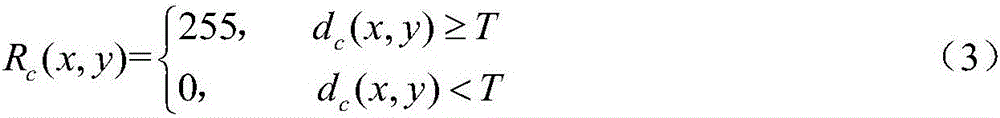Patents
Literature
162 results about "Differential function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Differentials Of Functions. The differential of a function provides a linear approximation of the function f ( x) at a particular point x. Taking the differential of a function results in its derivative. For a function f ( x ), . The differential of a multi-variable function can be found for any number of variables (so that for f ( x, y ),...
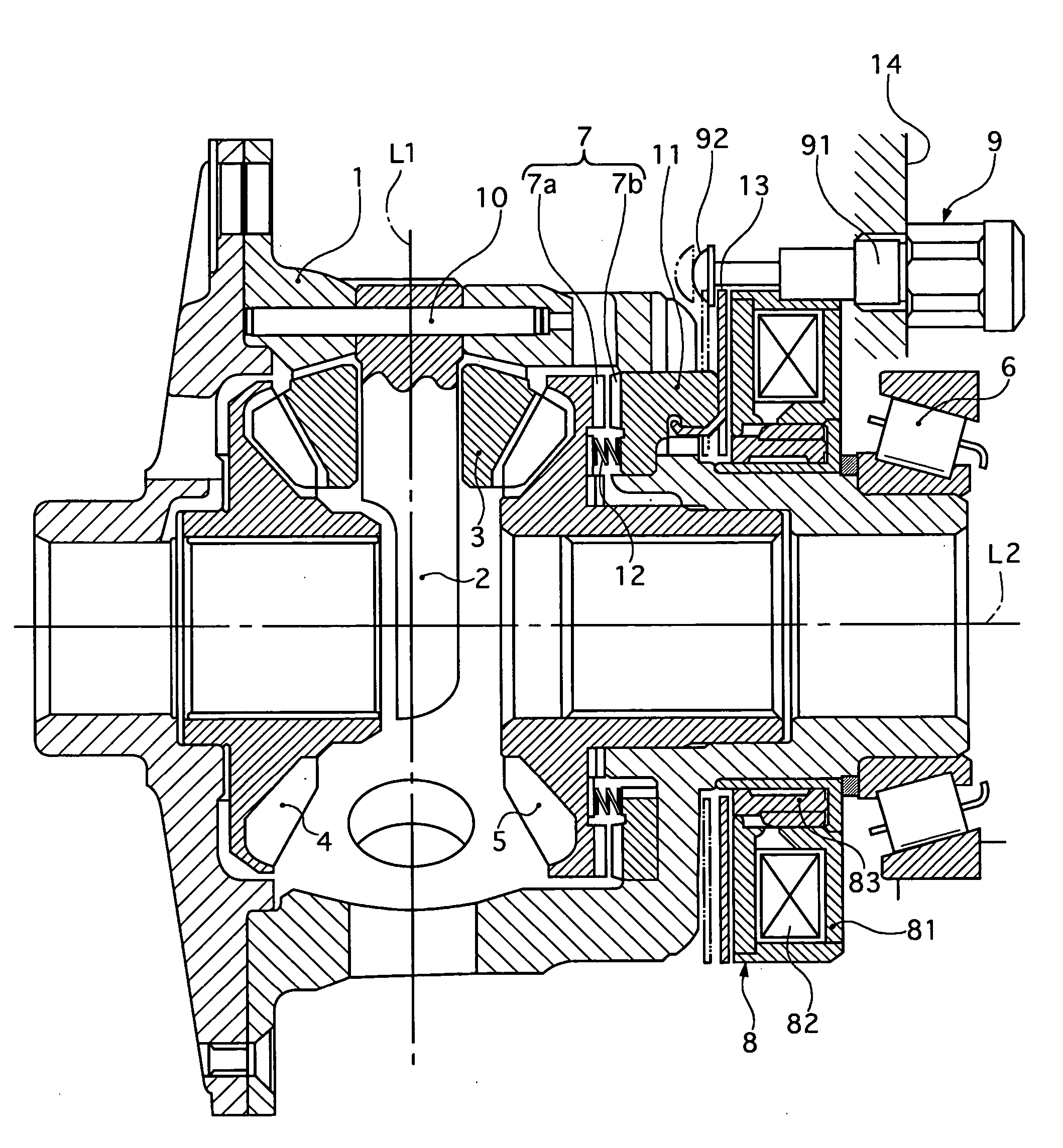
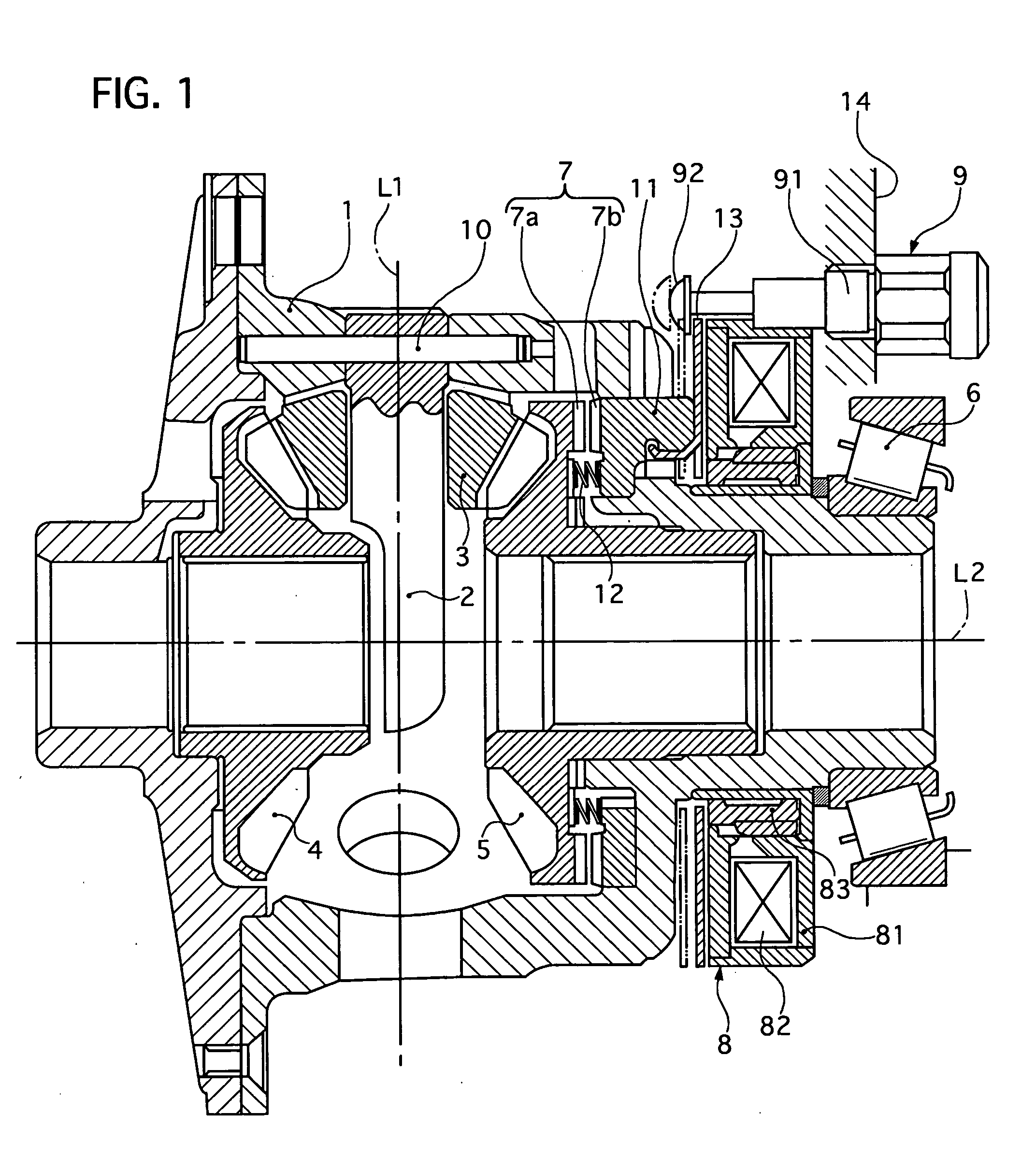
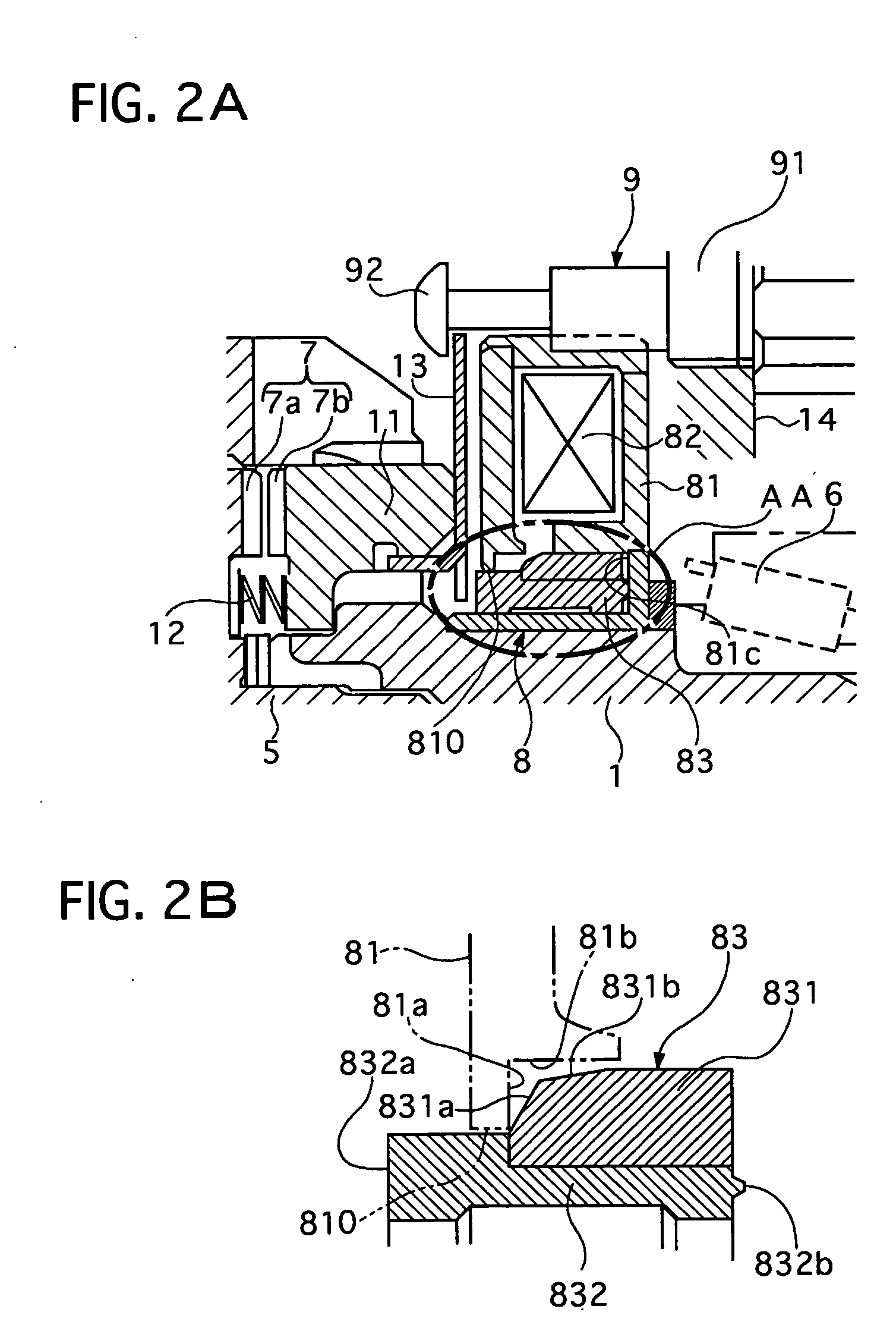
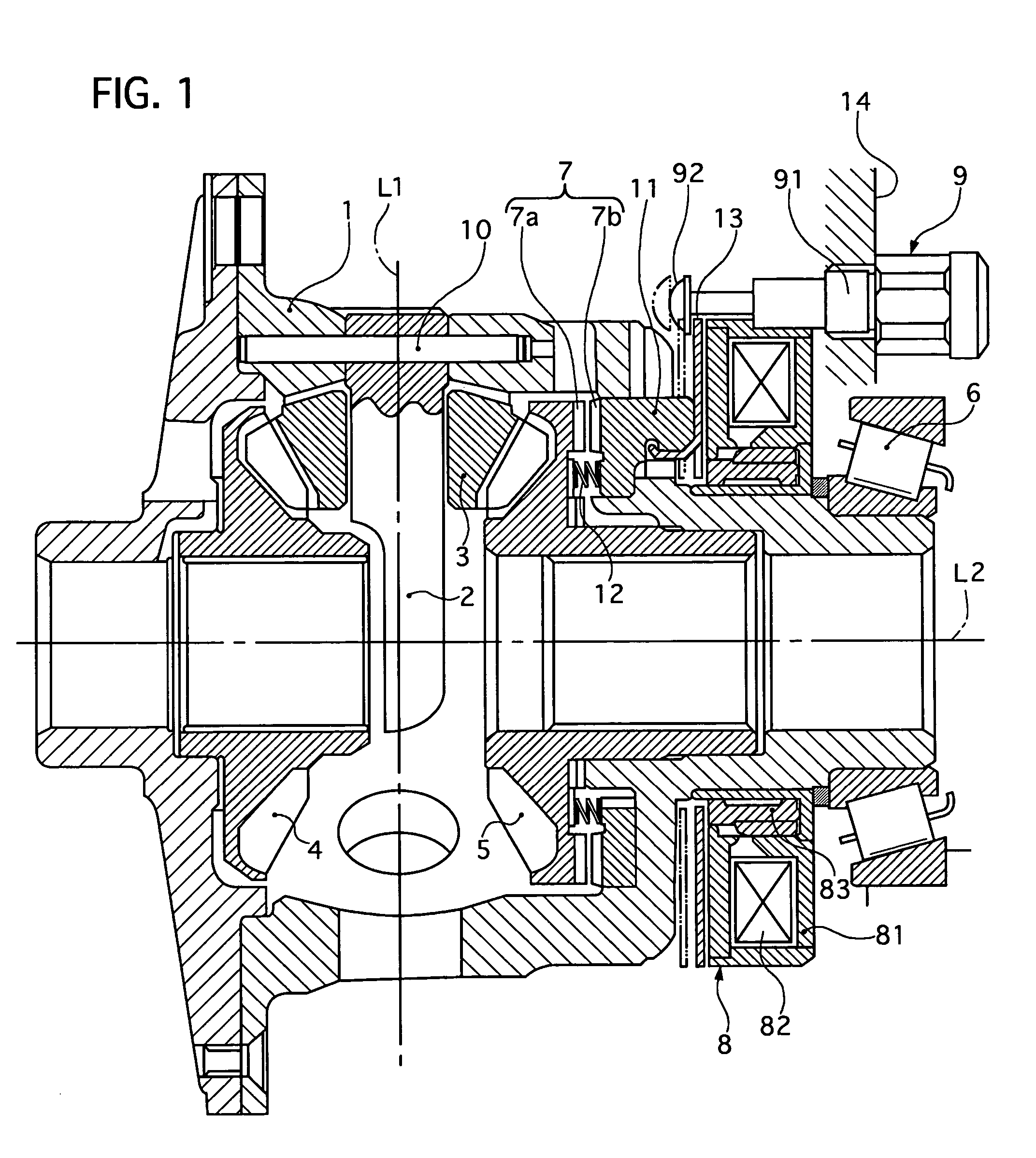
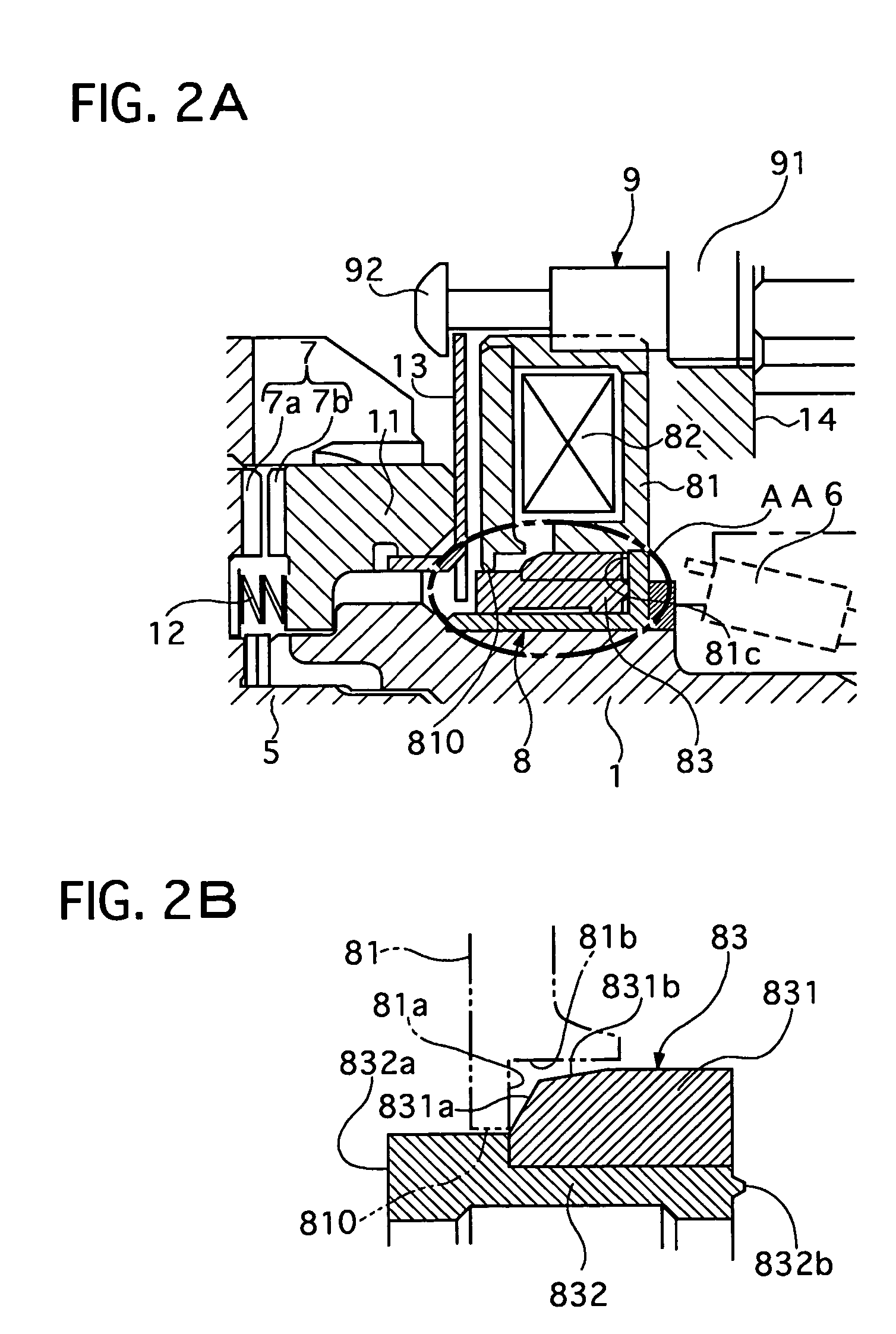
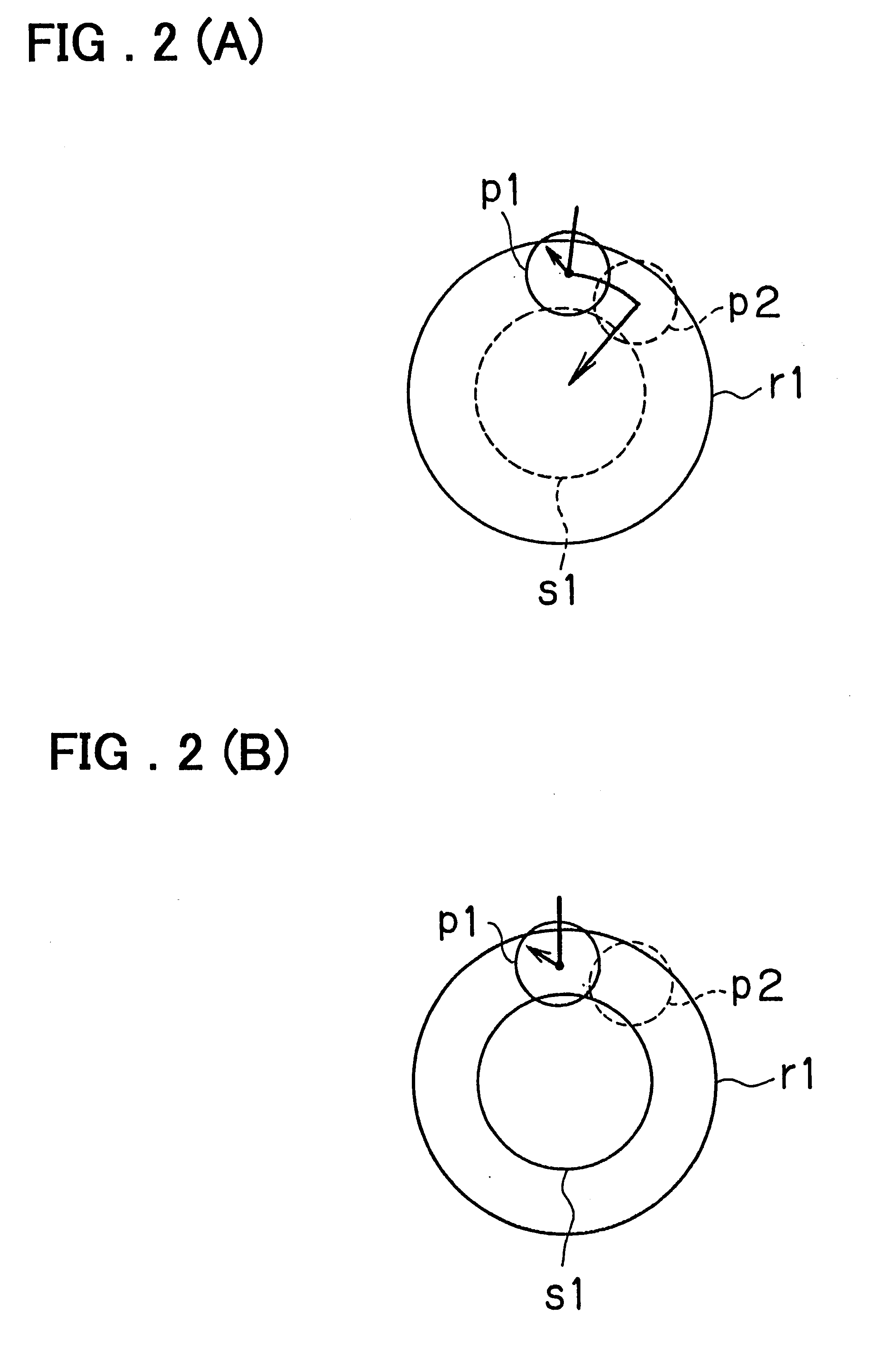
Limited slip differential device
ActiveUS20050187063A1Differential function is limitedMagnetically actuated clutchesDifferential gearingsDifferential functionLimited-slip differential
A limited slip differential device has differential gears, a clutch to limit the differential function of the differential gears, and a electromagnetic solenoid including a plunger and a coil. The plunger is set to move forward to engage the clutch by electromagnetic force of the coil in a differential limit state and move backward by a return spring to disengage said clutch in a differential limitless state. The plunger contacts with a contacting member in at least one state of the differential limit state and the differential limitless state, and their contact area is set smaller than a facing area between them in at least the one state.
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE TORQUE TECHNOLOGY KK +1
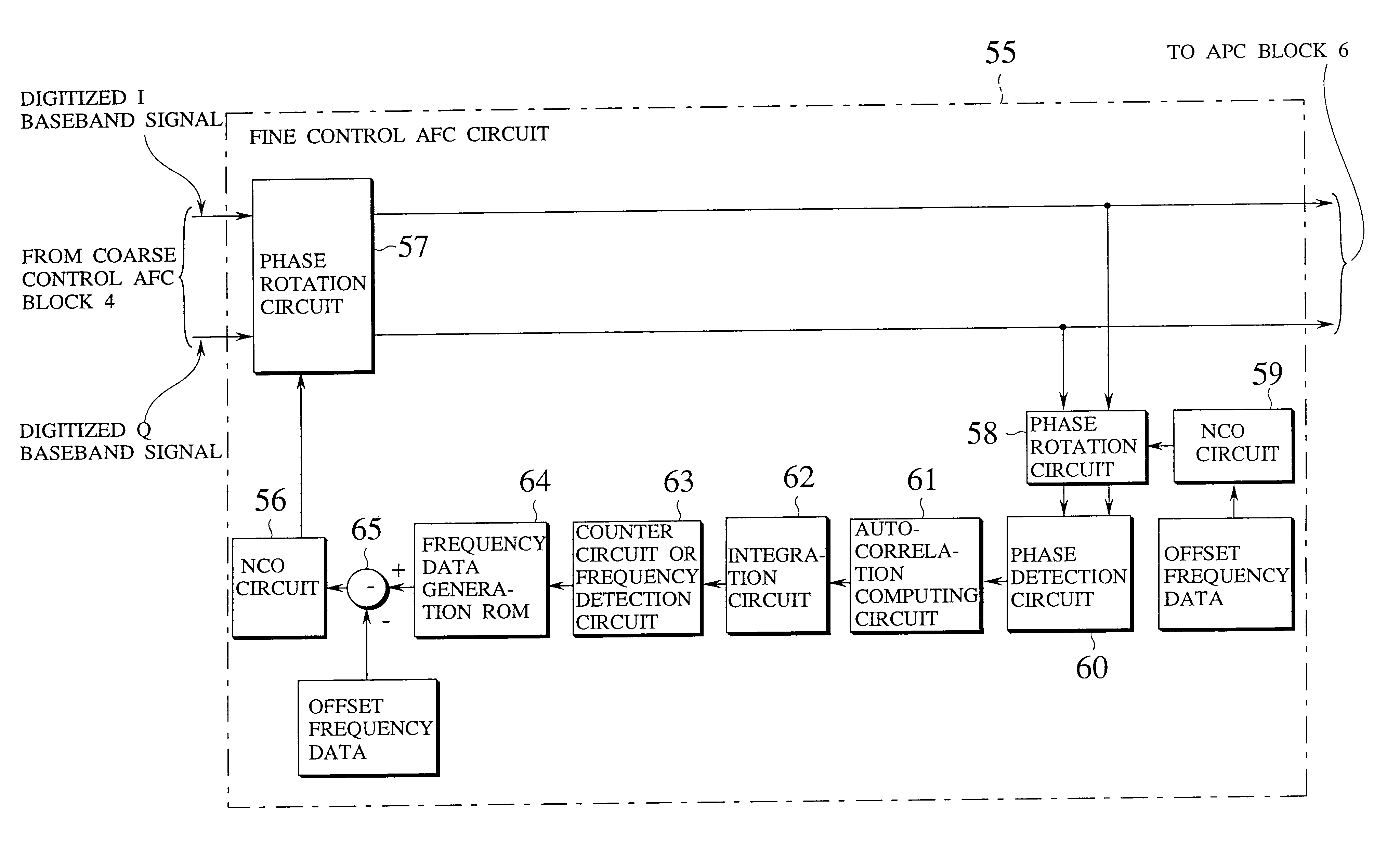
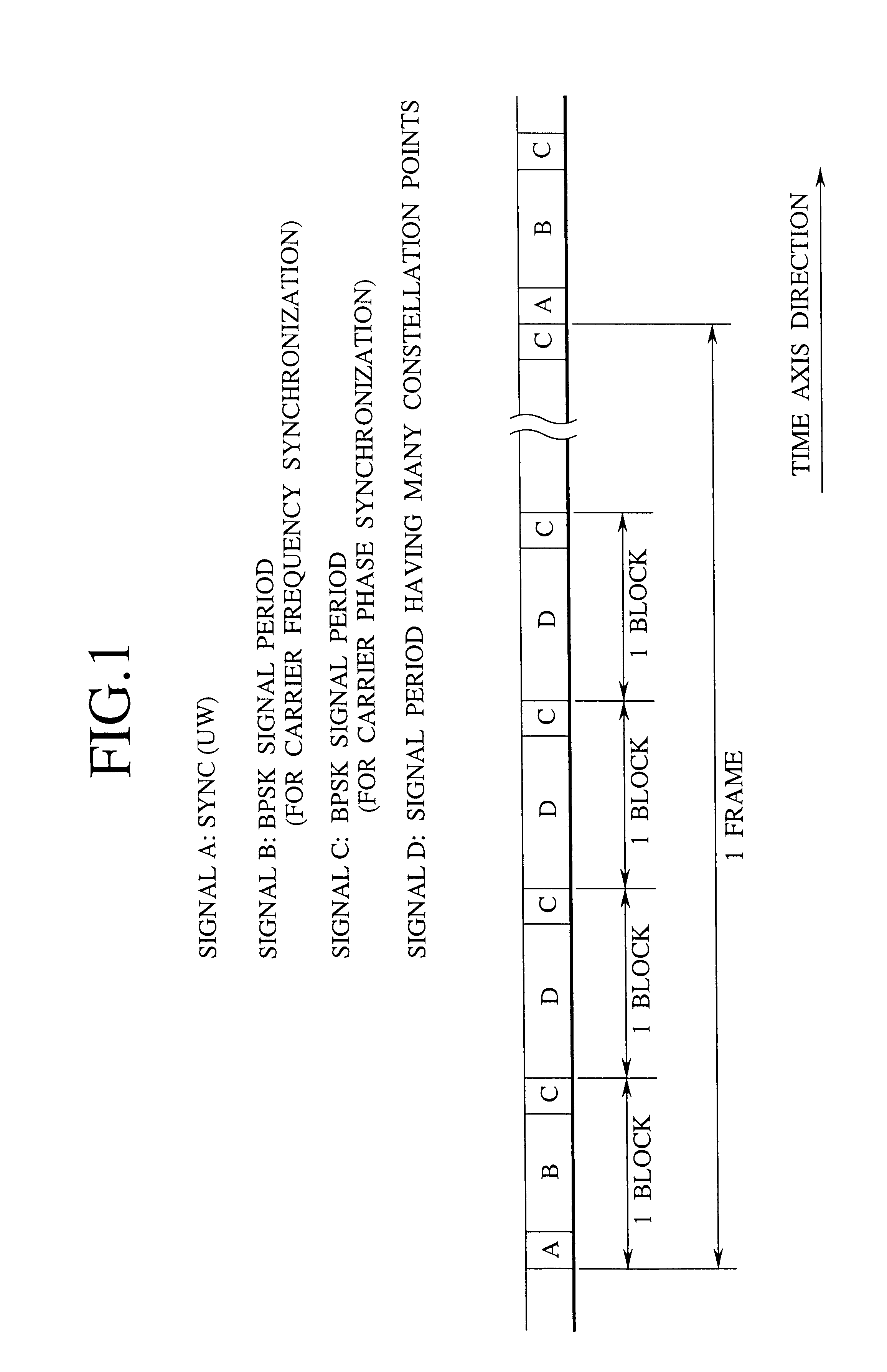
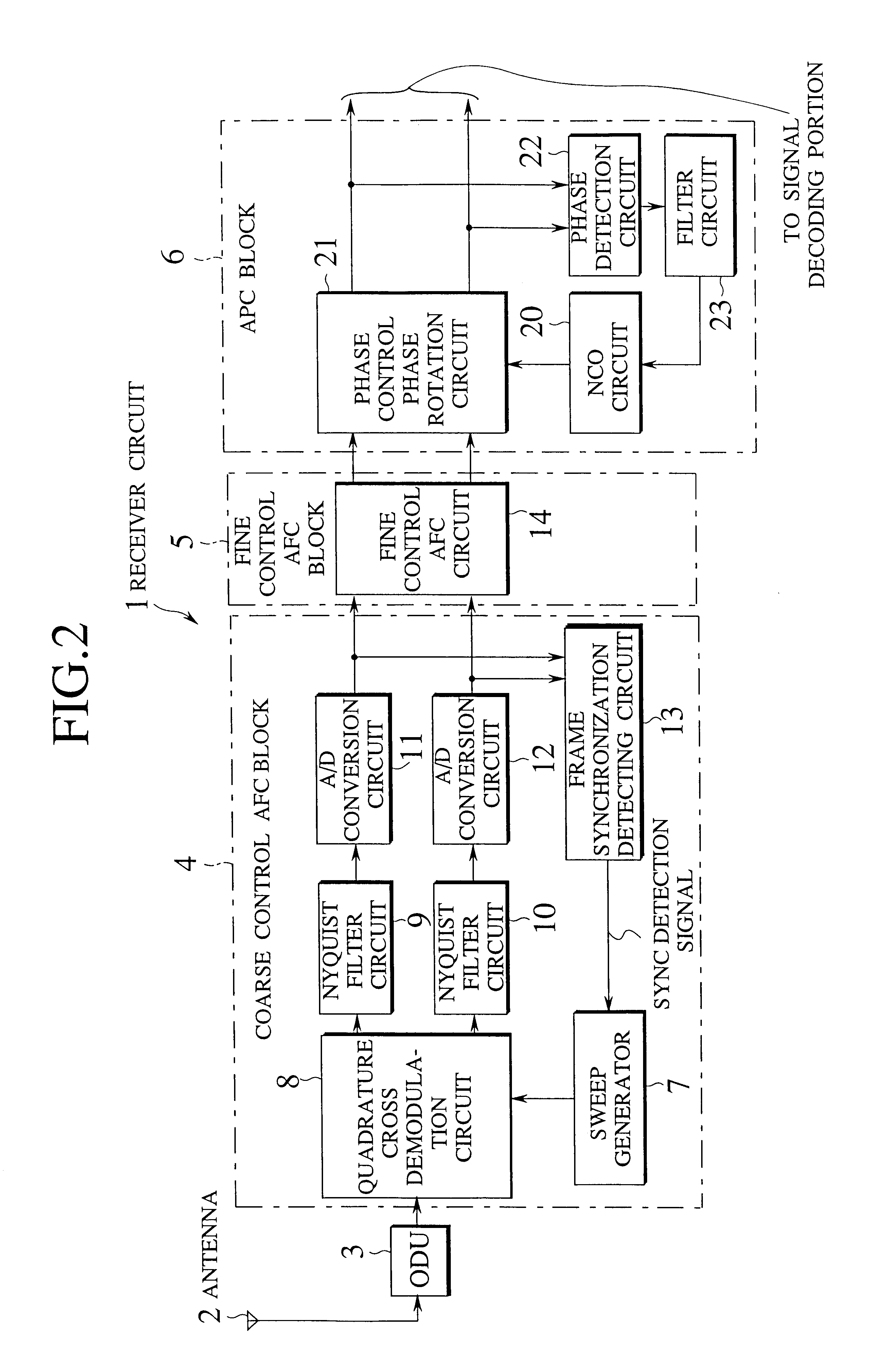
AFC circuit, carrier recovery circuit and receiver device capable of regenerating a carrier reliably even at the time of low C/N ratio
InactiveUS6490010B1Avoid it happening againEstimate degradedTelevision system detailsPulse automatic controlNumerical controlDifferential function
Stabilized carrier recovery is achieved even at the time of a low C / N ratio by measuring the phase of a signal and controlling VCO or NCO (Numerical Controlled Oscillator) using only a period having few constellation points. At this time, false lock phenomenon is avoided as follows. That is, relatively short SYNC modulated by an already-known pattern is entered into a modulation wave, VCO or NCO oscillation frequency is swept in a wide range and sweep is stopped at a frequency in which the SYNC can be received, thereby carrying out coarse control AFC. Further, a period having long to some extent, having few constellation points is provided in the modulation wave and then, a difference between the frequency of a received modulated signal and a local oscillation signal of VCO or NCO is obtained in this period. This frequency difference is analyzed according to the phase differential function method, self-correlation function method or count method, and the VCO or NCO is controlled based on this result of analysis.
