Patents
Literature
108 results about "Periplasmic space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the periplasmic space in gram-negative bacteria. Using cryo-electron microscopy it has been found that a much smaller periplasmic space is also present in gram-positive bacteria.
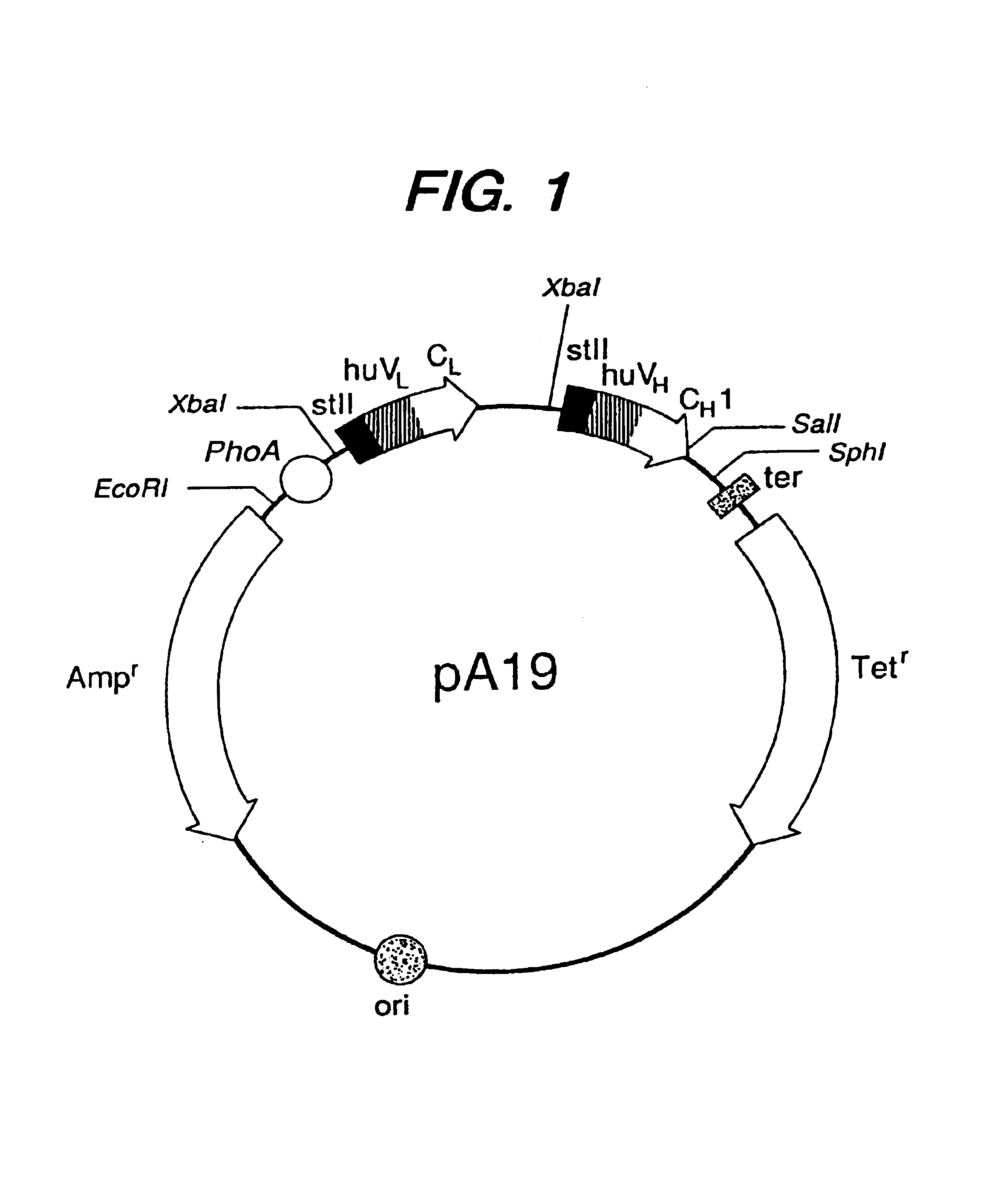
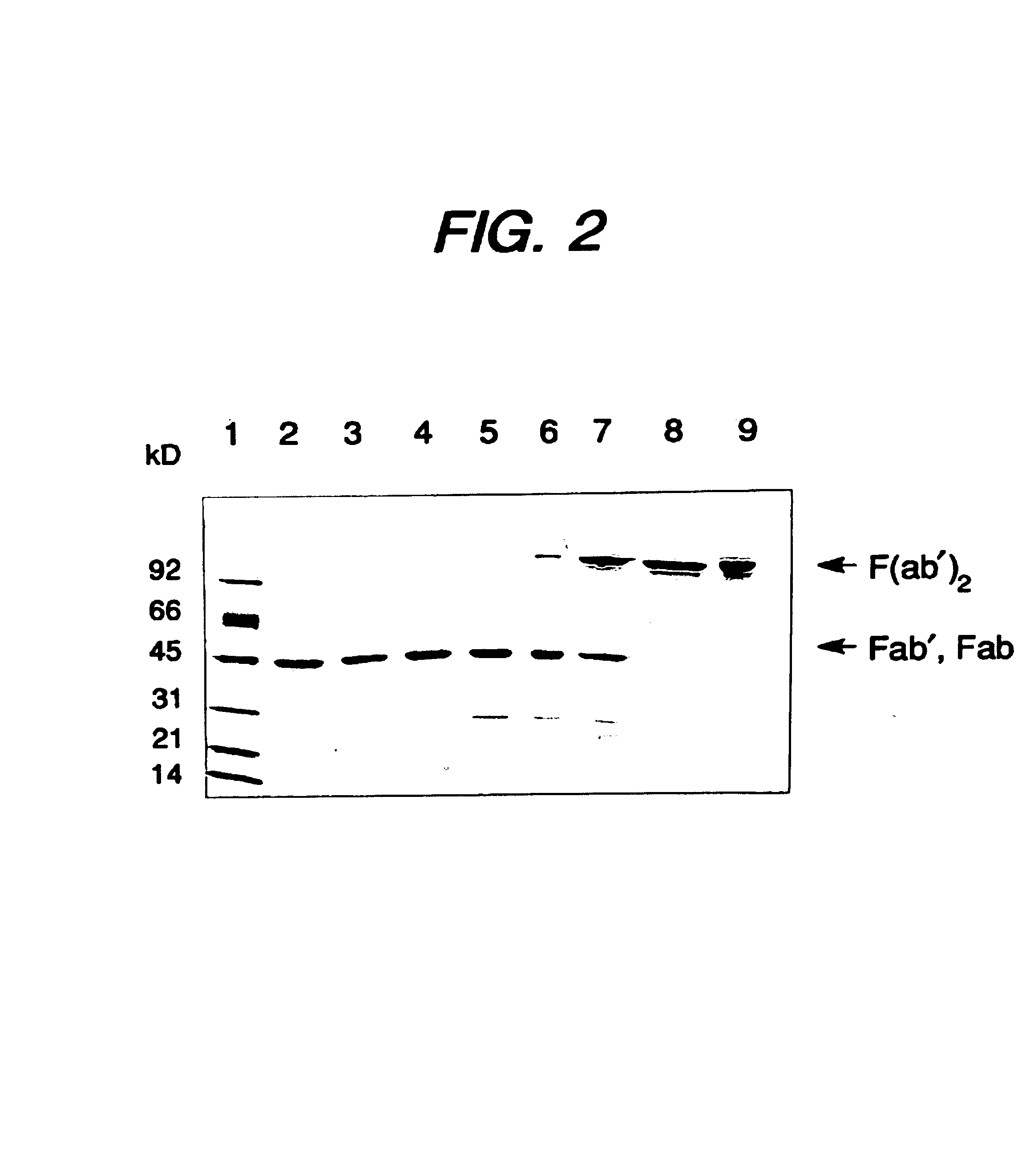
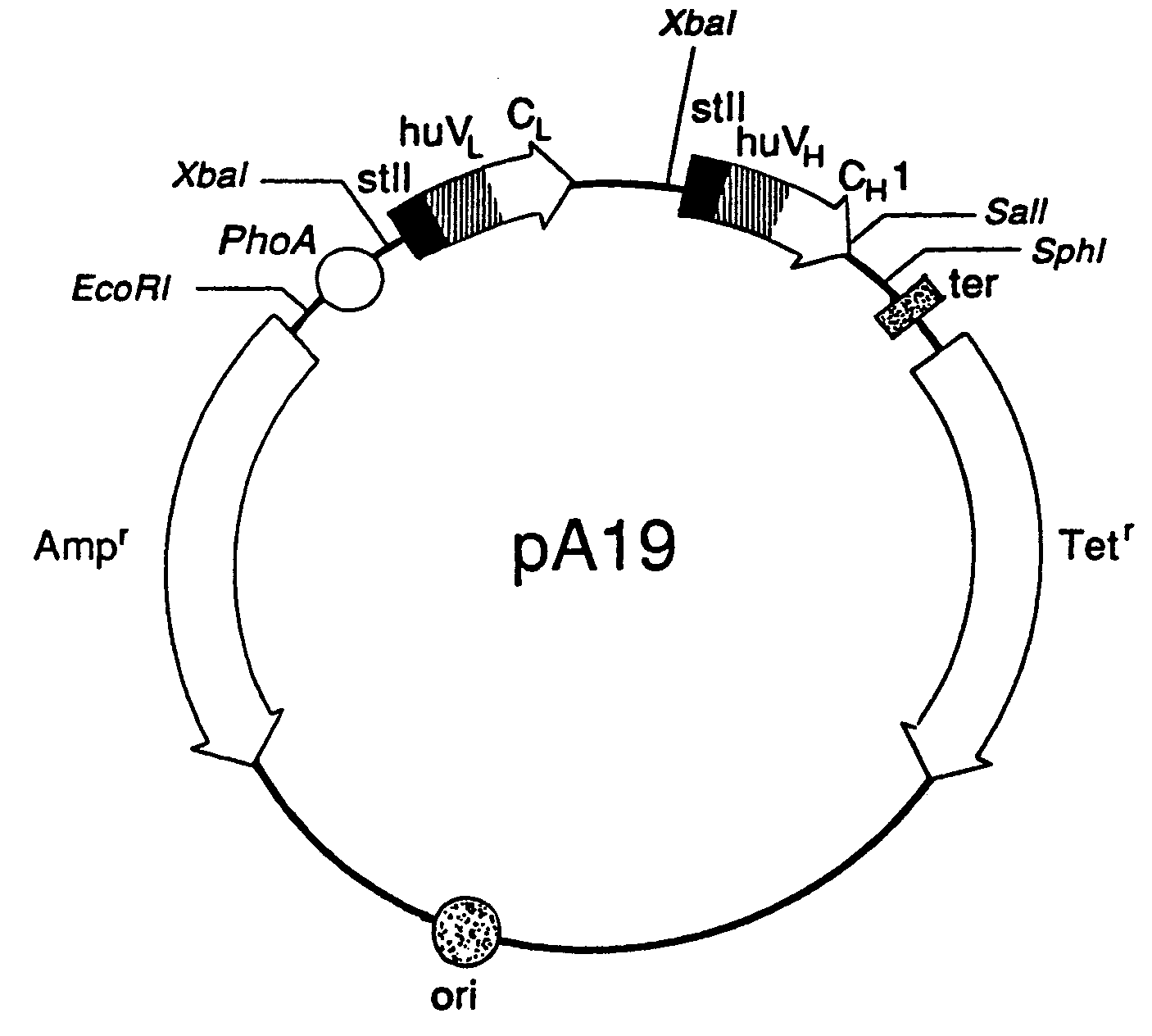
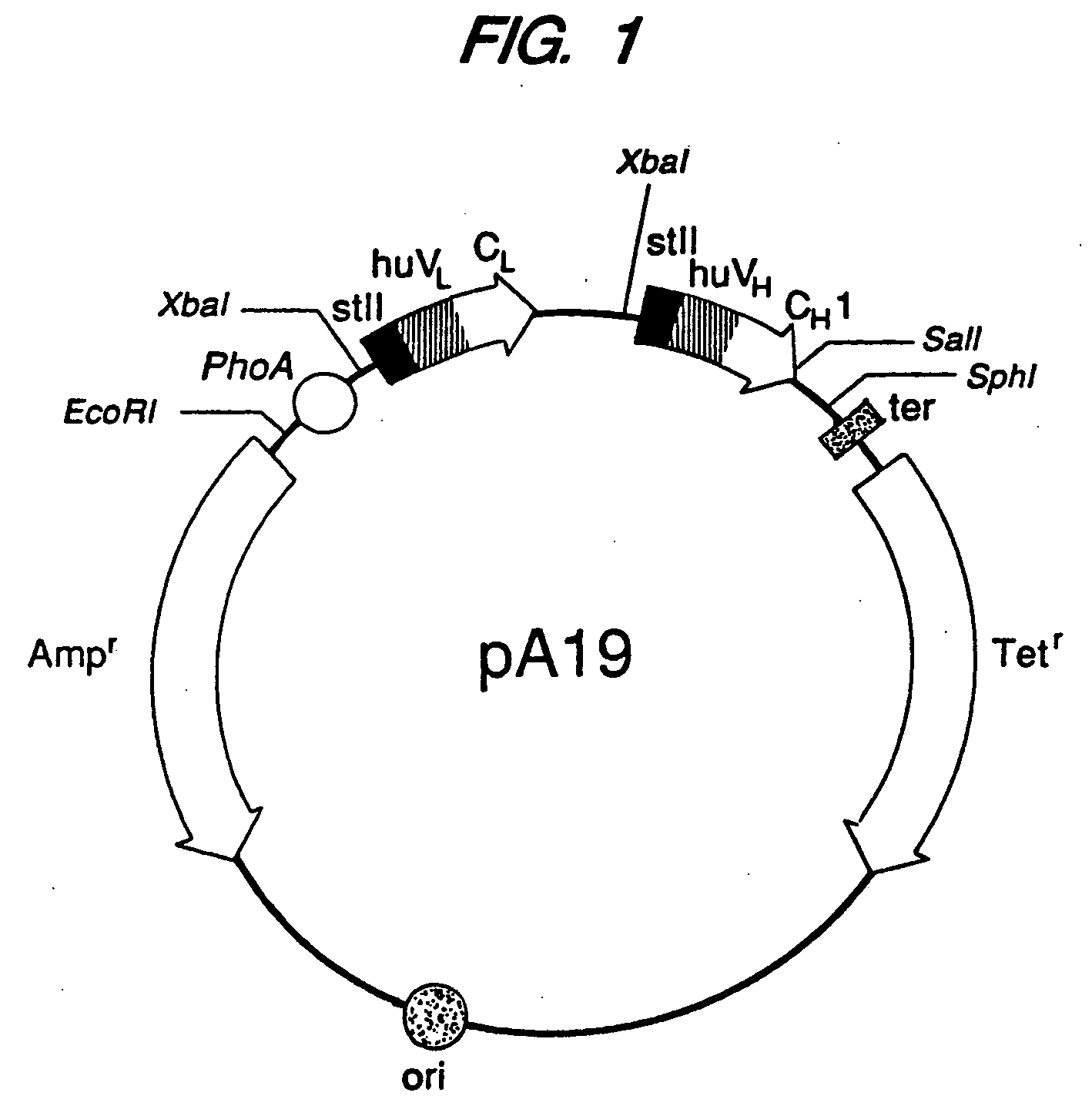
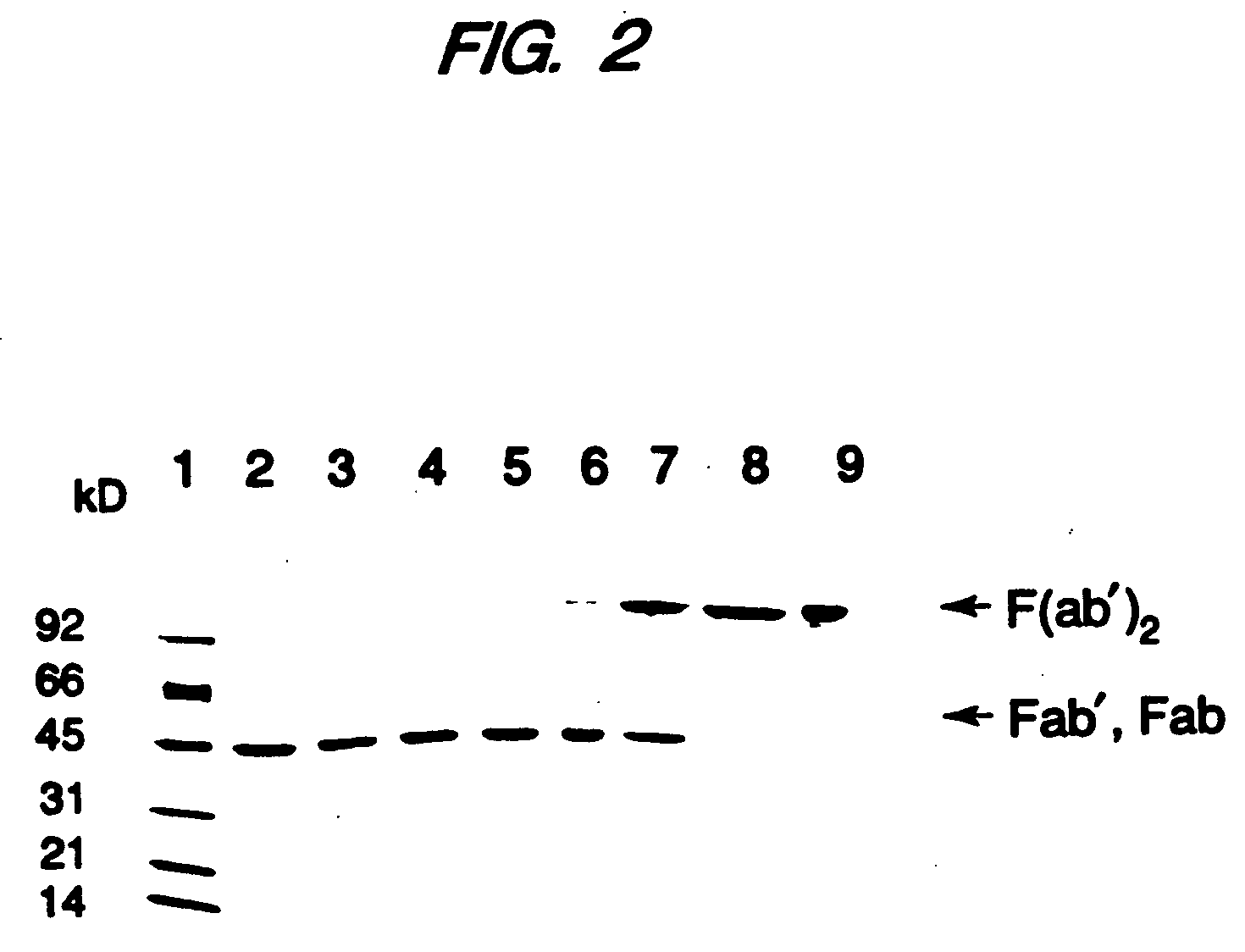
Expression of functional antibody fragments
InactiveUS7018809B1Easy to prepareFacilitated releaseHybrid immunoglobulinsSerum immunoglobulinsMicroorganismHeavy chain
Methods for the high yield production of antibody Fv-containing polypeptides, especially Fab′ and F(ab′)2 antibody fragments are provided. Expression of heavy and light chain Fv in a microbial secretory system is followed by recovery of Fv from the periplasm under conditions that maintain a cysteine residue as a free thiol. The free thiol is reacted with free thiol of an antibody fragment of the same or differing specificity, or with agents such as diagnostic labels or therapeutic moieties. The products offer advantages of homogeneity and purity not available through the use of known methods for preparing such derivatives.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for rapidly screening microbial hosts to identify certain strains with improved yield and/or quality in the expression of heterologous proteins
ActiveUS20080269070A1High yieldQuality improvementBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an array for rapidly identifying a host cell population capable of producing heterologous protein with improved yield and / or quality. The array comprises one or more host cell populations that have been genetically modified to increase the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein production, decrease the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein degradation, or both. One or more of the strains in the array may express the heterologous protein of interest in a periplasm compartment, or may secrete the heterologous protein extracellularly through an outer cell wall. The strain arrays are useful for screening for improved expression of any protein of interest, including therapeutic proteins, hormones, a growth factors, extracellular receptors or ligands, proteases, kinases, blood proteins, chemokines, cytokines, antibodies and the like.
