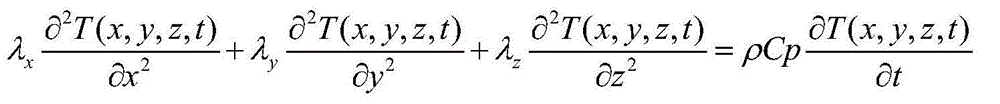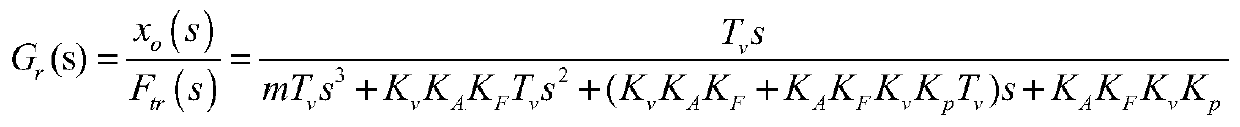Patents
Literature
34 results about "Inverse laplace transformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
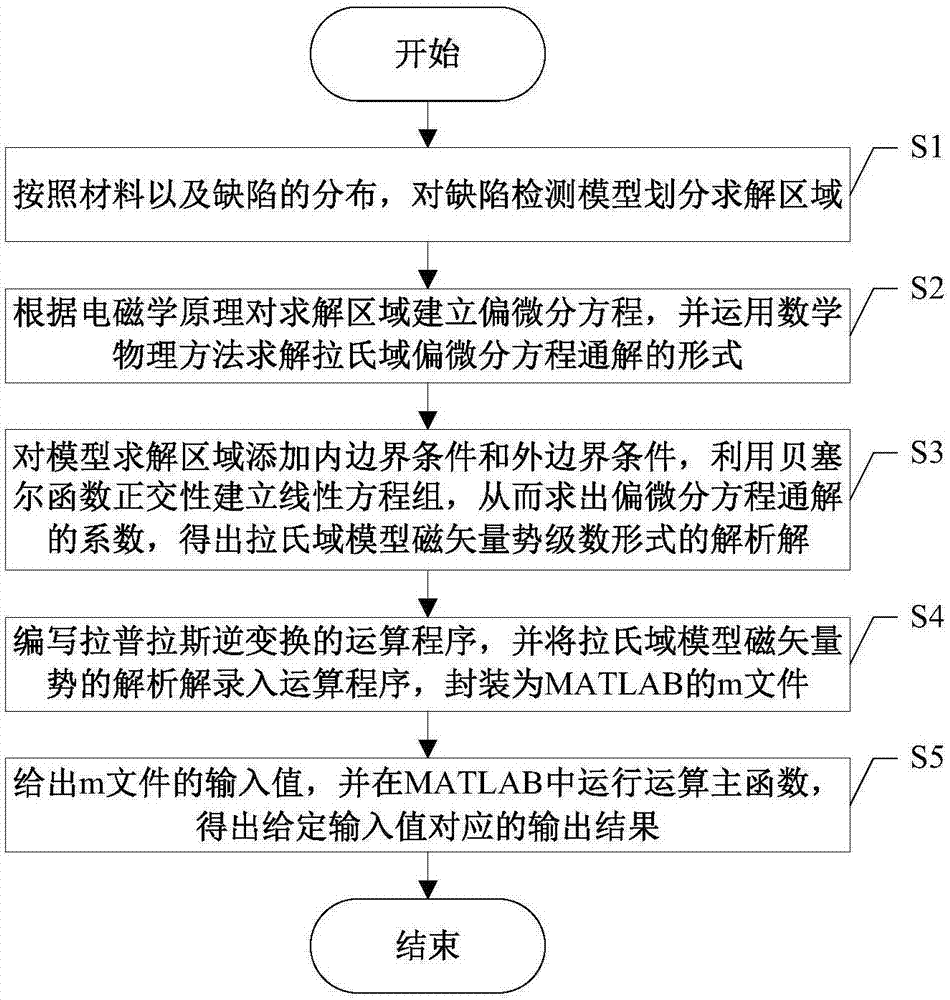
FDTD (Finite-Difference Time-Domain)-based three-dimensional induction-polarization double-field numerical simulation method
ActiveCN105893678AReduce usageEffective simulationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectromagnetic responseElectric field
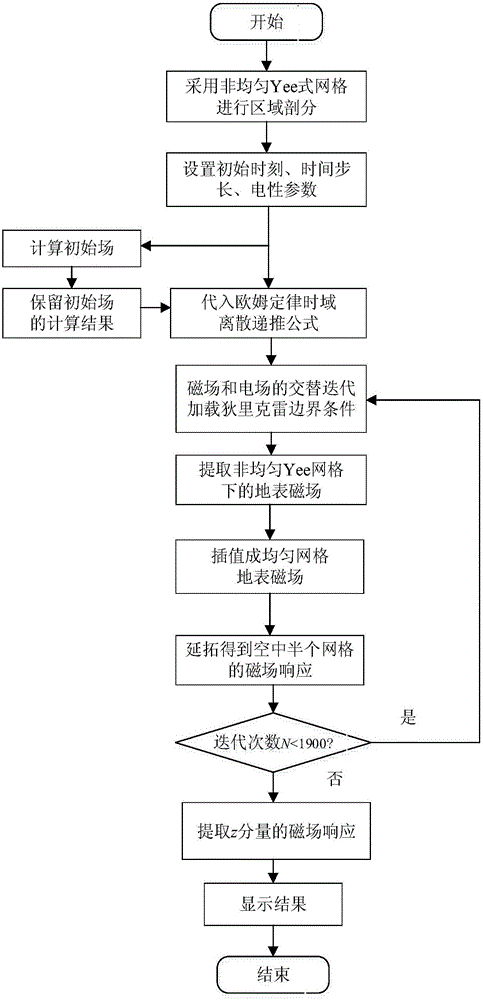
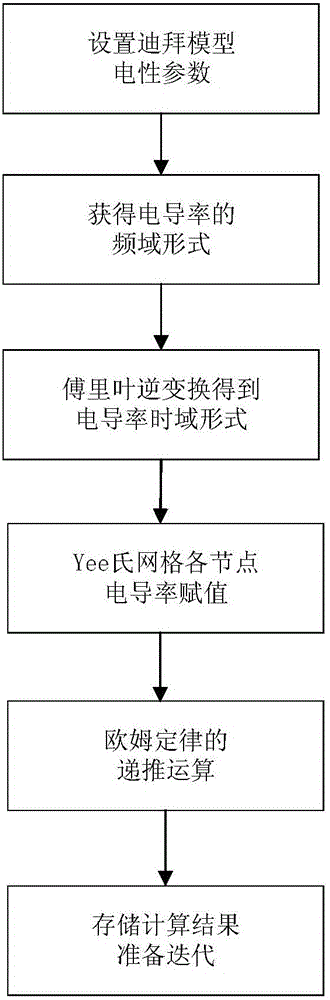
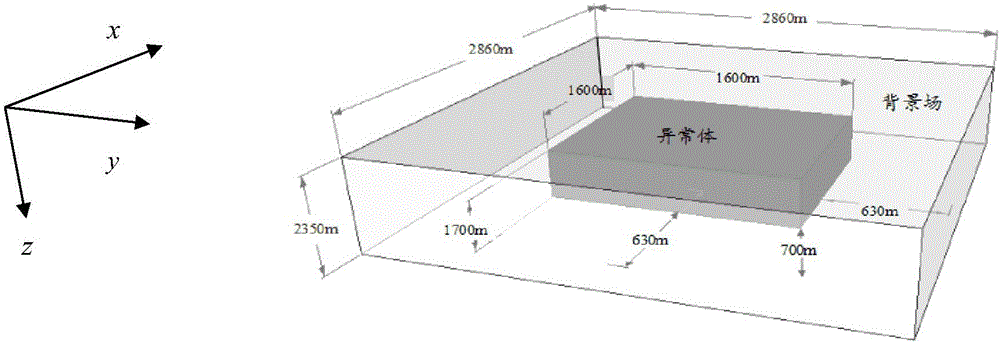
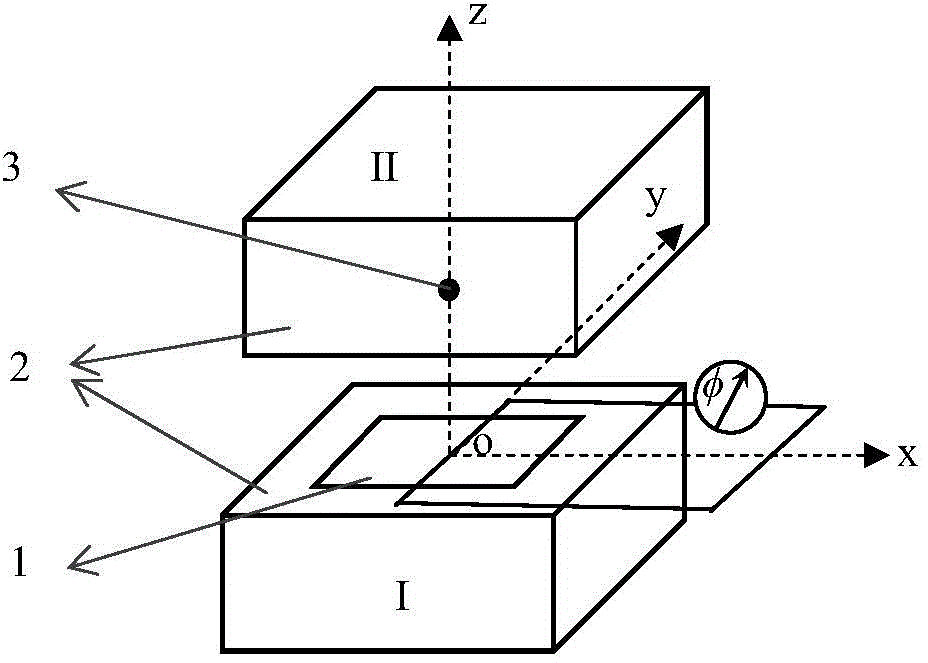
The invention relates to an FDTD (Finite Difference Time Domain)-based three-dimensional induction-polarized double-field numerical simulation method, which aims to quickly calculate electromagnetic response of induction-polarization double fields of a three-dimensional model. The FDTD-based three-dimensional induction-polarized double-field numerical simulation method mainly comprises the following steps of obtaining a time-domain expression of electric conductivity of a Dubai model by adopting inverse Laplace transformation; constructing an e index auxiliary equation of electric conductivity parameters; obtaining an ohm law time-domain discrete recursion expression through a trapezoidal integral method; reducing four-dimensional numeric operation into three-dimensional operation; substituting a formula into a passive Maxwell curl equation; deriving an iterative equation of an electric field and a magnetic field based on a three-dimensional FDTD method, thus completing electromagnetic response numerical calculation of the induction-polarization double fields of the three-dimensional model. The FDTD-based three-dimensional induction-polarized double-field numerical simulation method disclosed by the invention aims to solve the problems of long time-domain convolution operation of Ohm law, large memory occupation and the like, and the electromagnetic response numerical calculation of the induction-polarization double fields of the three-dimensional model is finally realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for measuring anisotropic material heat conductivity based on small-plane heat source
InactiveCN104597078AEasy to implementSimple stepsMaterial heat developmentTime domainLinear correlation
The invention discloses a method for measuring anisotropic material heat conductivity based on a small-plane heat source. The method comprises the following steps: building a three-dimensional heat transfer model of a measured sample in a right-angle coordinate system in a special form under the action of thermal interference; obtaining an analytical solution of temperature change in anisotropic material in a time domain by adopting Laplace transformation, variables separation, transcendental equation solving and inverse Laplace transformation methods; through sensitivity calculation, analyzing linear correlation of sensitivity coefficients of normal heat conductivity and tangential heat conductivity and the effects of parameters on temperature change; building an experiment measurement system, and collecting transient response data of the temperature; and simultaneously determining the normal heat conductivity and the tangential heat conductivity of the measured anisotropic material by an improved Gauss Newton parameter estimation method. The method has the advantages that the transient measurement method which is convenient to implement, fast in measurement and wide in application range and adopts simple steps is provided, and the normal heat conductivity and the tangential heat conductivity of the rectangular anisotropic material can be obtained by once measurement.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Fractional order electromagnetic anomalous diffusion three-dimensional simulation method of rational function approximation
ActiveCN107657137AQuick calculationMeet the dispersion characteristicsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsThree dimensional simulationElectromagnetic response
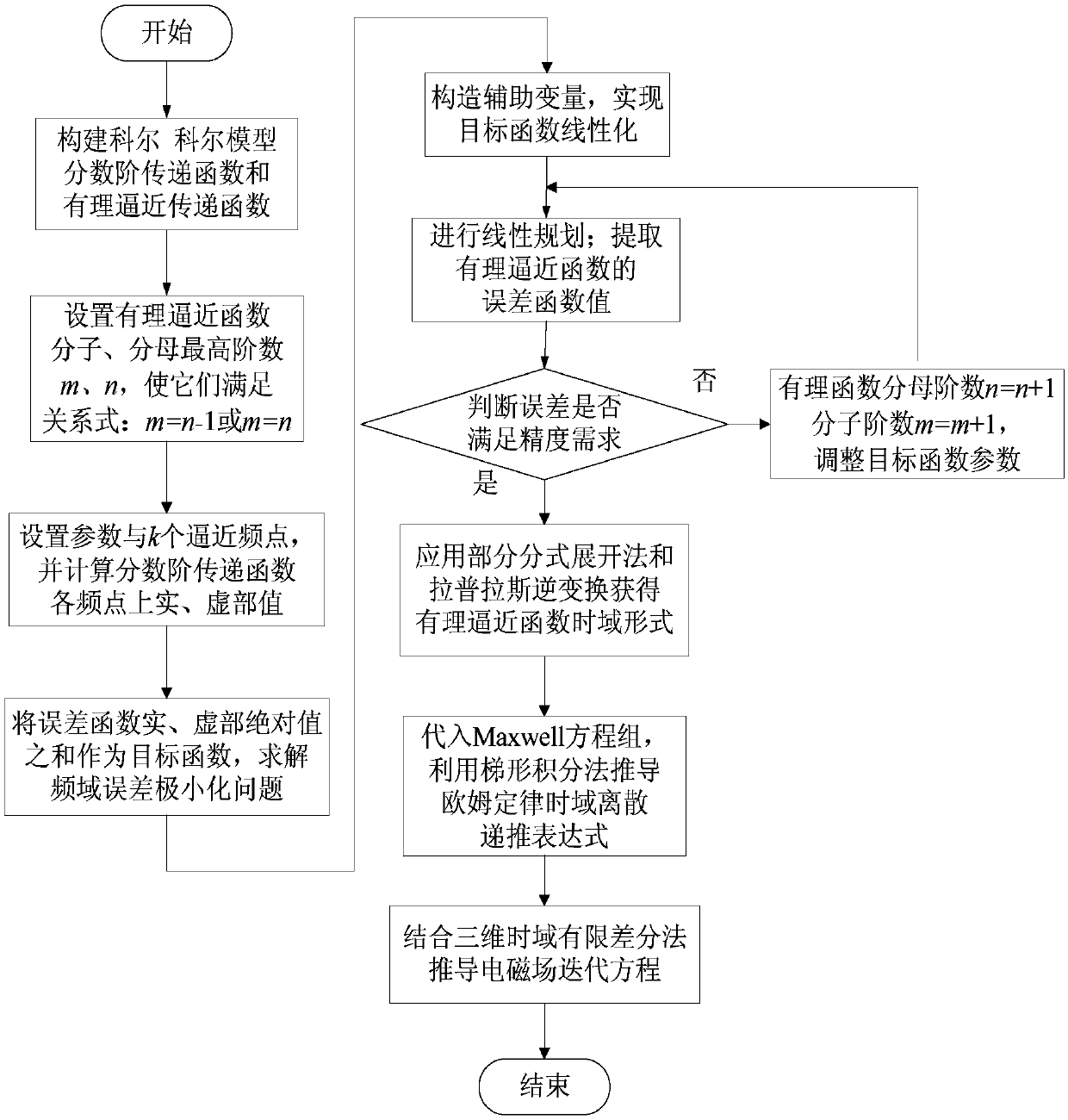
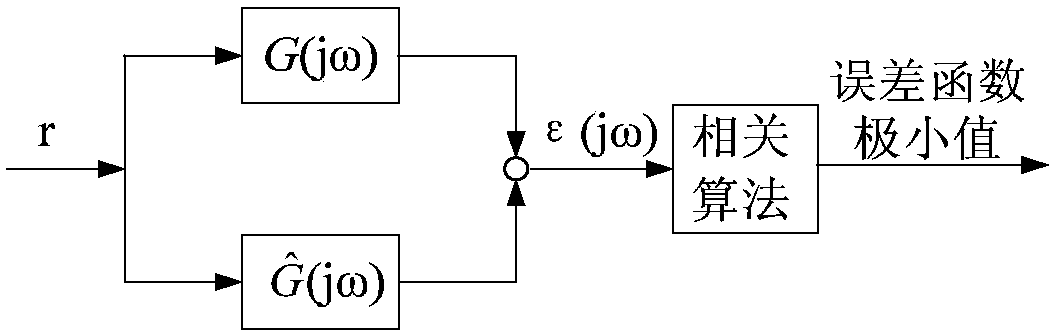
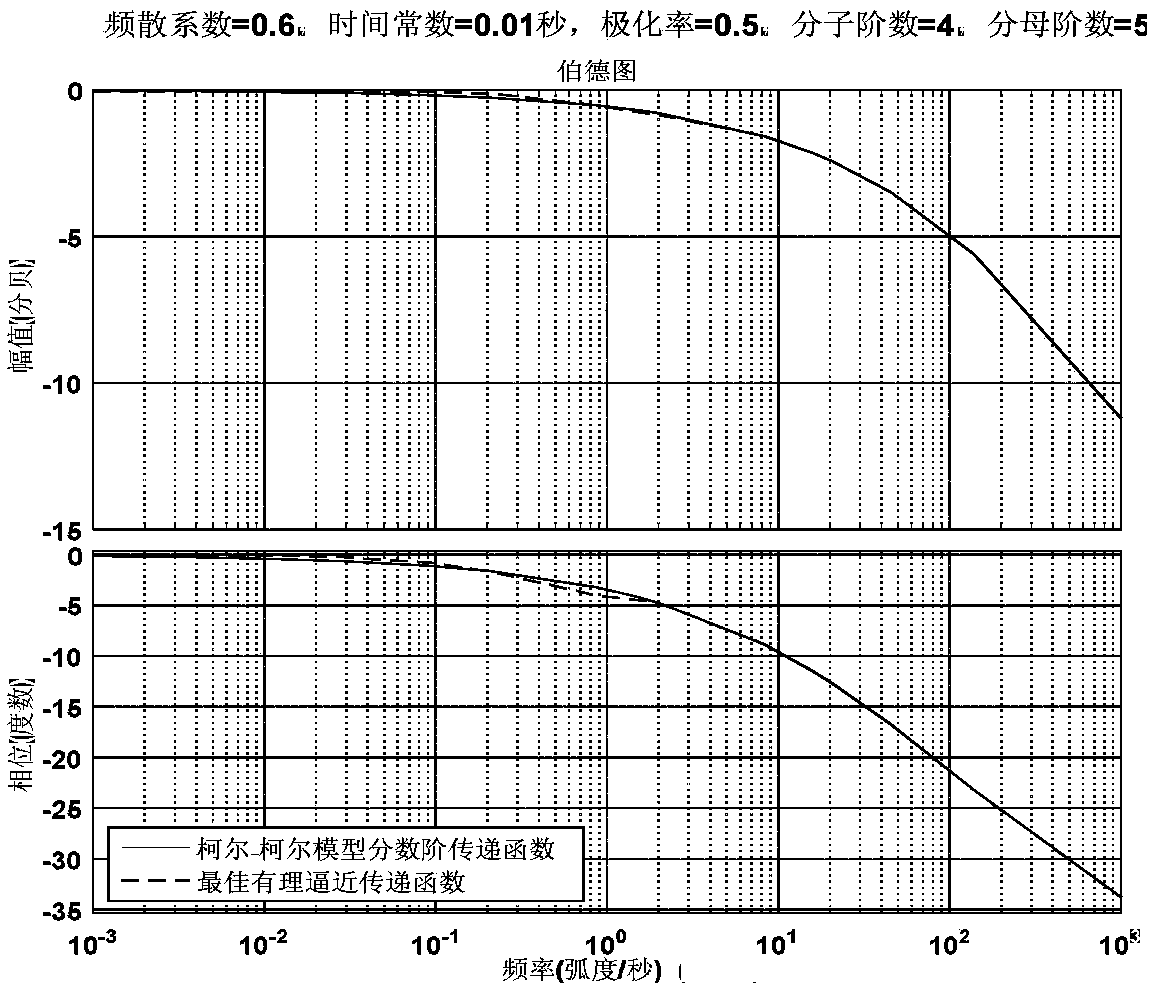
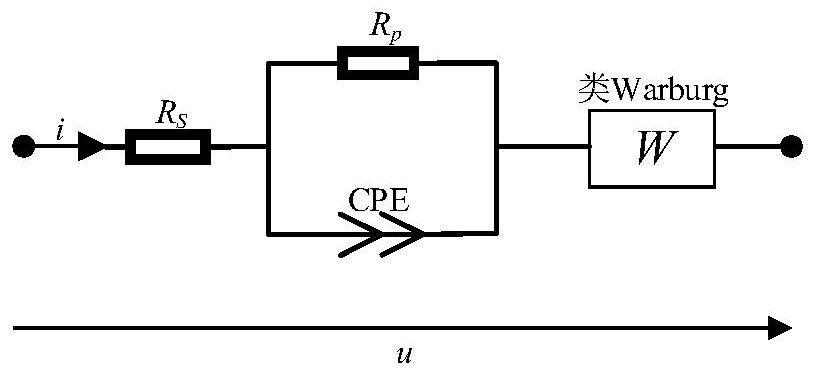
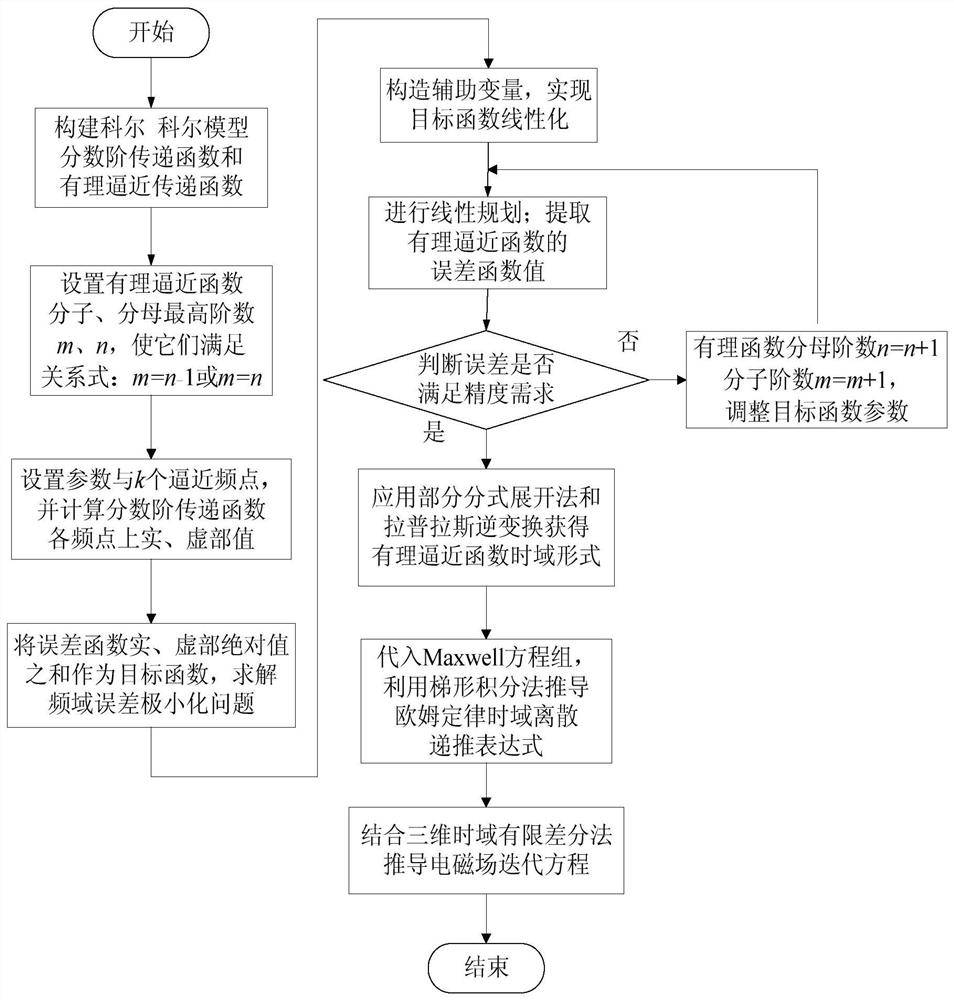
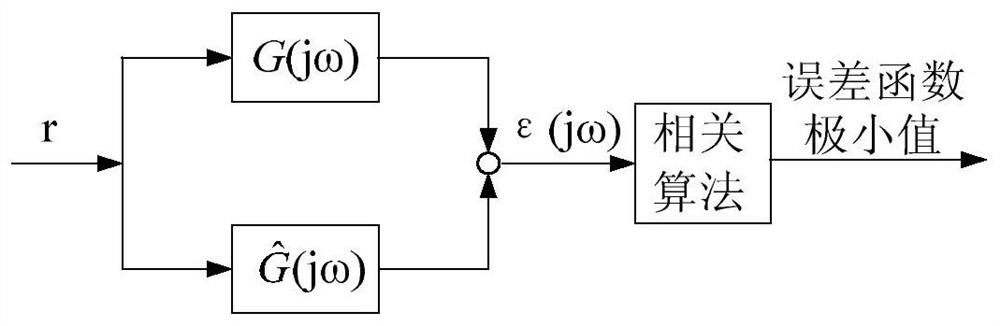
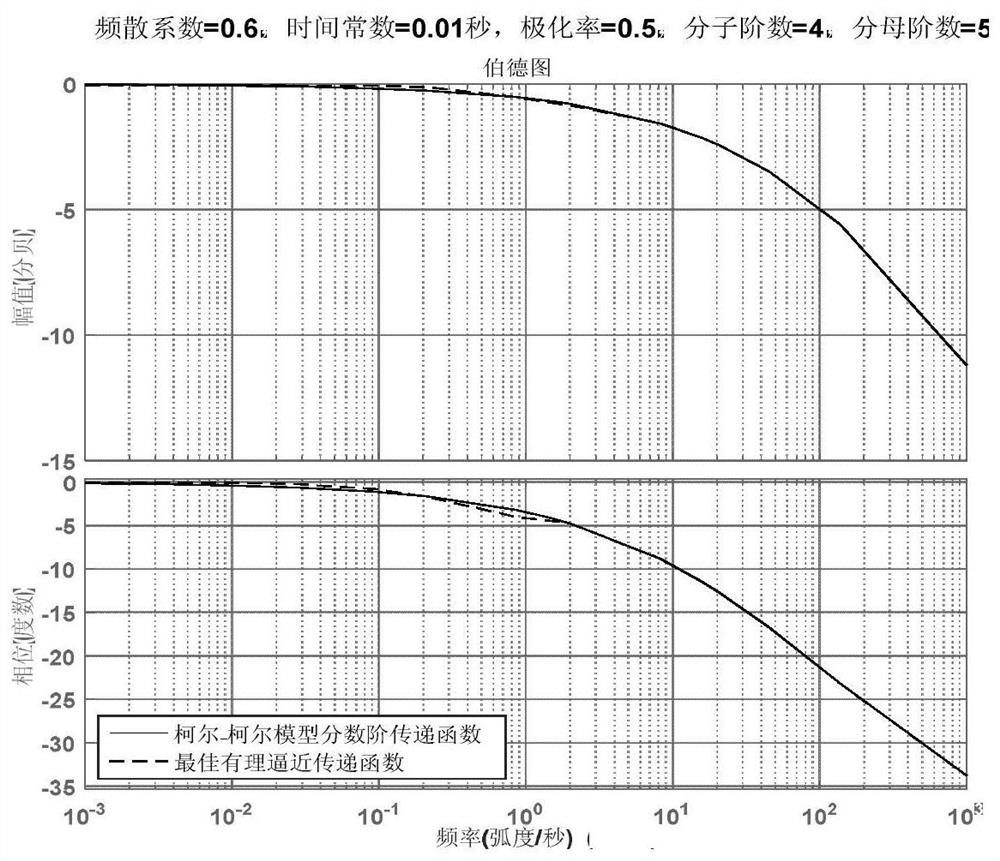
The invention relates to a fractional order electromagnetic anomalous diffusion three-dimensional simulation method of rational function approximation, and aims at calculating three-dimensional time-domain induction-polarization double field response of a fractional order Cole-Cole model. The method mainly comprises the steps of establishing a Cole-Cole model fractional order transfer function andan n-odrer rational approximation function based on a frequency domain rational function approximation method, and making the sum of the real part and the imaginary part of an error function as a target function; achieving linearization of the target function through an instrumental variable technique, and obtaining an optimal approximation rational function by adopting a linear programming approach; obtaining a time-domain mode of a conductivity by adopting a partial fraction expansion method and inverse laplace transformation; putting the time-domain mode in a Maxwell equation, deducing aniterative equation of an electromagnetic field based on a finite difference method, and achieving fractional order Cole-Cole model three-dimensional electromagnetic response value calculation. The fractional order electromagnetic anomalous diffusion three-dimensional simulation method of the rational function approximation has the advantages of fast and accurately simulating the fractional order Cole-Cole model three-dimensional time-domain electromagnetic response and providing theoretical foundation for research on abnormal electromagnetic diffusion in a polarization medium.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
