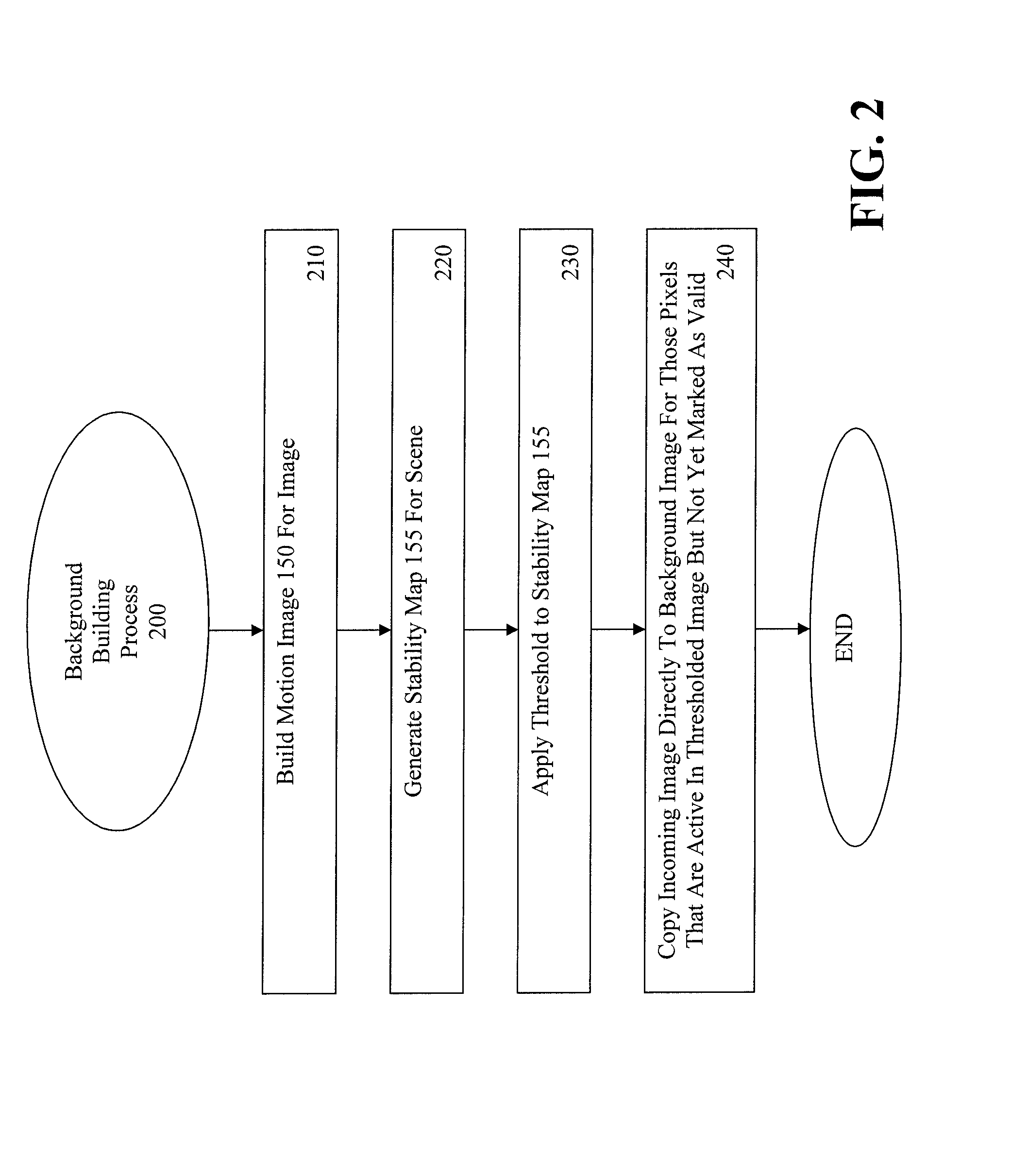
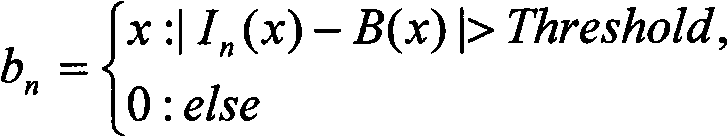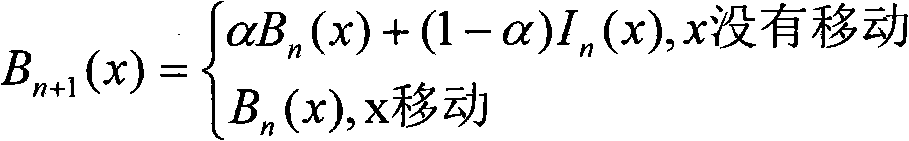Patents
Literature
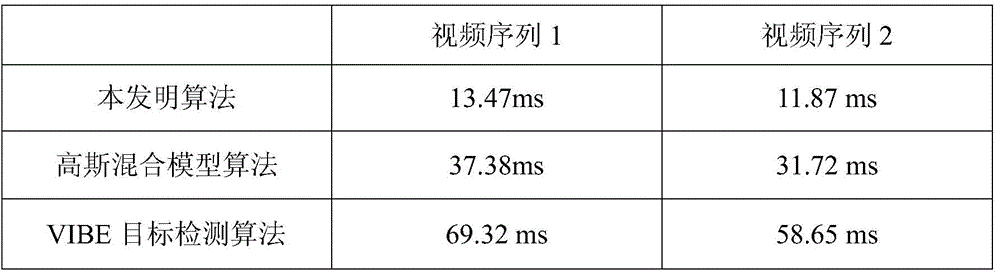
465 results about "Background subtraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
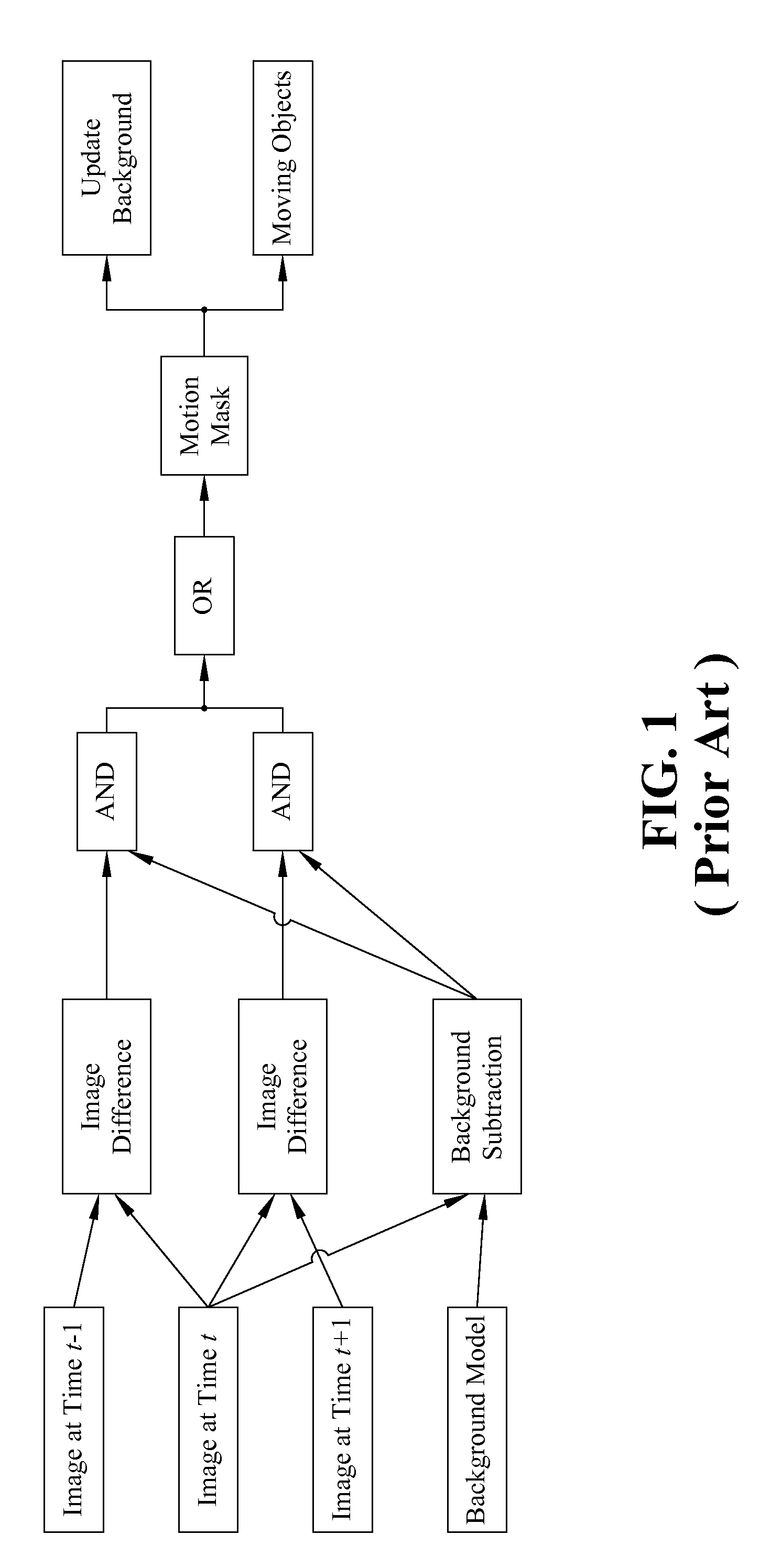
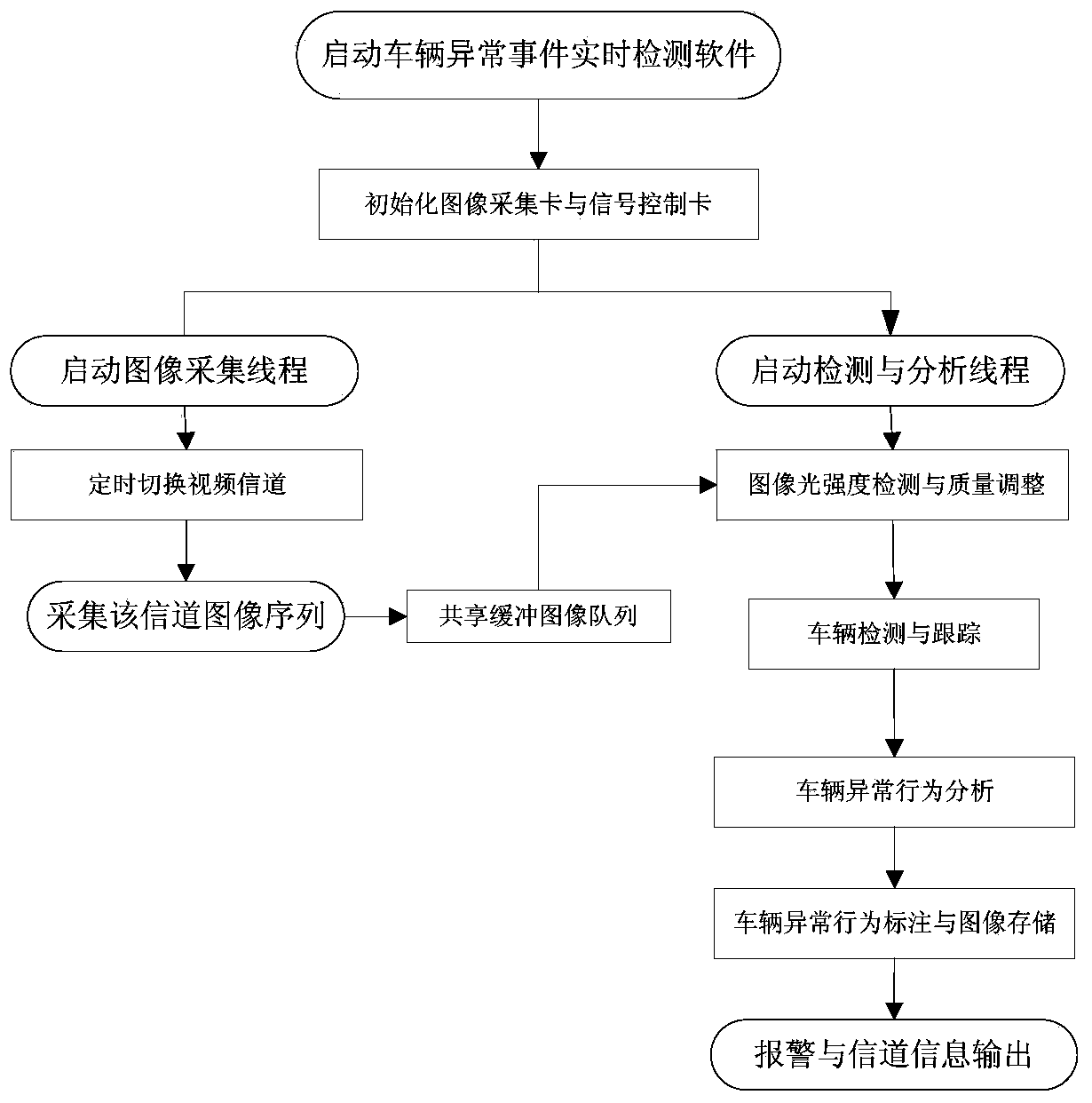
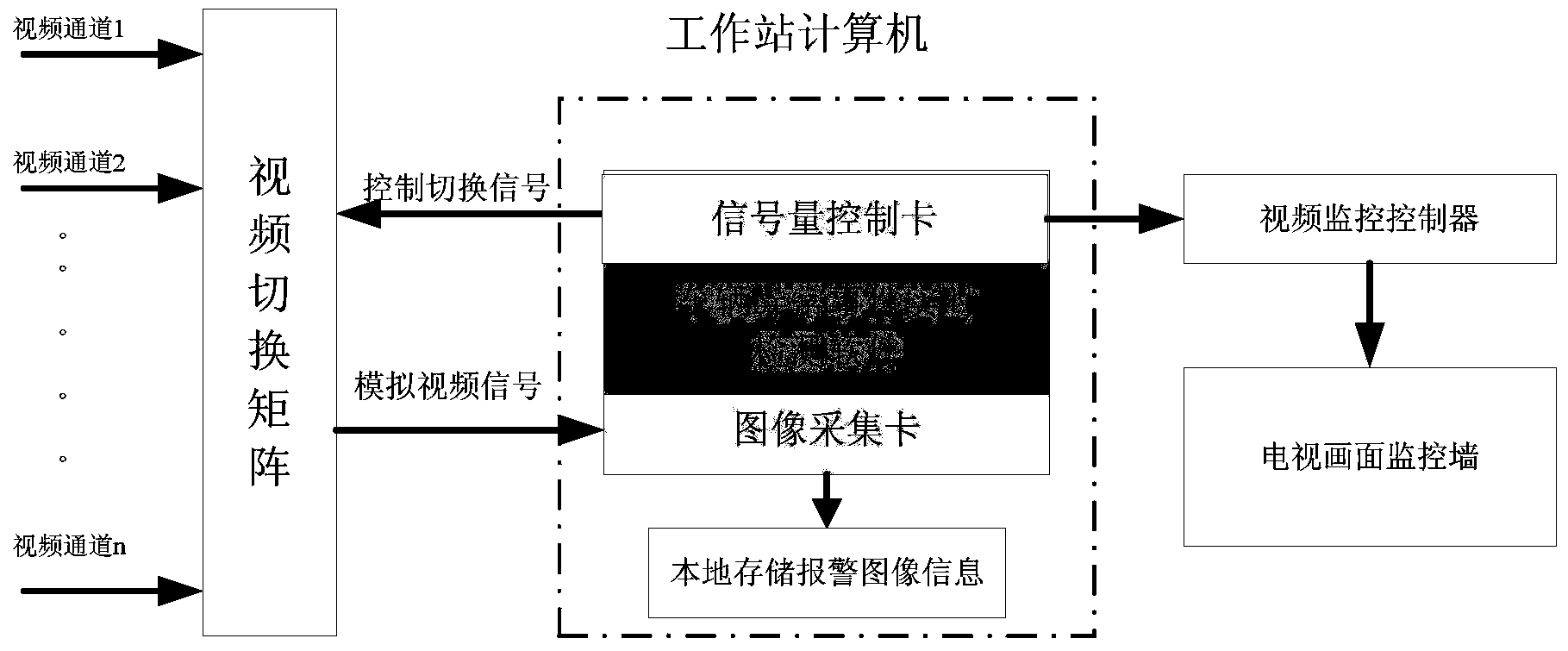
Background subtraction, also known as Foreground Detection, is a technique in the fields of image processing and computer vision wherein an image's foreground is extracted for further processing. Generally an image's regions of interest are objects in its foreground. After the stage of image preprocessing object localisation is required which may make use of this technique. Background subtraction is a widely used approach for detecting moving objects in videos from static cameras. The rationale in the approach is that of detecting the moving objects from the difference between the current frame and a reference frame, often called “background image”, or “background model”. Background subtraction is mostly done if the image in question is a part of a video stream. Background subtraction provides important cues for numerous applications in computer vision, for example surveillance tracking or human poses estimation. However, background subtraction is generally based on a static background hypothesis which is often not applicable in real environments. With indoor scenes, reflections or animated images on screens lead to background changes.
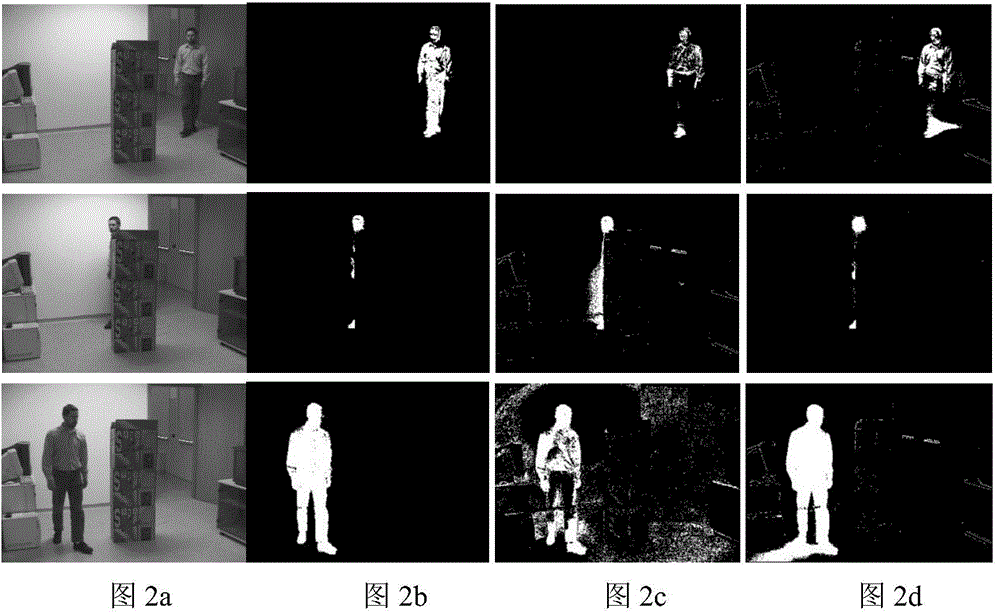
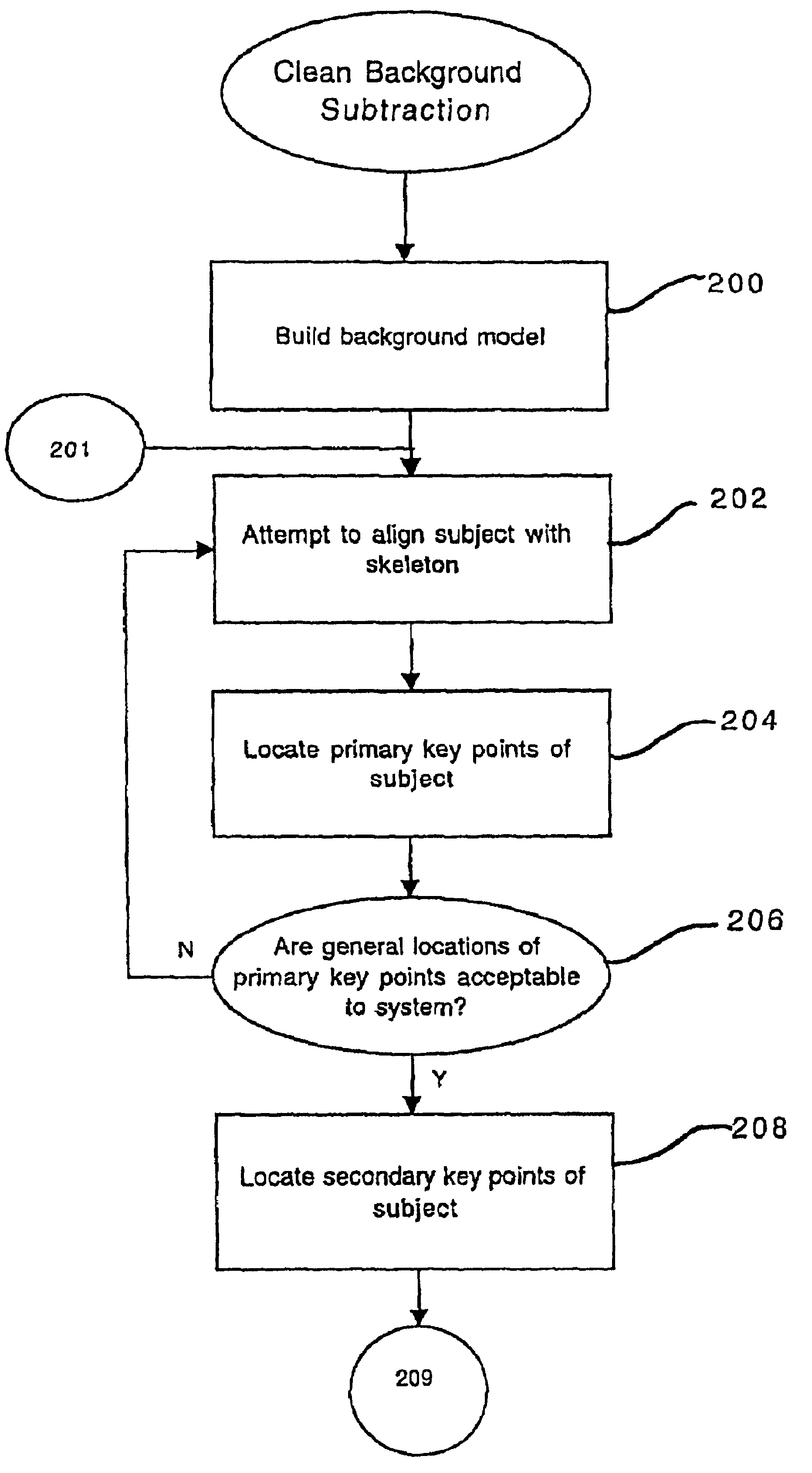
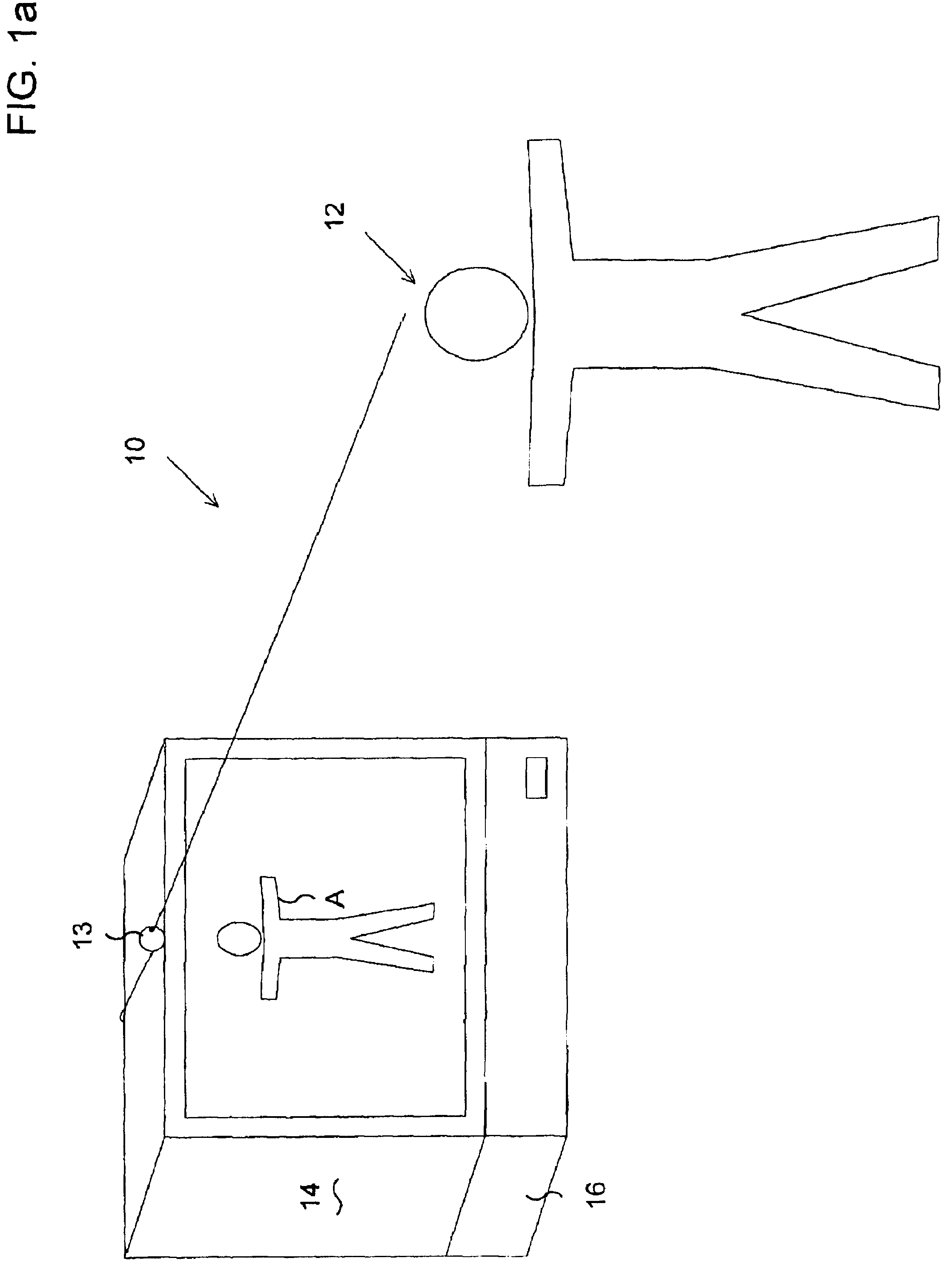
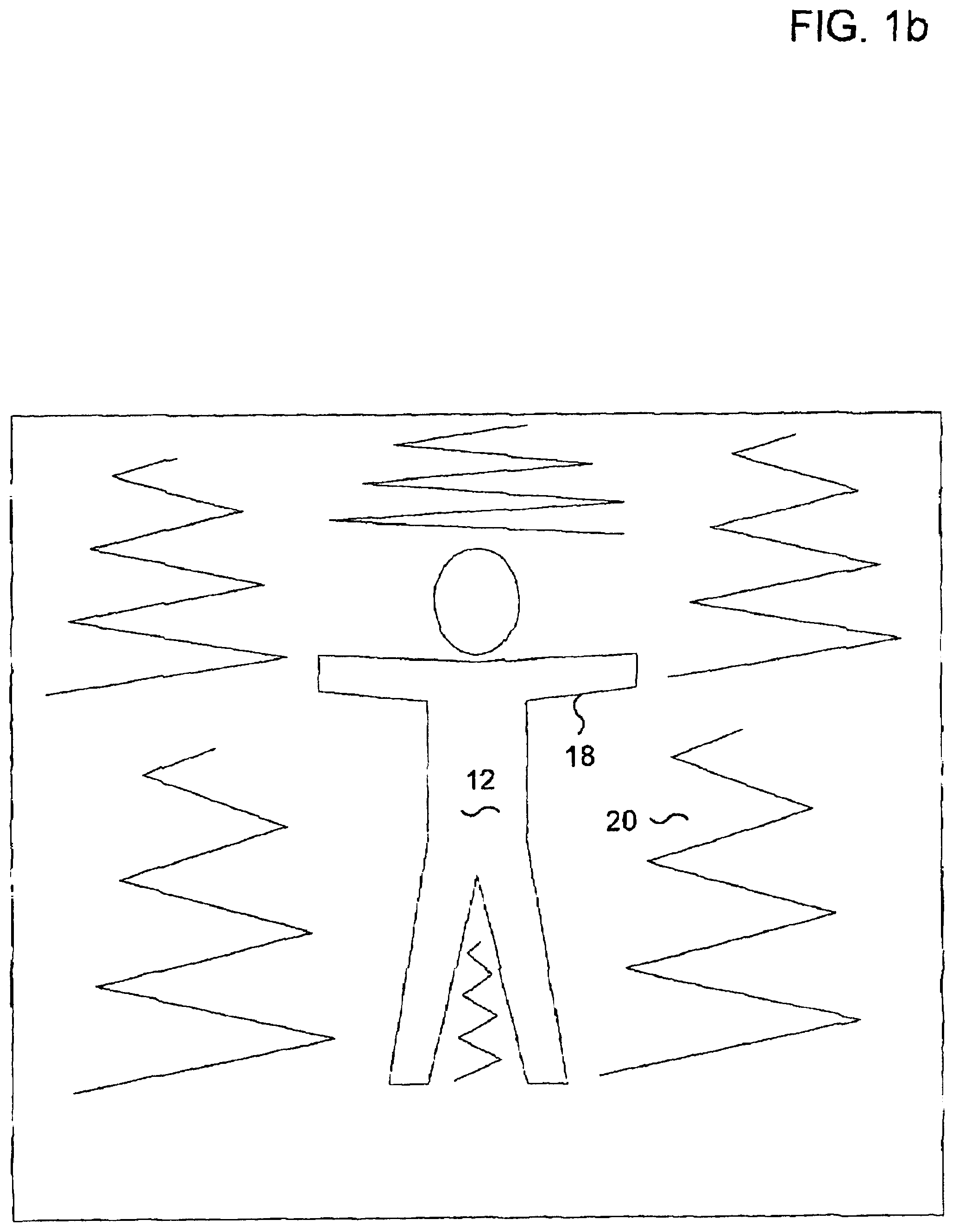
Method and apparatus for performing a clean background subtraction
InactiveUSRE42256E1Easy to determineReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisEdge extractionBackground image
A background subtraction apparatus of the present invention includes a key point locator for locating key points on a known object type, a boundary point locator for locating boundary points of the known object that make up the edges of the known object, and an edge processor for processing the edges to provide a clean-edged extraction of the known object from a background image. Preferably, the key point locator includes an alignment detector for detecting alignment of an image of the known object type with a skeleton image. Still more preferably, the skeleton image is an exoskeleton image and the known object type is a human being.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
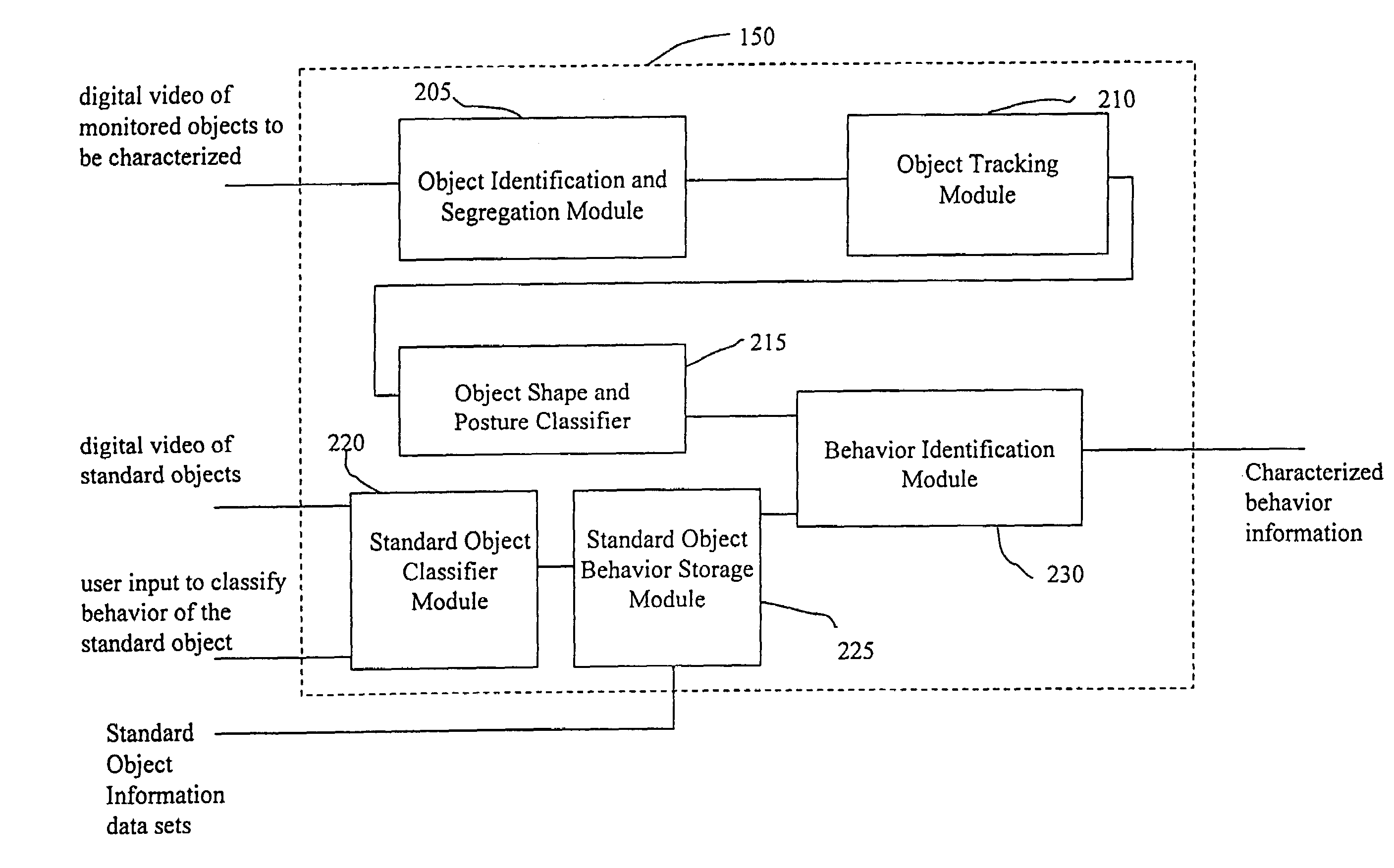
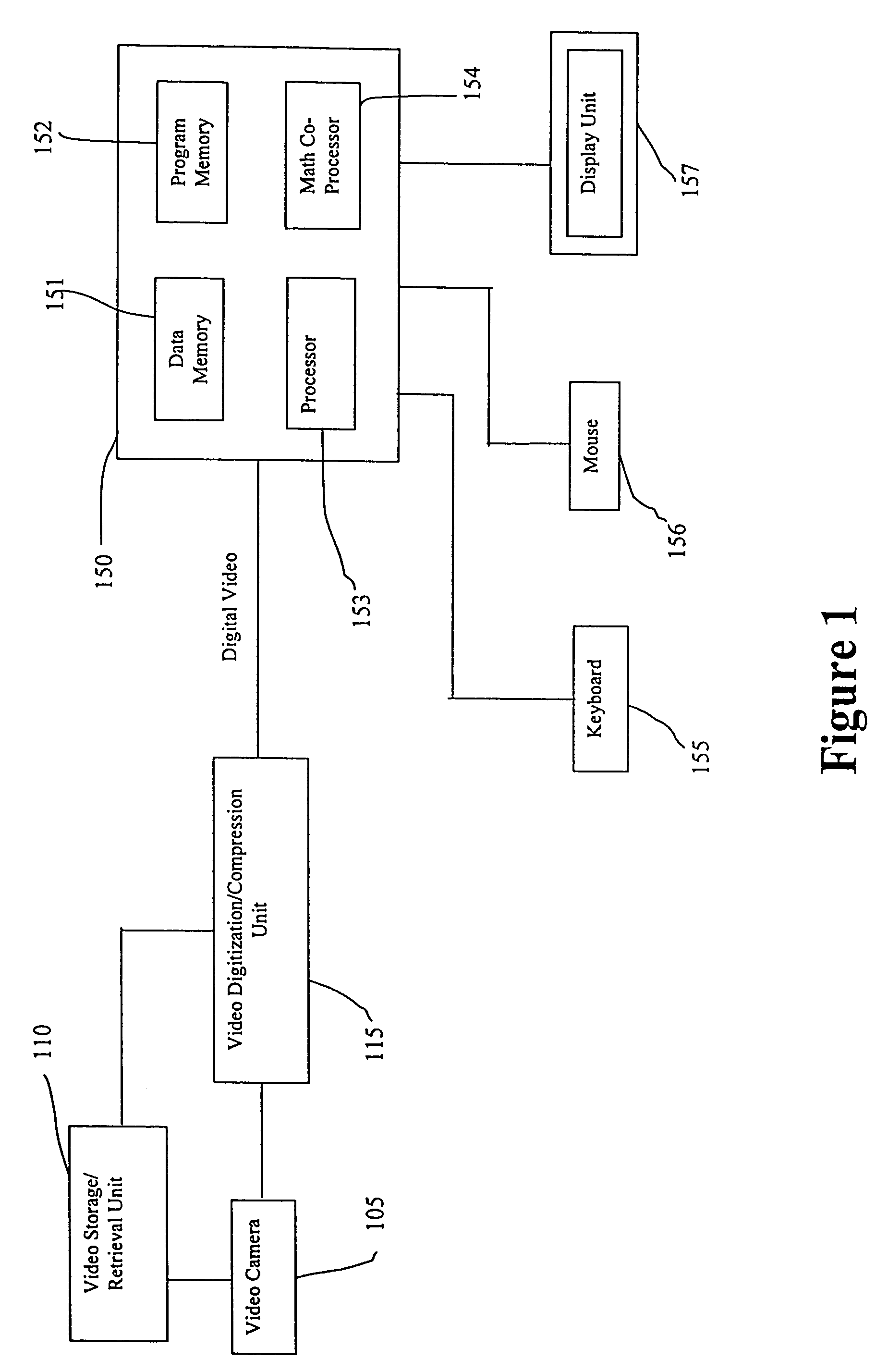
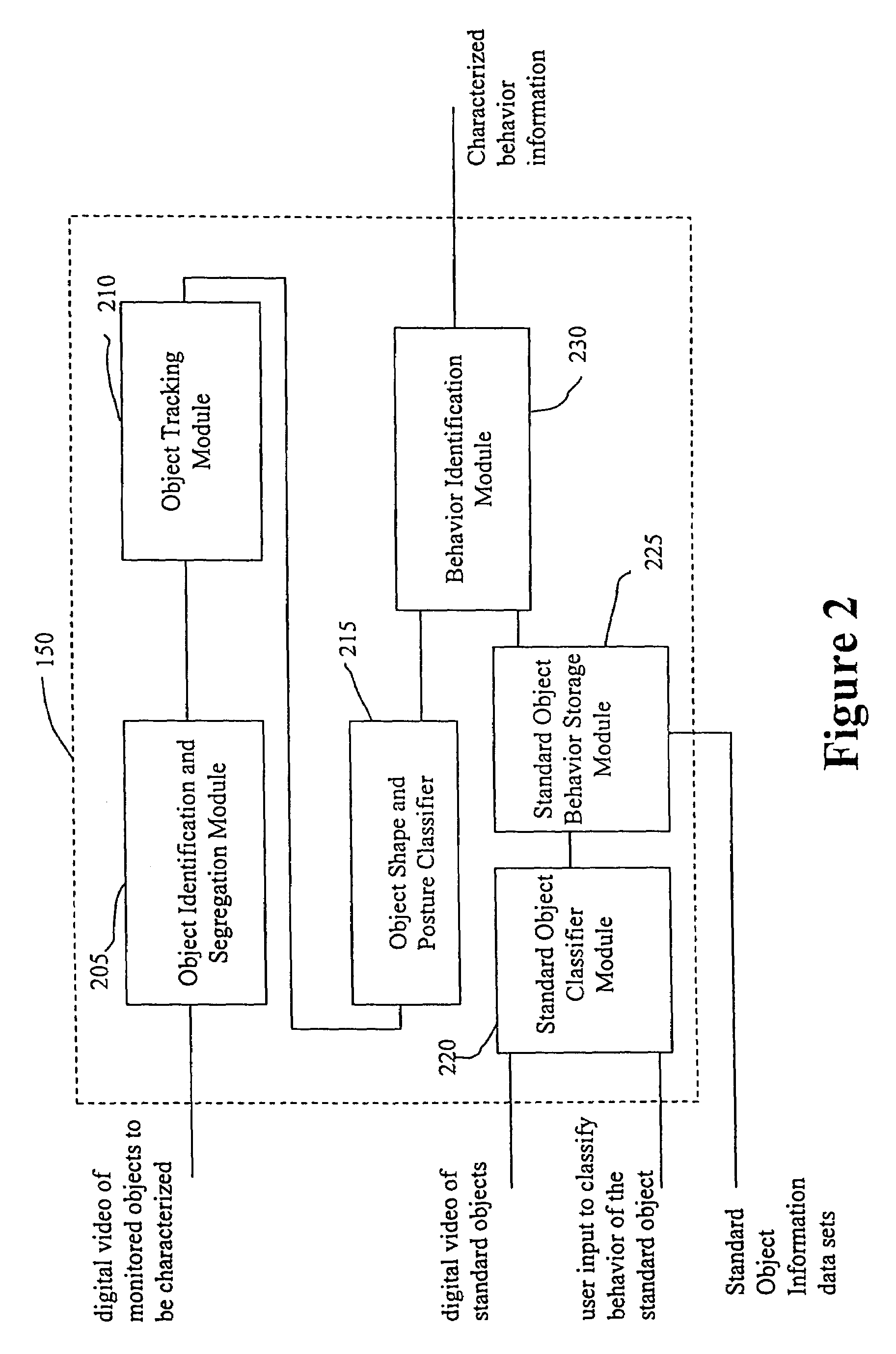
System and method for object identification and behavior characterization using video analysis
InactiveUS7068842B2Accurate identificationEfficient detectionImage enhancementImage analysisProbabilistic methodAnimal behavior
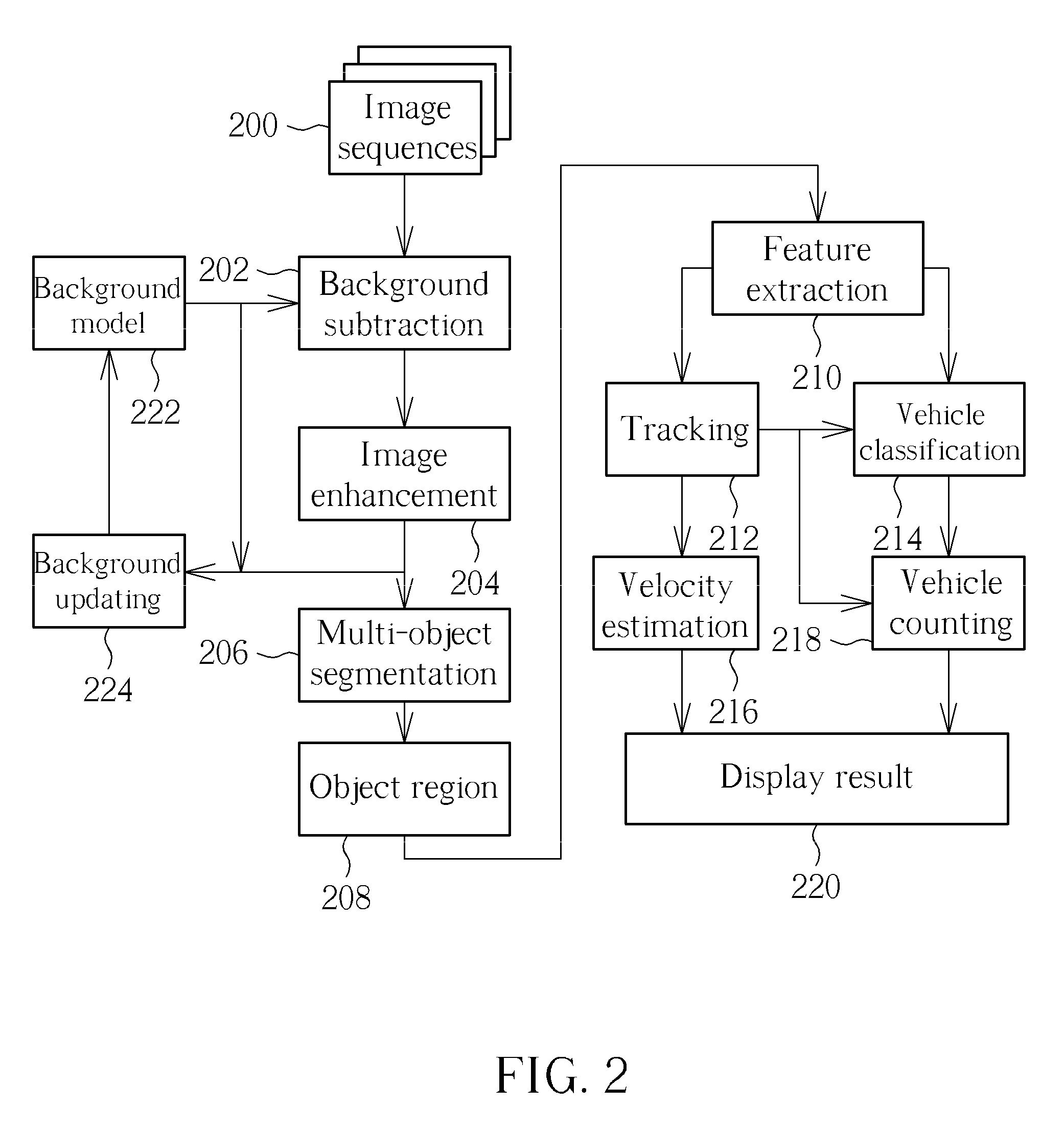
In general, the present invention is directed to systems and methods for finding the position and shape of an object using video. The invention includes a system with a video camera coupled to a computer in which the computer is configured to automatically provide object segmentation and identification, object motion tracking (for moving objects), object position classification, and behavior identification. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention may use background subtraction for object identification and tracking, probabilistic approach with expectation-maximization for tracking the motion detection and object classification, and decision tree classification for behavior identification. Thus, the present invention is capable of automatically monitoring a video image to identify, track and classify the actions of various objects and the object's movements within the image. The image may be provided in real time or from storage. The invention is particularly useful for monitoring and classifying animal behavior for testing drugs and genetic mutations, but may be used in any of a number of other surveillance applications.
Owner:CLEVER SYS
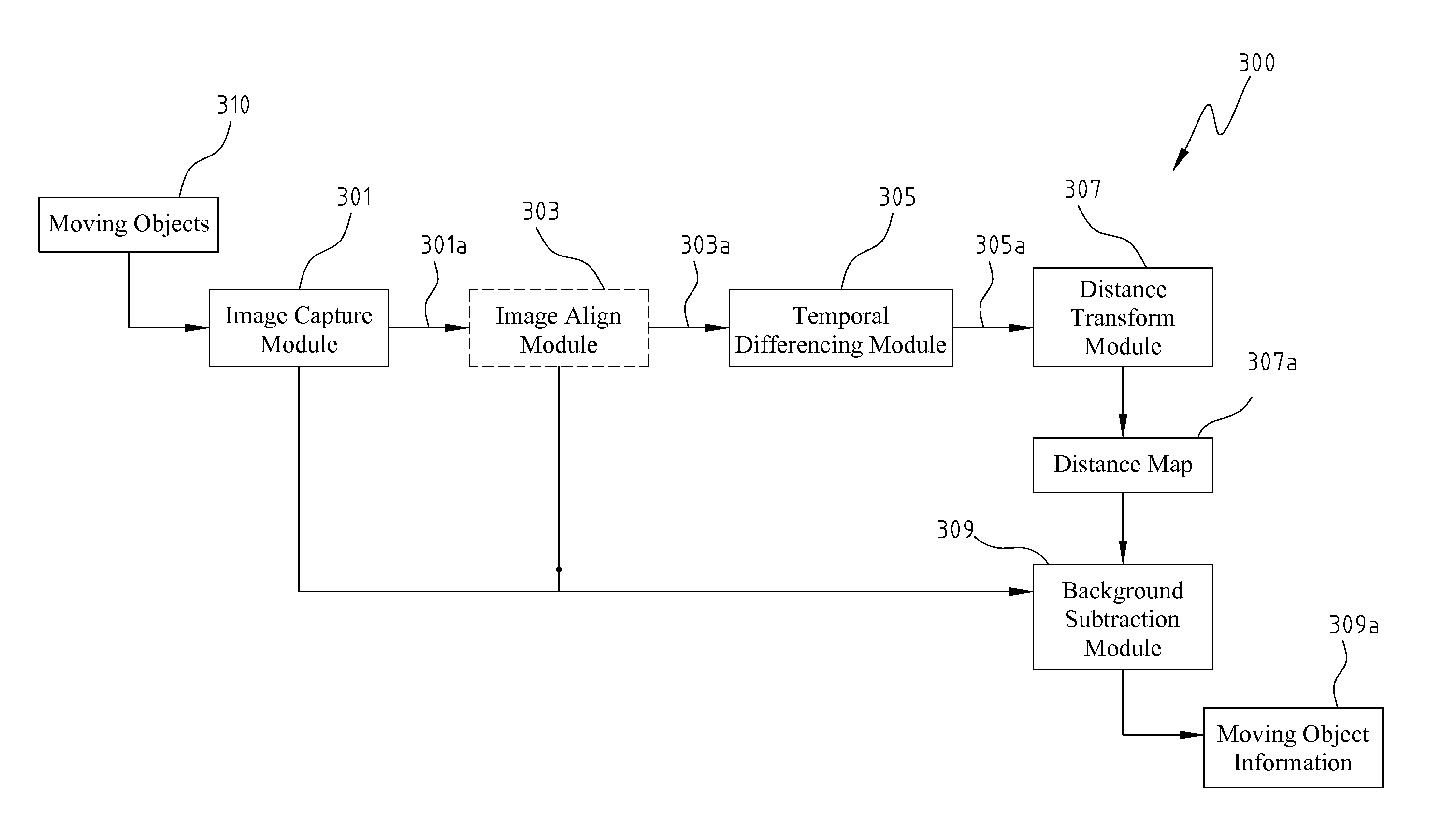
Moving object detection apparatus and method
