Patents
Literature
188 results about "Finite-difference time-domain method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
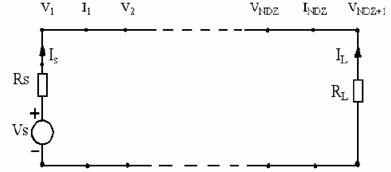
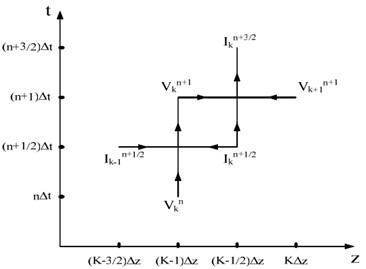
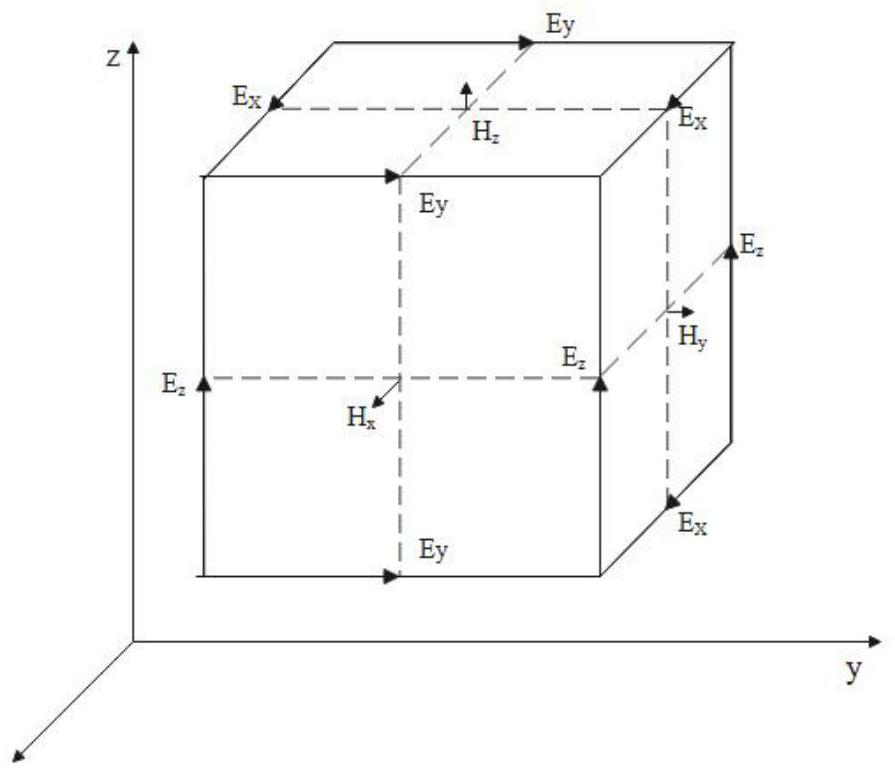
Finite-difference time-domain or Yee's method (named after the Chinese American applied mathematician Kane S. Yee, born 1934) is a numerical analysis technique used for modeling computational electrodynamics (finding approximate solutions to the associated system of differential equations). Since it is a time-domain method, FDTD solutions can cover a wide frequency range with a single simulation run, and treat nonlinear material properties in a natural way.
CD metrology analysis using a finite difference method
ActiveUS6919964B2Directly computeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyDirect evaluation
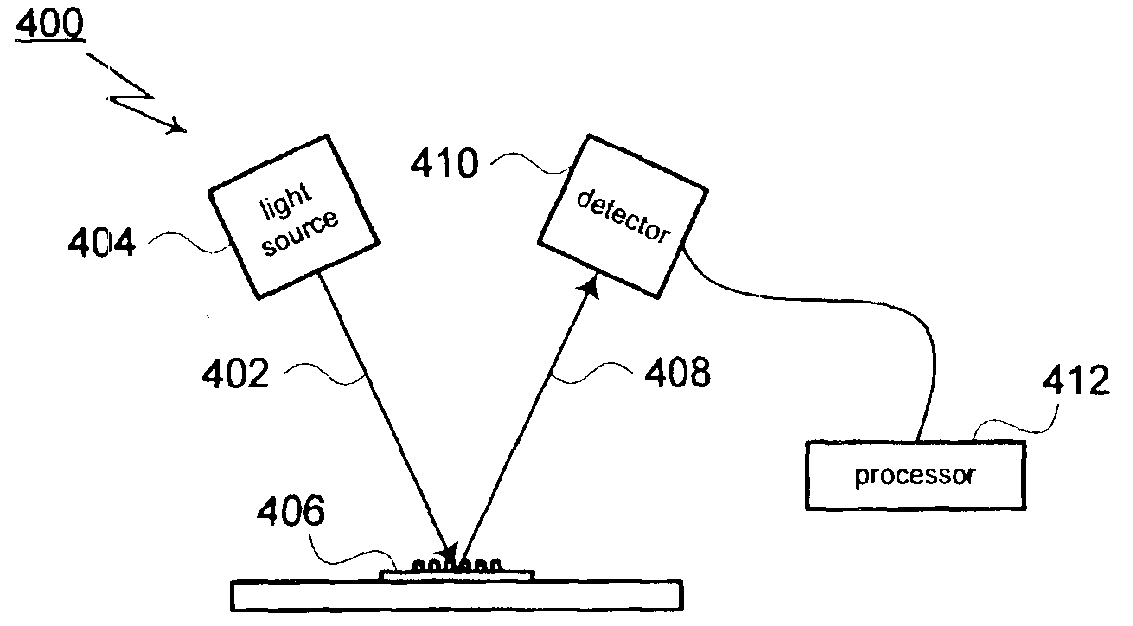
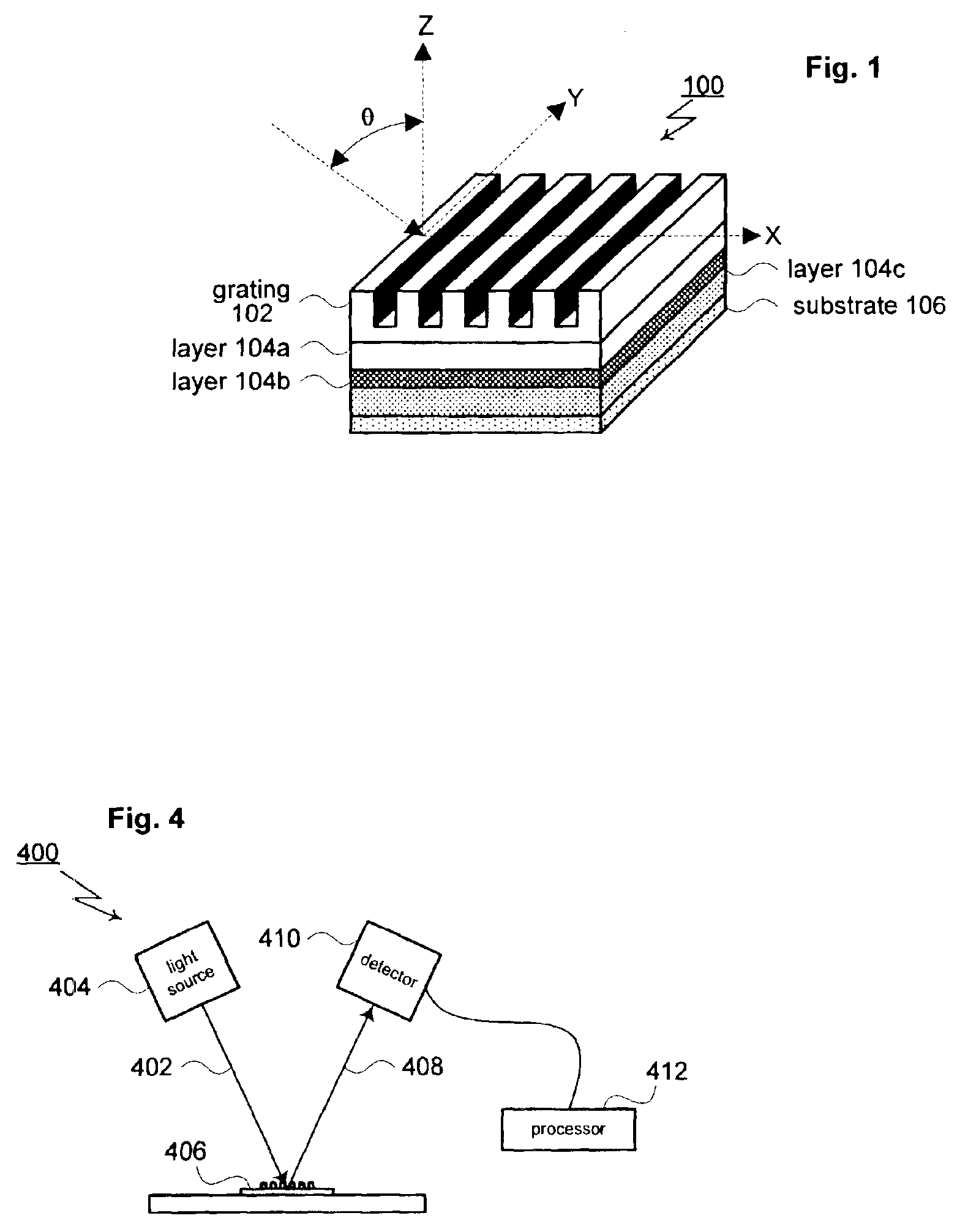
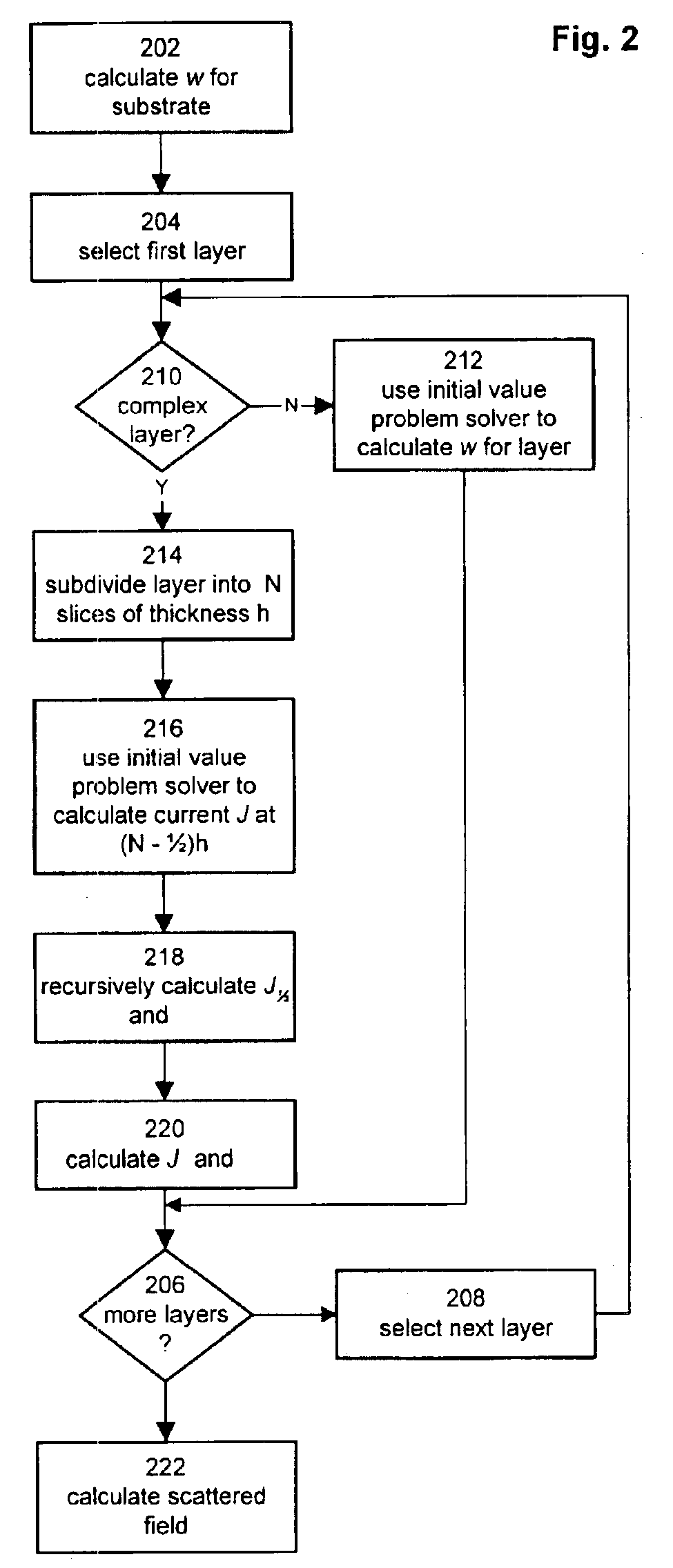
A method for modeling diffraction includes constructing a theoretical model of the subject. A numerical method is then used to predict the output field that is created when an incident field is diffracted by the subject. The numerical method begins by computing the output field at the upper boundary of the substrate and then iterates upward through each of the subject's layers. Structurally simple layers are evaluated directly. More complex layers are discretized into slices. A finite difference scheme is performed for these layers using a recursive expansion of the field-current ratio that starts (or has a base case) at the lowermost slice. The combined evaluation, through all layers, creates a scattering matrix that is evaluated to determine the output field for the subject.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
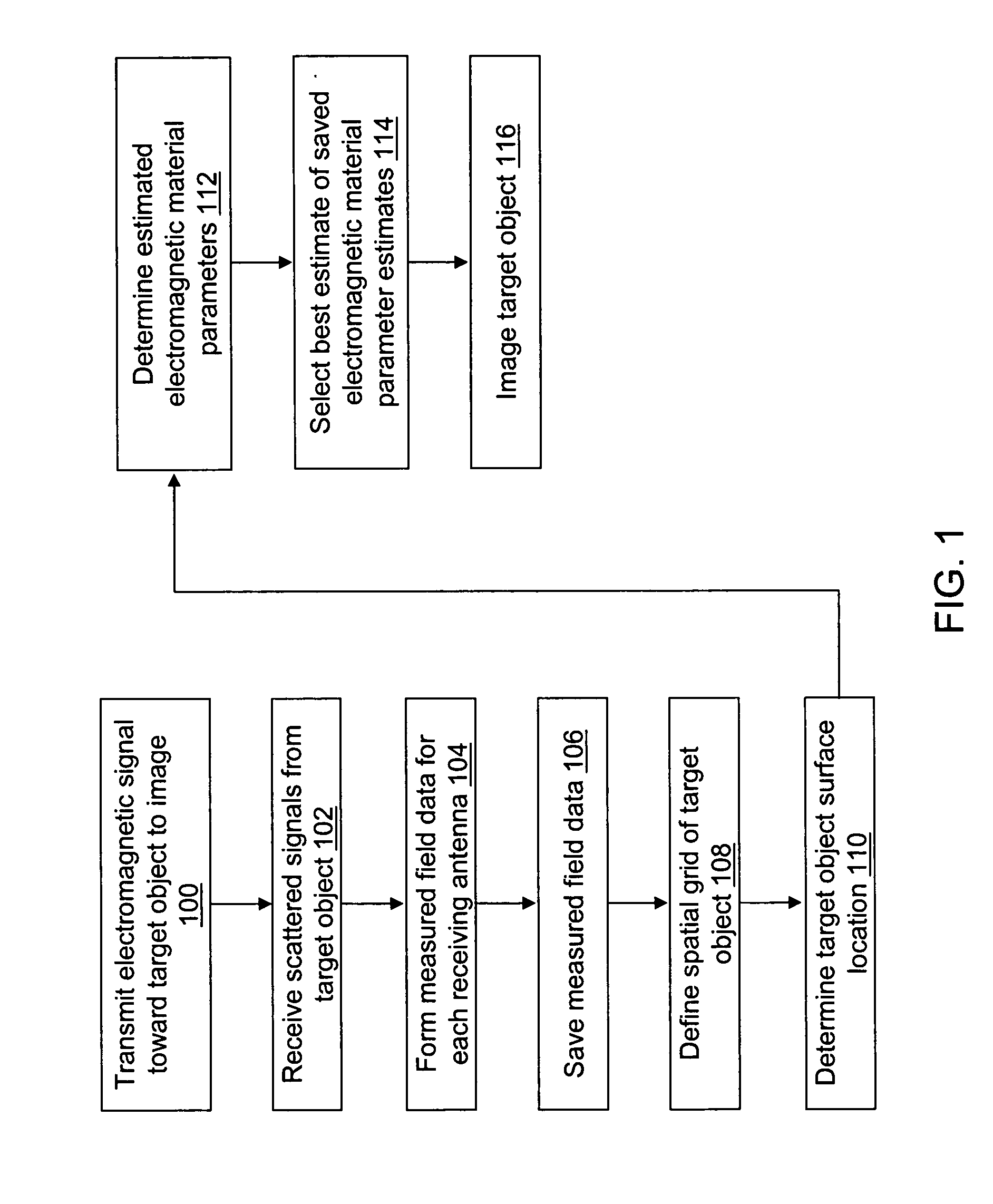
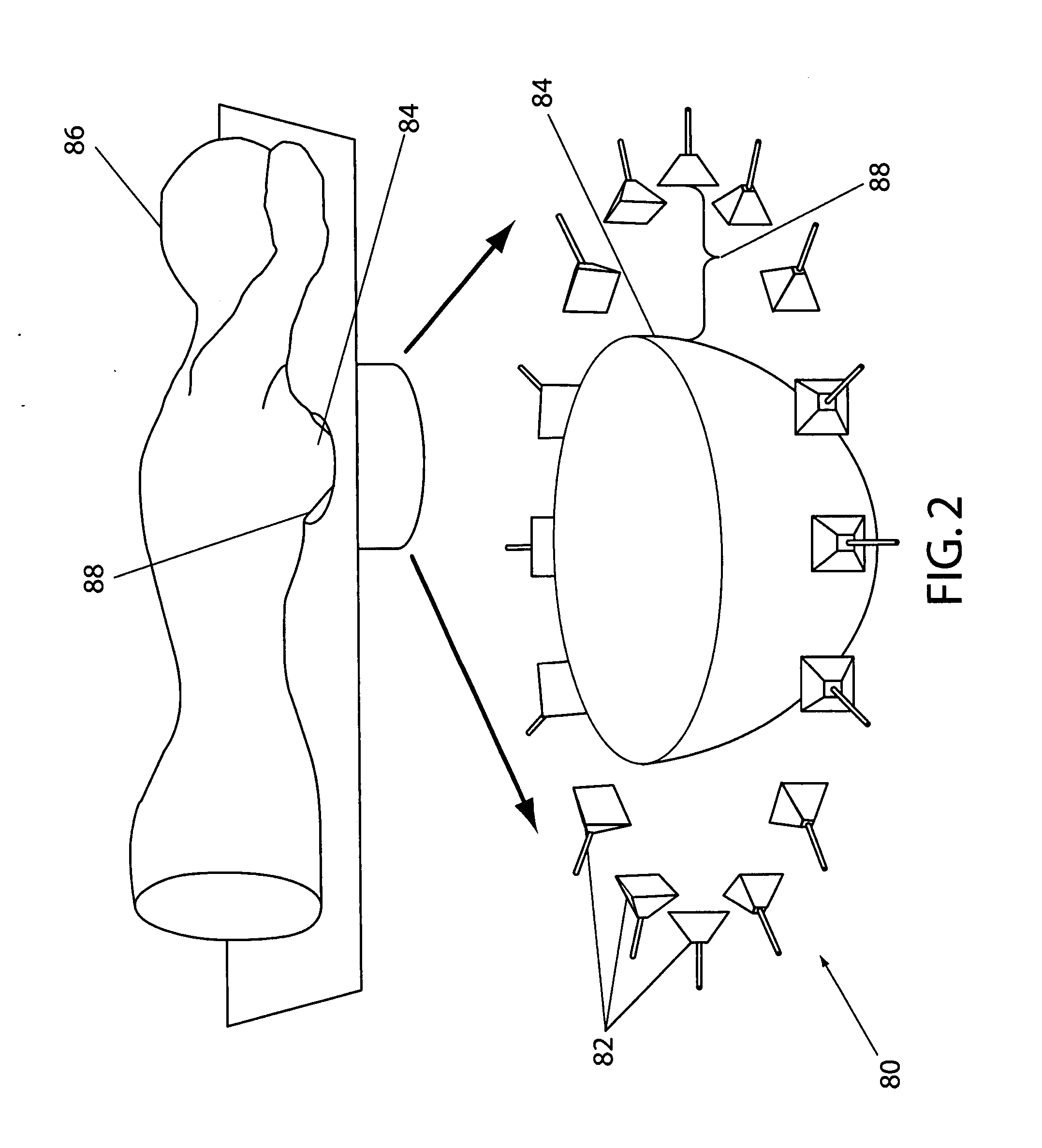
Time domain inverse scattering techniques for use in microwave imaging
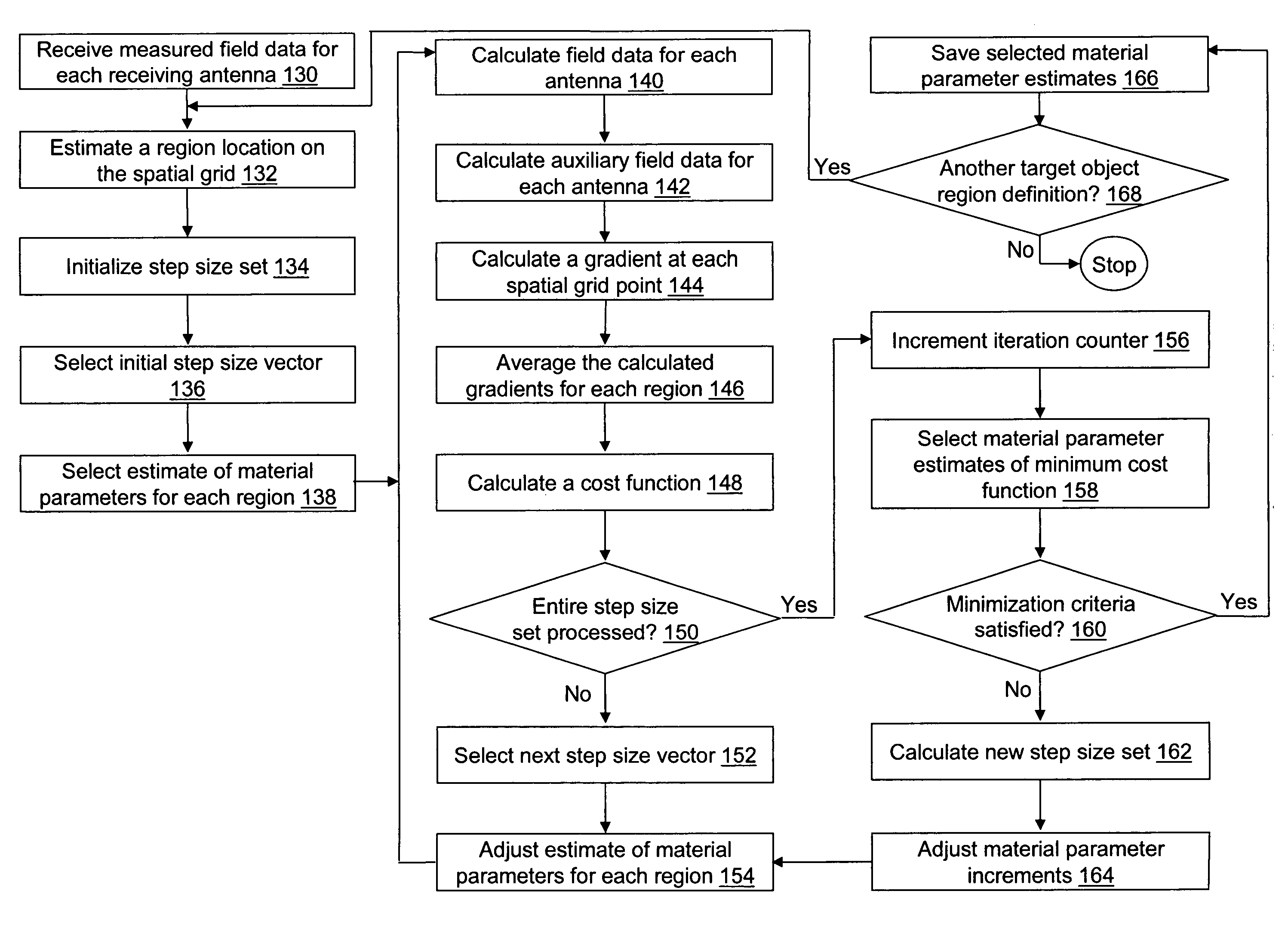
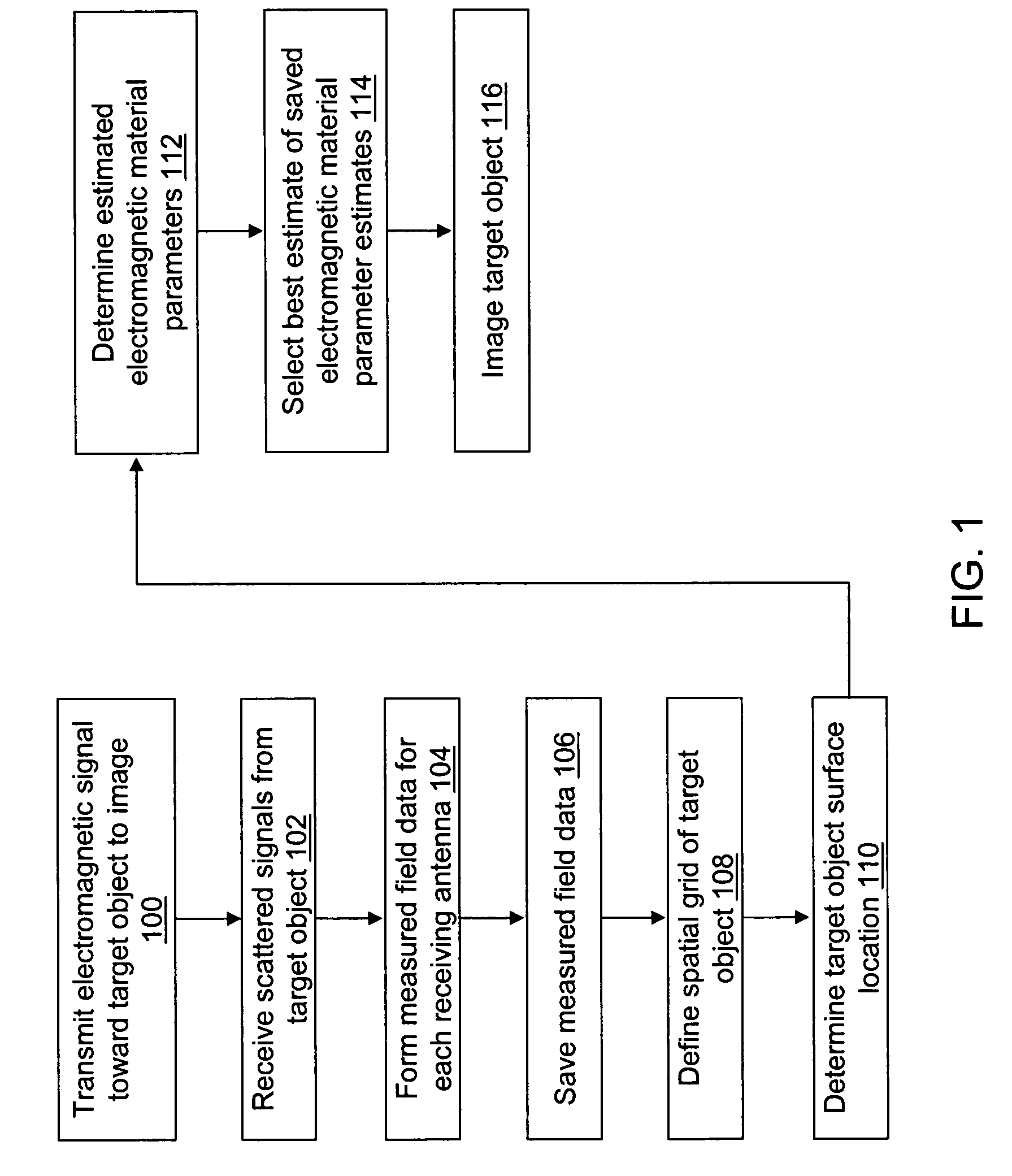
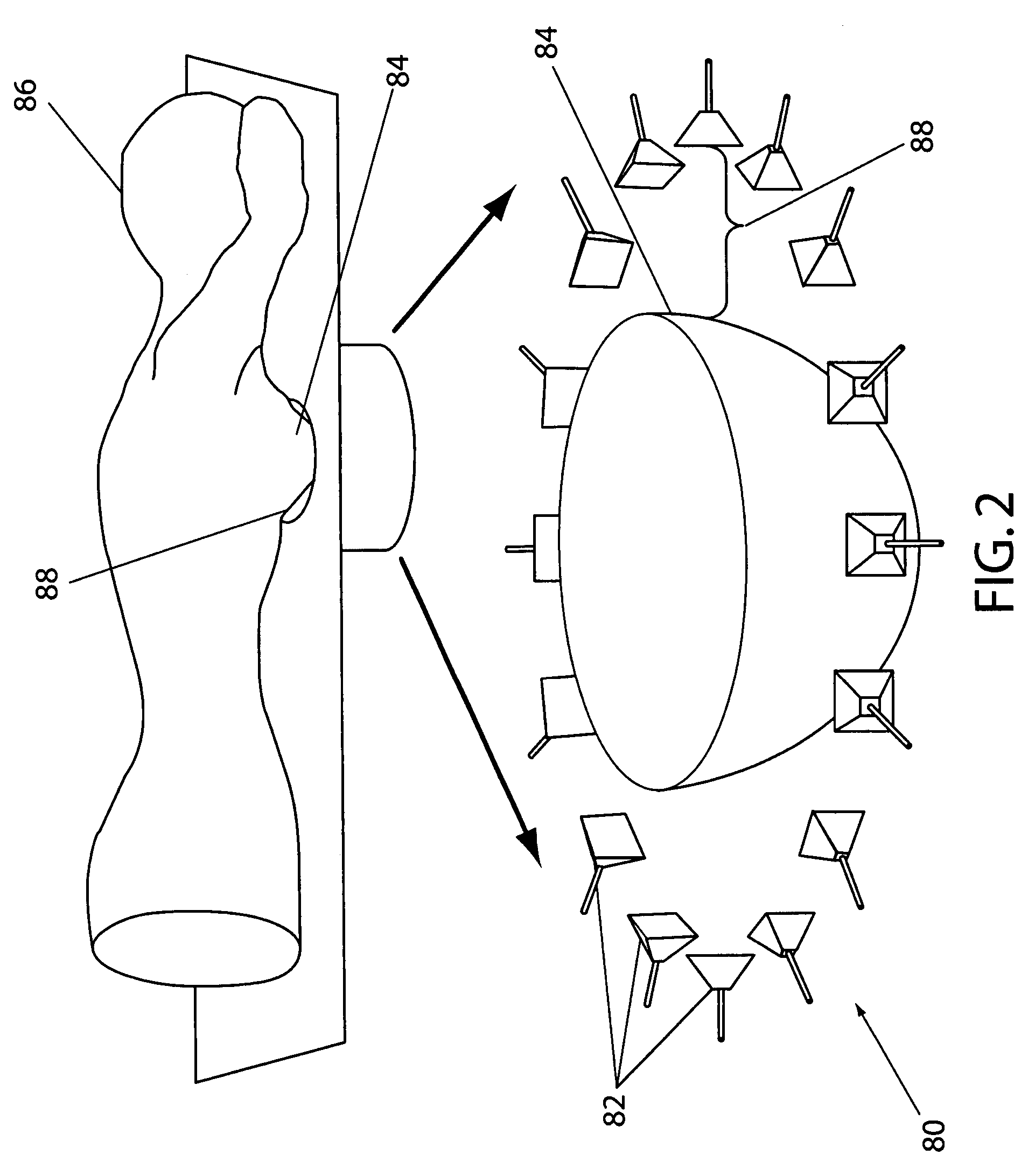
ActiveUS20060241409A1Accurate tumor localizationMinimize cost functionCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityTime domain
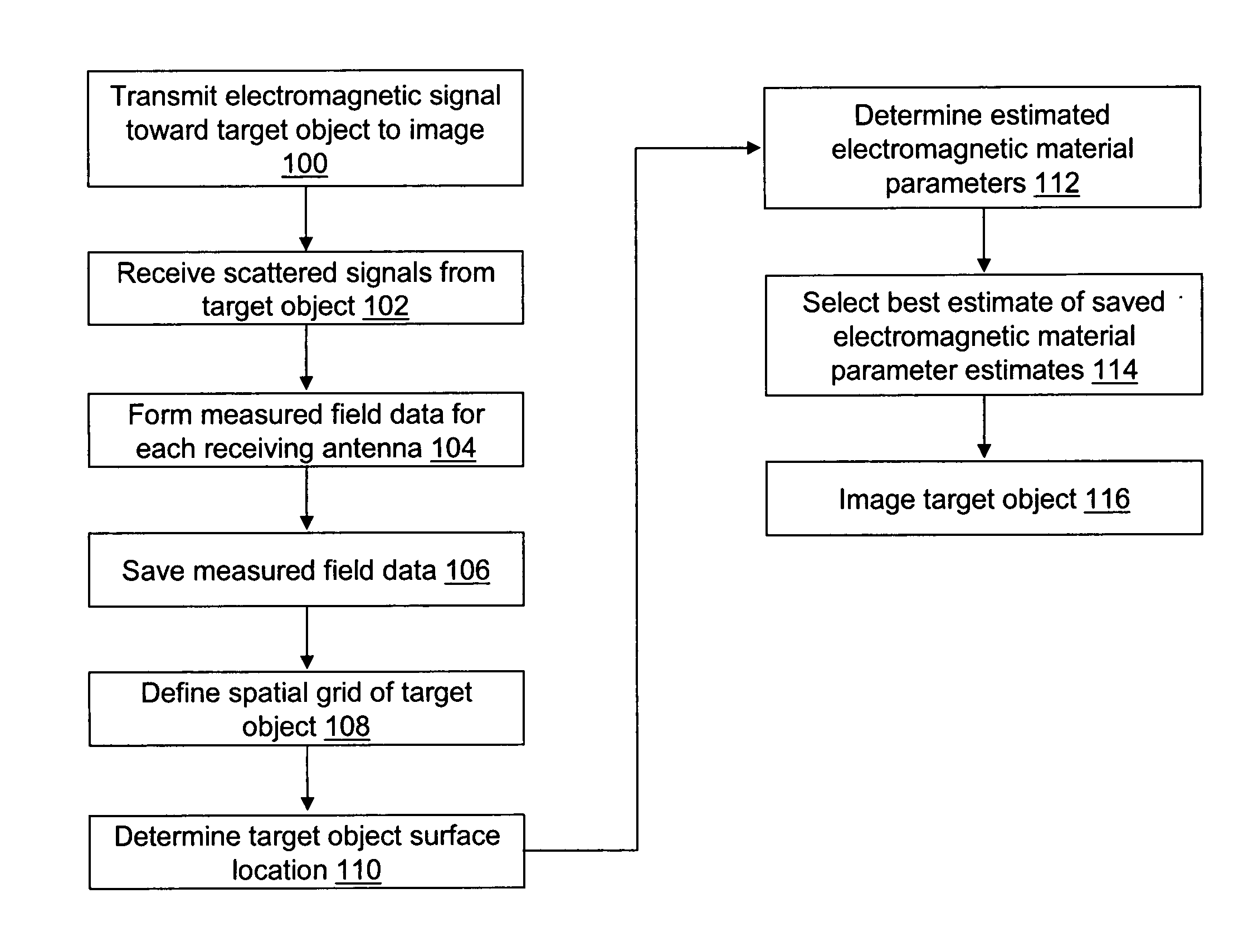
A system and a method are provided for estimating the average dielectric properties of a plurality of regions in space. The application of this technique is illustrated for determining the average properties of breast tissue. The knowledge of average properties is important when UWB microwave radar signal processing algorithms are used for tumor detection and localization. The method is an extension of a time-domain inverse scattering algorithm based on the finite-difference time-domain method. A hybrid conjugate gradient optimization is used to minimize a cost function defined between a measured and a calculated total electromagnetic field at a series of antennas. The output of the method is an average set of electromagnetic material parameters that describe specific regions of interest in either a non-dispersive heterogeneous medium or a dispersive heterogeneous medium.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
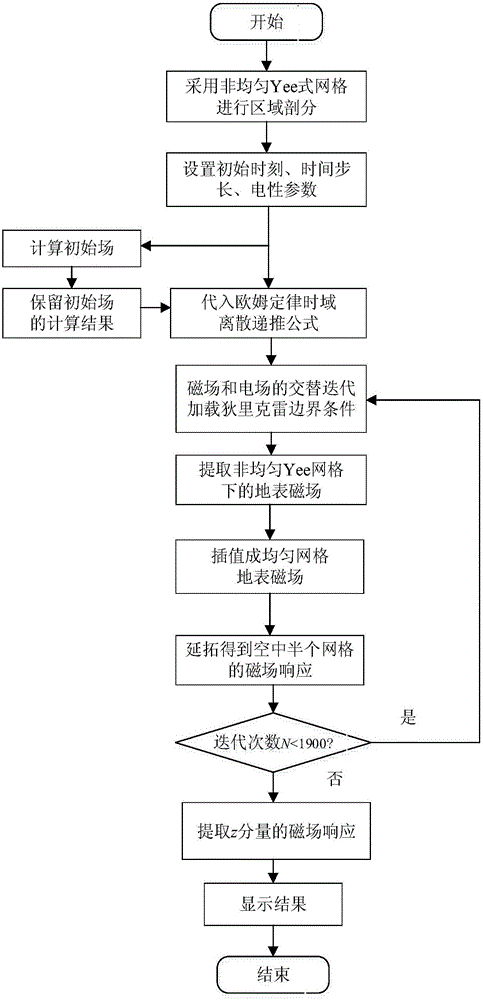
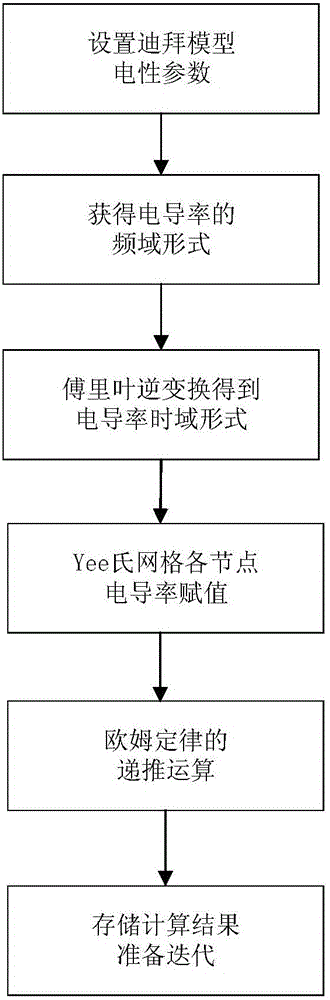
FDTD (Finite-Difference Time-Domain)-based three-dimensional induction-polarization double-field numerical simulation method
ActiveCN105893678AReduce usageEffective simulationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectromagnetic responseElectric field
The invention relates to an FDTD (Finite Difference Time Domain)-based three-dimensional induction-polarized double-field numerical simulation method, which aims to quickly calculate electromagnetic response of induction-polarization double fields of a three-dimensional model. The FDTD-based three-dimensional induction-polarized double-field numerical simulation method mainly comprises the following steps of obtaining a time-domain expression of electric conductivity of a Dubai model by adopting inverse Laplace transformation; constructing an e index auxiliary equation of electric conductivity parameters; obtaining an ohm law time-domain discrete recursion expression through a trapezoidal integral method; reducing four-dimensional numeric operation into three-dimensional operation; substituting a formula into a passive Maxwell curl equation; deriving an iterative equation of an electric field and a magnetic field based on a three-dimensional FDTD method, thus completing electromagnetic response numerical calculation of the induction-polarization double fields of the three-dimensional model. The FDTD-based three-dimensional induction-polarized double-field numerical simulation method disclosed by the invention aims to solve the problems of long time-domain convolution operation of Ohm law, large memory occupation and the like, and the electromagnetic response numerical calculation of the induction-polarization double fields of the three-dimensional model is finally realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Finite difference design method of magnatic resonance imaging (MRI) system gradient coil