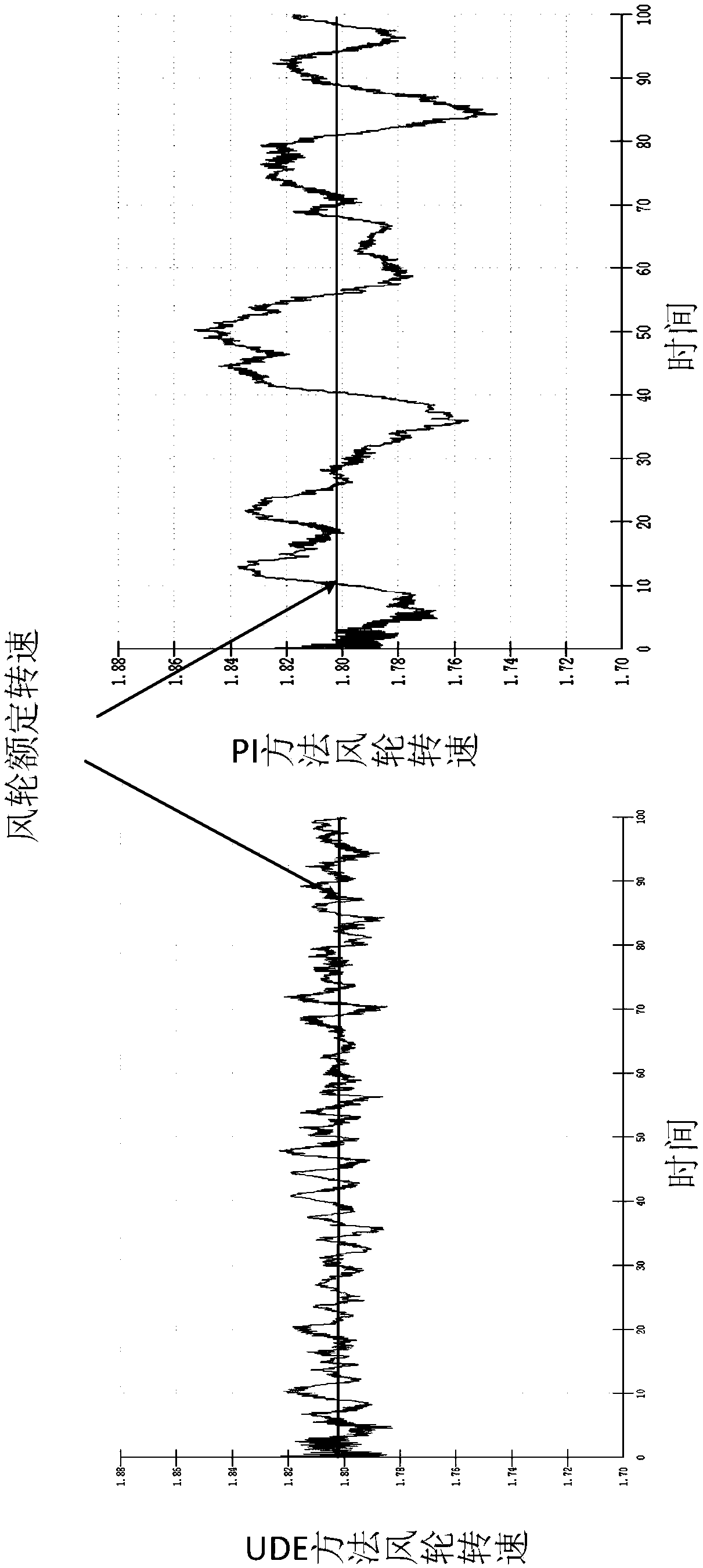
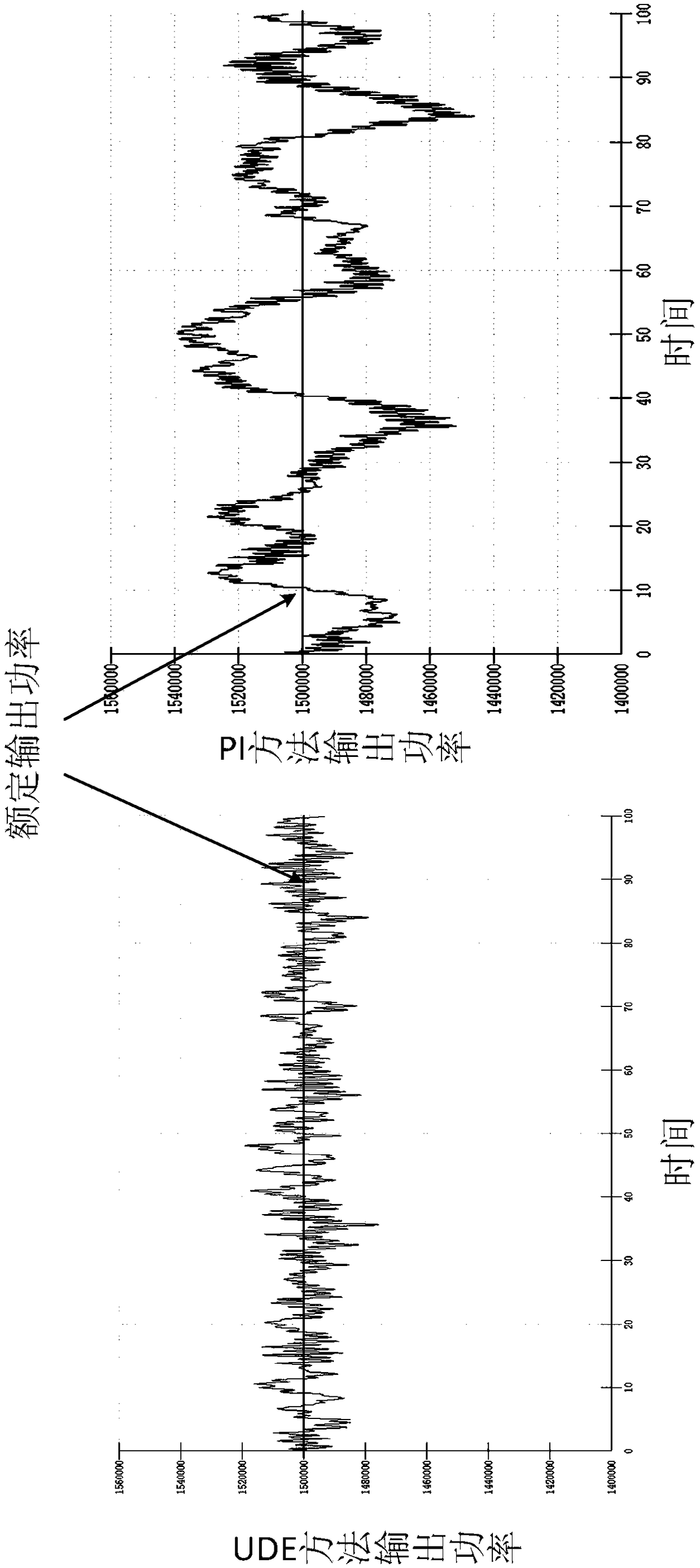
Variable-pitch robust control method based on UDE for wind generating set
ActiveCN105971819ASimple structureImprove anti-interference abilityWind motor controlMachines/enginesWind drivenAnti jamming
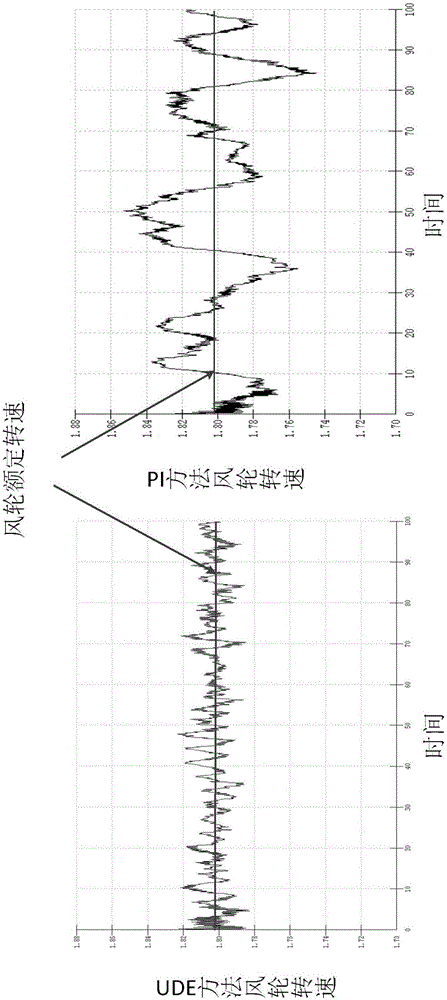
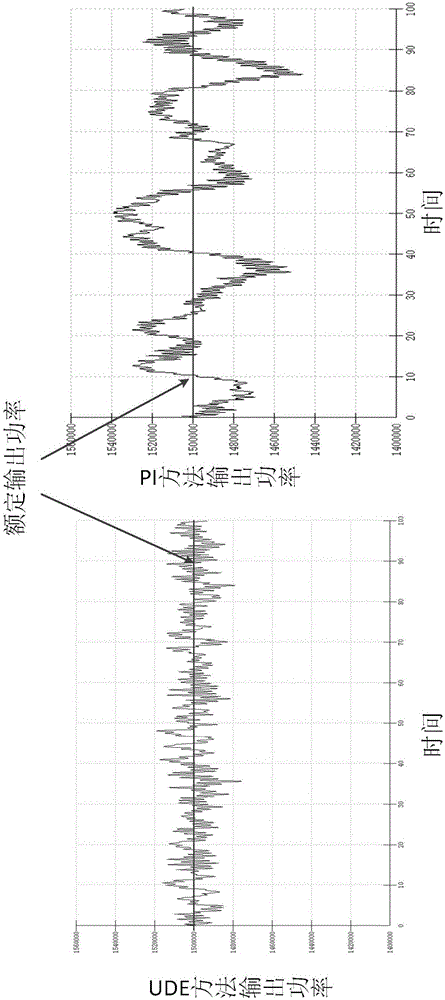
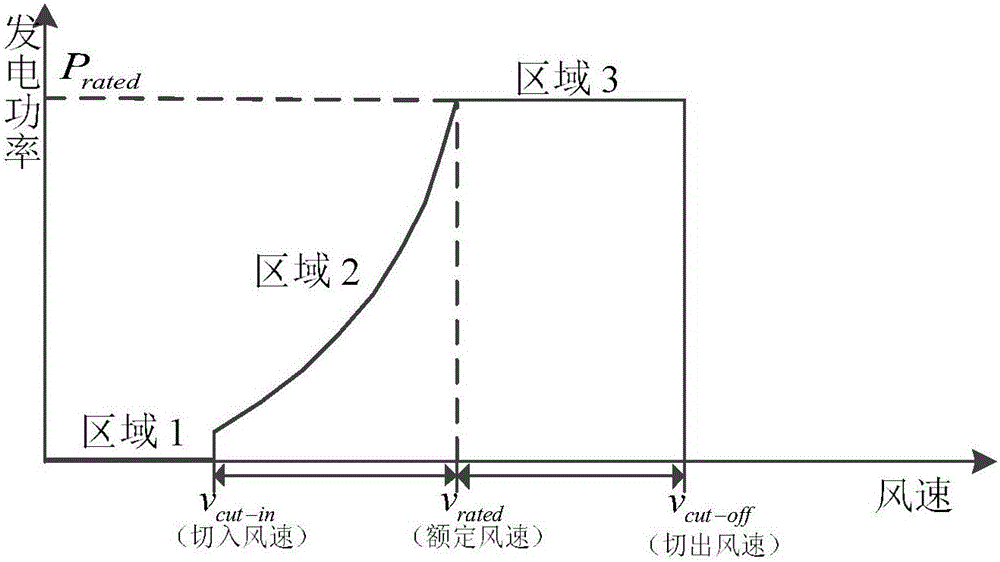
The invention discloses a variable-pitch robust control method based on a UDE for a wind generating set. The method comprises the steps of creating a dynamic model of wind-driven generators on the basis of unmodeled dynamics and disturbance of the wind generating set; defining dynamic characteristics of regulation errors and expectation errors; rewriting the dynamic model of the wind generating set and obtaining a preliminary expression of a pitch angle controller; arranging a low pass filter for carrying out approximation on non-affine uncertain items and disturbance terms of the dynamic model of the wind-driven generators, substituting the approximation result into the preliminary expression of the pitch angle controller, carrying out Laplace transformation, carrying out inverse Laplace transformation after merging and sorting and obtaining final pitch angle control signals. In the design process, the problem that the design of a non-affine system controller is difficult is solved, the unmodeled dynamics and the environmental disturbance of a system are fully considered, the structure of an obtained controller is simple, the number of needed parameters is small, the robustness is good, the anti-jamming capability is high, a more stable wind wheel rotation speed and more stable generation power can be provided, and high-quality electric energy can be provided for a power grid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
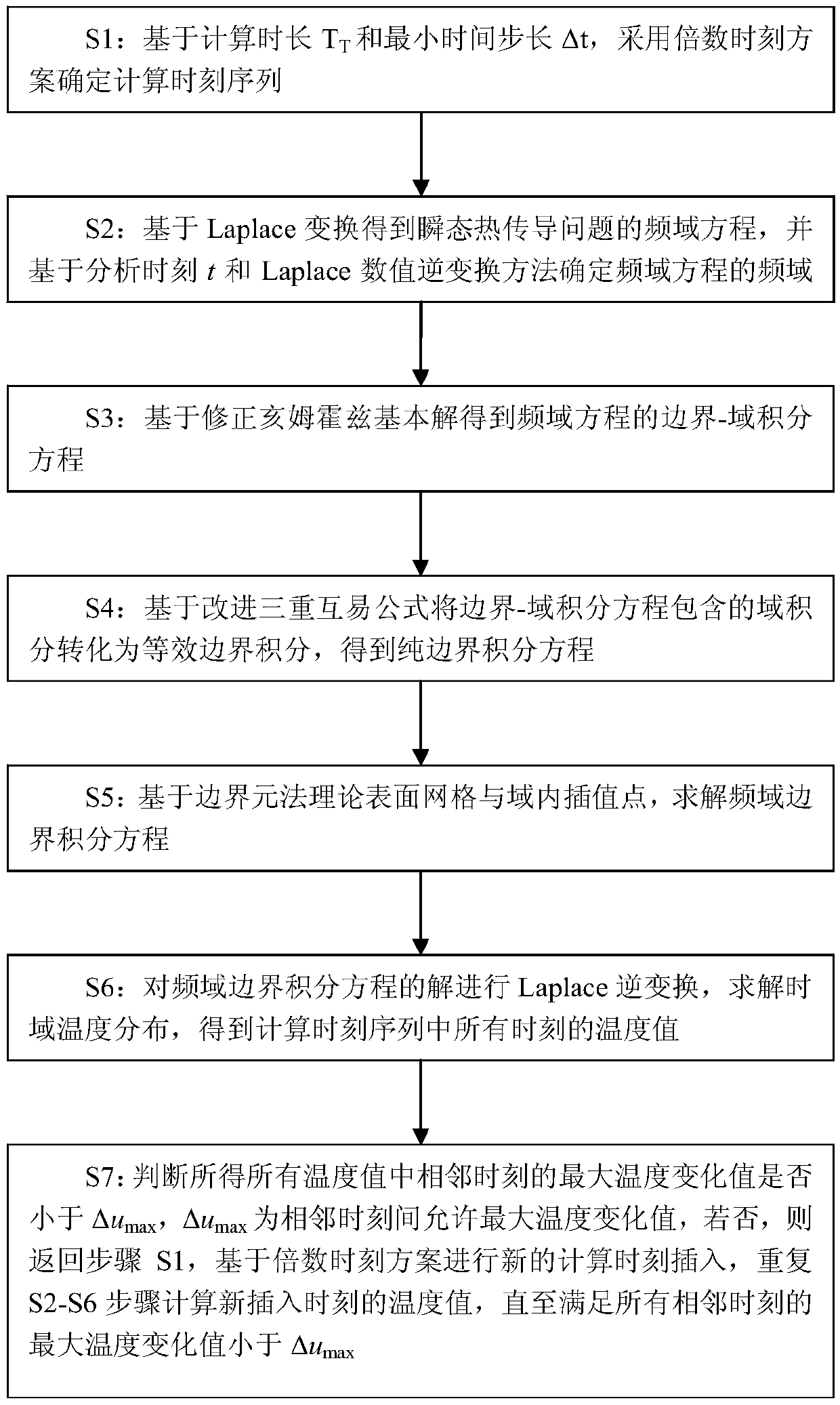
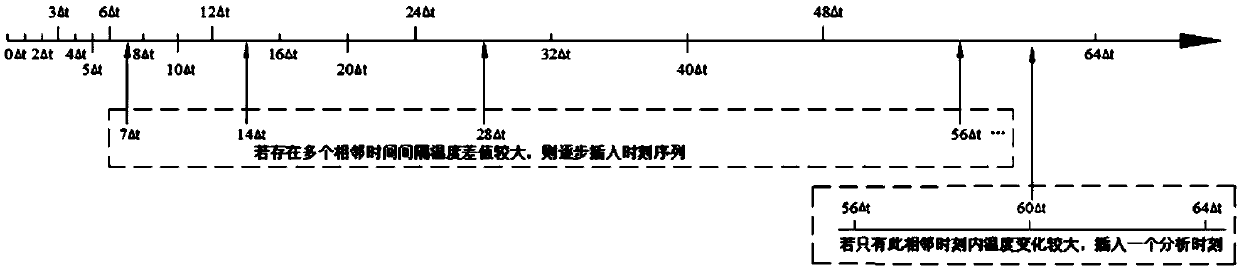
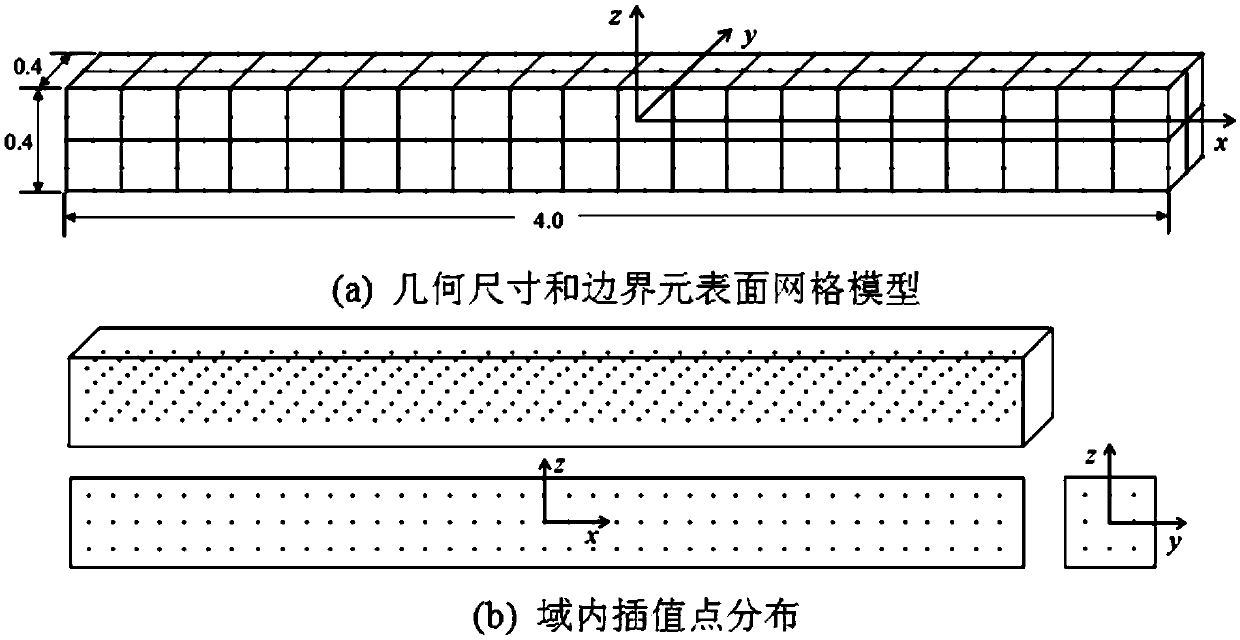
Transient temperature calculation method based on improved triple reciprocal boundary element method
ActiveCN108932392AReduce the number of computing momentsReduce computing timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsBoundary integral equationsFrequency domain equalization
The invention discloses a transient temperature calculation method based on an improved triple reciprocal boundary element method, comprising the following steps: adopting a multiple time scheme to determine a calculation time sequence; obtaining a frequency domain equation of a transient heat conduction problem based on Laplace transform, and determining frequency domain parameters of the frequency domain equation based on analysis time t and an inverse Laplace transformation method; obtaining a boundary-domain integral equation of the frequency domain equation based on a modified Helmholtz fundamental solution; based on an improved triple reciprocity formula, transforming a domain integral contained in the boundary-domain integral equation to equivalent boundary integral, to obtain a pure boundary integral equation; solving a frequency domain boundary integral equation based on a theoretical surface mesh of a boundary element method and intra-domain interpolation points; performing inverse Laplace transformation on a solution in frequency domain, and solving time domain temperature distribution. The invention provides an improved triple reciprocity method calculation formula withlow degree of freedom expression, thereby greatly reducing calculation time of the triple reciprocity method and saving storage space at the same time.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for building one-dimensional cumulates in two-storied foundation load in two stages
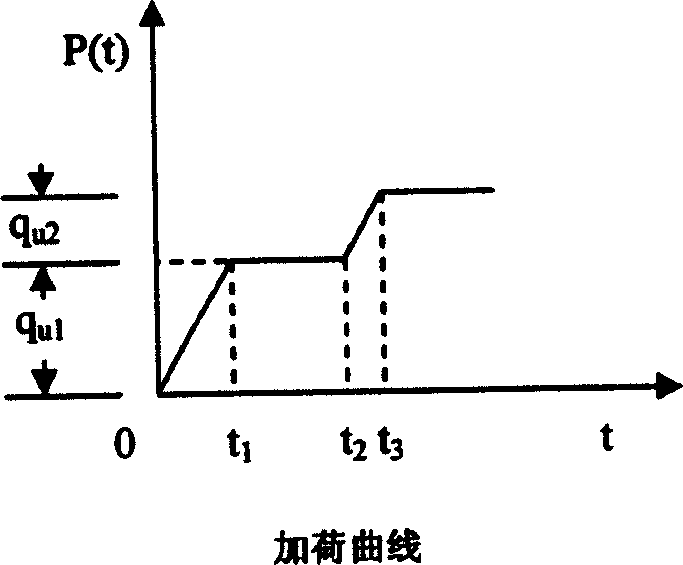
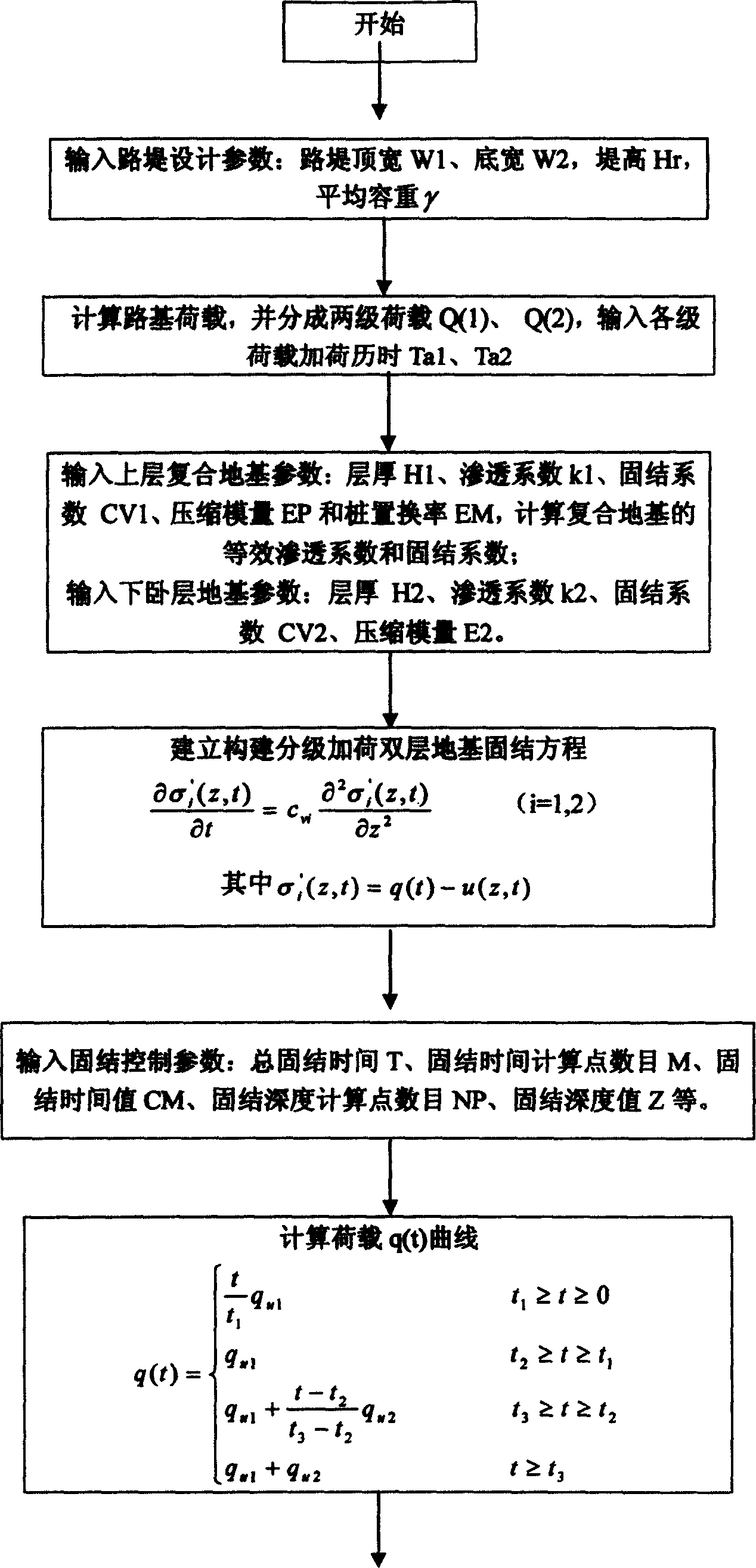
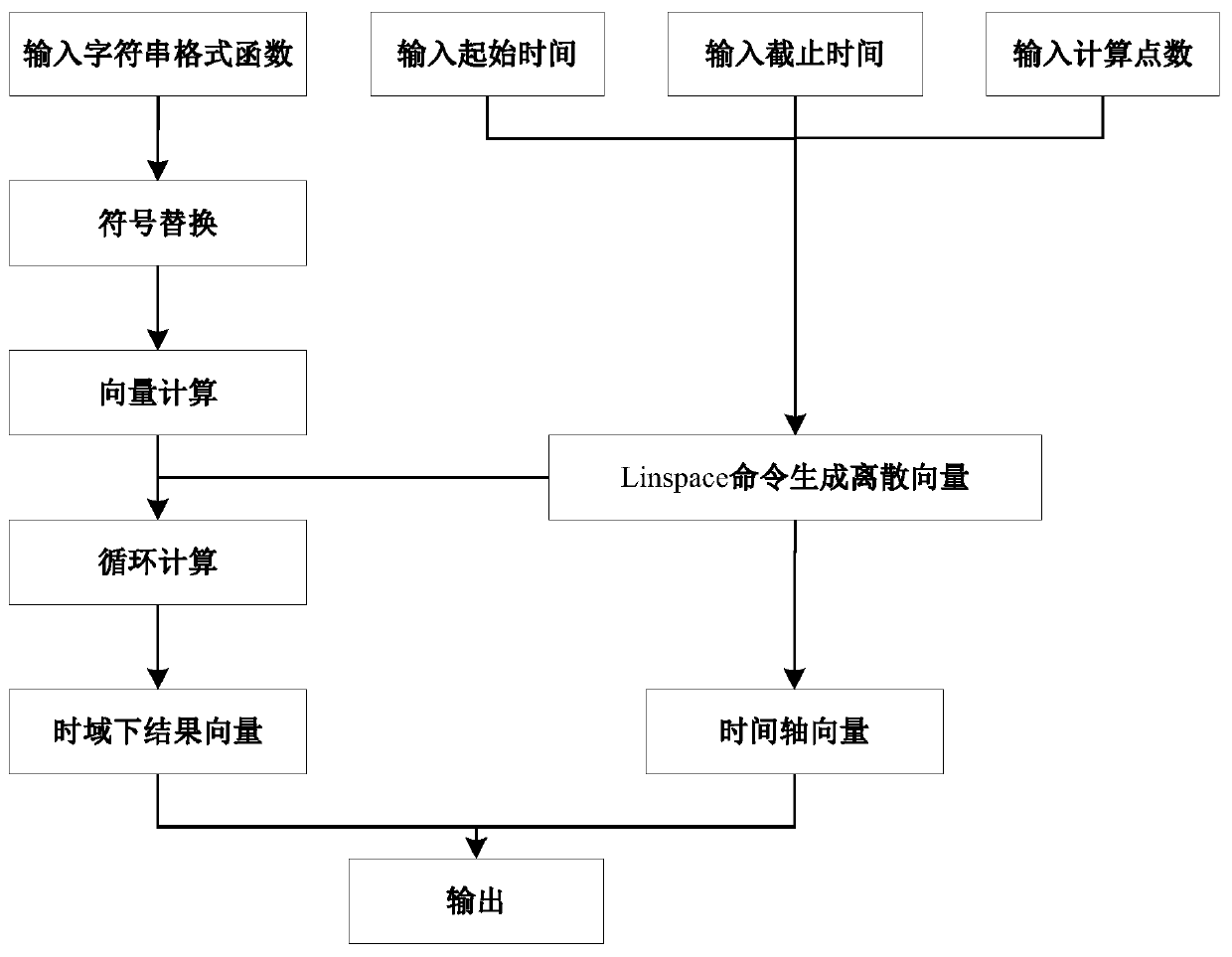