InactiveUS8000498B2Improve reliabilityEnhancing subtractionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage alignmentImage capture
Disclosed is directed to a moving object detection apparatus and method. The apparatus comprises an image capture module, an image alignment module, a temporal differencing module, a distance transform module, and a background subtraction module. The image capture module derives a plurality of images in a time series. The image alignment module aligns the images if the image capture module is situated on a movable platform. The temporal differencing module performs temporal differencing on the captured images or the aligned images, and generates a difference image. The distance transform module transforms the difference image into a distance map. The background subtraction module applies the distance map to background subtraction technology and compares the results with the current captured image, so as to obtain the information for moving objects.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for Automatic Detection and Tracking of Multiple Objects
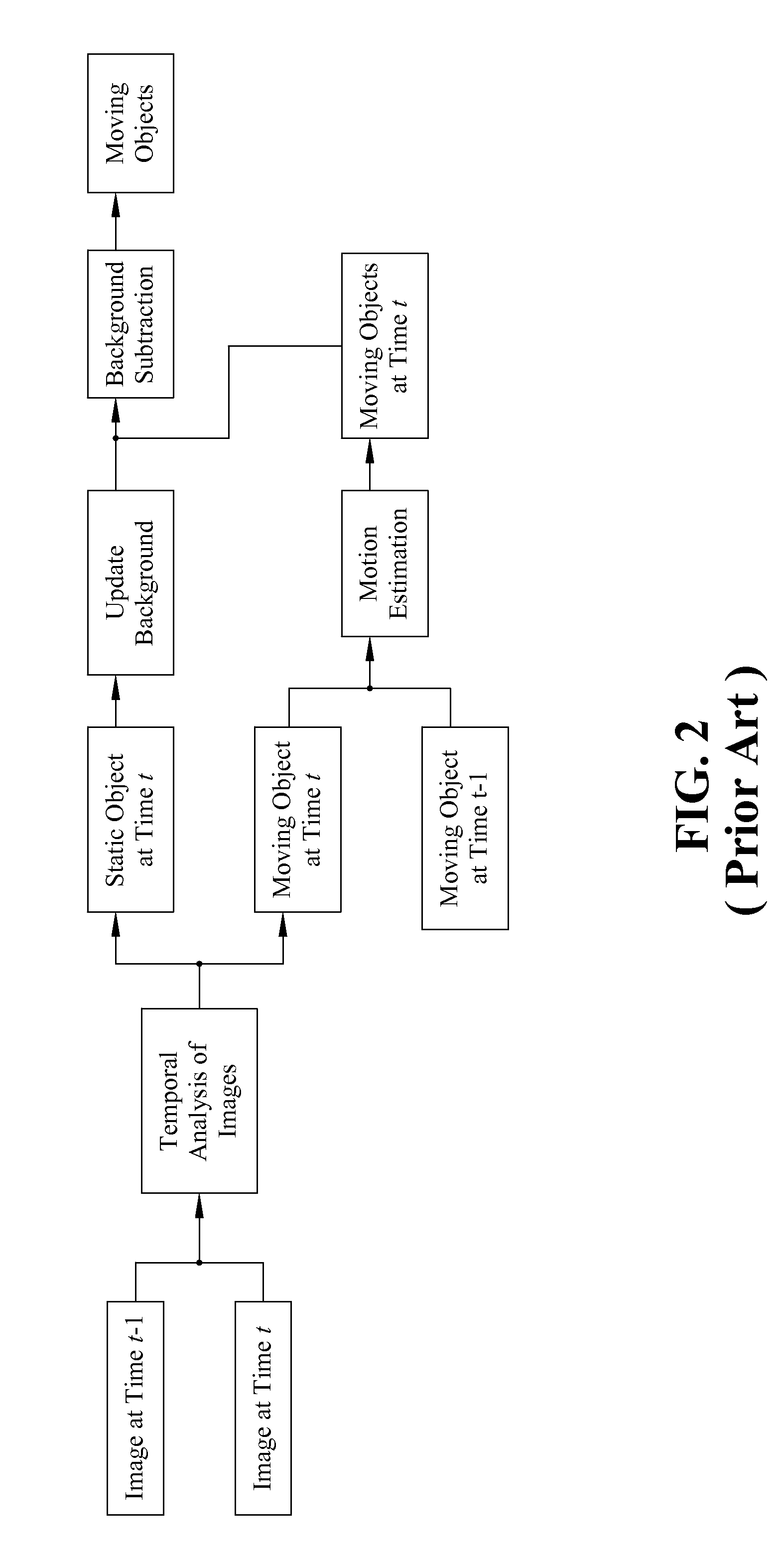
A method for automatically detecting and tracking objects in a scene. The method acquires video frames from a video camera; extracts discriminative features from the video frames; detects changes in the extracted features using background subtraction to produce a change map; uses the change map to use a hypothesis to estimate of an approximate number of people along with uncertainty in user specified locations; and using the estimate, track people and update the hypotheses for a refinement of the estimation of people count and location.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
Fast license plate locating method
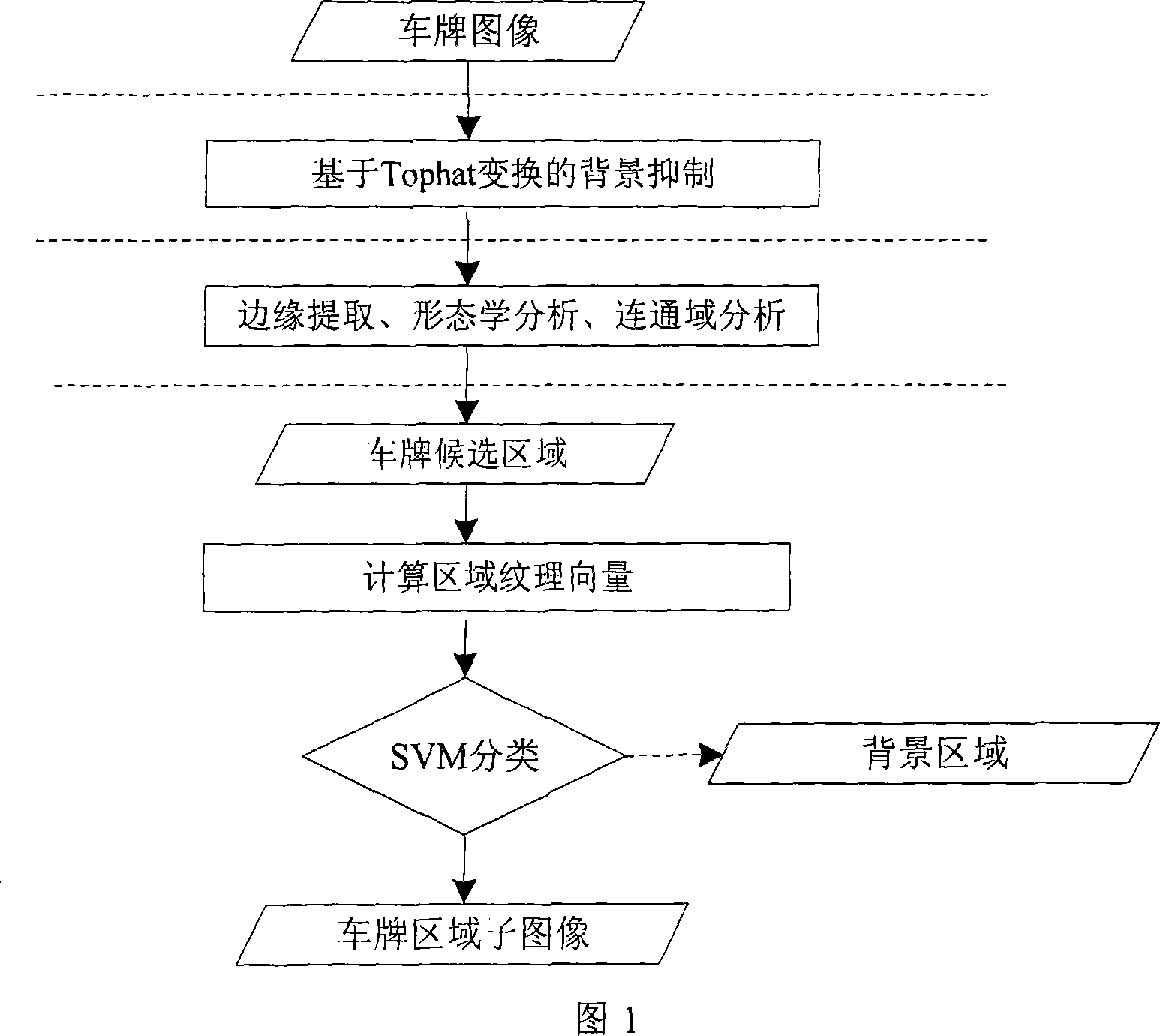
InactiveCN101246551AReduce distractionsImprove adaptabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputation complexity
A rapid vehicle license plate locating method is provided, which uses top hat transformation and character texture characteristic, and is divided into background subtraction, vehicle license plate region crude location and precision location three steps, specifically comprises: (1) background subtraction, converting obtained color vehicle license plate image into gray image, using top hat transformation to inhibit large-size background object, highlighting vehicle license plate region; (2) crude location phase, calculating image edge map and proceeding binaryzation, morphological dilation and connected components analysis and other operation, obtaining reasonable size vehicle license plate candidate region set; (3) precision location phase, extracting candidate region texture characteristic, using support vector machine classifier to classify candidate vehicle license plate region, thus accurately locating vehicle license plate region. The invention uses the top hat transformation to filter vehicle license plate image, reduces large-size background interference, so that greatly enhances environment adaptation; meanwhile, from crude to fine location method is more efficient, and reduces greatly computing complexity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method of detecting moving objects
InactiveUS20090309966A1Strong noise rejection abilitySimple calculationImage enhancementImage analysisMinimum bounding boxMinimum distance classifier
A method for detecting moving objects includes: (a) capturing and establishing a background image; (b) capturing at least one current image; (c) transforming the background image and the current image from an RGB color format into an HSI color format; (d) subtracting the background image from the current image according to a background subtraction rule for generating at least one moving object; (e) performing a vertical scanning and a horizontal scanning on the moving object for generating a minimum bounding box of the moving object; (f) calculating a characteristic datum of the moving object according to the minimum bounding box; (g) tracking the moving object according to the characteristic datum with a Euclidean distance rule; (h) classifying the moving object according to the characteristic datum, the tracking result generated by step (g) and a minimum distance classifier.
