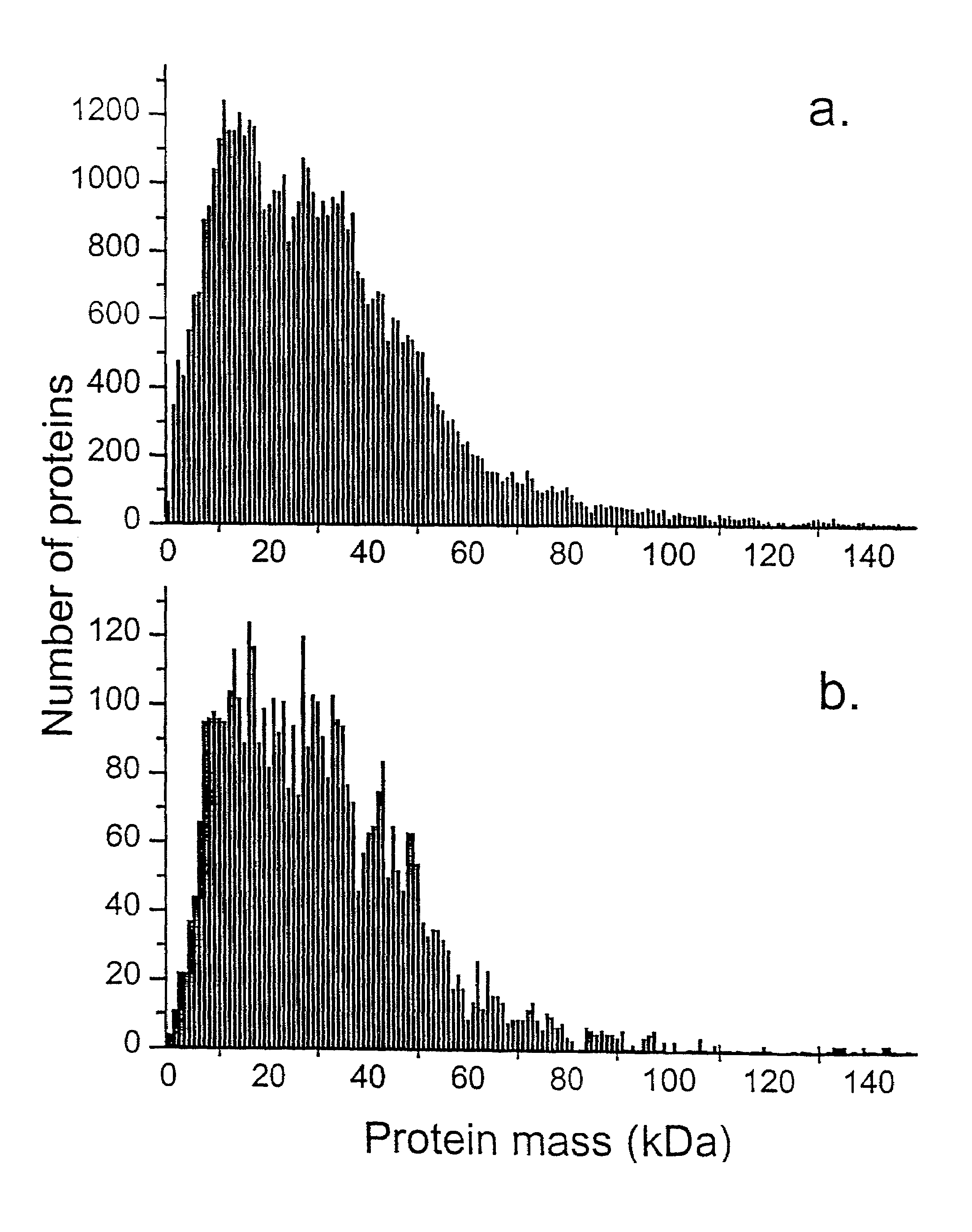
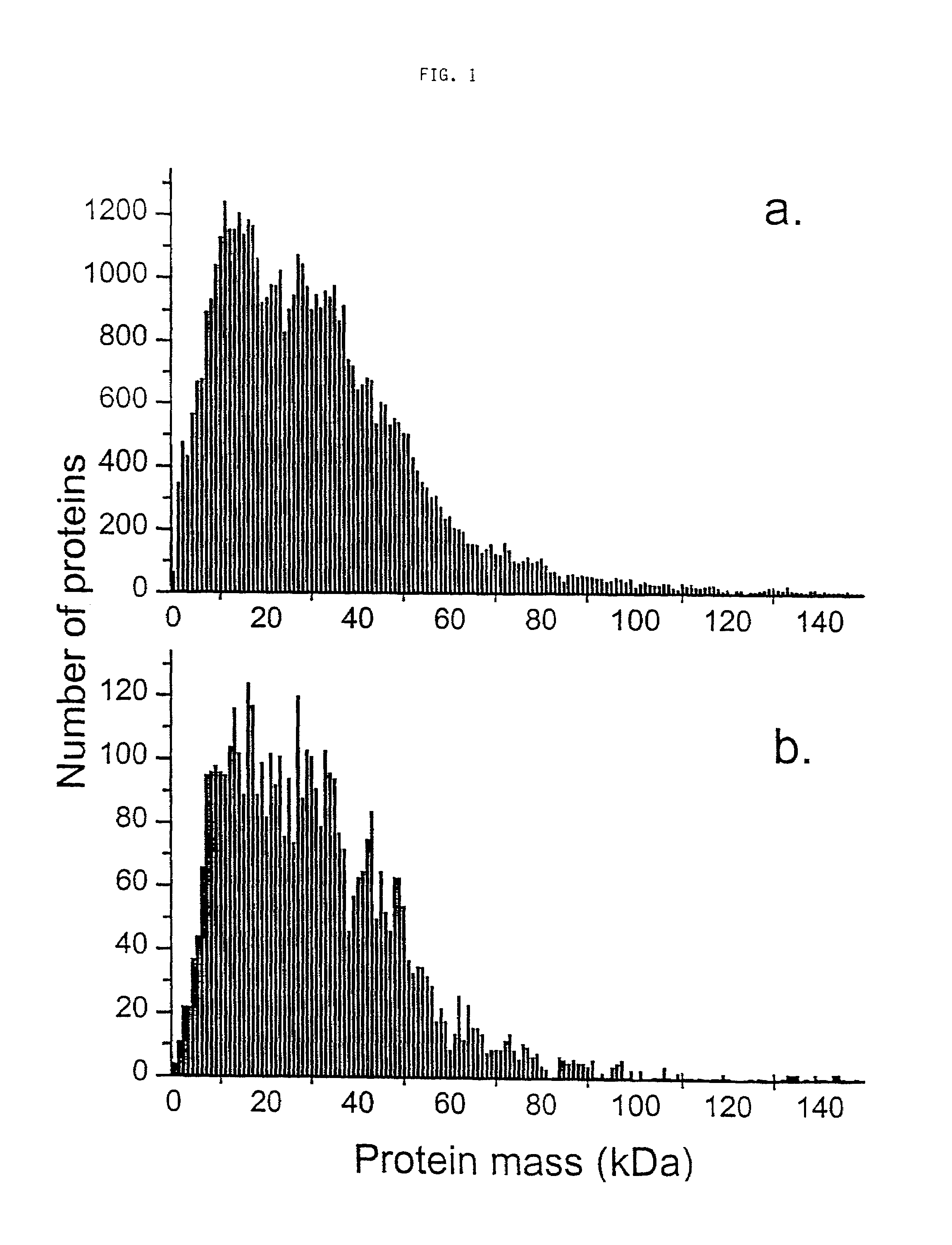
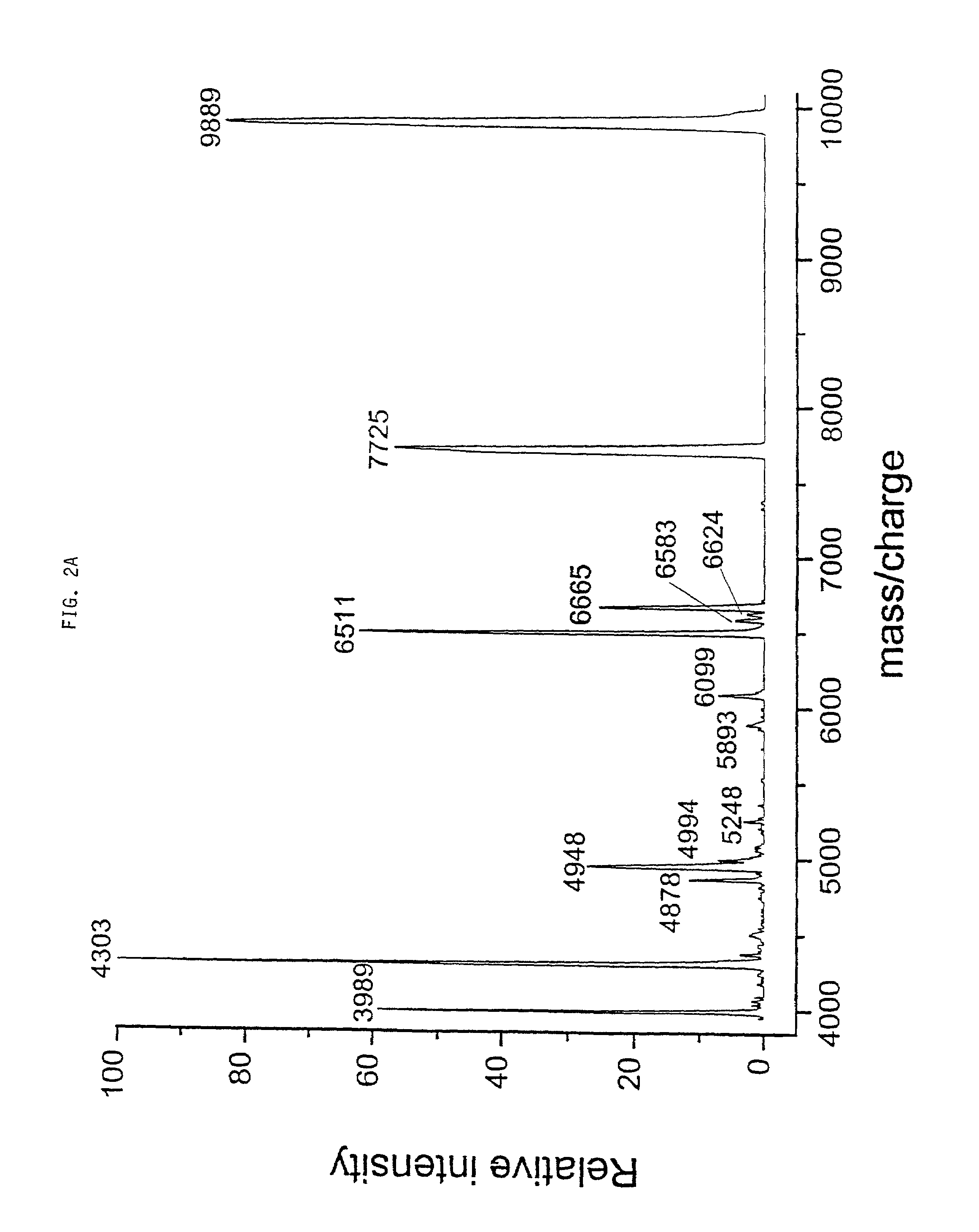
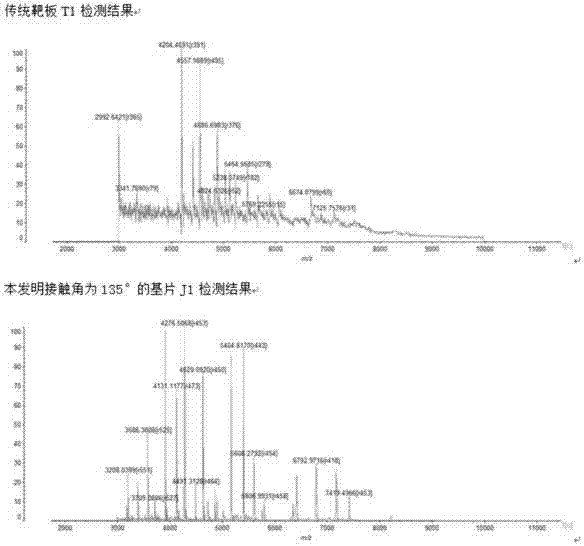
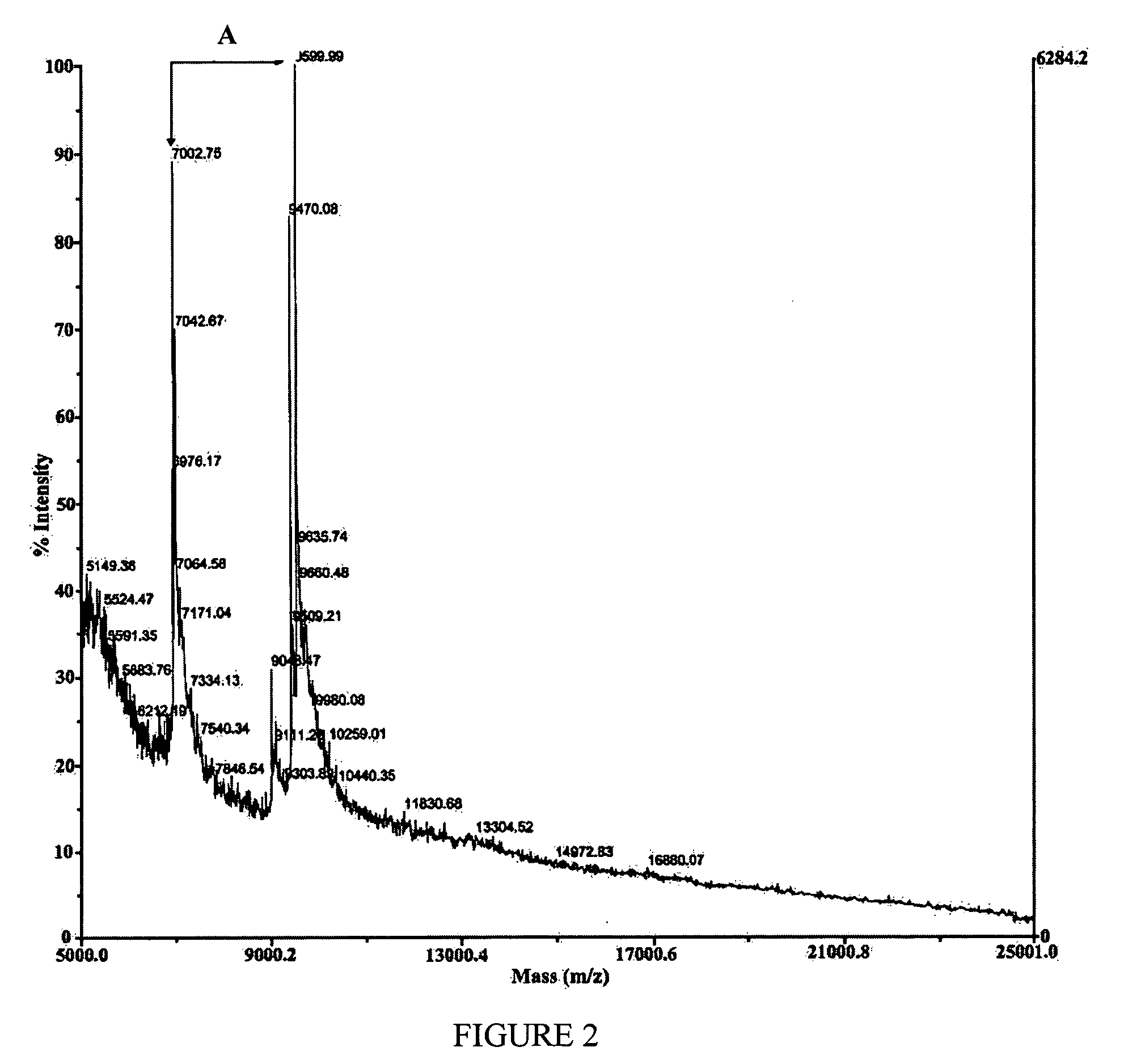
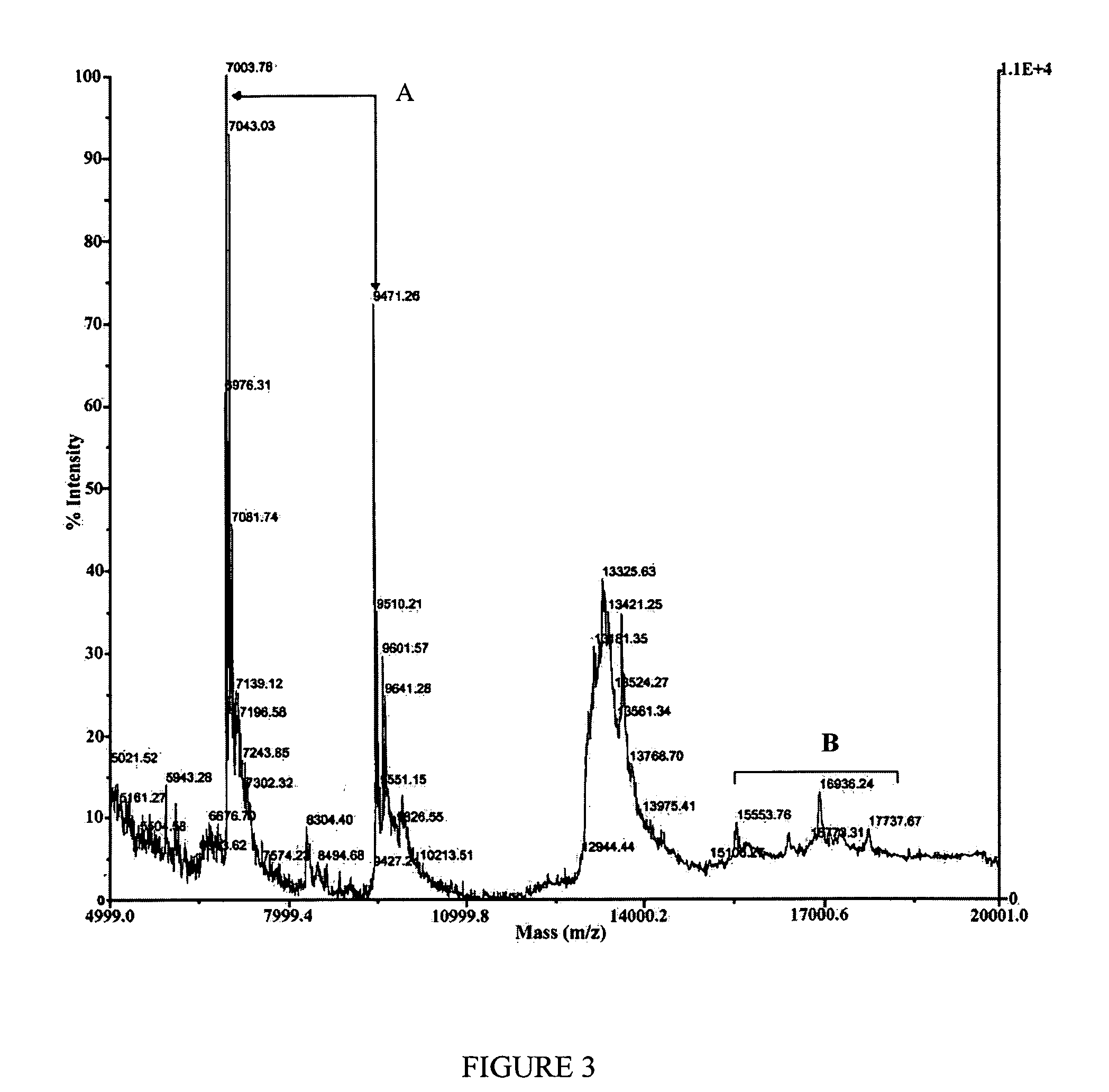
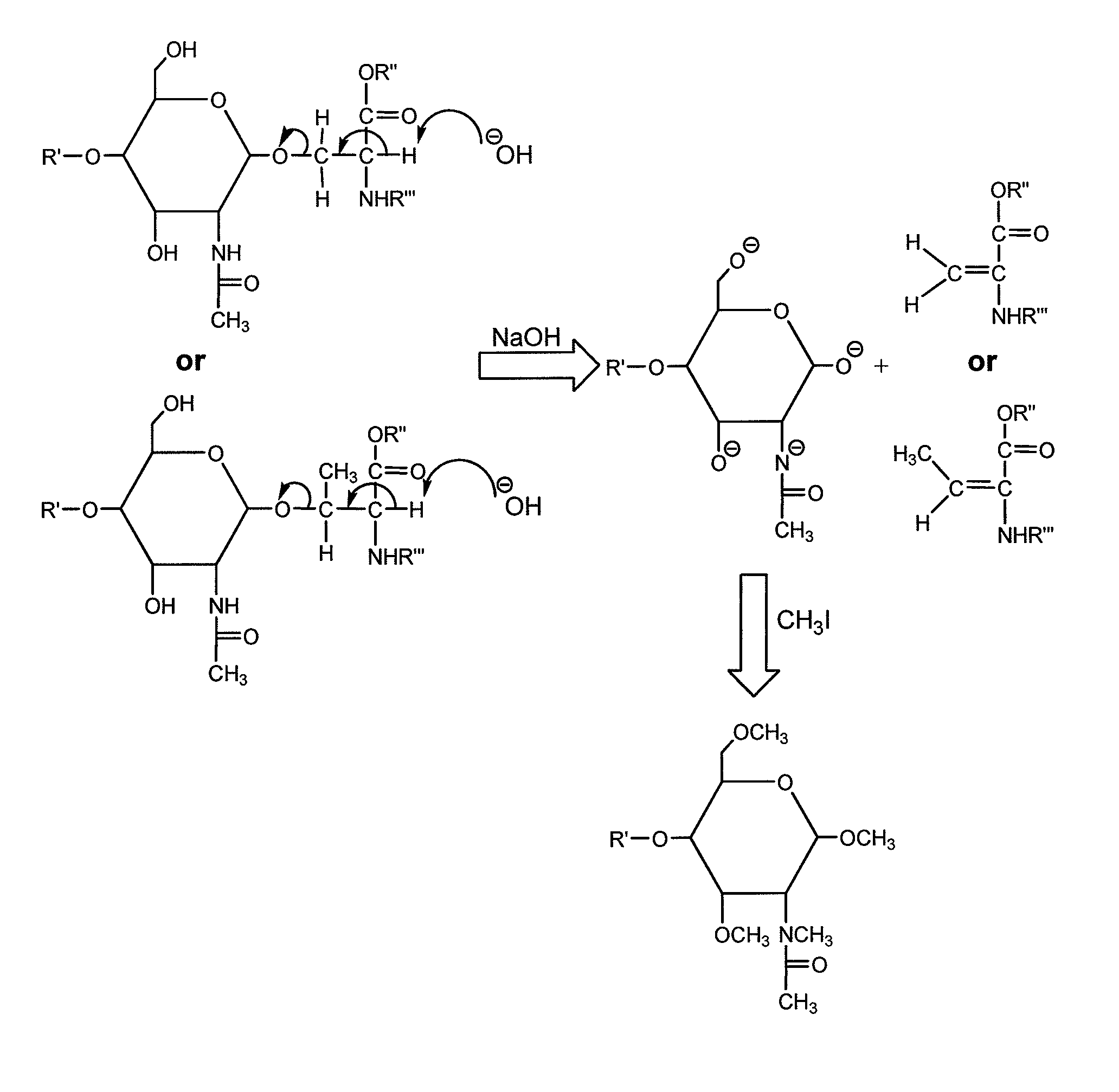
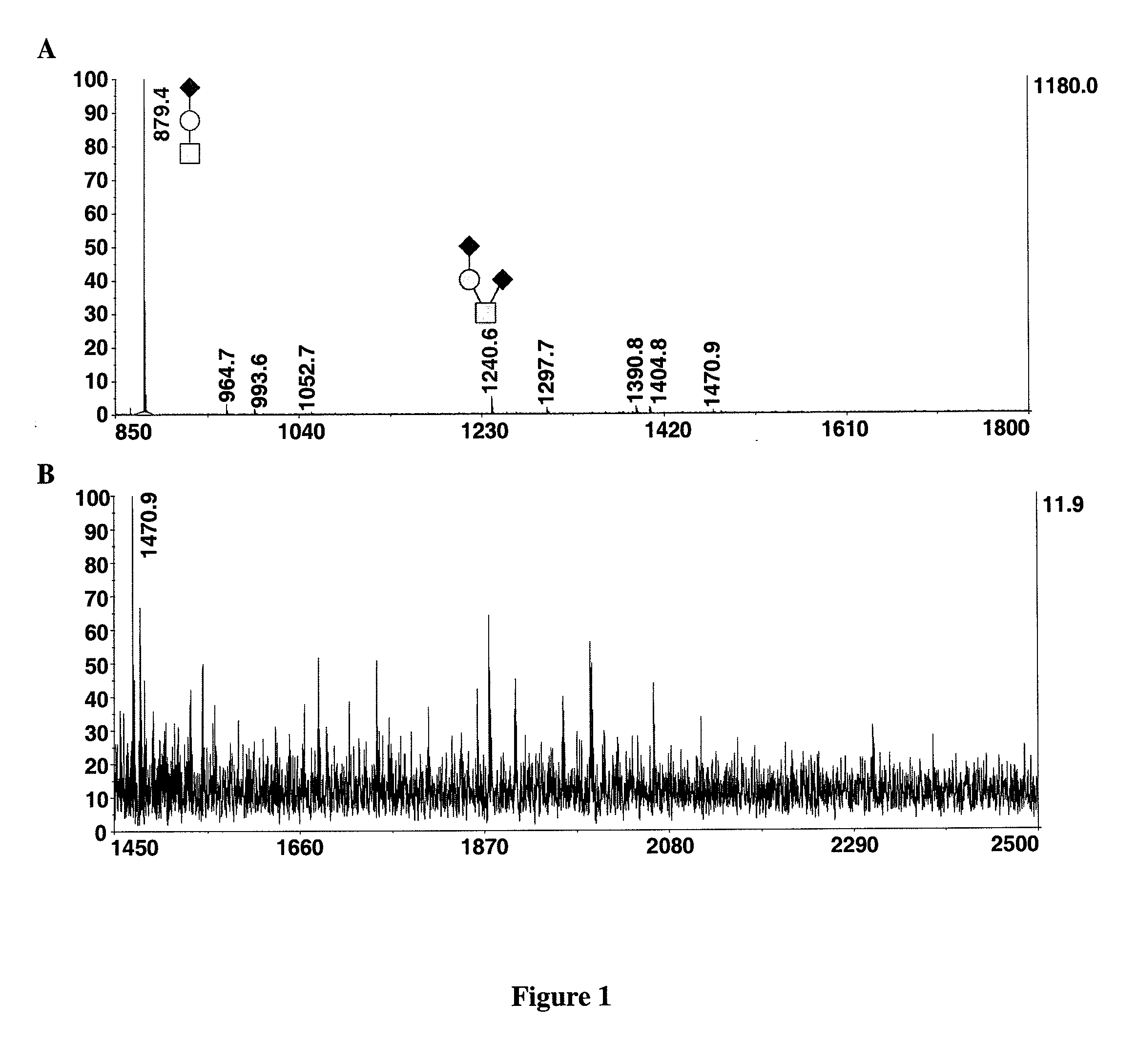
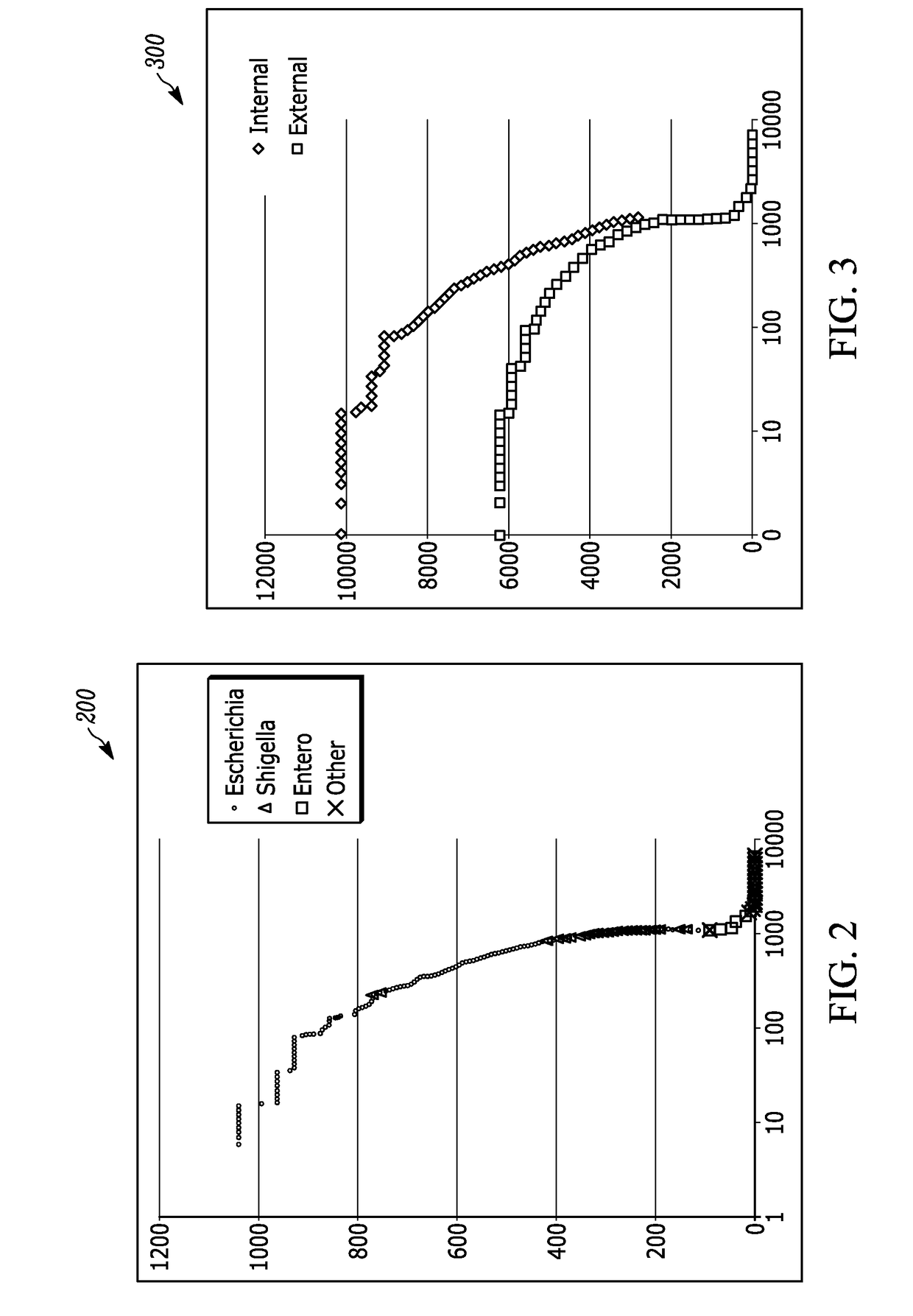
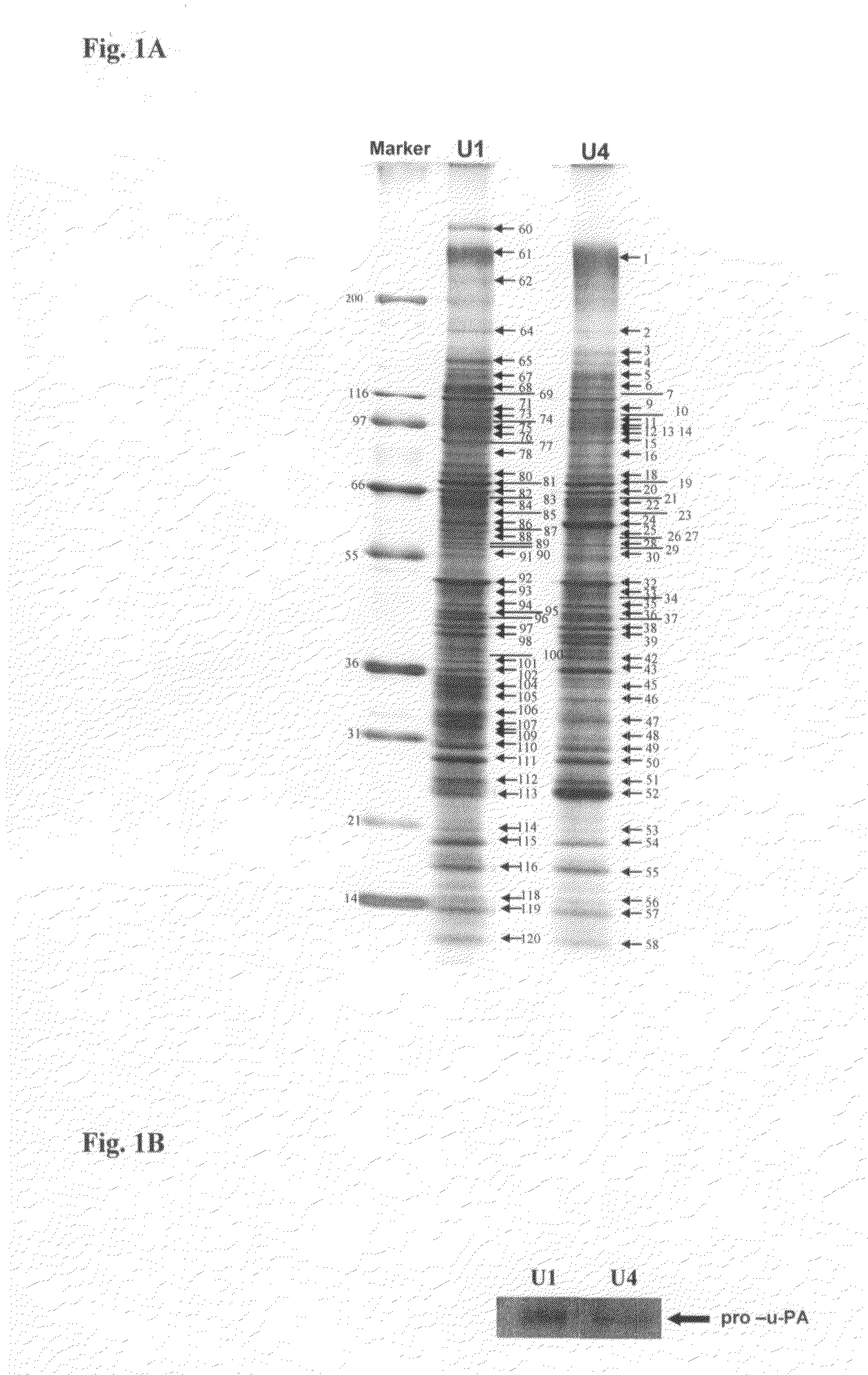Patents
Literature
33 results about "MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for interfacing separations techniques to MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060266941A1No significant loss in spatial resolution occursAccurate locationSamples introduction/extractionIsotope separationThin layerConductive materials
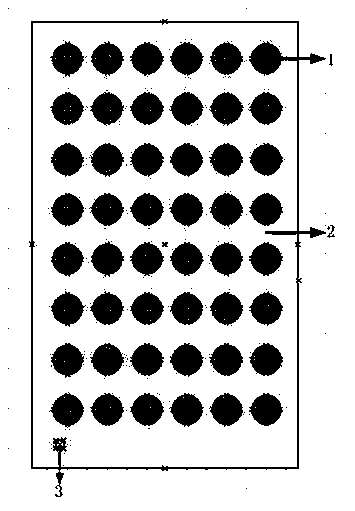
A sample plate for MALDI-TOF mass spectrography is provided which consists of a collimated hole structure intimately connected to a frame. The frame and at least one surface of the collimated hole structure are electrically conductive. The collimated hole structure may be formed from any material including glass, plastic, and metal and at least one surface may be rendered conductive by application of a thin layer of an electrically conductive material such as a metal, metal oxide, carbon, or organic or inorganic conductor or semi-conductor. The conductive surface is maintained in good electrical conduct with the conductive frame.