This is a kind of founding method for the two grade adding load double floor groundwork planar solidifying body. It's a kind of solidifying method directly used in the field of civil engineering. Its building method is as follows: build equivalent relation of grading adding load double floor groundwork planar solidification; input road embankment designed parameters, that is embankment top, fundus width, embankment height and average bearing weight; input composite groundwork parameters; input down lying floor groundwork parameters; input solidifying control parameters, that is total solidifying time, the calculating point number of solidifying time, the solidifying time value, the solidifying depth point number and the solidifying depth value; have numerical value calculation,; have Laplace transform on the double floor groundwork solidifying problem equation to do value calculation, then have Laplace counter transform to the image function of effective stress by the use of Stevest inversion formula, calculate to get the sedimentation distortion displacement and hole hydraulic pressure value of every depth point, forecast the after-building sedimentation according to the sedimentation distortion of the down lying floor; output the solidifying sedimentation calculating results of every depth point.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Anisotropic formation dip angle determination method based on transient multi-component induction logging
ActiveCN111058834AProvide accuratelyThe principle is simpleElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyWell loggingEngineering
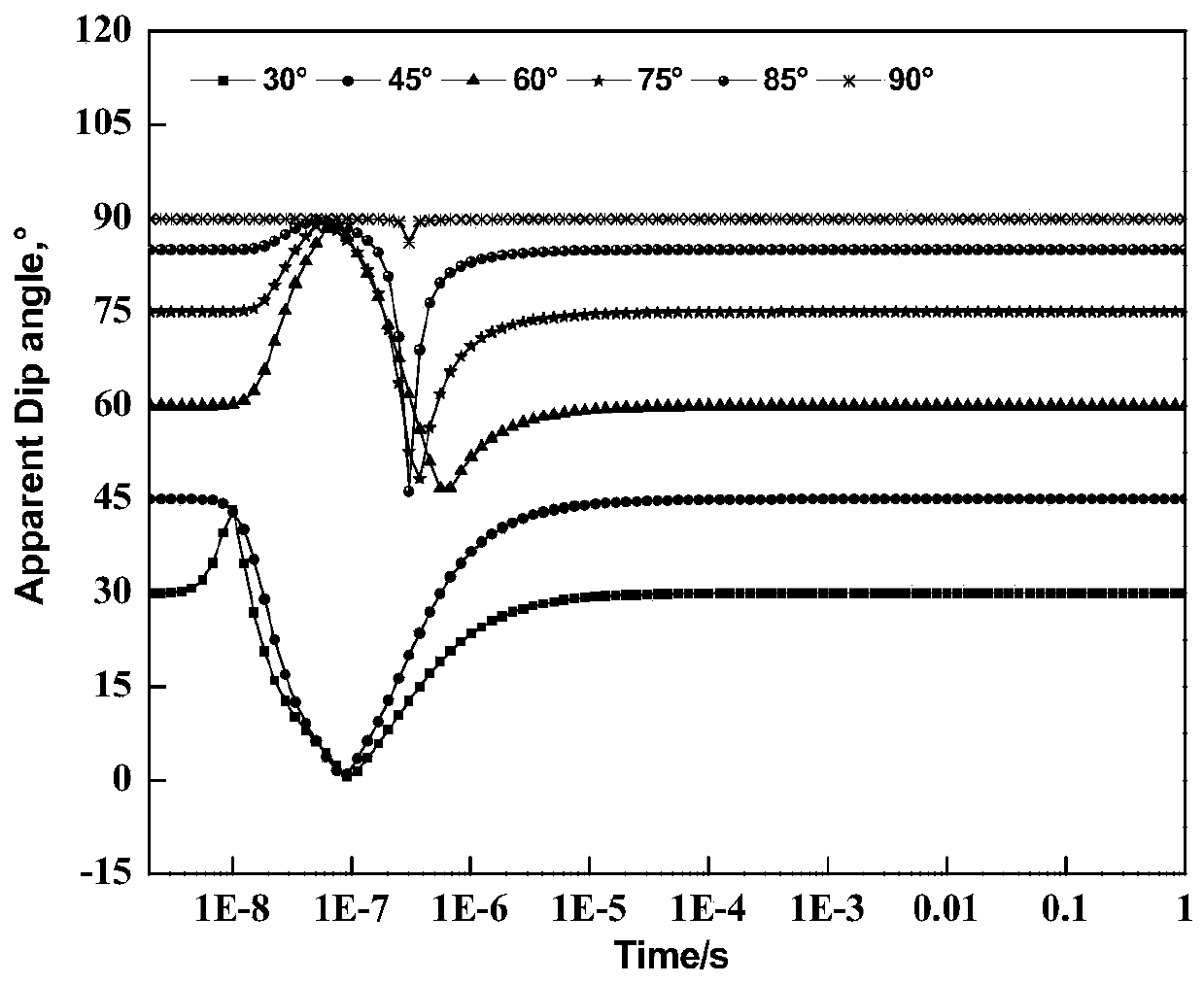
The invention discloses an anisotropic formation dip angle determination method based on transient multi-component induction logging. The method comprises the steps of (1) building a transverse isotropic formation model, and designing a multi-component transmitting and receiving antenna combination mode; (2) selecting a lower step signal source as an excitation source for transient multi-componentelectromagnetic wave logging, and measuring a pure secondary field in a formation after the excitation source is cut off; (3) adopting an inverse laplace transformation method for transforming a frequency domain multi-component induction logging tensor into a time domain, and obtaining an induced electromotive force for transient multi-component induction logging; (4) building an algebraic relation between a transient multi-component induction logging measurement signal and a formation dip angle; and (5) according to a change characteristic of an anisotropic formation dip angle in the time domain, determining a formation dip angle determination method. The anisotropic formation dip angle determination method based on transient multi-component induction logging provided by the invention can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, time consumption and solution multiplicity of current anisotropic formation dip angle inversion, and can quickly and accurately provide dip angle information for anisotropic formation evaluation and geological orientation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
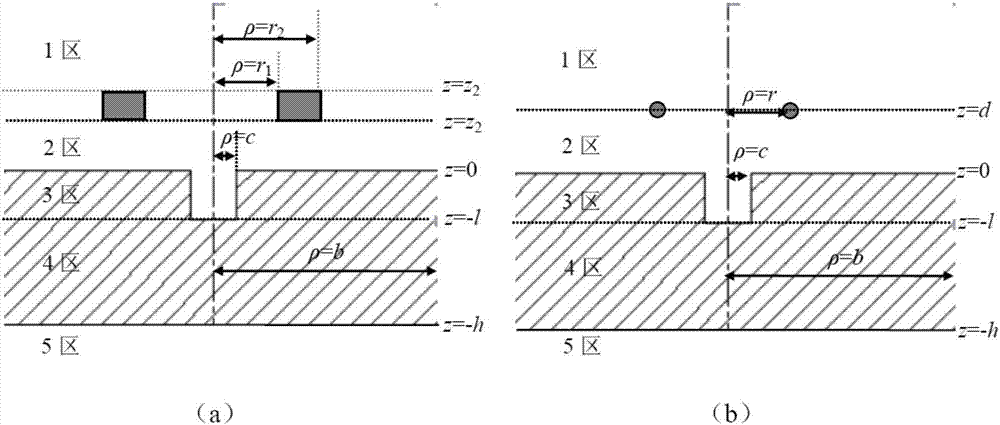
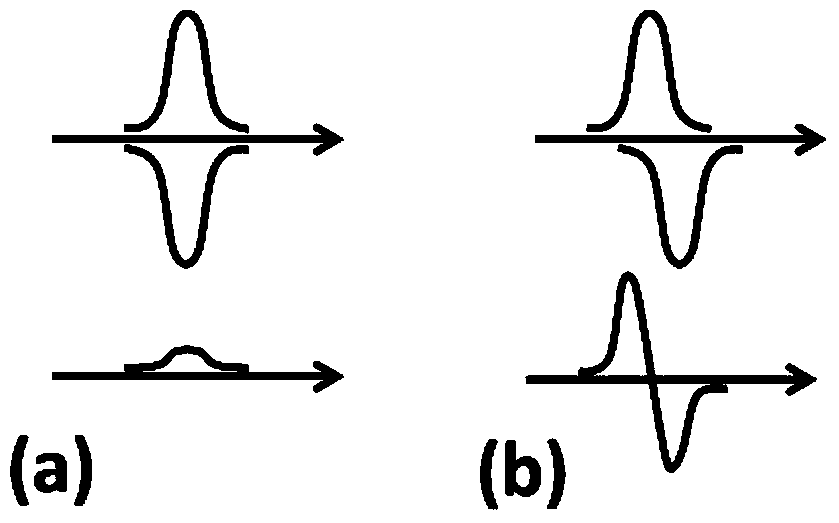
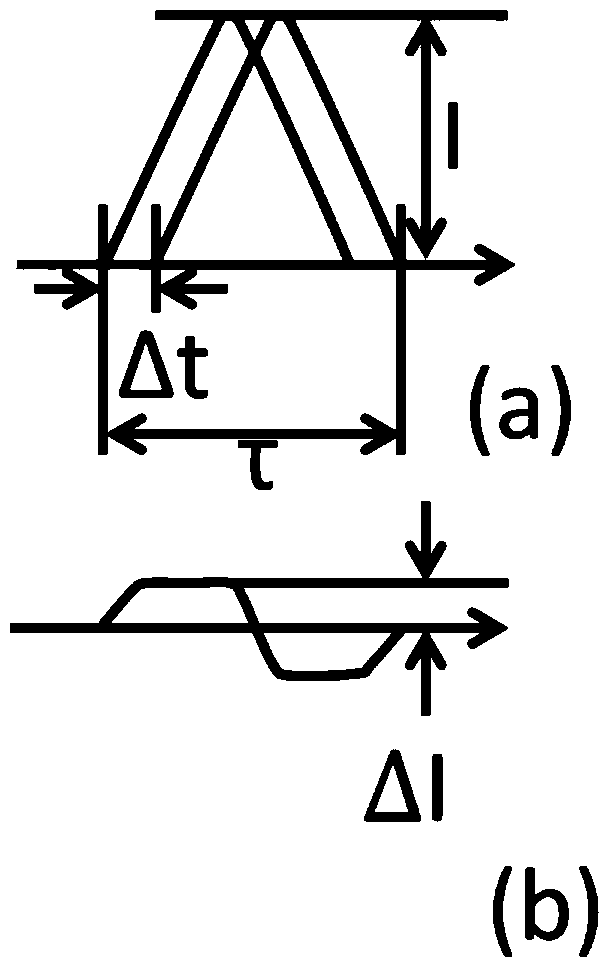
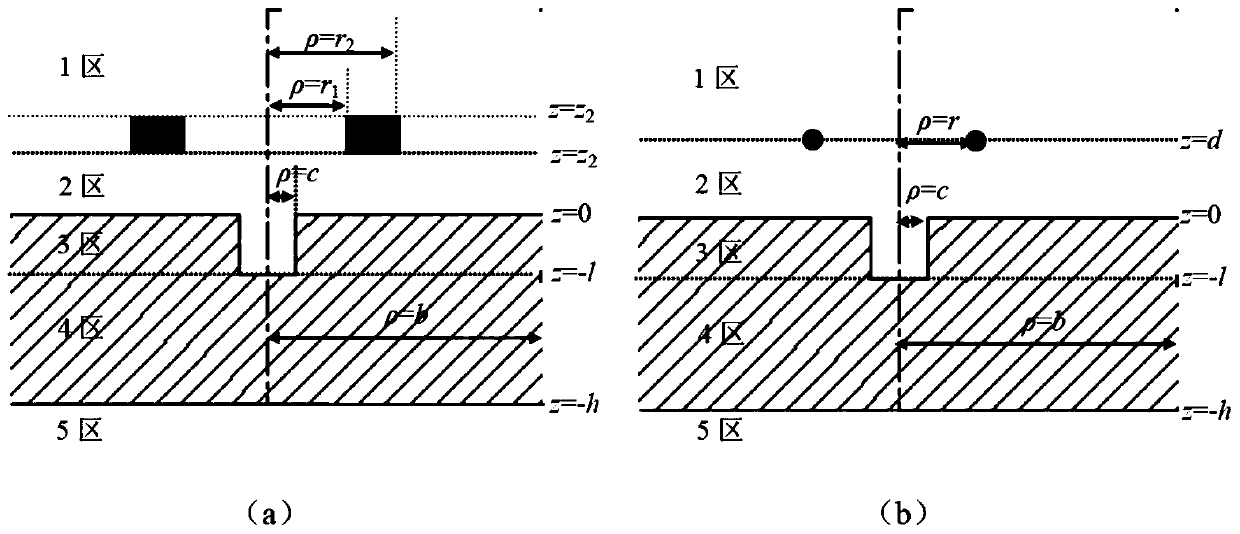
Semi-analytic calculation method for eddy nondestructive testing magnetic field containing column defect
ActiveCN107038302AImprove solution efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a semi-analytic calculation method for an eddy nondestructive testing magnetic field containing a column defect. According to the method, mathematical physics and electromagnetic field principles are utilized to obtain a precise analytic expression of magnetic vector potential under a Laplace domain, and numerical method inverse Laplace transformation is performed on a complex expression of a series form of the magnetic vector potential based on MATLAB to obtain a time-domain solution to an eddy nondestructive testing signal in a conductor containing the column defect. Through the method, the eddy nondestructive testing magnetic field of the conductor containing the column defect can be calculated accurately and efficiently, and a theoretical basis is provided for application of the eddy nondestructive testing technology in the defect quantitative recognition field.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Electromagnetic wave/particle beam spectroscopic method and electromagnetic wave/particle beam spectroscopic instrument
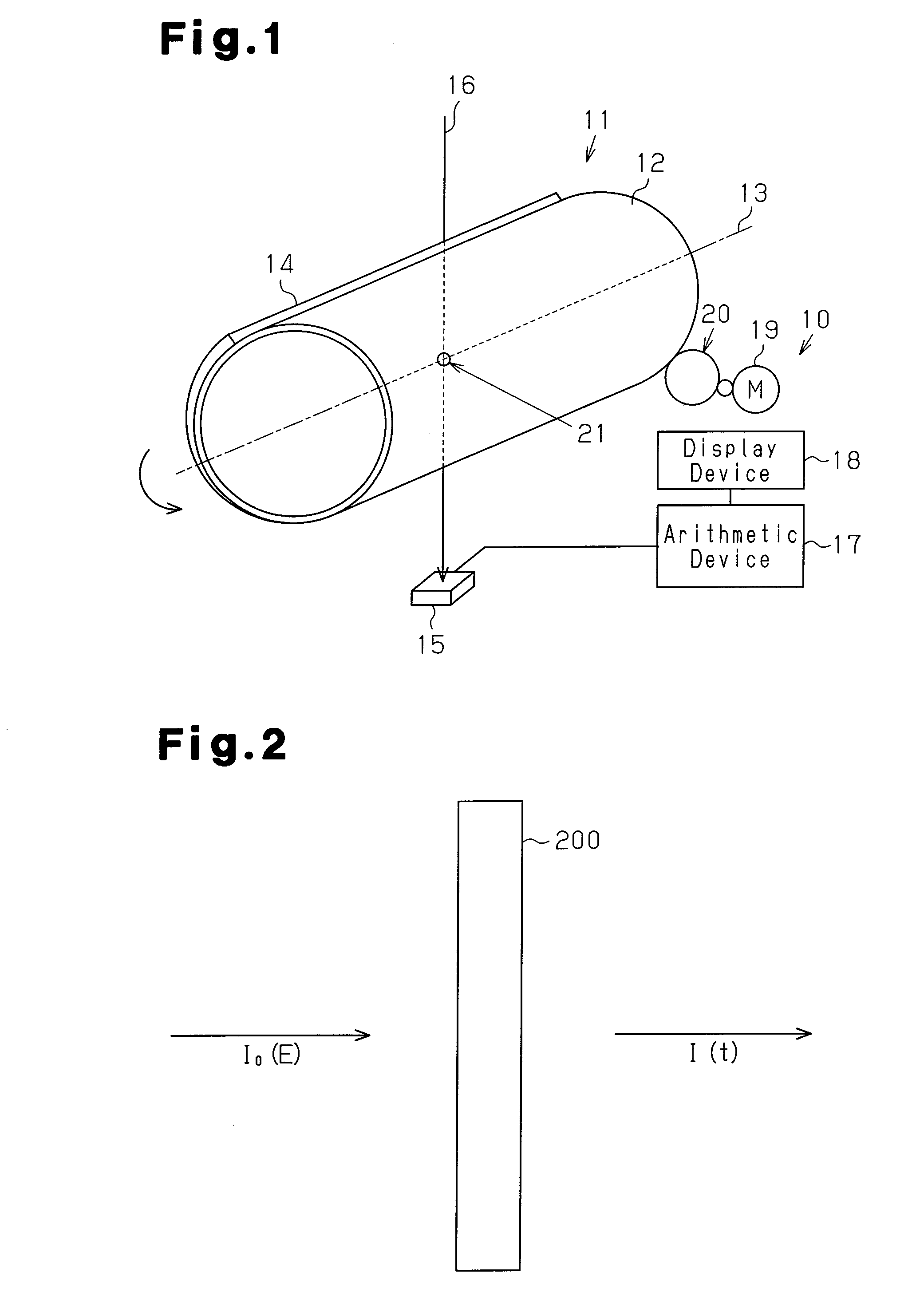
InactiveUS20100061513A1Wide measurement rangeHigh levelX-ray spectral distribution measurementParticle separator tubesParticle beamRadiation exposure
The present invention provides an electromagnetic wave / particle beam spectroscopic instrument that is not easily deteriorated in spectroscopic capability, and is resistant to electromagnetic noise, vibrations, heavy sound, heat and specific particle beams of interest, particle beams other than electromagnetic waves, electric noise due to electromagnetic waves, mechanical destruction, and recoiling of solid constituent atoms and is also more resistant to radiation exposure on the detection means than the conventional energy resolving technologies. A spectroscopic instrument 10 includes a Laplace transform filter 11 that performs Laplace transform on the intensity of an incident spectrum, a detection element 15 that detects a transmitted intensity of the incident spectrum, and an arithmetic device 17 that performs inverse Laplace transform on the detected transmitted intensity of the incident spectrum, thereby calculating the incident intensity of the incident spectrum that has entered the Laplace transform filter 11.
Owner:INTER UNIV RES INST NAT INST OF NATURAL SCI
Image subjective visual effect enhancement method based on Laplace pyramid
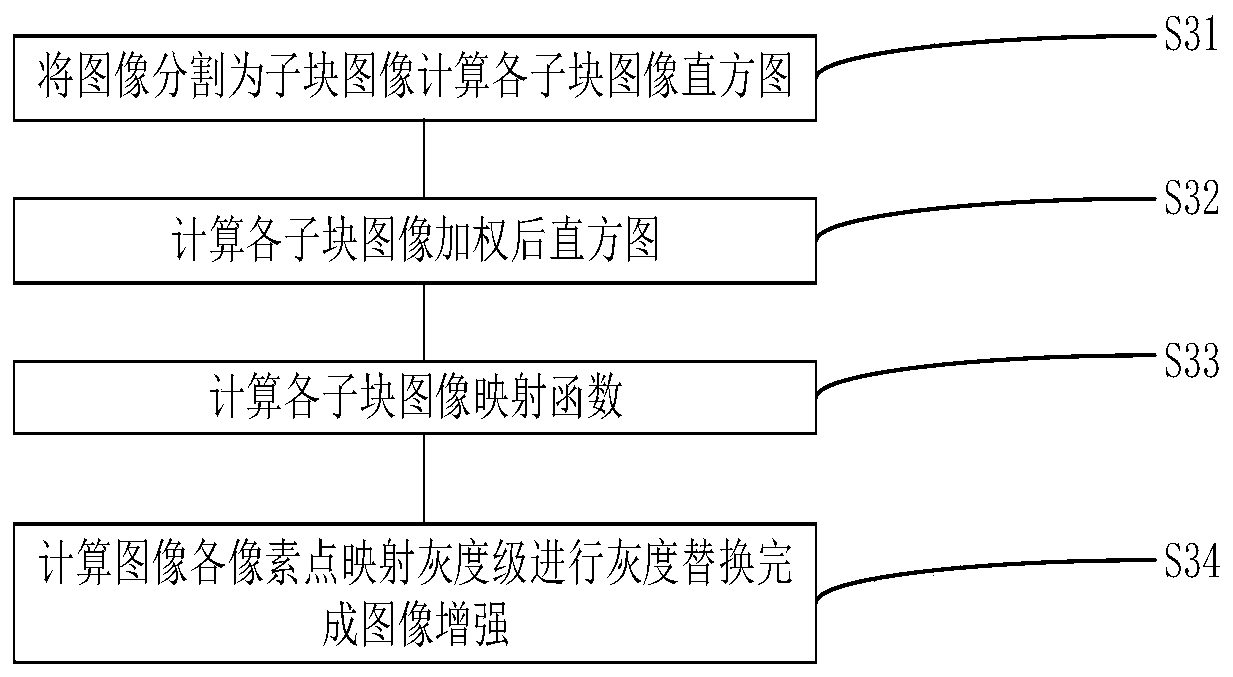
