Patents
Literature
608 results about "Parallel channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Parallel channel. (1) A channel that transmits data over several wires simultaneously, typically in increments of a byte (16, 32, 64 bits, etc.). (2) A parallel channel for IBM mainframes that transmits up to 4.5MB/sec.
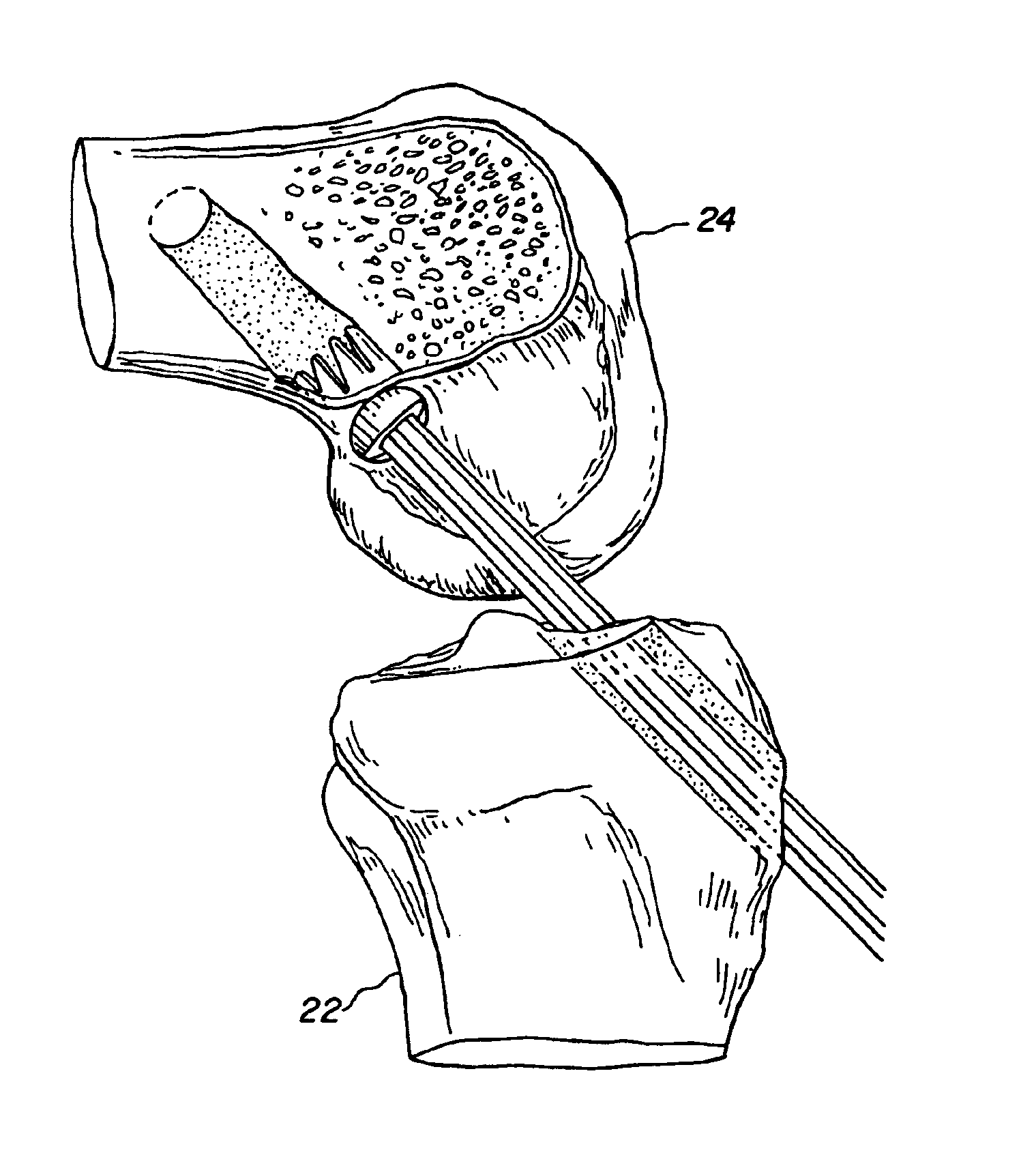
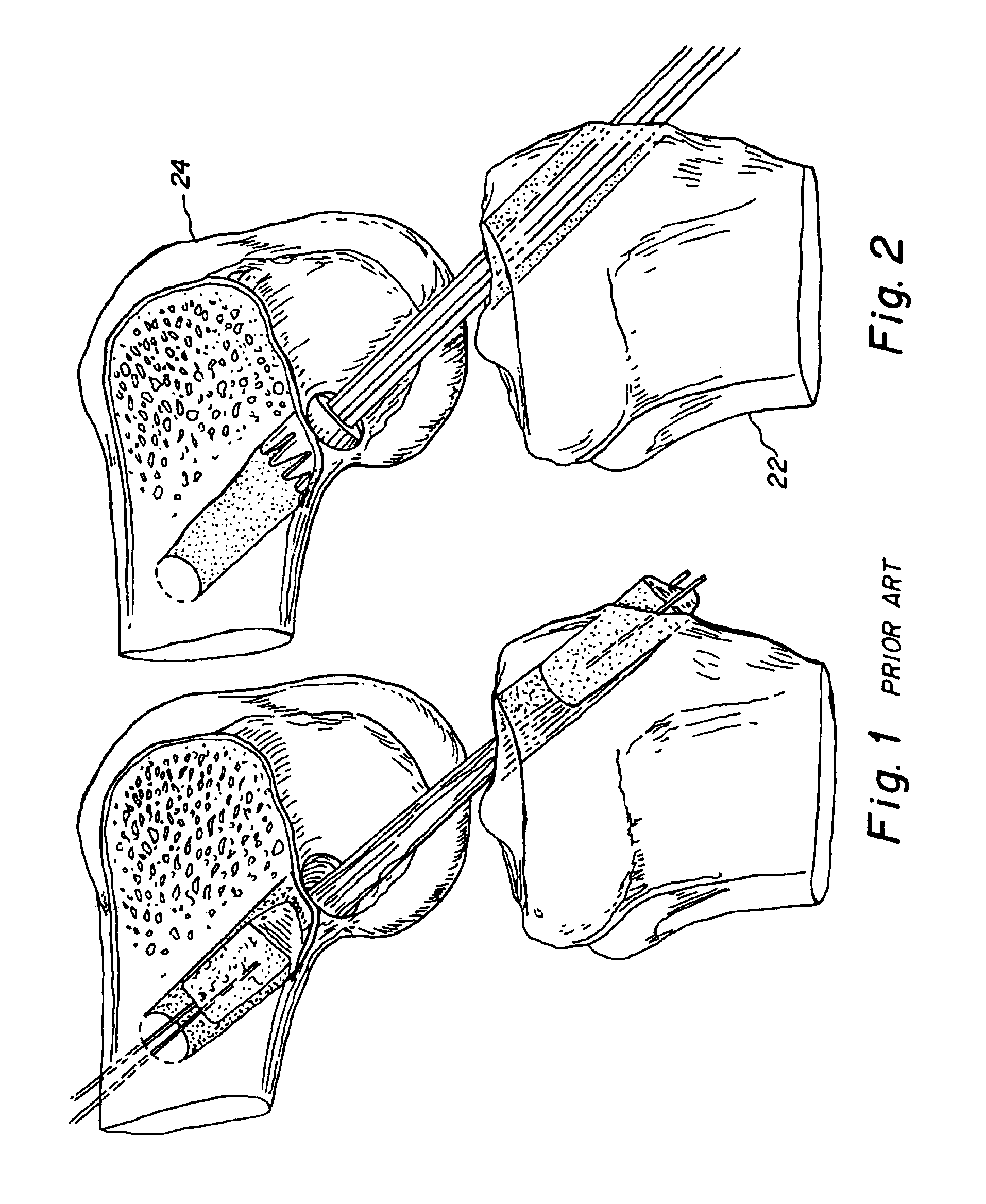
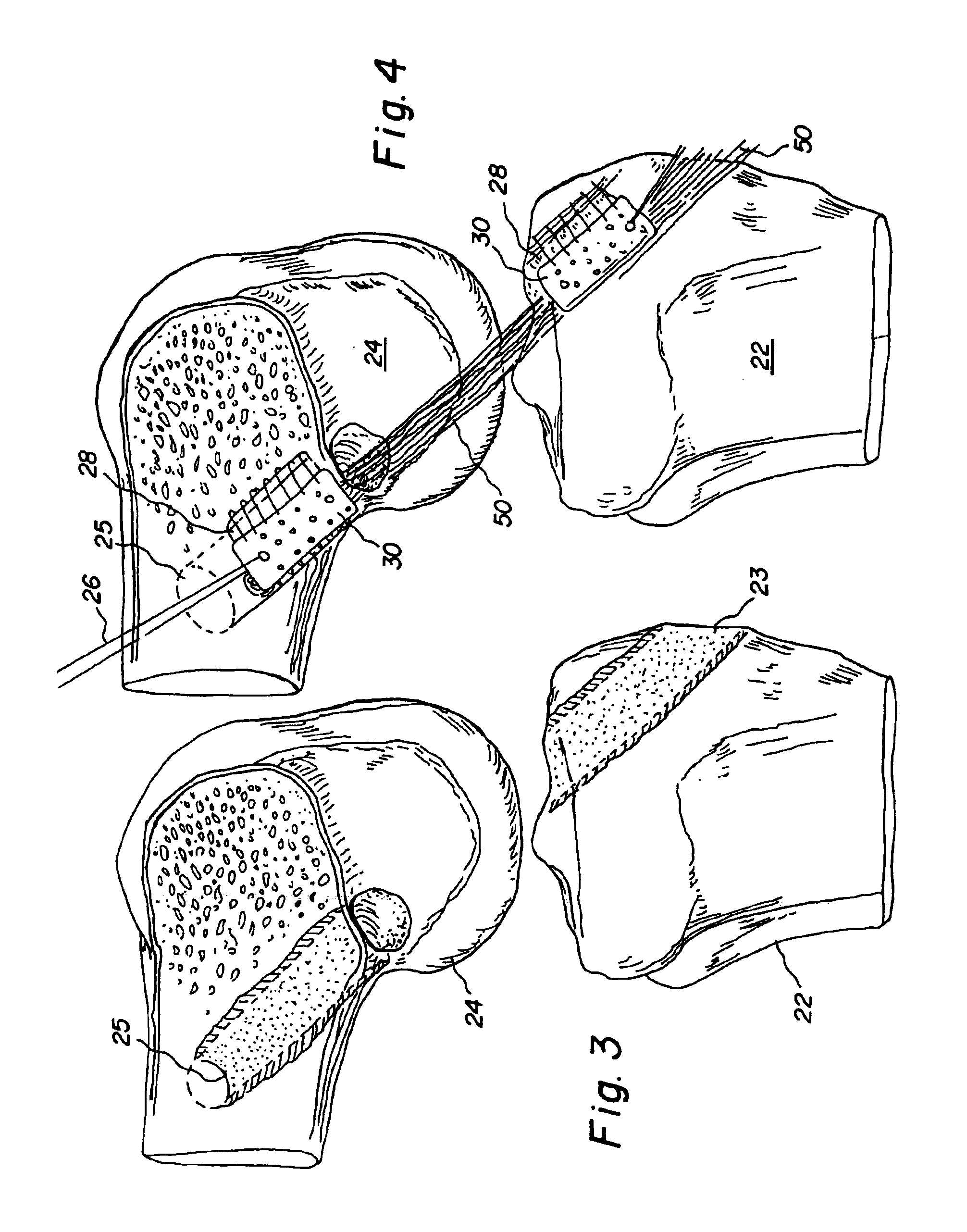
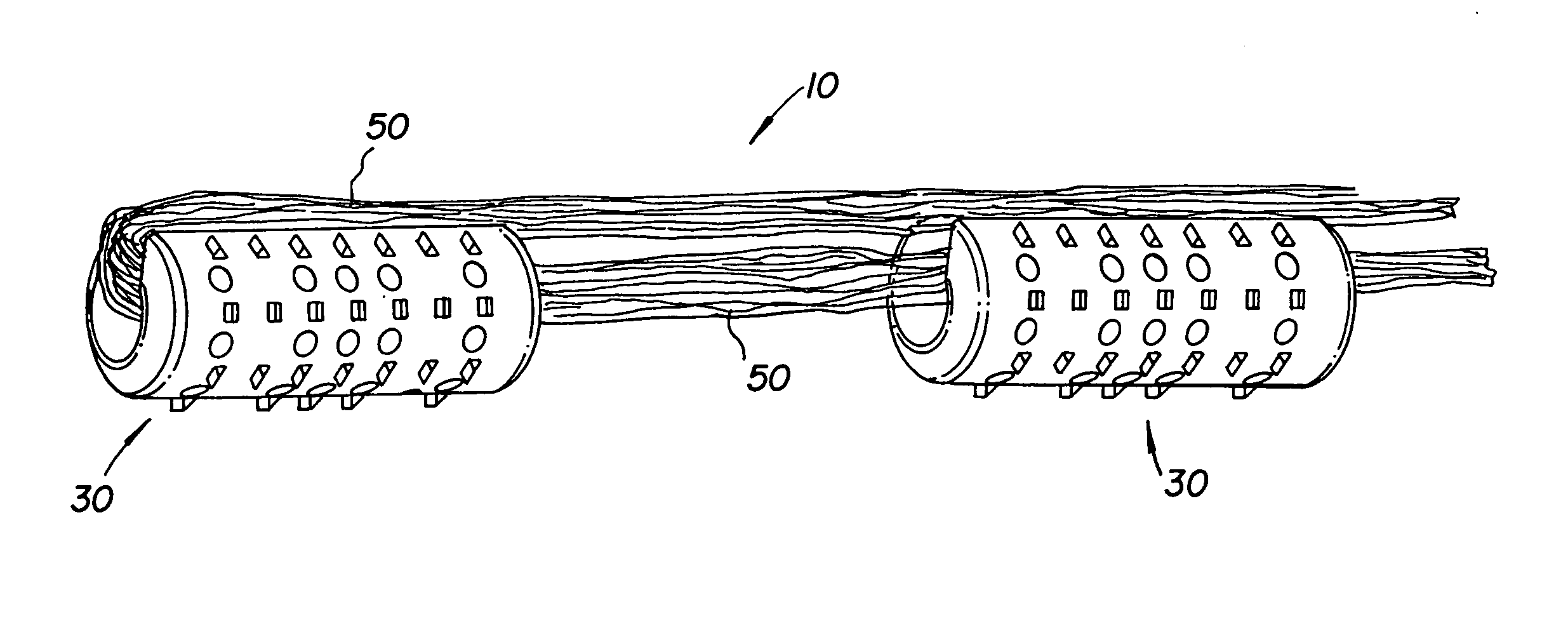
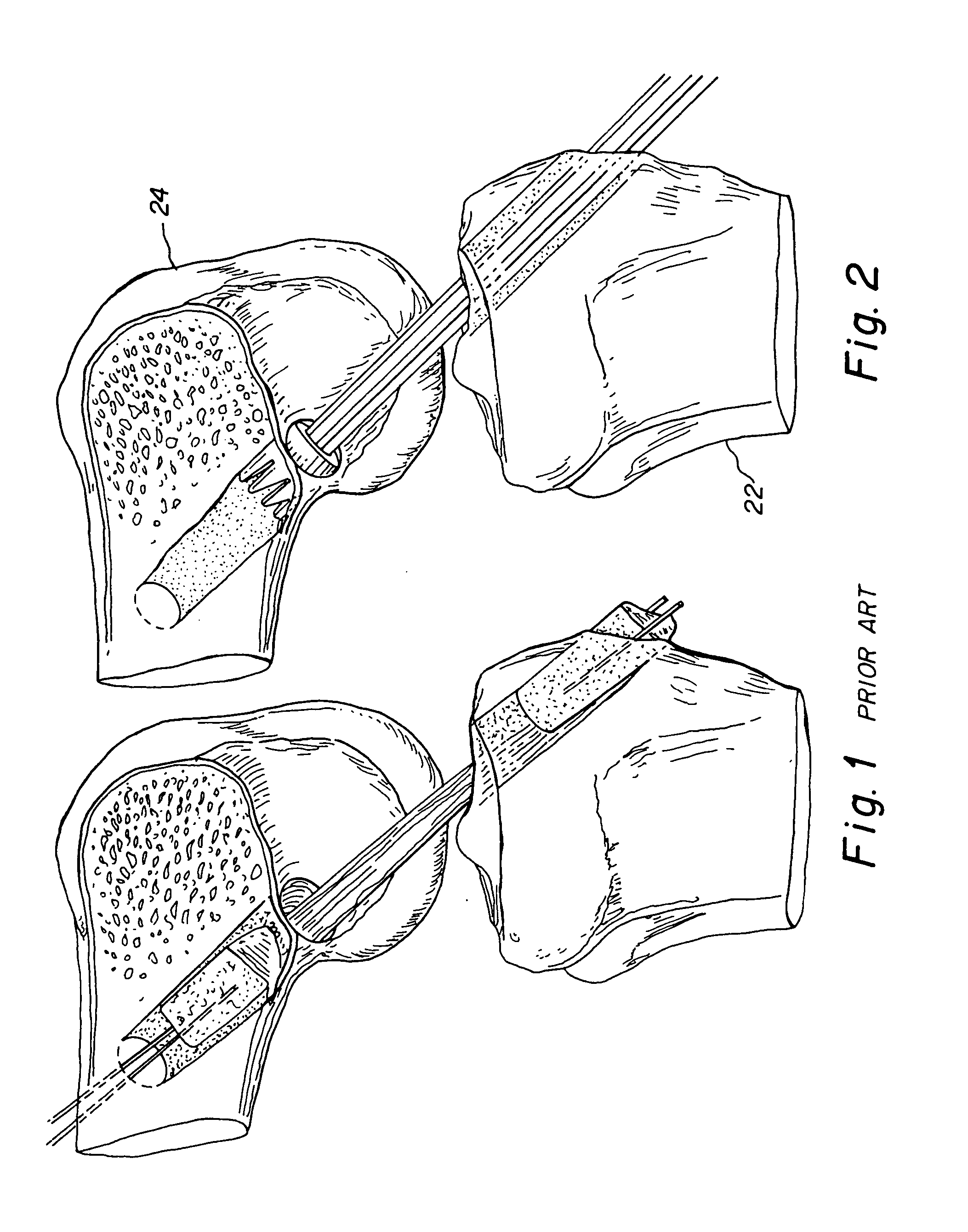
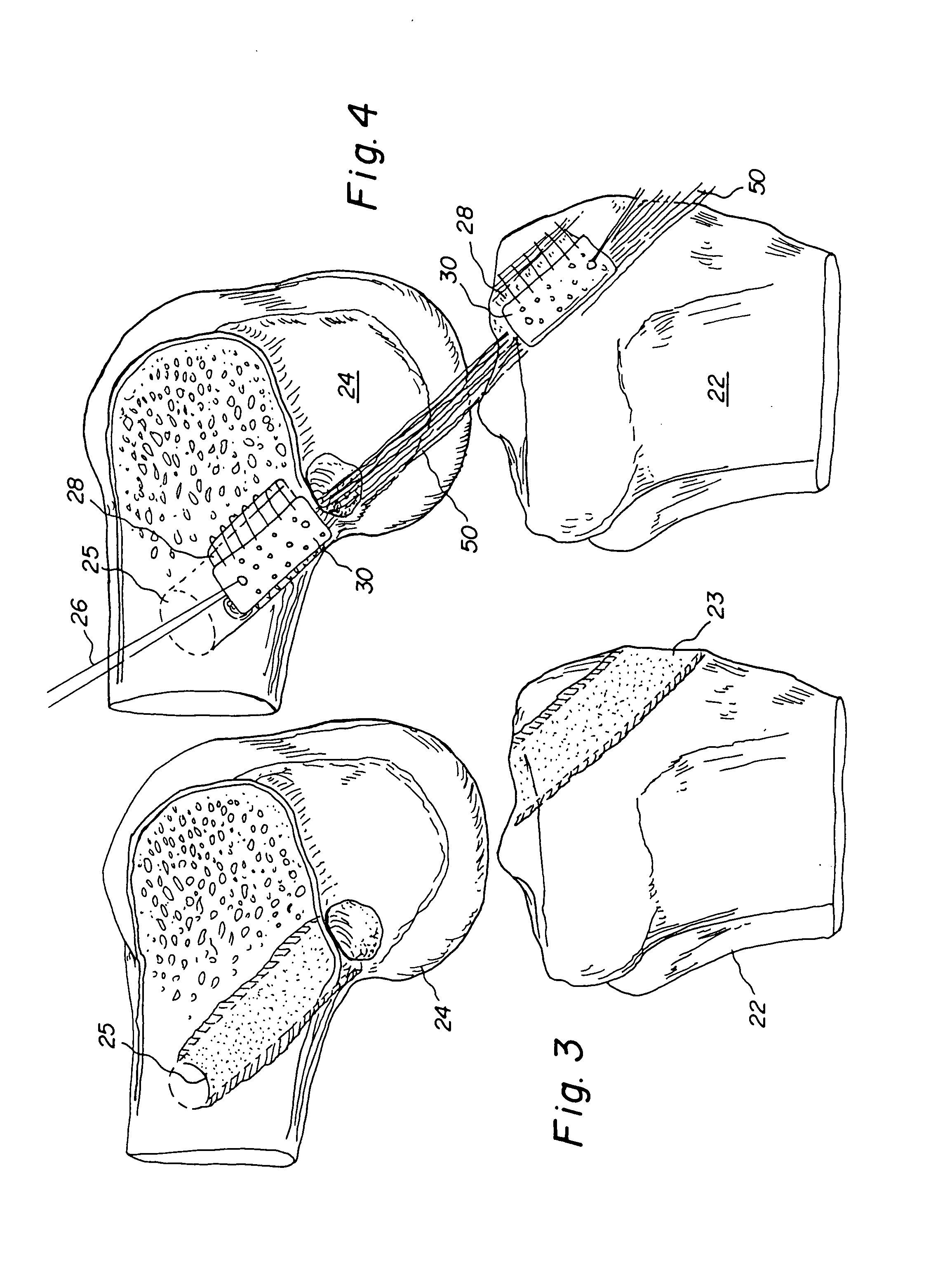
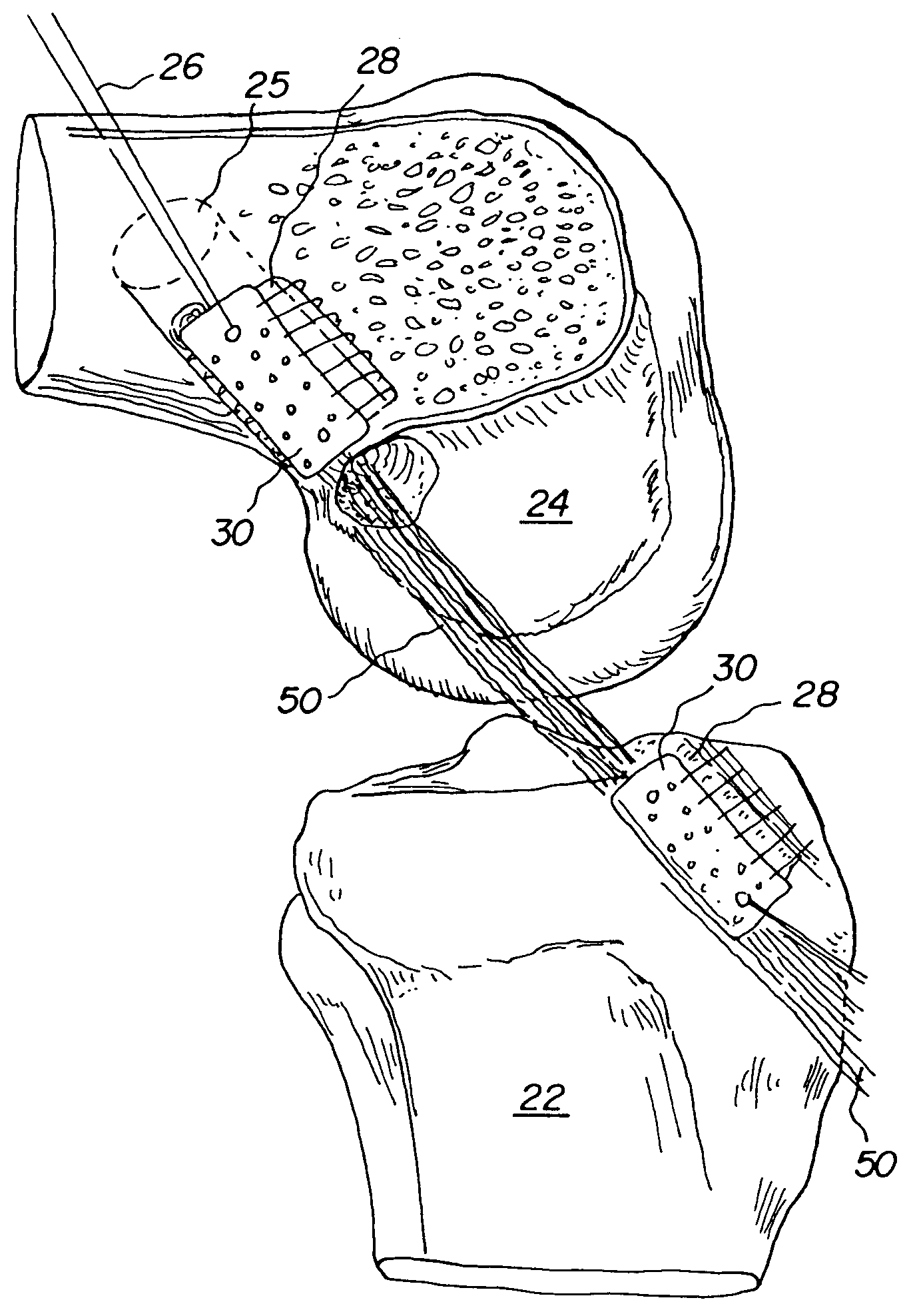
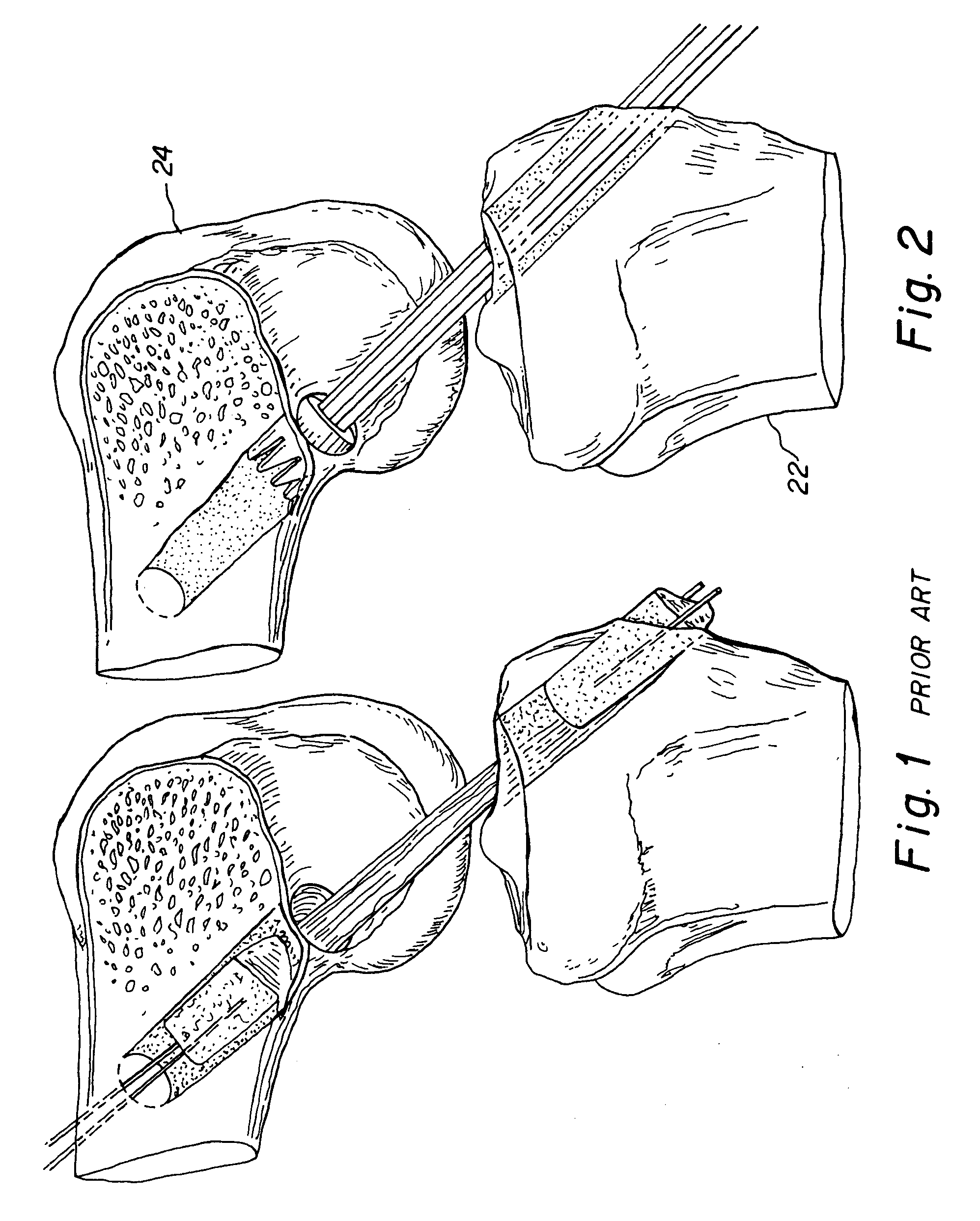
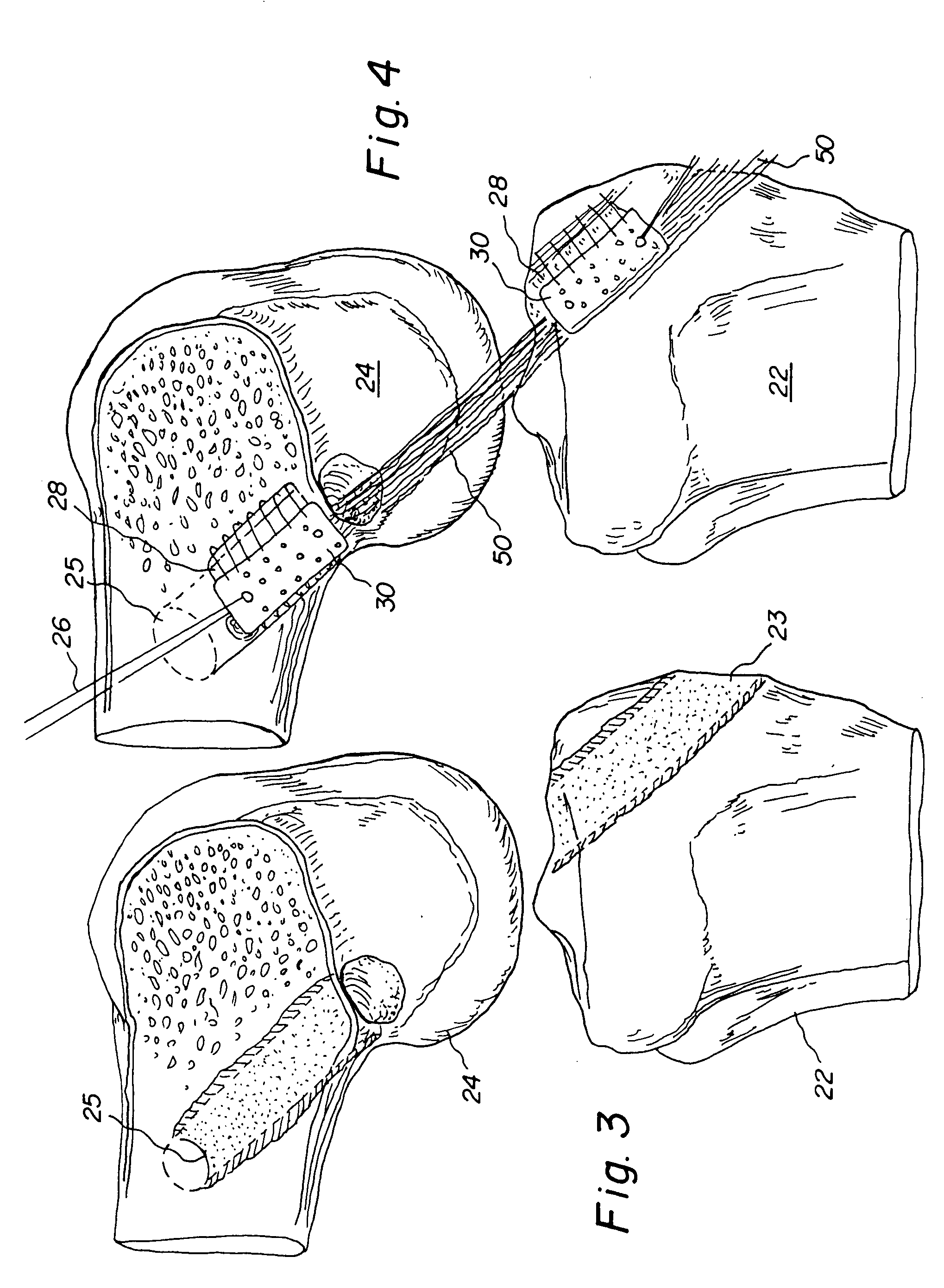
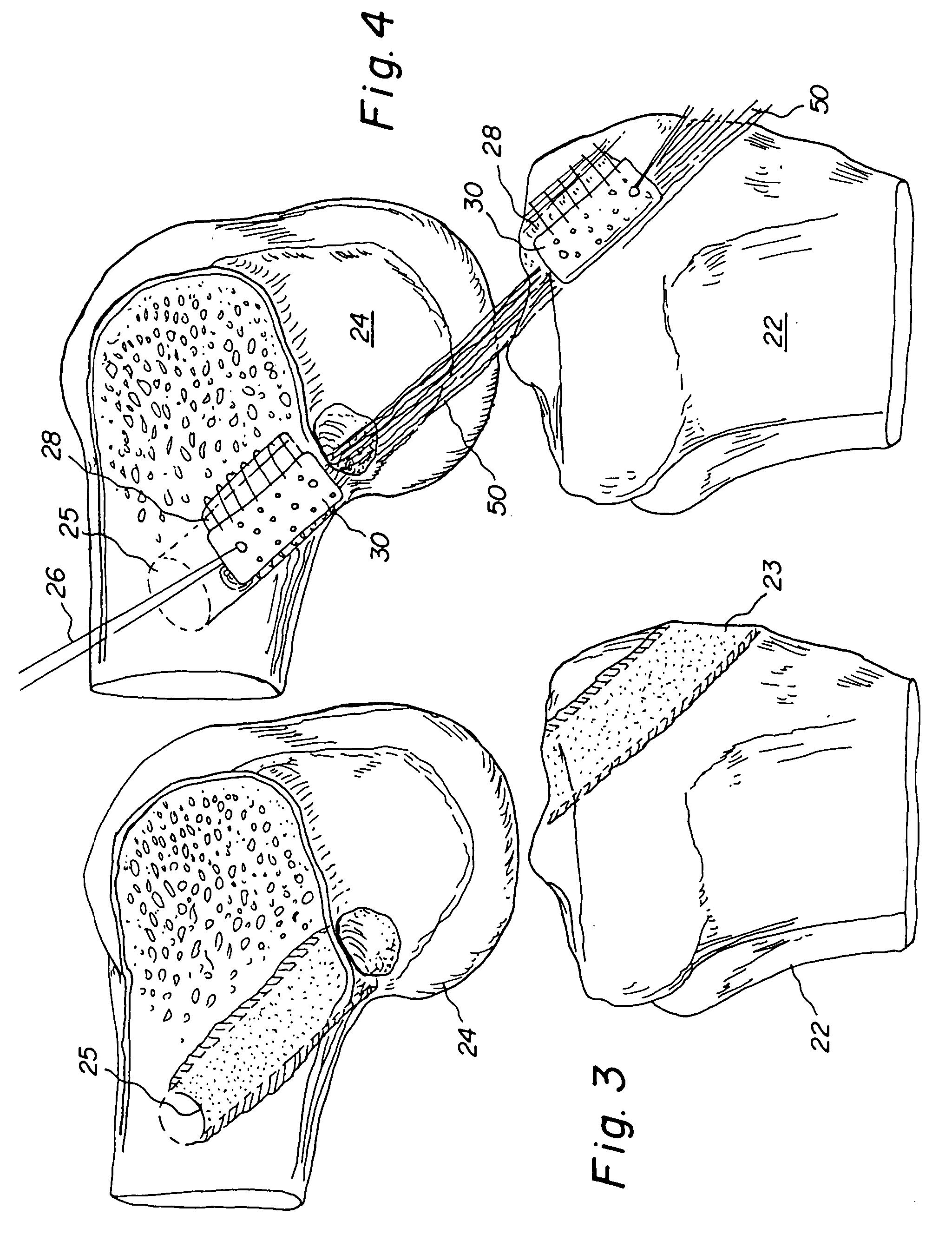
Bone-tendon-bone assembly with allograft bone block and method for inserting same
InactiveUS6890354B2Promote new bone growthPromote healingSuture equipmentsBone implantBone tunnelInterference screws
The invention is directed toward a bone block, a bone-tendon-bone assembly and method of tendon reconstruction in which at least one tendon replacement is extended between two bone blocks and fixed within each of two bone tunnels in the bones of a joint using interference screws. Each bone block has a central through going bore and at least one substantially parallel channel longitudinally cut in the exterior of the bone block body in which the ligament replacements are seated. One end of each bone block has a rounded recess leading from the central bore to the exterior parallel channel.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Random code length polar encoding method
InactiveCN103023618AImprove noise immunityError preventionCode conversionComputer hardwareCommunications system
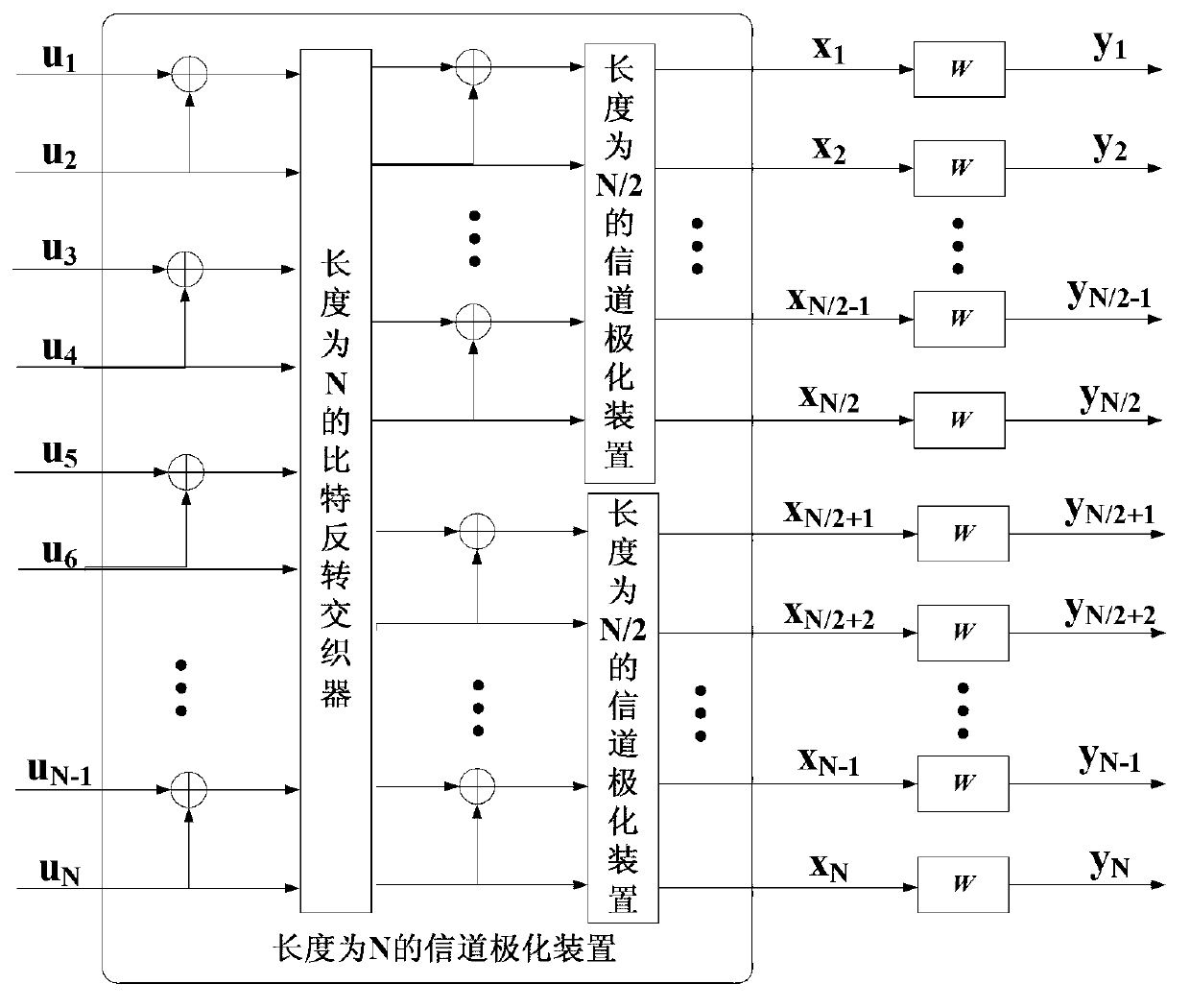
A random code length polar encoding method includes: during construction of a polar code, if the code length is not the power of 2, using a group of virtual channels with the capacity of zero for supplementing the channel number to be the power of 2; performing mixed mapping for each channel according to the capacity equalization principle; and performing polar conversion for the obtained channels, selecting the channels with higher capacity from converted channels according to the designed bitrate for transmitting information bit sequences, and using the rest channels for transmitting a known fixed bit sequence of a receiving end and a transmitting end. The method enables polar encoding to allow the code length to be an optional positive integer and is applicable to multi-carrier and high-order modulation systems, and the added perforating operation enables the encoding bit sequences outputted by an encoder to be optional in length; by means of channel mixed mapping, polar encoding can adapt to different component channels of parallel channels, so that anti-noise performance is good; and flexibility of using polar codes for a practical digital communication system is greatly improved, and accordingly the method has good application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
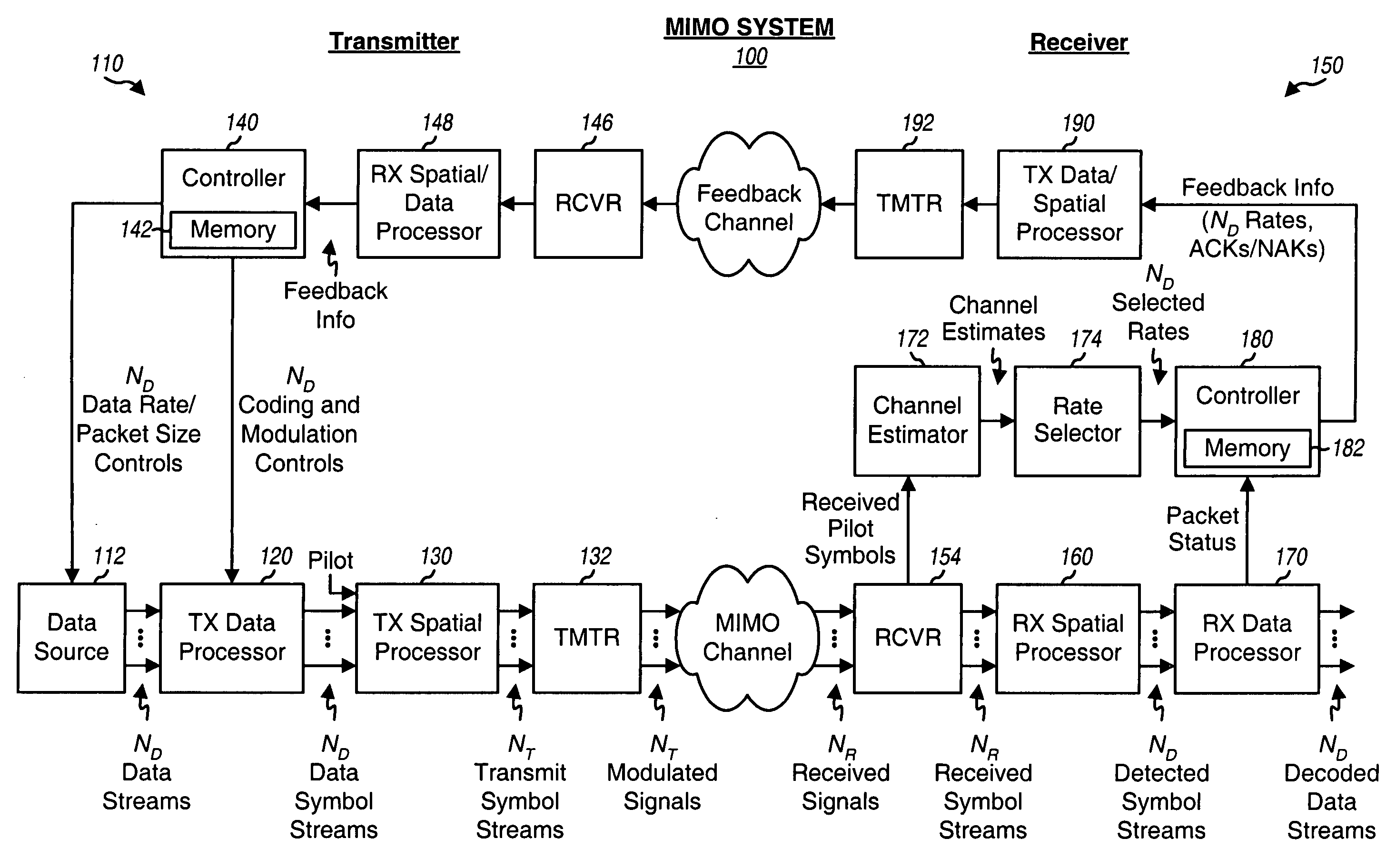
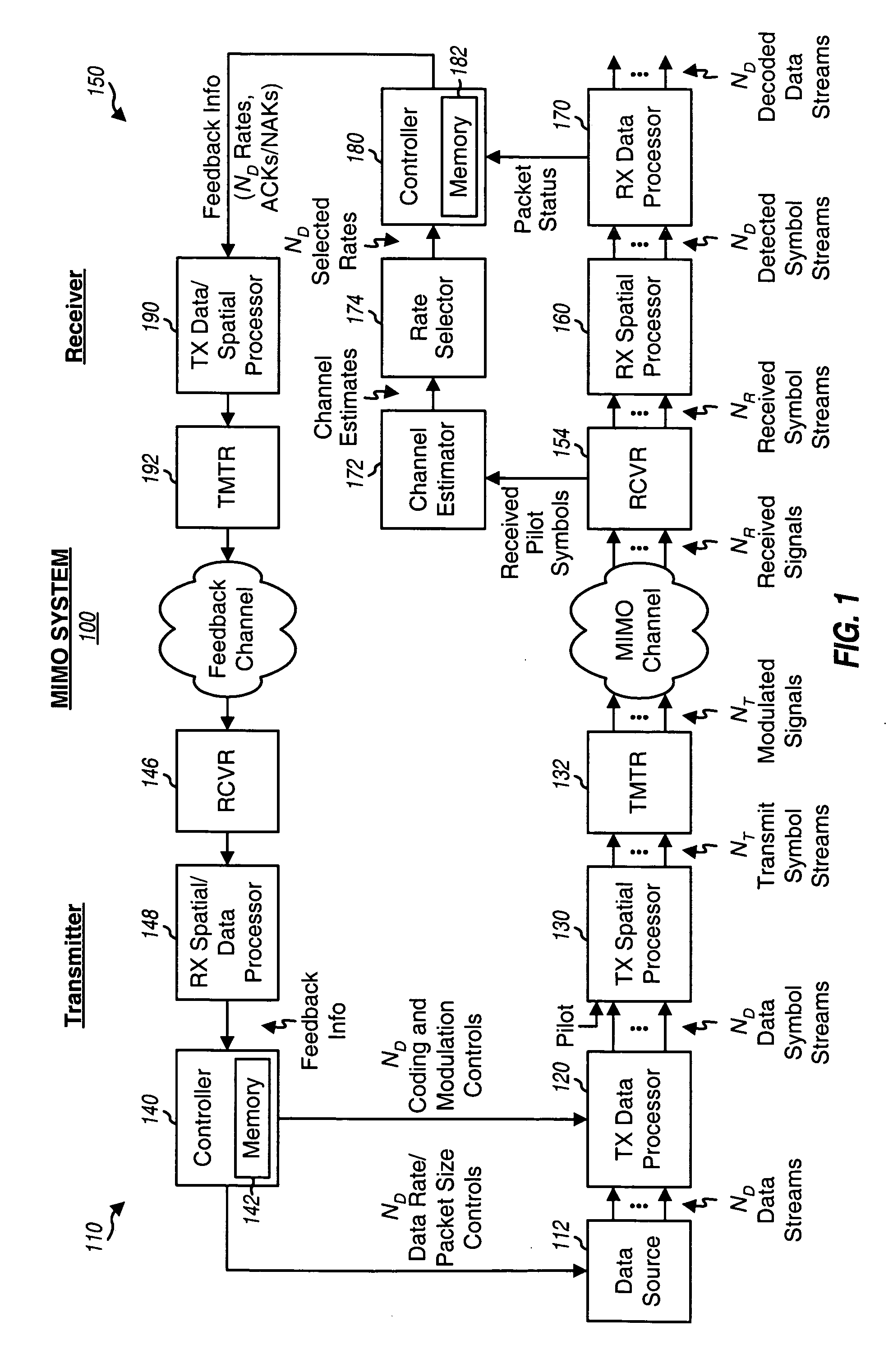
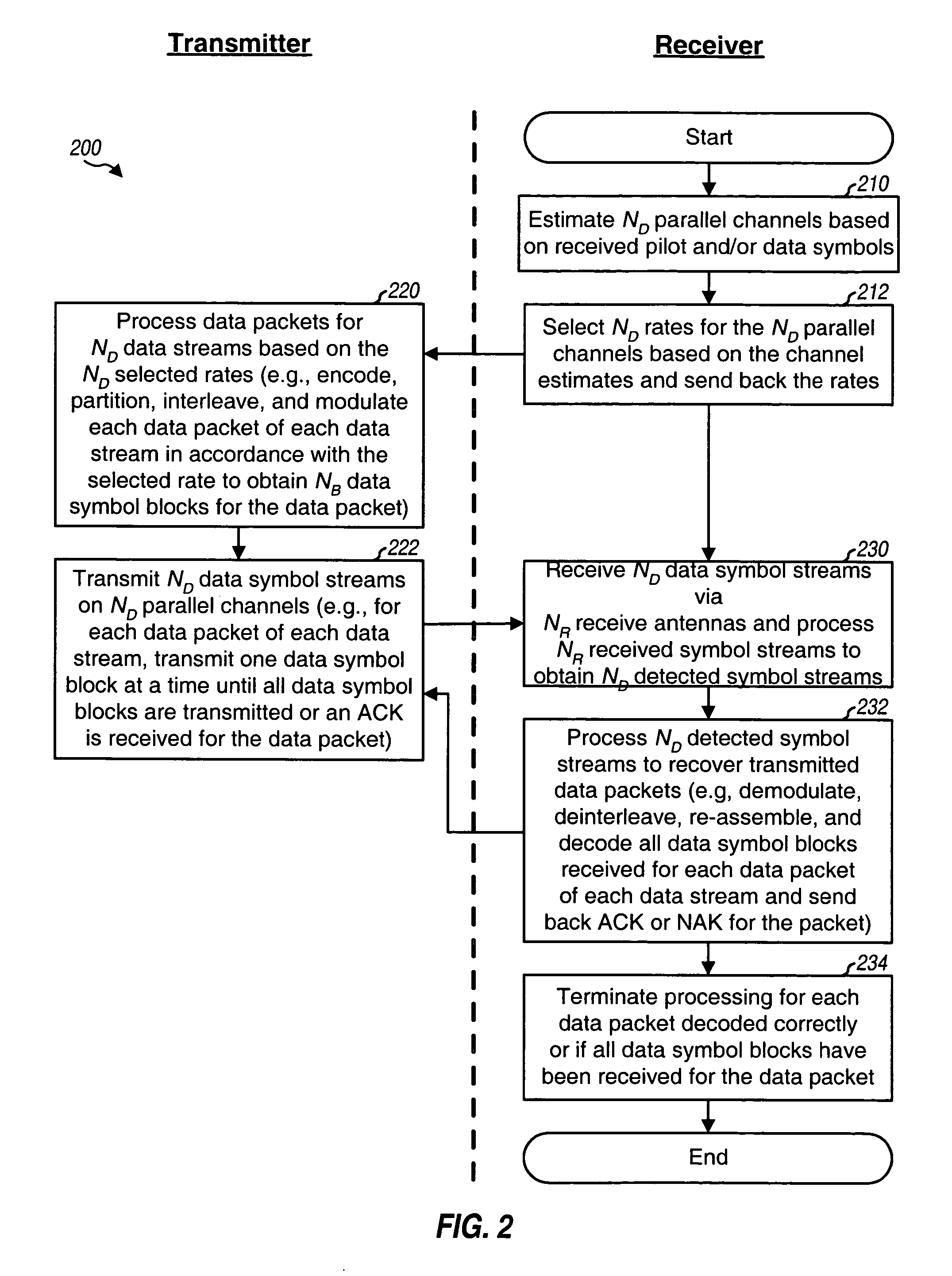
Incremental redundancy transmission for multiple parallel channels in a MIMO communication system
ActiveUS20050063378A1Increase chanceError prevention/detection by using return channelEnergy efficient ICTComputer scienceTransmitter
