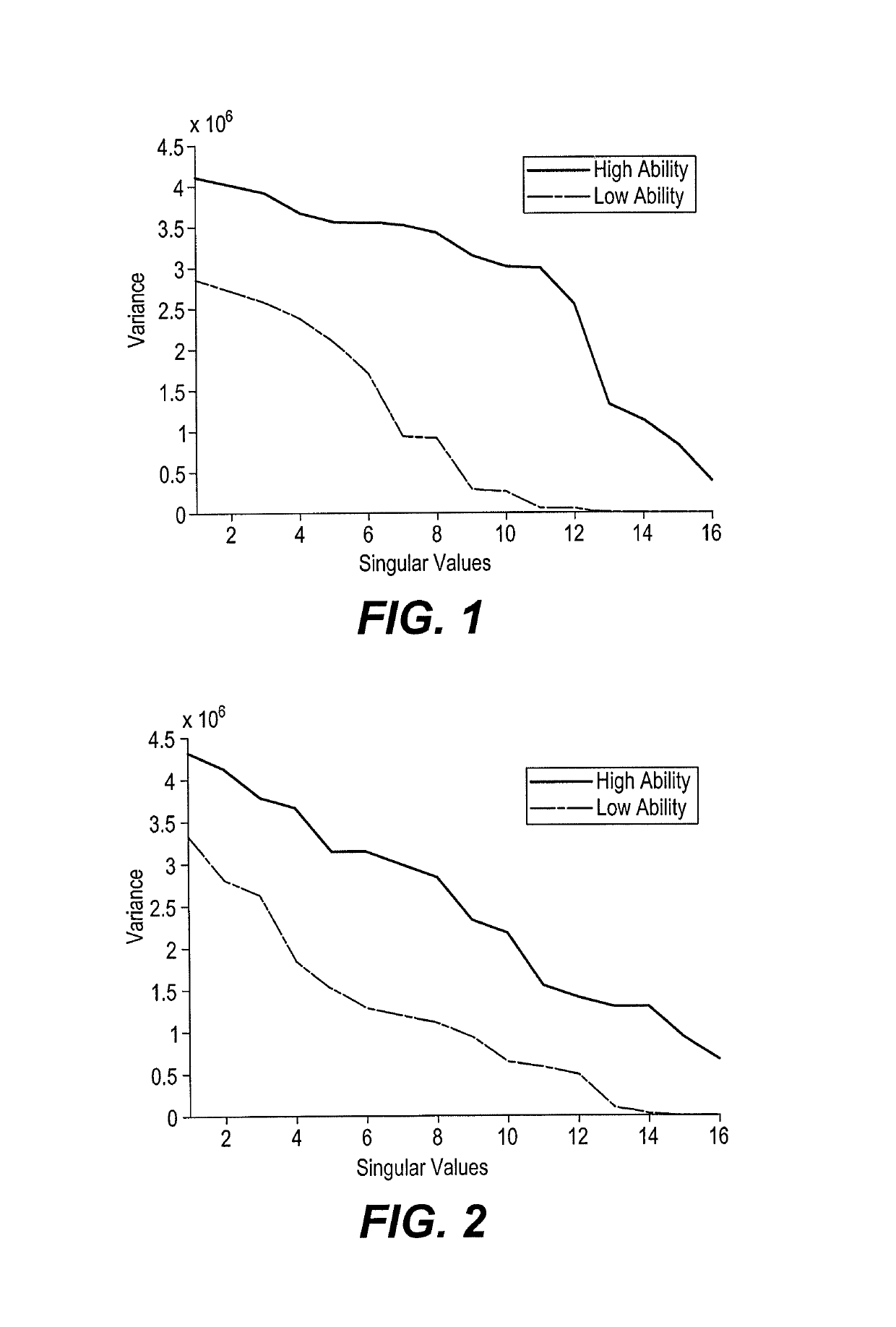
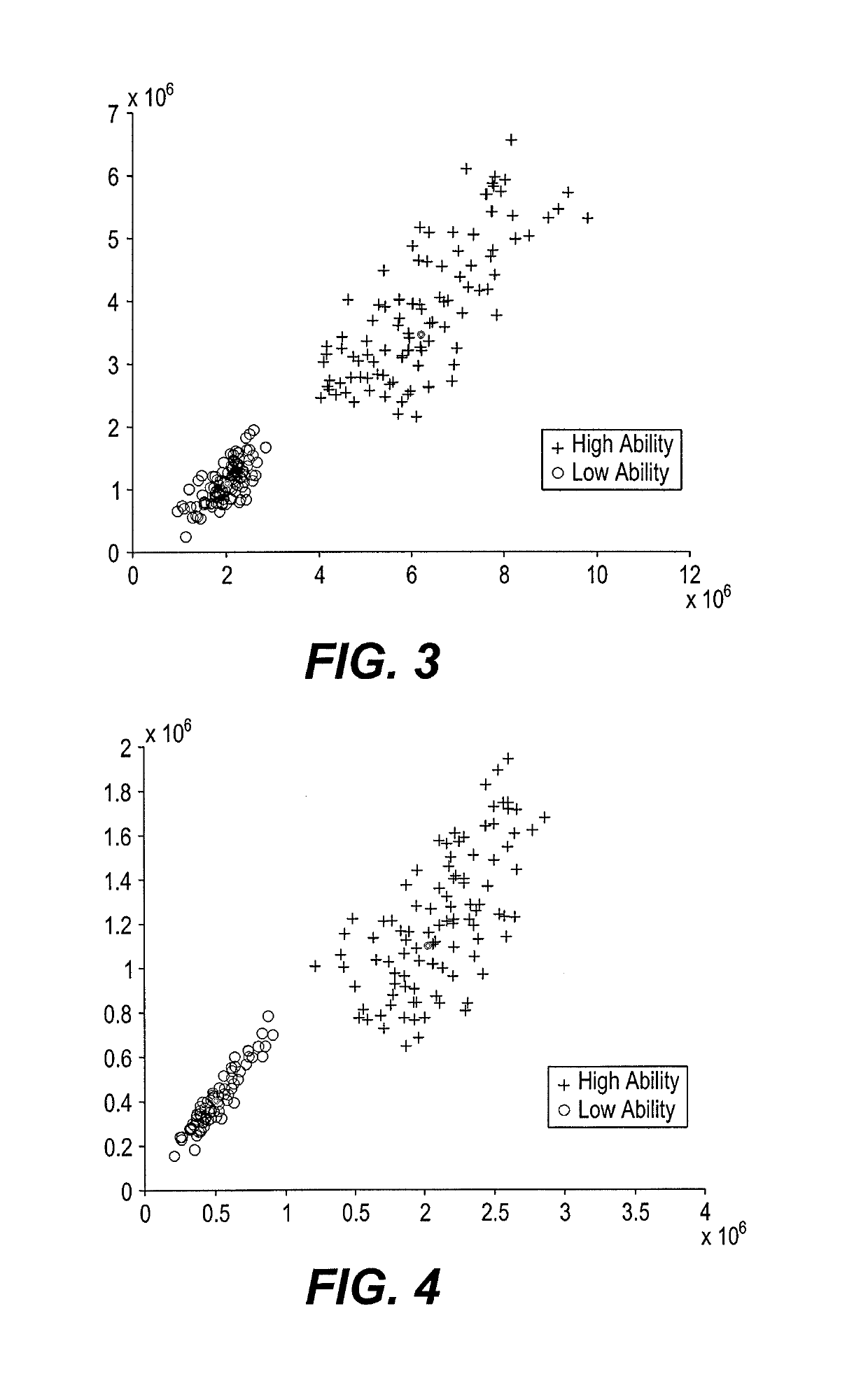
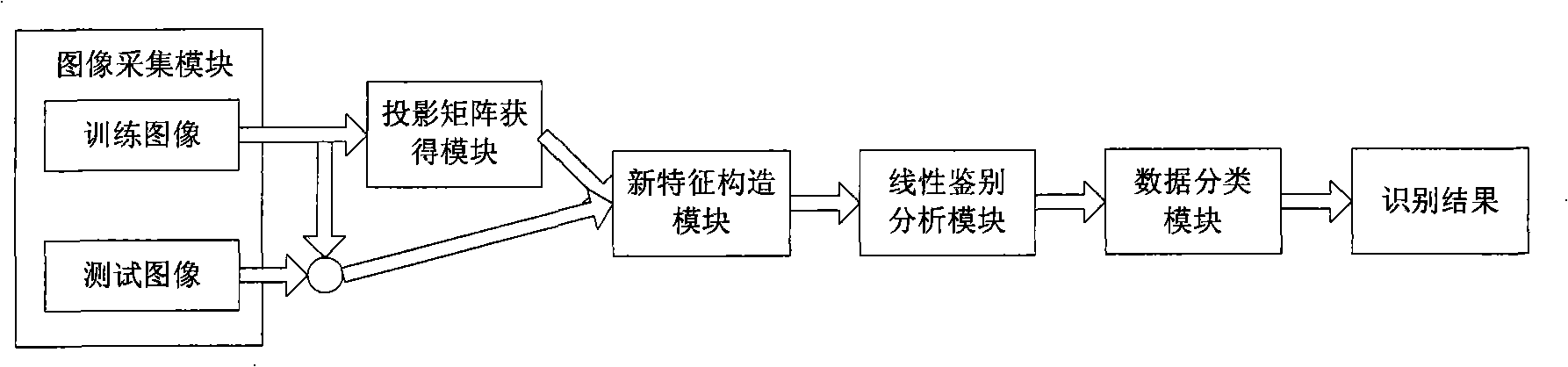
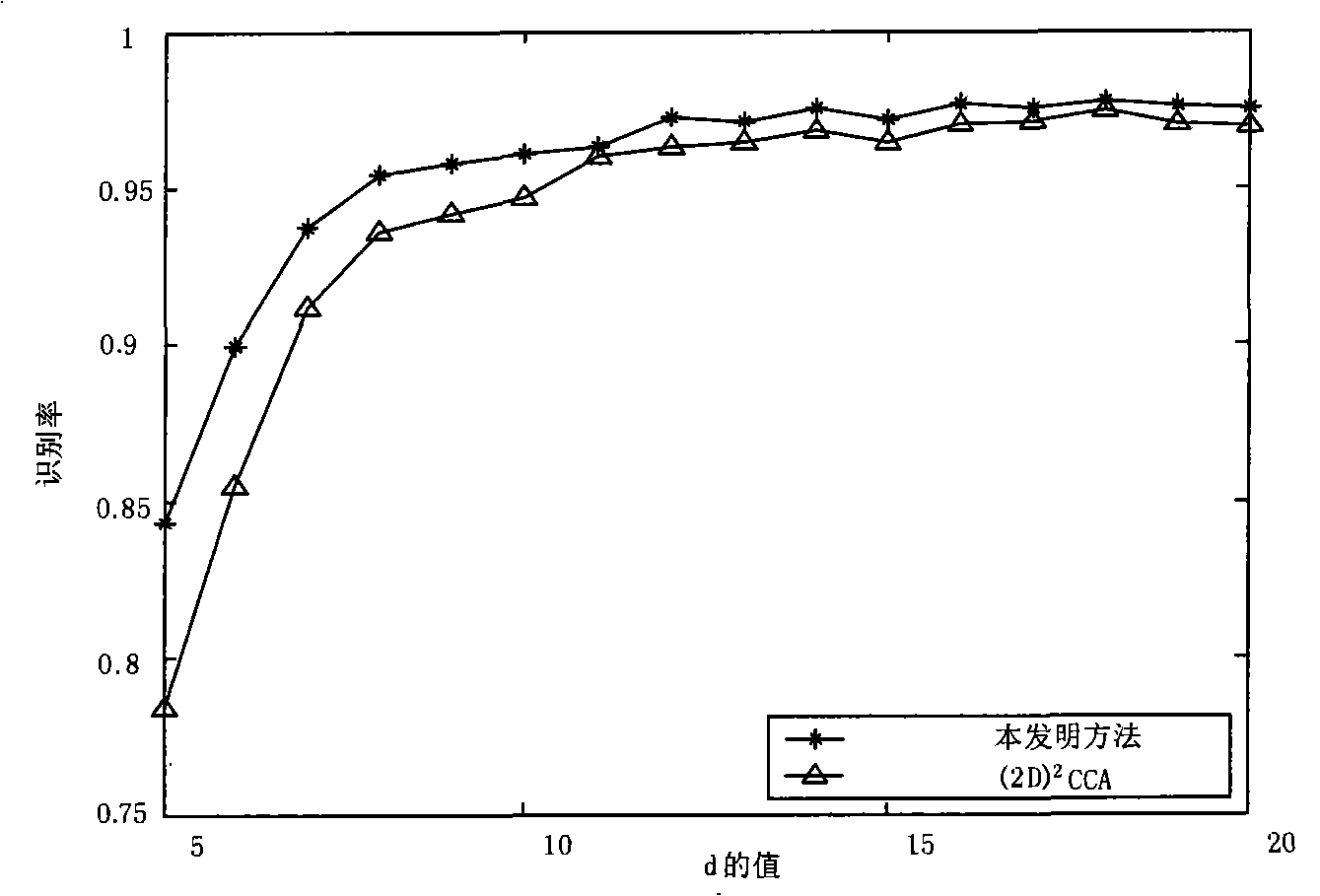
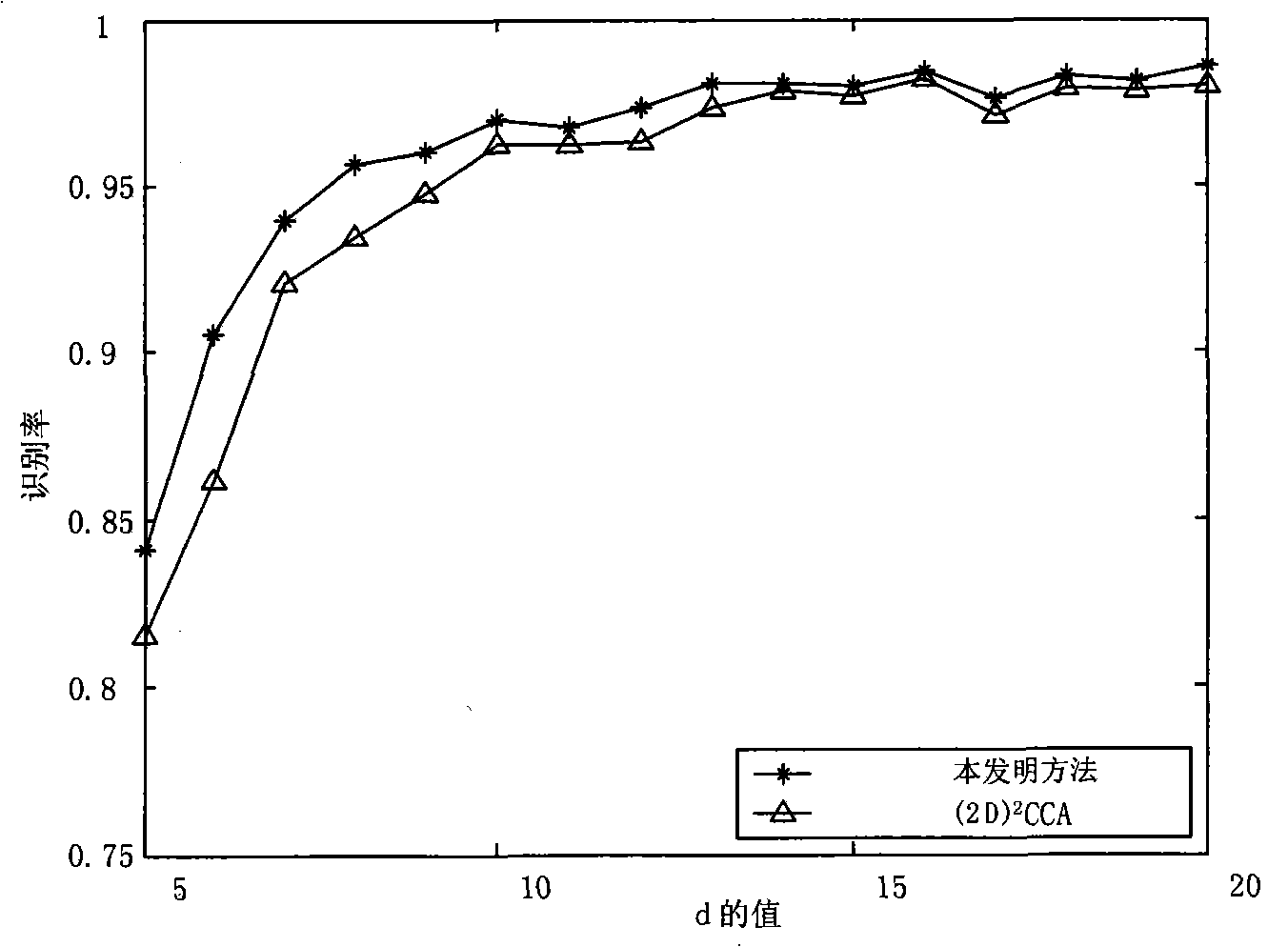
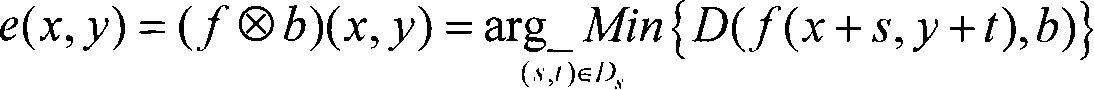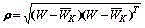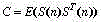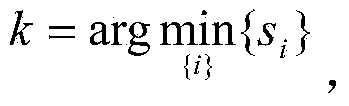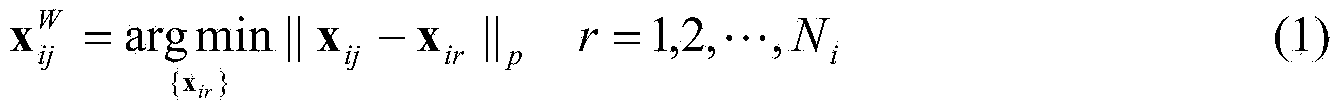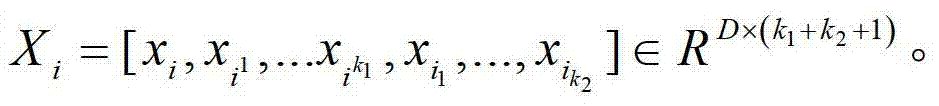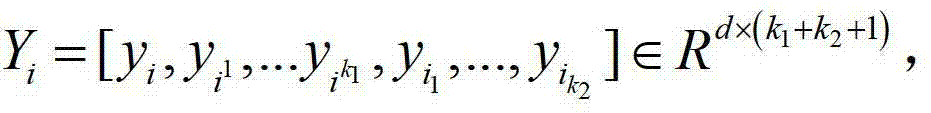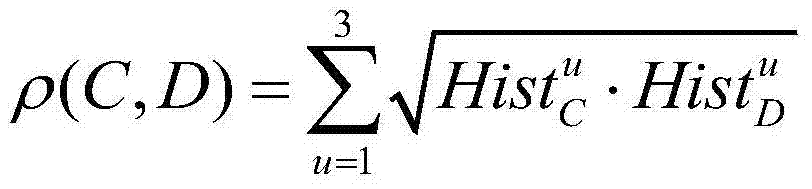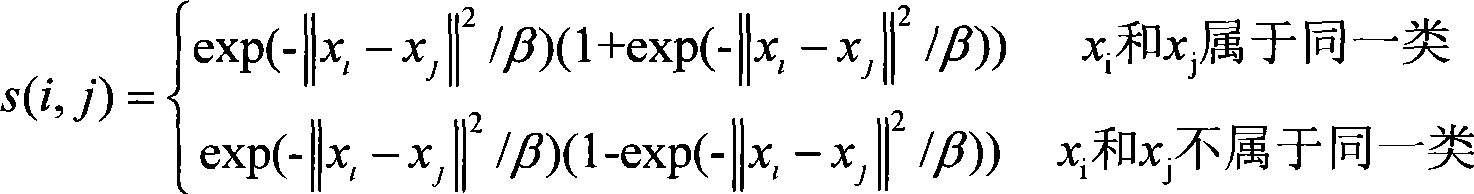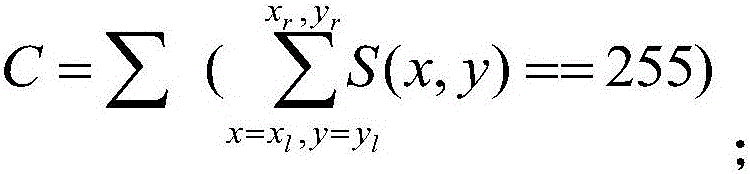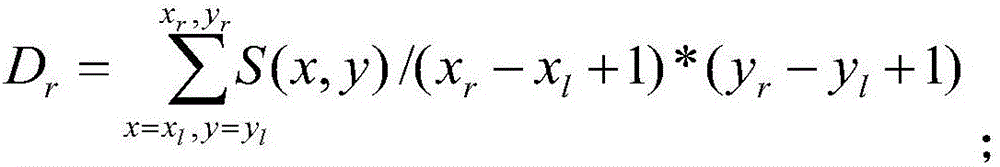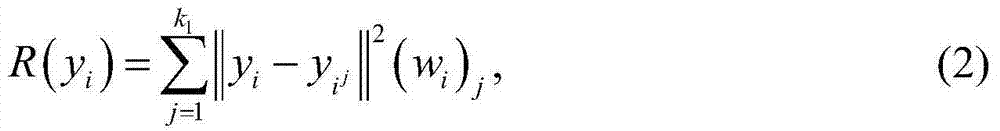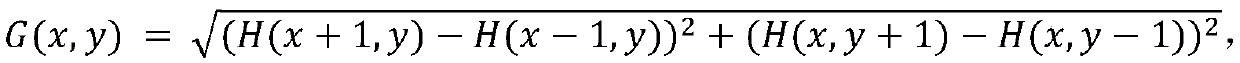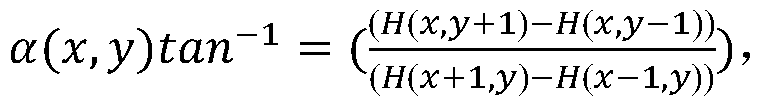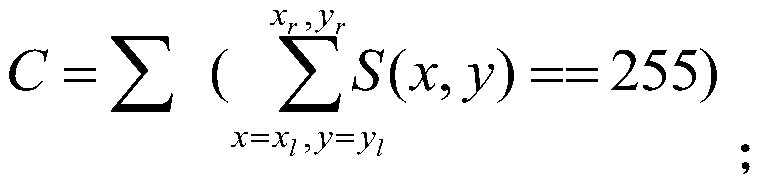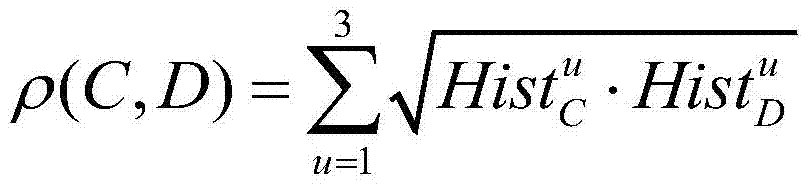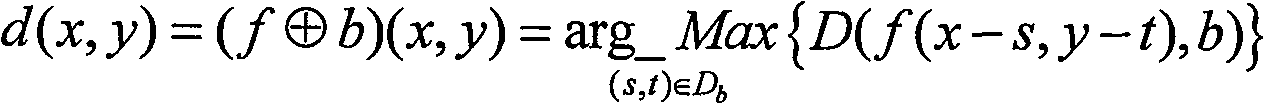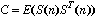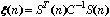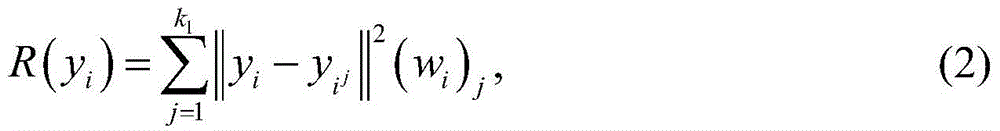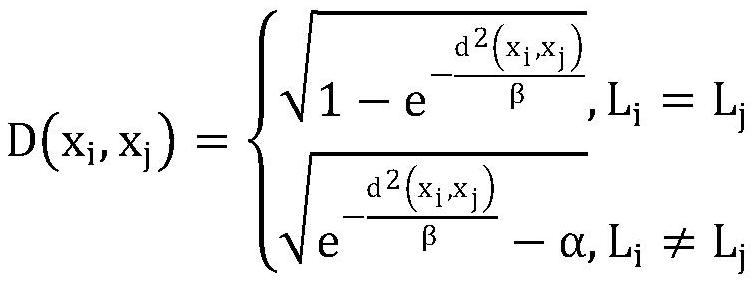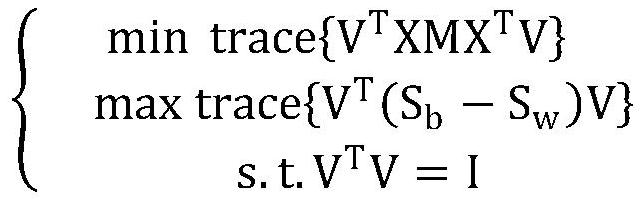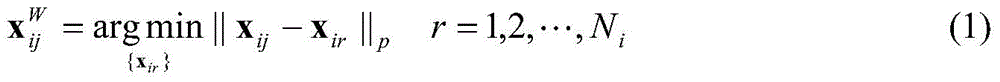Patents
Literature
32 results about "Minimum distance classifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
11.6 Minimum Distance Classifier. The minimum distance classifier is used to classify unknown image data to classes which minimize the distance between the image data and the class in multi-feature space.
