Application of nucleotide sequence of rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) ITS (internal transcribed spacer)-D3 region in establishment of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) bar code identification system for medicinal plants
An ITS-D3, nucleotide sequence technology, applied in the field of identifying medicinal plants using nucleotide sequences, can solve the problems of slow sequence evolution rate, lack of conserved regions, large workload, etc., achieving strong species differentiation ability and saving The effect of measuring time and sequence alignment is accurate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
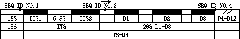
[0024] The design of the primer of the sequence shown in example 1SEQ ID No.1~4
[0025] The specific design method of the primers of the sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1~4 is as follows:
[0026] Reference Soltis et al. (Douglas E. Soltis, Anne E. Senters, Michael J. Zanis, Sangtae Kim, James D. Thompson, Pamela S. Soltis, Louis P. Ronse De Craene, Peter K. Endress and James S. Farris .Gunnerales are sister to other core eudicots: implications for the evolution of pentamery. American Journal of Botany, 2003, 90: 461-470.), download 206 additional taxa of seed plants from the nucleotide sequence database GenBank and EMBL 18S rDNA and 26S rDNA sequences, and downloaded the 9th chromosome sequence of japonica rice (Oryza sativa Japonica Group) (sequence number AP008225), and selected its rDNA complete sequence (from 2898bp to 8680bp, including 18S-ITS1-5.8S-ITS2-25S ). Multiple alignments were performed on the downloaded sequences using clustal X (version 1.83) (www.clustal.org),...
example 2
[0028] Example 2 establishes a DNA barcode database based on the nucleotide sequence of the ITS-D3 region
[0029] This example takes 50 kinds of medicinal plants as an example to illustrate the establishment of a DNA barcode database based on the nucleotide sequence of the ITS-D3 region. The specific steps are as follows:
[0030] 1. Collect the leaves of 50 species of medicinal plants in 19 families from the South China Medicinal Plant Germplasm Bank: Amomum villosum Lour.var.changguo., Alpinia officinarum Hance, Alpinia katsumadai Hayata , Alpinia galanga (Linn) Willd., Hedychium coronarium Koen., Aplinia pumila Hook.f., Crinum asiaticum L.var.sinicum (Roxb.ex Herb.), Hippeastrum vittatum (Ait.) Herb., Asparagus cochinchinensis (Lour.) Merr., Aloe vera L.var.chinesis (Haw.) Berger, Aloe arboresesens.Mill., Asarum sieboldii Miq., Teng San Boussingaultia gracilis Miers.var.baselloides Bail., Cajanus cajan(L.) Millsp., Schizonepeta tenuifolia(Benth.) Briq., Rhododendri mariae...
example 3
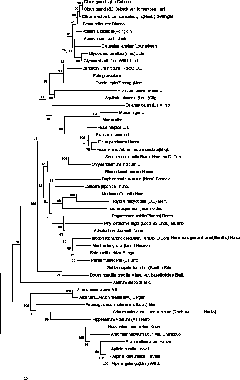
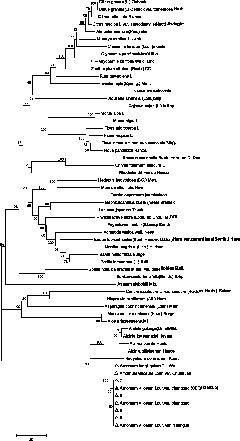
[0046] Example 3 Using the nucleotide sequence of the ITS-D3 region to distinguish each medicinal plant in the DNA barcode database and identify the relationship
[0047] In order to verify that the nucleotide sequence of the ITS-D3 region of the present invention has general and accurate beneficial effects as a medicinal plant DNA barcode, the ITS-D3 region nucleus of each medicinal plant in the DNA barcode database established in Example 2 is as follows The number of base differences in the nucleotide sequence is detected and the genetic relationship of each medicinal plant is identified.
[0048] 1. Detection of the number of base differences in paired samples of medicinal plants in the DNA barcode database
[0049] (1) The nucleotide sequences of the ITS-D3 regions of 50 kinds of medicinal plants obtained in Example 2 were multiple-aligned using clustal X (version1.83) (www.clustal.org), and the sequence alignment results were saved as aln file.
[0050] (2) Use MEGA 4 (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com