ActiveCN111292267AAvoid enhancementReduce the differenceImage enhancementImage analysisMachine learningHistogram
The invention relates to an image subjective visual effect enhancement method based on a Laplace pyramid, and belongs to the field of digital image processing. The method comprises the steps of 1, performing Laplace pyramid decomposition on an original image to obtain an approximate image and a multi-scale detail image; and 2, enhancing the approximate image based on an improved contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization algorithm; 3, enhancing the multi-scale detail image; and 4, performing Laplace inverse transformation on the enhanced approximate image and the multi-scale detail imageto obtain an enhanced image. Through the steps, the problems of boundary effect, over-enhancement, overlarge noise and the like possibly occurring in the image after traditional contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization enhancement can be effectively relieved, and the subjective visual effect of the image is remarkably improved.
Owner:北京锐影医疗技术有限公司
Steam-cured concrete damp-heat elastic response prediction method, system, storage medium and program
ActiveCN111625887AAccurately describe anomalous hot and humid behaviorGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationTime domainHeat flow
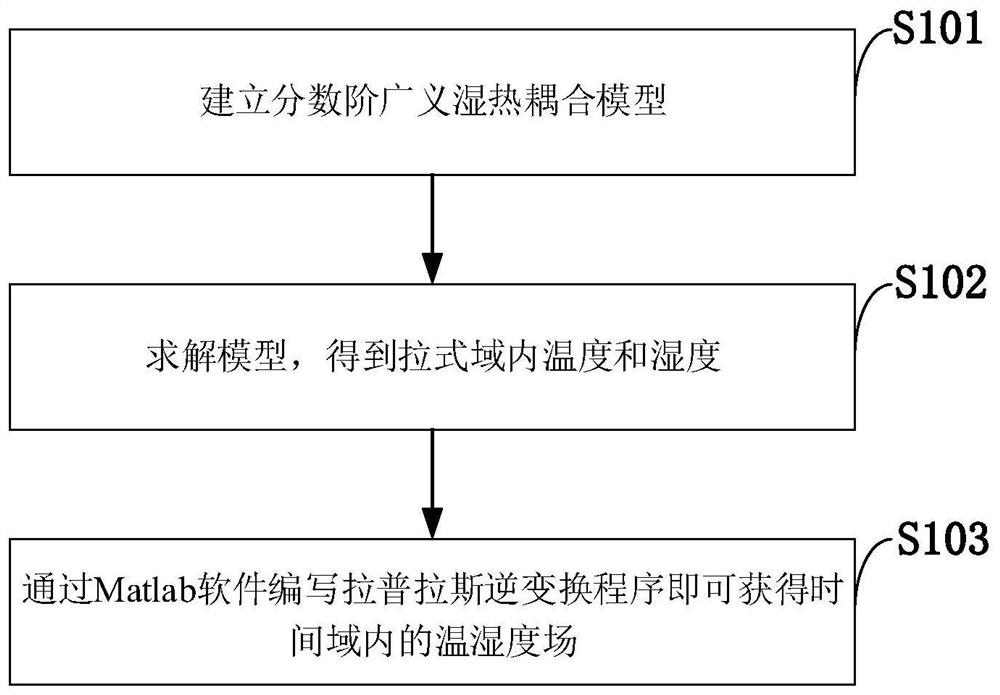
The invention belongs to the technical field of steam-cured concrete prefabricated parts, and discloses a steam-cured concrete damp-heat elastic response prediction method, a system, a storage mediumand a program. The steam-cured concrete damp-heat elastic response prediction method comprises the steps of establishing a fractional order generalized damp-heat coupling model; solving the model to obtain temperature and humidity in a pull-type domain; writing a Laplace inverse transformation program through Matlab software to obtain a temperature and humidity field in a time domain. According tothe model, the influence of the heat flow rate and the fractional order on heat conduction is considered, and the influence rule of the heat flow fractional order on temperature and humidity distribution under thermal shock is calculated. According to the model, the influence of the wet shunt rate and the fractional order on wet diffusion is considered, and the influence rule of the wet shunt fractional order on temperature and humidity distribution under thermal shock is calculated. By means of the fractional order generalized damp-heat coupling model established through the method, abnormaldamp-heat behaviors of the concrete in the high-temperature and high-humidity steam curing process can be accurately described.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for detecting high-temperature viscoelastic parameters of glass material
PendingCN112881196AOvercome the defect of easy breakageEffective and reliable measurementMaterial strength using steady bending forcesTime domainRelaxation modulus
A method for detecting high-temperature viscoelastic parameters of a glass material comprises the following steps: A, heating a glass test piece to a test temperature, applying force to the glass test piece for a preset time, and recording a curve of bending deformation of the glass test piece along with time; B, processing the measured data to obtain a curve of the creep compliance of the glass test piece along with time, and fitting the creep compliance of the glass test piece; C, performing Laplace transformation on the creep compliance obtained by fitting, obtaining Laplace transformation of the relaxation modulus according to a conversion relation between the creep compliance and the relaxation modulus, and then performing inverse Laplace transformation to obtain an expression equation of the relaxation modulus in a time domain; and D, judging whether the expression equation of the relaxation modulus is a Prony series expression form of the relaxation modulus or not, if yes, taking the expression equation as a detection result, otherwise, fitting the expression equation by using the Prony series, and taking the expression equation as a high-temperature viscoelastic parameter detection result. According to the invention, the defects of temperature limitation and easy breakage of the glass test piece can be overcome, and the viscoelastic parameters of the glass material in a high-temperature state can be effectively and reliably measured.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
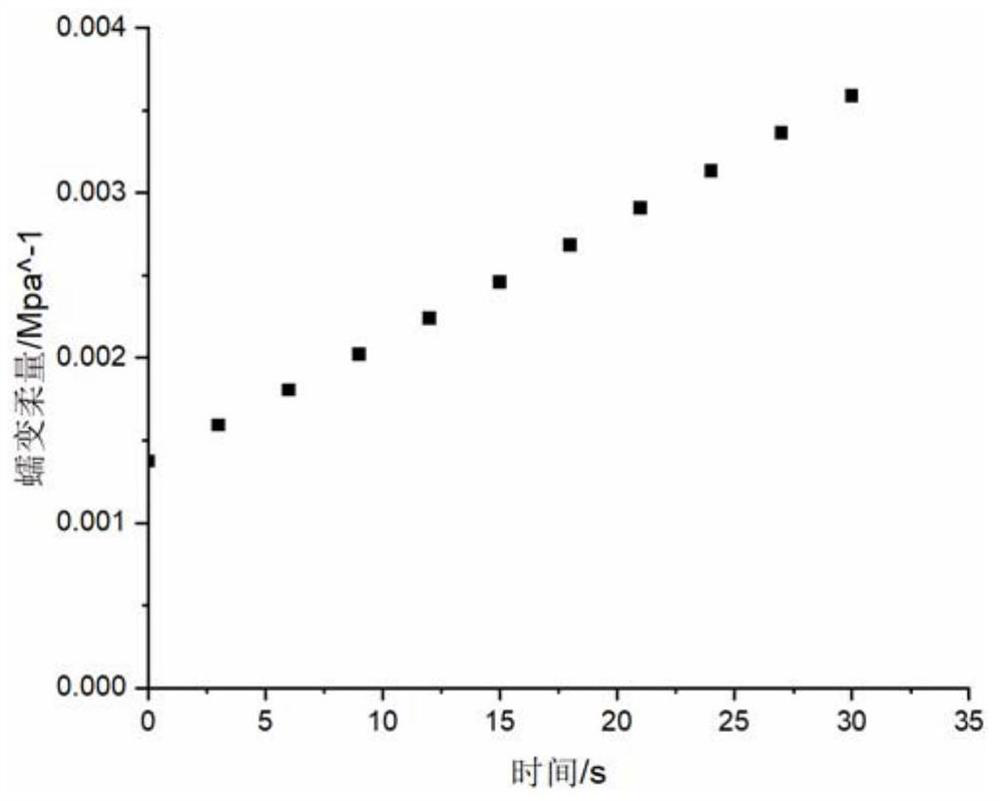
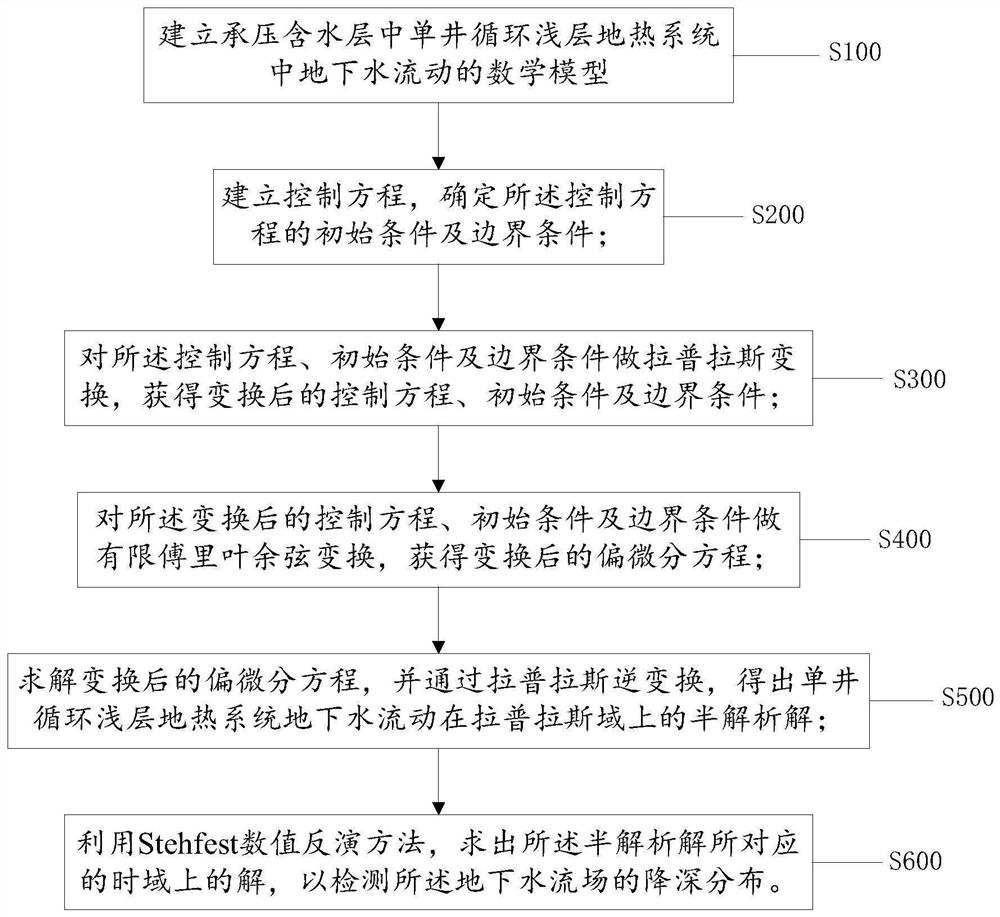
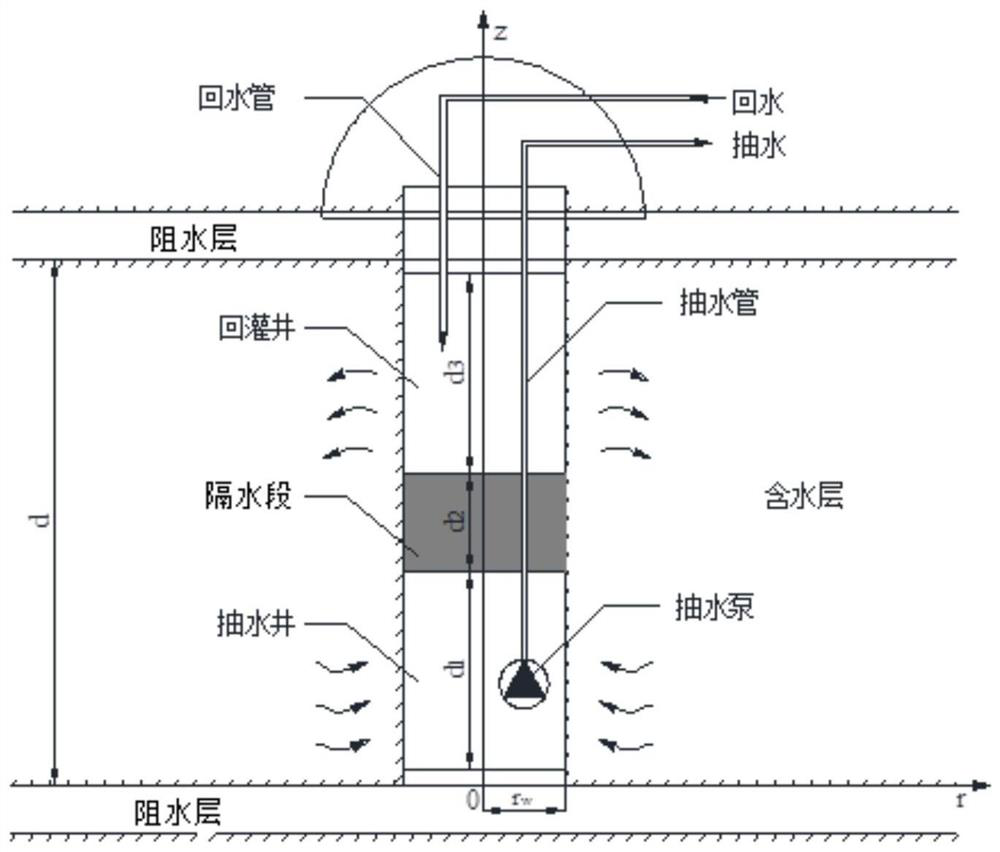
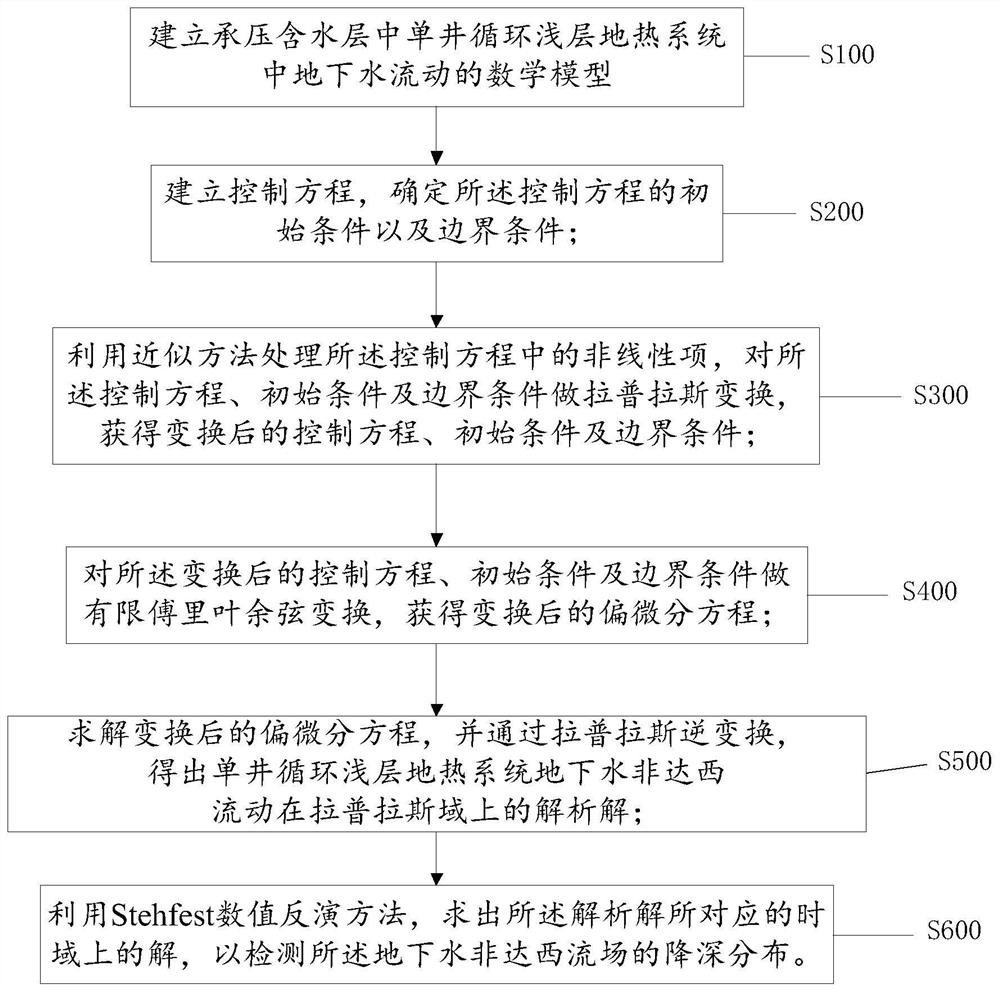
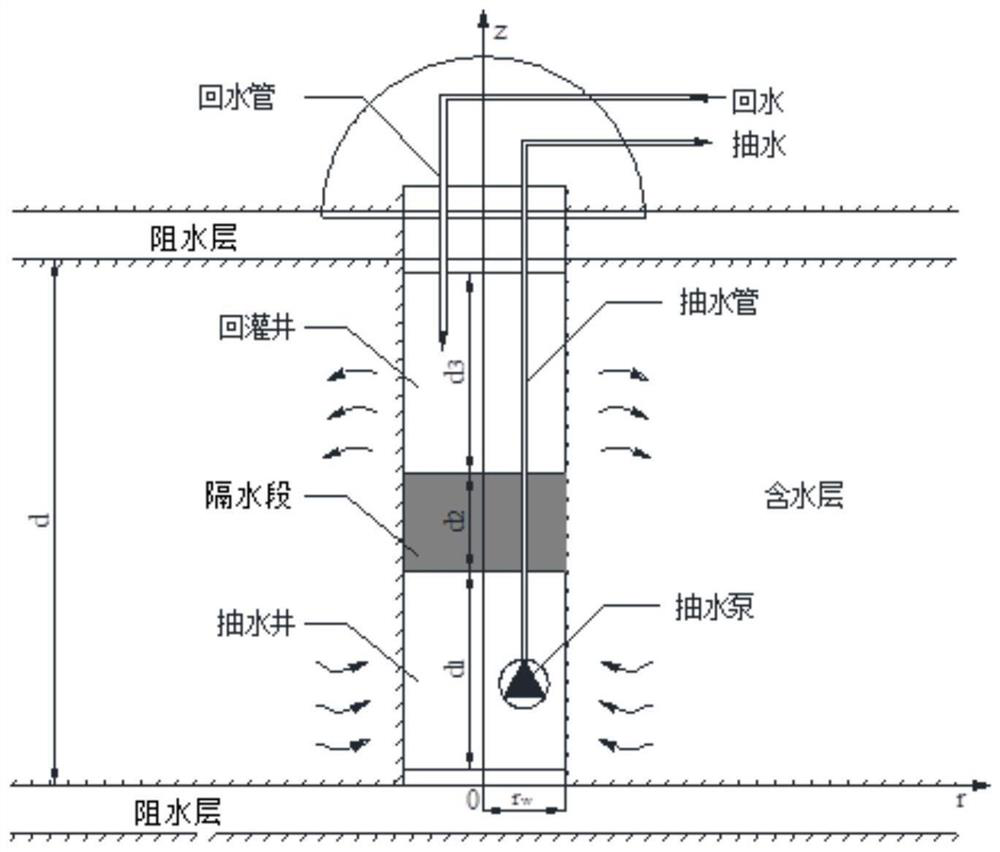
Method and device for detecting underground water flow field in single-well circulation shallow geothermal system
ActiveCN111767680ASolve temperature problemsGeothermal energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationTime domainMathematical model
