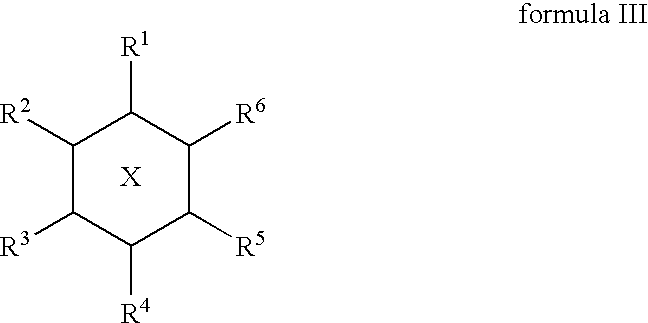
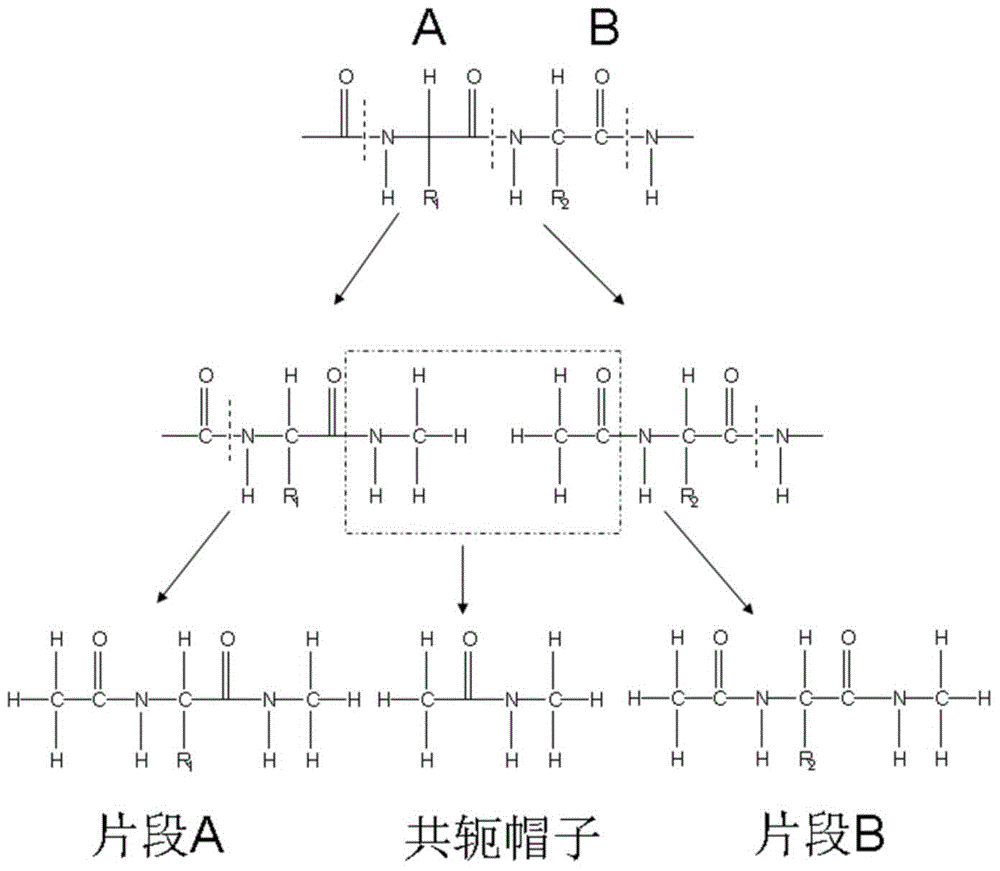
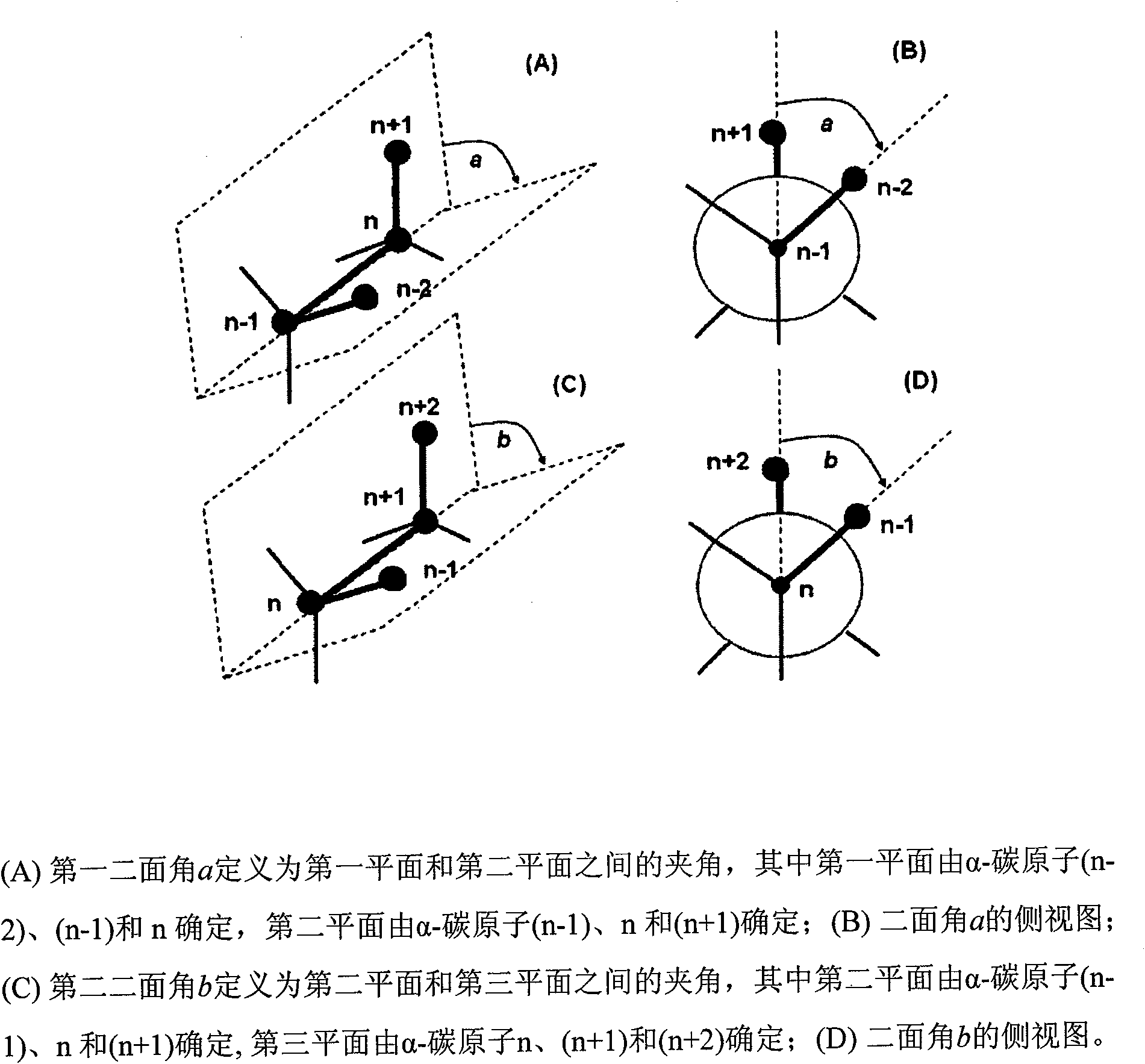
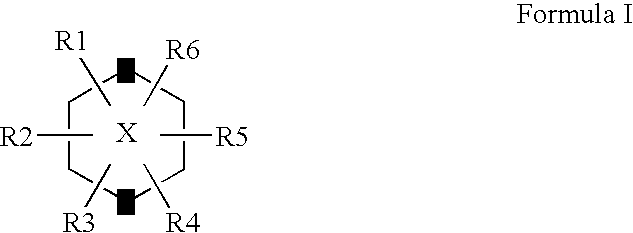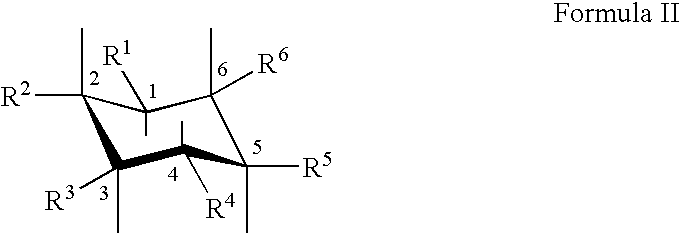Patents
Literature
155 results about "Protein folding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
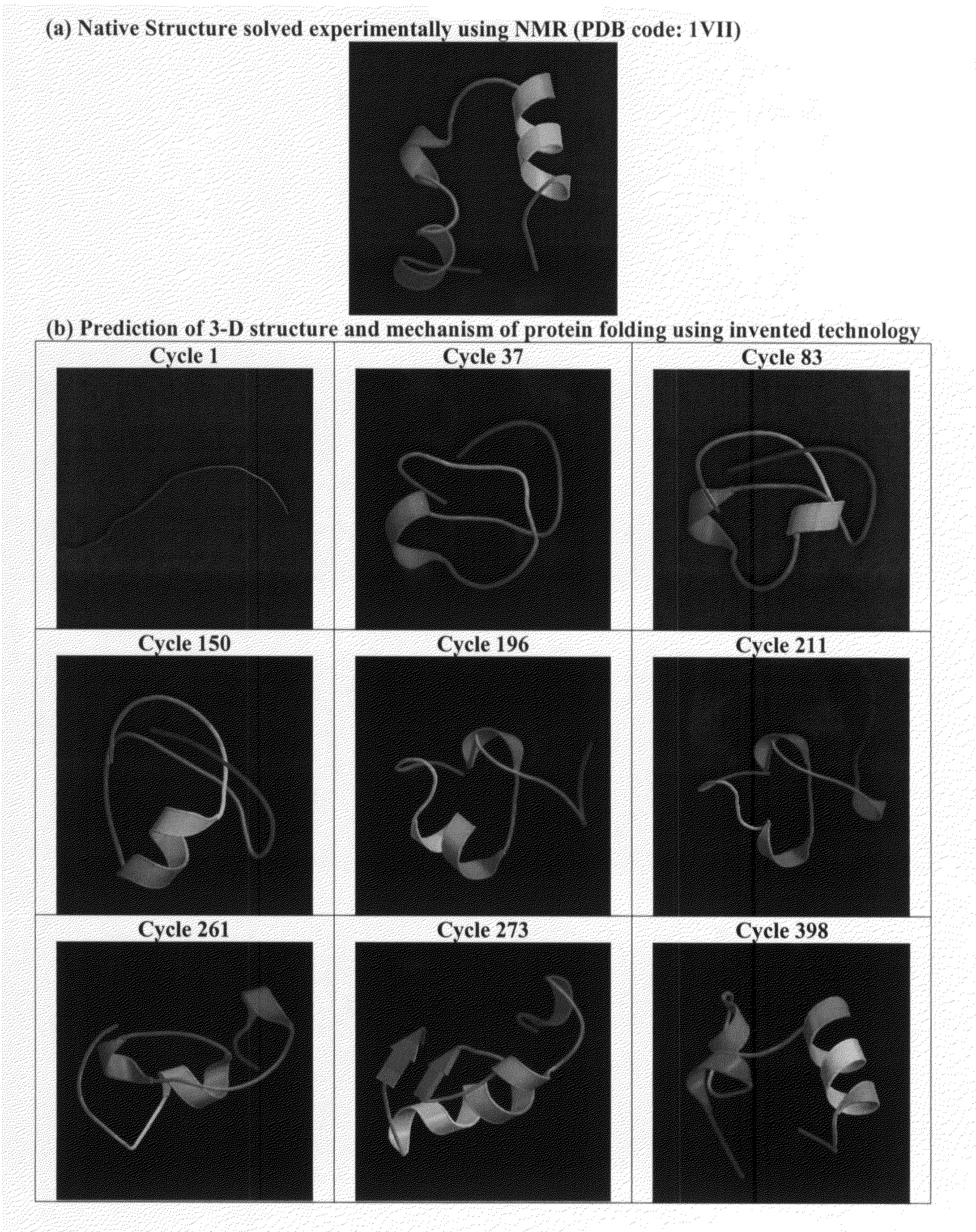
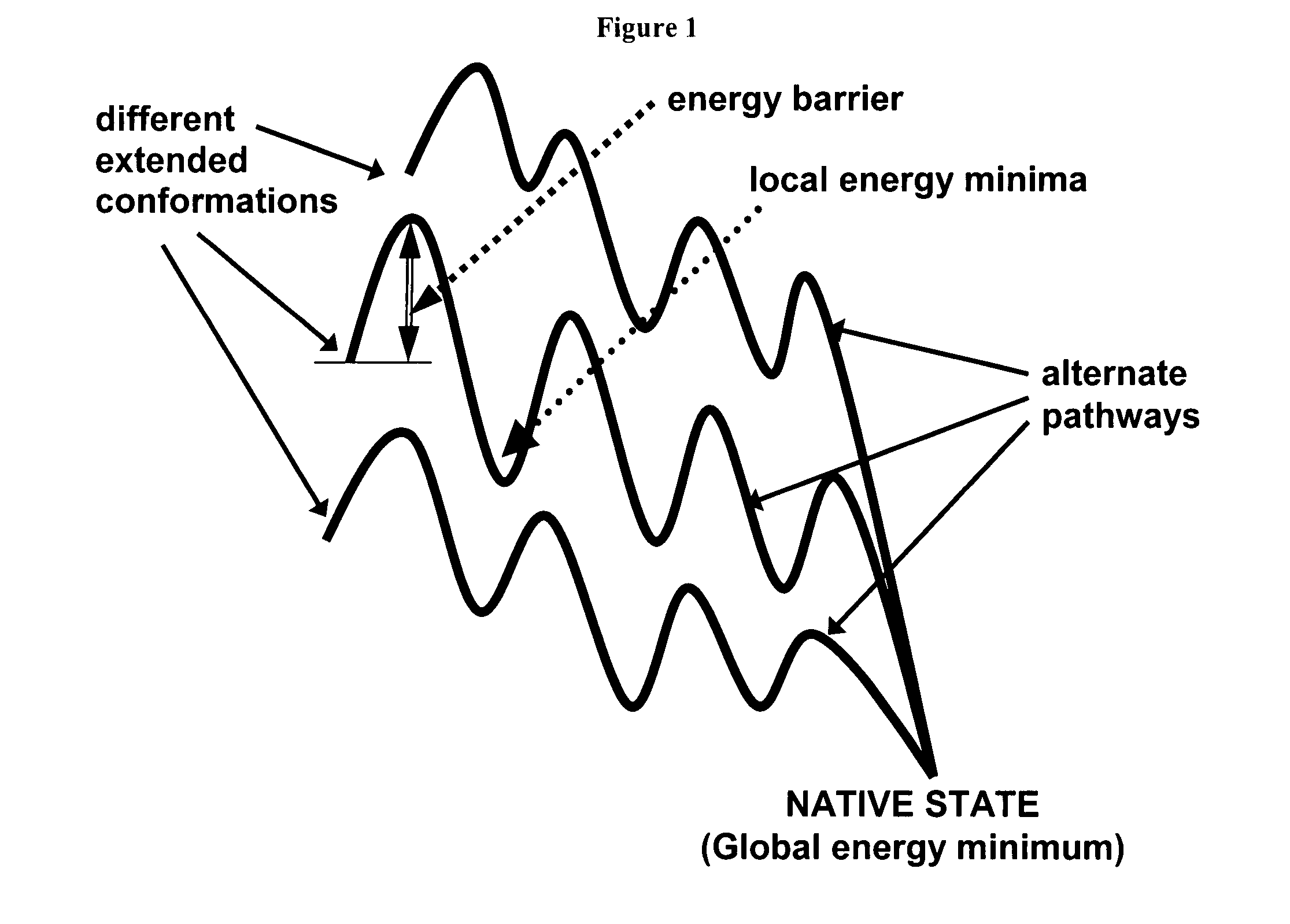
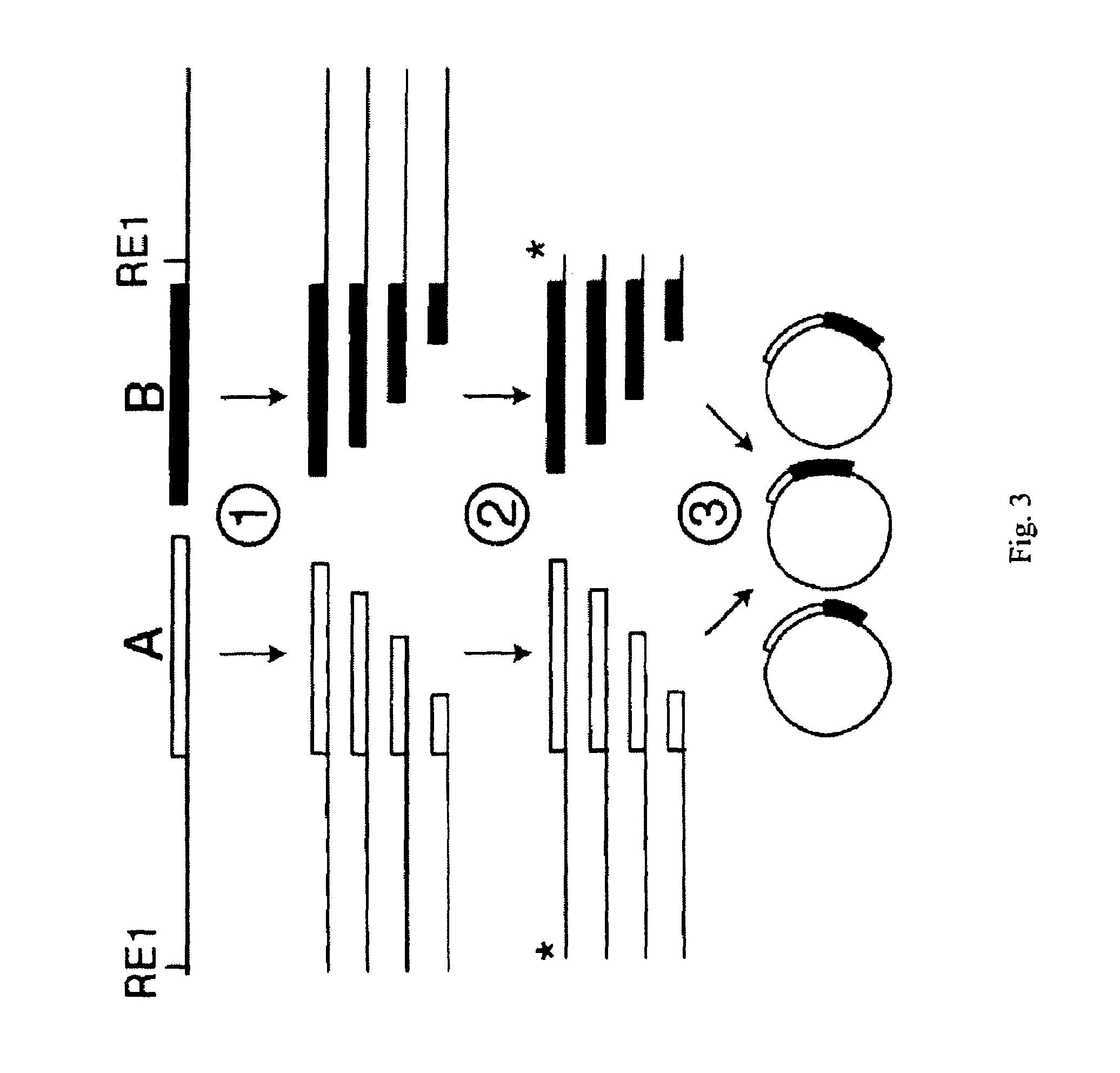
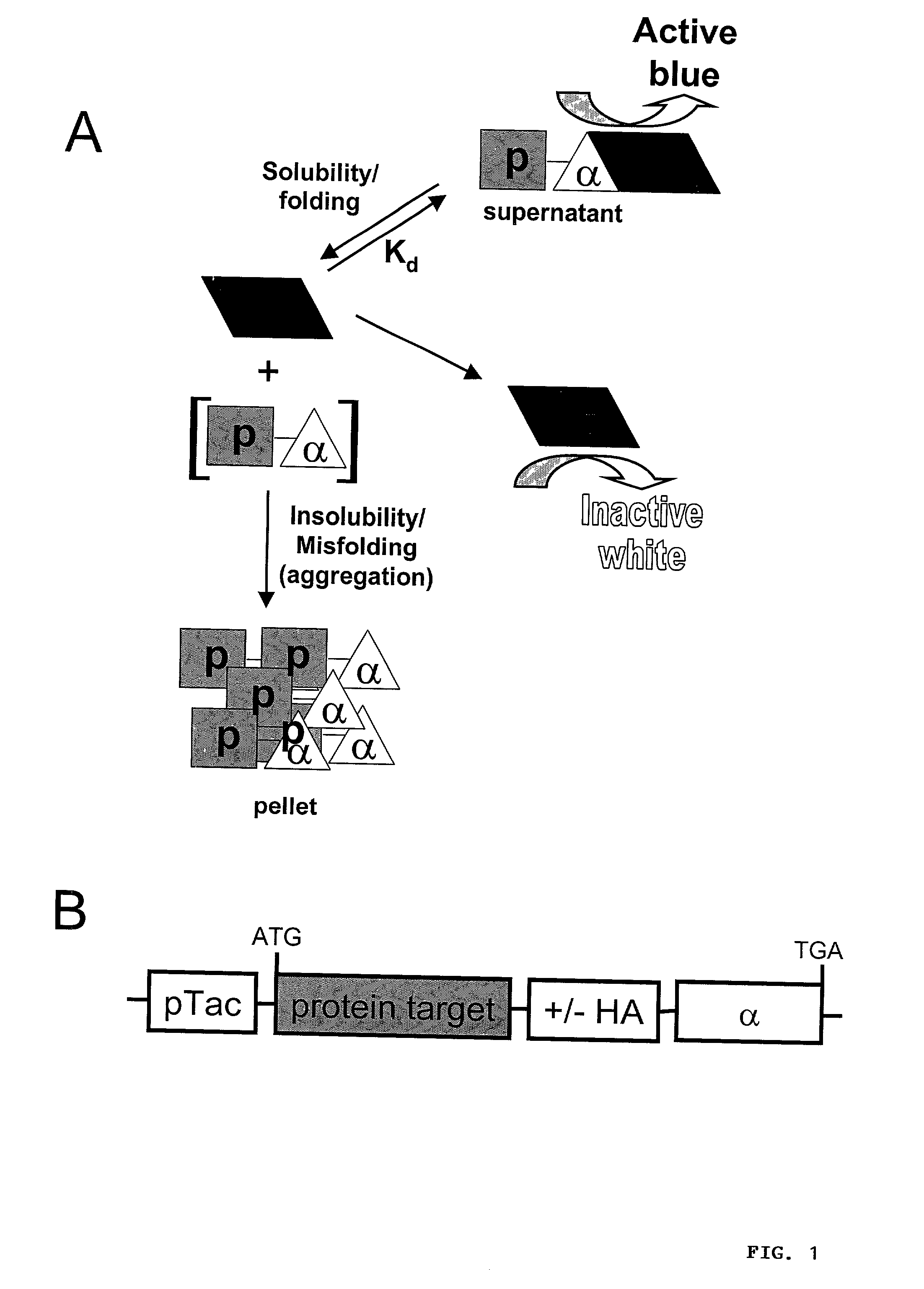
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein chain acquires its native 3-dimensional structure, a conformation that is usually biologically functional, in an expeditious and reproducible manner. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from a random coil. Each protein exists as an unfolded polypeptide or random coil when translated from a sequence of mRNA to a linear chain of amino acids. This polypeptide lacks any stable (long-lasting) three-dimensional structure (the left hand side of the first figure). As the polypeptide chain is being synthesized by a ribosome, the linear chain begins to fold into its three-dimensional structure. Folding begins to occur even during translation of the polypeptide