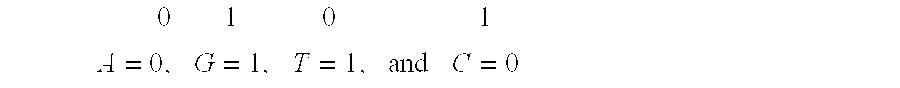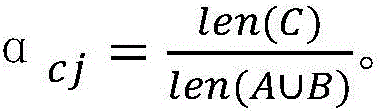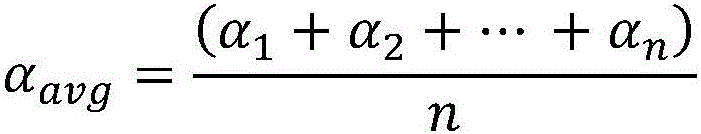Patents
Literature
269 results about "Sequence database" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the field of bioinformatics, a sequence database is a type of biological database that is composed of a large collection of computerized ("digital") nucleic acid sequences, protein sequences, or other polymer sequences stored on a computer. The UniProt database is an example of a protein sequence database. As of 2013 it contained over 40 million sequences and is growing at an exponential rate. Historically, sequences were published in paper form, but as the number of sequences grew, this storage method became unsustainable.
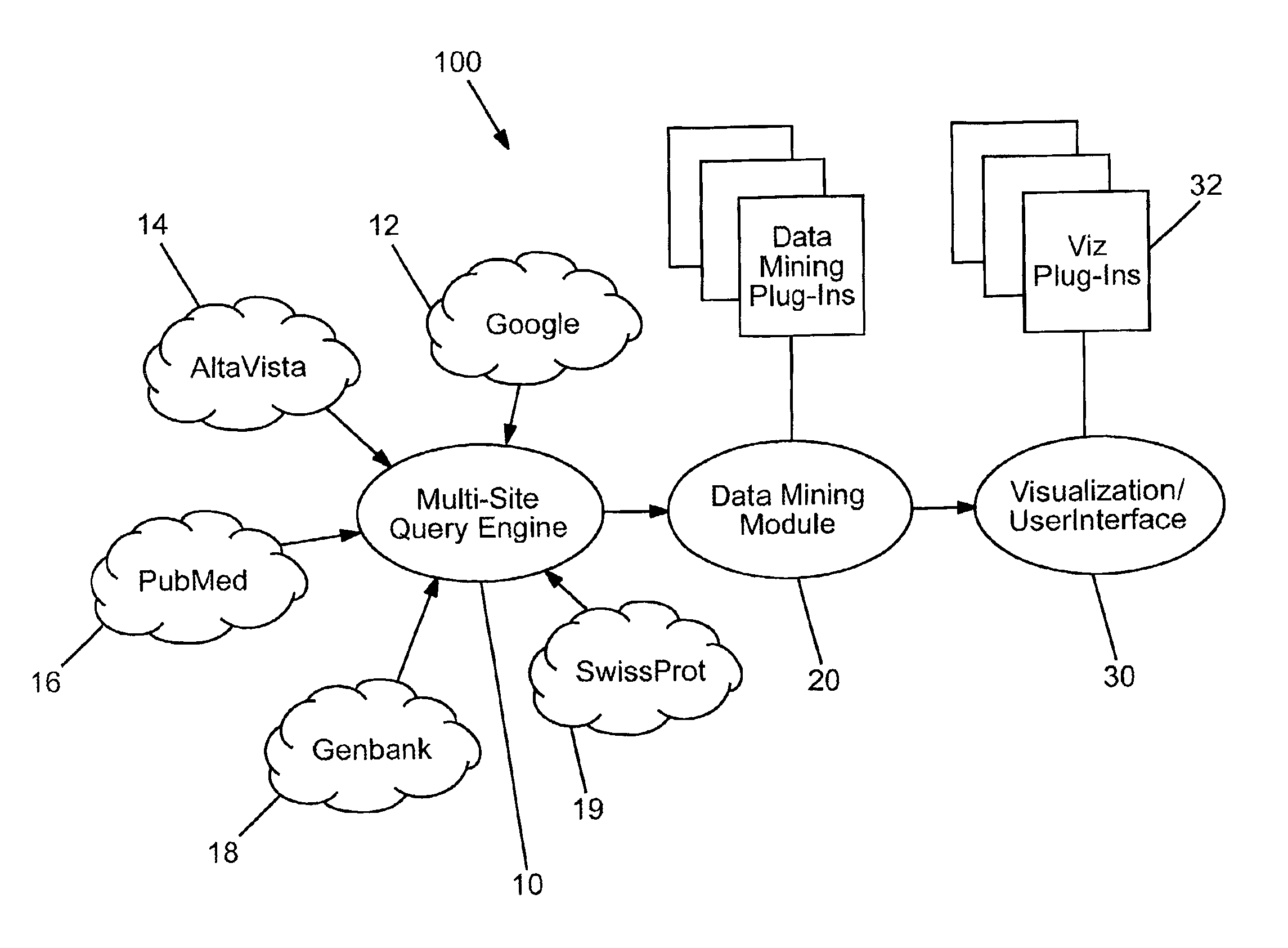
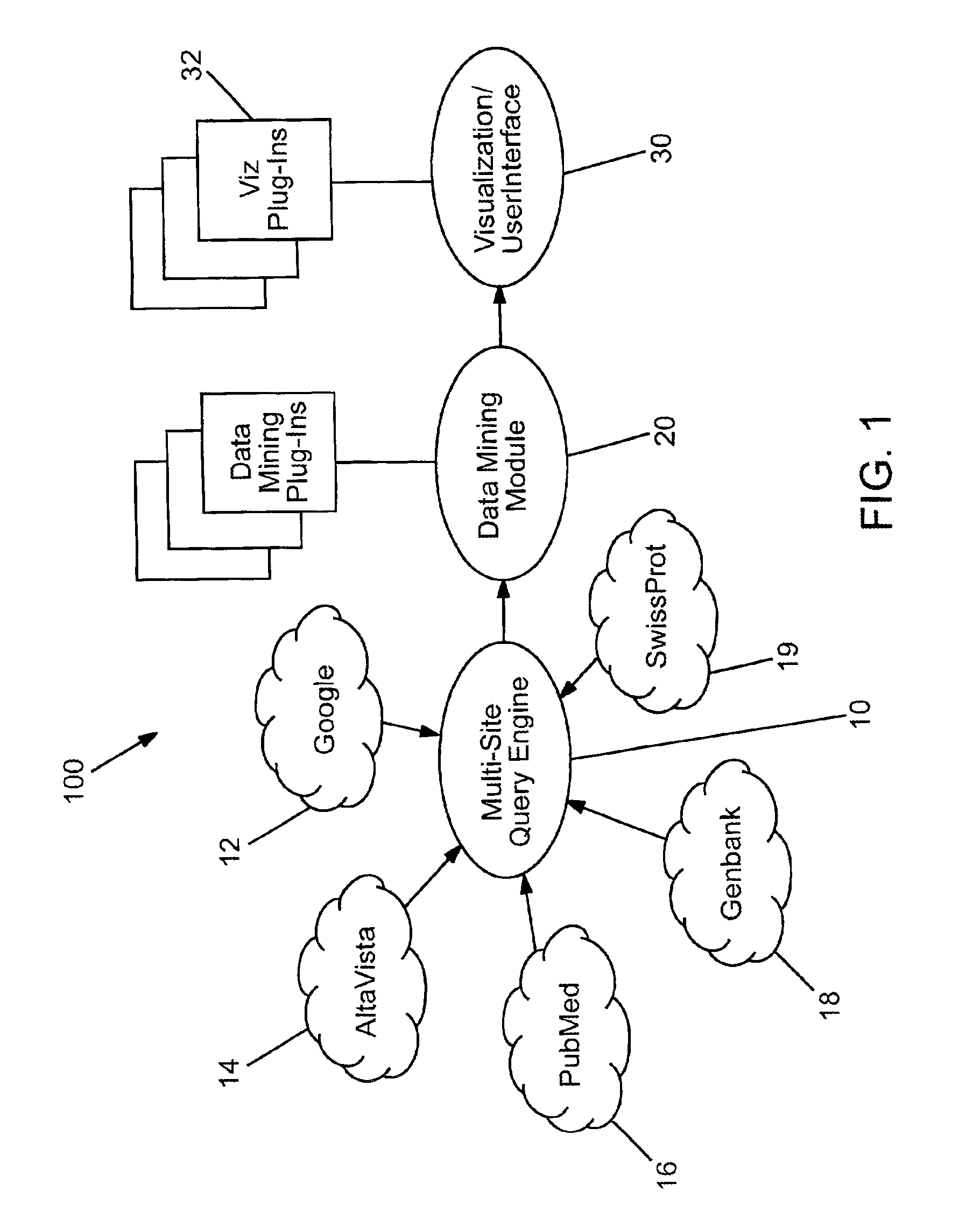
Domain specific knowledge-based metasearch system and methods of using
InactiveUS6920448B2Remove the burdenData processing applicationsWeb data indexingSequence databaseDocument preparation
A system and method for performing domain-specific knowledge based metasearches. A metasearch engine is provided for accessing a searching text-based documents using generic search engines while simultaneously being able to access publication based databases and sequence databases as well as in-house proprietary databases and any database capable of being interfaced with a web interface so as to produce search results in text format. A data mining module is also provided for organizing raw data obtained by unsupervised clustering, simple relevance ranking, and categorization, all of which are done independently of one another. The system is capable of storing previous search data for use in query refinement or subsequent searches based upon the stored data. A search results collection browser may be provided for analyzing current browsing patterns of the user for developing weighting factors to be used in ordering the results of future searches.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Rationally Designed, Synthetic Antibody Libraries and Uses Therefor
ActiveUS20090181855A1Peptide librariesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPolynucleotideSynthetic antibody
The present invention overcomes the inadequacies inherent in the known methods for generating libraries of antibody-encoding polynucleotides by specifically designing the libraries with directed sequence and length diversity. The libraries are designed to reflect the preimmune repertoire naturally created by the human immune system and are based on rational design informed by examination of publicly available databases of human antibody sequences.
Owner:ADIMAB LLC
System and method for pattern recognition in sequential data
InactiveUS20050187916A1Easy to useIncrease speedSequence analysisComparison of digital valuesMedical diagnosisSequential data
The present invention is based on the encoding of sequential data or sequences in a novel manner that permits efficient storage and processing of sequential data, as well as methods for searching sequences or databases of sequences. The methods and systems of the current invention may be adapted broadly to various fields of application and to a variety of sequences types. For example, the current invention has broad application including to the fields of bioinformatics, molecular biology, pharmacogenomics, phonetic sequences, lexicographic sequences, signal analysis, game playing, law enforcement, biometrics, medical diagnosis, equipment maintenance and micro-array data analysis.
Owner:ELORET CORP
System and method for indexing weighted-sequences in large databases
ActiveUS20050114298A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTimestampSequence database
The present invention provides an index structure for managing weighted-sequences in large databases. A weighted-sequence is defined as a two-dimensional structure in which each element in the sequence is associated with a weight. A series of network events, for instance, is a weighted-sequence because each event is associated with a timestamp. Querying a large sequence database by events' occurrence patterns is a first step towards understanding the temporal causal relationships among the events. The index structure proposed herein enables the efficient retrieval from the database of all subsequences (contiguous and non-contiguous) that match a given query sequence both by events and by weights. The index structure also takes into consideration the nonuniform frequency distribution of events in the sequence data.
Owner:SAP AG
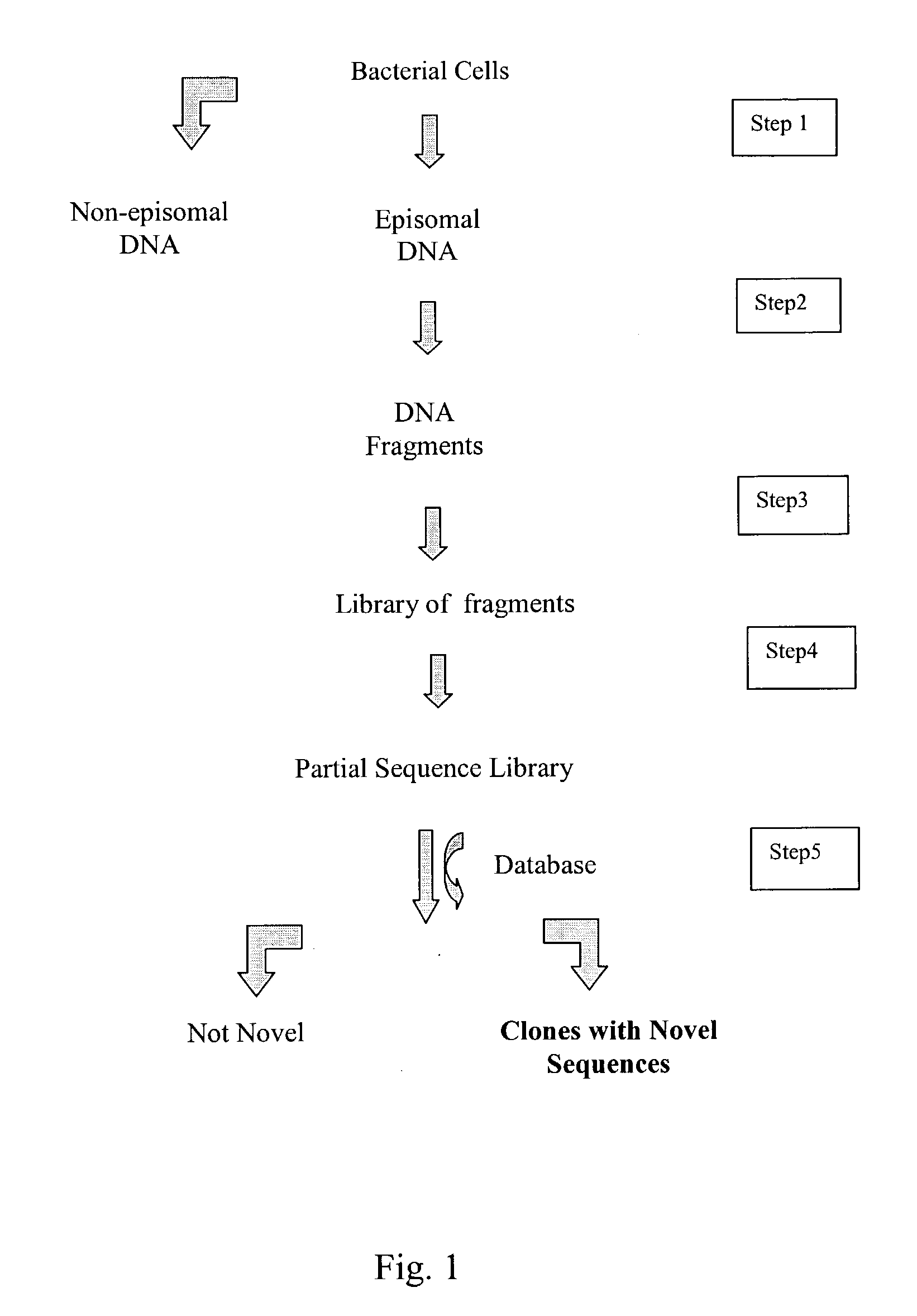
Integrated system for high throughput capture of genetic diversity
InactiveUS20040014091A1Rapid and highly efficient characterizationFast wayMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGenetic diversitySequence database
Compositions and methods for rapid and highly efficient characterization of genetic diversity in organisms are provided. The methods involve rapid sequencing and characterization of extrachromosomal DNA, particularly plasmids, to identify and isolate useful nucleotide sequences. The method targets plasmid DNA and avoids repeated cloning and sequencing of the host chromosome, thus allowing one to focus on the genetic, elements carrying maximum genetic diversity. The method involves generating a library of extrachromosomal DNA clones, sequencing a portion of the clones, comparing the sequences against a database of existing DNA sequences, using an algorithm to select said novel nucleotide sequence based on the presence or absence of said portion in a database, and identification of at least one novel nucleotide sequence. The DNA sequence can also be translated in all six frames and the resulting amino acid sequences can be compared against a database of protein sequences. The integrated approach provides a rapid and efficient method to identify and isolate useful genes. Organisms of particular interest include, but are not limited to bacteria, fungi, algae, and the like. Compositions comprise a mini-cosmid vector comprising a stuffer fragment and at least one cos site.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Determination of optimal local sequence alignment similarity score
InactiveUS7917302B2Low costShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyLocal sequence alignmentProtein function prediction
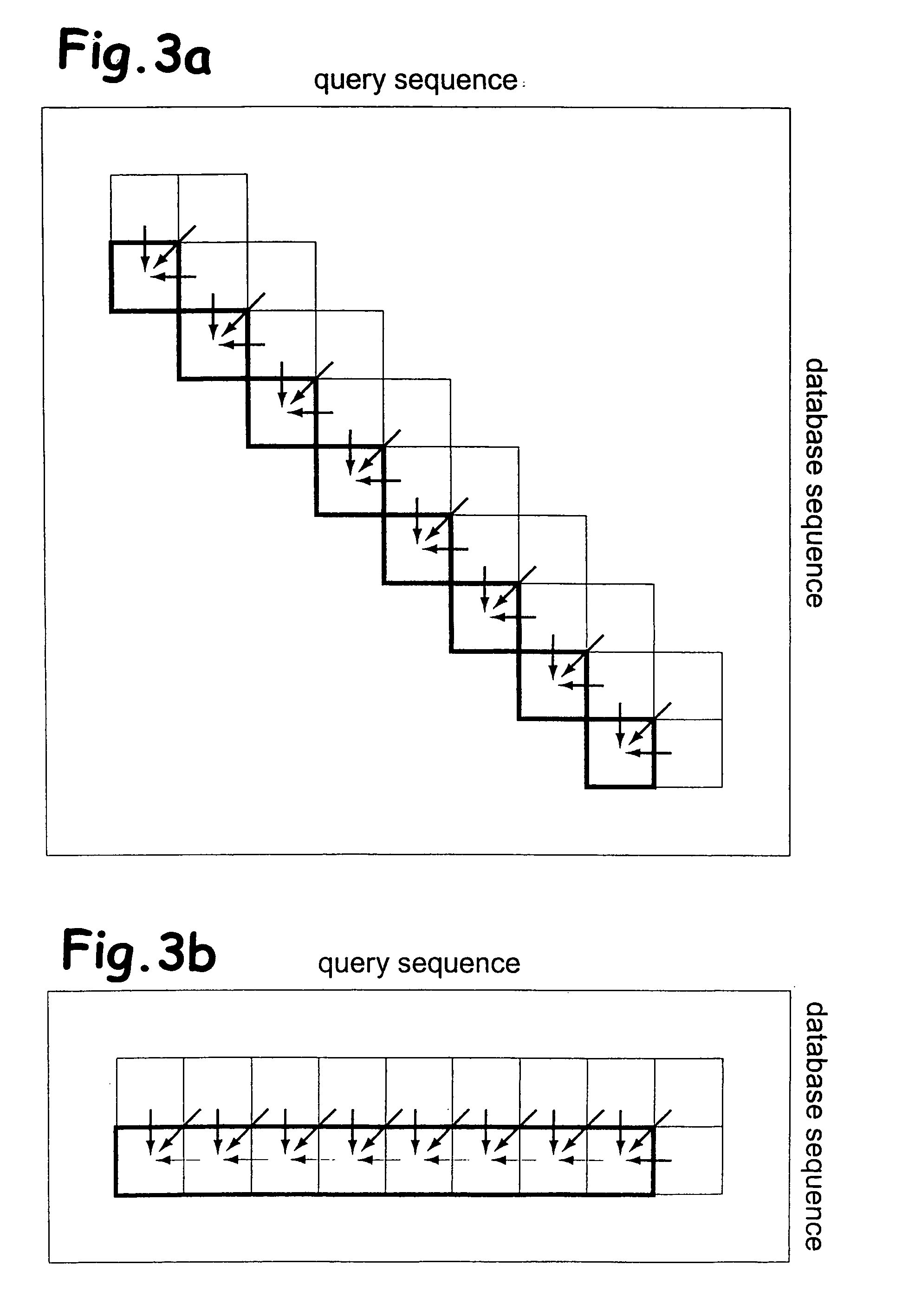
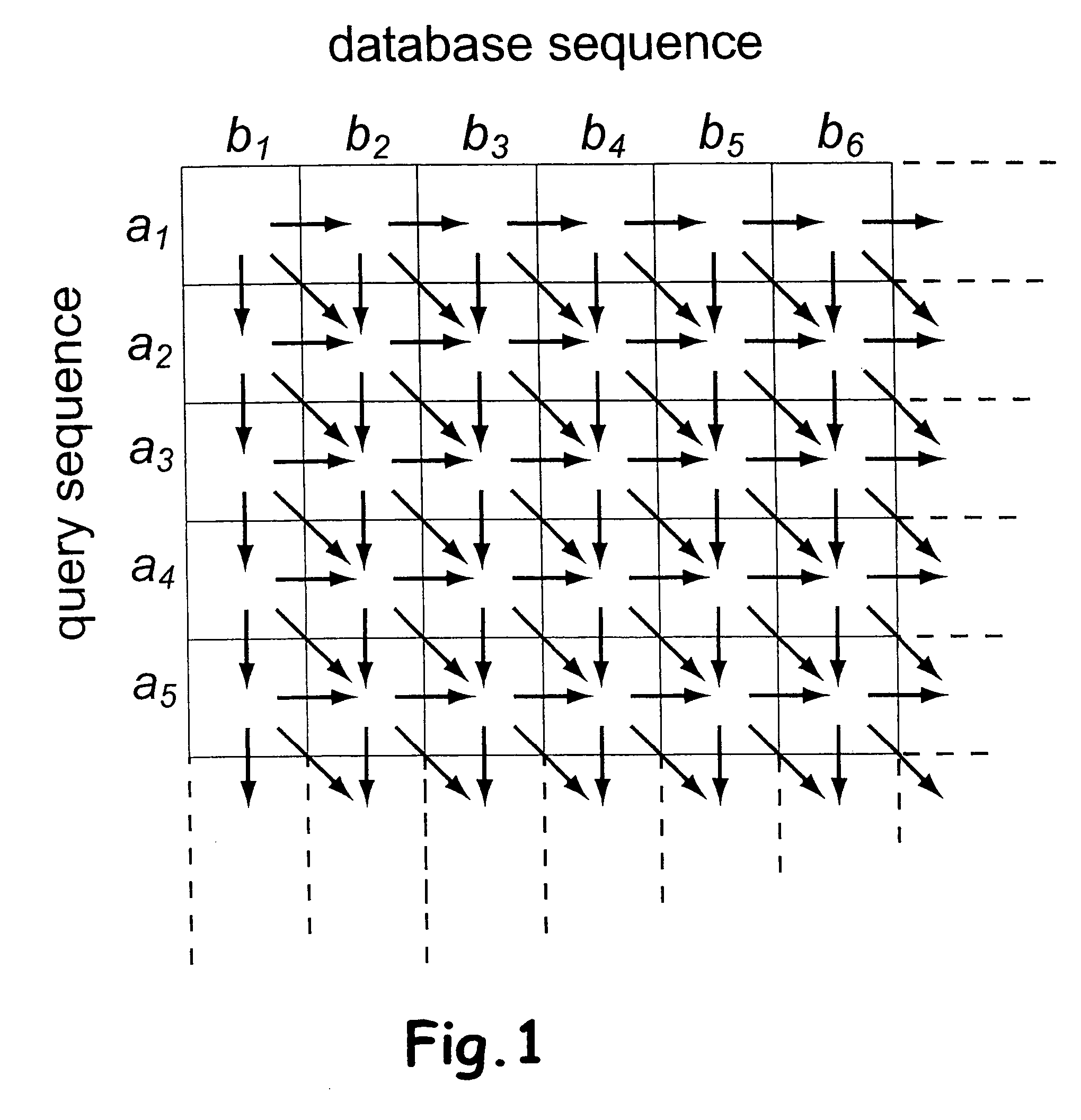
Sequence alignment and sequence database similarity searching are among the most important and challenging task in bio informatics, and are used for several purposes, including protein function prediction. An efficient parallelisation of the Smith-Waterman sequence alignment algorithm using parallel processing in the form of SIMD (Single-Instruction, Multiple-Data) technology is presented. The method has been implementation using the MMX (MultiMedia eXtensions) and SSE (Streaming SIMD Extensions) technology that is embedded in Intel's latest microprocessors, but the method can also be implemented using similar technology existing in other modern microprocessors. Near eight-fold speed-up relative to the fastest previously an optimised eight-way parallel processing approach achieved know non-parallel Smith-Waterman implementation on the same hardware. A speed of about 200 million cell updates per second has been obtained on a single Intel Pentium III 500 MHz microprocessor.