Owner:HUPER LAB
Method and device for detecting road traffic abnormal events in real time
InactiveCN103971521AImprove work efficiencyReduce work intensityDetection of traffic movementClosed circuit television systemsMultiple frameMerge algorithm
The invention provides a method and device for detecting road traffic abnormal events in real time. The method includes the steps of monitoring a road, obtaining a plurality of frames of continuous monitor images, extracting bright white segments from the monitor images, obtaining lane lines and lane end points through processing, building a lane model, determining a bidirectional detection area of a lane according to the lane model, detecting a moving object in the bidirectional detection area according to a Gaussian mixture model background subtraction method, determining the position of the moving object, building the mapping relation between the moving target and an actual vehicle according to the position of the moving target in the multiple frames of continuous monitor images by the adoption of a posterior probability splitting and merging algorithm and a feature point matching and tracking method, obtaining the running track and running speed of the actual vehicle, detecting the lane model and the running track and running speed of the actual vehicle according to a prestored road traffic abnormal behavior semantic model, and judging whether the road traffic abnormal events exist or not. The method has the advantages of being intelligent, high in accuracy and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
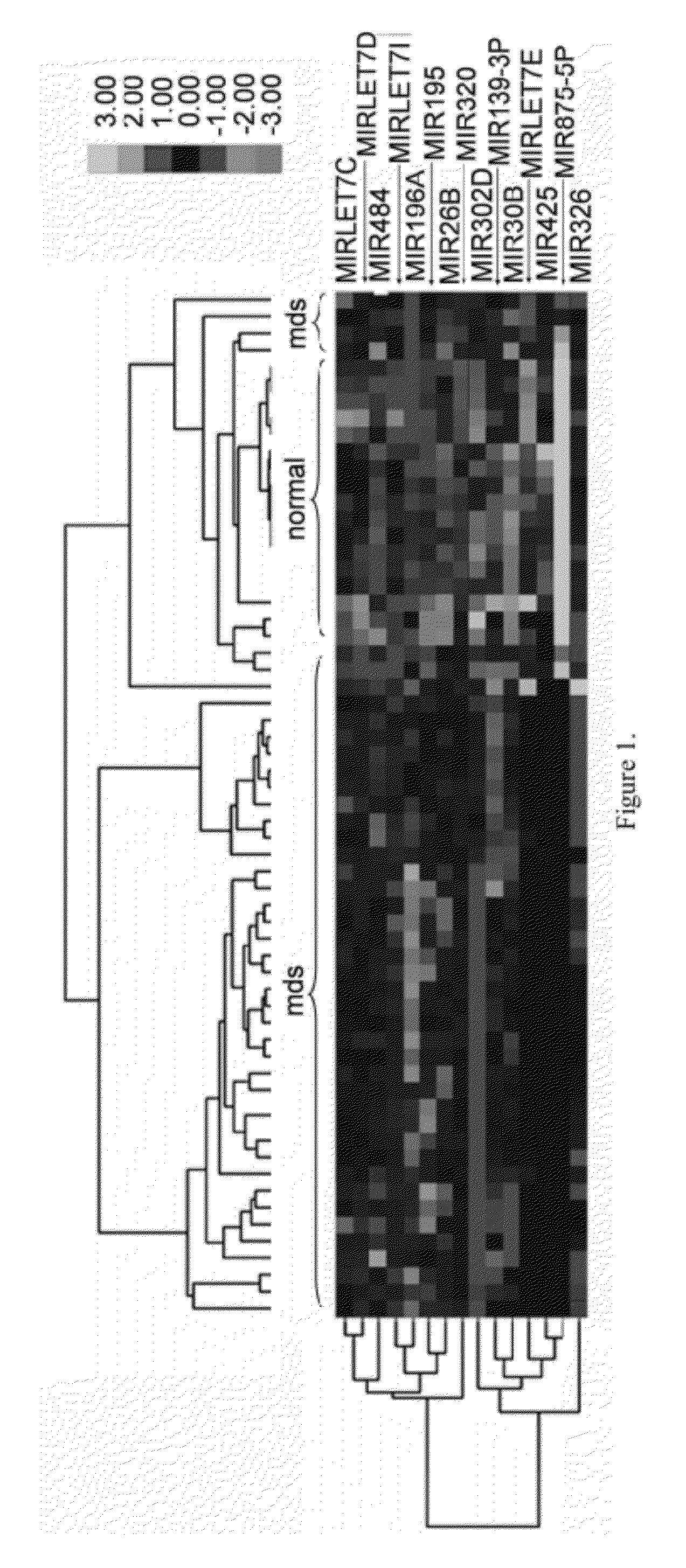
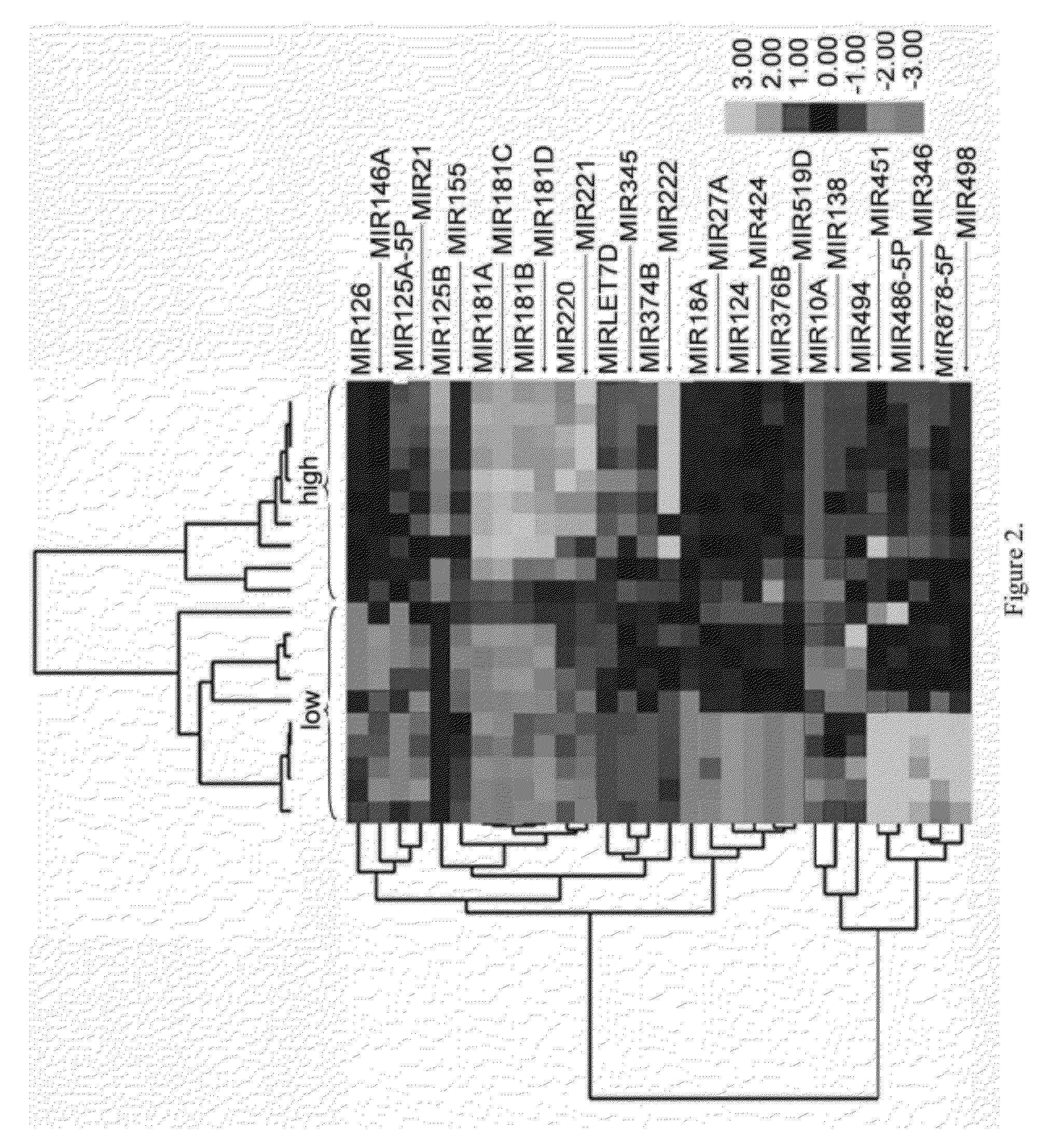
Method of Identifying Myelodysplastic Syndromes
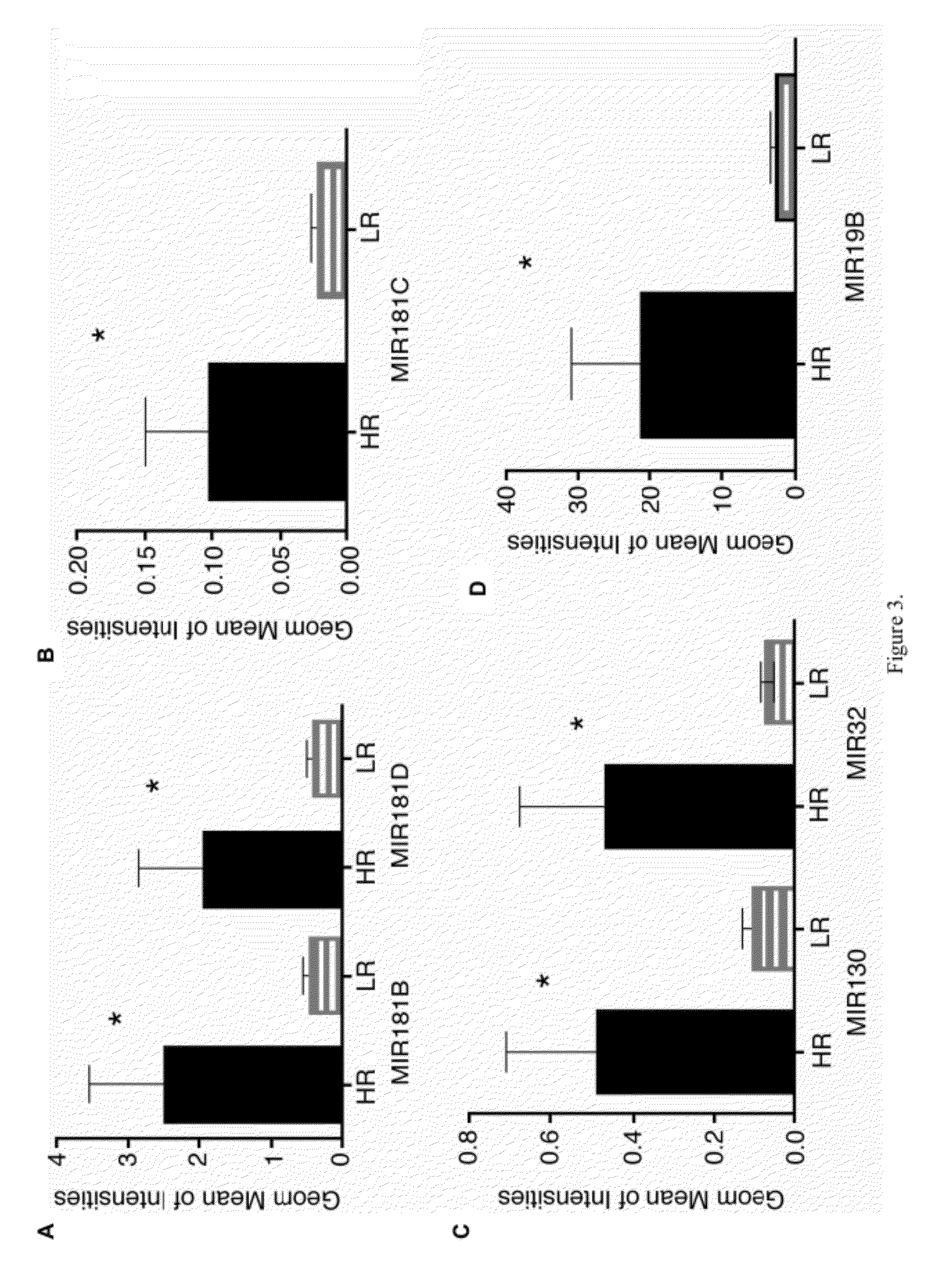
Myelodysplastic syndromes display both hematological and biological heterogeneity with variable leukemia potential. To determine whether microRNAs expression offers diagnostic discrimination or influences malignant potential in MDS, bone marrow miRNA expression was investigated from prognostically distinct MDS subsets using a microarray platform. After background subtraction and normalization, data were analyzed indicating thirteen miRNA signature with statistically significant differential expression, including down-regulation of members of a leukemia associated miRNA family. A unique signature consisting of 10 miRNAs was closely associated with International Prognostic Scoring System risk category permitting discrimination between lower and higher risk disease. Selective overexpression of miRNA-181 family members was detected in higher risk MDS, indicating pathogenetic overlap with acute myeloid leukemia. Analysis of miRNA expression profile offers diagnostic utility, and provides pathogenetic and prognostic discimination in MDS.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
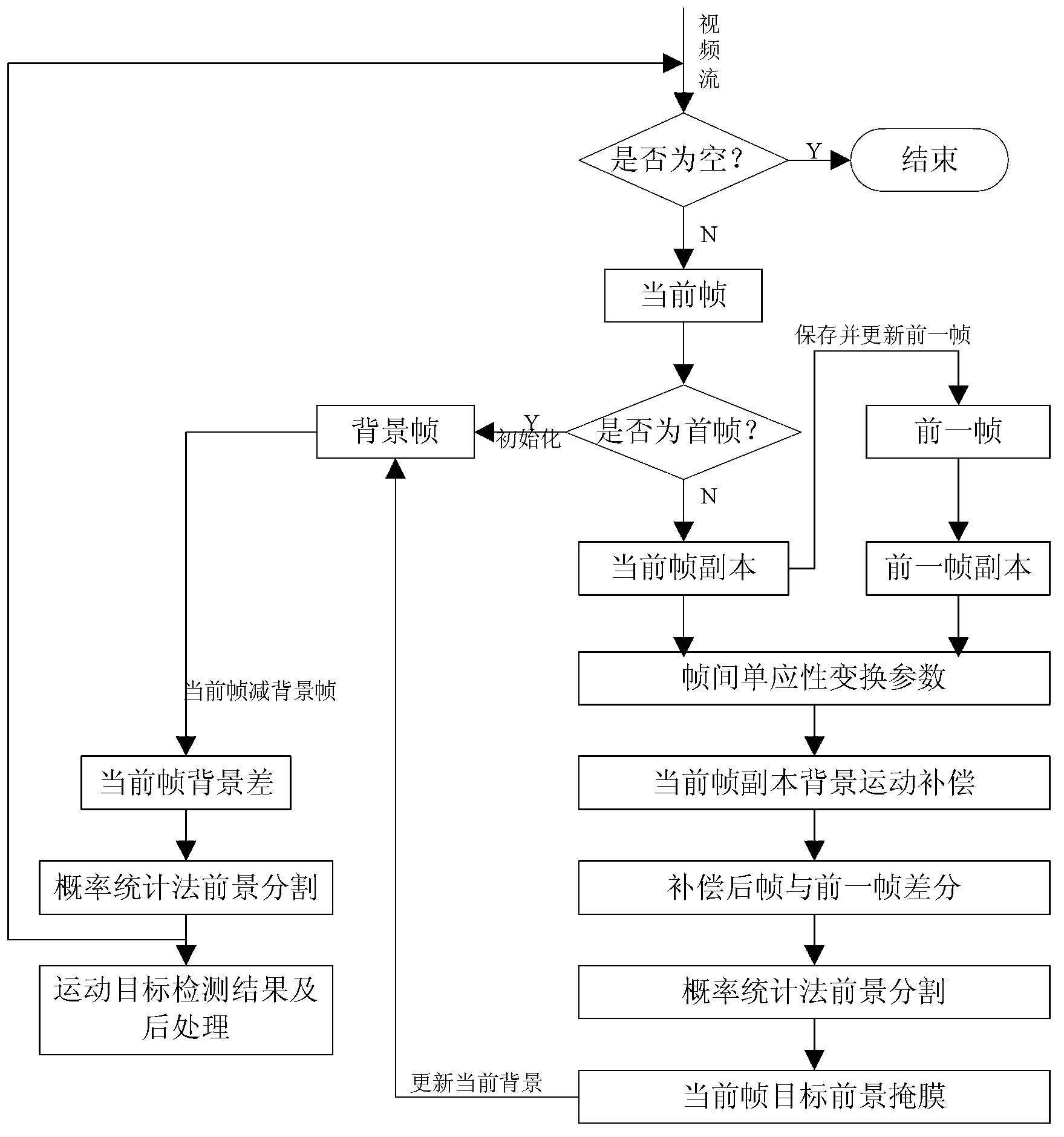
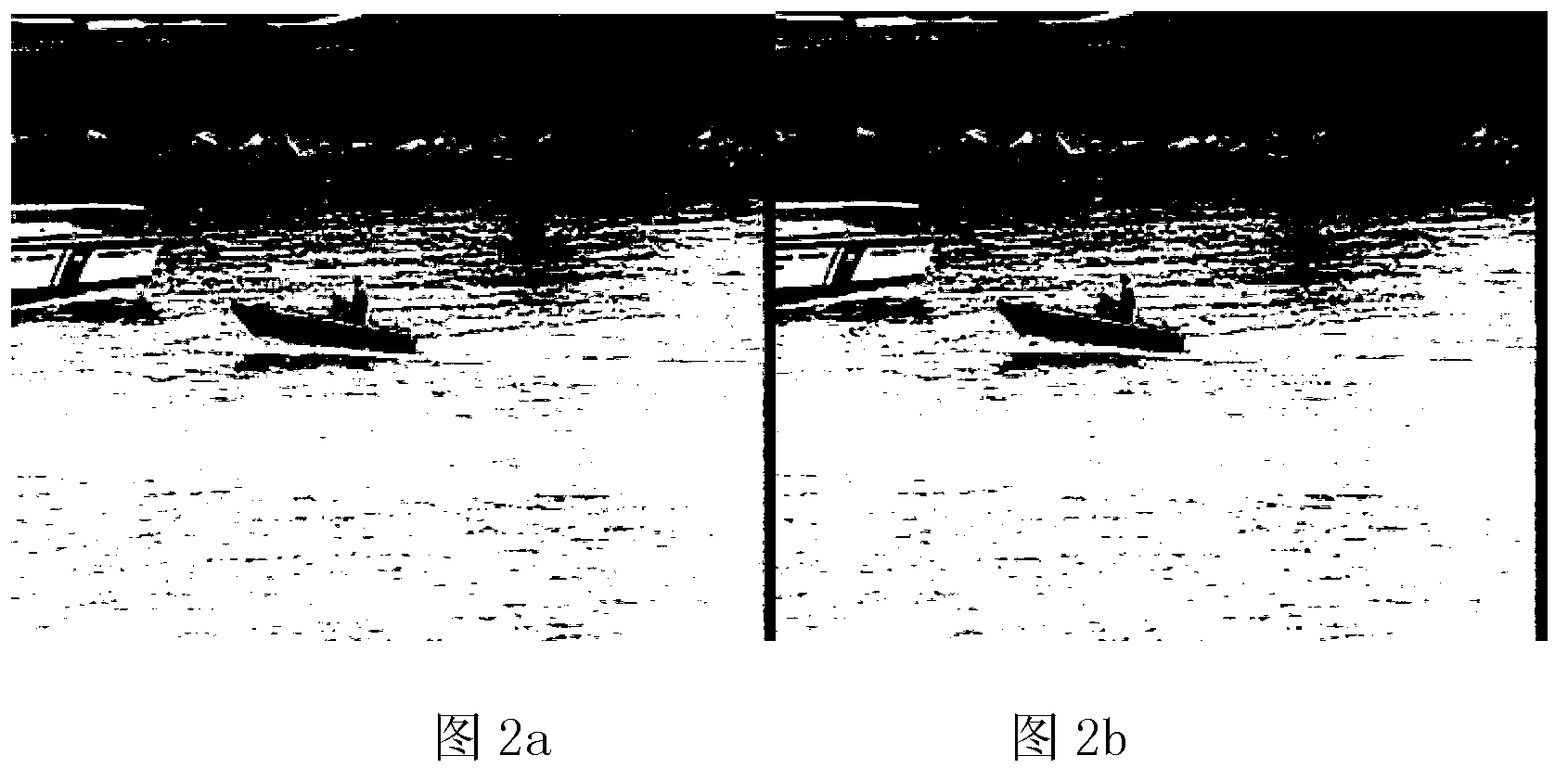
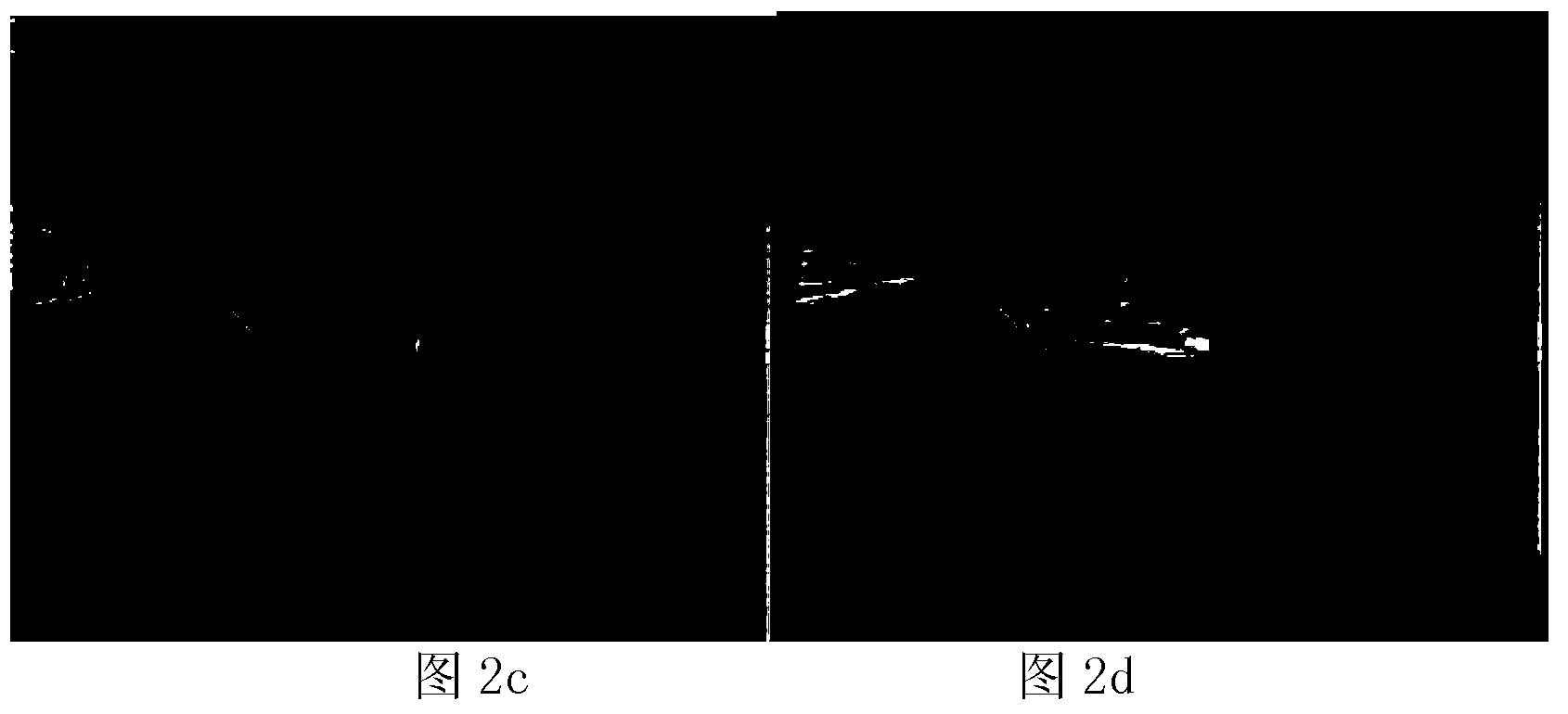
Quick detecting method for moving objects in dynamic scene
InactiveCN103325112AComplete exercise goalsSatisfy the rapidityImage analysisFrame differenceGray level
Provided is a quick detecting method for moving objects in a dynamic scene. The quick detecting method for the moving objects in the dynamic scene comprises carrying out sequence interframe registration on moving images by utilizing CenSurE feature points and a homography transformation model, obtaining a registering frame of a former frame taking a current frame as reference, carrying out subtraction on the registering frame with the current frame to obtain a frame difference image to generate a foreground mask, building a dynamic background updated in real time according to space distribution information of the foreground mask in the current frame, obtaining a background subtraction image based on a background subtraction method, carrying out statistics on the probability density of the gray level of each pixel in the frame difference image, when the sum of the probability density of the gray level of a pixel is larger than 2phi(k)-1, taking the gray level as a self-adaptation threshold value, judging pixels with values of gray levels larger than the threshold value as foreground pixels, and otherwise judging the pixels as background pixels. The quick detecting method for the moving objects in the dynamic scene can reach the processing speed of 15frame / s and can obtain relatively integral moving objects under the premise that the detecting speed is ensured, and therefore, index requirements such as rapidity, noise immunity, illumination adaptation, target integrity and the like of the detection of the moving objects in the dynamic scene can be met.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Accurate target detection system
InactiveUS20020084414A1Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansElectricityIntegrator
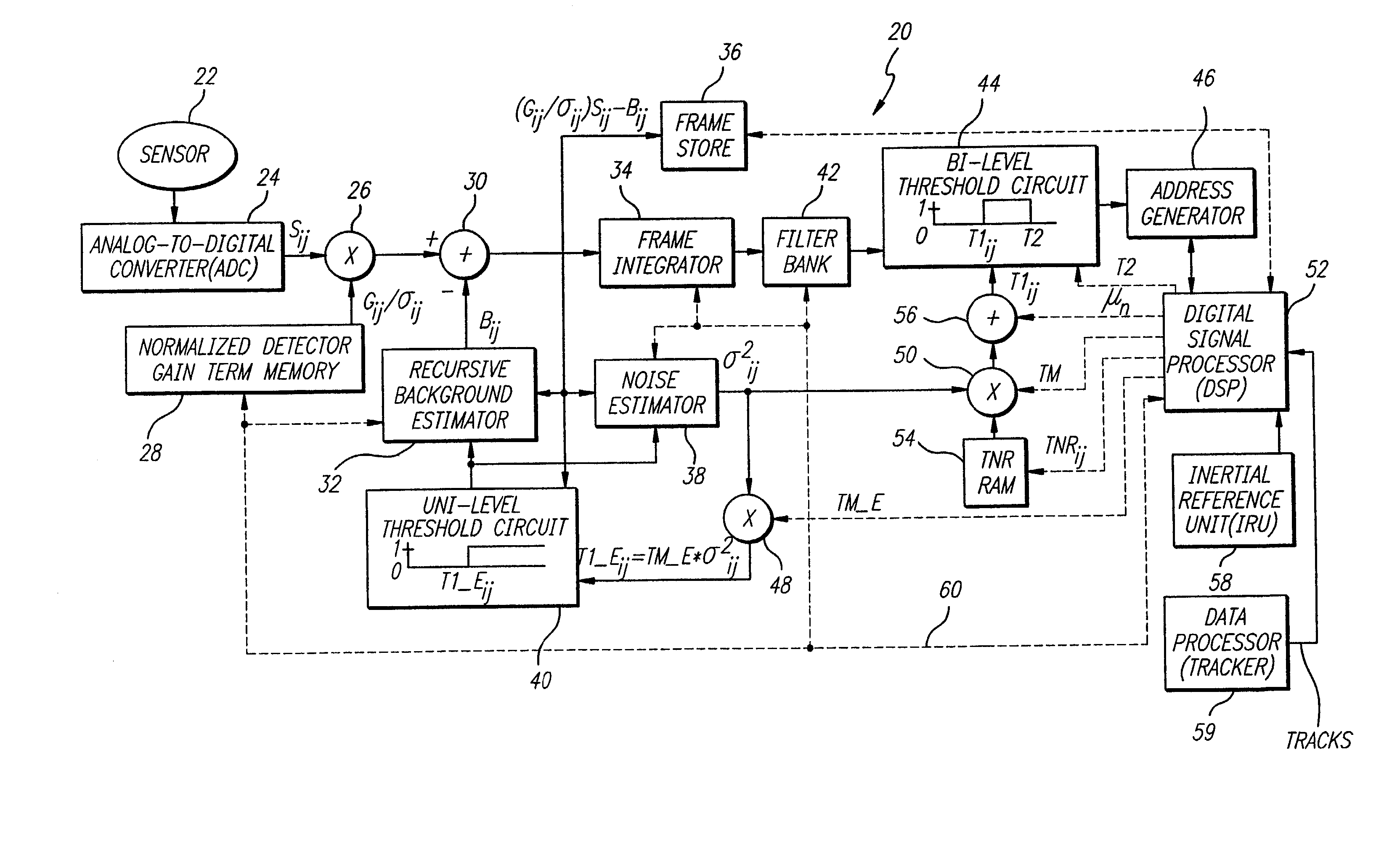
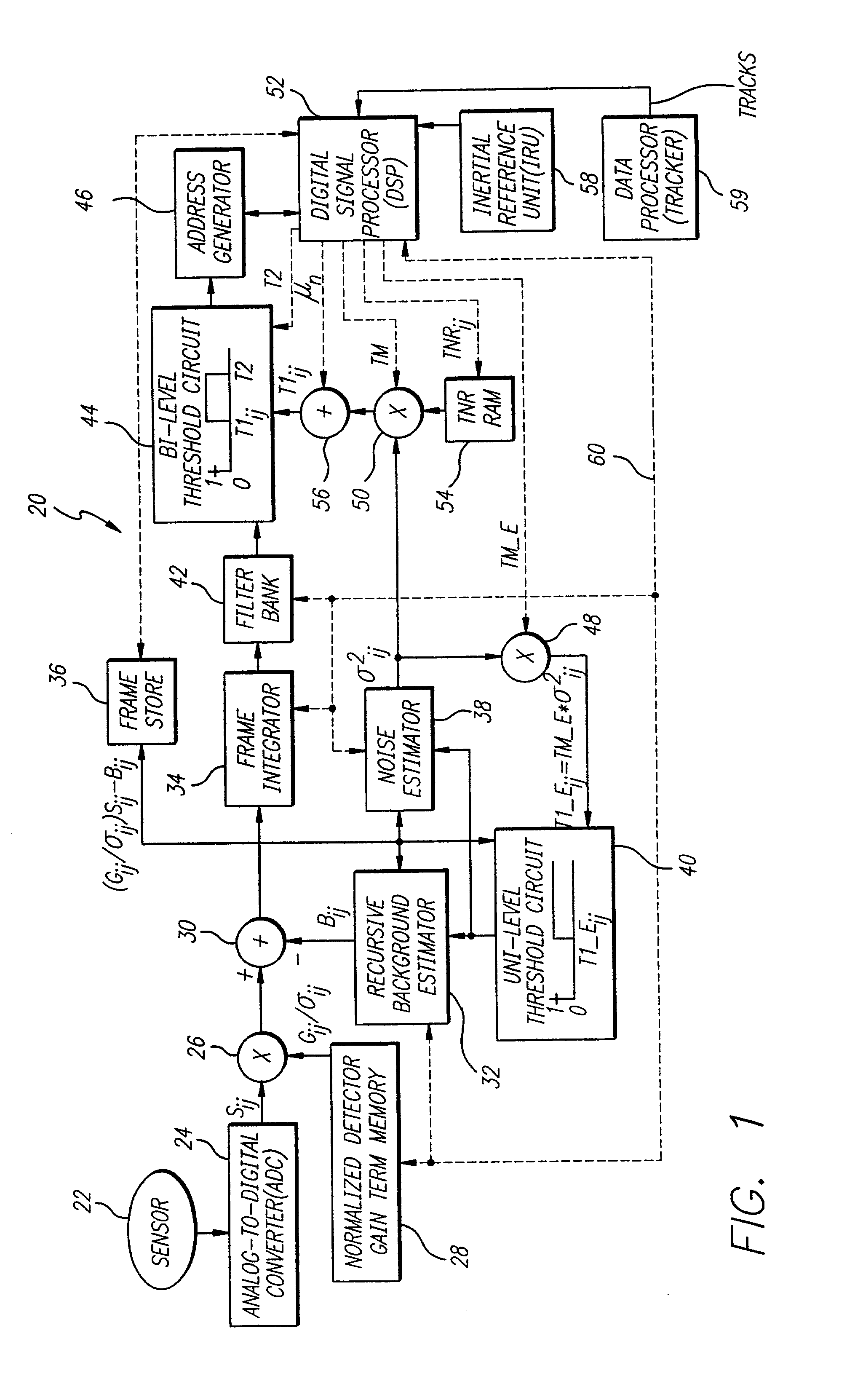
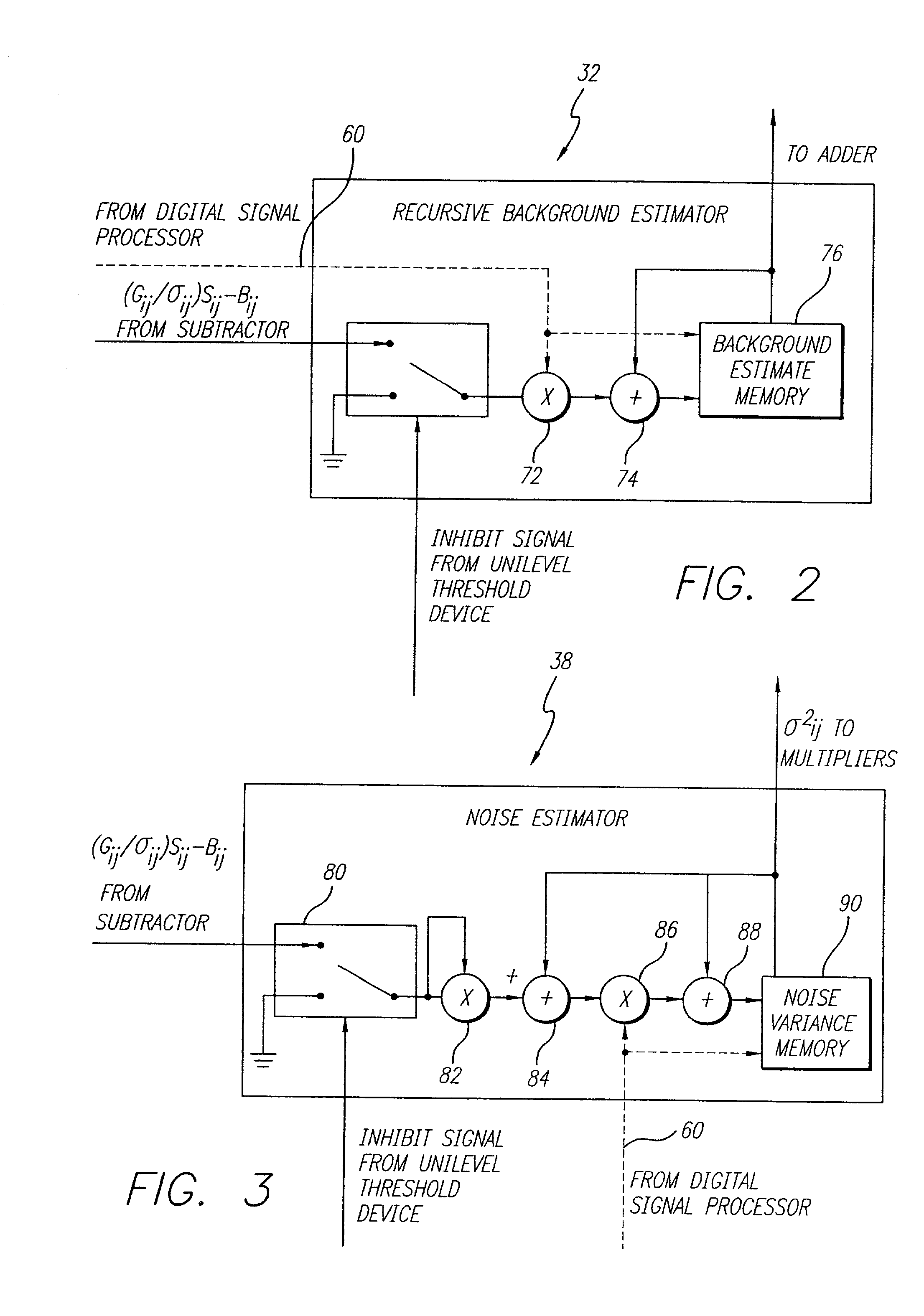
An accurate target detection system. The system includes a sensor (22) that receives electromagnetic signals and provides electrical signals in response thereto. A non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, 52) corrects non-uniformities in the sensor (22) based on the electrical signals and provides calibrated electrical signals in response thereto. A third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 52) determines if a target signal is present within the calibrated electrical signals and provides a target detection signal in response thereto. A fourth circuit (38, 40, 48) selectively activates or deactivates the non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, 52) based on the target detection signal. In a specific embodiment, the sensor (22) is an array of electromagnetic energy detectors (22), each detector providing an electrical detector output signal The non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, and 52) includes circuit for compensating for gain, background, and noise non-uniformities (28, 38, and 52) in the electromagnetic energy detectors. The non-uniformity correction circuit (28, 38, and 52) includes a detector gain term memory (28) for storing detector gain compensation values. The detector gain compensation values are normalized by noise estimates unique to each of the detectors. The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, and 52) includes a signal enhancement circuit for reducing noise (34, 42) in the calibrated electrical signals. The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, and 52) includes a noise estimation circuit (32, 38) that estimates noise in each of the detector output signals and provides noise estimates in response thereto. The noise estimation circuit (32, 38) further includes a noise estimator circuit (38) and a recursive background estimator (32). The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 52) further includes a subtractor (30) for subtracting background from the calibrated electrical signals and providing background subtracted signals in response thereto. The signal enhancement circuit (34, 42) includes a frame integrator circuit for adding frames of image data (34), each frame containing data corresponding to the background subtracted signals and providing summed frames in response thereto. The third circuit (30, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 52) includes a first threshold circuit (44) for comparing the filtered signal to a first threshold and a second threshold and providing a threshold exceedance signal if the filtered signal is between the first threshold and the second threshold.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
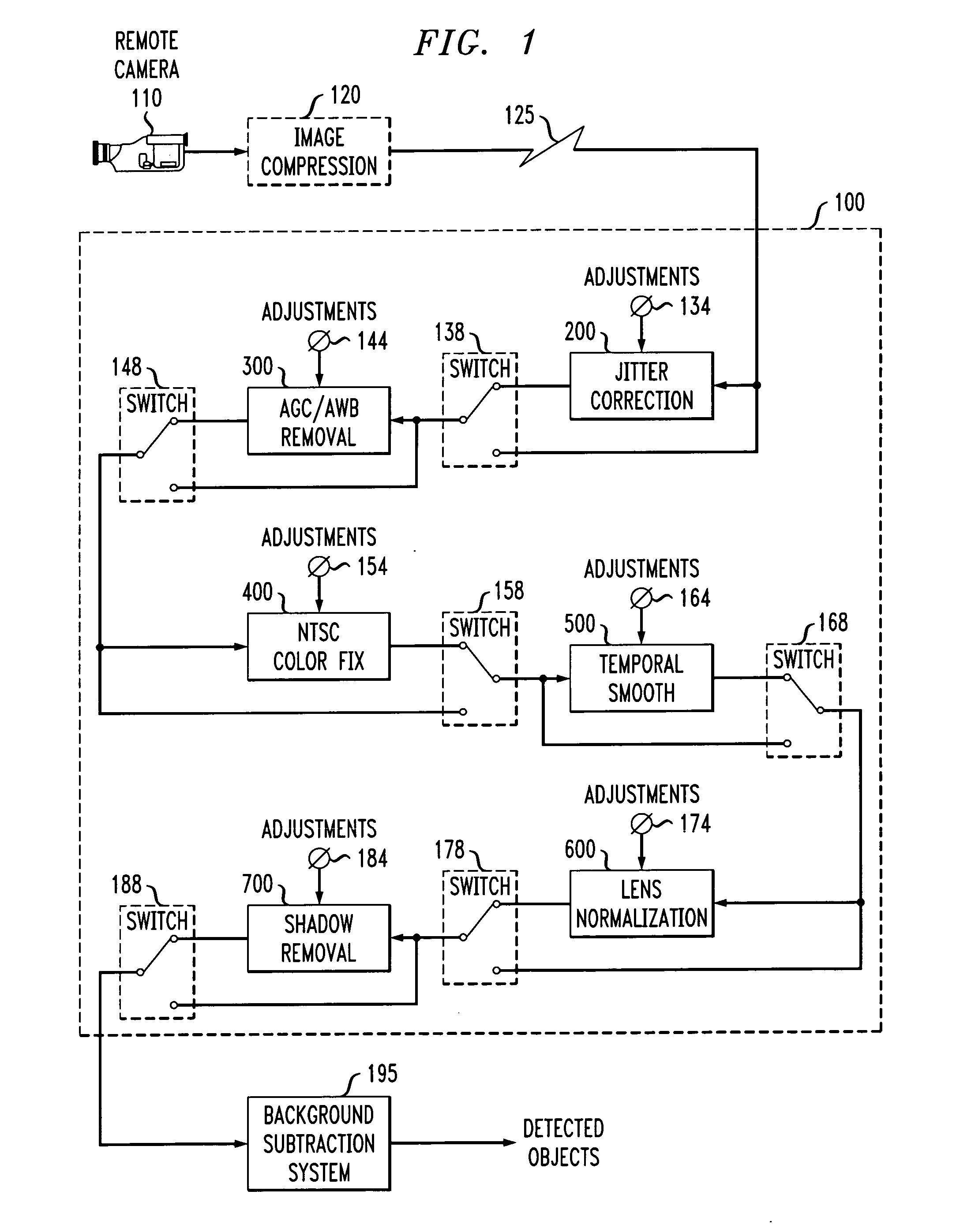
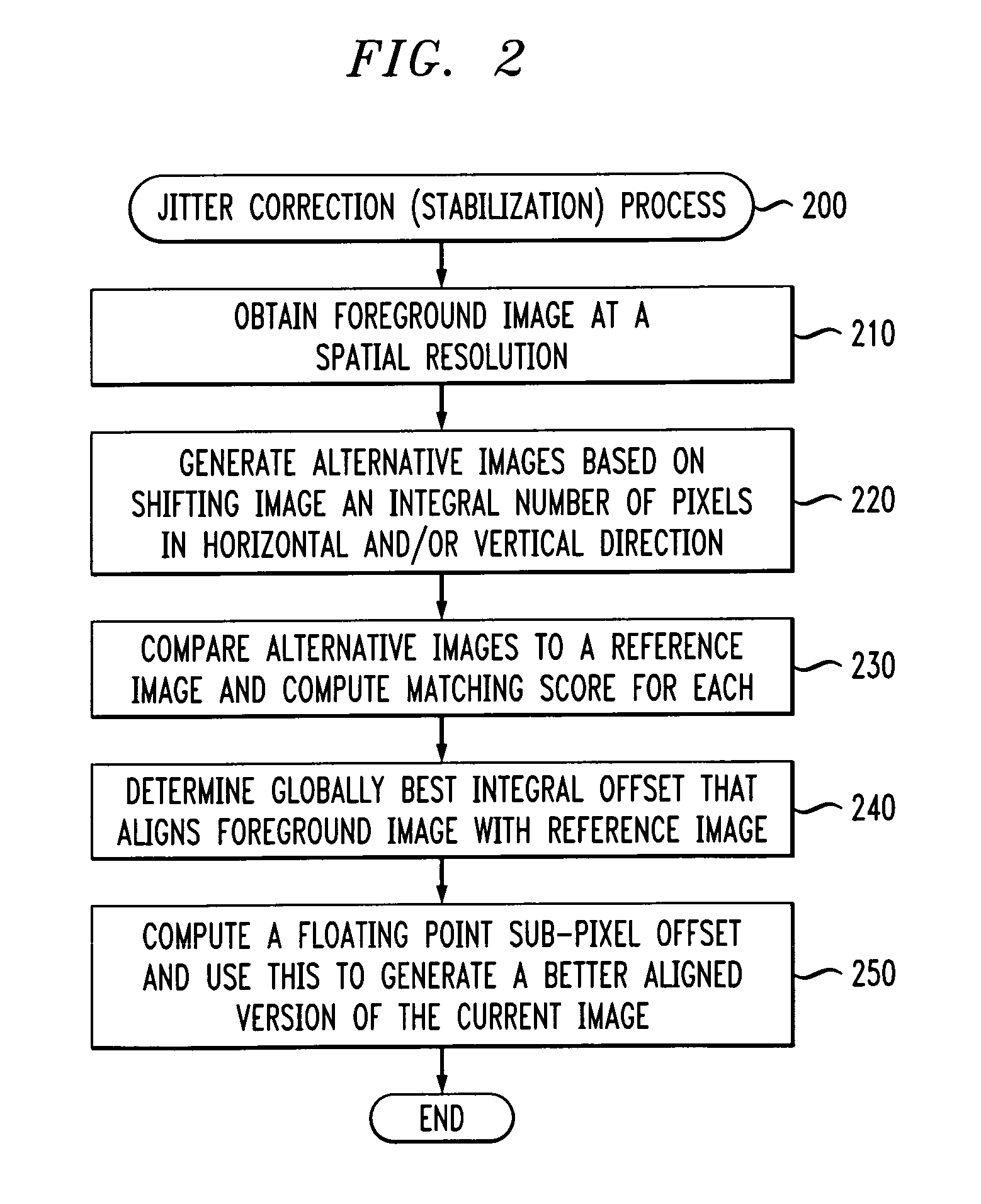
Method and apparatus for visual background subtraction with one or more preprocessing modules
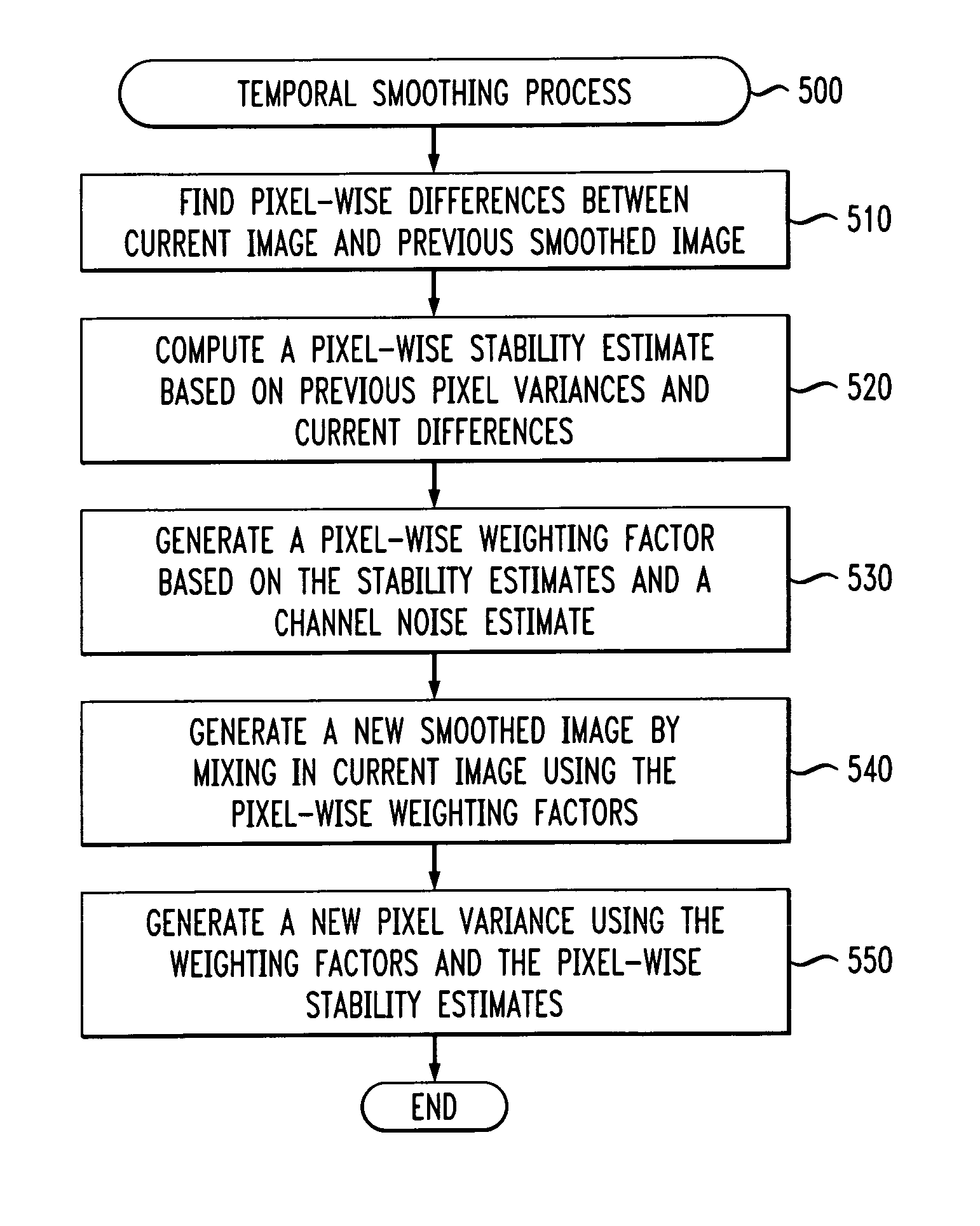
Methods and apparatus are provided for visual background subtraction using one or more preprocessing modules. One or more effects are detected in a received image signal and one or more blocks are selectively enabled to preprocess the image signal to compensate for the detected one or more effects. Visual analysis is then performed on the preprocessed signal using background subtraction. A spatially-variant temporal smoothing of the image signal is also disclosed. The spatially-variant temporal smoothing can be achieved by the mixing of a new intensity value with a previous intensity time-average as determined by a weighting matrix. The mixing can be influenced by a dynamic bias term that is a real-time estimate of a variance at the pixel, such as a degree of change, and the weighting can be determined by a relative stability of an observed value compared to a stability of the time-average.