One or more embodiments of the invention provide a method and device for detecting an underground water flow field in a single-well circulation shallow geothermal system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a mathematical model, establishing a control equation, determining an initial condition of the control equation, and establishing a boundary condition of the control equation; performing Laplace transformation on the control equation, the initial condition and the boundary condition to obtain a transformed control equation, initial condition and boundary condition; performing finite Fourier cosine transform on the transformed control equation, the initial condition and the boundary condition to obtain a transformed partial differential equation; solving the transformed partial differential equation, and obtaining a semi-analytical solution of the underground water flow of the single-well circulation shallow geothermal system on a Laplace domain through Laplace inverse transformation; and solving a solution on a time domain corresponding to the semi-analytical solution by utilizing a Stehfest numerical inversion method so as to detect the depth reduction distribution of the underground water flow field.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING) +2
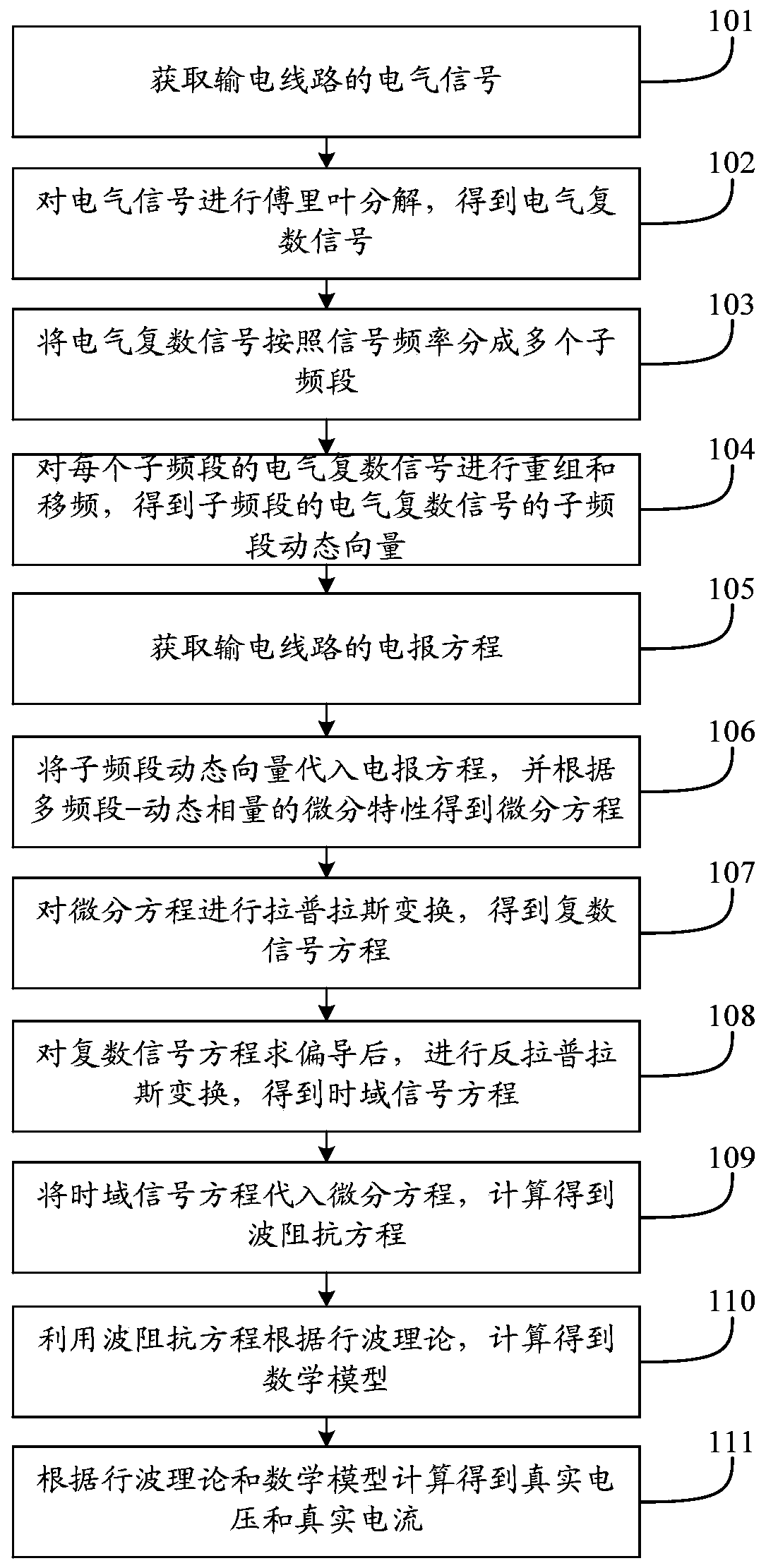
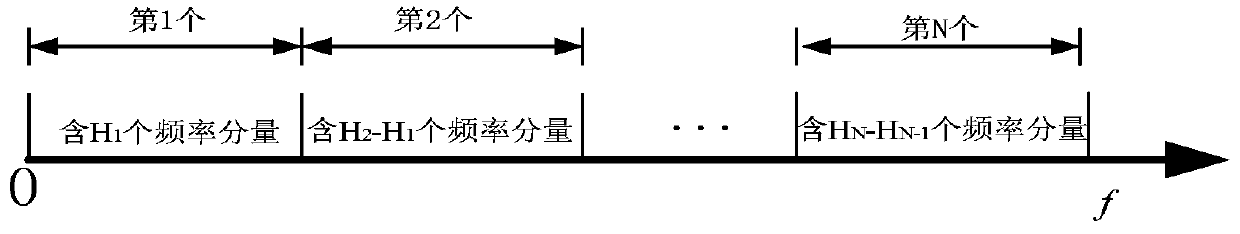
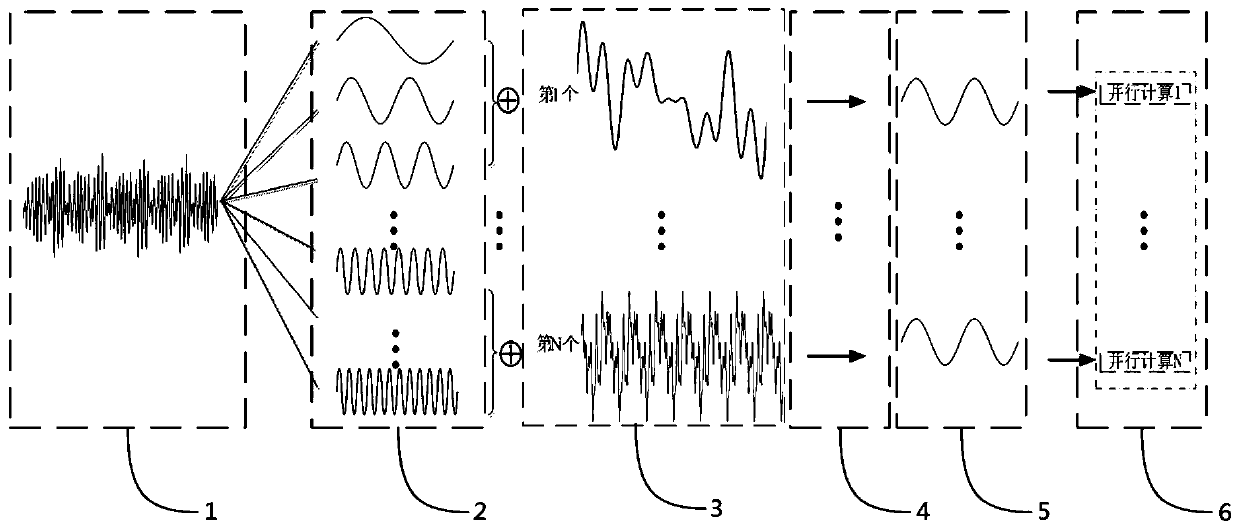
Power transmission line simulation method and system
ActiveCN110378021AImprove simulation speedImprove simulation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingDecompositionInverse laplace transformation
The invention discloses a power transmission line simulation method and system, and relates to the technical field of power systems. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an electrical signal, performing Fourier decomposition, dividing the electrical signal into a plurality of sub-bands according to a signal frequency, and performing recombination and frequency shift to obtain sub-band dynamic vectors; substituting the sub-band dynamic vectors into the obtained telegram equation to obtain a differential equation; performing Laplace transformation, partial derivative solving and inverse Laplace transformation on the differential equation in sequence to obtain a time domain signal equation; substituting the time domain signal equation into a differential equation, and calculating to obtain a mathematical model according to a traveling wave theory; and calculating to obtain real voltage and current according to a traveling wave theory and a mathematical model. Due to the fact that the sub-band dynamic vectors of the electric complex signals are the signals with the bandwidth, and the bandwidth meets the narrow-band condition, large-step simulation can be adopted to improve the simulation speed, and the power transmission line simulation method can effectively give consideration to the simulation efficiency and precision.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
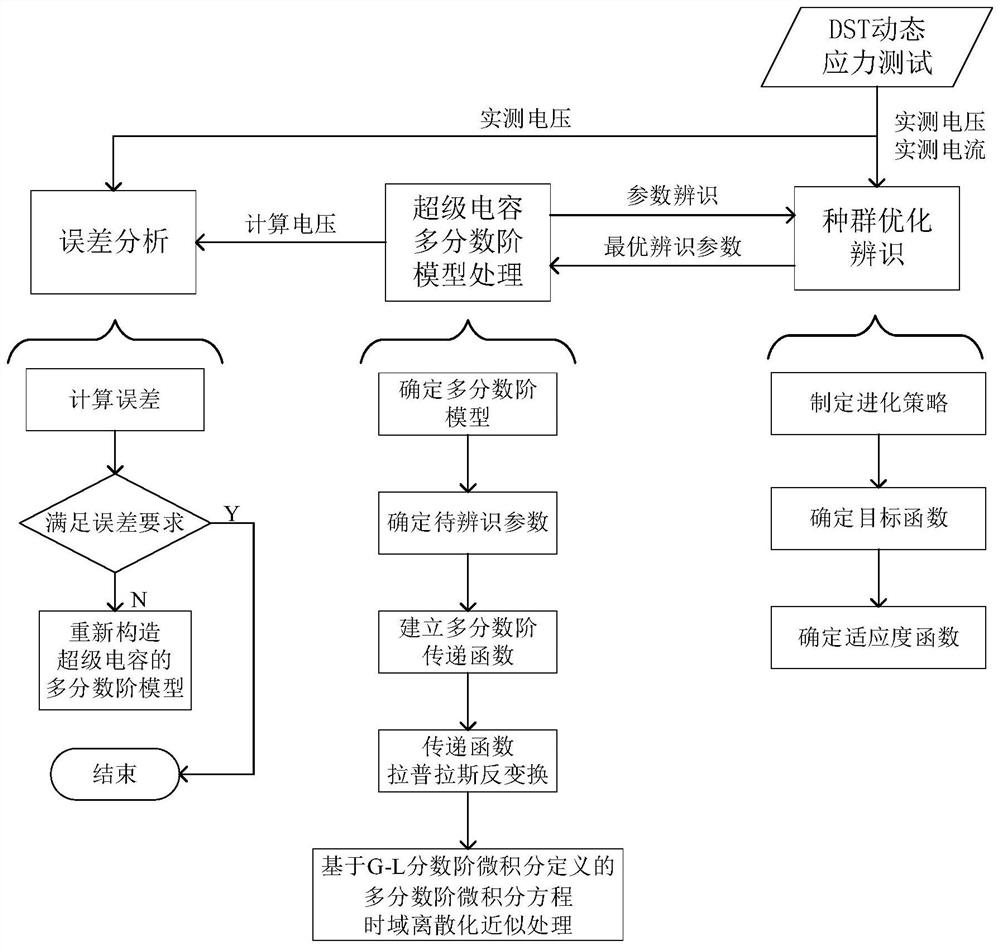
Super-capacitor multi-fractional-order model parameter identification method based on time domain discretization
PendingCN114372233AAvoid complex operationsHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsGenetic algorithmsCapacitanceTerminal voltage
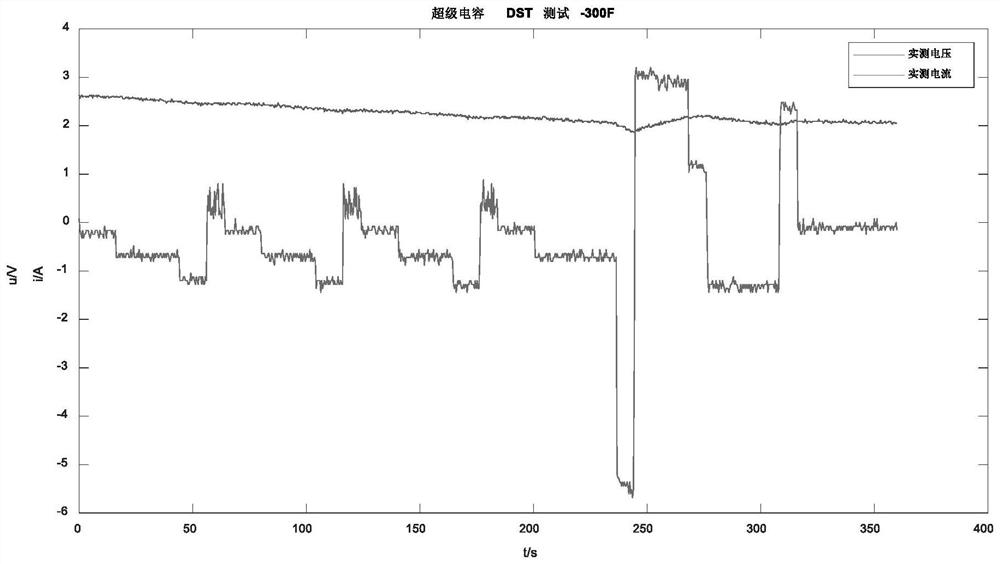
The invention discloses a super-capacitor multi-fractional-order model parameter identification method based on time domain discretization. The method comprises the following steps: 1) determining an appropriate super-capacitor multi-fractional-order model and to-be-identified parameters; 2) establishing a multi-fractional-order transfer function; 3) performing inverse Laplace transformation on a fractional calculus operator in the transfer function; 4) performing discretization approximate processing on the continuous multi-fractional calculus equation; 5) in order to obtain parameters to be identified in the equation, performing DST dynamic stress test on the super capacitor, and collecting actually measured voltage and current; 6) performing population optimization identification on the to-be-identified parameters; 7) substituting the optimal identification parameter into the multi-fractional-order model, and calculating the terminal voltage of the model; and 8) comparing the calculated voltage with the actually measured voltage, if the error meets the requirement, determining that the identification is successful, otherwise, reconstructing the super-capacitor multi-fractional-order model until the error meets the requirement. According to the method, the modeling precision of the super capacitor can be improved, and support is provided for precise charging and discharging control of the super capacitor.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A 3D Simulation Method of Fractional Electromagnetic Anomalous Diffusion Based on Rational Function Approximation
ActiveCN107657137BQuick calculationMeet the dispersion characteristicsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDimensional simulationElectromagnetic response
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Motion precision prediction method for direct-drive high-speed feed system with consideration of thrust harmonic characteristics
InactiveCN110308701AEfficient analysisOptimize servo parametersNumerical controlComplex mathematical operationsSystem parametersAnalysis models
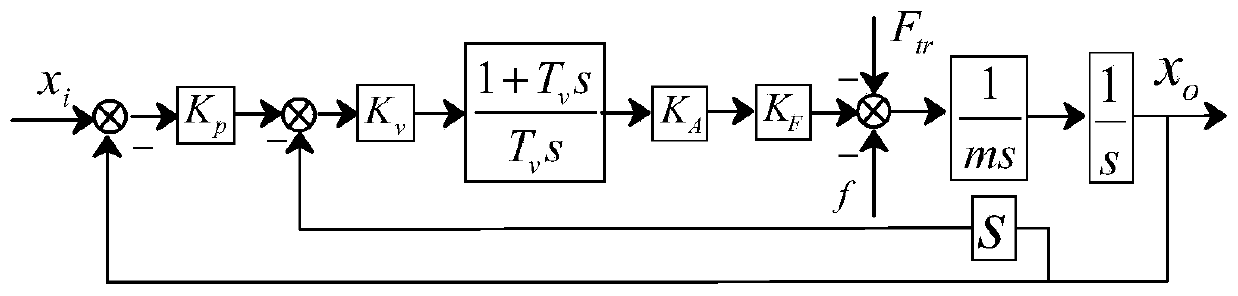
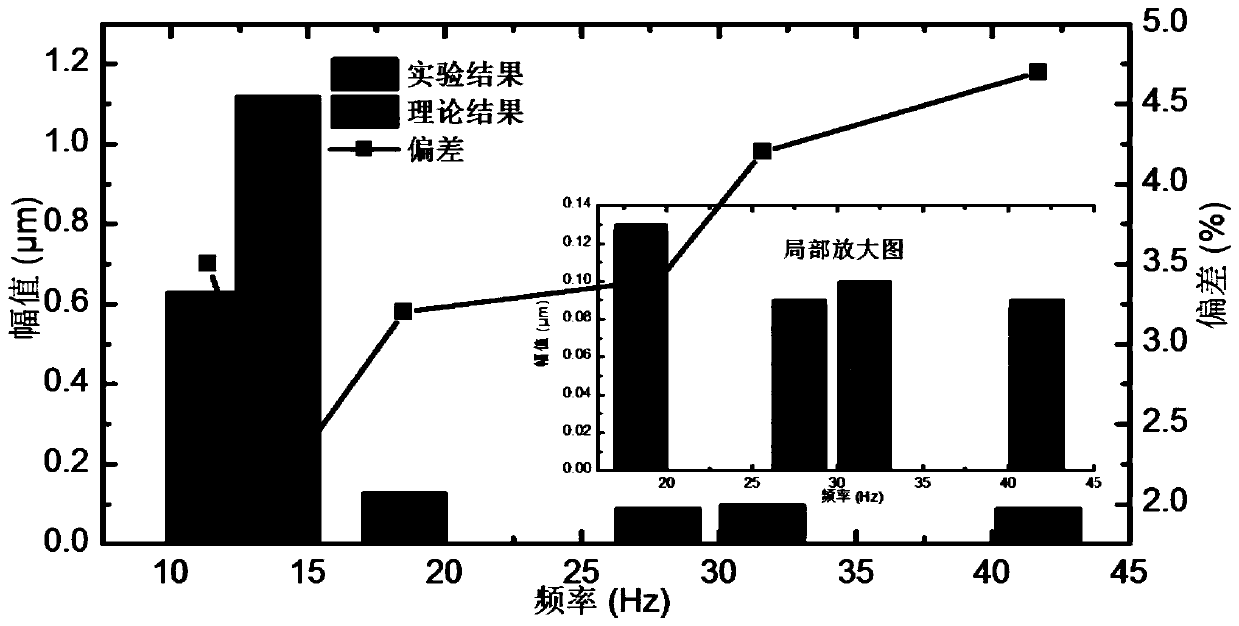
