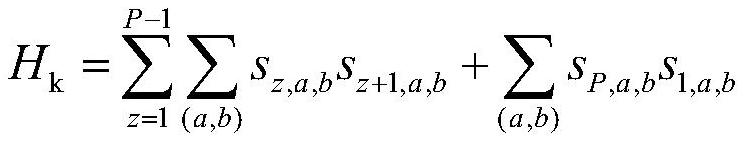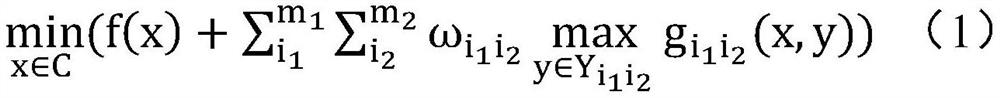Patents
Literature
50 results about "Quantum annealing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quantum annealing (QA) is a metaheuristic for finding the global minimum of a given objective function over a given set of candidate solutions (candidate states), by a process using quantum fluctuations. Quantum annealing is used mainly for problems where the search space is discrete (combinatorial optimization problems) with many local minima; such as finding the ground state of a spin glass. It was formulated in its present form by T. Kadowaki and H. Nishimori (ja) in "Quantum annealing in the transverse Ising model" though a proposal in a different form had been made by A. B. Finnila, M. A. Gomez, C. Sebenik and J. D. Doll, in "Quantum annealing: A new method for minimizing multidimensional functions".
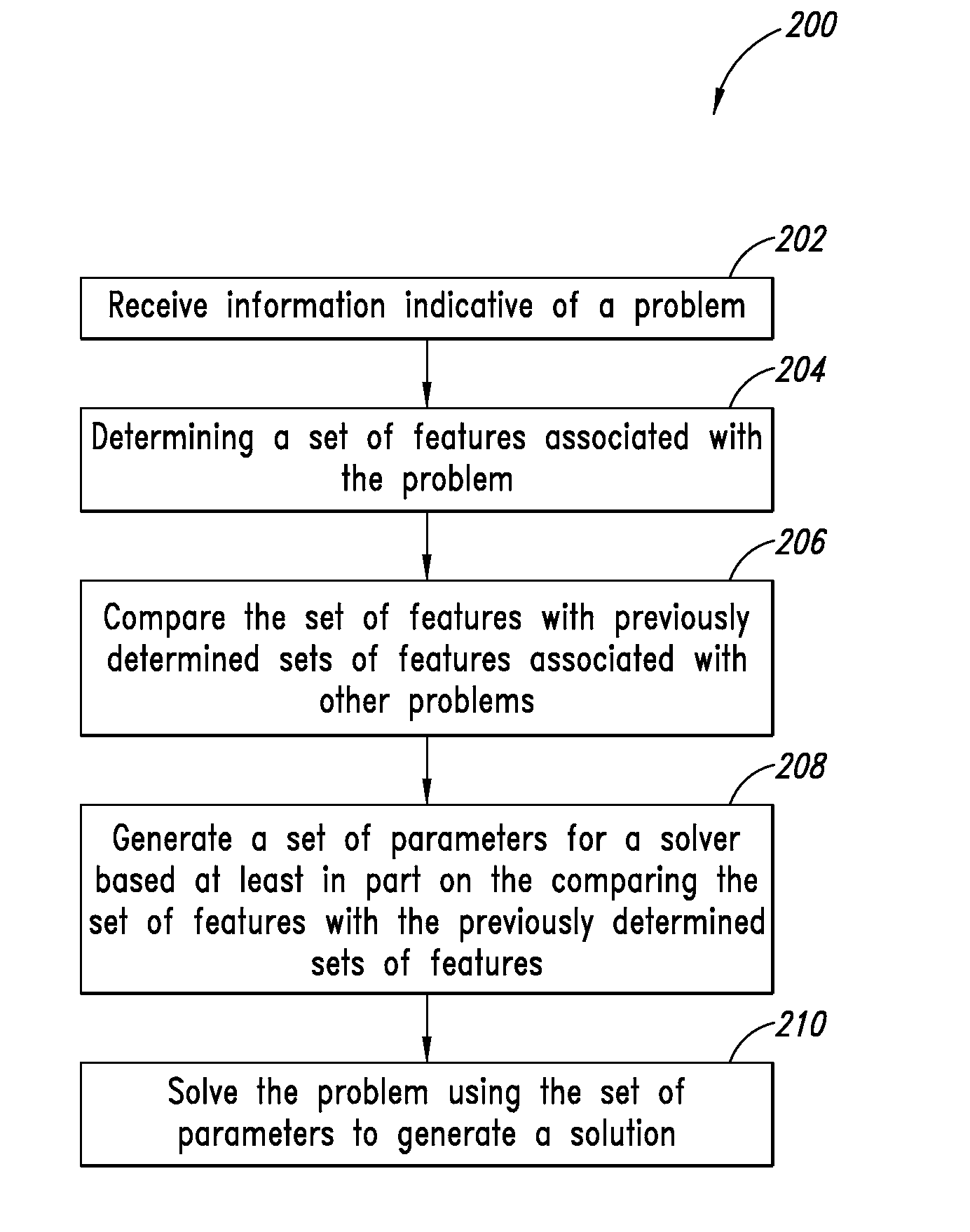
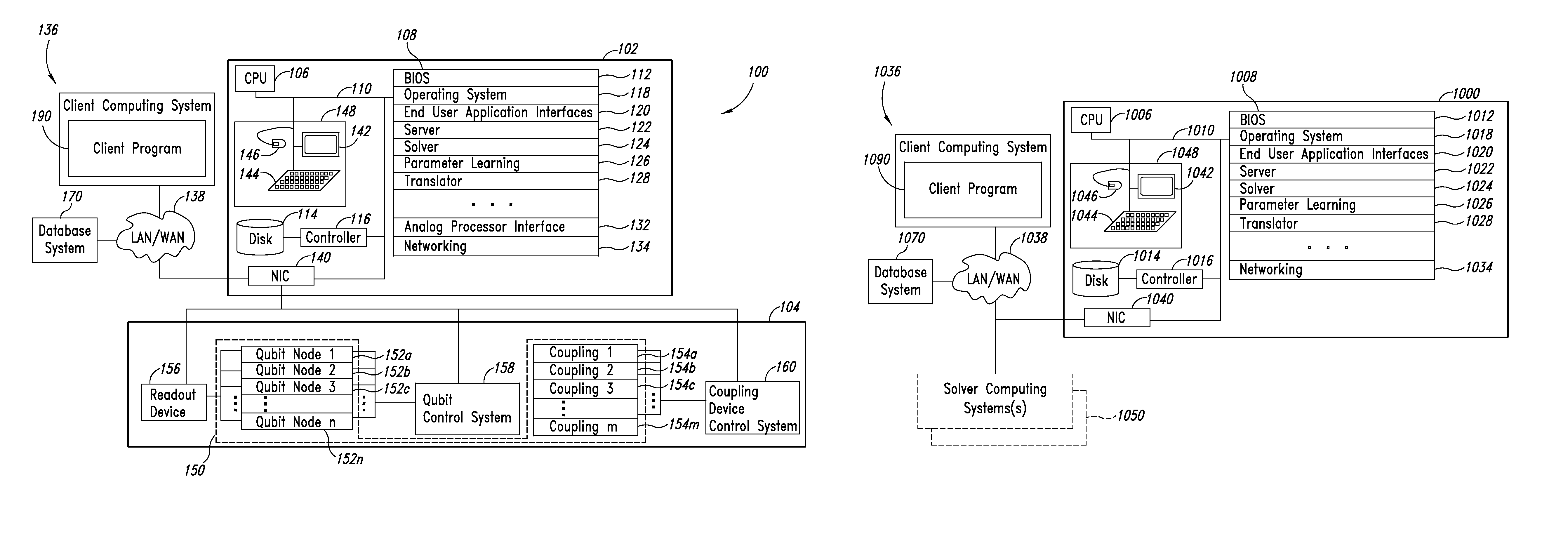
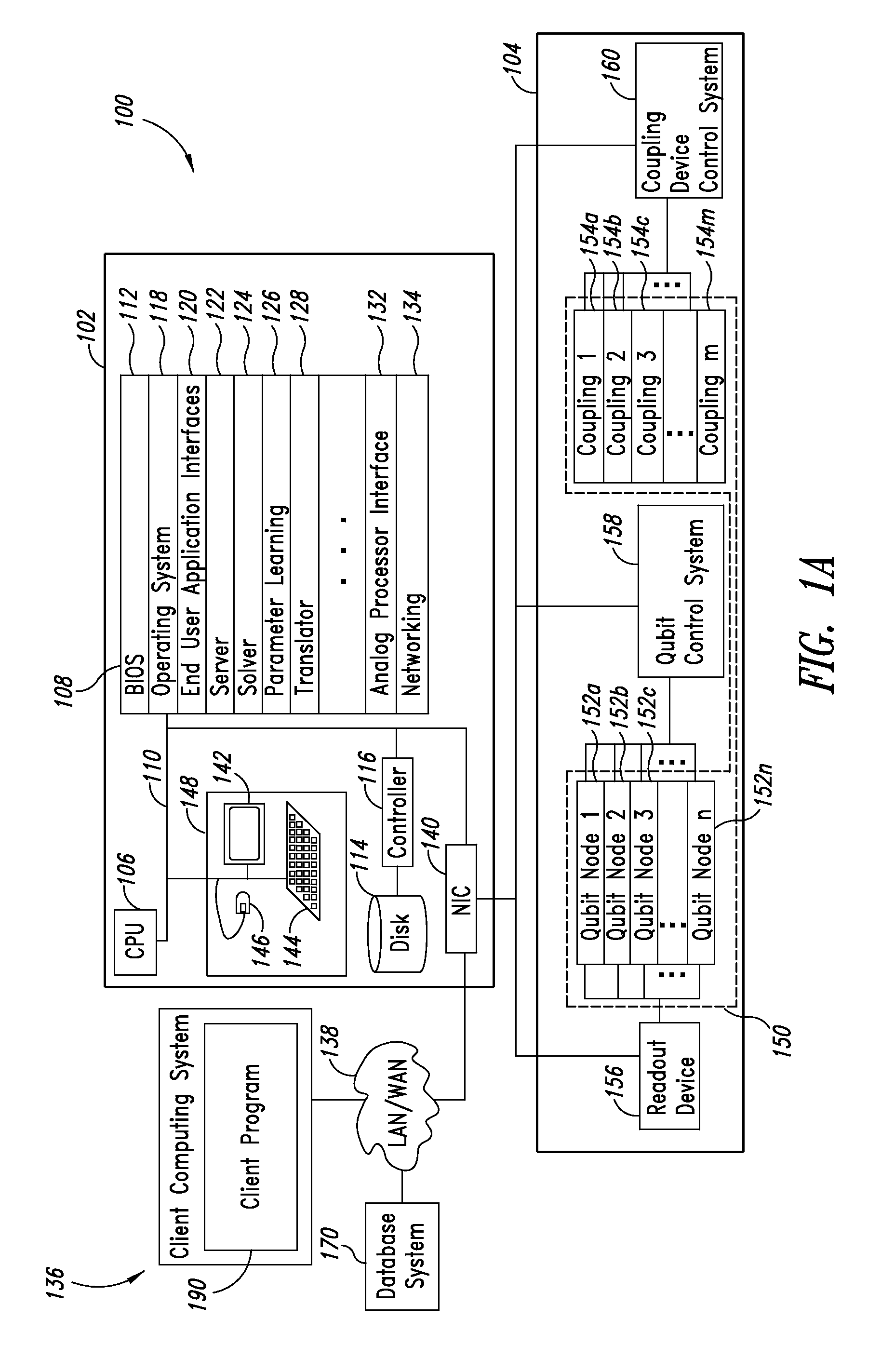
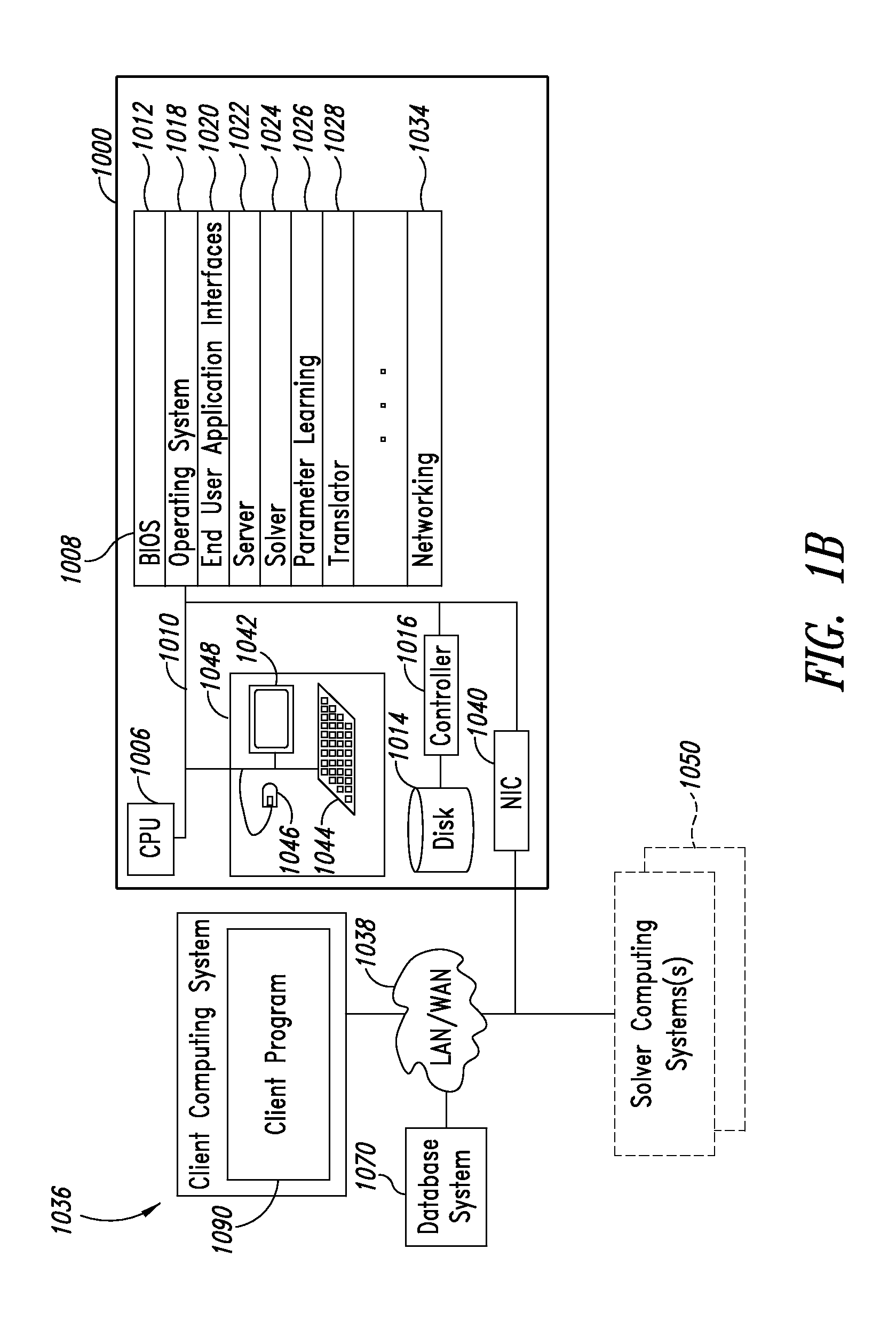
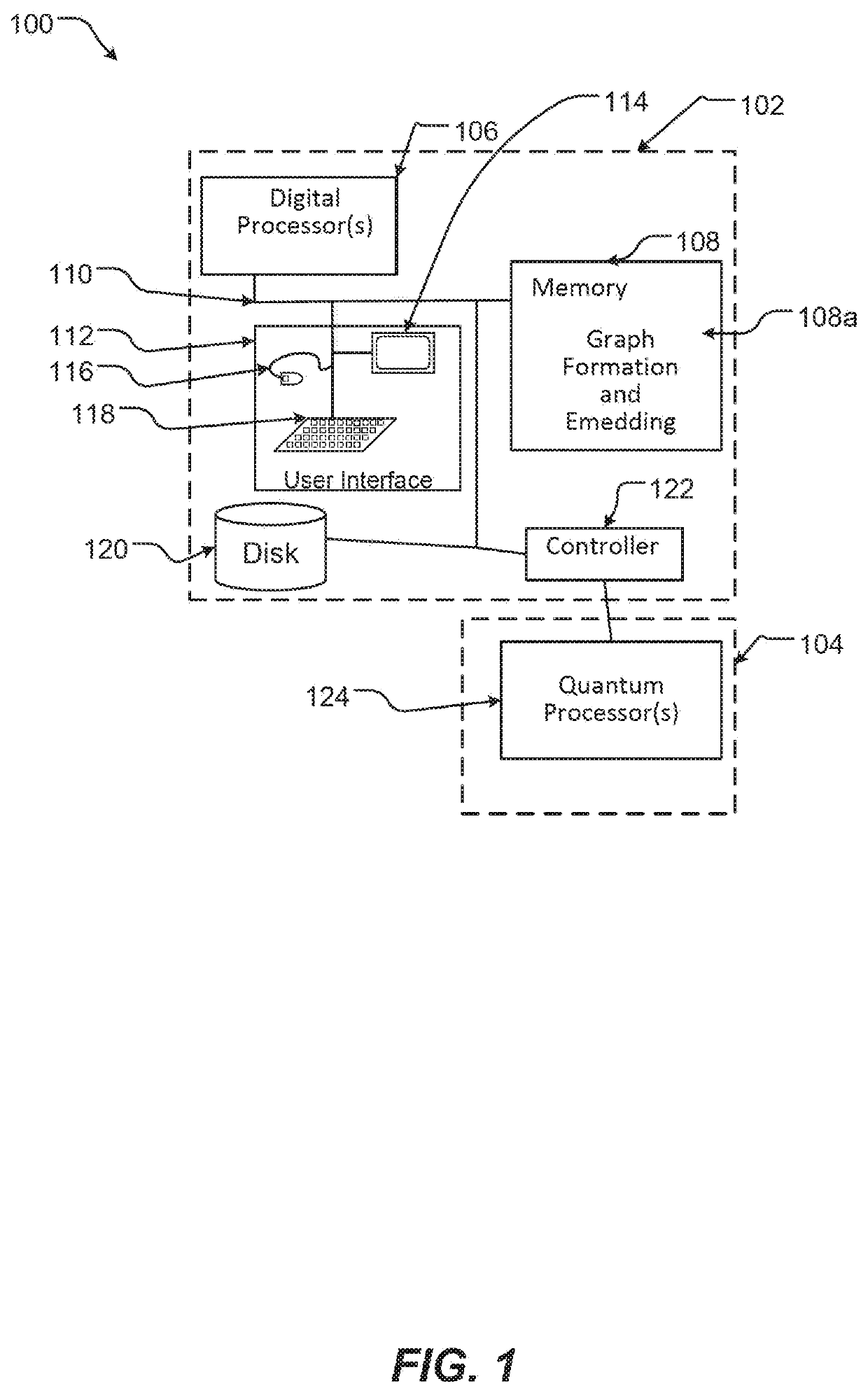
Quantum and digital processor hybrid systems and methods to solve problems
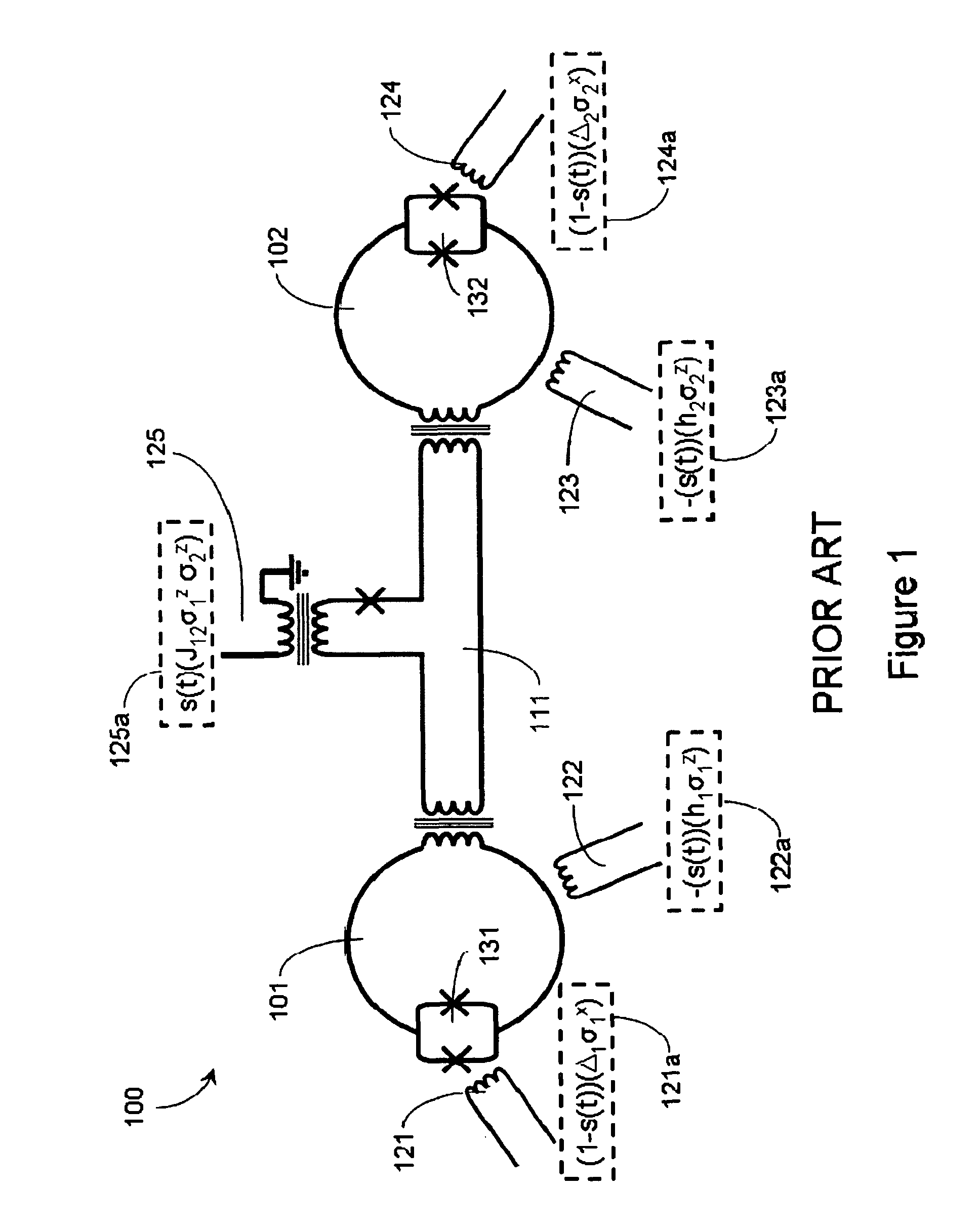
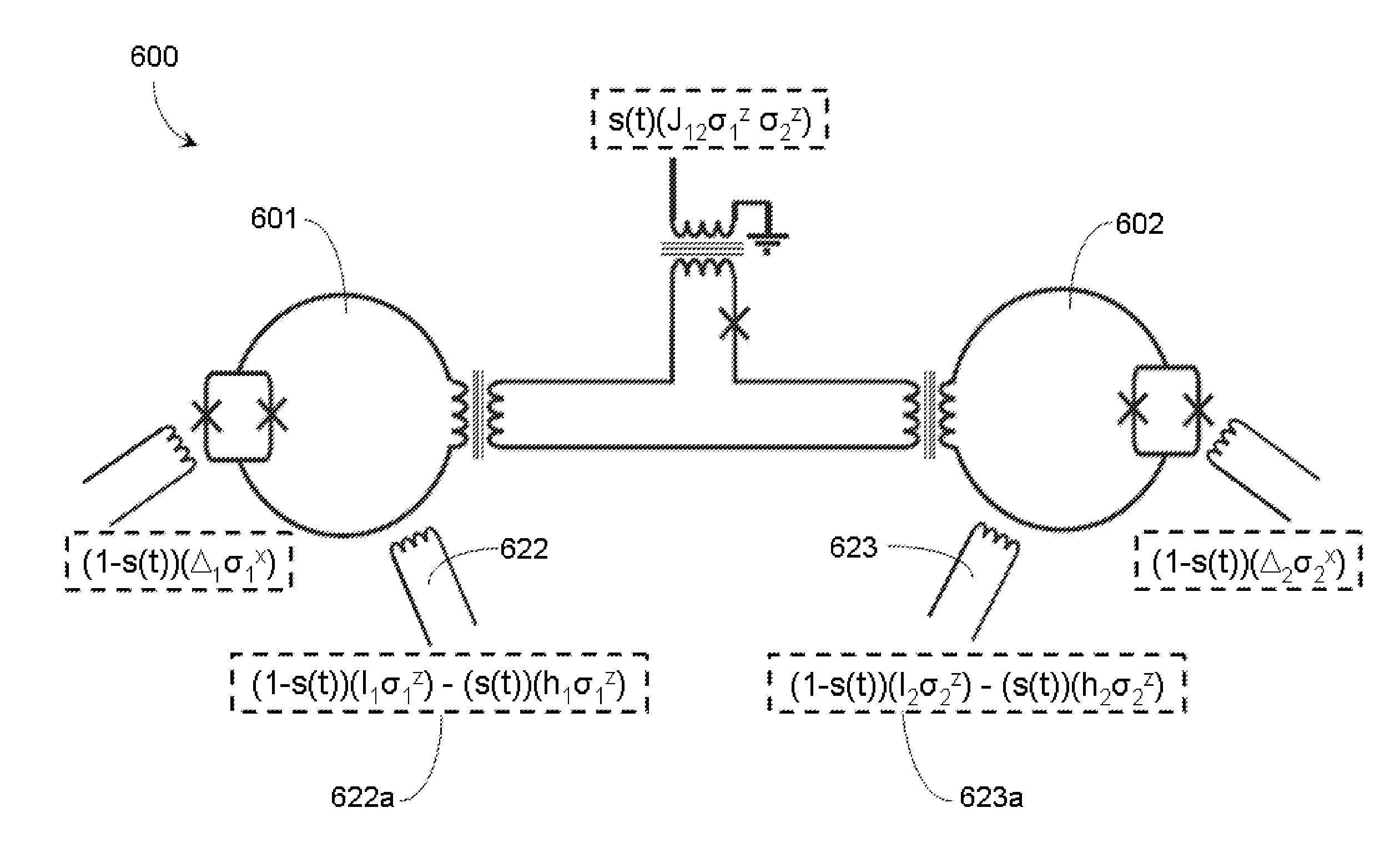
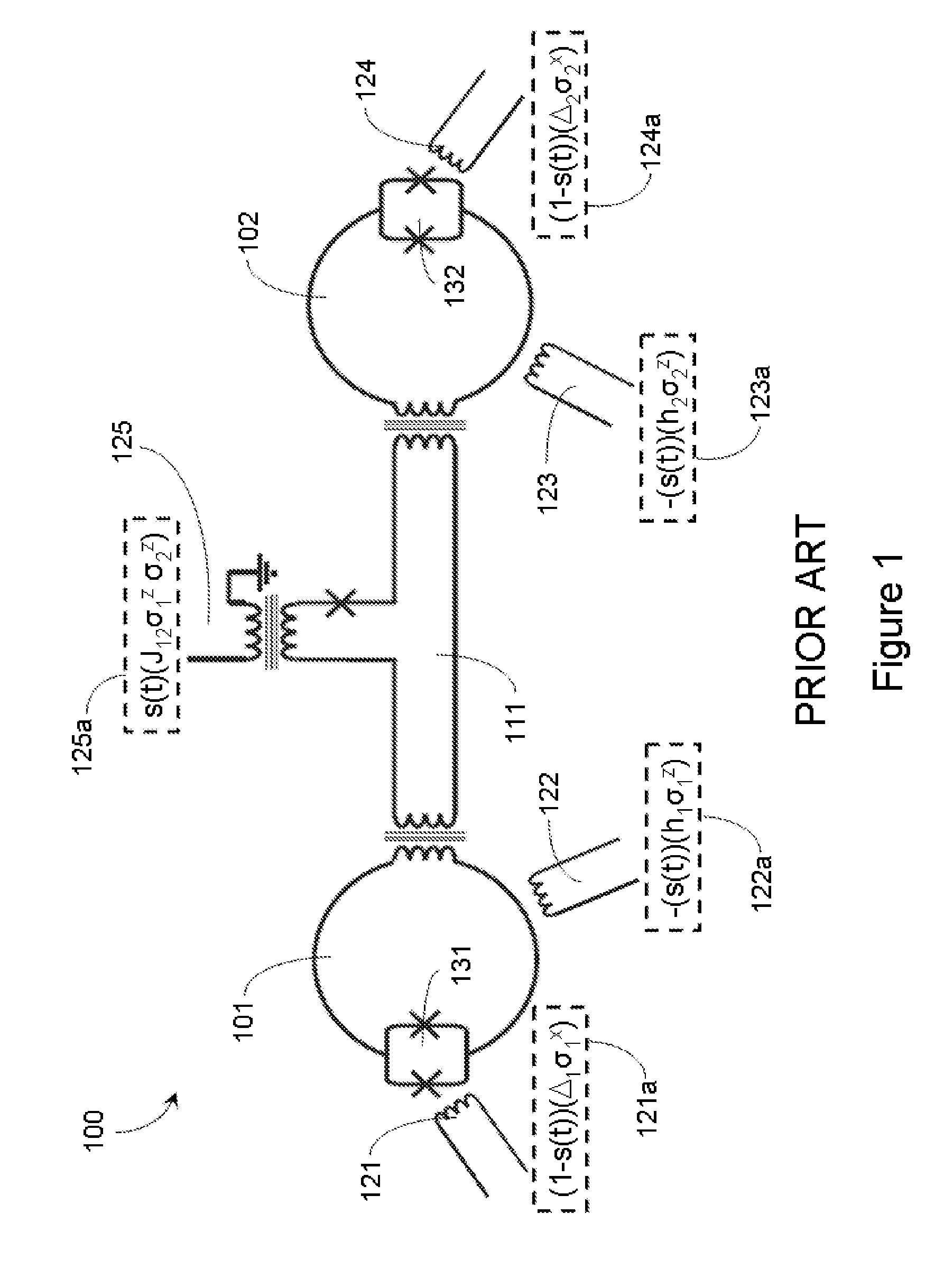
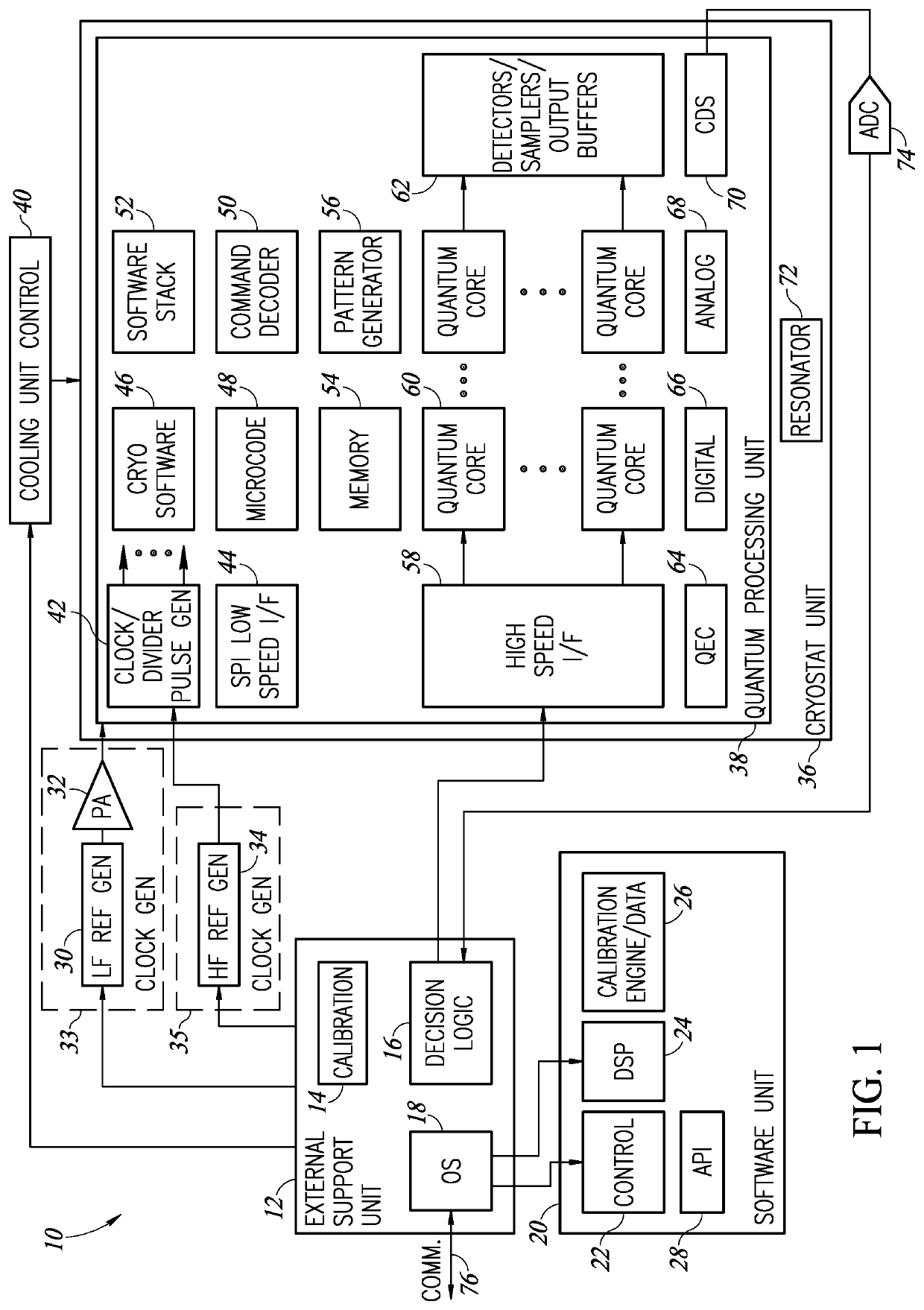
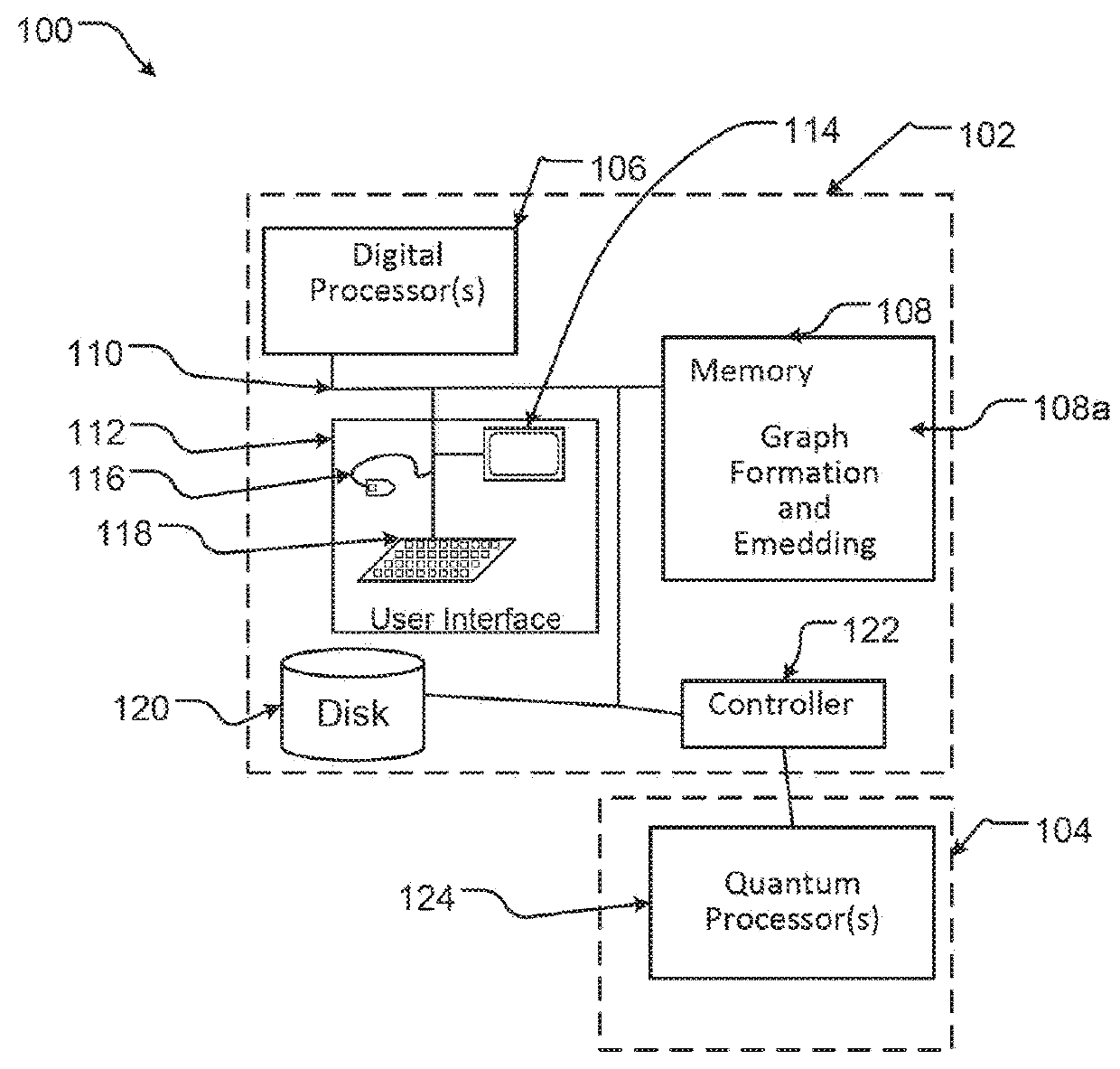
Quantum and digital processors are employed together to solve computational problems. The quantum processor may be configured with a problem via a problem Hamiltonian and operated to perform adiabatic quantum computation and / or quantum annealing on the problem Hamiltonian to return a first solution to the problem that is in the neighborhood of the global minimum of the problem Hamiltonian. The digital processor may then be used to refine the first solution to the problem by casting the first solution to the problem as a starting point for a classical optimization algorithm. The classical optimization algorithm may return a second solution to the problem that corresponds to a lower energy state in the neighborhood of the global minimum, such as a ground state of the problem Hamiltonian. The quantum processor may include a superconducting quantum processor implementing superconducting flux qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
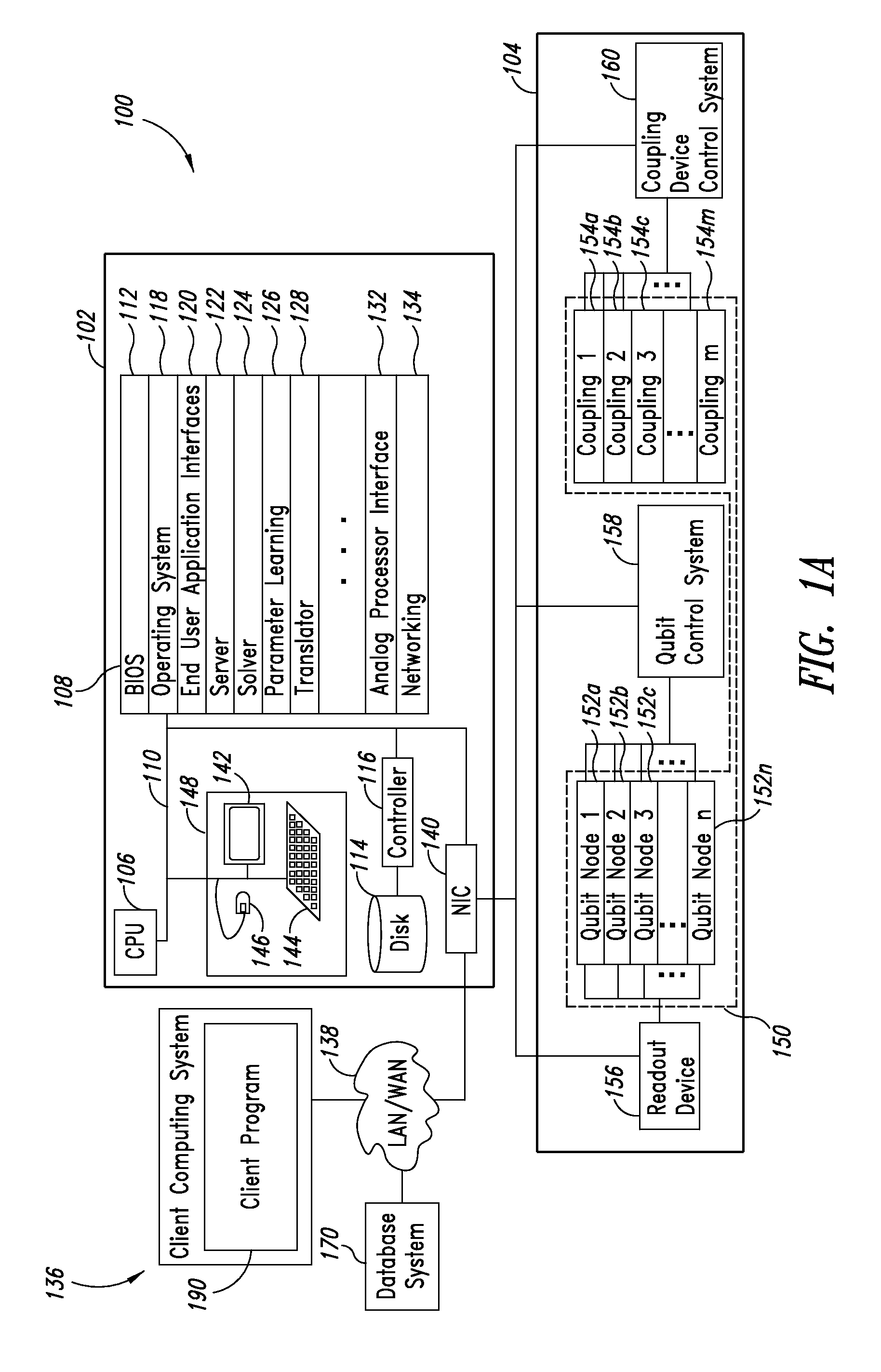
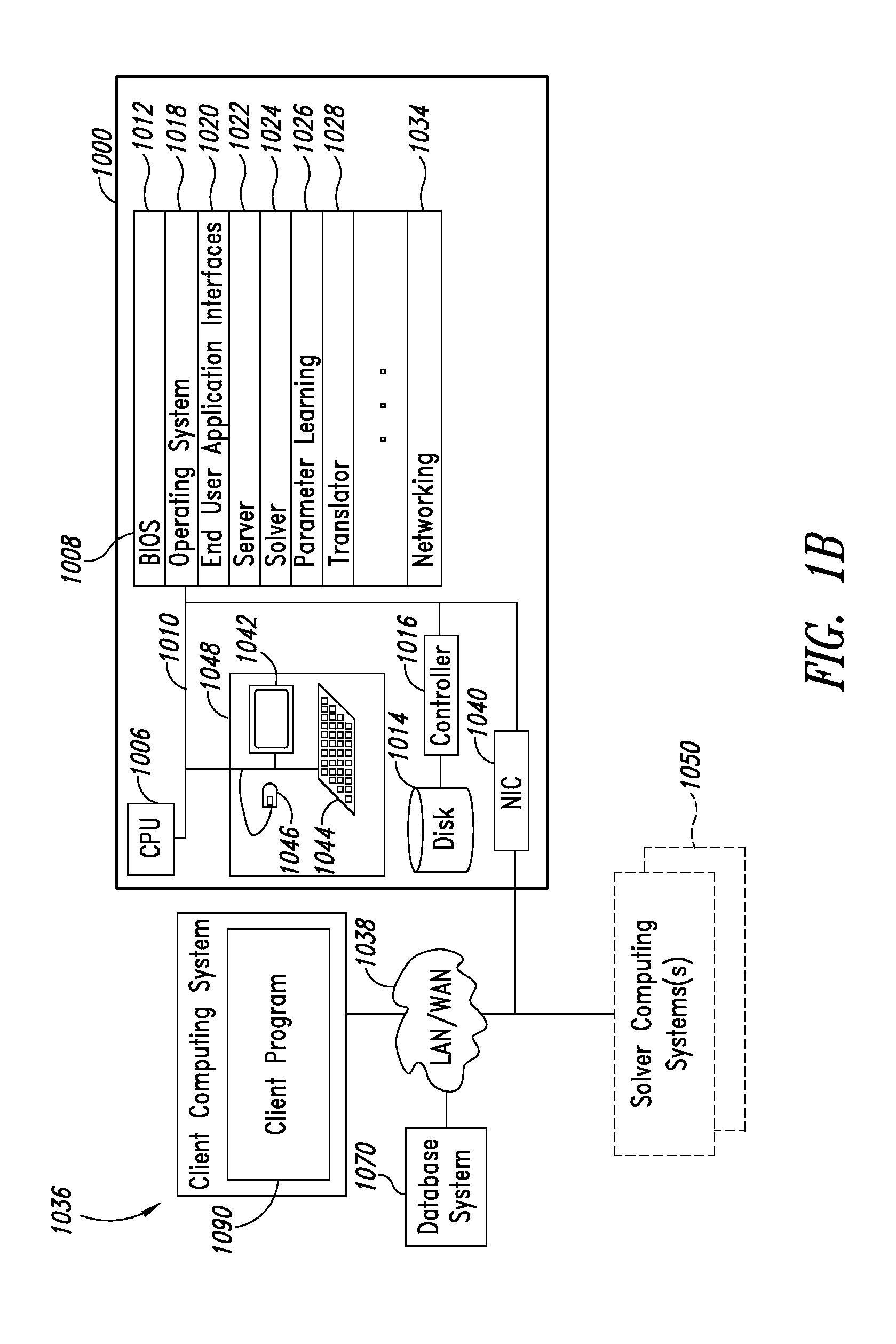
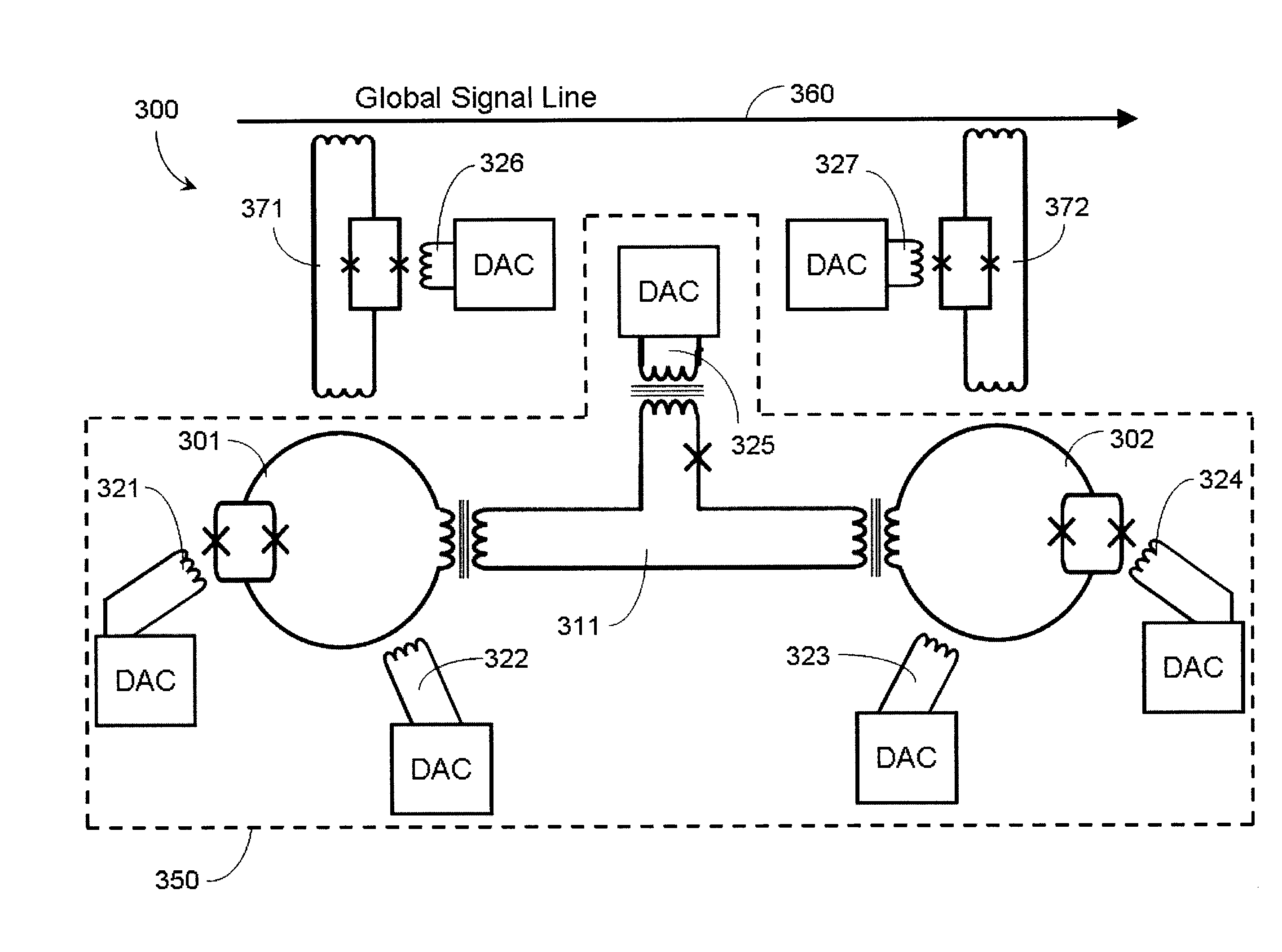
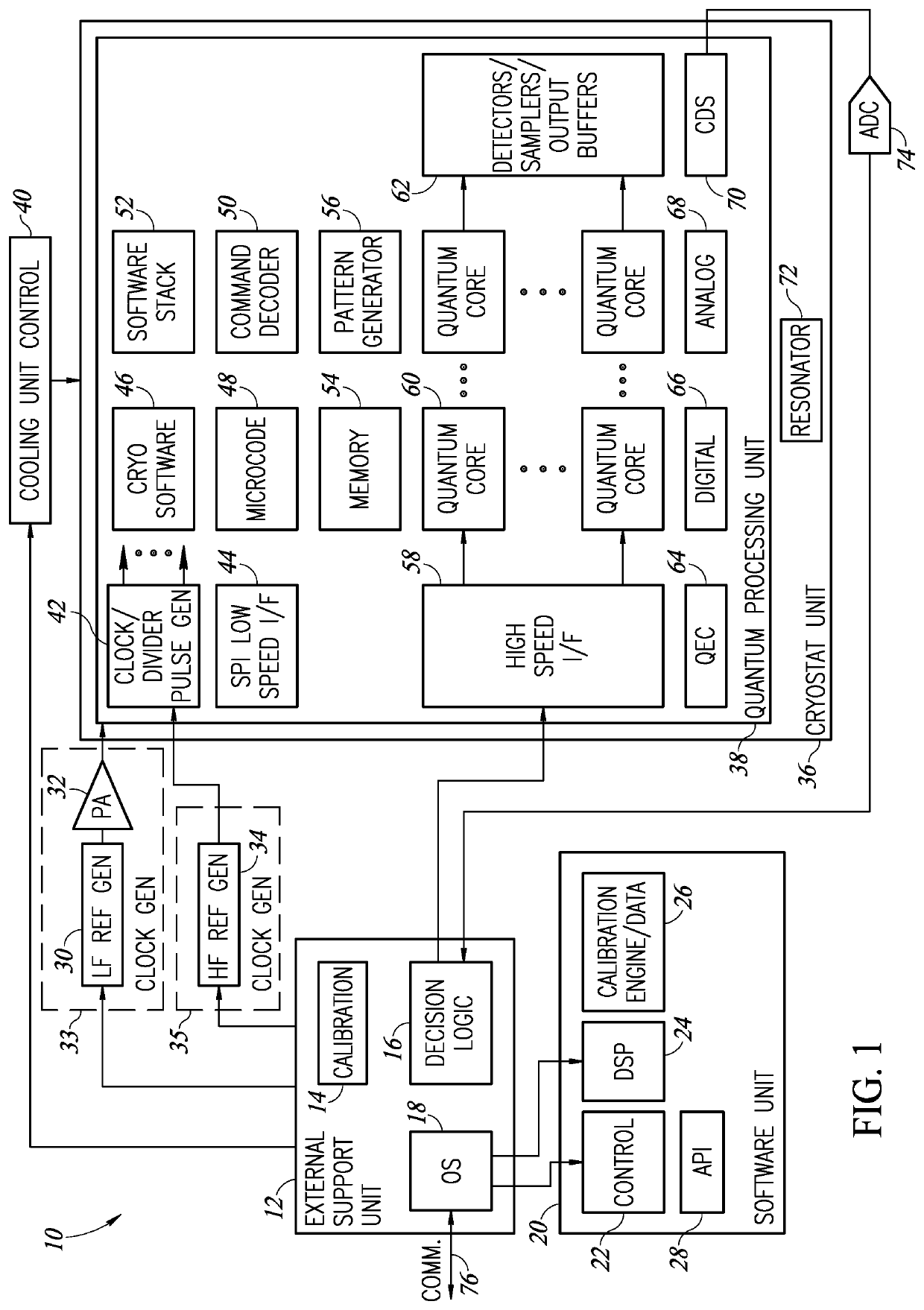
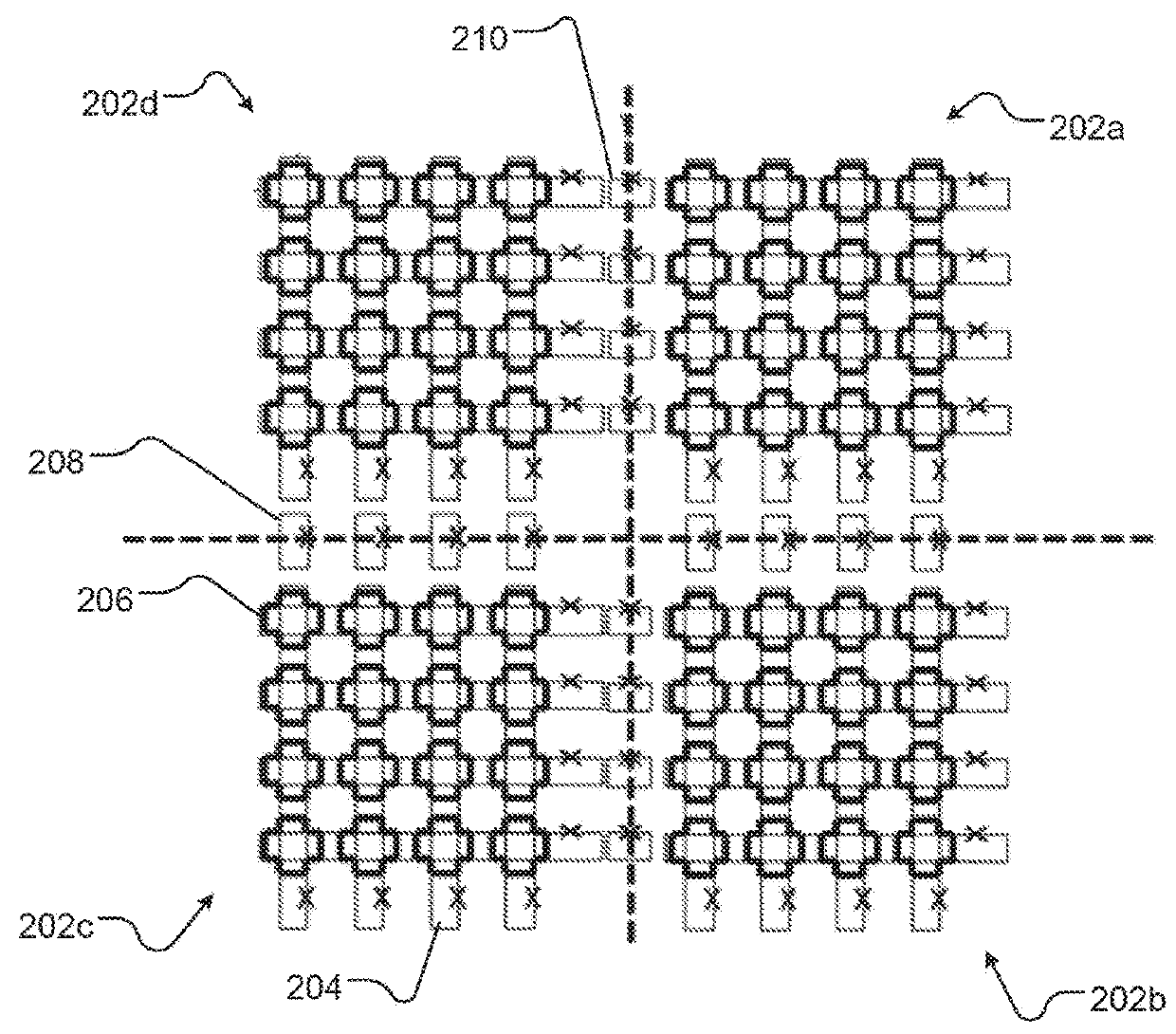
Systems, methods, and apparatus for calibrating, controlling, and operating a quantum processor
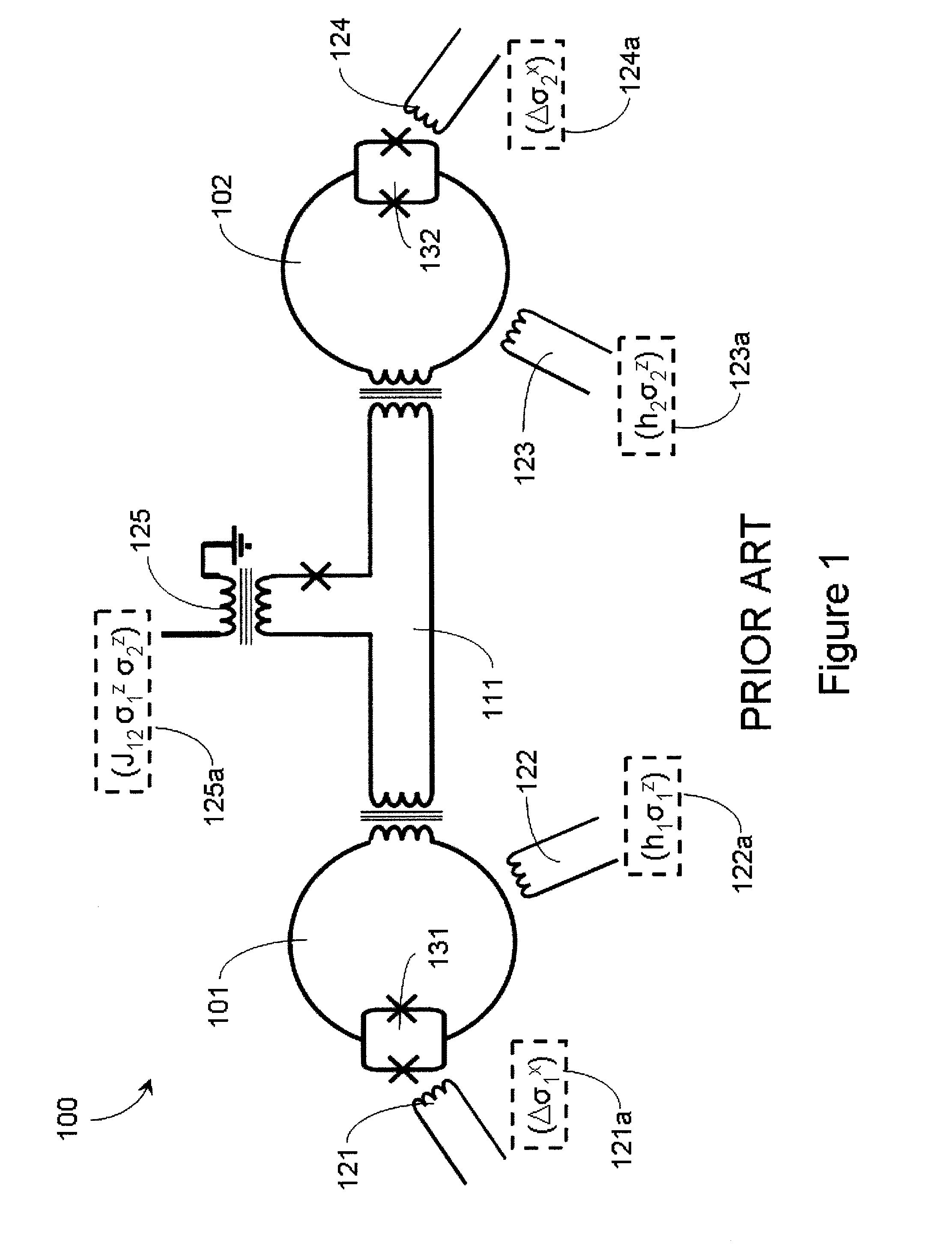
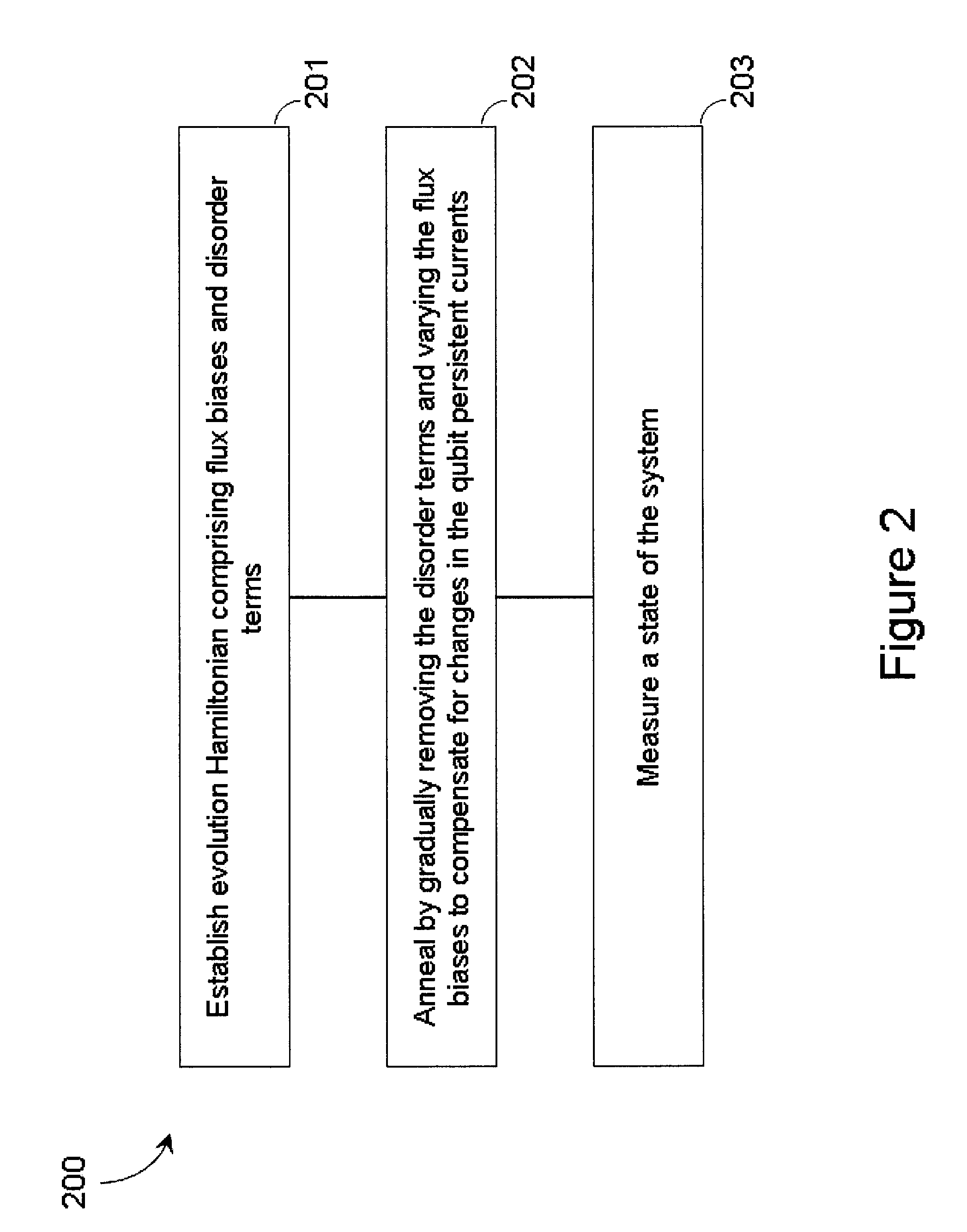
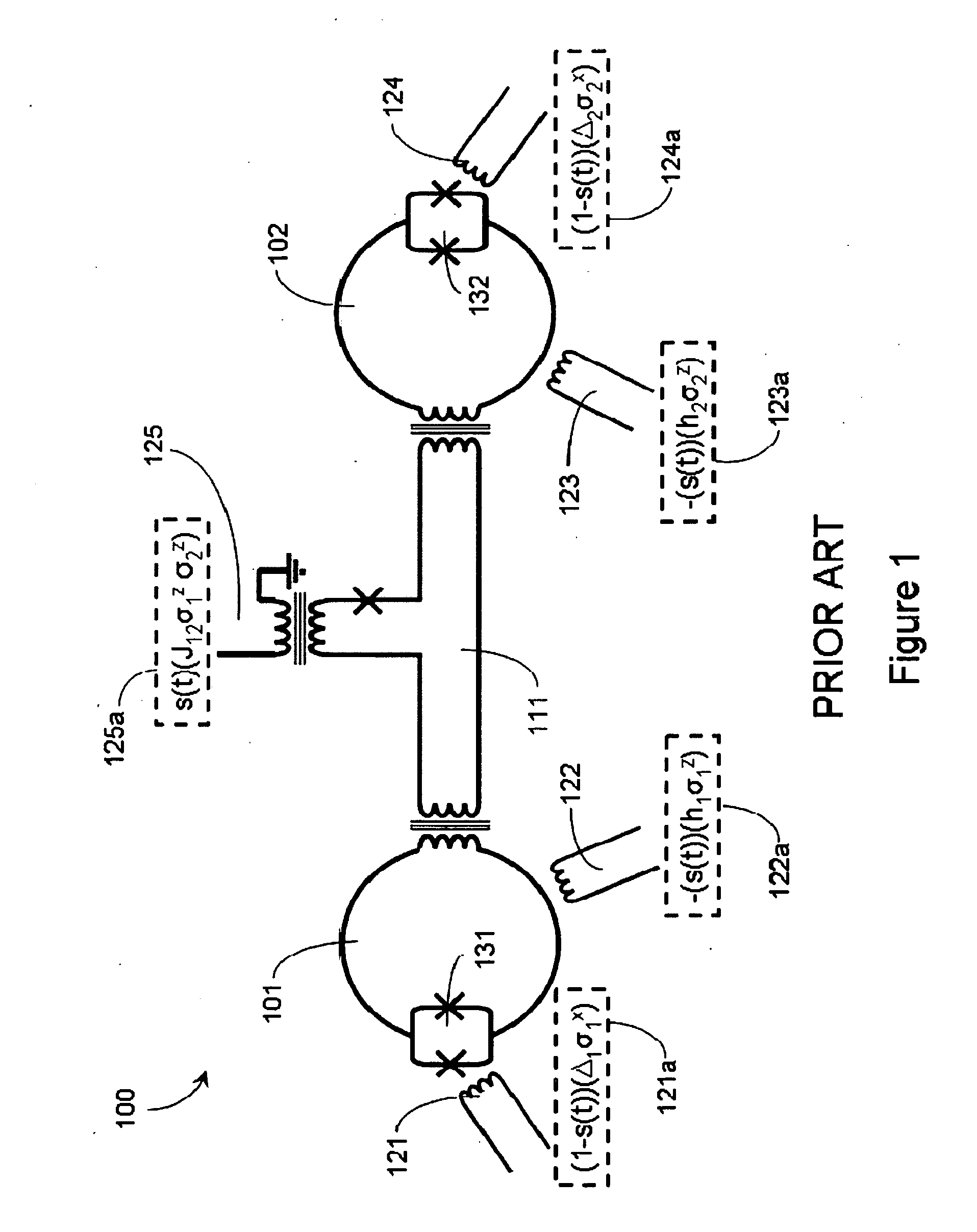
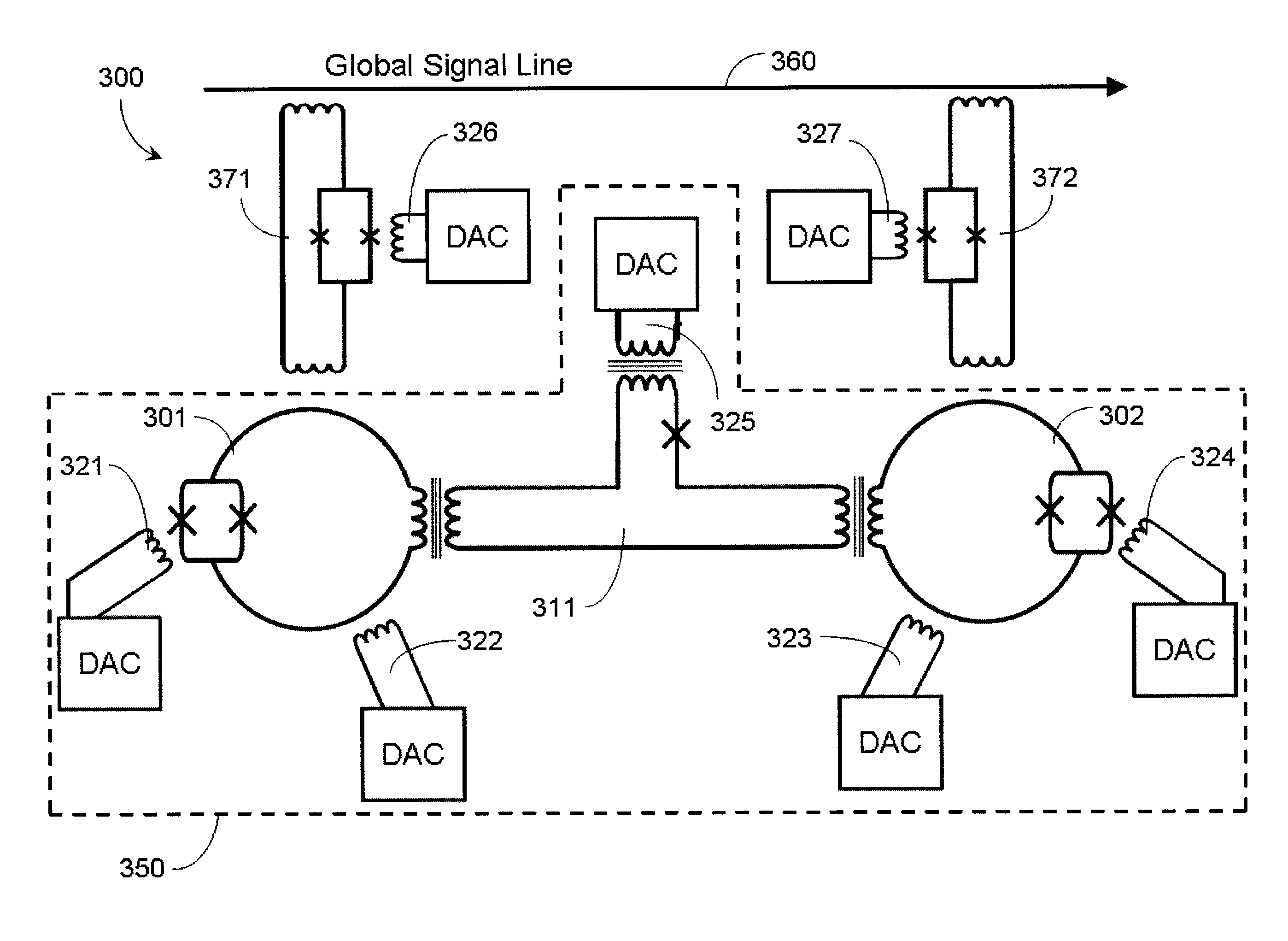
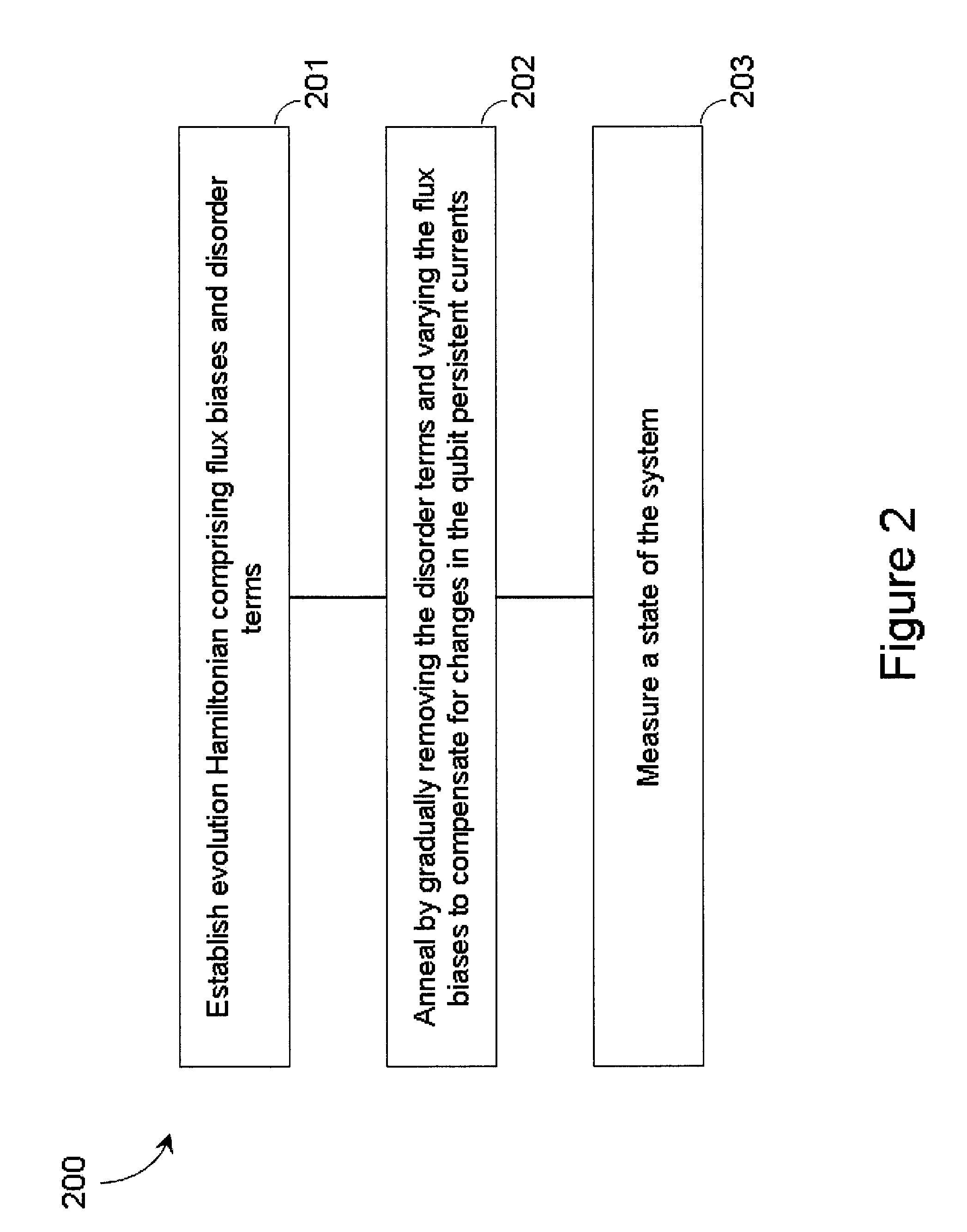
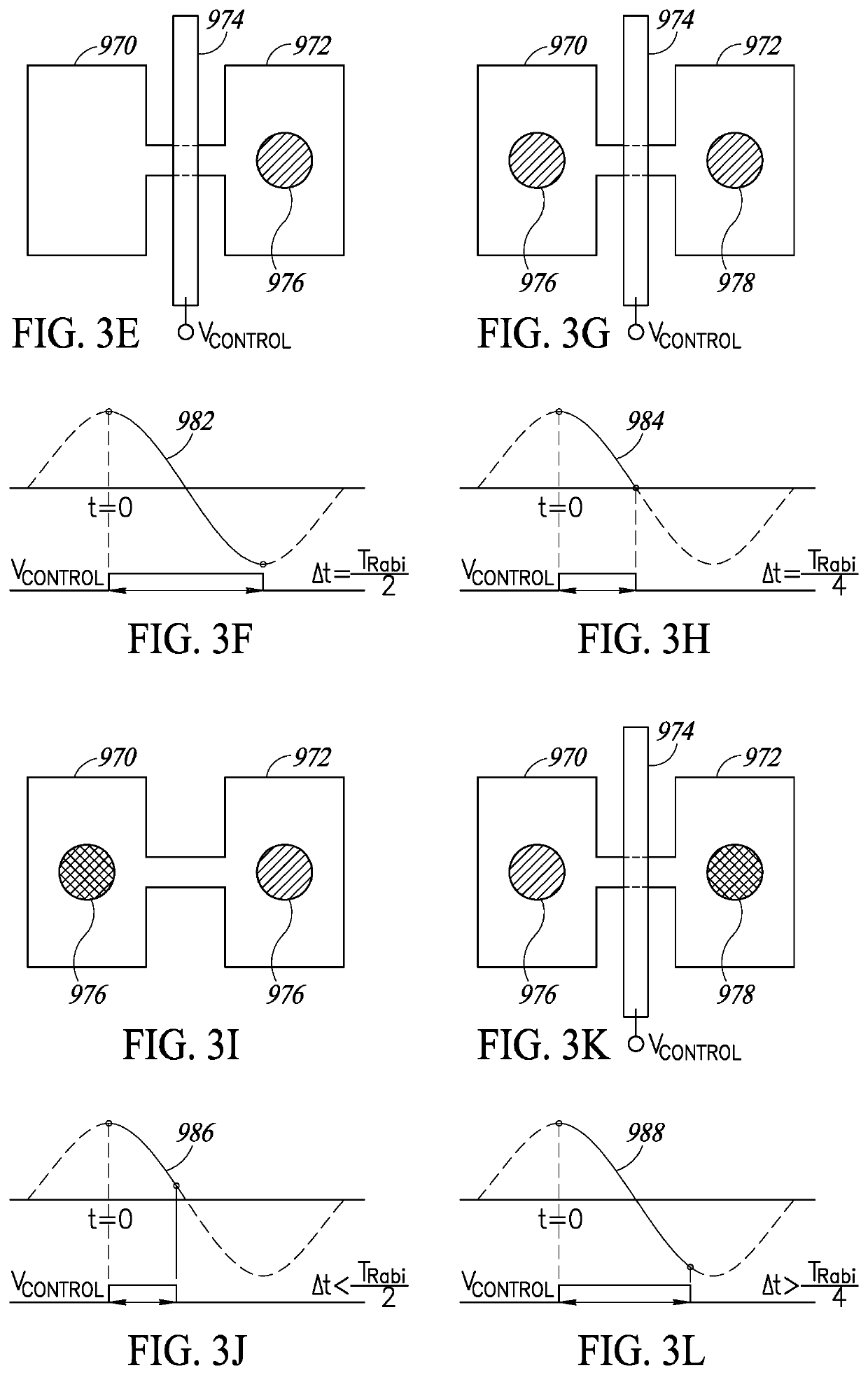
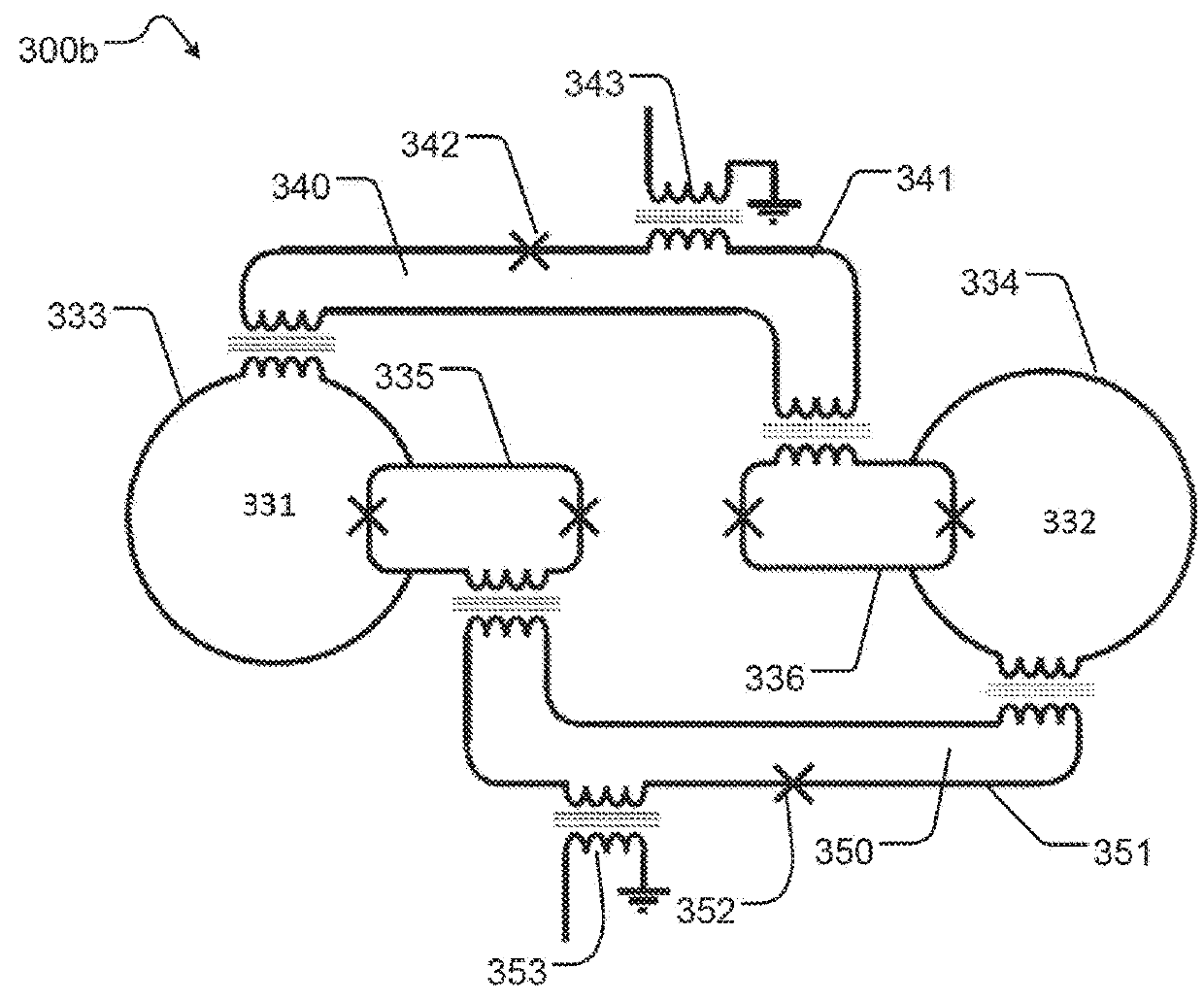
Quantum annealing may include applying and gradually removing disorder terms to qubits of a quantum processor, for example superconducting flux qubits of a superconducting quantum processor. A problem Hamiltonian may be established by applying control signals to the qubits, an evolution Hamiltonian established by applying disorder terms, and annealing by gradually removing the disorder terms. Change in persistent current in the qubits may be compensated. Multipliers may mediate coupling between various qubits and a global signal line, for example by applying respective scaling factors. Two global signal lines may be arranged in an interdigitated pattern to couple to respective qubits of a communicatively coupled pair of qubits. Pairs of qubits may be communicatively isolated and used to measure a response of one another to defined signals.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Method and apparatus for evolving a quantum system using a mixed initial hamiltonian comprising both diagonal and off-diagonal terms
