Patents
Literature
785 results about "Sequence alignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
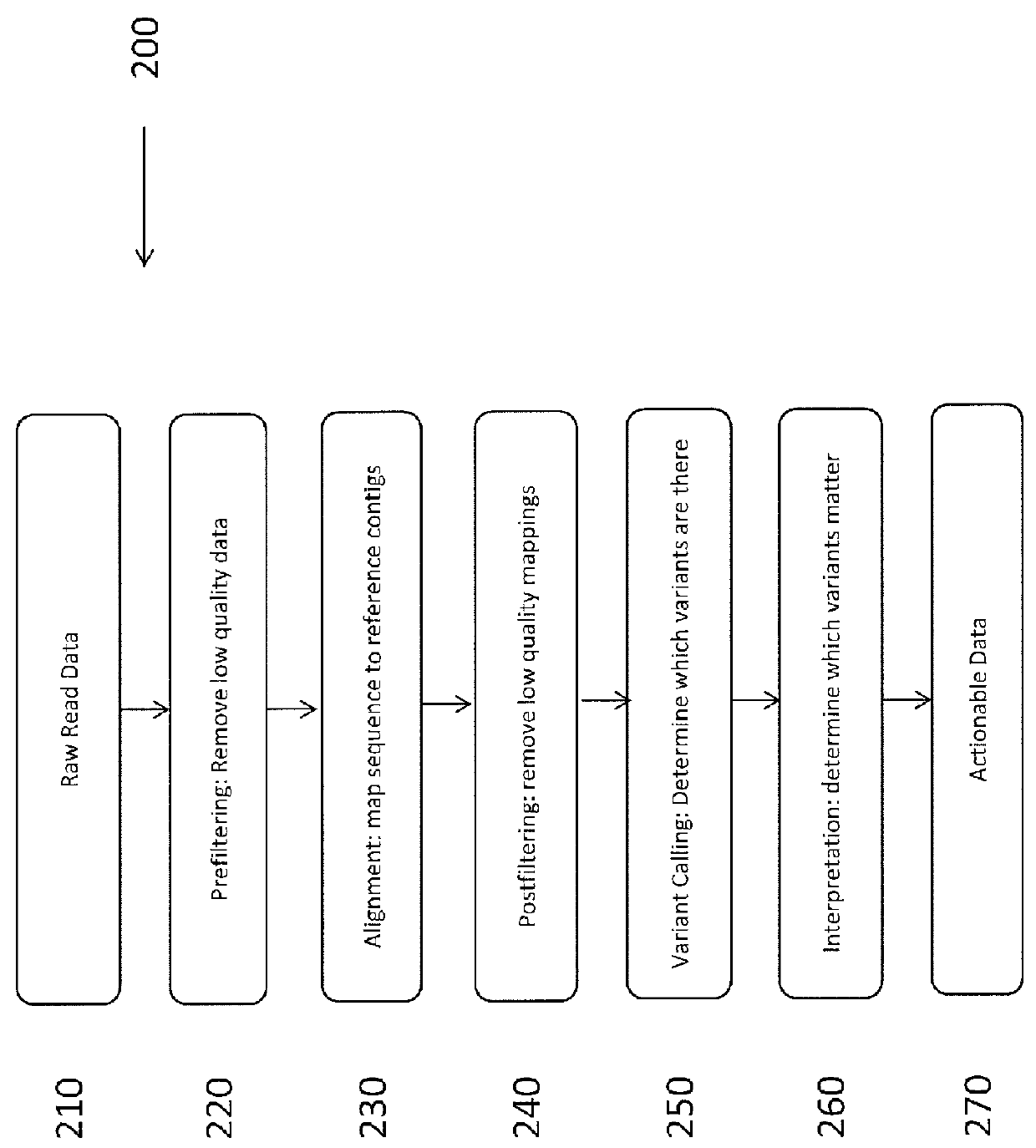
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix. Gaps are inserted between the residues so that identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. Sequence alignments are also used for non-biological sequences, such as calculating the distance cost between strings in a natural language or in financial data.
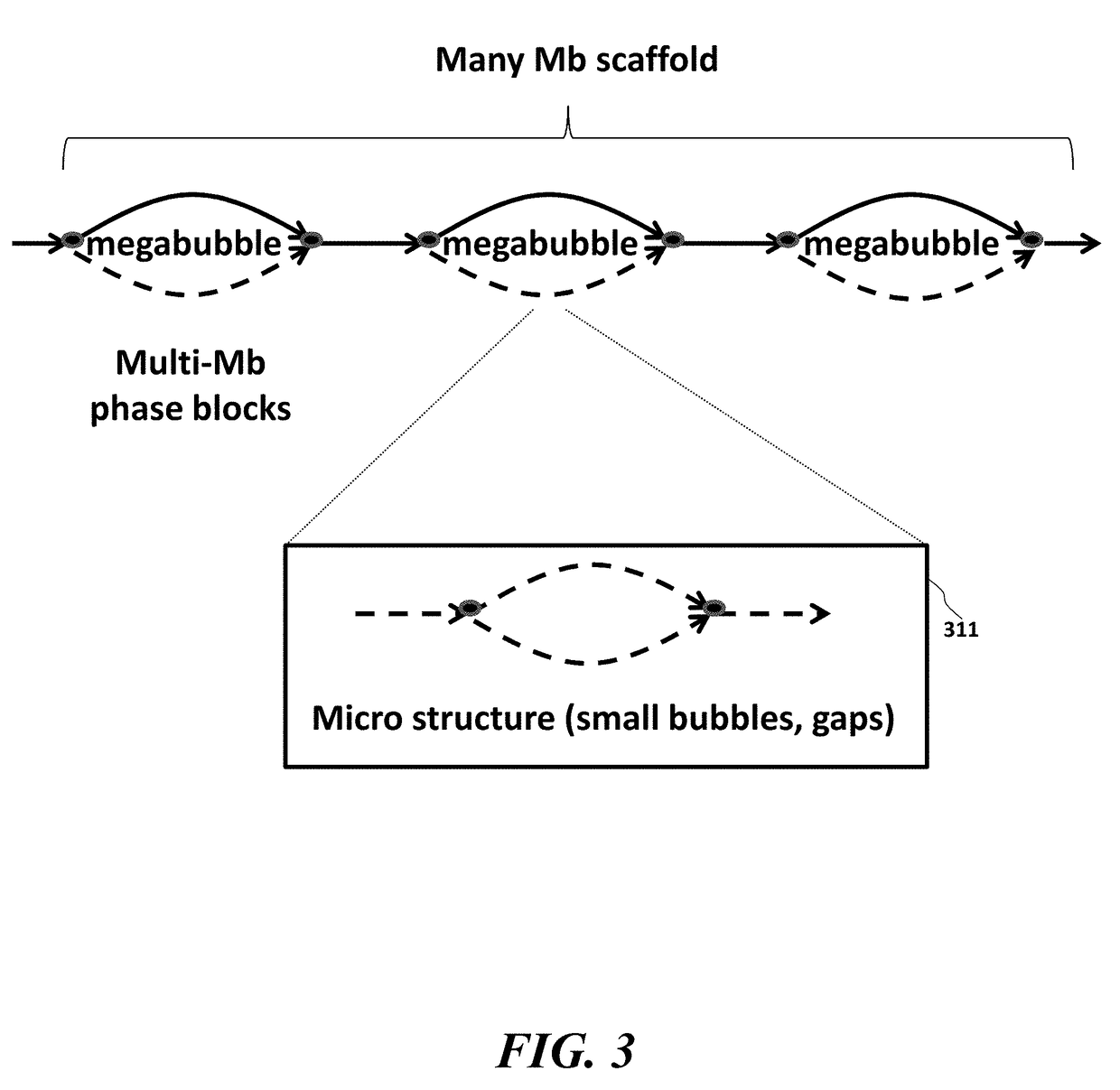
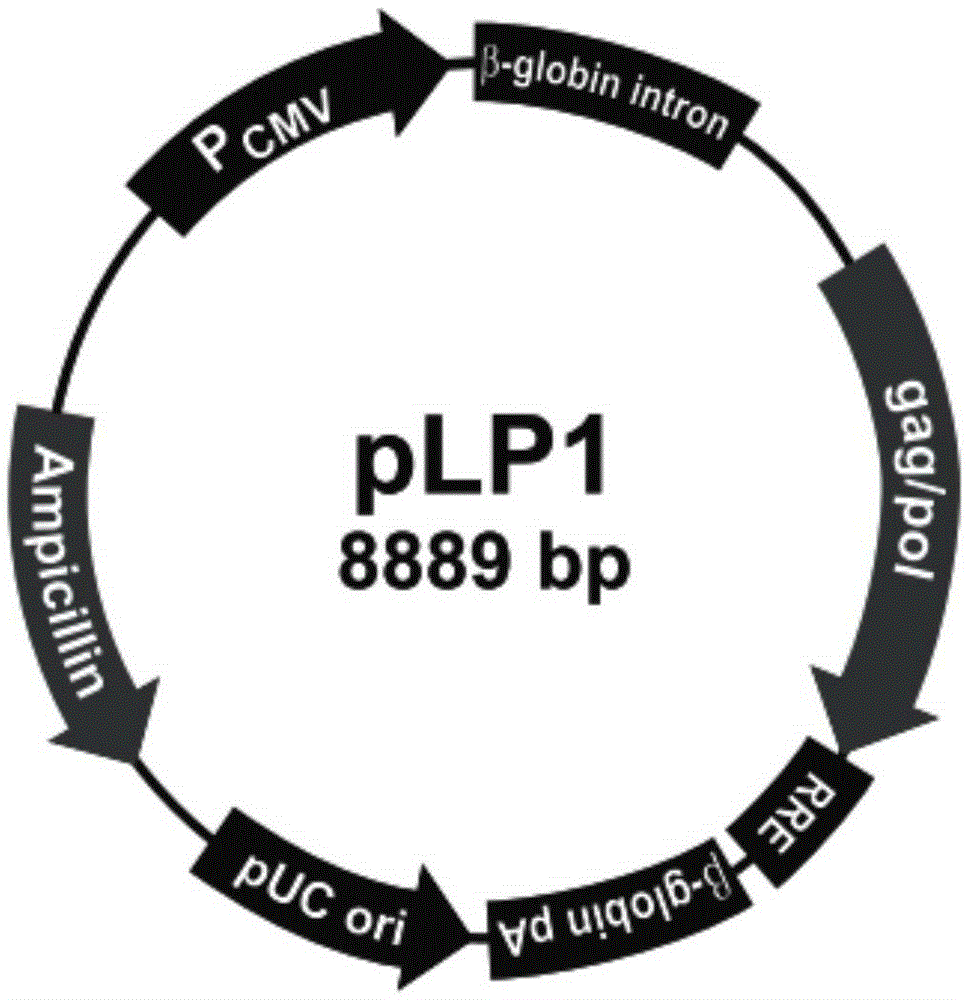
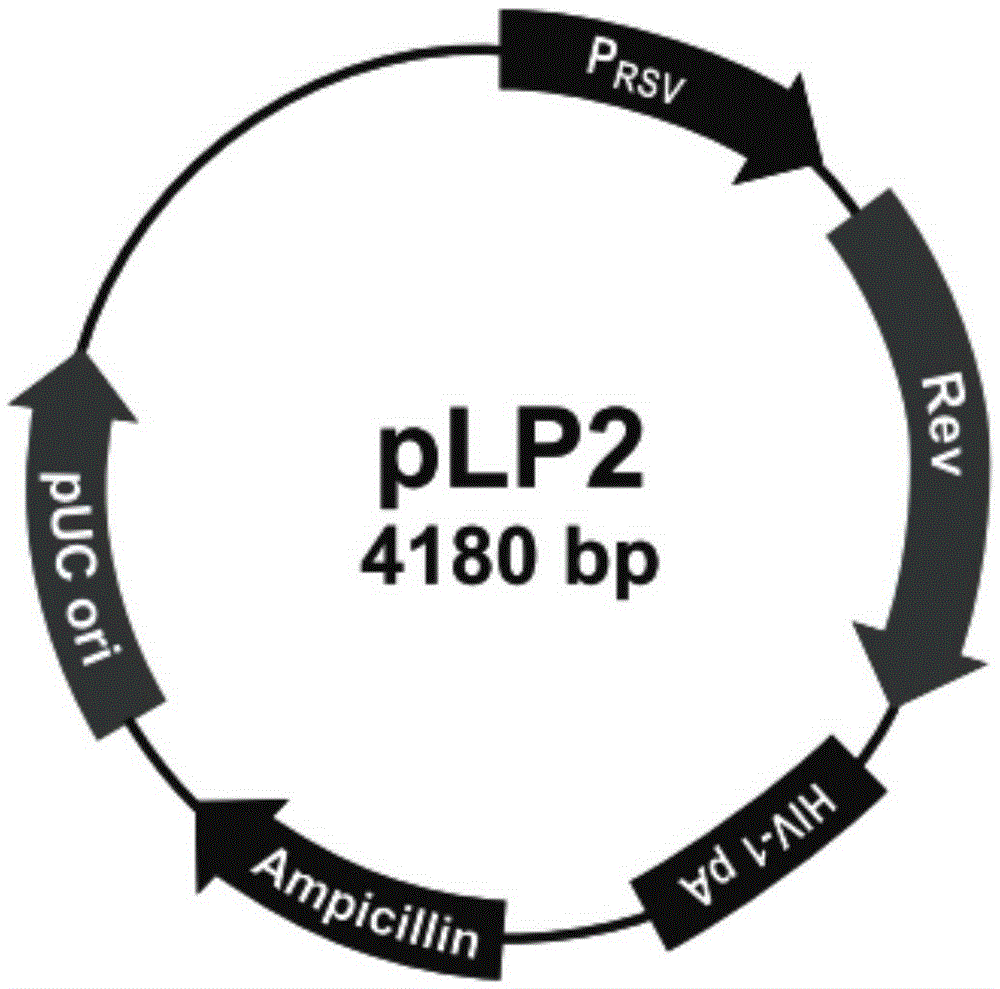
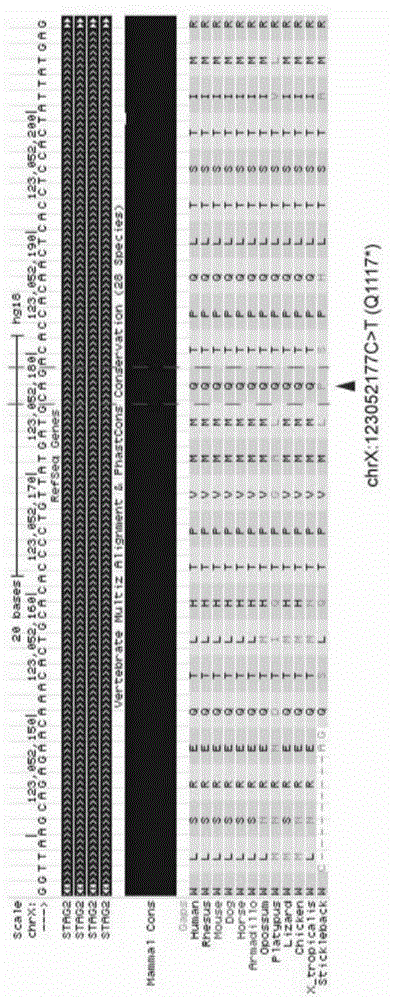
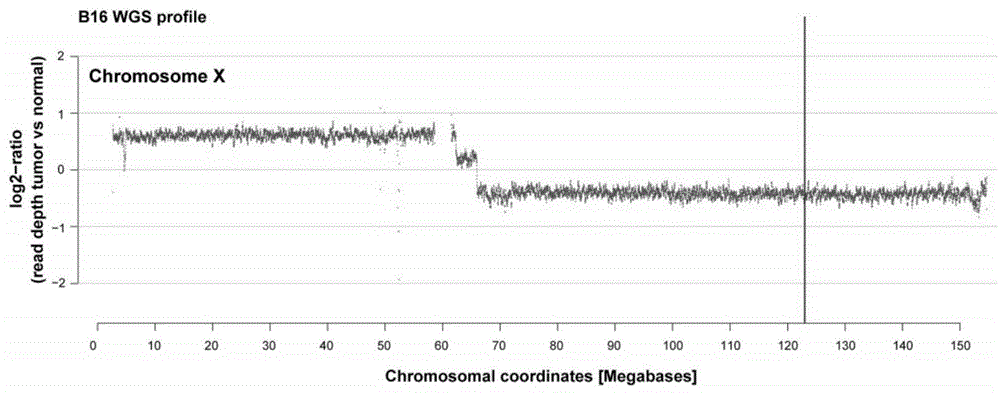
Systems and methods to detect copy number variation
InactiveUS20120046877A1Correction biasMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsData fileWorkstation
In one aspect, a system for implementing a copy number variation analysis method, is disclosed. The system can include a nucleic acid sequencer and a computing device in communications with the nucleic acid sequencer. The nucleic acid sequencer can be configured to interrogate a sample to produce a nucleic acid sequence data file containing a plurality of nucleic acid sequence reads. In various embodiments, the computing device can be a workstation, mainframe computer, personal computer, mobile device, etc.The computing device can comprise a sequencing mapping engine, a coverage normalization engine, a segmentation engine and a copy number variation identification engine. The sequence mapping engine can be configured to align the plurality of nucleic acid sequence reads to a reference sequence, wherein the aligned nucleic acid sequence reads merge to form a plurality of chromosomal regions. The coverage normalization engine can be configured to divide each chromosomal region into one or more non-overlapping window regions, determine nucleic acid sequence read coverage for each window region and normalize the nucleic acid sequence read coverage determined for each window region to correct for bias. The segmentation engine can be configured to convert the normalized nucleic acid sequence read coverage for each window region to discrete copy number states. The copy number variation identification engine can be configured to identify copy number variation in the chromosomal regions by utilizing the copy number states of each window region.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Systems, methods, and media for de novo assembly of whole genome sequence data
ActiveUS20170235876A1Sequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsComputer resourcesNucleic acid sequencing
Described are computer-implemented methods, systems, and media for de novo phased diploid assembly of nucleic acid sequence data generated from a nucleic acid sample of an individual utilizing nucleic acid tags to preserve long-range sequence context for the individual such that a subset of short-read sequence data derived from a common starting sequence shares a common tag. The phased diploid assembly is achieved without alignment to a reference sequence derived from organisms other than the individual. The methods, systems, and media described are computer-resource efficient, allowing scale-up.
Owner:10X GENOMICS
Method for detecting variation of copy numbers of genomes
ActiveCN105574361AIncreased sensitivityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsGC-contentBiology
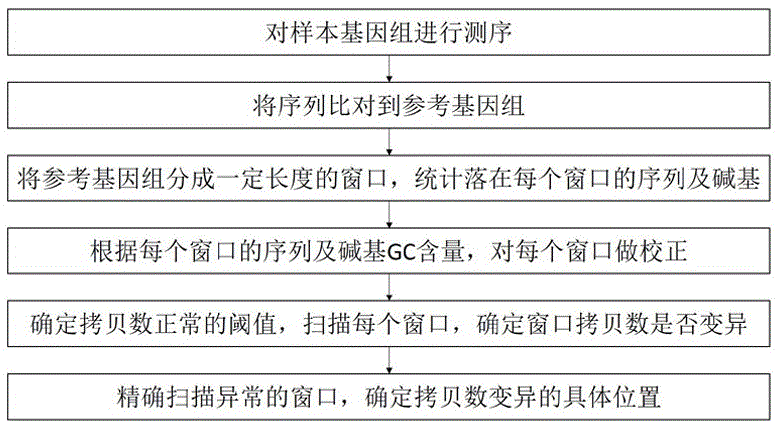
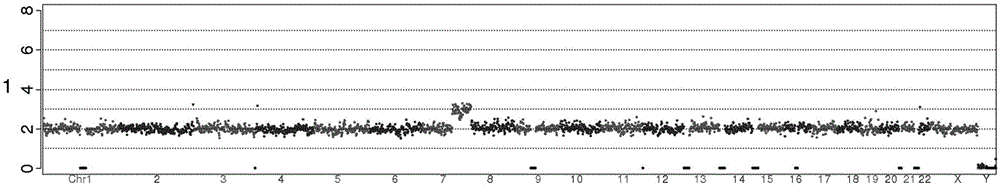
The invention relates to a method for detecting the variation of copy numbers of genomes. The method specifically comprises the following steps: sequencing sample genomes to obtain genome sequences; aligning the sequences to a reference genome to obtain the positions of the sequences on the genome; dividing the reference genome into windows with a certain length and carrying out statistics on the sequences and basic groups falling on the windows; correcting the windows according to the sequences and GC contents of the basic groups; determining threshold values with normal copy numbers, scanning the windows and determining whether the copy numbers of the windows varies; and precisely scanning the abnormal windows to determine the precise breakpoints and then determine the specific variation position of the copy numbers. According to the method, the sensitivity of the detection for the variation of the copy numbers of the genomes can be improved through utilizing three mean values, carrying out window correction, determining the threshold values with normal copy numbers, precisely scanning the abnormal windows and determining the precise breakpoints and the specific variation positions of the copy numbers; and the method is easy, simple and feasible to operate, high in efficiency, low in cost and beneficial for popularization and application.