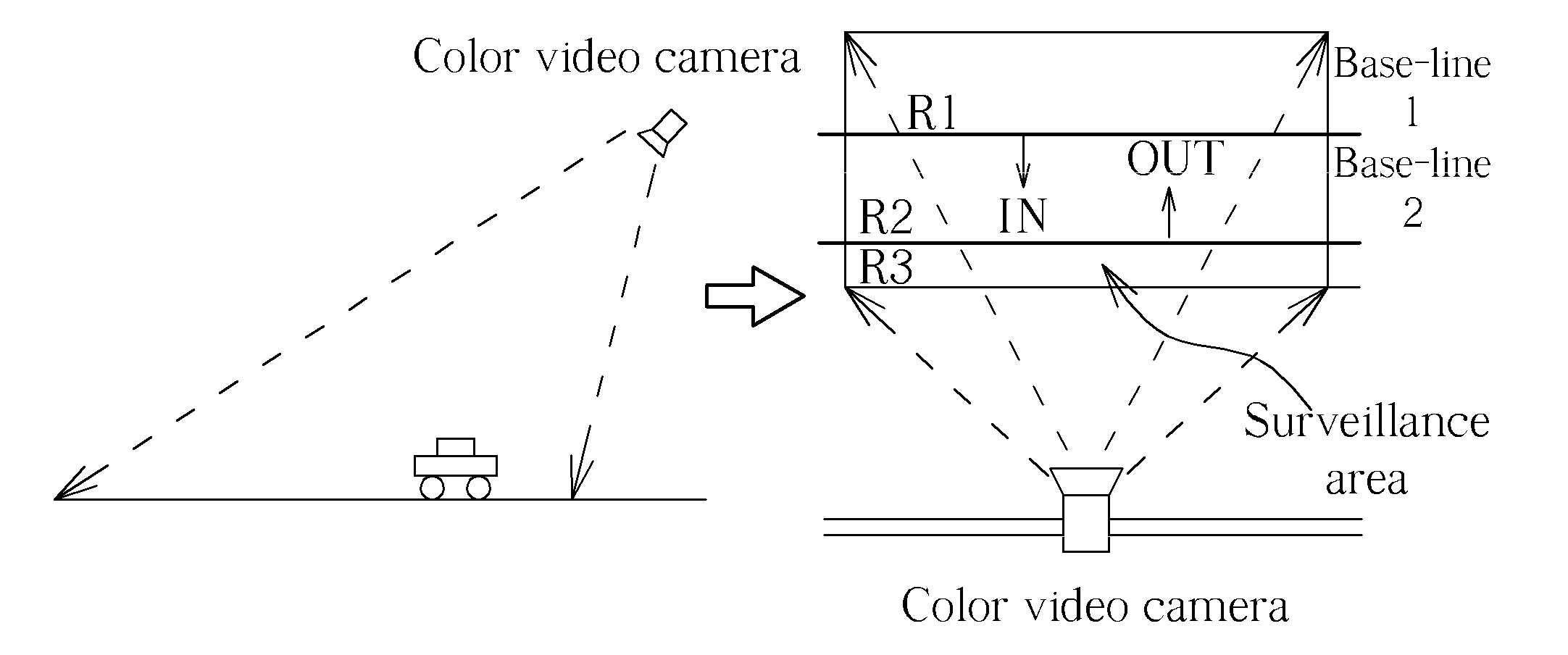
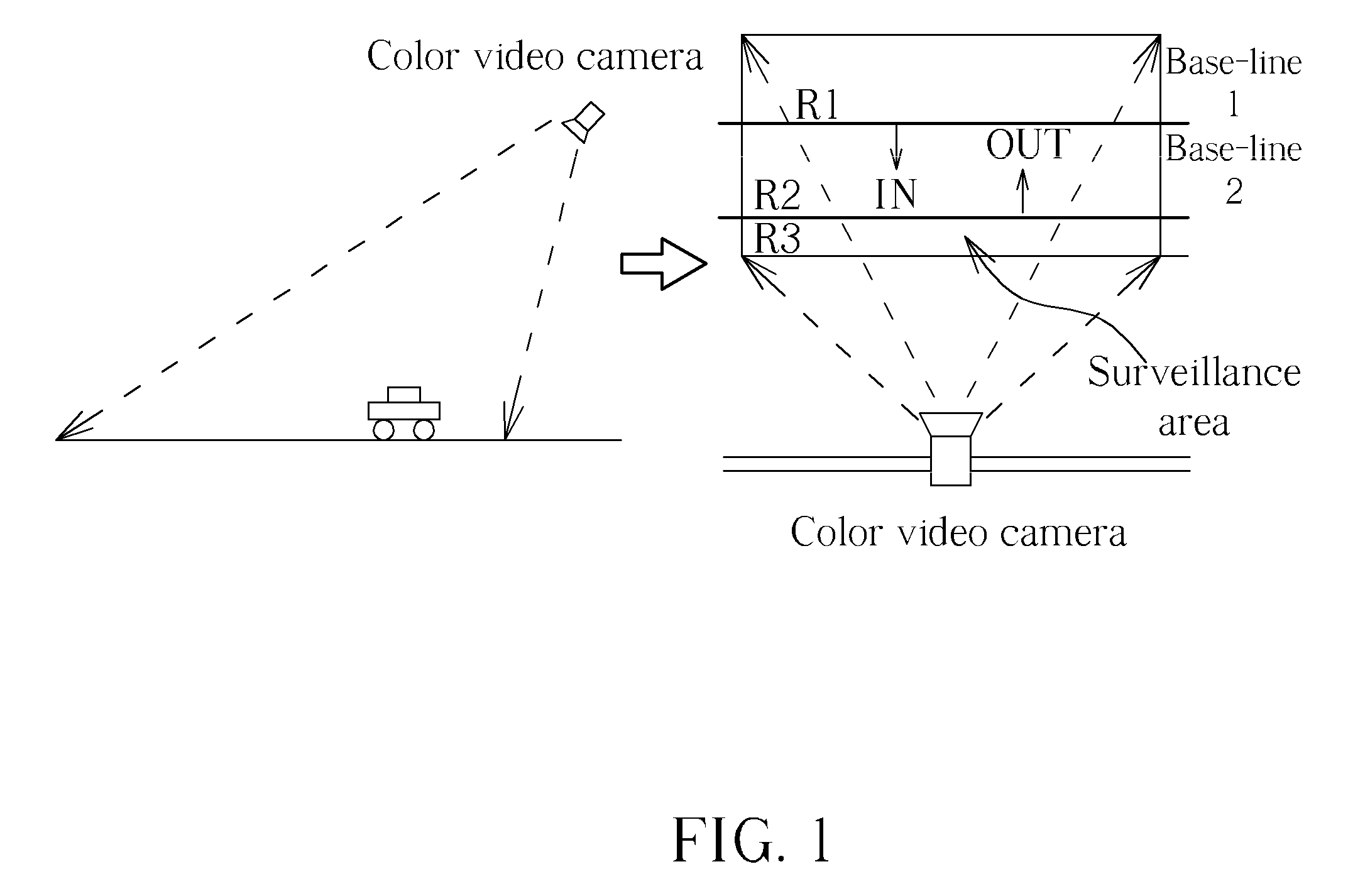
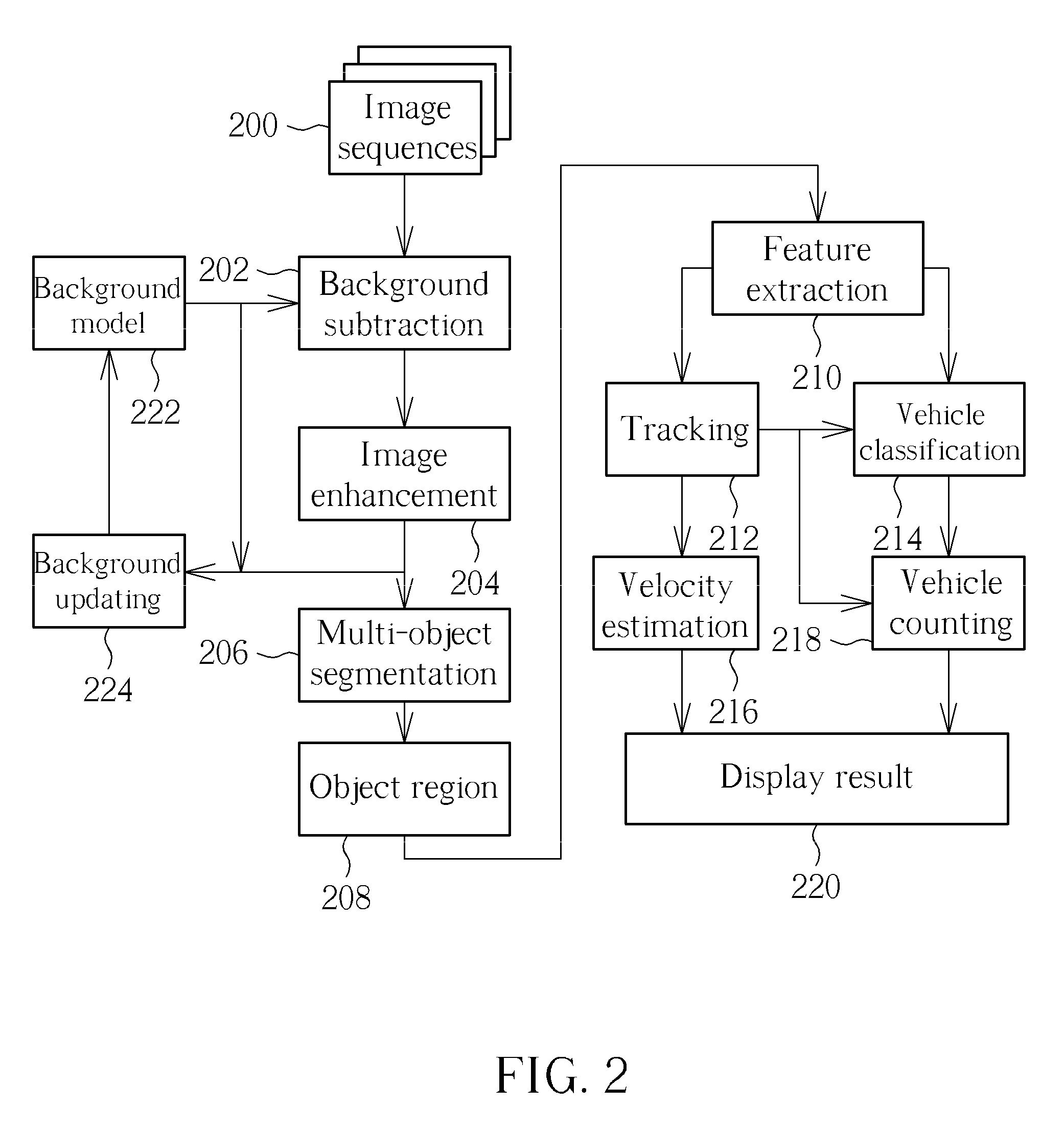
Method of detecting moving objects
InactiveUS20090309966A1Strong noise rejection abilitySimple calculationImage enhancementImage analysisMinimum bounding boxMinimum distance classifier
A method for detecting moving objects includes: (a) capturing and establishing a background image; (b) capturing at least one current image; (c) transforming the background image and the current image from an RGB color format into an HSI color format; (d) subtracting the background image from the current image according to a background subtraction rule for generating at least one moving object; (e) performing a vertical scanning and a horizontal scanning on the moving object for generating a minimum bounding box of the moving object; (f) calculating a characteristic datum of the moving object according to the minimum bounding box; (g) tracking the moving object according to the characteristic datum with a Euclidean distance rule; (h) classifying the moving object according to the characteristic datum, the tracking result generated by step (g) and a minimum distance classifier.
Owner:HUPER LAB
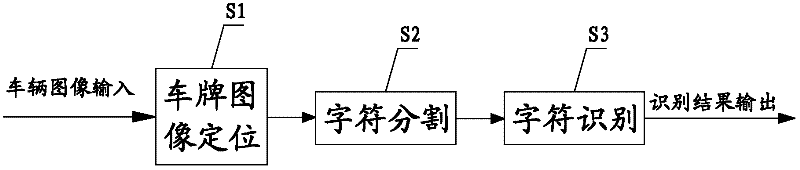
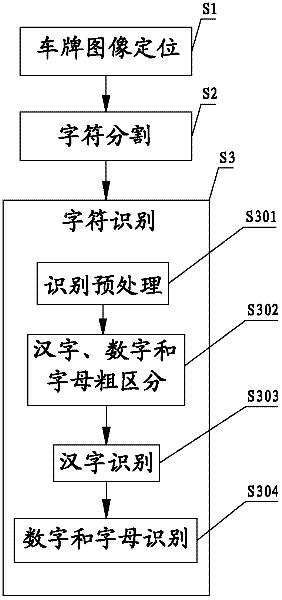
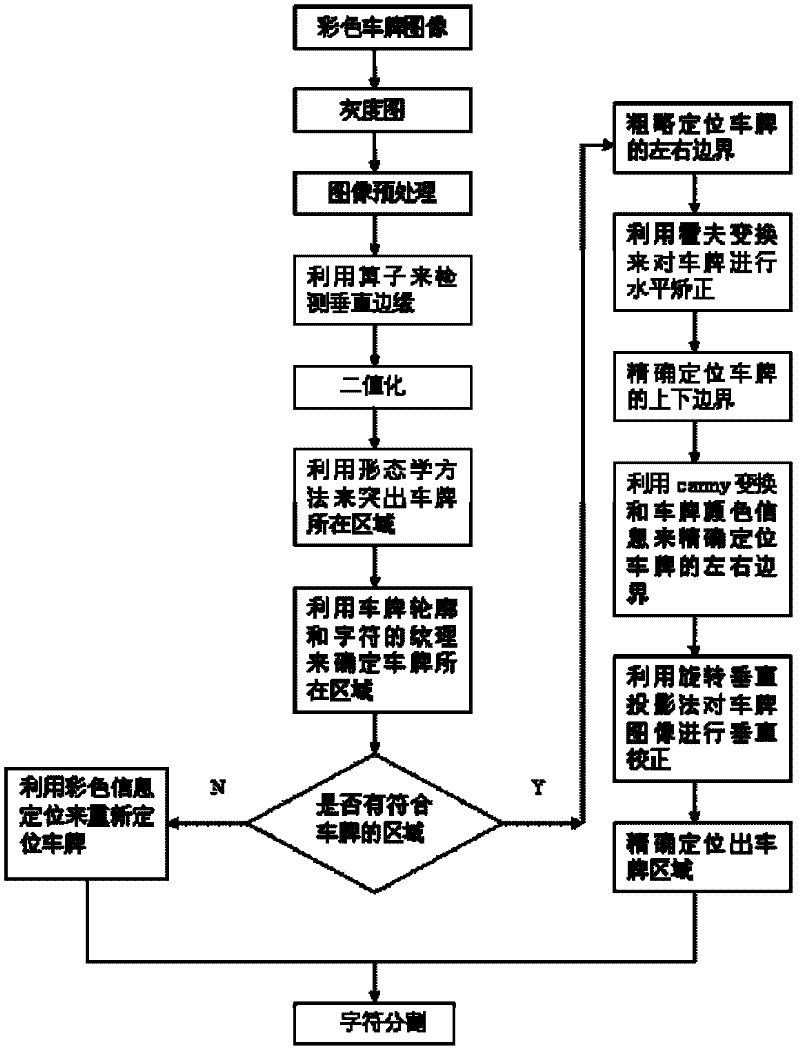
Number plate identification method and identification system thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of vehicle identification and particularly discloses a number plate identification method and an identification system of the number plate identification method. The method comprises the steps of number plate image positioning, character separation and character identification, wherein the character identification step comprises pre-treatment, coarse classification, Chinese character identification and number and letter identification. Through the improvement on a Chinese character identification method (through a Gabor filter and a minimum distance classifier) and a number and letter identification method (based on correlation feature selection (CFS) and a Bayes classifier), the number plate Chinese character identification rate and the number plate number and letter identification rate are greatly improved.