For incremental redundancy transmission on multiple parallel channels in a MIMO system, a transmitter processes (e.g., encodes, partitions, interleaves, and modulates) each data packet for each parallel channel based on a rate selected for the parallel channel and obtains multiple symbol blocks for the packet. For each data packet, the transmitter transmits one symbol block at a time on its parallel channel until a receiver recovers the packet or all blocks have been transmitted. The receiver performs detection and obtains symbol blocks transmitted on the parallel channels. The receiver recovers the data packets transmitted on the parallel channels independently or in a designated order. The receiver processes (e.g., demodulates, deinterleaves, re-assembles, and decodes) all symbol blocks obtained for each data packet and provides a decoded packet. The receiver may estimate and cancel interference due to recovered data packets so that data packets recovered later can achieve higher SINRs.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
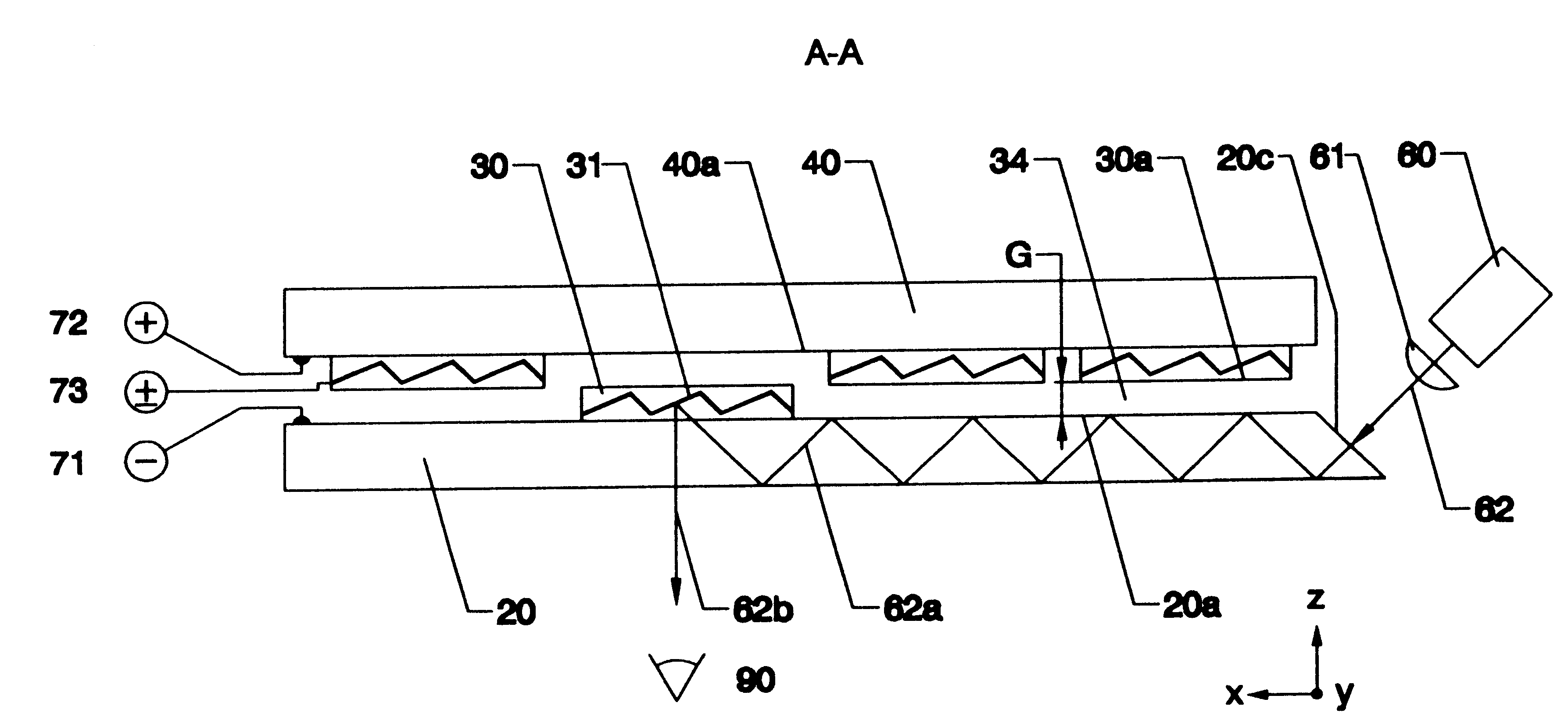
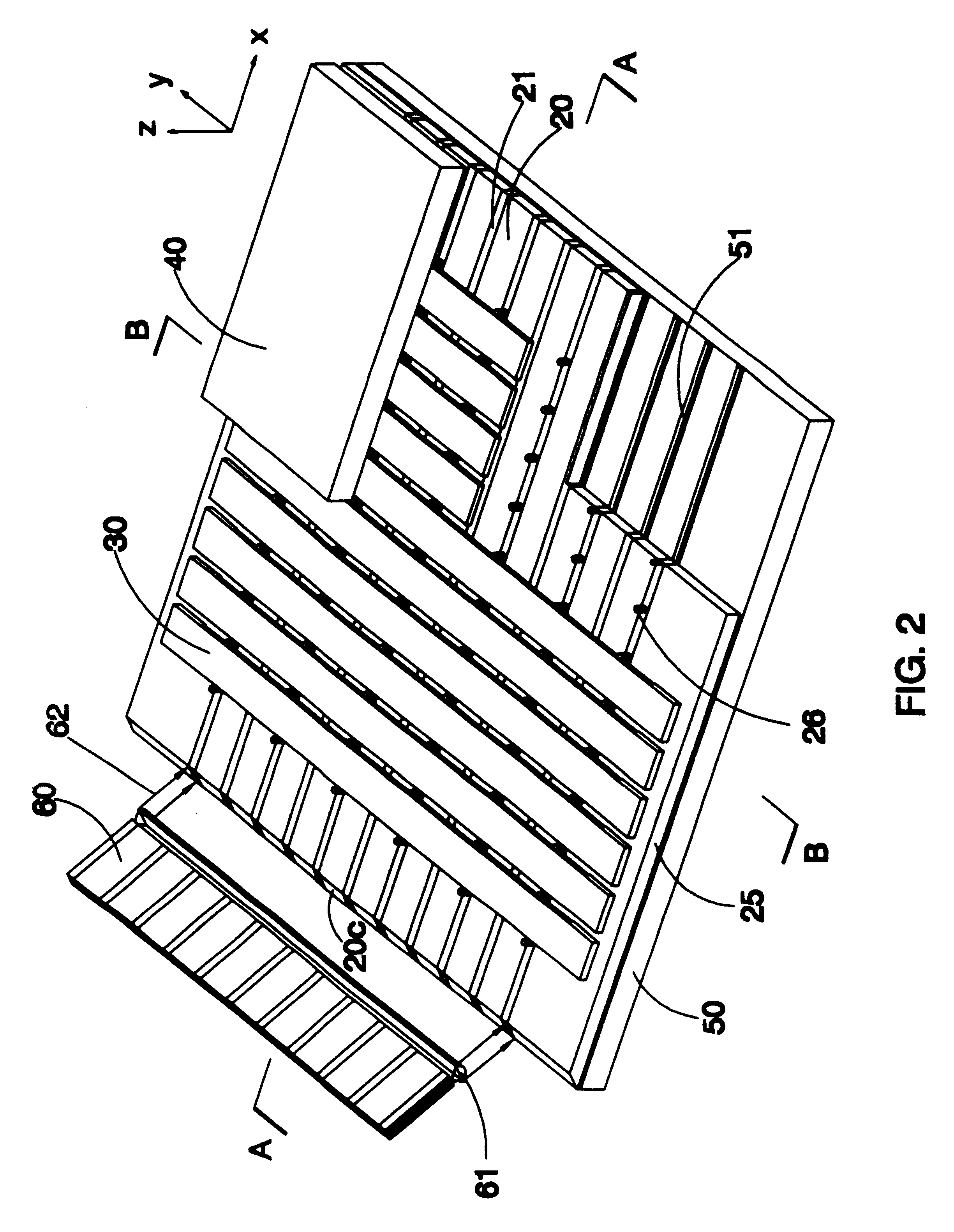
Optical device utilizing optical waveguides and mechanical light-switches
InactiveUS6650822B1High refractive indexReduction factorCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An optical device consists of one or more optical waveguides and mechanical light switches 30. When a light switch 30 is turned on, it extracts light beam 62a from a waveguide core 20 and redirect the light beam 62b into free space, it redirects an incoming light beam 80 from free space and injects the light beam 80a into the waveguide core 20, or it performs both functions at the same time, depending on specific applications. On and off states of a light switch 30 are achieved by pulling the light switch 30 into a close vicinity of the waveguide core 20 and by pushing the light switch 30 away from the waveguide core 20, respectively. An interactive fiat-panel display can be built based on this invention. A plurality of parallel channel waveguides forms a display panel. An array of light beams 62a, injected from an array light source 60, propagates along waveguide cores 20 until reaches a location where a light switch 30 is turned on. At this location, the light switch 30 redirects the light beams towards a viewer. An image is produced when the light switches 30 are turned on sequentially while the light-intensity distribution on the array light source 60 is synchronically updated. The panel display is capable of responding to an input optical signal by detecting an incoming light beam 80 from a light pen 100. An array of photodetectors 81 is used to identify the location of the incoming light beam 80 on the display panel and a computer is used to execute a corresponding action accordingly.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Bone tendon bone assembly with allograft bone block
InactiveUS20050203620A1Provide strengthProvide to structureSuture equipmentsBone implantBone tunnelInterference screws
The invention is directed toward a bone block, a bone-tendon-bone assembly and method of tendon reconstruction in which at least one tendon replacement is extended between two bone blocks and fixed within each of two bone tunnels in the bones of a joint using interference screws. Each bone block has a central through going bore and at least one substantially parallel channel longitudinally cut in the exterior of the bone block body in which the ligament replacements are seated. One end of each bone block has a rounded recess leading from the central bore to the exterior parallel channel.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
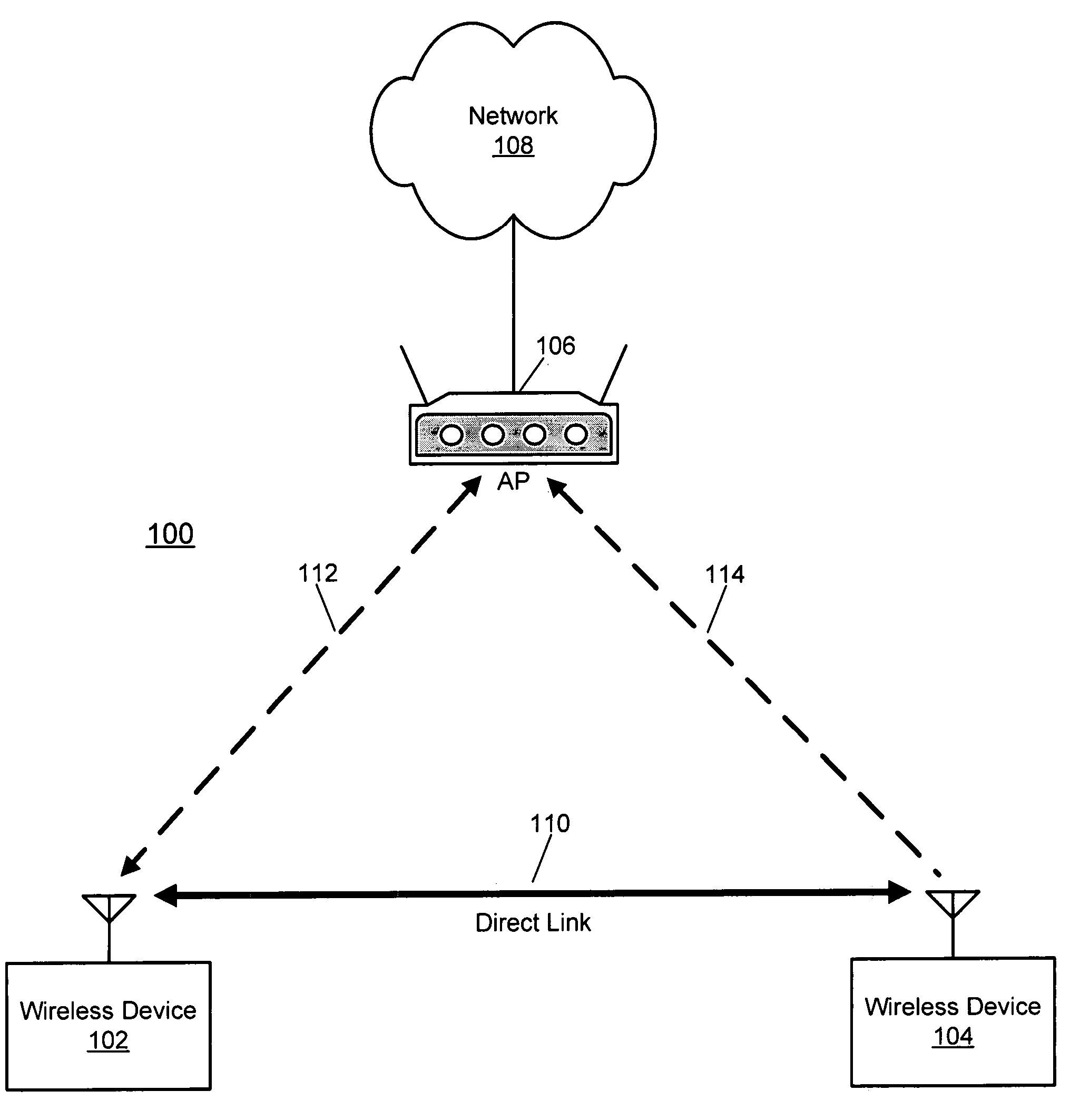
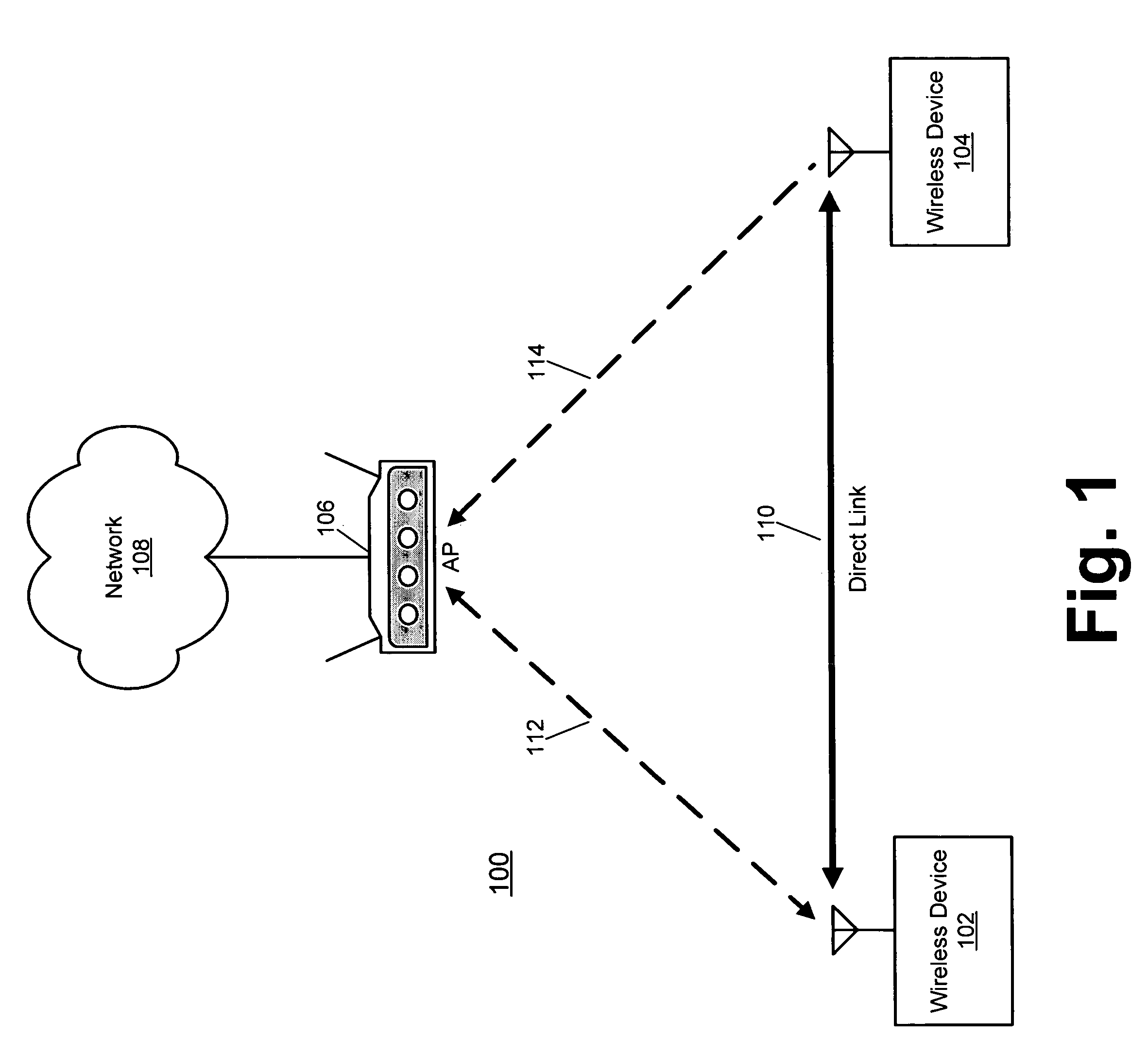
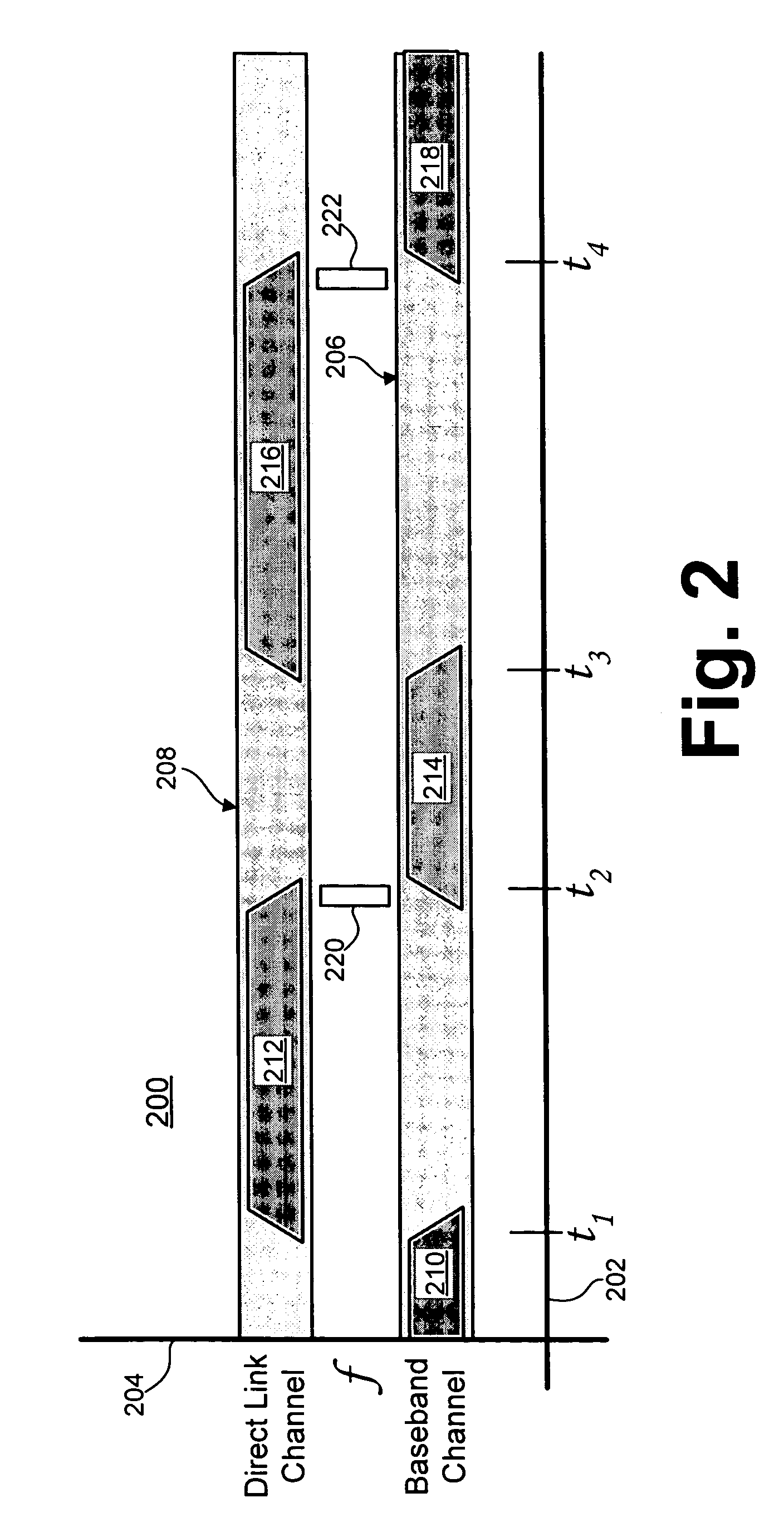
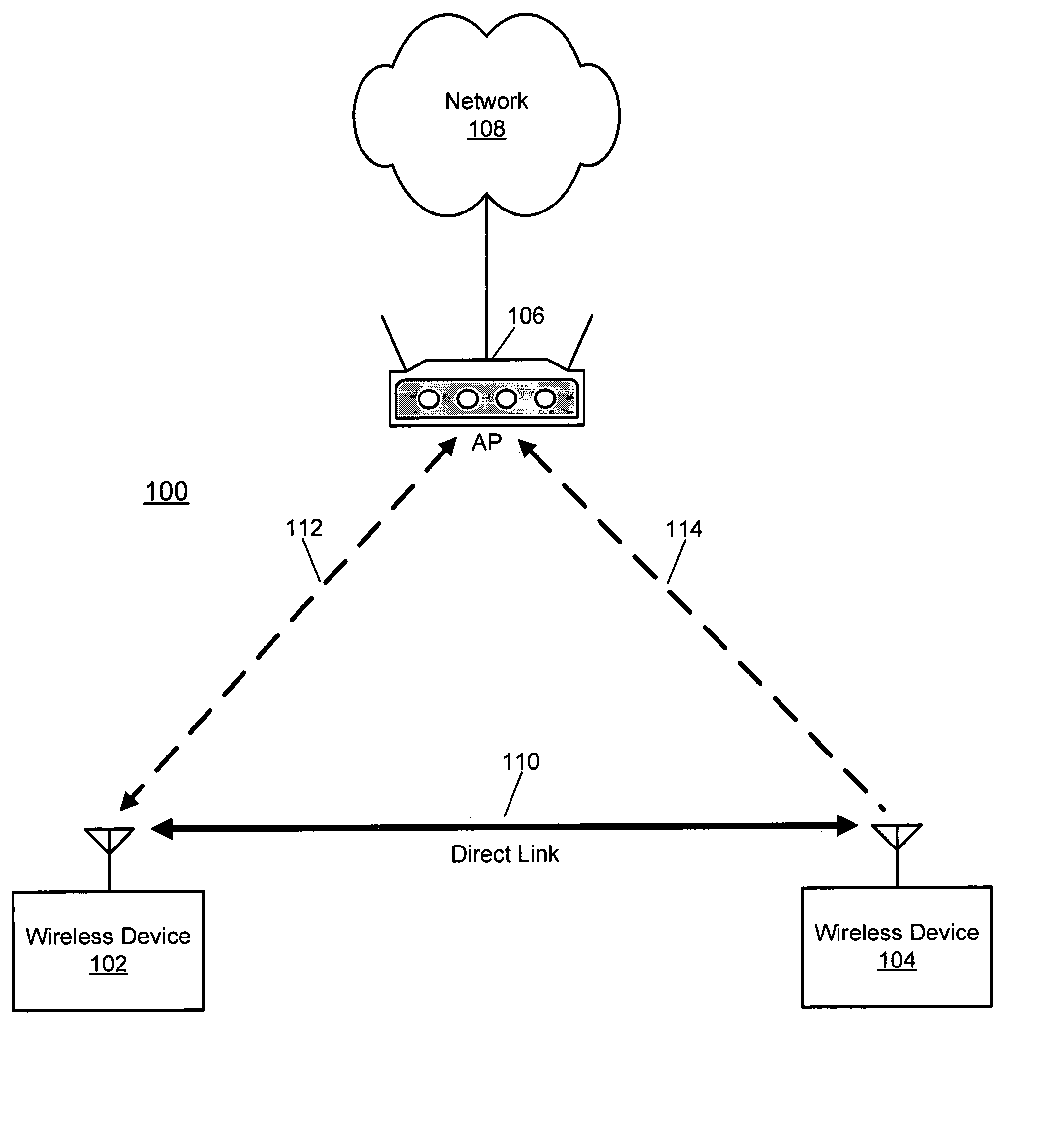
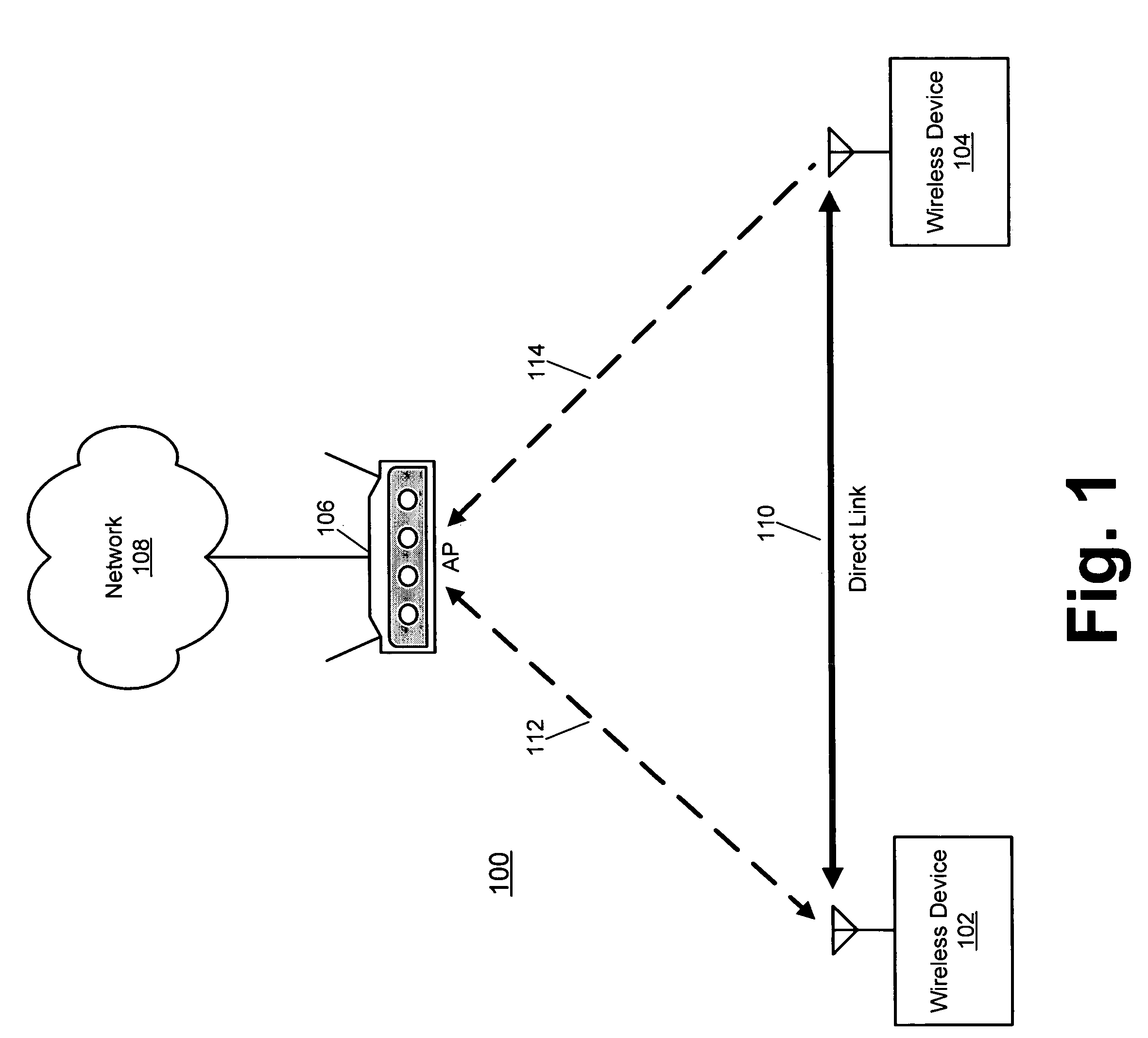
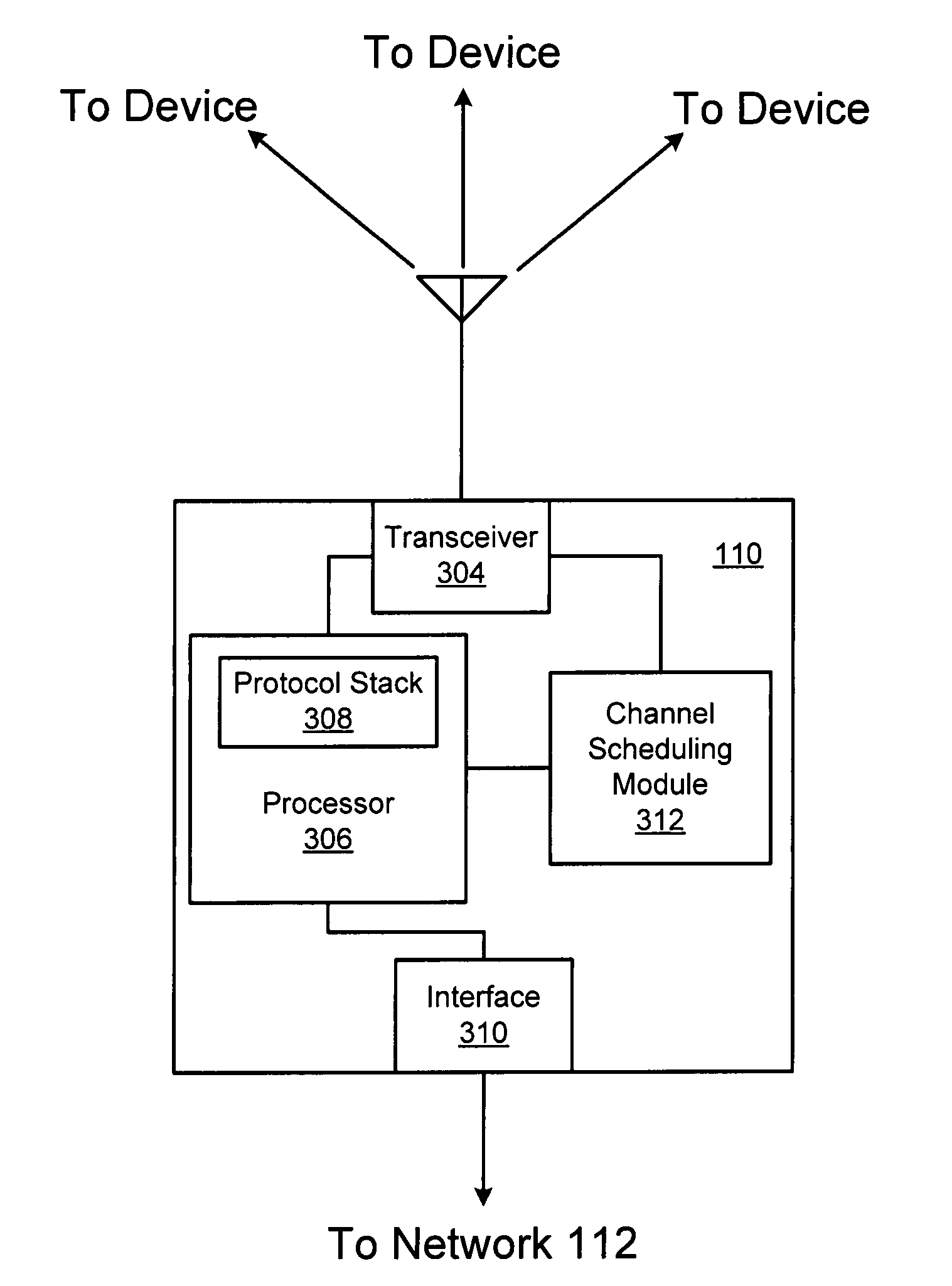