Owner:YIKON GENOMICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
Improvements in or relating to digital forensics
ActiveUS20120011153A1Quick identificationEasy translationDigital data processing detailsPlatform integrity maintainanceSystem callComputer science
New digital forensic techniques and systems are disclosed. System call information is collected from a device under test (DUT) and converted to a sequence format. Thereafter, sequence alignment methods and tools can be used to investigate and identify patterns of behaviour that are suspicious.
Owner:FORTINET
Method for detecting mutation information in multiplex amplification sequencing product of genome
ActiveCN106202991AEfficient identificationQuick identificationHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsReference genesNatural abundance
The invention discloses a method for detecting mutation information in a multiplex amplification sequencing product of a genome. The method comprises steps as follows: sequencing data are subjected to quality assessment and preprocessing; a recognizable sequencing sequence is selected for sequence assembling; the recognizable sequencing sequence or a sequence obtained through assembling is compared with a reference gene sequence, and preliminary variation information is obtained; fine calibration of sequence variation is performed according to different types of conditions; a calibrated sequencing fragment is obtained; the homozygosis or heterozygosis state of a target fragment is obtained according to the type of the sequencing fragment with the highest abundance; finally, the mutation information in the multiplex amplification sequencing product of the genome is obtained. By means of the method, the amplification product can be rapidly, efficiently and accurately recognized, and the calculation resources are saved; the sequence assembling process is compatible, and the problem of reduction of the quality value of basic groups produced in the sequencing process can be effectively solved; the homozygosis / heterozygosis state of variation information can be more effectively and stably judged, and random errors introduced in the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) process and the sequencing process are eliminated.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD +1
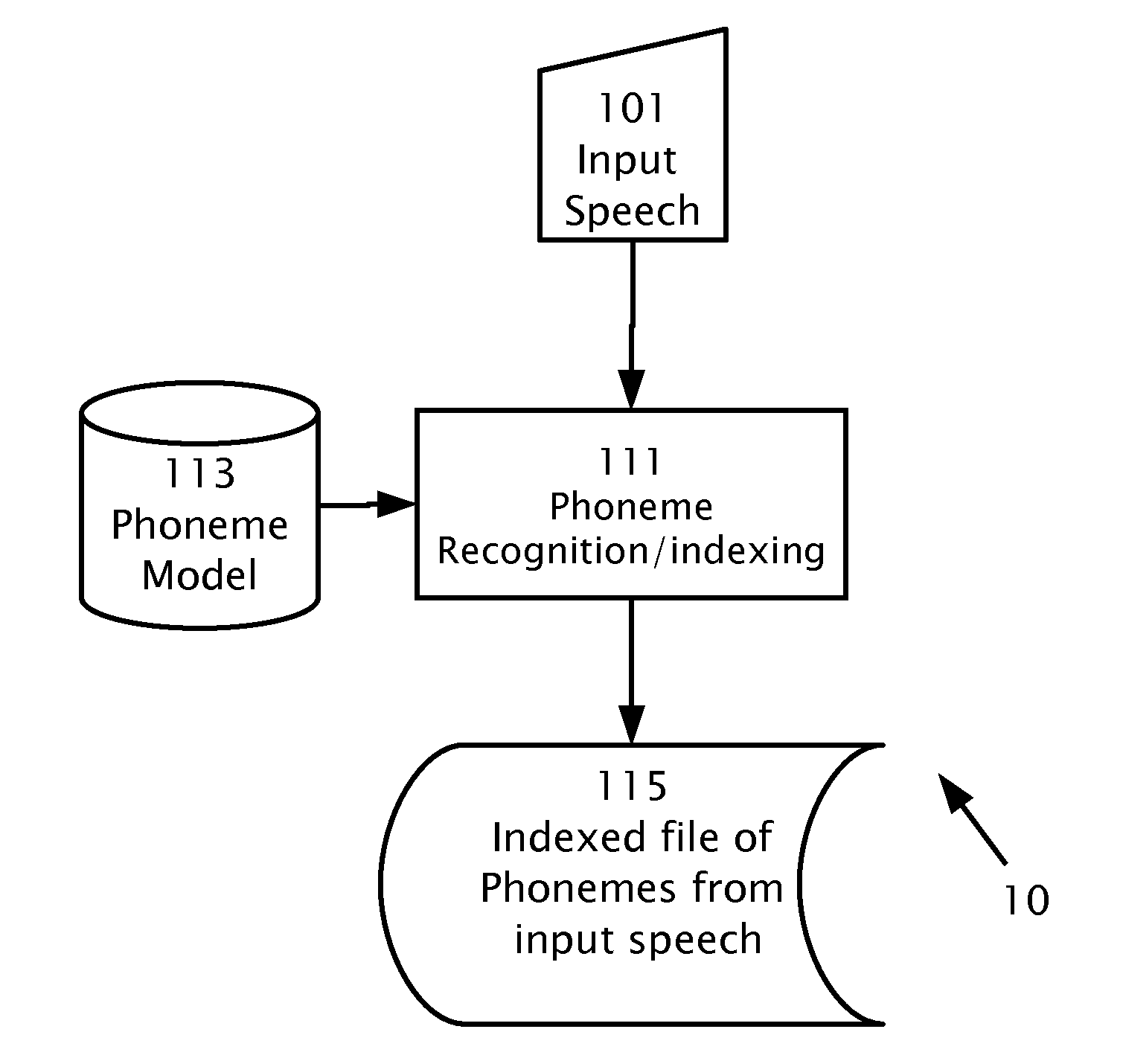
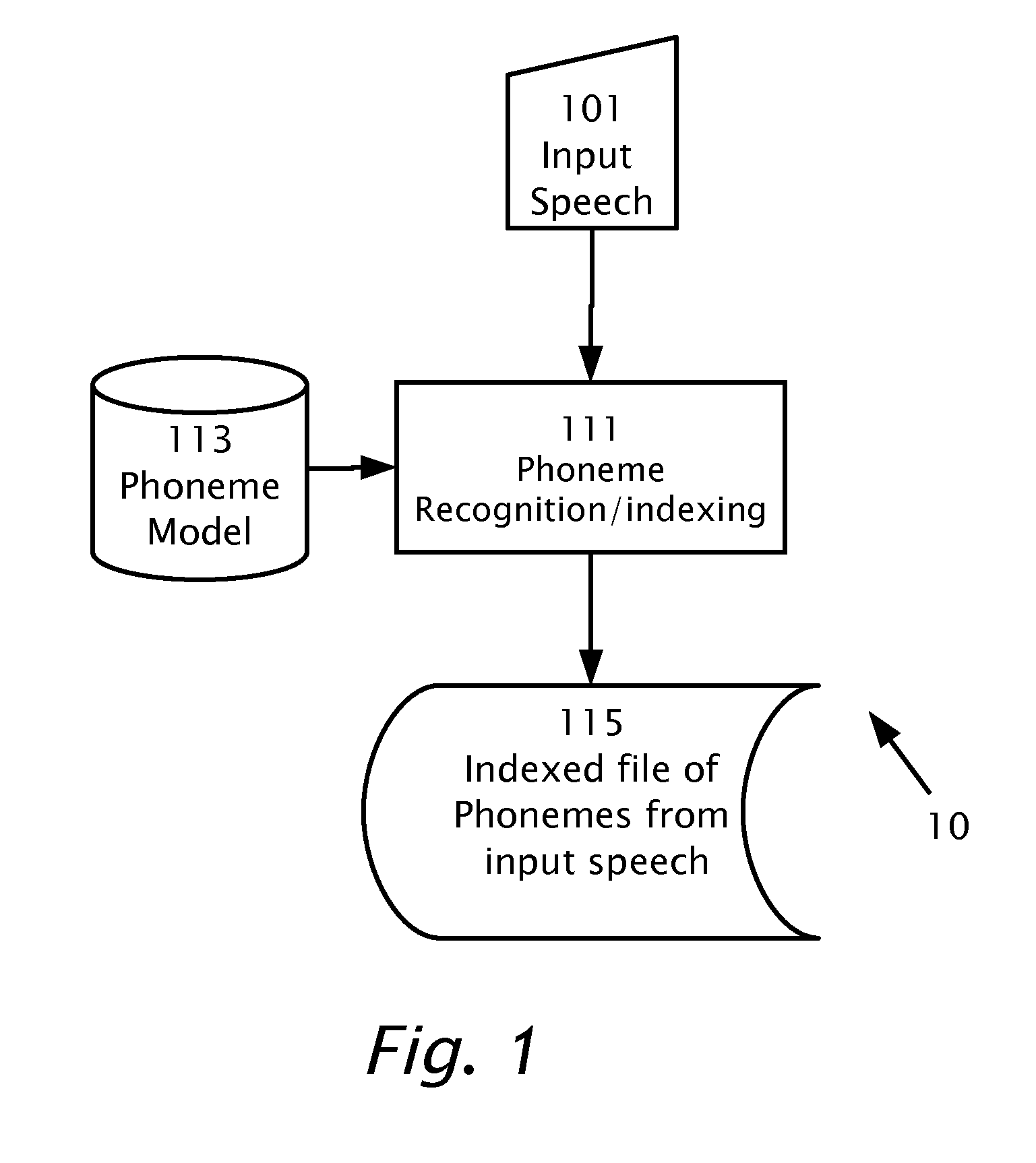
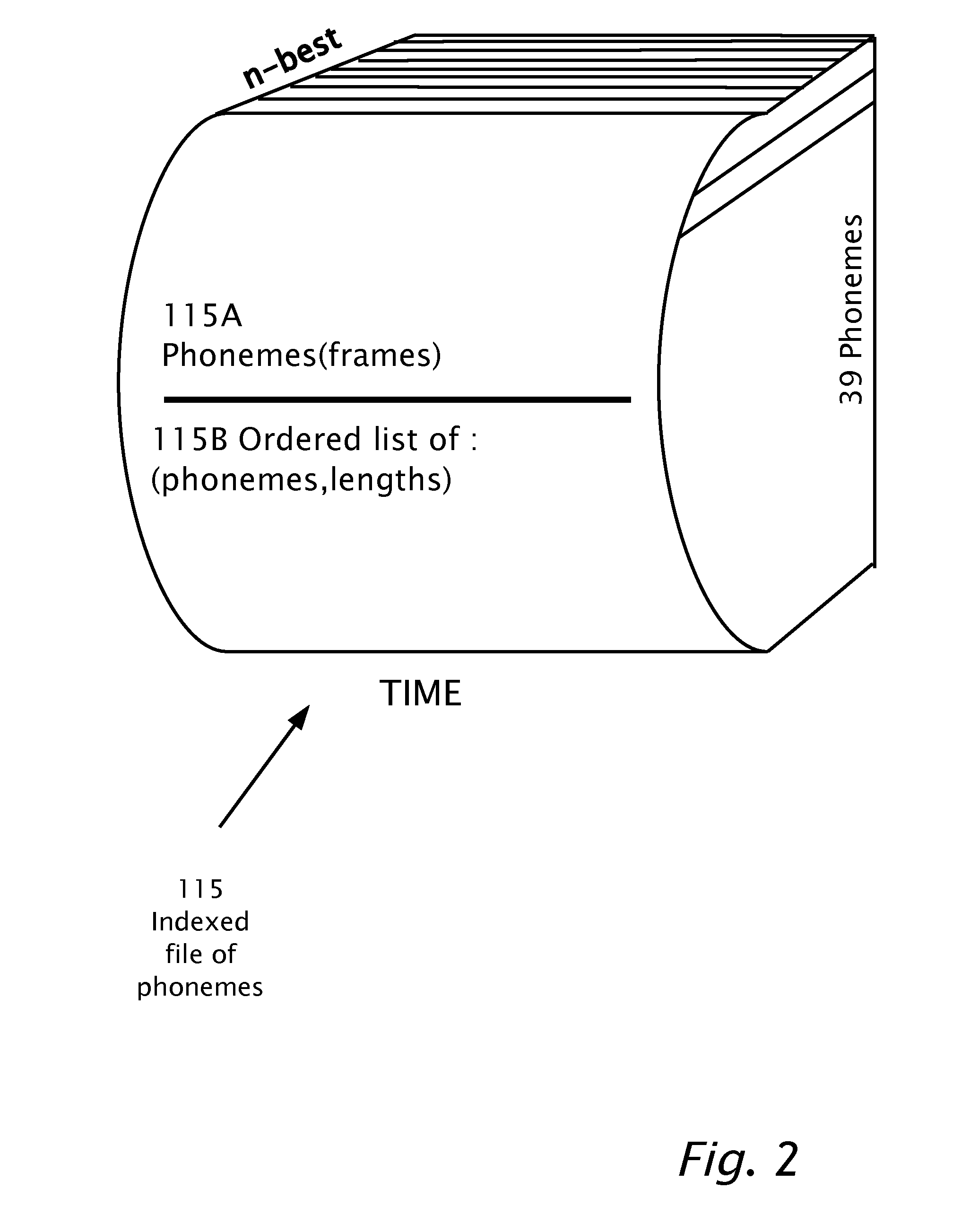
Searching in Audio Speech
A computerized method of detecting a target word in a speech signal. A speech recognition engine and a previously constructed phoneme model is provided. The speech signal is input into the speech recognition engine. Based on the phoneme model, the input speech signal is indexed. A time-ordered list is stored representing n-best phoneme candidates of the input speech signal and phonemes of the input speech signal in multiple phoneme frames. The target word is transcribed into a transcription of target phonemes. The time-ordered list of n-best phoneme candidates is searched for a locus of said target phonemes. While searching, scoring is based on the ranking of the phoneme candidates among the n-best phoneme candidates and based on the number of the target phonemes found. A composite score of the probability of an occurrence of the target word is produced. When the composite score is higher than a threshold, start and finish times are output which bound the locus. The start and finish times are input into an algorithm adapted for sequence alignment based on dynamic programming for aligning a portion of the phoneme frames with the target phonemes.
Owner:LNTS - LINQUISTECH SOLUTION
Method using CRISPR-Cas9 to specifically knock off pig PDX1 gene and sgRNA of PDX1 gene for specific targeting
