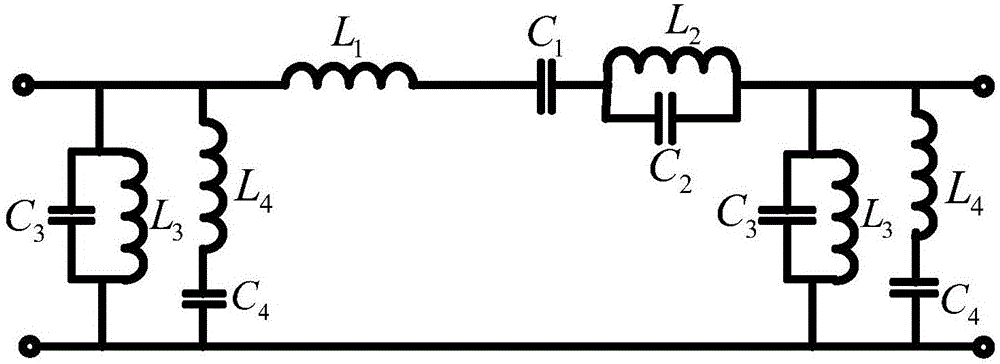
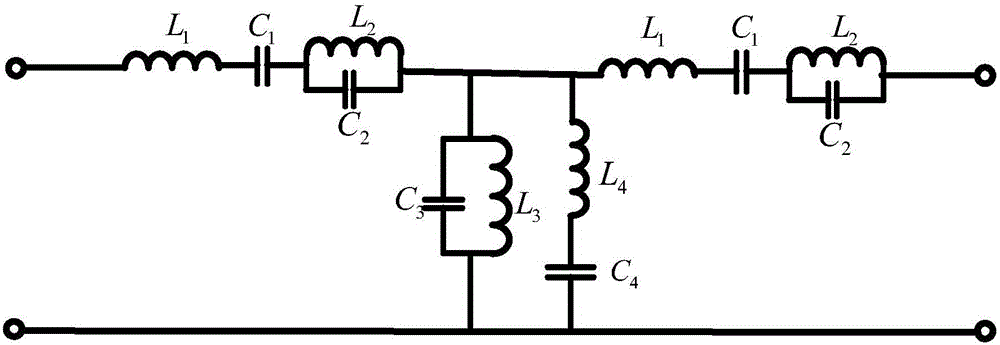
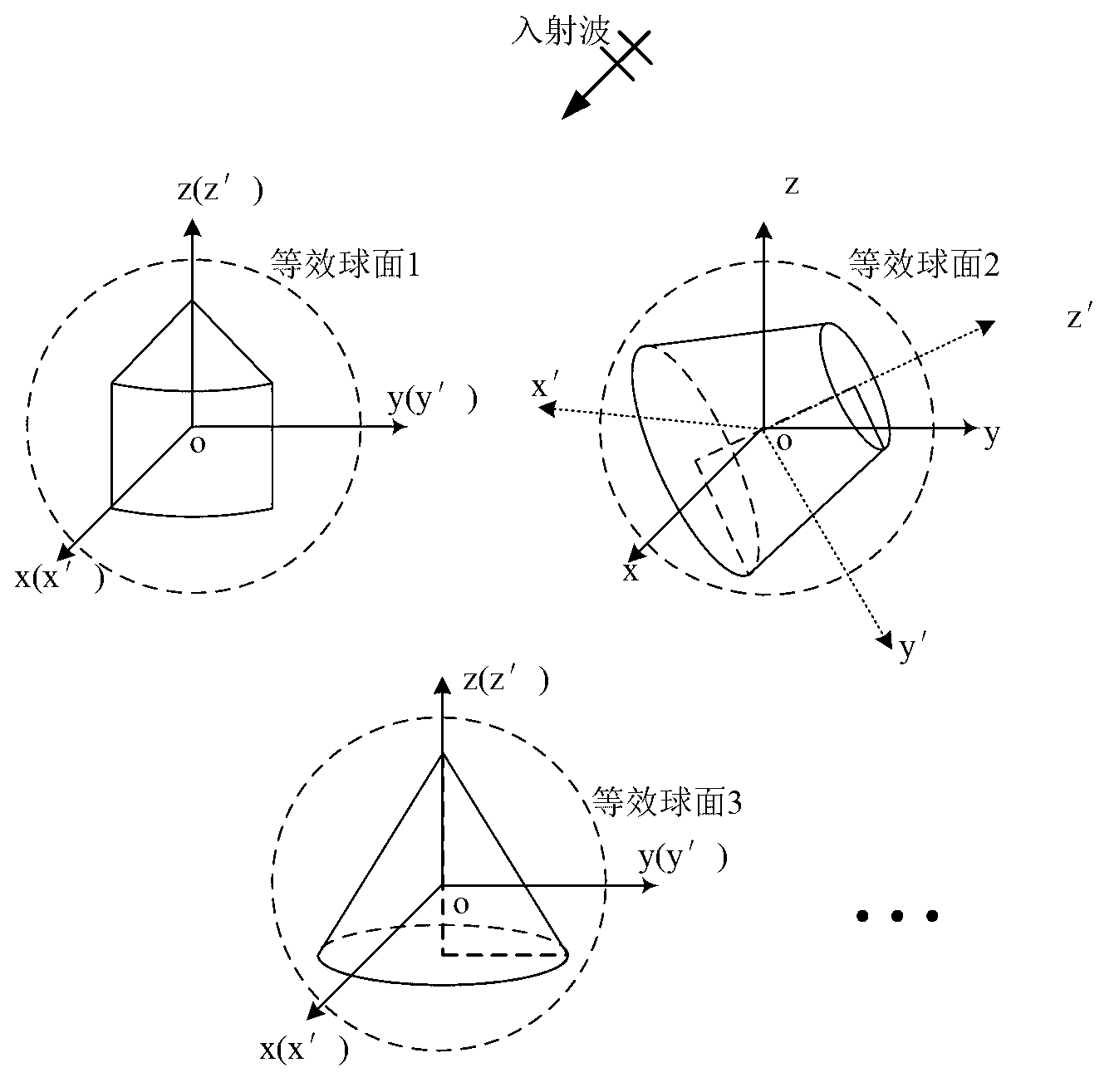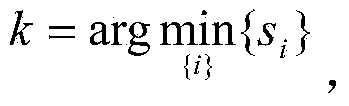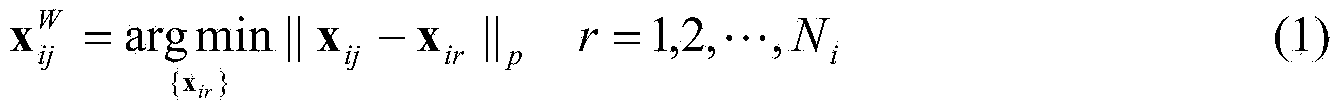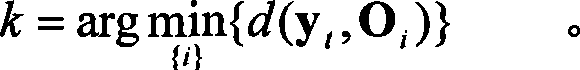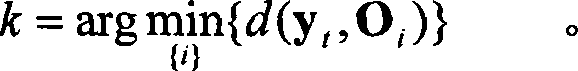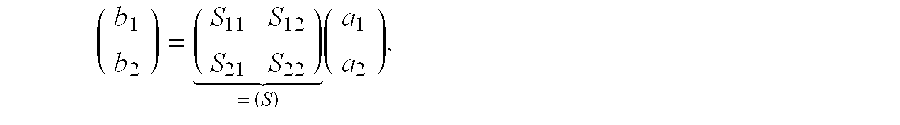Patents
Literature
153 results about "Scatter matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In multivariate statistics and probability theory, the scatter matrix is a statistic that is used to make estimates of the covariance matrix, for instance of the multivariate normal distribution.
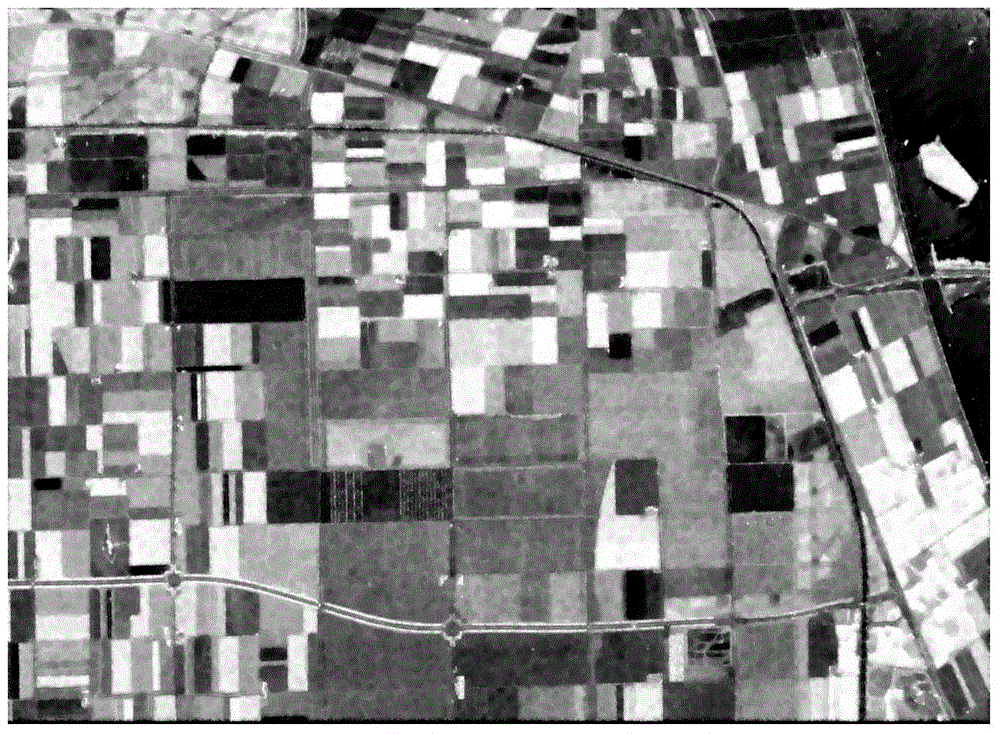
CD metrology analysis using a finite difference method
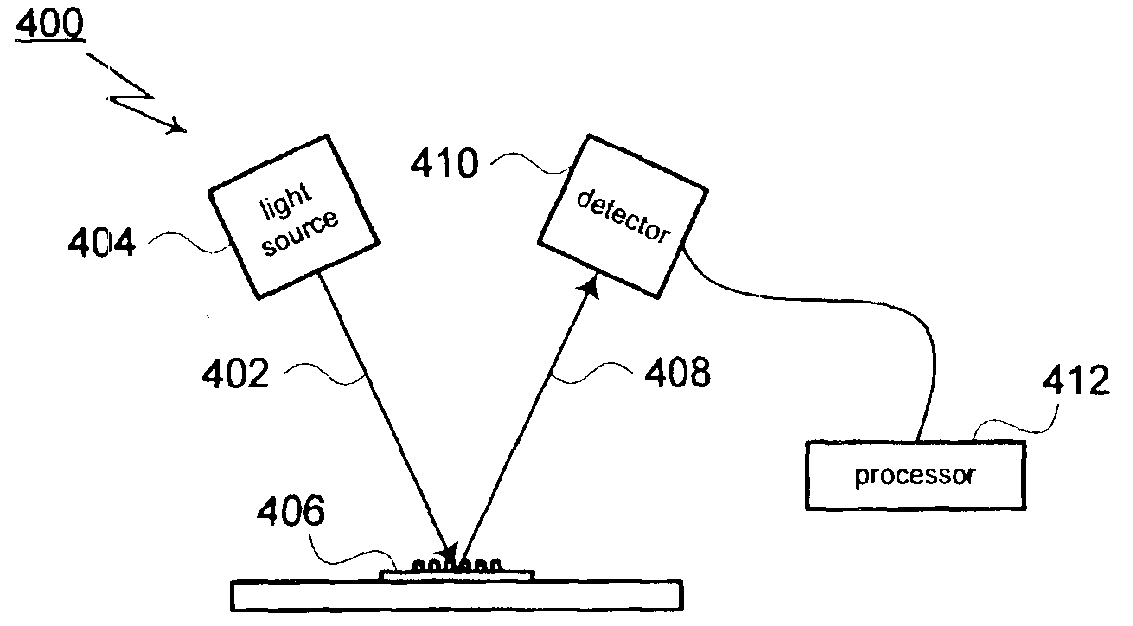
ActiveUS6919964B2Directly computeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyDirect evaluation
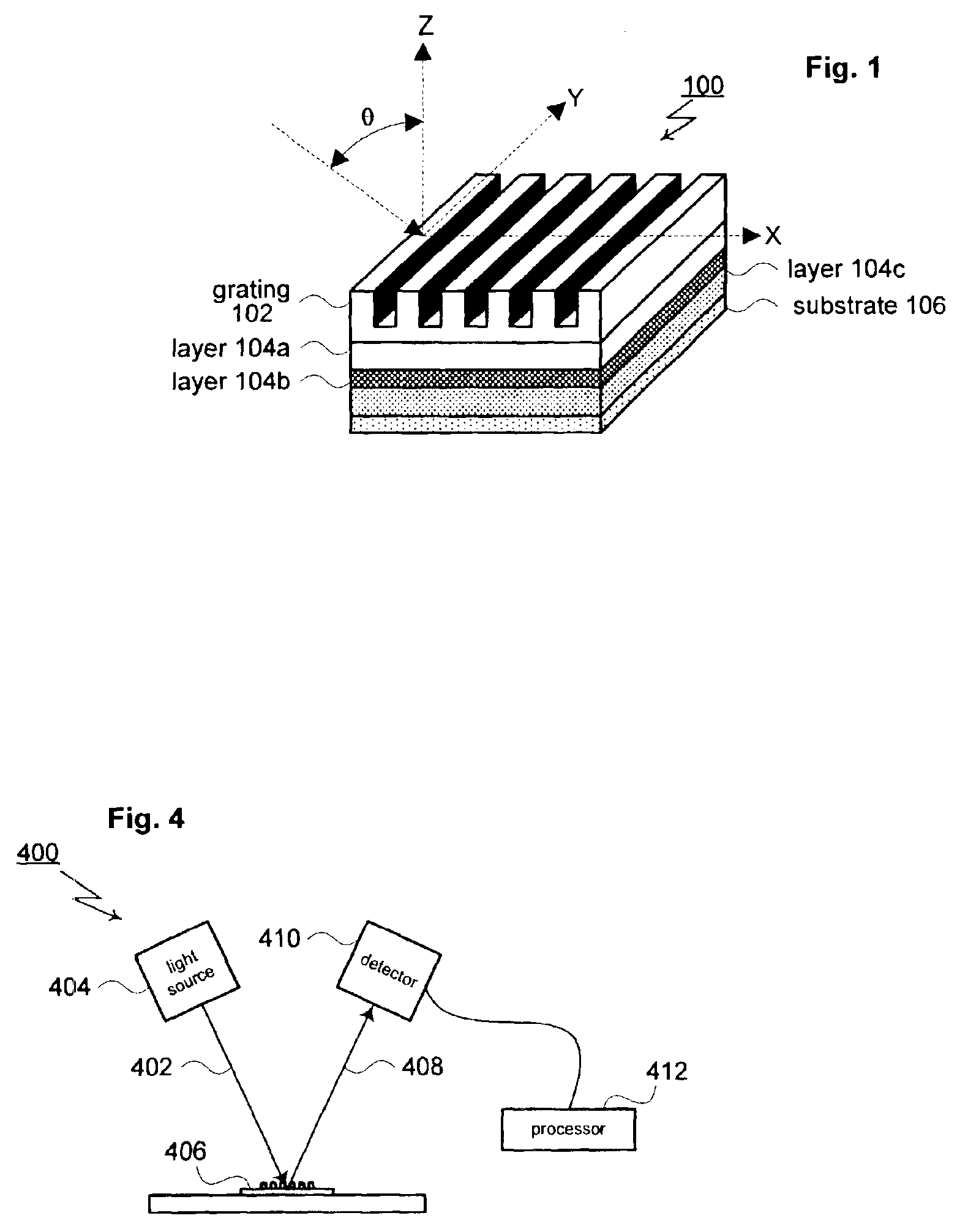
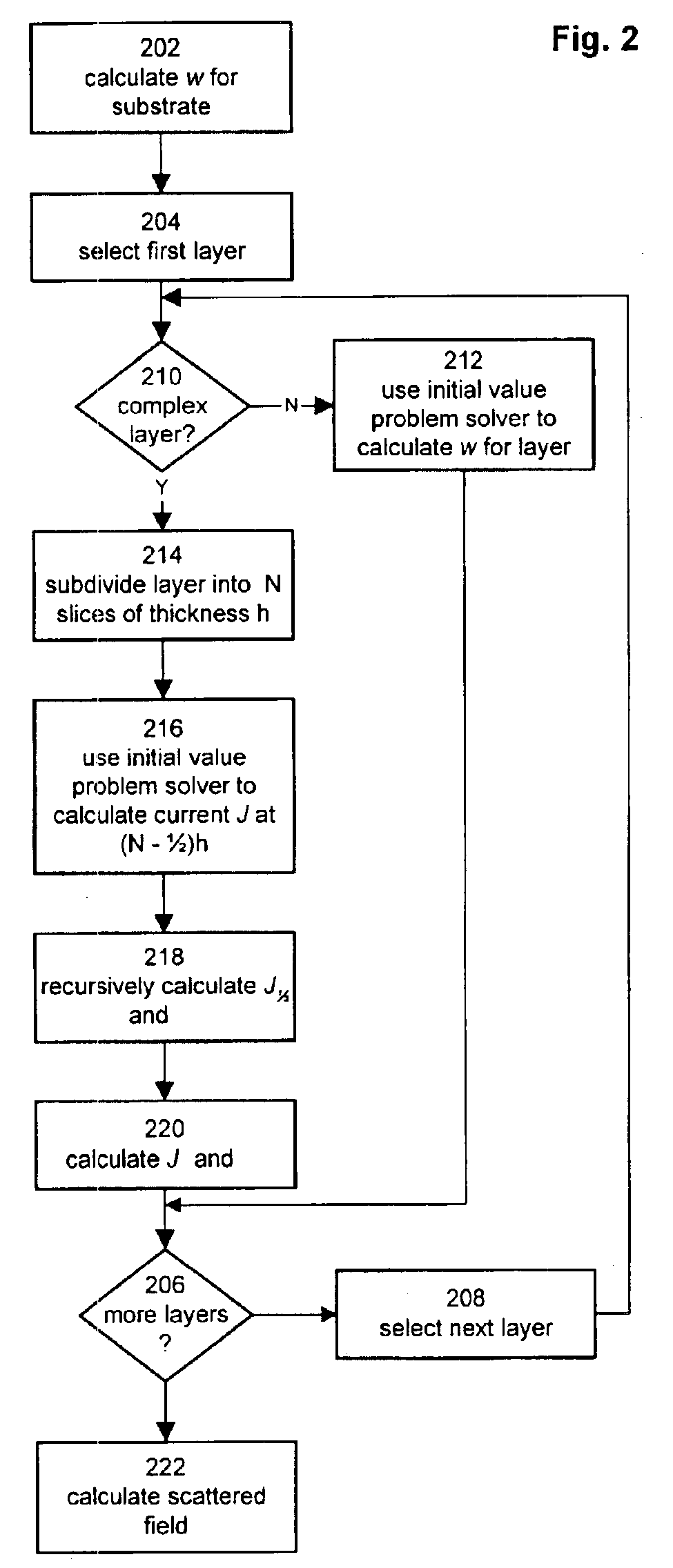
A method for modeling diffraction includes constructing a theoretical model of the subject. A numerical method is then used to predict the output field that is created when an incident field is diffracted by the subject. The numerical method begins by computing the output field at the upper boundary of the substrate and then iterates upward through each of the subject's layers. Structurally simple layers are evaluated directly. More complex layers are discretized into slices. A finite difference scheme is performed for these layers using a recursive expansion of the field-current ratio that starts (or has a base case) at the lowermost slice. The combined evaluation, through all layers, creates a scattering matrix that is evaluated to determine the output field for the subject.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