Owner:ZHUHAI YEARING TECH
Light spectrum and spatial information bonded high spectroscopic data classification method
InactiveCN101236106AAchieve fine classificationImprove reliabilityRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsMinimum distance classifierClassification methods
Disclosed is a hyperspectral data classification method which is combined spectrum and spatial information. The steps comprises (1) reading the hypersectral data, (2) confirming the minimum size of structural element, (3) calculating differentiation between picture elements in neighborhood of each structural element by extended mathematical morphology expansion and corrosion operation, (4) obtaining exponential value of morphology eccentricity by the extended expansion and the corrosion operation of step (3), (5), constantly repeating the above steps with the adding of the size of the structural element to achieve the maximum size of the structural element, (6), constantly updating the exponential value MEI of morphology eccentricity in iteration process via the obtained new value, and generating a final exponential value MEI of morphology eccentricity after the iteration process is finished, (7) realizing the extraction of the data characteristic by the image of the exponential value MEI of morphology eccentricity, namely generating ground object type information, and realizing sophisticated category of the ground object by a minimum-distance classifier. The method is an unsupervised classification method for hyperspectral ground object with strong stability, high reliability and high accuracy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
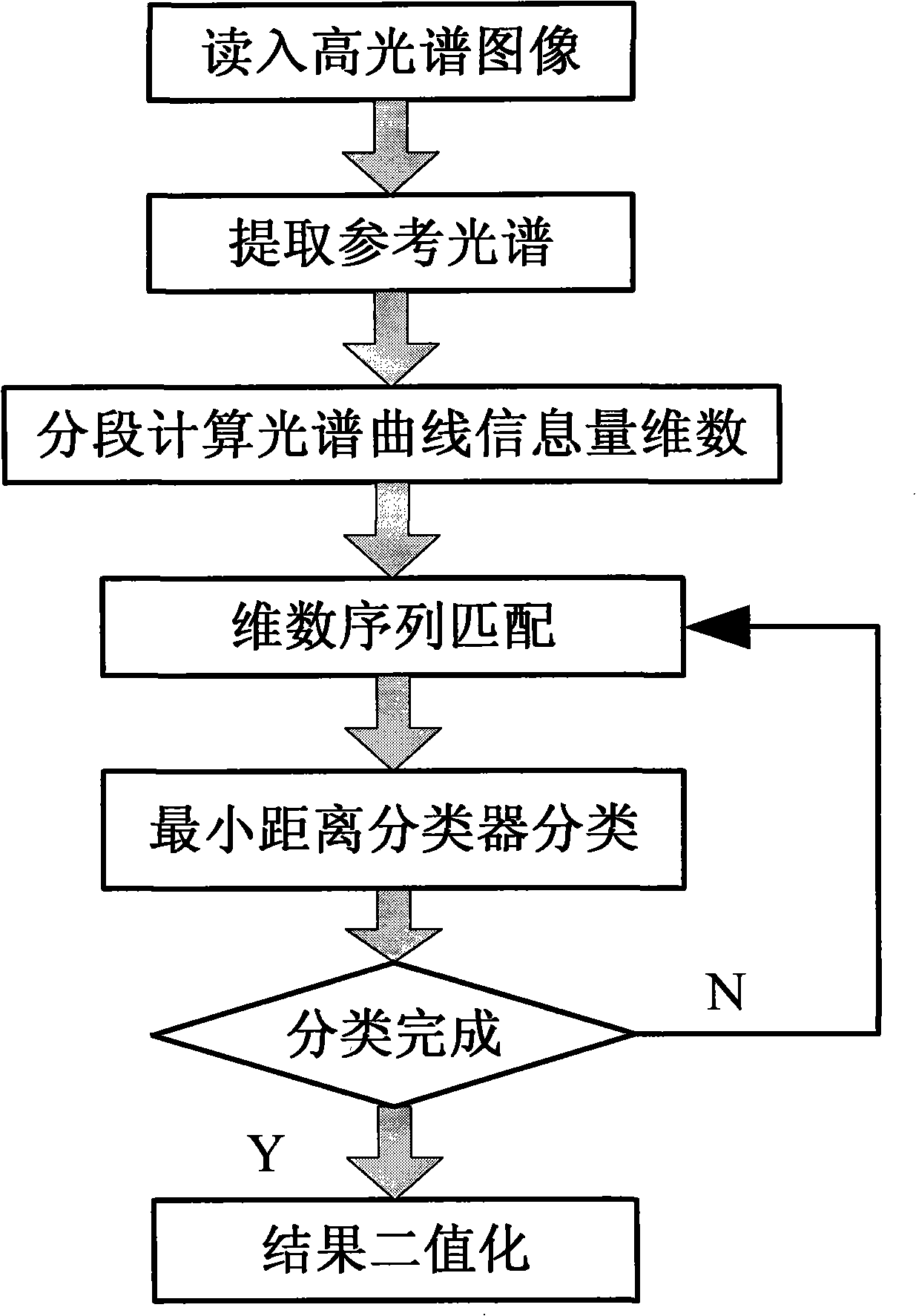
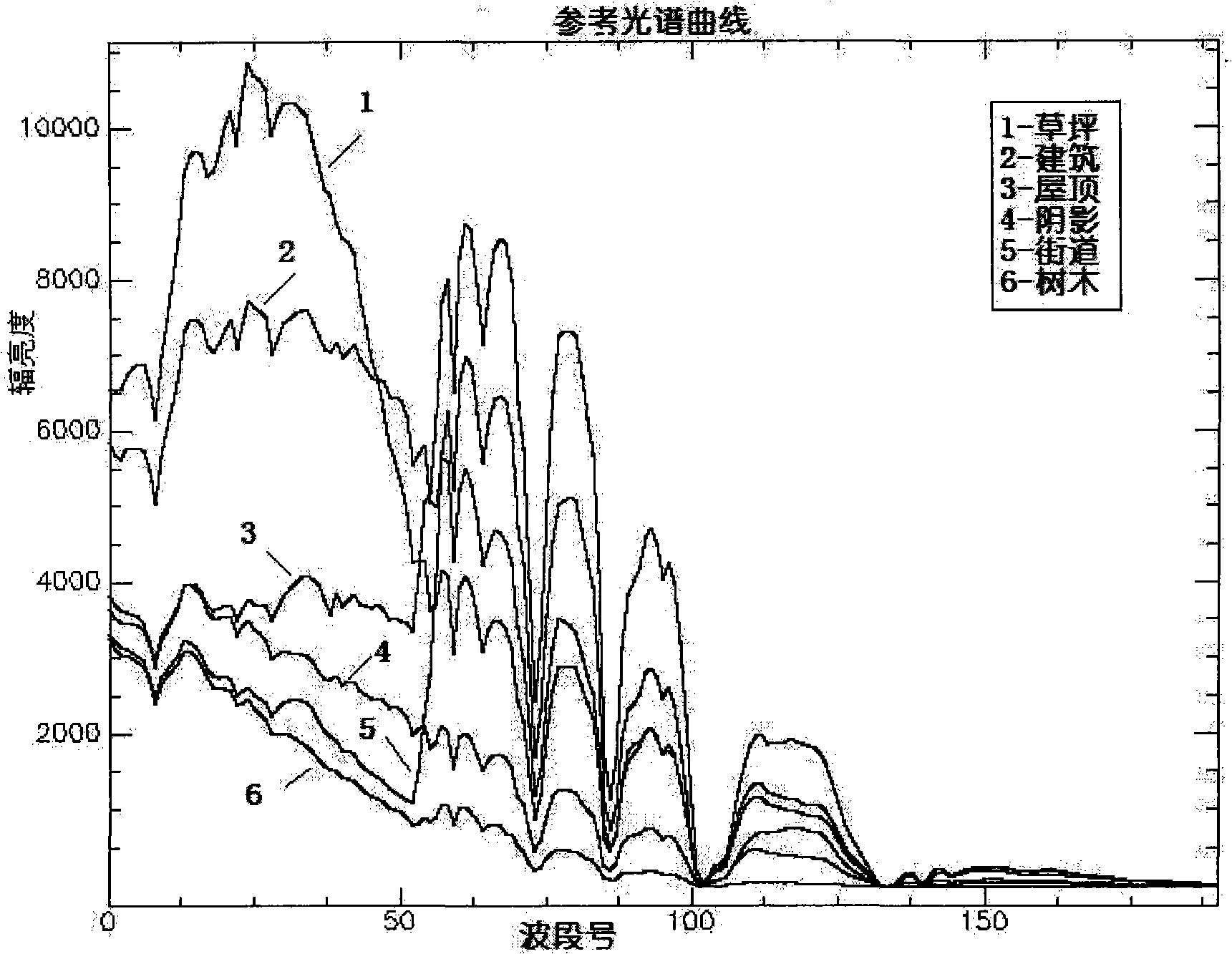
High spectroscopic data supervision classifying method based on information quantity dimensionality sequence
InactiveCN101299237AImprove classification efficiencyImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierInformation quantity
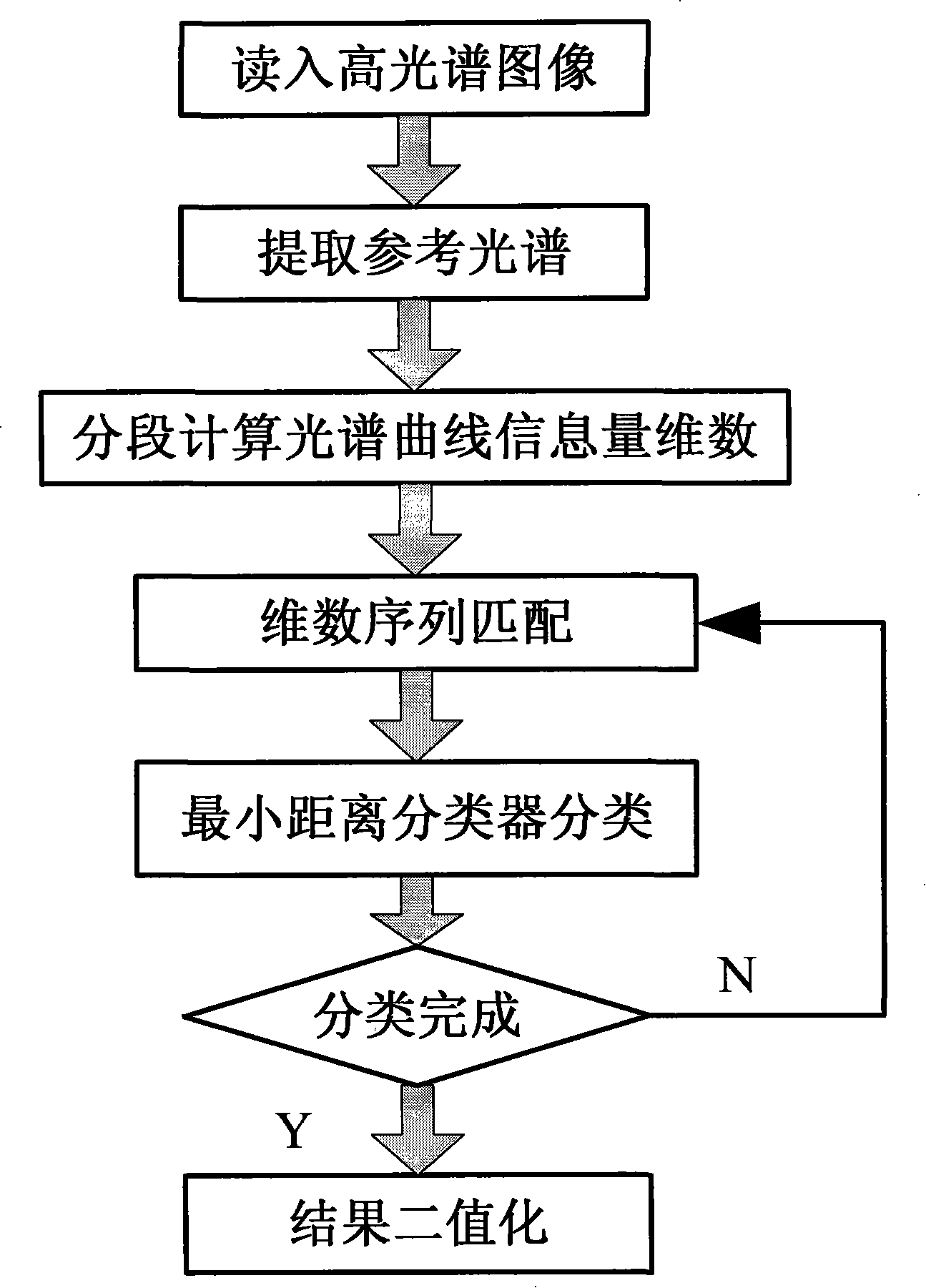
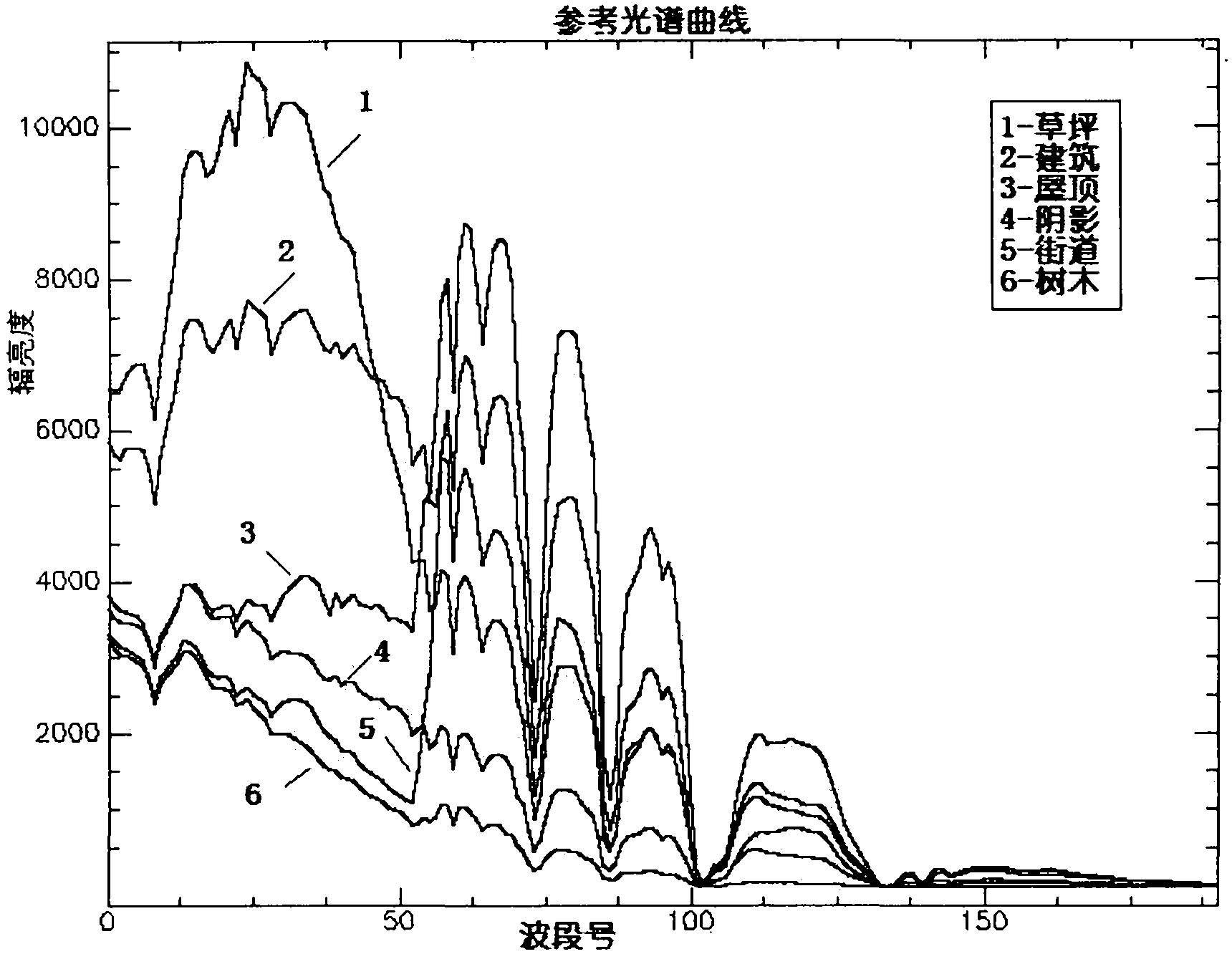
A high spectroscopic data supervision classification method based on information quantity dimensionality sequence includes the following steps: reading the high spectrum image data of a certain region; selecting a reference spectrum from the spectrum library or selecting the training sample from images to execute wave band average acquiring reference spectrum; calculating one by one the reference spectrum and all test spectral information quantity dimensionality sequence; executing vector angle matching one by one the test spectrum with all reference spectral information quantity dimensionality sequence, and using minimum distance classification machine to classify; result binarization matching, the matching result of each series of field culture is represented by the binary images, each image only includes a series of field culture. The high spectroscopic data classification method based on information quantity dimensionality sequence introduces the information quantity dimensionality into the spectrum domain analysis, synthetizes the advantages of the all band matching and partial quantization characteristic matching, can obtain higher classification effectiveness and classification accuracy, and has important value in the high spectroscopic data classification and object identification.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
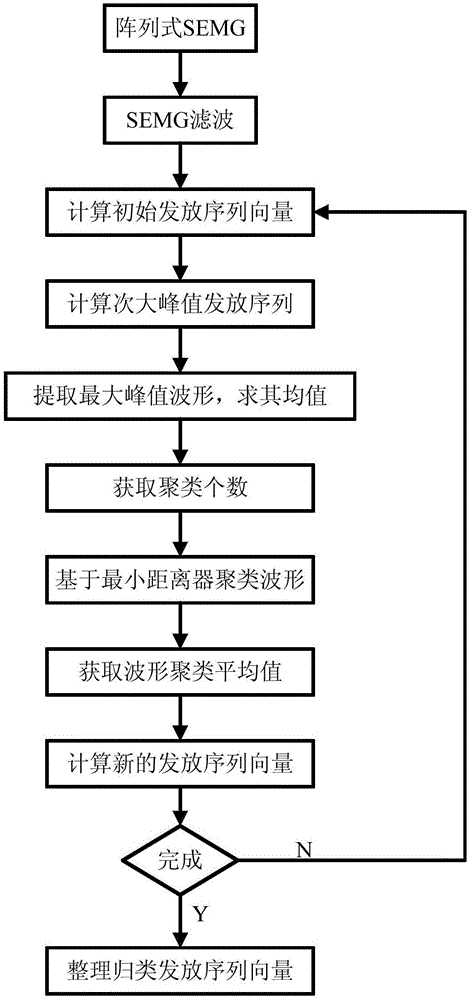
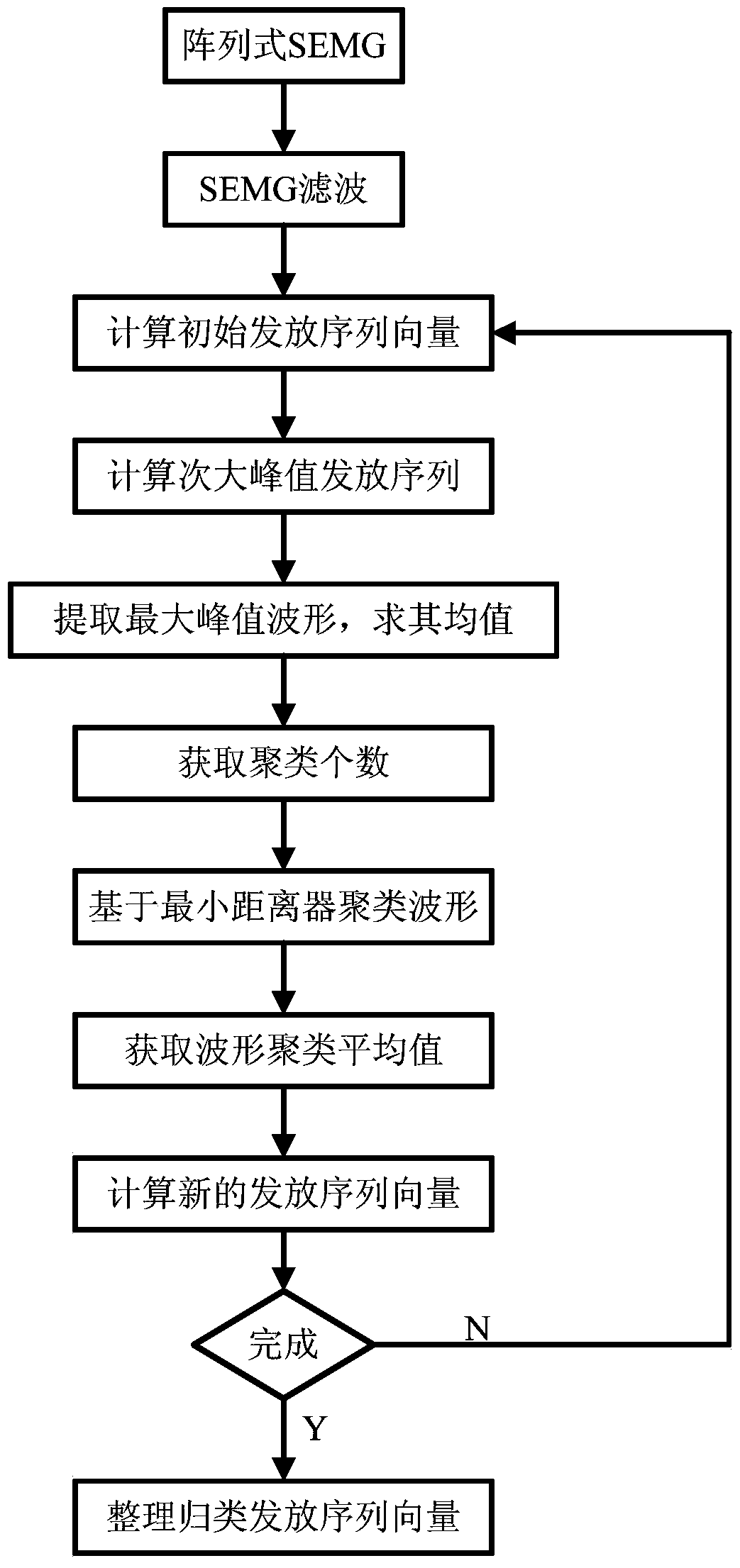
Automatic decomposition method of array type sEMG (surface EMG) signal
InactiveCN104997508AExact initial valueImprove decomposition accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTime domainMinimum distance classifier
The invention provides an automatic decomposition method of an array type sEMG (surface EMG) signal. The automatic decomposition method comprises the following steps: firstly, pretreating the array type sEMG signal, and calculating an initial distribution sequence vector; determining the number of kinematic units, namely, the cluster number, by using time domain subtraction; according to the cluster number, clustering array type sEMG waveforms by using a minimum distance classifier; finally, recalculating a new kinematic unit distribution sequence vector, circulating the executive routine till decomposition is finished, classifying all the distribution sequences, and optimizing the result. The decomposition method is high in accuracy, quick in calculation speed and easy to operate.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
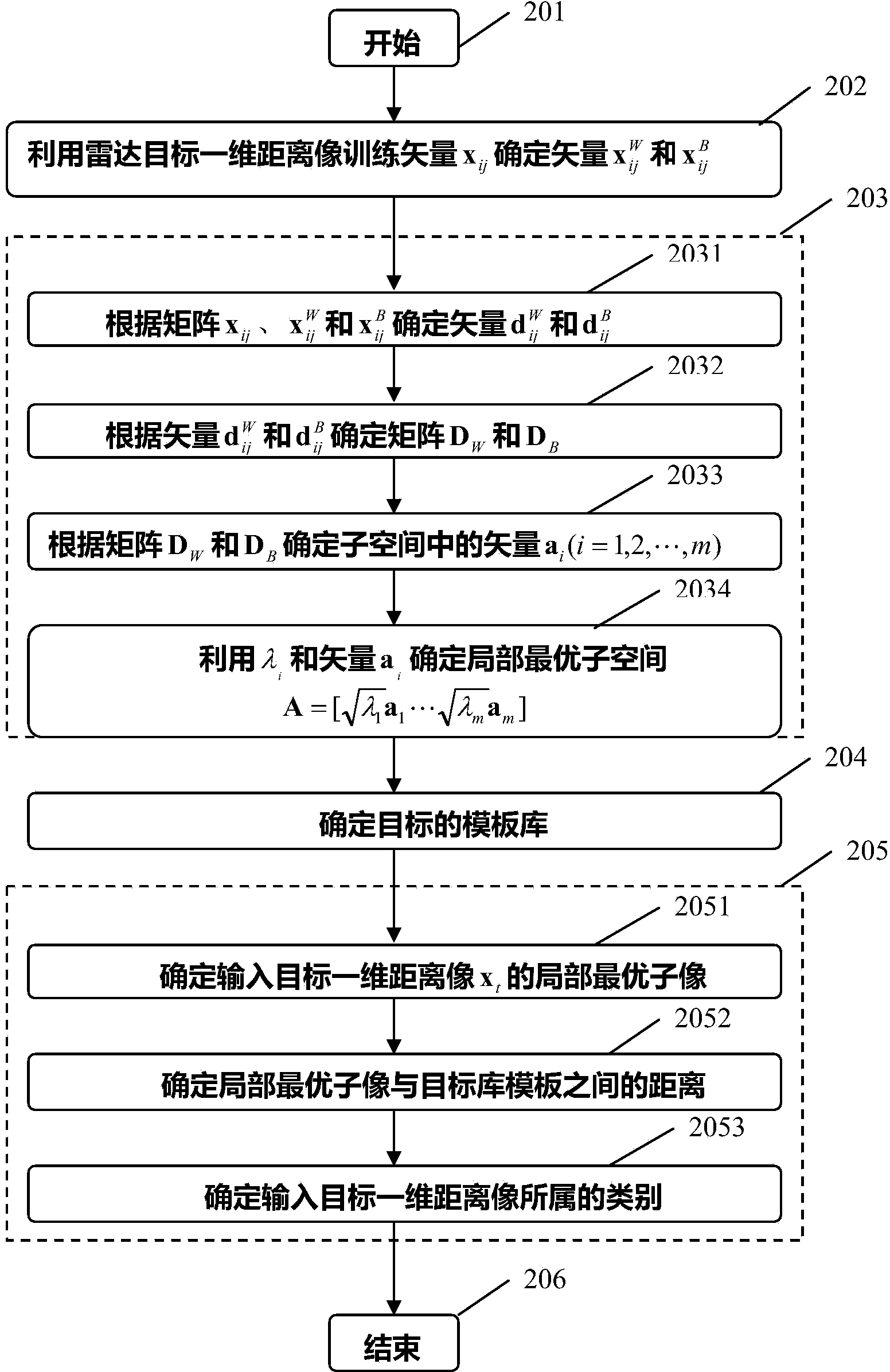
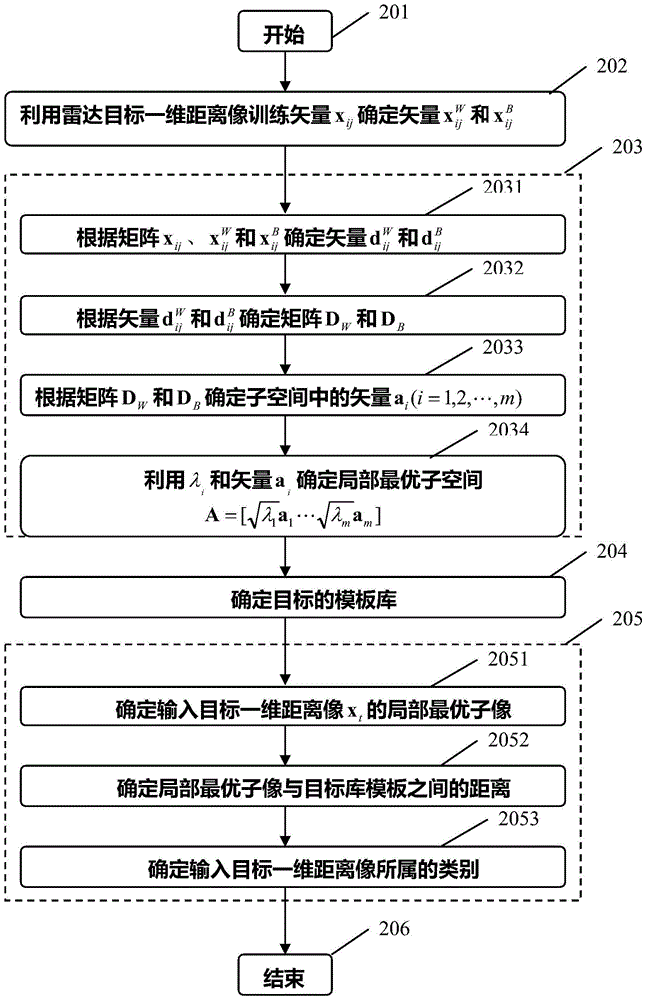
Radar target one-dimensional range profile local optimal sub-space recognition method
InactiveCN103941244AImprove object classification performanceEasy to identifyWave based measurement systemsMinimum distance classifierLocal optimum