The invention discloses a finite difference design method of a magnatic resonance imaging (MRI) system gradient coil, which comprises the following steps: firstly, dividing finite difference grids in the coil space, and establishing finite difference relation between a node stream function and grid current density on each grid node; subsequently, selecting a constraint field point in the magnetic field related region of the MRI system gradient coil, and computing the magnetic induction intensity on the constraint field point according to the design requirements; then, establishing a system of linear equations between the node stream function and the magnetic induction intensity of the constraint field point according to the Biot-Savart law; simultaneously, establishing a penalty function of the system of linear equations according to the actual engineering requirements; and finally, solving the system of linear equations by a method of regularization to acquire a node stream function value, and determining the current style of the coil by a constant stream function line. The invention is simple and effective and can be suitable for designing gradient coil systems in any structure.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for achieving wavefront modulation based on dielectric conformal metasurface
ActiveCN109164574AImplement custom functionsArbitrary regulationOptical elementsDielectricMicro nano
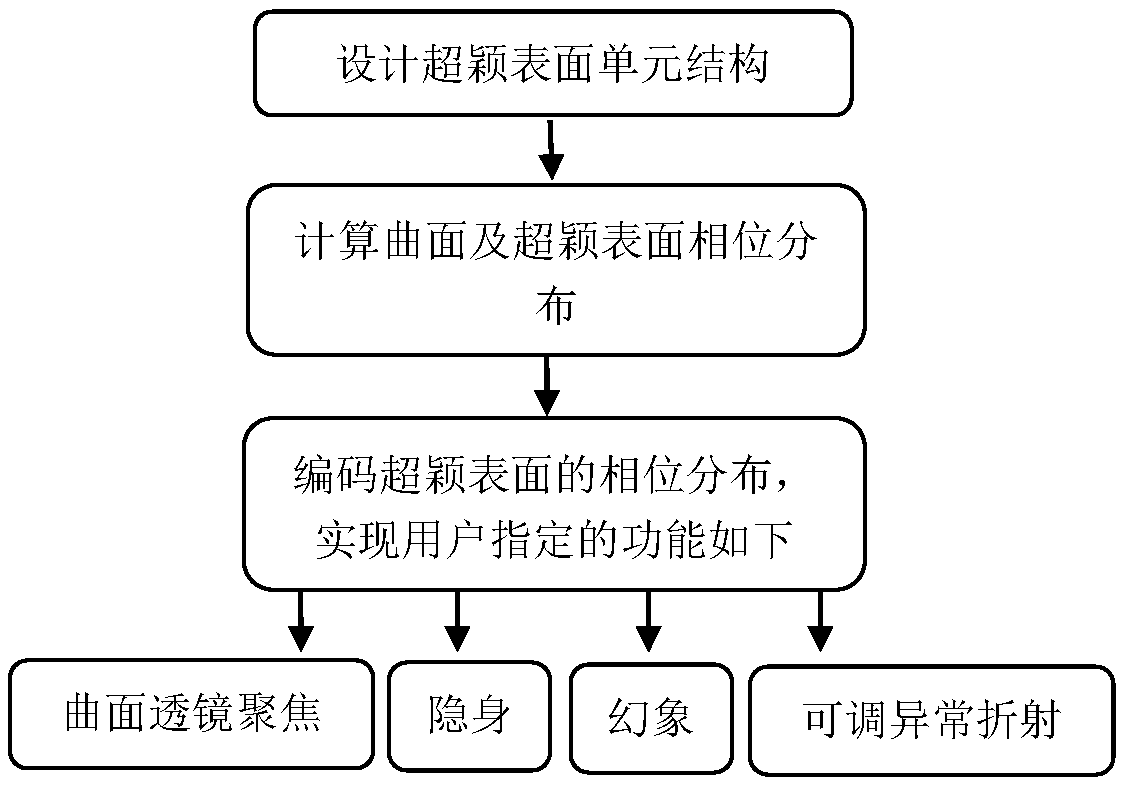
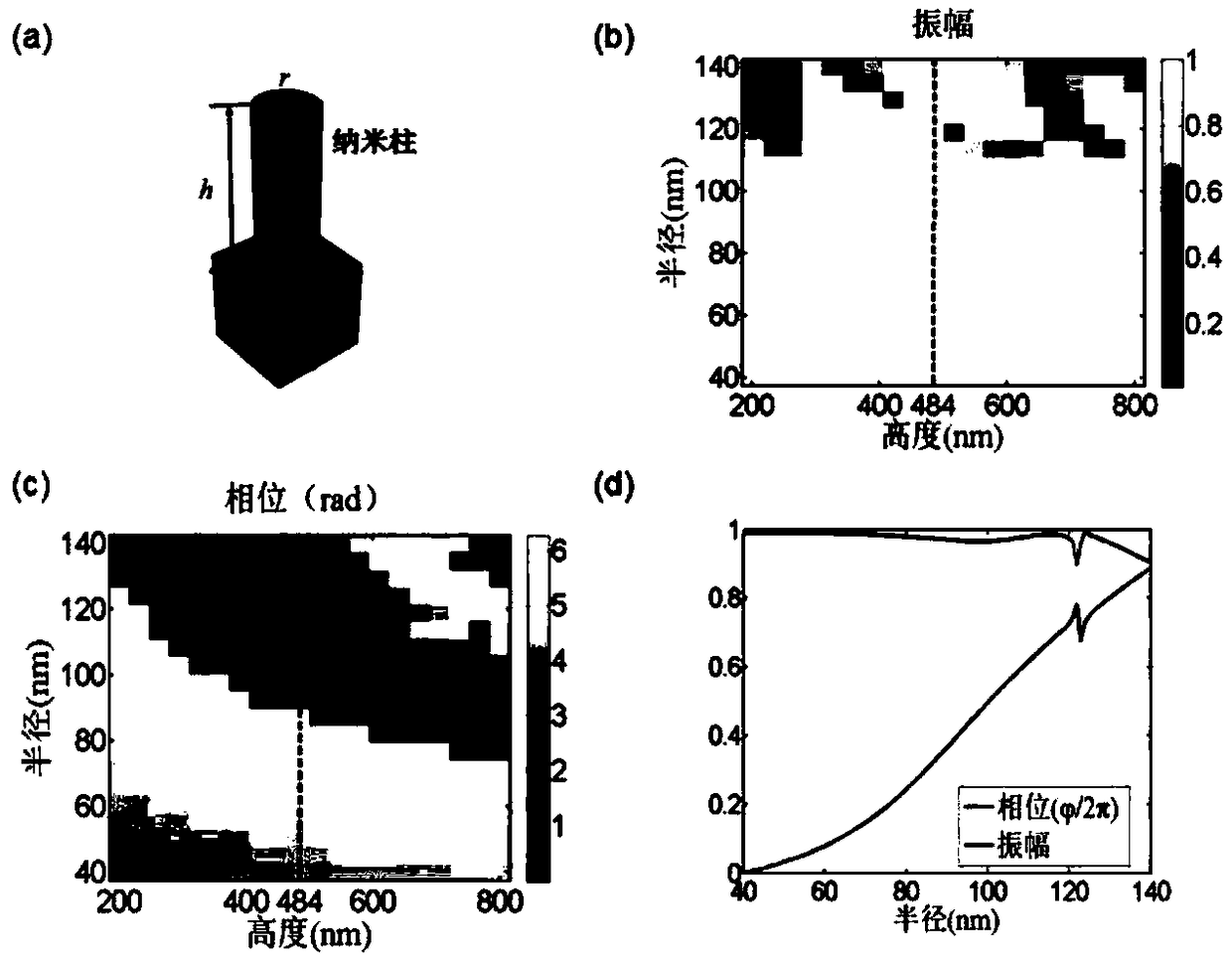
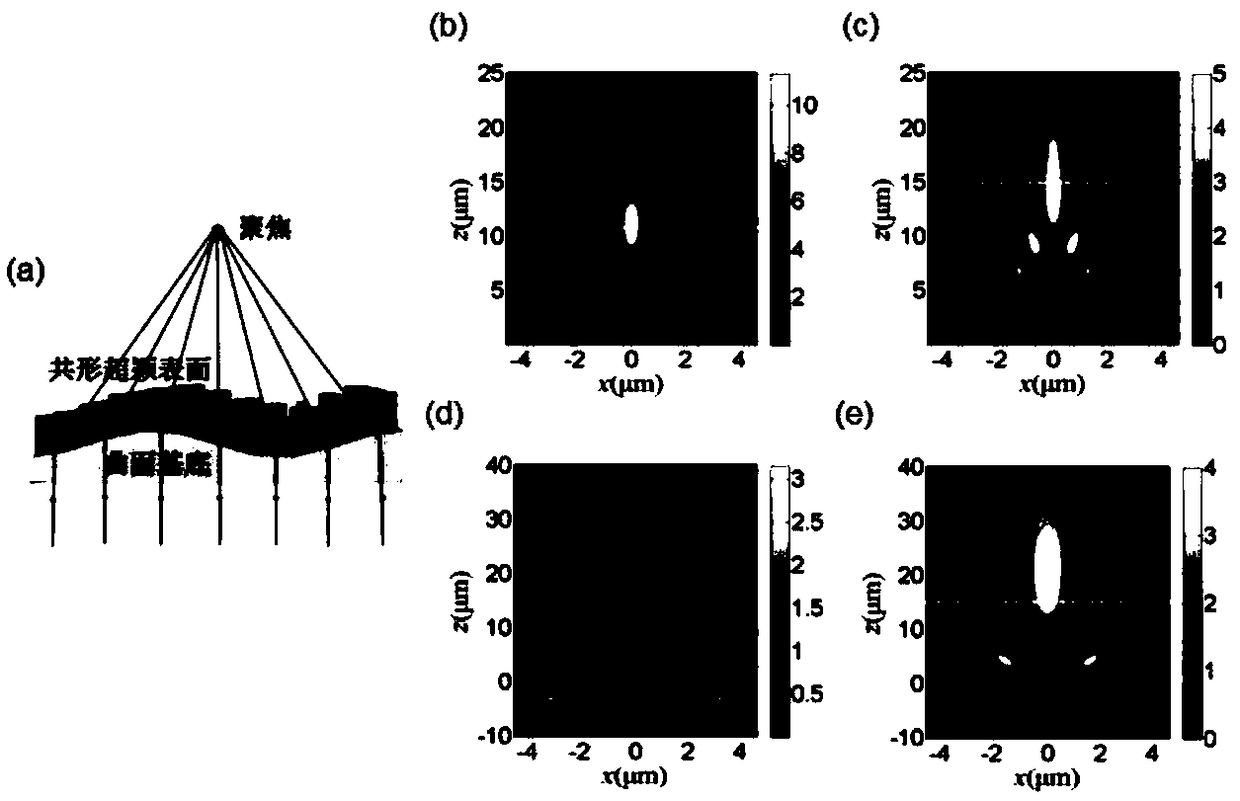
The invention discloses a method for achieving wavefront modulation based on a dielectric conformal metasurface, and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano optics and holography. The implementation method comprises the following steps of designing a unit structure of the metasurface, wherein the metasurface is composed of dielectric circular nanopillar arrays with different geometric sizes,and by changing the geometric radius and height of a nanopillar unit, the phase of an emergent light beam is randomly adjusted and controlled by the metasurface; when a single curved surface is considered only, calculating out phase distribution phi 0 of incident light passing the curved surface according to a ray tracing method or a finite-different time-domain (FDTD) method, and then calculatingout phase distribution phi d of user-customized functions according to a diffraction theory or a holographic principle analysis method, thereby compensating a phase difference phi p of the two by using the dielectric conformal metasurface; and carrying out coding on the phase of the metasurface. The user-customized functions include lens focusing, adjustable abnormal refraction, optical camouflage and illusion functions. According to the method, the corresponding technical problems in the field of wearable electronic products, medical equipment or photoelectric devices can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Rapid and accurate computation method for large-scale MIMO array antenna far-field radiation field
ActiveCN104992001AFast analysisImprove synthesis accuracySpecial data processing applicationsFull waveRadiation field
The present invention belongs to the field of electromagnetic value computing, and particularly relates to a rapid and accurate analysis method for large-scale MIMO array antenna far-field radiation. The method comprises: determining a structural parameter of an M*N-element plane array antenna; computing a relationship between an incident field and a scattered field of an element antenna; according to mutual coupling characteristics among element antennas, selecting a sub-array form and size of an extraction unit on an array environment condition; for an antenna sub-array of the extraction unit, computing a unit far-field radiation pattern of the sub-array; and according to the unit far-field radiation patterns of the array and a superposition principle, computing an array antenna far-field radiation pattern. According to the invention, by utilizing the accuracy of mutual coupling computation, the problems that the use of such methods as the moment method, the finite element method and the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method are limited by computing capacity of a single computer, and when the scale of the array antenna is too large, rapid and accurate computation of the antenna radiation field cannot be implemented with a full wave simulation method because of large consumption of memory and computing time, are effectively solved. The method provided by the invention is capable of analyzing the radiation pattern of a large and conformal array antenna, and has higher synthesizing accuracy and higher analysis speed.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
3D TTI double-phase medium seismic wave field value simulation method based on finite difference method
ActiveCN105044771AImplement iterative solutionEnables real-time propagation simulationSeismic signal processingDouble phaseFinite difference method