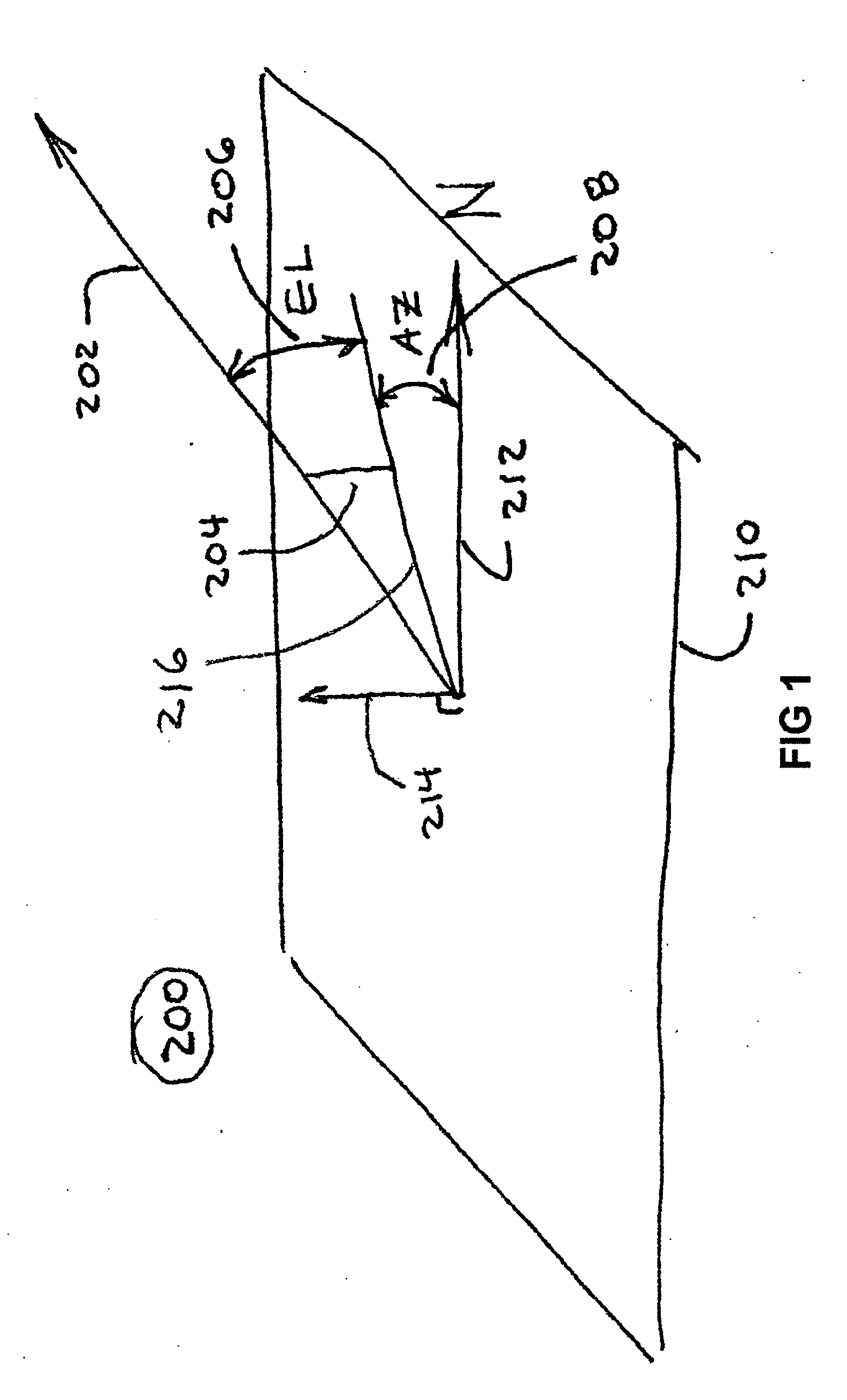
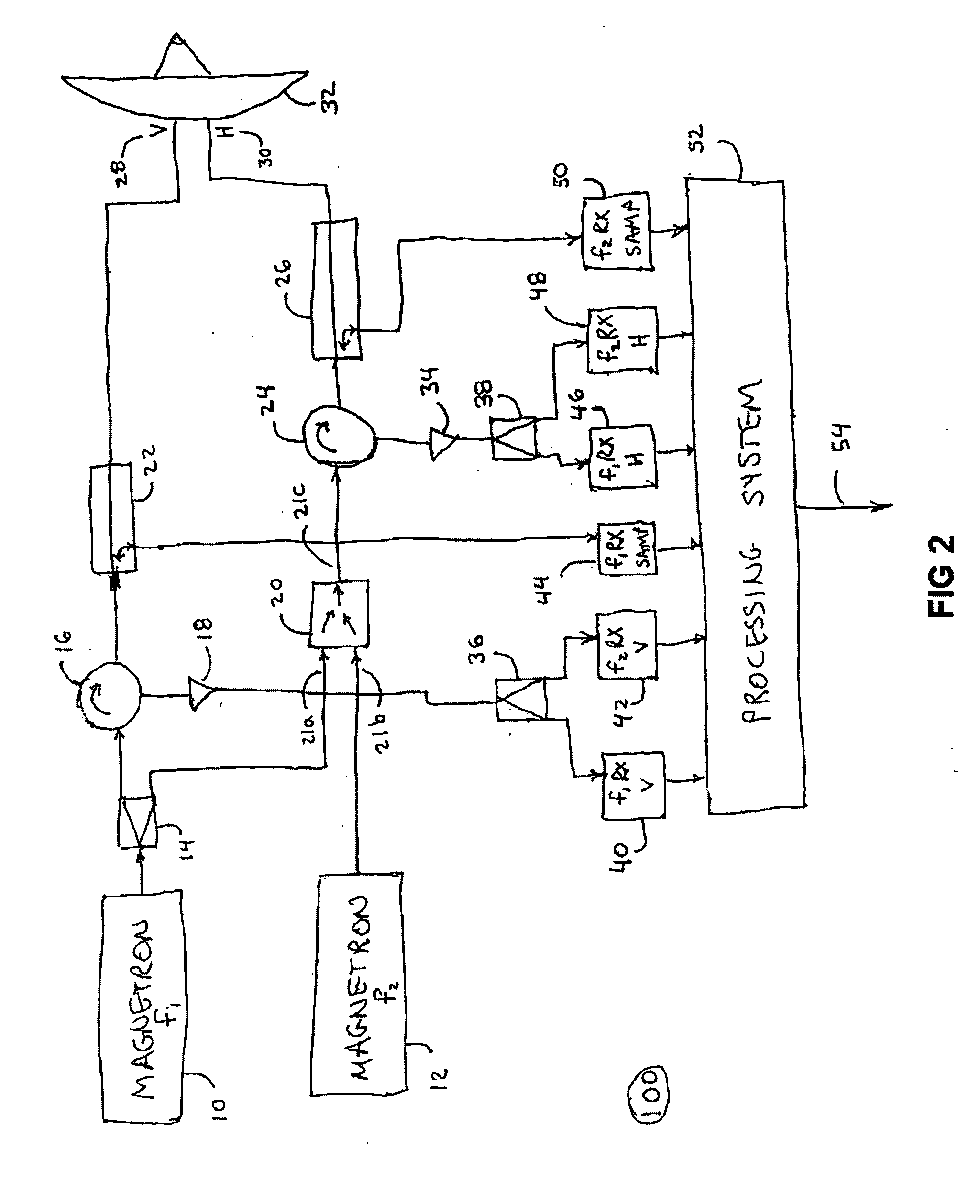
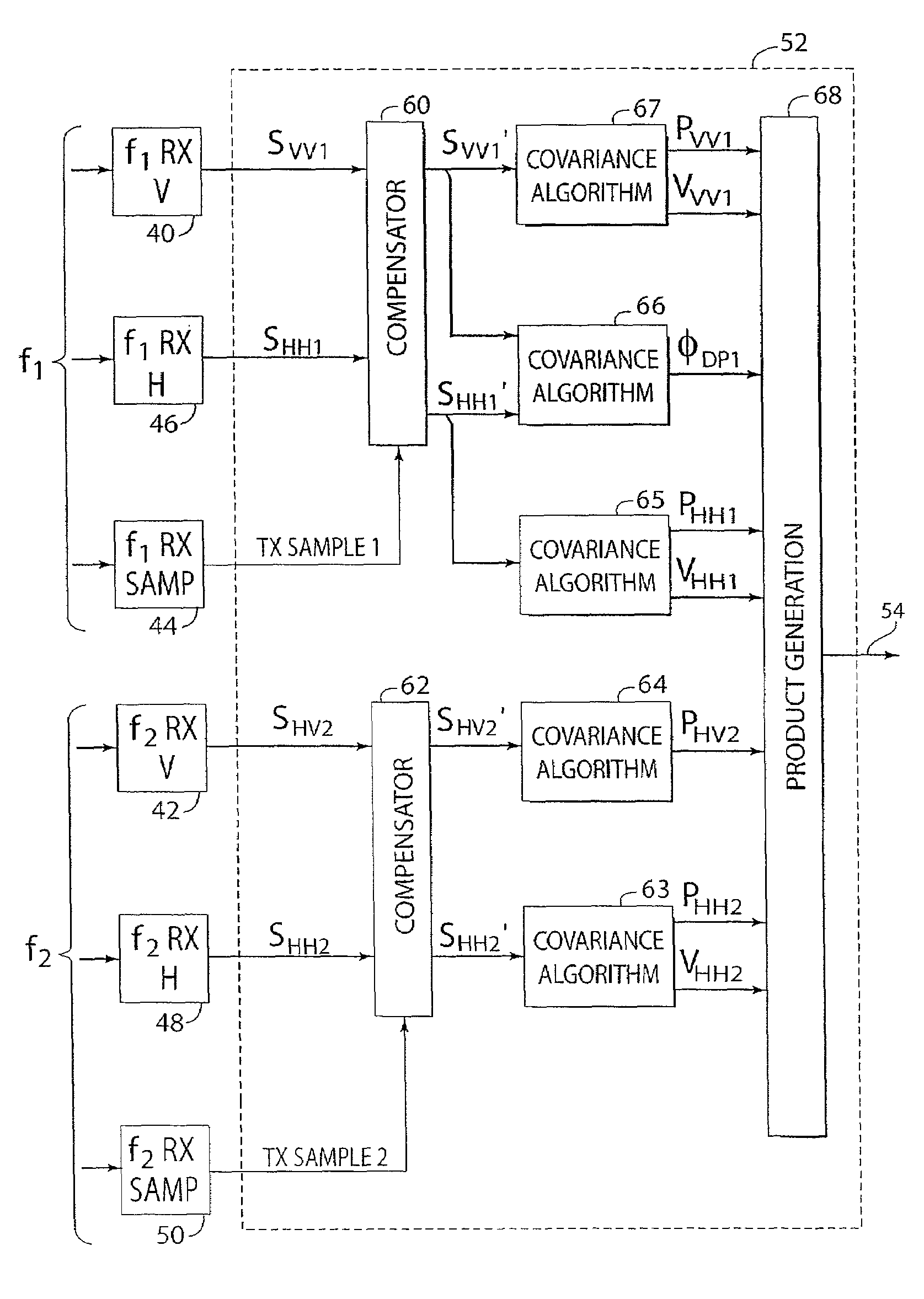
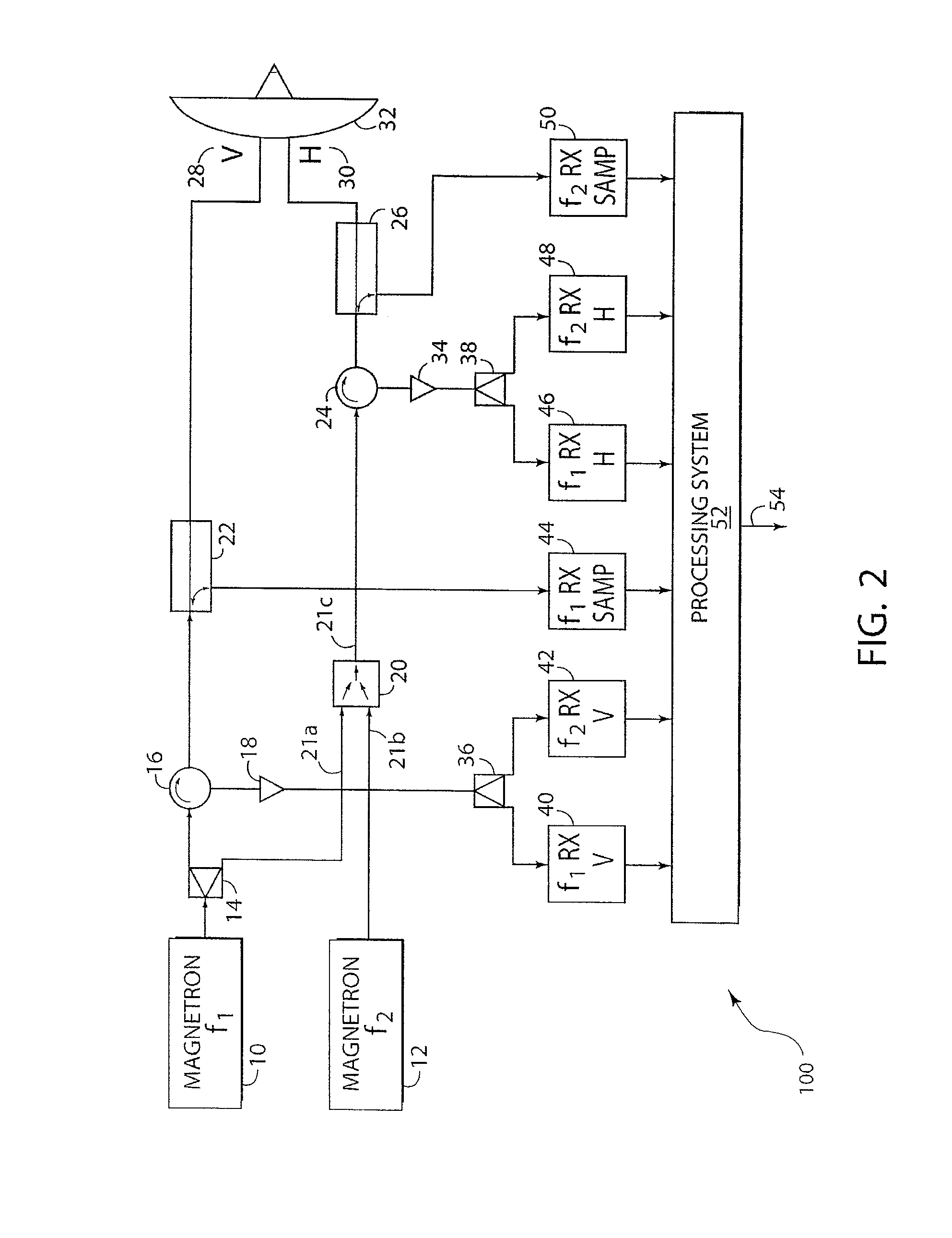
Polarization and frequency diverse radar system for complete polarimetric characterization of scatterers with increased scanning speed
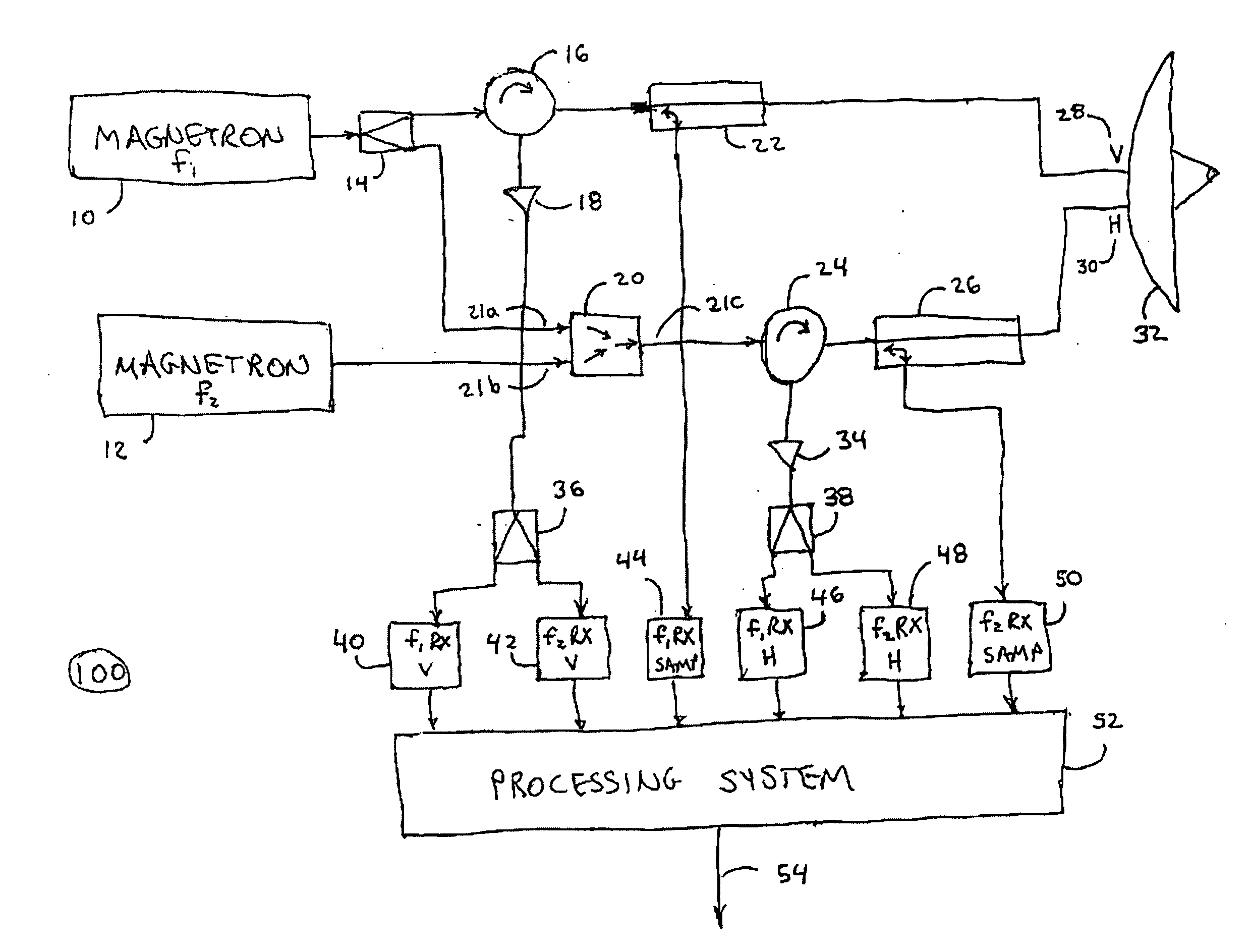
InactiveUS20070152867A1Maximize isolationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationDoppler velocityRadar systems
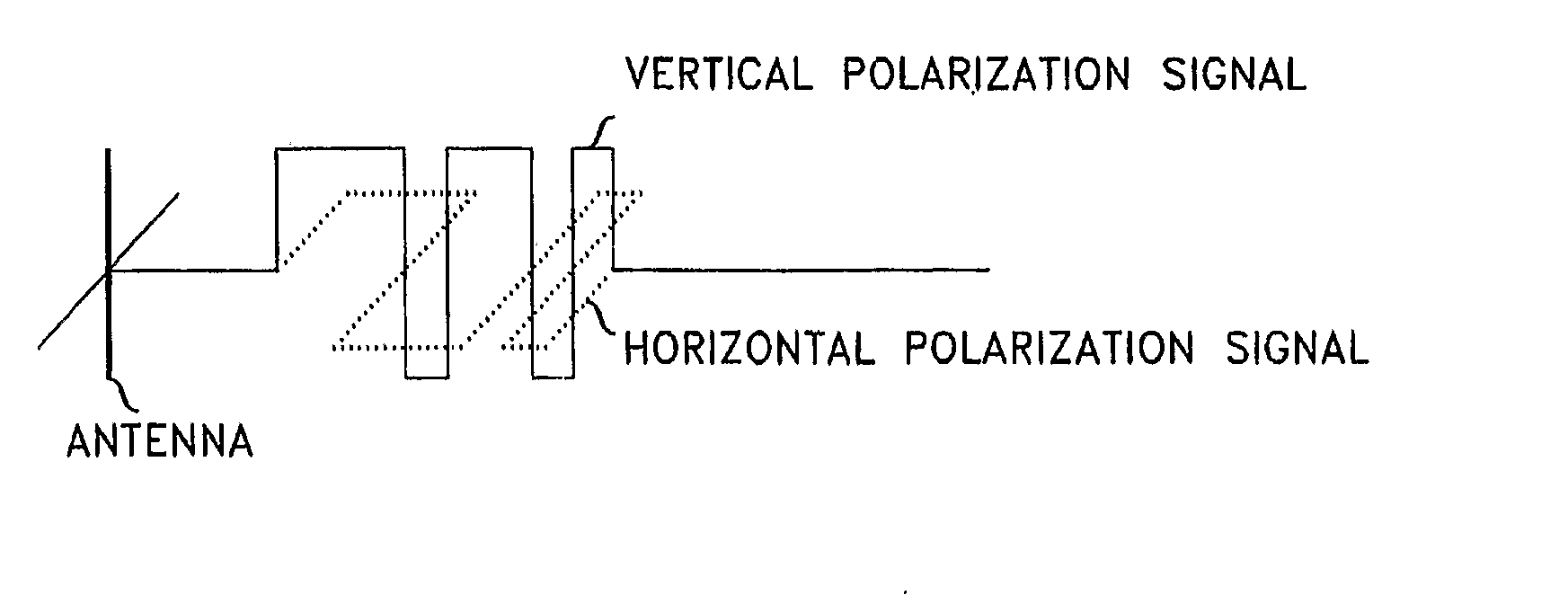
A method and apparatus is provided, whereby a scanning, polarization and frequency diverse radar system measures the complete polarimetric characterization of weather targets without loss of scanning speed and without an additional ambiguity in the Doppler velocity beyond that given by Nyquist's sampling theorem. In one embodiment, a linear combination of a horizontally and a vertically polarized signal are transmitted at a predetermined first frequency. Cotemporaneously or nearly cotemporaneously with the transmitted signal of the first frequency, a horizontally polarized signal is transmitted at a predetermined second frequency. Horizontal and vertical receive channels receive echoes at the predetermined first frequency to determine, but not limited to determine, the co-polar elements of the scattering matrix. Horizontal and vertical receive channels receive echoes at the predetermined second frequency to determine, but not limited to determine, the cross-polar elements of the polarization matrix. The predetermined first and second frequencies are selected to maximize isolation yet allow practical implementation.
