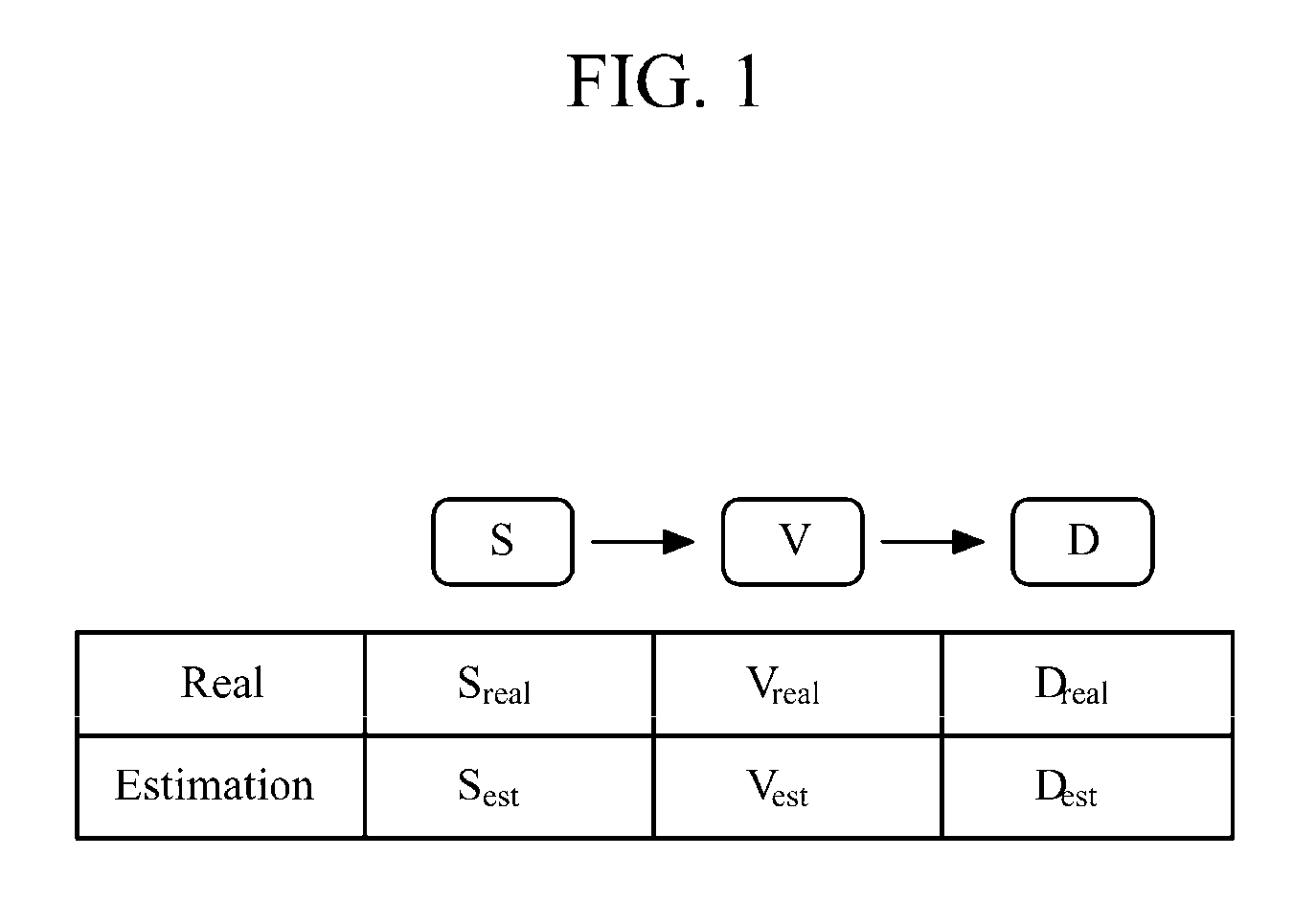
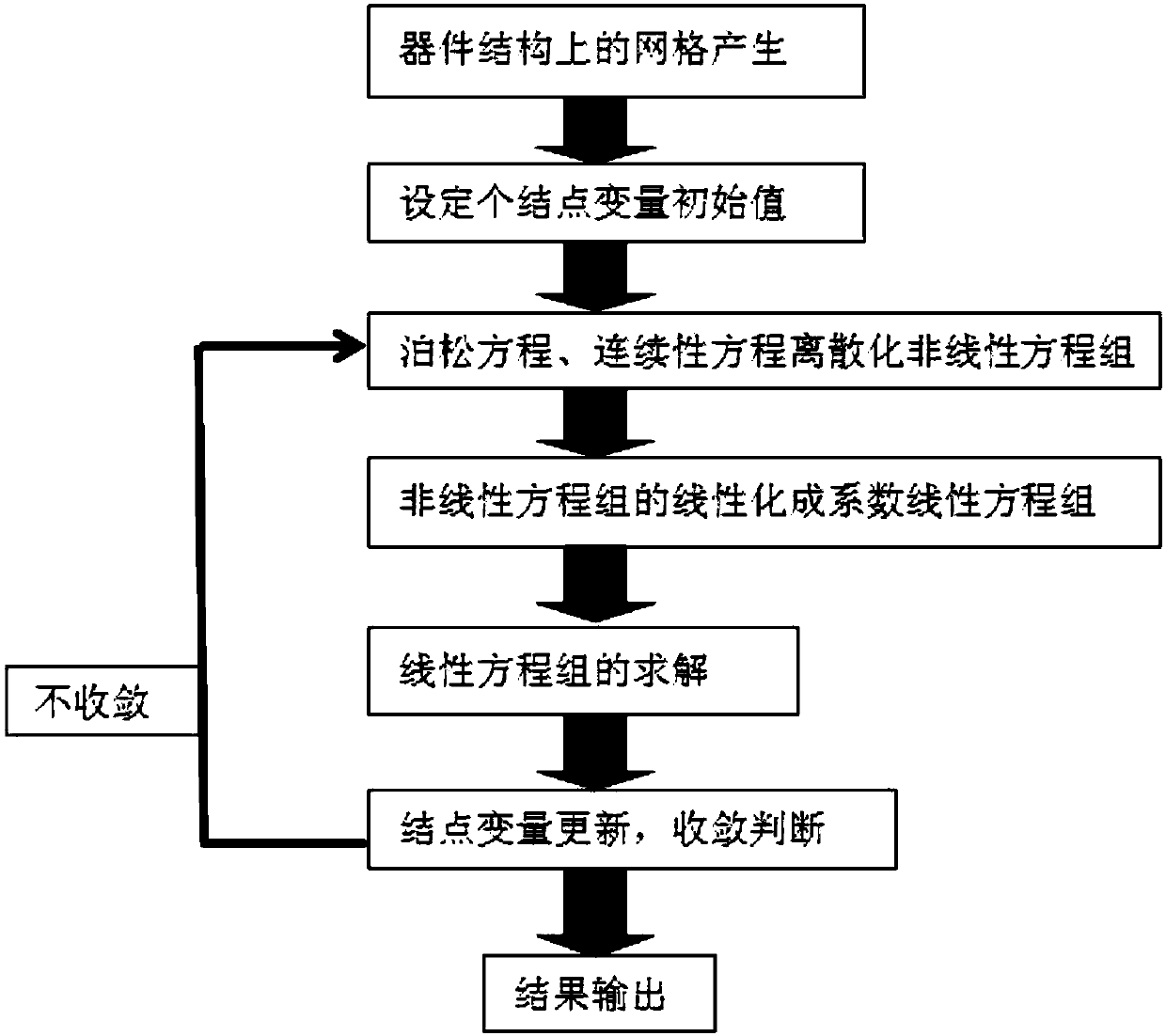
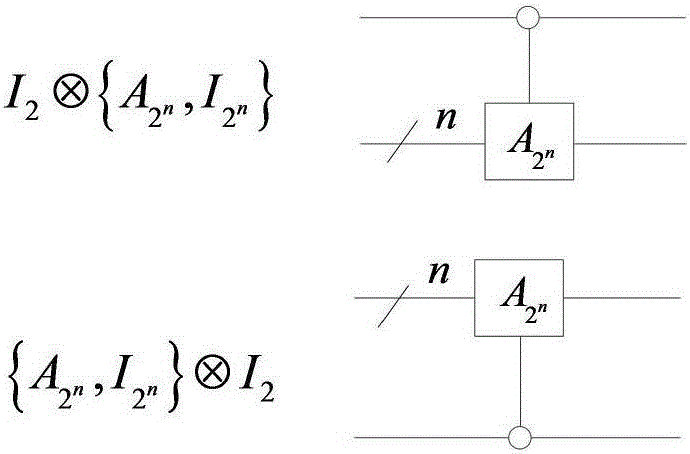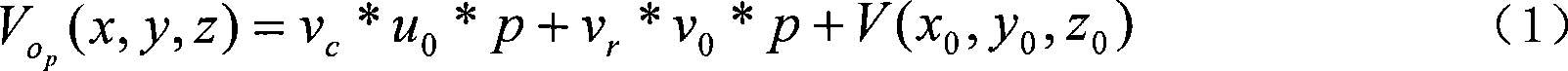Patents
Literature
69 results about "Mathematical physics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mathematical physics refers to the development of mathematical methods for application to problems in physics. The Journal of Mathematical Physics defines the field as "the application of mathematics to problems in physics and the development of mathematical methods suitable for such applications and for the formulation of physical theories". It is a branch of applied mathematics, but deals with physical problems.
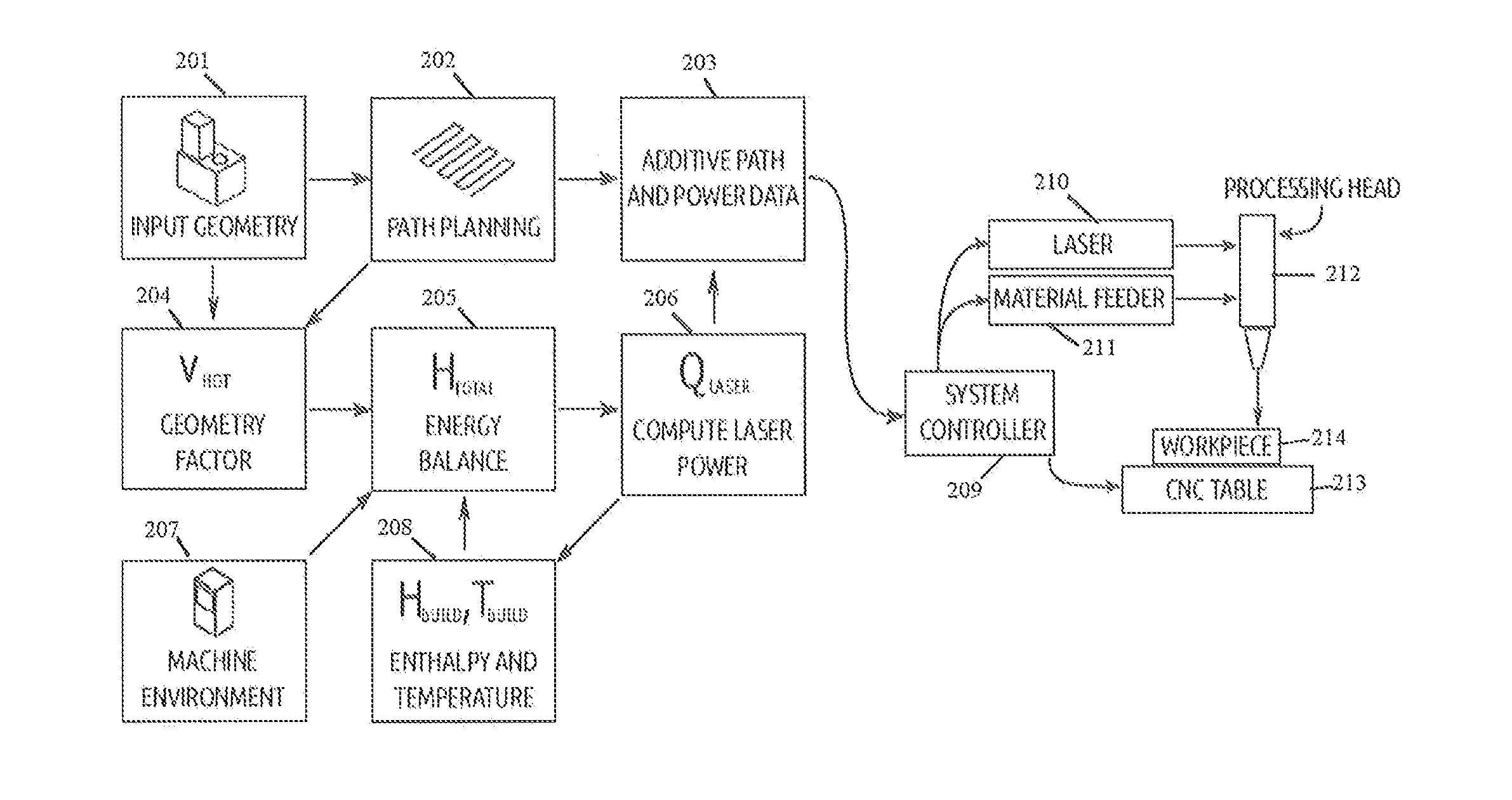
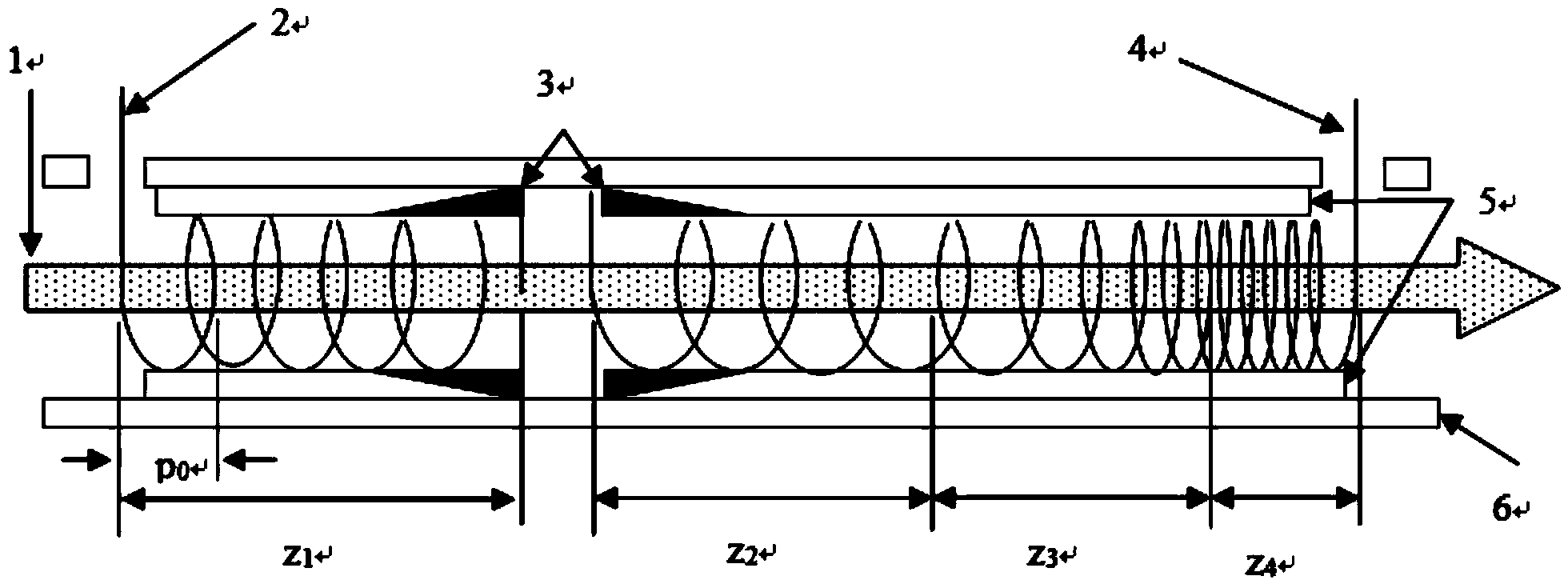
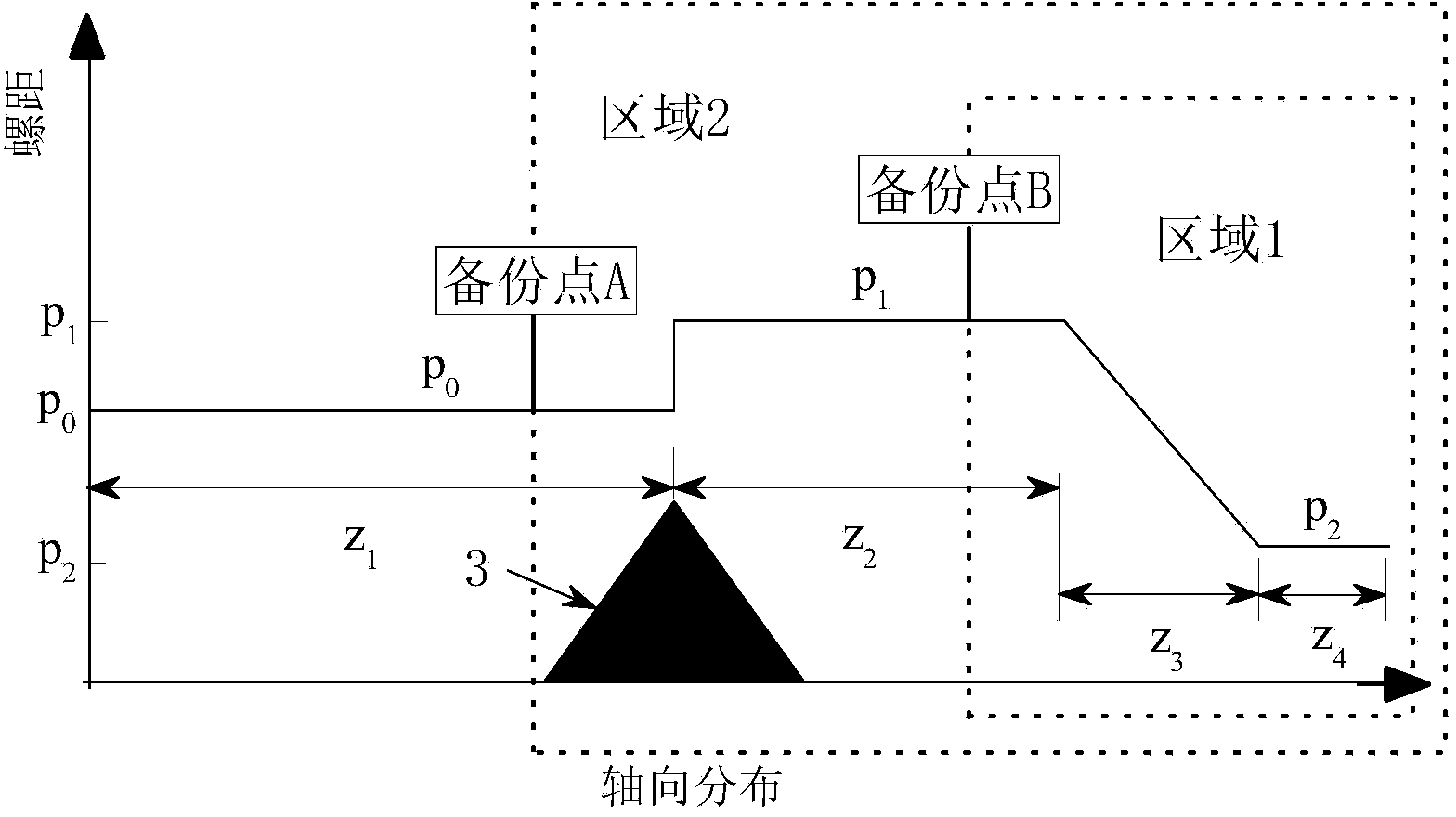
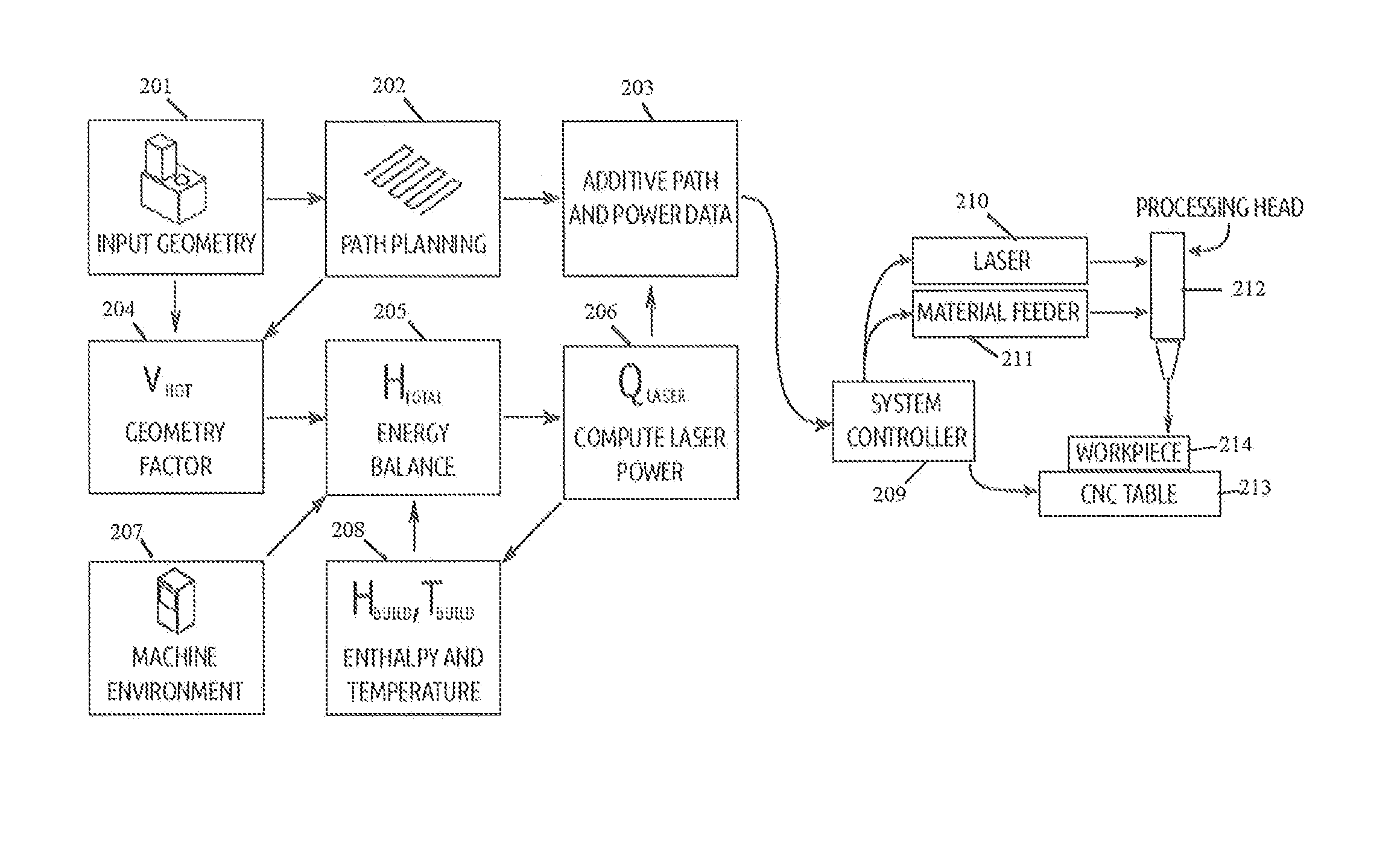
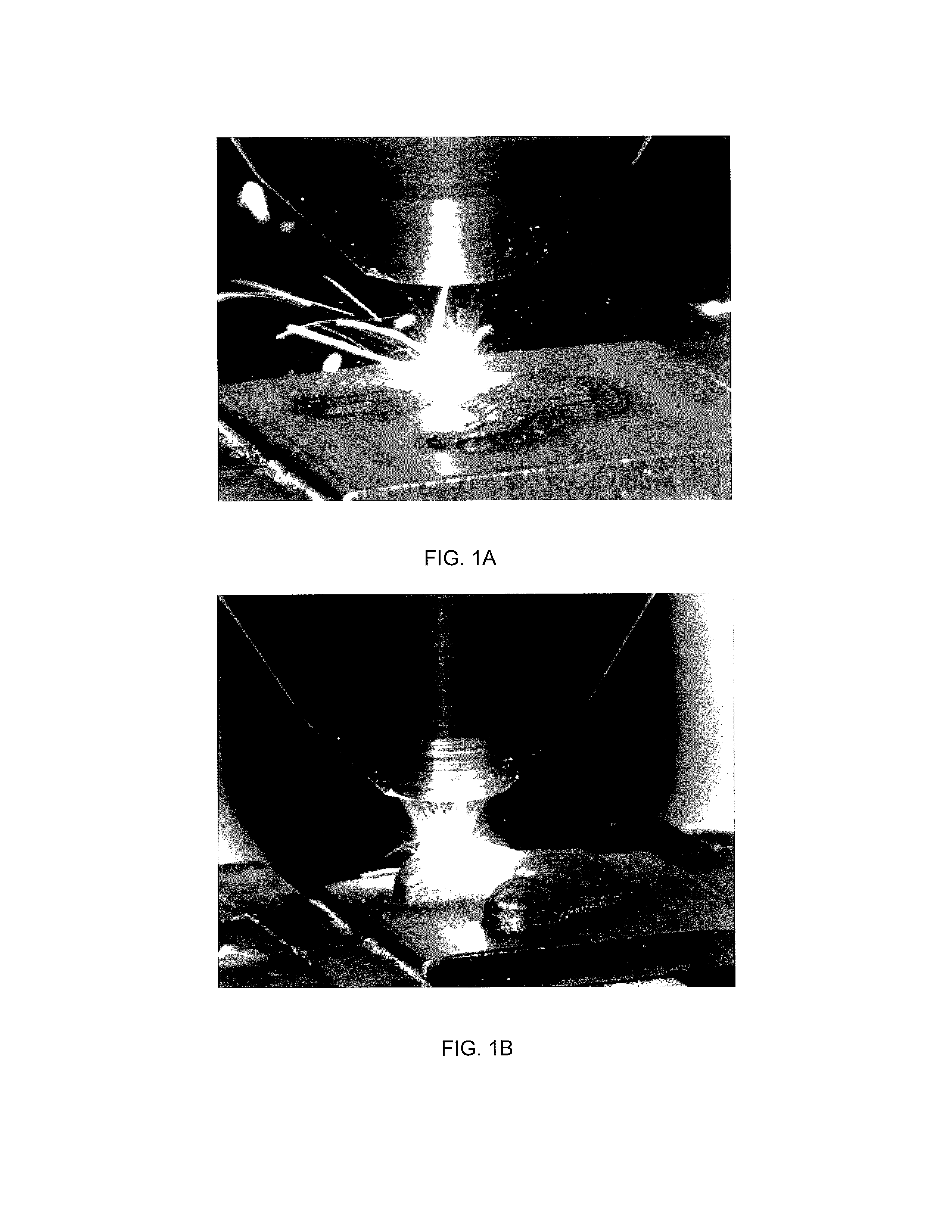
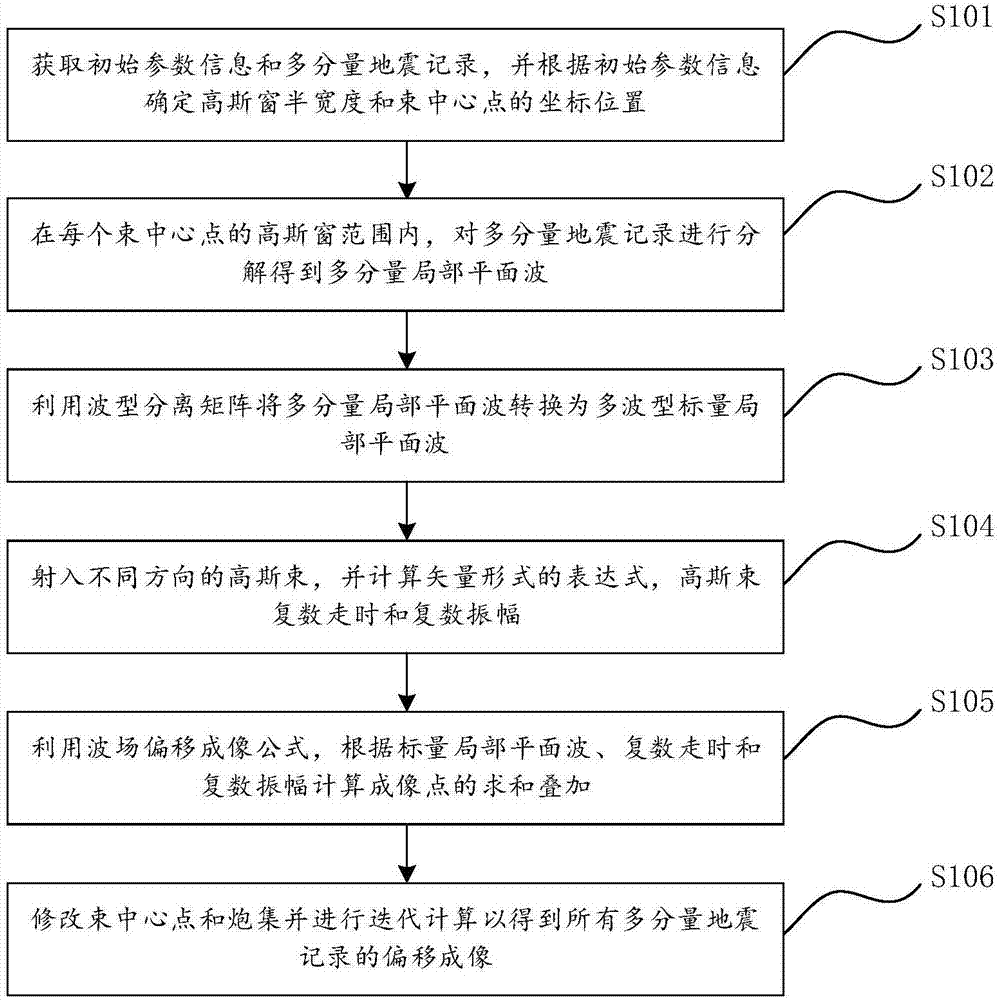
System and Method for Determining Beam Power Level Along an Additive Deposition Path
ActiveUS20160059352A1High frequencyImprove numerical stabilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusBeam sourceEnergy balanced
A power schedule calculation method utilizes an idealized geometry to predict laser power levels on an additive path during laser deposition. The method calculates beam power for any point along the path traveled to form a build having a geometry. Each point along the path has associated with it an idealized geometry comprising a melt pool, hot zone and bulk portion. The method comprises creating a geometric description representing the geometry of the build during the process, creating a path description representing the path of the beam source through space during the process, calculating the idealized geometry for the point on the path based upon the geometric description and path description, calculating an energy balance at the melt pool for the point on the path, calculating total energy needed at the point on the path and calculating optimum beam source power. In the calculations, build temperature is based upon a calculation of hot zone temperature derived from the idealized geometry.
