Patents
Literature
39results about How to "Minimizing adverse influence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
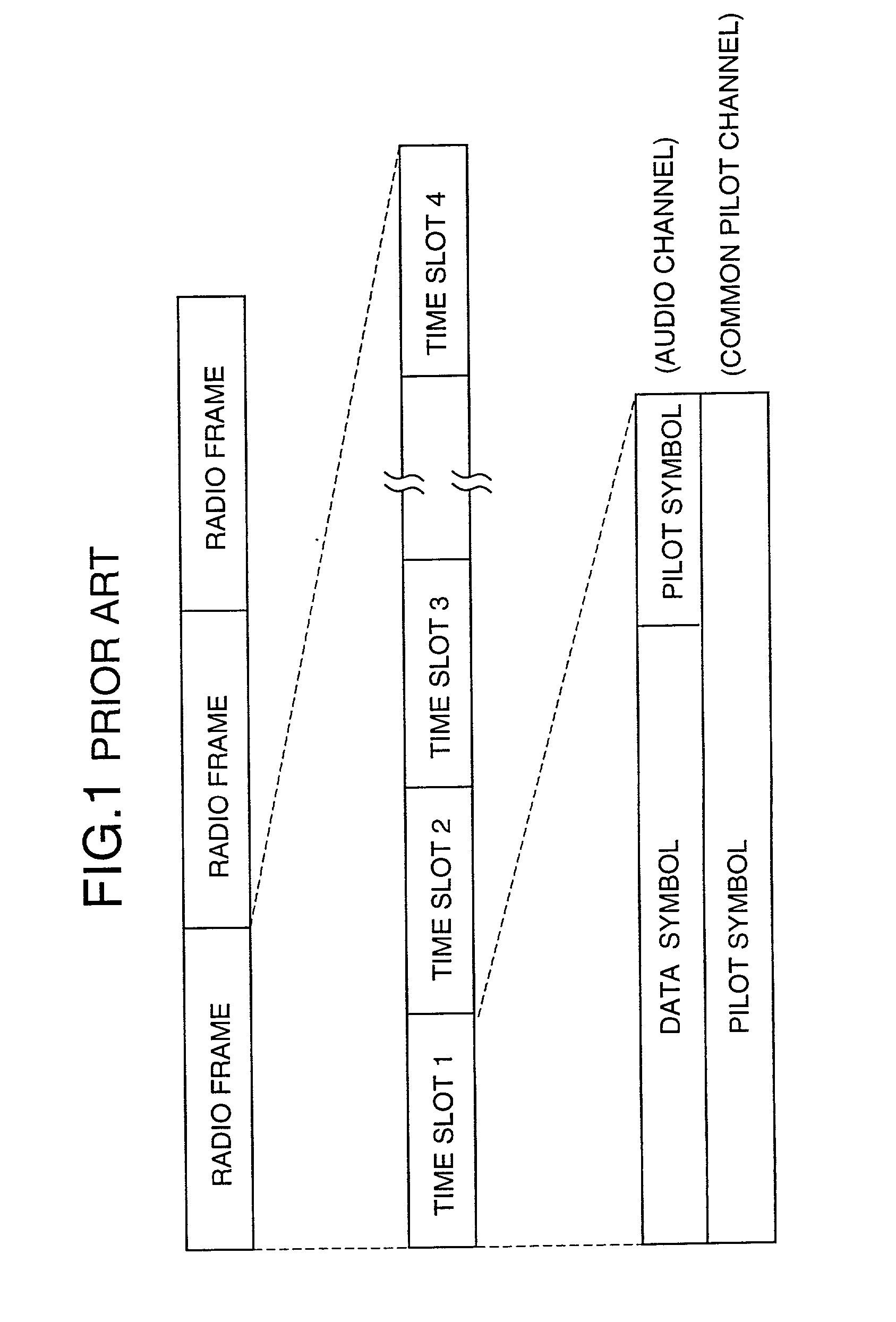
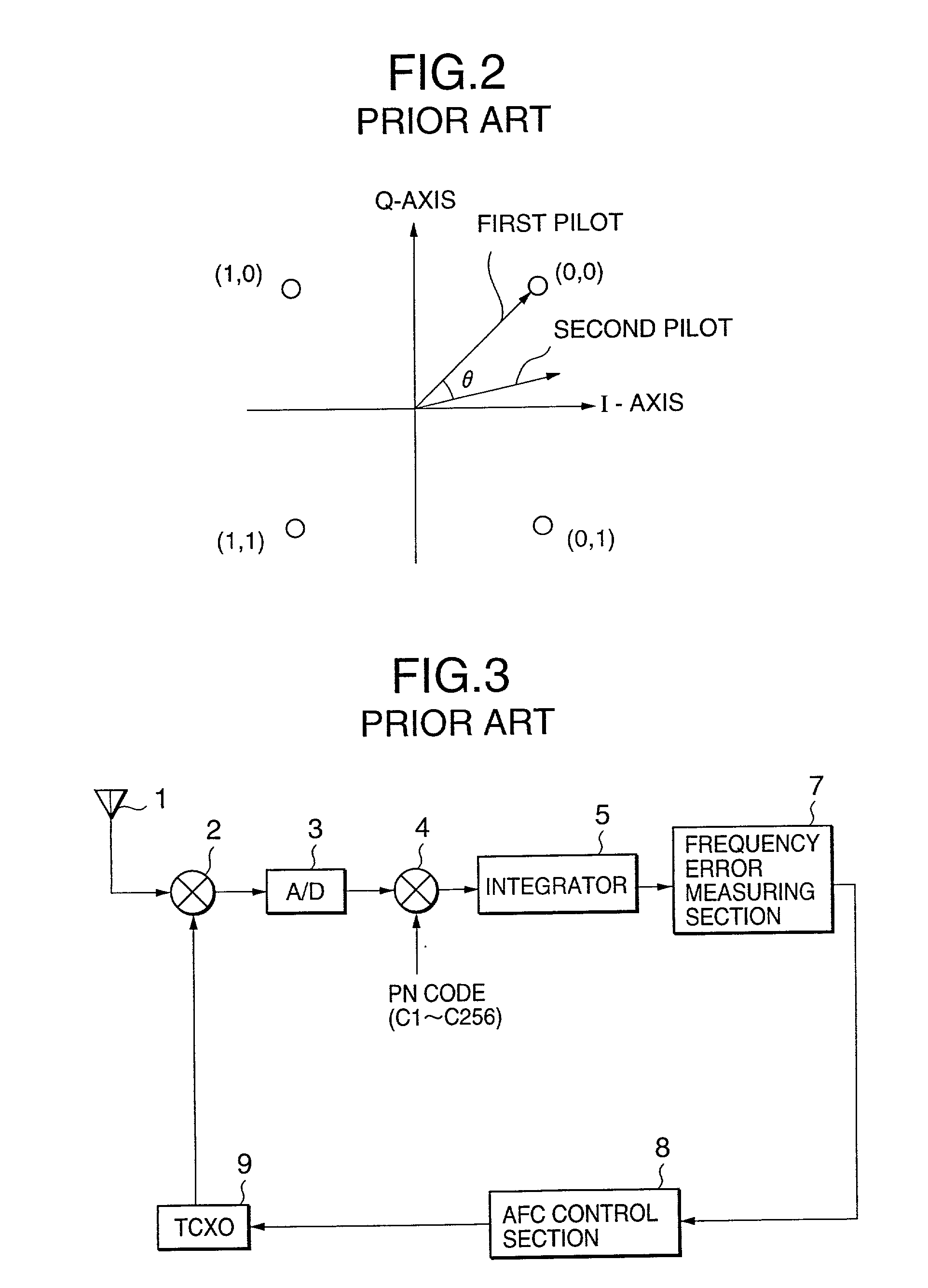
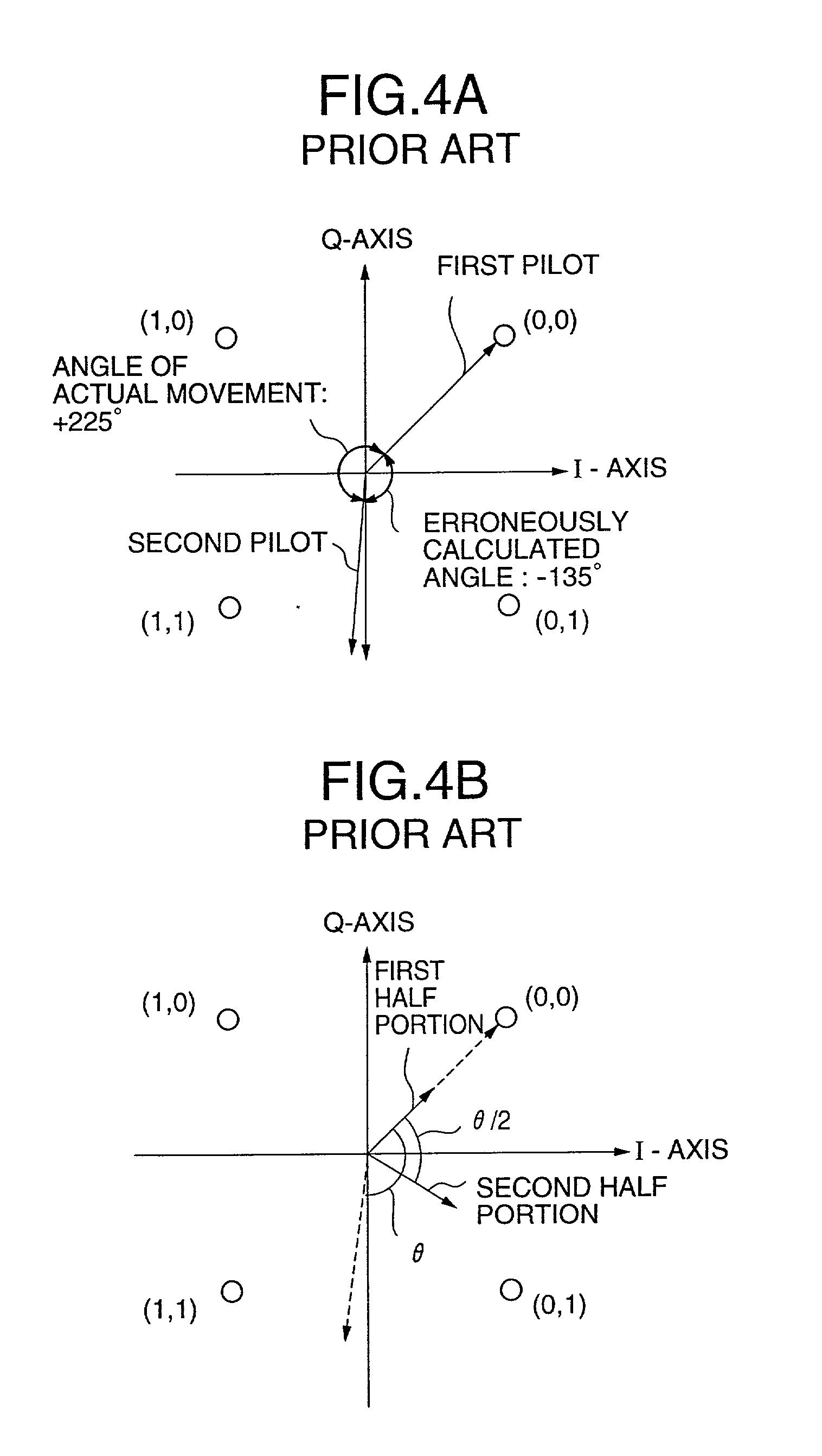
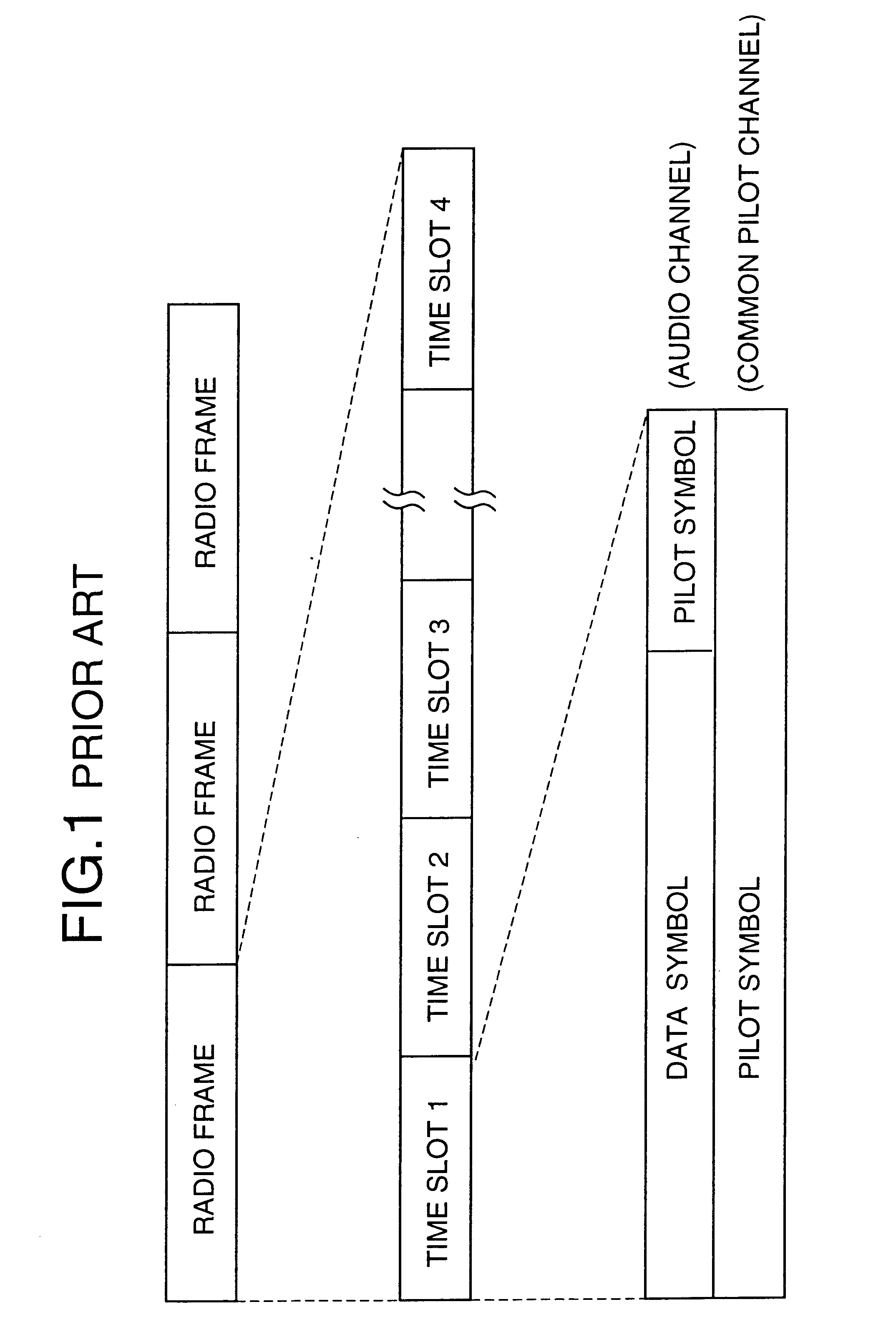
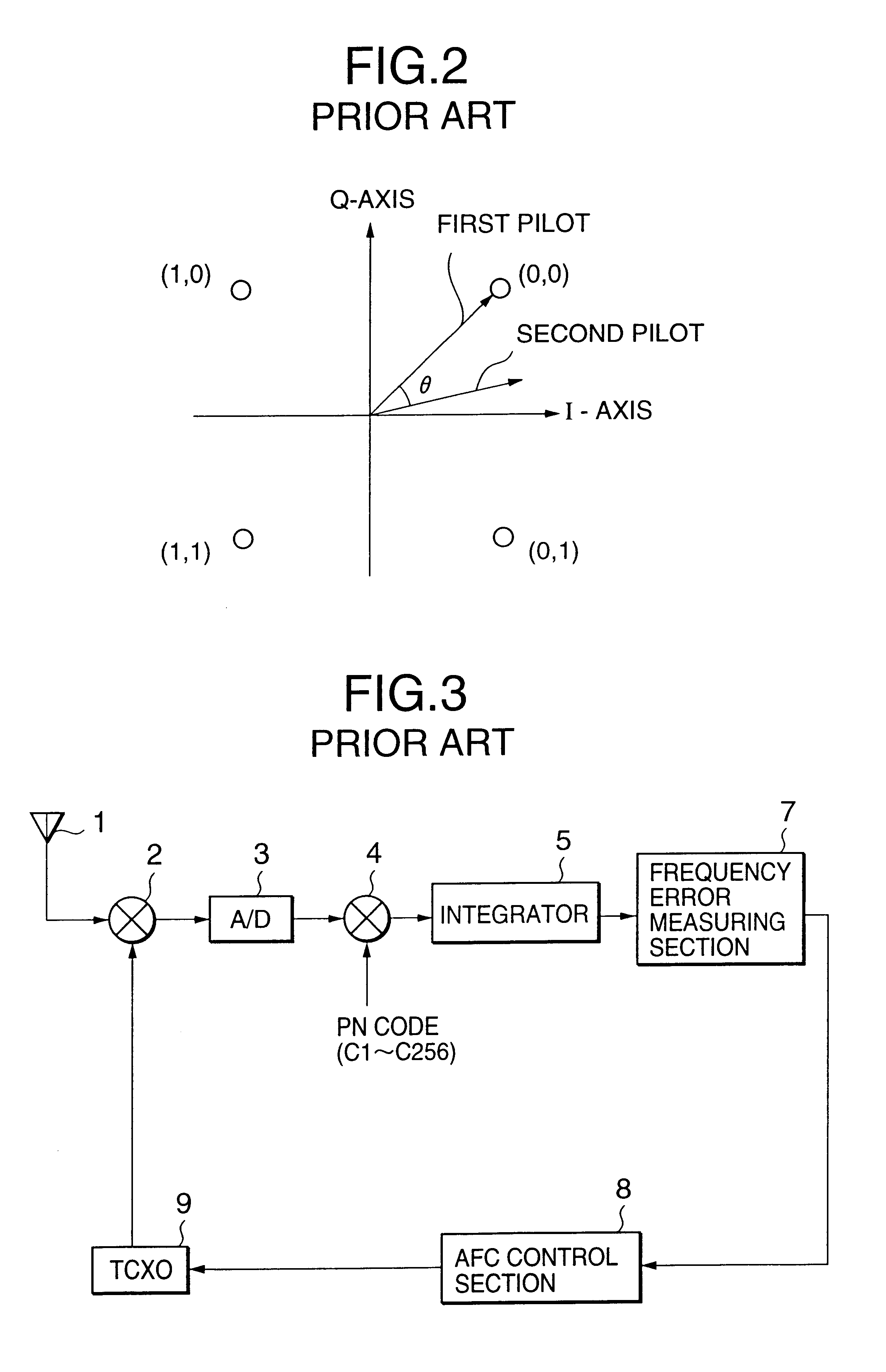
AFC control apparatus and method in mobile communication system and mobile communication equipment using the apparatus and method
InactiveUS20010004373A1No noiseMinimizing adverse influenceAutomatic frequency control detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase shiftedIntegrator
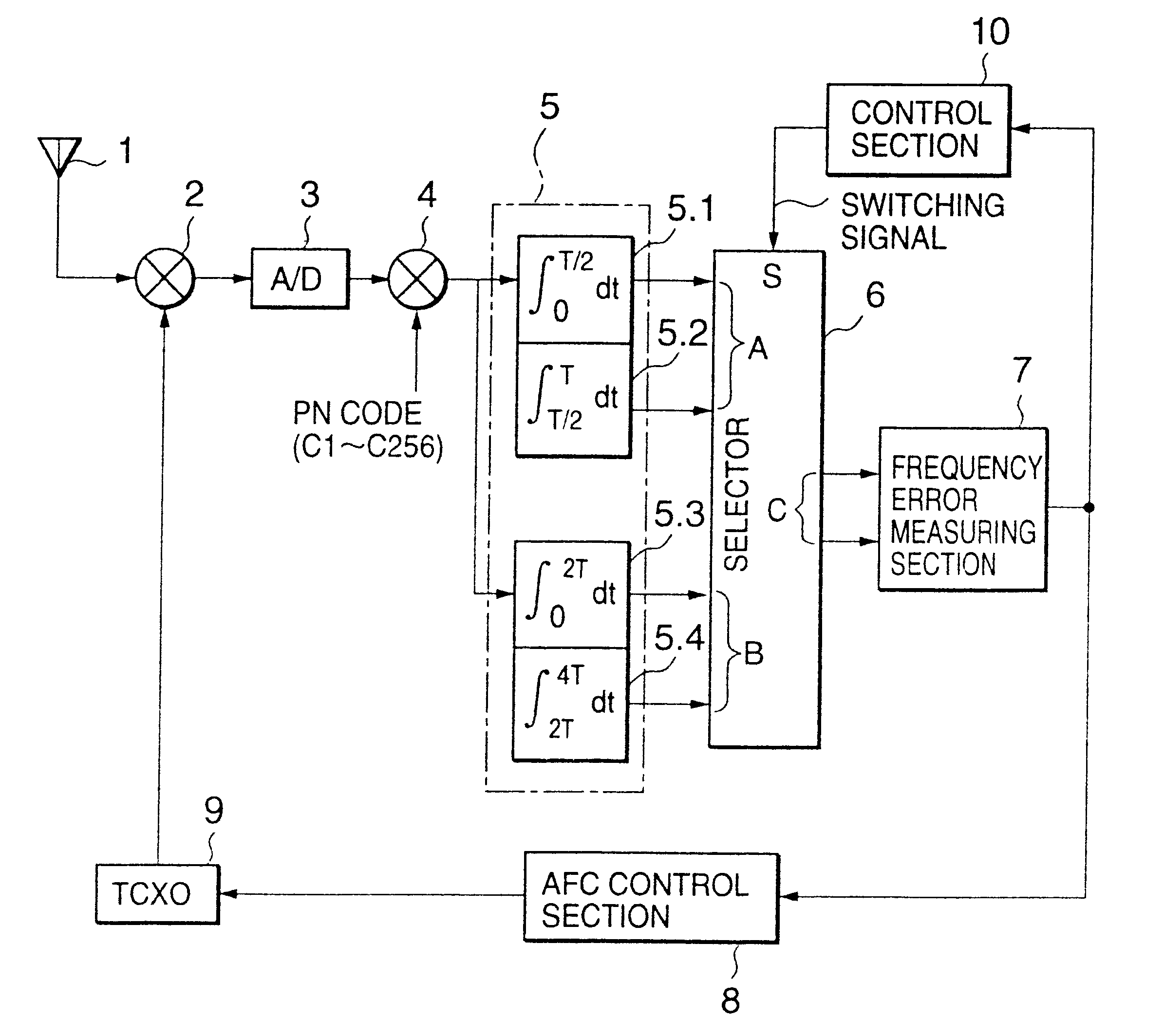
An AFC control apparatus in mobile communication equipment includes a depreading unit, first integrator, and control section. A despreading section despreads the reception signal. The first integrator integrates despread outputs obtained by despreading, of pilot symbols contained in a pilot channel of the reception signal, N (N is a number of 2 or more) consecutive first symbols and N second symbols succeeding the N first symbols, and generates first and second integral outputs. The control section detects any phase shift amount between the first and second integral outputs and controls the frequency of the local signal in accordance with the detected phase shift amount. An AFC control method and mobile communication equipment having the above apparatus and method are also disclosed.