Owner:NIPPON HOSO KYOKAI
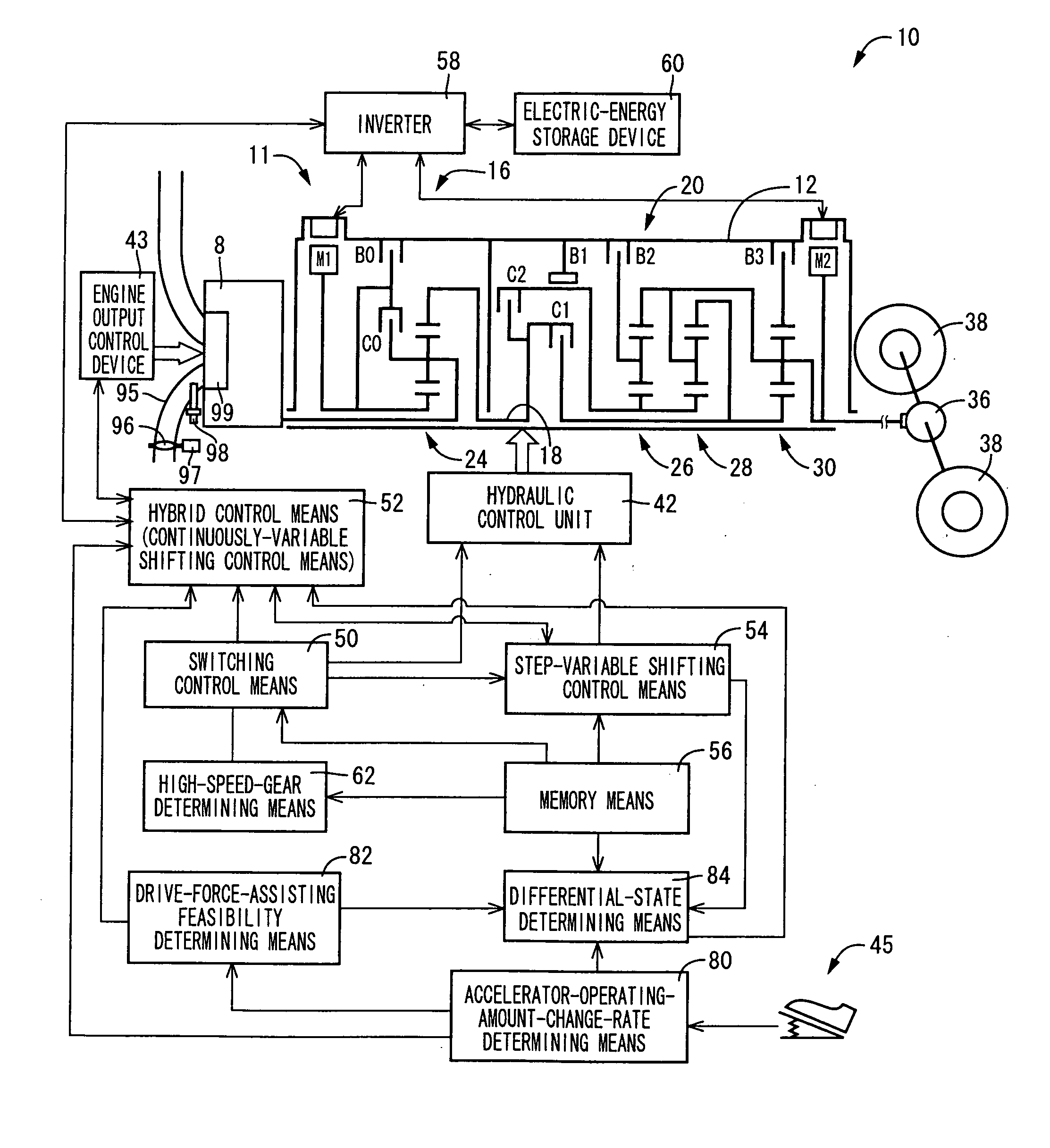
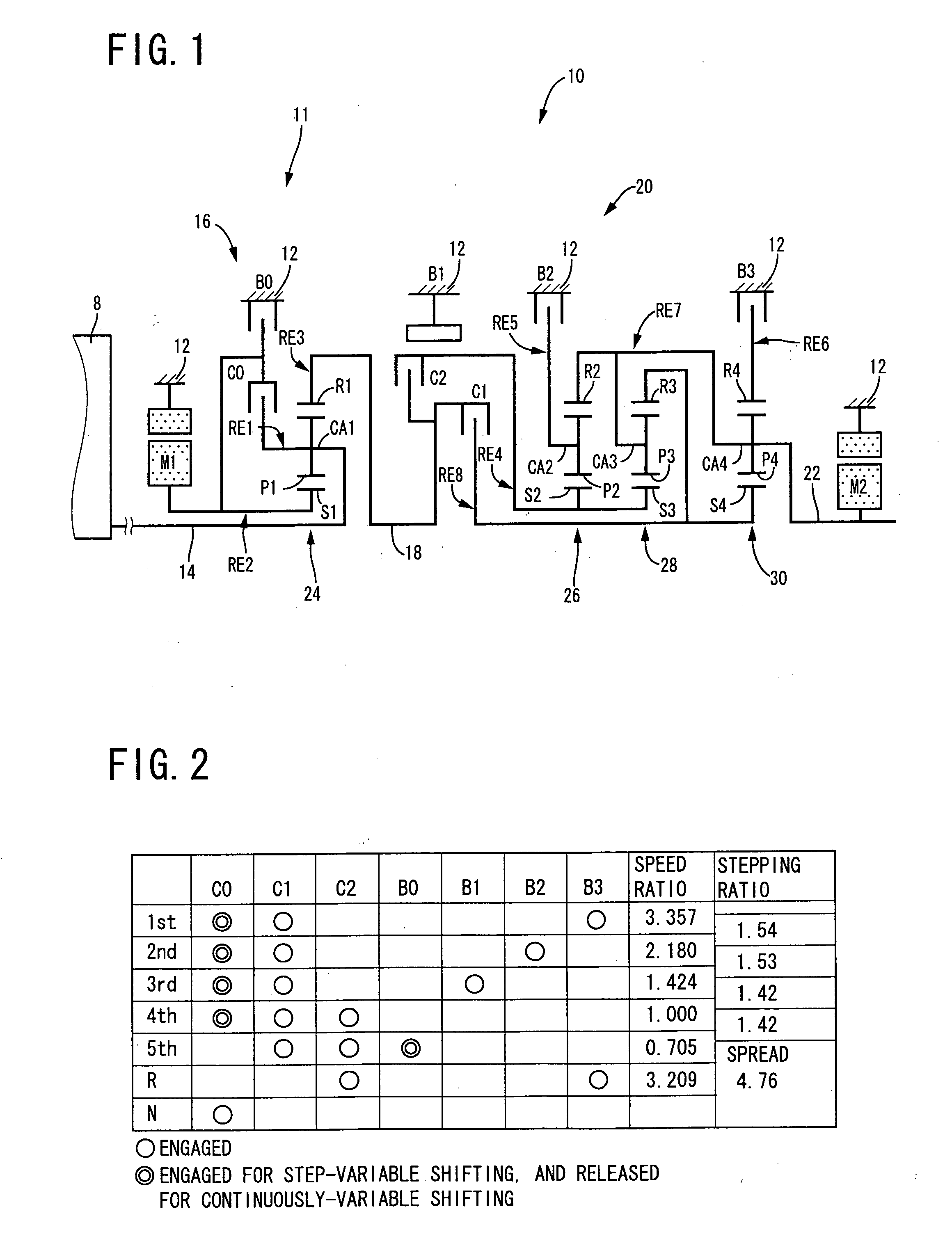
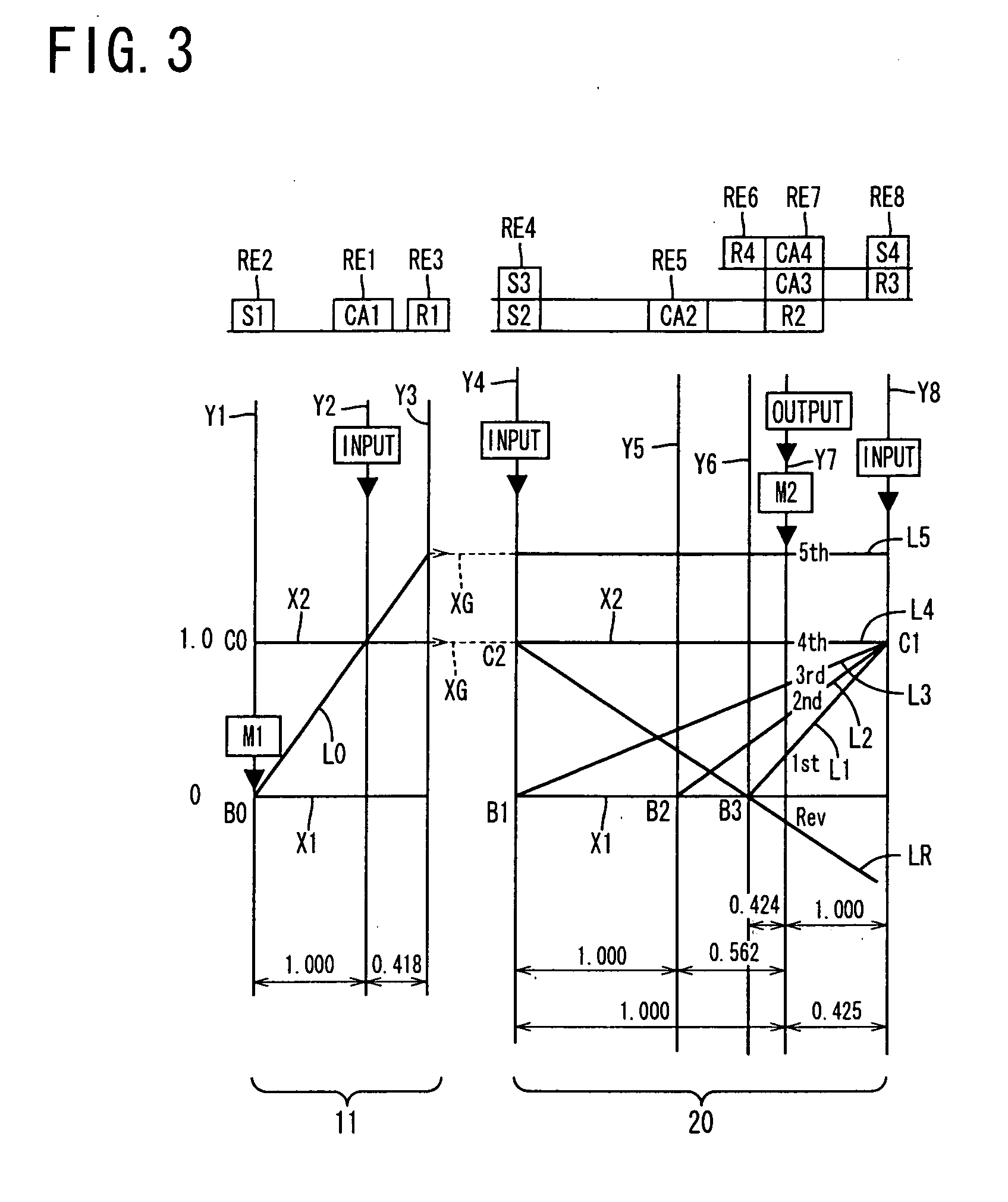
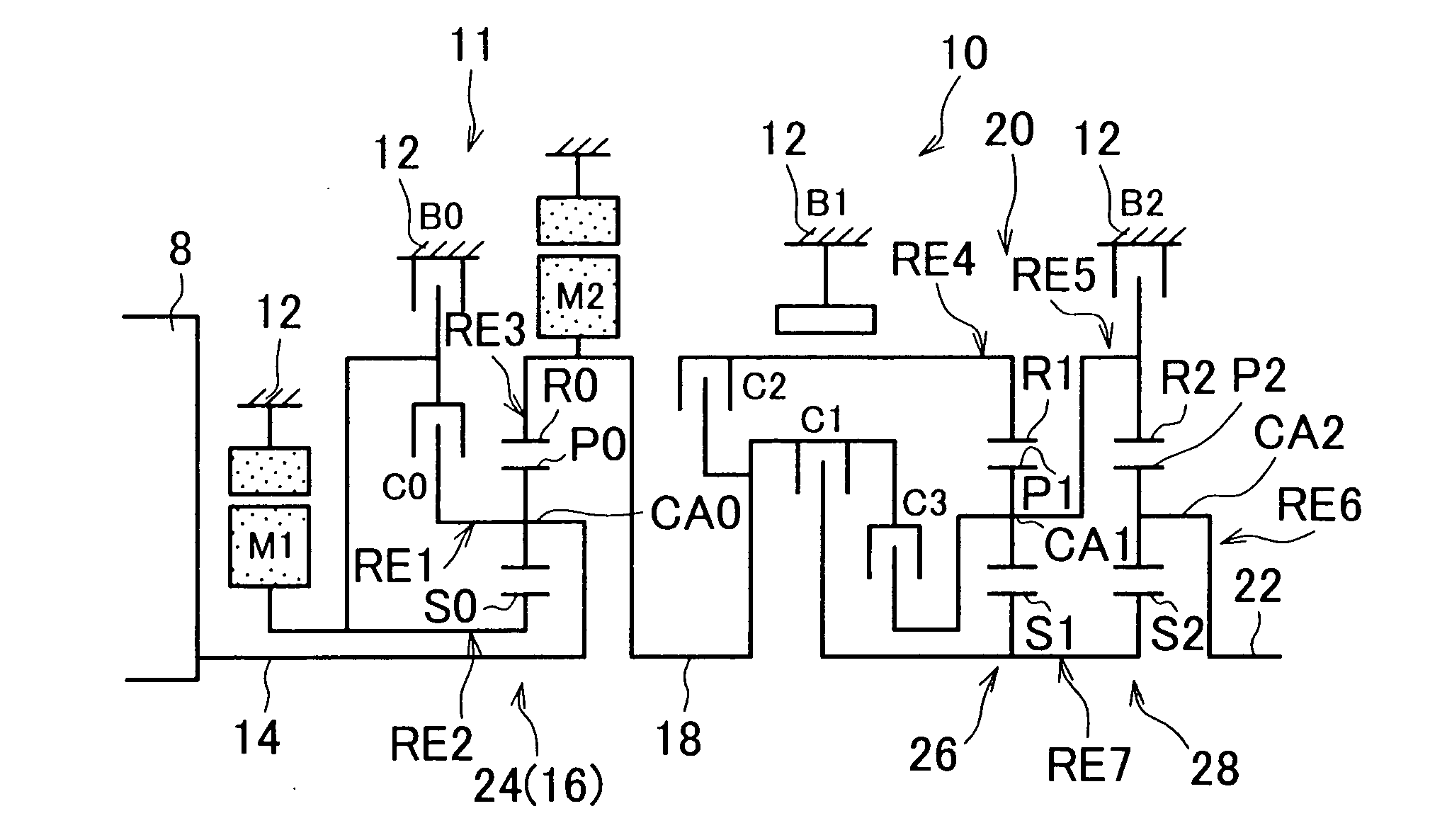
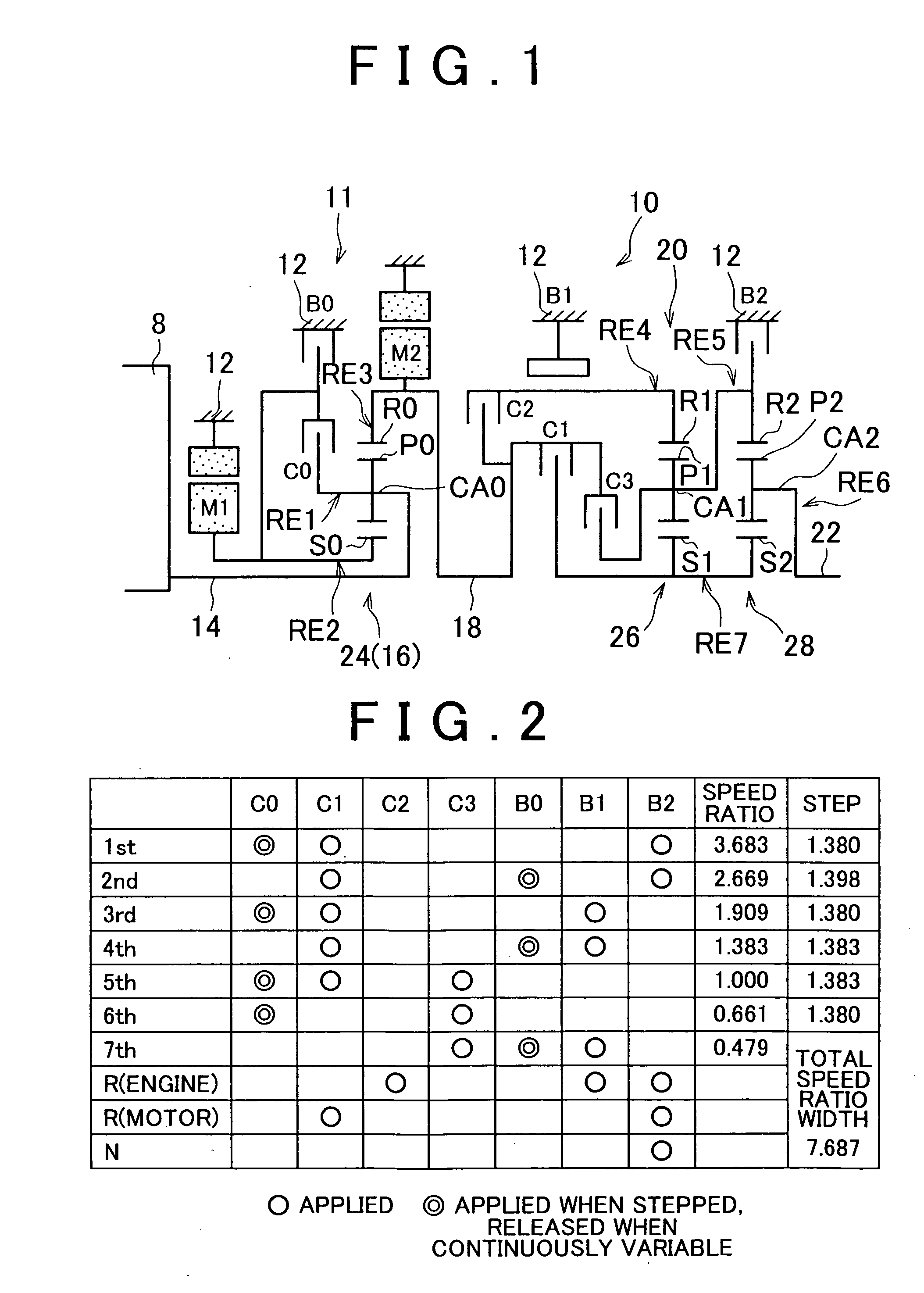
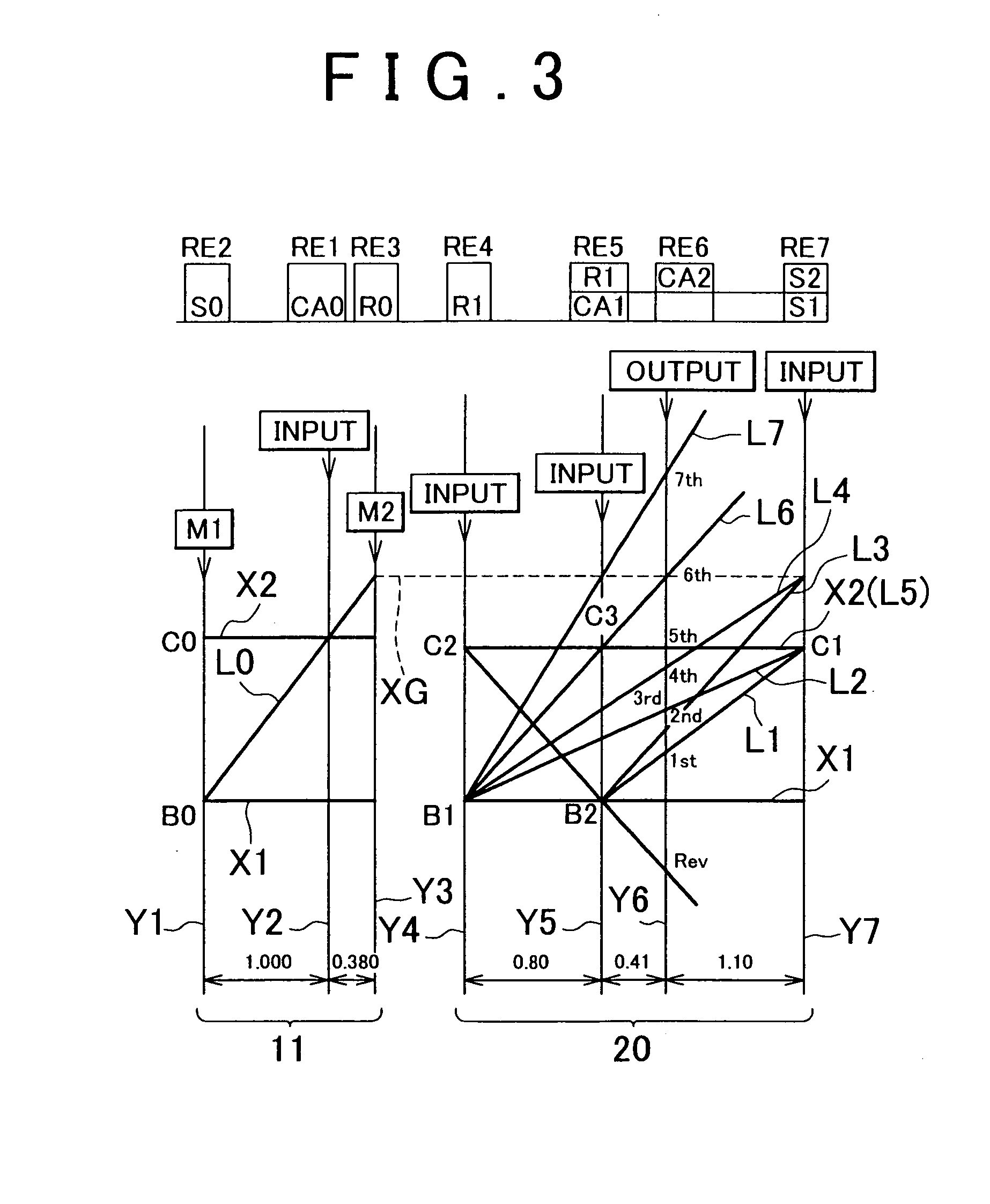
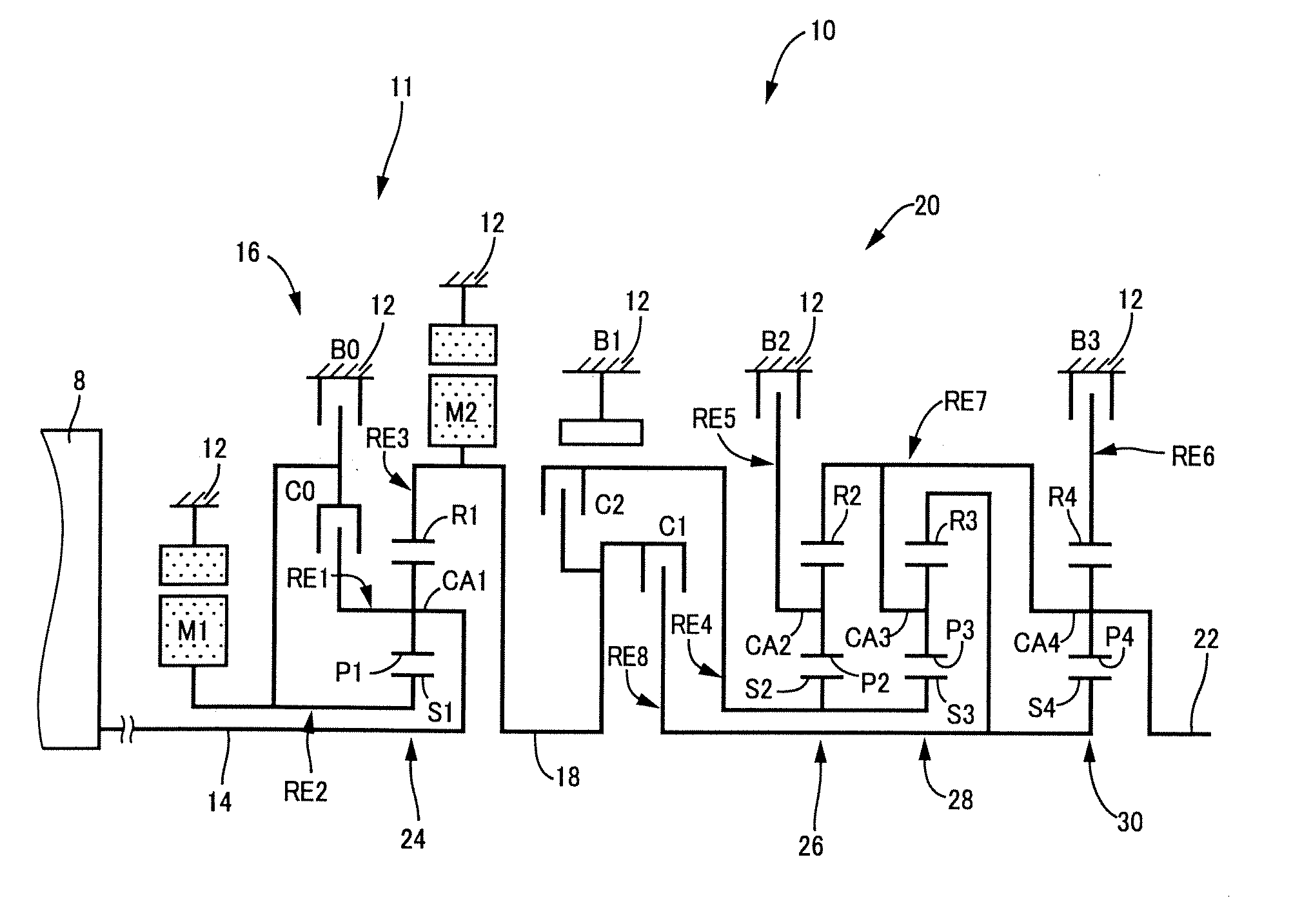
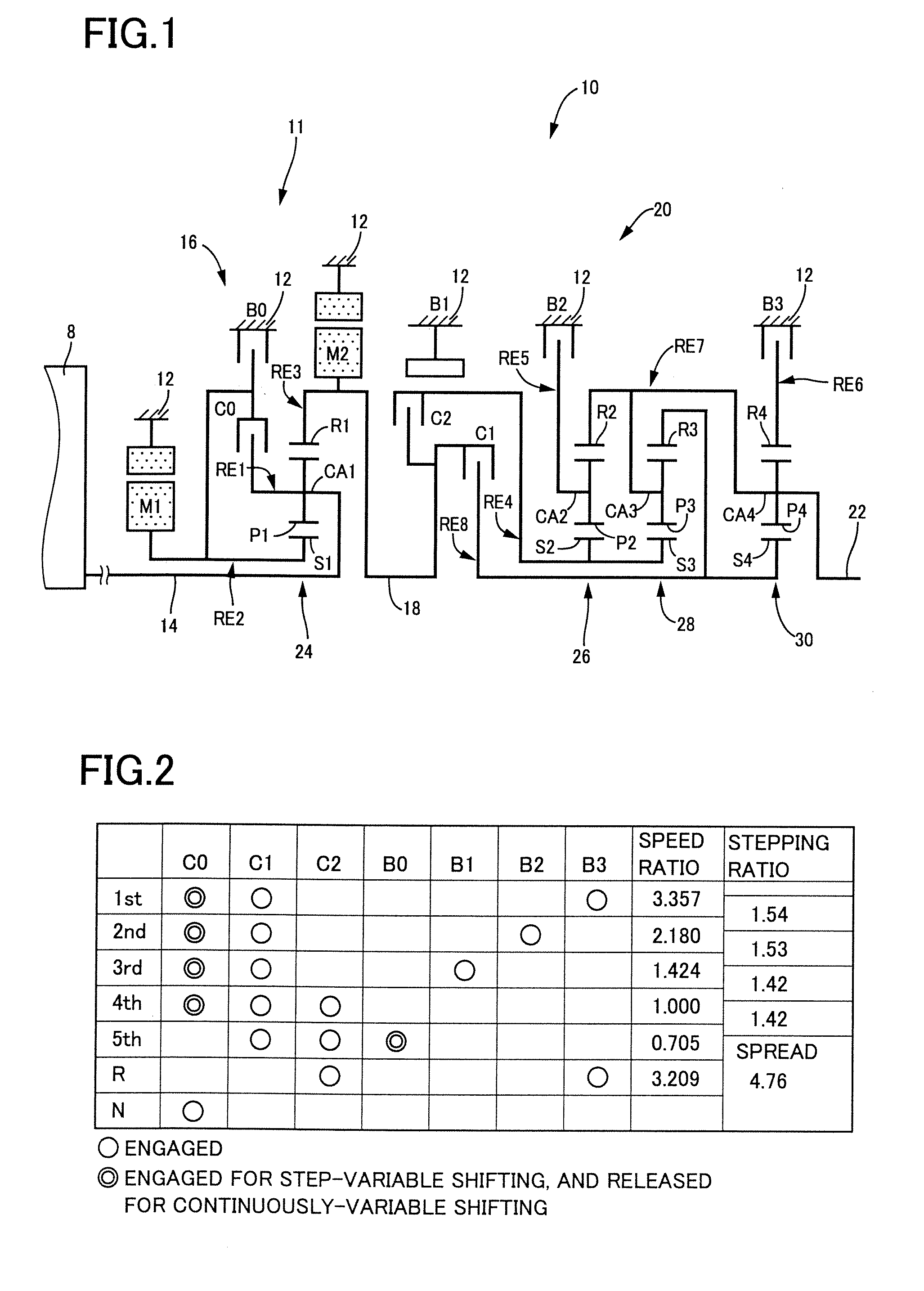
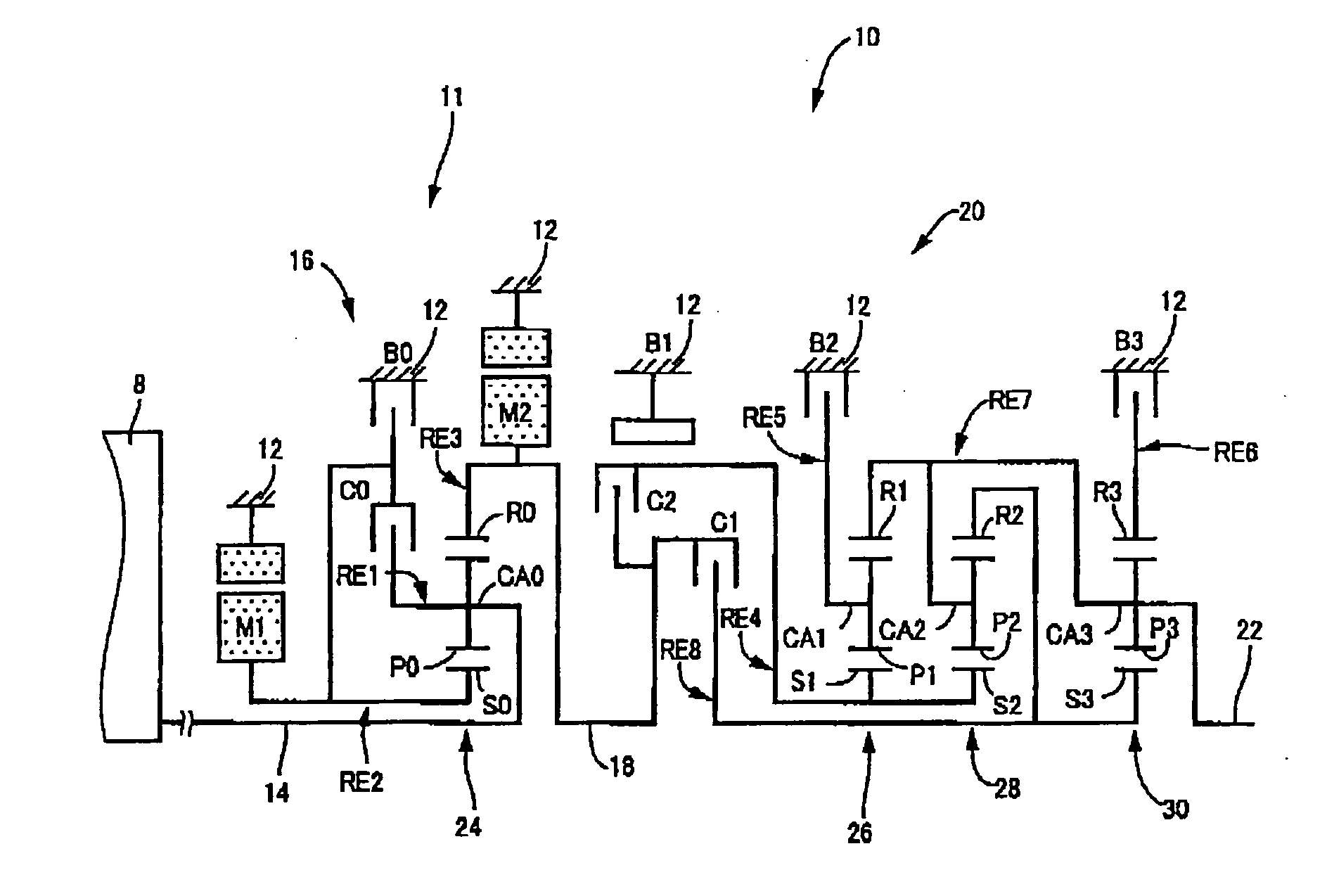
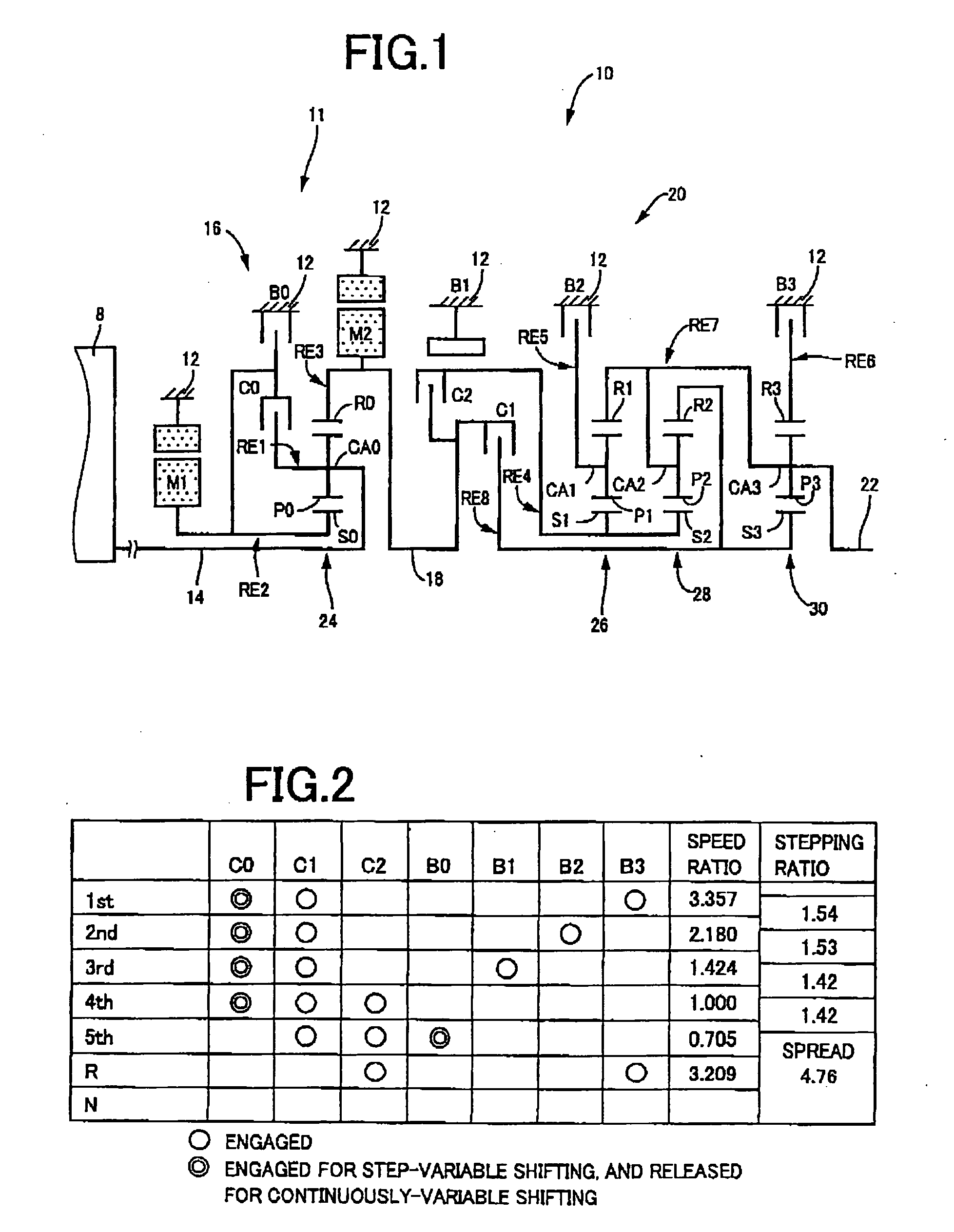
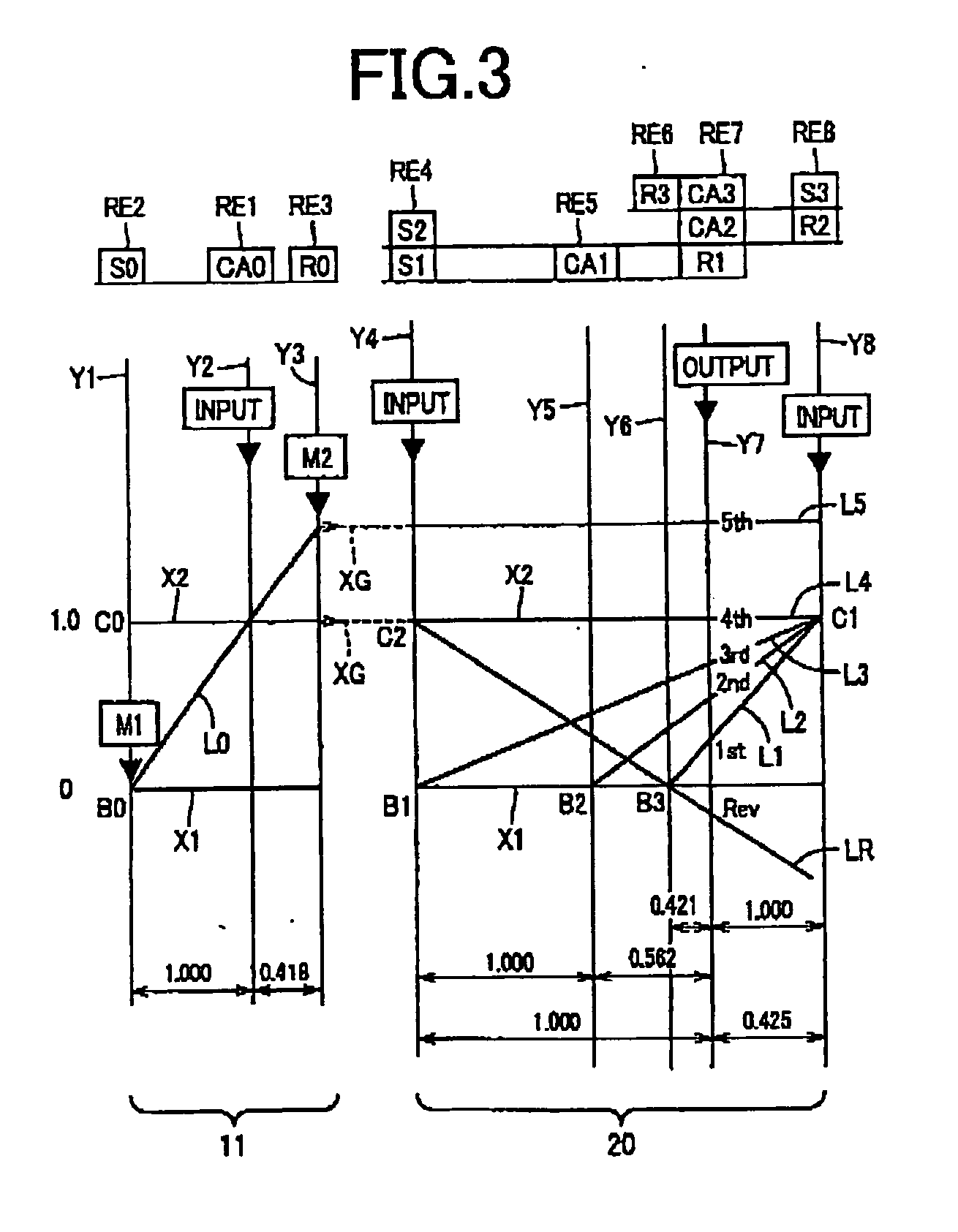
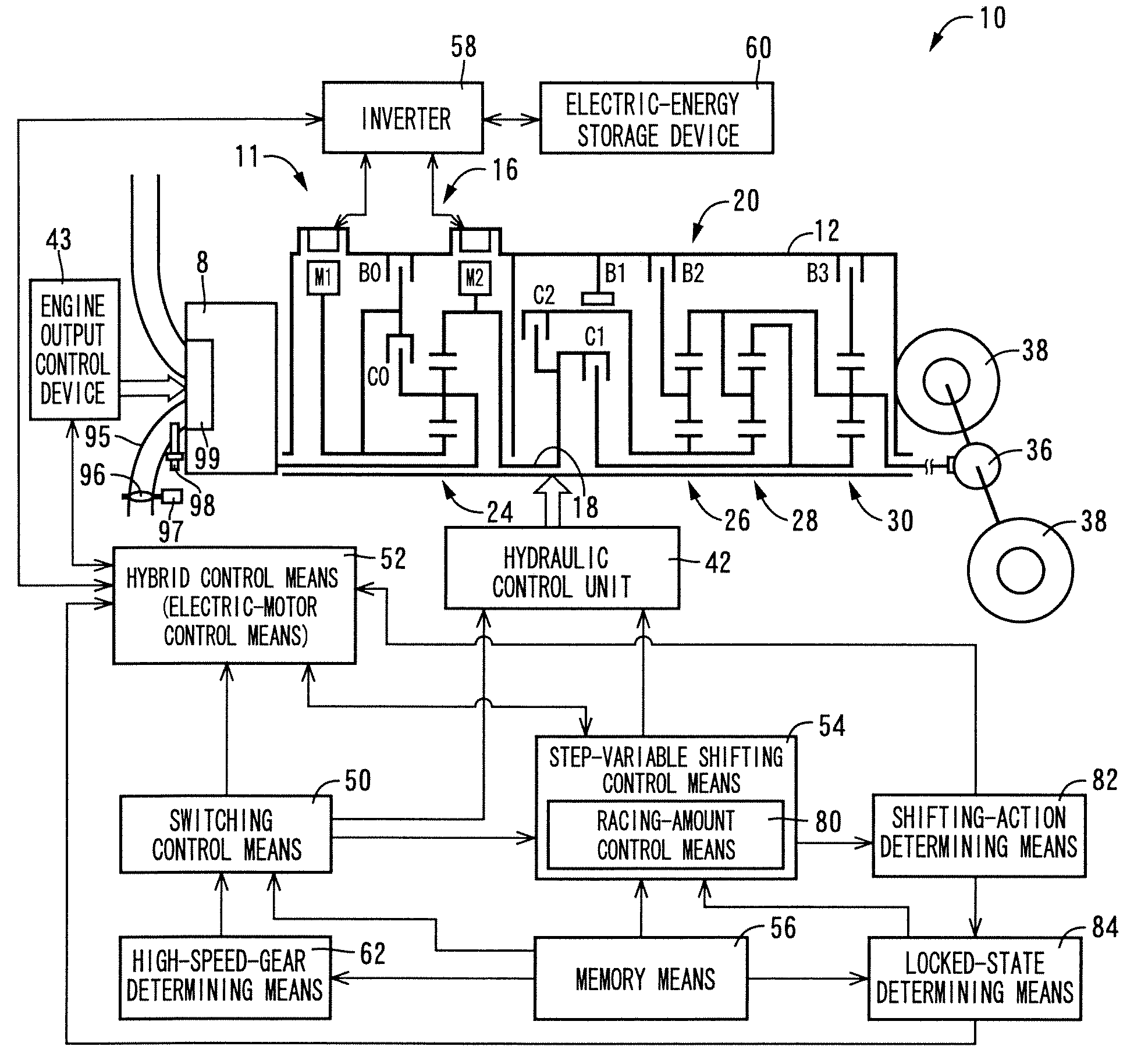
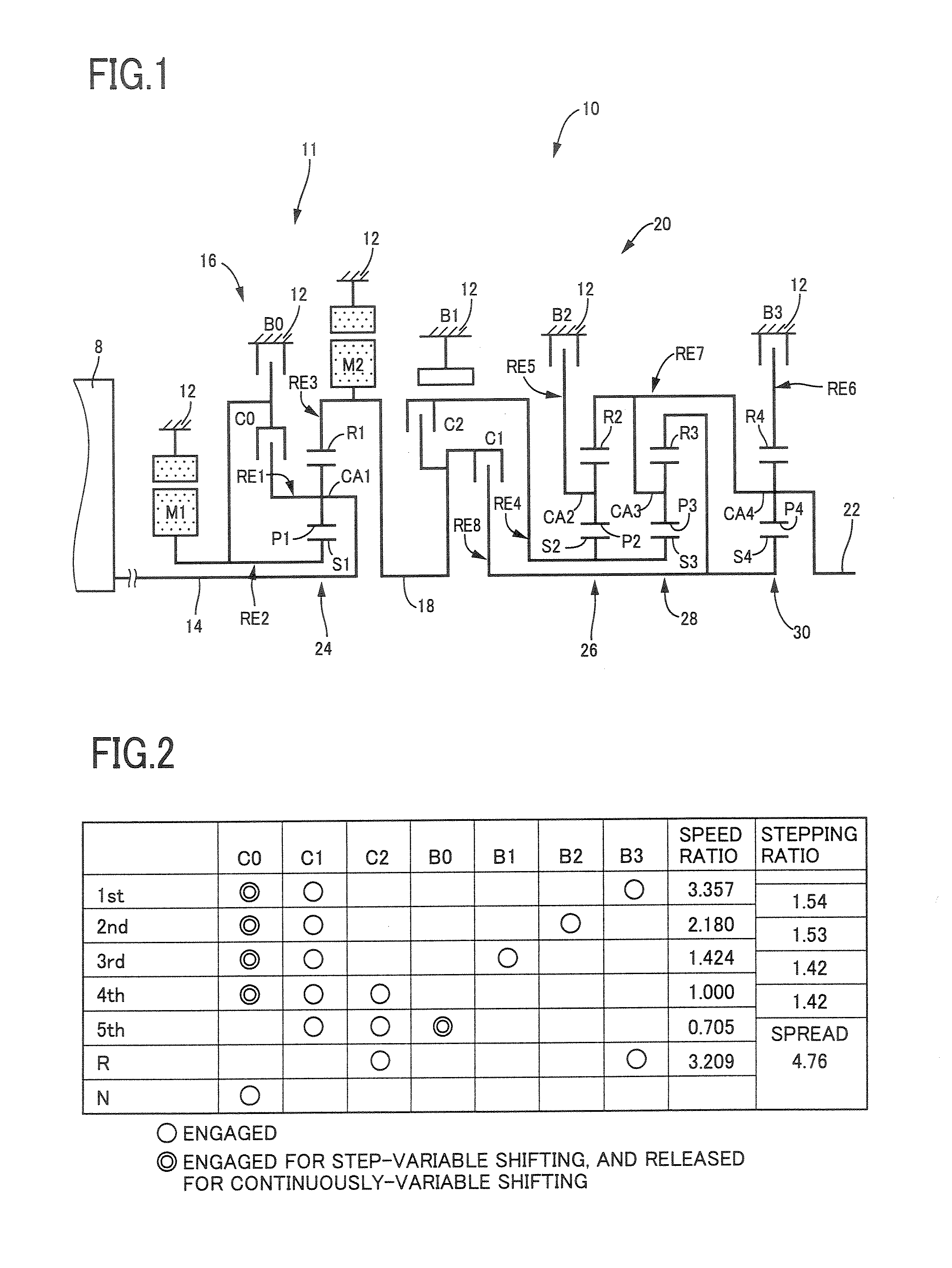
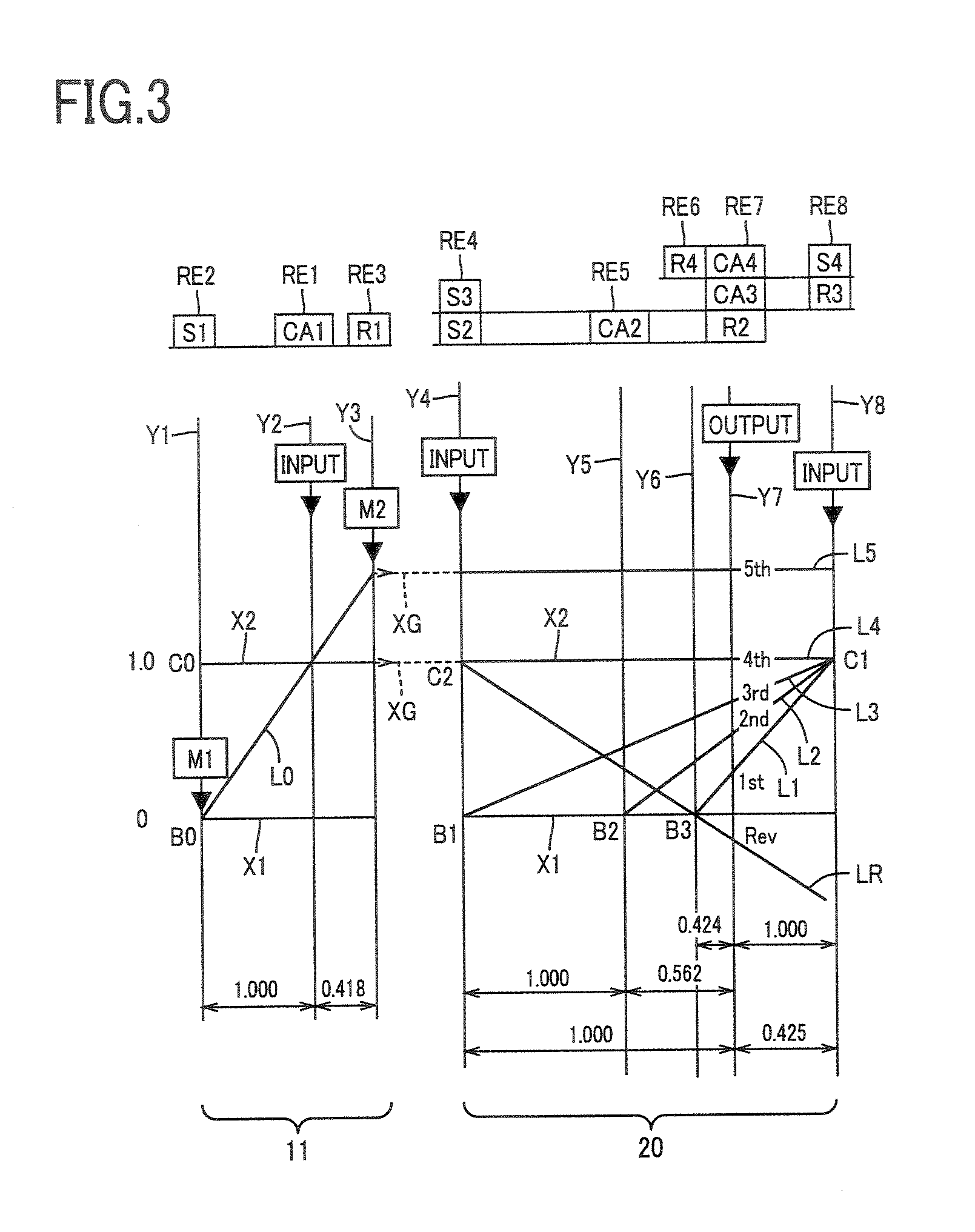
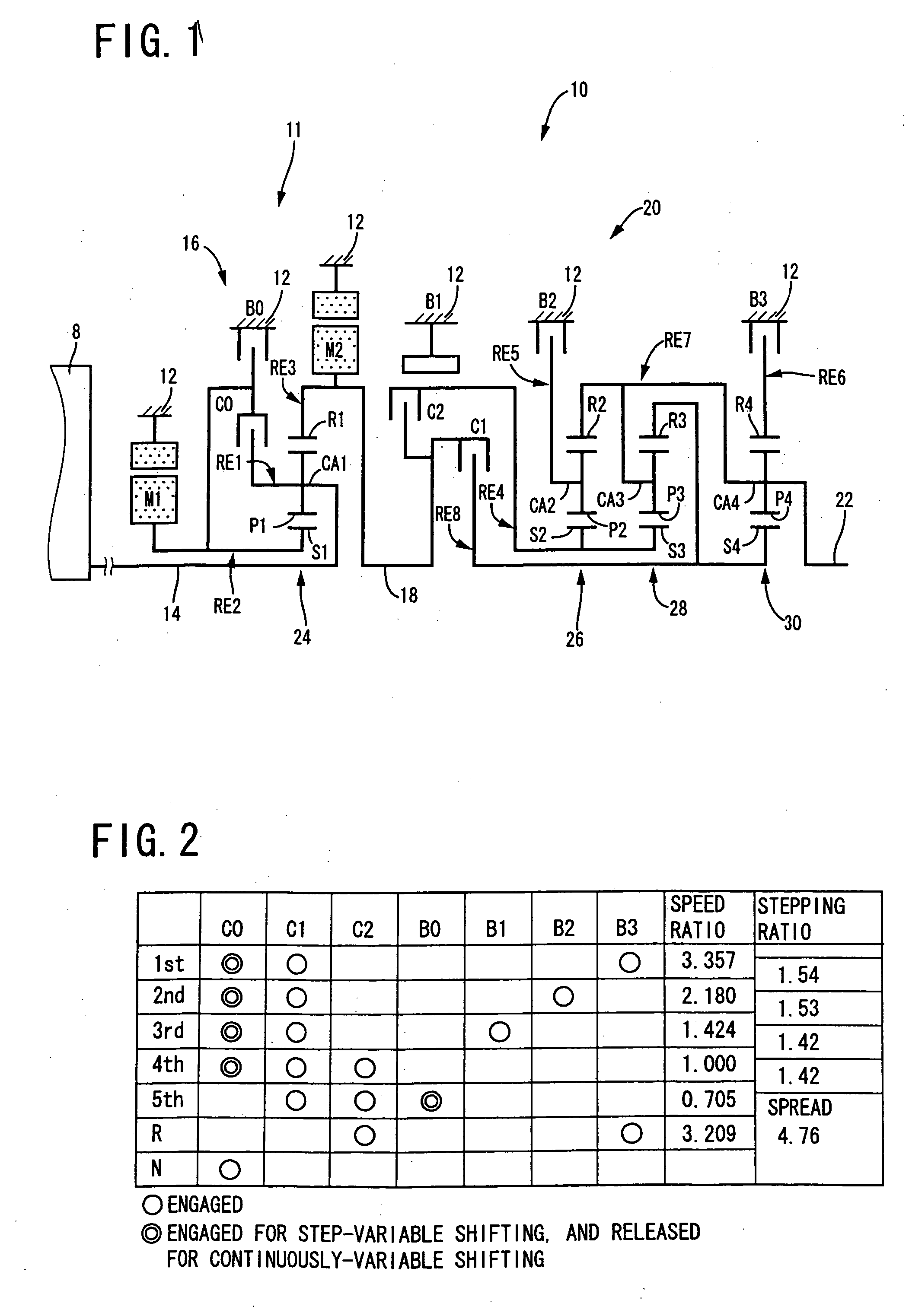
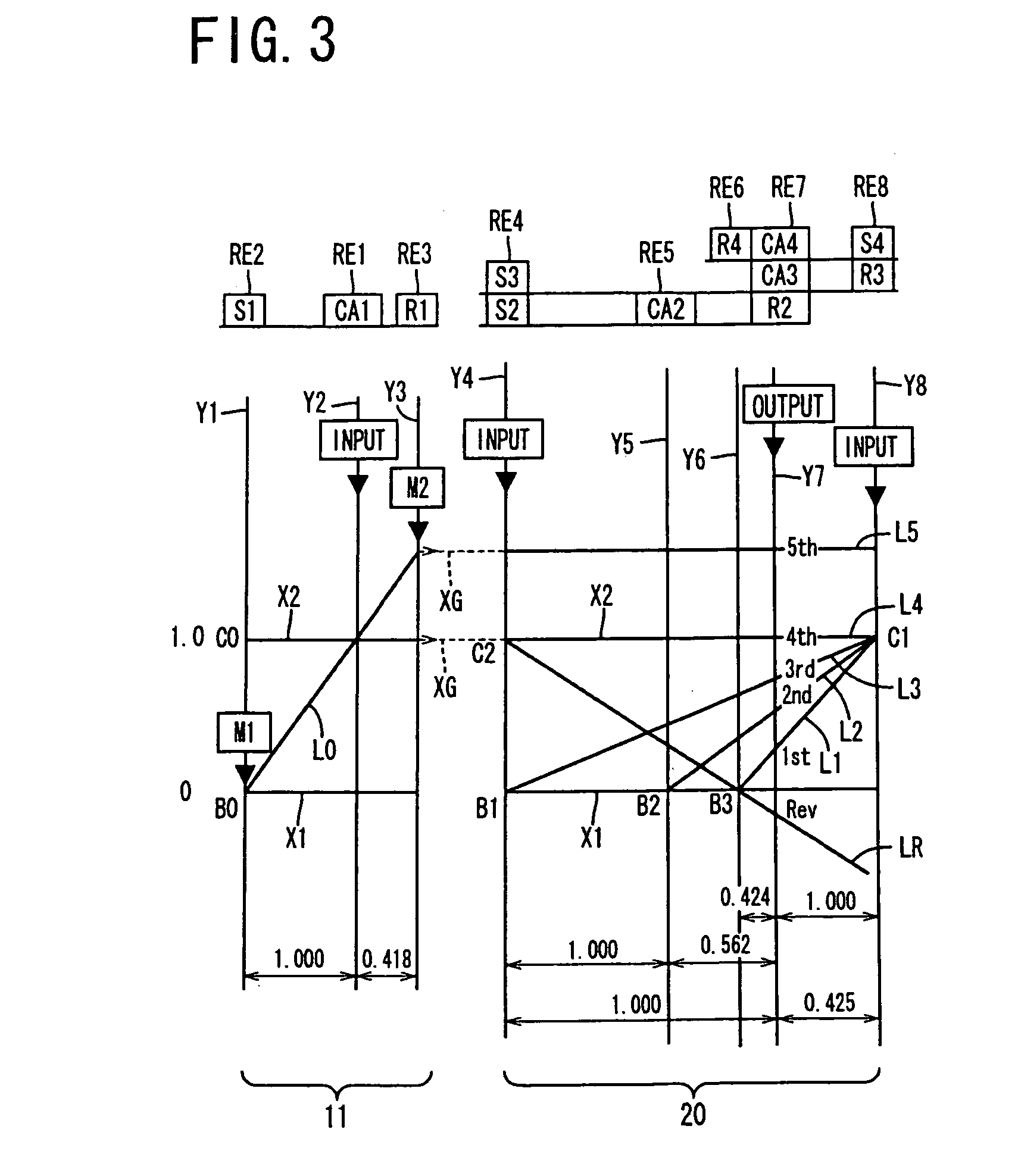
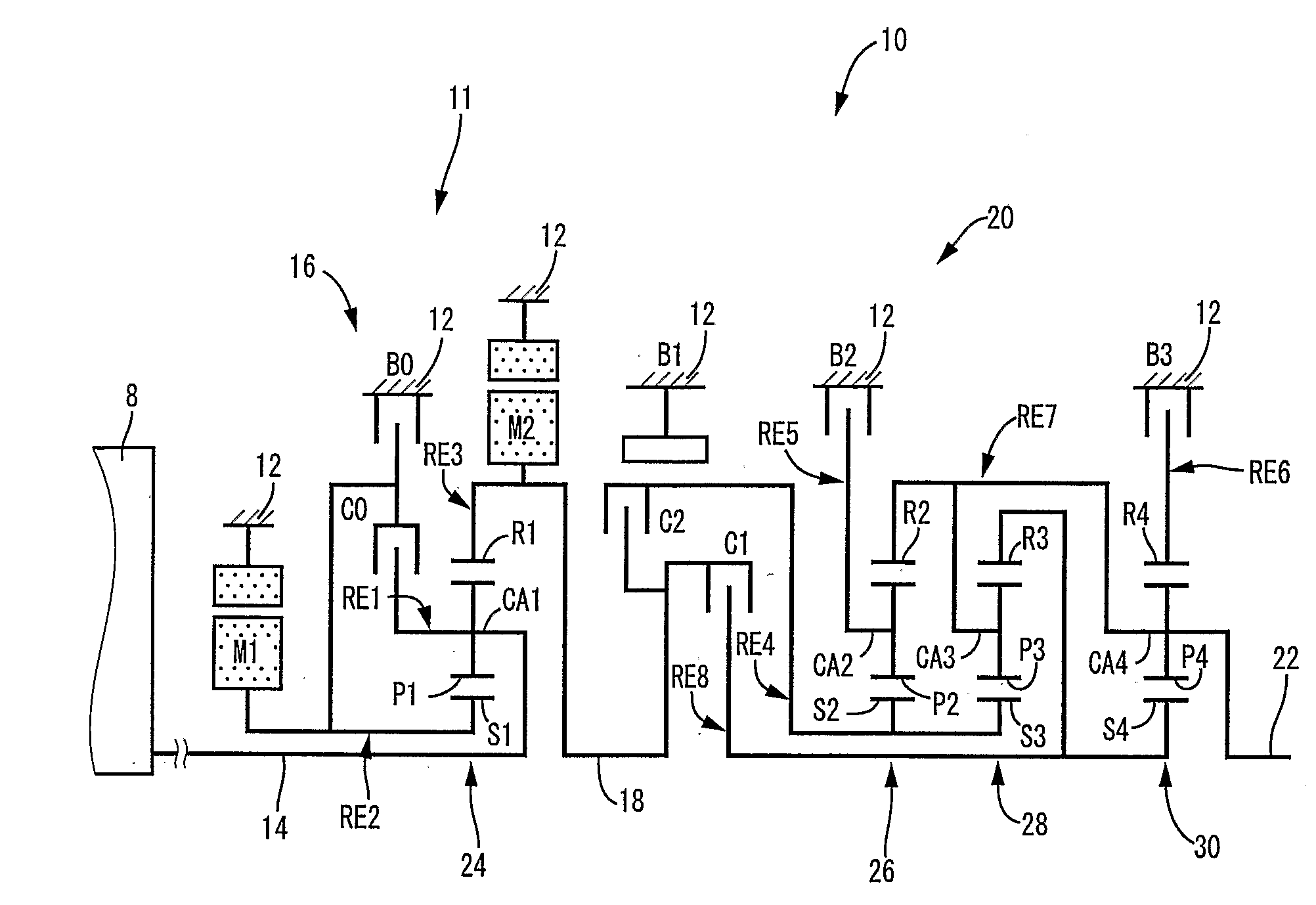
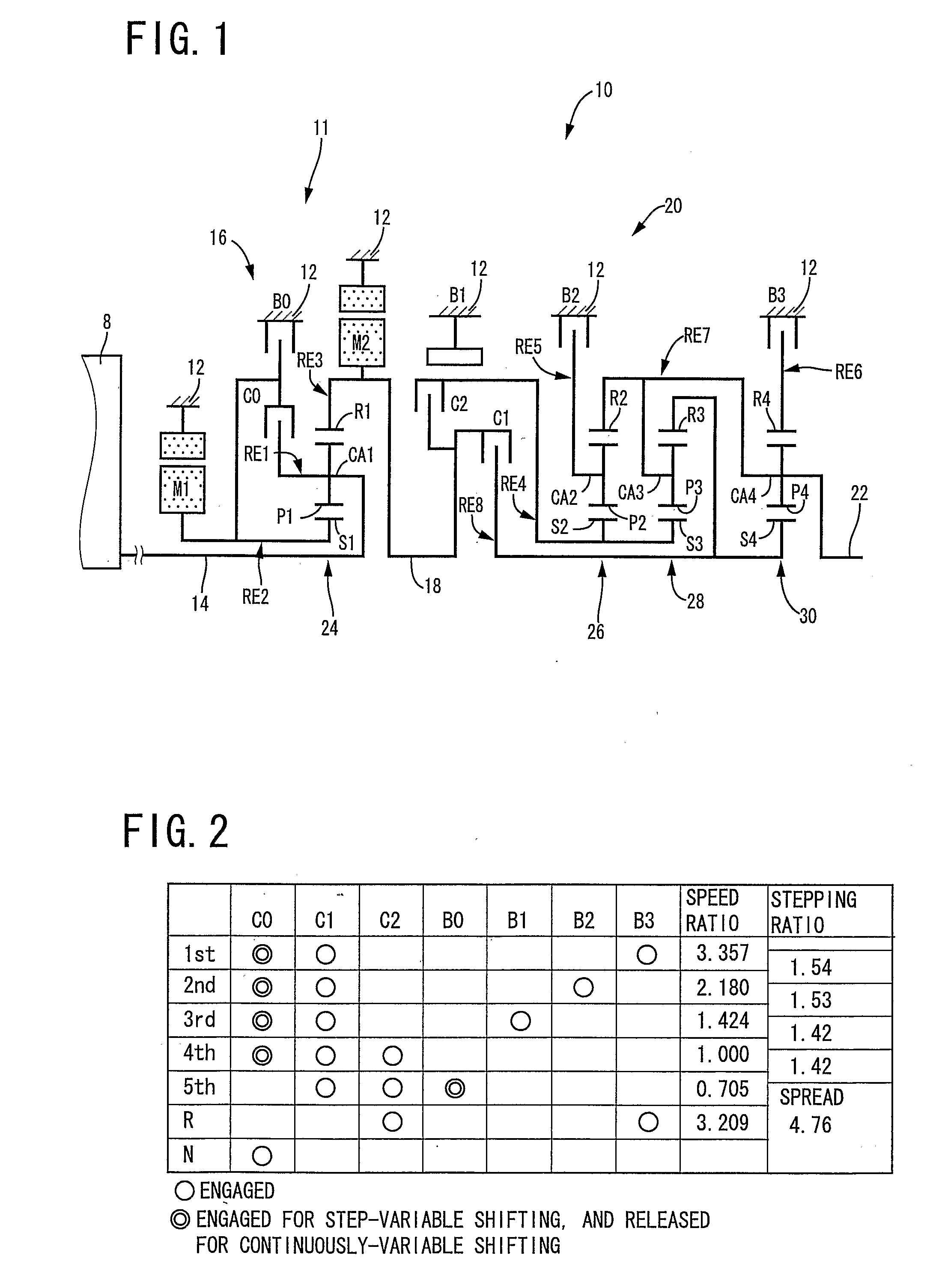
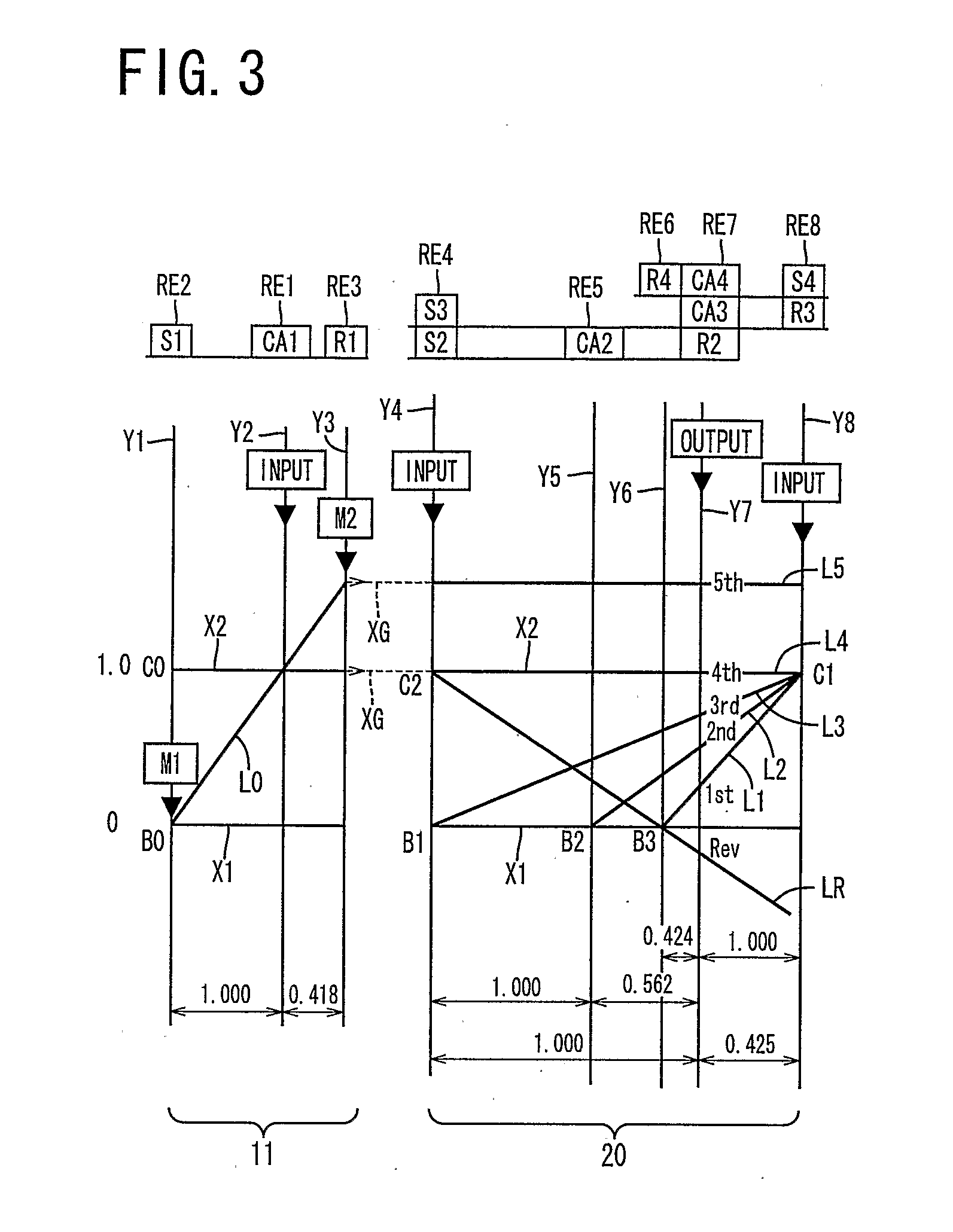
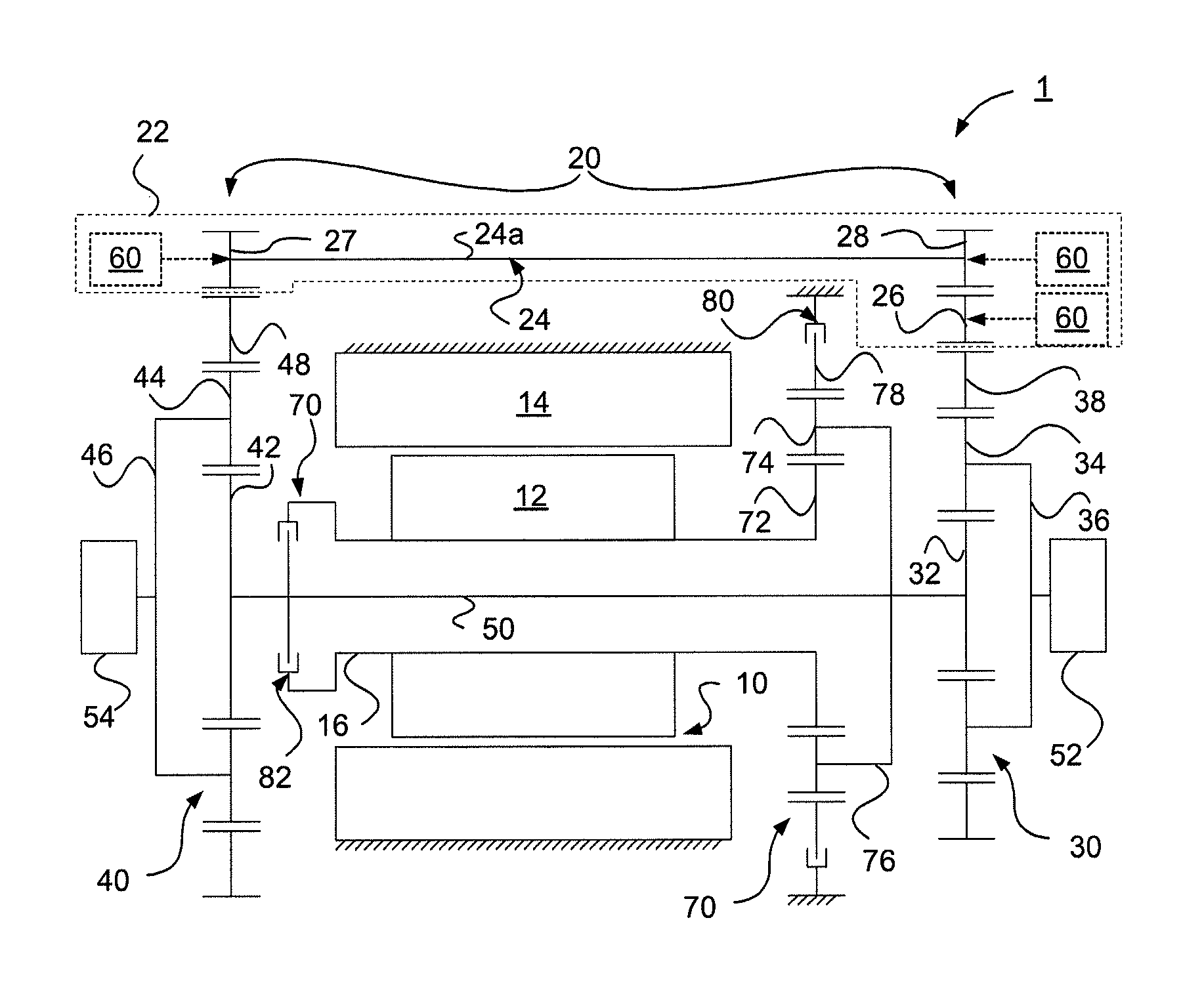
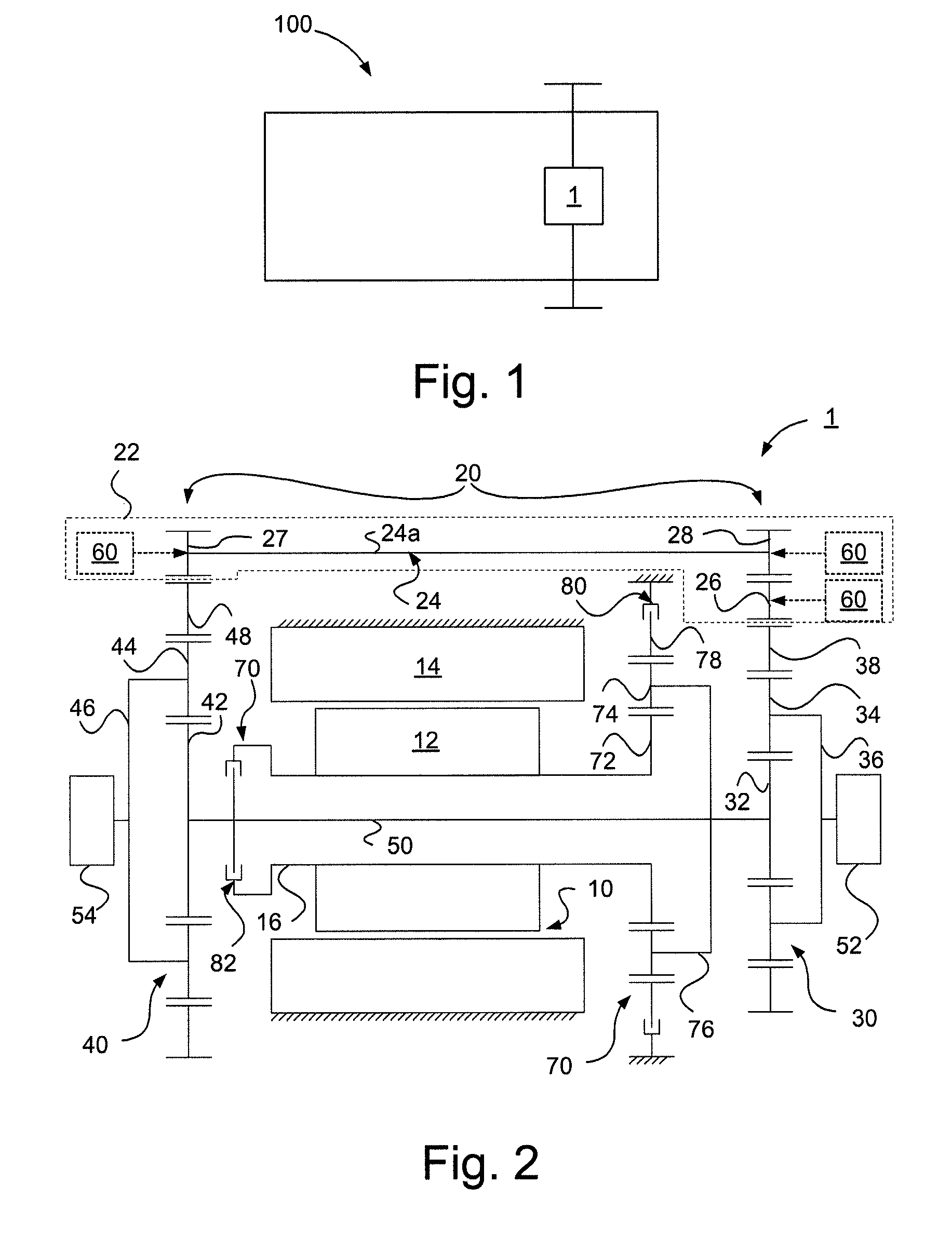
Control apparatus for vehicular drive system
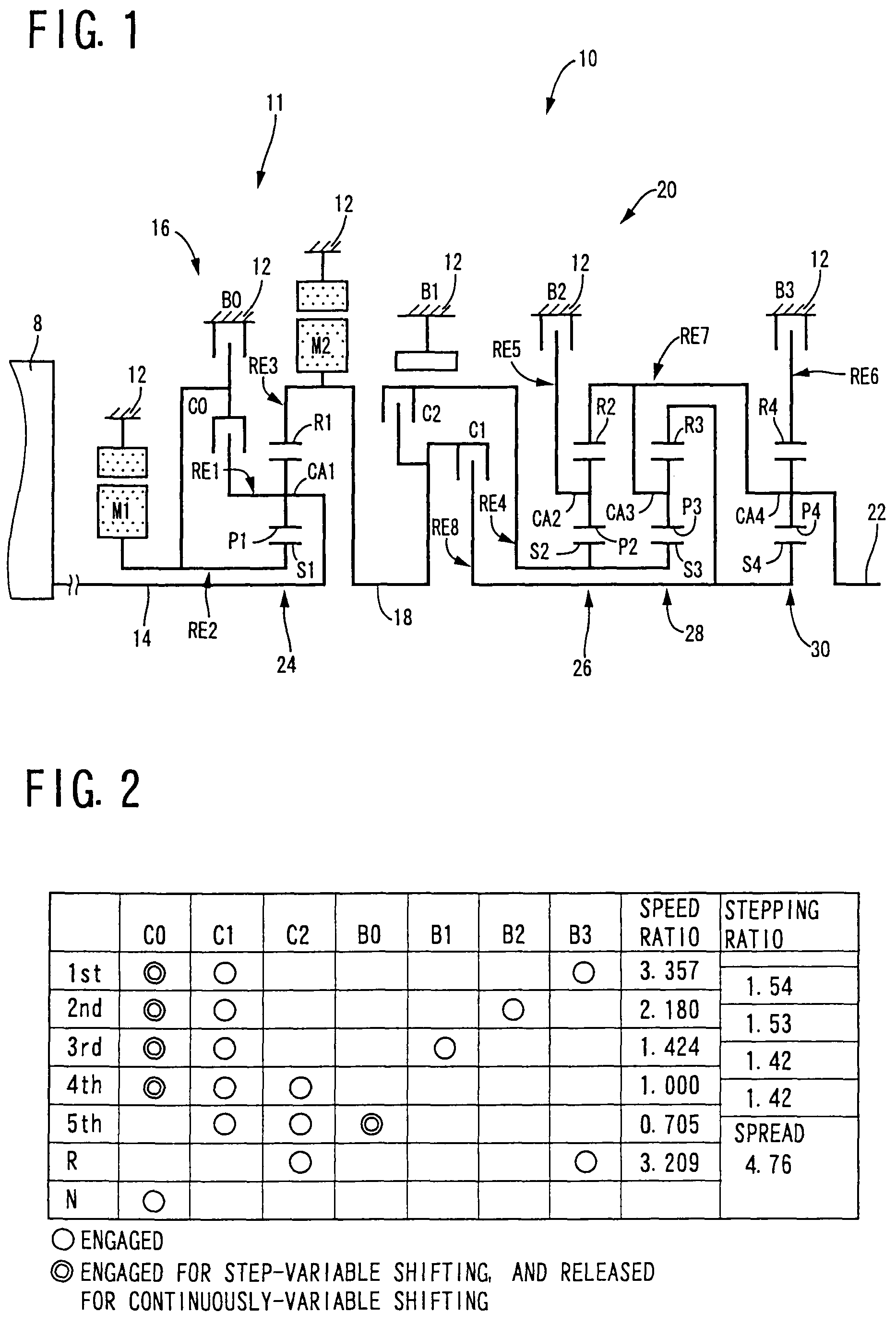
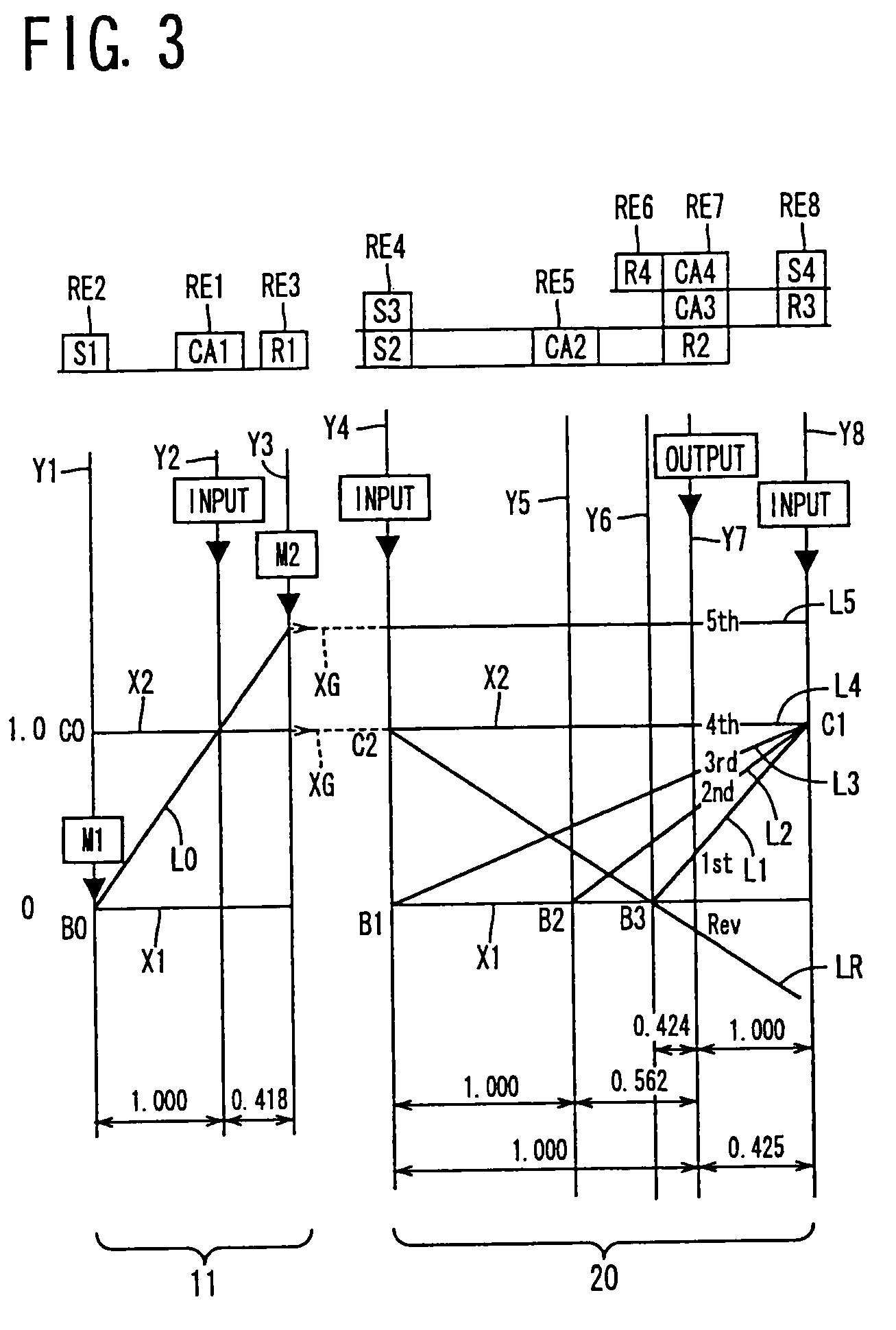
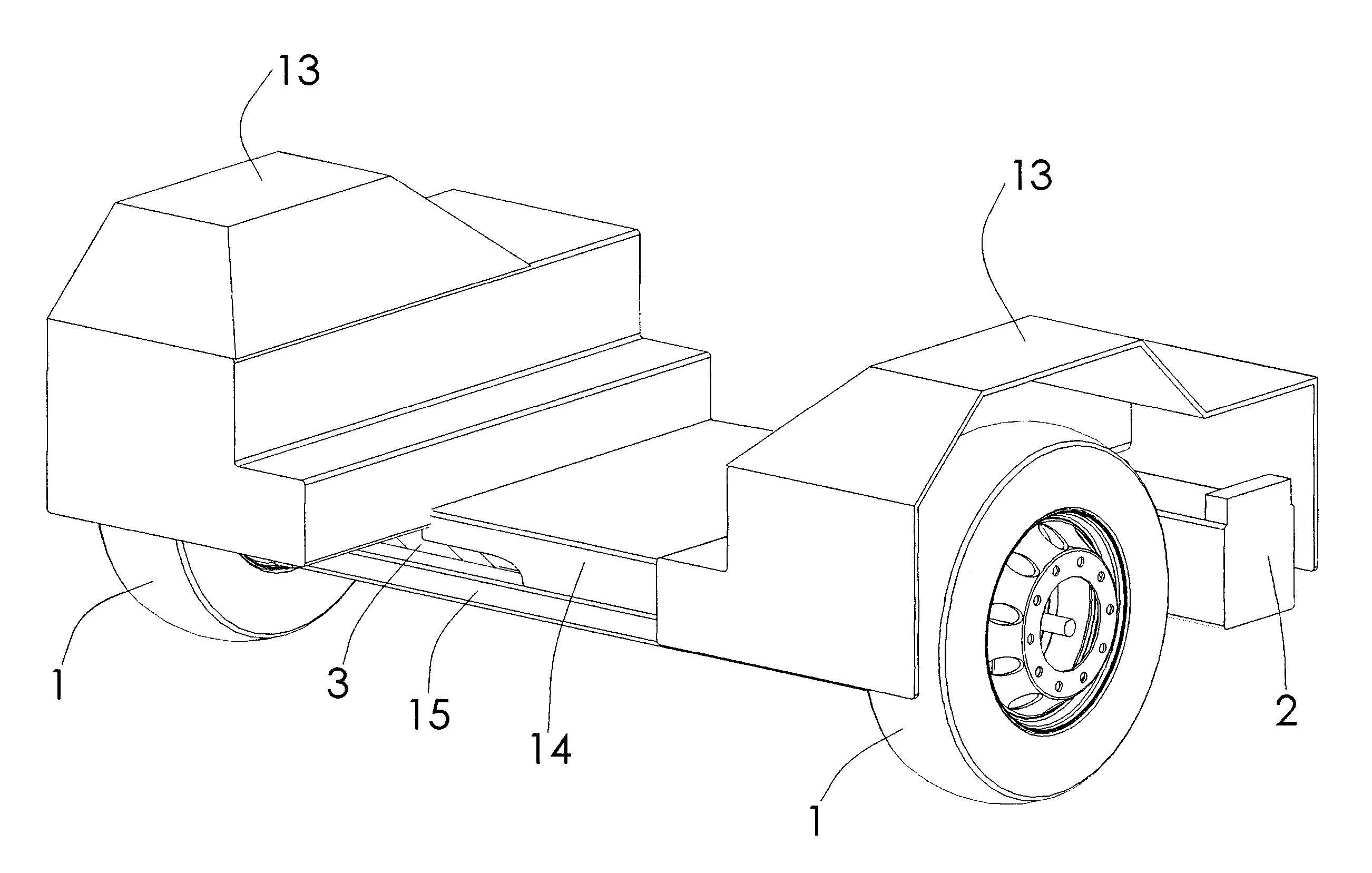
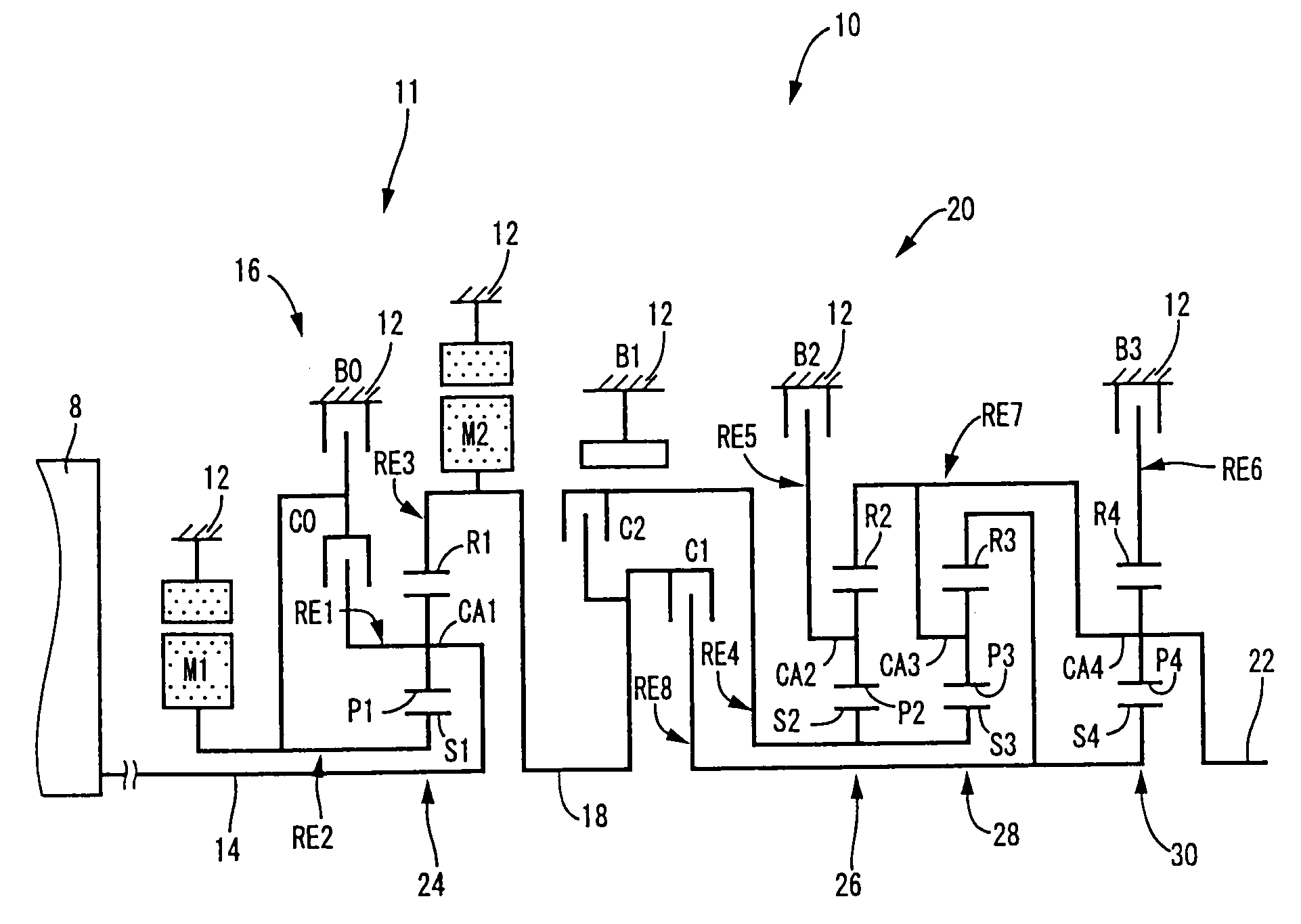
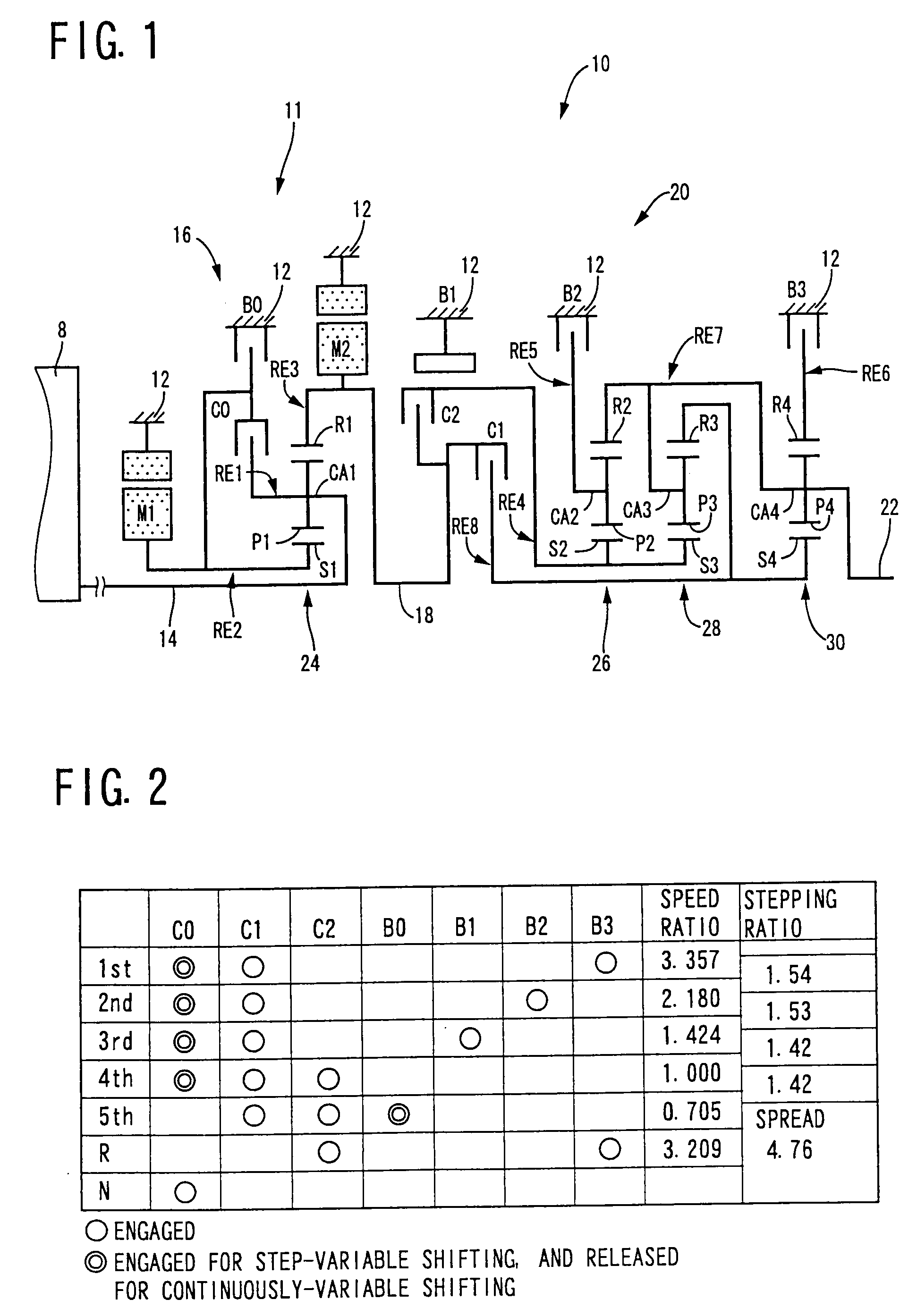
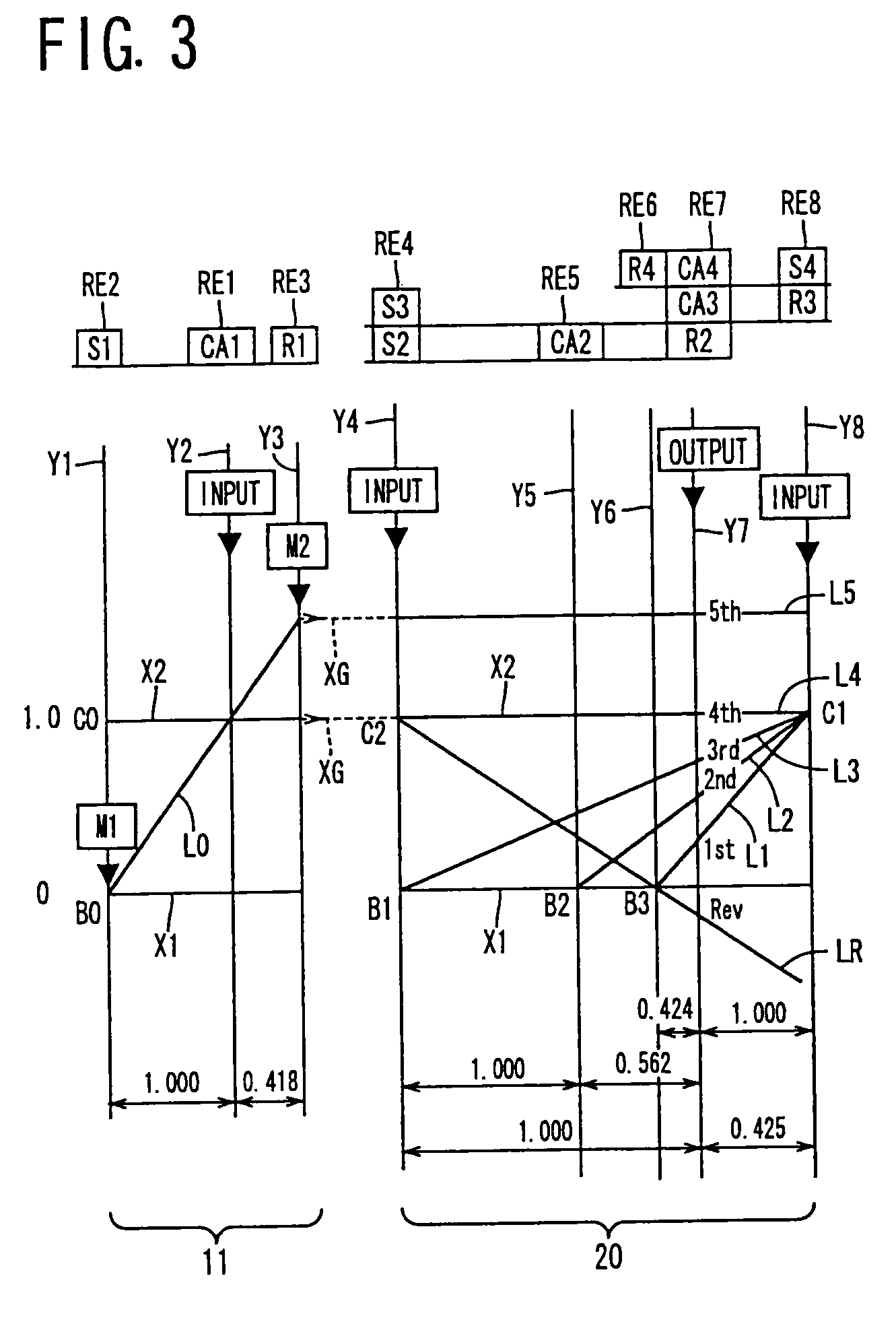
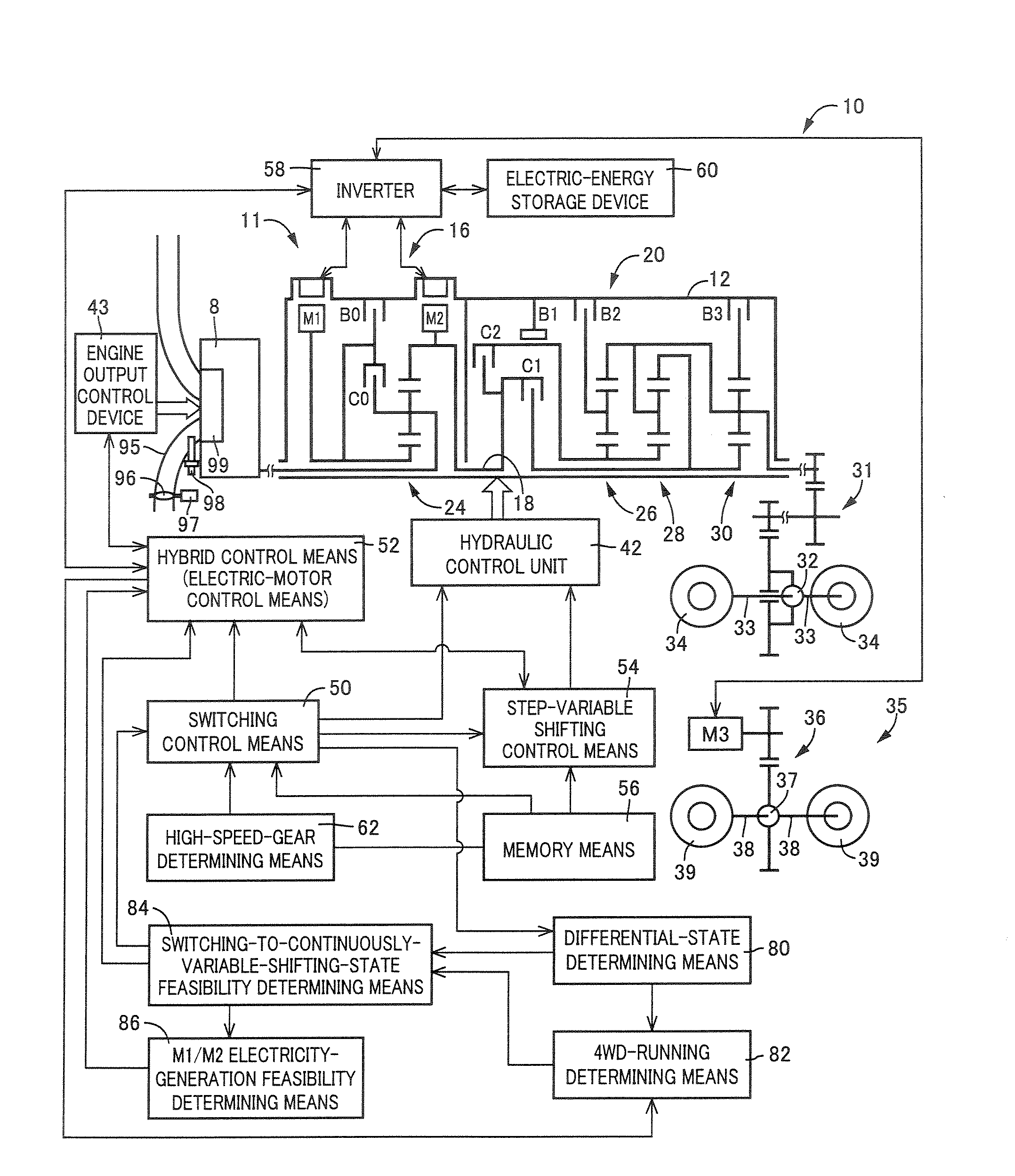
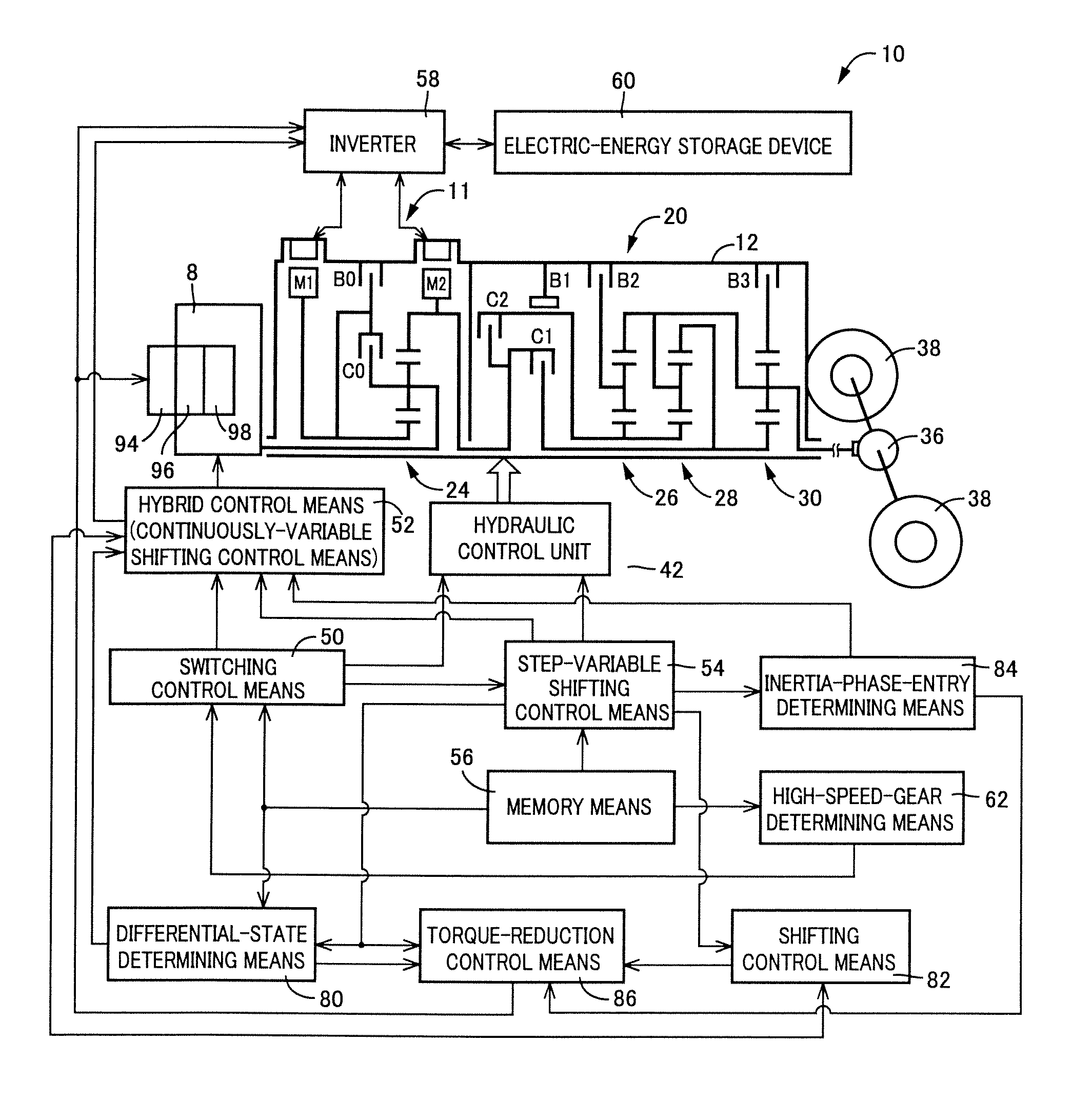
InactiveUS20070105679A1Improve efficiencySmooth changeHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingDrive wheelDifferential function
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a continuously-variable transmission portion operable as an electrically controlled continuously variable transmission, and a step-variable transmission portion, the continuously variable transmission portion having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, and a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel of a vehicle. The control apparatus including a differential-state limiting device provided in the differential mechanism, and operable to limit a differential function of the differential mechanism, for limiting an operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission, and an electric-motor control portion for controlling a drive-force assisting operation to generate an assisting drive force to drive the vehicle during a shifting action of the step-variable transmission portion, in different manners depending upon whether the continuously-variable transmission portion is placed in a continuously-variable shifting or a non-continuously-variable shifting state.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control Apparatus and control method for vehicular power transmitting apparatus
ActiveUS20080195286A1Increase in sizeWide rangeHybrid vehiclesInternal combustion piston enginesDifferential functionControl equipment