The invention discloses a 3D TTI double-phase medium seismic wave field value simulation method based on a finite difference method. The 3D TTI double-phase medium seismic wave field value simulation method comprises steps of obtaining a solid and fluid stress tensor and a solid and flow strain tensor and transforming the tensors to a constitutive equation, obtaining a geometry equation according to the corresponding relation of stress and the displacement, obtaining a motion differential equation according to the constitutive equation, the geometry equation and the fluid motion relative to the solid and the corresponding relation between the stress and the displacement, taking the divergence on two ends of the motion differential equation to obtain a first longitudinal wave equation and a second longitudinal wave equation of the seismic wave, as for the first longitudinal wave equation and the second longitudinal equation, enabling a partial derivative to y to be zero and performing difference discrete on the space partial derivative and the time partial derivative by employing an 2N order precision expansion formula and a 2-order precision center difference form to obtain a first difference equation and a second difference equation, and performing boundary absorbing condition processing on the first difference equation and the second difference equation to obtain the corresponding seismic wave field value. The invention realizes the real-time transmission simulation of the physics seismic wave field.
Owner:北京多分量地震技术研究院
Cartesian mesh generation technique
ActiveUS8059122B1Efficient data storageThe process is fast and accurate3D-image rendering3D modellingWorkstationByte
A highly accurate and robust cubic cell mesh generator “Cubegen” capable of a trillion plus cell meshes on a single processor 4-Gigabyte main memory workstation has been developed. The cells are generated in Yee format for the Finite Difference Time Domain method. Three key techniques were employed to achieve this capability: a highly efficient data storage ray tracing method, a highly accurate ray-facet intersection test, and a novel exact arithmetic tie-breaking algorithm for rays intersecting facet edges and vertices.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Imaging method of seismic wave fields between inclined wells
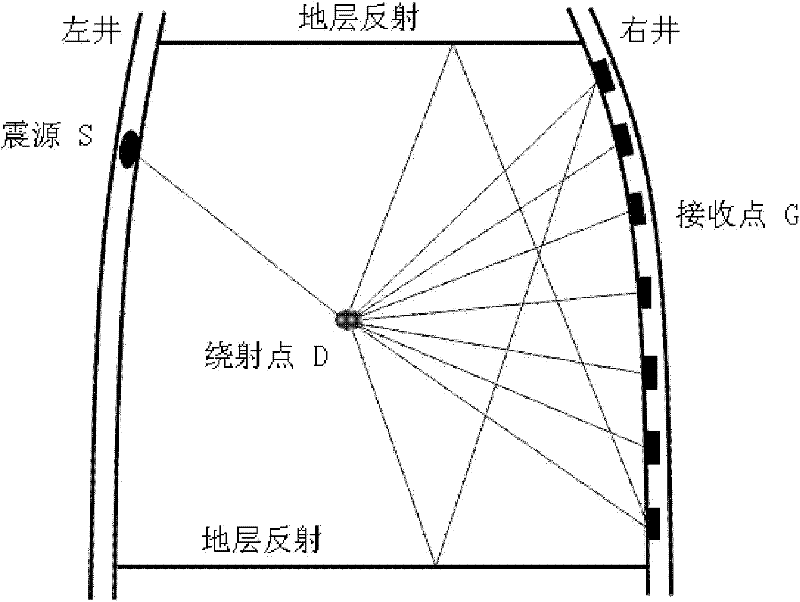
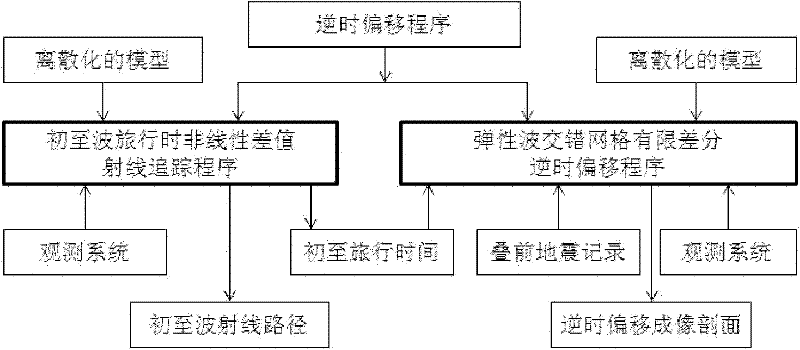
InactiveCN102162859AHigh precisionImprove reliabilitySeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingReverse timeWave field
The invention relates to an imaging method of seismic wave fields between inclined wells, comprising the following steps of: 1) scattering and gridding space areas between two adjacent inclined wells; taking each of the grid nodes as a secondary source point; 2) calculating the time TSD needed for transmitting a seismic focus S to each of the grid nodes according to a first-motion wave travel-time nonlinear interpolation ray-tracking method; 3) taking the actually recorded wave field as source by a receiving point; extrapolating the reverse time of each of the grid nodes to the TSD moment by using a speed-stress-first order differential equitation staggered gridding finite difference method, wherein the wave field at the moment is the image of the grid point; and 4) when the wave field is transmitted to a medium border, as the border wave impedance difference is large, using a completely matched layer to absorb the border, namely a PML layer; absorbing and attenuating the wave field so that the wave field cannot return to the medium and form interference.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
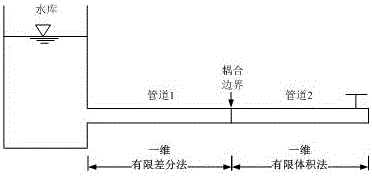
Multidimensional hydraulic system transient simulation method based on coupling of finite difference method and finite volume method
ActiveCN106503396ACalculation speedReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMultidimensional scalingCoupling
The invention discloses a multidimensional hydraulic system transient simulation method based on the coupling of a finite difference method and a finite volume method, and belongs to the field of simulation of a pipe network system hydraulic transient numerical value. The method adopts a one-dimensional pressure pipeline unsteady flow control equation, a one-dimensional open-channel shallow-water equation, a two-dimensional open-channel shallow-water equation and a three-dimensional flowing equation, and is based on an idea of the coupling of the finite difference method and the finite volume method, the same coupling method is adopted for coupling a one-dimensional pressure pipeline unsteady finite difference method with a one-dimensional pressure pipeline unsteady flow finite volume method, a one-dimensional open-channel unsteady flow finite volume method, a two-dimensional open-channel unsteady flow finite volume method and a three-dimensional complex flowing finite volume method respectively. On one hand, a coupling model utilizes the advantages of a one-dimensional finite difference method that the calculating speed is fast and the processing on boundary conditions is simple in the aspect of simulation of a complex hydraulic system, on the other hand, the coupling model utilizes the characteristic of a multidimensional finite volume method that the accuracy is high during complex flowing calculation, so that the optimal combination of efficiency and accuracy is realized.