chain. Amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, the folded protein (the right hand side of the figure), known as the native state. The resulting three-dimensional structure is determined by the amino acid sequence or primary structure (Anfinsen's dogma).
Methods of in vitro protein synthesis
InactiveUS7338789B2Enhanced in vitro synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyPhosphorylationBiological macromolecule
Biological macromolecules are synthesized in vitro under conditions and in a reaction composition wherein oxidative phosphorylation is activated and protein folding is improved.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods of preventing, treating and diagnosing disorders of protein aggregation
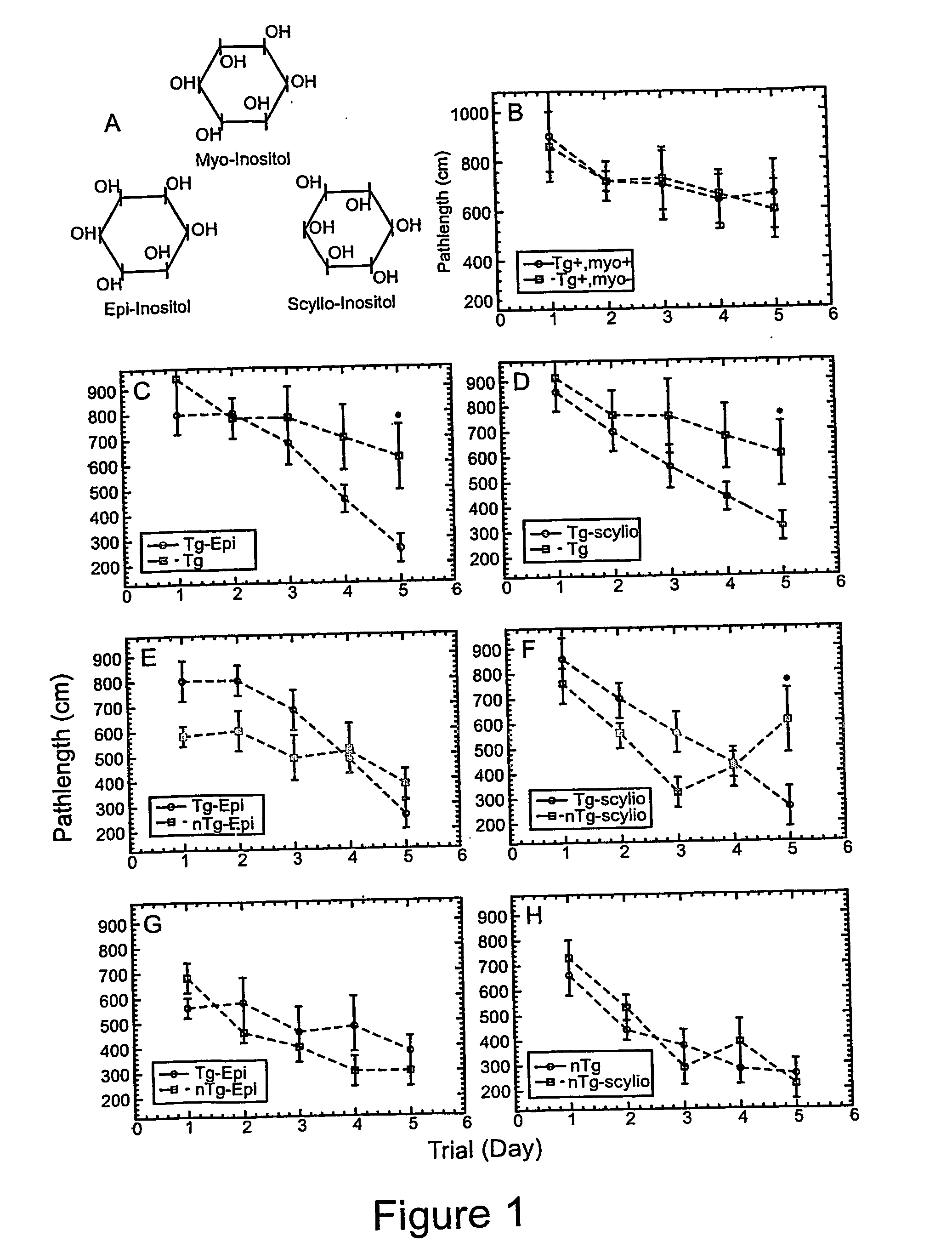
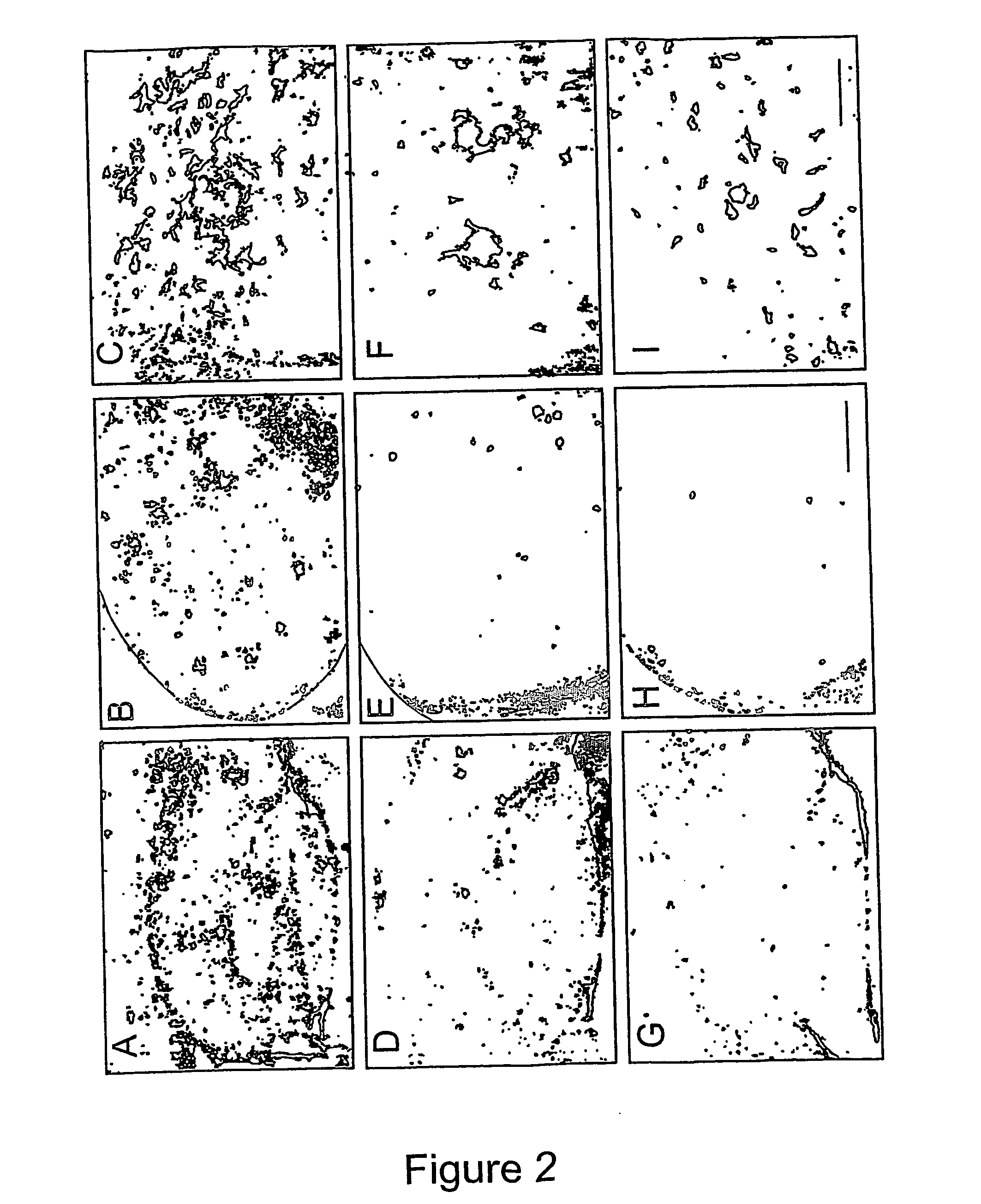
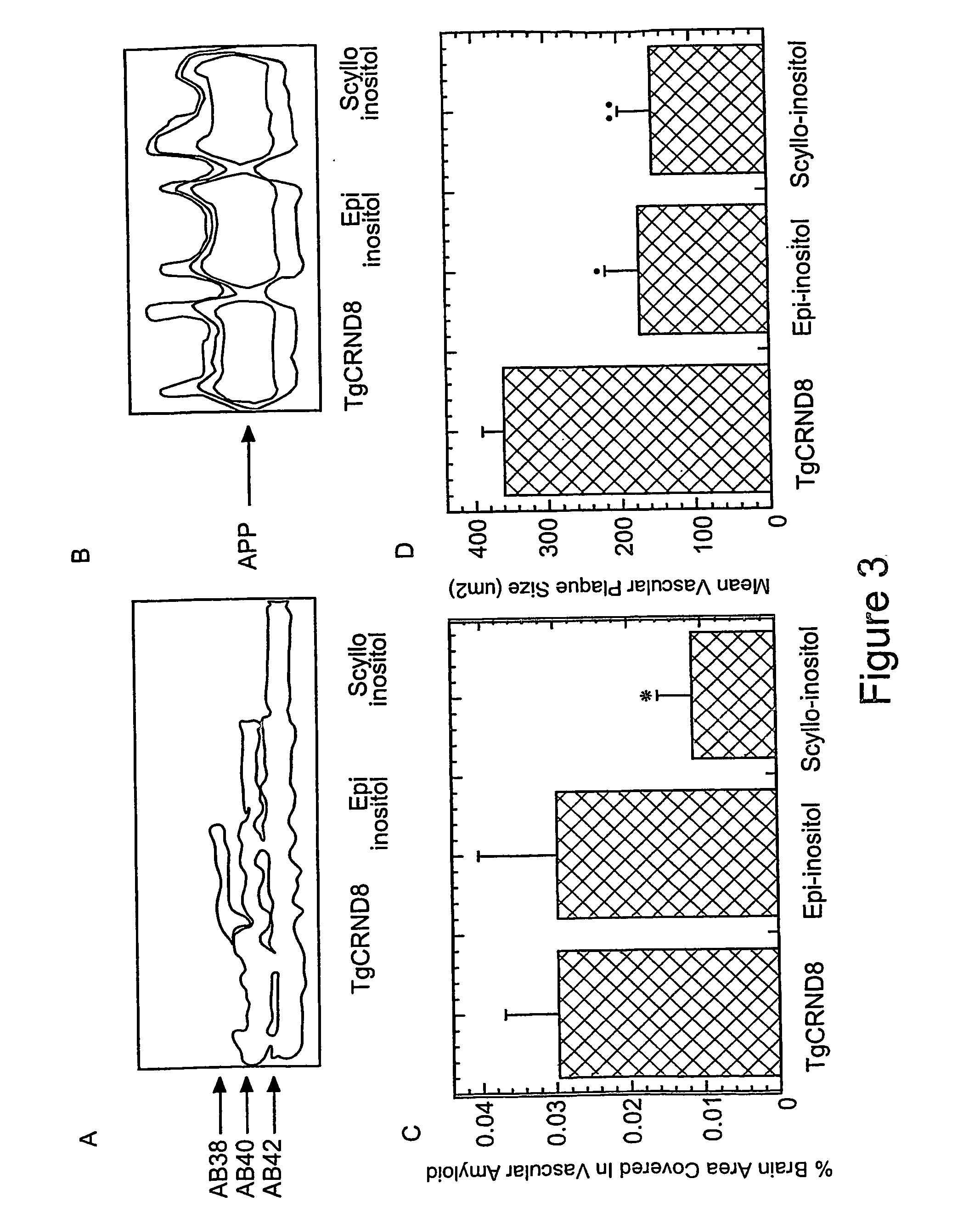
Disclosed are methods of preventing, treating, or diagnosing in a subject a disorder in protein folding or aggregation, or amyloid formation, deposition, accumulation, or persistence consisting of administering to said subject a pharmaceutically effective amount of inositol stereoisomers, enantiomers or derivatives thereof.
