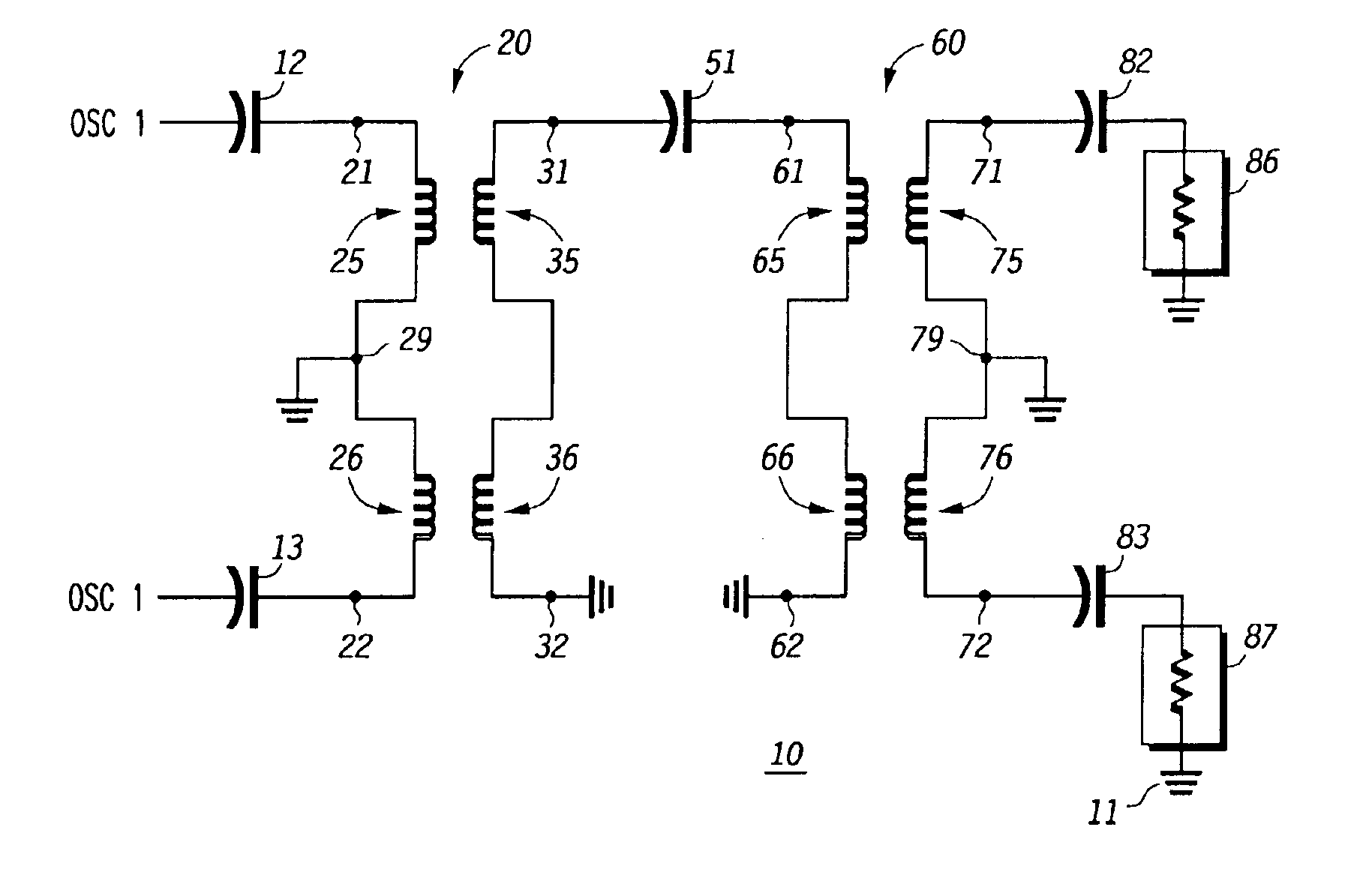Patents
Literature
158results about "Automatic frequency control details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
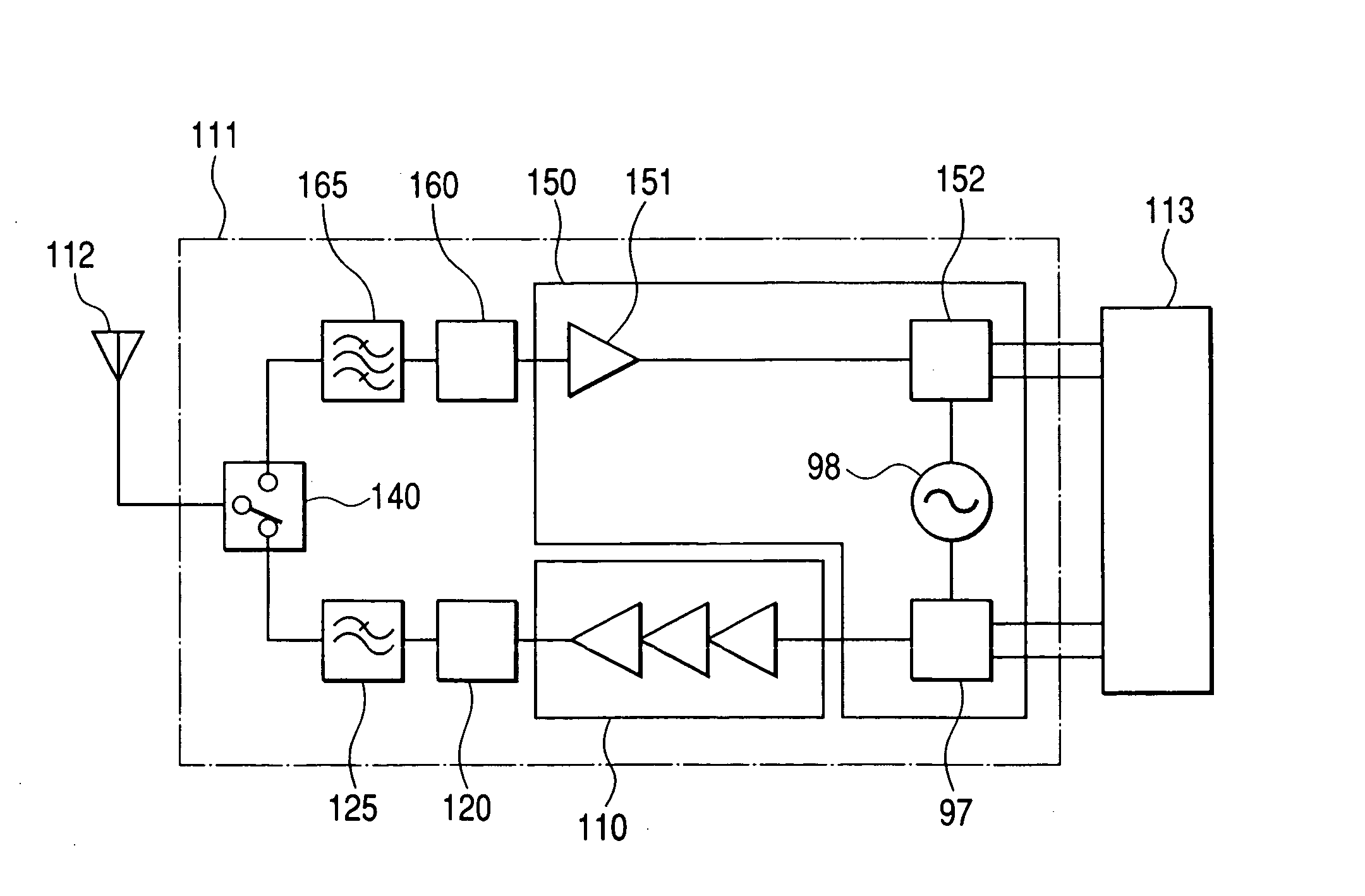
Radio communication semiconductor integrated circuit, data processing semiconductor integrated circuit and portable device
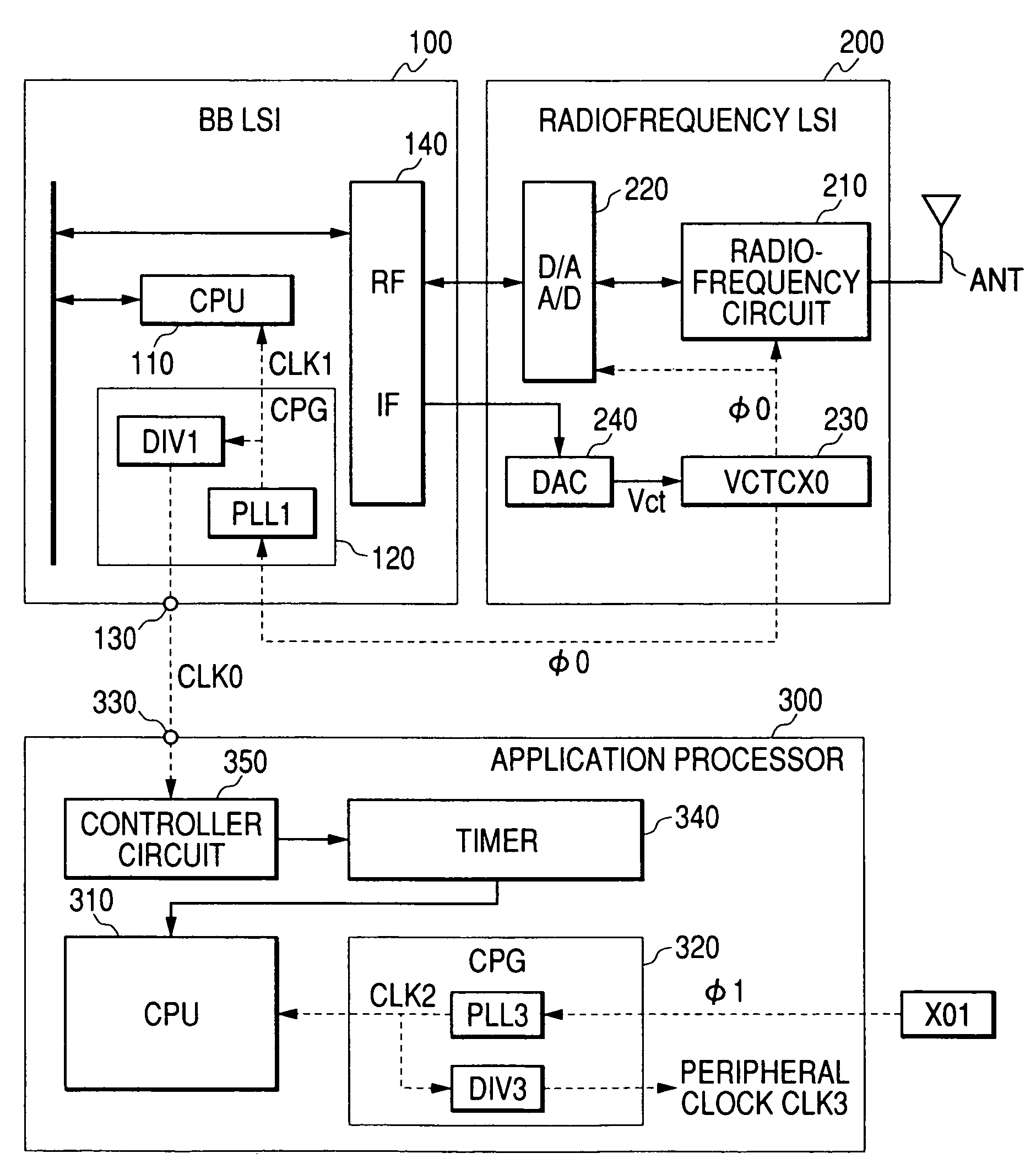
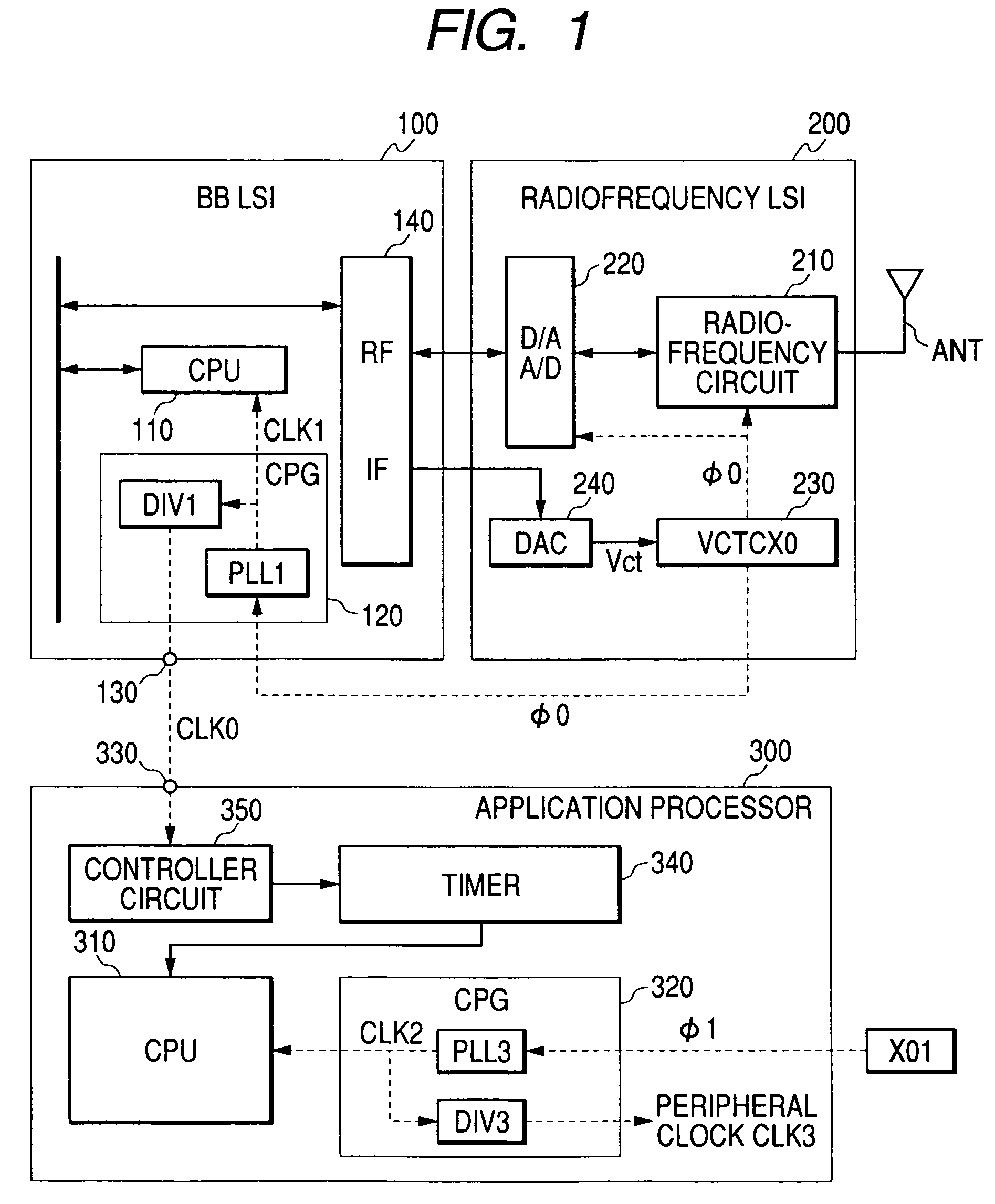
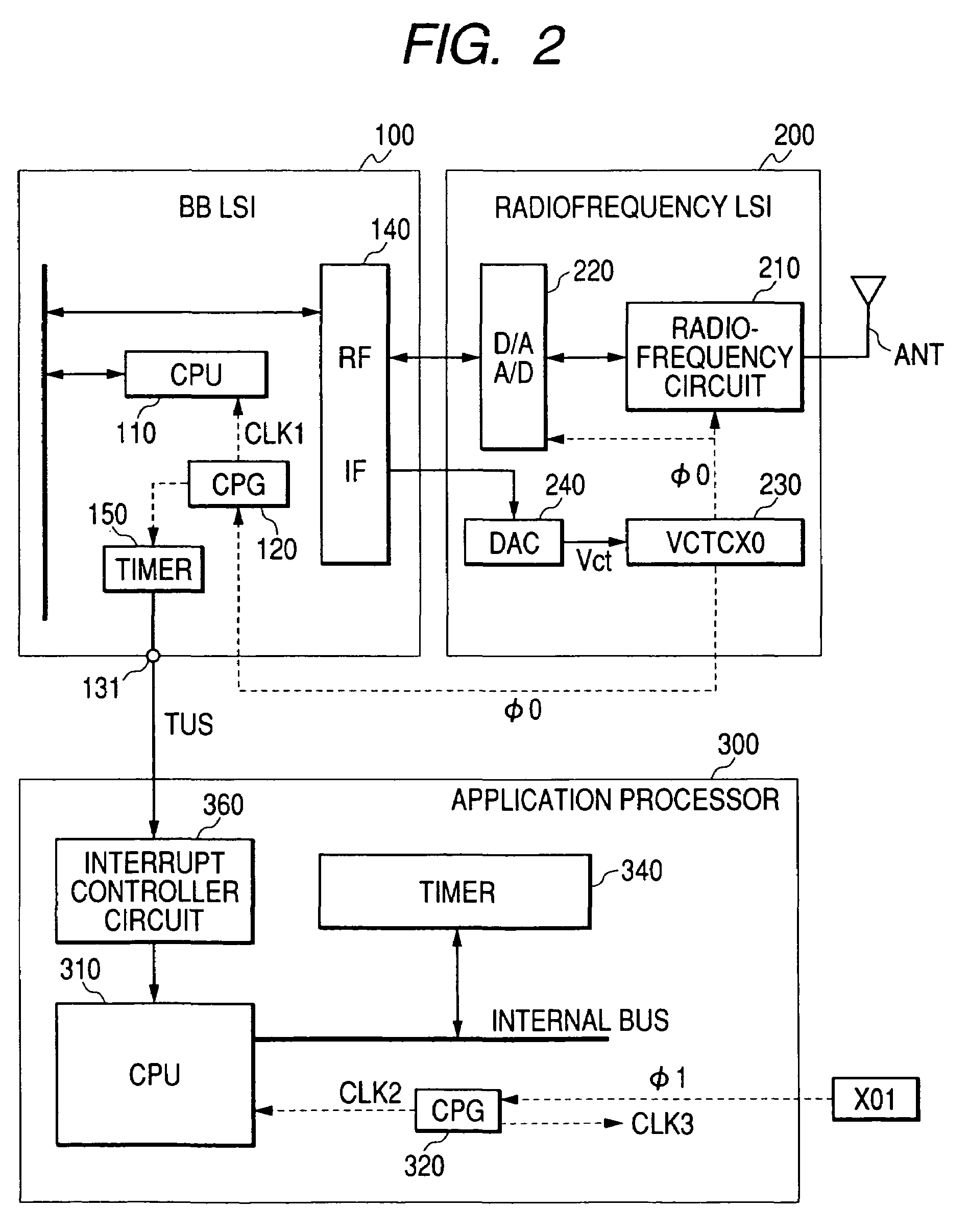
ActiveUS7444168B2Without lowering performanceAutomatic frequency control detailsData switching by path configurationEngineeringApplication processor
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
AFC control apparatus and method in mobile communication system and mobile communication equipment using the apparatus and method
InactiveUS20010004373A1No noiseMinimizing adverse influenceAutomatic frequency control detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase shiftedIntegrator
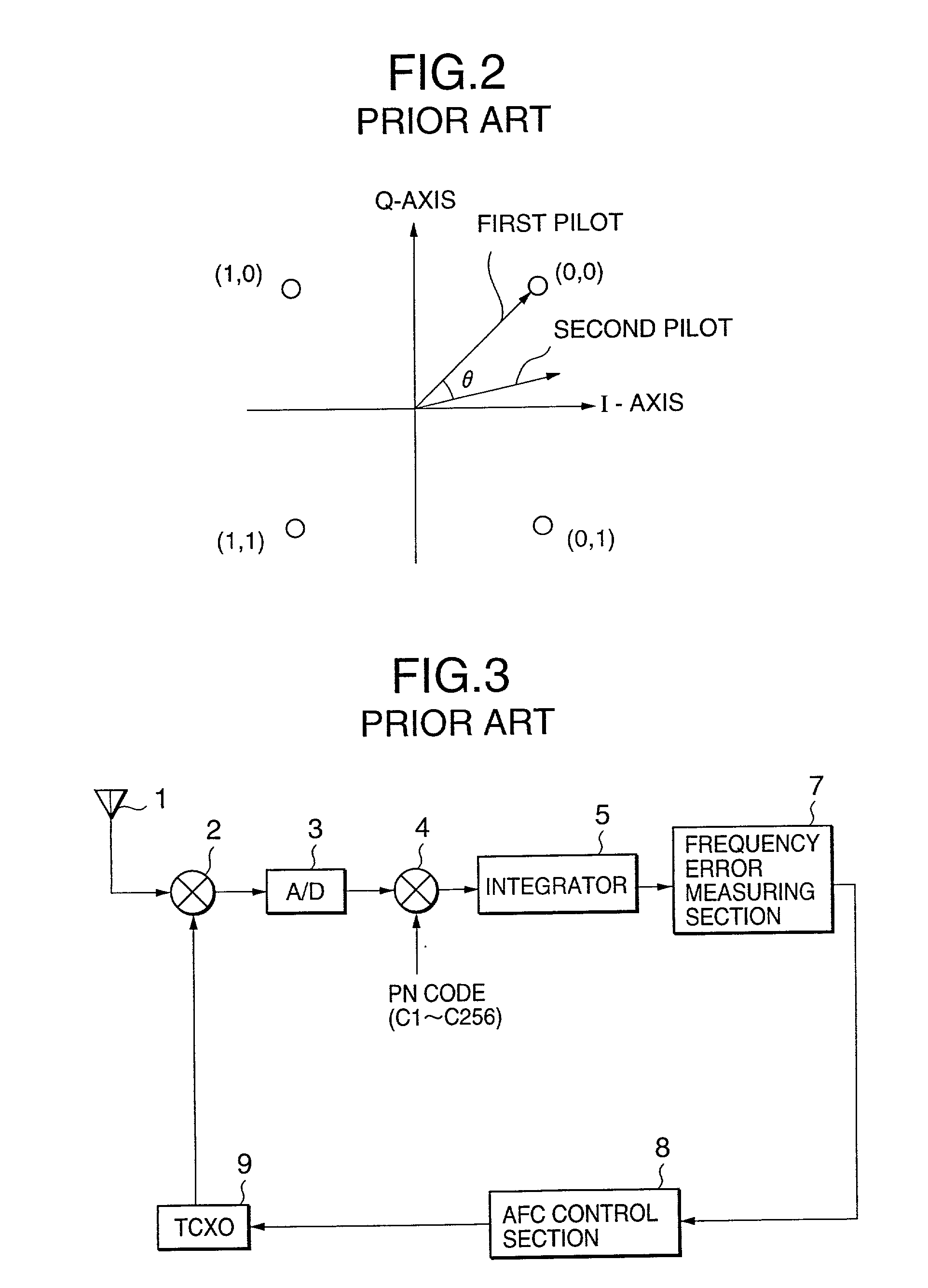
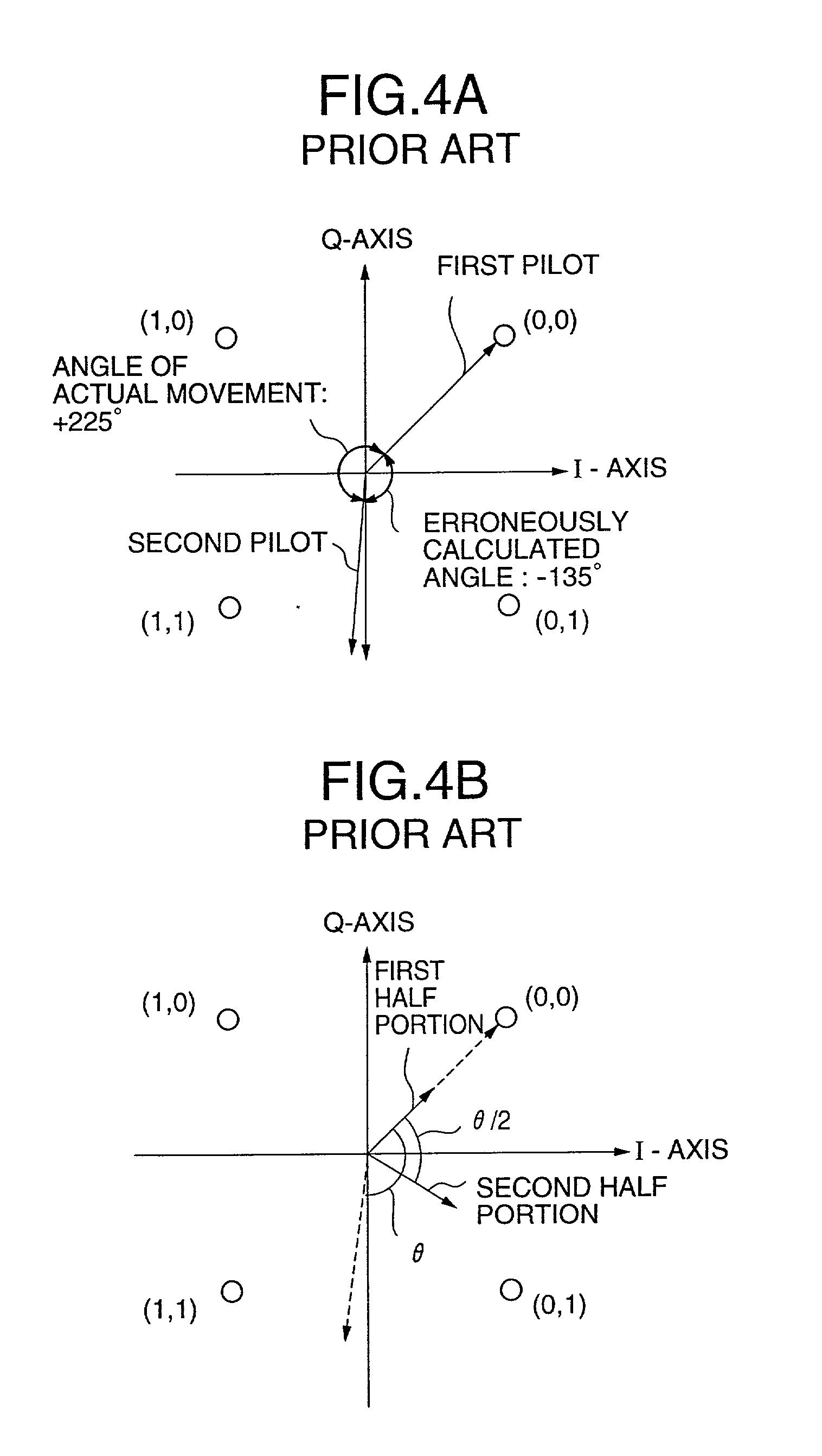
An AFC control apparatus in mobile communication equipment includes a depreading unit, first integrator, and control section. A despreading section despreads the reception signal. The first integrator integrates despread outputs obtained by despreading, of pilot symbols contained in a pilot channel of the reception signal, N (N is a number of 2 or more) consecutive first symbols and N second symbols succeeding the N first symbols, and generates first and second integral outputs. The control section detects any phase shift amount between the first and second integral outputs and controls the frequency of the local signal in accordance with the detected phase shift amount. An AFC control method and mobile communication equipment having the above apparatus and method are also disclosed.