The invention provides a radar target one-dimensional range profile local optimal sub-space recognition method which effectively improves the performance of recognizing a radar target. According to the method, firstly, a nearest intra-class distance scattering matrix and a nearest between-class distance scattering matrix are calculated through training data; then, a local optimal sub-space is set up according to an optimal ratio criteria, the characteristics of the target are extracted, and the characteristics are classified through a minimum distance classifier; finally, the classification where the input target belongs is determined. The method specifically includes the steps of determining a vector X<W>ij and a vector Xij through a radar target one-dimensional range profile training vector Xij; determining a vector d<W>ij and a vector dij; determining a matrix DW and a matrix DB; determining m vectors a1, a2...and am of the local optimal sub-space; determining the equation (please see the equation in the specification) of the local optimal sub-space according to lambdai and a vector ai, wherein i is 1 or 2 or 3...or m; determining a template library according to the projection of the training vectors in the sub-space A; determining the local optimal sub-image of an input target one-dimensional range profile Xt; determining the distance between the local optimal sub-image and a library template vector, and determining the classification where the input target range profile belongs through the minimum distance classifier.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Human behavior recognition method based on accelerometer
ActiveCN103500342AKeep fitEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierHat matrix
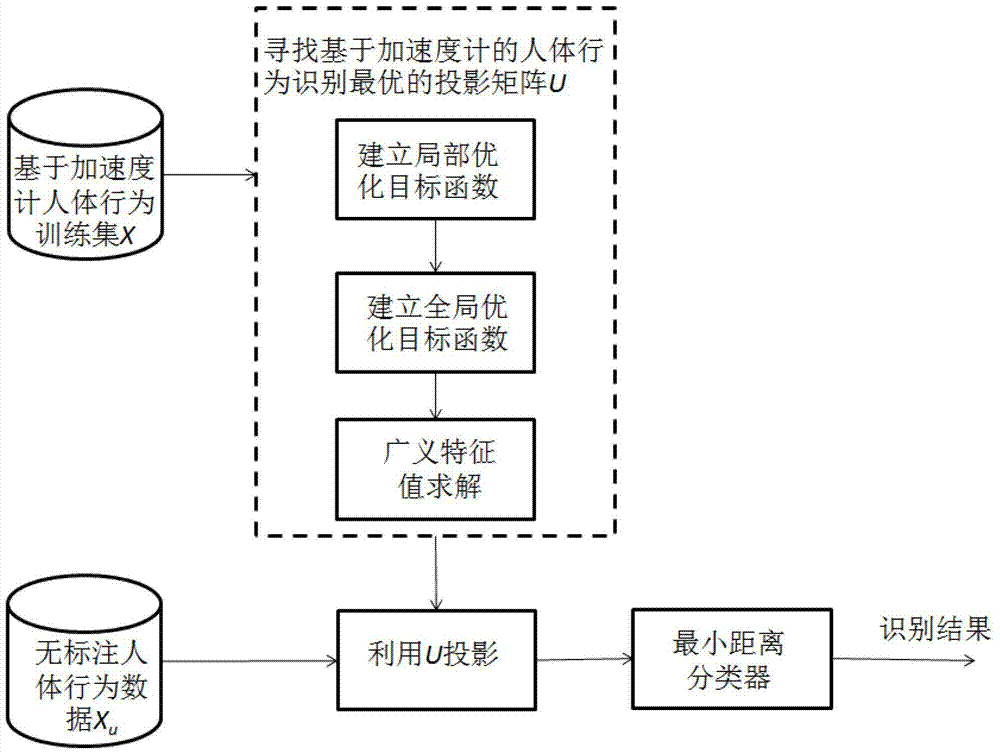
The invention discloses a human behavior recognition and classification method based on an accelerometer. The method includes the first step of collecting human behavior samples as a training set, the second step of searching for a projection matrix U which is optimal for the recognition and classification of the training set, the third step of carrying projection on no-labeled data, and the fourth step of classifying the projected data by using a minimum distance classifier to obtain a recognition result. According to the human behavior recognition method, a partial approximate linear hypothesis is carried out on adjacent blocks formed by labeled data so as to enable the distance between different types of samples on the blocks to be large enough, positional sequence information of the same type of samples is reserved as far as possible through class sigmoid function penalty factors, and finally a global objective function is established on the basis of the objective functions on all blocks. The human behavior recognition method can reserve the information of the distance between the samples in a higher dimensional space properly, and reduces dependence of recognition models on artificial tagging samples, and the recognition effect is superior to a representative human behavior recognition method based on linear discriminant analysis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
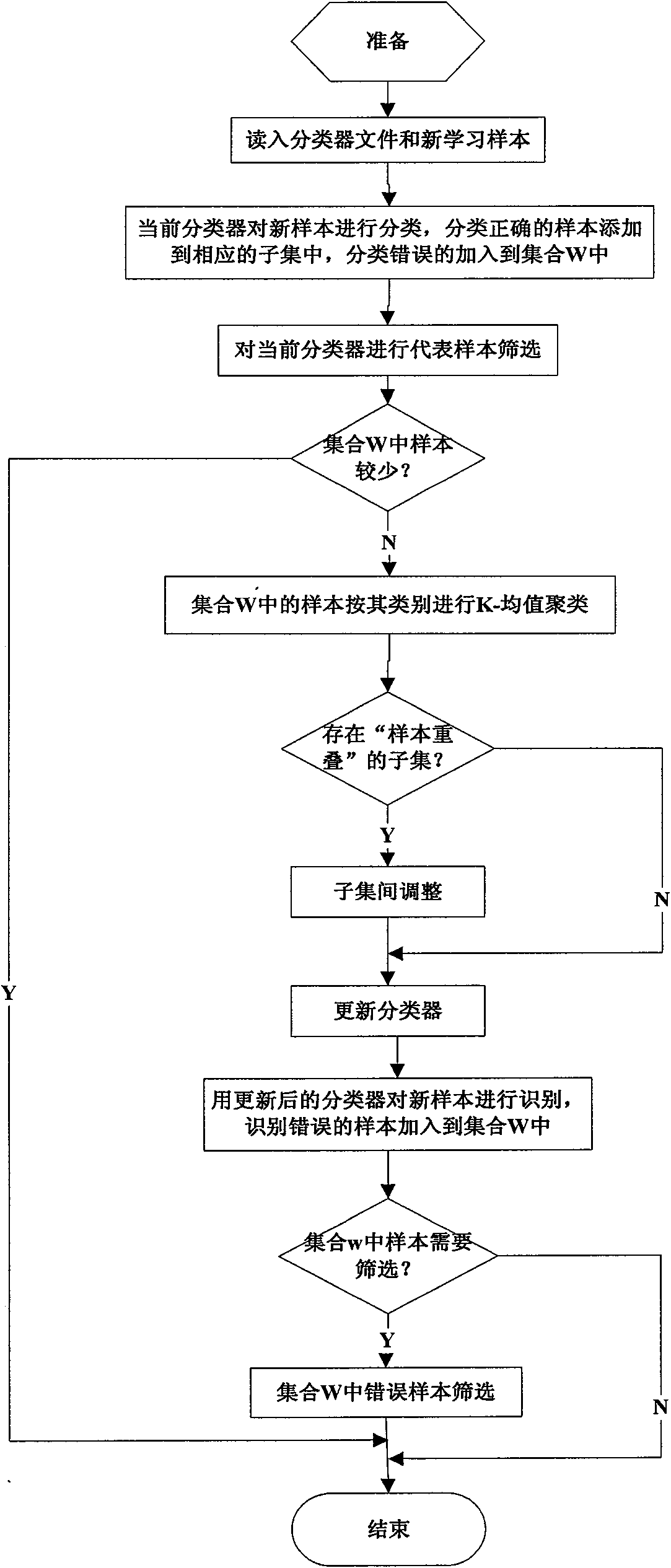
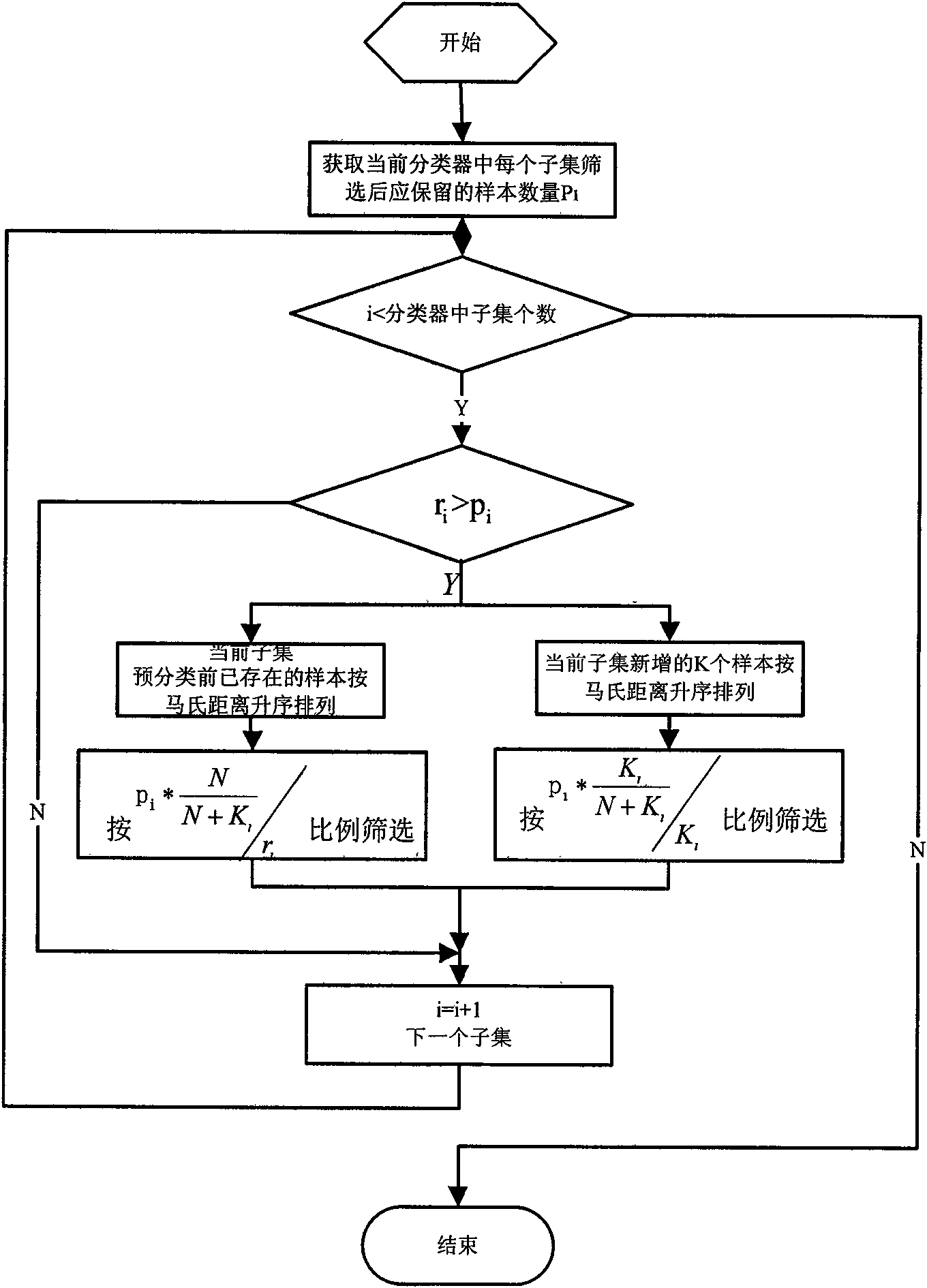
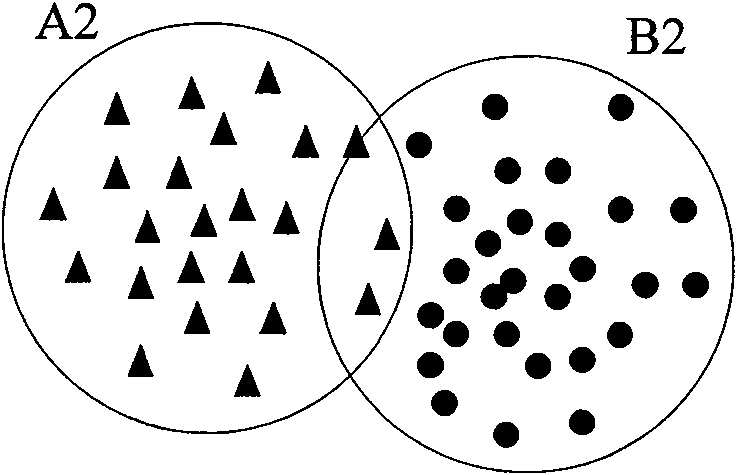
Increment study classification method under limited storage resources
InactiveCN101604394AEasy to identifyEffective studyCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierMisclassification error
The invention provides an increment study classification method under limited storage resources, which belongs to the technical field of pattern recognition. The method adopts a minimum distance classifier and comprises the following concrete steps: firstly, pre-classifying new samples, adding the new samples which are correctly pre-classified to the corresponding subset of the classifier, adding the new samples which are wrongly pre-classified to the set of wrong samples, and carrying out K-mean clustering on the samples in the set of wrong samples; then respectively selecting representative samples for each subset in the classifier and the set of wrong samples, adding the subsets in the set of wrong samples to the classifier after selection, and updating the classifier; and finally, adopting the updated classifier to classify the new samples. In the invention, by selecting the representative samples, not only the studied knowledge is saved, but also the new knowledge is acquired, and higher sample recognizing accuracy is achieved on the basis of reducing the storage cost and calculating the cost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
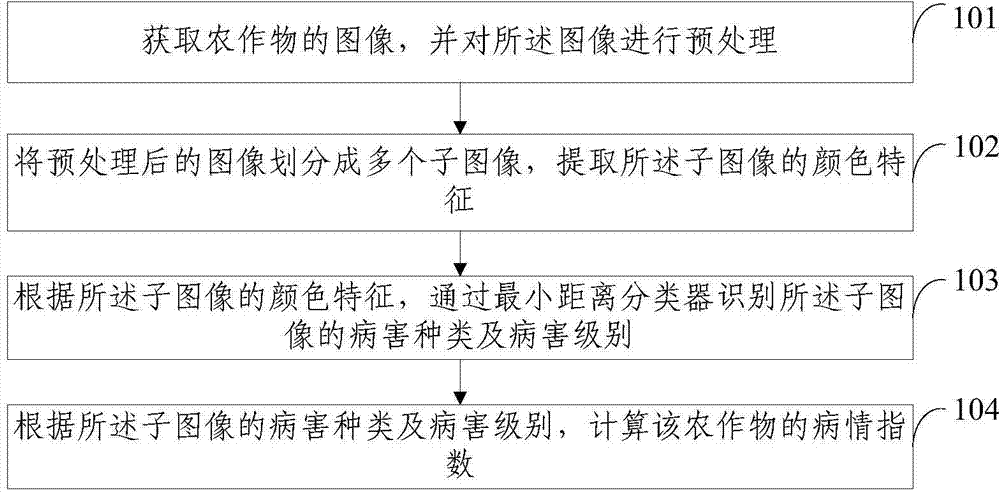
Computing method and system for crop disease index
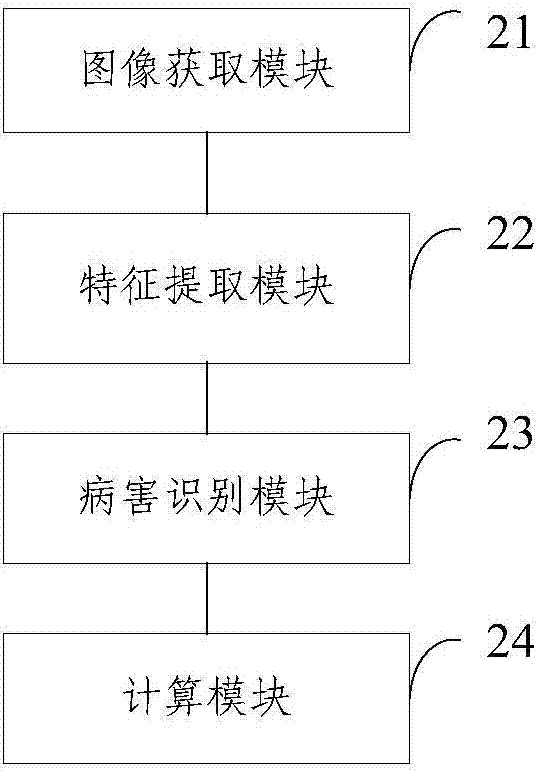
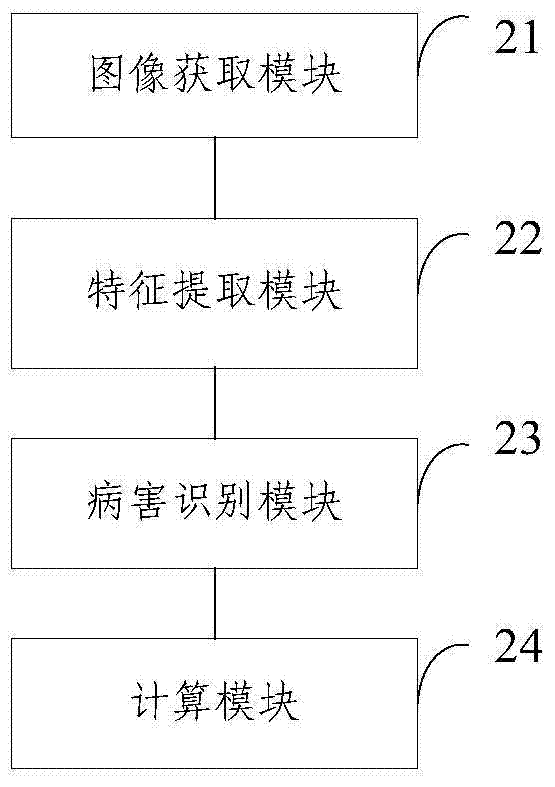
ActiveCN104751122AImprove the level of prevention and controlQuick implementationClimate change adaptationCharacter and pattern recognitionDiseaseMinimum distance classifier
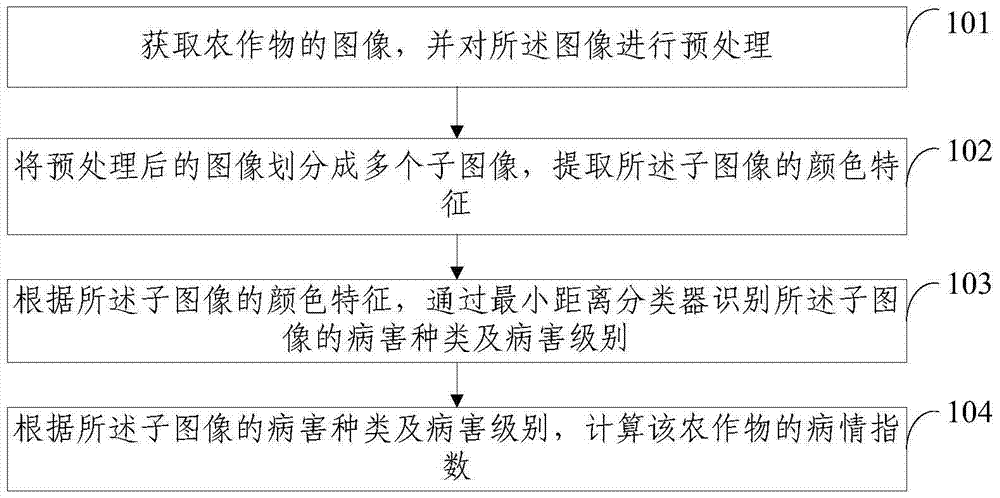
The invention discloses a computing method and a computing method system for crop disease index. The computing method comprises the following steps: acquiring image of crop and pre-processing the image; dividing the pre-processed image into multiple sub-images and extracting color characters of the sub-images; using a minimum distance classifier for identifying the disease types and disease level of the sub-images according to the color characters of the sub-images; computing the crop disease index according to the disease types and disease level of the sub-images. The method solves that the disease index computing of the prior art depends on experience and knowledge of pathology of field crop protection persons, the statistical result is inaccurate and manual computation is required. The method is conducive to improve the prevention and treatment level for crop disease index and promote the implementation of precision agriculture, and novel method and technology are provided for the crop disease prevention and treatment field.