The invention discloses a method using CRISPR-Cas9 to specifically knock off pig PDX1 gene and sgRNA of PDX1 gene for specific targeting. The target sequence of sgRNA of PDX1 gene for specific targeting on PDX1 gene is accord with the sequence alignment rule of 5'-N(20)NGG-3', wherein N(20) represents 20 continuous bases, and each N represent A, T, C or G; the target sequence of PDX1 gene is arranged in the first exon coding region on the N terminal of PDX1 gene or a junction between the coding region and neighbored intron, and the target sequence of PDX1 gene is unique. The provided method can rapidly, precisely, efficiently and specifically knock off PDX1 gene of pigs, and solves the problems of long period and high cost of pig PDX1 gene knocking.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
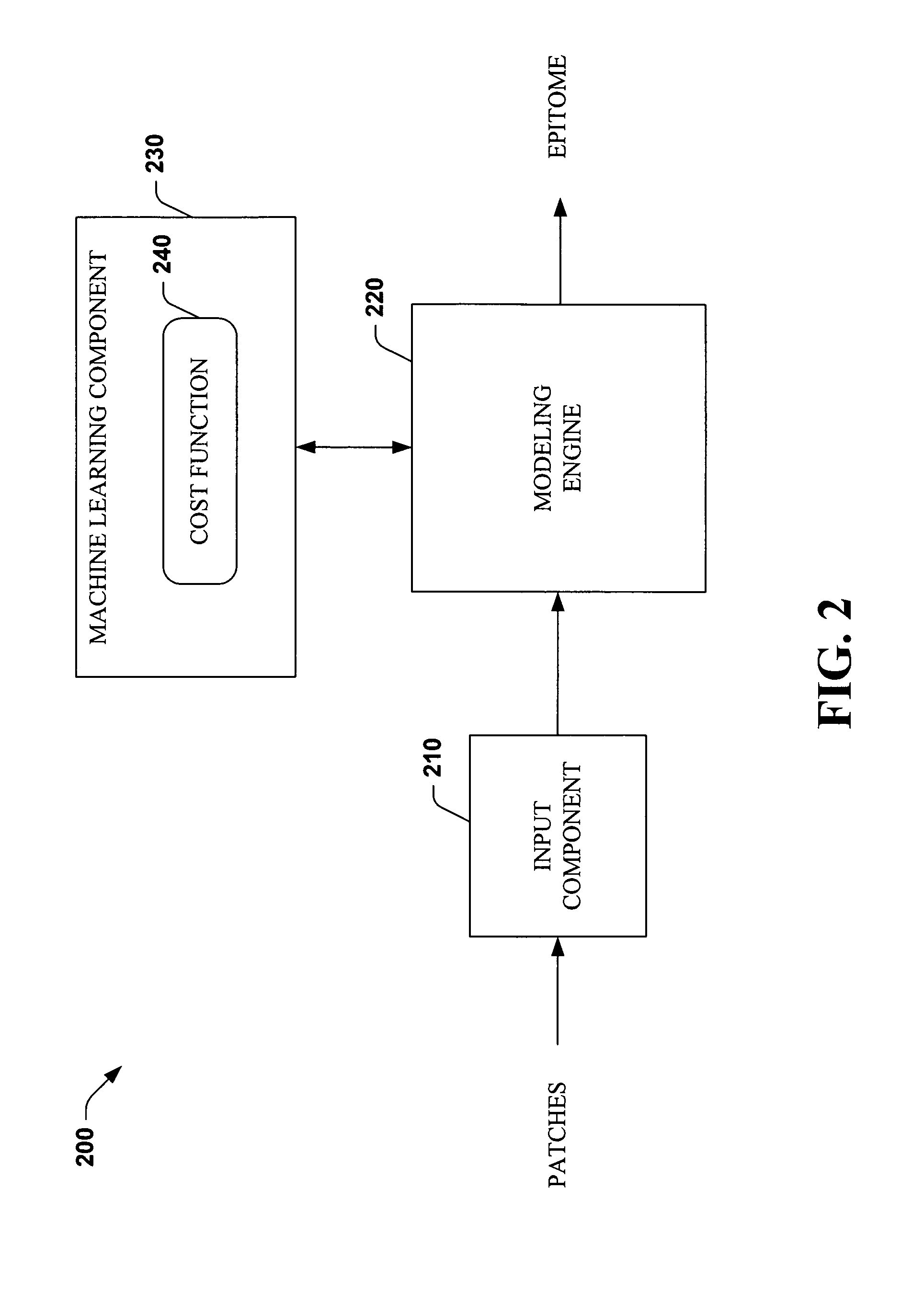
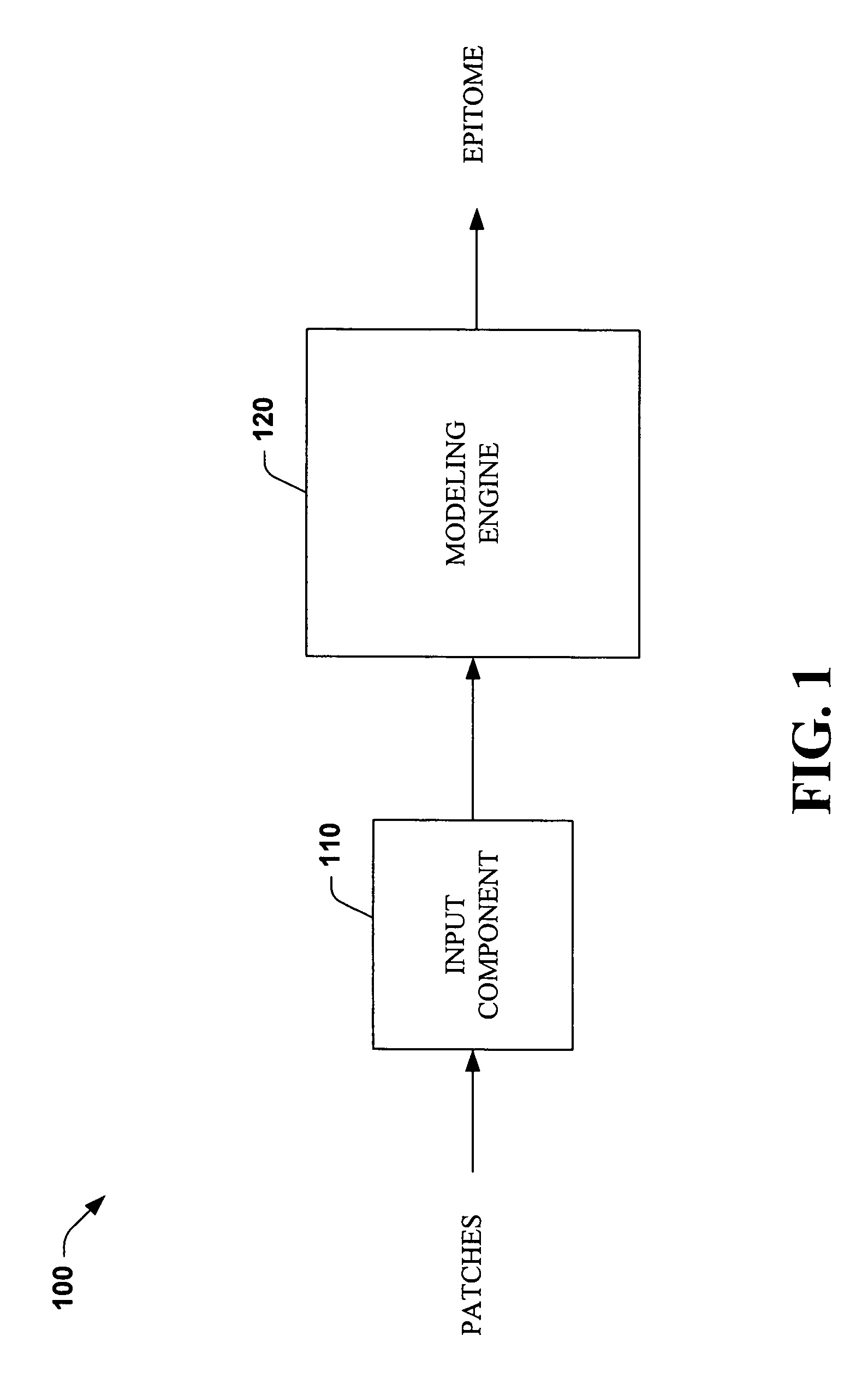
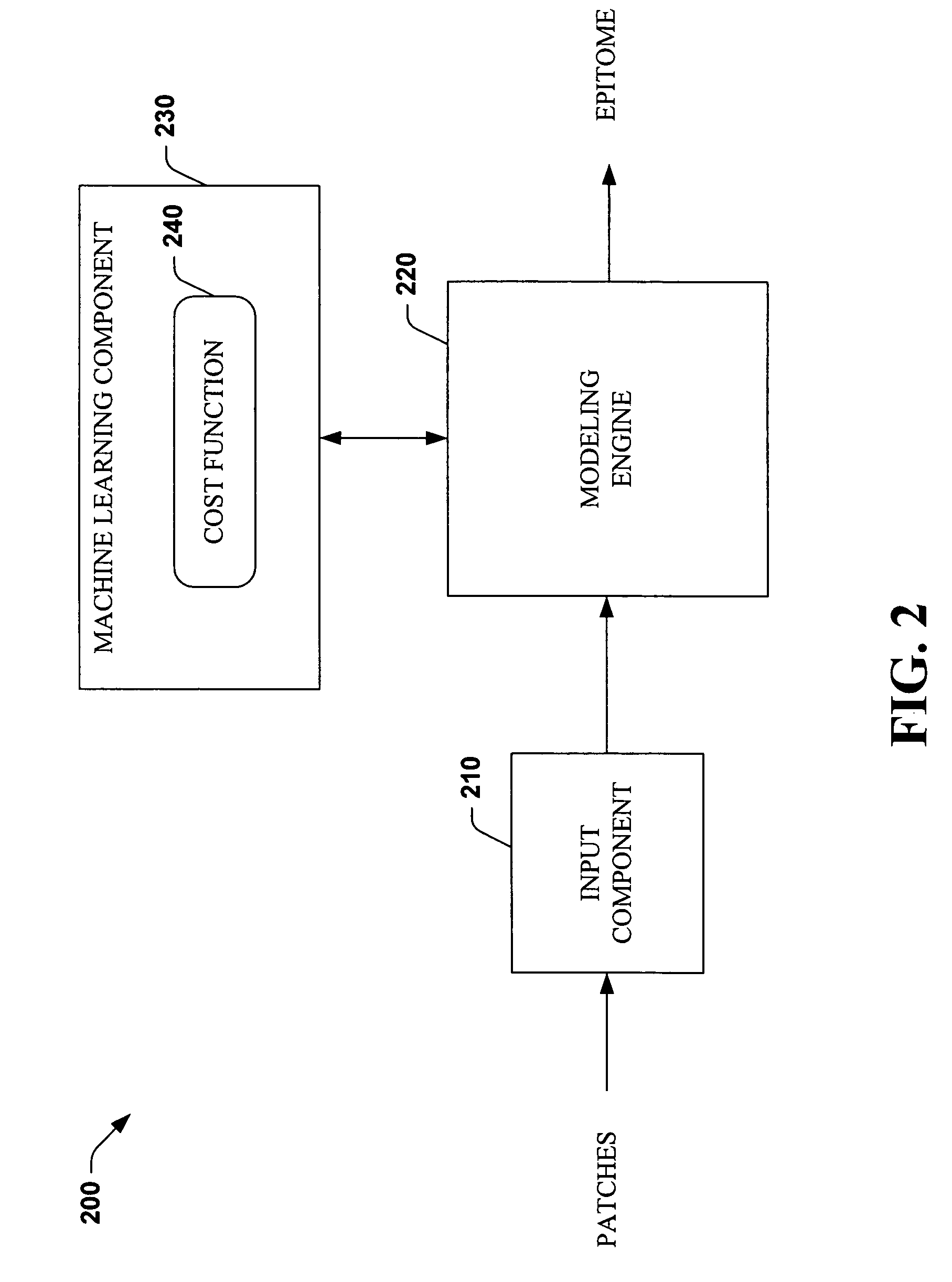
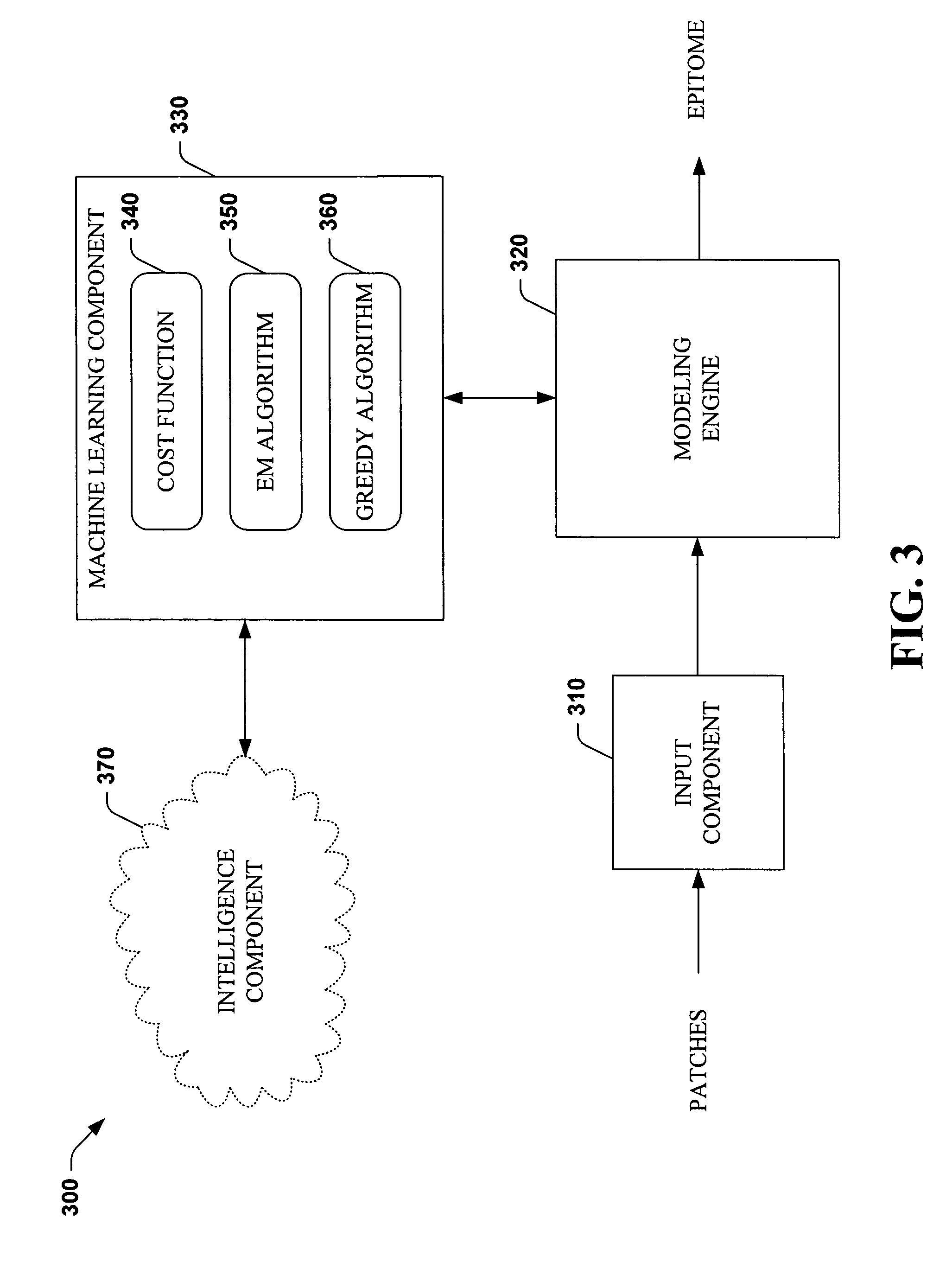
Systems and methods that utilize machine learning algorithms to facilitate assembly of aids vaccine cocktails
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
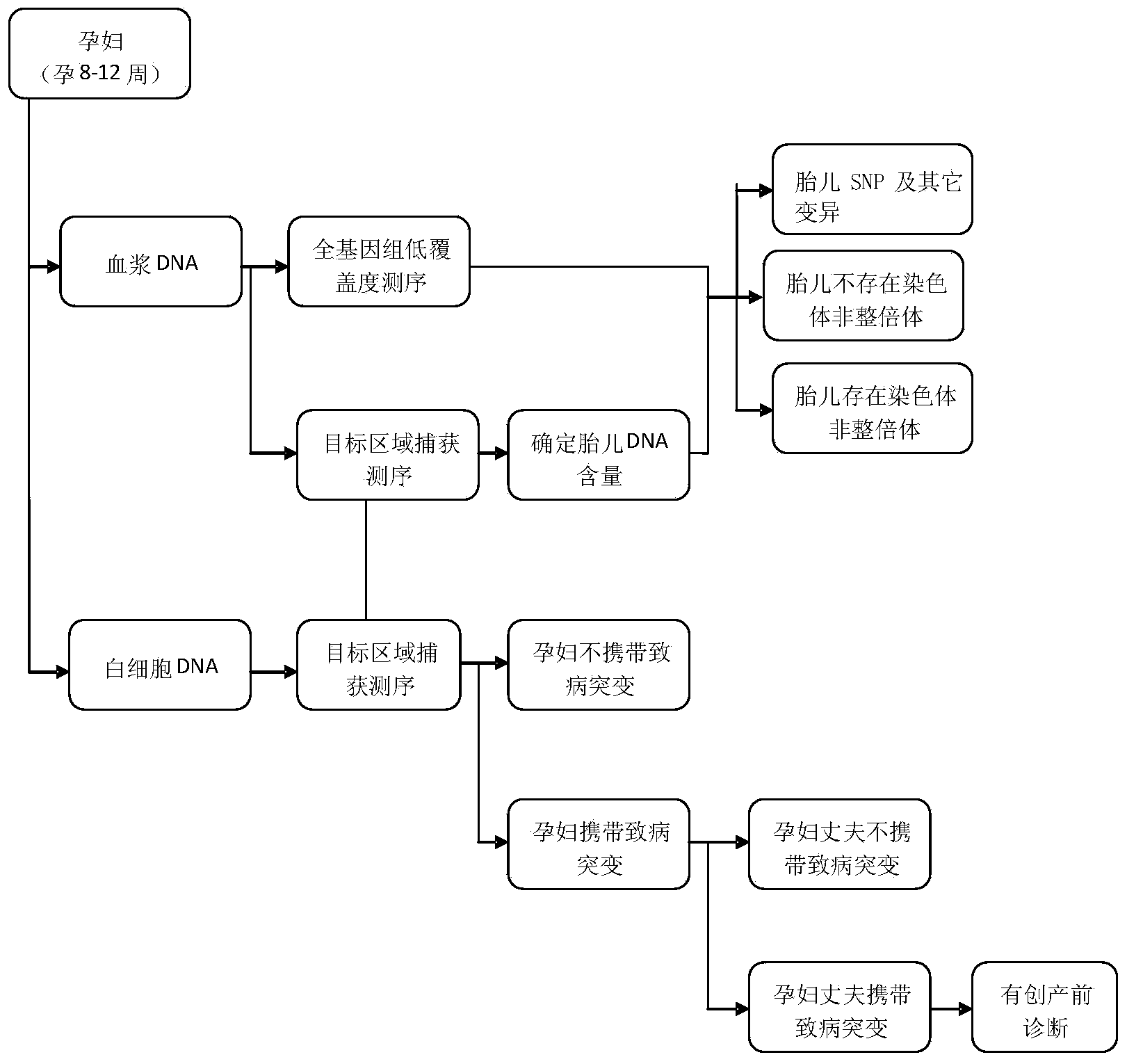
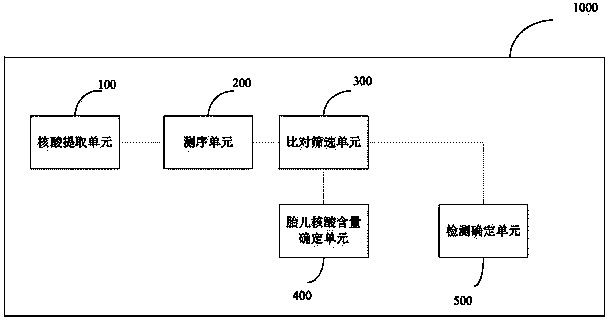
Method and device for simultaneously determining fetal nucleic acid content and aneuploidy of chromosome
ActiveCN104232777AAccurate detectionApplicable detectabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenotypeBiology
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI +2
Systems and methods that utilize machine learning algorithms to facilitate assembly of aids vaccine cocktails
The subject invention provides systems and methods that facilitate AIDS vaccine cocktail assembly via machine learning algorithms such as a cost function, a greedy algorithm, an expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm, etc. Such assembly can be utilized to generate vaccine cocktails for species of pathogens that evolve quickly under immune pressure of the host. For example, the systems and methods of the subject invention can be utilized to facilitate design of T cell vaccines for pathogens such HIV. In addition, the systems and methods of the subject invention can be utilized in connection with other applications, such as, for example, sequence alignment, motif discovery, classification, and recombination hot spot detection. The novel techniques described herein can provide for improvements over traditional approaches to designing vaccines by constructing vaccine cocktails with higher epitope coverage, for example, in comparison with cocktails of consensi, tree nodes and random strains from data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
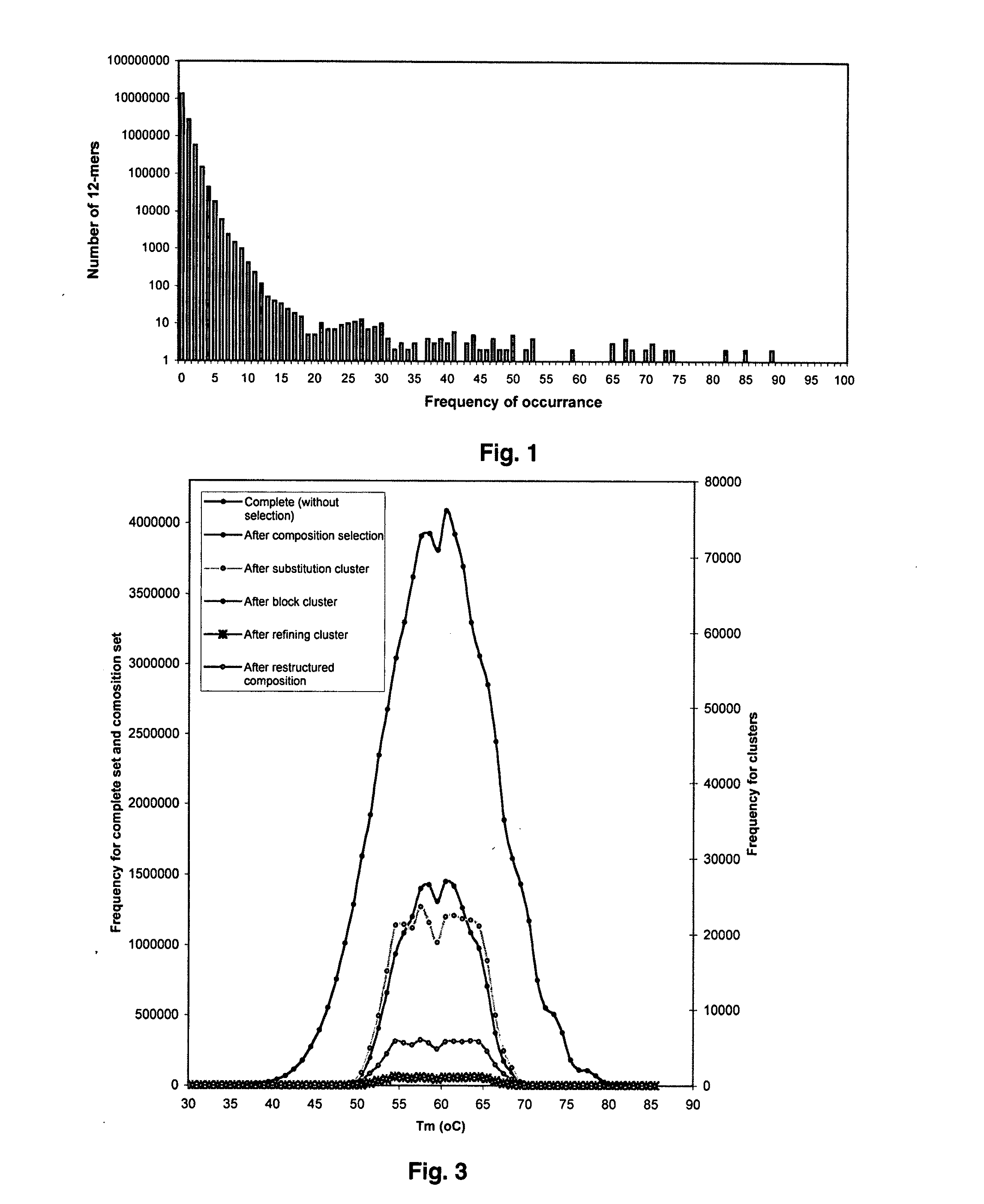
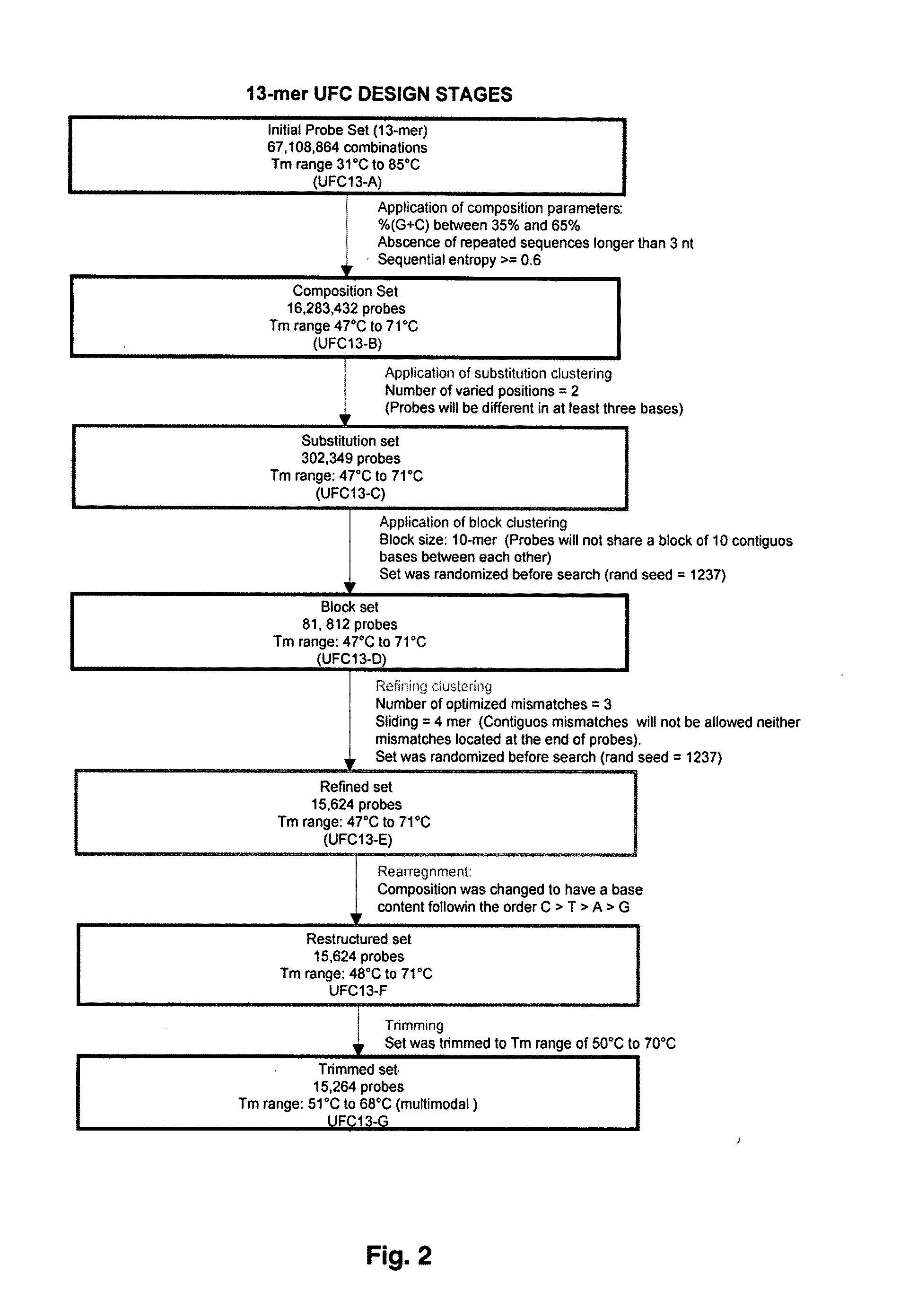
Universal fingerprinting chips and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110105346A1Avoid formingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideOrganism
The present invention discloses a designing strategy for constructing a set of probes useful for analyzing all or most prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. A set of capture probes with optimal fingerprinting properties and highly representative of all possible sequences of an organism can be selected by six sequential steps. Fingerprinting potential of such probes is validated by phylogenetic analysis, which generates results that strongly correlate with phylogenetic trees produced by sequence alignment. The probes generated by the instant methods can be used for detecting an organism, for establishing phylogenetic relationships between different organisms, for detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms and a wide variety of other applications that require genetic analysis.