Owner:NEC CORP
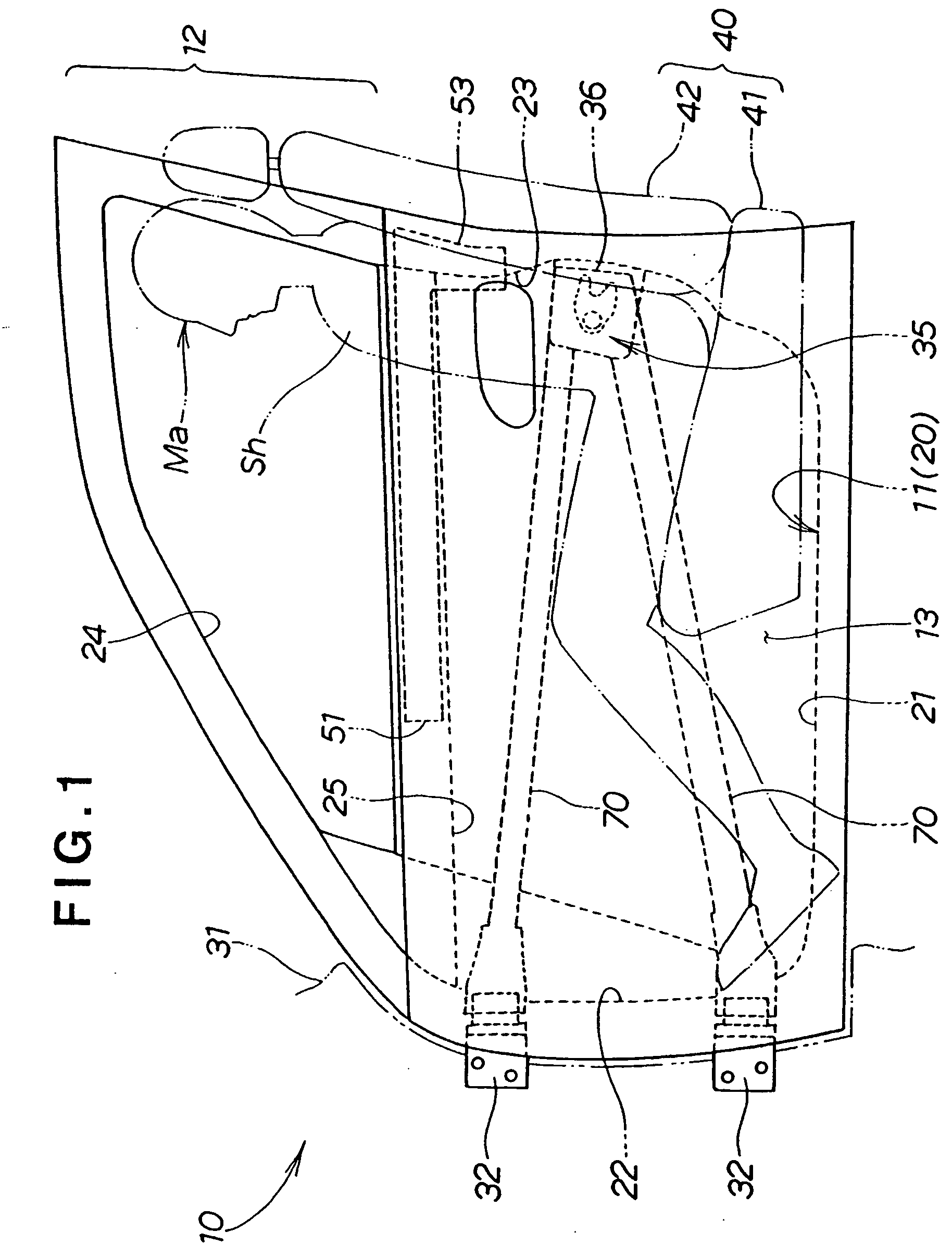
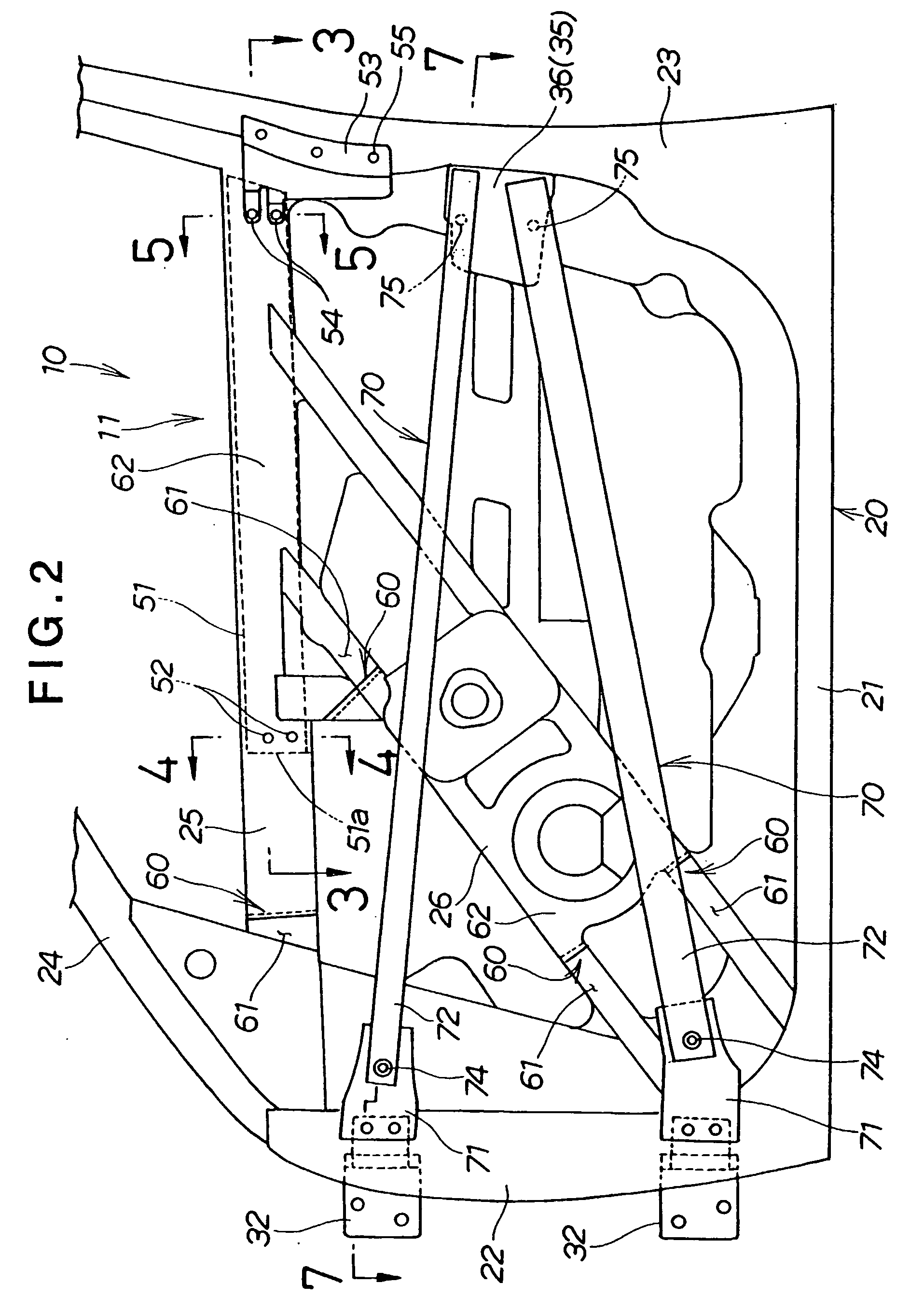
Vehicle door
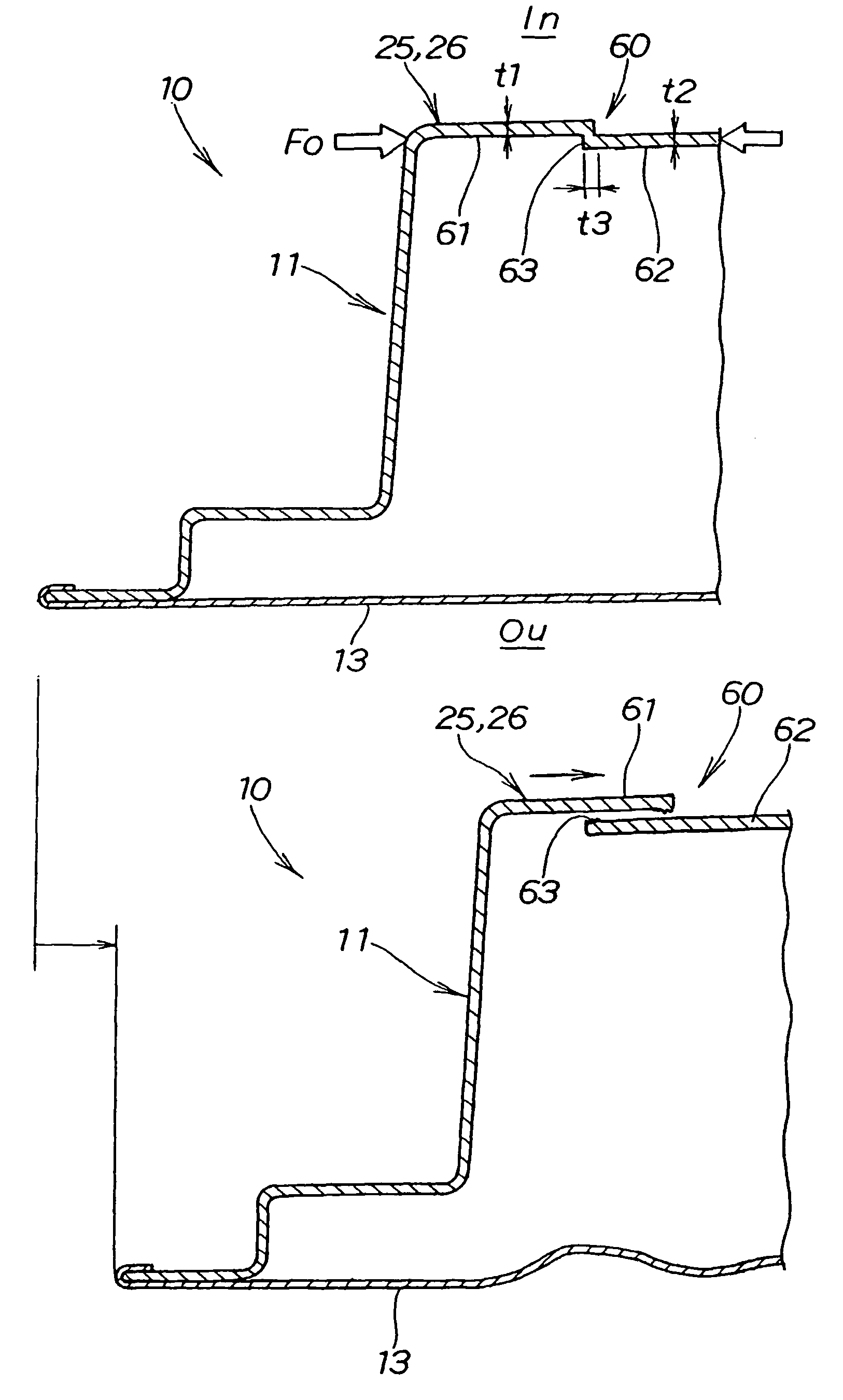
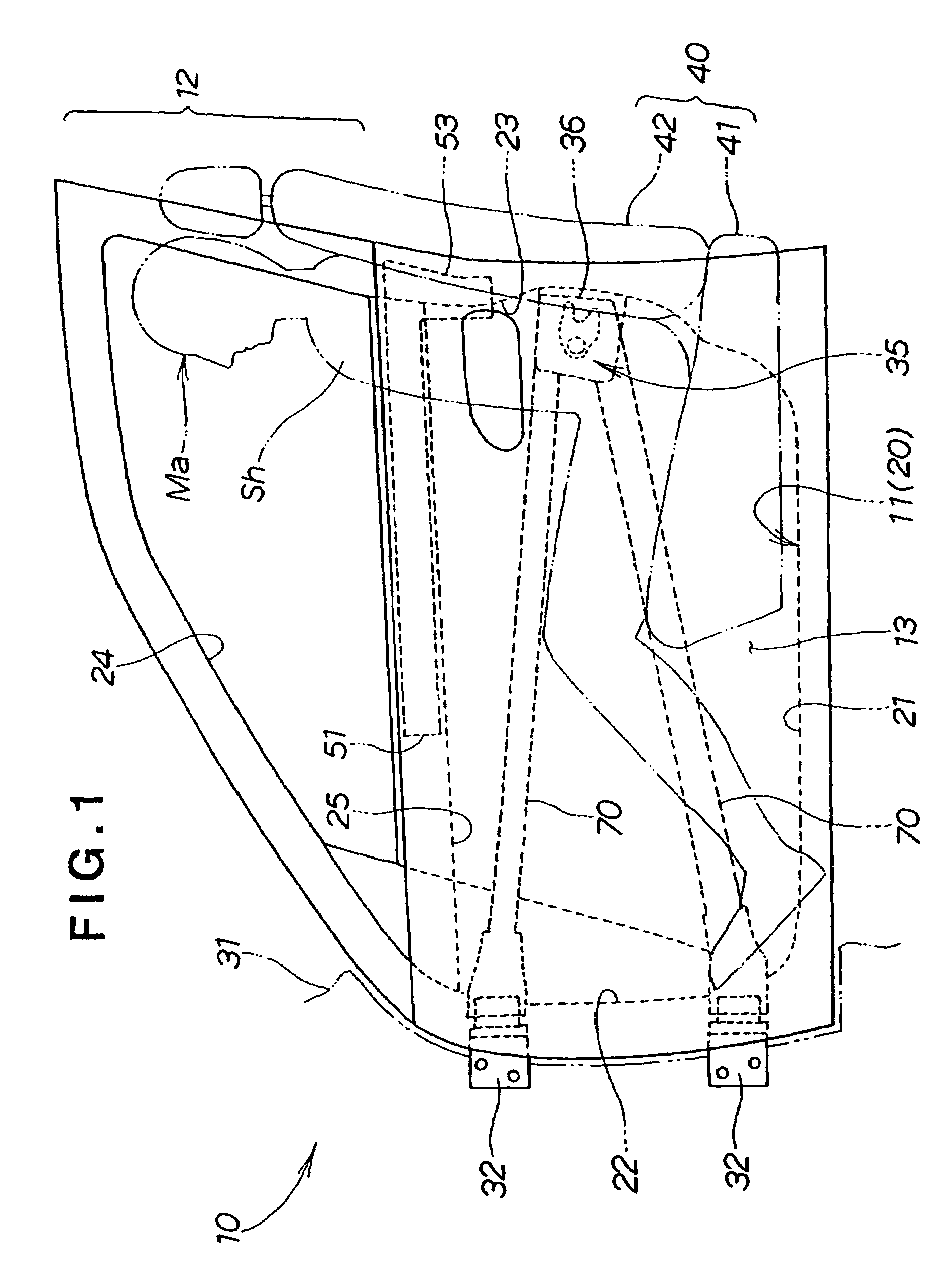
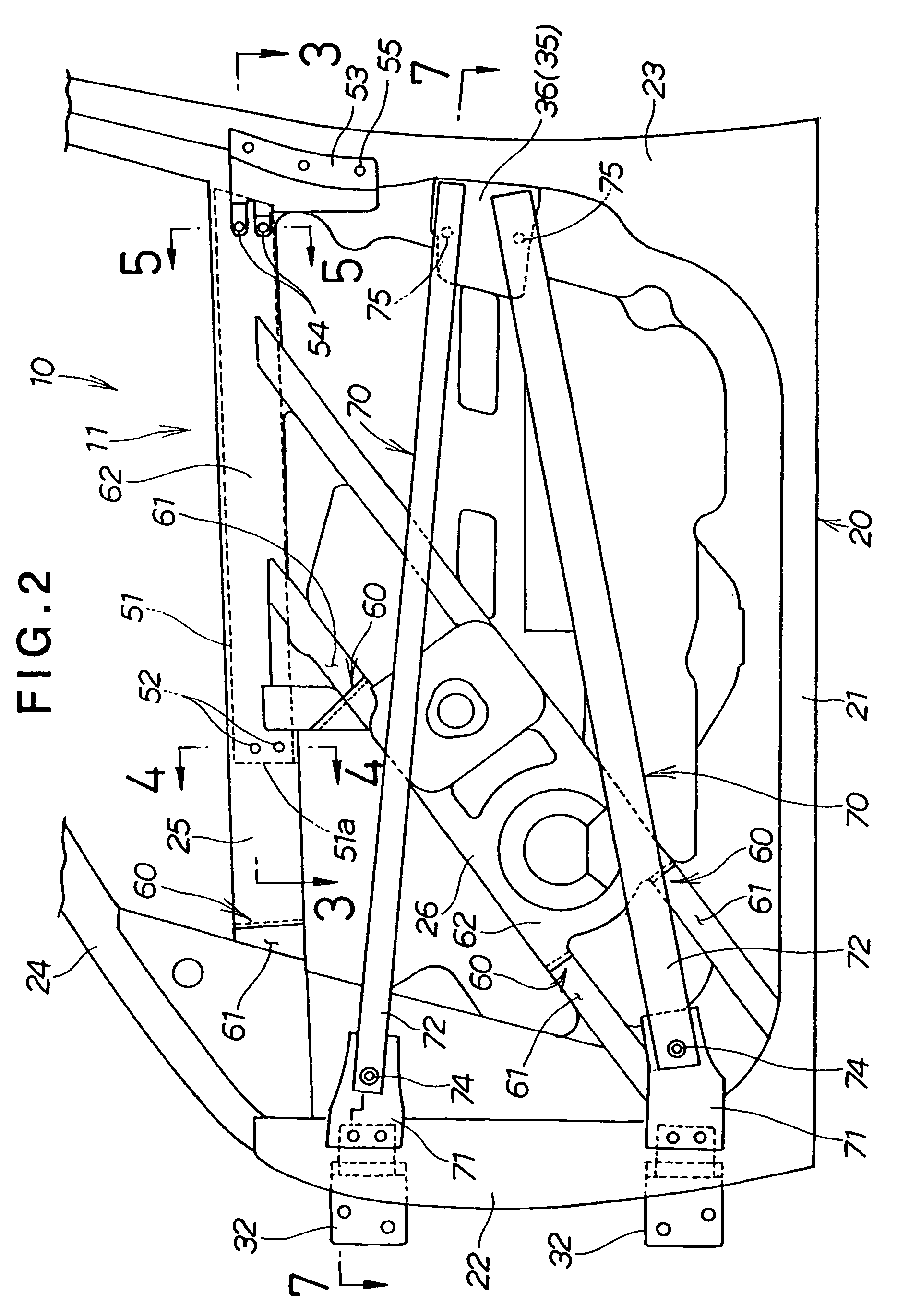
InactiveUS20050017538A1Reduce and absorb enough of collision energyImprove performanceVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringCar door
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
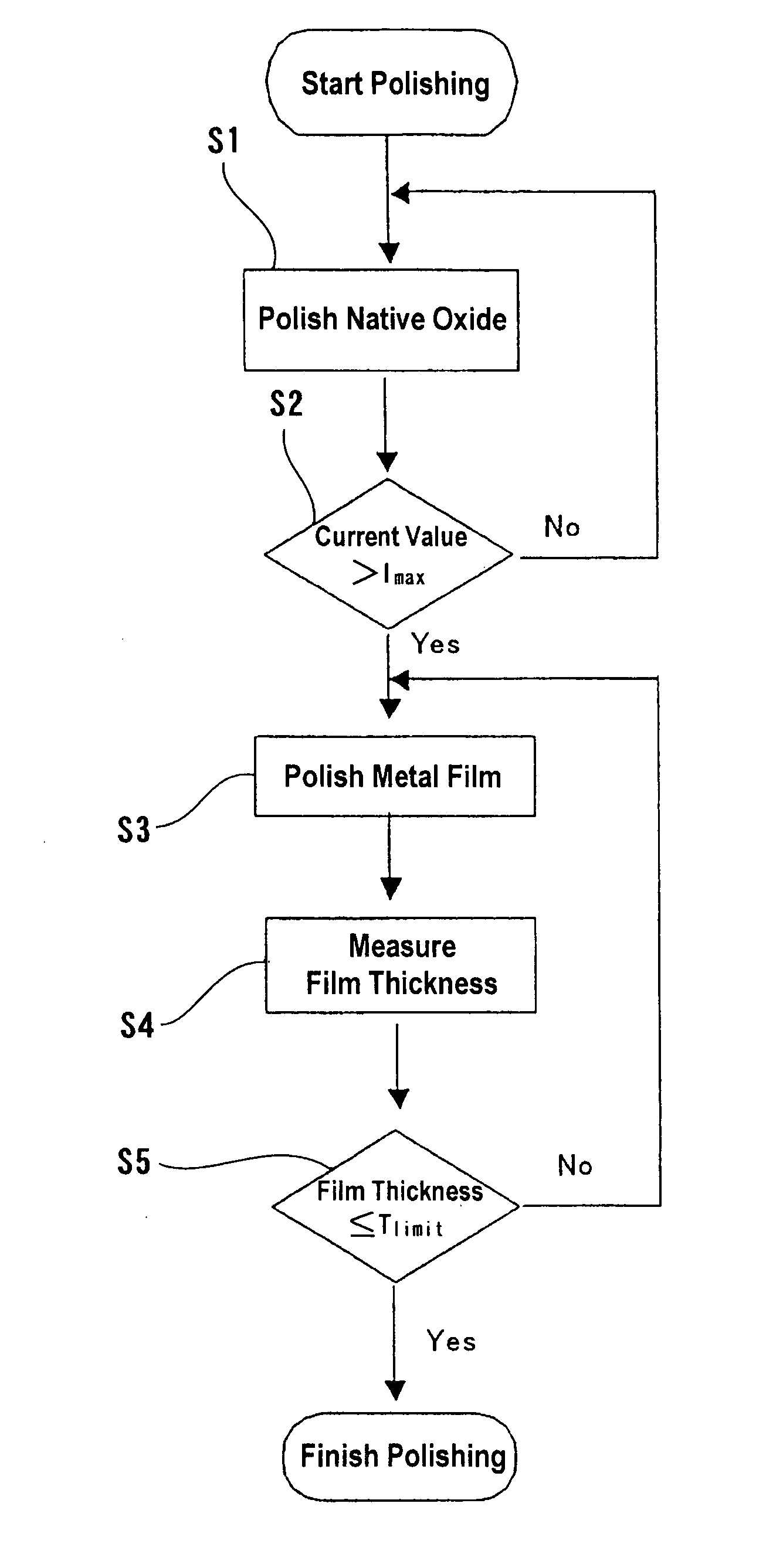
Substrate processing method and apparatus
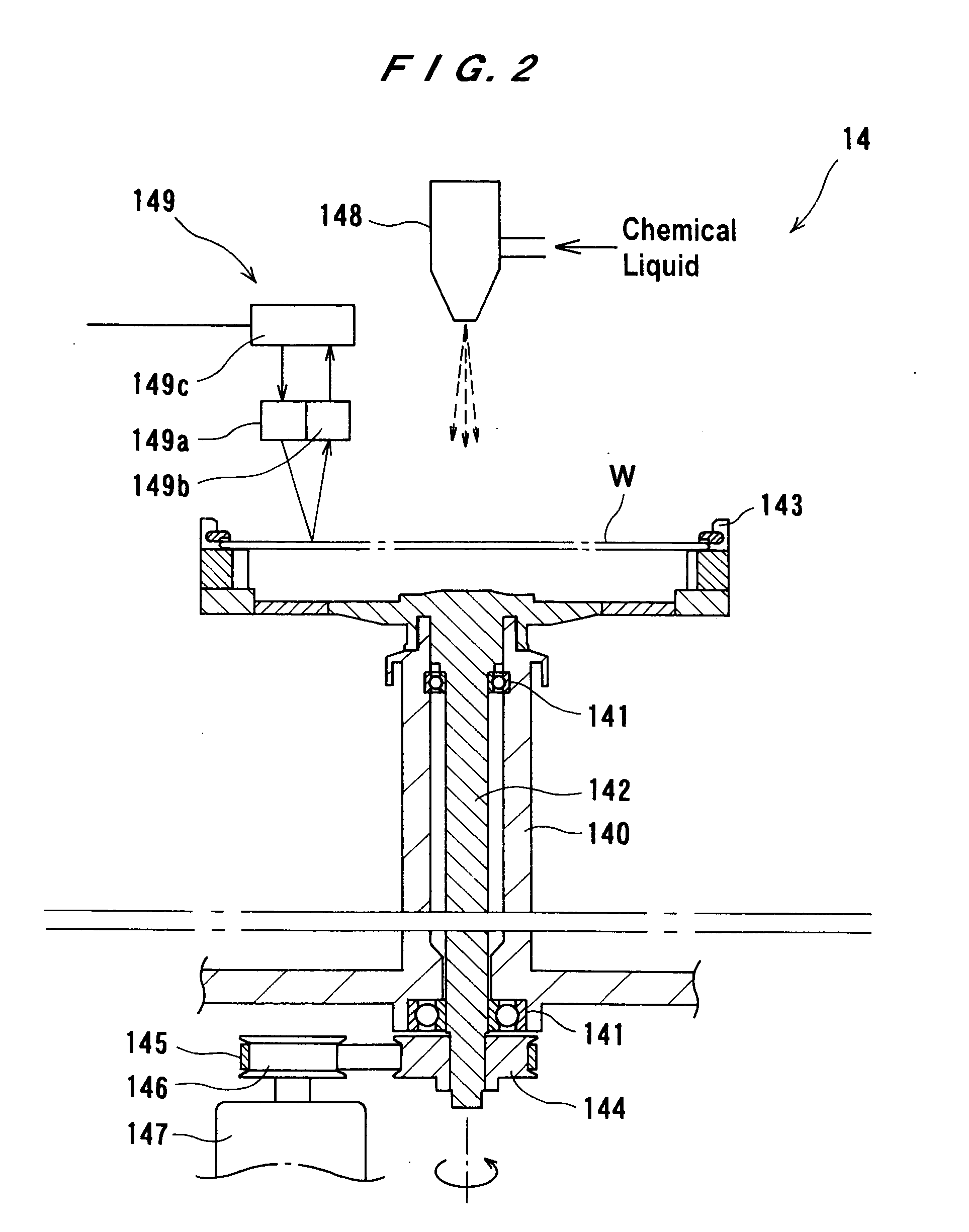
InactiveUS20050191858A1Uniform planarizationGood repeatabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesCompound (substance)Oxide
A substrate processing apparatus can process a substrate having a metal film formed thereon. The substrate processing apparatus has a process unit configured to remove a native oxide of a metal film formed on a surface of a substrate. The substrate processing apparatus also has a planarization unit configured to planarize the metal film of the substrate. The process unit may comprise a wet process unit configured to dissolve the native oxide of the metal film in a chemical liquid or a dry process unit configured to reduce or etch the native oxide of the metal film with a gas.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Low sulfated ash, low sulfur, low phosphorus, low zinc lubricating oil composition
ActiveUS20080076686A1Detergency may decreaseLow ashOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationAlkaline earth metalChemical composition
A low sulfated ash, tow sulfur, low phosphorus, low zinc lubricating, oil composition preferably employable for internal combustion engines using a low sulfur hydrocarbon fuel comprises a base oil having a saturated component of 85 wt. % or more, a viscosity index of 110 or more, and a sulfur content of 0.01 wt. % or less; an alkaline earth metal-containing detergent; a nitrogen-containing ashless dispersant of a weight average molecular weight of 4,500 or more; a phenolic or amine oxidation inhibitor; and a basic nitrogen-containing compound-oxymolybdenum complex.