Owner:PROD INNOVATION & ENG L L C
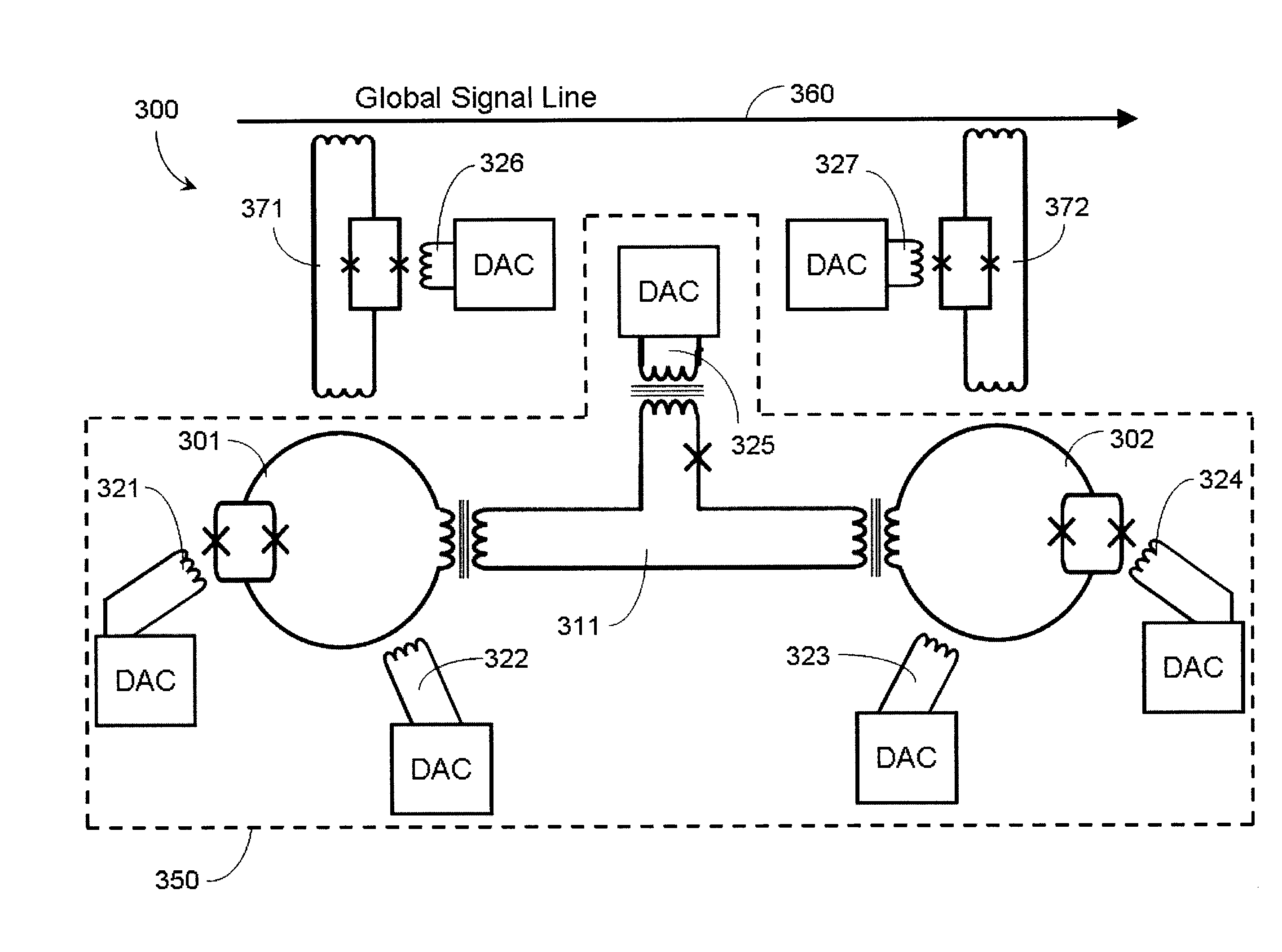
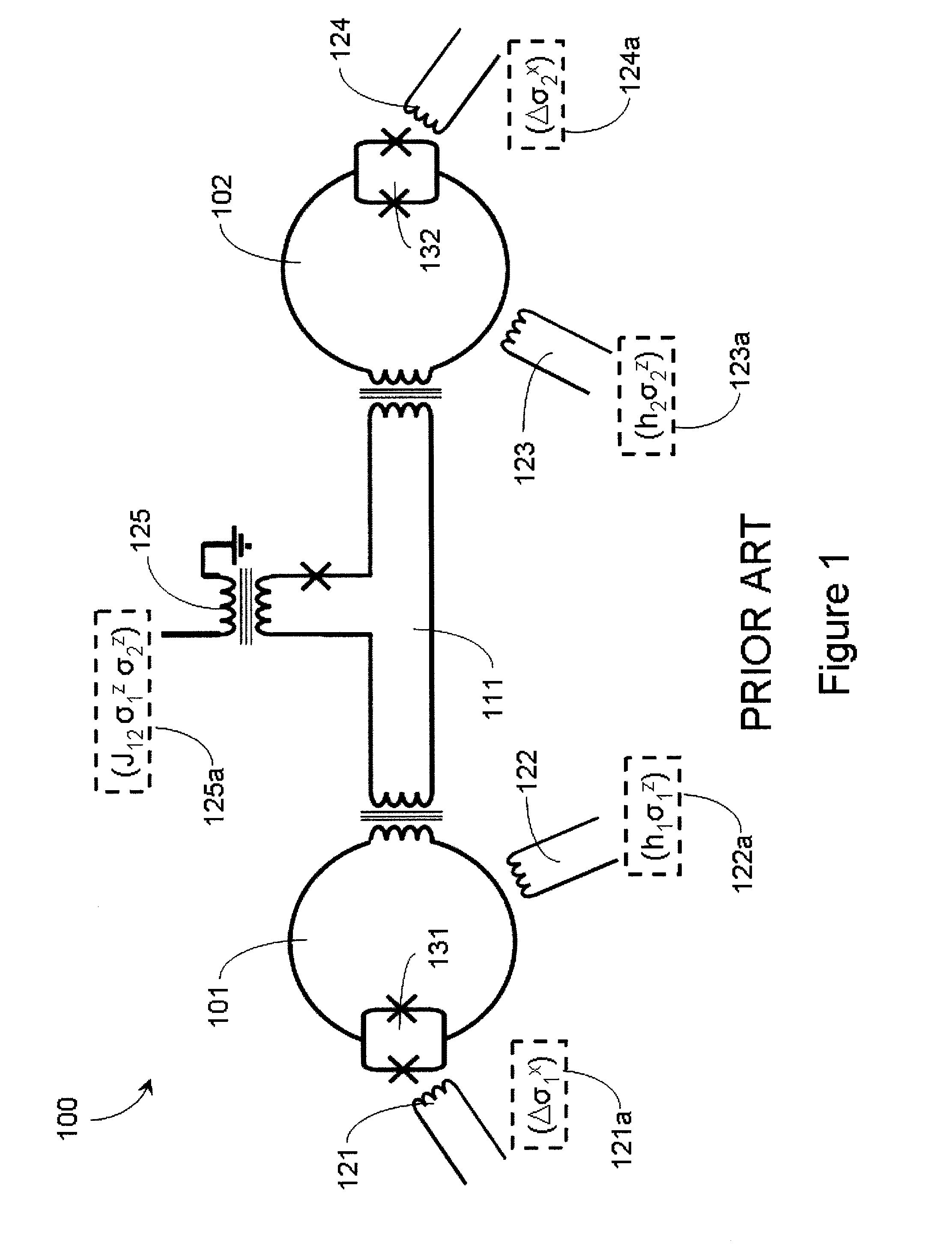
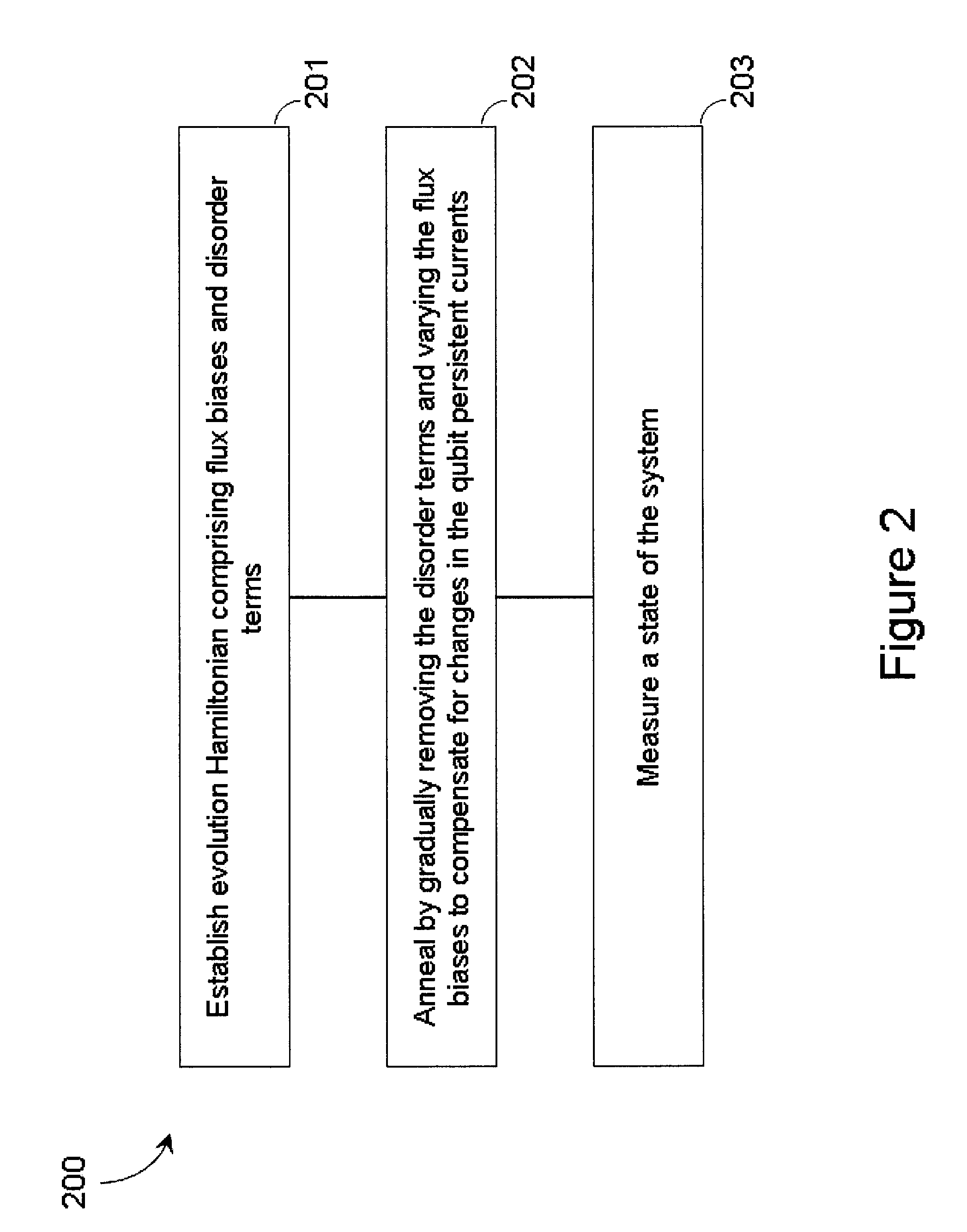
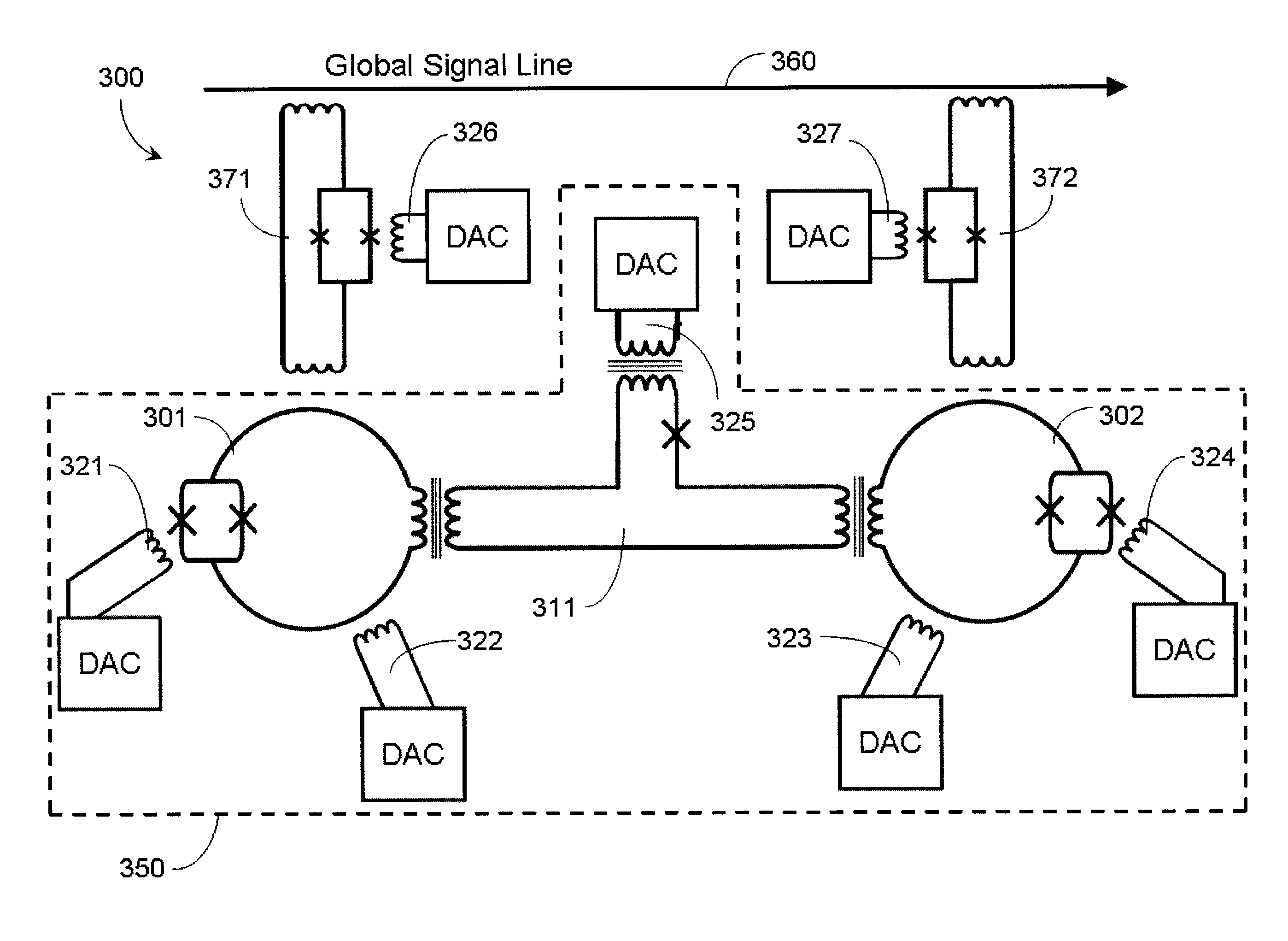
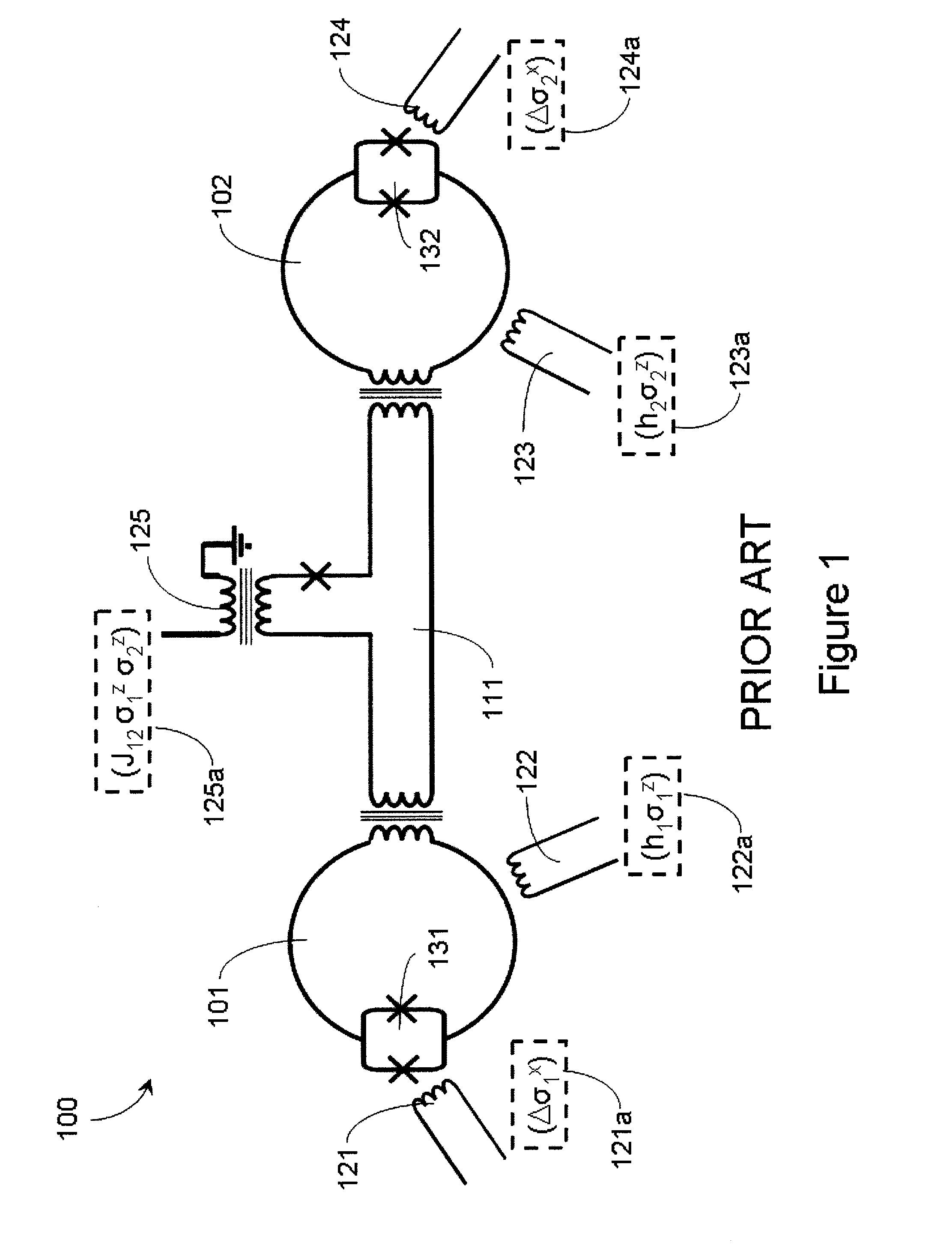
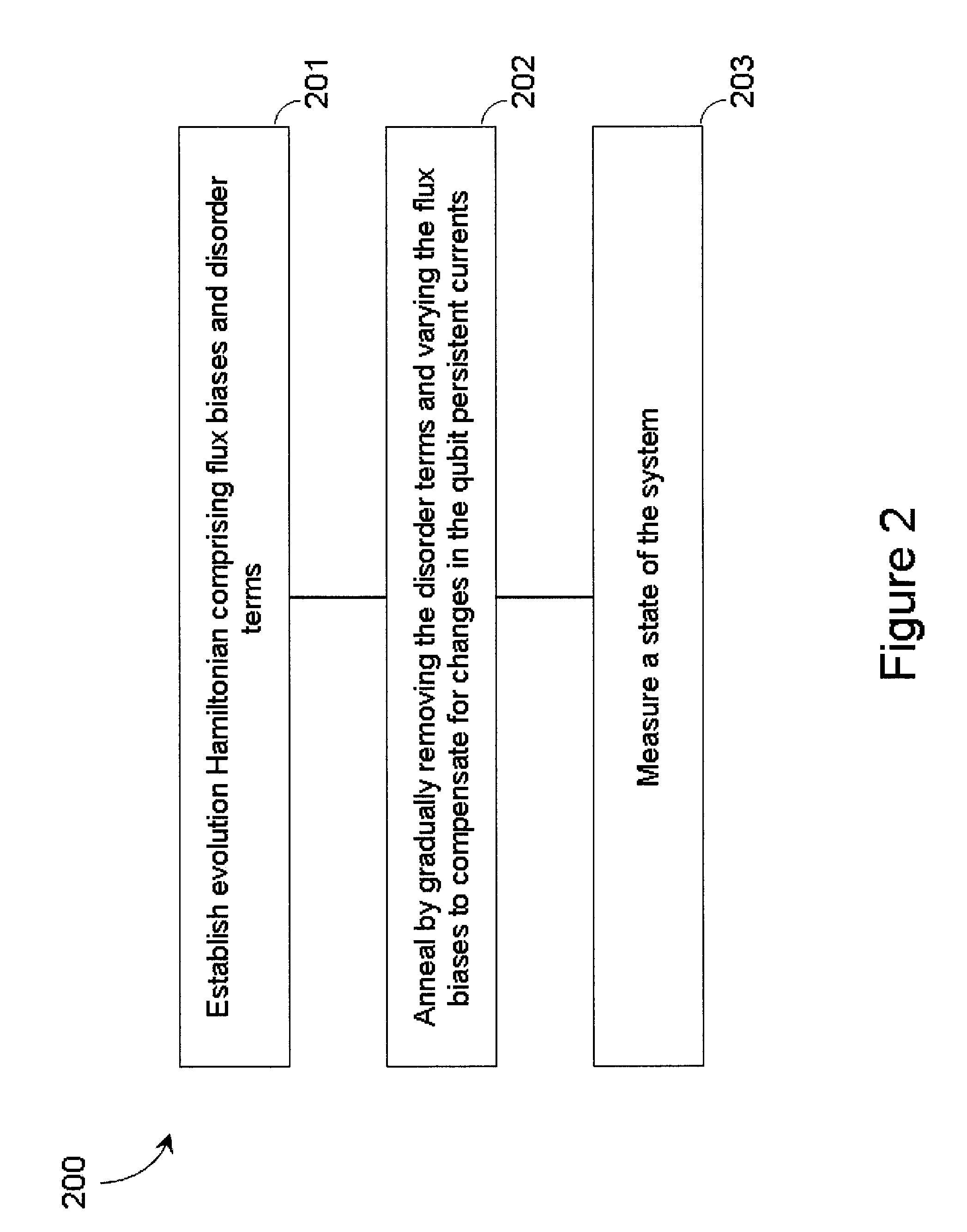
Systems, methods, and apparatus for calibrating, controlling, and operating a quantum processor
Quantum annealing may include applying and gradually removing disorder terms to qubits of a quantum processor, for example superconducting flux qubits of a superconducting quantum processor. A problem Hamiltonian may be established by applying control signals to the qubits, an evolution Hamiltonian established by applying disorder terms, and annealing by gradually removing the disorder terms. Change in persistent current in the qubits may be compensated. Multipliers may mediate coupling between various qubits and a global signal line, for example by applying respective scaling factors. Two global signal lines may be arranged in an interdigitated pattern to couple to respective qubits of a communicatively coupled pair of qubits. Pairs of qubits may be communicatively isolated and used to measure a response of one another to defined signals.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
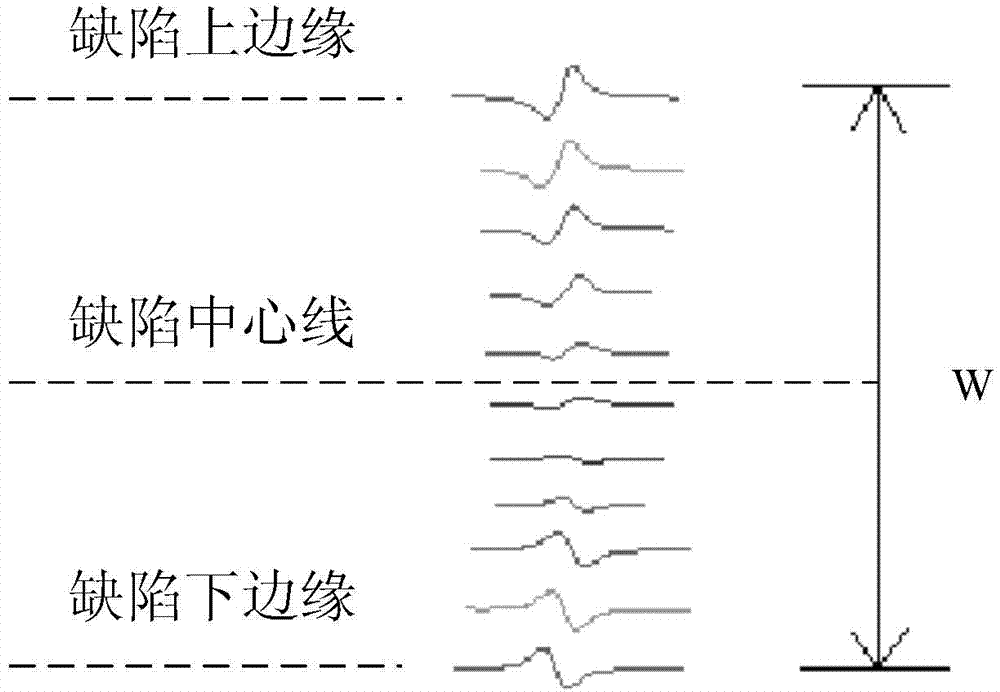
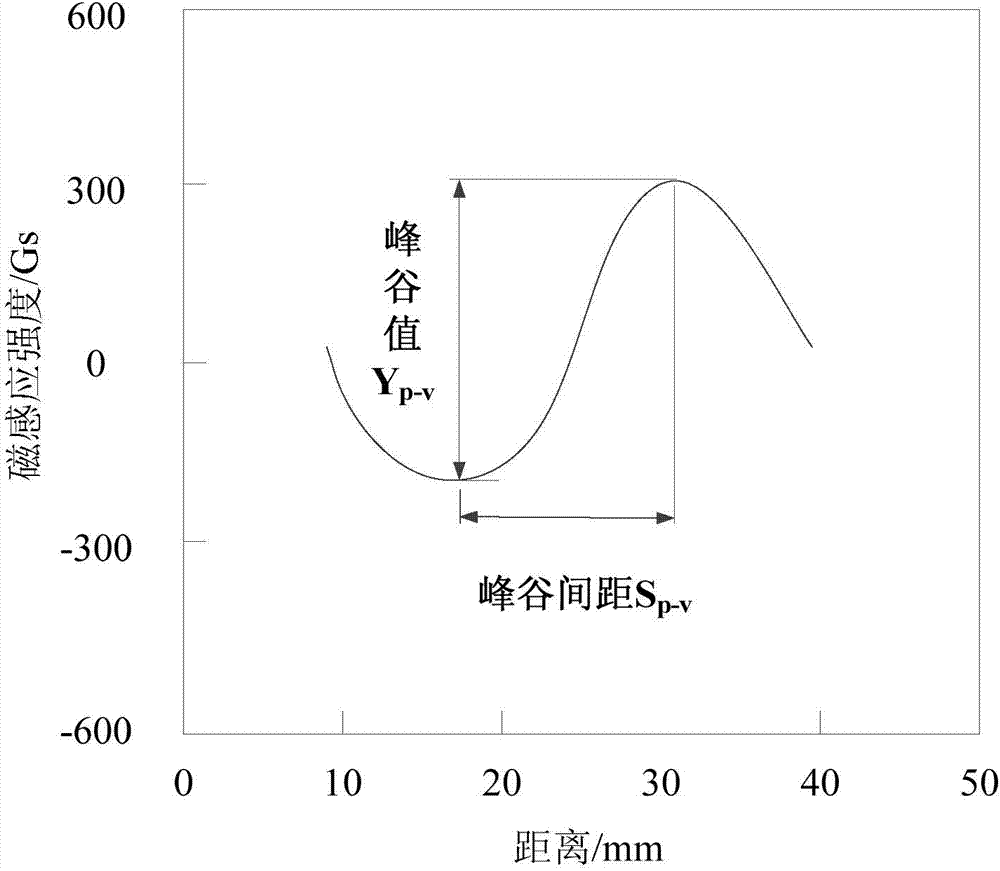
Three-dimensional pipeline flux leakage imaging defect quantizing method
ActiveCN104514987AOvercoming the shortcomings of axial magnetic flux leakage detection signal characteristics as evaluationImprove visibilityPipeline systemsMaterial magnetic variablesEngineeringSignal characteristic
The invention discloses a three-dimensional pipeline flux leakage imaging defect quantizing method which includes the steps: performing defect width quantization by taking circumferential flux leakage signal characteristics as evaluation criteria to obtain a defect width quantization formula; performing defect length quantization by taking radial flux leakage signal characteristics as evaluation to obtain a defect length quantization formula; performing defect depth quantization by taking axial flux leakage signal characteristics and the radial flux leakage signal characteristics as comprehensive evaluation to obtain a defect depth quantization formula; acquiring axial, radial and circumferential discrete three-dimensional flux leakage detection data of a detected component, filtering the axial, radial and circumferential discrete three-dimensional flux leakage detection data to extract defect flux leakage signal characteristic values, and substituting the characteristic values into the formulas to obtain the sizes and distribution situations of defects. Multiple flux leakage signal characteristics are comprehensively and collectively evaluated, the method is high in distinguishing degree and accurate, simple and easy in calculation, and the identification ability and the quantization accuracy of various irregular defects and applicability are improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
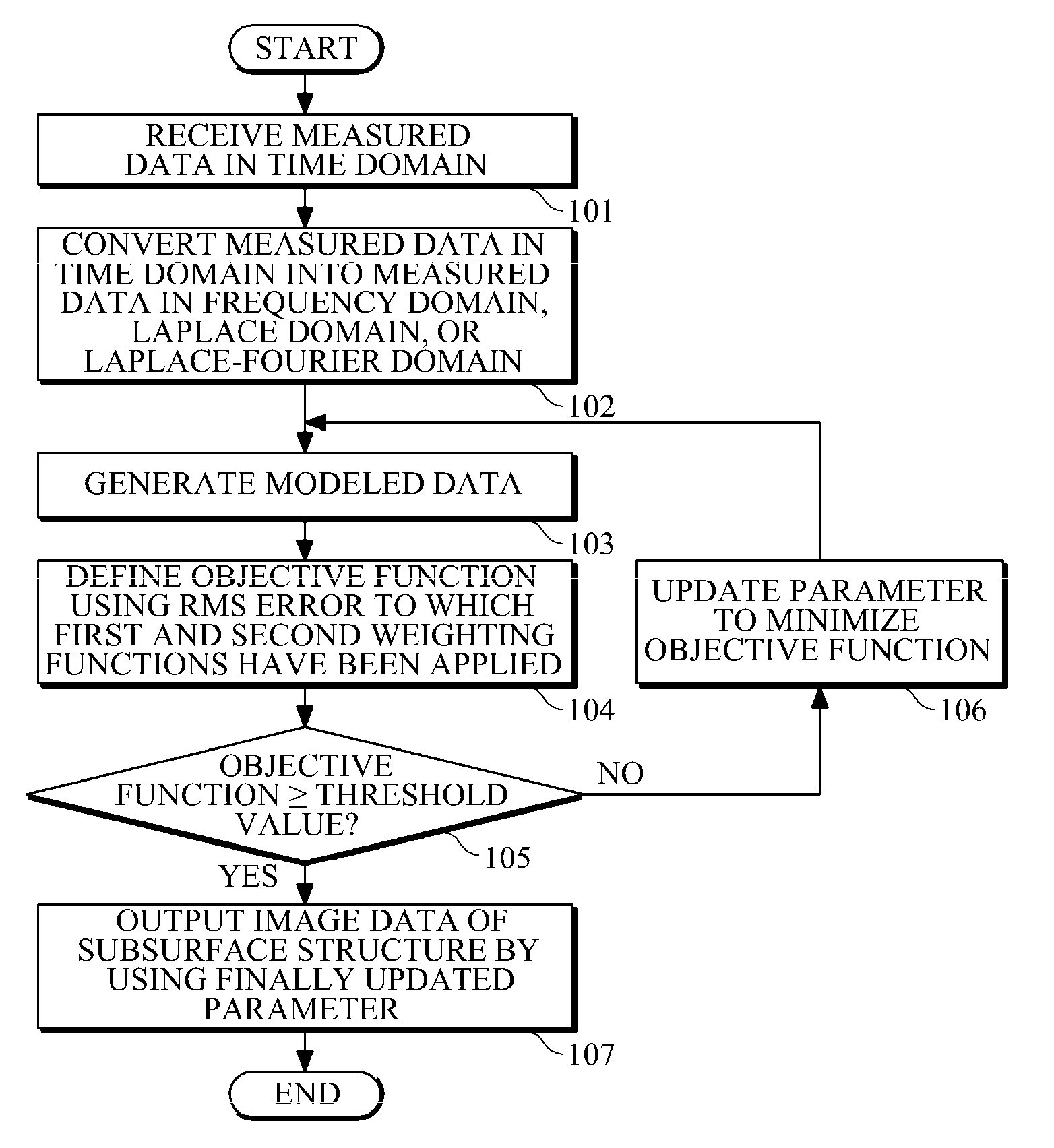
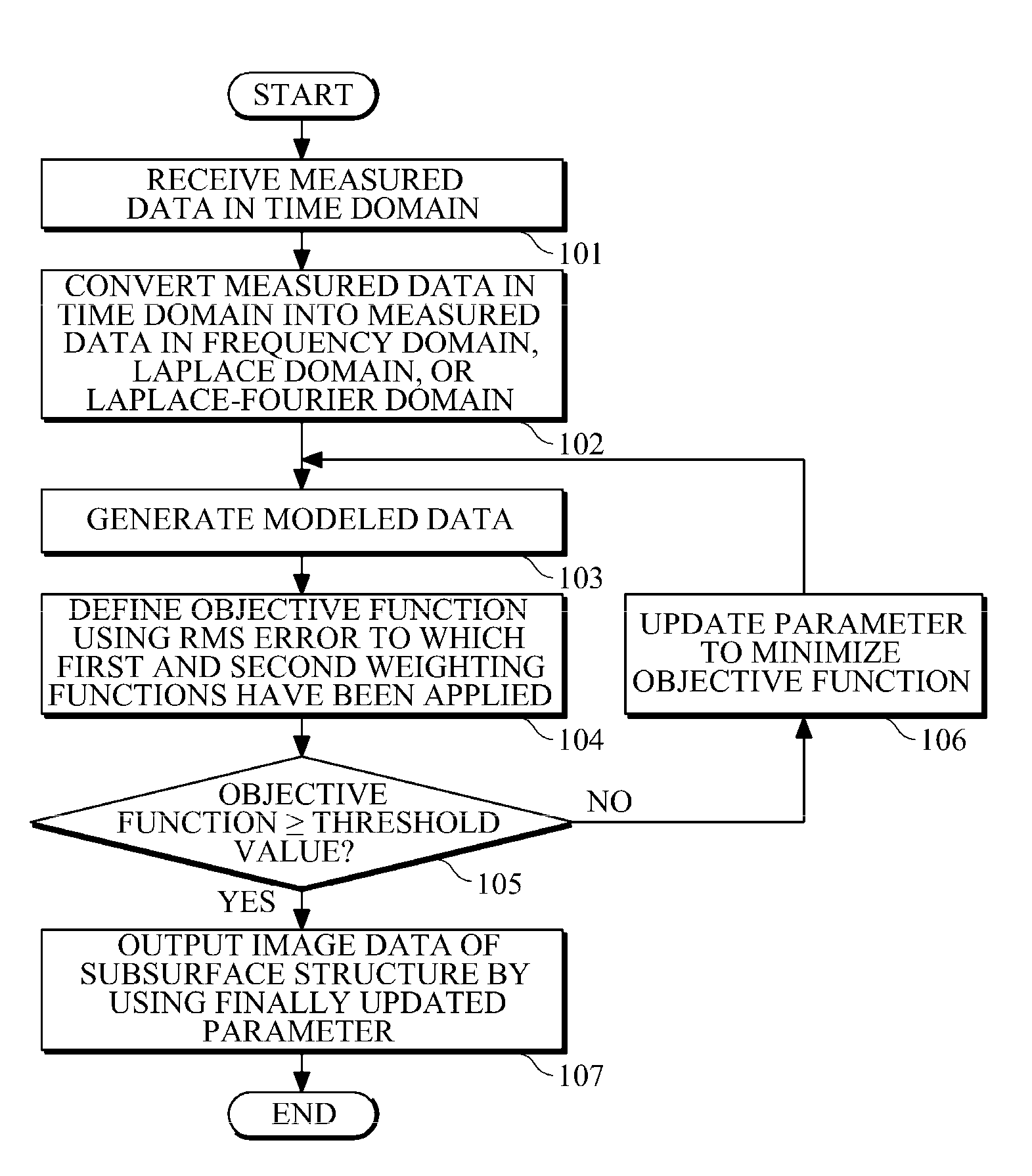
Apparatus and method for imaging subsurface structure of target area by using waveform inversion
ActiveUS20100322032A1Efficient use ofEvenly distributedSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsDamping constantObject function
Provided are an apparatus and method for imaging the subsurface structure of a target area by using waveform inversion. In the apparatus and method, the subsurface structure of a target area is estimated using waveform inversion of a seismic signal in the frequency domain, the Laplace domain, or the Laplace-Fourier domain, and an objective function is defined by applying a weighting function such that the objective function makes a different contribution for each frequency, each Laplace damping constant, or each Laplace-Fourier damping constant. The objective function is not limited to a particular type of objective function and a weighting function can be automatically determined when a gradient vector for each frequency, each Laplace damping constant, or each Laplace-Fourier damping constant is normalized. In addition, a gradient direction for all frequencies can be defined by applying another weighting function to the sum of respective gradient vectors for all frequencies, all Laplace damping constants, or all Laplace-Fourier damping constants, wherein the weighting function can also be automatically determined by normalization.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
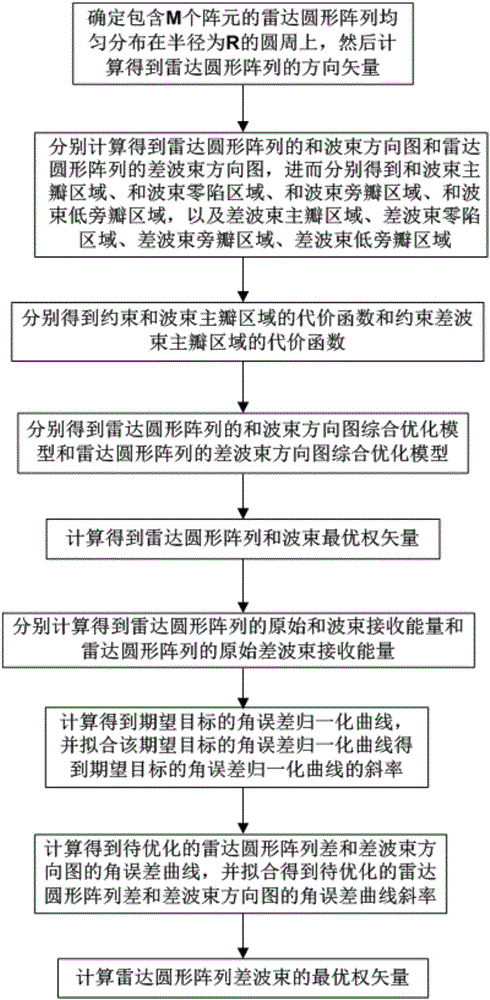
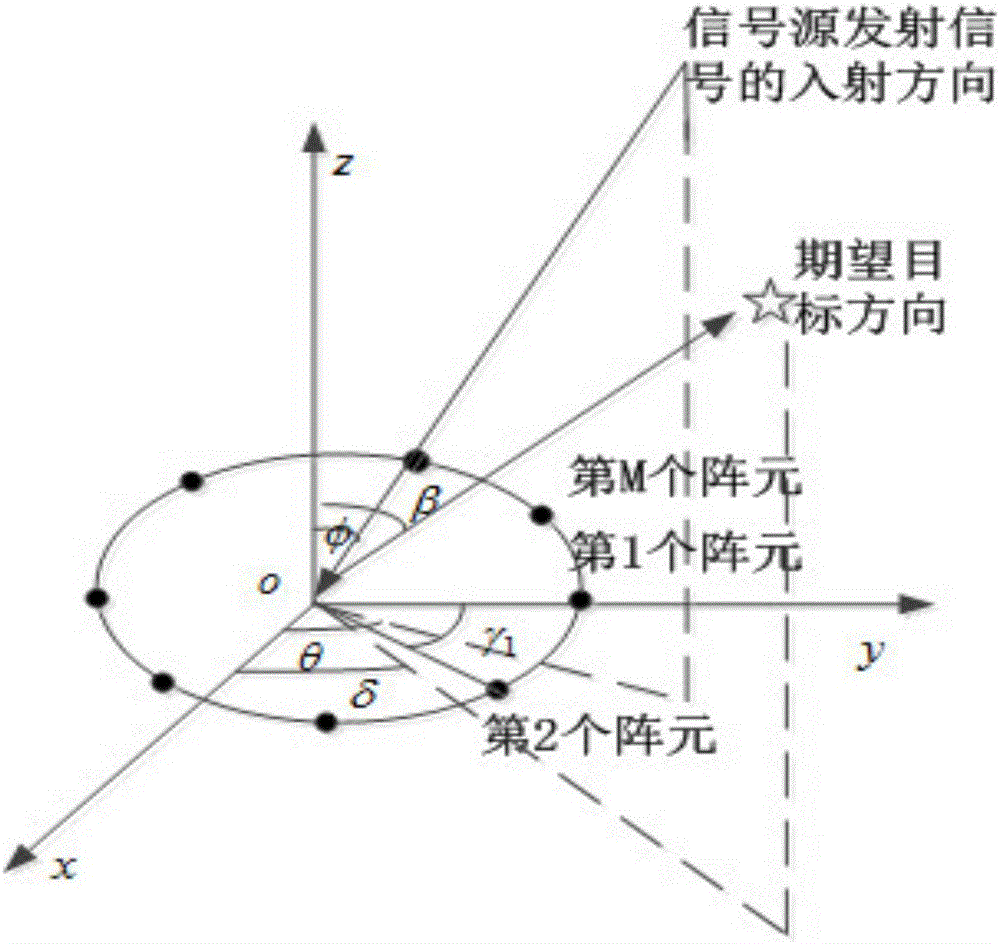
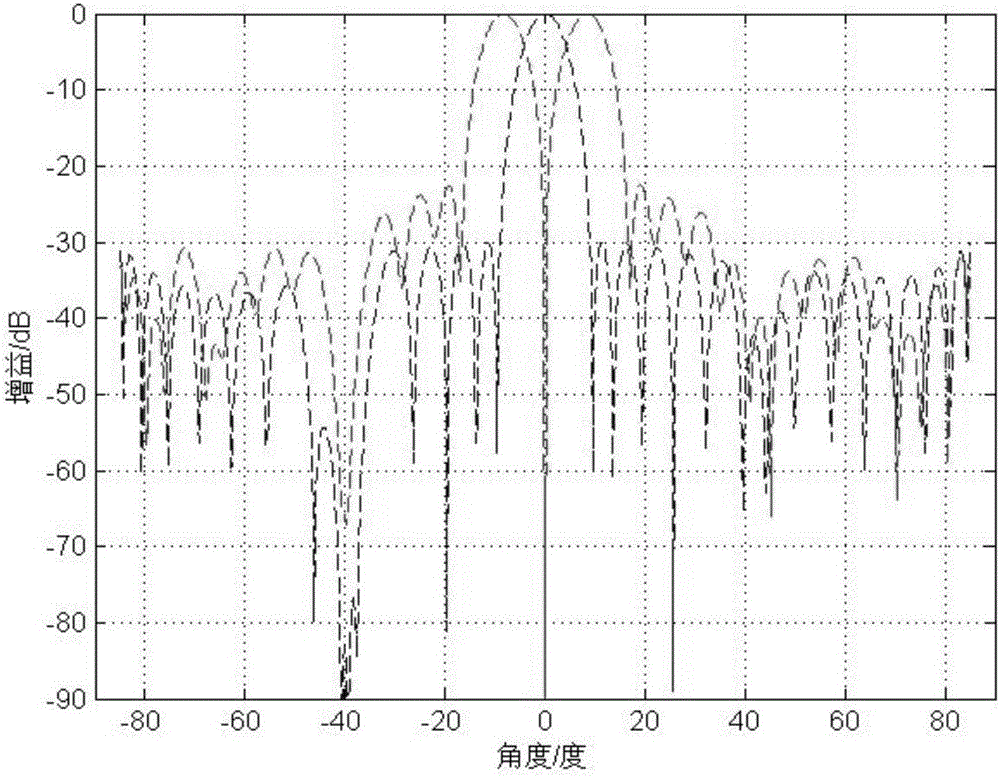
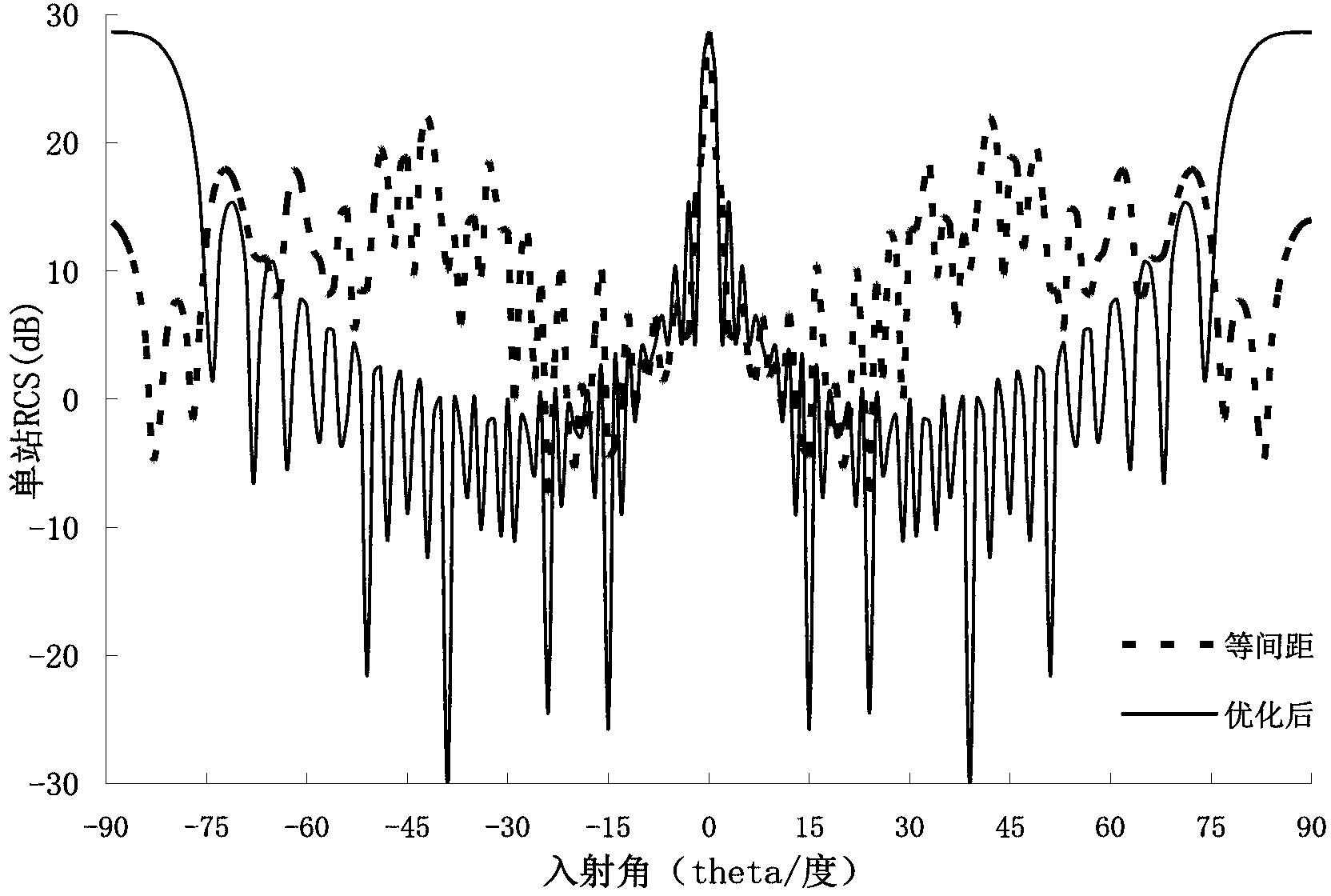
Convex optimization algorithm-based radar array sum-difference beam directional diagram optimization method
ActiveCN106772260AImproved clutter suppression performanceSide lobe lowWave based measurement systemsInternal combustion piston enginesOptimal weightRadar