Owner:PFENEX
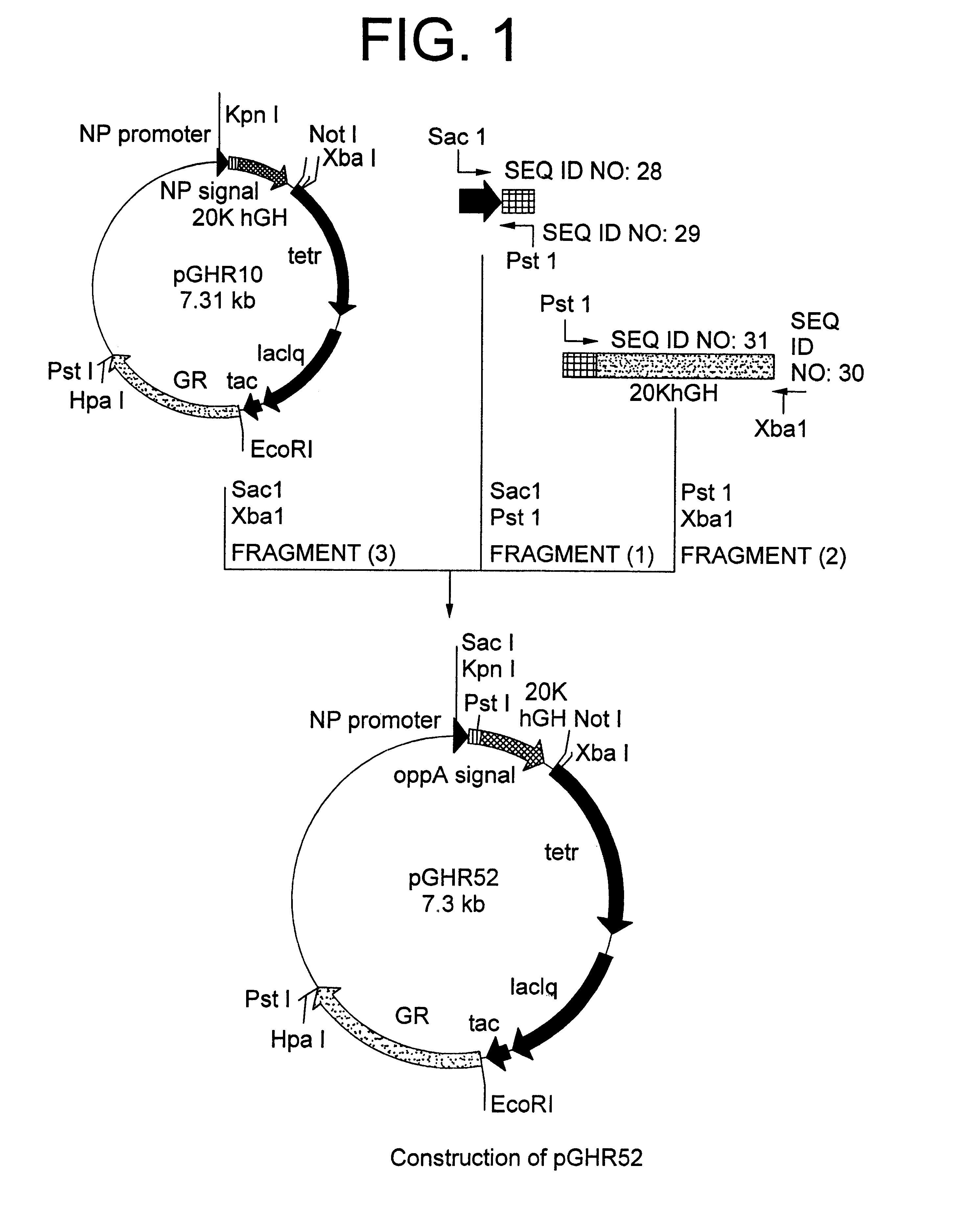
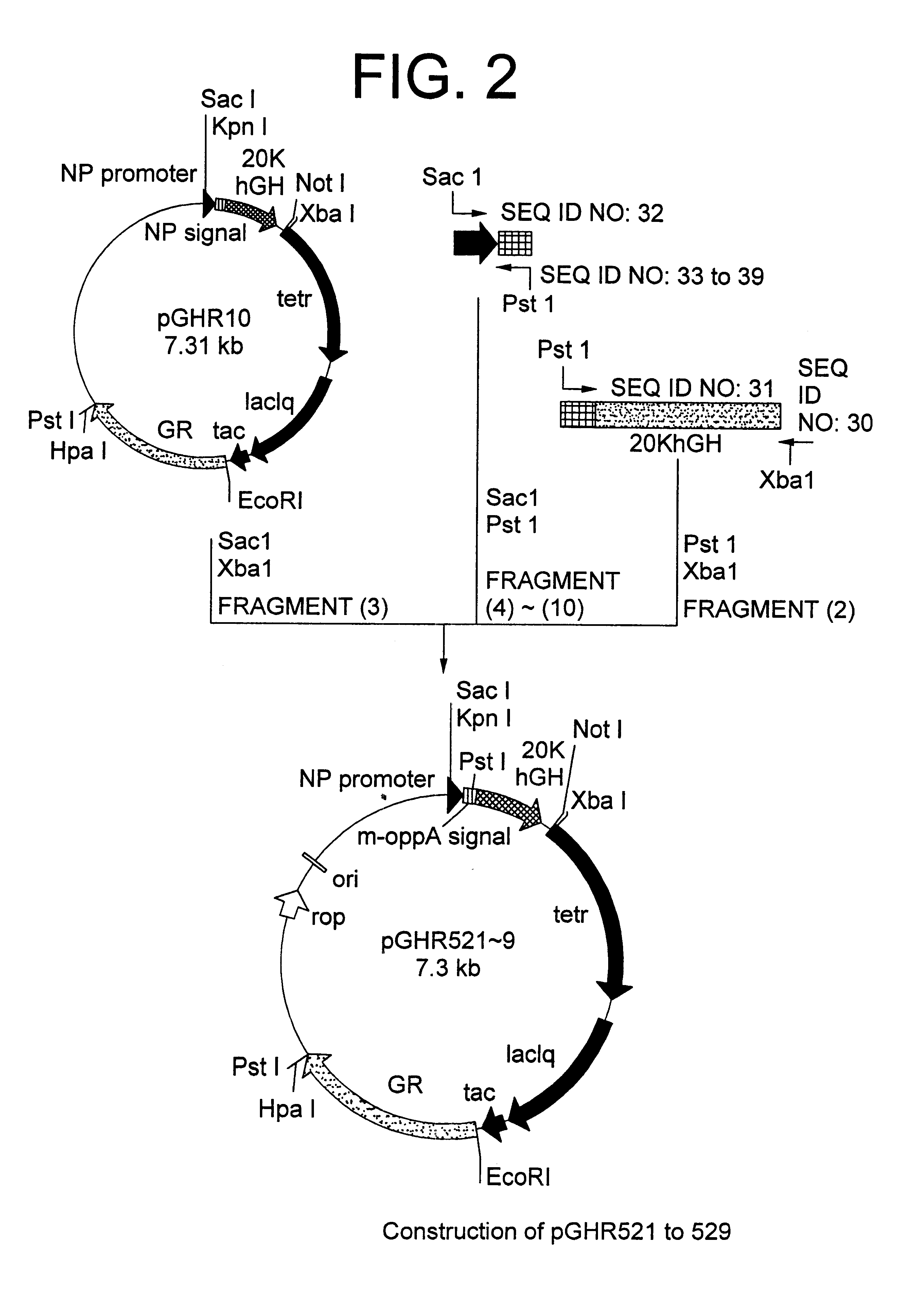
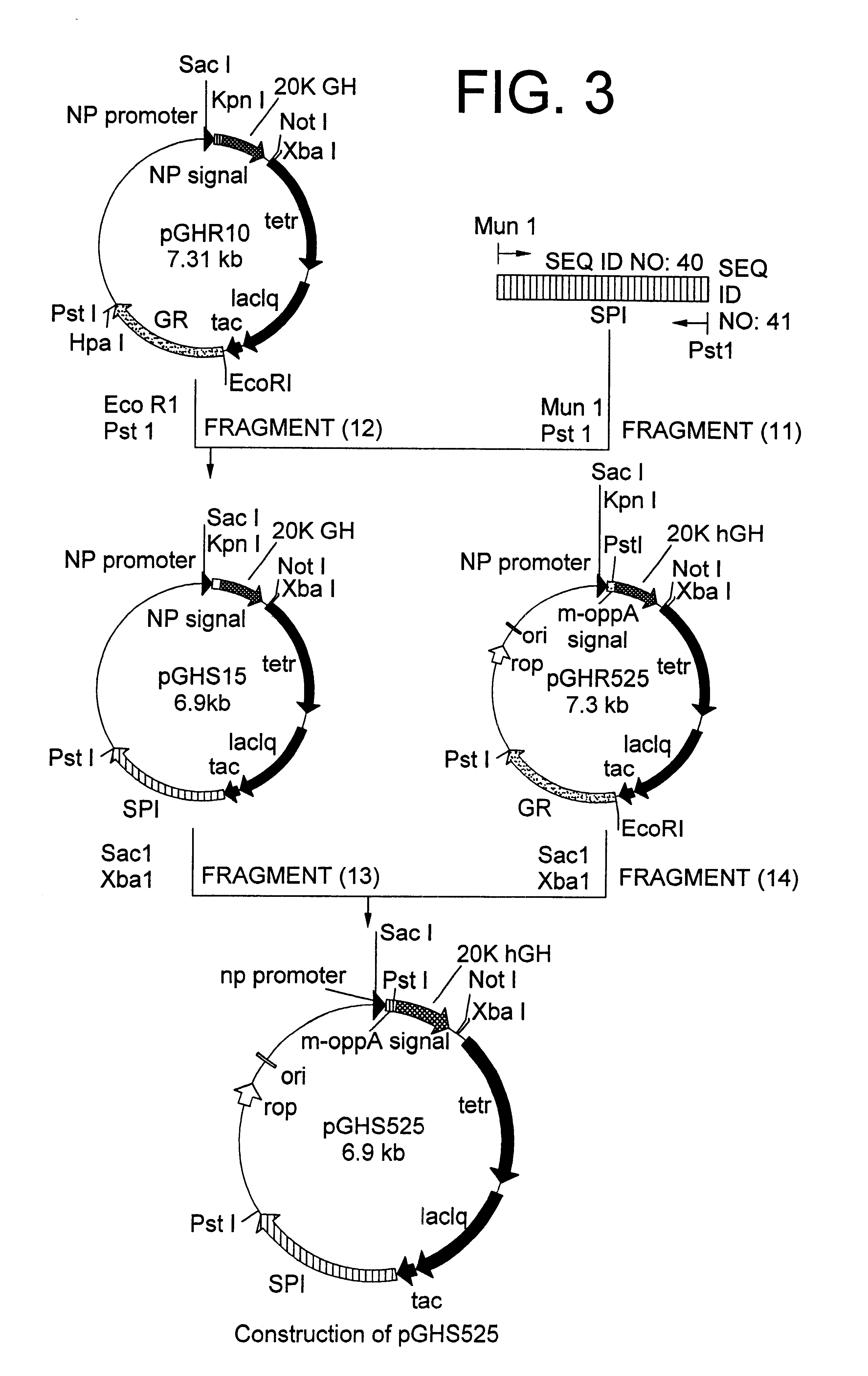
Method for secretory production of human growth hormone
InactiveUS6436674B1Increase productionDecreased tendency for lysisBacteriaHydrolasesHuman growth hormoneA-DNA
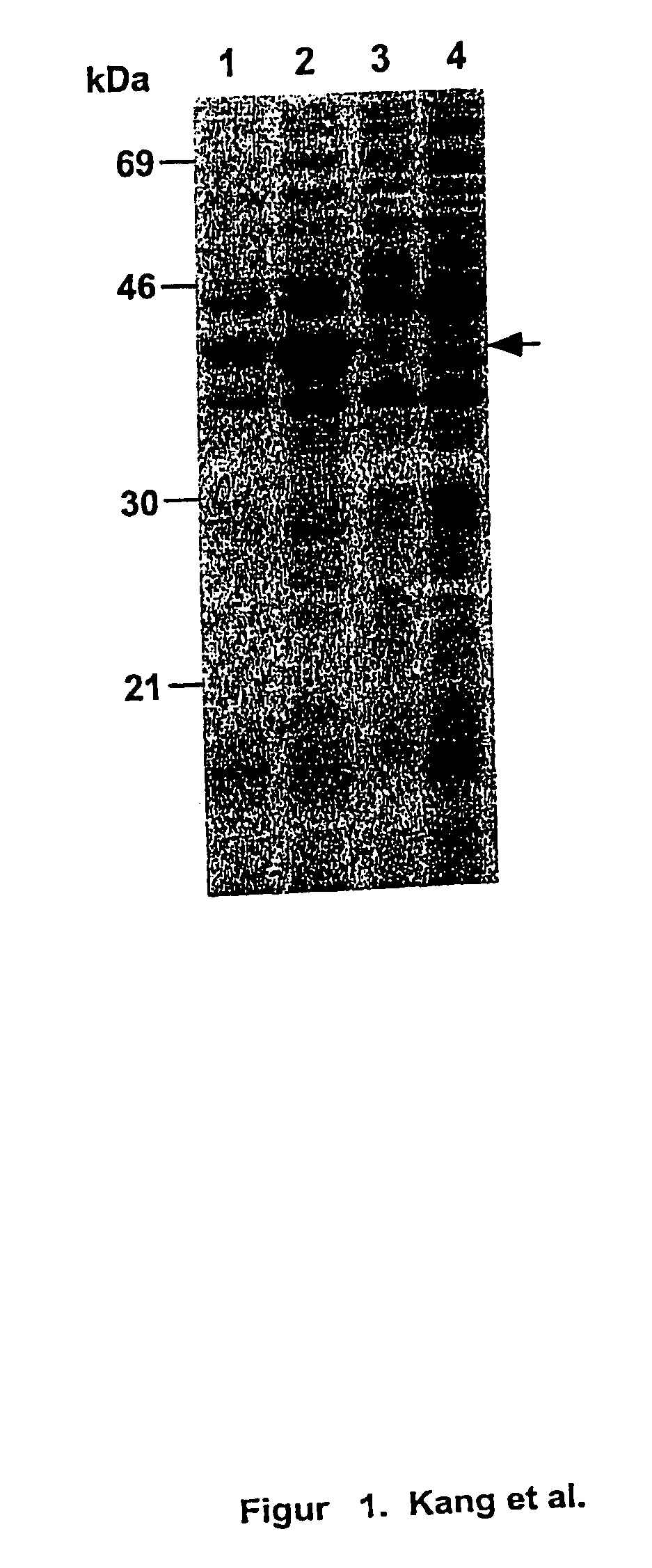
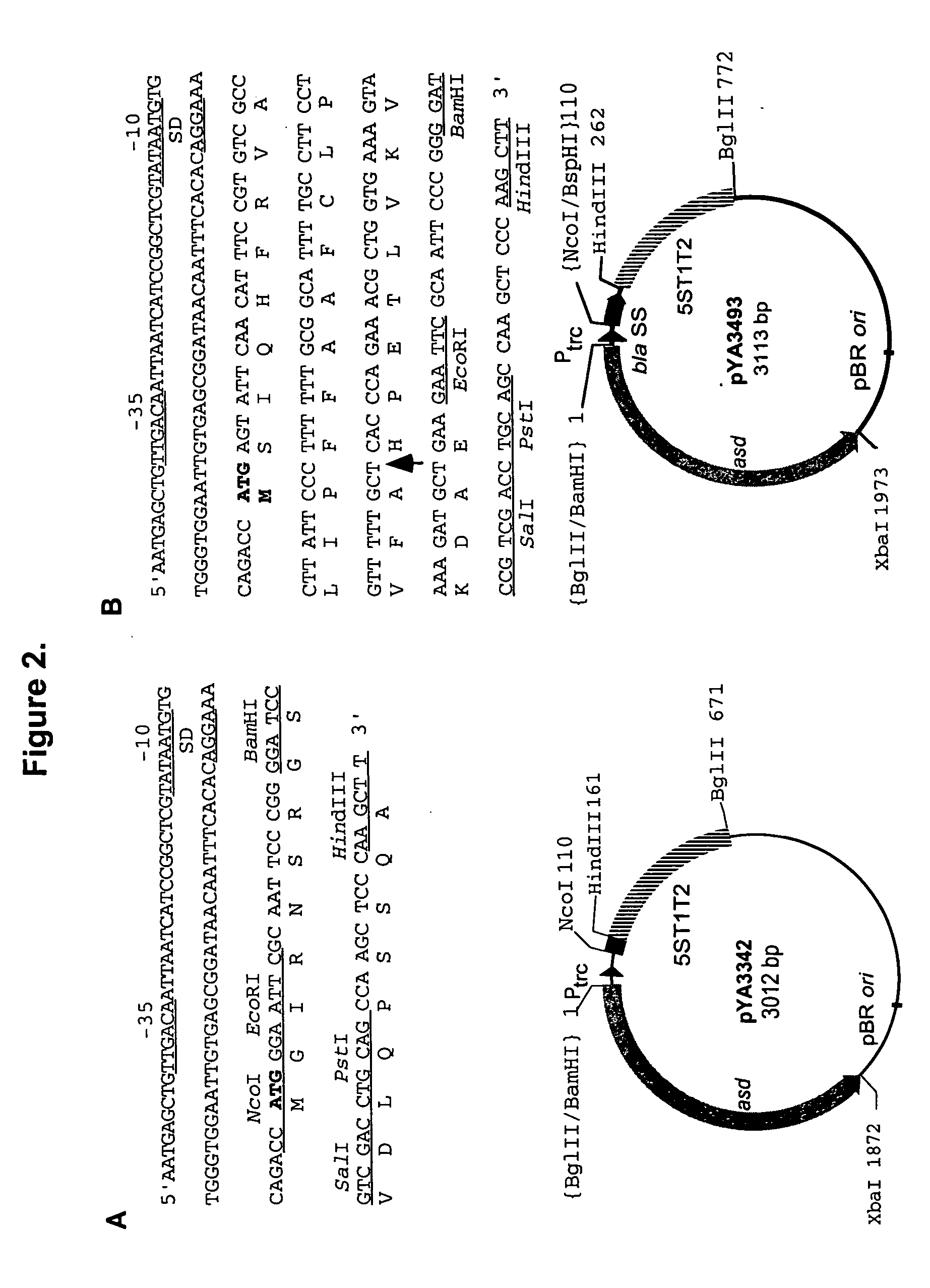
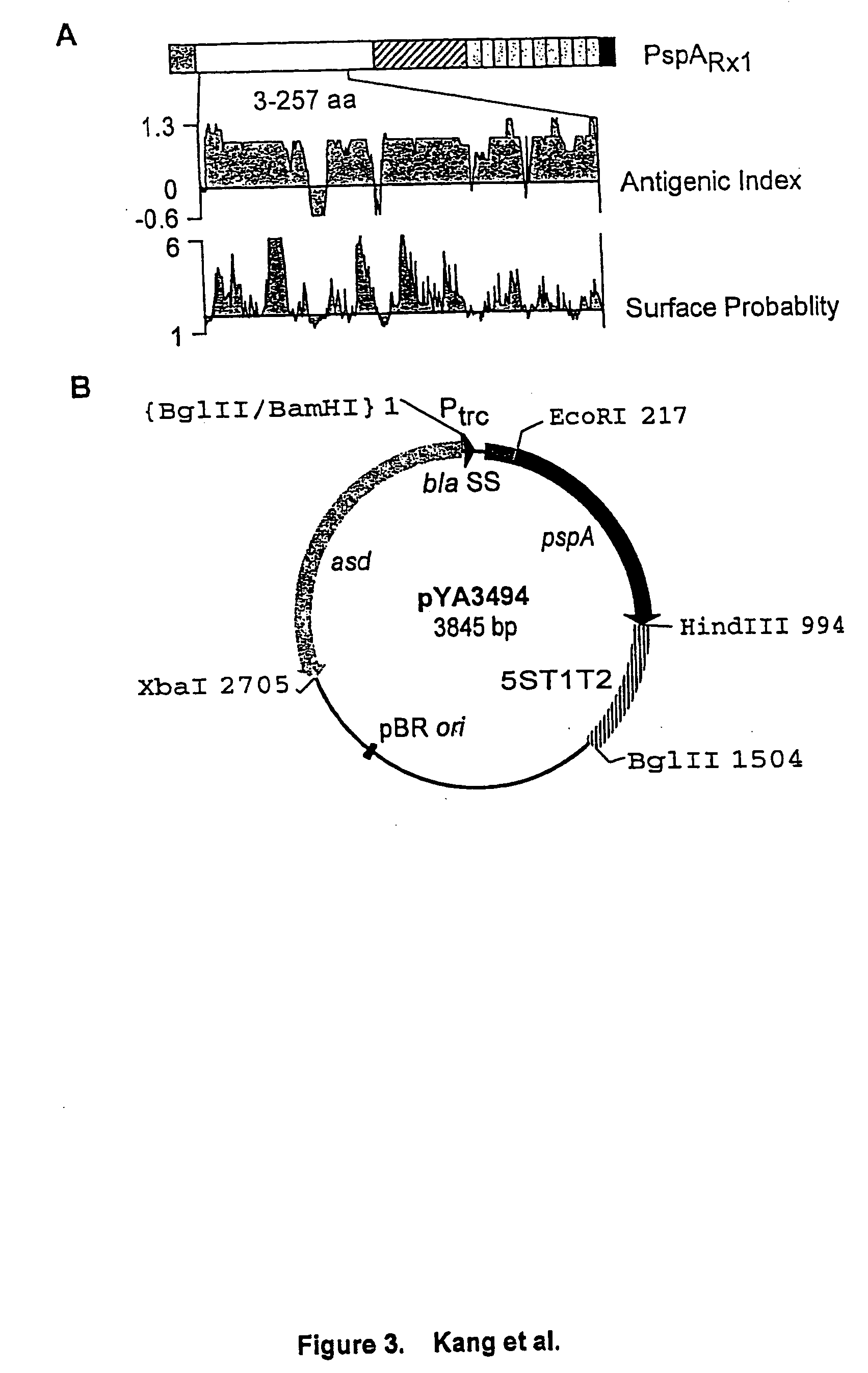
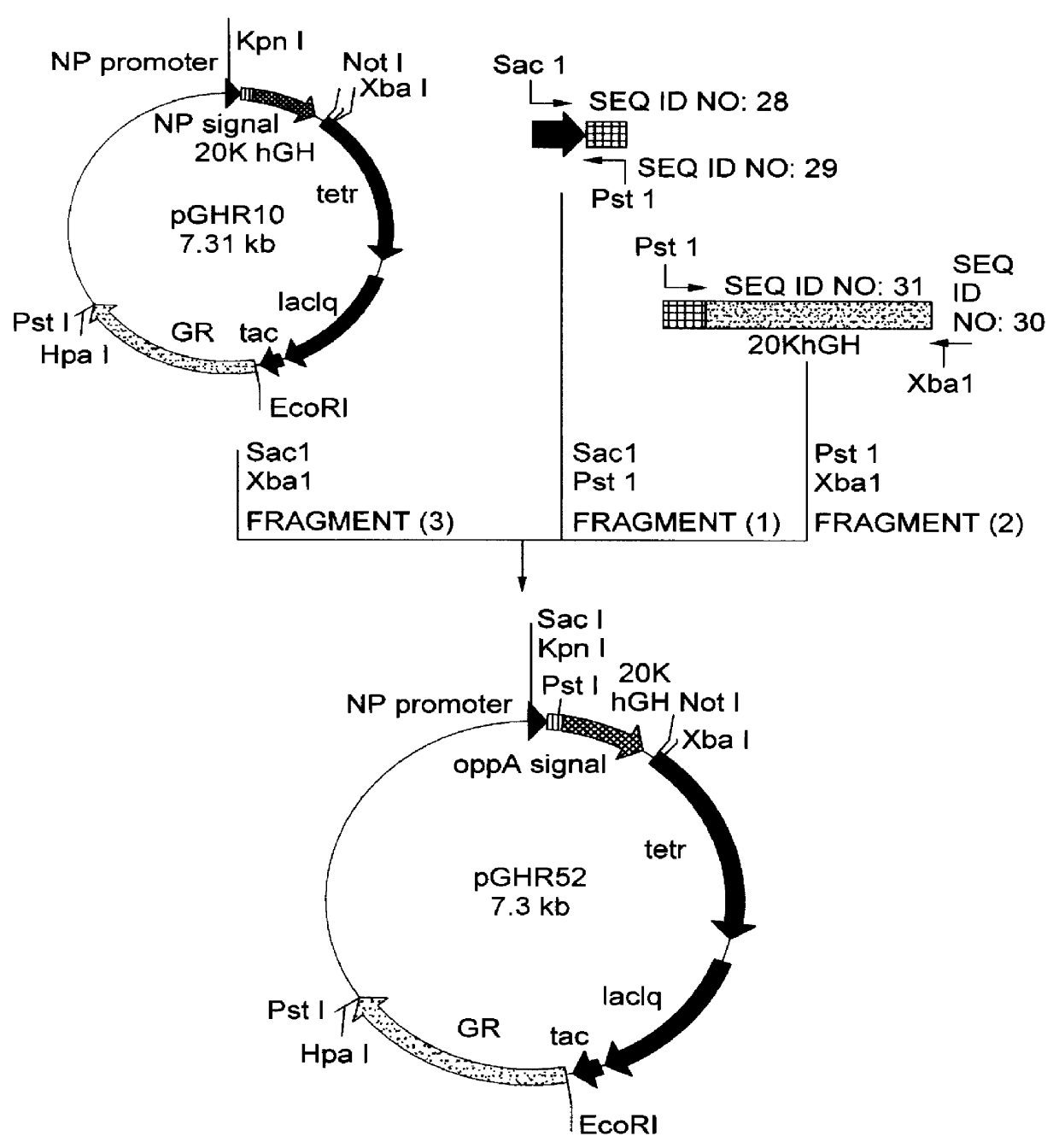
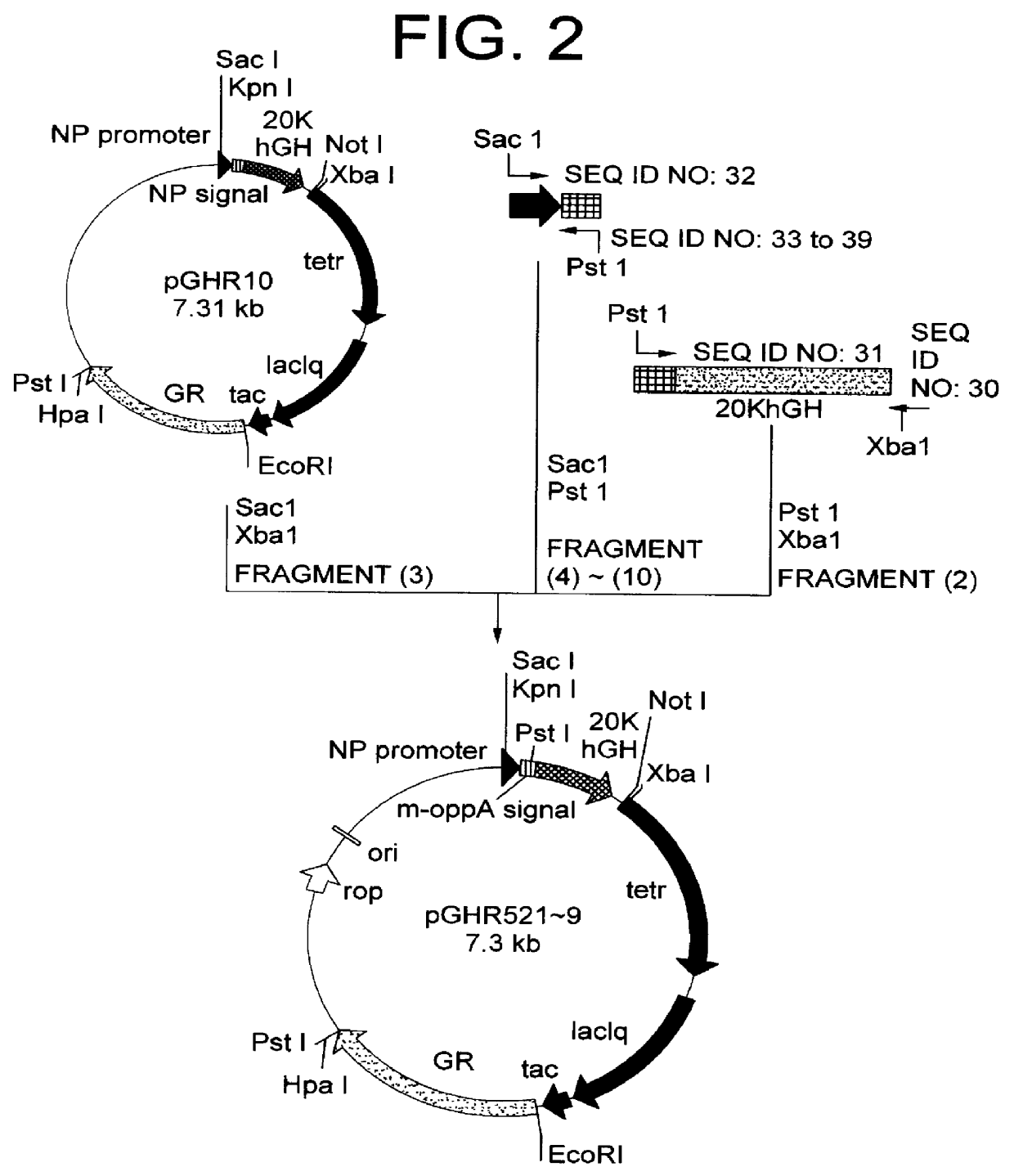
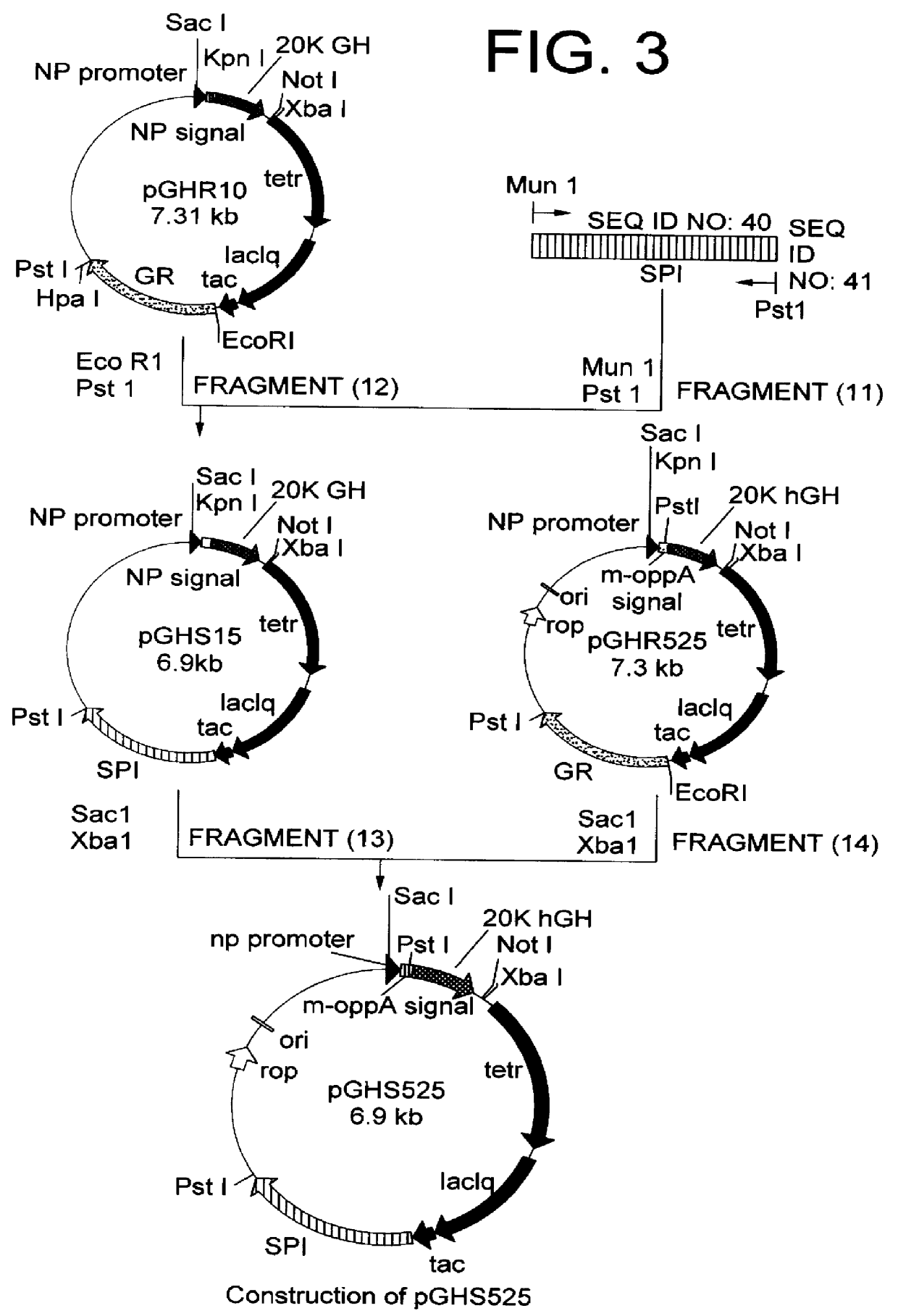
A DNA encoding 20K hGH is connected directly to a gene encoding Escherichia coli OppA protein secretion signal, or a modified form thereof, and a DNA encoding signal peptidase 1 to construct a recombinant plasmid, E. coli is transformed by the plasmid and cells of the resulting E. coli transformant strain are cultured for secretory production of the 20K hGH in the E. coli periplasm. This method enables efficient secretory production of 20K hGH and easy isolation and purification of 20K hGH from the periplasm fraction because the level of impure proteins in the E. coli periplasm is low.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
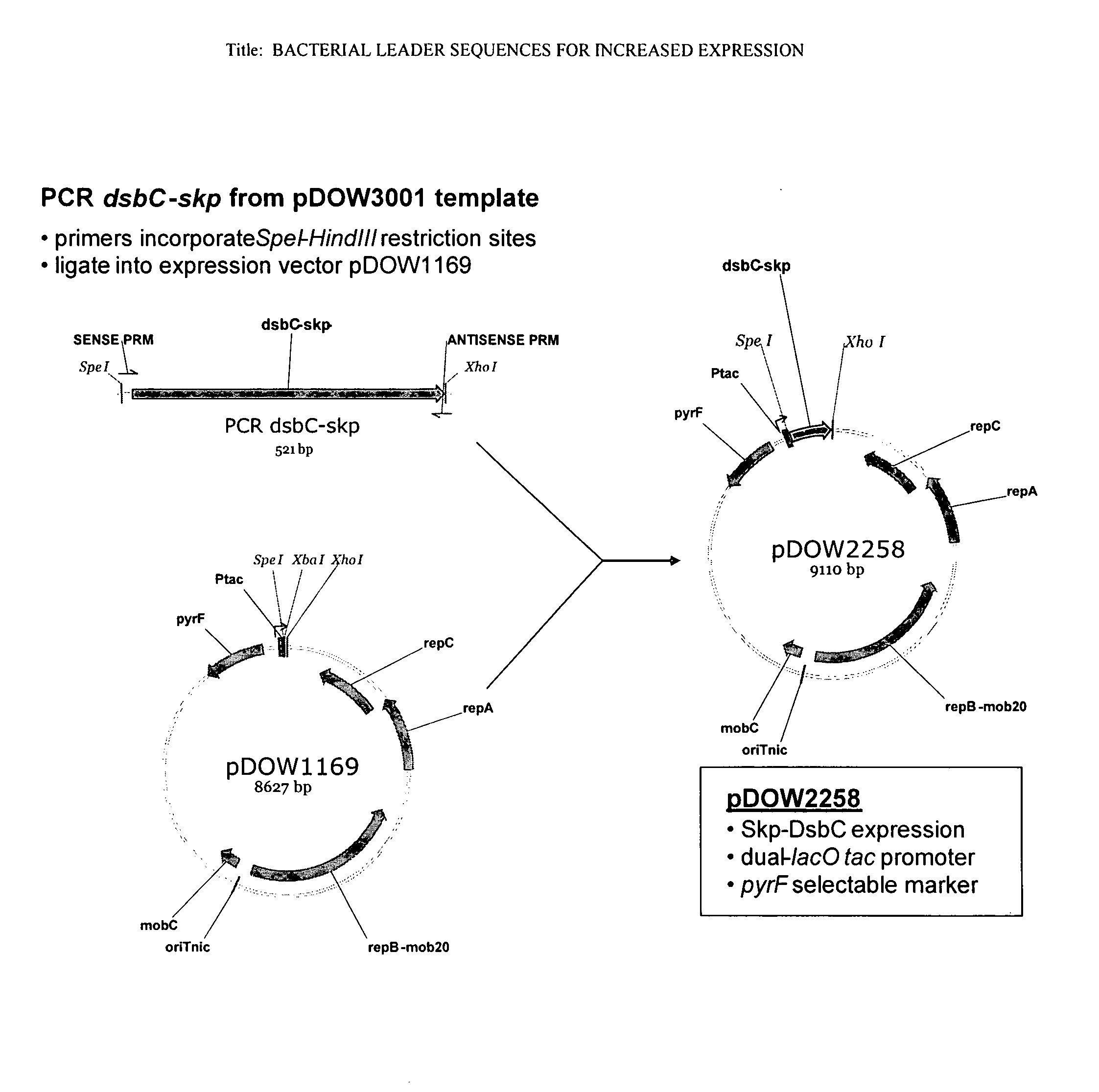
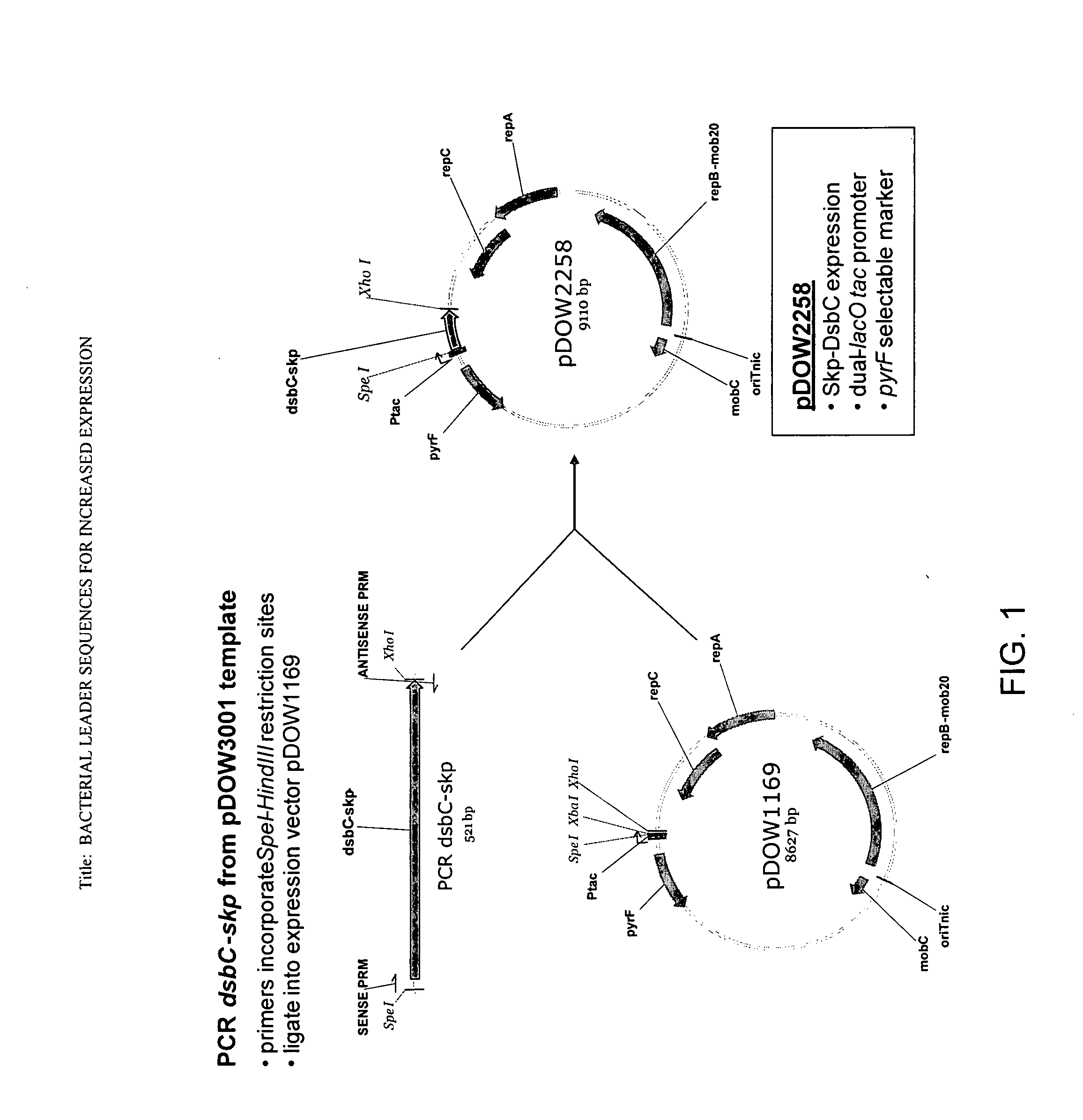
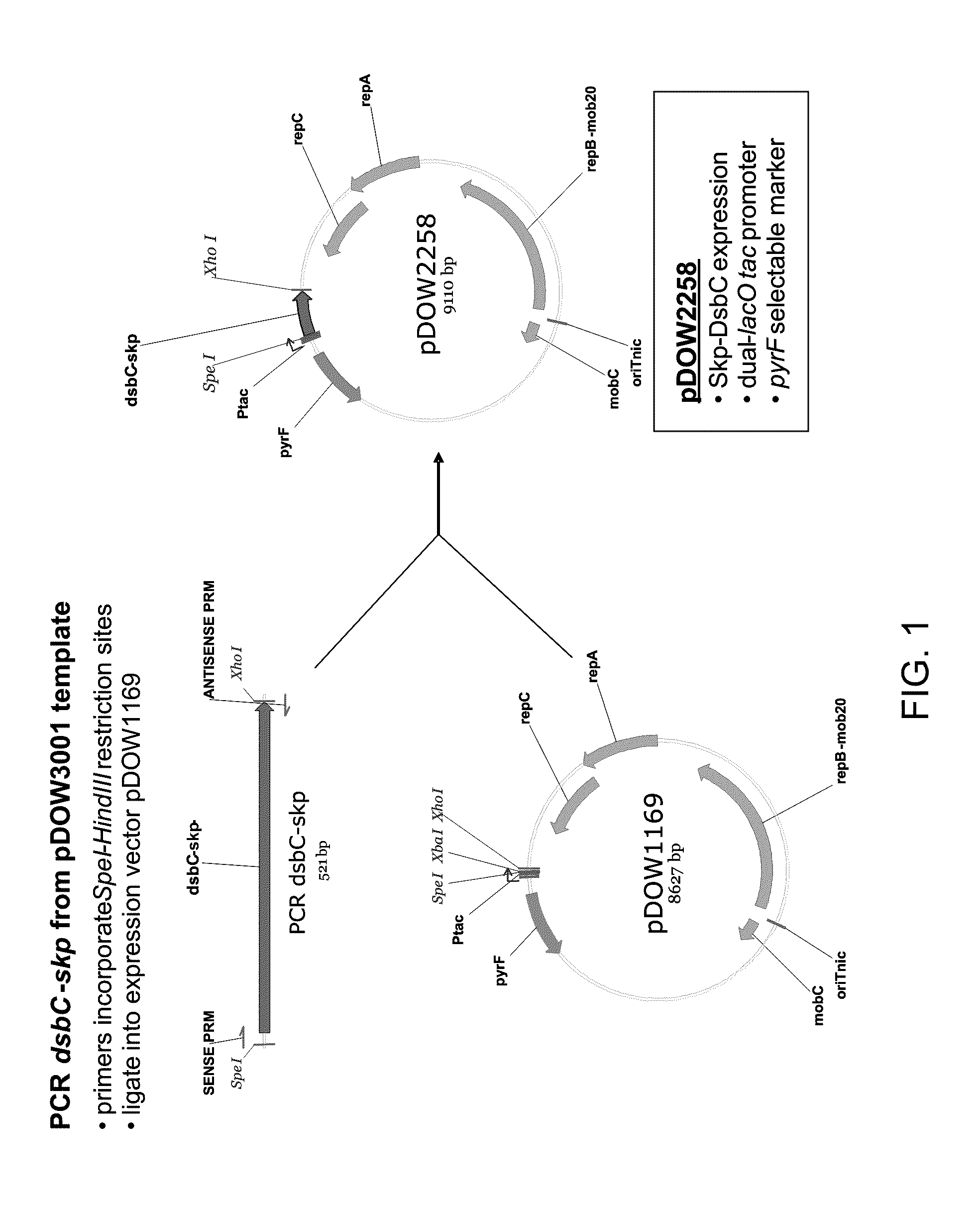
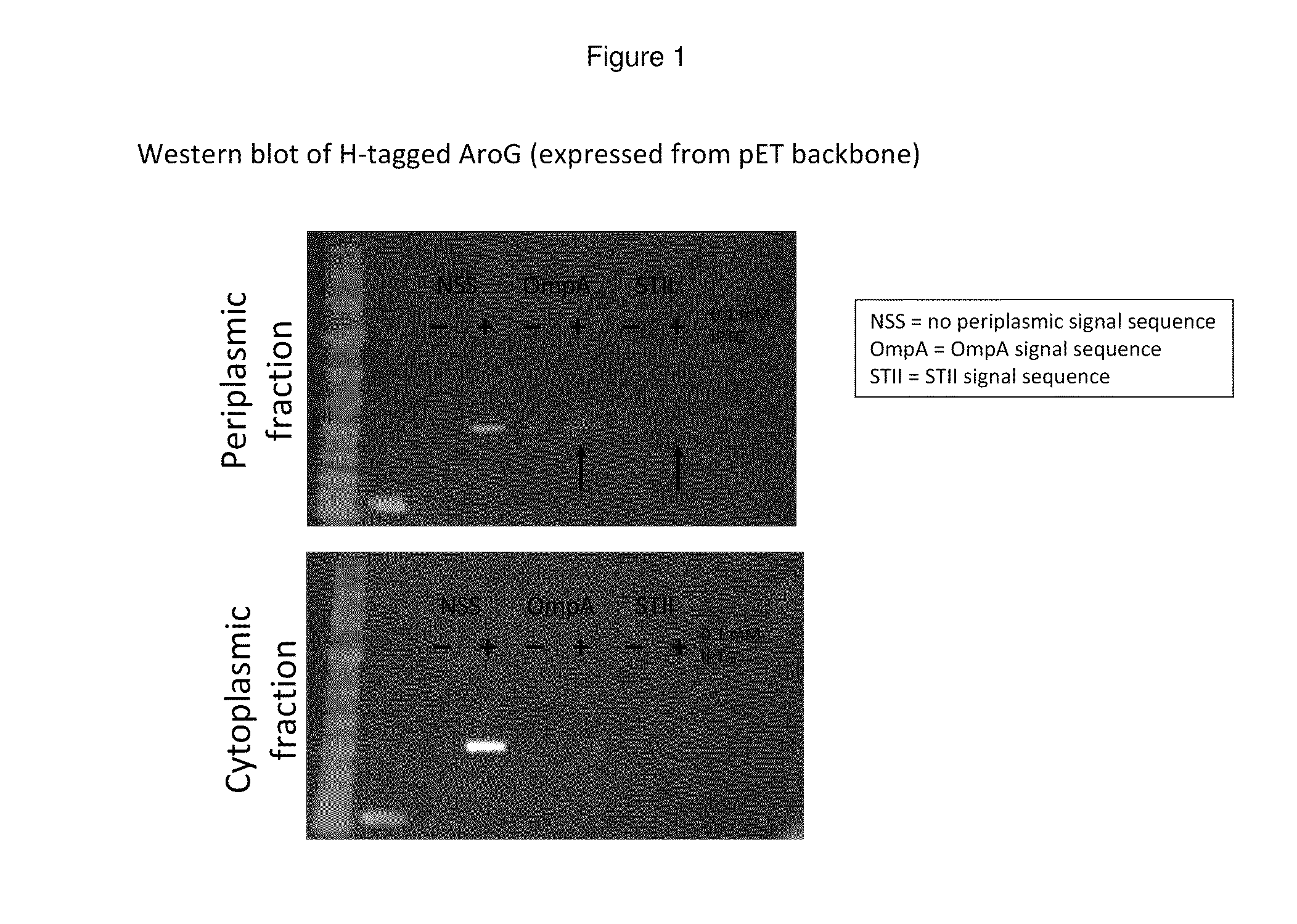
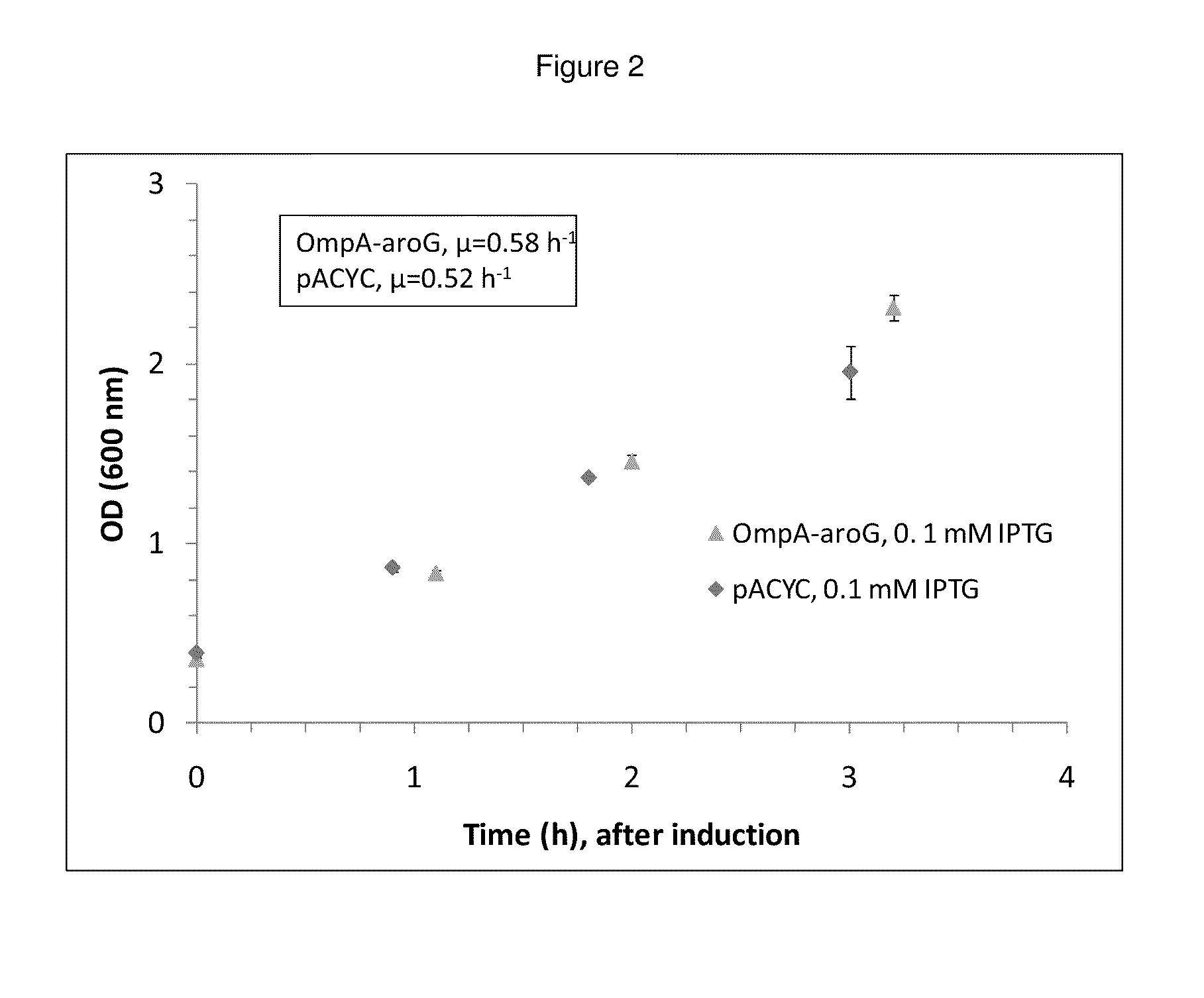
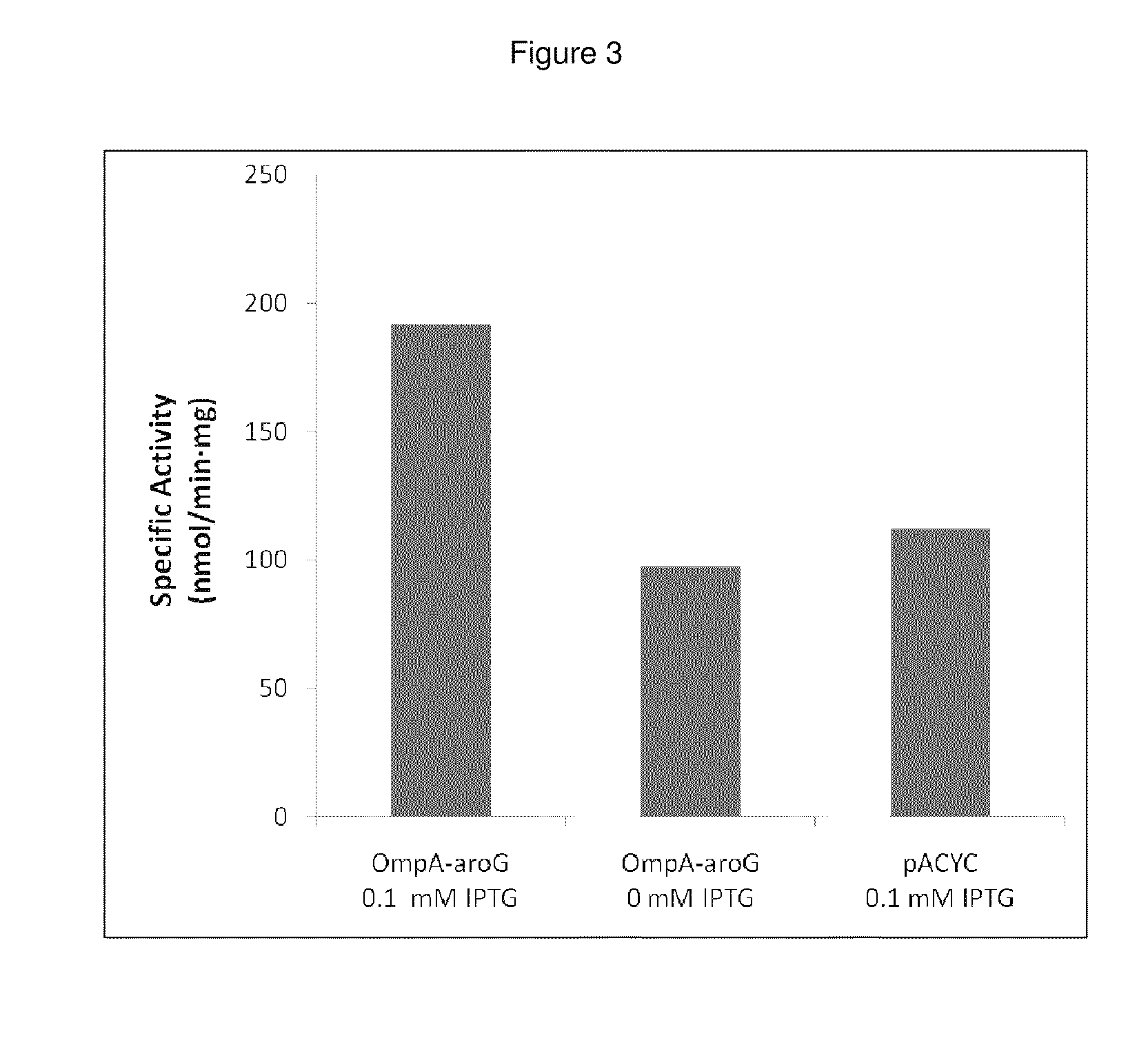
Bacterial leader sequences for increased expression
ActiveUS20080193974A1Promote targetingSimple compositionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
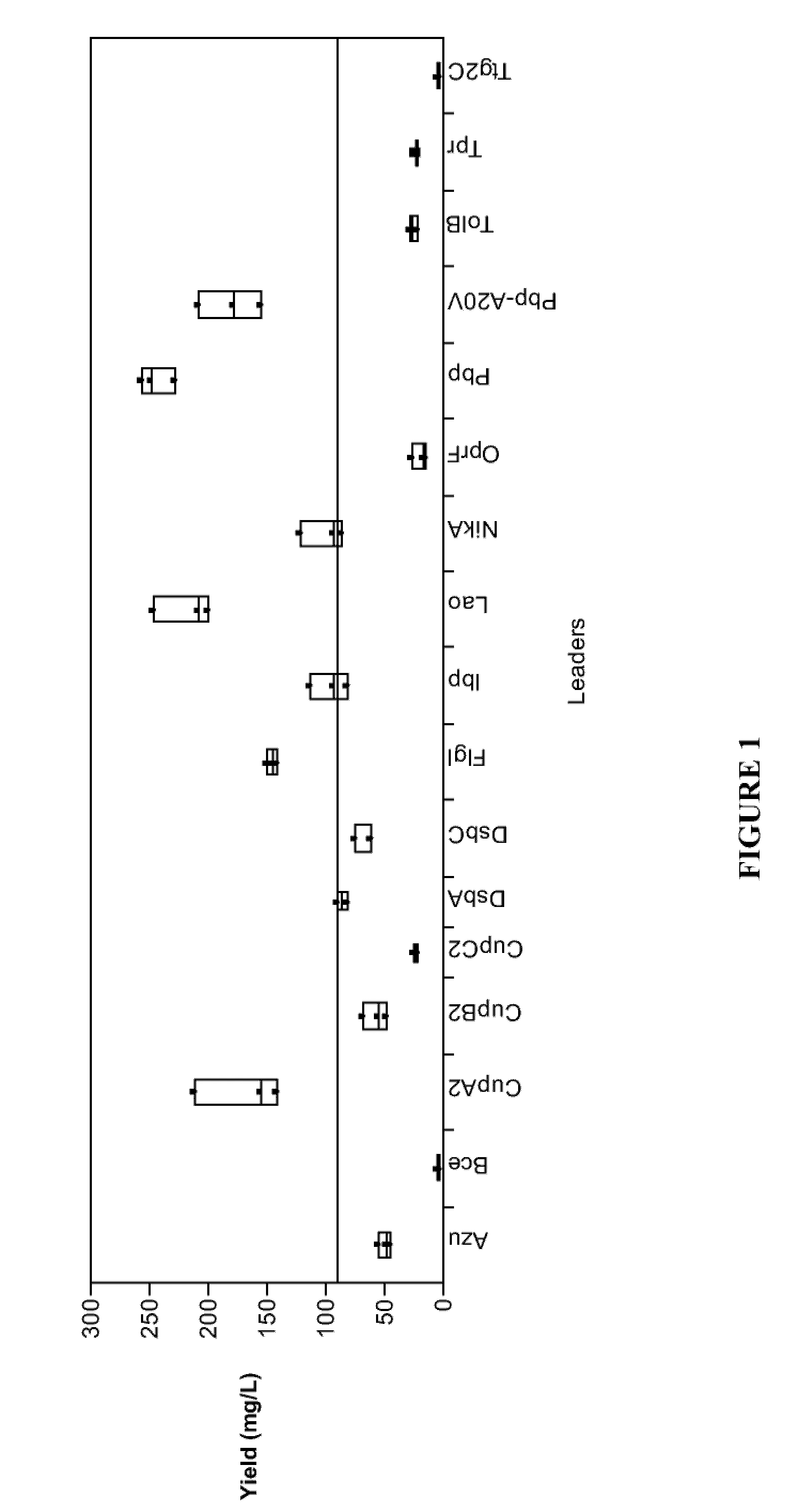
Compositions and methods for improving expression and / or secretion of protein or polypeptide of interest in a host cell are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a bacterial secretion signal peptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in vector constructs or expression systems for transformation and expression of a protein or polypeptide of interest in a host cell. The compositions of the invention are useful for increasing accumulation of properly processed proteins in the periplasmic space of a host cell, or for increasing secretion of properly processed proteins from the host cell. In particular, isolated secretion signal peptide-encoding nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the nucleic acid molecules are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, and 24, and the nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, and 23, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:PFENEX
Bacterial leader sequences for increased expression
ActiveUS7618799B2Reduce environmental pollutionHigh expressionBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsADAMTS ProteinsAmino acid
Compositions and methods for improving expression and / or secretion of protein or polypeptide of interest in a host cell are provided. Compositions comprising a coding sequence for a bacterial secretion signal peptide are provided. The coding sequences can be used in vector constructs or expression systems for transformation and expression of a protein or polypeptide of interest in a host cell. The compositions of the invention are useful for increasing accumulation of properly processed proteins in the periplasmic space of a host cell, or for increasing secretion of properly processed proteins from the host cell. In particular, isolated secretion signal peptide-encoding nucleic acid molecules are provided. Additionally, amino acid sequences corresponding to the nucleic acid molecules are encompassed. In particular, the present invention provides for isolated nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, and 24, and the nucleotide sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, and 23, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Expression of functional antibody fragments