A control apparatus for a vehicular power transmitting apparatus includes, in series, i) a differential portion which is provided with a differential mechanism having a differential function with respect to an input shaft and an output shaft, in which the differential mechanism is switched between a differential state and a non-differential state, and ii) a stepped shifting portion that shifts between a plurality of gears in a stepped manner. During a shift with a switch between the differential state and the non-differential state in the differential portion, the control apparatus either maintains the gear at that time or shifts into a gear that is adjacent to that gear.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control device for vehicular drive system
ActiveUS20060027413A1Improve fuel economyFurther reduction of the resonance phenomenonHybrid vehiclesGas pressure propulsion mountingDifferential functionDrive wheel
A control device for a vehicular drive system including (a) a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine (8) to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, (b) a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel of a vehicle, and (c) a differential-state switching device operable to place the differential mechanism selectively in one of a differential state in which the differential mechanism is operable to perform a differential function and a locked state in which the differential mechanism is not operable to perform the differential function, the control device including an engine-stop switching control portion operable to control the differential-state switching device to place the differential mechanism in the differential state, upon stopping of the engine, so that the engine speed can be rapidly lowered to zero by controlling the first electric motor in the differential state of the differential mechanism, so as to reduce a possibility of occurrence of a resonance phenomenon of the drive system and a resultant vibration of the vehicle when the engine is stopped.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Limited slip differential device
ActiveUS7247118B2Differential function is limitedMagnetically actuated clutchesDifferential gearingsDifferential functionLimited-slip differential
A limited slip differential device has differential gears, a clutch to limit the differential function of the differential gears, and a electromagnetic solenoid including a plunger and a coil. The plunger is set to move forward to engage the clutch by electromagnetic force of the coil in a differential limit state and move backward by a return spring to disengage said clutch in a differential limitless state. The plunger contacts with a contacting member in at least one state of the differential limit state and the differential limitless state, and their contact area is set smaller than a facing area between them in at least the one state.
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE TORQUE TECHNOLOGY KK +1
Control device for vehicle drive device
InactiveUS20090037061A1Improve fuel economyImprove power transfer efficiencyHybrid vehiclesBraking element arrangementsDifferential functionAutomatic transmission