Owner:BEATTIE KENNETH L +4
Bacillus subtilis highly producing tetramethylpyrazine and method thereof for fermentation producing tetramethylpyrazine
InactiveCN101445786AIncrease productionRich sourcesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharumSucrose
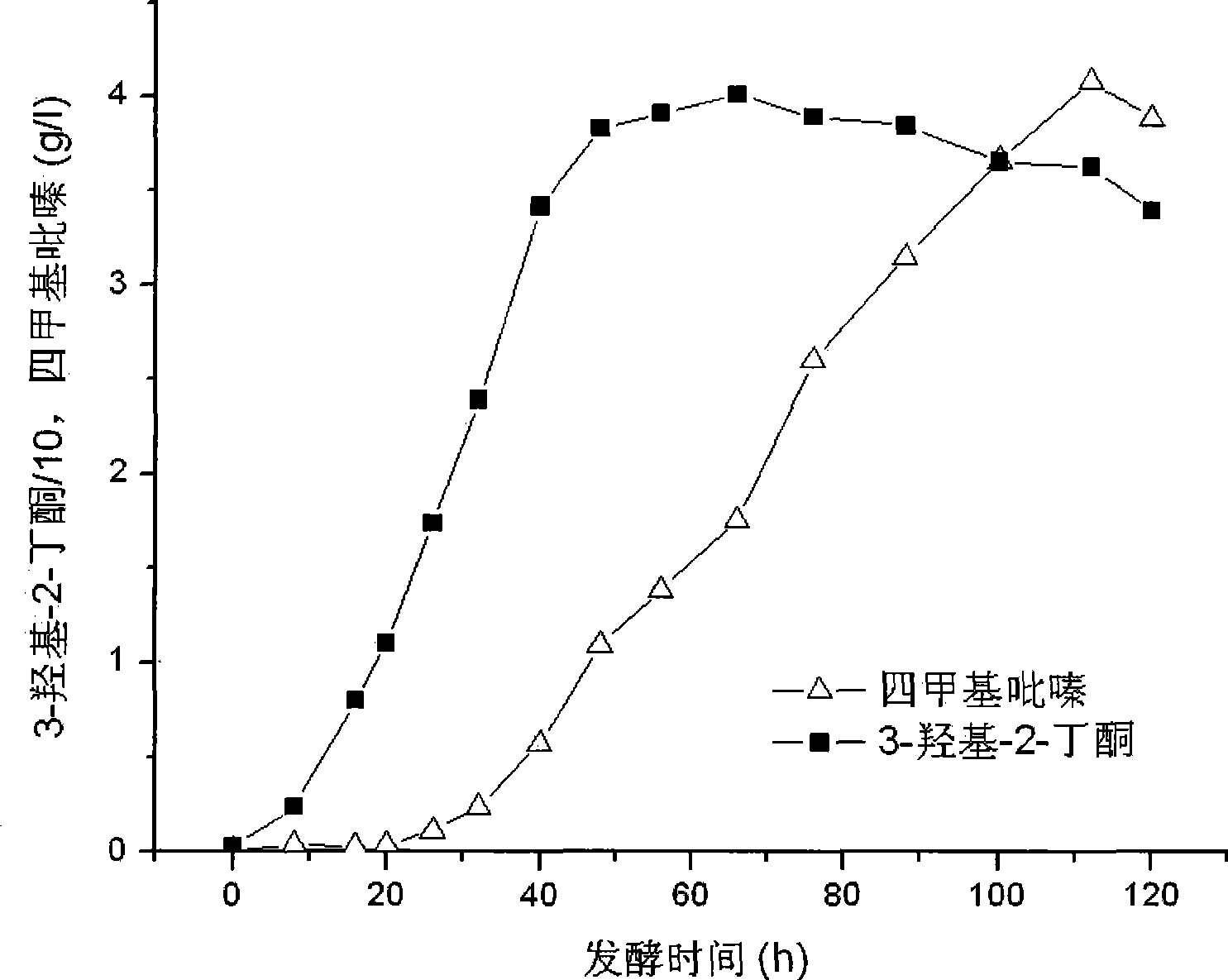
The invention relates to a bacillus subtilis highly producing tetramethylpyrazine and a method thereof for fermentation producing tetramethylpyrazine, and belongs to the technical field of bio-engineering. The invention discloses a Bacillus subtilis XZ1124 which can highly produce tetramethylpyrazine, and is preserved in CCTCC, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 208157. The strain is made of Maotai-flavor liquor and high temperature Daqu; the strain is identified as Bacillus subtilis based on colony, cell form, physiological and biochemical characteristics and 16S rRNA gene sequence comparative result thereof. The strain can utilizes glucose, sucrose, molasses and soybean cake powder as substrate, and increases the output of tetramethylpyrazine through accumulating a great deal of endogenous precursors, so as to solve the problems of low product density, exogenous adding precursor requirement, and low precursor utilization rate in tetramethylpyrazine production through microbe fermentation. When sucrose and soybean cake powder are used as substrate, 4.08 g / L of tetramethylpyrazine can obtained through shaking culture of the raw material for 120 h at the temperature of 37 DEG C.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Low allergenic protein variants
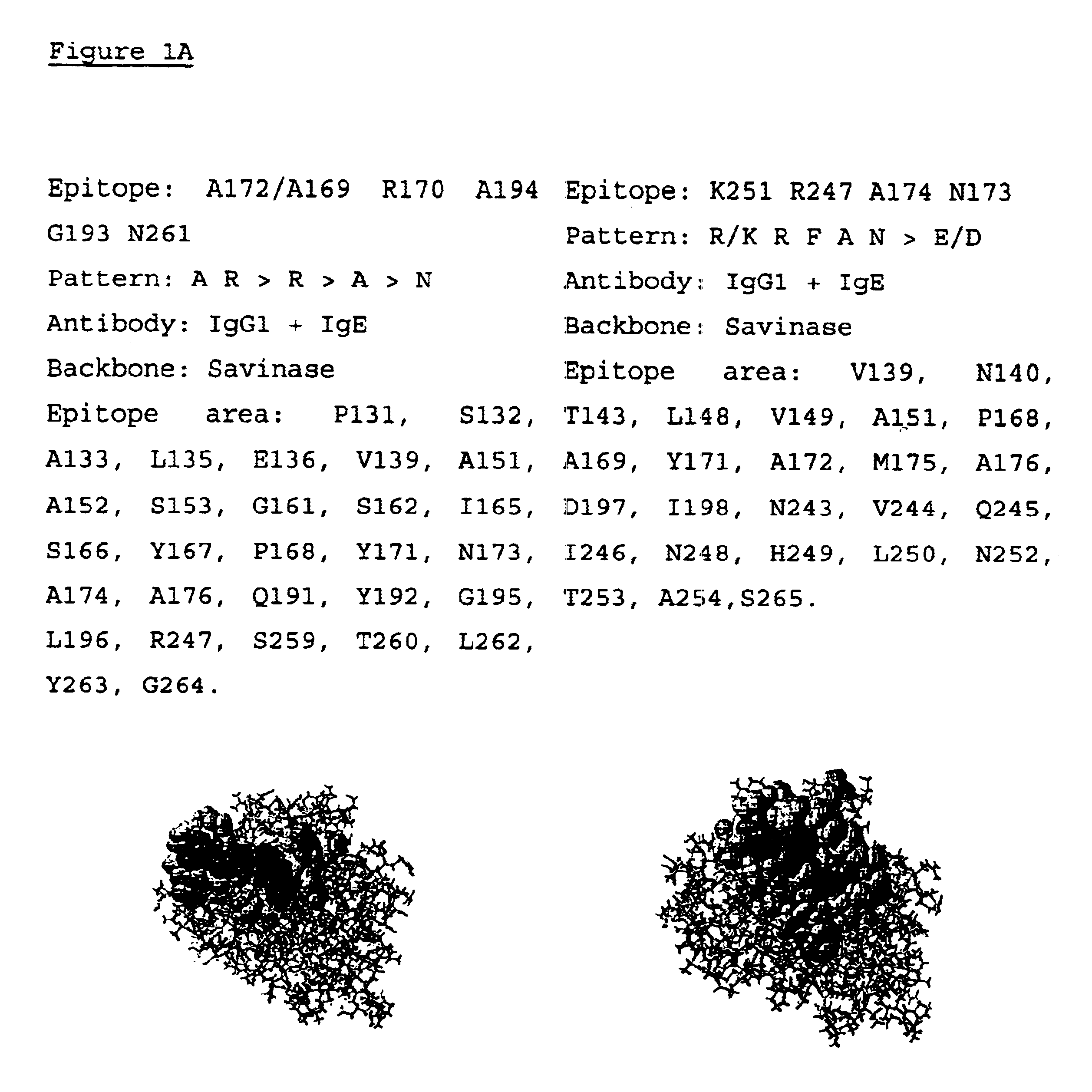
The present invention relates to a method of selecting a protein variant having reduced immunogenicity as compared with the parent protein. This method includes the steps of screening a random peptide display package library with antibodies raised against any protein of interest, sequencing the amino acid sequence of the antibody binding peptides, or the DNA sequence encoding the antibody binding peptides, identifying epitope patterns of a protein by sequence alignment of the reactive peptide sequence, localization of epitope patterns on the primary 3-dimensional structure of the parent protein, defining an epitope area including amino acids situated within 5 Å from the epitope amino acids, and affecting antibody binding to the epitope, changing the localized epitope patterns, or amino acids defining the epitope area of the parent protein by genetic engineering mutations of a DNA sequence encoding the parent protein without impairing functionality of the protein using the emerging epitode database for eliminating amino acid substitutions creating new or duplicating existing epitope patterns, introducing the mutated DNA sequence into a suitable host, culturing the host and expressing the protein variant, and evaluating the immunogenicity of the protein variant using the parent protein as reference. The invention further relates to the protein variant and its use, as well as to a method for producing said protein variant.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method and device for quick contrast and analysis of short sequence for second-generation sequencing
ActiveCN106295250AImprove time and efficiencyFaster thanSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsReference genesArray data structure
The invention discloses a method and a device for quick contrast and analysis of a short sequence for second-generation sequencing, which can solve the problems of low contrast efficiency and high memory occupation ratio of sequencing data. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) short sequence obtained by sequencing, and respectively mapping and encoding the DNA short sequence by a first hash algorithm and a second hash algorithm, so as to respectively obtain a first index and a second index; according to a preset index query library, the first index and the second index, contrasting the DNA short sequence and a reference gene group, wherein the index query library consists of an unit structure array, and each unit structure comprises value and index 2; storing the array index offset of each unit structure as the corresponding index 1, namely the index value corresponding to the structure array, wherein K is the length of segment sequence; according to the contrast result, when the contrast result is correct, obtaining the value of the K-mer segment contrasted with the corresponding DNA short sequence, and determining the chromosome number of the corresponding DNA short sequence and the site on the chromosome.
Owner:北京普康瑞仁医学检验所有限公司
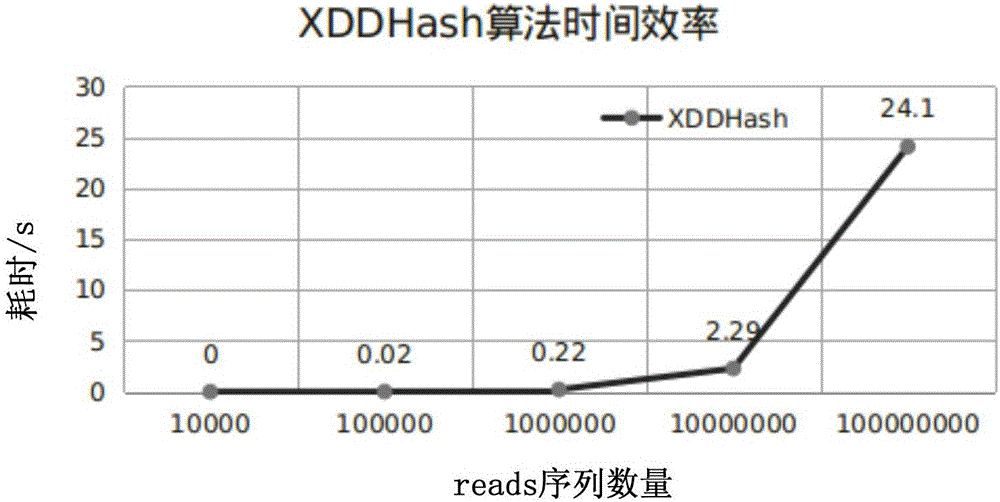
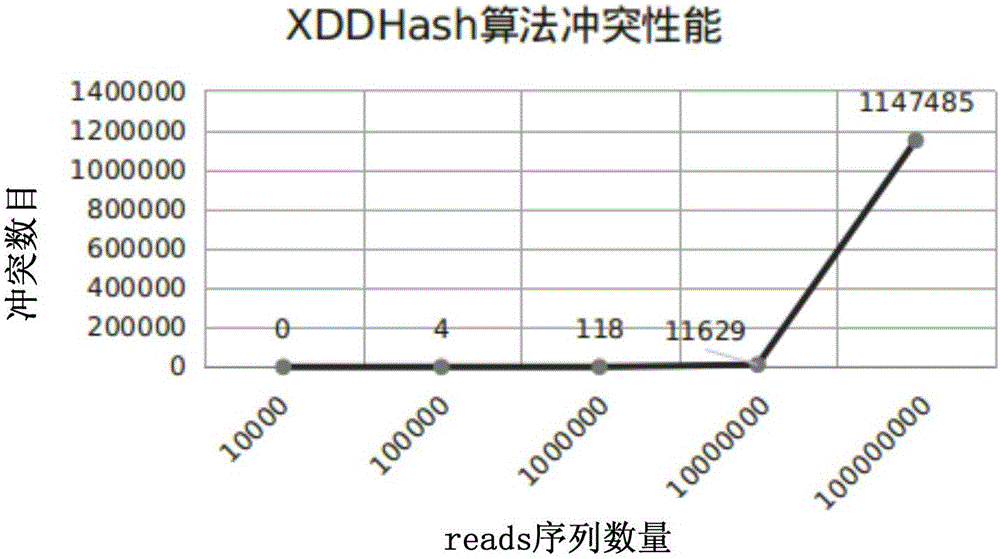
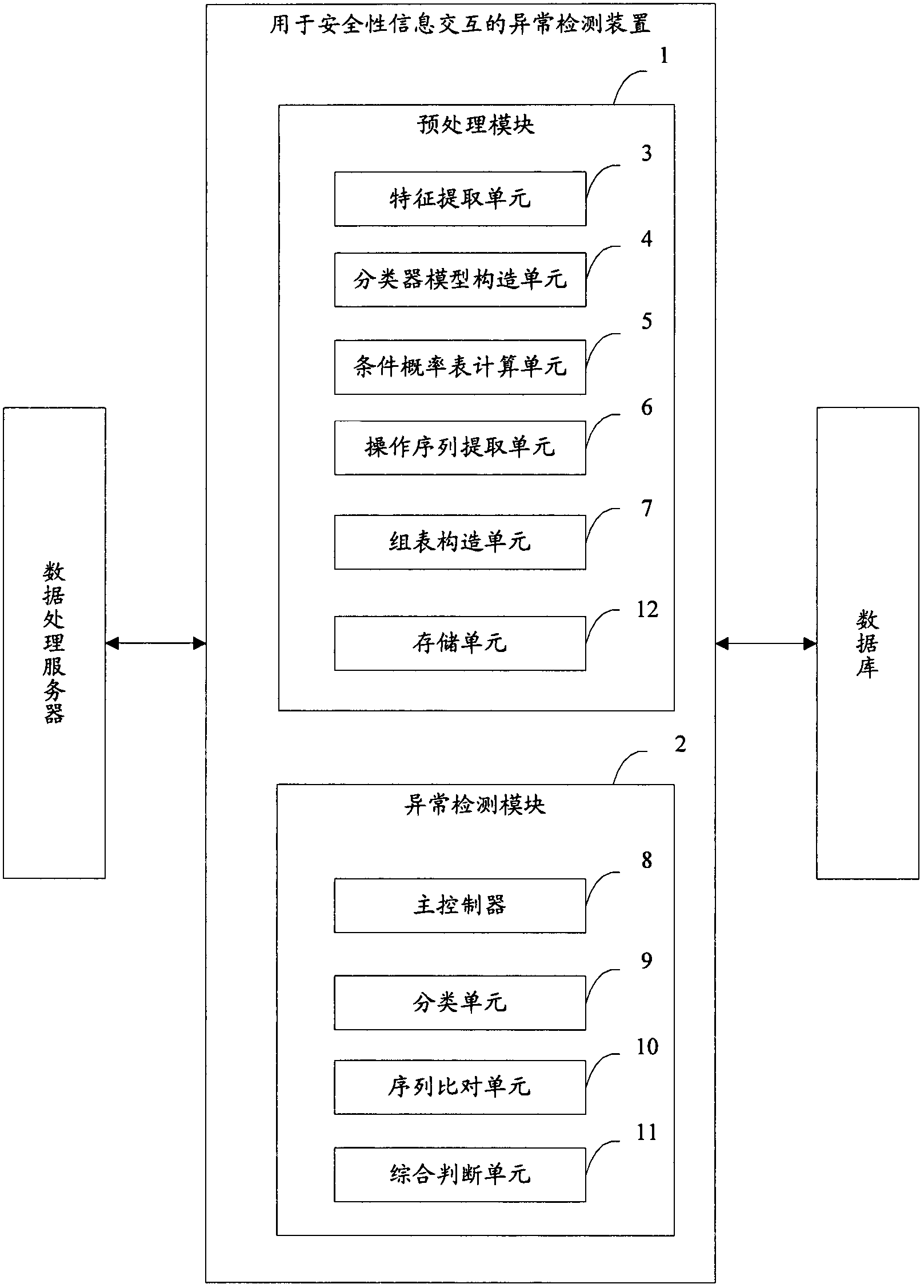
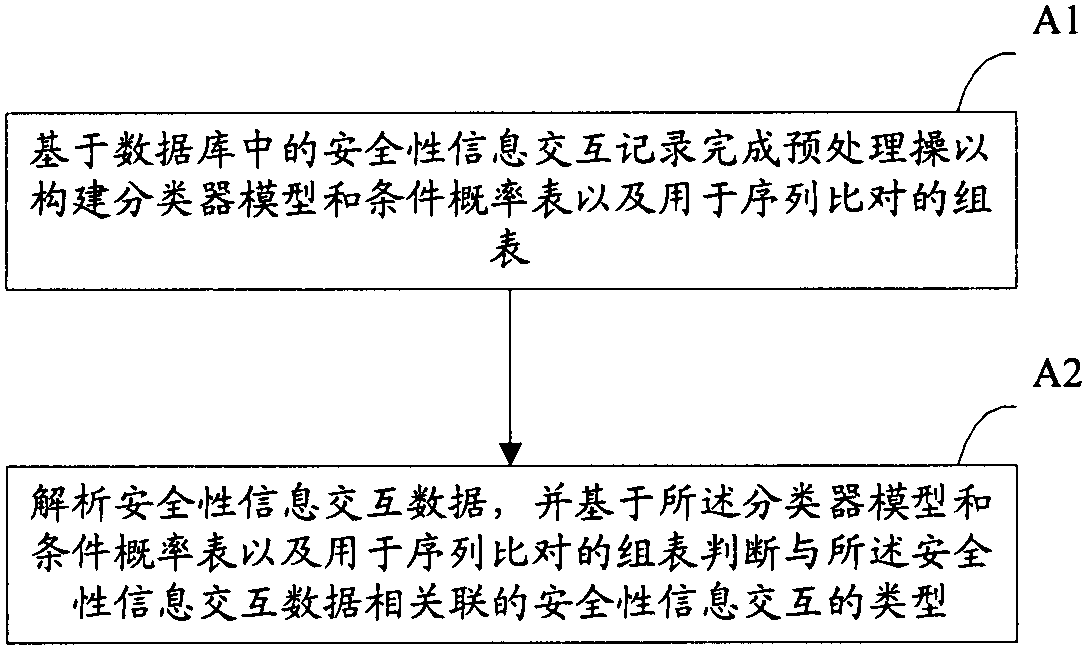
Anomaly detection device and method for security information interaction
ActiveCN103544429AImprove securityReduce false alarm ratePlatform integrity maintainanceAnomaly detectionReporting rate
The invention provides an anomaly detection device and method for security information interaction. The method includes the following steps of completing preprocessing operation on the basis of security information interaction records in a database to build a classifier model and conditional probability table and a group table for sequence alignment, analyzing security information interaction data, and judging the types of security information interaction related to the security information interaction data on the basis of the classifier model and conditional probability table and the group table for sequence alignment. The anomaly detection device and method for security information interaction have high security, the low false alarm rate and the low missing report rate.