Owner:VIRGIN INSTR CORP
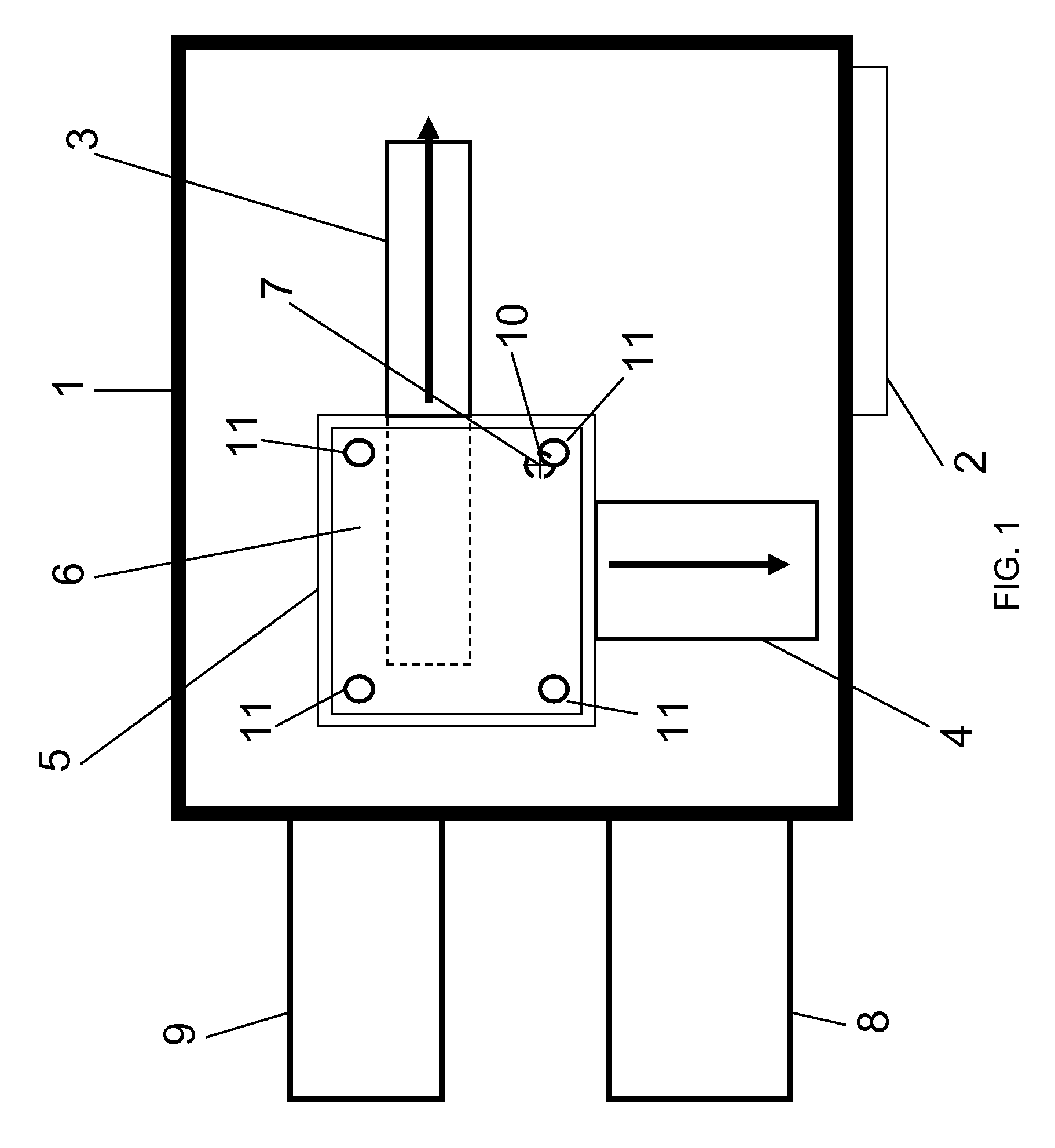
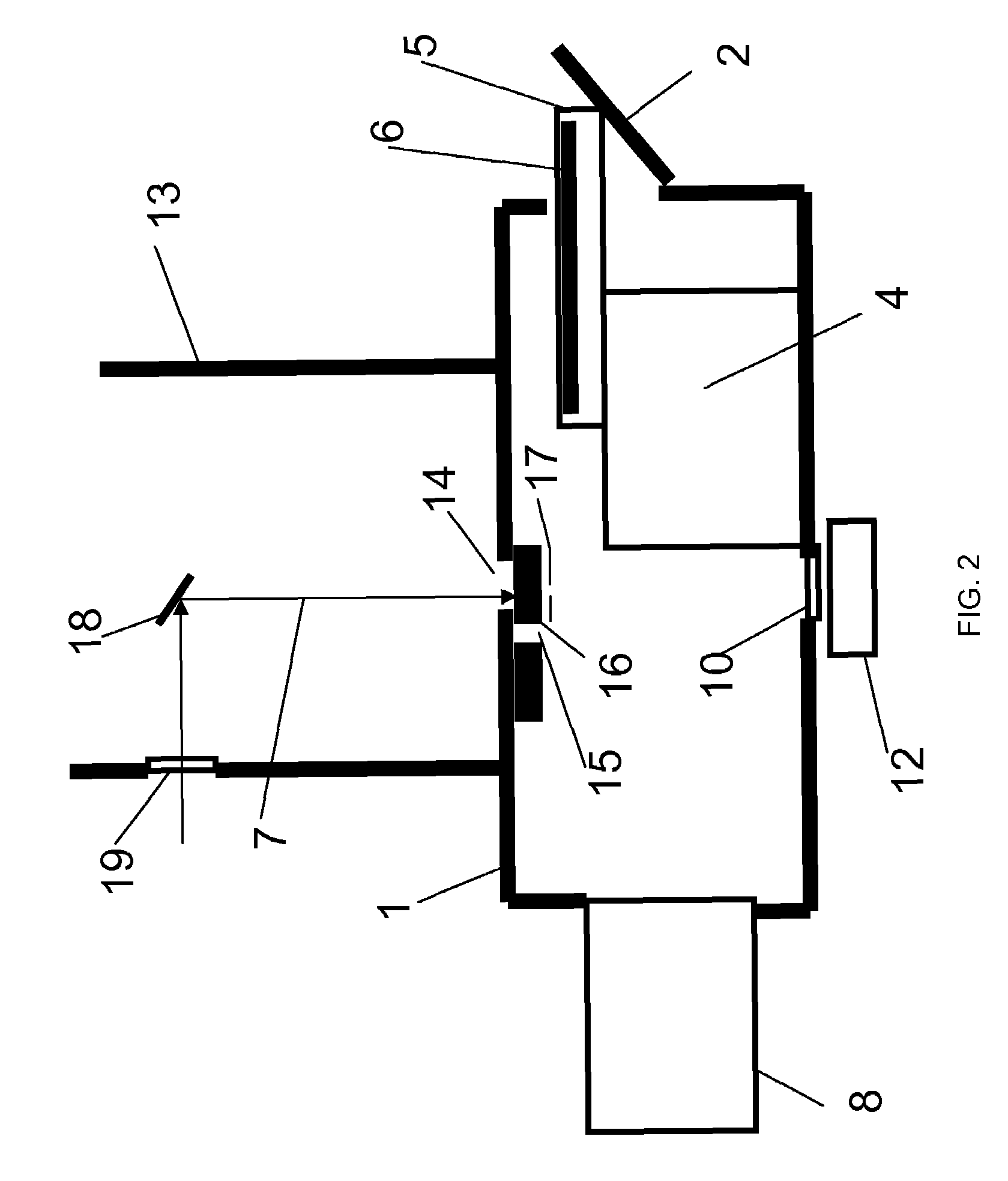
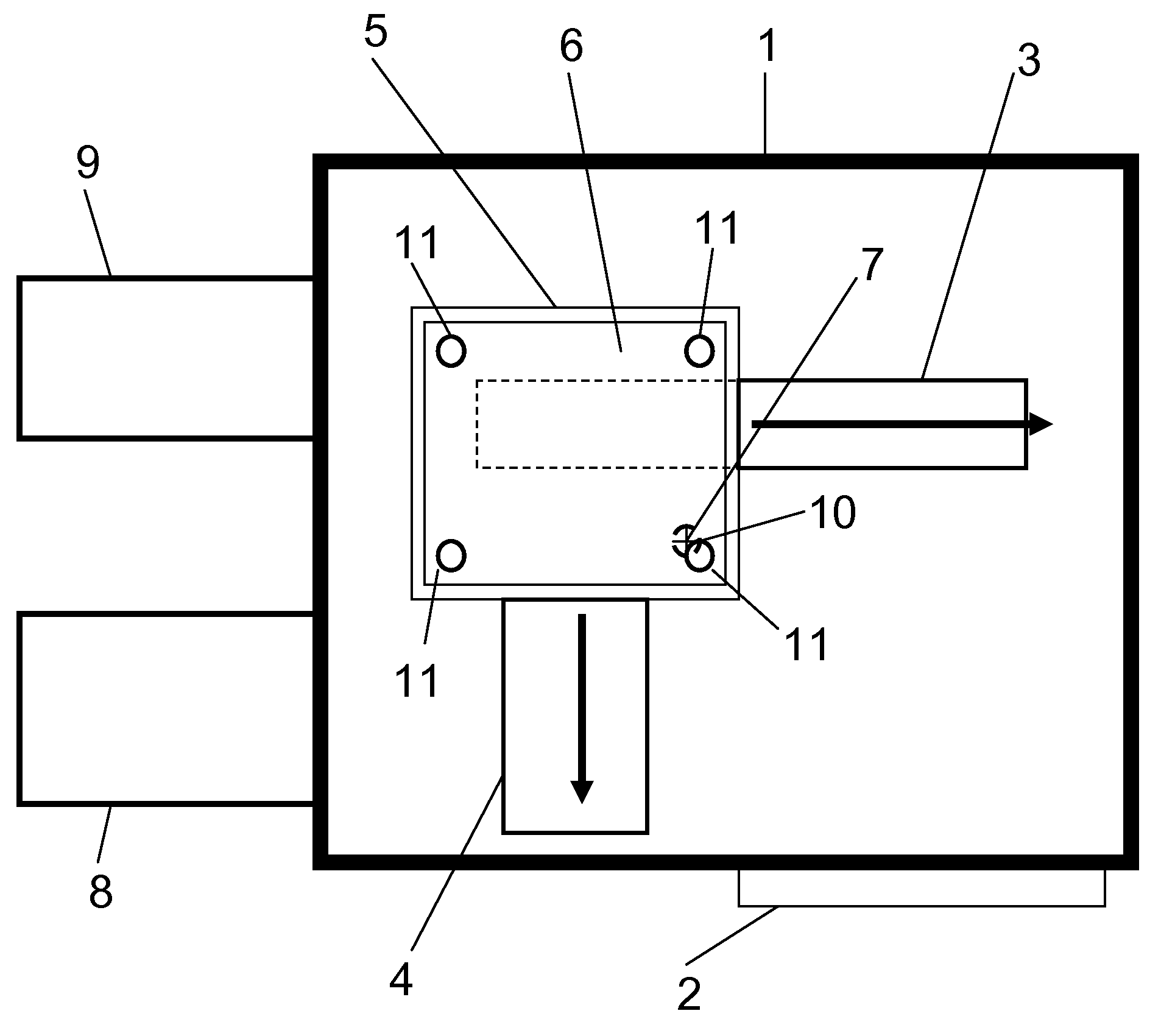
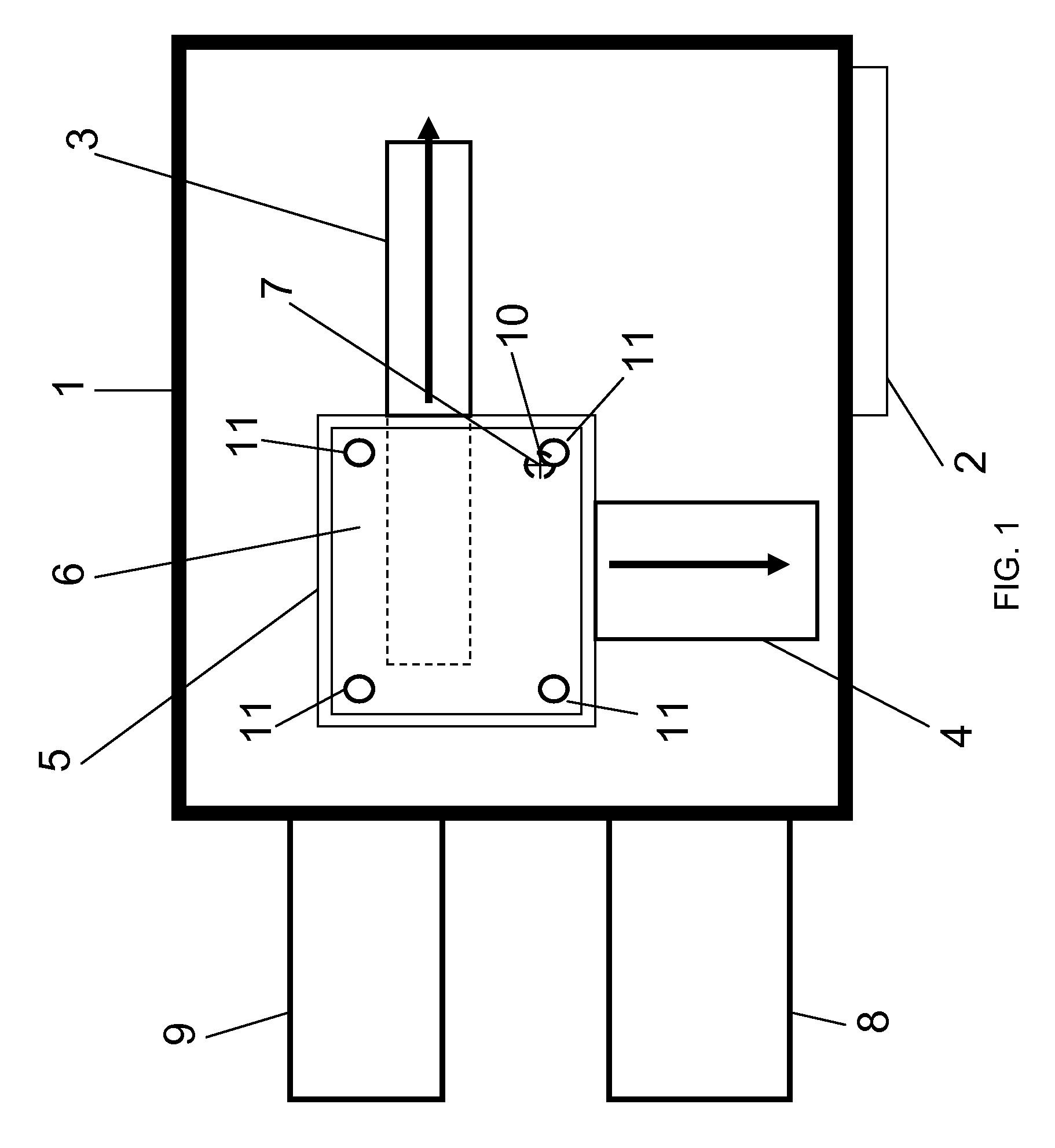
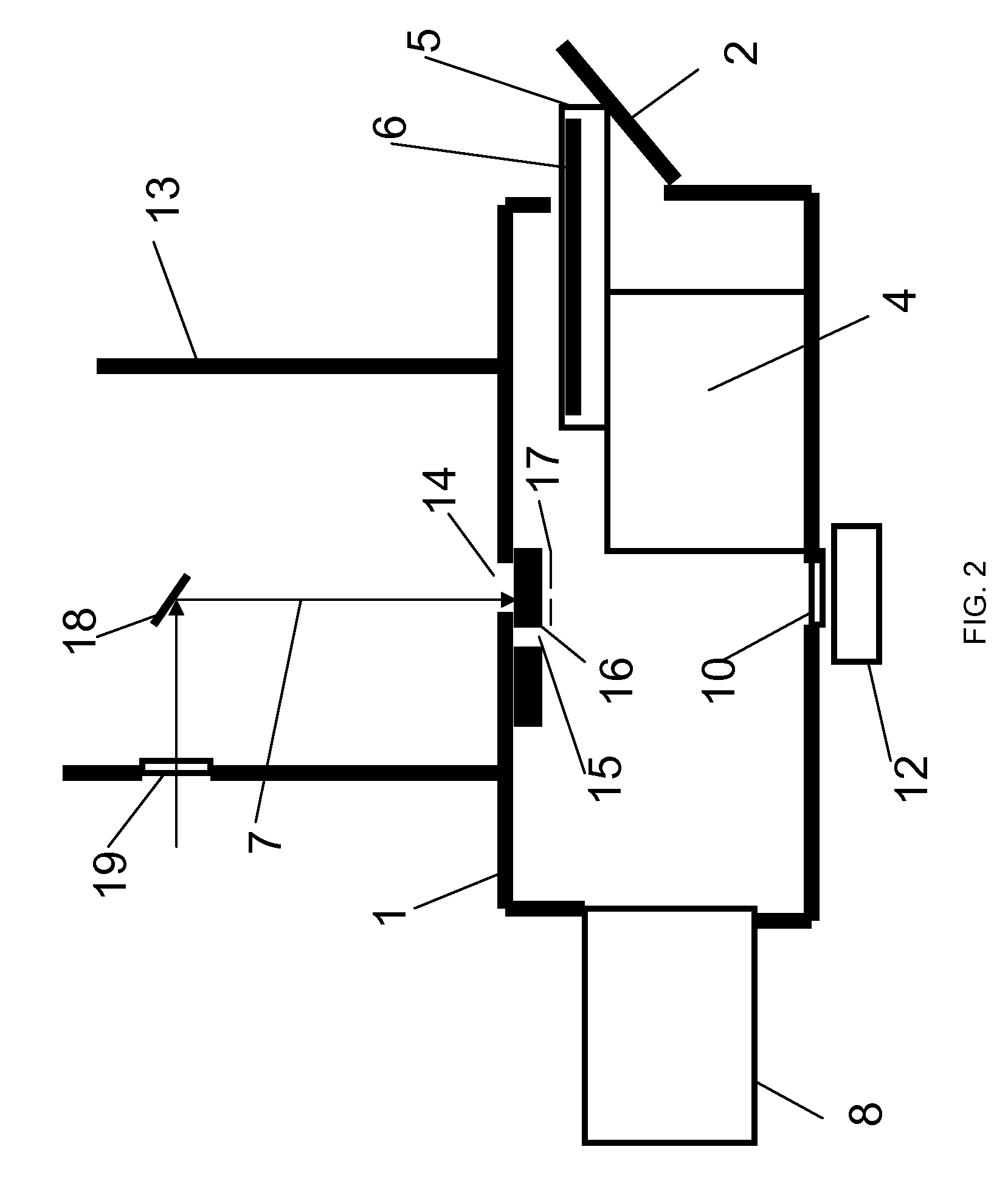
Vacuum housing system for MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7564028B2Improve performanceOvercome limitationsSamples introduction/extractionLighting and heating apparatusState of artMass analyzer
The present invention is directed to ion source and vacuum housings for use in MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry which operates with any type of mass analyzer including linear, reflector, or tandem TOF-TOF instruments. By removing the requirement for the vacuum lock, the present invention allows operation of the ion source vacuum chamber at a pressure at least two orders of magnitude higher than conventional instruments. The present invention also requires only a single valve that isolates the ion source vacuum housing from the TOF analyzer vacuum housing. This is a significant improvement over vacuum locks in the art where the valve opening must be sufficiently large to allow the sample plate to pass through.
Owner:VIRGIN INSTR CORP
Vacuum Housing System for MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
InactiveUS20080272286A1Overcome limitationsImprove performanceLighting and heating apparatusIon sources/gunsMass analyzerVacuum chamber
The present invention is directed to ion source and vacuum housings for use in MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry which operates with any type of mass analyzer including linear, reflector, or tandem TOF-TOF instruments. By removing the requirement for the vacuum lock, the present invention allows operation of the ion source vacuum chamber at a pressure at least two orders of magnitude higher than conventional instruments. The present invention also requires only a single valve that isolates the ion source vacuum housing from the TOF analyzer vacuum housing. This is a significant improvement over vacuum locks in the art where the valve opening must be sufficiently large to allow the sample plate to pass through.