InactiveUS20050244929A1Easy to prepareFacilitated releaseHybrid immunoglobulinsBacteriaMicroorganismHeavy chain
Methods for the high yield production of antibody Fv-containing polypeptides, especially Fab′ and F(ab′)2 antibody fragments are provided. Expression of heavy and light chain Fv in a microbial secretory system is followed by recovery of Fv from the periplasm under conditions that maintain a cysteine residue as a free thiol. The free thiol is reacted with free thiol of an antibody fragment of the same or differing specificity, or with agents such as diagnostic labels or therapeutic moieties. The products offer advantages of homogeneity and purity not available through the use of known methods for preparing such derivatives.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Immunogenic compositions and vaccines comprising carrier bacteria that secrete antigens
InactiveUS20040101531A1Snake antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesMucosal Immune ResponsesAntigen delivery
Disclosed are vaccines and immunogenic compositions which use live attenuated pathogenic bacteria, such as Salmonella, to deliver ectopic antigens to the mucosal immune system of vertebrates. The attenuated pathogenic bacteria are engineered to secrete the antigen into the periplasmic space of the bacteria or into the environment surrounding the bacteria. The vertebrate mounts a Th2-mediated immune response toward the secreted antigen.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method for secretory production of human growth hormone
InactiveUS6160089AIncrease productionDecreased tendency for lysisBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPlasmidPeriplasmic space
A DNA encoding 20K hGH is connected directly to a gene encoding Escherichia coli OppA protein secretion signal, or a modified form thereof, and a DNA encoding signal peptidase 1 to construct a recombinant plasmid, E. coli is transformed by said plasmid and cells of the resulting E. coli transformant strain are cultured for secretory production of the 20K hGH in the E. coli periplasm. This method enables efficient secretory production of 20K hGH and easy isolation and purification of 20K hGH from the periplasm fraction because the level of impure proteins in the E. coli periplasm is low.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Method for Rapidly Screening Microbial Hosts to Identify Certain Strains with Improved Yield and/or Quality in the Expression of Heterologous Proteins
ActiveUS20100137162A1High yieldQuality improvementLibrary screeningMicroorganism librariesHeterologousProtein Degradations
The present invention provides an array for rapidly identifying a host cell population capable of producing heterologous protein with improved yield and / or quality. The array comprises one or more host cell populations that have been genetically modified to increase the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein production, decrease the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein degradation, or both. One or more of the strains in the array may express the heterologous protein of interest in a periplasm compartment, or may secrete the heterologous protein extracellularly through an outer cell wall. The strain arrays are useful for screening for improved expression of any protein of interest, including therapeutic proteins, hormones, a growth factors, extracellular receptors or ligands, proteases, kinases, blood proteins, chemokines, cytokines, antibodies and the like.