Owner:CHEVRON JAPAN
Electrical receptacle
InactiveUS20120071032A1Minimize adverse influence of crosstalk and electromagnetic interferenceAssembly complexity be reduceElectric discharge tubesCoupling device detailsElectrical and Electronics engineeringEngineering
Owner:TSAI CHOU HSIEN
Vehicle door
InactiveUS6969107B2Reduce and absorb enough of collision energyImprove performanceVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementEngineeringCar door
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method for Producing a Light-Emitting Semiconductor Component and Light-Emitting Semiconductor Component
InactiveUS20130313604A1Improve stabilityEffective lightingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor chipElectrical connection
A method for producing a light-emitting semiconductor component is specified. A light-emitting semiconductor chip is arranged on a mounting area of a carrier. The semiconductor chip is electrically connected to electrical contact regions on the mounting area. An encapsulation layer is applied to the semiconductor chip by means of atomic layer deposition. All surfaces of the semiconductor chip which are free after mounting and electrical connection are covered with an encapsulation layer. Furthermore, a light-emitting semiconductor component is specified.
Owner:OSRAM OPTO SEMICONDUCTORS GMBH
Touch control structure of an amoled display screen
ActiveUS20160306479A1Low costFlexible Touch ControlStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesPolymer foilActive matrix
The present invention discloses a touch control structure of an active-matrix organic light-emitting diode display screen which is disposed on a display screen substrate, the touch control structure comprises a transmitting structure and a receiving structure that are mutually inductive, the transmitting structure further comprises a first encapsulation film, a first patterned electrode and a second encapsulation film, wherein the first encapsulation film is formed on an organic light-emitting diode device disposed on the display screen substrate, the first patterned electrode is formed on the first encapsulation film, and the second encapsulation film is formed upon the first patterned electrode; the receiving structure further comprises a flexible polymer foil sheet and a second patterned electrode formed on the flexible polymer foil sheet, wherein the flexible polymer foil sheet is adhered to the second encapsulation film, and the first patterned electrode and the second patterned electrode are oppositely disposed. By configuring the transmitting structure and the receiving structure that are mutually inductive, the present invention significantly simplifies the manufacture process, reduces the cost, and can also achieve flexible touch control.