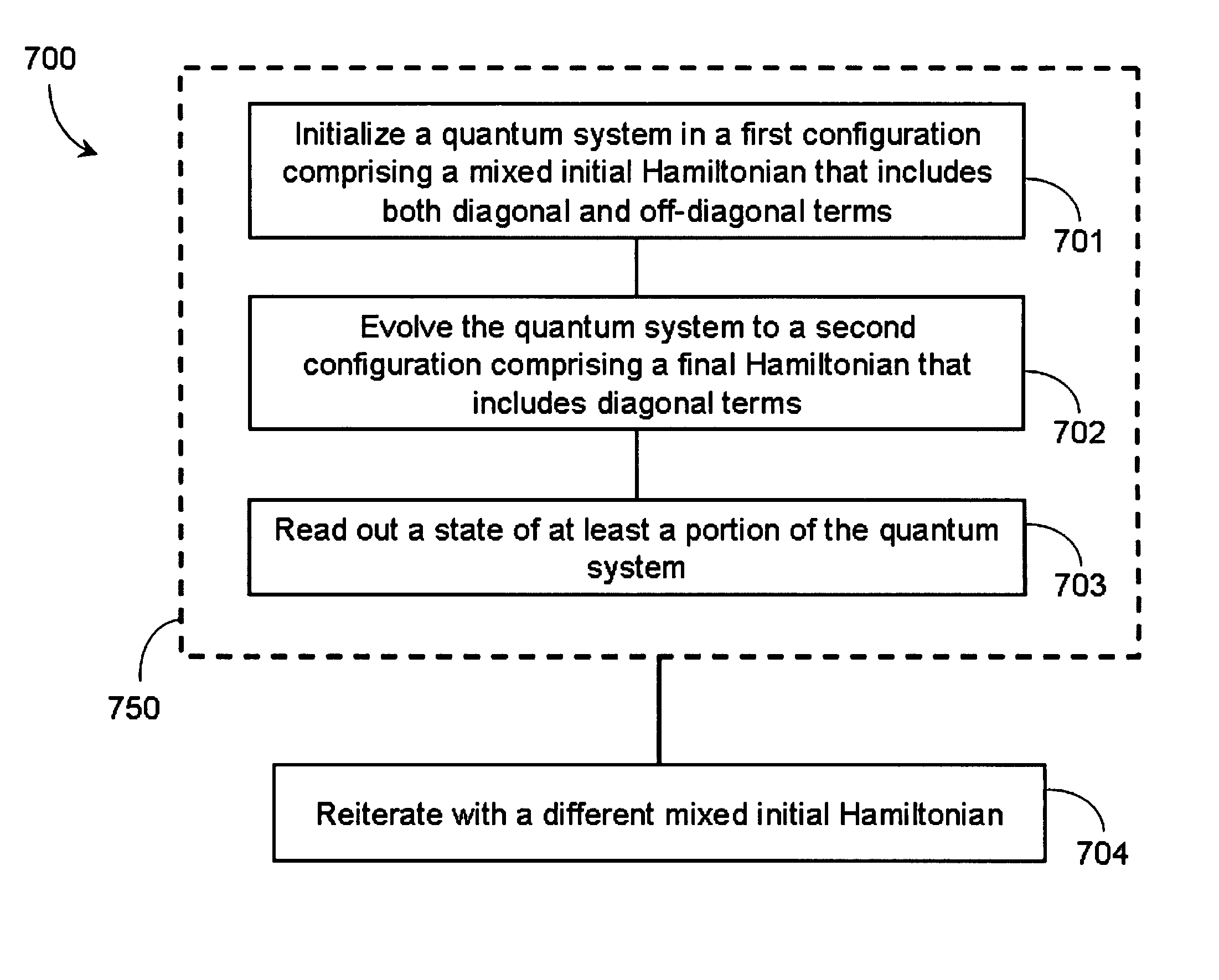
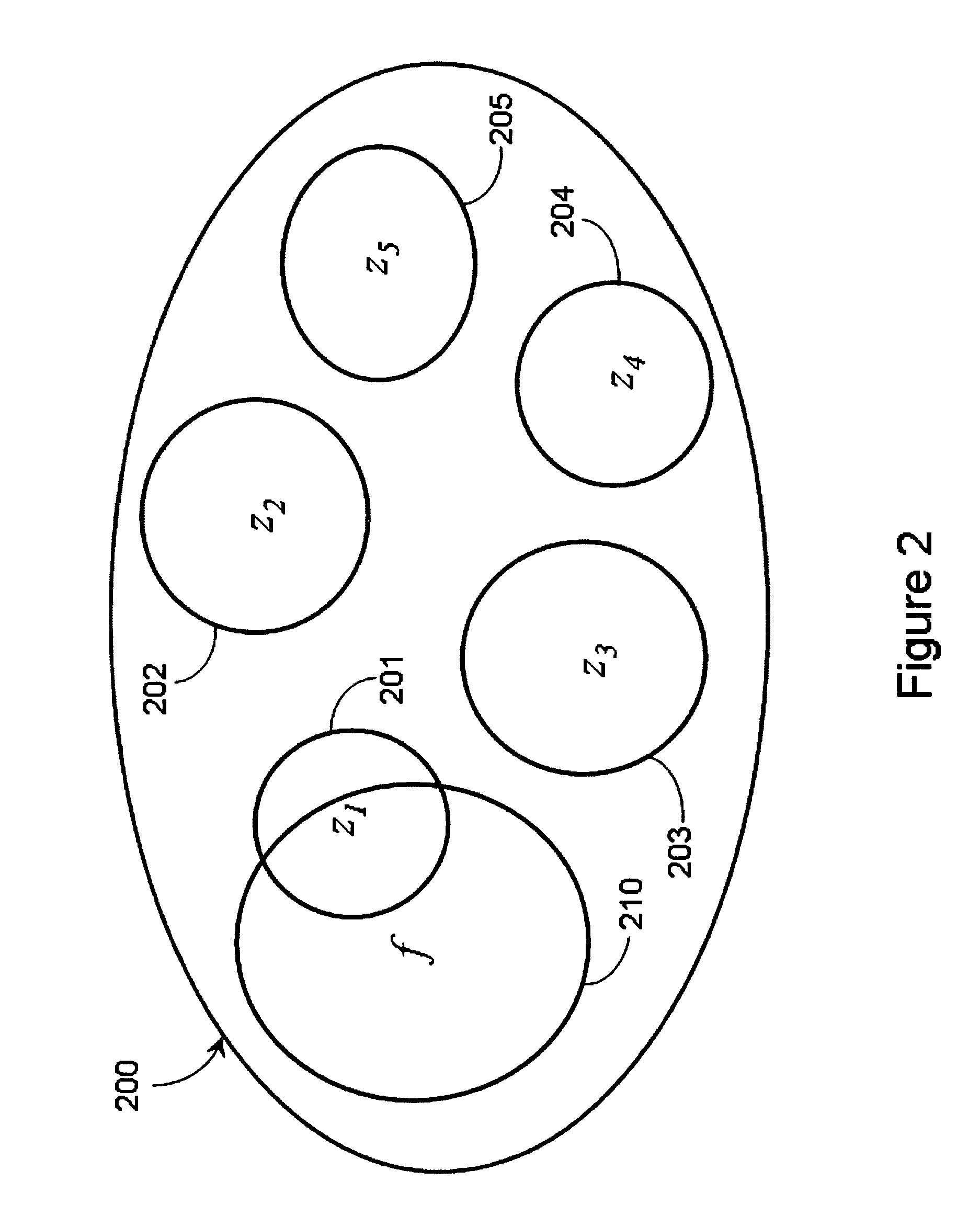
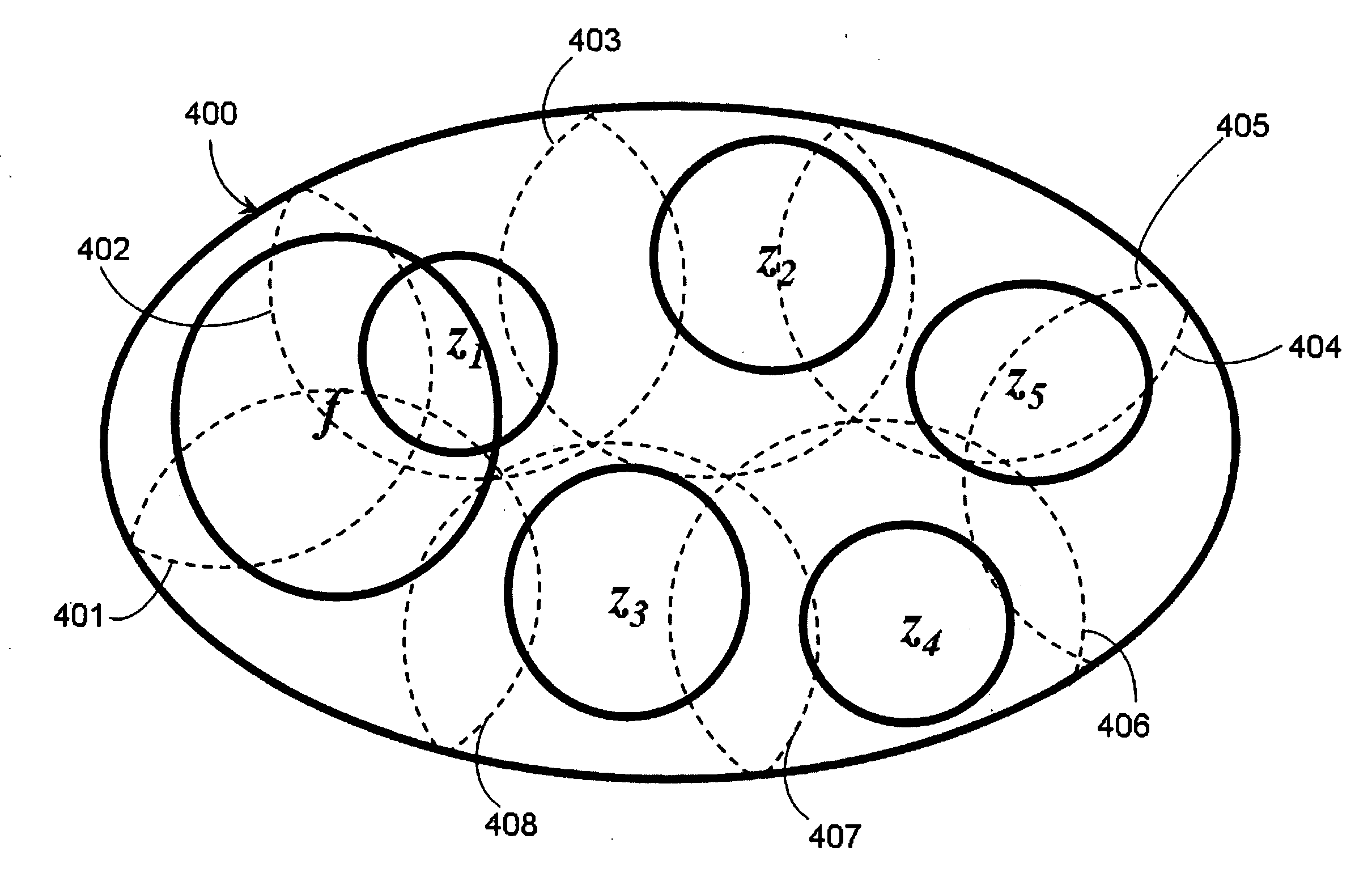
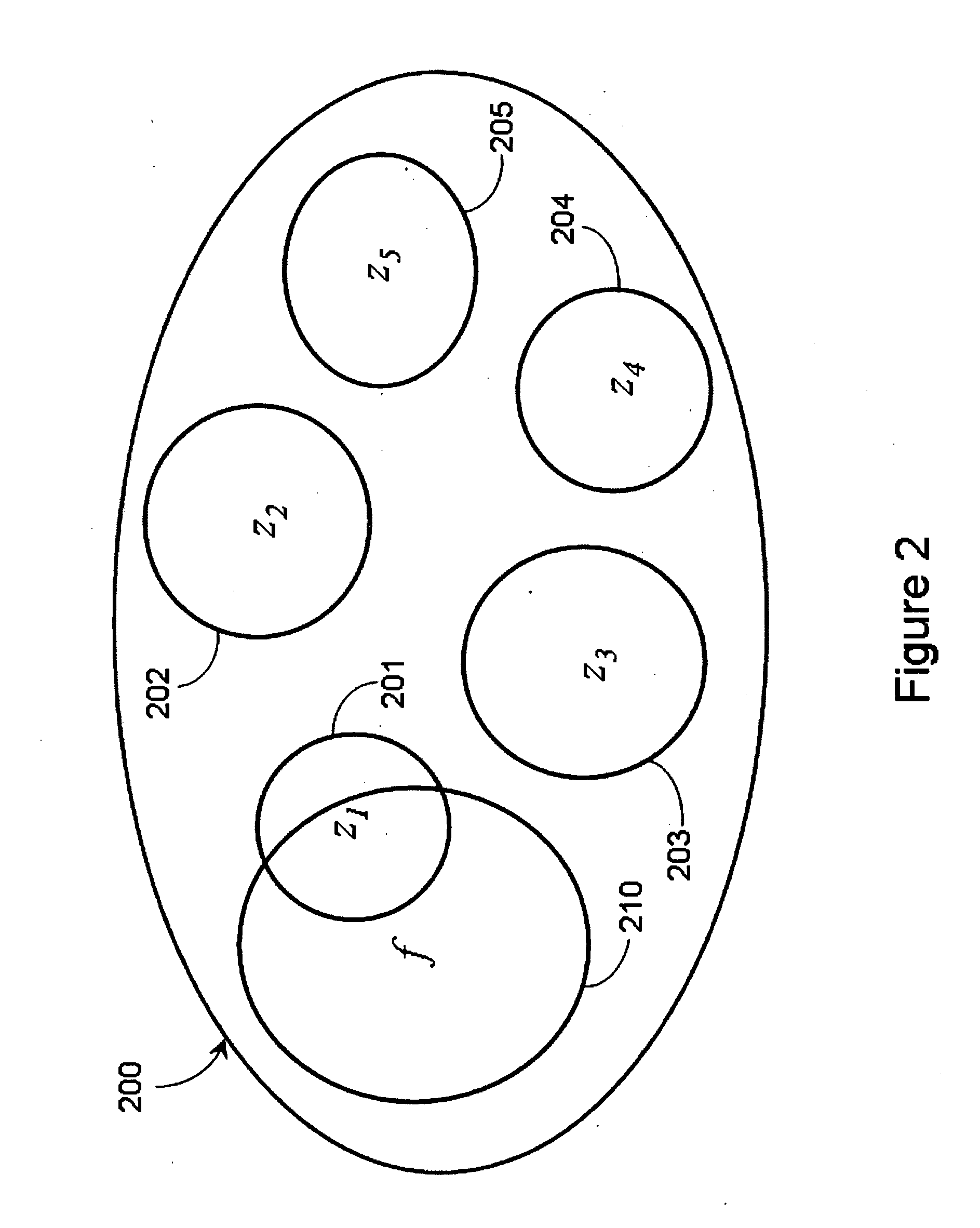
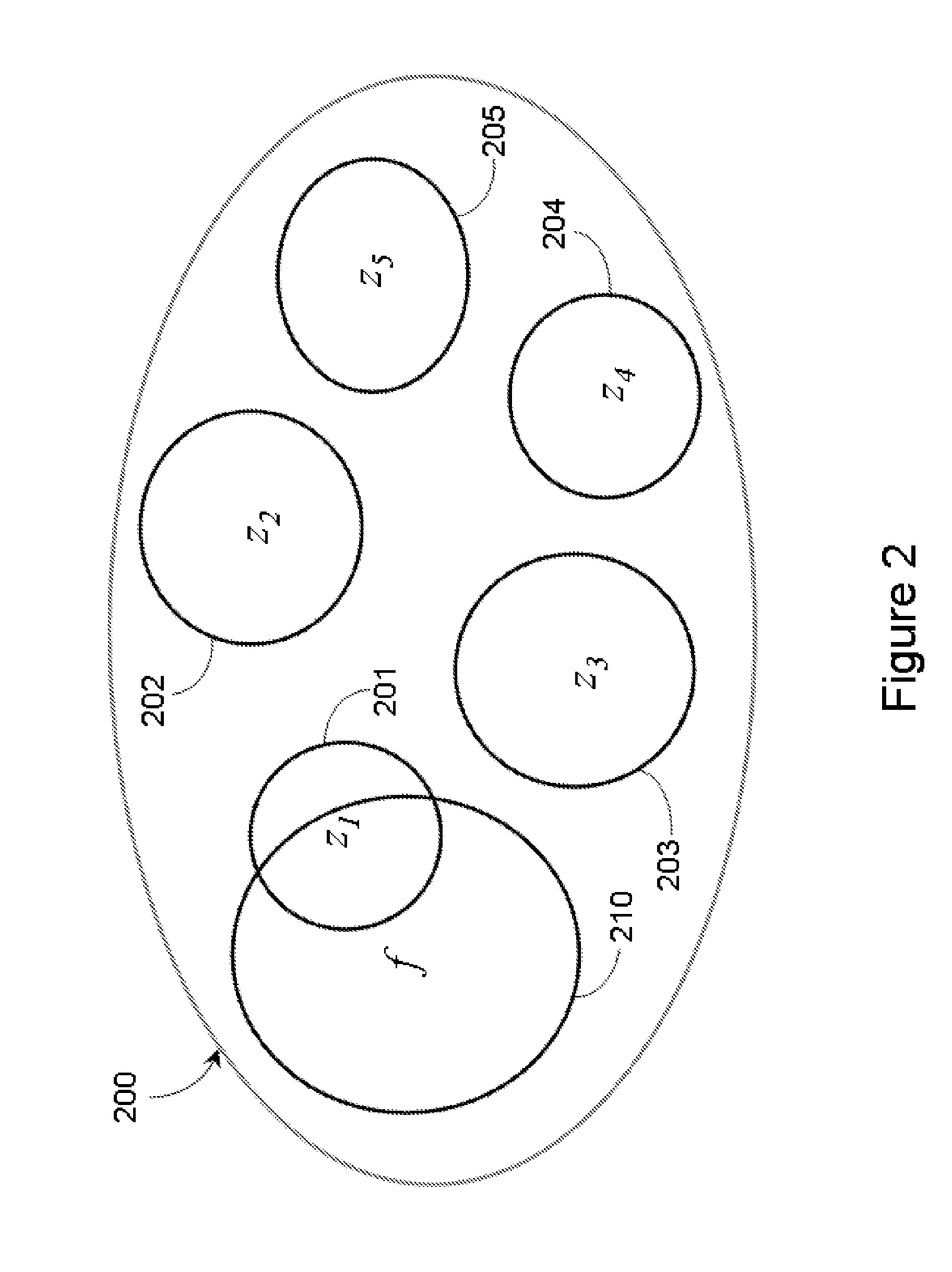
Various adaptations to adiabatic quantum computation and quantum annealing are described. These adaptations generally involve tailoring an initial Hamiltonian so that a local minimum is avoided when a quantum processor is evolved from the initial Hamiltonian to a problem Hamiltonian. The initial Hamiltonian may represent a mixed Hamiltonian that includes both diagonal and off-diagonal terms, where the diagonal terms at least partially define a center point of a first computation space that is at least partially contained within a second computation space. A problem Hamiltonian may be evolved into a low energy state by inhomogeneously inducing disorder in the qubits of the quantum processor. A higher degree of disorder may be induced in a subset of qubits predicted to contribute to a local minimum of the problem Hamiltonian.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems, methods and apparatus for adiabatic quantum computation and quantum annealing
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Quantum and digital processor hybrid systems and methods to solve problems
Quantum and digital processors are employed together to solve computational problems. The quantum processor may be configured with a problem via a problem Hamiltonian and operated to perform adiabatic quantum computation and / or quantum annealing on the problem Hamiltonian to return a first solution to the problem that is in the neighborhood of the global minimum of the problem Hamiltonian. The digital processor may then be used to refine the first solution to the problem by casting the first solution to the problem as a starting point for a classical optimization algorithm. The classical optimization algorithm may return a second solution to the problem that corresponds to a lower energy state in the neighborhood of the global minimum, such as a ground state of the problem Hamiltonian. The quantum processor may include a superconducting quantum processor implementing superconducting flux qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
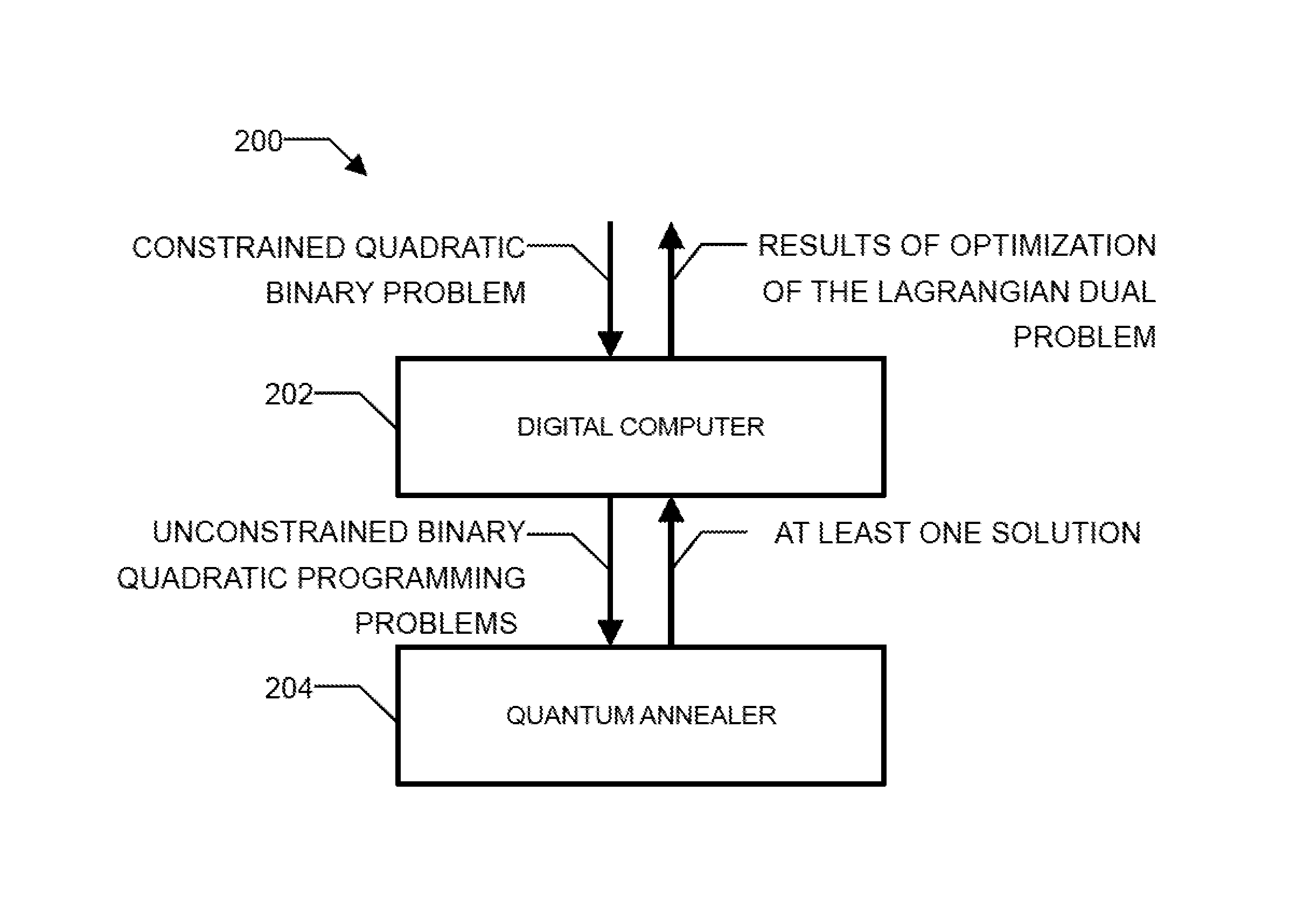
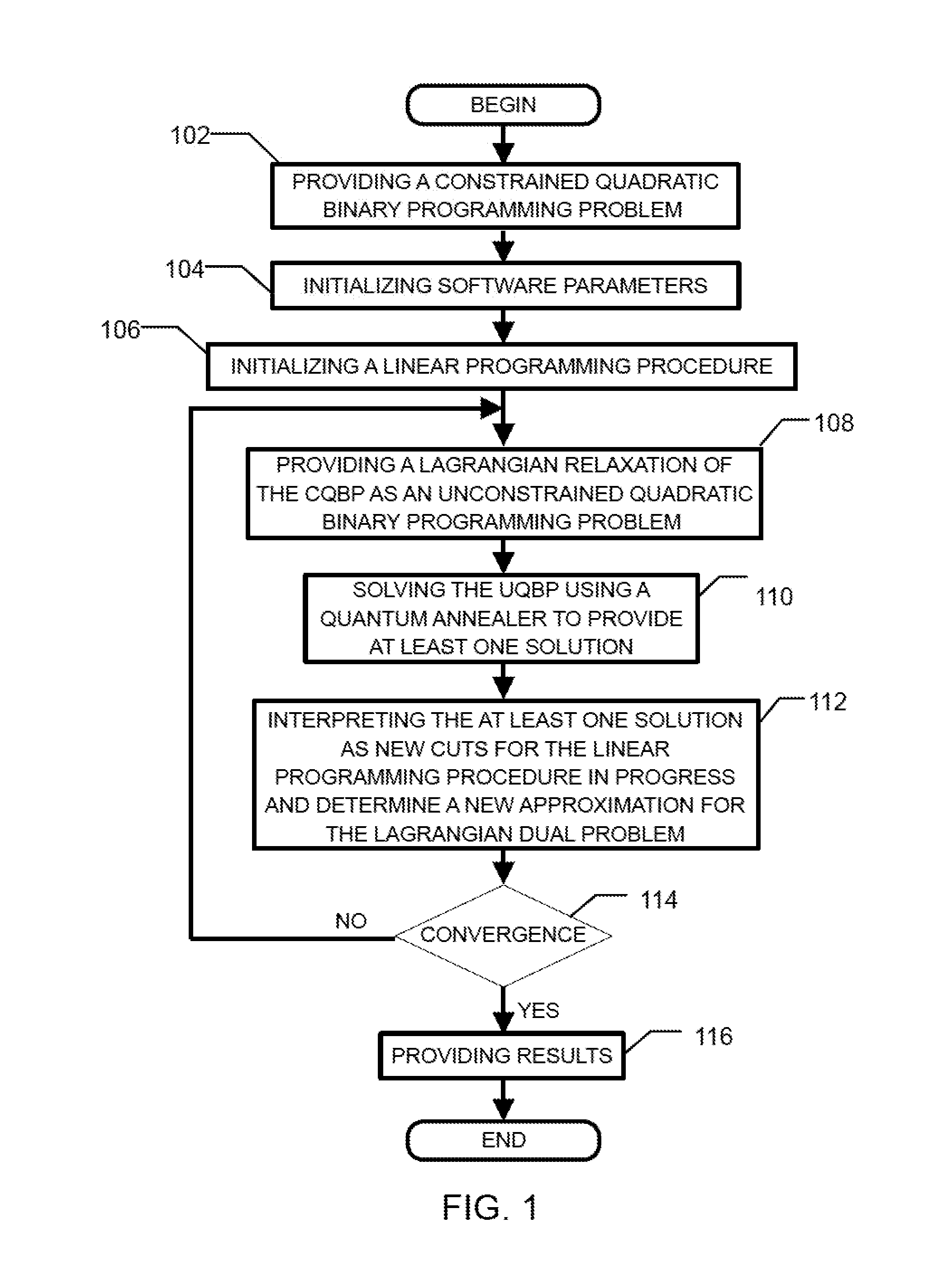
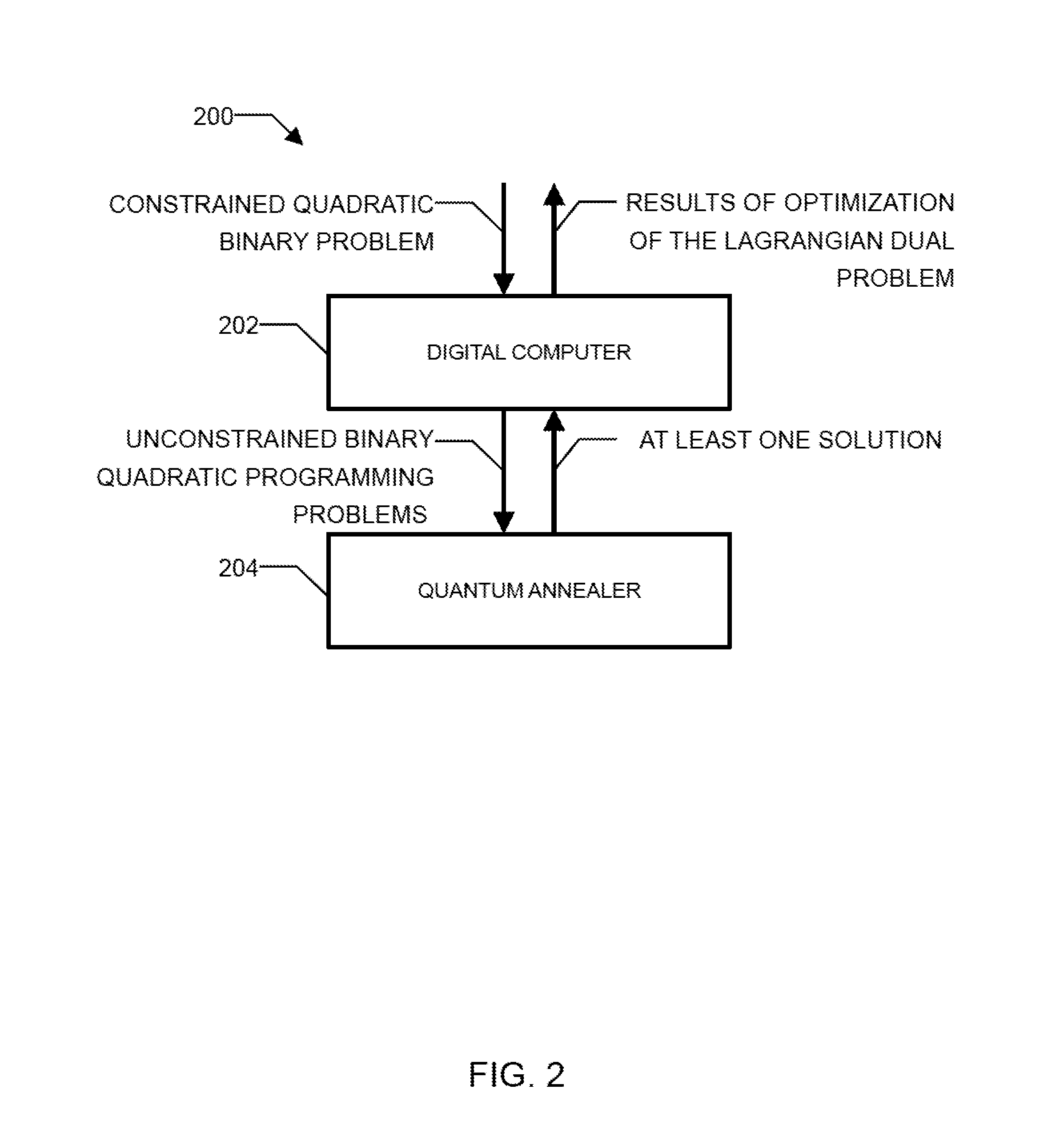
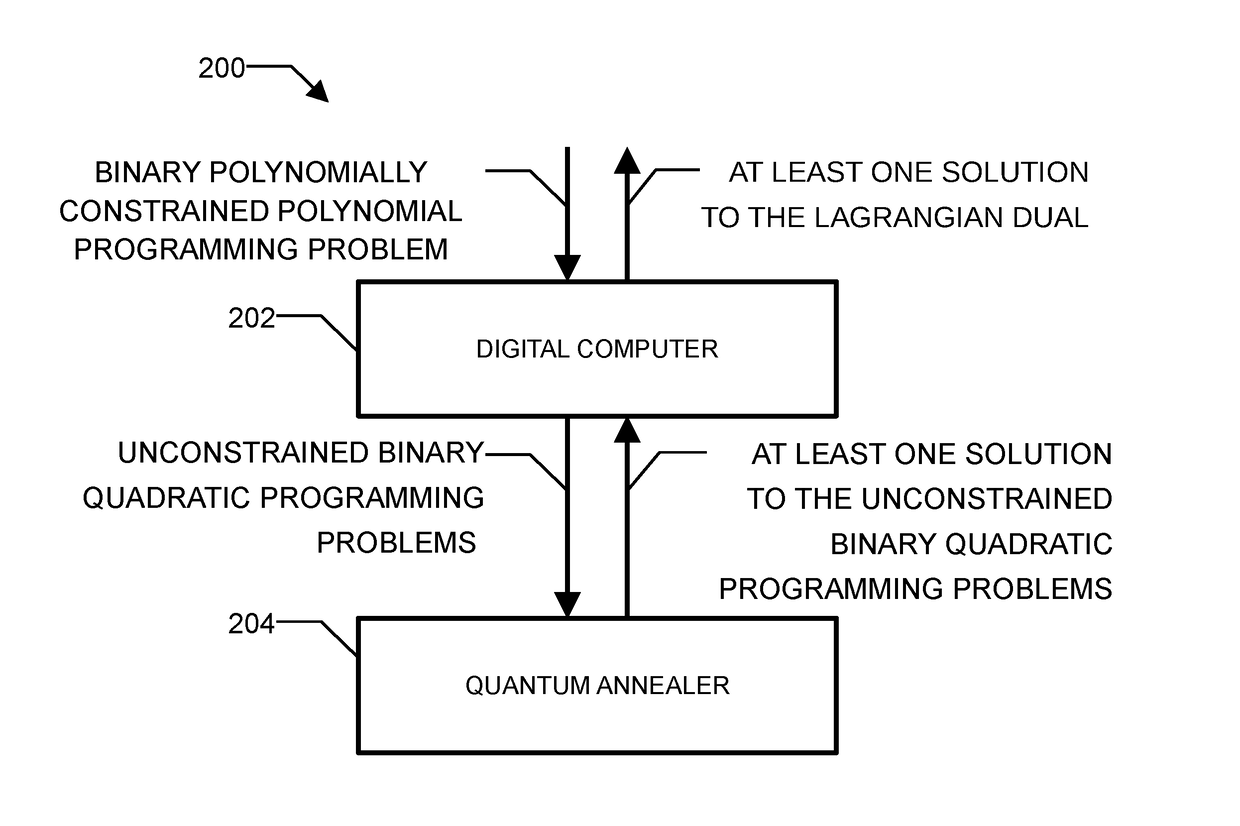
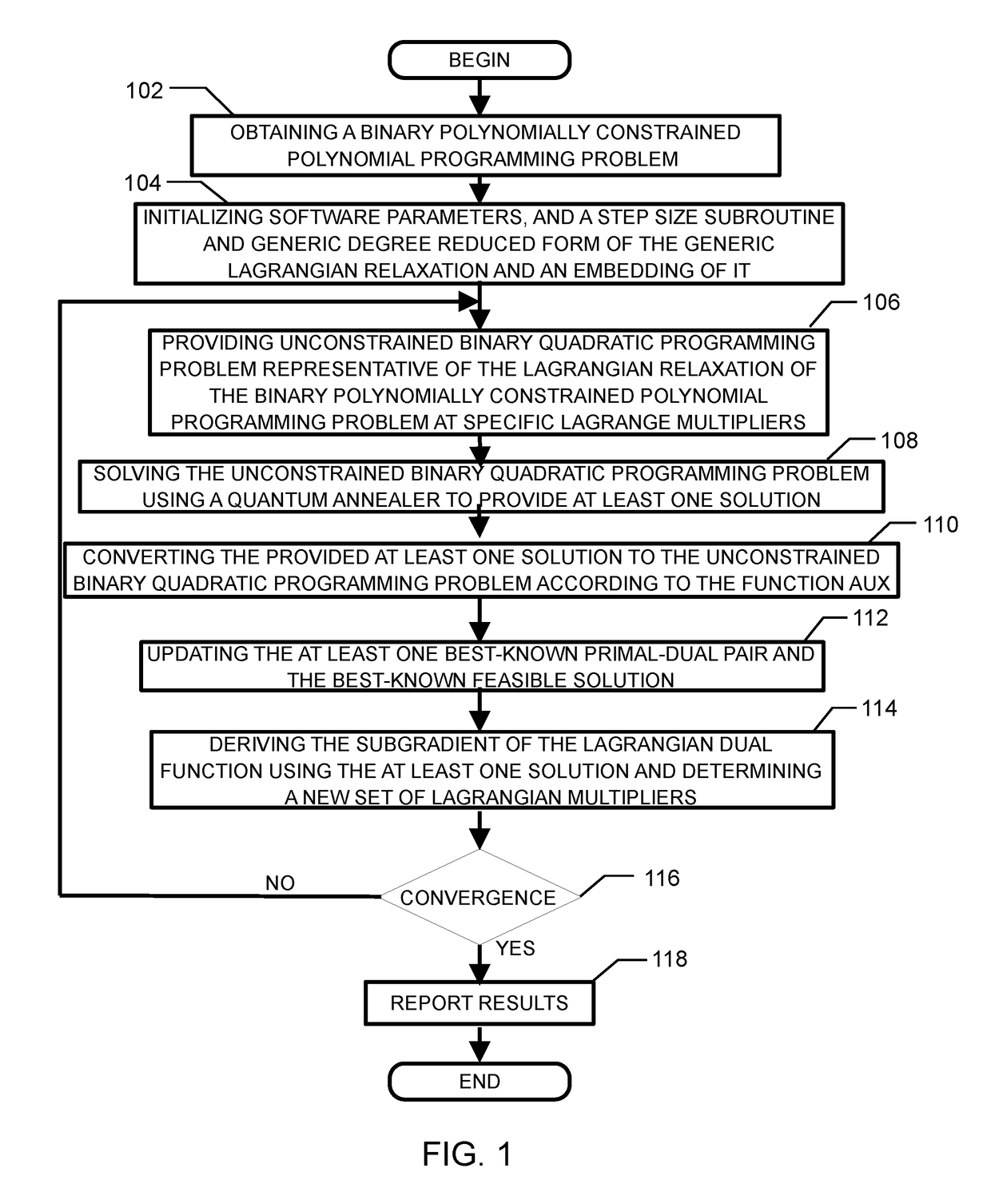
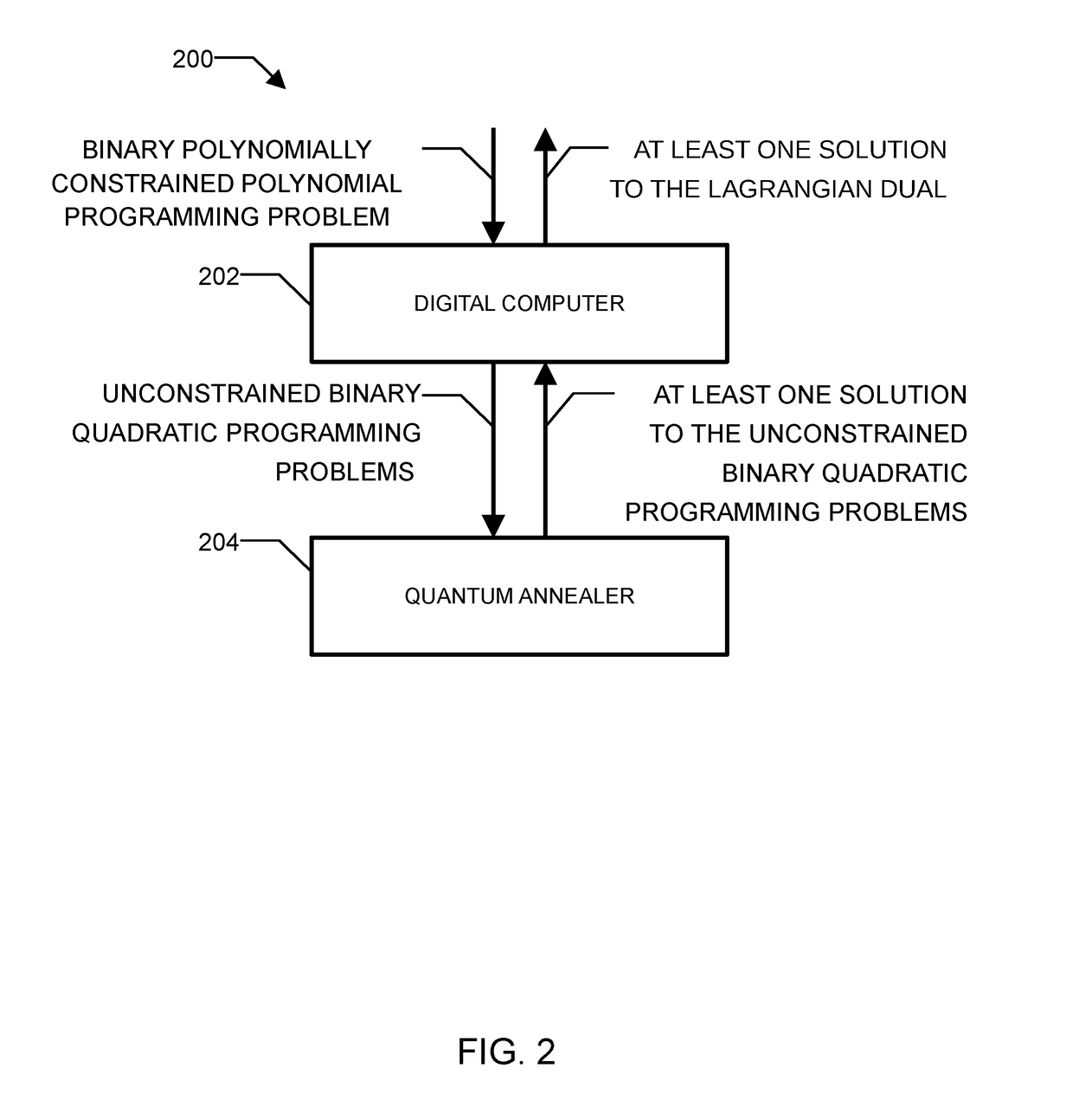
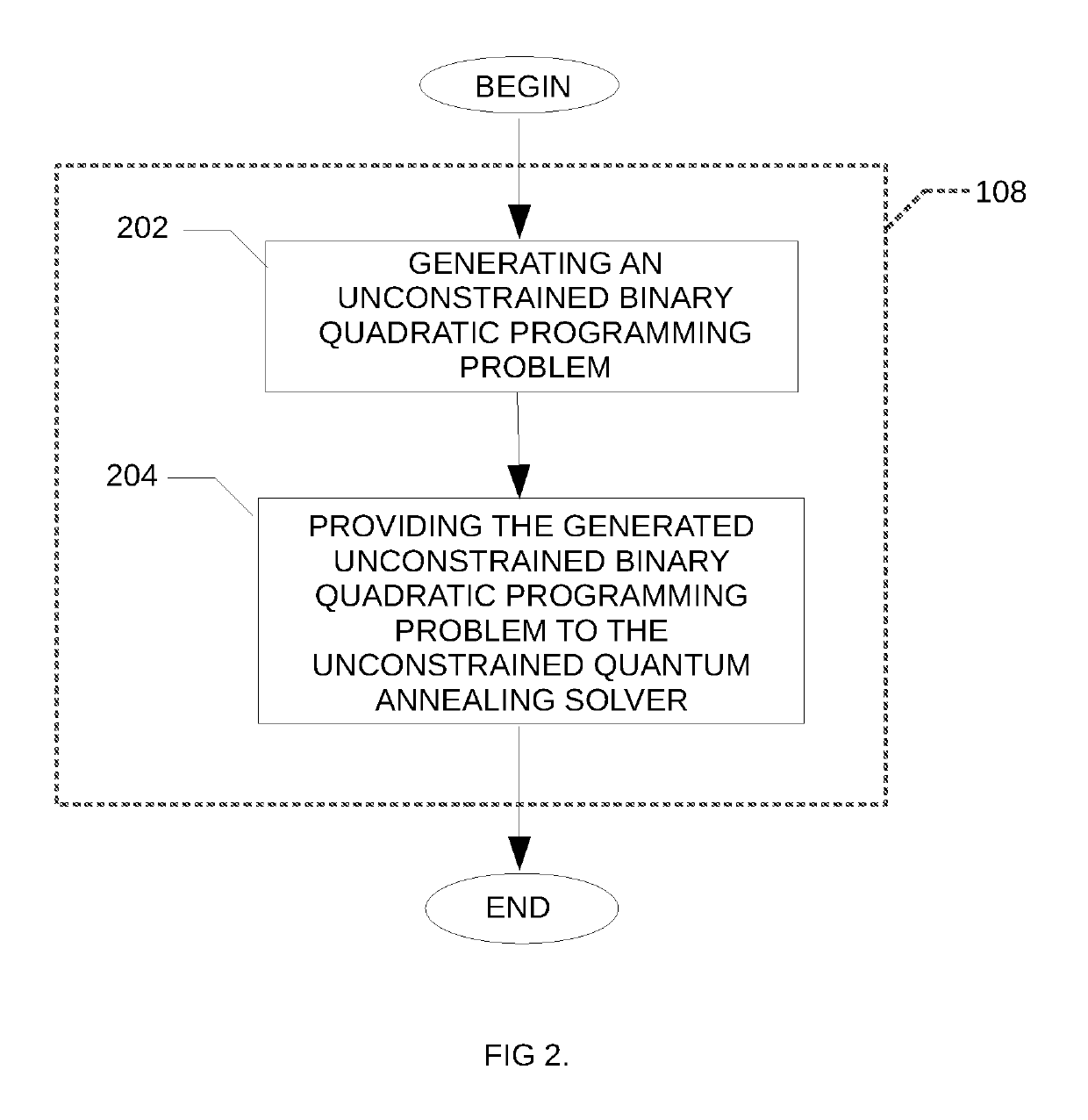
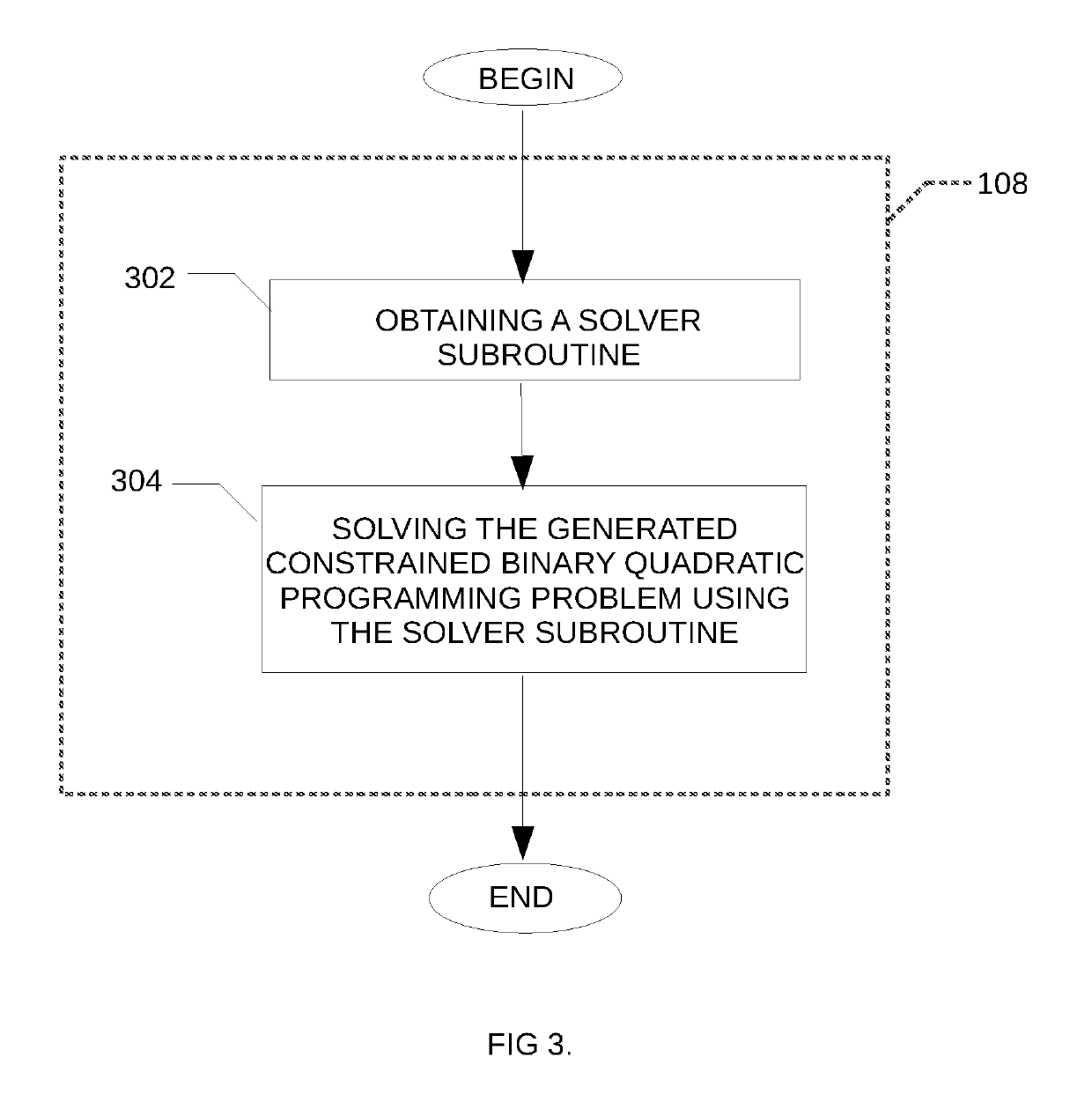
Method and system for solving the lagrangian dual of a constrained binary quadratic programming problem using a quantum annealer
InactiveUS20160224515A1Speed up the processQuantum computersComplex mathematical operationsComputer scienceQuantum
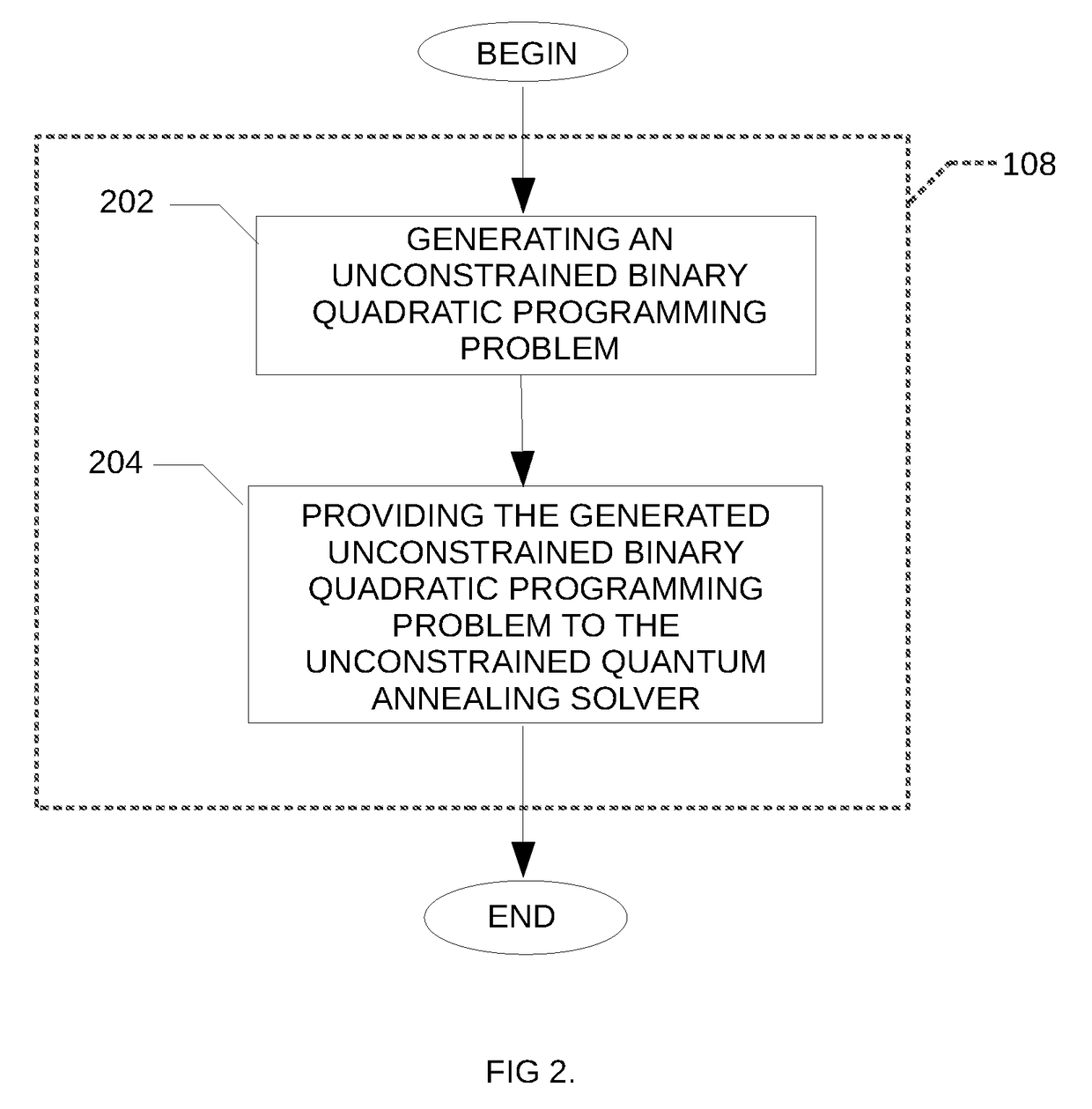