Owner:NEC CORP
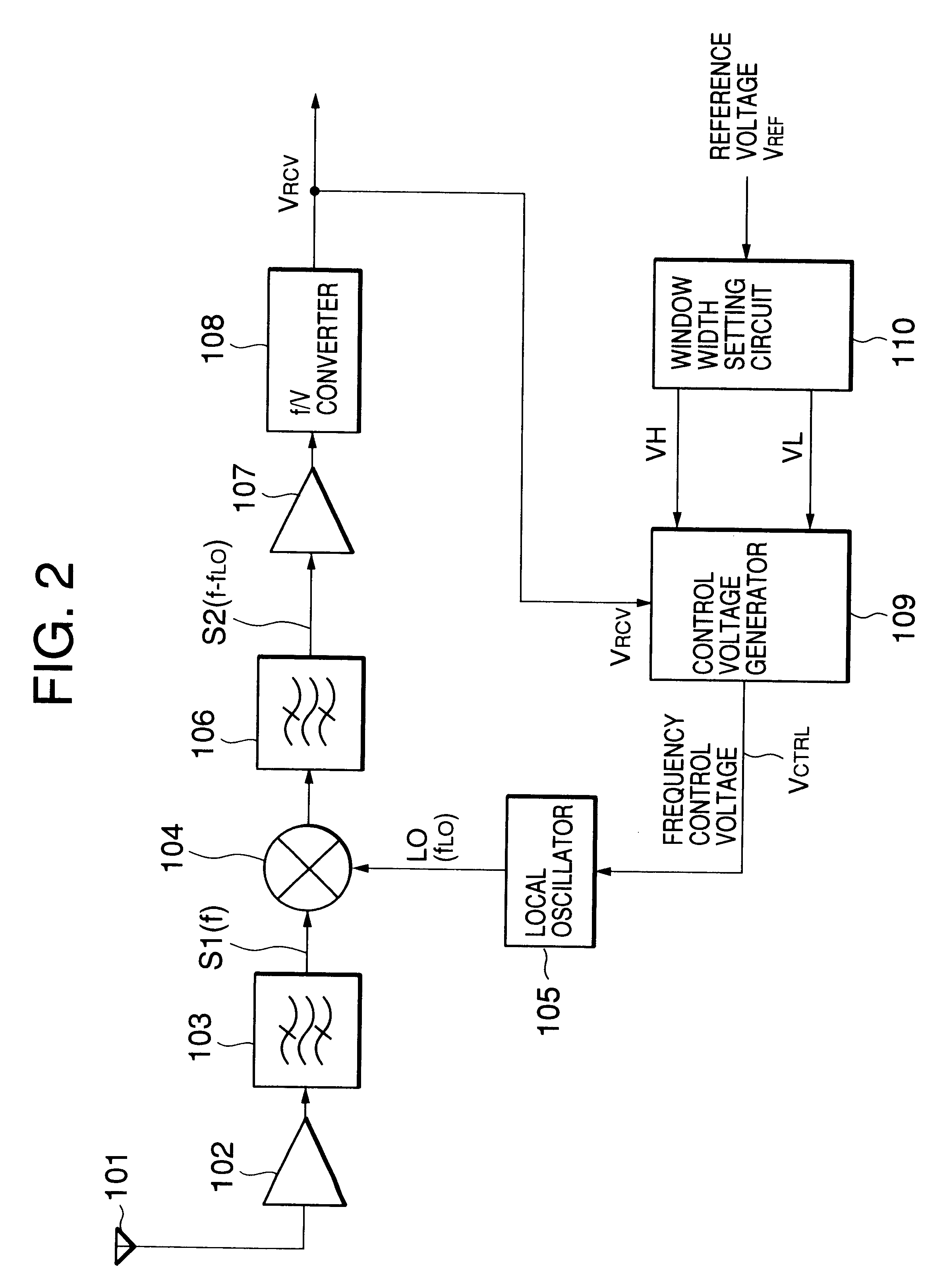
Automatic frequency control in FSK receiver using voltage window deviation
InactiveUS6332007B1Pulse automatic controlAutomatic frequency control detailsLocal oscillatorEngineering
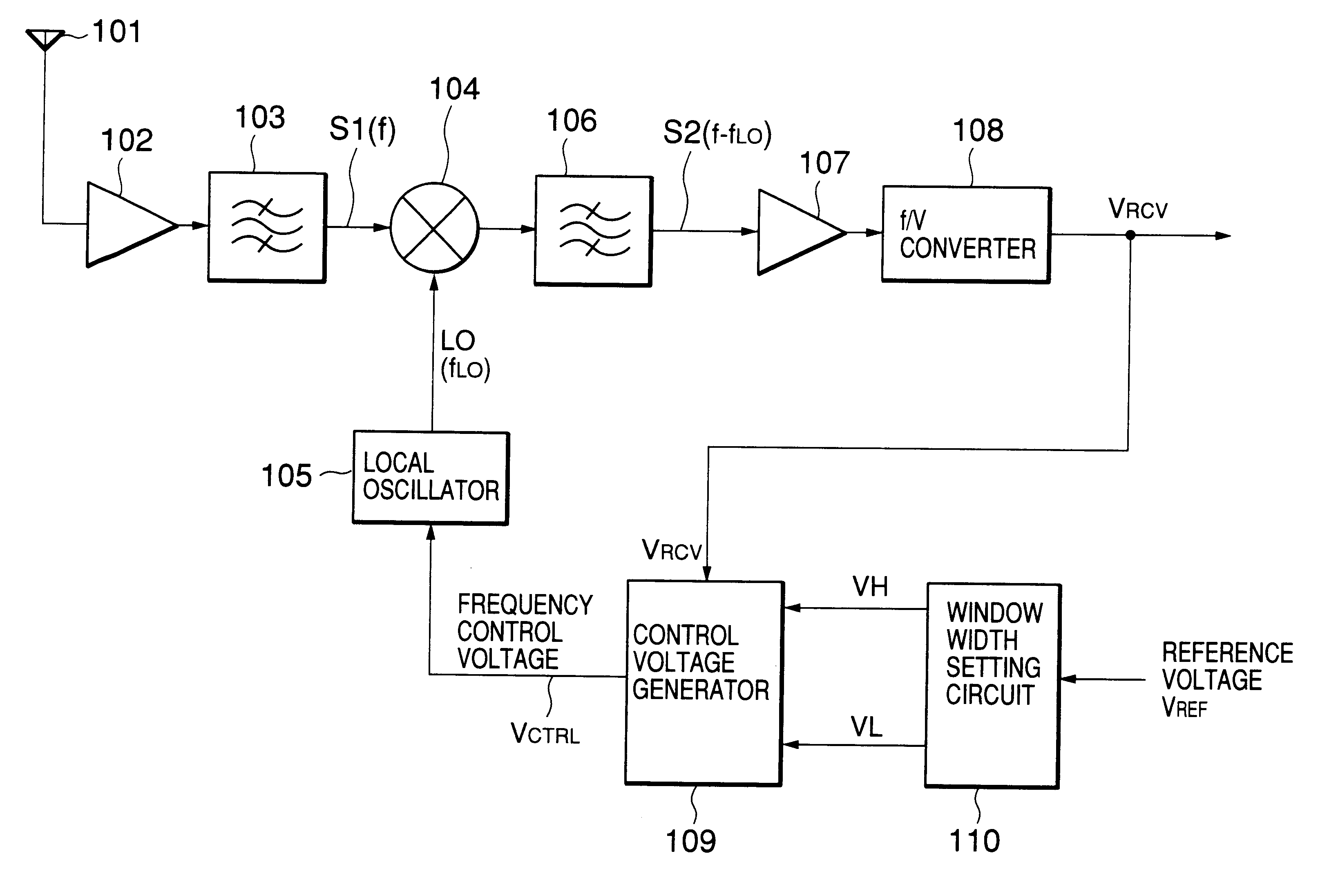
An AFC circuit for controlling an oscillation frequency of a local oscillator is disclosed. An f / V converter converts a frequency of an FSK signal to a received signal voltage varying depending on the frequency of the FSK signal. A window generator generates a voltage window including a reference voltage corresponding to a center frequency of the FSK signal. The oscillation frequency of the local oscillator is controlled depending on a deviation of the received signal voltage from the voltage window so that the received signal voltage falls into the voltage window.
Owner:NEC CORP
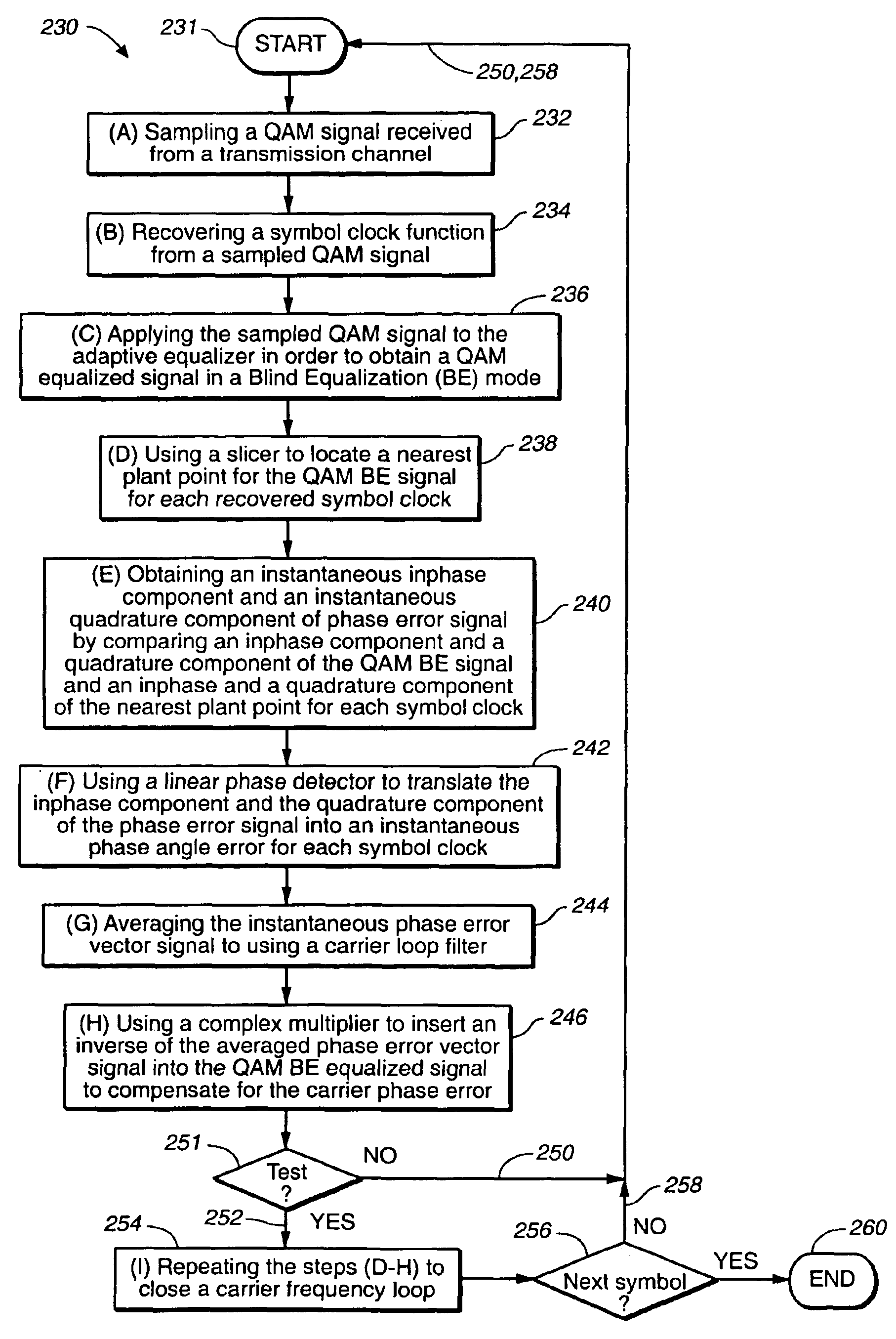
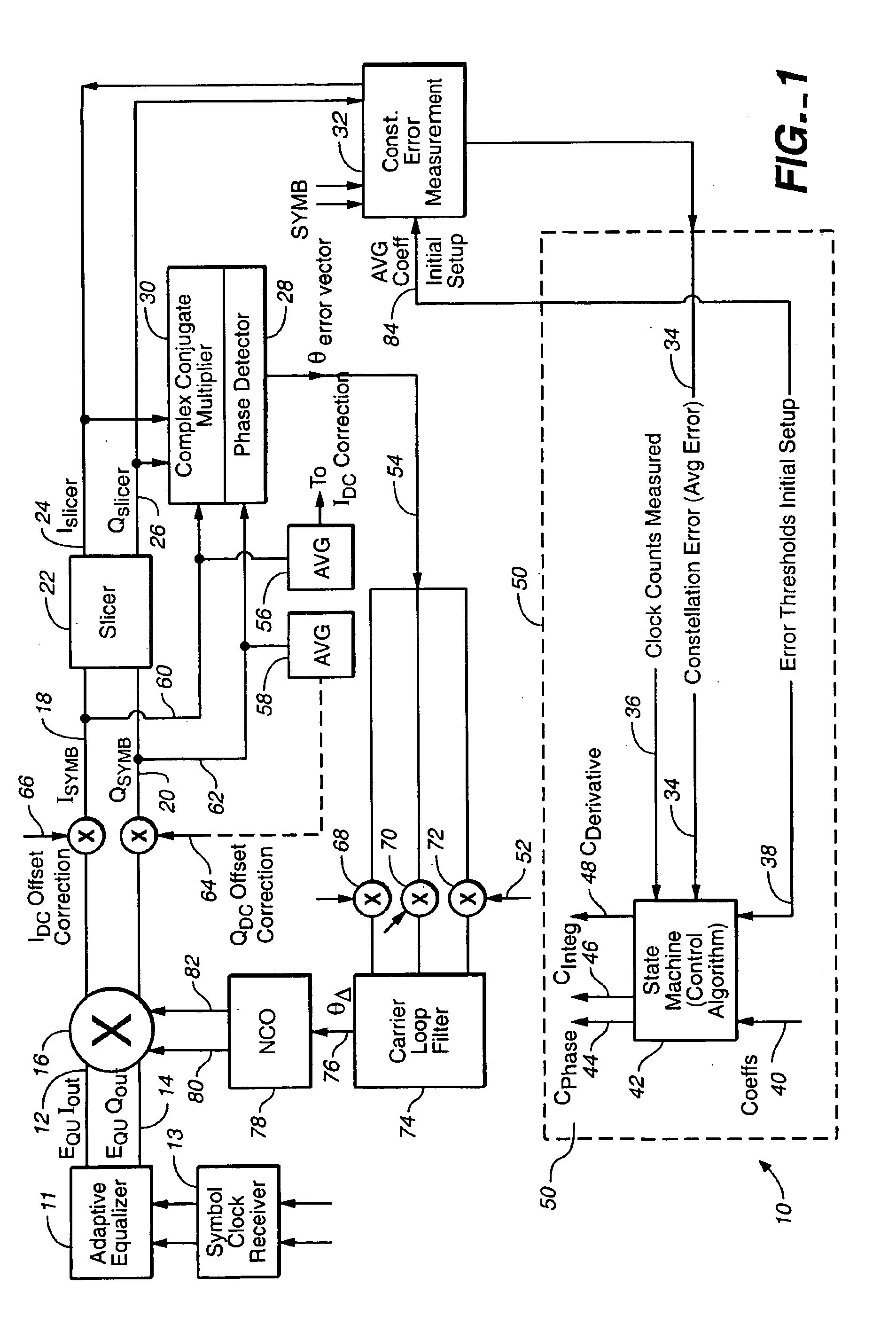
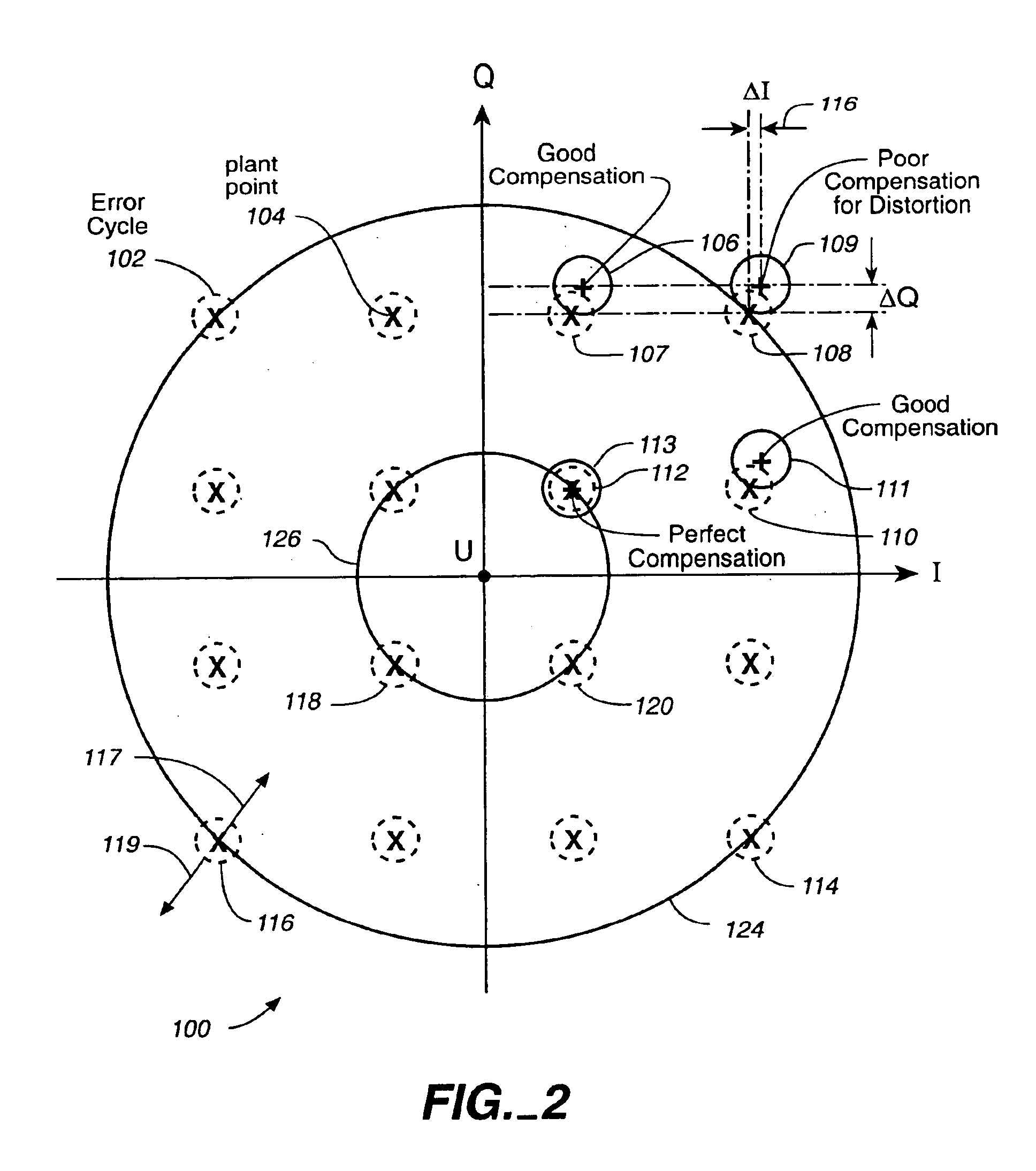
Linear phase robust carrier recovery for QAM modems
InactiveUS6904098B1Large loop bandwidthLower latencyDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAutomatic frequency control detailsQam modulationBlind equalization
In a QAM demodulator including an adaptive equalizer, a method of carrier tracking comprising the following steps is disclosed: (A) sampling a QAM signal received from a transmission channel; (B) recovering a symbol clock function from the sampled QAM signal; (C) applying the sampled QAM signal to the adaptive equalizer in order to obtain a QAM equalized signal in a Blind Equalization (BE) mode; (D) using a slicer to locate a nearest plant point for the QAM Blind equalized signal for each recovered symbol clock; (E) using a complex conjugate multiplier to obtain an instantaneous inphase component and an instantaneous quadrature component of a phase angle error signal; (F) using a linear phase detector to obtain an instantaneous phase angle error for each symbol clock; (G) averaging the instantaneous phase angle error signal by using a carrier loop filter; (H) using a complex multiplier to insert an inverse of the averaged phase angle error signal into the QAM Blind equalized signal to compensate for the carrier phase angle error; and (I) repeating the steps (D-H) to close a carrier frequency loop.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
Detection of large carrier offsets using a timing loop
A method and apparatus for the detection and correction of large carrier offsets. A set of known correction carrier offsets are used to translate an input signal having a carrier offset. After applying each correction carrier offset, a state of a timing recovery loop is evaluated. The set of known correction carrier offsets are sequentially used to translate the input signal until the timing recovery loop is locked. The carrier offset is substantially acquired when the timing recovery loop is locked.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Tag communications with access point