Owner:VIRGIN INSTR CORP
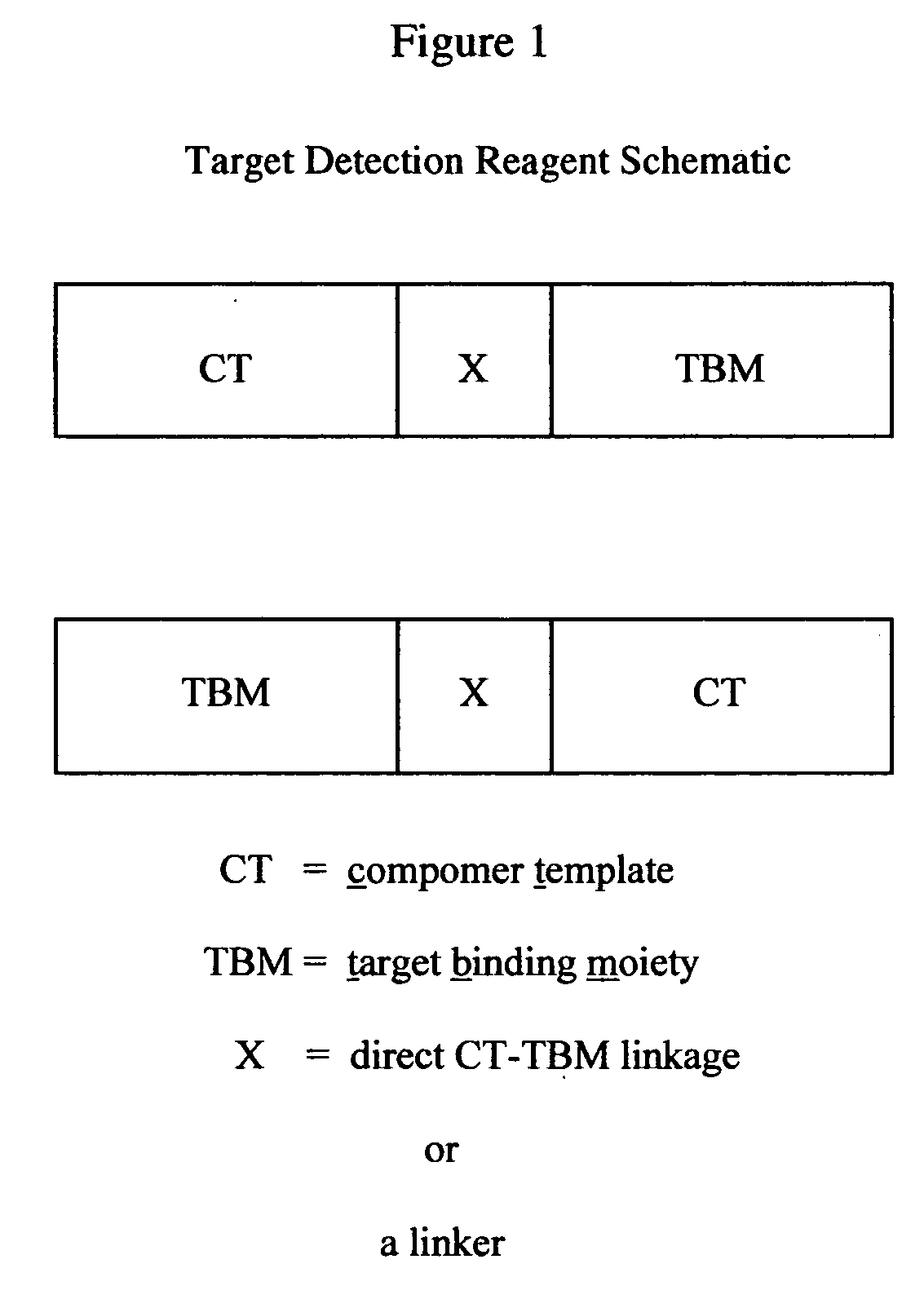
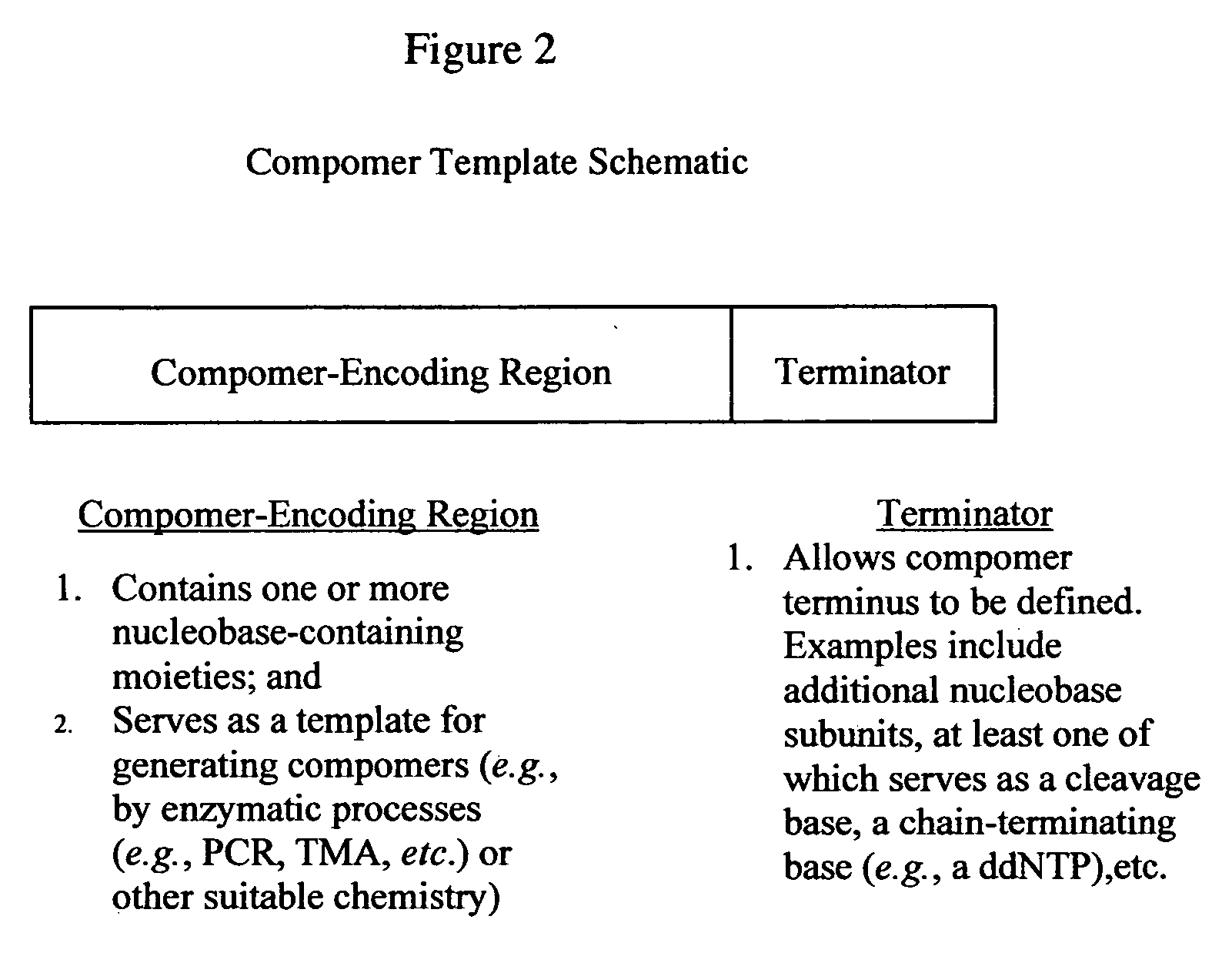
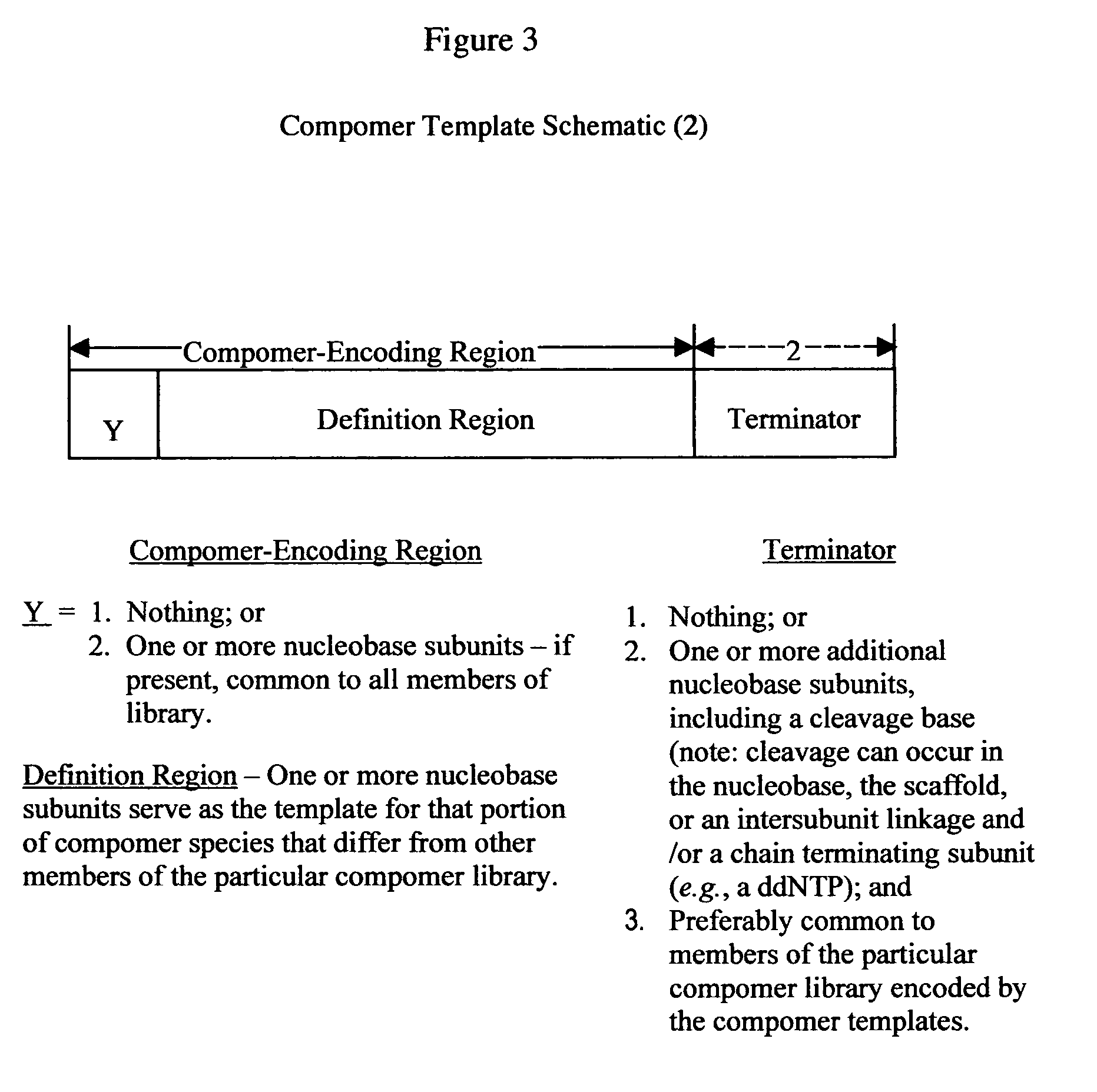
Target-specific compomers and methods of use
InactiveUS20050287533A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLipid formationMass increment
The present invention provides a novel class of molecules, termed “compomers,” that enable the indirect detection of target molecules, as well as novel target detection reagents and compomer templates that encode compomers. Compomers are linear polymers generated from the compomer template portion of a target detection reagent during the course of an assay. In a given assay, each compomer species is correlated with a different target molecule, e.g., a carbohydrate, lipid, polypeptide, or target nucleic acid, particularly a specific nucleotide sequence within a target nucleic acid molecule. When, for example, a target nucleic acid is present in an assay, a compomer species specifically and uniquely correlated with the particular target (e.g., a known SNP or other genetic variant) is generated directly from a target-specific detection reagent (or indirectly from a larger precursor encoded by the compomer template and from which it is subsequently released), after which it can readily be detected, even in an assay where tens, hundreds, or thousands of different compomer species may be generated, as each compomer species is engineered to differ from the others by a small, resolvable defined characteristic (e.g., a mass increment, a difference in subunit composition, sequence, size, length, etc.). When coupled with highly sensitive detection techniques (e.g., MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, nucleic acid hybridization, nuclear magnetic resonance, etc.), a large number of different compomer species can be detected in a single reaction, thereby facilitating highly multiplexed analyses of complex samples.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Matrix for MALDI analysis based on porous polymer monoliths
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
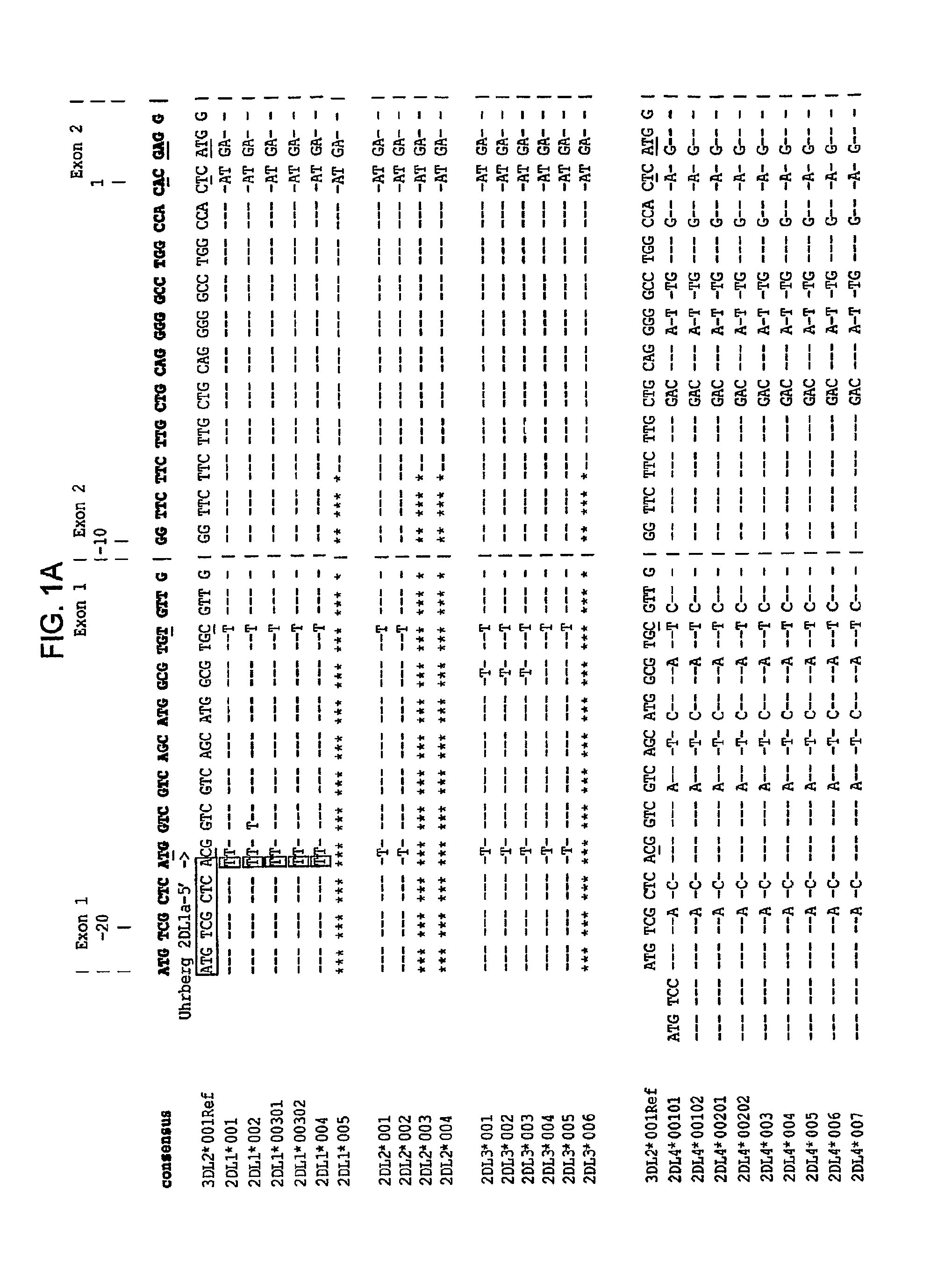
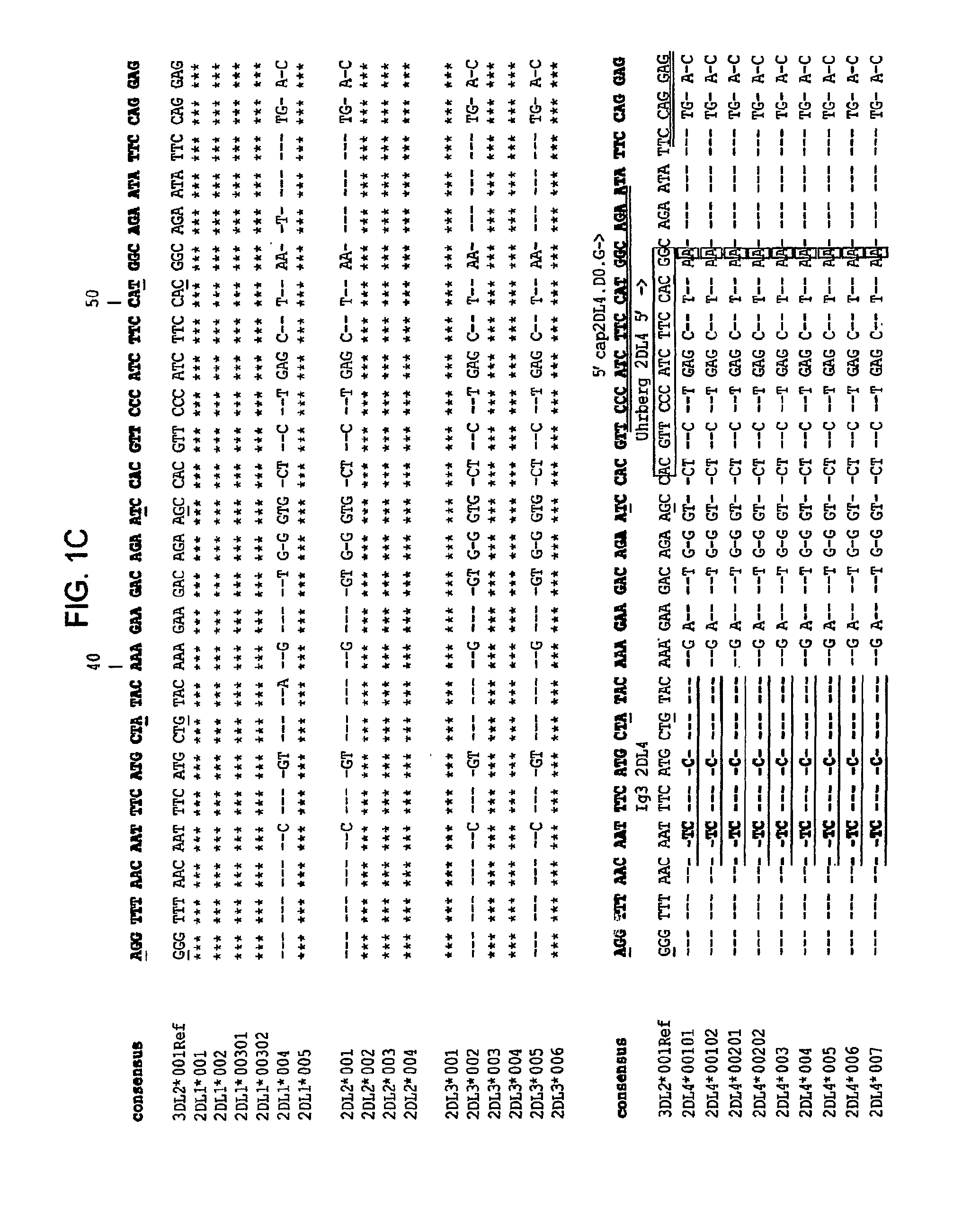
Methods and Compositions for Kir Genotyping
InactiveUS20080213787A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene clusterIonization time of flight
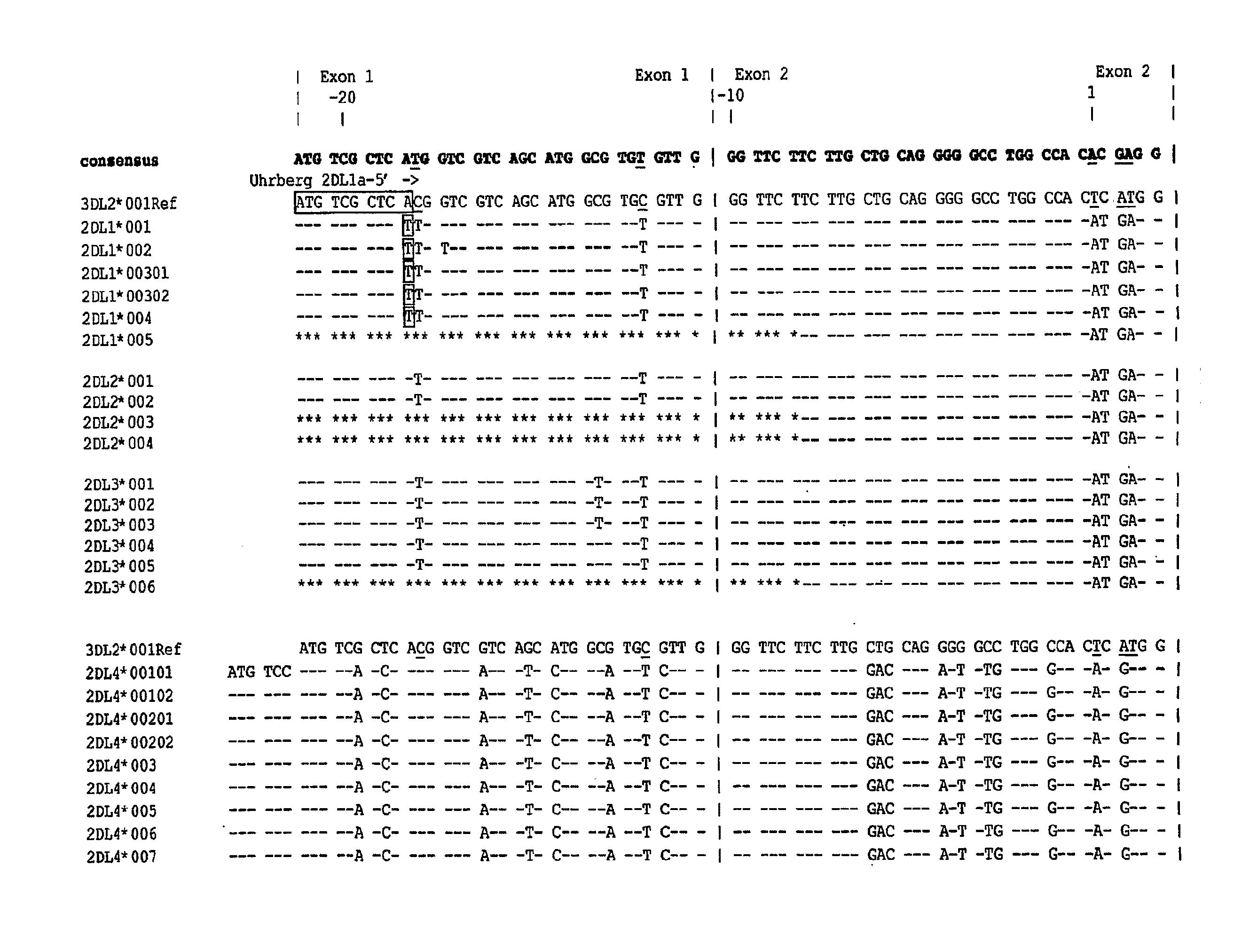
The present invention provides methods for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene cluster genotyping using the matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometer. In general, the methods involve amplifying a plurality of target sequences of a plurality of KIR genes, and detecting the presence or absence of a plurality of single SNPs of the plurality of KIR genes by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The invention also features compositions, including arrays of capture primers and optionally extension primers on a substrate surface, and kits, for use in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
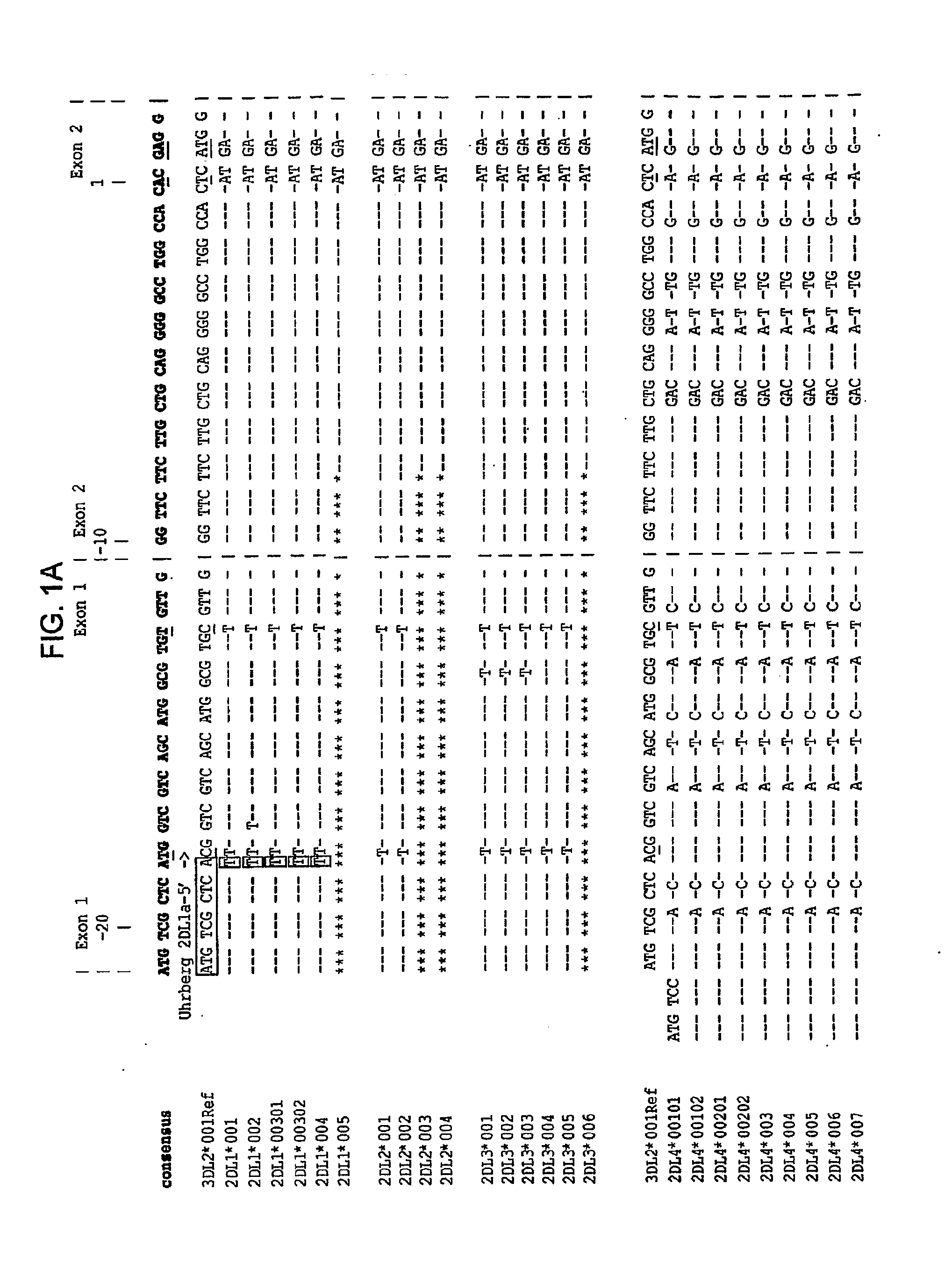
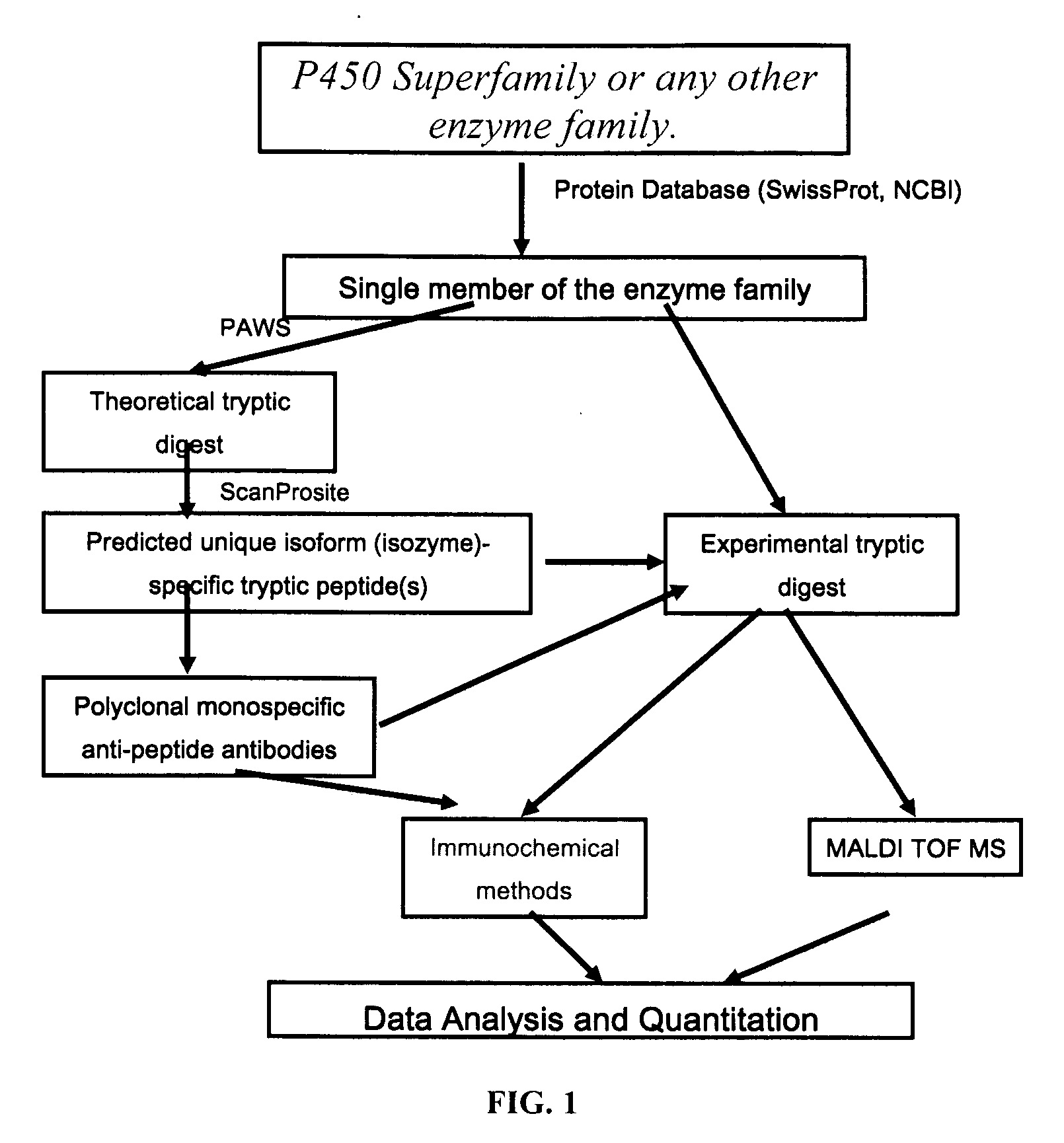
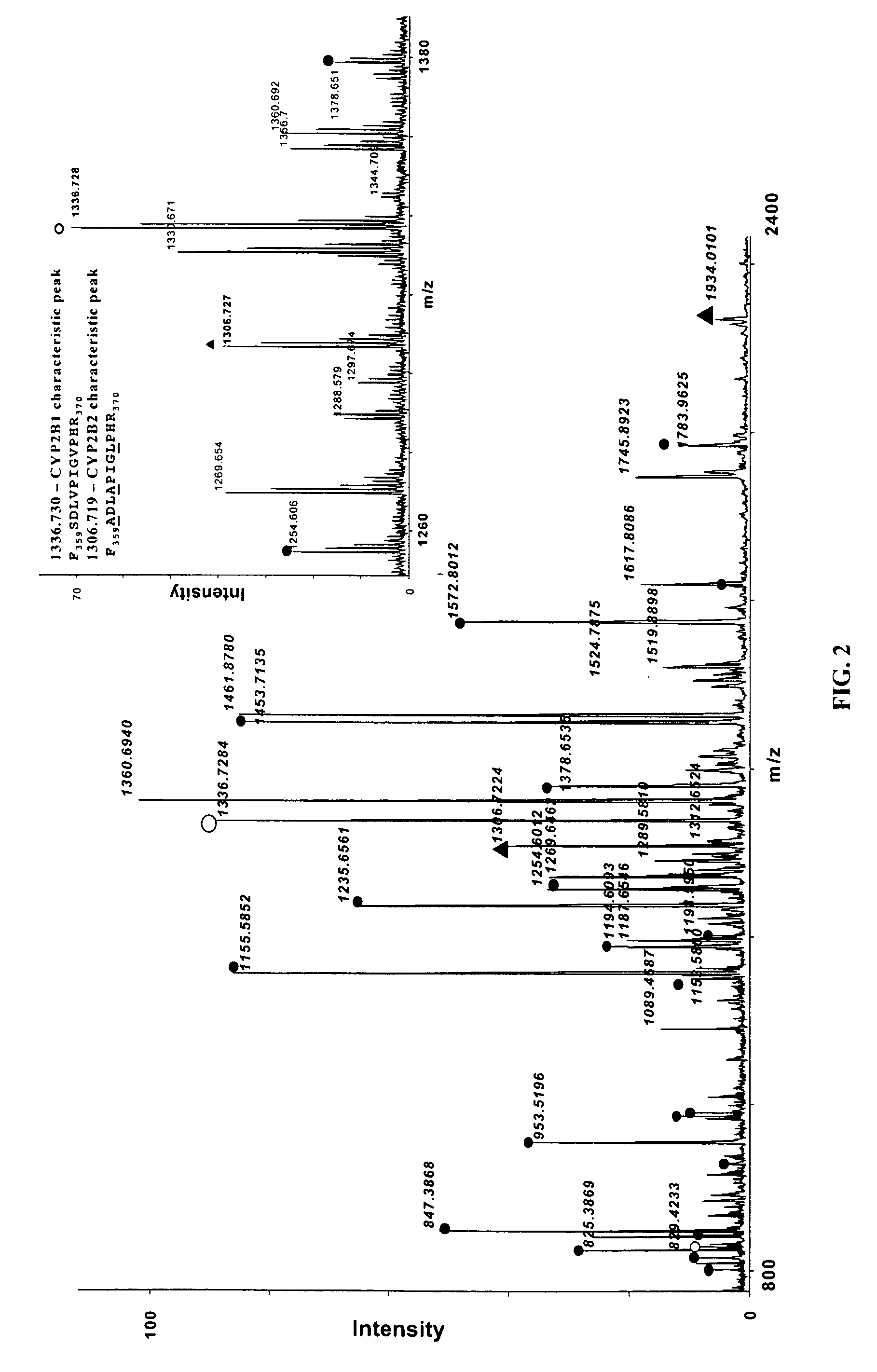
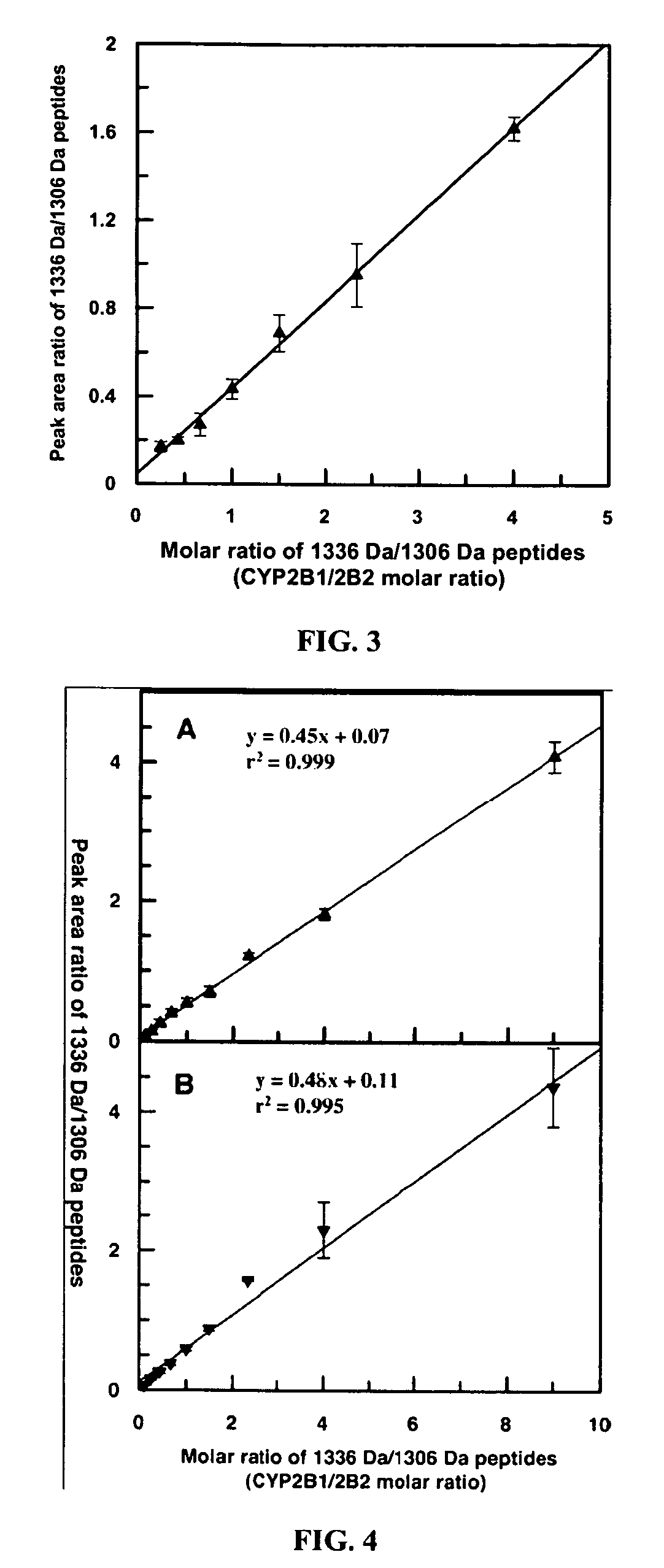
Analysis of protein isoforms using unique tryptic peptides by mass spectrometry and immunochemistry
InactiveUS20070092926A1Accurate measurementReliable detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisIsozymeMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting a protein isoform (p450 isozyme) in a sample using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry or immunochemistry using a unique proteolytic peptide for the isoform. Relative and absolute quantitation can be performed using calibration curves with P450 isozyme-specific peptide standards.