A method is disclosed for solving the Lagrangian dual of a constrained binary quadratic programming problem. The method comprises obtaining a constrained quadratic binary programming problem; until a convergence is detected, iteratively, performing a Lagrangian relaxation of the constrained quadratic binary programming problem to provide an unconstrained quadratic binary programming problem, providing the unconstrained quadratic binary programming problem to a quantum annealer, obtaining from the quantum annealer at least one corresponding solution, using the at least one corresponding solution to generate a new approximation for the Lagrangian dual bound; and providing a corresponding solution to the Lagrangian dual of the constrained binary quadratic programming problem after convergence.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
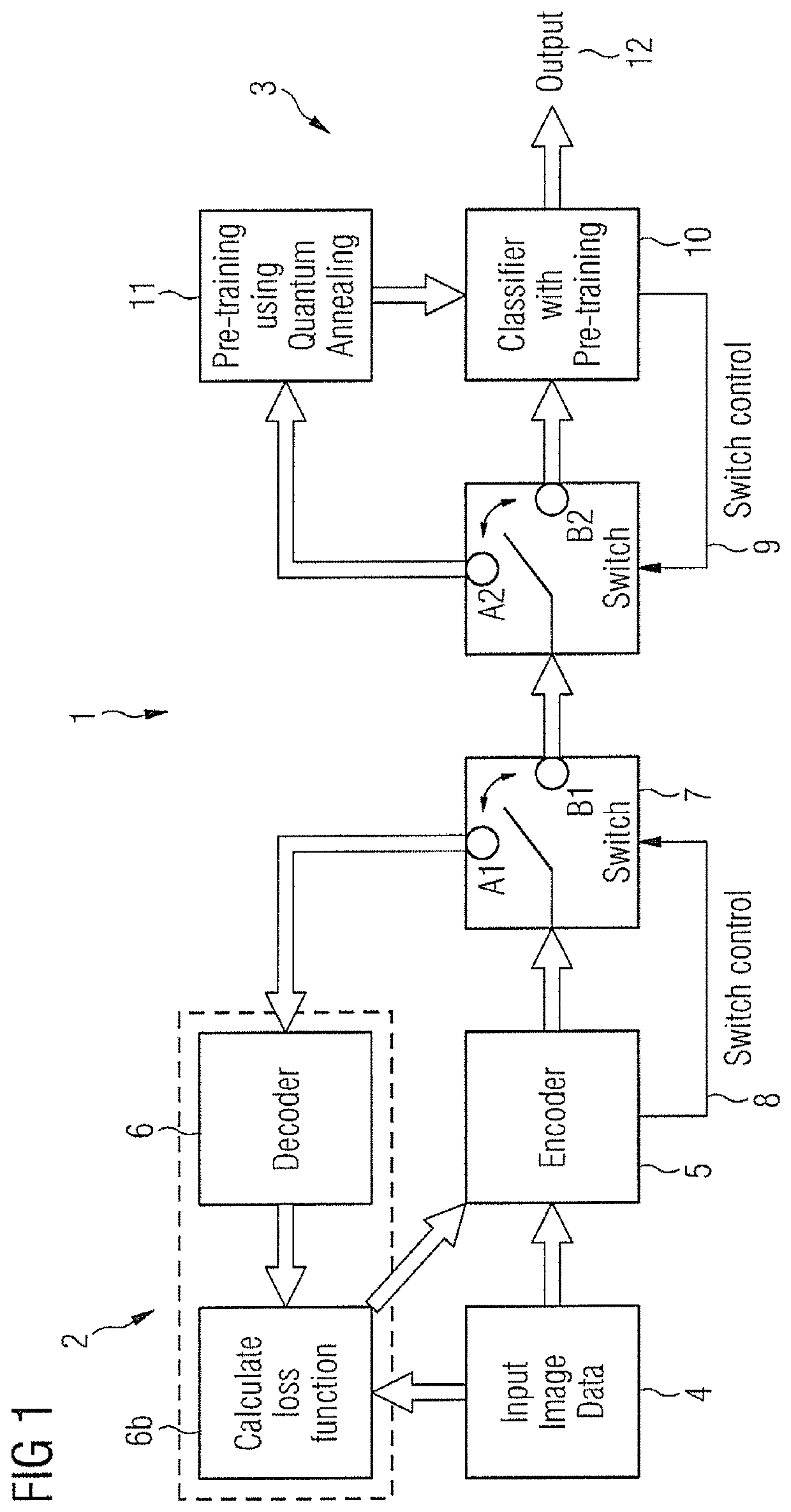
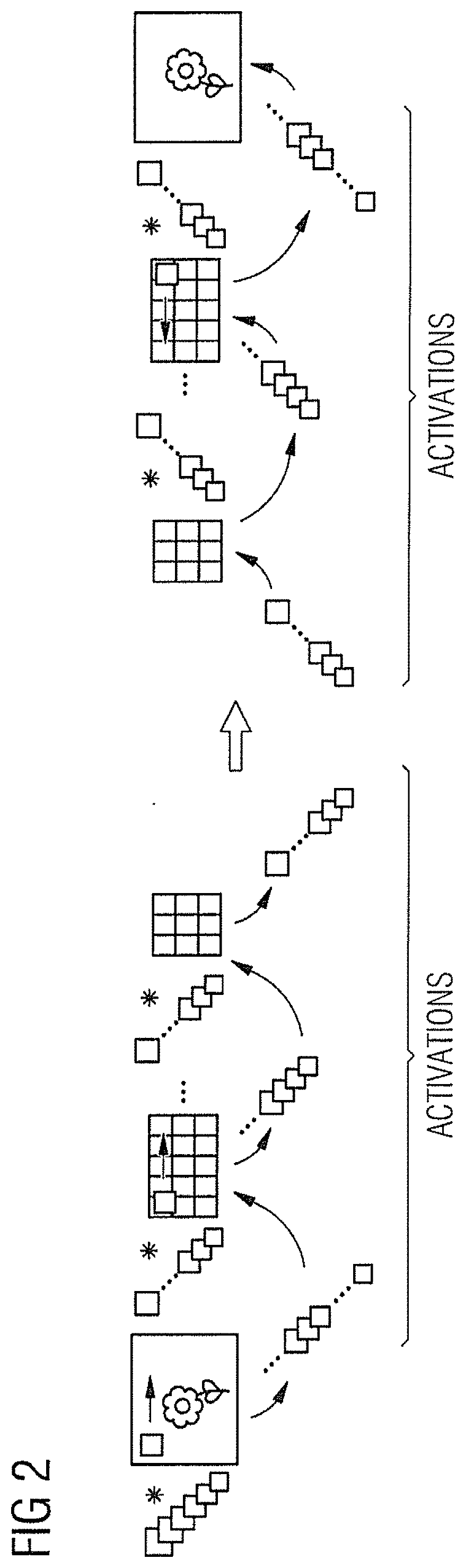
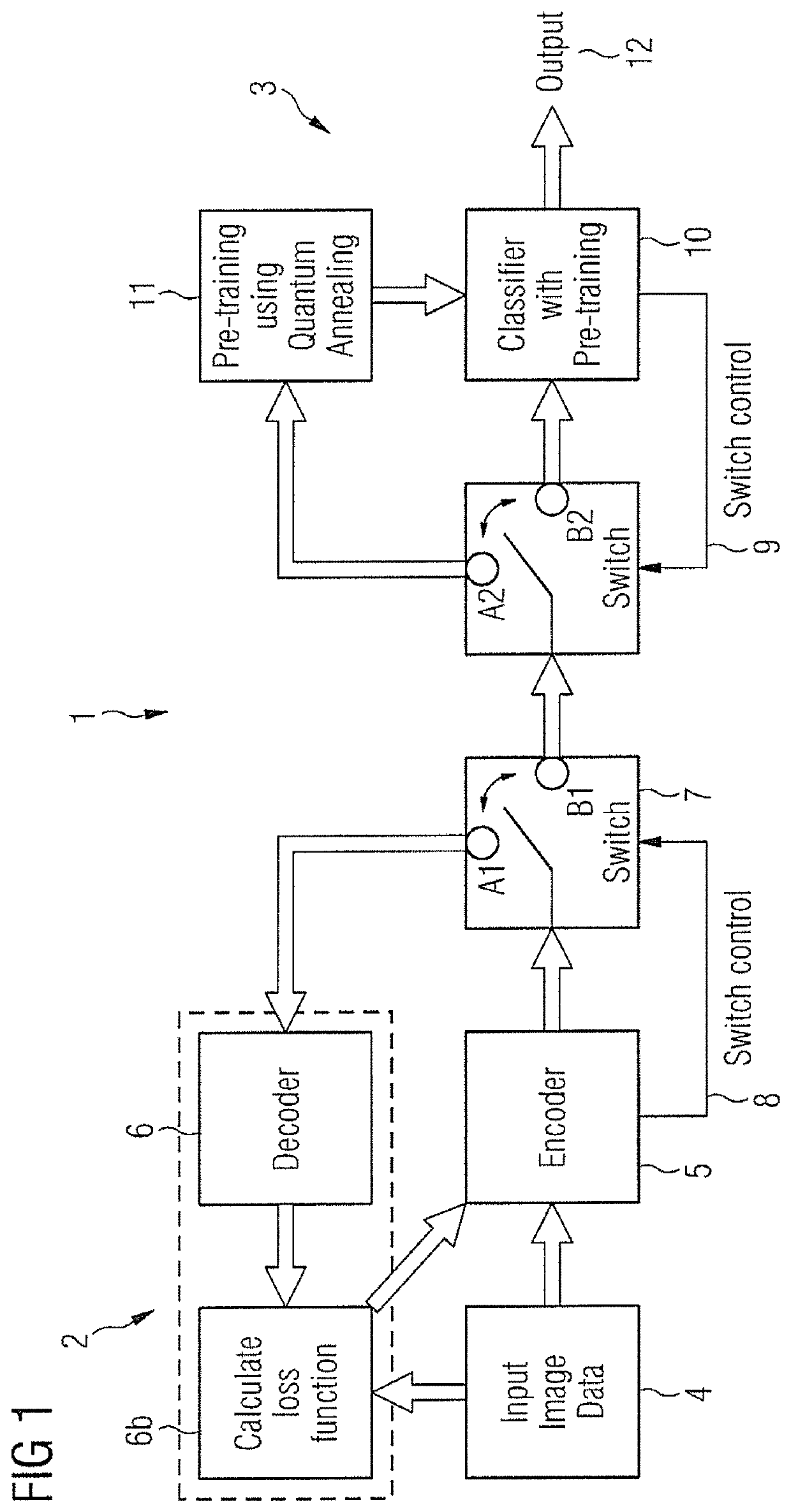
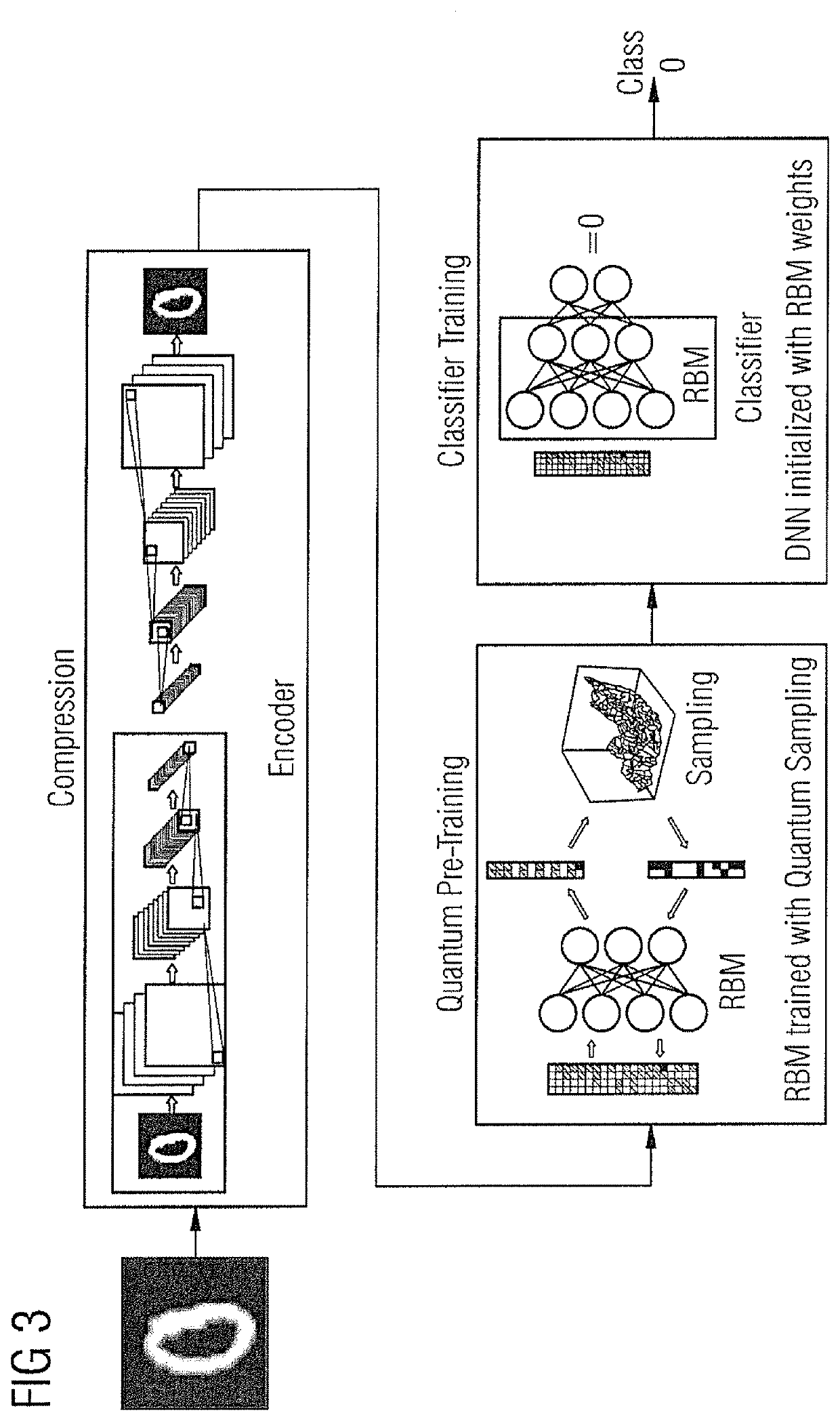
Data encoding and classification
ActiveUS20200005154A1Quantum computersEnsemble learningPattern recognitionRestricted Boltzmann machine
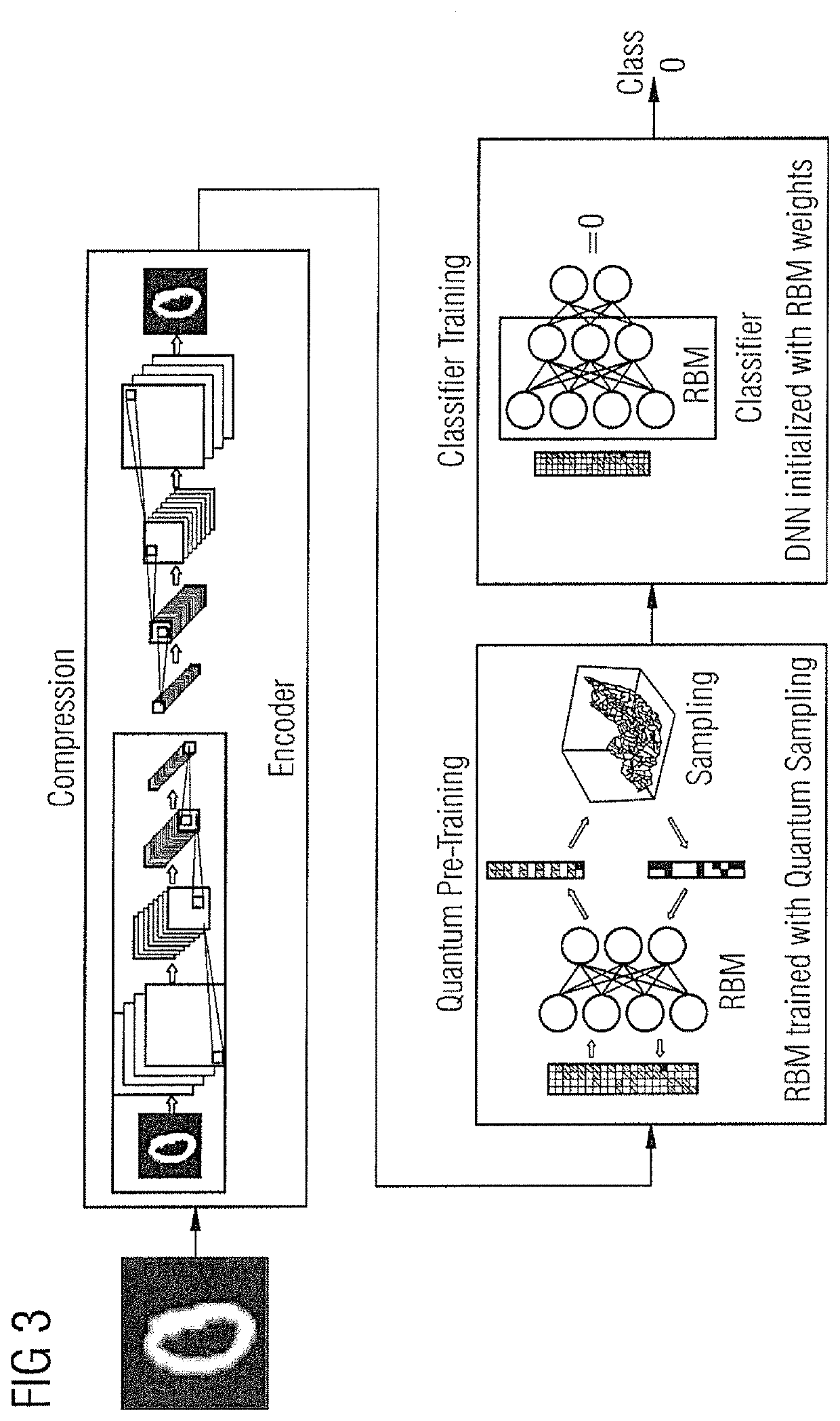
In a method and apparatus for training a computer system for use in classification of an image by processing image data representing the image, image data are compressed and then loaded into a programmable quantum annealing device that includes a Restricted Boltzmann Machine. The Restricted Boltzmann Machine is trained to act as a classifier of image data, thereby providing a trained Restricted Boltzmann Machine; and, the trained Restricted Boltzmann Machine is used to initialize a neural network for image classification thereby providing a trained computer system for use in classification of an image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE LTD +1
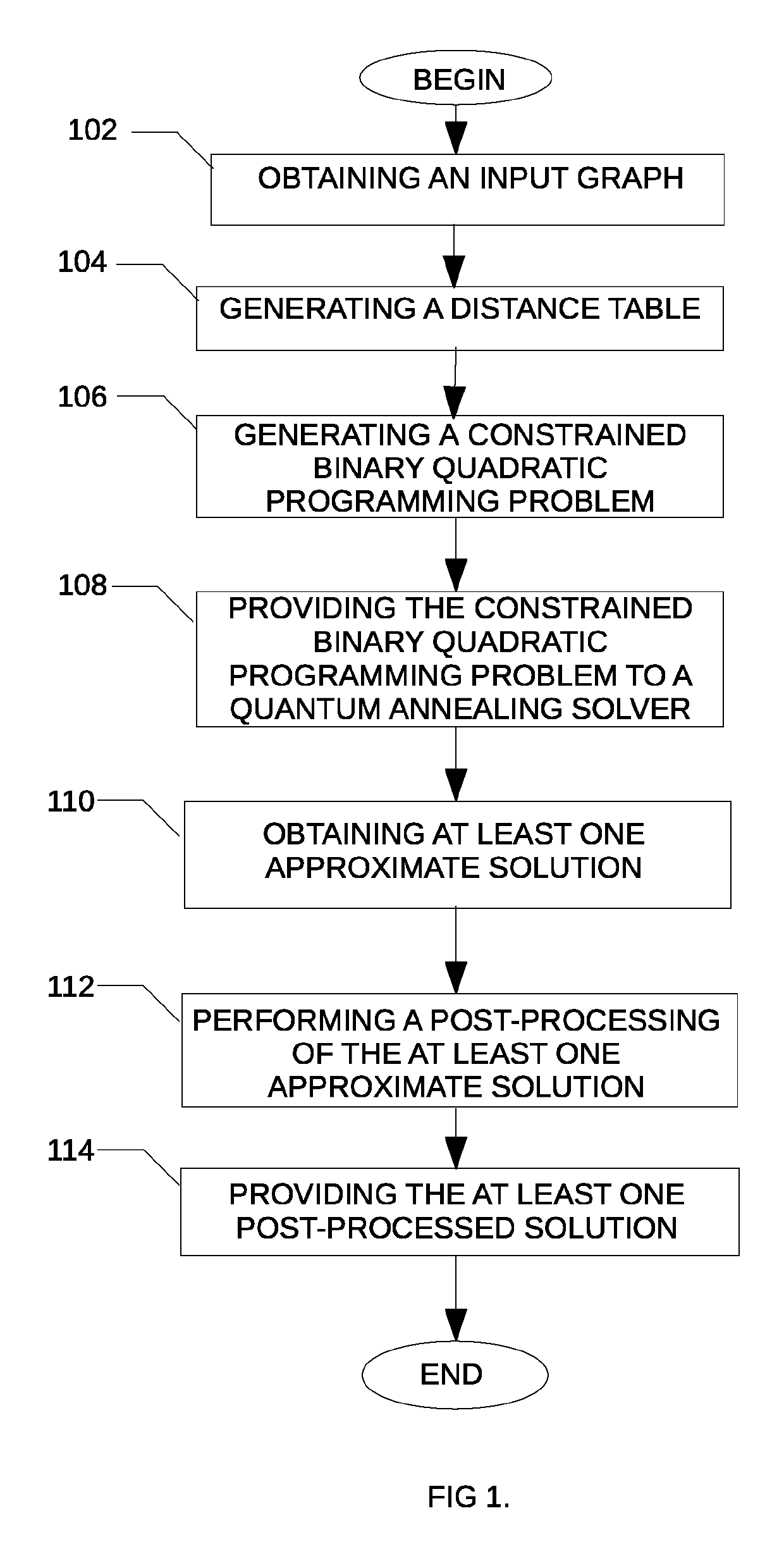
Method and system for solving a minimum connected dominating set problem using quantum annealing for distance optimization
ActiveUS20170286852A1Less timeProcessing problemForecastingMachine learningNODALConnected dominating set
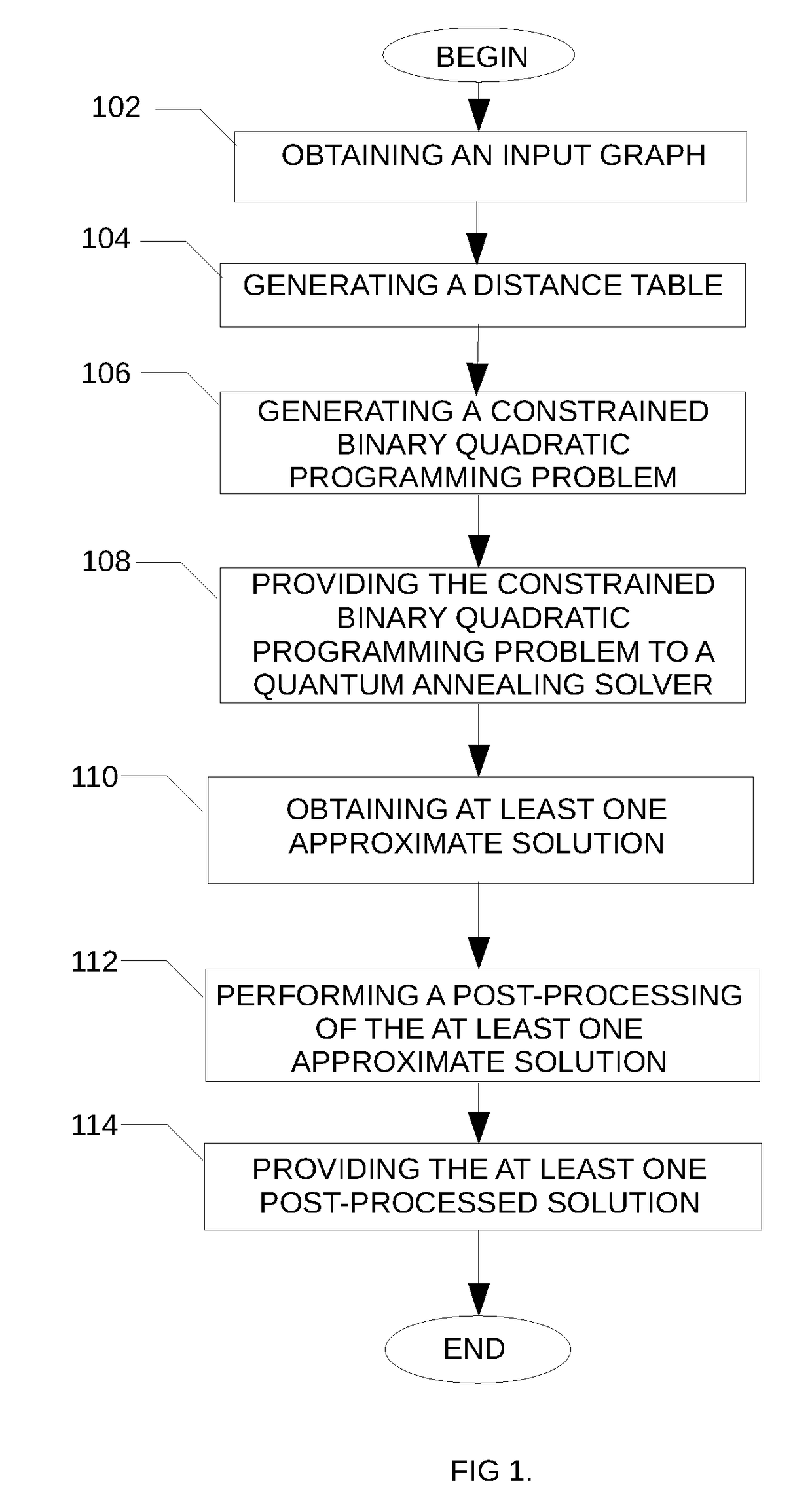
A method is disclosed for determining a minimum connected dominating set in a graph, the method comprising obtaining an indication of an input graph, the input graph comprising a plurality of nodes and a plurality of edges; generating a distance table comprising for each node of the input graph, an indication of a distance between the given node and each of the other node of the plurality of nodes; generating a corresponding constrained binary quadratic programming problem using the generated distance table; providing the corresponding constrained binary quadratic programming problem to a quantum annealing solver; obtaining at least one approximate solution from the quantum annealing solver; post-processing the at least one approximate solution and providing the post-processed at least one approximate solution.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
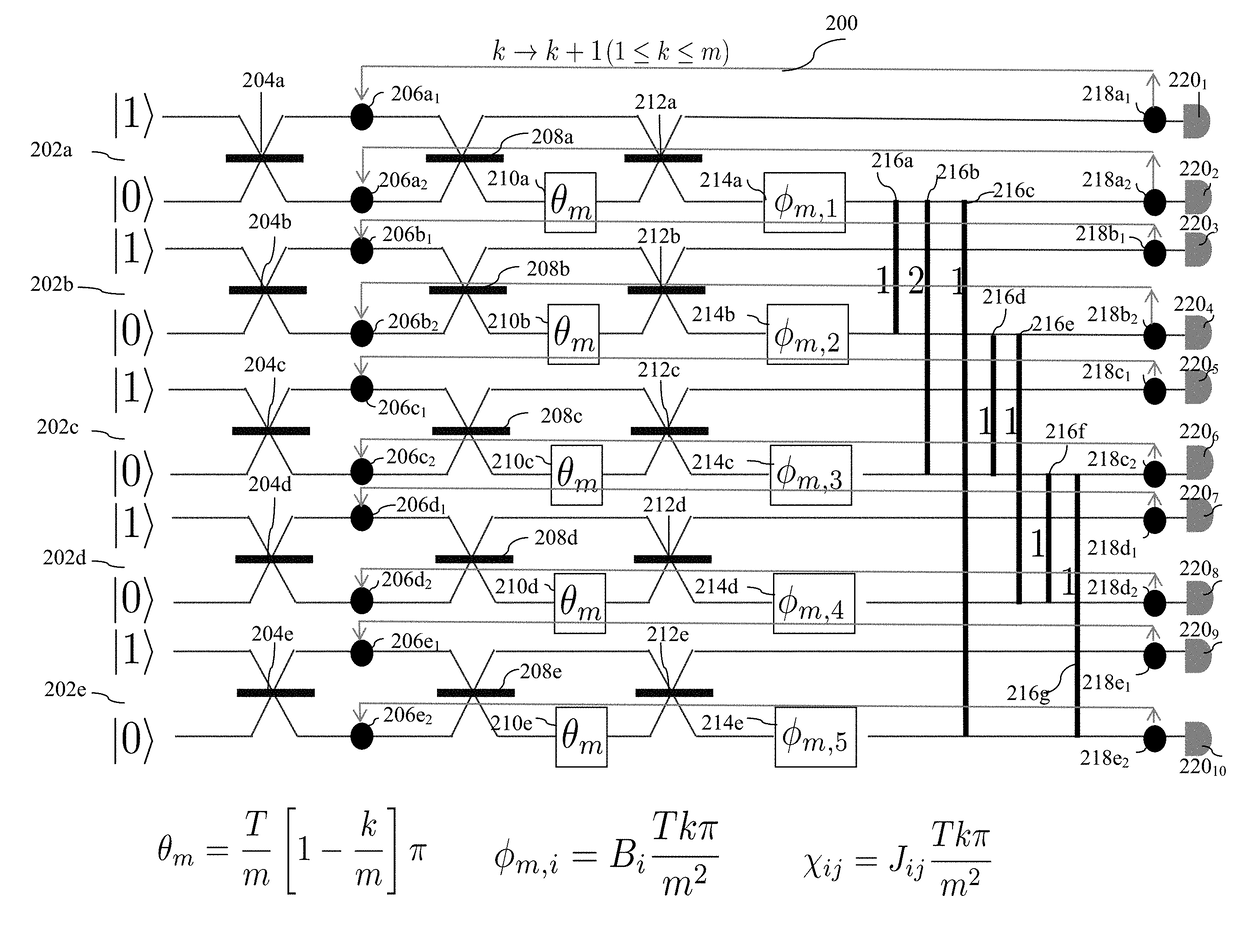
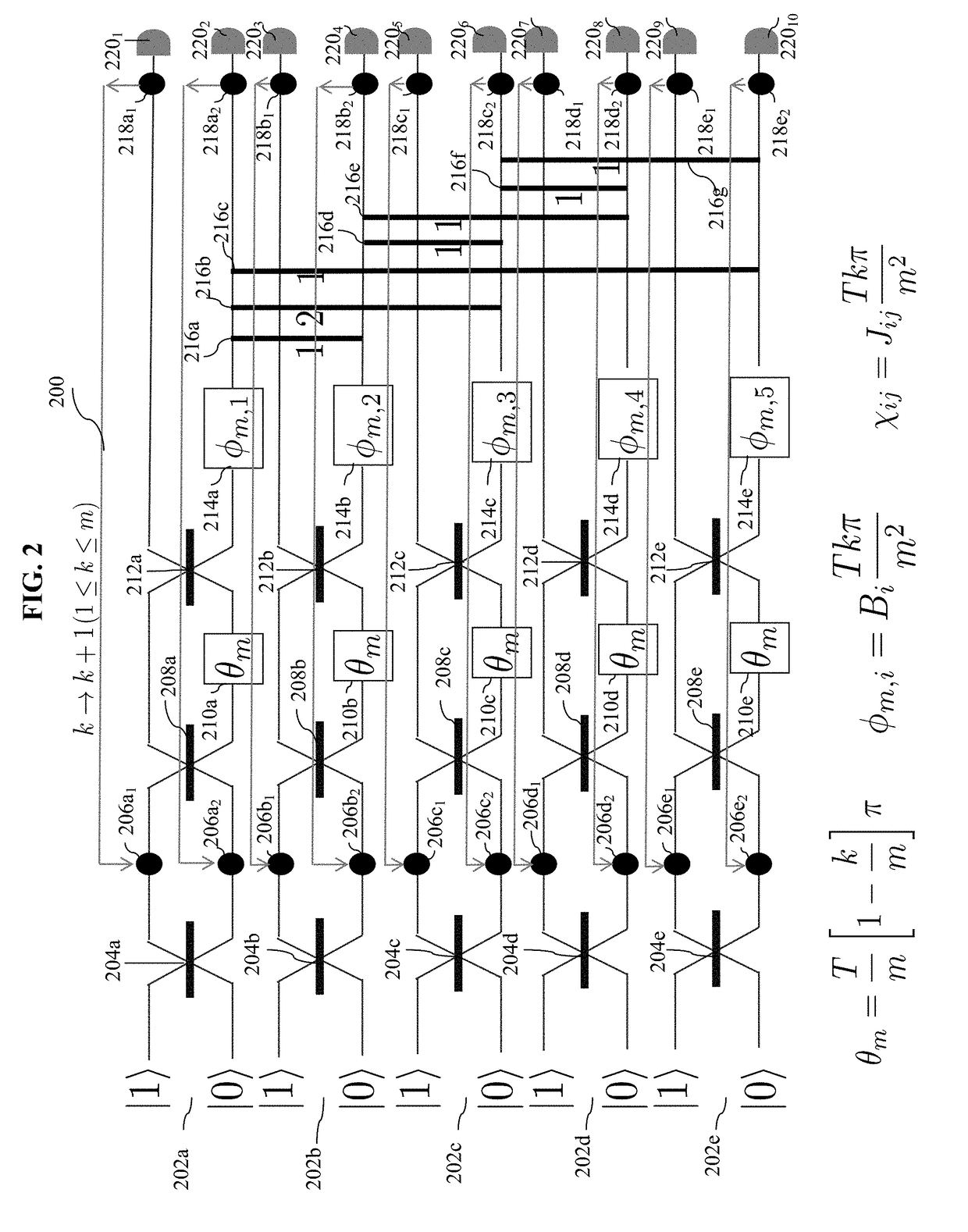
Optical ising-model solver using quantum annealing
ActiveUS20170264373A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsQuantum computersBeam splitterIsing model
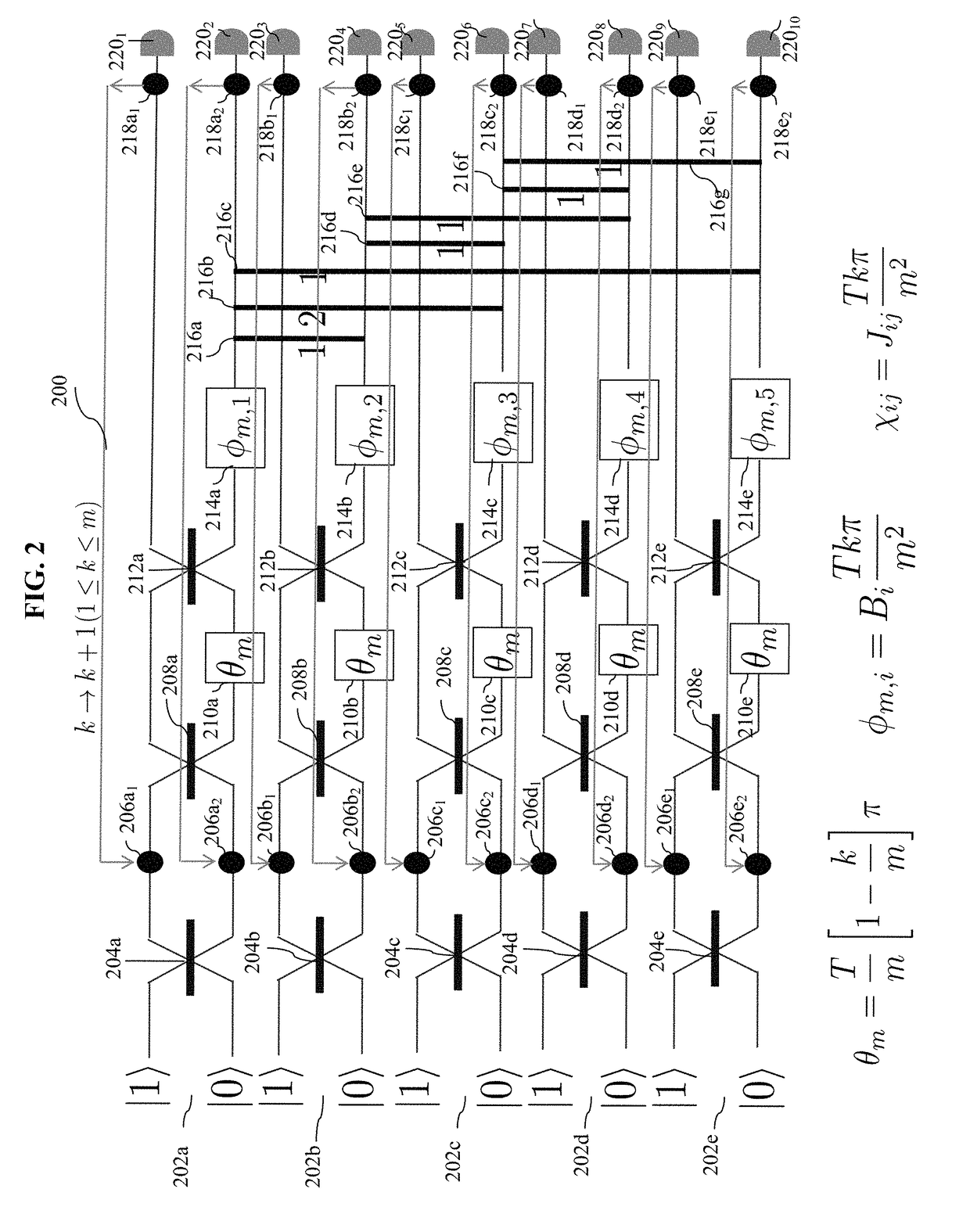
A method implemented by an optical circuit, including beam splitter, phase shifters and cross-phase modulators, for solving Ising-model using quantum annealing discretizes a continuous time-dependent Hamiltonian function over a time period T, into a plurality of smaller portions; implements each of said smaller portions with a non-linear optical medium, and iterates over said smaller portions to output a solution of the Ising Hamiltonian problem, using the optical components.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Method and system for solving the lagrangian dual of a binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem using a quantum annealer