Owner:POWER CHINA KUNMING ENG CORP LTD
Simulation method for super speed aircraft conformal sub-grid electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis
ActiveCN105653747AFit closelyImprove adaptabilitySpecial data processing applicationsFinite difference methodRadar cross-section
The invention discloses a simulation method for super speed aircraft conformal sub-grid electromagnetic scattering characteristic analysis. The simulation method includes the following steps: performing aerothermodynamics simulation according to an aerodynamic configuration, the flight speed and the flight height of an aircraft, and determining the plasma collision frequency and the plasma oscillation frequency of all parts through simulation information; performing subdivision on an aircraft model and a plasma sheath through a tetrahedron to obtain structure information of the aircraft model; mapping flow field point information to ridges of a finite difference time domain computing grid, and determining a zone with a relative dielectric constant more than 6 according to the collision frequency and the oscillation frequency on the ridges to perform sub-grid processing; processing junctions between the ridges of the finite difference time domain computing grid and a metal surface through a finite difference universal time domain method; and computing the plasma zone through an iterative formula of plasma to finally determine the radar cross section of the super speed aircraft. The simulation method has good adaptability and high computational efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Finite element and finite difference coupling method for fast calculating rolled piece section temperature
InactiveCN104298884AFast Calculation of Transient Temperature FieldCalculation speedSpecial data processing applicationsCouplingFinite difference method
The invention discloses a finite element and finite different coupling method for fast calculating rolled piece section temperature. The method includes the steps of firstly, mapping finite element grids before rolling of each gate with finite difference grids before rolling, and transmitting finite different grid node temperature before rolling to the finite element grids before rolling according to position relations; secondly, transmitting finite element node temperature before rolling to finite element nodes after rolling, and adding rolling temperature rise; thirdly, performing finite difference grid division on rolled pieces according to the finite element grid data of the rolled piece after the rolling of each gate, and judging in-surface, out-surface and boundary point positions; fourthly, mapping the finite element grid node temperature to finite difference nodes according to position relations; fifthly, using finite difference grids to perform gap temperature calculating after rolling. By the method, the instant temperature fields at optional moment during rolling of the rolled pieces with various sections can be calculated fast, calculation speed is increased greatly, manual intervention is not needed, and high automation level is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
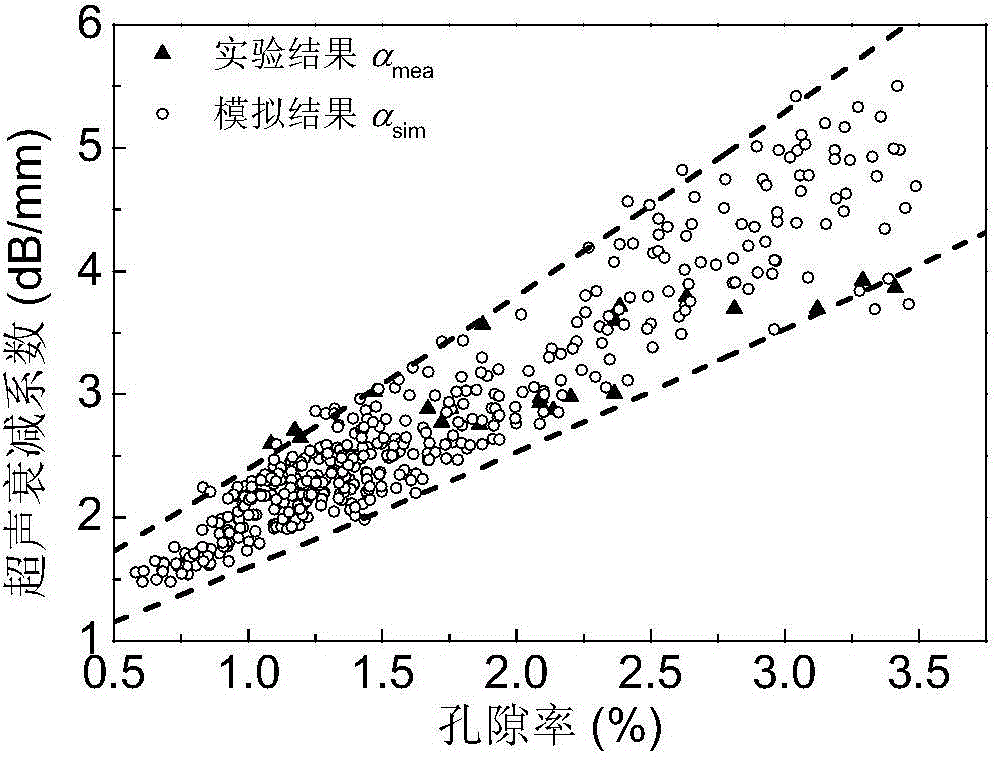
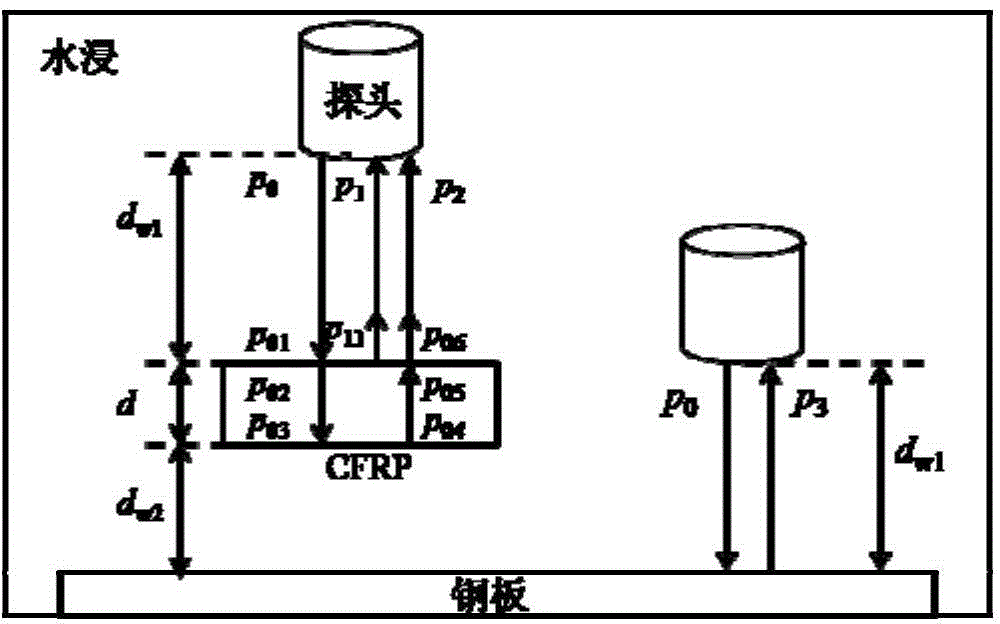
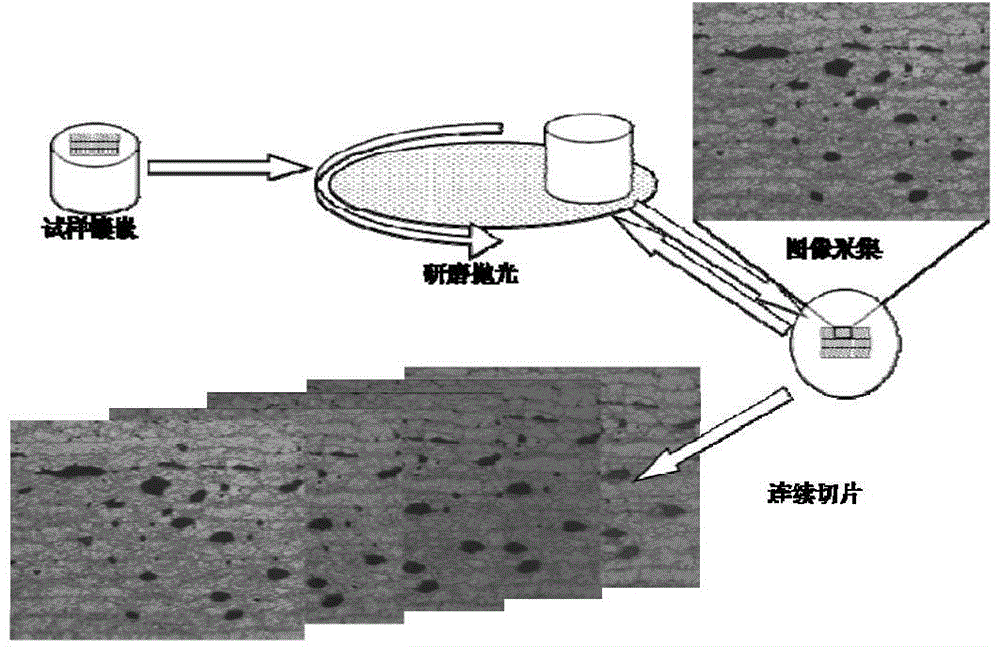
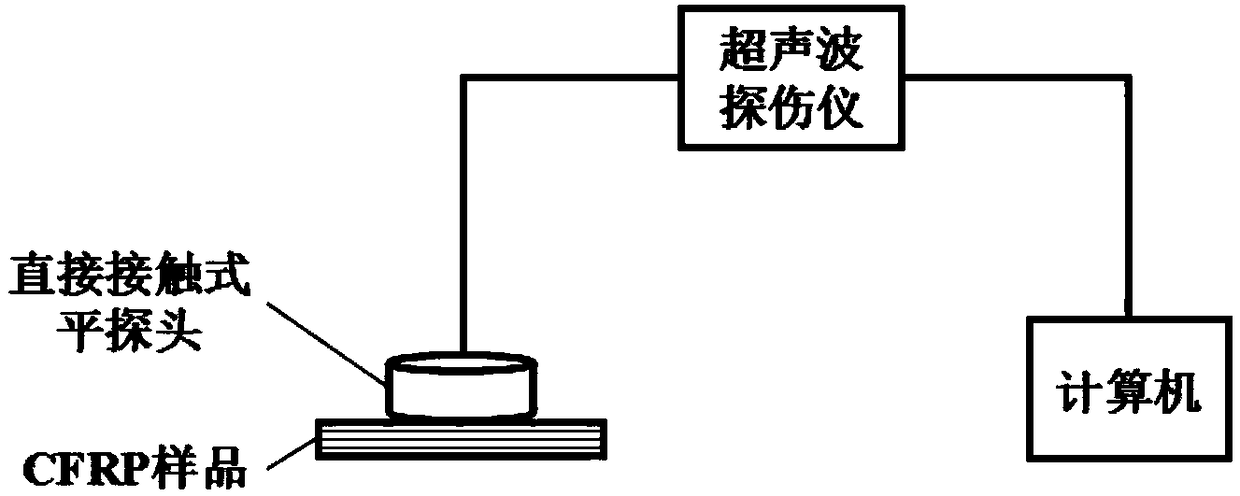
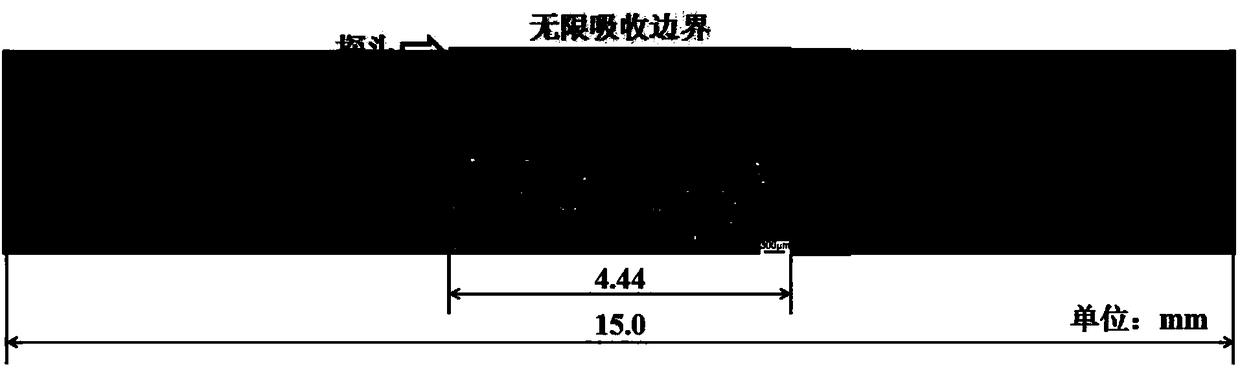
Method for confirming relation between porosity of CFRP (carbon fiber reinforced plastics) and ultrasonic attenuation coefficient
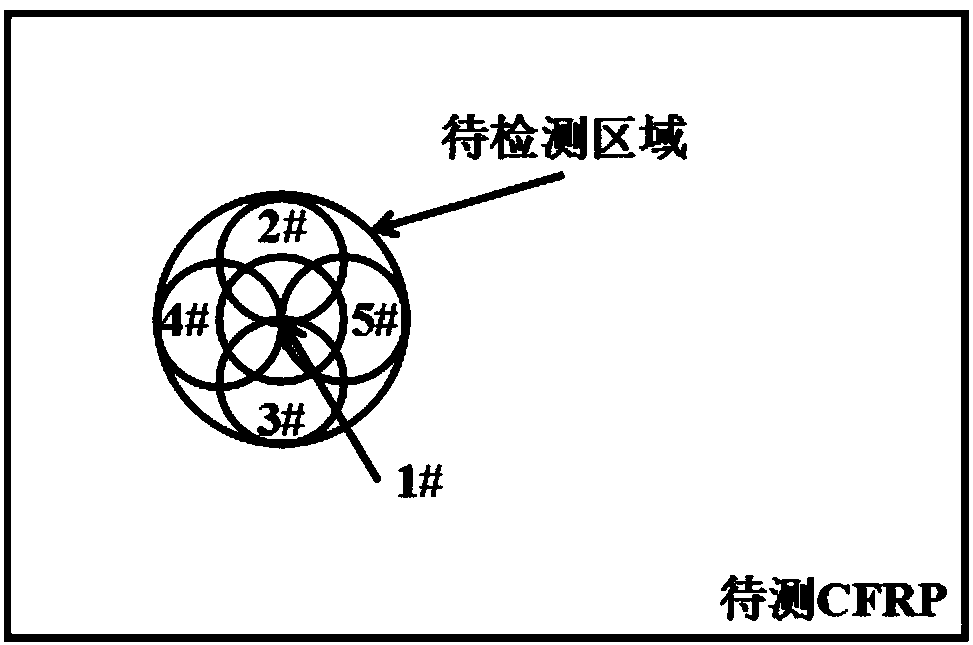
The invention discloses a method for confirming the relation between the porosity of CFRP (carbon fiber reinforced plastics) and the ultrasonic attenuation coefficient and belongs to the technical field of ultrasonic non-destructive testing. Firstly, by the aid of an ultrasonic C scanning testing method, an area with the relatively uniform primary bottom surface reflection echo amplitude of a CFRP laminated board is selected as a research object, a metallograph of the area is obtained through continuous microtomy, and an in-situ image containing real morphological pores is acquired with a median filter method and the like. A real morphological pore model is further established with a time-domain finite difference method, the multi-value corresponding relation between the porosity P of the CFRP and the ultrasonic attenuation coefficient alpha is obtained through numerical calculation, and support of experimental data is obtained. By the aid of the method, the multi-value corresponding relation between P and alpha is confirmed firstly, and a more effective model basis is provided for deep elaboration of the ultrasonic attenuation mechanism of the complex morphological pores of the CFRP.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
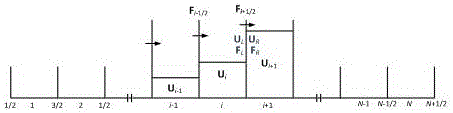
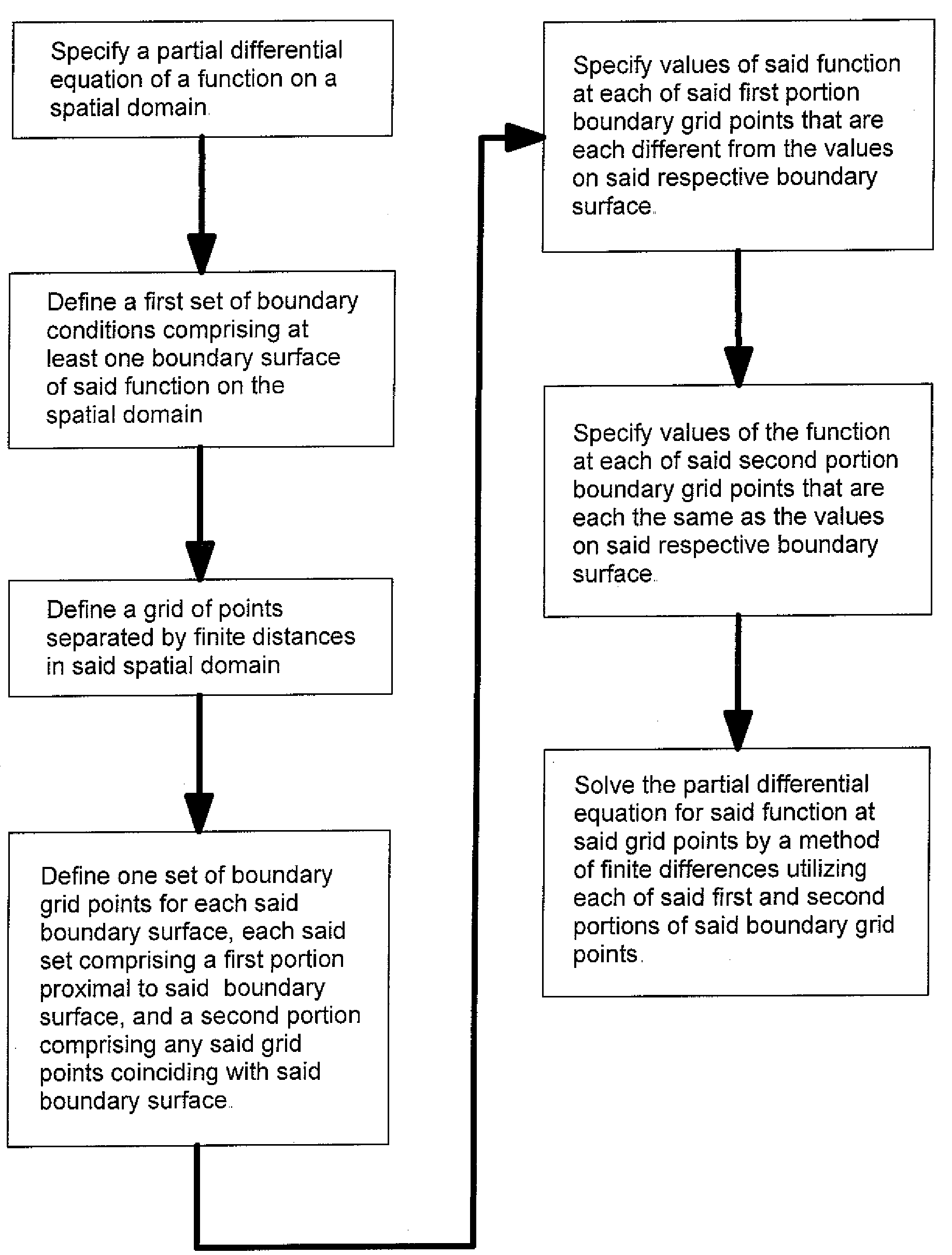
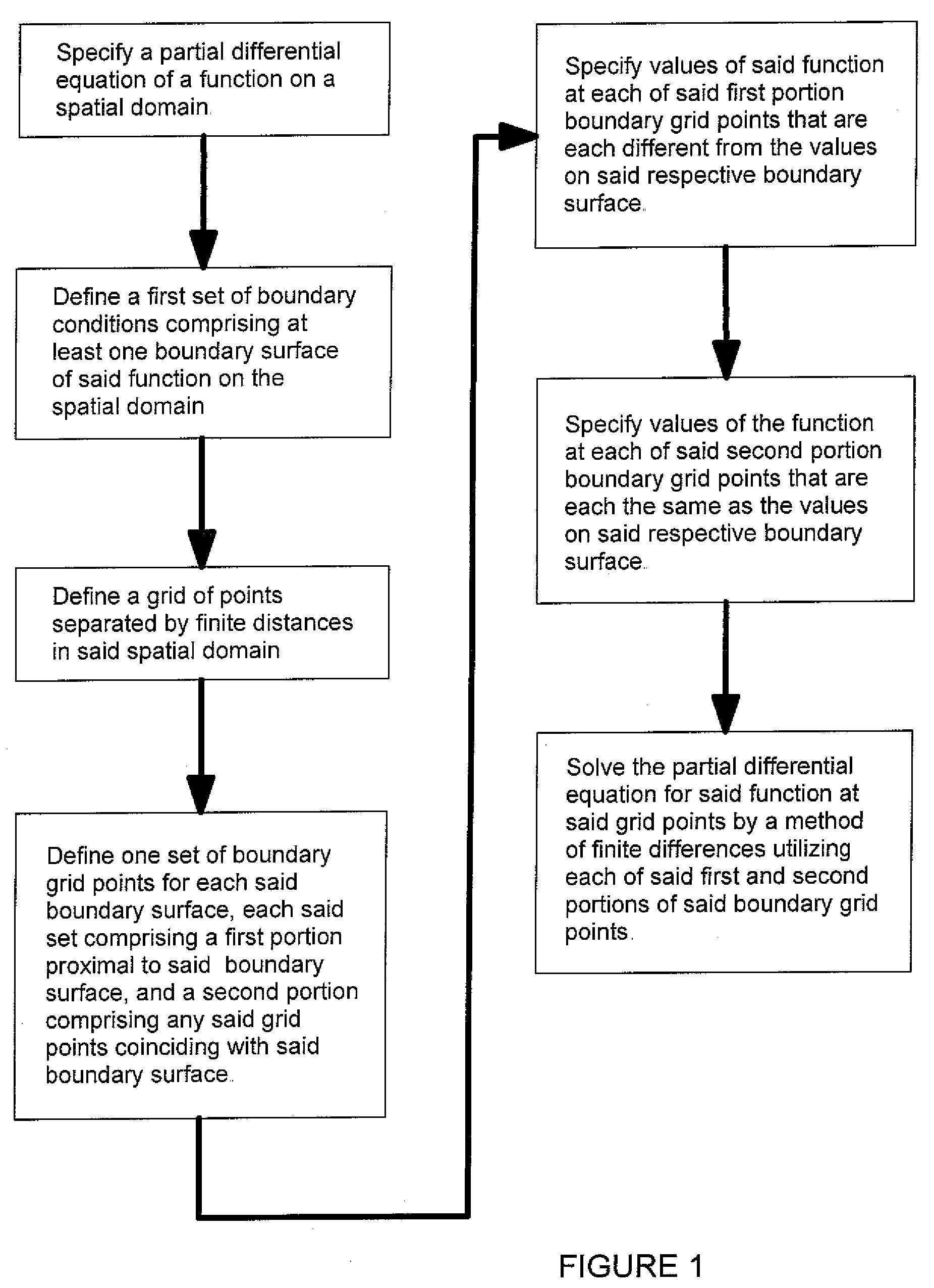
Finite differences methods
ActiveUS20090083356A1Improved accuracy in the calculation of the function fMeet growth requirementsDigital differential analysersDesign optimisation/simulationBoundary valuesDiscretization
The application of finite differences methods to solve boundary value problems typically involves a discretization of such a problem across an orthogonal array of discrete grid points. This leads to an array of difference equations which is solved numerically within the constraints of the boundary conditions to yield solutions at the grid point locations. However, the accuracy of the solutions is limited with conventional finite differences methods when the boundary conditions are not represented exactly within the orthogonal array of discrete grid points, as when the boundary conditions are curved or slanted surfaces. The invention described herein provides finite differences methods for solving boundary value problems more accurately than with conventional finite differences methods, particularly when curved or slanted boundary surfaces correspond to terminations of a known analytical function.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Method for calculating lightning induction voltage of overhead power line tower