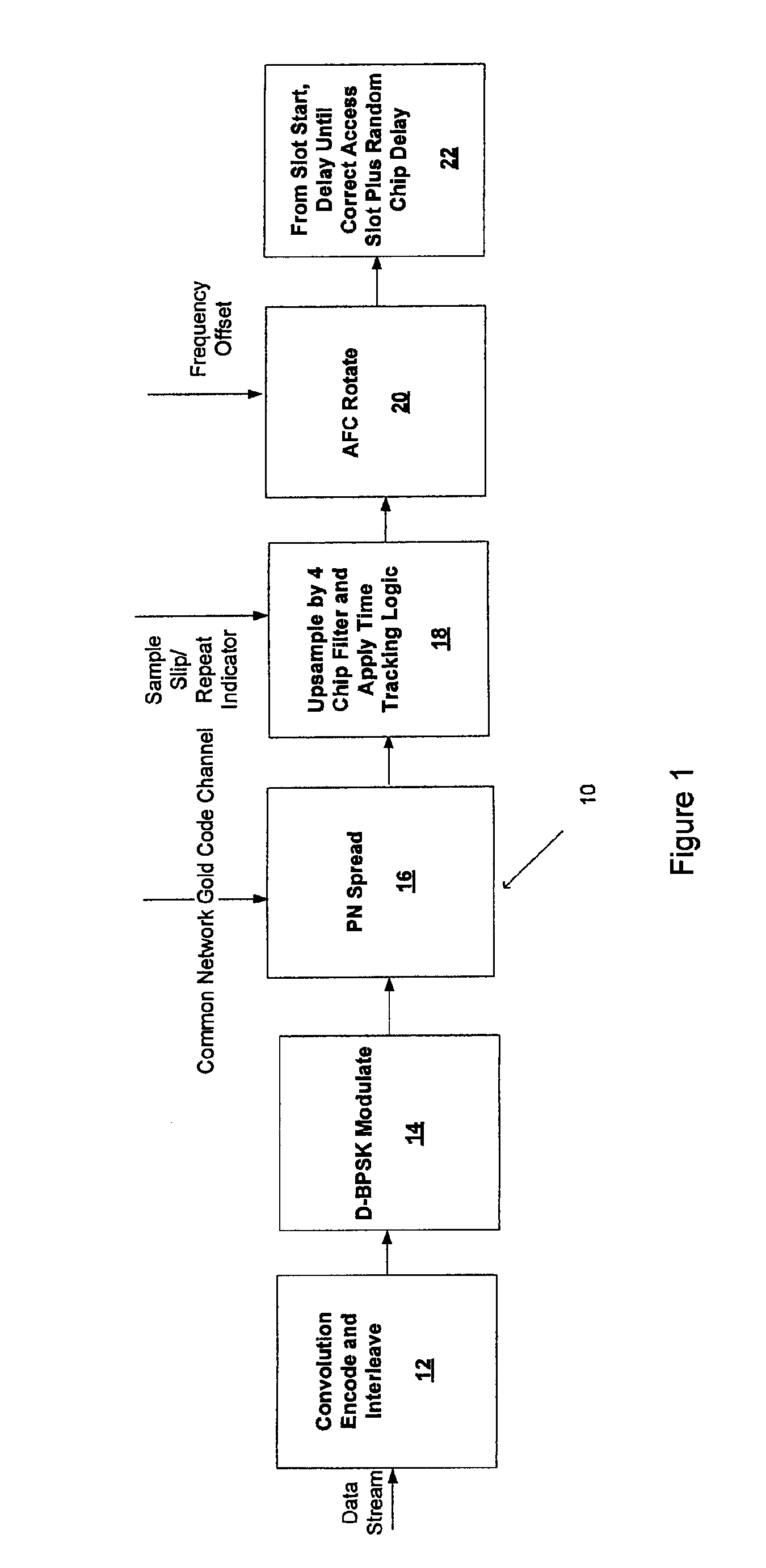
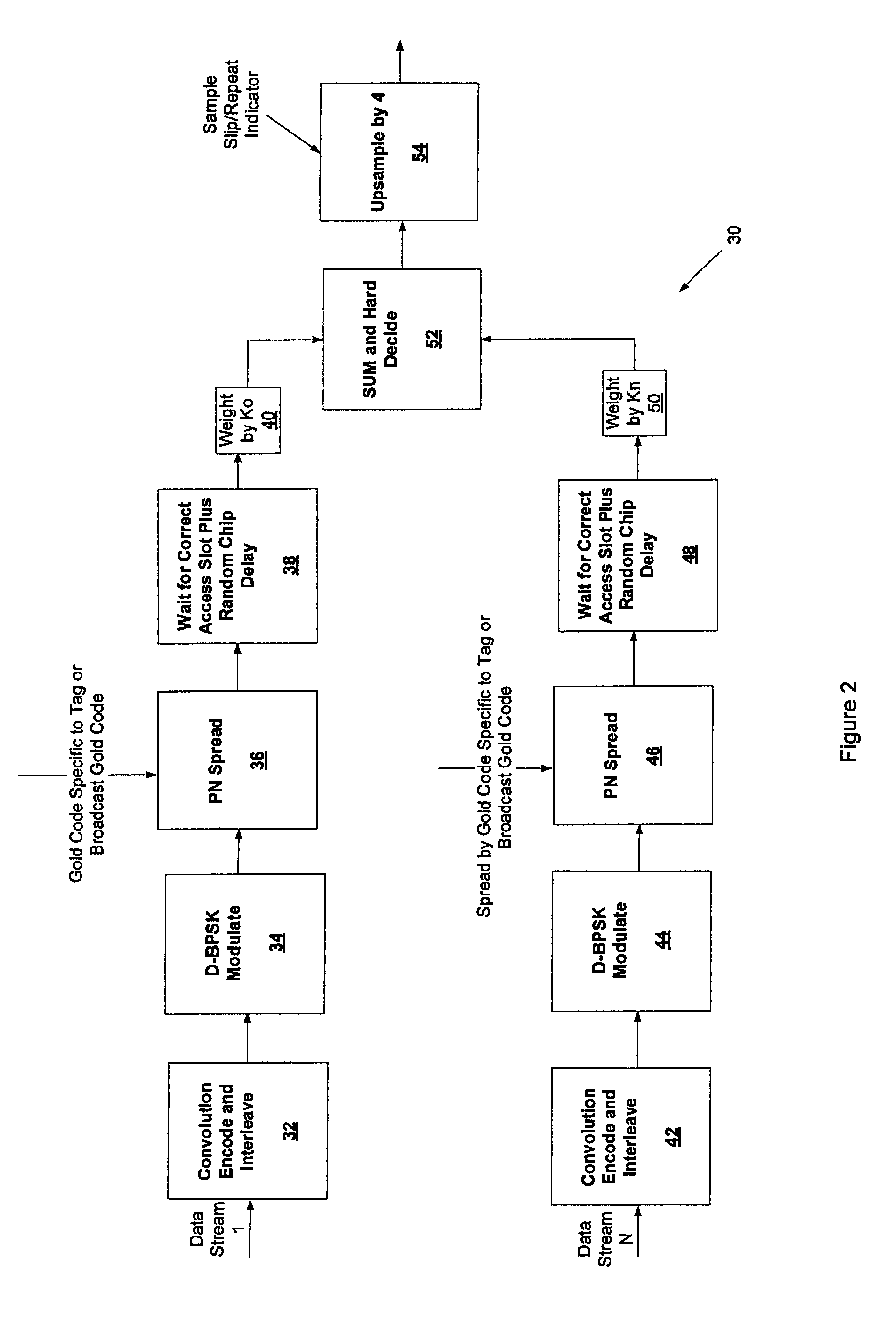
ActiveUS7526013B1Easy accessProvide securityReceiver initialisationError prevention/detection by using return channelData streamCheque
A method of establishing communication at a tag includes calculating a metric for each of a plurality of automatic frequency control (AFC) hypotheses where the plurality of AFC hypotheses correspond to a timing used by an access point; based on the calculated metrics, identifying one or more relevant AFC hypotheses; performing a check on a demodulated data stream identified using the one or more relevant AFC hypotheses; identifying a valid AFC hypothesis based at least in part on the check; and determining where a frame starts based at least in part on the check.
Owner:INGENU INC
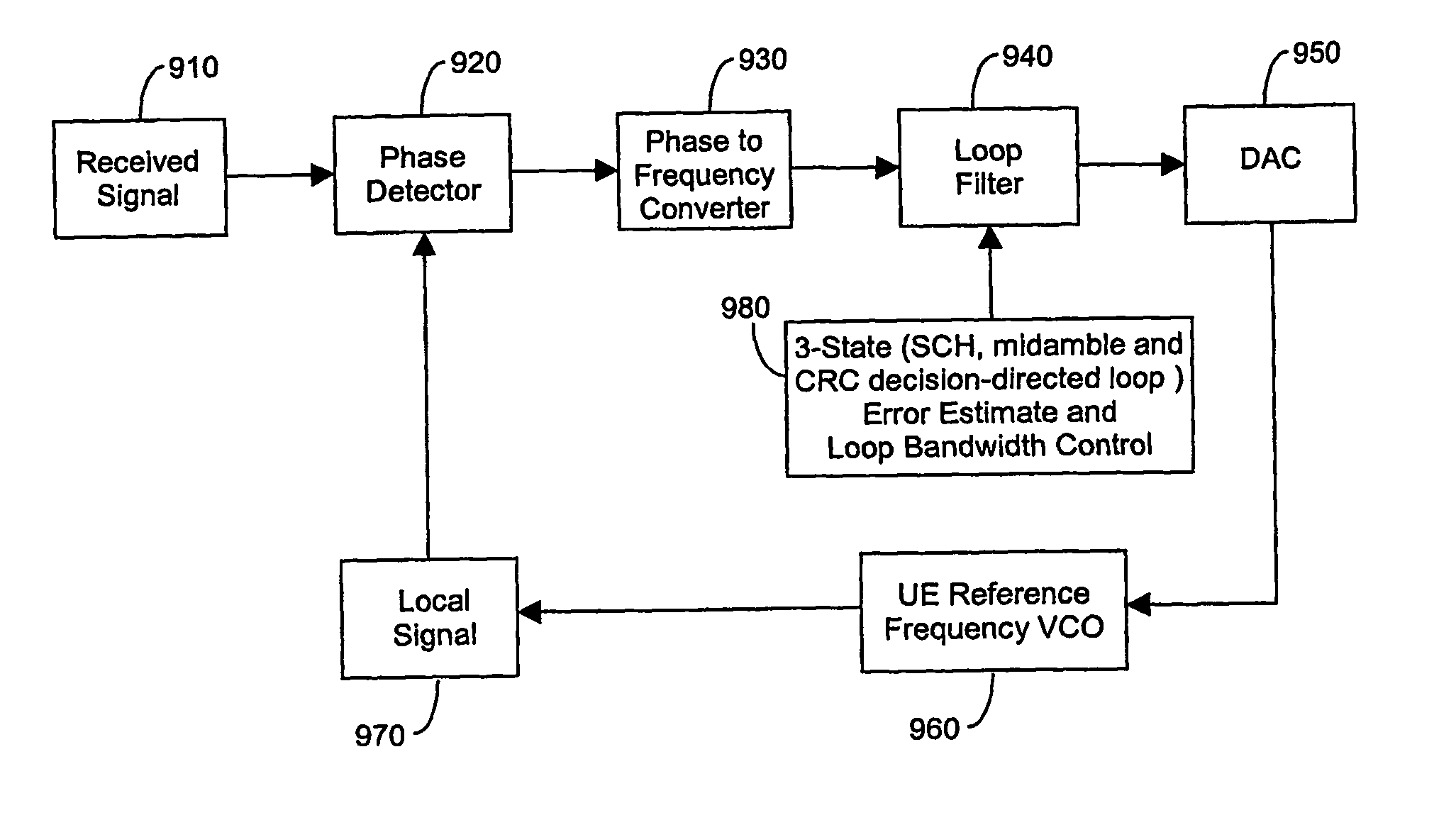
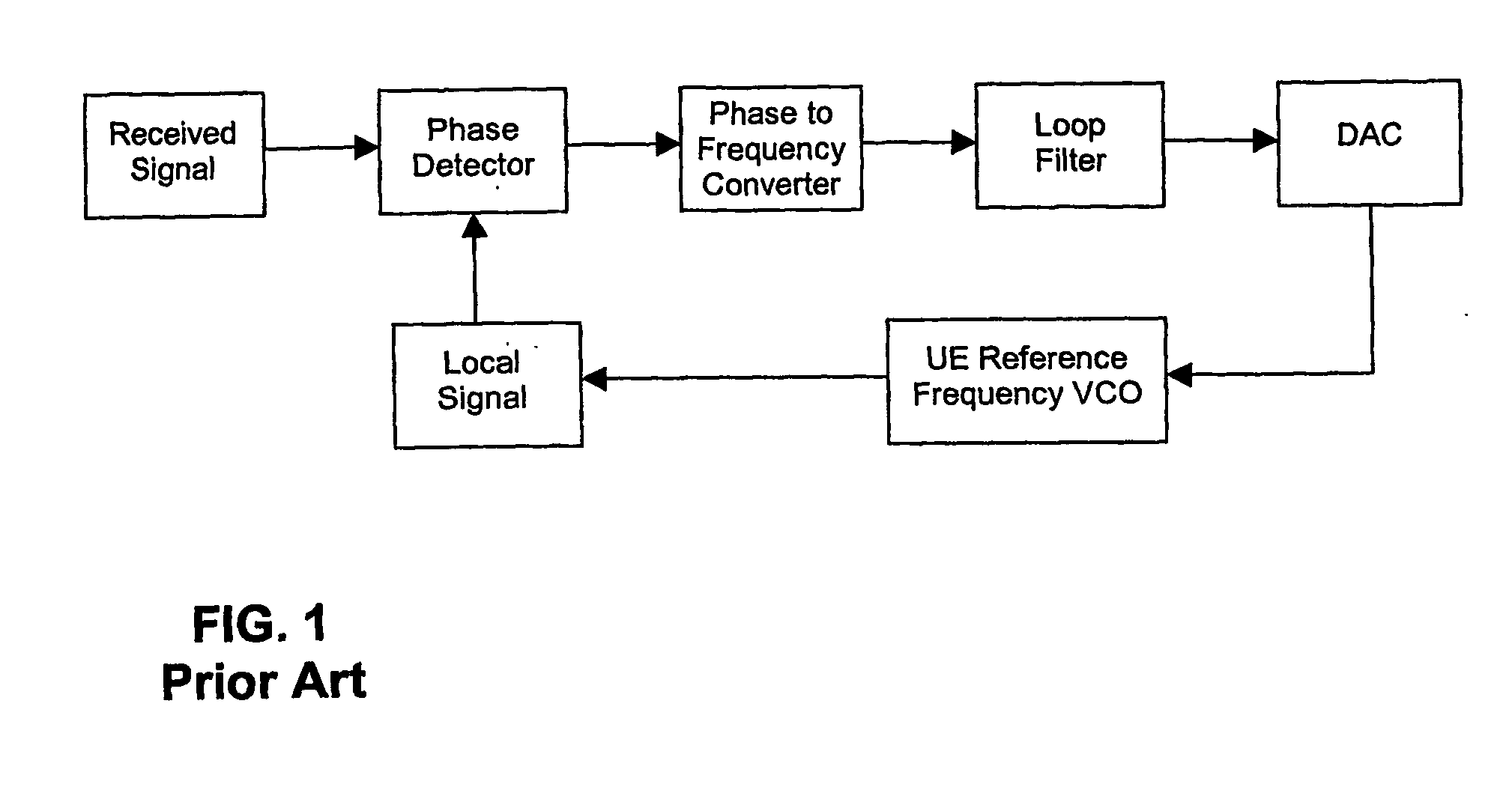
Method and arrangement for automatic frequency control in a communication system
ActiveUS20070140386A1Pulse automatic controlAutomatic frequency control detailsCommunications systemEngineering
An arrangement (900), method and unit for AFC in a communication system (100) having: a frequency estimator (980) producing a decision-directed frequency estimate from a received signal; and an AFC loop receiving the decision-directed frequency estimate and performing therewith frequency control. The AFC process may use a CRC-decision directed frequency estimate as the final stage in a multi-stage AFC process (preceded by SCH- and midamble-derived frequency estimate stages), such that a verified received data sequence is used to re-construct a local copy of the ideal received data symbols expected at the output of a detector. This local copy is then correlated with the actual detector output and the results used to estimate the frequency error present on the received signal. The AFC process is inherent suited for discontinuous receive (DRX) applications. This provides the advantage of allowing required frequency correction accuracy to have minimal impact on the error rate of the received data in various channel configurations.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
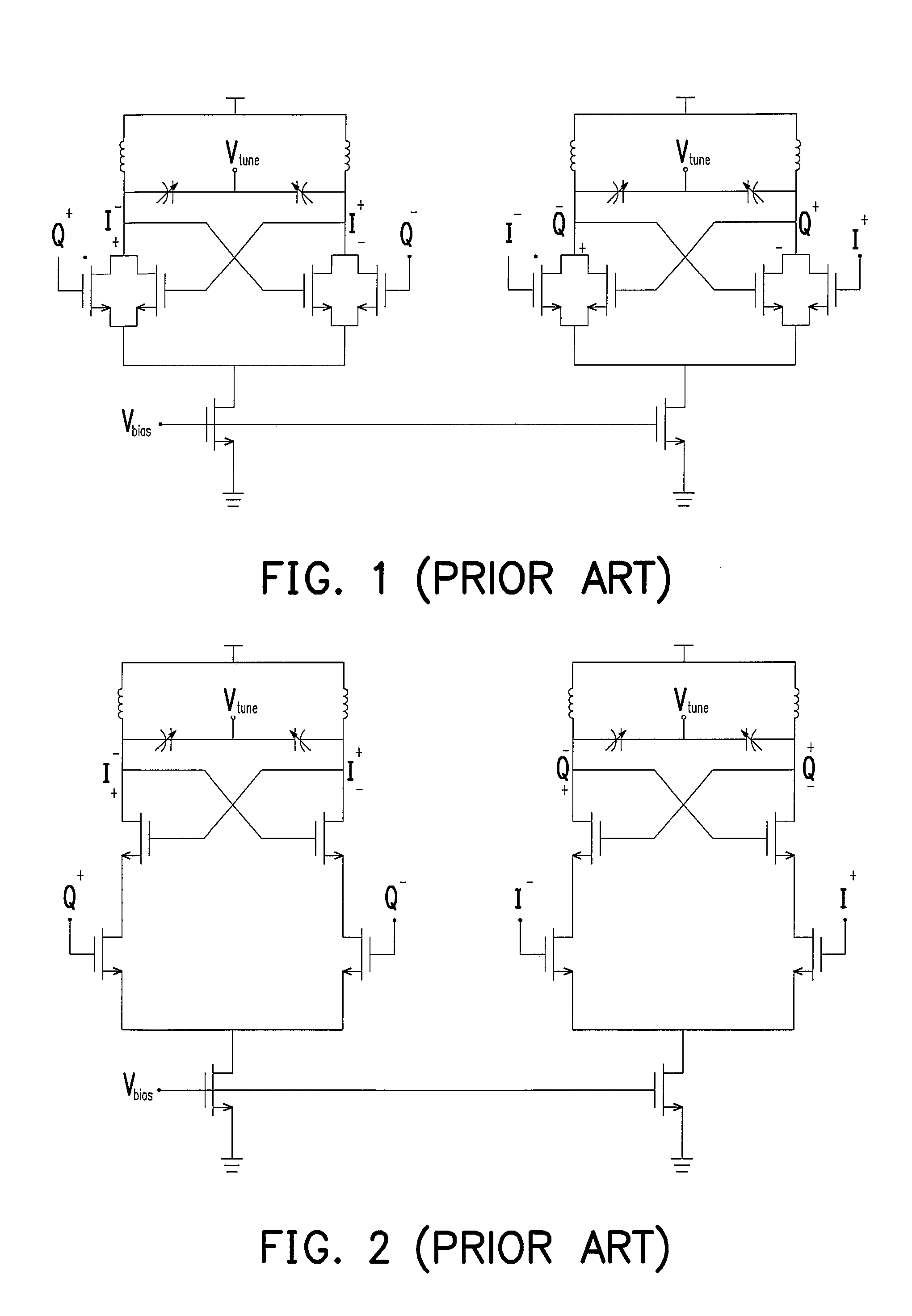
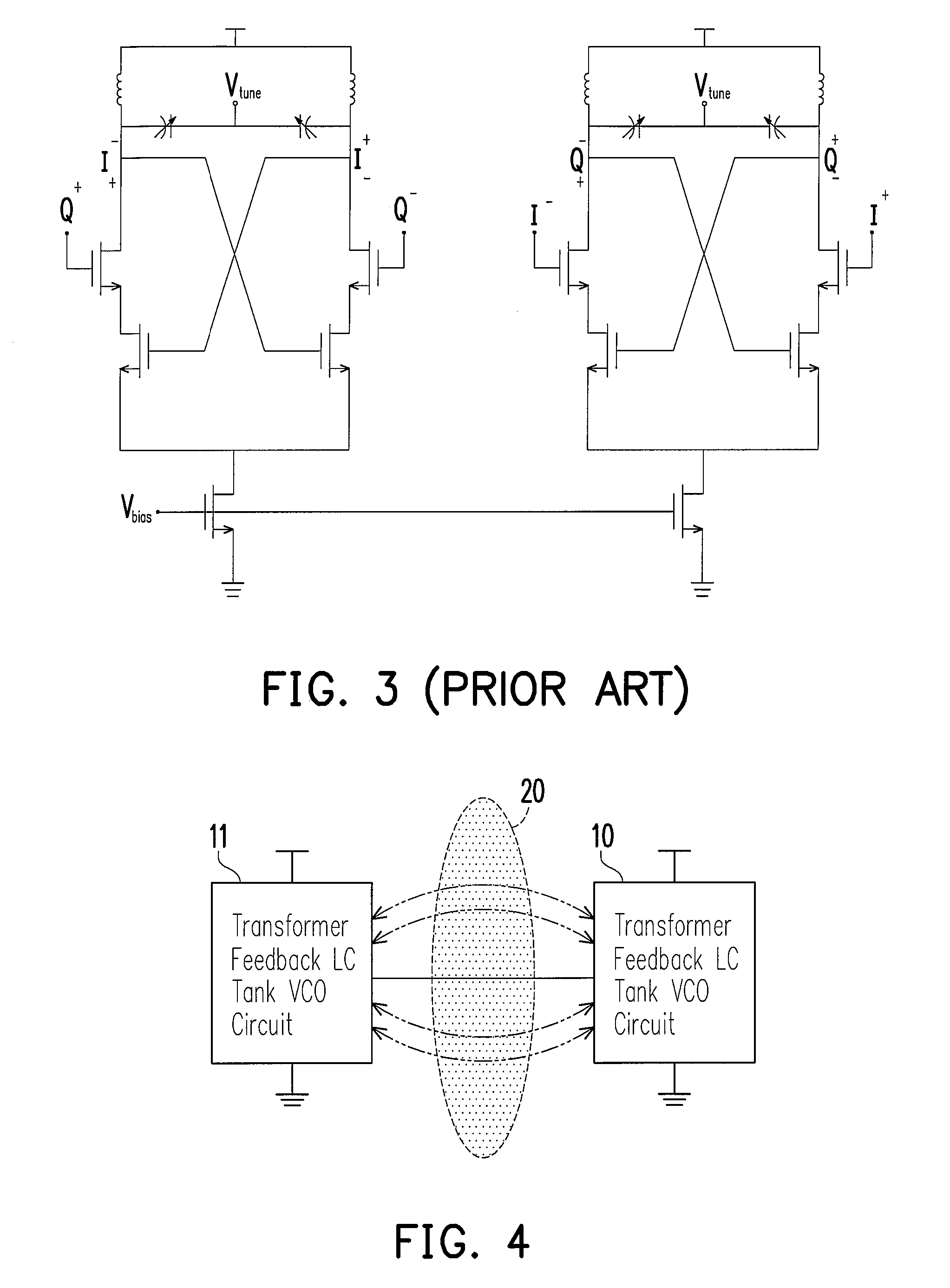
Transformer coupled oscillator and method
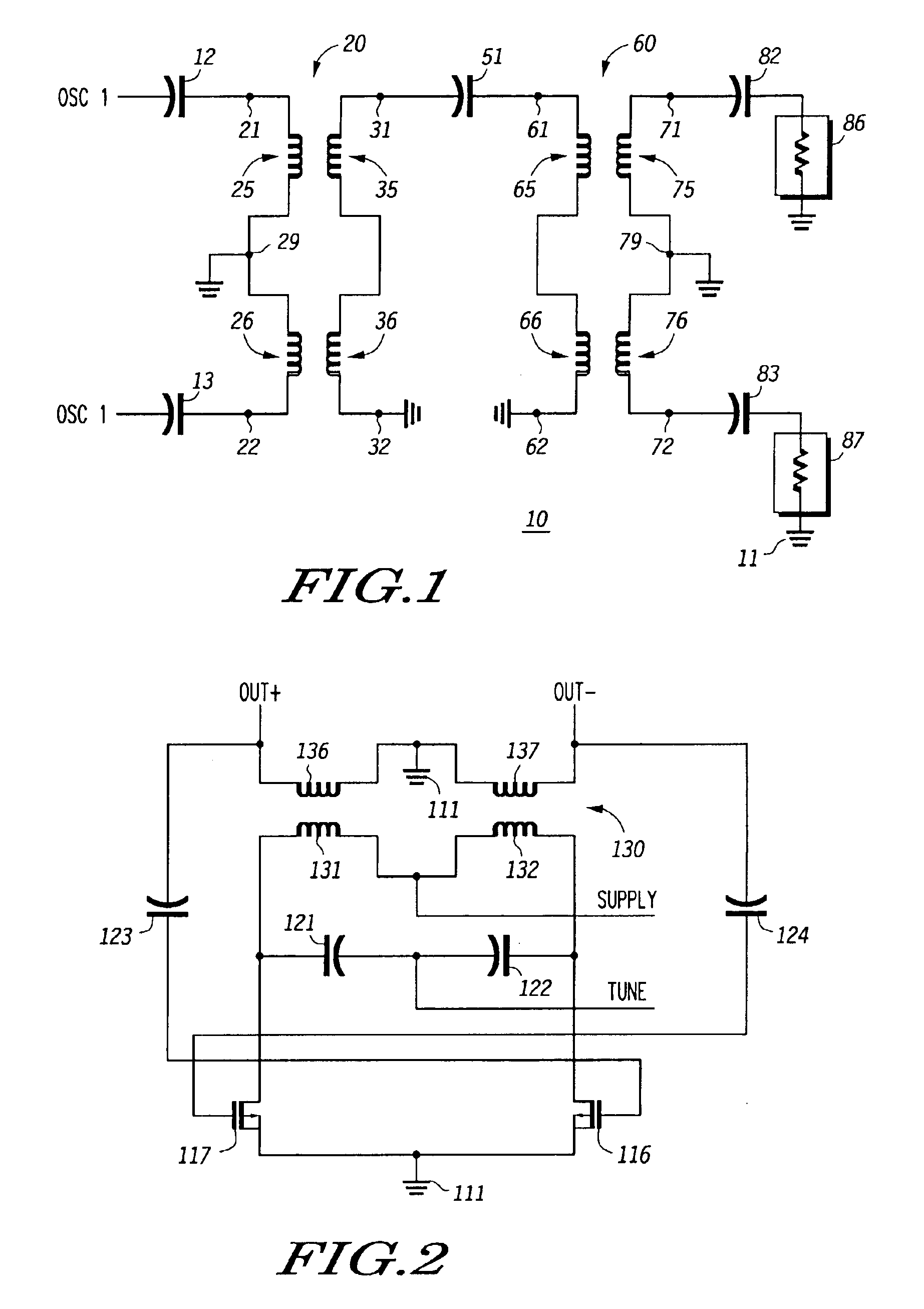
InactiveUS6982605B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceEngineering
In a particular embodiment, an oscillator adjustment circuit is disclosed. The oscillator adjustment circuit includes a resonator portion comprising a capacitive element coupled to an inductive element and a signal balancing portion comprising a secondary coil of the transformer. The inductive element comprises a primary coil of a transformer. The secondary coil has a grounded center tap.