Owner:KANSAS UNIV OF
Methods for identifying and classifying organisms by mass spectrometry and database searching
InactiveUS7020559B1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingSequence databaseProtein molecules
A method for rapid identification of biological materials is presented, which exploits the wealth of information contained in genome and protein sequence databases (5). In a preferred embodiment, the method utilizes the masses of a set of ions by MALDI TOF mass spectrometry of intact or treated cells (1). Subsequent correlation (4) of each ion in the set to a protein, along with the organismic source of the protein, is performed by searching a database comprising protein molecular weights (9).
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +1
Mass spectrometry substrate as well as preparation method and application
InactiveCN106872562ASuitable for large-scale useEasy to makeFixed microstructural devicesPreparing sample for investigationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMirror effect
Owner:毅新兴业(北京)科技有限公司
Kit for detecting deafness susceptibility genes
InactiveCN106367491AReduce usageReduce lossMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal DeafnessMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
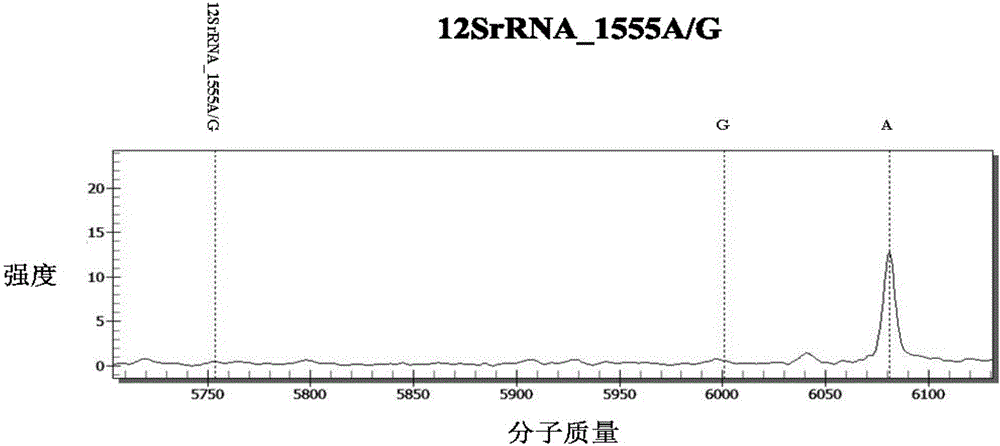
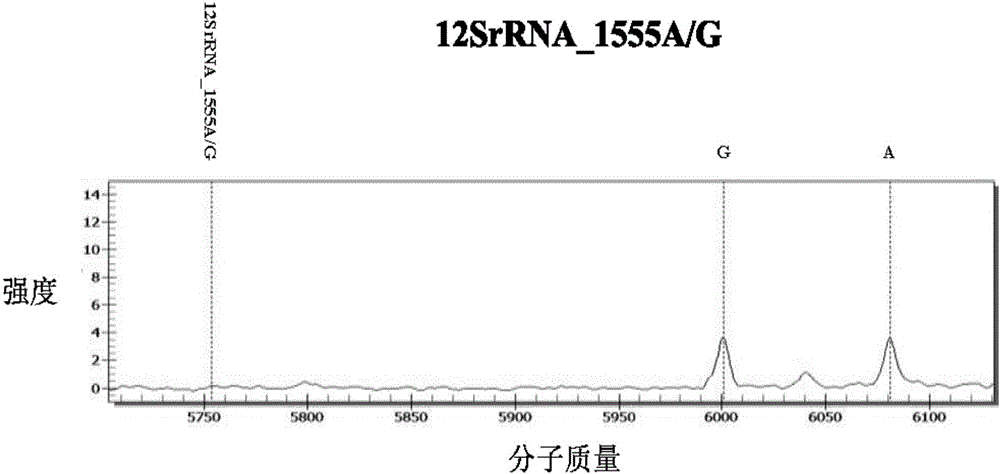
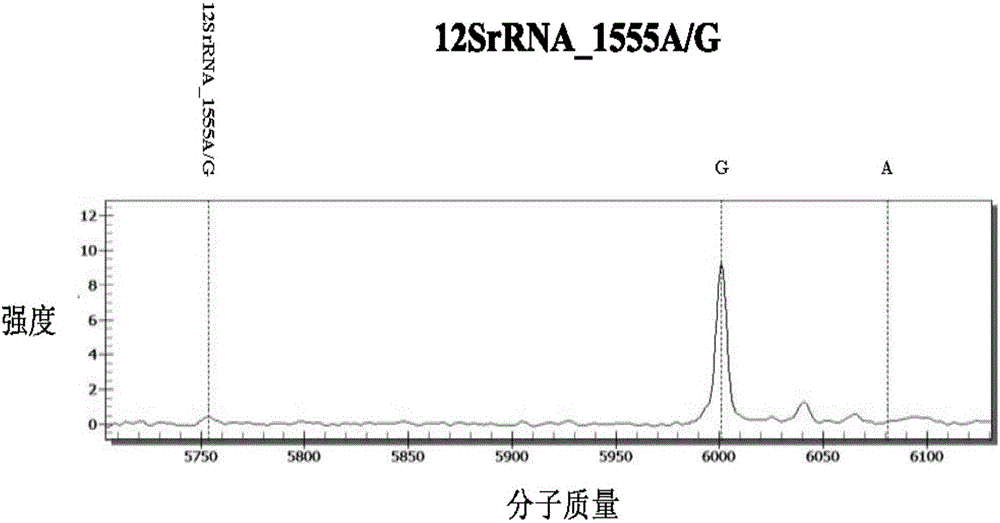
The invention discloses a kit for detecting deafness susceptibility genes, namely the invention provides a kit for rapidly and accurately detecting the GJB2, SLC26A4 and 12SrRNA deafness susceptibility genes by virtue of an MALDI-TOF mass-spectrometry technique. The kit mainly consists of the following ingredients: PCR amplification products shown as SEQ ID NO:1-SEQ ID NO:32 and mass-spectrometry extension primers shown as SEQ ID NO:33-SEQ ID NO:48. The kit provided by the invention, by combining the mass-spectrometry technique and a multi-primer extension technique, is relatively simple in adopted reagent consumables, low in cost and stable, and dozens to thousands of samples are analyzed in one reaction, so that loss caused by reagent preparation is reduced; and the kit is quite high in sensitivity, accuracy and detection consistency, and detection throughput is improved.
Owner:DALIAN GENTALKER BIO-TECH CO LTD
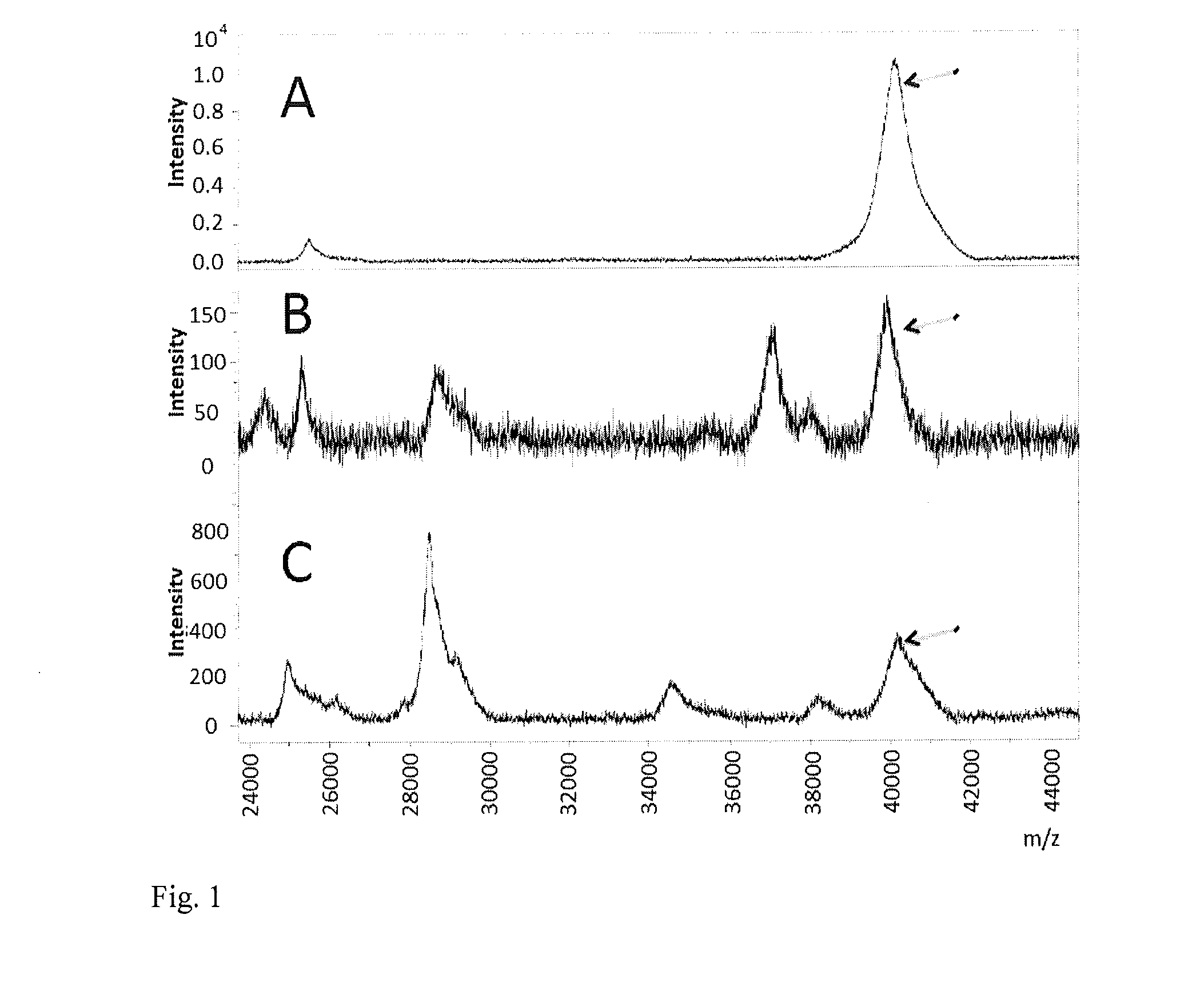
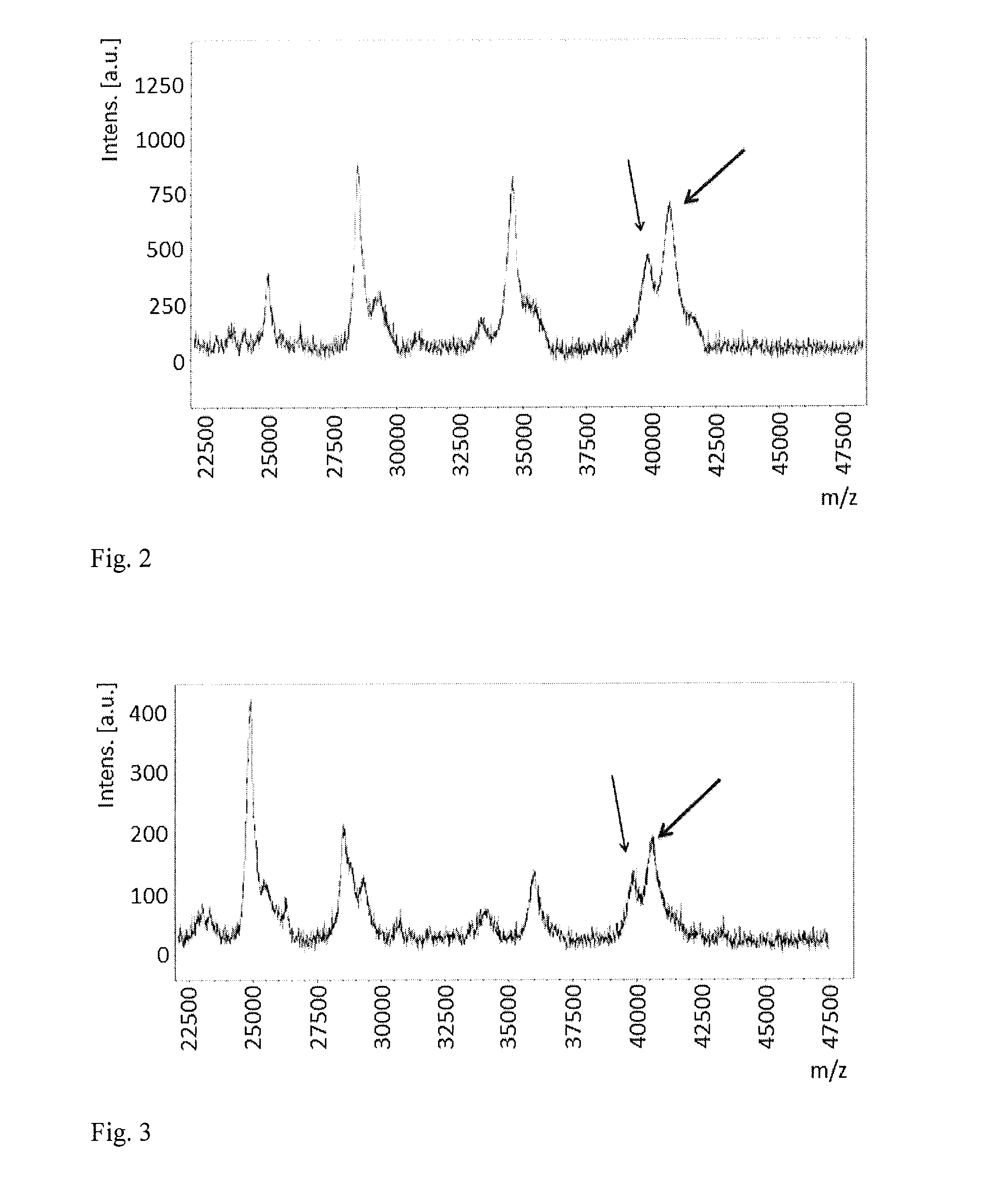
Deep-maldi tof mass spectrometry of complex biological samples, e.g., serum, and uses thereof
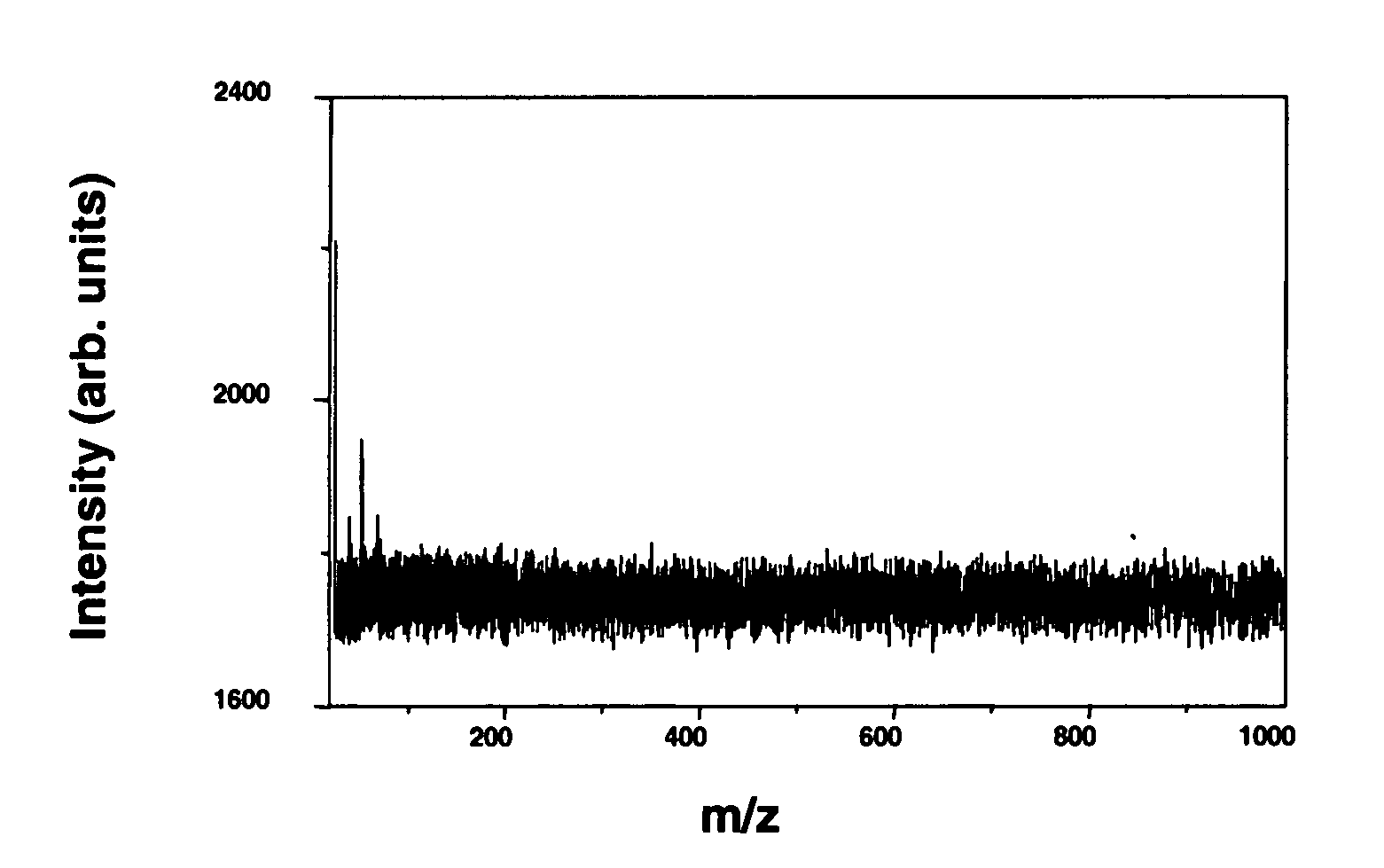
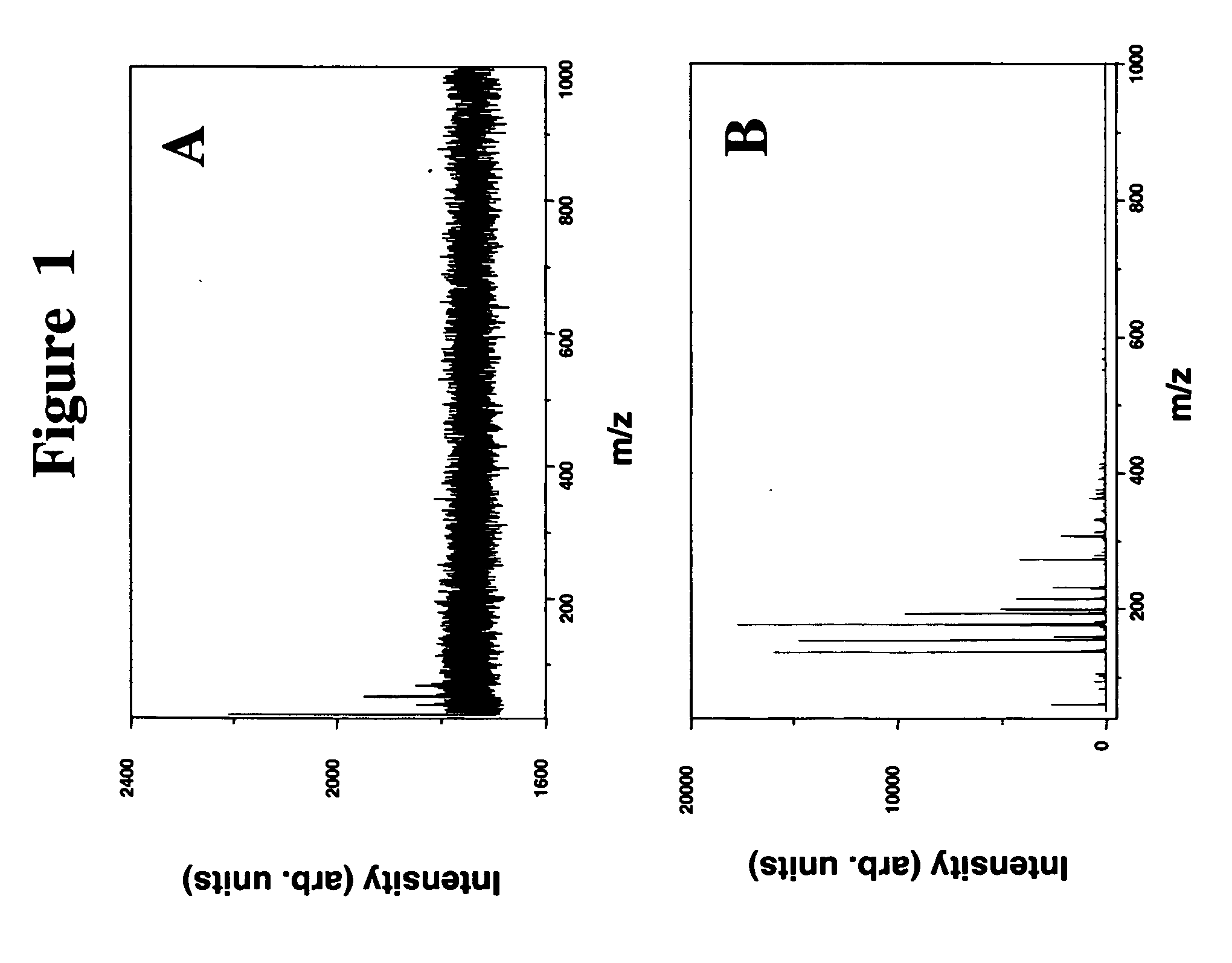
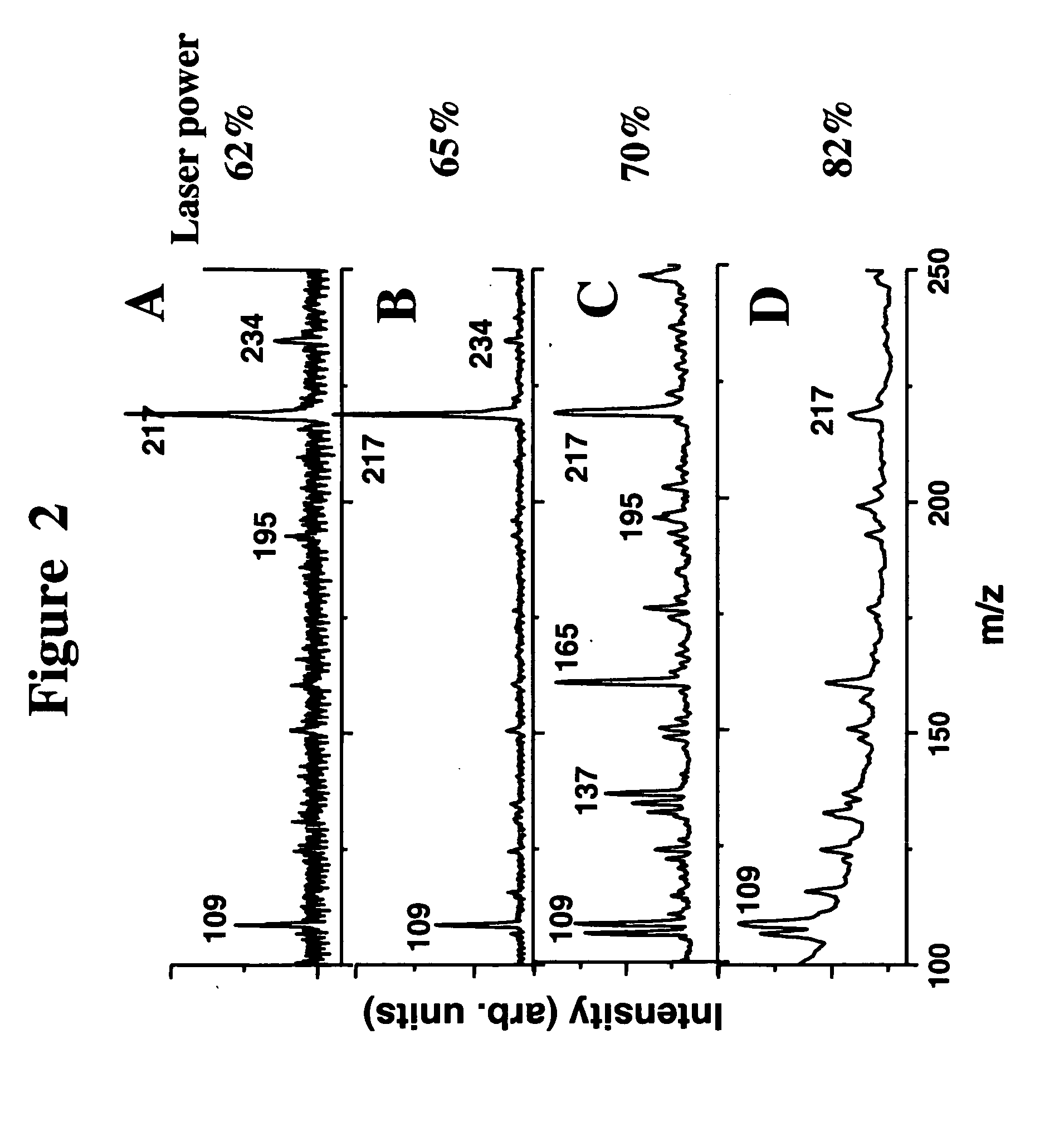
A method of analyzing a biological sample, for example serum or other blood-based samples, using a MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer instrument is described. The method includes the steps of applying the sample to a sample spot on a MALDI-TOF sample plate and directing more than 20,000 laser shots to the sample at the sample spot and collecting mass-spectral data from the instrument. In some embodiments at least 100,000 laser shots and even 500,000 shots are directed onto the sample. It has been discovered that this approach, referred to as "deep-MALDI", leads to a reduction in the noise level in the mass spectra and that a significant amount of additional spectral information can be obtained from the sample. Moreover, peaks visible at lower number of shots become better defined and allow for more reliable comparisons between samples.