Owner:北京市农林科学院信息技术研究中心
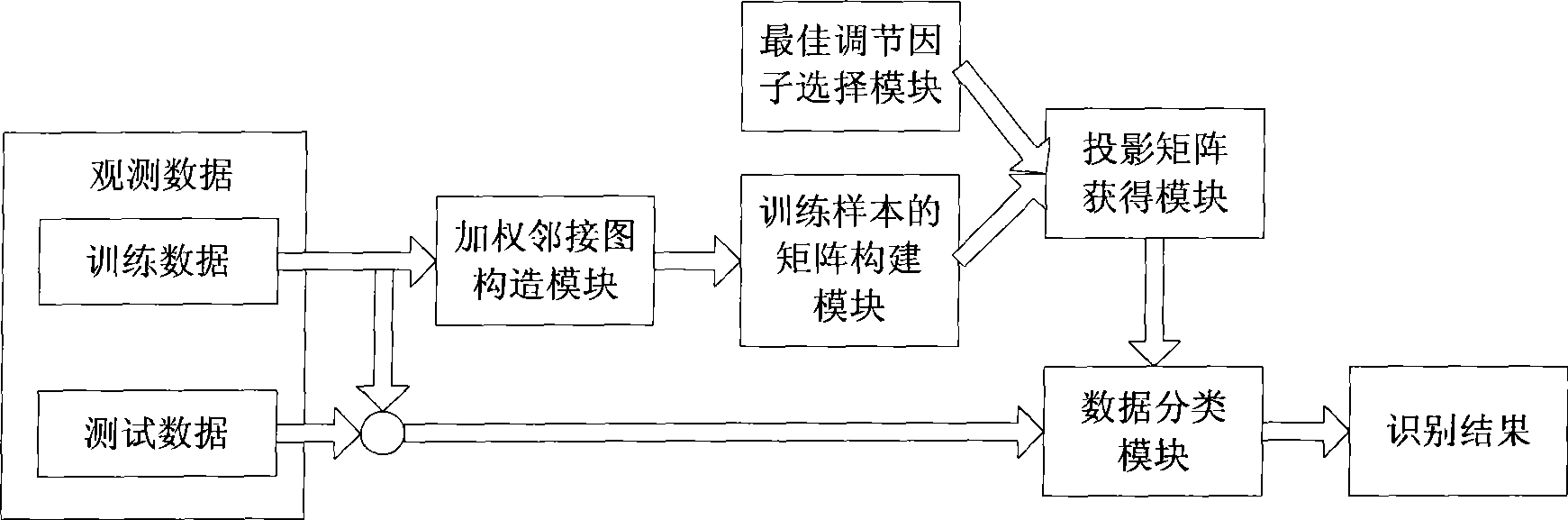
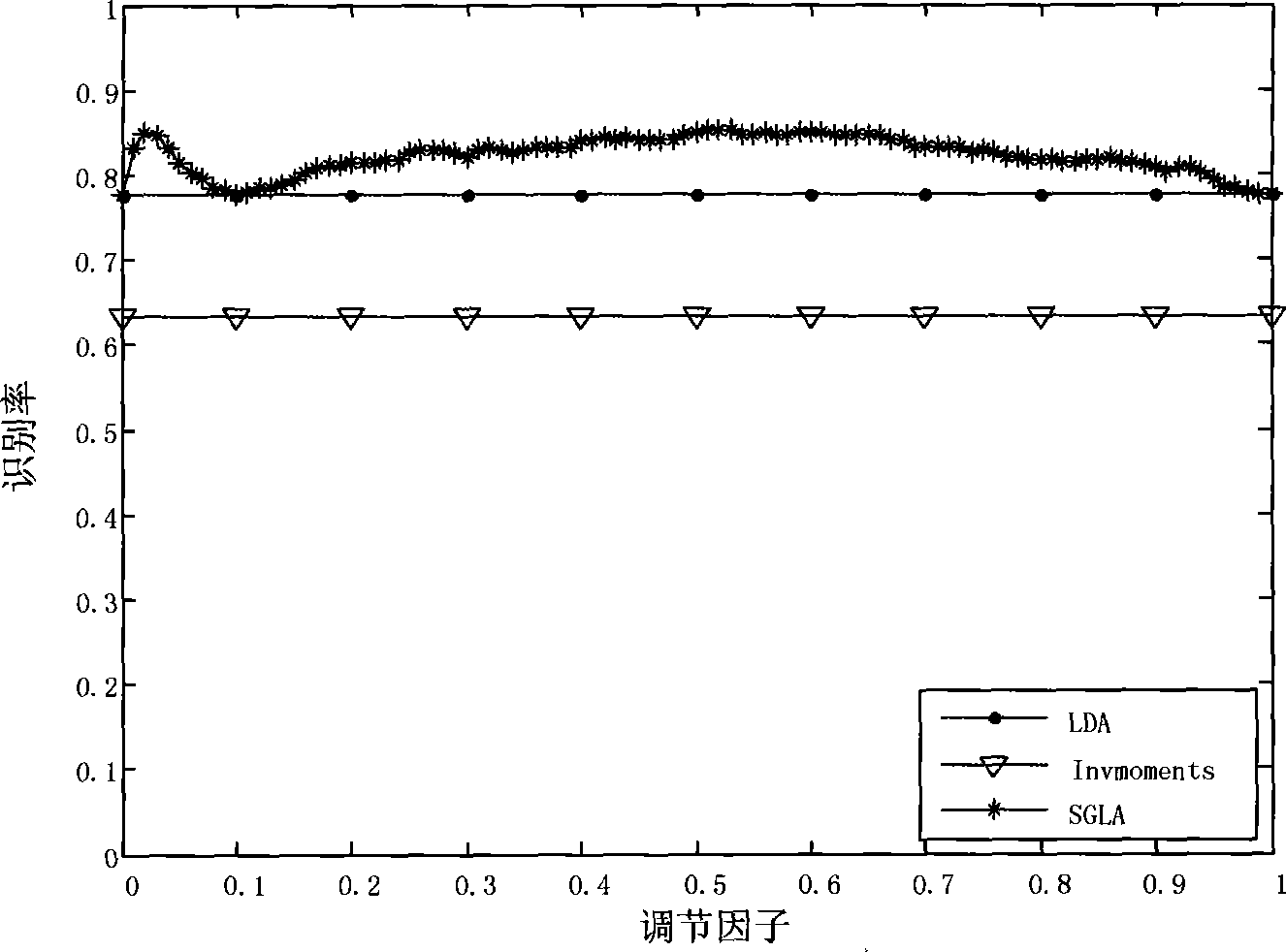
Integral and local characteristic fuse recognition system facing to identification
InactiveCN101441716APreserve the manifold structureAccurate portrayalCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierHat matrix
The invention provides an identification-oriented integral-local feature fusion-recognition system in the technical field of pattern recognition. In the system, a weighted adjacency graph construction module establishes a weighted adjacency graph, and acquires the similarity weight between any two vertices according to category information; a matrix construction module of a training sample receives the similarity weight, and establishes a similar matrix, a degree matrix, a laplacian matrix of the graph, an intra-class scatter matrix and an inter-class scatter matrix for the training sample according to the nearest neighbor principle; a selection module for an optimal regulatory factor selects a regulatory factor value allowing the recognition rate of the training sample to reach maximum as an optimal value of regulatory factors; a projection-matrix acquisition module selects eigenvectors corresponding to top minimum feature values in all feature values as base vectors, so as to form a projection matrix; and a data classification module adopts a minimum distance classifier to recognize the category of test data. The system utilizes the category information of data to depict data relation more accurately, thereby gaining higher recognition performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
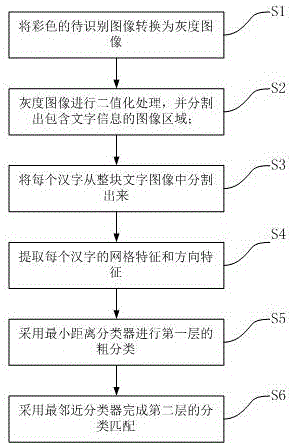
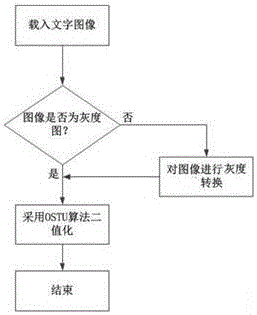
Multi-classifier integration-based image character recognition method
InactiveCN106127198AImprove anti-interference abilityEffect of Strong Stroke WidthCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierAnti jamming
The invention provides a multi-classifier integration-based image character recognition method. The method comprises the following steps of: converting a colored to-be-identified image into a grayscale image; carrying out binary processing on the grayscale image and segmenting an image region with character information; segmenting each Chinese character from a whole character image; extracting grid features and direction features of each Chinese character; selecting stroke density total length features to carry out first-layer rough classification by adoption of a minimum distance classifier; and respectively selecting peripheral features, the grid features and the direction features to complete second-layer classification matching by adoption of a nearest-neighbor classifier. The method has the advantages that the character recognition has relatively strong anti-jamming capability and relatively strong character local structure description capability, and is less influenced by stroke widths; by adoption of a classifier integration technology of complementing and combining the minimum distance classifier and the nearest-neighbor classifier, a system is more reliable; and the characters can be intelligently recognized, so that the adaptability of the system is improved and the recognition rate is high.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
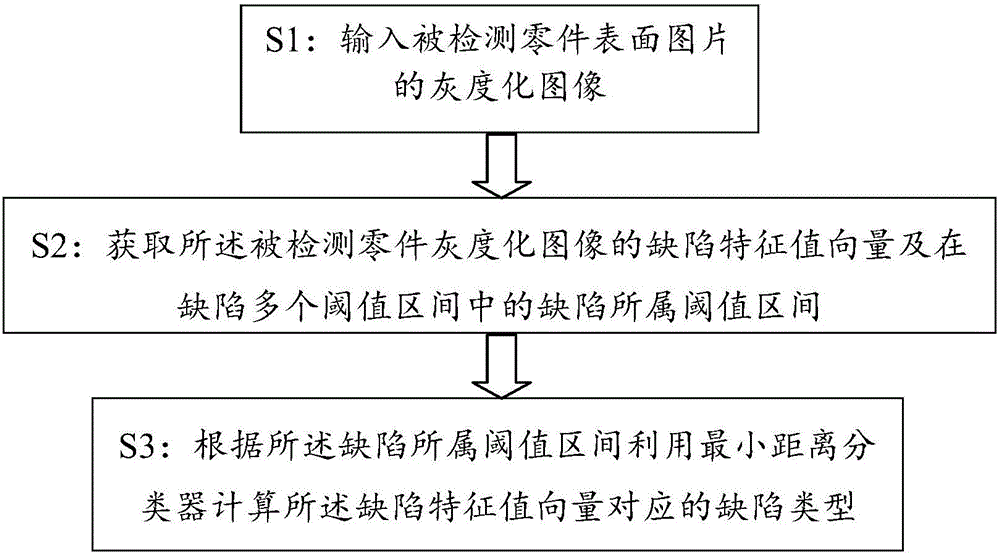
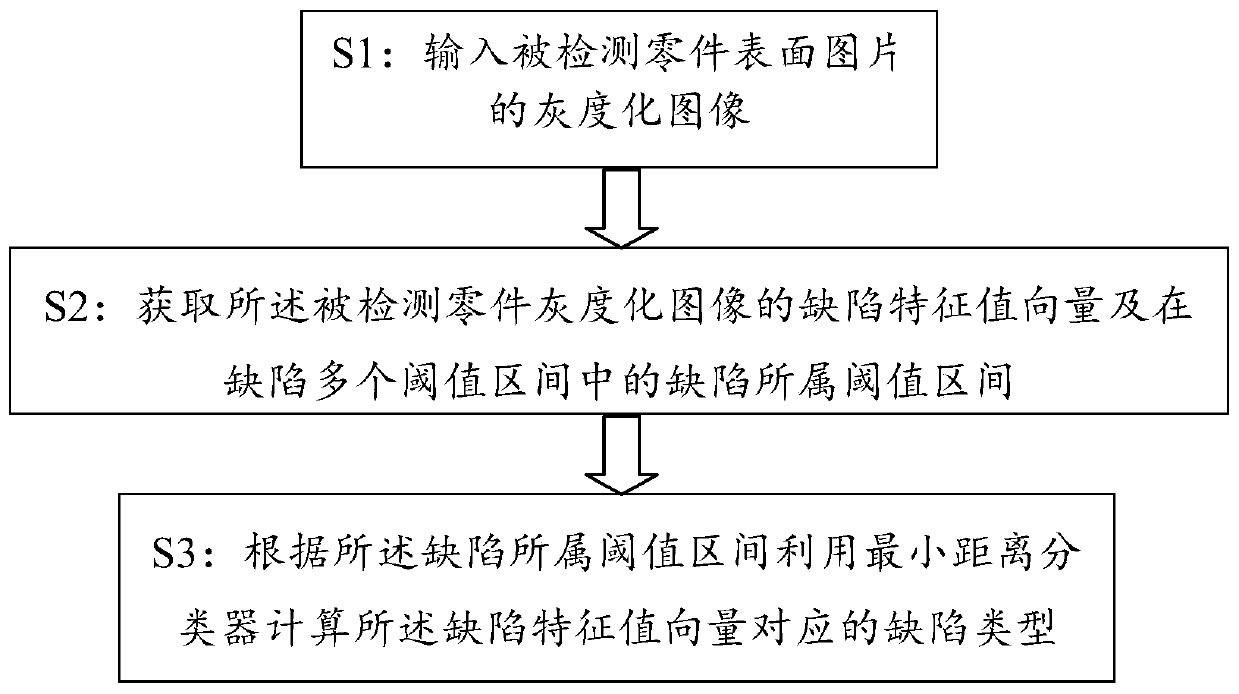
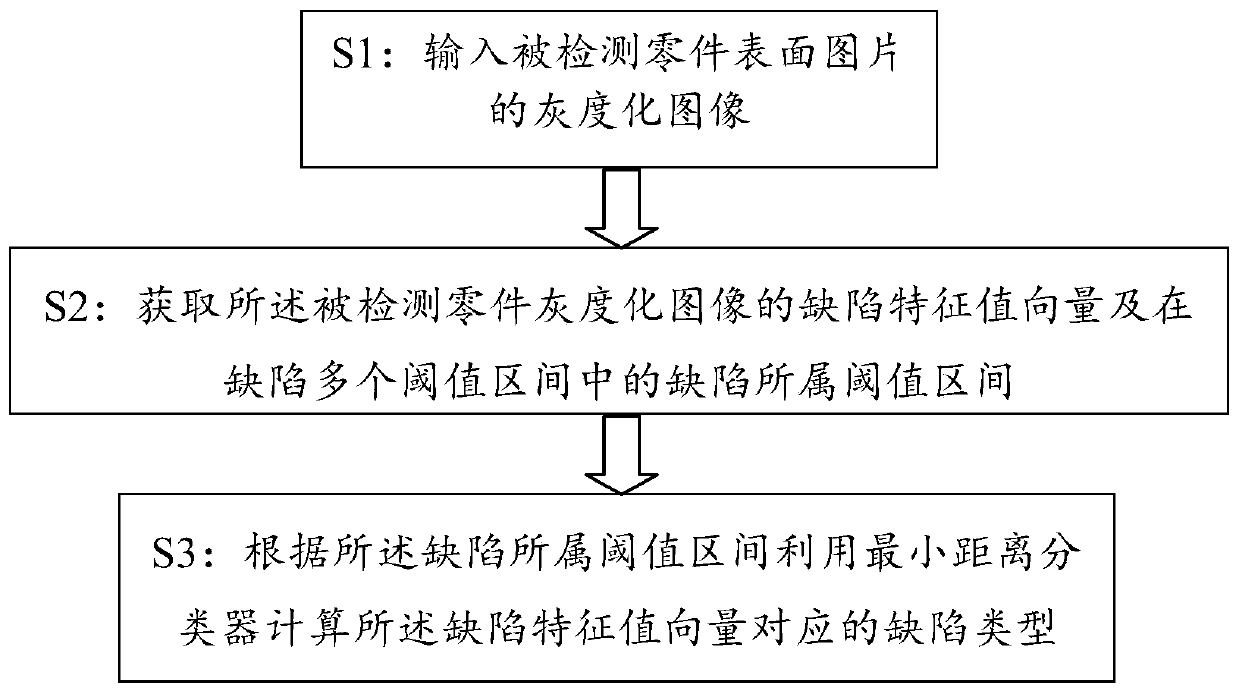
Plastic part defect detection method based on multiple threshold intervals
ActiveCN106770321ASolve the detection speed is slowImprove detection accuracyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPattern recognitionMinimum distance classifier
The invention provides a plastic part defect detection method based on multiple threshold intervals. The method comprises the following steps: S1, inputting a grayed image of a surface picture of a detected part; S2, obtaining a defect eigenvalue vector of the grayed image of the detected part and a defect threshold interval in multiple threshold intervals of the defect; and S3, calculating a defect type corresponding to the defect eigenvalue vector by using a least distance classifier according to the defect threshold interval. Through the plastic part defect detection method, multiple threshold intervals are set, and the least distance classifier is used; the automation detection of the surface defects of the plastic parts is achieved; the detection efficiency of the surface defects of the plastic parts is improved; the manpower, the material resources and the financial resources are reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
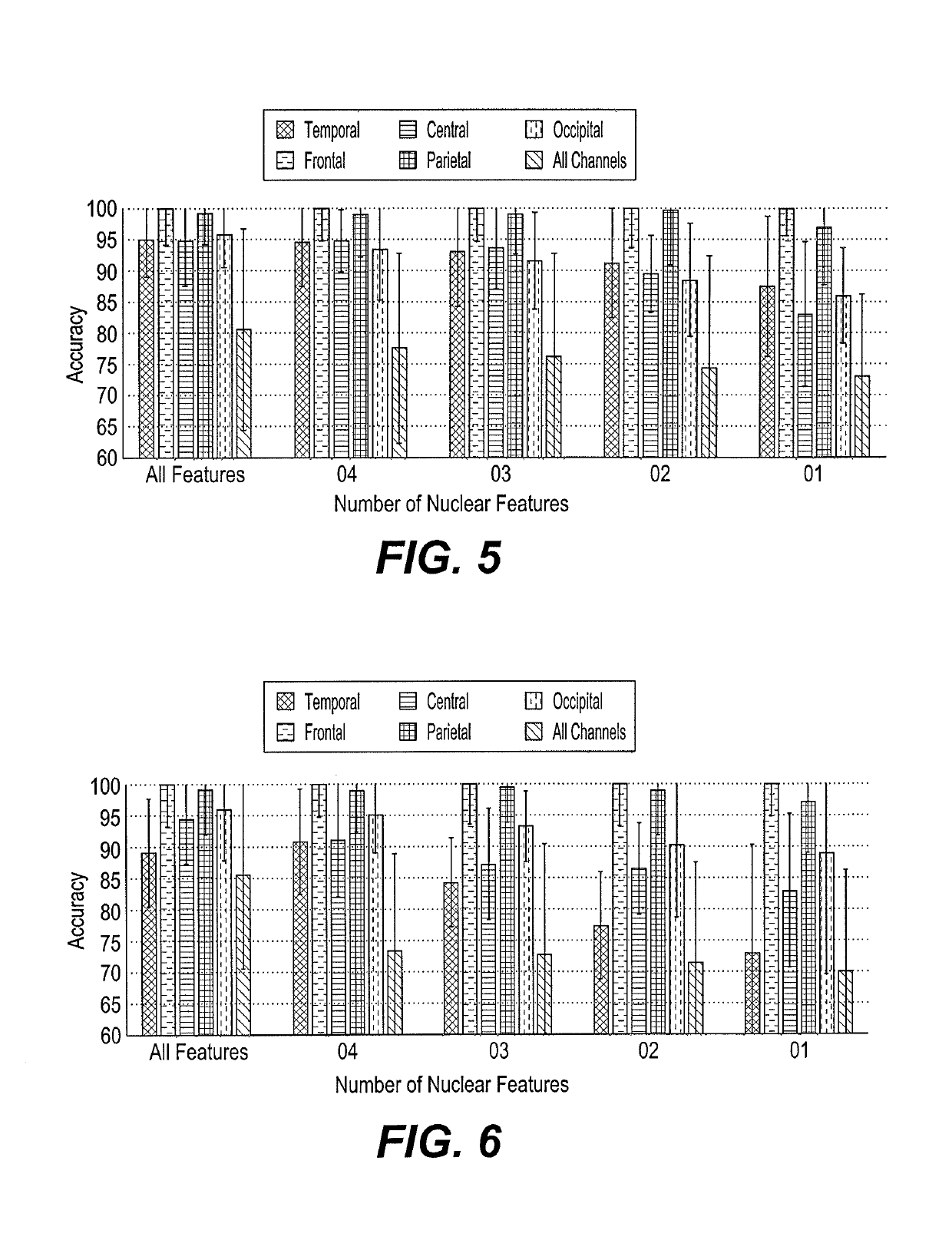
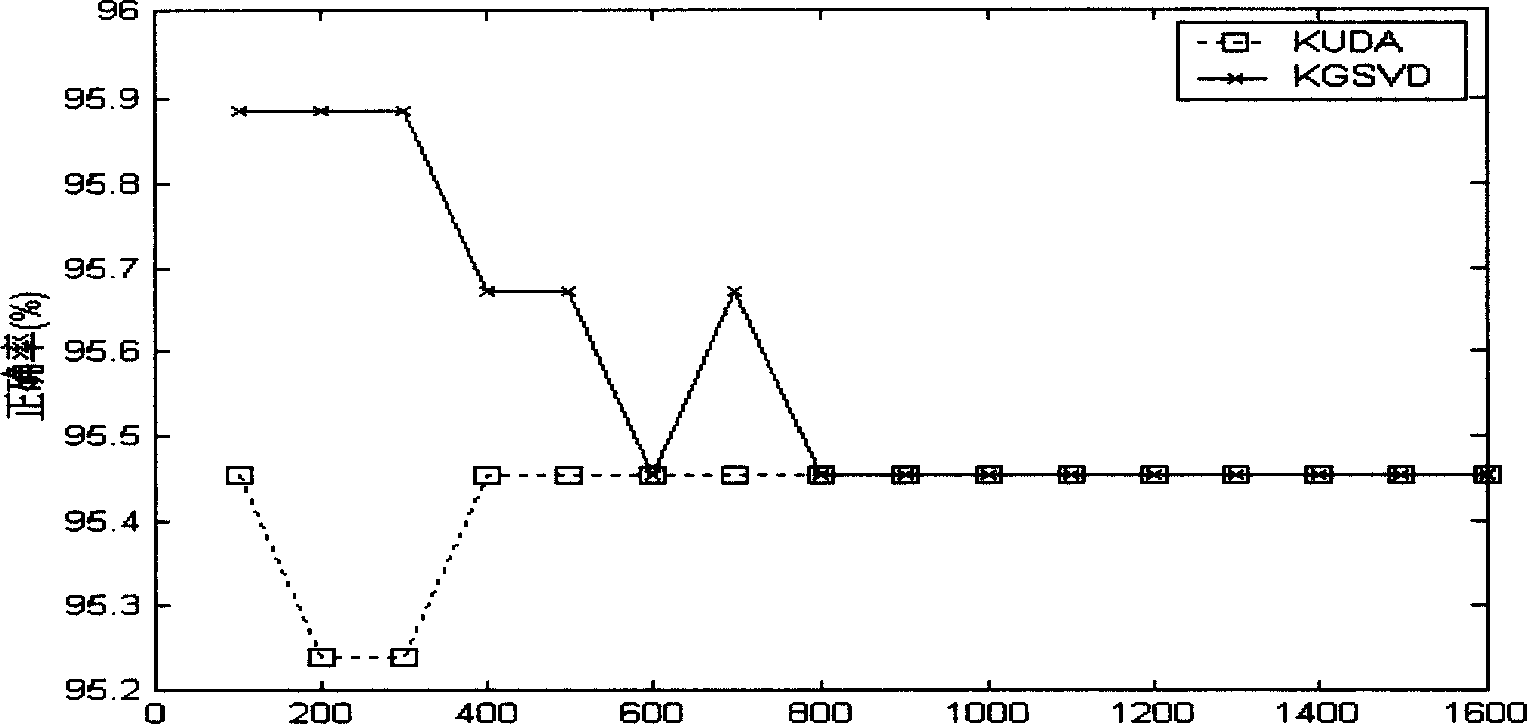
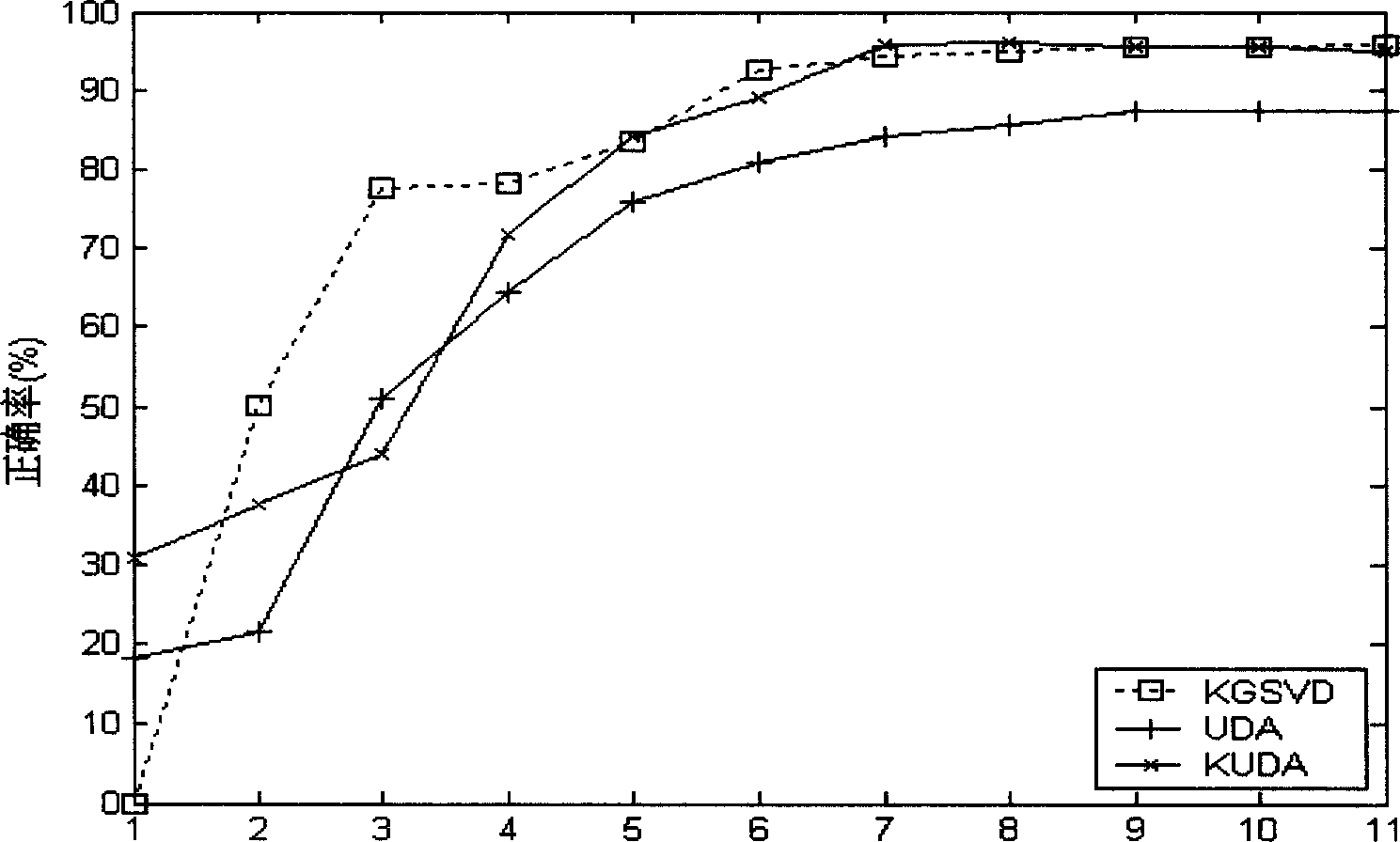
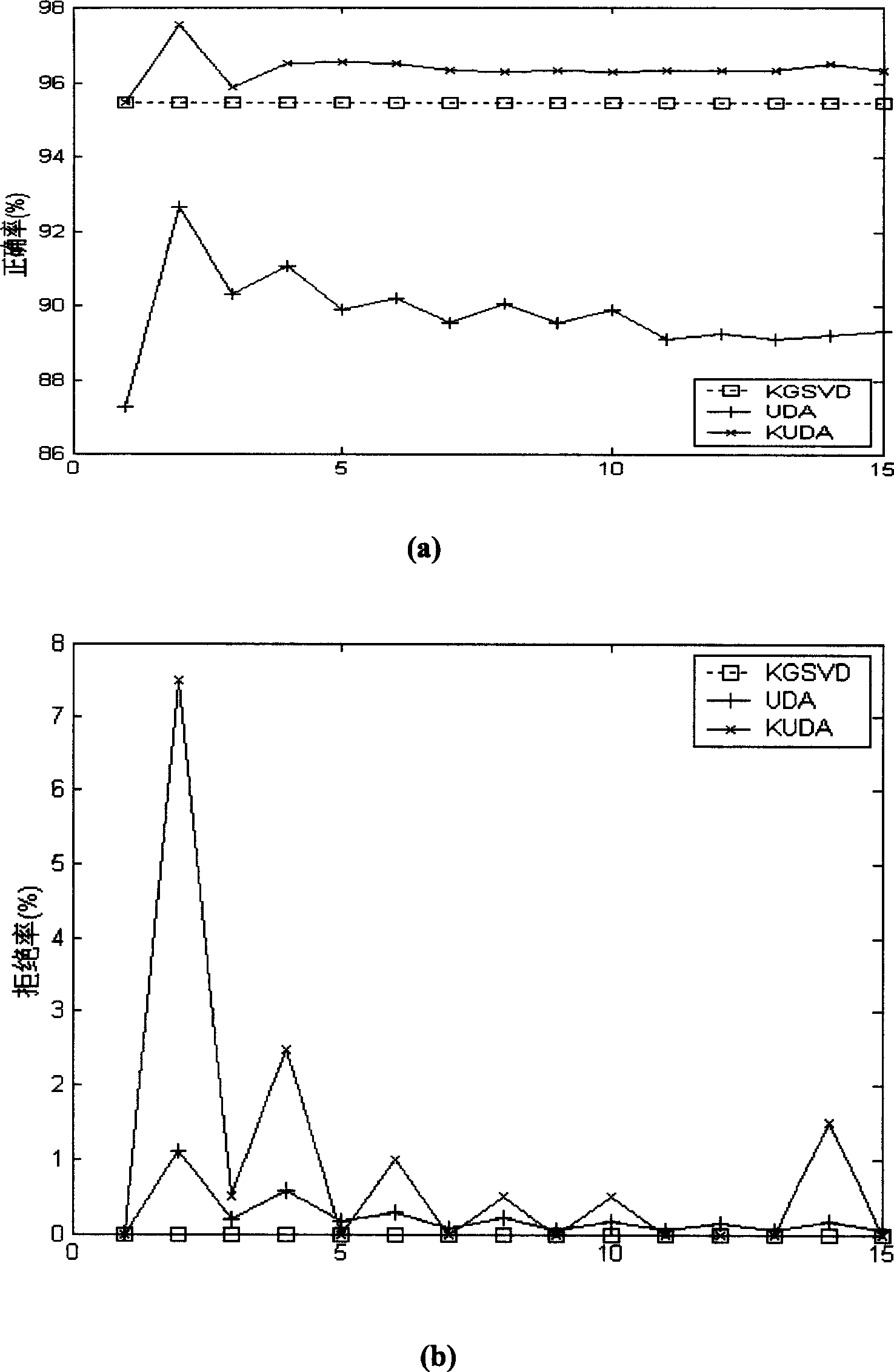
Method of classifying raw EEG signals
InactiveUS10299694B1Improve abilitiesLow abilityElectroencephalographyMedical data miningSingular value decompositionMinimum distance classifier
The method of classifying raw EEG signals uses a classification method based on nuclear features extracted as dominant singular values from an EEG signal segment using singular value decomposition (SVD) and a class means-based minimum distance classifier (CMMDC) to classify a patient's EEG signals. From a mean EEG signal, a set of zero-centered EEG signals are calculated, and from the zero-centered EEG signals and a standard deviation of the EEG signals, a unit variance is calculated for each component. Using the standardized component signals a nuclear matrix is calculated, to which singular value decomposition is applied to generate a set of singular values. The CMMDC is applied to class means associated with first and second classes and a nuclear feature vector to classify the patient's EEG signals as belonging in either the first or second class.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
Hand writing number identification method based on kernel function
InactiveCN1624712ASmall amount of calculationEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierShortest distance
A hand-written number identification method based on nuclear function, including character extraction and identification of the hand-written number, at the phase of the extraction, firstly map the low-dimension character to the high-dimension space via nonlinear mapping function to make the problem of the character space become linear dividable or near linear dividable and further uses the nuclear function to extract the characters; at the character identification phase, use simple k-NN distance classifier and shortest distance classifier to identify.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Discrimination-oriented correlated characters fusion recognition system of an image
InactiveCN101515330AAvoid singularity problemsAvoid difficultiesCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierHat matrix
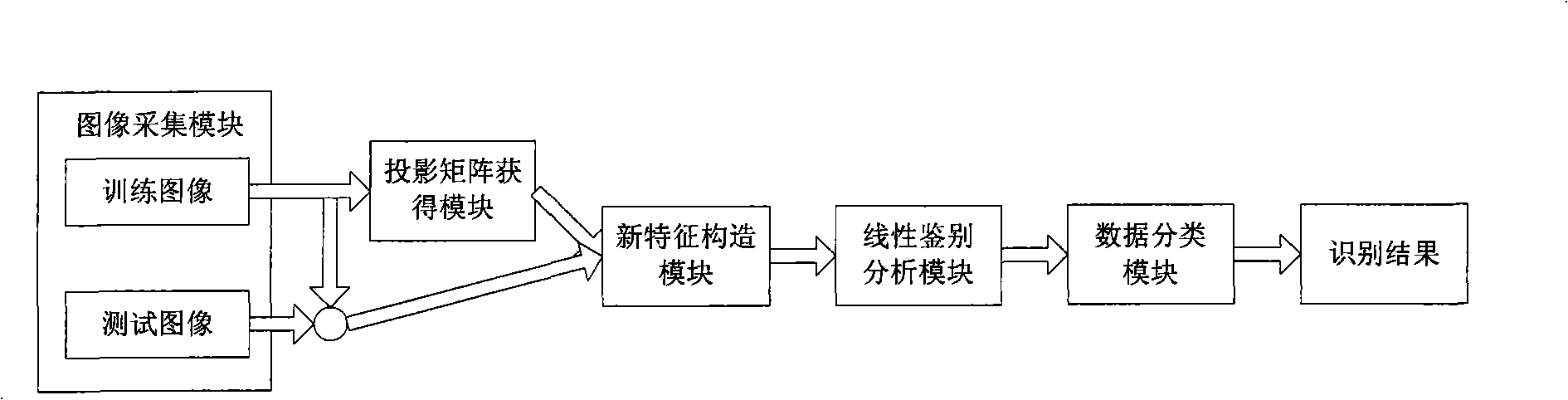