Owner:CHINA UNIONPAY
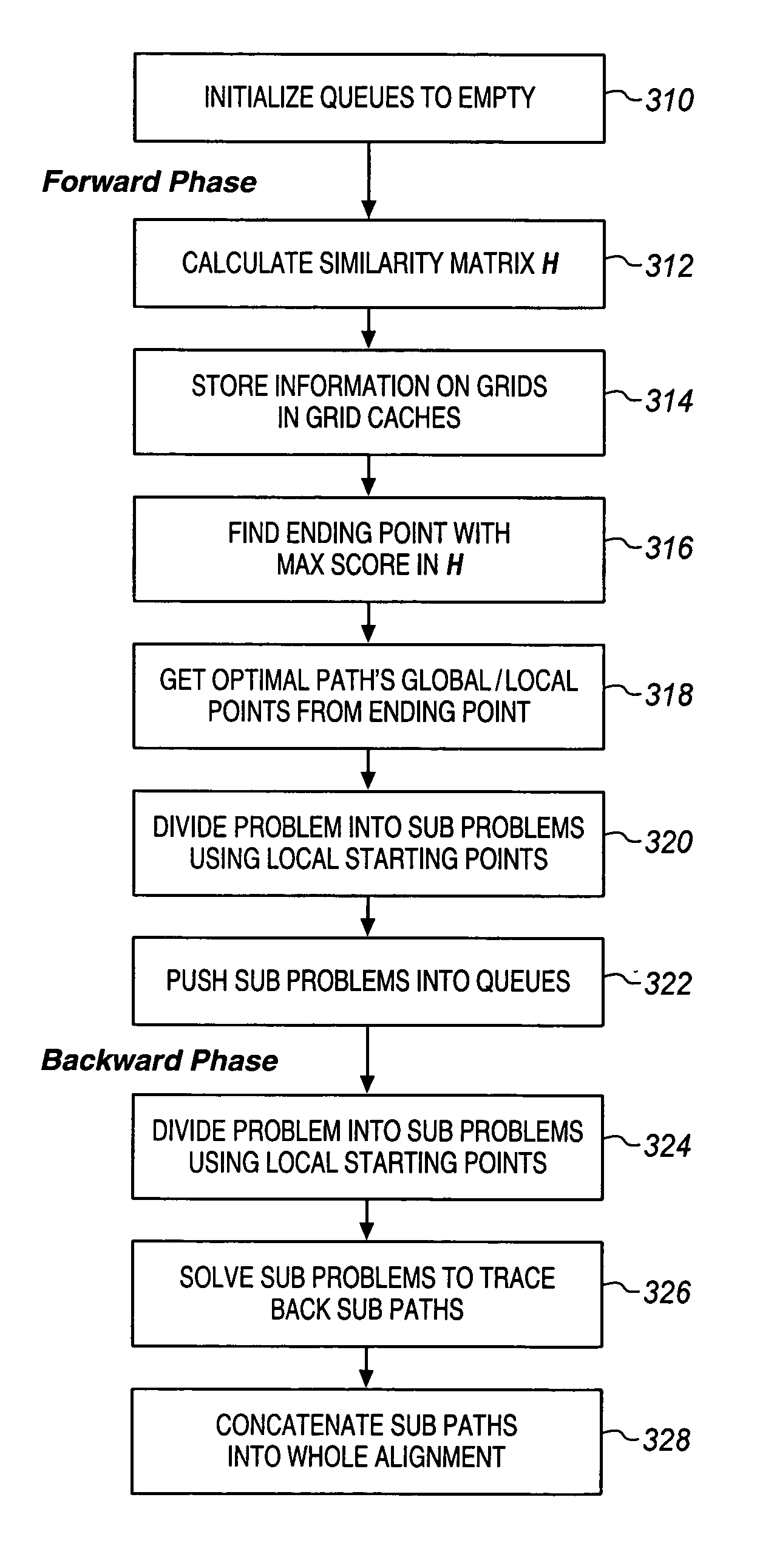
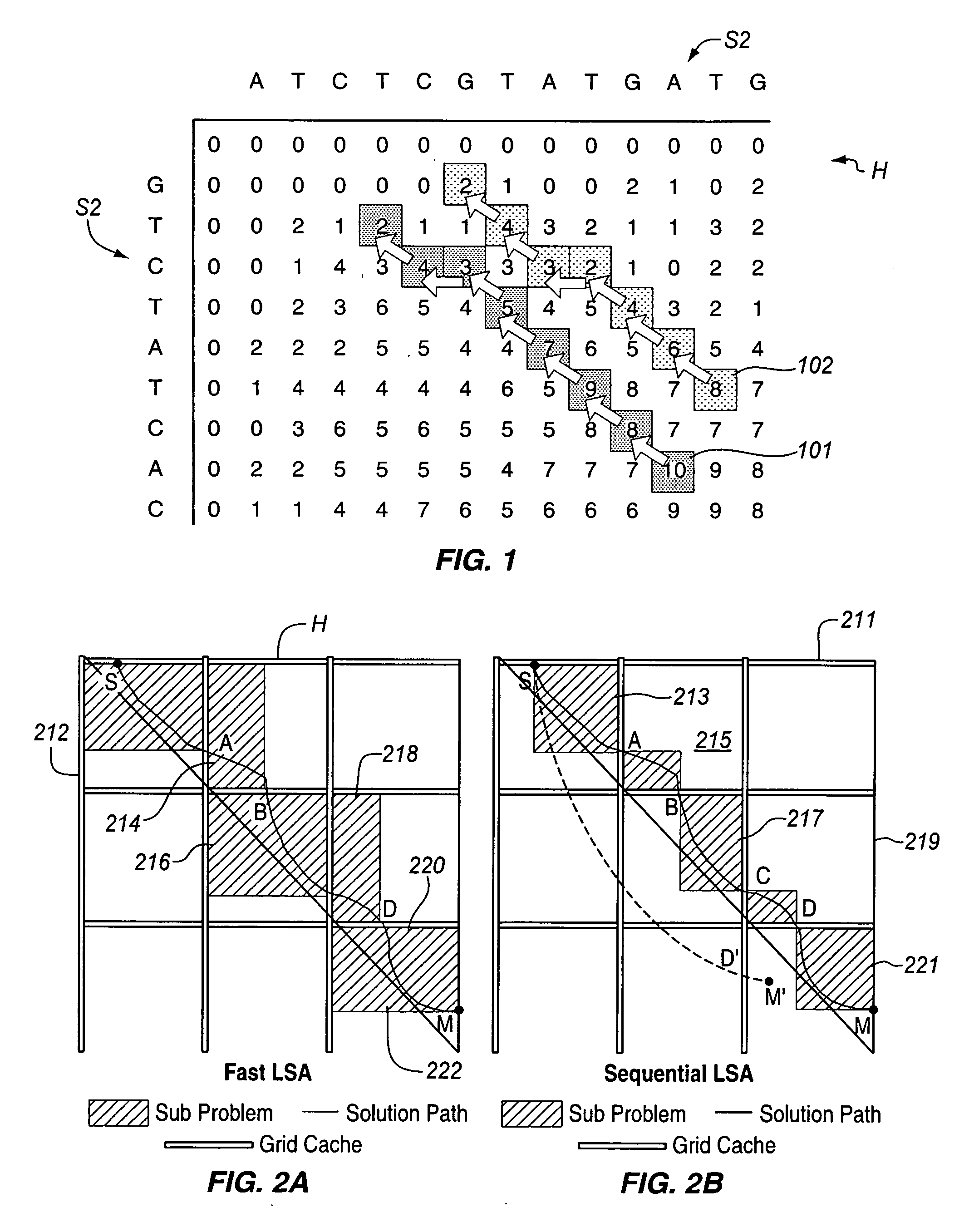
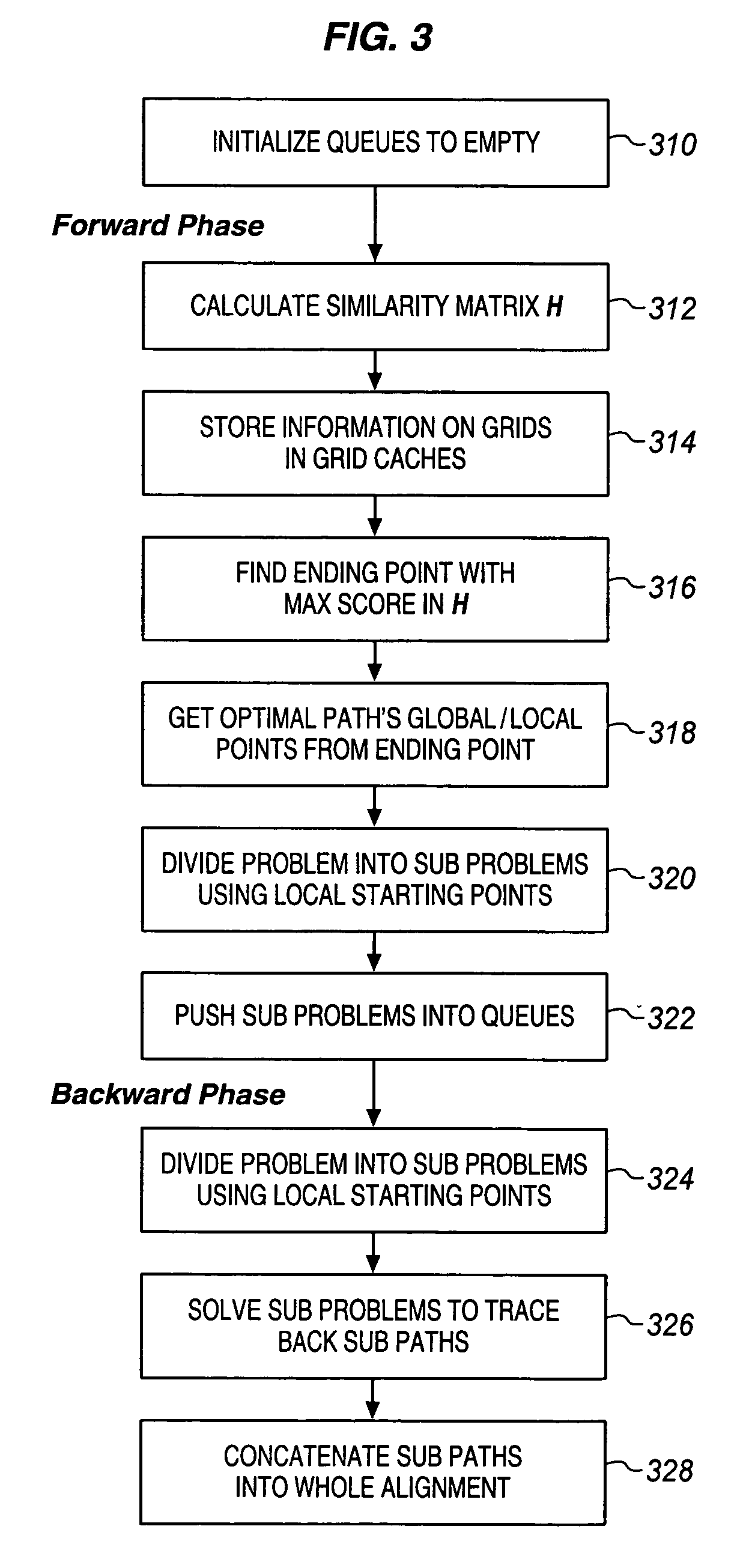
Fast alignment of large-scale sequences using linear space techniques
InactiveUS20070076936A1Character and pattern recognitionBiological testingMinimum cost pathSpace techniques
Large scale sequences and other types of patterns may be matched or aligned quickly using a linear space technique. In one embodiment, the invention includes, calculating a similarity matrix of a first sequence against a second sequence, determining a lowest cost path through the matrix, where cost is a function of sequence alignment, dividing the similarity matrix into a plurality of blocks, determining local start points on the lowest cost path, the local start points each corresponding to a block through which the lowest cost path passes, dividing sequence alignment computation for the lowest cost path into a plurality of independent problems based on the local start points, solving each independent problem independently, and concatenating the solutions to generate an alignment path of the first sequence against the second sequence.
Owner:INTEL CORP
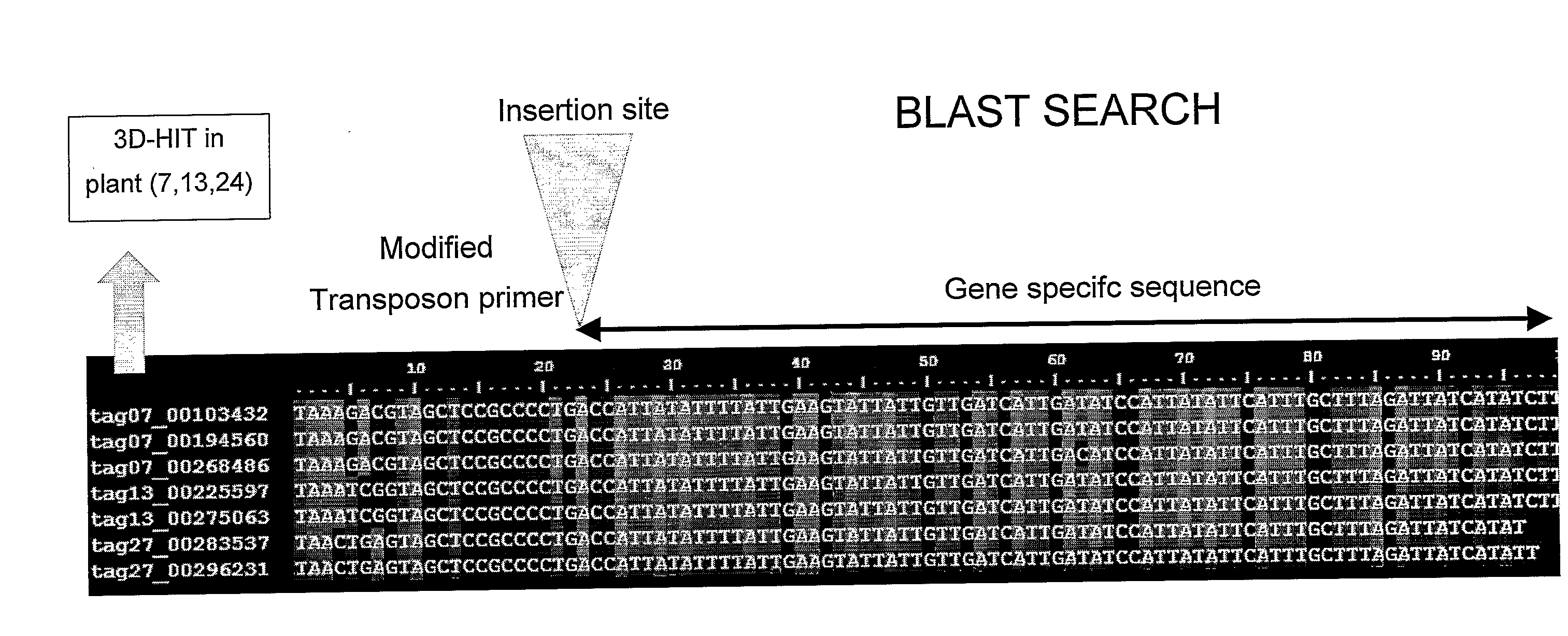
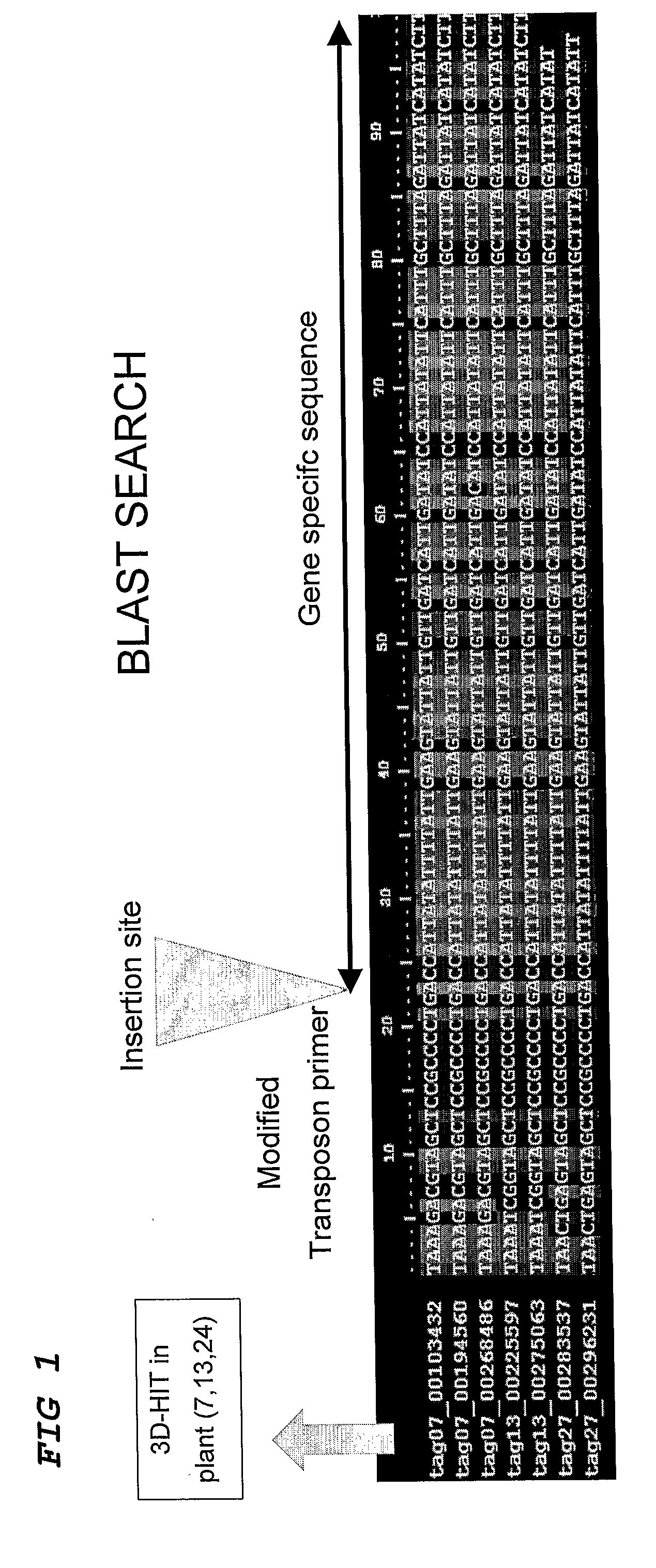
Method for the High Throughput Screening of Transposon Tagging Populations and Massive Parallel Sequence Identification of Insertion Sites
InactiveUS20090208943A1Efficient screeningImprove signal-to-noise ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsGenomic DNA
Method for the identification of a gene in a transposon population, comprising isolating genomic DNA, optionally pooling the DNA, restrict the DNA in the pools using an enzyme, ligate adaptors, amplifying the adaptor-ligated fragments with primers, one of which is a primer complementary to a border of a transposon sequence, high throughput sequencing of the fragments, aligning the fragments with known sequences in a database and thereby identifying gene candidates.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
CNV detection method and CNV detection apparatus
The invention provides a CNV detection method which including the steps of: 1) acquiring a genome sequencing result of a target individual; 2) comparing the sequencing result with a reference sequence to obtain a comparison result, wherein the reference sequence comprises a plurality of windows; 3) on the basis of the comparison result, calculating initial comparison ratio of each window, which is the number of reads in the windows on the comparison dividing the average value of the number of the reads in the windows on the comparison, wherein the average value of the number of the reads in the windows on the comparison is the total number of reads in all windows on the comparison dividing the number of the windows; 4) combining a plurality of adjacent windows of which the initial comparison ratios have no significant difference, and defining the combined adjacent windows as a primary zone, and the rest individual windows are respectively called the primary zones; and 5) if the comparison ratio of the primary zone is not equal to a preset comparison ratio, determining existence of CNV in the primary zone.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD
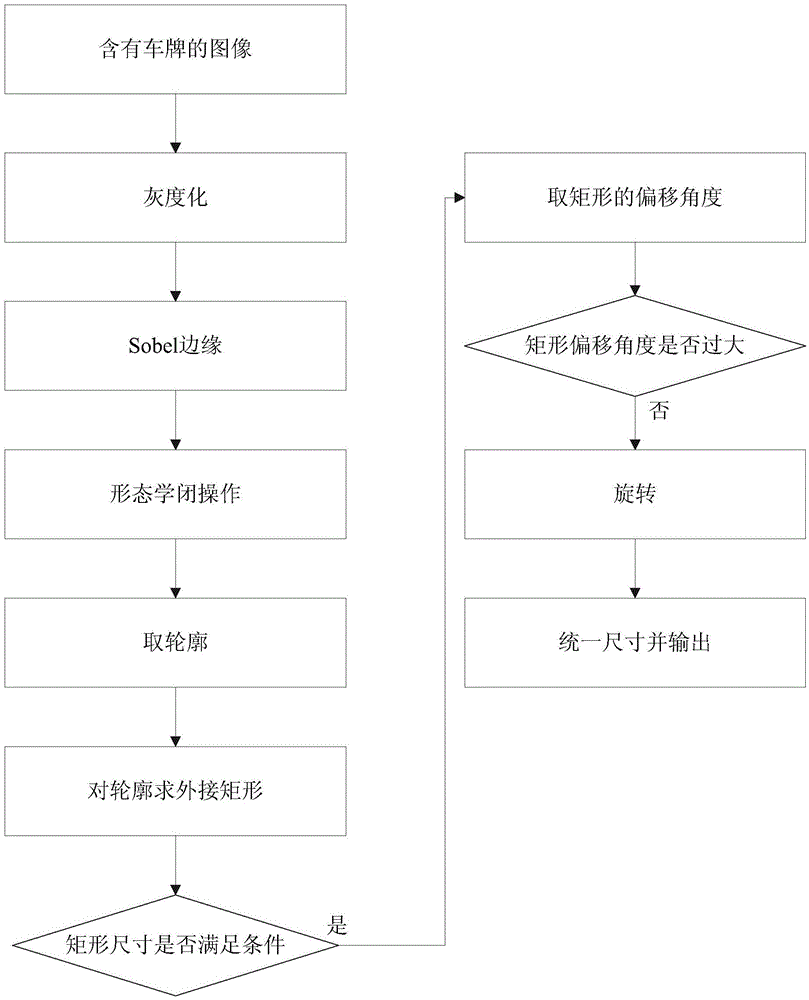
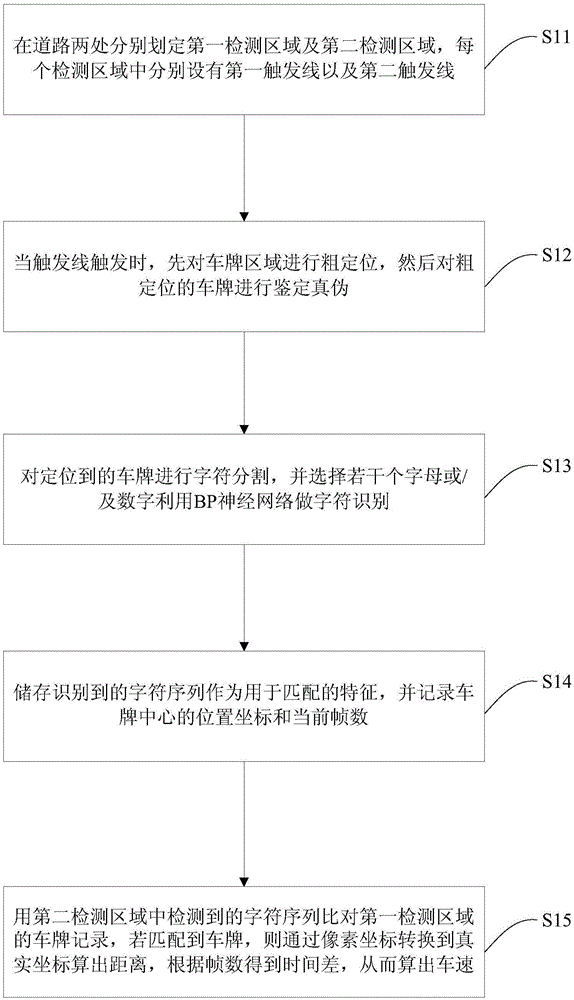
Speed detection method based on license plate characteristic matching
InactiveCN105551264ASolve the problem of insufficient matching accuracySolve instabilityRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmTime difference
The invention provides a speed detection method based on license plate characteristic matching. The method comprises the following steps of 1) delimiting a first detection area and a second detection area and setting a triggering line; 2) when the triggering line is triggered, carrying out coarse positioning on a license plate area and carrying out identification of true and false; 3) carrying out character segmentation on a positioned license plate and carrying out character identification; 4) storing an identified character sequence and taking as a matching characteristic, and recording a position coordinate of a license plate center and a current frame number; 5) using a character sequence detected in the second detection area to compare with a license plate record in the first detection area, calculating a distance through converting a pixel coordinate into a real coordinate, according to the frame number, acquiring a time difference so as to calculate a speed. The license plate adopted in the invention is served as a characteristic of vehicle matching and a problem that matching precision is insufficient by using a speed measurement method based on characteristic point characteristic matching can be effectively solved. And through recording the license plate characteristic of each area and current position information, an unstable problem existing in multi-vehicle speed measurement can be solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