Owner:ADVANCED RADAR CORP
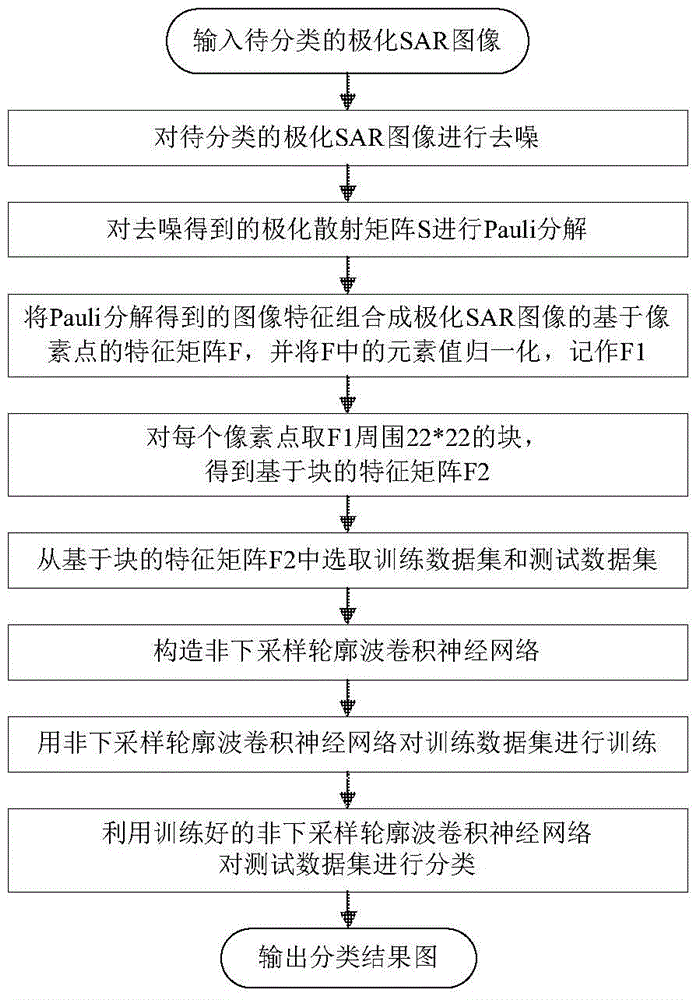
Polarized SAR image classification method based on nonsubsampled contourlet convolutional neural network
InactiveCN105718957AReduce the effect of coherence speckleImprove classification accuracyBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setDecomposition
The invention discloses a polarized SAR image classification method based on a nonsubsampled contourlet convolutional neural network, and mainly at solving the problems that influence of speckle noises is hard to avoid and the classification precision is low in the prior art. The method comprises the steps that a polarized SAR image to be classified is denoised; Pauli decomposition is carried out on a polarized scattering matrix S obtained by denoising; image characteristics obtained via Pauli decomposition are combined into a characteristic matrix F, and the characteristic matrix F is normalized and recorded as F1; 22*22 blocks surrounding the F1 are taken for each pixel point to obtain a block based characteristic matrix F2; a training data set and a test data set are selected from the F2; the nonsubsampled contourlet convolutional neural network is established to train the training data set; and the trained nonsubsampled contourlet convolutional neural network is used to classify the test data set. The polarized SAR image classification method improves the expression capability and the classification precision of the features of the polarized SAR image, and can be used for target identification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Light ground mass industrial machine-shaping process technology
InactiveCN101253845AReduce labor intensityProtect environmentBio-organic fraction processingBiofuelsEcological environmentEngineering
A technology for industrialized processing and molding of a light matrix includes the steps of crushing agricultural and forest waste first, composting the waste with beneficial microbes, namely EM bacteria for fermentation, conducting rational sifting and matrix matching, using a light-matrix processing and molding machine to process the scattered matrix into an enteroid matrix container with a diameter of 35mm to 50mm, and then cutting the matrix container into small sections, namely matrix sections in the length of 80mm to 100mm, thereby suiting both the cultivation of eucalyptus grafts and the upper bag of the seedling container for tissue-culture rooting. The technology, which can be used for industrialized matrix production, greatly reduces labor intensity and protects ecological environment. The matrix, belonging to composite matrix, can be used for seeding, cuttage and transplant of plants and for the cultivation of other seedlings for greening purpose, with a high survival rate and robust root systems.
Owner:CHINA EUCALYPT RES CENT
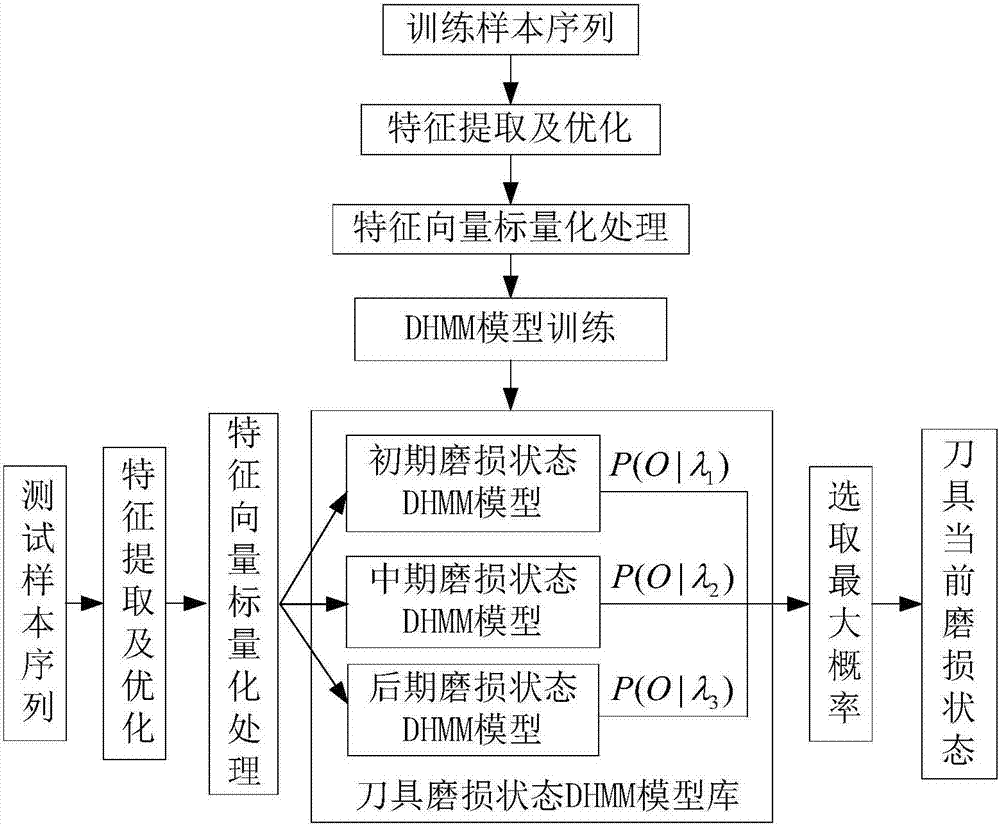
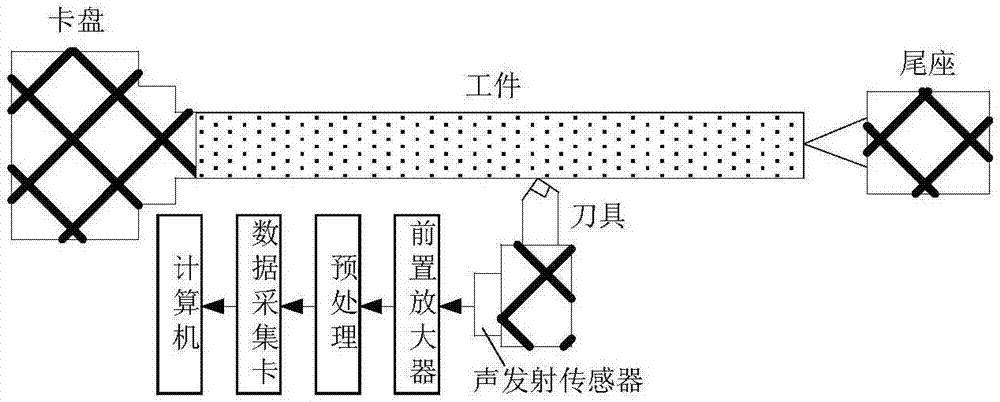
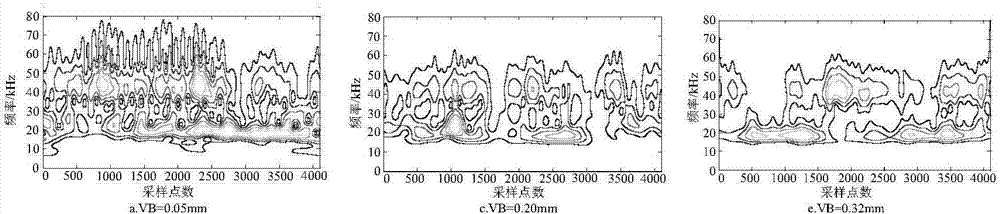
Monitoring method based on image features and LLTSA algorithm for tool wear state
ActiveCN107378641ARealization of wear status monitoringFully automatedMeasurement/indication equipmentsTime–frequency analysisTool wear
The invention relates to a monitoring method based on image features and an LLTSA algorithm for a tool wear state. According to the method, an image texture feature extraction technology is introduced into the field of tool wear fault diagnosis, and monitoring for the tool wear state is realized in combination with three flows of ' signal denoising', 'feature extraction and optimization' and 'mode recognition'. The method comprises the steps of firstly, acquiring an acoustic emission signal in a tool cutting process through an acoustic emission sensor, and carrying out signal denoising processing through an EEMD diagnosis; secondly, carrying out time-frequency analysis on a denoising signal through S transformation, converting a time-frequency image to a contour gray-level map, extracting image texture features through a gray-level co-occurrence matrix diagnosis, and then further carrying out dimensionality reduction and optimization on an extracted feature vector through a scatter matrix and the LLTSA algorithm to obtain a fusion feature vector; and finally training a discrete hidden Markov model of the tool wear state through the fusion feature vector, and establishing a classifier, thereby realizing automatic monitoring and recognition for the tool wear state.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
Fisher judged null space based method for decomposing mixed pixels of high-spectrum remote sensing image
InactiveCN101692125ASmall spectral differenceReduce the impactWave based measurement systemsImage analysisDecompositionComputer science
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image processing, and particularly discloses a Fisher judged null space based method for decomposing mixed pixels of a high-spectrum remote sensing image. A Fisher judged null space method is provided aiming at the problem that the decomposition precision is reduced due to the phenomenon of same objects and different spectrums generally existing in the mixed pixel decomposition. The method comprises the following steps: analyzing a training sample consisting of pure pixel spectrums of an end member, constructing an intra-class scattering matrix null space of the training sample, making the spectrum difference in the end member become null, searching a judgment vector causing the scattering degree of the intra-class scattering matrix to be maximum in the null space, and making the separation degree of end member spectrums of different classes maximum so as to furthest reduce the decomposition error caused by the same objects and different spectrums. The method of the invention has particularly important application values in the aspects of high-precision surface feature decomposition of the high-spectrum remote sensing image and detection and identification of ground targets.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