Owner:SEEBERG ERLING CHRISTEN +1
Methods and devices for measuring differential gene expression
InactiveUS6355423B1Efficient and accurateImprove search efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence databaseNucleic Acid Sequence Databases
This invention includes methods for identifying nucleic acids in a sample of nucleic acids by observing sequence sets present in the nucleic acids of the sample and then identifying those sequences in a nucleic acid sequence database having the sequence sets observed. In a preferred embodiment, a sequence set consists of two primary subsequences and an additional subsequence having determined mutual relationships. The methods include those for observing the sequence sets and those for performing sequence database searches. This invention also includes devices for recognizing in parallel the additional subsequences in a sample of as well as methods for the use of these devices. In a preferred embodiment, the devices include probes bound to a planar surface that recognize additional subsequence by hybridization, and the methods of use include features to improve the specificity and reproducibility of this hybridization.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Method and apparatus for identifying classifying or quantifying DNA sequences in a sample without sequencing
InactiveUS6141657ARapid and economical and quantitative and precise determination and classificationSufficient discrimination and resolutionData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSequence databaseDNA Sequence Databases
This invention provides methods by which biologically derived DNA sequences in a mixed sample or in an arrayed single sequence clone can be determined and classified without sequencing. The methods make use of information on the presence of carefully chosen target subsequences, typically of length from 4 to 8 base pairs, and preferably the length between target subsequences in a sample DNA sequence together with DNA sequence databases containing lists of sequences likely to be present in the sample to determine a sample sequence. The preferred method uses restriction endonucleases to recognize target subsequences and cut the sample sequence. Then carefully chosen recognition moieties are ligated to the cut fragments, the fragments amplified, and the experimental observation made. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the preferred method of amplification. Another embodiment of the invention uses information on the presence or absence of carefully chosen target subsequences in a single sequence clone together with DNA sequence databases to determine the clone sequence. Computer implemented methods are provided to analyze the experimental results and to determine the sample sequences in question and to carefully choose target subsequences in order that experiments yield a maximum amount of information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Methods and apparatus for high-speed approximate sub-string searches
InactiveUS6931401B2Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence searchSequence database
A method and system for conducting sequence searches in a sequence database wherein in one embodiment, the method includes: combining a plurality of query sequences into a combined query sequence; determining a plurality of subdivisions of the sequence database; performing a plurality of searches, wherein each search includes a comparison of the combined query sequence against one of the plurality of subdivisions of the database to produce a plurality of word matches; extending the length of the plurality of word matches to produce a plurality of High-scoring Segment Pairs, combining the plurality of High-scoring Segment Pairs; and producing a plurality of reports, each report representing the highest scoring matches for one of the plurality of query sequences.
Owner:PARACEL
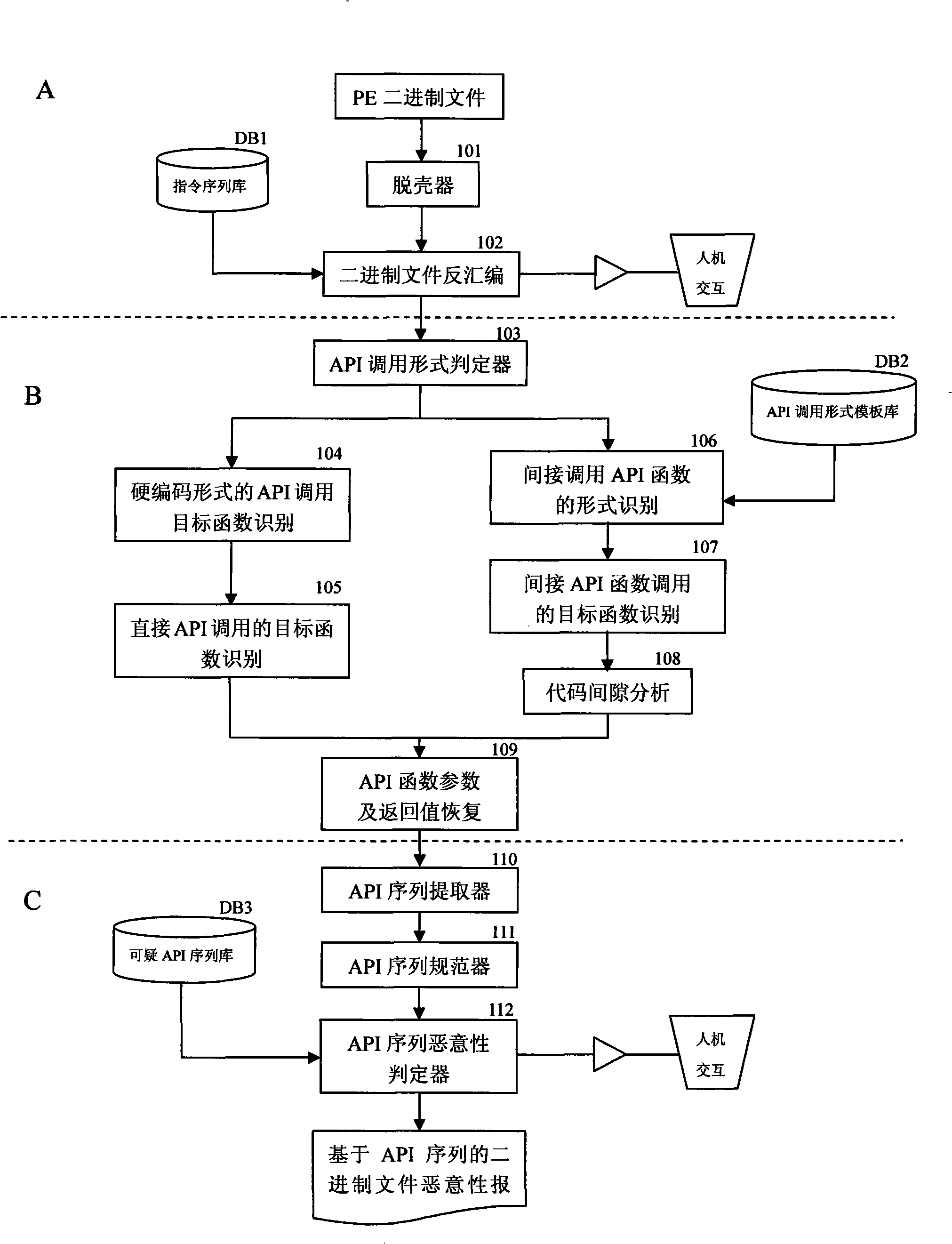
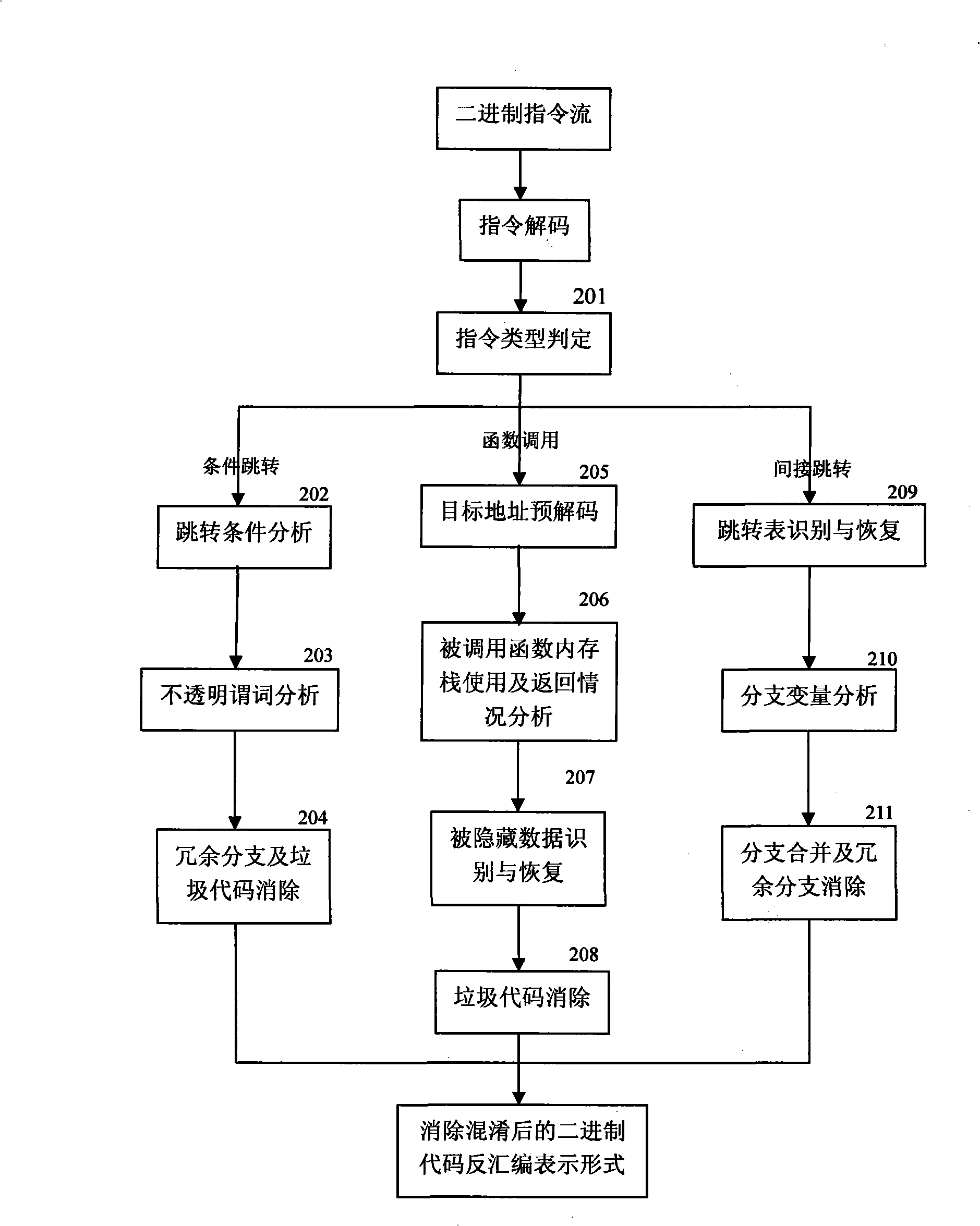
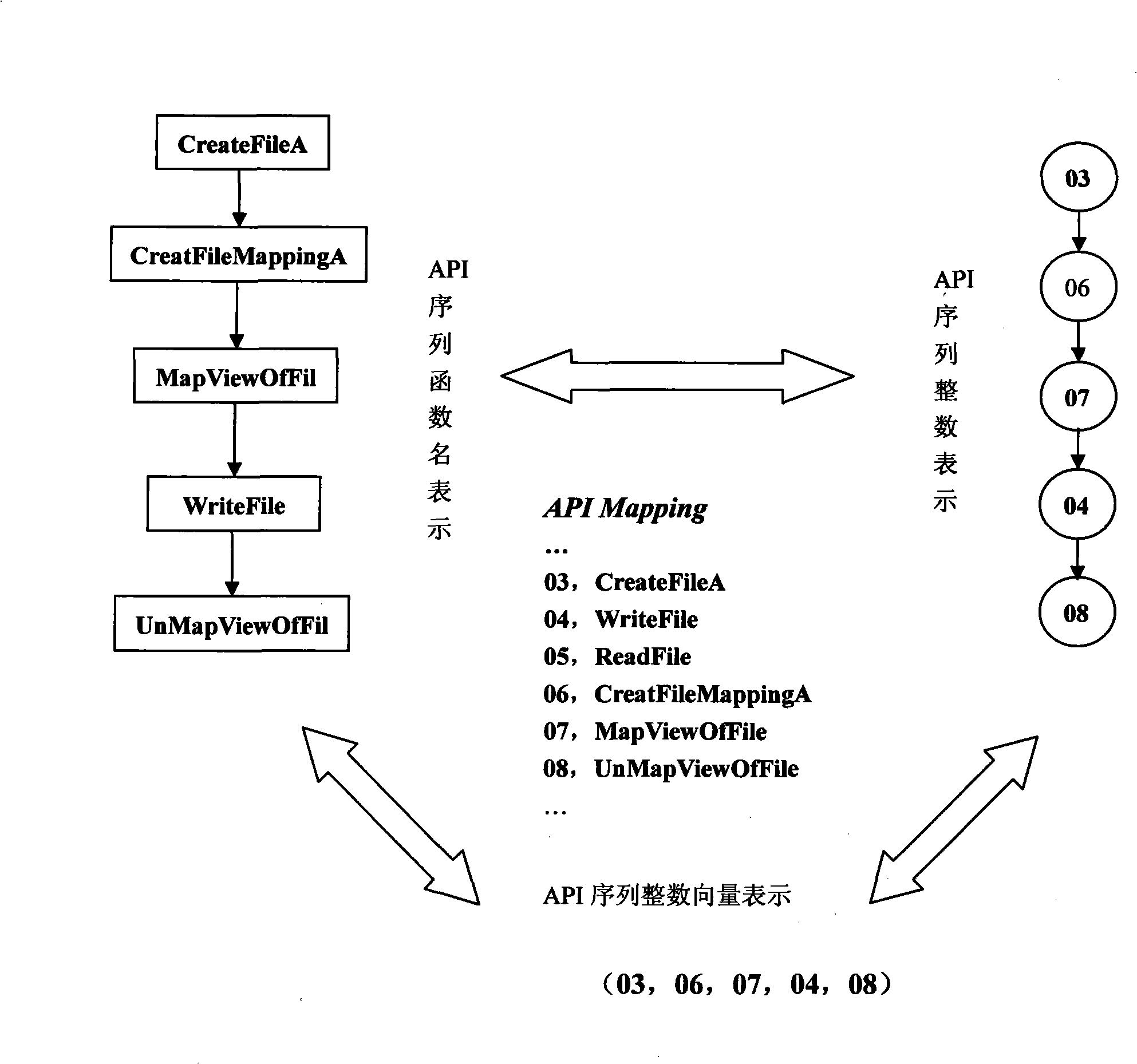
API use action discovering and malice deciding method after confusion of multi-tier synergism
InactiveCN101359352ASolve the problem that it is difficult to find the behavior of API function callsEasy to understandPlatform integrity maintainanceProgram controlSequence databaseConfusion
The invention relates to a stratification synergic detection and judgment method for detecting the confused API call behavior and judging the maliciousness of the call behavior; the detection and judgment method includes three steps: firstly, the binary code for being analyzed is disassembled to establish the control flow graph (CFG) of the program; the known unconventional instruction or data sequence provided with the API function call capability and stored in the database DB1 is adopted to recognize the unconventional call behavior of the API function; secondly, the generation operation of the API sequence called by the target program is finished; the API function is recognized and recovered in the aspects of direct call and indirect call; finally, the extraction of the API sequence and the maliciousness judgment operation are finished; the extraction of the sequence is finished and based on the control flow graph (CFG) of the program; then the obtained sequence is normalized according to the format stored in the suspected API sequence database; the invention provides a stratification synergic detection and judgment method for detecting the confused API call behavior and judging the maliciousness of the call behavior, which has the advantages of wide recognition range, accurate recognition and high efficiency.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Methods and devices for measuring differential gene expression
InactiveUS20030003463A1Efficient and accurateImprove search efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence databaseNucleic Acid Sequence Databases
This invention includes methods for identifying nucleic acids in a sample of nucleic acids by observing sequence sets present in the nucleic acids of the sample and then identifying those sequences in a nucleic acid sequence database having the sequence sets observed. In a preferred embodiment, a sequence set consists of two primary subsequences and an additional subsequence having determined mutual relationships. The methods include those for observing the sequence sets and those for performing sequence database searches. This invention also includes devices for recognizing in parallel the additional subsequences in a sample of as well as methods for the use of these devices. In a preferred embodiment, the devices include probes bound to a planar surface that recognize additional subsequence by hybridization, and the methods of use include features to improve the specificity and reproducibility of this hybridization.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
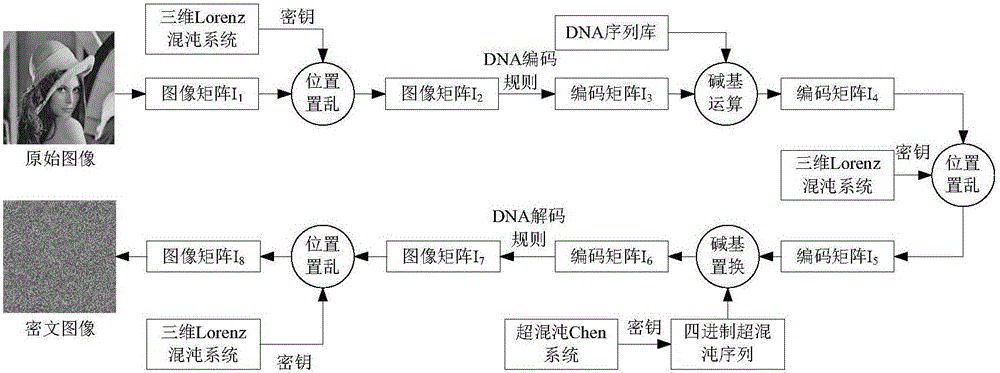
Digital image encryption method based on chaotic system and nucleotide sequence database
InactiveCN105046636AEnhanced confusionImprove featuresImage data processing detailsInformation processingSequence database