Owner:BIODESIX
Protein markers for the diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian and breast cancer
ActiveUS20080213907A1Peptide librariesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsProtein markersADAMTS Proteins
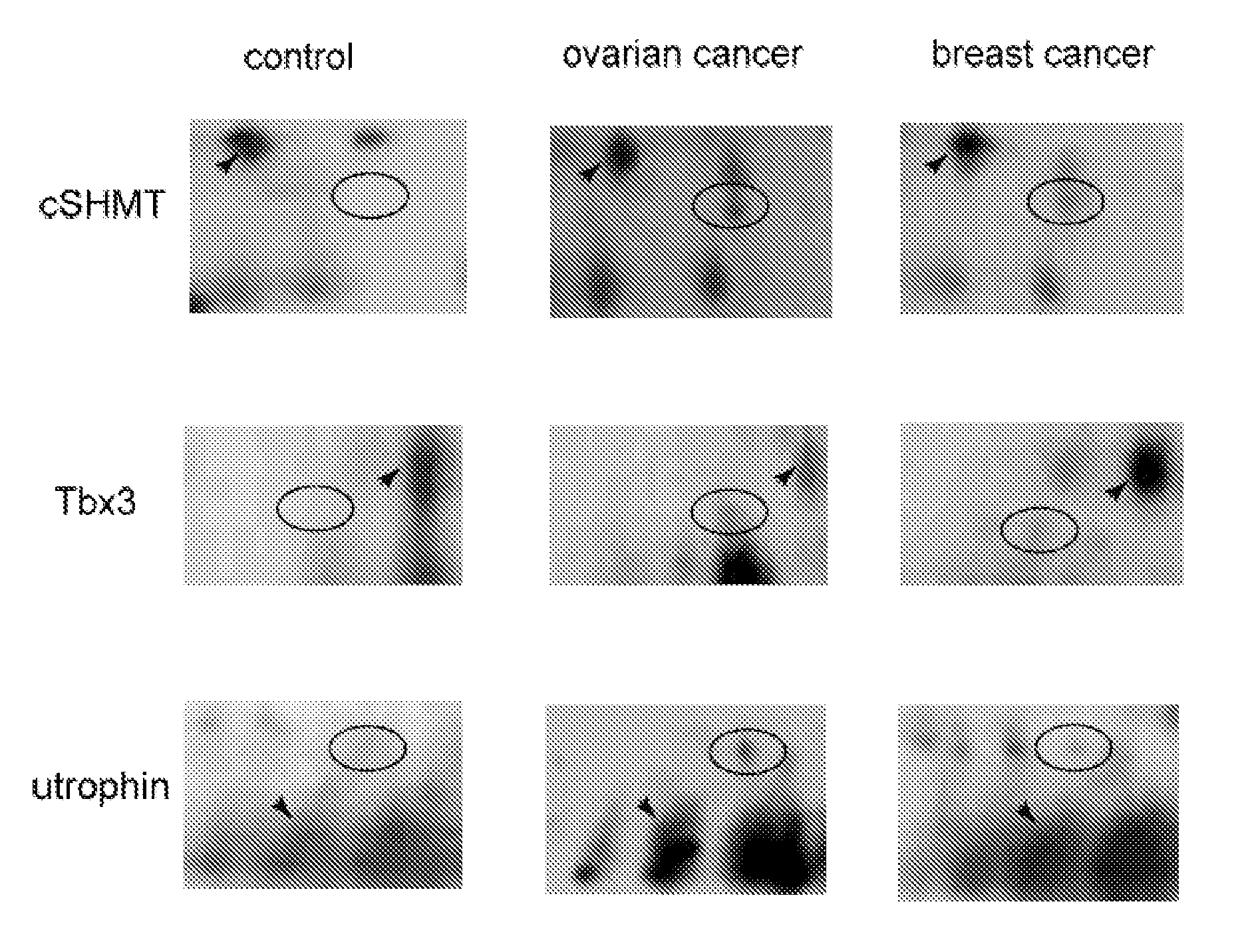
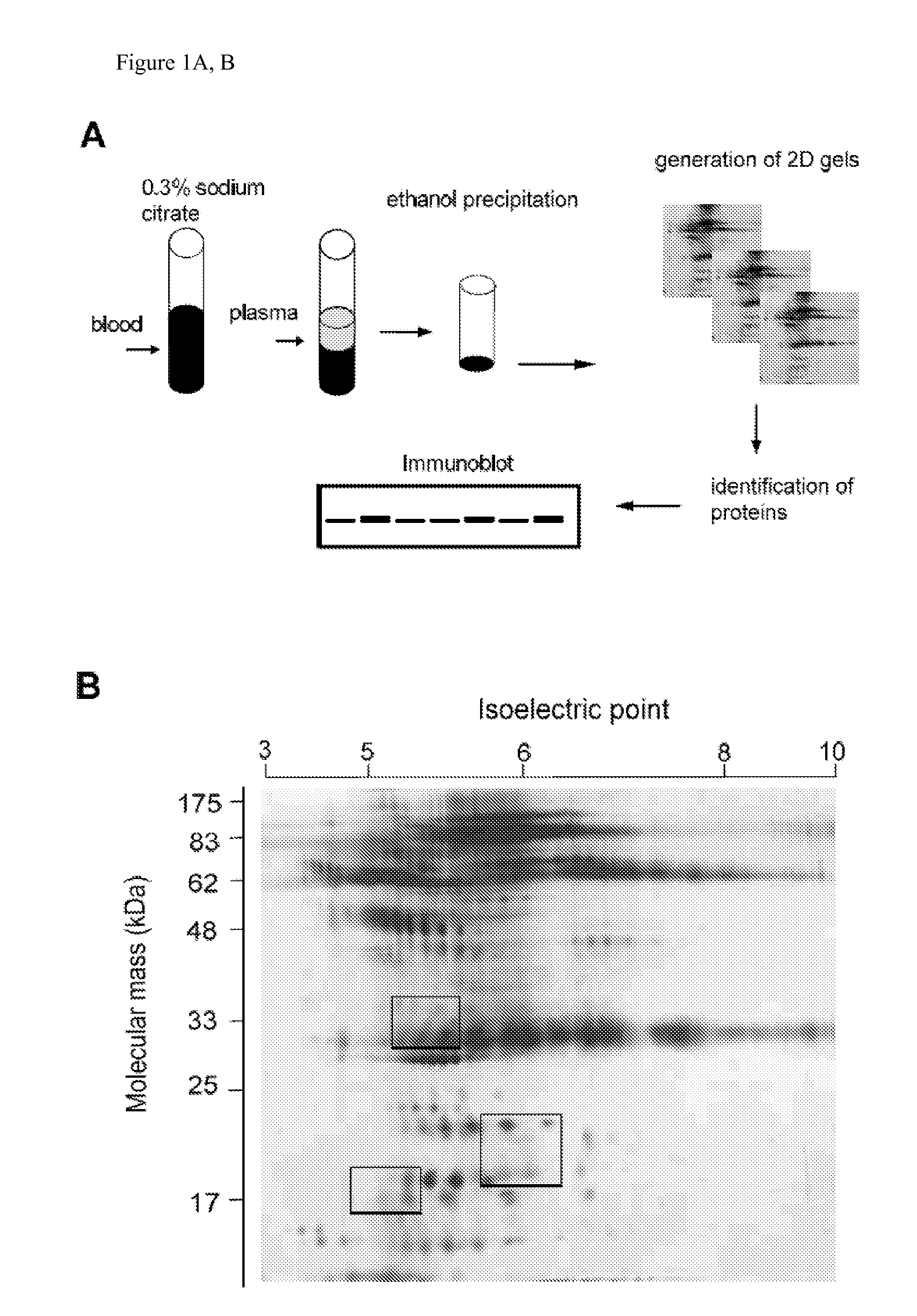
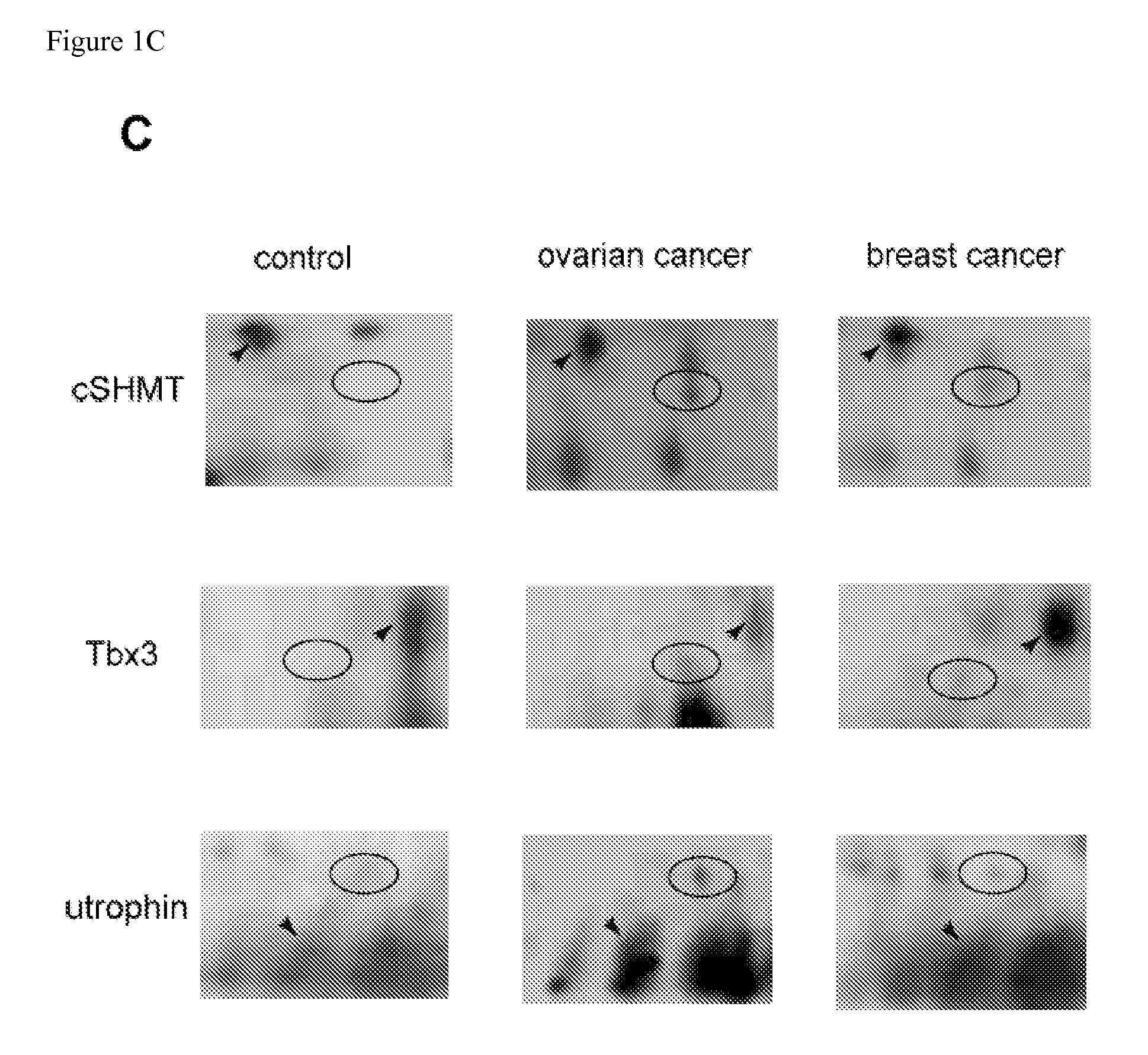
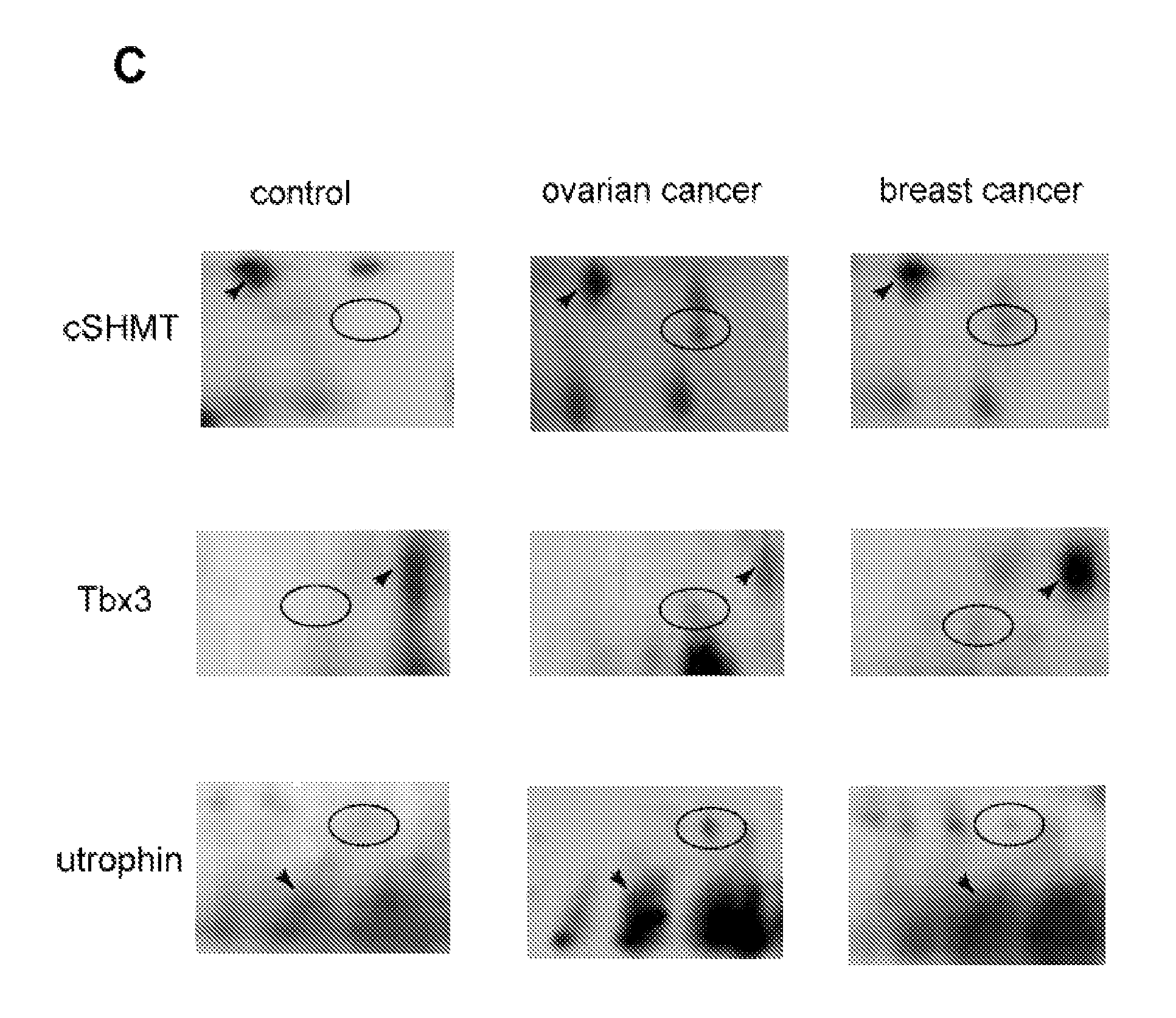
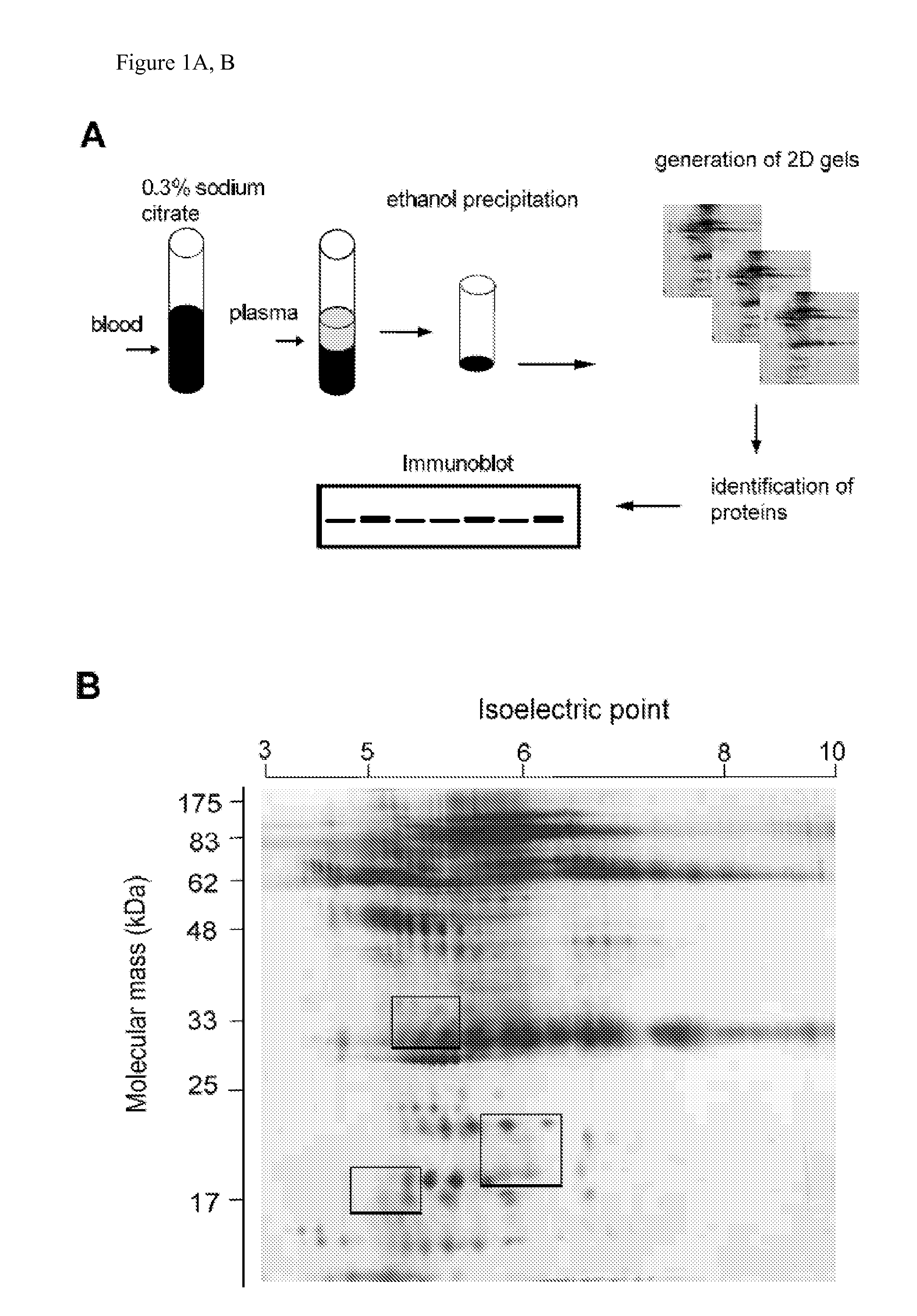
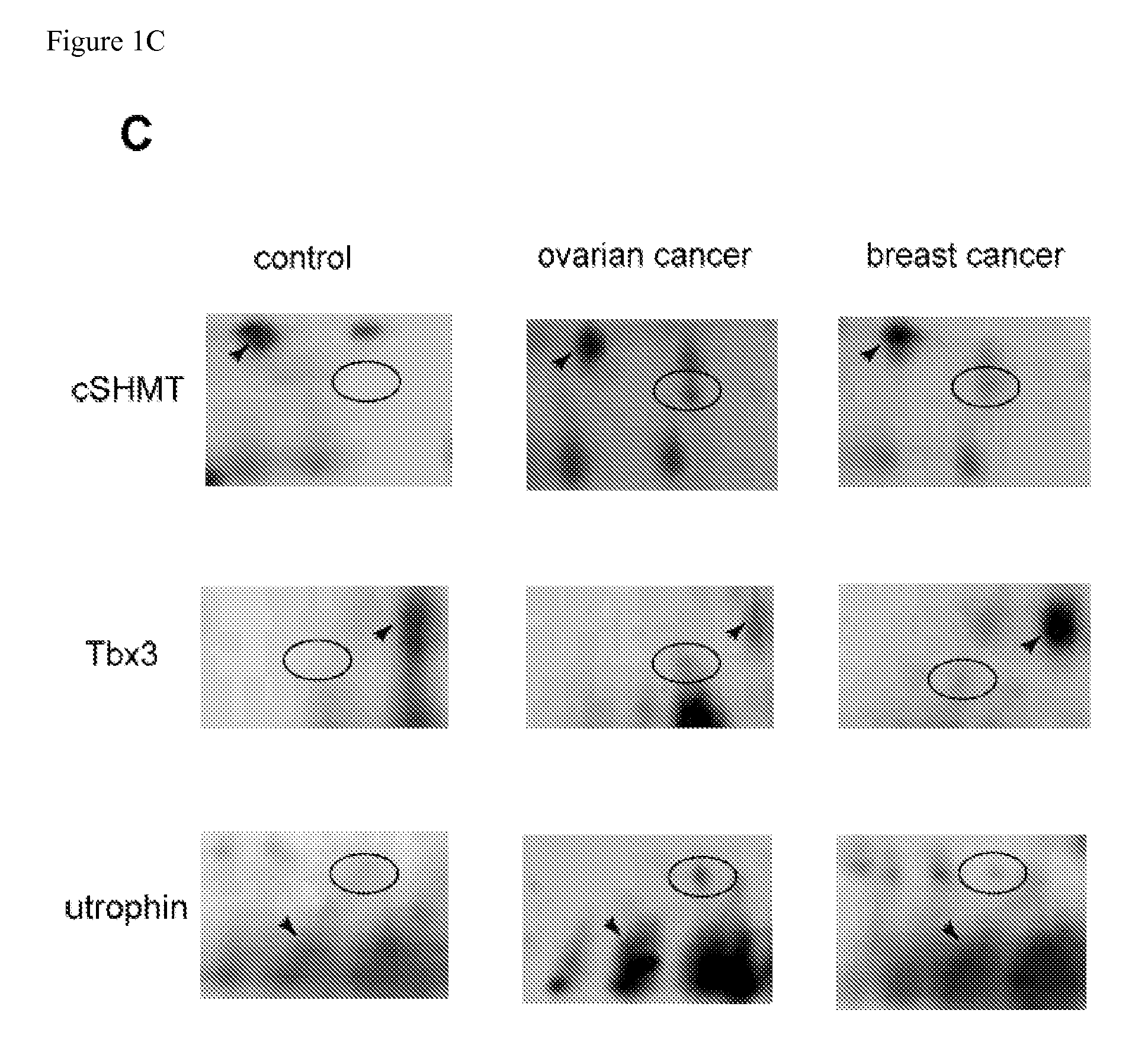
Plasma samples of ovarian and breast cancer patients were used to search for markers of cancer, using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and MALDI TOF mass spectrometry. Truncated forms of cytosolic serine hydroxymethyl transferase (cSHMT), T-box transcription factor 3 (Tbx3) and utrophin were aberrantly expressed in samples from cancer patients, as compared to samples from noncancer cases. Aberrant expression of proteins was validated by immunoblotting of plasma samples with specific antibodies to cSHMT, Tbx3 and utrophin. A cohort of 79 breast and 39 ovarian cancer patients, and 31 individuals who were either healthy or had noncancerous conditions was studied. We observed increased expression of truncated cSHMT, Tbx3 and utrophin in plasma samples obtained from patients at early stages of disease. The results indicate that cSHMT, Tbx3, utrophin and truncated forms thereof can be used as components of multiparameter monitoring of ovarian and breast cancer.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES
Method for Developing and Applying Databases for Idenfication of Microorganisms by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
InactiveUS20160350475A1Time-of-flight spectrometersLibrary screeningMicroorganismRelative probability
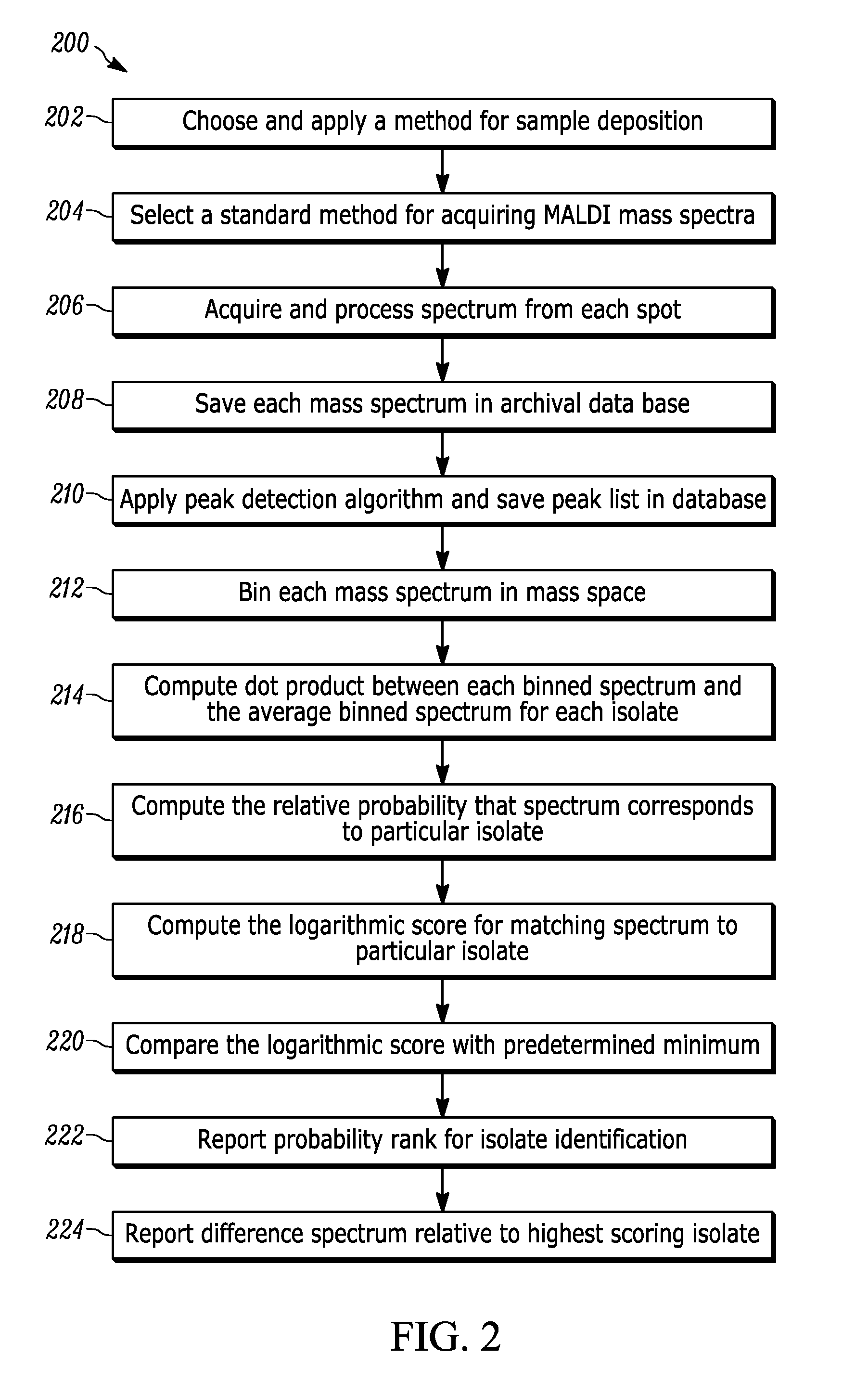
A method for organism identification using MALDI TOF mass spectrometry includes generating a searchable database. A mass spectrum is acquired from a sample. Peak detection of the acquired mass spectrum is performed, binned, and a vector is generated. Dot products are computed between the generated vector of peak detected mass spectrum and averaged binned spectrum for each isolate. A relative probability that acquired mass spectrum matches a spectrum from each isolate in the searchable database is computed. A logarithmic score for matching the acquired mass spectrum with the mass spectrum is computed from each isolate. The logarithmic score for matching the acquired mass spectrum is compared with the mass spectrum from each isolate to a predetermined minimum passing score. A list of isolates is generated with greater than the predetermined minimum score. The probability rank and logarithmic score are then reported for each isolate with a minimum passing score.
