Patents
Literature
50 results about "Gigabyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The gigabyte (/ˈɡɪɡəbaɪt, ˈdʒɪɡə-/) is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The prefix giga means 10⁹ in the International System of Units (SI). Therefore, one gigabyte is 1000000000bytes. The unit symbol for the gigabyte is GB.
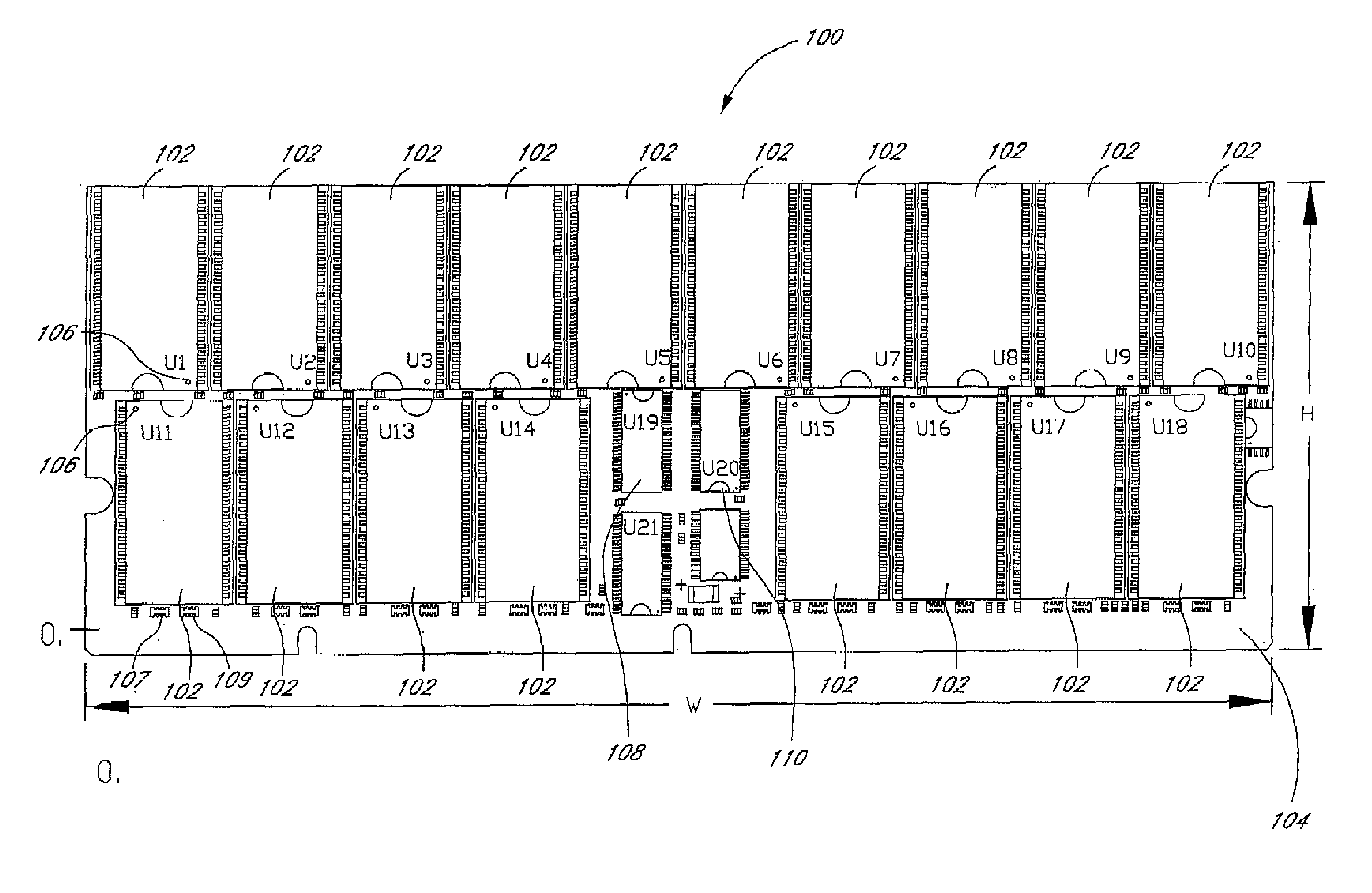
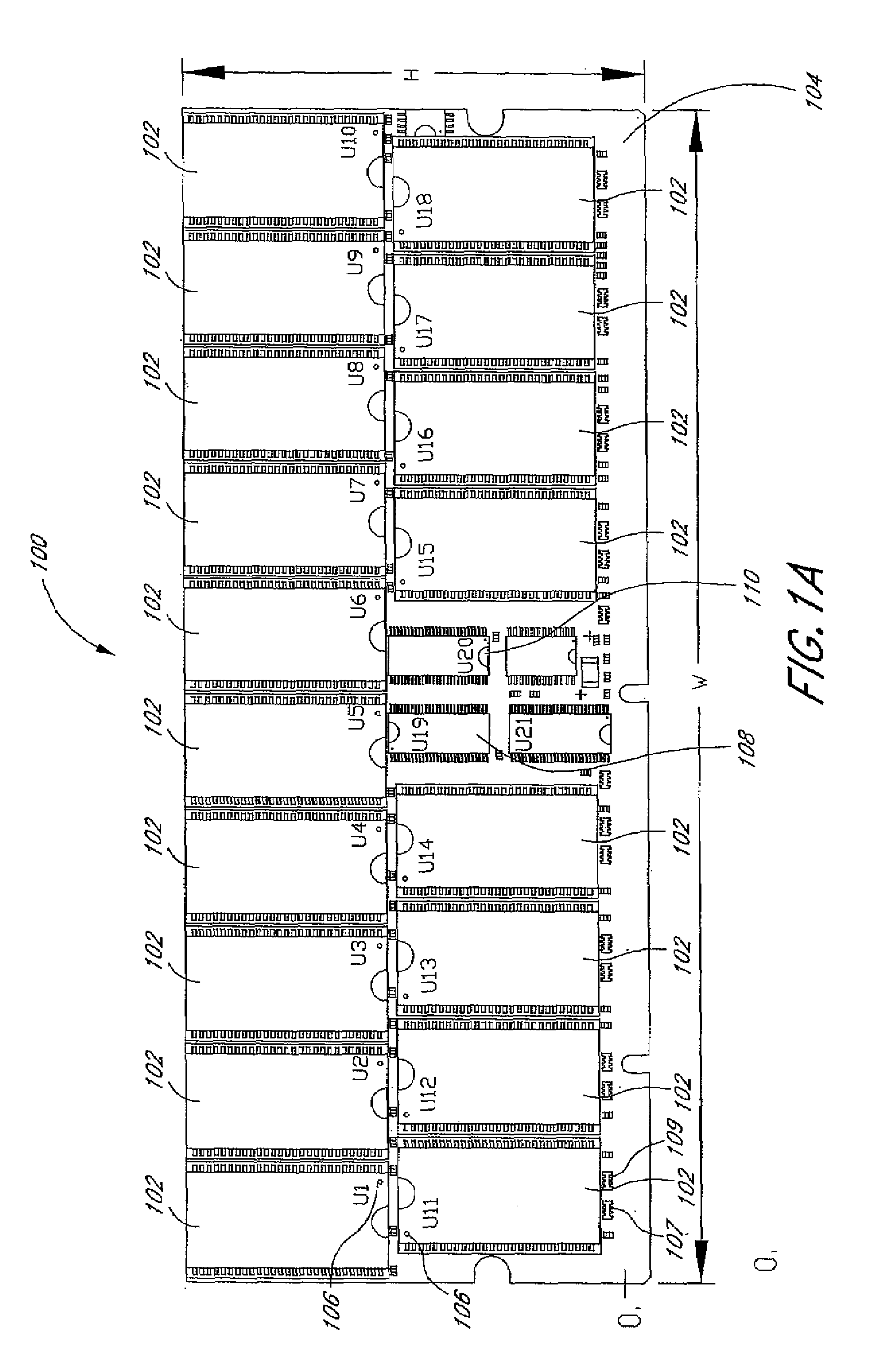
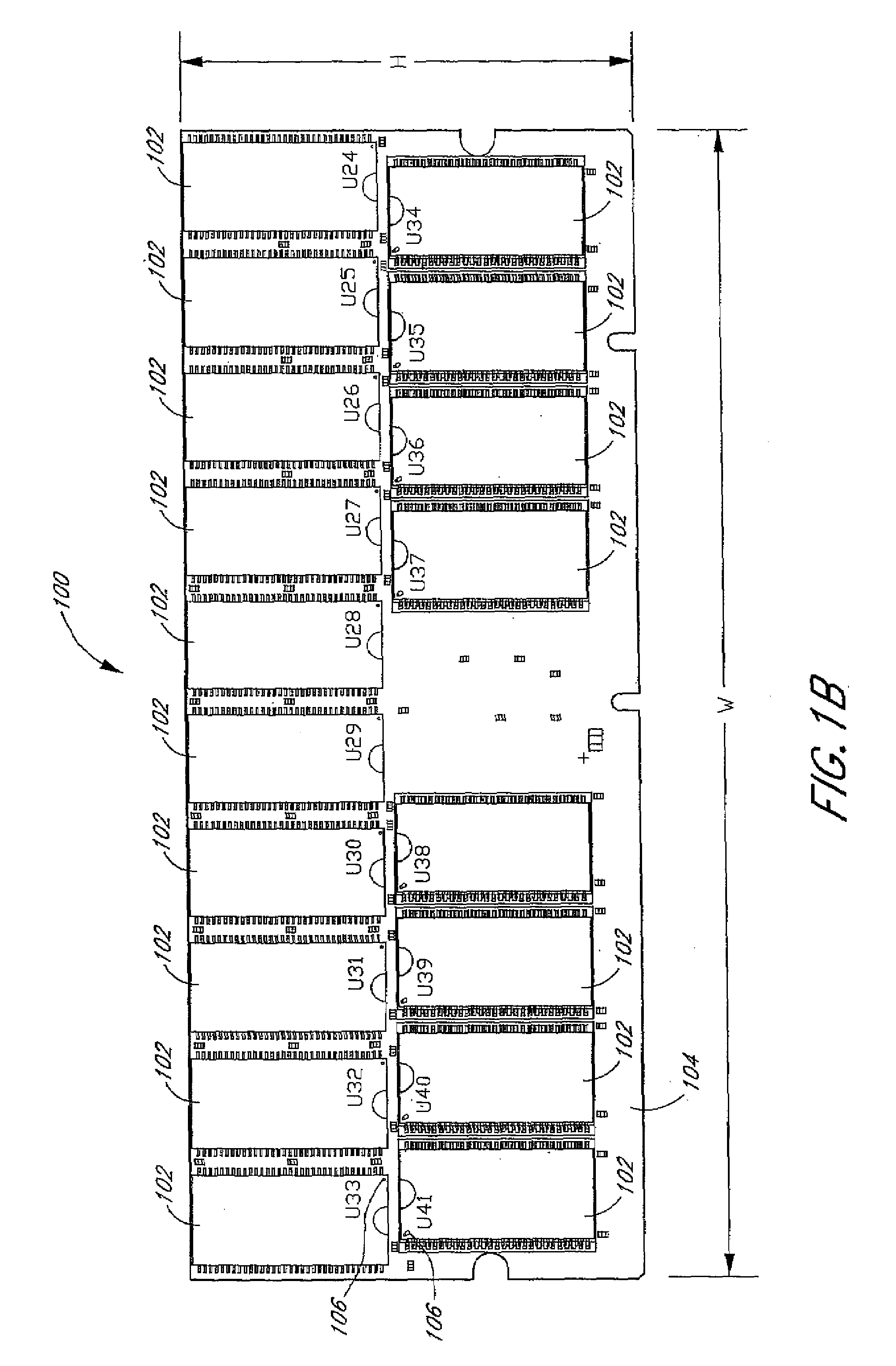
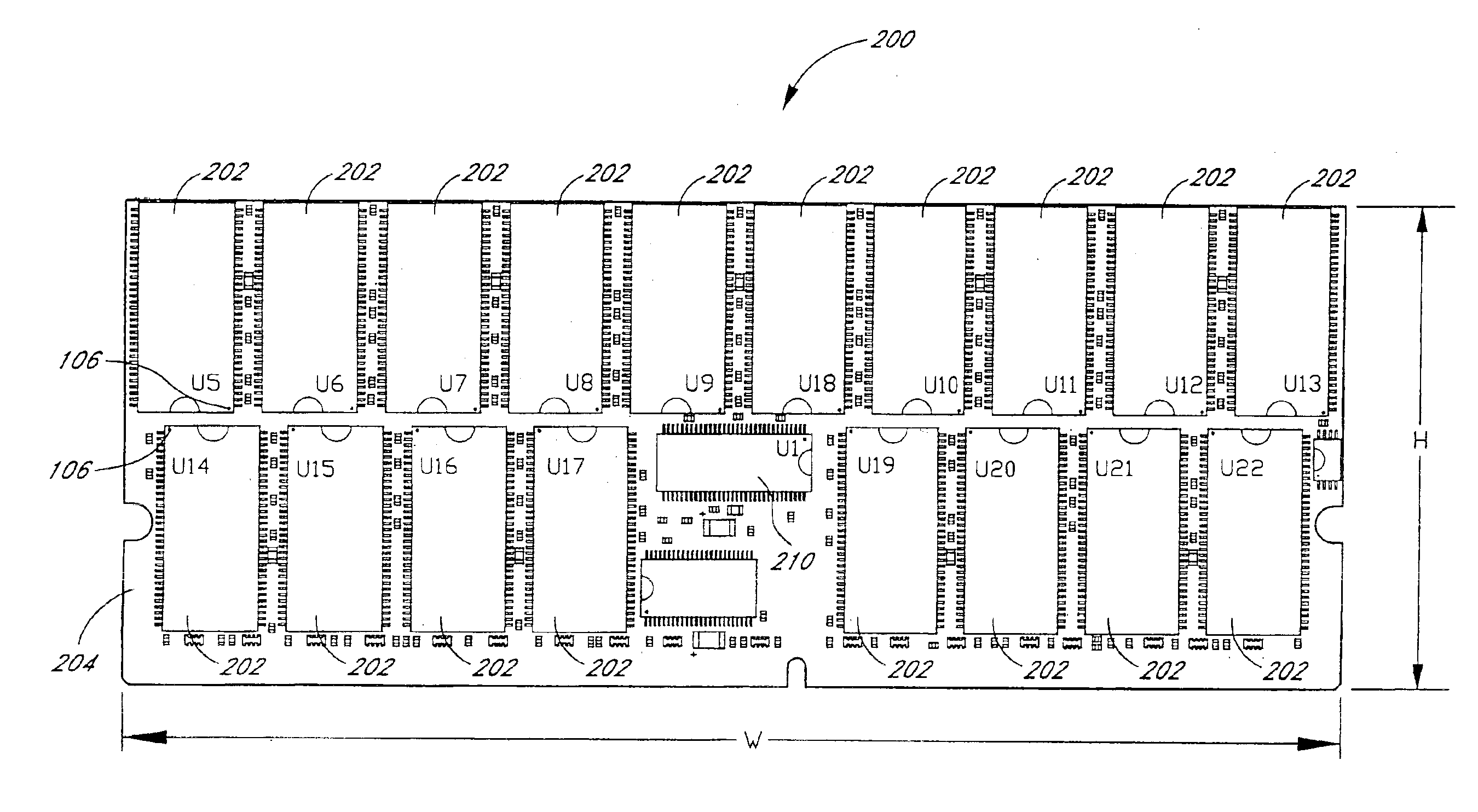
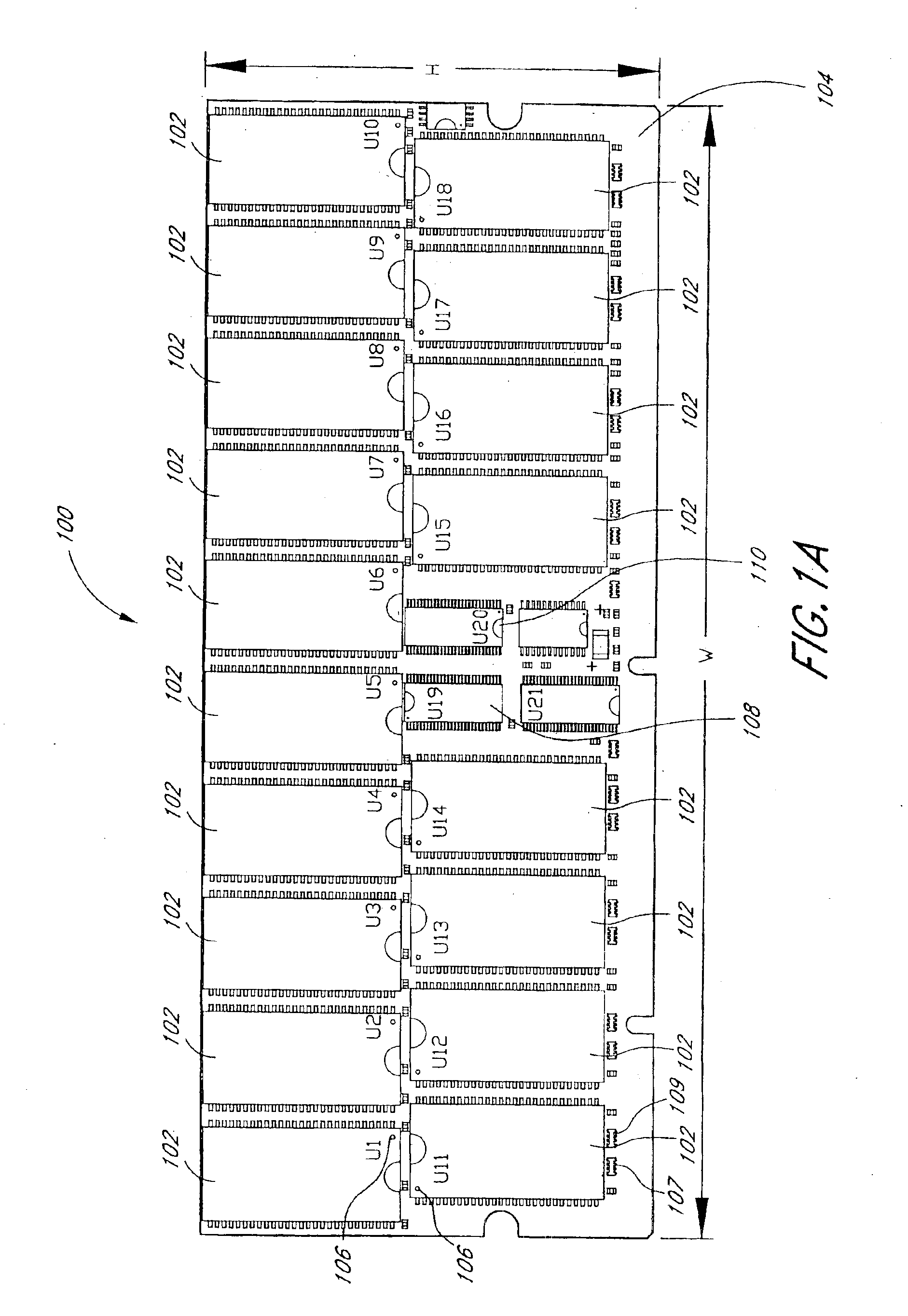
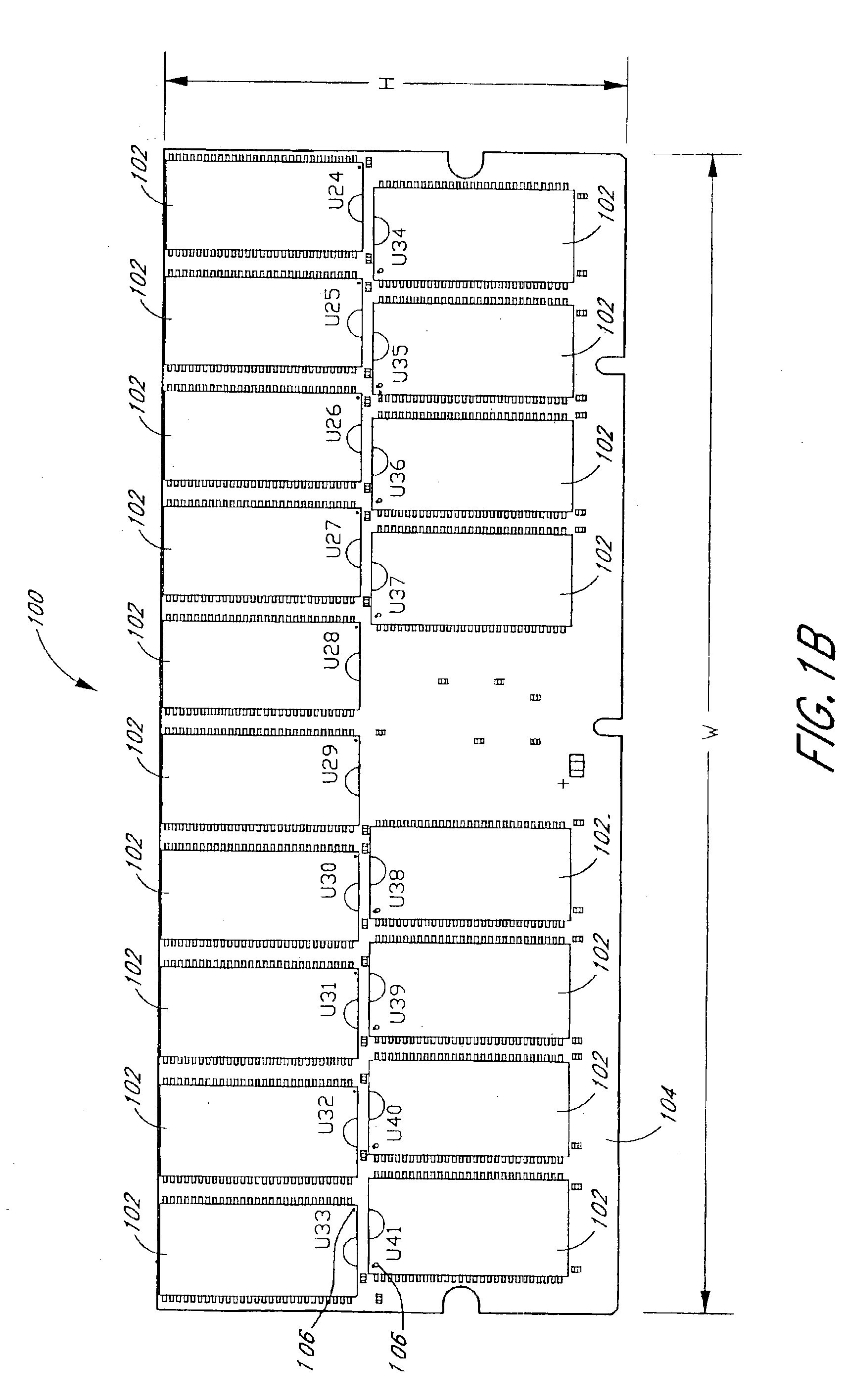
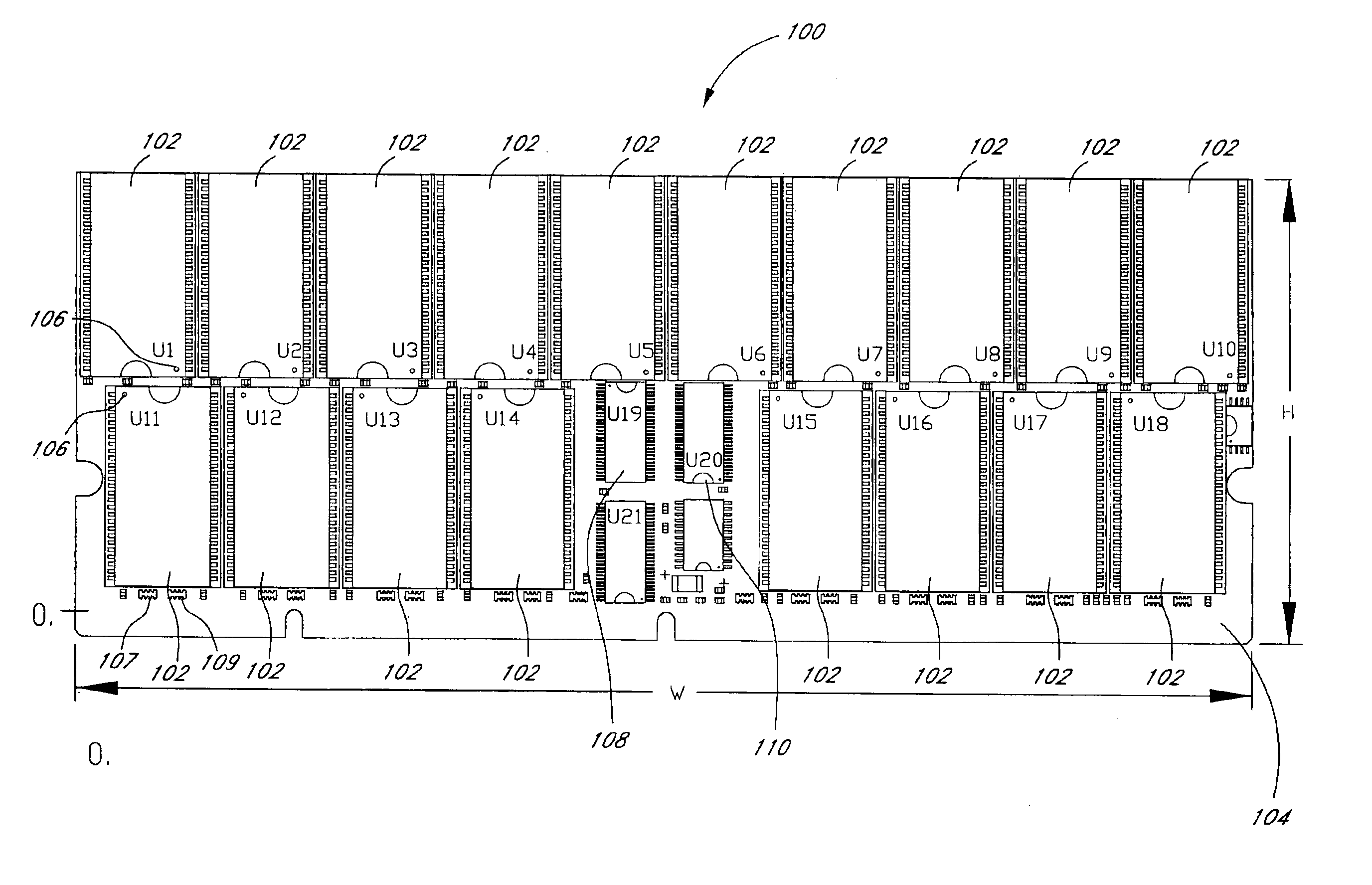
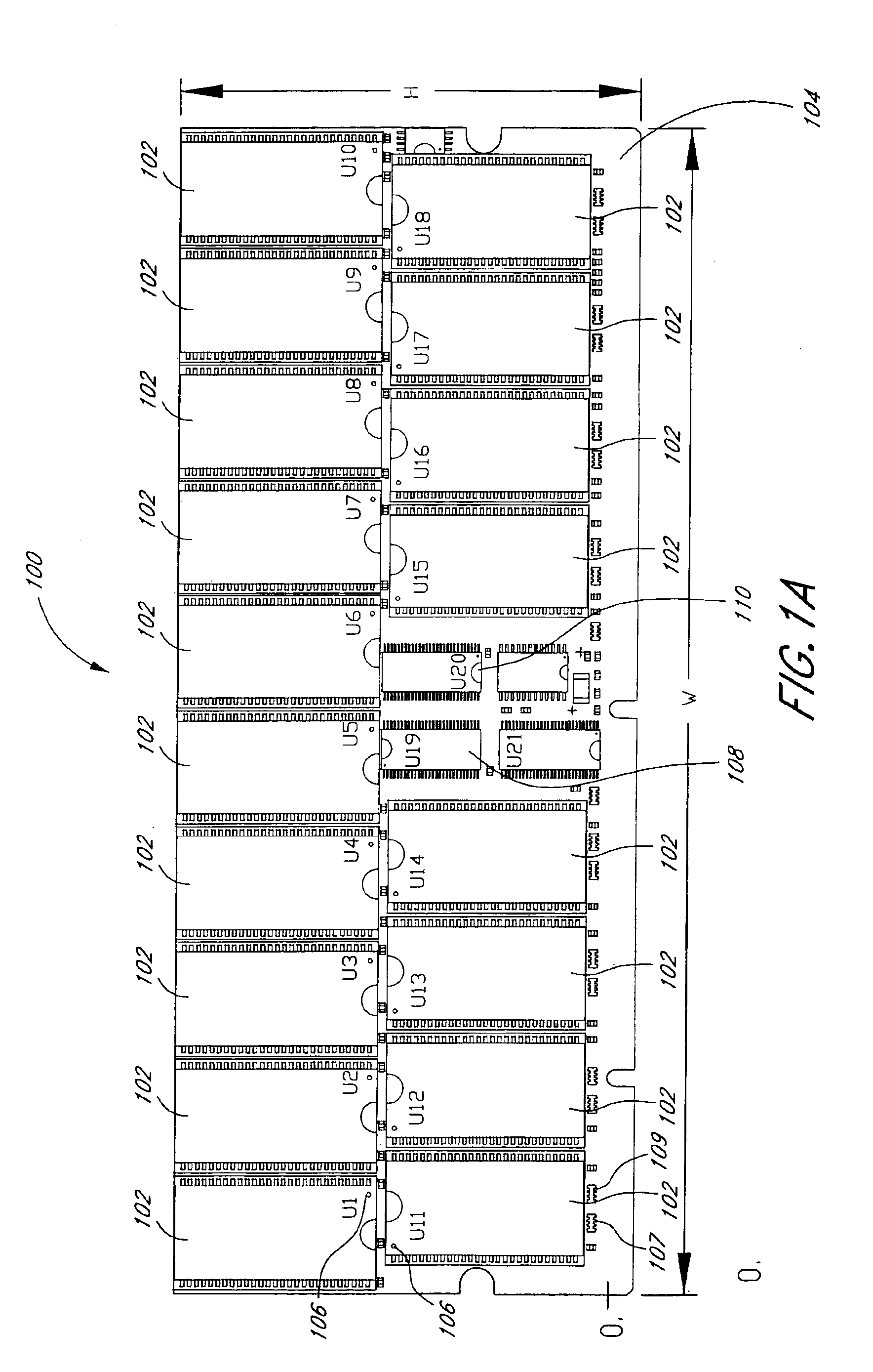
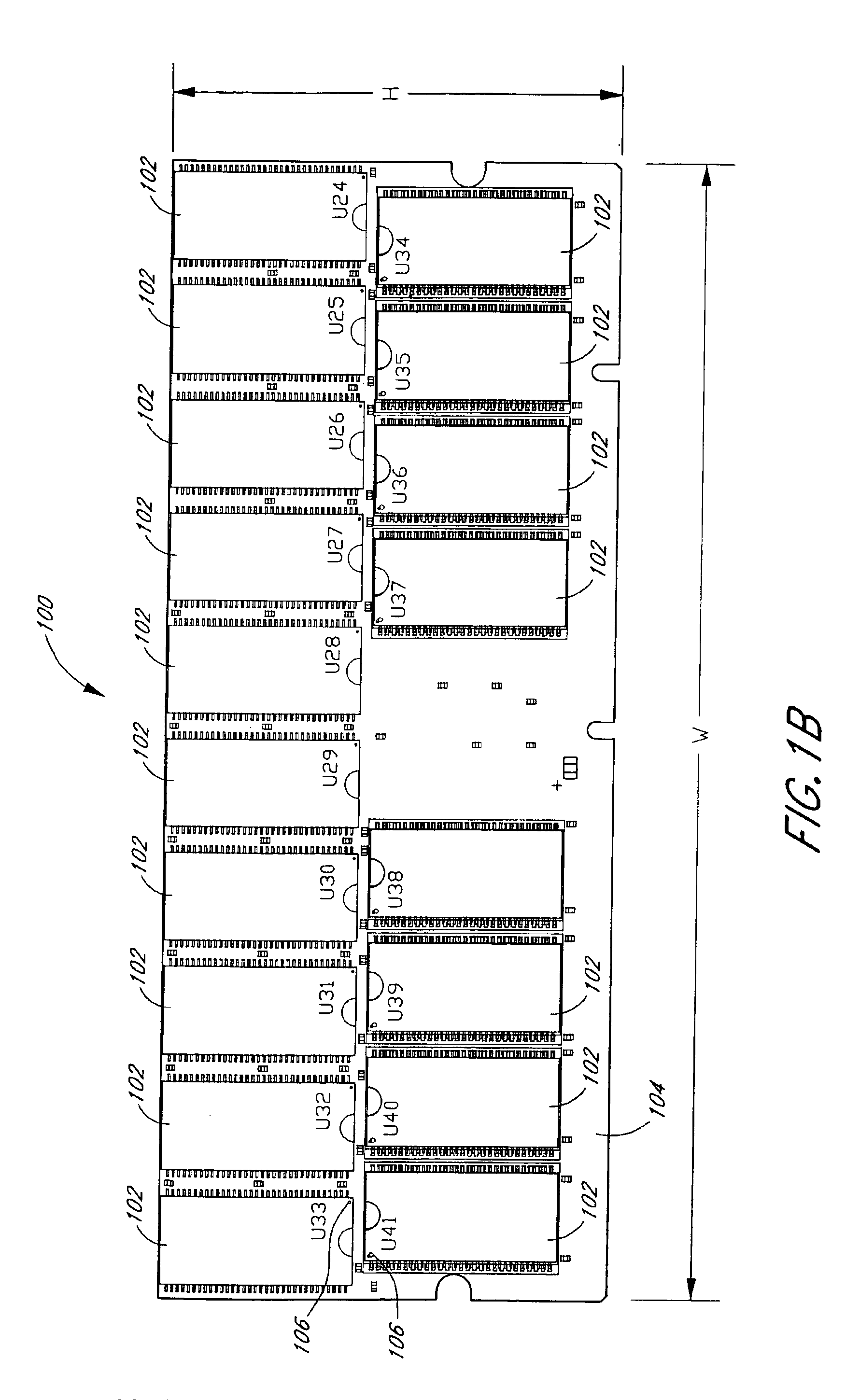
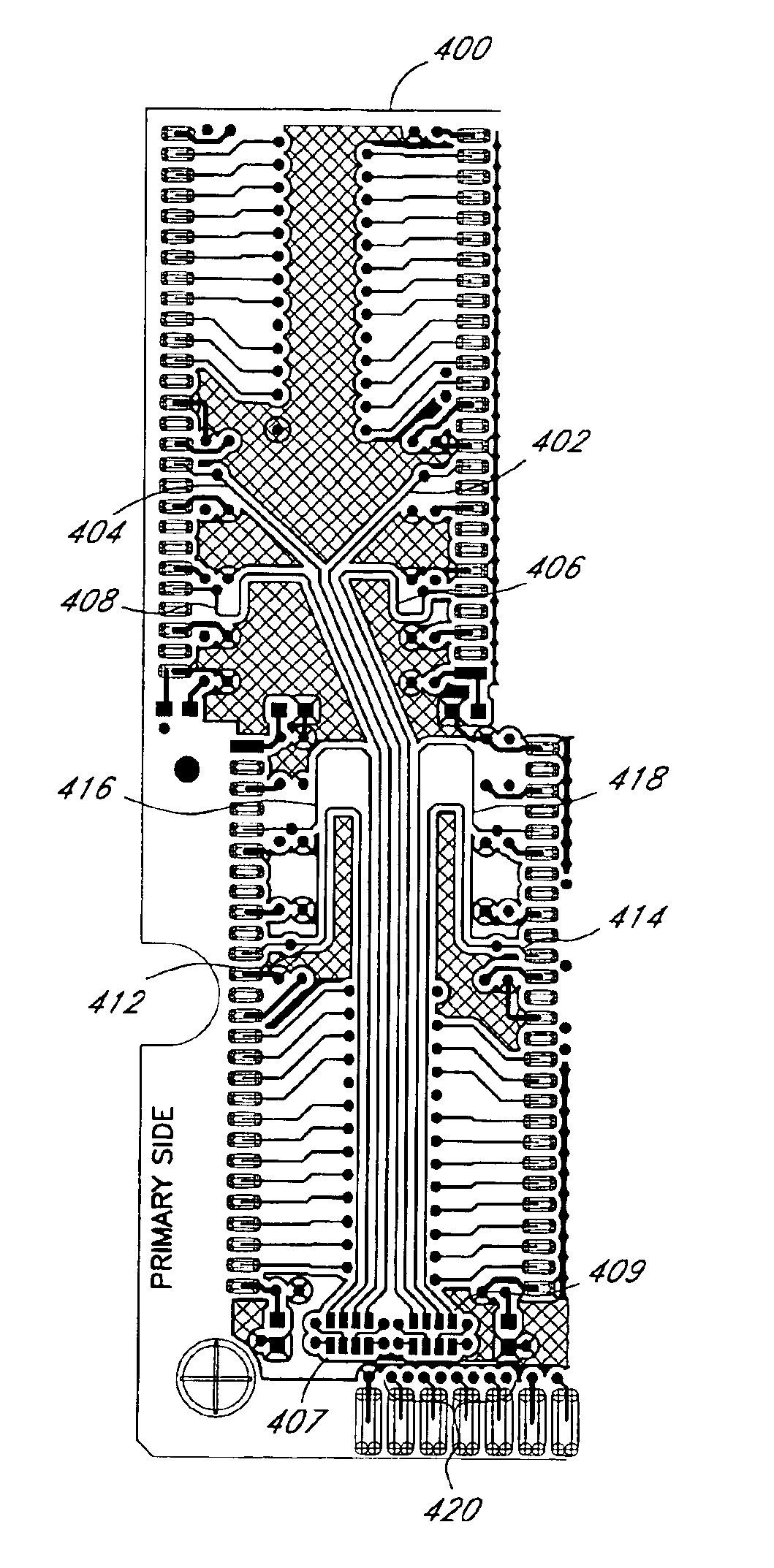
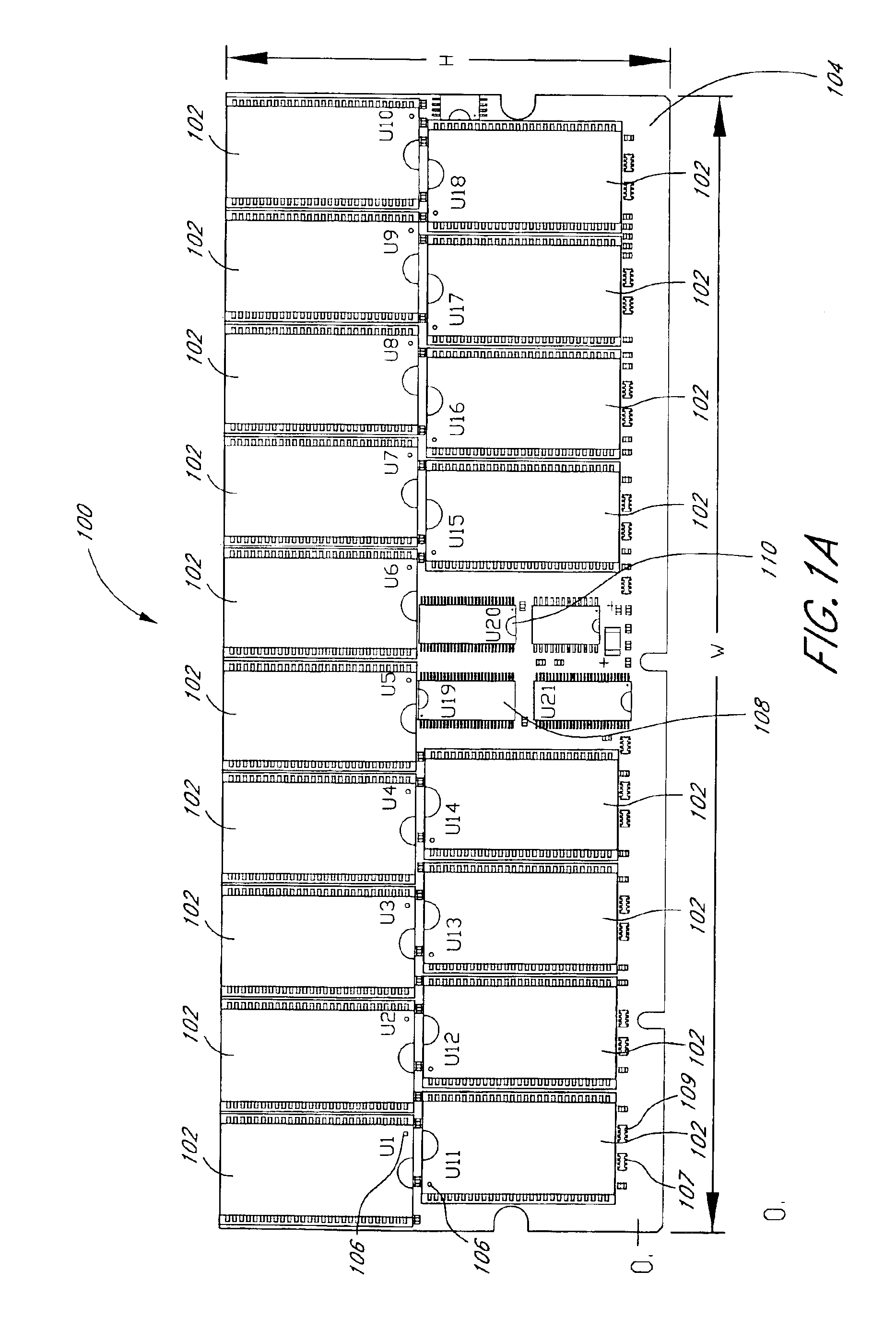
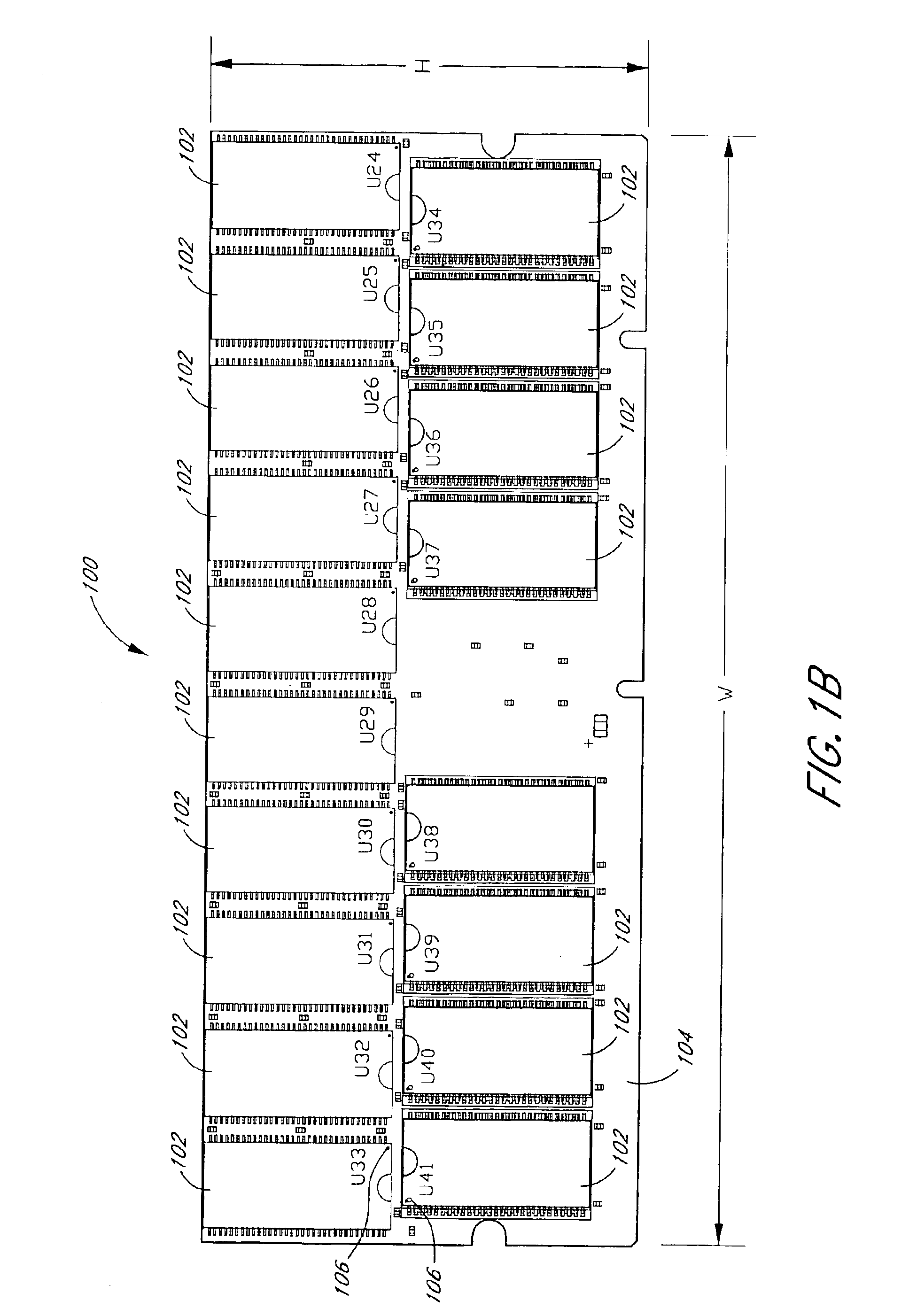
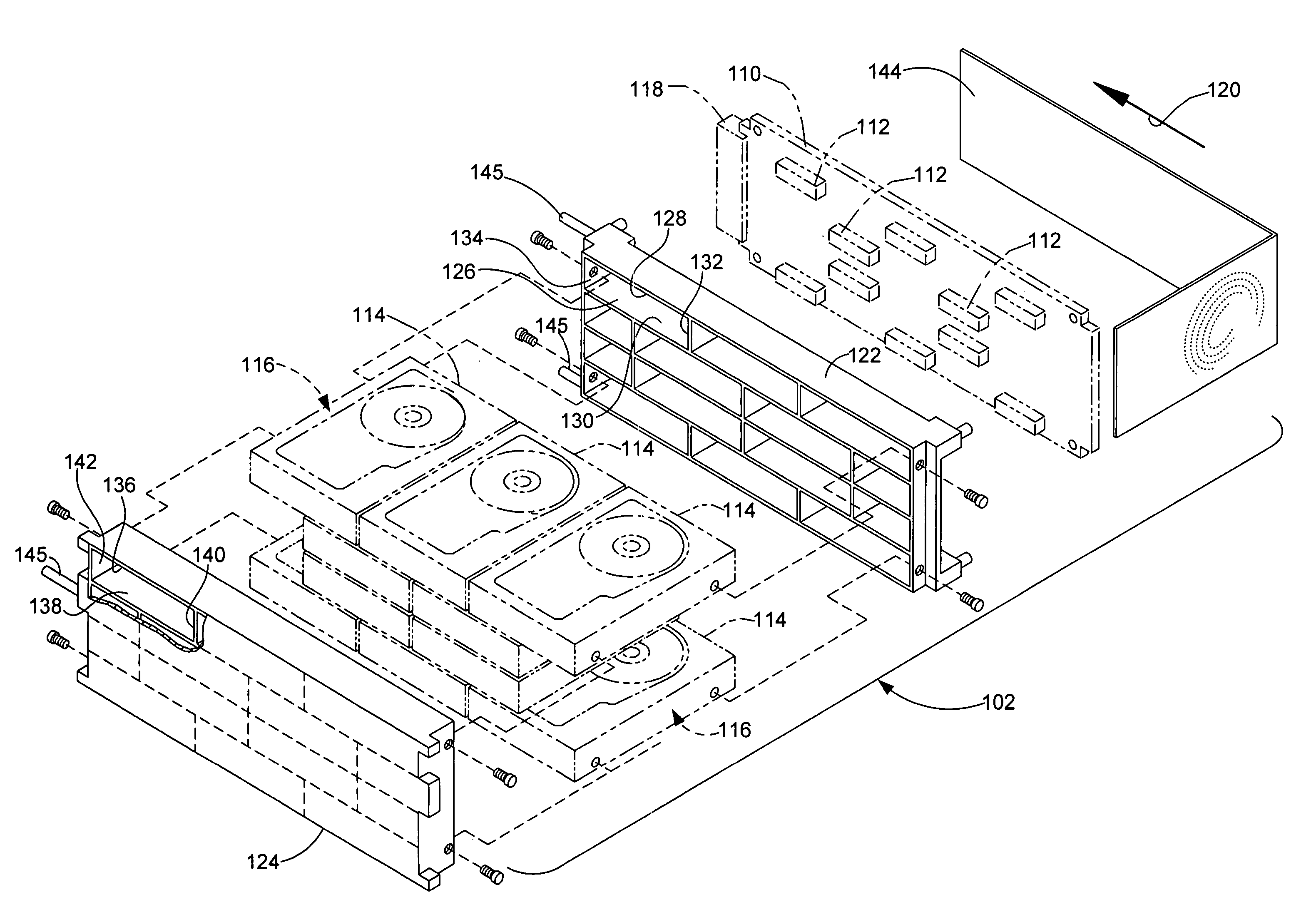
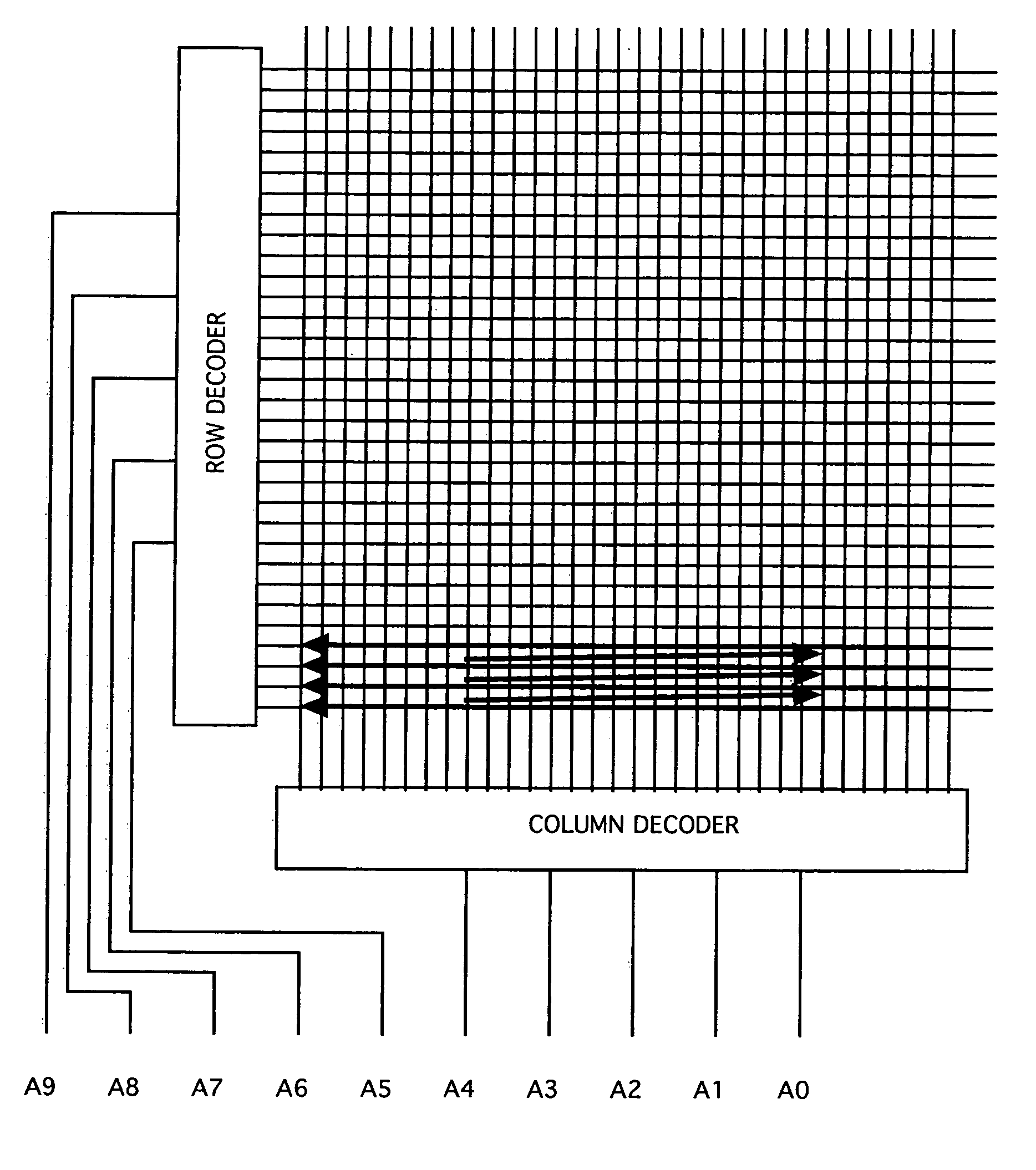
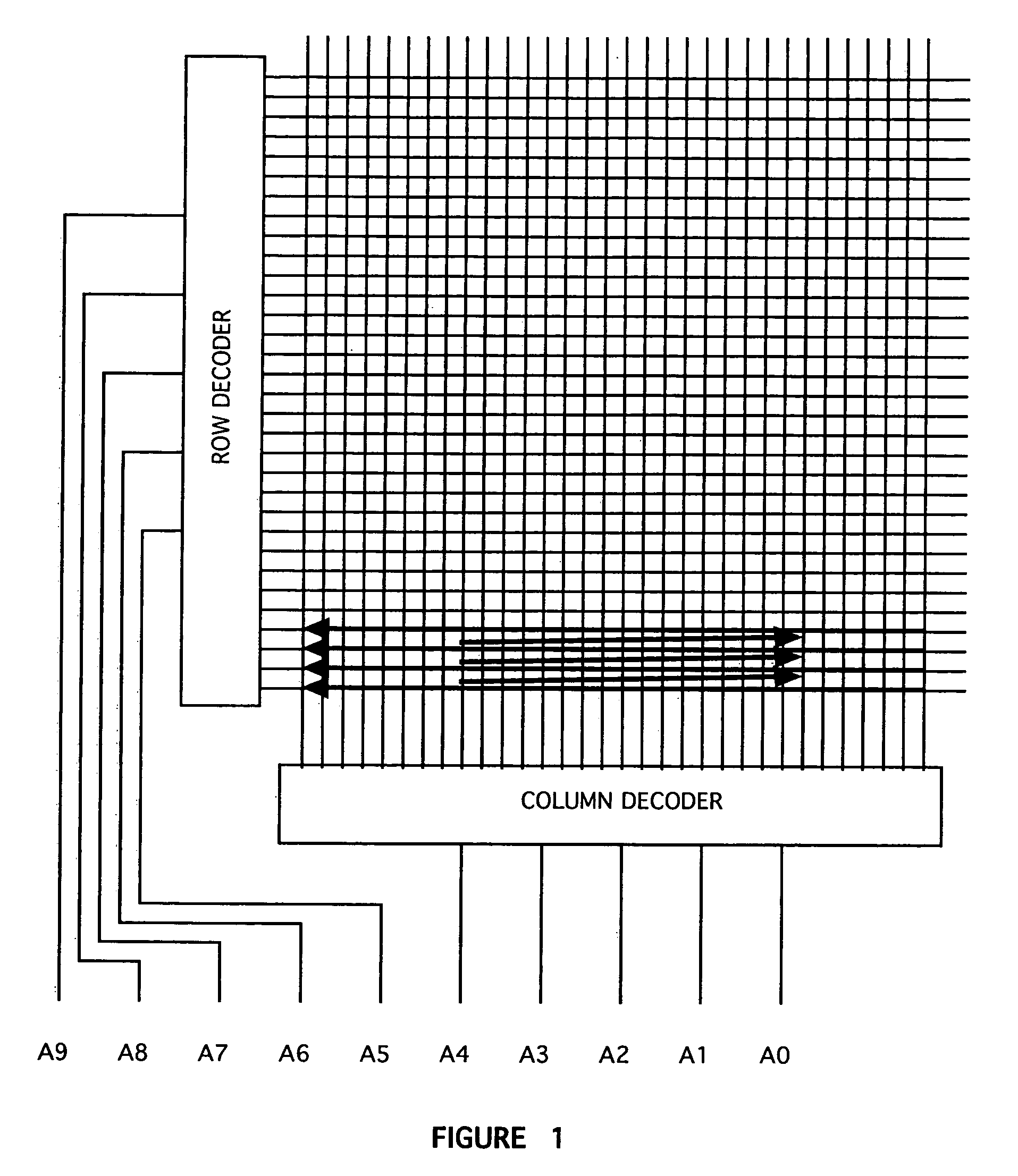
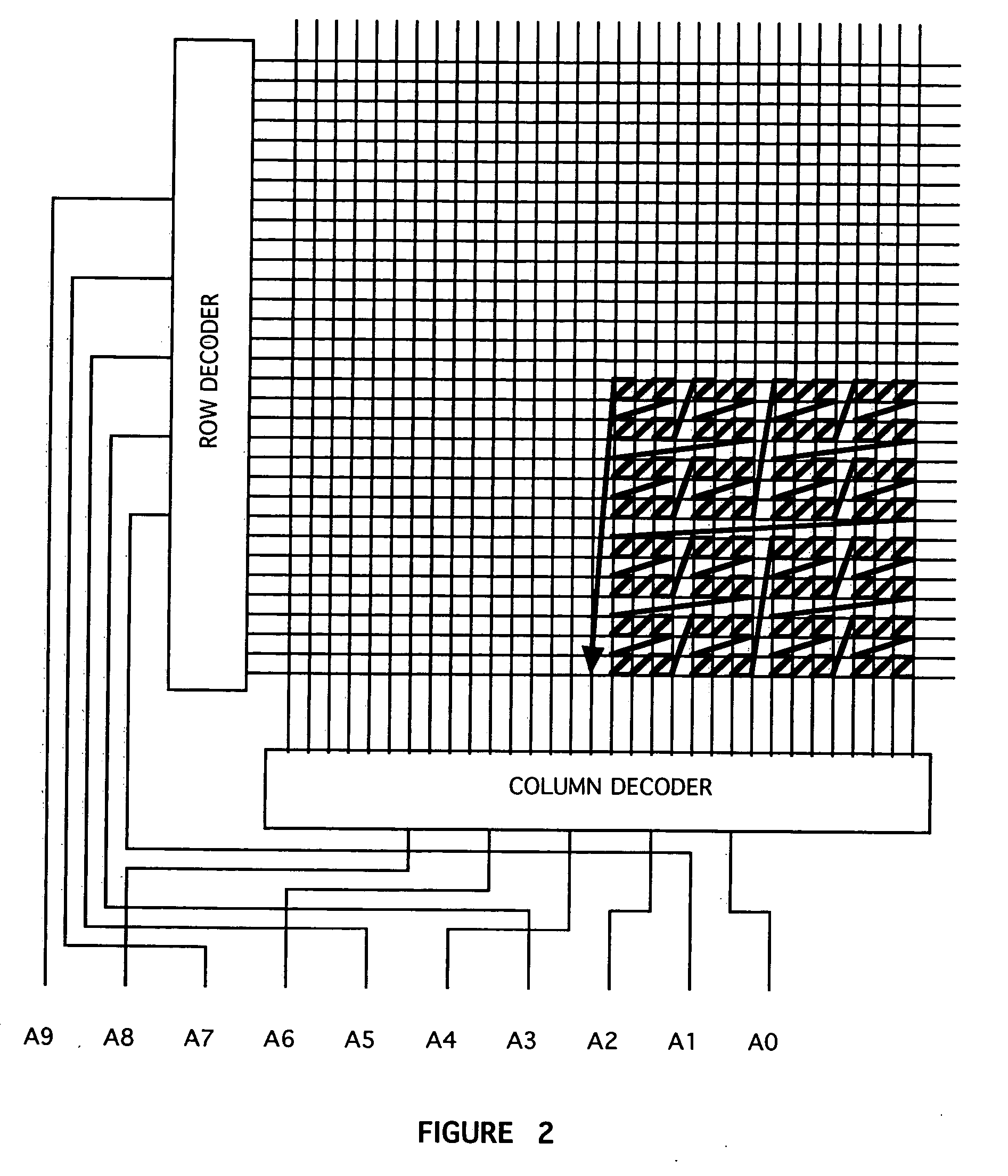
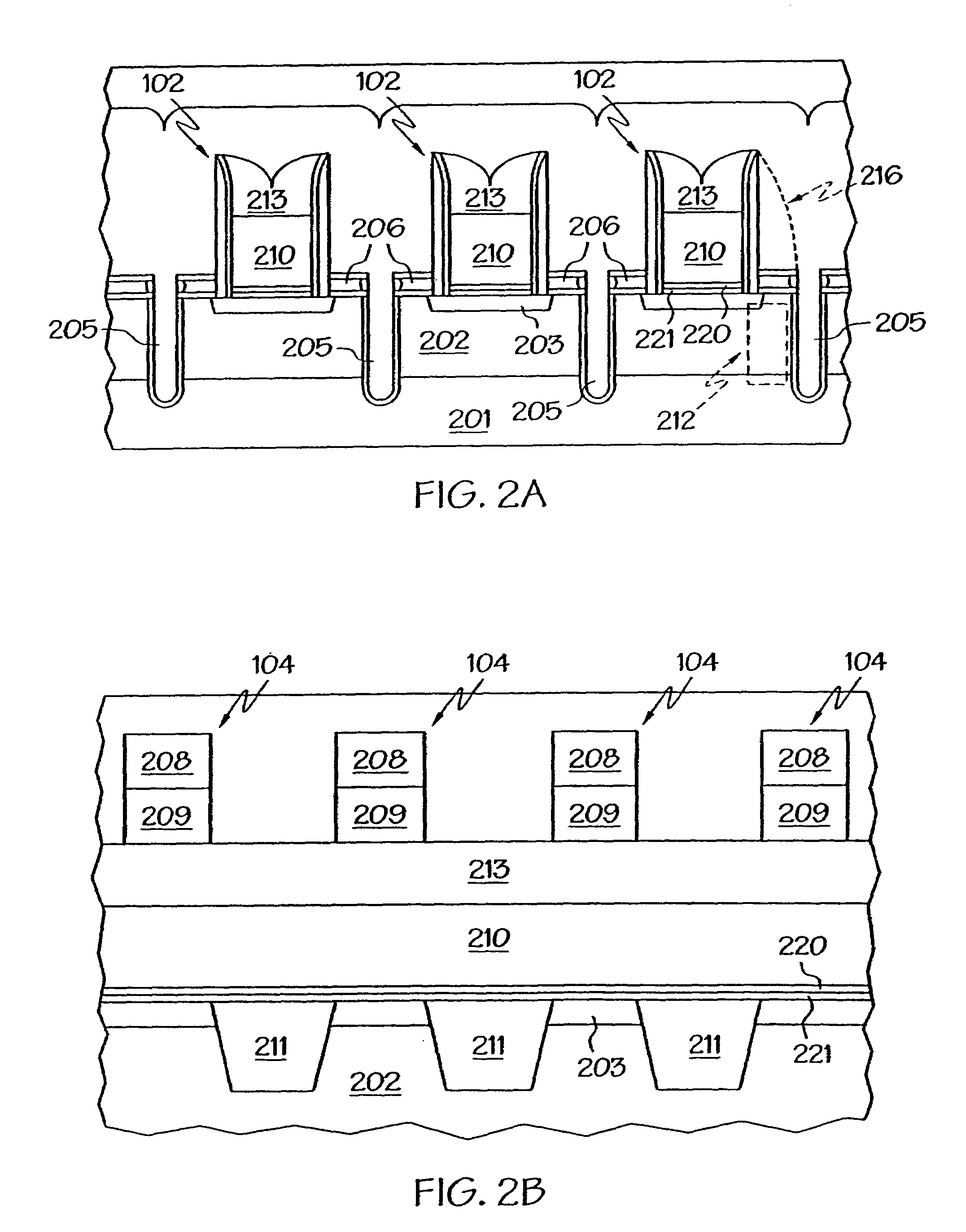
Arrangement of integrated circuits in a memory module
InactiveUS20050018495A1Final product manufactureCross-talk/noise/interference reductionGigabyteProcessor register
Abstract of the Disclosure Integrated circuits utilizing standard commercial packaging are arranged on a printed circuit board to allow the production of one-Gigabyte, two-Gigabyte, and four-Gigabyte capacity memory modules. A first row of integrated circuits is oriented in an opposite orientation to a second row of integrated circuits. The integrated circuits in the first row on a first lateral portion of the printed circuit board and in the second row on the first lateral portion are connected to a first addressing register with two register integrated circuits. The integrated circuits in the first row on the second lateral portion and in the second row on the second lateral portion are connected to a second addressing register with two register integrated circuits. Each addressing register processes a non-contiguous subset of the bits in each data word.