The invention provides a digital image encryption method based on a chaotic system and a nucleotide sequence database. The method comprises the following steps: image pixel positions are scrambled by chaotic mapping index sequence; an image pixel value undergoes DNA coding, and the DNA-coded image pixel value and a DNA sequence in a nucleotide sequence database undergo base operation; and the DNA-coded pixel undergoes base replacement according to a quanternary hyperchaos sequence generated by a hyperchaos Chen system, and confusion and diffusion properties are further enhanced by iteration of a ciphertext feedback and chaotic system. By means of sensibility and pseudo-randomness of chaotic mapping to initial conditions, by combining inherent spatial configuration and unique information processing capability of DNA molecules and through transformation and operation between two chaotic sequences, a DNA sequence database and pixel gray value, the purpose of confusion and diffusion is achieved so as to realize encryption of digital images. It shows through experimental results that the method has a large keyspace, has strong sensitivity to a secret key and can effectively defense attack operations such as statistical analysis, exhaustion analysis and the like.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
System and method for pattern recognition in sequential data
InactiveUS8280640B2Easy to useIncrease speedBiological testingComparison of digital valuesSequential dataMedical diagnosis
The present invention is based on the encoding of sequential data or sequences in a novel manner that permits efficient storage and processing of sequential data, as well as methods for searching sequences or databases of sequences. The methods and systems of the current invention may be adapted broadly to various fields of application and to a variety of sequences types. For example, the current invention has broad application including to the fields of bioinformatics, molecular biology, pharmacogenomics, phonetic sequences, lexicographic sequences, signal analysis, game playing, law enforcement, biometrics, medical diagnosis, equipment maintenance and micro-array data analysis.
Owner:ELORET CORP
Method for developing mung bean simple sequence repeat (SSR) primer based on transcriptome sequencing
InactiveCN103642912AImprove design success rateSimple designMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence databaseTranscriptome Sequencing
The invention provides a method for developing a mung bean simple sequence repeat (SSR) primer based on transcriptome sequencing. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a set of mung bean genome-wide transcription, and forming a sequence database; splicing sequencing sequences into a transcriptome by Trinity; taking the longest transcript in each gene as Unigene; carrying out bioinformatics analysis of a Unigene sequence; carrying out SSR detection on the Unigene by adopting MISA1.0; carrying out SSR primer design by using a Primer 3, and carrying out SSR primer polymorphism identification. 13134 pairs of SSR primers are successfully designed by application of the method; 50 pairs of primers are randomly selected to verify 8 parts of mung bean deoxyribonucleic acids (DNAs) from different countries, wherein 32 pairs of polymorphic primers are formed in all; the mung bean materials with different geographical origins can be distinguished by using the 32 pairs of SSR primers. The method disclosed by the invention is convenient, fast and accurate, and low in cost, and a new thought is provided for development of the mung bean SSR primer.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for mining attack frequent sequence mode from Web log
ActiveCN105721427ATransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsSequence databaseUniform resource locator
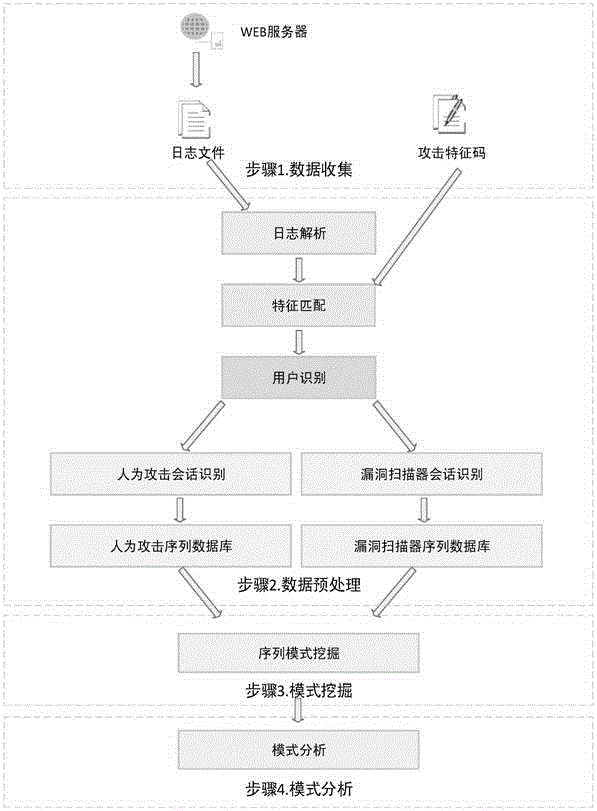
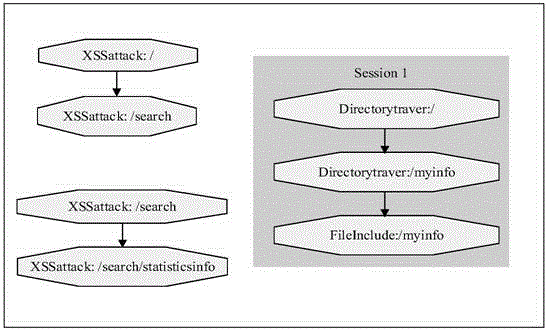
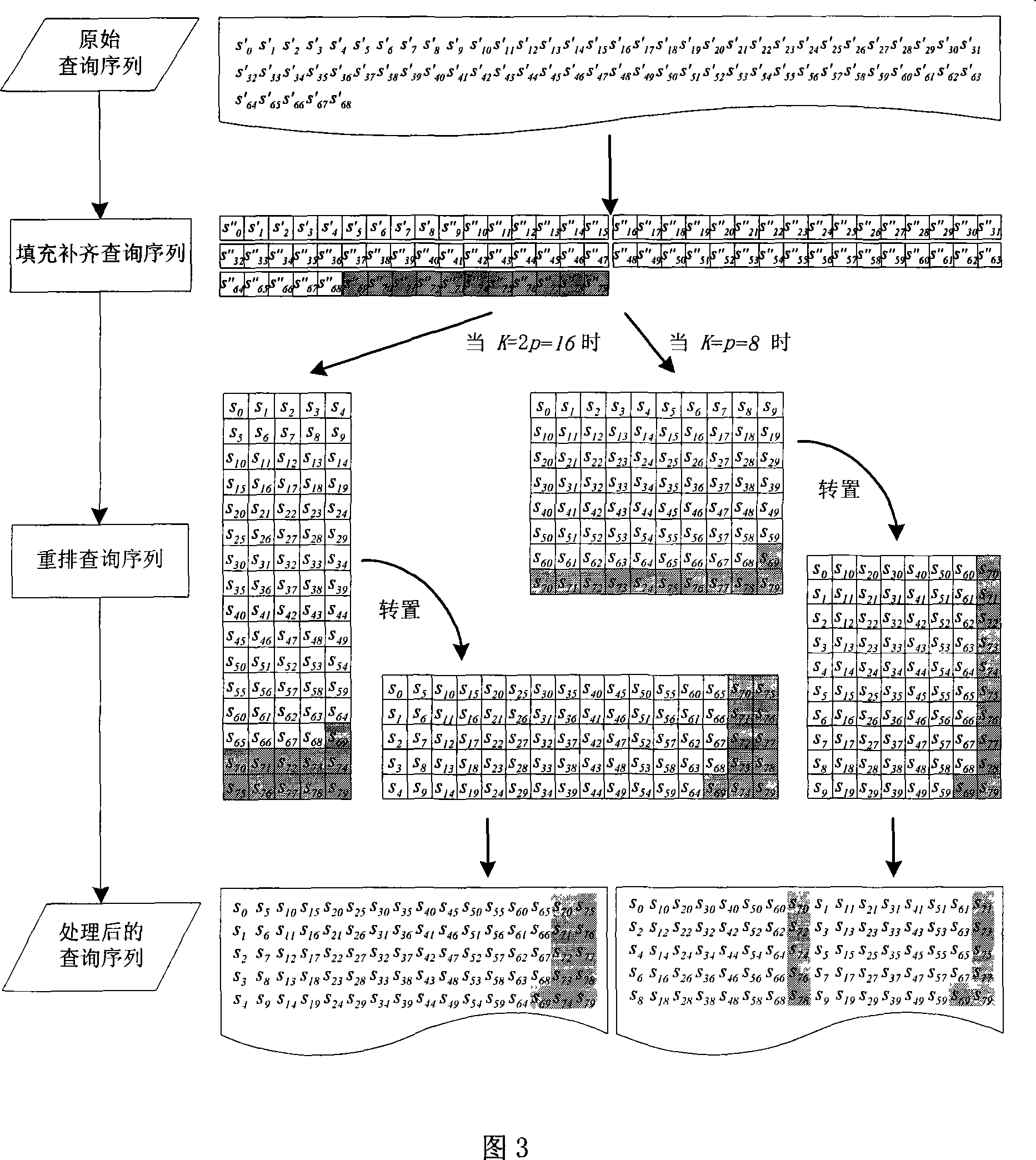
The invention relates to data mining in the field of network security and especially relates to a method for mining an attack frequent sequence mode from a Web log. The method comprises the following steps: collecting website access log files, website information and attack feature codes; analyzing a website log structure, matching analyzed URLs with the collected attack feature codes, obtaining attack records, and clearing up the URLs; performing user identification on attack log data and distinguishing manual attacks and attacks of a loophole scanner; respectively performing session identification to obtain a sequence database of the manual attacks and a sequence database of the loophole scanner; converting a character string database into a digital database, and respectively mining a frequent sequence of the sequence database by use of a sequence mode mining method; and maximizing the frequent sequence obtained through mining and converting a sequence mode into visual figure language. The process is indicated in the first graph. The method provided by the invention can realize visualization of an attack mode and explores a scanning sequence in the loophole scanner.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for recognizing mouse gesticulation
InactiveCN101408824AEasy to operateFast recognitionInput/output processes for data processingSequence analysisSequence database
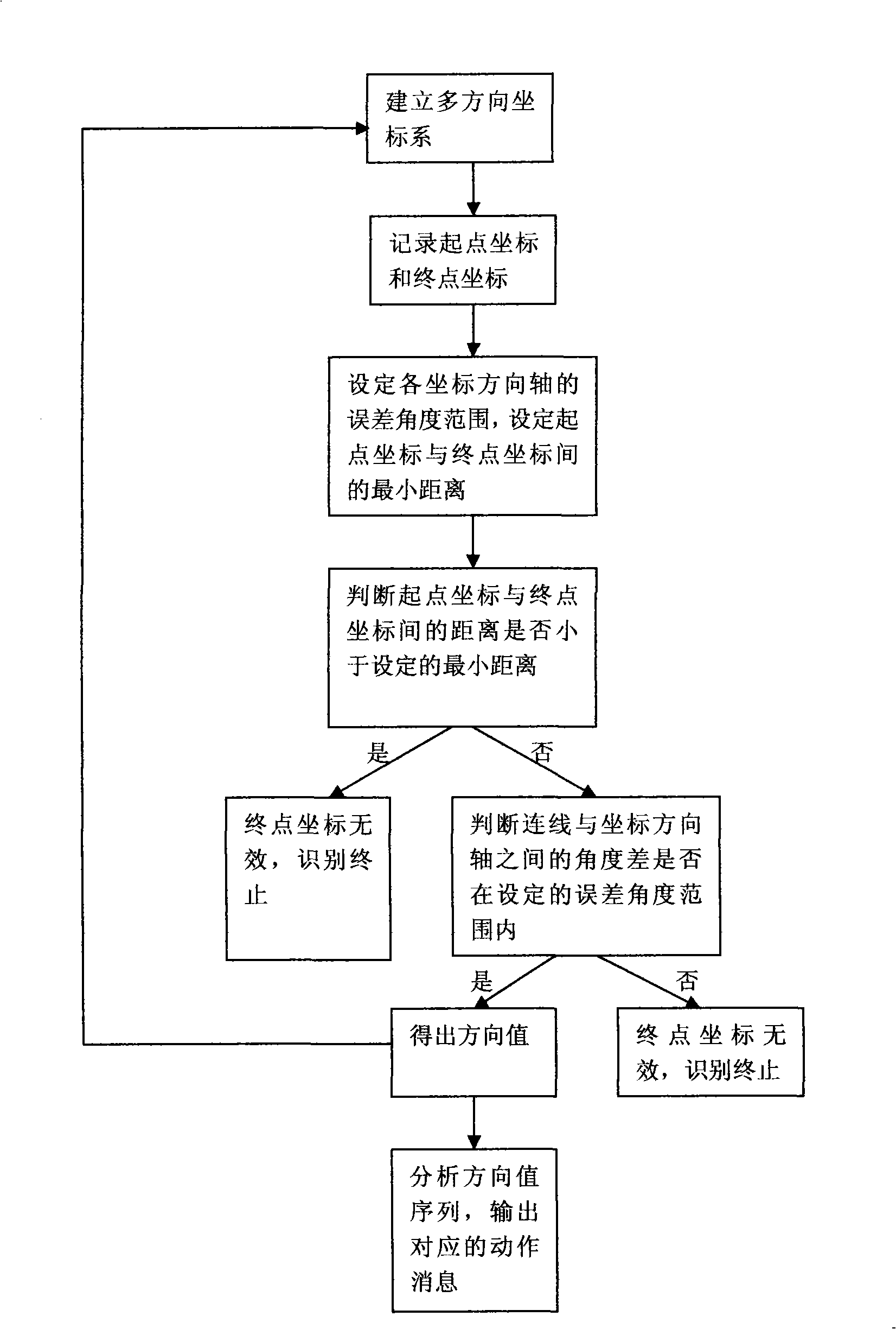
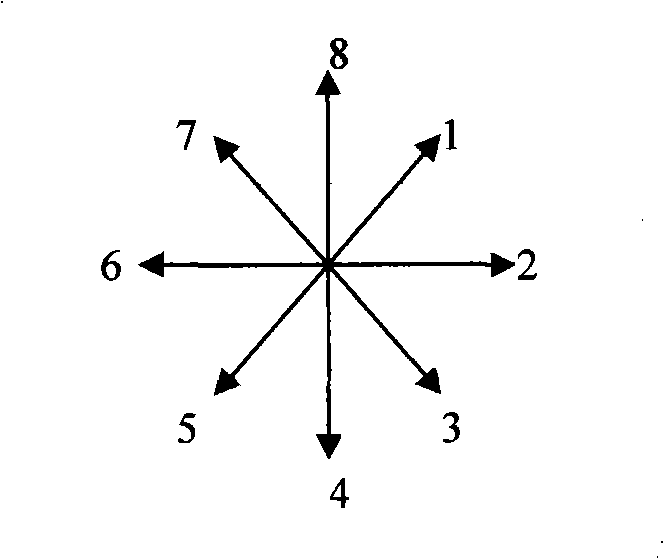
The invention provides a mouse gesture identification method. A starting point coordinate and an end point coordinate before and after the movement of a mouse cursor point are recorded by a message processing module by establishing a multidirectional coordinate system and then calculated in a gesture computing module to judge the moving direction of the mouse cursor point; after the circulation of the steps, the direction value sequence obtained is sent to a sequence analysis module; and the group that is best matched is found in a feature sequence database by comparison and the corresponding action information is output. The method of the invention has fast computing speed and high identification efficiency, thus being convenient for the operation of a touch screen user on software greatly; meanwhile, a control manufactured by adopting the method is greatly convenient for the programmers for secondary development to develop the touch screen application program.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTRON TECH CO LTD
Determination of optimal local sequence alignment similarity score
InactiveUS20040024536A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyLocal sequence alignmentProtein function prediction
Sequence alignment and sequence database similarity searching are among the most important and challenging task in bio informatics, and are used for several purposes, including protein function prediction. An efficient parallelisation of the Smith-Waterman sequence alignment algorithm using parallel processing in the form of SIMD (Single-Instruction, Multiple-Data) technology is presented. The method has been implementation using the MMX (MultiMedia eXtensions) and SSE (Streaming SIMD Extensions) technology that is embedded in Intel's latest microprocessors, but the method can also be implemented using similar technology existing in other modern microprocessors. Near eight-fold speed-up relative to the fastest previously an optimised eight-way parallel processing approach achieved know non-parallel Smith-Waterman implementation on the same hardware. A speed of about 200 million cell updates per second has been obtained on a single Intel Pentium III 500 MHz microprocessor.