Owner:KUNSHAN NEW FLAT PANEL DISPLAY TECH CENT +1
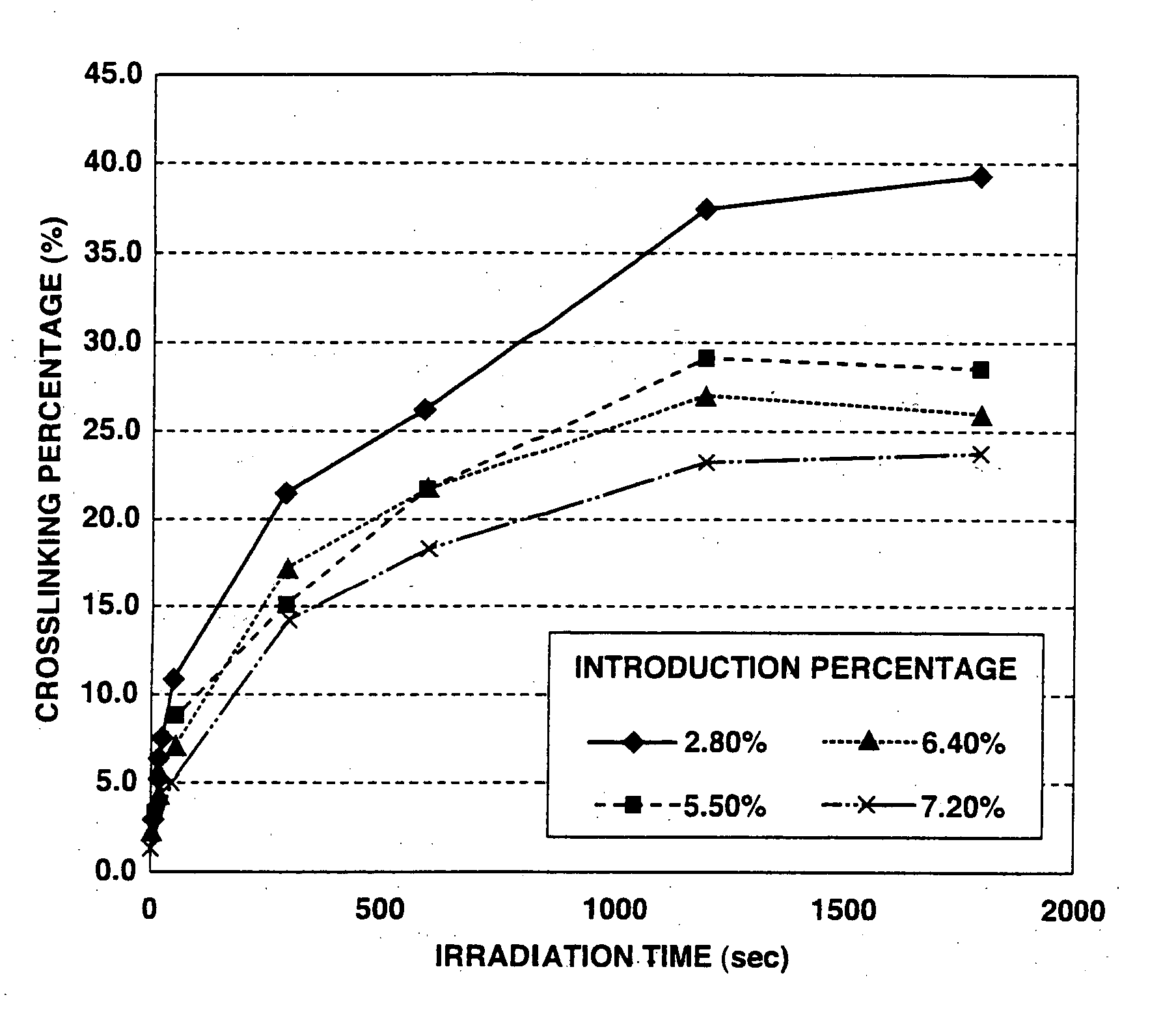
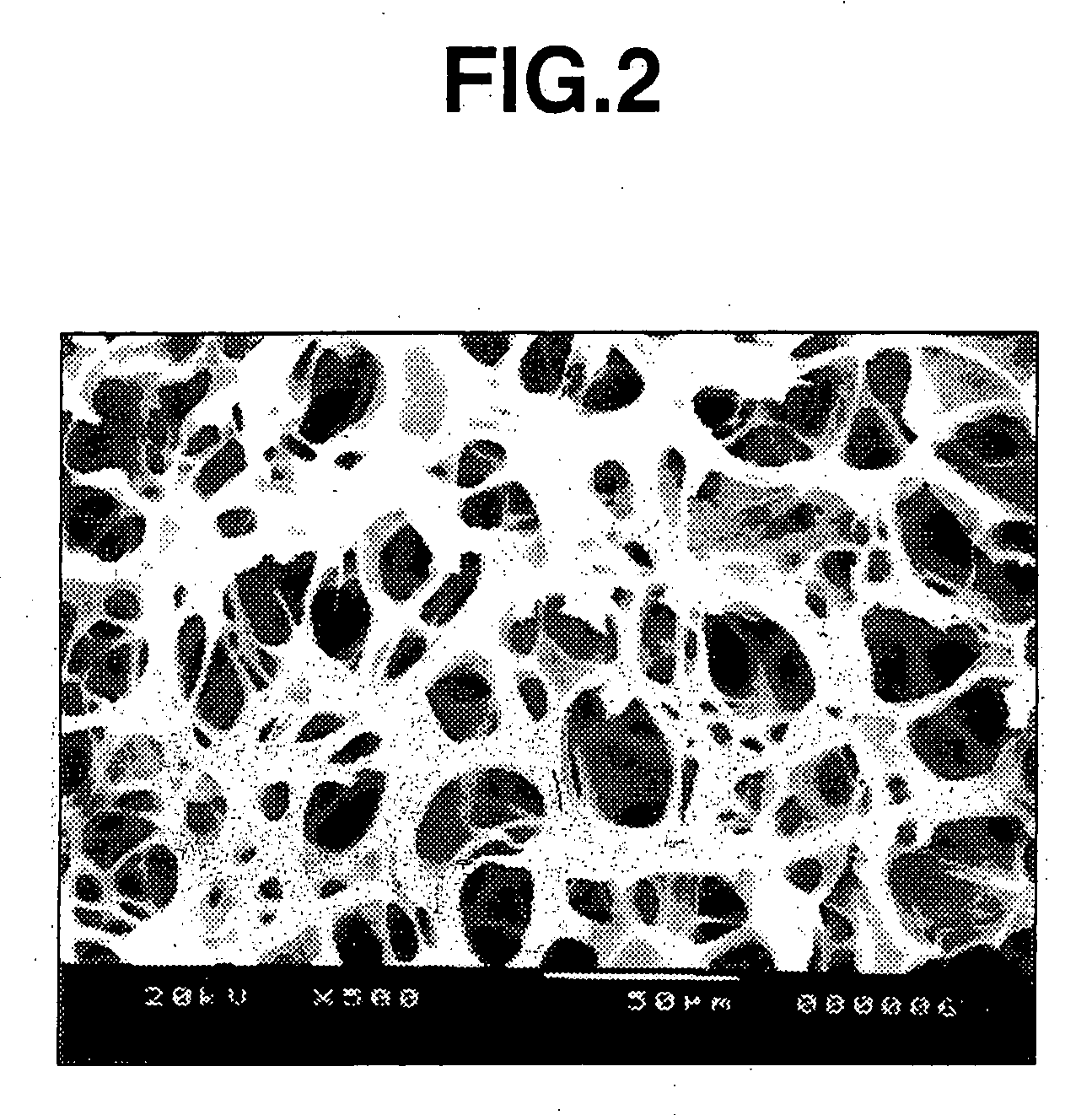
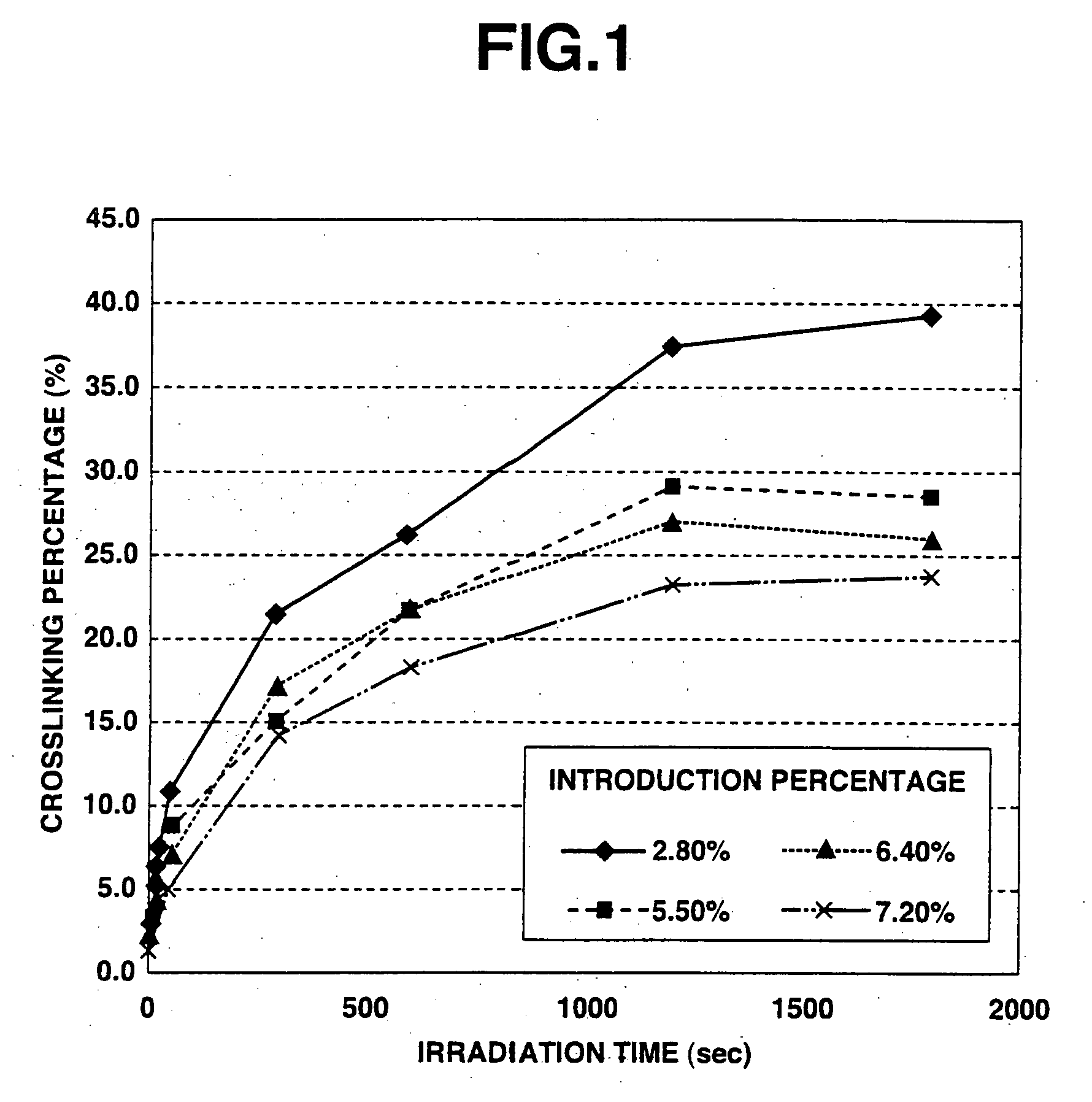
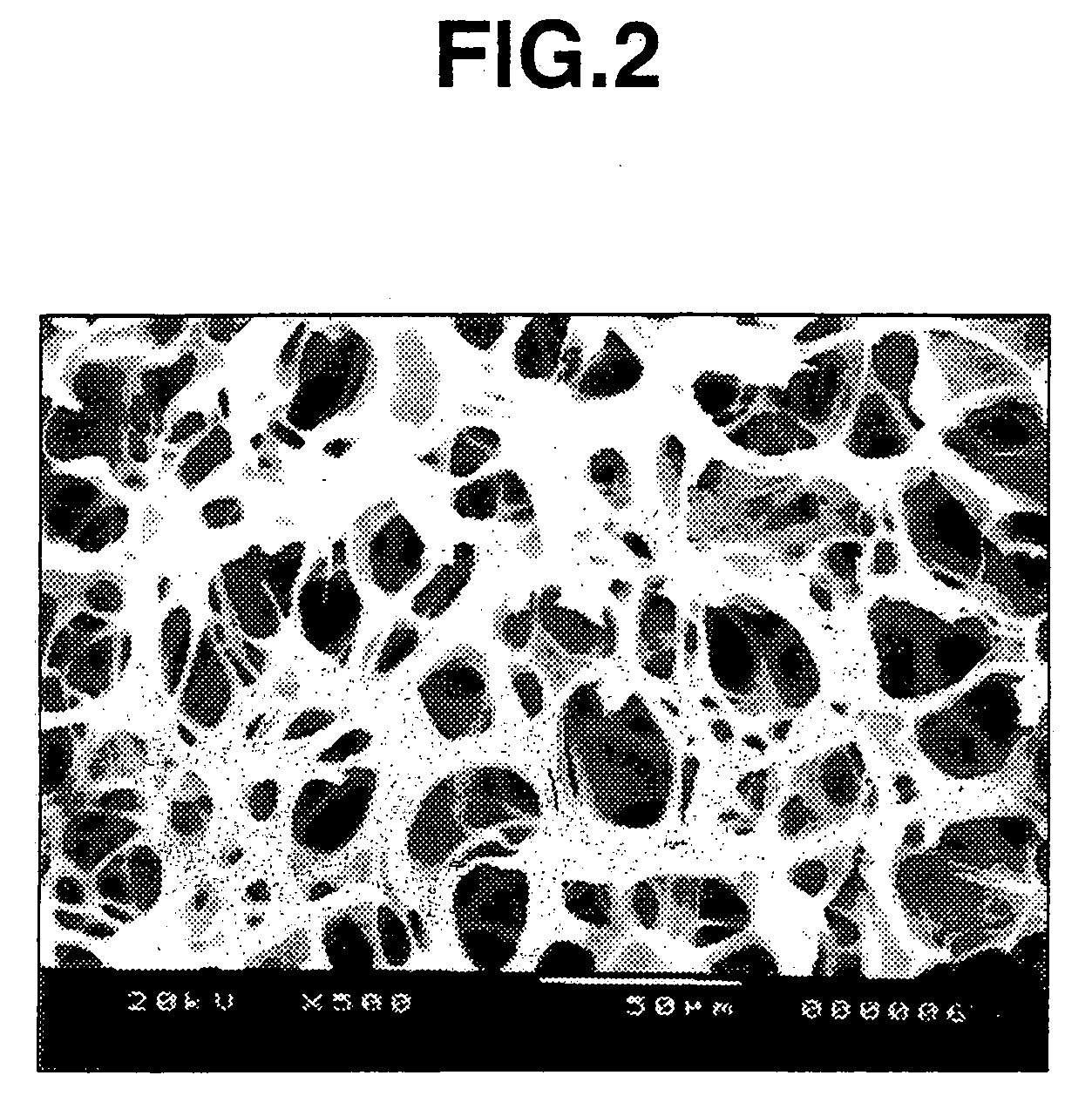
Crosslinked polysaccharide sponge
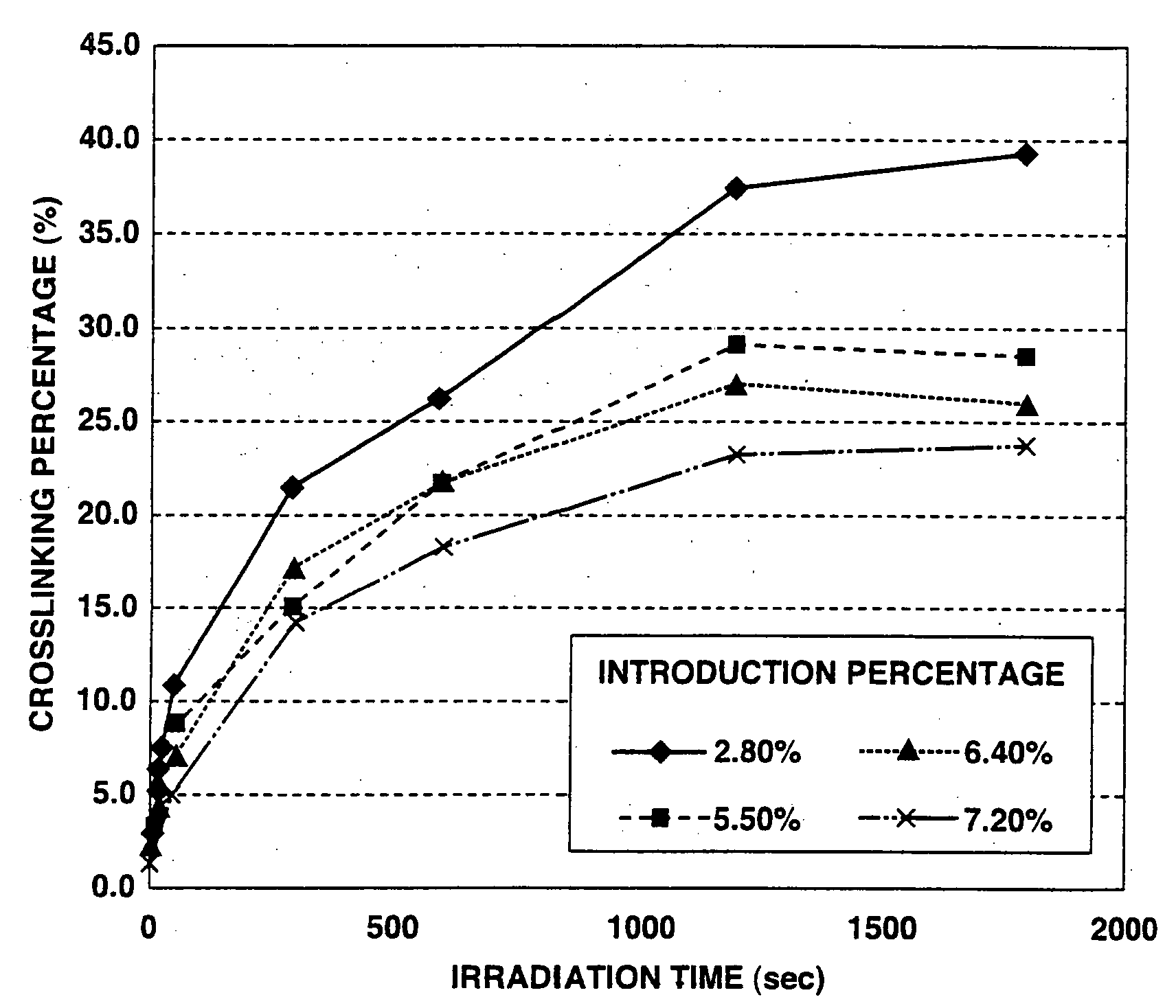
InactiveUS20080071001A1Easy to excludeImprove securitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSolventPhotochemistry
A process for producing a polysaccharide sponge comprises the steps of (A) freezing a photoreactive polysaccharide solution, and (B) irradiating the frozen photoreactive polysaccharide solution with light to crosslink the photoreactive polysaccharide, thereby obtaining the polysaccharide sponge. The process includes simplified steps requiring no removal of solvent, and has such an advantage that impurities are easily removed therefrom.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
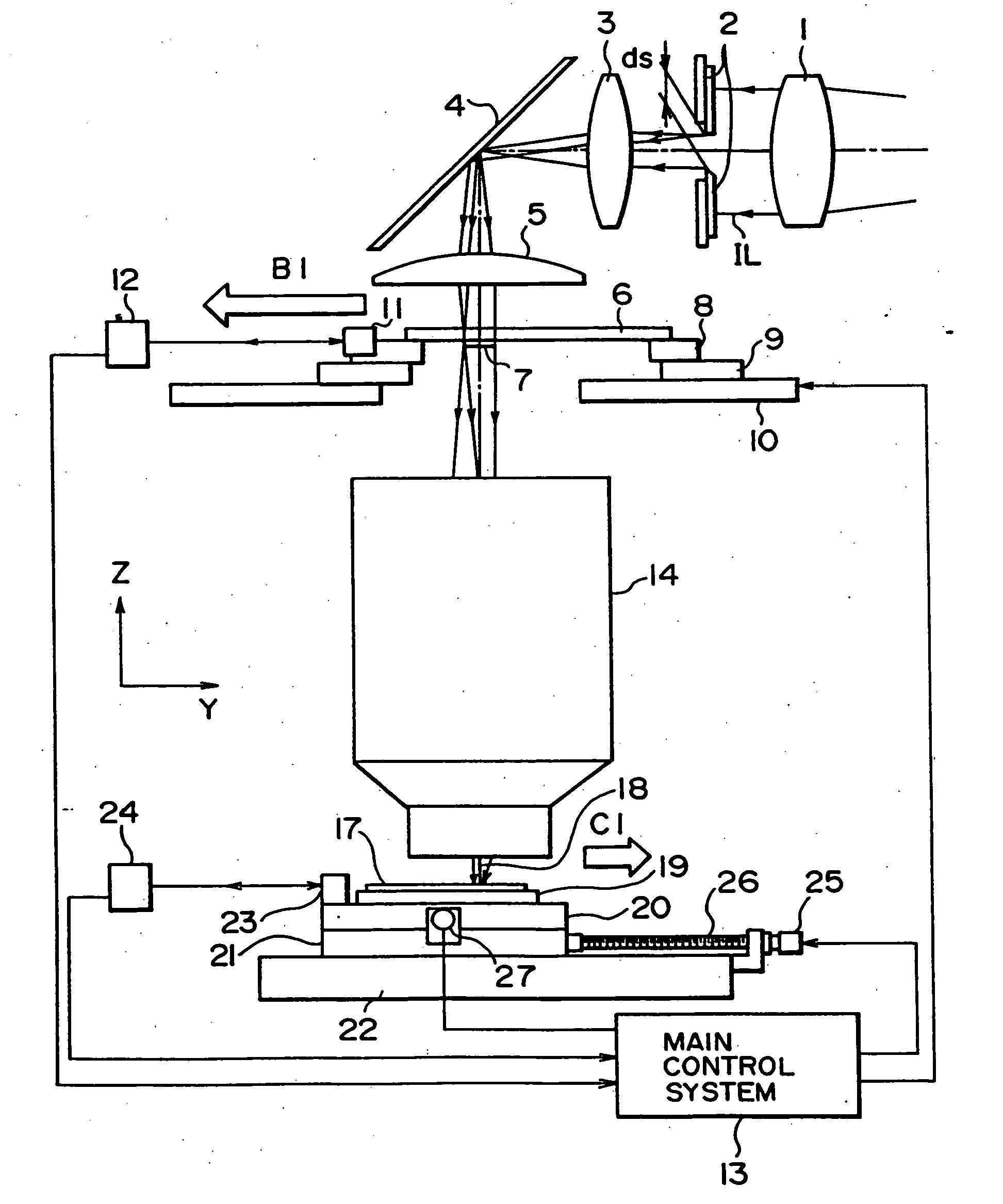
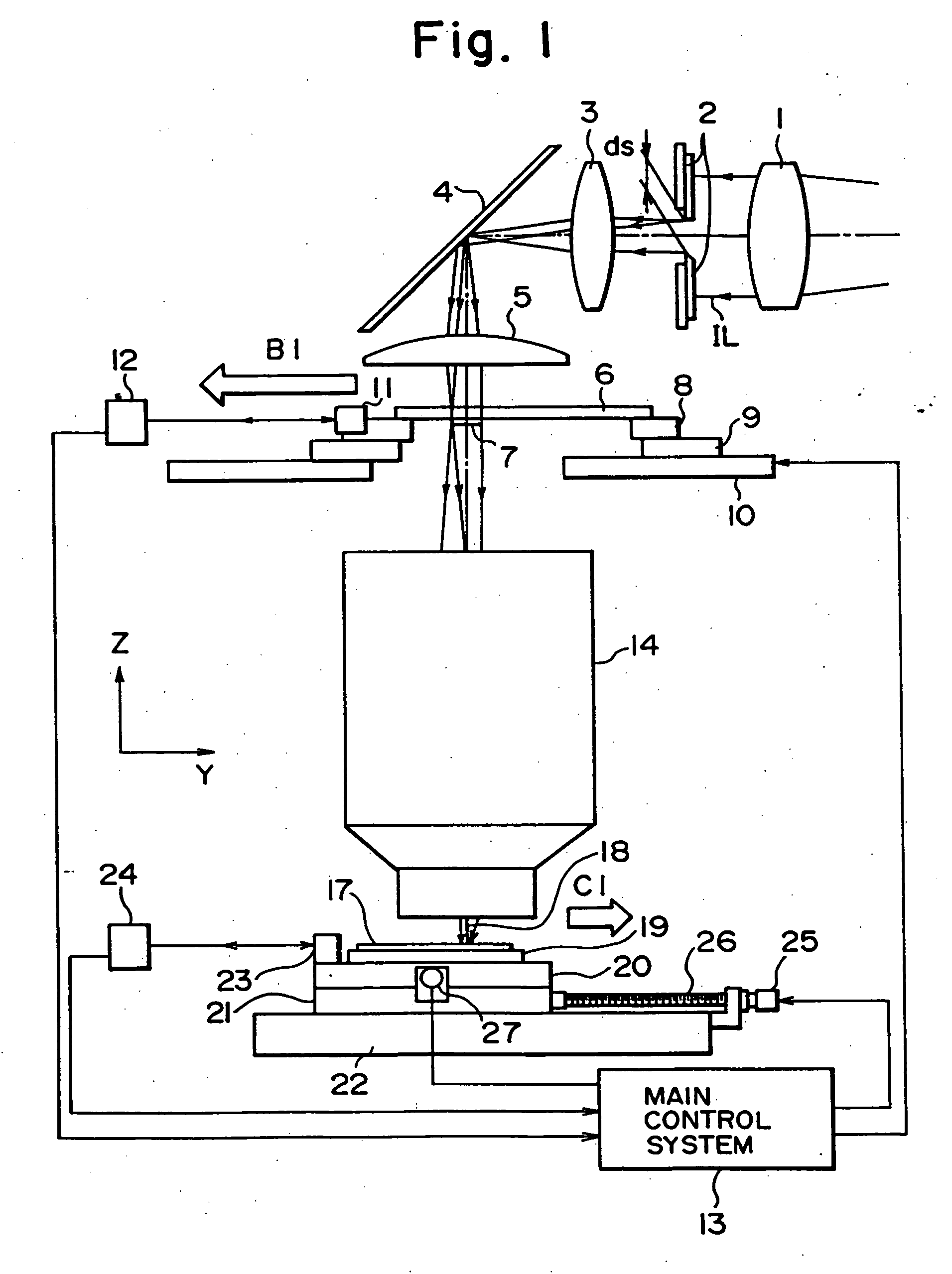
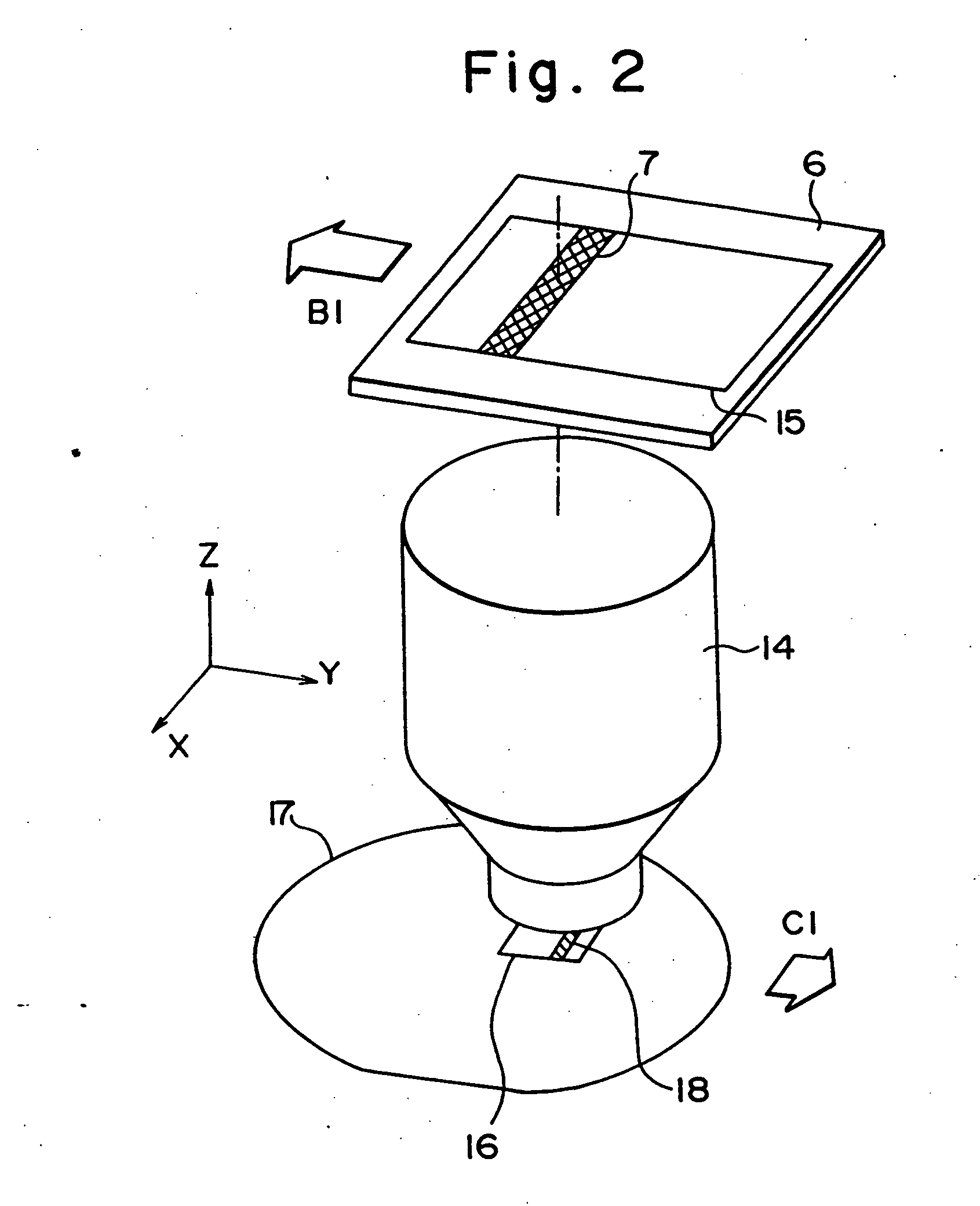
Stage unit, drive table, and scanning exposure apparatus using same
InactiveUS20050133732A1Minimize amount of heat generatedHigh measurement accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
An exposure method for manufacturing a liquid crystal display utilizes a scanning exposure apparatus to expose a pattern of a mask onto a glass plate. The exposure method includes a step of moving a mask stage that holds the mask in a scanning direction by a first electromagnetic actuator. The first electromagnetic actuator moves the mask stage associating with a guide member that extends in the scanning direction. The method also includes the step of moving the mask stage in a non-scanning direction different from the scanning direction by a second electromagnetic actuator. The second electromagnetic actuator moves the mask stage associating with no guide member, and a moving distance in the non-scanning direction by the second electromagnetic actuator is shorter than a moving distance in the scanning direction by the first electromagnetic actuator.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor light emitting device, semiconductor light emitting device, method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, semiconductor device, method of manufacturing a device, and device
InactiveUS7091056B2Maintain good propertiesReliable and reliableOptical wave guidancePolycrystalline material growthVolumetric Mass DensityDislocation
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Precision variable area flowmeter apparatus
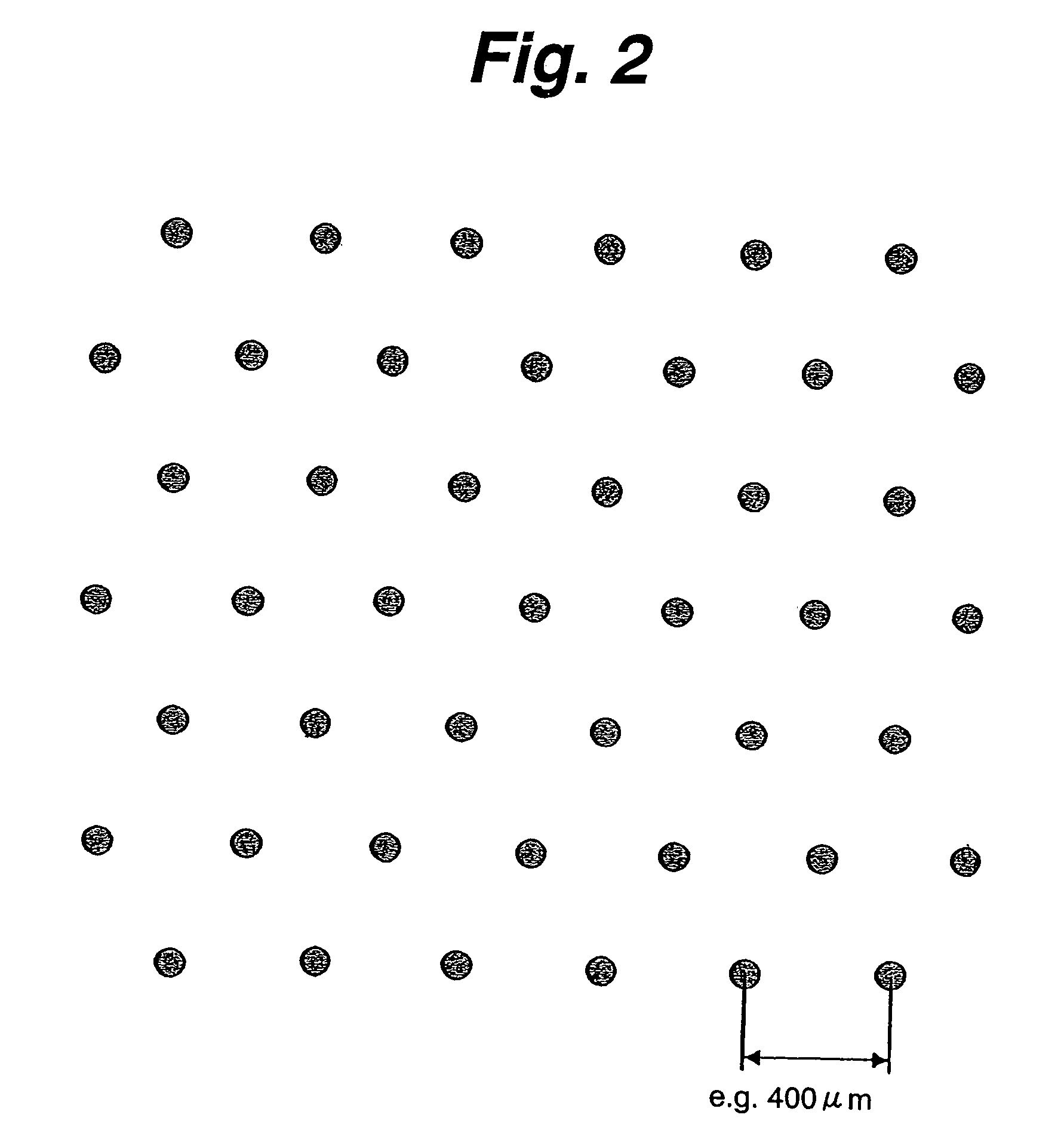
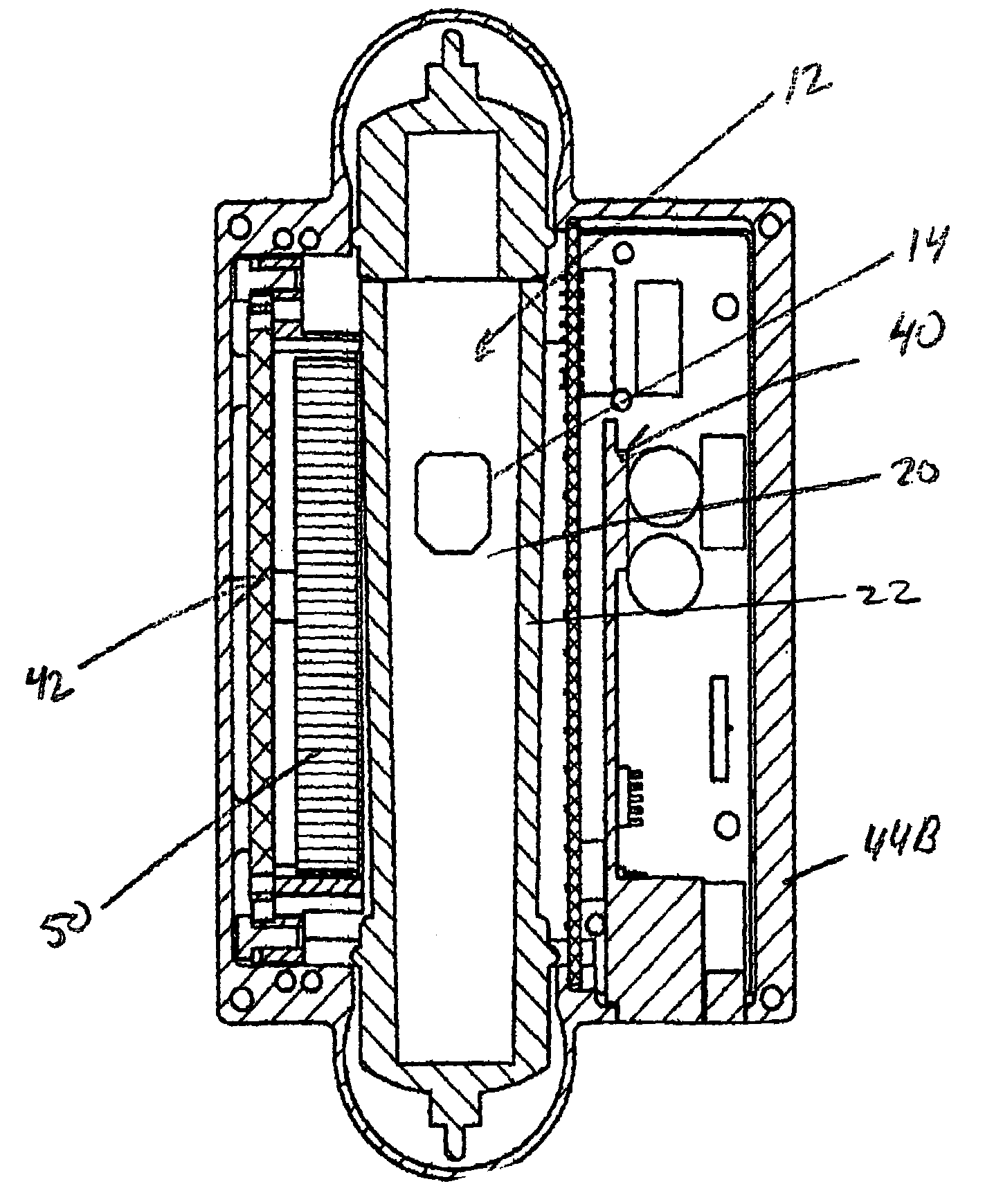
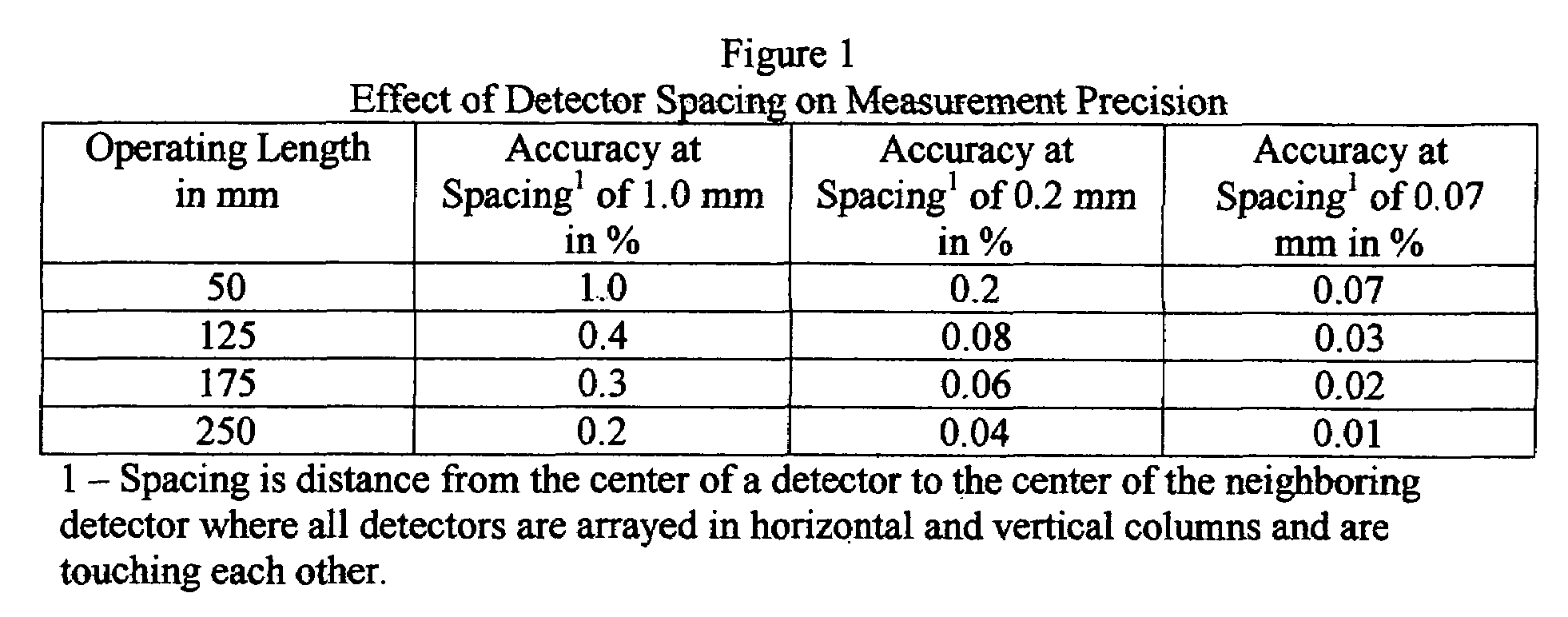
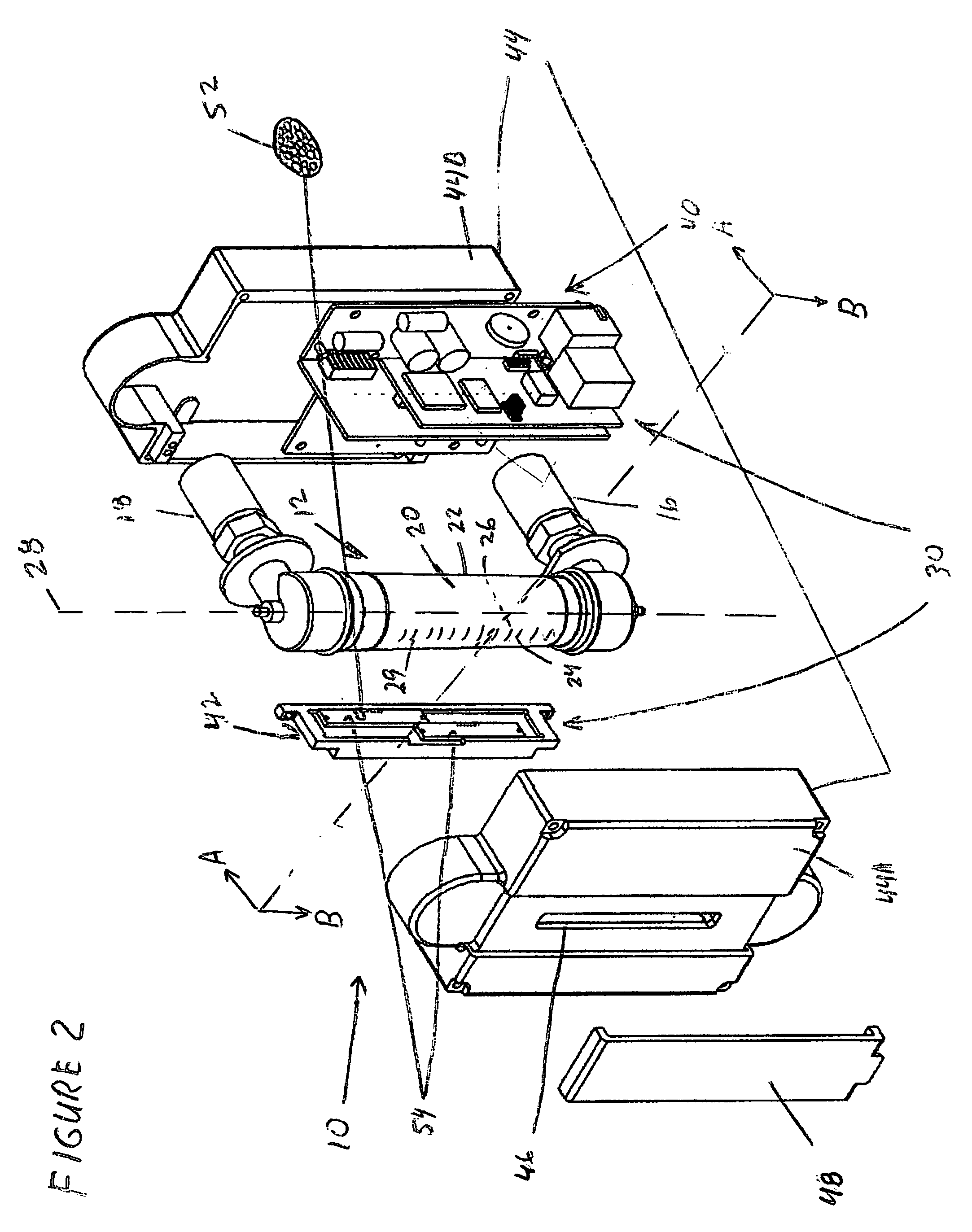
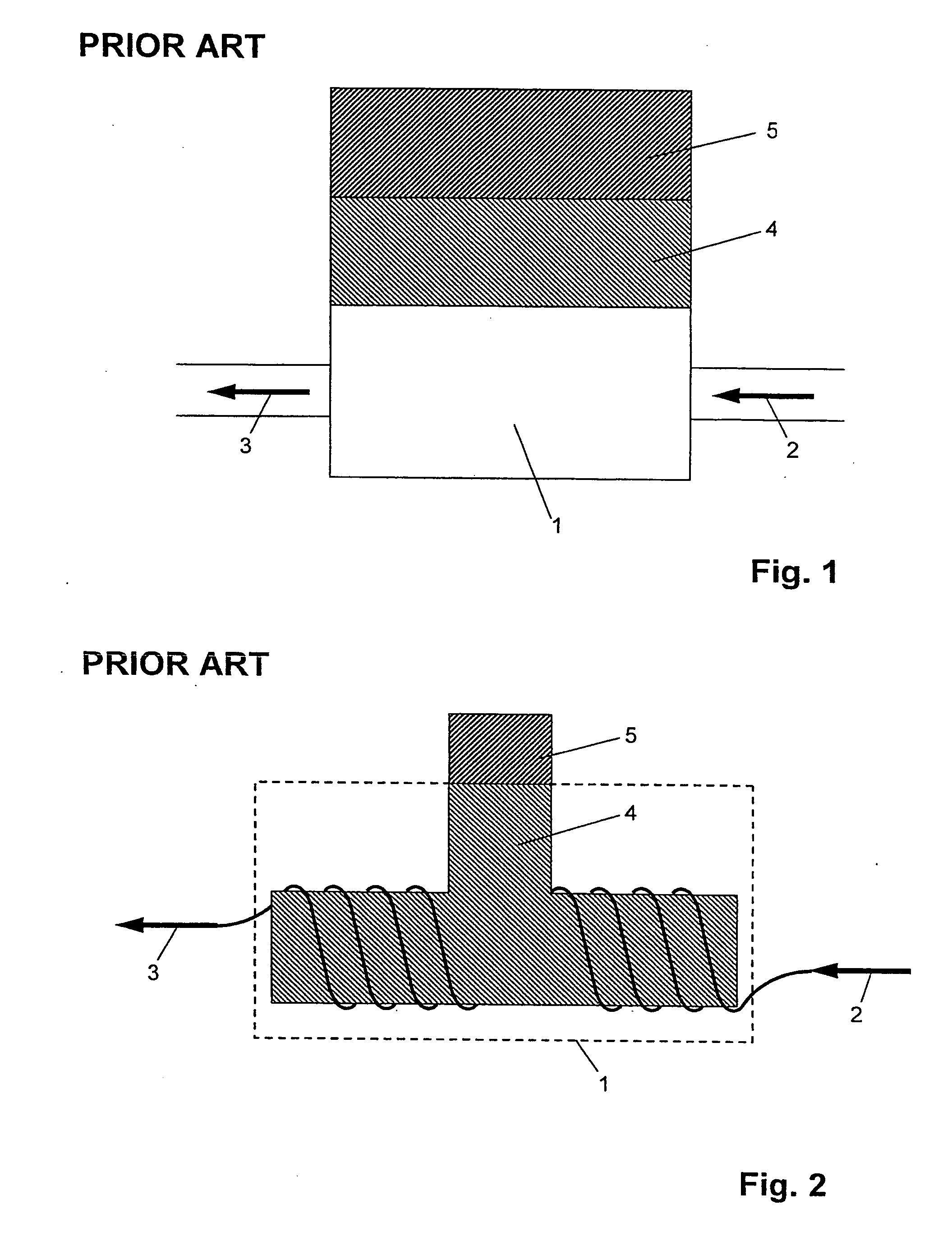
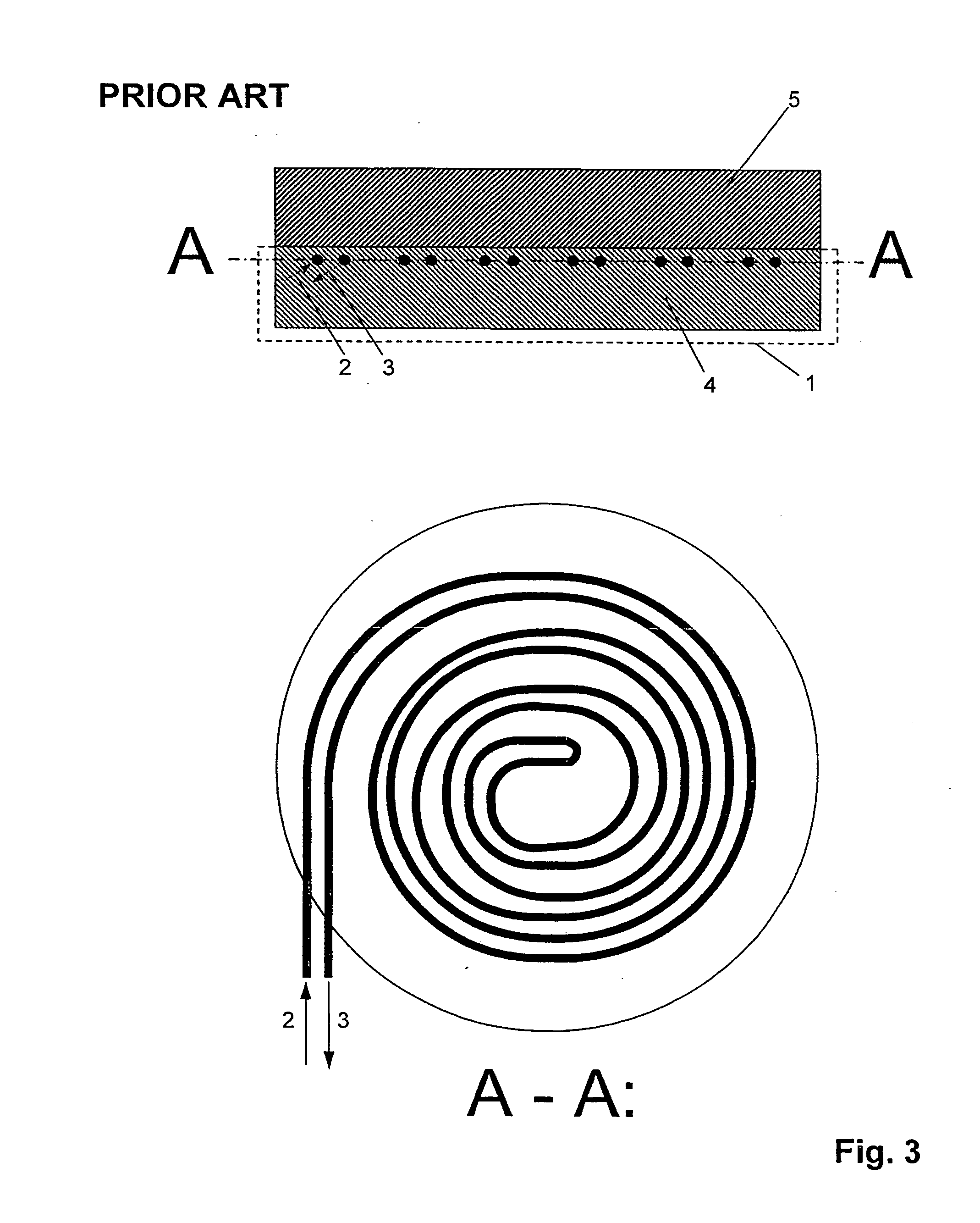
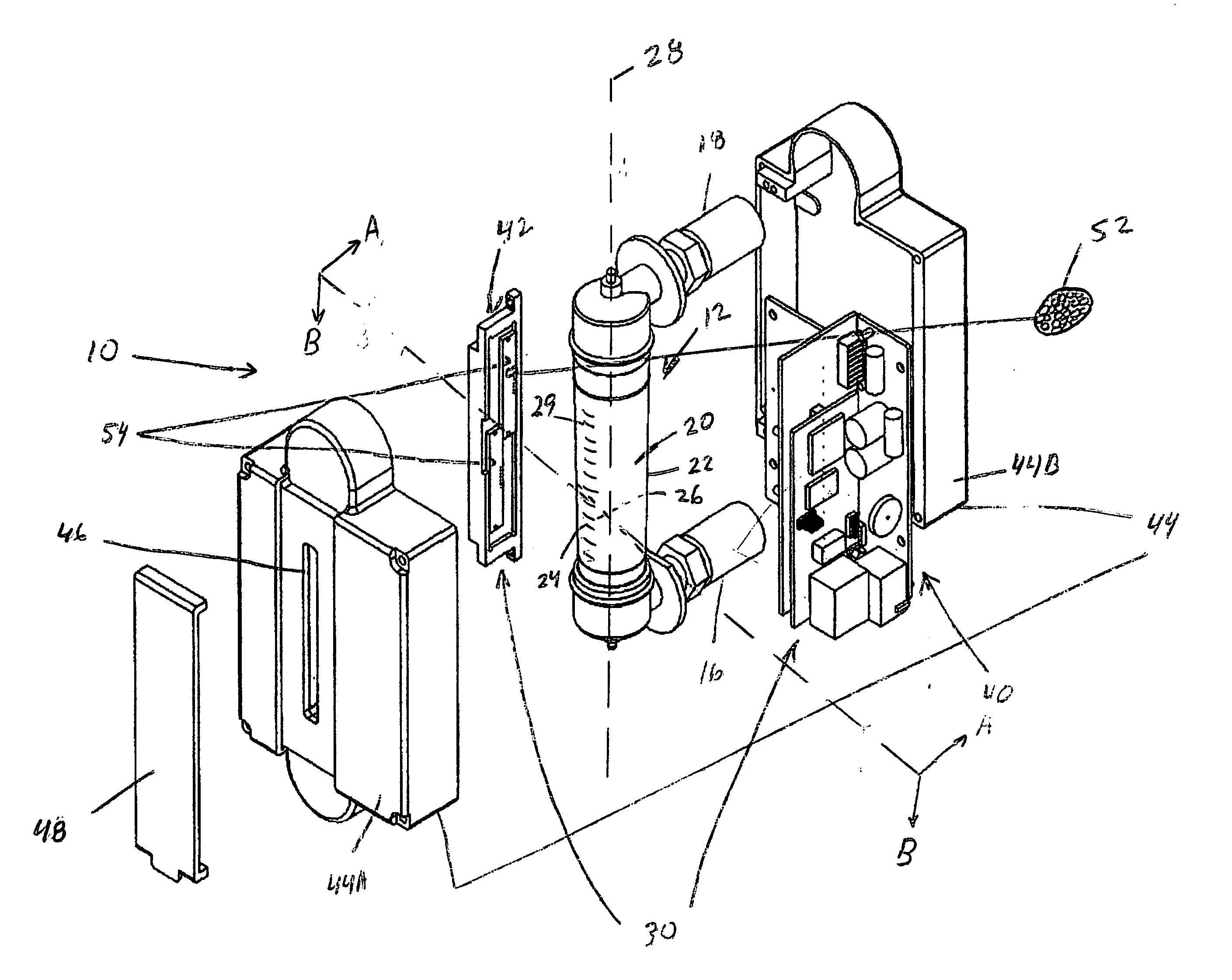