Owner:MCLAURIN JOANNE
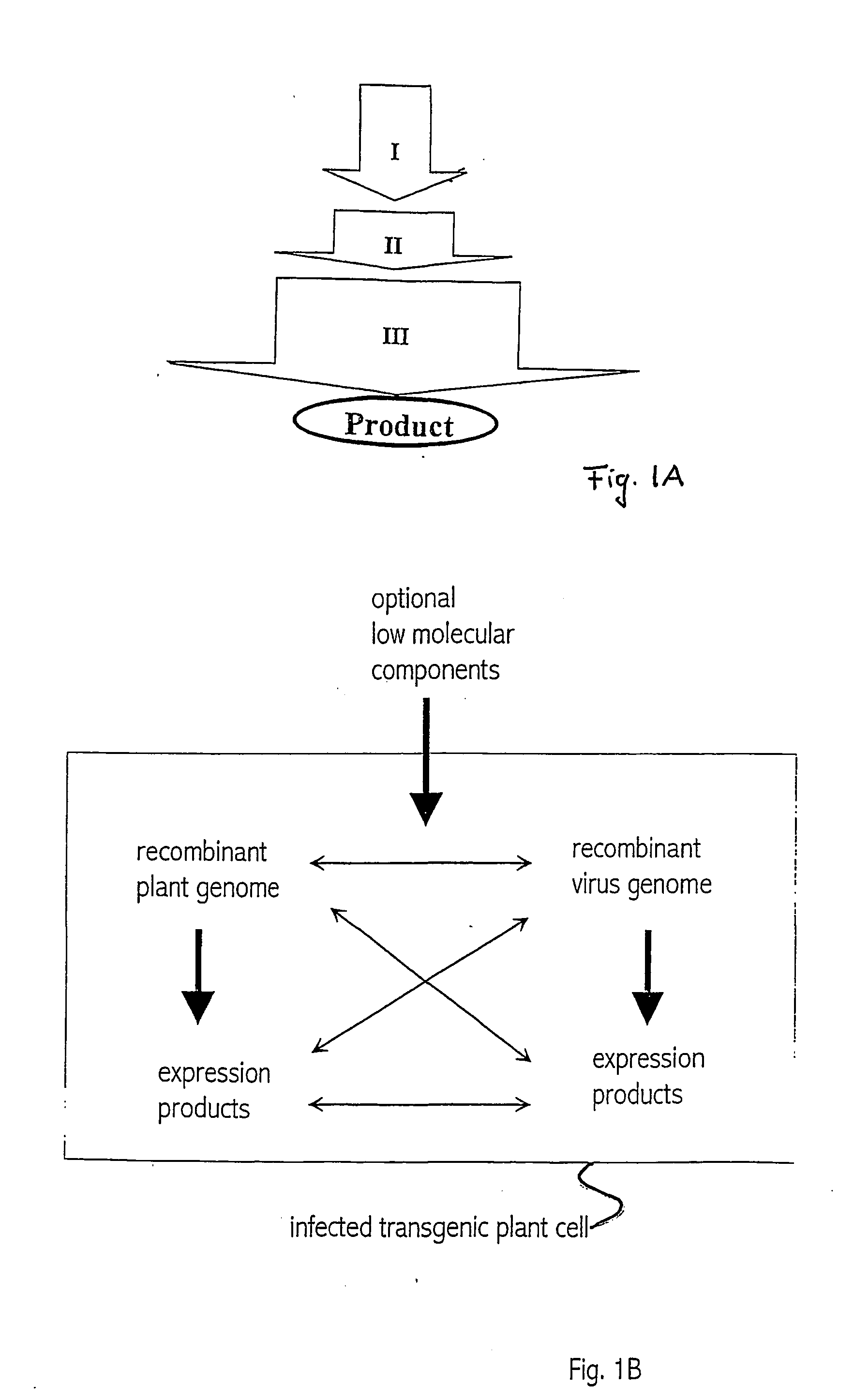
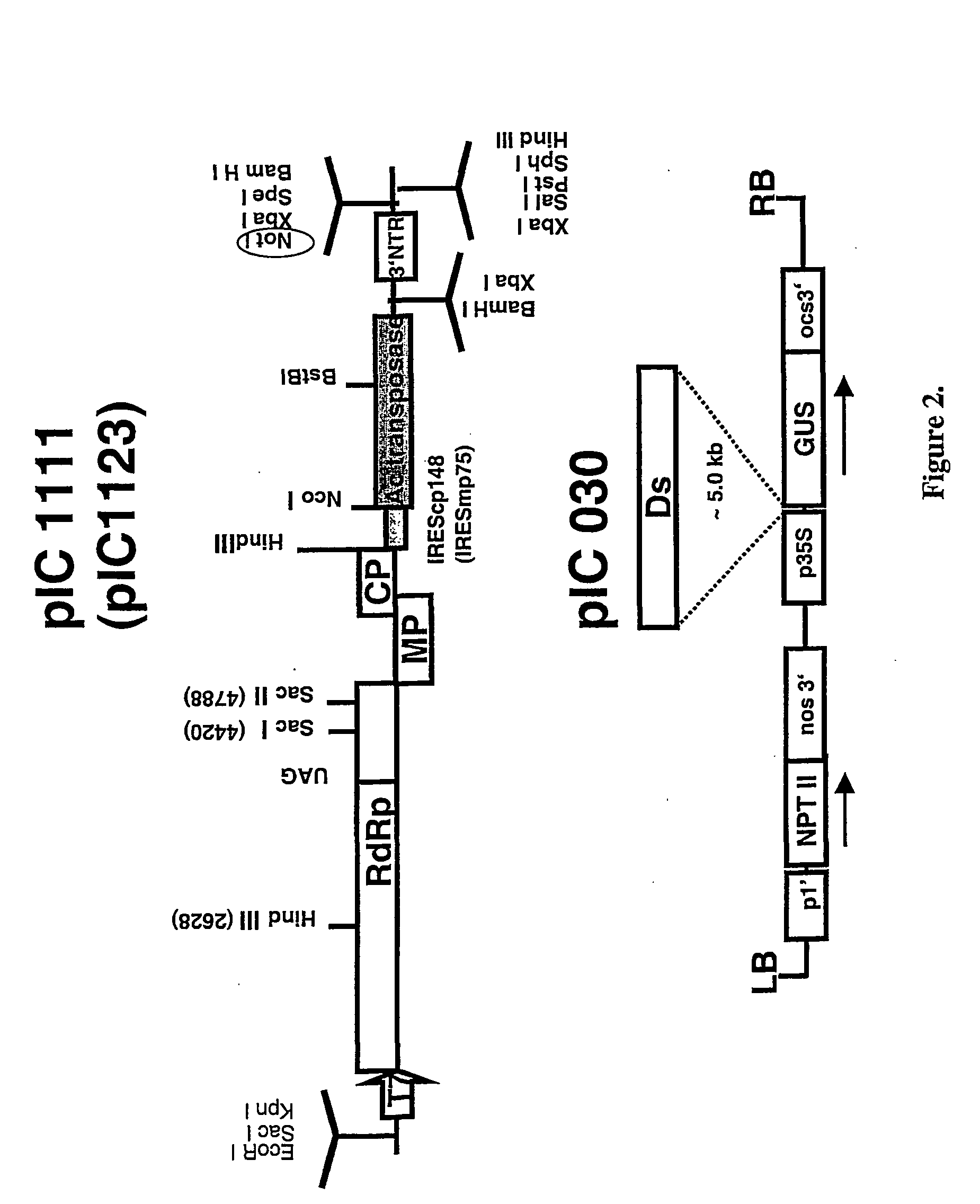
Recombinant viral switches for the control of gene expression in plants
InactiveUS20050091706A1Improve interferenceGrowth retardationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationHeterologousPlant virus
Owner:ICON GENETICS
Compositions and methods for monitoring and altering protein folding and solubility
InactiveUS20070026012A1Improve solubilityBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityProtein Biochemistry
The present invention relates to the fields of microbiology, molecular biology and protein biochemistry. More particularly, it relates to compositions and methods for analyzing and altering (e.g., enhancing or inhibiting) protein folding and solubility.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
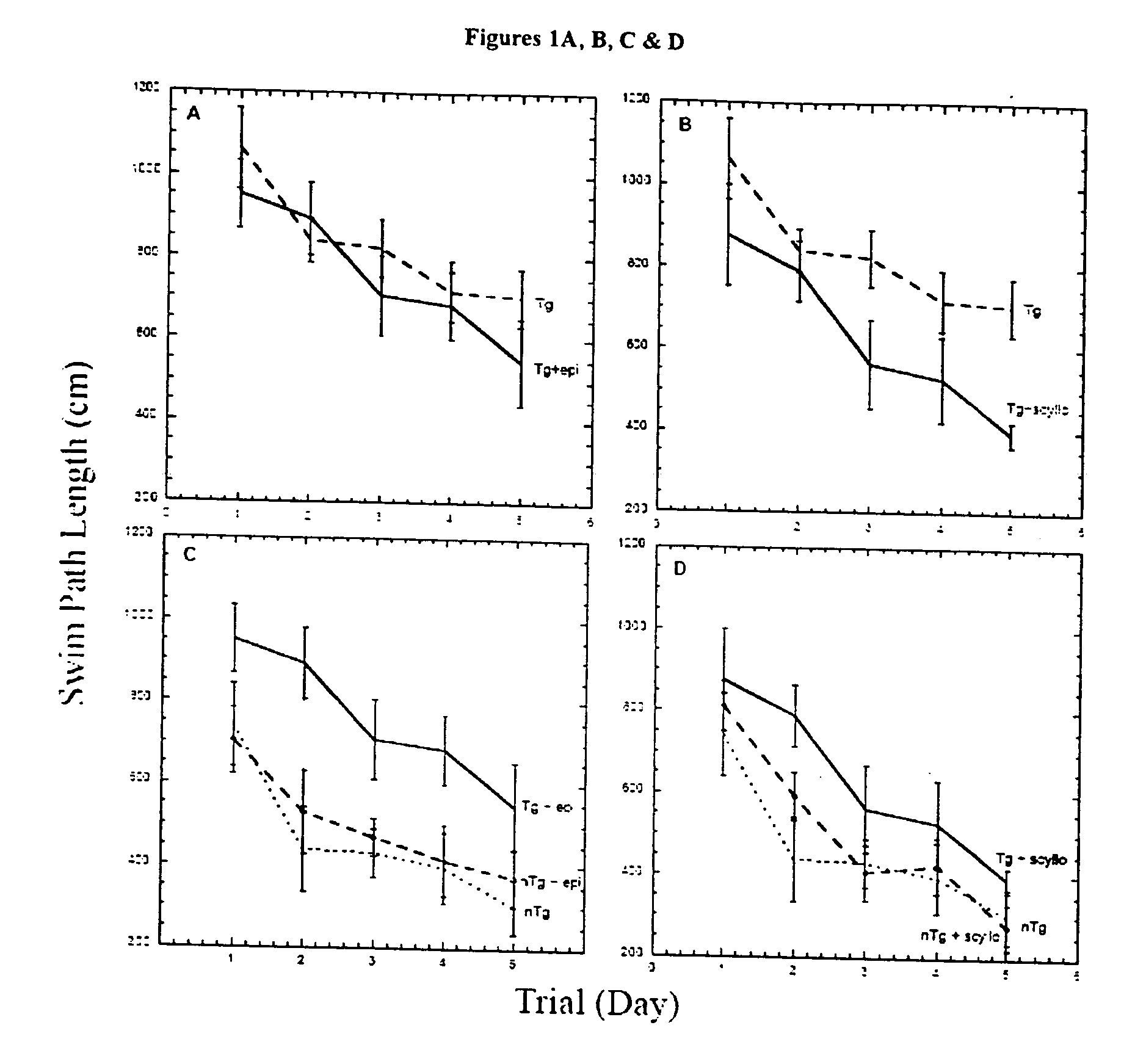
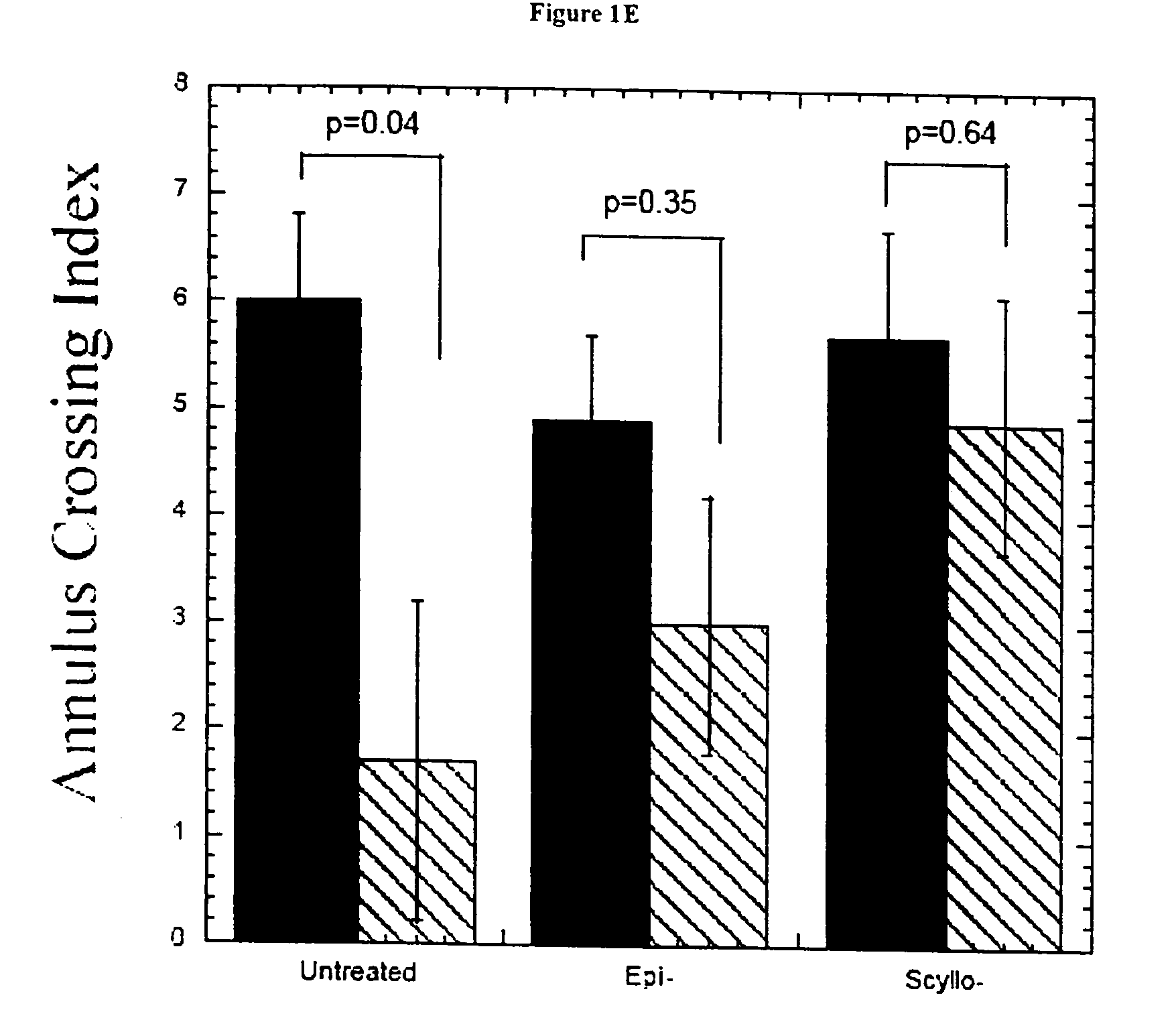
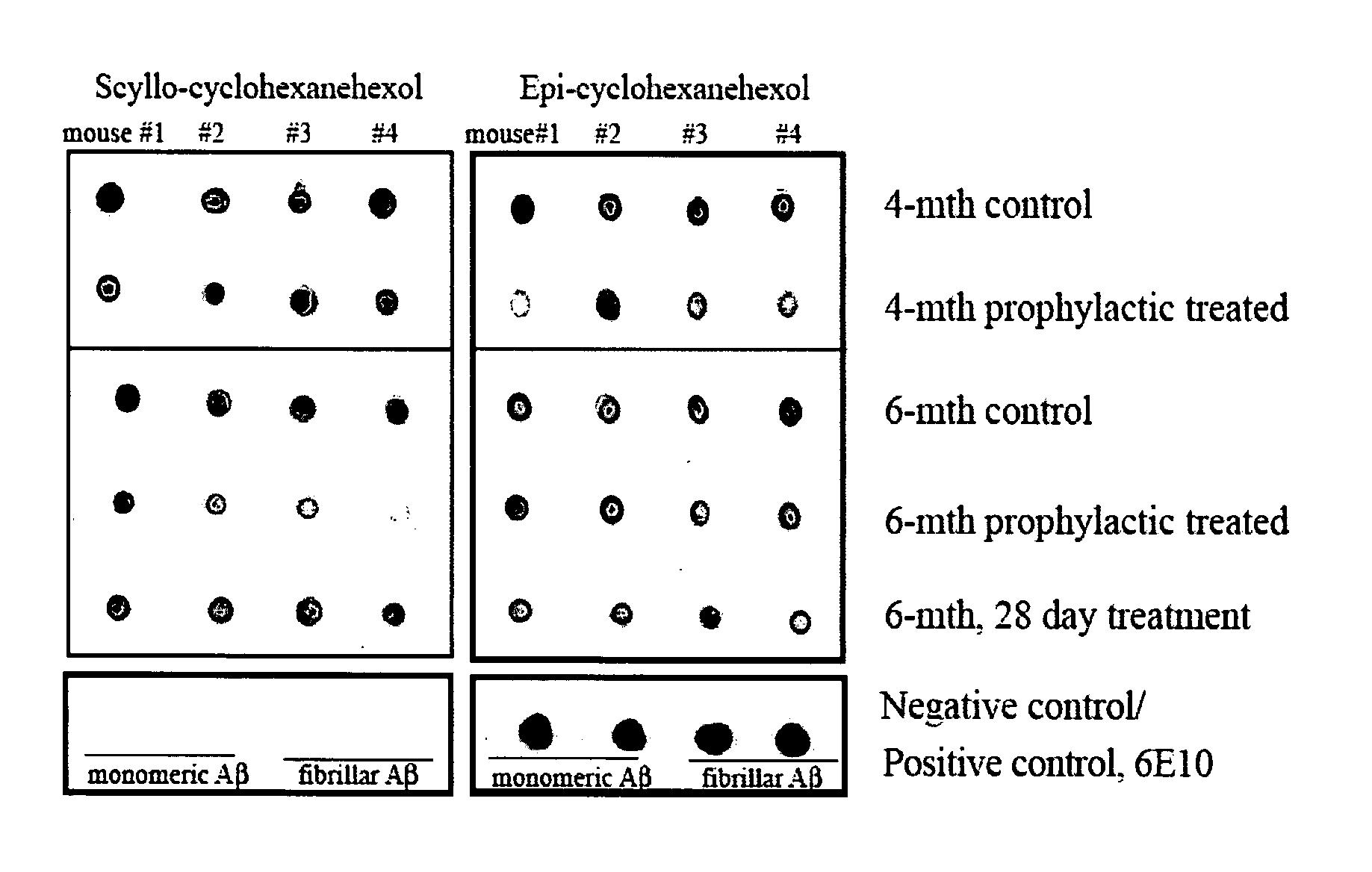
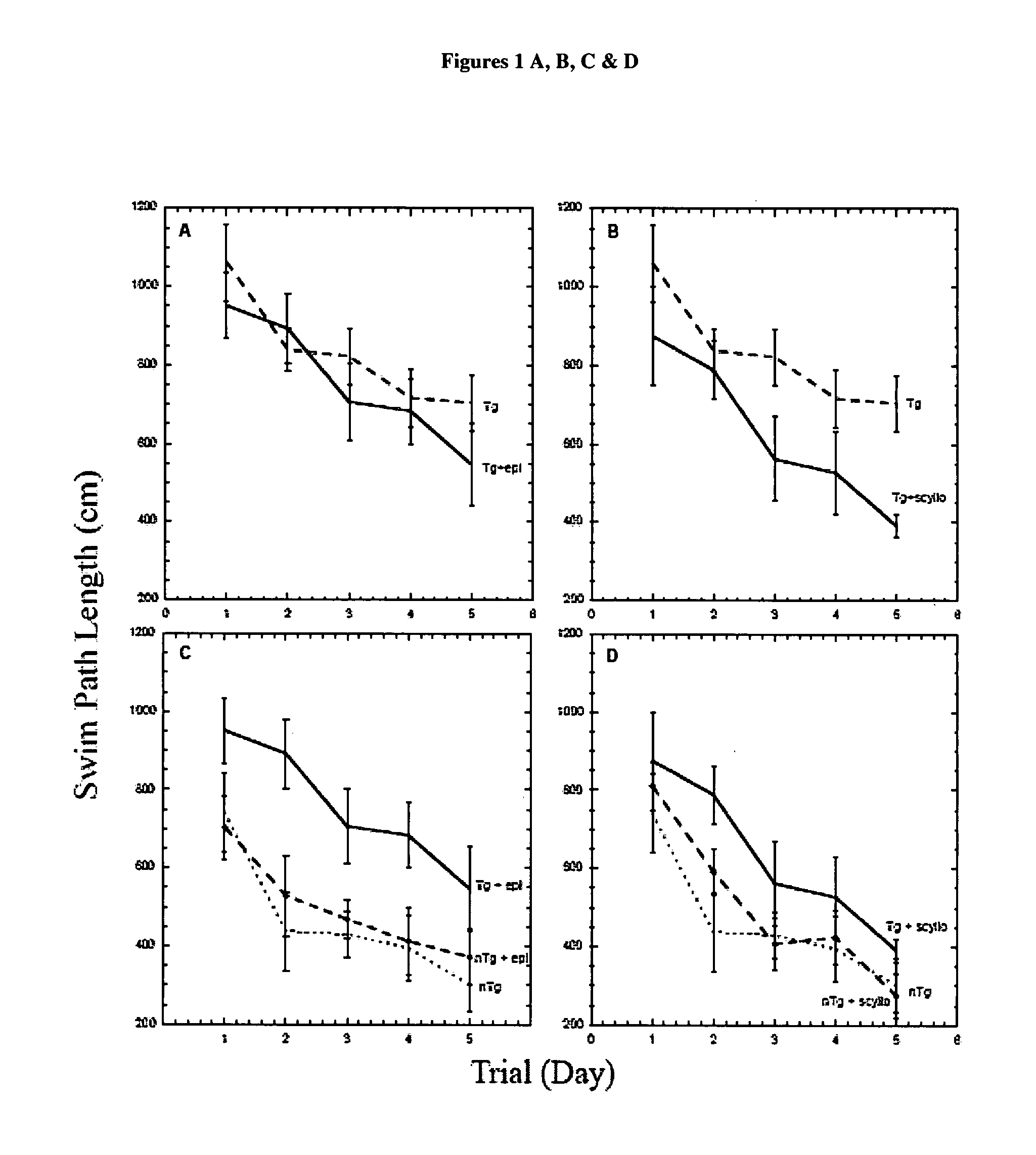
The Combination of a Cyclohexanehexol and a NSAID for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
InactiveUS20100173960A1Preventing and reducing aggregation of AβMaintaining synaptic functionBiocideNervous disorderNeuro degenerationProtein folding
The invention relates generally to novel compositions and methods comprising one or more cyclohexanehexol and one or more NSAID. The compositions and methods provide beneficial effects in the treatment and prevention of diseases involving a disorder in protein folding and / or aggregation, and / or amyloid formation, deposition, accumulation, or persistence, in particular neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:WARATAH PHARMA INC
Method of preventing, treating and diagnosing disorders of protein aggregation
Disclosed are methods of preventing, treating, or diagnosing in a subject a disorder in protein folding or aggregation, or amyloid formation, deposition, accumulation, or persistence consisting of administering to said subject a pharmaceutically effective amount of inositol stereoisomers, enantiomers or derivatives thereof.