Owner:SEEBERG ERLING CHRISTEN +1
Protein expression profile database
InactiveUS20050048564A1Peptide librariesLibrary screeningSequence databaseProtein expression profile
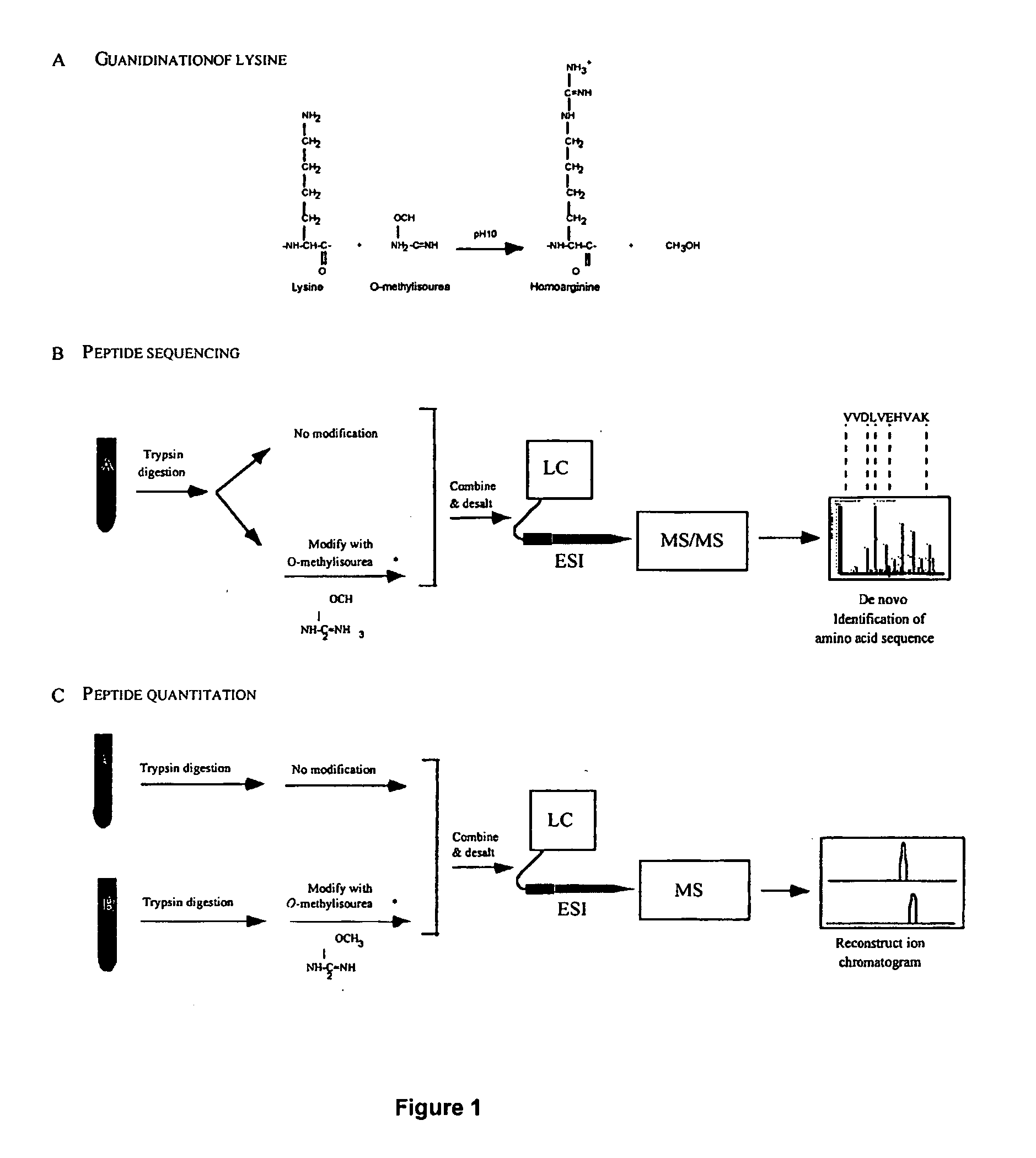
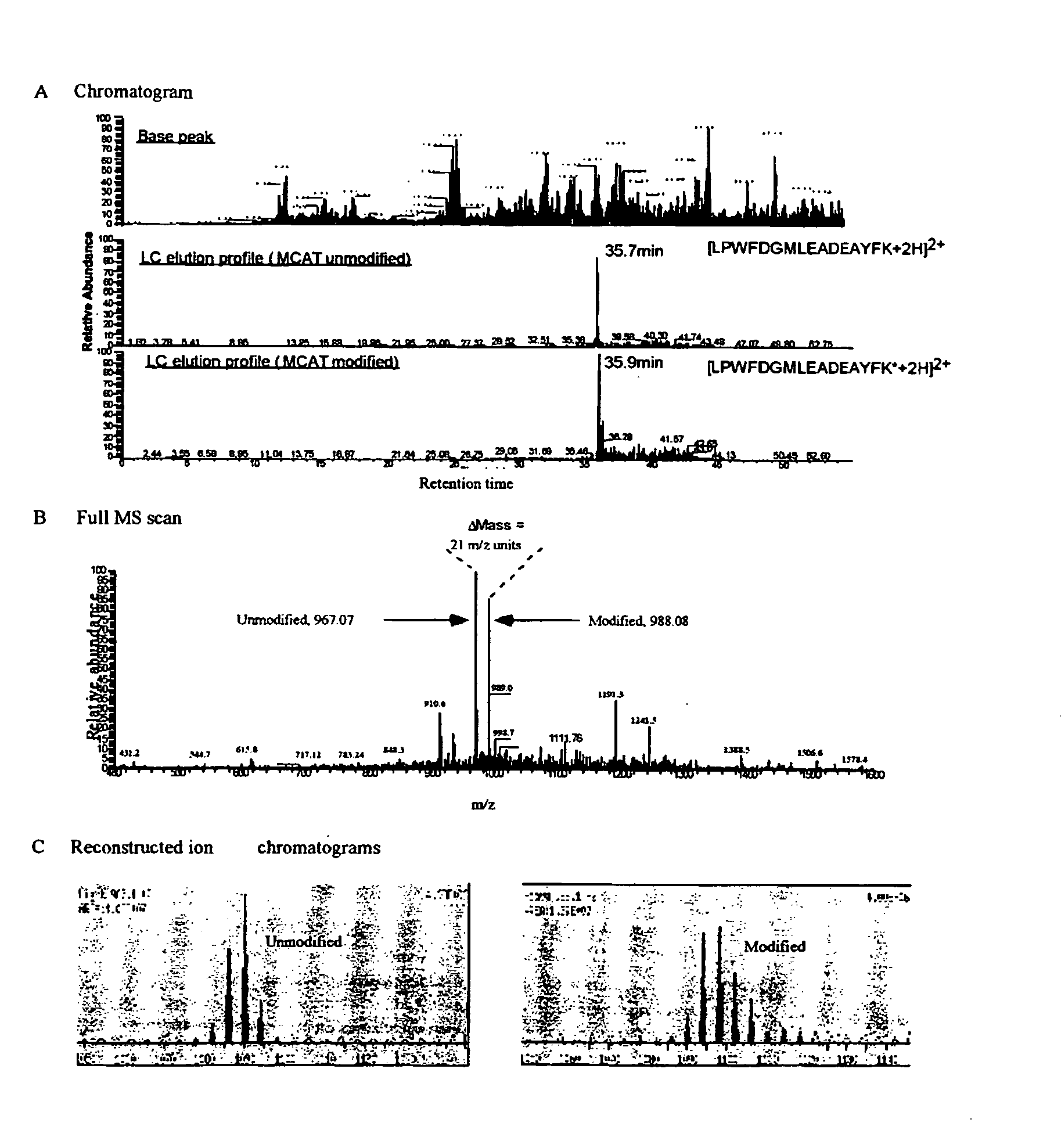
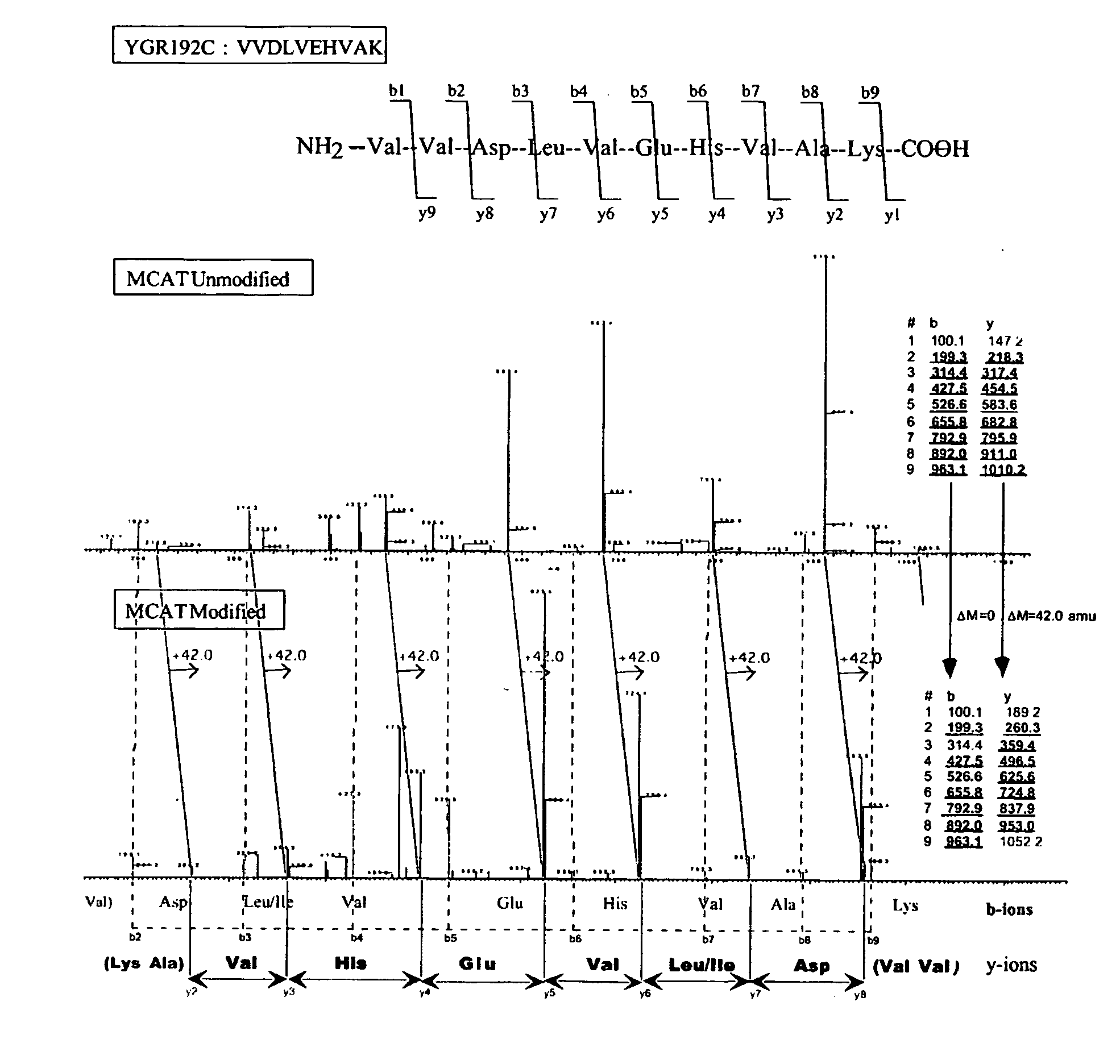
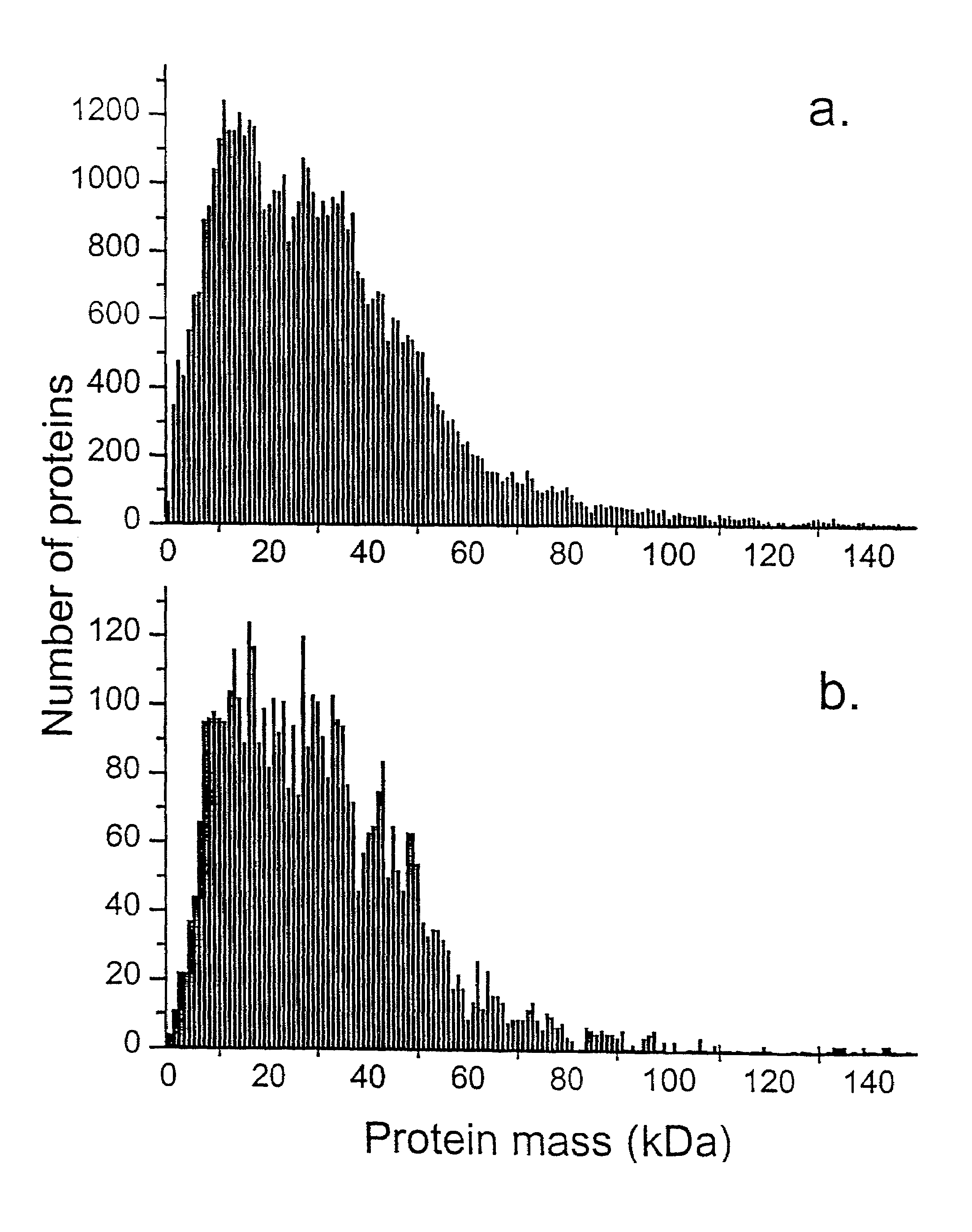
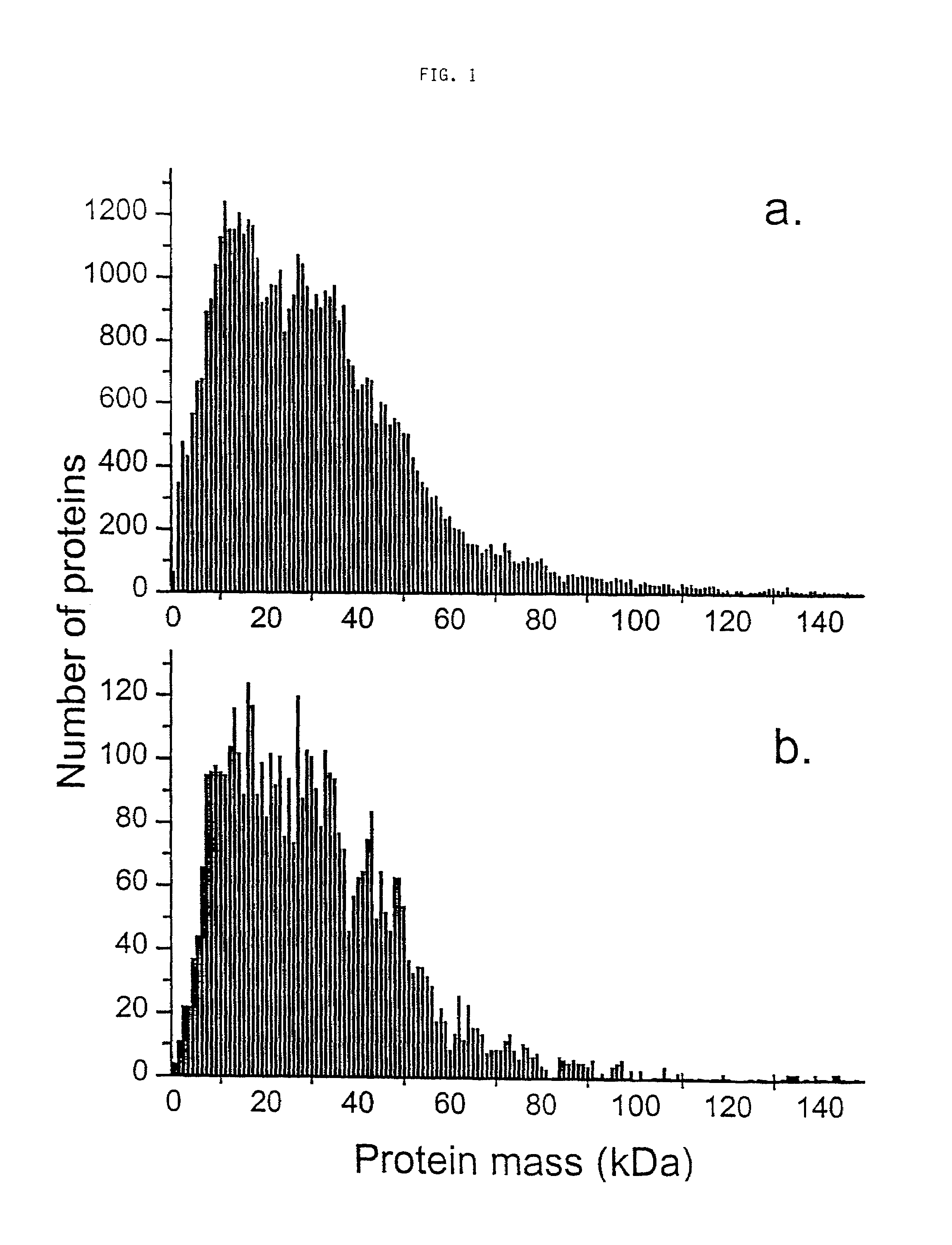
This invention describes the use of peptide profiling to identify, characterize, and classify biological samples. In complex samples, many thousands of different peptides will be present at varying concentrations. The invention uses liquid chromatography and similar methods to separate peptides, which are then identified and quantified using mass spectrometry. By identification it is meant that the correct sequence of the peptide is established through comparisons with genome sequence databases, since the majority of peptides and proteins are unannotated and have no ascribed name or function. Quantification means an estimate of the absolute or relative abundance of the peptide species using mass spectrometry and related techniques including, but not limited to, pre- or post-experimental stable or unstable isotope incorporation, molecular mass tagging, differential mass tagging, and amino acid analysis.