Owner:IBM CORP
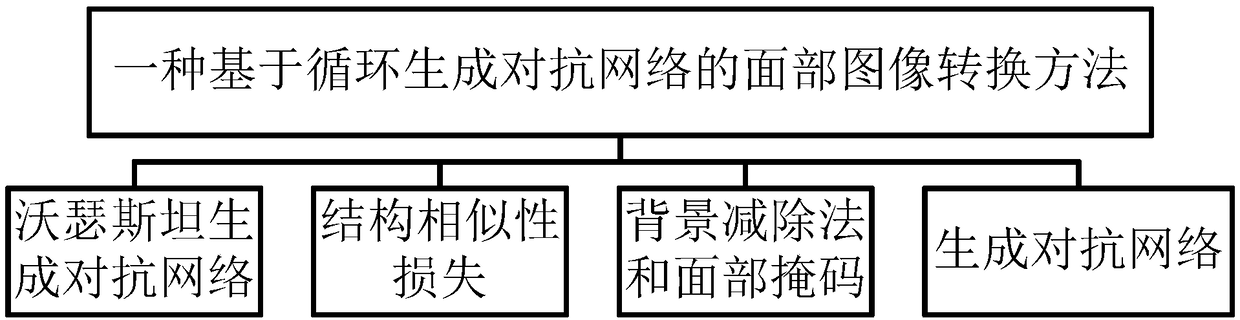
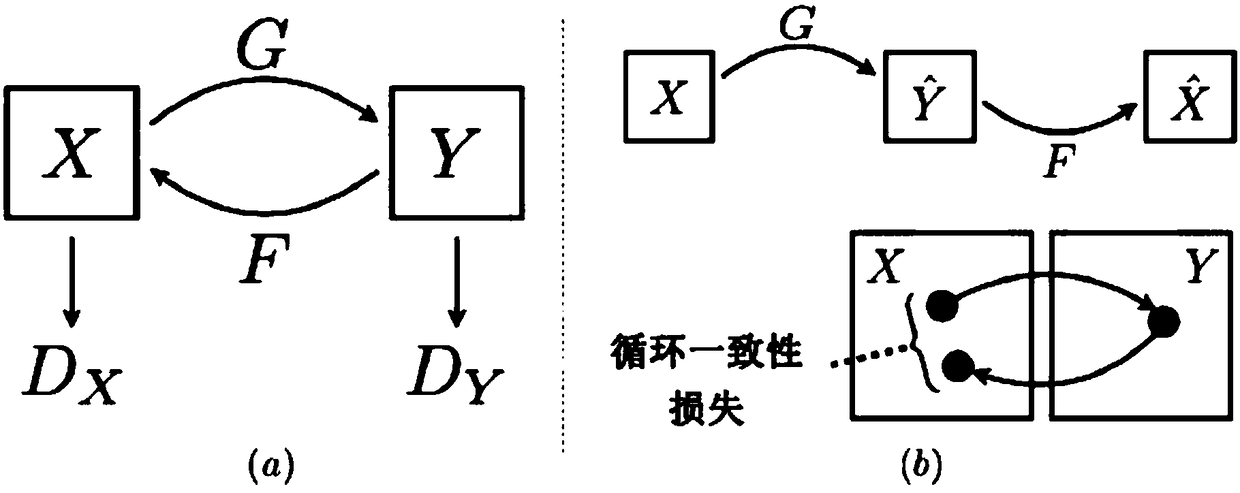
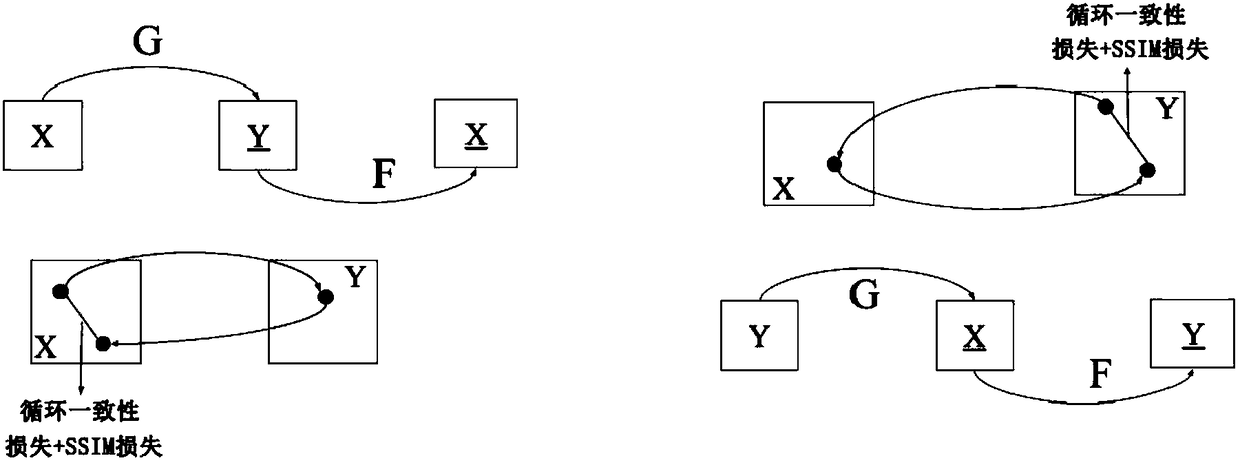
Facial image conversion method based on cycle generative adversarial network
InactiveCN108182657AEnlarging capacityReduce random noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionNetwork structure
The invention provides a facial image conversion method based on a cycle generative adversarial network. The main content of the method comprises a Wasserstein generative adversarial network (WGAN), astructural similarity (SSIM) loss, background subtraction method and face mask and a generative adversarial network (GAN). The method comprises the steps of using a generator network and a discriminator network to compete against each other, forming the cycle GAN by using a traditional GAN loss function and a new cyclic consistency loss function, improving the WGAN, improving the training of the GAN through loss, matching the SSIM loss and brightness, contrast and structural information of a generated image and an input image, inputting a binary mask and the images during training, and applying an element product to reconstruct the loss. According to the method, the cycle generative adversarial network is used, the method has higher consistency and stability in converting facial expressions, facial details and edge details can be processed well, and thus a converted image is more natural and more realistic.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
Gradient calculating camera board
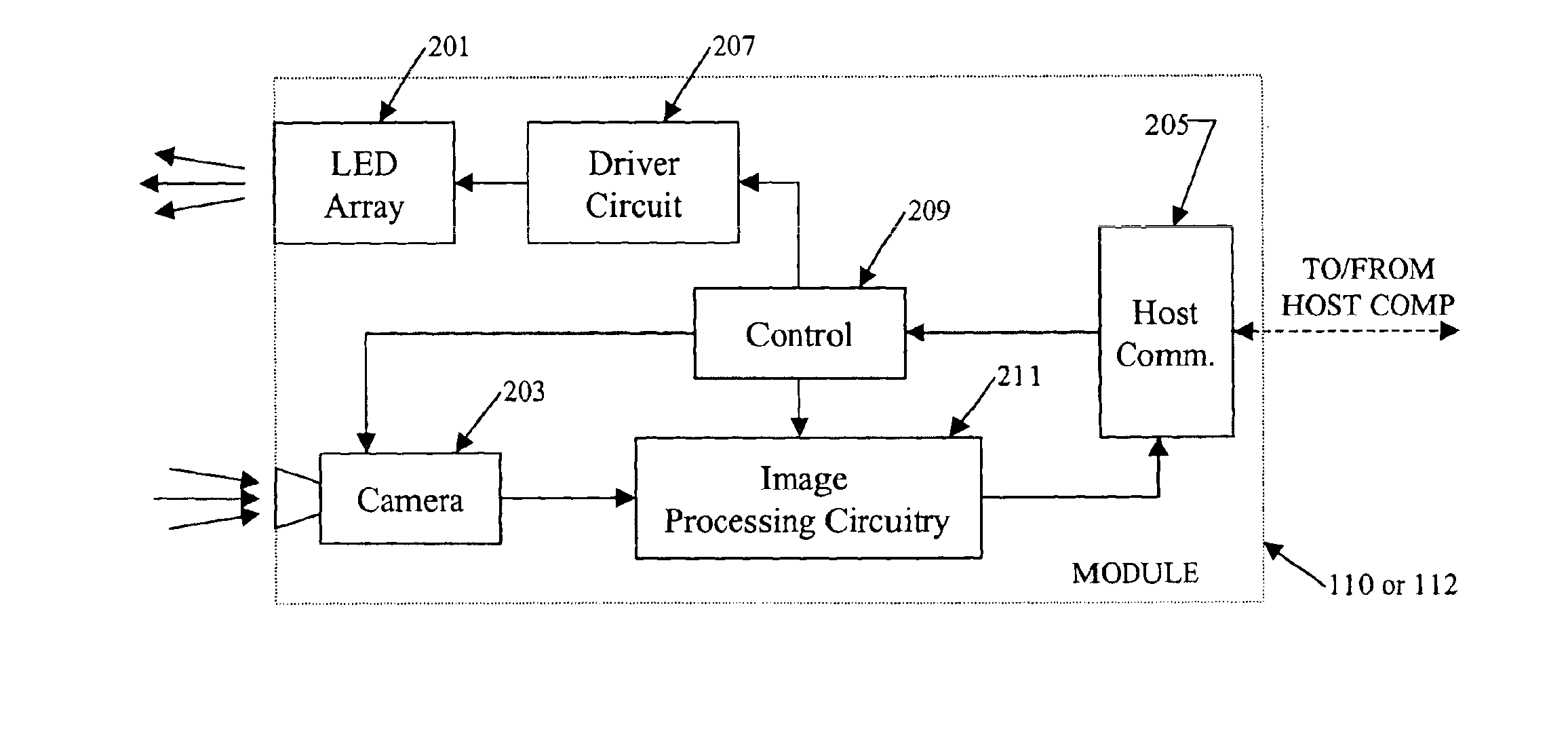
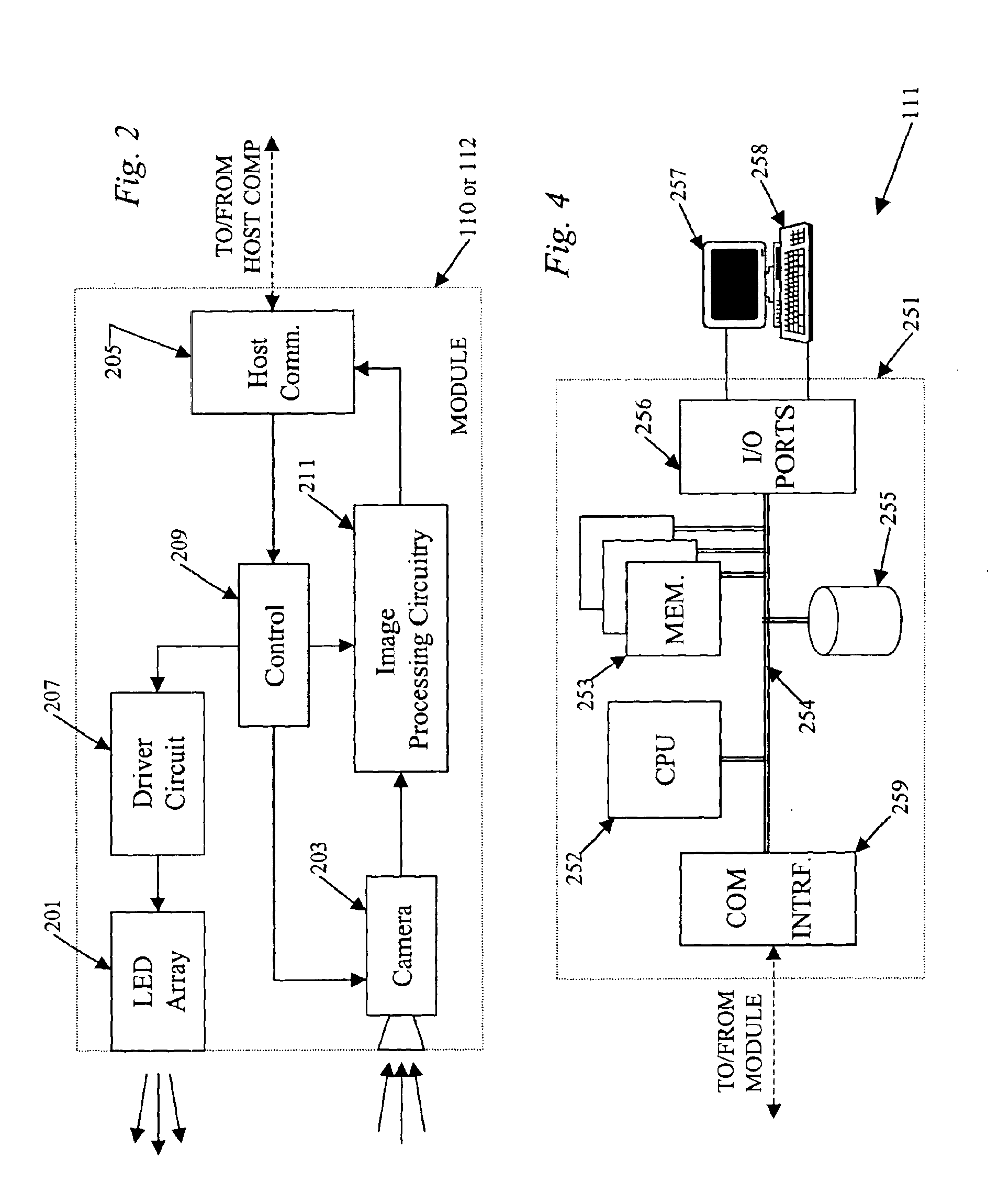
InactiveUS6871409B2Reduce bandwidth requirementsNot require as complex (or expensive) hardwareAngles/taper measurementsAngle measurementCamera controlVisual perception
In a machine vision system utilizing computer processing of image data, an imaging module incorporates the image sensor as well as pre-processing circuitry, for example, for performing a background subtraction and / or a gradient calculation. The pre-processing circuitry may also compress the image information. The host computer receives the pre-processed image data and performs all other calculations necessary to complete the machine vision application, for example, to determine one or more wheel alignment parameters of a subject vehicle. In a disclosed example useful for wheel alignment, the module also includes illumination elements, and the module circuitry provides associated camera control. The background subtraction, gradient calculation and associated compression require simpler, less expensive circuitry than for typical image pre-processing boards. Yet, the pre-processing at the imaging module substantially reduces the processing burden on the host computer when compared to machine vision implementations using direct streaming of image data to the host computer.
Owner:SNAP ON INC
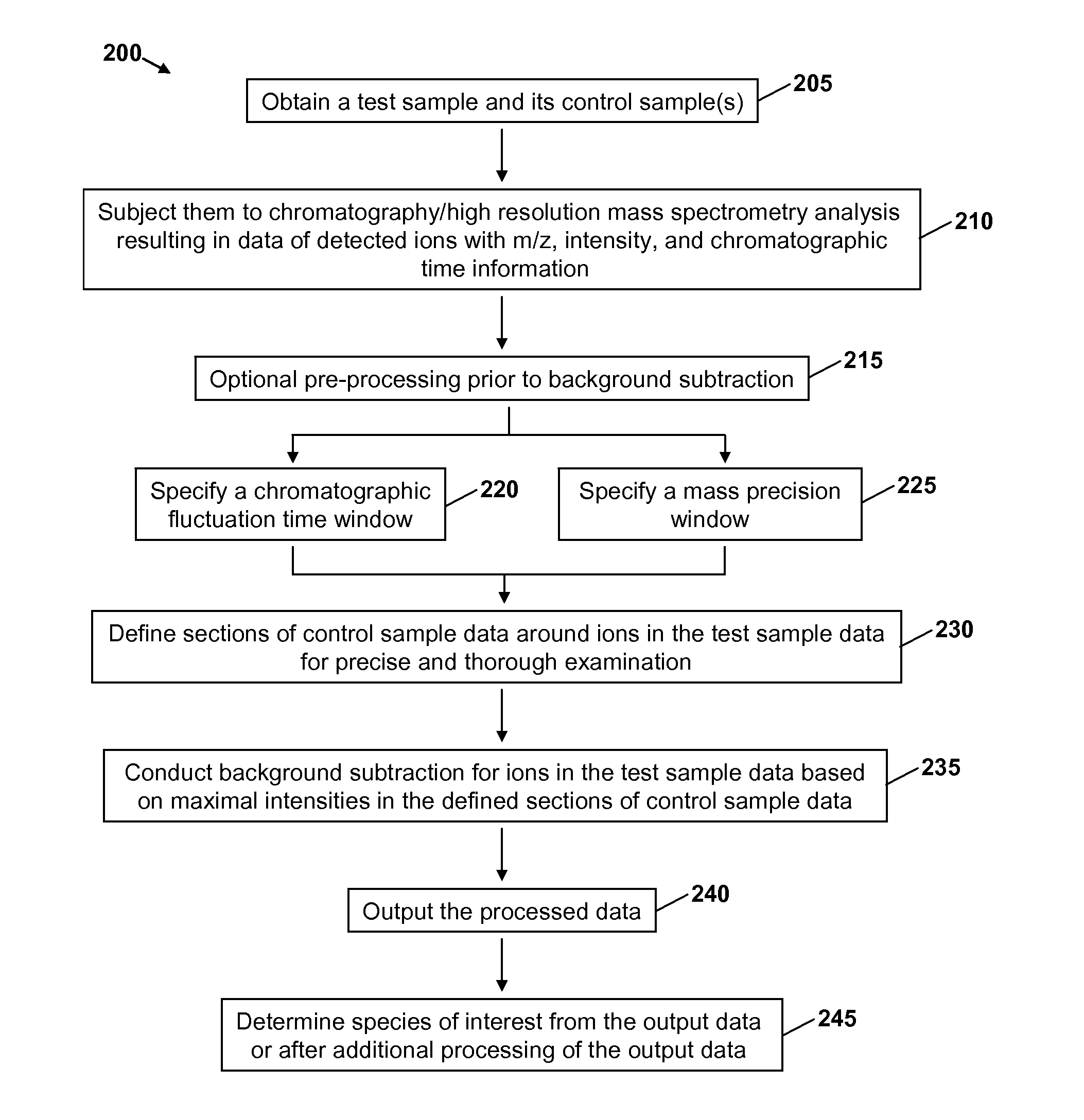
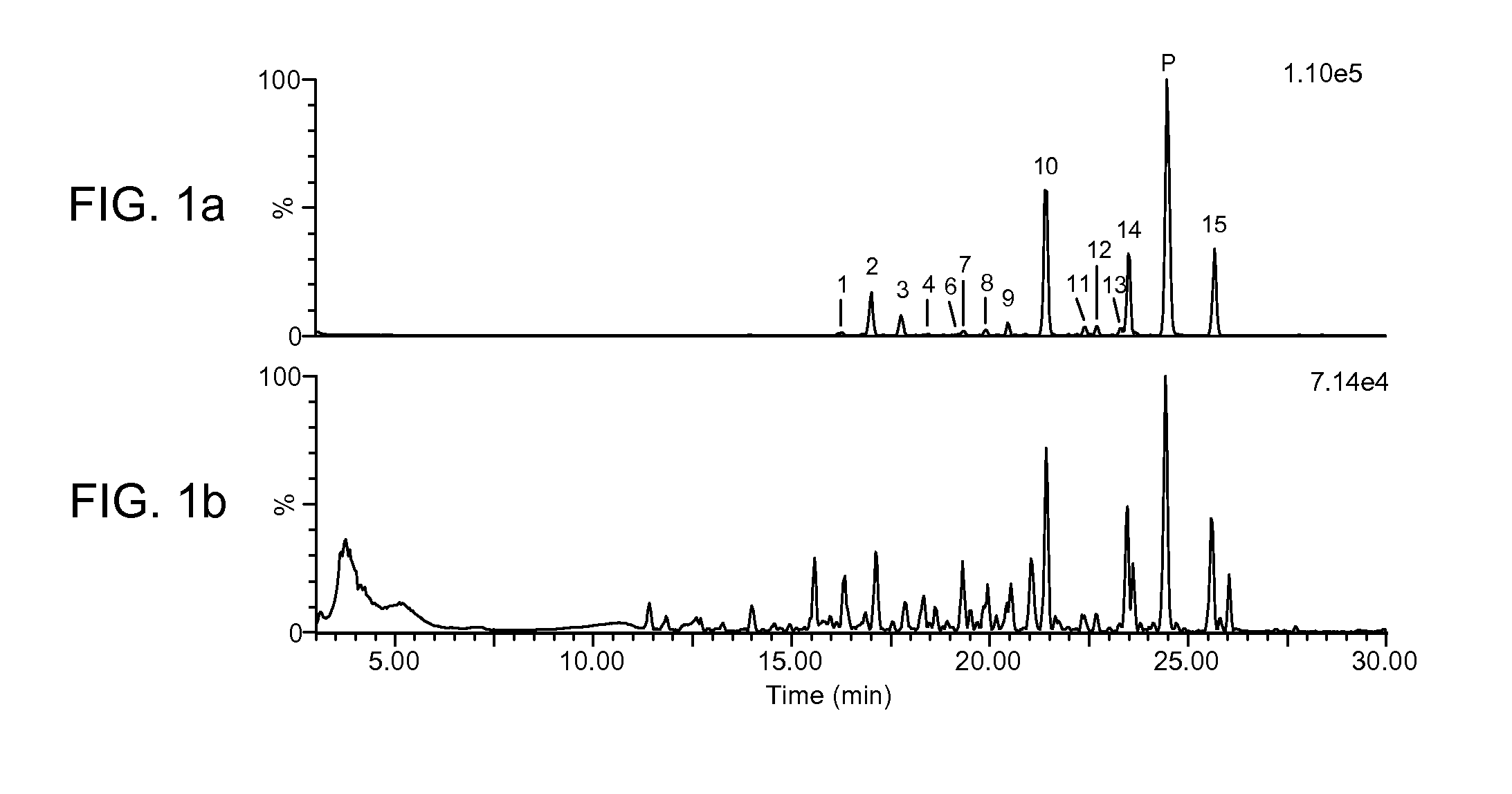
Precise and thorough background subtraction
ActiveUS20100213368A1Avoid enteringIsotope separationMass spectrometersTest sampleMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A method for identifying and characterizing components of interest in complex samples includes subjecting both a sample and its control samples to chromatography / high resolution mass spectrometry analysis to detect ions of the samples. The method includes defining sections of control sample data within specified chromatographic fluctuation time and mass precision windows around each ion or each group of the same ions of question in the test sample data. The defined sections of the control sample data are examined and the maximal intensities are subtracted from respective ions in the test sample. Components of interest are determined from the resultant data of the test sample. The method can be used for identifying molecular ions and / or their fragment ions for components of interest in complex samples.