InactiveUS20170242824A1Less sensitive to errorSpeed up the processQuantum computersComplex mathematical operationsPolynomial programmingPosynomial
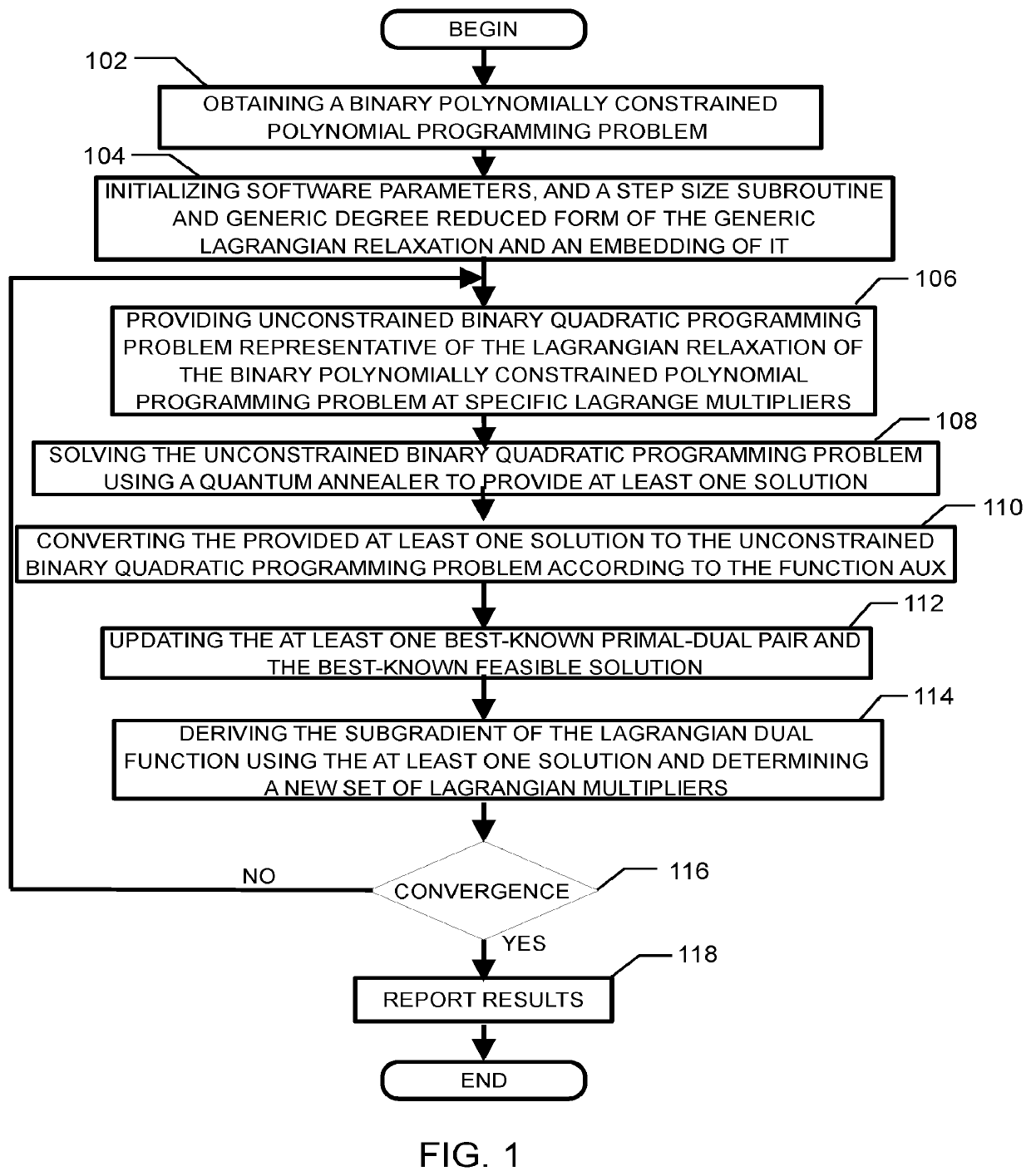
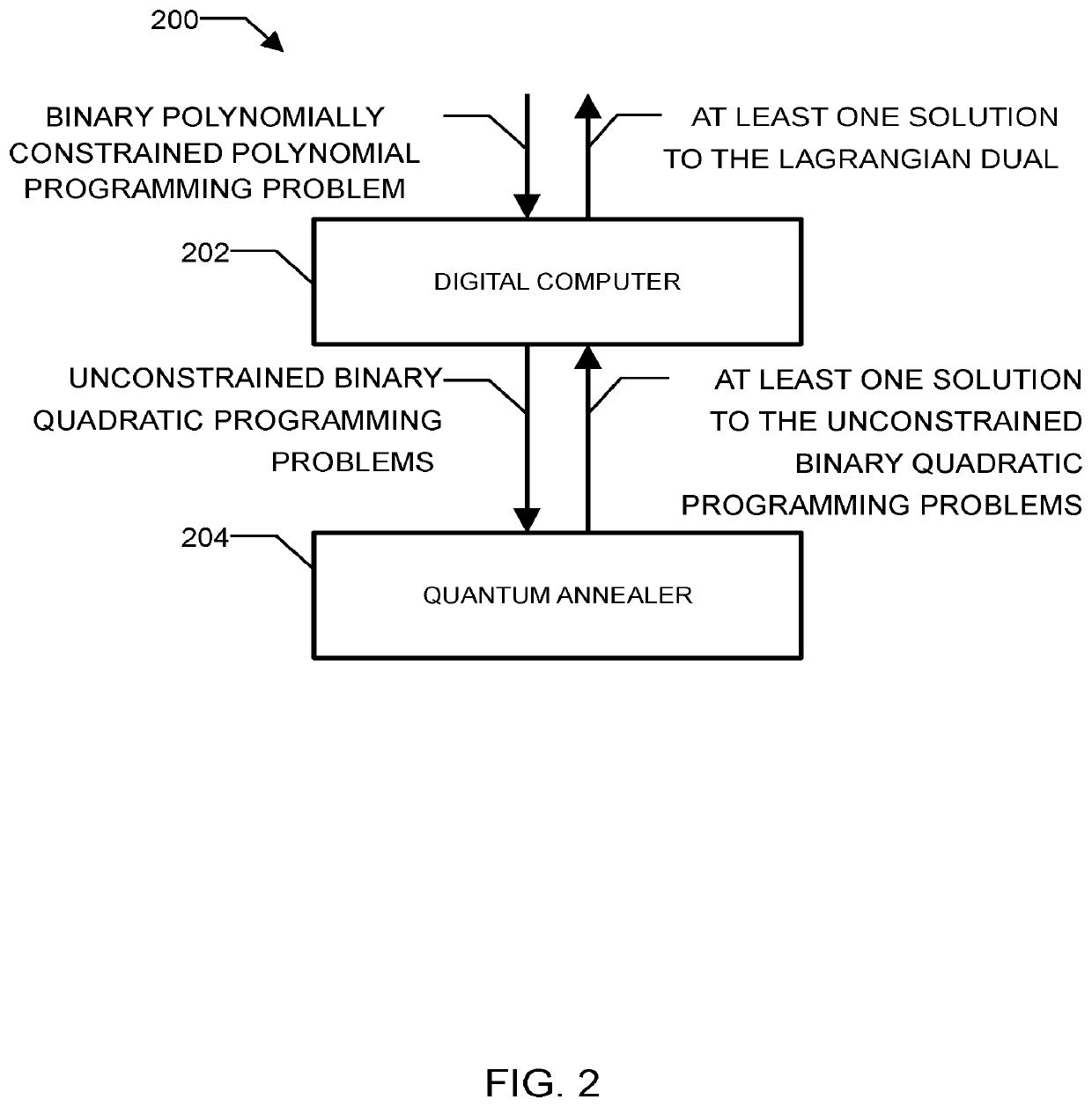
A method for solving the Lagrangian dual of a binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem comprises obtaining a binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem; until a convergence is detected, iteratively, providing a set of Lagrange multipliers, providing an unconstrained binary quadratic programming problem representative of the Lagrangian relaxation of the binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem at these Lagrange multipliers, providing the unconstrained binary quadratic programming problem to a quantum annealer, obtaining from the quantum annealer at least one corresponding solution, using the at least one corresponding solution to generate a new set of Lagrange multipliers; and providing all corresponding best-known primal-dual pairs and best-known feasible solutions after convergence.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method and apparatus for evolving a quantum system using a mixed initial hamiltonian comprising both diagonal and off-diagonal terms
Various adaptations to adiabatic quantum computation and quantum annealing are described. These adaptations generally involve tailoring an initial Hamiltonian so that a local minimum is avoided when a quantum processor is evolved from the initial Hamiltonian to a problem Hamiltonian. The initial Hamiltonian may represent a mixed Hamiltonian that includes both diagonal and off-diagonal terms, where the diagonal terms at least partially define a center point of a first computation space that is at least partially contained within a second computation space. A problem Hamiltonian may be evolved into a low energy state by inhomogeneously inducing disorder in the qubits of the quantum processor. A higher degree of disorder may be induced in a subset of qubits predicted to contribute to a local minimum of the problem Hamiltonian.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems, methods, and apparatus for calibrating, controlling, and operating a quantum processor
Quantum annealing may include applying and gradually removing disorder terms to qubits of a quantum processor, for example superconducting flux qubits of a superconducting quantum processor. A problem Hamiltonian may be established by applying control signals to the qubits, an evolution Hamiltonian established by applying disorder terms, and annealing by gradually removing the disorder terms. Change in persistent current in the qubits may be compensated. Multipliers may mediate coupling between various qubits and a global signal line, for example by applying respective scaling factors. Two global signal lines may be arranged in an interdigitated pattern to couple to respective qubits of a communicatively coupled pair of qubits. Pairs of qubits may be communicatively isolated and used to measure a response of one another to defined signals.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Data encoding and classification
In a method and apparatus for training a computer system for use in classification of an image by processing image data representing the image, image data are compressed and then loaded into a programmable quantum annealing device that includes a Restricted Boltzmann Machine. The Restricted Boltzmann Machine is trained to act as a classifier of image data, thereby providing a trained Restricted Boltzmann Machine; and, the trained Restricted Boltzmann Machine is used to initialize a neural network for image classification thereby providing a trained computer system for use in classification of an image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE LTD +1