Owner:APPLE INC
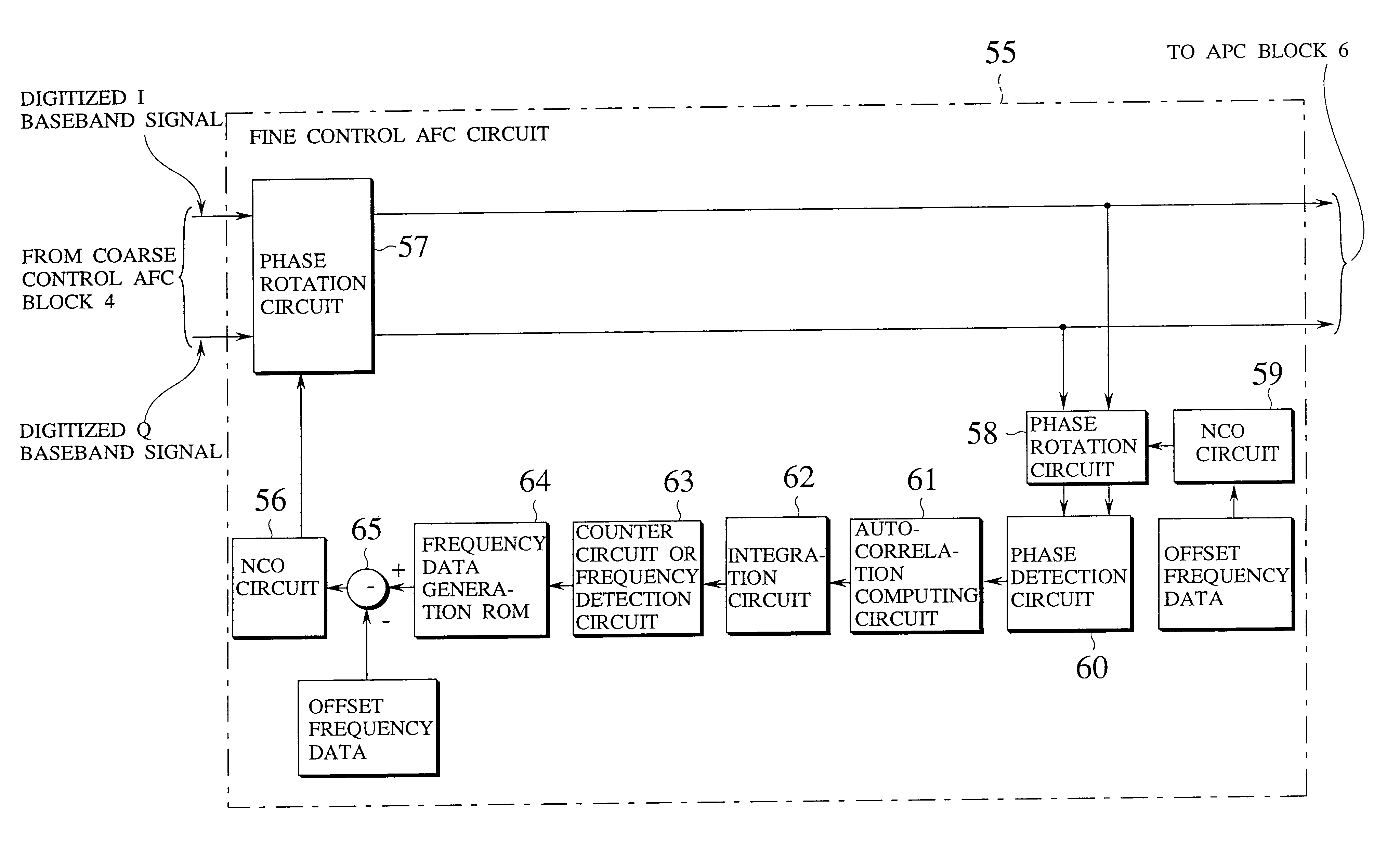
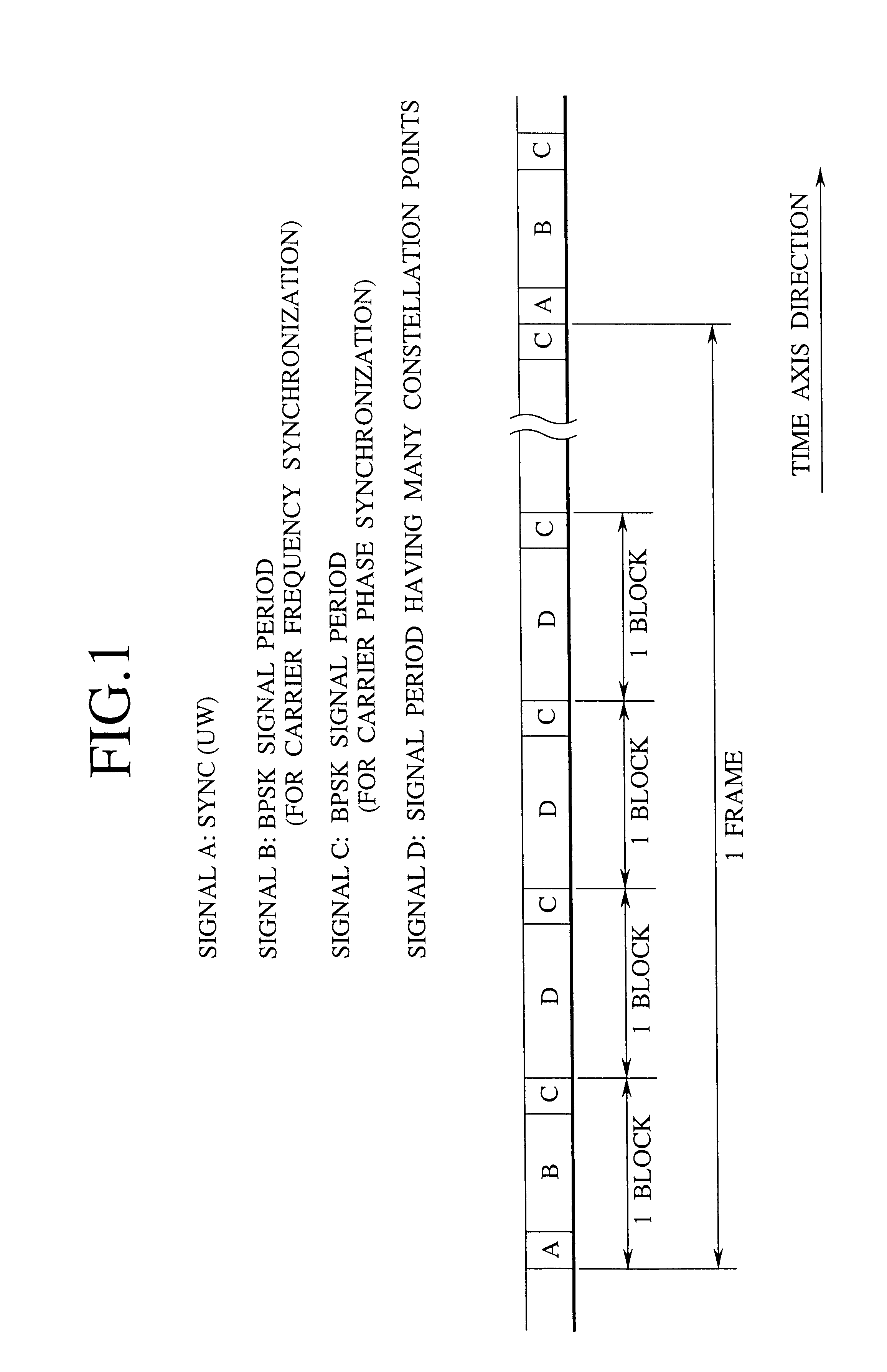
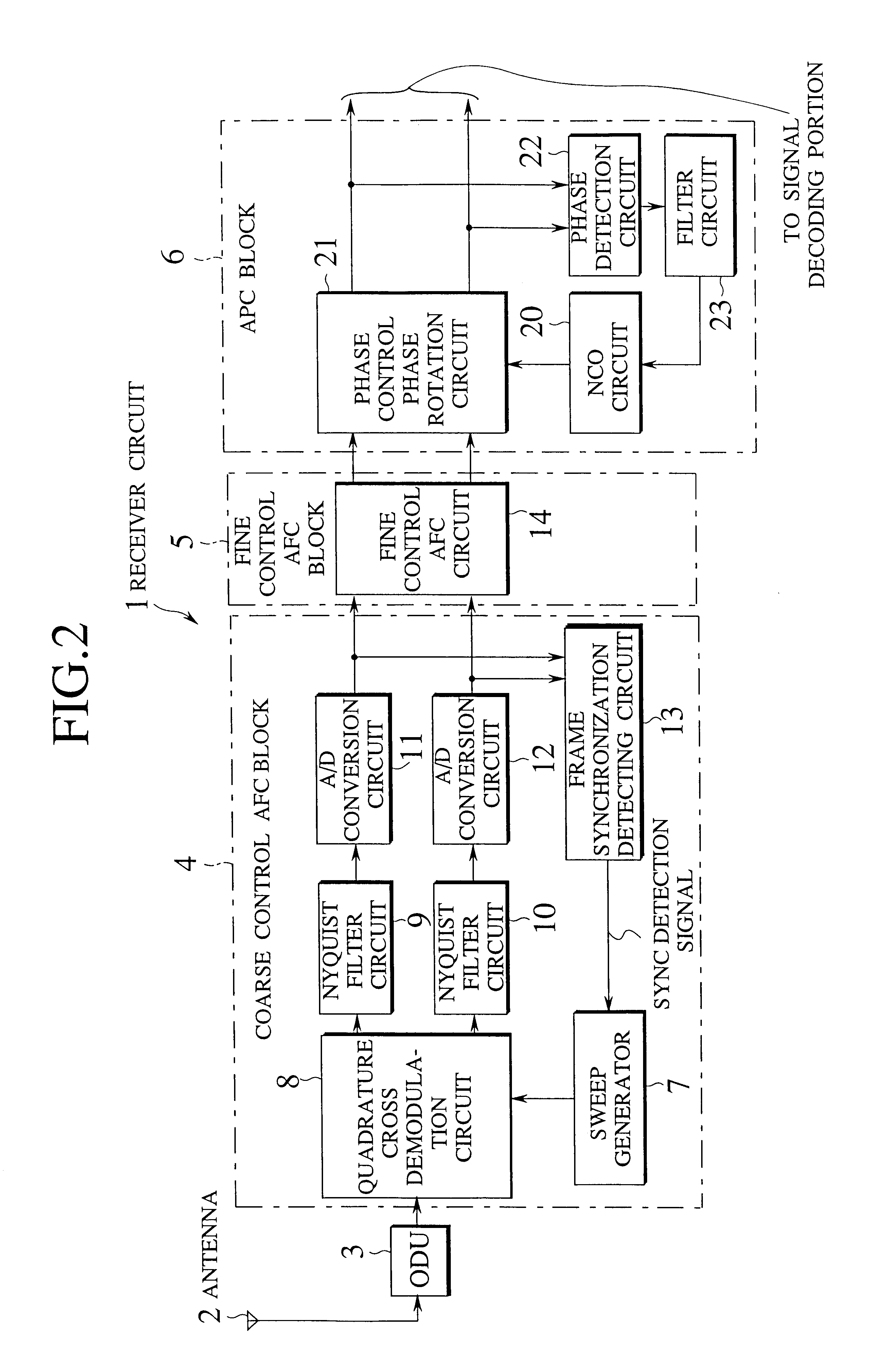
AFC circuit, carrier recovery circuit and receiver device capable of regenerating a carrier reliably even at the time of low C/N ratio
InactiveUS6490010B1Avoid it happening againEstimate degradedTelevision system detailsPulse automatic controlNumerical controlDifferential function
Stabilized carrier recovery is achieved even at the time of a low C / N ratio by measuring the phase of a signal and controlling VCO or NCO (Numerical Controlled Oscillator) using only a period having few constellation points. At this time, false lock phenomenon is avoided as follows. That is, relatively short SYNC modulated by an already-known pattern is entered into a modulation wave, VCO or NCO oscillation frequency is swept in a wide range and sweep is stopped at a frequency in which the SYNC can be received, thereby carrying out coarse control AFC. Further, a period having long to some extent, having few constellation points is provided in the modulation wave and then, a difference between the frequency of a received modulated signal and a local oscillation signal of VCO or NCO is obtained in this period. This frequency difference is analyzed according to the phase differential function method, self-correlation function method or count method, and the VCO or NCO is controlled based on this result of analysis.
Owner:NIPPON HOSO KYOKAI
Multi-phase voltage-control oscillator
InactiveUS7551038B2Improve performancePulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInductorEngineering
A multi-phase voltage-control oscillator including a first voltage-control oscillator circuit and a second voltage-control oscillator circuit is provided. The first voltage-control oscillator circuit includes a first LC tank and a first inductor assembly unit. The second voltage-control oscillator circuit includes a second LC tank and a second inductor assembly unit. A mutual inductance effect is generated between the inductors of the first voltage-control oscillator and the inductors of the second voltage-control oscillator.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Semiconductor devices with inductors
ActiveUS20060038621A1Reduce distractionsInhibitionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCarrier signalLocal oscillator
Semiconductor devices provided with high performance high-frequency circuits that reduce interference caused by inductors are provided. In the semiconductor device including a modulator circuit to modulate a carrier wave by a base band signal to output an RF signal and a demodulator circuit to demodulate the RF signal by use of the carrier wave to gain the base band signal and a local oscillator to generate the carrier wave, inductors respectively having a closed loop wire are adopted. Interference caused by mutual inductance is reduced by the closed loop wire. For example, where inductors are adopted in the modulator circuit, a closed loop wire is disposed around the outer periphery of the inductors.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Integrated electronic circuit comprising a tunable resonator
ActiveUS7187240B2Improve performanceEasy to adjustAngle modulation detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringInductor
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Phase locked loop, voltage controlled oscillator, and phase-frequency detector
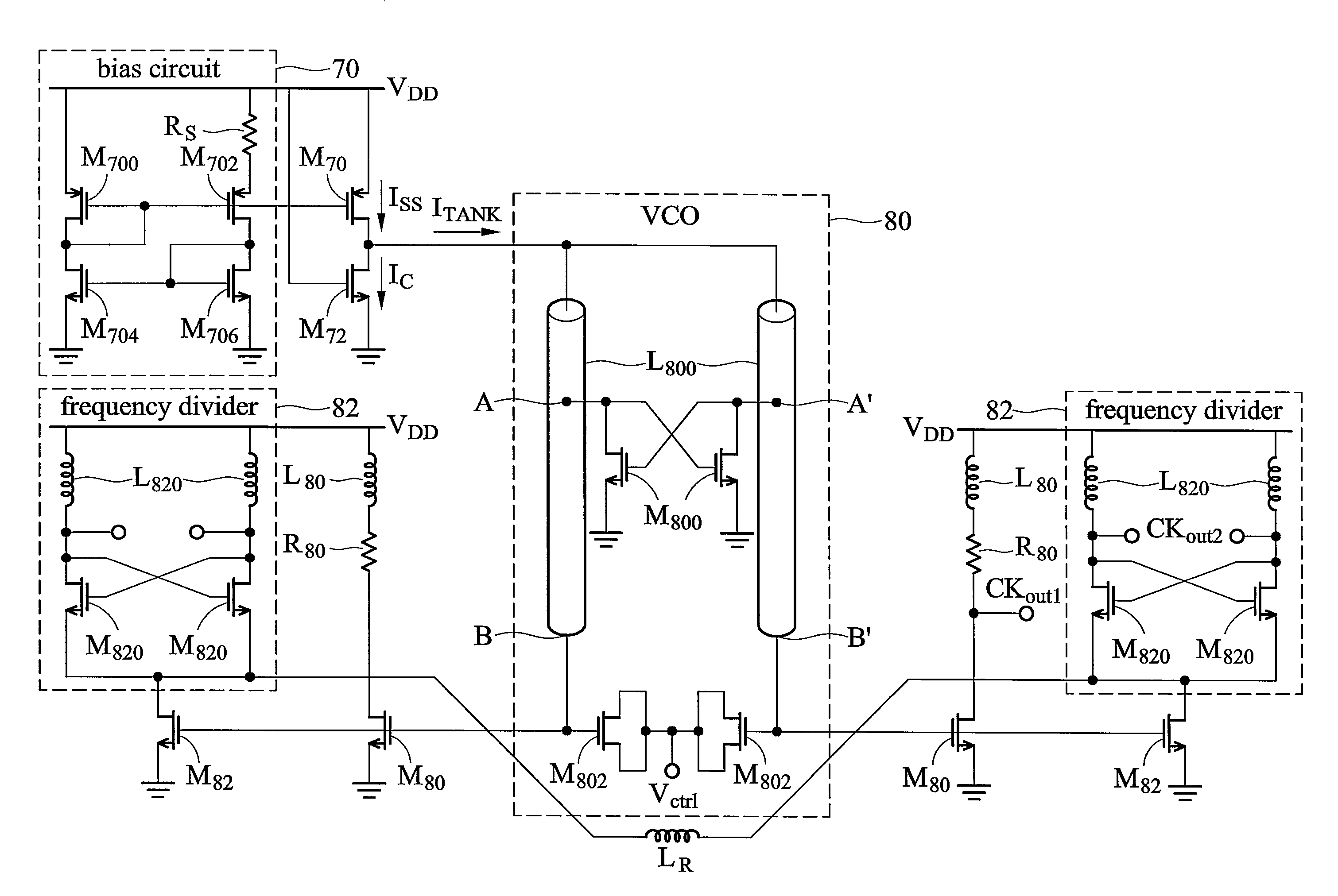
ActiveUS7830212B2Pulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLoop filterPhase frequency detector
A phase locked loop, voltage controlled oscillator, and phase-frequency detector are provided. The phase locked loop comprises a phase-frequency detector (PFD), a loop filter (LF), a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO), and a 3-stage frequency divider. The PFD receives a reference signal and a feedback signal to determine phase and frequency errors. The LF), coupled to the phase-frequency detector, filters the phase and frequency errors to generate a control voltage. The VCO, coupled to the loop filter, generates a VCO output signal according to the control voltage. The 3-stage frequency divider, coupled to the voltage controlled oscillator, divides the frequency of the VCO output signal 3 times to generate the feedback signal.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC +1
Automatic frequency control communication system
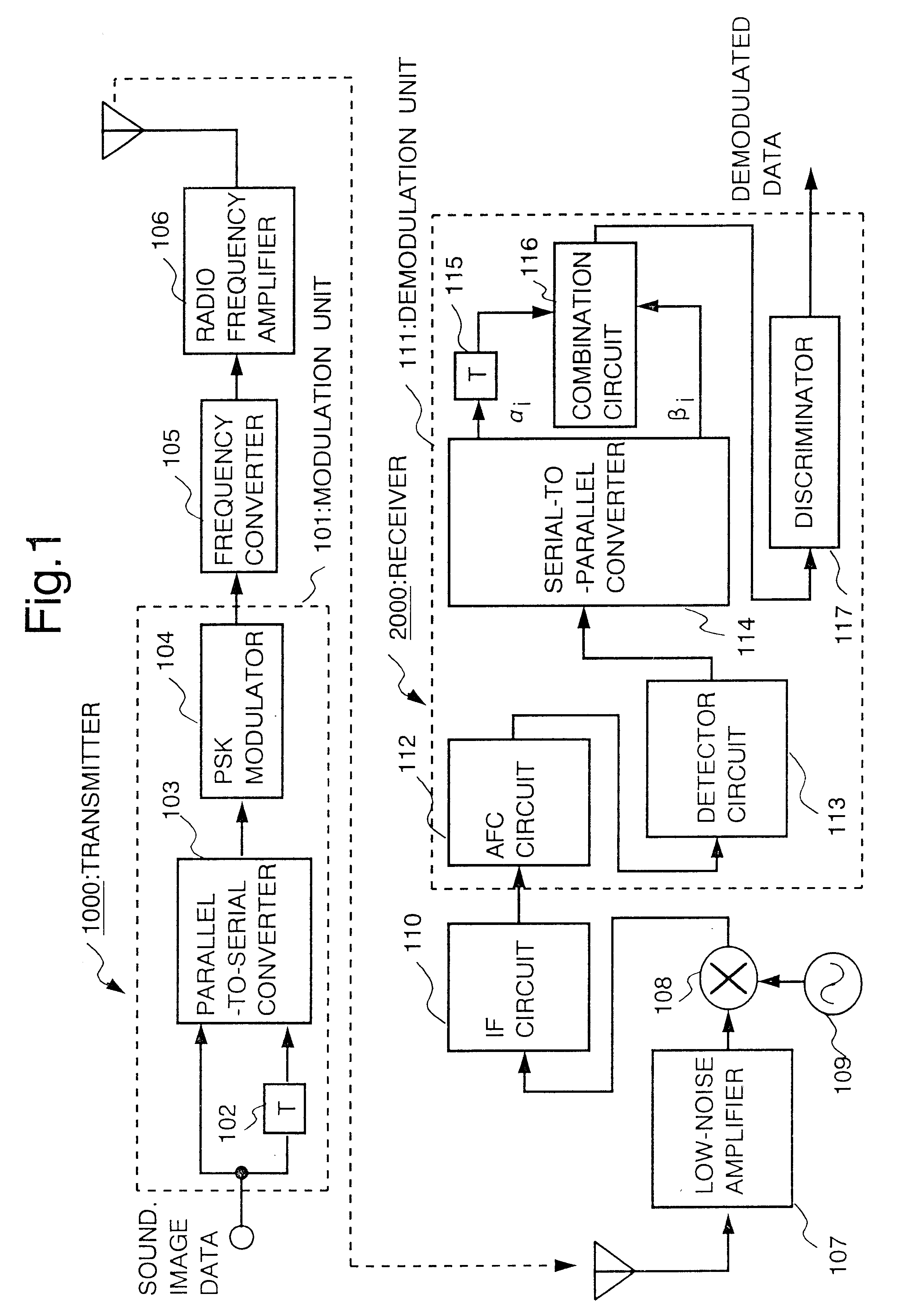
InactiveUS6456672B1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemIntegrator
In a communication system using the time diversity transmission scheme, the communication system provided with the stable automatic frequency control circuit with the wide frequency pull-in range and under low CN ratio transmission is achieved by removing the modulation phase from the received data through the application of the data correlation of the time diversity. The frequency offset in the received signal is compensated as the phase rotator rotates the phase of the received signal, the phase converter converts the phase rotator output into a phase, the serial-to-parallel converter converts the phase converter outputs into serial-to-parallel sequence, the delay units gives a delay to the serial-to-parallel converter output, the phase adder adds the serial-to-parallel converter output to the delay unit output, the multiplier multiplies the phase adder output by a certain value, the integrator integrates the multiplier output, another integrator integrates the integrator output, and the phase rotator controls the phase of the received signal based on the other integrator output.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
PLL circuit including a voltage controlled oscillator and a method for controlling a voltage controlled oscillator
InactiveUS6853257B2Angle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlSwitching signalCarrier signal
A voltage controlled oscillator having a wide oscillation frequency band, desirable carrier-noise characteristic, and desirable linearity of the oscillation frequency relative to a control voltage. The voltage controlled oscillator includes an oscillation unit and a control unit. The oscillation unit generates an output signal having an oscillation frequency corresponding to the control voltage in one of a plurality of oscillation frequency bands. The oscillation unit includes a switching unit for selecting one of the plurality of oscillation frequency bands in accordance with a switching signal. The control unit generates the switching signal in accordance with the control voltage.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
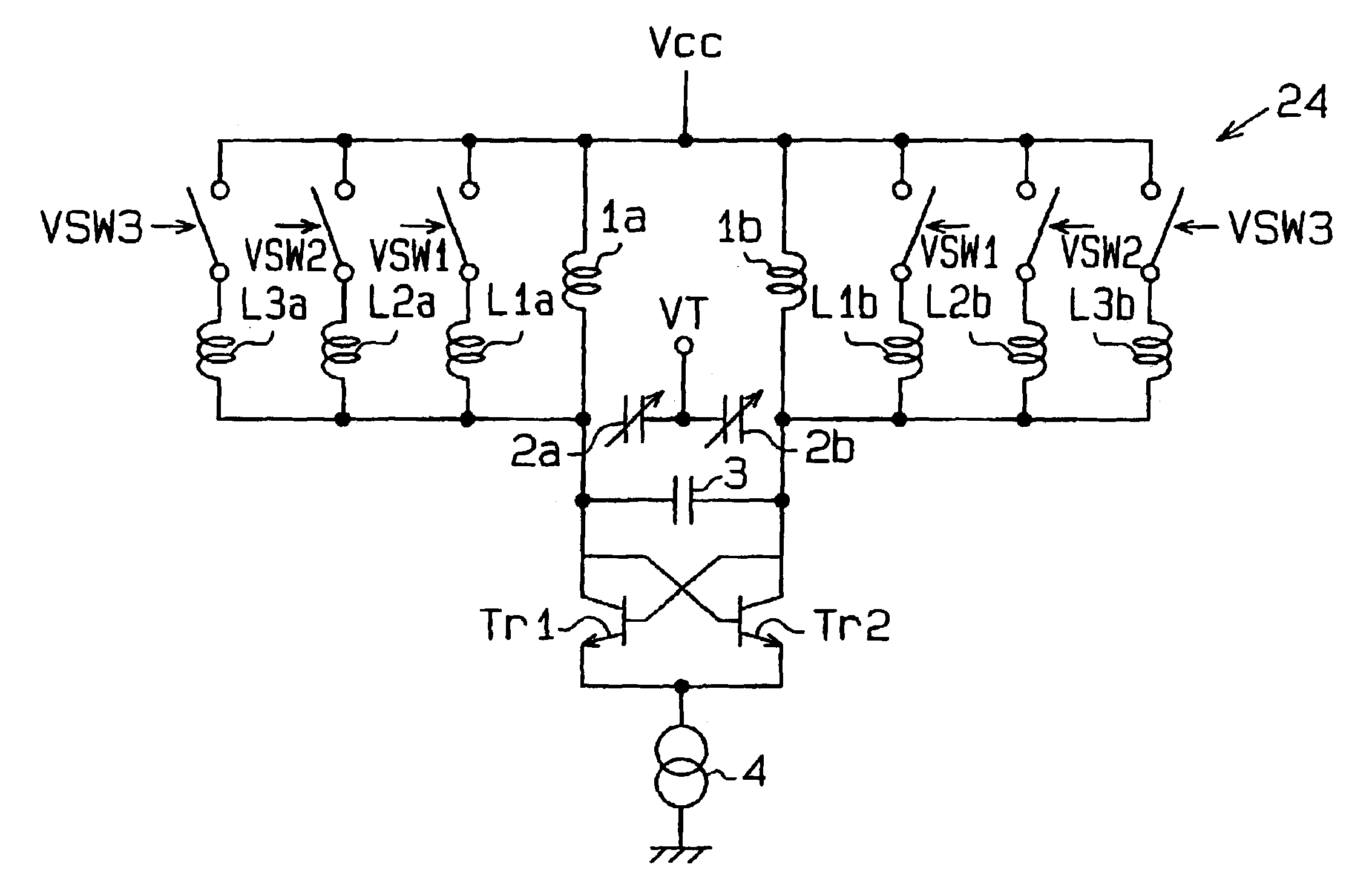
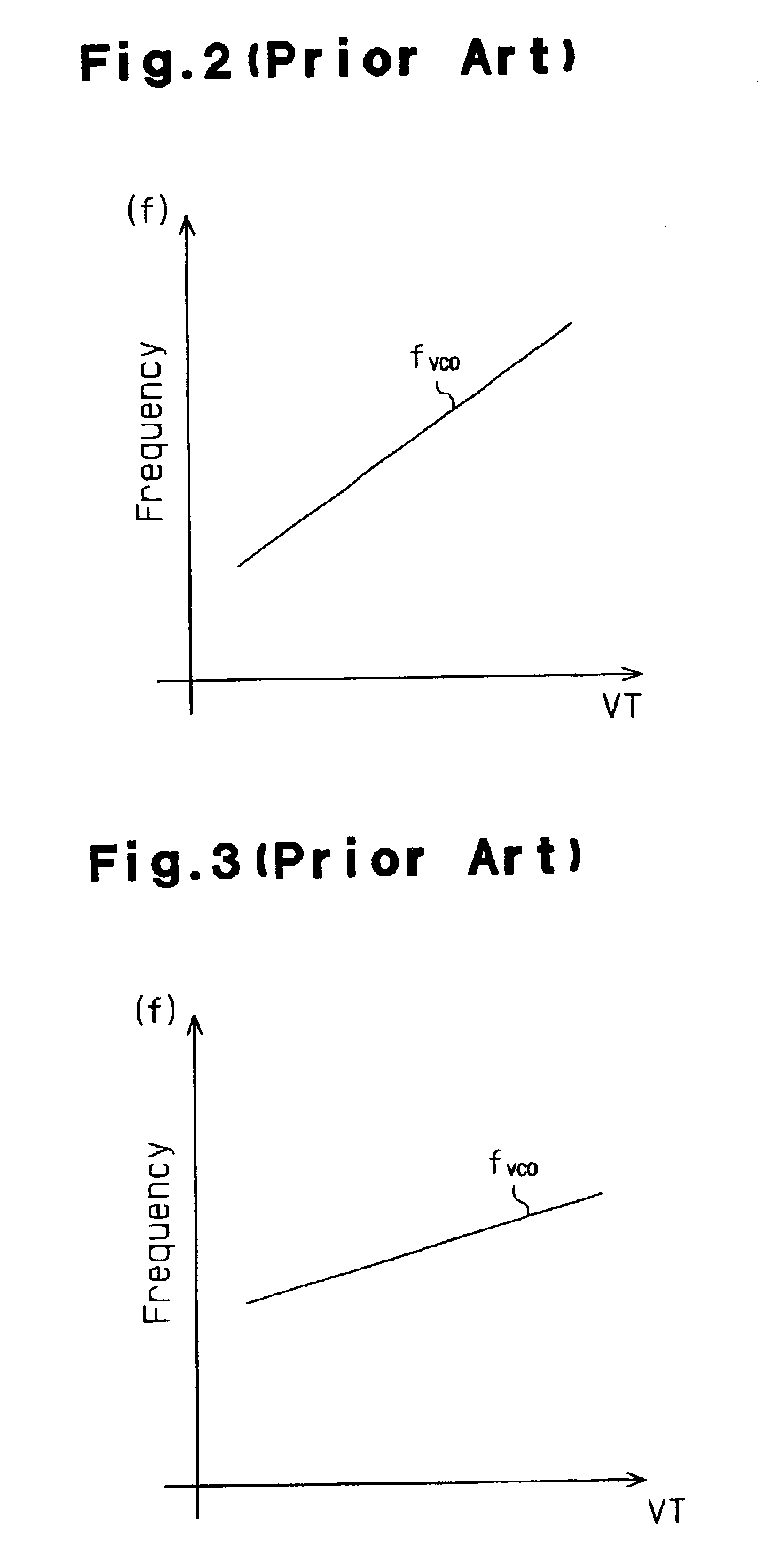
Variable frequency oscillator circuit
InactiveUS6255913B1Reduce inductanceIncrease working frequencyAngle modulation by variable impedenceContinuous tuning detailsInductorEngineering
A variable frequency oscillator (VFO) circuit having an increased frequency tuning range to selectively obtain operating frequencies above and below a set frequency. The circuit includes a tank inductor connected in parallel with a tank capacitor for primarily defining the set oscillating frequency of the VFO circuit. A switchable capacitor is included for selectively providing a predetermined step-wise decrease of the oscillating frequency to a frequency value below the set frequency of the circuit, and a varactor is included for accommodating selective tuning of the oscillating frequency within a range of frequency values below the set frequency. The inventive circuit selectively includes a switchable inductance element which is selectively electromagnetically coupled to the tank inductor to decrease the overall inductance value of the VFO circuit and, thereby, selectively increase the oscillating frequency above the set frequency value.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
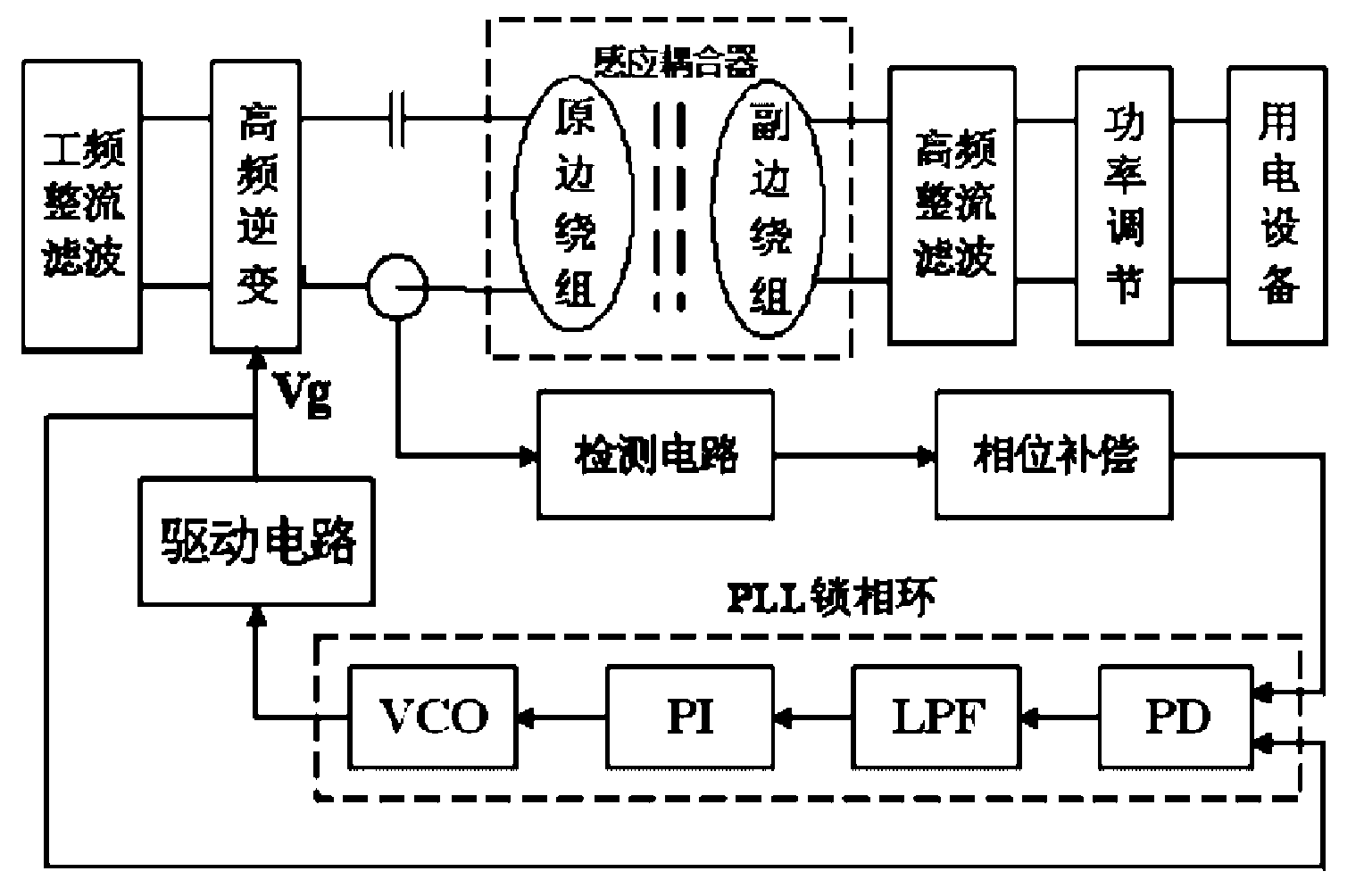
Self-adapting resonance control method for transmitting non-contact electric energy
InactiveCN101557227AGuaranteed separation effectPulse automatic controlDc-dc conversionPhase differenceTransmission technology
The invention discloses a self-adapting resonance control method for transmitting non-contact electric energy, which is characterized by obtaining a phase difference by detecting and calculating the voltage and current outputted by a non-contact electric energy transmitting system contravariant mechanism, and adjusting the driving frequency of the inverter by outputting the electric energy to a PI adjustor and an oscillating element. After a transient state process, the phase difference of the voltage and current outputted by the inverter is zero, thus achieving self-adapting resonance control of circuits. The method guarantees separability between the receiving mechanism and the transmitting mechanism of the system only by detecting the voltage and current outputted by the contravariant mechanism, with the self-adapting resonance control function completely achieved by hardware circuits, while complicated control algorithm is not required. The method not only has self-adapting control capability on load change, but also has adjustment actions to the parameter variations of all the components after the output of the contravariant mechanism; besides, the method has the advantages of guaranteeing the system always works under a resonance condition, ensuring the output power and transmission efficiency reach the maximum value, and promoting the practicability process of the transmission technology of the non-contact electric energy.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Wireless communication receiver that determines frequency offset
InactiveUS6952570B2Improve transmission efficiencyAccurate frequencyCarrier regulationAutomatic frequency control detailsSignal onEngineering