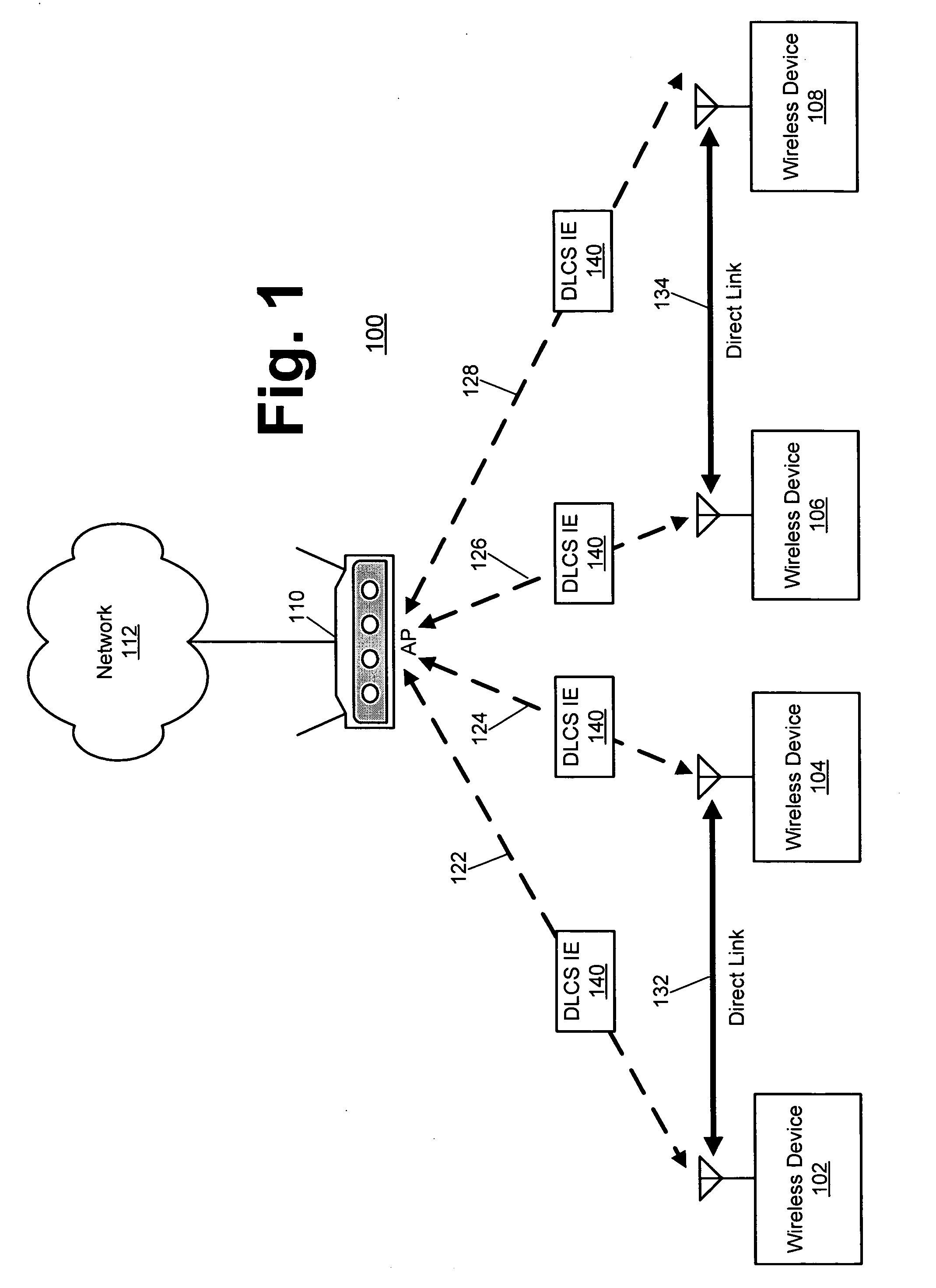
Event-based multichannel direct link
InactiveUS20050036469A1Improve economyTransparent operationPower managementTransmission control/equalisingTelecommunicationsBeacon frame
Disclosed herein are exemplary techniques for the communication of information in a wireless system by using multiple wireless channels. A direct link between two or more wireless devices may be established by performing a direct link setup between two or more wireless devices using an access point, where the direct link setup is conducted over a base channel and the direct link is established on a parallel channel. The two or more wireless devices may switch to the parallel channel and use the established direct link to communicate information directly without the access point as an intermediary. In anticipation of a predetermined event, such as the transmission of a delivery traffic indication map (DTIM) beacon frame by the access point, the two or more wireless devices may switch back to the base channel so that uplink, downlink and / or peer-to-peer information may be transmitted and / or received.
Owner:OZMO LICENSING LLC
Event-based multichannel direct link
InactiveUS7251235B2Improve economyTransparent operationPower managementTransmission control/equalisingBeacon framePeer-to-peer
Disclosed herein are exemplary techniques for the communication of information in a wireless system by using multiple wireless channels. A direct link between two or more wireless devices may be established by performing a direct link setup between two or more wireless devices using an access point, where the direct link setup is conducted over a base channel and the direct link is established on a parallel channel. The two or more wireless devices may switch to the parallel channel and use the established direct link to communicate information directly without the access point as an intermediary. In anticipation of a predetermined event, such as the transmission of a delivery traffic indication map (DTIM) beacon frame by the access point, the two or more wireless devices may switch back to the base channel so that uplink, downlink and / or peer-to-peer information may be transmitted and / or received.
Owner:OZMO LICENSING LLC
Local communication system
InactiveUS6865188B1Reduce smoothnessMeet growth requirementsTime-division multiplexHybrid transportRing latencyControl channel
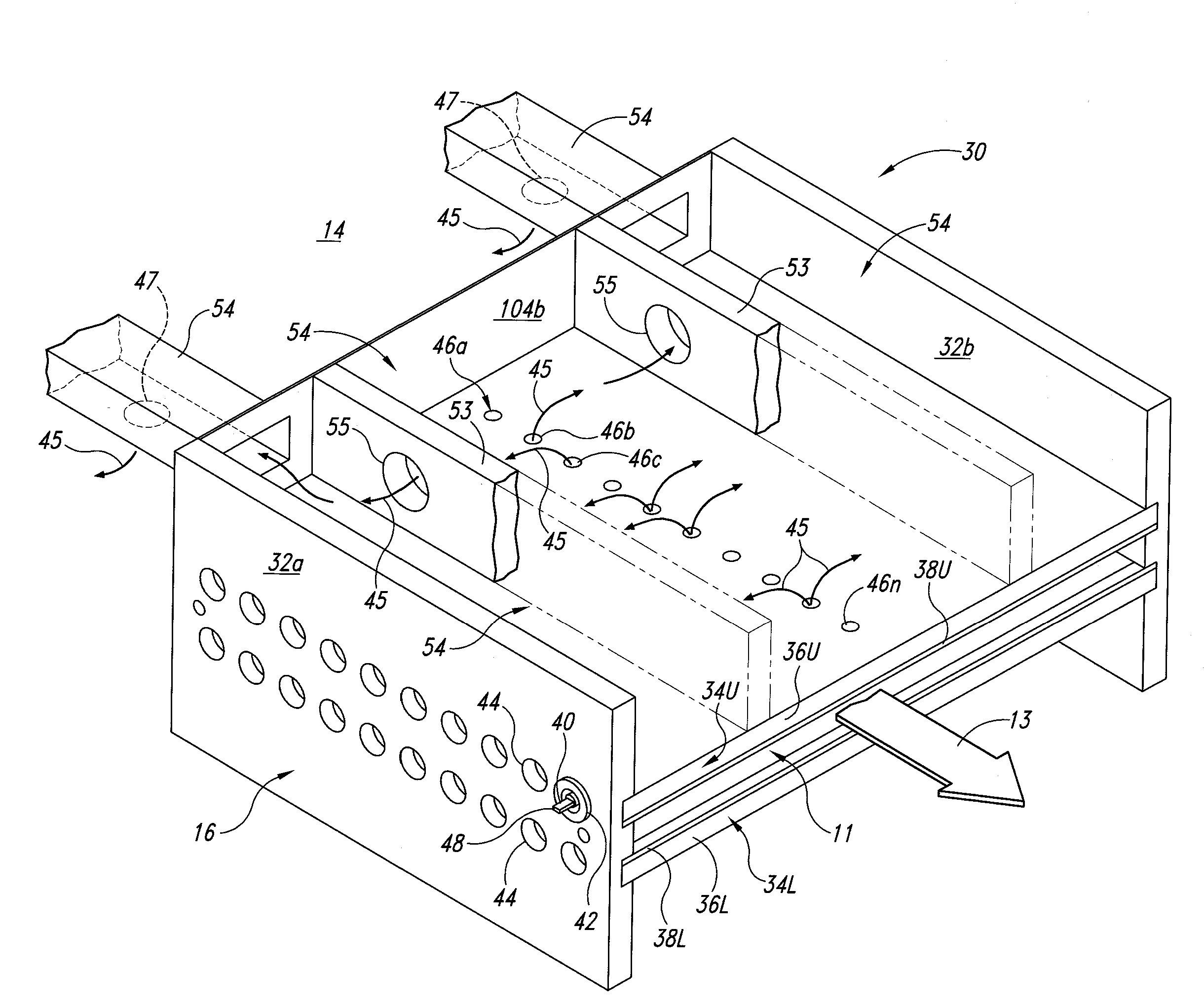
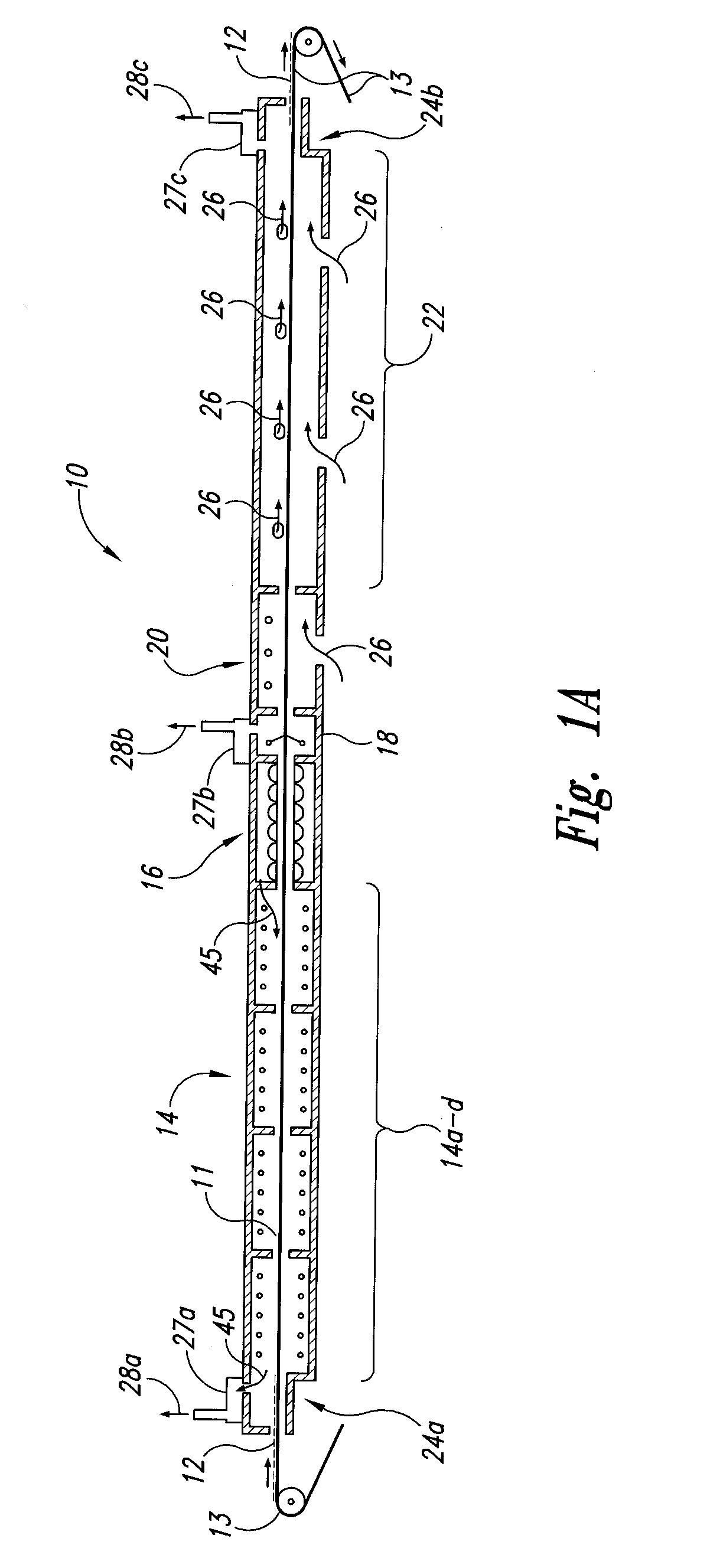
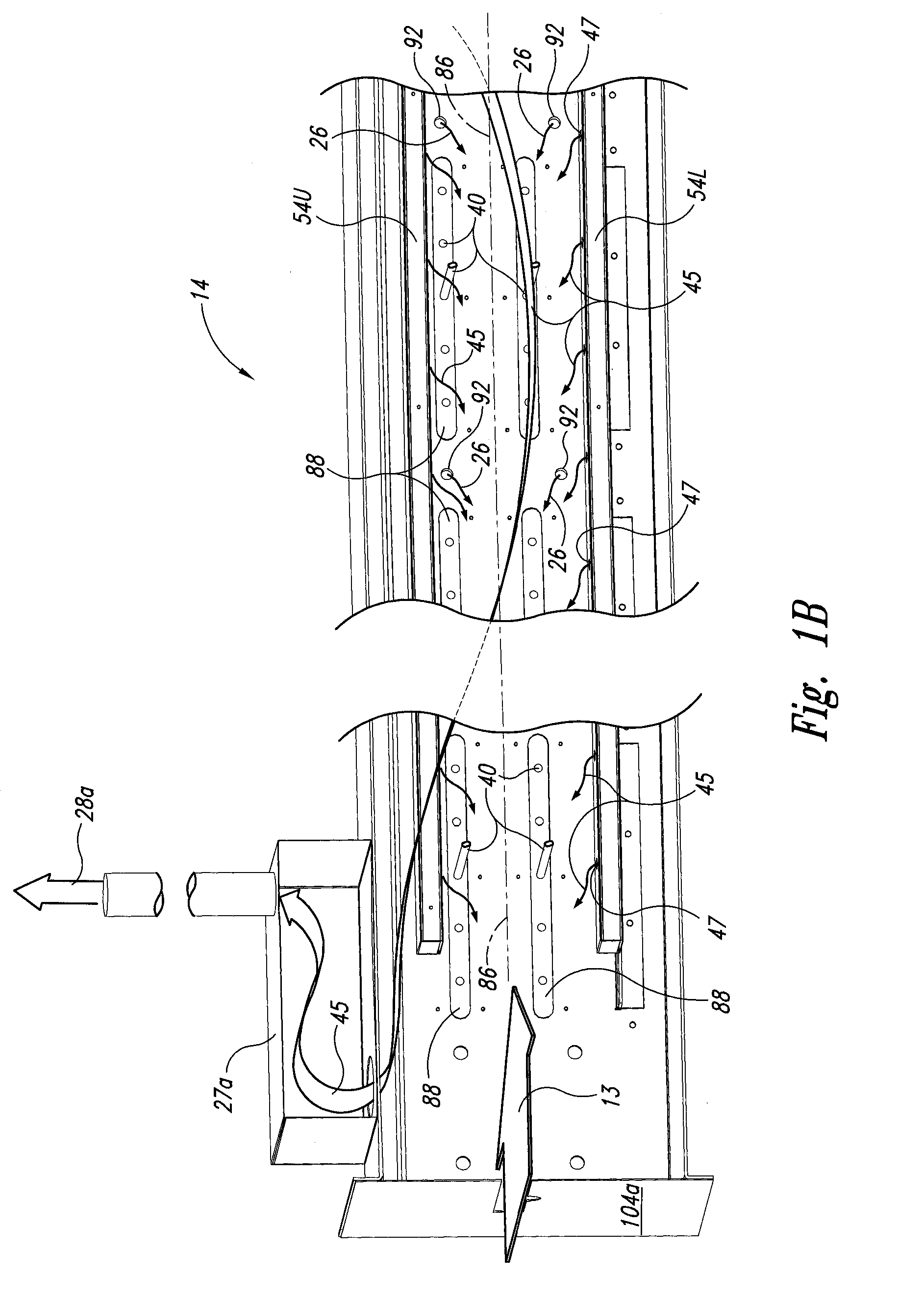
Examples of local communication systems are disclosed, based on a ring of point-to-point links, providing for transport of fixed rate synchronous, fixed rate asynchronous data and variable rate data in a flexible format. Different segments of the ring network can carry data at different bit rates, while remaining synchronized to a common frame rate and having a common control channel structure, for compatibility with earlier systems. Parallel channels are provided, either permanently or when required, for signalling errors of source data, data validity / padding, flow control. Parallel variable width channels are defined with free content (stream or packet). Null data symbols are defined for padding on a byte-by-byte basis. The allocation of capacity among variable width channels is revised block by block, and a transition period is defined to allow for ring latency. Calculations for allocation of capacity are performed during one block for the next block, locally at each source station, according to predetermined rules. Information as to bandwidth requirements is exchanged prior to the calculation via a special connection signalling channel and message format.