The invention provides a motion precision prediction method for a direct-drive high-speed feed system with consideration of thrust harmonic characteristics. The method comprises the following steps: step one, according to a motion precision analysis model of a direct-drive high-speed feed system considering thrust harmonic characteristics, acquiring a system interference transfer function; step two, extracting a characteristic equation according to the system interference transfer function obtained in the step one; step three, introducing actual system parameters into the characteristic equation obtained in the step two to obtain a root of the characteristic equation and determining the root of the characteristic equation; step four, on the basis of the determination result in the step three, carrying out inverse laplace transformation by using the system interference transfer function Gr(s) obtained in the step one to obtain system motion precision under the single thrust harmonic action; and step five, repeating the step four to obtain the motion precision of the direct-drive high-speed feed system under all thrust harmonics. According to the invention, the linear motor thrust fluctuation problem in the conventional analysis is extended to the motion accuracy of the final feed system; and thus the method has the important guidance significance in evaluating the influence degree of the thrust fluctuation phenomenon of the linear motor in the actual CNC machine tool.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Characterization method for porous structure of regenerated cellulose material
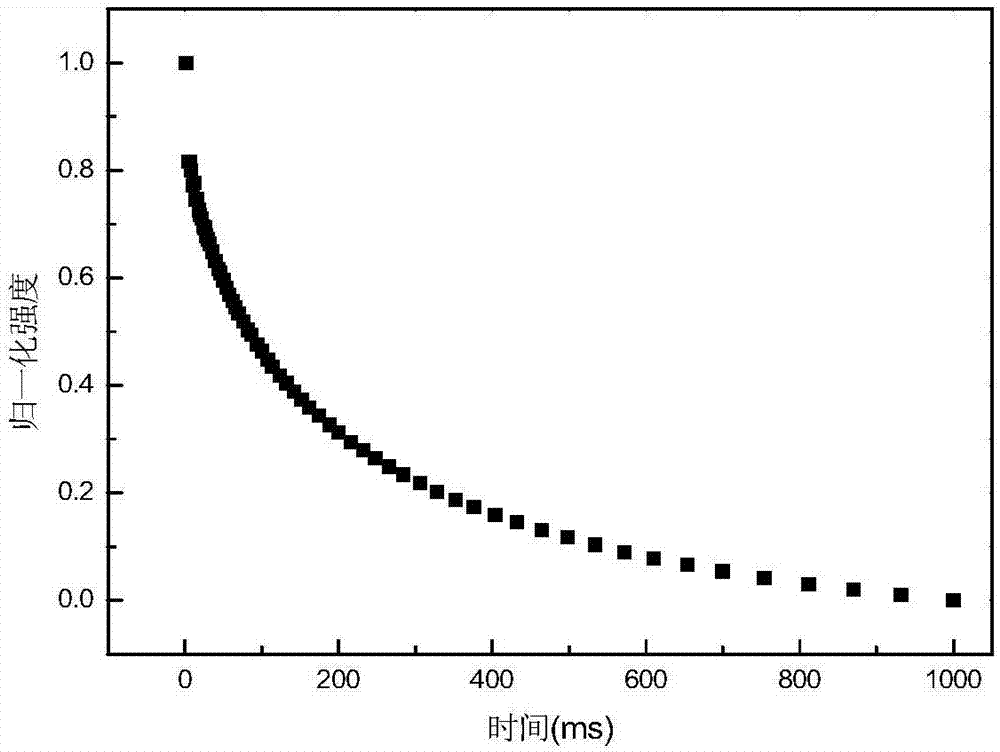
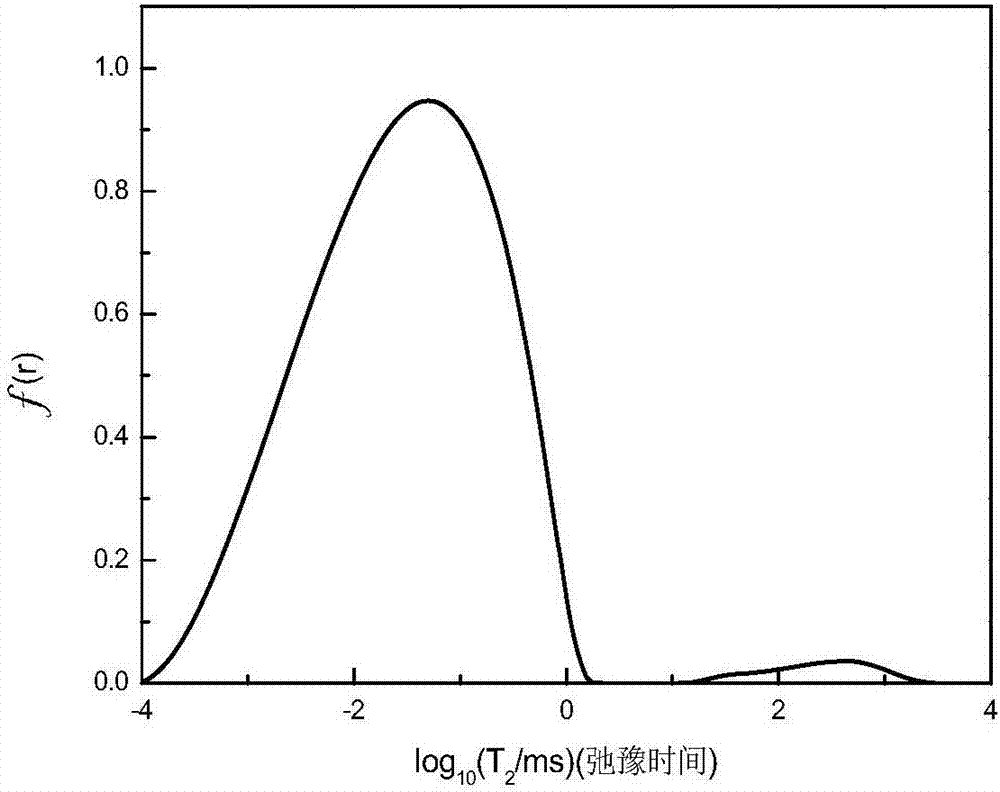
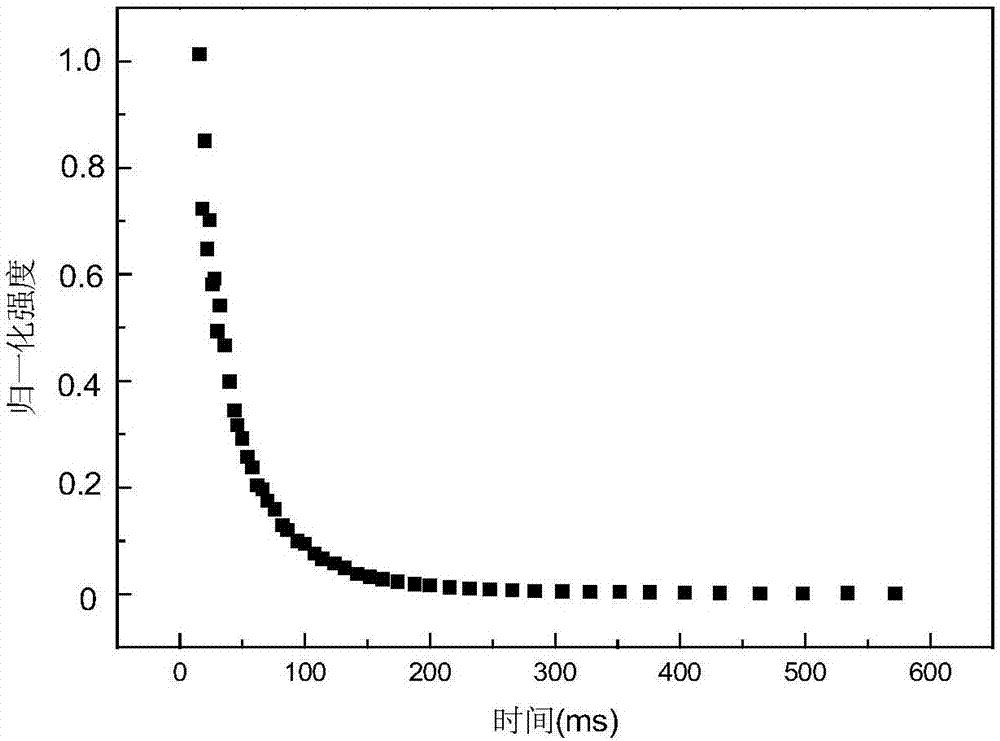
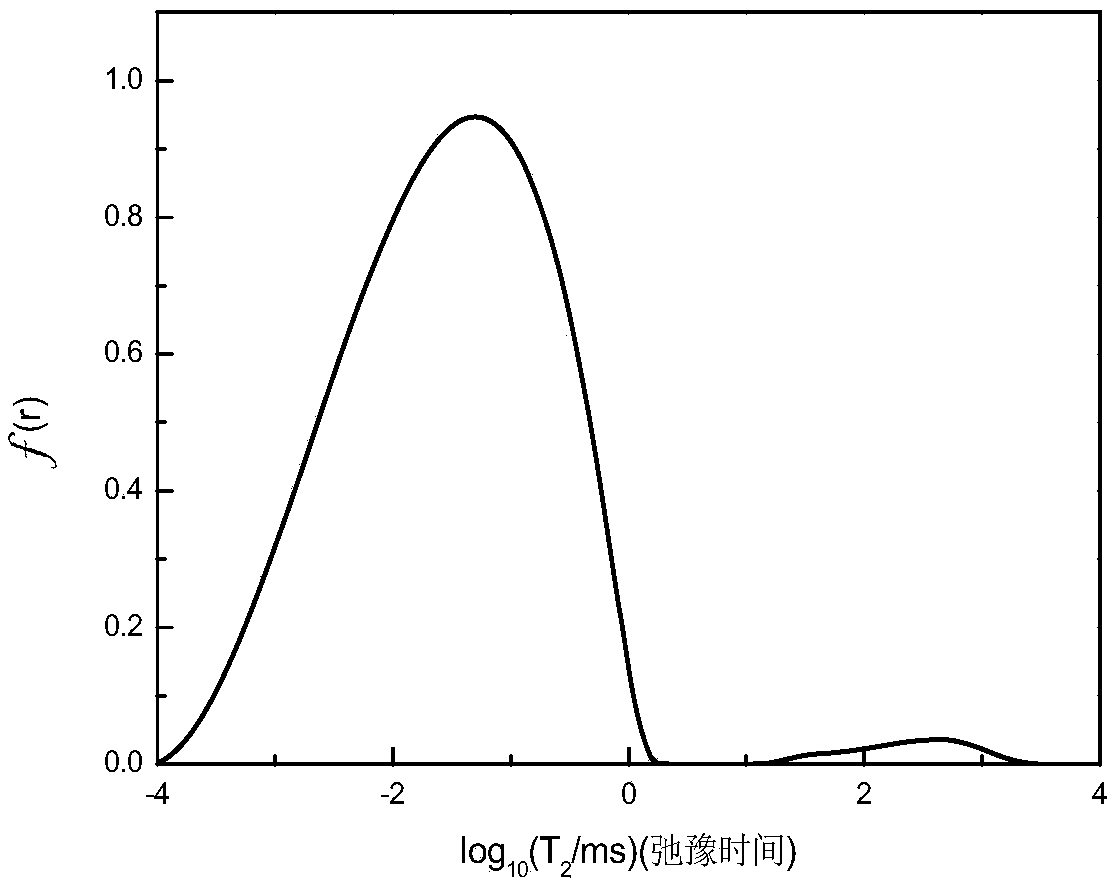
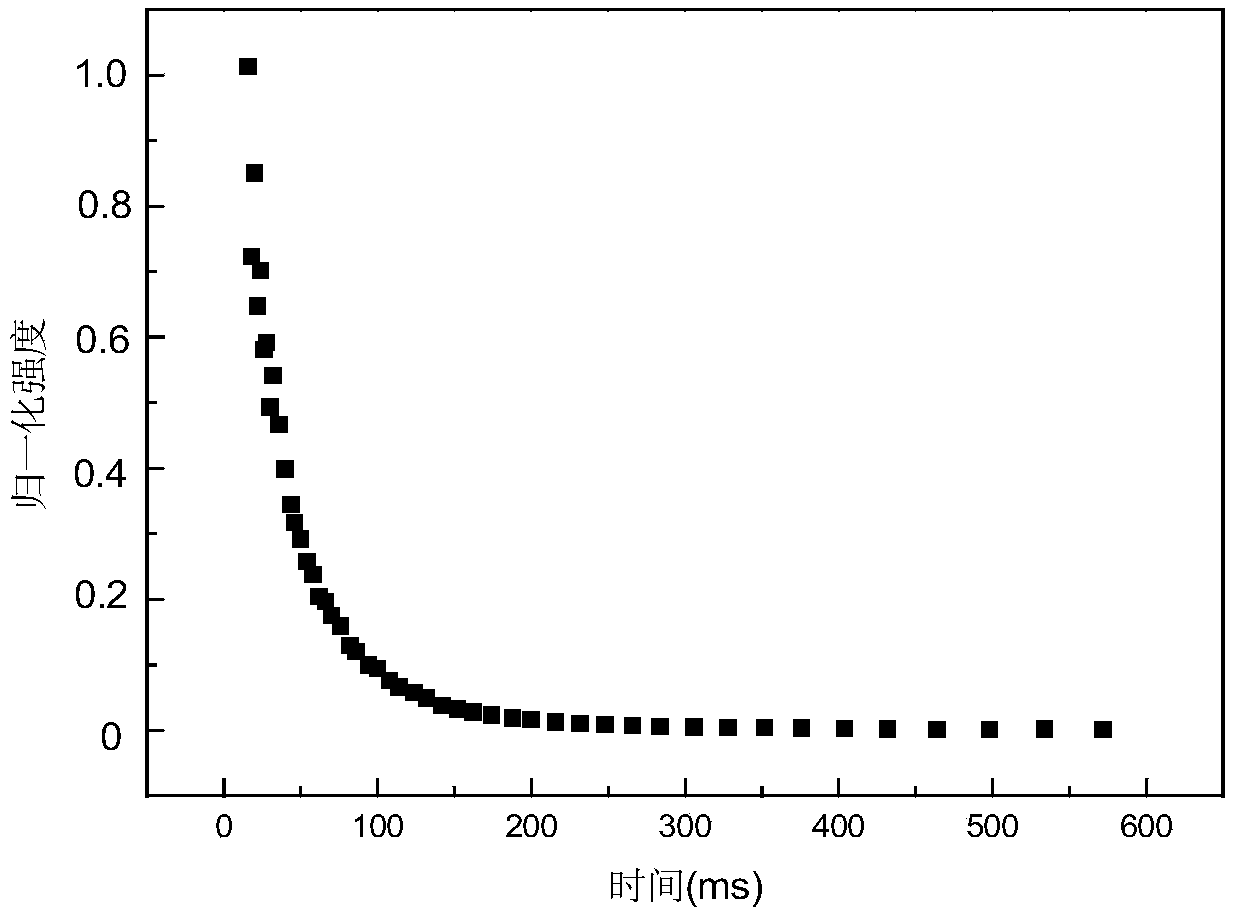
ActiveCN107202809ADescription sizeKeep it pristineAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceHydrogenFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a characterization method for a porous structure of a regenerated cellulose material. The characterization method comprises the following steps: firstly, soaking regenerated cellulose into liquid and oscillating; secondly, carrying out nuclear magnetic relaxation hydrogen spectrum test on the regenerated cellulose treated in the first step; thirdly, carrying out inverse laplace transformation on a nuclear magnetic relaxation attenuation curve obtained by the nuclear magnetic relaxation hydrogen spectrum test to obtain parameters for characterizing the porous structure of the regenerated cellulose. According to the characterization method disclosed by the invention, the relationship that relaxation time (logarithms and horizontal coordinates) is in direct proportion to the content of pores (longitudinal coordinates) can be obtained, therefore, the sizes of the pores can be qualitatively explained; if specific values of the sizes of the pores need to be determined, different formulas are adopted for calculating according to difference of samples. According to the characterization method disclosed by the invention, drying or freeze-drying treatment of samples is not needed, so original states of the samples can be well kept.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
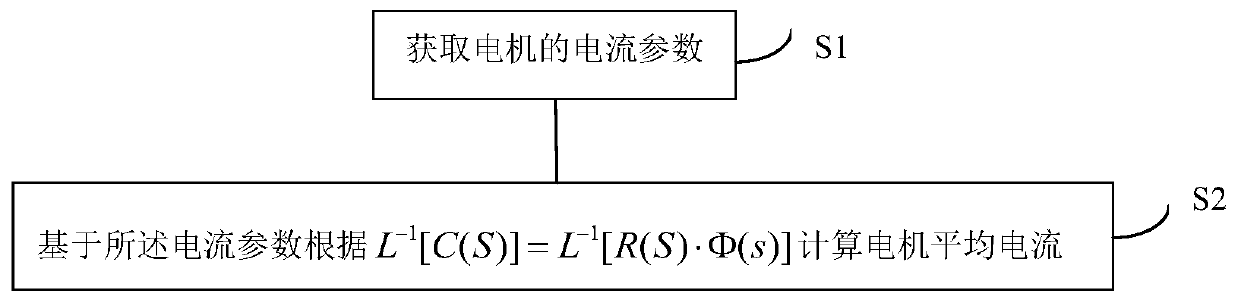
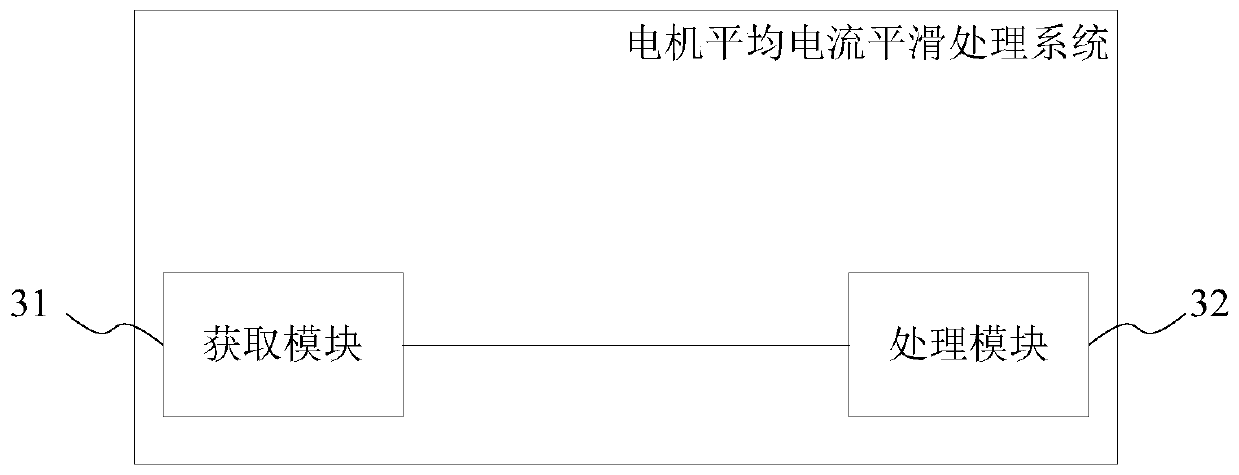
Motor average current smoothing method and system and motor current sampling equipment
ActiveCN111130414AEasy to handleFast operationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsElectric machine
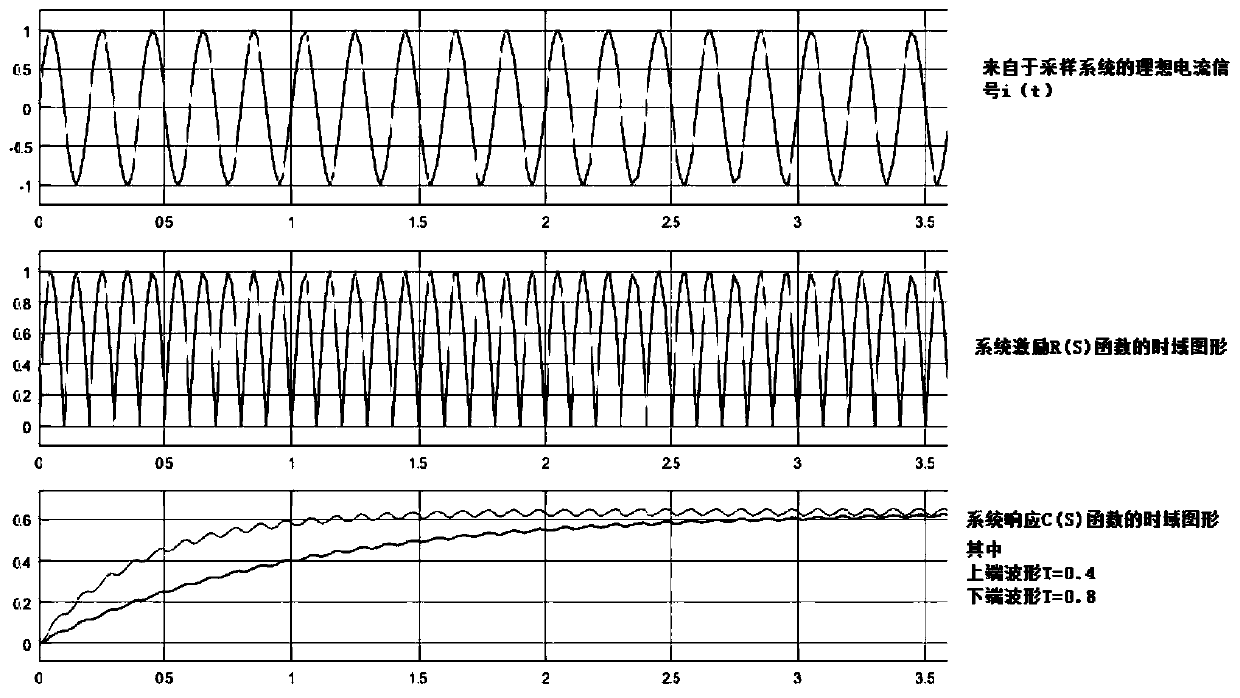
The invention provides a motor average current smoothing method and system, and motor current sampling equipment. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a current parameter of a motor; calculating the average current of the motor according to L-1[C(S)] = L-1[R(S)*phi(s)] based on the current parameter, wherein L-1 represents inverse Laplace transformation, im is a current peak value,omega is the angular velocity of the motor rotor, and gamma is an adjustable system constant. According to the motor average current smoothing method and system and the motor current sampling device,the multi-phase current collected from the motor can be rapidly processed, and a continuous and smooth motor current average value is provided.
Owner:SYMG SHANGHAI INTELLIGENCE SYST CO LTD
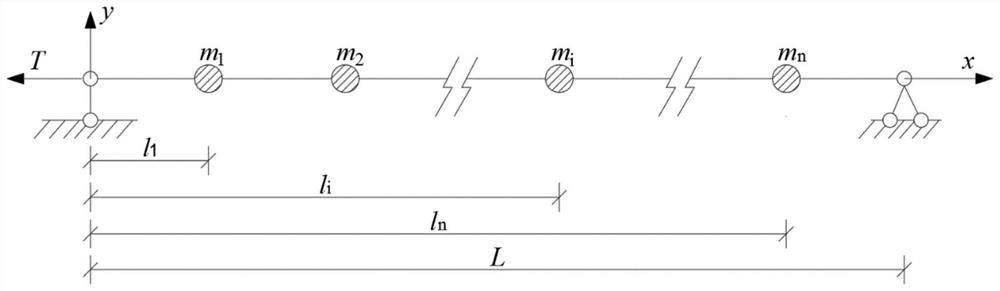
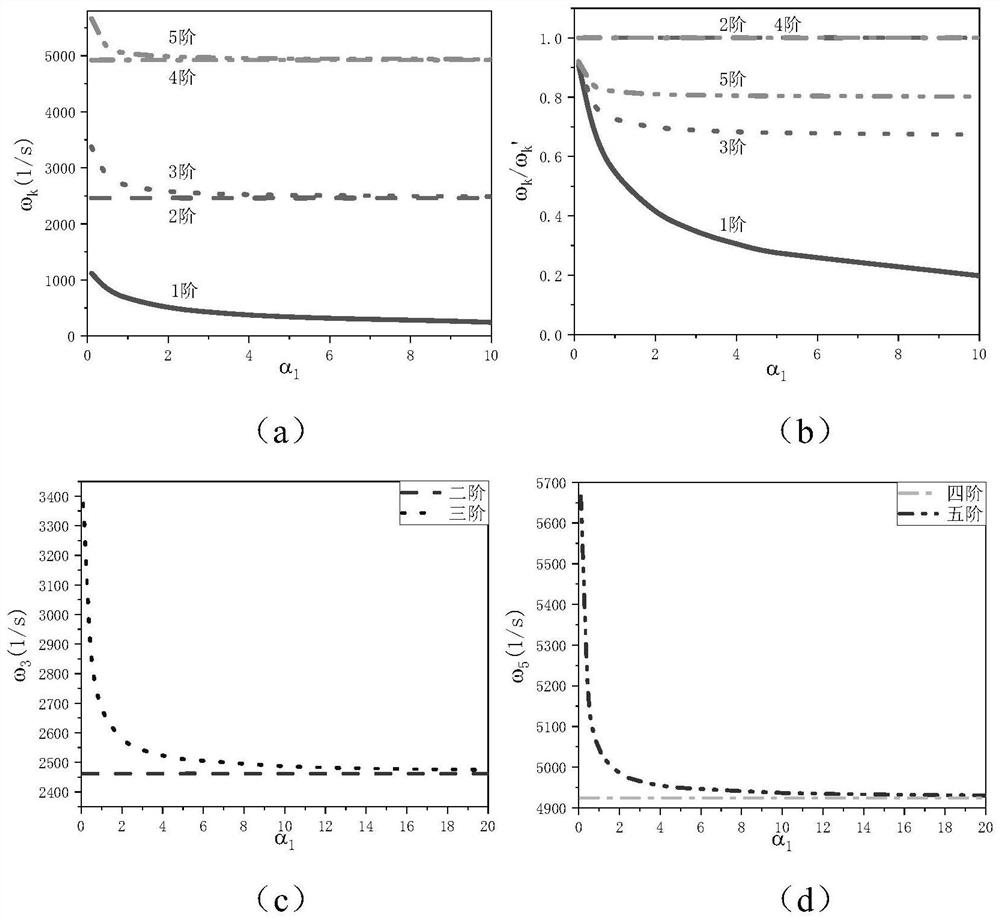
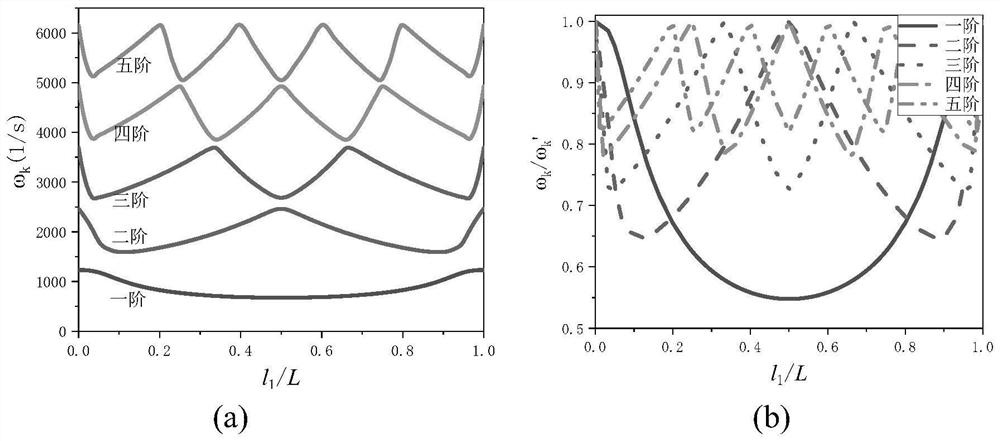
Singular function model analysis method for inherent frequency of string pulling combined structure
PendingCN114357796AEfficient analysisDoes not increase natural frequencyDesign optimisation/simulationClassical mechanicsEngineering
The invention relates to a singular function model analysis method for inherent frequency of a string pulling composite structure, and belongs to the technical field of building structure model analysis. Comprising the following steps: simplifying a concentrated mass string pulling combination structure; the concentrated mass is converted into distributed mass in the cable length direction through a Dirac function; solving a function of the vibration mode of the inhaul cable relative to the time t and the position x; laplace transformation is carried out on a vibration equation of transverse free vibration in a tensioning chord plane; performing inverse Laplacian transformation on the result of the step 4; and solving to obtain a vibration mode equation of the concentrated mass pull string structure model, and obtaining a singular function model, thereby obtaining the frequency of each order of the concentrated mass pull cable combined structure. The singular function model can well predict the influence of the concentrated quality on the inherent frequency of the pull string composite structure.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