A frequency offset correction value estimation section (21) receives a signal including a predetermined fixed pattern from a transmission side, thereafter, selects a combination of fixed patterns used in a process of estimating a frequency offset is selected depending on the state of a channel, and an estimation result of the frequency offset calculated by the combination of the fixed patterns is output as a correction value of a determined frequency offset. A frequency offset correction section (22) receives the received signal obtained after the correction is performed for correcting a frequency offset of the received signal on the basis of the correction value, and an equalizer (23) demodulates the received signal by using a predetermined algorithm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
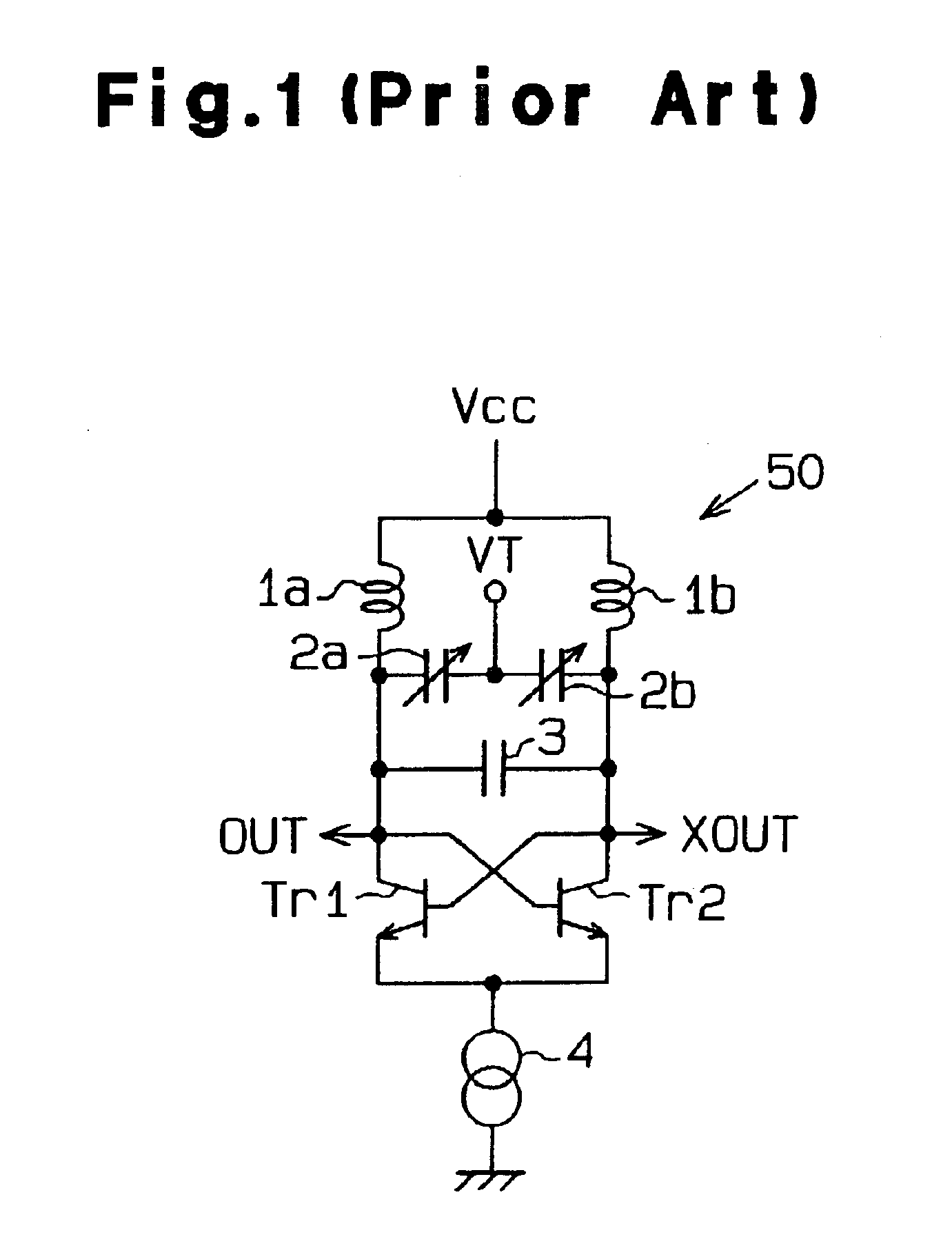
Voltage-controlled oscillator with LC resonant circuit
InactiveUS6861913B1Pulse automatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhase noiseLc resonant circuit
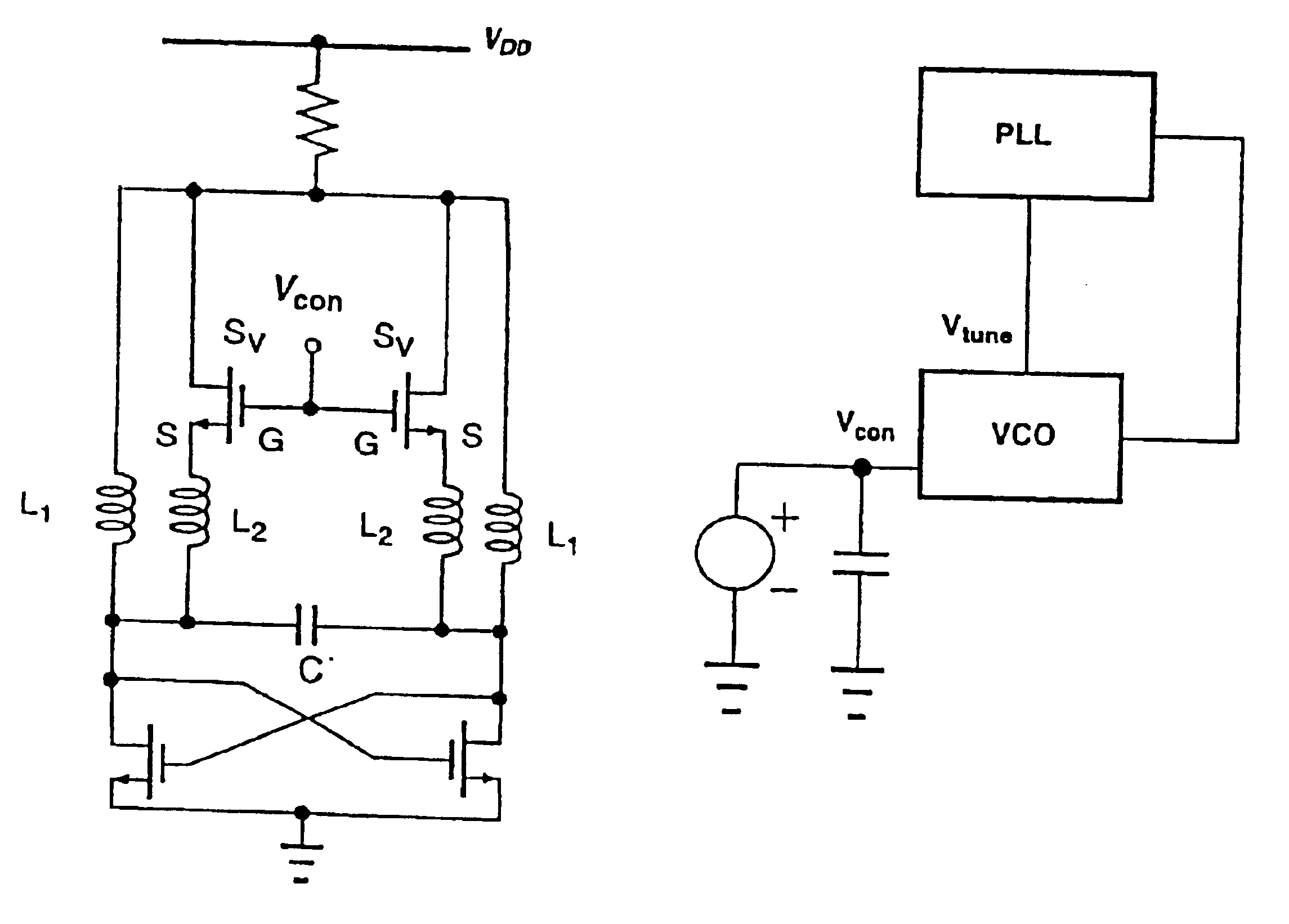
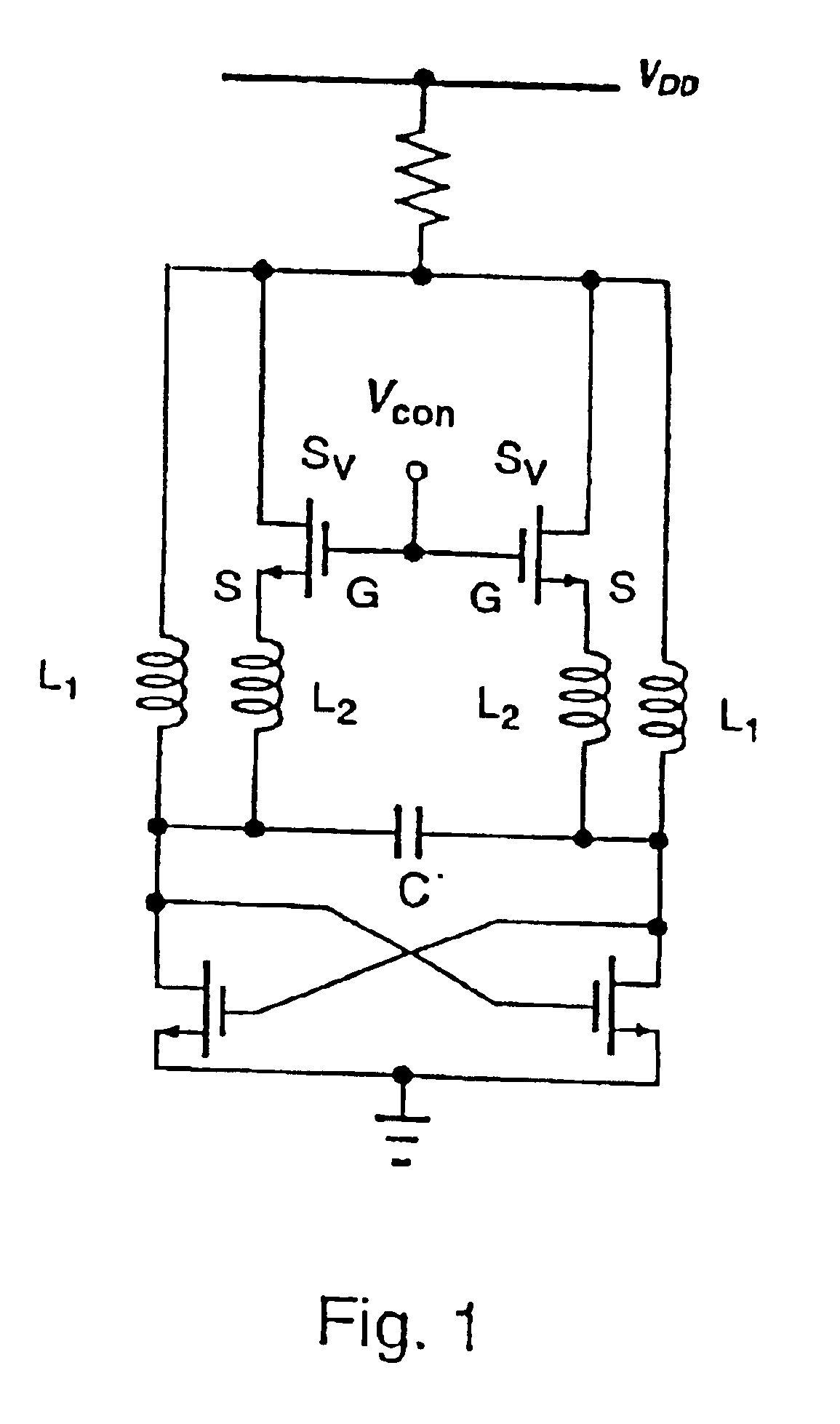
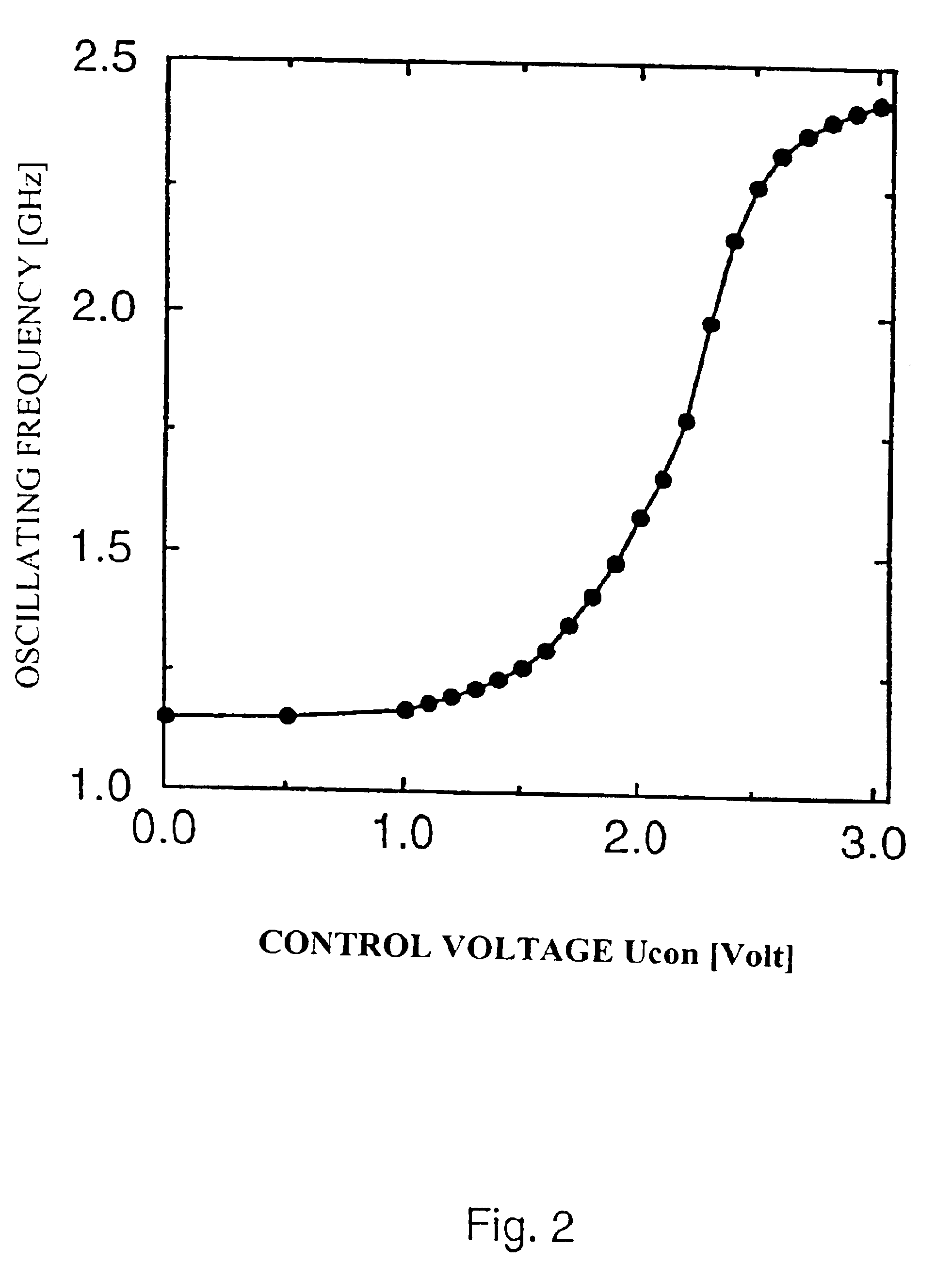
A voltage-controlled oscillator device with an LC-resonant circuit, in particular for implementing integrated voltage-controlled oscillators for the lower GHz range, is disclosed. The device achieves continuous frequency tunability in a wide range in particular with a low level of phase noise and phase jitter. In the voltage-controlled oscillator, a second inductor can be periodically switched in parallel and / or in series with at least one first inductor of the LC-resonant circuit by way of a switching means actuated with the oscillator frequency. A control input of the switching means is connected to a variable dc voltage. In that respect the relationship of the duration of the conducting state and the duration of the non-conducting state of the switching means is variable within an oscillation period of the oscillator in dependence on the value of the control voltage. In accordance with the relationship of the duration of the conducting state and the duration of the non-conducting state of the switching means within an oscillation period of the oscillator the time-averaged effective inductance is variable in dependence on the value of the control voltage.
Owner:IHP GMBH INNOVATIONS FOR HIGH PERFORMANCE MICROELECTRONICS LEIBNIZ INST FUR INNOVATIVE
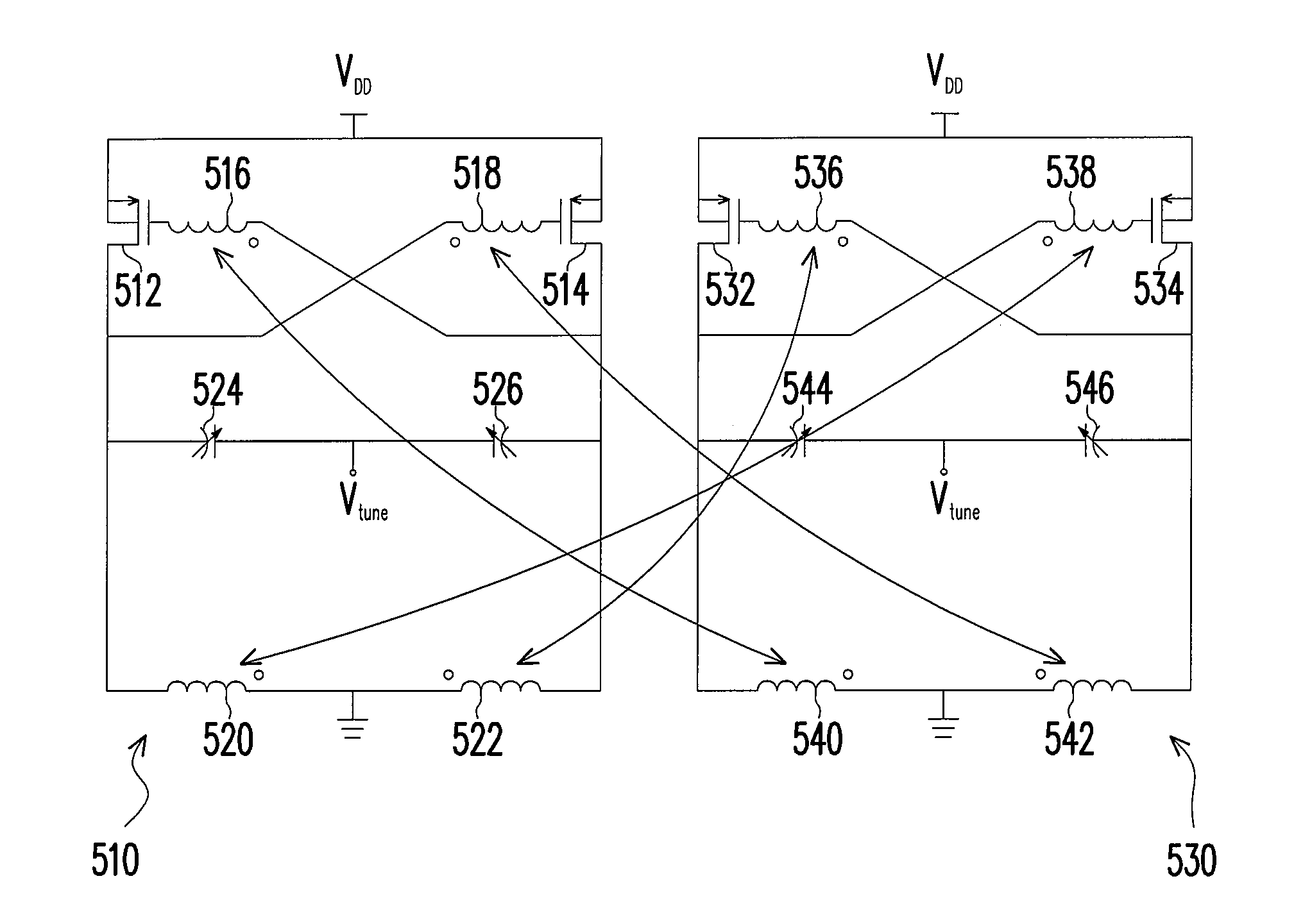
Transformer-based VCO for both phase noise and tuning range improvement in bipolar technology
ActiveUS20060181355A1Improve noiseIncrease rangeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhase noiseEngineering
A silicon bipolar VCO implementing a double-coupled transformer is disclosed. The VCO circuit, which is suitable in the field of integrated RF circuits, has been integrated into a universal LNB having a down-converter block and PLL merged into a single die and implemented in silicon bipolar technology. The integrated transformer is formed by three turns of stacked metal layers, where the topmost metal layer is employed for the resonator inductance. The VCO is missing conventional biasing resistors and decoupling capacitors, thus improving phase noise and tuning range performance.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Method and system for frequency feedback adjustment in digital receivers
InactiveUS20050181729A1Modulated-carrier systemsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionTransceiverEngineering
In RF transceivers, a method and a system for a frequency feedback adjustment in digital receivers are provided. A DC offset may result from the difference in frequencies between an RF transmitter and an RF receiver. An adjustment of the receiver's frequency may be implemented after synchronization occurs and may be performed by utilizing the Forward Error Correction (FEC) repetition rate in a header of a Bluetooth packet. The adjustment may be performed when the frequency difference exceeds a threshold value. In another aspect, adjusting the frequency of the RF receiver may be performed by modifying and / or changing a phase locked loop (PLL) trimmer register. This approach may allow an RF receiver to operate, in some instances, without the need for an equalizer. In this regard, the power consumed by the RF receiver may be minimized and / or the overall cost of the RF receiver may be reduced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Channel acquisition processing for a television receiver
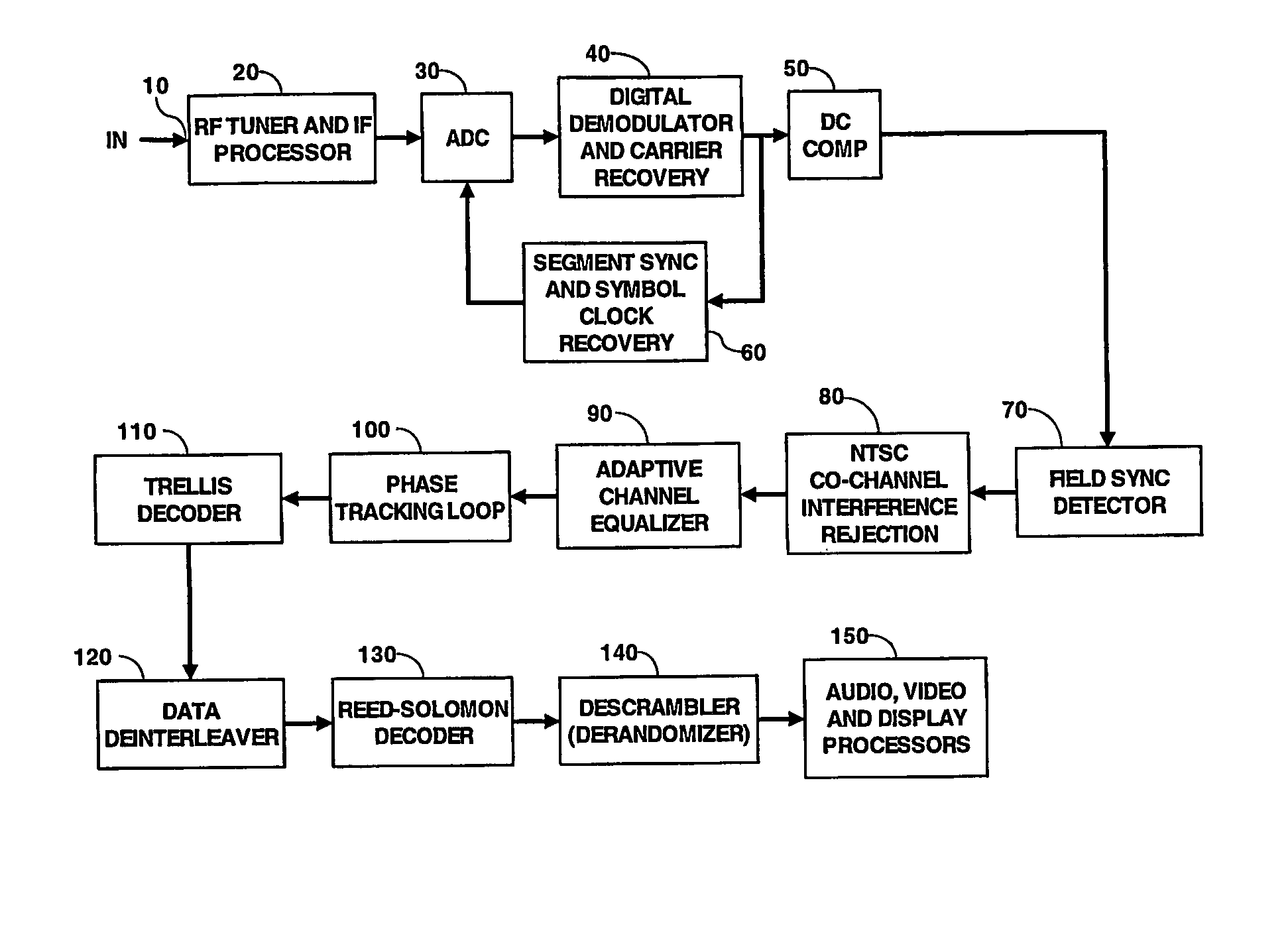
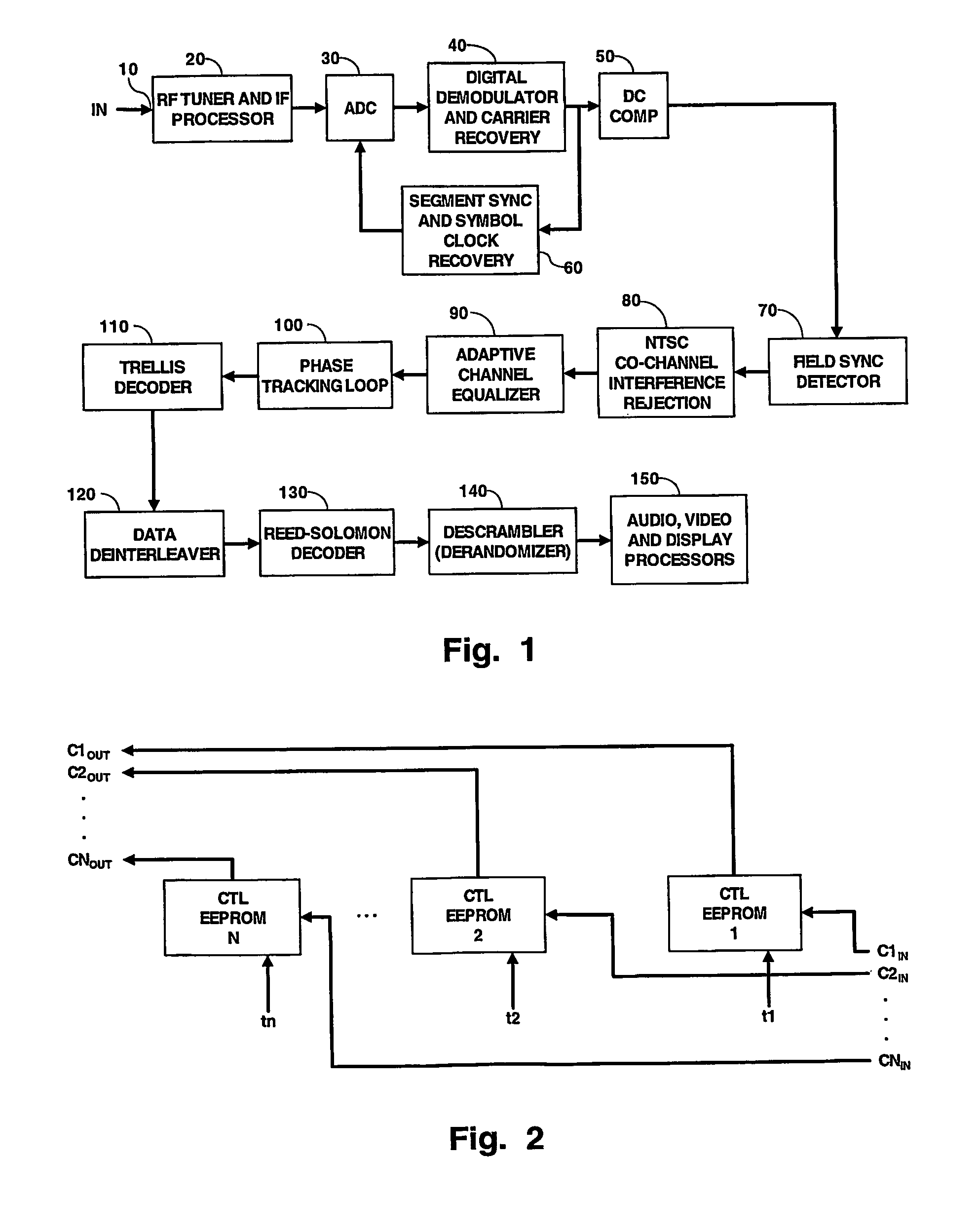
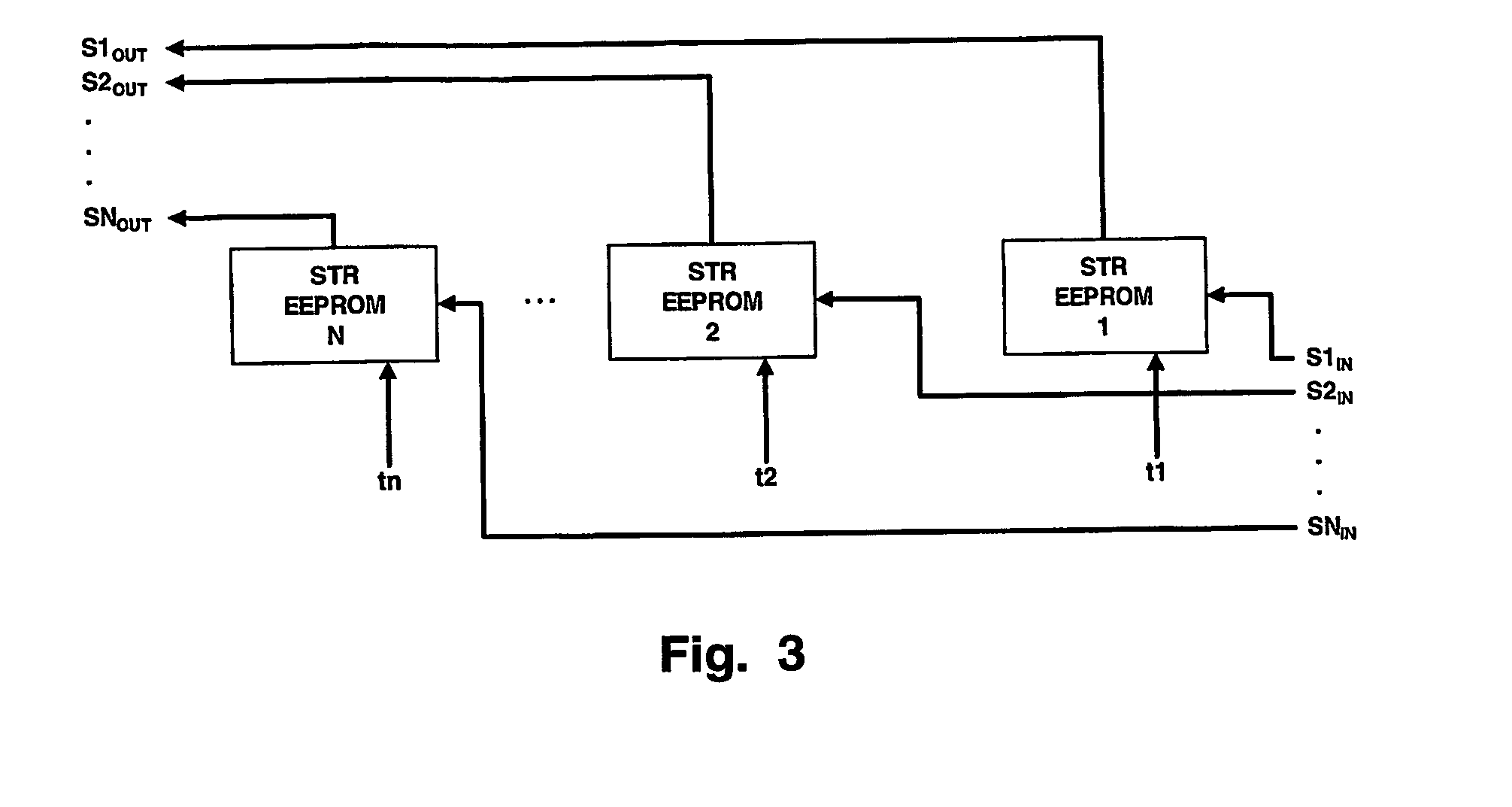
ActiveUS7230654B2Less timeSpeed up channel acquisition timeTelevision system detailsCarrier regulationTelevision receiversCarrier signal
Channel acquisition in a digital television signal receiver is improved by determining the carrier tracking loop frequency offsets and the symbol timing recovery offsets for each channel in the television receiver. Offsets are stored in respective EEPROMs for each channel. When a channel is to be acquired in the TV receiver the tune command will be applied to the appropriate EEPROMs and the respective values are conveyed to the VSB demodulator to start acquisition of the channel.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Enhanced GPS receiver utilizing wireless infrastructure