Owner:COMM & CONTROL ELECTRONICS
Heat exchangers having baffled manifolds
InactiveUS20100206535A1Prevent maldistributionEvaporators/condensersStationary conduit assembliesGas phaseEngineering
A heat exchanger for a fluid having a vapor-phase and a liquid-phase is provided. The heat exchanger includes a first manifold, a second manifold, a plurality of parallel channels, a mixing device, and one or more baffles. The parallel channels are in fluid communication with the first and second manifolds. The mixing device mixes the fluid flowing into the first manifold so that the fluid is a substantially homogeneous two-phase mixture of the vapor and liquid phases. The baffles are within the first manifold and ensure that the fluid enters the parallel channels as the substantially homogeneous two-phase mixture.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
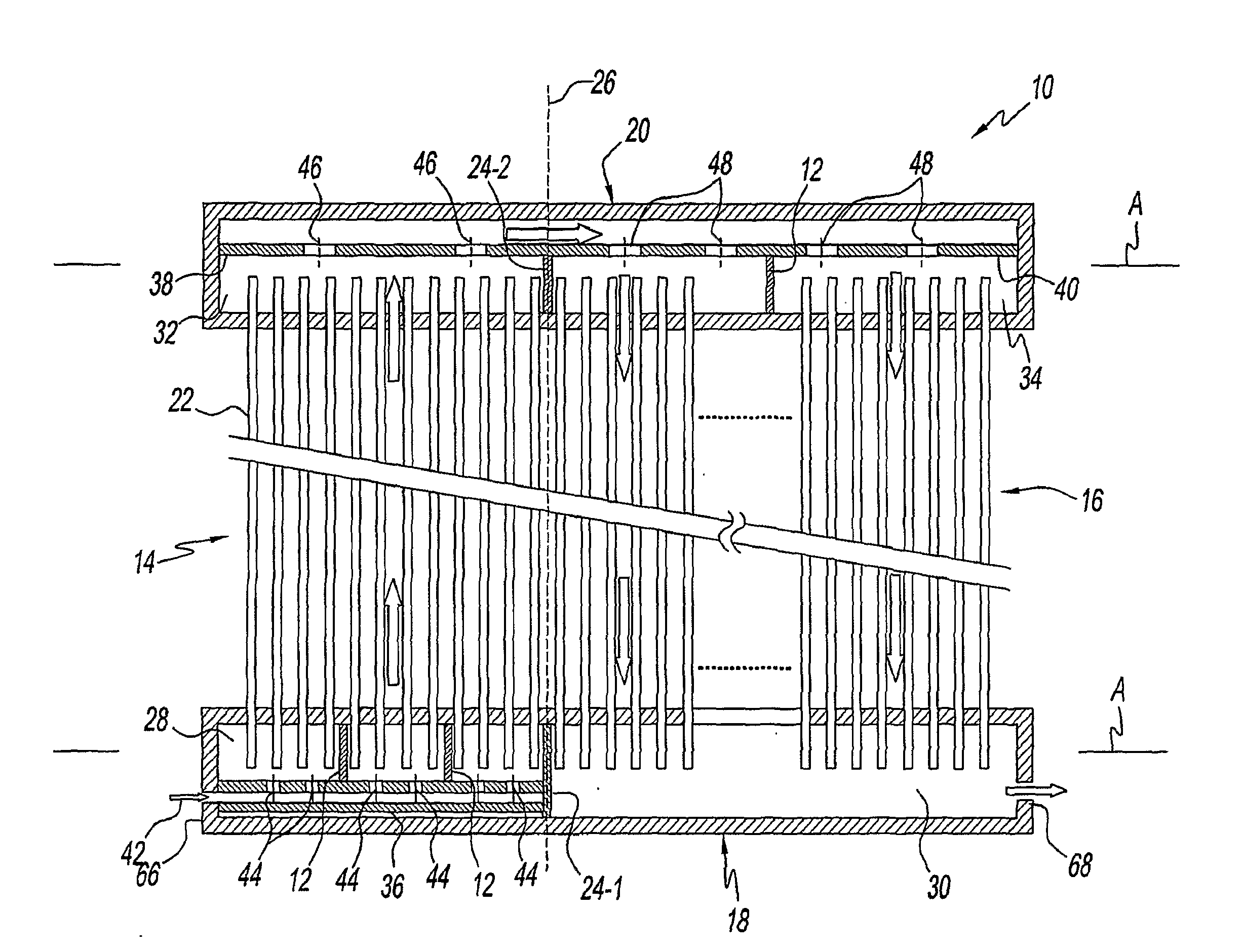
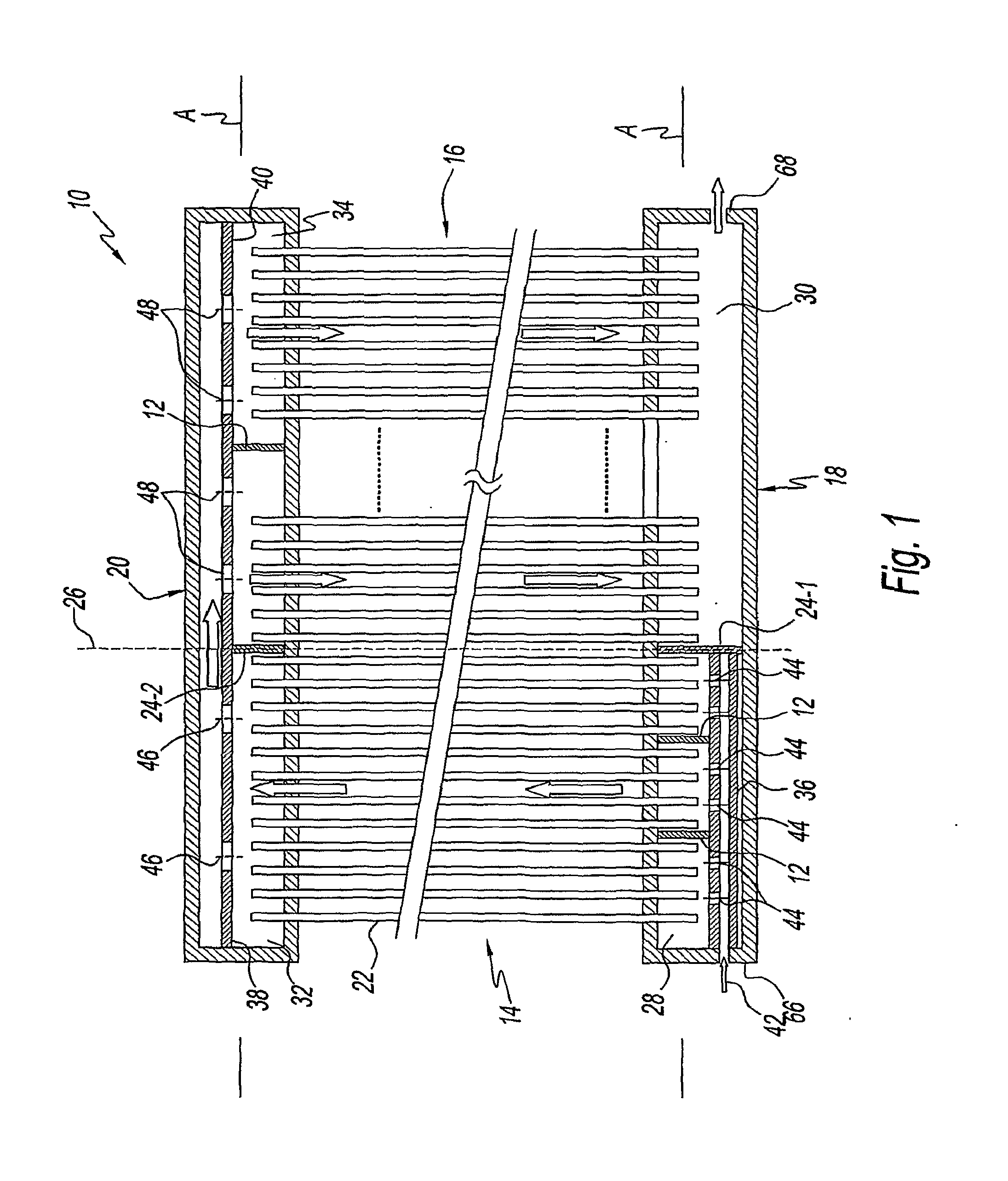
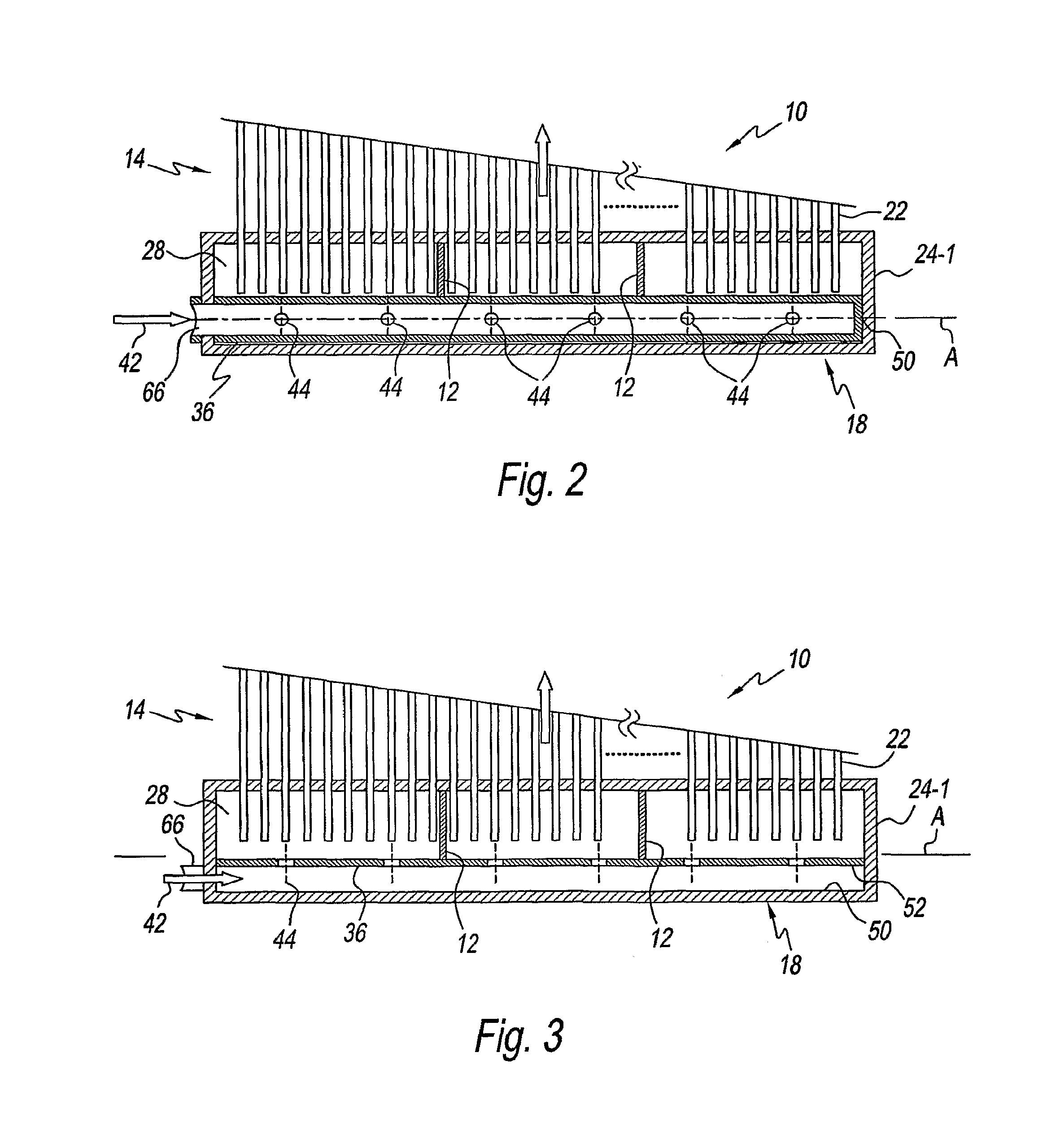
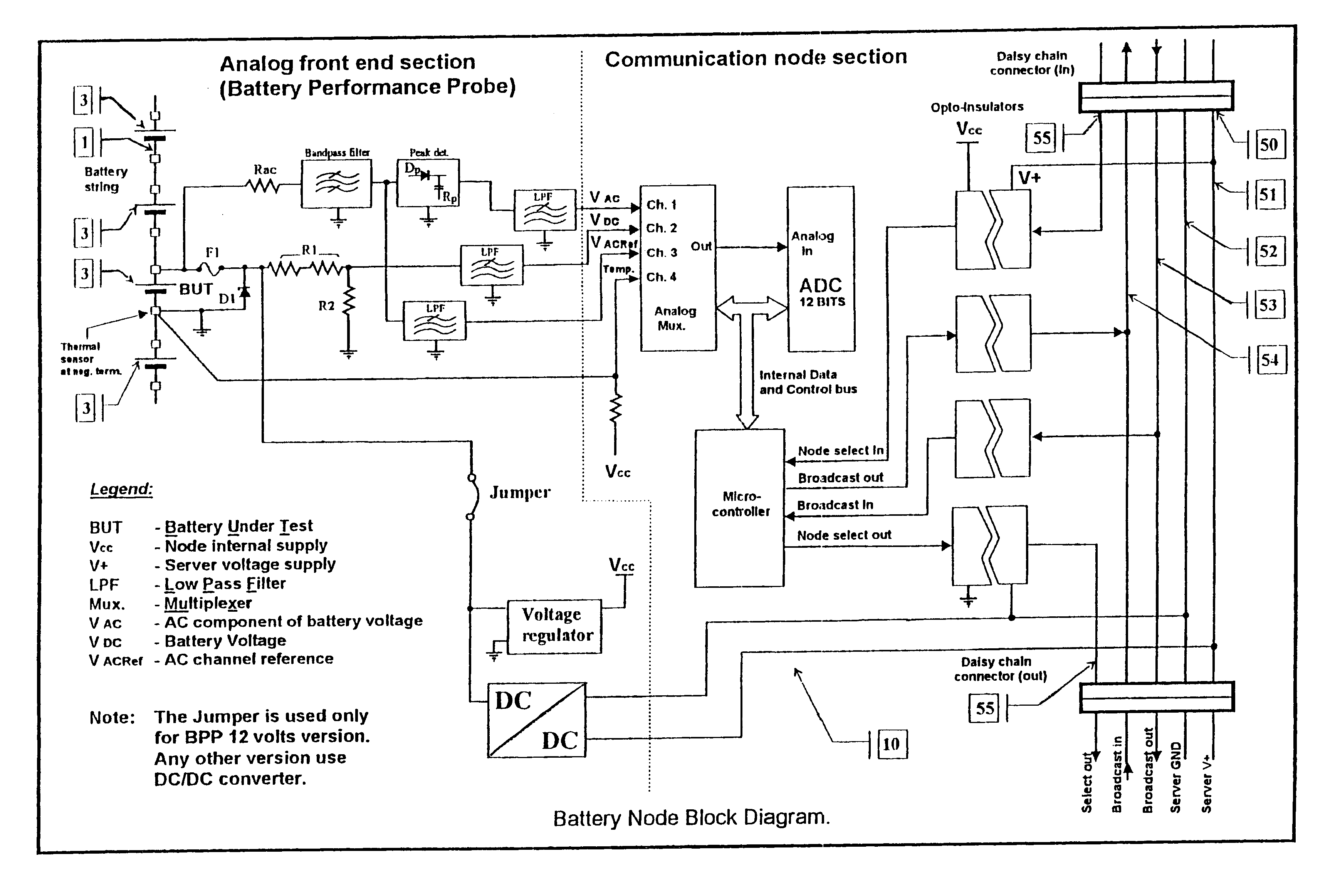
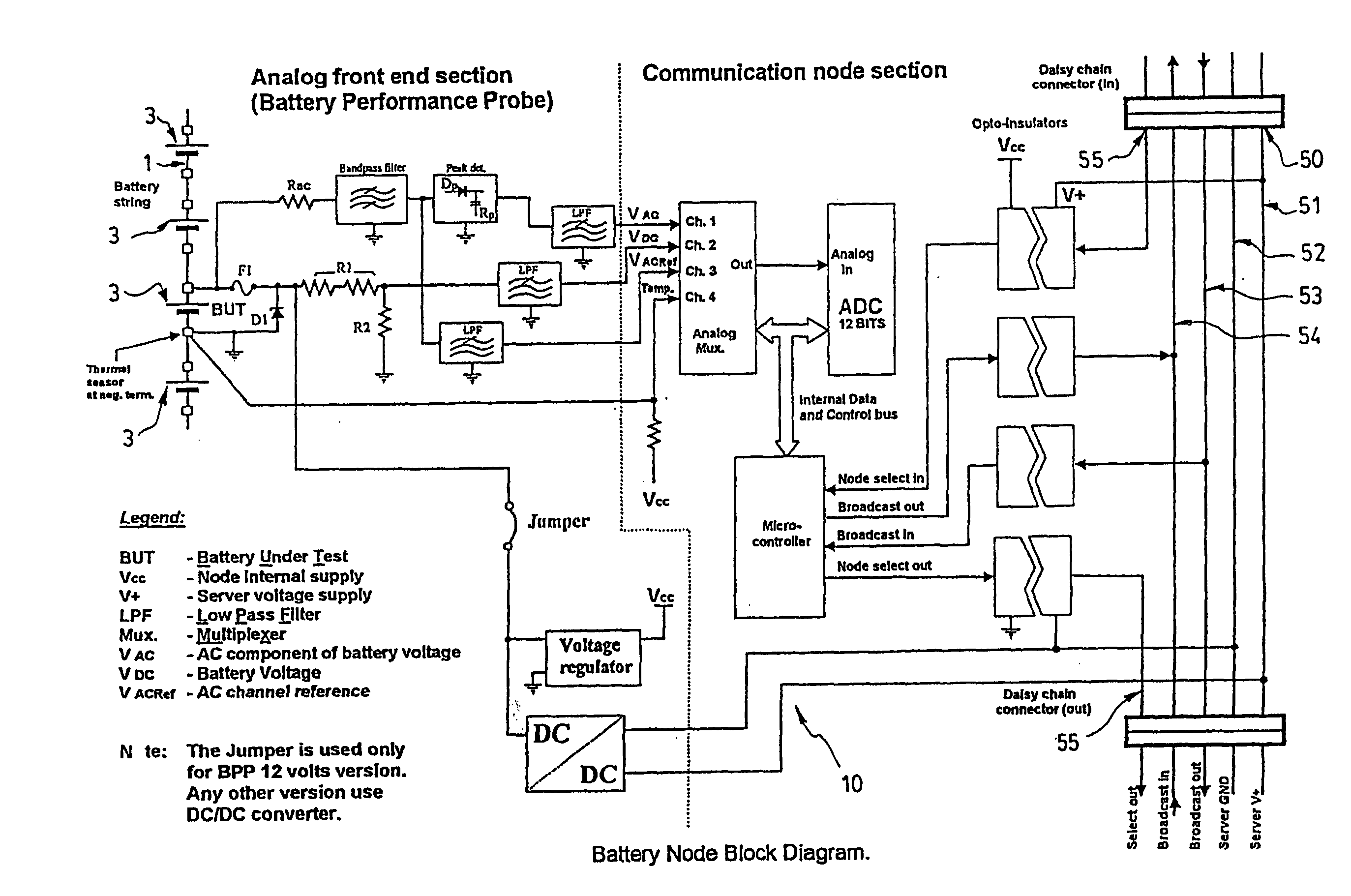
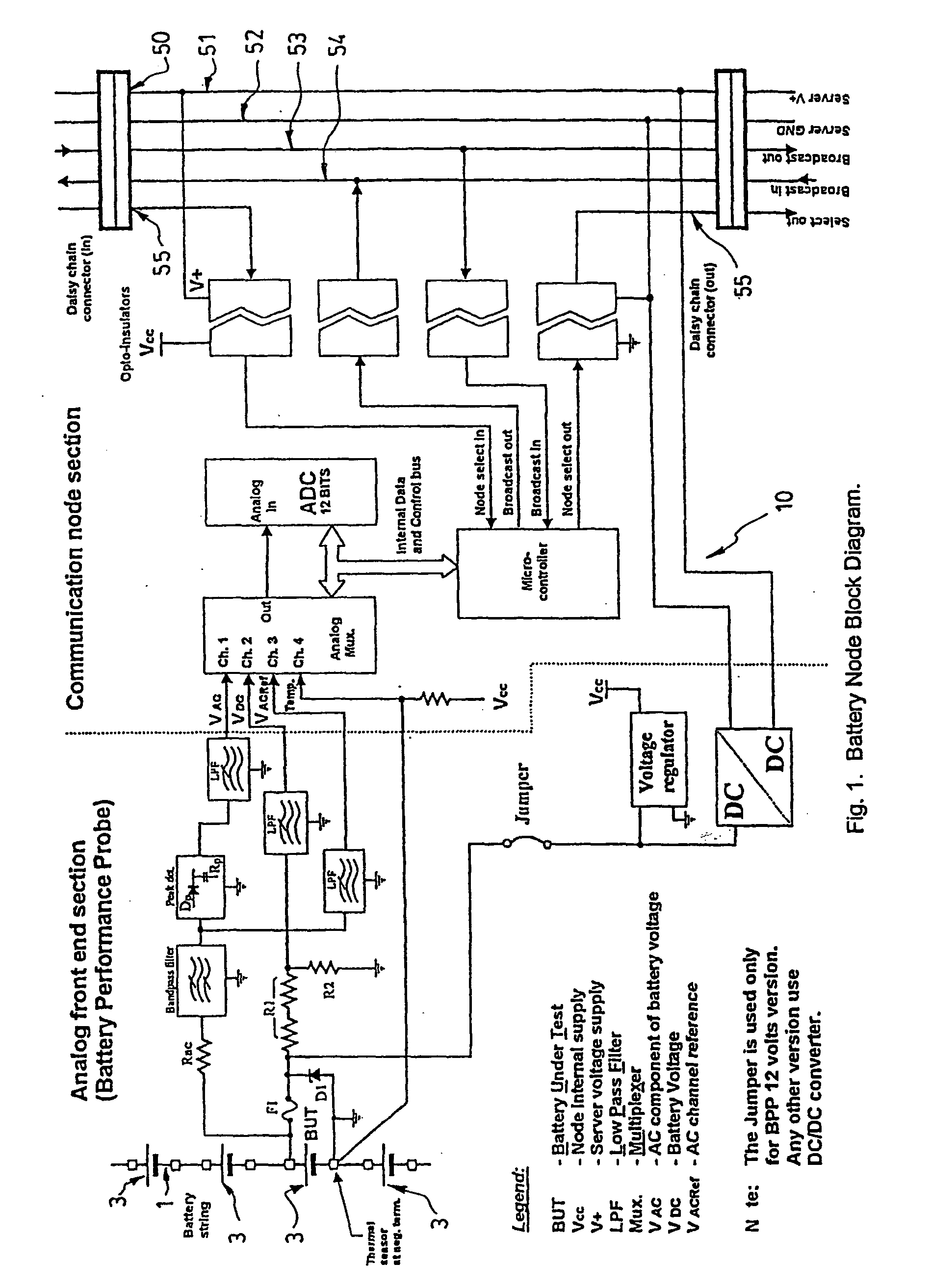
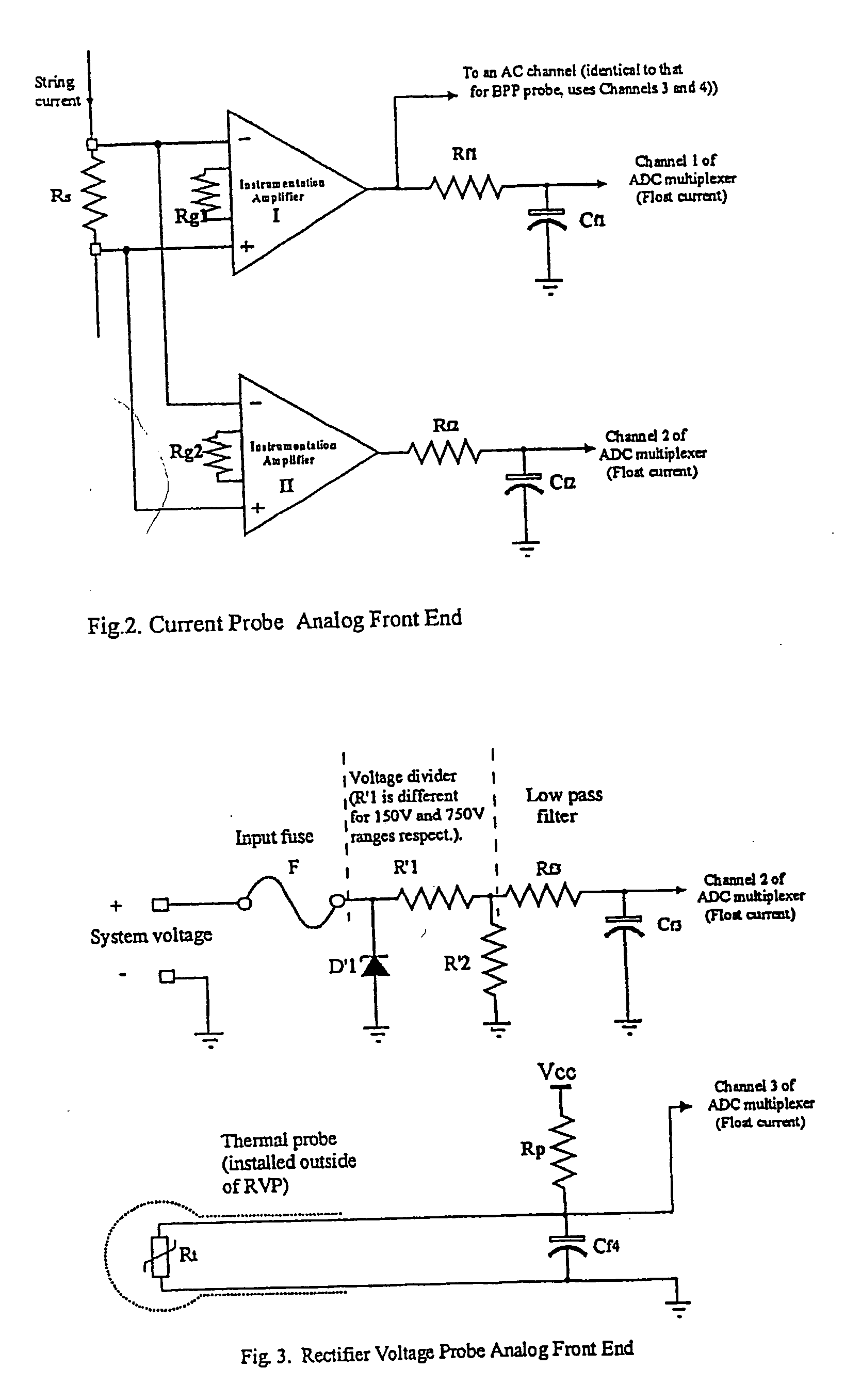
Method and apparatus for the continuous performance monitoring of a lead acid battery system
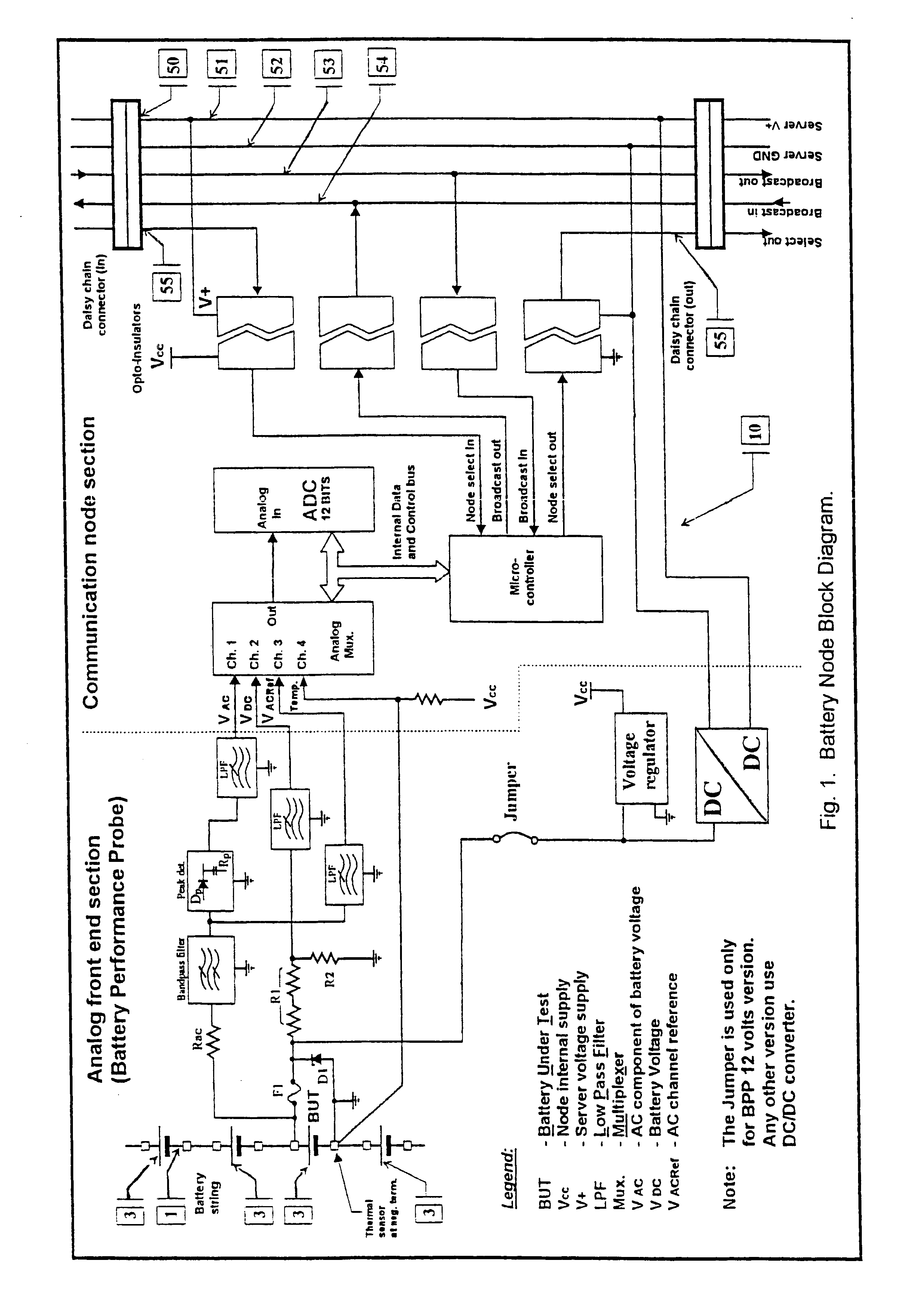
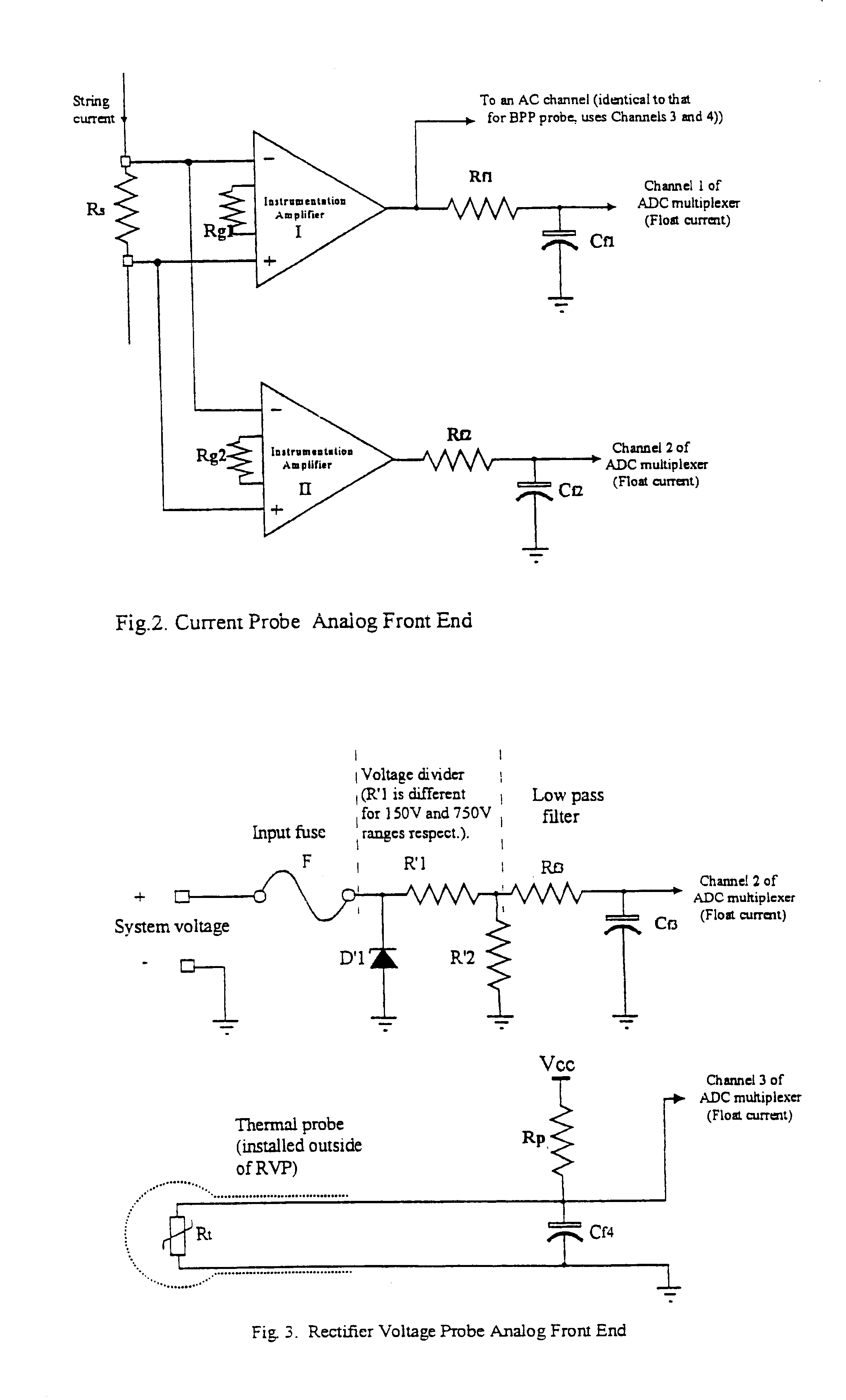
InactiveUS6611774B1Simple and accurate measurementBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingDaisy chainMonitoring system
The present invention concerns a battery monitoring system for monitoring a plurality of batteries serially connected to form a string. The battery monitoring system includes a number of probes connected to at least a portion of the string, a daisy chain bus having a select channel for serially interconnecting the probes, the bus having other, parallel channels for data communication and power, and a system server. The probes each have a sensing module and a communication module. The sensing module senses characteristics of at least a portion of the string, such as voltage or current. The communication module receives the sensed characteristics and converts them into digital form for broadcast to the system server over the bus. The communication module of the probes have a memory for storing an address assigned to the corresponding probe upon reception of an initialization signal sent by the system server via the bus.