Owner:NETLIST INC
Arrangement of integrated circuits in a memory module
Integrated circuits utilizing standard commercial packaging are arranged on a printed circuit board to allow the production of 1-Gigabyte and 2-Gigabyte capacity memory modules. A first row of integrated circuits is oriented in an opposite orientation to a second row of integrated circuits. The integrated circuits in a first half of the first row and in the corresponding half of the second row are connected via a signal trace to a first register. The integrated circuits in a second half of the first row and in the corresponding half of the second row are connected to a second register. Each register processes a non-contiguous subset of the bits in each data word.
Owner:NETLIST INC
Arrangement of integrated circuits in a memory module
Integrated circuits utilizing standard commercial packaging are arranged on a printed circuit board to allow the production of 1-Gigabyte and 2-Gigabyte capacity memory modules. A first row of integrated circuits is oriented in an opposite orientation to a second row of integrated circuits. The integrated circuits in a first half of the first row and in the corresponding half of the second row are connected via a signal trace to a first register. The integrated circuits in a second half of the first row and in the corresponding half of the second row are connected to a second register. Each register processes a non-contiguous subset of the bits in each data word.
Owner:NETLIST INC
Arrangement of integrated circuits in a memory module
Integrated circuits utilizing standard commercial packaging are arranged on a printed circuit board to allow the production of 1-Gigabyte and 2-Gigabyte capacity memory modules. A first row of integrated circuits is oriented in an opposite orientation to a second row of integrated circuits. The integrated circuits in a first half of the first row and in the corresponding half of the second row are connected via a signal trace to a first register. The integrated circuits in a second half of the first row and in the corresponding half of the second row are connected to a second register. Each register processes a non-contiguous subset of the bits in each data word.
Owner:NETLIST INC
Content distribution using CD/DVD burners, high speed interconnects, and a burn and return policy
InactiveUS20050204019A1Additional revenue opportunityIncrease opportunitiesRecord information storageMultiple digital computer combinationsContent distributionHard disc drive
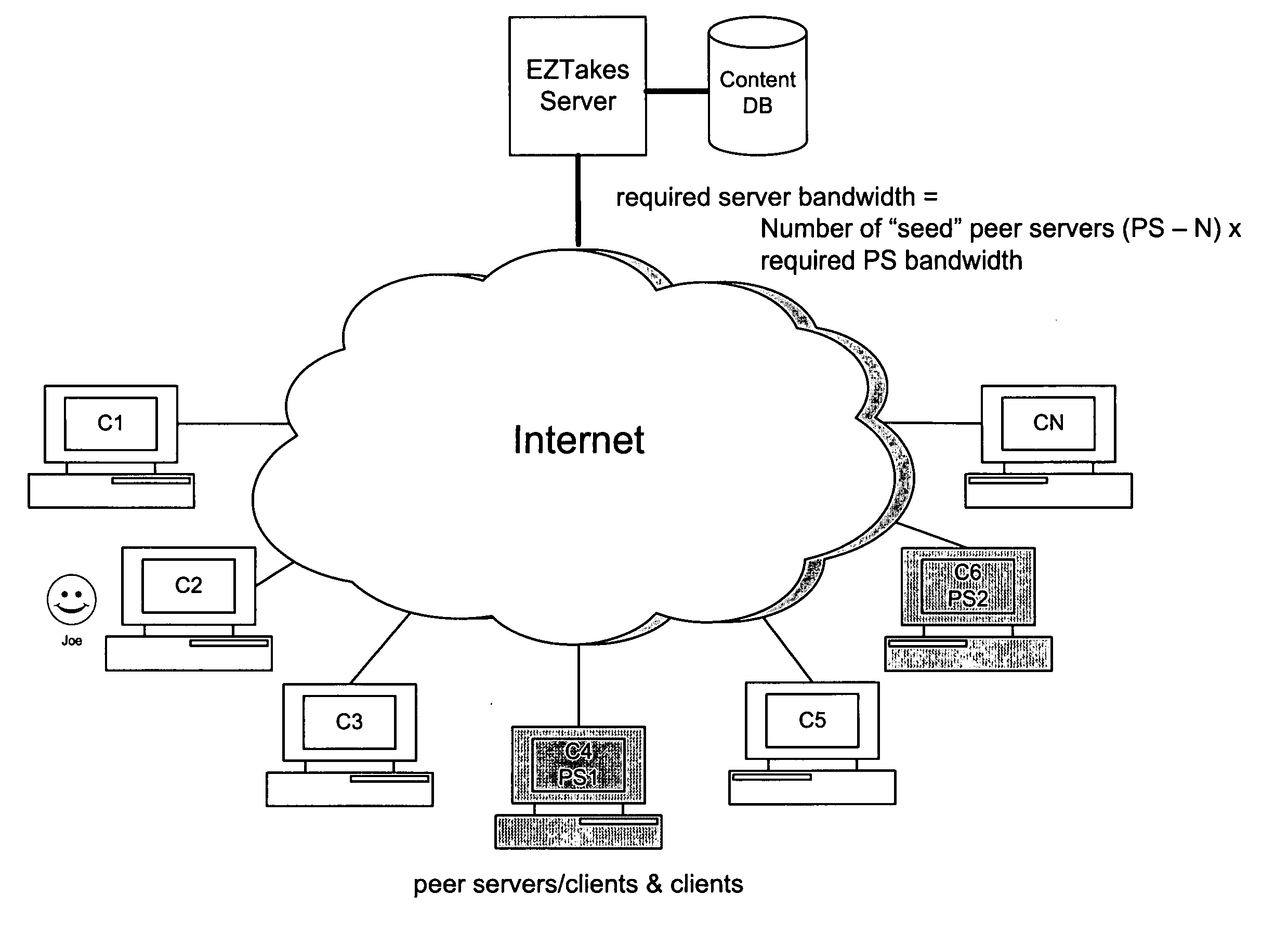
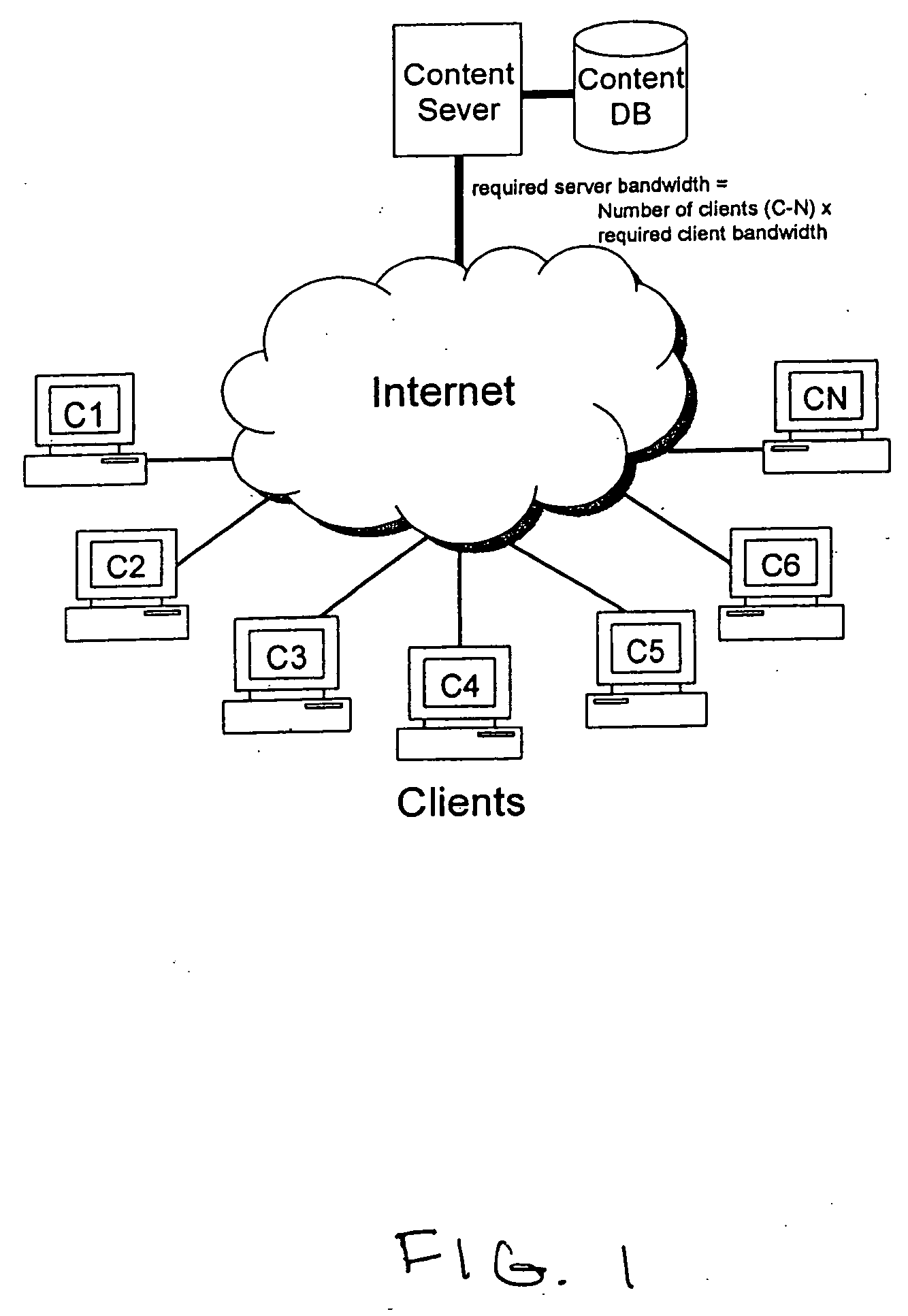
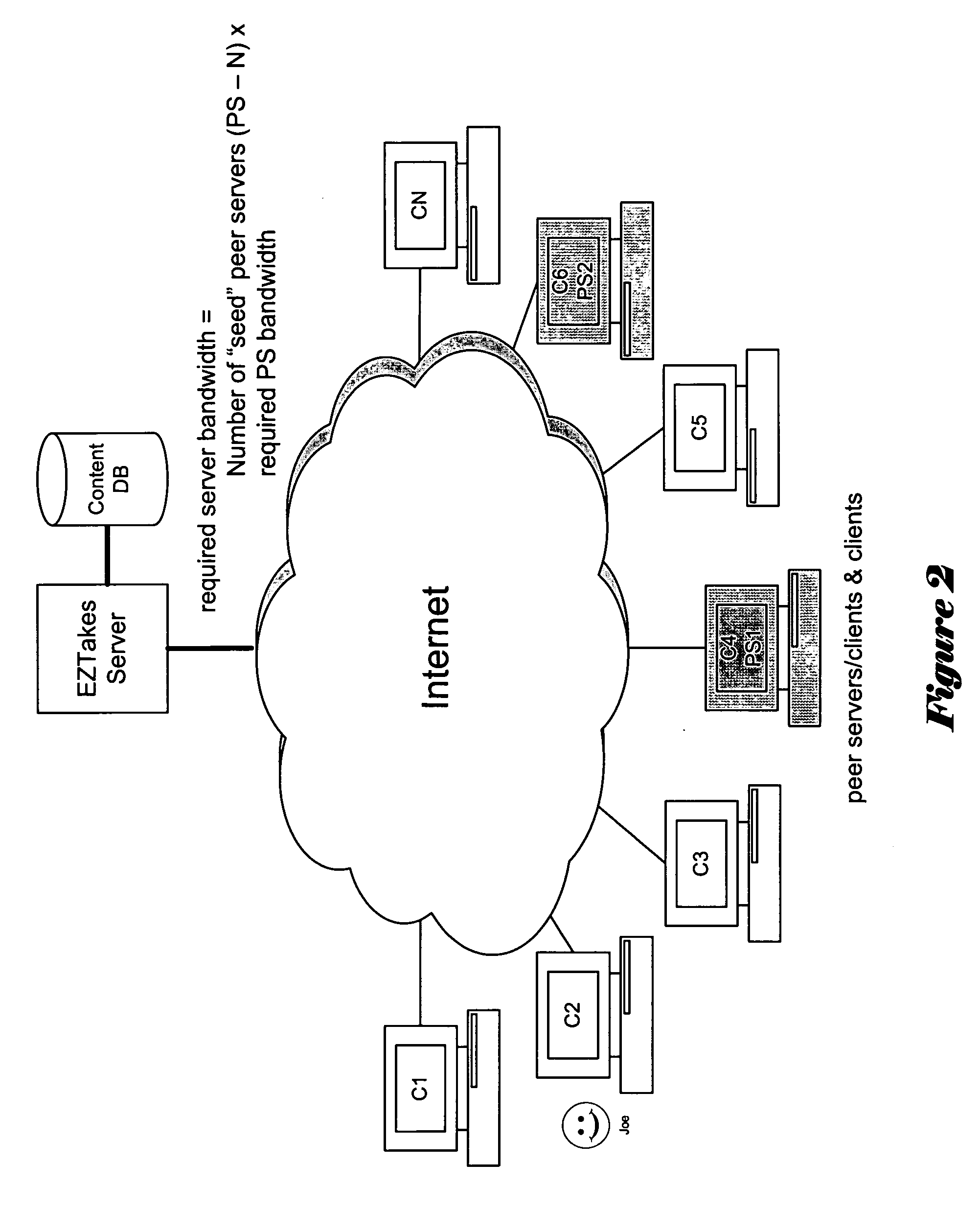
Embodiments of the present invention provide services that enable individuals to rent and / or purchase content over the Internet and to receive it electronically, referred to below as “EZTakes.” This content may include movies, TV shows, music, games and other information typically distributed on CD / DVD. EZTakes leverages high-speed broadband Internet connections, peer-to-peer networking, digital rights management (DRM) and the growing prevalence of home computers that now typically feature large hard drives (e.g. 180+gigabytes) and have the capability to “burn” (i.e. create) DVDs and / or CDs. EZTakes bridges the gap between the home computer and the living room by using standard technologies that consumers already own and are already familiar with: home computers, DVD media, DVD players and the Internet. EZTakes also promotes the interests of content owners (e.g. movie production companies) by expanding their revenue opportunities through enabling them to distribute their content assets over the Internet. EZTakes also includes technical control mechanisms, such as digital watermarking, that could not easily be exploited when using physical DVD / CD distribution channels.
Owner:EZTAKES
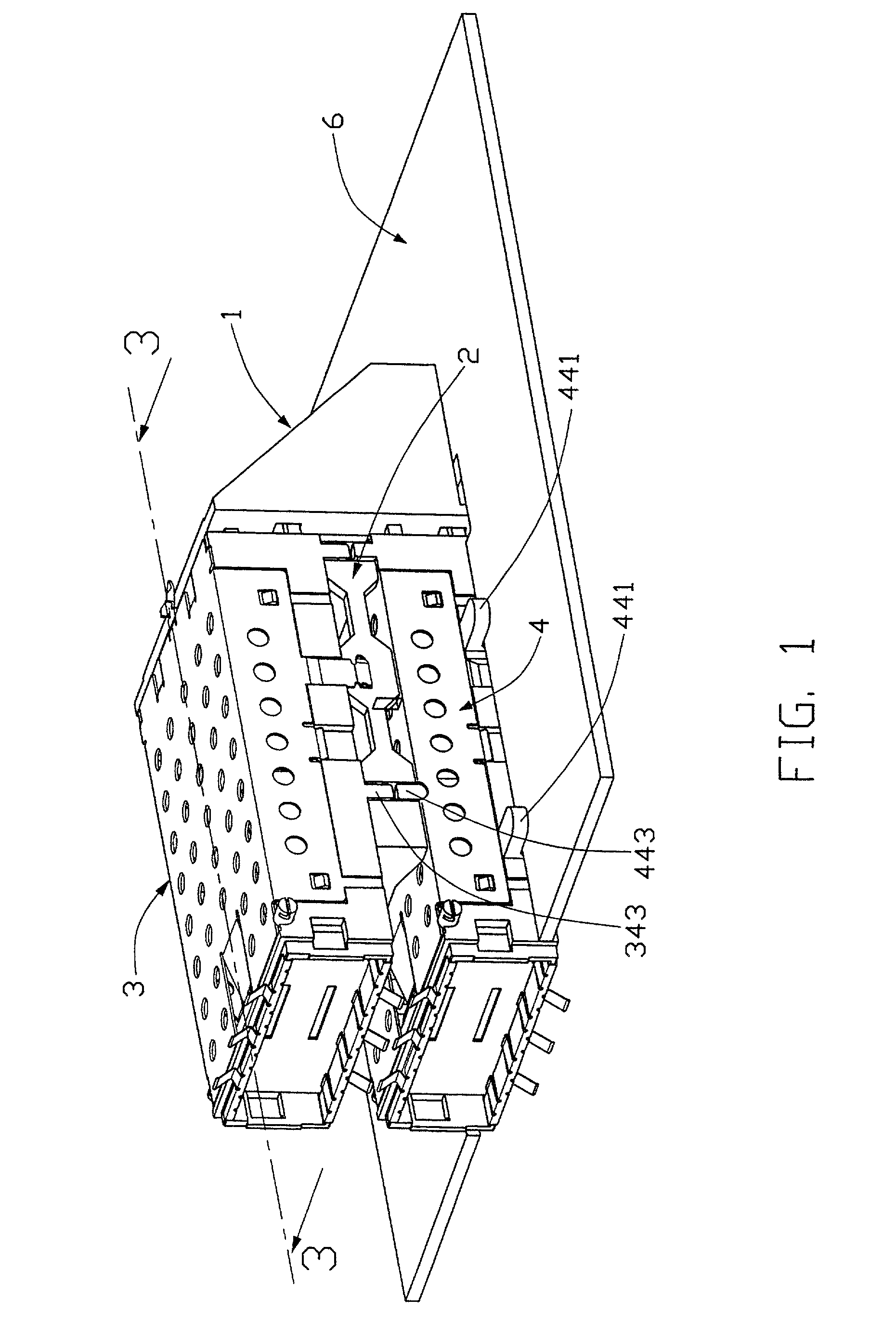
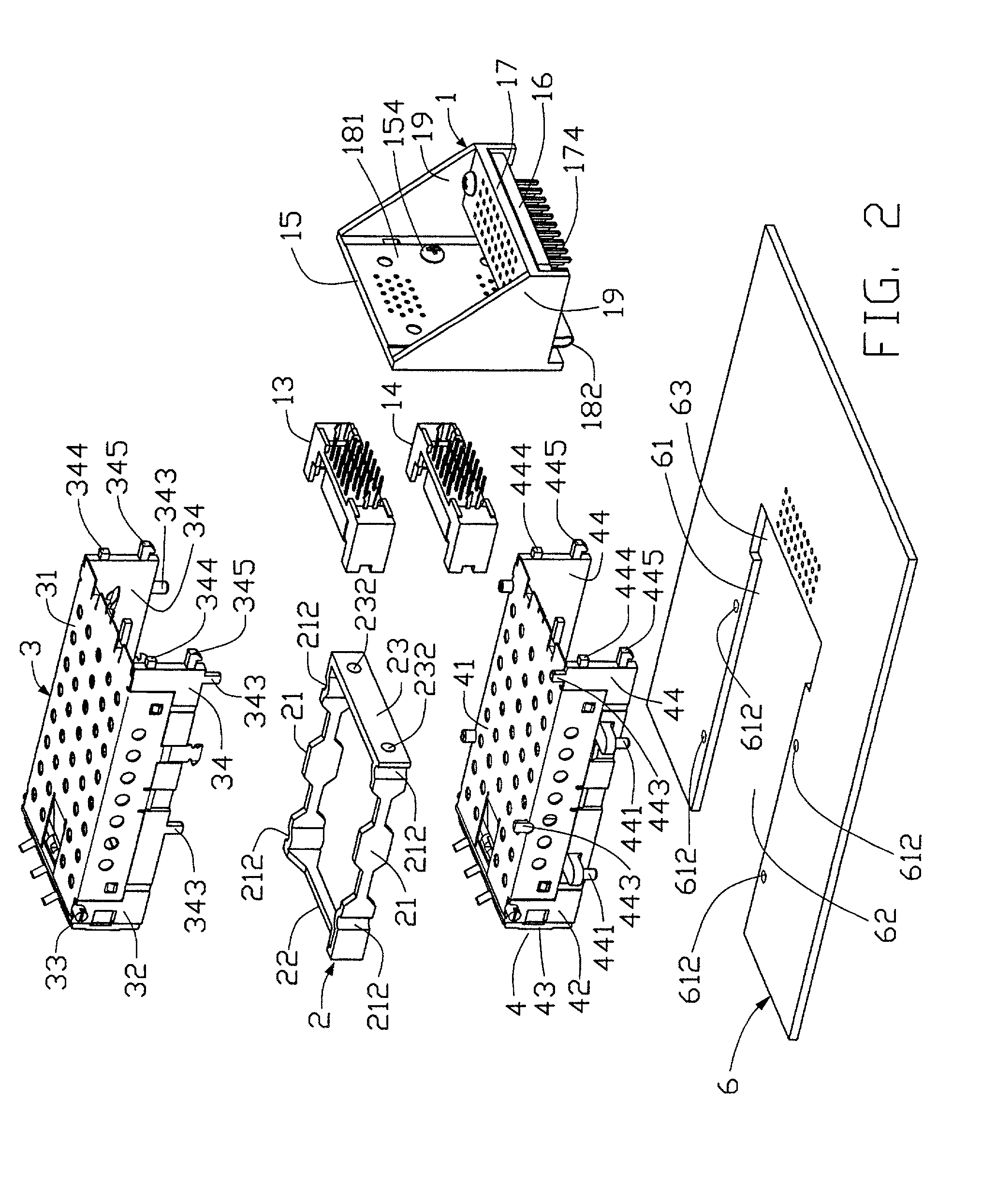
Stacked GBIC guide rail assembly
InactiveUS20020197043A1Computer periphery connectorsTwo-part coupling devicesTransceiverComputer module
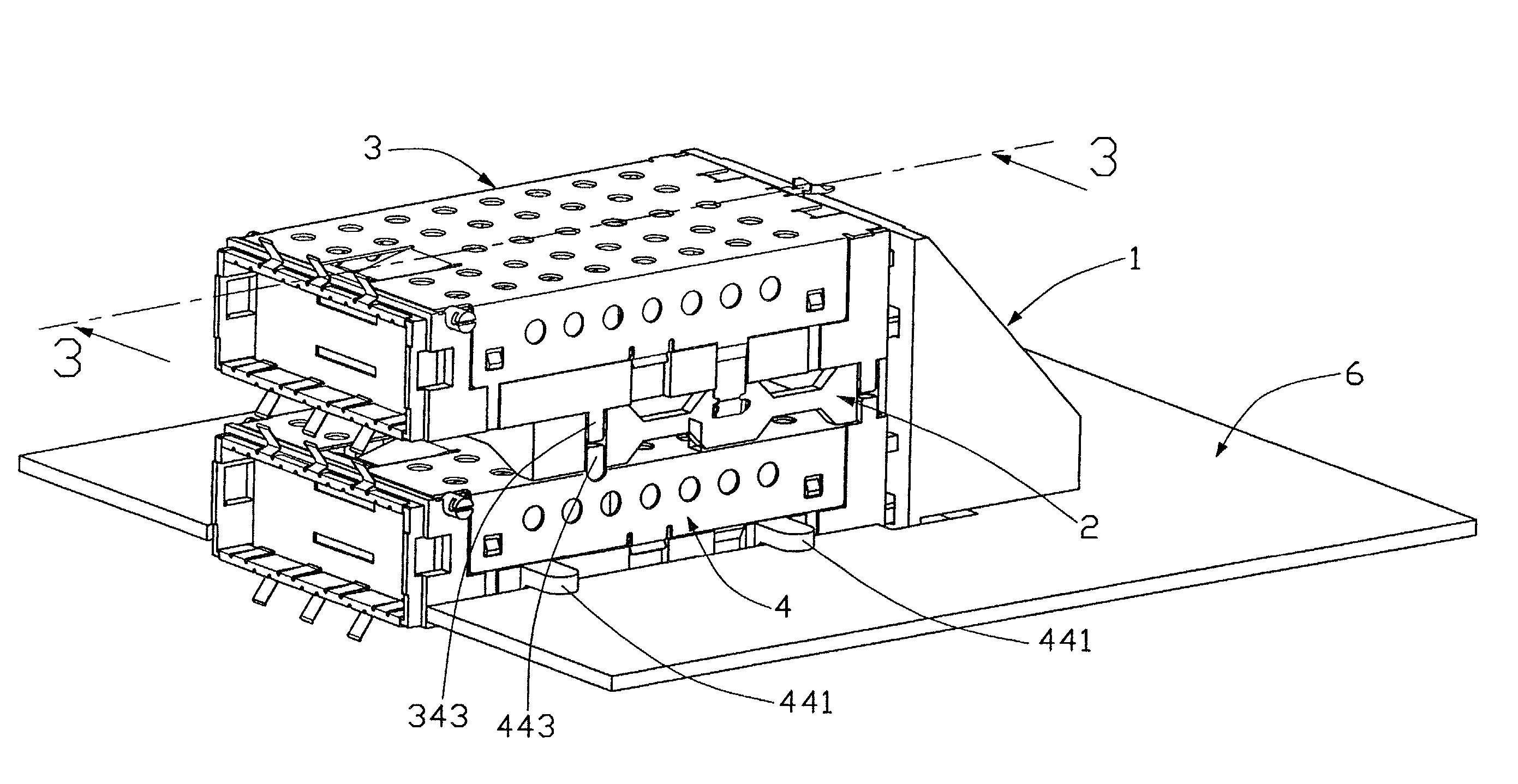
A stacked Gigabyte Interface Converter (GBIC) guide rail assembly for removable optoelectronic modules includes a raiser mounted on a circuit board, a plurality of guide rails fixed to the raiser, and a plurality of spacers spacing the guide rails from each other. The guide rails receive and accommodate transceivers therein for forming a dense arrangement of the transceivers. The lowest guide rail is mounted and supported on the circuit board.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
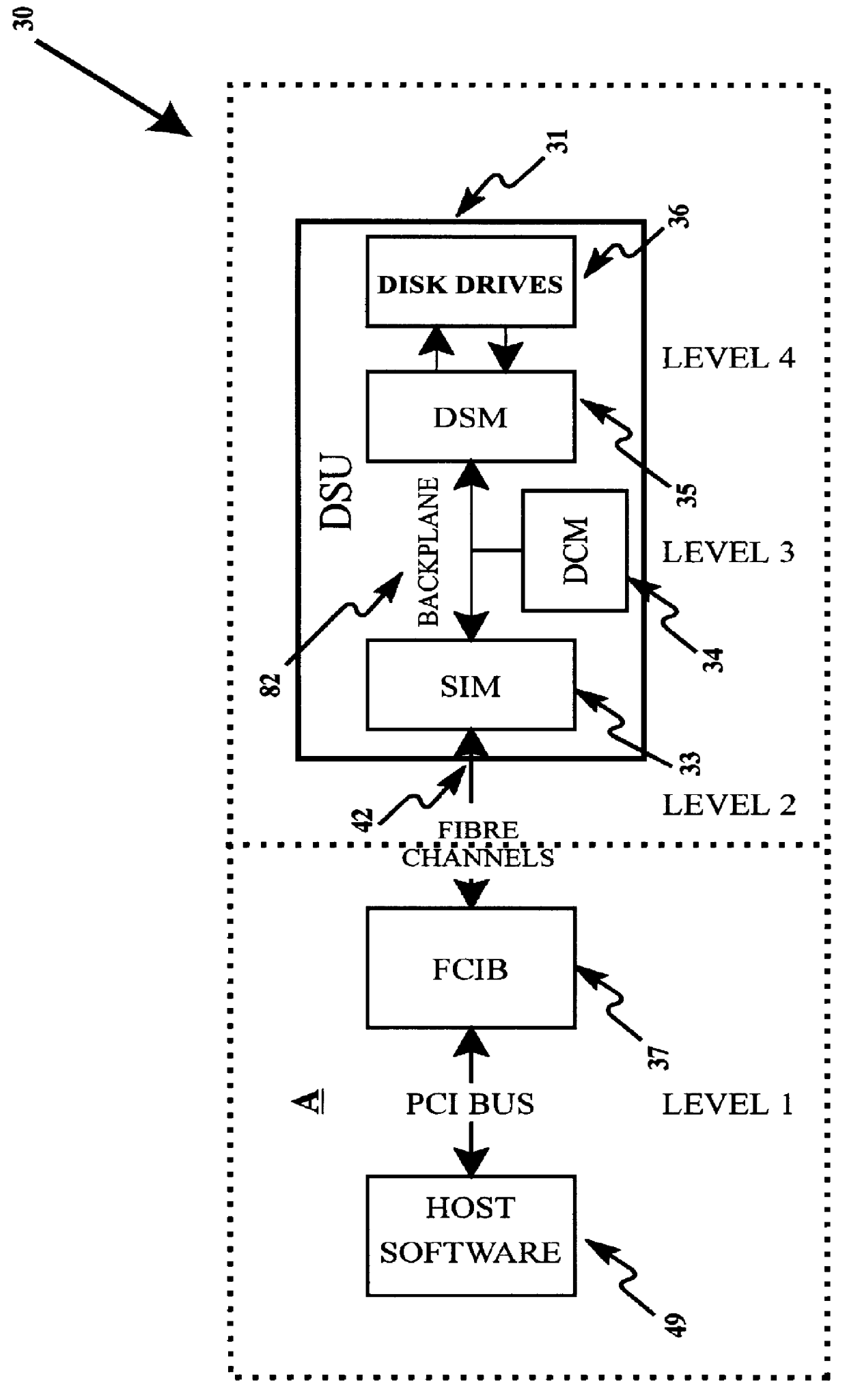
Modular disk memory apparatus with high transfer rate
InactiveUS6112276AIncrease chanceLarge capacityInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsFiberHard disc drive
A modular disk memory apparatus provides a modularly expandable, multi-gigabyte auxiliary memory for a computer or other host electronic device, and includes multiple, parallel serial data channels to maximize bidirectional data transfer rates between the apparatus and the host device. Maximization of READ / WRITE data transfer rates within the apparatus is achieved by utilizing a large number of small hard disk drives, typically eight 2.5-inch drives on each of a plurality of Disk Storage Modules, each including a plug-in printed circuit board capable of holding two 5-+E,fra 1 / 4+EE inch drives, thereby increasing the maximum data transfer rate per unit volume of the modules by a factor of two. Maximization of bidirectional data transfer rates between the apparatus and host device over that attainable using a single serial data channel such as a coaxial, quadaxial or fiber optic cable, is achieved by parsing or demultiplexing data to be transmitted from a single parallel channel onto p paralleled cables, thereby increasing the maximum transmittal rate by p. Data received over the parallel data channels is multiplexed or concatenated to comprise a data stream on a single parallel channel. Reconstruction data is embedded in data contained in the p parallel data channels specifying the number q of channels employed, where 1< / =q< / =p thereby configuring the demultiplexer to concatenate that number of data channels onto a single parallel data bus.