The invention discloses a convex optimization algorithm-based radar array sum-difference beam directional diagram optimization method. The method comprises the steps of determining that a radar circular array containing M array elements is uniformly distributed on a circumference with the radius being R, and then determining a sum beam main lobe area, a sum beam null steering area, a sum beam side lobe area, a sum beam low side lobe area, a difference beam main lobe area, a difference beam null steering area, a difference beam side lobe area and a difference beam low side lobe area; respectively obtaining a cost function for restraining the sum beam main lobe area and a cost function for restraining the difference beam main lobe area; further obtaining a sum beam directional diagram comprehensive optimization model of the radar circular array and a difference beam directional diagram comprehensive optimization model of the radar circular array, and calculating a radar circular array sum beam optimal weight vector; sequentially obtaining a slope of an angle error normalization curve of an expected target and a curve slope of an angle error curve of a radar circular array sum-difference beam directional diagram to be optimized, and calculating an optimal weight vector of a radar circular array difference beam.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-resolution precondition method for analyzing aerial radiation and electromagnetic scattering
ActiveCN102156764AGood mannersIterative convergence is fastSpecial data processing applicationsLow demandElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a multi-resolution precondition method for analyzing aerial radiation and electromagnetic scattering problems in electromagnetic simulation. The method is a method for generating a multi-resolution basis function by using a geometrical mode on a laminar grid constructed in a grid aggregation mode and further generating multi-resolution preconditions, wherein the multi-resolution basis function is formed by linear combination of a classical vector triangle basis function (RWG), and can be conveniently applied to the conventional moment method electromagnetic simulation program to effectively improve the behavior of a matrix formed in the moment method electromagnetic simulation process so as to realize acceleration of the iterative solution process of a matrix equation and fulfill the purpose of accelerating the moment method electromagnetic simulation process. Meanwhile, the multi-resolution pre-processing technology can also be conveniently combined with a quick algorithm such as a quick multi-pole algorithm. The method has the advantages of short calculation time and capability of ensuring high precision of the program and low demand of a computing memory, and can effectively improve the computing efficiency of the conventional electromagnetic simulation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gradient coil design method in nuclear magnetic resonance system
InactiveCN102096053AArbitrary constraint lengthExcellent design resultMagnetic measurementsLinearitySimulated annealing
The invention discloses a gradient coil design method in a nuclear magnetic resonance system. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a mathematical relation between a field expansion harmonic component and a cylindrical surface current distribution harmonic component under a spherical coordinate system based on a current distribution harmonic component coefficient capable of generating a specific target field through solving; combining the traditional harmonic method with a target field method; and introducing a simulated annealing algorithm to optimize and obtain the global optimum current distribution. The gradient coil design method can be used for designing a self-shielding gradient coil with cylindrical surface current distribution and optionally restraining the coil length, and ensures excellent linearity while the higher coil efficiency is achieved through comprehensively considering a plurality of design indexes. Since the gradient coil design method is optimized by utilizing a global search algorithm-simulated annealing algorithm, a global optimum design result is ensured. Meanwhile the position information of the actual distribution of a current lead is directly output by the design result, therefore, the engineering processing and manufacturing are facilitated.
Owner:SUZHOU LONWIN MEDICAL SYST
Array antenna radar cross section reduction method based on space mapping
InactiveCN103246781AGuaranteed accuracyReduce optimization timeSpecial data processing applicationsScattering cross-sectionFull wave analysis
The invention discloses an array antenna radar cross section reduction method based on space mapping. The array antenna radar cross section reduction method based on the space mapping comprises the steps of establishing an array antenna model, enabling unit amplitude uniform plane wave to illuminate on an array antenna, and determining a total scattering field of the array antenna; deducing a radar cross section formula of the array antenna according to a pattern multiplication, establishing a space mapping rough model of the array antenna, optimizing the rough model and determining an optimum design parameter of the rough model; utilizing a method of moments of a full-wave analysis in a fine model; enabling the response of the rough model to approach that of the fine model through parameter extraction, and establishing a mapping relation of a rough model parameter and a fine model parameter; and utilizing the optimum design parameter of the rough model and the inverse mapping of the established mapping relation to obtain a prediction parameter of the fine model, and if the prediction parameter of the fine model does not meet a design requirement, subjecting the mapping relation to iteration updating until the prediction parameter of the fine model meets the design requirement. The array antenna radar cross section reduction method based on the space mapping subjects the design parameter to a global optimization and saves time under the premise of guaranteeing the accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