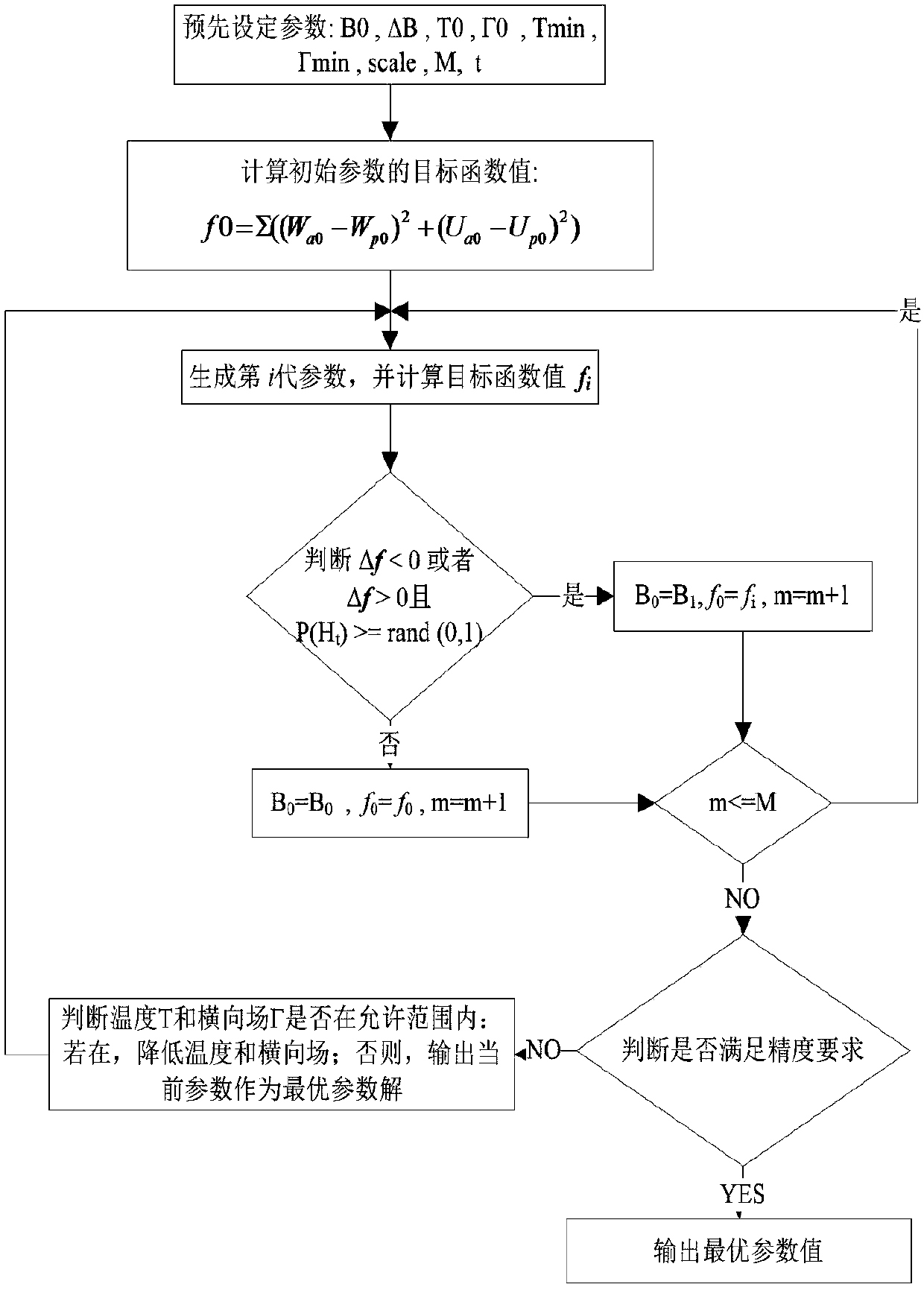
Parameter inversion method of probability integral method based on quantum annealing method
InactiveCN108491641APrecise inversionReliable inversionArtificial lifeDesign optimisation/simulationGlobal optimizationInversion methods
The present invention relates to a parameter inversion method of a probability integral method based on a quantum annealing method. The method comprises: giving an initial value B0 of a parameter of the probability integral, and determining a temperature and transverse field variation function, a fluctuation range + / -[delta]B of each parameter of the probability integral, the maximum allowable step length scale of the parameter, and the number of times M of internal loops; by calculating the objective function under the gradually decreased temperature and transverse field, determining an optimal parameter solution at each temperature; and finally outputting the optimal parameter solution by determining the accuracy requirement or whether the minimum temperature and the transverse field arereached. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, based on inheriting the advantages of the simulated annealing method, the thermal fluctuation mechanism of the simulated annealingmethod is replaced by the quantum fluctuation mechanism, so that the shortcomings of the simulated annealing algorithm are effectively overcome; and compared with the parameter inversion method of the probability integral based on the simulated annealing, by using the method disclosed by the present invention, the convergence speed and the possibility of jumping out of the local optimal solutionare effectively improved, the global optimization ability is enhanced, and the parameter inversion of the probability integral can be more accurate and reliable.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
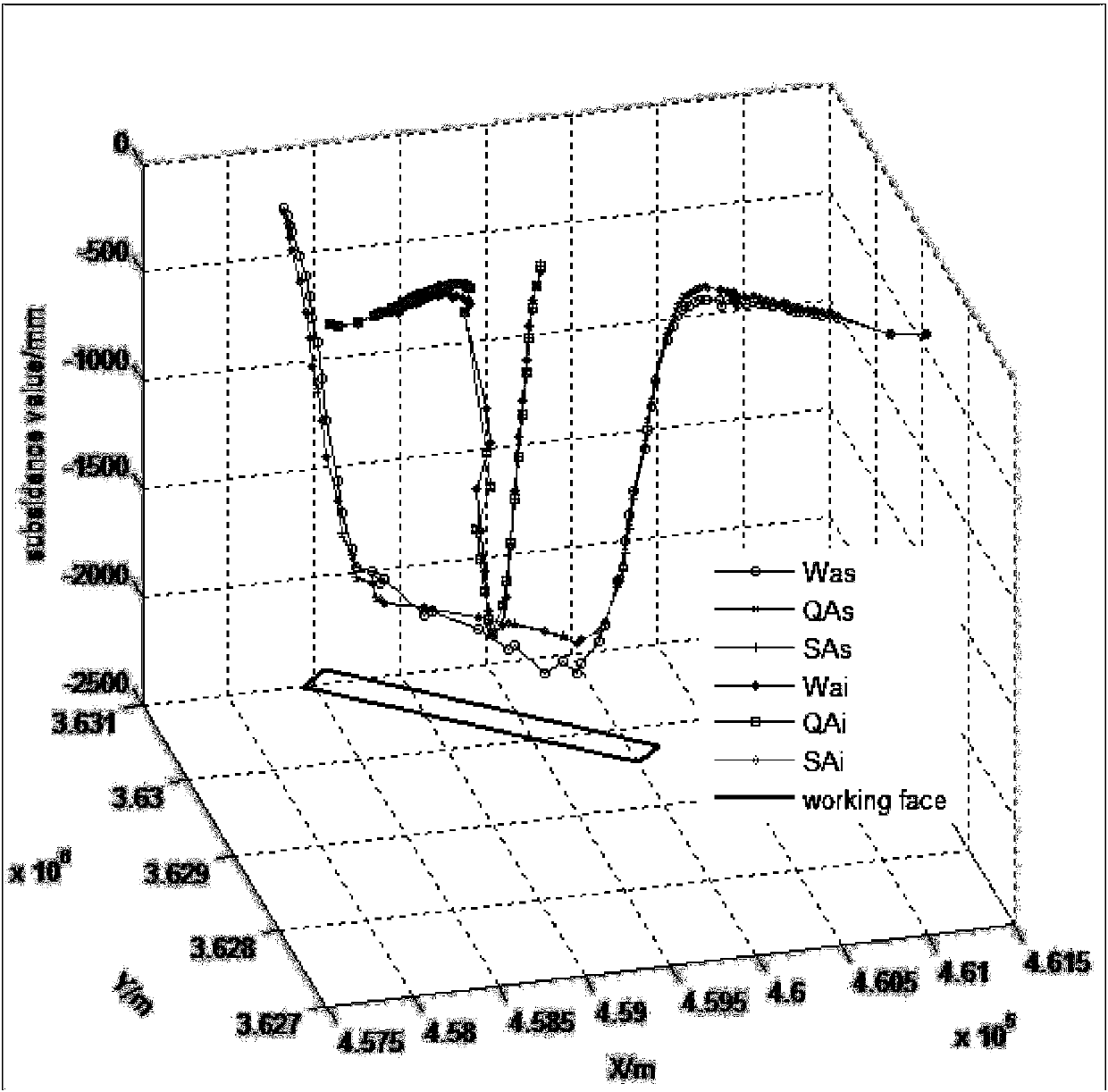
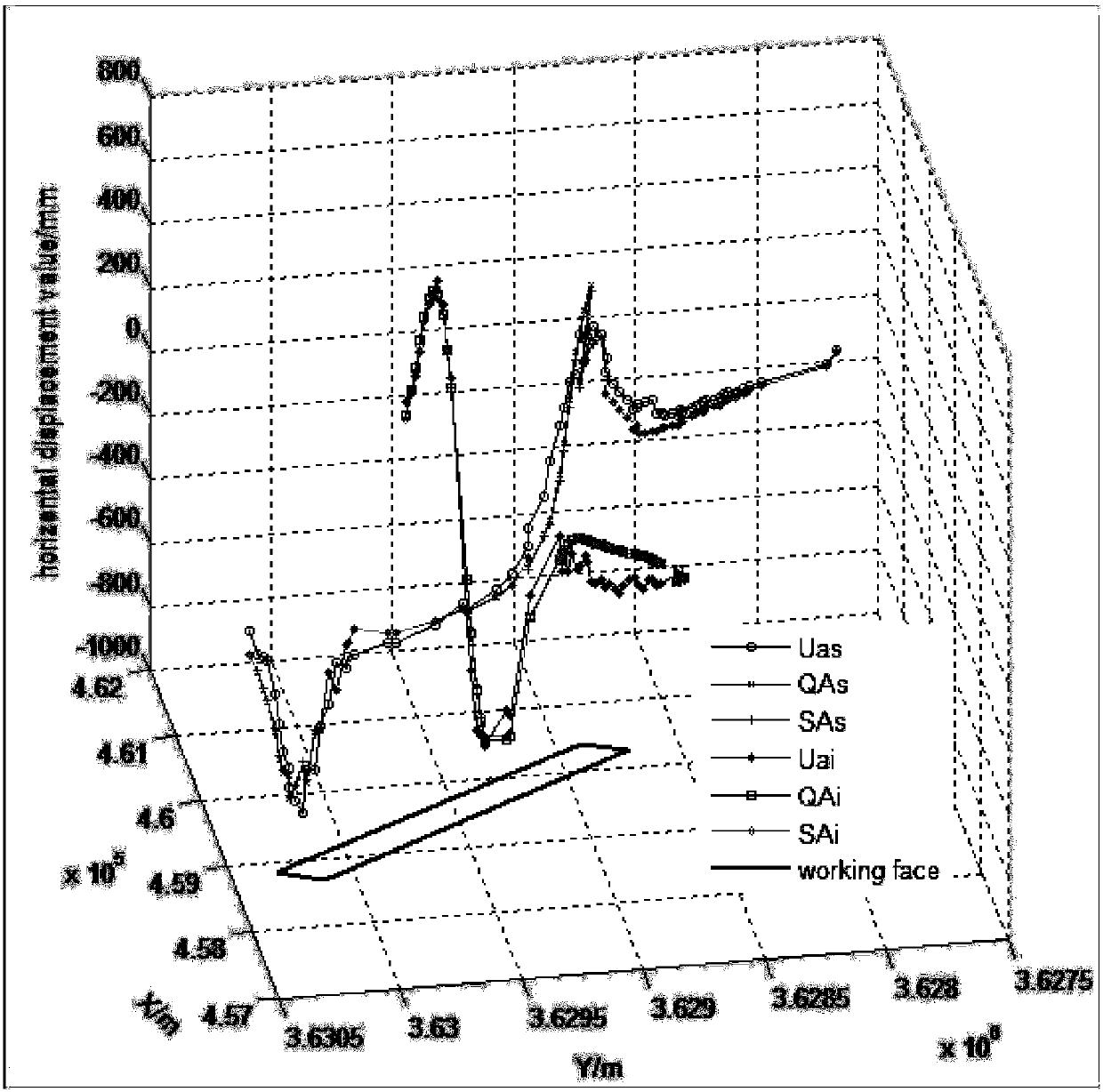
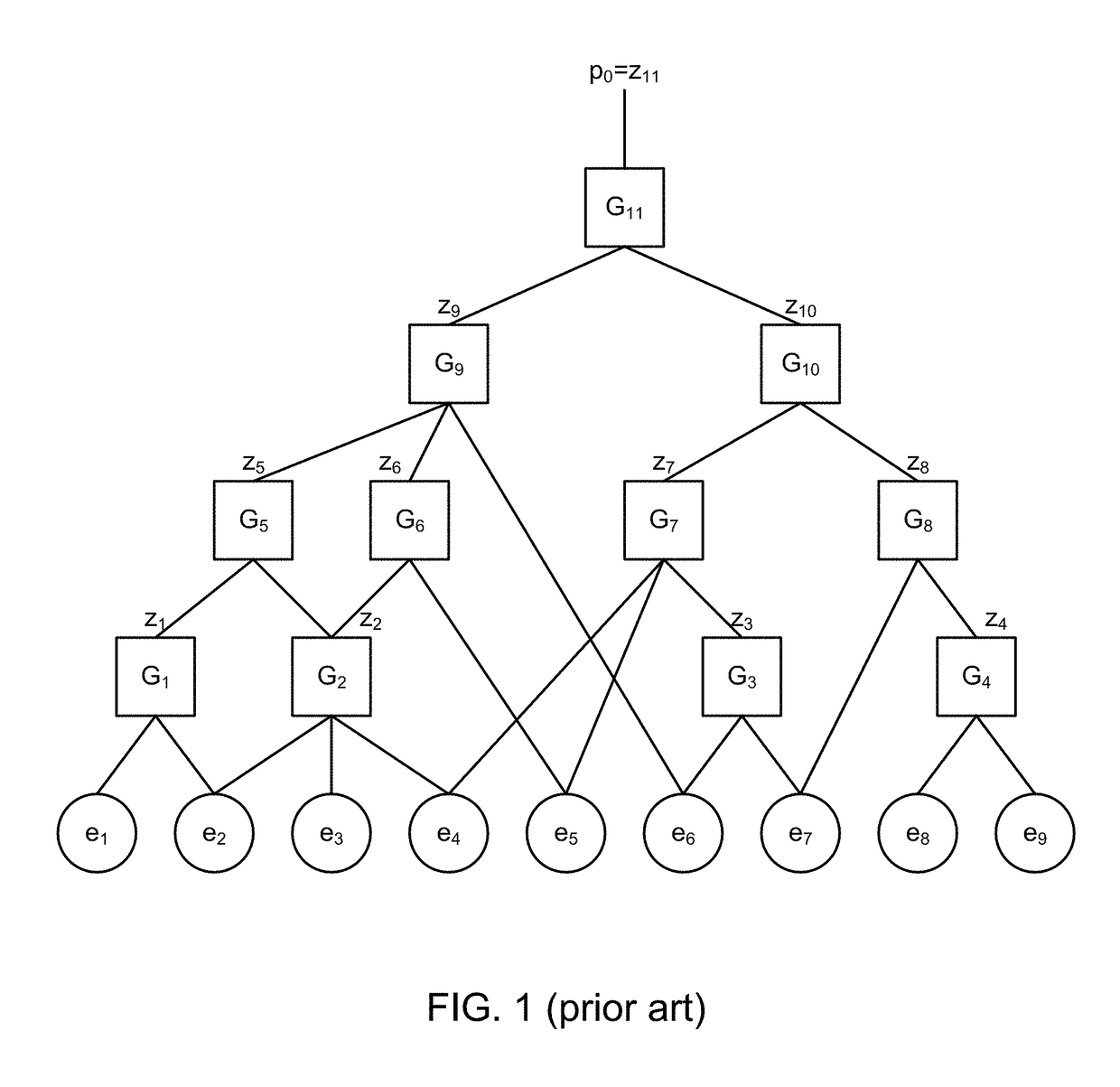
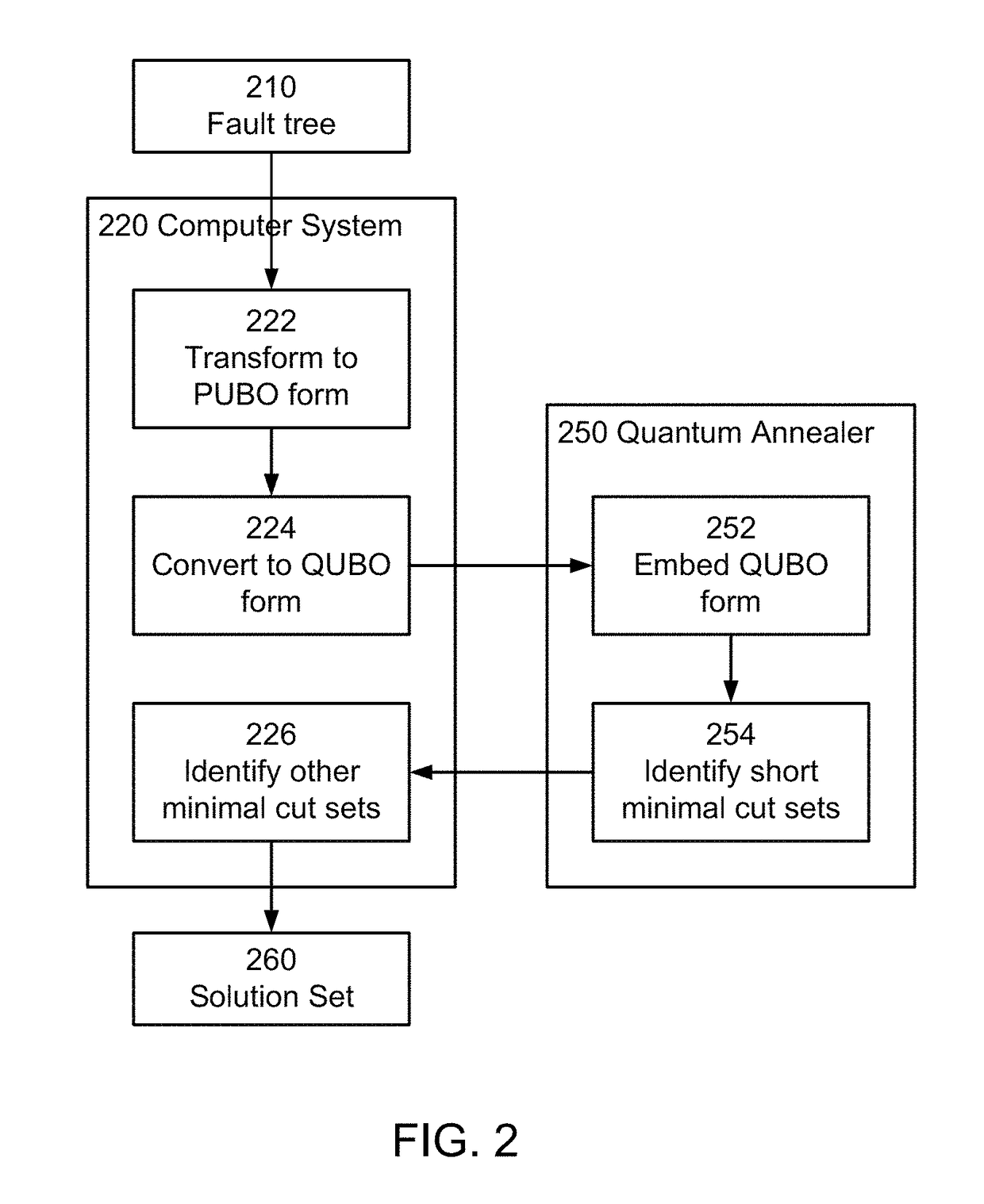
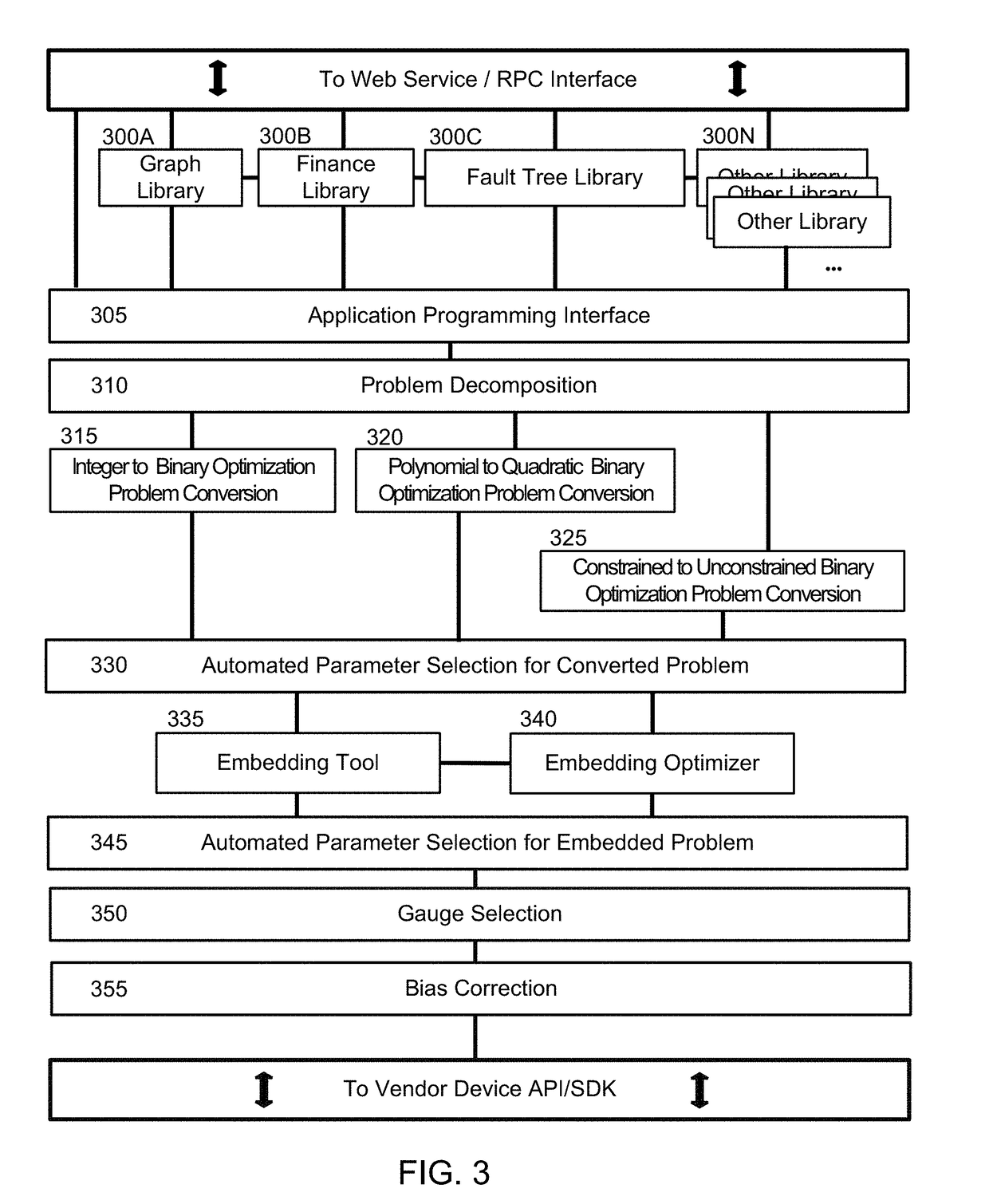
Performing fault tree analysis on quantum computers
Fault tree analysis is performed using a combination of digital computer systems and quantum processing devices. For example, quantum annealers may be configured to analyze a fault tree for minimal cut sets. The quantum annealer may be particular good at identifying smaller minimal cut sets. Digital computer systems may be used to identify the remaining minimal cut sets. If the quantum annealer identifies one of the minimal cut sets of smallest size (i.e., lowest cardinality), this can be used as a constraint for the digital computer system, thus speeding up its search for other minimal cut sets.
Owner:QC WARE CORP
Semiconductor controlled quantum swap interaction gate
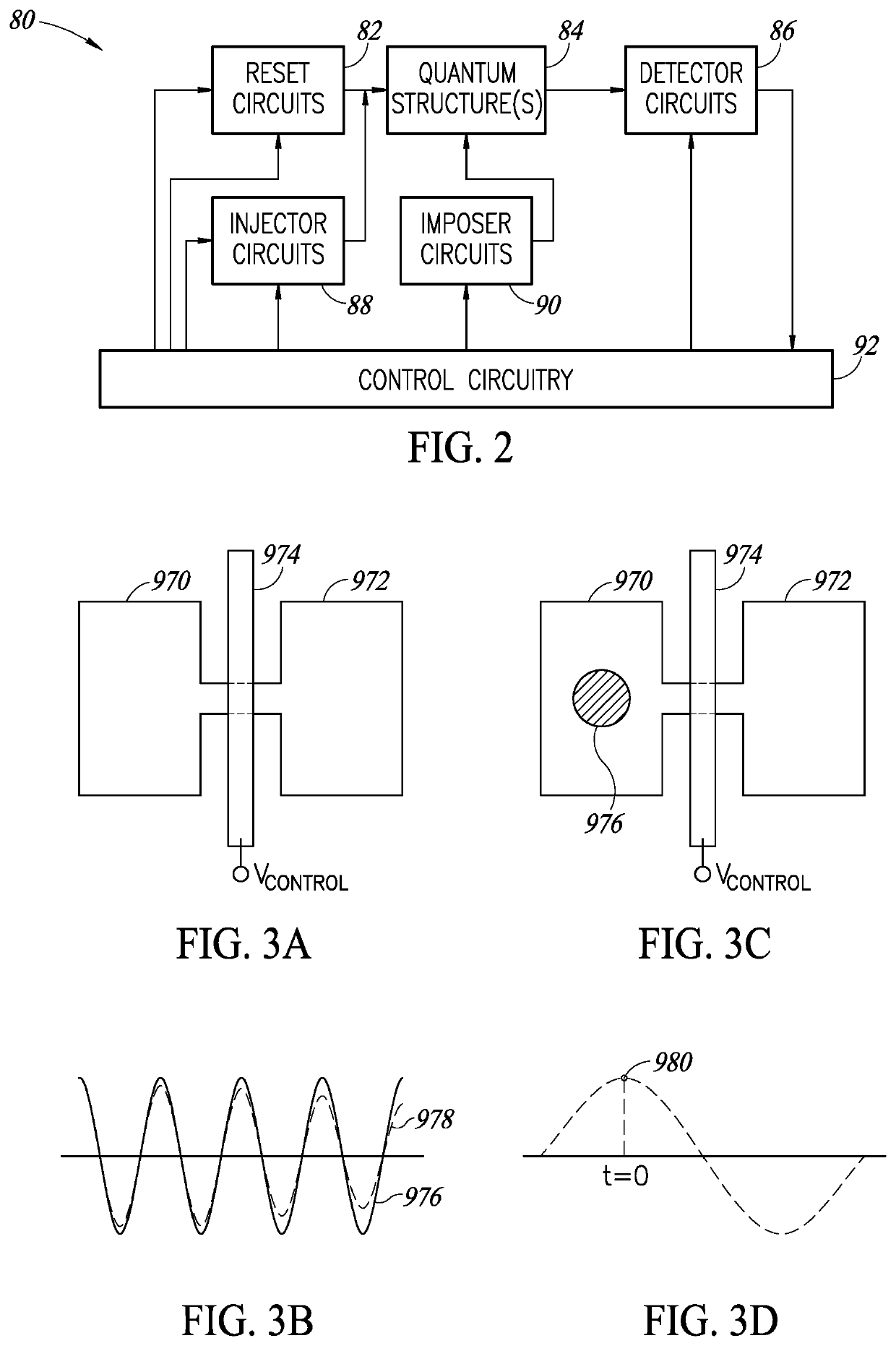
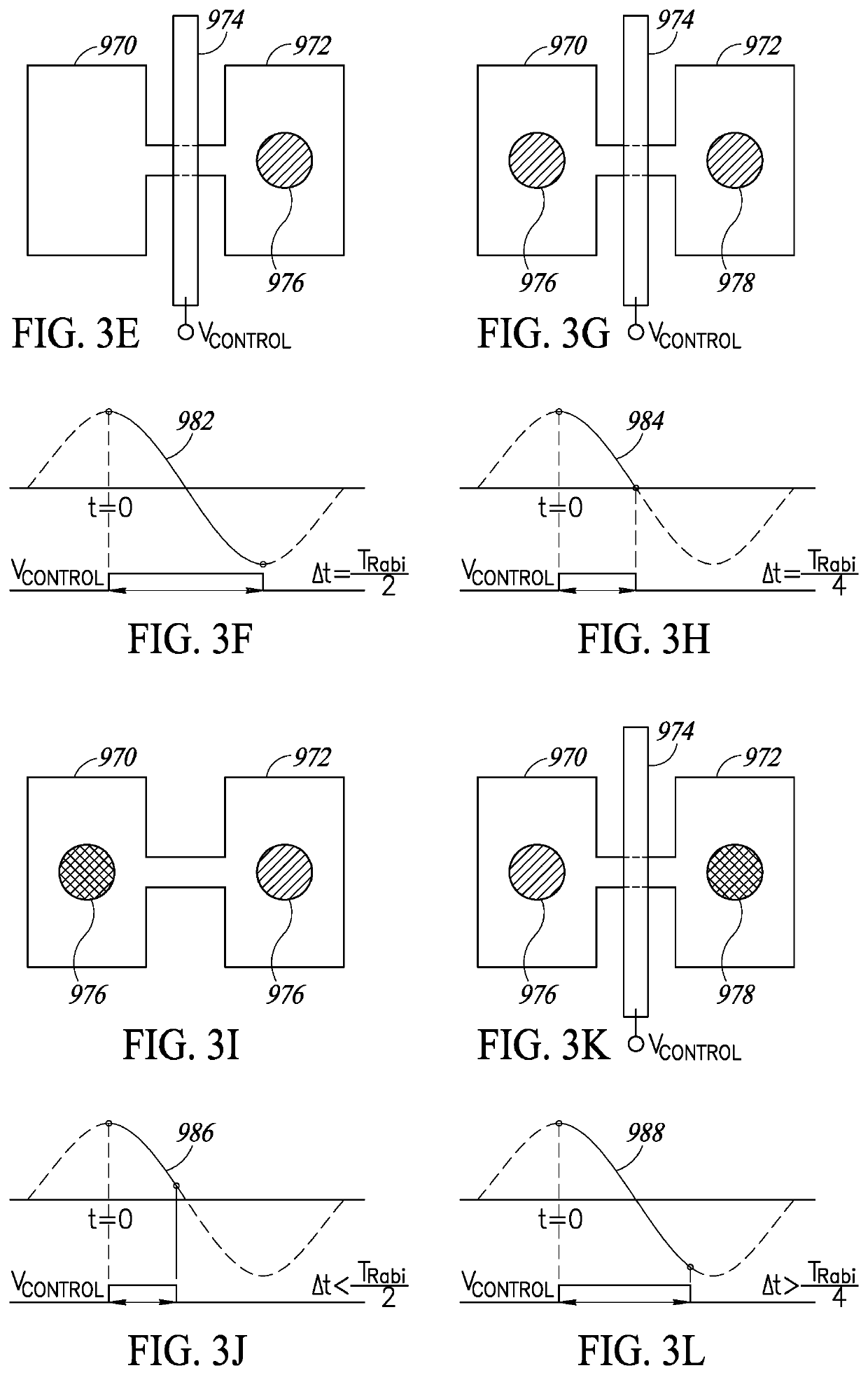
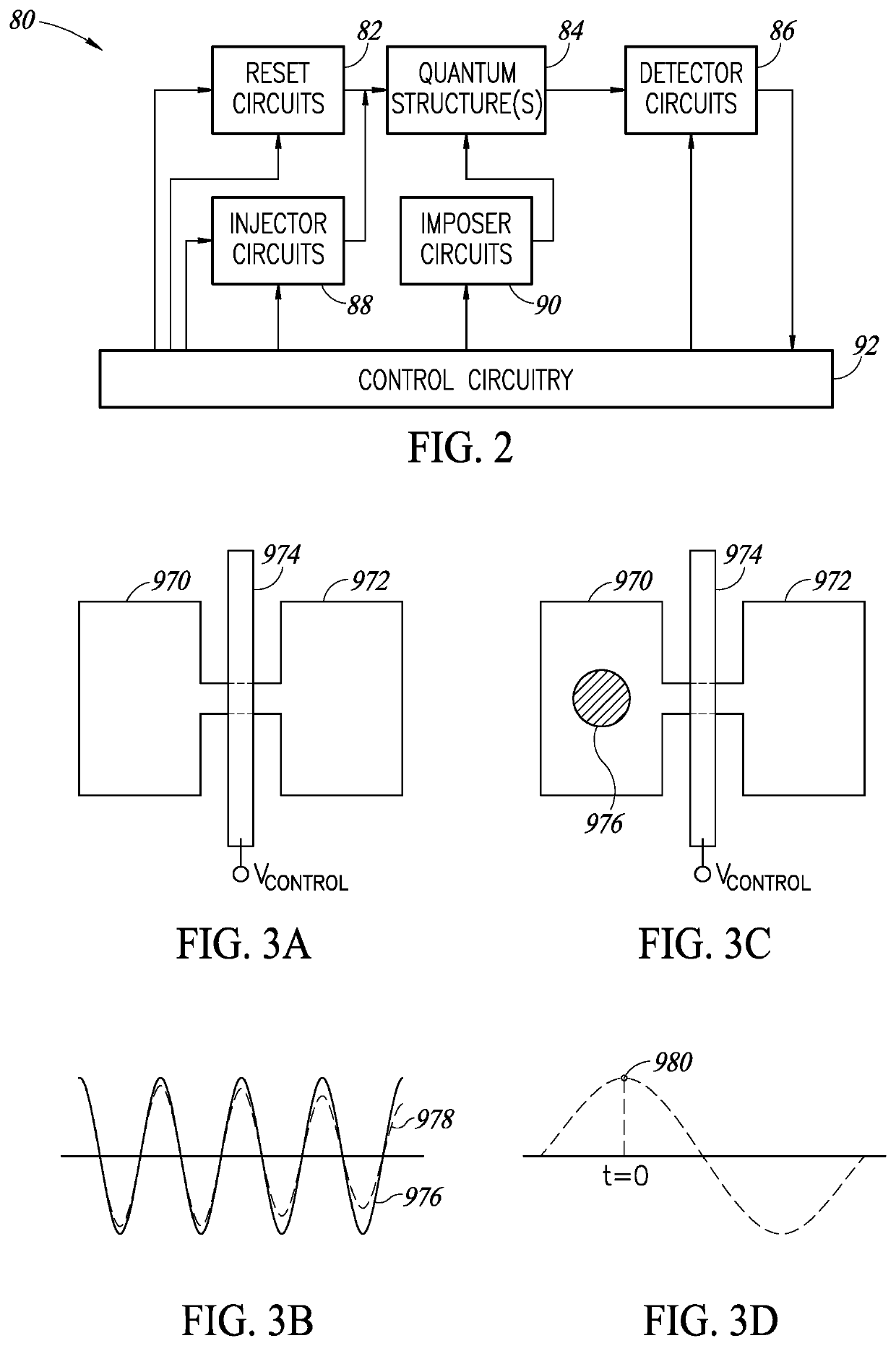
ActiveUS20190393399A1Digital data processing detailsNanoinformaticsQuantum electrodynamicsSemiconductor