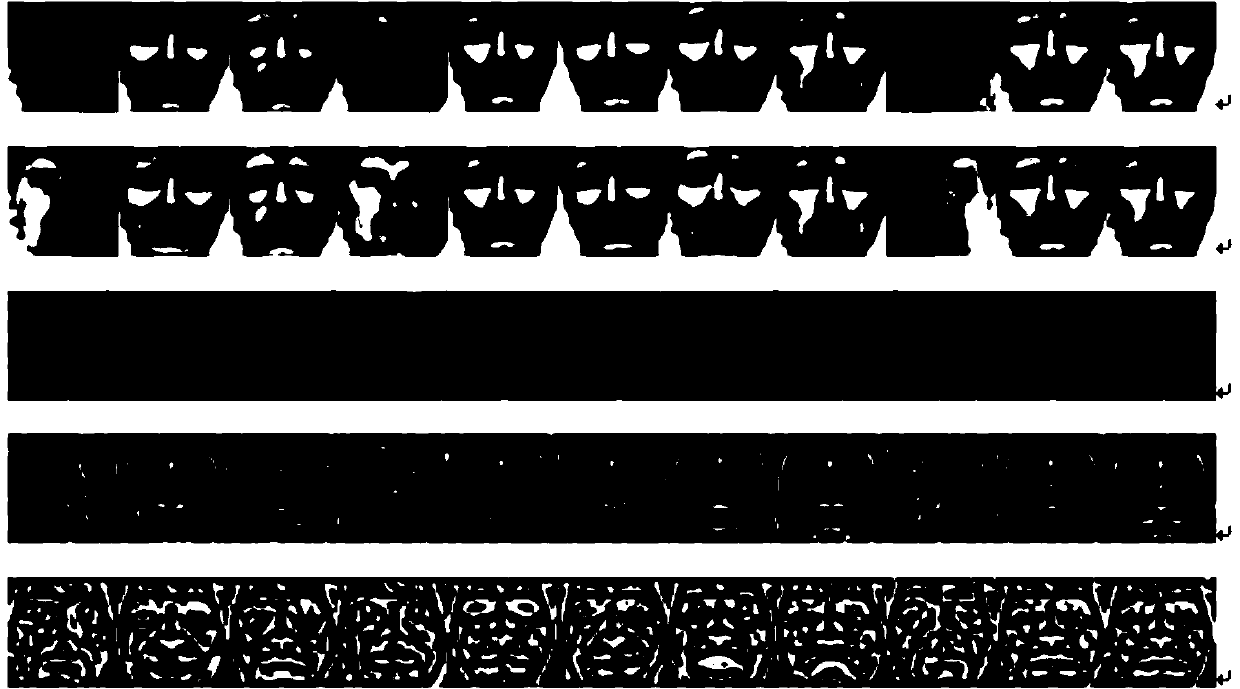
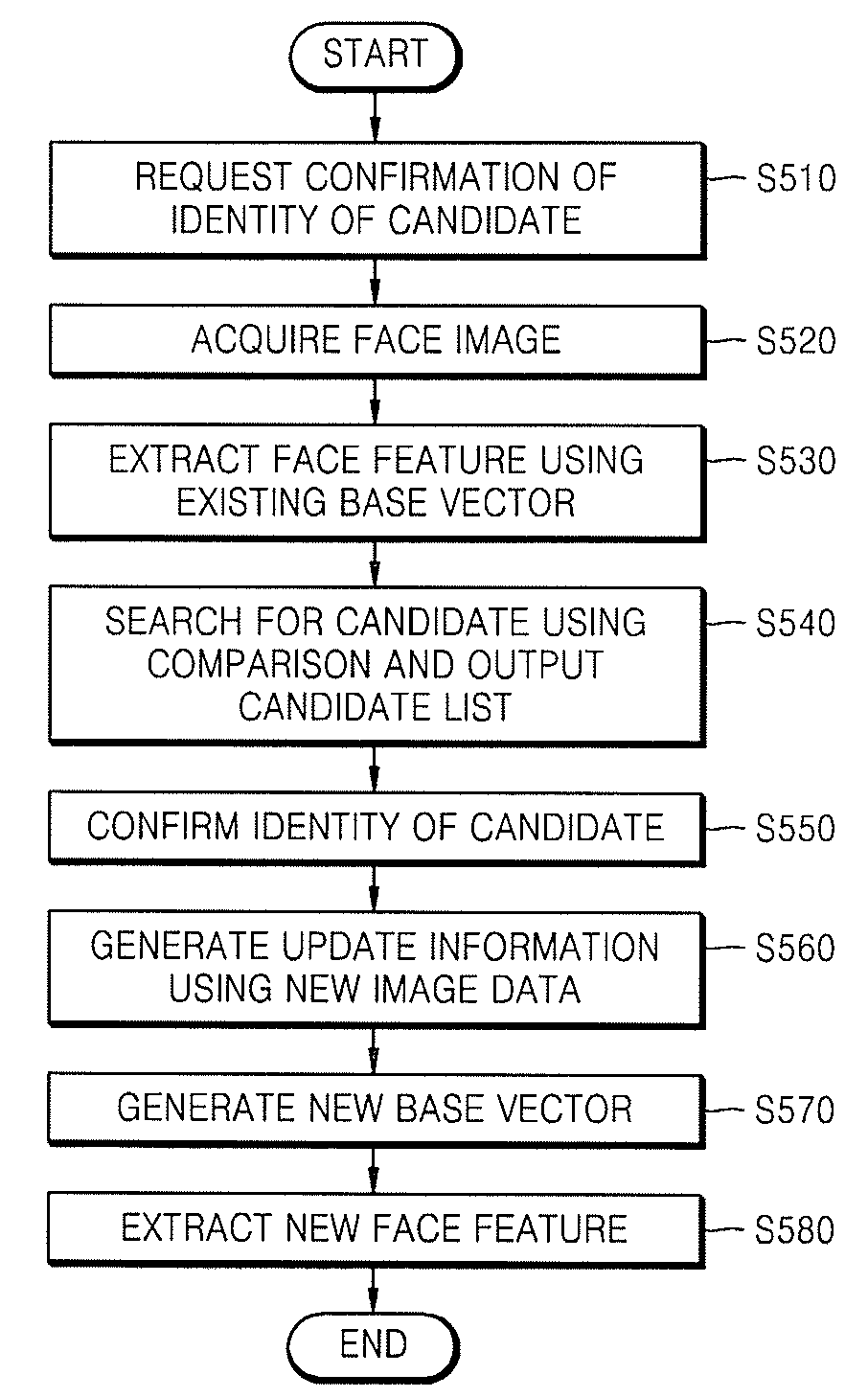
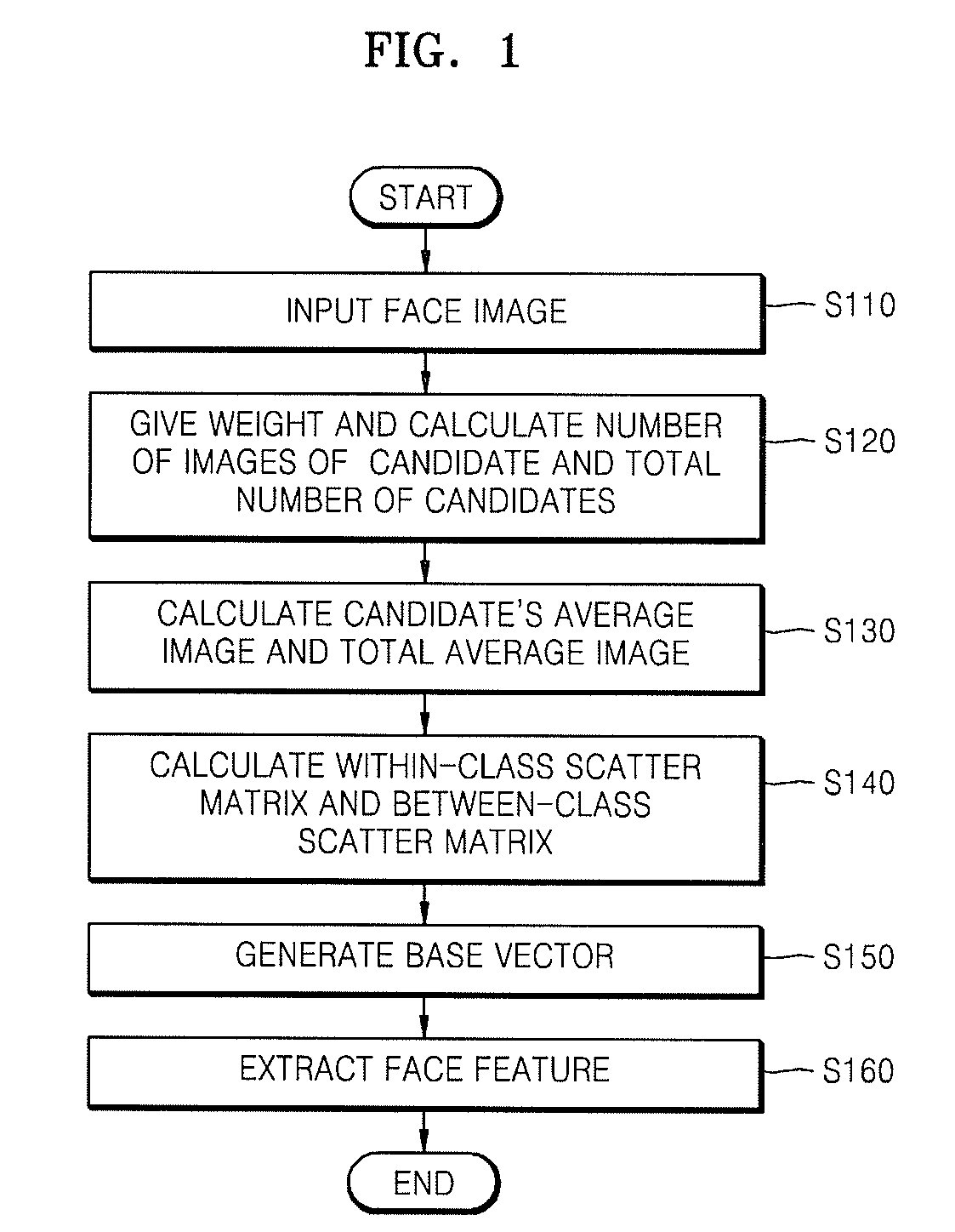
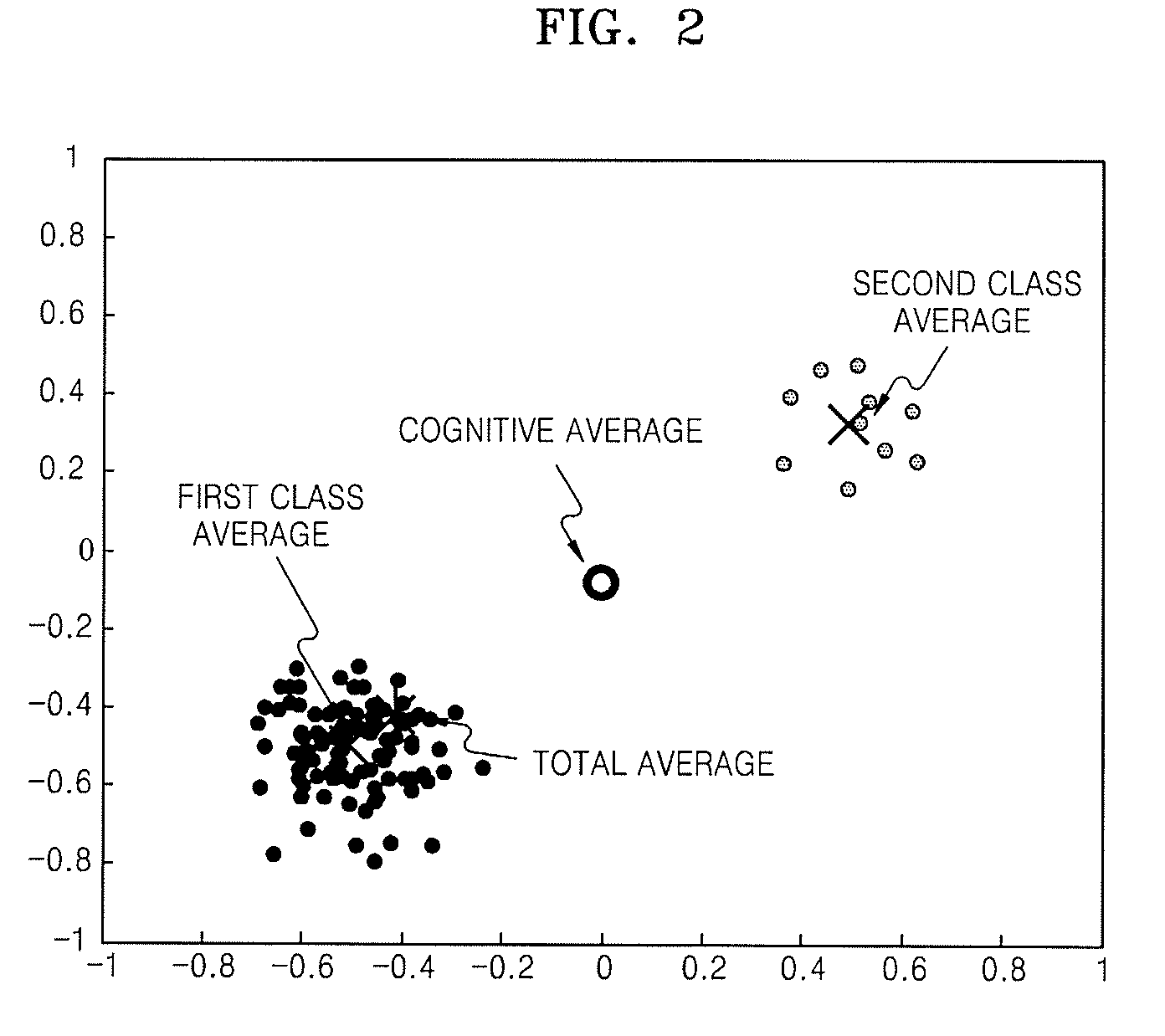
Method and apparatus for extracting face feature
InactiveUS20080130962A1Improve recognition rateEffectively featureImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionVector maximizationScatter matrix
A method and apparatus for extracting a face feature to construct a face search system having a high recognition rate are provided. The method includes calculating an average image of each of a plurality of candidates having one or more face images to which different weights are given according to an order in which the face images are acquired and calculating a total average image of all face images of the plurality of candidates, calculating a between-class scatter matrix based on a difference between each candidate's average image and the total average image and a within-class scatter matrix based on a difference between each candidate's average image and each candidate's predetermined face image of the one or more face images, and generating a base vector that maximizes a criterion defined by a ratio between the between-class scatter matrix and the within-class scatter matrix.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
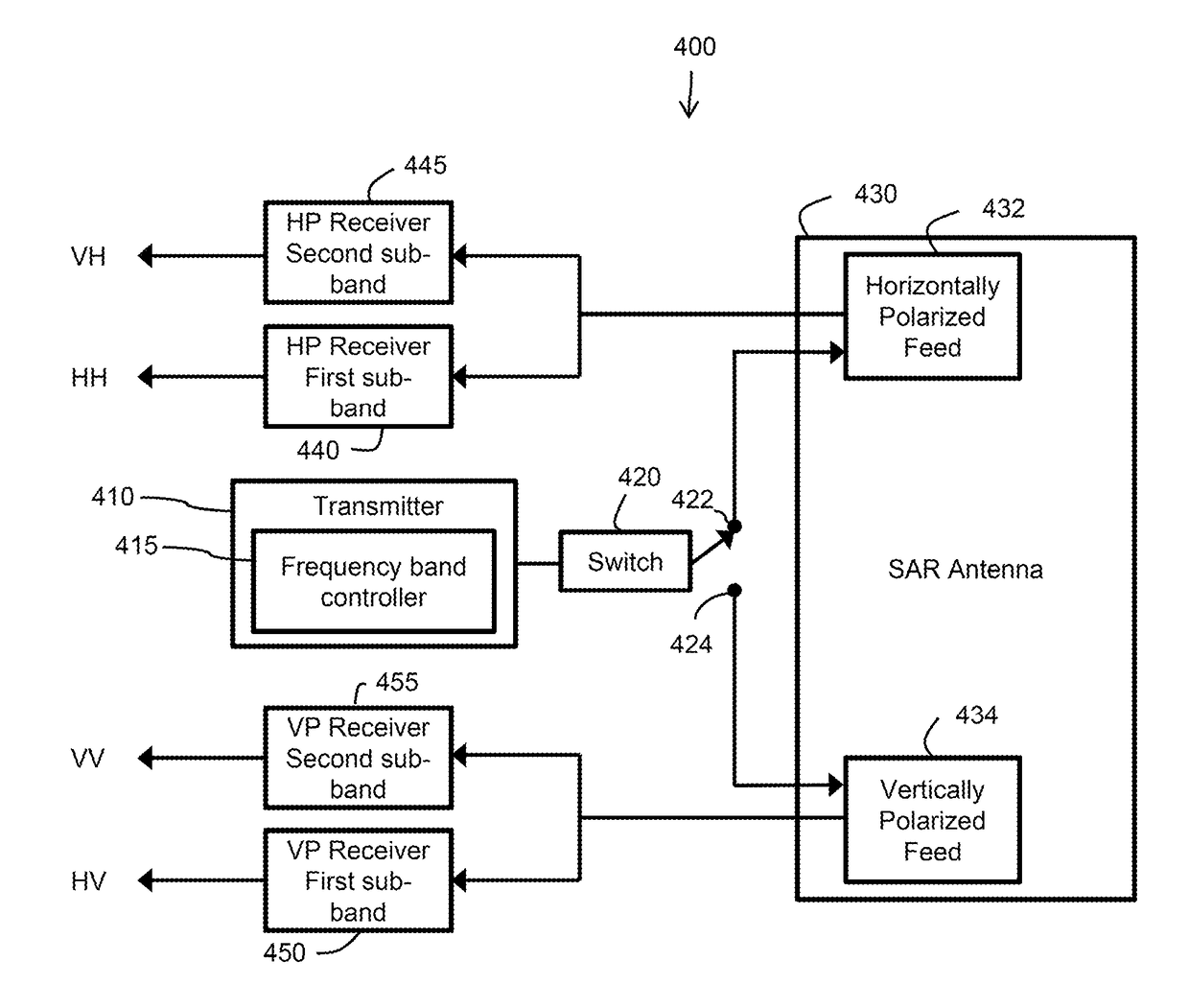
Apparatus and methods for quad-polarized synthetic aperture radar
InactiveUS20180335518A1Accurate measurementLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarClassical mechanics
A quad-pol synthetic aperture radar (SAR) system reduces the effects of range ambiguities in a quad-pol SAR data. Pulses are transmitted in two sub-bands at respective ones of two different linear orientations. For each sub-band and orientation, returns are received in two orientations, and filtered to attenuate the other sub-band. A scattering matrix may be determined from the results. Additionally or alternatively, a Faraday rotation angle associated with acquired quad-pol SAR data is estimated, and used to correct a scattering matrix. Estimation may occur before, after, or both before and after acquisition of the quad-pol SAR data.
Owner:URTHECAST CORP
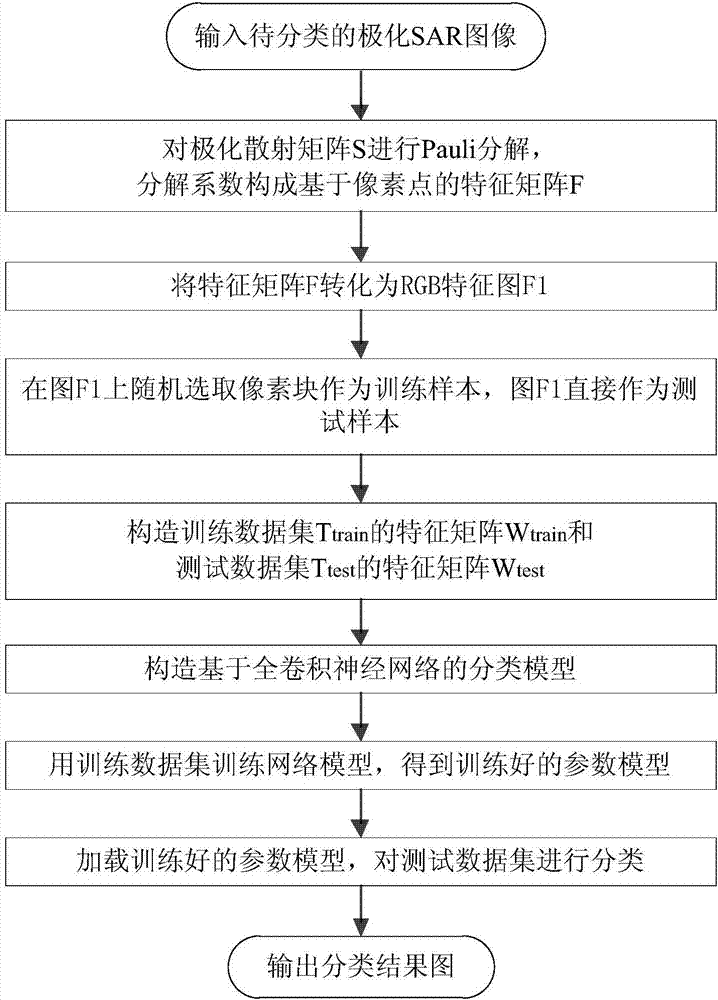
Polarized SAR land feature classification method based on full convolution neural network
InactiveCN107239797AImplement classificationReduce network parametersCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsDecompositionRgb image
The invention discloses a polarized SAR land feature classification method based on a full convolution neural network, comprising: performing Pauli decomposition on a to-be-classified polarized scattering matrix S to obtain the odd scattering coefficient, the even scattering coefficient and the volume scattering coefficient; using the odd scattering coefficient, the even scatter coefficient and the volume scattering coefficient as the three-dimensional image characteristics F of the polarized SAR image; then converting the obtained three-dimensional image characteristics matrix F into an RGB image F1; randomly selecting m x n pixel blocks in the RGB image F1 as training samples; using the whole RGB image F1 as a testing sample; re-constructing a full convolution neural network model; training the training samples through the full convolution neural network to obtain a trained model; and then, through the trained model, classifying the test set and obtaining the classification result. The method of the invention can solve the problem of low time efficiency in the prior art and shorten the running time under the condition of high classification accuracy.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Onboard P-waveband polarization synthetic aperture radar (SAR) calibration method under non-ideal calibrator condition
ActiveCN103091666AAvoid changeHigh precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarRadar
The invention provides an onboard P-waveband polarization synthetic aperture radar (SAR) calibration method under a non-ideal calibrator condition, and relates to radar techniques. The method is used for calibrating polarization discrimination, polarization channel imbalance and other system errors of the SAR. The non-ideal condition indicates non-ideal performance of scattering matrixes led in by posture changes of a calibrator and an aerial carrier. The method corrects the scattering matrixes of the ideal calibrator, carries out correction on antenna direction pictures, accordingly overcomes the occasion that calibration parameters change with visual angles (distance direction) of an antenna, takes consideration of the fact that polarizing angle changes caused by the postures of the aerial carrier change the scattering matrixes of the calibrator, corrects a polarizing calibration model based on the preceding steps, carries out calibration treatment to obtain an emission distortion matrix and a receiving distortion matrix of a system, and accordingly carries out polarizing correction for the polarization SAR pictures.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
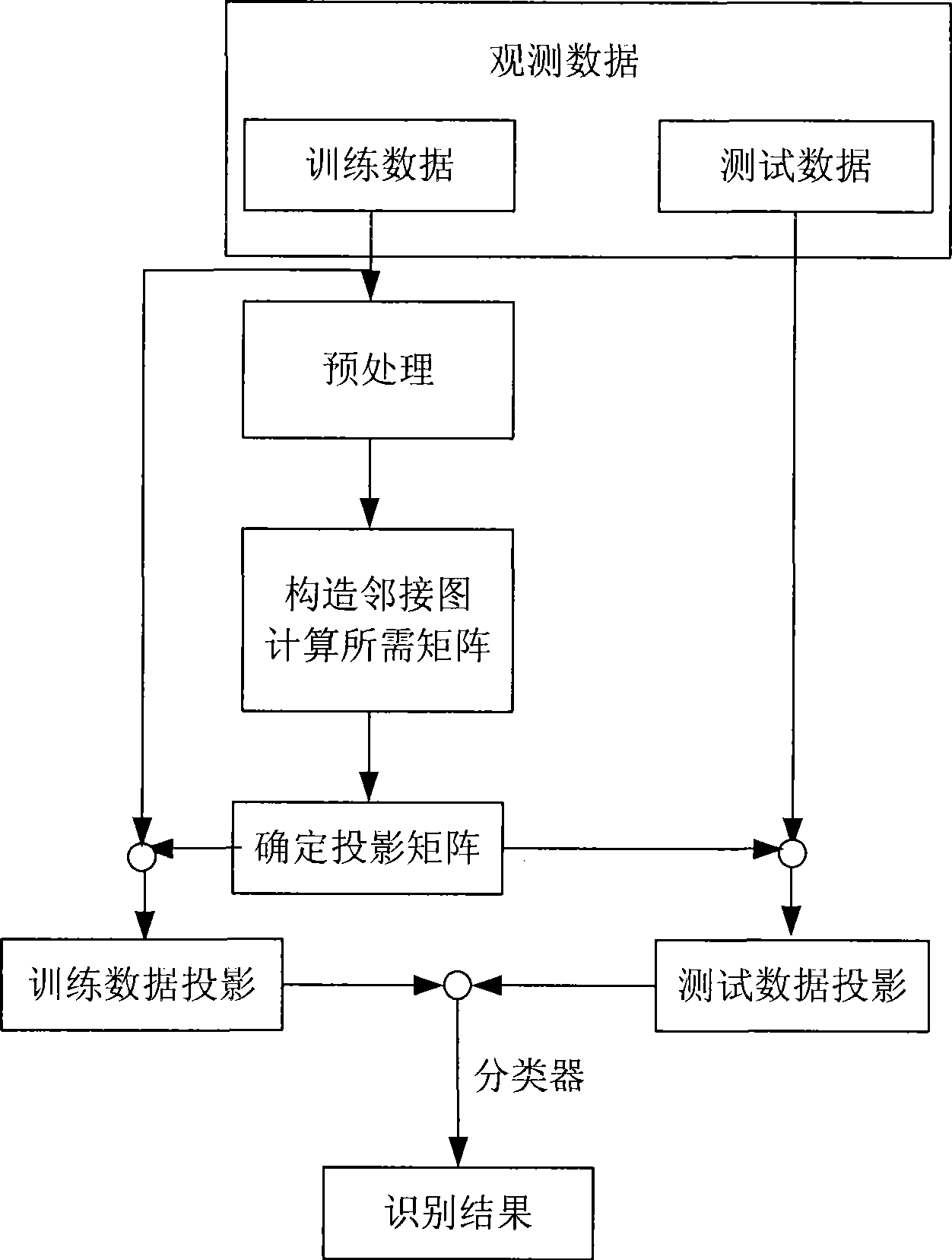
Image characteristics extraction method based on global and local structure amalgamation
Provided is an image feature extraction method based on global and local structure fusion, characterized by comprising: 1) constructing a weight adjacent map; 2) determining laplacian matrix of similar matrix, degree matrix and images, 3) determining scatter matrix inside the kind and between the kind; 4) determining projection matrix, 5) identifying. The invention provides a feature extraction method of fusing the global structure information and the local structure information, wherein complex features fused of the global feature and the local feature are extracted, thereby the method has strong resolving power. The method not only has the characteristics of holding the reflection method locally, namely holding the characteristics of manifold structure of data; moreover has the characteristics of linear discrimination analysis method, namely assembling the date of the kind more compact to enlarge the distance between the kinds. The invention is applied in image recognition, thereby increasing identifying performance.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Polarization and frequency diverse radar system for complete polarimetric characterization of scatterers with increased scanning speed