Owner:PFENEX
Combinatorial protein library screening by periplasmic expression
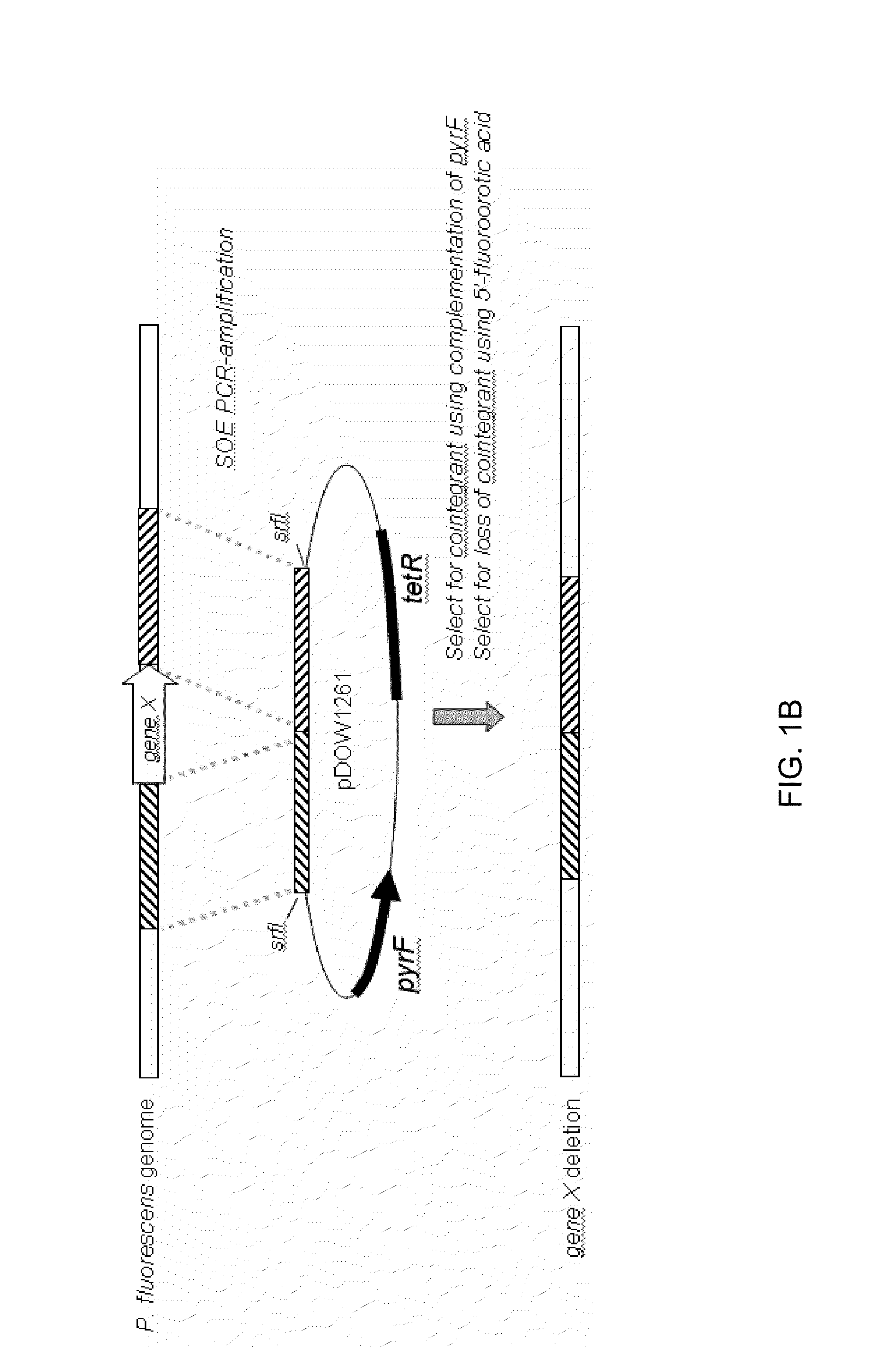
InactiveUS20060029947A1Improve breathabilityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaScreening techniquesSurface expression
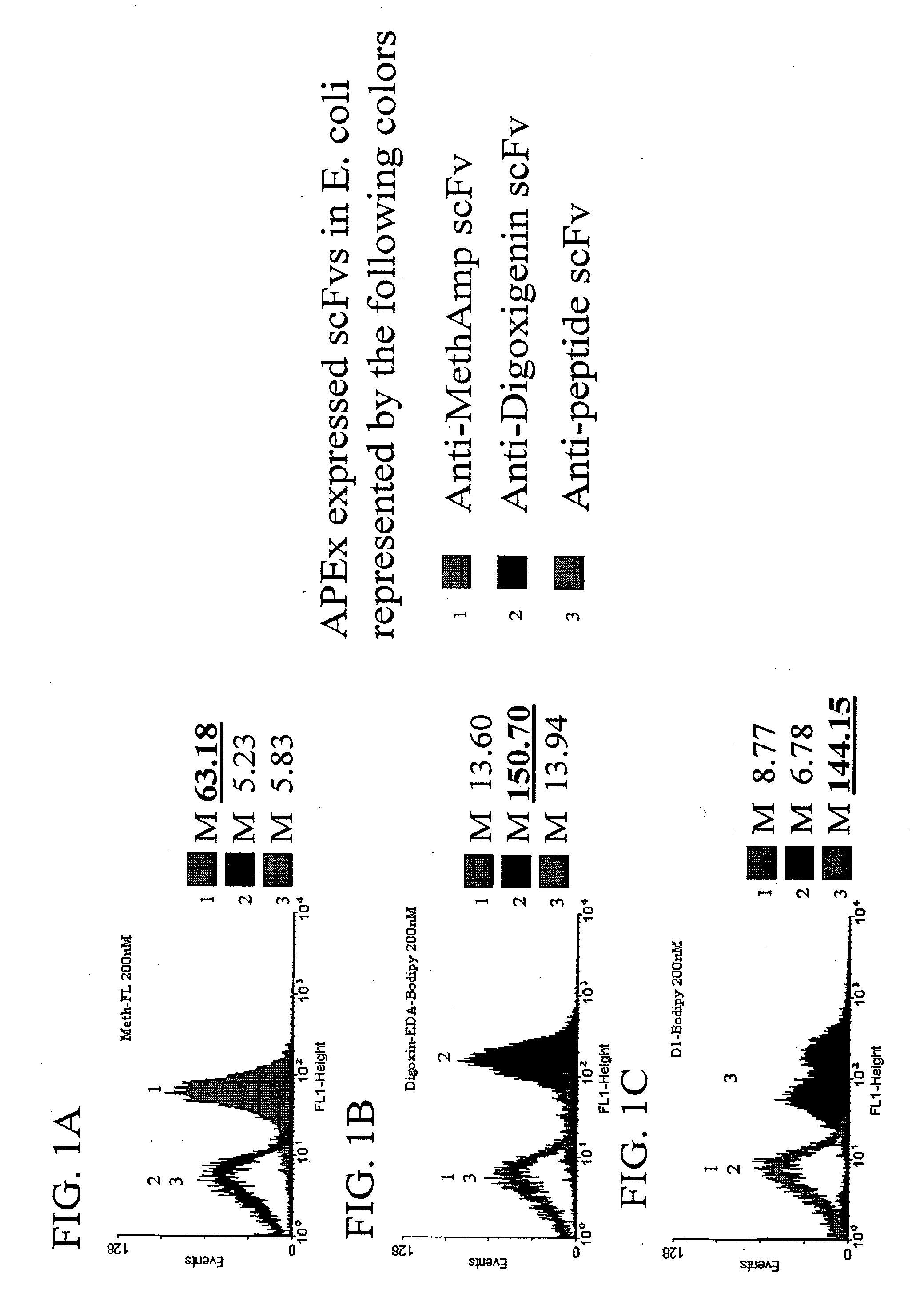
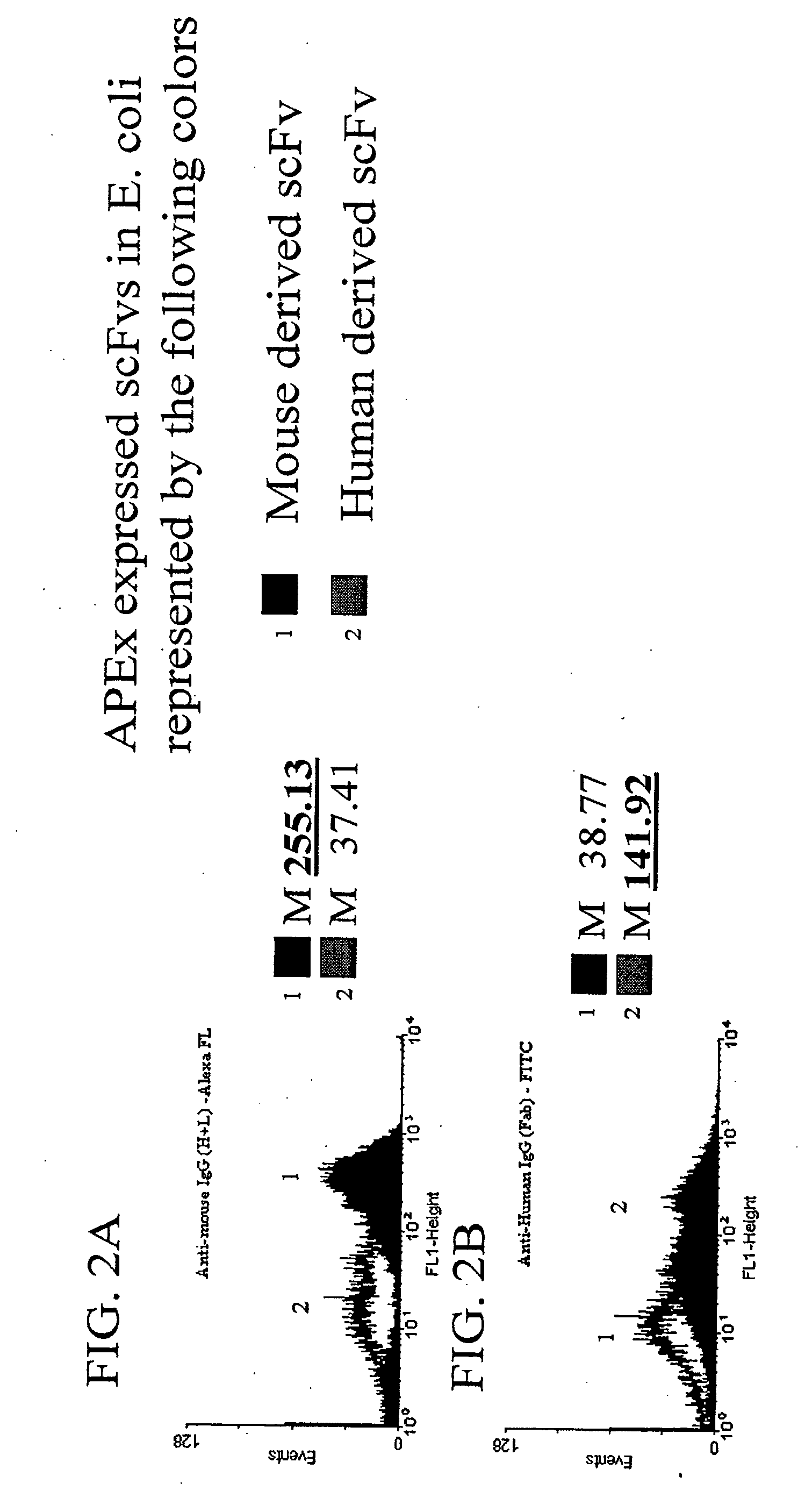
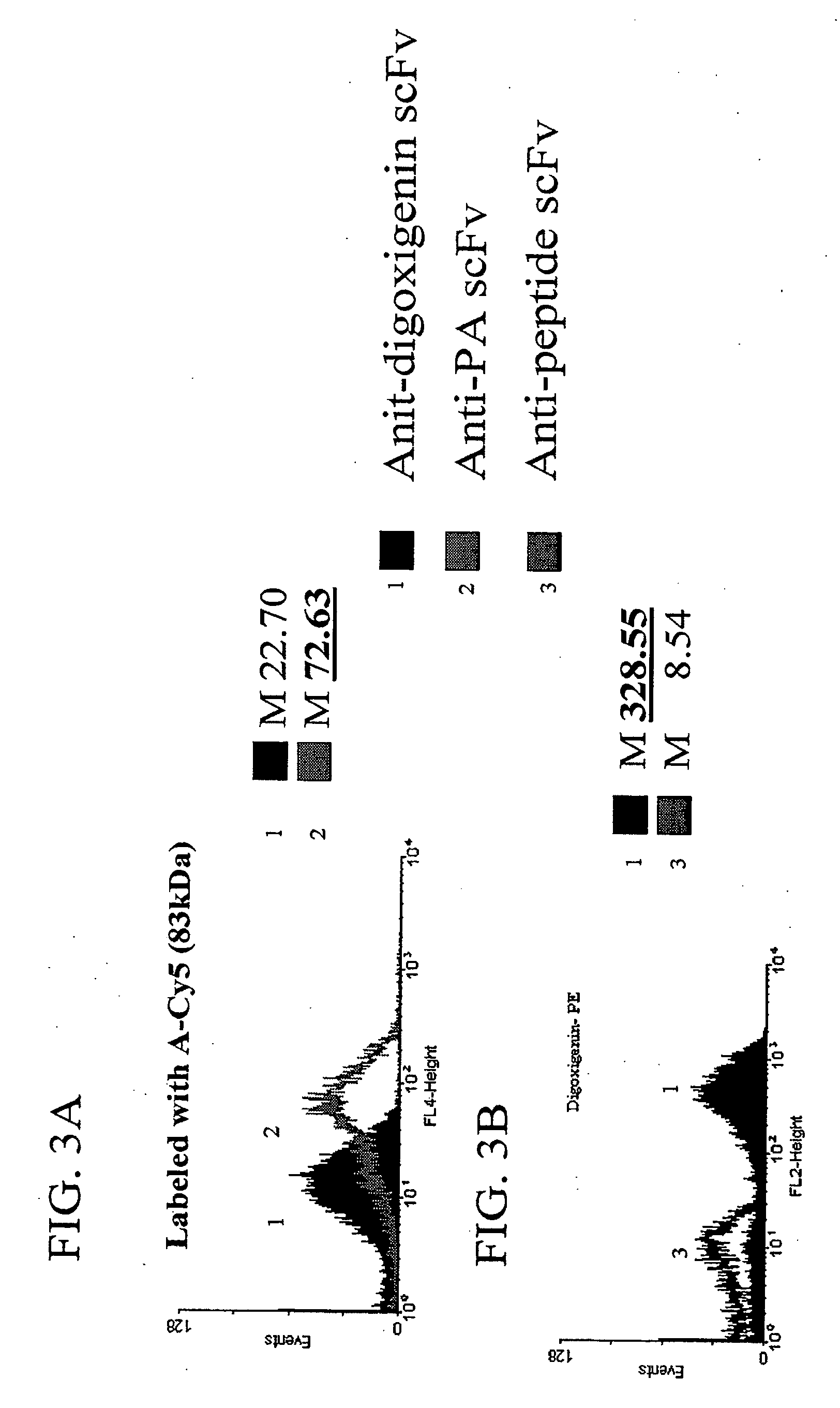
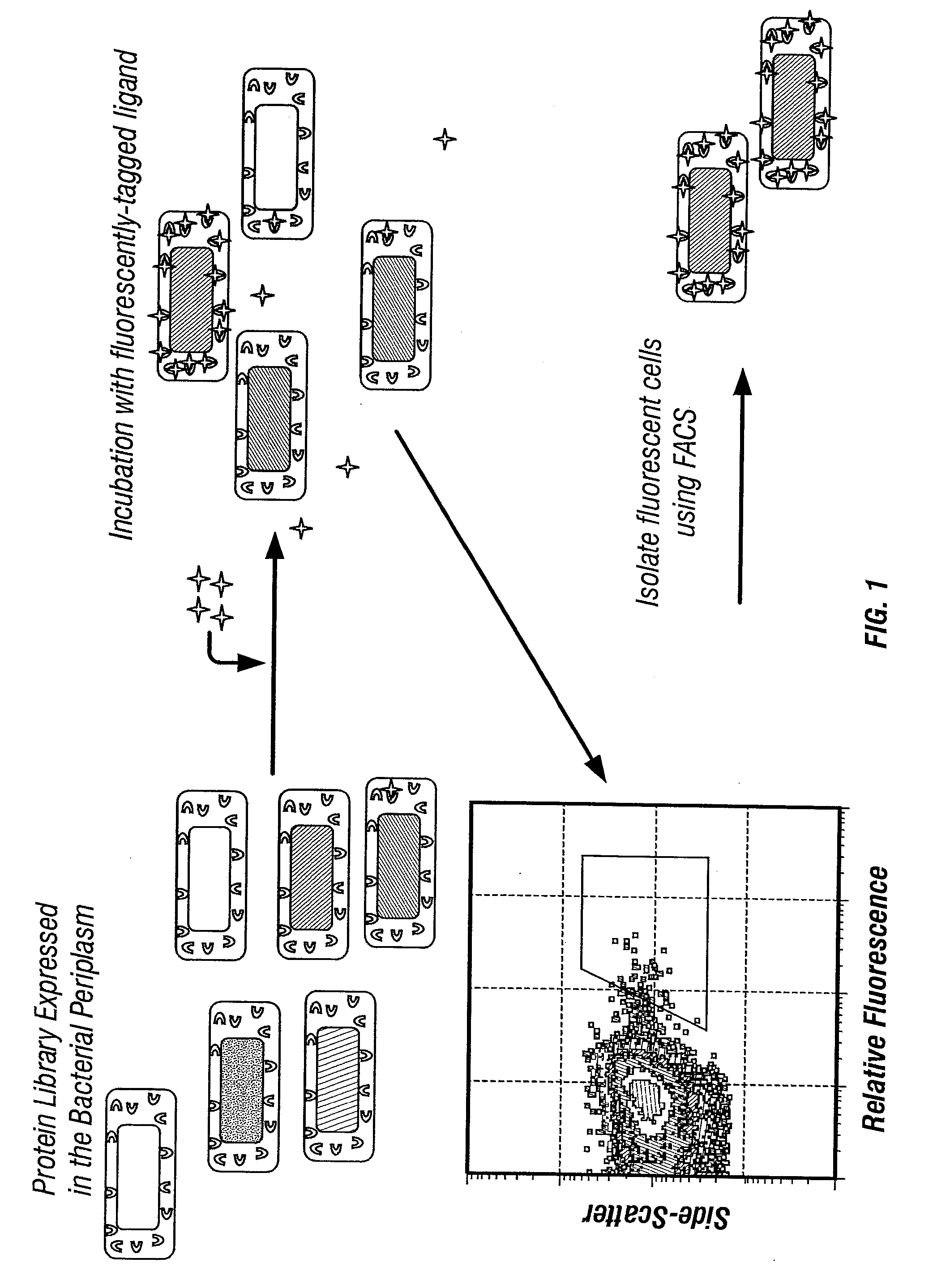
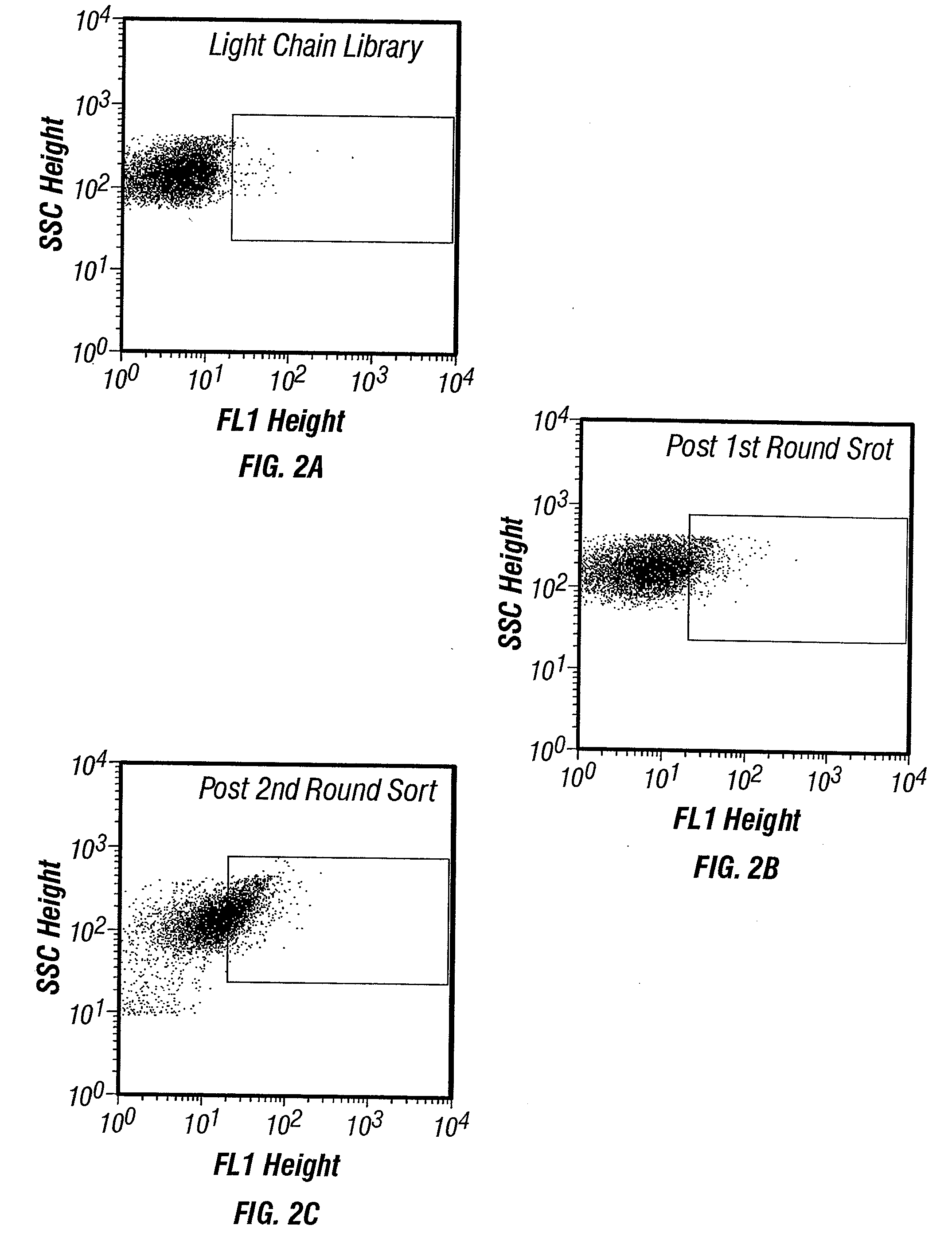
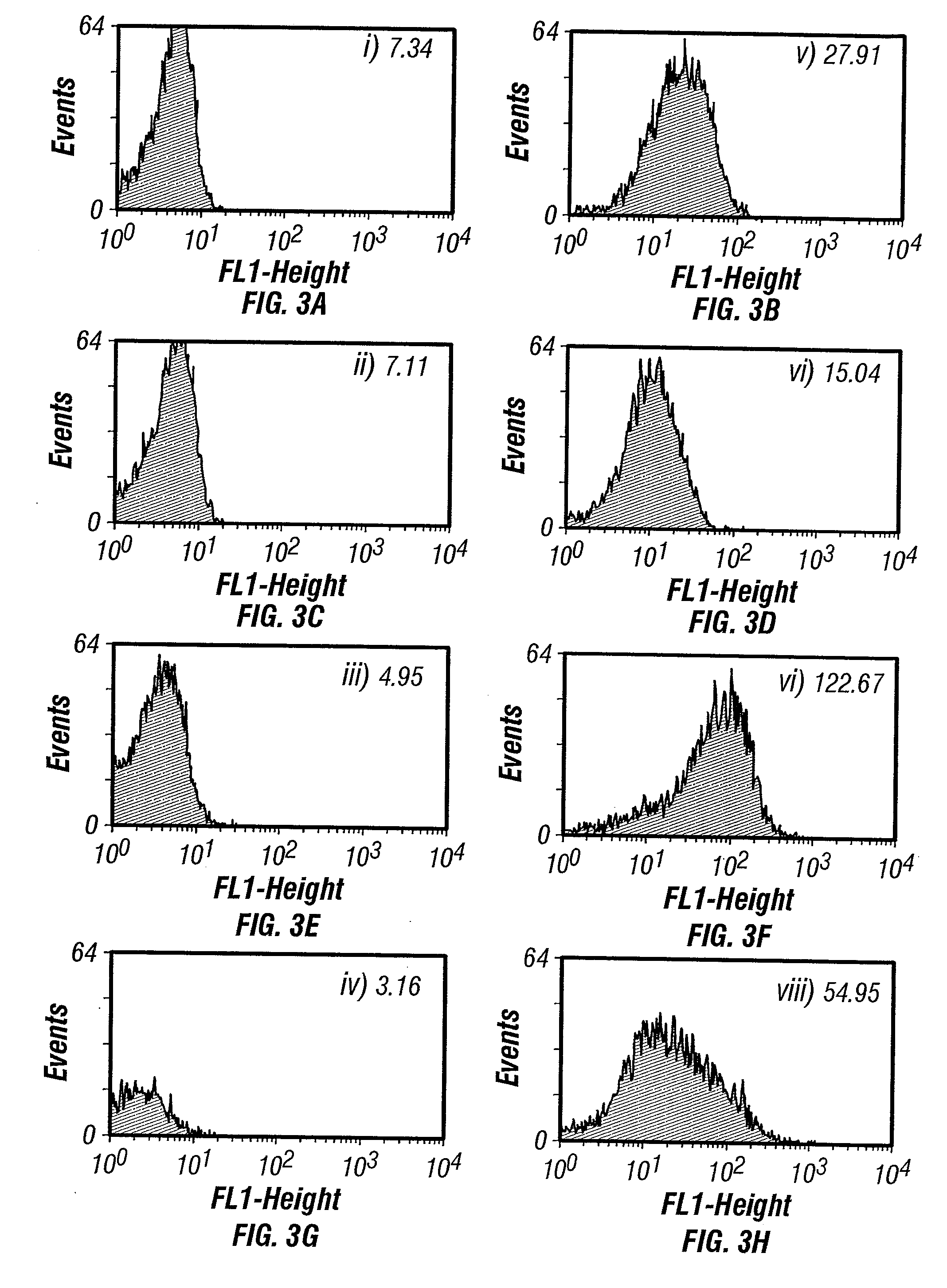
The invention overcomes the deficiencies of the prior art by providing a rapid approach for isolating binding proteins capable of binding small molecules and peptides. In the technique, libraries of candidate binding proteins, such as antibody sequences, may be expressed in the periplasm of gram negative bacteria with at least one target ligand. In clones expressing recombinant polypeptides with affinity for the ligand, the ligand becomes bound and retained by the cell even after removal of the outer membrane, allowing the cell to be isolated from cells not expressing a binding polypeptide with affinity for the target ligand. The target ligand may be detected in numerous ways, including use of direct fluorescence or secondary antibodies that are fluorescently labeled, allowing use of efficient screening techniques such as fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). The approach is more rapid and robust than prior art methods and avoids problems associated with the outer surface-expression of ligand fusion proteins employed with phage display.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Combinatorial protein library screening by periplasmic expression
The invention overcomes the deficiencies of the prior art by providing a rapid approach for isolating binding proteins capable of binding small molecules and peptides. In the technique, libraries of candidate binding proteins, such as antibody sequences, are expressed in the periplasm of gram negative bacteria and mixed with a labeled ligand. In clones expressing recombinant polypeptides with affinity for the ligand, the concentration of the labeled ligand bound to the binding protein is increased and allows the cells to be isolated from the rest of the library. Where fluorescent labeling of the target ligand is used, cells may be isolated by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). The approach is more rapid than prior art methods and avoids problems associated with the outer surface-expression of ligand fusion proteins employed with phage display.