Novel and useful quantum structures that provide various control functions. Particles are brought into close proximity to interact with one another and exchange information. After entanglement, the particles are moved away from each other but they still carry the information contained initially. Measurement and detection are performed on the particles from the entangled ensemble to determine whether the particle is present or not in a given qdot. A quantum interaction gate is a circuit or structure operating on a relatively small number of qubits. Quantum interaction gates implement several quantum functions including a controlled NOT gate, quantum annealing gate, controlled SWAP gate, a controlled Pauli rotation gate, and ancillary gate. These quantum interaction gates can have numerous shapes including double V shape, H shape, X shape, L shape, I shape, etc.
Owner:EQUAL1 LABS INC
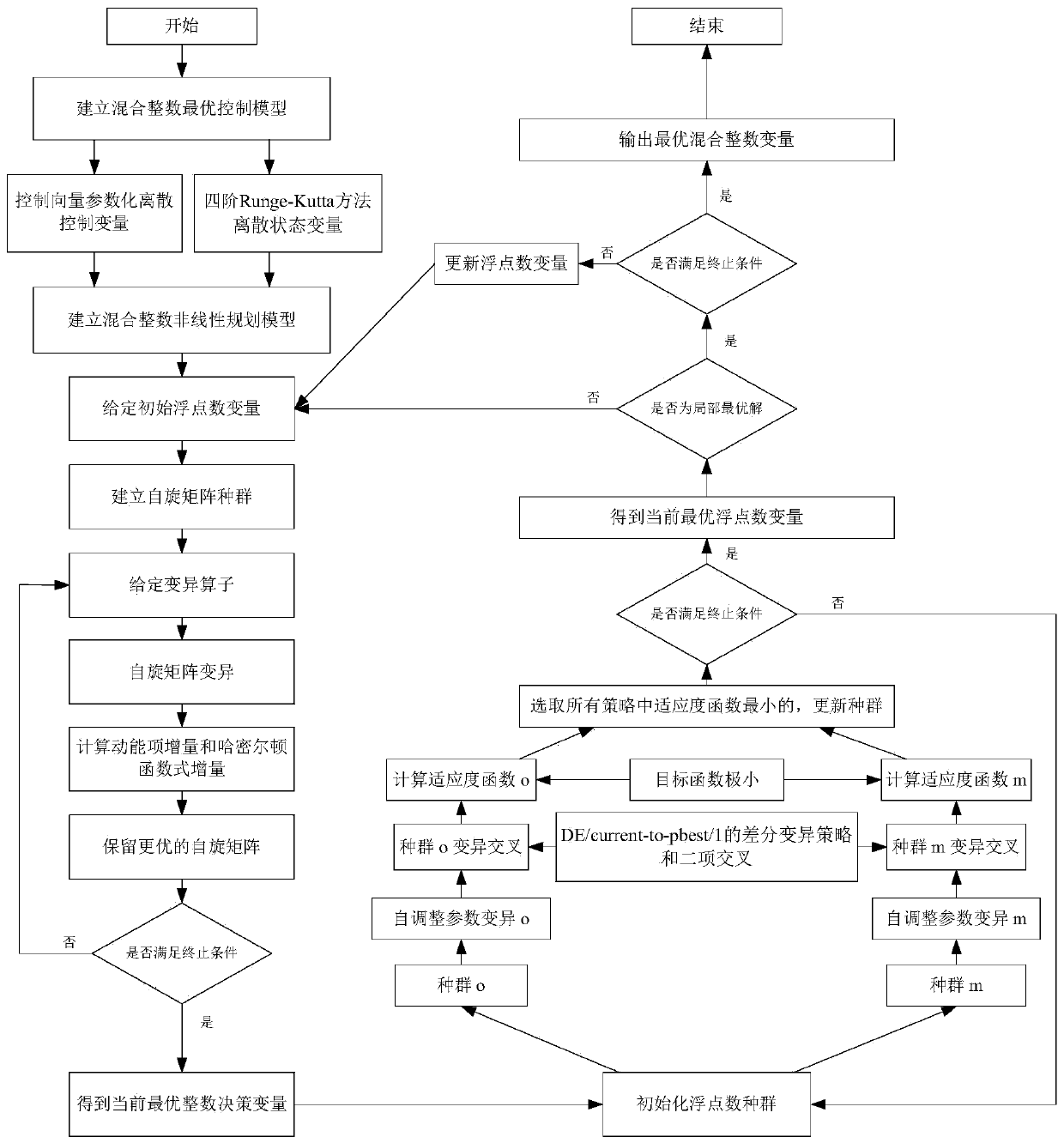
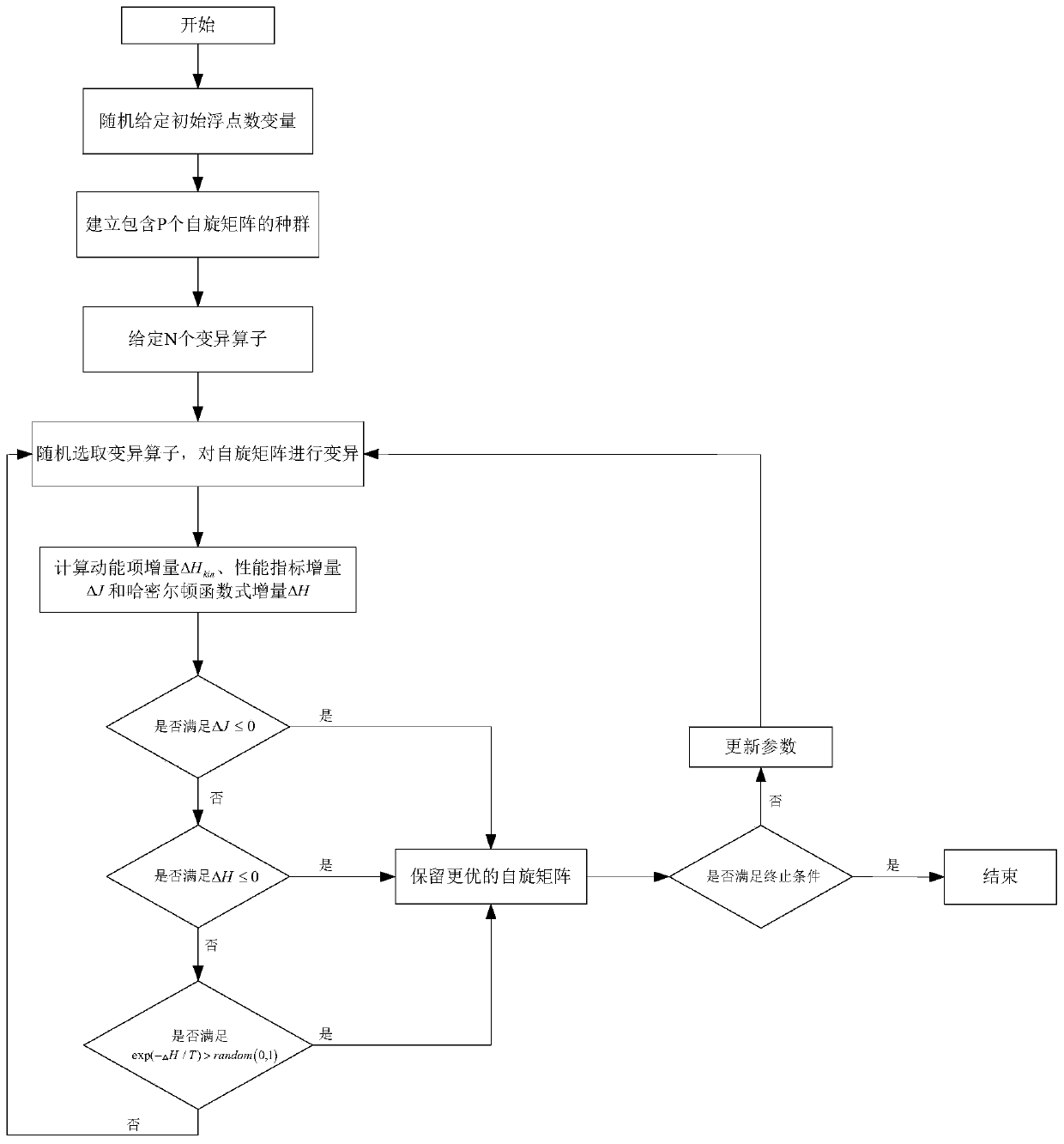
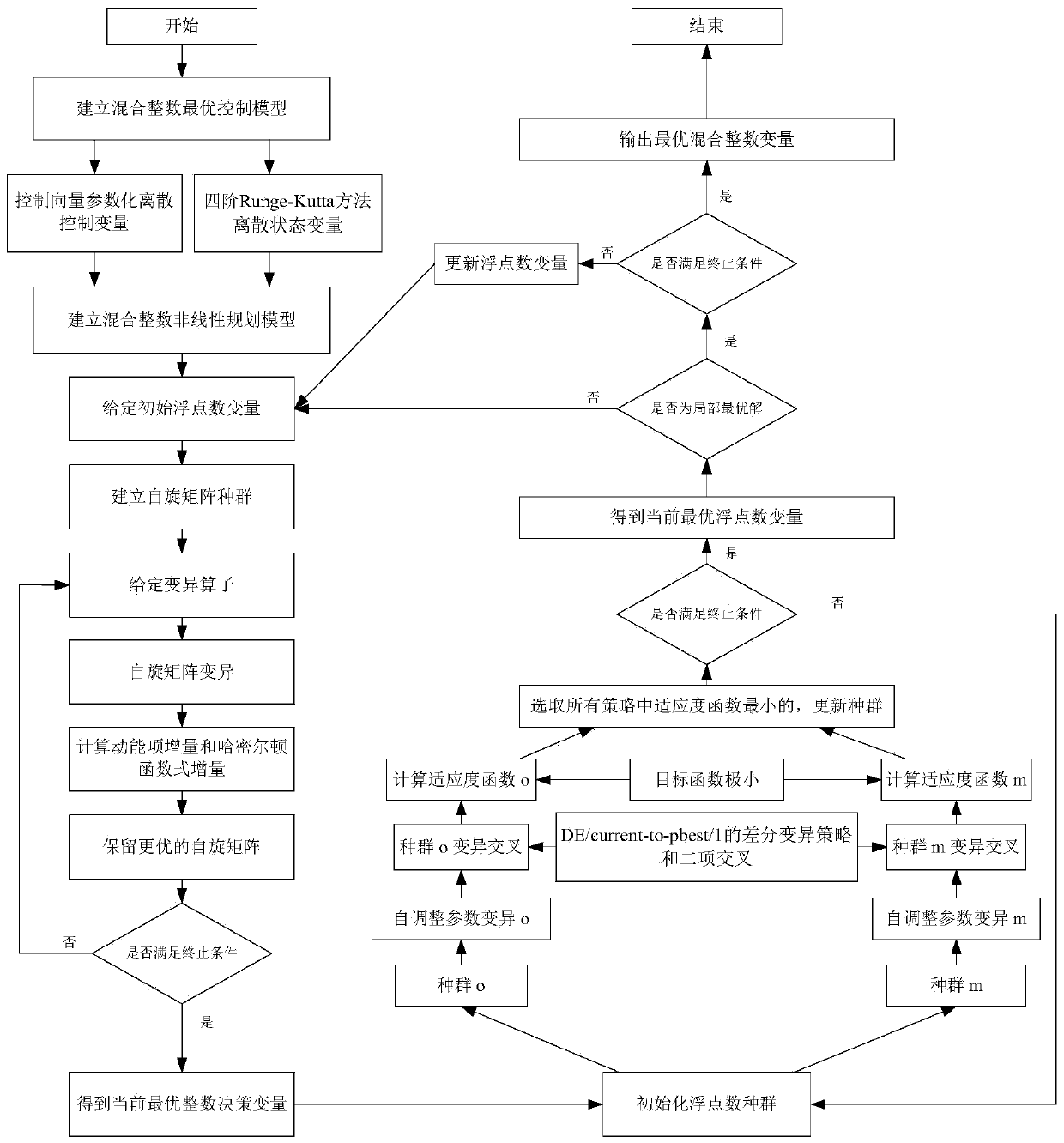
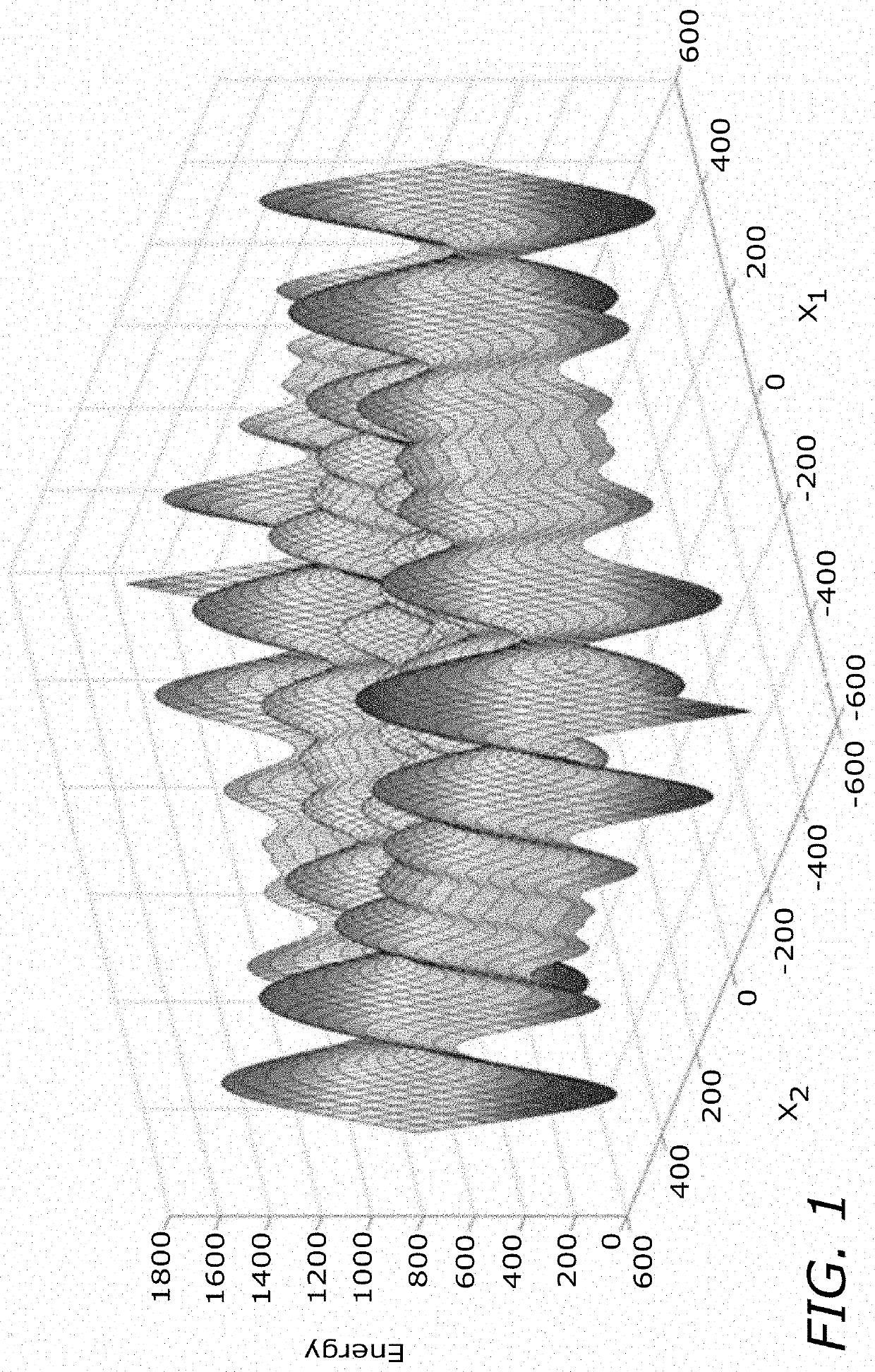
Mixed integer optimal control numerical solution method based on quantum annealing
A mixed integer optimal control problem is one of the most important problems in the daily life and industrial production. In order to solve the computational complexity of solving an integer decisionvariable, the invention proposes a mixed integer optimal control numerical solution method based on quantum annealing. Firstly, a mixed integer optimal control model is established to describe a mixed integer optimal control problem. Then, the mixed integer optimal control model is converted into a mixed integer nonlinear programming model by using a control vector parameterization and fourth-order Runge-Kutta method. Thirdly, compared with the traditional intelligent optimization algorithm, a quantum annealing algorithm with a higher convergence speed and stronger global search ability is proposed, an integer decision variable is solved by using the quantum annealing algorithm, and an optimal floating point number control variable i solved by using a parallel differential evolution algorithm. Finally, an optimal mixed integer control decision is obtained by two-part interactive iterative optimization.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Using noise to speed convergence of simulated annealing and markov monte carlo estimations
ActiveUS20200090071A1Quantum computersDigital data processing detailsComputer scienceRate of convergence
The invention shows how to use noise-like perturbations to improve the speed and accuracy of Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) estimates and large-scale optimization, simulated annealing optimization, and quantum annealing for large-scale optimization.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Optical ising-model solver using quantum annealing
A method implemented by an optical circuit, including beam splitter, phase shifters and cross-phase modulators, for solving Ising-model using quantum annealing discretizes a continuous time-dependent Hamiltonian function over a time period T, into a plurality of smaller portions; implements each of said smaller portions with a non-linear optical medium, and iterates over said smaller portions to output a solution of the Ising Hamiltonian problem, using the optical components.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Method and system for solving the lagrangian dual of a binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem using a quantum annealer
InactiveUS20200272684A1Less sensitive to errorSpeed up the processQuantum computersComplex mathematical operationsPolynomial programmingAlgorithm