Owner:EMILI ANDREW +1
Software security flaw detection method based on sequential pattern mining
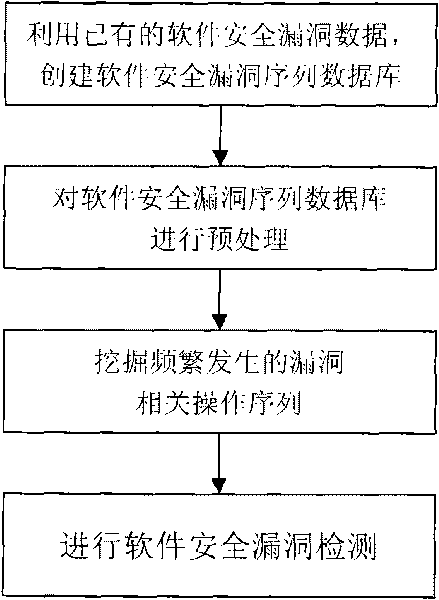
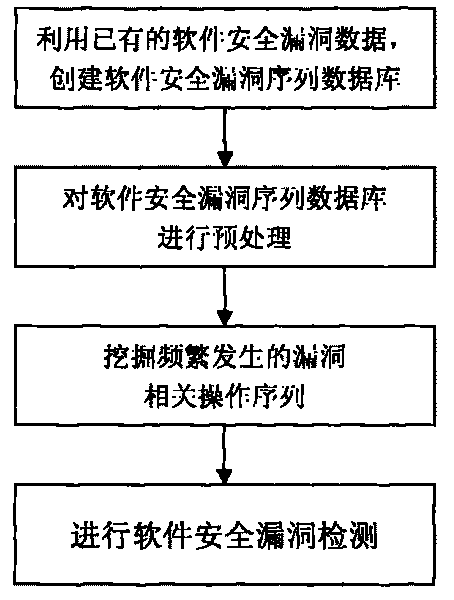
InactiveCN101710378AImprove detection efficiencyReduce the false negative rate of vulnerability detectionPlatform integrity maintainanceSpecial data processing applicationsSequence databaseSoftware system
The invention provides a software security flaw detection method based on sequential pattern mining. Firstly, a great quantity of relevant operation sequence data of a detected software security flaw is used for building a relevant operation sequence database of the security flaw; then, a closed sequential pattern mining arithmetic in the data mining is used to mine frequently appearing relevant operation sequence of the flaw; the mined frequently appearing relevant operation sequence of the flaw is used for detecting the security flaw of the current software system so as to lower flaw detection missing report rate as well as improve security flaw detection efficiency. Along with the accumulation of flaw data, the advantage of high security flaw detection efficiency of the invention is more outstanding.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +2
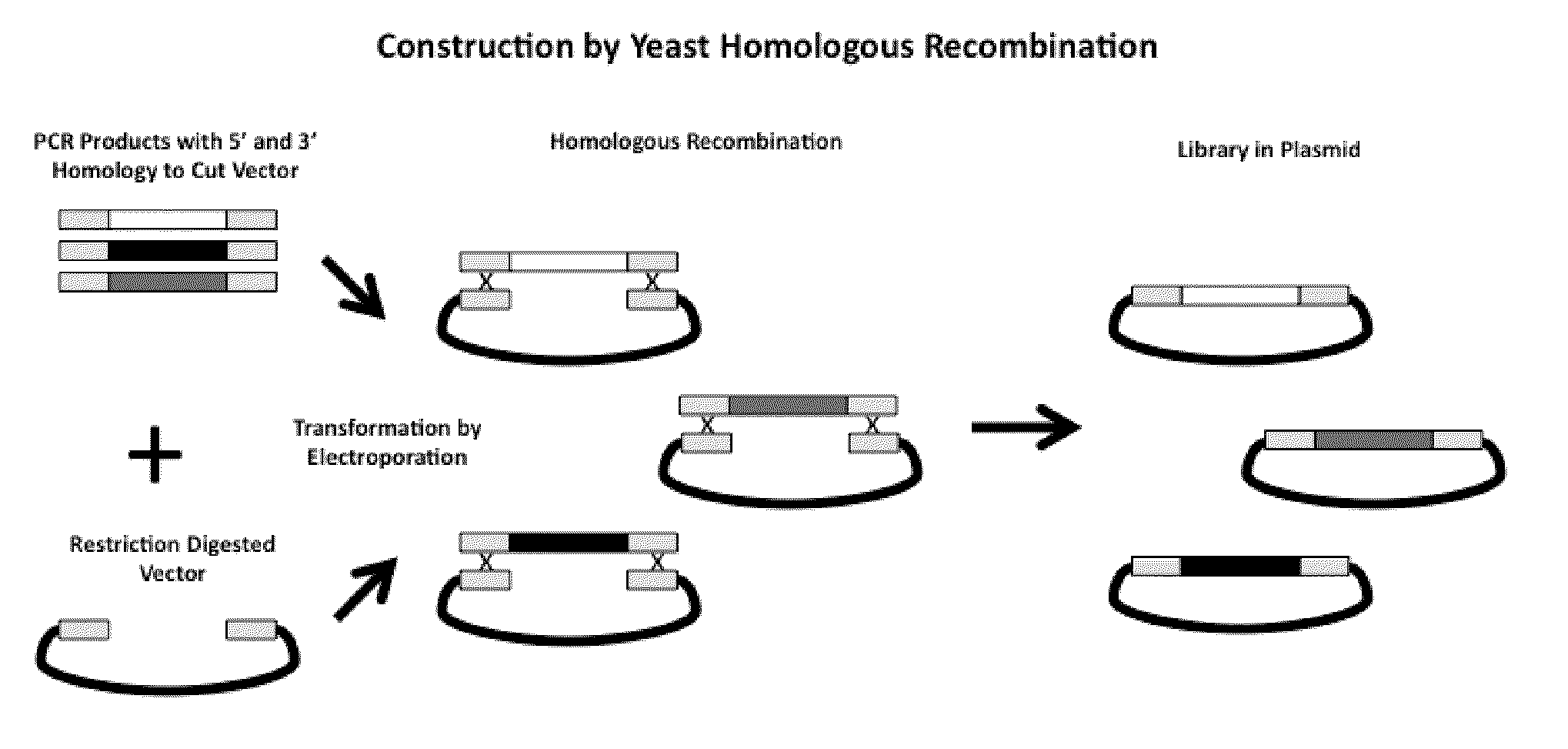
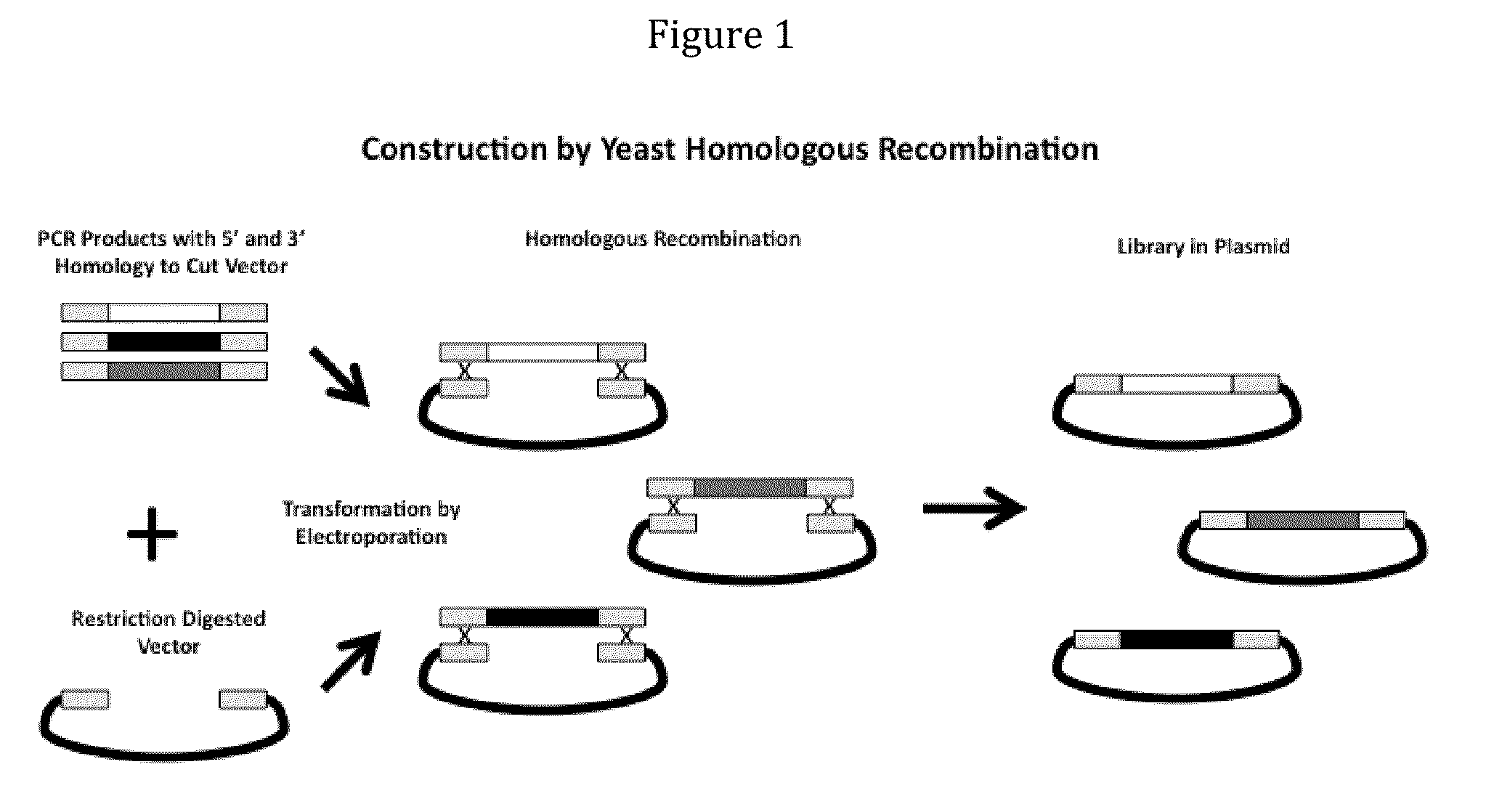
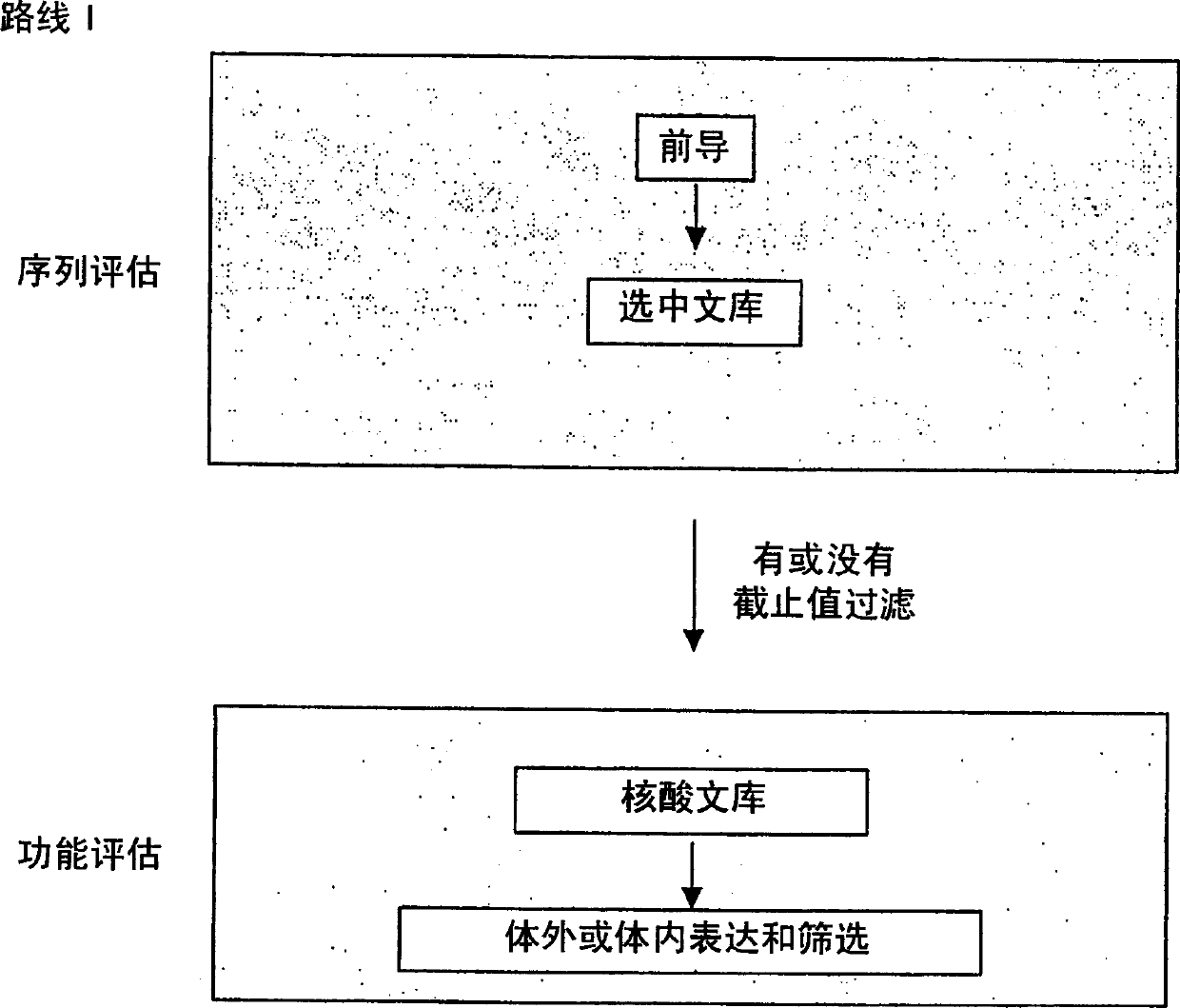
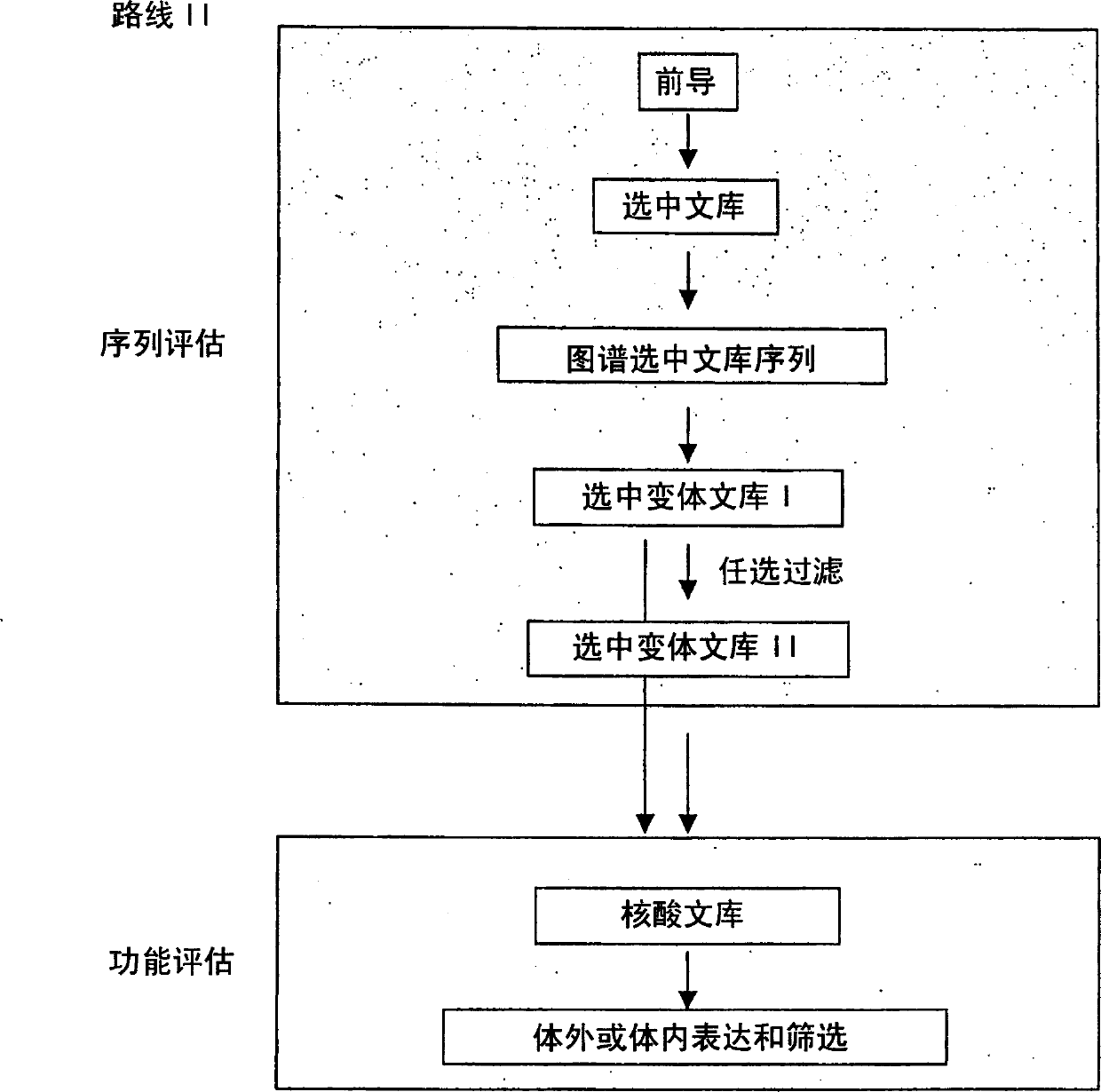
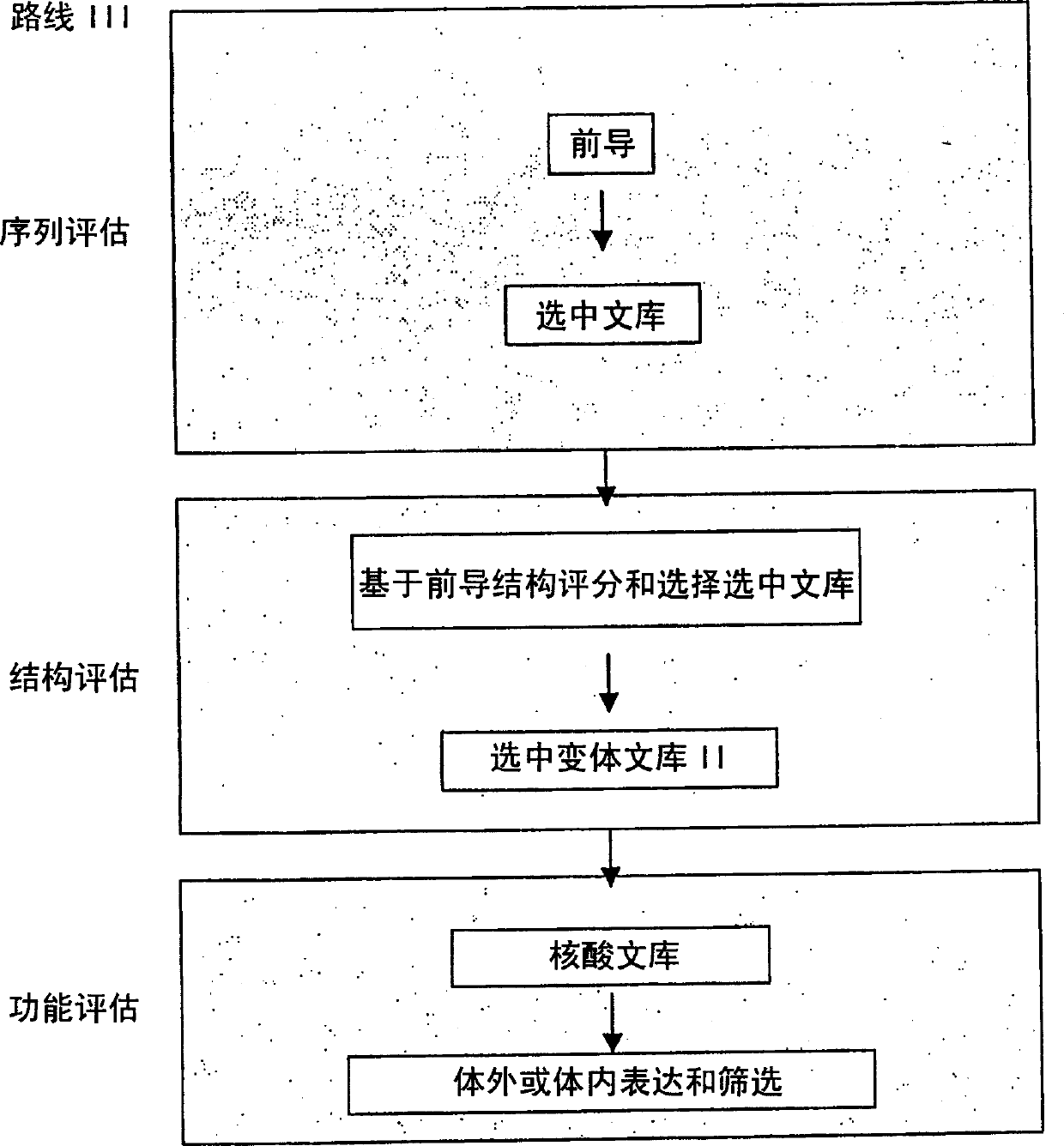
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
The present invention provides methods for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimal proteins with desired biological functions, such as improved binding affinity for biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The method is performed in silico in a high-throughput fashion by mining the ever-expanding database of protein sequences in all living things, especially humans. In one embodiment, a method of constructing a designer protein library comprises the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, referred to as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of test protein sequences; Select at least two peptide fragments having at least 15% sequence identity with the leader sequence from each test protein sequence, and the selected peptide fragments form a selection library; a library of designed proteins is formed by replacing the leader sequence with the selection library. Libraries of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to generate libraries of recombinant proteins that can be screened for new or improved functions relative to lead proteins, such as antibodies against a therapeutically important target.
Owner:埃博马可西斯公司
Biological sequence data-base searching multilayered accelerating method based on flow process
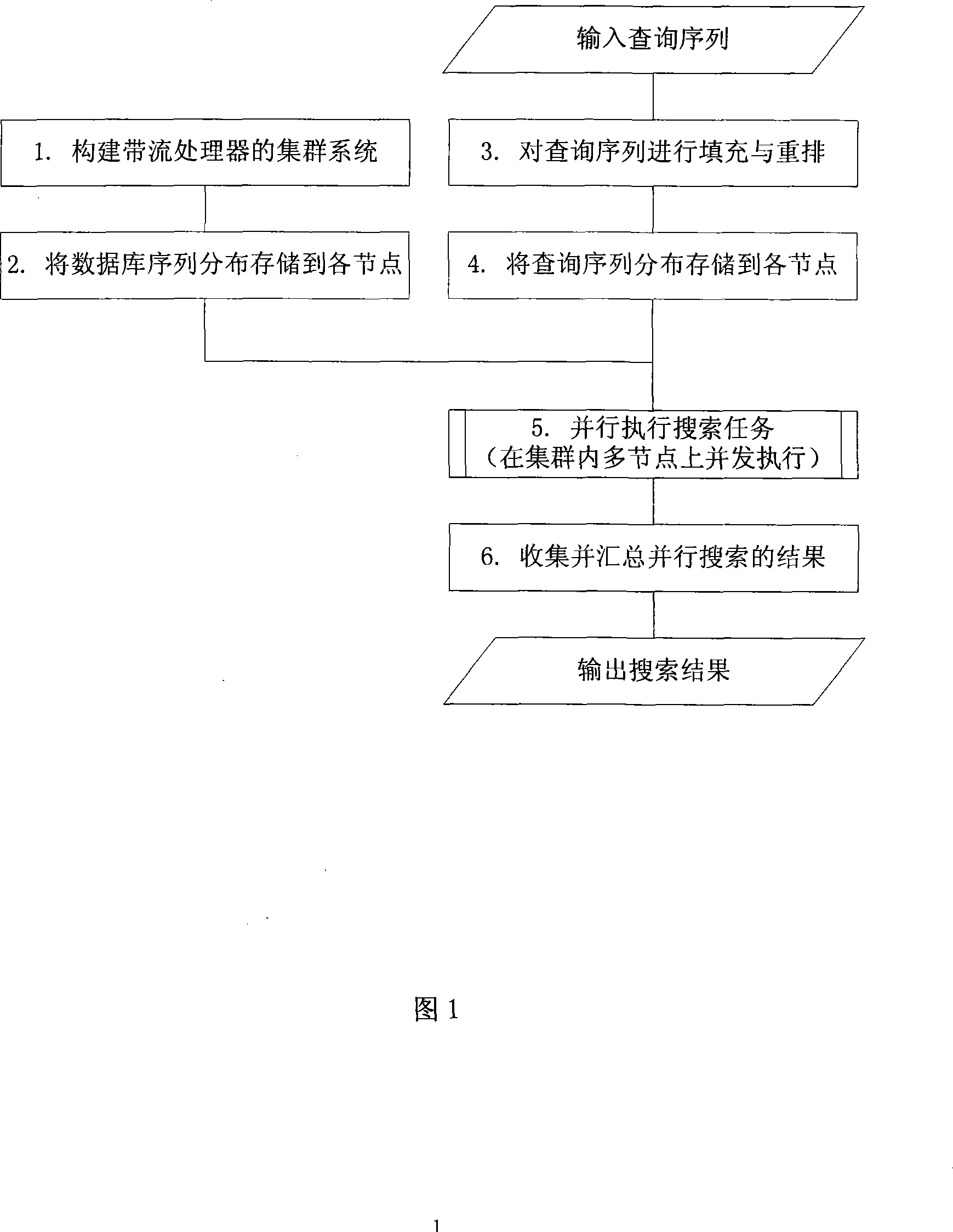
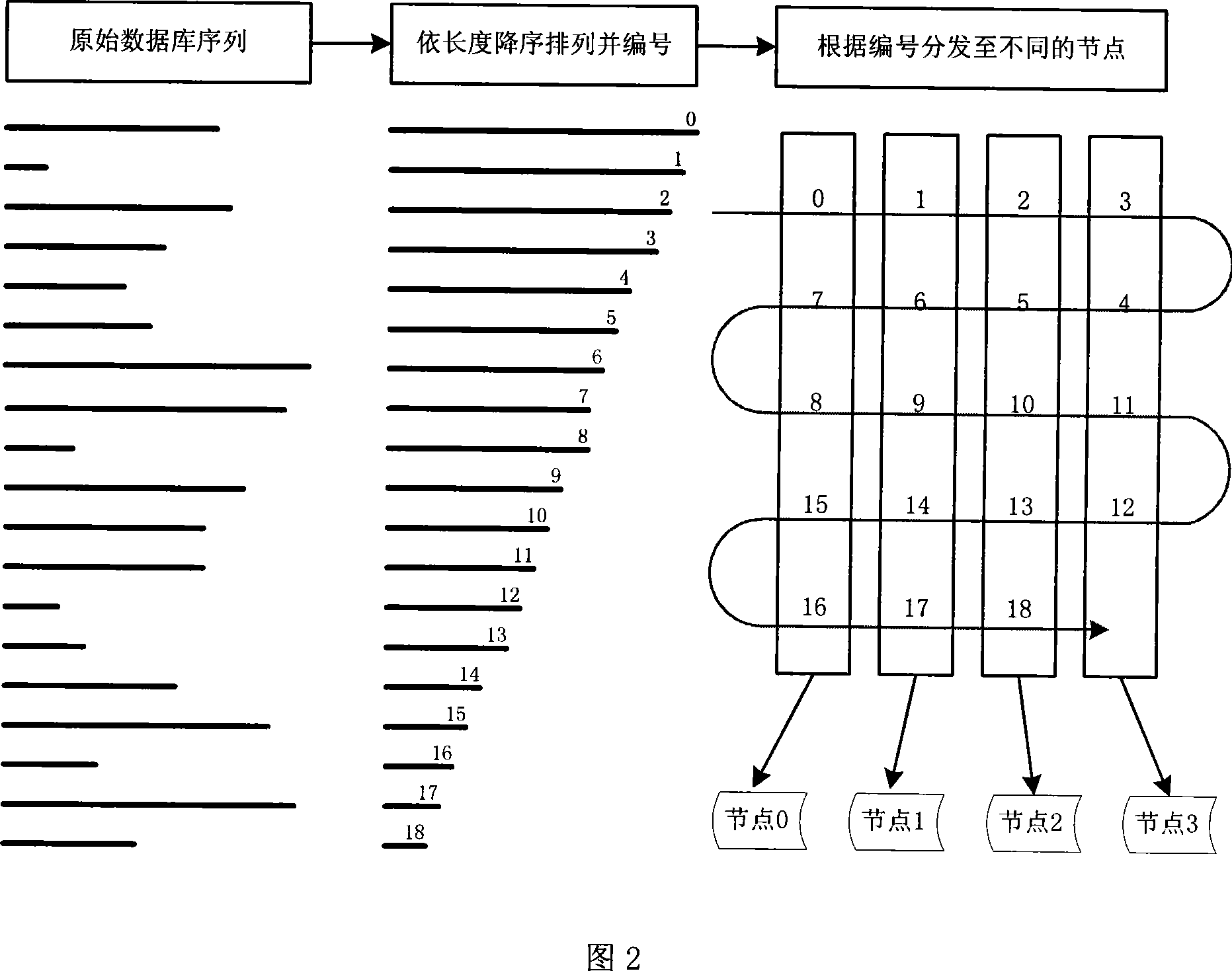
InactiveCN101158952AImprove search speedIncrease computing speedSpecial data processing applicationsCluster systemsSequence database