Owner:MASSDEFECT TECH
System and method for searching for changes in surveillance video
ActiveUS20050078853A1Reduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisBackground imageRegion of interest
Systems and methods for determining when a change has occurred in an area-of-interest included in an image region are disclosed. The system and methods may perform a specially modified background subtraction method. The systems and methods may initialize a background image region and then comparing a first image region from a second frame to the background image region to classify pixels as foreground pixels or background pixels. The foreground pixels are then classified based on predetermined characteristics. The background image region may then be updated to include foreground pixels that did not have the predetermined characteristics. The systems and methods allow for searching for background updates to thereby determine when a change has occurred in the area-of-interest.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TYCO IP HLDG LLP
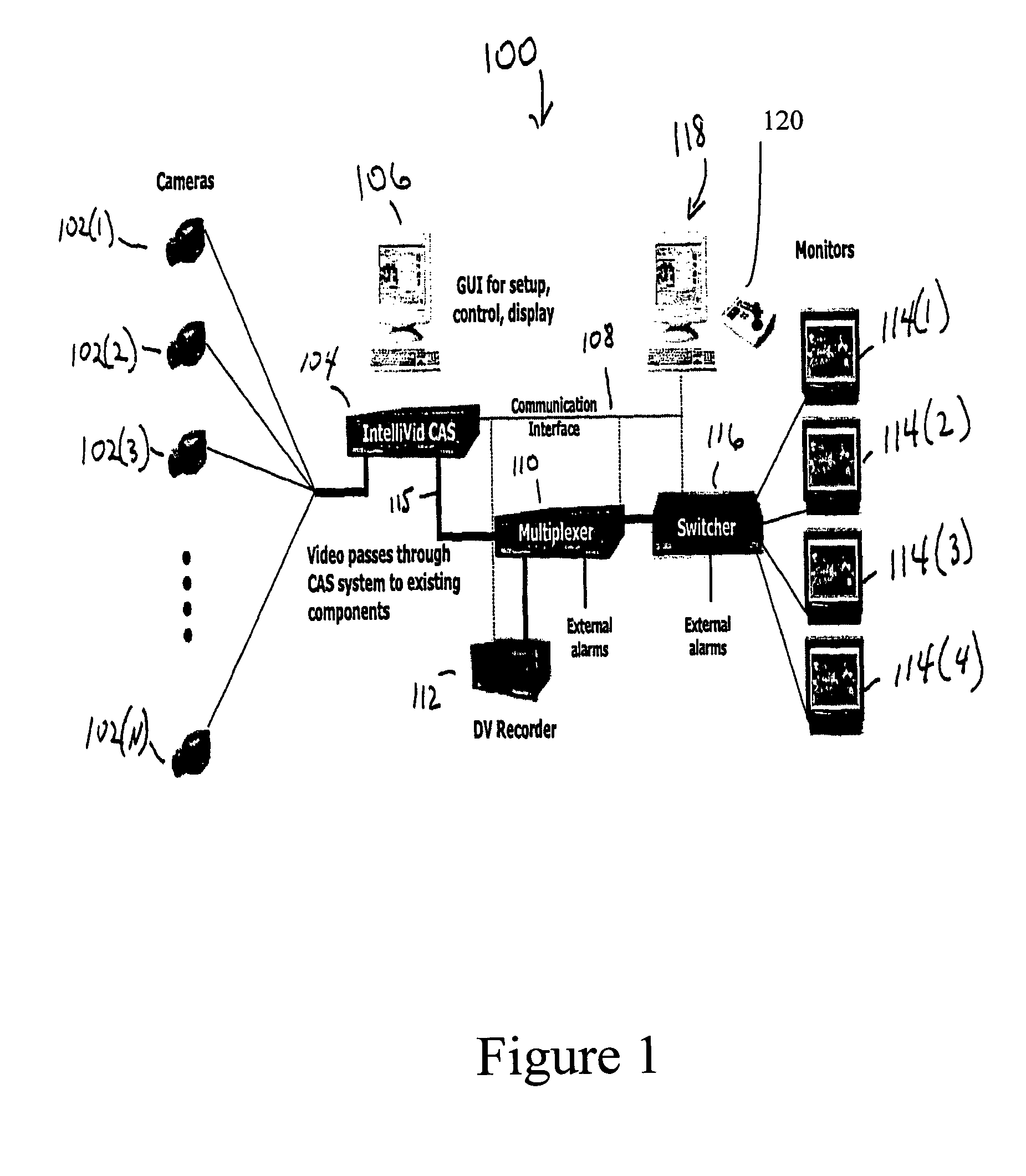
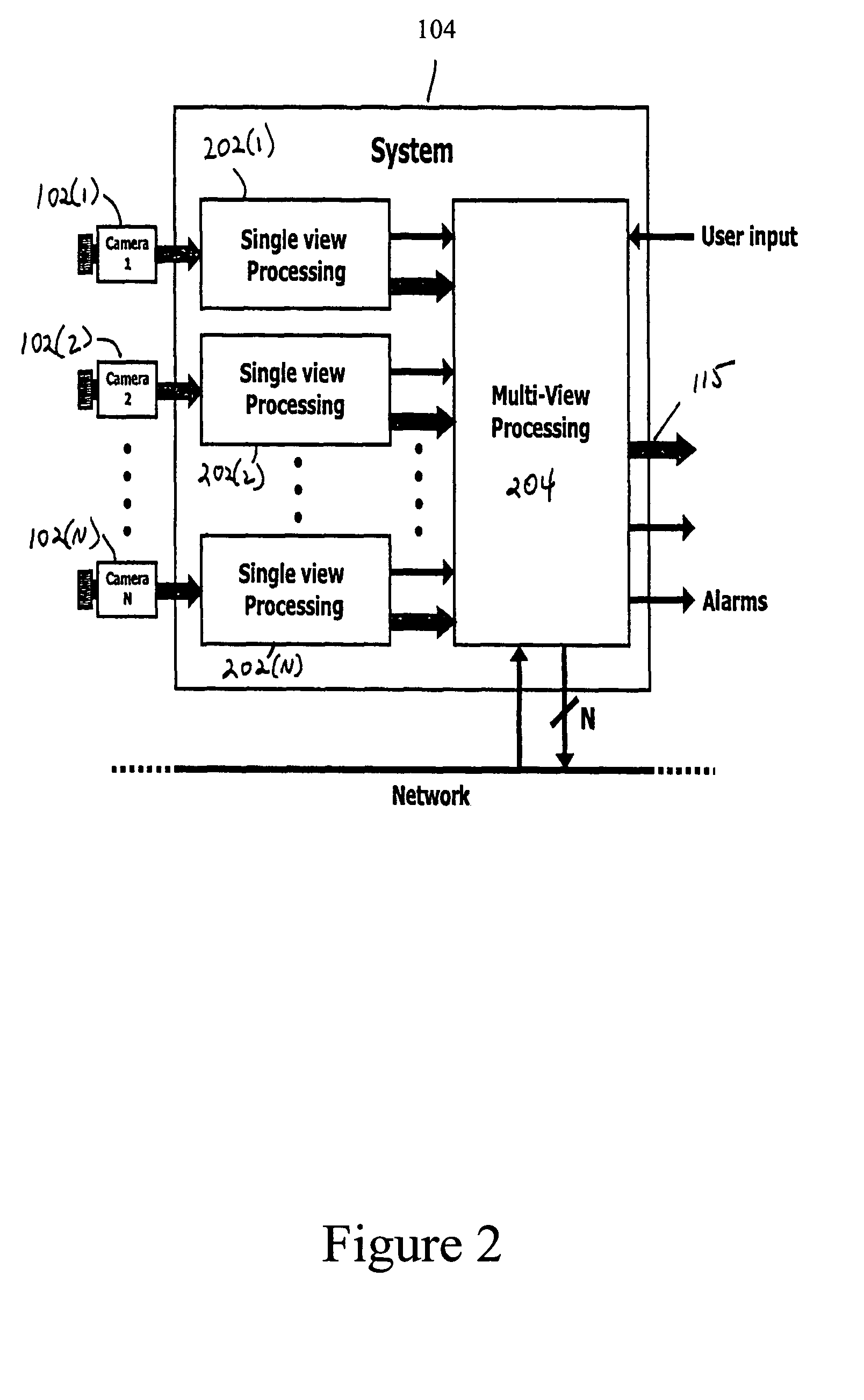
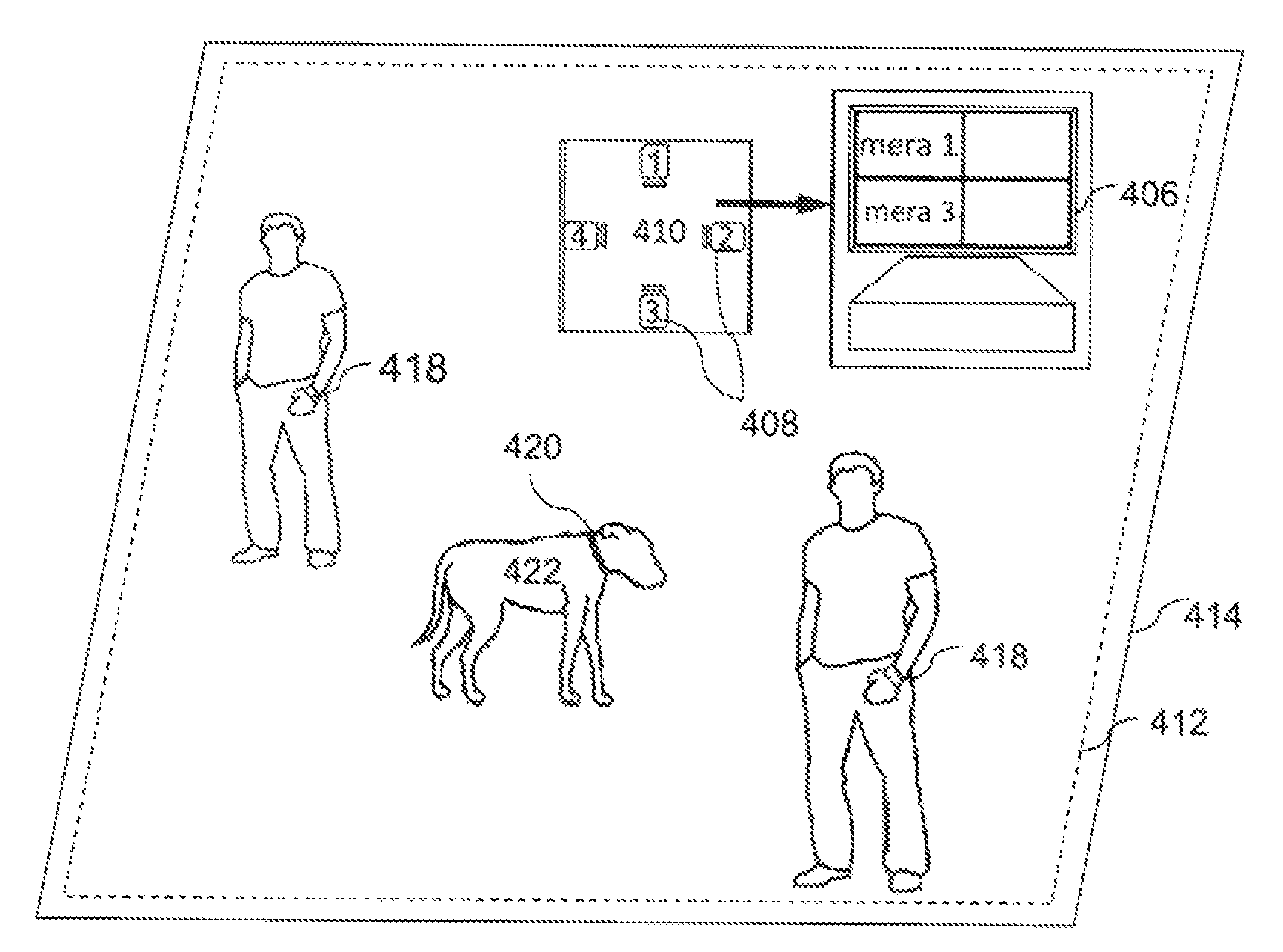
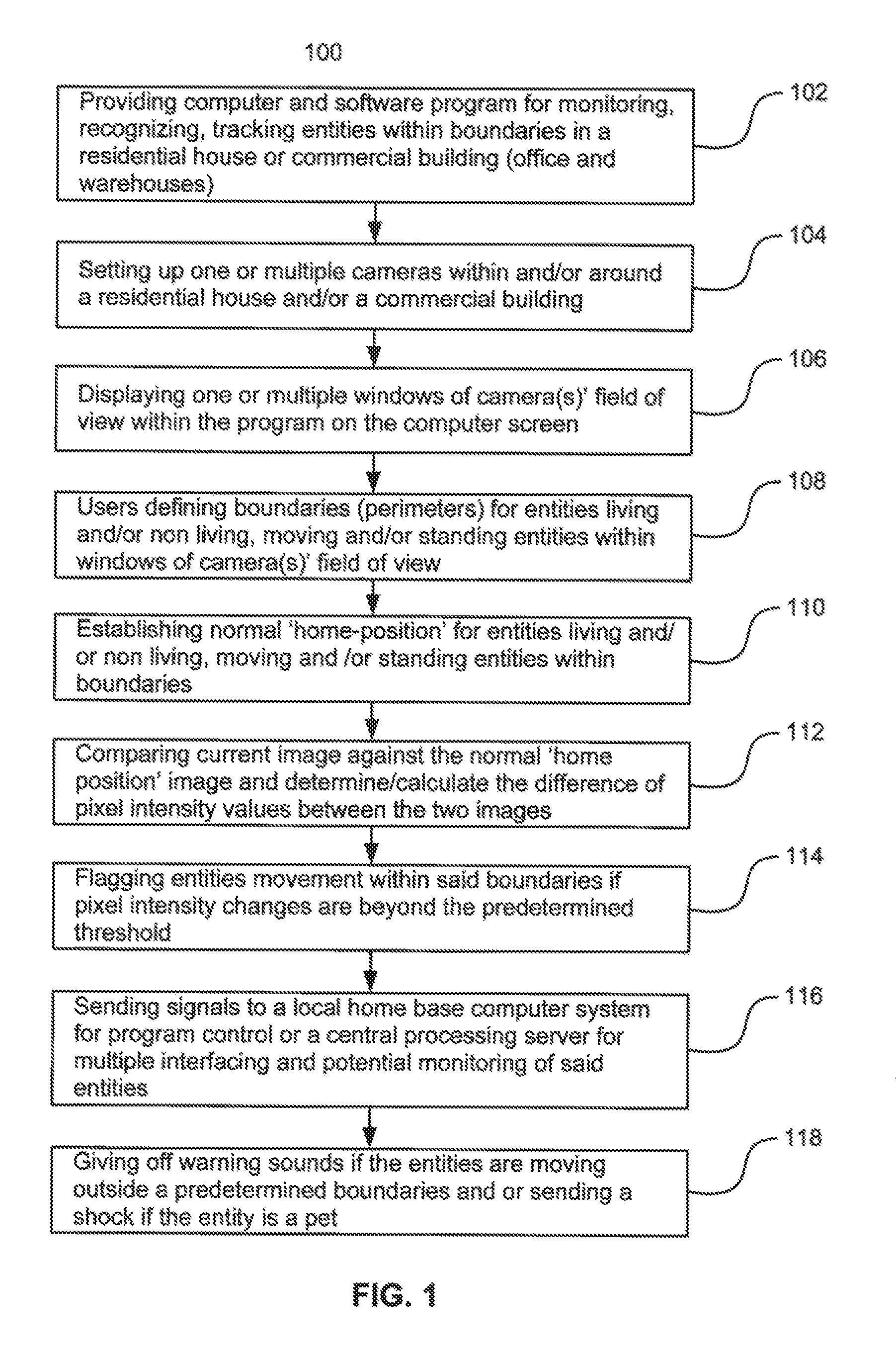
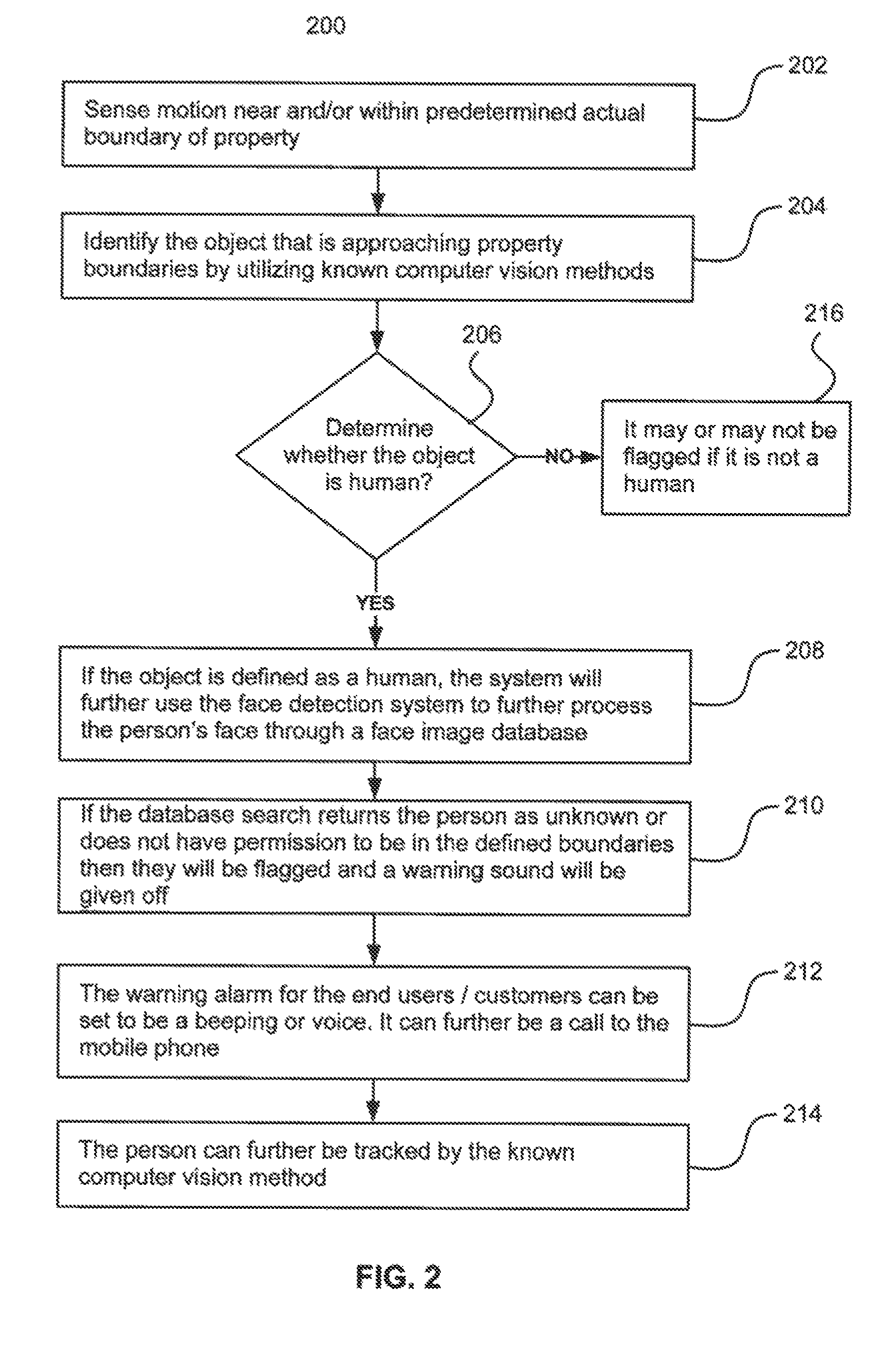
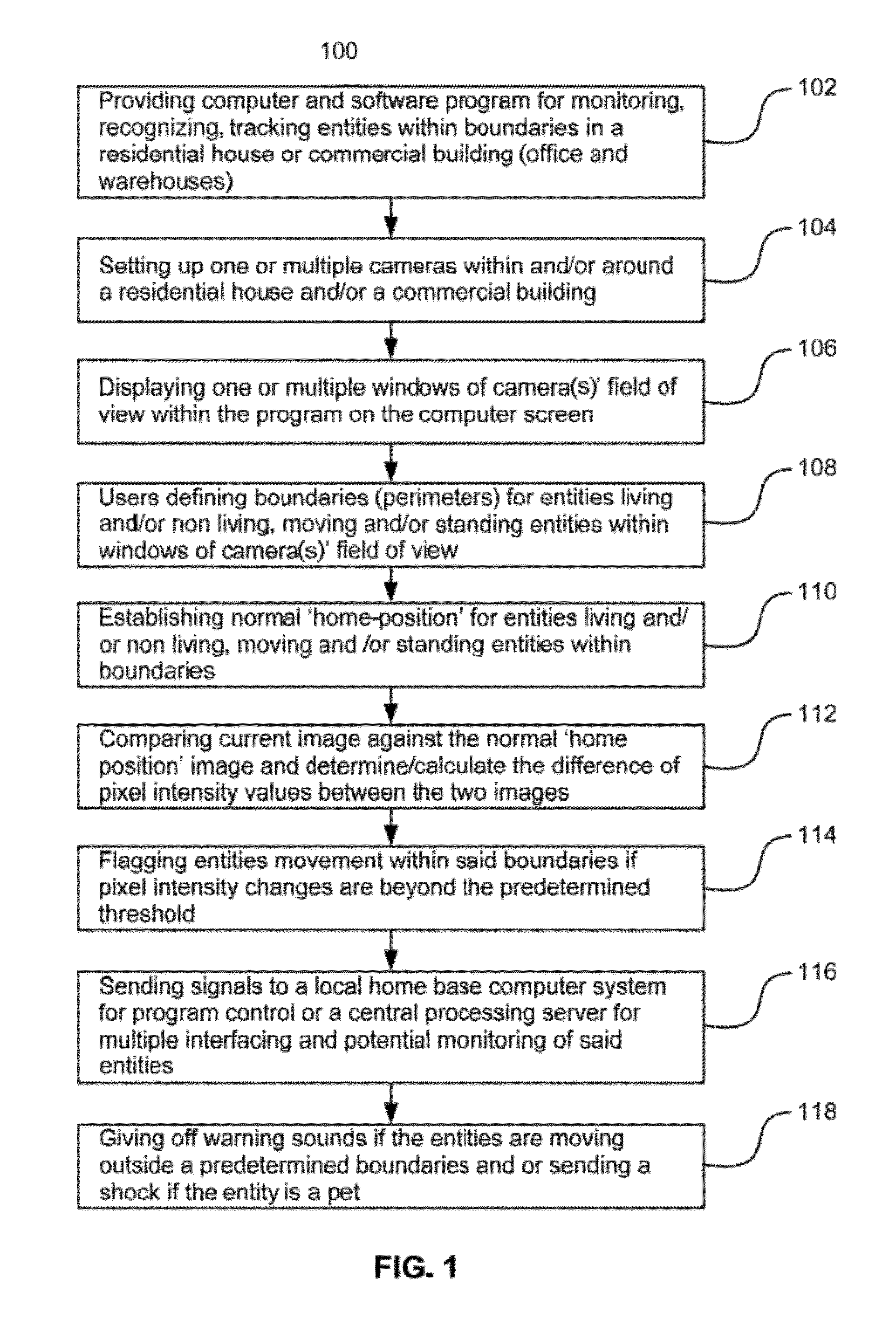
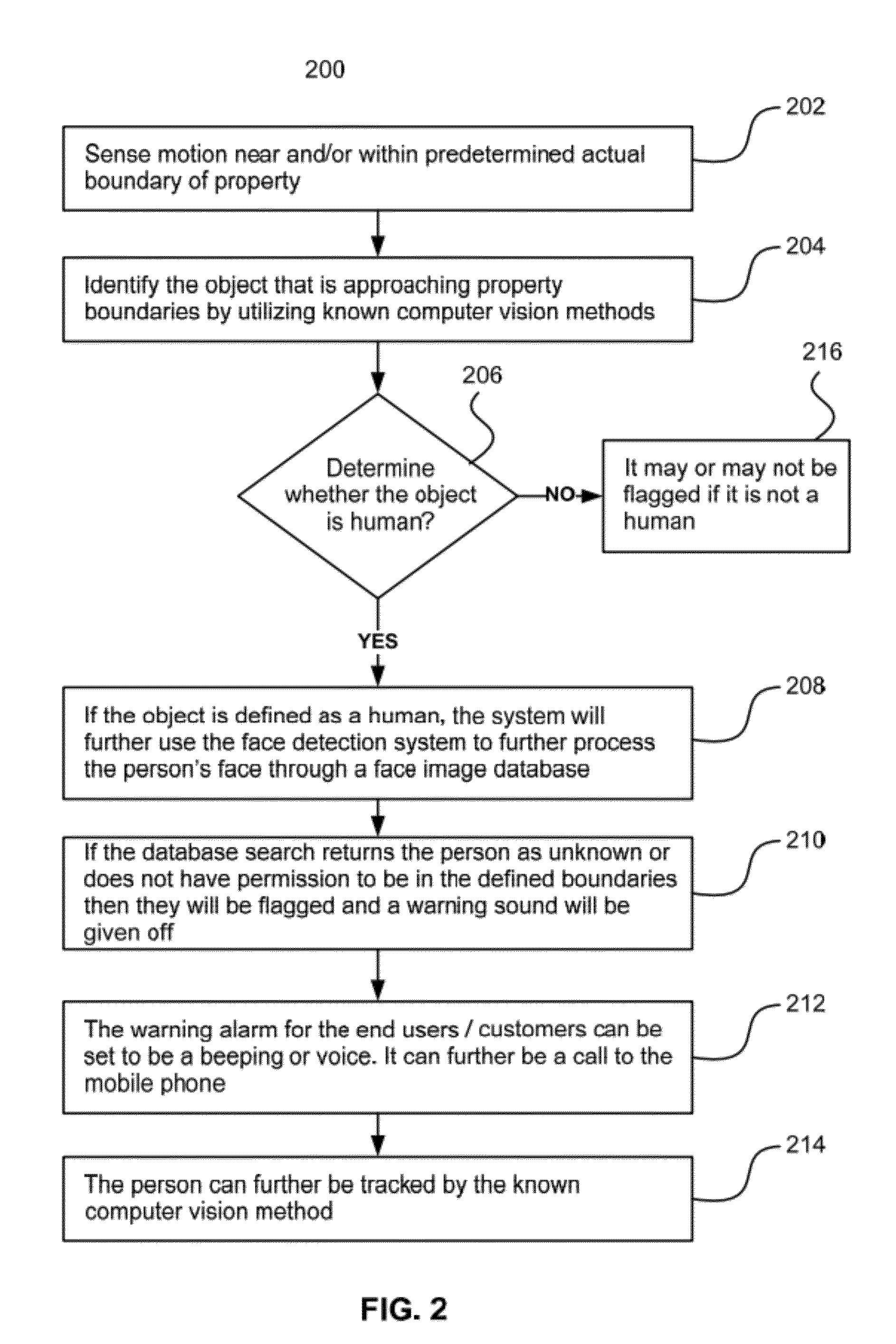
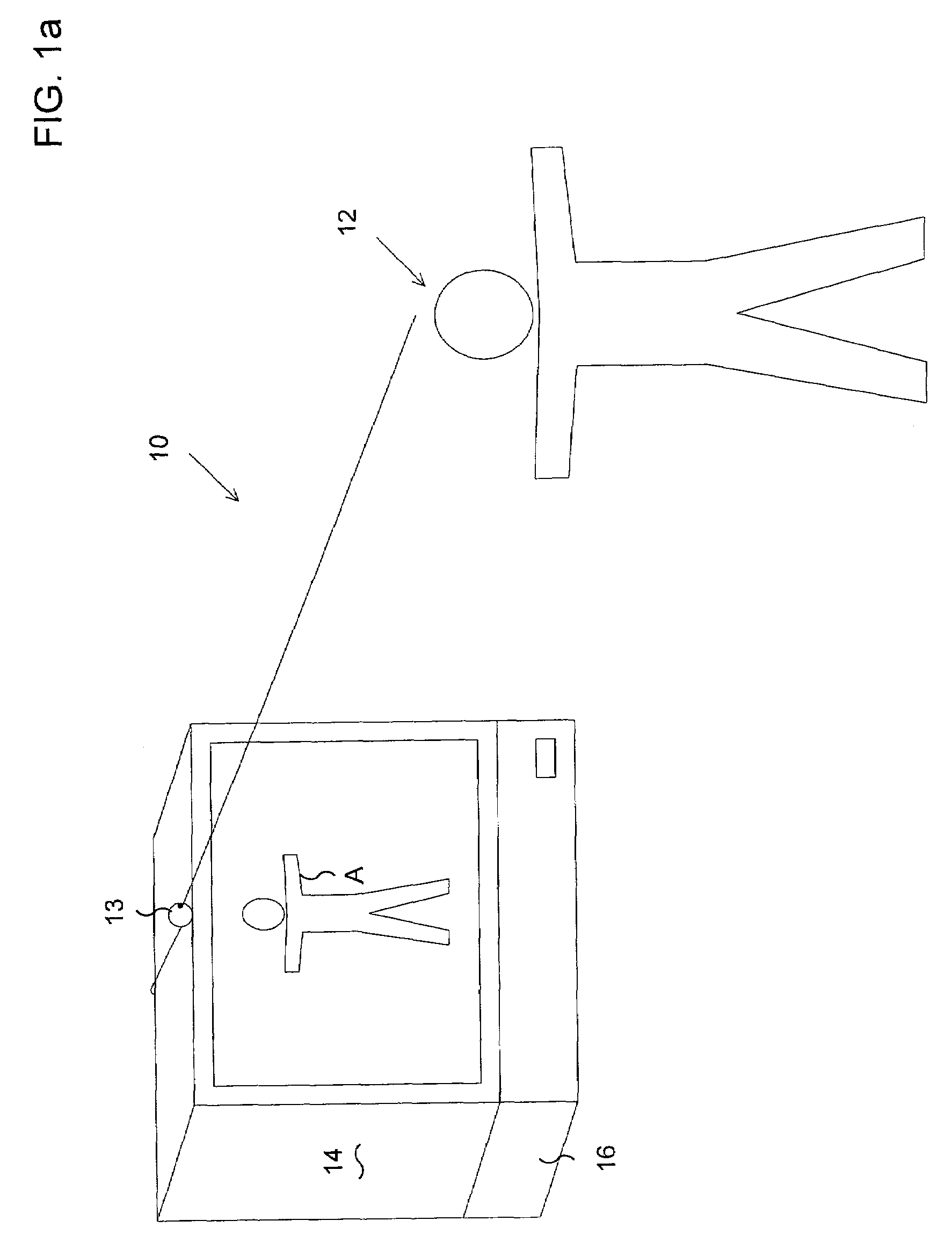
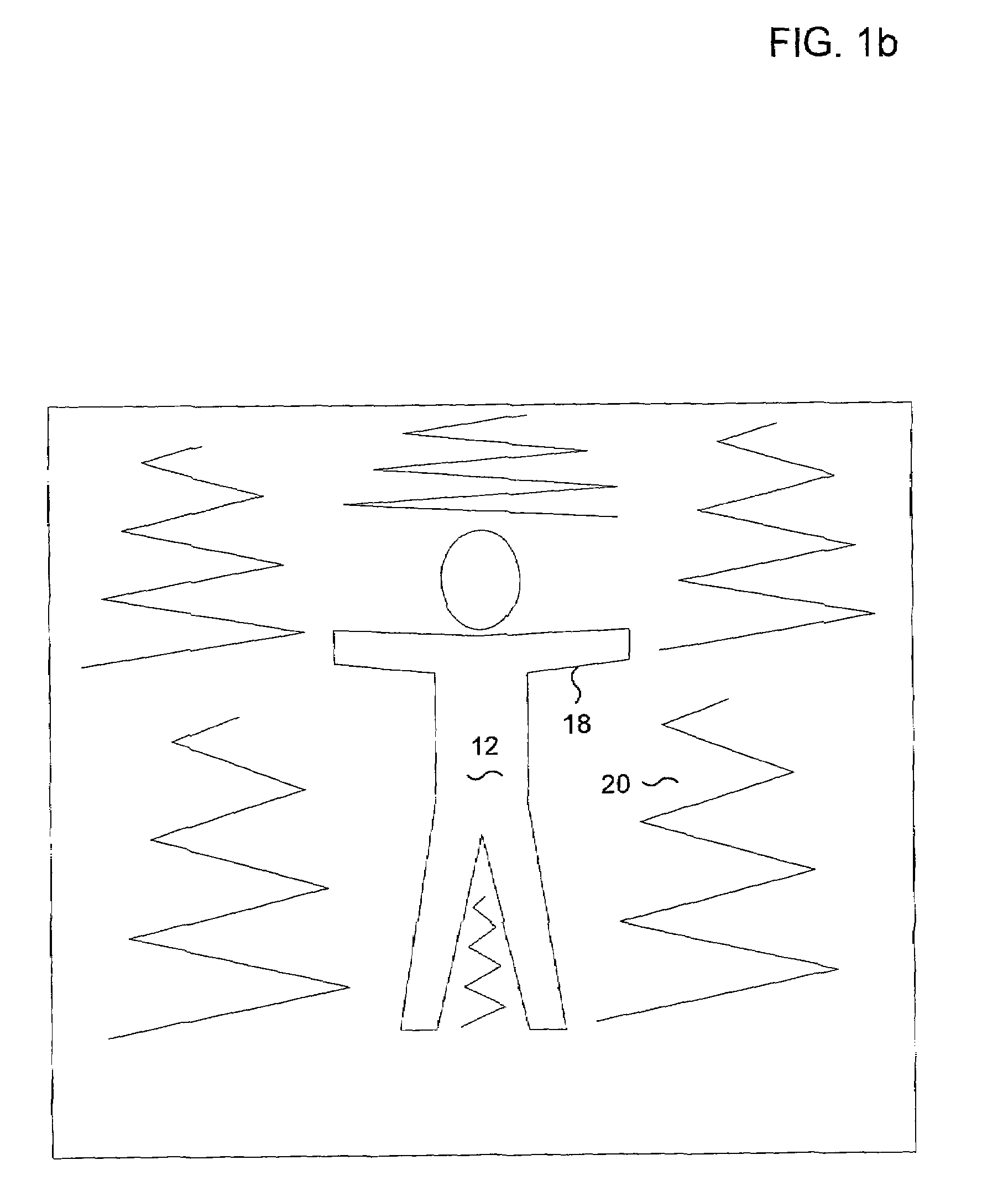
Surveillance systems and methods to monitor, recognize, track objects and unusual activities in real time within user defined boundaries in an area
InactiveUS8908034B2Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsNon real timeMonitoring system
A surveillance system and method that utilize computer vision technology and background subtraction to monitor, recognize, and track objects or unusual activities within user specified boundaries. The system and method comprises at least one camera and at least one computer with a software program showing one or multiple windows of camera's field of views in real time. The program allows users to define one or multiple boundaries within any window. The program further utilizes background subtraction technique to establish normal “home-position” of objects within defined boundaries. The program compares current image of the objects against the normal “home-position” to determine / calculate the difference of pixel intensity values. If the difference is beyond the predetermine threshold, the program will flag the movement of the object and give off alert.