A method for solving the Lagrangian dual of a binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem comprises obtaining a binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem; until a convergence is detected, iteratively, providing a set of Lagrange multipliers, providing an unconstrained binary quadratic programming problem representative of the Lagrangian relaxation of the binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem at these Lagrange multipliers, providing the unconstrained binary quadratic programming problem to a quantum annealer, obtaining from the quantum annealer at least one corresponding solution, using the at least one corresponding solution to generate a new set of Lagrange multipliers; and providing all corresponding best-known primal-dual pairs and best-known feasible solutions after convergence.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
Problem solving using quantum annealer, useful for example in sequencing, for instance nucleic acid sequencing
Quantum annealers as analog or quantum processors can find paths in problem graphs embedded in a hardware graph of the processor, for example finding valid paths, shortest paths or longest paths. A set of input, for example nucleic acid reads, can be used to set up a graph with edges between nodes denoting overlap (i.e., common base pairs) between the reads with constraints applied to perform sequence alignment or sequencing of a nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) strand or sequence, finding a solution that has a ground state energy. At least a portion of the described approaches can be applied to other problems, for instance resource allocations problems, e.g., job scheduling problems, traveling salesperson problems, and other NP-complete problems.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Method and system for solving a minimum connected dominating set problem using quantum annealing for distance optimization
ActiveUS10268964B2Less timeProcessing problemForecastingMachine learningConnected dominating setDominating set
A method is disclosed for determining a minimum connected dominating set in a graph, the method comprising obtaining an indication of an input graph, the input graph comprising a plurality of nodes and a plurality of edges; generating a distance table comprising for each node of the input graph, an indication of a distance between the given node and each of the other node of the plurality of nodes; generating a corresponding constrained binary quadratic programming problem using the generated distance table; providing the corresponding constrained binary quadratic programming problem to a quantum annealing solver; obtaining at least one approximate solution from the quantum annealing solver; post-processing the at least one approximate solution and providing the post-processed at least one approximate solution.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
Semiconductor controlled quantum ancillary interaction gate
ActiveUS20190393400A1Digital data processing detailsNanoinformaticsQuantum electrodynamicsSemiconductor
Novel and useful quantum structures that provide various control functions. Particles are brought into close proximity to interact with one another and exchange information. After entanglement, the particles are moved away from each other but they still carry the information contained initially. Measurement and detection are performed on the particles from the entangled ensemble to determine whether the particle is present or not in a given qdot. A quantum interaction gate is a circuit or structure operating on a relatively small number of qubits. Quantum interaction gates implement several quantum functions including a controlled NOT gate, quantum annealing gate, controlled SWAP gate, a controlled Pauli rotation gate, and ancillary gate. These quantum interaction gates can have numerous shapes including double V shape, H shape, X shape, L shape, I shape, etc.