Owner:ENERSAFE
System and Methods for ACK/NAK Feedback in TDD Communications
ActiveUS20110002276A1Guaranteed normal transmissionError preventionTransmission path divisionCommunications systemTelecommunications network
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Bone tendon bone assembly with cylindrical allograft bone block
InactiveUS20050203623A1Provide strengthProvide to structureSuture equipmentsBone implantInterference screwsBone tendon bone
The invention is directed toward a bone block, a bone-tendon-bone assembly and method of tendon reconstruction in which at least one tendon replacement is extended between two bone blocks and fixed within each of two bone tunnels in the bones of a joint using interference screws. Each bone block has a central through going bore and at least one substantially parallel channel longitudinally cut in the exterior of the bone block body in which the ligament replacements are seated. One end of each bone block has a rounded recess leading from the central bore to the exterior parallel channel.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAT TRANSPLANT FOUND
PSA pressure measurement and control system
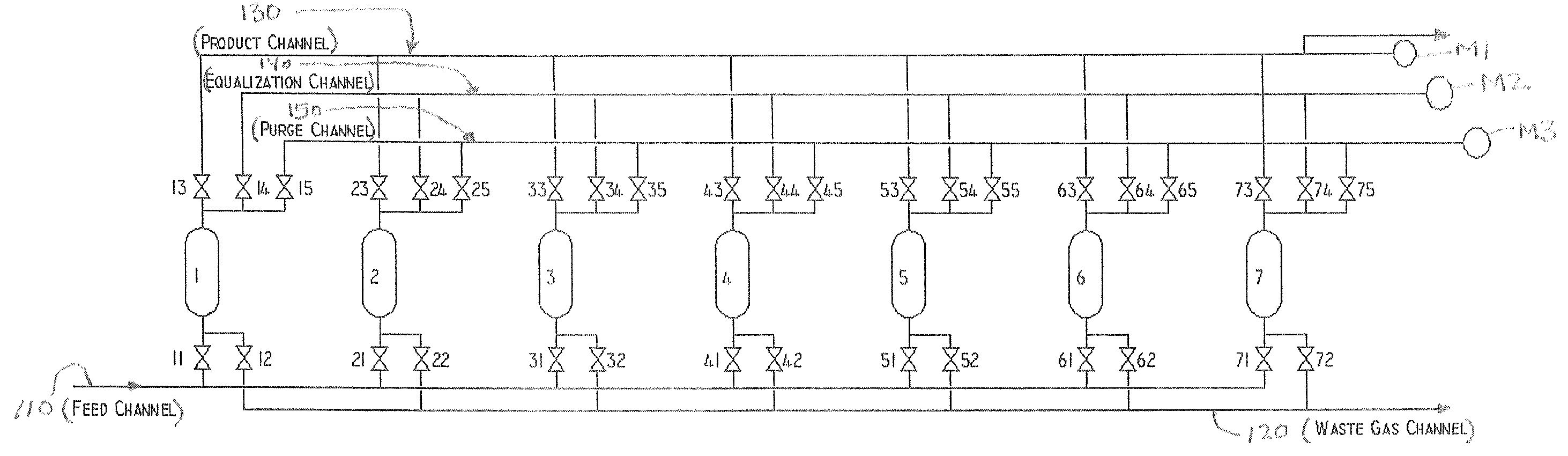
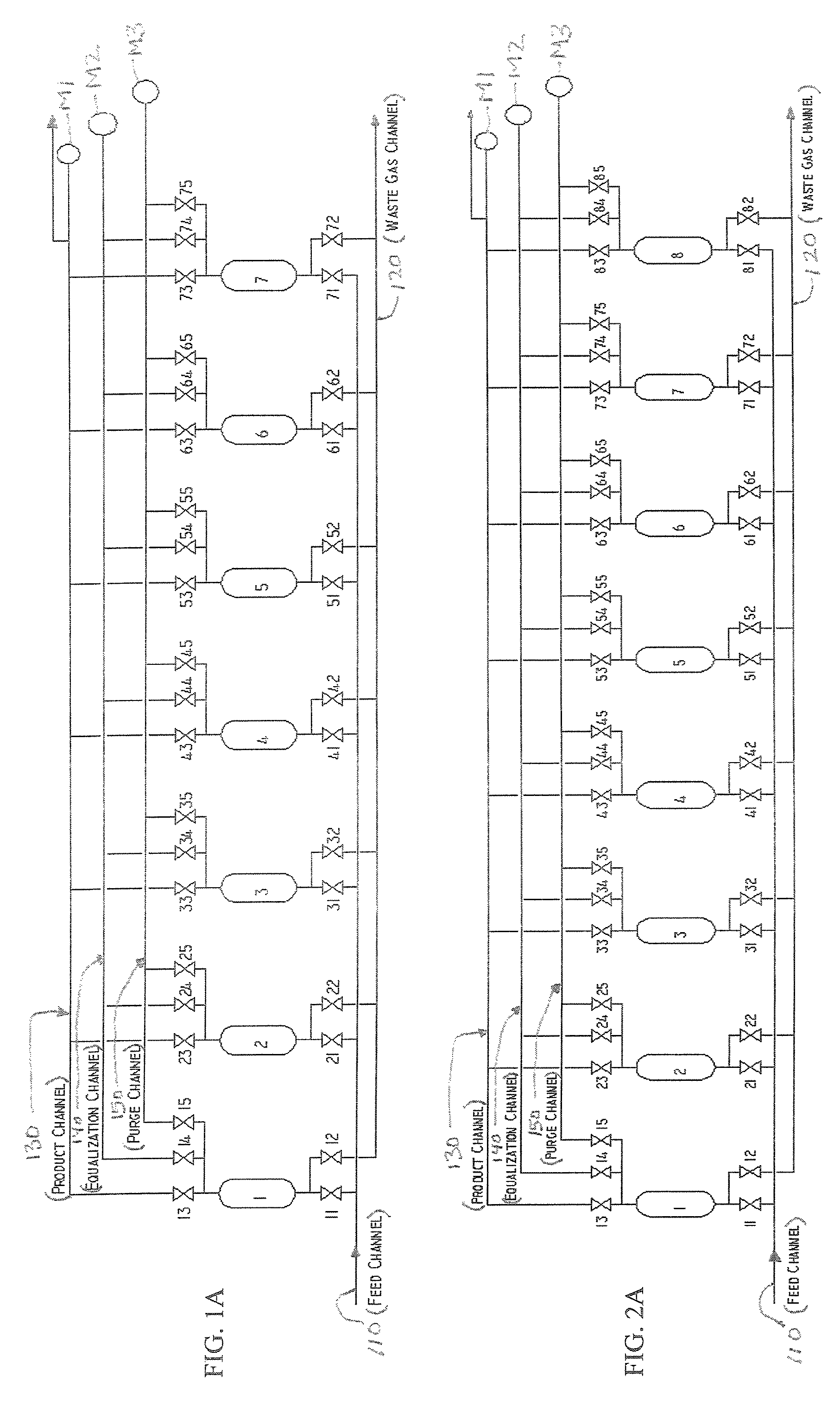
A pressure swing adsorption system including a plurality of vessels having one or more layers of adsorbent material therein, a feed gas channel, a waste channel, and a product channel. The system also includes at least one parallel channel connected to each of the vessels via a respective conduit with a valve. At least one pressure measuring device i configured to measure a pressure within the parallel channel. And, a controller is provided that is configured to monitor the at least one pressure measured by the at least one pressure measuring device during a PSA cycle performed within the PSA system, in order to determine the performance of the cycle and monitor proper operation of the system.
Owner:LUMMUS TECH INC
Method and apparatus for determining a data rate in a high rate packet data wireless communications system
InactiveUS6973098B1High packet data rateLower latencyPower managementTransmission control/equlisationHigh rateCommunications system
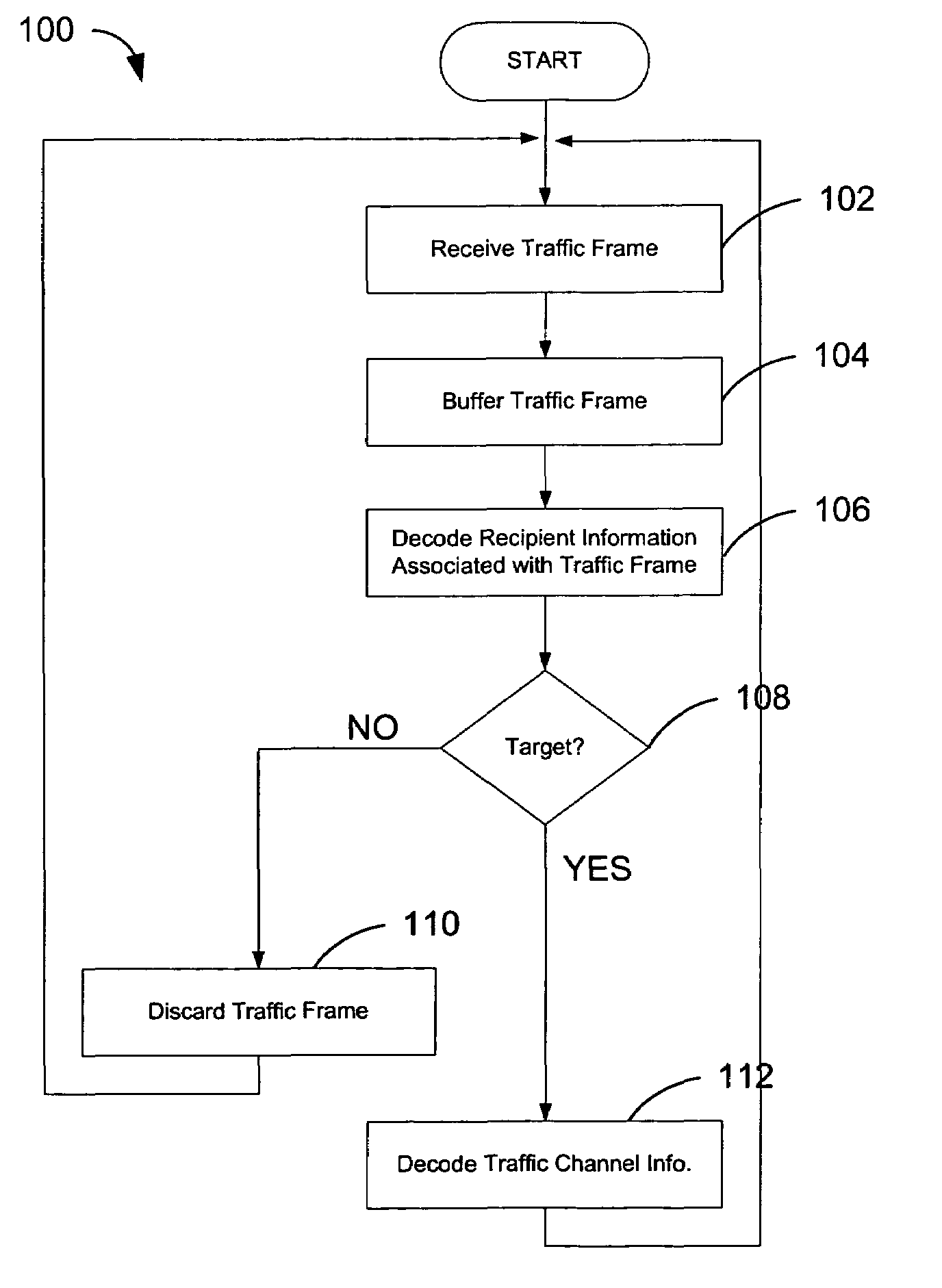
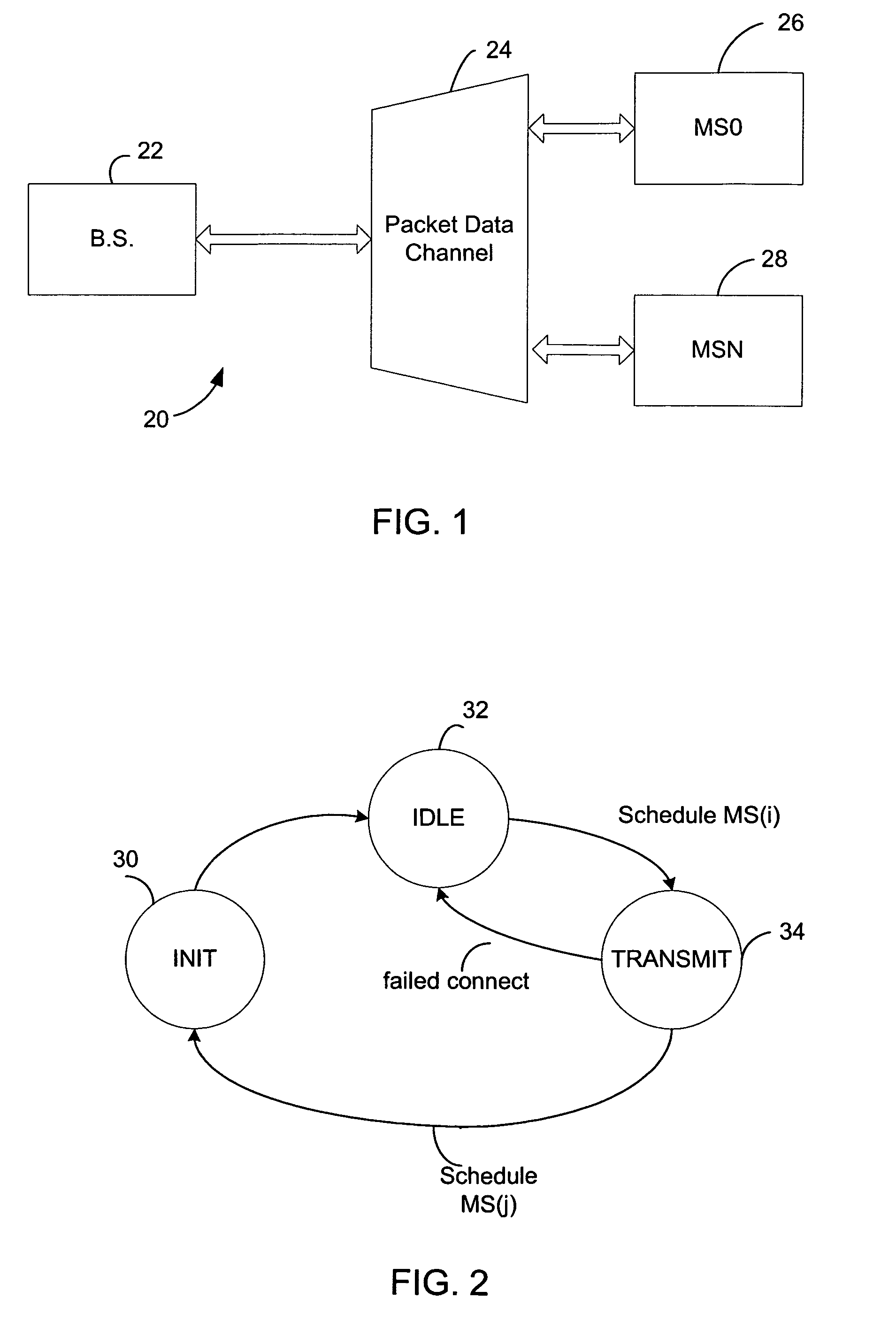
In a wireless communication system a method for combination transmission of packet data and low delay data. In one embodiment a parallel signaling channel provides a message to receivers indicating a target recipient of packet data. The message also identifies the transmission channels used for packet data transmissions. Each receiver may then selectively decode only packets where the message identifies the receiver as a target recipient. The data packets stored in a buffer are ignored if the target recipient is another mobile unit. In one embodiment, the message is sent concurrently with the data packet on a parallel channel. In one embodiment, the message is punctured into the high rate packet data transmission.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
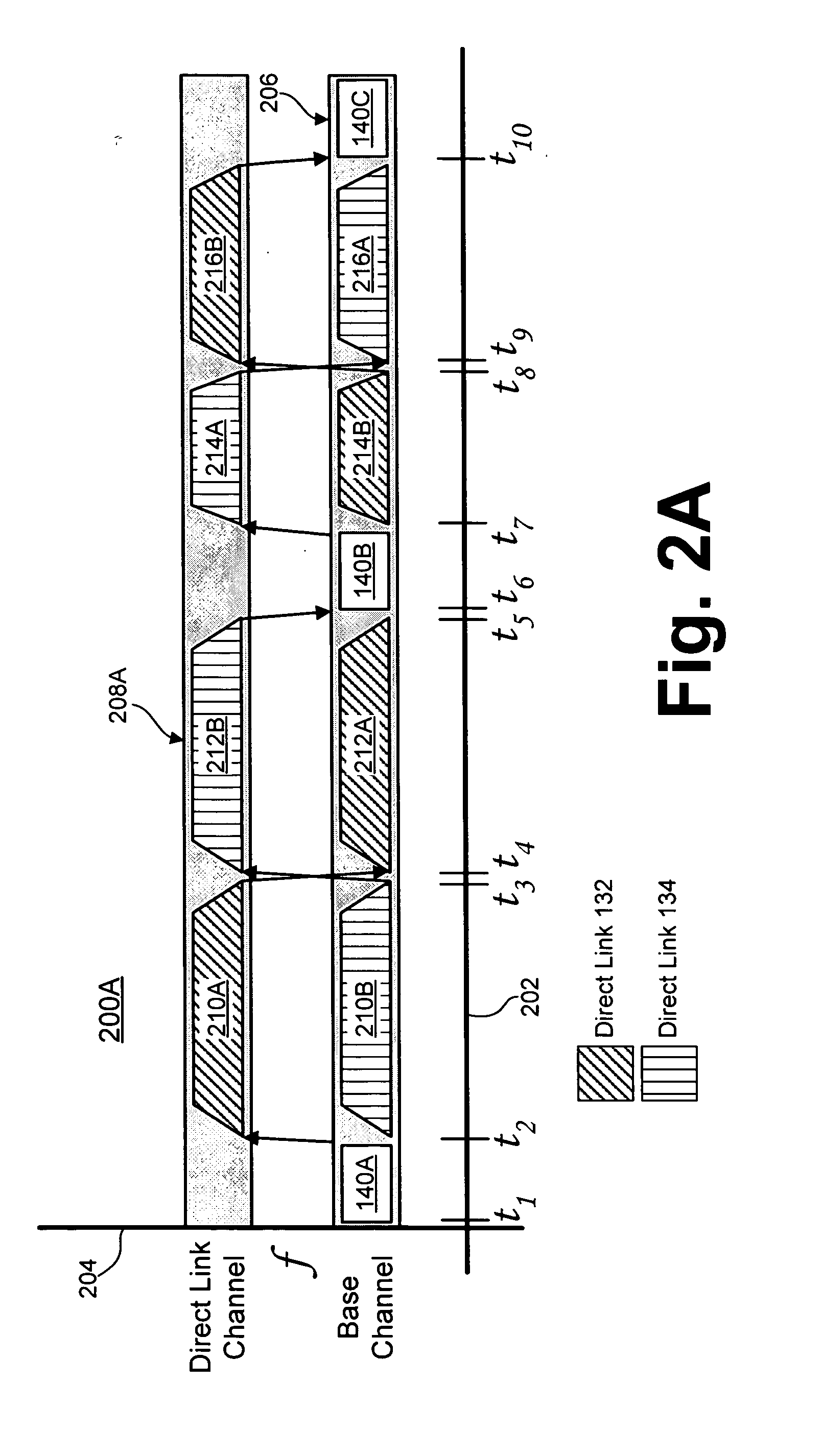
Time-scheduled multichannel direct link
InactiveUS20050157674A1Transparent operationLow costPower managementTransmission control/equalisingTime scheduleComputer network
Disclosed herein are exemplary techniques for communicating information in a wireless system using multiple wireless channels. A direct link between two or more wireless devices may be established by performing a direct link setup between two or more wireless devices using an access point. The two or more wireless devices may switch to a parallel channel and use the established direct link to communicate information directly without the access point as an intermediary. Switching the wireless devices between a base channel and one or more parallel channels may be accomplished using one or more predetermined channel schedules.
Owner:XOCYST TRANSFER
Rapid Thermal Firing IR Conveyor Furnace Having High Intensity Heating Section
InactiveUS20080012499A1Effectively doubling heating rate and furnace processing throughputIncrease productionSoldering apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNameplate capacityCooling curve
Isolation IR heat lamp module and method of firing multi-zone IR furnaces for solar cell processing comprising lamps disposed in individual parallel channels in a reflector / insulator body to provide a cooling air channel surrounding each tube; the channels are covered with IR-transmissive plate material to isolate each lamp from adjacent lamps and the process zone. Cooling air is exhausted and recycled upstream for energy conservation. Lamp spacing can be varied and power to each lamp individually controlled to provide infinite control of temperature profile in each heating zone. For a spike zone, and in combination with downstream quench control and annealing zones, steep heating and cooling curves with very short dwell (sharp) peak temperature profiles permit faster throughput due to operation of the lampsm at essentially 100% rated capacity, at a 2× or greater heating and throughput rate without compromising lamp life, while producing solar cells with improved output efficiency.
Owner:TP SOLAR OF USA
Modular disk memory apparatus with high transfer rate
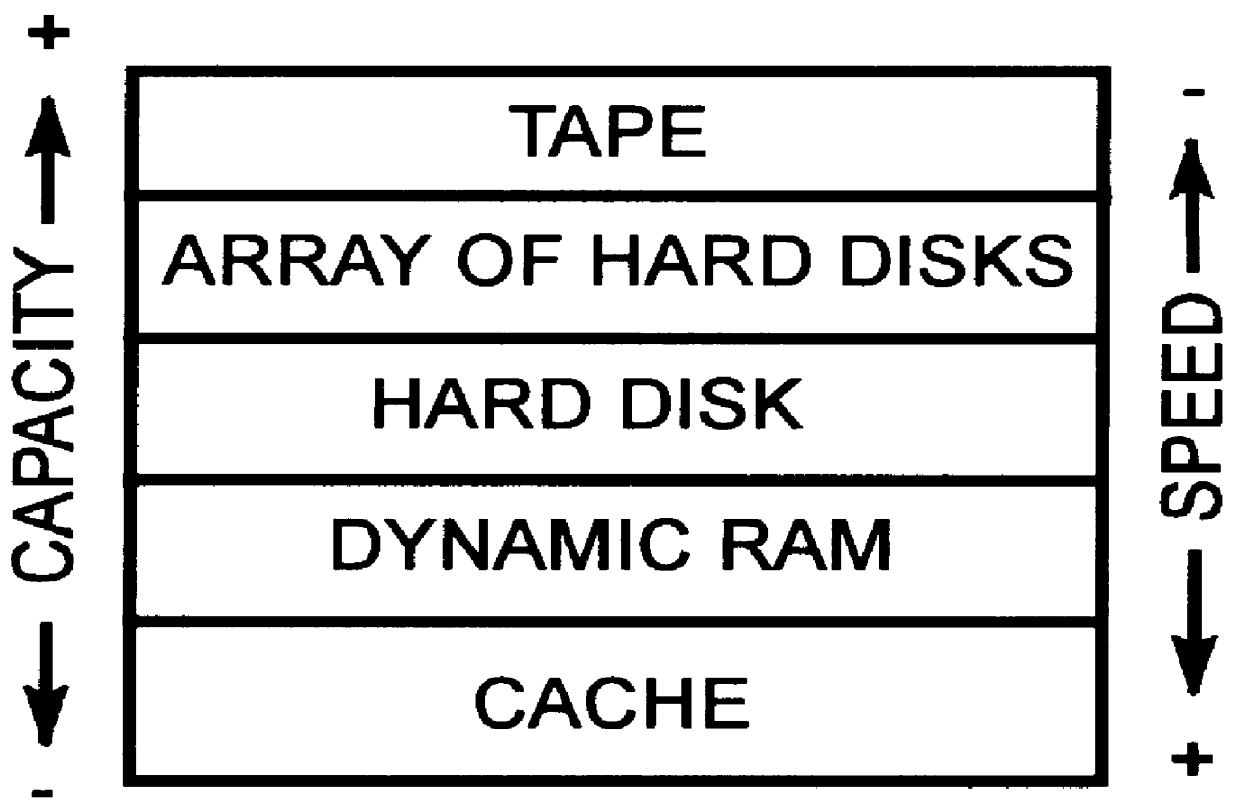
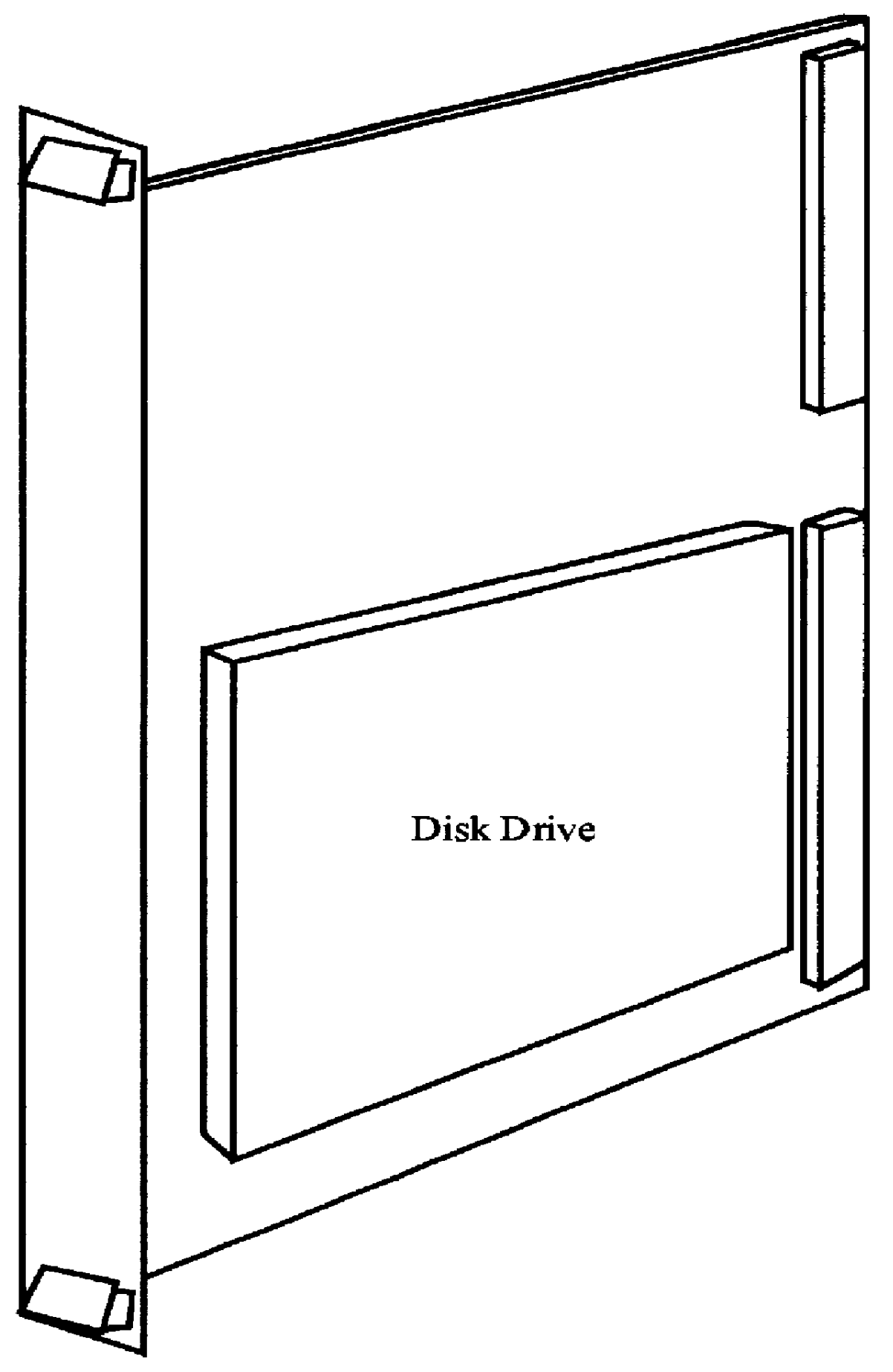
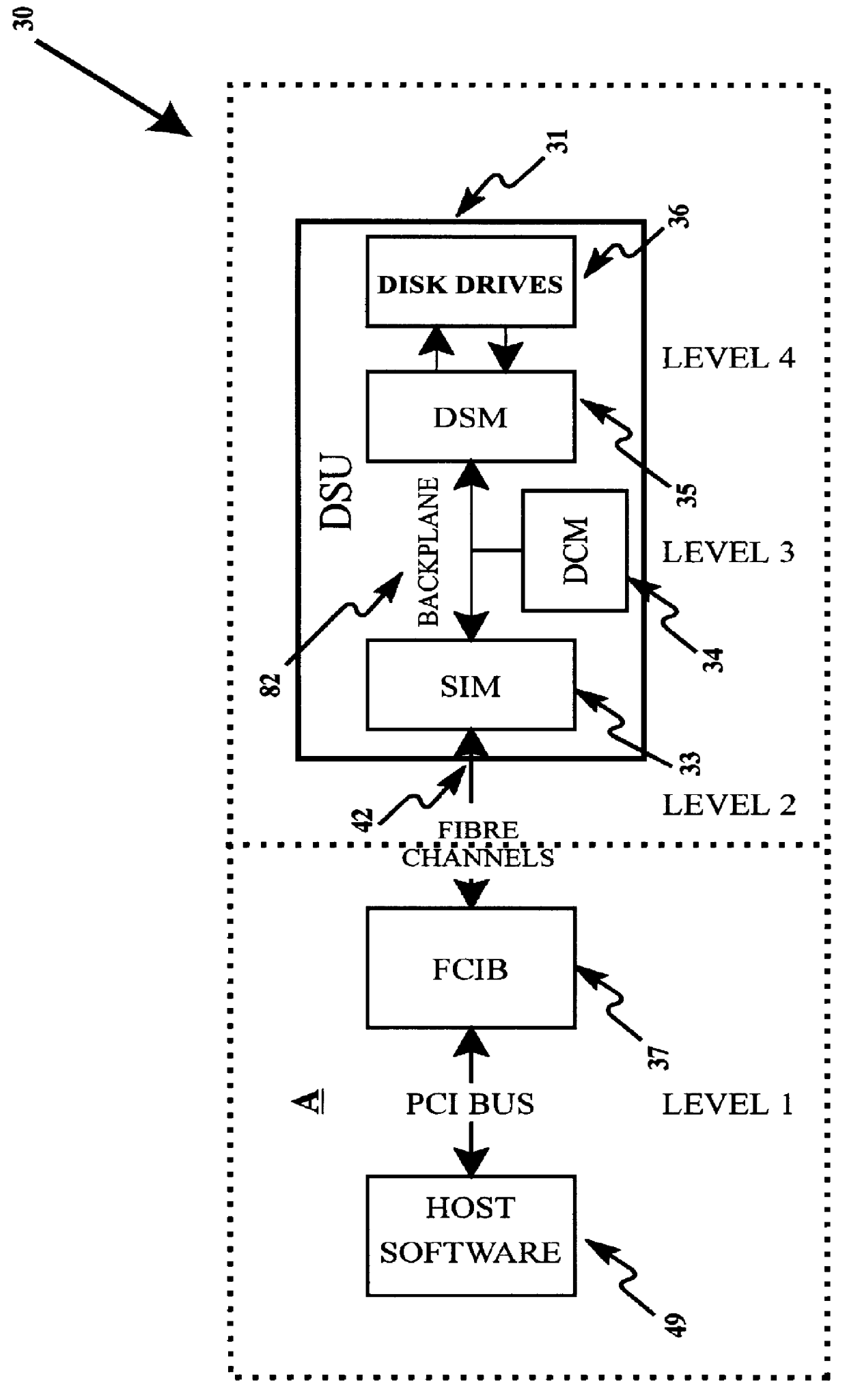
InactiveUS6112276AIncrease chanceLarge capacityInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsFiberHard disc drive
A modular disk memory apparatus provides a modularly expandable, multi-gigabyte auxiliary memory for a computer or other host electronic device, and includes multiple, parallel serial data channels to maximize bidirectional data transfer rates between the apparatus and the host device. Maximization of READ / WRITE data transfer rates within the apparatus is achieved by utilizing a large number of small hard disk drives, typically eight 2.5-inch drives on each of a plurality of Disk Storage Modules, each including a plug-in printed circuit board capable of holding two 5-+E,fra 1 / 4+EE inch drives, thereby increasing the maximum data transfer rate per unit volume of the modules by a factor of two. Maximization of bidirectional data transfer rates between the apparatus and host device over that attainable using a single serial data channel such as a coaxial, quadaxial or fiber optic cable, is achieved by parsing or demultiplexing data to be transmitted from a single parallel channel onto p paralleled cables, thereby increasing the maximum transmittal rate by p. Data received over the parallel data channels is multiplexed or concatenated to comprise a data stream on a single parallel channel. Reconstruction data is embedded in data contained in the p parallel data channels specifying the number q of channels employed, where 1< / =q< / =p thereby configuring the demultiplexer to concatenate that number of data channels onto a single parallel data bus.