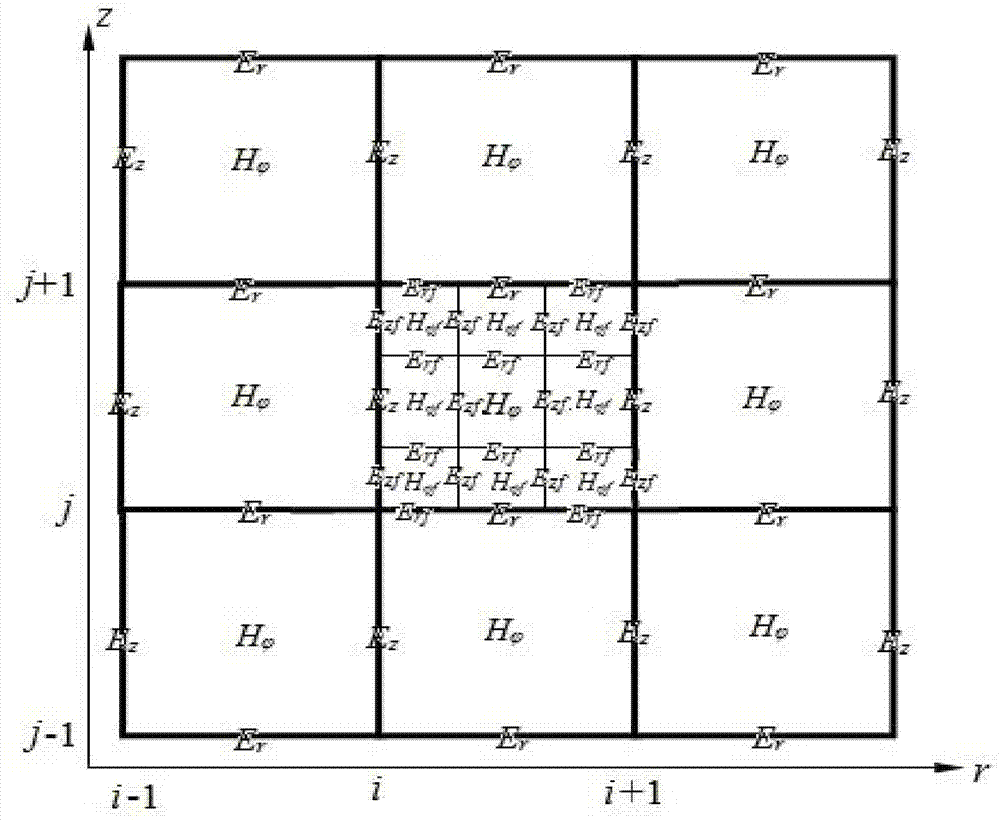
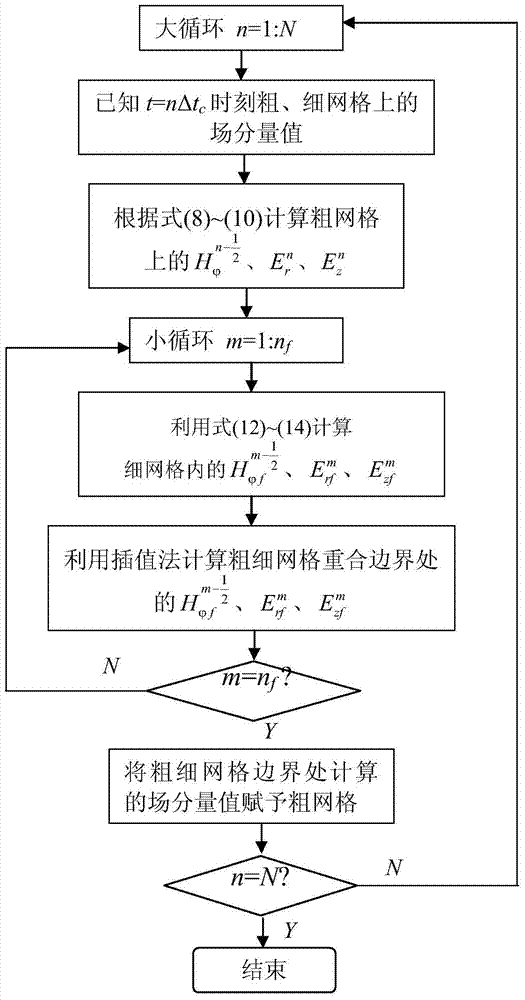
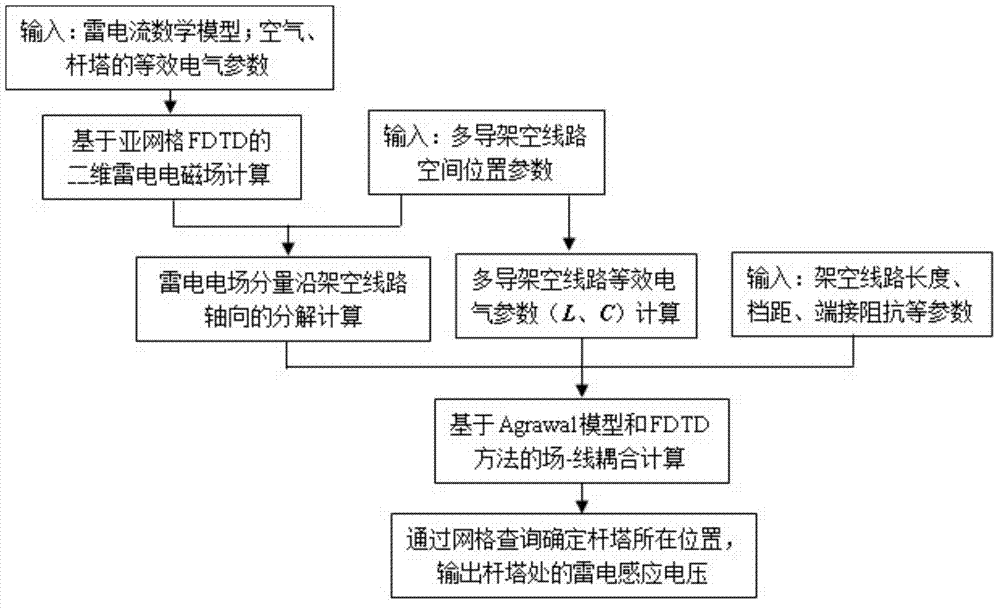
InactiveCN104850738AThe calculation result is accurateSmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsCoarse meshEngineering
The present invention discloses a method for calculating lightning induction voltage of an overhead power line tower. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) calculating a space lightning electromagnetic field while the influence of the tower is taken into consideration, wherein a sub-grid technology based finite-difference time-domain method is adopted in which a coarse mesh is generated for air space and a fine mesh is generated for the tower; (2) applying a two-dimensional calculation result of the lightning electromagnetic field to field decomposition of a three-dimensional space structure formed by an overhead power line and a lightning current return stroke channel, wherein the lightning electromagnetic field is generated by stimulation of lightning return stroke current; and (3) calculating the lightning induction voltage of the overhead power line and extracting the lightning induction voltage of the tower, wherein the lightning induction voltage of the overhead power line is calculated by using an Agrawal model and an FDTD method, and the tower position is located by grid query and the lightning induction voltage of the tower is extracted. The method can be used for effectively and more accurately estimating the lightning induction voltage of the overhead power line and the lightening induction voltage of insulators and lightning arresters of the tower.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method of calculating far extrapolation of transient field of electromagnetic scattering through finite difference time domain
ActiveCN104573376ASimple calculationImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsArray data structureTime domain response
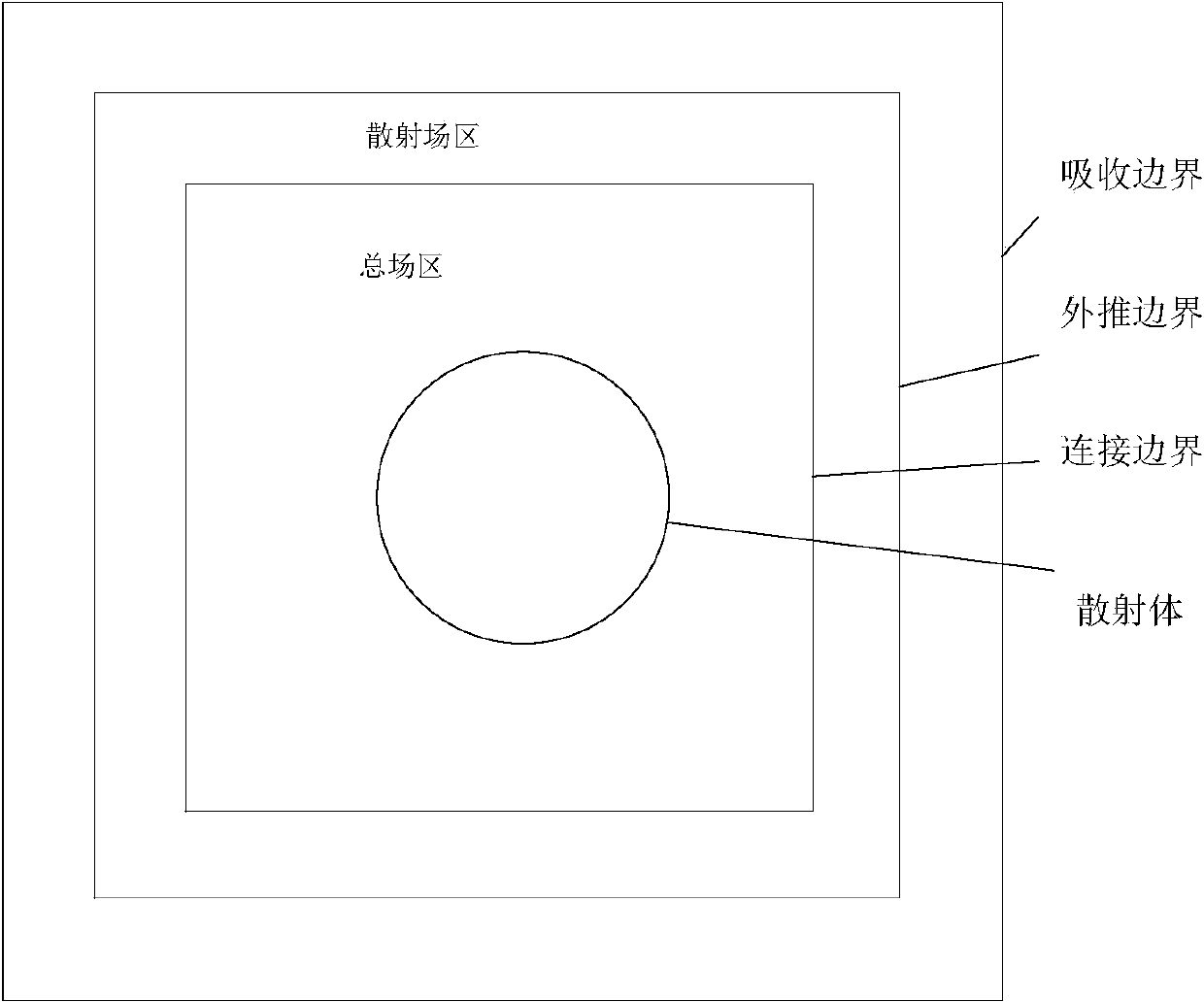
A method of calculating far extrapolation of a transient field of electromagnetic scattering through finite difference time domain includes the steps of 1 dividing an area to be calculated into a main field area and a scattering field area according to the connecting boundary; 2 setting an extrapolation boundary in the scattering field area, and extrapolating electric fields and magnetic fields on the extrapolation boundary to obtain a far field; 3 setting transient incident waves, and sequentially updating the electric fields and the magnetic fields at each time step until the electromagnetic field distribution becomes steady; 4 writing the far field into a product of frequency factors and integral factors, and performing inverse Fourier transform on the integral factors to obtain a time domain expression; 5 setting an integral factor far field time domain response array; 6 performing Fourier transform on integral factor far field time domain response to obtain integral factor far field frequency domain response; 7 using far field and incident wave frequency domain response to obtain RCS (Radar Cross Section) changes with frequency. The method of calculating far extrapolation of the transient field of electromagnetic scattering through finite difference time domain writes the far field into the form of the product of the frequency factors and the integral factors due to the fact that the forms of frequency-time transform and time-frequency transform of the integral factors are simple, thereby simplifying the calculation and improving the efficiency.
Owner:北京博奥瑞科技有限公司
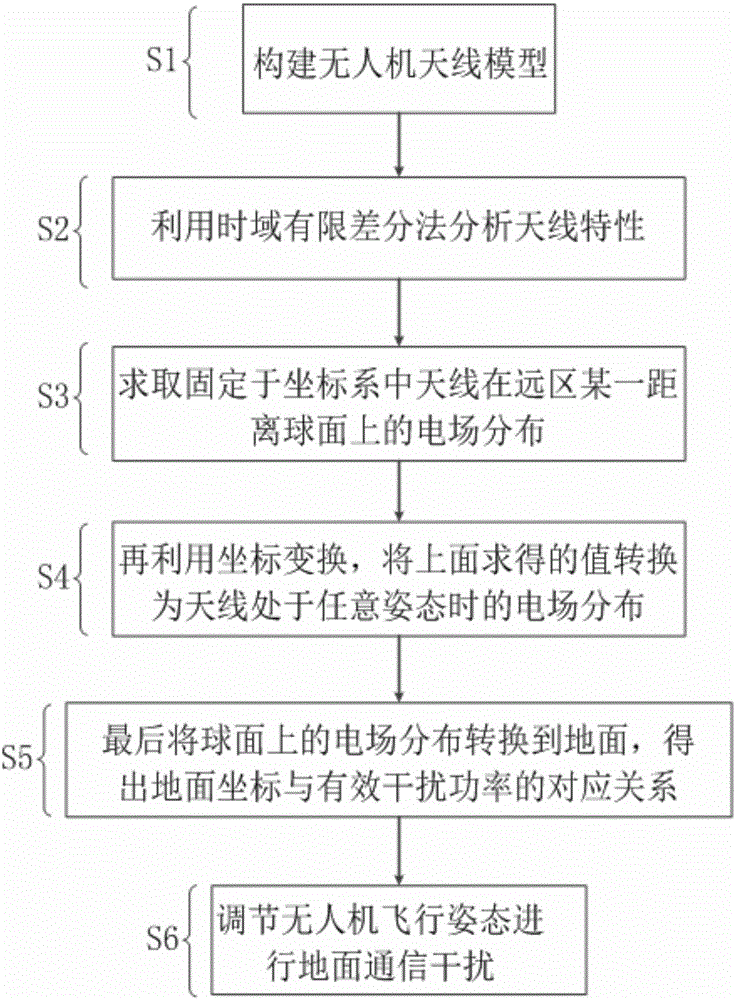
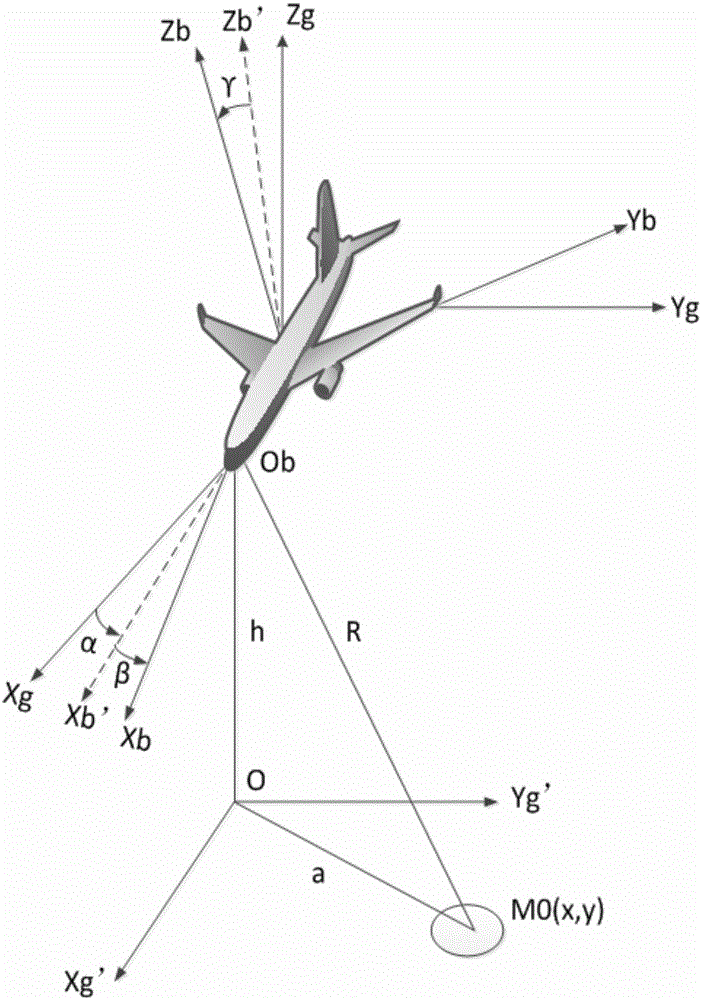
Unmanned plane communication interference countermeasure method based on real-time embedded control system
ActiveCN105119683ARadiation area is largeImprove antenna efficiencyCommunication jammingTime domainCommunications system
The invention relates to an unmanned plane communication interference countermeasure method based on a real-time embedded control system and belongs to the technical field of unmanned plane communication countermeasure. The method comprises steps of: S1, constructing an unmanned plane antenna model; S2: analyzing the characteristic of the antenna by using a time-domain finite difference method; S3, acquiring the field distribution of the antenna fixed in a coordinate system on a spherical surface at a certain distance in a far area; S4, transforming an acquired value into field distribution of the antenna in any attitude by using transformation of coordinates; S5, transforming the field distribution on the spherical surface into ground in order to obtain a relation between ground coordinates and effective interference power; and S6, adjusting the flying attitude of an unmanned plane in order to perform ground communication interference. The method may effectively and accurately adjust the flying attitude of the unmanned plane in order to maximize the interference effect of the unmanned plane on a ground communication system and effectively prevent defects of conventional ground communication countermeasure, and has high application value in the field of unmanned plane communication countermeasure.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and device for quantitatively evaluating stratum heterogeneity
ActiveCN109490965ASeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingTime domainScattering attenuation
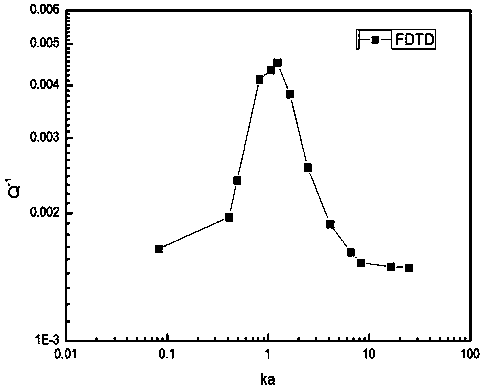
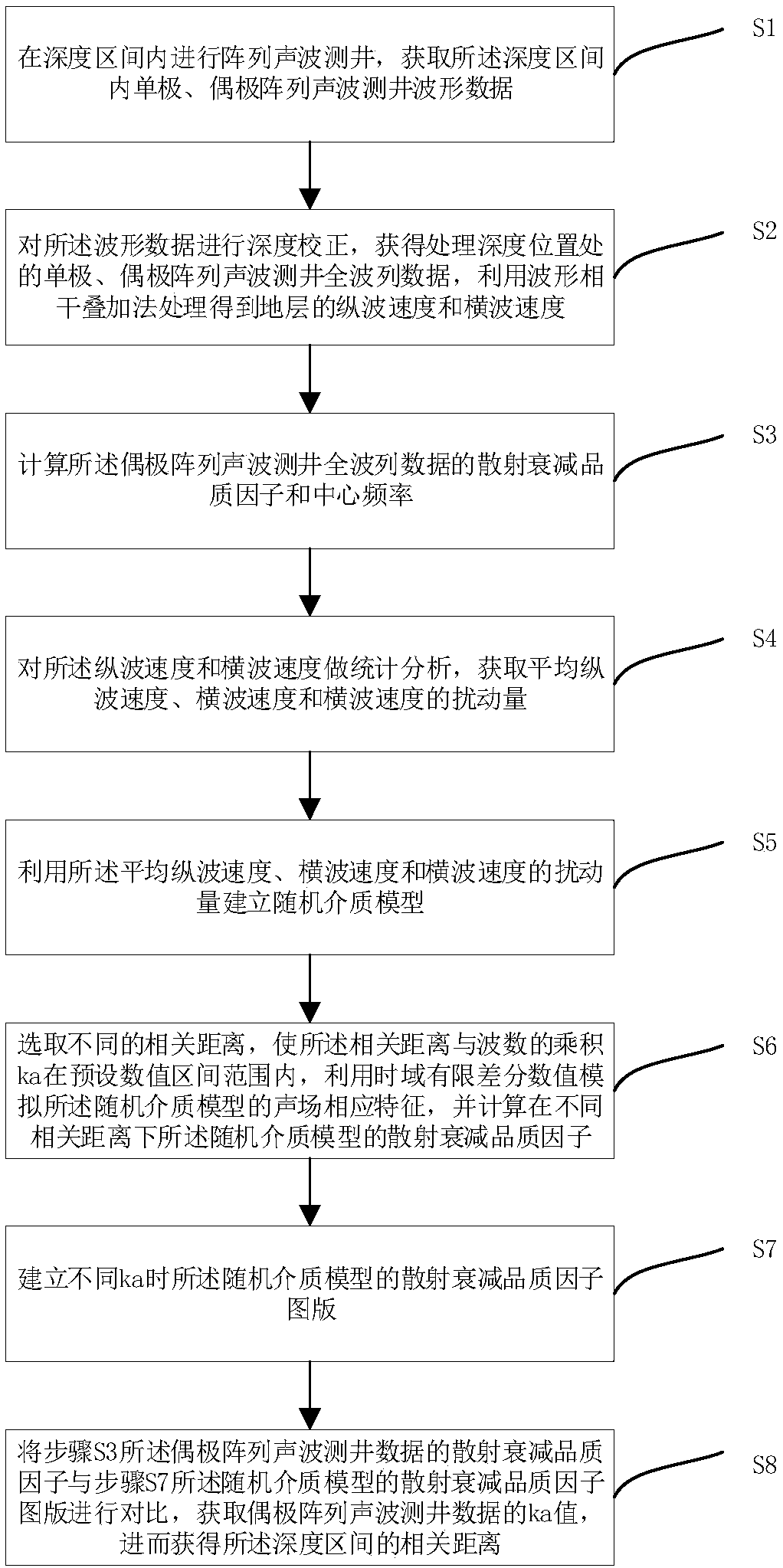