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a differential mechanism including an electric motor. The drive system includes a switching clutch and switching brake to switch the transmission mechanism between a continuously-variable shifting state and a step-variable shifting state. A shifting control mechanism changes a manner of controlling shifting action of the transmission mechanism during shifting action of an automatic transmission portion, for reducing a shifting shock, depending upon whether a differential portion is placed in the continuously-variable shifting state in which engine speed is variable due to differential function irrespective of rotating speed of power transmitting member, or the non-continuously-variable shifting state in which the engine speed is more difficult to be variable than in the continuously-variable shifting state.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control apparatus for vehicular drive system
InactiveUS7566288B2Improve fuel economyHigh power transmissionHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerDrive wheelDifferential function
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a continuously-variable transmission portion operable as an electrically controlled continuously variable transmission having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, and a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel of a vehicle. The control apparatus includes: (a) a differential-state limiting device provided in the differential mechanism, and operable to limit a differential function of the differential mechanism, for limiting an operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission; and (b) a differential-state switching controller operable, when acceleration or deceleration of the vehicle is required, for removing the limitation imposed by the differential-state limiting device on the operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control apparatus for hybrid vehicle power transmitting system
ActiveUS20090036263A1Easy to operateImprove fuel economyHybrid vehiclesVehicle sub-unit featuresElectric power transmissionDifferential function
A control apparatus for a power transmitting system of a hybrid vehicle including (a) a differential portion which has a differential mechanism operatively connected to an engine and a first electric operatively connected to the differential mechanism, and a differential state of which is controlled by controlling an operating state of the first electric motor, and (b) a differential-state switching device which is incorporated in the differential mechanism and which is operable according to a differential-state switching condition, to switch the differential mechanism between a differential state in which the differential mechanism is operable to perform a differential function and a non-differential state in which the differential mechanism is not operable to perform the differential function, the control apparatus including a differential-state-switching-condition changing portion operable to change a differential-state switching condition for switching the differential-state switching device to switch the differential mechanism between the differential and non-differential states, when a temperature of the power transmitting system is lower than a predetermined threshold value.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Controller of driver for vehicles