Owner:SIGNATEC
Annotating graphs to allow quick loading and analysis of very large graphs
InactiveUS20060150168A1Easy post-processingImprove visualizationSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsGraphicsInformation processing
A method, information processing system, and computer readable medium for annotating graphs to allow for subsequent quick loading and analysis of very large graphs is described. The present invention encompasses a way to order and annotate nodes of a graph into a data stream that allows for optimization of subsequent processing of nodes in later analysis. For example, a very large reference graph representing heap snapshots may be annotated to facilitate post-processing and visualization of the heap for memory leak analysis. In such an example, the present invention reduces the number of objects and references to be modeled in memory, while still capturing the essence of the non-modeled portions. In this example, the present invention may process reference graphs on the scale of one hundred million live objects per snapshot using a computer with one gigabyte of memory.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Method for the secure and timely delivery of large messages over a distributed communication network
InactiveUS20030126303A1Lower latencyMinimum delayUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsGigabyteThe Internet
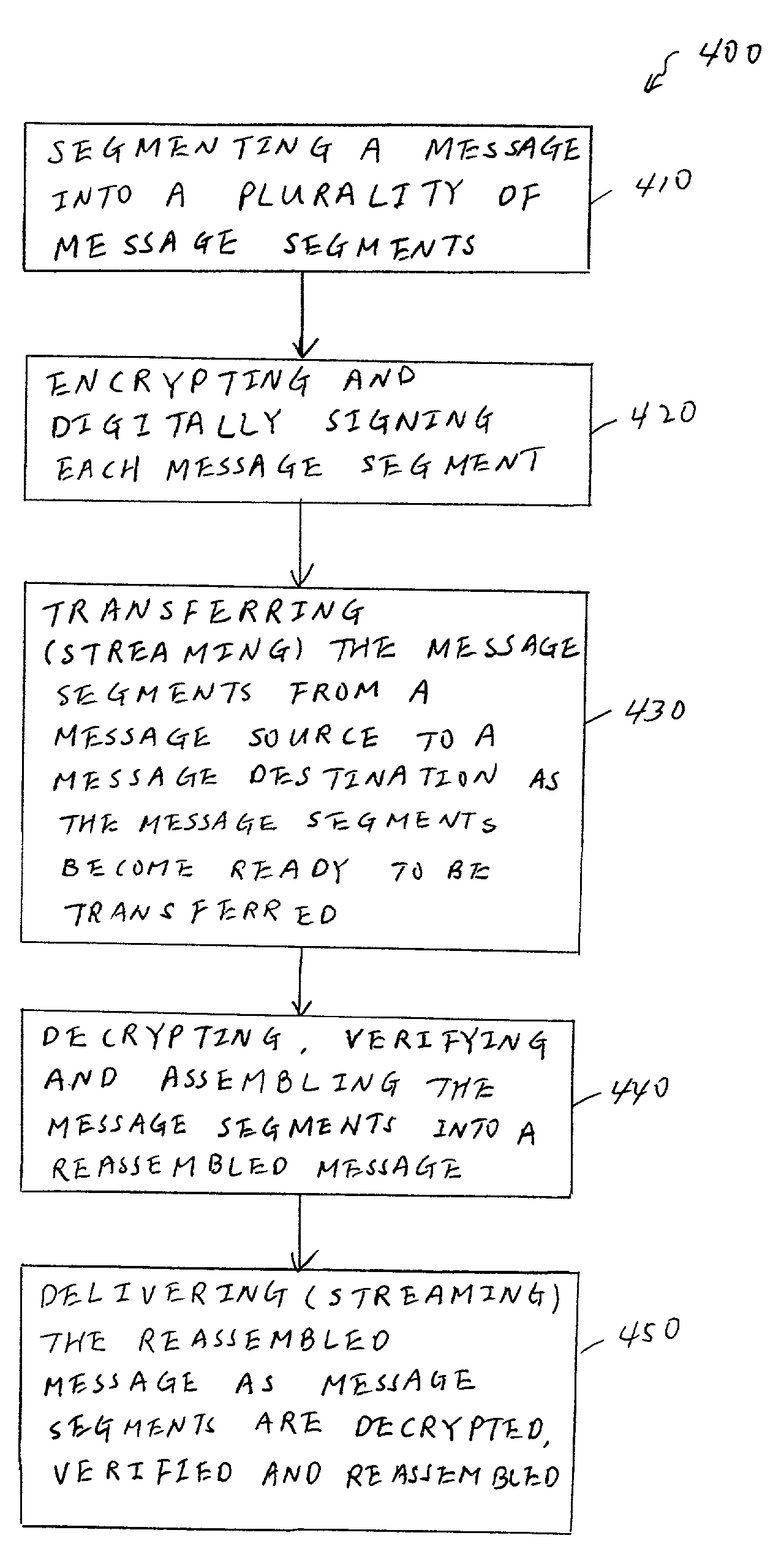
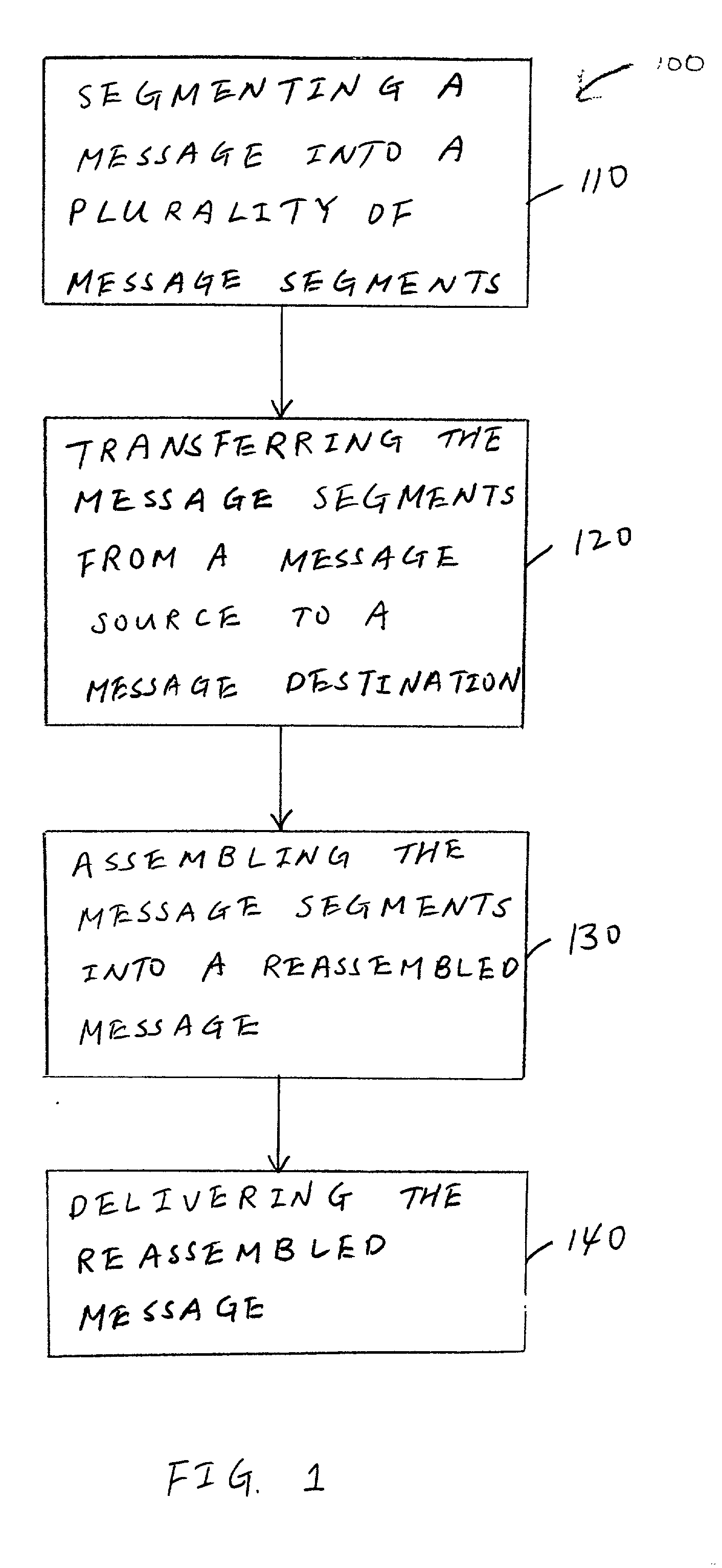
A method for transferring messages between a sending application program and a receiving application program across a distributed communication network (e.g., the Internet) that includes a message source coupled to a message destination. The method includes segmenting a message (e.g., a relatively large message of one gigabyte or more) being received at the message source from the sending application program into a plurality of message segments. While this segmentation is occurring, a common message identifier and a unique sequence number are assigned to each of the plurality of message segments. The method also includes transferring the plurality of message segments from the message source to the message destination, along with the common message identifier and unique sequence number assigned to the plurality of message segments, with at least one of the plurality of message segments being transferred as the message is being received at the message source. In other words, prior to the entire message being received at the message source and segmented, message segments that have already been segmented from the message are transferred (i.e., sent) to the message destination. At the message destination, the plurality of message segments that have been transferred from the message source are assembled into a reassembled message as the plurality of message segments are received at the message destination. At least a portion of the reassembled message is delivered to the receiving application while the assembling is occurring.
Owner:CLOUDPRIME
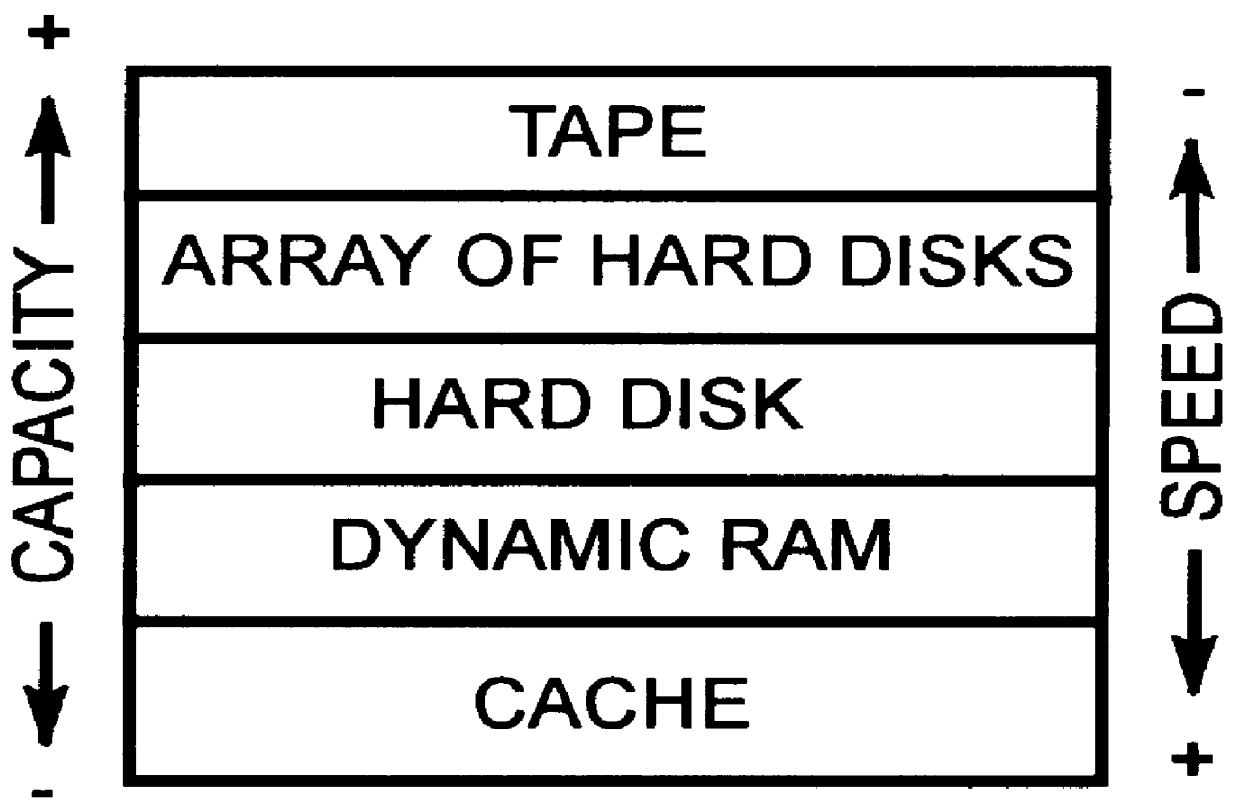
High speed and high capacity data storage array
InactiveUS7375923B2Reducing temperature influence on carrierDigital data processing detailsActuatorByte
A data storage array is provided such as for a distributed storage system or a consumer electronics device wherein increased data storage capacity is provided at the cost of increased power consumption in relation to industry standard power consumption rates. The array has a plurality of data storage devices, each having an actuator operably disposed in a data storing and retrieving relationship with a data storage medium. The data storage medium is rotated at a speed of substantially greater than 10,000 revolutions per minute, and each of the data storage mediums has a data storage capacity of substantially greater than 100 gigabytes. The increased heat created by the relatively faster rotation speed is handled through improved airflow made possible by a multiple device array constructed in accordance with embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
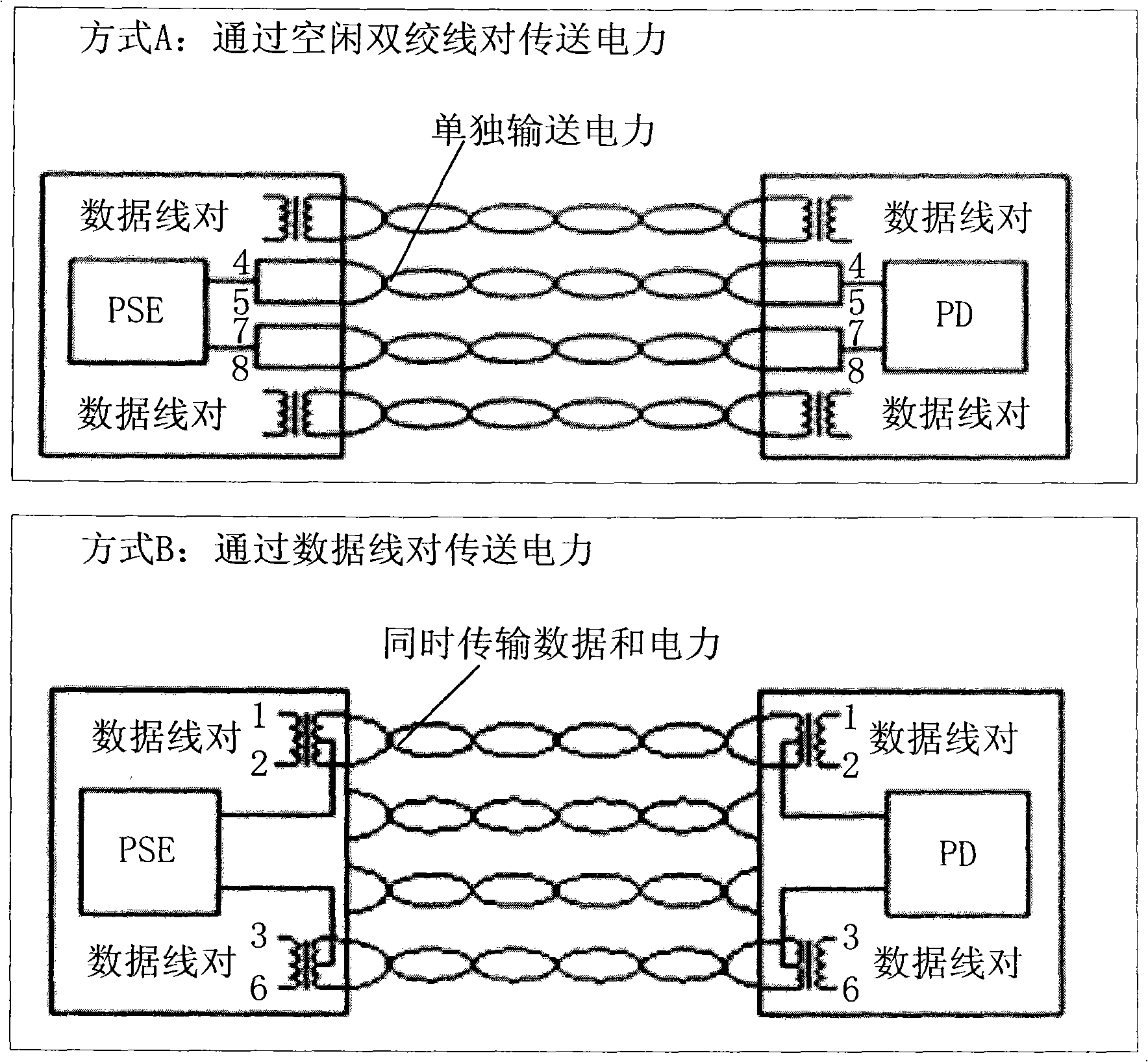
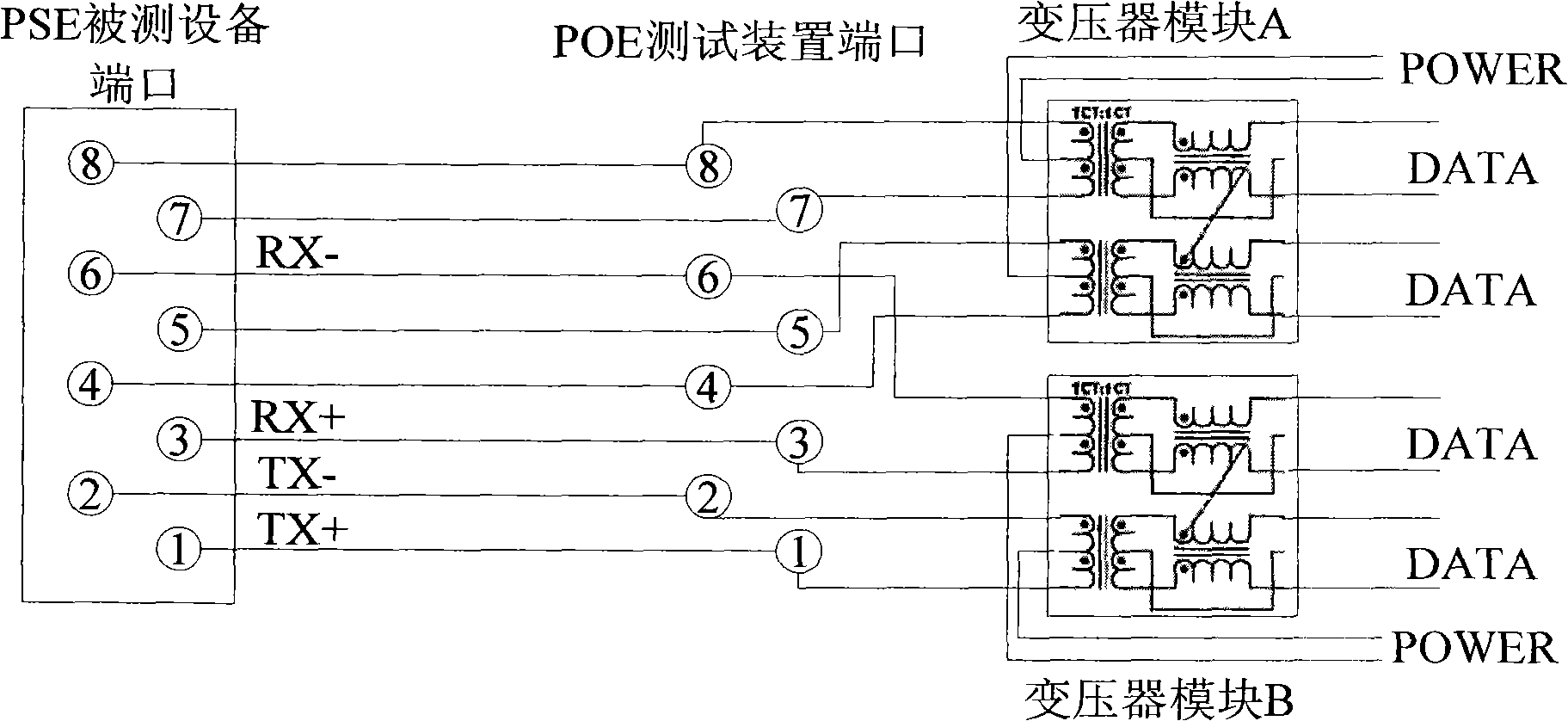
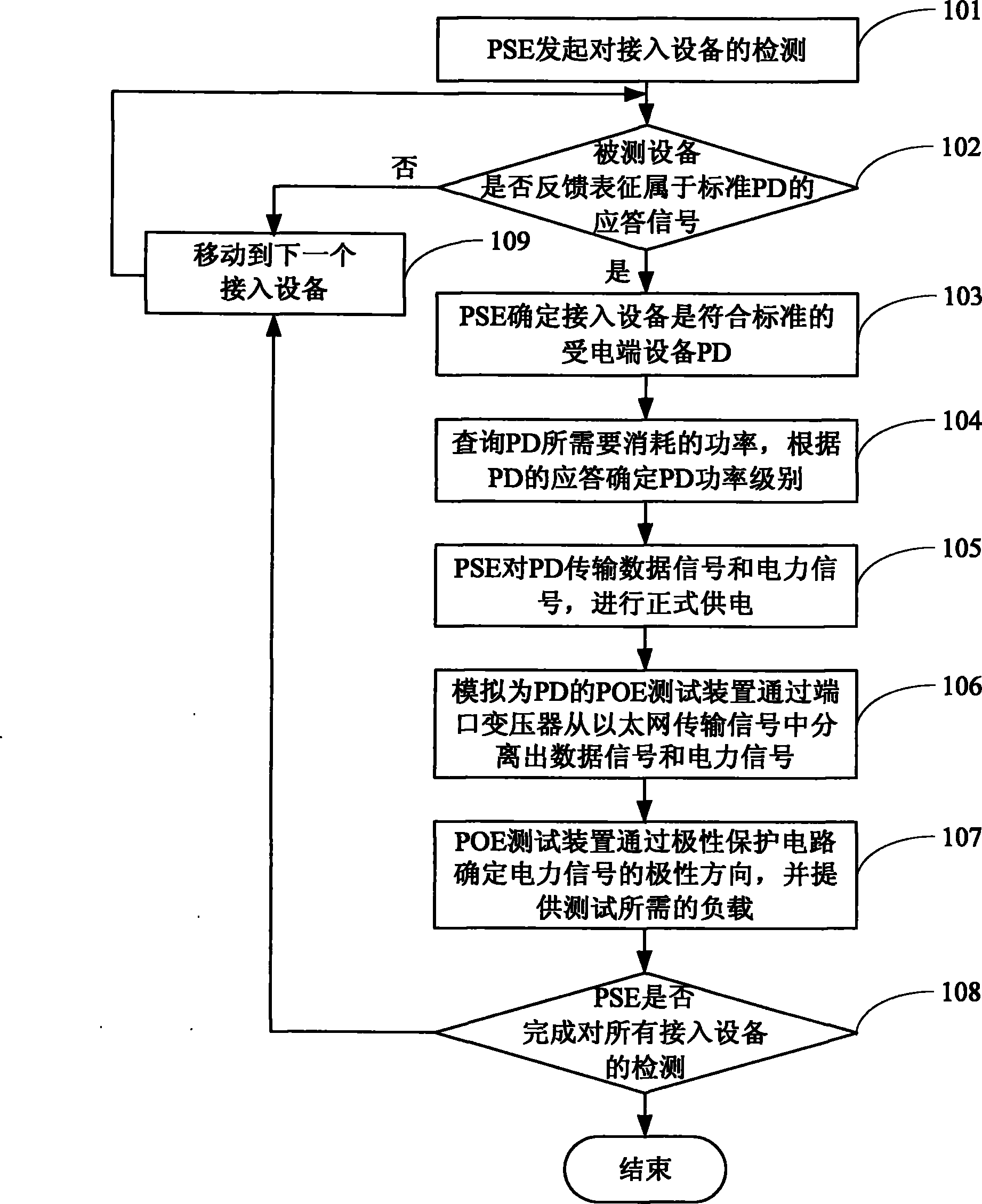
System, device and method for testing power over Ethernet (POE) function
ActiveCN101793930ALow costEasy to operateElectrical testingData switching by path configurationTest powerMegabyte
The invention discloses a system, a device and a method for testing a power over Ethernet (POE) function. The system comprises tested power sourcing equipment (PSE) ports and a power over Ethernet (POE) function test device, wherein the tested PSE ports connect Ethernet line pairs carrying data signals and electric signals with corresponding ports of the POE function test device respectively; and the POE function test device has ports and transformers, is used for connecting all the Ethernet line pairs which are led in through the ports with corresponding transformers respectively, and separates the electric signals and the data signals through the transformers. The system, the device and the method are compatible with test on the POE function of the Ethernet PSE having different power supply schemes and also compatible with test on POE function of the Ethernet PSE of gigabytes and megabytes, and have the advantages of low cost and simple operation.