Owner:BORDONARO JAMES
Method and device for detecting lost articles in security monitoring
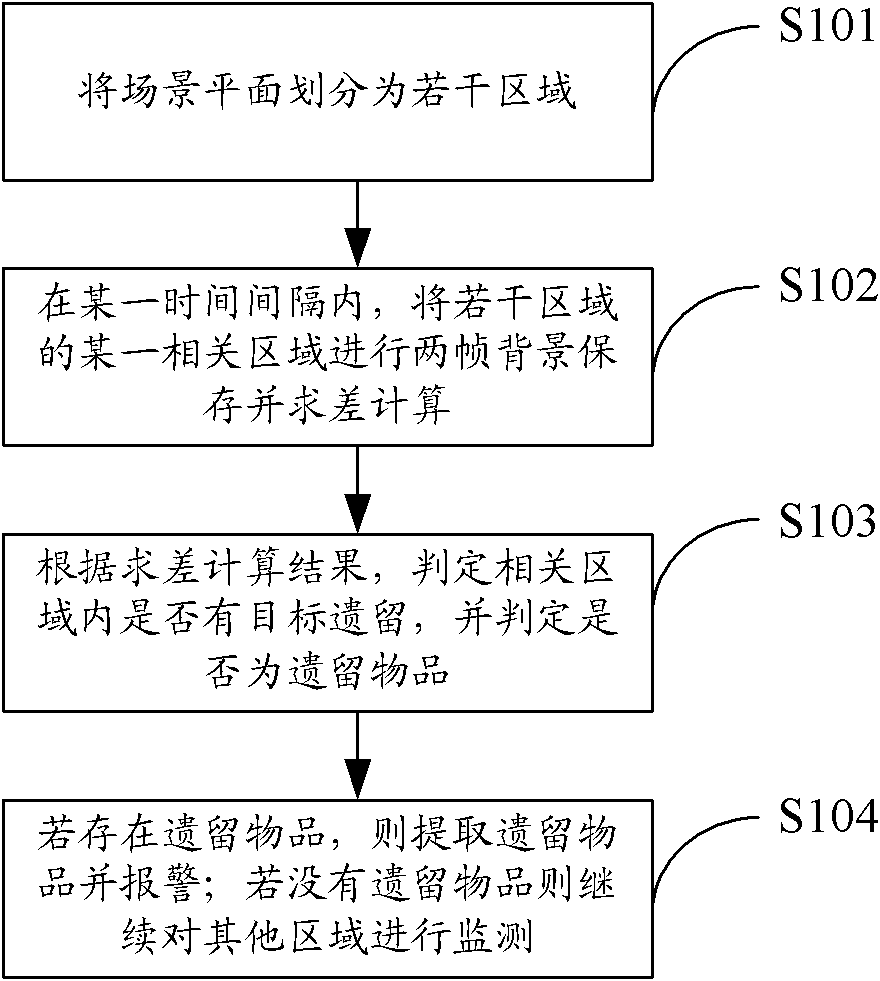
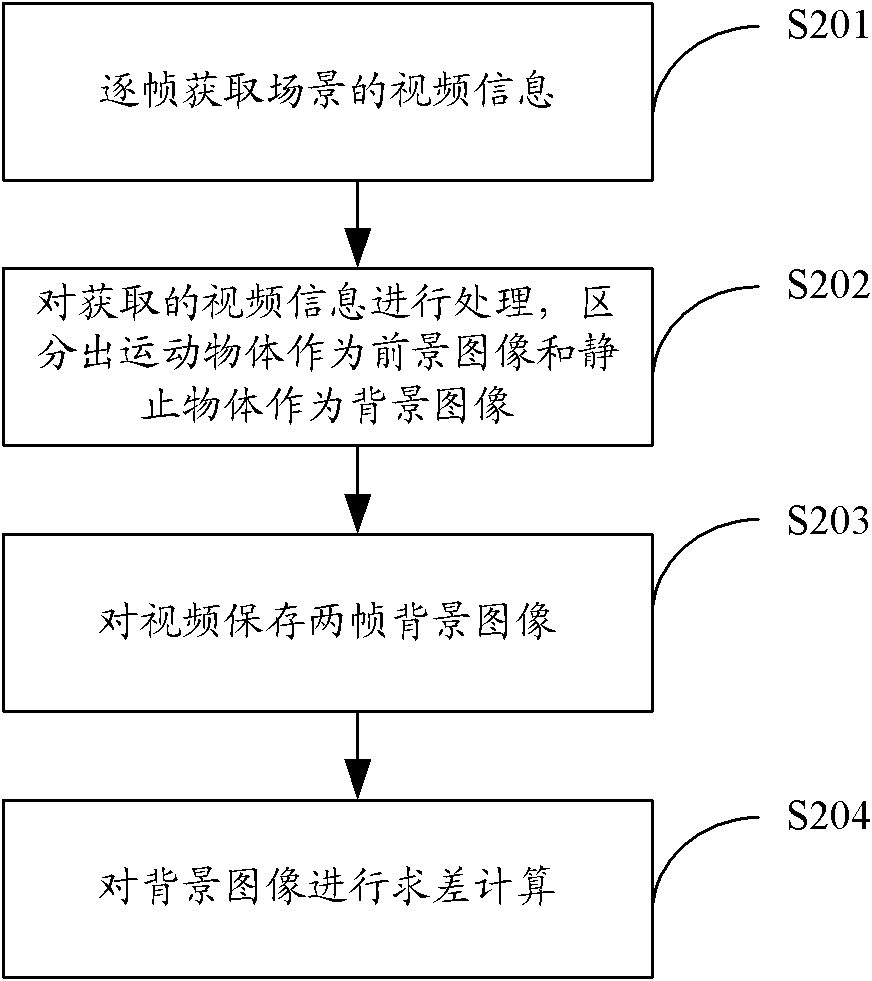
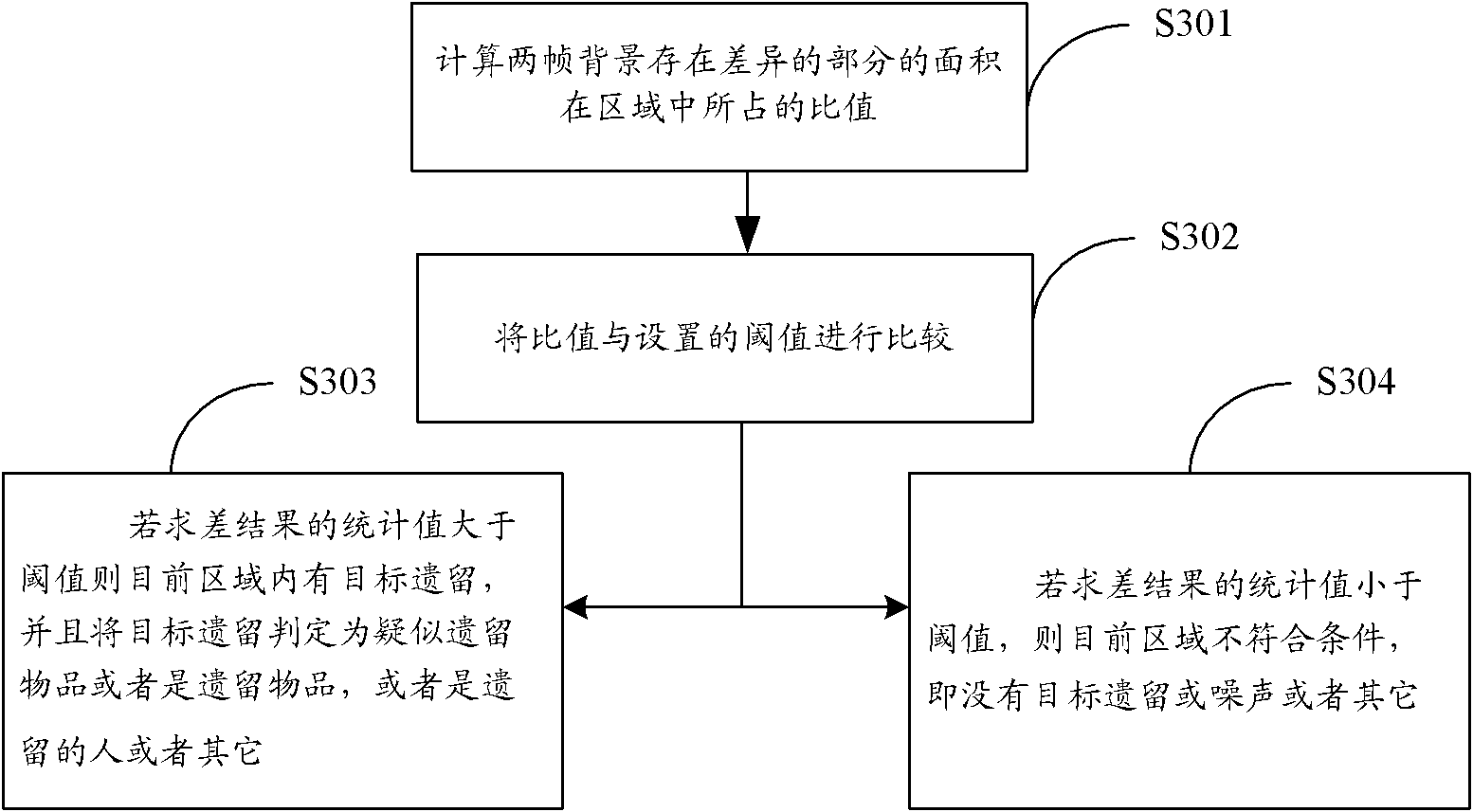
ActiveCN102063614AIncreased complexityAvoid Misjudgment SituationsImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionVideo monitoringSecurity monitoring
The invention provides a method and device for detecting lost articles in security monitoring, belonging to the field of video monitoring. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing a scene plane into a plurality of regions; carrying out two-frame background storage on a certain relevant region of the plurality of regions and performing subtraction within a certain interval; judging whether a target lost article exists in the relevant region according to the subtraction result, and judging whether a found article is the target lost article; if the target lost article exists, extracting the lost article and alarming; and if no lost article exists, continuously monitoring other regions. By adopting a moving detection and two-frame background subtraction method, the invention avoids algorithm complexity increase caused by incapability of accurately tracking or stricter requirement for a tracking strategy when a moving object moves too fast or background updating speed is overhigh and even the object is distorted in order to meet a hardware requirement is avoided, and erroneous judgment caused by temporarily shielding the object is also avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN YAAN TECH CO LTD
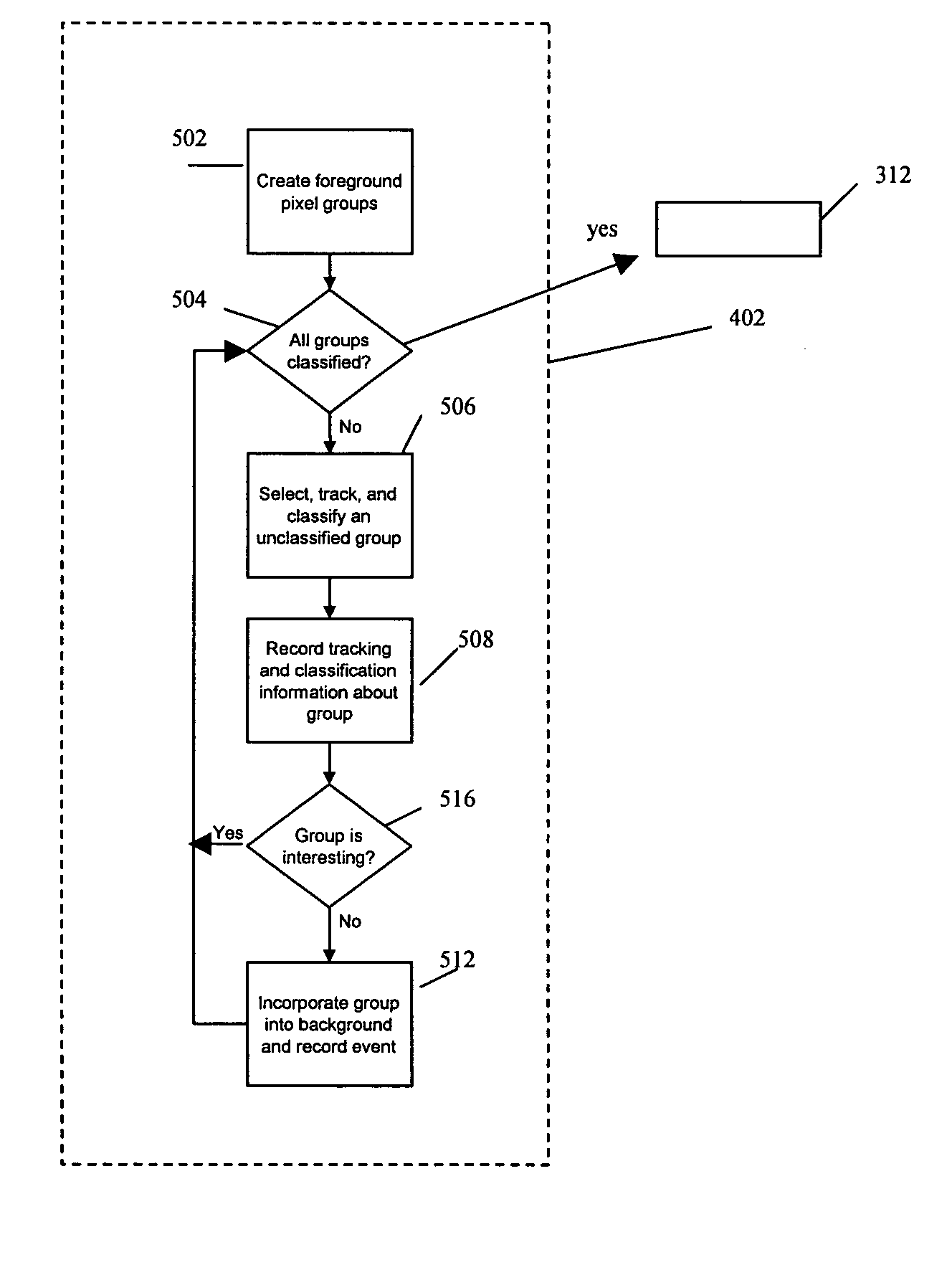
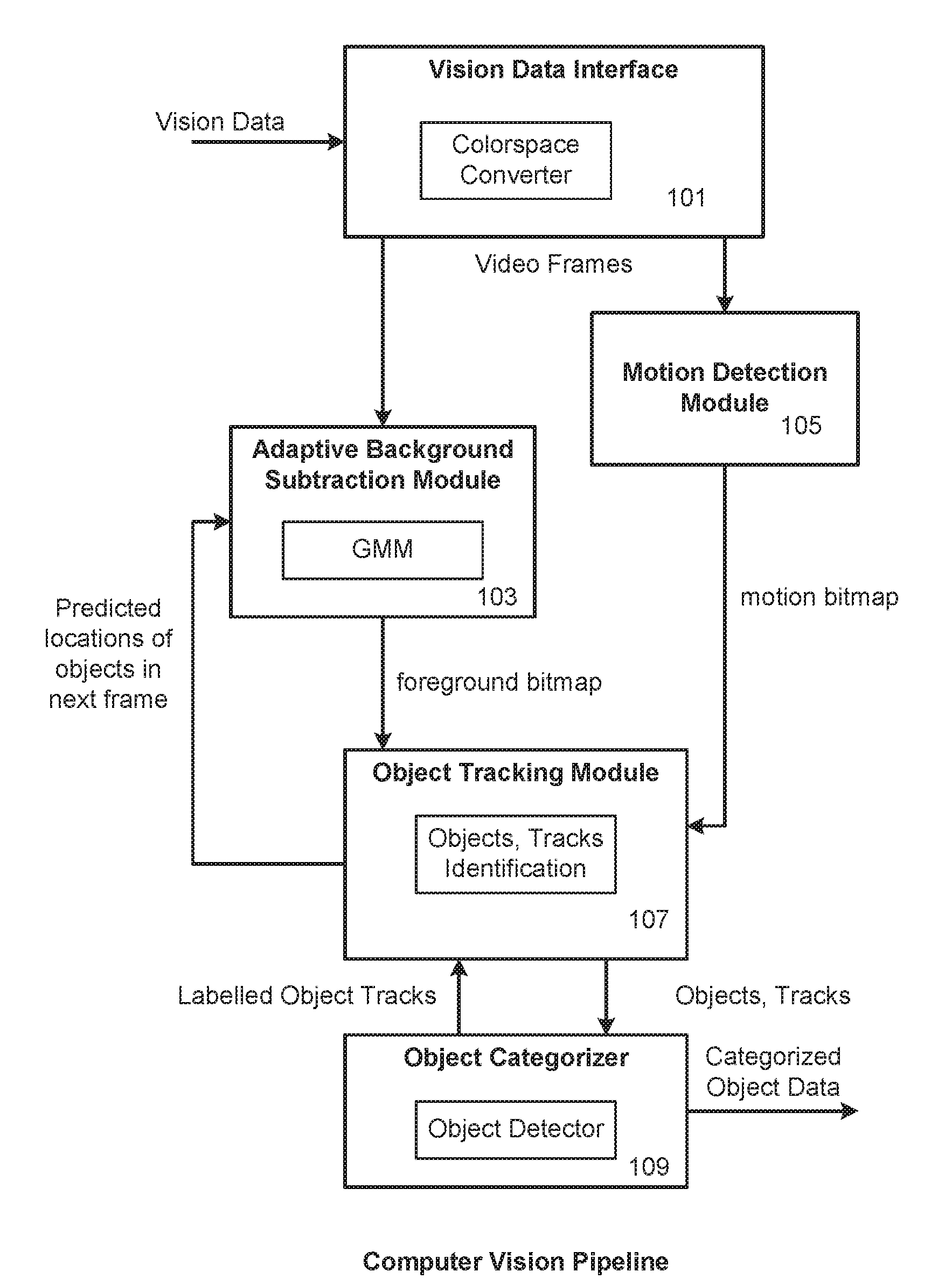
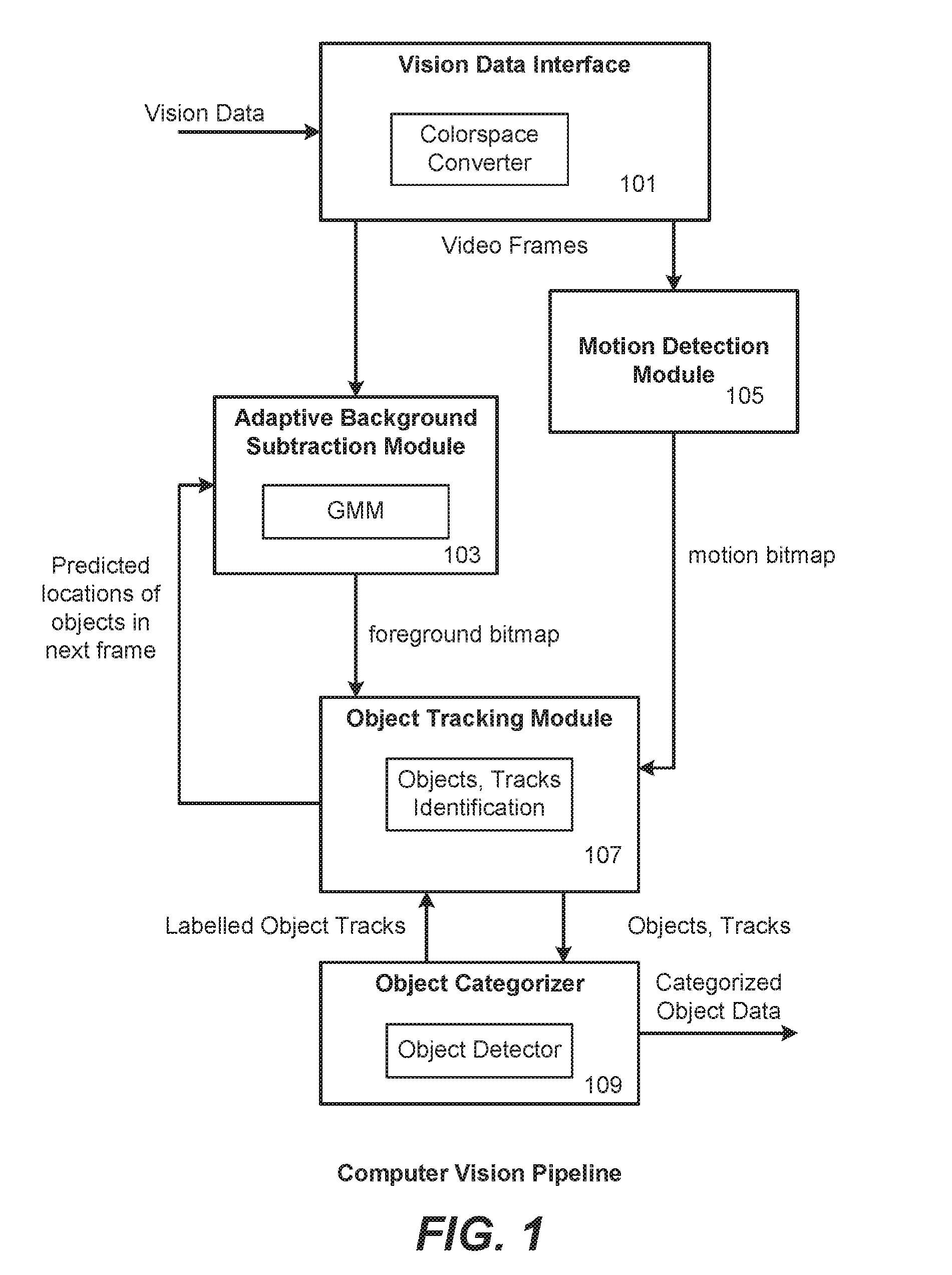
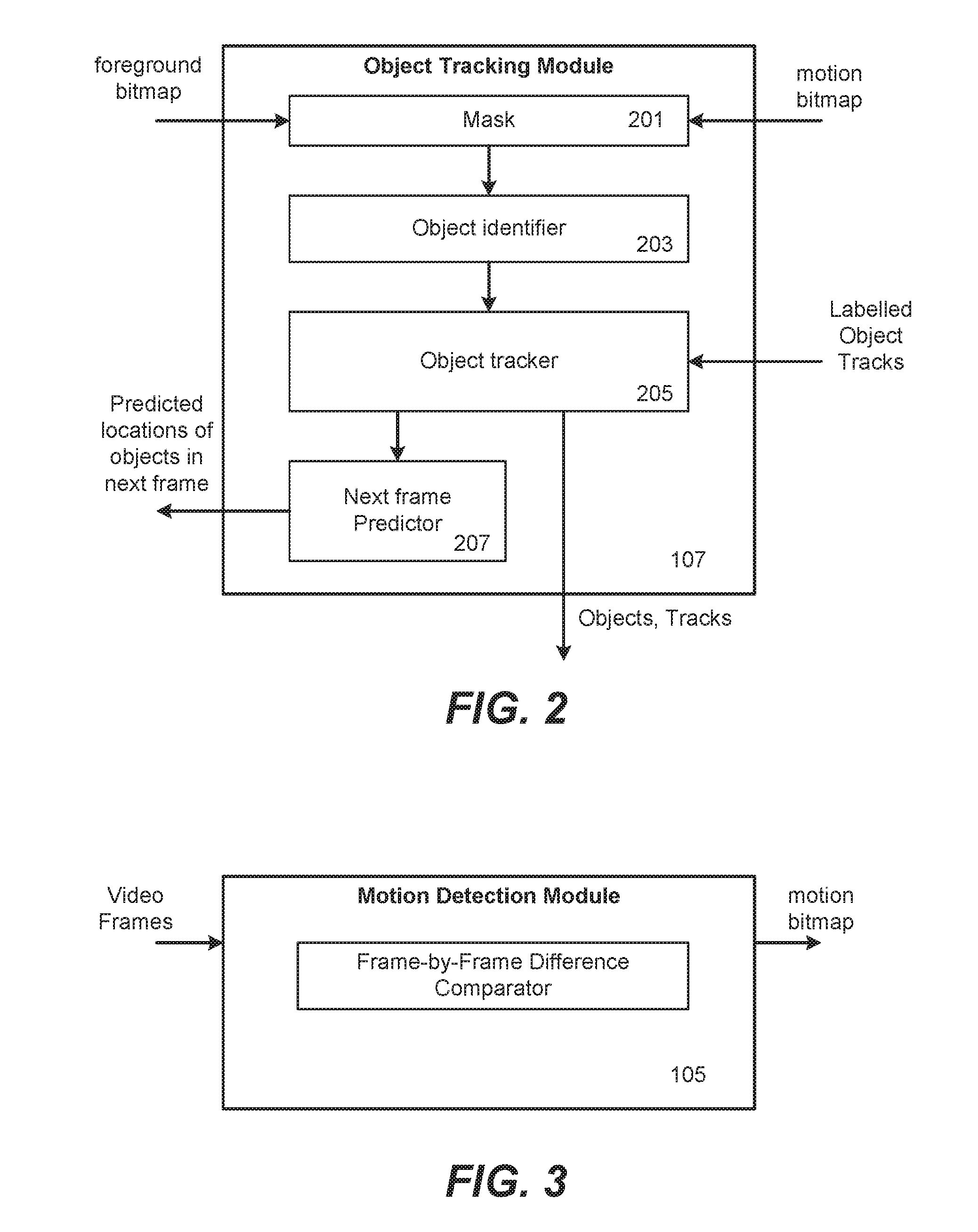
Computer Vision Pipeline and Methods for Detection of Specified Moving Objects
A computer vision pipeline detects tracks and classifies people or other specified class of objects in a steam of video. The ability to not only detect motion, but to distinguish people or other specified objects, can improve the systems usefulness in applications like security monitoring. A motion detection module provides a motion bitmap and a background subtraction module provides a foreground bitmap, and an object tracking module uses these bitmaps identify and track the specified classes of objects. From these objects and tracks, categorized object data can then be generated.
Owner:SIGHTHOUND
Surveillance systems and methods to monitor, recognize, track objects and unusual activities in real time within user defined boundaries in an area
InactiveUS20120188370A1Optimization definitionColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsNon real timeMonitoring system
A surveillance system and method that utilize computer vision technology and background subtraction to monitor, recognize, and track objects or unusual activities within user specified boundaries. The system and method comprises at least one camera and at least one computer with a software program showing one or multiple windows of camera's field of views in real time. The program allows users to define one or multiple boundaries within any window. The program further utilizes background subtraction technique to establish normal “home-position” of objects within defined boundaries. The program compares current image of the objects against the normal “home-position” to determine / calculate the difference of pixel intensity values. If the difference is beyond the predetermine threshold, the program will flag the movement of the object and give off alert.
Owner:BORDONARO JAMES
Method and apparatus for performing a clean background subtraction
InactiveUS7162082B2Reduce noiseEasy to determineImage enhancementImage analysisEdge extractionBackground image
A background subtraction apparatus of the present invention includes a key point locator for locating key points on a known object type, a boundary point locator for locating boundary points of the known object that make up the edges of the known object, and an edge processor for processing the edges to provide a clean-edged extraction of the known object from a background image. Preferably, the key point locator includes an alignment detector for detecting alignment of an image of the known object type with a skeleton image. Still more preferably, the skeleton image is an exoskeleton image and the known object type is a human being.
Owner:ELET SYST
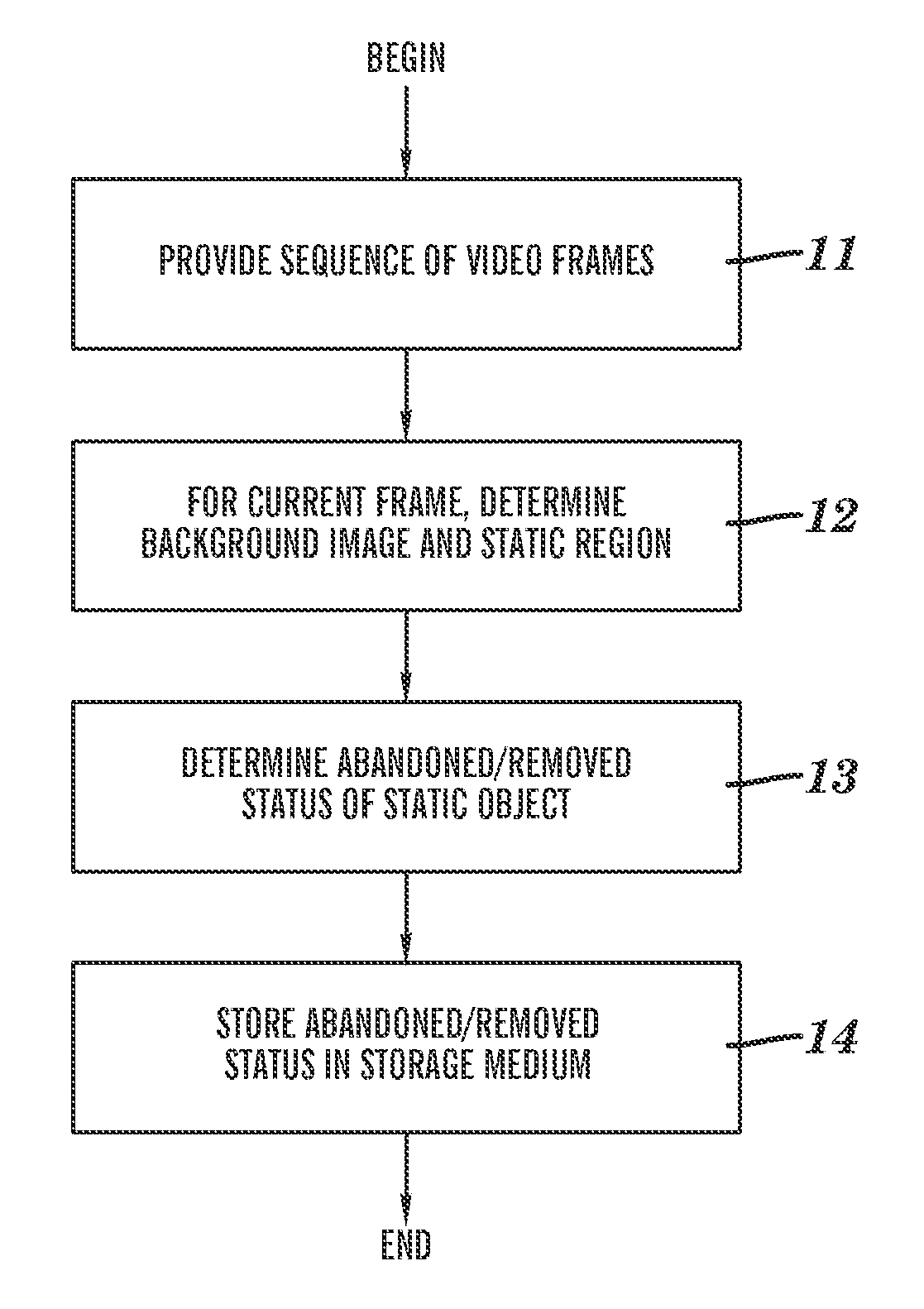
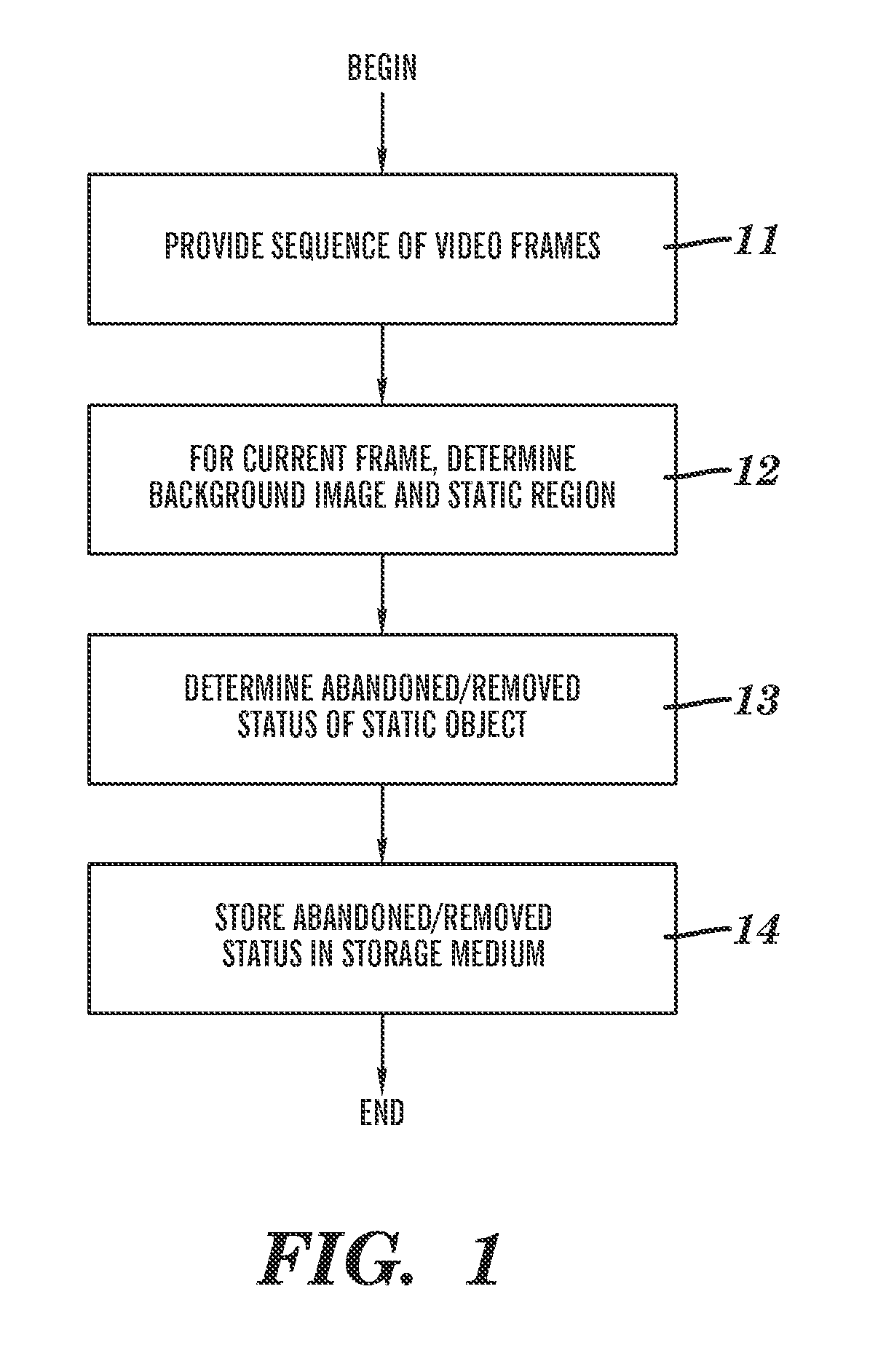
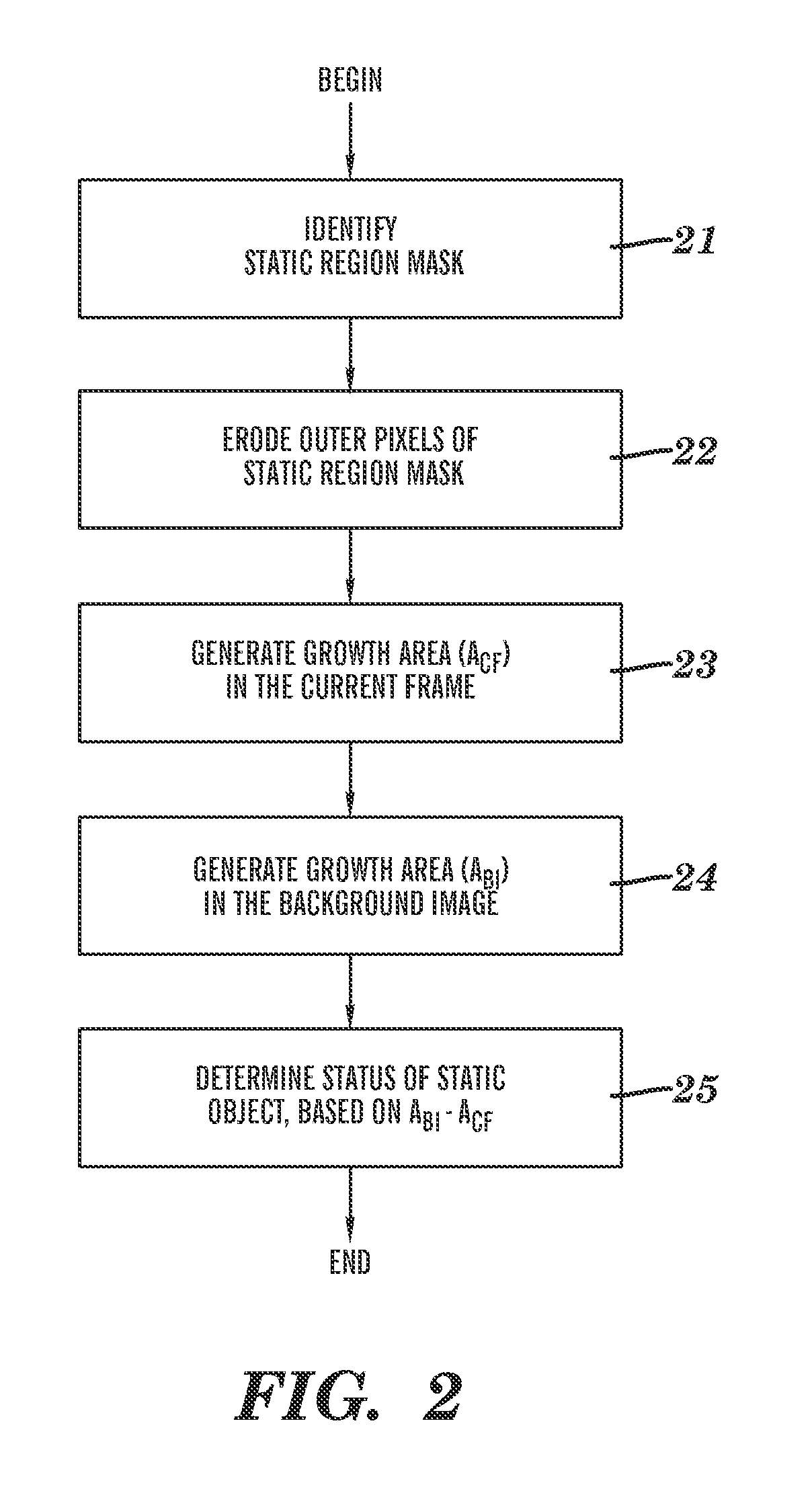
Detection of abandoned and removed objects in a video stream
A method for processing a time-ordered sequence of video frames. The method is implemented by execution of program code on a processor of a computer system. Each frame includes a two-dimensional array of pixels and a frame-dependent color intensity at each pixel. A current frame and at least one frame occurring prior to the current frame in the sequence are analyzed via a background subtraction on the at least one frame to determine a background image and a static region mask associated with a static region. The background subtraction determines an existence of a static object relating to the static region. A status of the static object is determined, the status being either that the static object is an abandoned object or that the static object is a removed object. The determined status is stored in a data storage medium of the computer system.