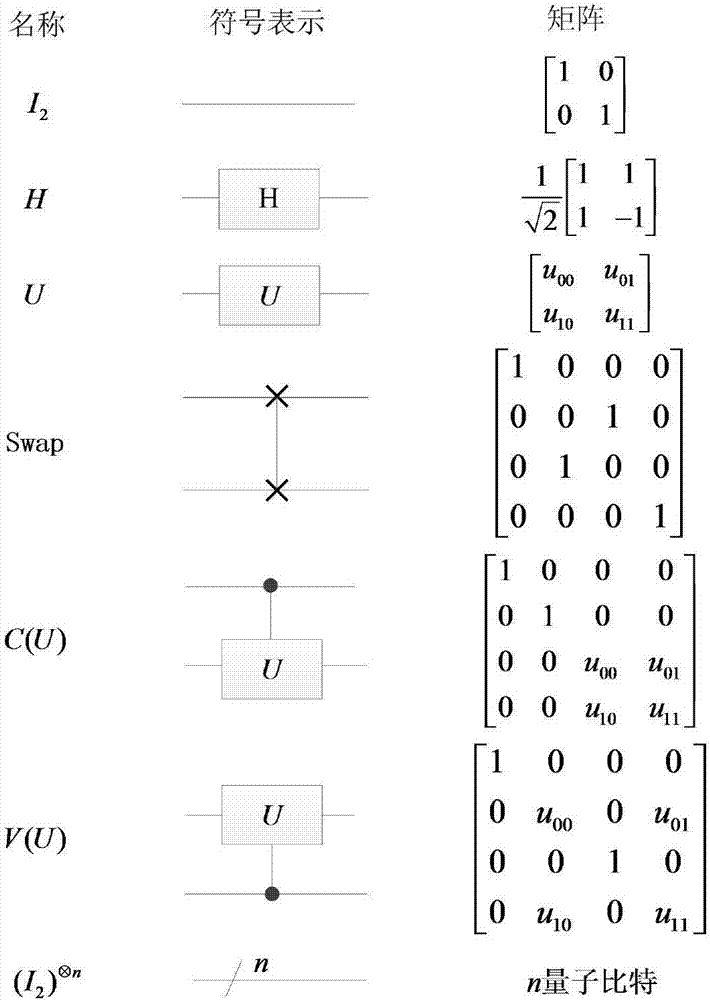
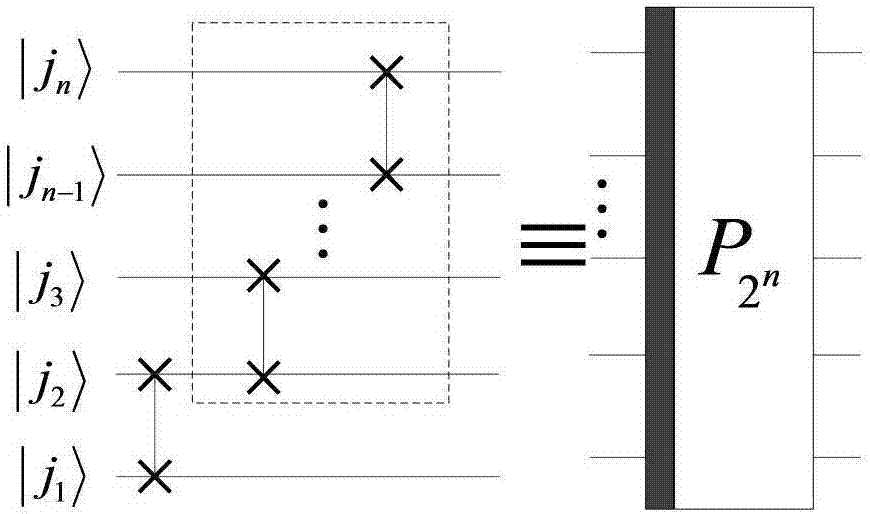
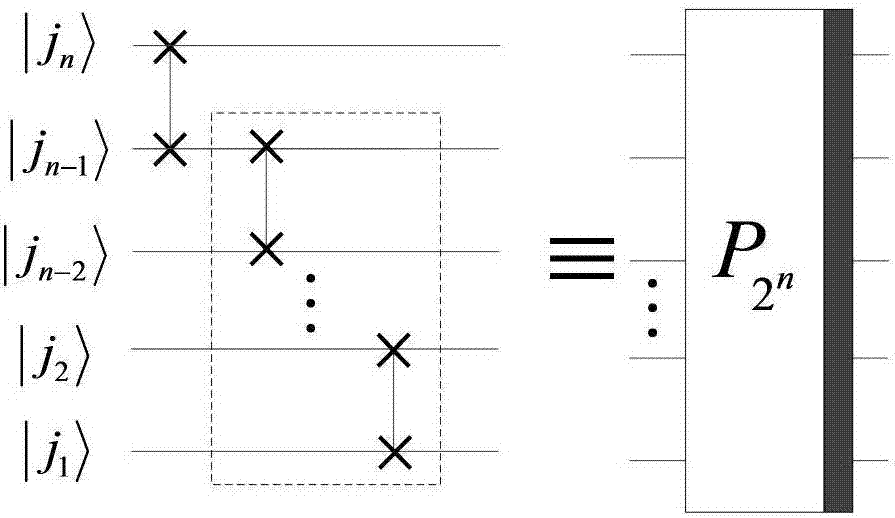
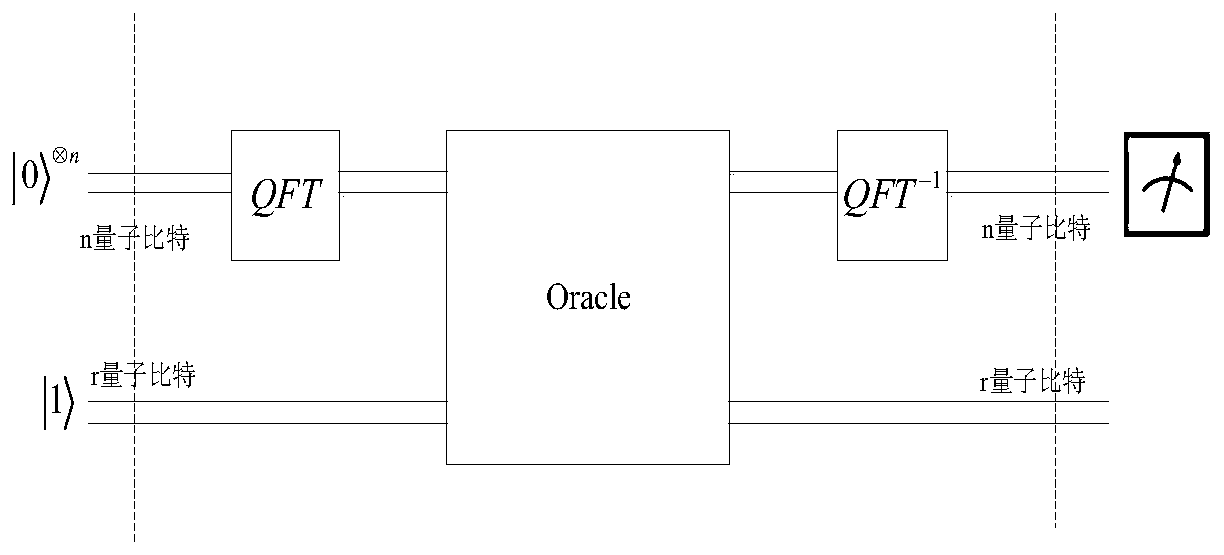
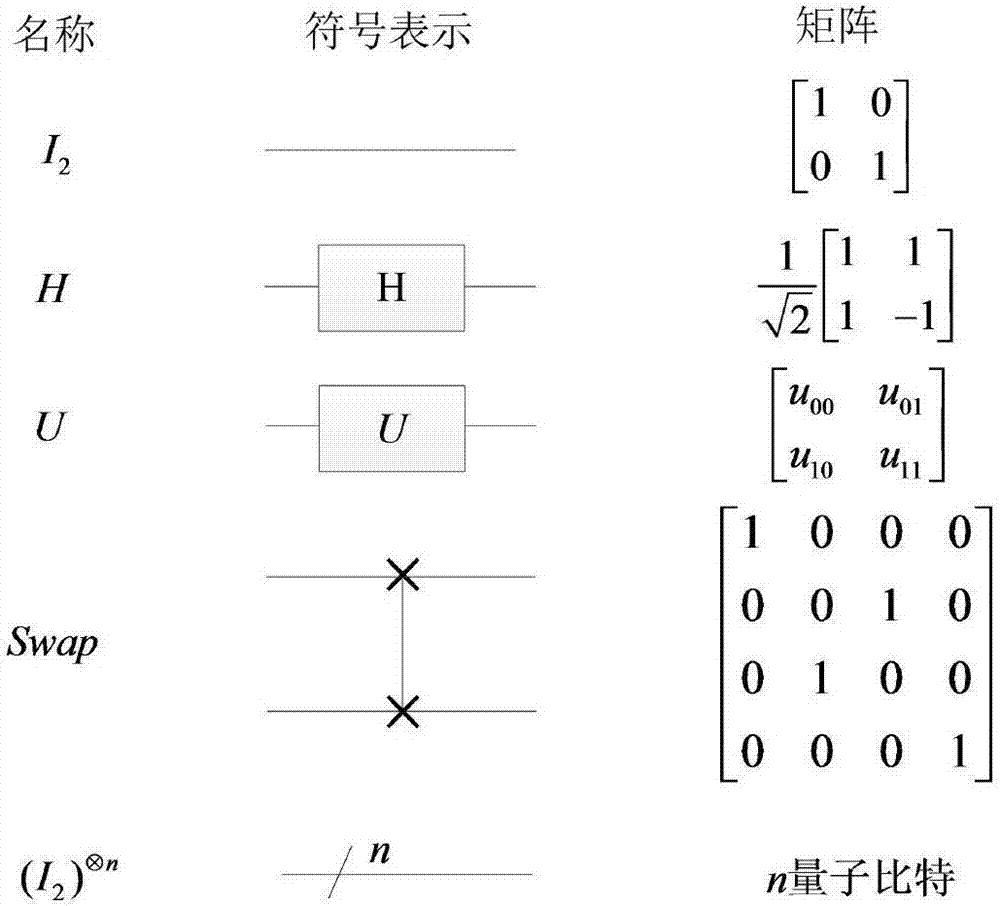
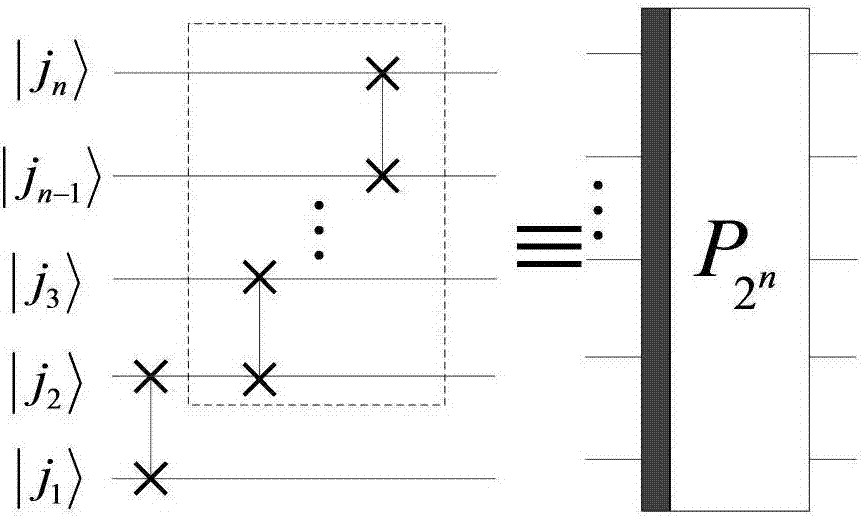
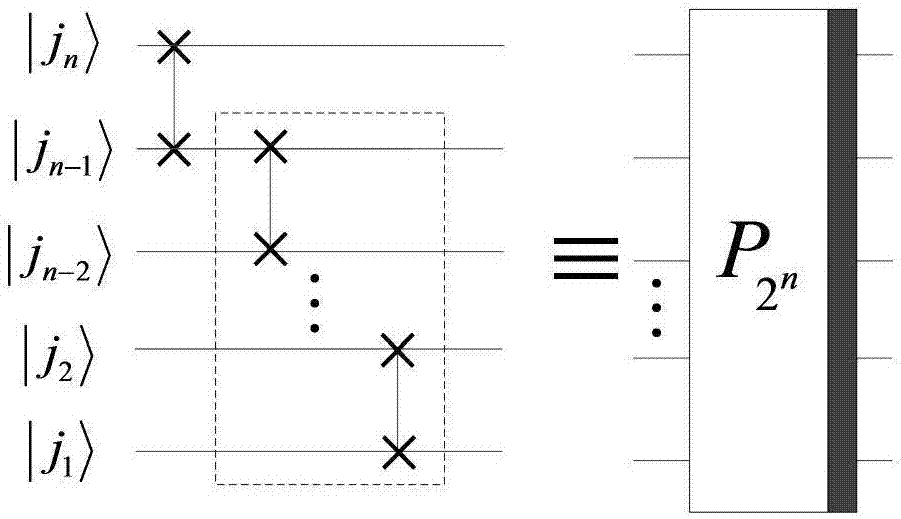
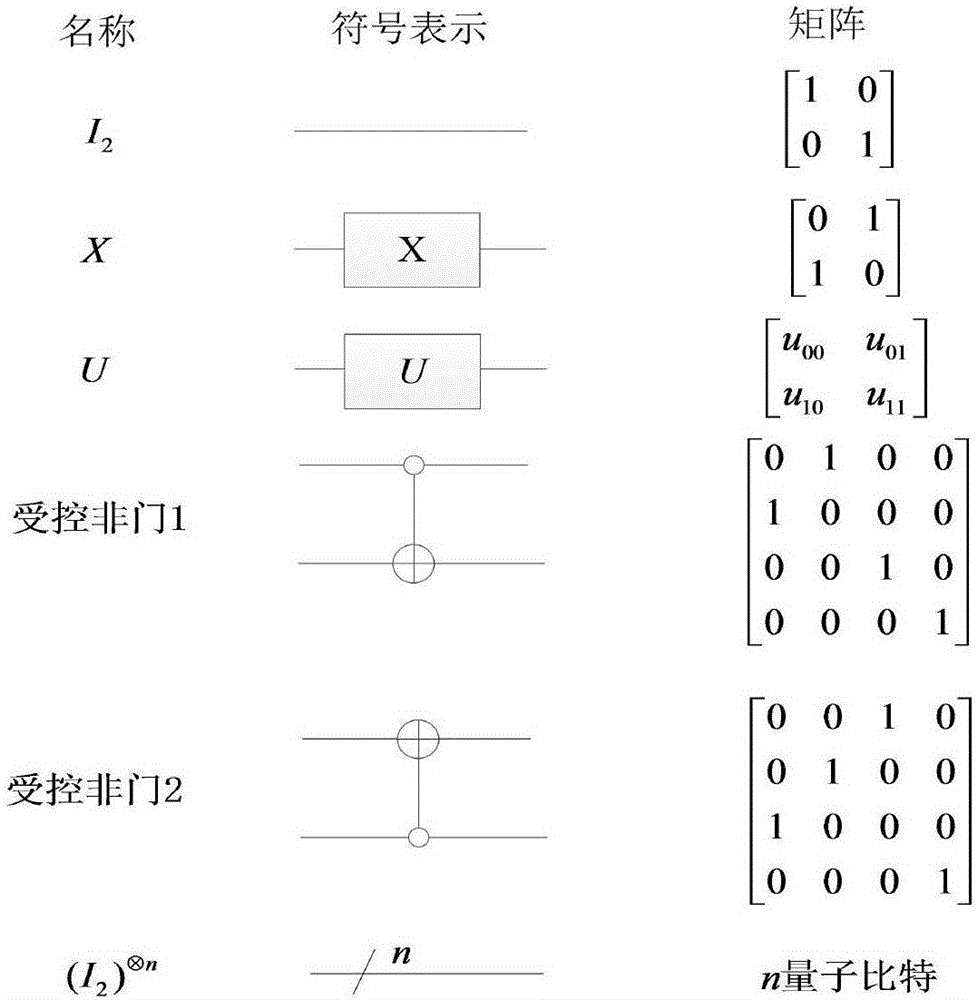
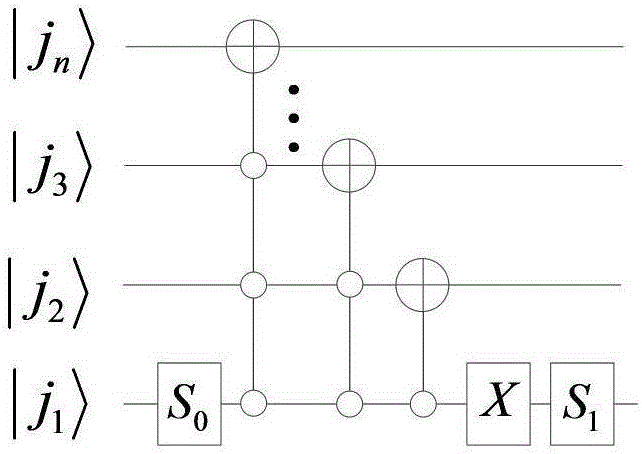
Method for realizing quantum circuit design through quantum Fourier transform
The invention provides a method for realizing quantum circuit design through quantum Fourier transform and belongs to the field of circuit design. A conventional quantum Fourier transform implementation technology is perfected and improved with the method due to the fact that a Bit Reverse circuit is absent in conventional quantum Fourier transform implementation circuits. Four quantum Fourier transform implementation circuits are constructed by an extended tensor product and basic quantum bit gates including quantum bit controlled gates and single quantum bit gates; on the basis of analysis for complexity of the quantum Fourier transform implementation circuits, complexity of the four quantum Fourier transform implementation circuits is theta(n<2>) in terms of a data set comprising 2<n> elements, which cannot be achieved by any other classic fast Fourier transform. The method is suitable for many application fields of actual information processing, for instance, efficient Fourier transform is required for algorithms of image compression, denoising, encryption, decryption and the like, and the method has great significance in perfection of the quantum computing theory and popularization of application.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
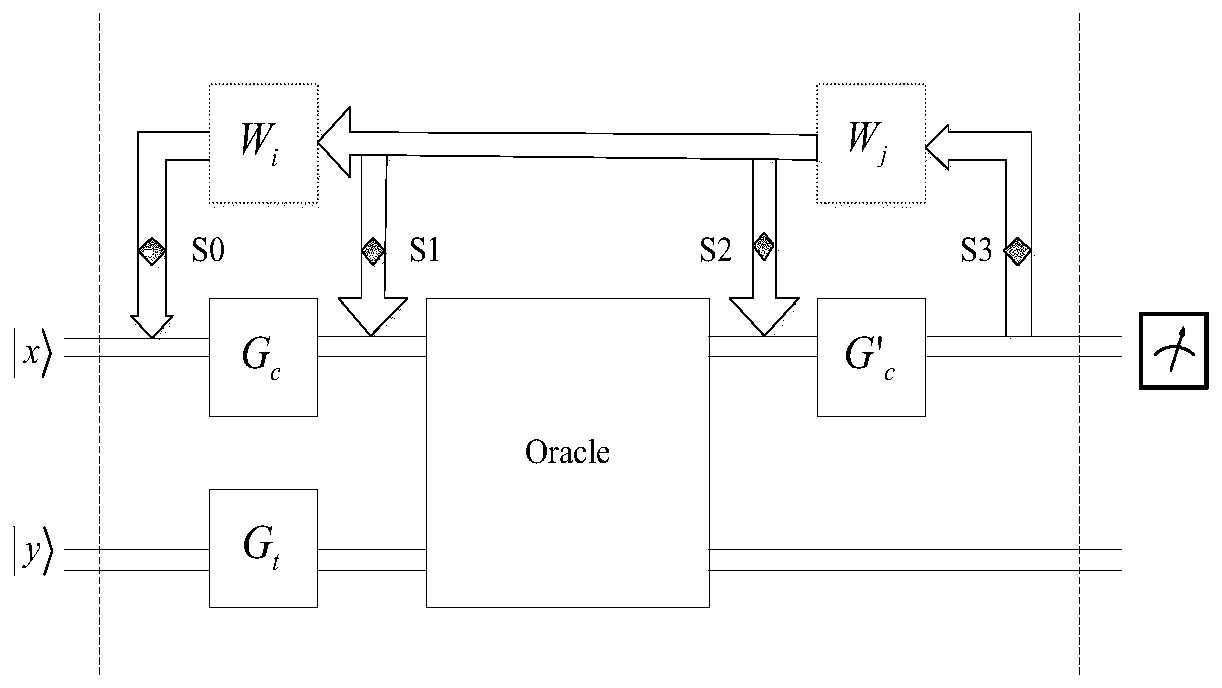
Quantum computer quantum processing unit, quantum circuit and quantum circuit quantum algorithm
ActiveCN110490327AAchieve performanceGuaranteed cycle lookupQuantum computersEnergy efficient computingQuantum circuitDecomposition
The invention relates to a quantum computer quantum processing unit, a quantum circuit and a quantum circuit quantum algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of computers. The quantum processingunit (QPU) is composed of five modules and is controlled by a classic device. The quantum circuit defines two n quantum bit inputs |x) and |y) based on an SHOR algorithm. A control register and a target register are arranged. Gates Gc, G'c and Gt are defined for each algorithm. The quantum circuit quantum algorithm is a design scheme of a quantum processing architecture based on a Shor algorithm.The influence of feedback control on the proposed architecture is considered. The period searching during large number decomposition can be effectively ensured by utilizing feedback adjustment, so that the optimal performance of the quantum algorithm is effectively realized.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Systems, methods, and apparatus for calibrating, controlling, and operating a quantum processor
Quantum annealing may include applying and gradually removing disorder terms to qubits of a quantum processor, for example superconducting flux qubits of a superconducting quantum processor. A problem Hamiltonian may be established by applying control signals to the qubits, an evolution Hamiltonian established by applying disorder terms, and annealing by gradually removing the disorder terms. Change in persistent current in the qubits may be compensated. Multipliers may mediate coupling between various qubits and a global signal line, for example by applying respective scaling factors. Two global signal lines may be arranged in an interdigitated pattern to couple to respective qubits of a communicatively coupled pair of qubits. Pairs of qubits may be communicatively isolated and used to measure a response of one another to defined signals.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
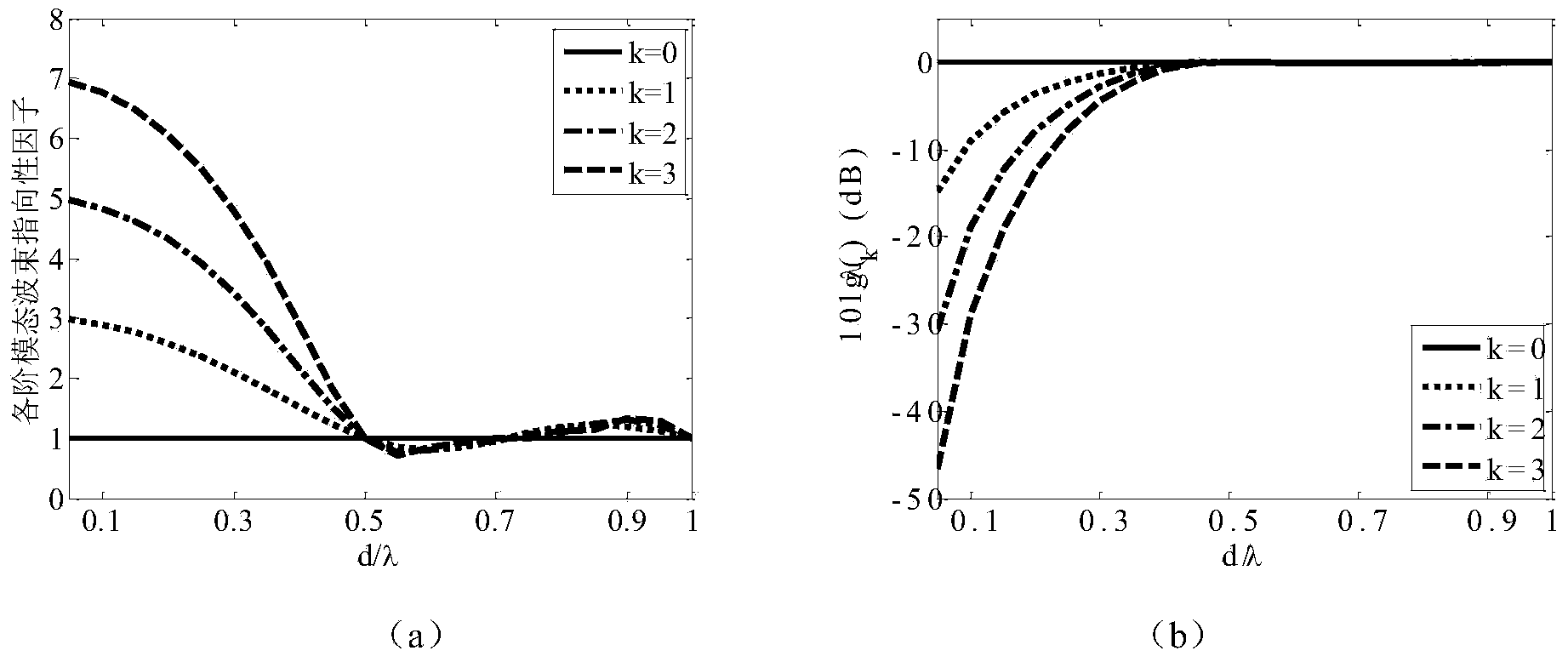
Super-directivity beam forming method based on modal decomposition and synthesis
ActiveCN103902831APrecise recursive calculation formulaEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsGram schmidtOrthogonal transformation
The invention relates to an super-directivity beam forming method based on modal decomposition and synthesis. The super-directivity beam forming method comprises the steps of firstly, decomposing the optimal solution on the basis of the beam forming theory, representing the optimal solution as a matrix form, then utilizing Gram-Schmidt orthogonal transformation for giving a solution formula of a related matrix, and then utilizing the matrix form of the optimal solution for decomposing the optimal beam into various-order modal beams with different directivities and robustness, wherein the factor with the maximum directivity is obtained by overlaying directivity factors of the various-order modal beams. Finally, a uniformity rectilinear figure array is used as an example, and the final robust super-directivity beam is obtained by selecting the proper modal beam to carry out synthesis. According to the super-directivity beam forming method based on modal decomposition and synthesis, the detects that in the prior art, accuracy is not enough, and the application range is limited are overcome according to the characteristics that the optimal solution of the beam forming theory is not limited by the matrix form, and the accurate recursion formula is used for the Gram-Schmidt orthogonal transformation.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for realizing quantum circuit design through quantum Haar wavelet transformation