Owner:ZTE CORP
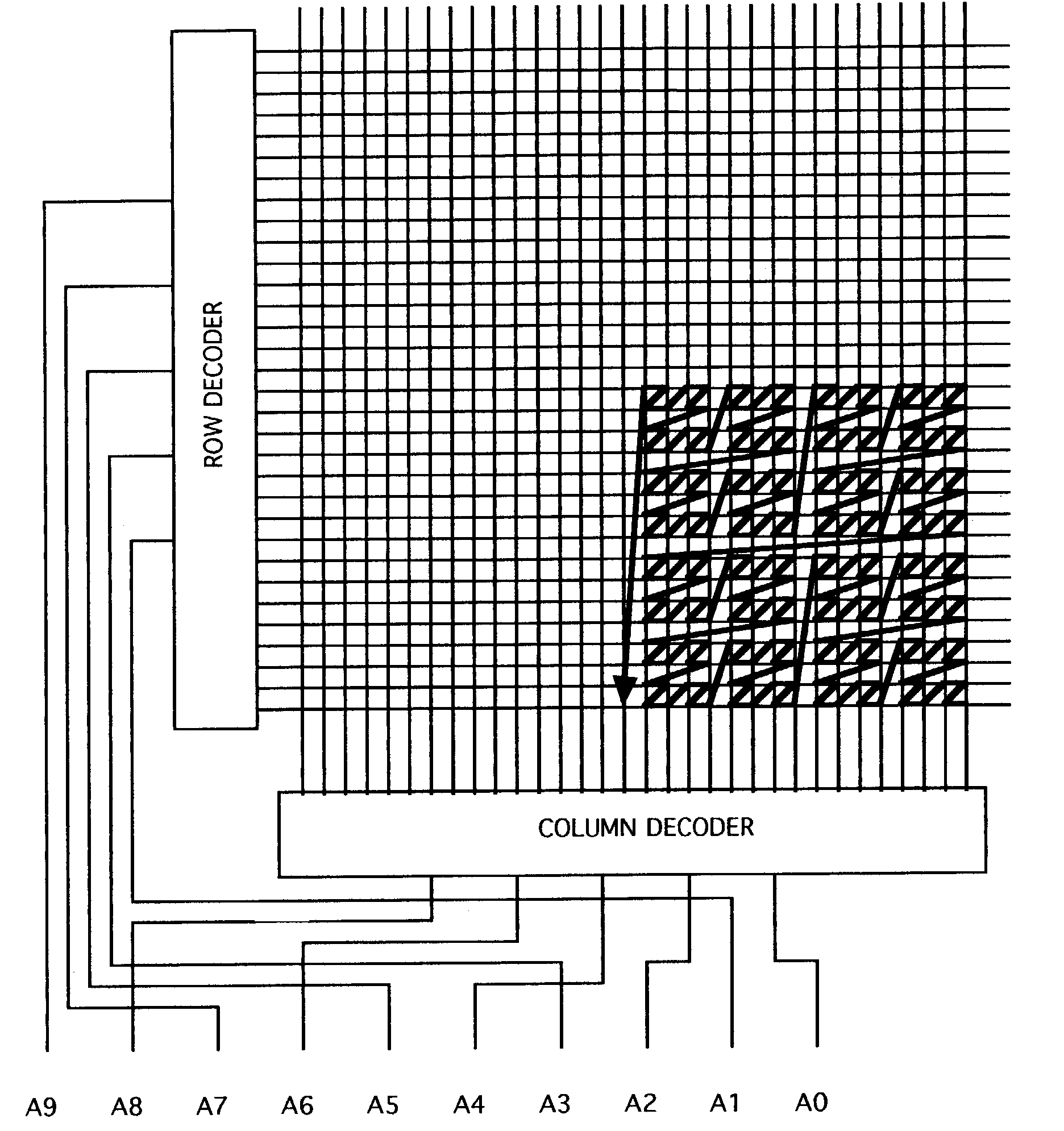
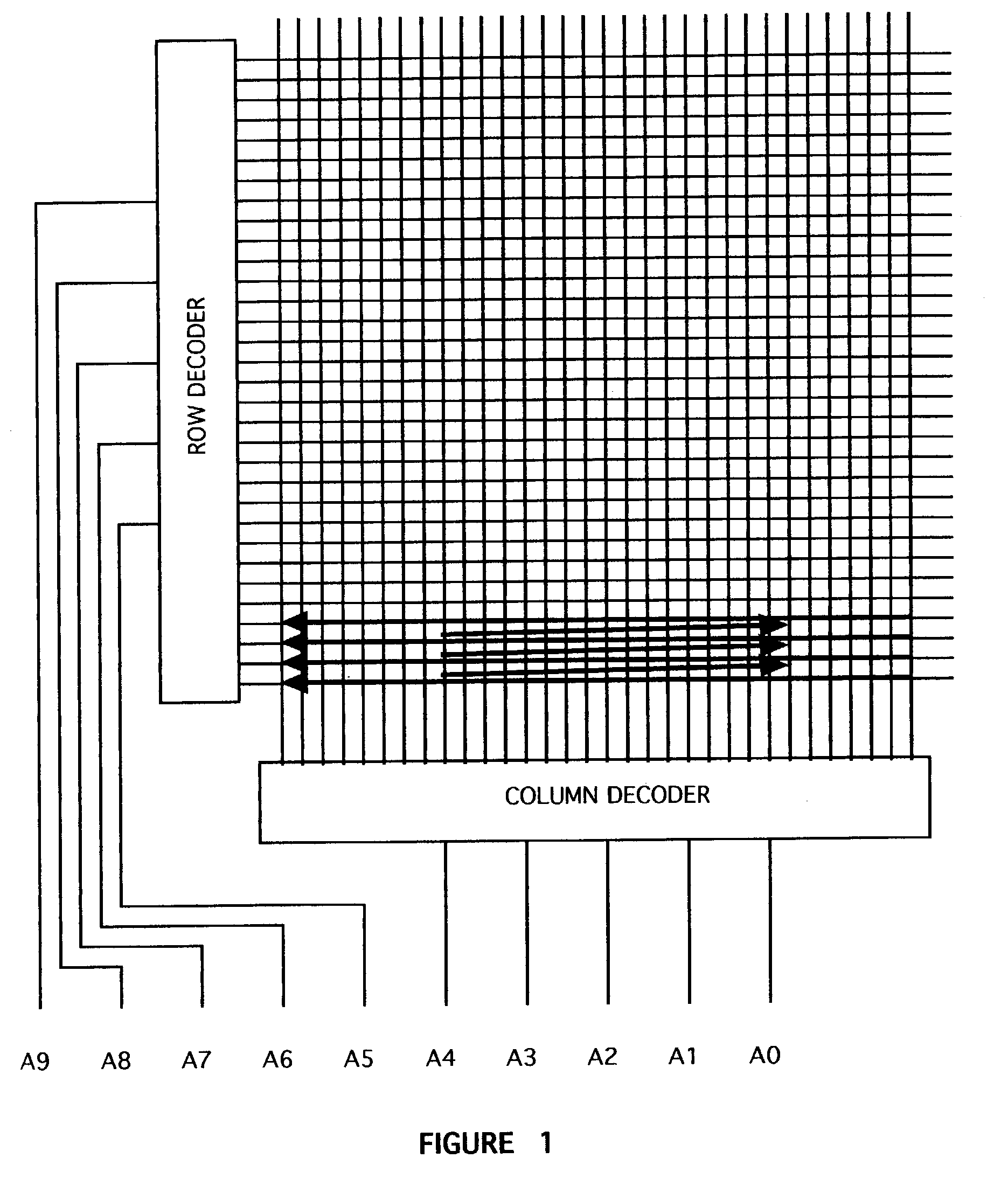
Error correcting memory access means and method
ActiveUS7149934B2Low costEfficiently utilize error correctingCode conversionCoding detailsData streamByte
As advances continue to be made in the area of semiconductor memory devices, high capacity and low cost will be increasingly important. In particular, it will be necessary to create memory devices for which the testing of the device must be minimized in order to minimize costs. Current memory manufacturing costs are significant and will grow as the capacity of the devices grows—the higher the memory's capacity, the more storage locations that must be tested, and the longer the testing operation will take. The cost of the testing can be calculated by dividing the amortized cost of the test equipment by the number of devices tested. As memory devices enter the Gigabyte range and larger, the number of devices that can be tested by a given piece of test equipment will go down. As a result, the cost per unit attributable to testing will rise. The present invention is a means and a method for accessing streams of data stored within a memory device so as to minimize the cost of device testing and thereby the cost of the device itself. By incorporating error-correcting bits in the data stream, the individual data bits need not be tested. Then, by accessing the memory locations so as to avoid having error correcting techniques fail due to common memory device faults, testing costs can be significantly reduced while maintaining high device yields. A sequential access of the memory device will access data bits in a somewhat diagonal path across the two-dimensional array. The key to the present invention is that the sequential data stream stored in the device is stored such that sequential access of that data will not dwell on a single (or a small number of) row or column line. In a three or more dimensional array, the sequential data stream stored in the device is stored such that sequential access of that data will not dwell on a single value in a given dimension for which bulk errors are considered likely.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
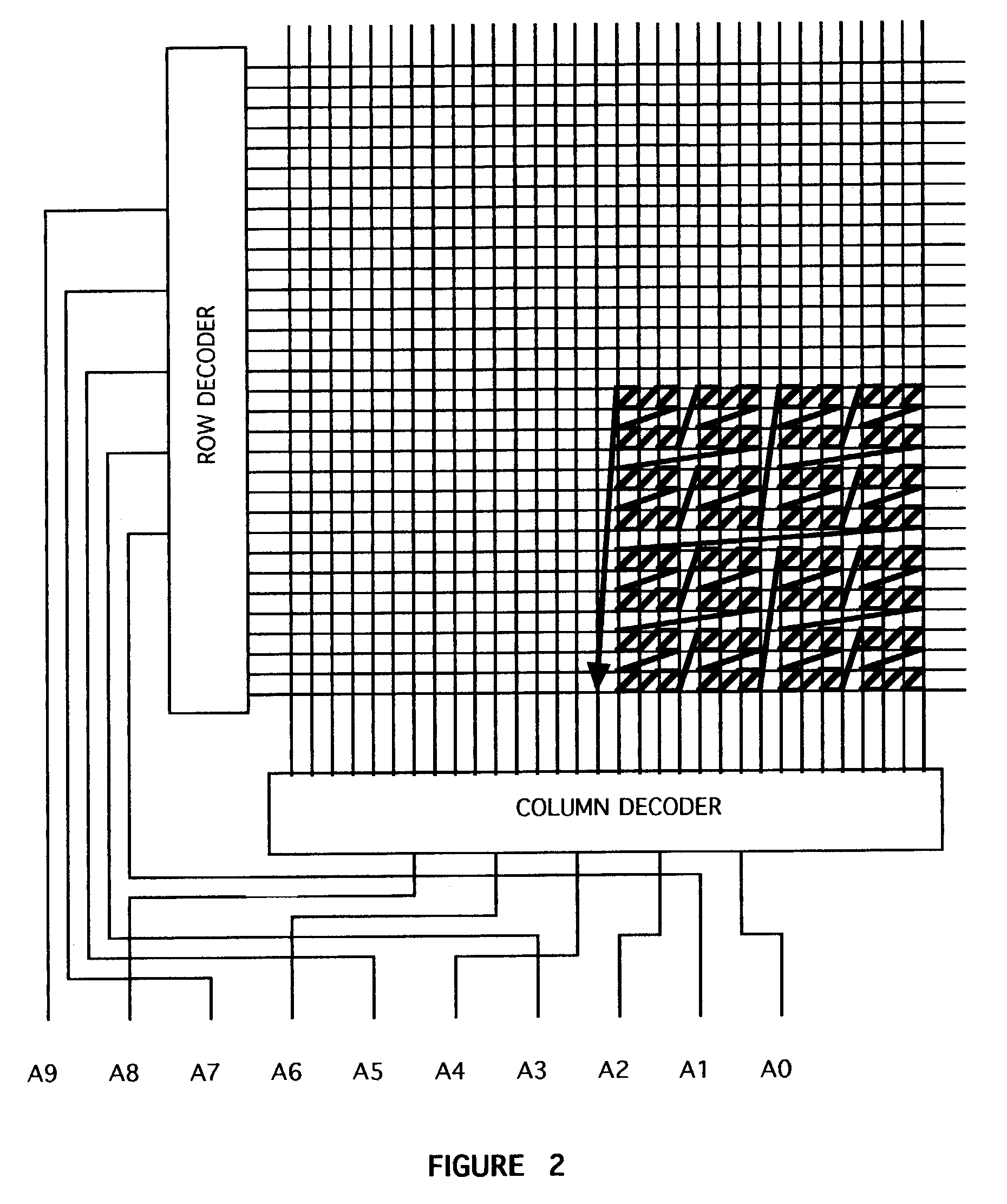
Error correcting memory access means and method
ActiveUS20070028150A1Low costEfficiently utilize error correctingCode conversionCoding detailsData streamTerm memory
As advances continue to be made in the area of semiconductor memory devices, high capacity and low cost will be increasingly important. In particular, it will be necessary to create memory devices for which the testing of the device must be minimized in order to minimize costs. Current memory manufacturing costs are significant and will grow as the capacity of the devices grows—the higher the memory's capacity, the more storage locations that must be tested, and the longer the testing operation will take. The cost of the testing can be calculated by dividing the amortized cost of the test equipment by the number of devices tested. As memory devices enter the Gigabyte range and larger, the number of devices that can be tested by a given piece of test equipment will go down. As a result, the cost per unit attributable to testing will rise. The present invention is a means and a method for accessing streams of data stored within a memory device so as to minimize the cost of device testing and thereby the cost of the device itself. By incorporating error-correcting bits in the data stream, the individual data bits need not be tested. Then, by accessing the memory locations so as to avoid having error correcting techniques fail due to common memory device faults, testing costs can be significantly reduced while maintaining high device yields. A sequential access of the memory device will access data bits in a somewhat diagonal path across the two-dimensional array. The key to the present invention is that the sequential data stream stored in the device is stored such that sequential access of that data will not dwell on a single (or a small number of) row or column line. In a three or more dimensional array, the sequential data stream stored in the device is stored such that sequential access of that data will not dwell on a single value in a given dimension for which bulk errors are considered likely.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
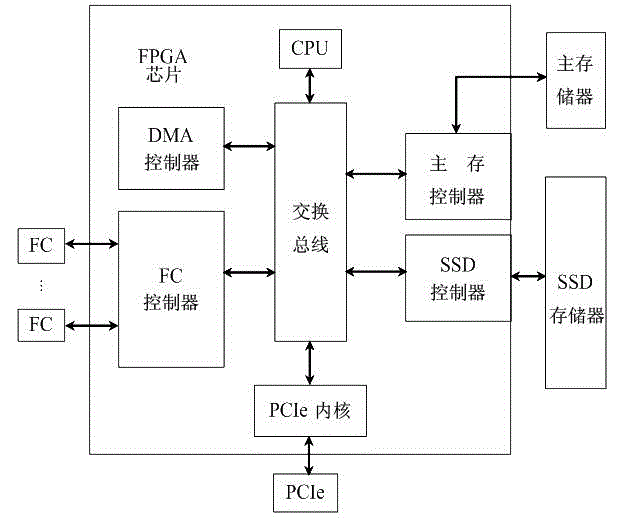
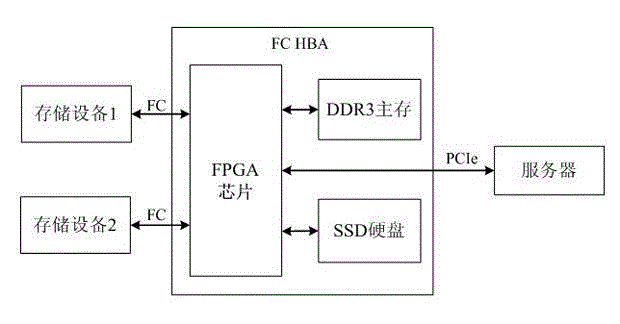
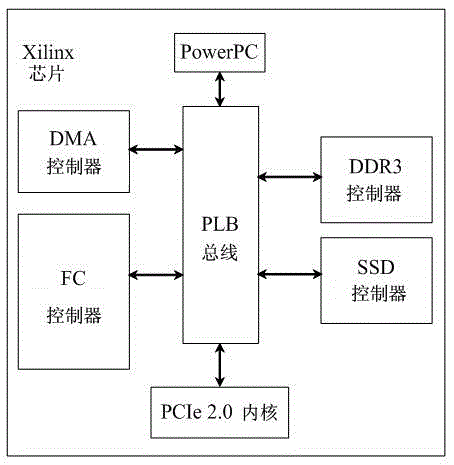
FC HBA (fiber channel host bus adapter) based on SSD (solid state disk) cache and design method thereof
ActiveCN103336745AReduce data latencySSD improvedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGigabyteEngineering
The invention discloses an FC HBA (fiber channel host bus adapter) based on an SSD (solid state disk) cache and a design method thereof. An SSD memory is used as the buffer memory of the FC HBA, a server is communicated with the FC HBA through a PCIe (peripheral component interface express) interface, a memory device is communicated with the FC HBA through an FC interface; and the SSD buffer memory stores the transmitted data in a buffer manner, and the transmitted data includes the data transmitted between the server and the memory device, and the data transmitted between the memory device and another memory device. The SSD memory is used as the data cache of the FC HBA, namely a large-capacity high-speed buffer memory is provided for the FC HBA, the capacity of the buffer memory can reach 100 GB (gigabyte)-2TB(trillionbyte), or even a larger range. The server only needs to access to the SSD buffer memory in the FC HBA to obtain required data without accessing to the memory device, so that the data delay between the server and the memory device is reduced, and the IOPS (input / output operations per second) of the system is effectively improved. Besides, the SSD memory is used as the cache of the FC HBA, so that the transfer rate of stored network data is effectively improved.
Owner:无锡北方数据计算股份有限公司
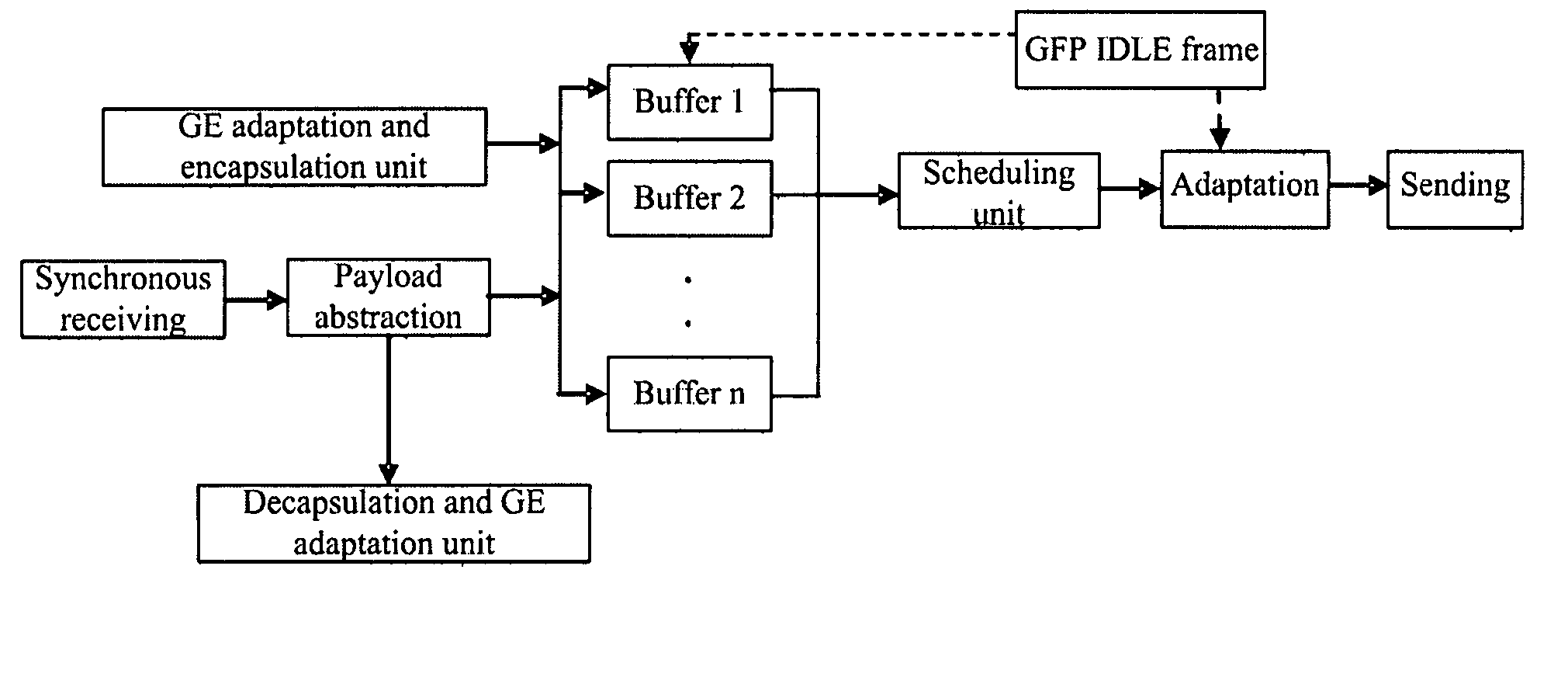
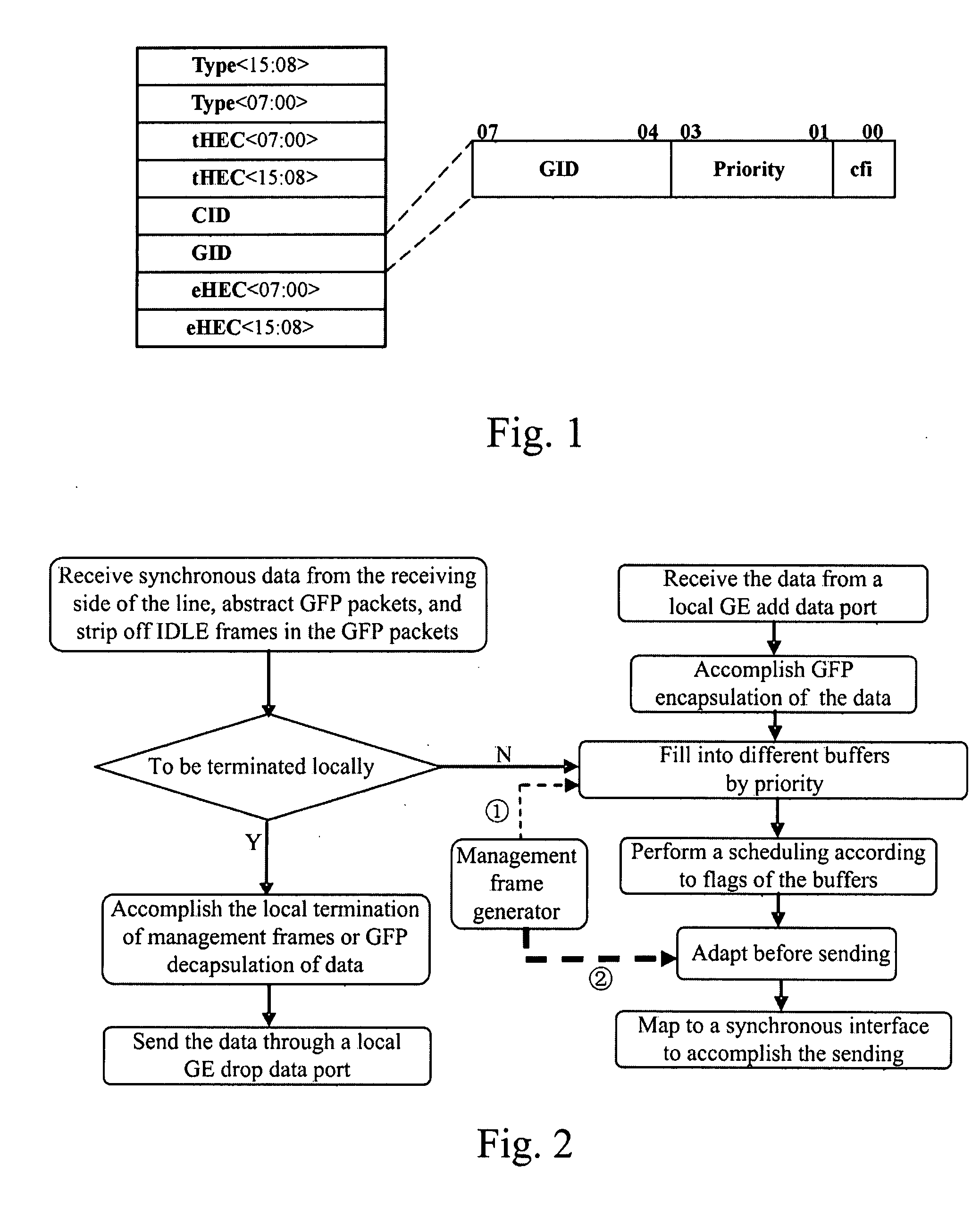
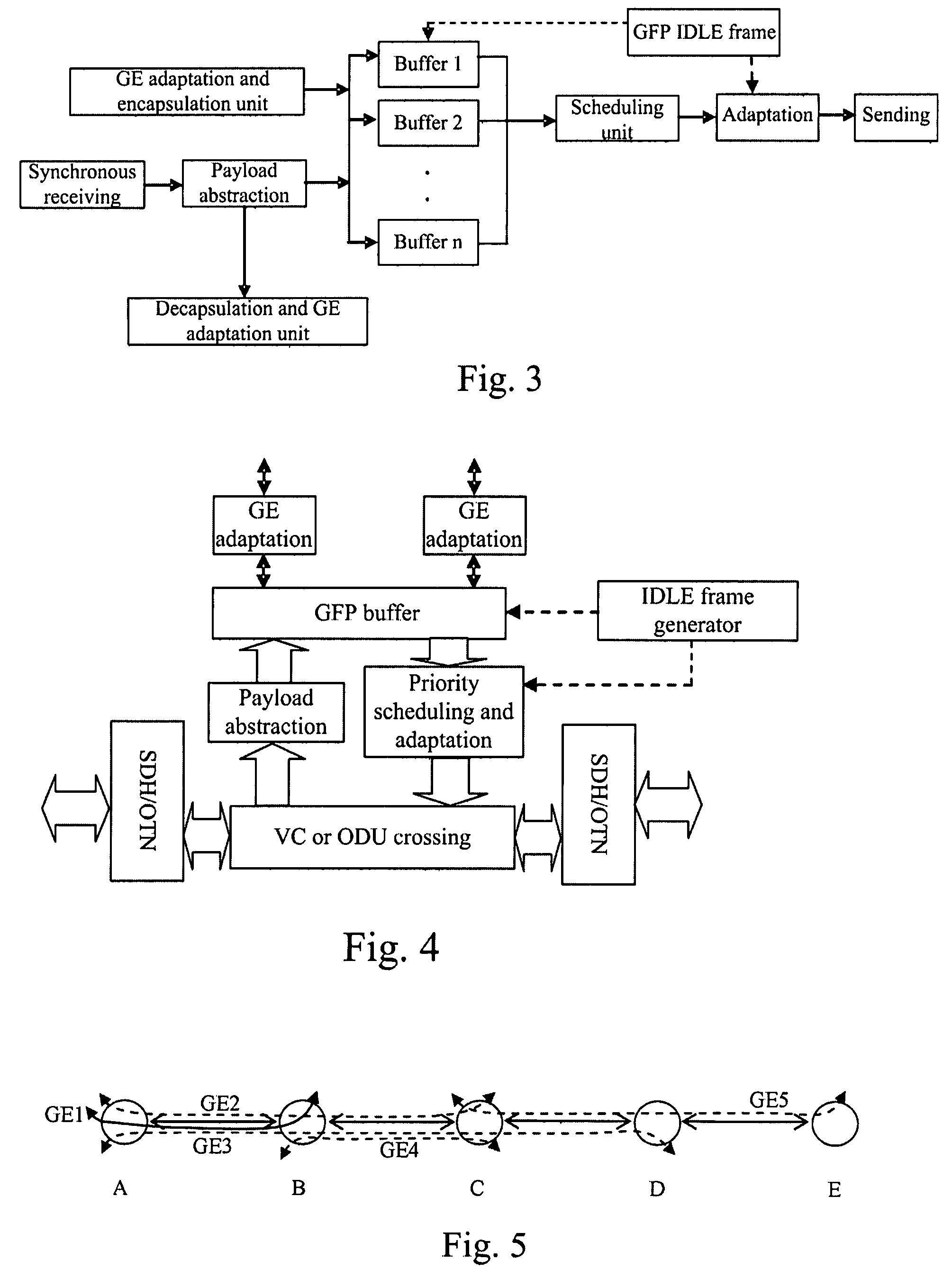
Add drop multiplexing method, apparatus and system based on GFP
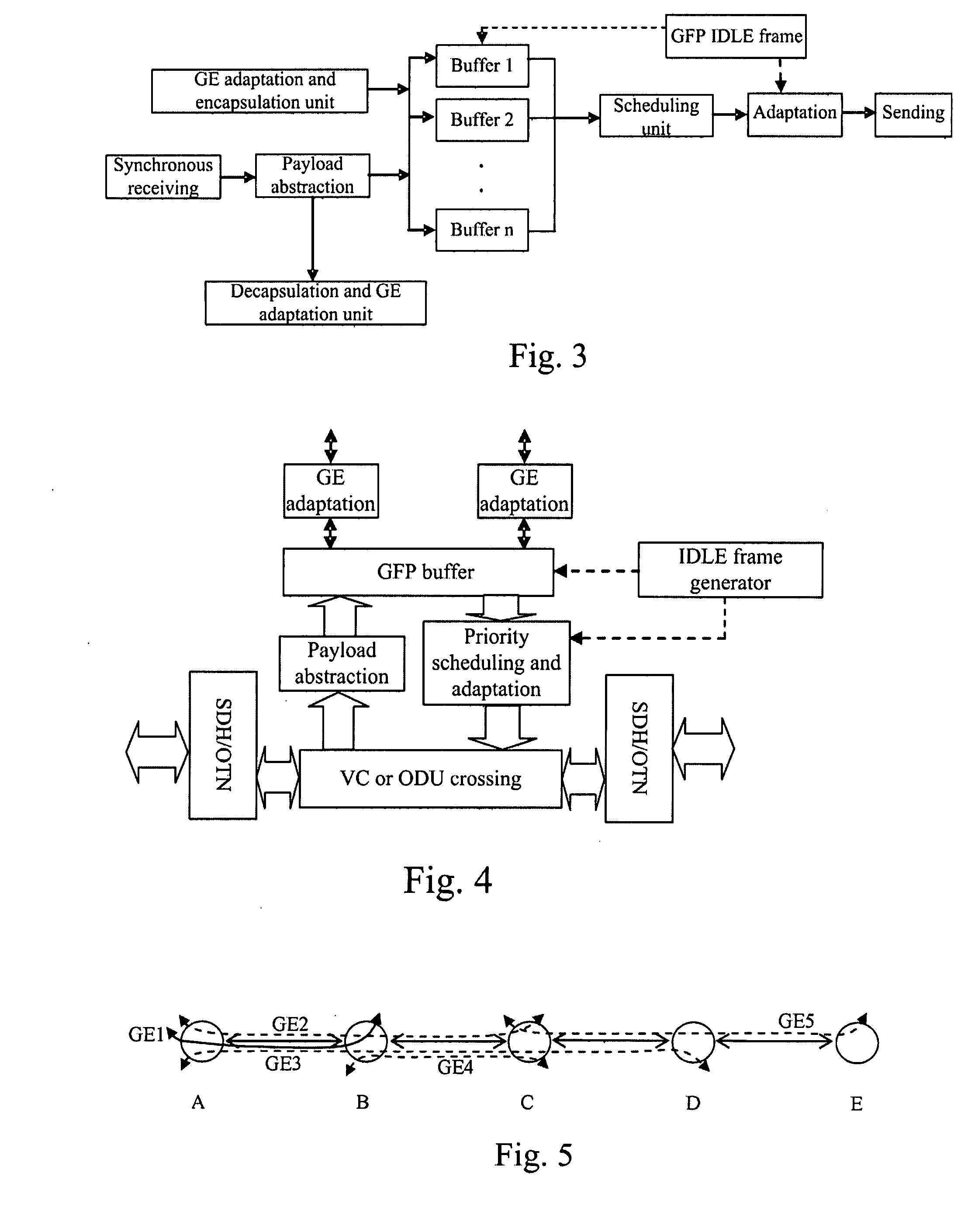
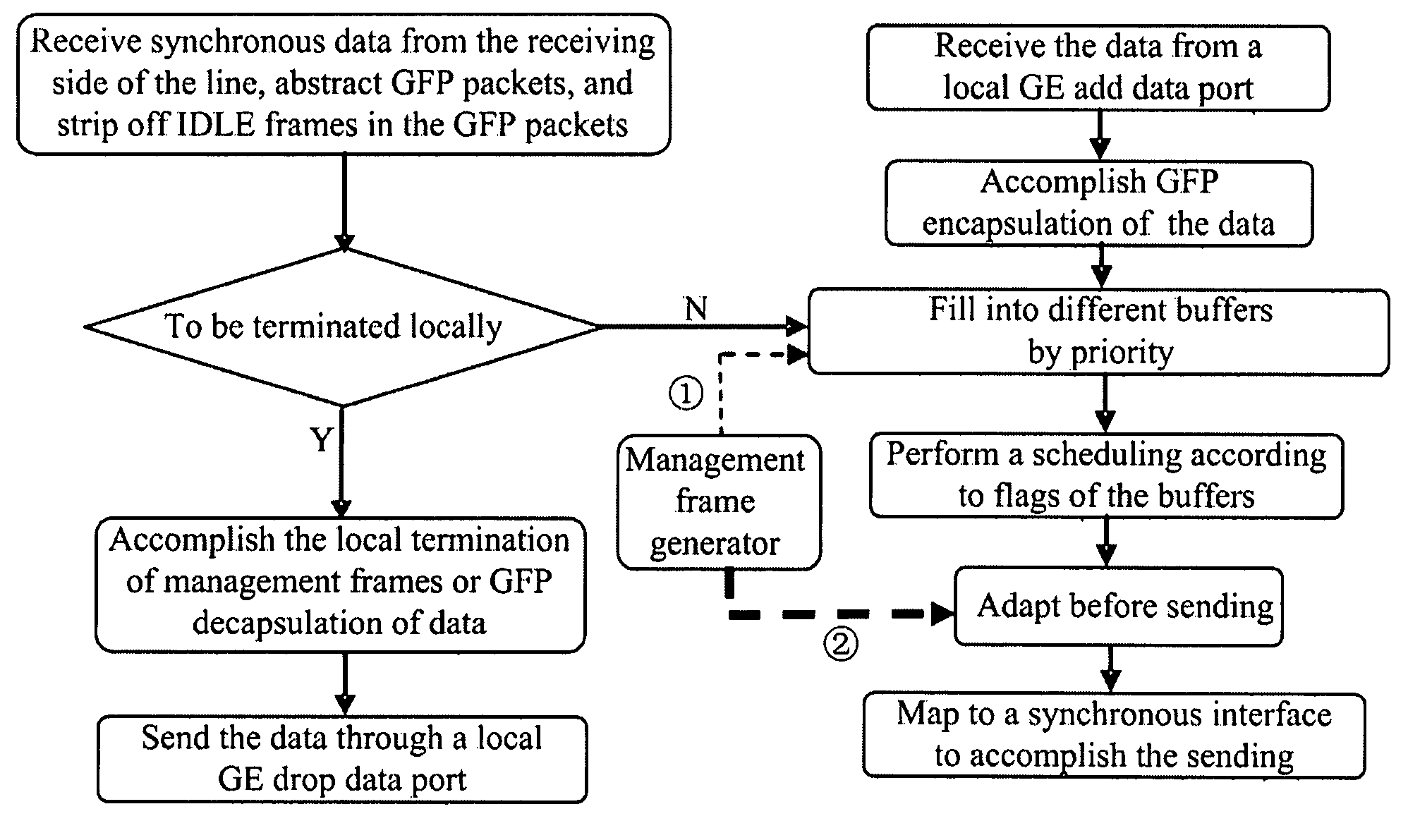
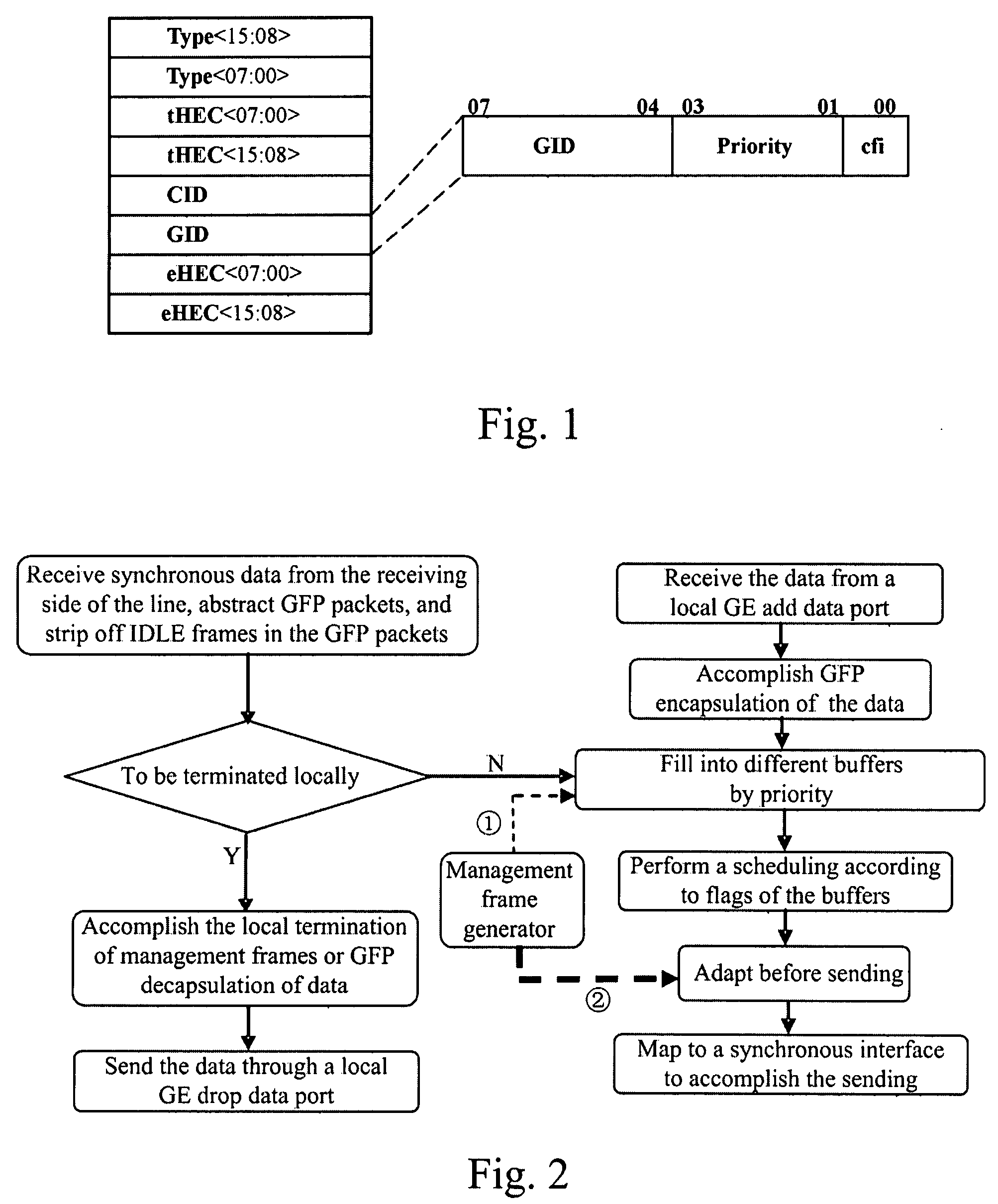
ActiveUS20070230495A1Improve bandwidth utilizationReduce complexityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiplexingGigabyte
The present invention relates to network transmission technologies, and provide a Generic Framing Procedure (GFP)-based add / drop multiplexing (add / drop multiplexing) method, apparatus and system to improve add / drop multiplexing utilization, in which multiple Gigabyte Ethernet (GE) connections among multiple nodes are multiplexed in GFP to a byte synchronous interface for transmission, wherein a bandwidth of the byte synchronous interface is smaller than a sum of peak bandwidths of the group of GE connections borne on the byte synchronous interface; statistical multiplexing is carried out on effective data borne on the multiple GEs by means of buffers, and the effective data are treated by priority in the case of network congestion. The present invention implements statistical add / drop multiplexing for multiple data services in various types, and can be used in implementing a statistical ADM for diverse data services in burst mode, even a statistical ADM for multiple mixed services.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
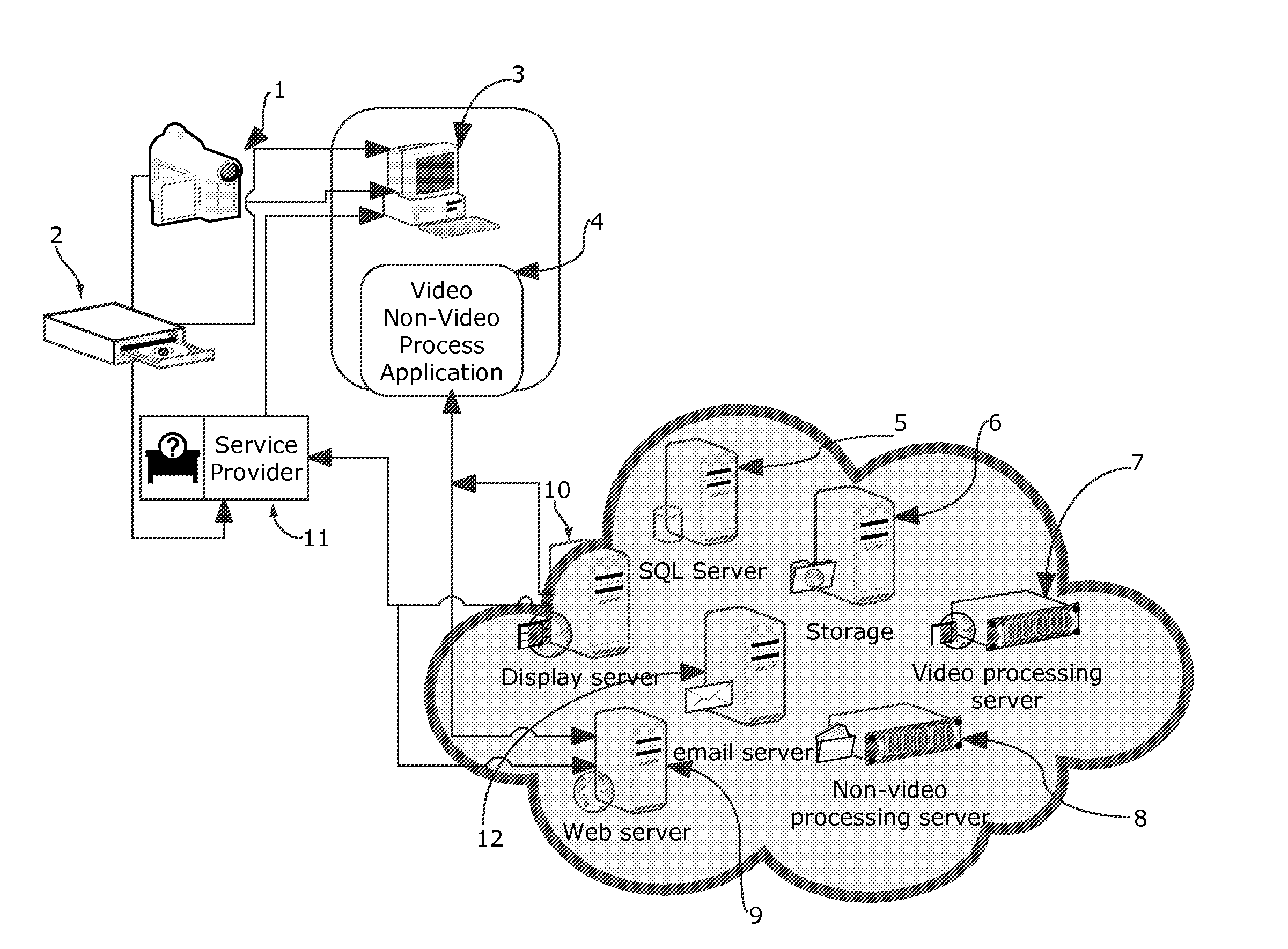
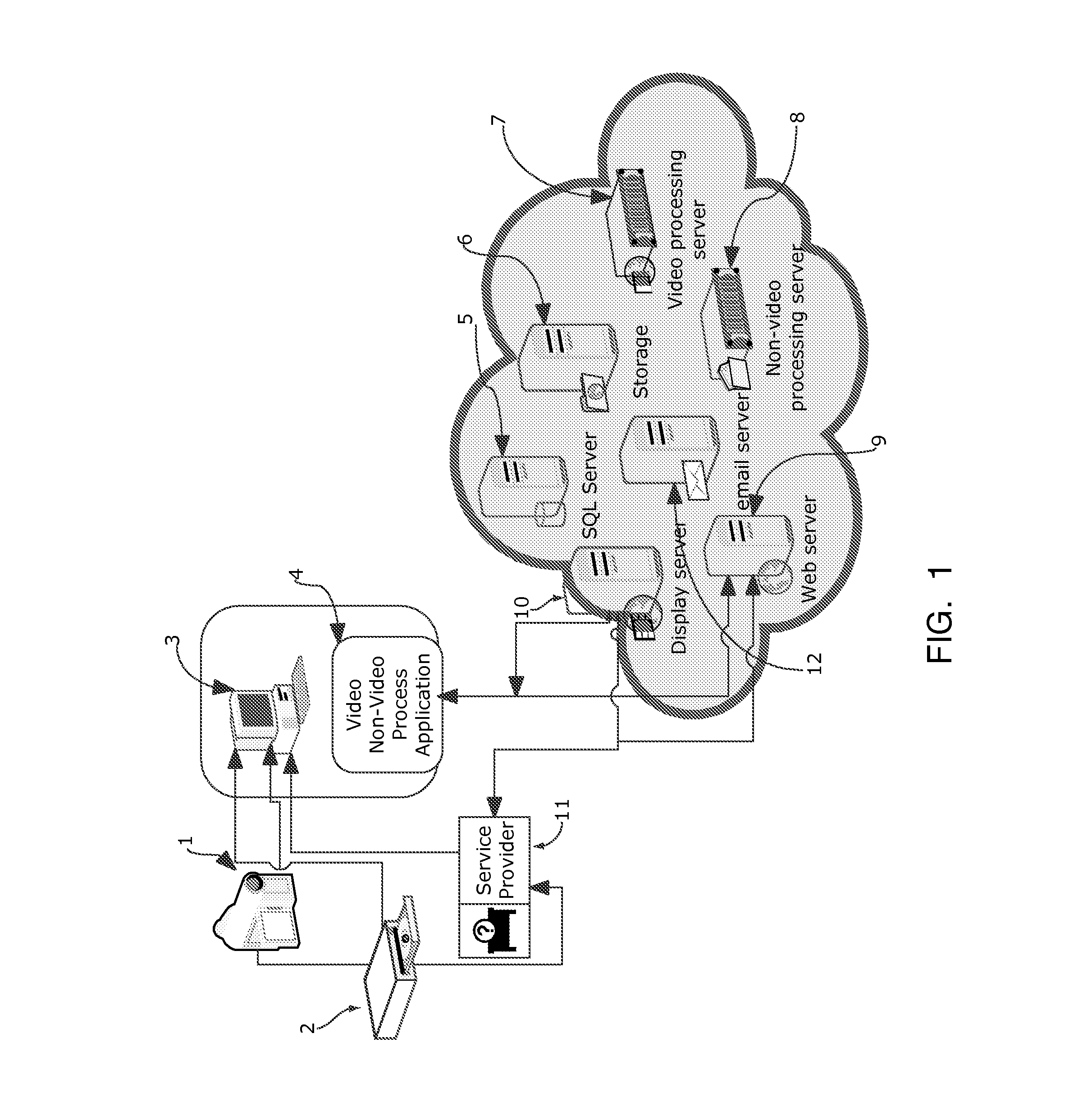
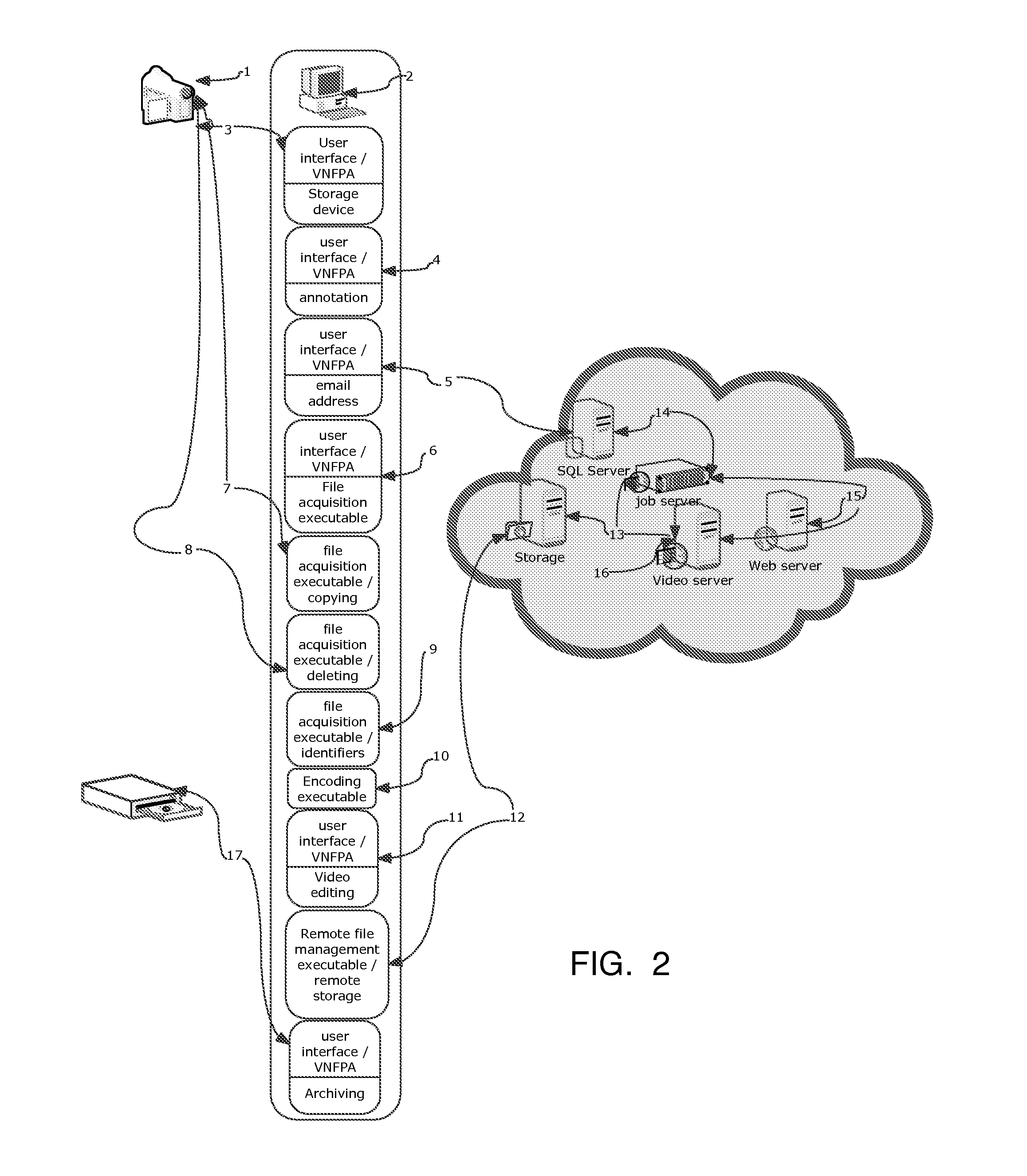
Systems for the integrated design, operation and modification of databases and associated web applications
InactiveUS20130132523A1Simple codingReliable methodMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDigital videoThe Internet
The described embodiment of the system includes business methods and software and hardware that acquires up to multi-gigabyte digital video files from digital cameras and other storage media, encodes the video files into formats in general use for playback on the Internet, acquires and manages all types of non-video files and delivers digital video and non-video files to remote storage for display using encryption algorithms and file compression algorithms. The system consists of digital cameras, personal computers, software and remote servers. The video-file-management software manages the process of acquiring video files from removable storage and all types of files from personal computers, manages the process of encoding movie files, annotating and editing movie files, annotating non-movie files, and compressing, encrypting and uploading such files to remote storage. The video-file-management software divides long movie files into two-minute segments to make editing, recombining and uploading simpler and more reliable.
Owner:LOVE THOMAS +1
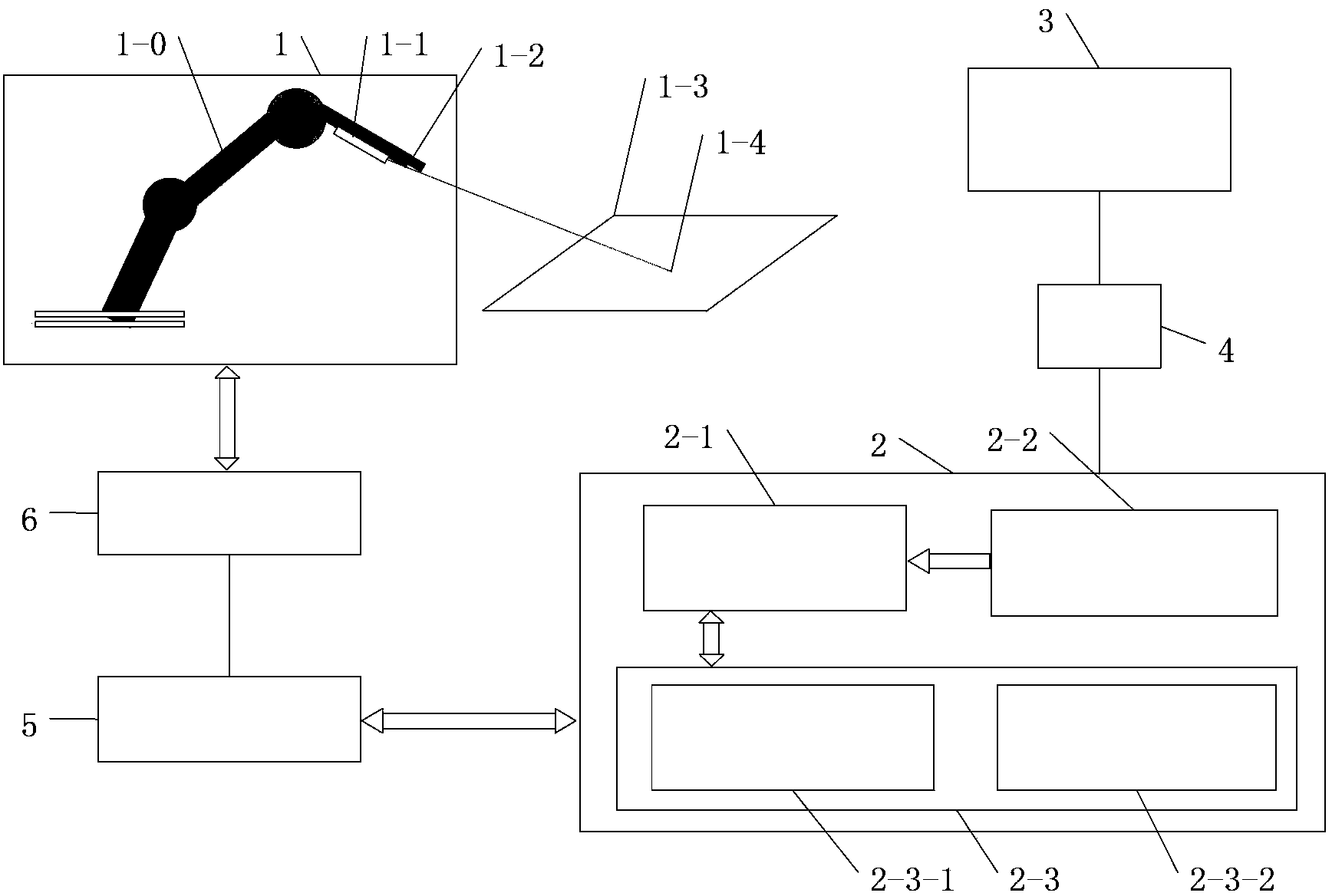
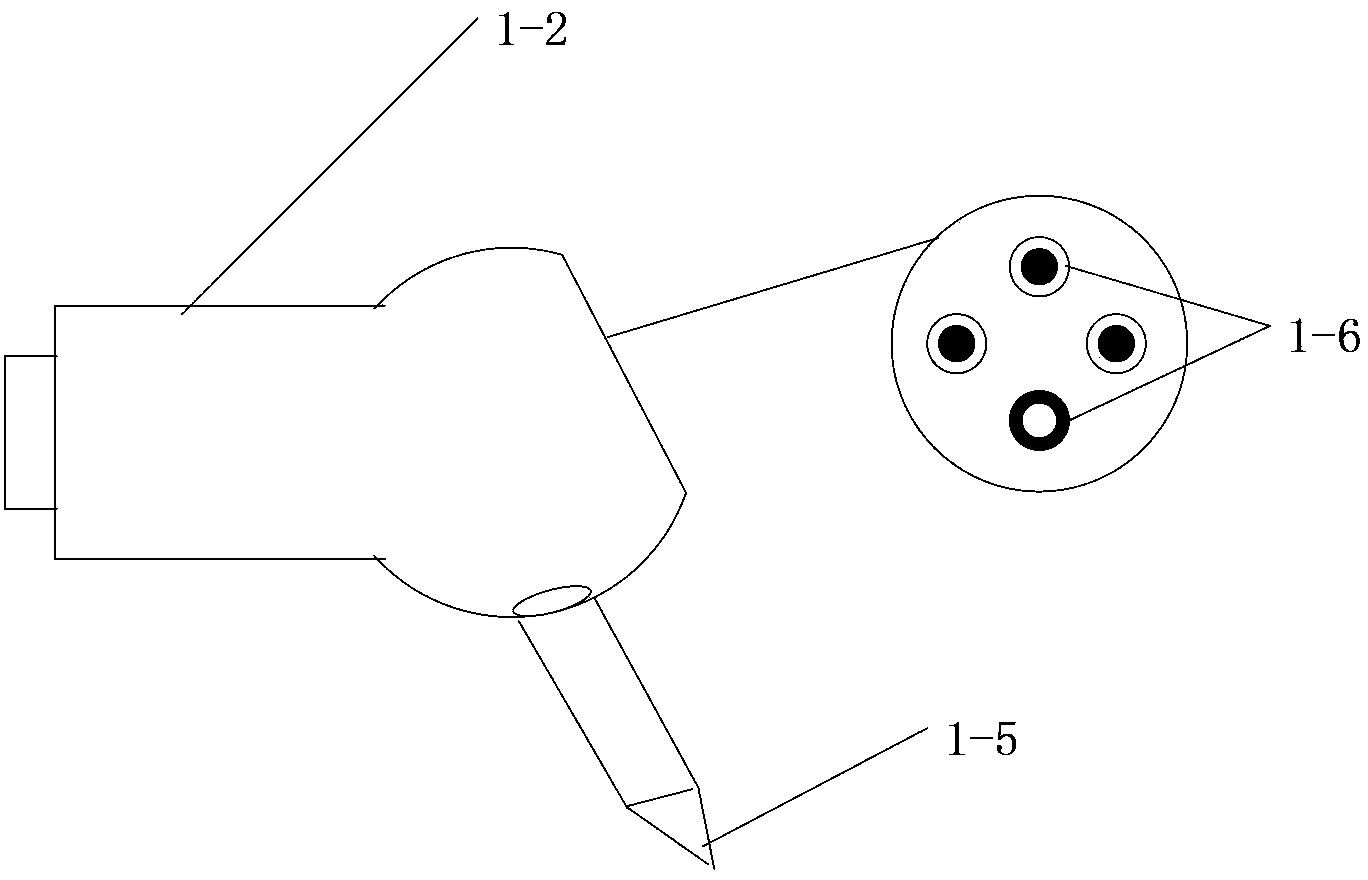
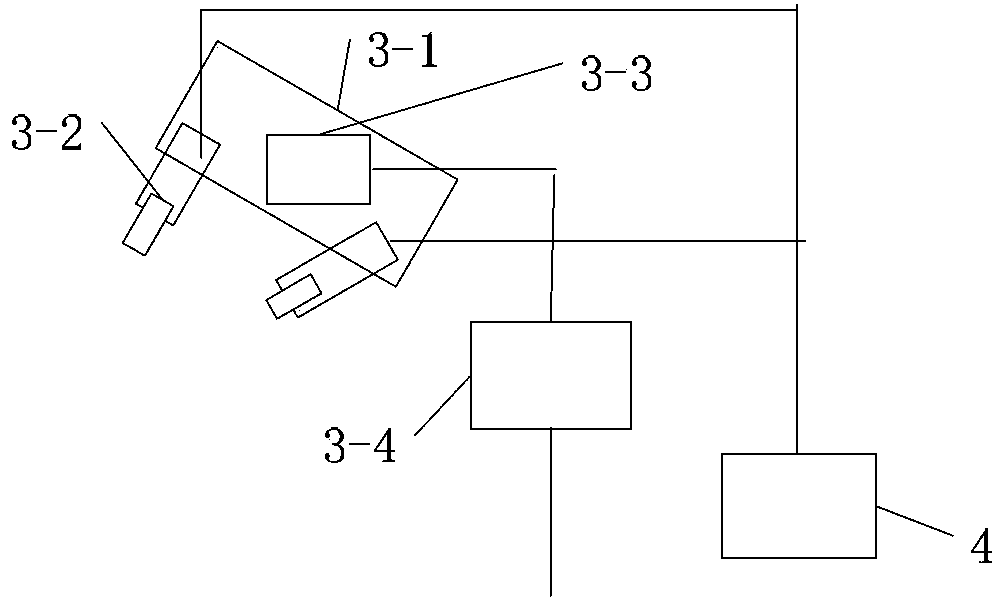
Industrial robot three-dimensional real-time and high-precision positioning device and method
ActiveCN104298244AHigh positioning accuracySimple and fast operationPosition/course control in three dimensionsWide fieldMulti camera
The invention discloses an industrial robot three-dimensional real-time and high-precision positioning device and method. The device comprises an industrial robot system, an industrial computer and a camera unit, wherein the industrial computer is connected with the industrial robot controller through a first gigabyte Ethernet, and then is connected into the industrial robot system, the industrial computer is connected with the camera unit through a second gigabyte Ethernet, and the camera unit is an active camera unit or a multi-camera unit. The method includes the following steps that: the position state of the camera unit is set according to the positions of a feature point and an actual target point; a mapping relationship of three-dimensional coordinates in a robot space and two-dimensional coordinates in a camera space is established; the position of a target point in the three-dimensional robot space is obtained, the industrial robot controller sends a command so as to control a robot to move to the target point and position the robot on the target point; and finally, the robot is positioned on the actual target point through judgment. The industrial robot three-dimensional real-time and high-precision positioning device and method of the invention have the advantages of no need for calibration, high precision, wide field of vision and high real-time performance.