Owner:SIGNATEC
Liftable turfing systems
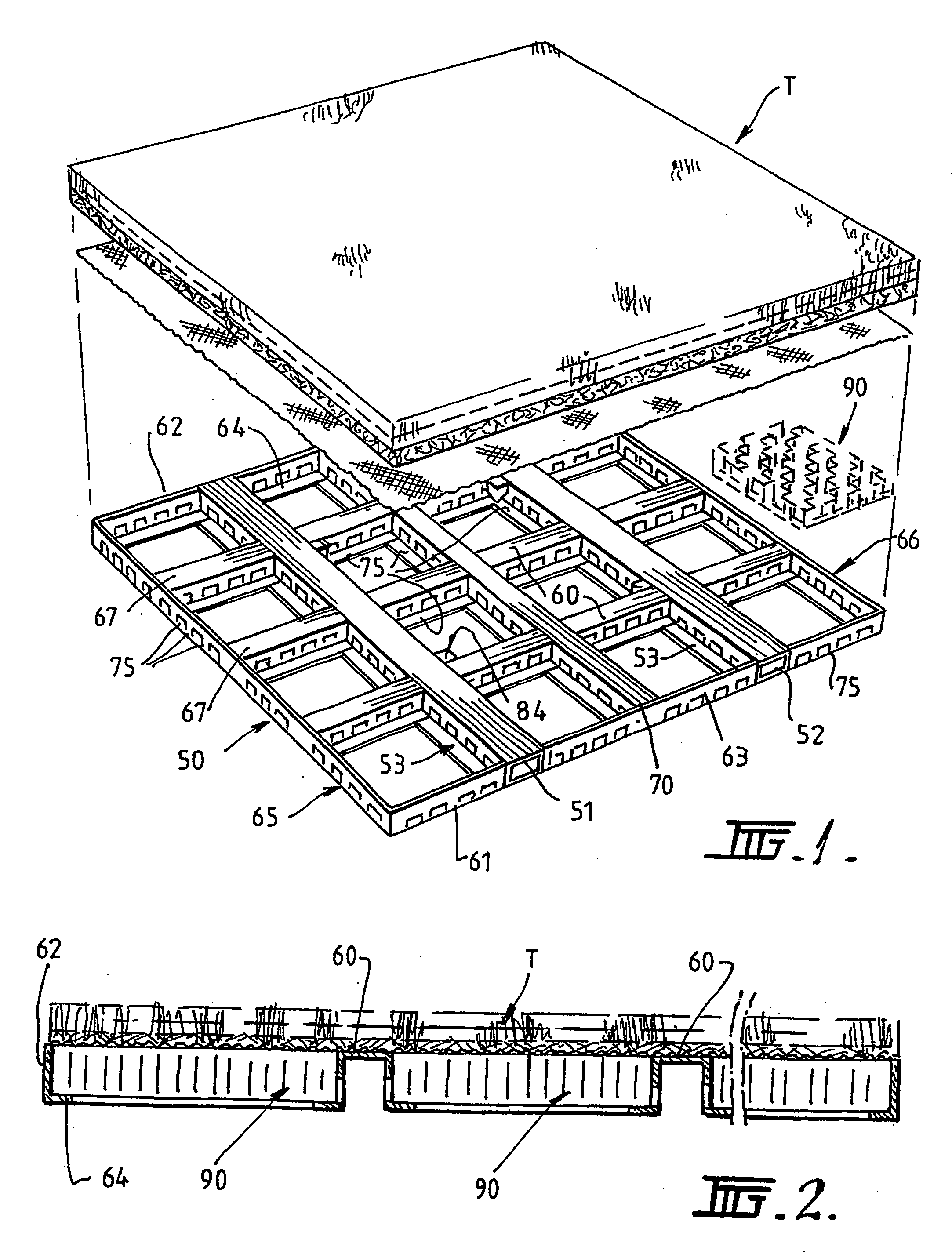
InactiveUS20060242901A1Precise positioningEasy loading and unloadingSki bindingsTurf growingArtificial turfEngineering
A liftable support structure for a turf system, the support structure comprising a skeletal framework having an open based structure with upstanding sides and at least two parallel spaced cross beams, the framework defining open subsections, each subsection having a base defining a ledge structure, each subsection supporting a latticework panel that sits on the ledge structure, the framework having a plurality of spaced lifting points and the cross beams defining access to forklift tines. A pallet for natural or artificial turf comprising a structure moulded in foamed plastics to have a closed planar top surface supported by a lattice work of mutually perpendicular walls defining a flexible open base, the structure defining a pair of elongate spaced parallel channels extending across each side to facilitate forklift tine entry.
Owner:STRATHAYR
Multi-channeled micro-structured reactor
ActiveCN1736577AHigh selectivityIncrease throughputChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesLiquid-gas reaction processesEngineeringParallel channel
Disclosed is amultichannel reactor with microstructure. Continuous phase inlet pipe and distribution chamber, discontinuous phase inlet pipe and distribution chamber, mixture phase buffer chamber and fluid outlet pipe connects separately, and they compose the lower cavity. Porous distribution medium is sealed in the upper distribution chamber of discontinuous phase. A parallel channel plate of continuous phase is located above the lower cavity and the upper is sealed. The continuous phase liquid flows into the reactor from the distribution chamber of inlet pipe; the discontinuous liquid flows into the parallel channel of continuous phase following through the distribution medium, distributes into minute drop or air bubble with the floating shearing force of continuous phase liquid, and then connects with the continuous phase liquid to realize the rapid mixture and reaction of the two- phase liquid; then the liquid flows out of the reactor. With the invention, the area of mass transfer is big, the reaction conversion rate is high, and large scale production can be realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
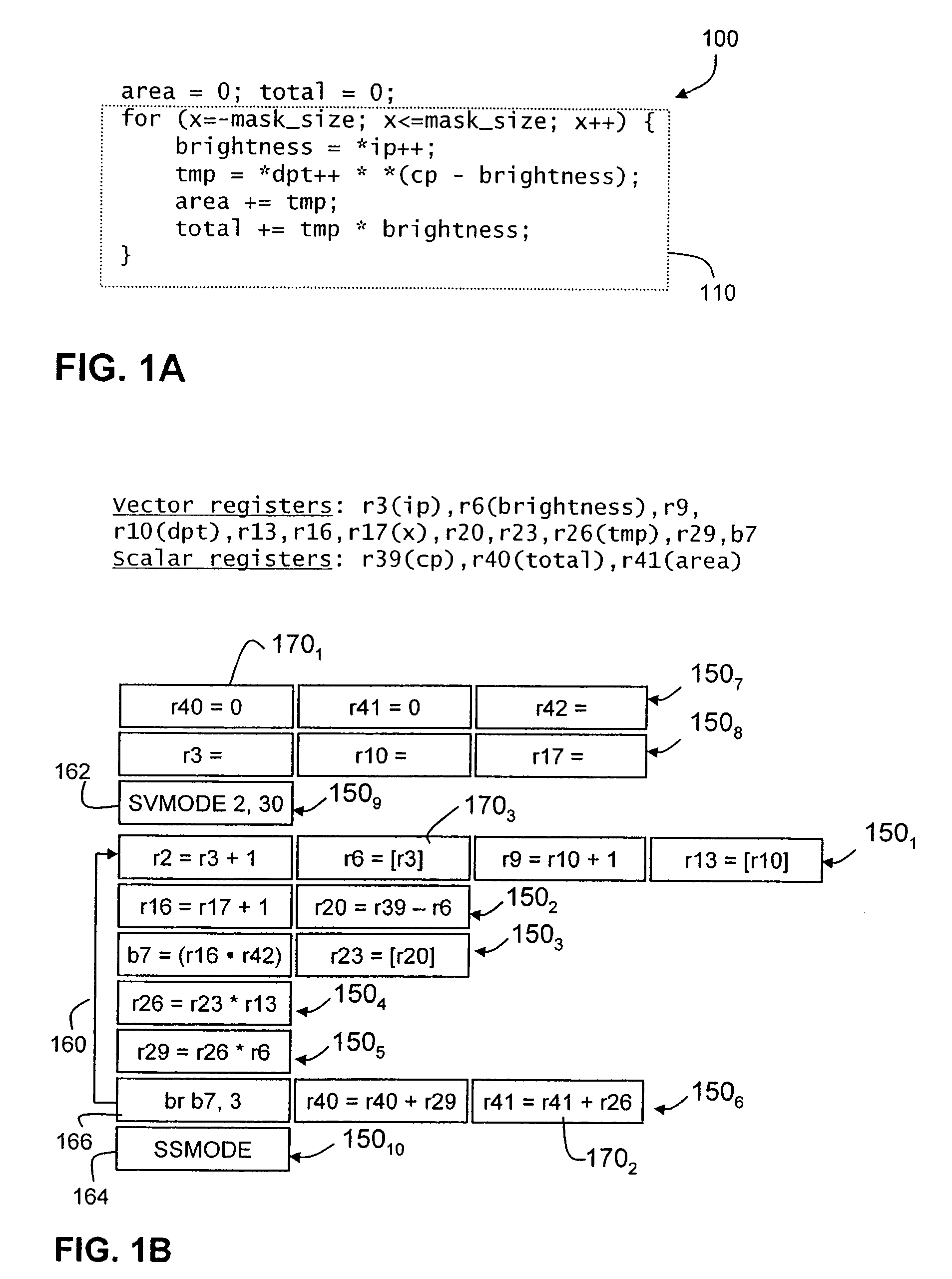
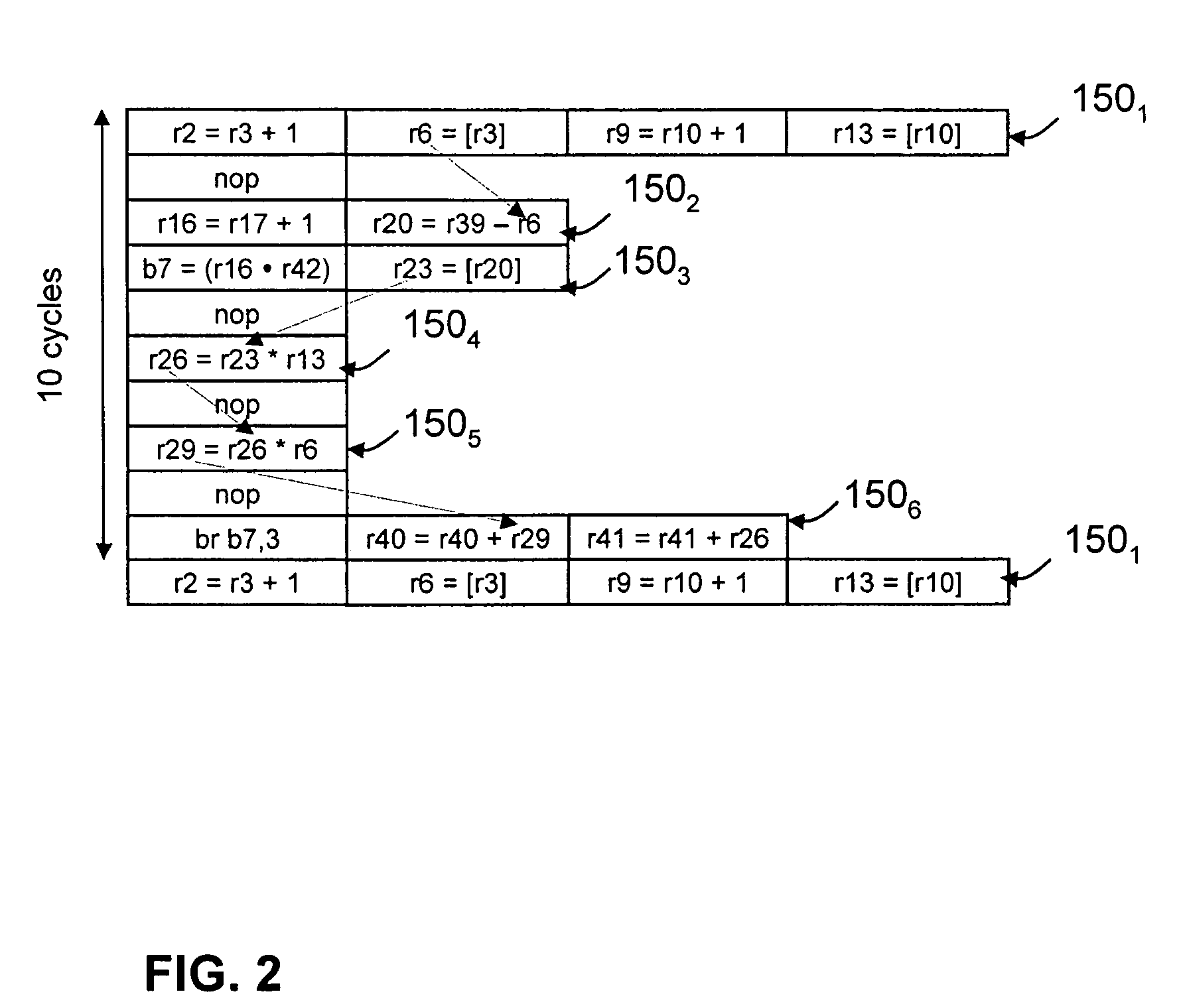
Instruction vector-mode processing in multi-lane processor by multiplex switch replicating instruction in one lane to select others along with updated operand address
ActiveUS7493475B2Register arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerMultiplexingScalar processor
An improved superscalar processor. The processor includes multiple lanes, allowing multiple instructions in a bundle to be executed in parallel. In vector mode, the parallel lanes may be used to execute multiple instances of a bundle, representing multiple iterations of the bundle in a vector run. Scheduling logic determines whether, for each bundle, multiple instances can be executed in parallel. If multiple instances can be executed in parallel, coupling circuitry couples an instance of the bundle from one lane into one or more other lanes. In each lane, register addresses are renamed to ensure proper execution of the bundles in the vector run. Additionally, the processor may include a register bank separate from the architectural register file. Renaming logic can generate addresses to this separate register bank that are longer than used to address architectural registers, allowing longer vectors and more efficient processor operation.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
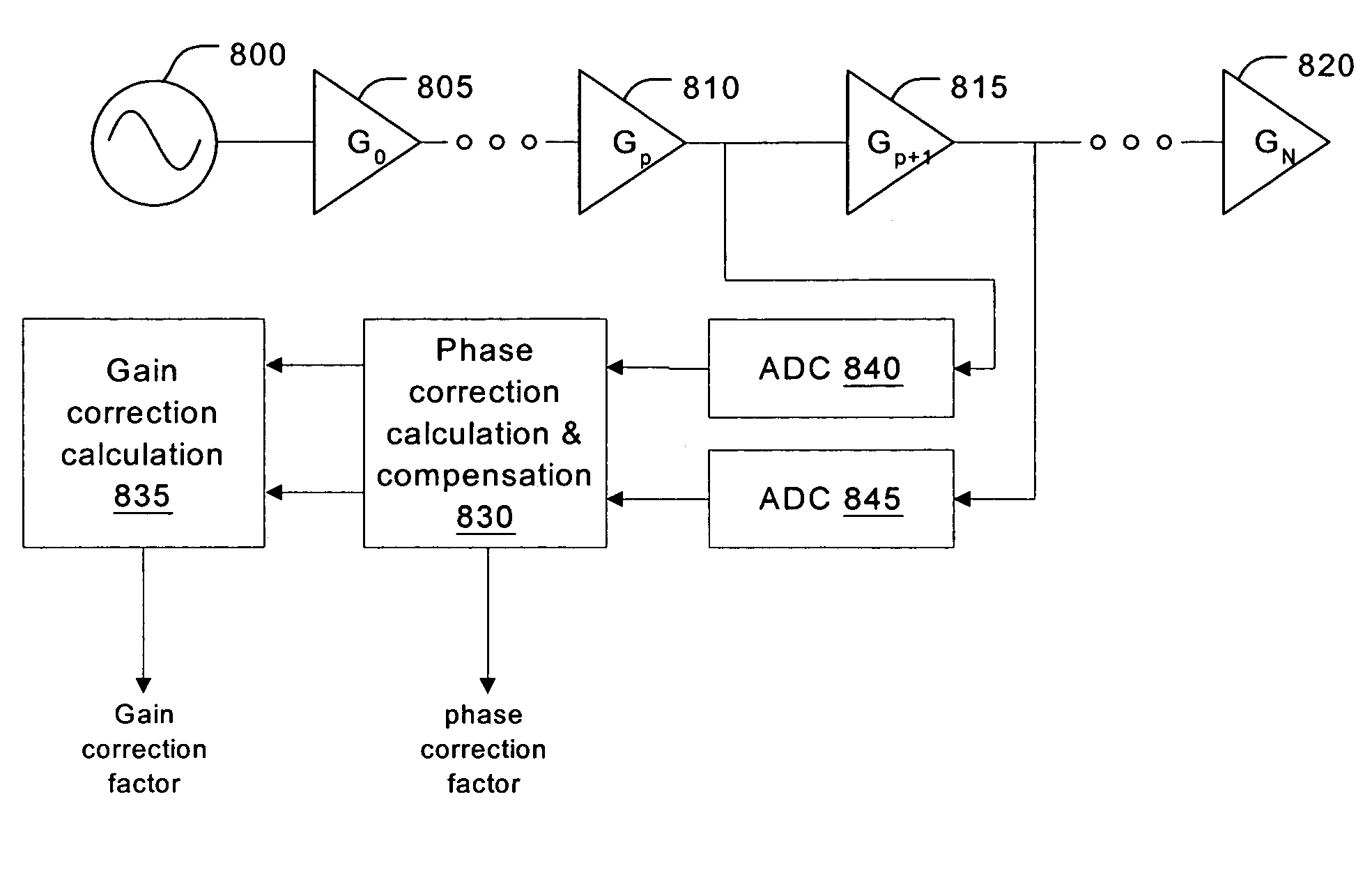
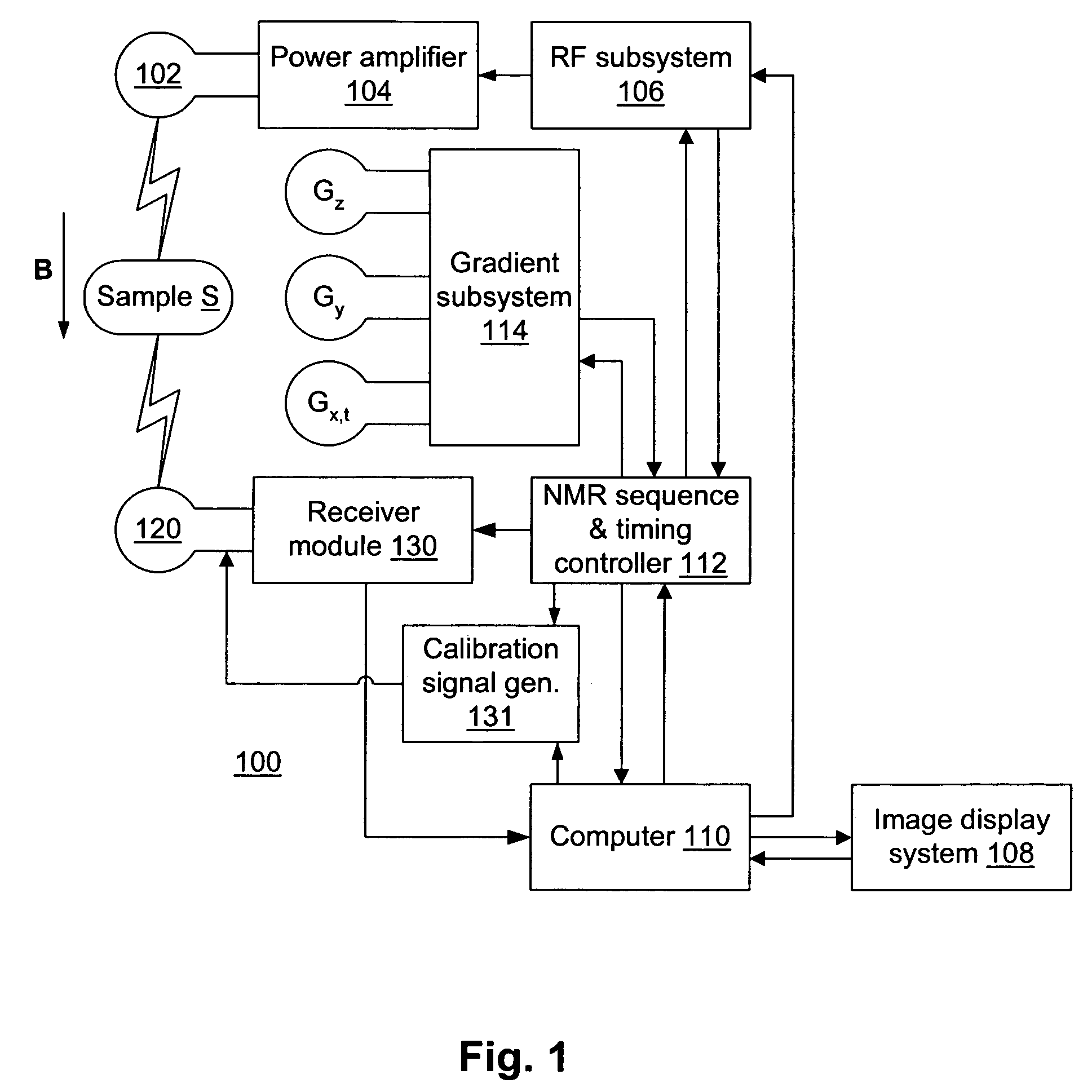
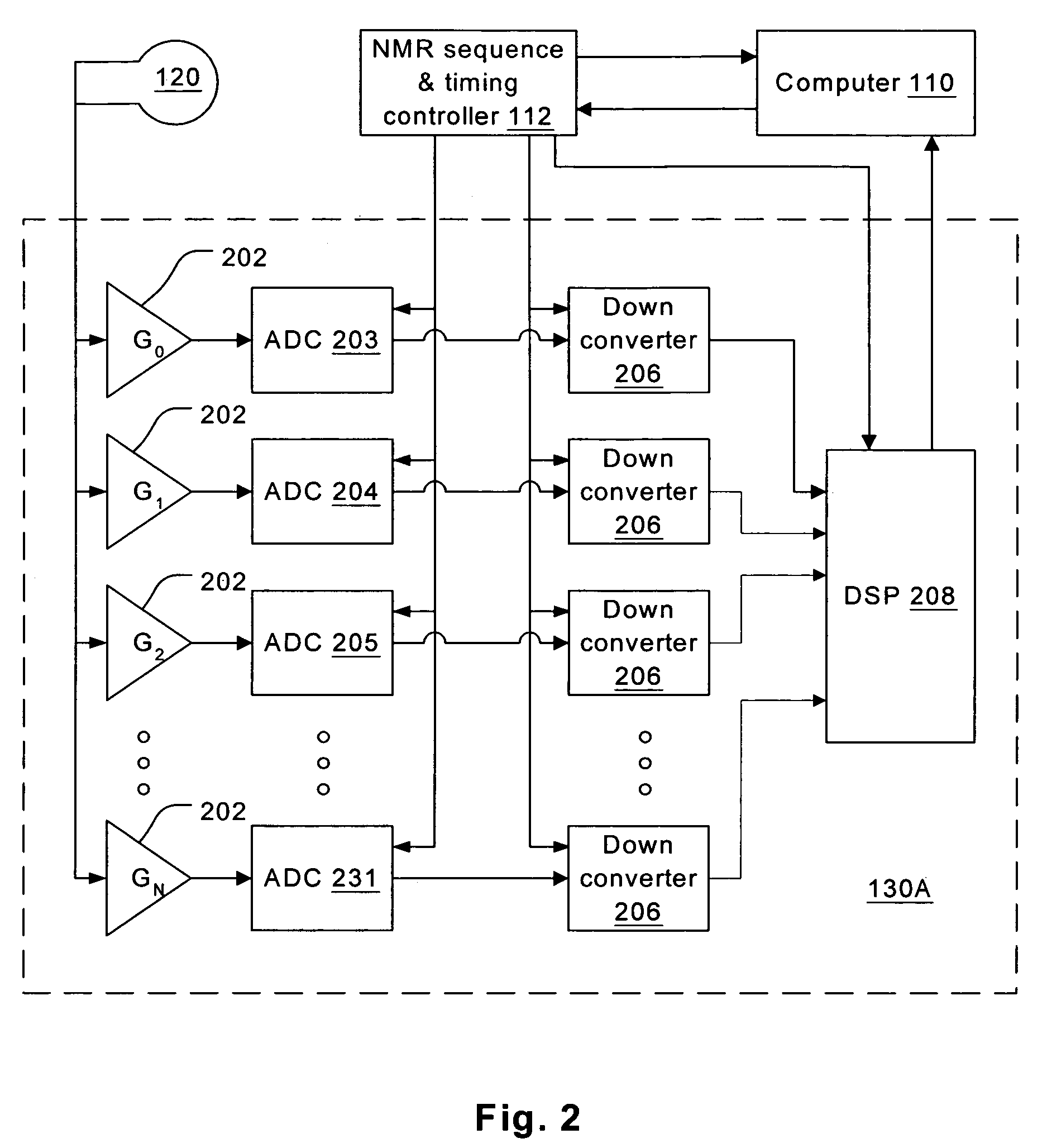
Adaptive dynamic range receiver for MRI
InactiveUS7403010B1Avoid the needLimited dynamic rangeElectric signal transmission systemsMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoRapid imaging
A receiver for a resonance signal of a magnetic resonance imaging system generates a baseband signal for image processing by dividing a raw resonance signal among multiple parallel channels, each amplified at a respective gain. A digital channel selector determines, at any given moment, a lowest-distortion channel to be further processed. Amplitude and phase error compensation are handled digitally using complex multipliers, which are derived by a calibration, based on a simple Larmor oscillator, which can be done without the need for a sample and without repeating when measurement conditions are changed. One of the important benefits of the invention is that it provides for gain selection without repeated calibration steps. This is particularly important in systems that employ fast imaging techniques such as fast spin echo, where the invention can speed imaging substantially.
Owner:FONAR
Method and apparatus for the continuous performance monitoring of a lead acid battery system
InactiveUS20040095249A1Simple and accurate measurementTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsElectrical testingSignal onMonitoring system
The present invention concerns a battery monitoring system for monitoring a plurality of batteries serially connected to form a string. The battery monitoring system includes a number of probes connected to at least a portion of the string, a daisy chain bus having a select channel for serially interconnecting the probes, the bus having other, parallel channels for data communication and power, and a system server. The probes each have a sensing module and a communication module. The sensing module senses characteristics of at least a portion of the string, such as voltage or current. The communication module receives the sensed characteristics and converts them into digital form for broadcast to the system server over the bus. The communication module of the probes have a memory for storing an address assigned to the corresponding probe upon reception of an initialization signal sent by the system server via the bus. In order to readdress all of the probes, a reset signal is transmitted to all of the probes. The probes clear the present address, and wait until they are selected through the select channel. Once the probe has been selected, it receives an address from the system server, stores the address in its memory, acknowledges this to the system controller, and sends a signal on the select channel to the next probe. Accordingly, initialization of a battery monitoring system is easily performed. The invention also lies in an interface device for use with a battery monitoring system.