Owner:MCLAURIN JOANNE
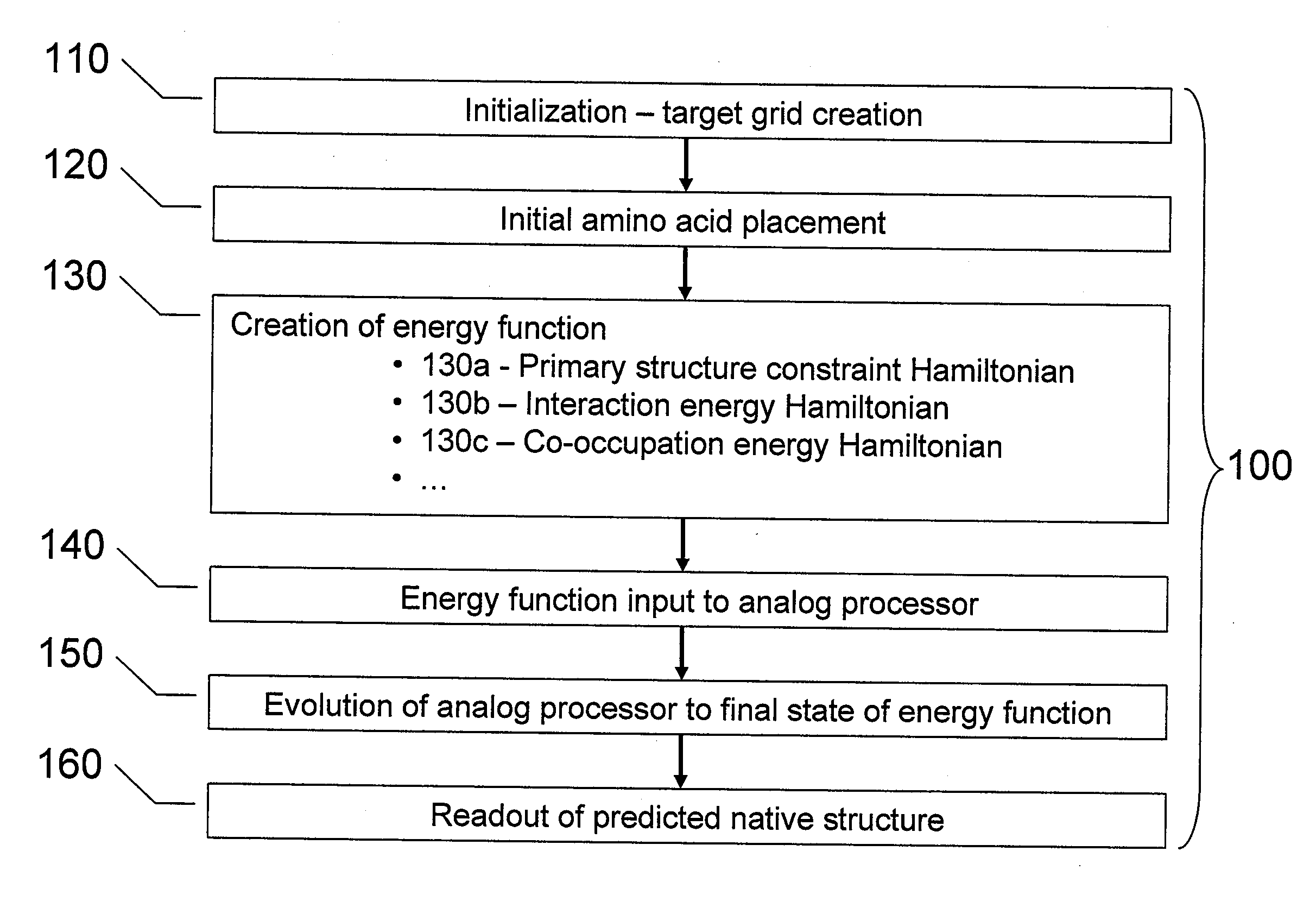
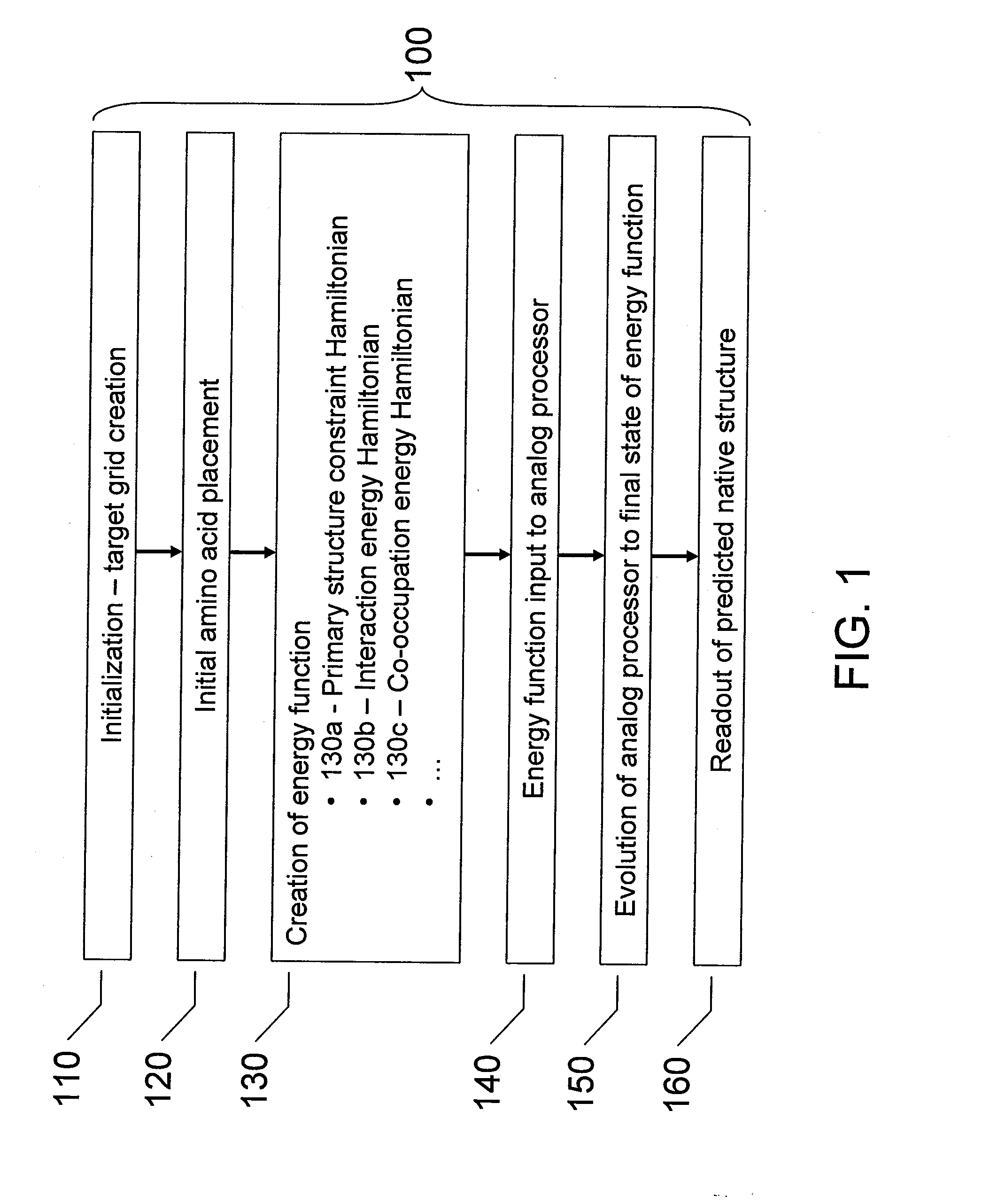
Systems, methods and apparatus for protein folding simulation
InactiveUS20080052055A1Improve legibilityAnalogue computers for chemical processesSpecial data processing applicationsNative structureAnalog processor
Analog processors such as quantum processors are employed to predict the native structures of proteins based on a primary structure of a protein. A target graph may be created of sufficient size to permit embedding of all possible native multi-dimensional topologies of the protein. At least one location in a target graph may be assigned to represent a respective amino acid forming the protein. An energy function is generated based assigned locations in the target graph. The energy function is mapped onto an analog processor, which is evolved from an initial state to a final state, the final state predicting a native structure of the protein.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
High-throughput screening of expressed DNA libraries in filamentous fungi
InactiveUS7122330B2Minimizes and eliminates formationLow culture viscosityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyCDNA library
The invention provides a method for the expression of exogenous DNA libraries in filamentous fungi. The fungi are capable of processing intron-containing eukaryotic genes, and also can carry out post-translational processing steps such as glyclosylation and protein folding. The invention provides for the use of fungi with altered morphology, which permits high-throughput screening and directed molecular evolution of expressed proteins. The same transformed fungi may be used to produce larger quantities of protein for isolation, characterization, and application testing, and may be suitable for commercial production of the protein as well.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