InactiveUS7803086B2Improve fuel economyImprove power transfer efficiencyHybrid vehiclesVehicle sub-unit featuresDriver/operatorDifferential function
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including (a) a differential portion having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a vehicle drive wheel, and a switching clutch and a switching brake provided in the differential mechanism and operable to limit a differential function of the differential portion, and (b) a step-variable automatic transmission portion constituting a part of the power transmitting path and operable to perform a clutch-to-clutch shifting action by a releasing action of a coupling device and an engaging action of another coupling device, the control apparatus including a step-variable shifting control configured to change an amount of racing of an input speed of the automatic transmission portion during the clutch-to-clutch shifting action, depending upon whether the differential function of the differential portion is limited by the switching clutch and brake.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
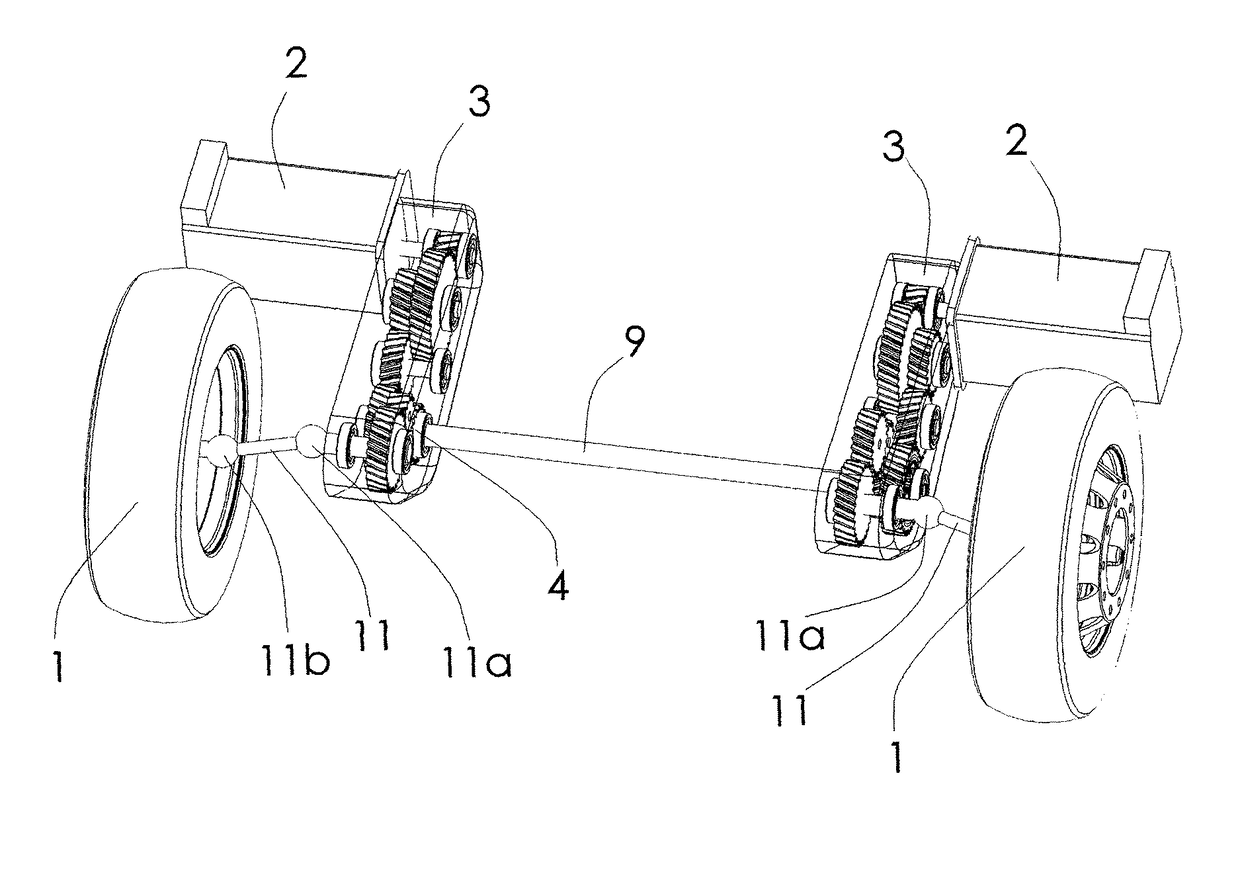
System for driving the drive wheels of an electric or hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20150096823A1Optimize architectureElectric propulsion mountingMotor depositionDrive wheelDifferential function
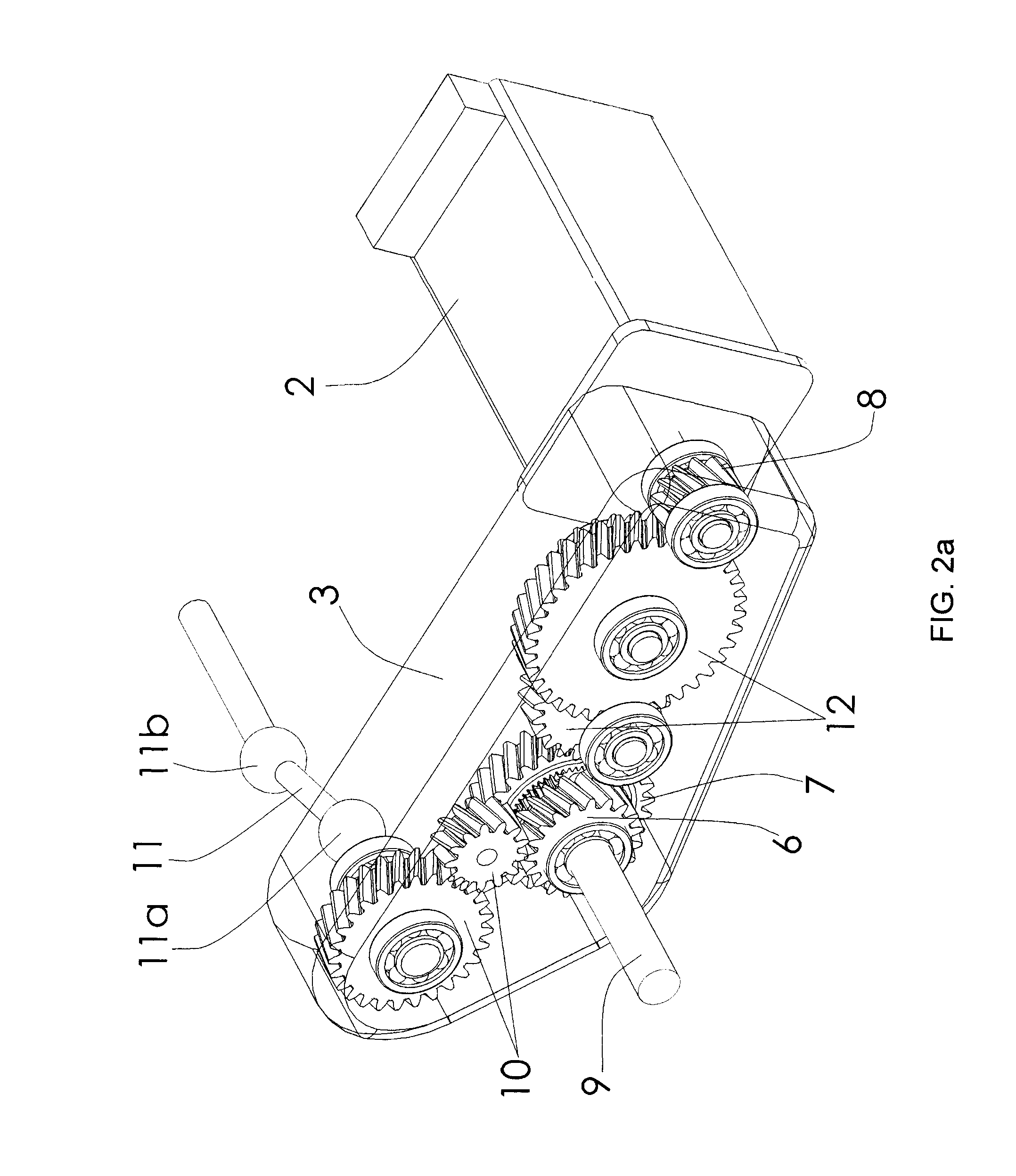
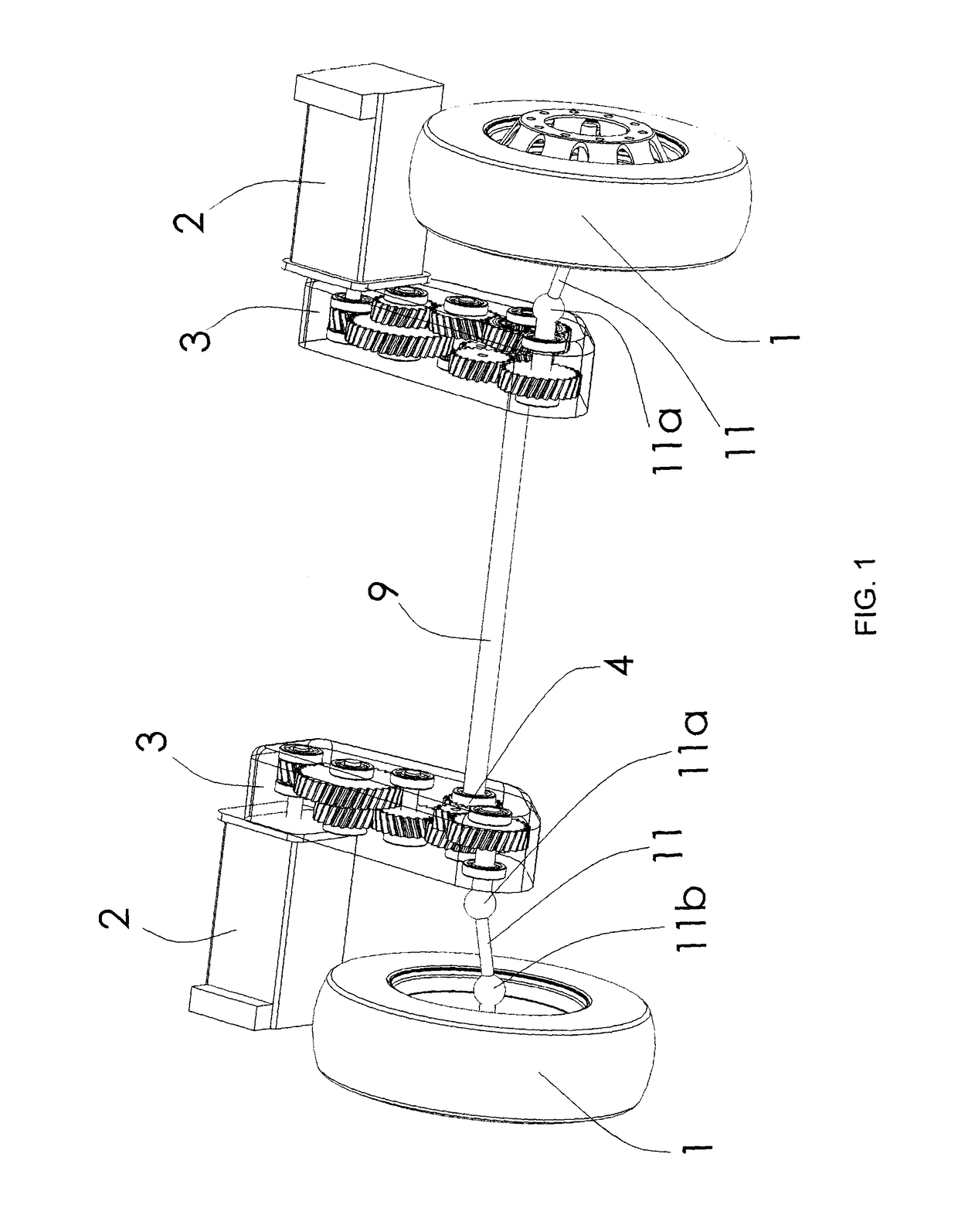
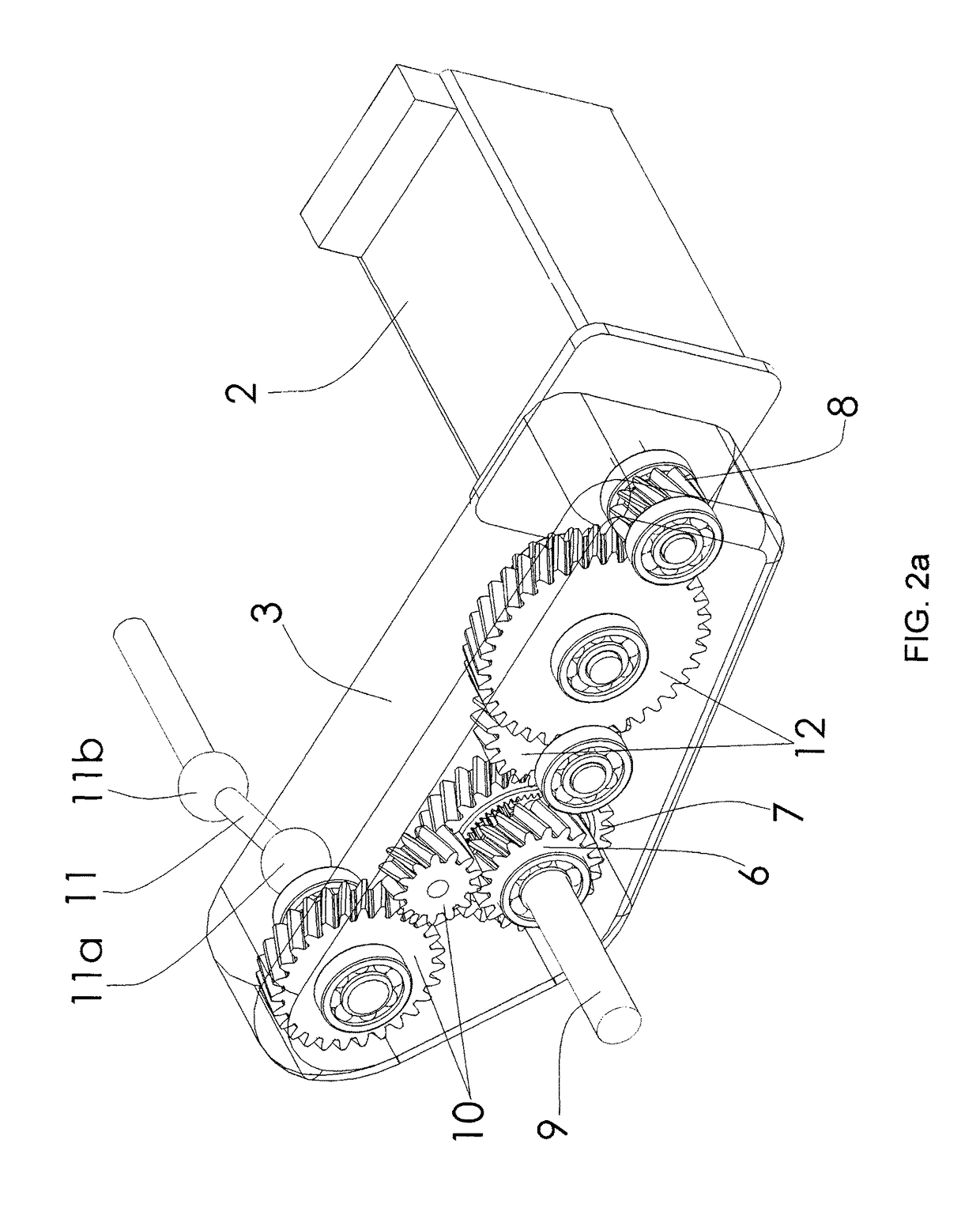
The invention relates to a system for driving the drive wheels (1) of a vehicle, comprising two sets of electric motors (2) and casings (3) (left and right). Each of the casings (3) comprises an input pinion (8) which rotates interdependently with the rotor of one of the electric motors (2) as well as with a set of gears (12) driving the ring gear (7) of a planetary gear set (4). The two planetary gear sets (4) are connected to one another by a connecting means (9) that rotates interdependently with each of the two sun gears (5) (inner planetaries). The planet carrier (6) of each of the planetary gear sets (4) rotates interdependently with a connecting means (11) of one of the drive wheels (1). The two planetary gear sets (4) perform a double differential function. The invention also relates to a method for controlling the electric motors (2) that allows the drive system to be used as a torque converter. The drive system can be fixed to the chassis frame of the vehicle. In addition, the two casings (3) can be located in the wheel cages (13). The connecting means (9) that rotates interdependently with the two sun gears (5) can be located inside the casing of the floor pan (14) of the vehicle. The two electric motors (2) can be located just behind the driven wheels (1).