Owner:HARVEY BARRETT R +2
Microbial strains and processes for the manufacture of biomaterials
InactiveUS20090226962A1Increase enzyme activityHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCell culture media
DNA constructs and genetically engineered microbial strains constructed using these DNA constructs, which produce a nuclease enzyme with specificity for DNA and / or RNA, are provided. These strains secrete nuclease into the periplasm or growth medium in an amount effective to enhance productivity and / or recovery of polymer, and are particularly suited for use in high cell density fermentation processes. These constructs are useful for modifying microbial strains to improve production and recovery processes for polymers such as intracellular proteins, such as enzymes, growth factors, and cytokines; for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates; and for producing extracellular polysaccharides, such as xanthan gum, alginates, gellan gum, zooglan, hyaluronic acid and microbial cellulose.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for rapidly screening microbial hosts to identify certain strains with improved yield and/or quality in the expression of heterologous proteins
ActiveUS9580719B2High expressionReduce expressionLibrary screeningMicroorganism librariesHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an array for rapidly identifying a host cell population capable of producing a heterologous protein with improved yield and / or quality. The array comprises one or more host cell populations that have been genetically modified to increase the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein production, decrease the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein degradation, or both. One or more of the strains in the array may express the heterologous protein of interest in a periplasm compartment or may secrete the heterologous protein extracellularly through an outer cell wall. The strain arrays are useful for screening for improved expression of any protein of interest including therapeutic proteins, hormones, growth factors, extracellular receptors or ligands, proteases, kinases, blood proteins, chemokines, cytokines, antibodies and the like.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
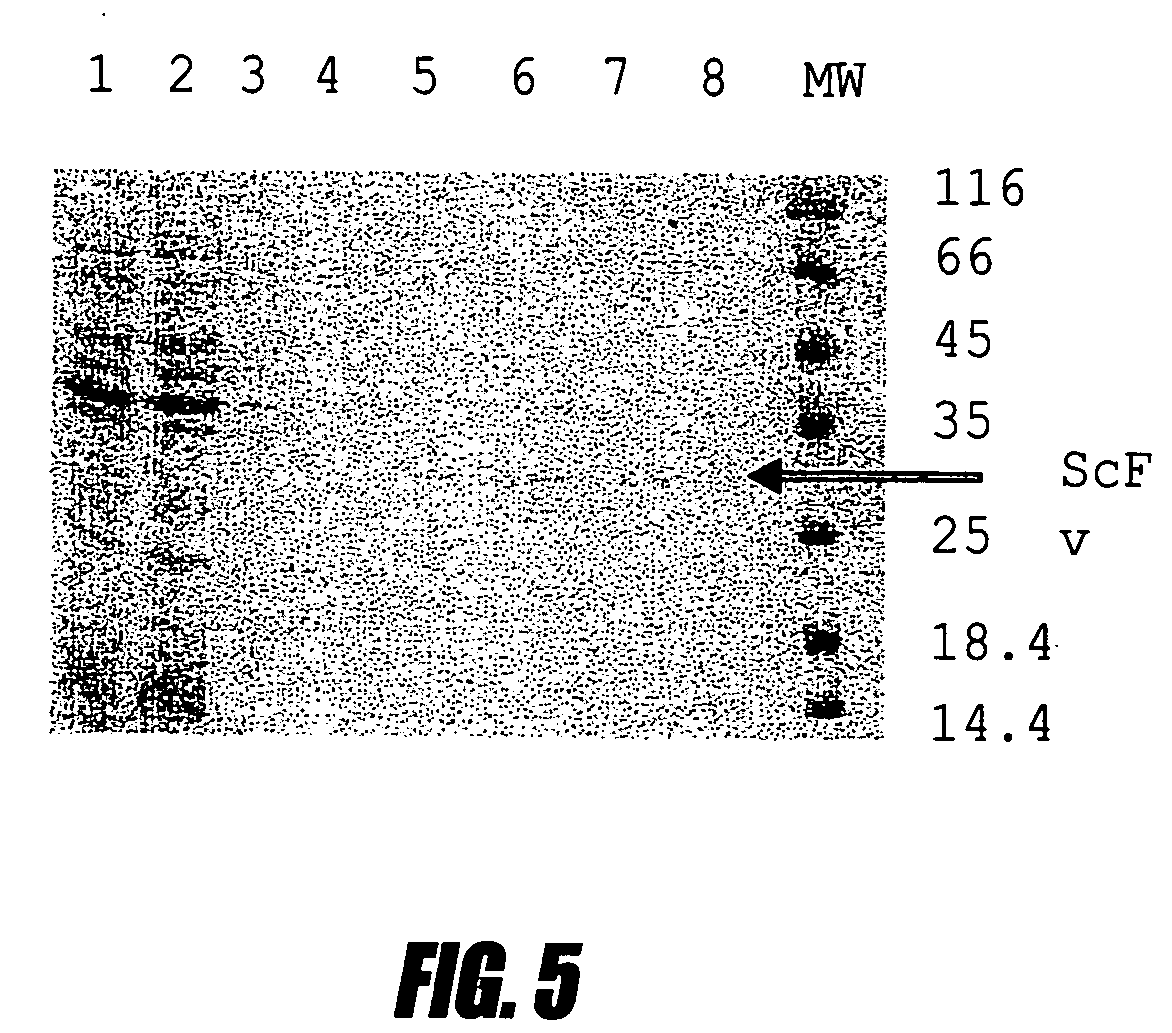
Method for obtaining single chain antibodies to human interferon alpha2b
A bacterial high-expression system which is applicable for simultaneous screening of large numbers of recombinant clones from combinatorial antibody libraries is disclosed. The method pertains to screening of single chain antibodies from libraries expressed in the periplasm of E. coli by secretion. By this approach, approximately 104 clones can be screened in a single round. After screening, the clones, which express the recombinant antibodies to the desired antigen, can be directly used for production of large quantities of antibodies from microorganism culture. The system is especially attractive for fast screening of antibody libraries from a hybridoma source. A refolding method for the large-scale production of biologically active scFv-6 his proteins from bacterial inclusion bodies is also disclosed.
Owner:NEW TECH HLDG
Methods for control of flux in metabolic pathways through enzyme relocation
Genetically manipulated cells, lysates of such cells, systems, and methods of use thereof are provided, where one or more enzymes in a pathway of interest are genetically modified to incorporate a peptide sequence that provides for relocation of the protein, e.g., to the periplasm, so as to sequester the enzyme, and where the enzyme controls flux in the pathway of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
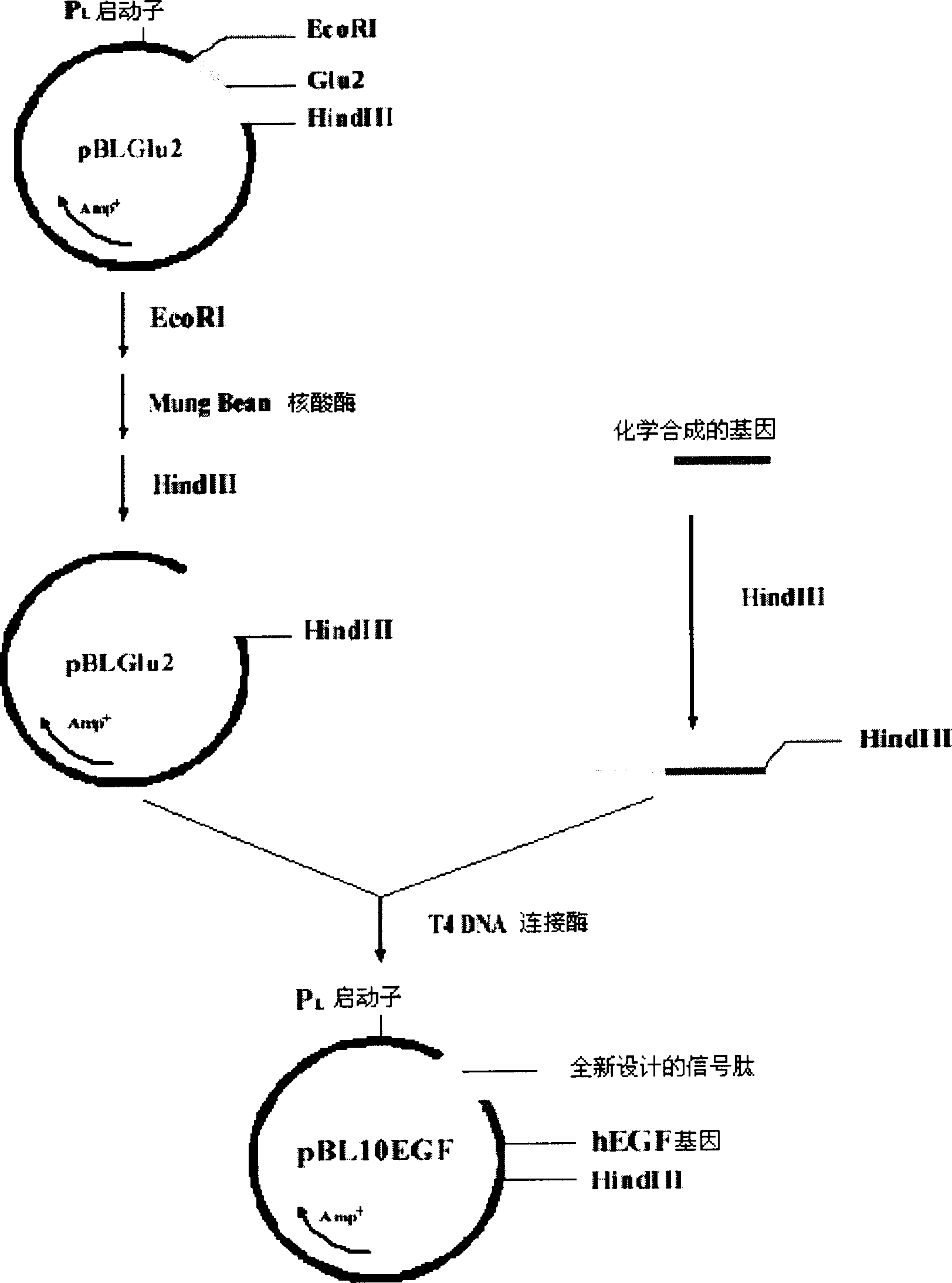
Escherichia expression system of secretory expression recombinant human epidermal growth factor
This invention includes signal peptide gene phoAspL10, expression plasmid pBL10EGF, host cell of bacillus coli BL21 (DE3) inverted by expression plasmid pBL10EGF, engineering strain BE-2 screened from the host cell and preparation method of rhEGF. The strain BE-2 can excrete and express rhEGF directly into culture after fermentation and the quantity is 384mg / l.The purity is more than 95% and specific activity more than 1.0*106IU / mg protein. The product rhEGF reserves crude space configuration and shows high biological activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAOHAI BIOLOGICAL TECH
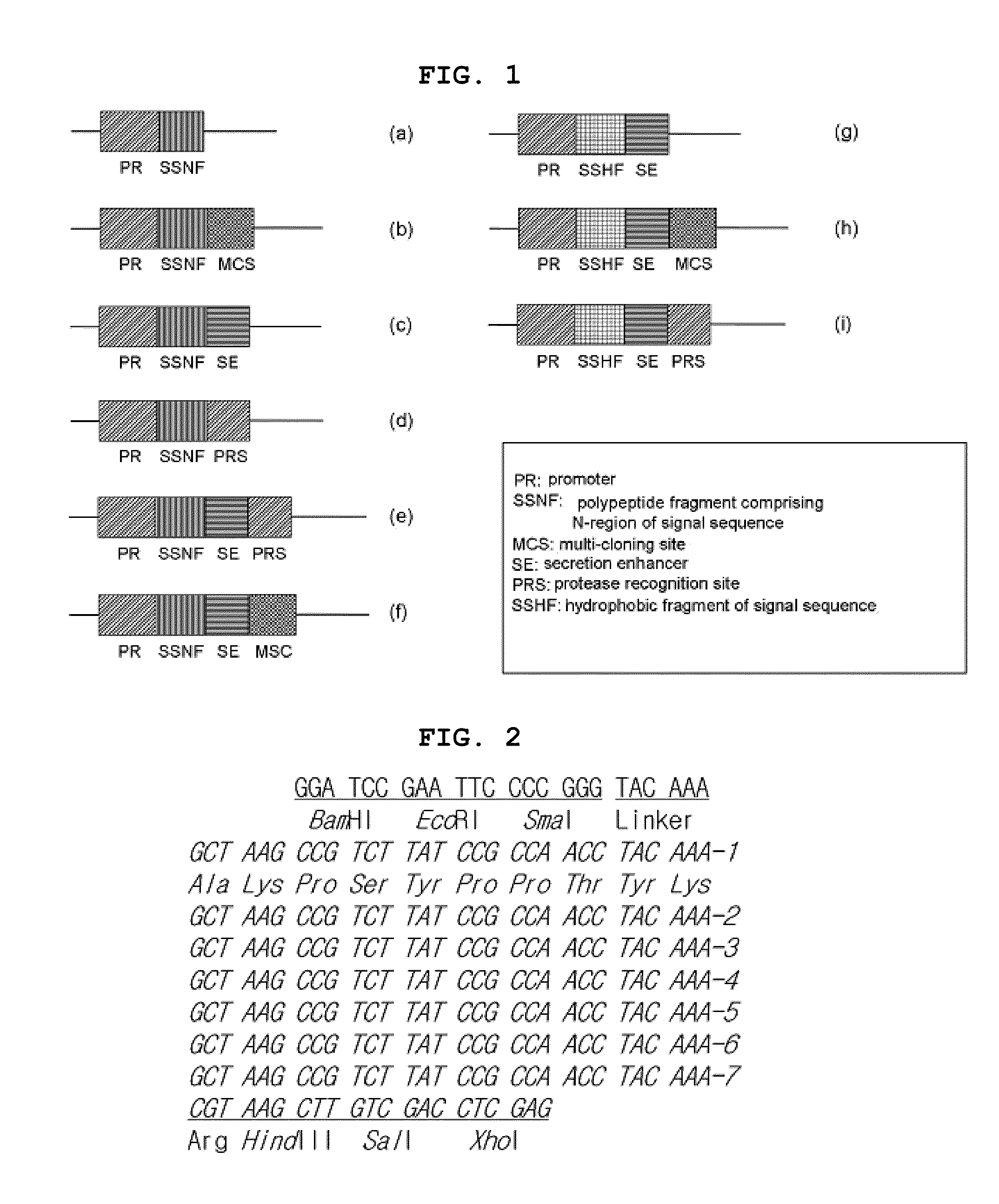
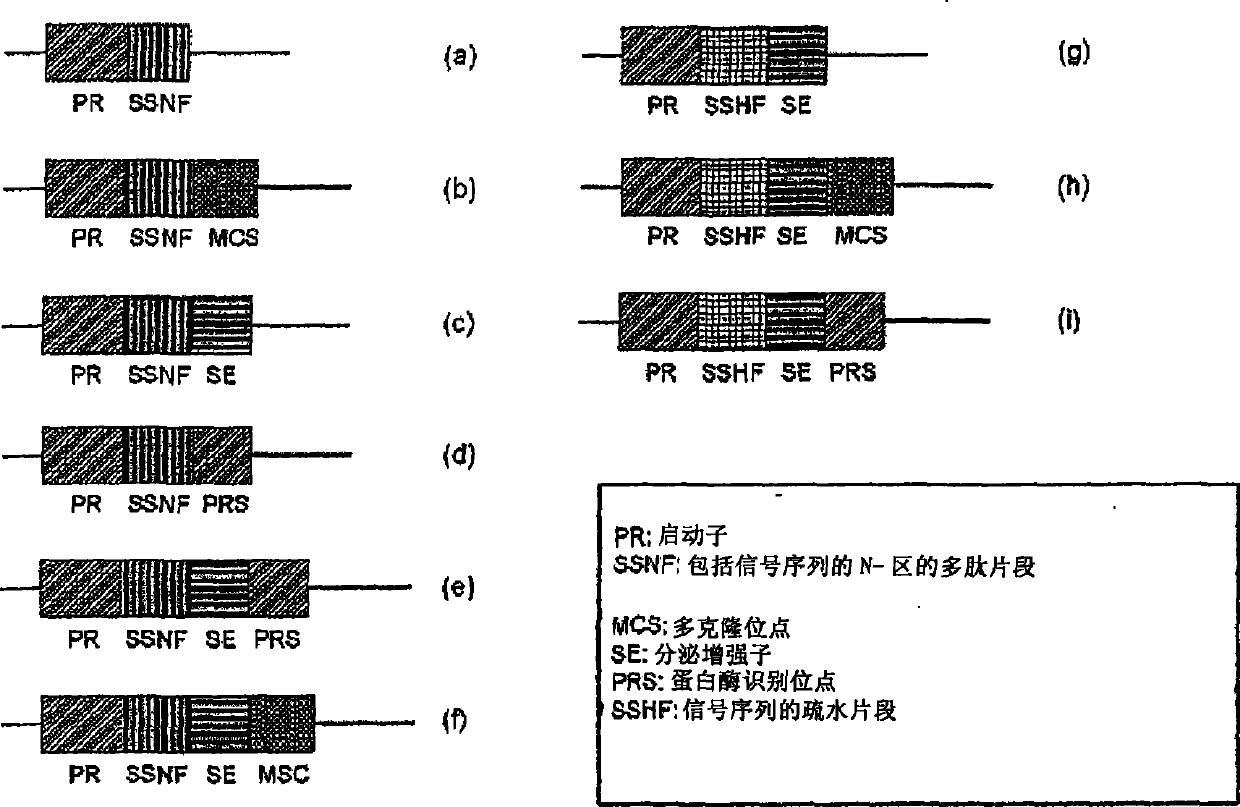
Production of a soluble native form of recombinant protein by the signal sequence and secretional enhancer
InactiveUS20090011995A1Efficient productionImprove efficiencyFungiNervous disorderBiotechnologyMembrane permeability
The present invention is drawn to a method for enhancing secretional efficiency of a heterologous protein using a secretional enhancer consisting of a modified signal sequence which comprises the N-region of a signal sequence and / or a hydrophobic fragment of the said signal sequence comprising the said N-region and / or the hydrophilic polypeptide. The method of the present invention can be used not only for production of recombinant heterologous proteins by inhibiting insoluble precipitation and enhancing secretional efficiency of the recombinant protein into the periplasm or the extracellular fluid and but also for transduction of therapeutic proteins by enhancing membrane-permeability of the recombinant protein using a strong secretional enhancer.