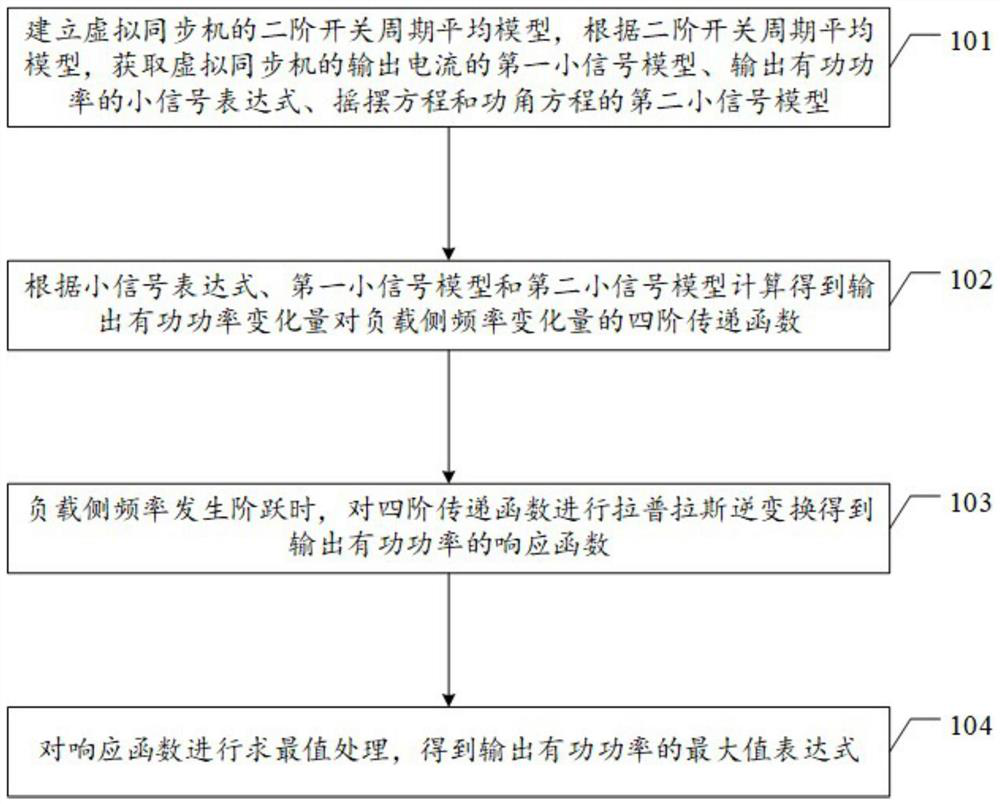
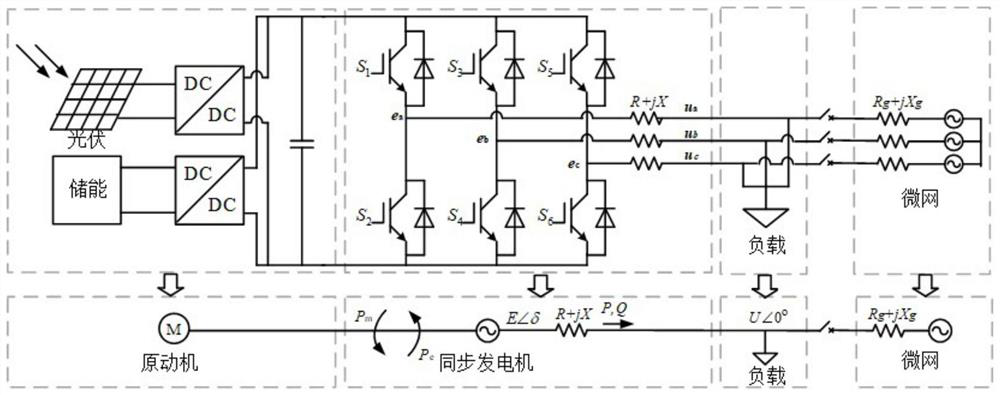
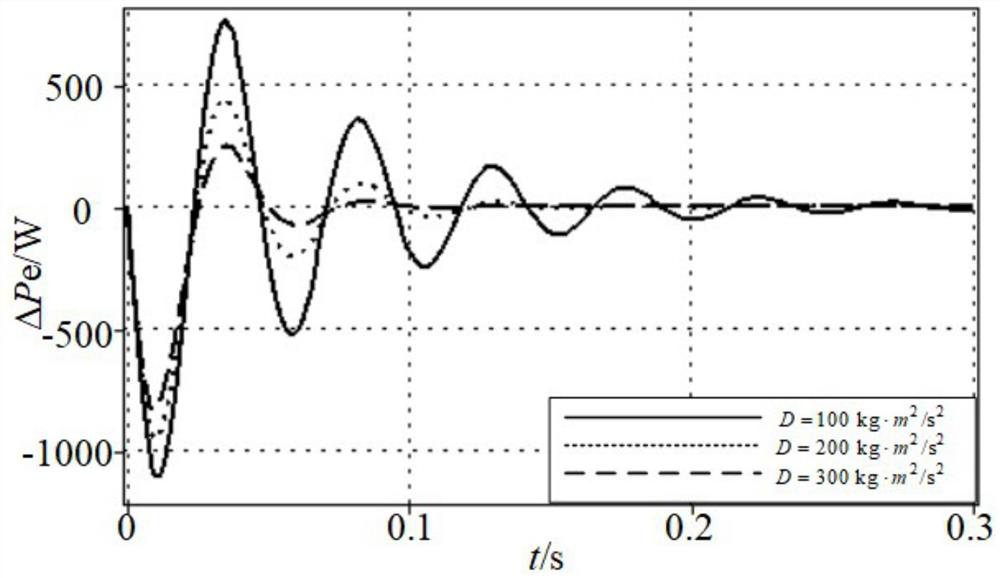
A virtual synchronous machine damping configuration method and device
The embodiment of the present invention discloses a virtual synchronous machine damping configuration method and device. The method includes: establishing a second-order switching cycle average model of the virtual synchronous machine, and obtaining the second-order switching cycle average model of the virtual synchronous machine according to the second-order switching cycle average model. A small-signal model, a small-signal expression of the output active power, a second small-signal model of the rocking equation and a power angle equation; the output active power change is calculated according to the small-signal expression, the first small-signal model, and the second small-signal model The fourth-order transfer function of the variable to the load-side frequency change; when the load-side frequency has a step, the response function of the output active power is obtained by performing inverse Laplace transformation on the fourth-order transfer function; the response function is calculated for the maximum value, Get the maximum expression of the output active power. The invention provides a clear and effective damping configuration method for matching the energy storage capacity of the virtual synchronous machine, which is convenient for people to configure damping for the virtual synchronous machine.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Method and device for detecting underground water non-Darcy flow field in single-well circulating geothermal system
ActiveCN111764367ASolve temperature problemsGeothermal energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationTime domainMathematical model
The invention provides a method and device for detecting an underground water non-Darcy flow field in a single-well circulating geothermal system. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a mathematical model, establishing a control equation, determining an initial condition of the control equation, and establishing a boundary condition of the control equation; processing a nonlinear term in the control equation by using an approximation method, and performing Laplace transformation on the control equation, the initial condition and the boundary condition to obtain a transformed control equation, a transformed initial condition and a transformed boundary condition; performing finite Fourier cosine transformation on the transformed control equation, the transformed initialcondition and the transformed boundary condition to obtain a transformed partial differential equation; solving the transformed partial differential equation, and performing inverse Laplace transformation to obtain an analytical solution of underground water non-Darcy flow of a single-well circulating shallow geothermal system in a Laplace domain; and solving a solution in a time domain corresponding to the analytical solution by using a Stehfest numerical inversion method to detect the depth-reducing distribution of the underground water non-Darcy flow field.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING) +2
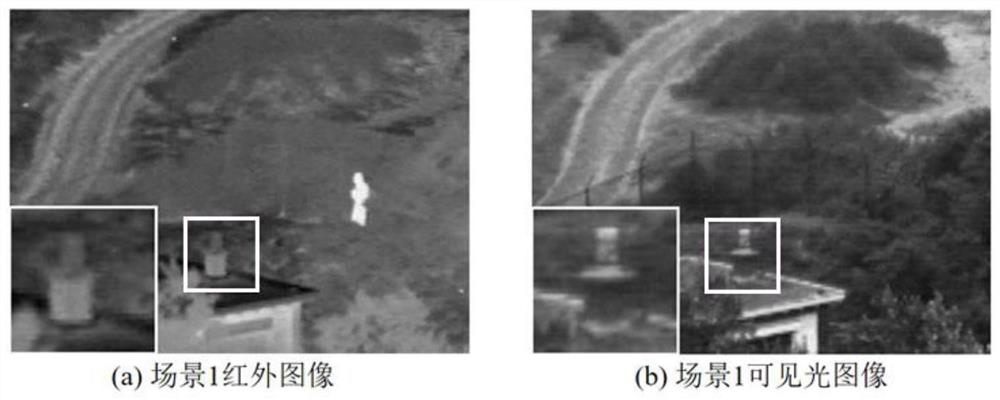
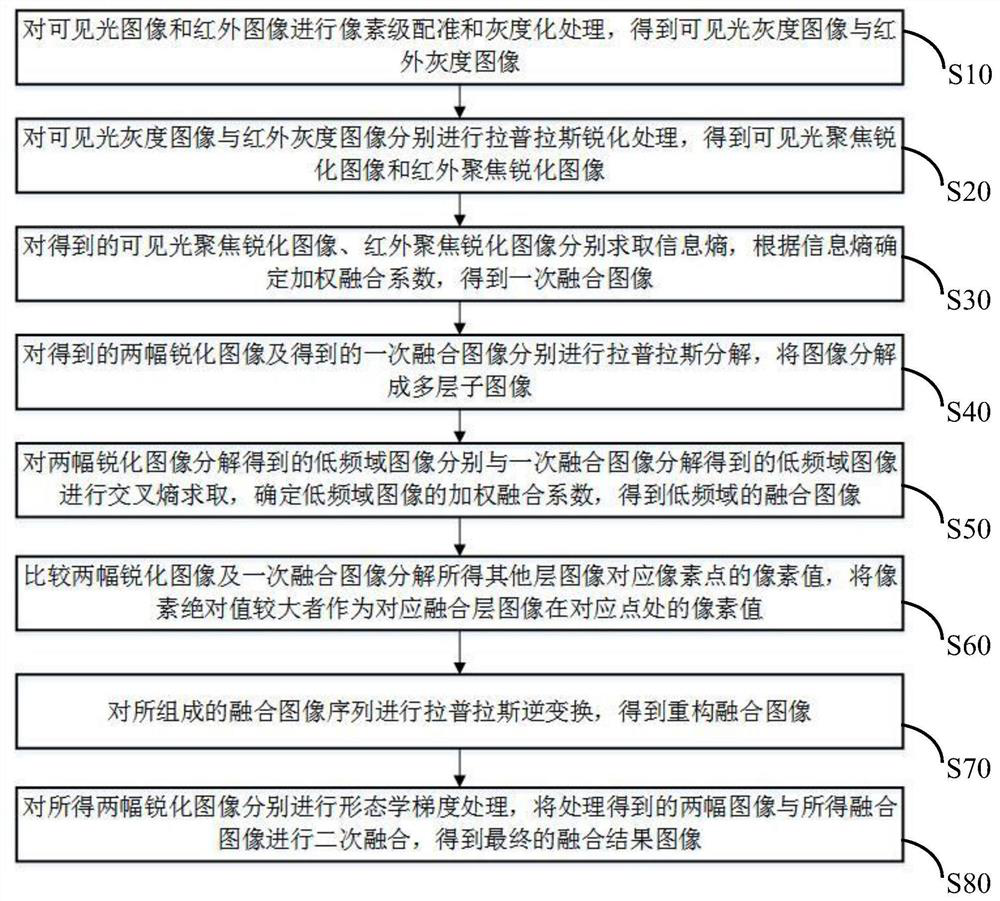
Visible light image and infrared image fusion method based on Laplace pyramid
PendingCN112184606AReduce noiseMultiple structure informationImage enhancementImage analysisSource imageArtificial intelligence
The invention provides a visible light image and infrared image fusion method based on a Laplace pyramid. The method comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the preprocessing and Laplace sharpeningof a visible light image and an infrared image, obtaining corresponding focusing sharpened images, solving the information entropy of the obtained focusing sharpened images, and carrying out the primary fusion; performing Laplace decomposition, performing cross entropy calculation on the low-frequency domain image, determining a weighted fusion coefficient of the low-frequency domain image, obtaining a fused image of the low-frequency domain, calculating a pixel value, taking the image with a relatively large pixel absolute value as a pixel value of the corresponding fused layer image at a corresponding point, and performing Laplace inverse transformation to obtain a reconstructed fused image; finally, carrying out morphological gradient processing, and secondary fusion is carried out, andobtaining a final fusion result image. According to the visible light image and infrared image fusion method provided by the invention, a fusion result contains less noise, and more structural information and edge information of a source image are reserved.