Owner:VIRGIN INSTR CORP
METHOD OF IDENTIFICATION OF SPORE-FORMING Bacillus spp. BY DIRECT In-situ ANALYSIS OF MALDI-TOF MASS SPECTROMETRY, AND ANALYSIS SYSTEM
InactiveUS20150024428A1High-precision detectionEasily and rapidlyTime-of-flight spectrometersMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyTime of flight
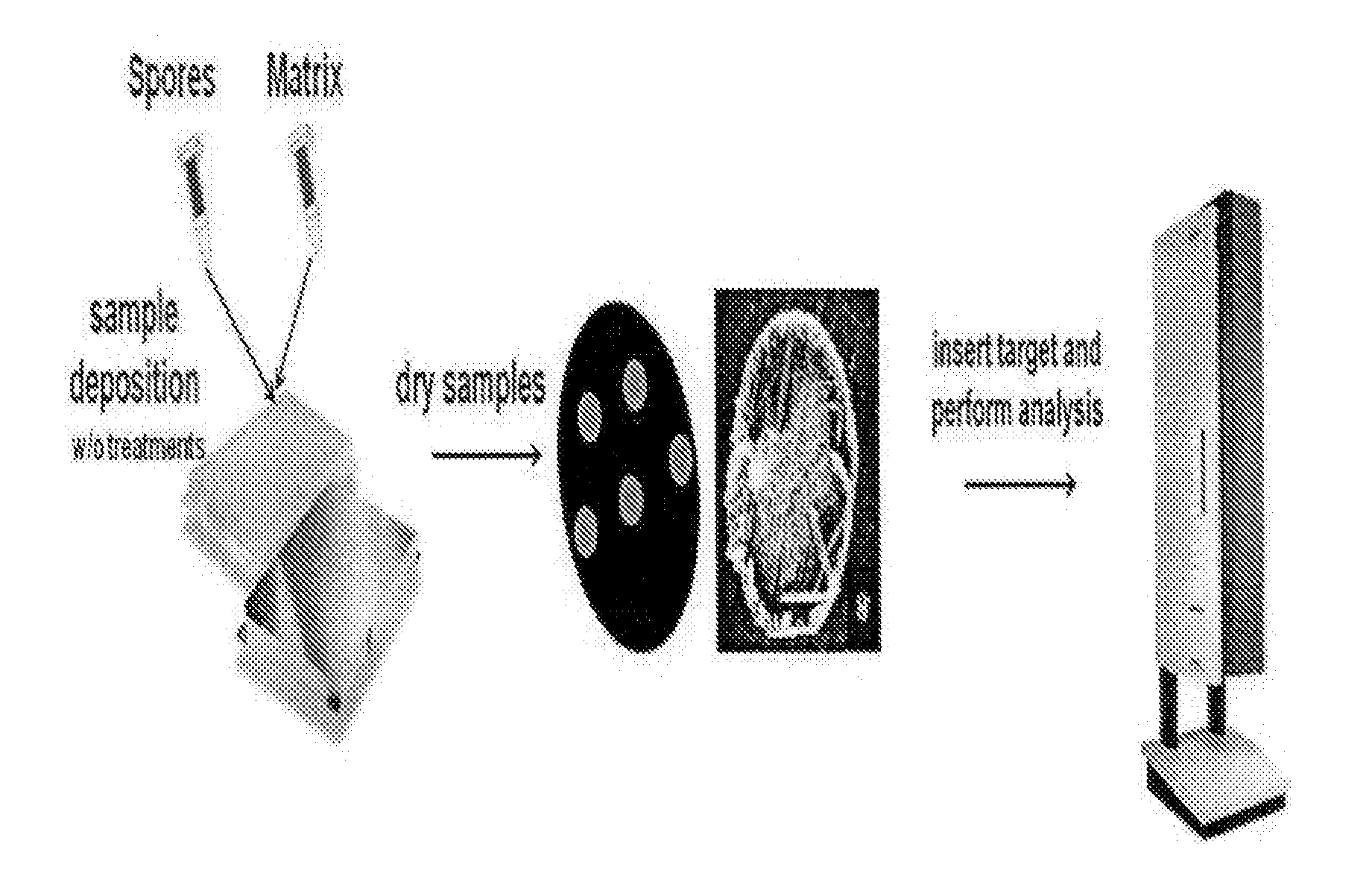
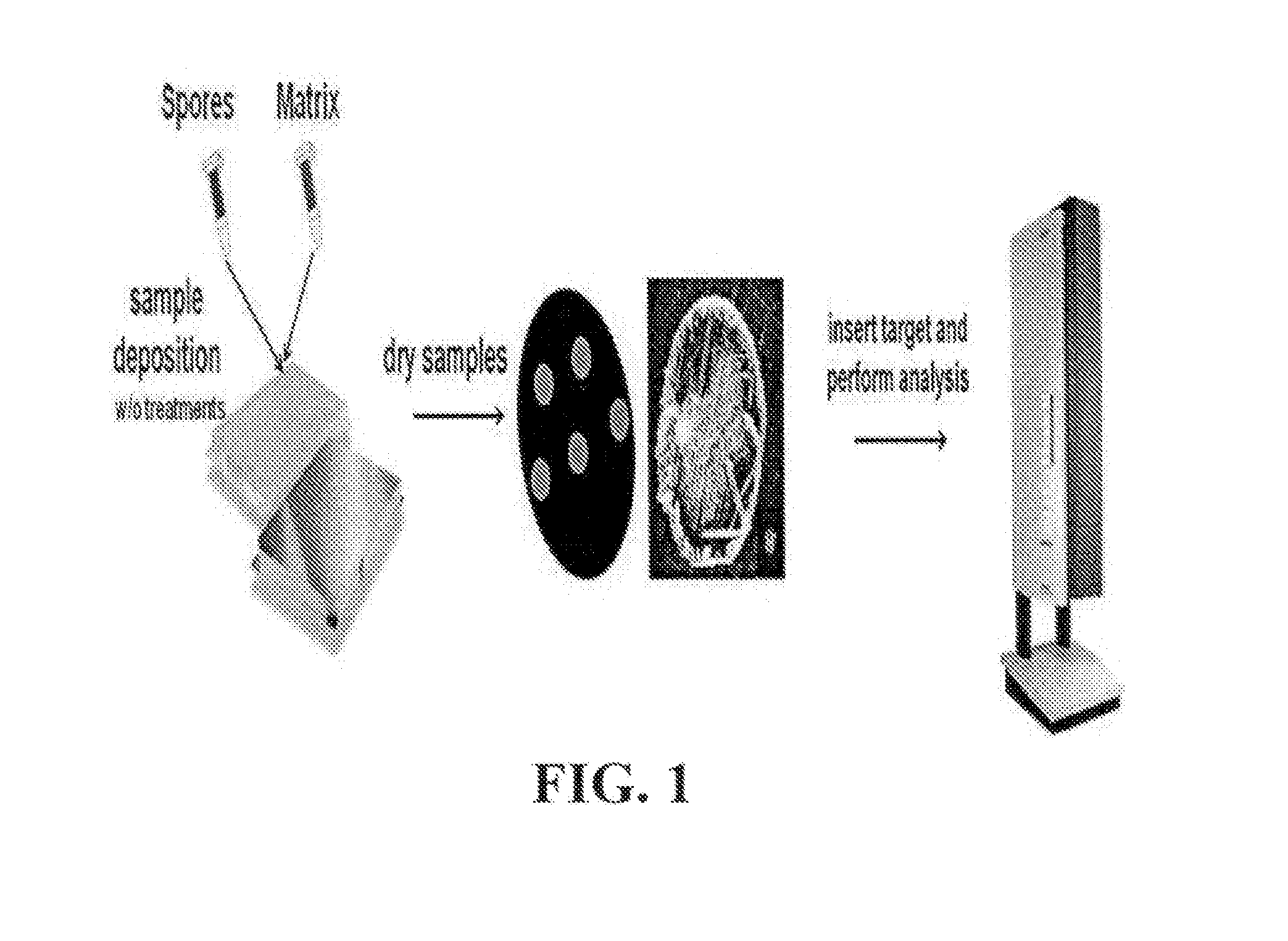
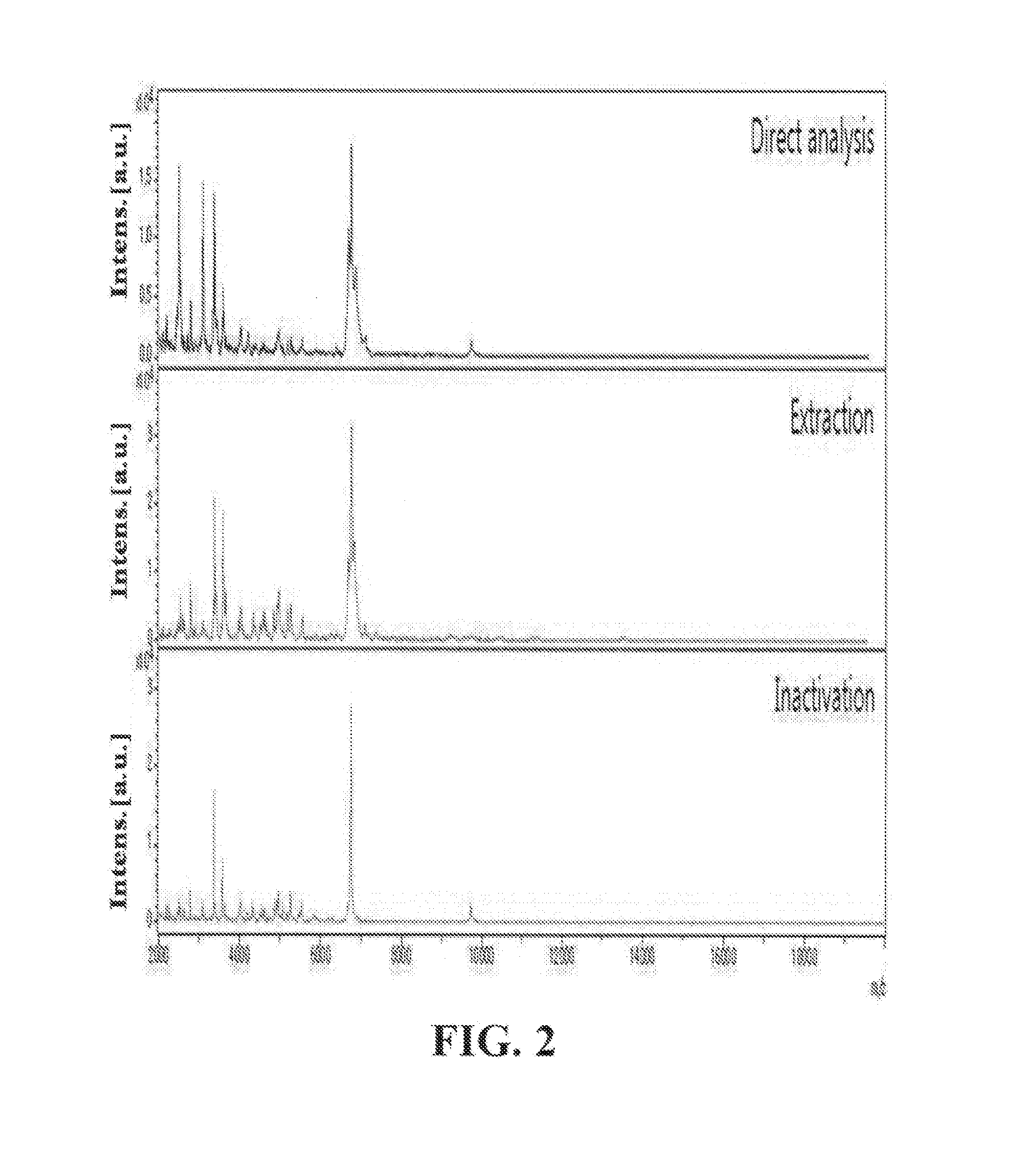
A method of the identification of Bacillus species by direct in-situ analysis of MALDI-TOF MS (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption / Ionization Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectometry) in which spore-forming bacteria are applied intact without any pretreatment, and an analysis system of distinctive biomarkers which allow Bacillus spores to be distinguished. Rapid and accurate detection and identification of Bacillus species can be achieved by the method and analysis system.
Owner:AGENCY FOR DEFENSE DEV
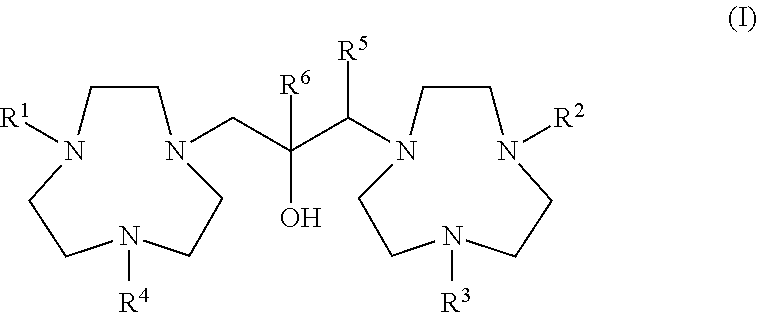
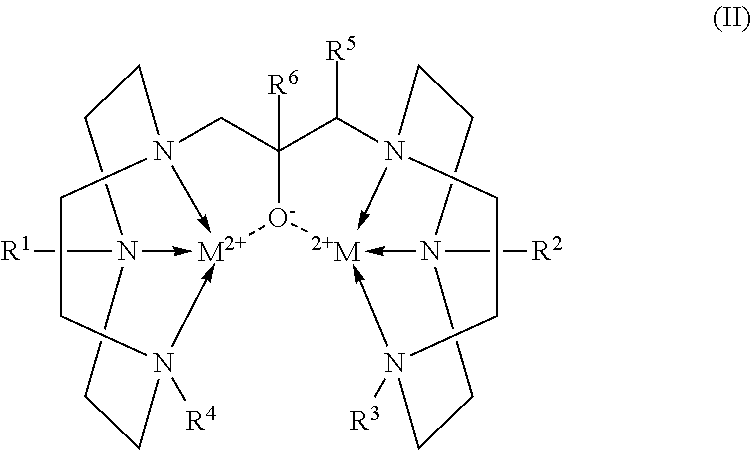
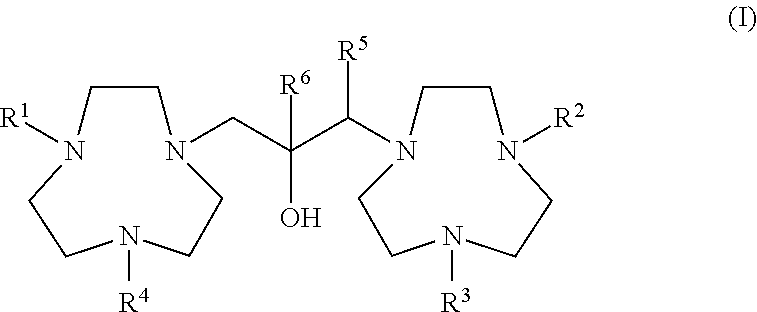
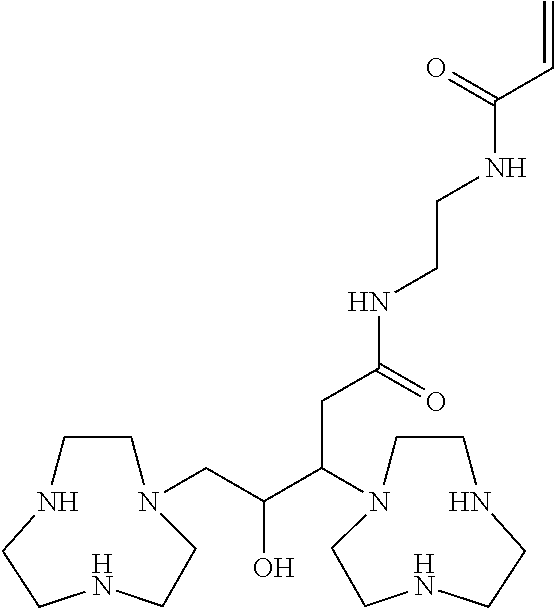
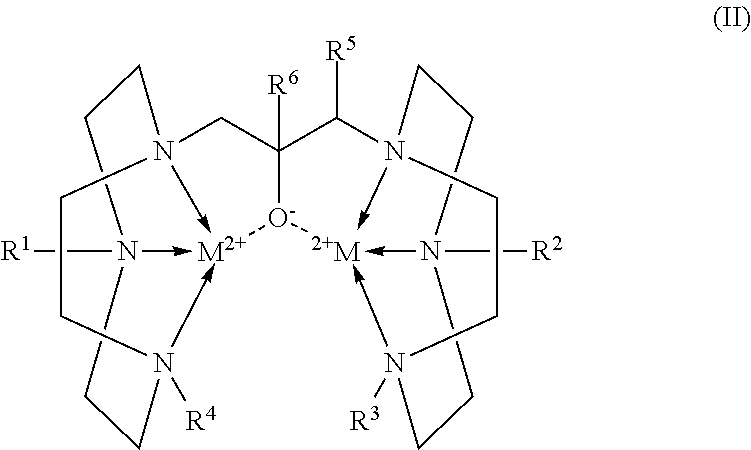
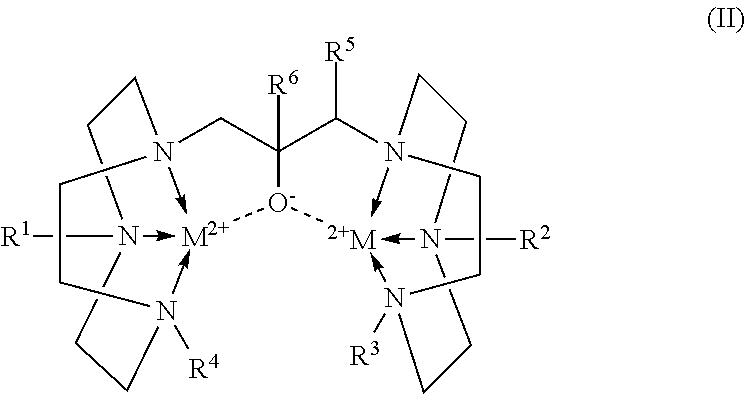
Conjugates of 1,4,7-triazacyclononanes, dinuclear metal complexes of such conjugates, and methods of use for both 1,4,7-triazacyclononanes and conjugates
ActiveUS20120058565A1Organic active ingredientsParticle separator tubesBiological speciesOrganophosphate
Conjugates of 1,3-bis(1,4,7-triazacyclonon-1-yl)-2-hydroxypropanes with a variety of conjugating members are used in the formation of dinuclear metal complexes which bind to phosphate esters. By virtue of their conjugated forms, the complexes are incorporated into chromatographic media, affinity binding reagents, and dyes, which make the complexes useful in a wide range of assays, separations, and purifications. In addition, dinuclear metal complexes of 1,3-bis(1,4,7-triazacyclonon-1-yl)-2-hydroxypropanes that are not so conjugated are used in the detection of phosphate esters of biological species by either MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry or by dye displacement.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
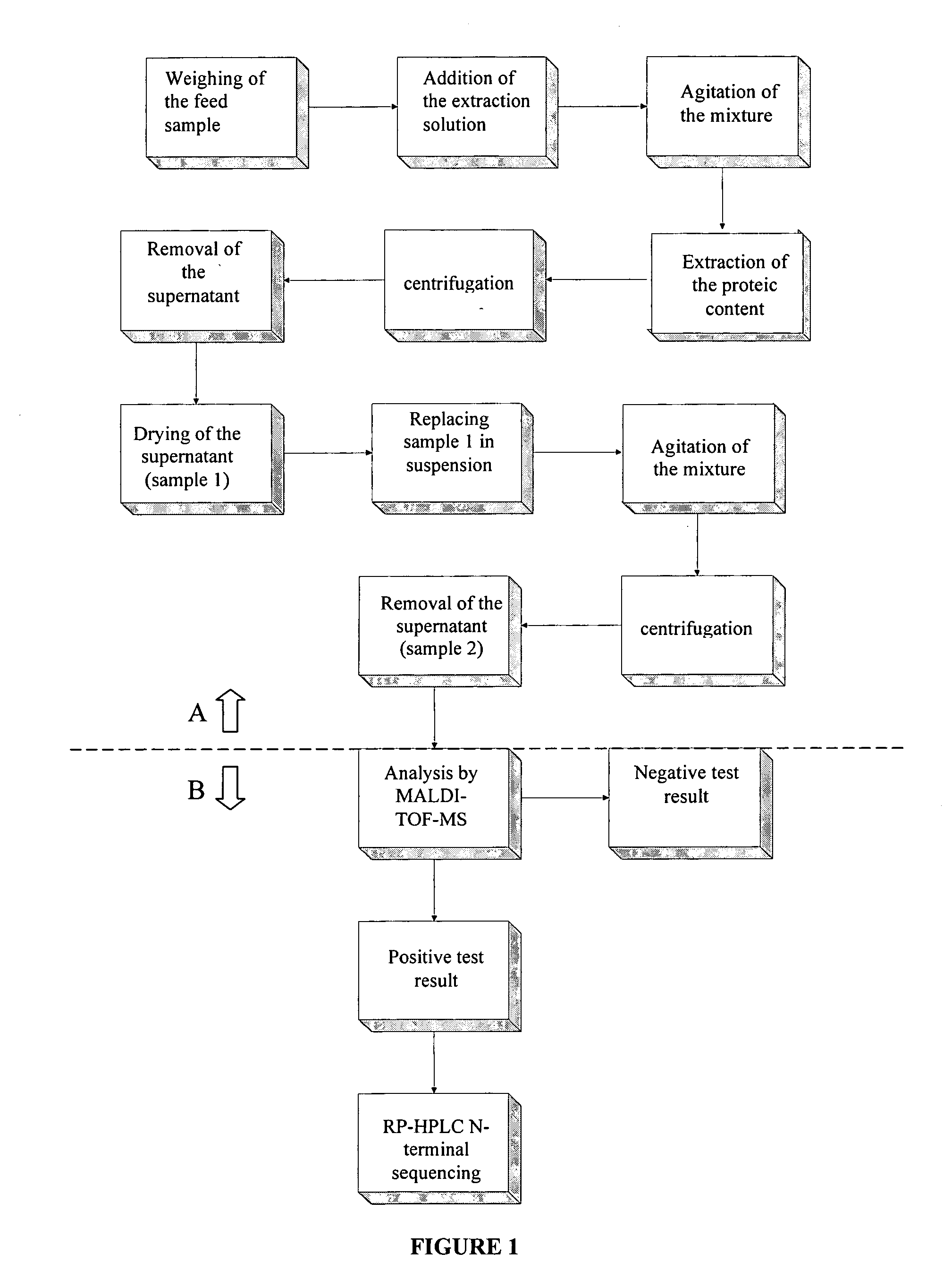
Method for the detection of proteins of animal origin in complex mixtures
InactiveUS20050118720A1Avoid spreadingLow impurity contentNervous disorderComponent separationHigh concentrationLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
The purpose of the present invention is to evaluate the quality of feed for ruminants and consequently, avoid the transmission of TSEs through the detection of animal proteins in these foods. This purpose is embodied in the form of a method for detecting proteins of animal origin in complex mixtures comprising the stages of: (i) extraction of the proteic matter in high concentration from a sample of the initial complex mixture in a manner as to substantially remove all interferents; (ii) preparation of the matrix-analyte in a manner as to maintain low levels of impurities and an adequate matrix-analyte molar rate; (iii) analysis of the material obtained in the prior stage by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry; (iv) optionally, fractionation of the samples or isolation of the components by RP-HPLC and identification of the components by means of automatic sequencing of the N-terminal region and sequencing of its peptidic fragments by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC / MS / MS). The present invention also contemplates the use of this method in the detection of proteins of animal origin in feed for ruminants, which permits the interruption of transmission of Transmittable Spongiform Encephalopathies, and more particularly Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathies (BSE).