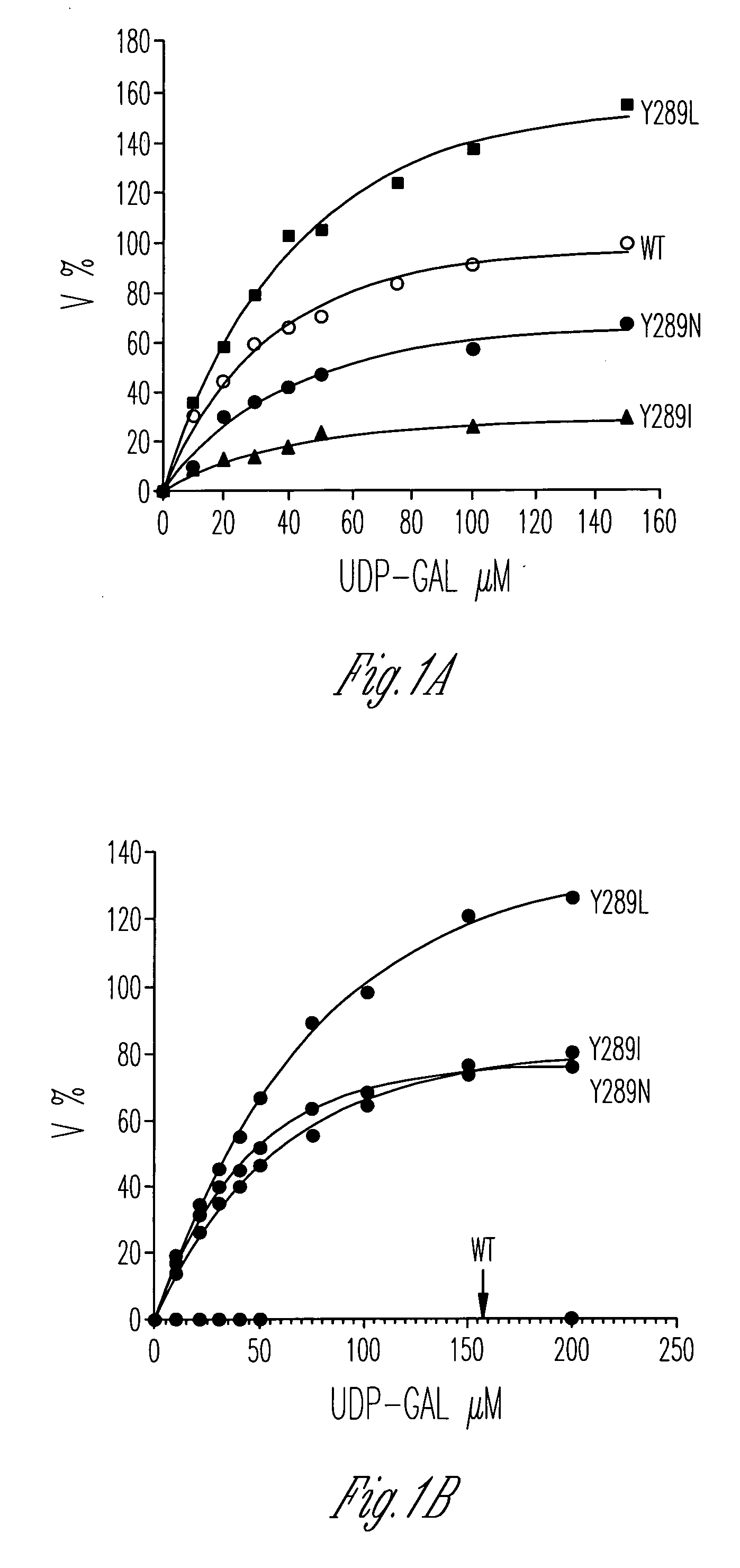
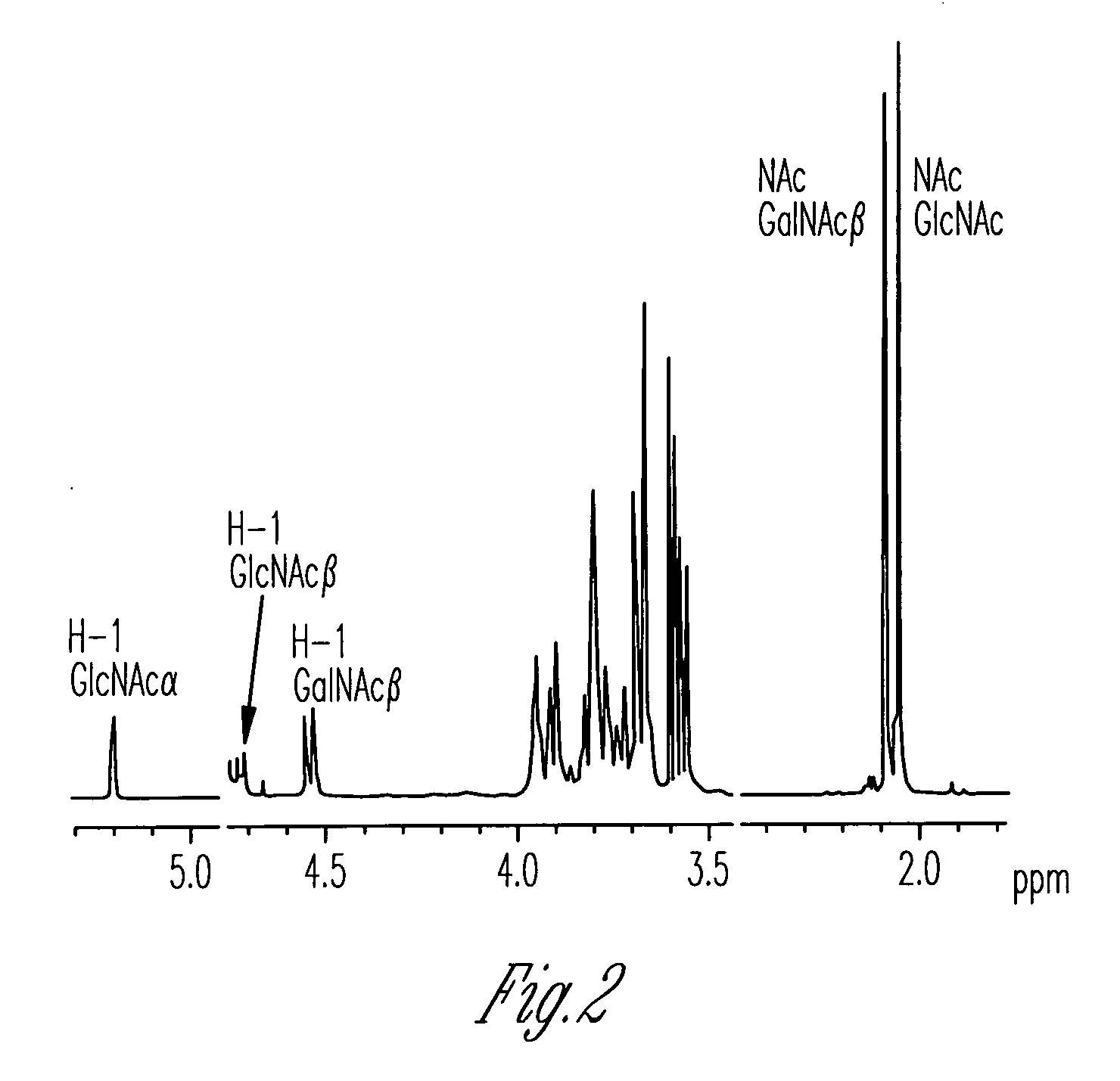
Catalytic domains of beta(1,4)-galactosyltransferase I having altered donor and acceptor specificities, domains that promote in vitro protein folding, and methods for their use
ActiveUS20060084162A1Improving immunogenicitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGreek letter betaMutant
Disclosed are methods and compositions that can be used to synthesize oligosaccharides; mutants of galactosyltransferases having altered donor and acceptor specificity; methods for increasing the immunogenicity of an antigen; and polypeptide stem regions that can be used to promote in vitro folding of polypeptides, such as the catalytic domain from a galactosyltransferase.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Compositions and methods for treatment of disorders of protein aggregation
InactiveUS20060189582A1Good treatment effectSustained effectBiocideNervous disorderMedicineCell Aggregations
The invention provides compositions, methods and uses comprising a scyllo-inositol compound that provide beneficial effects in the treatment of a disorder and / or disease including a disorder in protein folding and / or aggregation, and / or amyloid formation, deposition, accumulation, or persistence.
Owner:MCLAURIN JOANNE
Osmolyte Mixture for Protein Stabilization
ActiveUS20110053795A1Speed up the processInhibit aggregationLibrary screeningEnzyme stabilisationProtein insertionOsmolyte
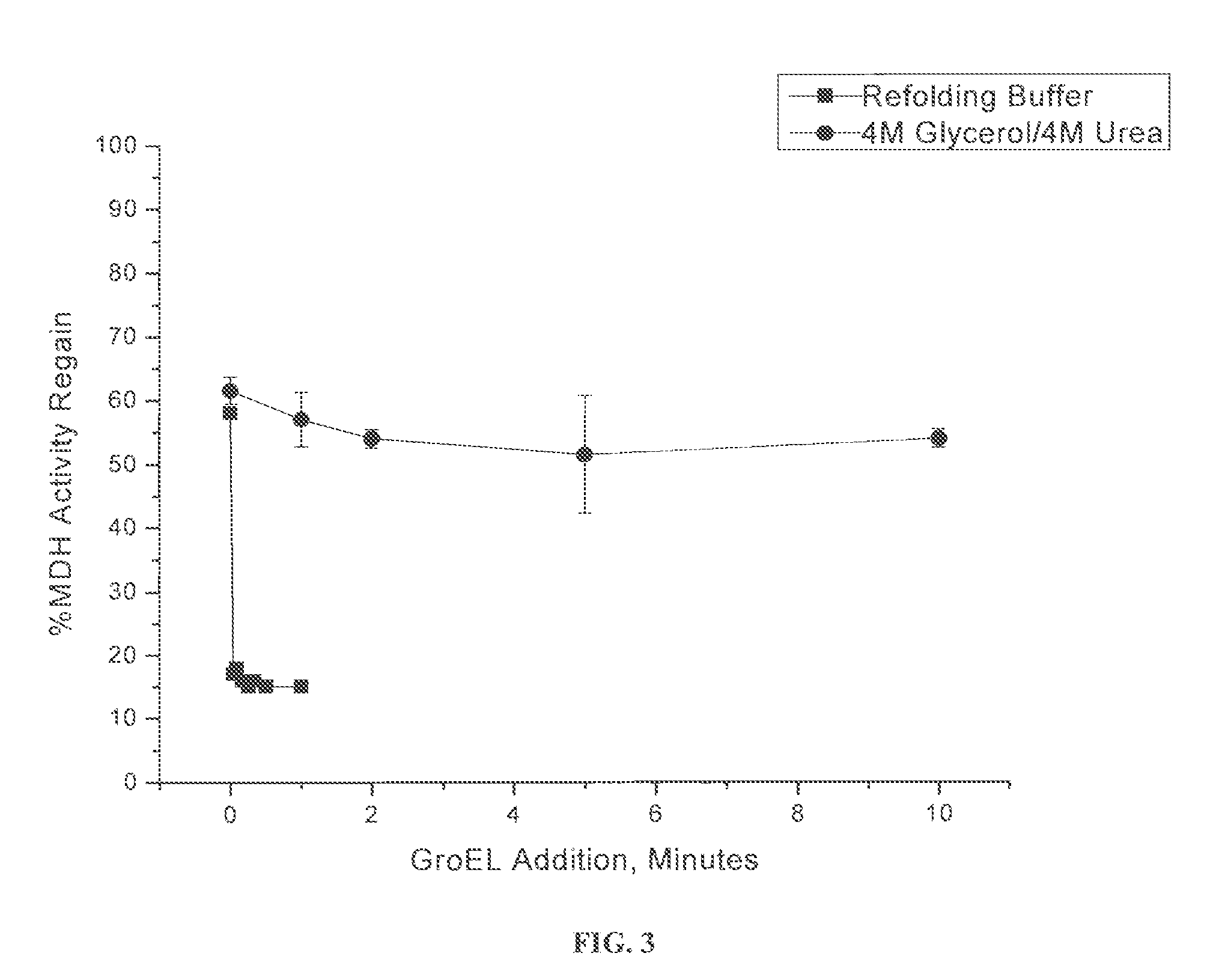
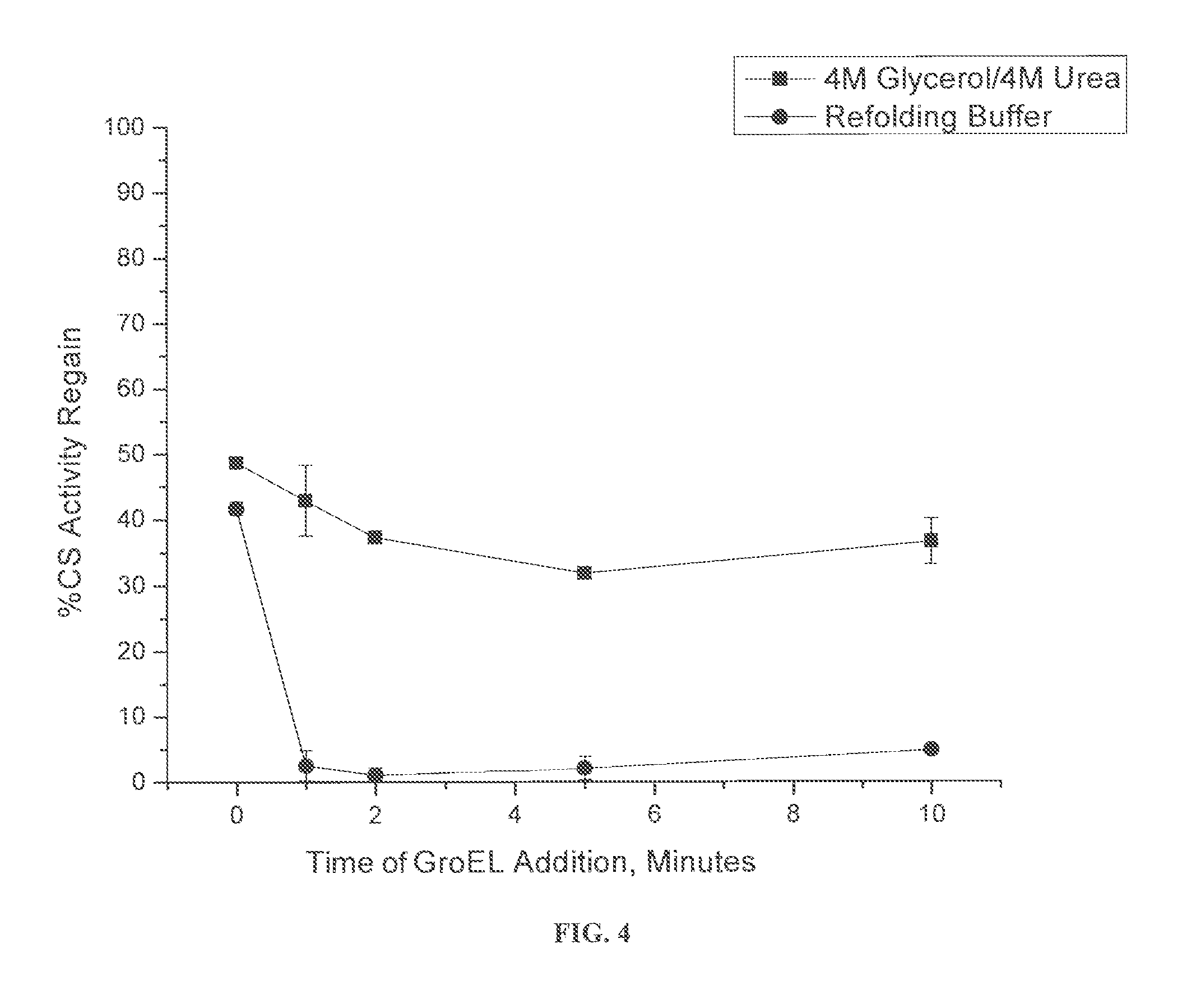
An osmolyte composition comprising 4 M glycerol and 4M urea for stabilizing previously transient protein folding intermediates as long-lived stable forms. A method to search for other possible stabilizing osmolyte mixtures using a screening array is also provided. These additional osmolyte mixtures may complement or augment the successful 4M glycerol / 4 M urea mixture.