InactiveUS7355546B2Maximize isolationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationDoppler velocityRadar systems
Owner:ADVANCED RADAR CORP
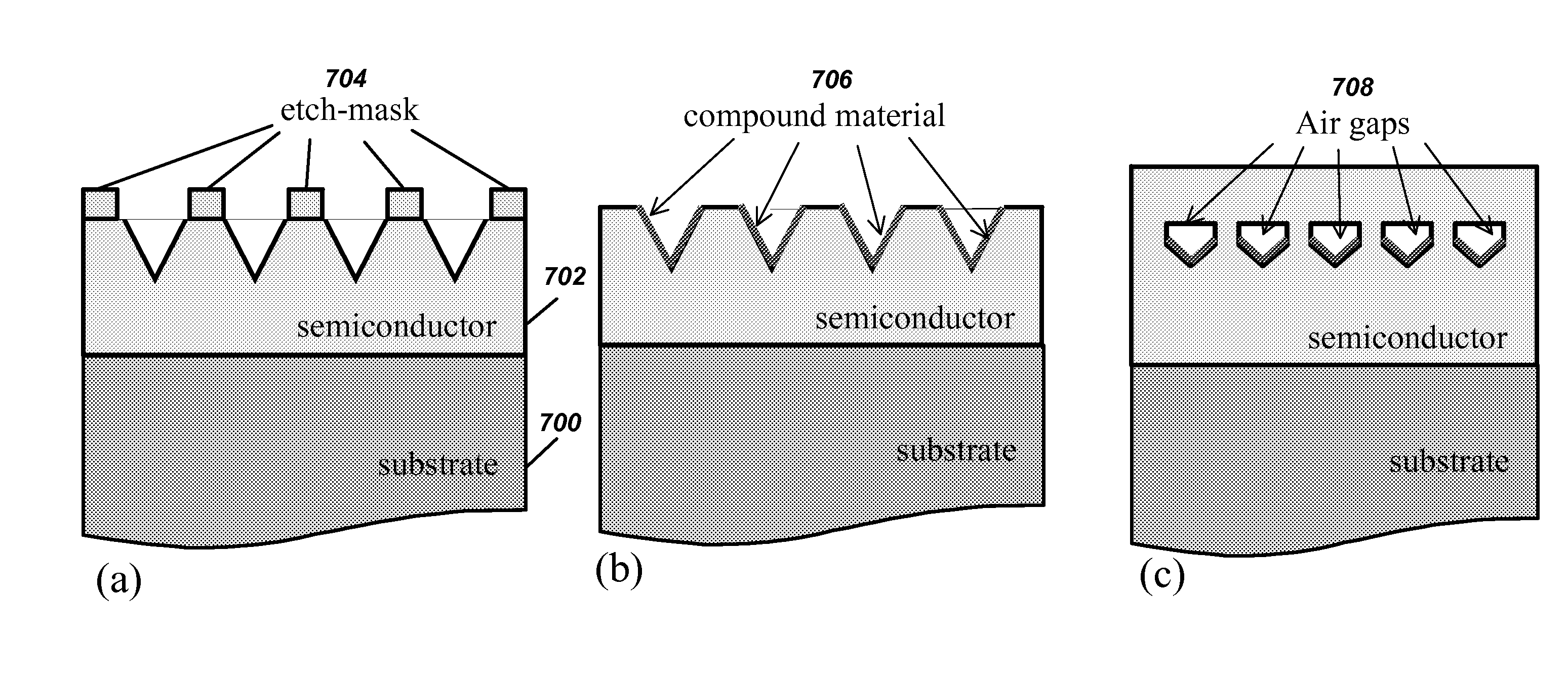
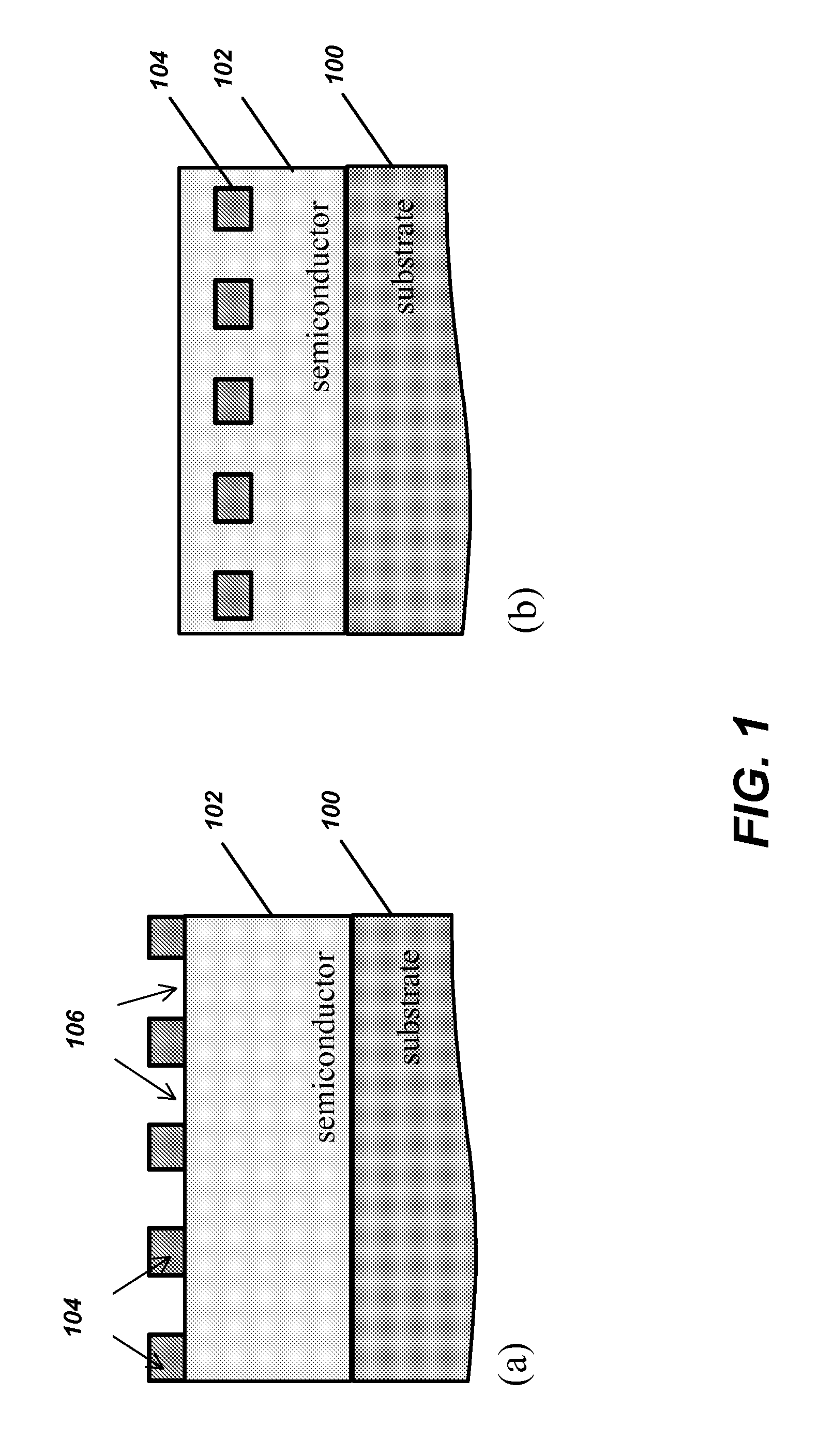
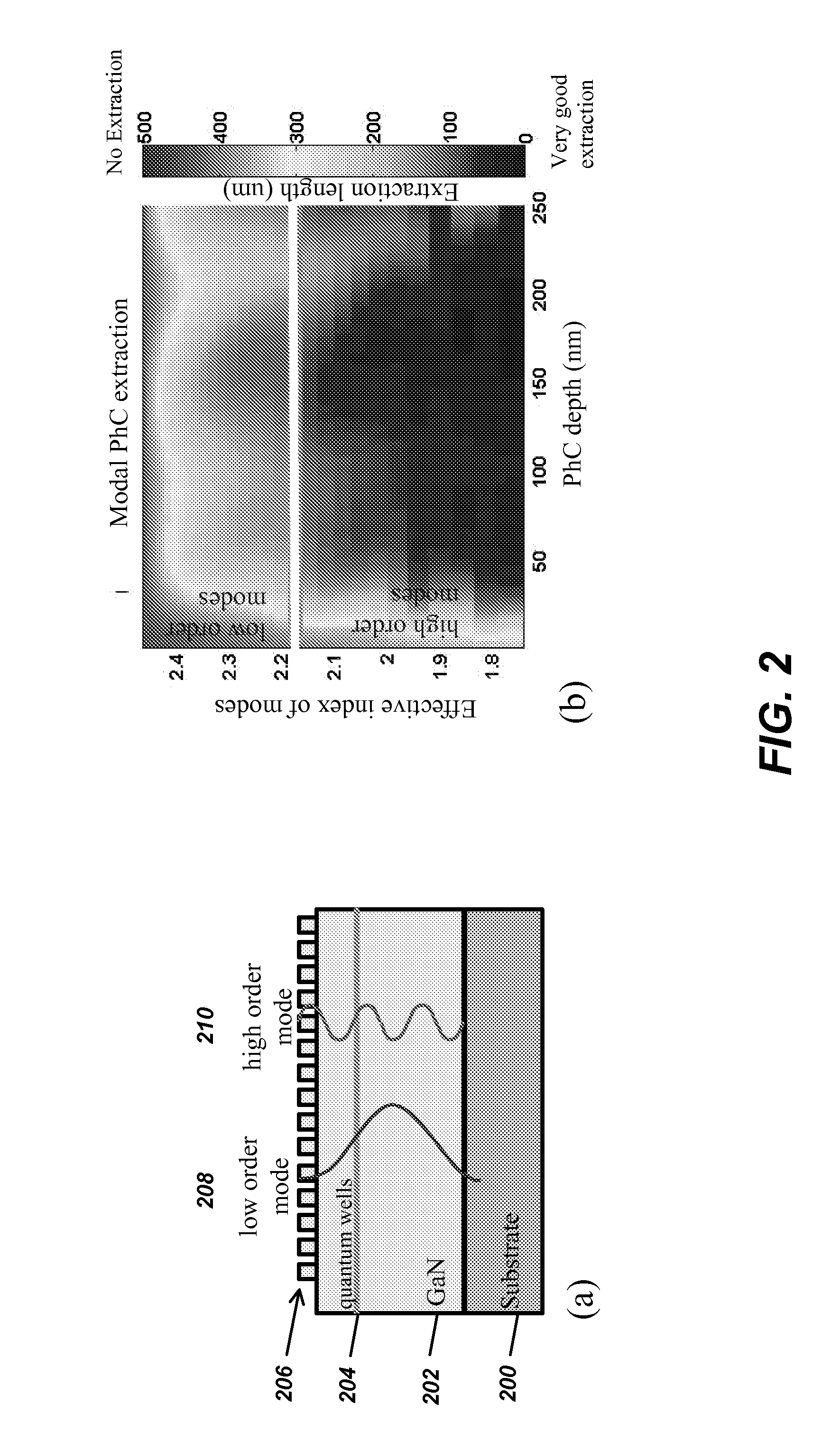
Optoelectronic devices with embedded void structures
An optoelectronic structure, and method of fabricating same, comprised of semiconductors having growth-embedded void-gap gratings or photonic crystals in one or two dimensions, which are optimized to yield high interaction of the guided light and the photonic crystals and planar epitaxial growth. Such structure can be applied to increase light extraction efficiency in LEDs, increase modal confinement in lasers or increase light absorption in solar cells. The optimal dimensions of the growth-embedded void-gap gratings or photonic crystals are calculated by numerical simulation using scattering matrix formalism. The growth-embedded void-gap gratings are applicable to any semiconductor device, as well as optoelectronic devices, such as light-emitting diodes, laser diodes and solar cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Rotatable double-antenna PARC (polarimetric active radar calibrator) and polarimetric active radar calibration method thereof
ActiveCN104659498AImprove polarization isolationPlays the role of filtering out cross-polarization couplingTransmitters monitoringPolarised antenna unit combinationsMultiple formsAntenna design
The invention discloses a rotatable double-antenna PARC (polarimetric active radar calibrator) and a polarimetric active radar calibration method thereof. According to the PARC, polarization filters are additionally mounted at apertures of a receiving antenna and a transmitting antenna; the rotatable double-antenna design is adopted, and different posture combinations of the receiving antenna and the transmitting antenna can form different polarization combinations. Each antenna of the designed rotatable double-antenna PARC can rotate independently, the receiving antenna and the transmitting antenna of the PARC are controlled to be combined in different polarization manners, and multiple forms of polarimetric scattering matrixes of the PARC can be obtained. During mounting of the PARC, the delay parameter is adjusted, and a rotating mechanism is controlled, and the PARC rotates at constant and slow speeds, and any to-be-calibrated objects can be calibrated. The polarization filters are additionally mounted at the apertures of the antennas, so that the polarimetric isolation of each of the receiving antenna and the transmitting antenna can be greatly increased, and the polarimetric calibration accuracy is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
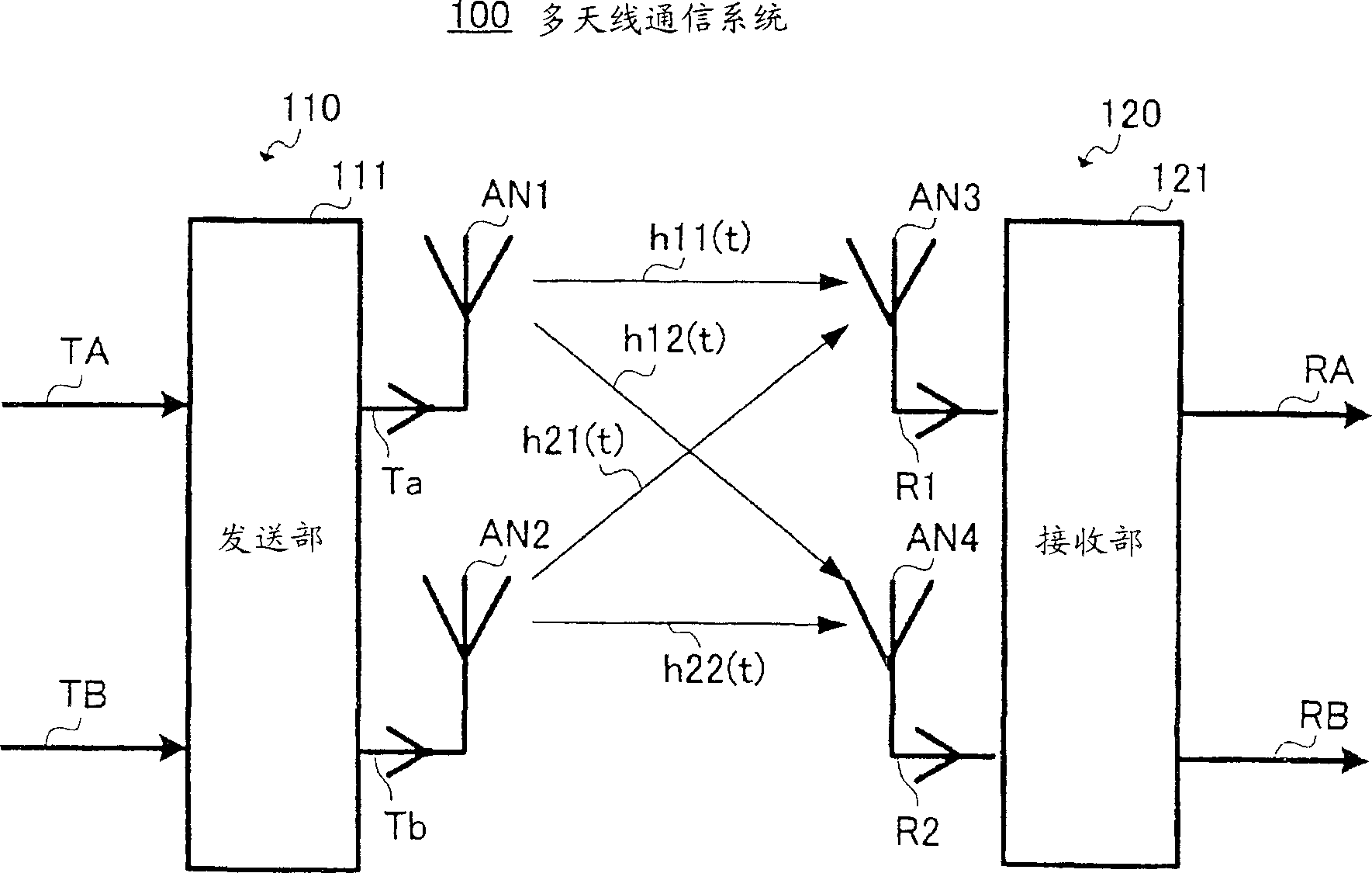
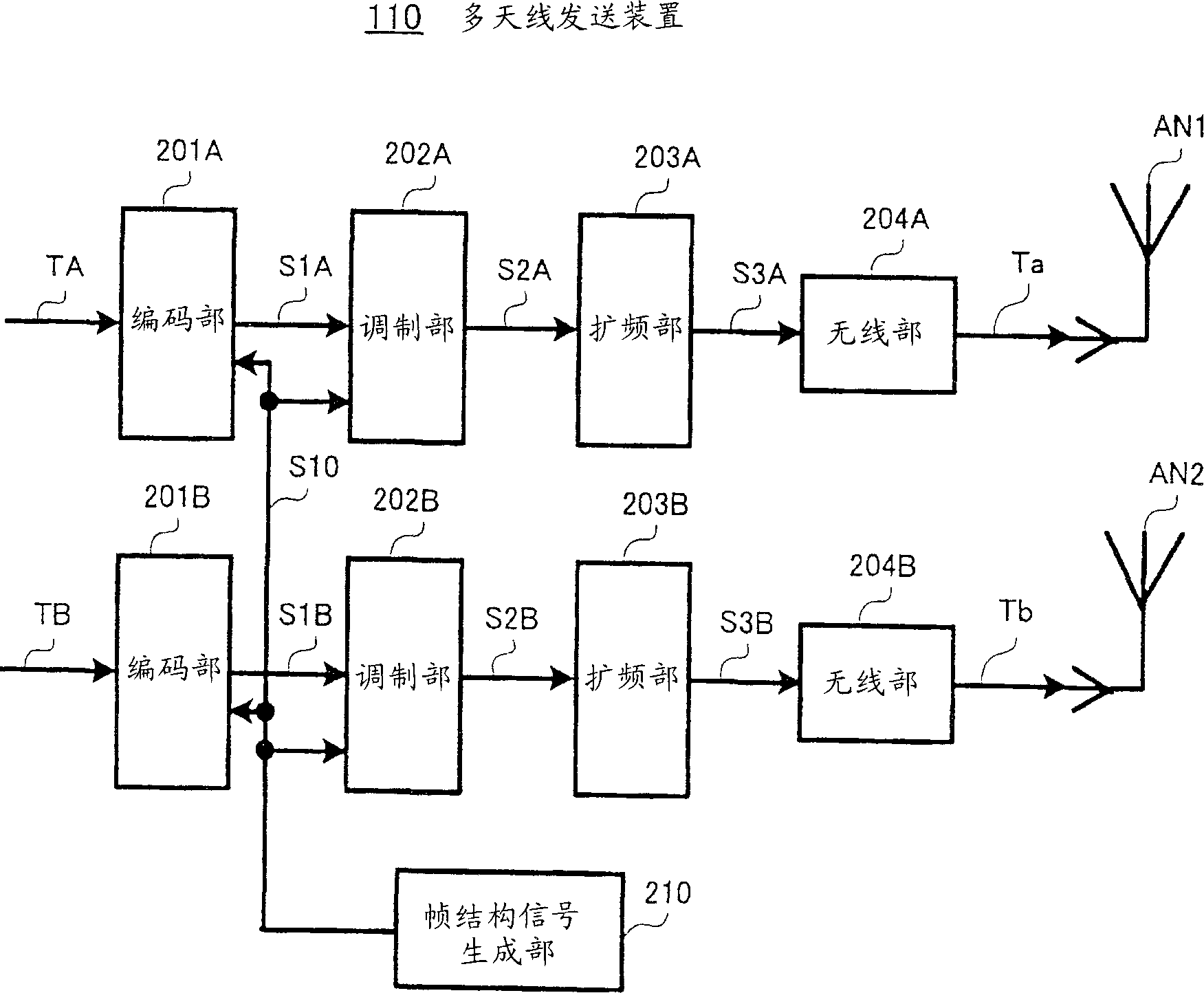
Multi-antenna receiving apparatus, multi-antenna receiving method, multi-antenna transmitting apparatus, and multi-antenna communication system
ActiveCN1883145ANo reduction in data transfer efficiencyReduce the number of operationsSpatial transmit diversityMultiplex communicationCommunications systemEngineering
Soft decision parts (503,506) perform temporary decisions of modulated signals (502,505) as separated by a separating part (501) using an inverse matrix calculation of a channel scatter matrix. Signal point reduction parts (508,510,514,516) use the temporary decision results (504,507) to reduce the number of candidate signal points of multiplexed modulated signals. Soft decision parts (512,518) use the candidate signal points as reduced to perform precise decisions, thereby obtaining reception data of the modulated signals (RA,RB). In this way, a smaller number of calculations is used to successfully obtain the reception data (RA,RB) having an improved error rate characteristic without degradation of the data transmission efficiency.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
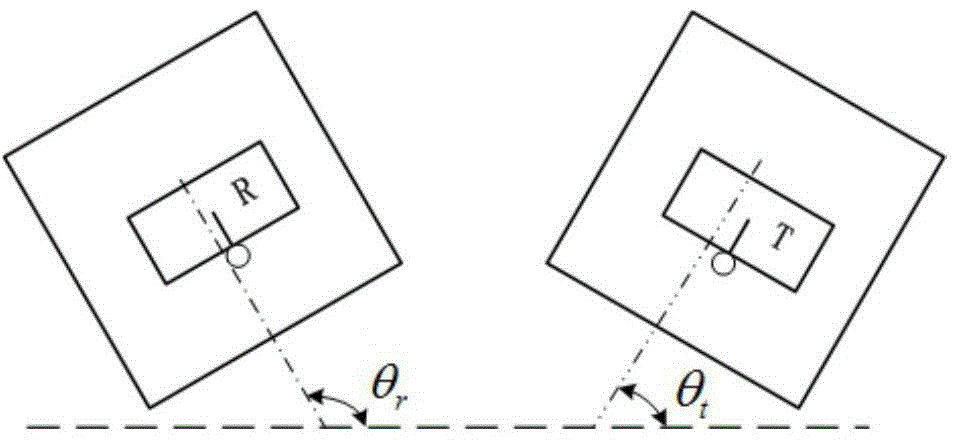
Face identification algorithm under different illumination conditions
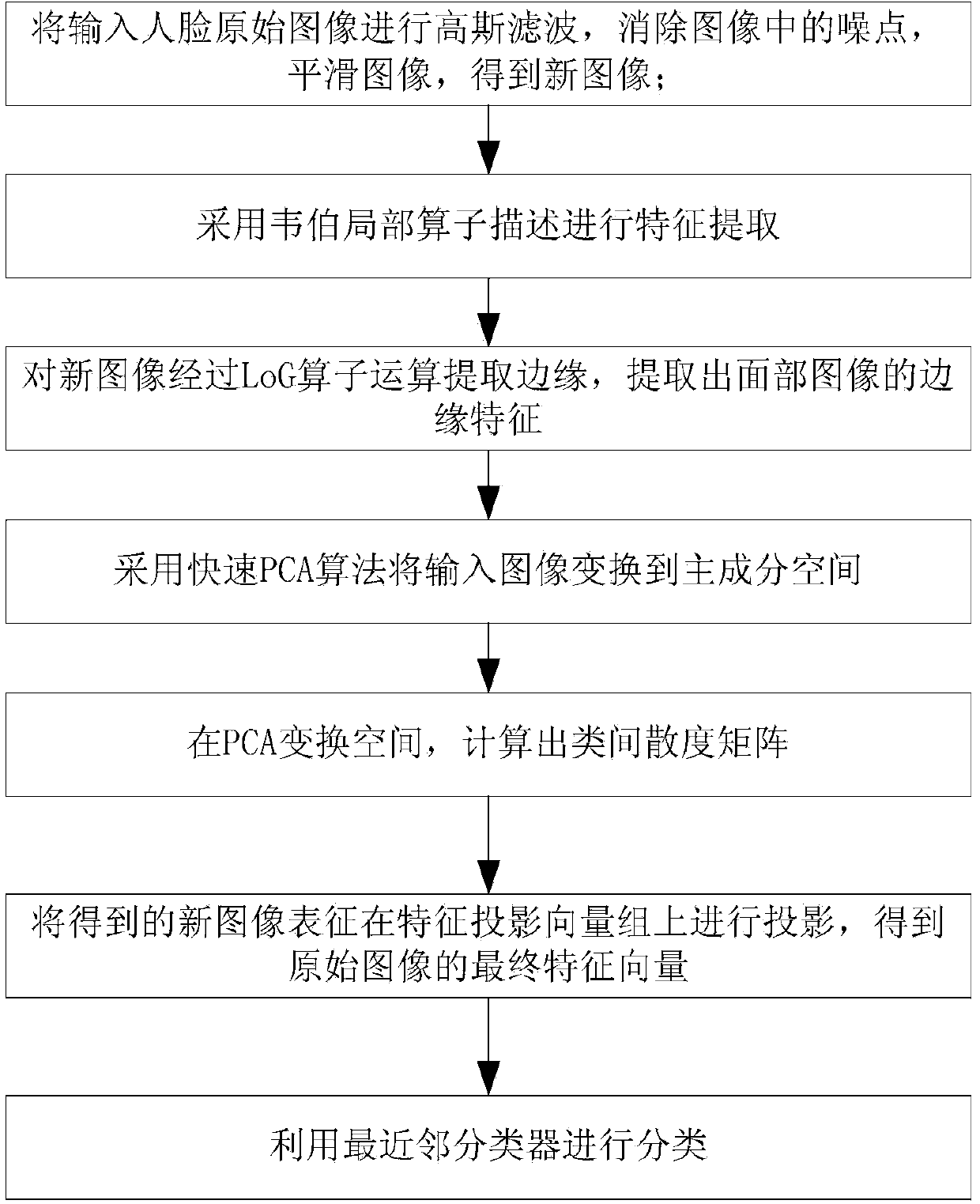
InactiveCN103745237AClear outlineObvious structureCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging FeatureNearest neighbor classifier
The invention discloses a face identification algorithm under different illumination conditions, comprises the steps that: (1) the inputted face original image F(x, y) is subjected to Gaussian filter so as to eliminate noise point in the image and smooth the image, thereby obtaining a new image F'(x, y); (2) the F' (x, y) is subjected to feature extraction by using a Weber local operator description; (3) an edge is extracted from a new image WF(x, y) by LoG operator operation; (4) the inputted image is converted to a principal component space by using fast PCA algorithm; (5) in the PCA transform space, a inter-class scatter matrix is calculated (img file='DDA0000447013750000011.TIF' wi ='45' he='65' / ); (6) the obtained new image feature WF'(x, y) is projected on a feature projection vector group Phi; (7) finally, a nearest neighbor classifier carries out classification. The invention carries out feature extraction of the image operated by the LoG operator, more complete identification information of the original imagely can be extracted, the data from the above experiment shows that the new algorithm can obtain the prominent face identification rate from all three face databases, and also completely meet the real-time requirements in the speed.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Instantaneous radar polarimetry
Owner:CALDERBANK ARTHUR ROBERT +2