Owner:PANTERO TECH
Controller of Driver for Vehicles
InactiveUS20090011895A1Small sizeImprove efficiencyHybrid vehiclesVehicle sub-unit featuresDrive wheelDifferential function
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including (a) a differential portion having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a vehicle drive wheel, and a switching clutch and a switching brake provided in the differential mechanism and operable to limit a differential function of the differential portion, and (b) a step-variable automatic transmission portion constituting a part of the power transmitting path and operable to perform a clutch-to-clutch shifting action by a releasing action of a coupling device and an engaging action of another coupling device, the control apparatus including a step-variable shifting control configured to change an amount of racing of an input speed of the automatic transmission portion during the clutch-to-clutch shifting action, depending upon whether the differential function of the differential portion is limited by the switching clutch and brake.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Distributed power system state estimation method
InactiveCN102623993AImprove iteration efficiencyImprove development efficiencyComplex mathematical operationsAc network circuit arrangementsDifferential functionEstimation methods
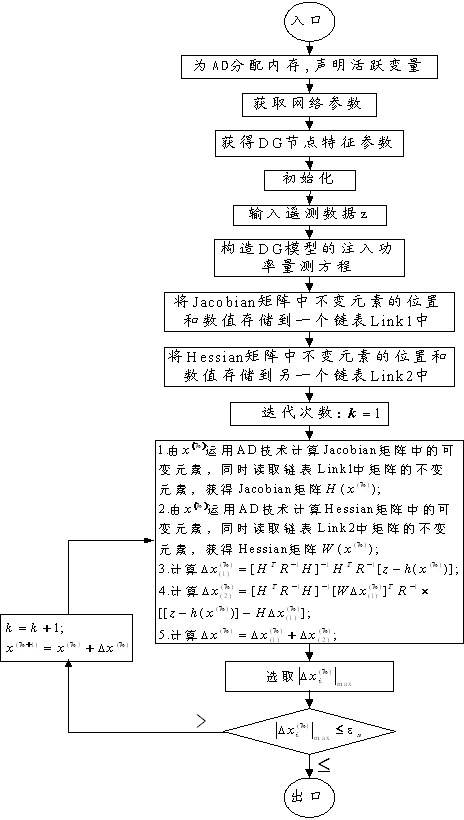
The invention discloses a distributed power system state estimation method. A distributed power system state estimation model is established in consideration of distributed generation (DG) characteristics so that the real-time accurate operational state of each node in the power grid can be obtained, and the real-time accurate operational state of the DG can also be obtained; secondly, a preserving non-linear method is introduced to the state estimation, and the truncation error is avoided so that the state estimation is provided with a higher computational accuracy and the iteration efficiency of an algorithm is improved; and finally, the Jacobian matrix and the Hessian matrix of a function is calculated and measured in the preserving non-linear method of the state estimation, the work load of manually calculating a large quantity of differential functions and compiling differential codes is large, and the work is too cumbersome and easy to produce errors so that the distributed power system state estimation method utilizes the automatic differentiation technique to replace the traditional manual compiling differential codes to calculate the Jacobian matrix and the Hessian matrix, the workload of the manual compiling codes is reduced, and the development efficiency of procedures is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Control apparatus for vehicular drive system
InactiveUS20100041511A1Small sizeImprove efficiencyHybrid vehiclesGearing controlElectricityDrive wheel
A transmission mechanism including a switching clutch or brake is switchable between a continuously-variable shifting state and a step-variable shifting state, and provides improved fuel economy by a transmission with an electrically variable speed ratio and high power transmitting efficiency by a gear type power transmitting device constructed for mechanical transmission of power. During four-wheel drive vehicle running with second drive wheels driven by a third electric motor, a switching control switches a differential portion to a continuously-variable shifting state, so that an operating speed of a first electric motor operated by an output of an engine as an electric generator is controlled to assure a higher degree of electricity generating efficiency, owing to the differential function of the differential portion, than when the differential portion is placed in a non-continuously-variable shifting state in which first electric motor speed and engine speed are determined by vehicle running speed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control apparatus for vehicular drive system
InactiveUS20070111848A1Improve fuel economyHigh power transmissionHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerDifferential functionDrive wheel
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a continuously-variable transmission portion operable as an electrically controlled continuously variable transmission, the continuously-variable transmission portion having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, and a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel of a vehicle. The control apparatus includes: (a) a differential-state limiting device provided in the differential mechanism, and operable to limit a differential function of the differential mechanism, for limiting an operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission; and (b) a differential-state switching controller operable, when acceleration or deceleration of the vehicle is required, for removing the limitation imposed by the differential-state limiting device on the operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
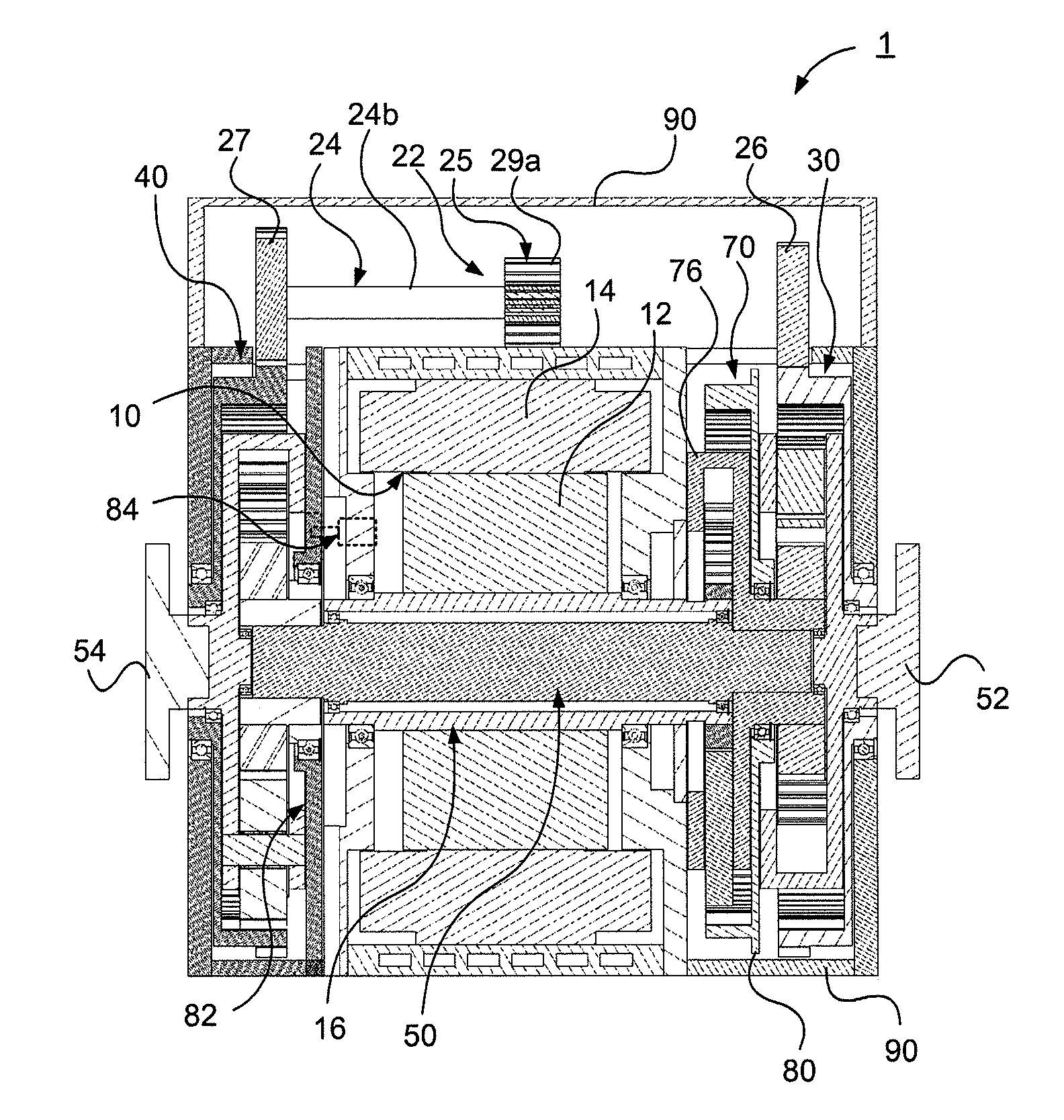
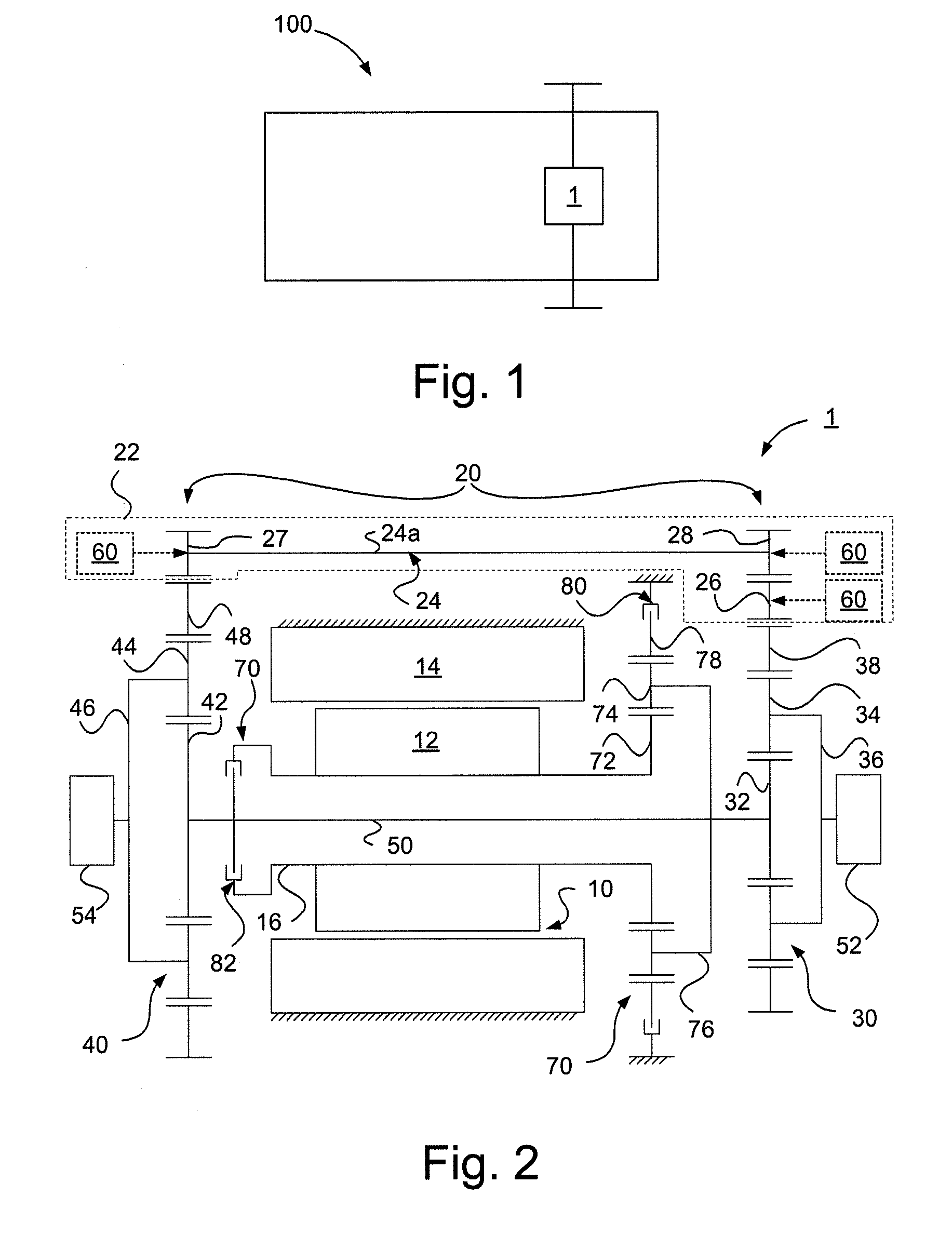
Control Device For Vehicular Drive System
ActiveUS20080146408A1Small sizeImprove fuel economyHybrid vehiclesGearing controlDrive wheelDifferential function
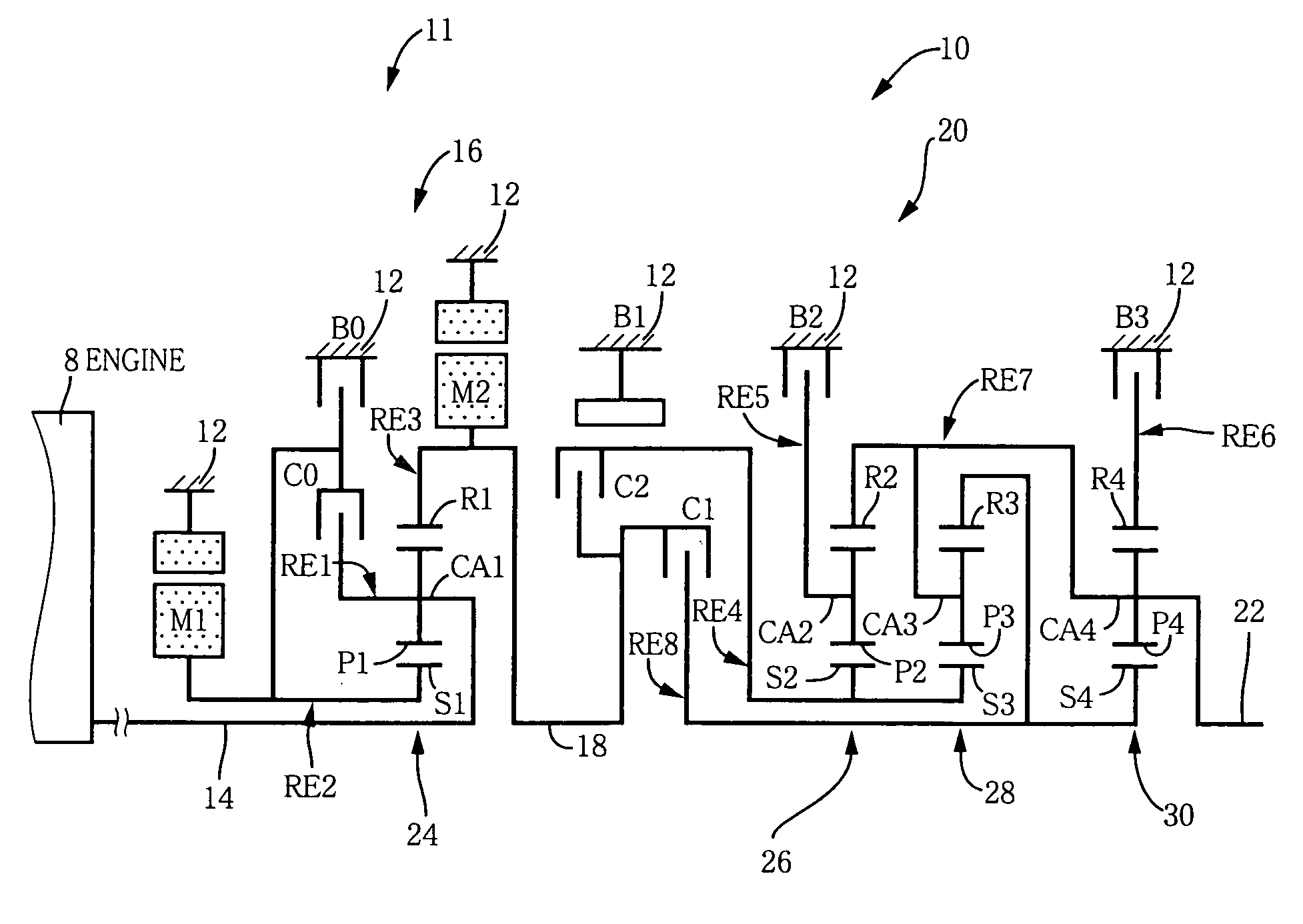
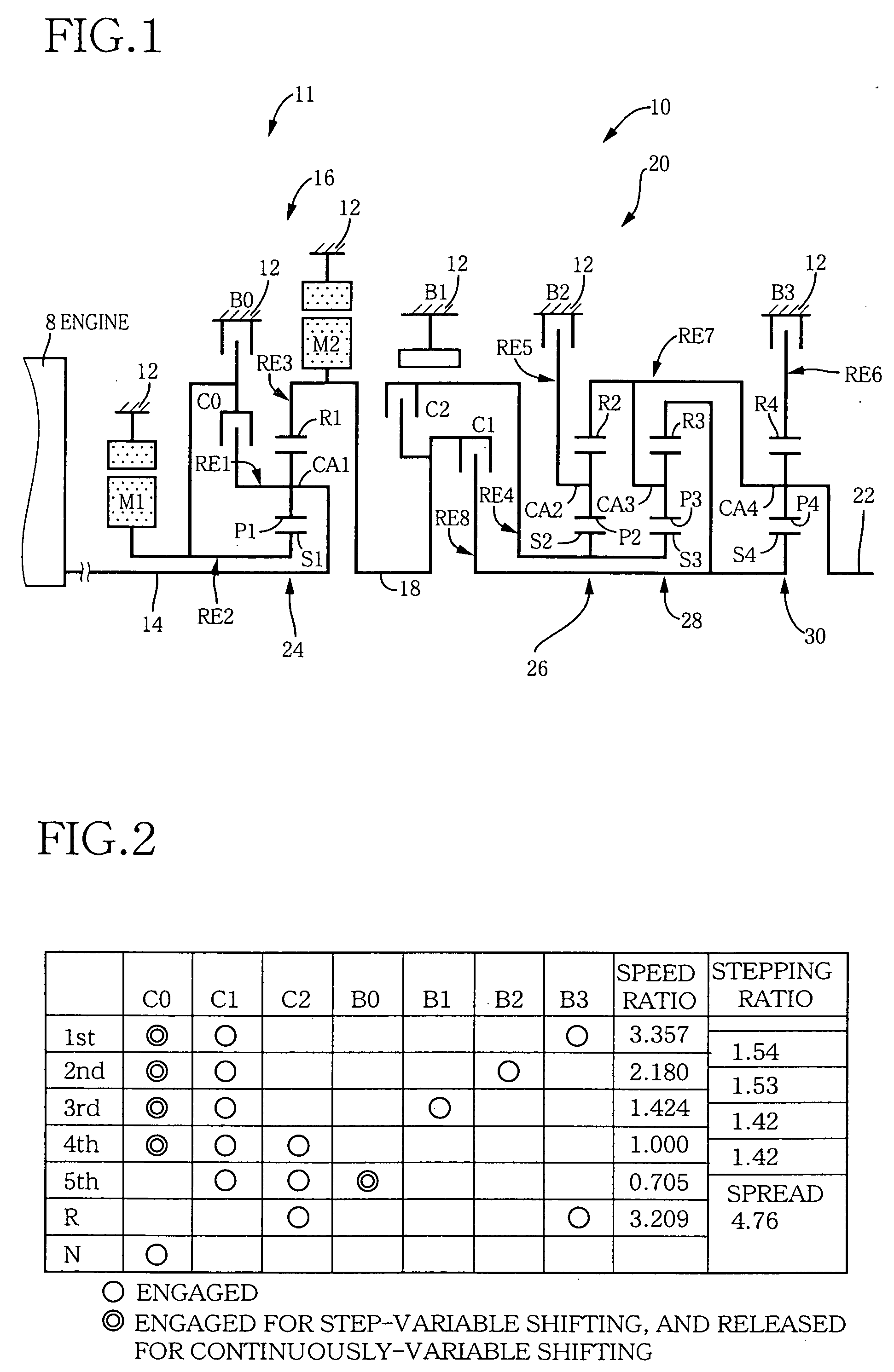
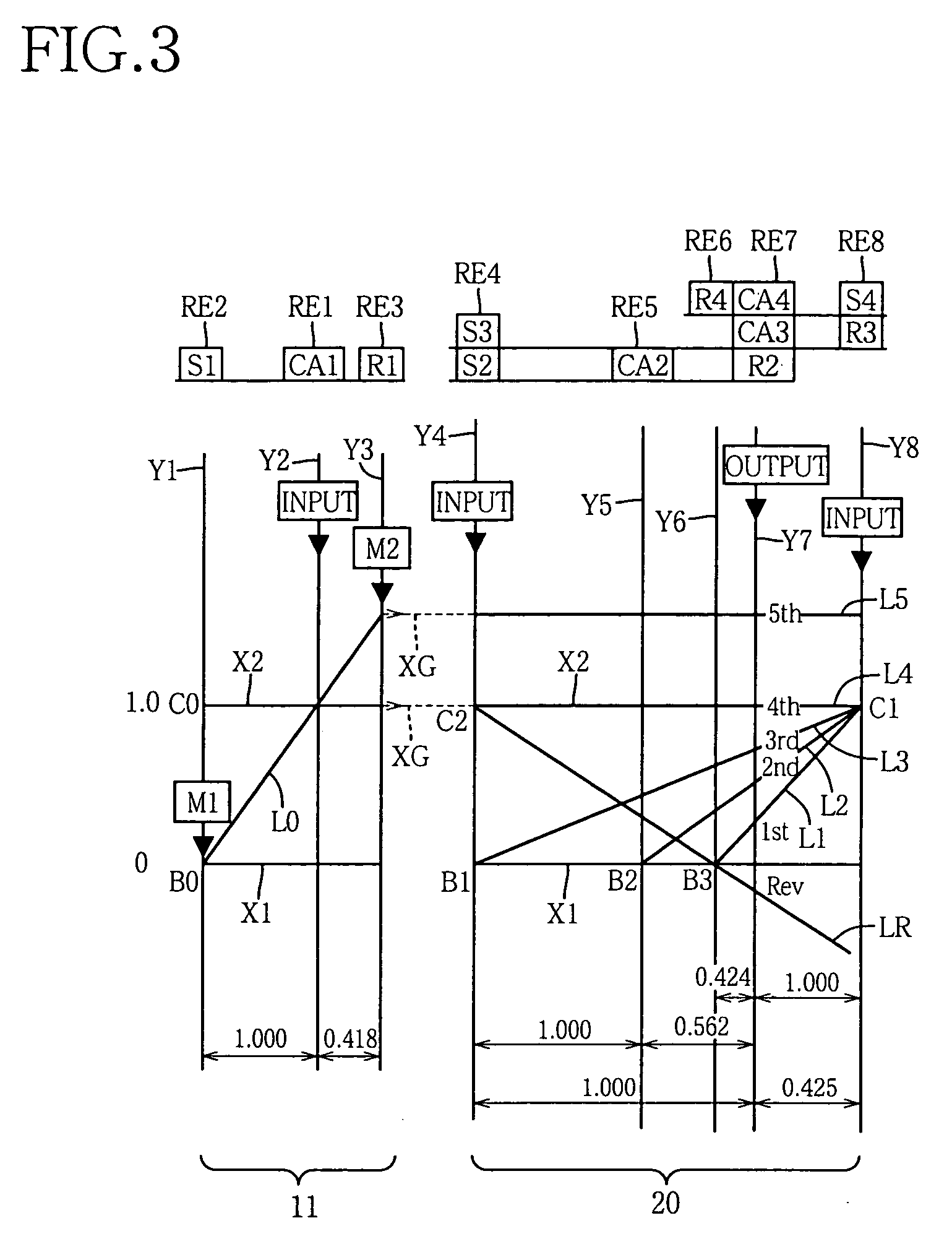
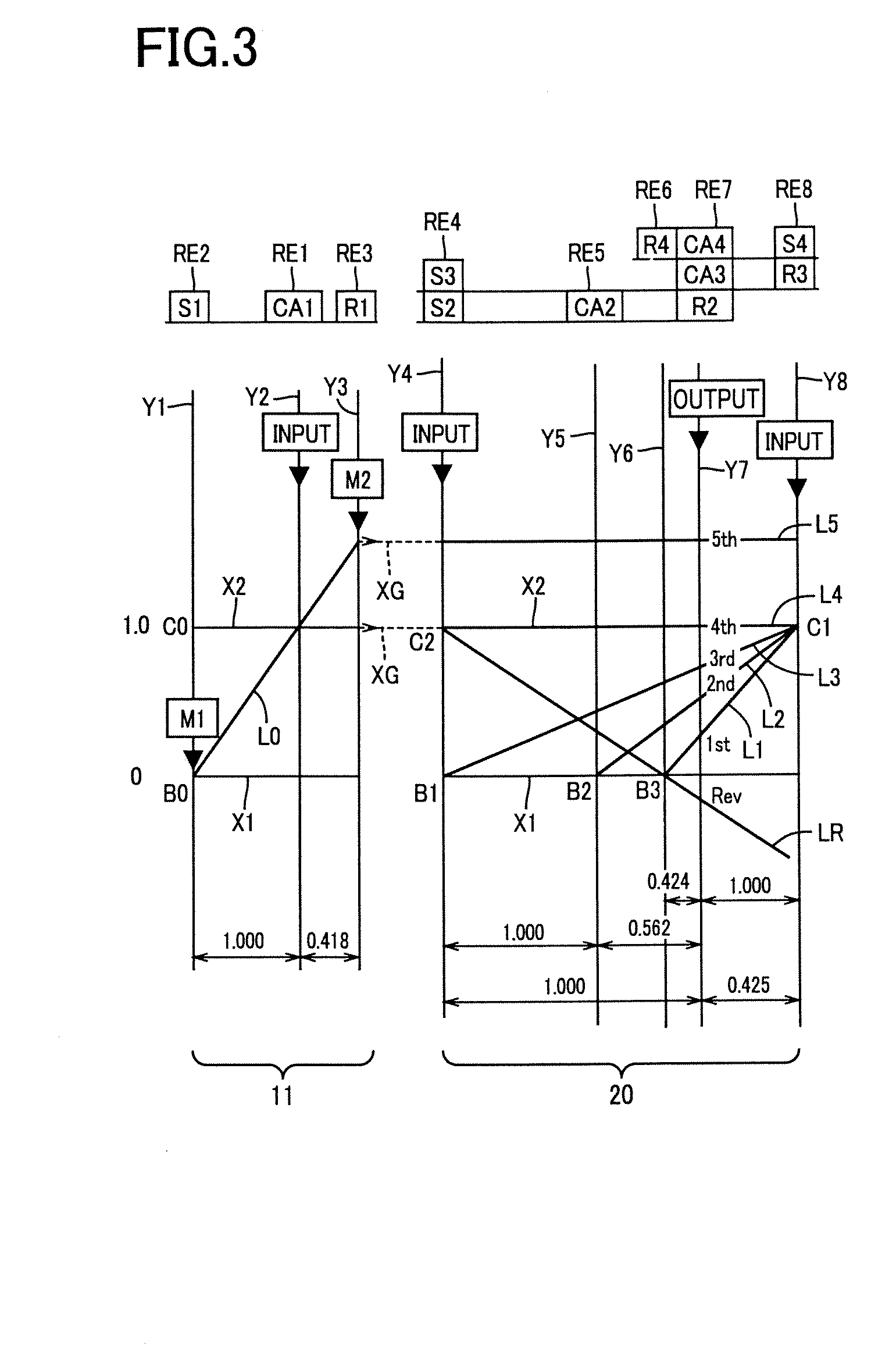
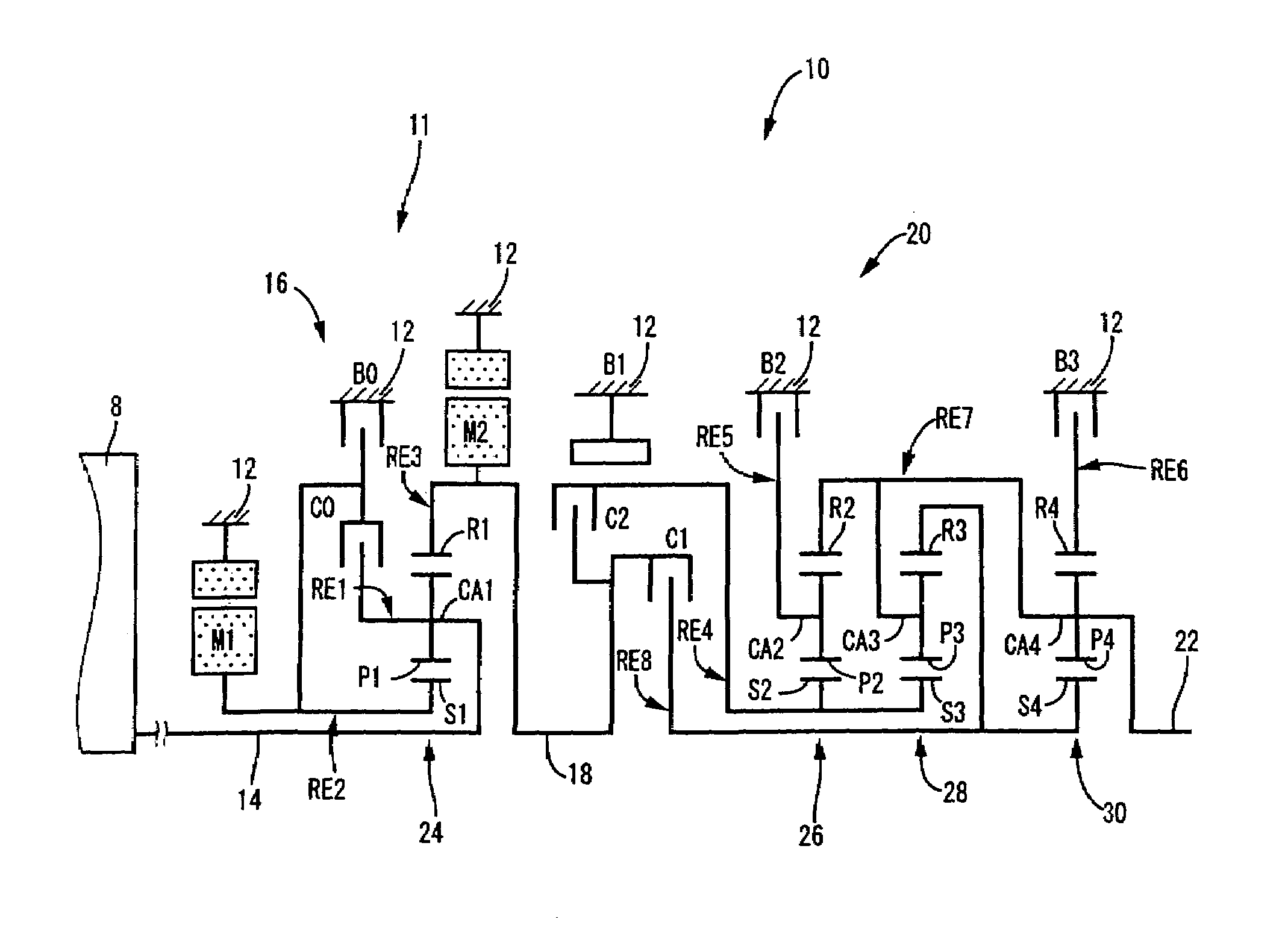
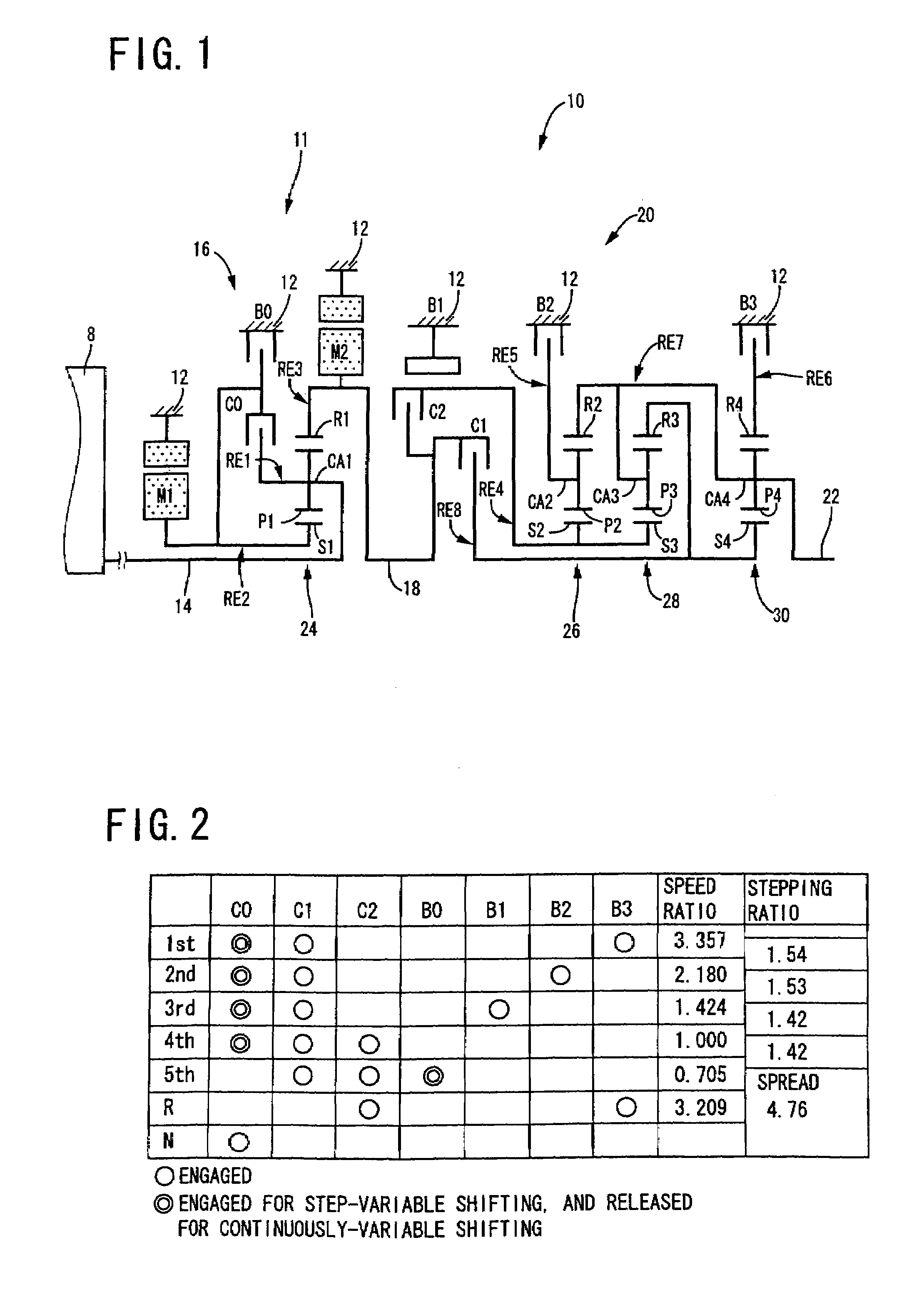
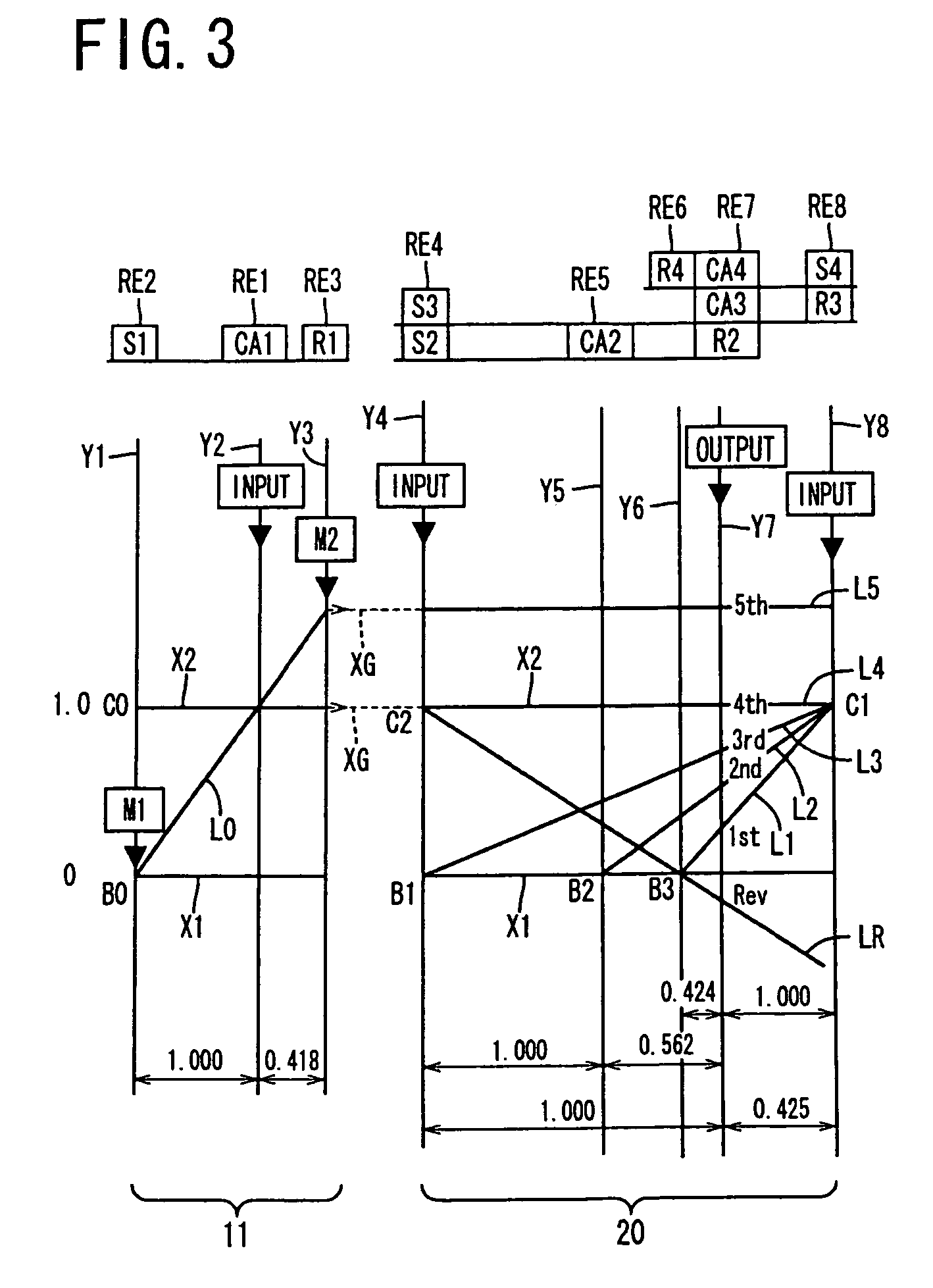
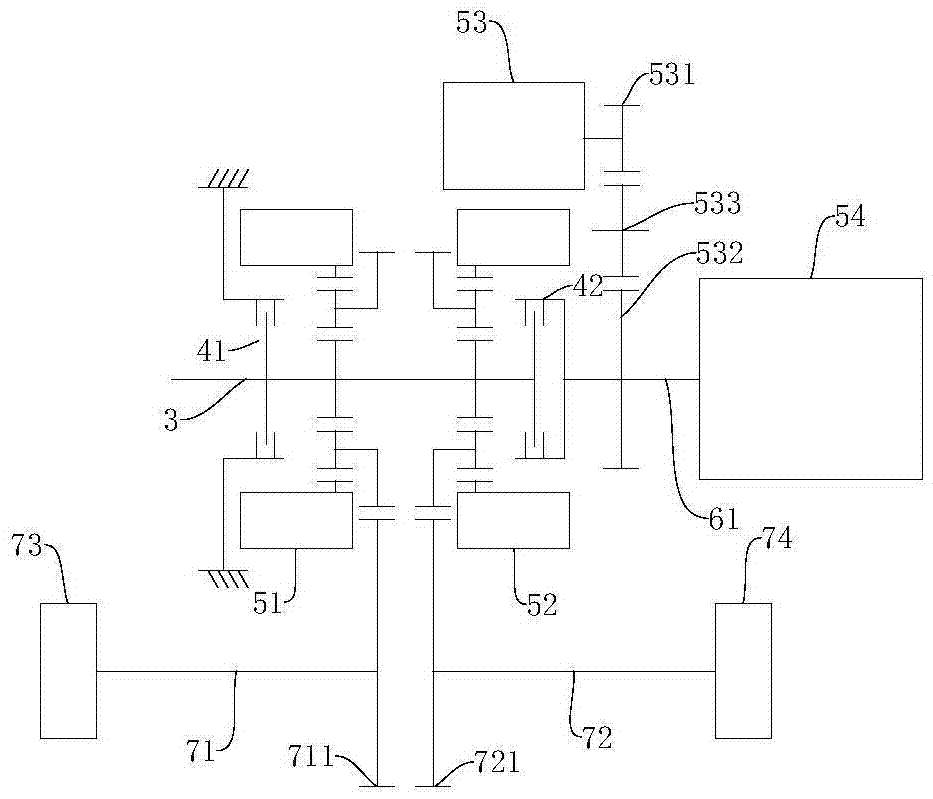
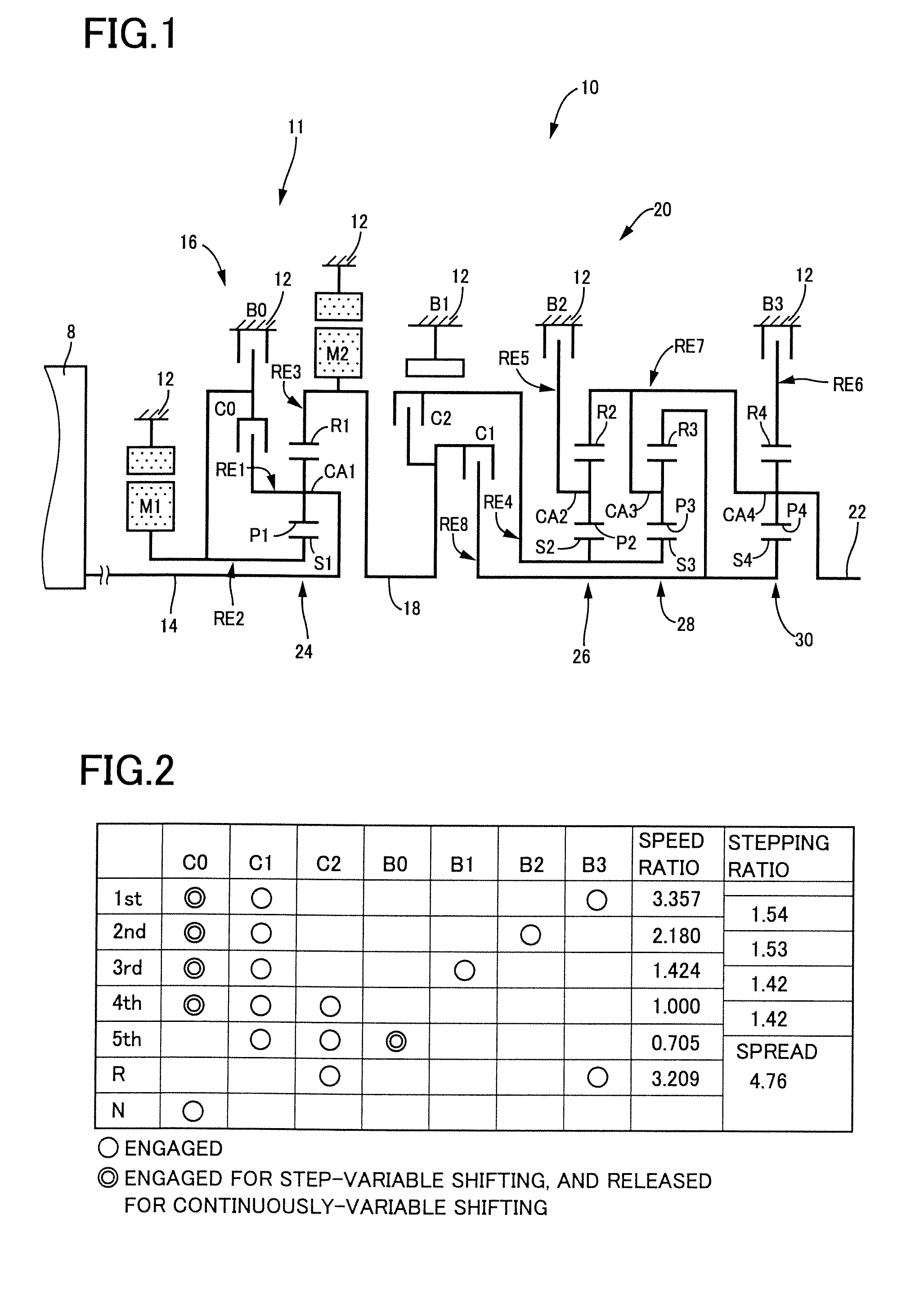
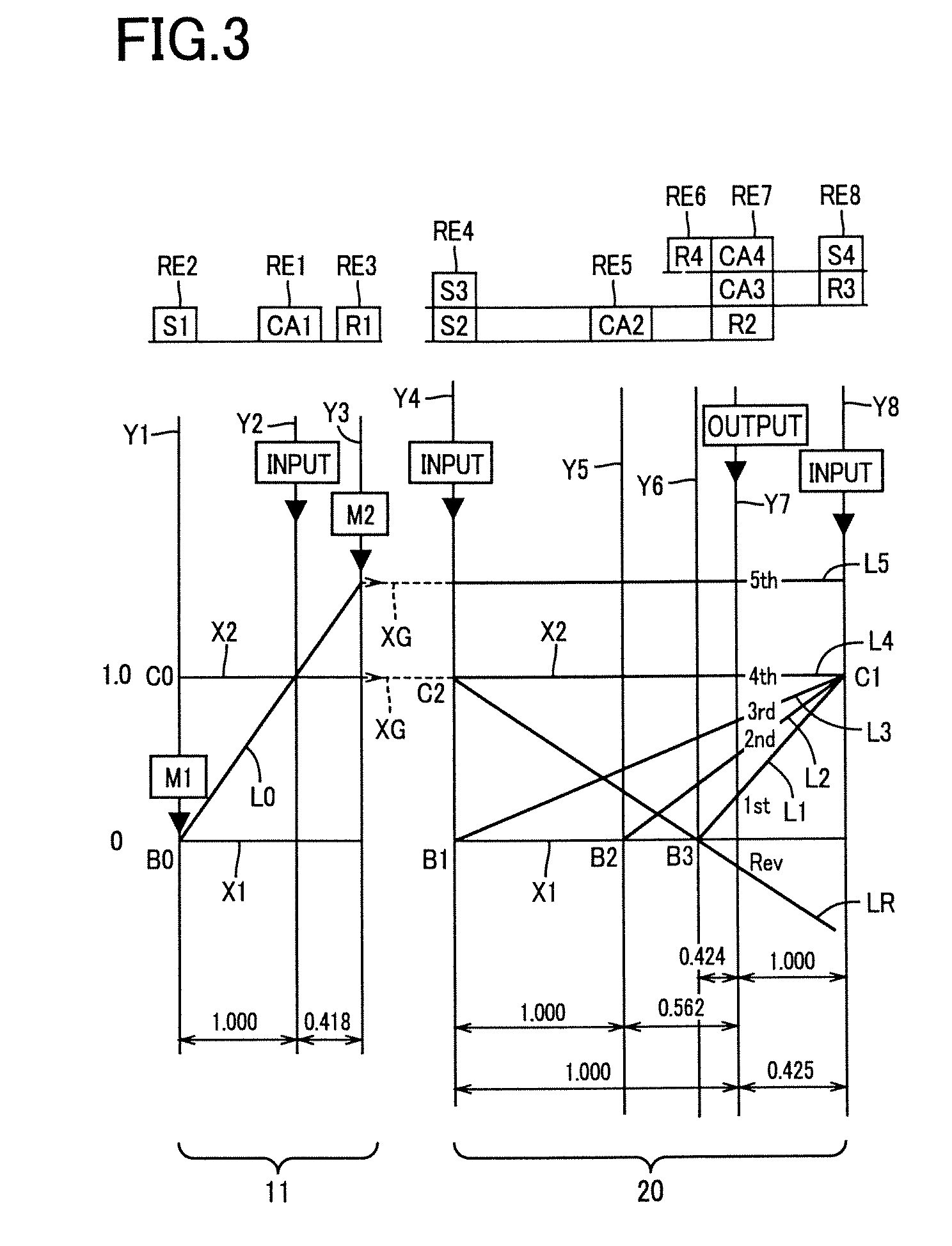
A control device for a vehicular drive system including a differential portion (11) having a differential mechanism (16) operable to distribute an output of an engine (8) to a first electric motor (M1) and a power transmitting member (18), and a second electric motor (M2) disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel (38) of a vehicle, the control device including a differential limiting device (C0, B0) provided in the differential mechanism (16) and operable to limit a differential function of the differential mechanism for thereby limiting a differential function of the differential portion (11), and torque-response control means (84) for controlling a response of a change of an input torque of the differential portion to an operation of a manually operable vehicle accelerating member (45), depending upon whether the differential function of the differential mechanism (16) is limited or not.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Steering conveying system
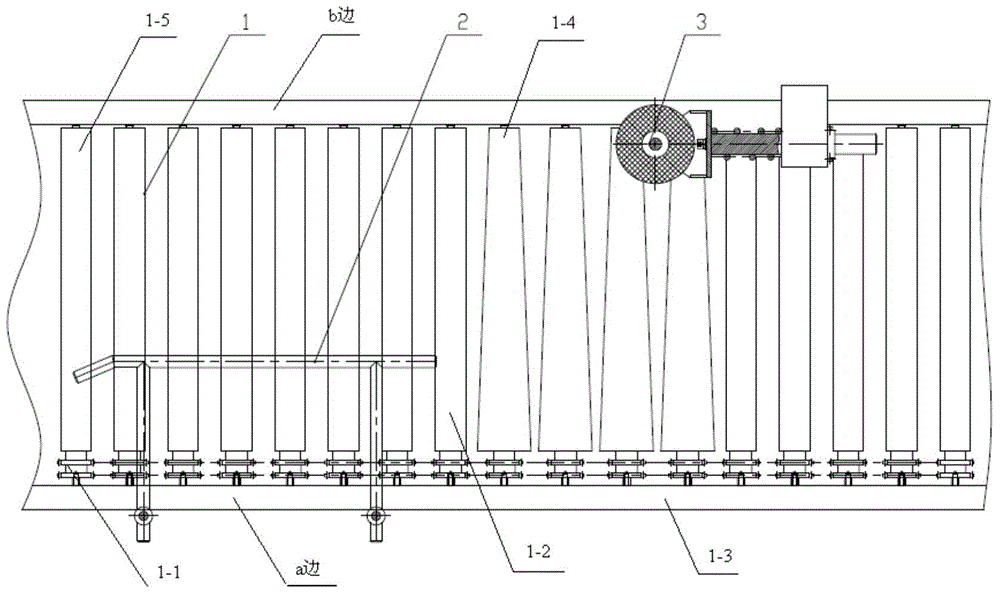
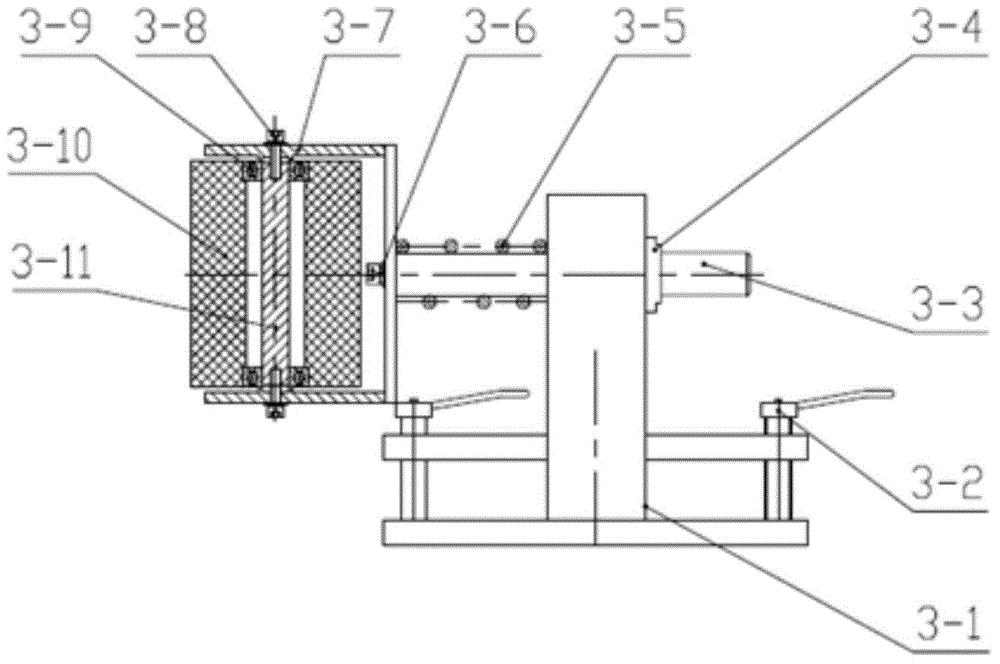
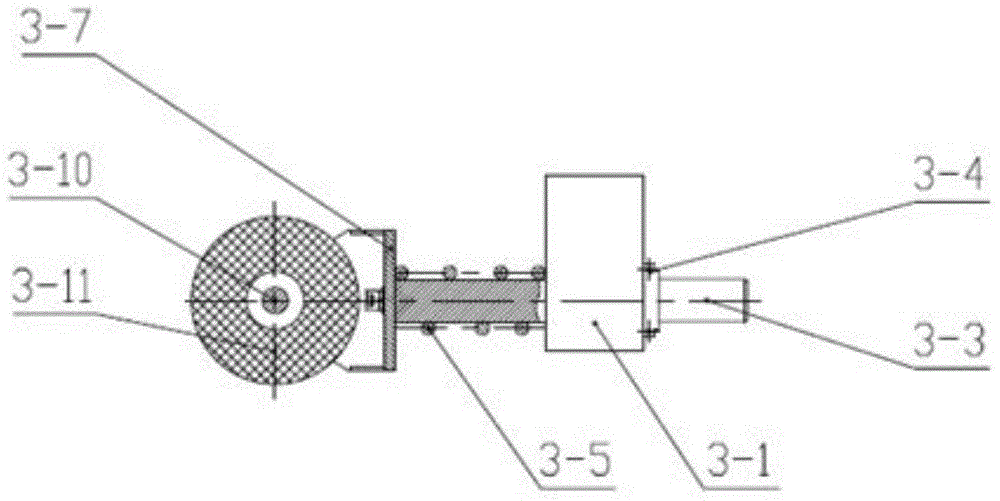
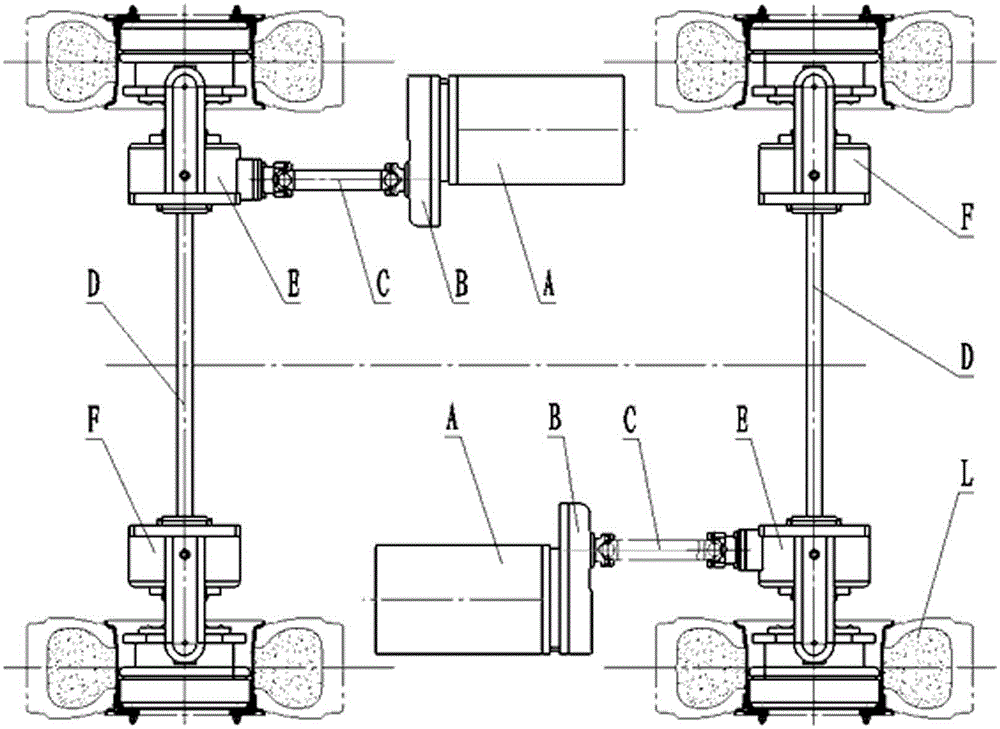
InactiveCN104590865AAchieve steeringReliable steeringConveyor partsRoller-waysDifferential functionMechanical engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of packing conveying equipment, in particular to a steering conveying system. The steering conveying system is characterized by comprising a packing material conveying line (1), a guide guardrail (2) and a steering mechanism (3), wherein the packing material conveying line (1) comprises a driving device, a conveying roller line and connecting side plates; the driving device is used for driving the conveying roller line to move; multiple conical power rollers are arranged in the middle of the conveying roller line, and the rest are common power rollers; the connecting side plates are positioned at the two sides of the conveying roller line; the guide guardrail (2) is positioned in front of the area of the conical power rollers, and is used for adjusting the position of a packing material; and the steering mechanism (3) is mounted on the connecting side plate at the side b of the packing material conveying line (1), and is positioned in the area of the conical power rollers. The steering conveying system has the beneficial effects of fully using the differential function of the conical rollers for realizing the steering of the packing material, designing an adjusting handle for conveniently adjusting and fixing the position and designing a spring buffer device for protecting the steering conveying system and the packing material from being intensely collided.