The invention discloses a multi-level acceleration method of flow-based biological sequence database search, which is to accelerate the search speed of a biological sequence database on the premise of ensuring search accuracy and relatively low cost. The technical proposal is that a cluster system composed of a plurality of personal computers shall be created firstly, and a master control node machine is assigned; the master control node machine distributes the database sequence and stores into each node machine in the cluster system, so as to fill and rearrange an inquiry sequence, and distribute the inquiry sequence to all the node machines in the cluster system; each node machine executes the search task in parallel, so as to be responsible for the completion of search tasks of the inquiry sequence in a local database sequence; the master control node machine collects, summarizes and outputs the results of parallel search tasks on all the node machines. The invention makes the search tasks be executed in parallel between the n node machines of the cluster, each node machine distributes the comparative calculation task of two sequences to p hardware calculation clusters to be conducted in parallel, thereby realizing the multi-level acceleration objective in parallel of three layers including a cluster node layer, a flow-level calculation layer, as well as a flow inner core command layer.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and apparatus for identifying, classifying, or quantifying DNA sequences in a sample without sequencing
InactiveUS20010007985A1Sufficient discriminationSolve the lack of resolutionData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSequence databaseDNA Sequence Databases
This invention provides methods by which biologically derived DNA sequences in a mixed sample or in an arrayed single sequence clone can be determined and classified without sequencing. The methods make use of information on the presence of carefully chosen target subsequences, typically of length from 4 to 8 base pairs, and preferably the length between target subsequences in a sample DNA sequence together with DNA sequence databases containing lists of sequences likely to be present in the sample to determine a sample sequence. The preferred method uses restriction endonucleases to recognize target subsequences and cut the sample sequence. Then carefully chosen recognition moieties are ligated to the cut fragments, the fragments amplified, and the experimental observation made. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the preferred method of amplification. Another embodiment of the invention uses information on the presence or absence of carefully chosen target subsequences in a single sequence clone together with DNA sequence databases to determine the clone sequence. Computer implemented methods are provided to analyze the experimental results and to determine the sample sequences in question and to carefully choose target subsequences in order that experiments yield a maximum amount of information.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
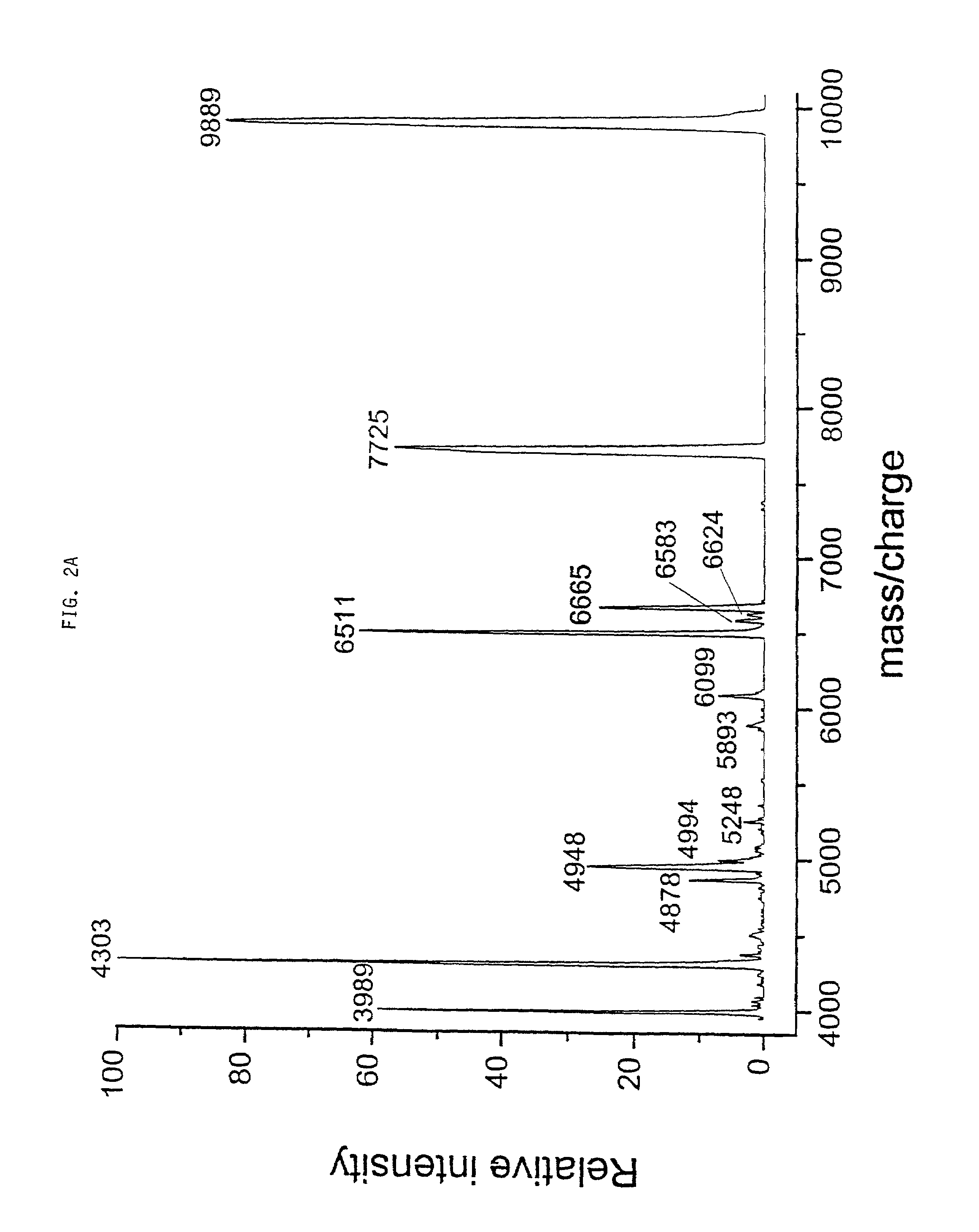
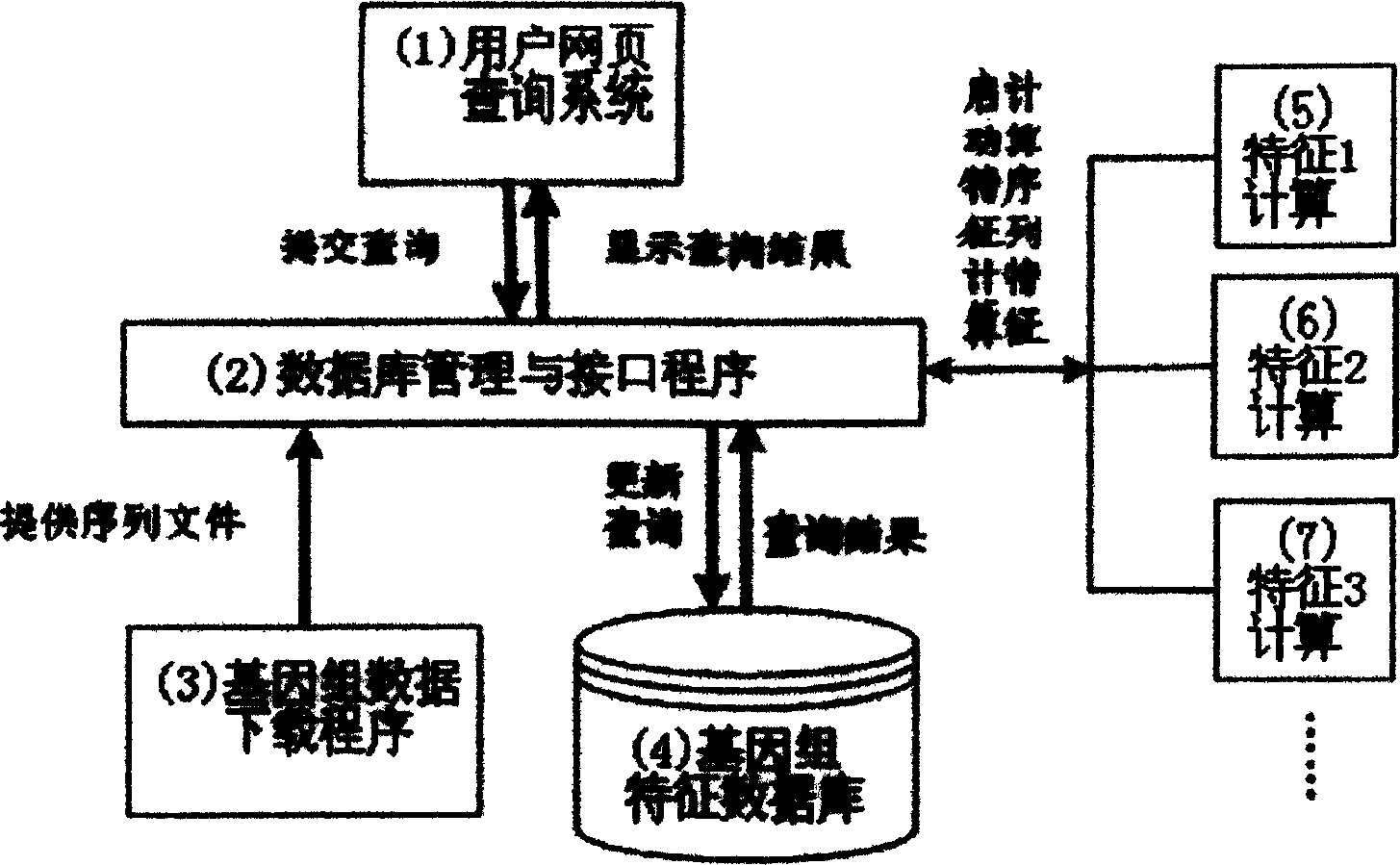
Methods for identifying and classifying organisms by mass spectrometry and database searching
InactiveUS7020559B1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence databaseProtein molecules
A method for rapid identification of biological materials is presented, which exploits the wealth of information contained in genome and protein sequence databases (5). In a preferred embodiment, the method utilizes the masses of a set of ions by MALDI TOF mass spectrometry of intact or treated cells (1). Subsequent correlation (4) of each ion in the set to a protein, along with the organismic source of the protein, is performed by searching a database comprising protein molecular weights (9).