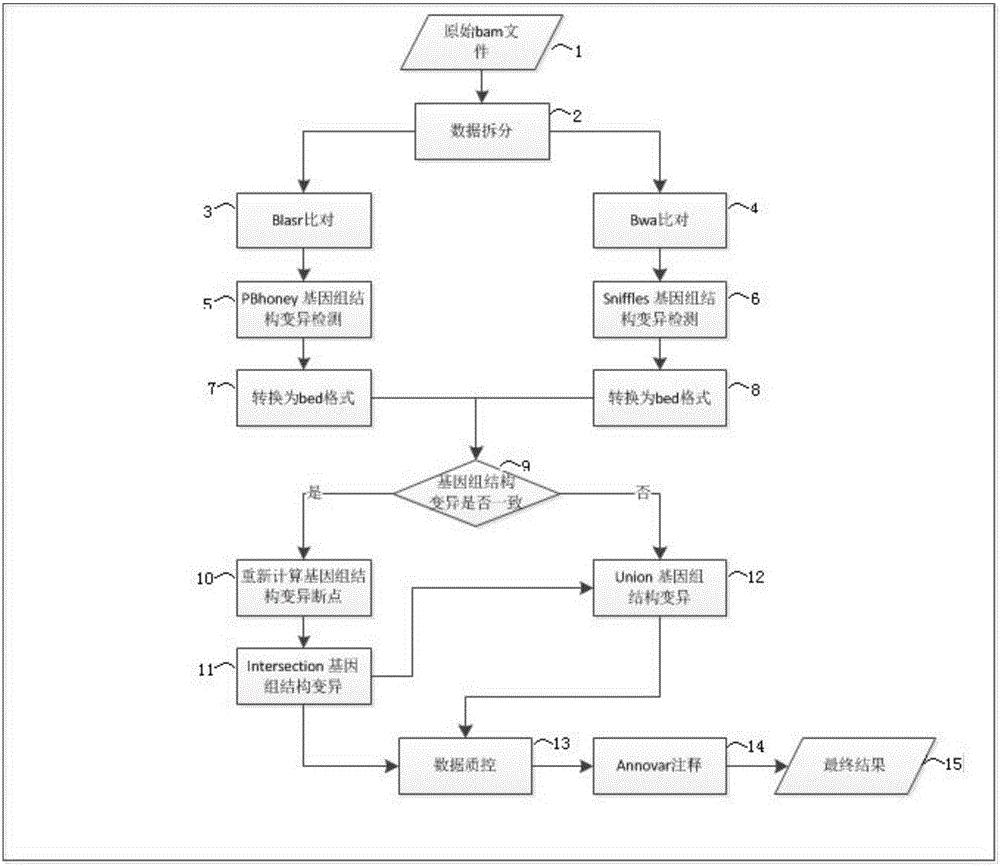
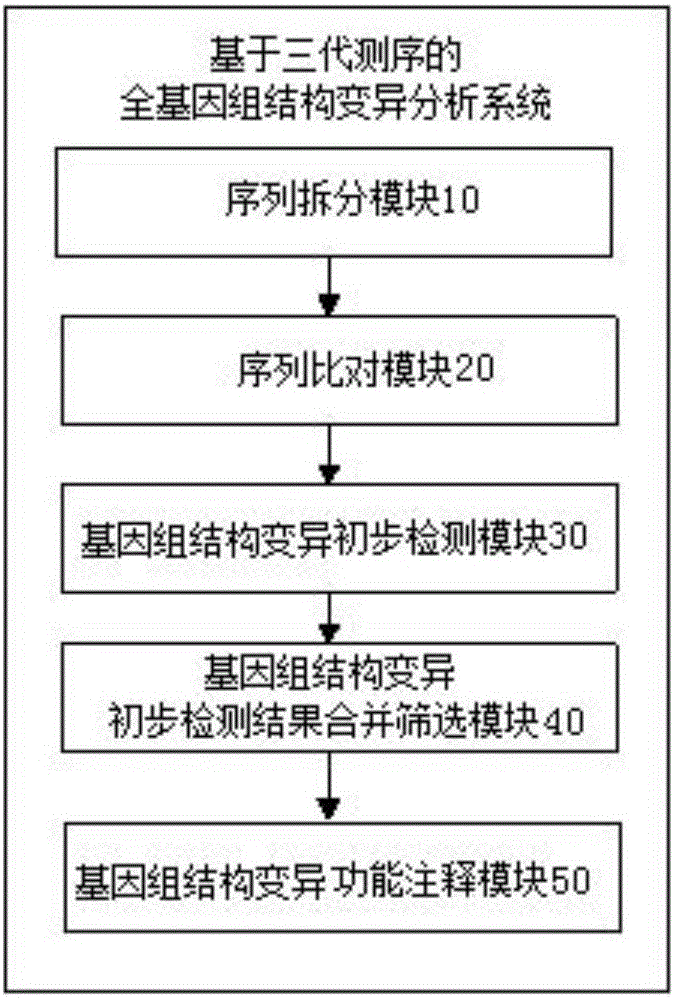
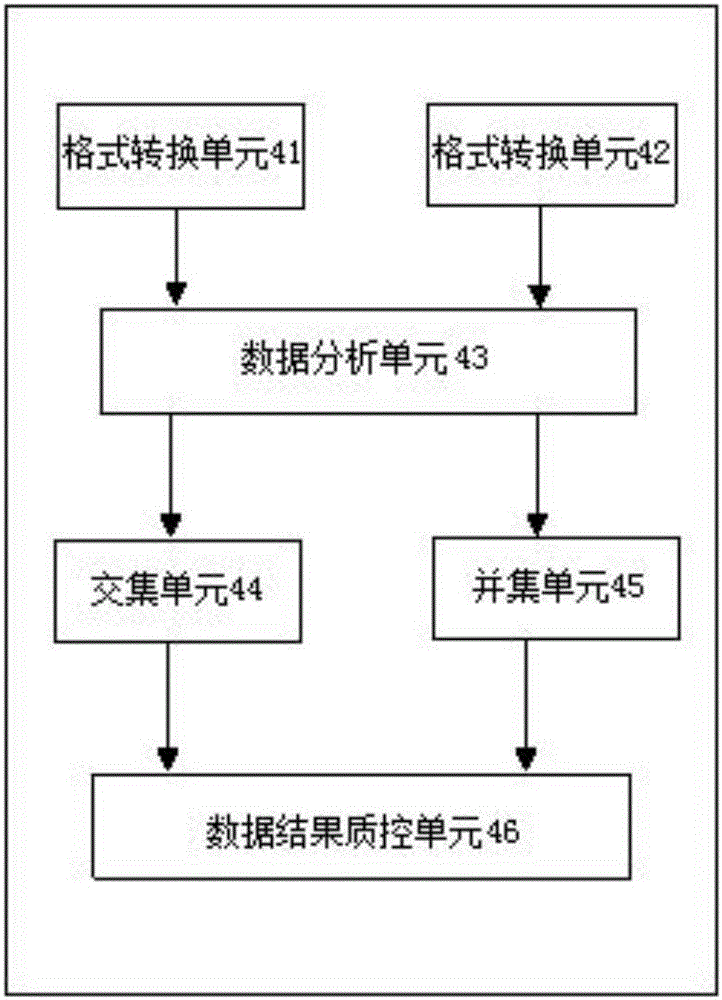
Three-generation sequencing-based whole genome structure variation analysis method and system
The invention discloses a three-generation sequencing-based whole genome structure variation analysis method and system. The method comprises the steps of 1) performing sequence splitting; 2) performing sequence comparison; 3) performing genome structure variation preliminary detection; 4) combining and screening genome structure variation preliminary detection results; and 5) performing genome structure variation function annotation. The system comprises a sequence splitting module, a sequence comparison module, a genome structure variation preliminary detection module, a genome structure variation preliminary detection result combining and screening module and a genome structure variation function annotation module. According to the method and the system, by integrating existing three-generation genome structure variation detection technologies PBhoney and Sniffles, the accuracy and sensitiveness of genome structure variation detection under low coverage degree can be effectively improved, and the reliability of the detection results is ensured while the detection cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING GRANDOMICS BIOTECH
Application of nucleotide sequence of rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) ITS (internal transcribed spacer)-D3 region in establishment of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code identification system for medicinal plants
InactiveCN102191318AImprove versatilitySequence alignment is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsNucleotideDNA barcoding
The invention relates to a method for identifying medicinal plants by utilizing nucleotide sequences, in particular to an application of a nucleotide sequence of an rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) ITS (internal transcribed spacer)-D3 region in establishment of a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code identification system for medicinal plants. The application comprises the following steps of: firstly, detecting the nucleotide sequences of the ITS-D3 regions of medicinal plants, and establishing a DNA bar code database; then, detecting the nucleotide sequence of the ITS-D3 region of a sample to be identified; constructing a clustering tree by the detected nucleotide sequence and the nucleotide sequences of the ITS-D3 regions in the DNA bar code database; determining the medicinal plant having the closest genetic relationship with the sample to be identified in the DNA bar code database according to the clustering tree, and comparing the difference between the nucleotide sequences of the ITS-D3 regions of the medicinal plant and the sample to be identified; and then, by taking the name of the species of the medicinal plant having the closest genetic relationship with the sample to be identified in the database as a reference and combining information such as morphological characteristics and the like, determining the name of the species of the sample to be identified. In the invention, the DNA bar codes have the characteristics of good primer universality, accurate sequence comparison and strong species distinguishing capability.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE +1
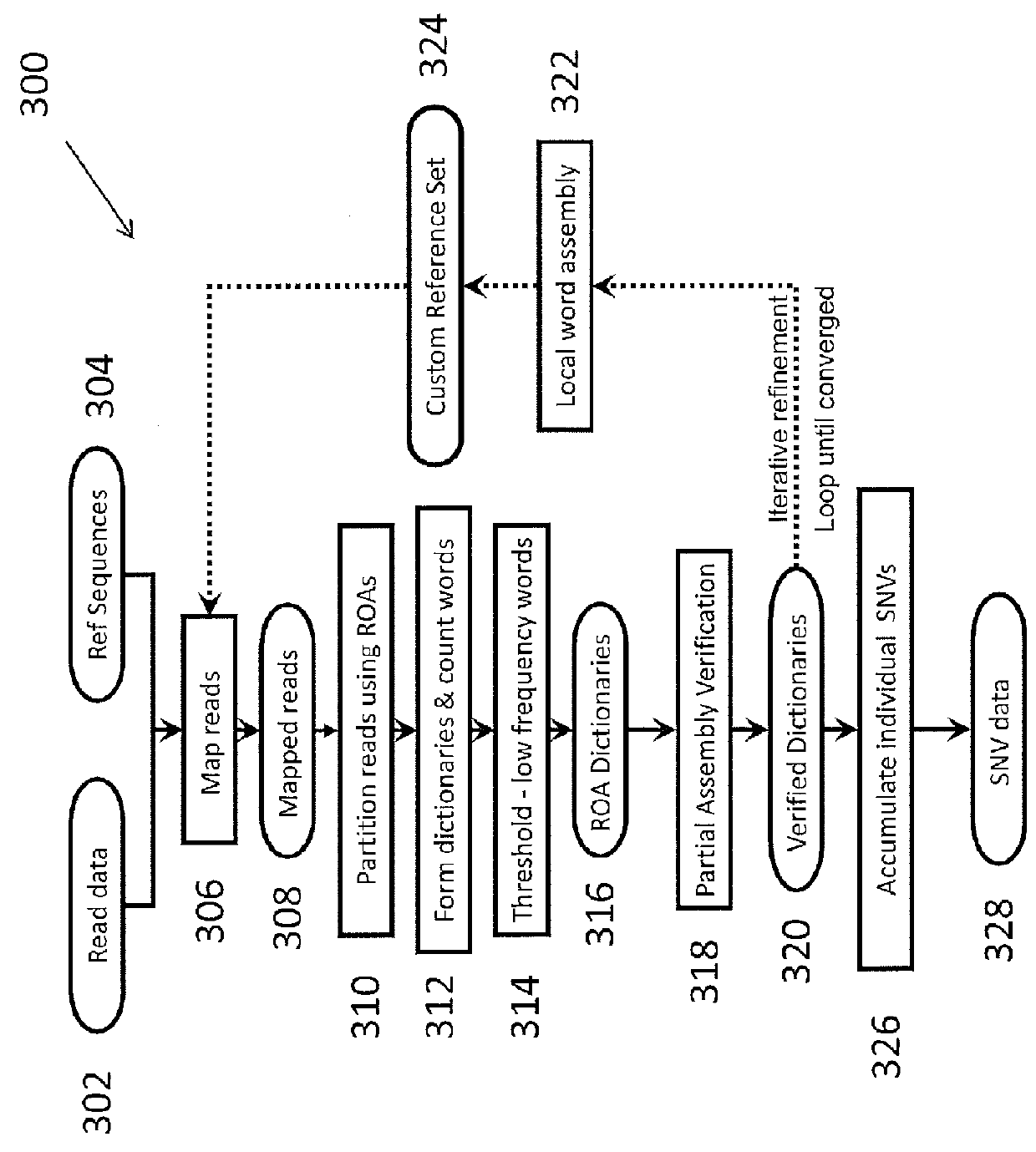
System and Method for Detecting Population Variation from Nucleic Acid Sequencing Data
InactiveUS20160034638A1Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsPopulation variationNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to a method of identifying genetic variants within a population of sequences. The method includes the steps of aligning a set of sequence data reads to reference sequences, dividing reference sequences into multiple tracks of overlapping regions of analysis (ROAs), partitioning each read into a ROA, identifying a plurality of sequence patterns in the reads, setting a sequence pattern frequency threshold value, eliminating any sequence pattern that has a value below the frequency threshold value forming a plurality of dictionaries from the sequence patterns having a value above the frequency threshold value, and cross-validating sequence patterns via partial sequence assembly. The method may optionally include amending the reference sequences used in iterative re-alignment of sequence data.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Detection device and method for gene fusion
