FDTD (Finite-Difference Time-Domain)-based three-dimensional induction-polarization double-field numerical simulation method
A finite difference in time domain and numerical simulation technology, applied in design optimization/simulation, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing the use of memory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
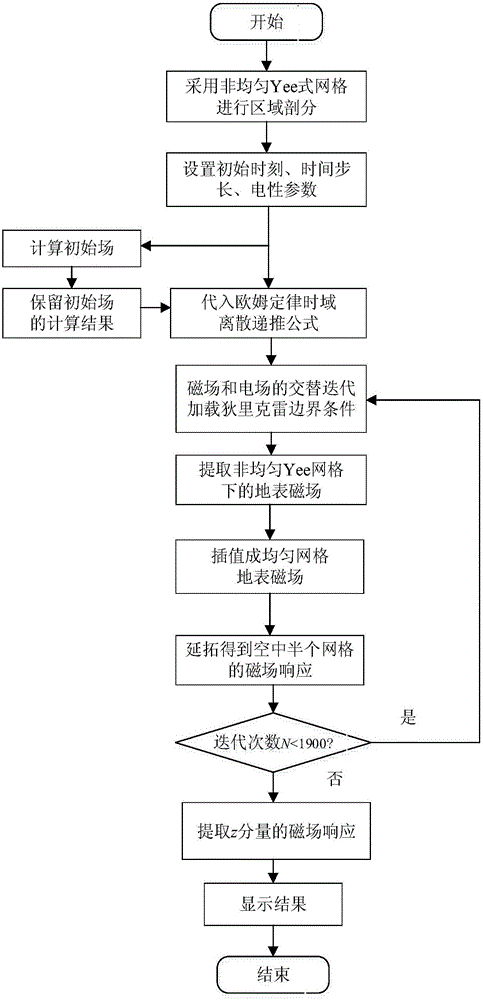
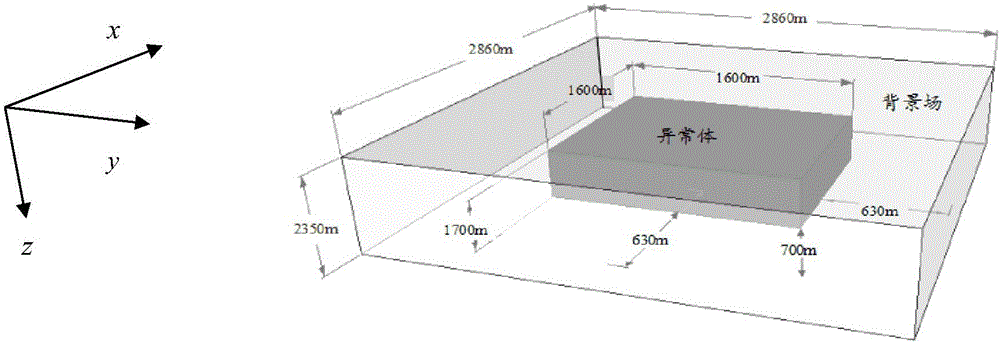
[0045] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention more clear, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the examples. Taking the uniform half-space model, the layered earth model, and the three-dimensional anomalous body model as examples, the three-dimensional induction-polarization dual-field electromagnetic response calculation of the time-domain finite difference is carried out. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention. see figure 1 to combine figure 2 As shown, a finite-difference time-domain three-dimensional induction-polarization dual-field numerical simulation method includes:
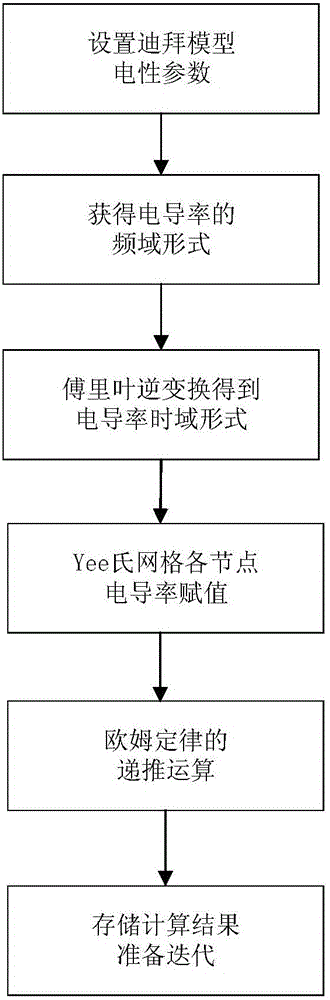
[0046] 1. Based on the Dubai model (Cole-Cole complex resistivity model when the frequency correlation coefficient c=1), first obtain the frequency domain form of the Dubai model conductivity, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com