Owner:BEIJING AREOSTANARD NEW TECH +2
Heavy shuttle car hub driving system integrating differential respective drive and wet-type brake
ActiveCN105197020APower balance without overloadImprove power utilizationElectric motor propulsion transmissionManufacturing technologyDifferential function
The invention belongs to the technical field of design and manufacturing of underground coal mine subsidiary transport equipment parts, and provides a heavy shuttle car hub driving system integrating differential respective drive and wet-type brake. The problem that the existing shuttle car brake system is poor in steering differential function, large in brake impact and the like is solved. A drive front axle and a drive rear axle of a shuttle car are respectively controlled by two driving systems which are connected with each other in parallel; each driving system comprises a motor, a single-reduction gearbox, a hub reduction gear I and a hub reduction gear II; each hub reduction gear I and the corresponding hub reduction gear II are symmetrically mounted at two ends of a transverse transmission shaft of a corresponding shuttle car drive axle, and are positioned on the inner side of a corresponding walking rubber wheel of the shuttle car; the hub reduction gears I are connected with an outputting end of the single-reduction gearbox through transmission shafts; and the single-reduction gearbox is driven by the motors. By the two driving systems which are connected with each other in parallel, problems of abrasion of tires, eccentric load of the hub reduction gears and the like are solved, and motor power utilization rate is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN INST OF CHINA COAL TECH & ENG GROUP +1
Gene transduction method with nano granule as carrier based on ultrasonic intervention guiding
InactiveCN1687427ALow priceEasy to operateImmobilised enzymesOther foreign material introduction processesParticulatesCell wall
A gene transduction method ultrasonic-based, which using the nano particulate as the carrier. It consists of animal transgenic gene method and plant transgenic gene method. The outer gene joins with the particulate with the effect of static form together to form the gene carrier, which can protect the DNA being broken by ultrasonic. The ultrasonic synchronously give effect to particulate gene carrier, cells, organize and apparatus, the carrier can run efficiently through the short period alleyway of cell wall, cell film, core film cell, enables the outer gene constructs with the gene group in cell. This method has a high efficiency, and is provided with convenient manipulation, high efficiency, no request of differential function e.g. other merits. It can be applied widely to these range, animal and plant transgenic technology and genic cure of human being.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
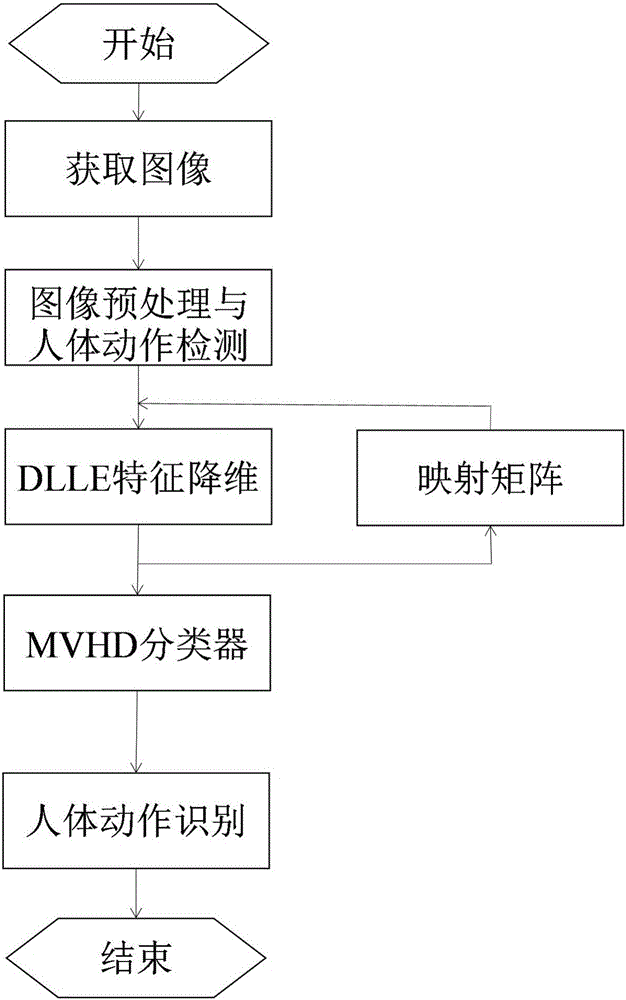
DLLE model-based data dimension reduction and characteristic understanding method
InactiveCN106127112AHigh precisionProof of validityCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyKey frame
The invention discloses a DLLE (Linear Local Embedding of Difference) model-based data dimension reduction and characteristic understanding method, and belongs to the field of computer vision. The method comprises the steps of firstly, obtaining an image sequence through a visual sensor, then analyzing an input motion image sequence, extracting a foreground human body contour region through a background subtraction method, performing binarization, researching a periodic characteristic of a motion, performing key frame extraction on each motion sequence, and extracting a complete motion periodic sequence; performing manifold dimension reduction through a DLLE algorithm to obtain a low-dimensional eigenvector, and storing the low-dimensional eigenvector in a motion database; and performing identification through a nearest neighbor classifier by comparing a mean Hausdorff distance between a test sequence and a motion sequence in a training sample library. According to the method, the application of a differential function and category information-based neighborhood preserving embedding algorithm to human body motion identification is proposed; a DLLE model can not only keep a manifold local geometric structure during dimension reduction but also fully utilize category information of original high-dimensional data; and the extension from unsupervised extension to supervised extension is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Electric drive system
InactiveUS20110124460A1Efficient driveEasy to changeSpeed controllerElectric propulsion mountingElectricityDifferential function
An electric drive system including an electric motor arranged to rotate a drive shaft. A differential includes a first planetary gear being drivingly connected to a first output assembly. A second planetary gear configuration is in driving engagement with the first planetary gear configuration via an output shaft. The second planetary configuration is drivingly connected to a second output assembly. The motor is disposed between the first and second planetary gear configuration. The first planetary gear configuration is arranged to co-act with the second planetary gear configuration so as to provide a differential function. The ring gears of the first and second planetary gear configurations are engaged via a reversing assembly for the differential function. Also, a motor driven unit, such as a motor vehicle.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS HAGGLUNDS AKTIEBOLAG
System for driving the drive wheels of an electric or hybrid vehicle
The invention relates to a system for driving the drive wheels (1) of a vehicle, comprising two sets of electric motors (2) and casings (3) (left and right). Each of the casings (3) comprises an input pinion (8) which rotates interdependently with the rotor of one of the electric motors (2) as well as with a set of gears (12) driving the ring gear (7) of a planetary gear set (4). The two planetary gear sets (4) are connected to one another by a connecting means (9) that rotates interdependently with each of the two sun gears (5) (inner planetaries). The planet carrier (6) of each of the planetary gear sets (4) rotates interdependently with a connecting means (11) of one of the drive wheels (1). The two planetary gear sets (4) perform a double differential function. The invention also relates to a method for controlling the electric motors (2) that allows the drive system to be used as a torque converter. The drive system can be fixed to the chassis frame of the vehicle. In addition, the two casings (3) can be located in the wheel cages (13). The connecting means (9) that rotates interdependently with the two sun gears (5) can be located inside the casing of the floor pan (14) of the vehicle. The two electric motors (2) can be located just behind the driven wheels (1).