InactiveUS7140262B1Minimizing adverse influenceMinimize impactVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectLong axisEngineering
We have invented an improved apparatus for electronically measuring fluid flow. The apparatus includes a radiation detection means for indicating the position of a flow indicator in a chamber of a variable area flowmeter and has a reliability, versatility and functional accuracy not obtainable with known variable area flowmeters. The invention may also include a variable area flowmeter with the flow indicator in a tapered fluid flow chamber with a wall and a long axis, the chamber having a front side, a back side, and an operational length substantially parallel to the long axis. The invention has no moving parts and is not intrusive so mechanical malfunction and unwanted leaks can not occur. Useful embodiments include, for example, compact self contained apparatus useful for fitting around existing flowmeters, systems that include flowmeters and systems able to work with some fluids that are visually opaque.
Owner:VAUGHN TONI CLINE +1
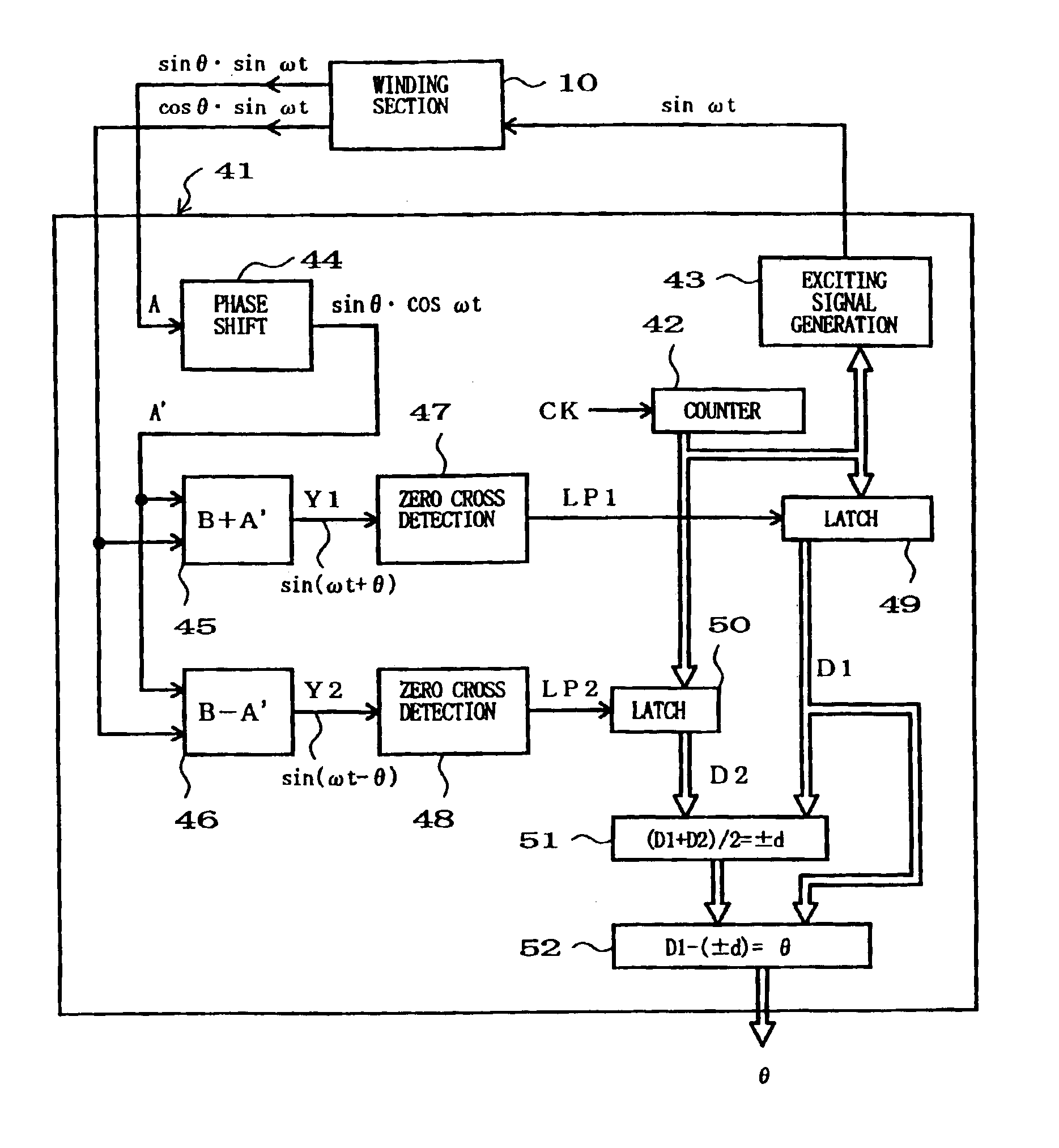
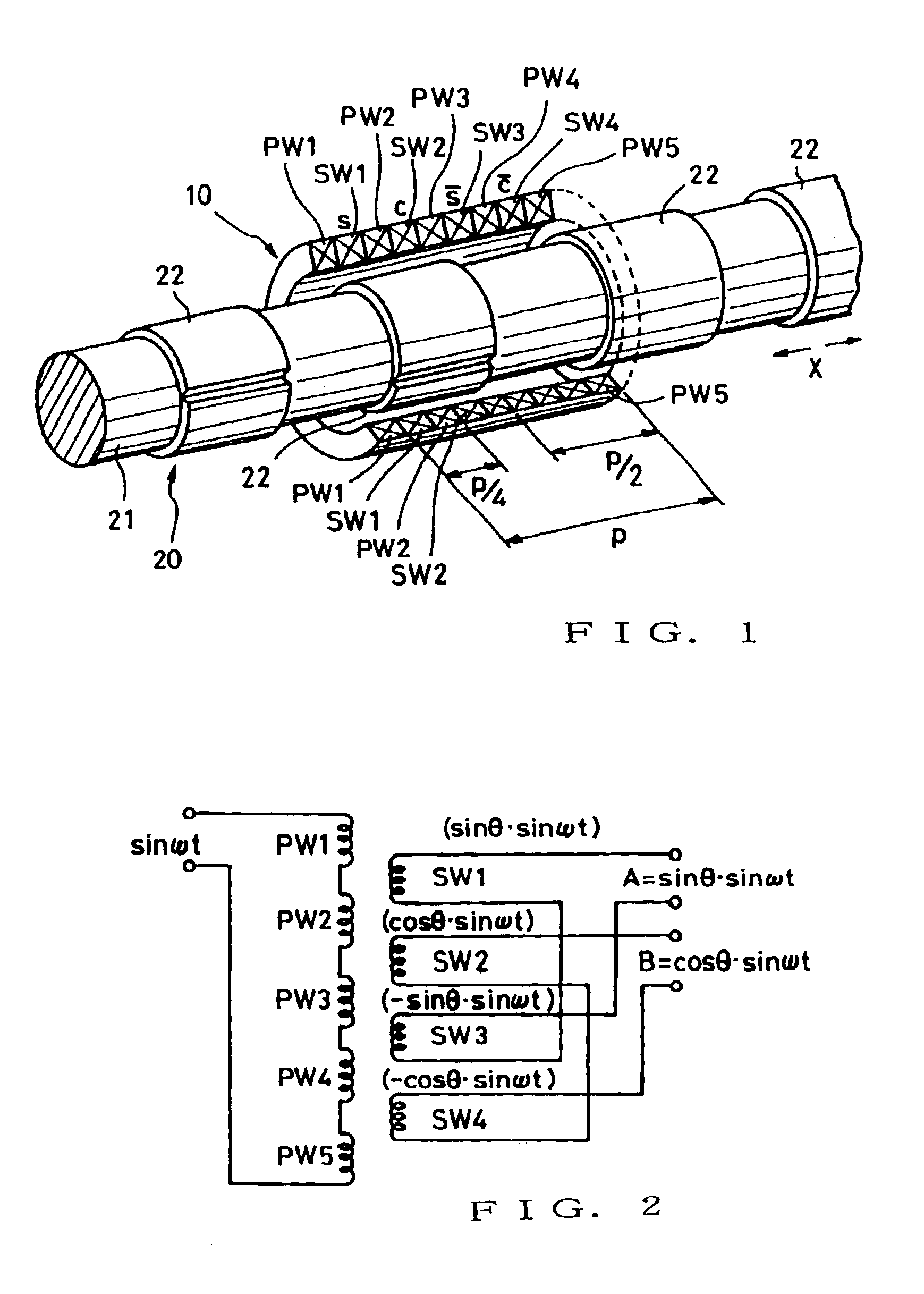
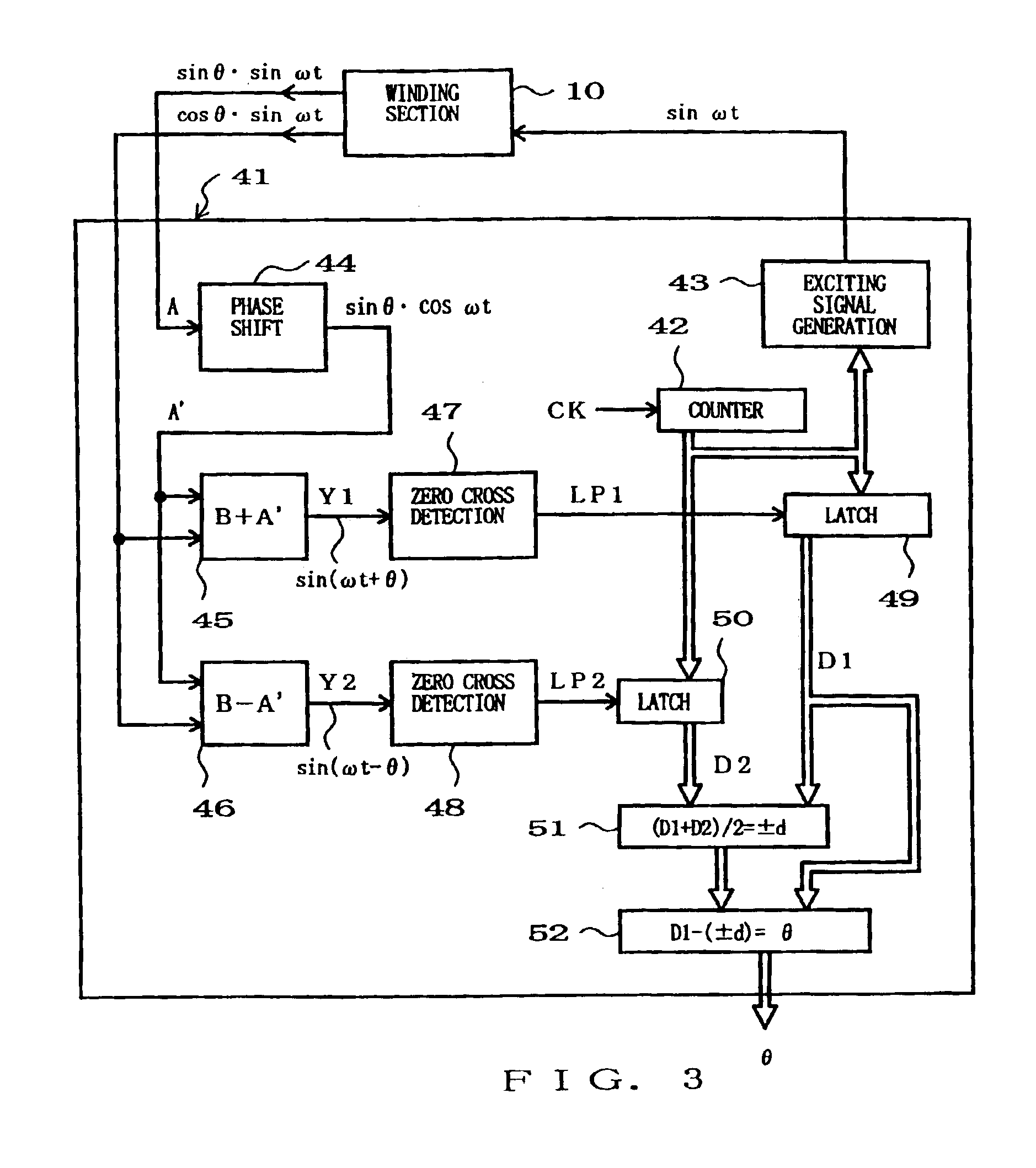
Phase difference detection device and method for a position detector
InactiveUS6885310B2Minimizing adverse influenceImprove response characteristicsElectric signal transmission systemsMagnetic measurementsPhase variationElectricity
Two A.C. output signals amplitude-modulated in accordance with two function values (sine and cosine) differing from each other in correspondence to a position-to-be-detected are received from a position sensor such as a resolver. By performing an addition or subtraction between a signal derived by shifting the electric phase of one of the received A.C. output signals by a predetermined angle, and the other received signal, two electric A.C. signals (sin(ωt±d+θ), sin((ωt±d−θ)) are electrically synthesized which have electric phase angles (θ) corresponding to the position-to-be-detected and are phase-shifted in opposite directions. “±d” here represents phase variation error caused by factors, other than the position-to-be-detected, such as temperature change. In the synthesized two signals, the phase variation errors (±d) appear in the same direction, while the phase differences (θ) corresponding to the position are shifted in opposite, positive and negative, directions. Thus, by measuring the respective phase shift amounts (±d+θ, ±d−θ) and performing appropriate operation, it is allowed to cancel out or extract the error (±d) so that an accurate phase difference (θ) can be detected. Position detection data indicative of the detected phase difference (θ) is converted into a pulse-width-modulated signal and transmitted in the pulse-width-modulated form.