Owner:ZACCARIA ROBERT
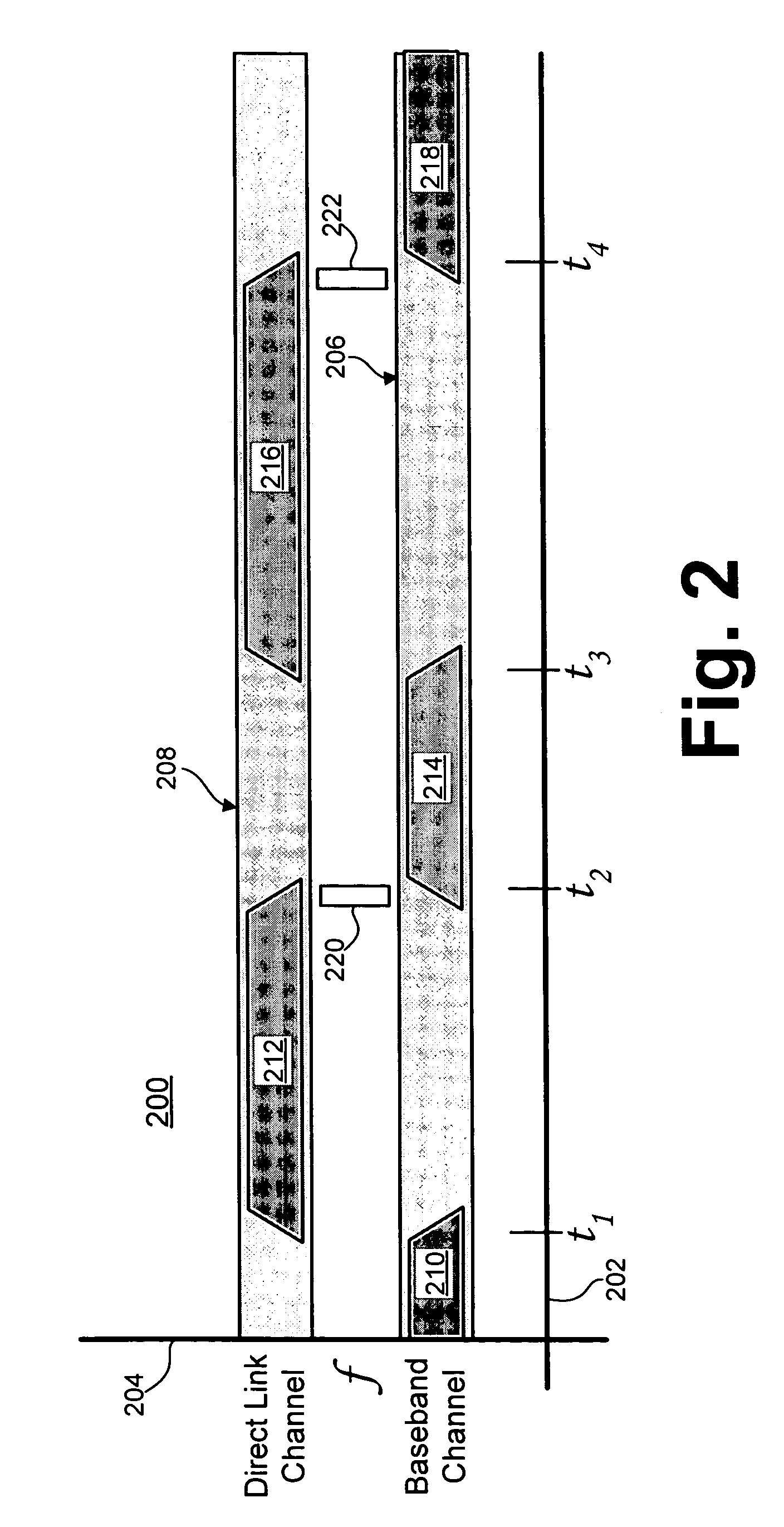
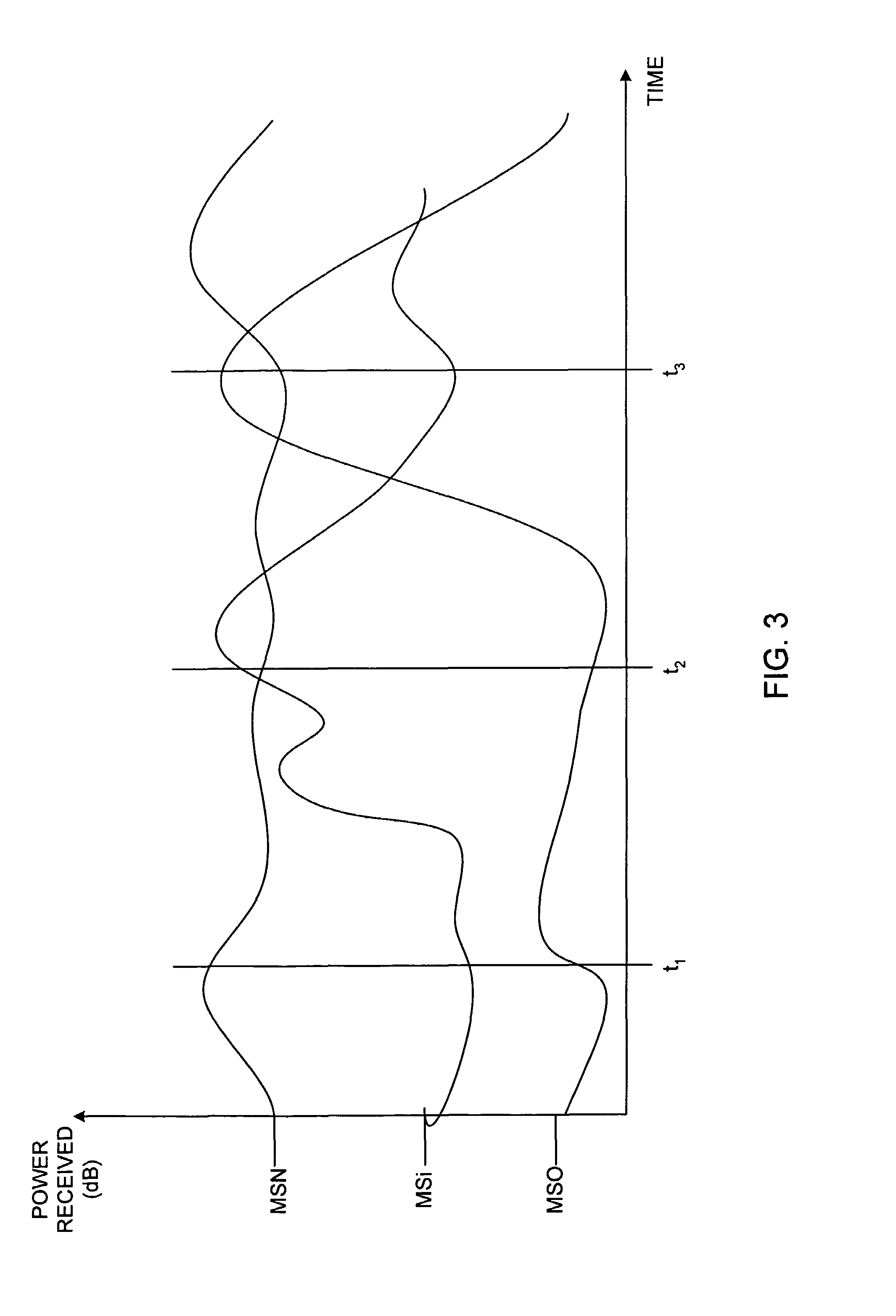
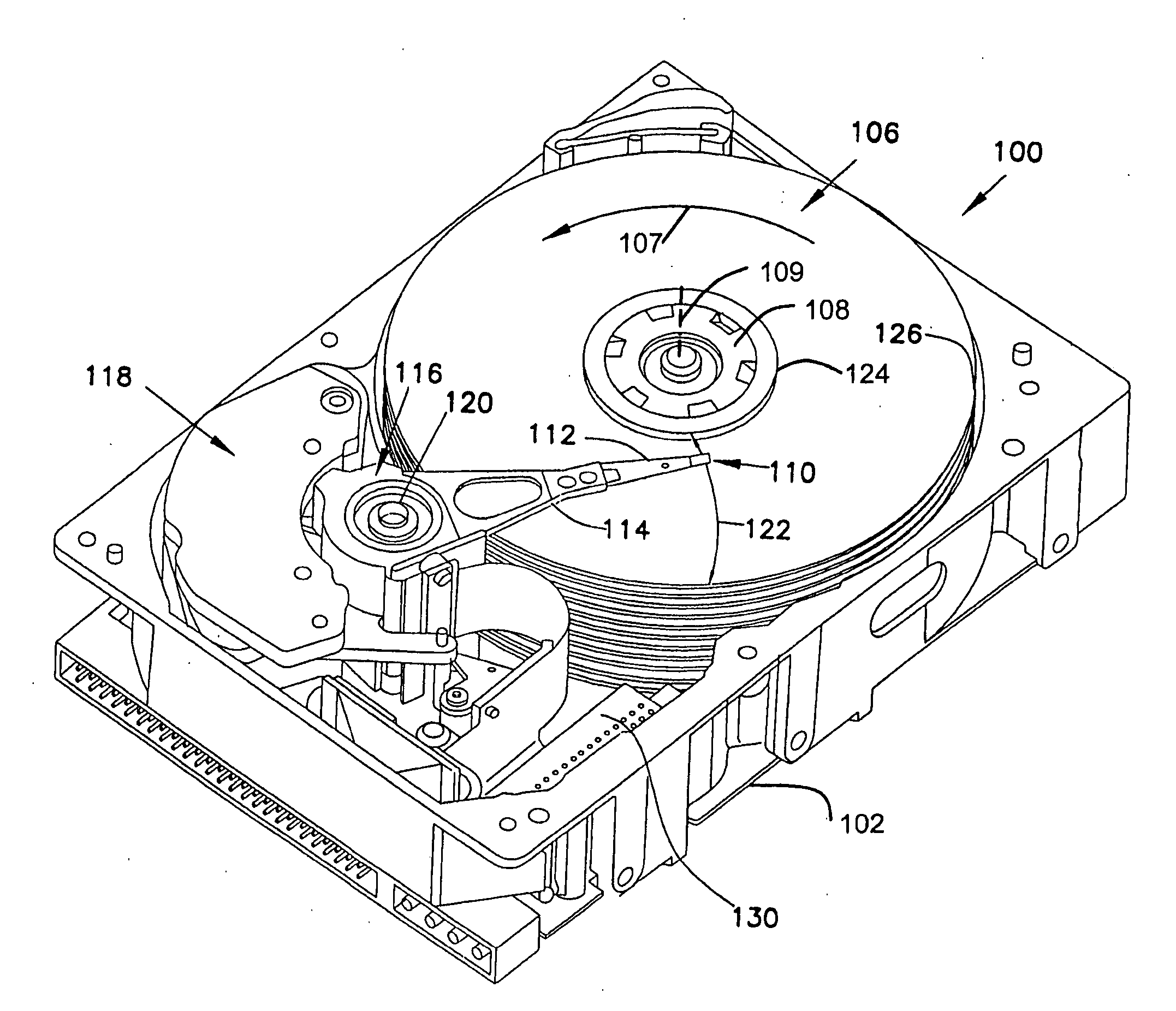
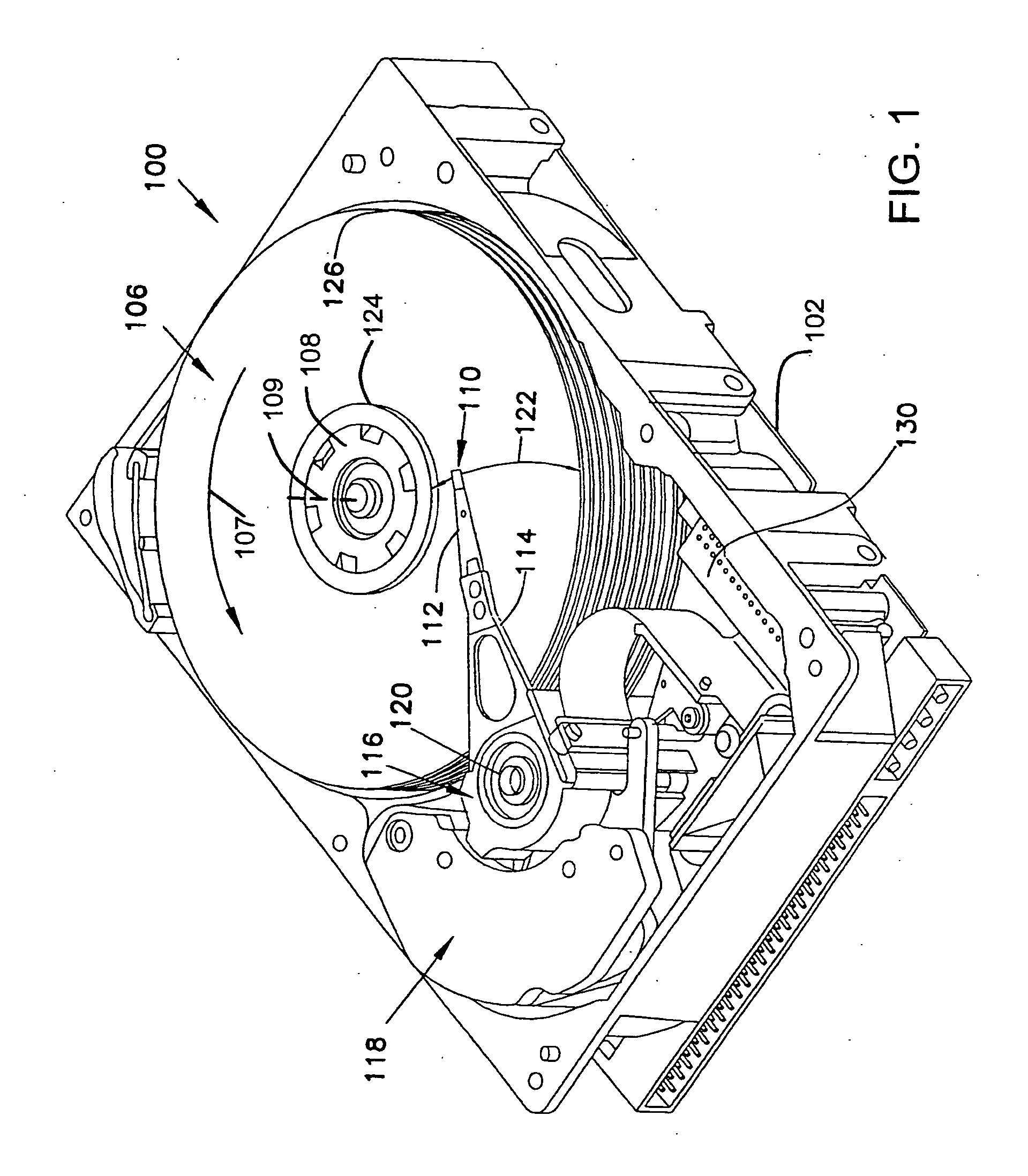
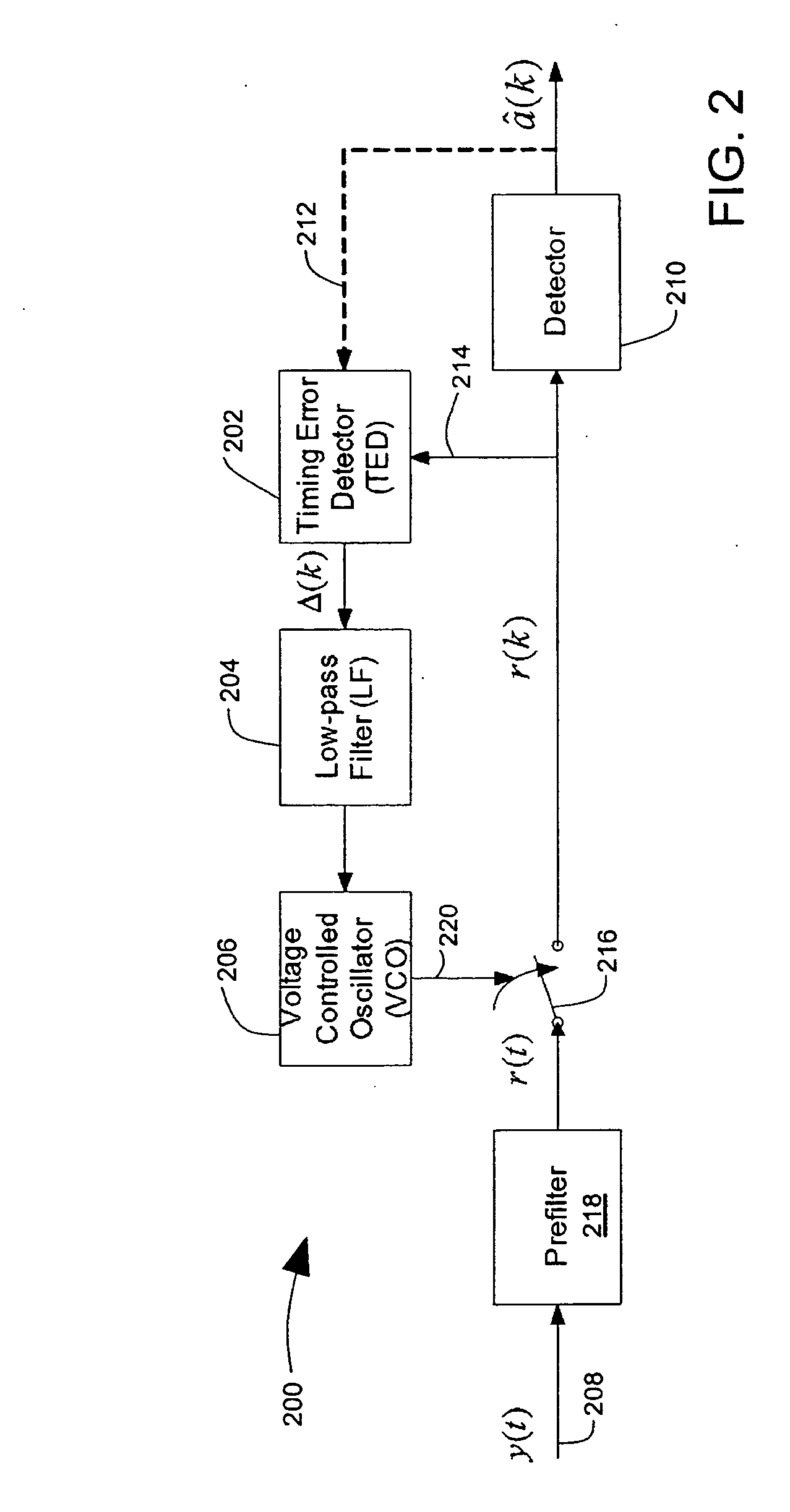
Timing recovery in a parallel channel communication system
ActiveUS20060210002A1Modification of read/write signalsSynchronisation error detectionCommunications systemDiscrete-time signal
A parallel channel timing recovery circuit. The parallel timing recovery circuit comprises multiple prefilters receiving parallel channel outputs and providing prefilter outputs. Multiple sampling filters receive the prefilter outputs and provide multiple discrete time signal samples. A self-timing circuit has multiple inputs receiving the multiple discrete time signal samples. The self-timing circuit provides a sampling control output to the sampling filters. The sampling control output is based on a composite of the multiple discrete time signal samples. Each of the sampling filters generates a discrete time signal sample based on the sampling control output and the prefilter outputs.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
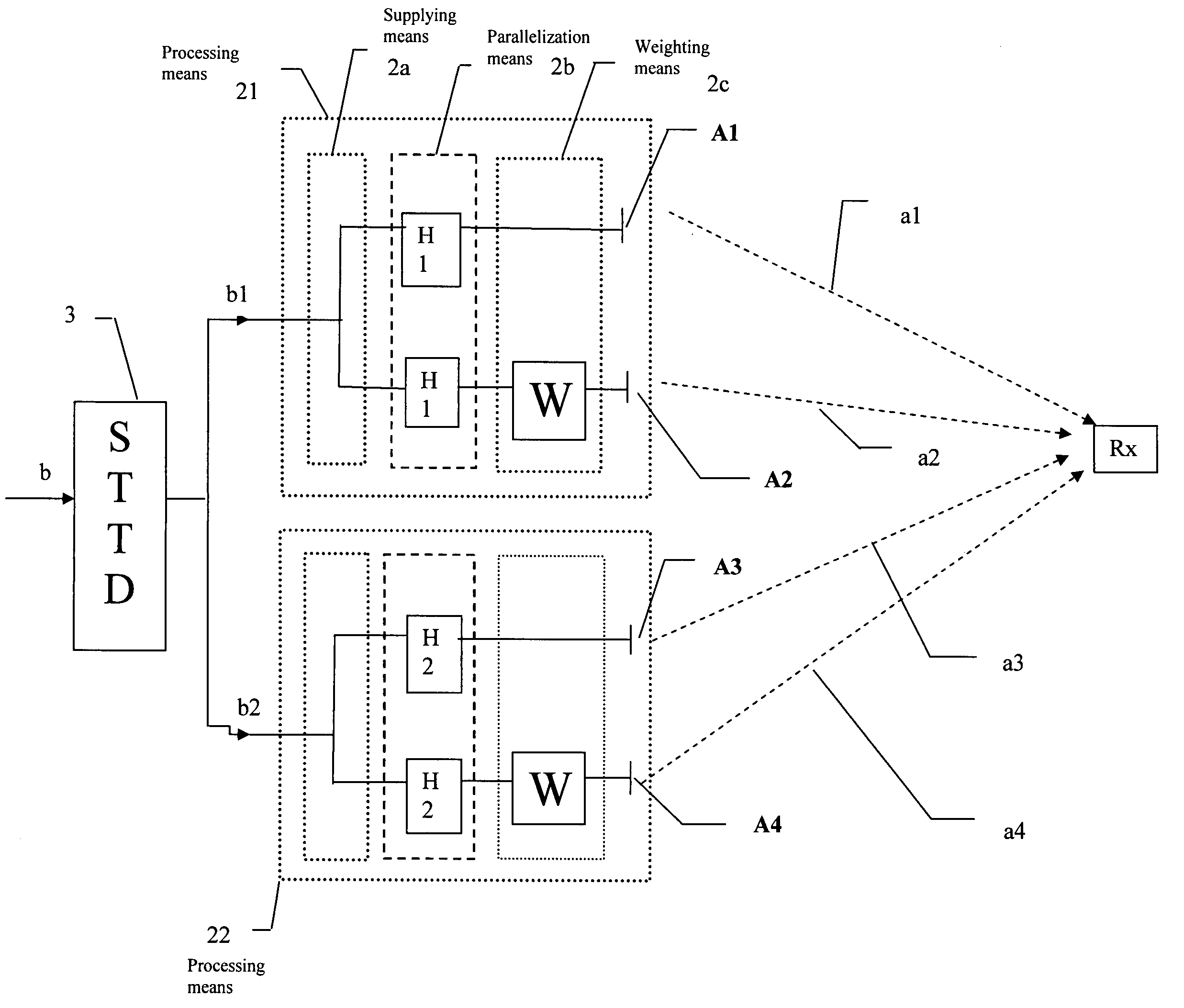
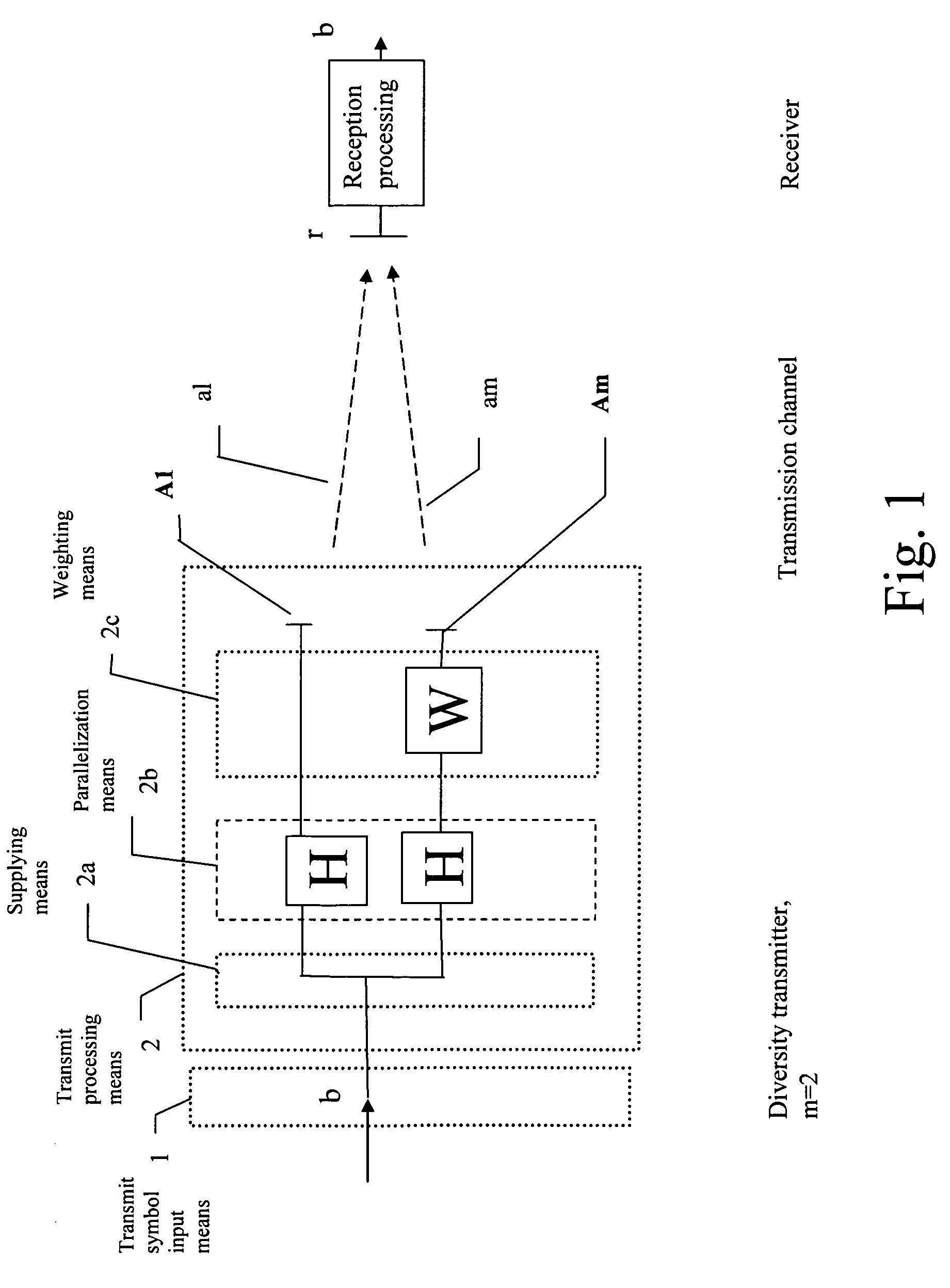
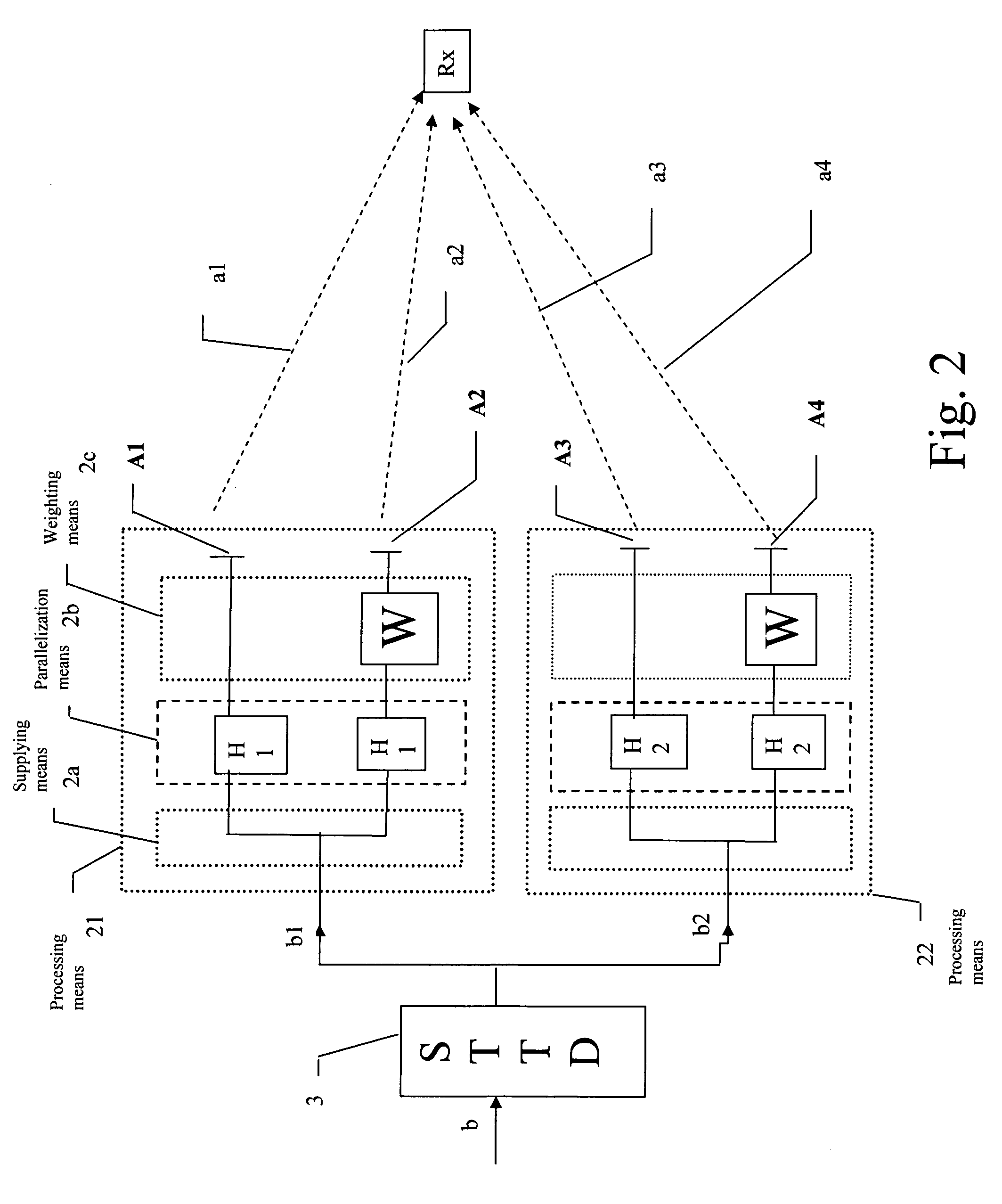
Diversity transmitter and diversity transmission method
InactiveUS7158579B2Improve performanceNo distractionSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsEngineeringDiversity scheme
The present invention concerns a diversity transmitter and a corresponding diversity transmission method. A symbol matrix is input for being processed, the processing comprising supplying columns of the symbol matrix to a plurality of at least two branches, each branch being supplied to a respective one of spatial channels for transmission. Parallelization is performed so as to provide within each branch at least two parallel channels allocated to a respective user. The symbol matrix signals is subjected on at least one of the branches to an invertible linear transformation with at least one fixed complex weight, the complex weight being different for at least two parallel channels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Bone tendon bone assembly
InactiveUS20050203622A1Provide strengthProvide to structureSuture equipmentsBone implantBone tunnelInterference screws
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Therapeutic Device for Treating Soft Tissue Swelling and Fibrosis
InactiveUS20080086071A1Reduce swellingProvide stabilizing and constrictive forcePhysical therapyFeet bandagesTherapeutic DevicesFibrosis
Owner:WEATHERLY KATHY JO
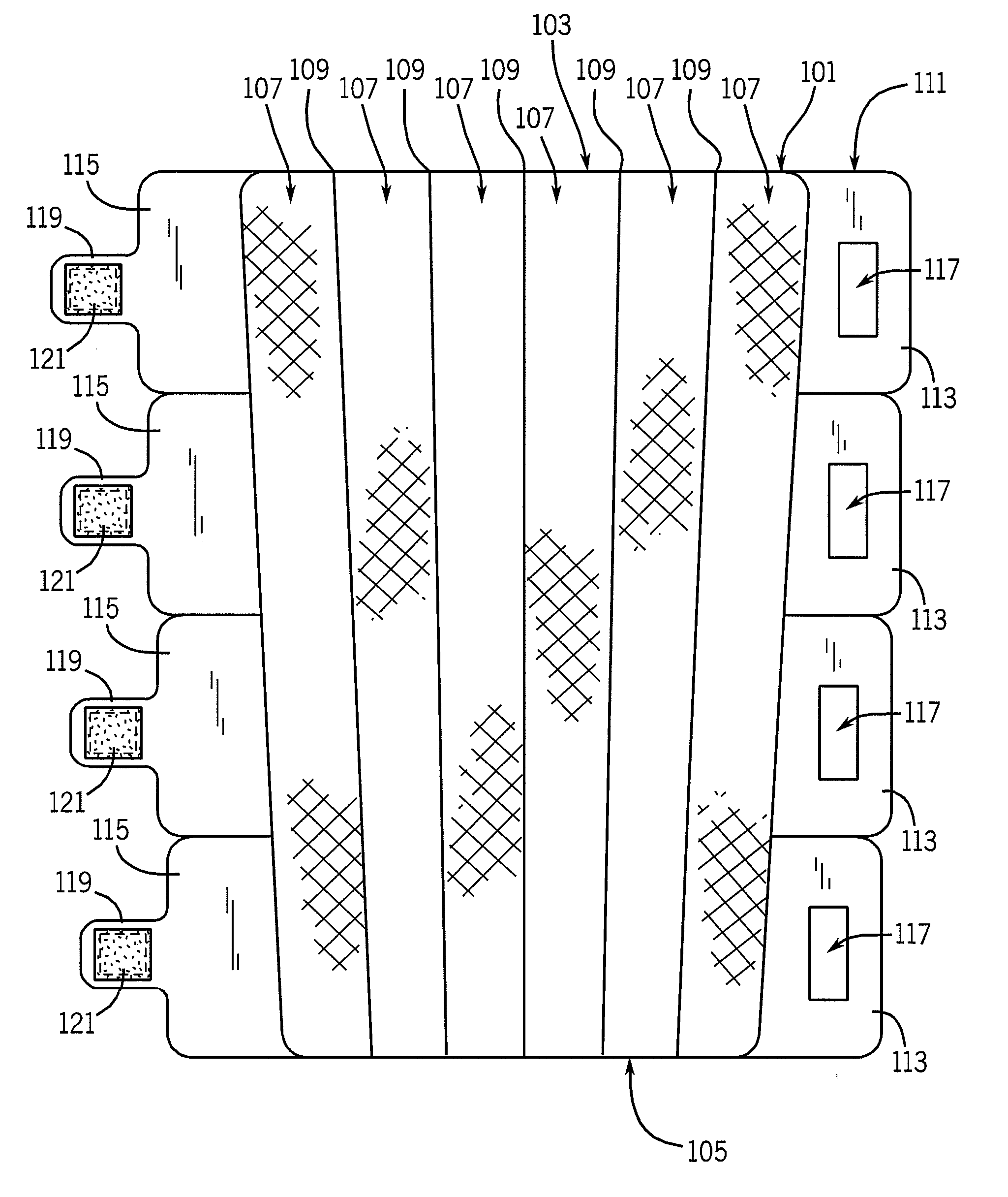
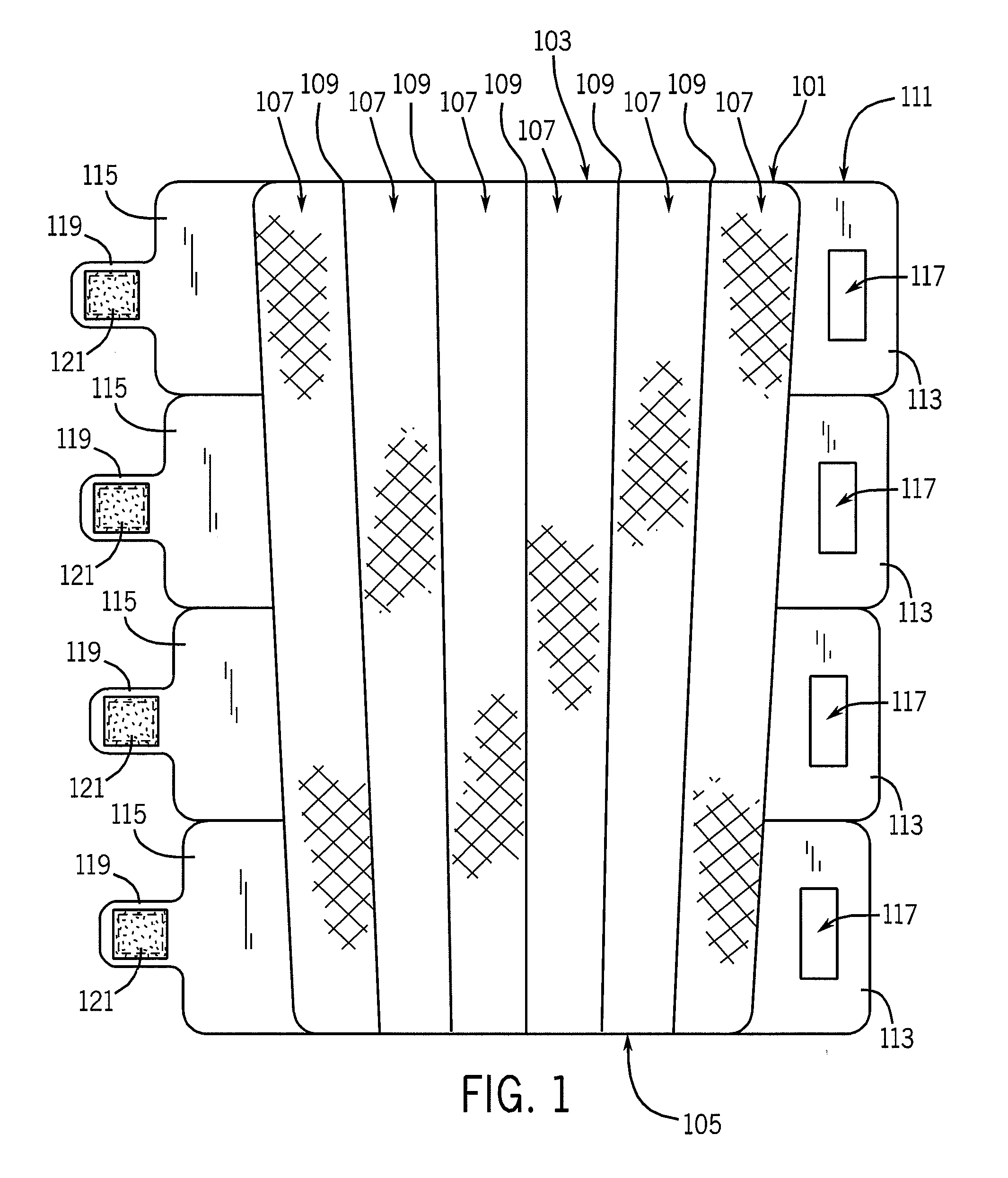
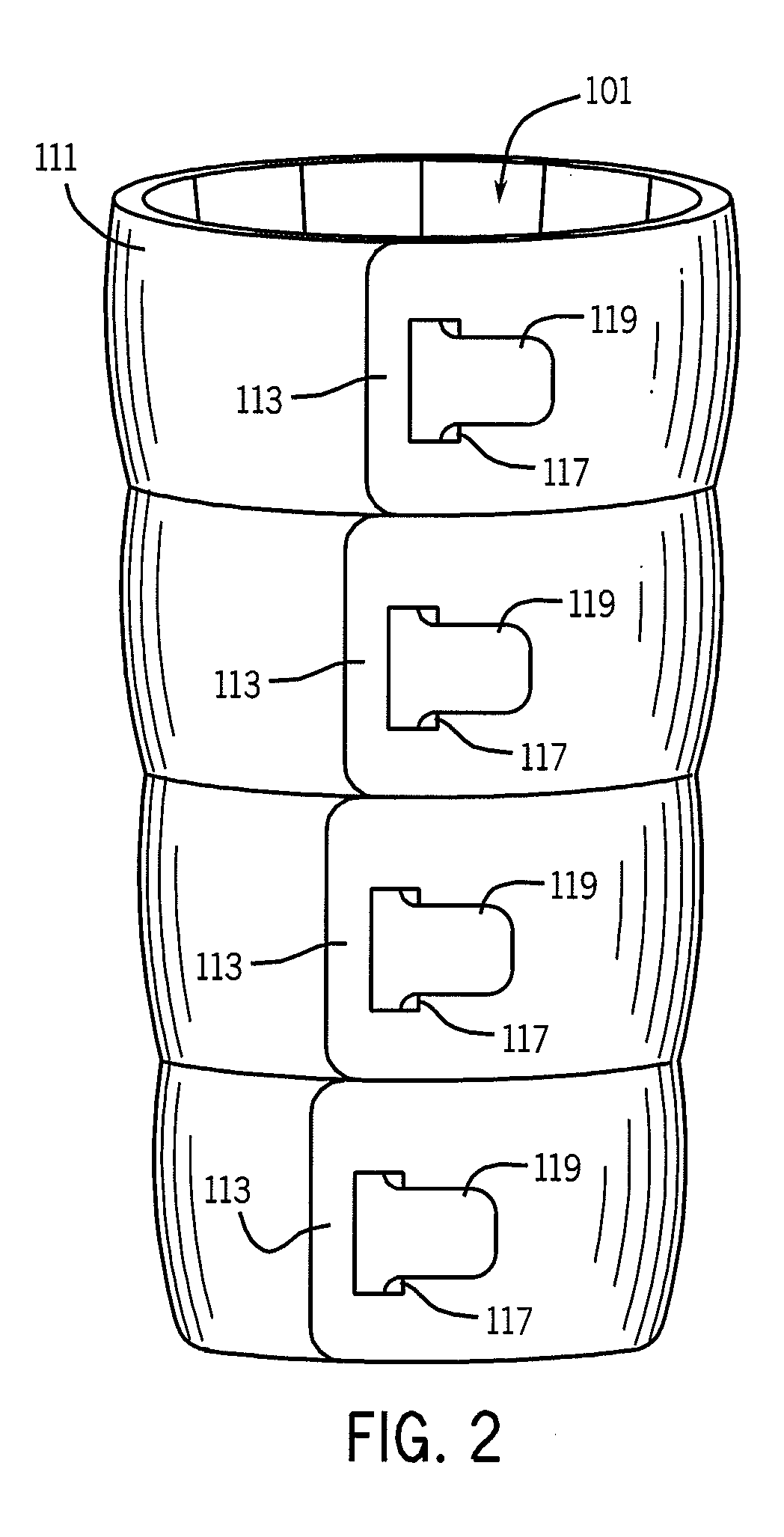
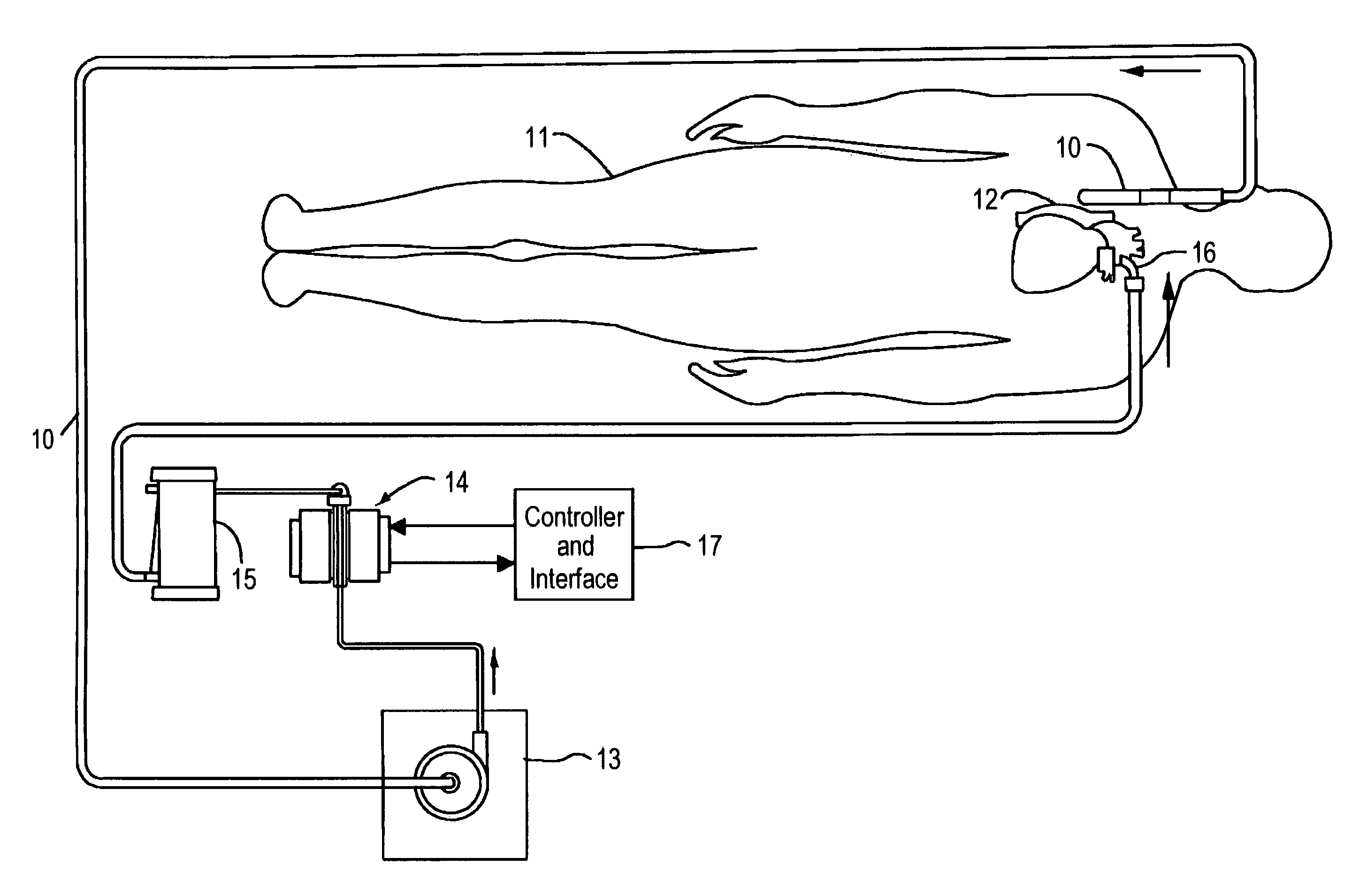
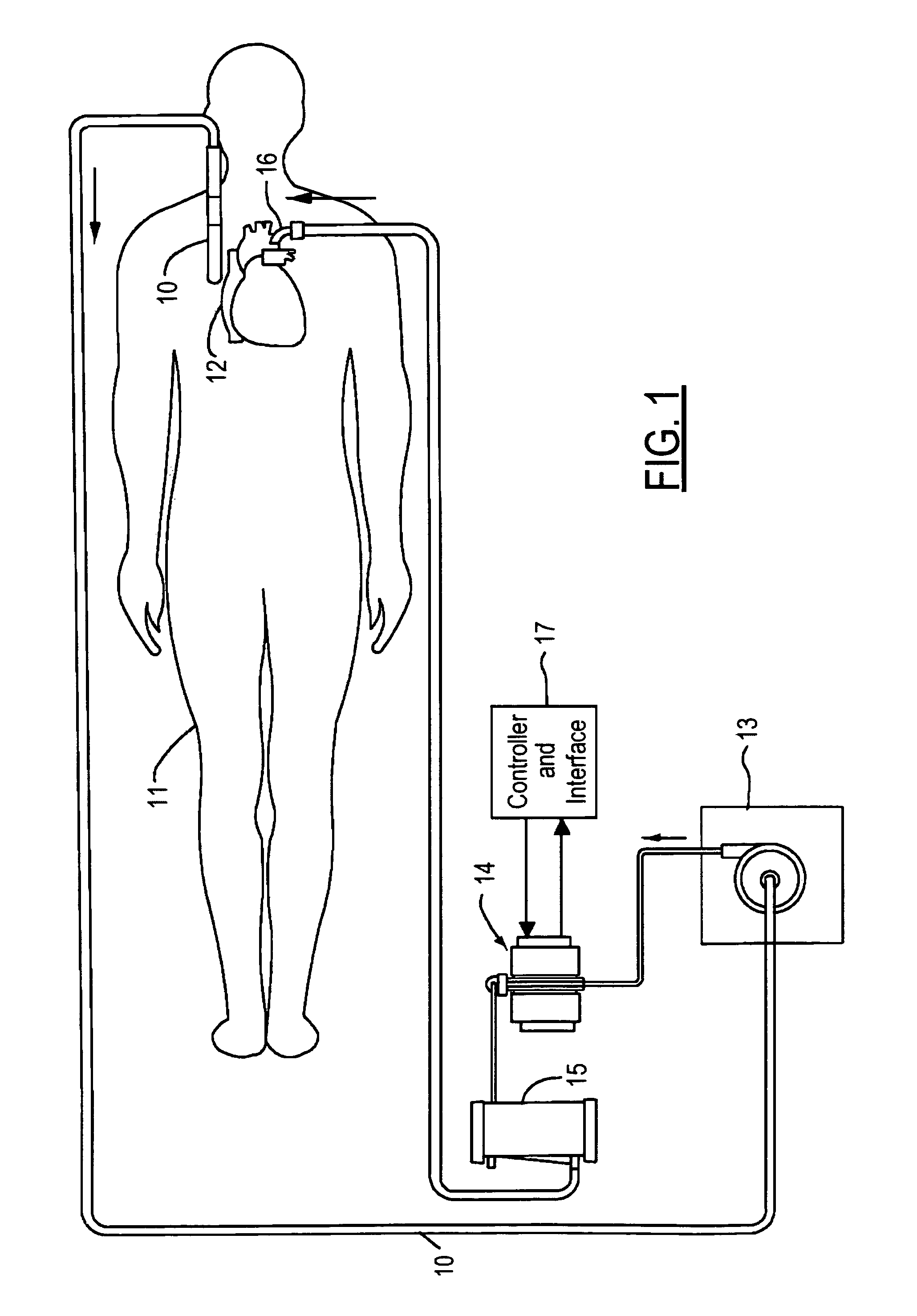
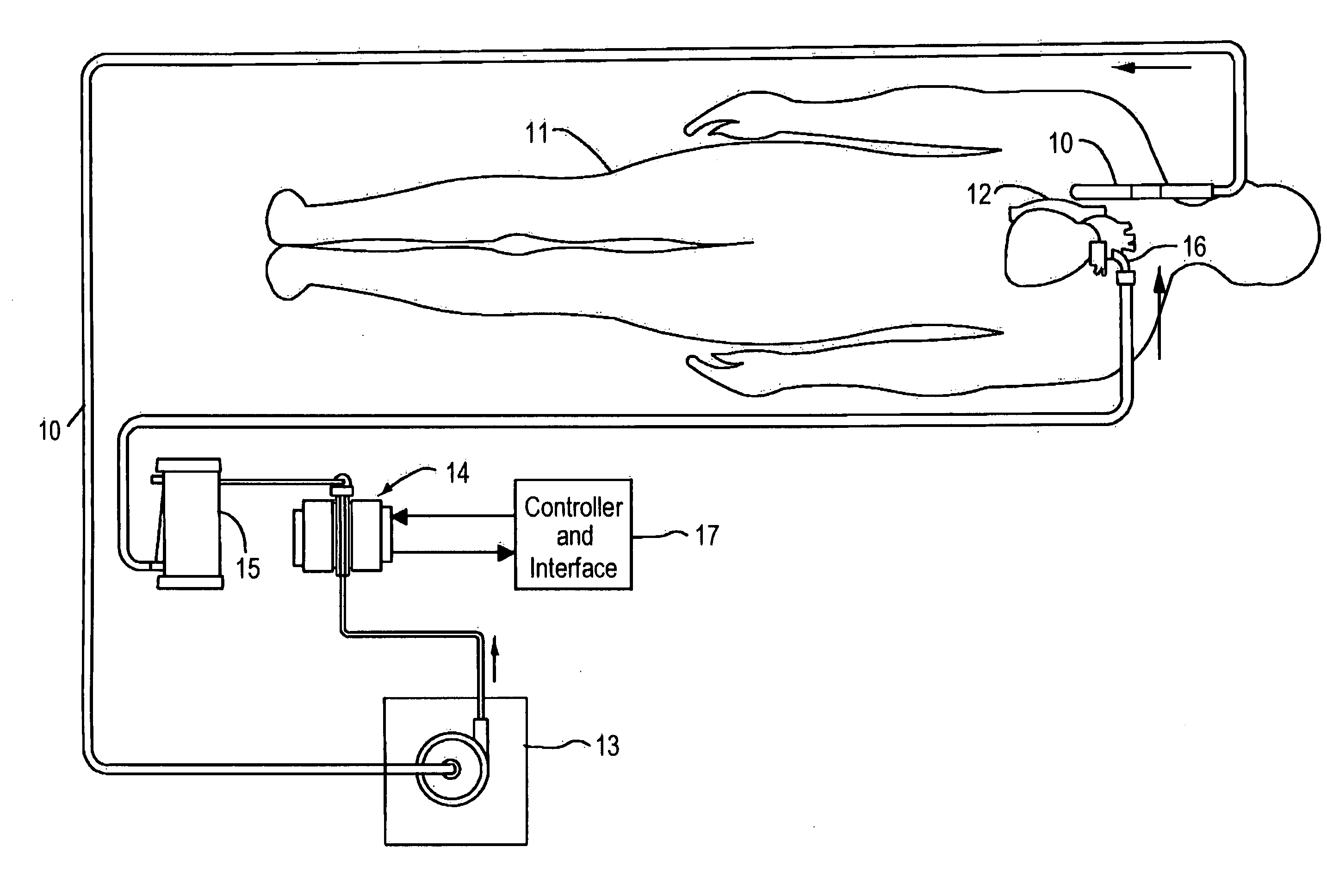
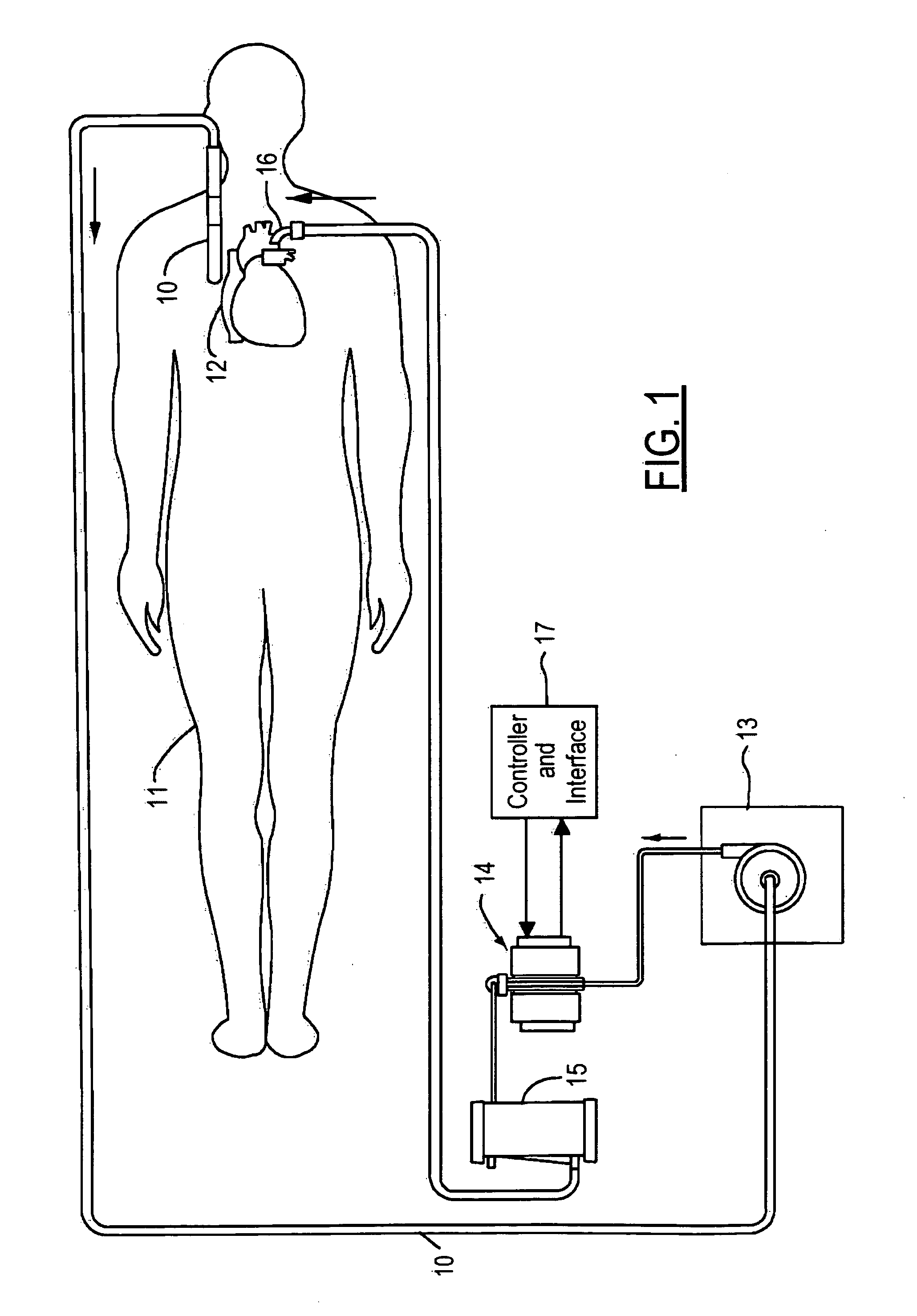
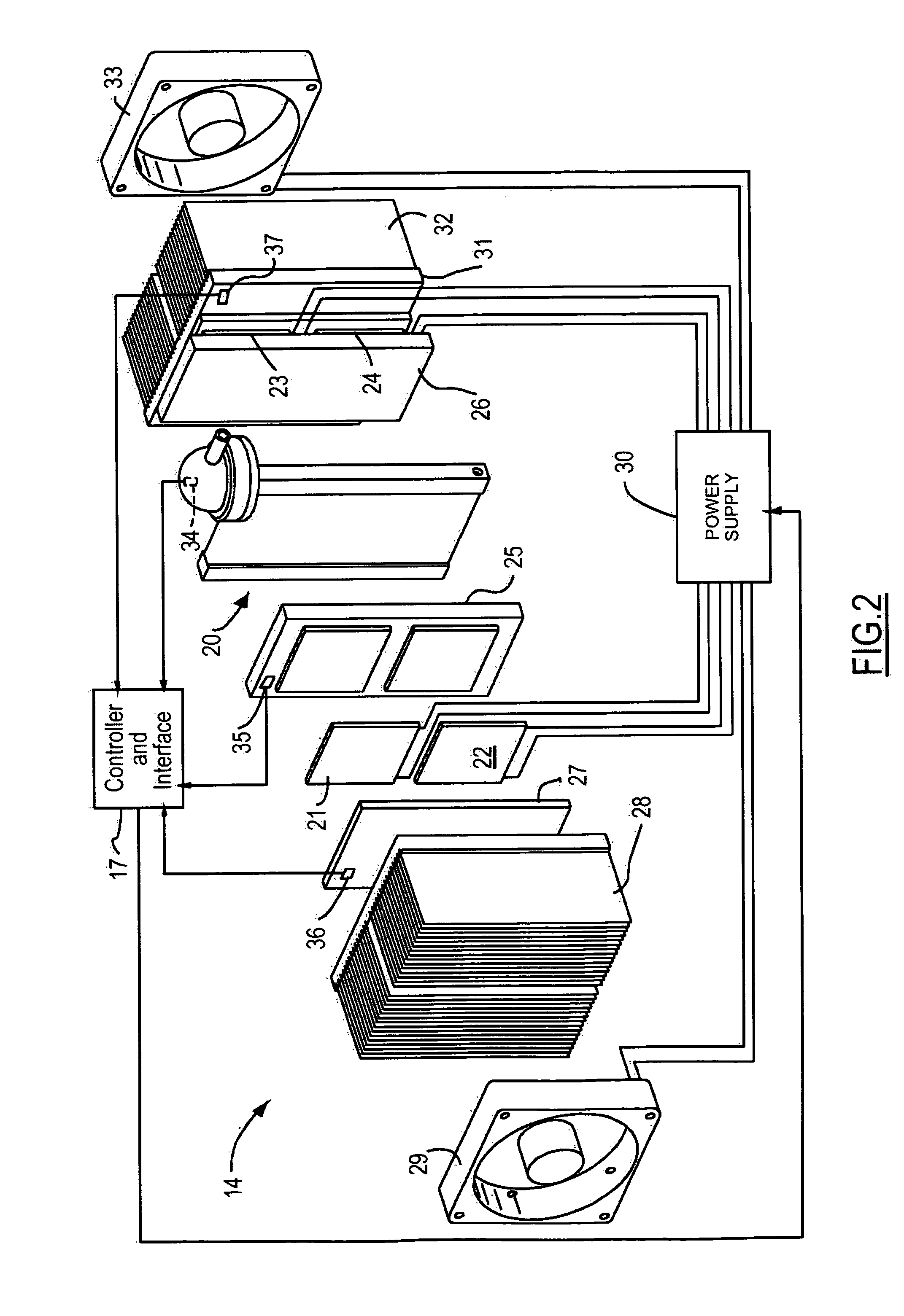
Thermoelectric temperature control for extracorporeal blood circuit
ActiveUS7588549B2Improve efficiencyReduce blood volumeTeeth fillingMedical devicesTemperature controlBlood flow
A waterless blood heater / cooler device directly controlling temperature of blood flowing through an extracorporeal blood circuit. A thermoelectric module is coupled to a supply voltage to generate a temperature difference. A heat exchanger cassette comprising a core and first and second laminar flow guides is in thermal contact (directly or indirectly) with the thermoelectric module. The cassette has a plurality of tubes for carrying parallel channels of the blood. The first and second laminar flow guides provide an inlet and an outlet for coupling to the extracorporeal blood circuit and respective intermediate chambers for receiving respective ends of the tubes in order to guide the blood to and from respective tubes in a substantially laminar flow.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