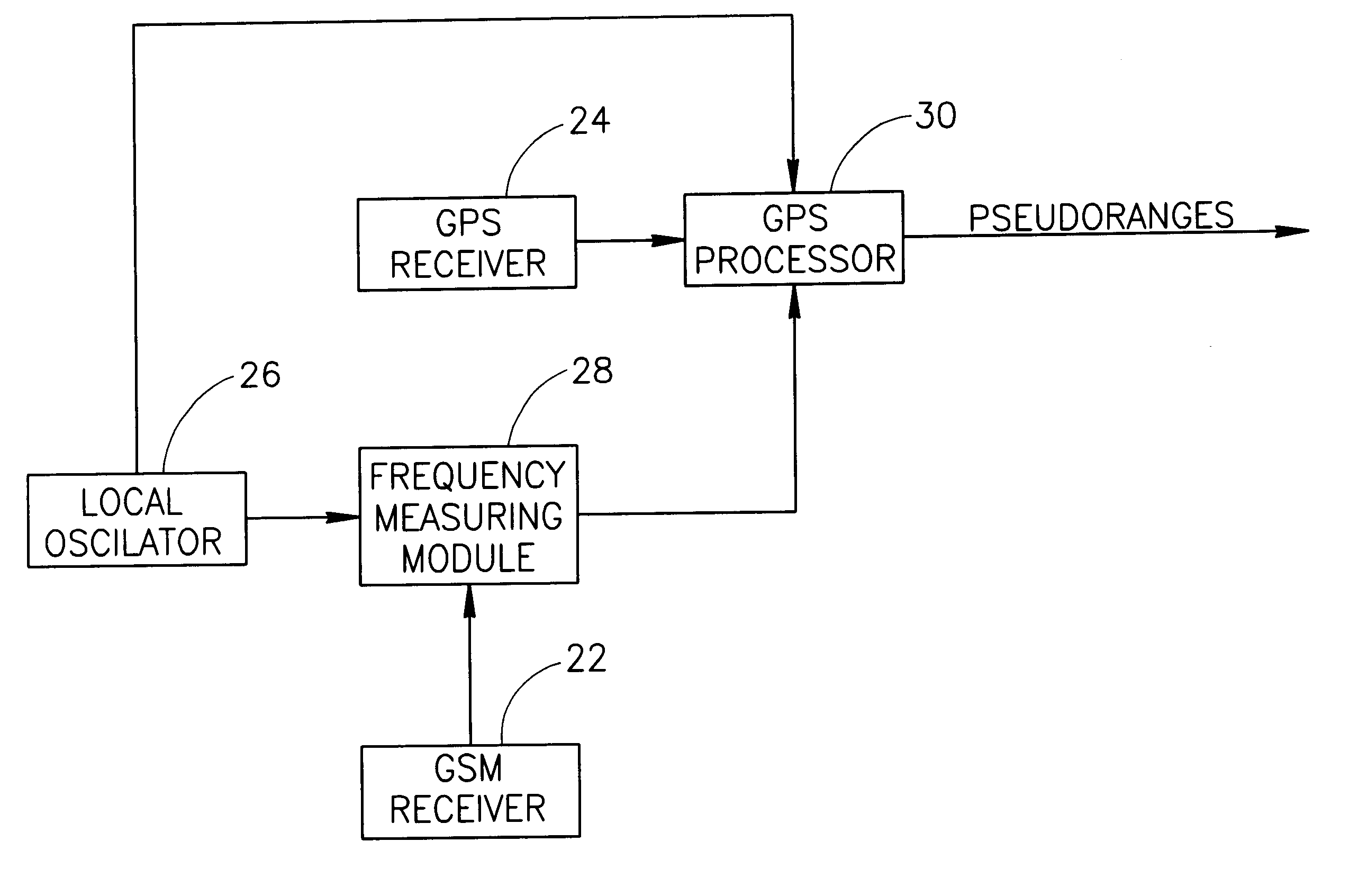
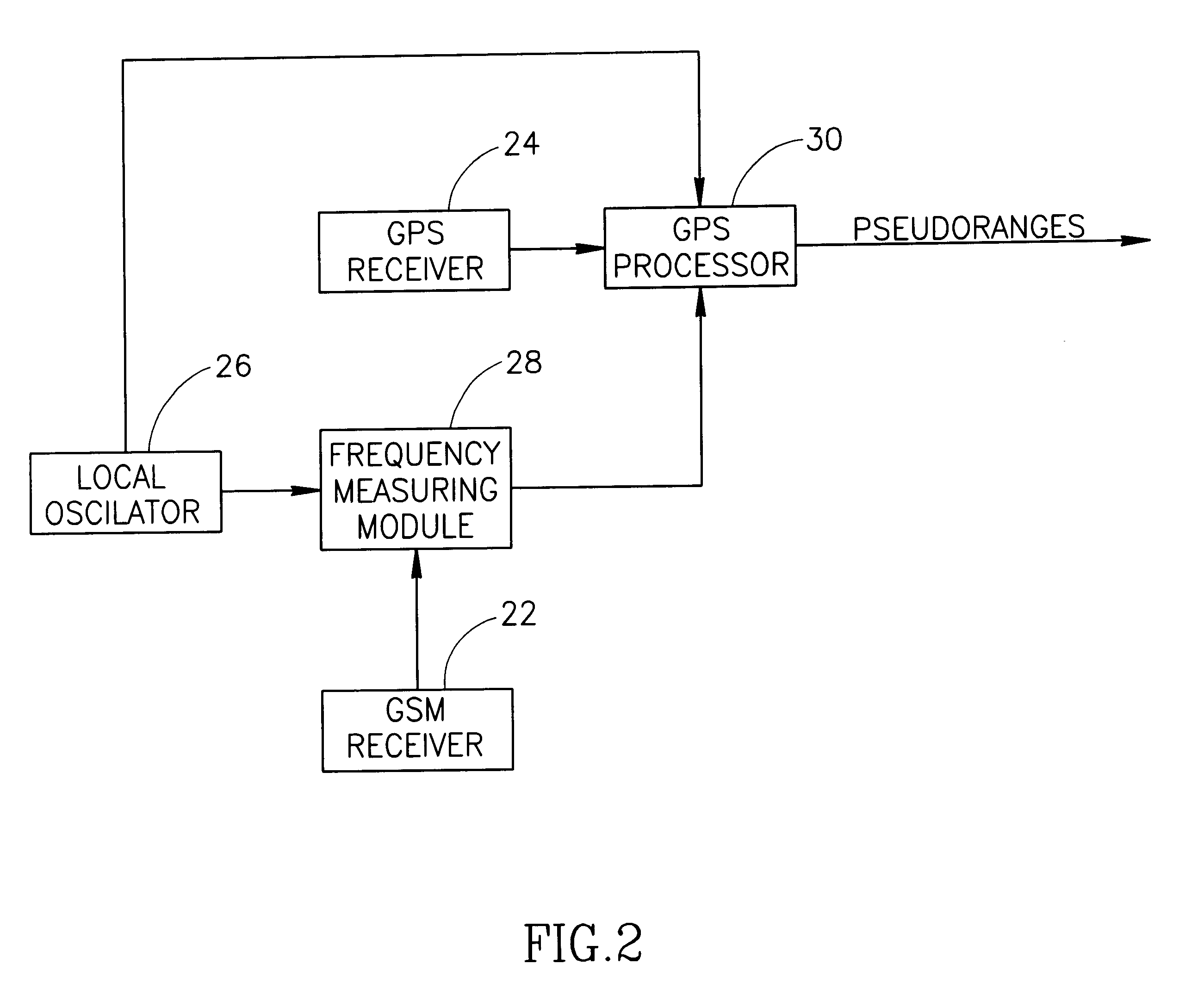
InactiveUS6839547B2Improve accuracyShorten the timeActive radio relay systemsAutomatic frequency control detailsDigital numberGps receiver
A locator using Navstar constellation signals for determining geographical location of a mobile receiver. The locator is integrated with a mobile unit of a cellular network, which derives its reference frequency from a local oscillator (26). A frequency measuring module (28) counts the number of digital numbers derived from the local oscillator passing between two consecutive time-tagged indicators of the cellular network. The estimated frequency is calculated by dividing the number of digital numbers by the nominal time interval (T0) between the indicators.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC +1
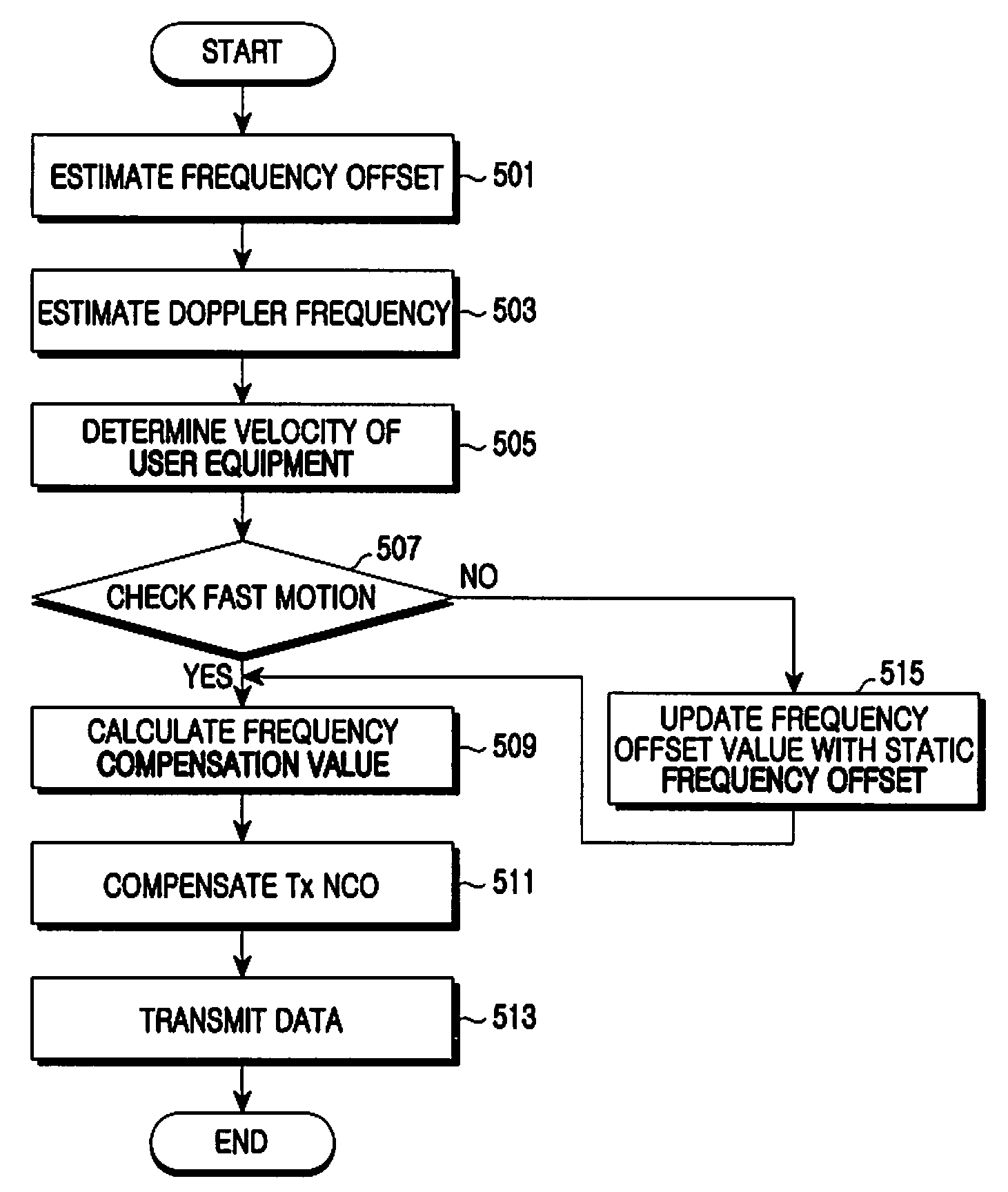
Apparatus and method for controlling frequency in mobile communication system
ActiveUS20090197535A1Reduce distractionsEcho effect reductionAutomatic frequency control detailsCommunications systemMobile communication systems
An apparatus and a method for mitigating interference between uplink signals of a user equipment in a mobile communication system are provided. The apparatus includes a frequency regulator for, when fast movement of a user equipment is confirmed, changing a transmit frequency by calculating a frequency offset compensation value which compensates for a frequency required for a transmit frequency band.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
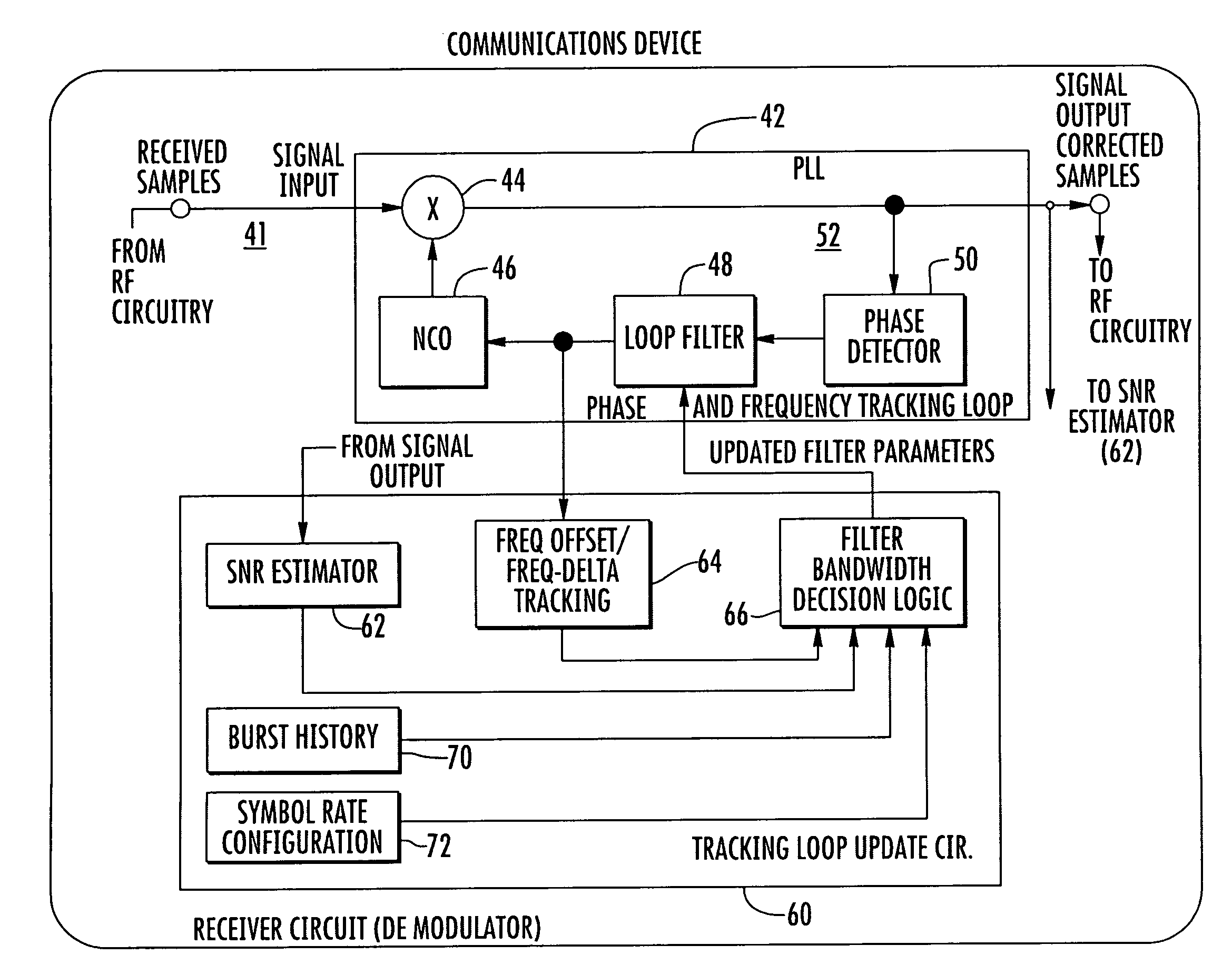
Communications device using measured signal-to-noise ratio to adjust phase and frequency tracking
InactiveUS20100067619A1Automatic frequency control detailsCarrier regulationLoop filterSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A communications device includes a phase and frequency tracking loop having a signal input and adjustable loop filter that establishes a predetermined tracking loop bandwidth for samples of communication signals received at the signal input and processed within the tracking loop. A tracking loop update circuit updates the loop filter operating parameters. It is operative with the loop filter for increasing or decreasing the tracking loop bandwidth of the phase and frequency tracking loop based on the measured signal-to-noise ratio in the received samples of communication signals at the signal output by the tracking loop and on the known or measured apriori tracking capabilities of demodulator based on the symbol rate of communication signal.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
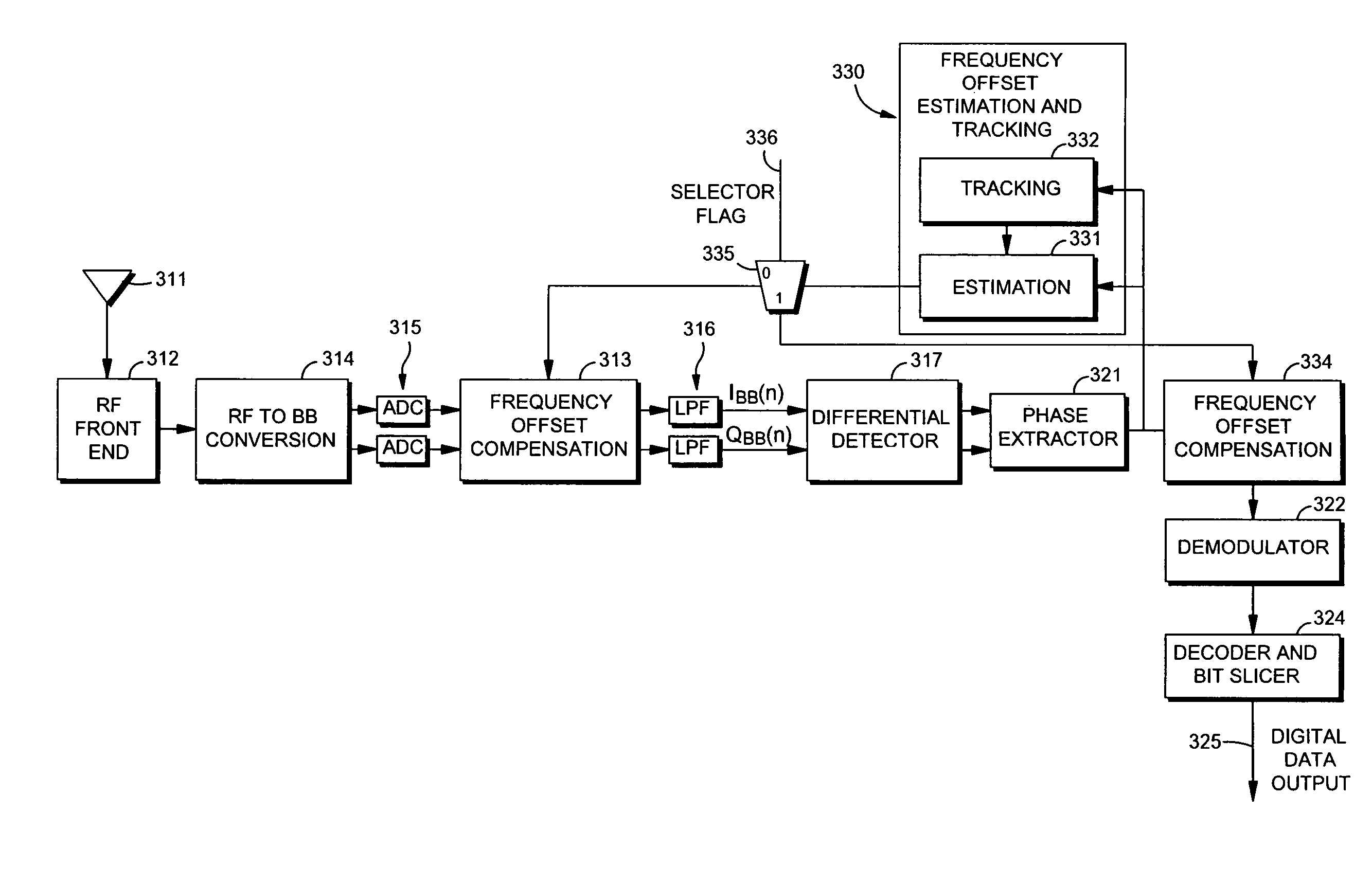
Differential receiver with frequency offset compensation
ActiveUS7809083B1Wider estimation rangeArea consumption reducedAutomatic frequency control detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsEngineeringFrequency offset
A differential receiver which provides for estimation and tracking of frequency offset, together with compensation for the frequency offset. Estimation and tracking of the frequency offset is undertaken in the phase domain, which reduces computational complexity and allows frequency offset estimation and tracking to be accomplished by sharing already-existing components in the receiver. Compensation for the frequency offset can be performed either in the time domain, before differential detection, or in the phase domain, after demodulation, or can be made programmably selectable, for flexibility.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method for correcting Doppler frequency difference of high speed moving body
InactiveCN101378276AQuality assuranceAccurate correctionModulated-carrier systemsAutomatic frequency control detailsCommunication qualityCorrection method
The invention provides a high-speed moving body Doppler frequency difference correction method which comprises downward frequency difference correction and upward frequency difference correction; wherein, the downward frequency difference correction corrects the Doppler frequency difference of a carrier frequency signal by superposing a pilot signal generated by a standard VCO in a downward carrier frequency signal and detecting the frequency difference of the pilot signal at a mobile terminal; by detecting the frequency difference of the downward pilot signal and pre-superposing the Doppler frequency difference in the carrier frequency signal at the mobile terminal, the upward frequency difference correction corrects an upward signal g received at a fixed terminal due to Doppler frequency shift. The whole correction method evades the changes of an arrival angle and the speed of the mobile terminal, the correction is accurate and timely, and the communication quality is guaranteed to be stable and reliable.