Owner:NANJING XIAOZHUANG UNIV
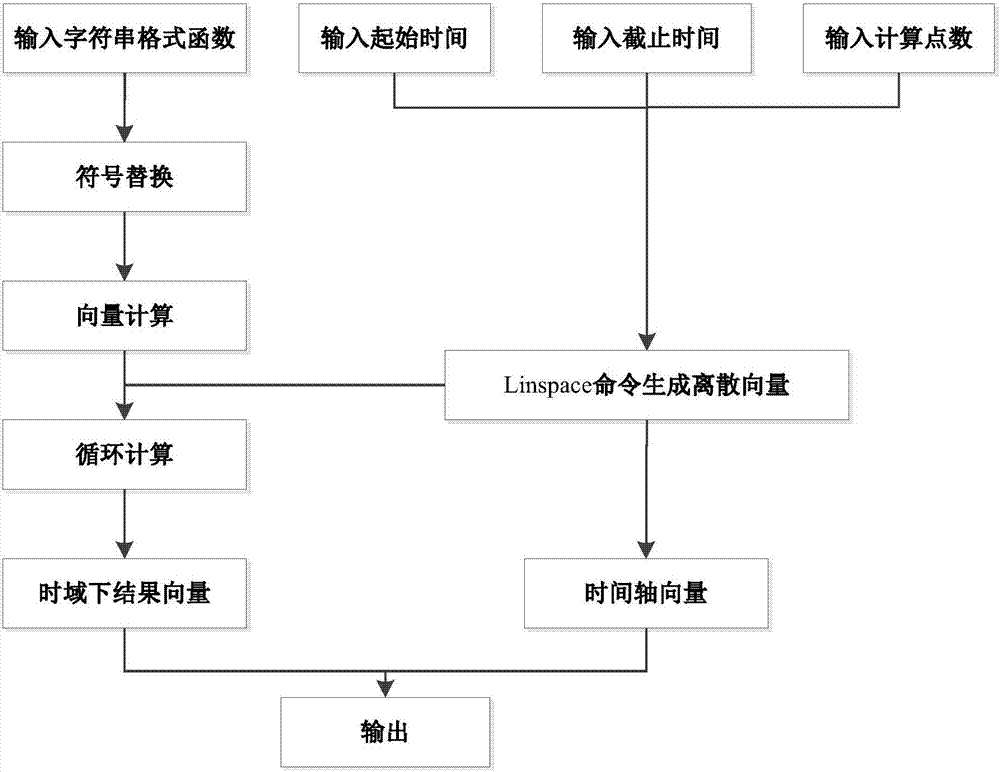
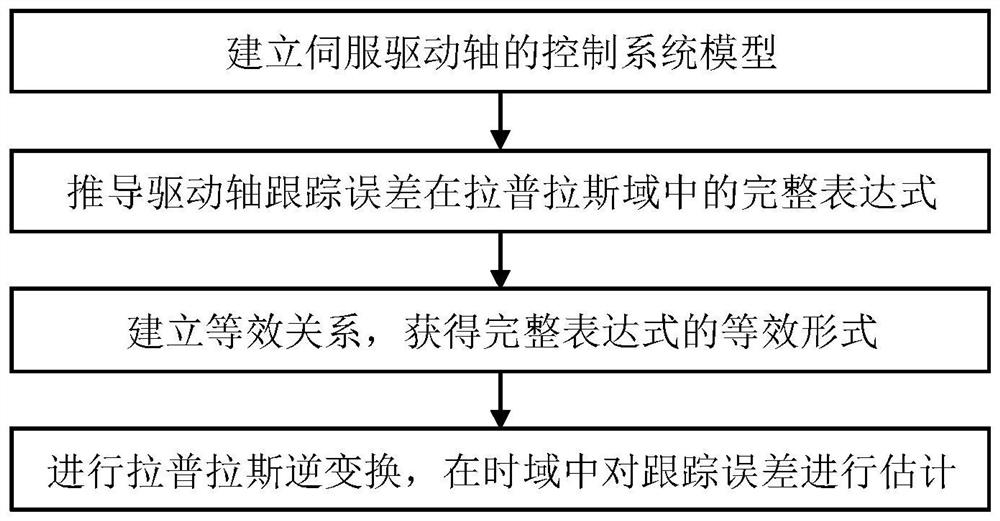
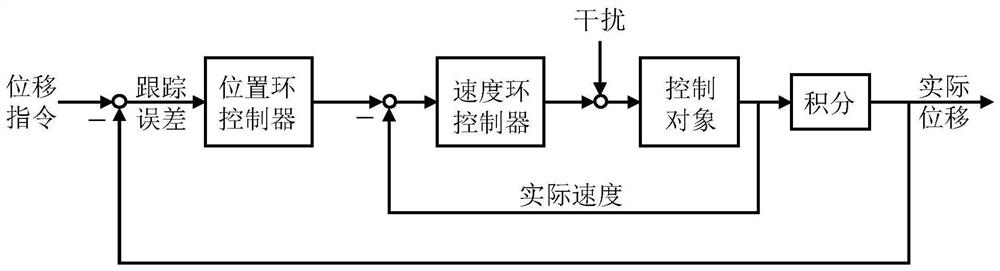
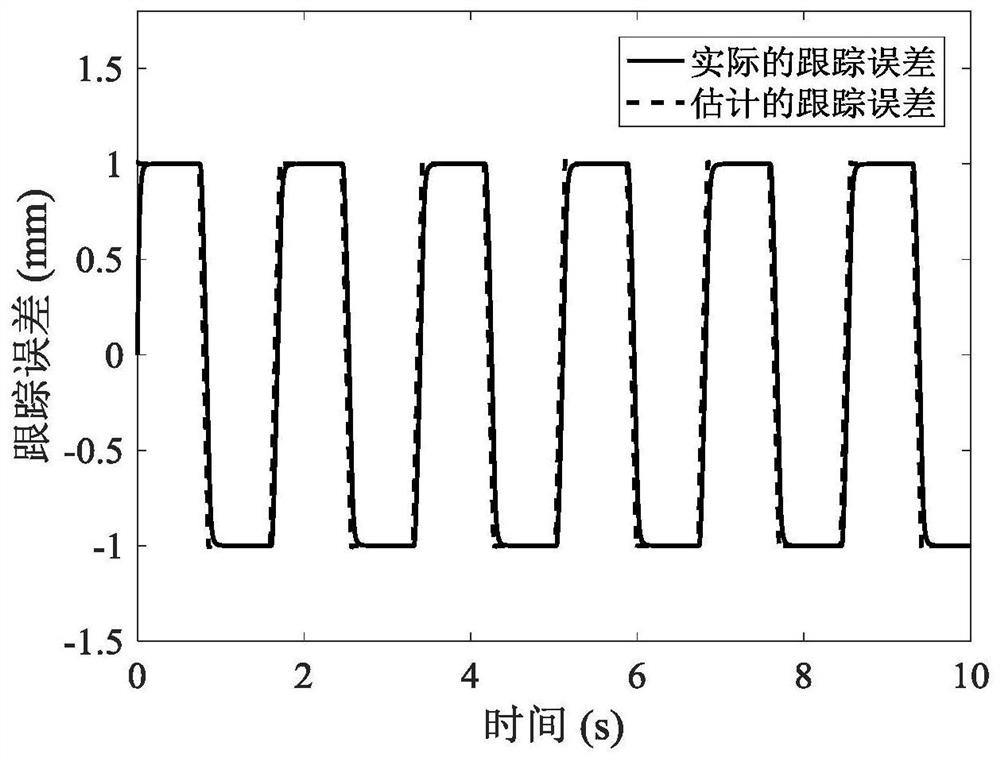
A Tracking Error Estimation Method for Servo Drive Axis
The invention discloses a tracking error estimation method for a servo drive shaft, belonging to the technical field of electromechanical integration. This method first establishes the control system model of the servo drive shaft, and derives the complete expression of the tracking error in the Laplace domain; further, according to the composition characteristics of the displacement command signal, the equivalent form of the complete expression is obtained; finally, through the Laplace Inverse Steinian transform to estimate the tracking error of a servo-driven shaft in the time domain. Using the proposed method, the fast and accurate estimation of the tracking error of the servo drive shaft is realized in the time domain, which overcomes the problems of difficult operation and low efficiency of the traditional method, and provides an accurate and convenient tool for field engineers and technicians .
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ultrafast laser balance detection photoelectric pulse signal shaping method and realization circuit
InactiveCN104702248BImprove high-frequency noise suppressionSimple compositionPulse shapingHemt circuitsEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical electronic devices and particularly relates to an ultrafast laser balanced detection photoelectric pulse signal shaping method and an implementation circuit. Shaping broadening processing is performed on photocurrent through an electrical means, so that differential signals caused by waveform mismatching are reduced, and the adverse effect on the balance effect is reduced. The transfer function H used by shaping broadening processing is: (imag file= 'dest_path_image 002. TIF' wi= '169' he = '24' / ), wherein s is a complex variable, (imag file= 'dest_path_image 004. TIF' wi= '23' he = '15' / ) is an inverse Laplace transformation mark, (imag file= 'dest_path_image 006. TIF' wi= '120' he = '16' / ) is a different real parameter, and the dimension is time. Various specific implementation circuits exist. The electrical shaping mode has to additional advantages of two circuits of improving the circuit high-frequency noise suppression capacity, simplifying experiment equipment, reducing the cost and improving the data accuracy and signal to noise rate.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
A Semi-Analytical Calculation Method of Magnetic Field for Eddy Current Nondestructive Testing Containing Columnar Defects
ActiveCN107038302BImprove solution efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a semi-analytical calculation method for the magnetic field of eddy current non-destructive testing containing columnar defects. Using mathematical physics and electromagnetic field principles, the precise analytical expression of the magnetic vector potential in the Lagrangian domain is obtained, and the magnetic vector potential level is calculated based on MATLAB. The complex expressions in numerical form are inversely transformed by numerical Laplace, and the time-domain solution of eddy current nondestructive testing signals in conductors with columnar defects is obtained. The invention can accurately and efficiently calculate the eddy current non-destructive testing magnetic field of the conductor containing columnar defects, and provides a theoretical basis for the eddy current non-destructive testing technology in the field of defect quantitative identification.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
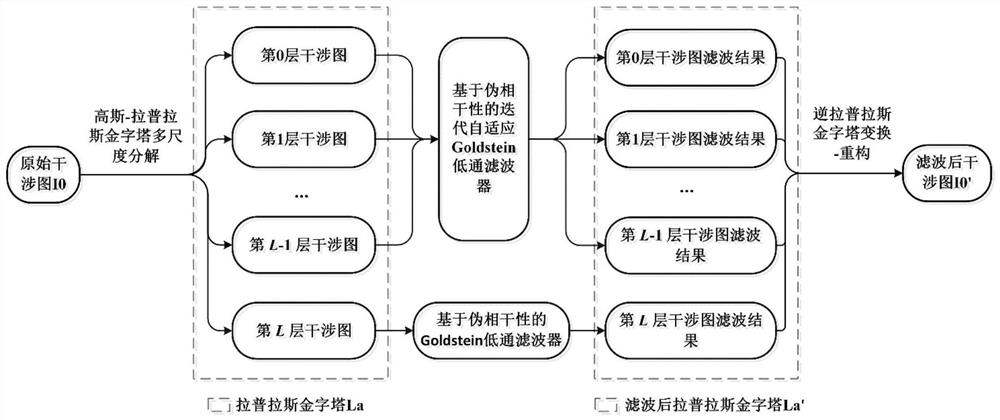
SAR interferogram filtering method based on multi-scale decomposition-reconstruction
PendingCN112419206AImprove filtering effectImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMultiscale decomposition
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Robust pitch control method for wind turbines based on ude
ActiveCN105971819BSimple structureImprove anti-interference abilityWind motor controlMachines/enginesWind drivenAnti jamming
The invention discloses a variable-pitch robust control method based on a UDE for a wind generating set. The method comprises the steps of creating a dynamic model of wind-driven generators on the basis of unmodeled dynamics and disturbance of the wind generating set; defining dynamic characteristics of regulation errors and expectation errors; rewriting the dynamic model of the wind generating set and obtaining a preliminary expression of a pitch angle controller; arranging a low pass filter for carrying out approximation on non-affine uncertain items and disturbance terms of the dynamic model of the wind-driven generators, substituting the approximation result into the preliminary expression of the pitch angle controller, carrying out Laplace transformation, carrying out inverse Laplace transformation after merging and sorting and obtaining final pitch angle control signals. In the design process, the problem that the design of a non-affine system controller is difficult is solved, the unmodeled dynamics and the environmental disturbance of a system are fully considered, the structure of an obtained controller is simple, the number of needed parameters is small, the robustness is good, the anti-jamming capability is high, a more stable wind wheel rotation speed and more stable generation power can be provided, and high-quality electric energy can be provided for a power grid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A method for characterizing the pore structure of regenerated cellulose materials
ActiveCN107202809BKeep it pristineTrue and reliableAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceHydrogenFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a characterization method for a porous structure of a regenerated cellulose material. The characterization method comprises the following steps: firstly, soaking regenerated cellulose into liquid and oscillating; secondly, carrying out nuclear magnetic relaxation hydrogen spectrum test on the regenerated cellulose treated in the first step; thirdly, carrying out inverse laplace transformation on a nuclear magnetic relaxation attenuation curve obtained by the nuclear magnetic relaxation hydrogen spectrum test to obtain parameters for characterizing the porous structure of the regenerated cellulose. According to the characterization method disclosed by the invention, the relationship that relaxation time (logarithms and horizontal coordinates) is in direct proportion to the content of pores (longitudinal coordinates) can be obtained, therefore, the sizes of the pores can be qualitatively explained; if specific values of the sizes of the pores need to be determined, different formulas are adopted for calculating according to difference of samples. According to the characterization method disclosed by the invention, drying or freeze-drying treatment of samples is not needed, so original states of the samples can be well kept.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Infrared and visible light image fusion method based on multi-scale analysis and VGG-19
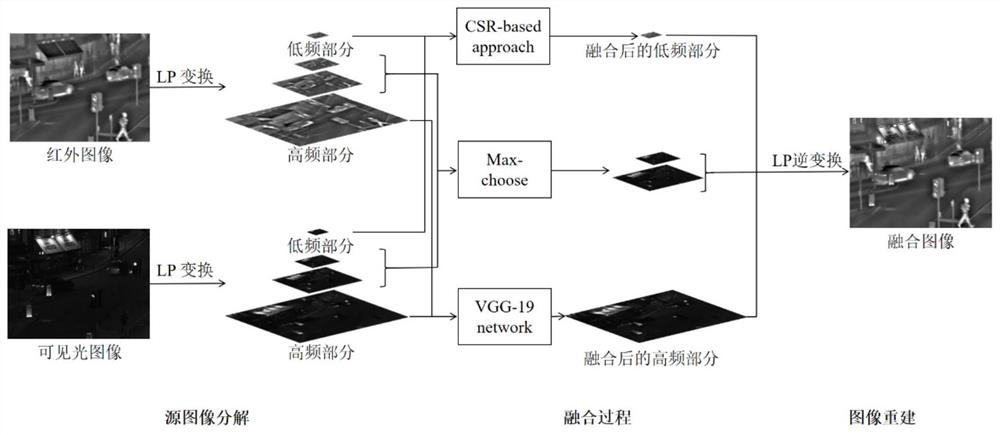
ActiveCN114862730AEasy to keepRetain structural informationImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmLow contrast
The invention discloses an infrared and visible light image fusion algorithm based on multi-scale analysis and VGG-19, belongs to the field of image processing, and mainly solves the problems of detail loss, low contrast and edge blurring in the current fusion method. Comprising the following steps: step 1, performing Laplacian pyramid decomposition on a source image to obtain sub-bands; 2, for the Nth layer of sub-band, extracting image features by adopting a neural network (VGG-19)-based method, and performing feature fusion by adopting a maximum selection mode; 3, fusing the first layer of sub-bands by adopting a method based on convolutional sparse representation (CSR); fusing the second layer to the Nth layer of sub-bands by adopting a'maximum selection 'strategy; and step 4, carrying out Laplace inverse transformation on the fused sub-bands to obtain a fused image. The invention provides a new fusion framework, and the obtained fusion image has superiority in subjective and objective evaluation compared with other classic fusion algorithms.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com