Owner:REPUBLIC OF KOREA (NAT FISHERIES RES & DEV INST)
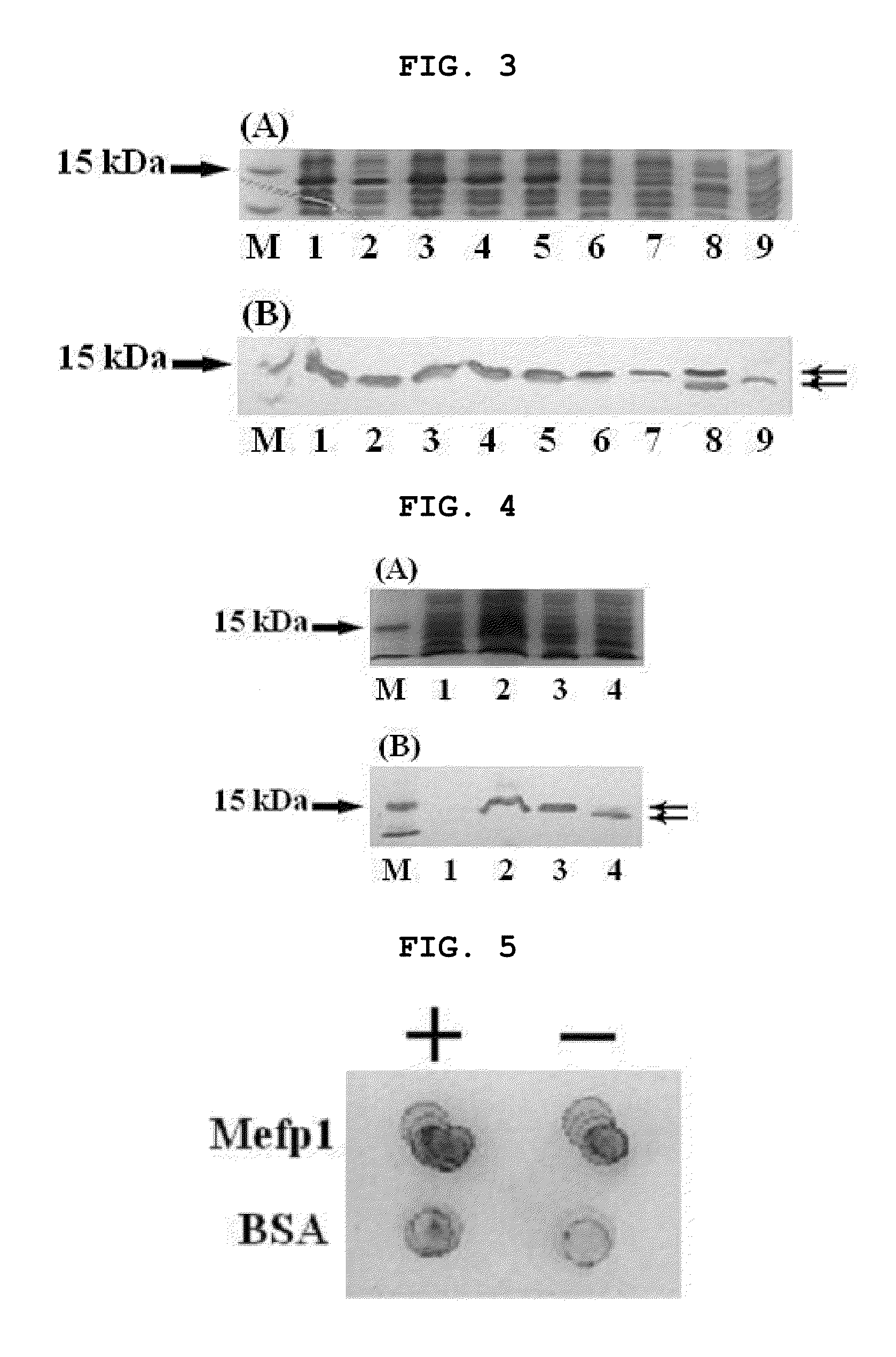
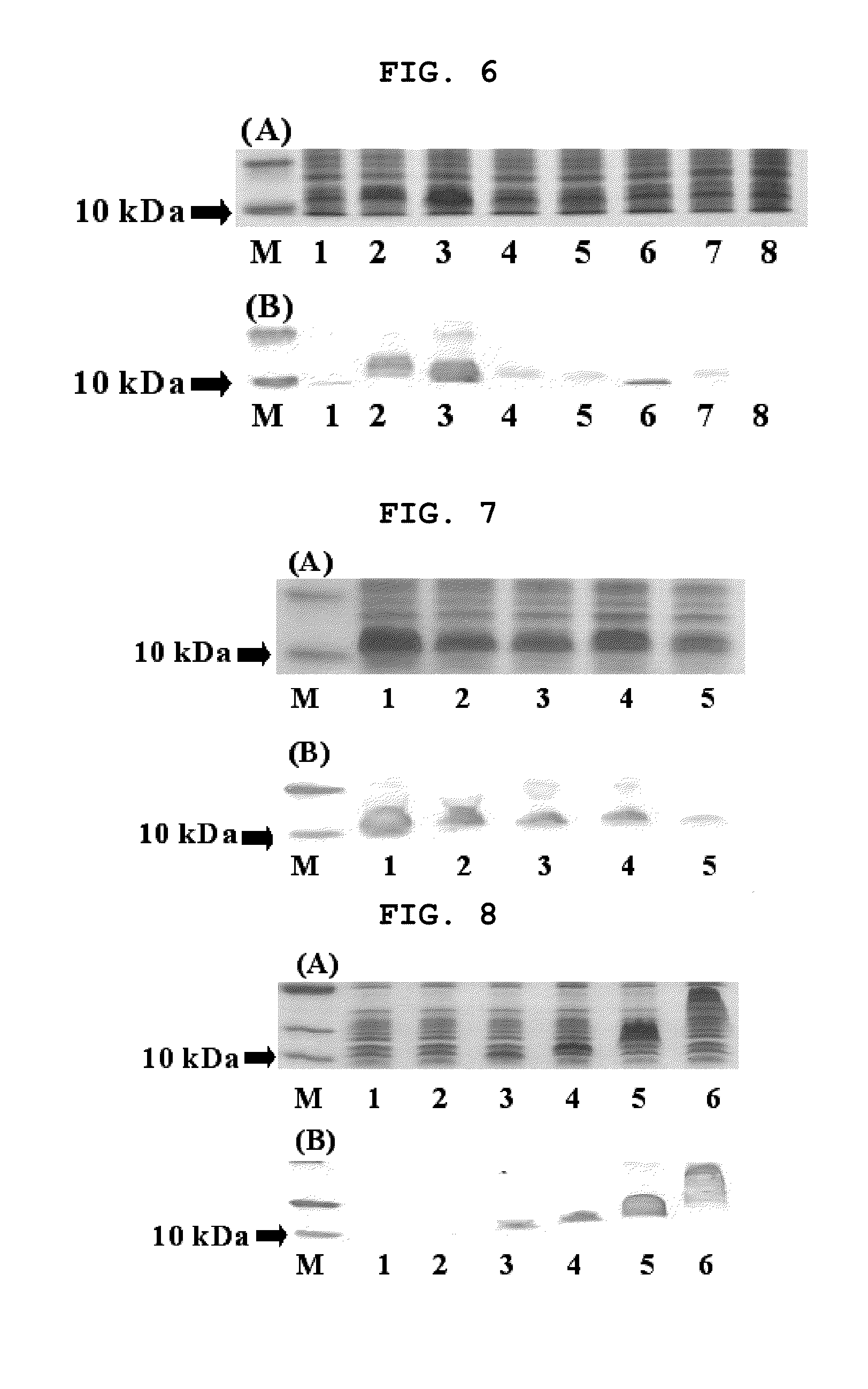
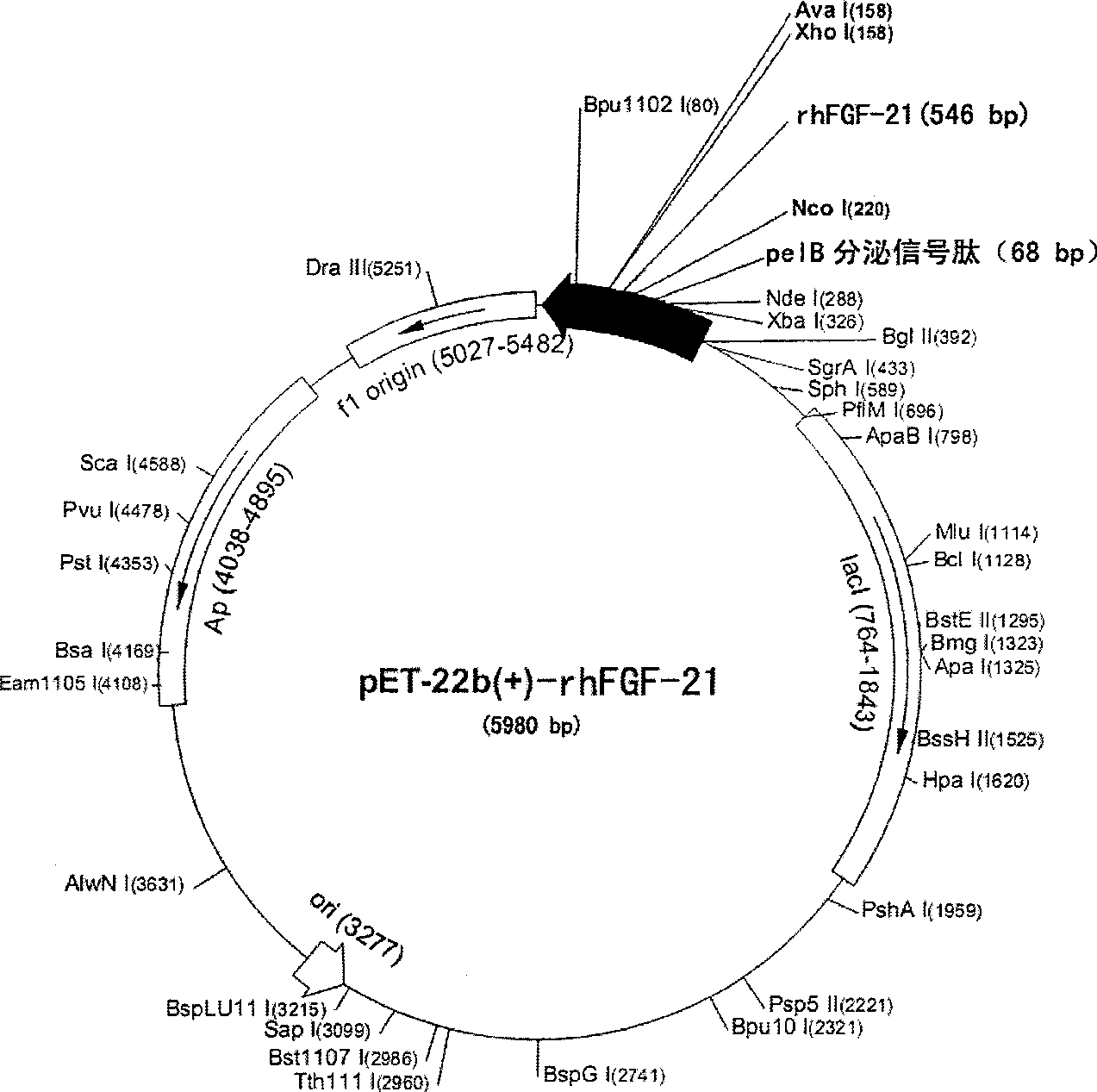
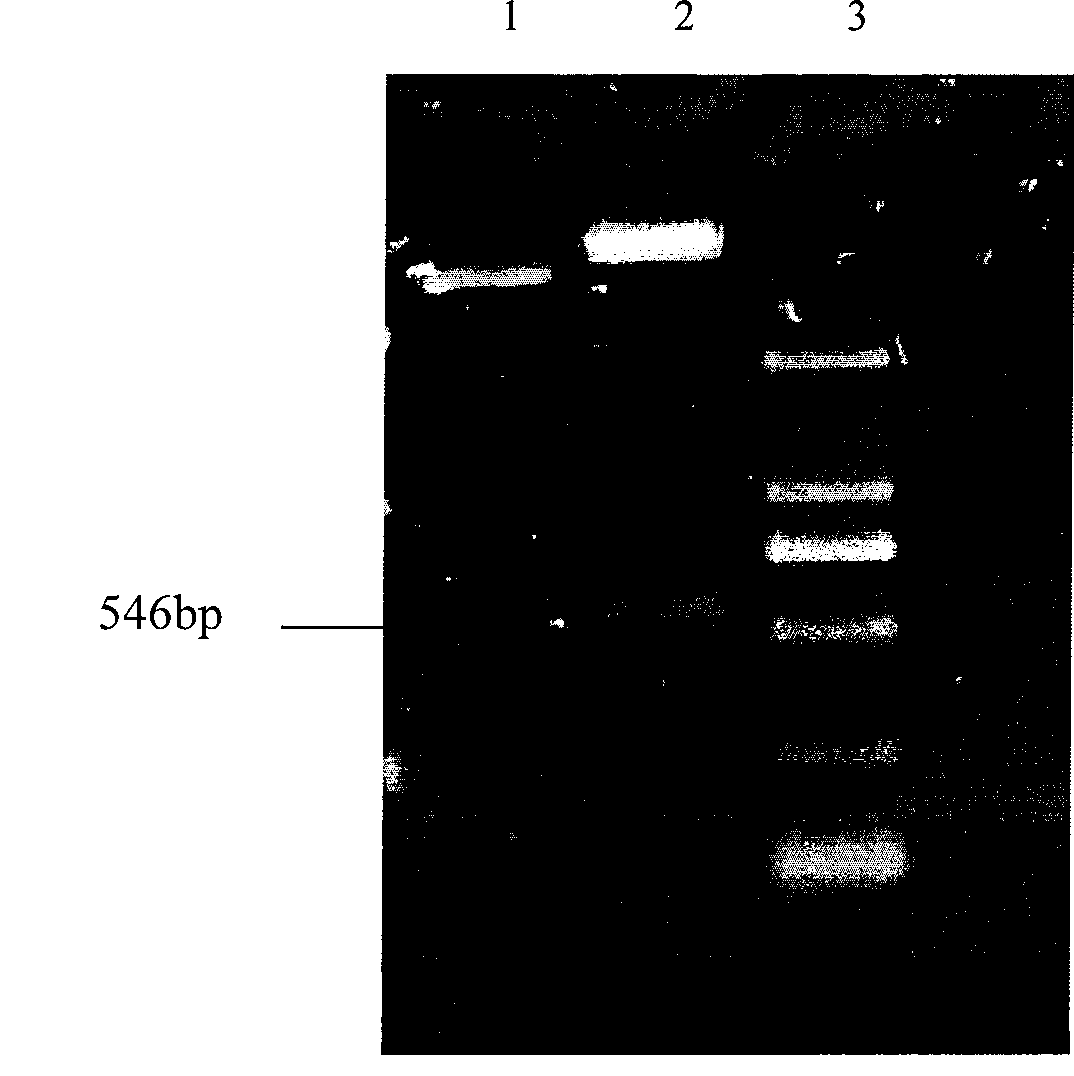
Method for producing secretion expression recombinant human fibroblast growth factor-21
ActiveCN101376888ASimple purification processImprove yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSecretion expressionNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides a method for producing FGF21. The invention first designs and synthetizes full-length FGF21 nucleotide sequence which is integrated with secreted signal peptide to be structured into an expression carrier capable of secreting and expressing FGF21 protein; the expression carrier is led into an appropriate host cell; under the guidance of the secreted signal peptide, FGF21 is expressed in cell periplasm, so that the purification procedure is convenient, the finished product ratio is improved and the mass production of rhFGF-21 becomes possible.
Owner:李校堃 +2
Method for obtaining single chain antibodies to human interferon alpha2b
A bacterial high-expression system which is applicable for simultaneous screening of large numbers of recombinant clones from combinatorial antibody libraries is disclosed. The method pertains to screening of single chain antibodies from libraries expressed in the periplasm of E. coli by secretion. By this approach, approximately 104 clones can be screened in a single round. After screening, the clones, which express the recombinant antibodies to the desired antigen, can be directly used for production of large quantities of antibodies from microorganism culture. The system is especially attractive for fast screening of antibody libraries from a hybridoma source. A refolding method for the large-scale production of biologically active scFv-6 his proteins from bacterial inclusion bodies is also disclosed.
Owner:NEW TECH HLDG
Isolation of binding proteins with high affinity to ligands
The invention overcomes the deficiencies of the prior art by providing a rapid approach for isolating binding proteins capable of binding small molecules and peptides via “display-less” library screening. In the technique, libraries of candidate binding proteins, such as antibody sequences, are expressed in soluble form in the periplasmic space of gram negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, and are mixed with a labeled ligand. In clones expressing recombinant polypeptides with affinity for the ligand, the concentration of the labeled ligand bound to the binding protein is increased and allows the cells to be isolated from the rest of the library. Where fluorescent labeling of the target ligand is used, cells may be isolated by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS). The approach is more rapid than prior art methods and avoids problems associated with the surface-expression of ligand fusion proteins employed with phage display.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods for control of flux in metabolic pathways through enzyme relocation
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Methods for optimizing the secretion of protein in prokaryotes
Methods are provided for producing recombinant proteins by utilizing expression vectors carrying nucleic acids encoding the proteins, and secretory signal sequences to direct the secretion of the proteins to the periplasm or extracellular medium. Expression vectors which encode a fusion protein comprising a carrier protein and the protein are also provided, as are host cells transformed with the expression vectors.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Methods for producing recombinant proteins
ActiveUS7754447B2High protein yieldQuality improvementBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPeriplasmic spaceProtein C
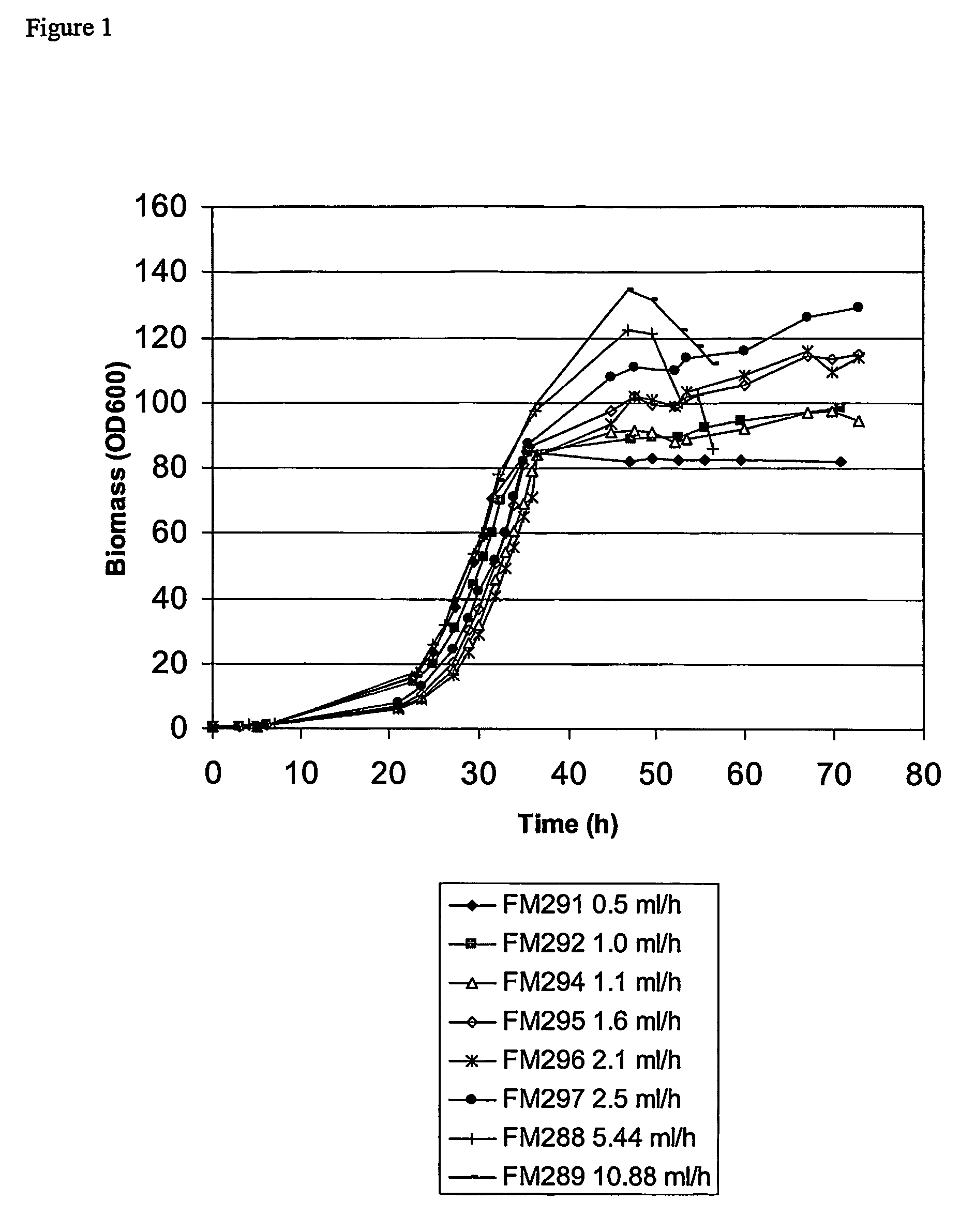
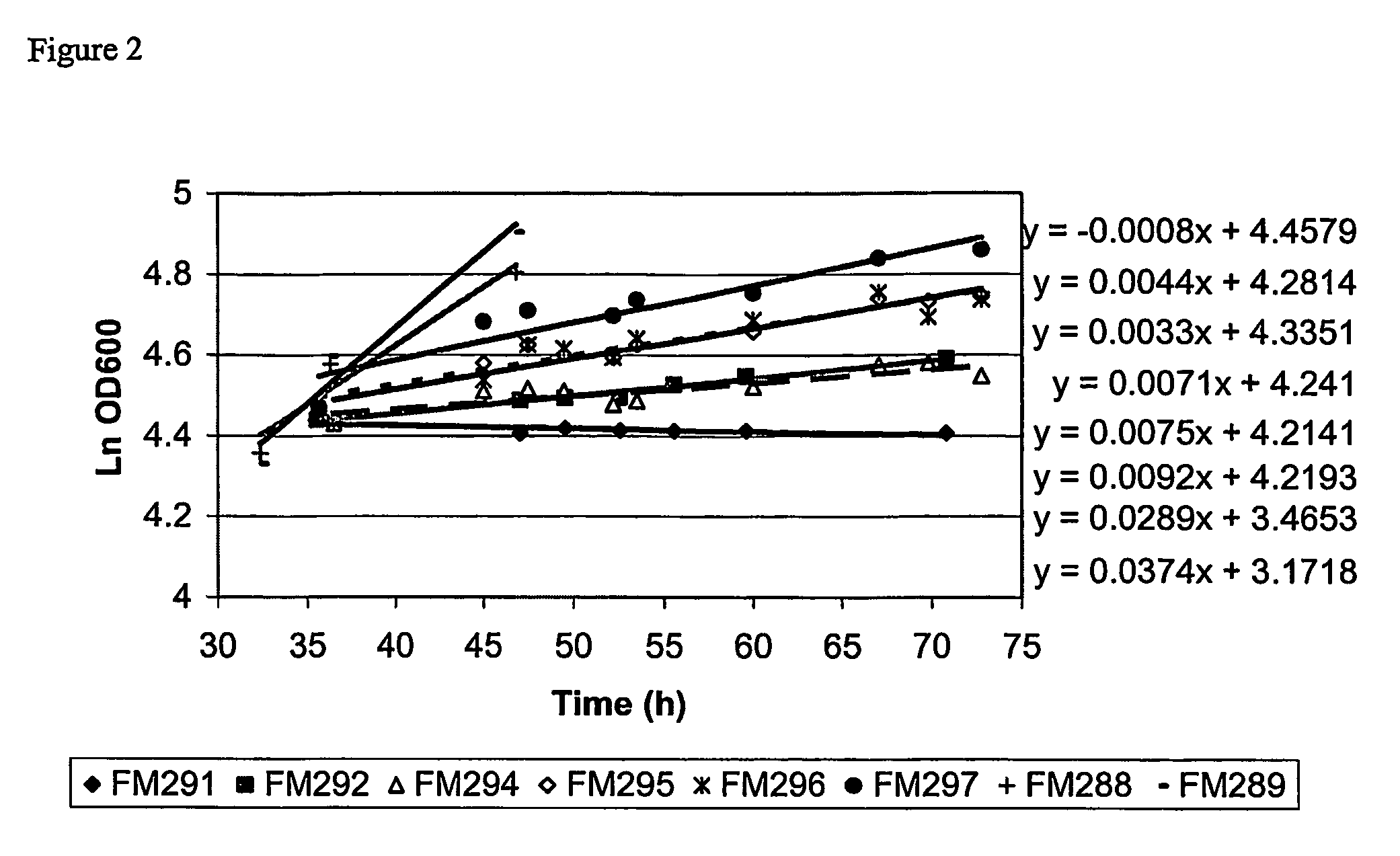
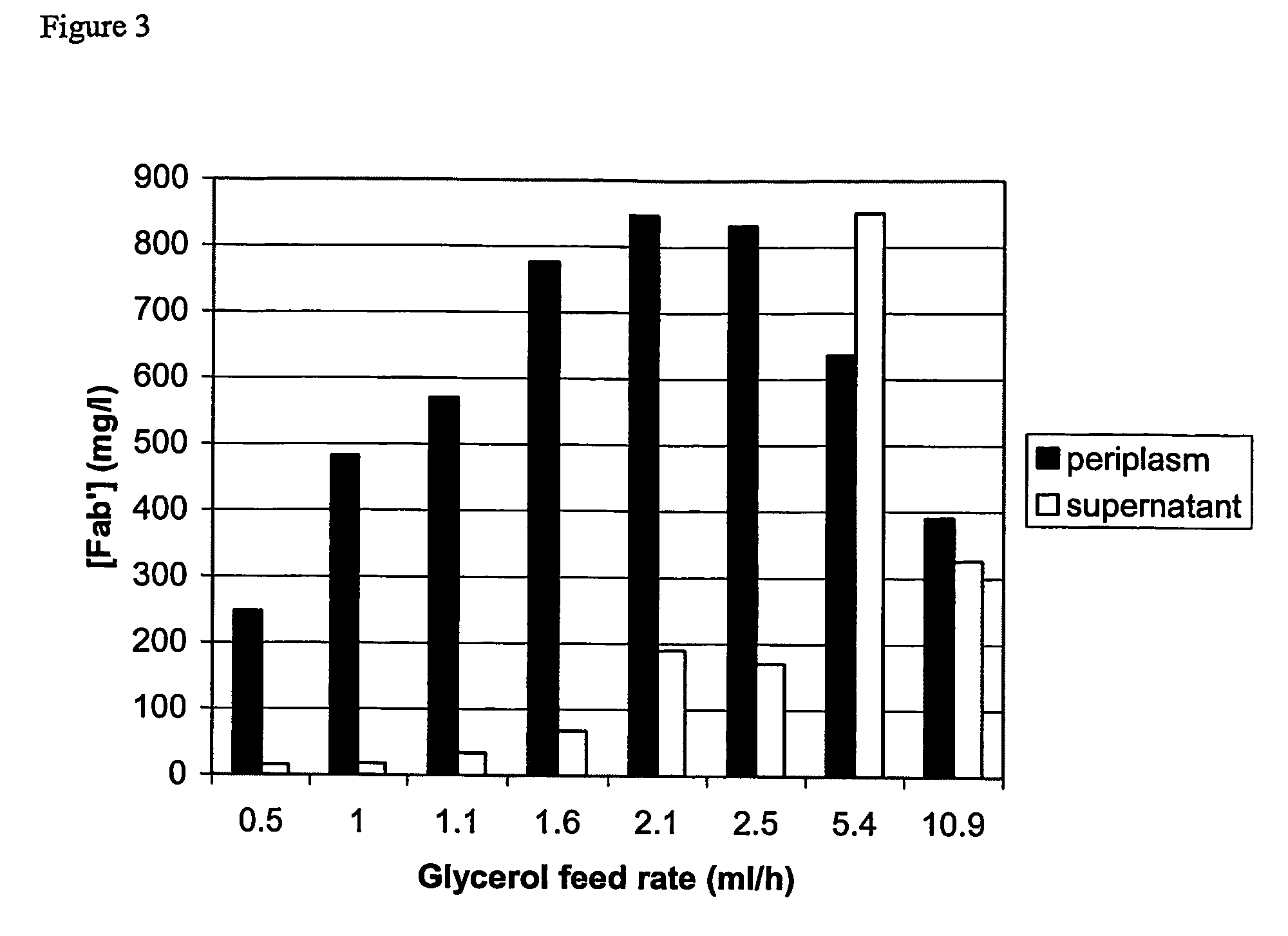
The present invention provides a method for controlling the partitioning of a recombinant protein between the supernatant and the periplasm in E. coli host cell cultures wherein expression of the recombinant protein by said cells is under the control of an inducible system, which method comprises: a) providing an E. coli host cell culture b) changing the growth rate of the E. coli host cells c) inducing expression of the recombinant protein wherein steps (b) and (c) can be performed in any order or simultaneously; and subsequently d) determining the yield of recombinant protein in the culture supernatant and the E. coli host cell periplasm e) comparing the yield determined in step (d) with the yield determined when at least one other growth rate has been used in step (b) f) selecting a growth rate from the comparison made in step (e) in which the partitioning of the recombinant protein between the supernatant and the periplasm is most suited to the primary recovery of the recombinant protein.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