Owner:EQUAL1 LABS INC
Parallel quantum annealing target point distribution calculation method
ActiveCN106902480AReduce experienceImprove efficiencyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor targetGamma ray
The invention discloses a parallel quantum annealing target point distribution calculation method which comprises the steps of establishing a tumor target area and damaged organ data model through CT or MR data image analysis and doctor diagnosis; then, performing quick calculation of key point dosage distribution through a Gamma ray three-dimensional orientation rotating focusing radiotherapy machine beam characteristic, comparing the key point dosage distribution with a clinically required radiotherapy target, defining a target function according to a prescription dosage of the target area and the tolerable dosage of the damaged organ, setting a choice rule according to a simulated annealing algorithm, and performing new calculation comparison, and finally obtaining an anticipated result; and finally, performing accurate calculation on dosage distribution according to the parameter which corresponds with the calculated anticipated result, and obtaining final dosage distribution in the irradiation area. According to the parallel quantum annealing target point distribution calculation method, automatic machine calculation is utilized in a calculation process, thereby reducing subjective factors such as physicist experience, realizing no requirement for calculation process intervention by a plan designer, and realizing relatively objective calculation result. Furthermore, reversed plan designing realizes advantages of reducing subjective factors such as physicist experience, increasing plan designing speed, improving economic benefit and social benefit of radiotherapy, and realizing better satisfaction for a clinical requirement.
Owner:西安一体医疗科技有限公司
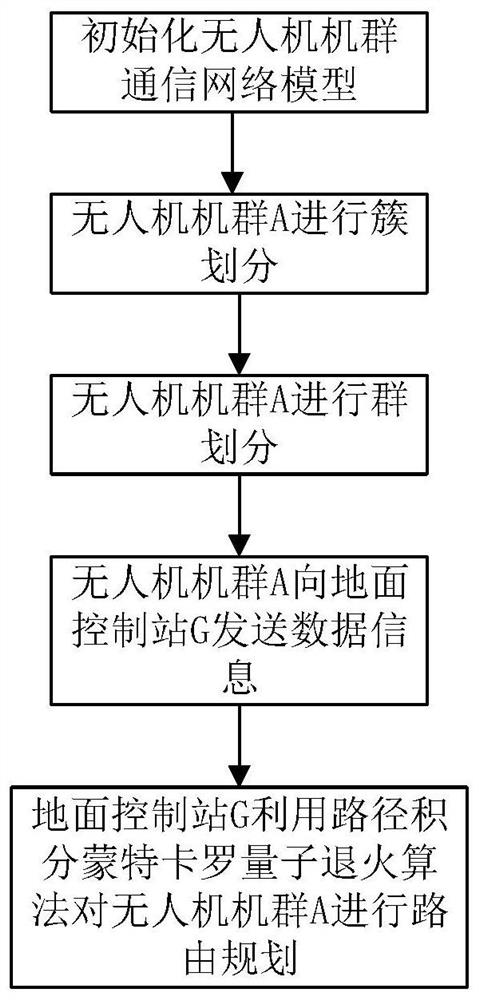
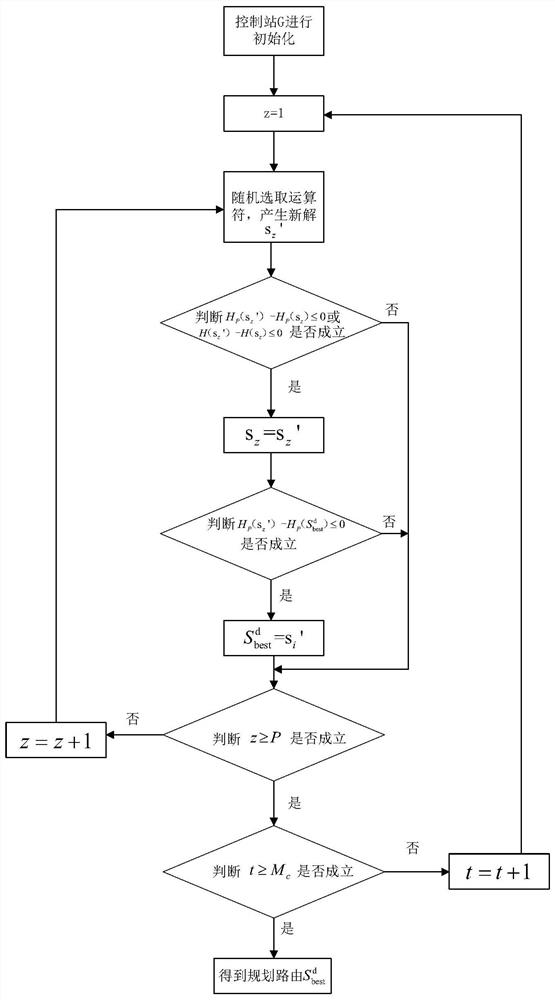
Unmanned aerial vehicle communication network route planning method based on quantum annealing algorithm
ActiveCN112954584AReduce route planning timeAvoid getting stuck in a local optimal solution problemParticular environment based servicesBroadcast service distributionAlgorithmSimulation
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle communication network route planning method based on a quantum annealing algorithm, and aims to improve the route planning efficiency of an unmanned aerial vehicle group communication network, reduce the communication energy consumption of the unmanned aerial vehicle network, realize load balancing and prolong the service life of the unmanned aerial vehicle group network. The method comprises the following steps: initializing an unmanned aerial vehicle group communication network model; performing cluster division on the unmanned aerial vehicle group A; performing group division on the unmanned aerial vehicle group A; enabling the unmanned aerial vehicle group A to send data information to the ground control station G; and enabling the ground control station G to perform route planning on the unmanned aerial vehicle group A by using a path integral Monte Carlo quantum annealing algorithm.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
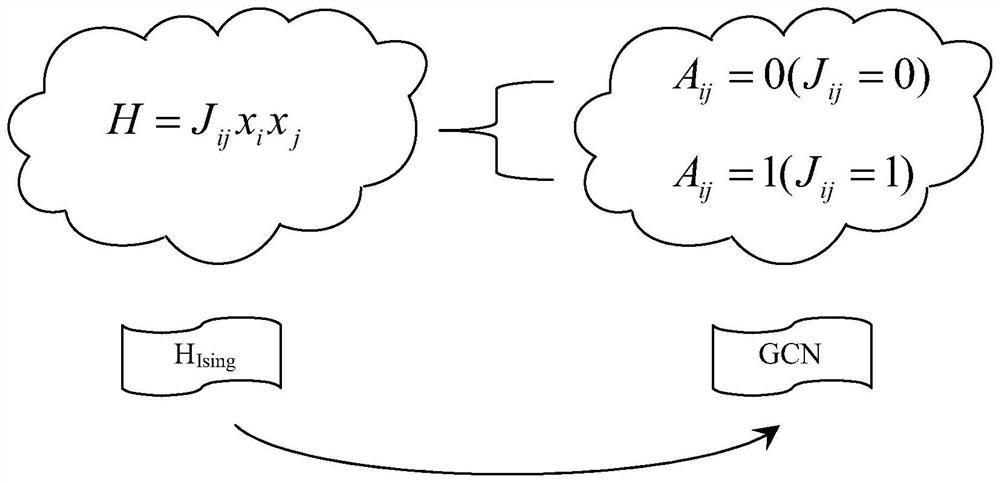
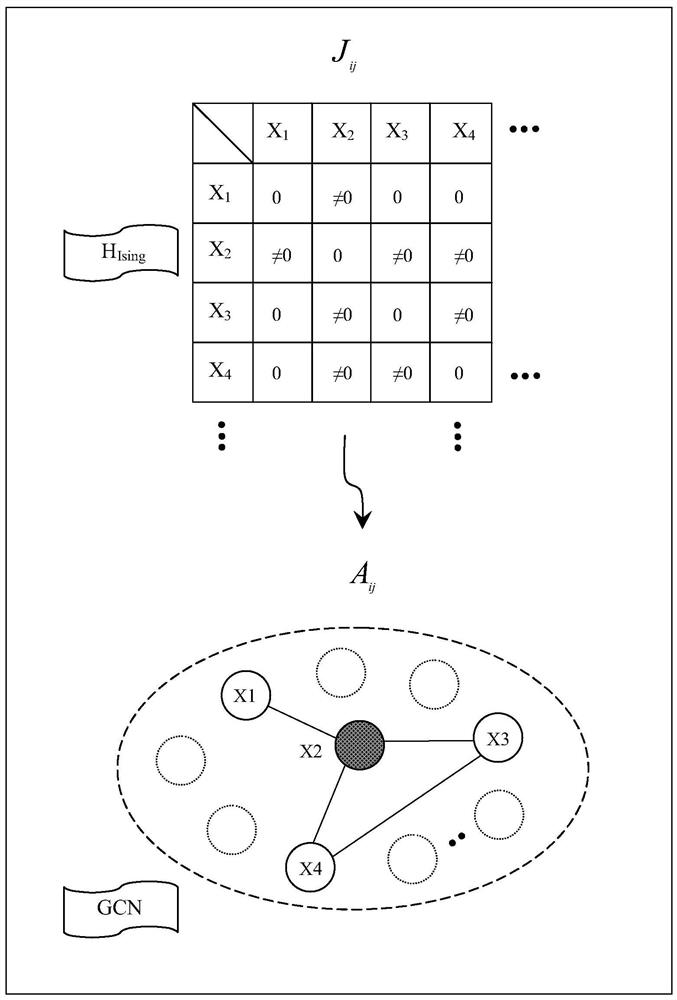
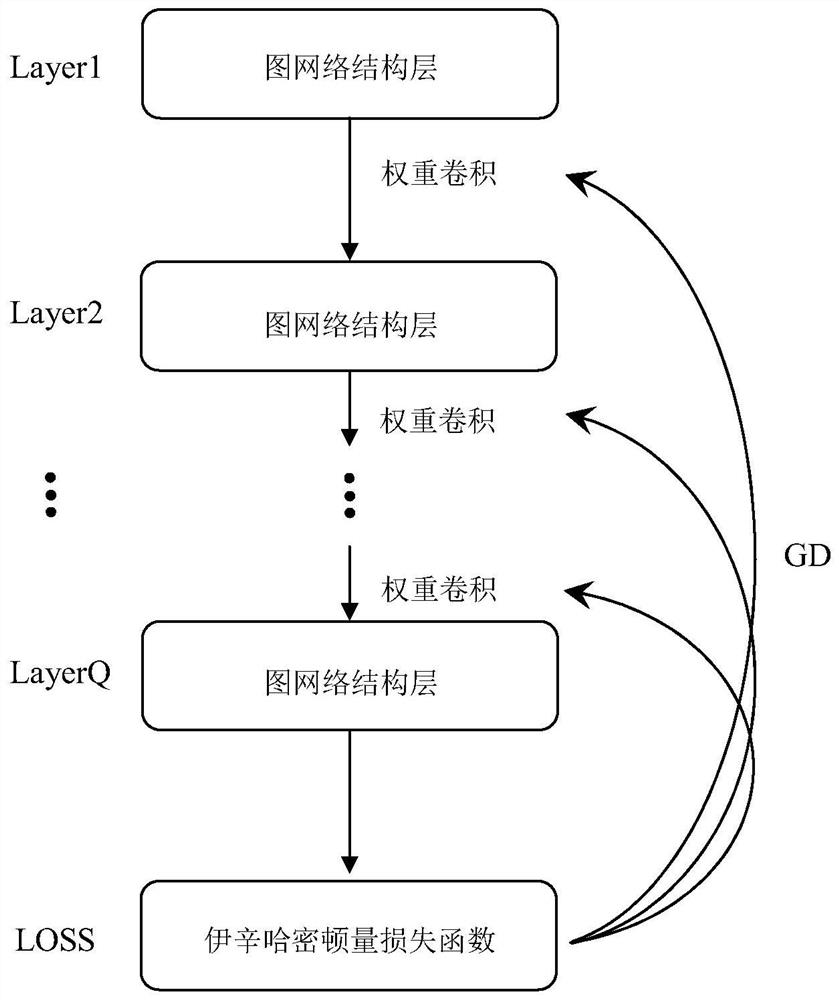
Isin solver based on graph convolutional neural network and method for realizing Isin model
The invention relates to an Isin solver based on a graph convolutional neural network and a method for realizing an Isin model. The first module in the two core modules is used for the configuration of a graph convolutional network architecture, and the second module is used for the optimization of an equivalent loss function of the Isin Hamiltonian amount. The structure of the graph network is constructed in the first module according to the form of the Isin Hamiltonian quantity. And in the second module, due to the binary property of the Isin Hamiltonian ground state solution and the arbitrariness of the output value of the final convolutional layer, function processing is performed on the output value of the final convolutional layer. An Isin solver using a graph neural network is designed on the basis that a sufficiently strong association action is performed on a GCN structure and a Hamiltonian of quantum annealing, and an NP-hard problem containing large-scale variables can be solved.
Owner:上海图灵智算量子科技有限公司
Systems and methods for stochastic optimization of a robust inference problem
PendingCN111670438ATechnical convenienceSolving Robust Inference ProblemsQuantum computersKernel methodsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The present disclosure provides methods and systems for stochastic optimization of a robust inference problem using a sampling device. Specifically, the methods and systems of the present disclosure enable smoothing of objective functions, thereby making such functions amenable to computation via stochastic-gradient methods using sampling in place of solving the inference problem exactly. Such methods and systems advantageously connect the gradient of the smoothed function approximation to a Boltzmann distribution, which can be sampled by a sampling device, such as a Gibbs sampler, using a simulated process and / or quantum process, in particular quantum-annealing process, thermal or adiabatic relaxation of a classical computer, semi-classical computer, or a quantum processor / device, and / orother physical process.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
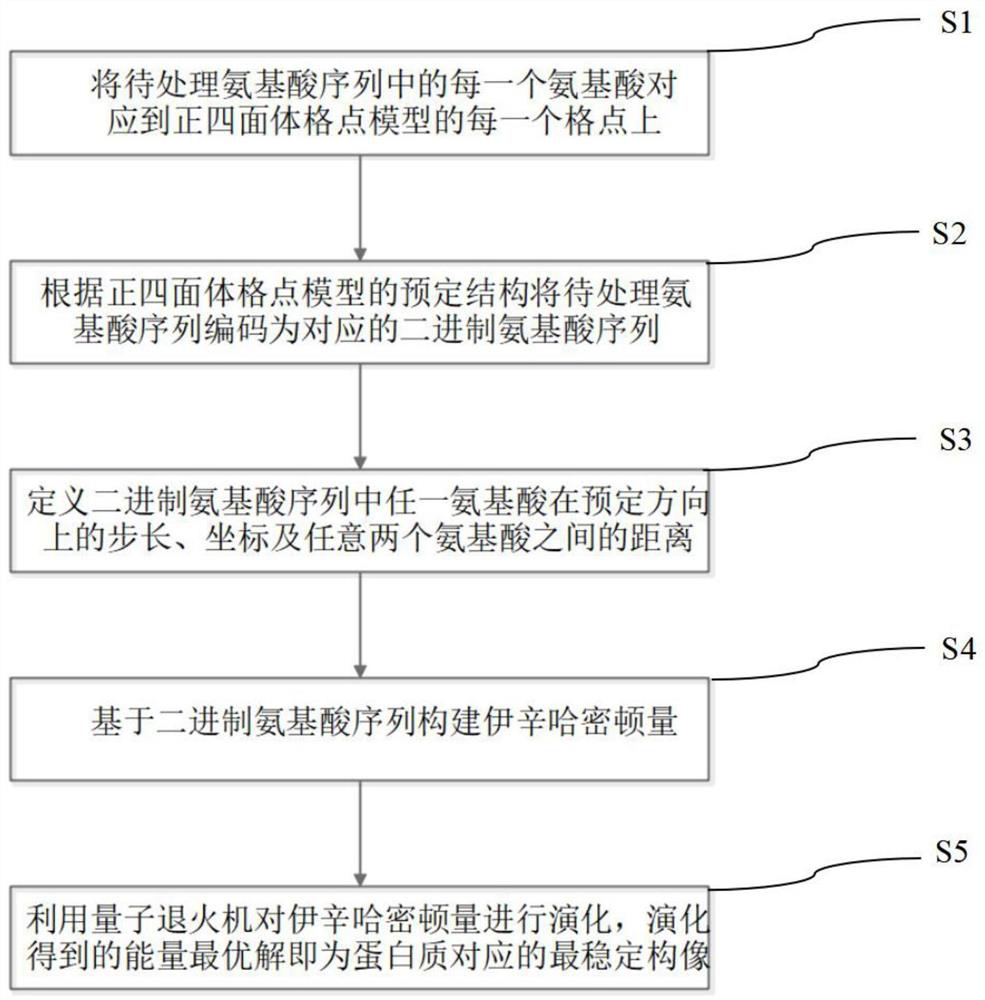
Protein folding method based on quantum annealing
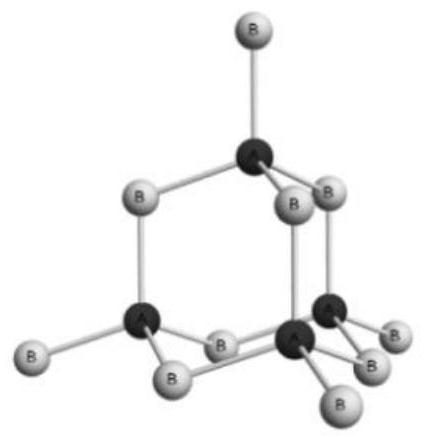
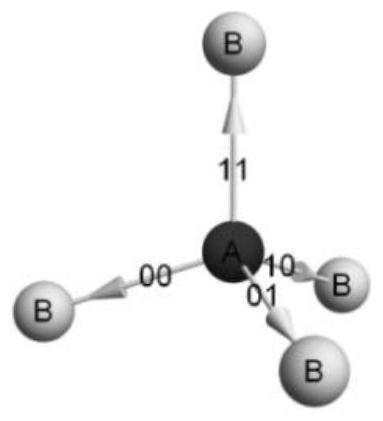
PendingCN114446391ACompressed Space ComplexityCompressed Time ComplexityQuantum computersDesign optimisation/simulationChemical physicsThree-dimensional space
The invention provides a protein folding method based on quantum annealing, and belongs to the technical field of quantum computing. According to the method, a protein folding problem is encoded into a computable optimization problem (QUBO form), and specifically, a regular tetrahedron lattice point model is adopted to simulate the composition of amino acid polypeptide chain molecules in a three-dimensional space; the method comprises the steps of coding binary amino acid sequences, defining the step length and coordinates of any amino acid in the coded binary amino acid sequences in a predetermined direction and the distance between any two amino acids, constructing a corresponding Isin Hamiltonian by adding constraint conditions, and finally evolving the Isin Hamiltonian by utilizing quantum annealing to obtain a final evolution result. The energy optimal solution obtained through evolution is the most stable conformation corresponding to the protein. Therefore, the method utilizes the quantum tunneling effect in quantum annealing to solve the protein problem, the space and time complexity can be greatly reduced, the consumed time is less, and the method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:上海图灵智算量子科技有限公司
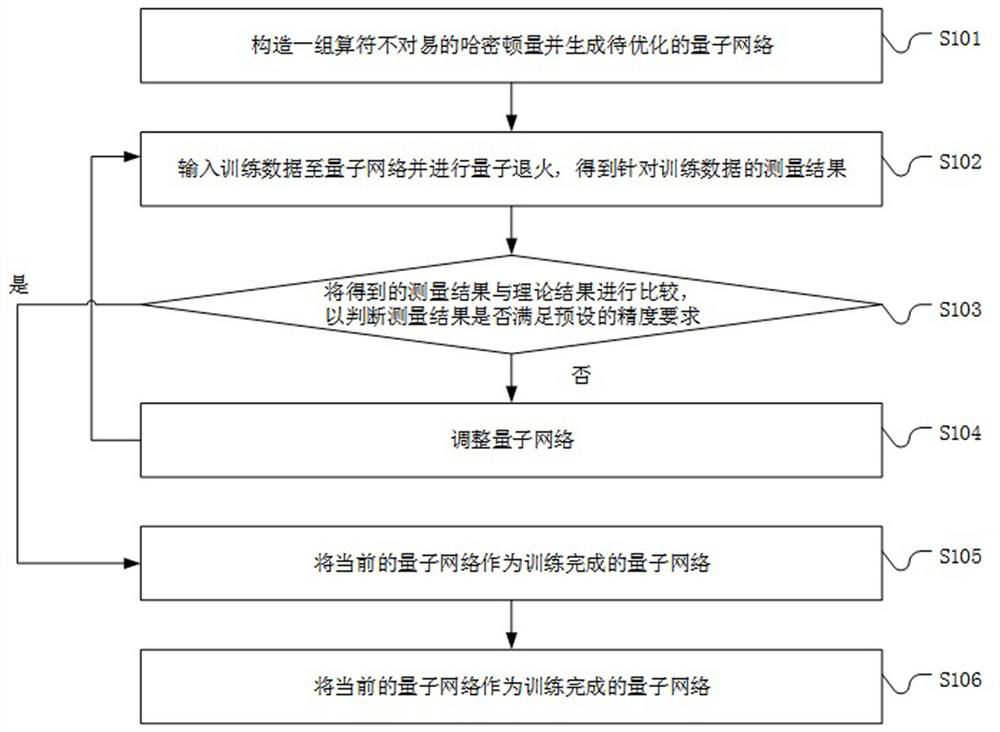
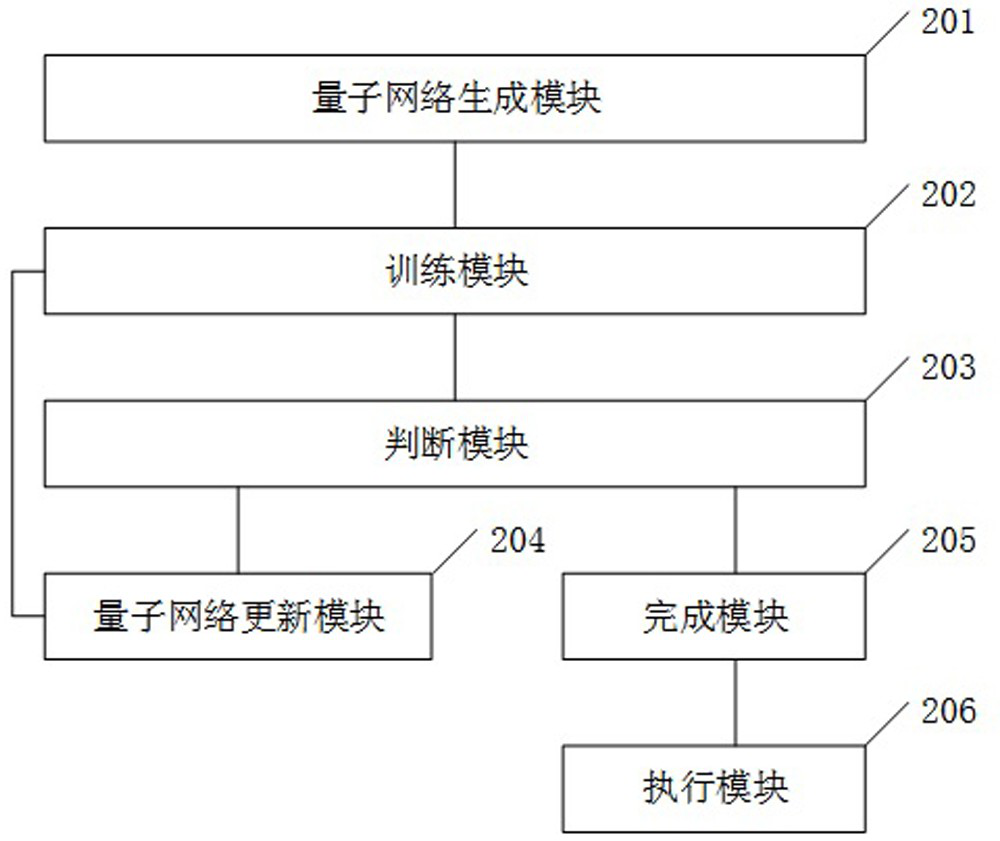
Identification method, system and device based on quantum network and storage medium
InactiveCN114169469AImprove performanceIncrease flexibilityQuantum computersCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringComputational physics
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Problem solving using quantum annealer, useful for example in sequencing, for instance nucleic acid sequencing
Quantum annealers as analog or quantum processors can find paths in problem graphs embedded in a hardware graph of the processor, for example finding valid paths, shortest paths or longest paths. A set of input, for example nucleic acid reads, can be used to set up a graph with edges between nodes denoting overlap (i.e., common base pairs) between the reads with constraints applied to perform sequence alignment or sequencing of a nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) strand or sequence, finding a solution that has a ground state energy. At least a portion of the described approaches can be applied to other problems, for instance resource allocations problems, e.g., job scheduling problems, traveling salesperson problems, and other NP-complete problems.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com