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +1
Establishment method of gene library of fecal flora based on high-throughput gene sequencing
InactiveCN105937053AFast database buildingImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSequence databaseGenomic library
An establishment method of a gene library of fecal flora based on high-throughput gene sequencing employs a ''nested PCR'' method for enrichment amplification on 16S rDNA, so as to reduce the host and food residue genome pollution by the maximum; and V3 and V6 are combined for specific amplification and massive parallel sequencing, so as to obtain the a target gene sequence database of the flora. The library can increase the identification of the bacterial flora from Genus level to Species level. The method can maximally avoid the interference of host cell nucleic acid, and completely and efficiently detect 16SrDNA tag sequence of all bacteria varieties, so as to accurately determine the ecological structure of the intestinal flora.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SAGENE BIOTECH
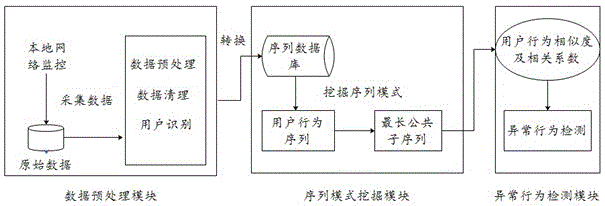
Detection method for abnormal behaviors based on user access sequence
ActiveCN106657410AEfficient extractionThe analysis result is accurateData switching networksPattern recognitionCorrelation coefficient
The invention discloses a detection method for abnormal behaviors based on a user access sequence. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1) capturing data from a local network, preprocessing the data, and performing serializing treatment on the acquired data; 2) storing a sequence formed in the step 1 into a sequence database, and generating a behavior sequence of each user on the basis of time; and 3) calculating the behavior similarity and the correlation coefficient between users according to the behavior sequence of each user, comparing the correlation coefficient for detecting the abnormal behaviors, and searching for the abnormal behaviors of the user. According to the method, on the basis of sequence pattern excavation, factors, such as, time and user behavior characteristics, are fully considered, an improved more accurate user behavior similarity algorithm is utilized to calculate, and the sequence rule of the user access is effectively extracted, so that an analysis result is more accurate and the defects of other analysis methods are overcome. Besides, on the basis of the user behavior similarity algorithm, the method has obvious advantages in noise interference, the used resources are few, and the running efficiency is high.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Rapid efficacy assessment method for lung cancer therapy
InactiveUS20070048750A1Rapid efficacy assessmentHigh correlationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence databaseEfficacy
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Network water army behavior detection method and system based on mixed Dirichlet process
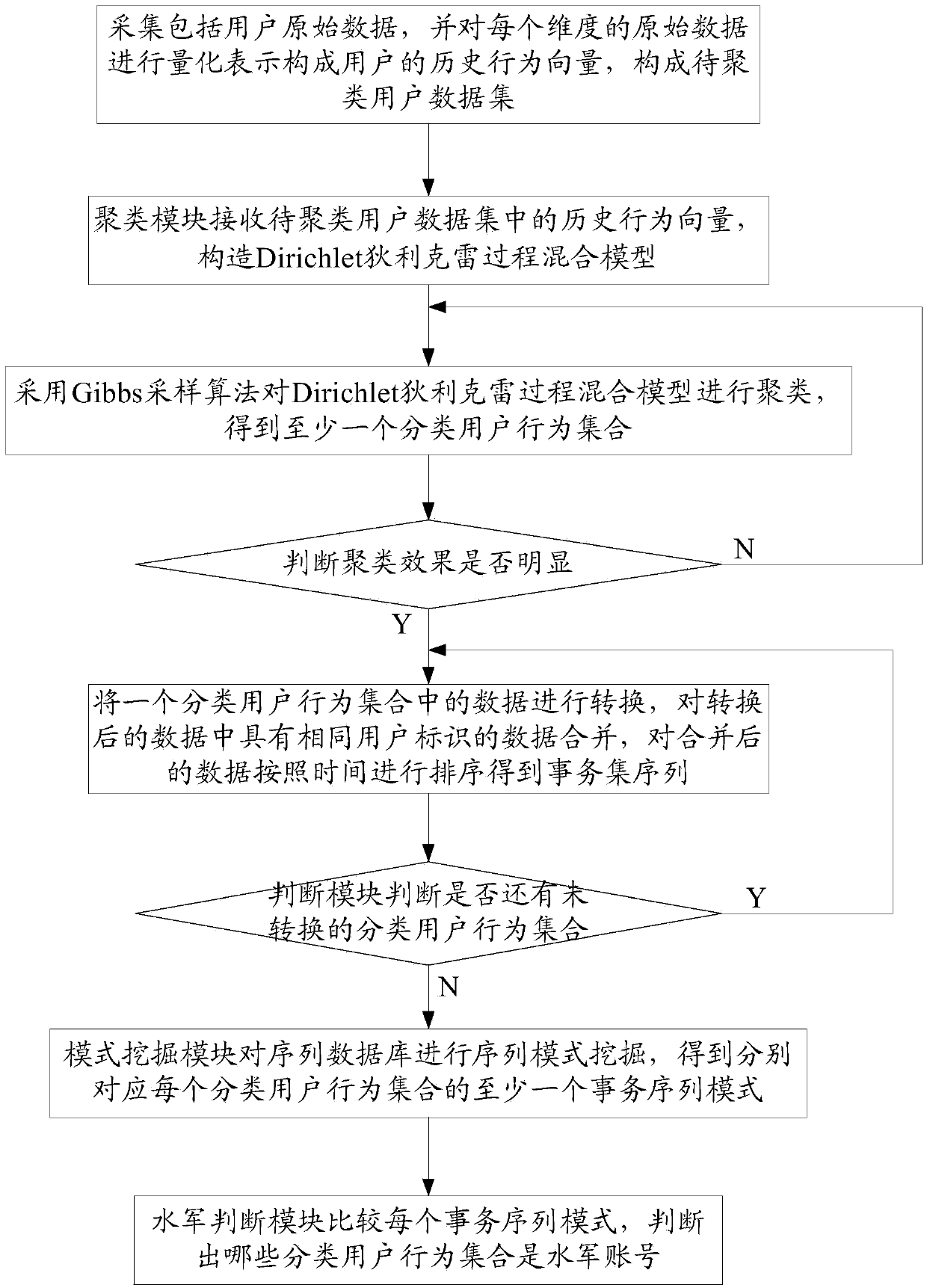
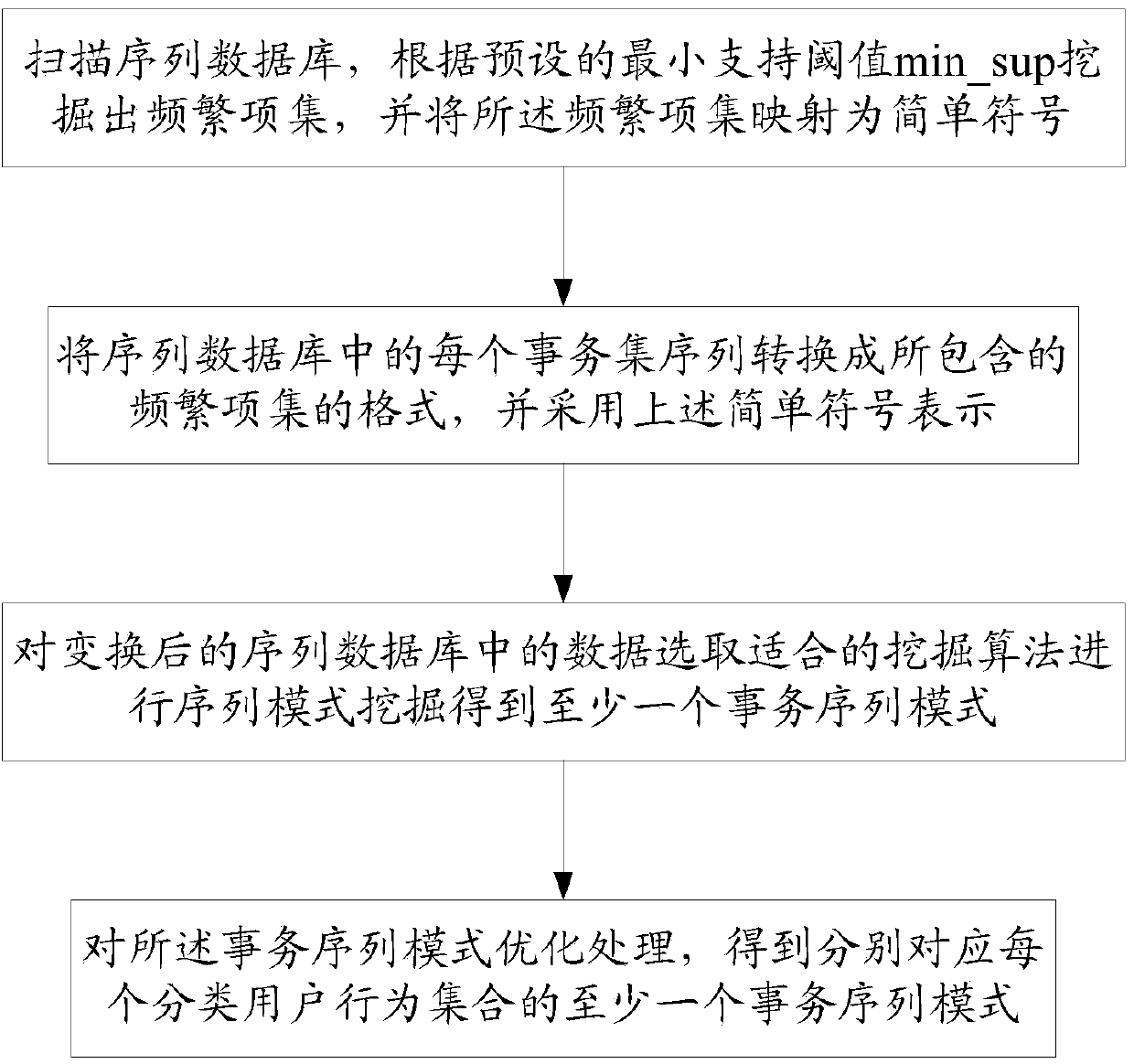
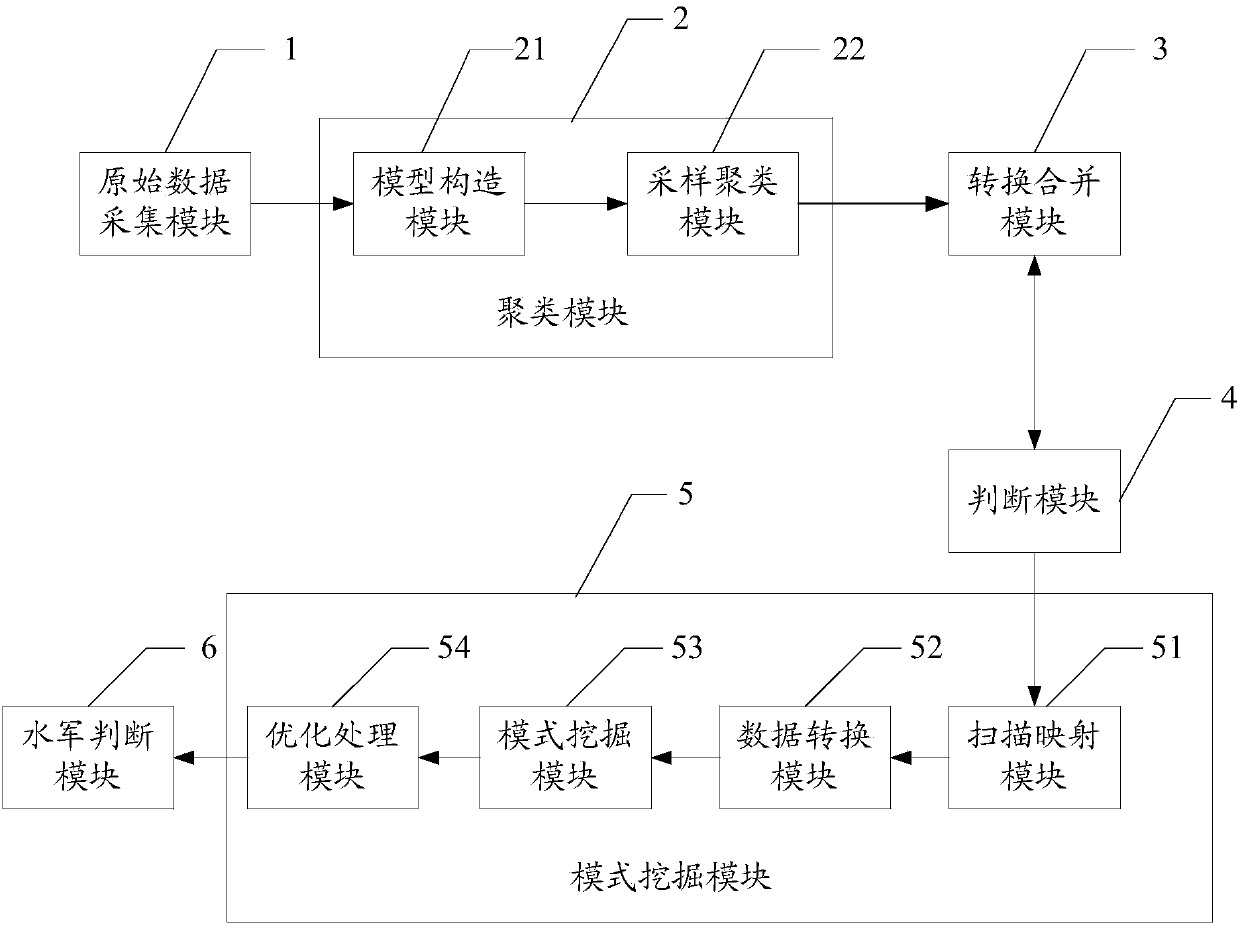
ActiveCN103812872ARealize identificationThe analysis result is accurateTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionData set
The invention relates to a network water army behavior detection method and a network water army behavior detection system based on a mixed Dirichlet process. The network water army behavior detection method includes: collecting original data comprising user behavior features and content features, performing quantization representation on the original data of each dimensionality so as to form history behavior vectors of a user, and forming a user data set to be clustered; clustering the history behavior vectors in the user data set to be clustered so as to obtain at least one classification user behavior set; converting data in the at least one classification user behavior set, and merging data with the same user identification in the data after being converted so as to obtain a sequence database; performing sequence pattern excavation on the sequence database through a pattern excavation module so as to obtain at least one affair sequence pattern corresponding to each classification user behavior set; judging out the classification user behavior set which is a water army username by comparing each affair sequence pattern through a water army judging module. The network water army behavior detection method and the network water army behavior detection system based on the mixed Dirichlet process can easily recognize which category belongs to the water army username.