Owner:UNIV KANSAS MEDICAL CENT
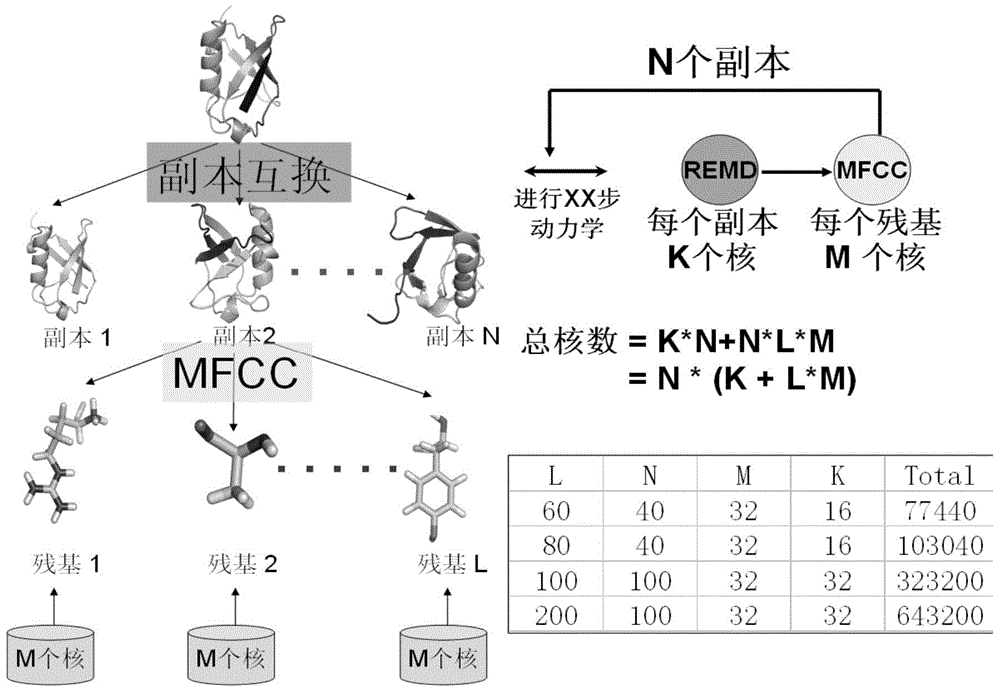
Protein folding parallel predicting method
InactiveCN105787292APolarization cannot be ignoredThe result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsProtein structureAmino acid
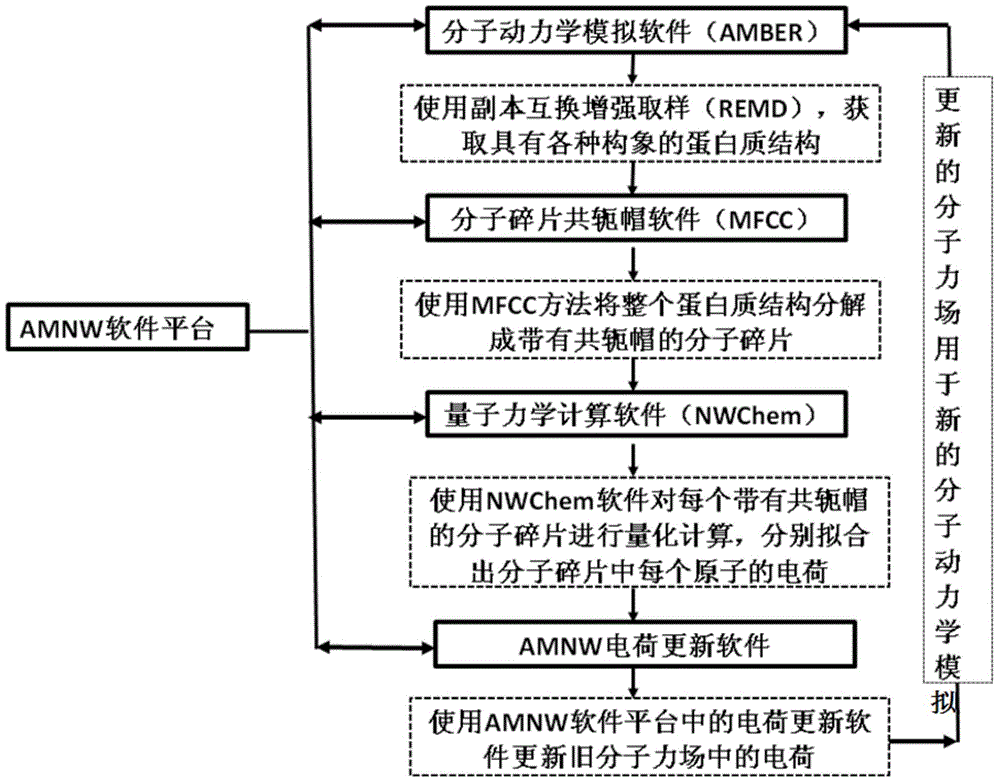
The invention relates to a protein folding parallel predicting method. The method includes the following steps: obtaining different protein structures through molecular dynamics simulation; setting different temperatures, and obtaining more protein structures with different conformations; partitioning the protein structures with different conformations through a conjugate cap molecule partitioning method, decomposing amino acids from proteins, and wearing a conjugate cap on each amino acid; calculating out the electrostatic potential of molecular fragments through quantum mechanics software to fit out the electric charge of each atom in each amino acid molecular fragment, and updating the electric charge of atoms in a molecule force field. To research protein folding, the scheme of considering a protein polarization effect and a copy interchange-based method are organically integrated, and then two difficult problems of atom interaction potential and a sampling technique in dynamics simulation can be overcome in order to achieve a good effect in protein folding simulation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Agents for the inhibition of virus replication through regulation of protein folding
The invention concerns agents for the treatment of acute and chronic infections with human and animal pathogenic viruses which assemble along the cell membrane and are released through budding on the surface of the cell. Hereunto count especially causative agents of infectious diseases such as AIDS, hepatitis, hemorrhagic fever, SARS, smallpox, measles, polio or the flu. The subjects of the invention are agents that contain inhibitors of the protein folding as active components. Hereunto count inhibitors of cellular folding enzymes (the enzymatic chaperones) as well as substances that disturb the folding of proteins through chemical chaperones. The following substance classes and their derivates belong thereunto: Geldanamycin, Deoxyspergualin, 4-PBA or Herbimycin A. Due to these agents the highly organised processes of the assembly and the proteolytical maturation of virus structure proteins is disturbed. As a result the release and production of infectious decendent viruses is prevented.
Owner:VIROLOGIK GMBH
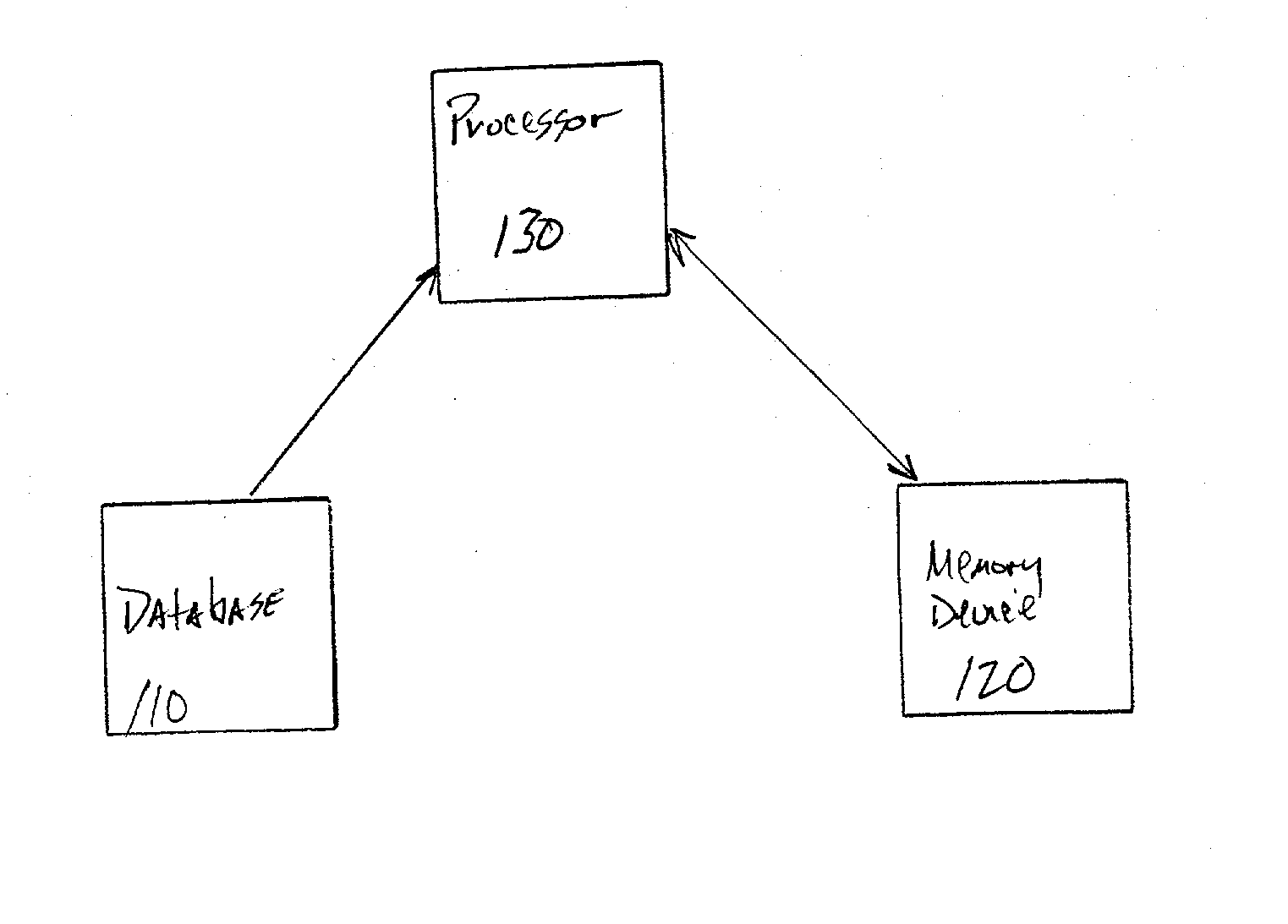
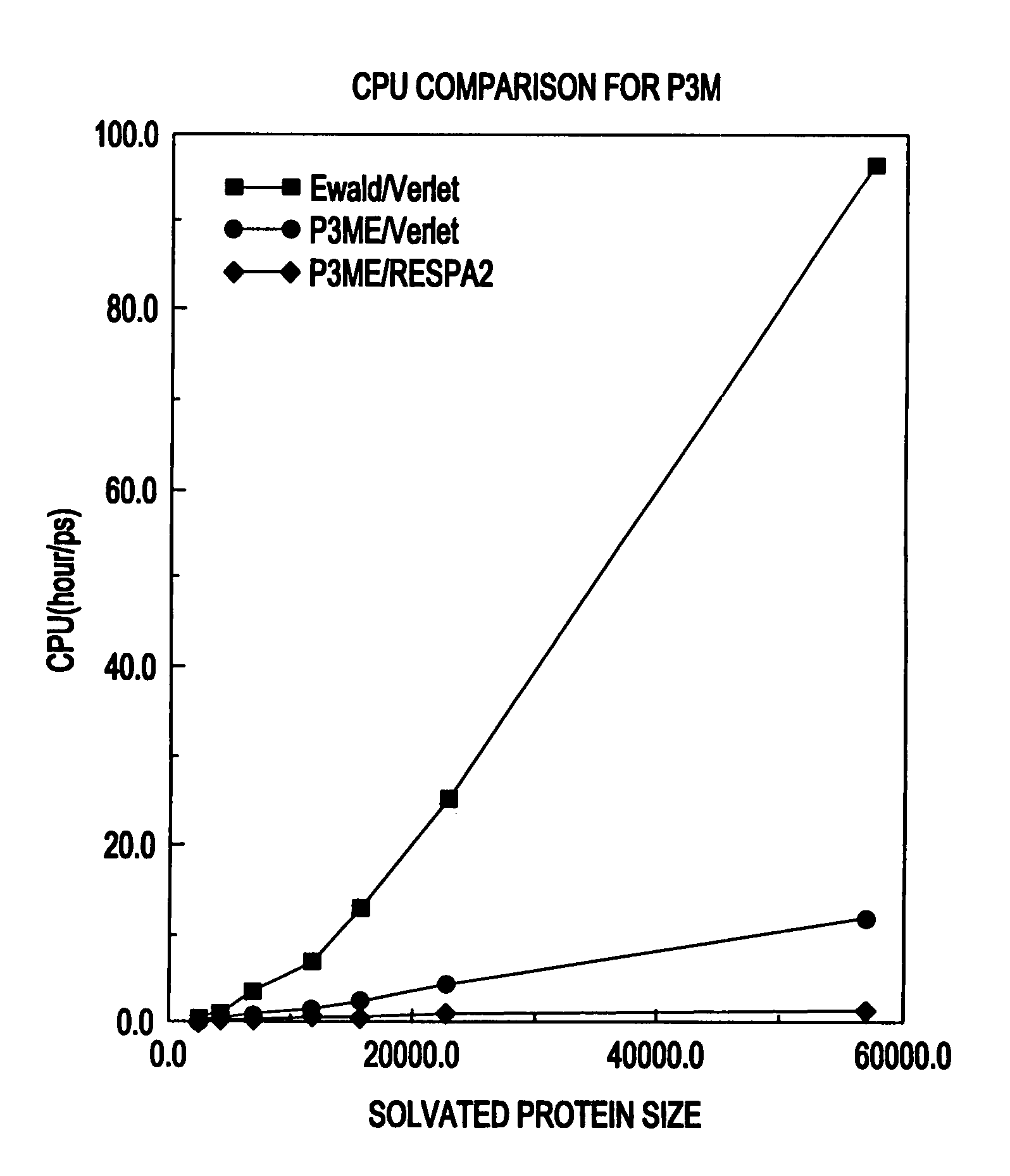
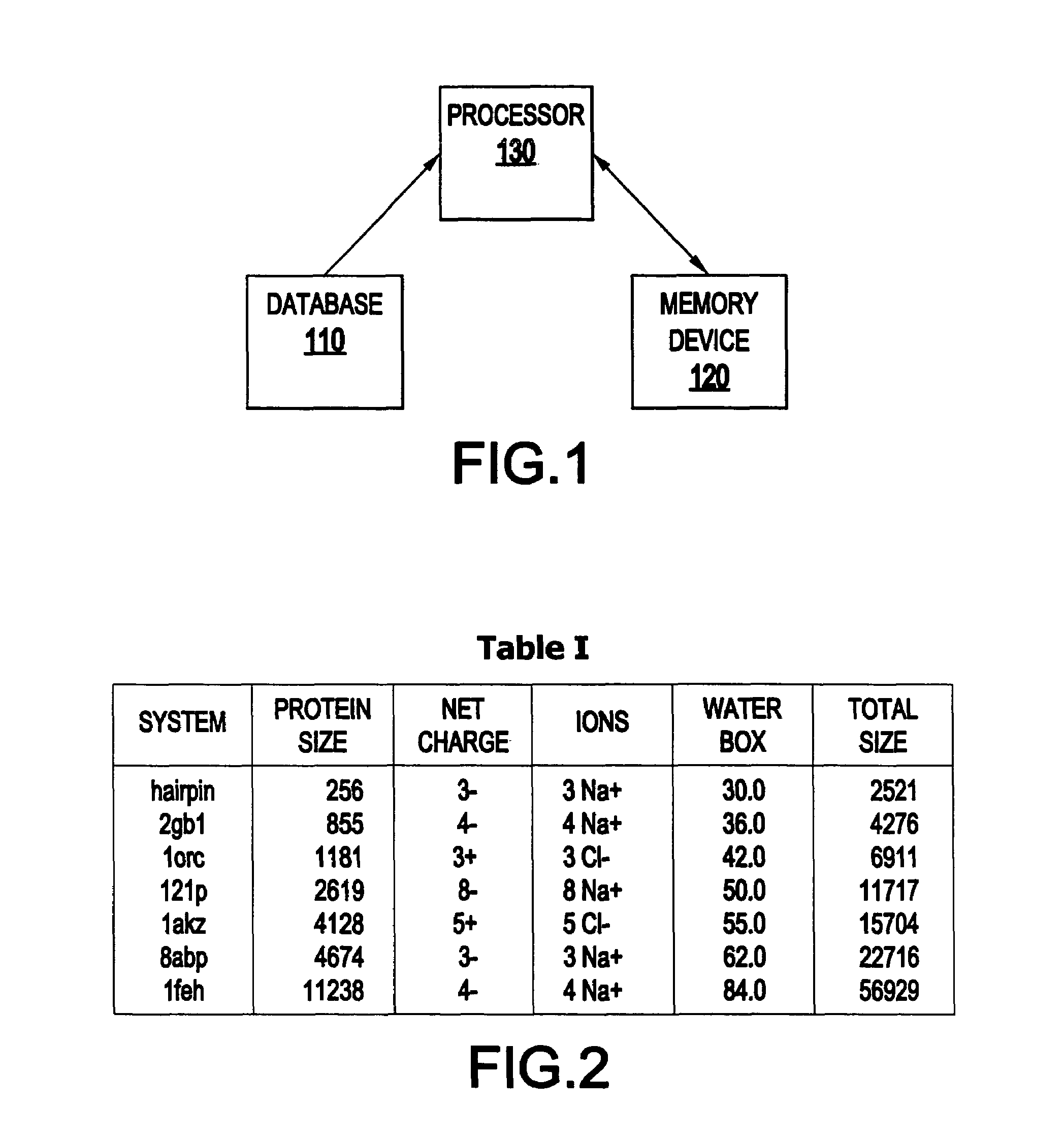
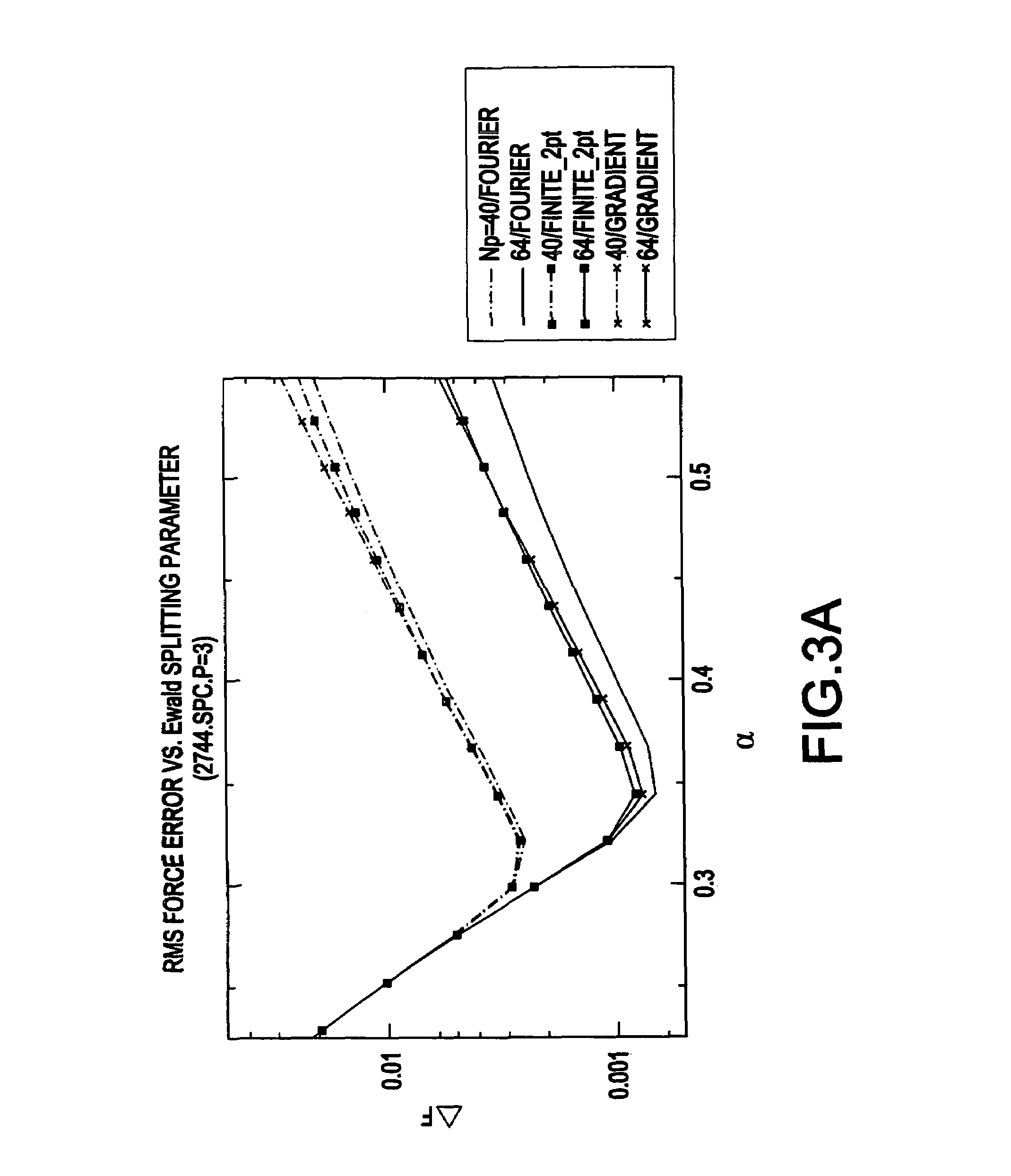
System and method for molecular dynamic simulation
InactiveUS20030014231A1Analogue computers for chemical processesSpecial data processing applicationsProtein solutionProtein molecules