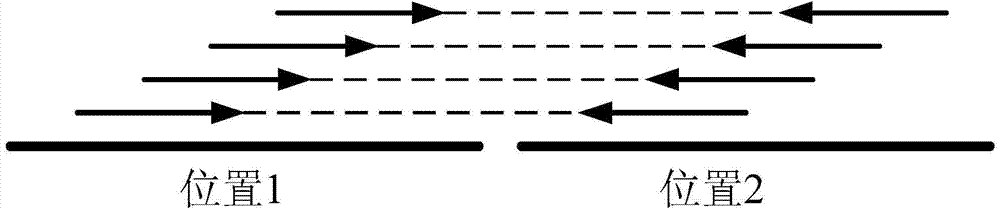
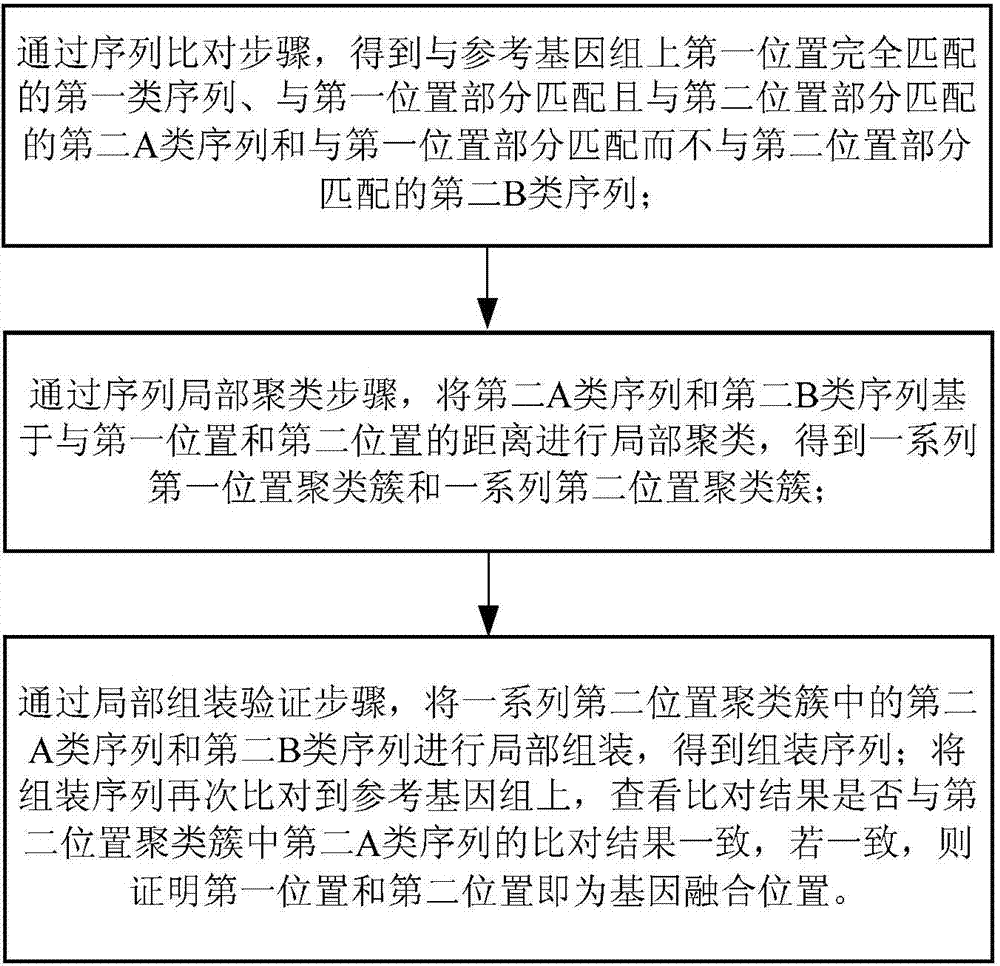
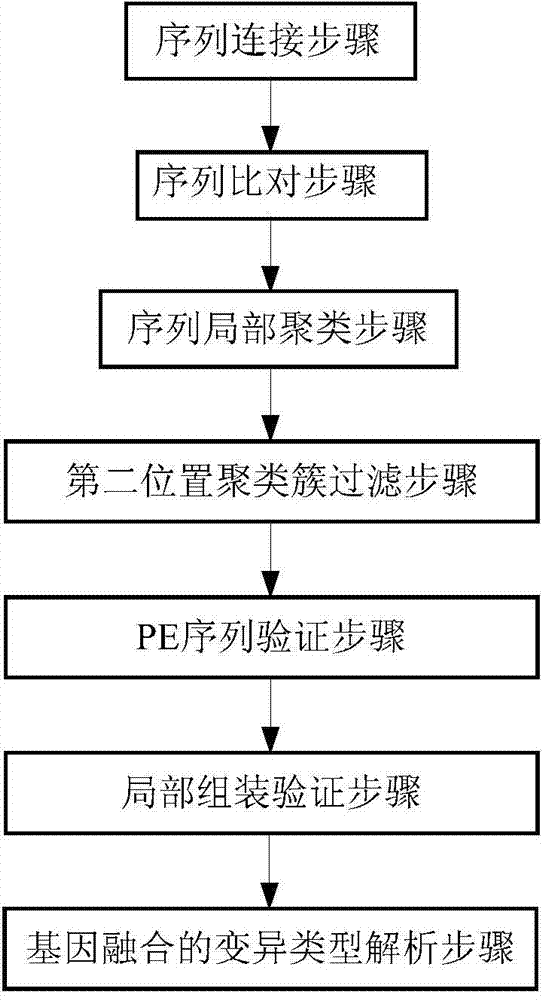
ActiveCN104298892AReduce false positive rateSpecial data processing applicationsTrue positive rateLocal sequence
The invention discloses a detection device and method for gene fusion. The detection method is executed between sequence alignment and local assembly verification and comprises the step of local sequence clustering. The method for local sequence clustering comprises the steps that local clustering is conducted on a second A type sequence which is partially matched with a first position and is also partially matched with a second position of a reference genome and a second B type sequence which is partially matched with the first position and is not partially matched with the second position based on the distance between the first position and the second position, so that a series of first position clusters and a series of second position clusters are obtained; local assembly is conducted on second A type sequences and second B type sequences in the series of second position clusters, so that an assembly sequence is obtained; the assembly sequence is compared with the reference genome again, whether the comparison result of the assembly sequence is consistent with a comparison result for second A type sequences in the second position clusters is checked, if yes, it is proved that the first position and the second position are the gene fusion positions. According to the detection method, the true positive rate is high, and the result is more reliable.
Owner:天津诺禾致源生物信息科技有限公司
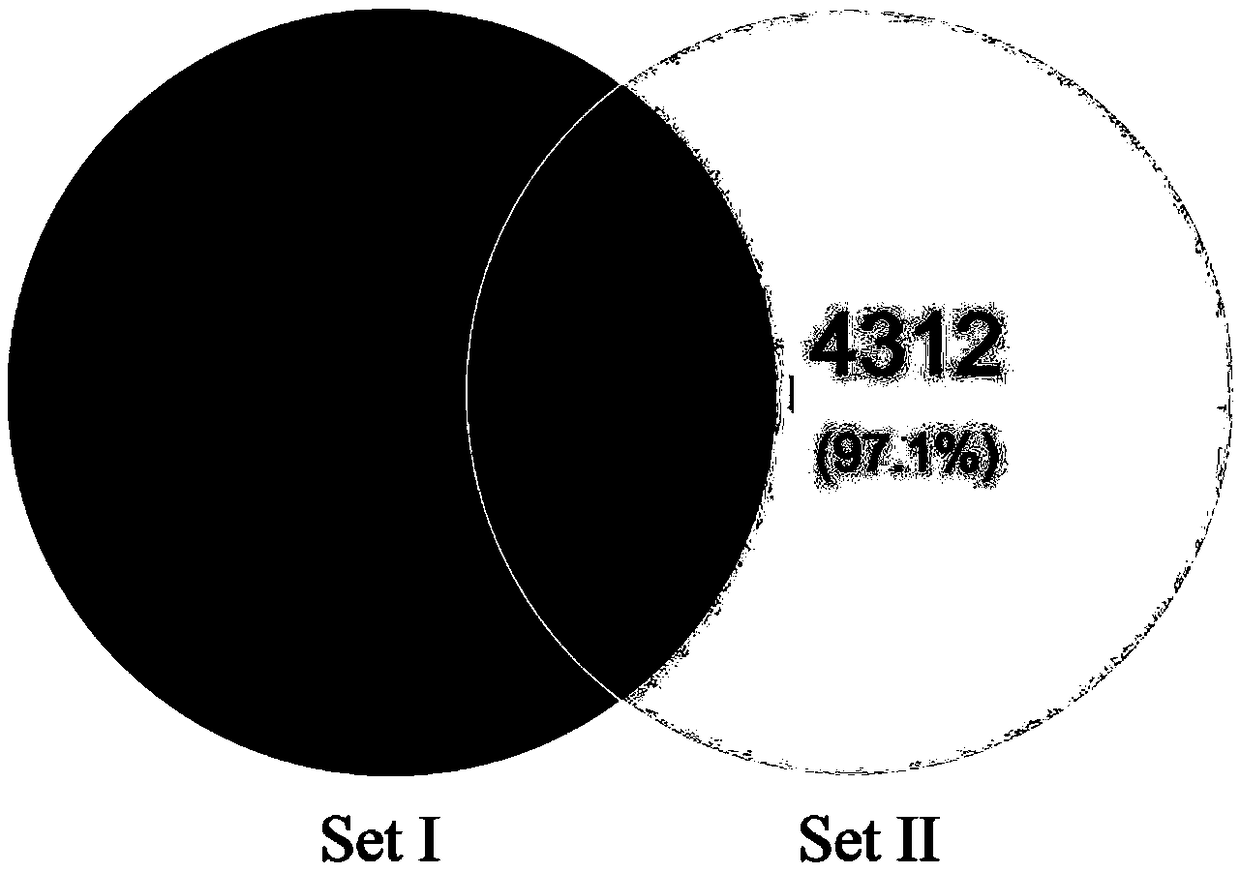
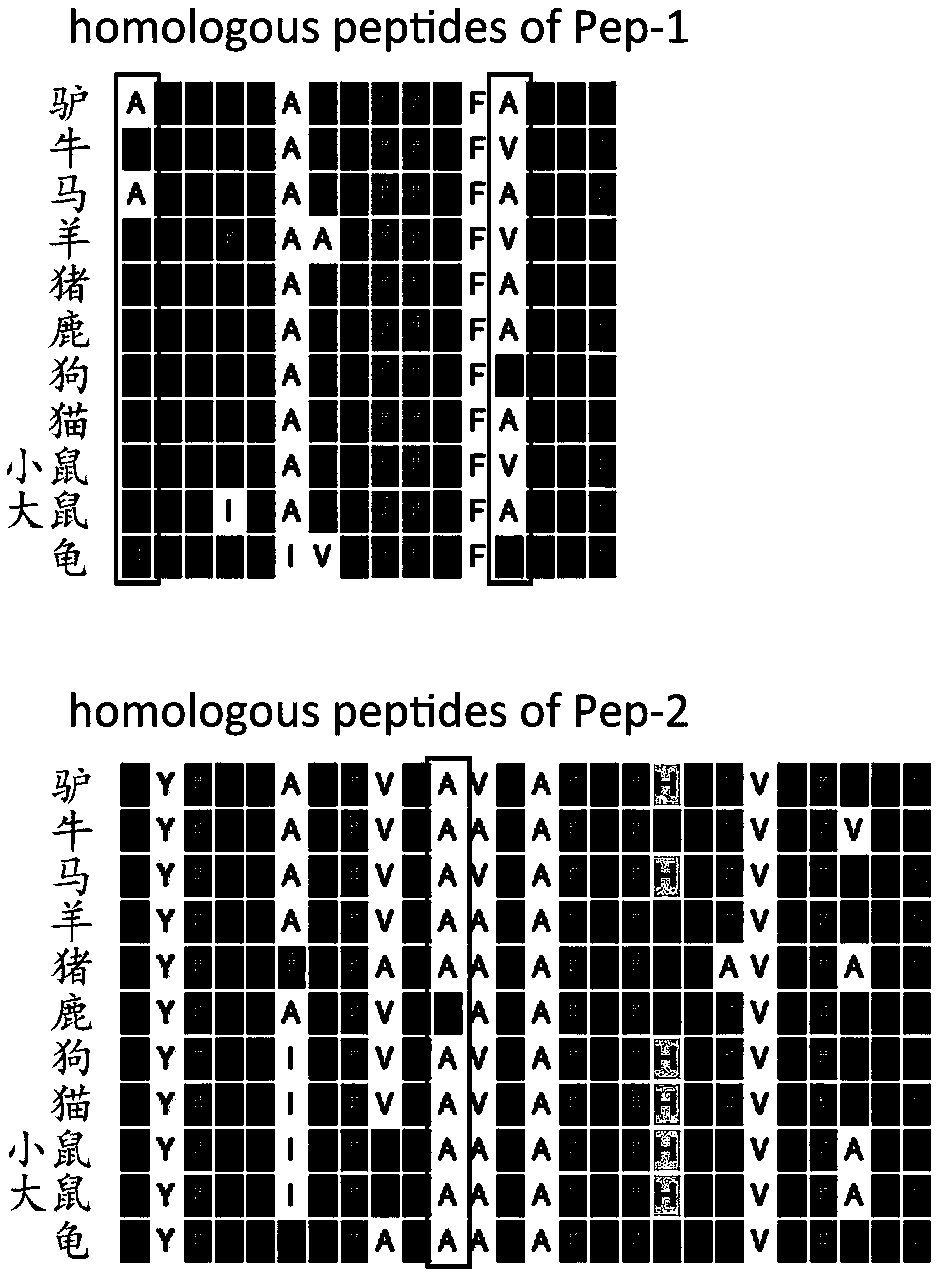
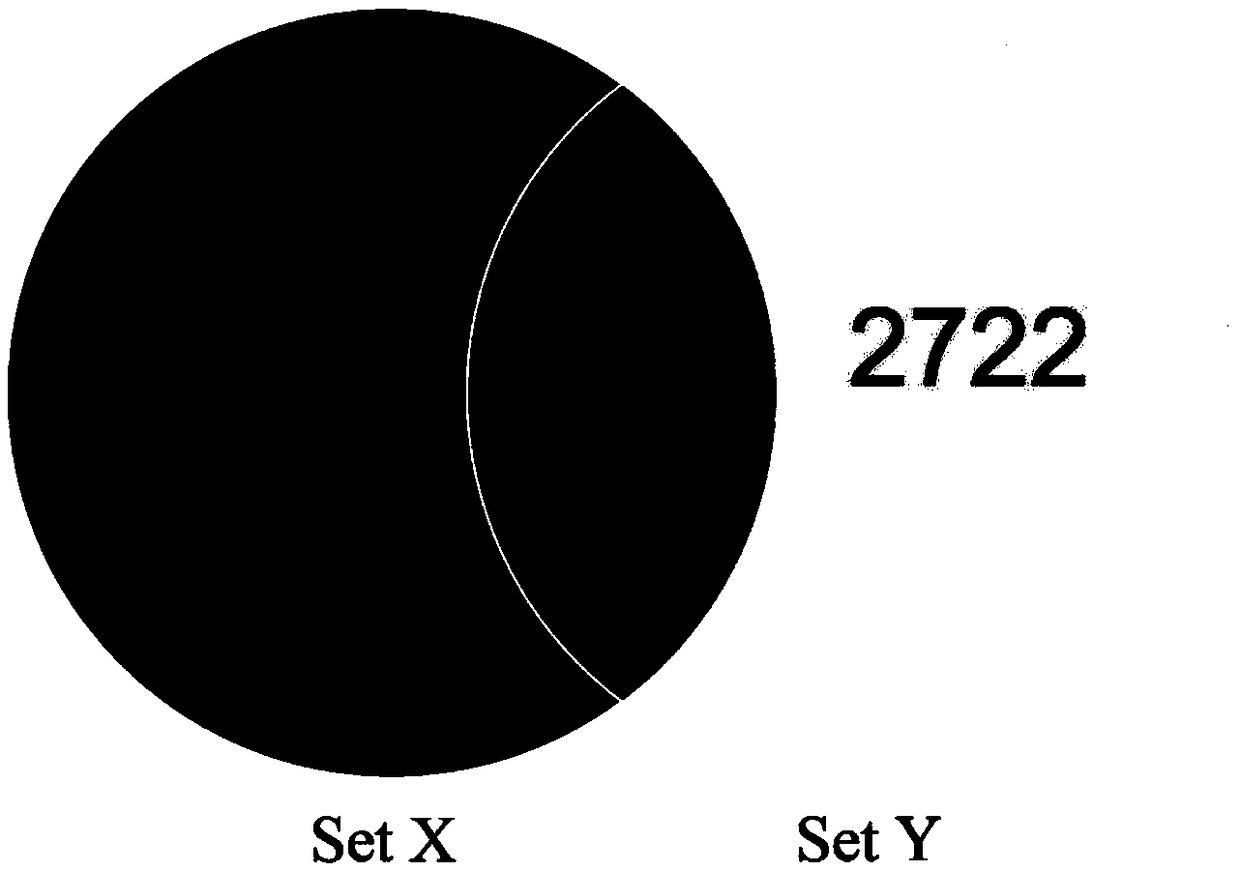
Method for identifying specific peptides of Chinese medicine containing protein
The invention discloses a method for identifying specific peptides of a Chinese medicine containing protein. The method comprises the following steps of: screening through a large number of experiments; taking a sample and performing enzymatic hydrolysis by using preferred enzyme; performing a desalination treatment; performing a high-throughput identification on peptide sequences using the best Nano LC-MS / MS method; verifying specific peptides by comparing differences in homologous protein sequences between different species of different samples; validating the specificity of the specific peptides in authentic products using the preferred LC-QQQ MS analysis. The method is scientific and easy to operate, and can be used to identify authentic and fake products of Chinese medicine, animal drugs, foods and aquatic products, and has important application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
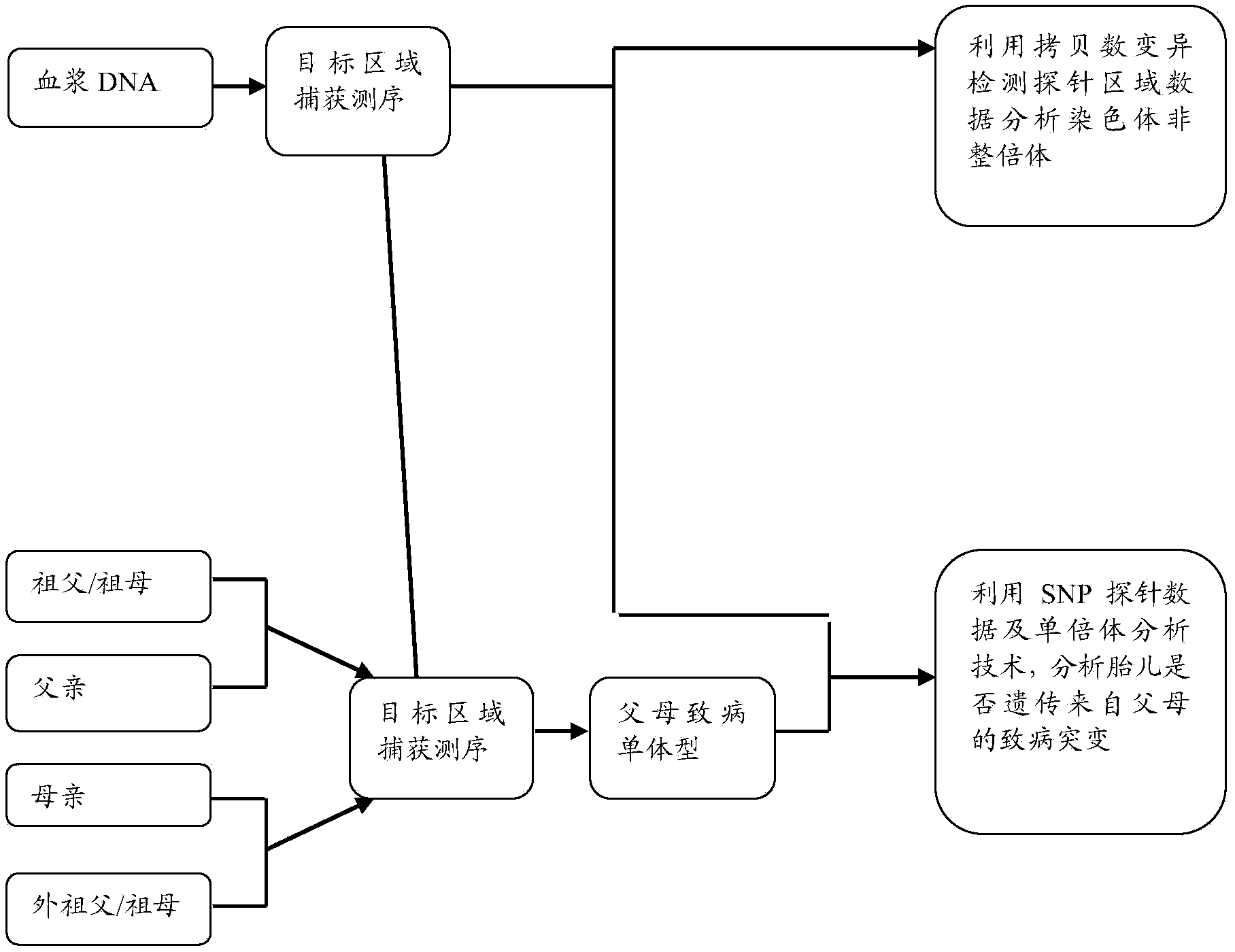
Method and device for simultaneously determining fetal haplotype and aneuploidy of chromosome
ActiveCN104232778ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHaplotypeBody fluid sample
The invention provides a method and a device for simultaneously determining a fetal haplotype and the aneuploidy of chromosome. The method comprises the steps of (1) respectively extracting a first DNA, a second DNA and a third DNA from a body fluid sample of a pregnant woman and a sample of the father of a fetus, wherein the first DNA is a mixture of the DNA of the mother and the DNA of the fetus, the second DNA is a genome DNA of the mother, and the third DNA is the DNA of the father; (2) simultaneously or respectively sequencing the first DNA, the second DNA and the third DNA of at least one part so as to correspondingly obtain a first reading section, a second reading section and a third reading section; (3) respectively comparing the first reading section, the second reading section and the third reading section with a reference sequence, and performing (a) or (b) according to an obtained comparison result to screen out a specific polymorphic site; (4) determining the fetal nucleic acid content of the body fluid sample of the pregnant woman according to the quantity of the reading sections, which support the screened specific polymorphic site, in the comparison result of the first reading section; (5) simultaneously determining the fetal haplotype and the aneuploidy of the chromosome according to the comparison result and the fetal nucleic acid content.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI +2
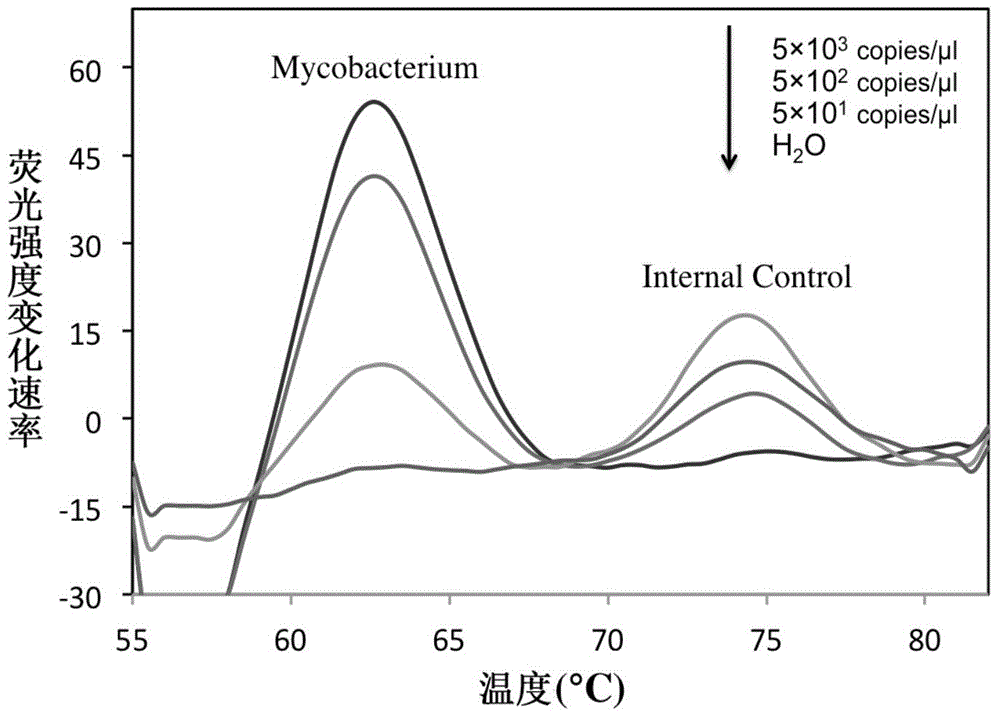
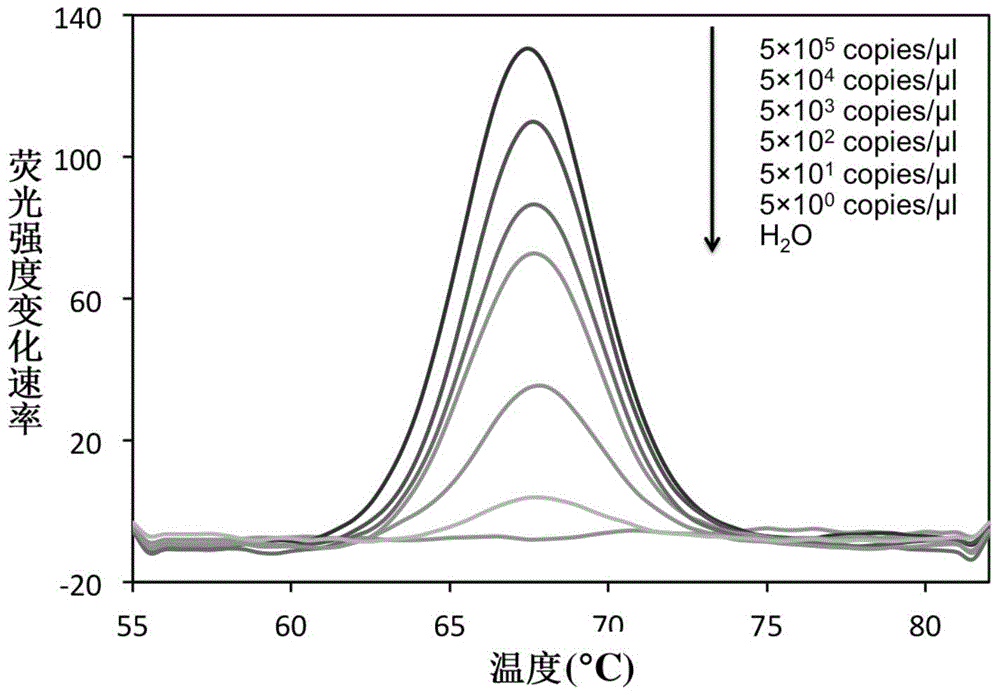
Rapid identification method and kit for MTBC (mycobacterium tuberculosis complex)
InactiveCN104561245AShorten diagnostic timeSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceRapid identification