Owner:南京赫曼机器人自动化有限公司
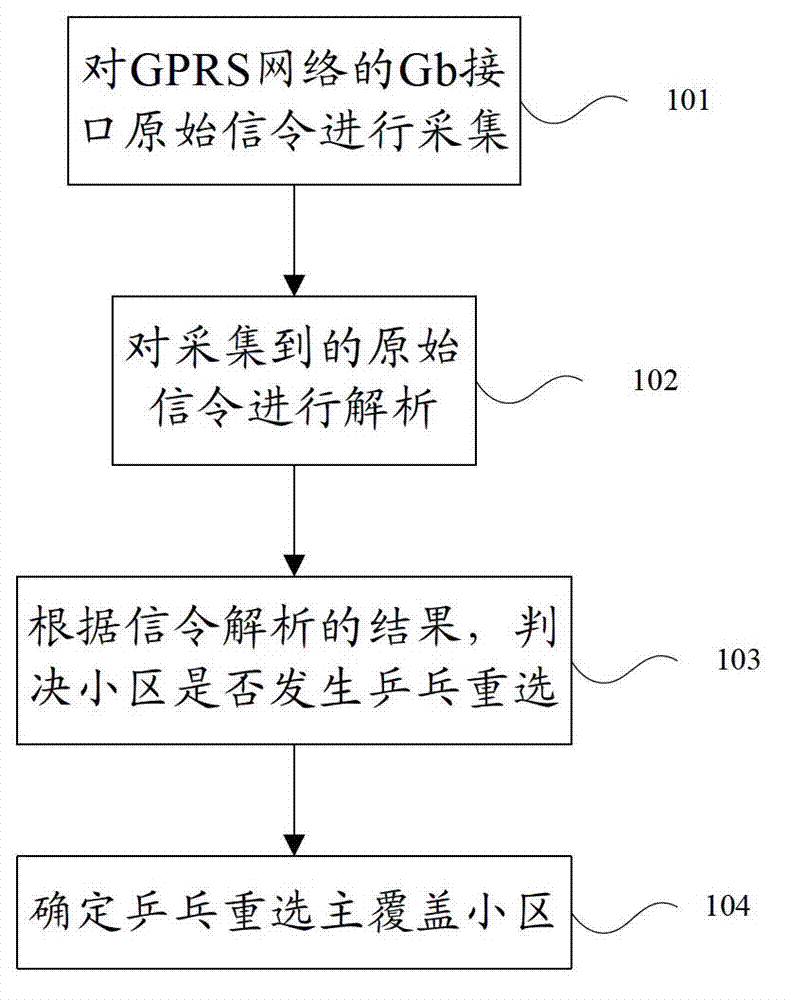
Analytical method of data traffic neighborhood ping-pong reselection
The invention discloses an analytical method of data traffic neighborhood ping-pong reselection, and belongs to the field of mobile communications. The analytical method comprises the following steps: collecting original signaling of a gigabyte (Gb) port of a general packet radio service (GPRS) network, analyzing the collected original signaling; judging whether the ping-pong reselection occurs in a neighborhood according to the result of signaling analysis, and determining a main covering neighborhood of the ping-pong reselection. Through acquisition and analysis of the signaling of the Gb port, the phenomenon of the neighborhood ping-pong reselection occurring in the data traffic using process of users is judged and analyzed by combining a certain algorithm, and thereby analysis of the influence of the neighborhood ping-pong reselection on all data traffic users in the range of a whole network is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING TUOMING COMM TECH
Fabricating a 2F2 memory device with a horizontal floating gate
Methods and devices are disclosed which provide for memory devices having reduced memory cell square feature sizes. Such square feature sizes can permit large memory devices, on the order of a gigabyte or large, to be fabricated on one chip or die. The methods and devices disclosed, along with variations of them, utilize three dimensions as opposed to other memory devices which are fabricated in only two dimensions. Thus, the methods and devices disclosed, along with variations, contains substantially horizontal and vertical components.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High capacity ancillary storage unit removably attachable to mobile cellular telephone member
InactiveUS20060058057A1Substation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsGigabyteThird generation
Cellular telephones embodying 3G system protocols with a storage drive that can add upwards of two to four gigabytes of data storage to the mobile wireless cellular telephone member in a portable attachment that is readily integratable with any standard cellular 3G telephone housing. A high function Third Generation (3G) cellular telephone with high functions, such as teleconferencing and multimedia, is enhanced with a high capacity ancillary storage unit removably attached to the telephone that includes a housing having means for receiving the ancillary storage unit. The ancillary storage unit preferably has a USB I / O slot for removably receiving a USB key drive.
Owner:IBM CORP
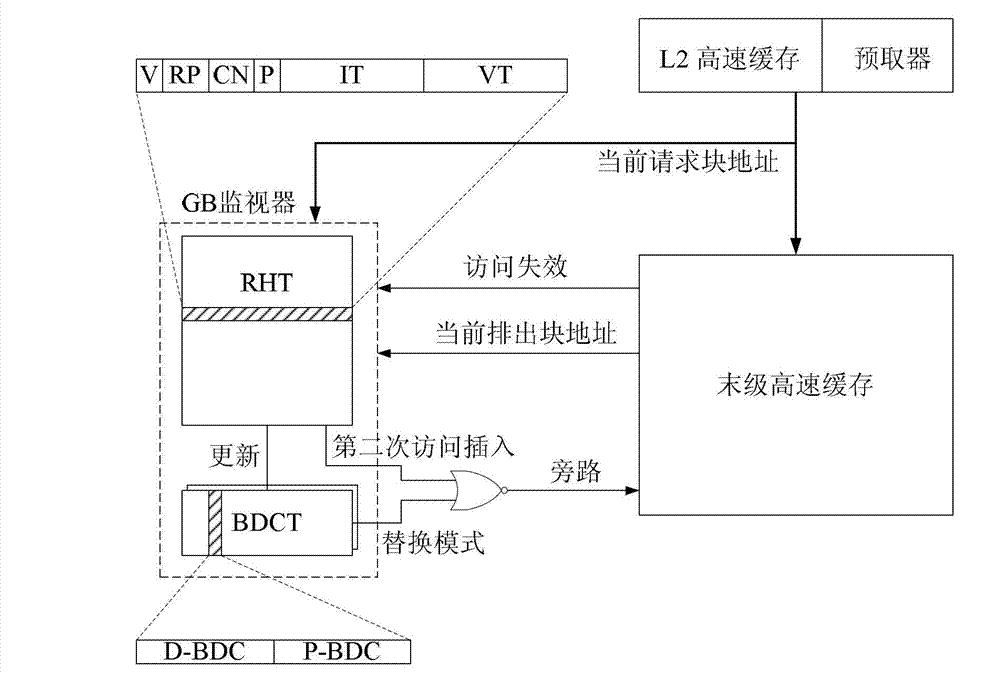
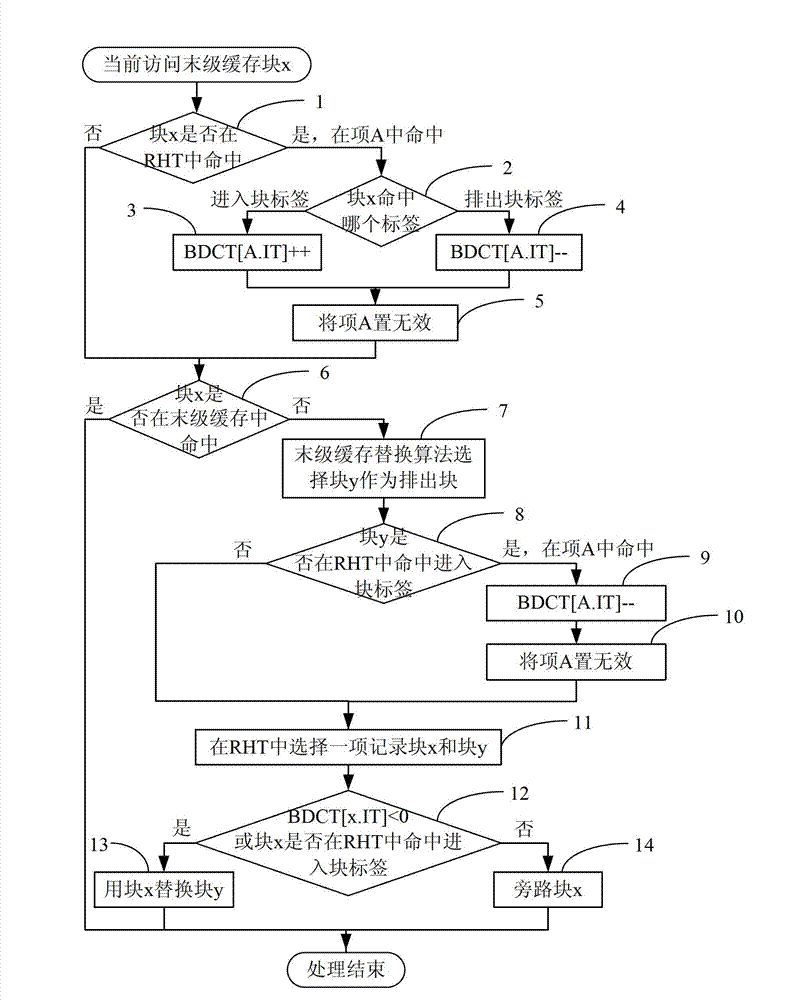
Management system and method of processor last level high-speed buffer
The invention discloses a management system and a method of processor last level high-speed buffer. The management system of the processor last level high-speed buffer comprises recording a couple of an access block and a discharge block every time when a last level buffer fails to access by a gigabyte (GB) monitor, switching a replacement pattern or a bypass pattern by studying behavior guide of an optimal bypass algorithm, wherein action of the optimal bypass algorithm is formed through actions of selection and adoption of a replacement method and a bypass method according to conditions of the optimal bypass algorithm occurred in follow-up access of the last level high-speed buffer in an accumulation mode; judging a first condition which satisfies the optimal bypass algorithm according to an access block tag and a discharge block tag of a present record in once occurrence of failure of the last level high-speed buffer, and adopting the replacement method when reusable distance of the access block is smaller than the reusable distance of the discharge block, and otherwise, adopting the bypass method. Bypass and replacement are treated as the same strategy to be switched in the management system and the method of the processor last level high-speed buffer.
Owner:北京北大众志微系统科技有限责任公司
Method for fast scanning dirty page bitmap of full-virtualization virtual machine
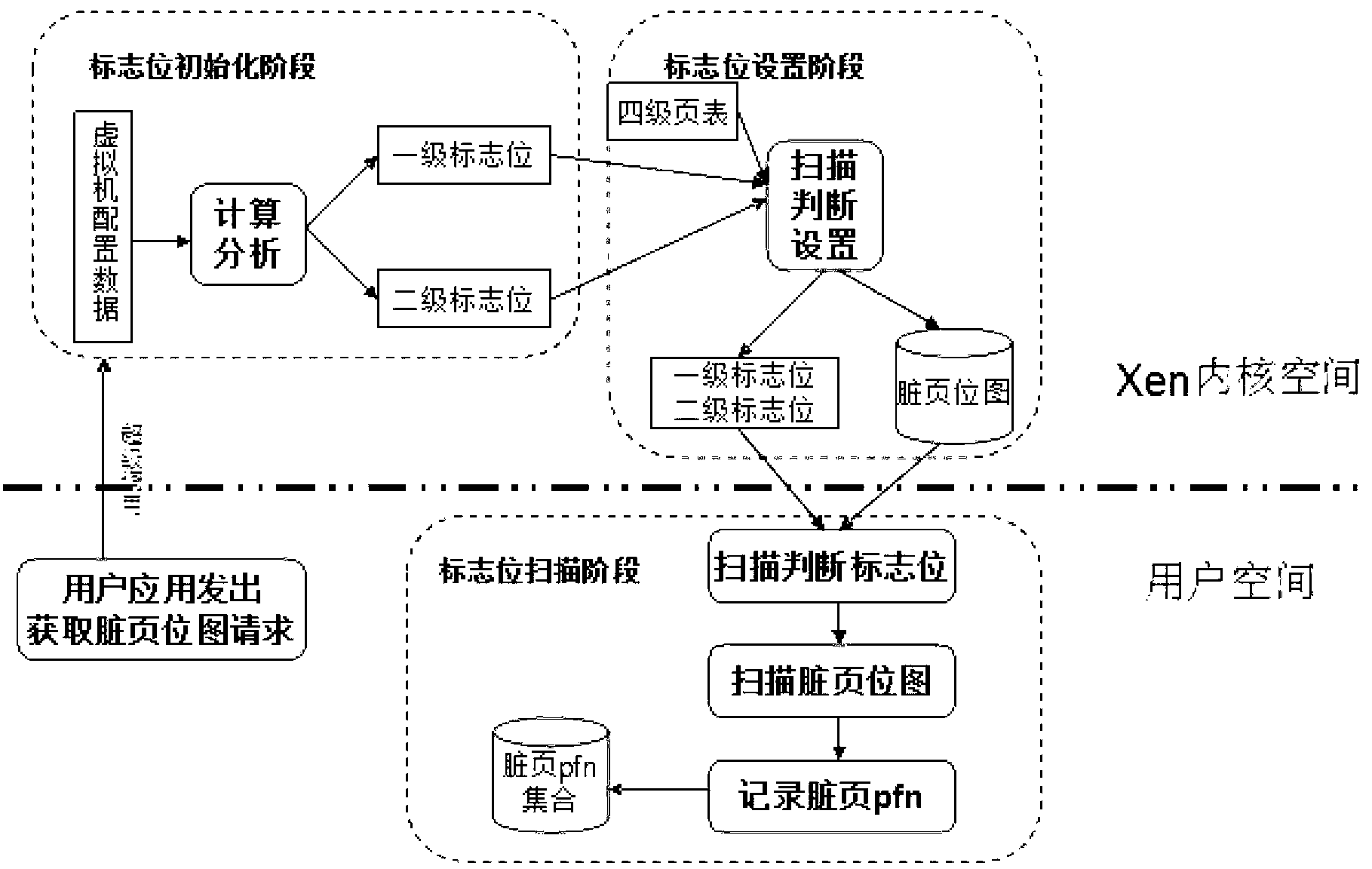
InactiveCN102981962AEasy to useReal-time adaptabilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDirty pageGigabyte
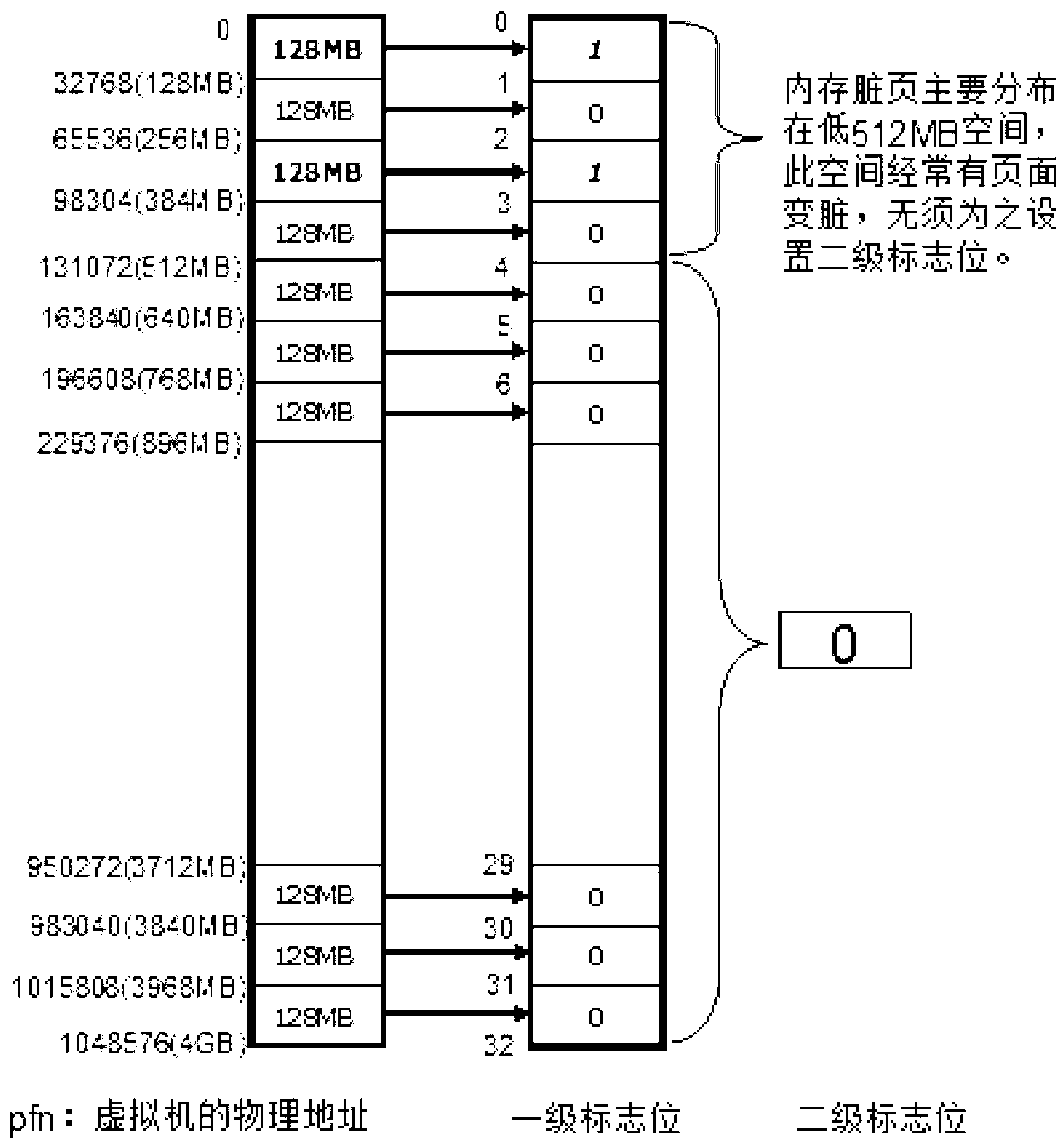
The invention discloses a method for fast scanning a dirty page bitmap of a full-virtualization virtual machine. The method comprises the following steps: a zone bit initialization phase, allocating a first class zone bit and a second class zone bit for 4 gigabyte (GB) memory space of the full-virtualization virtual machine in Xen address space, and meanwhile, initializing the first class zone bit and the second class zone bit into zero, wherein the number of the first class zone bit is 4GB / 128MB=32, and the number of the second class zone bit is one; a zone bit setting phase, reading an address in a second class page table entry of an Xen and setting the values of the first class zone bit and the second class zone bit according to the address; and a zone bit scanning phase, scanning the dirty page bitmap of the full-virtualization virtual machine according to the values of the first class zone bit and the second class zone bit so as to obtain a dirty page number. According to the method for fast scanning the dirty page bitmap of the full-virtualization virtual machine, the time for suspending the virtual machine caused by scanning of the dirty page bitmap in a dynamic migration or a Remus HA system of the virtual machine is reduced, so that the calculated performance and the service quality of the virtual machine are enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical six-dimensional multilayer storage technology using two-photon absorption writing and erasure as well as optical coherence tomography scan reading
The invention provides a six-dimensional optical multilayer storage method using two-photon absorption writing and erasure as well as optical coherence tomography scan reading and a device designed on the basis of the method. The storage capacity is increased and the storage performance is improved by combining three spatial dimensions with three physical dimensions including light wavelength, light intensity and light polarization. Each optical disk of DVD size of the device has large storage capacity more than 32 terabytes, ultrafast reading speed of 25 gigabits per second and ultrafast reading / erasing speed of 10 gigabits per second, the system has low light noise during data writing and erasure, and the signal-noise ratio during data reading is up to 76 decibels. Moreover, the storage capacity of each optical disk of DVD size of the device has the potential more than 1 gigabyte. The system device and the optical disk have relatively simple optical structures, facilitate light addressing on a storage unit in a fast rotating disk, and have high compatibility with CDs and DVDs. The method and the device are practical optical large-capacity storage technology.
Owner:李忠奇
Transmission system of network data
ActiveCN102984038AImprove network operation stabilityAvoid noiseOptical transmission adaptationsData switching by path configurationAccess networkTransceiver
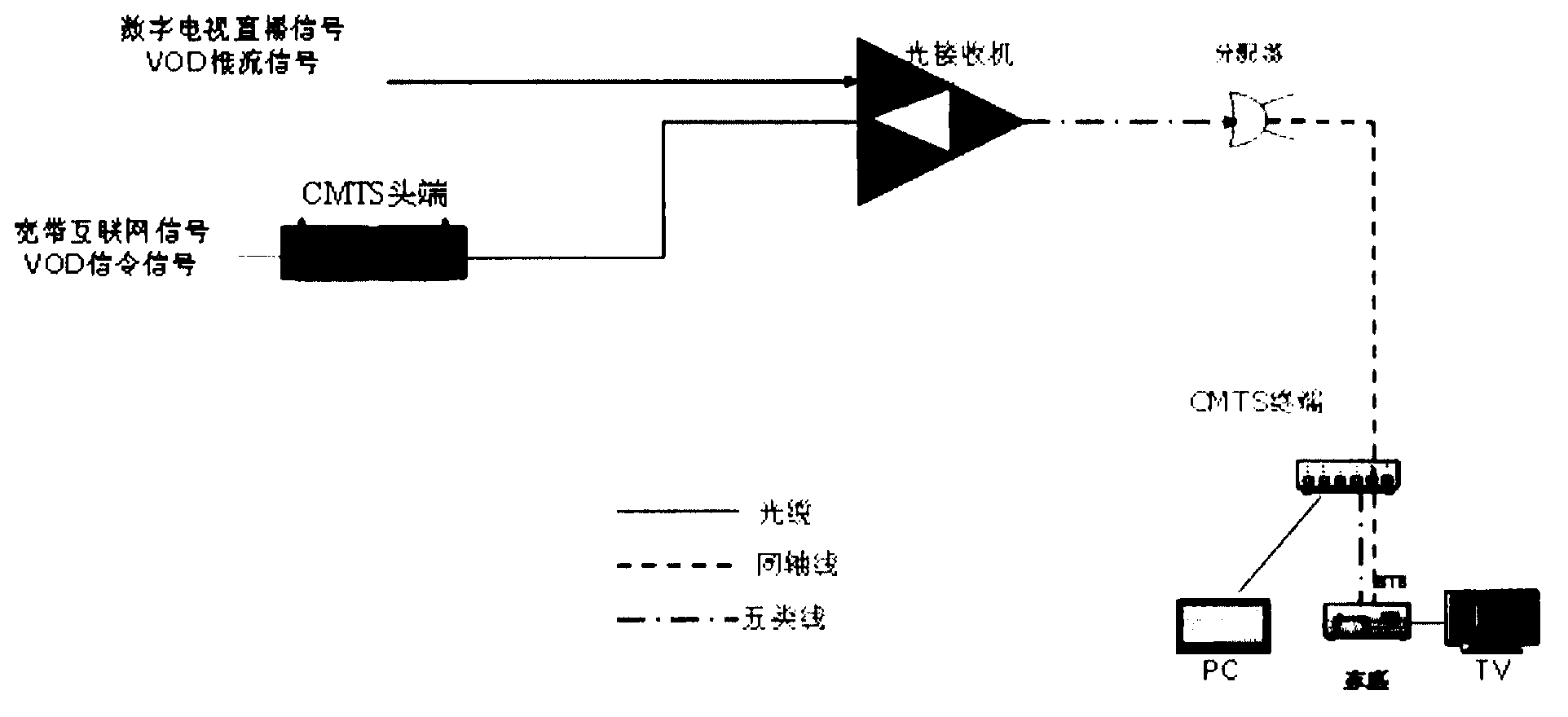
The invention provides a transmission system of network data. The transmission system of the data comprises a data transmission front end, a transmission network, an access network and a data receiving terminal. The data transmission front end comprises a convergence switch with a transceiver port being arranged to be used only for sending mandatorily, and the convergence switch is used for encoding and internet protocol (IP) packing of data such as audio and video and transmitting an IP data package out through the convergence switch in an IP broadcast mode or a multicast mode. The transmission network is used for transmitting the IP package in a rate of 1 Gigabyte (Gb) or more than 1 Gb in single and transparent modes. The access network comprises a first switch of a broadcast switch or a multicast switch, and the access network is used for acquiring the IP package from the transmission network through the first switch. The data receiving terminal is used for acquiring the IP package from the access network and unpacking and encoding for the IP package so that the data of the audio and the video can be displayed.
Owner:BEIJING JISHI HUITONG TECH CO LTD
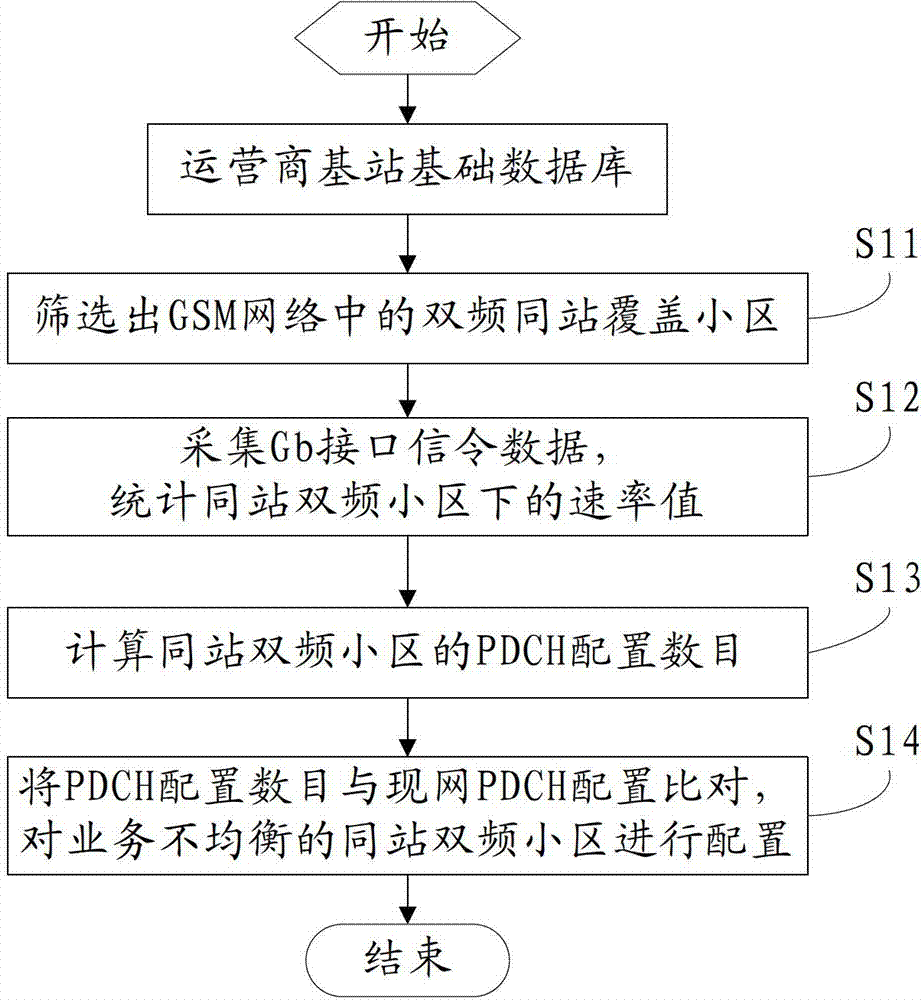
Global system for mobile communications (GSM) double frequency co-located station cell resource leveling method based on gigabyte (Gb) interface signaling
The invention discloses a global system for mobile communications (GSM) double frequency co-located station cell resource leveling method based on gigabyte (Gb) interface signaling. According to the method, double frequency co-located station coverage cells in a GSM network are screened out according to a base station foundation database at first; then, Gb interface signaling data is collected, rate values under the co-located station double frequency cells are counted, and the configuration number of packet data channels (PDCH) under the condition that the co-located station double frequency cells meet requirements of different user sensing is calculated according to the rate value under the co-located station double frequency cells; and at last, the calculated PDCH number is compared with PDCH configuration of an existing network, and configuration for co-located station double frequency cells with unbalanced business is achieved. According to the method, cell resource balance is achieved through reasonable configuration for cell PDCH resources, configuration information of the cells is just changed, conditions of reselection parameters, coverage and power are not changed, influences on network quality, performance and test indexes of a speech network are little, and reasonable configuration for the cells can be achieved according to the level of user sensing.