A discrimination-oriented correlated characters fusion recognition system of an image belongs to the technical field of telecommunication, comprising the following steps: first, determining a projection matrix via an iterative process according to a training image; second, respectively projecting the training image and test image to a characteristic space by utilizing the projection matrix, extracting the training characteristic and test characteristic and then carrying out parallel fusion respectively on the characteristics to form a new characteristic; at last, extracting characteristics with more discriminability by utilizing linear discriminant analysis method and adopting minimum distance classifier, thus identifying the category to which the test image belongs. The system can more naturally depict the relation between row vectors and the relation between column vectors of an image matrix; the extracted characteristics can more intensively reflect the image information; further discrimination-oriented processing can extract characteristics with more discriminability; and the system can improve not only processing speed but also recognition performance by being applied to the image recognition.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
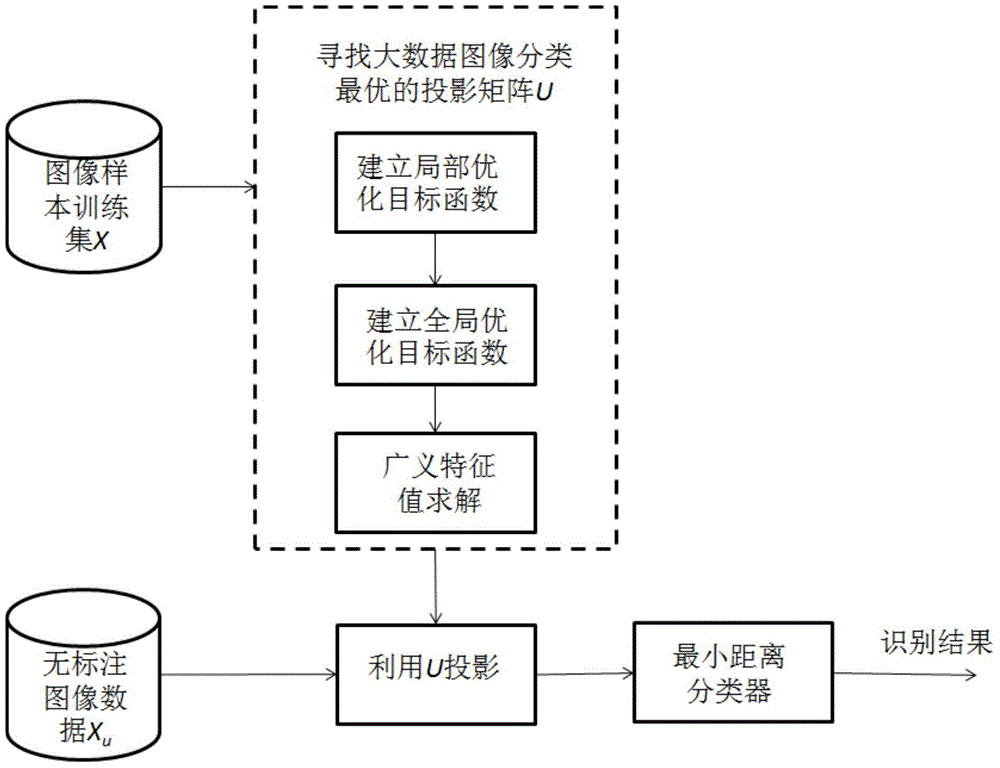
Big data image classification method
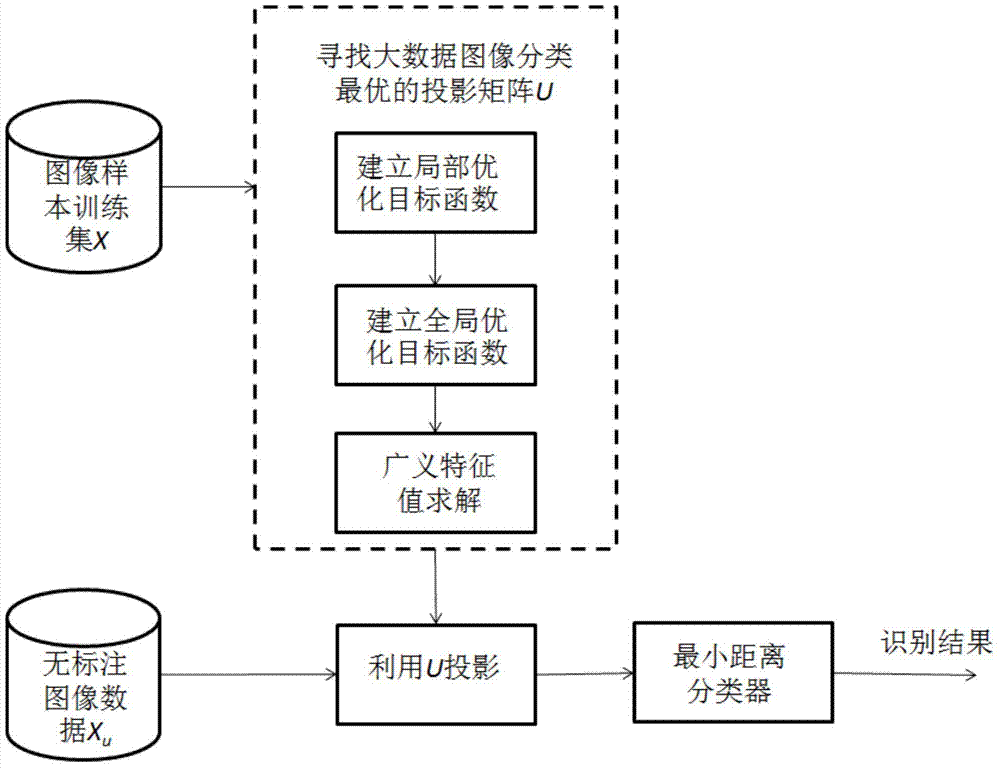
ActiveCN103488744AImprove accuracyReduce dependenceCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHat matrixMinimum distance classifier
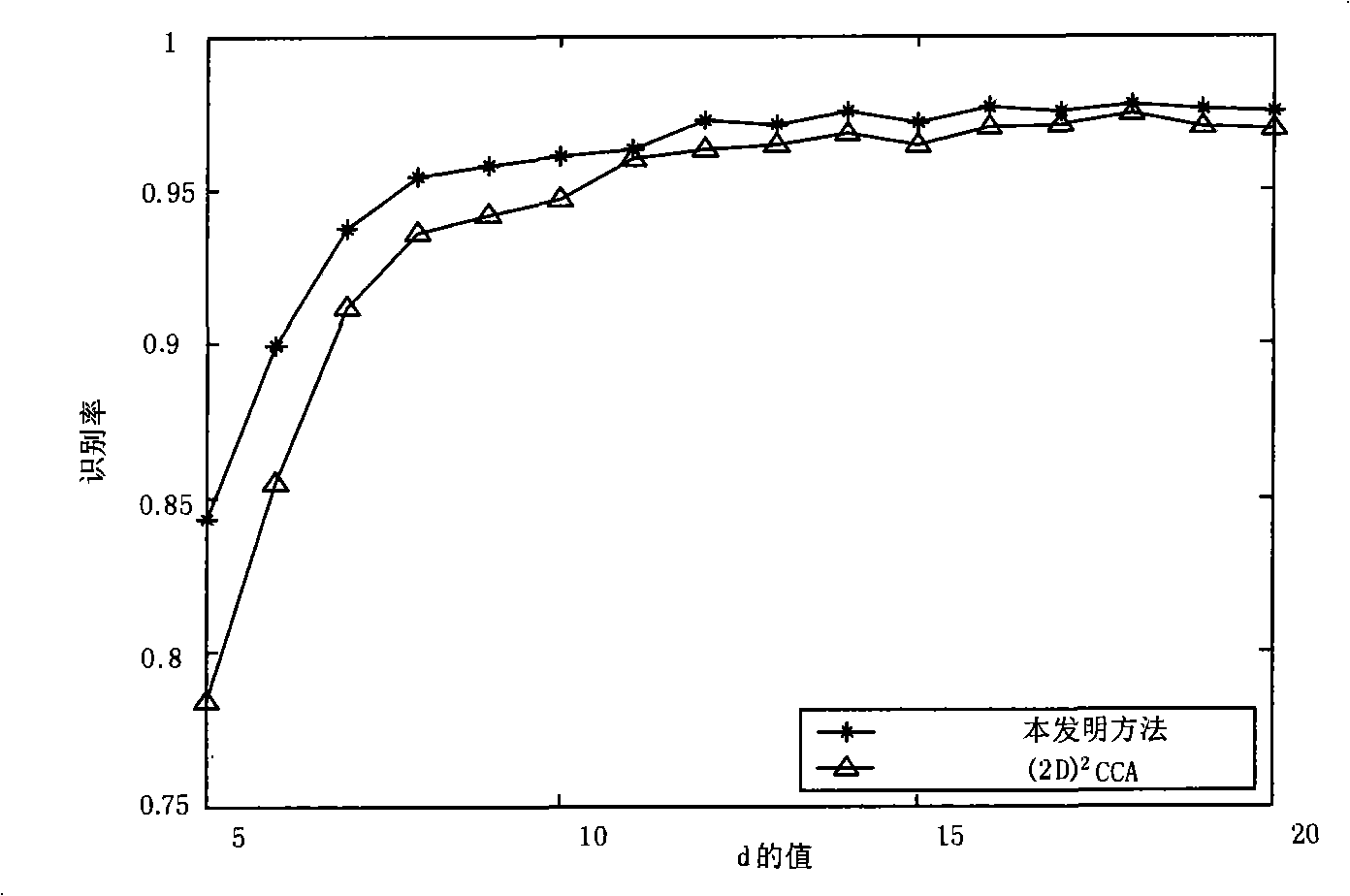
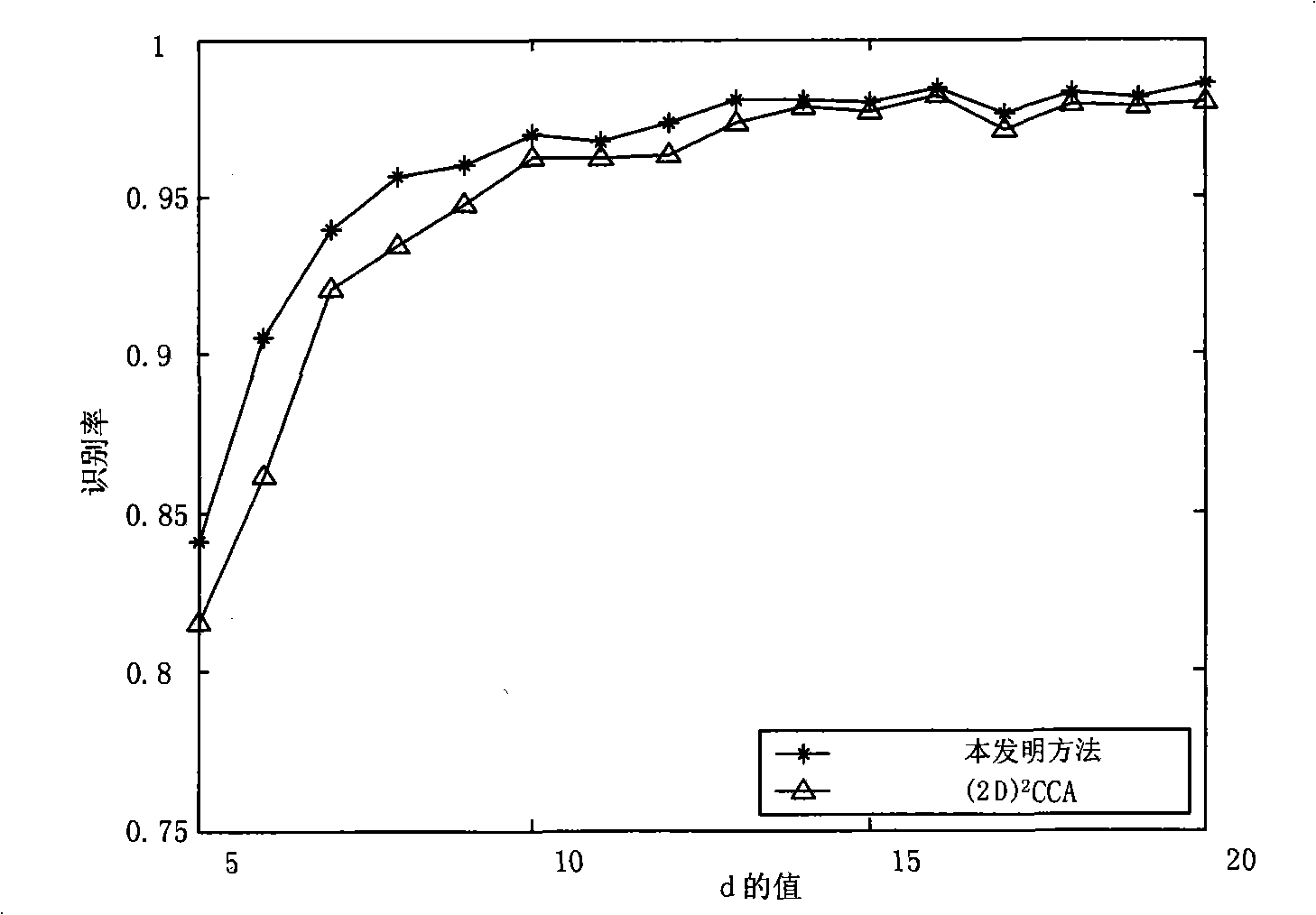
The invention discloses a big data image classification method. The big data image classification method comprises a first step of enabling image samples to be collected to serve as a training set, a second step of searching a projection matrix optimal in big data image classification, a third step of performing projection on data without marks and a fourth step of adopting a minimum distance classifier to classify the samples after projection. According to the method, local geometric information of sample distribution can be effectively utilized, classified discrimination information is extracted, dependence of big data image classification on manually marked samples is reduced, storage cost in the training process is effectively reduced, and the big data image classification method has higher classification accuracy than a representative image classification method based on linear discrimination analysis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
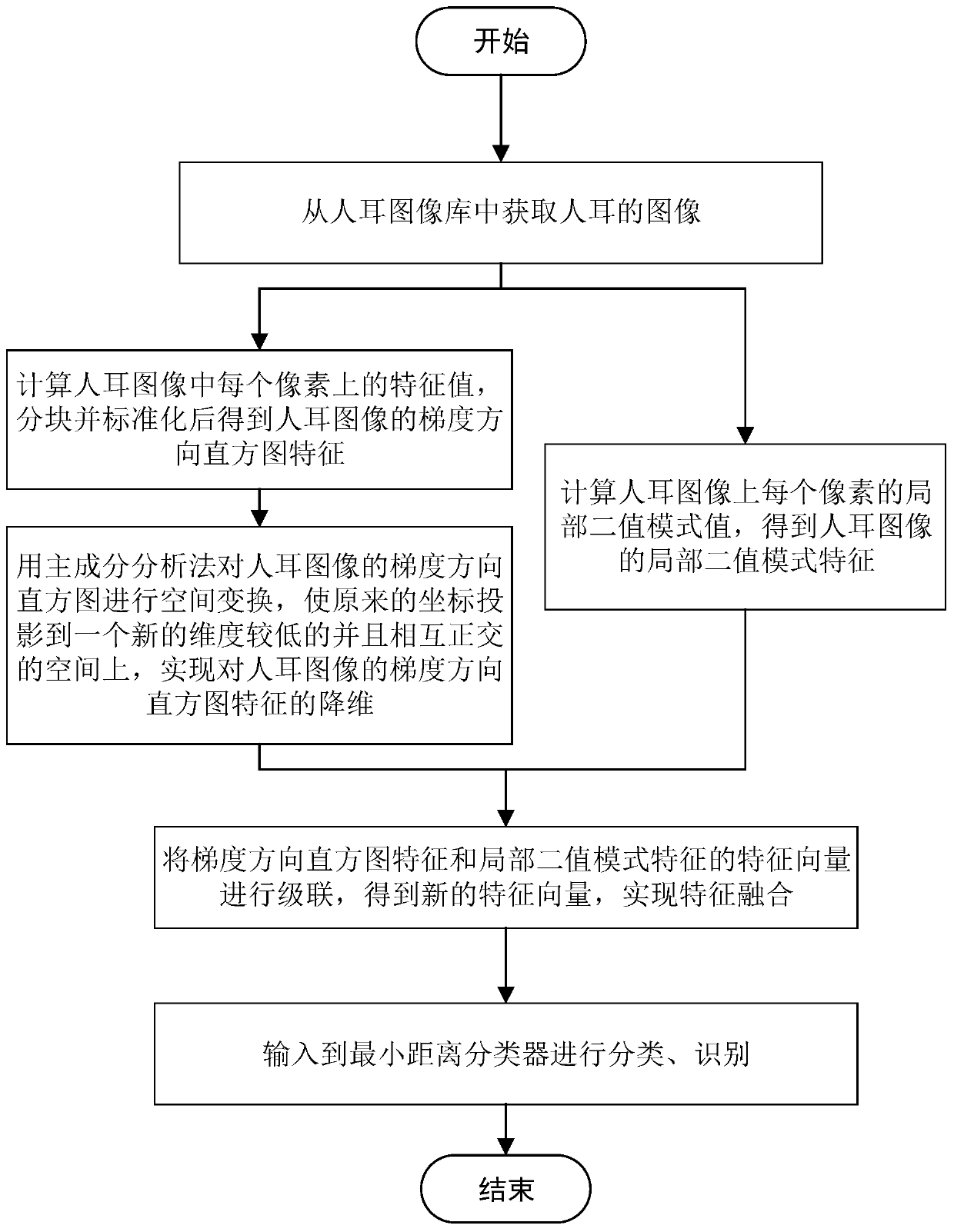
Human ear recognition method based on fusion of gradient direction histogram and local binary pattern
ActiveCN110188646AImprove accuracyHigh speedCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a human ear recognition method based on fusion of a gradient direction histogram and a local binary pattern, which solves the problem of low human ear recognition rate in a human ear image. According to the method, firstly, the gradient direction histogram of the image is extracted, dimensionality reduction is carried out through a principal component analysis method, thenthe texture features of the image are extracted through the local binary pattern, then the two features are fused, and finally classification is carried out through a minimum distance classifier. According to the invention, through the multi-feature fusion, the recognition rate of human ear recognition is improved, and the method has good implementability and effectiveness.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
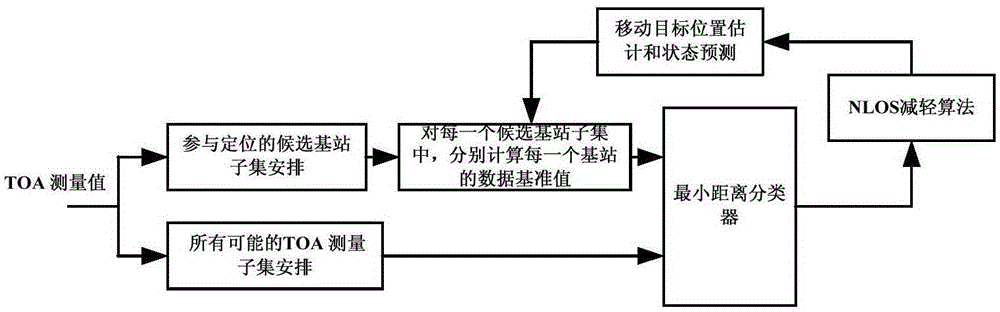
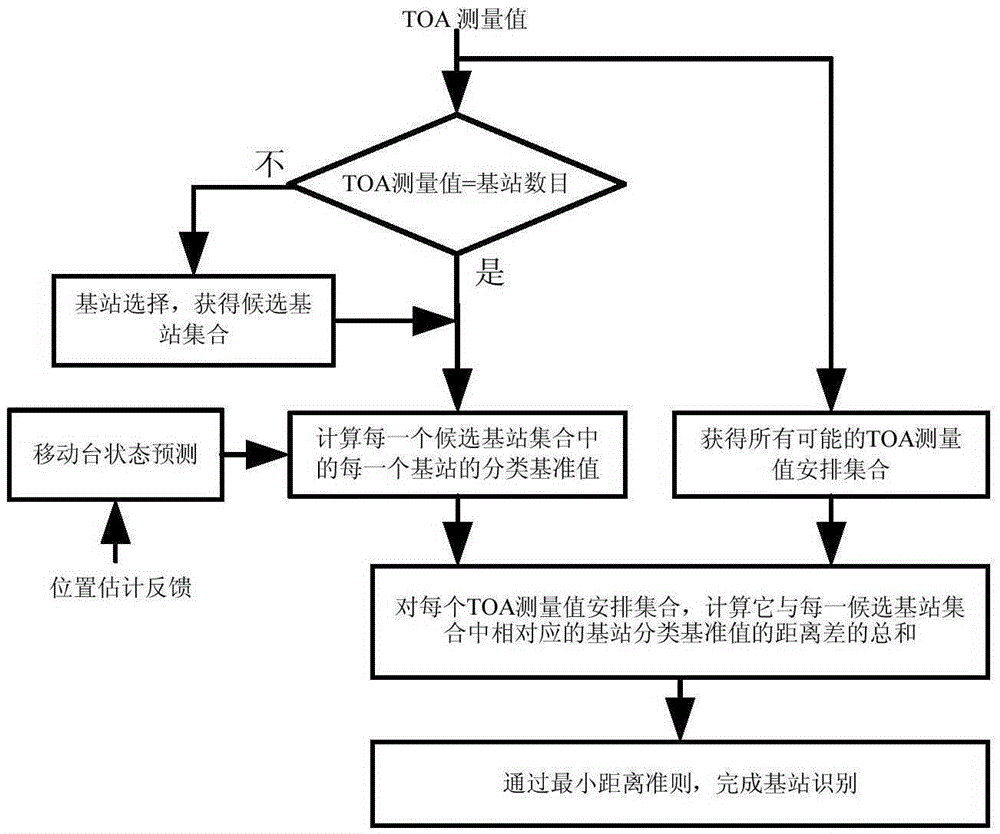
Base station identification method in single-frequency network positioning system
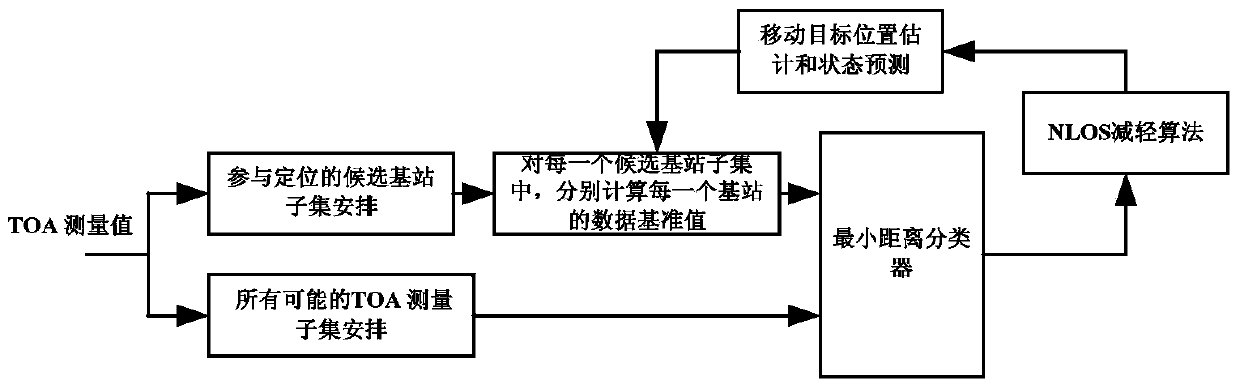
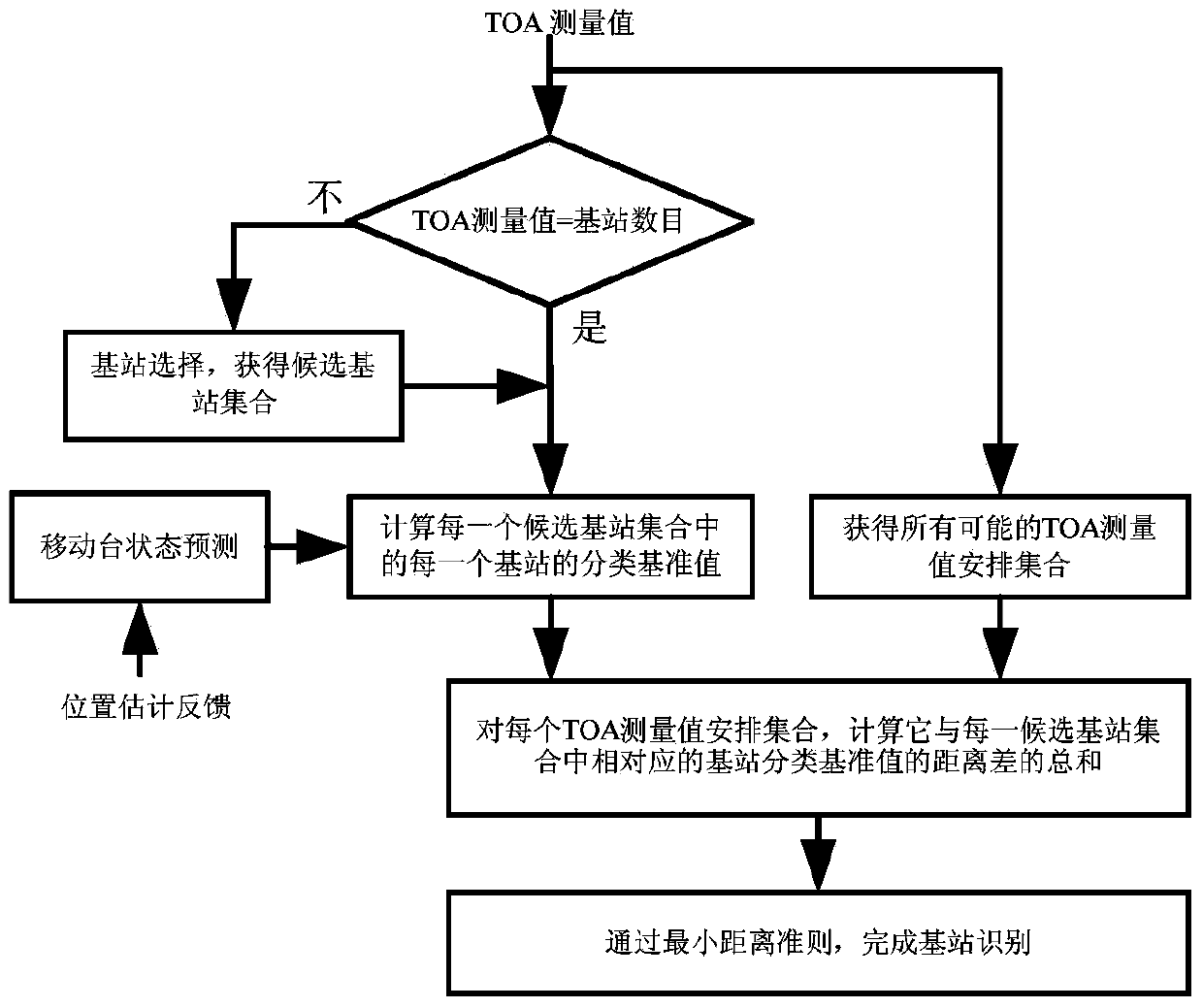
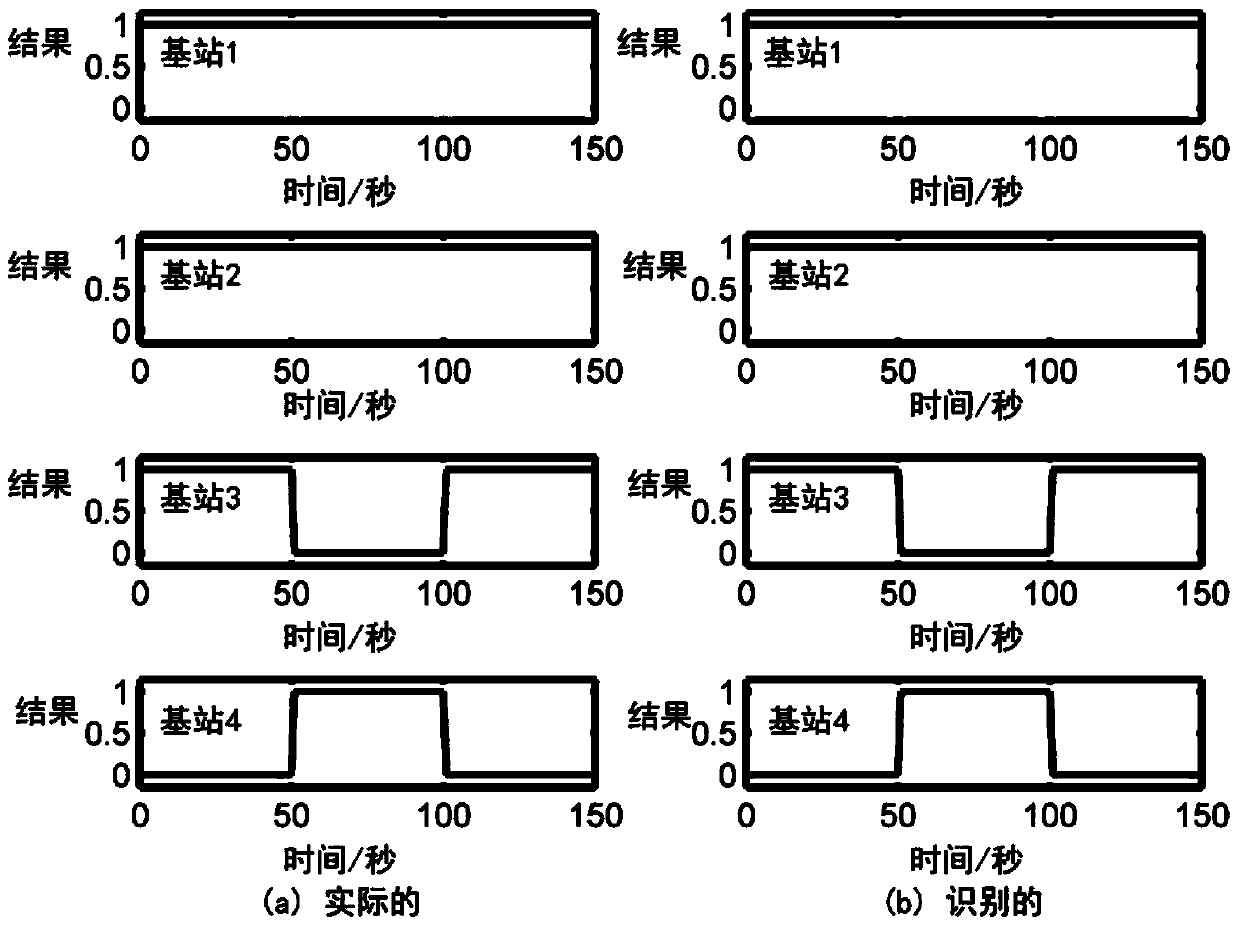
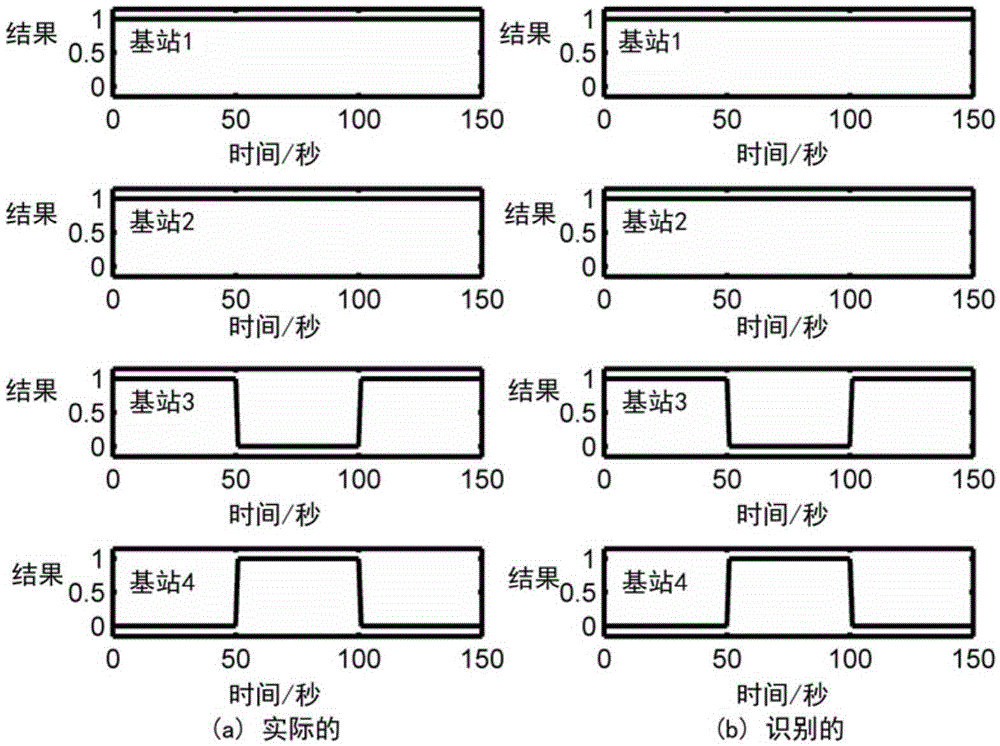
ActiveCN103744051AEasy to identifyAccurate target informationPosition fixationMinimum distance classifierState prediction
The invention provides a base station identification method in a single-frequency network positioning system. The method, based on the positioning system, converts the problem of base station identification to the problem of data classification, and the base station identification is realized through a minimum-distance classifier; a state prediction model is utilized to estimate motion parameters of a mobile station, and thus hardware requirement of the system is lowered; and to get a better base station identification effect in a non-line-of-sight environment, an interaction multi-model method is utilized to reduce non-line-of-sight effect, and thus more accurate mobile station object information is obtained. Two different functions, position estimation and base station identification, of the positioning system are closely associated, so that the method is economic and effective, and is suitable for all digital television standards.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
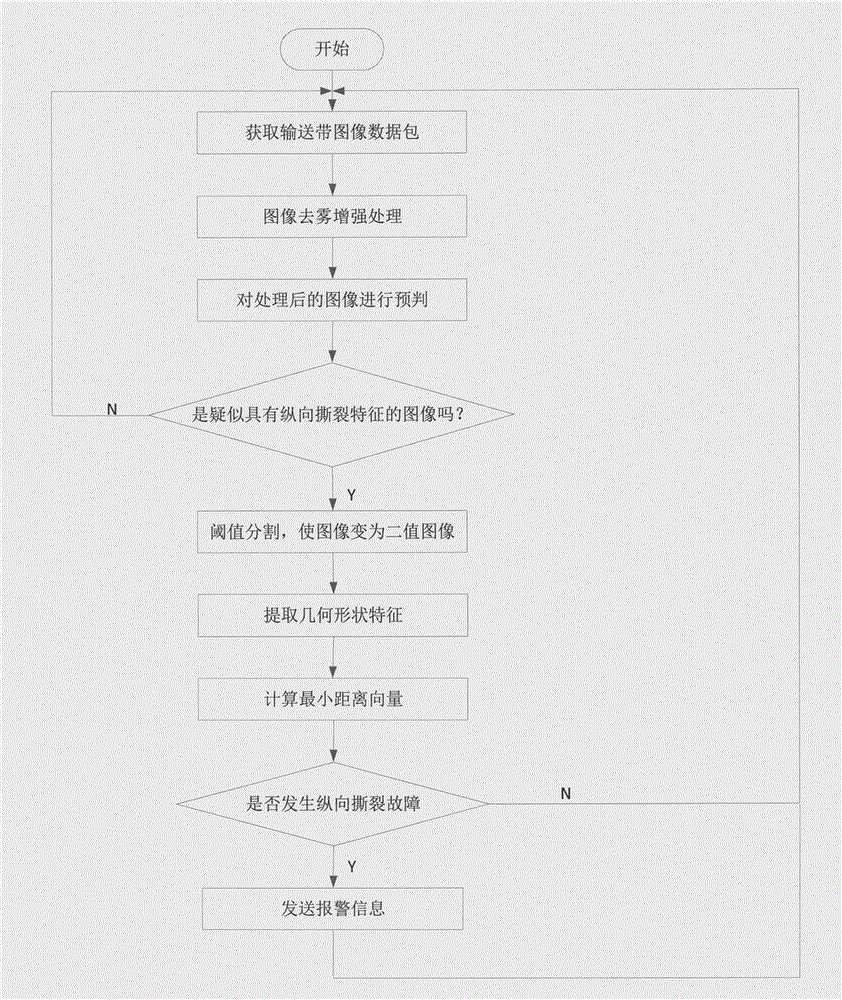
Method for online detection of longitudinal tear fault of conveyor belt
InactiveCN105083916AImprove reliabilityImprove real-time performanceControl devices for conveyorsMinimum distance classifierImaging quality
The invention provides a method for online detection of a longitudinal tear fault of a conveyor belt, and belongs to the field of non-destructive testing. The purpose of online detection of the longitudinal tear fault of the conveyor belt is achieved, and the accuracy and the real-time performance of detection are improved. According to the invention, defogging enhancement processing is conducted on acquired conveyor belt images in terms of a gray level morphology gradient and a defogging enhancement algorithm of a single-scale Retinex (SSR) algorithm, and therefore the image quality of the conveyor belt images is improved; conveyor belt binary images are acquired in terms of a threshold segmentation algorithm of an improved genetic algorithm of a gray level average method; and a conveyor belt longitudinal tear image feature extraction and fault recognition algorithm with the combination between a conveyor belt longitudinal tear fault pre-judgment and geometric feature statistical method and a minimum distance classifier is adopted, and therefore the accuracy and the real-time performance of online detection of the longitudinal tear fault are improved. The method has high use value in the process of industrial application.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV +1
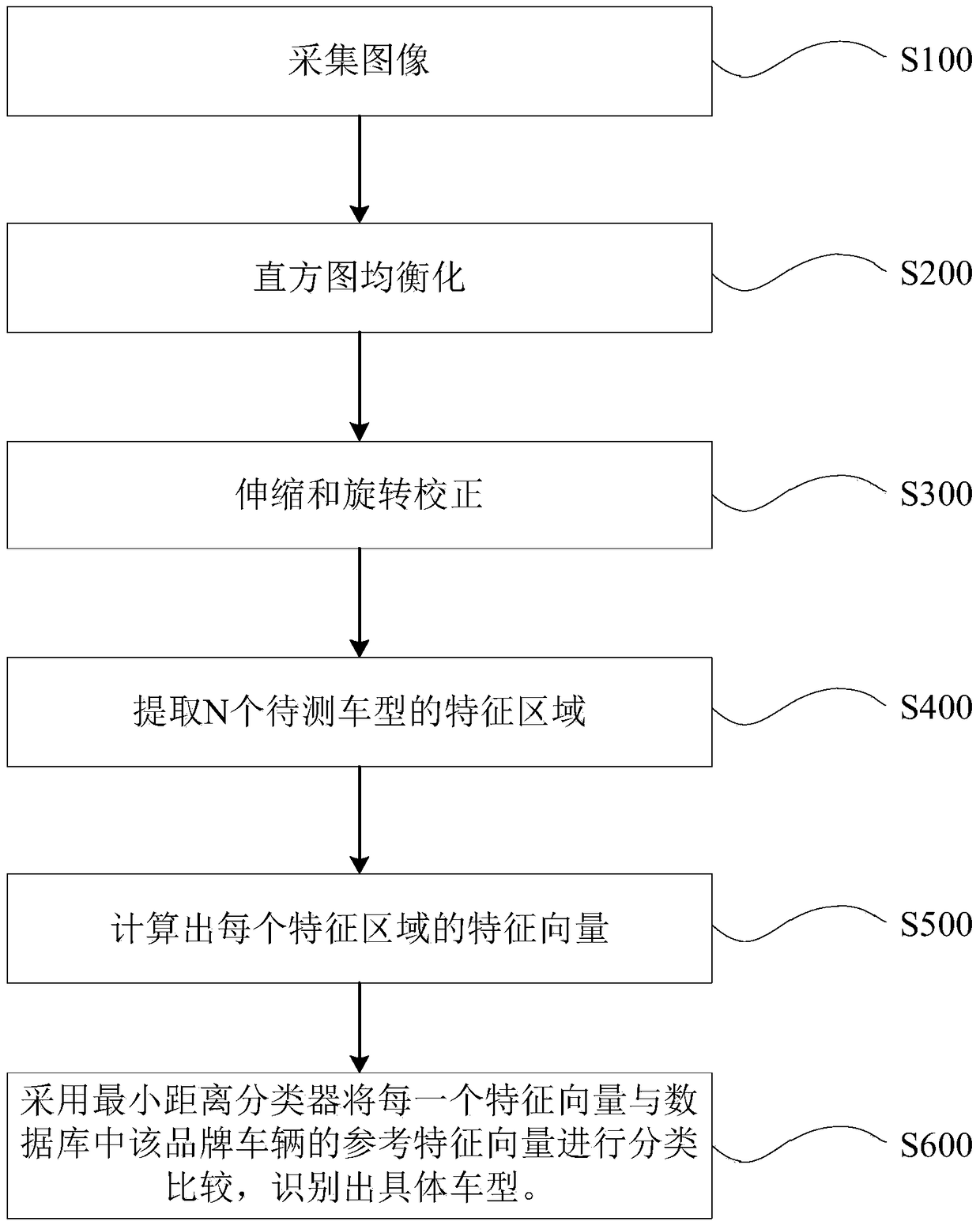
Vehicle model recognition method of the same brand based on spatial location information
InactiveCN103500327BReduce misidentificationImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierFeature vector