Owner:TERRACE LICENSING LLC
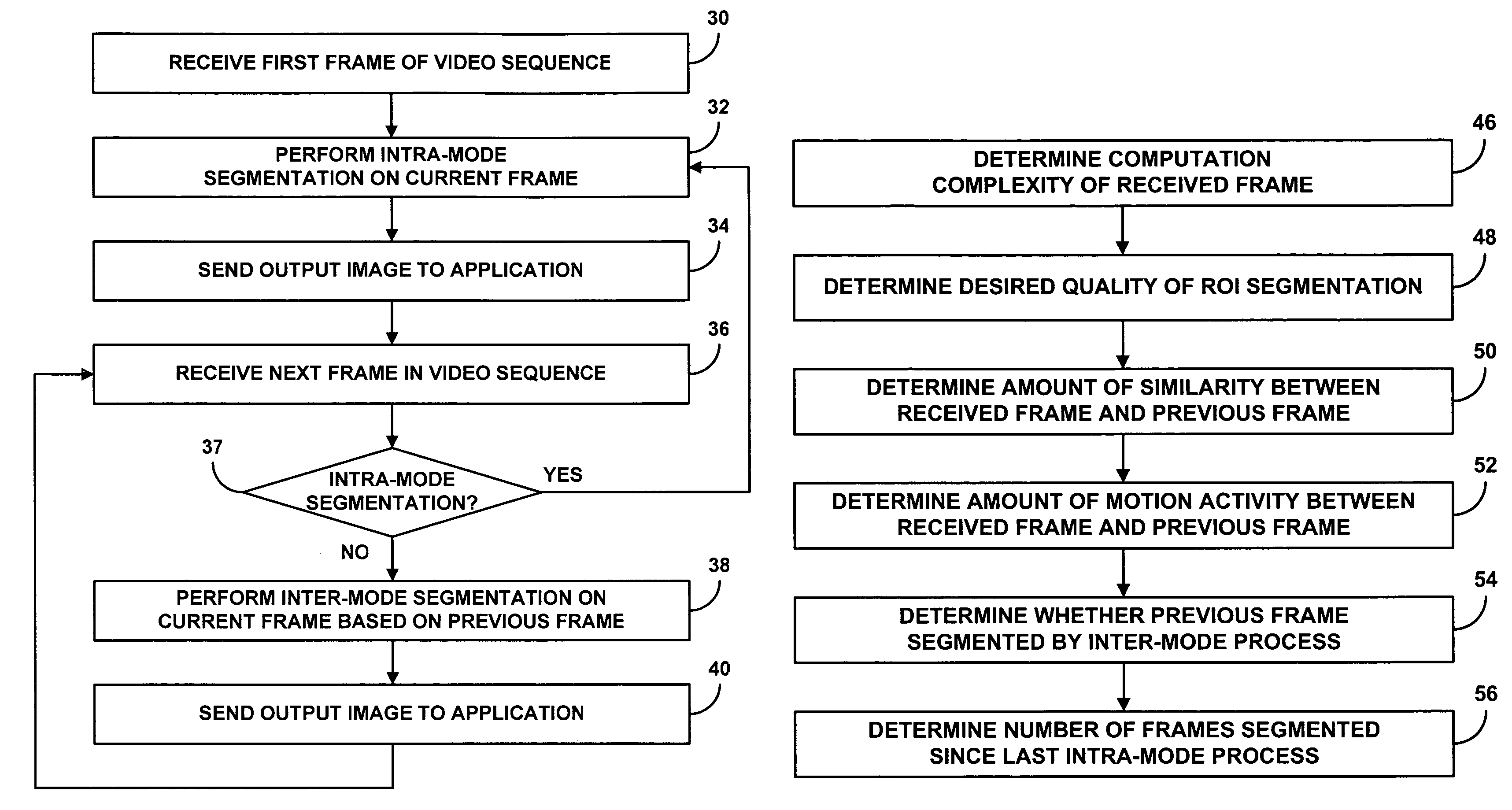
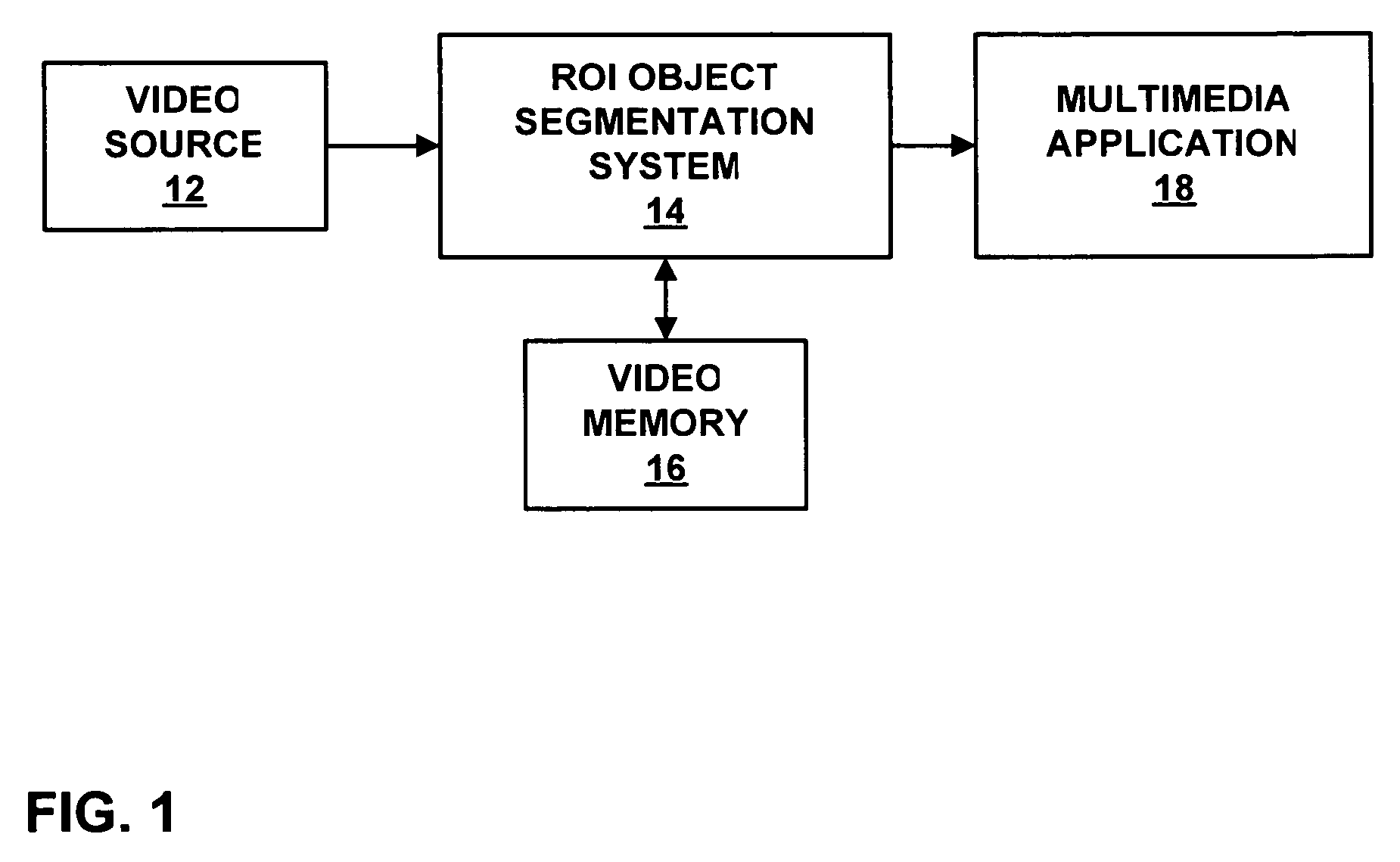
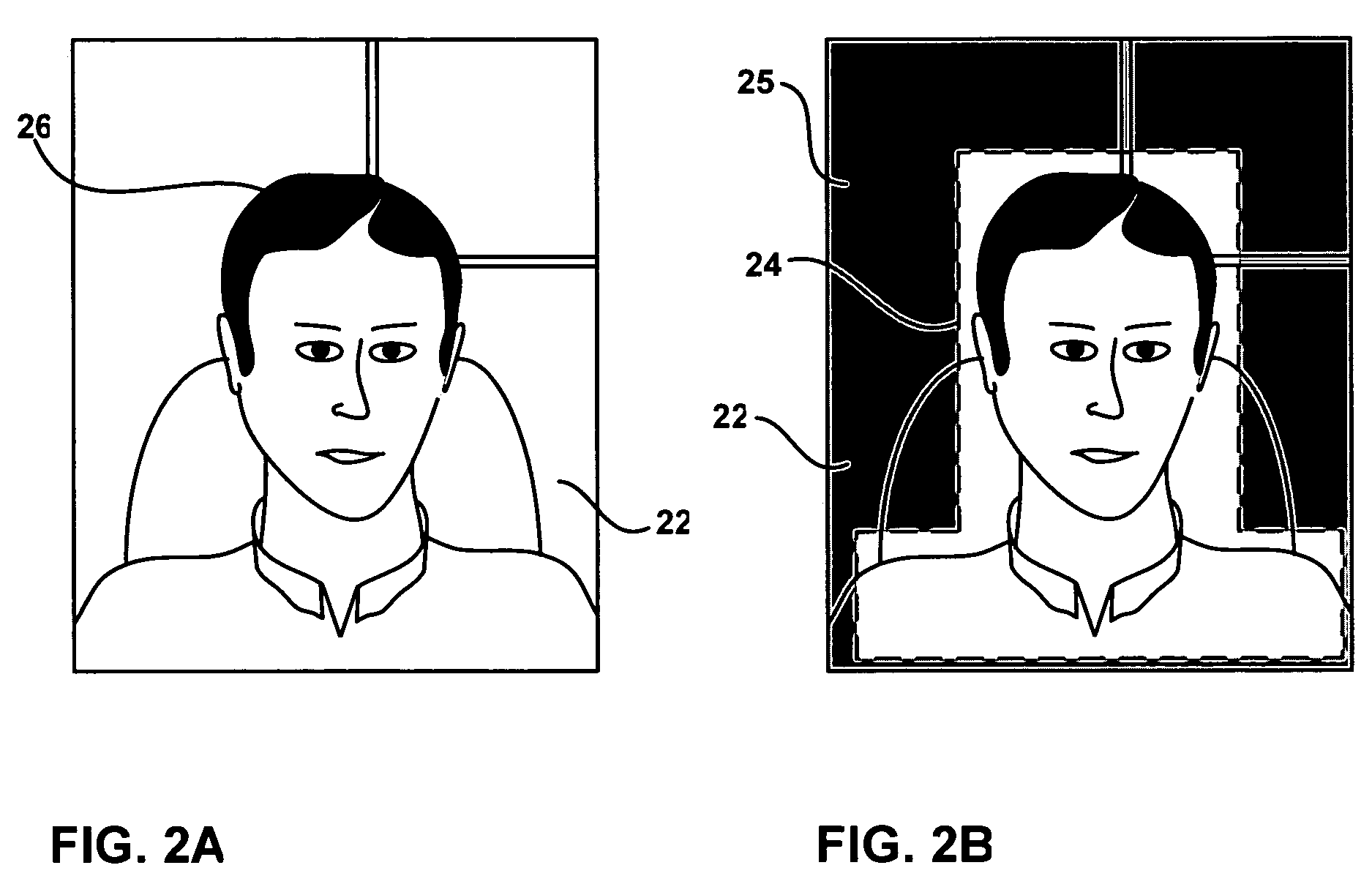
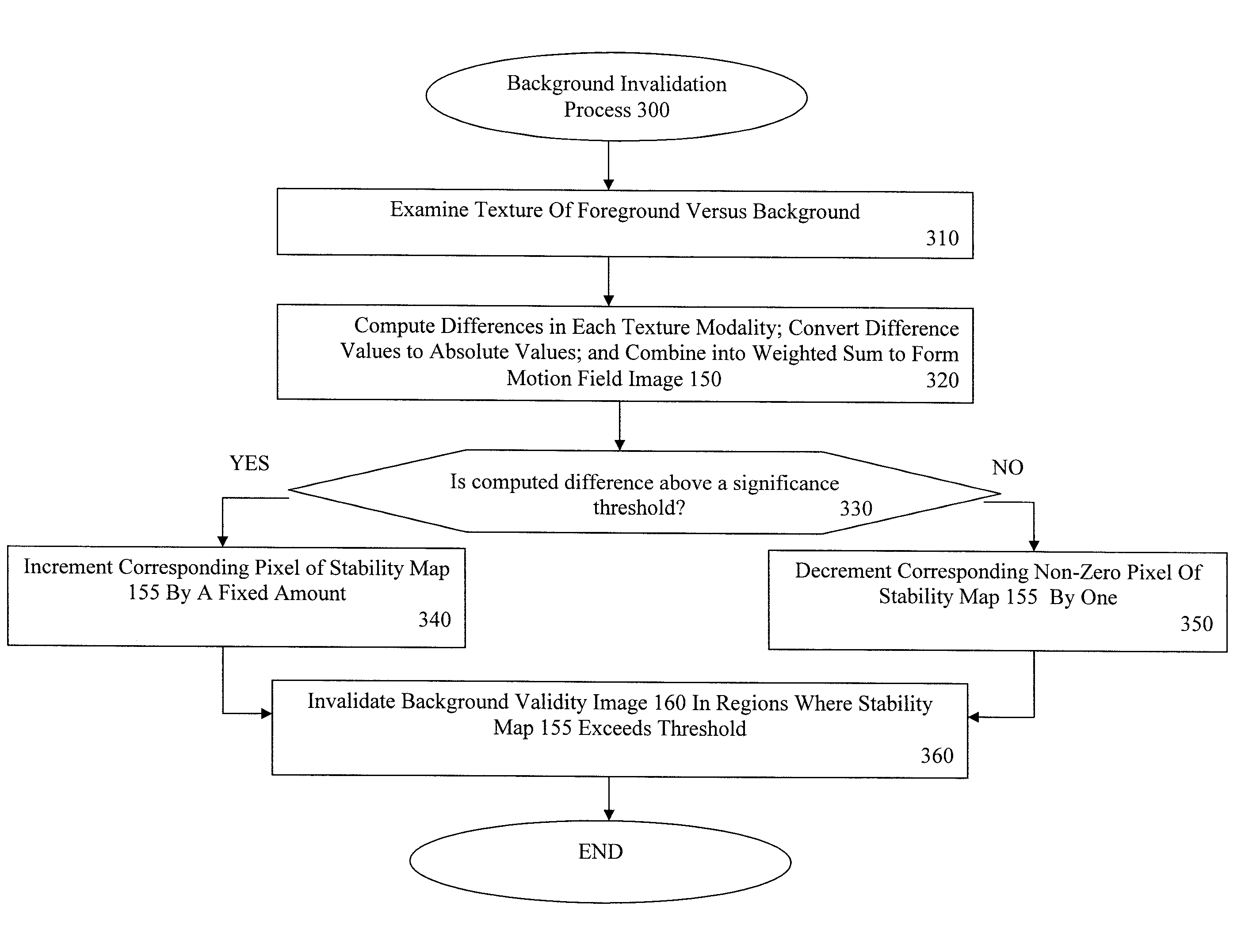
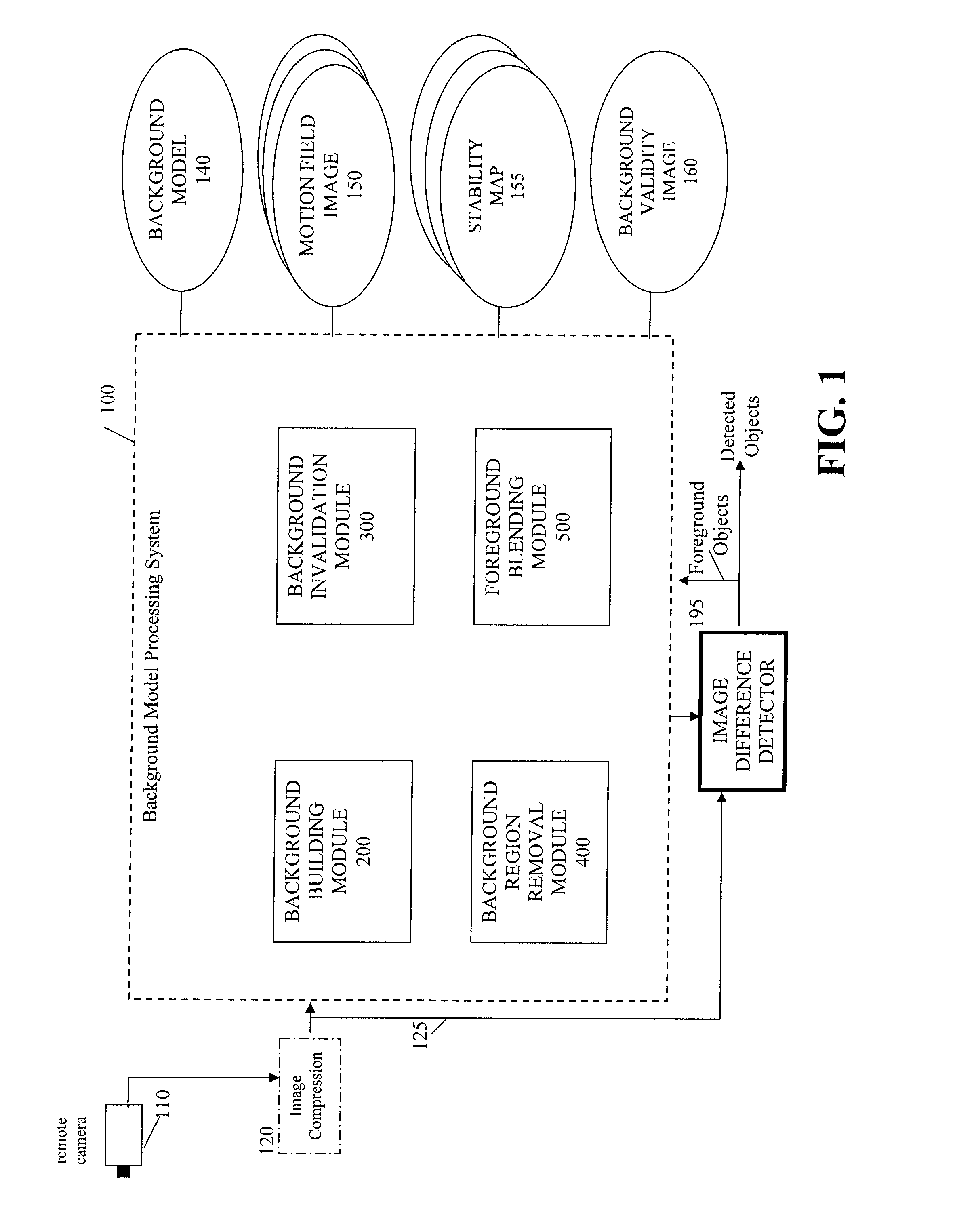
Multi-mode region-of-interest video object segmentation
ActiveUS8150155B2Generate accuratelyAccurate feature detectionImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationVideo sequence
The disclosure is directed to techniques for automatic segmentation of a region-of-interest (ROI) video object from a video sequence. ROI object segmentation enables selected ROI or “foreground” objects of a video sequence that may be of interest to a viewer to be extracted from non-ROI or “background” areas of the video sequence. Examples of a ROI object are a human face or a head and shoulder area of a human body. The disclosed techniques include a hybrid technique that combines ROI feature detection, region segmentation, and background subtraction. In this way, the disclosed techniques may provide accurate foreground object generation and low-complexity extraction of the foreground object from the video sequence. A ROI object segmentation system may implement the techniques described herein. In addition, ROI object segmentation may be useful in a wide range of multimedia applications that utilize video sequences, such as video telephony applications and video surveillance applications.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and Apparatus for Maintaining a Background Image Model in a Background Subtraction System Using Accumulated Motion
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
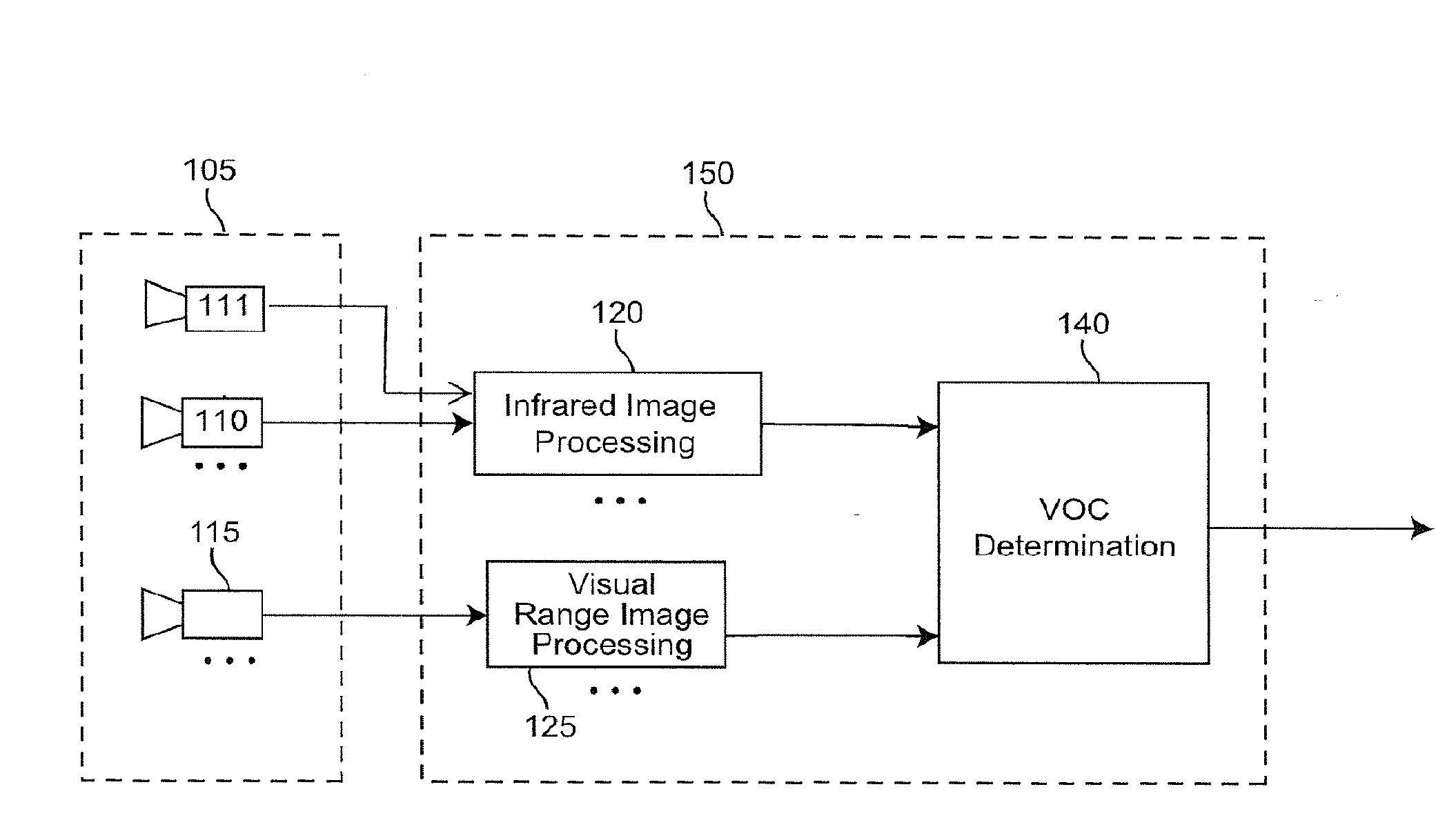
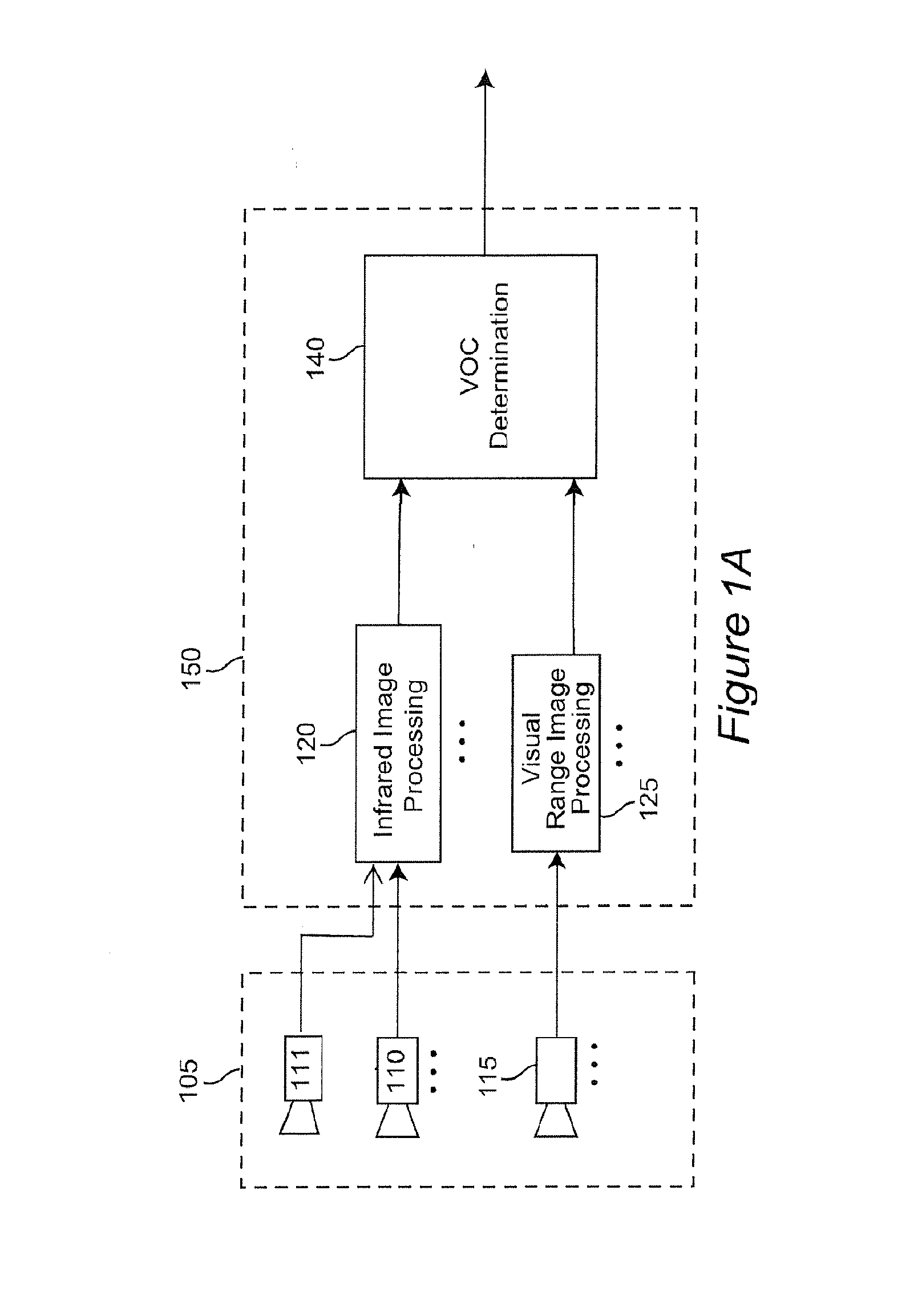
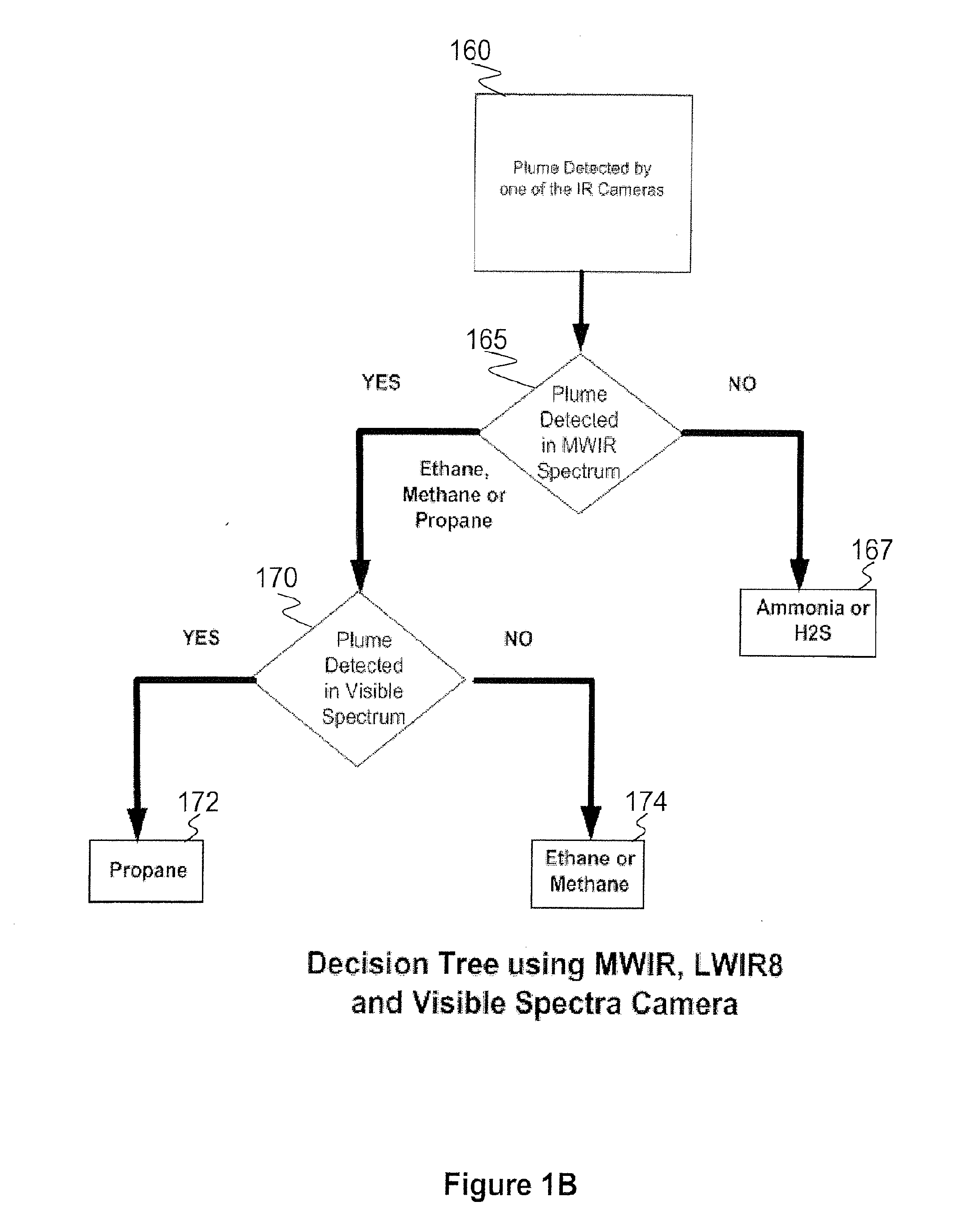
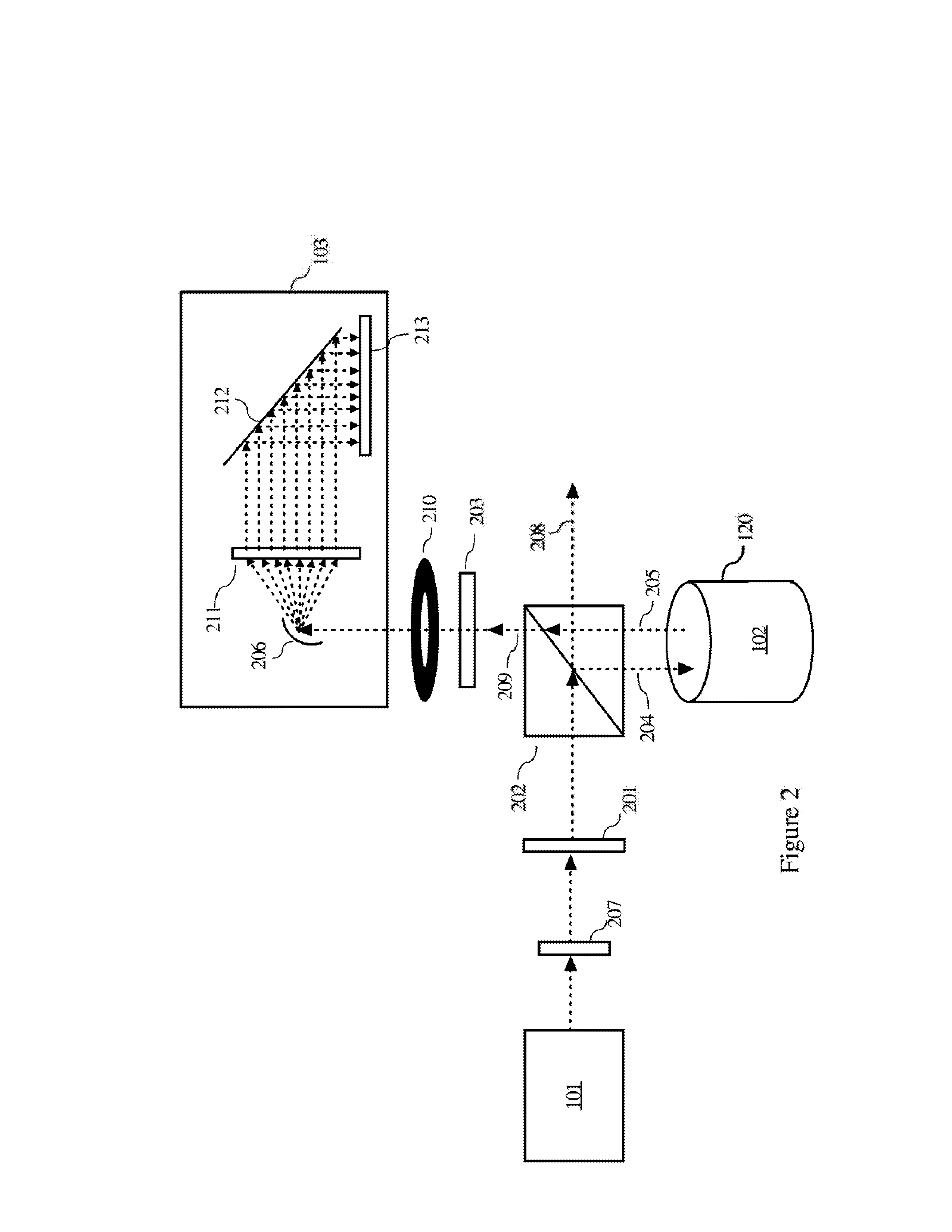
Method, device and system for determining the presence of volatile organic compounds (VOC) in video
InactiveUS20130286213A1Television system detailsImage enhancementOrganic compoundAnalytical technique
A video based method to detect volatile organic compounds (VOC) leaking out of components used in chemical processes in petrochemical refineries. Leaking VOC plume from a damaged component has distinctive properties that can be detected in realtime by an analysis of images from a combination of infrared and optical cameras. Particular VOC vapors have unique absorption bands, which allow these vapors to be detected and distinguished. A method of comparative analysis of images from a suitable combination of cameras, each covering a range in the IR or visible spectrum, is described. VOC vapors also cause the edges present in image frames to loose their sharpness, leading to a decrease in the high frequency content of the image. Analysis of image sequence frequency data from visible and infrared cameras enable detection of VOC plumes. Analysis techniques using adaptive background subtraction, sub-band analysis, threshold adaptation, and Markov modeling are described.