The invention provides a method for realizing quantum circuit design through quantum Haar wavelet transformation, and belongs to the field of quantum information processing. According to the method, the existing quantum Fourier transform implementing technology is perfected and improved, and implementing circuits of two pieces of multi-layer quantum Haar wavelet transformation and two pieces of multi-layer quantum Haar wavelet inverse transformation are established separately by using extended tensor product and basic quantum bit gate (comprising quantum bit controlled door and single quantum bit gate). Based on analysis of the complex rates of the implementing circuits of the quantum Haar wavelet transformation and the quantum Haar wavelet inverse transformation, the complex rates of the implementing circuits of the two pieces of multi-layer quantum Haar wavelet transformation and the two pieces of multi-layer quantum Haar wavelet inverse transformation are Theta(n2) for one data set with 2n elements, and other typical and rapid Haar wavelet transformation cannot achieve the aim. The method is suitable for the fields of algorithms such as compression, denoising, encryption and decryption of images of actual information processing application, and has important significance in popularization of perfection and application of a quantum computing theory.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
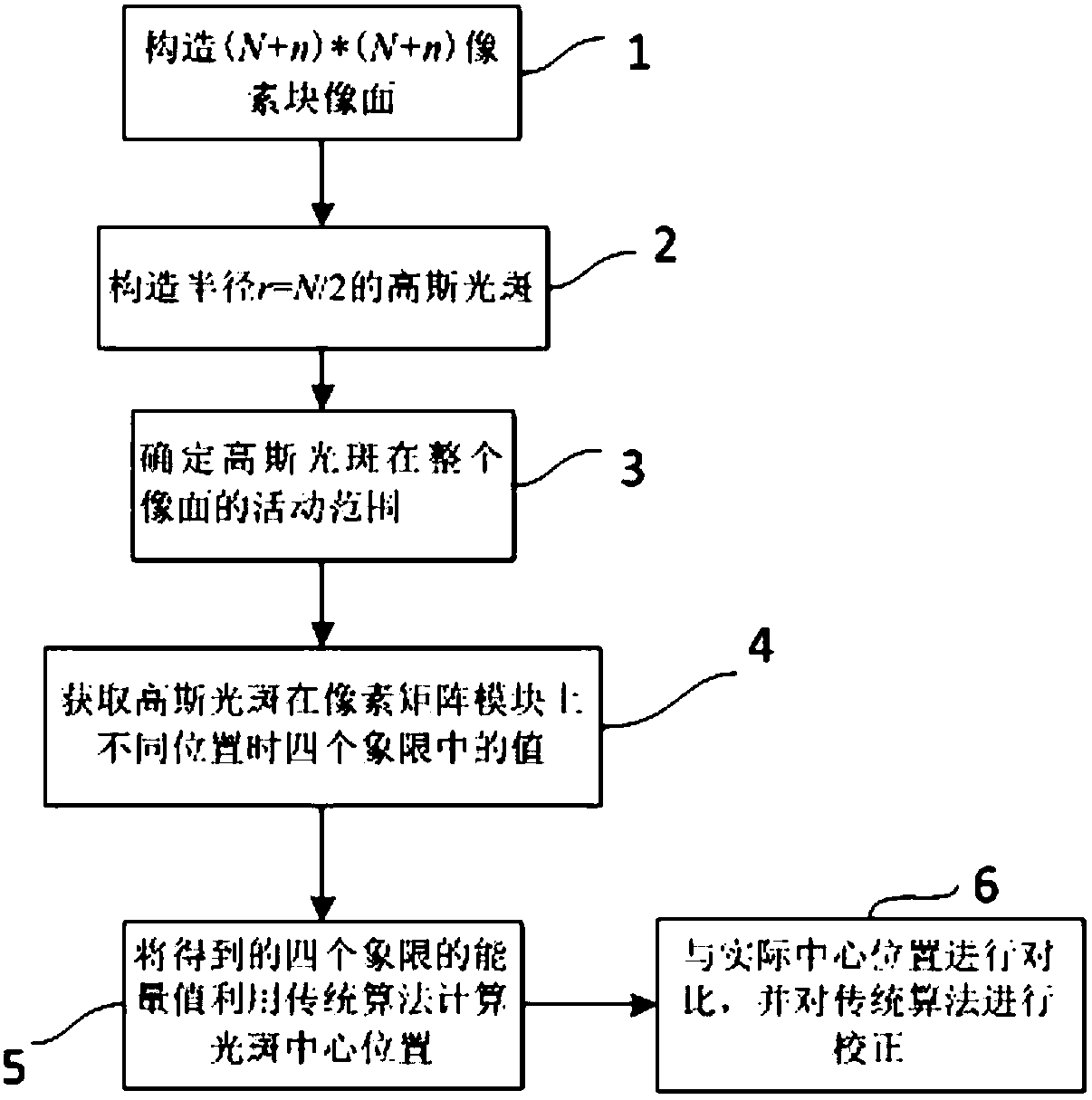
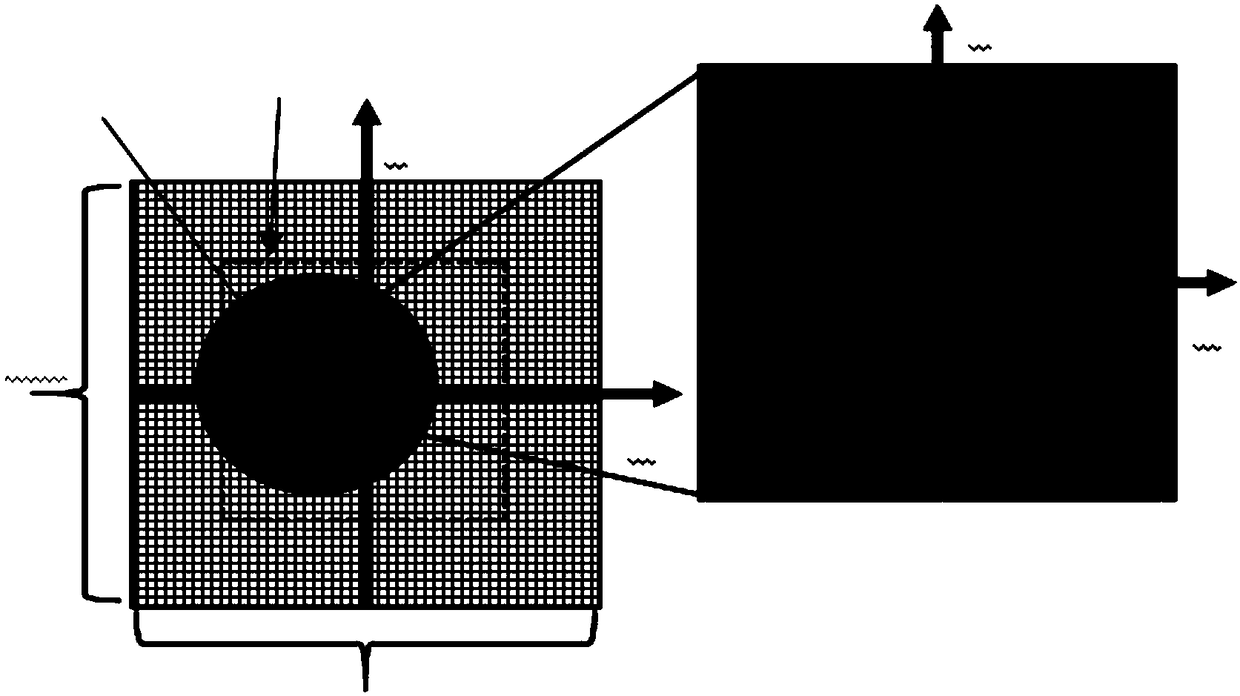
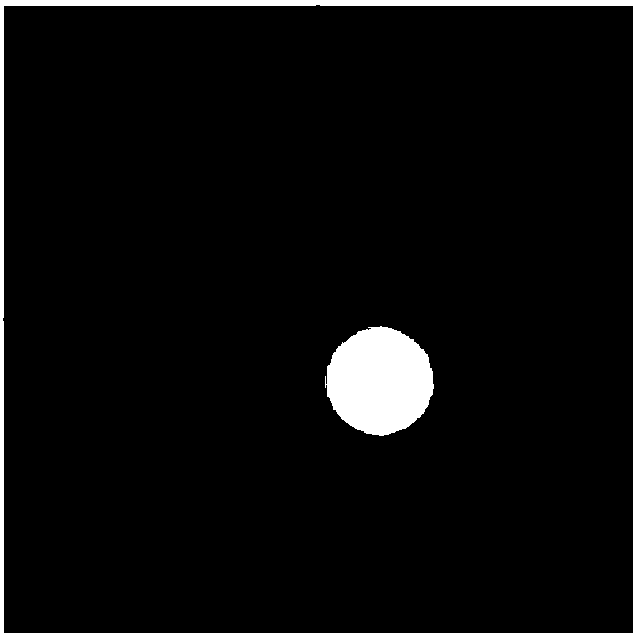
Method for obtaining high-precision positioning of Gaussian beam based on four-quadrant detector
The invention discloses a method for obtaining high-precision positioning of a Gaussian beam based on a four-quadrant detector. The method comprises the following steps: to begin with, establishing apixel matrix module, the initial value of which is 0, according to image plane size of the four-quadrant detector; then, according to a Gaussian distribution function, establishing a light spot, the energy of which obeys the Gaussian distribution, to simulate imaging information of the Gaussian beam on the image plane of the four-quadrant detector after passing through an optical system; obtainingvalues of the Gaussian light spot in four quadrants at different positions within a certain range on the pixel matrix module respectively; calculating a theoretical light spot center coordinate basedon the four values by utilizing a conventional positioning algorithm; and finally, carrying out comparison analysis on the theoretical center coordinate and actual center coordinate, and obtaining ahigh-precision positioning algorithm through a polynomial fitting method. The obtained Gaussian beam positioning algorithm has the advantages of high precision, fast processing speed and high resolution and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
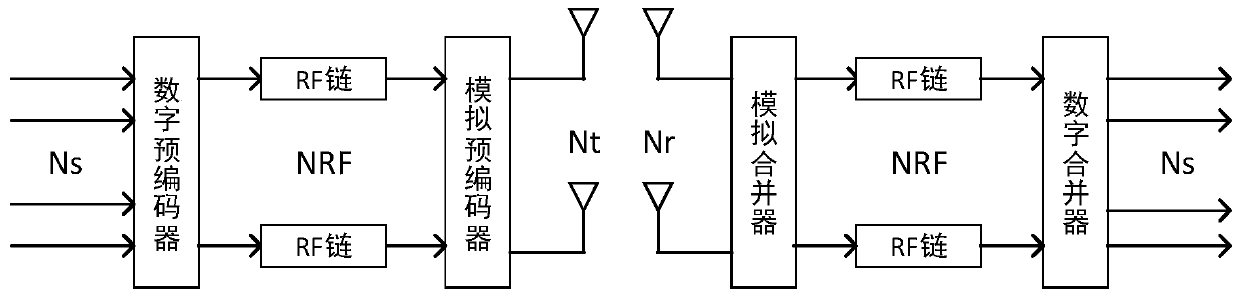
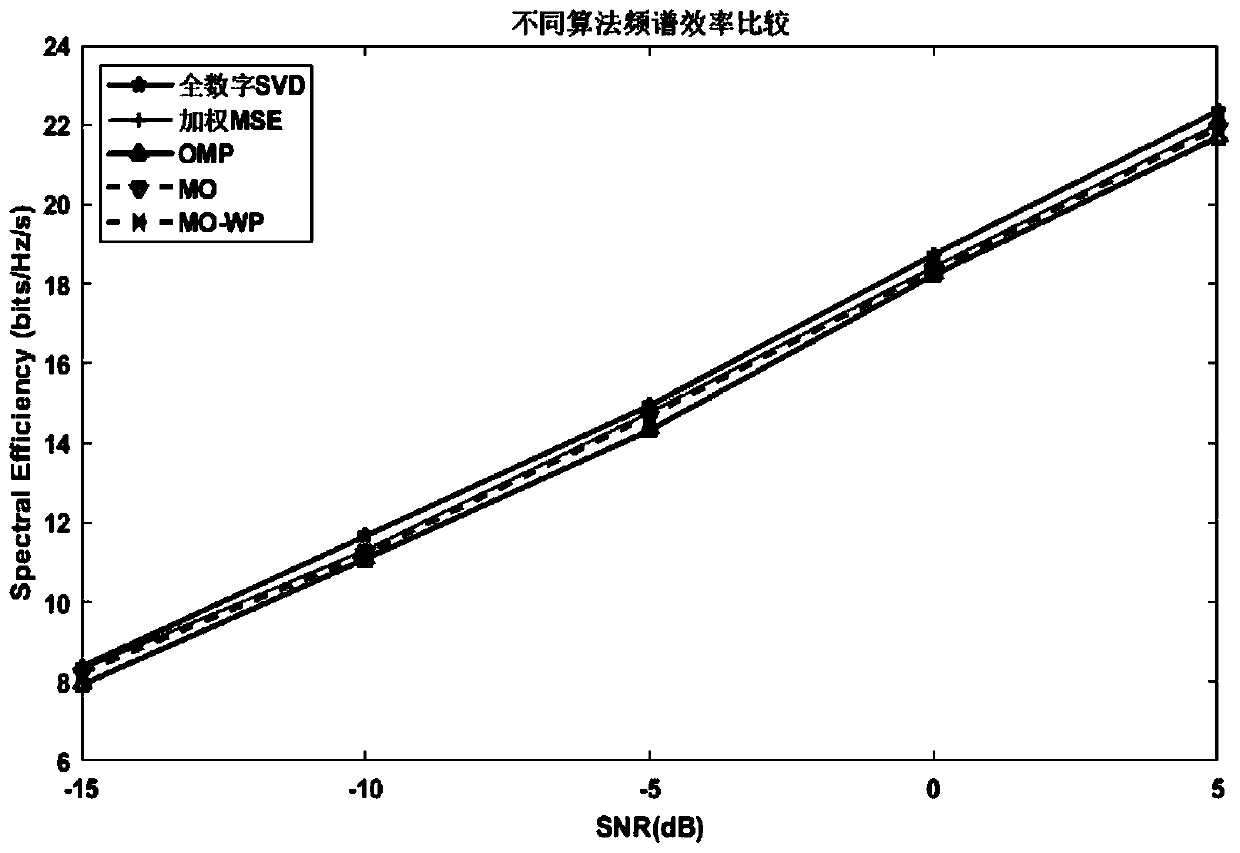
Millimeter wave hybrid analog/digital beam forming method based on improved Riemann manifold optimization
InactiveCN110611526AReduce bit error rateReduce complexityRadio transmissionHybrid beamformingFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a millimeter wave hybrid analog / digital beam forming method based on improved Riemann manifold optimization. The millimeter wave hybrid analog / digital beam forming method comprises the following steps of projecting conjugate gradients to a tangent space to obtain Riemann gradients; searching a point in the tangent space along the Riemann gradient, determining a step lengthby using a Wolfe-Powell criterion, and backtracking the search point to the Riemann manifold; and when a stop condition is met, obtaining an analog beam forming matrix and a digital beam forming matrix through calculation. According to the method, while the algorithm complexity is reduced, the problem that minimum points are missed in the search process is avoided, so that the calculation time isgreatly shortened, the bit error rate is reduced, and the problems that the full-digital beam forming spectral efficiency cannot be achieved through hybrid beam forming and the algorithm complexity istoo high are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Optimization method of traveling-wave tube beam wave interaction distribution structure