Owner:AMITEQ
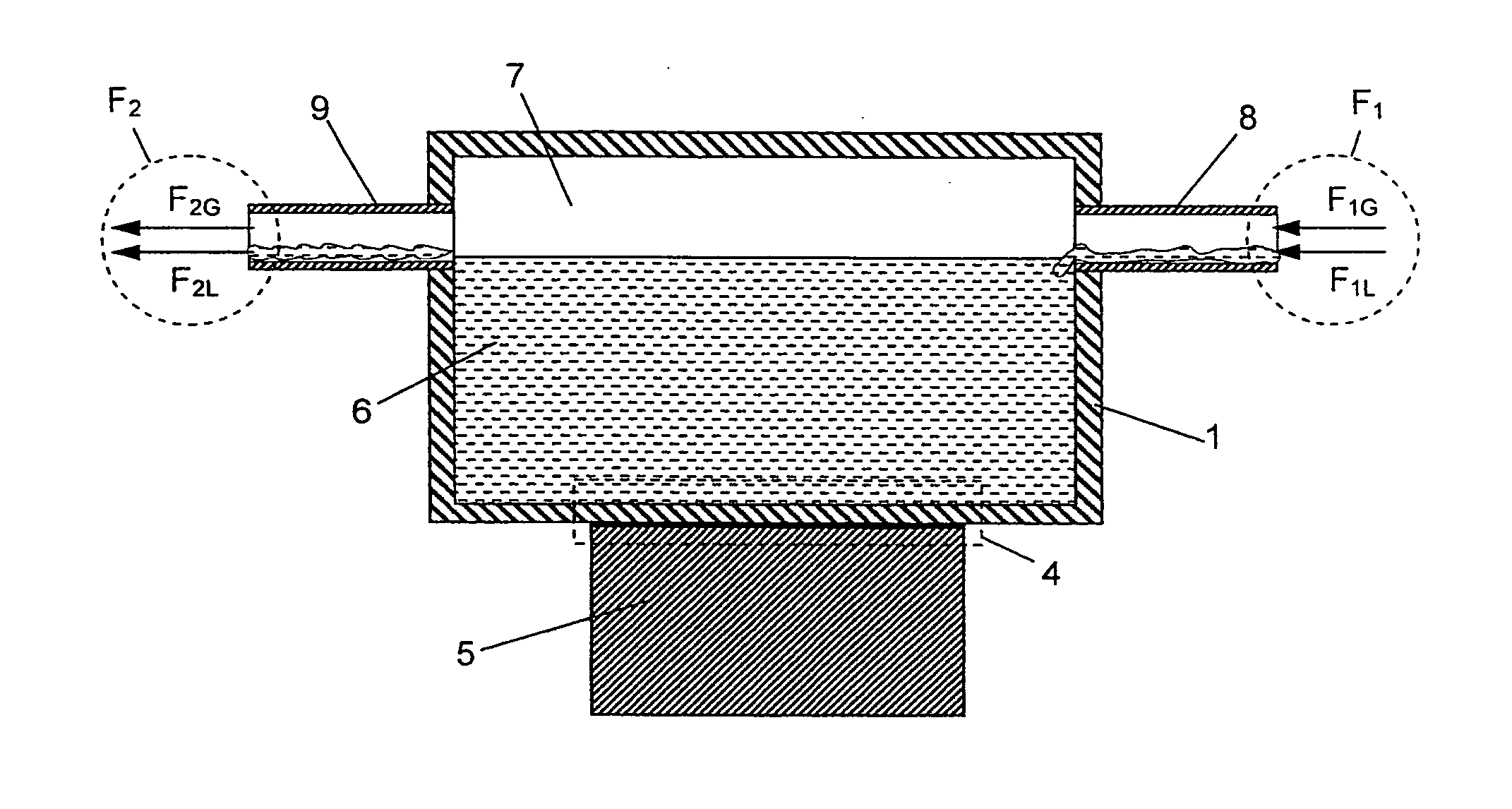
Cooling device for cryogenic cooling of an NMR detection system with the assistance of a container filled with a cryogenic fluid
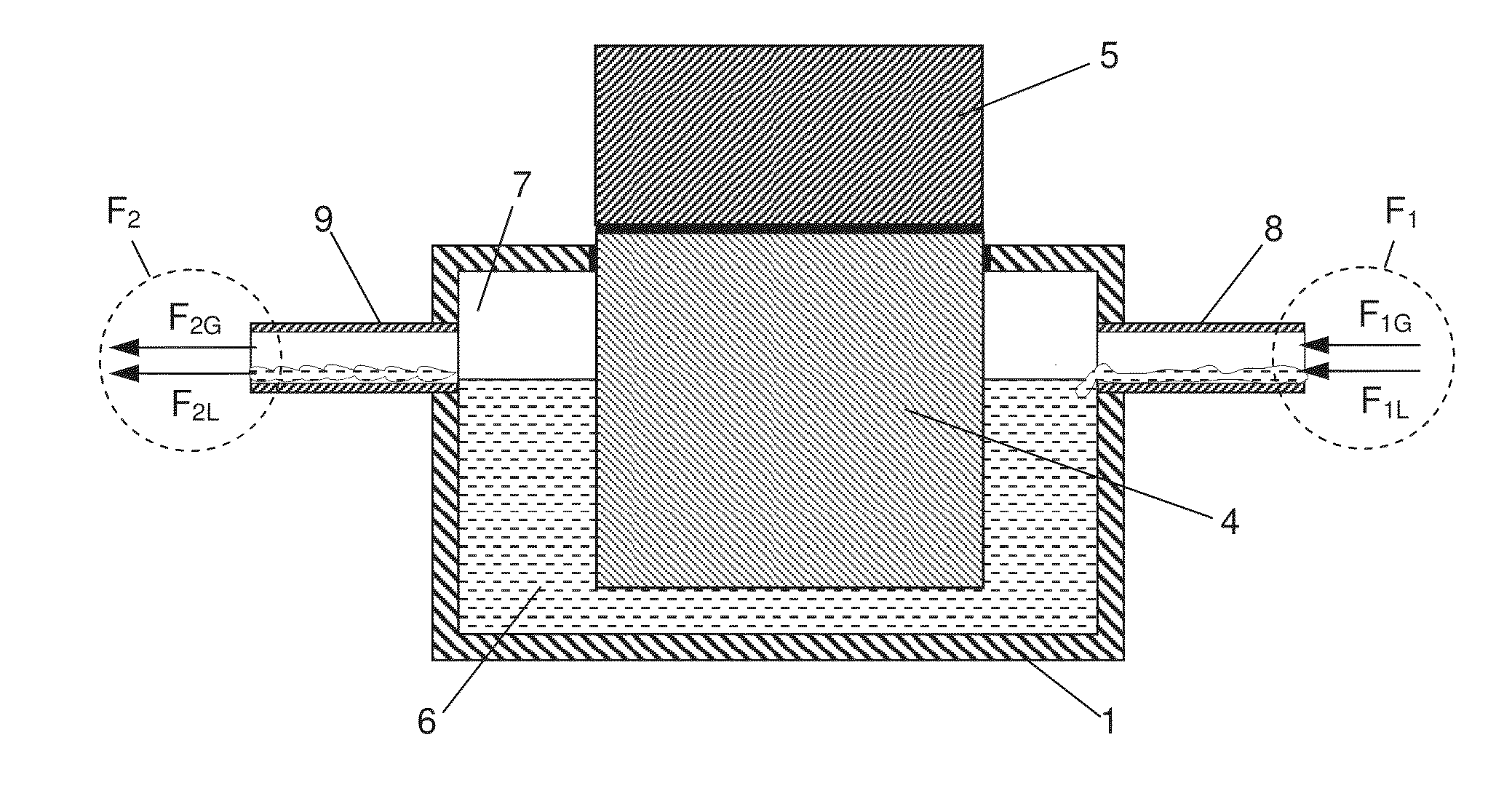
InactiveUS20110100027A1Undesirable influenceReduce consumptionLevel controlTemperatue controlProcess engineeringThermal contact
A cryo probe head for the transmission / reception of RF signals for NMR measurements with a heat exchanger (1) for cooling heat sources (5), the heat exchanger having a contact element (4.2) for thermal connection between a cryogenic fluid and the heat source, is characterized in that the heat exchanger comprises a container having an interior volume VB into which a first cryogenic fluid F1 that has a liquid component F1L and a gaseous component F1G flows through an inflow conduit (8) and from which a second cryogenic fluid F2 that has liquid component F2L and a gaseous component F2G flows out through an outflow conduit (9). The inflow conduit has a flow cross-section QZ and a circumference UZ from which a characteristic conduit volume VZ=4·Q2Z / UZ results, wherein VB>10·VZ, and the outflow conduit has a flow diameter QA wherein QA≧QZ. The contact element is in close thermal contact with both the liquid volume component VL of the cryogenic fluid and with the heat source. A device for setting the inflow quantity of the first cryogenic fluid F1 into the container is provided that ensures a state F1L / F1G>F2L / F2G during operation. In this way, vibrations due to the cooling process can be largely reduced and the consumption of cryogenic fluid minimized.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Precision variable area flowmeter apparatus
InactiveUS20060248962A1Increase reliabilityFunctional accuracyVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectMoving partsLong axis
We have invented an improved apparatus for electronically measuring fluid flow. The apparatus includes a radiation detection means for indicating the position of a flow indicator in a chamber of a variable area flowmeter and has a reliability, versatility and functional accuracy not obtainable with known variable area flowmeters. The invention may also include a variable area flowmeter with the flow indicator in a tapered fluid flow chamber with a wall and a long axis, the chamber having a front side, a back side, and an operational length substantially parallel to the long axis. The invention has no moving parts and is not intrusive so mechanical malfunction and unwanted leaks can not occur. Useful embodiments include, for example, compact self contained apparatus useful for fitting around existing flowmeters, systems that include flowmeters and systems able to work with some fluids that are visually opaque.
Owner:VAUGHN TONI CLINE +1
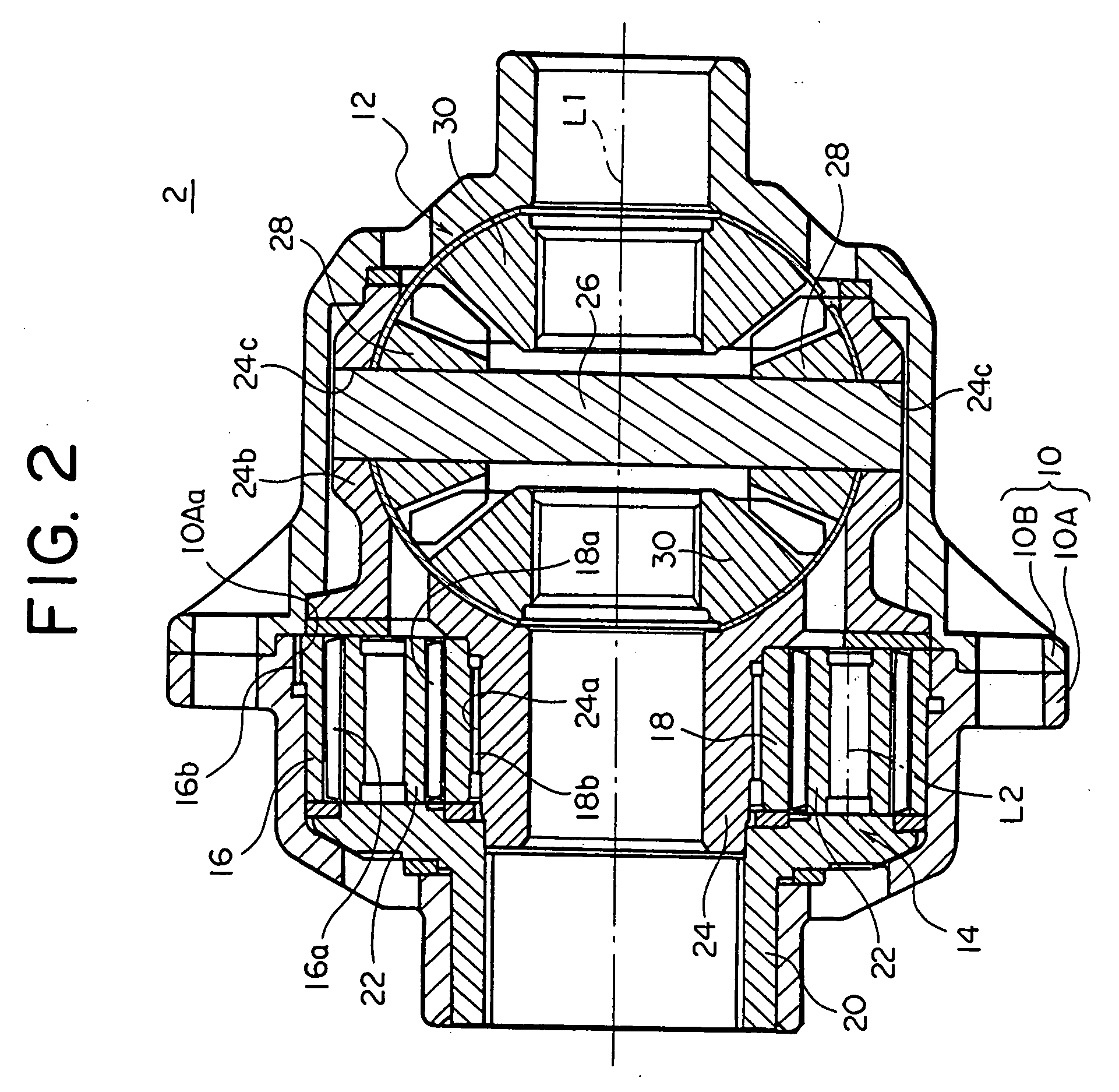
Vibration damping device and power transmission device
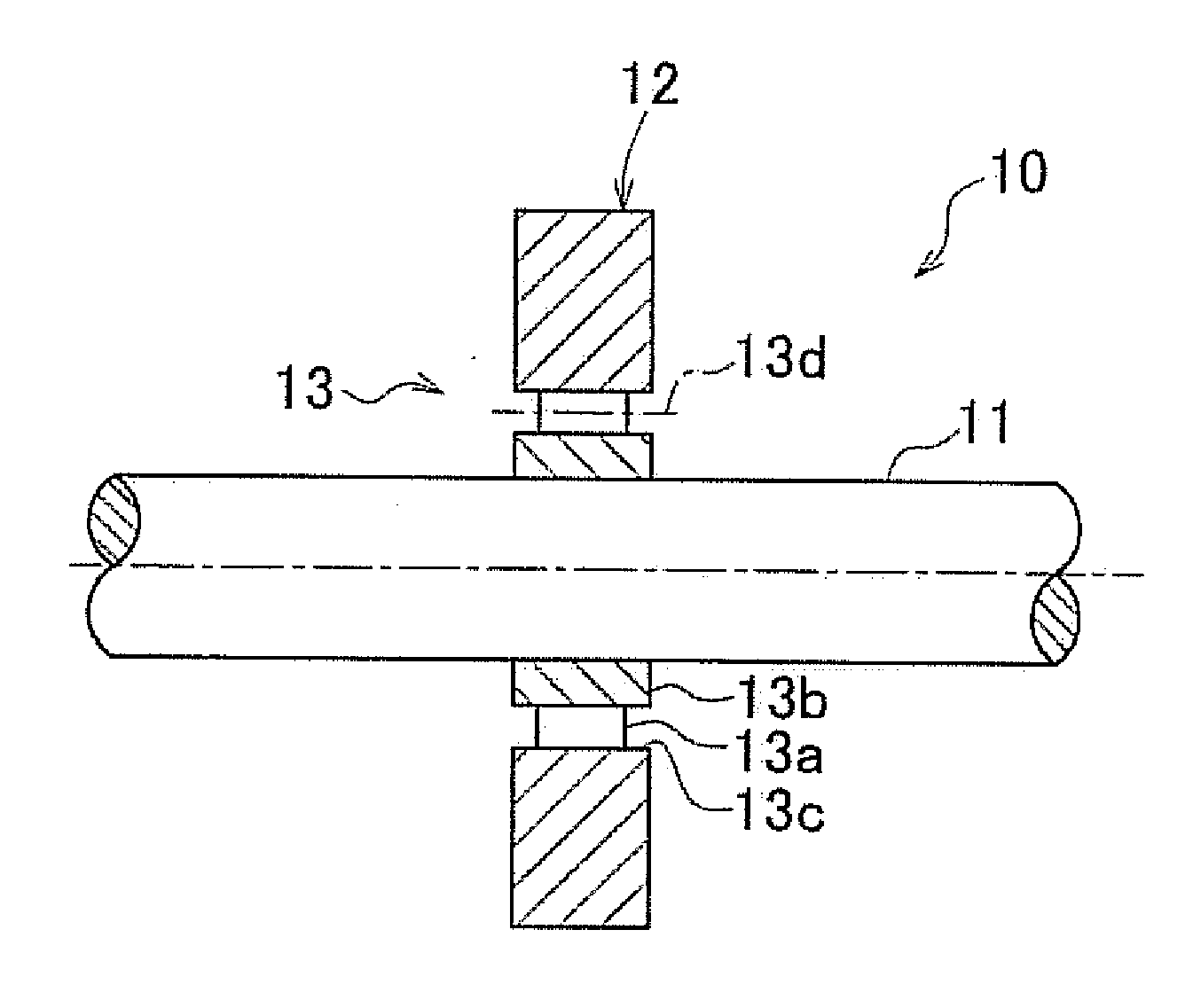
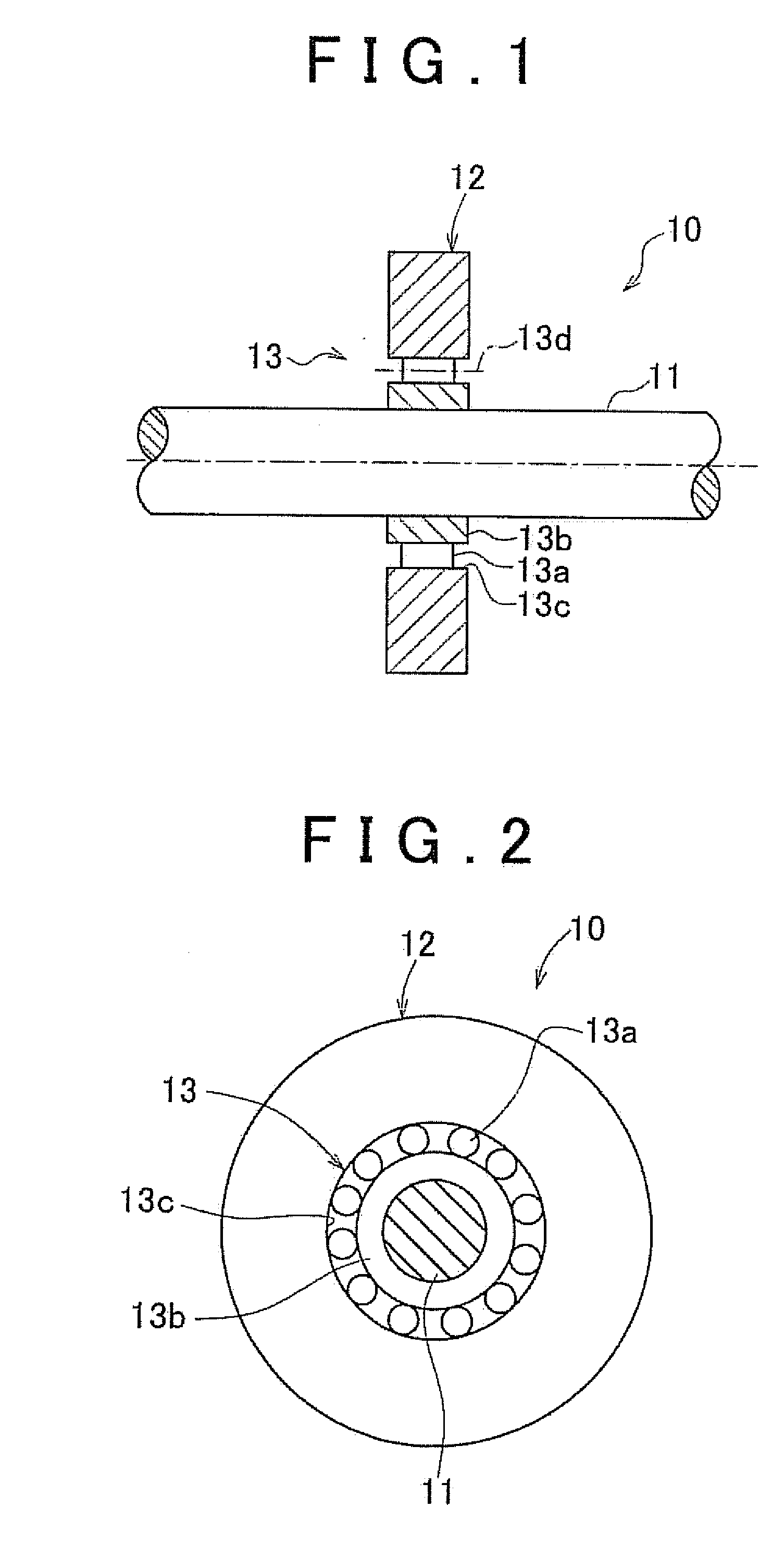
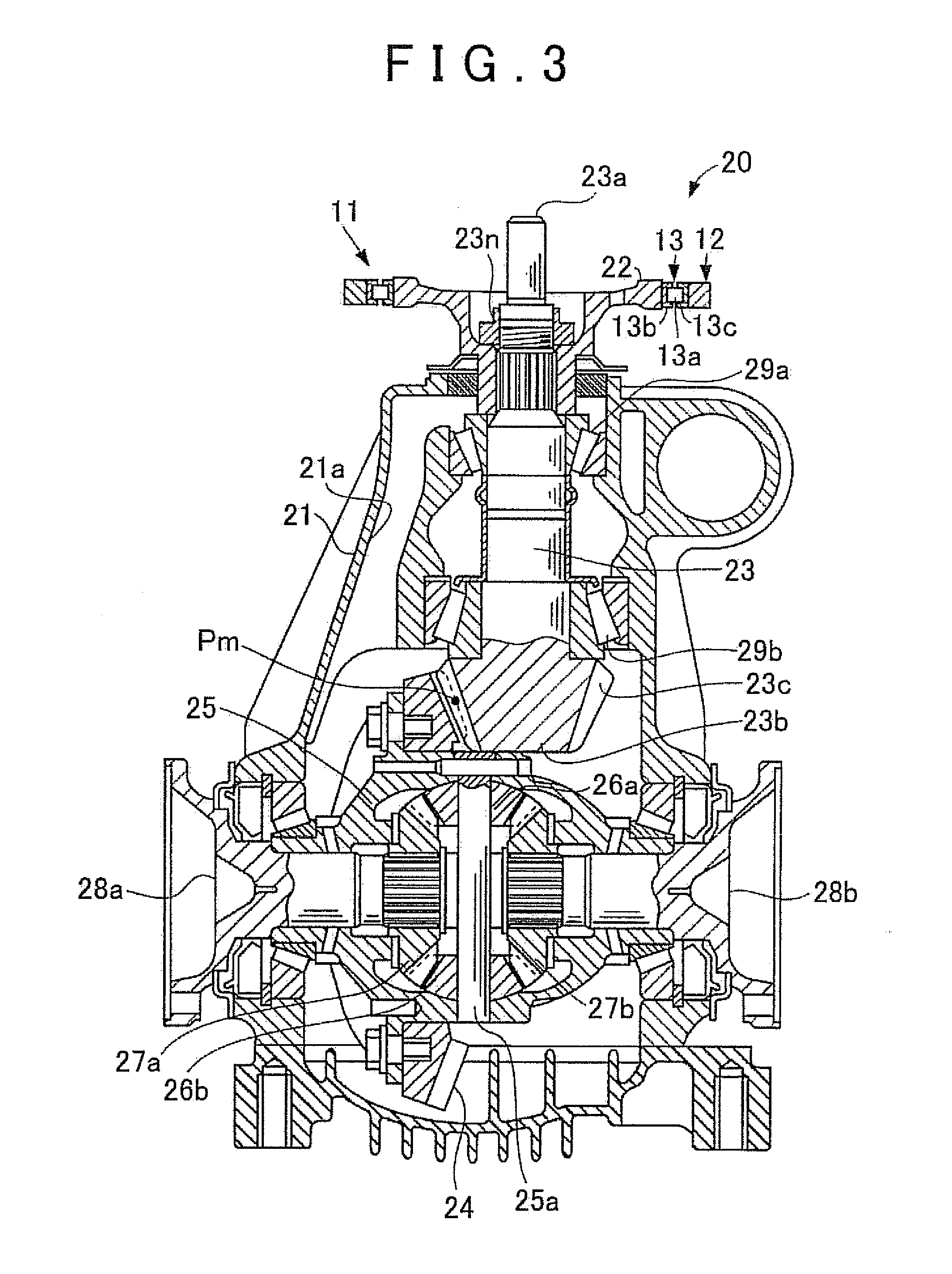
InactiveUS20090258749A1Minimizing adverse influenceLower Level RequirementsRotating vibration suppressionDifferential gearingsRotational axisRolling-element bearing
A vibration damping device is equipped with a mass body disposed spaced apart from a rotational center axis of a rotary shaft by a certain distance, and a rolling bearing that rotatably supports the mass body with respect to the rotary shaft and holds a support posture of the mass body with respect to the rotational center axis of the rotary shaft constant.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method of driving light emitting element array
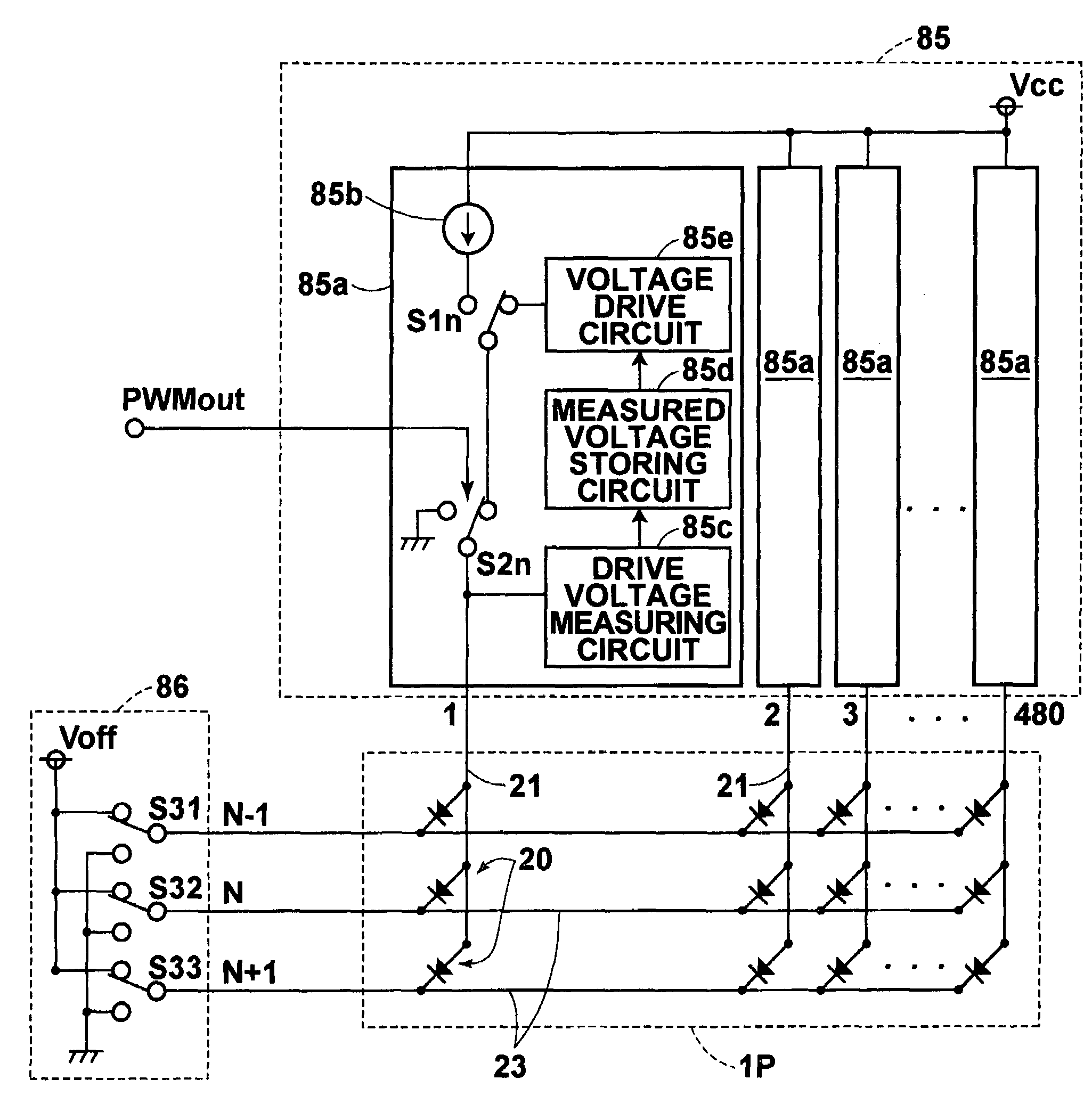
ActiveUS7385575B2Suppress fluctuation in response and light emissionImprove featuresPhotometry using reference valueStatic indicating devicesAnode voltageExposure period