Owner:PANTERO TECH
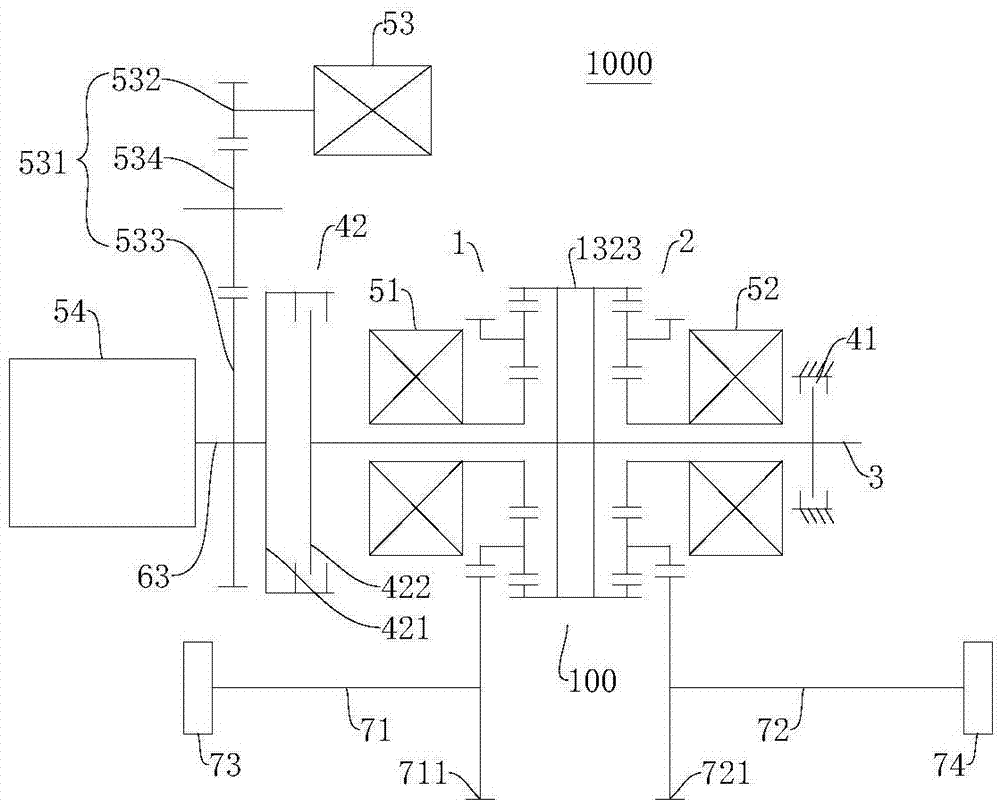
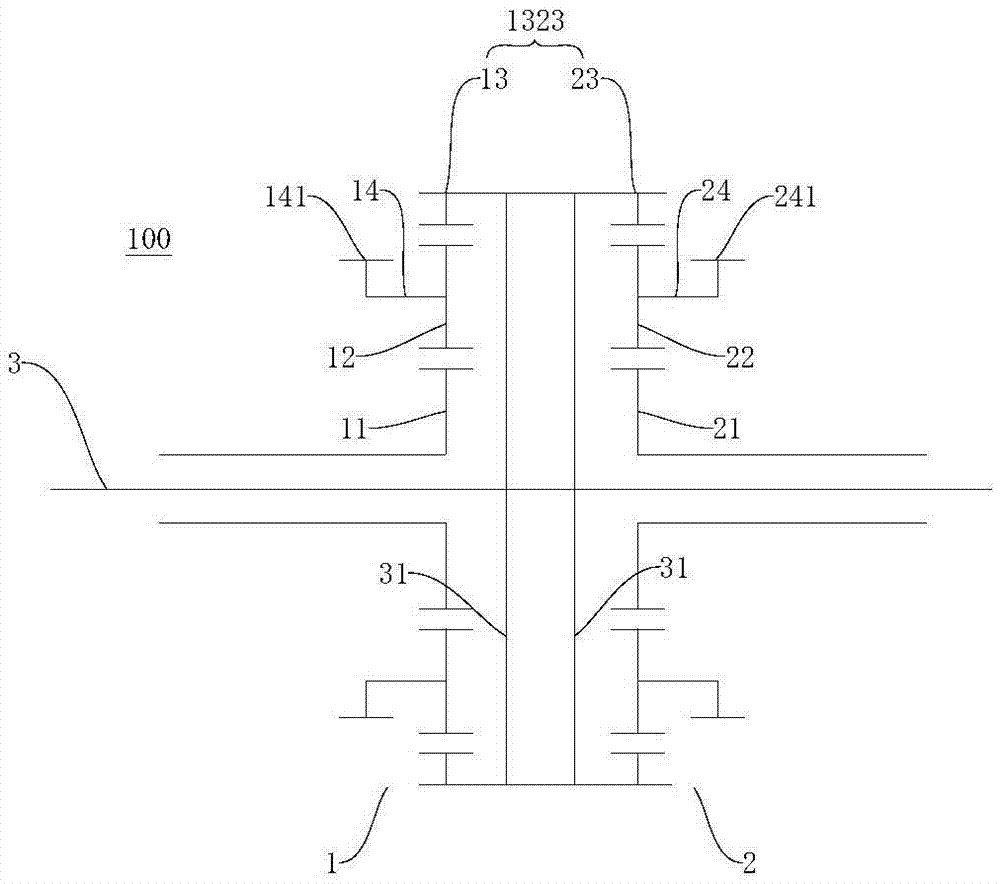
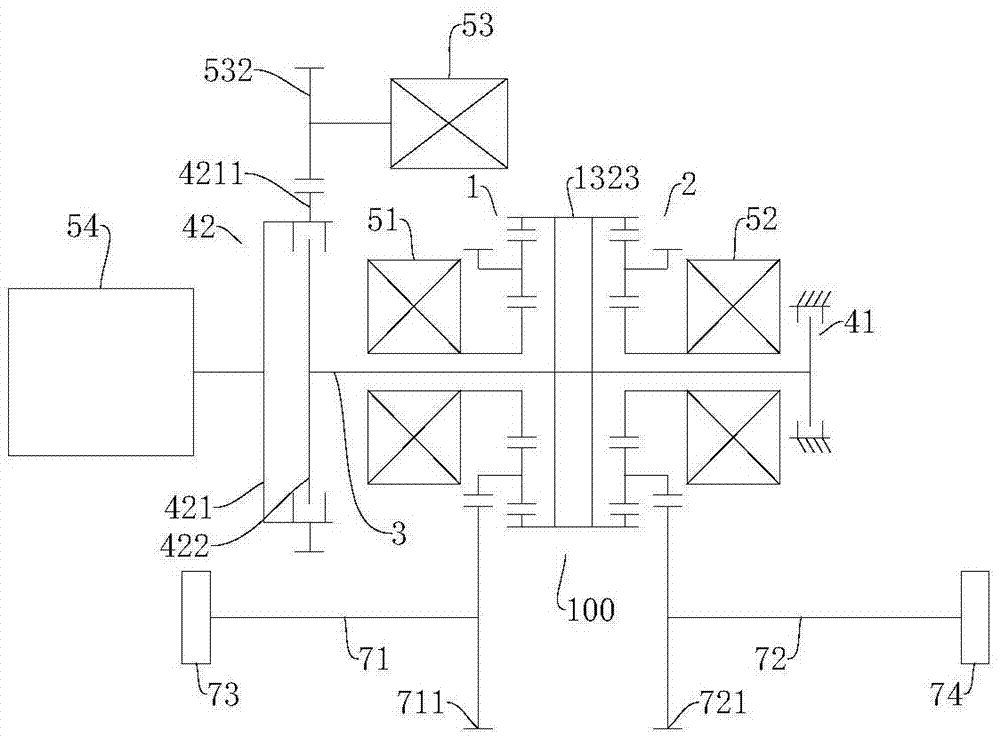
Power driving system and vehicle with power driving system
ActiveCN106915245ARealize the differential functionRich transmission modeHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingDifferential functionDynamic coupling
The invention discloses a power driving system and a vehicle with the power driving system. The power driving system comprises a dynamic coupling device, a power transmission unit, a power source, a first motor generator, a second motor generator and a first brake device. The dynamic device comprises a first sun wheel, a first planet carrier, a first gear ring, a second sun wheel, a second planet carrier and a second gear ring. The power transmission unit is coaxially in linkage with the first sun wheel and the second sun wheel. The power source is set to selectively joint the power transmission unit. The first motor generator is in linkage with the first gear ring. The second motor generator is in linkage with the second gear ring. The first brake device is used for braking the power transmission unit directly or indirectly. According to the power driving system, the differential function is realized on the basis of omitting a conventional mechanical differential mechanism. The power driving system is rich in transmission mode.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Hydraulic circuit of the differential telescopic system and aerial work platform using hydraulic circuit of the differential telescopic system
InactiveCN106438521ADoes not increase the difficulty of layoutEasy to controlServomotorsServometer circuitsDifferential functionSolenoid valve
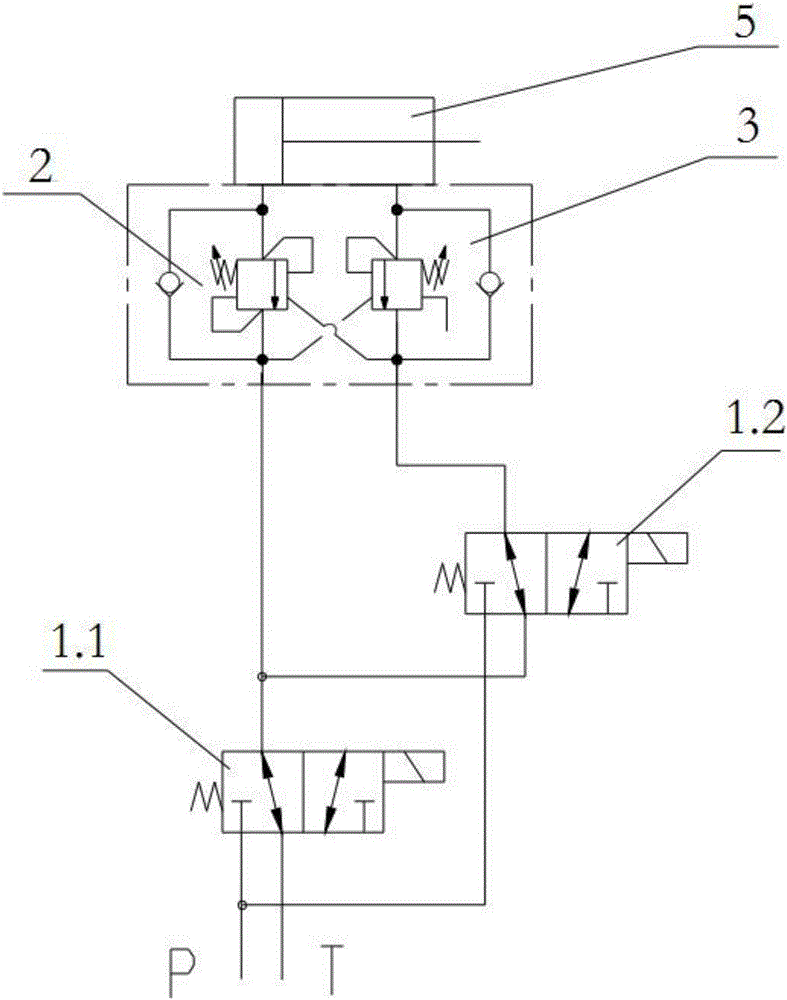
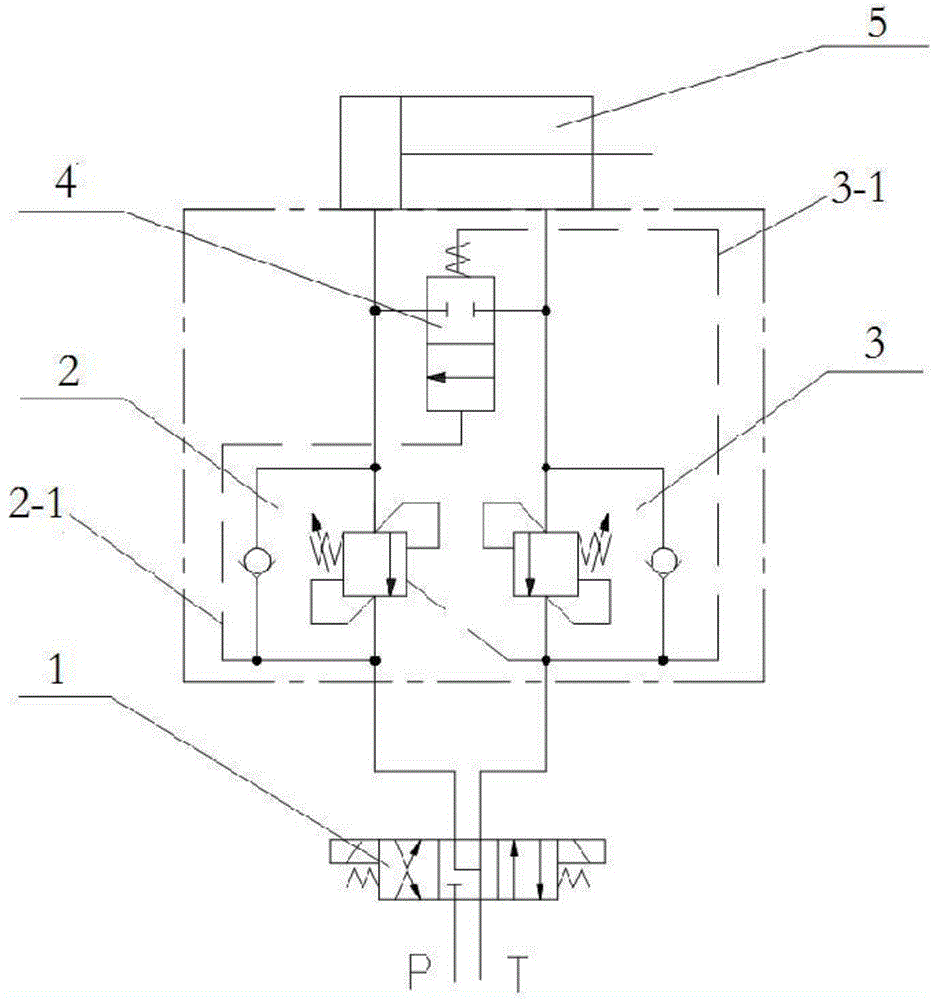
This invention discloses the hydraulic circuit of the differential telescopic system. The hydraulic circuit of the differential telescopic system includes the single solenoid valve (1), which passes through the balance valve without the rod cavity (2) and the balance valve with the rod cavity (3) connecting with the rod cavity of the telescopic cylinder (5) and the rodless cavity of the telescopic cylinder (5). The hydraulic check valve (4) is installed between the balance valve without the rod cavity (2) and the balance valve with the rod cavity (3). The controllable oil circuit I is formed between the balance valve without the rod cavity (2) and the hydraulic check valve (4). The controllable oil circuit II is formed between the balance valve with the rod cavity (3) and the hydraulic check valve (4). The hydraulic circuit of the differential telescopic system also includes the aerial work platform adopting the hydraulic circuit of the differential telescopic system. The hydraulic circuit of the differential telescopic system uses the single solenoid valve, which will not increase the difficulty of arranging the valve. The balance valve is the ordinary one, which can reduce the cost effectively. Meanwhile, the hydraulic control valve, which will automatically switch the differential function, can improve the telescopic efficiency. The full working process of this hydraulic circuit of the differential telescopic system will not pollute the air for the reason that there will be no leakage of the oil without hydraulic pressure.
Owner:XCMG FIRE FIGHTING SAFETY EQUIP CO LTD
Control device for vehicle drive device
InactiveUS8036801B2Improve fuel economyImprove power transfer efficiencyHybrid vehiclesBraking element arrangementsAutomatic transmissionDifferential function
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Transfer for four-wheel drive vehicle
InactiveUS6485390B2Weight increaseSimple structureToothed gearingsControl devicesDifferential functionControl theory
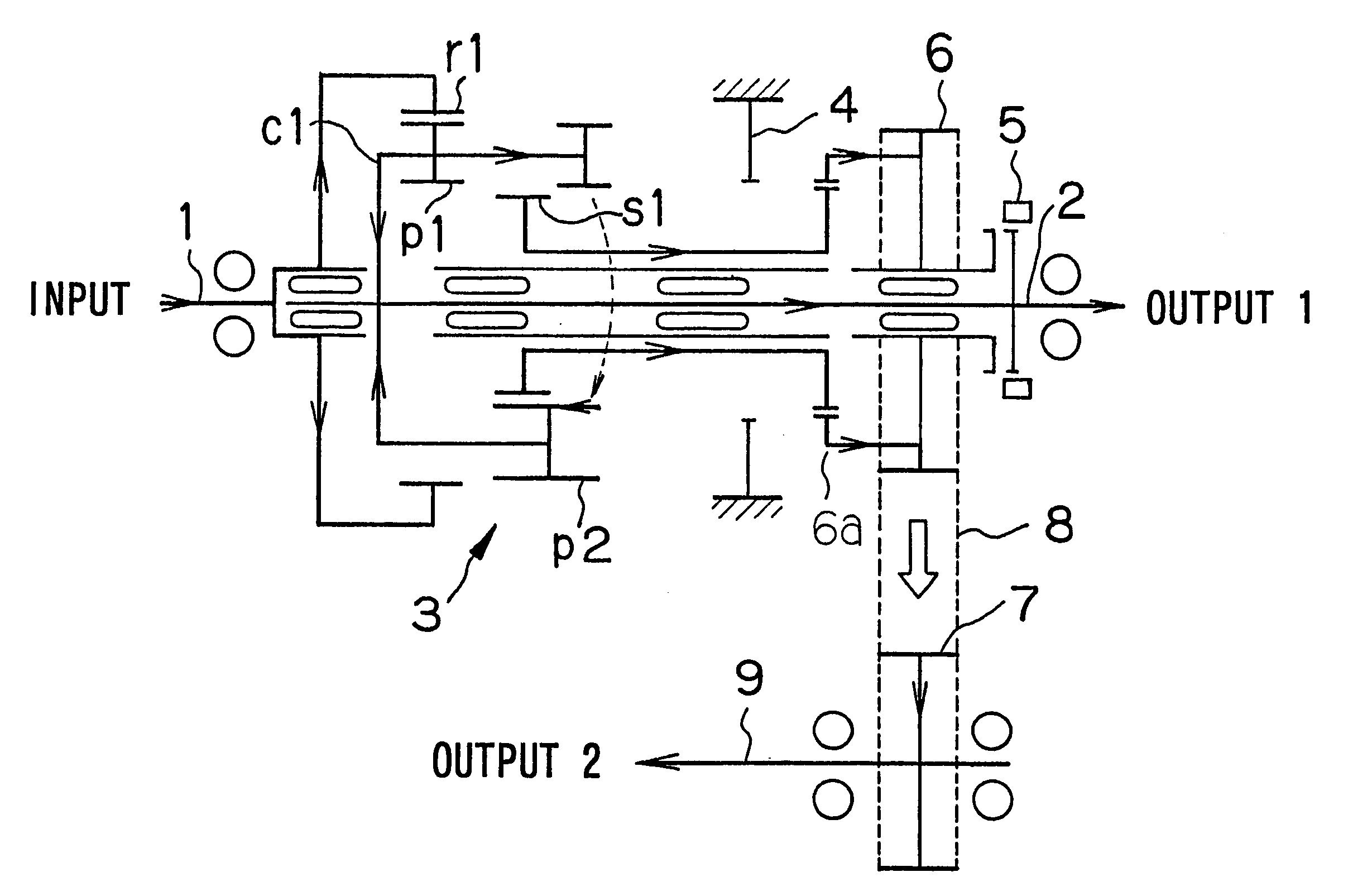
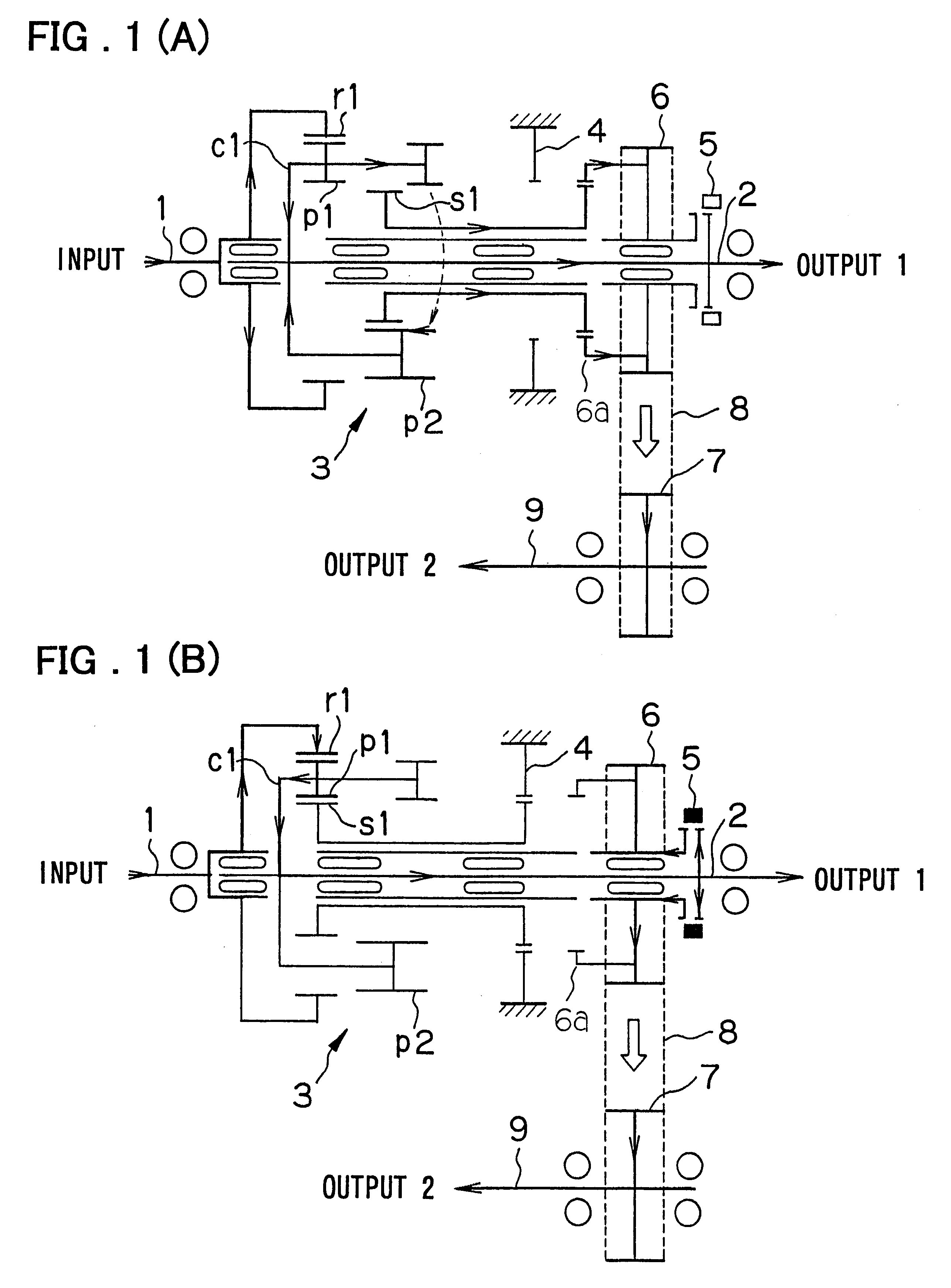
A transfer for a four-wheel drive vehicle of simplified structure in which speed-reducing and center differential functions are implemented by a single planetary gear set includes an input shaft; a first output shaft disposed coaxially with respect to the input shaft; a ring gear which co-rotates with the input shaft; a first pinion meshed with the ring gear; a second pinion in mesh with the first pinion at all times; a carrier for axially supporting the first and second pinions; a sun gear which, by being slid, selectively meshes with the first pinion or the second pinion; a brake for locking the sun gear when the sun gear and the first pinion mesh (the low position of the transfer); a driving gear which meshes with the sun gear when the sun gear and the second pinion mesh (the high position of the transfer); a sleeve mounted on the first output shaft and shifted for engaging the driving gear with the first output shaft in the direction of rotation; a second output shaft disposed in parallel with the first output shaft; and a driven gear which co-rotates with the second output shaft and to which torque is transmitted from the driving gear via a chain.
Owner:AISIN AI CO LTD
Power driving system and vehicle with same
InactiveCN106915236ARealize the differential functionRich transmission modeHybrid vehiclesGas pressure propulsion mountingPower couplingDifferential function
The invention discloses a power driving system. The power driving system comprises a power coupling device, a power source, a first electric power generator, a second electric power generator and a first brake device, wherein the power coupling device comprises a first sun gear, a first planet carrier, a first gear ring, a second sun gear, a second planet carrier and a second gear ring, wherein the first gear ring is coaxially connected with the second gear ring; the power source is arranged to be selectively linked with the first gear ring and the second gear ring; the first electric power generator is linked with the first sun gear; the second electric power generator is linked with second sun gear; and the first brake device is used for directly or indirectly braking the first gear ring and the second gear ring. The power driving system has the advantages that a differential function is realized on the premise of eliminating the traditional mechanical differential mechanism and rich transmission modes are also realized.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Electric drive system
InactiveUS8343000B2Simple and compact structureReduce lossesSpeed controllerElectric propulsion mountingElectricityDifferential function
An electric drive system including an electric motor arranged to rotate a drive shaft. A differential includes a first planetary gear being drivingly connected to a first output assembly. A second planetary gear configuration is in driving engagement with the first planetary gear configuration via an output shaft. The second planetary configuration is drivingly connected to a second output assembly. The motor is disposed between the first and second planetary gear configuration. The first planetary gear configuration is arranged to co-act with the second planetary gear configuration so as to provide a differential function. The ring gears of the first and second planetary gear configurations are engaged via a reversing assembly for the differential function. Also, a motor driven unit, such as a motor vehicle.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS HAGGLUNDS AKTIEBOLAG
Locking differential and automobile
ActiveCN104482163AGuaranteed uptimeIncrease output torqueDifferential gearingsDifferential functionActuator
The invention provides a locking differential and an automobile. The locking differential comprises a differential left shell, a differential right shell and a differential lock and is provided with a left half shaft and a right half shaft connected with the automobile, both the left half shaft and the right half shaft are connected with half shaft gears, a pin is arranged in the differential, a bevel planet gear is fixed by the pin, the differential lock comprises an inner canine tooth ring, an outer canine tooth ring and a hydraulic actuator, the inner canine tooth ring is connected with the left half shaft, a canine tooth groove is formed in the inner canine tooth ring, the outer canine tooth ring sleeves the inner canine tooth ring and axially slides on the inner canine tooth ring, canine teeth are arranged on the outer canine tooth ring, the outer canine tooth ring is circumferentially connected with the differential left shell, a first spring ring is arranged between the outer canine tooth ring and the inner canine tooth ring, the hydraulic actuator is fixed on the inner canine tooth ring, and an oil cavity is formed in the hydraulic actuator and communicated with an oil supply device. When the automobile slides or falls into a mud pit, the hydraulic actuator pushes the outer canine tooth ring to axially move, so that the first spring ring is compressed, the canine teeth are meshed with the canine tooth groove, power is directly transmitted to the left half shaft through the inner canine tooth ring, the differential loses a differential function, output torque is improved, sliding is prevented, and normal running of the automobile is ensured.
Owner:GREAT WALL MOTOR CO LTD
Object defect depth measuring method with defect size being considered
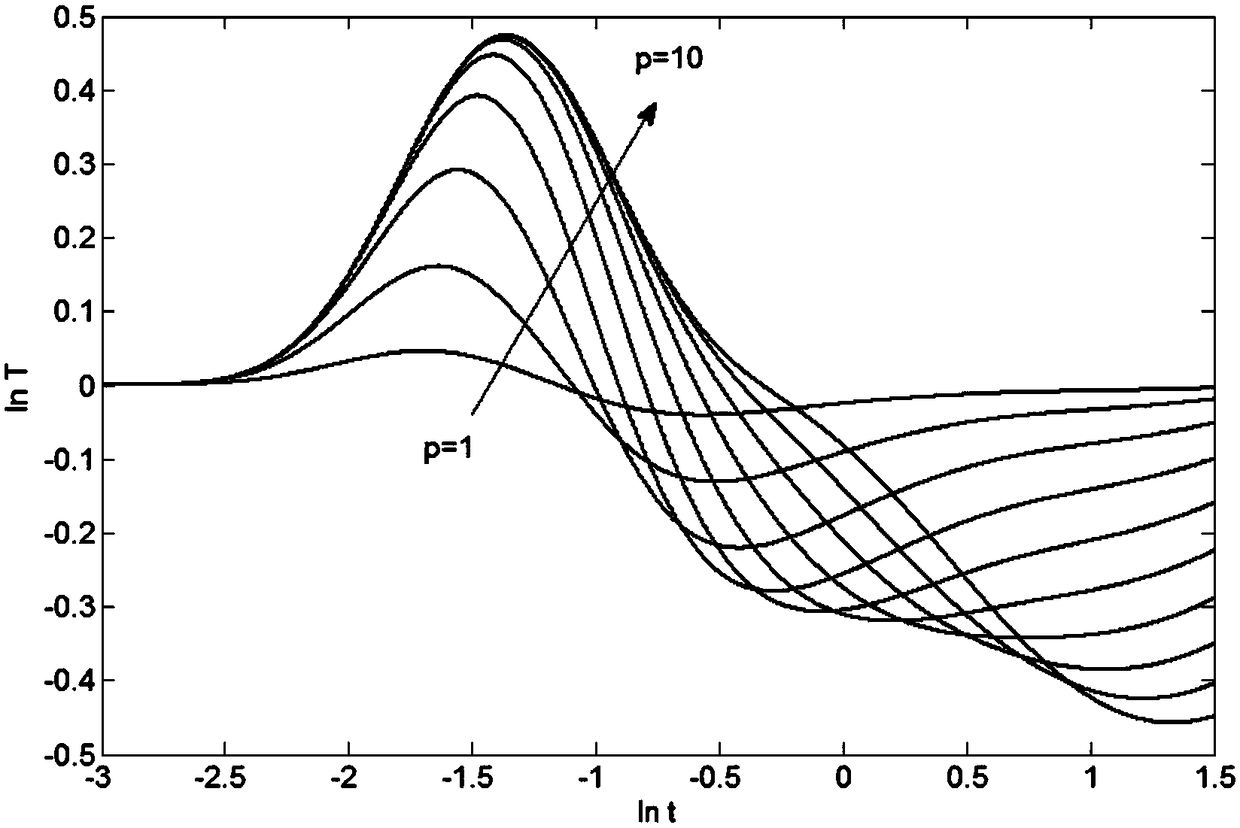
ActiveCN108072337AHigh measurement accuracyUsing wave/particle radiation meansDifferential functionDefect size
The invention discloses an object defect depth measuring method with the defect size being considered, which comprises the steps of S1, heating a measured object by pulse heating equipment, and obtaining thermographic sequence data of the surface of the measured object by an infrared thermal imaging device; S2, solving a second-order differential function of the logarithmic temperature-logarithmic time of the thermographic sequence data in allusion to the obtained thermographic sequence data, and extracting a corresponding time of peak tLPSD in the second-order differential function; S3, acquiring the defect diameter D of the measured object by using a full width at half maximum algorithm in allusion to the obtained thermographic sequence data; and S4, calculating the defect depth of themeasured object by using the correction method provided by the invention. According to the invention, the defect depth is measured on the condition that the defect size is considered, so that errors in the existing measurement technologies can be effectively reduced.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com