The invention discloses an optimization method of a traveling-wave tube beam wave interaction distribution structure. The optimization method of the traveling-wave tube beam wave interaction distribution structure aims to improve the optimization efficiency of a traveling-wave tube beam wave interaction optimization algorithm. The optimization method combines the optimization algorithm with the internal mechanism of beam wave interaction and relates to a nest algorithm, through the beam wave interaction process sequencing computation characteristic and whether the relative phase angle phi meets the condition that phi > pi / 2 or phi < -pi / 2, computation is ended in advance. For an ordinary high-efficiency screw pitch distribution structure, the efficiency of the optimization method is improved by three to four times compared with an ordinary optimization method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
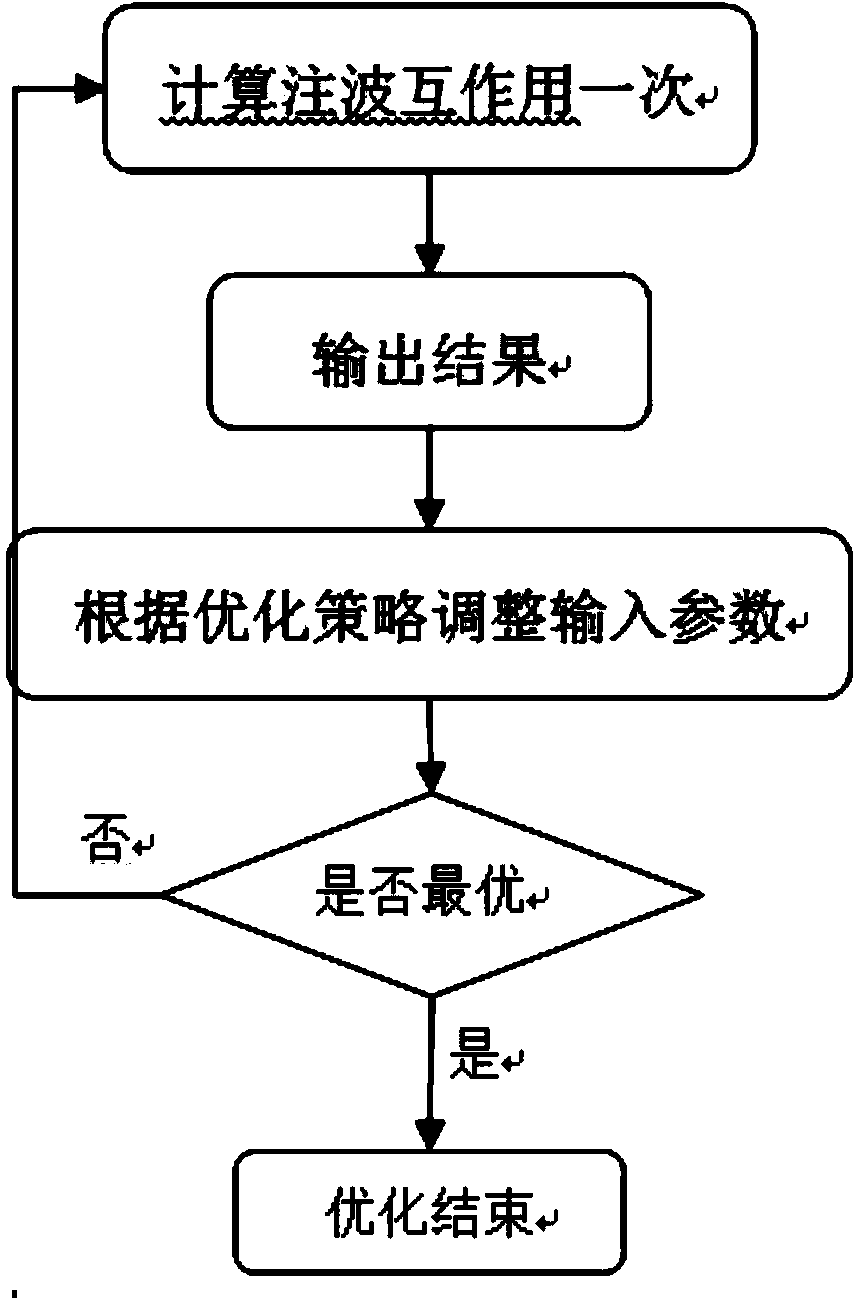
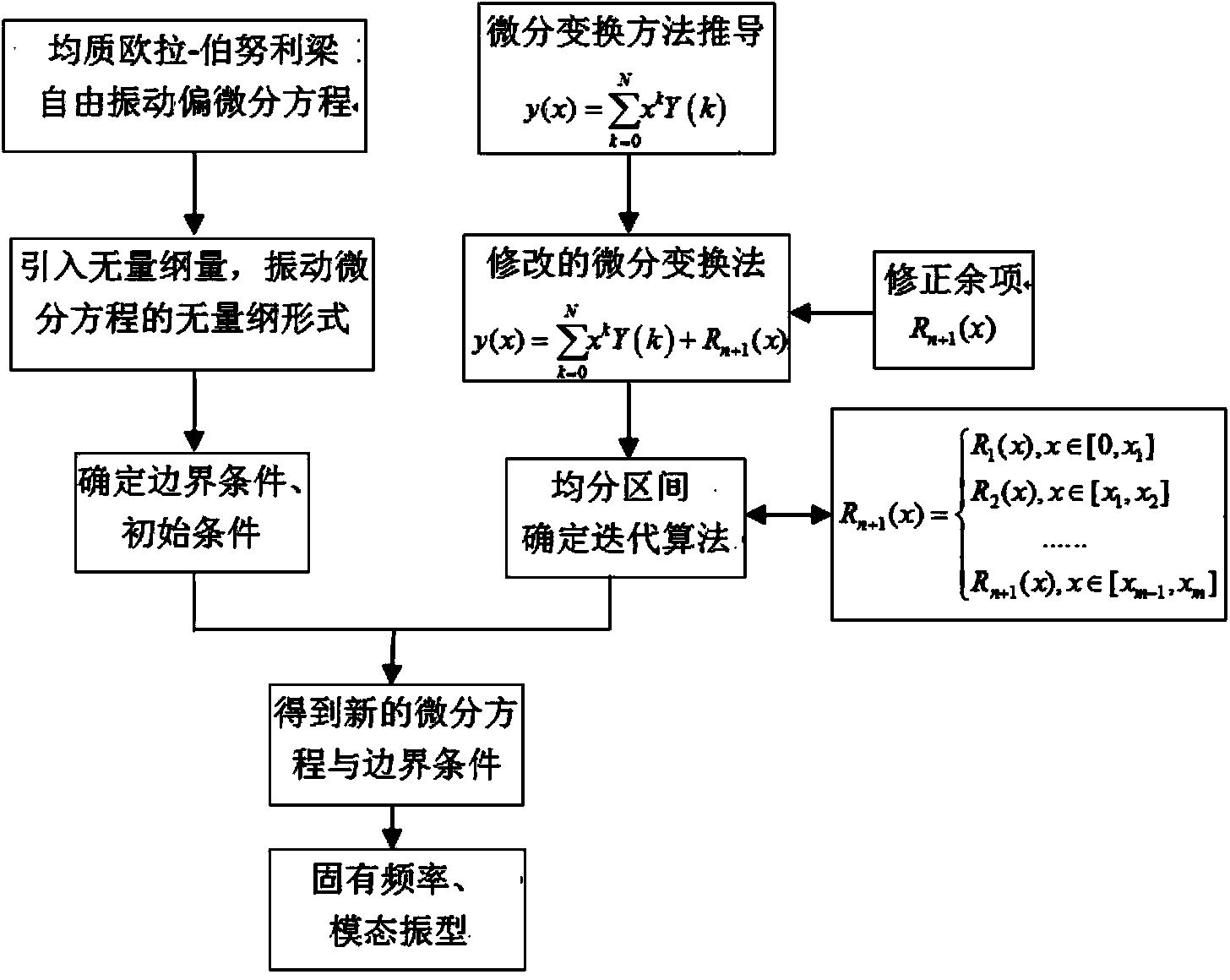
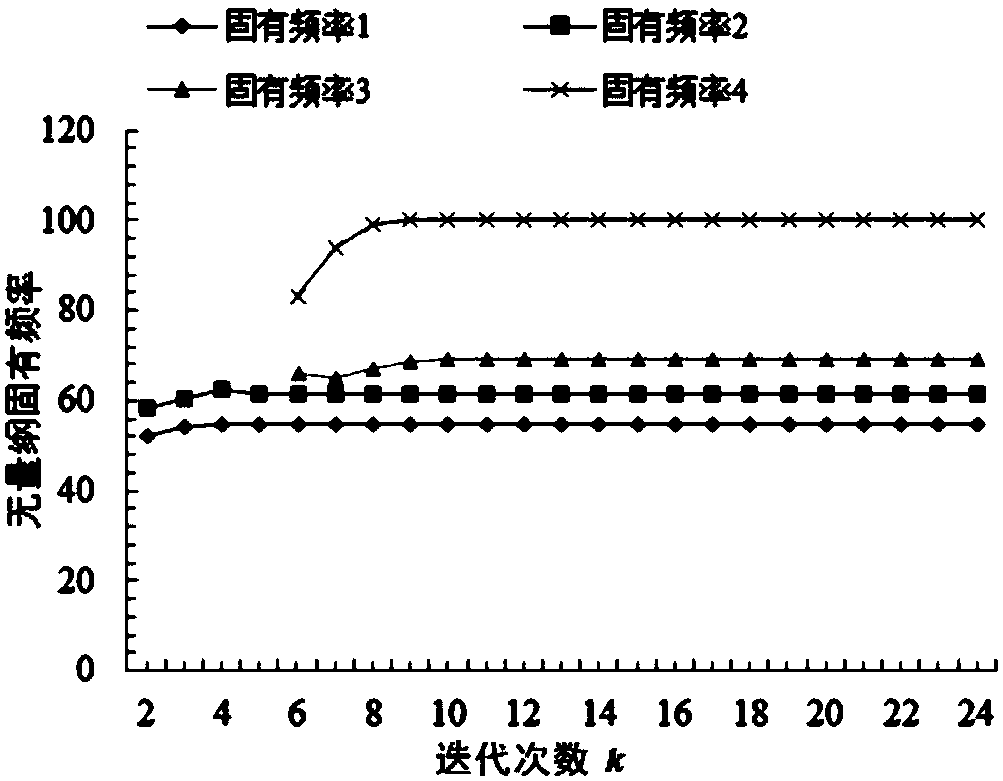
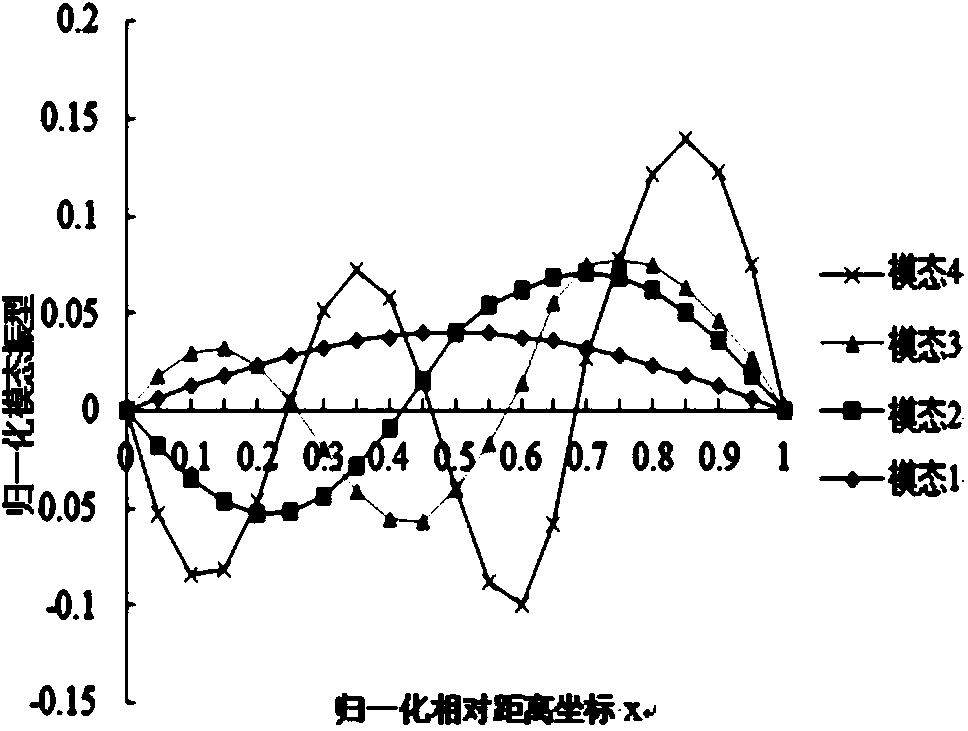
Method for calculating inherent frequency of Euler-Bernoulli beam through improved differential transformation method
InactiveCN103902504ASolve problems such as computational complexityThe calculation process is fast and accurateComplex mathematical operationsDifferential transform methodAlgebraic equation
The invention relates to a method for calculating the inherent frequency of a Euler-Bernoulli beam through an improved differential transformation method. The method comprises the steps that the improved differential transformation method is deduced on the basis of a differential transformation method; a corresponding oscillatory differential equation is built, the improved differential transformation method is used for solving the free vibration problem of the homogeneous Euler-Bernoulli beam with two freely-supported ends, a control differential equation is converted into an algebraic equation, and boundary conditions are changed to an algebraic frequency equation convenient to calculate; corresponding algebraic operation is carried out to obtain the inherent frequency and the modal shape of any order of the differential equation. According to the method for calculating the inherent frequency of the Euler-Bernoulli beam through the improved differential transformation method, the improved differential transformation method is used for solving the free vibration problem of the homogeneous Euler-Bernoulli beam, an approximate solution of a nonlinear problem is obtained in the mode that iteration is carried out to converge the series, closed-form solutions such as the four-order inherent frequency and the modal shape are obtained, the solution of a Taylor expansion power series can be converged at a larger time interval, and the calculation process is rapider and more accurate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
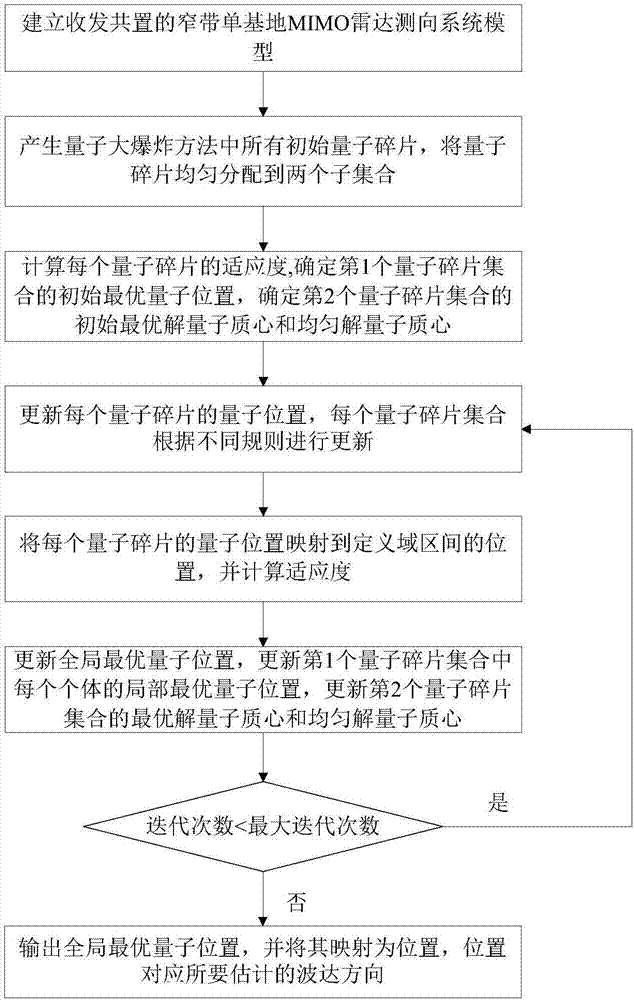
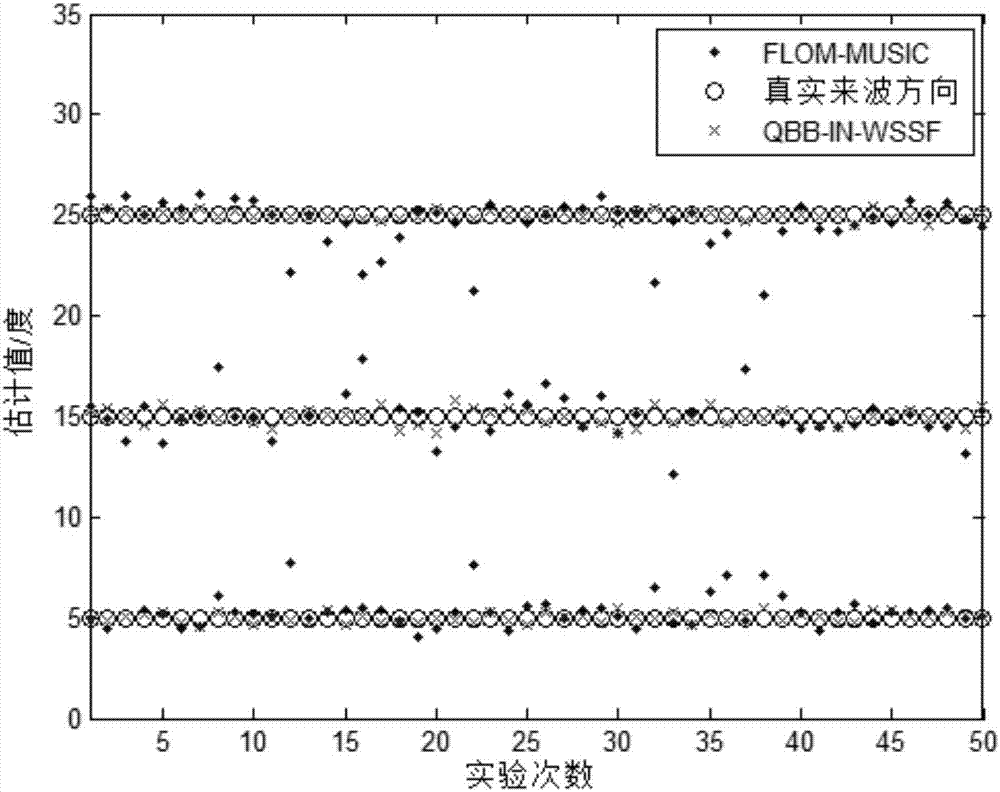
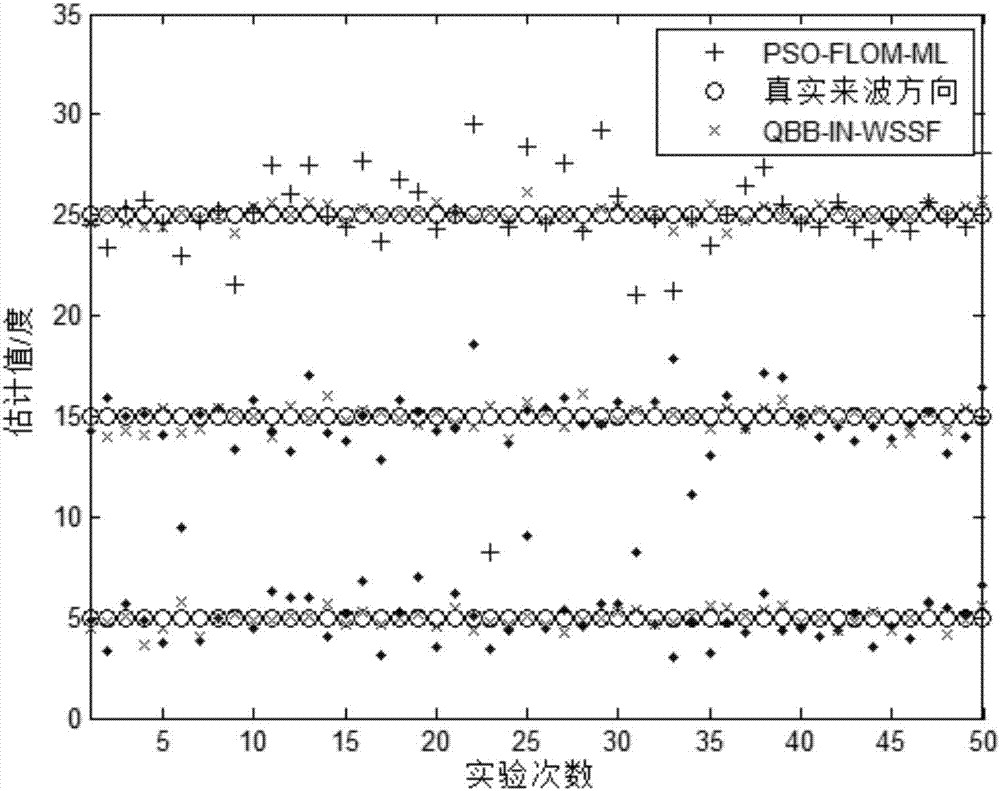
Monostatic MIMO radar direction finding method for quantum explosion
ActiveCN107290732ASolve the problem of robust and high-precision direction findingExcellent direction finding performanceWave based measurement systemsMulti inputRadar
The invention provides a monostatic MIMO (Multi-Input Multi-Output) radar direction finding method for quantum explosion. The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing a transceiving co-located narrowband monostatic MIMO radar system direction finding model; (2) determining all quantum fragments in a quantum explosion algorithm, and uniformly allocating the quantum fragments to two subsets; (3) calculating the adaptability of each quantum fragment, and determining the initial optimal quantum position of the first quantum fragment set, and the initial optimal solution quantum centroid and uniform solution quantum centroid of the second quantum fragment set; (4) updating the quantum position of each quantum fragment; (5) mapping the quantum position of each quantum fragment to the position of a defined interval, and calculating the adaptability value; (6) updating a global optimal quantum position; and (7) outputting the global optimal quantum position, and mapping the global optimal quantum position to the wave arrival direction to be estimated. The method can realize fast and high-precision direction finding under the complex environment of impulse noise and the like, and has excellent direction finding performance.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
System and method for determining beam power level along an additive deposition path
ActiveUS9573224B2High frequencyIncrease the number ofAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyEnergy balancingMelting tank
A power schedule calculation method utilizes an idealized geometry to predict laser power levels on an additive path during laser deposition. The method calculates beam power for any point along the path traveled to form a build having a geometry. Each point along the path has associated with it an idealized geometry comprising a melt pool, hot zone and bulk portion. The method comprises creating a geometric description representing the geometry of the build during the process, creating a path description representing the path of the beam source through space during the process, calculating the idealized geometry for the point on the path based upon the geometric description and path description, calculating an energy balance at the melt pool for the point on the path, calculating total energy needed at the point on the path and calculating optimum beam source power. In the calculations, build temperature is based upon a calculation of hot zone temperature derived from the idealized geometry.