An exposure system is provided with a light emitting element array formed by a plurality of light emitting elements formed at the intersections of anodes and cathodes arranged in matrix so that a photosensitive material is exposed to an image formed on the light emitting element array. A method of driving the light emitting element array includes the steps of driving the light emitting elements in constant-current drive before and / or during an exposure period, measuring and storing in a memory means the anode voltage of each light emitting element at that time, and driving the light emitting elements in constant-voltage drive at a voltage equal to the measured anode voltage at least during beginning of the subsequent exposure periods.
Owner:UDC IRELAND +1
AFC control apparatus and method in mobile communication system and mobile communication equipment using the apparatus and method
InactiveUS6816540B2No noiseMinimizing adverse influenceAutomatic frequency control detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase shiftedIntegrator
An AFC control apparatus in mobile communication equipment includes a depreading unit, first integrator, and control section. A despreading section despreads the reception signal. The first integrator integrates despread outputs obtained by despreading, of pilot symbols contained in a pilot channel of the reception signal, N (N is a number of 2 or more) consecutive first symbols and N second symbols succeeding the N first symbols, and generates first and second integral outputs. The control section detects any phase shift amount between the first and second integral outputs and controls the frequency of the local signal in accordance with the detected phase shift amount. An AFC control method and mobile communication equipment having the above apparatus and method are also disclosed.
Owner:NEC CORP
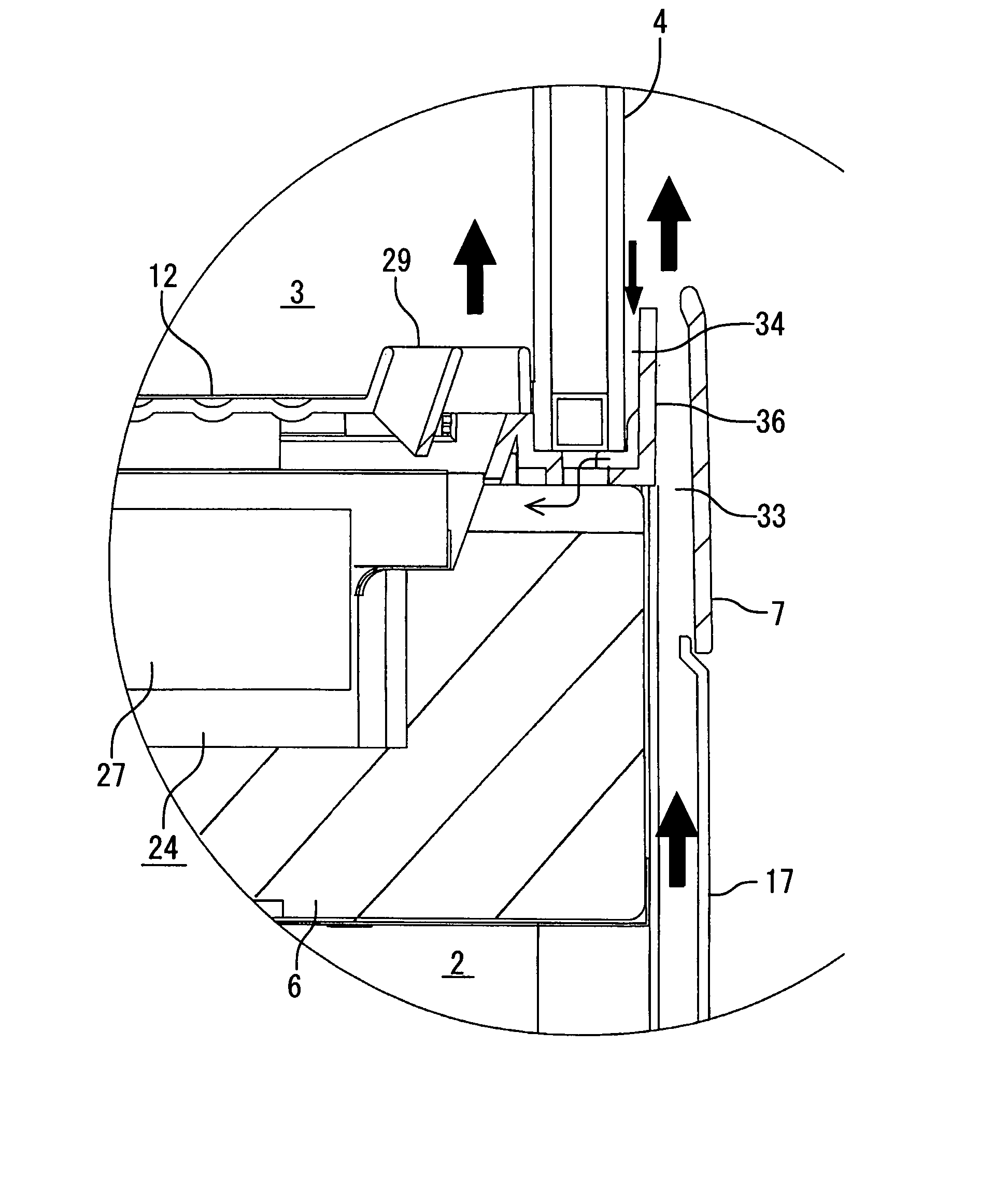
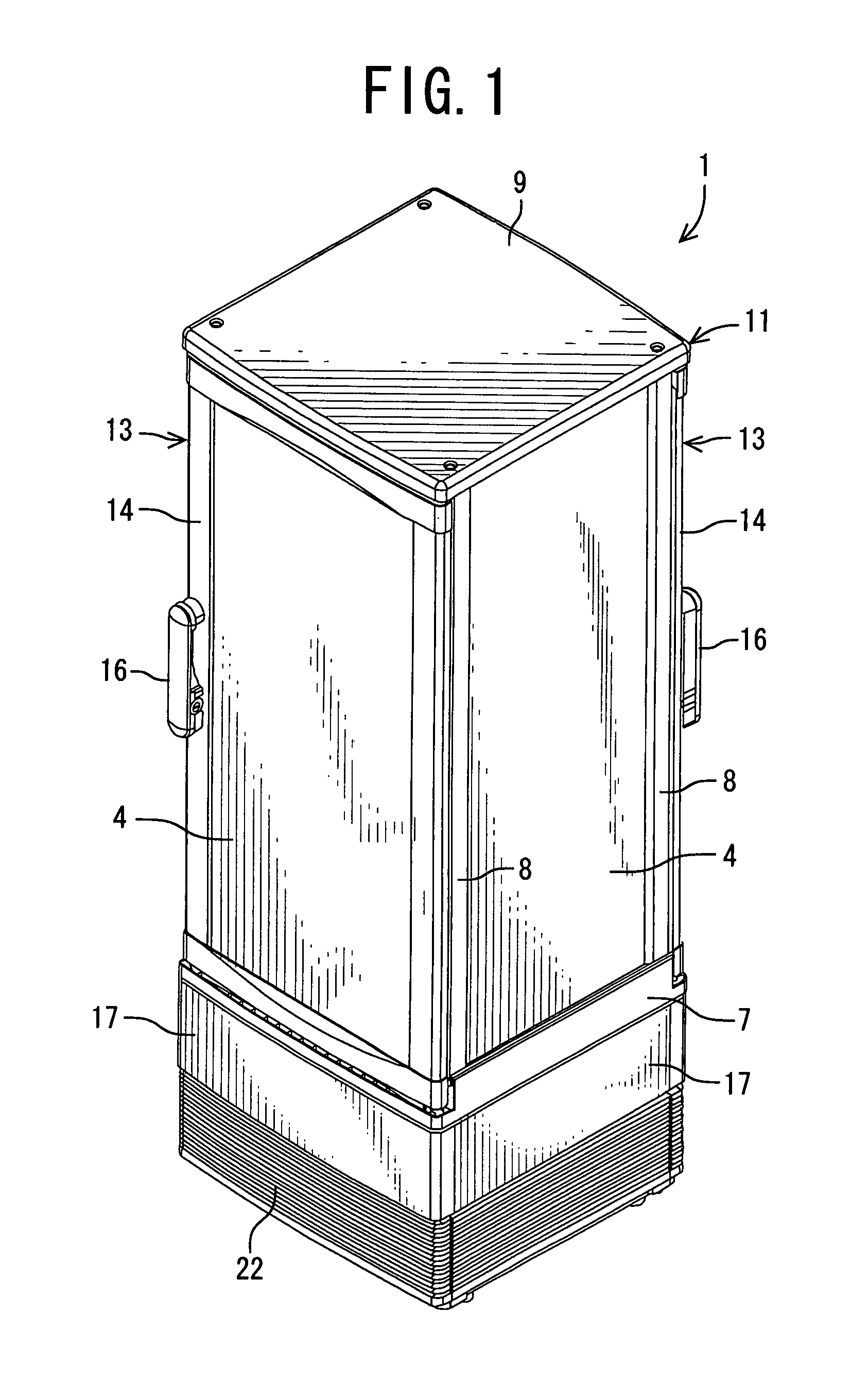
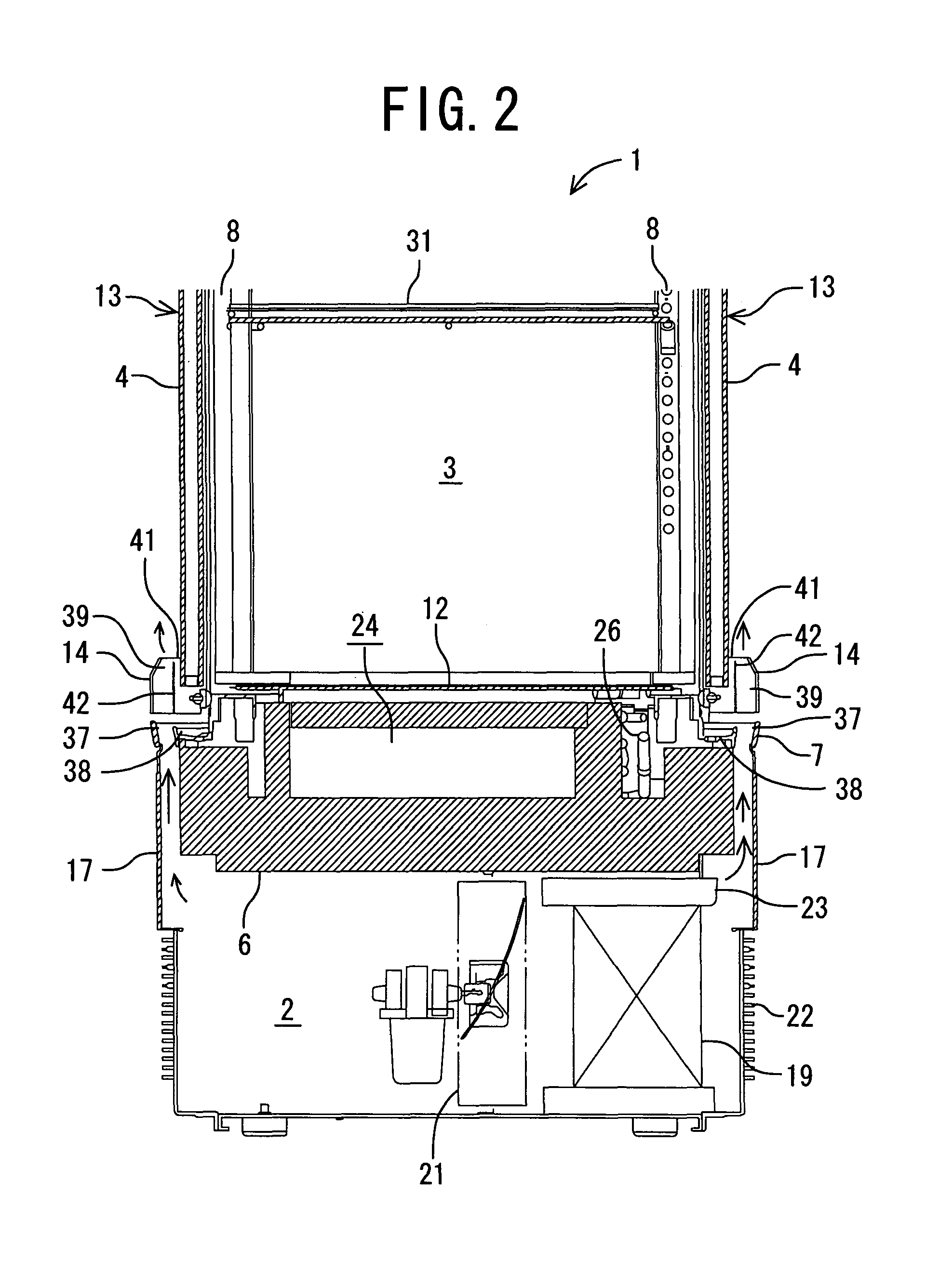
Low-temperature showcase
InactiveUS8104302B2Process stabilityEliminate and suppress dew condensationShow cabinetsCorrosion preventionWater flowDew
There is disclosed a low-temperature showcase in which dew condensation water from outer surfaces of transparent walls is securely treated and in which air can smoothly be blown from a mechanical chamber to the outer surfaces of the transparent walls. The low-temperature showcase includes a showroom having the transparent walls, the mechanical chamber constituted under this showroom, and a cooling unit constituted of a compressor, a condenser, a fan for the condenser and the like arranged in the mechanical chamber. The low-temperature showcase further comprises blow-off portions which are formed at lower portions of the transparent walls and which blow air discharged from the fan for the condenser in the mechanical chamber toward outer surfaces of the transparent walls, and water receiving portions which are defined between the blow-off portions and the outer surfaces of the transparent walls and which allows inflow of dew condensation water flowing down along the outer surfaces of the transparent walls.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
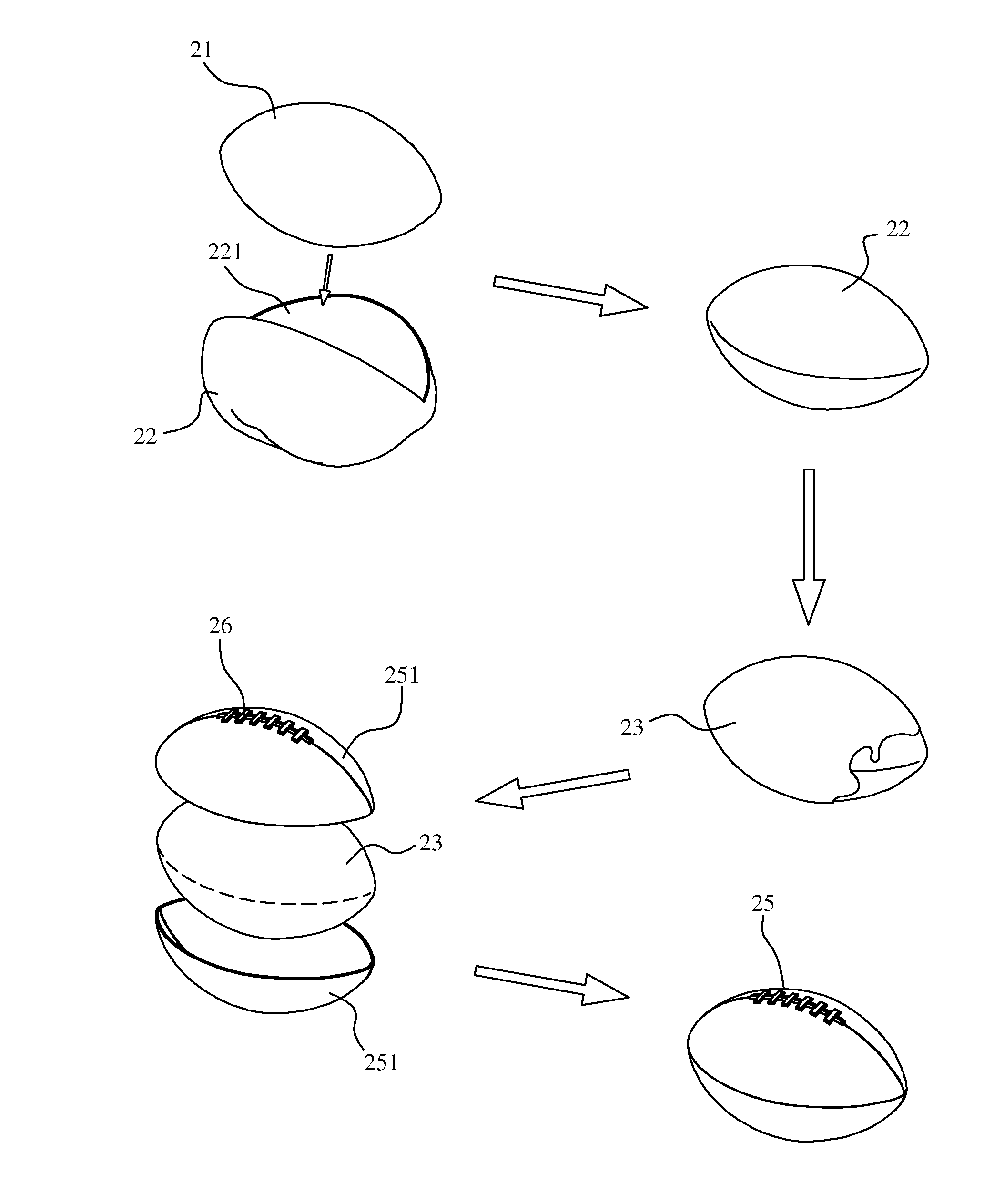
Stitch-free Football Structure and Method of Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20110237368A1Reduced bad yieldImprove smoothnessLabelling non-rigid containersLamination ancillary operationsYarnThermal compression
A stitch-free football structure includes a ball bladder formed by providing a yarn layer on an outer surface of an inflatable bladder and a glue layer on an outer side of the yarn layer, and a prolate-spheroidal structure formed by adjoining curved panels having configuration corresponding to the ball bladder and glued to an outer side of the glue layer; and a lacing-shaped patch glued to a seam between two adjoining curved panels to meet a required football configuration. In a method of manufacturing the stitch-free football structure, a plurality of curved panels is prepared in advance by hot press molding, and the curved panels are joined and attached to a ball bladder by gluing. Thus, the procedures for manufacturing a football are simplified, the bad yield in manufacturing is reduced, and the produced football is more durable for use, has more precise dimensions, and beautiful and even exterior appearance.