Owner:泉州泽仕通科技有限公司
Method and system for frequency feedback adjustment in digital receivers
InactiveUS7599662B2Modulated-carrier systemsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionTransceiverEngineering
In RF transceivers, a method and a system for a frequency feedback adjustment in digital receivers are provided. A DC offset may result from the difference in frequencies between an RF transmitter and an RF receiver. An adjustment of the receiver's frequency may be implemented after synchronization occurs and may be performed by utilizing the Forward Error Correction (FEC) repetition rate in a header of a Bluetooth packet. The adjustment may be performed when the frequency difference exceeds a threshold value. In another aspect, adjusting the frequency of the RF receiver may be performed by modifying and / or changing a phase locked loop (PLL) trimmer register. This approach may allow an RF receiver to operate, in some instances, without the need for an equalizer. In this regard, the power consumed by the RF receiver may be minimized and / or the overall cost of the RF receiver may be reduced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
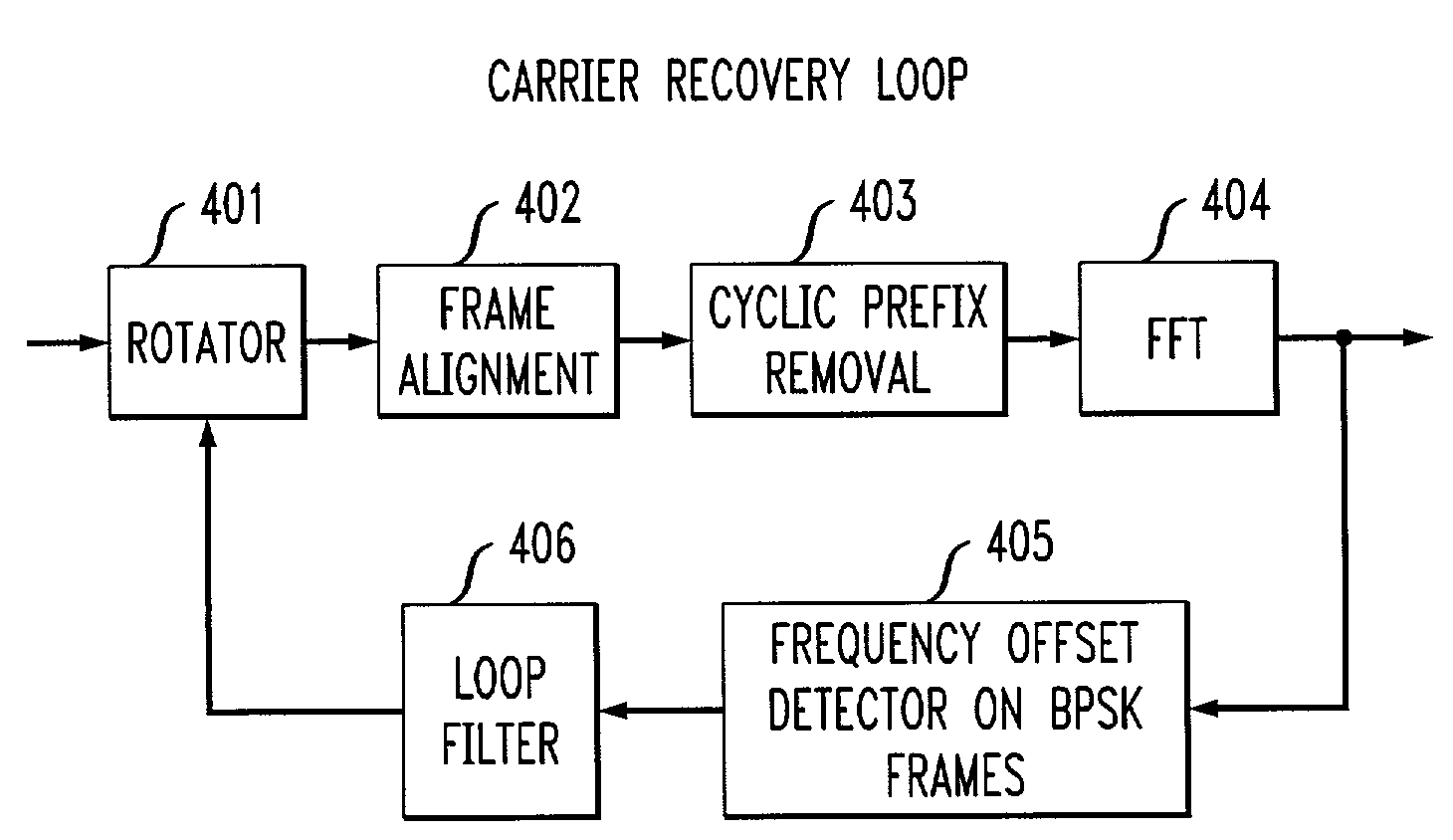
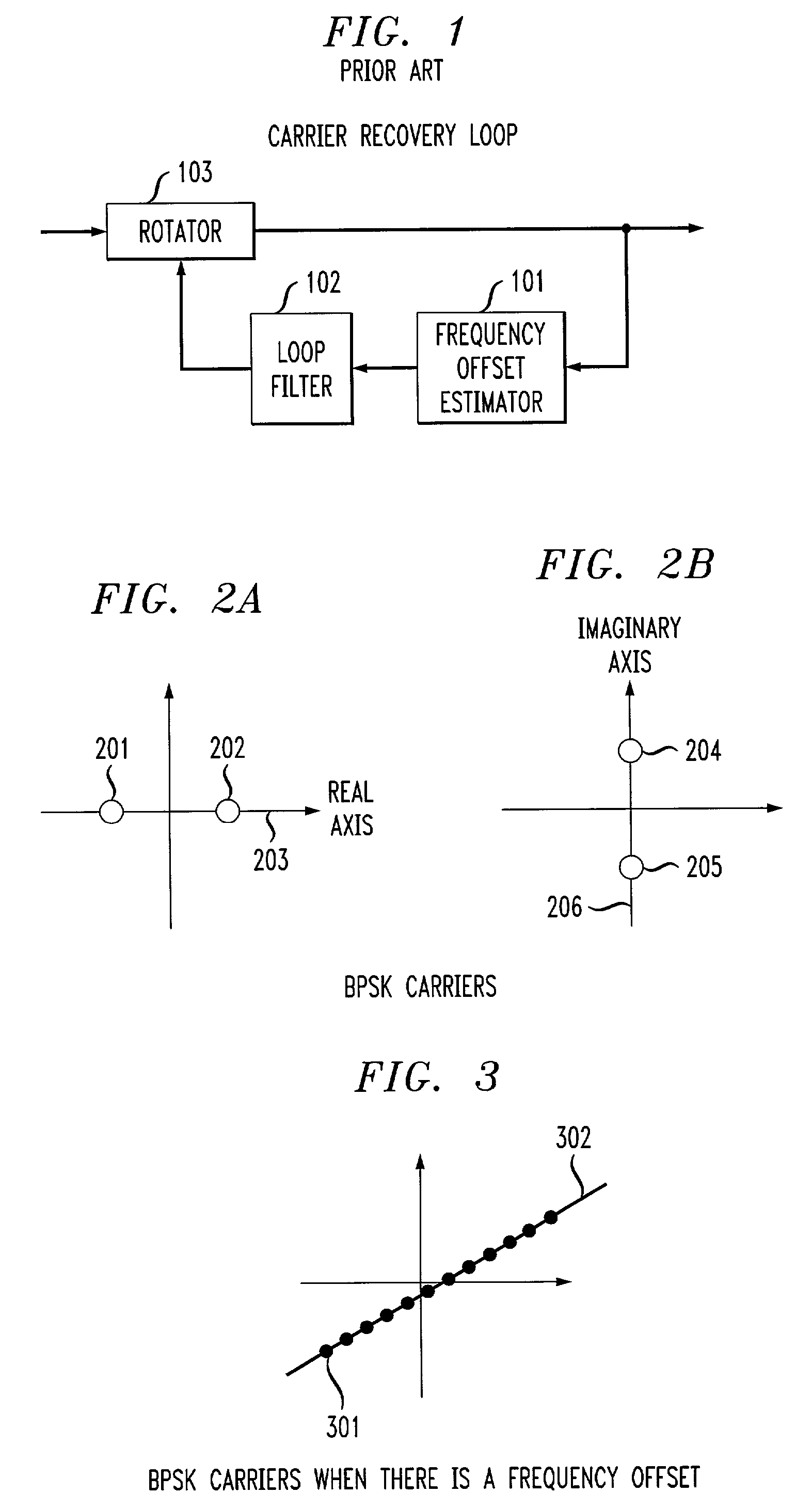
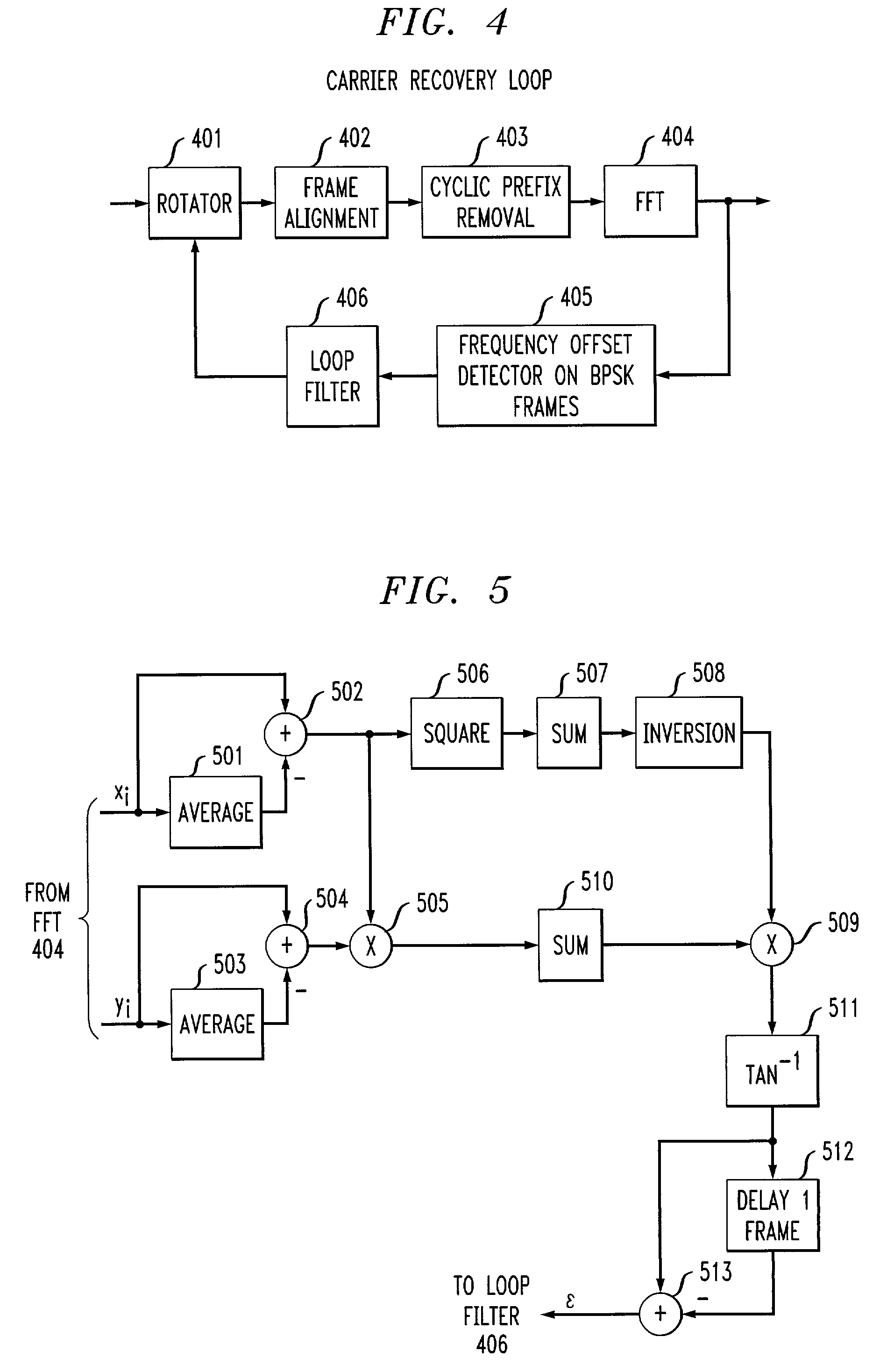
Carrier frequency offset estimator for OFDM systems
InactiveUS7266162B2Accurate estimateImprove performanceAutomatic frequency control detailsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationPhase-shift keyingCarrier frequency offset
A frequency offset estimator is employed that estimates the frequency offset in signal frames that include only binary Phase-Shift Keying (BPSK) carriers in OFDM systems. Specifically, the offset frequency estimator takes advantage of those OFDM systems in which some OFDM symbols only have carriers with either zero or the BPSK constellations. In many WLAN systems such as the system described in standard IEEE802.11a, transmission frames include only BPSK symbols, which are used for training and other services. By making use of these BPSK symbols in each frame, a very accurate estimate of frequency offset can be obtained. By advantageously employing the frequency offset estimator of this invention, a carrier recovery system can achieve high performance even under strong ISI and low SNR. In a specific embodiment of the invention, BPSK carriers spread to be on a line in a complex plane at an angle to the real axis. An estimate of the angle of the line including the BPSK carriers is then employed to obtain an estimate of the frequency offset.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
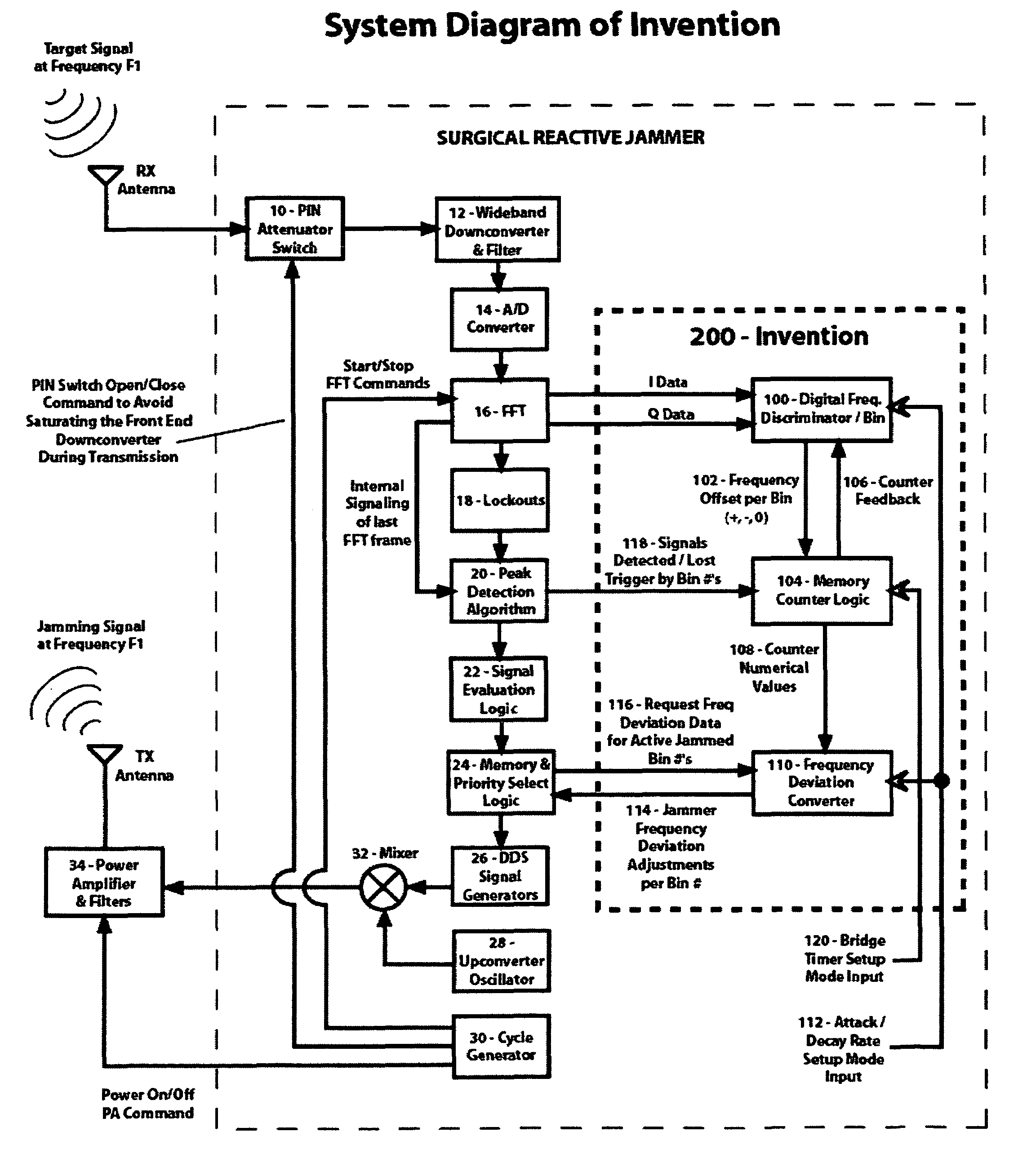
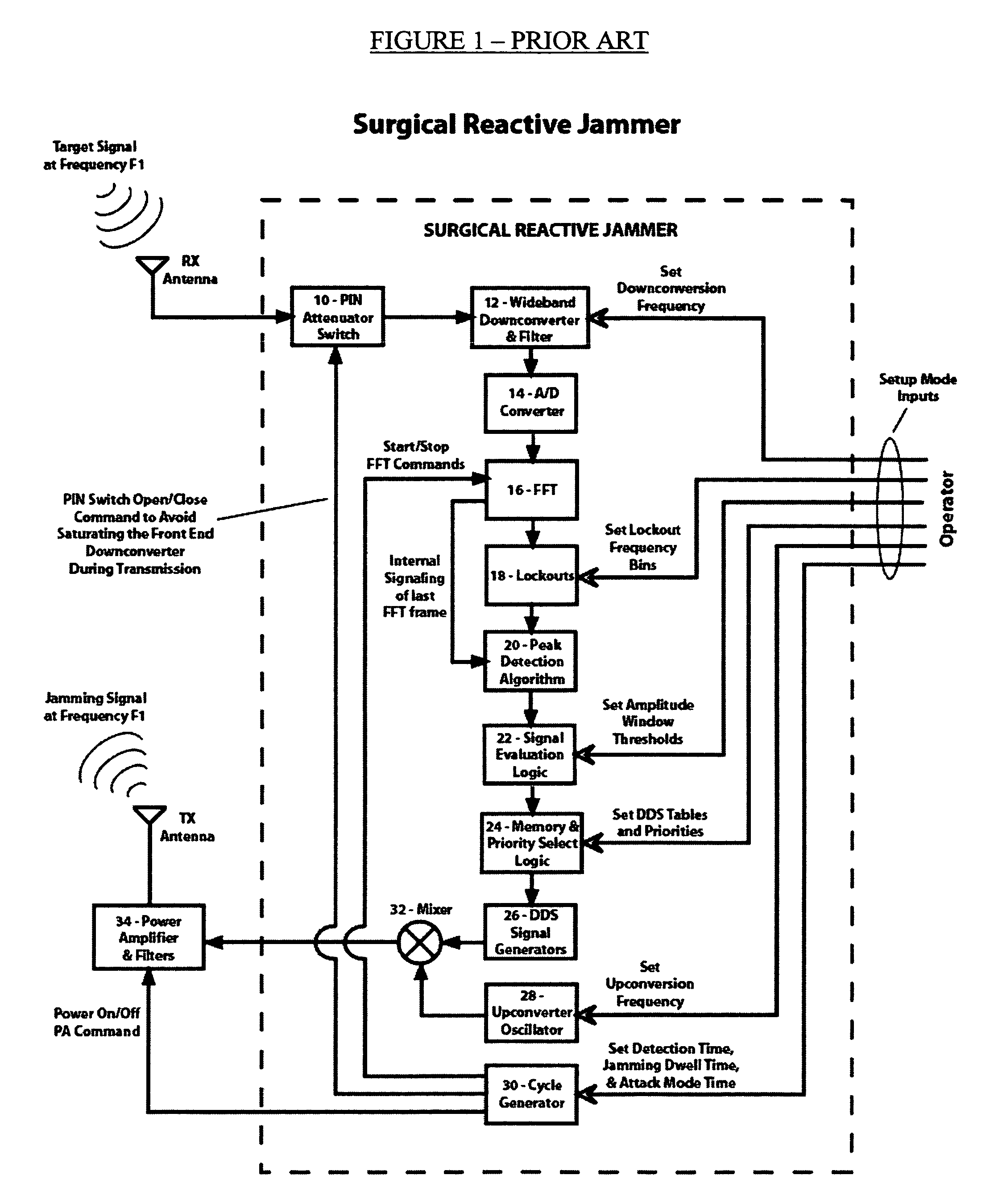
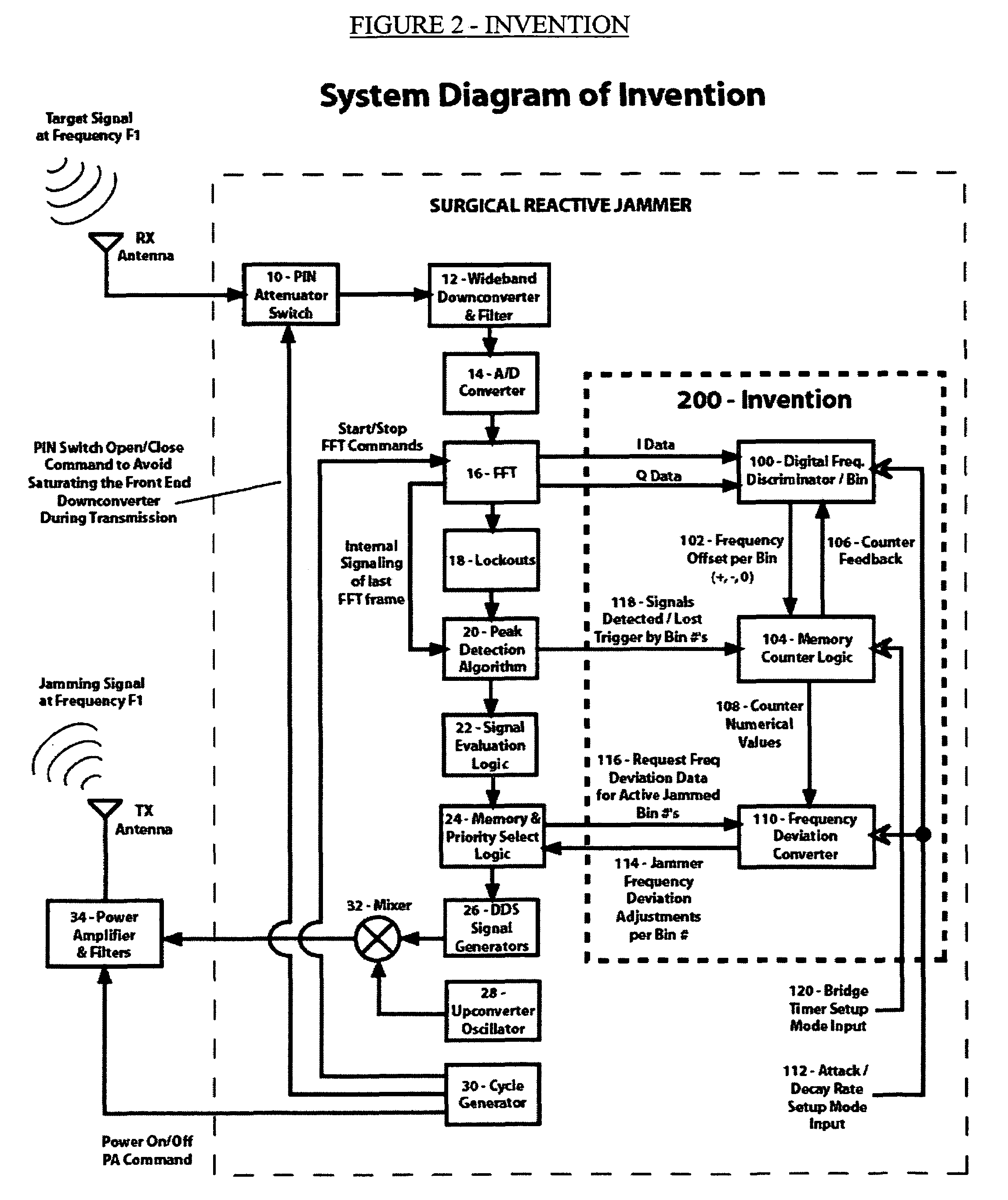
Method and apparatus for automatic jammer frequency control of surgical reactive jammers
InactiveUS7095779B2Improve efficiencyIncrease capacityWave based measurement systemsAutomatic frequency control detailsEnd systemEngineering
A Method and Apparatus for Automatic Jammer Frequency Control of Surgical Reactive Jammers is disclosed. The system and method to autonomously and selectively jam frequency-hopping signals in near real-time. The system has the ability to automatically detect short duration signals (such as those output from frequency hoppers), to automatically determine if detected signal(s) should be jammed, and subsequently to automatically and extremely quickly activate the jamming transmitter on the frequency-hopper transmitter's frequency. Furthermore, the system improves upon the FFT-based front-end system by incorporating a module that automatically and iteratively comparing the digital FFT results to the analog RF signal to the arrive at a total frequency offset between the FFT results and the analog signal so that the transmitted jamming signal will be more accurately applied on the desired or target frequency. Finally, the system provides a programmable user interface so that operators can set up the system to act autonomously as intended, such that operator intervention is unnecessary when the system is placed in jamming operation mode.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com