Owner:PROD INNOVATION & ENG L L C
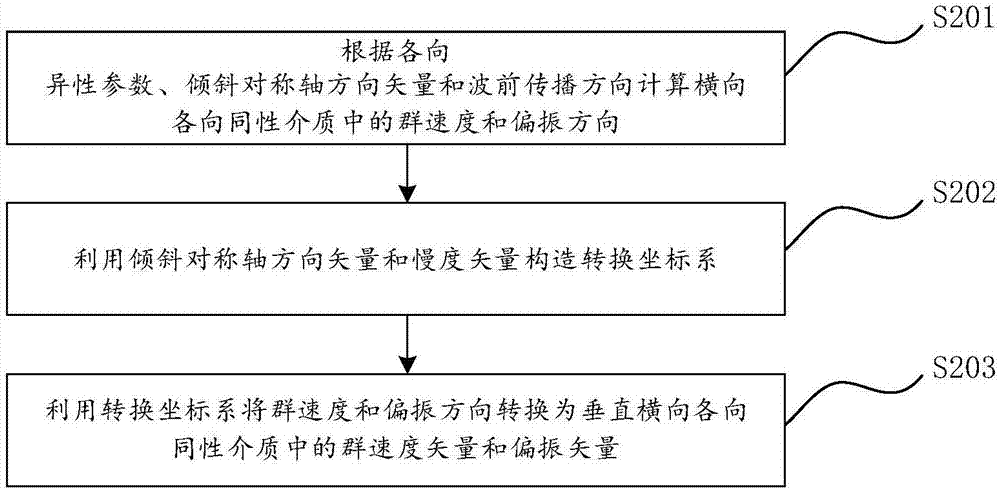
Elastic Gaussian beam migration imaging method and system
The present invention provides an elastic Gaussian beam migration imaging method and a system. The method includes the steps of acquiring the initial parameter information and a multi-component seismic record, and determining the half width of a Gaussian window and the coordinate position of a beam center point; within the range of the Gaussian window of each beam center point, decomposing the multi-component seismic record to obtain a multi-component locally plane wave; based on a wave-type separation matrix, converting the multi-component locally plane wave into a multi-wave type scalar local plane wave; shooting Gaussian beams in different directions, calculating an expression in the vector form, the complex travel time of Gaussian beams and the complex amplitude thereof; based on a wave-field migration imaging formula, calculating the summing superimposition of imaging points according to the scalar local plane wave, the complex travel time and the complex amplitude; modifying the beam center point and the shot gather so as to obtain the migration imaging through iterative computation. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the complete and effective 3D elastic Ti-medium multi-component Gaussian beam migration method is designed. In the vector representation form, wave-field propagation properties are described. Therefore, a reasonable migration imaging formula is provided. The method and the system are high in applicability.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
Design method for quantum multiplier
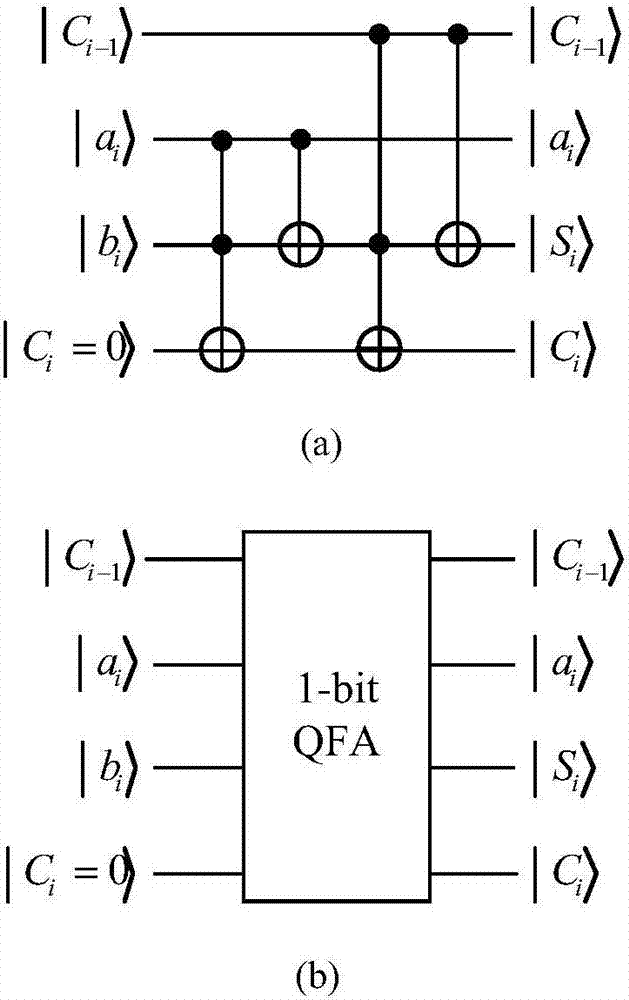
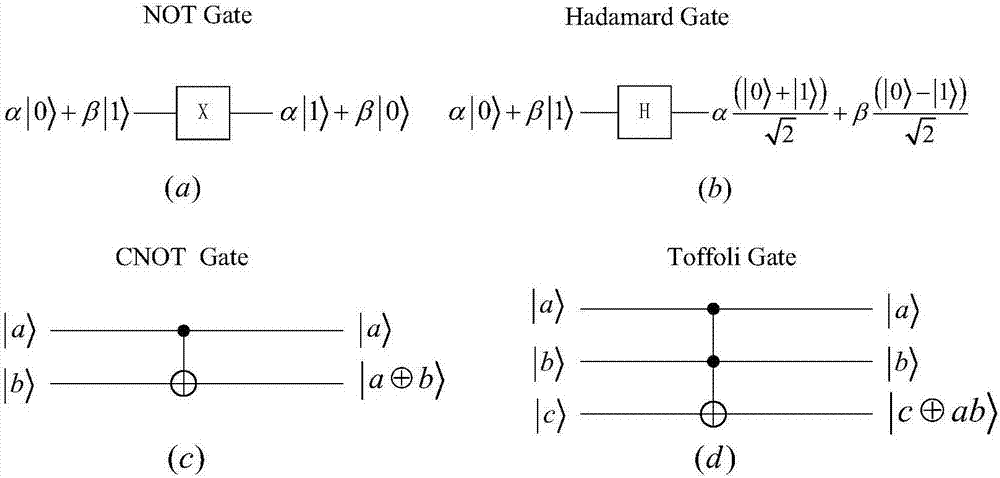
ActiveCN107066234AEfficient designSave resourcesDigital data processing detailsRight shiftDesign methods
The invention discloses a design method for a quantum multiplier. The design method comprises the following steps of 1, designing a one-bit quantum full adder by utilizing a quantum gate, and superposing n one-bit quantum full adders together for designing a n-bit quantum full adder, thereby realizing a sum of two n-bit binary numbers; 2, designing a zero setting circuit by utilizing two controlled-NOT gates, and designing a quantum right shift operator by using the zero setting circuit; and 3, improving a binary number multiplication step, and designing the quantum multiplier by using the quantum full adder and the quantum right shift operator according to the improved binary multiplication step. According to the method, the blank of the quantum multiplier in algorithm design is successfully filled up; and the efficient quantum multiplier is designed.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Quick calculation method for terahertz band surface rough target electromagnetic scattering
ActiveCN104992035ASave storage spaceScatter fastSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfaceTarget surface
The invention proposes a quick calculation method for terahertz band surface rough target electromagnetic scattering. The method is a patch grading semi-deterministic target modeling method, and in the method a full-wave theory proposed by E.Bahar for the rough surface scattering problem is used to implement electromagnetic scattering calculation of surface rough target. The patch grading based semi-deterministic target modeling method can satisfy a requirement that a shape of a target are depicted and rough features of the target surface are reflected, and meanwhile, can reduce storage space occupied by a target model. The full-wave theory based rough surface quick calculation method has good adaptability to roughness parameters in a relatively wide range, and is high in calculation efficiency, thereby implementing quick calculation of a rough target scattering.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for calculating load coefficient of uniform cross-section and simply-supported beam under action of blast load
ActiveCN109580193AThe calculated value is accurateReliable calculationMachine part testingBlast loadLoad model
The invention discloses a method for calculating a load coefficient of a uniform cross-section and simply-supported beam comprising near-field blast and far-field blast. The method comprises the stepsof: firstly, establishing a uniform load model of a uniform cross-section and simply-supported beam under the action of near-field blast and far-field blast, and establishing a coordinate by taking the mid-span position of the uniform cross-section and simply-supported beam as the coordinate origin, the horizontal rightward parallel beam direction as the x axis direction and the direction vertical to the x axis direction as the y axis direction; and, selecting the mid-span cross section of the uniform cross-section and simply-supported beam as an observation position, wherein constraint conditions of two end parts of the uniform cross-section and simply-supported beam are same, solving a first-order vibration mode function by adopting Taylor's third-order substitution, selecting a typicalblast impact wave overpressure peak parameter value and an explosive equivalent, and thus, determining the blast load coefficient of the uniform cross-section and simply-supported beam comprising near-field blast and far-field blast. A uniform calculation formula obtained by the method can provide relatively accurate calculation numerical value for structural design calculation; and the design risk due to ignoring of the near-field blast in the traditional method can be reduced.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Near field source direction finding method based on quantum whale optimization mechanism
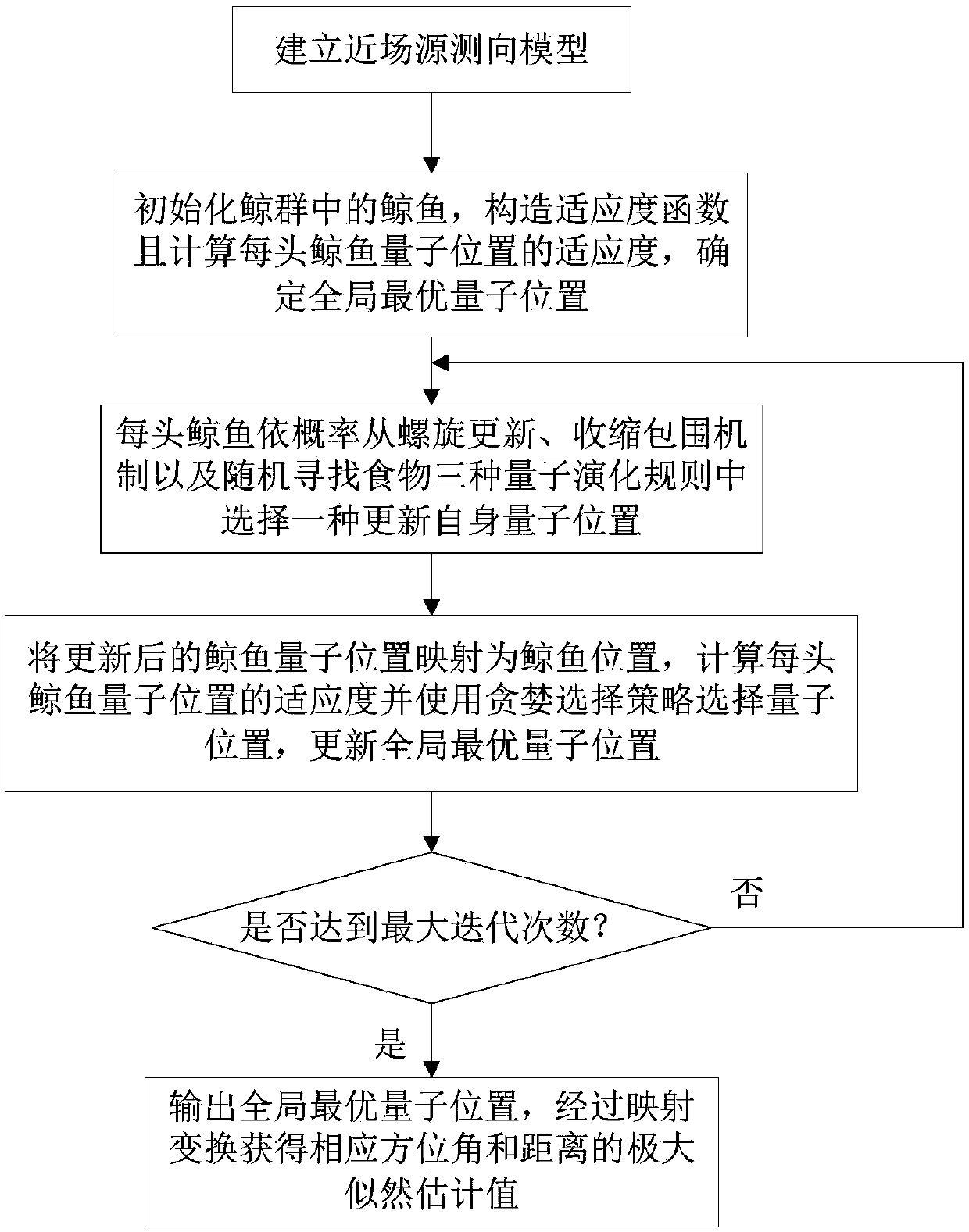
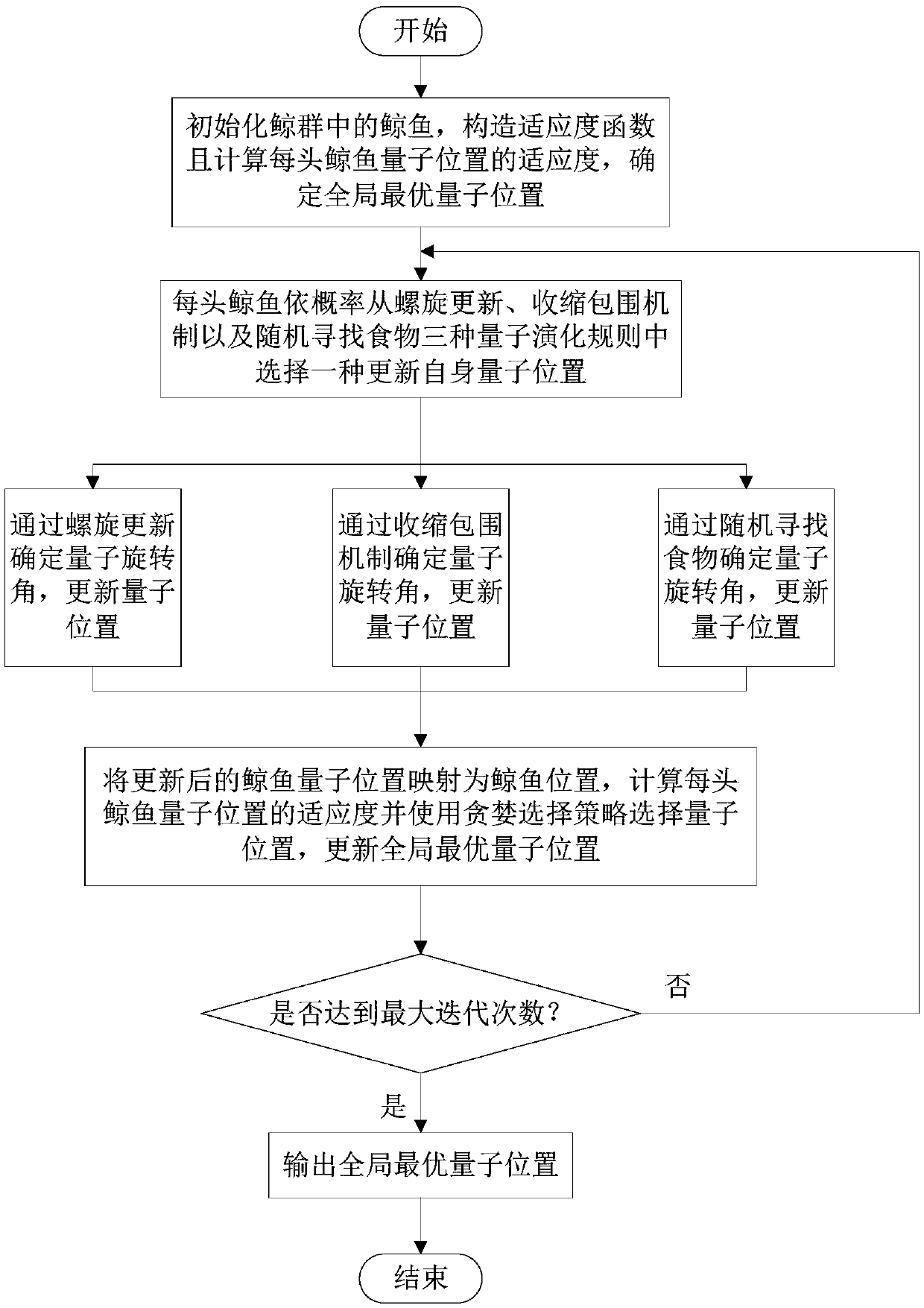
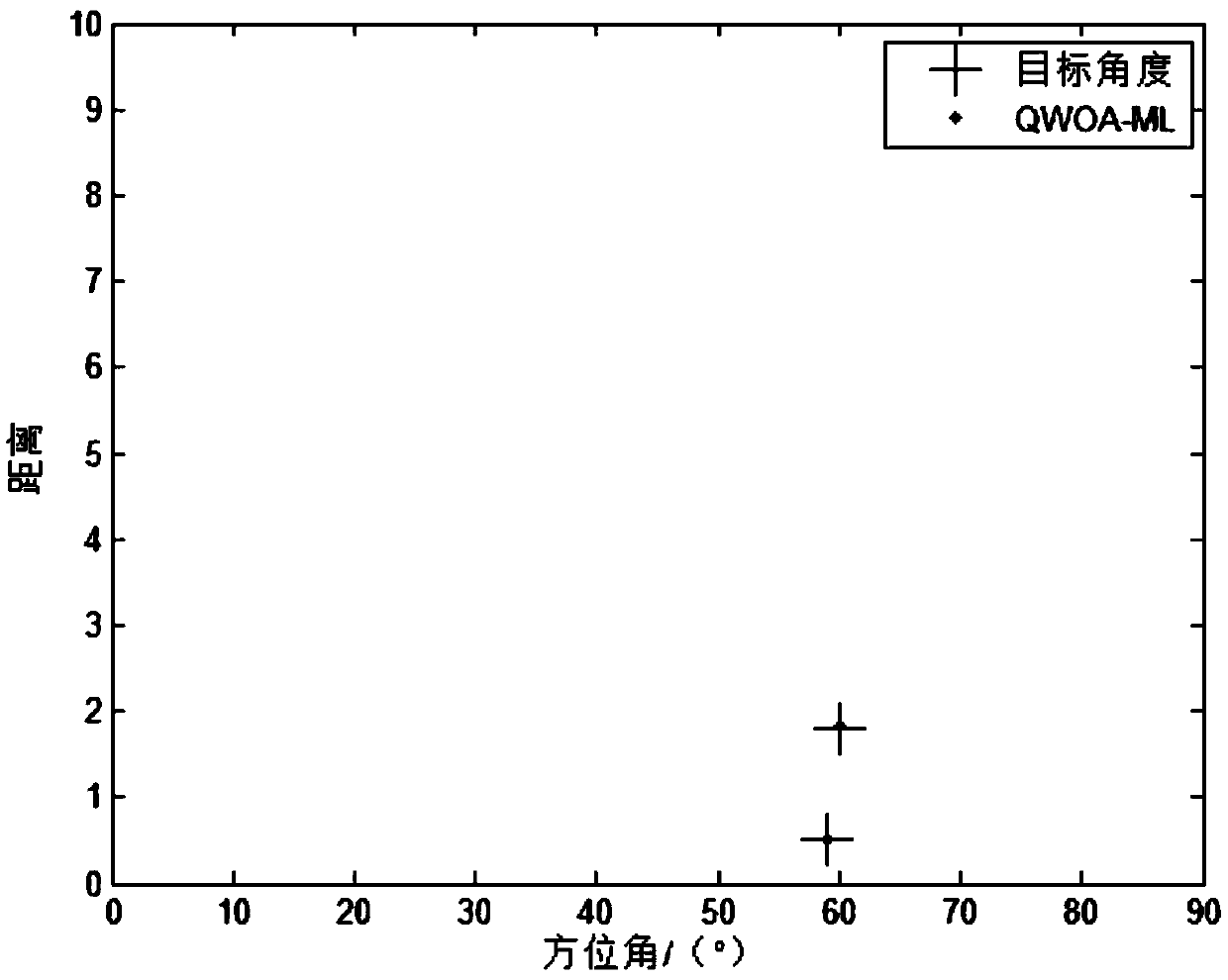
PendingCN108983142AEfficient solutionSmall amount of calculationRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsGlobal optimalFindings methods
The invention provides a near field source direction finding method based on a quantum whale optimization mechanism. A near field source direction finding model is established; whales in a whale groupare initialized, a fitness function is constructed, the fitness of each whale quantum position is calculated, and a global optimal quantum position is determined; each whale selects one from quantumevolution rules including spiral update, a contracted bounding mechanism and random food searching according to the probability to update the quantum position of itself; the updated whale quantum position is mapped to the whale position, the fitness of each whale quantum position is calculated, a greedy selection strategy is used to select the quantum position, and the globally optimal quantum position is updated; and the globally optimal quantum position is output, and maximum likelihood estimated values of the corresponding azimuth and distance are obtained by mapping transformation. The method can be used to carry out high-precision range finding on coherent near field sources, and the quantum whale optimization mechanism is used to realize the high-precision range finding method.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Apparatus and method for imaging subsurface structure of target area by using waveform inversion
ActiveUS8422335B2Efficient use ofEvenly distributedSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsDamping constantPerformed Imaging
Provided are an apparatus and method for imaging the subsurface structure of a target area by using waveform inversion. In the apparatus and method, the subsurface structure of a target area is estimated using waveform inversion of a seismic signal in the frequency domain, the Laplace domain, or the Laplace-Fourier domain, and an objective function is defined by applying a weighting function such that the objective function makes a different contribution for each frequency, each Laplace damping constant, or each Laplace-Fourier damping constant. The objective function is not limited to a particular type of objective function and a weighting function can be automatically determined when a gradient vector for each frequency, each Laplace damping constant, or each Laplace-Fourier damping constant is normalized. In addition, a gradient direction for all frequencies can be defined by applying another weighting function to the sum of respective gradient vectors for all frequencies, all Laplace damping constants, or all Laplace-Fourier damping constants, wherein the weighting function can also be automatically determined by normalization.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Method for realizing quantum circuit design by quantum D(4) wavelet transform