A system and method for molecular dynamic simulation includes a database for storing data pertaining to at least one biomolecular system, a memory device for storing instructions for performing at least one algorithm having an electrostatic interaction calculating function and a multiple time step function, and subdividing forces on a basis of distance over which the forces act, and a processor for processing the data by executing the instructions in order to propagate the biomolecular system from a first set of coordinates to a second set of coordinates. The system and method significantly speed up the molecular dynamics simulation of biomolecular systems in which there are long-range and short-range electrostatic interactions and in which there are fast and slow motions, and make practicable the simulation of large protein solutions and thus, can be used to simulate protein folding and the binding of substrates to protein molecules.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Novel method for characterizing and multi-dimensionally representing the folding process of proteins
InactiveUS20130130294A1Simple designHigh activityDiscounts/incentivesFinanceComputer-aidedComputer aid
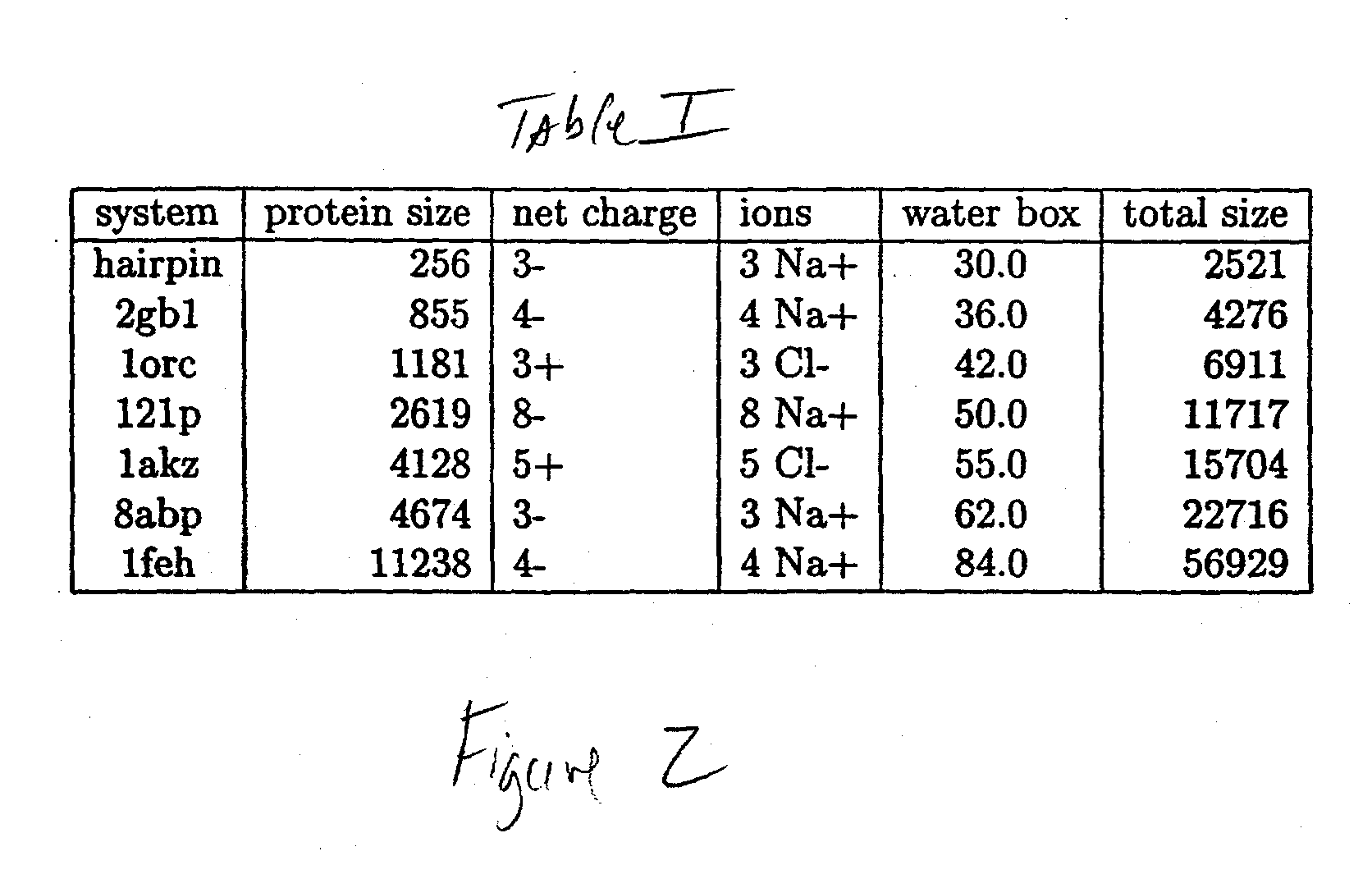
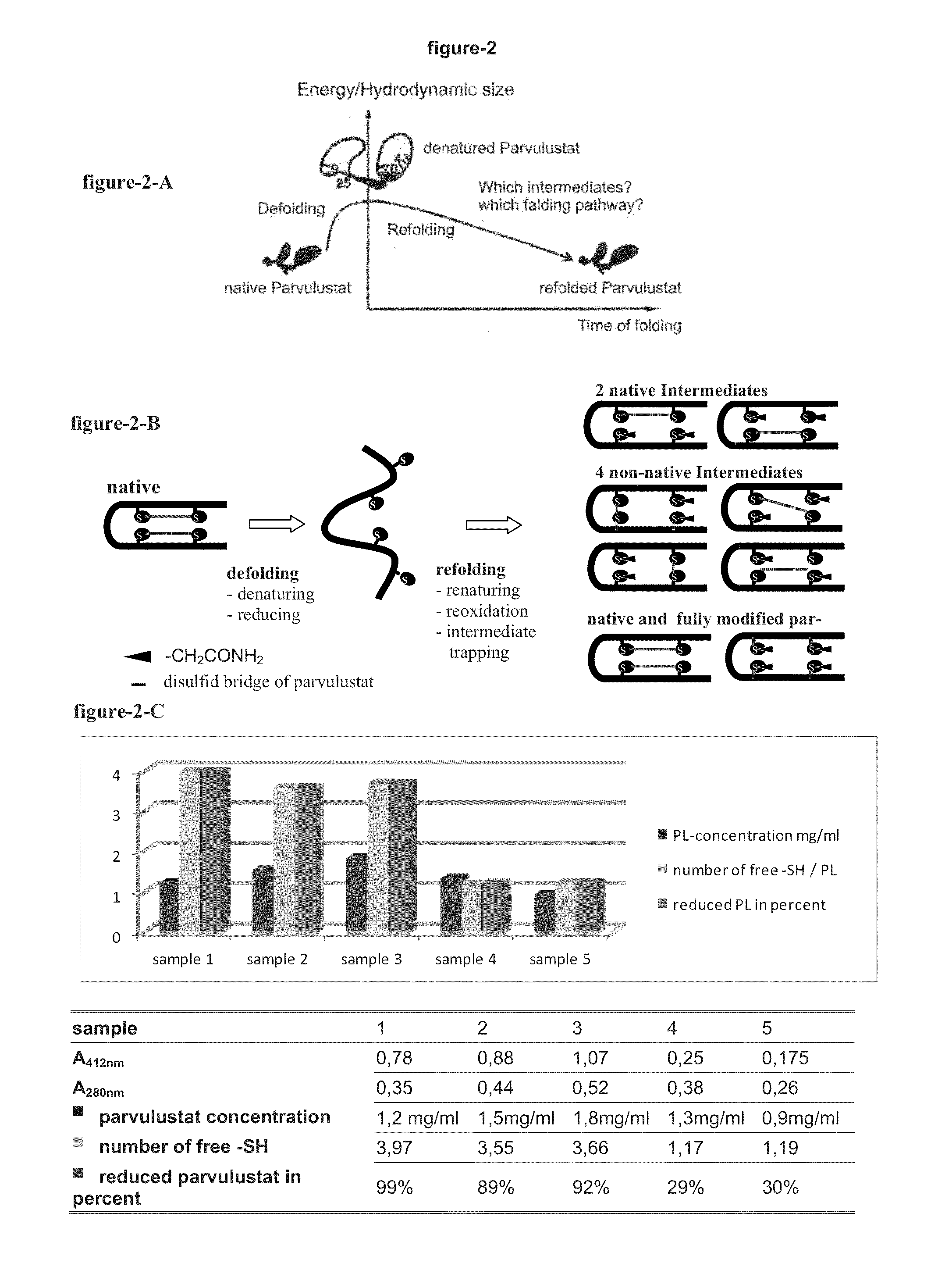
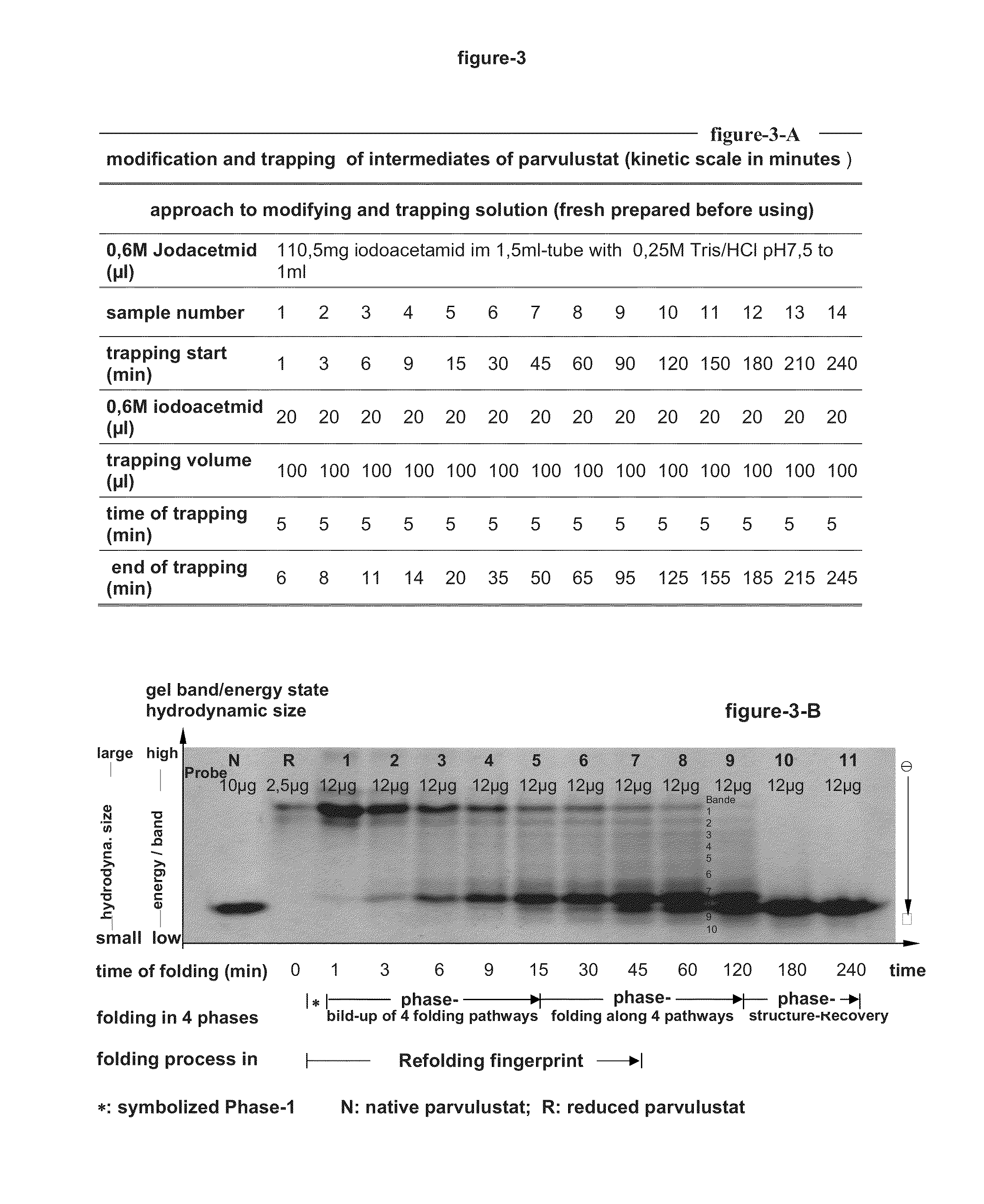
The invention relates to a novel method for characterizing and multi-dimensionally representing the folding process of proteins (FIG. 9). Said method comprises, in a methodically novel combination, kinetically arranging the hydrodynamic size of the refolding and thus modified protein, associating the proteolytically fragmented intermediates on the basis of the bioinformatic detection patterns, classifying the folding pathway association of the intermediates, characterizing the folding sequences, and multi-dimensionally visualizing the characterized folding process in a computer-aided manner. Said method is characterized in that all intermediates modified during the refolding and thus structurally blocked are identified and digitalized according to the four individual characteristics of said intermediates, namely the hydrodynamic size, the formation time, the folding pathway association, and amount. Said novel method has many applications in the field of research of protein folding and proteopathy, protein engineering, antibody engineering, molecular biology, therapeutic medicine, biotechnology, biotechnological production of protein pharmaceuticals, protein taxonomy, and nanotechnology for developing and producing novel functional protein materials. According to the invention, many and varied products in the form of different assay kits, devices, software, and machines can be produced and used to carry out said method.