The invention provides a method and device for quantitatively evaluating the stratum heterogeneity, and belongs to the field of oil and gas resource exploration. The method comprises the steps that waveform data in a depth interval is obtained; depth correction is conducted, a waveform coherent stacking method is utilized for treatment, and the longitudinal wave speed and transverse wave speed ofa stratum are obtained; a scattering attenuation quality factor and center frequency of the waveform data are calculated; the average longitudinal wave speed, the transverse wave speed and the disturbance quantity of the transverse wave speed are obtained; a random medium model is built; different correlation distances are selected, corresponding characteristics of a sound field of the random medium model are simulated by means of a finite-difference time-domain value, and scattering attenuation quality factors of the random medium model under the different correlation distances are calculated; a scattering attenuation quality factor chart of the random medium model is built; a measured data scattering attenuation quality factor is compared with the scattering attenuation quality factor chart, and the correlation distance of the depth interval is obtained. Accordingly, by adopting the correlation distance of rock, the heterogeneity of the rock is quantitatively evaluated.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Method for simulating transmission property of partial discharge signal in power cable
InactiveCN102156788ASolve the difficult problem of decouplingAccurate detectionSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringElectric cables
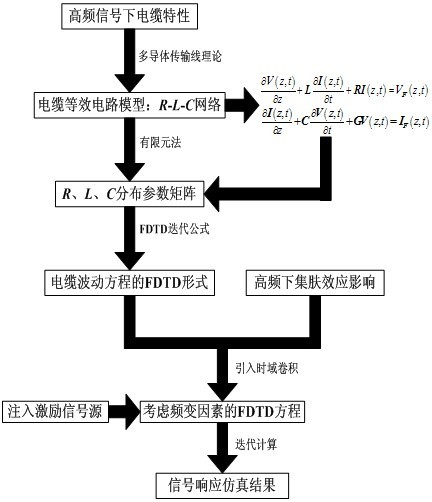
The invention discloses a method for simulating transmission property of a partial discharge signal in a power cable, comprising the following steps of: step 1, creating an equivalent circuit model of a coaxial cable under a high frequency signal through an R-L-C network according to electrical parameters of the power cable, and calculating R, L and C distribution parameter matrixes of the equivalent circuit model through a finite element method; step 2, creating a frequency varying factor related finite-different time-domain method iterative model according to the R, L and C distribution parameter matrixes; and step 3, simulating the transmission property of the signal in the cable through the finite-different time-domain method iterative model. The method offers effective help for in-depth study on the transmission property of the partial discharge in the cable, particularly on high-frequency transmission mechanism, and implementing accurate detection and positioning of partial discharge.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
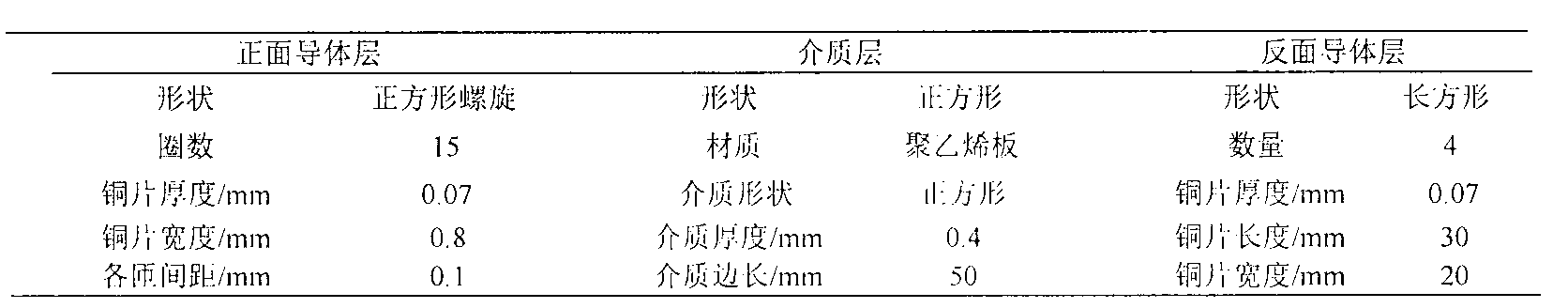
Small-size resonator and magnetic coupling resonance wireless energy transmission system
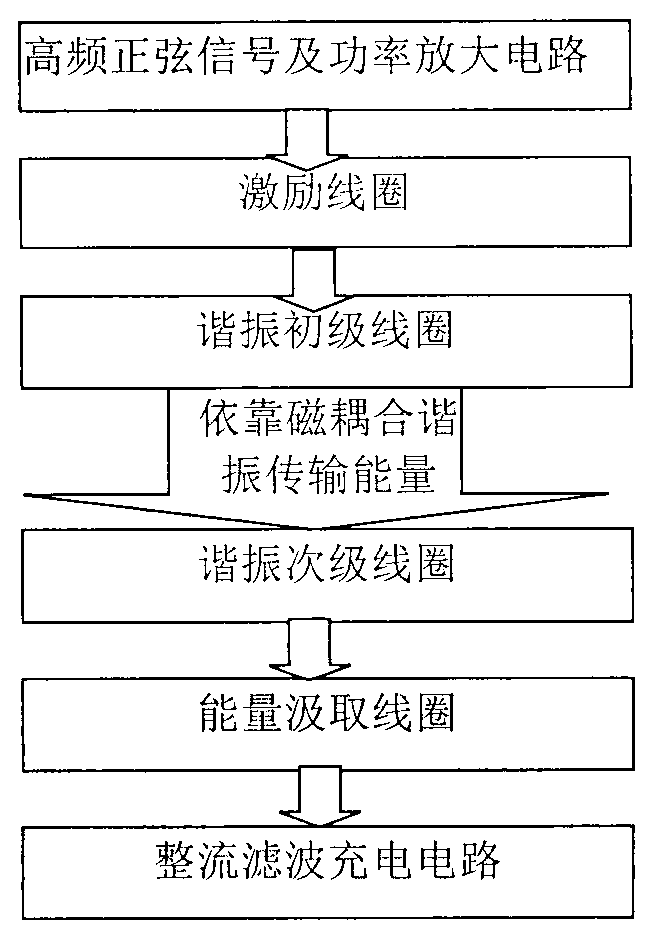
InactiveCN102983637ARaise the resonant frequencyVerify securityElectromagnetic wave systemTransformersCapacitanceElectrical conductor
Magnetic coupling resonance wireless energy transmission is a new technology which utilizing magnetic coupling resonance to achieve middle-distance electric energy wireless transmission, and has good application prospects. The invention provides a small-size plane-spiral resonance coil made by a printed board directly, the front face and the back face of the coil are all coated with copper, inductance generated on a front conductor layer and capacitance generated on an overlapped section of the front conductor layer and a back conductor layer form a needed resonator through a complex series-parallel connection circuit for energy transmission, and the size of the resonator is only 1.35 cm<3>. Through establishment of human head three-dimensional numerical model and implantation of a coil model into a body, a time-domain finite difference method is applied to the calculate head specific absorption rate and the electric-field magnetic field strength. Results show that when the magnetic coupling resonance wireless energy transmission technology is applied for the energy transmission of components implanted in the head, the I0g specific absorption rate (SAR) average value of the human head is 9.2627*10-6W / kg, the maximum value of root-mean-square of the electric-field magnetic field strength is respectively 4.64 V / m and 0.057 A / m, and the values are lower than the international safety limit standard.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
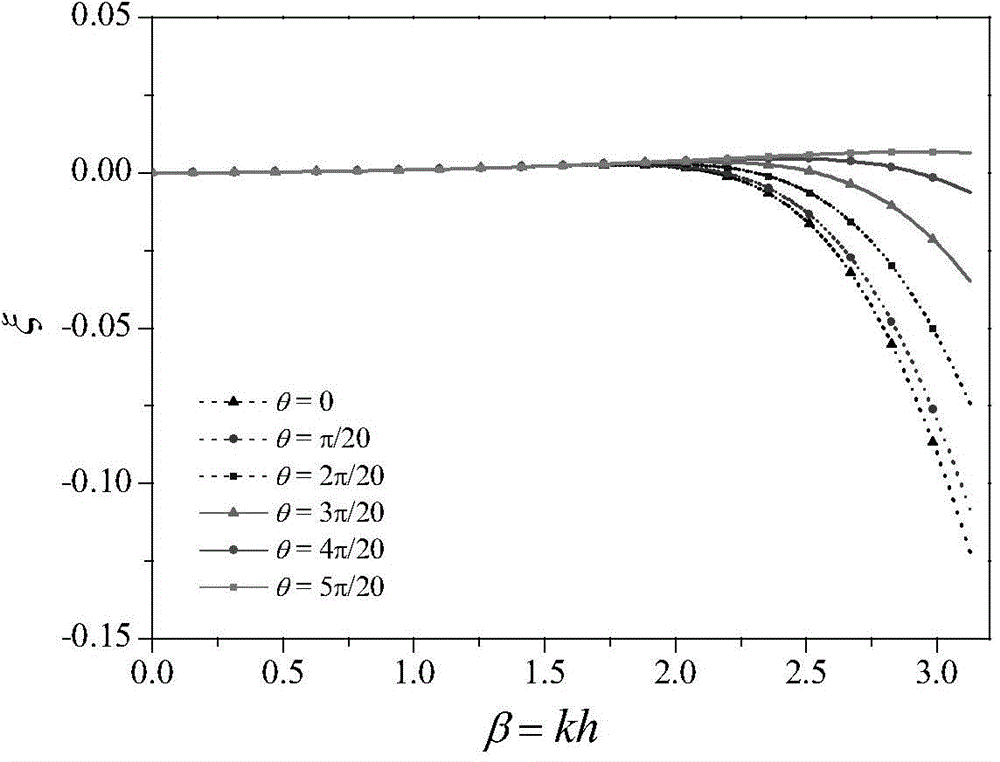
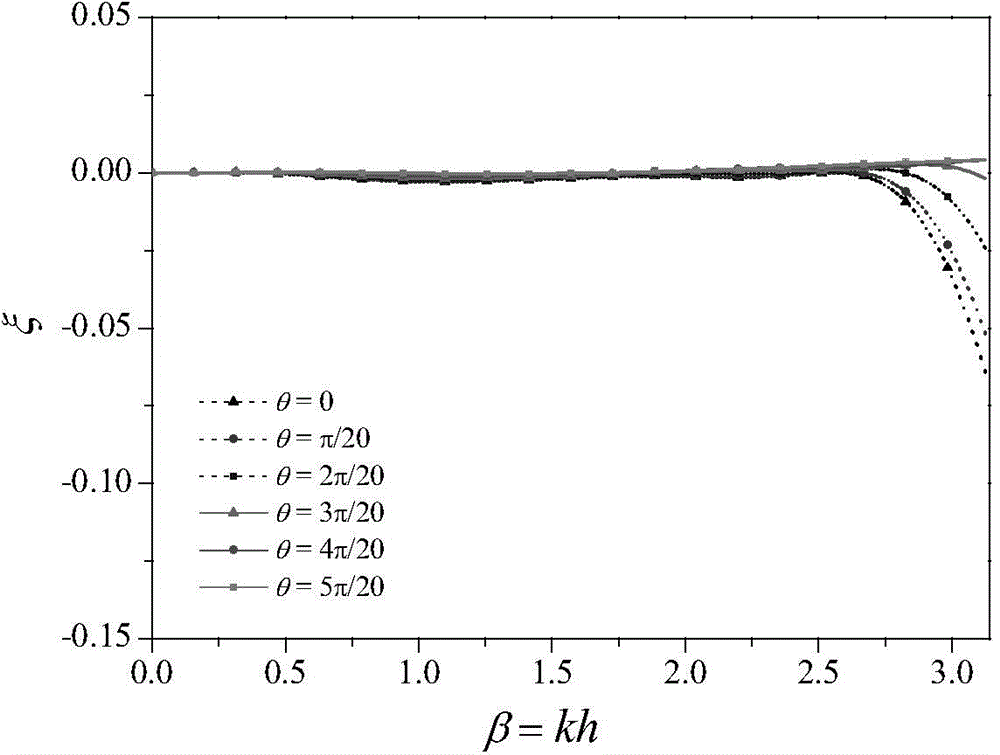
Optimum design method of finite difference template of non-equiangular long-grid wave equation
ActiveCN104597488AMeet the analog accuracy requirementsSeismic signal processingWave equationAcoustic wave
The invention discloses an optimum design method of a finite difference template of a non-equiangular long-grid wave equation. The method comprises the following steps: according to a time sampling interval and a spatial sampling interval, mesh subdivision is executed to the simulating region of an actual geologic model; according to the maximum appointed permissible error and the wave number range, the corresponding operator lengths of different acoustic velocities are calculated; based on the finite difference method of the least square optimization time space domain and the corresponding operator length, the optimized finite difference coefficient of the grid is acquired; the acquired optimized finite difference coefficient is brought into the wave equation with a difference scheme to perform forward modeling of the wave equation. According to the method, the finite difference method of the time space domain only applied to square and cube grids is expanded into the rectangular or rectangular parallelepiped grids, thus a special simulation precision requirement and a requirement for saving a calculated amount are met in actual production.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Time domain inverse scattering techniques for use in microwave imaging
ActiveUS7809427B2Minimize cost functionAccurate tumor localizationCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringTime domainElectromagnetic field