Owner:BEIJING TUOMING COMM TECH
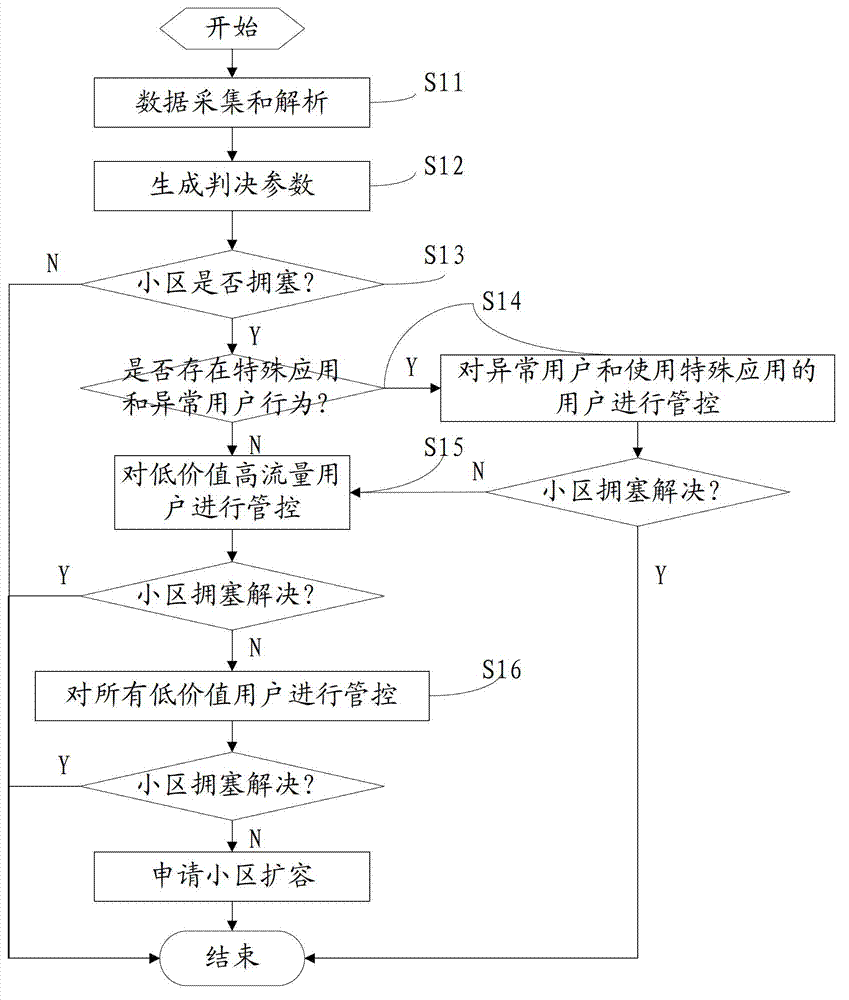
Data business flow control method based on signaling analyzing
ActiveCN103096386APerfect management and control strategyResolve stressful situationsNetwork traffic/resource managementGeneral Packet Radio ServiceTraffic capacity
The invention discloses a data business flow control method based on signaling analyzing. According to the method, at first, original signaling of a gigabyte (Gb) interface of a general packet radio service (GPRS) network and home location register (HLR) data of a user and business analysis system data are collected, and analyzing for signaling data is achieved; then, a cell congestion judgment parameter is set, and whether a cell is overloaded or not is judged according to the judgment parameter; and for a congestion cell, the modes of sequential control for abnormal users and special application users in the cell, low-value high-flow users in the cell, and all the low-value users in the cell are achieved to achieve scheduling of resources of the congestion cell, the network congestion problem is resolved, and the network resource utilization rate is improved.
Owner:BEIJING TUOMING COMM TECH
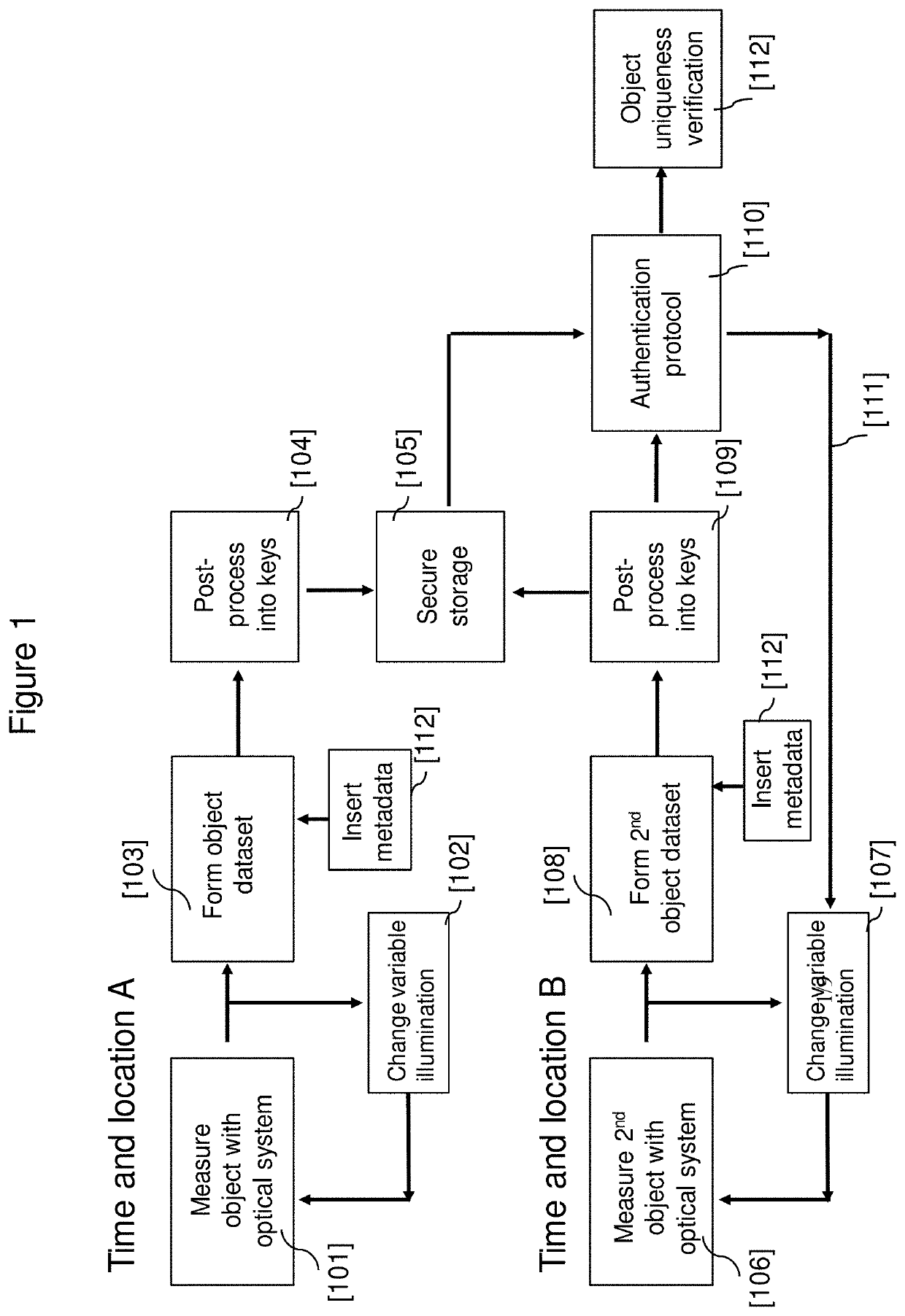
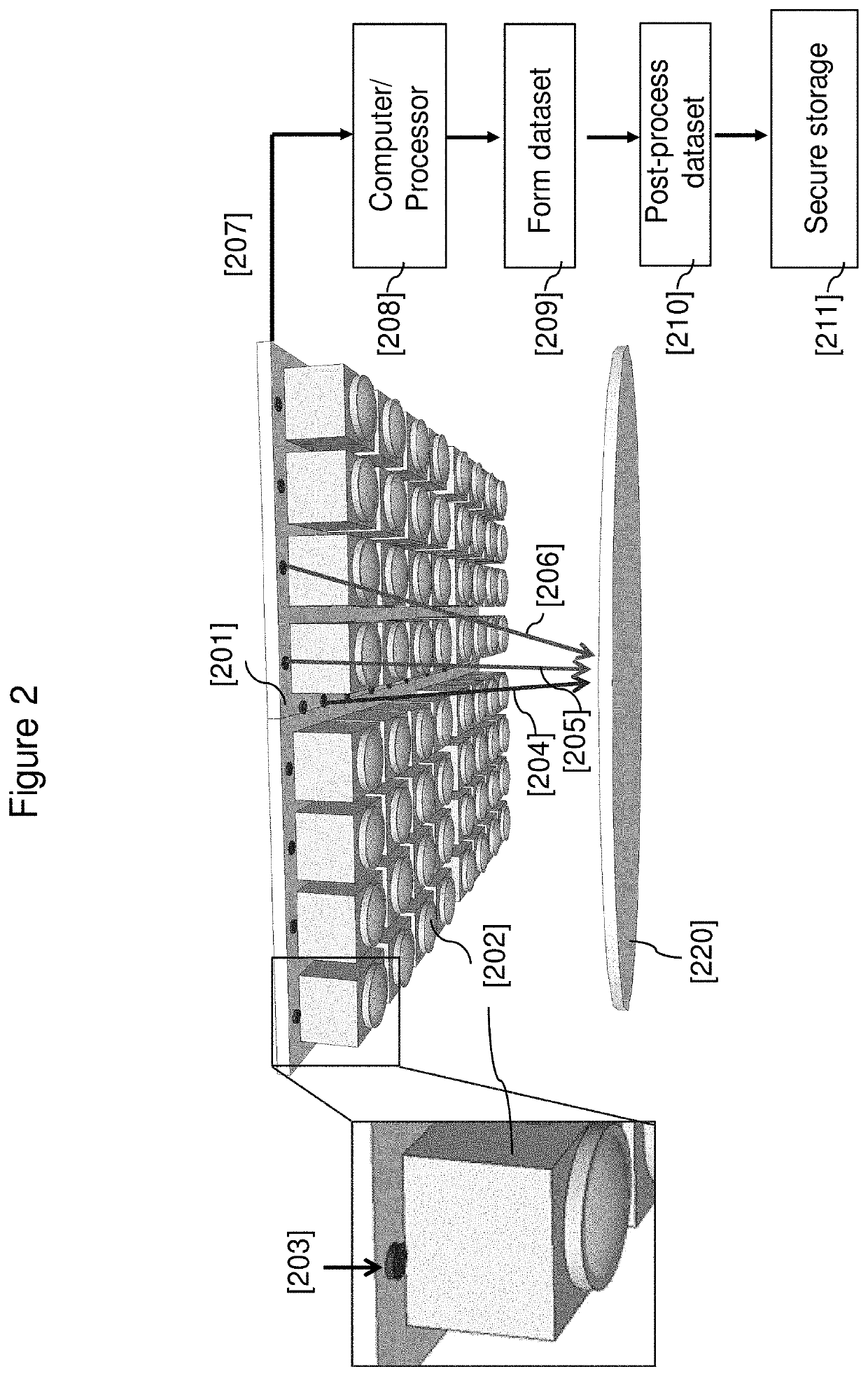
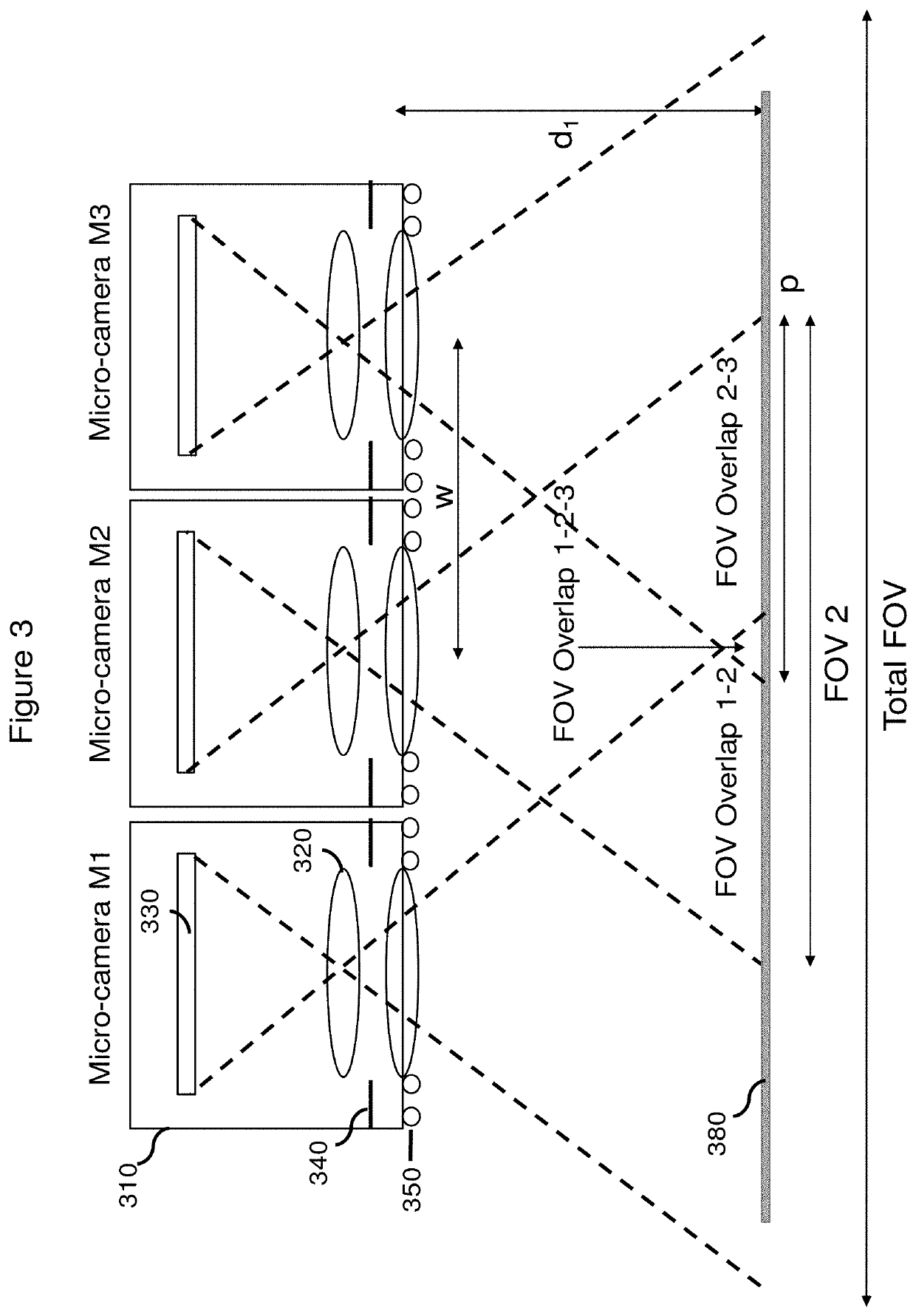
System and method to optically authenticate physical objects
PendingUS20200143032A1High degreeEnsure uniquenessCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital data authenticationCamera imageData set
A system and method to verify the authenticity of a physical object, based on the efficient acquisition and digital post-processing of a large amount of optical data. An optical system, comprised of an array of microscope-type “micro-cameras” and a patterned illumination source, acquires spatial, spectral and angular information about the physical object in the form of micro-camera images. The set of all acquired images comprise one object dataset, which a post-processing system then digitally transforms into a multi-gigabyte set of semi-random keys. Authentication takes place at a later date following a challenge-and-response protocol. The high resolution (<15 μm) of the acquired data presents a significant challenge to attempted duplication of the physical object, and the large size (>1 Gigabyte) of the key set similarly prevents both physical and digital forgery attempts.
Owner:RAMONA OPTICS INC
High-speed security hard disk design method
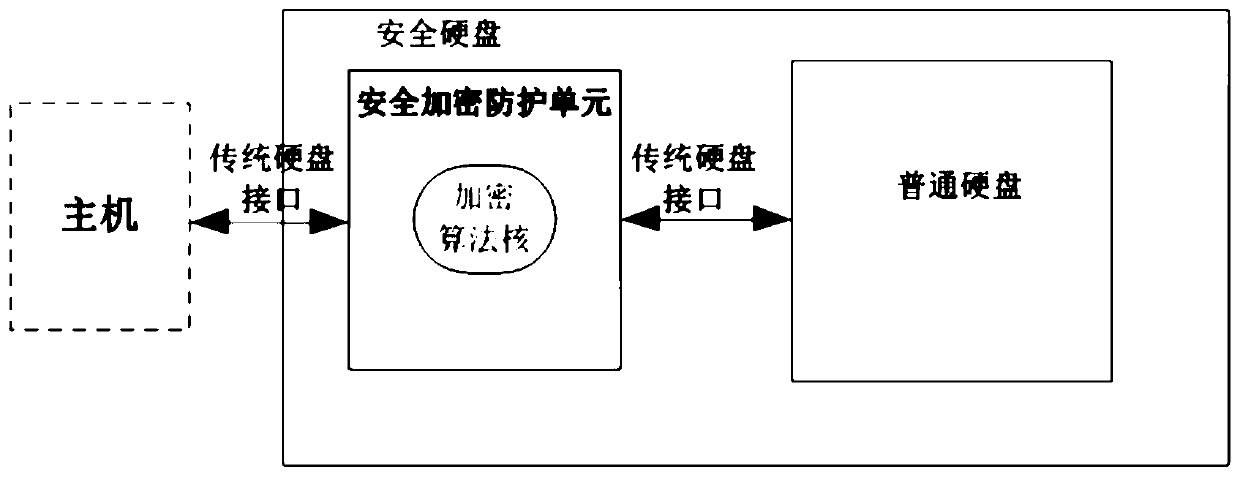
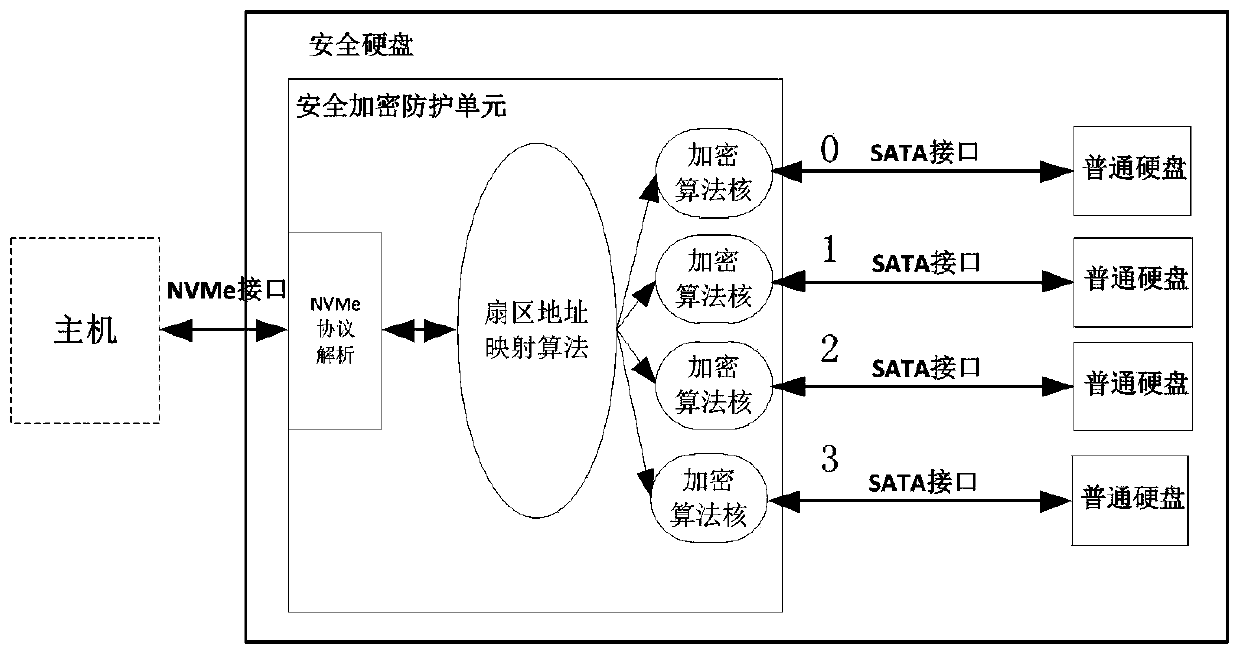
ActiveCN110163011AImprove performanceLower latencyInternal/peripheral component protectionGigabyteLow delay
The invention relates to a high-speed security hard disk design method, and relates to the technical field of computer storage. The NVMe interface with lower delay and higher speed is connected with the host, a security encryption protection unit is provides a plurality of encryption algorithms to check data for encryption and decryption and is provided with a plurality of hard disks to access data in parallel, the data throughput rate can reach the magnitude order of gigabyte per second, and the performance of the security hard disks is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF COMP TECH & APPL
Add drop multiplexing method, apparatus and system based on GFP
ActiveUS7656910B2Improve bandwidth utilizationWithout limiting demandError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiplexingGigabyte
The present invention relates to network transmission technologies, and provide a Generic Framing Procedure (GFP)-based add / drop multiplexing (add / drop multiplexing) method, apparatus and system to improve add / drop multiplexing utilization, in which multiple Gigabyte Ethernet (GE) connections among multiple nodes are multiplexed in GFP to a byte synchronous interface for transmission, wherein a bandwidth of the byte synchronous interface is smaller than a sum of peak bandwidths of the group of GE connections borne on the byte synchronous interface; statistical multiplexing is carried out on effective data borne on the multiple GEs by means of buffers, and the effective data are treated by priority in the case of network congestion. The present invention implements statistical add / drop multiplexing for multiple data services in various types, and can be used in implementing a statistical ADM for diverse data services in burst mode, even a statistical ADM for multiple mixed services.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
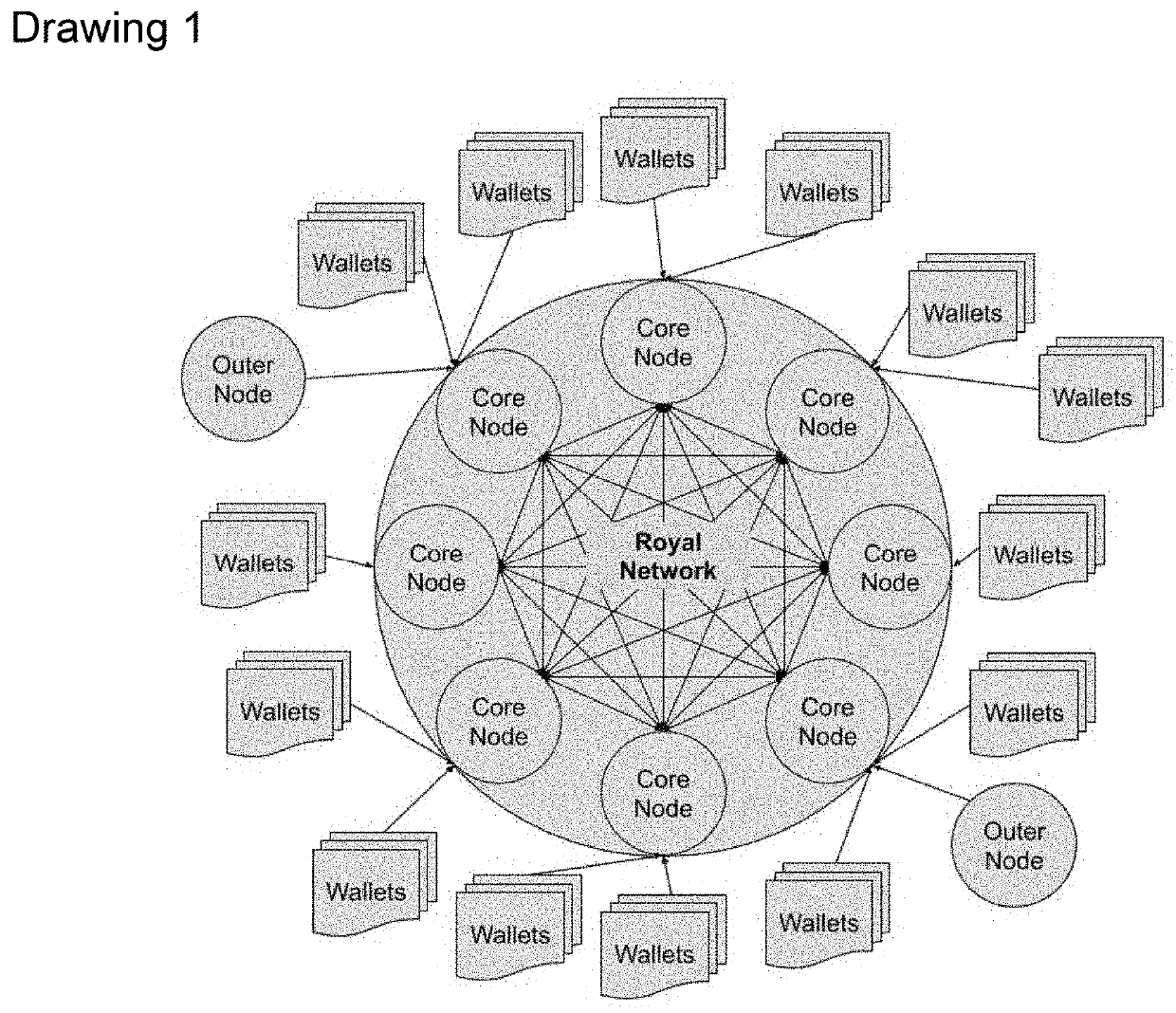
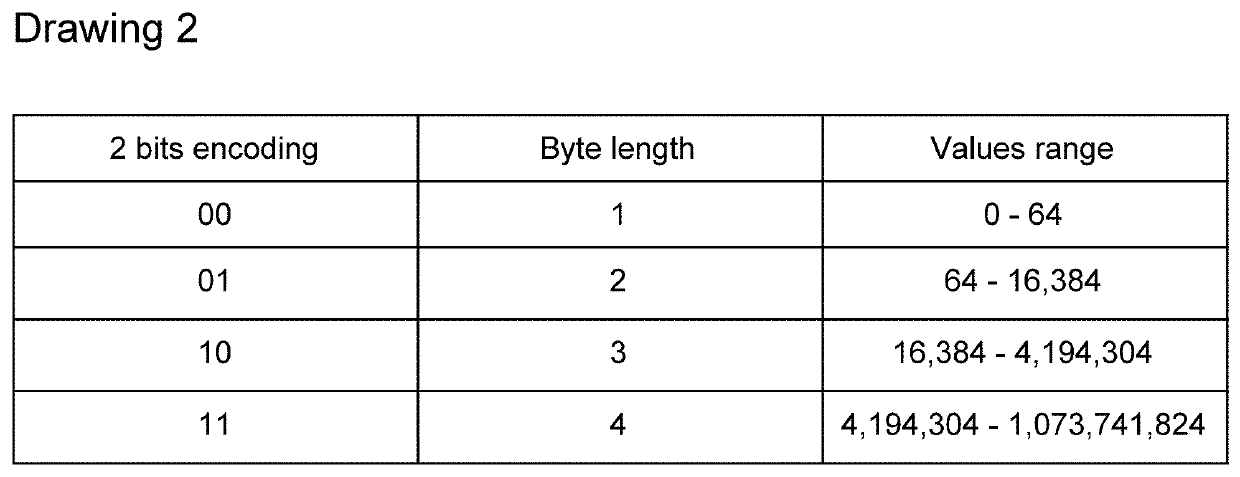
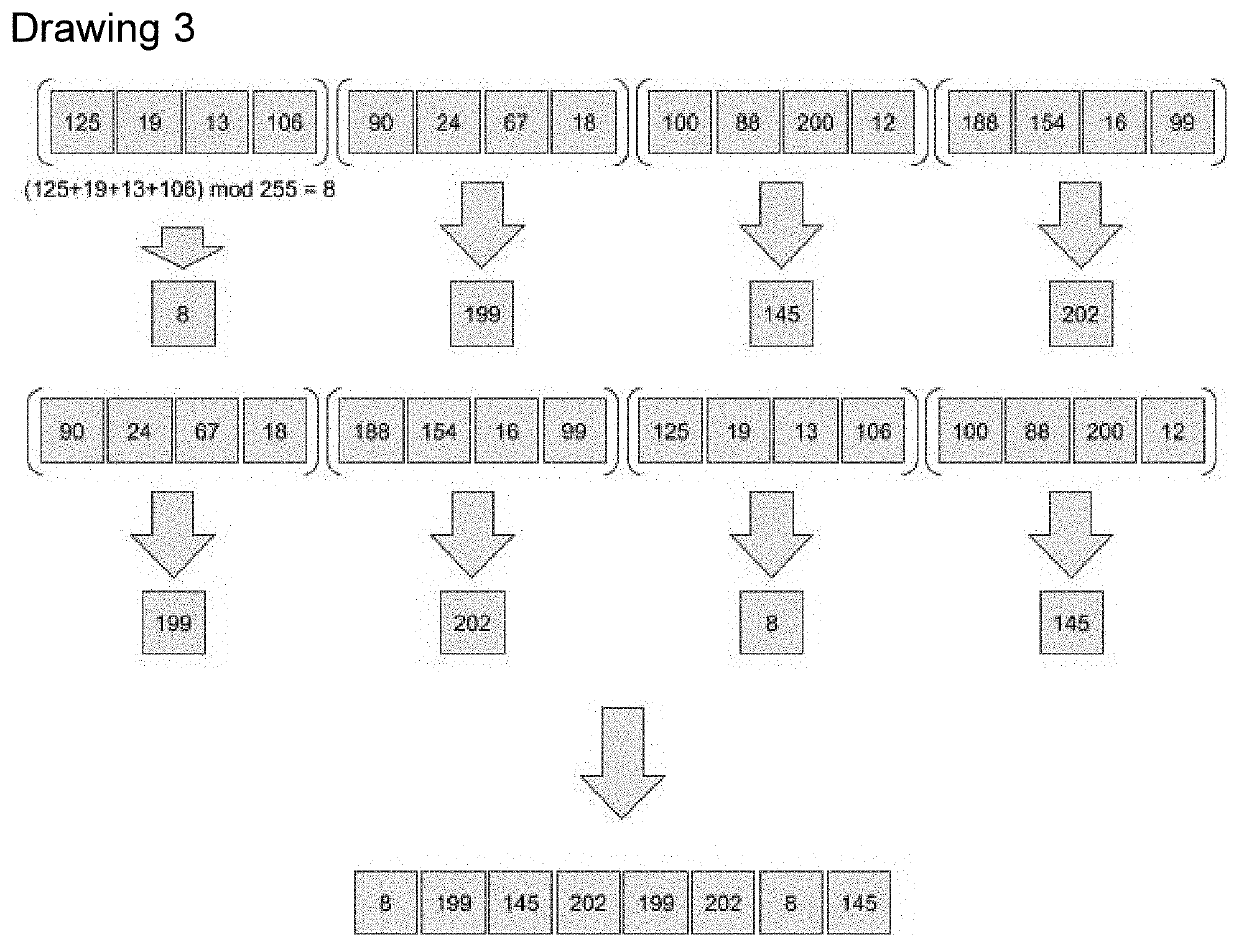
Cryptocurrency with Royal Network, Decentralized Trusted Party and Automated Smart Contracts
InactiveUS20200364680A1Increase in sizeReduce transactionCryptography processingPayment protocolsPaymentGigabyte
Confidence coin, in short Coco, is an upgrade to the cryptocurrency technology, it replaces P2P network with Royal Network and using a special block encoding that together allows blocks as big as Gigabytes of data. It offers micro and macro transactions via Decentralized Trusted Parties. It also increases users privacy and helps government regulators to protect the system from illegal trades and fraudulent activities. Coco upgrades smart contracts to Automated Smart Contracts that allow automatic payments. And it has a leadership organization, founded by Coco system itself with a single purpose of making Coco great.
Owner:GAZMAN ILYA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com