The invention belongs to the field of a detection reagent, and relates to a detection and identification kit for MTBC (mycobacterium tuberculosis complex) and an identification method of the MTBC. According to the method, fluorescence probes and amplification primers for detecting the MTBC are designed through sequence alignment, mycobacterium and the MTBC specific SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) loci on an rrs gene are detected based on a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) platform and with an asymmetric PCR amplification technology and a probe melting curve analysis technology, so that mycobacteria are identified, and the MTBC and NTM (nontuberculosis mycobacteria) are further identified. The method has the characteristics of convenience in operation, short detection time and high specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Molecular marker for identifying amur sturgeon germplasm and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN105063192AThe experiment is accurate and fastSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGermplasmSturgeon
The invention provides a molecular marker for identifying amur sturgeon germplasm and a method for identifying amur sturgeon germplasm by virtue of the molecular marker. Amur sturgeon or a finished product thereof can be directly identified through sequence alignment on the basis of an interspecific sequence difference of an fzd8 gene segment obtained from PCR amplification of a specific primer between the amur sturgeon and other sturgeons. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention, which is used for analyzing and identifying an SNP site on the fzd8 nuclear gene segment screened from acipenseridae fishes, has the advantages of being accurate in experiment, reliable and rapid in identification, convenient and simple in operation, and the like.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES CORPORATION +1
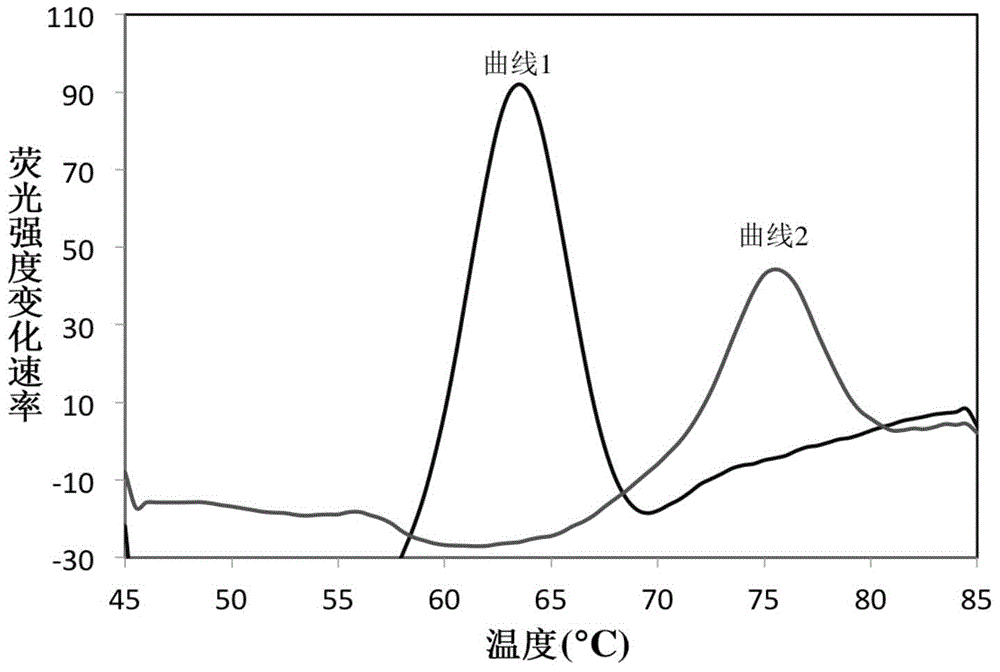
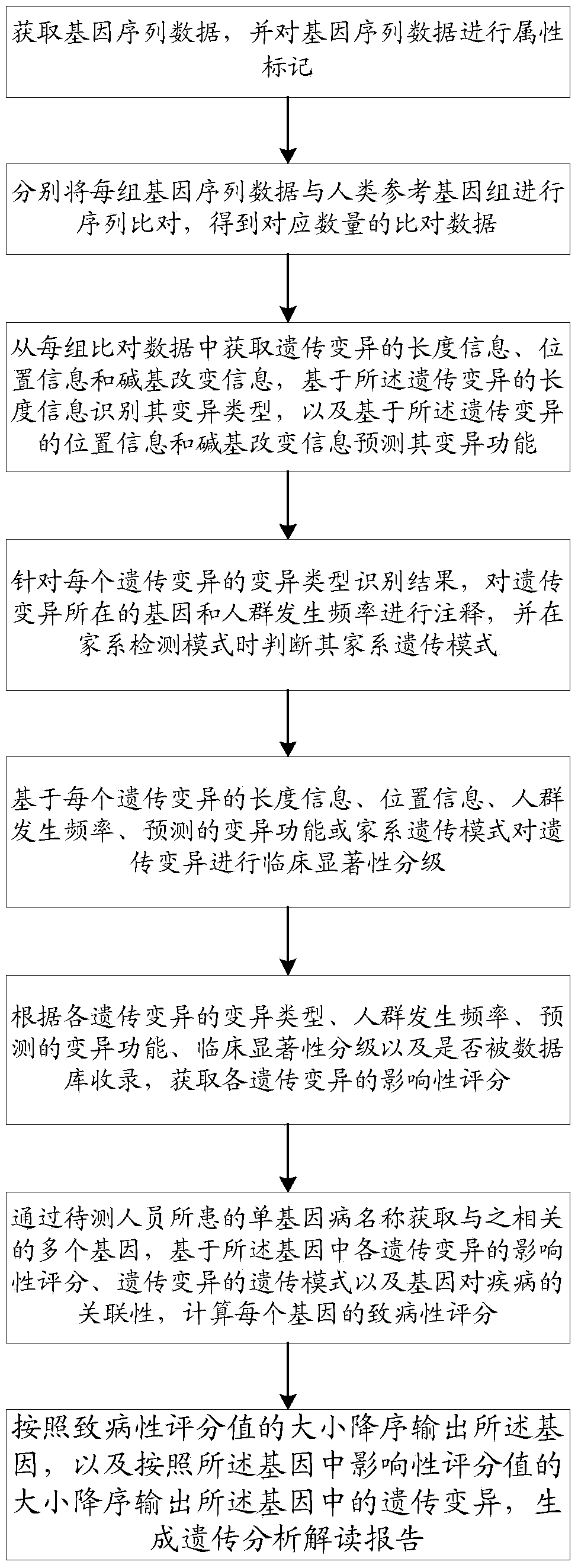
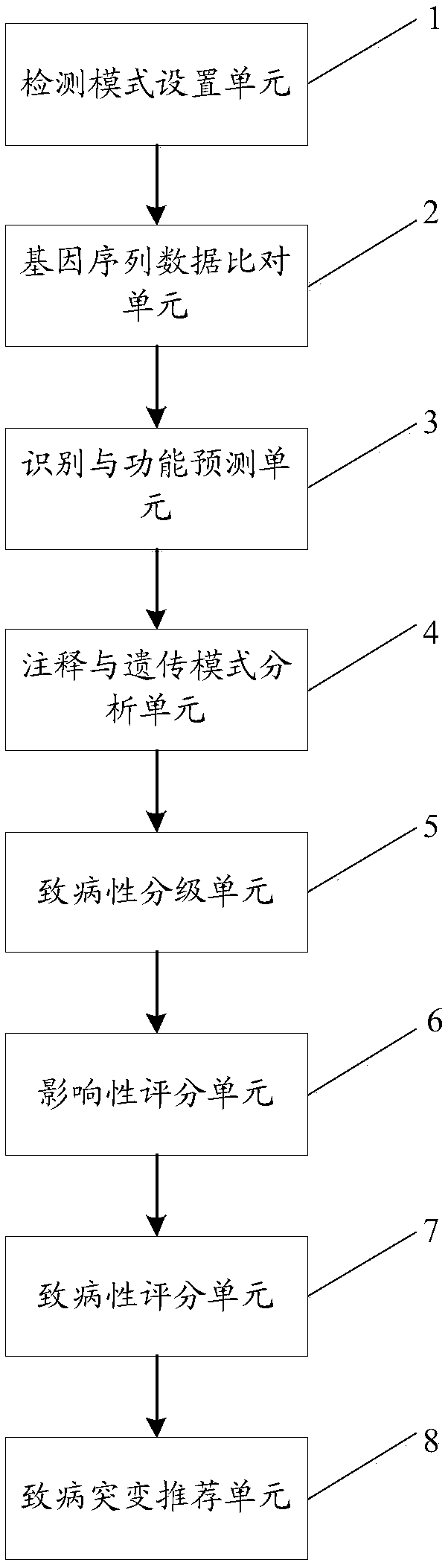
A method and system for intelligently interpreting and reporting genetic variation of monogenic diseases
ActiveCN109086571ARealize full automationReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsCrowdsSequence alignment
The invention discloses a method and a system for intelligently interpreting and reporting the genetic variation of a single gene disease, which can automatically analyze the genetic variation resultbased on the original sequence data of a gene of a patient, and provide a professional genetic variation analysis report, thereby improving the diagnosis and treatment efficiency of the genetic variation. The method comprises the following steps of: gene sequence data is acquired and attribute marking is performed on the gene sequence data; sequence alignment of each set of gene sequence data withhuman reference genome is performed to obtain corresponding amount of alignment data; based on the length information of genetic variation, the variation type is identified, and the variation function is predicted based on the position information and base change information of genetic variation. According to the identification results of each genetic variation type, the gene and population frequencies of genetic variation were annotated, and the family genetic pattern was judged when the family detection mode was used. The system comprises the method proposed in the technical proposal.
Owner:国家卫生健康委科学技术研究所
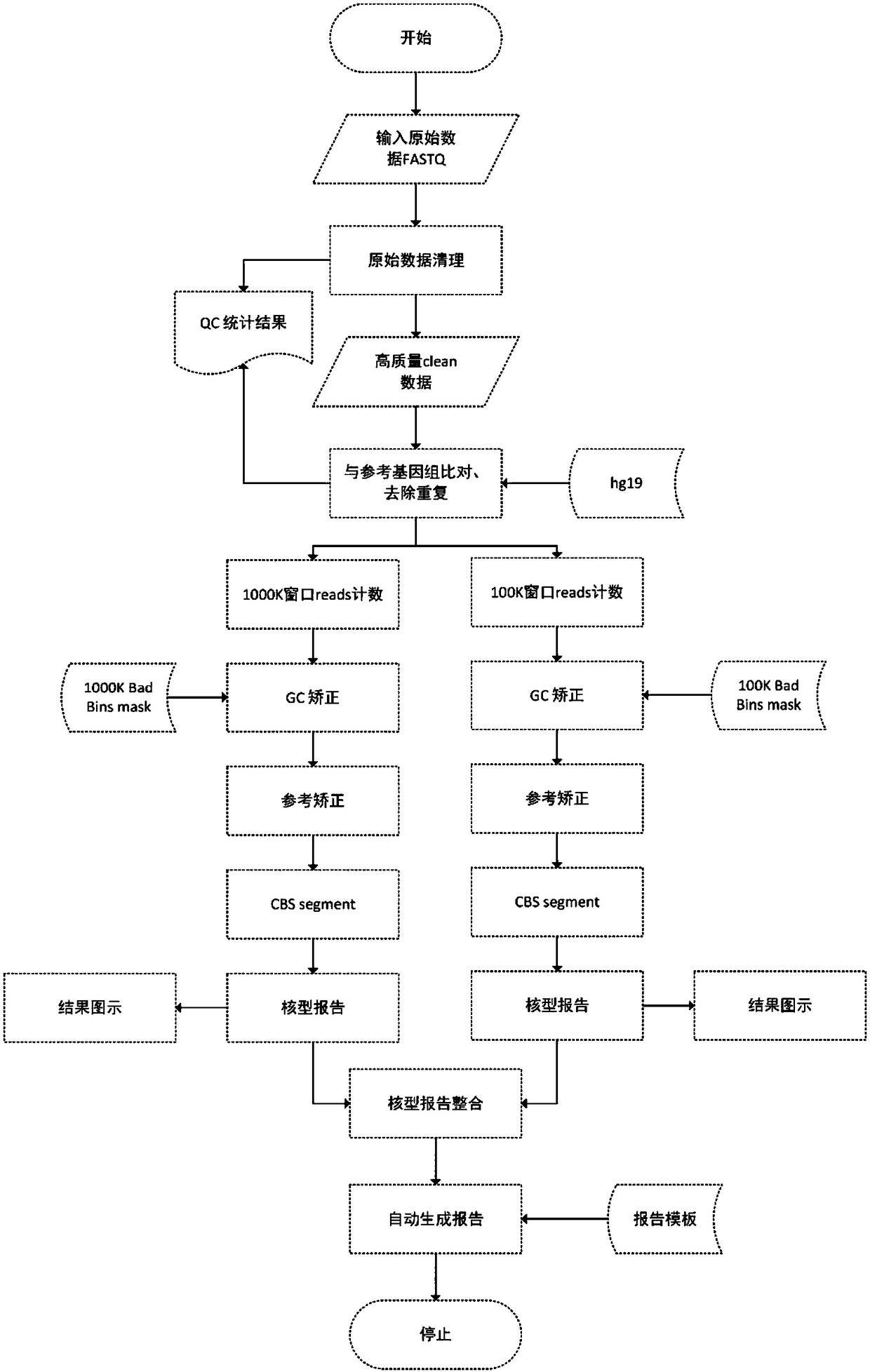
Detection method for genomic copy number variation and device comprising same
The invention provides a detection method for genomic copy number variation and a device comprising the method. The method comprises the following steps: inputting original data, cleaning quality control, aligning sequences to a reference genome, calculating a unique alignment sequence number by using windows of different sizes, performing GC correction and reference correction, shielding undetectable areas, segmenting CBS, integrating karyotype reports and generating reports, a complete set of the detection methods and devices is established through experimental exploration and optimization,through successive application of the specific sequential steps, the step of the reference correction is creatively adopted, and the windows with different sizes are used for performing alignment andintegration, the steps cooperate mutually, and finally the sensitivity and specificity are improved, so that the detection accuracy and result forms can conform to clinical demands, and the detectionmethod for the genomic copy number variation and the device comprising the method are high in automation degree, easy to expand, high in detection accuracy, capable of lowering the cost of data analysis, and extremely high in application value.
Owner:YIKON GENOMICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com