A system and a method are provided for estimating the average dielectric properties of a plurality of regions in space. The application of this technique is illustrated for determining the average properties of breast tissue. The knowledge of average properties is important when UWB microwave radar signal processing algorithms are used for tumor detection and localization. The method is an extension of a time-domain inverse scattering algorithm based on the finite-difference time-domain method. A hybrid conjugate gradient optimization is used to minimize a cost function defined between a measured and a calculated total electromagnetic field at a series of antennas. The output of the method is an average set of electromagnetic material parameters that describe specific regions of interest in either a non-dispersive heterogeneous medium or a dispersive heterogeneous medium.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
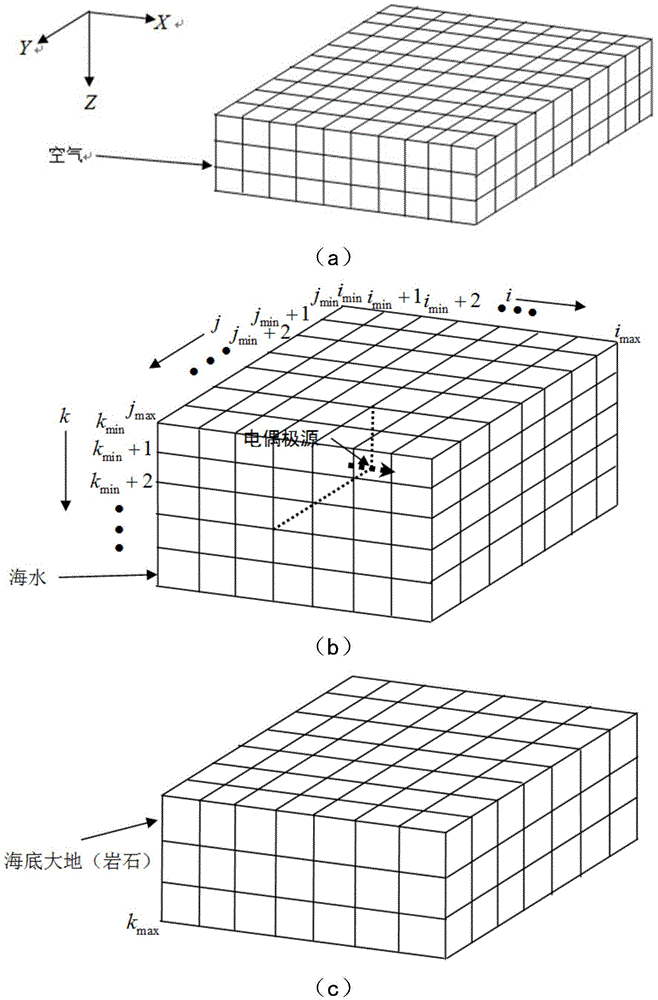
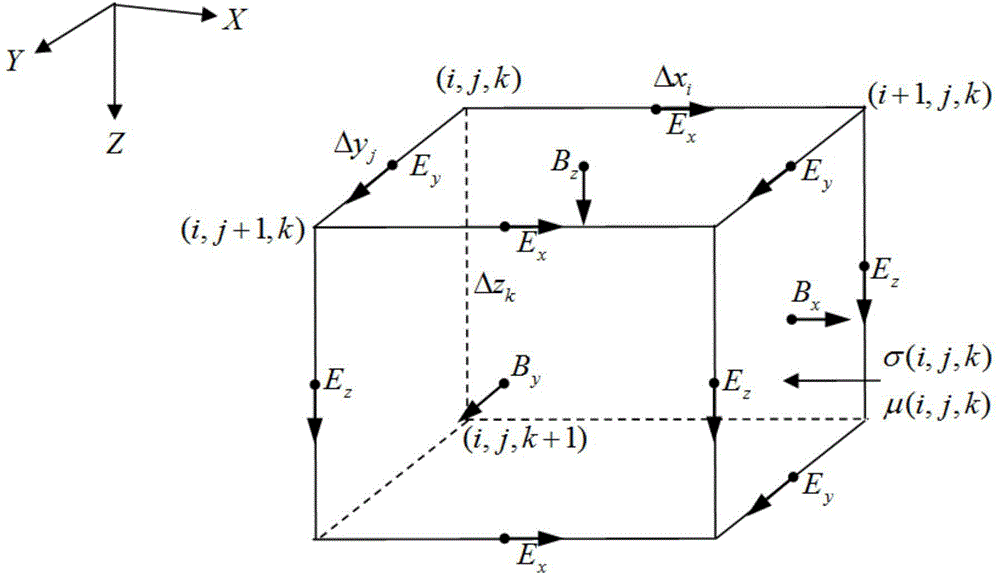
Electric dipole source three-dimensional time domain finite difference direct interpretation imaging method
InactiveCN104408021AFlexible width adjustmentRich low frequency signalComplex mathematical operationsICT adaptationOcean bottomMaxwell's equations
The invention relates to an electric dipole source three-dimensional time domain finite difference direct interpretation imaging method. The method includes the steps of loading Gaussian pulses on an electric dipole source, establishing Maxwell equations and constitutive equations for the ocean air space, the seawater space and the seabed ground space, conducting uniform mesh generation on prism object models of the three spaces, obtaining difference equations of seawater and the seabed ground through a time domain finite difference method according to meshes obtained through mesh generation by consuming that the conductivities and the magnetic conductivities of all the meshes obtained through mesh generation are unchanged, processing the Maxwell equations of ocean air through analysis solutions, calculating the electromagnetic field of the air above the sea surface, processing the boundary conditions of the generation space, setting stabilization conditions, solving the established difference equations through the combination with the processing results of the boundary conditions and the set stability conditions, and obtaining the distribution of the electromagnetic field of the seawater and the seabed ground at any moment.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composite material void ratio characterization method based on ultrasoundtwo-parameter
ActiveCN108226007AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPermeability/surface area analysisCarbon fibersSonification
The invention relates to a carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composite material void ratio characterization method based on an ultrasound two-parameter. The method belongs to the technical field ofnondestructive testing, and comprises the steps of adopting a set of void ratio detecting system comprising an ultrasonic fault detector, a direct contact type flat probe and a computer; acquiring amaterial parameter through a CFRP (Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics) mark to be detected, building a real morphology void model with a complex void morphology characteristic and a material property based on a random mediumtheory and a digital picture processing technique, building a relationship between void ratio P and an ultrasonic attenuation coefficient alpha sim through simulating calculationof a finite difference time domain software, and linearly fitting to obtain a P-alpha sim relational expression; selecting an area to be detected according to an ultrasonic C-scan result, adopting acontact type impulse reflection process to carry out multi-point acquisition on the selected area, and experimentally calculating alpha exp and an attenuation spectrum tilt K relevant to the void morphology characteristic; realizing CFRP void ratio characterization through the P-alpha sim relational expression and the K value. The method realizes CFRP void ratio characterization on the basis of considering the void morphology characteristic.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
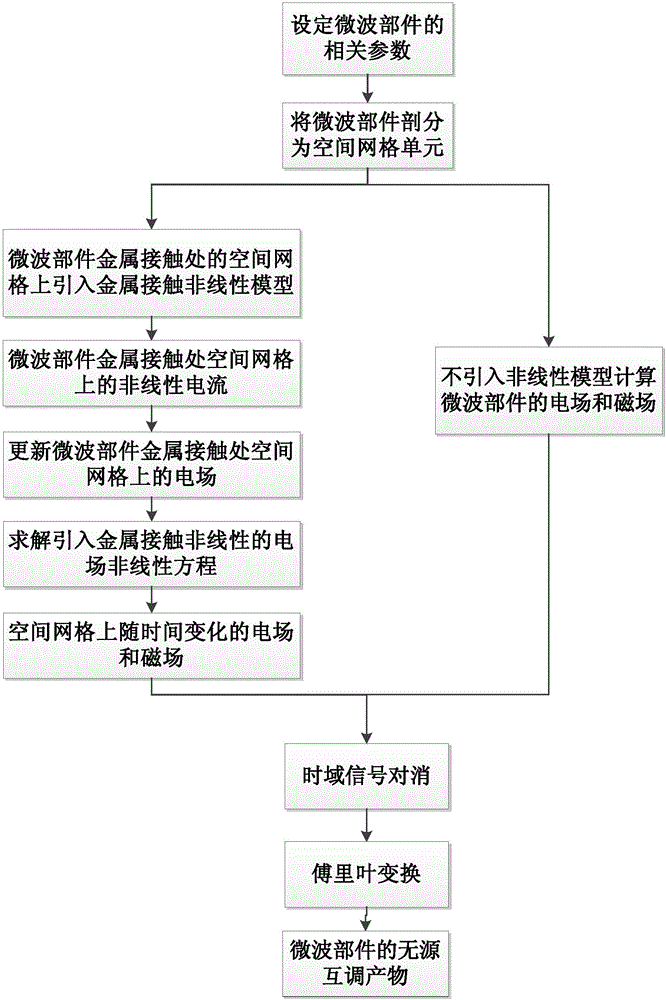
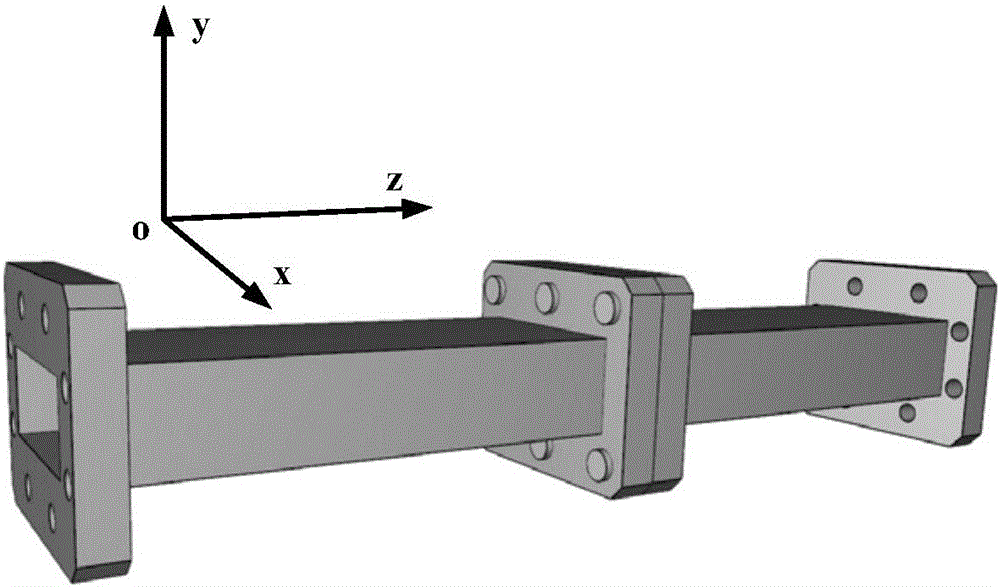
Time domain finite difference based microwave part passive inter-modulation numerical analysis method
ActiveCN105069247ASolve the problem of lack of numerical analysis meansAccurate analysisSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainMicrowave
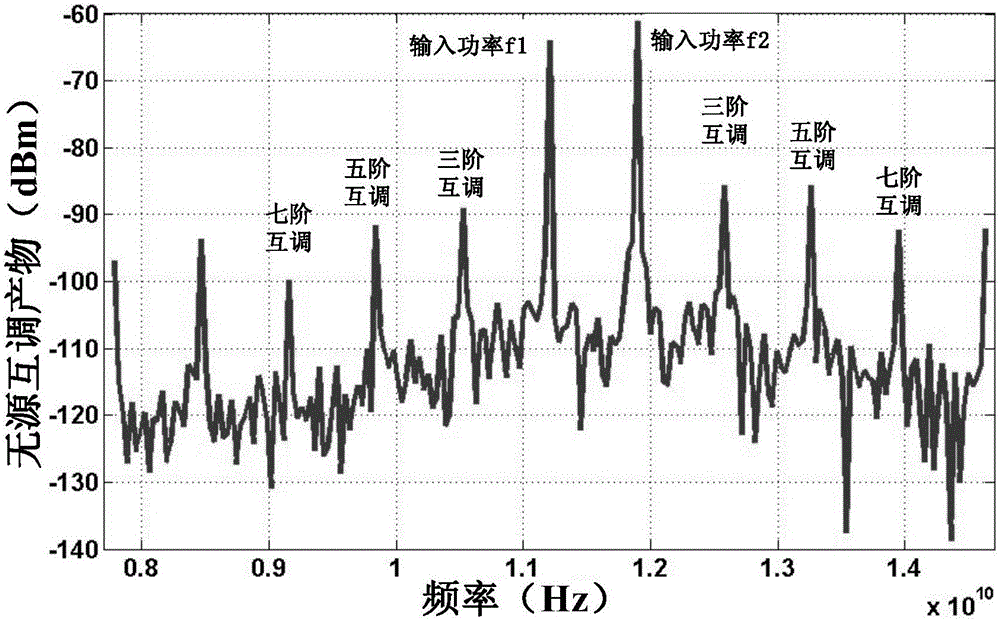
The present invention discloses a time domain finite difference based microwave part passive inter-modulation numerical analysis method, and discloses a method for introducing a micro-morphology and contact-state metallic contact nonlinear model of a metallic contact part of a microwave part. By adopting the method, the electromagnetic field analysis of a microwave part taking metallic contact non-linearity into consideration is realized, the electromagnetic field of an output port of a microwave part not taking metallic contact non-linearity into consideration is computed by adopting a time domain finite difference method and two signals are subjected to time domain cancellation, so that the interference of errors in numerical computation is reduced, a passive inter-modulation small signal is highlighted, a computation result of a passive inter-modulation product of the microwave part is more accurate, and the difficult problem that the passive inter-modulation of the microwave part is short of a numerical analysis means is solved.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
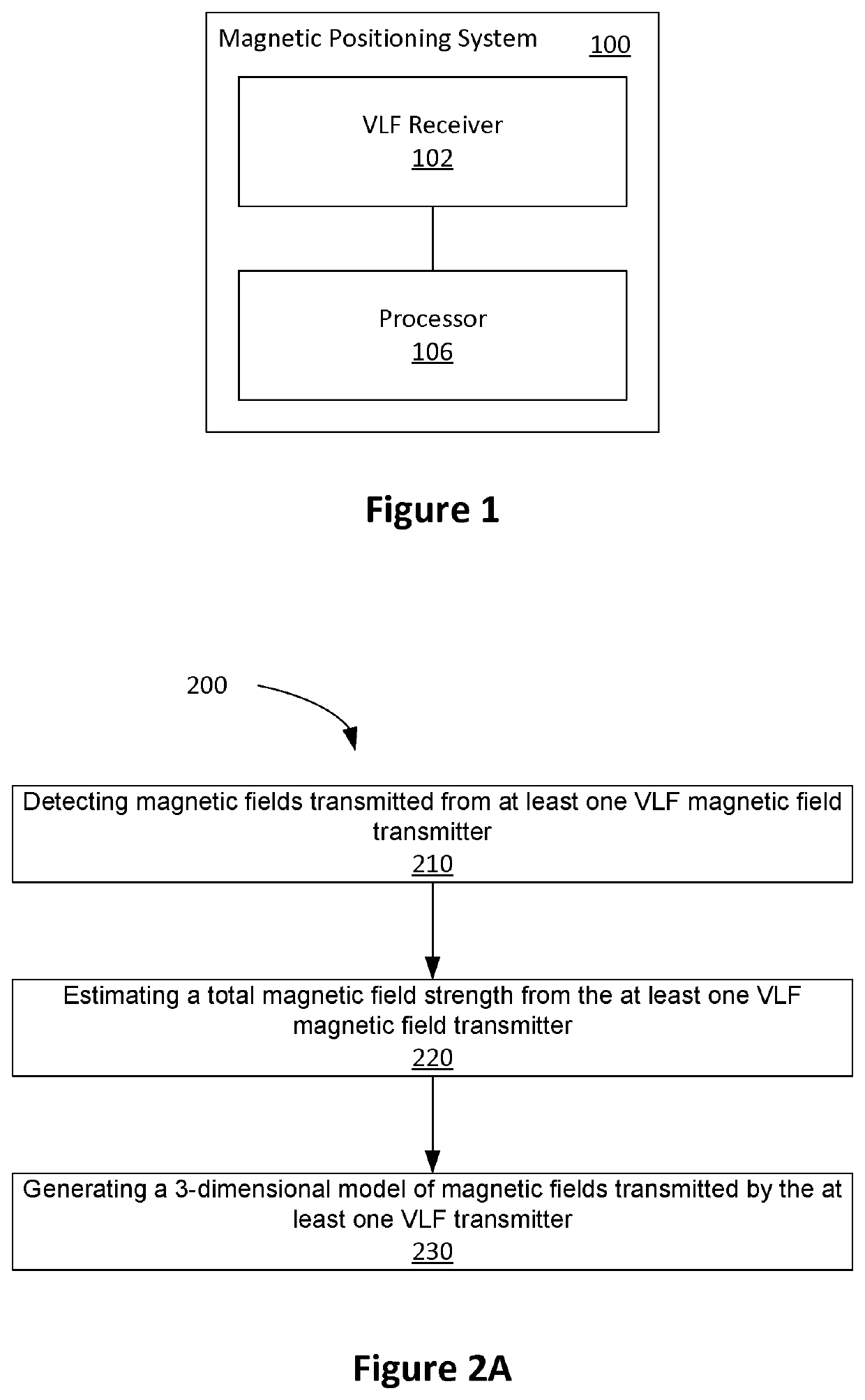
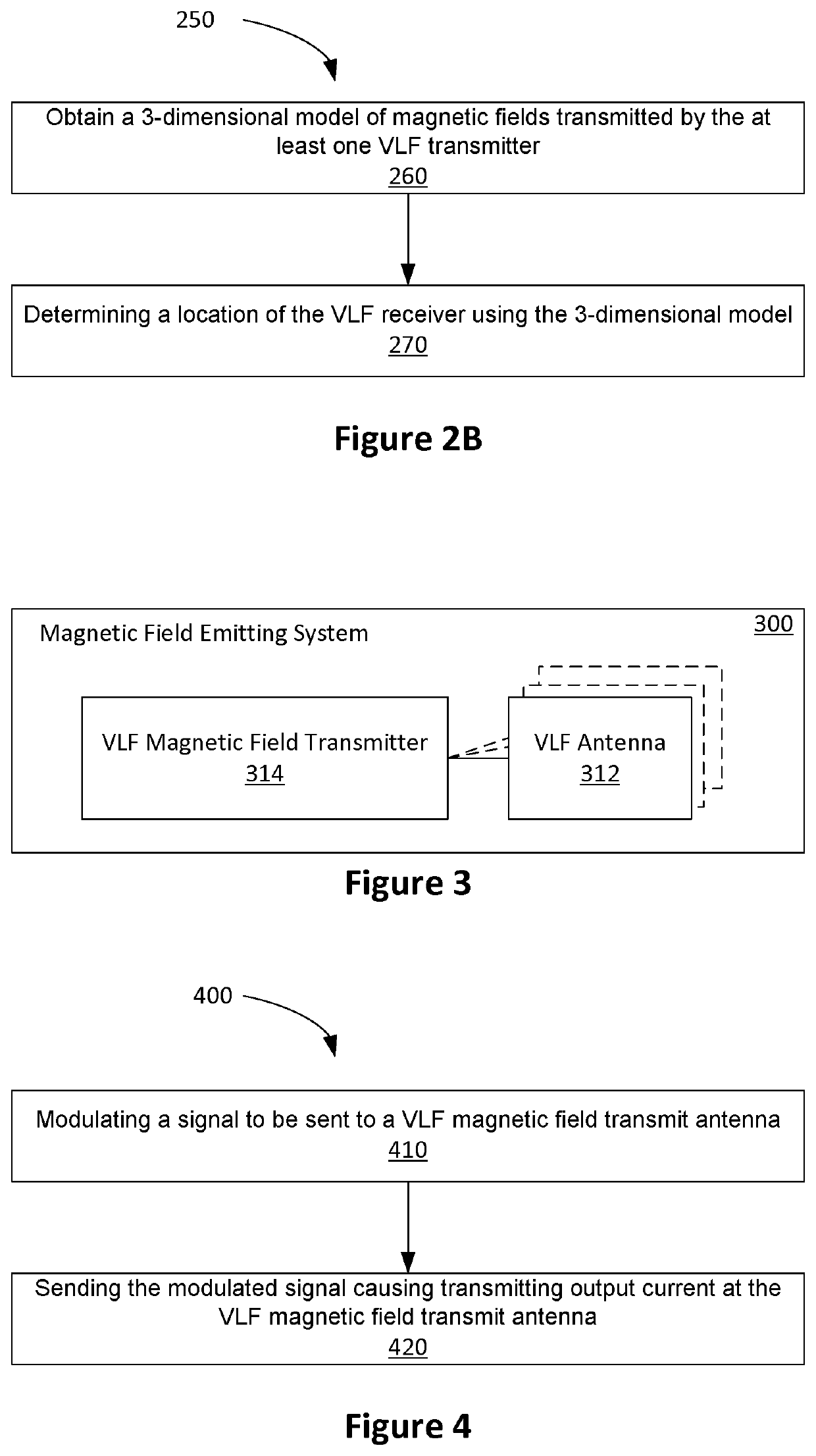
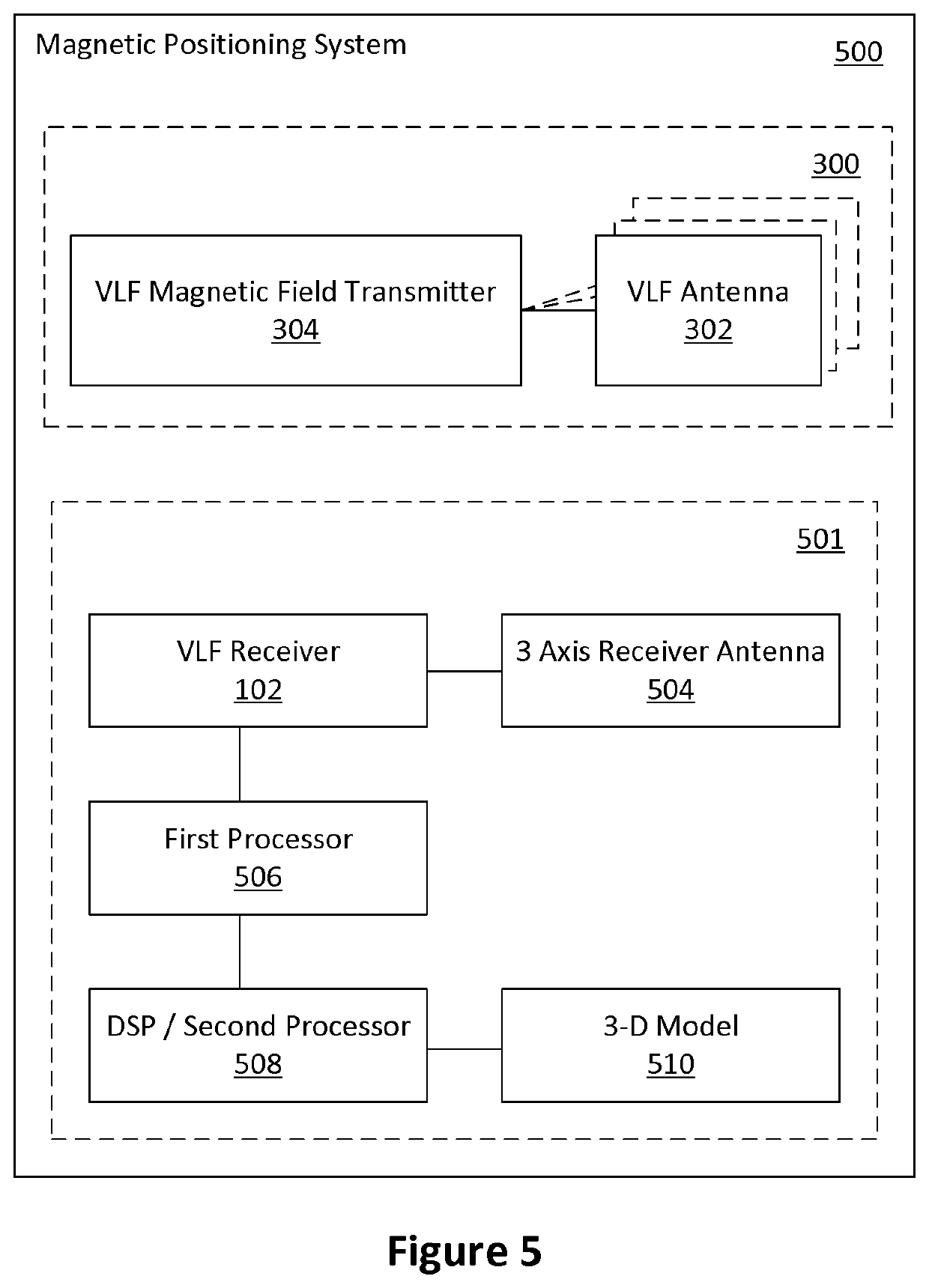
Magnetic positioning system
ActiveUS20190383619A1Accurate modelingMinimizing misfitMagnetic measurementsNavigational calculation instrumentsTime domainConductive materials
Embodiments described herein relate to a magnetic positioning system and method that allows the position of a receiver to be determined in environments containing conducting material such as concrete. A number of transmitters create modulated magnetic fields which are distorted as they propagate through the conducting materials. A finite difference time domain (FDTD) simulation of the environment is used to generate an accurate model of the fields within the environment. A receiver is used to measure the field strength of each transmitter. The receiver position is determined by evaluating the misfit between the received fields and the values in the FDTD model.