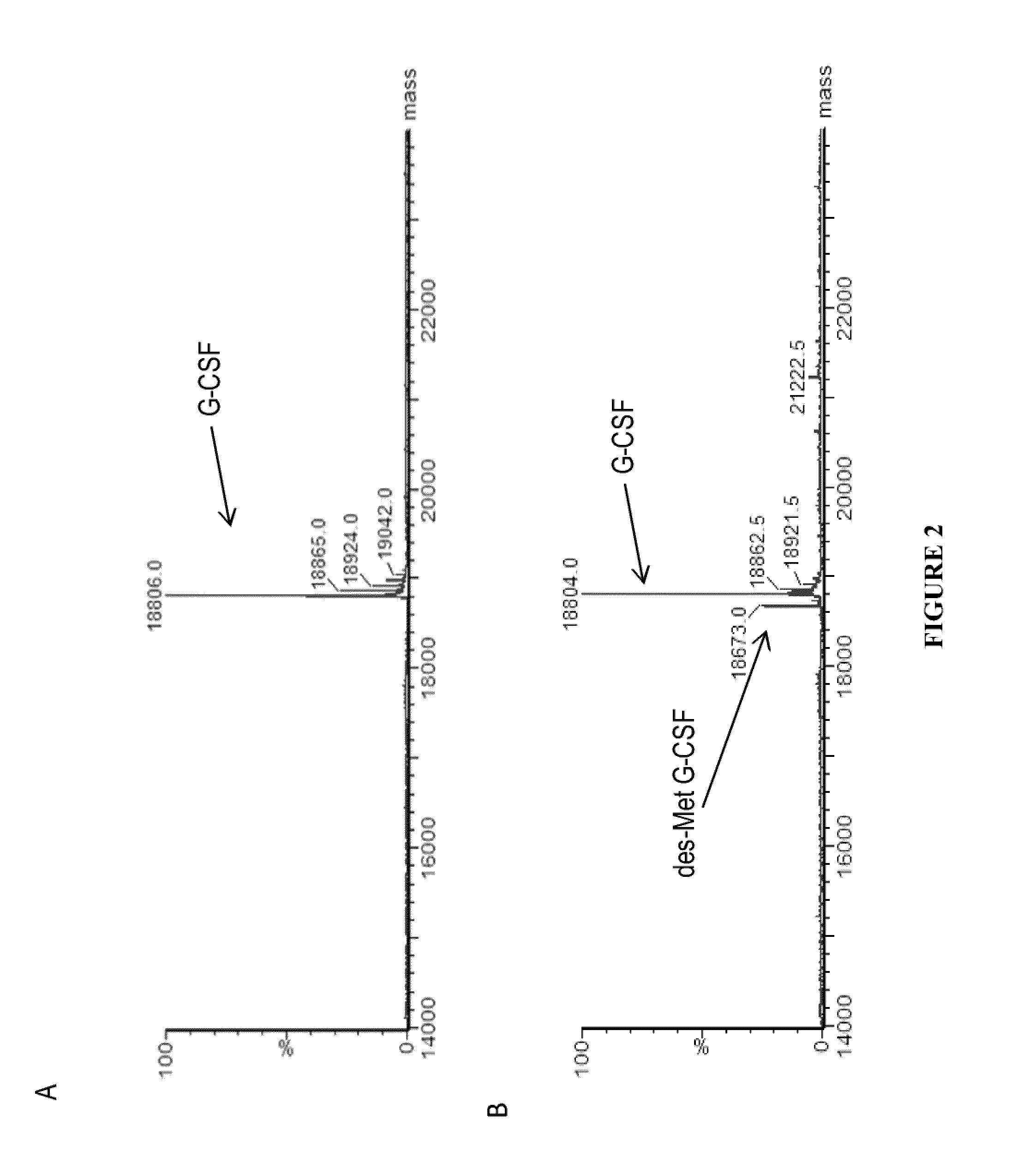
Methods for G-CSF production in a Pseudomonas host cell
ActiveUS8455218B2High yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyPeriplasmic space
The present invention relates to the field of recombinant protein production in bacterial hosts. It further relates to expression of soluble, active recombinant protein by using secretion signals to direct the protein to the periplasmic space of a bacterial cell. In particular, the present invention relates to a production process for obtaining soluble hG-CSF protein from a bacterial host.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
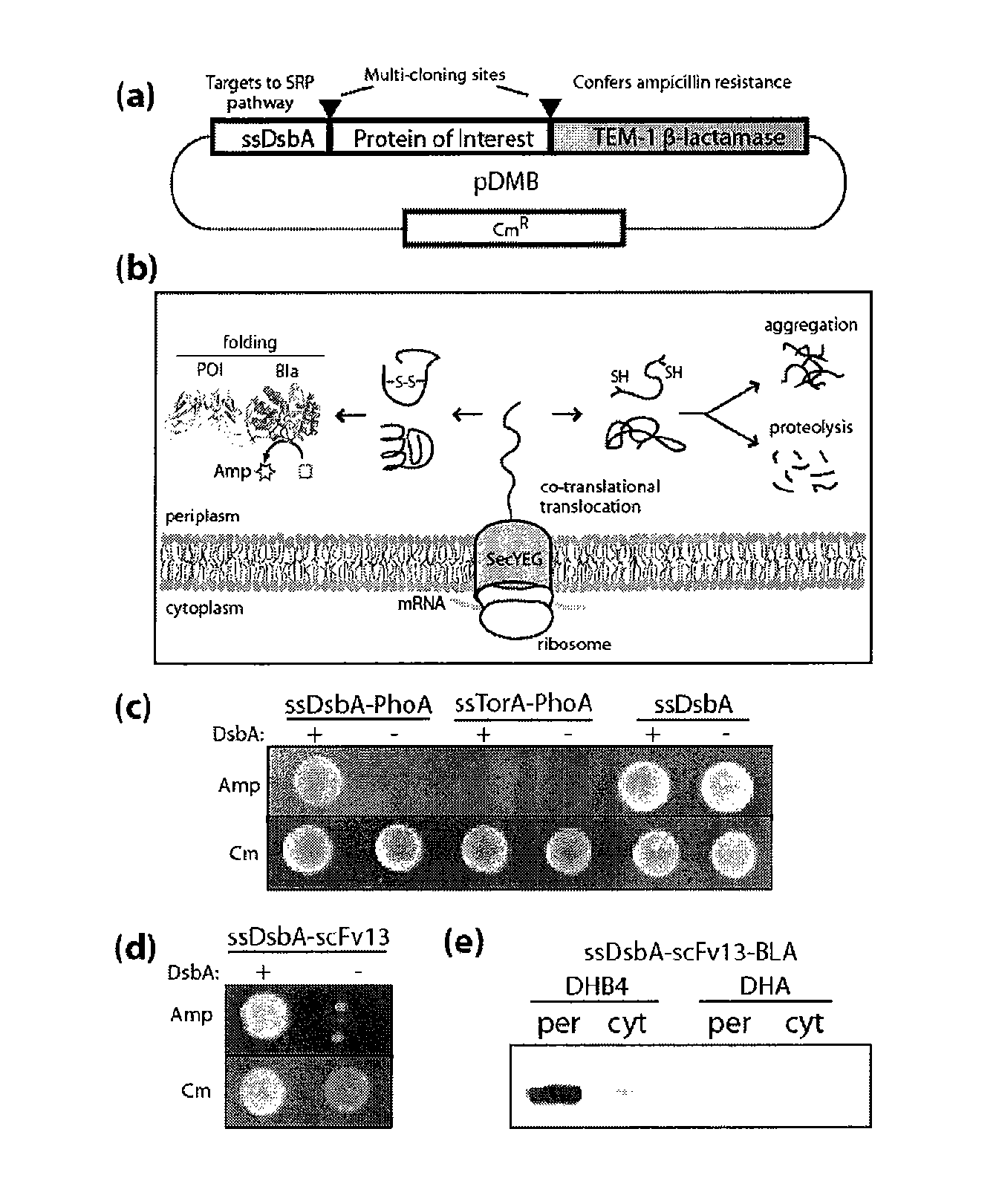
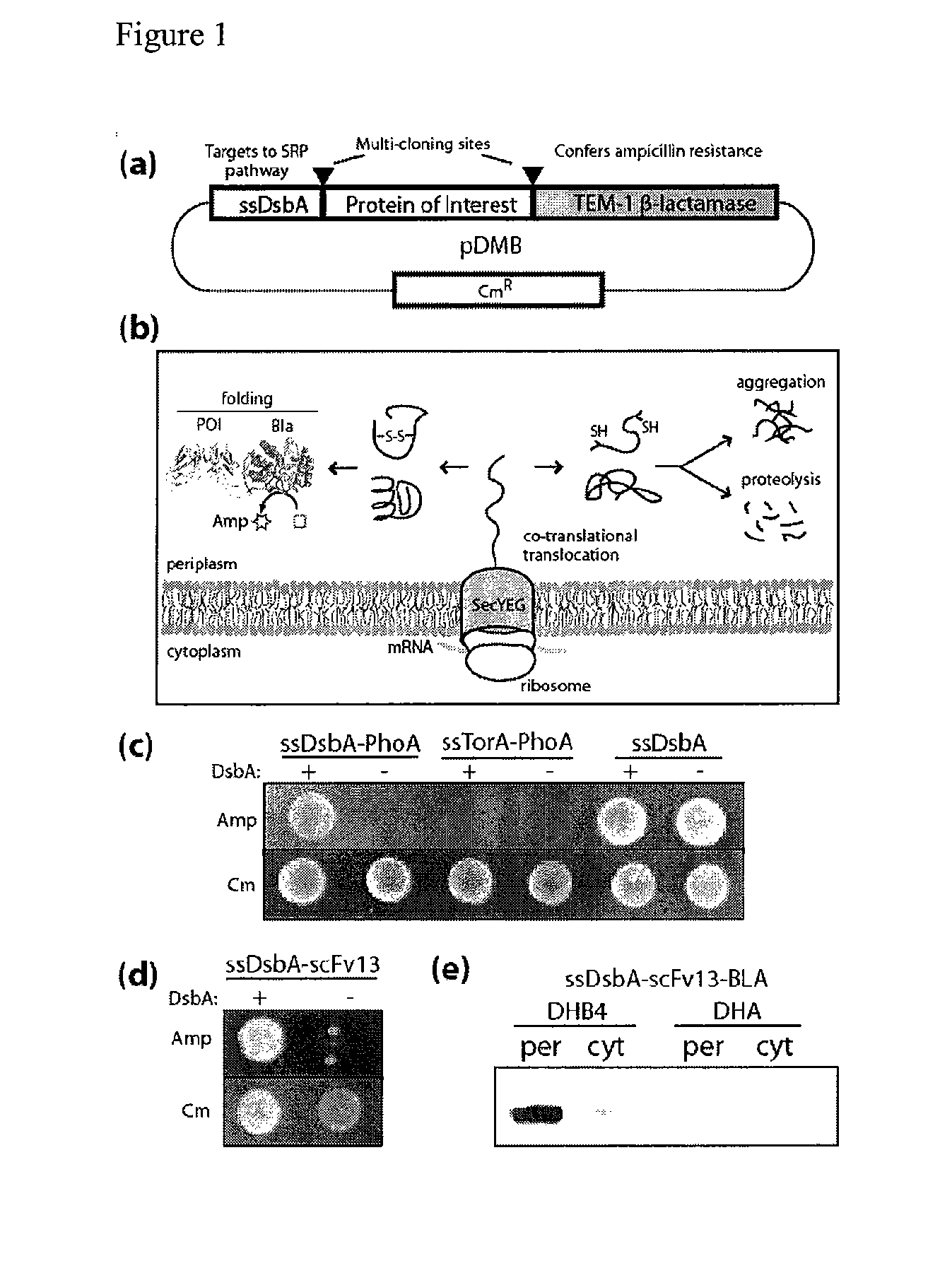
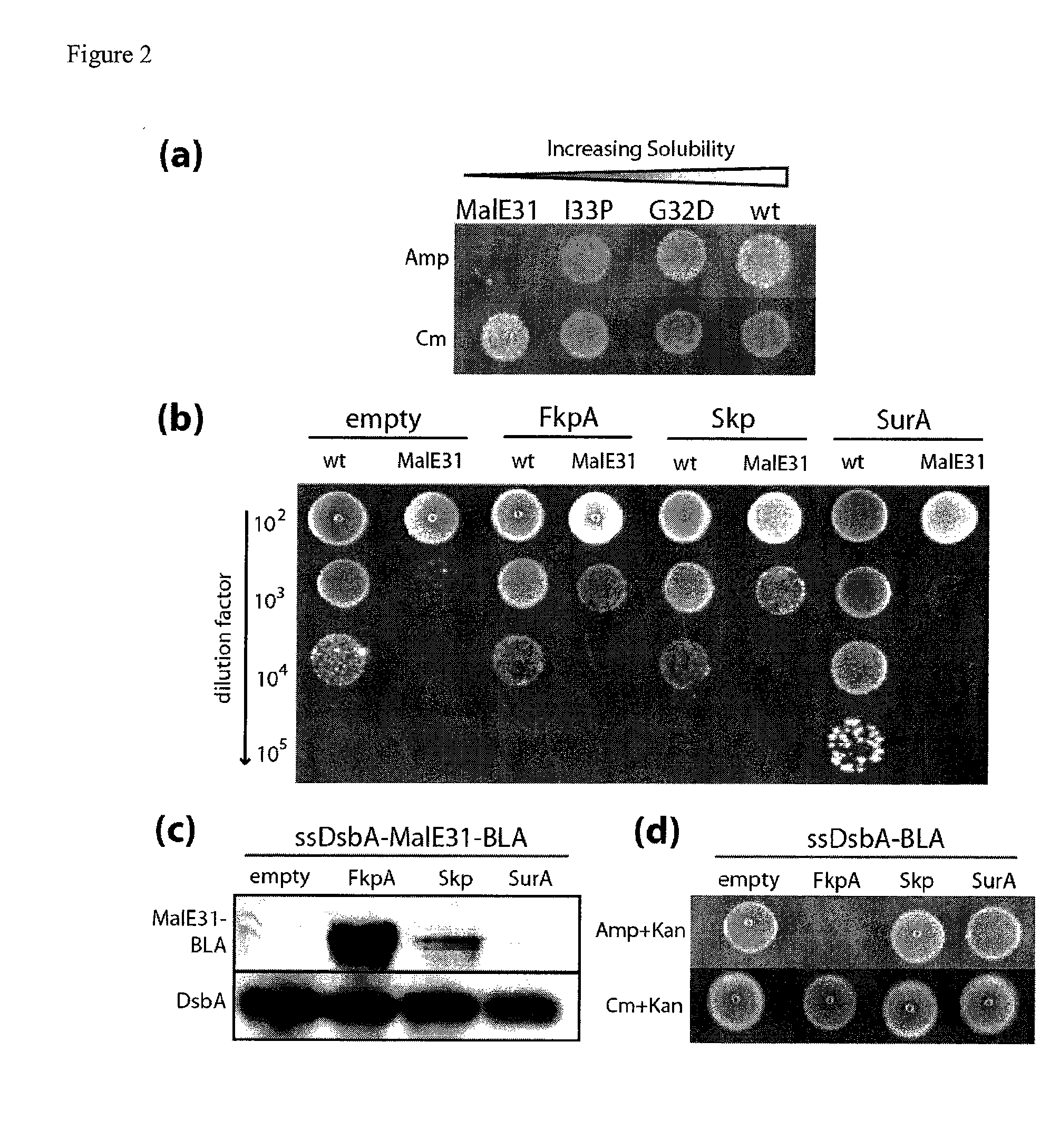
Genetic selection for protein folding and solubility in the bacterial periplasm
ActiveUS20100144546A1Sugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSignal recognition particleSolubility
The present invention relates to the fields of microbiology, molecular biology and protein biochemistry. More particularly, it relates to compositions and methods for analyzing and altering (e.g., enhancing or inhibiting) protein folding and solubility (e.g., within periplasm). The present invention provides an engineered assay for protein folding and solubility in the E. coli periplasm based on co-translational translocation of a chimera comprising a protein of interest fused to TEM-I β-lactamase that is targeted for export via the signal recognition particle (SRP)-dependent pathway. Using an array of native and heterologous proteins, it is demonstrated that periplasmic folding behavior of proteins is intimately coupled to in vivo β-lactamase activity. As a result of this coupling, the reporter is useful for (1) facile discovery of extrinsic periplasmic factors that affect protein folding and solubility; and (2) genetic selection of solubility-enhanced proteins.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
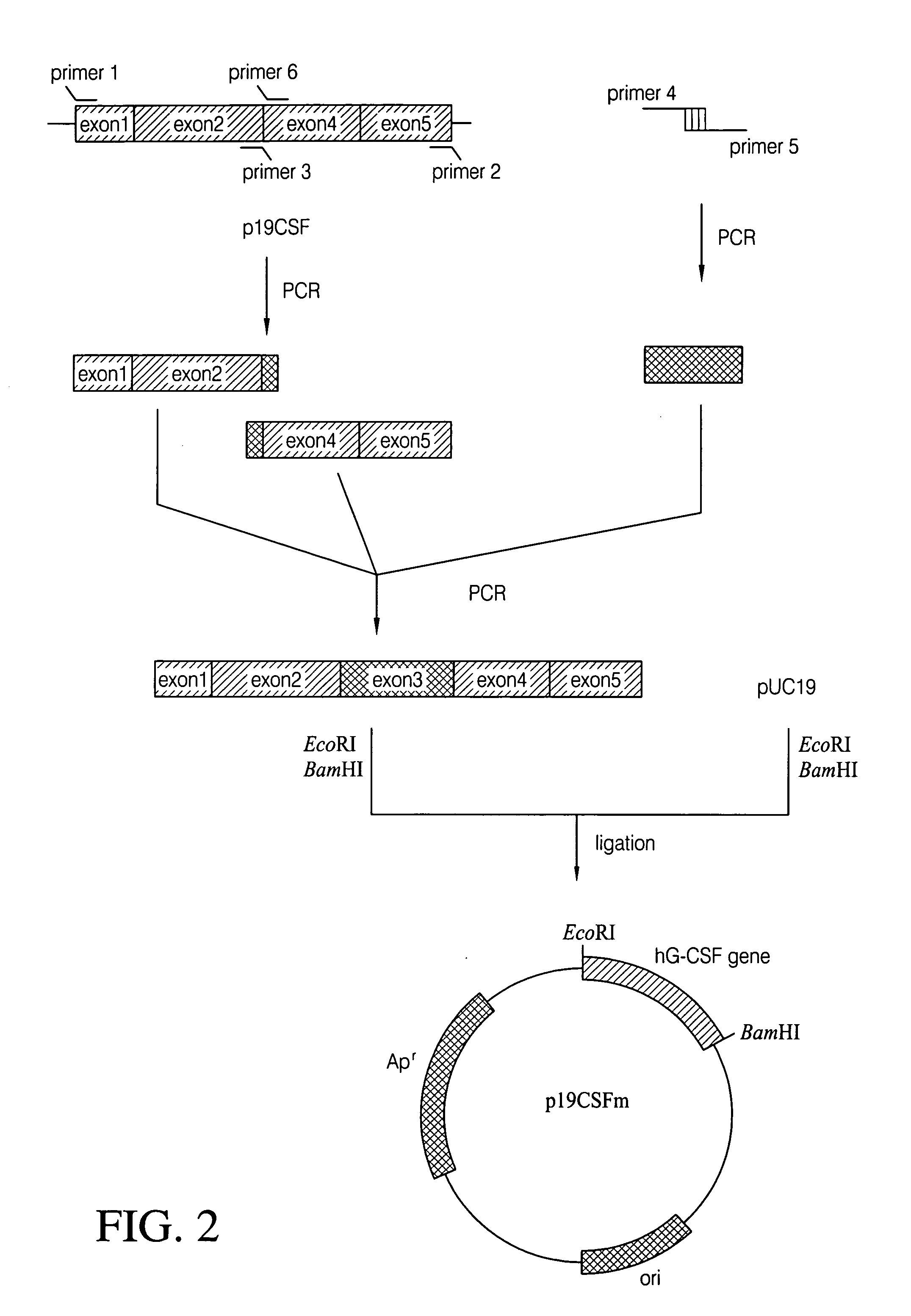
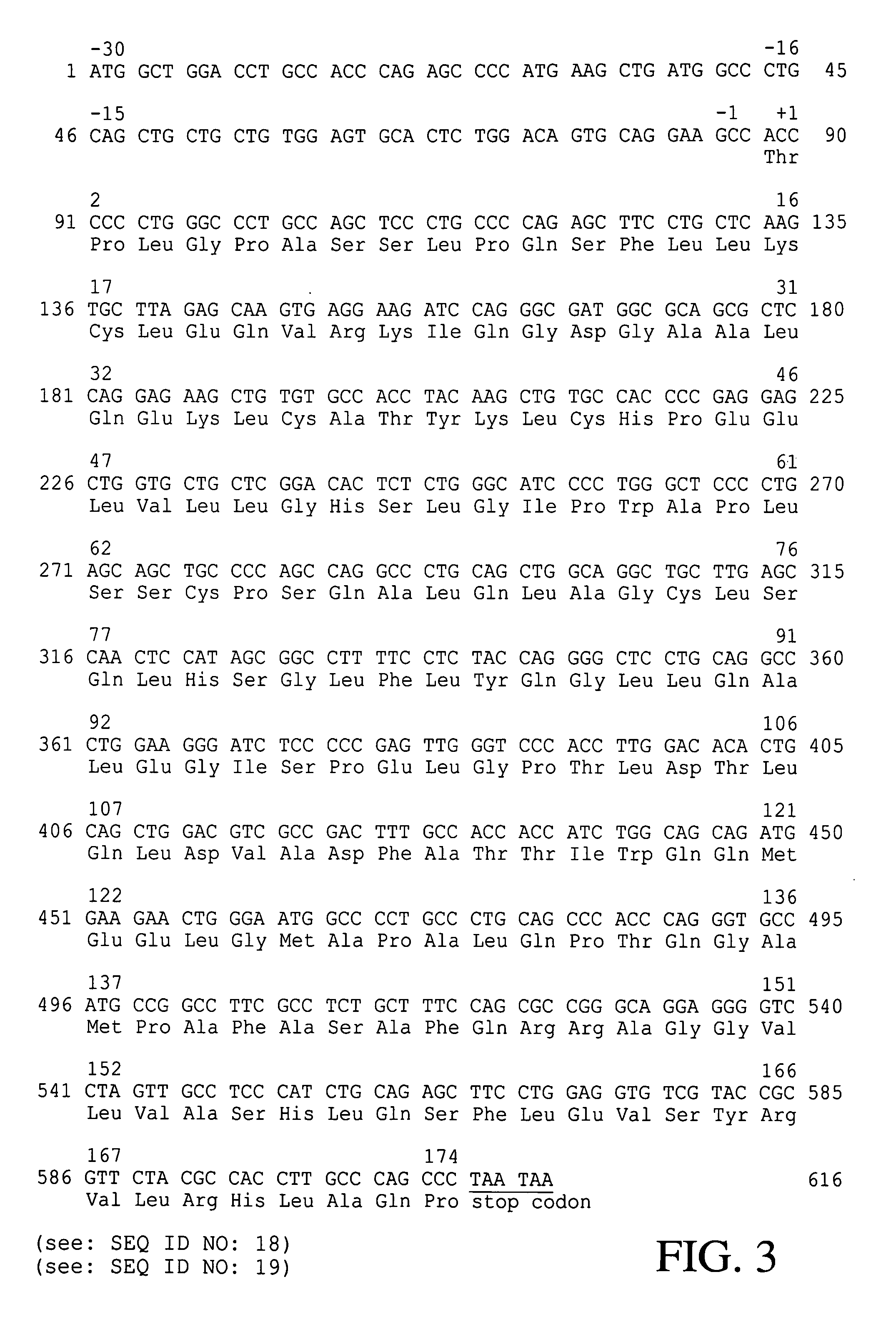
Escherichia coli strain secreting human granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF)
The present invention provides a recombinant plasmid vector comprising a kanamycin resistance gene, a promoter, an endoxylanase signal sequence, a nucleotide sequence coding for an oligopeptide consisting of 13 amino acids including 6 consecutive histidine residues, and a human granulocyte colony stimulating factor(hG-CSF) gene; an E. coli transformed with the said vector; and, a process for producing complete hG-CSF protein with high purity from the protein pool secreted by the said microorganism. In accordance with the invention, the hG-CSF protein can be prepared with high purity through rather simple process facilitating secretion of large amount of hG-CSF fusion protein into the periplasm, which does not require complicated processes such as solubilization and subsequent refolding required for isolation of the hG-CSF protein produced in cytoplasm as insoluble inclusion bodies by conventional techniques, thus, the hG-CSF protein can be widely used as an active ingredient in the development of supplementary agents for anticancer therapy.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Production of a soluble native form of recombinant protein by the signal sequence and secretional enhancer
The present invention is drawn to a method for enhancing secretional efficiency of a heterologous protein using a secretional enhancer consisting of a modified signal sequence which comprises the N-region of a signal sequence and / or a hydrophobic fragment of the said signal sequence comprising the said N-region and / or the hydrophilic polypeptide. The method of the present invention can be used not only for production of recombinant heterologous proteins by inhibiting insoluble precipitation and enhancing secretional efficiency of the recombinant protein into the periplasm or the extracellular fluid and but also for transduction of therapeutic proteins by enhancing membrane-permeability of the recombinant protein using a strong secretional enhancer.