Owner:LONG WAY ENTERPRISE
Method for cryogenic cooling of an NMR detection system with the assistance of a container filled with a cryogenic fluid
ActiveUS20140283530A1Constant heating temperatureMinimize signalingFluid transferredMachines using refrigerant evaporationCatheterProcess engineering
A method for the transmission / reception of RF signals for NMR measurements uses a heat exchanger (1) for cooling heat sources (5), the heat exchanger having a contact element (4.2) for thermal connection between a cryogenic fluid and the heat source, is characterized in that the heat exchanger comprises a container having an interior volume V.sub.B into which a first cryogenic fluid F.sub.1 that has a liquid component F.sub.1L and a gaseous component F.sub.1G flows through an inflow conduit (8) and from which a second cryogenic fluid F.sub.2 that has liquid component F.sub.2L and a gaseous component F.sub.2G flows out through an outflow conduit (9). The inflow conduit has a flow cross-section Q.sub.Z and a circumference U.sub.Z from which an associated parameter V.sub.Z=4Q.sup.2.sub.Z / U.sub.Z results, wherein V.sub.B>10V.sub.Z, and the outflow conduit has a flow diameter Q.sub.A wherein Q.sub.A.gtoreq.Q.sub.Z. The contact element is in close thermal contact with both the liquid volume component V.sub.L of the cryogenic fluid and with the heat source. A device for setting the inflow quantity of the first cryogenic fluid F.sub.1 into the container is provided that ensures a state F.sub.1L / F.sub.1G>F.sub.2L / F.sub.2G during operation. In this way, vibrations due to the cooling process can be largely reduced and the consumption of cryogenic fluid minimized.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
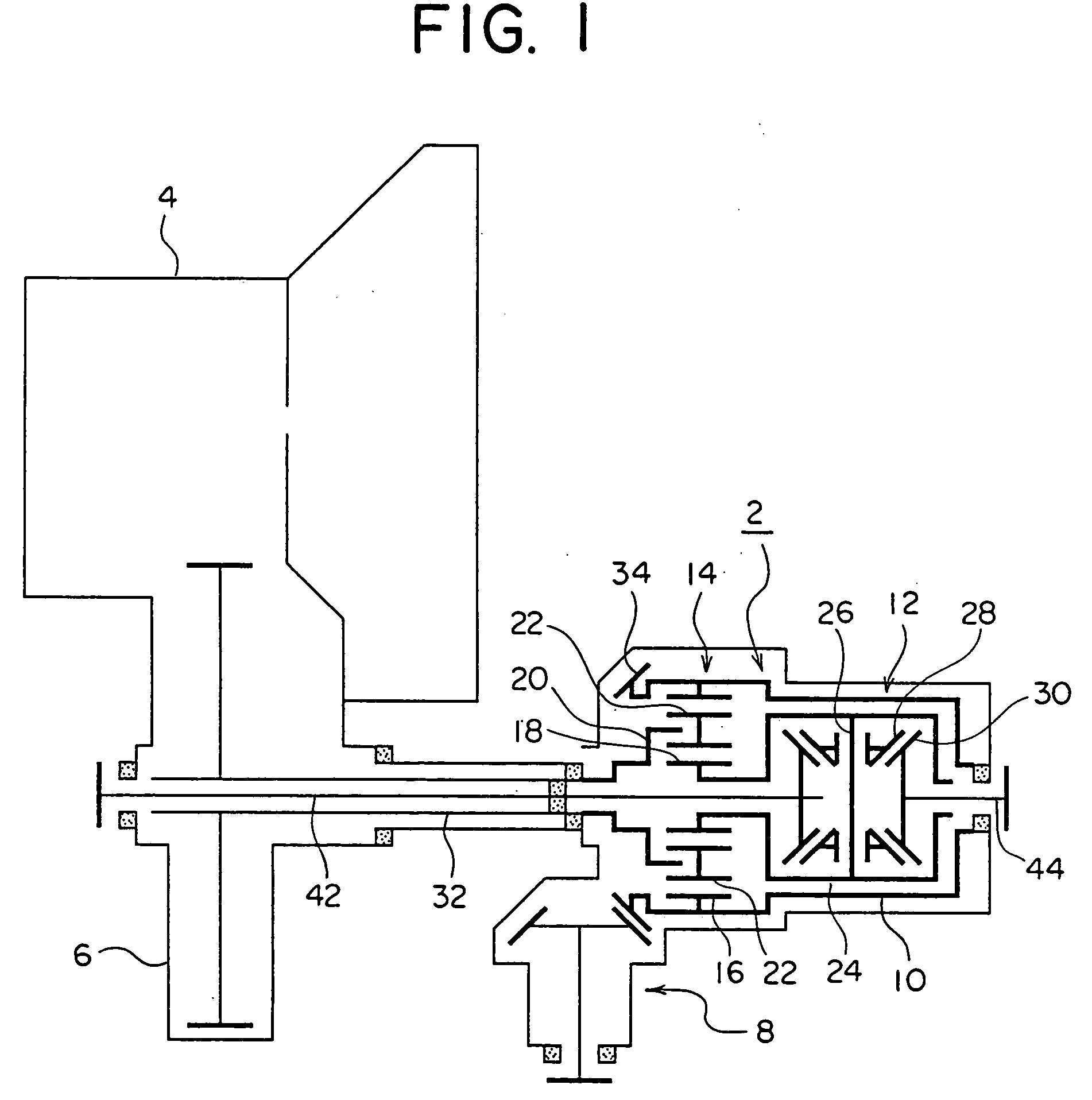
Power transmission system for vehicle
InactiveUS20050090356A1Minimizing adverse influenceToothed gearingsDifferential gearingsDrivetrainEngineering
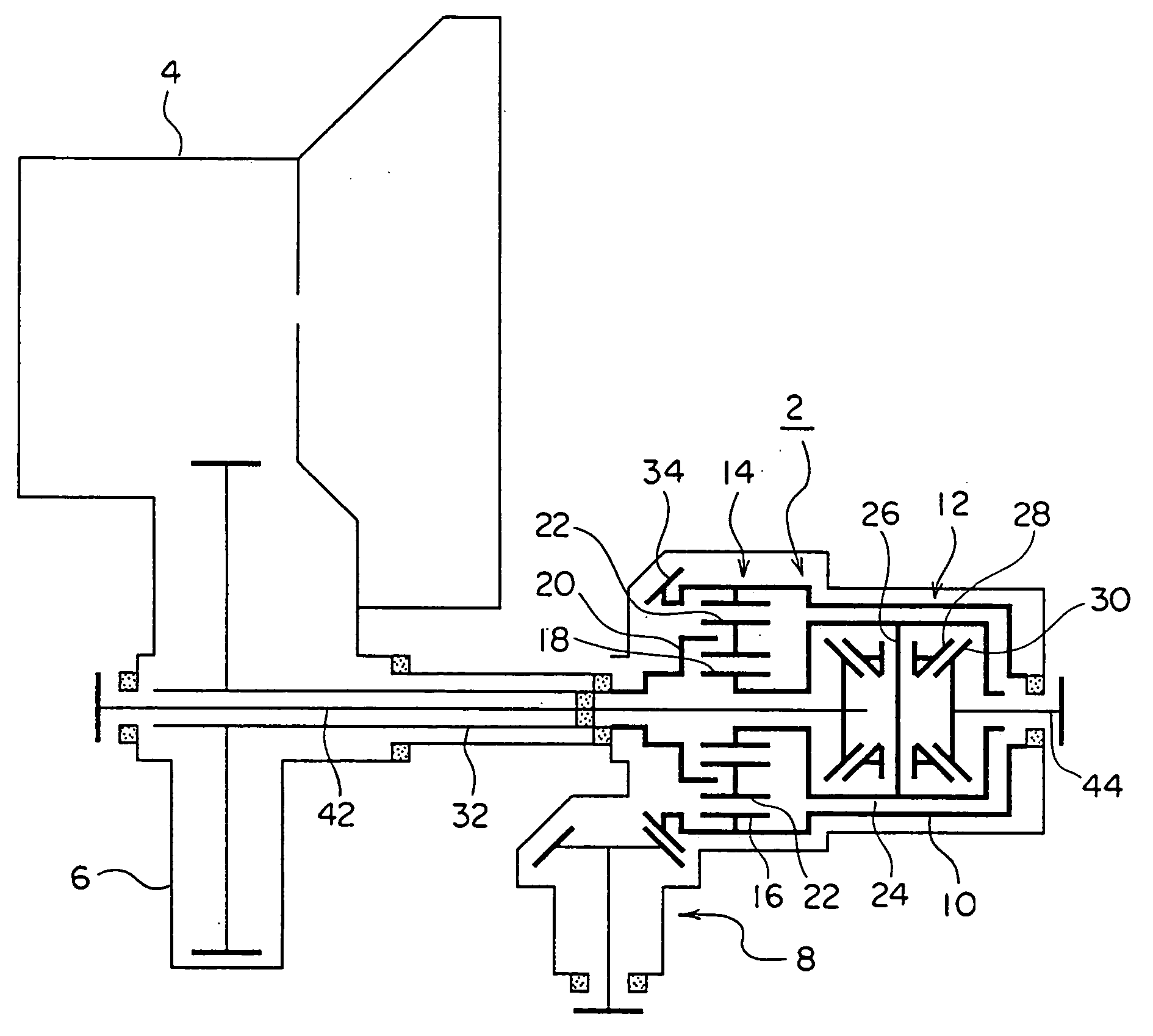
A differential gearing 2 of twin differential type including a center differential unit 14 of planetary gear type and a front differential unit 12 of bevel gear type which are received within a housing 10 is separated from a gear box 6 of a transmission 4, and is disposed within PTO (power transfer off) 8. A common specification can be used for the twin differential unit, and influences by the oil variety can be avoided, assuring a given performance in any application.
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD
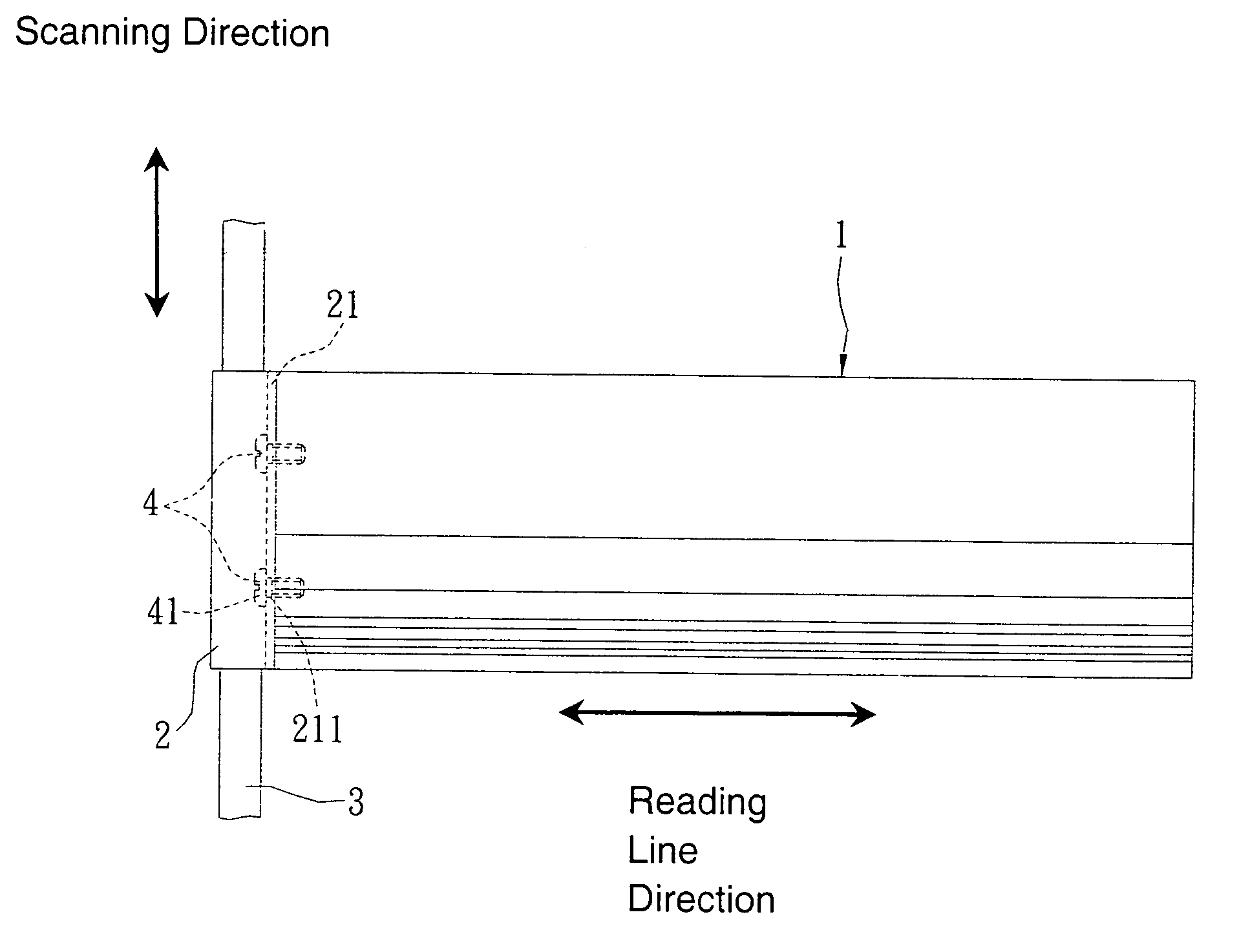
Reading-line adjusting device of image scanner
InactiveUS20060039043A1Minimizing adverse influenceBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringImage sensing
A reading-line adjusting device of an image scanner includes an image sensing module, a shaft, a bush member, and a fixing and adjusting member. The image sensing module has a reading line for sensing an electronic signal of an image. The shaft is arranged in a first direction. The bush member includes a base and a bushing body. The base is coupled with the image sensing module. The bushing body is sleeved around the shaft and moved along the shaft. The fixing and adjusting member is used for fixing the base of the bush member onto the image sensing module and adjusting an angle between the base and the image sensing module such that the reading line of the image sensing module is arranged in a second direction.
Owner:TECO IMAGE SYST
Internal antenna of mobile terminal
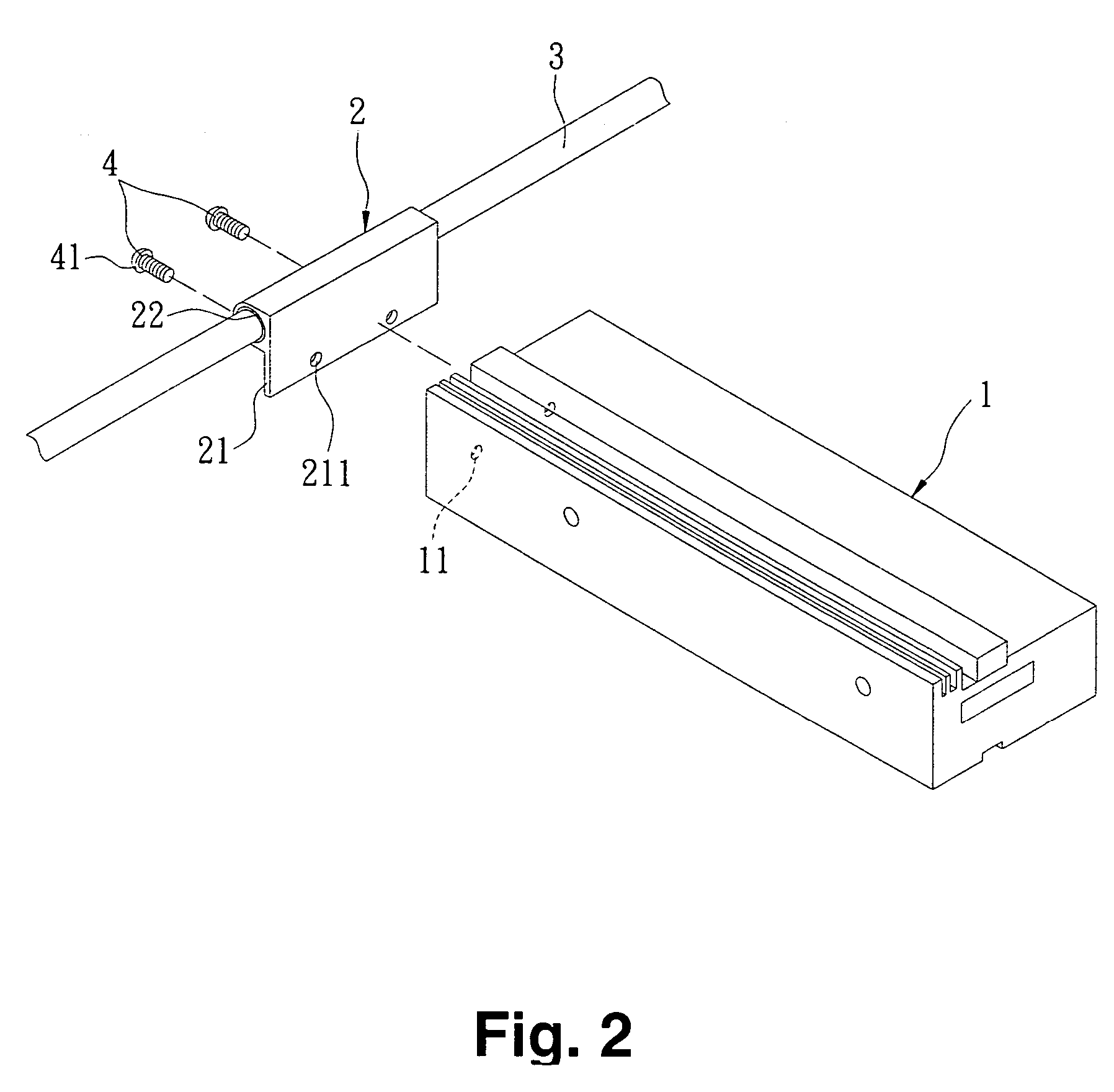
ActiveUS20140043192A1Small thicknessMinimizing adverse influenceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsPrinted circuit boardFront cover
An antenna of a mobile includes at least two internal antennas and a printed circuit board disposed between a front cover and a rear cover. The printed circuit board includes at least one first antenna mounted on an upper surface and the printed circuit board having at least one fastening opening therein. A second antenna is mounted in an upper portion of a side surface of the printed circuit board and included a protruded portion of one end protruded from a body and in which the protruded portion is fastened to the fastening opening to be fastened to a side surface of the printed circuit board and the mobile terminal can be produced having a reduced thickness.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Vibration damping device and power transmission device
InactiveUS20110245011A1Minimizing adverse influenceDecrease in levelRotating vibration suppressionShaftsRotational axisRolling-element bearing
A vibration damping device is equipped with a mass body disposed spaced apart from a rotational center axis of a rotary shaft by a certain distance, and a rolling bearing that rotatably supports the mass body with respect to the rotary shaft and holds a support posture of the mass body with respect to the rotational center axis of the rotary shaft constant.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Crosslinked polysaccharide sponge
InactiveUS7700747B2Improve securityMinimizing adverse influenceOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNo removalSolvent
A process for producing a polysaccharide sponge comprises the steps of (A) freezing a photoreactive polysaccharide solution, and (B) irradiating the frozen photoreactive polysaccharide solution with light to crosslink the photoreactive polysaccharide, thereby obtaining the polysaccharide sponge. The process includes simplified steps requiring no removal of solvent, and has such an advantage that impurities are easily removed therefrom.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Touch Control Structure of an Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode Display Screen
ActiveUS20190018531A1Minimizing adverse influenceReduce difficultyStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesPolymer foilActive matrix
Owner:KUNSHAN NEW FLAT PANEL DISPLAY TECH CENT +1
Low sulfated ash, low sulfur, low phosphorus, low zinc lubricating oil composition
ActiveUS8361940B2Low ashReduce contentOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationAlkaline earth metalInternal combustion engine
A low sulfated ash, tow sulfur, low phosphorus, low zinc lubricating, oil composition preferably employable for internal combustion engines using a low sulfur hydrocarbon fuel comprises a base oil having a saturated component of 85 wt. % or more, a viscosity index of 110 or more, and a sulfur content of 0.01 wt. % or less; an alkaline earth metal-containing detergent; a nitrogen-containing ashless dispersant of a weight average molecular weight of 4,500 or more; a phenolic or amine oxidation inhibitor; and a basic nitrogen-containing compound-oxymolybdenum complex.
Owner:CHEVRON JAPAN
Recording apparatus
ActiveUS20190016138A1Reduce riskMinimizing adverse influenceOther printing apparatusEngineeringElectric field
A recording apparatus includes an electric field forming section including a conductive member and configured to form an electric field, and the conductive member includes at least one first portion and a second portion, each of the at least one first portion being disposed at a position being nearer the recording head than a position of the second portion and included in a corresponding one of at least one liquid discarding region each of which, in an execution of borderless recording, is used for the ejection of the liquid onto an outside of a corresponding one of at least one edge whose position corresponds to each of at least one predetermined size of a medium, the second portion being disposed in a recording region other than the at least one liquid discarding region.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Crosslinked polysaccharide sponge
InactiveUS20080071050A1Easy to excludeImprove securitySugar derivativesThin material handlingSolventNo removal
A process for producing a polysaccharide sponge comprises the steps of (A) freezing a photoreactive polysaccharide solution, and (B) irradiating the frozen photoreactive polysaccharide solution with light to crosslink the photoreactive polysaccharide, thereby obtaining the polysaccharide sponge. The process includes simplified steps requiring no removal of solvent, and has such an advantage that impurities are easily removed therefrom.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com