The invention relates to a method for identifying vehicle types of vehicles of the same brand based on spatial position information. The method includes: collecting images of the vehicles; performing histogram equalization on the images of the vehicles; setting the size of the license plate, and adjusting the histogram The image after image equalization is stretched and rotated; the feature area of N vehicle models to be tested is extracted according to the position of the corrected image relative to the license plate; the feature vector of each feature area is calculated; the minimum distance classifier is used to classify each feature vector Classify and compare with the reference feature vector of the brand vehicle in the database to identify the specific model. The method of the invention extracts the feature area of the license plate and then identifies the relevant parameters of the feature area, thereby improving the recognition accuracy of the vehicle type.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A defect detection method for plastic parts based on multiple threshold intervals
ActiveCN106770321BSolve the detection speed is slowImprove detection accuracyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPattern recognitionMinimum distance classifier
The invention provides a plastic part defect detection method based on multiple threshold intervals. The method comprises the following steps: S1, inputting a grayed image of a surface picture of a detected part; S2, obtaining a defect eigenvalue vector of the grayed image of the detected part and a defect threshold interval in multiple threshold intervals of the defect; and S3, calculating a defect type corresponding to the defect eigenvalue vector by using a least distance classifier according to the defect threshold interval. Through the plastic part defect detection method, multiple threshold intervals are set, and the least distance classifier is used; the automation detection of the surface defects of the plastic parts is achieved; the detection efficiency of the surface defects of the plastic parts is improved; the manpower, the material resources and the financial resources are reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
A base station identification method in a single frequency network positioning system
ActiveCN103744051BEasy to identifyAccurate target informationPosition fixationMinimum distance classifierState prediction
The invention provides a base station identification method in a single-frequency network positioning system. The method, based on the positioning system, converts the problem of base station identification to the problem of data classification, and the base station identification is realized through a minimum-distance classifier; a state prediction model is utilized to estimate motion parameters of a mobile station, and thus hardware requirement of the system is lowered; and to get a better base station identification effect in a non-line-of-sight environment, an interaction multi-model method is utilized to reduce non-line-of-sight effect, and thus more accurate mobile station object information is obtained. Two different functions, position estimation and base station identification, of the positioning system are closely associated, so that the method is economic and effective, and is suitable for all digital television standards.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
High spectroscopic data supervision classifying method based on information quantity dimensionality sequence
InactiveCN101299237BImprove classification efficiencyImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierInformation quantity
A high spectroscopic data supervision classification method based on information quantity dimensionality sequence includes the following steps: reading the high spectrum image data of a certain region; selecting a reference spectrum from the spectrum library or selecting the training sample from images to execute wave band average acquiring reference spectrum; calculating one by one the referencespectrum and all test spectral information quantity dimensionality sequence; executing vector angle matching one by one the test spectrum with all reference spectral information quantity dimensionality sequence, and using minimum distance classification machine to classify; result binarization matching, the matching result of each series of field culture is represented by the binary images, each image only includes a series of field culture. The high spectroscopic data classification method based on information quantity dimensionality sequence introduces the information quantity dimensionality into the spectrum domain analysis, synthetizes the advantages of the all band matching and partial quantization characteristic matching, can obtain higher classification effectiveness and classification accuracy, and has important value in the high spectroscopic data classification and object identification.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Calculation method and system for crop disease index
ActiveCN104751122BImprove the level of prevention and controlQuick implementationClimate change adaptationCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierTreatment field
The invention discloses a computing method and a computing method system for crop disease index. The computing method comprises the following steps: acquiring image of crop and pre-processing the image; dividing the pre-processed image into multiple sub-images and extracting color characters of the sub-images; using a minimum distance classifier for identifying the disease types and disease level of the sub-images according to the color characters of the sub-images; computing the crop disease index according to the disease types and disease level of the sub-images. The method solves that the disease index computing of the prior art depends on experience and knowledge of pathology of field crop protection persons, the statistical result is inaccurate and manual computation is required. The method is conducive to improve the prevention and treatment level for crop disease index and promote the implementation of precision agriculture, and novel method and technology are provided for the crop disease prevention and treatment field.
Owner:北京市农林科学院信息技术研究中心
Light spectrum and spatial information bonded high spectroscopic data classification method
InactiveCN100590402CAchieve fine classificationImprove reliabilityRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsMinimum distance classifierClassification methods