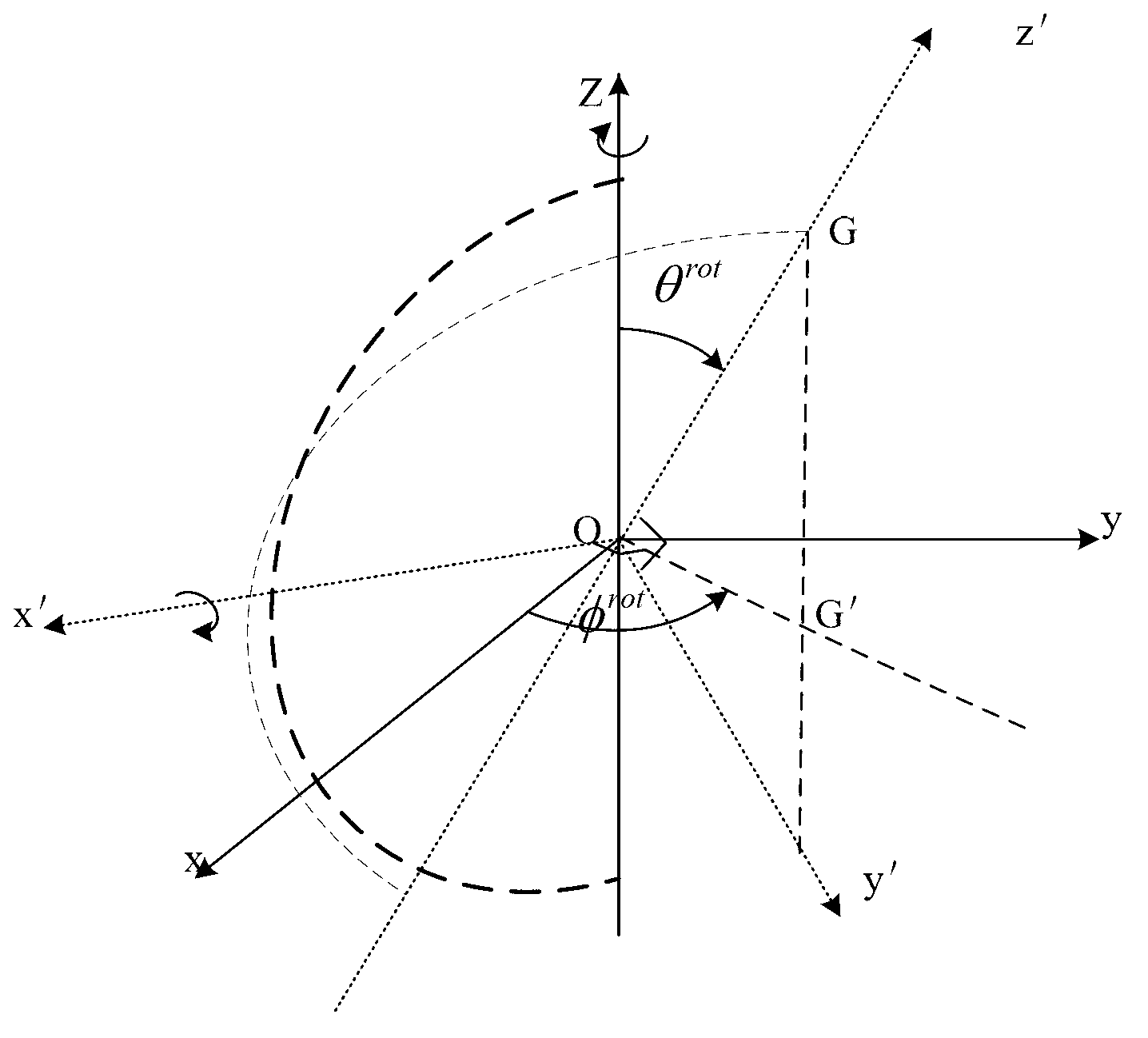
Simulation method for electromagnetic scattering characteristic of plurality of non-coaxial rotating symmetric bodies
ActiveCN103217675AFast simulationReduce memory consumptionWave based measurement systemsTransmission matrixRectangular coordinates
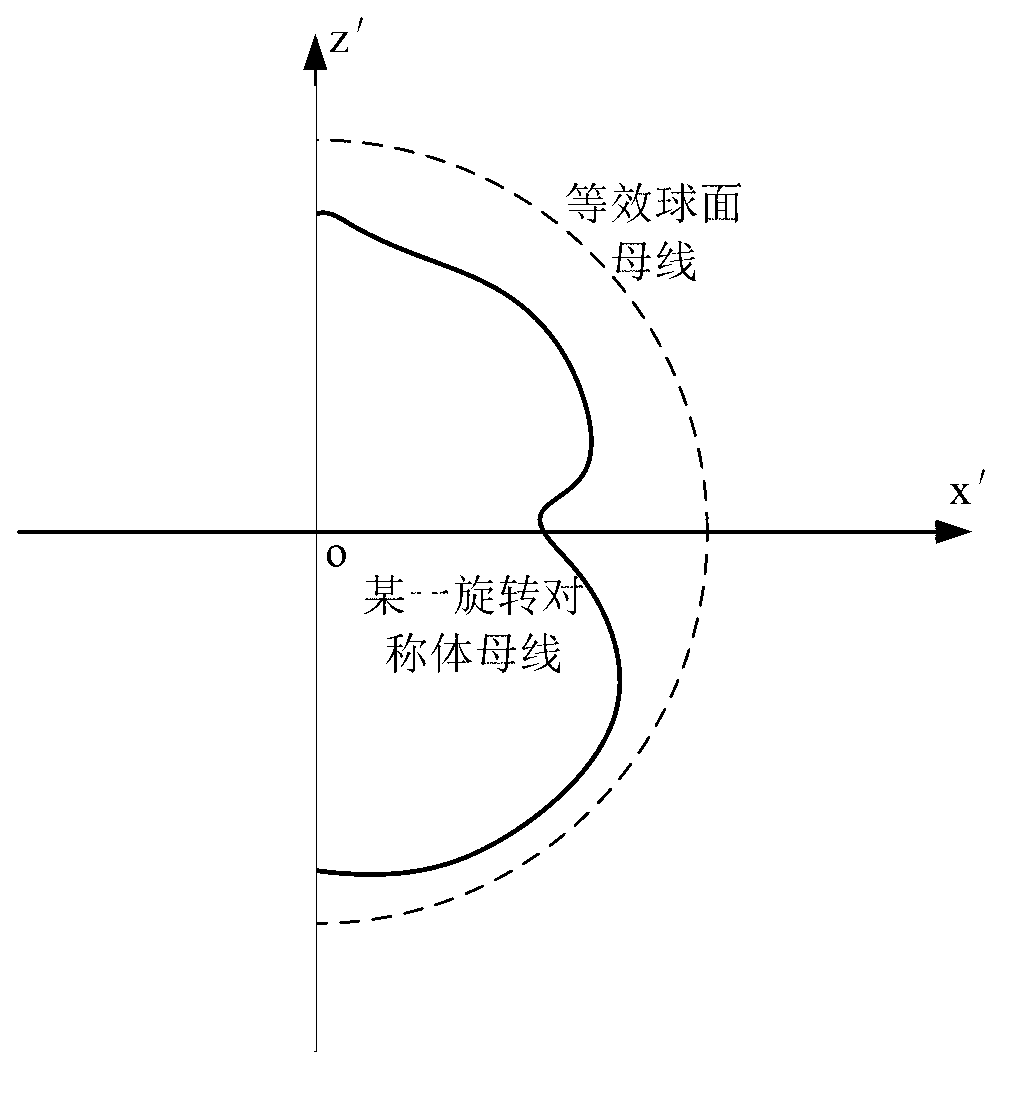
The invention discloses a simulation method for electromagnetic scattering characteristic of a plurality of non-coaxial rotating symmetric bodies. The simulation method comprises the following steps of: building a model of each rotating symmetric body and a corresponding equivalent sphere; respectively building first and second local rectangular coordinate systems on each rotating symmetric body; determining the excitation vectors by using plane wave as an excitation source; respectively building scattering matrixes in the first local coordinate system of each rotating symmetric body; building a third local rectangular coordinate system for every two equivalent spheres and determining the transmission matrix between the two equivalent spheres; building rotating matrixes among the first, second and third local rectangular coordinate systems; building an equation set and obtaining equivalent electromagnetic flow on each equivalent sphere by using an iteration method; and determining the scattering field of a remote area, thus obtaining the radar scattering section area. The simulation method disclosed by the invention provides a quick and efficient solution for electromagnetic scattering simulation of a plurality of rotating symmetric bodies, saves spatial resources, and can accurately and quickly simulate the electromagnetic scattering characteristic of the plurality of non-coaxial rotating symmetric bodies.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Radar target one-dimensional range profile local optimal sub-space recognition method
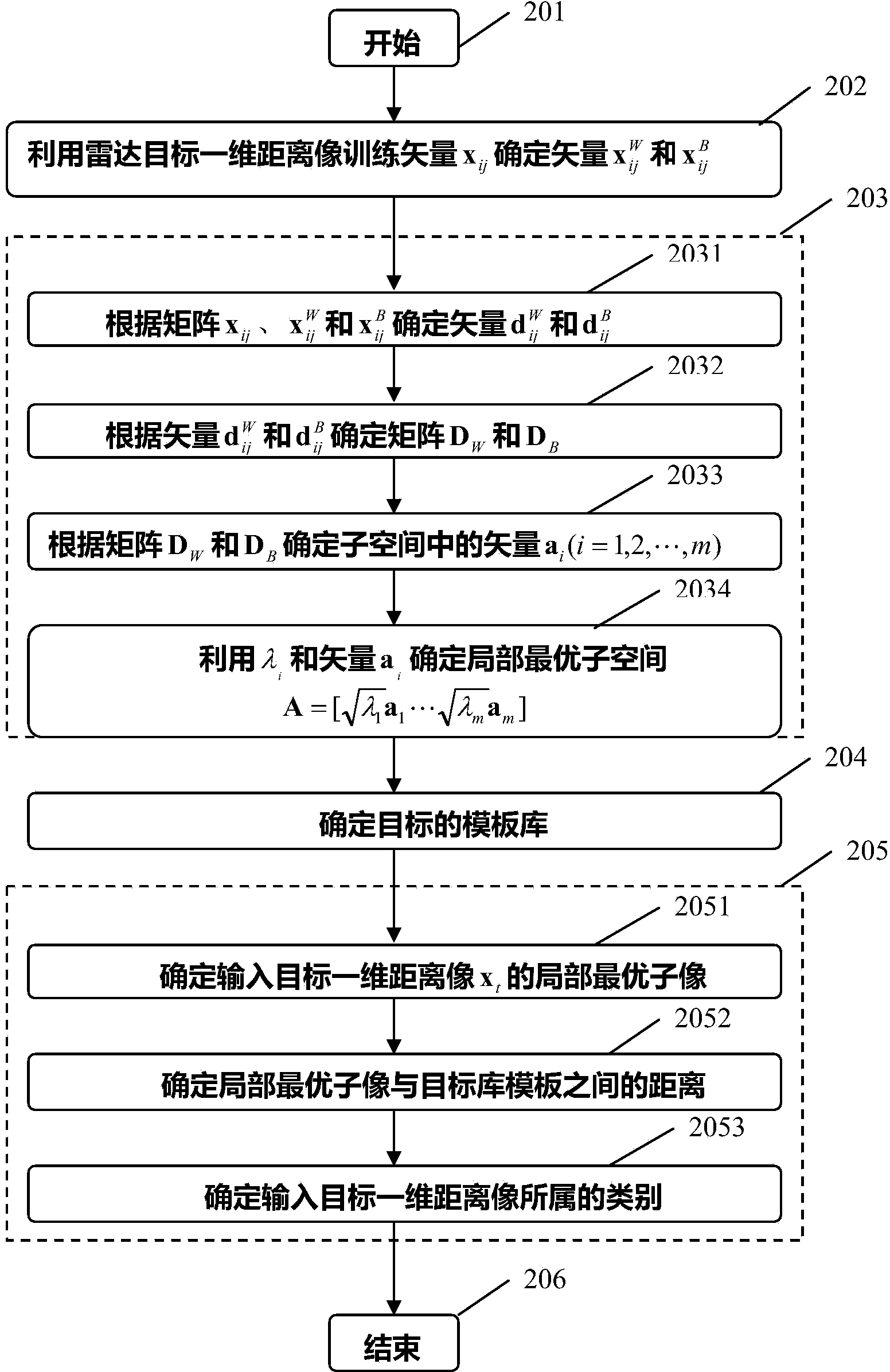
InactiveCN103941244AImprove object classification performanceEasy to identifyWave based measurement systemsMinimum distance classifierLocal optimum
The invention provides a radar target one-dimensional range profile local optimal sub-space recognition method which effectively improves the performance of recognizing a radar target. According to the method, firstly, a nearest intra-class distance scattering matrix and a nearest between-class distance scattering matrix are calculated through training data; then, a local optimal sub-space is set up according to an optimal ratio criteria, the characteristics of the target are extracted, and the characteristics are classified through a minimum distance classifier; finally, the classification where the input target belongs is determined. The method specifically includes the steps of determining a vector X<W>ij and a vector Xij through a radar target one-dimensional range profile training vector Xij; determining a vector d<W>ij and a vector dij; determining a matrix DW and a matrix DB; determining m vectors a1, a2...and am of the local optimal sub-space; determining the equation (please see the equation in the specification) of the local optimal sub-space according to lambdai and a vector ai, wherein i is 1 or 2 or 3...or m; determining a template library according to the projection of the training vectors in the sub-space A; determining the local optimal sub-image of an input target one-dimensional range profile Xt; determining the distance between the local optimal sub-image and a library template vector, and determining the classification where the input target range profile belongs through the minimum distance classifier.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Linear discriminant analysis dimension reduction method based on cosine similarity weighting
InactiveCN107273926AGood dimensionality reduction effectCharacter and pattern recognitionCosine similarityHat matrix
The invention discloses a linear discriminant analysis dimension reduction method based on cosine similarity weighting. The method comprises steps: 1, a to-be-acquired initial feature F of each sample in a data set X is read; 2, based on an LLE algorithm, the initial feature F is subjected to initial dimension reduction to acquire a temporary feature F'; 3, sample feature data are acquired, and the temporary feature F' serves as an input feature; 4, a mean value m of each sample class and a mean value m of the total samples in the data set X are calculated; 5, based on the sample feature data, the m and the m, a within-class scatter matrix based on cosine similarity weighting and a corresponding between-class scatter matrix are acquired; 6, an objective function based on the cosine similarity weighting is built to carry out further dimension reduction on the sample feature data; and 7, according to a projection matrix generated in the step 6, the input feature is mapped to new dimension space. The method has better within-class coupling and between-class scatter, and better dimension reduction effects are achieved.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Transmission coefficient method for AVO seismic analysis
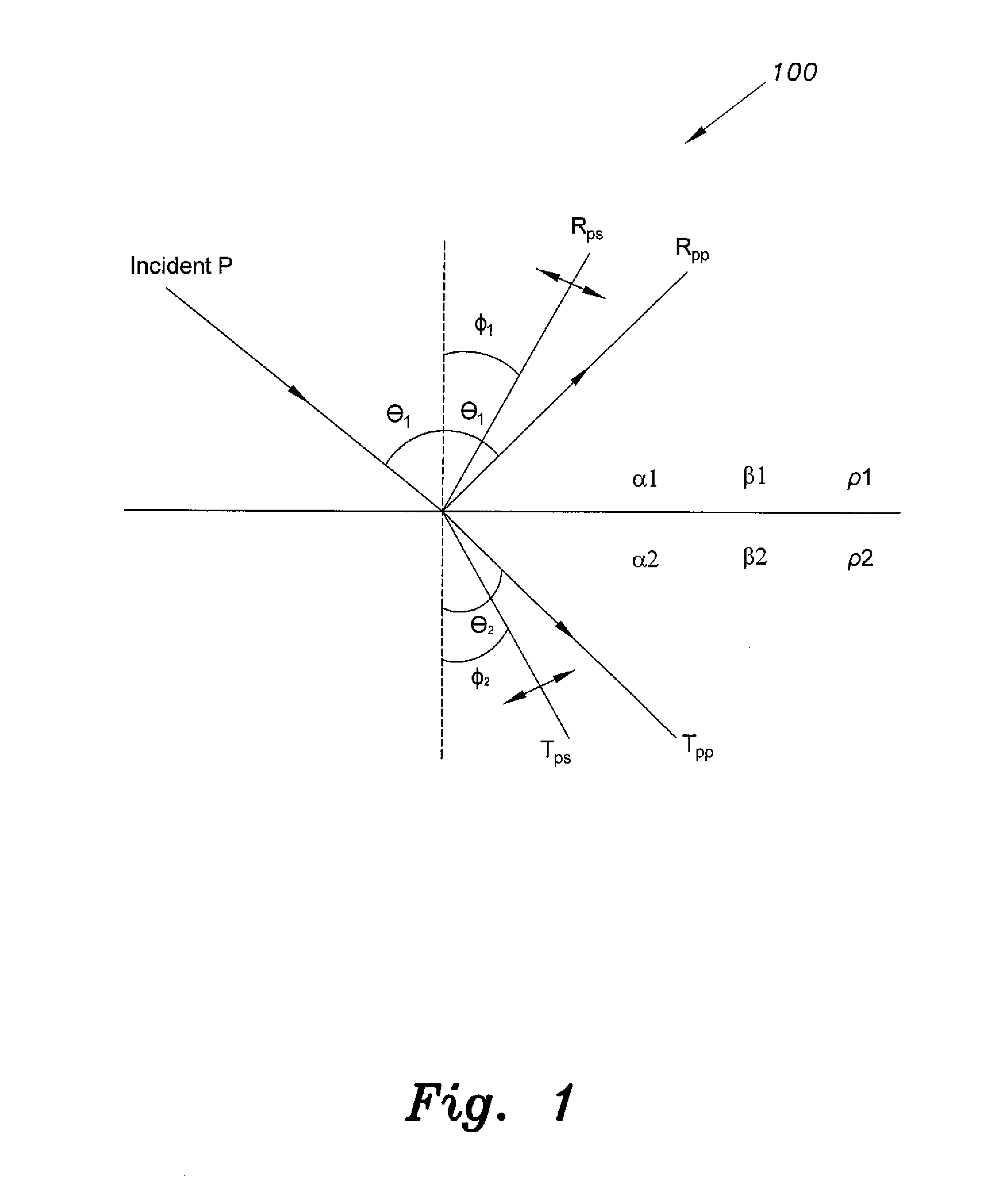
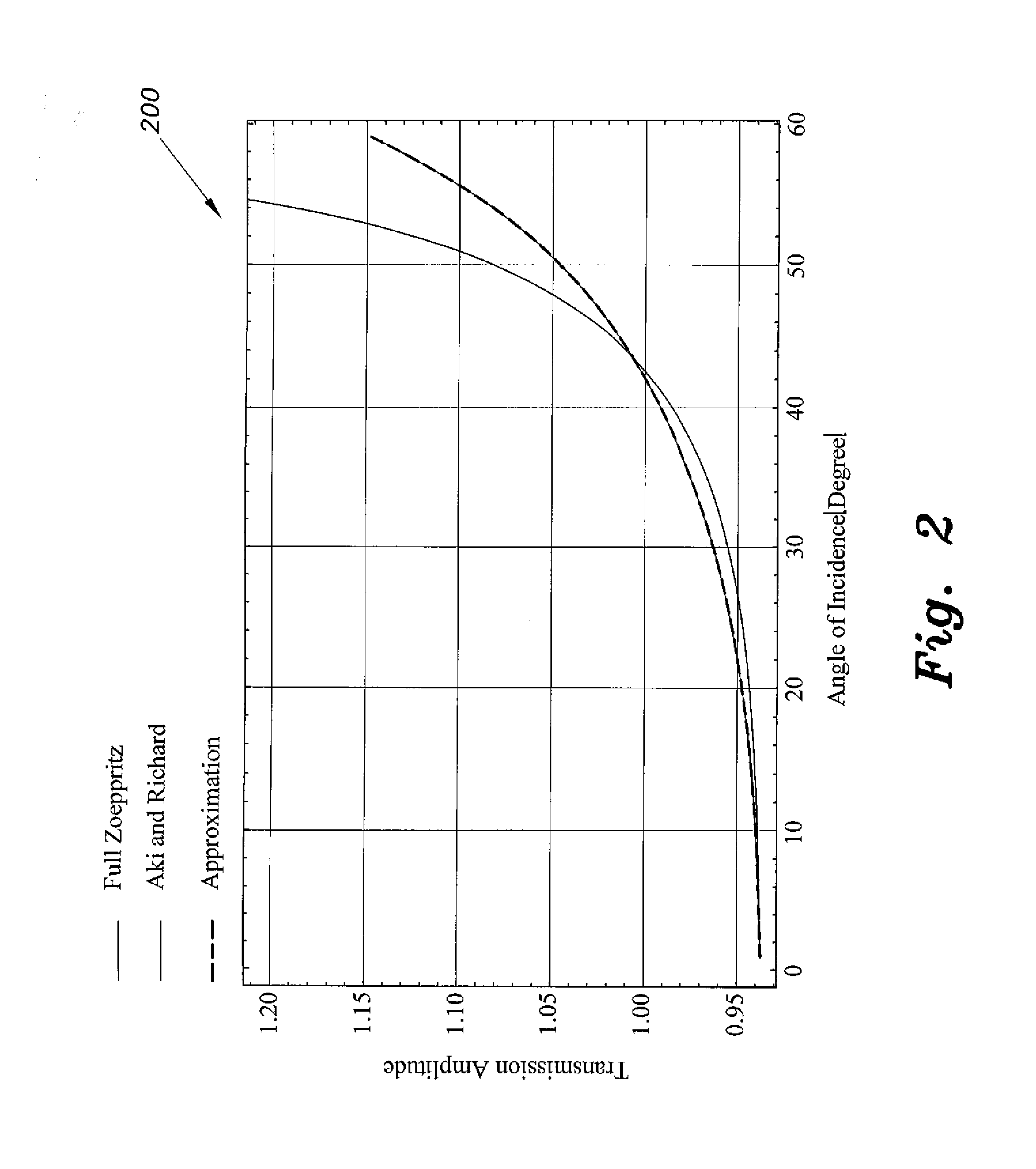
InactiveUS20140324354A1Simple calculationEasy to analyzeSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsPresent methodZoeppritz equations
The transmission coefficient method for AVO (amplitude variation with offset) seismic analysis computes incident-to-transmitted pressure wave and incident-to-transmitted shear wave data in a manner that is compatible with existing AVO applications for analysis on the transmission coefficients of VSP data. Amplitude variation with offset (AVO) computation techniques known in the art provide estimates of pressure wave, shear wave and pseudo-Poisson's reflectivity. Such estimates are based on the Aki-Richards approximation of Zoeppritz's formulation of reflection amplitude and polarity variation with respect to incidence angle. The Zoeppritz equations describe the amplitudes of body waves when incident on an interface, resulting in a scattering matrix in which all possible incident and generated modes are addressed. The present method further simplifies the Aki and Richards computations to facilitate further AVO analysis.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