Owner:DELACOM DETECTION SYST
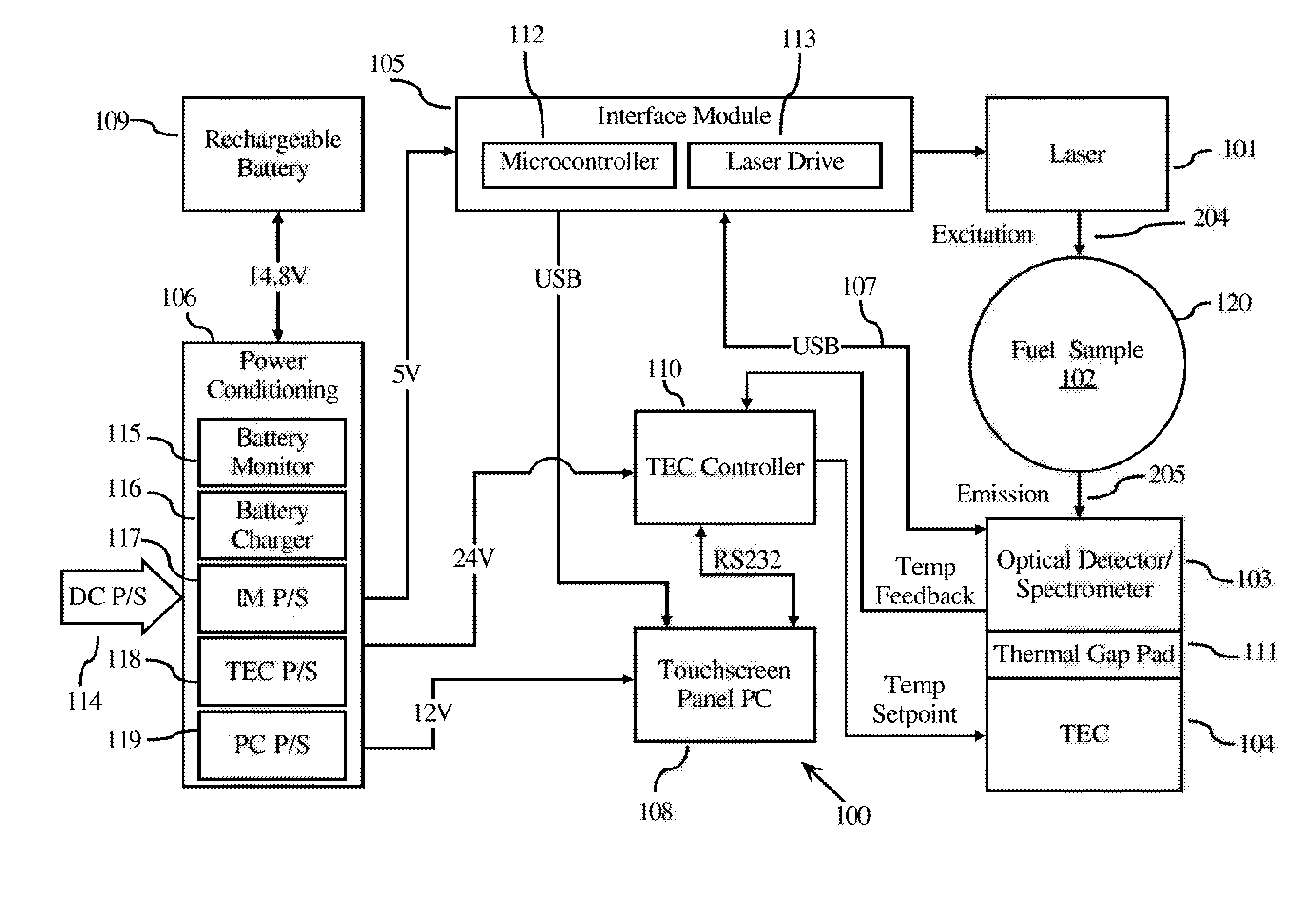
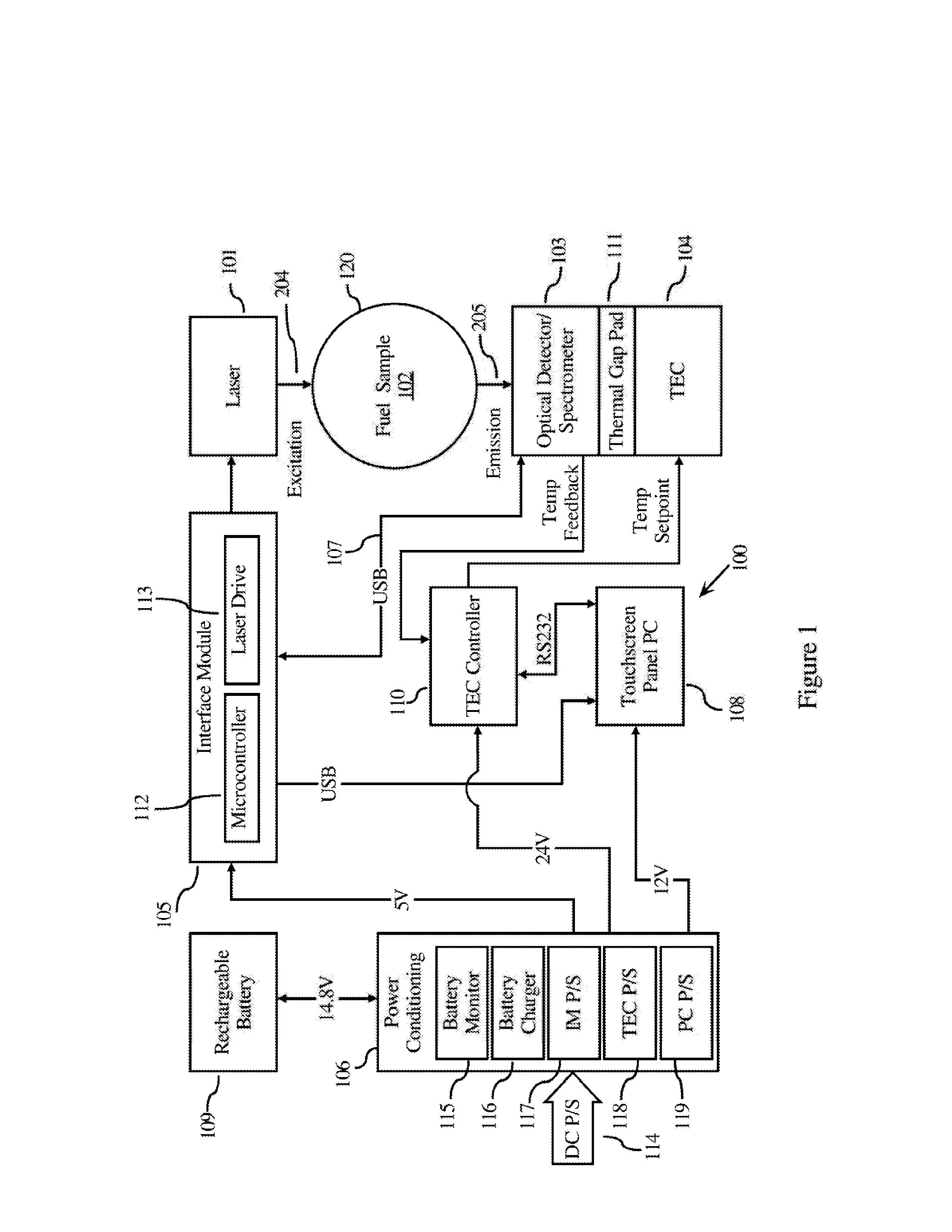
Determining the Quantity of a Taggant in a Liquid Sample
Device and methods for detecting / quantifying a fluorescent taggant in a liquid sample. Generally, the liquid samples are fuels having low concentrations (measured in ppb) of a fluorescent taggant. The detection / quantification generates a predicted concentration of the fluorescent tagging compound using a process selected from the group of a multivariate process, a background subtraction process, or a combination of both. The invention addresses the detection of an adulteration of gasoline and diesel fuels.
Owner:AUTHENTIX INC
Target detection algorithm in combination of statistical matrix model and adaptive threshold
The invention discloses a target detection algorithm in combination of a statistical matrix model and an adaptive threshold. The target detection algorithm comprises the steps of initializing a background image through the front frames of a video; initially extracting foreground by the background subtraction method; continuously accumulating the occurrence times of pixel points with small pixel value variation amplitude in the foreground area by the frame difference method; storing the times of accumulation variation of the corresponding pixel points through a statistical matrix; updating the current foreground as the background point when the times exceed a certain value so as to obtain the accurate background image for the subsequent background subtraction method; then performing binarization segmentation through the adaptive threshold to obtain a target area; the binarization threshold of each pixel point is determined according to the difference value between all the current pixel values and the background pixel value in the point window. With the adoption of the algorithm, the background can be quickly updated, and the target can be accurately detected.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
NaI (TI) scintillation detector gamma energy spectrum high-resolution inversion analysis process and method based on gauss response matrix
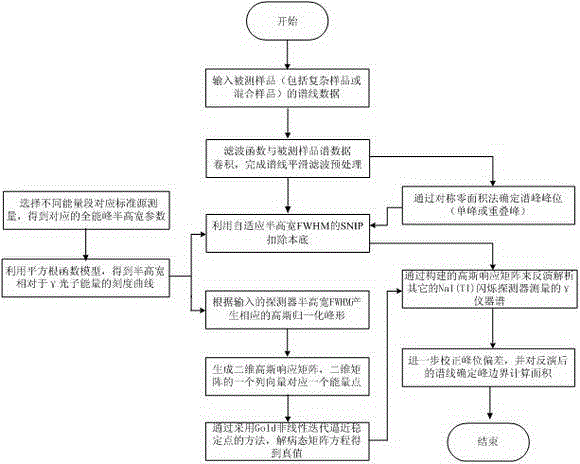
ActiveCN103913764AImprove analytical abilityX-ray spectral distribution measurementGamma energyFull width at half maximum
The invention relates to an NaI (TI) scintillation detector gamma energy spectrum high-resolution inversion analysis process and method based on a gauss response matrix. The analysis process comprises the steps of spectral line pretreatment, peak searching and peak boundary treatment, resolution ratio ruling, background subtraction, gauss response matrix generation and inversion analysis. According to the feature of an NaI (TI) scintillation detector and the physical property of the spectrum forming process, response, in the detector, of different energy gamma photons corresponds to different full widths at half maximum of a photo peak, and the photo peak is approximate to a gauss function in shape. The parameters of the full widths at half maximum of a spectral line are extracted, the background is subtracted from the full widths at half maximum adaptively, the universal gauss response matrix between a radioactive source and a gamma spectrum is constructed, and finally the response matrix is used for inversion analysis of other gamma instrument spectrums measured by the NaI (TI) scintillation detector. The result analyzed through the method is an energy point corresponding to the measured spectral line under the response matrix or is approximate to the solution of a physical spectral line in theory, and the ability of the method to analyze the spectral line is obviously improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Fast object recognition algorithm
InactiveCN102222214AImprove robustnessEasy to divideImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainRecognition algorithm
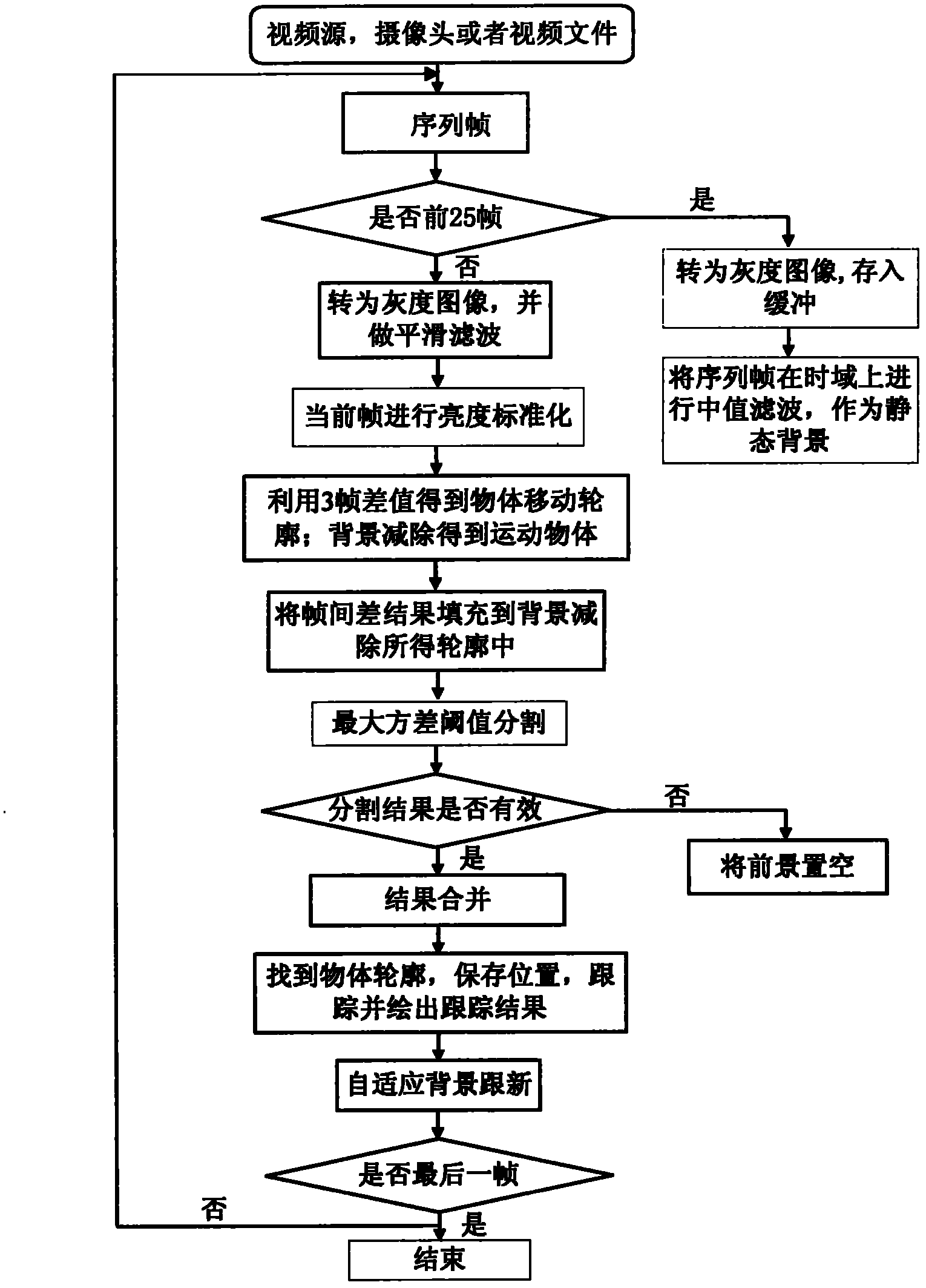
The invention relates to a fast object recognition algorithm comprising the following steps of: firstly, carrying out median filtering on approximately one second sequence frame in time domain so as to be taken as a static background; secondly, determining a moving object by utilizing the fusion algorithm of background subtraction and interframe difference; thirdly, carrying out binaryzation on the obtained result by utilizing maximum variance threshold segmentation, and simultaneously analyzing the effectiveness of the segmentation; and finally, merging the results of the effective segmentation, and tracking by utilizing Kalman filtering. The intelligent video object-tracking method has good tracking effect and high robustness, dispenses with manual intervention and effectively avoids the phenomena of tracking and alarming by mistake.
Owner:SUZHOU YISIKANG INFORMATION TECH
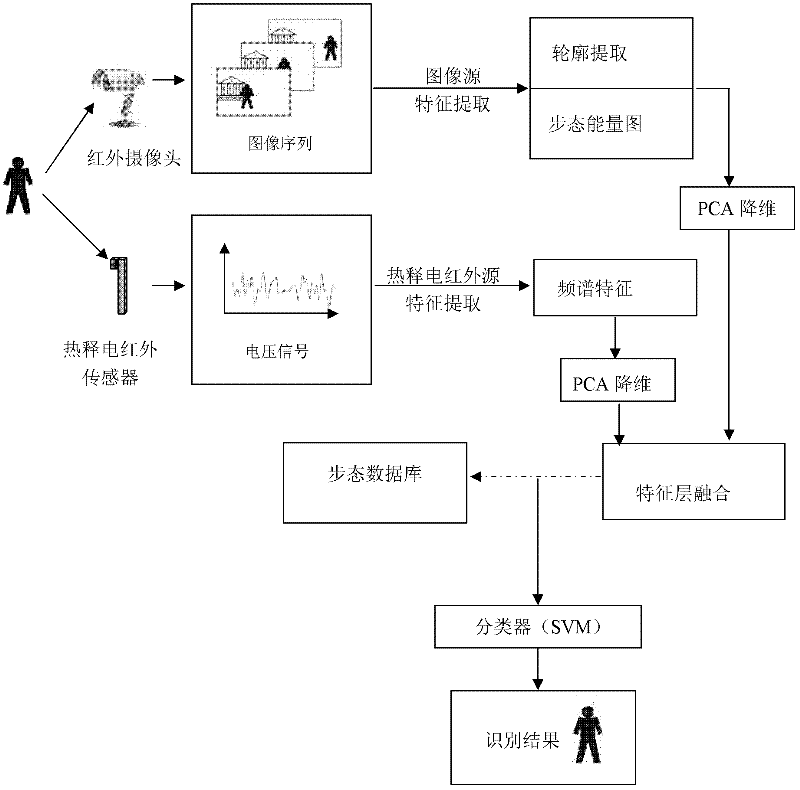
Infrared gait dual-channel feature fusion recognition method
InactiveCN102289672AEasy to implement in real timeMethod is easyCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency spectrumData acquisition
An infrared gait dual-channel feature fusion recognition method, the steps are: infrared image preprocessing, firstly using the background subtraction method of the mixed Gaussian model to realize the detection of moving human body; then performing morphological processing, that is, using morphological filtering to eliminate binary values Noise in the image and fill in the lack of moving targets; infrared image feature extraction, first of all, it is necessary to divide the cycle of the gait sequence, and determine the gait cycle based on the periodicity of the contour width; determine the gait energy map; infrared pyroelectric features Extraction, first of all, data collection, then denoising processing on the collected voltage signal, and then performing Fourier transform on the time domain signal to obtain its spectrum, and then use PCA to reduce the dimension to obtain the feature vector; classification and identification. In the present invention, the one-dimensional voltage signal collected by infrared pyroelectricity during human movement is easy to realize in real time, and the infrared image is not sensitive to the shape change of the carrying objects such as bags, umbrellas, backpacks, etc. when people walk, and it can also be used at night working.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
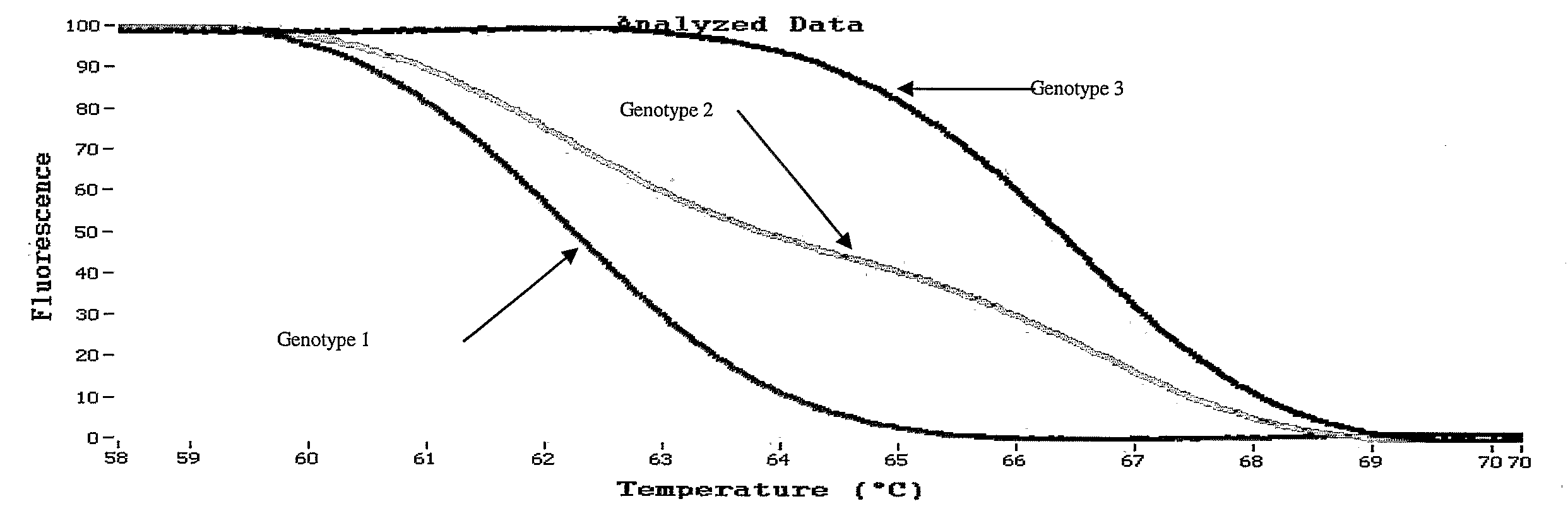
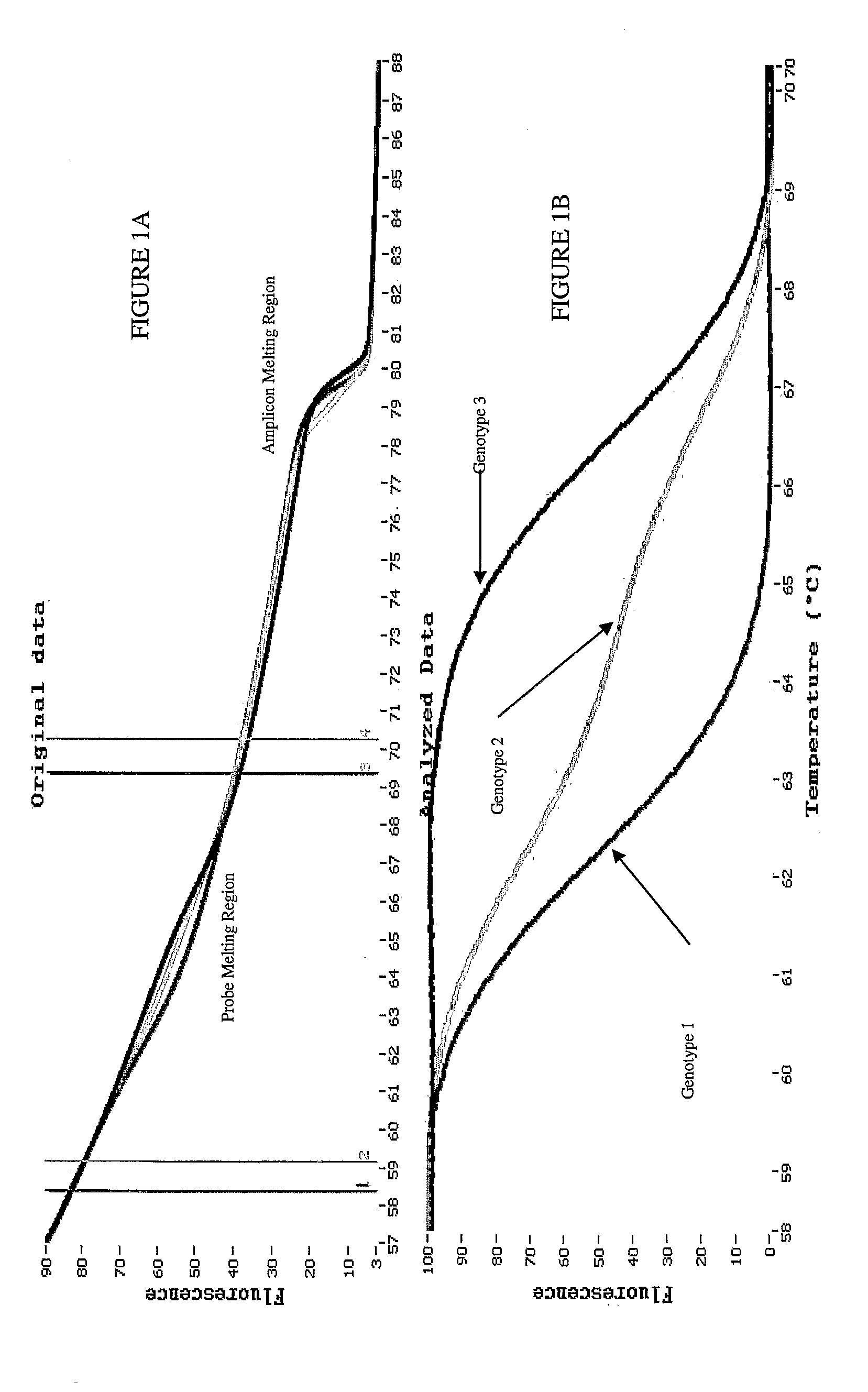
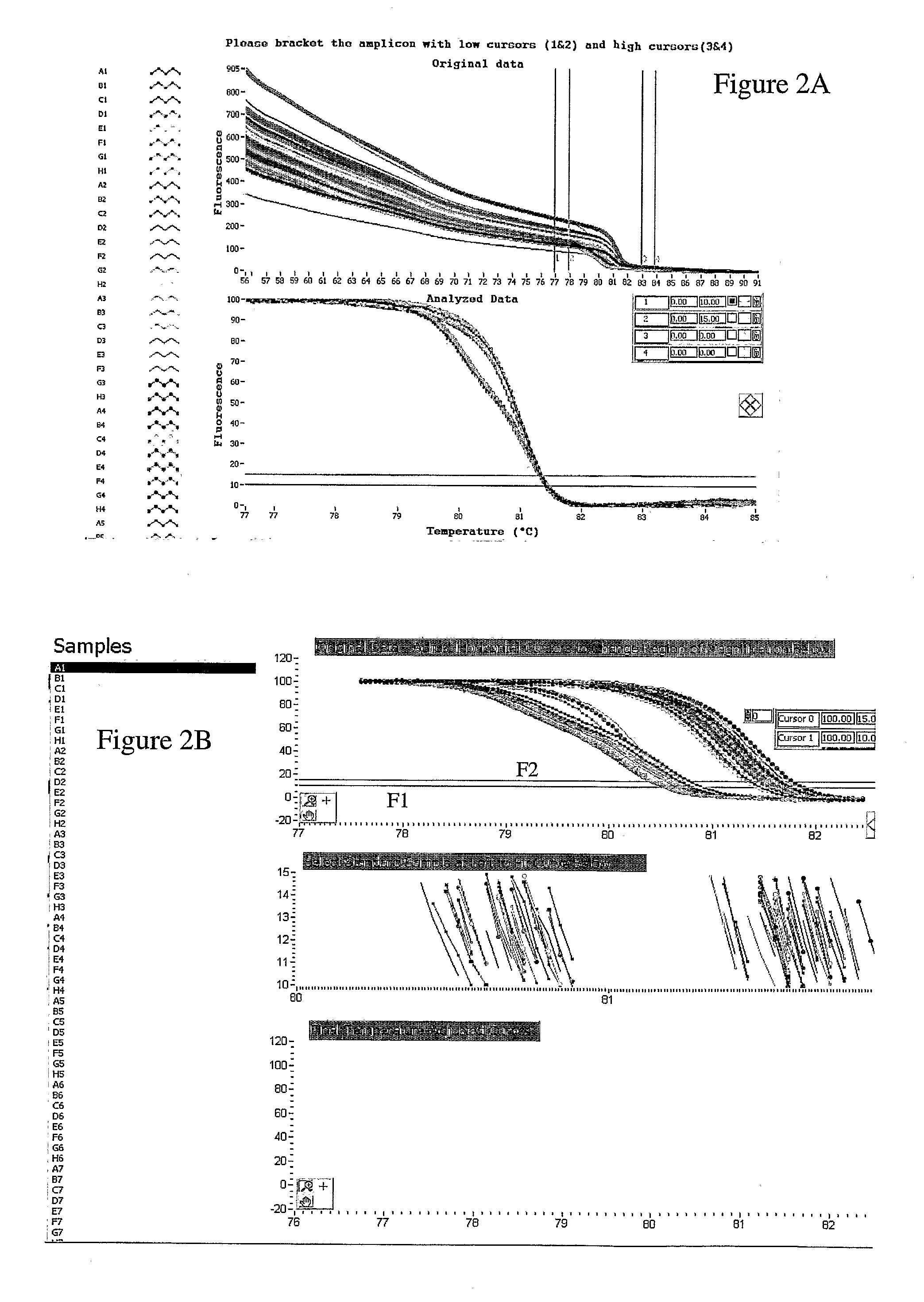
Melting Curve Analysis with Exponential Background Subtraction
A system and methods are provided for melting curve genotyping analysis of nucleic acids. Melting curves are generated by plotting fluorescence of a sample as a function of temperature. In one illustrative example, an exponential algorithm is employed to remove the background from generated melting curves and thereby perform comparative analysis to other melting curves. Additional illustrative examples provide for measuring the differences between two or more melting curves and clustering the genotypes of the provided sample nucleic acids.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com