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUARIA EMBRAPA
Method for the analysis of o-linked oliosacharides
InactiveUS20110143386A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAnalysis methodMass spectrometric
A method of analyzing O-linked oligosaccharides in a sample is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of digesting a glycoprotein with a proteolytic enzyme, performing solid-phase permethylation of the oligosaccharide, then analyzing the permethylated and non-reduced O-linked oligosaccharides using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for sample preparation and direct spotting eluants onto a MALDI-TOF target
InactiveUS20060263259A1Eliminating transfer stepAnalysis using chemical indicatorsTime-of-flight spectrometersSolid phase extractionMALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
A single- or multi-well sample preparation apparatus and method for desalting, concentrating and depositing samples prior to further analysis such as by MALDI TOF mass spectrometry. The apparatus in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention includes a plurality of wells each in fluid communication with a respective outlet or drainage opening, optionally containing a three dimensional membrane structure preferably comprising a plurality of sorptive particles entrapped in a porous polymer matrix so as to form a device capable of carrying out solid phase extraction. The apparatus is designed to allow for direct spotting onto a MALDI target, thereby eliminating a transfer step. Also disclosed is a method of sample preparation, deposition and analysis using the apparatus of the present invention.
Owner:CHERNOKALSKAYA ELENA +2
Method of identifying cancer biomarkers and cancer progression
InactiveUS20080318263A1Efficient and effectiveEfficiently detecting cancer progressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisWestern blotWilms' tumor
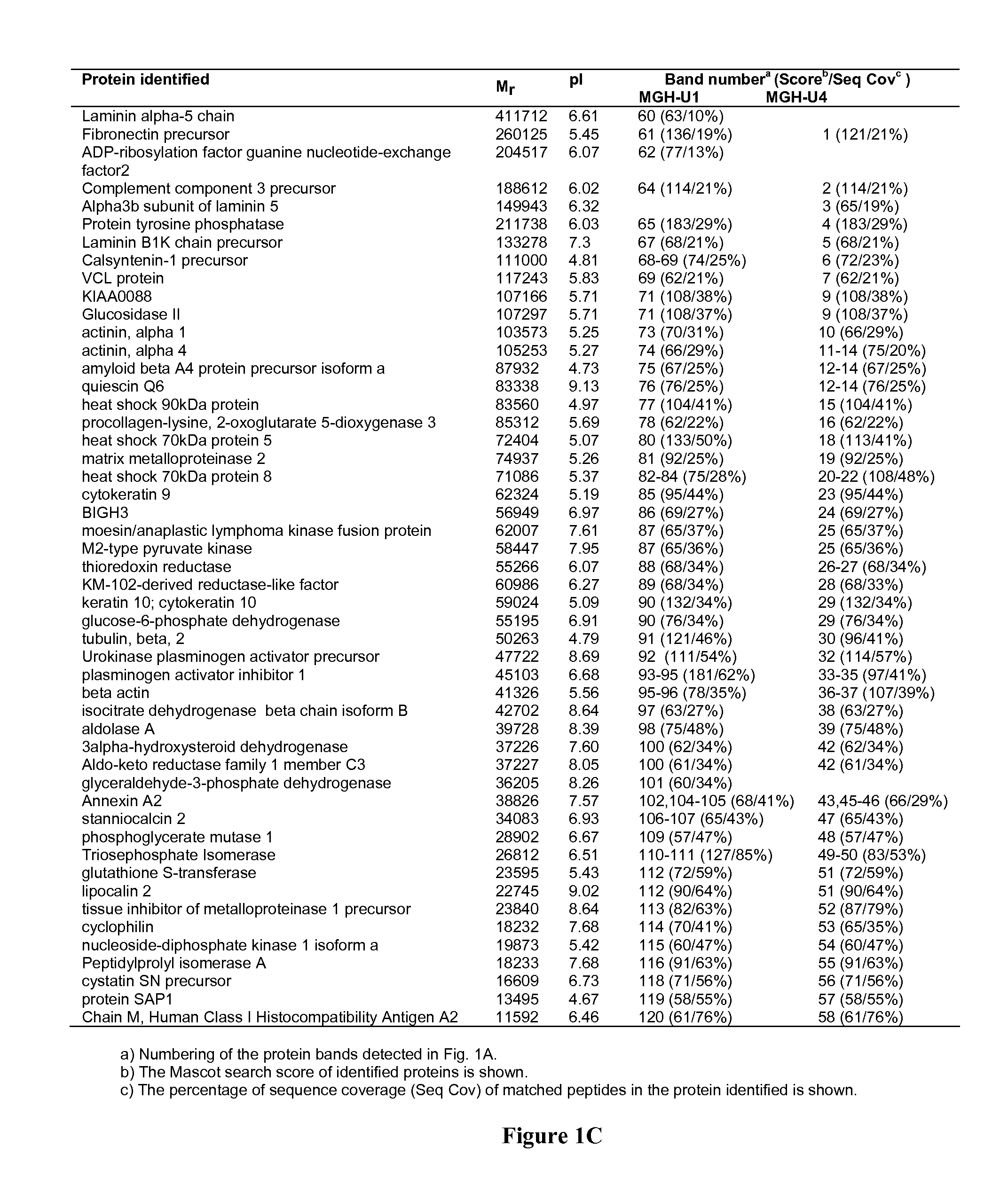
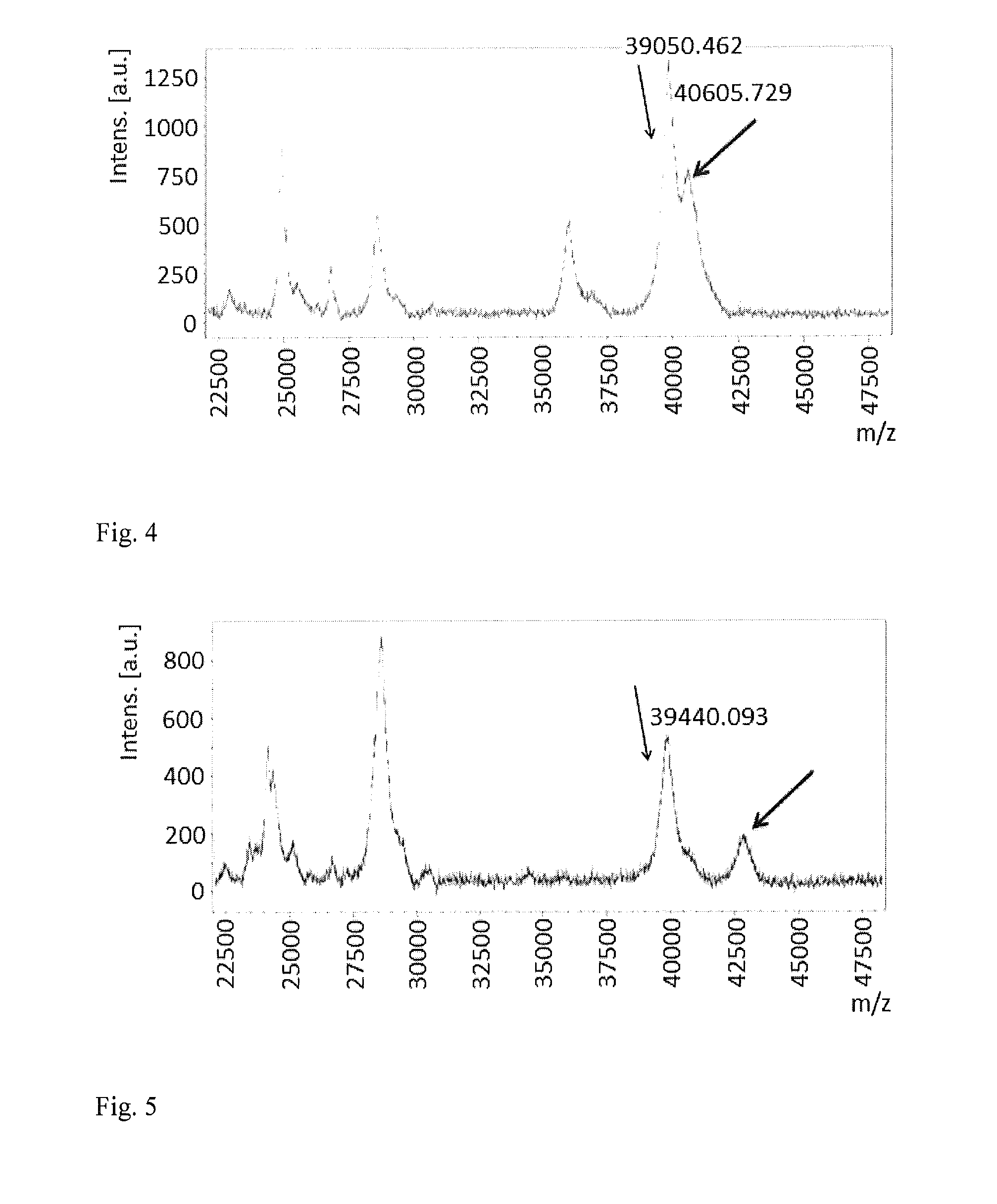
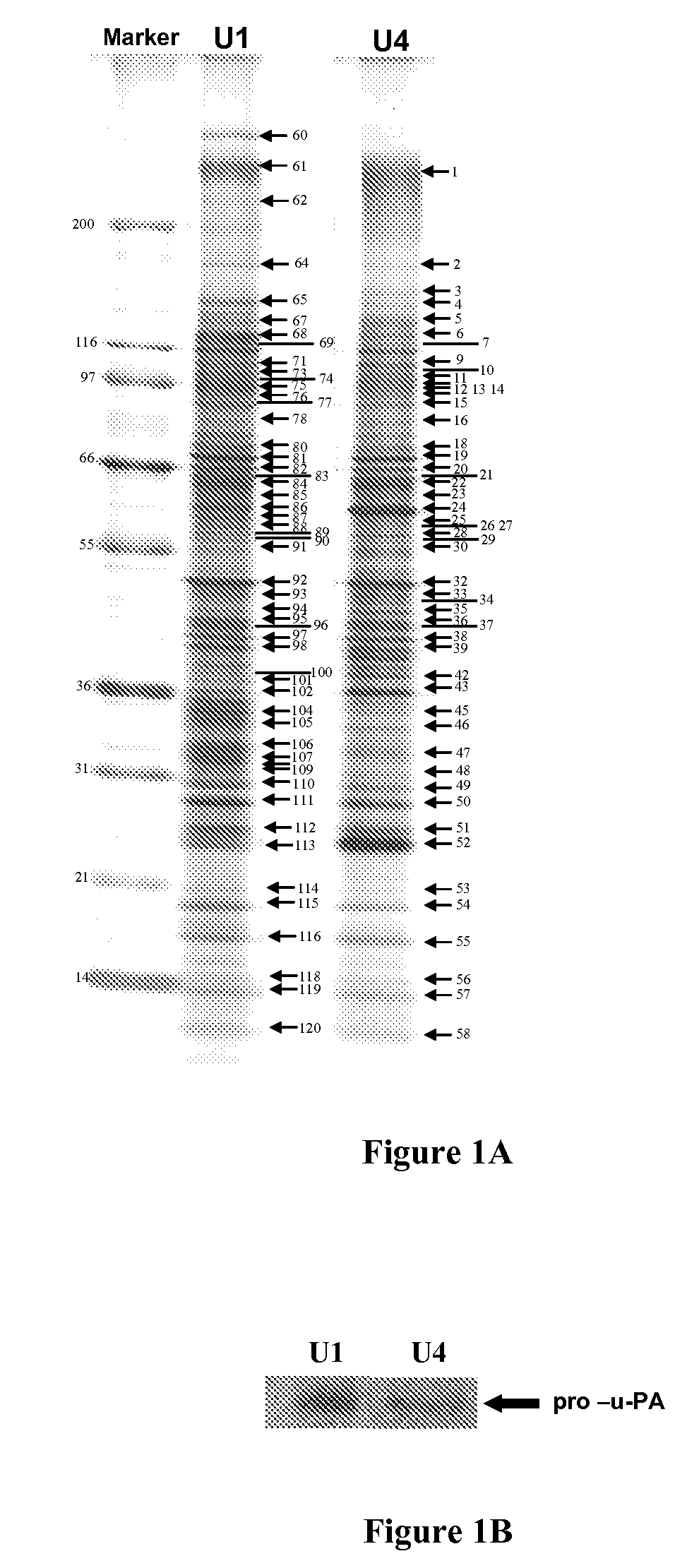
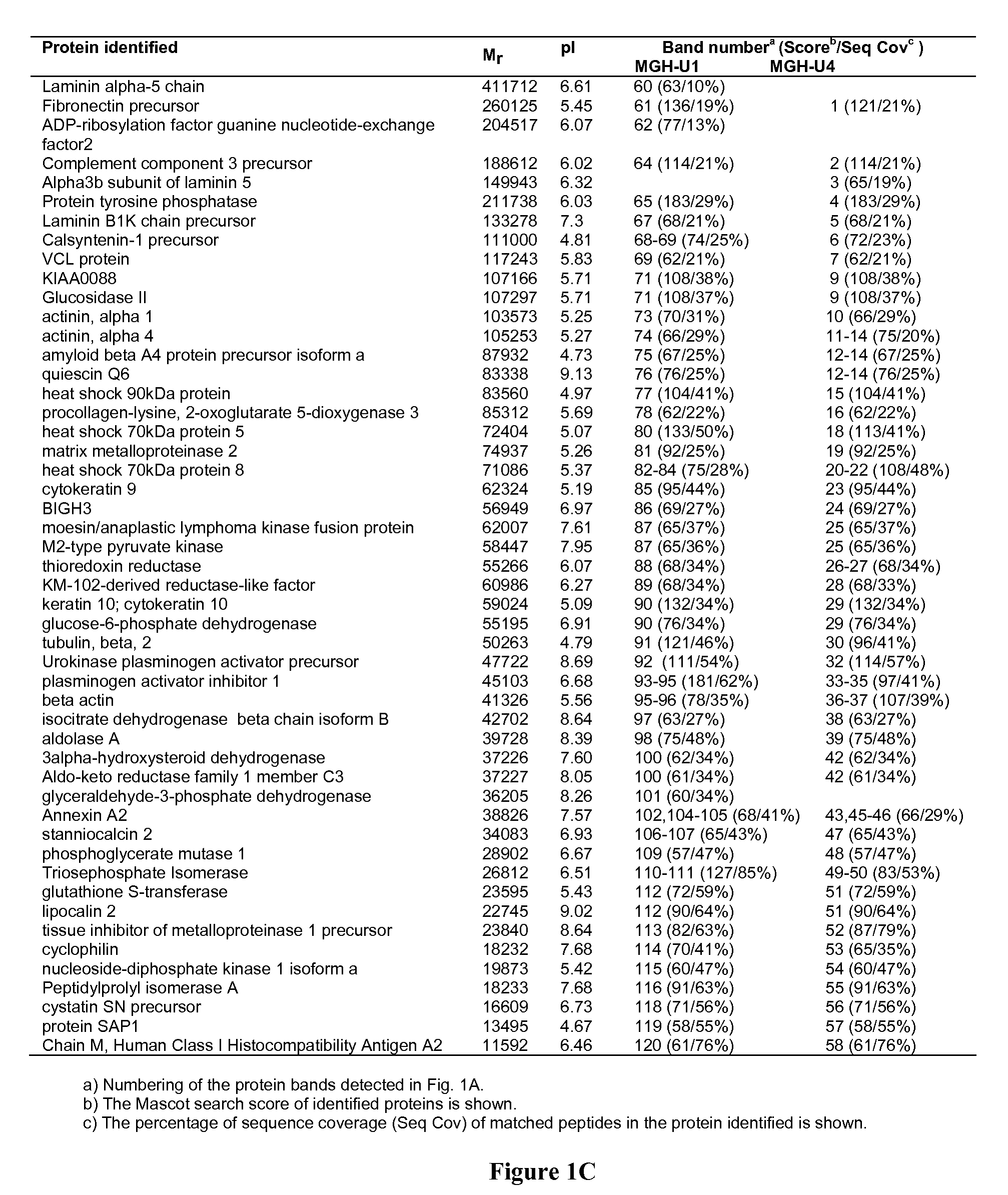
An efficient method for identifying important cancer biomarkers and identifying progression of bladder cancer using pro-u-PA as a clinical tool is provided. Searching for biomarkers critical for bladder carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis, secreted proteomes of highly malignant U1 and pre-malignant U4 cell lines are first analyzed. Proteins in the cultured media of the U1 and U4 cell-lines were systematically examined by SDS-PAGE combined with MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Expression of pro-u-plasminogen activator (pro-u-PA) was confirmed by Western blot analysis and further evaluated. A statistically significant relationship between the low level and absence of pro-u-PA in urine with high stages and grades of the tumor samples was established. Constitutive expression of Ras dominant negative protein led to increased expression of pro-u-PA in cultured media, indicating the loss of pro-u-PA is associated with oncogenic transformation. The loss of pro-u-PA in urine has been identified as a marker of more advanced bladder carcinoma.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Method For Using Protein Databases To Identify Microorganisms
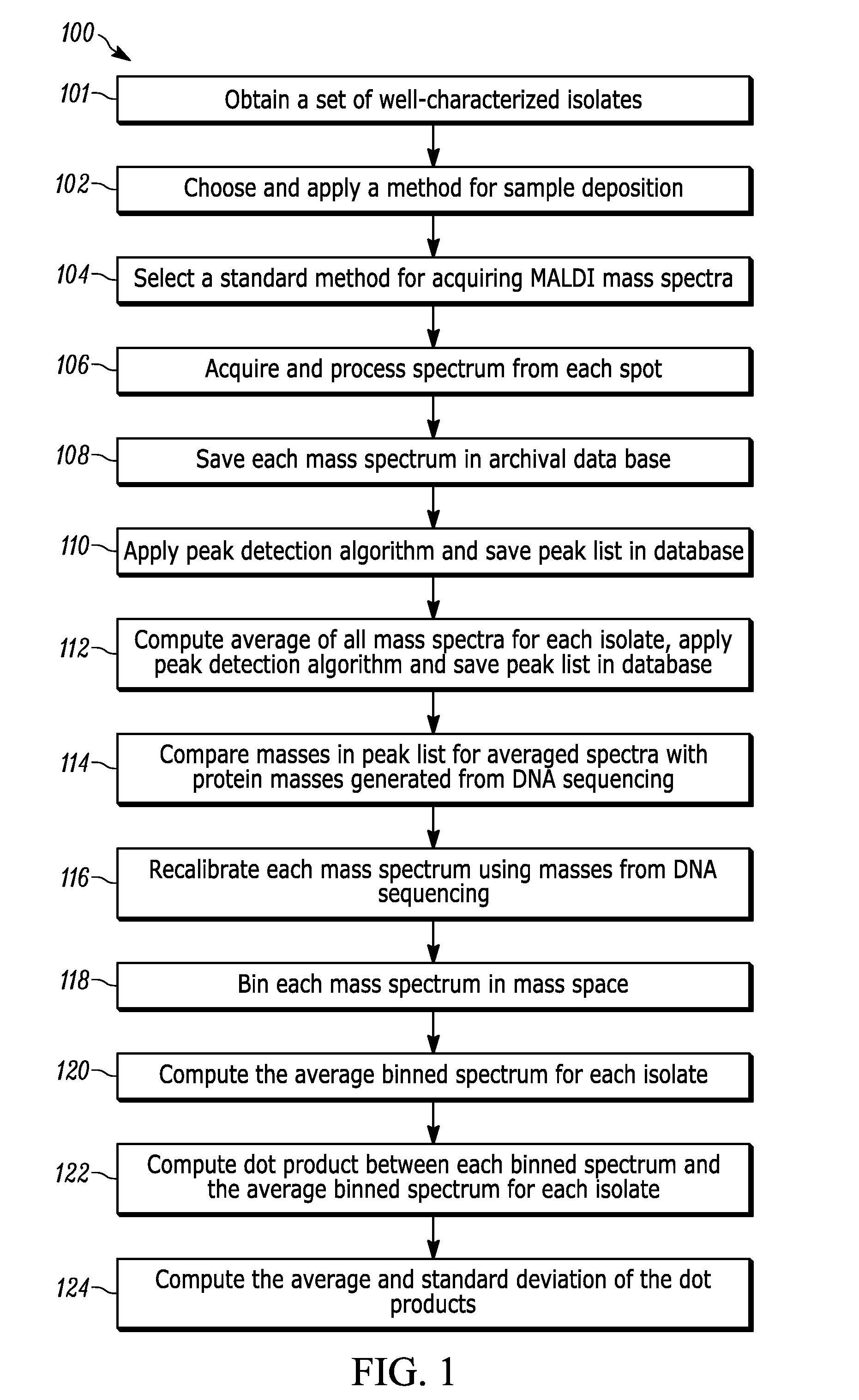
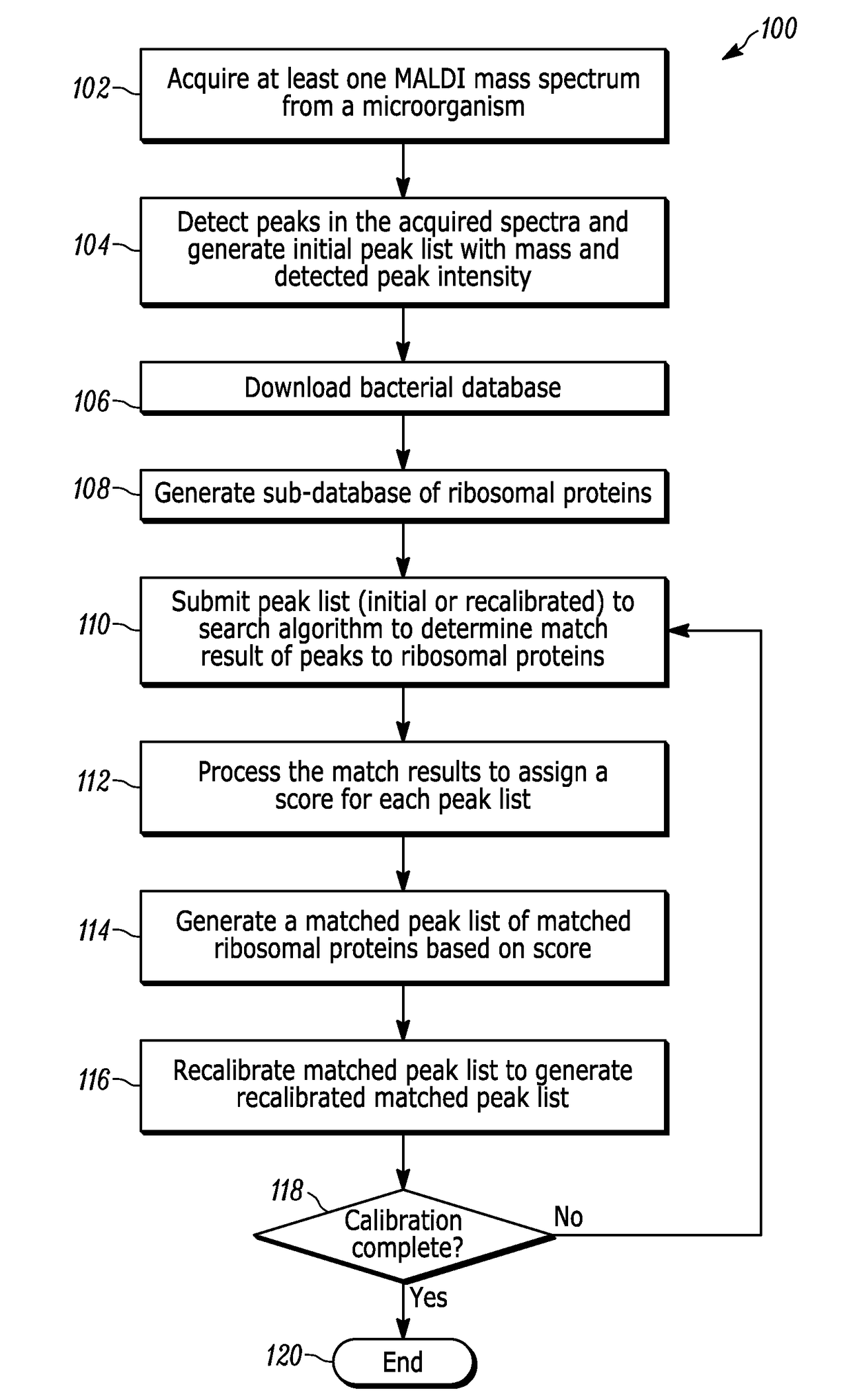
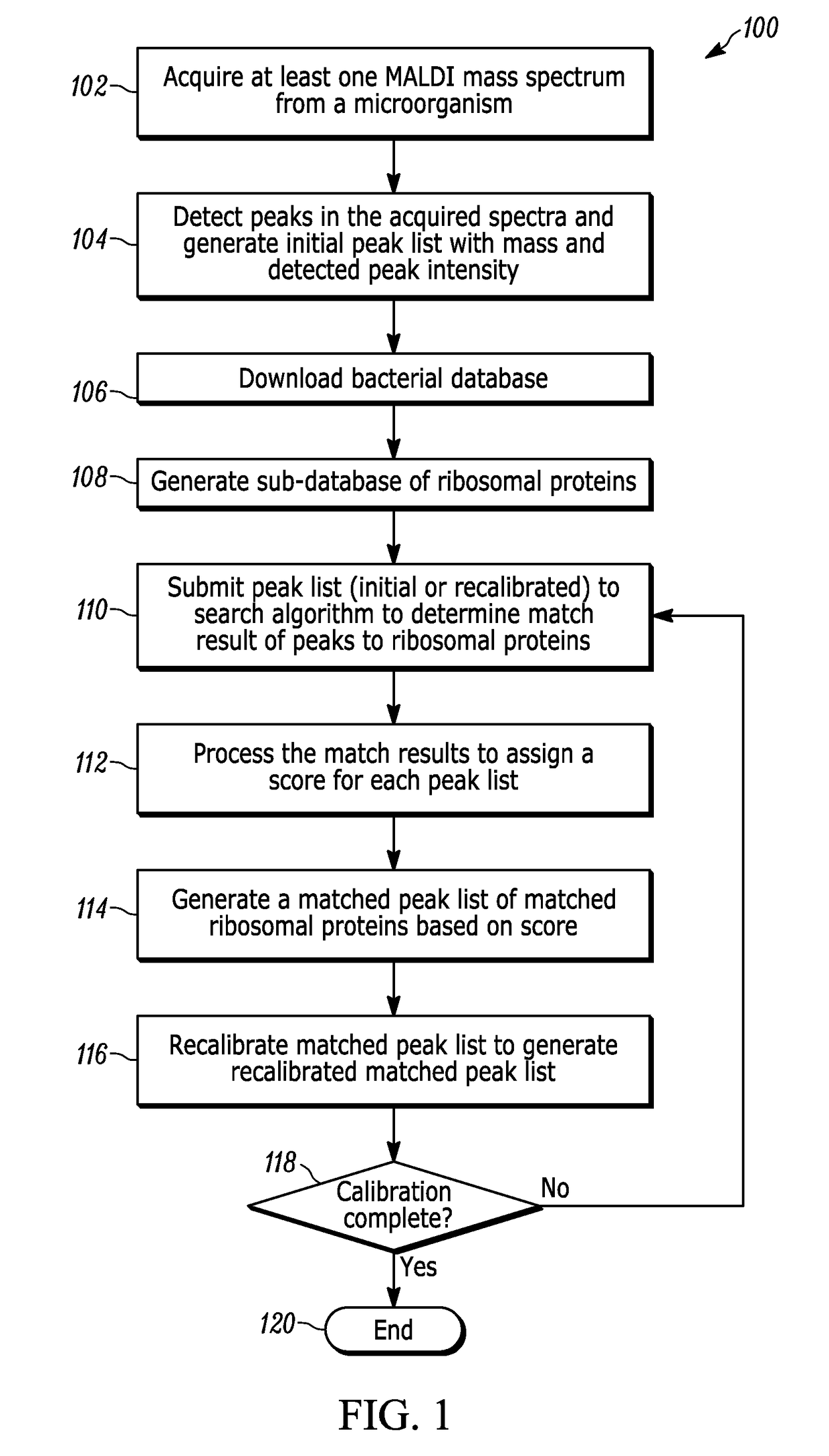
A method for identifying microorganisms by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry includes acquiring a MALDI mass spectrum of a microorganism, detecting peaks in the acquired MALDI spectrum, generating a peak list comprising mass and intensity from the detected peaks in the acquired MALDI spectrum, acquiring a database of protein sequences deduced from DNA sequences for microorganisms, generating a sub-database of ribosomal proteins from the protein sequences and their masses in the database, matching masses of the detected peaks in the acquired MALDI spectrum to masses of the ribosomal proteins in the generated sub-database, scoring the matches obtained above for each represented microorganism, generating a peak list of accurate masses of matched ribosomal proteins, recalibrating the peak list comprising mass and intensity with the peak list of accurate masses of matched ribosomal proteins, identifying a microorganism with the highest score, and repeating until a desired improvement in the recalibrated peak list or a validated identification is achieved.