MIMO radar target blind detection method based on characteristic values under correlated noise background
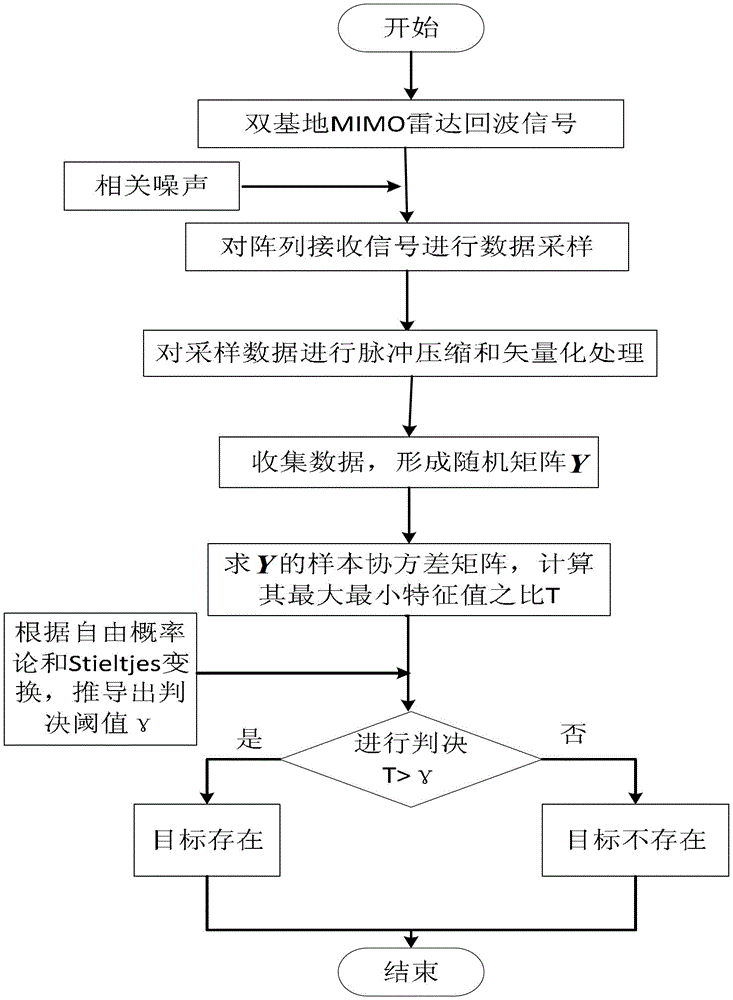
ActiveCN104360334AImprove robustnessSolve the defect of object detection performance degradationWave based measurement systemsPattern recognitionObservation data
The invention provides an MIMO radar target blind detection method based on characteristic values under a correlated noise background. The method is suitable for large-array bistatic MIMO radar with the receiving and transmitting number of array elements and the snapshot number being close. The method comprises the steps that a random matrix theory is used as a tool, the defects that in the prior art, the snapshot number is insufficient and the target detection performance under the correlated noise background is lowered are overcome, and a random matrix model of observation data is established by echo signals under the correlated noise background; the ratio of the maximum characteristic value and the minimum characteristic value of an echo data covariance matrix is calculated to be used as the detection statistical magnitude; the freedom probability theory and Stieltjes conversion are used for deriving a threshold value expression of target detection under the correlated noise background; the threshold value is used as a judgment threshold for detecting a target. Simulation experiments show that the method is suitable for blind detection under the condition that a noise variance and a target scattering matrix are unknown, and the robustness of target detection under the correlated noise environment is obviously improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Range image non-linear subspace recognition method
InactiveCN101241184ALarge amount of informationEasy to handleRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFeature vectorRadar
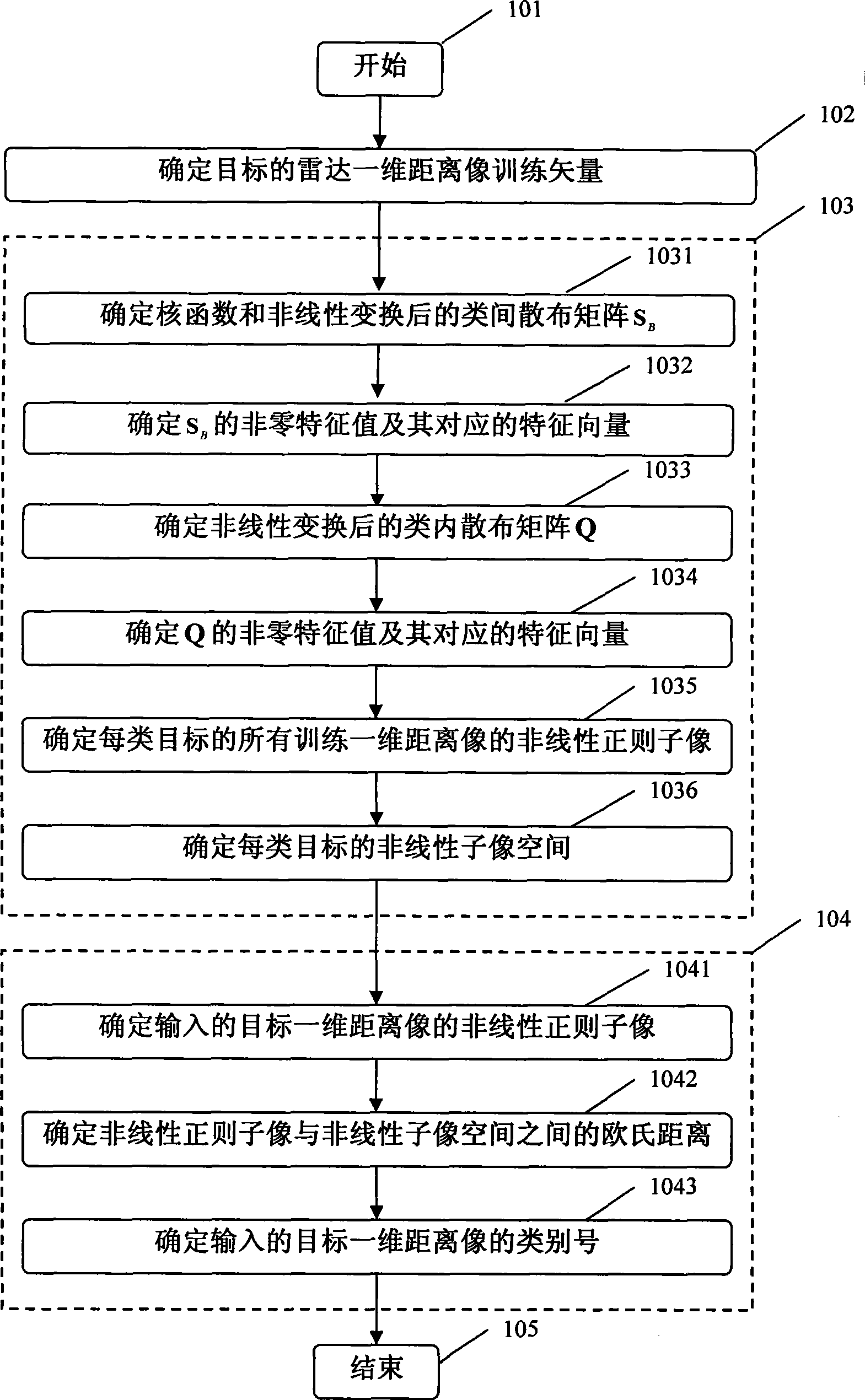
The present invention provides a method for distinguishing nonlinear subspace of one-dimensional distance image which belongs to field of radar target recognition. Target one-dimensional distance image is transferred nonlinearly and mapped to high-dimensional characteristic space, nonlinear regular sub-image characteristics of each kind of target is obtained by characteristic transform matrix of high-dimensional characteristic space to form nonlinear sub-image space of each kinds of target, when the radar one-dimensional distance image of target is input, the sort of one-dimensional distance image is determined according to Euclidean distance between nonlinear regular sub-image and nonlinear sub-image space. Step: radar one-dimensional distance image training vector of target is determined; between-class scatter matrix sB after nonlinear transform and kernel function are determined; nonzero eigenvalue of C and corresponding eigenvector are determined; kind-in scatter matrix Q is determined; nonzero eigenvalue of Q and corresponding eigenvector are determined; all training one-dimensional distance image nonlinear regular sub-image of each kind target are determined; nonlinear sub-image space of each kind of target is determined; input one-dimensional distance image nonlinear regular sub-image of target is dertermined; Euclidean distance between nonlinear regular sub-image and nonlinear sub-image space is determined; sort number of input target one-dimensional distance image is determined.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for extracting features of one-dimensional range profile of radar true/false target in maximum margin subspace
InactiveCN107678006AIncrease the spread distanceReduce overlapWave based measurement systemsFeature vectorFeature Dimension
The invention discloses a method for extracting the features of the one-dimensional range profile of a radar true / false target in a maximum margin subspace, which belongs to the technical field of radar target recognition. First, a maximum margin subspace matrix W is trained based on a training sample set about the one-dimensional range profile of a radar target. Then, during training, an objective equation for solving W is constructed based on a between-class scatter matrix SB and a within-class scatter matrix SW of a training sample xij. Finally, based on the trained matrix W, the one-dimensional range profile of a radar true / false target of which the sub image features are to be extracted is mapped to the matrix W to get sub image features. By increasing the between-class scatter distance and reducing the within-class scatter distance, the between-class separation interval reaches the maximum, and between-class overlap is reduced. Moreover, the dimension of the feature vector obtained by the method is not restricted by the number of classes, a more favorable feature dimension can be obtained, and therefore, the efficiency of target recognition is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Instantaneous Radar Polarimetry
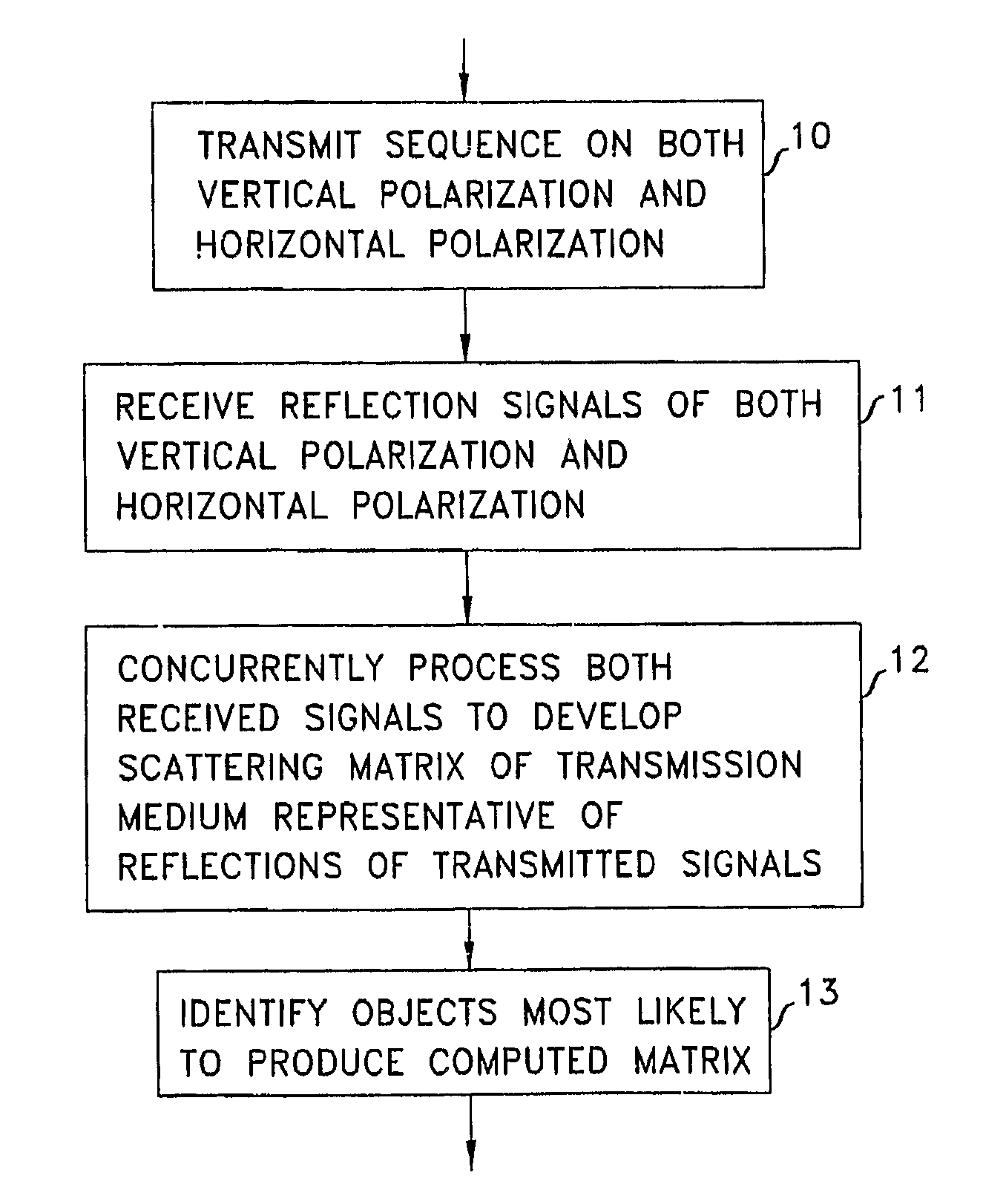
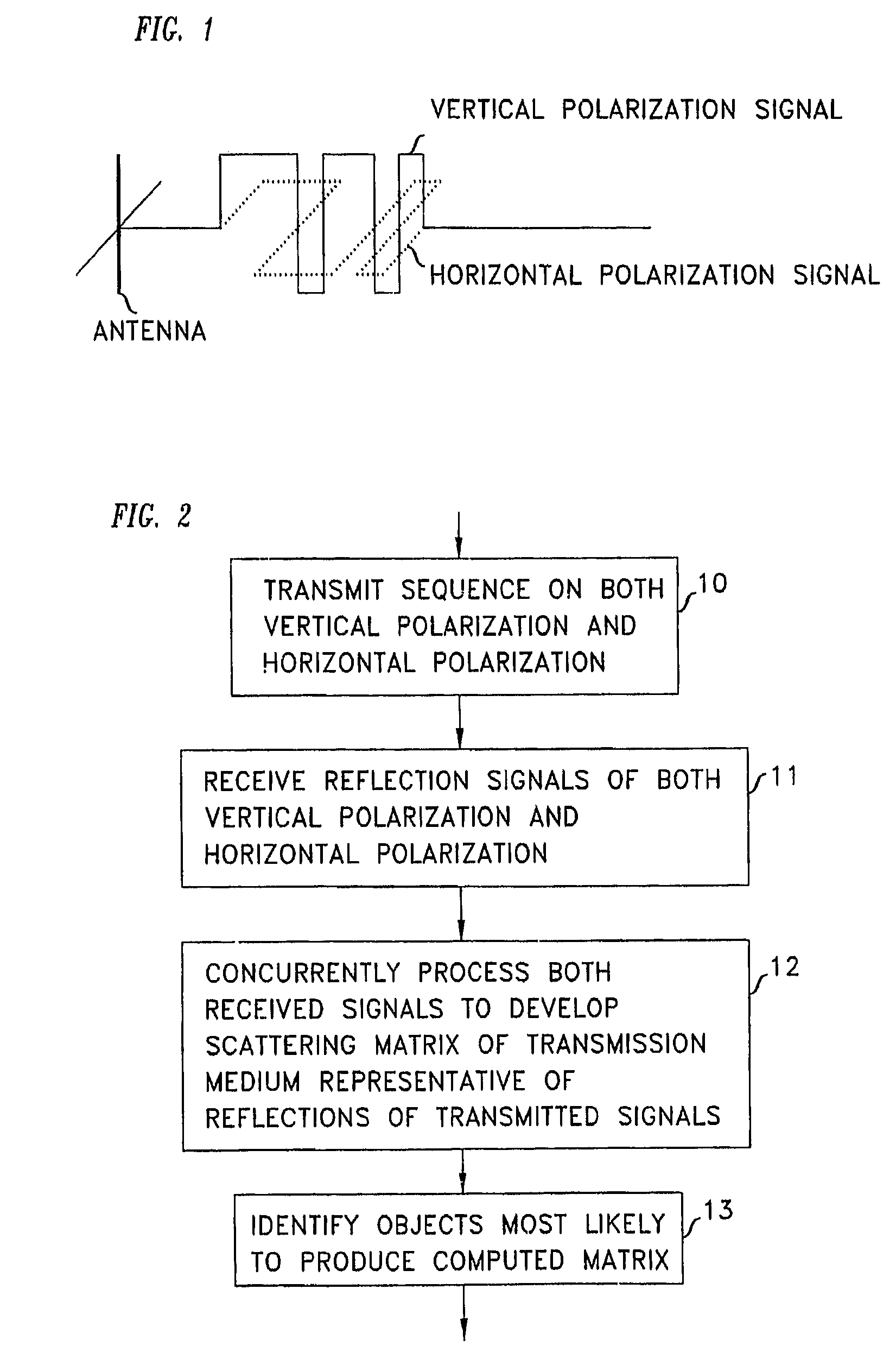
A radar system and method that employs polarization-time diversity in transmitting signals and concurrently processing received reflections from both polarization modes provides information about the scattering matrix of a target without loss of information. Illustratively, the transmitted signals from Golay pairs, and the processing method employs a complex-conjugate time reversal operand. The received reflected signals are processed for a particular distance in mind to develop a scattering matrix of the medium at that distance. By comparing the scattering matrix to known scattering matrices an identification of the target from where the transmitted signals were reflected is obtained.