Disclosed is a hyperspectral data classification method which is combined spectrum and spatial information. The steps comprises (1) reading the hypersectral data, (2) confirming the minimum size of structural element, (3) calculating differentiation between picture elements in neighborhood of each structural element by extended mathematical morphology expansion and corrosion operation, (4) obtaining exponential value of morphology eccentricity by the extended expansion and the corrosion operation of step (3), (5), constantly repeating the above steps with the adding of the size of the structural element to achieve the maximum size of the structural element, (6), constantly updating the exponential value MEI of morphology eccentricity in iteration process via the obtained new value, and generating a final exponential value MEI of morphology eccentricity after the iteration process is finished, (7) realizing the extraction of the data characteristic by the image of the exponential valueMEI of morphology eccentricity, namely generating ground object type information, and realizing sophisticated category of the ground object by a minimum-distance classifier. The method is an unsupervised classification method for hyperspectral ground object with strong stability, high reliability and high accuracy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Discrimination-oriented correlated characters fusion recognition system of an image
InactiveCN101515330BAvoid singularity problemsAvoid difficultiesCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierHat matrix
A discrimination-oriented correlated characters fusion recognition system of an image belongs to the technical field of telecommunication, comprising the following steps: first, determining a projection matrix via an iterative process according to a training image; second, respectively projecting the training image and test image to a characteristic space by utilizing the projection matrix, extracting the training characteristic and test characteristic and then carrying out parallel fusion respectively on the characteristics to form a new characteristic; at last, extracting characteristics with more discriminability by utilizing linear discriminant analysis method and adopting minimum distance classifier, thus identifying the category to which the test image belongs. The system can more naturally depict the relation between row vectors and the relation between column vectors of an image matrix; the extracted characteristics can more intensively reflect the image information; further discrimination-oriented processing can extract characteristics with more discriminability; and the system can improve not only processing speed but also recognition performance by being applied to the image recognition.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Automatic decomposition method of arrayed semg signal
InactiveCN104997508BImprove decomposition accuracyImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMinimum distance classifierTime domain
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A Big Data Image Classification Method
ActiveCN103488744BImprove accuracyReduce dependenceCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHat matrixMinimum distance classifier
The invention discloses a big data image classification method, comprising the following steps: 1) collecting image samples as a training set; 2) finding the optimal projection matrix for big data image classification; 3) projecting unlabeled data; 4) The projected samples are classified using a minimum distance classifier. The method proposed by the invention can effectively utilize the local geometric information of sample distribution, and extract the identification information of classification, reduce the dependence of big data image classification on manually labeled samples, effectively reduce the storage cost in the training process, and its classification accuracy is higher than Representative image classification methods based on linear discriminant analysis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Radar target identification method based on adaptive neighborhood preserving projection
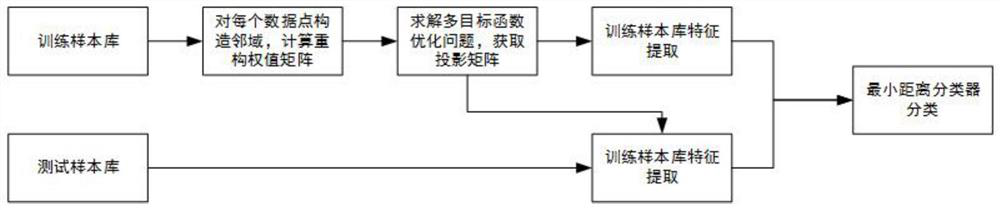
PendingCN113947104AImprove generalization abilityEffective classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionMinimum distance classifierAlgorithm
The invention discloses a radar target identification method based on adaptive neighborhood preserving projection, which is mainly suitable for a coherent radar to classify and identify hovering helicopters and small sea surface targets. The method mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a variation difference distance, constructing a neighborhood for each data point in a training sample library according to the variation difference distance, and calculating a reconstruction weight matrix; then solving a multi-objective function optimization problem to obtain a projection matrix; after the projection matrix is obtained, carrying out feature extraction on data in the training sample library and the test sample library; and finally, carrying out hovering helicopter and sea surface small target classification identification by adopting a minimum distance classifier. According to the method, internal information of the data is deeply mined and fused into a feature extraction process, low-dimensional features containing rich identification information in the JEM data are extracted, and classification and identification of a hovering helicopter and a small sea surface target by a radar are realized.
Owner:中国船舶集团有限公司第七二四研究所
A Locally Optimal Subspace Recognition Method for One-Dimensional Range Profiles of Radar Targets
InactiveCN103941244BImprove object classification performanceEasy to identifyWave based measurement systemsLocal optimumMinimum distance classifier
The invention provides a radar target one-dimensional range profile local optimal sub-space recognition method which effectively improves the performance of recognizing a radar target. According to the method, firstly, a nearest intra-class distance scattering matrix and a nearest between-class distance scattering matrix are calculated through training data; then, a local optimal sub-space is set up according to an optimal ratio criteria, the characteristics of the target are extracted, and the characteristics are classified through a minimum distance classifier; finally, the classification where the input target belongs is determined. The method specifically includes the steps of determining a vector X<W>ij and a vector Xij through a radar target one-dimensional range profile training vector Xij; determining a vector d<W>ij and a vector dij; determining a matrix DW and a matrix DB; determining m vectors a1, a2...and am of the local optimal sub-space; determining the equation (please see the equation in the specification) of the local optimal sub-space according to lambdai and a vector ai, wherein i is 1 or 2 or 3...or m; determining a template library according to the projection of the training vectors in the sub-space A; determining the local optimal sub-image of an input target one-dimensional range profile Xt; determining the distance between the local optimal sub-image and a library template vector, and determining the classification where the input target range profile belongs through the minimum distance classifier.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com