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Primer, method and kit for detecting animal clonorchiasis sinensis specificity
InactiveCN101586161AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence databaseUltraviolet lights
The present invention discloses a primer, a method and a kit for detecting the animal clonorchiasis sinensis specificity, a nucleotide sequence of an upstream primer of the primer is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, a nucleotide sequence of a downstream primer is represented by SEQ ID NO:2. the present invention implements an PCR amplification to a detectingformwork DNA by the primer, an amplifying outcome yield is processed by an agarose gel electrophoresis and observed under an ultraviolet light, if it is a positive result, there will be a specificity amplifying band, otherwise there will not be a band. According to an ITS zone sequence database OF THE animal clonorchiasis sinensis, the invention designs the primer, builds a rapid, special and sensitive PCR method, and it is capable of authenticating the animal clonorchiasis sinensis accurately. The operation of the kit of the invention is simple and programmable, the method specificity is strong, the sensibility is high, the result judgement is objective, and the invention is capable of being used for diagnosing the animal clonorchiasis sinensis and inquiring epidemiology.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Seaching method of genome sequence data based on characteristic
InactiveCN1598821AImprove search efficiencyImprove scalabilitySpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataSequence database
The invention relates to an approach of searching gene group sequence database based on characters. Approximate sequence is searched in database according to sequence statistic character. The search method is as follows: search approximate sequence according to distance of statistic character, namely, basic information of different species' sequence group serial data, including sequence's database login number, species name, chromosome number, original data, basic group composition character and base pair relativity character is memorized in database. For any a gene snippet submitted by client, its eigenvalue is computed according to client's request and distance between the eigenvalue and all corresponding eigenvalue in database is computed to compare approximate sequence; the most approximate sequence is arranged and displayed by distance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and apparatus for mRNA assembly
InactiveUS20050079504A1Eliminate the problemEasy to createMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence databaseNucleic acid sequencing
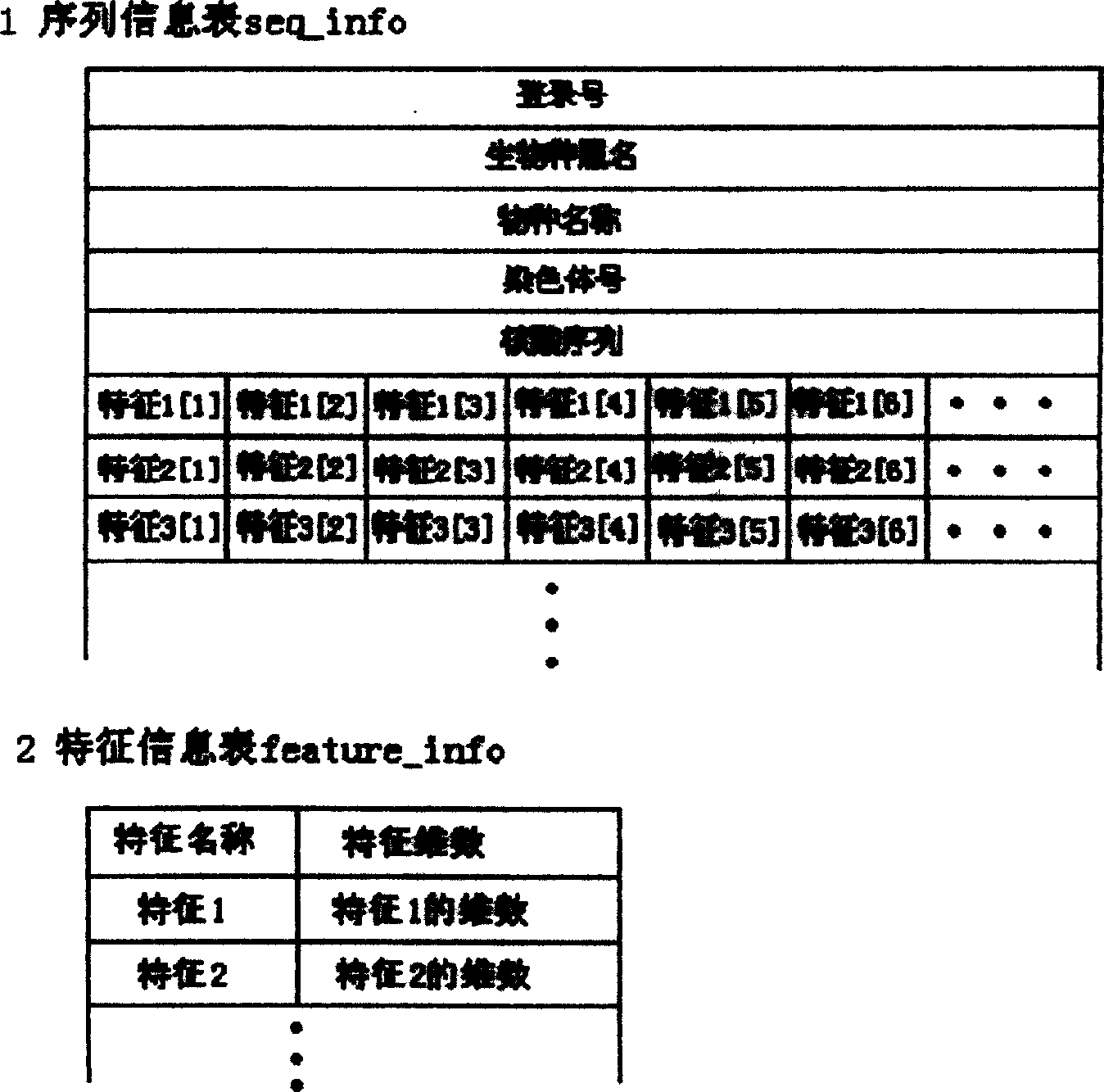
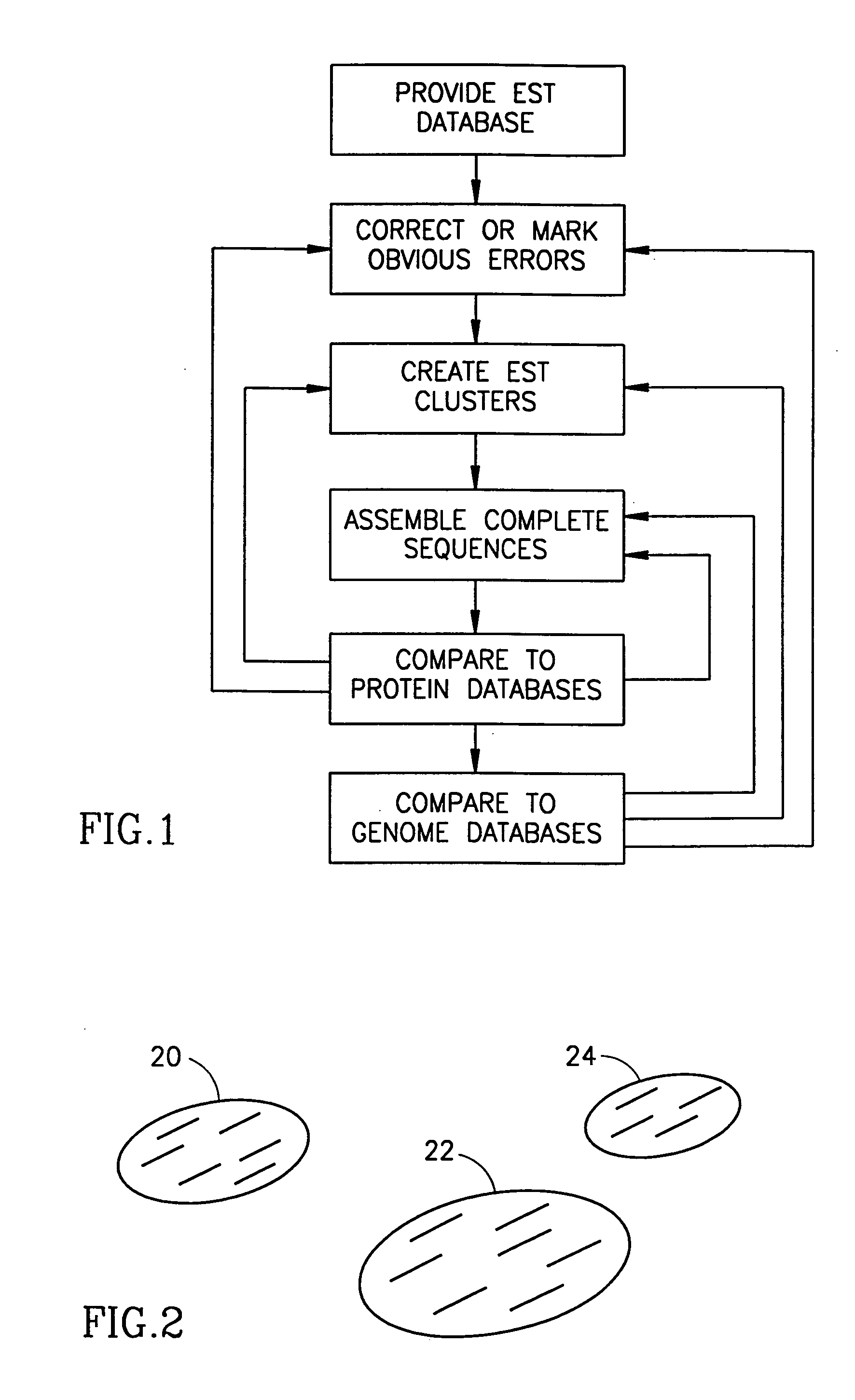
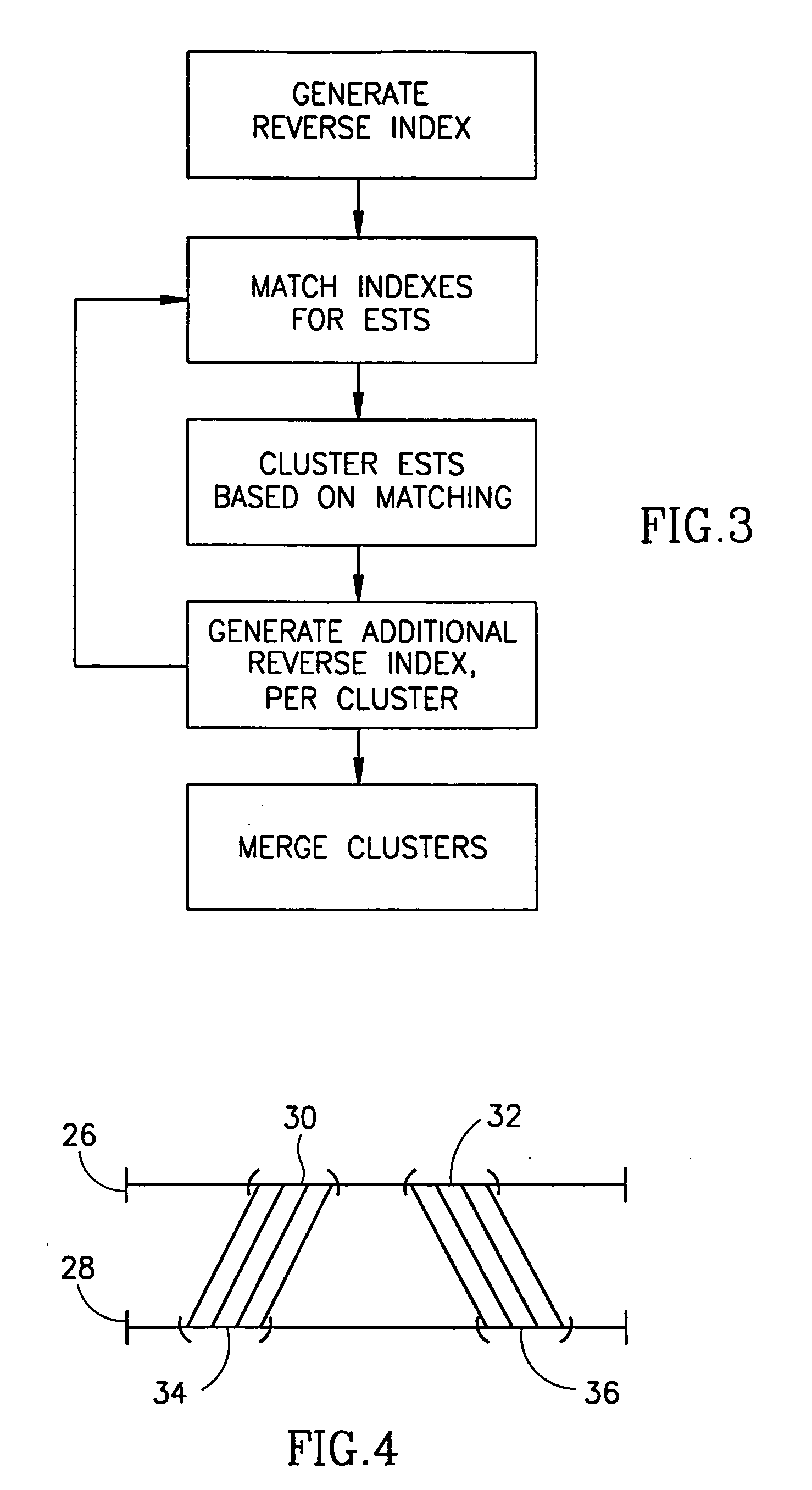
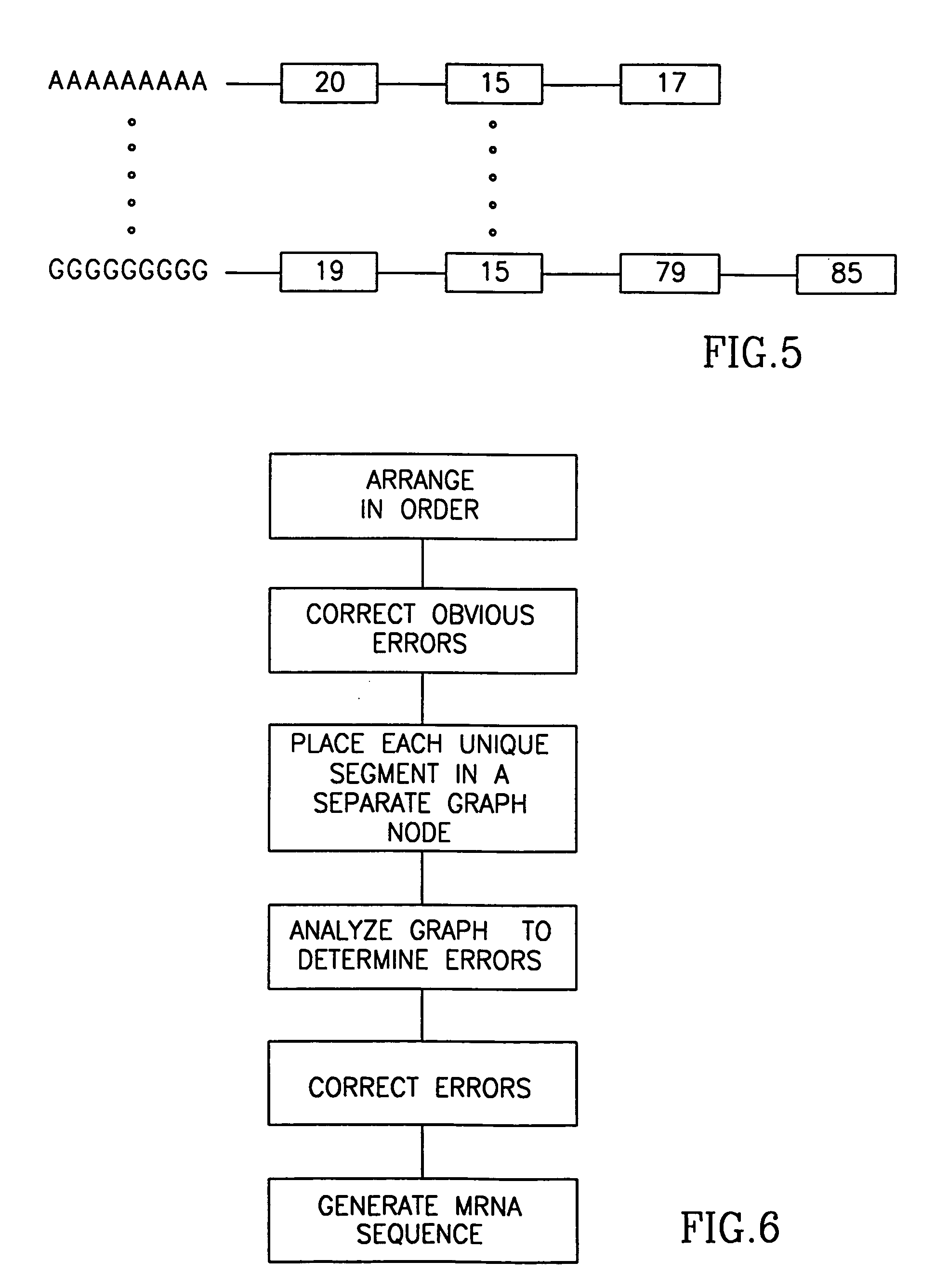
A method of comparing nucleic acid sequences being ESTs included in a first database of sequences and nucleic acid sequences included in a second database of sequences to form groups of sequences from the two databases that all relate to the same gene. For each one or more n-groups of sequences of one of the two databases, associating therewith lists of nucleic acid sequences, each from one of said two databases, each sequence on the list containing the n-groups, and matching sequences on the lists to generate said group.
Owner:COMPUGEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com