Owner:国立水产科学院 +1
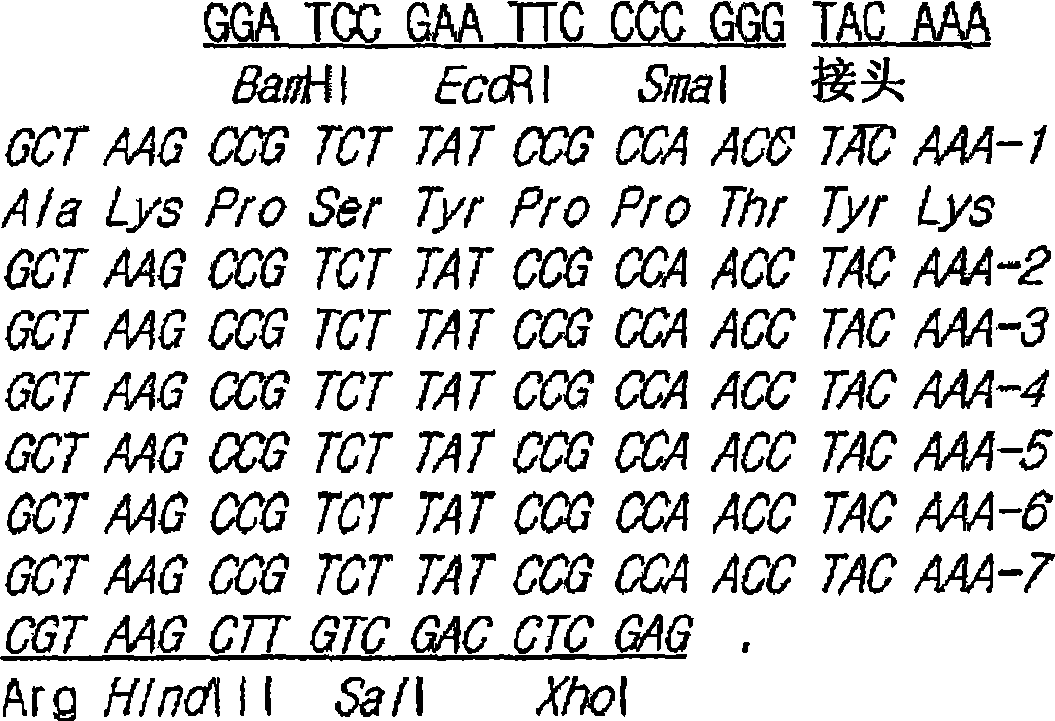
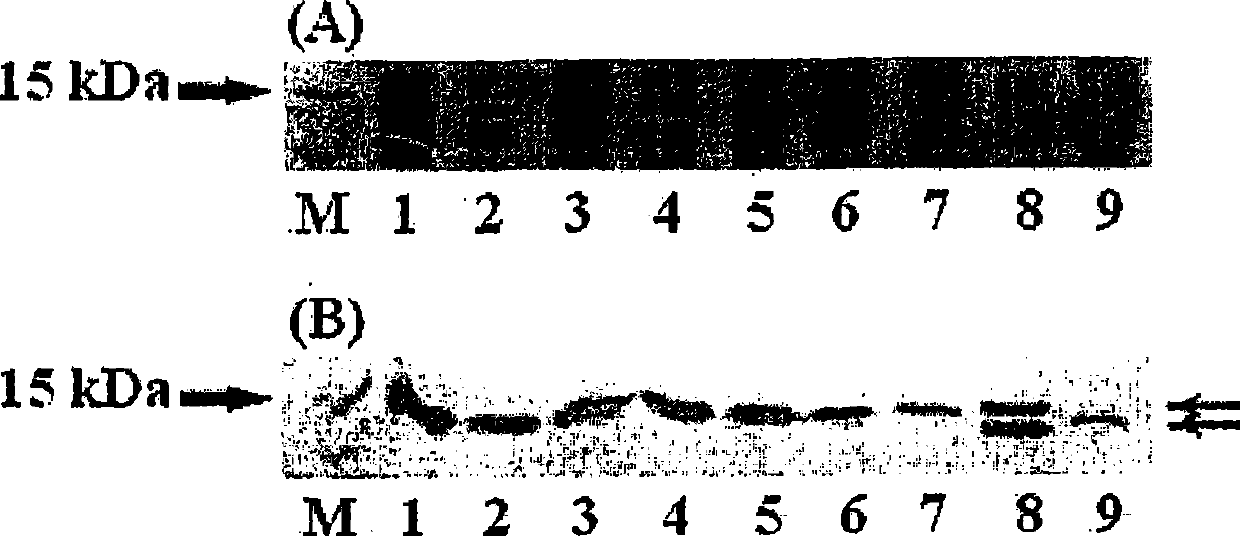
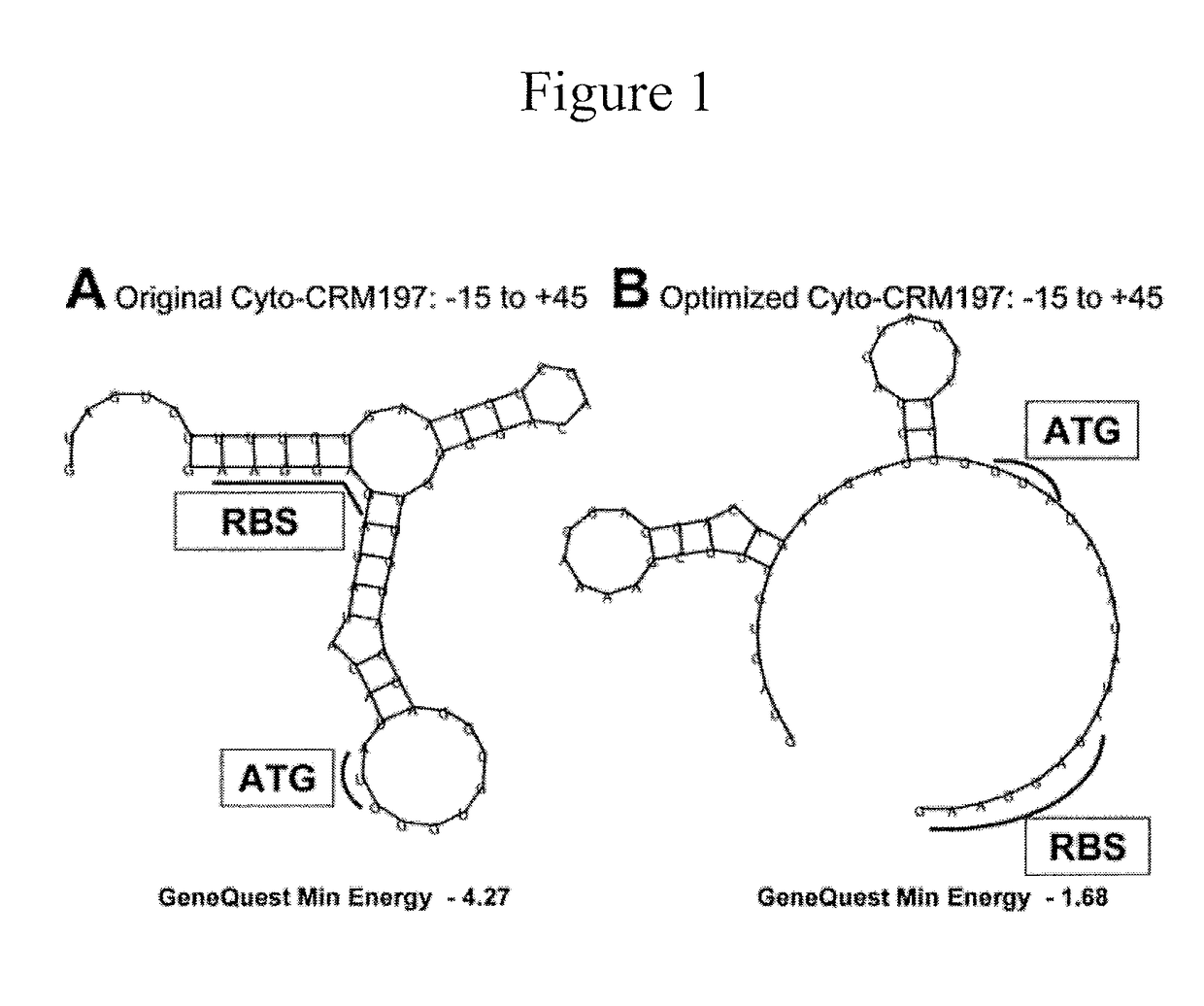
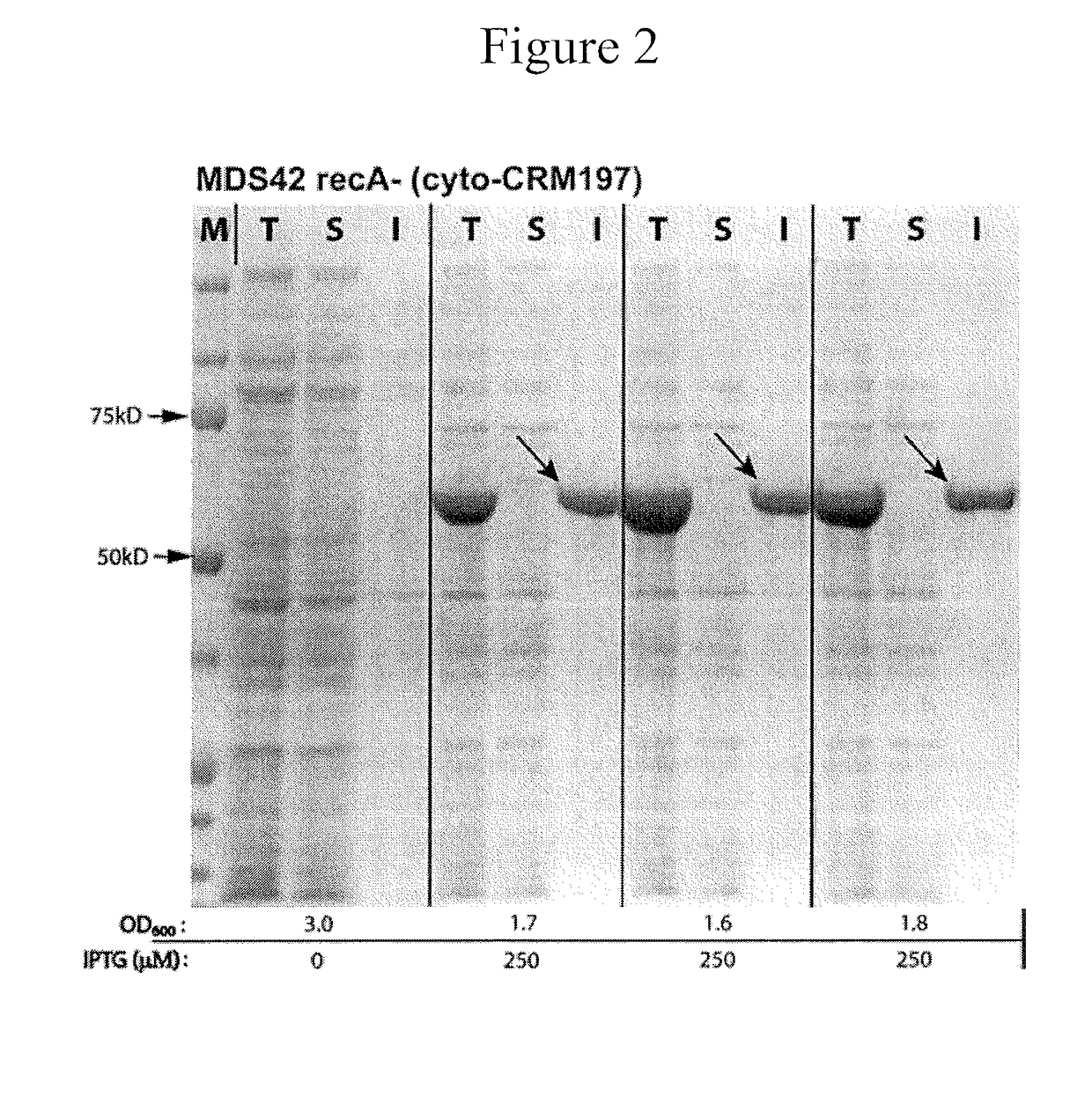
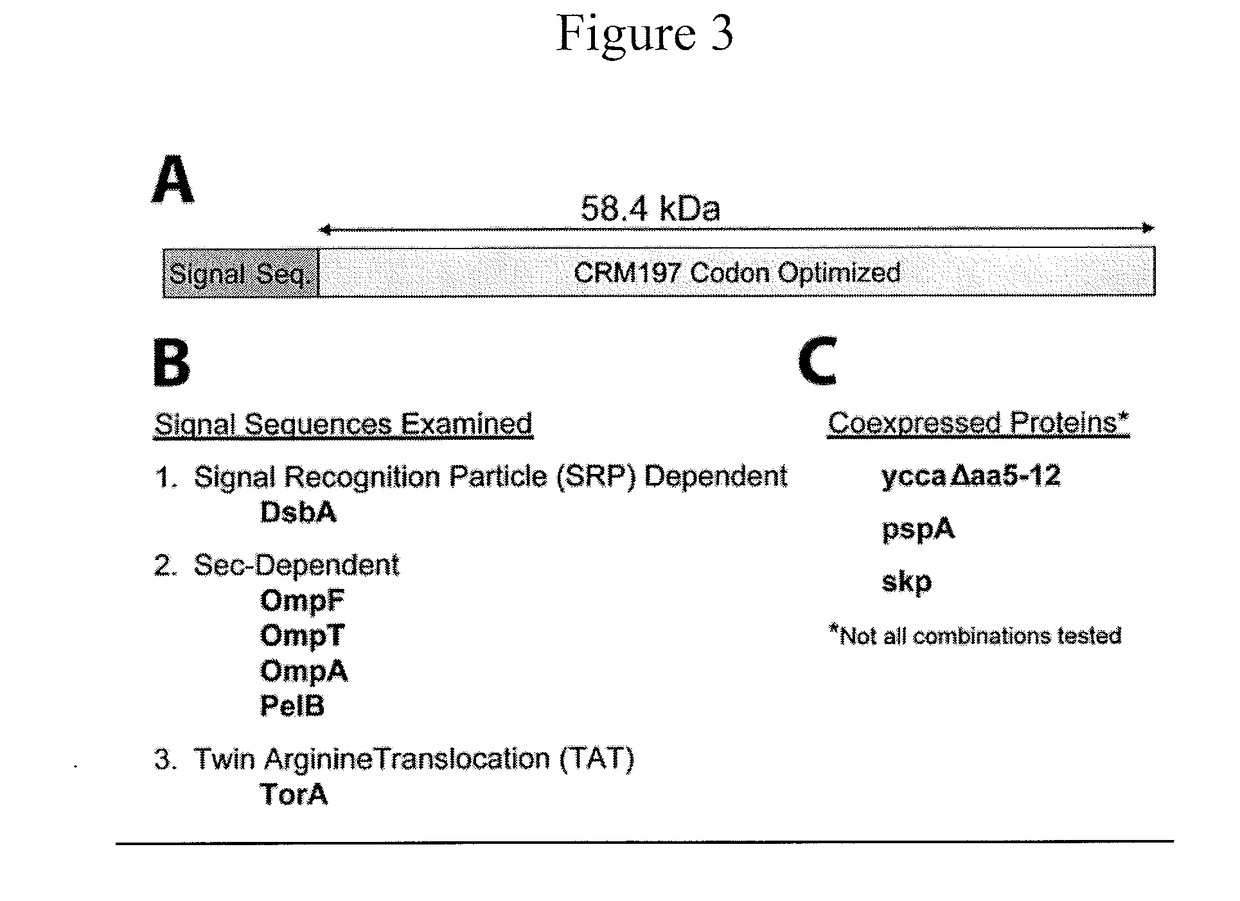
Enhanced Production of Recombinant CRM197 in E. coli
Rediced genome or native K12 strain E. coli bacteria comprising expression vectors encoding a recombinant CRM197 protein and their use in the production of CRM 197 is provided. The CRM 197 protein may be fused to a signal sequence that directs the expressed CRM197 protein to the periplasm of the E. coli host.
Owner:SCARAB GENOMICS LLC
Method for preparing recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor-2 by secretion expression
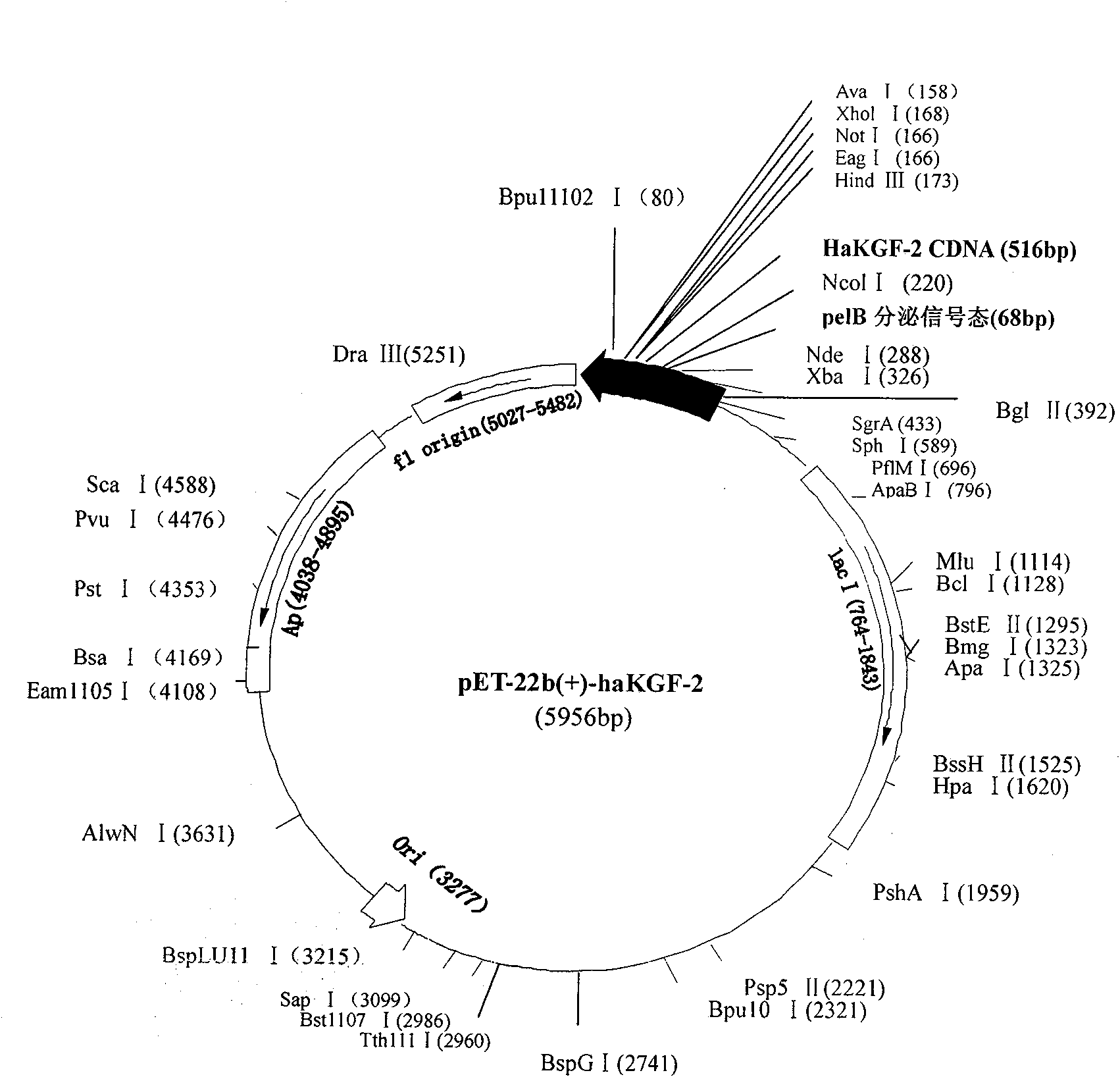
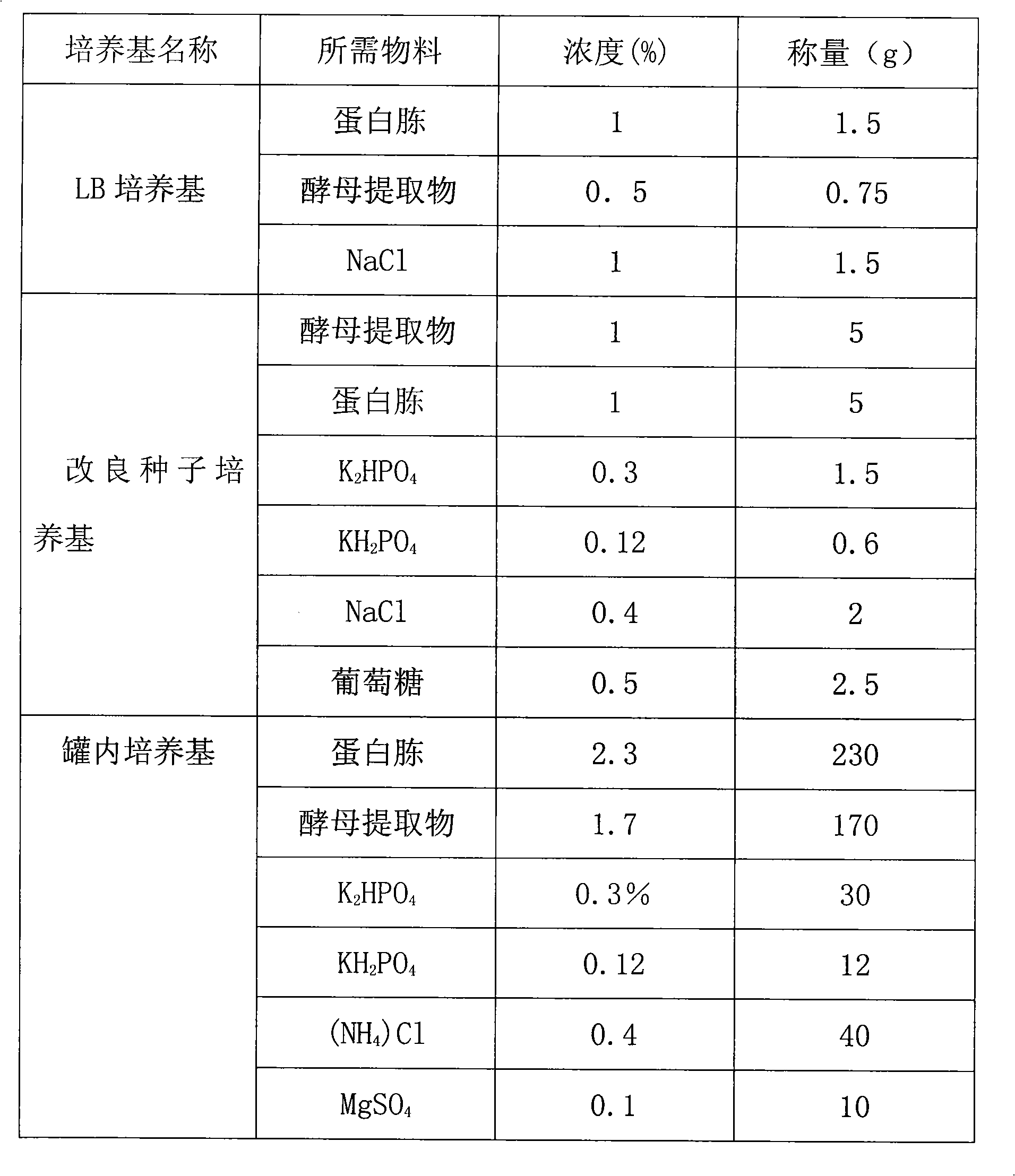
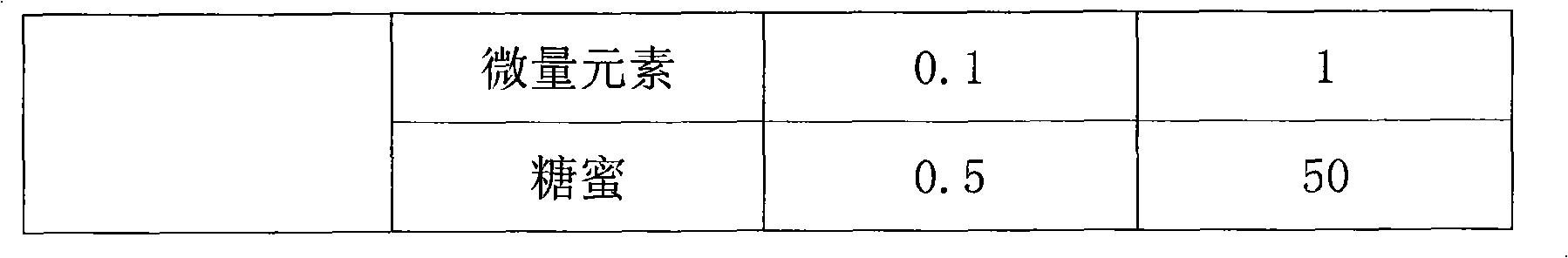
InactiveCN101538571AThe expression process is simpleHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRecombinant Human Keratinocyte Growth FactorFreeze thawing
The invention provides a method for preparing recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor-2 by secretion expression. The method provides an expression vector of the recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor-2, which contains an secretion signal peptide coding sequence and can secrete KGF-2 protein in periplasm for expression; and when a host cell containing the recombinant plasmid is subjected to repeated freeze thawing at a low temperature, the recombined protein can be released in a buffer solution under the condition of not damaging inner membranes of bacilli and the activity of the protein.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV +2
Engineering bacteria based on manganese peroxidase and implementation method of engineering bacteria
InactiveCN104232555AStable enzymatic propertiesAchieve periplasmic space expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionProtein target
The invention provides engineering bacteria based on manganese peroxidase in the field of the genetic engineering and an implementation method of the engineering bacteria. The genome DNA of the streptomyces griseorubens is taken as a template, and PCR amplification is performed on the template and a primer containing an enzyme digestion site and a polyhistidine label so that the nucleotide sequence coding the manganese peroxidase can be obtained; next, the gene sequence obtained by amplification is connected to an expression vector, and then the obtained connection product is transferred into an escherichia coli expressed strain, and finally, the over-expressed recombinant strain of the manganese peroxidase is obtained. The engineering bacteria based on the manganese peroxidase are used for overcoming the shortage of seriously restricted application range and application effect because the manganese peroxidase mostly is an endoenzyme in vivo and is low in expression amount, and in-vitro mass expression and synthesis of the manganese peroxidase are realized by use of a genetic engineering method; besides, the purity of the purified manganese peroxidase is also guaranteed while the protein activity is improved by use of the method of adding the polyhistidine label to the C end of the expressed recombinant protein; in addition, the periplasmic space expression of the target protein is realized by use of a vector signal peptide and the activity of the manganese peroxidase is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com