Owner:VITAL ALERT COMM
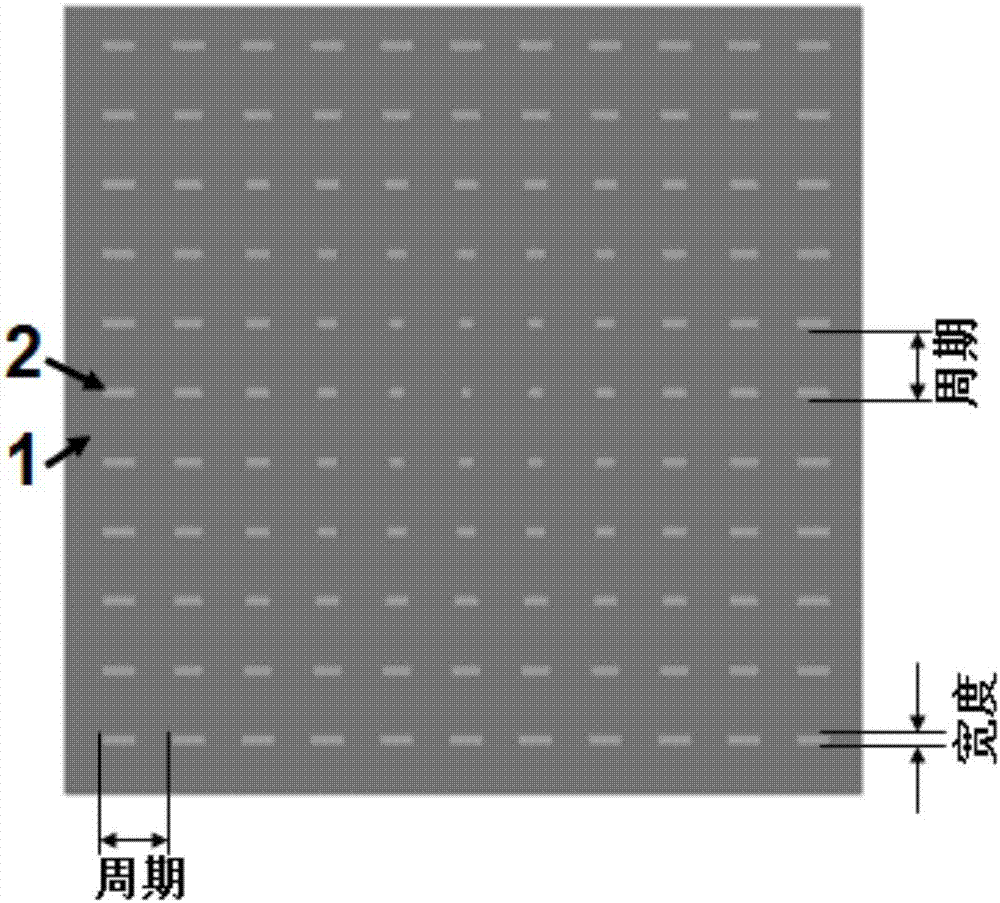
Plasmon refractive index sensor based on nano pattern and sensing method thereof
ActiveCN106940296AImplement detectionWide light sourcePhase-affecting property measurementsRefractive indexColor changes
The invention discloses a plasmon refractive index sensor based on a nano pattern and a sensing method thereof. The sensor comprises a layer of plasmon nano antenna array and a flat transparent substrate supporting the antenna array, the plasmon nano antenna array is a periodic array structure, the period is 50 to 1000 nanometers, and the thickness is 10 to 100 nanometers; the size of a single nano antenna of the array structure gradually changes according to a certain law, and the changing range is from 10 to 10000 nm. The sensor uses an imaging device to detect brightness and color change of a finite difference time domain method nano antenna array on the sensor in to-be-tested medium environment or position change of a resonance nano antenna under monochromatic light or white light irradiation to achieve medium refractive index sensing. The plasmon refractive index sensor has the advantages of simple detection technique, high sensitivity, good stability, low cost of needed detection equipment, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
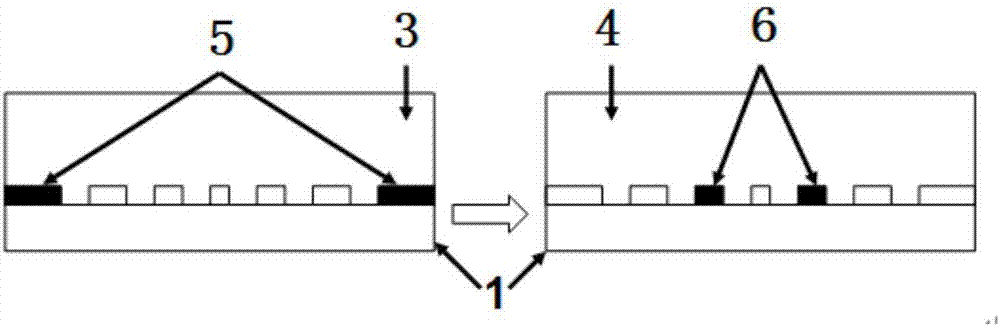
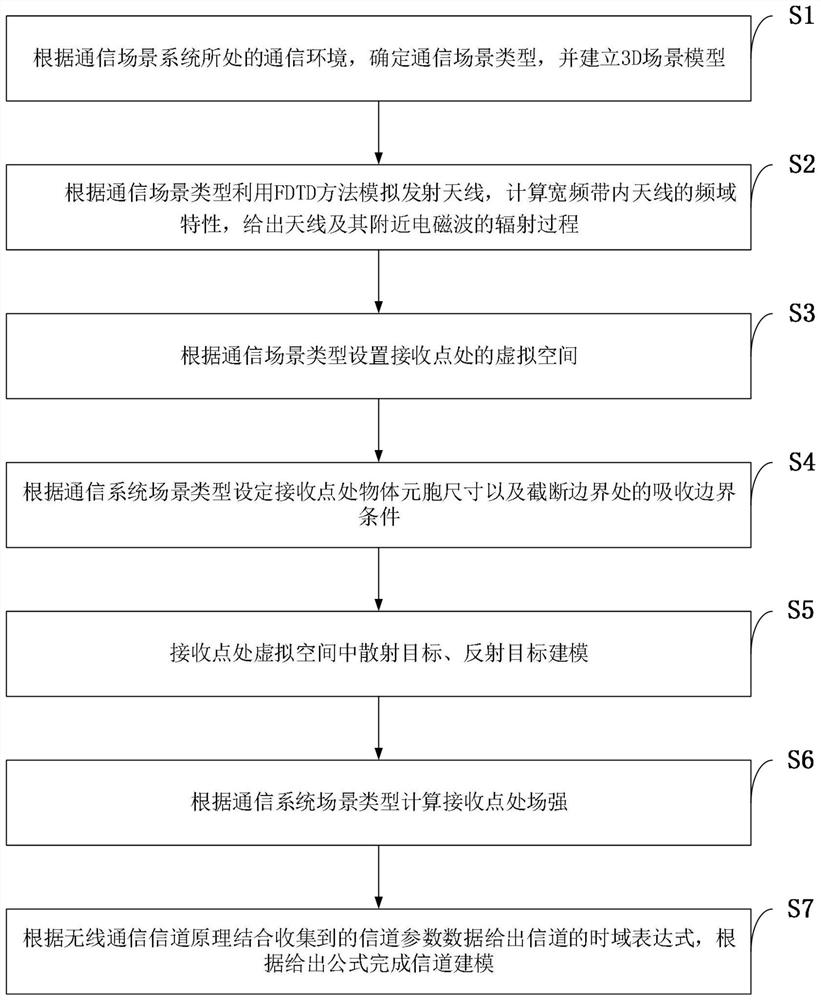
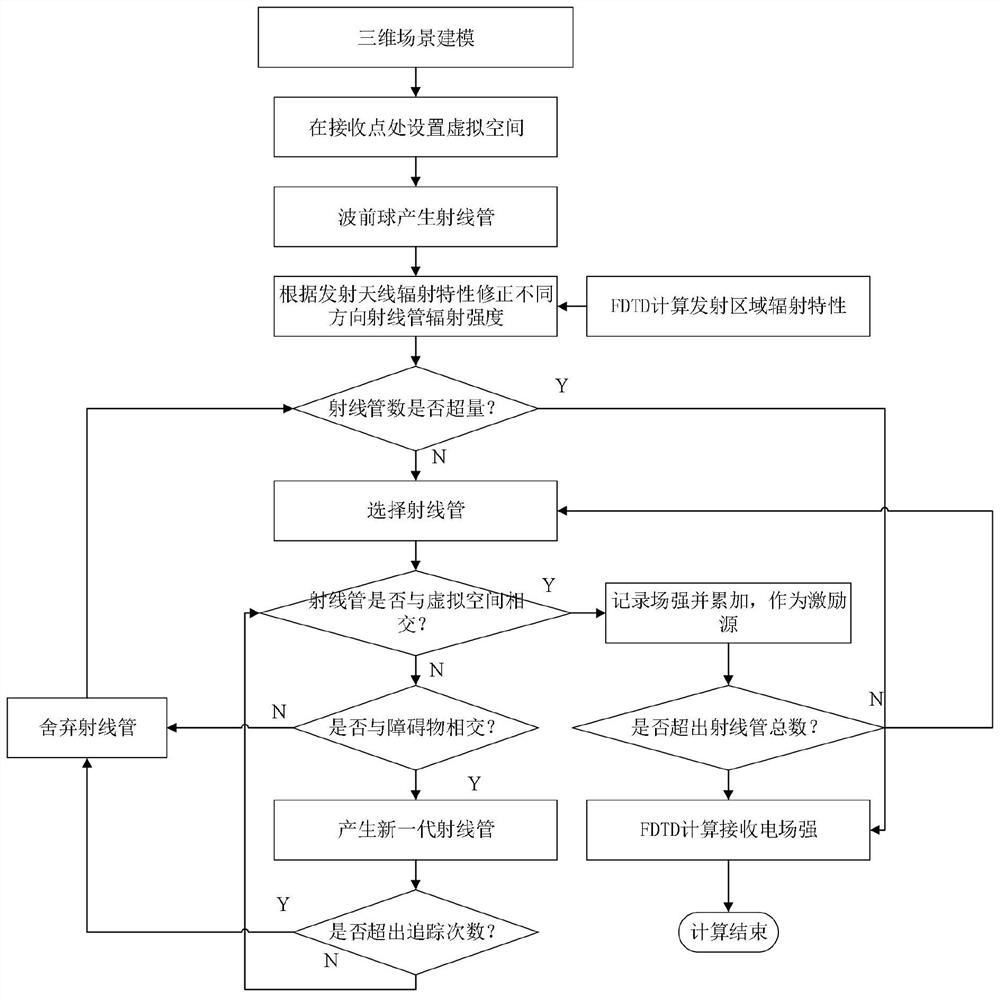
Channel modeling method combining ray tracing method and finite difference time domain method
InactiveCN112865883AEasy to switchReduce the amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationTransmission monitoringTime domainChannel parameter
The invention belongs to the technical field of radio frequency wireless communication, particularly relates to a channel modeling method combining ray tracing and a finite difference time domain method, adopts a channel modeling method based on ray tracing and FDTD (finite difference time domain method), and aims to solve the problems in the prior art. Various characteristic parameters in an electromagnetic wave propagation process are obtained by using a ray tracing technology, characteristic parameters such as amplitude, angle, phase and time delay can be obtained for each path so as to perform analysis and calculation, and in addition, simulation analysis is performed on an antenna and an electromagnetic wave radiation process close to the antenna at a transmitting end in combination with an FDTD method. And meanwhile, a virtual space is established at a receiving end to carry out modeling analysis on a receiving antenna and a scatterer, so that corresponding electromagnetic parameters are obtained. And finally, channel modeling is given according to channel parameters obtained in the ray propagation process.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
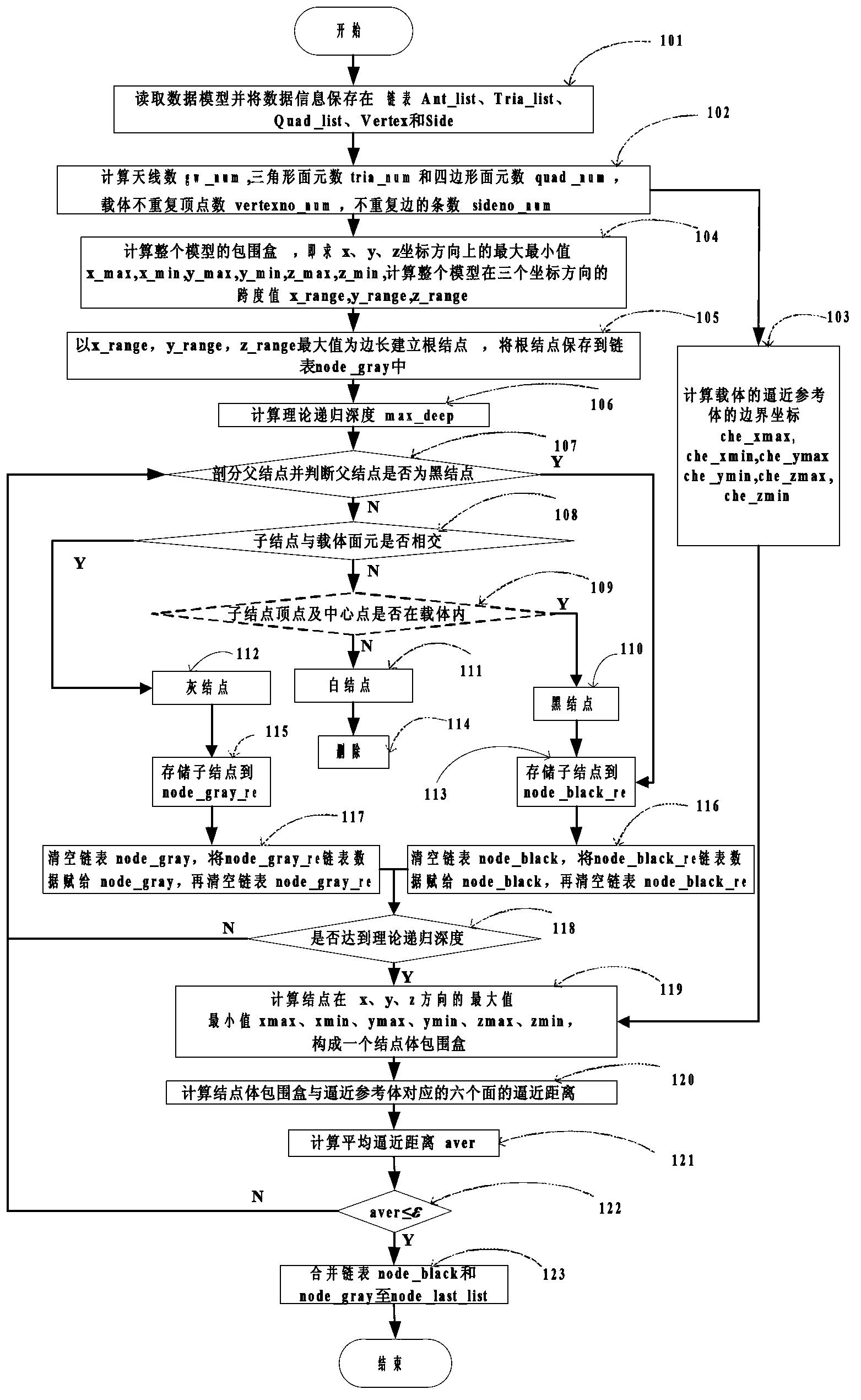
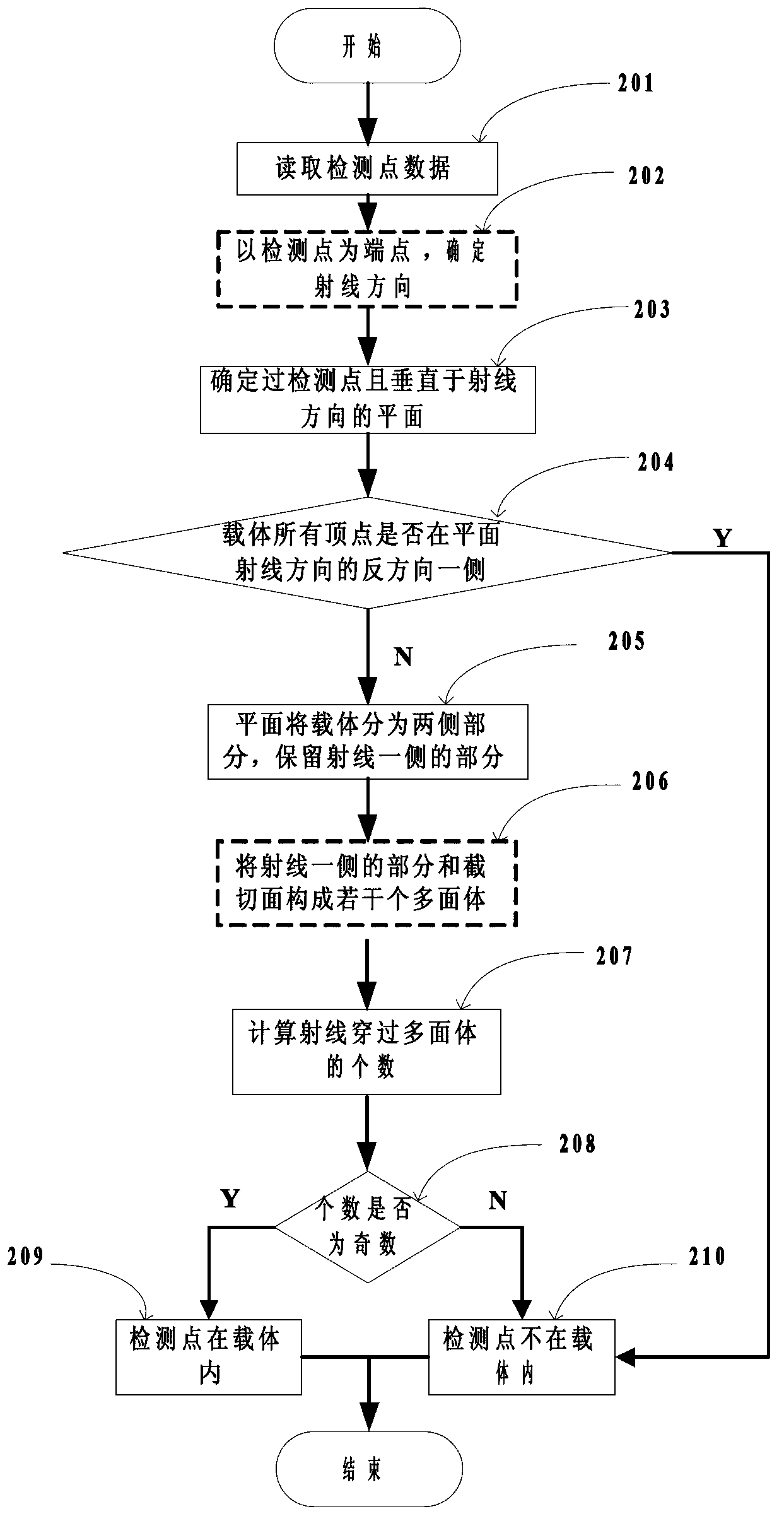
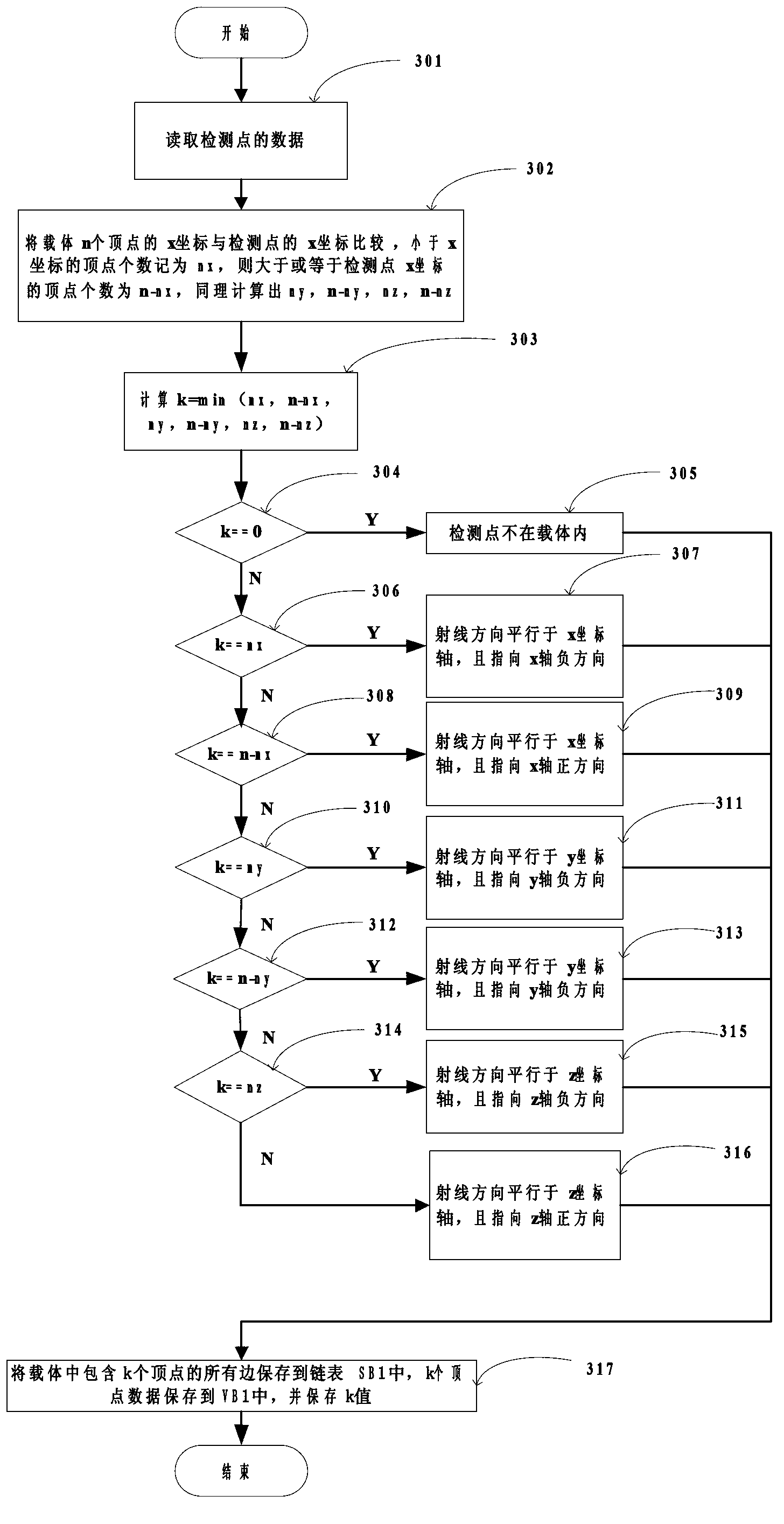
Finite difference time domain electromagnetic calculation carrier meshing method
InactiveCN103310069AHigh degree of geometric approximationThe calculation result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsTime domain electromagneticsGrid partition
The invention discloses a finite difference time domain electromagnetic calculation carrier meshing method. According to the method, the mesh size is jointly controlled by the discrete electrical dimensional accuracy and the carrier surface approximation accuracy, the geometrical approximation degree between the divided mesh model and the carrier model is high especially under the situation of low frequency with large wavelength, finite difference time domain electromagnetic calculation is performed on the basis of the mesh model, and the calculation result is relatively accurate; surface approximation accuracy controlling parameters for meshing the mesh model are provided, the blindness of meshing precision control of the conventional direct subdivision method is avoided, and the calculated amount for meshing can be effectively controlled; when mesh refinement is required, all that is needed is to perform octree recursive subdivision to the black nodes in the bottommost layer, and mesh refinement is easy to realize.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
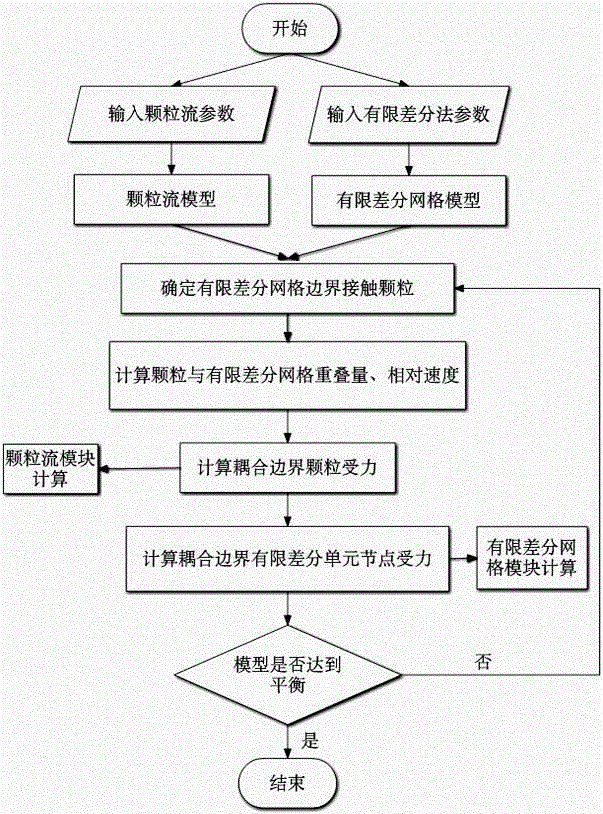
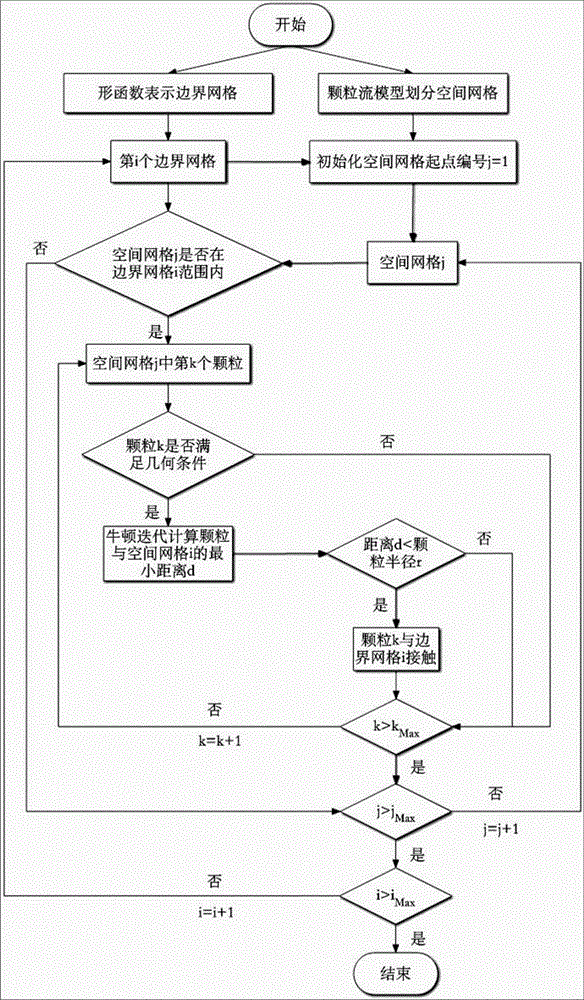
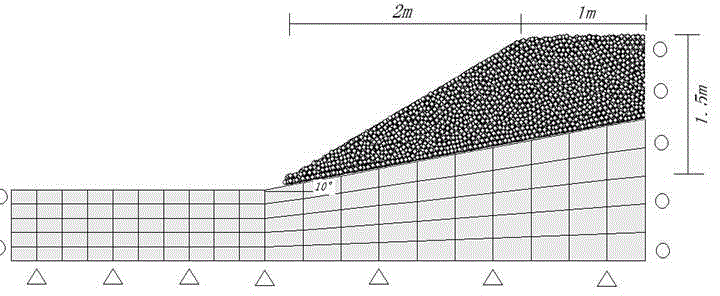
Coupling calculation method based on granular flow and finite difference method
InactiveCN104091009AAccurately analyze mesoscopic propertiesAccurately analyze macroscopic propertiesSpecial data processing applicationsCouplingComputational simulation
The invention relates to a coupling calculation method based on granular matter mechanics and a finite difference method, and belongs to the technical field of calculation of rock mechanics. In terms of limitation of an existing discrete medium and continuous medium computational simulation method, a method that any position on the surface of granular flow / finite difference grid is coupled is adopted to achieve transmission of interaction force of boundaries of two different media, granular flow and finite difference grids are calculated with the newton second law as a basis, and a rock and soil material calculation model with consideration of full coupling of discrete media and continuous media is established. According to the method, boundary coupling calculation of discrete media and continuous media can be effectively achieved, multiscale analysis can be conducted on stress characteristics of rock and soil bodies, and application of the granular flow and the finite difference method on the geotechnical engineering technical field is propelled forcefully.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com