Owner:CALDERBANK ARTHUR ROBERT +2
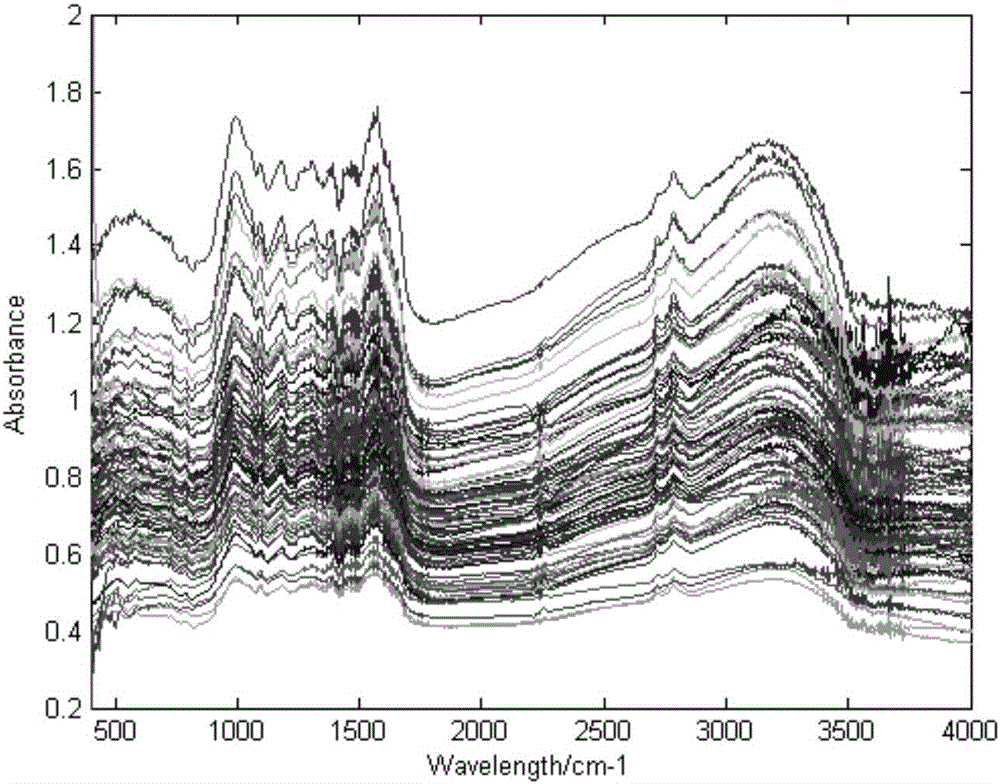
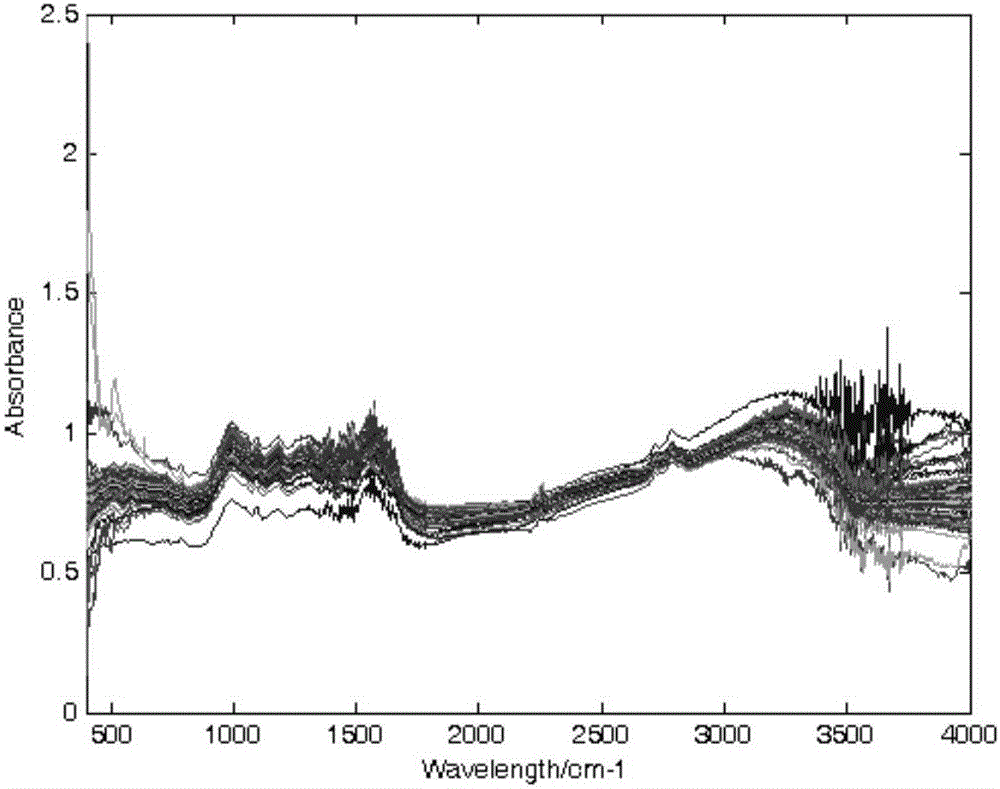
Tea infrared spectrum classification method of fuzzy discrimination clustering
InactiveCN106408012AFew training samplesImplement extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorTest sample
The invention discloses a tea infrared spectrum classification method of fuzzy discrimination clustering. A linear discrimination analyzing method is employed to extract the identification information of 14-dimensional training sample data, and 14-dimensional test sample data is projected to a discrimination vector to obtain the two-dimensional test sample data. The two-dimensional test sample data are subjected to fuzzy C-means clustering. A fuzzy interclass scattering matrix is calculated according to an initial clustering center, and the fuzzy total scattering matrix is calculated. An eigenvector is calculated according to the fuzzy interclass scattering matrix and the fuzzy total scattering matrix. A clustering central value is calculated in a characteristic space through the fuzzy membership function value. The average value of each 14-dimensional training sample is calculated respectively, and the Euclidean distance of the average values of the clustering central value and the training samples of the test samples. If the Euclidean distance from the clustering central value to the training samples is minimal, the tea belonging to the clustering central value is of the same type with the tea of the training samples, thereby realizing correct classification of different tea types.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
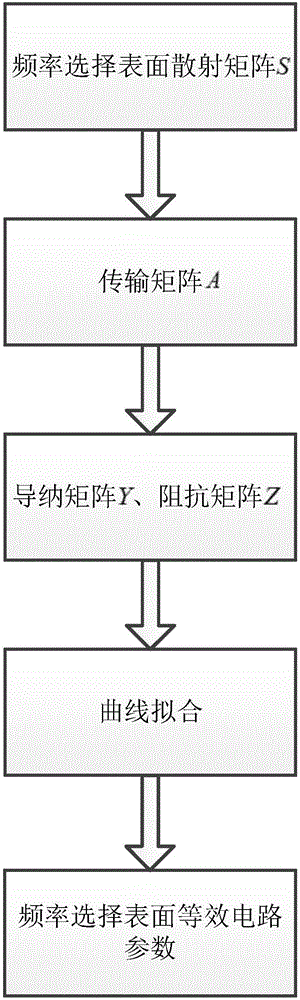
Method for extracting equivalent circuit parameter of dual-frequency-band frequency selective surface
ActiveCN105069235AOvercome limitationsAccurately reflectSpecial data processing applicationsDual frequencyTransmission matrix
The invention discloses a method for extracting an equivalent circuit parameter of a dual-frequency-band frequency selective surface, and mainly solves the boundedness problem in the prior art that an empirical formula is depended to extract the equivalent circuit parameter. The method comprises the following implementation steps: 1) converting a scattering matrix of the frequency selective surface into a transmission matrix; 2) obtaining an admittance matrix and an impedance matrix of an equivalent circuit through the transmission matrix; 3) expressing the admittance matrix and the impedance matrix by lumped elements in the equivalent circuit; and 4) adopting a curve fitting optimization algorithm to extract the parameter in the equivalent circuit. The method can extract the equivalent circuit parameter of any dual-frequency-band frequency selective surface, improves the precision of the equivalent circuit parameter of the dual-frequency-band frequency selective surface and can be used for quickly and accurately analyzing the characteristics of the dual-frequency-band frequency selective surface.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
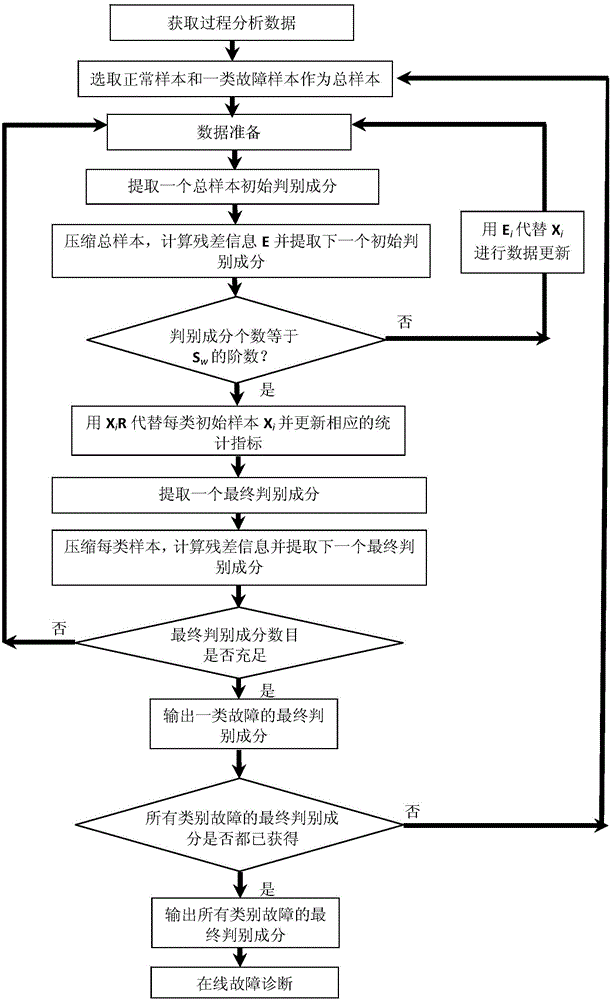
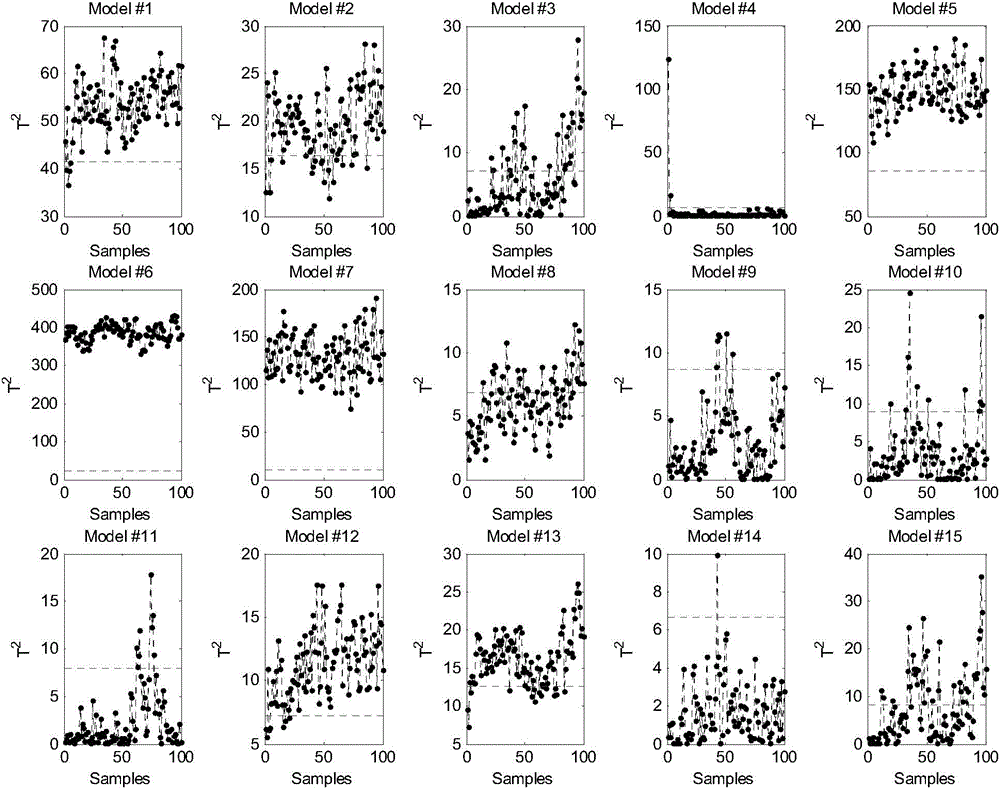
Fault diagnosis method based on nested iterative Fisher discriminant analysis
ActiveCN104536439APursuit of high qualityEffectively distinguish fault categoriesElectric testing/monitoringLinear correlationDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis method based on nested iterative Fisher discriminant analysis, which overcomes the problem of singularity of a within-class scatter matrix, the problem of number limit of discriminant components and a linear correlation problem of the discriminant components in the conventional method, fully explores potential information contained in process data and can be used for effectively differentiating the process data in different types. The method is simple and easy to implement, the performance of online fault diagnosis is greatly improved, the reliability and credibility of actual online fault diagnosis are enhanced, and faults can be accurately repaired by industrial engineers, so that safe and reliable operation of actual production and high quality pursuit of the product can be guaranteed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for estimating Faraday rotation angle (FRA) in satellite borne complete polarization synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data
InactiveCN103197286ANot affected by phase imbalanceWave based measurement systemsSynthetic aperture radarDiagonal
The invention provides a method for estimating a Faraday rotation angle (FRA) in satellite borne complete polarization synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data. The technical scheme comprises that the method comprises the steps of using measurement vector quantity of a satellite borne complete polarization SAR scattering matrix as input, (1) obtaining a polarimetric covariance matrix (PCM), obtaining the corresponding PCM of the measurement vector quantity according to the measurement vector quantity of the scattering matrix, (2) constructing a complex number for estimating the FRA, constructing the complex number relevant to the FRA through a real part of a non-diagonal element of the corresponding PCM of the measurement vector quantity and a diagonal element of the corresponding PCM of the measurement vector quantity, (3) estimating the FRA, and achieving the FRA estimation through the fact that the operations of angle taking and angle halving are carried on the complex number constructed in the step (2). The method for estimating the FRA of the satellite borne complete polarization SAR data is essentially free of influences of unbalanced system phases and steady in property.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Calibration method for carrying out multiport measurements on semiconductor wafers
InactiveUS7130756B2Considerable reproducibility of measurementHigh precisionResistance/reactance/impedenceTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesContinuous measurementCalculation error
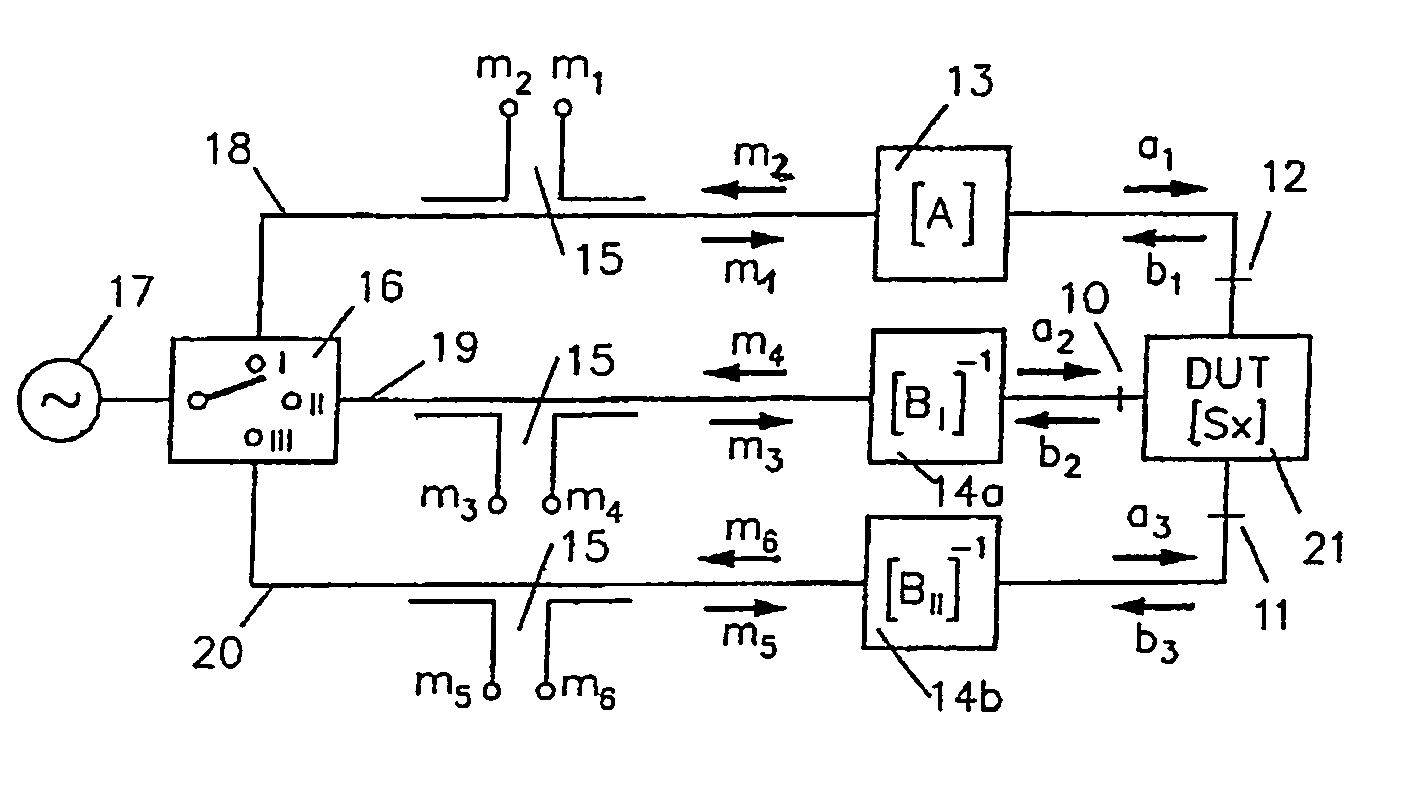
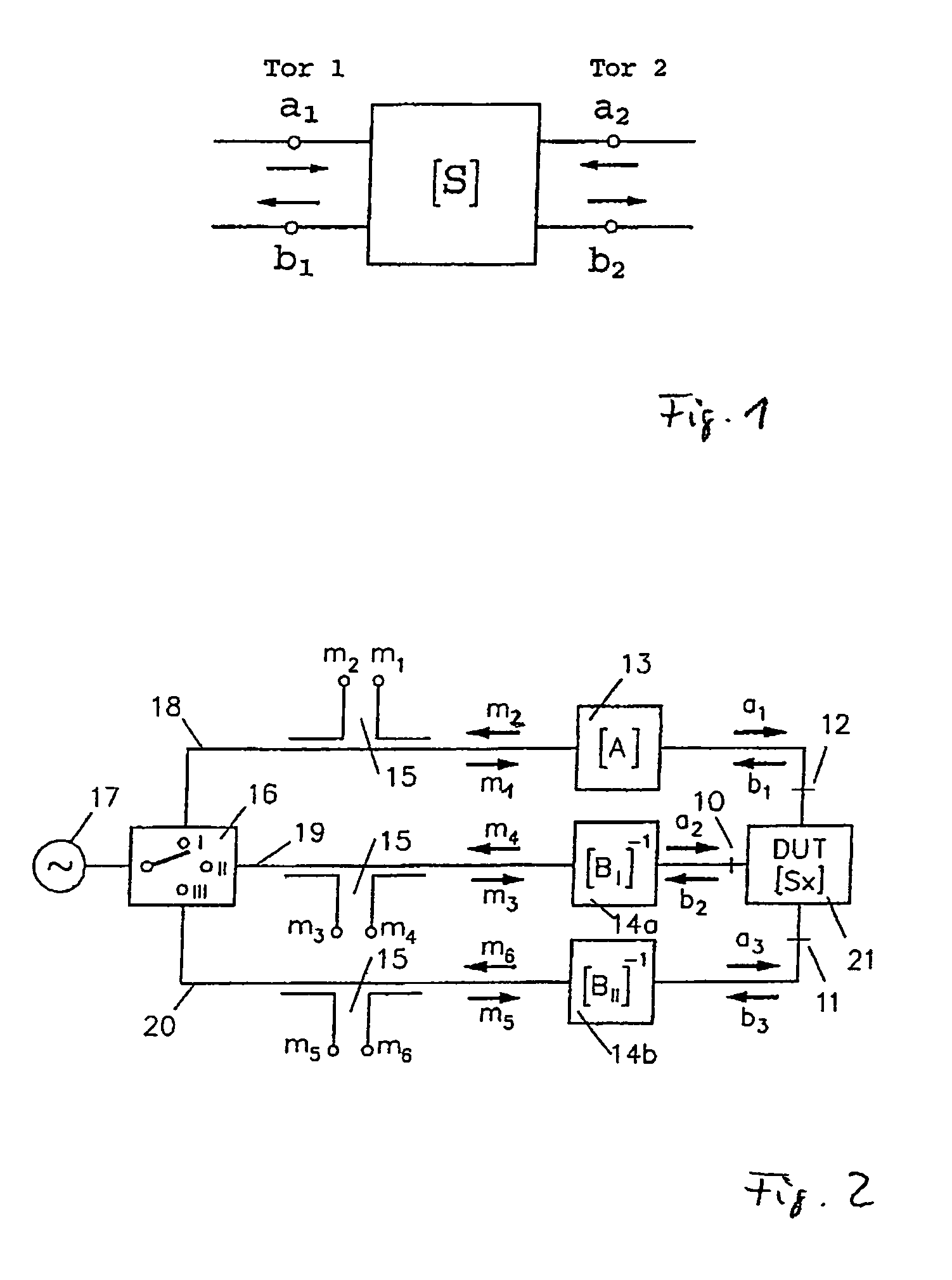
The invention relates to a method for calibrating a vectorial network analyzer having n measurement ports and at least 2n measurement locations (n>1) by successive measurement of the reflection and transmission parameters at different two-port calibration standards, which are connected between the measurement ports in any desired order and must all have a transmission path, and three different n-port calibration standards, which are connected between the measurement ports in any desired order and which are not permitted to show transmission and by calculation of error coefficient and scattering matrix [Sx] with the 10-term or 7-term multiport method. An object of the invention is to propagate a method for calibrating these vectorial network analyzer used for multiport measurement which permits a calibration with increased precision and considerable reproducibility of measurement.
Owner:CASCADE MICROTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com