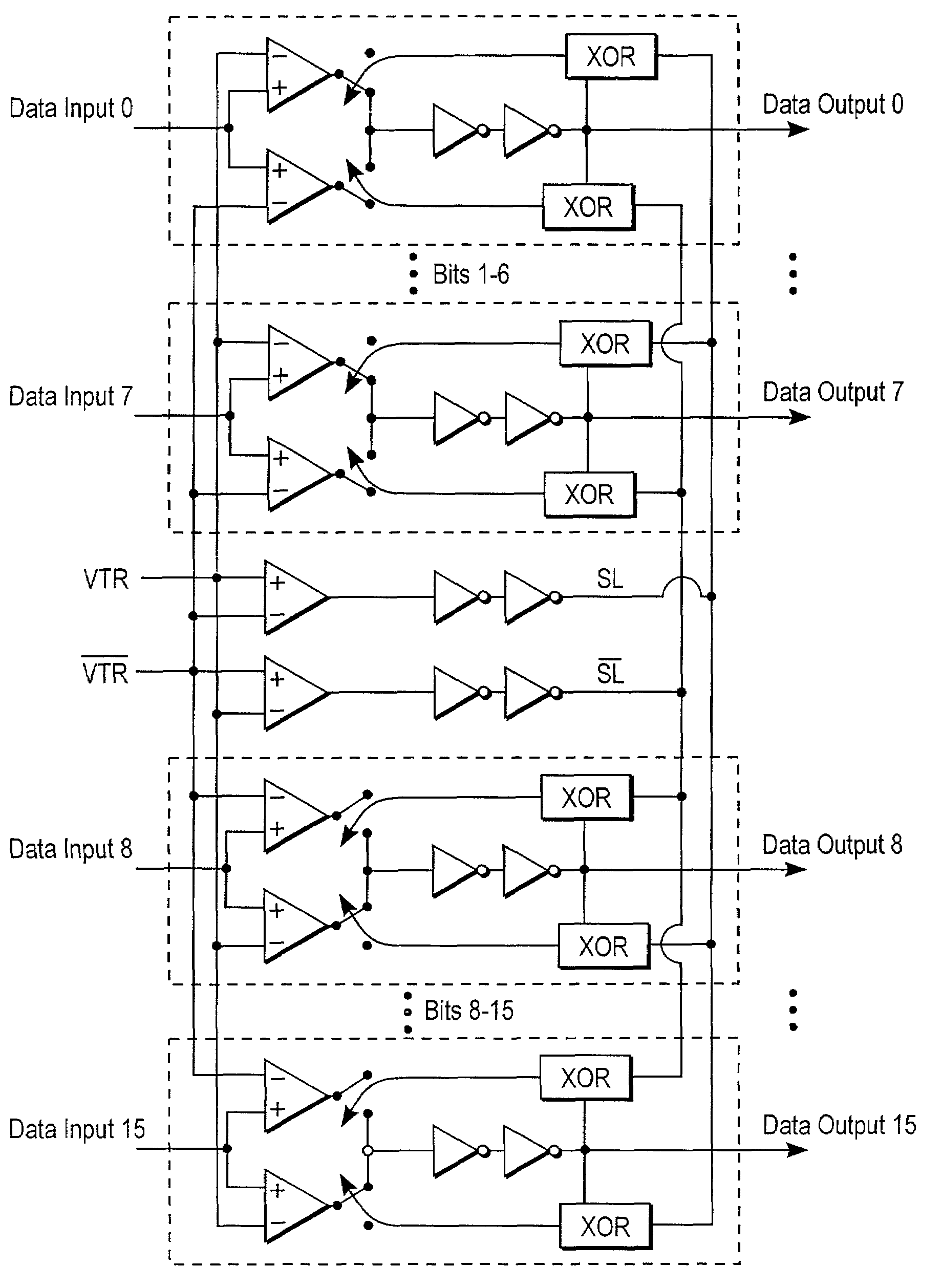
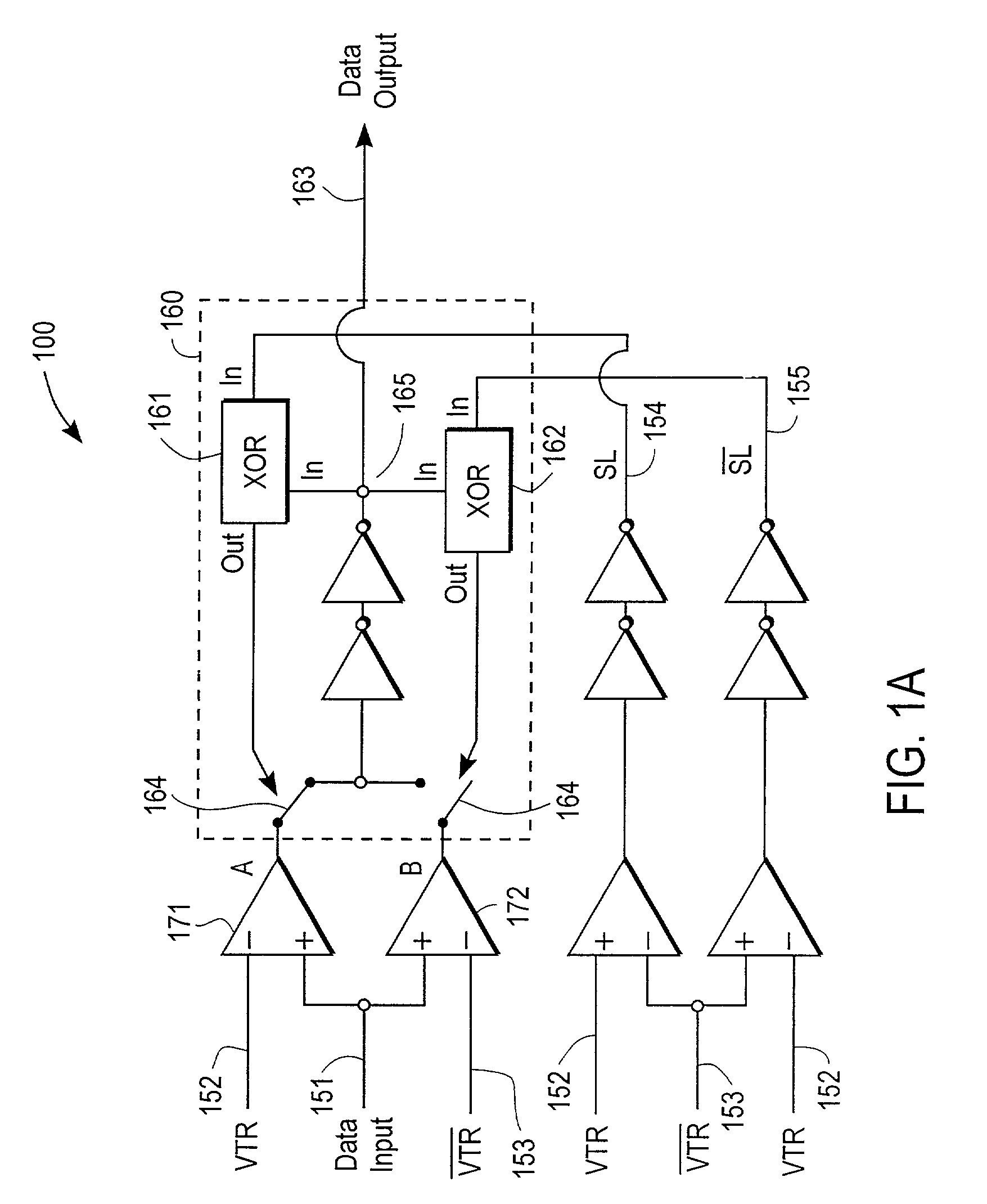
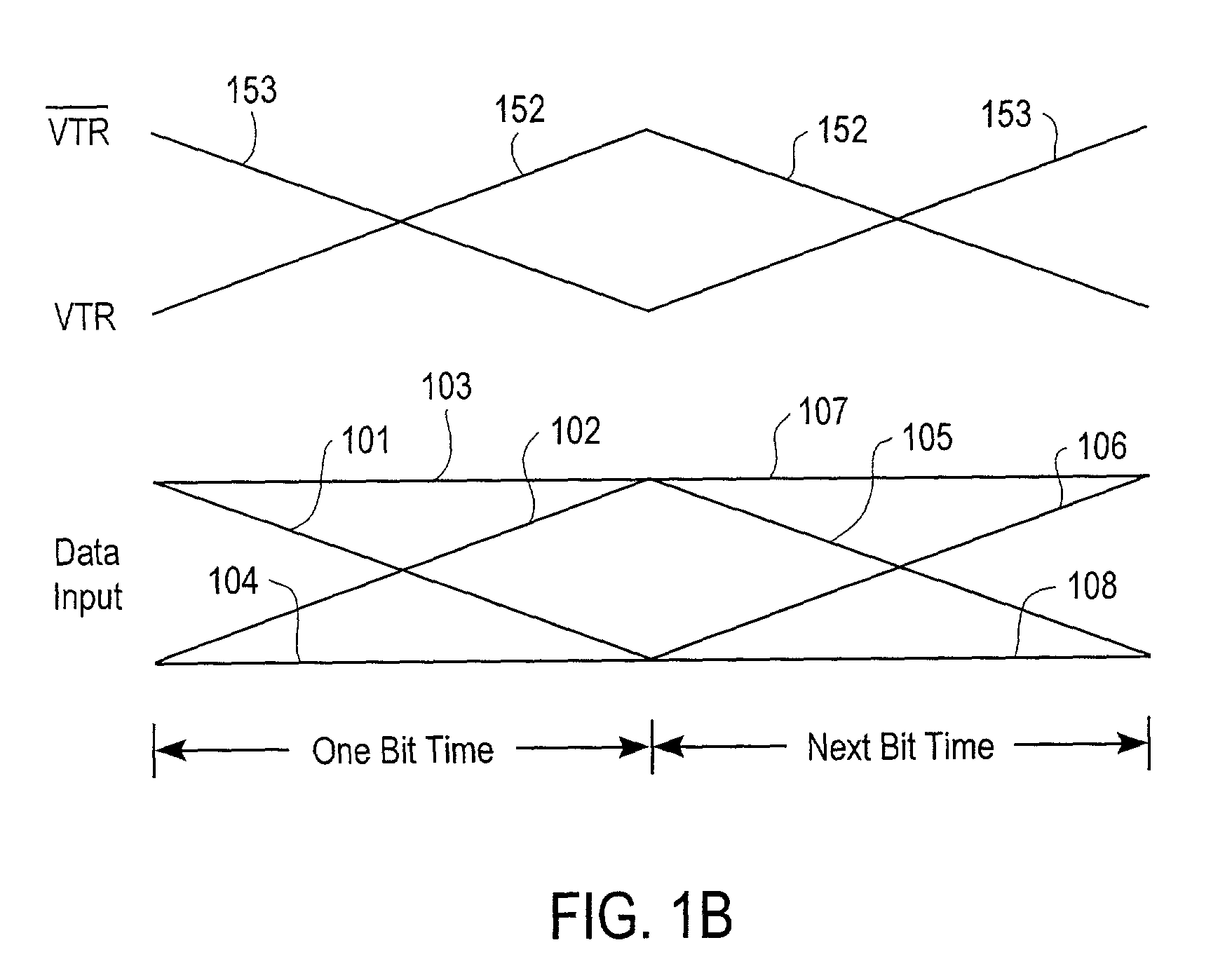
Method and system for deskewing parallel bus channels to increase data transfer rates
ActiveUS7123660B2Reliable receptionReliable transmissionChannel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsSignal onEngineering
In one embodiment, a system for deskewing signals on parallel bus channels includes several parallel channels that carry several data input signals and a pair of complementary voltage and timing reference (VTR) signals. The system also includes several receivers, with each receiver coupled to receive a data input signal and the pair of complementary VTR signals. The output of each receiver is based in part on a comparison of the received data input signal with the pair of complementary VTR signals. In one embodiment, a pair of VTR signals is selected from several pairs of VTR signals to widen the skew band on each channel. In one embodiment, each channel is skewed using a programmable delay circuit having a delay value based on the alignment of a data input signal relative to a pair of complementary VTR signals.
Owner:JAZIO
Multi-user parallel channel access in WLAN systems
ActiveUS20170231009A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork topologiesClear to sendResource allocation
Methods and apparatuses are related to multi-user parallel channel access (MU-PCA). For example, a wireless transmit / receive unit (WTRU) is provided that is one of a plurality of WTRUs operable to simultaneously communicate via a plurality of channels managed by an access point (AP). The WTRU includes a receiver configured to receive, from the AP, over at least one channel of the plurality of channels, a group request-to-send (G-RTS) message that includes a resource allocation that indicates at least one assigned channel for the WTRU; a transmitter configured to transmit a clear-to-send (CTS) message, to the AP, over the at least one assigned channel of the plurality of channels; and the receiver further configured to receive a data message, from the AP, over at least one channel of the plurality of channels.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Thermoelectric temperature control for extracorporeal blood circuit
ActiveUS20080031773A1Improve efficiencyReduce blood volumeMedical devicesSuction devicesTemperature controlTemperature difference
A waterless blood heater / cooler device directly controlling temperature of blood flowing through an extracorporeal blood circuit. A thermoelectric module is coupled to a supply voltage to generate a temperature difference. A heat exchanger cassette comprising a core and first and second laminar flow guides is in thermal contact (directly or indirectly) with the thermoelectric module. The cassette has a plurality of tubes for carrying parallel channels of the blood. The first and second laminar flow guides provide an inlet and an outlet for coupling to the extracorporeal blood circuit and respective intermediate chambers for receiving respective ends of the tubes in order to guide the blood to and from respective tubes in a substantially laminar flow.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com