Owner:VIRGIN INSTR CORP
Conjugates of 1,4,7-triazacyclononanes, dinuclear metal complexes of such conjugates, and methods of use for both 1,4,7-triazacyclononanes and conjugates
Conjugates of 1,3-bis(1,4,7-triazacyclonon-1-yl)-2-hydroxypropanes with a variety of conjugating members are used in the formation of dinuclear metal complexes which bind to phosphate esters. By virtue of their conjugated forms, the complexes are incorporated into chromatographic media, affinity binding reagents, and dyes, which make the complexes useful in a wide range of assays, separations, and purifications. In addition, dinuclear metal complexes of 1,3-bis(1,4,7-triazacyclonon-1-yl)-2-hydroxypropanes that are not so conjugated are used in the detection of phosphate esters of biological species by either MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry or by dye displacement.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Methods and compositions for KIR genotyping
InactiveUS7919279B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene clusterIonization time of flight
The present invention provides methods for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene cluster genotyping using the matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometer. In general, the methods involve amplifying a plurality of target sequences of a plurality of KIR genes, and detecting the presence or absence of a plurality of single SNPs of the plurality of KIR genes by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The invention also features compositions, including arrays of capture primers and optionally extension primers on a substrate surface, and kits, for use in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Method of detection of gram-negative bacteria periplasmic space and cell wall outer membrane proteins by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20160138068A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMatrix solutionBeta lactam antibiotic
The invention relates to a method of detection of Gram-negative bacteria periplasmic space and cell wall outer membrane proteins by mass spectrometry, wherein the periplasmic space and cell wall outer membrane proteins are extracted from the bacteria, and the proteins to be detected are stabilized by an inhibitor and / or a substrate of the given protein, the proteins are then dissolved, placed onto a MALDI-TOF plate, covered with matrix solution, measured by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, and the resulting spectra are compared to the reference peaks of the given protein. Preferably, the proteins are beta-lactamases and their detection can be used to quickly determine the bacterial resistance against beta-lactam antibiotics, minimizing the false-positive results.
Owner:UNIVERZITA KARLOVA V PRAZE LEKARSKA FAKULTA V PLZNI
Method of identifying cancer biomarkers and cancer progression
InactiveUS20090208980A1Efficient and effectiveEfficiently detecting cancer progressionDisease diagnosisWestern blotWilms' tumor
An efficient method for identifying important cancer biomarkers and identifying progression of bladder cancer using pro-u-PA as a clinical tool is provided. Searching for biomarkers critical for bladder carcinoma diagnosis and prognosis, secreted proteomes of highly malignant U1 and pre-malignant U4 cell lines are first analyzed. Proteins in the cultured media of the U1 and U4 cell-lines were systematically examined by SDS-PAGE combined with MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Expression of pro-u-plasminogen activator (pro-u-PA) was confirmed by Western blot analysis and further evaluated. A statistically significant relationship between the low level and absence of pro-u-PA in urine with high stages and grades of the tumor samples was established. Constitutive expression of Ras dominant negative protein led to increased expression of pro-u-PA in cultured media, indicating the loss of pro-u-PA is associated with oncogenic transformation. The loss of pro-u-PA in urine has been identified as a marker of more advanced bladder carcinoma.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Mass spectrometry substrate and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN106872562BSuitable for large-scale useEasy to makeFixed microstructural devicesPreparing sample for investigationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Mass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention provides a dedicated substrate carrying a BIOMARK in MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry detection. The substrate comprises a hole-outside hydrophobic region made of a chemical surface modifier, an intra-circle hydrophilic region modified by a special chemical reagent, surface round holes or square holes for titrating a BIOMARK sample, a substrate material having tough texture and good flatness, and a substrate surface having a single-side polished mirror effect. Besides, the substrate can further include a two-dimensional code for identification. The micro / nano structural substrate can effectively enrich the sample, crystal grows uniformly, the mass spectrometry curve sample for BIOMARK biological detection is high in peak accuracy, the signal-to-noise ratio is high, and the base line is low.
Owner:毅新兴业(北京)科技有限公司
Conjugates of 1,4,7-triazacyclononanes, dinuclear metal complexes of such conjugates, and methods of use for both 1,4,7-triazacyclononanes and conjugates
ActiveUS20140057293A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansSolid sorbent liquid separationBiological speciesOrganophosphate
Conjugates of 1,3-bis(1,4,7-triazacyclonon-1-yl)-2-hydroxypropanes with a variety of conjugating members are used in the formation of dinuclear metal complexes which bind to phosphate esters. By virtue of their conjugated forms, the complexes are incorporated into chromatographic media, affinity binding reagents, and dyes, which make the complexes useful in a wide range of assays, separations, and purifications. In addition, dinuclear metal complexes of 1,3-bis(1,4,7-triazacyclonon-1-yl)-2-hydroxypropanes that are not so conjugated are used in the detection of phosphate esters of biological species by either MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry or by dye displacement.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Protein markers for the diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian and breast cancer
ActiveUS8187889B2Peptide librariesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseProtein markers
Plasma samples of ovarian and breast cancer patients were used to search for markers of cancer, using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and MALDI TOF mass spectrometry. Truncated forms of cytosolic serine hydroxymethyl transferase (cSHMT), T-box transcription factor 3 (Tbx3) and utrophin were aberrantly expressed in samples from cancer patients, as compared to samples from noncancer cases. Aberrant expression of proteins was validated by immunoblotting of plasma samples with specific antibodies to cSHMT, Tbx3 and utrophin. A cohort of 79 breast and 39 ovarian cancer patients, and 31 individuals who were either healthy or had noncancerous conditions was studied. We observed increased expression of truncated cSHMT, Tbx3 and utrophin in plasma samples obtained from patients at early stages of disease. The results indicate that cSHMT, Tbx3, utrophin and truncated forms thereof can be used as components of multiparameter monitoring of ovarian and breast cancer.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES
Mass Spectrometry Method And Apparatus For Clinical Diagnostic Applications
ActiveUS20160291047A1Sufficient massSufficient powerTime-of-flight spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryComputerized system
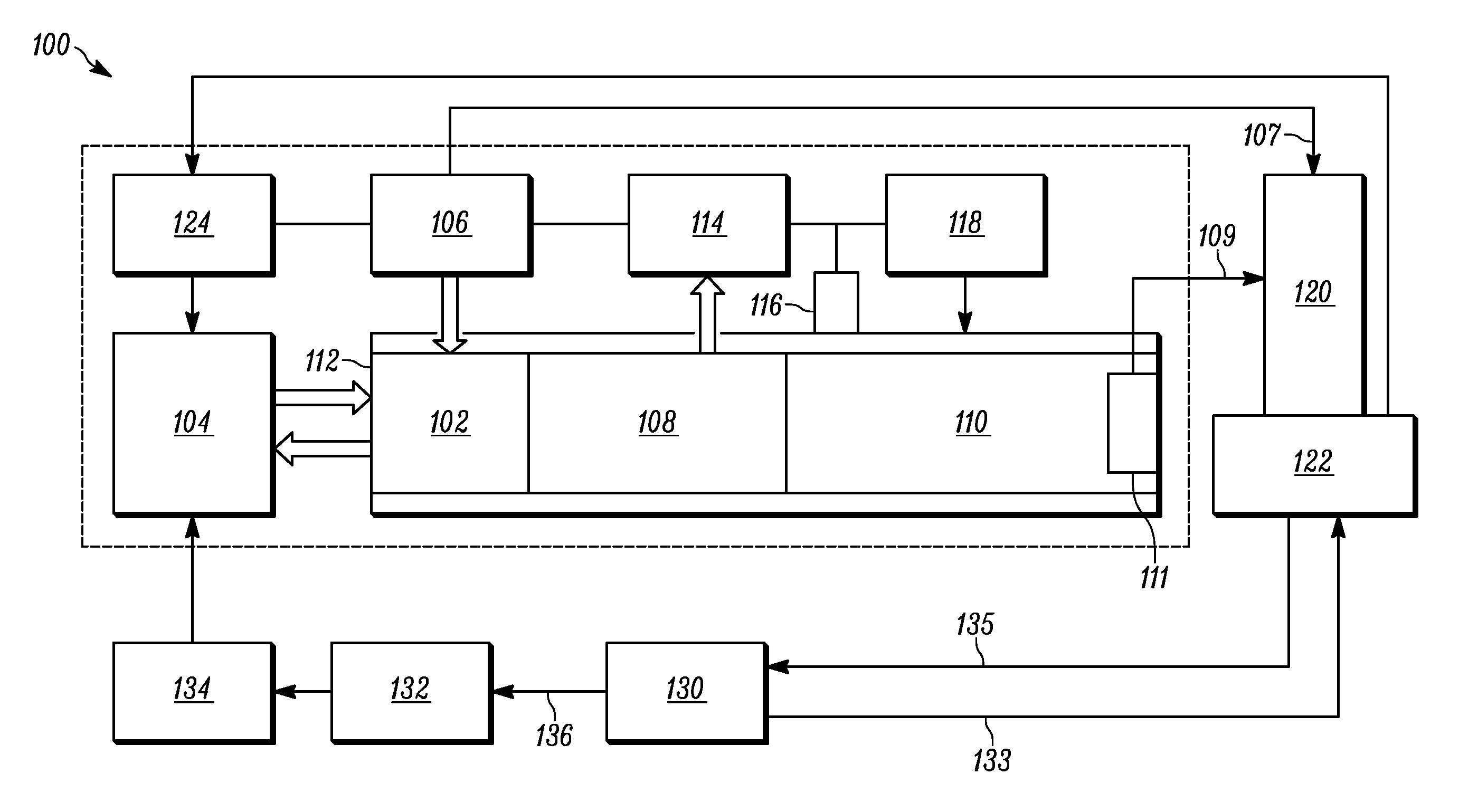
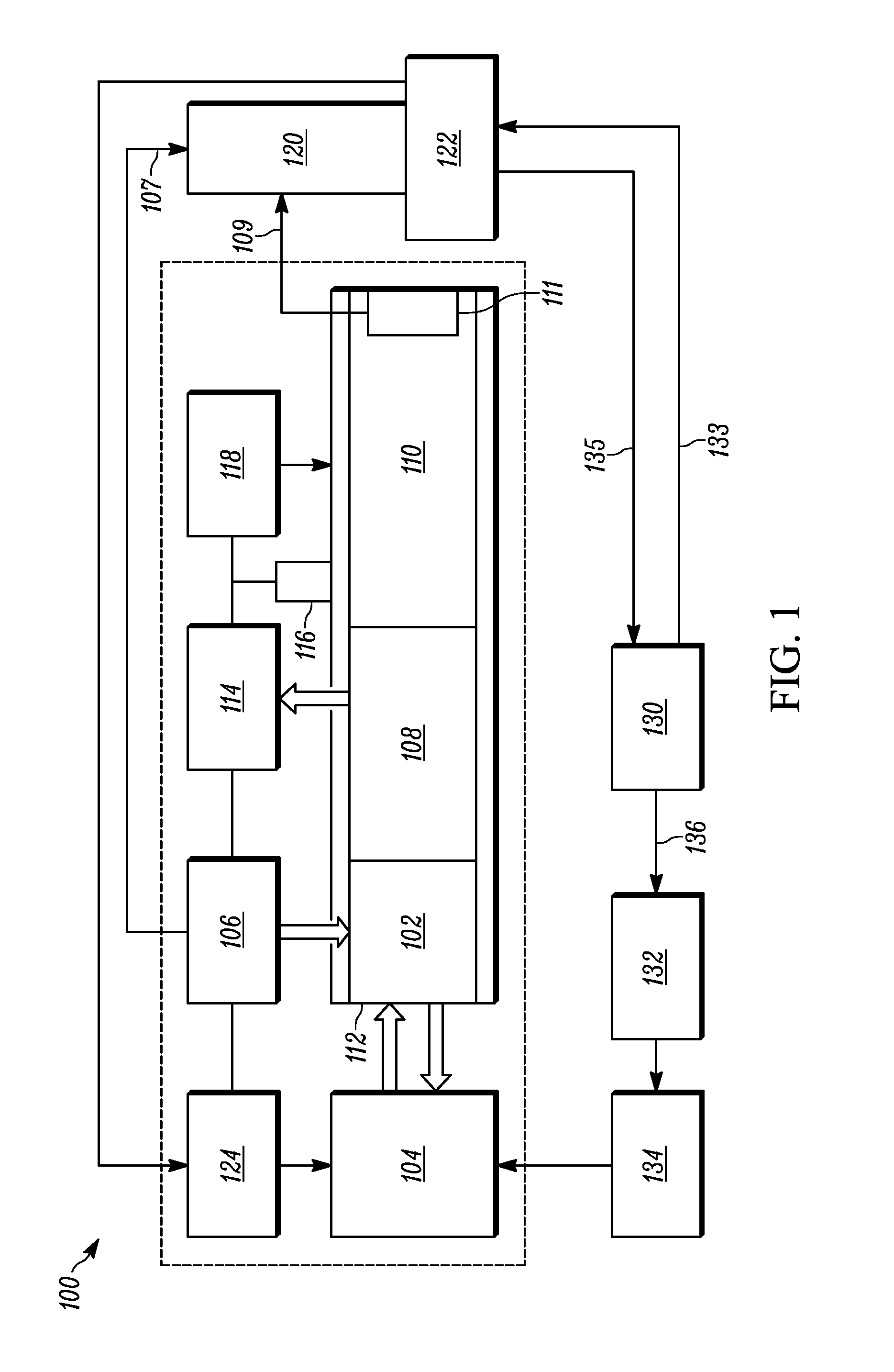
A mass spectrometer system for analysis of clinical samples includes a source of clinical samples. A controller receives the clinical samples from the source of clinical samples. A sample preparation system receives clinical sample from the controller and processes the samples to produce an extract suitable for analysis by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and deposits the extract on a sample plate together with a MALDI matrix. A sample plate loading mechanism transports sample plates from the sample preparation system into an evacuated ion source of a MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer. A MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer ionizes and analyzes samples on the sample plate and generates a mass spectrum of components in the clinical samples. A computer system receives data from the MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer and processes and interprets the data to generate a mass spectrum.
Owner:VIRGIN INSTR CORP
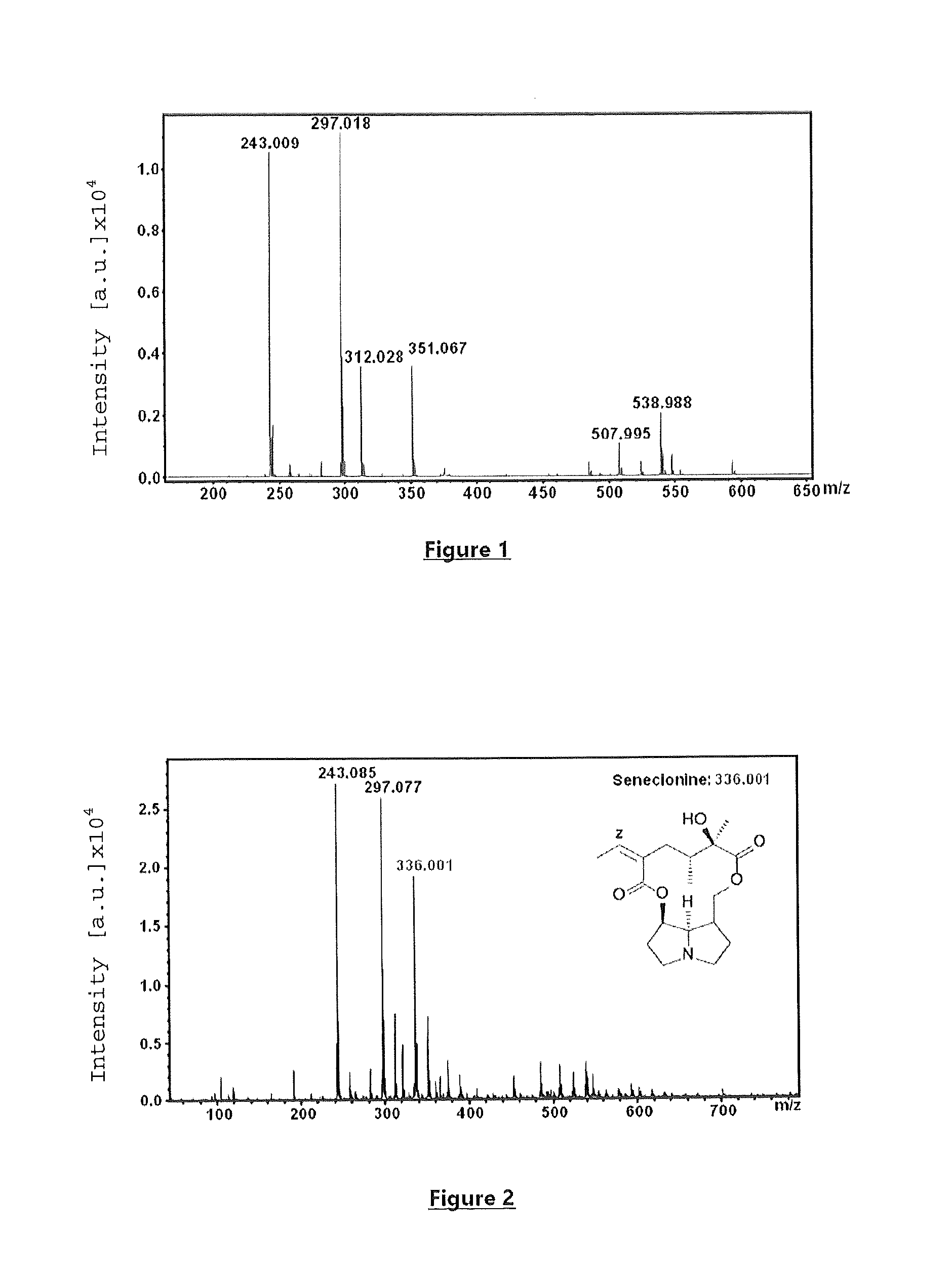
New use for a compound as a matrix in the specific detection, identification and/or quantification of alkaloids by maldi-tof mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20140319331A1High selectivityHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryParticle spectrometer methodsTime-of-flight mass spectrometrySpecific detection
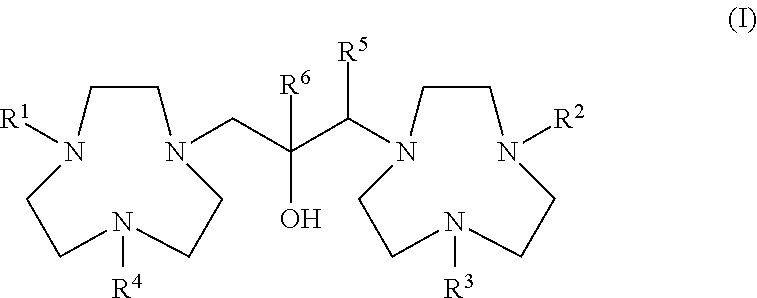
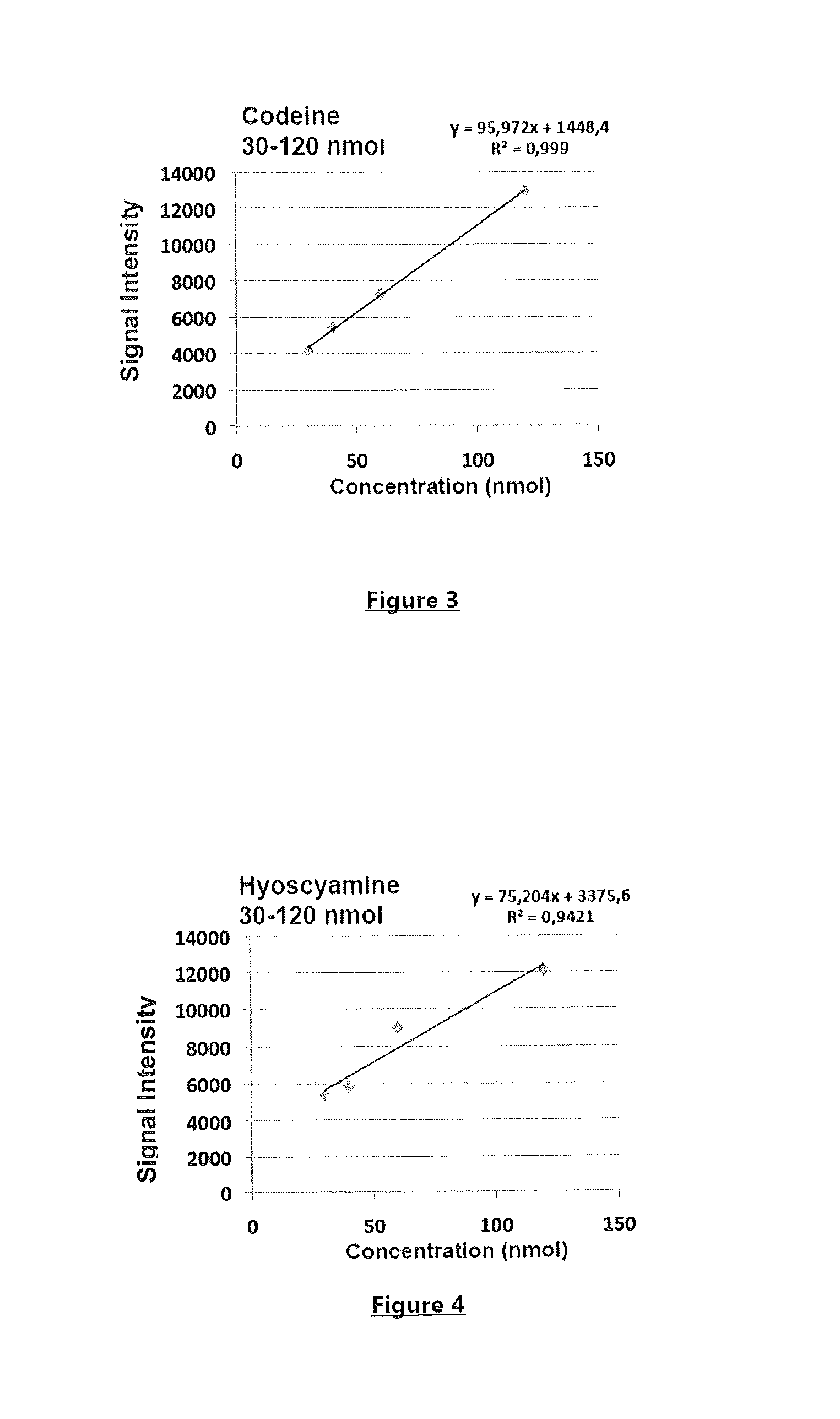
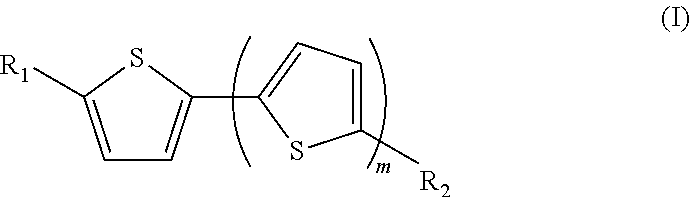
There is provided (i) a method of analysing small molecules that may have a mass of <800 Da, in particular alkaloids, said method being generally referred to as MALDI-TOF-MS (or MALDI time-of-flight mass spectrometry), which is an acronym for a method of analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Also provided is (ii) a molecule according to formula (I) and the use of the molecule as a matrix in the analysis method.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ANGERS +1
In vitro diagnostic method for an invasive fungal infection using MALDI-TOFF mass spectrometry
ActiveUS9360470B2Increased contact surface areaEasy to separateComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid formationFungal microorganisms
A method for the in vitro diagnosis of an invasive fungal infection by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The method involves, providing a liquid biological sample from a mammal, said biological sample containing, in particular, proteins and / or lipids and / or salts and / or polysaccharides and / or oligosaccharides and / or monosaccharides capable of forming complexes with said proteins and / or lipids and / or salts; treating said sample with biological liquid so as to extract said polysaccharides and / or oligosaccharides and / or monosaccharides; determining, by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, whether or not there is present among said extracted polysaccharides, oligosaccharides and / or monosaccharides, at least one given compound of interest coming from said fungal microorganism and chosen from polysaccharides, oligosaccharides and monosaccharides; and deducing, if said given compound of interest is present in said sample, that said mammal is suffering from an invasive fungal infection.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALER & UNIV DE LILLE +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com