The invention provides a method for realizing quantum circuit design by quantum D(4) wavelet transform, and belongs to the field of quantum information processing. The method designs single-layer quantum D(4) wavelet transform, uses two rotary matrixes to replace a general unitary matrix and is an innovation for an existing quantum D(4) wavelet transform technology on an aspect of methods. From the complexity analysis of the implementation circuit of the quantum D(4) wavelet transform and quantum D(4) wavelet inverse transform, for a dataset which contains 2n pieces of elements, the complexities of the circuits of the quantum D(4) wavelet transform and the quantum D(4) wavelet inverse transform are both [Theta](n2) which can not be achieved by other classic quick D(4) wavelet transform. The method is suitable for a plurality of practical information processing application fields, for example, algorithms, including image compression, denoising, encryption, decryption and the like, all need efficient D(4) wavelet transform, and the method has an important meaning for the perfection and the application of a quantum computing theory.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
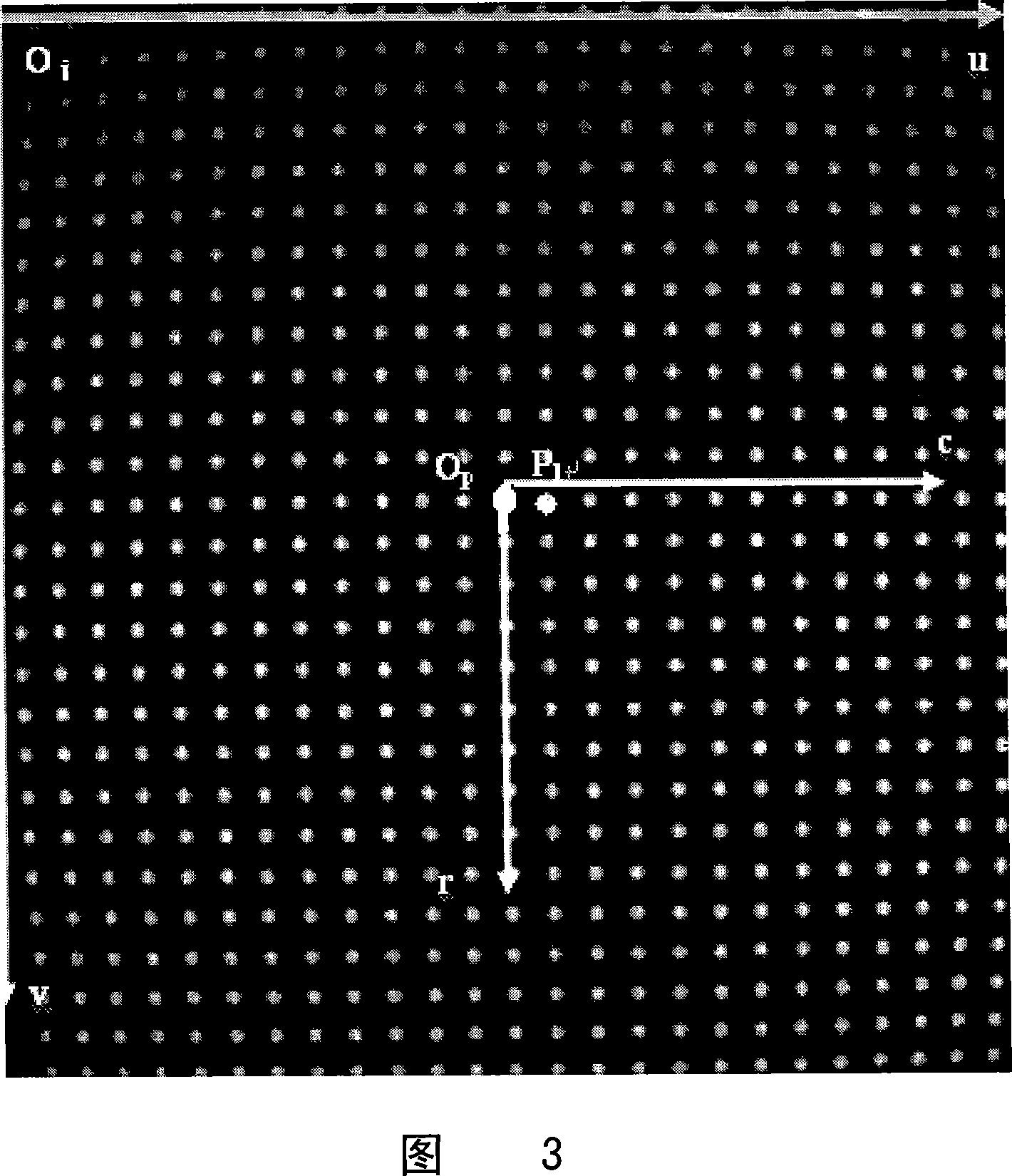
Magnetic resonance image-forming system gradient field spherical harmonic coefficient obtaining method
ActiveCN101216541AImprove accuracySteps to Simplify ImplementationImage enhancementMagnetic measurementsResonanceSpherical harmonics
The invention relates to a method for acquiring spherical harmonic coefficient of gradient field of magnetic resonance imaging system, which comprises the following steps of : (a) constructing a water model coordinate system selecting a mark point Pc(u0, v0) closest to the image center as the original point Op, selecting the u axis direction of an MRI image as the c axis direction, selecting the v axis direction in the image as the r axis direction, and selecting the direction forming a right-handed coordinate system with the c and the r axes as the s axis direction; (b) calculating the MRI coordinates of the mark point Pi according to the water model coordinate system by following steps: (1) ignoring the rotation of the water model in the plane thereof and the translation of the original point; (2) considering the rotation by a theta angle in the plane of the water model around the center of Op and a shaft in the direction of a scan layer slice; and (3) considering the translation of the coordination original point of the water model; and (c) obtaining a linear equation group concerning spherical harmonic coefficients a and b if the magnetic field intensity parameters gamma, theta, phi and image coordinates of a certain point are known, and calculating the coefficients a and b by solving the linear equation group.
Owner:SYMBOW MEDICAL TECH
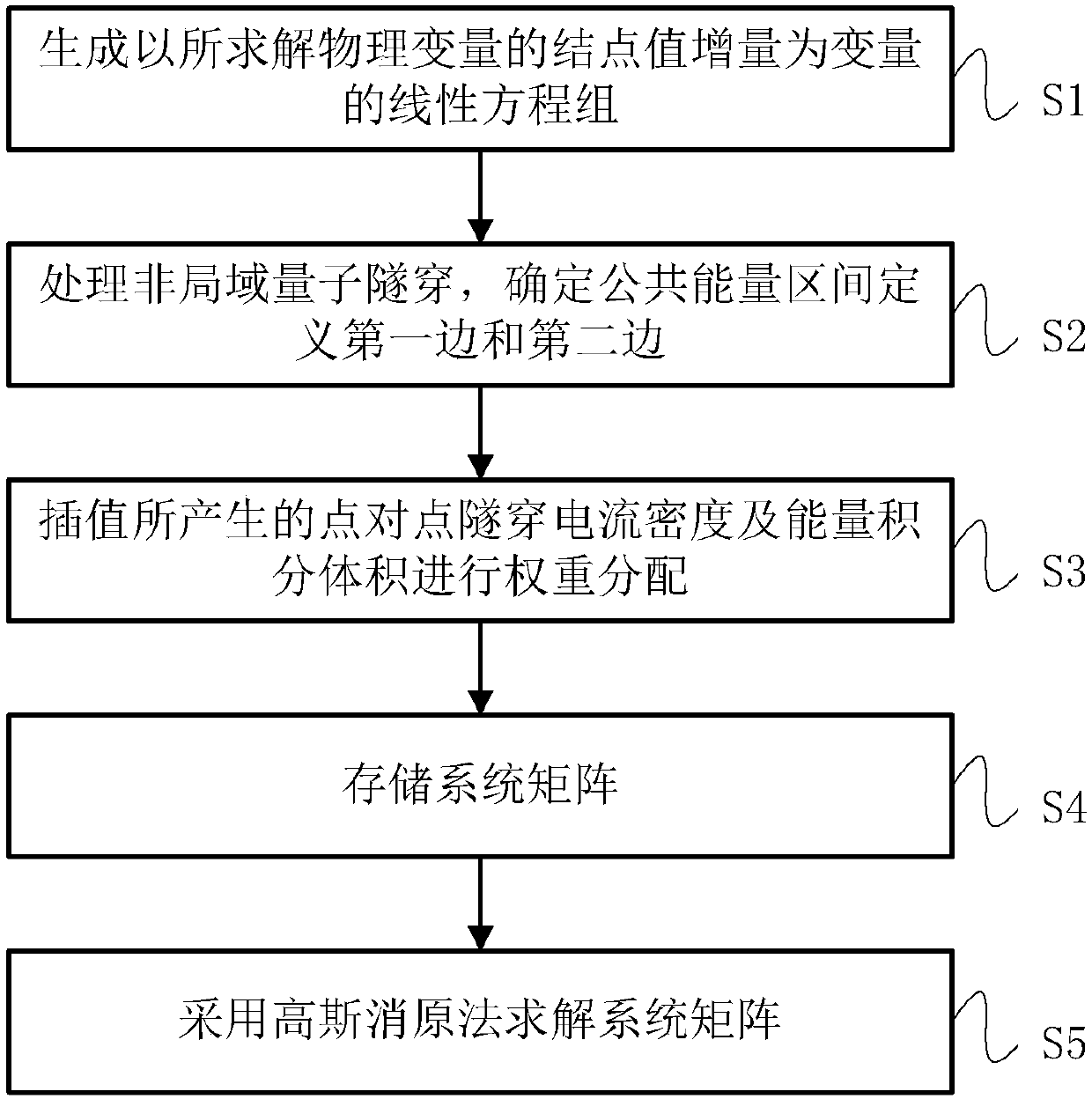
Energy interband non-local quantum tunneling simulation method with current conservation characteristic
ActiveCN106339562AGuaranteed conservationEliminate errorsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSimulation errorOrdinary differential equation
The invention discloses an energy interband non-local quantum tunneling simulation method with a current conservation characteristic. The method comprises the steps of generating a linear equation system which adopts a nodal value increment of a solved physical variable as a variable in a dispersing semiconductor device physical region; processing non-local quantum tunneling, determining a public energy zone for defining a first side and a second side; carrying out weight distribution on point-to-point tunneling current density and energy integral volume produced by interpolation; dividing a coefficient matrix of the linear equation system into a principal matrix caused by general differential equation dispersing and an additional coefficient matrix caused by non-local quantum tunneling with the current conservation characteristic, and storing; adopting a Gaussian origin eliminating method to solve the coefficient matrix. According to the energy interband non-local quantum tunneling simulation method with the current conservation characteristic provided by the invention, the non-local quantum tunneling current conservativeness is ensured, and the simulation error and the uncertainty brought by non-conservation are eliminated; by utilizing a method combining the principal matrix and an auxiliary incidence matrix, the coefficient linear equation system obtained through linearizing a non-linear equation system can be quickly solved, and the solving efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPACE POWER SOURCES
Reduced order model-based free vibration analysis method for beam structure
ActiveCN106294975AReduce adverse effectsImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsReduced modelFine structure
The invention belongs to the field of aerospace complex beam structure component calculation, and provides a reduced order model-based free vibration analysis method for a beam structure. The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining a mass matrix and a stiffness matrix of a fine structure by using finite element software; 2) using a polynomial interpolation function to construct a reduced base vector, so as to realize order reduction of an original complex beam structure; and 3) solving a kinetic equation of the reduced order model, and obtaining the overall frequency and part of low-order frequencies of the structure. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, the polynomial interpolation function is used to construct the reduced base vector, nodes in a finite element model of the complex structure are condensed to the section centroid in the form of displacement interpolation so as to realize the order reduction of the original structure, and the calculation precision of the reduced order model can be controlled by polynomial orders. The method disclosed by the present invention has the advantages that: without depending on the experience of the user, the adverse influence of the difference of selection of the master and slave freedom degrees on the calculation precision is reduced; a large amount of matrix operation is not needed, so that the calculation efficiency of order reduction of the model is improved; and the obtained reduced order model has a wide application range.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
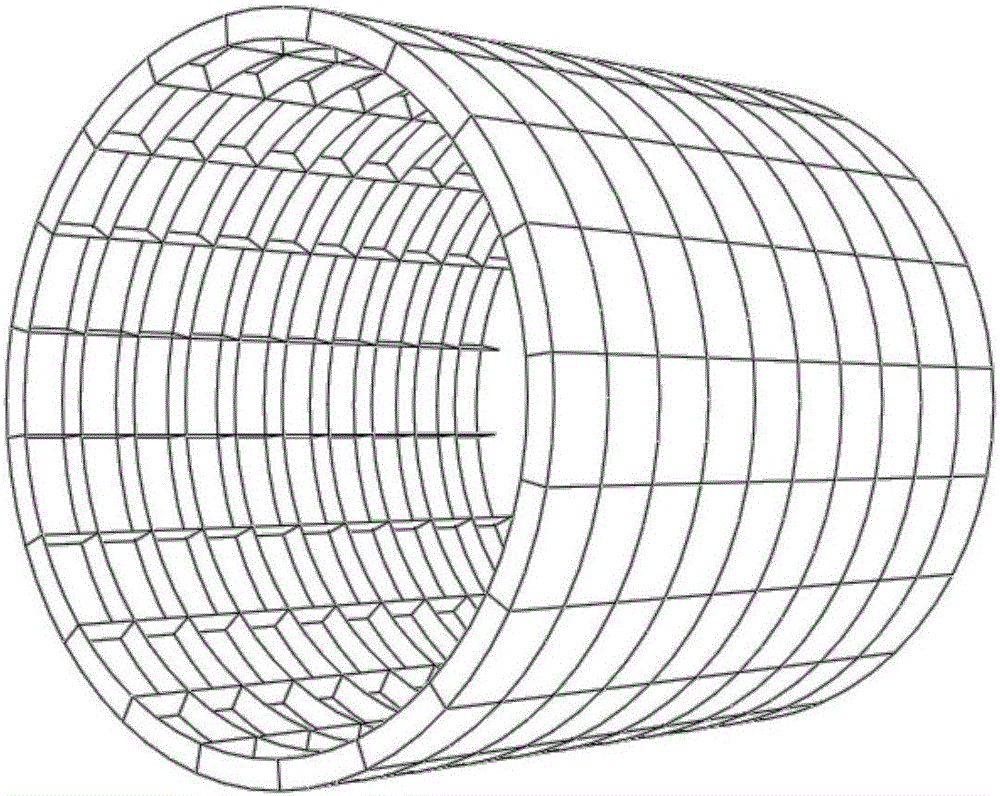
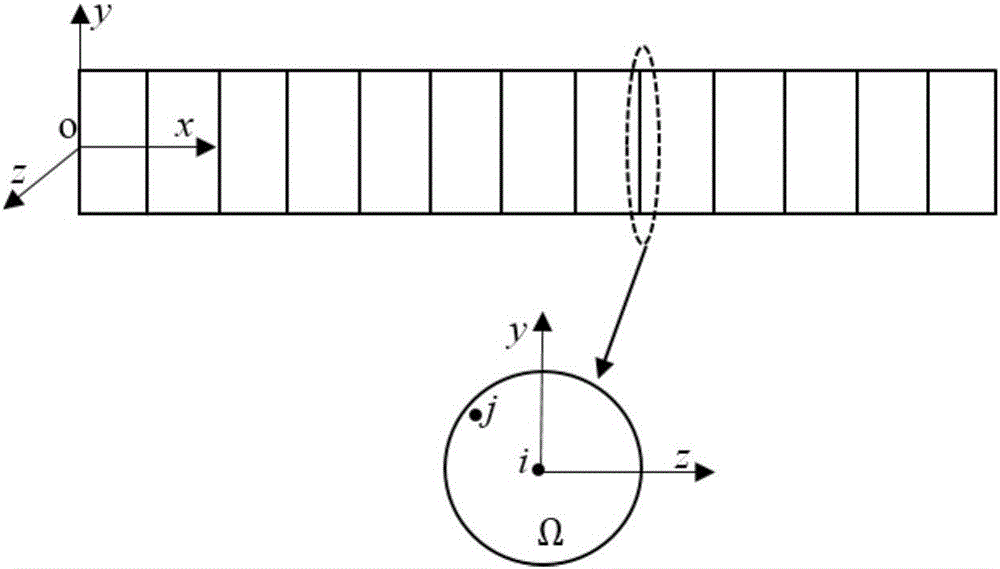
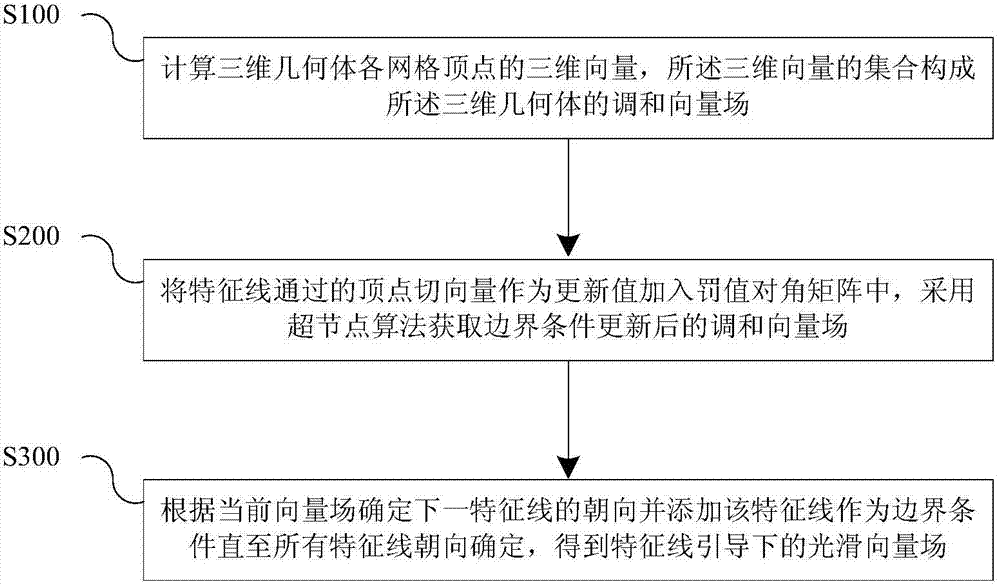
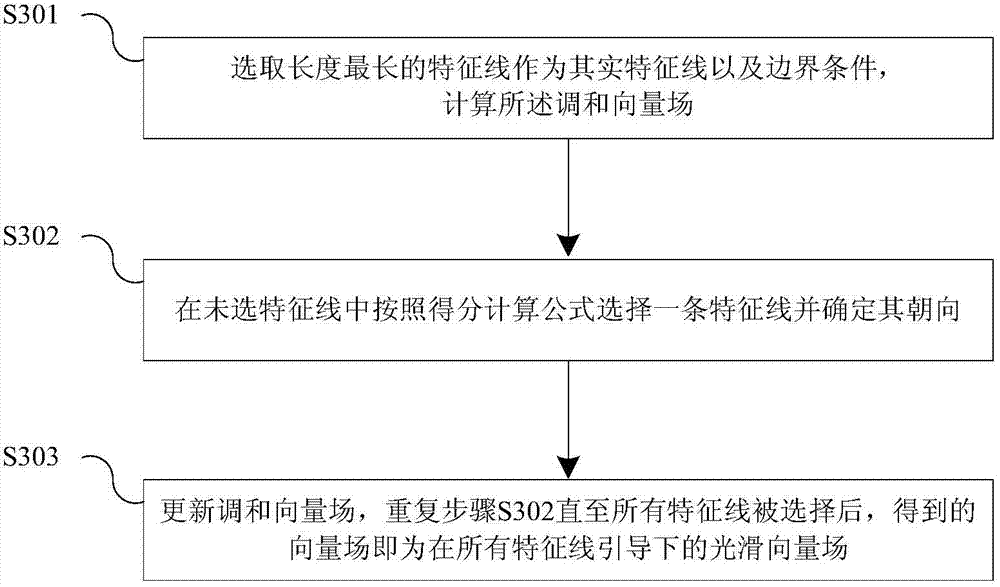
Three-dimensional geometric body surface smooth vector field calculating method under guidance of typical line
The invention brings forward a three-dimensional geometric body surface smooth vector field calculating method under the guidance of a typical line. The method comprises the following steps: S100, calculating three-dimensional vectors at the grid summits of a three-dimensional geometric body, a set of the three-dimensional vectors constituting a harmonic vector field of the three-dimensional geometric body; S200, introducing the typical line as a boundary condition, by taking all summit tangential vectors which the typical line passes through as updating values, adding the updating values into a penalty diagonal matrix, and employing a supernode algorithm to obtain a harmonic vector field after the boundary condition is updated; and S300, utilizing a greedy algorithm to calculate a vector field by taking the current typical line as a boundary condition, and obtaining a smooth vector field under the guidance of the typical line. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: in the prior art, only a surface smooth vector field can be calculated, and a vector field under the guidance of a typical line cannot be calculated, however, the method provided by the invention realizes rapid calculation of typical line orientation by use of a dynamically updated harmonic vector field.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com