Owner:HAN SIGENG
System and method for molecular dynamic simulation
InactiveUS7096167B2Doubles speedStep of become largeComputation using non-denominational number representationBiological testingProtein solutionProtein molecules
A system and method for molecular dynamic simulation includes a database for storing data pertaining to at least one biomolecular system, a memory device for storing instructions for performing at least one algorithm having an electrostatic interaction calculating function and a multiple time step function, and subdividing forces on a basis of distance over which the forces act, and a processor for processing the data by executing the instructions in order to propagate the biomolecular system from a first set of coordinates to a second set of coordinates. The system and method significantly speed up the molecular dynamics simulation of biomolecular systems in which there are long-range and short-range electrostatic interactions and in which there are fast and slow motions, and make practicable the simulation of large protein solutions and thus, can be used to simulate protein folding and the binding of substrates to protein molecules.
Owner:LINKEDIN
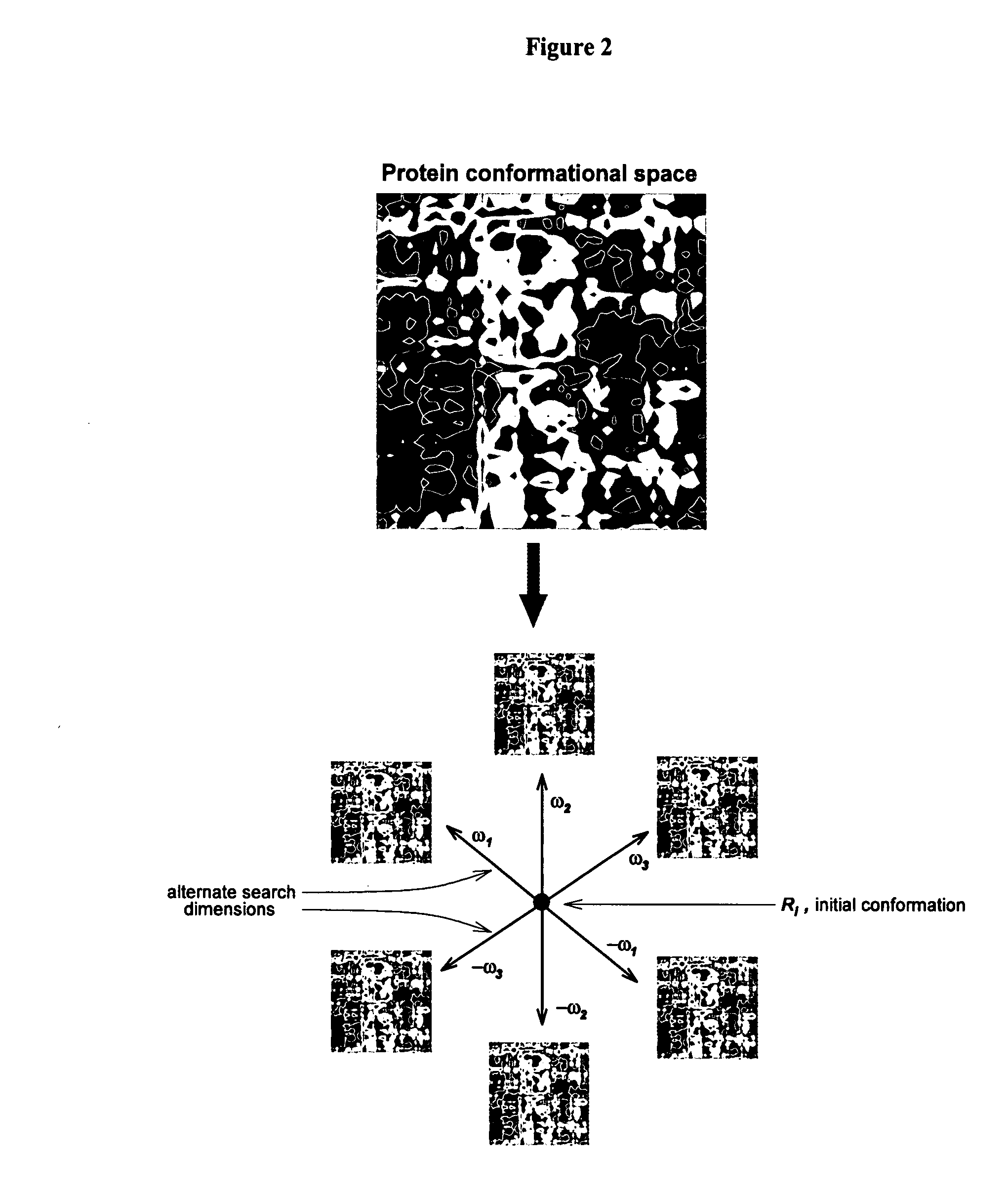
Methods, systems, algorithyms and means for describing the possible conformations of actual and theoretical proteins and for evaluating actual and theoretical proteins with respect to folding, overall
Methods, systems, algorithms and means for describing, analyzing and predicting protein folding motifs and other structures are provided. In one aspect, the Protein Folding Shape Code (PFSC) methods,systems, algorithms and means of the present invention apply generally to all of the categories of protein analysis and description, and are especially relevant to the geometric analyses and descriptions of proteins from their respective sequences or sequence portions. In a novel approach, the present inventions render analyses with respect to the alpha carbons of five-amino acid elements of a protein, utilizing available data to derive torsion angles and pitch distances, to thereby generate a series of overlapping analyses that can be expressed by a plurality of 27 vectors. Methods, systems and algorithms of the invention can be embodied in any computing device or portion thereof, and are adaptable to describe, analyze and predict the folding and other three-dimensional aspects of the structures of biomolecules such as nucleic acids, carbohydrates and glycoproteins. As yet another advantage, the present invention is adaptable as a tool for describing the conformations of many other organic molecules, and are thus especially suitable for use in the design of drugs, and the discovery and design of molecules which are to be adapted to interact with drugs.
Owner:MICRO PHARMATECH
Methods of diagnosis and treatment of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-related conditions
InactiveUS20140348857A1Diminishment of extentDelay slowingOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningDiabetes mellitusReticulum cell
The present invention relates to methods for treating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-related conditions (e.g., cancer, protein folding / misfolding disease, diabetes mellitus) and for identifying compounds for treating ER stress-related conditions in a subject (e.g., a human). The invention also provides methods for diagnosing an ER stress-related condition in a subject and kits for the treatment of same.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
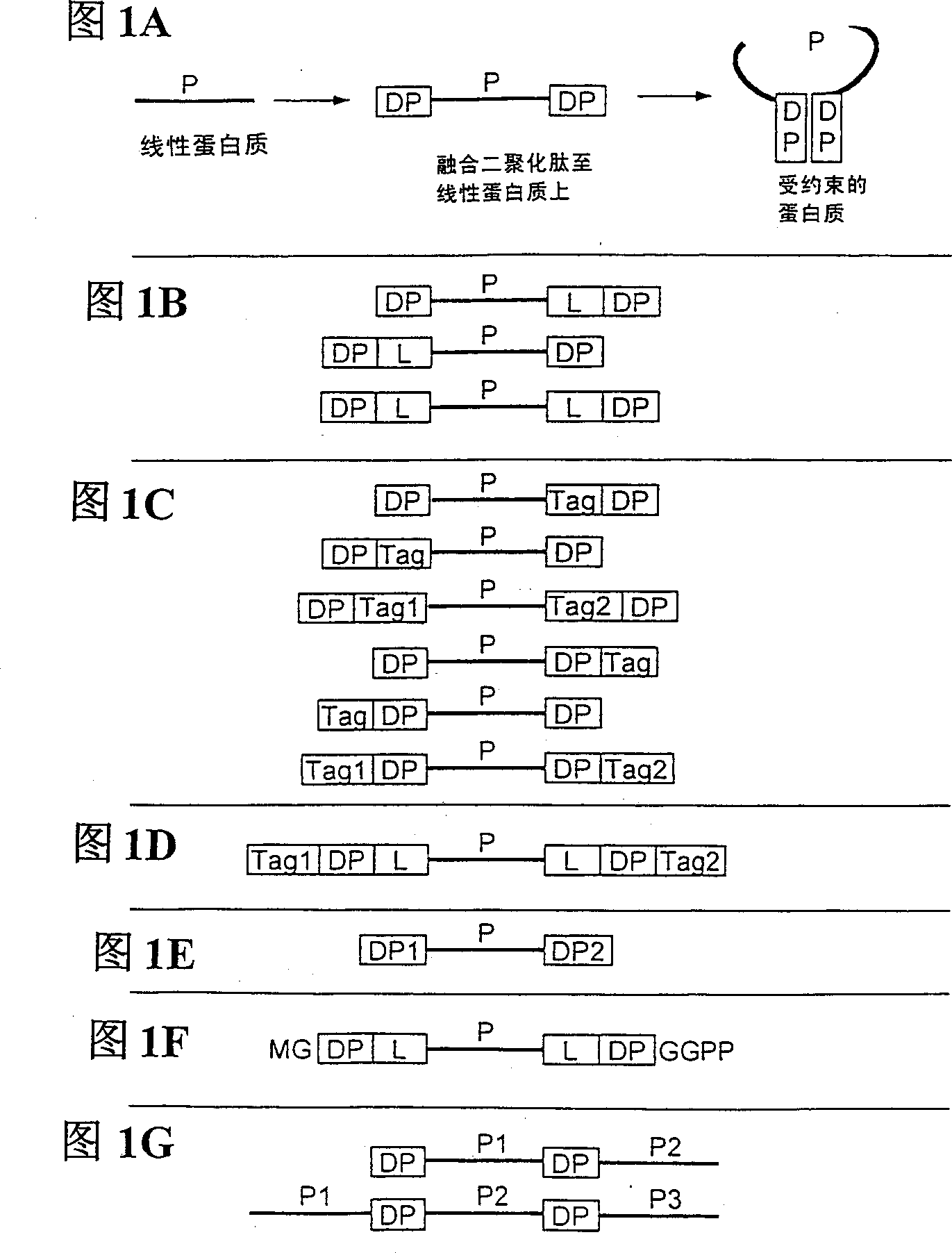
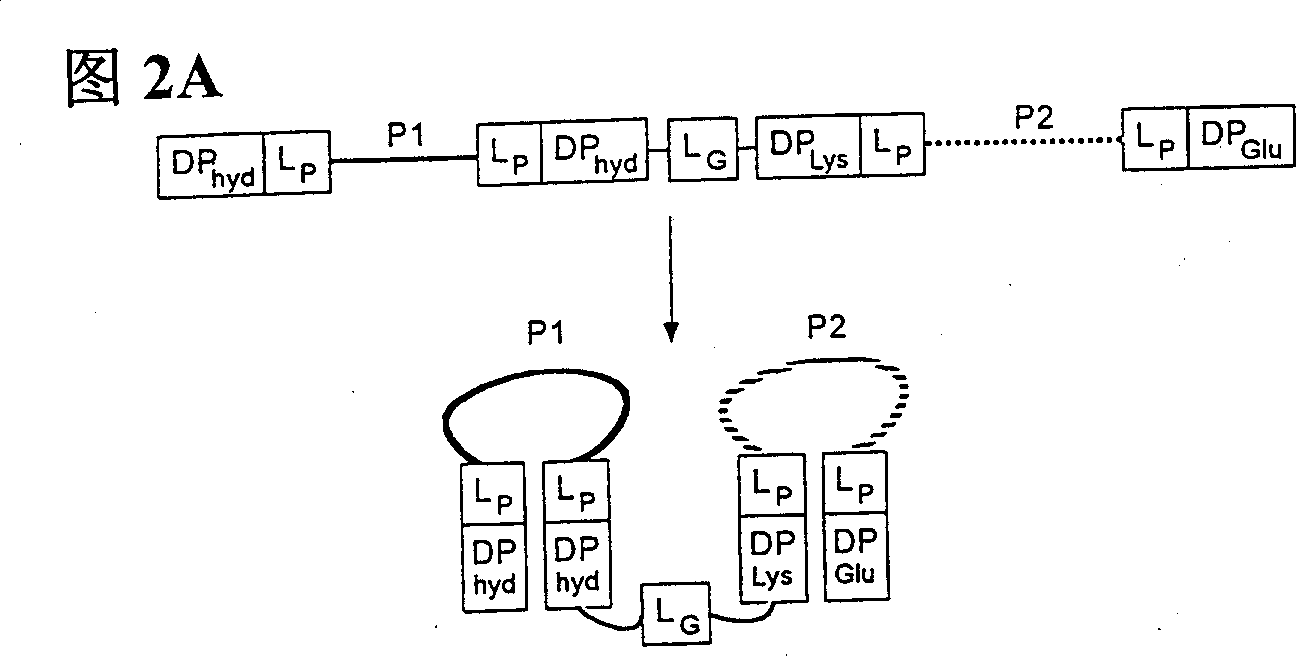
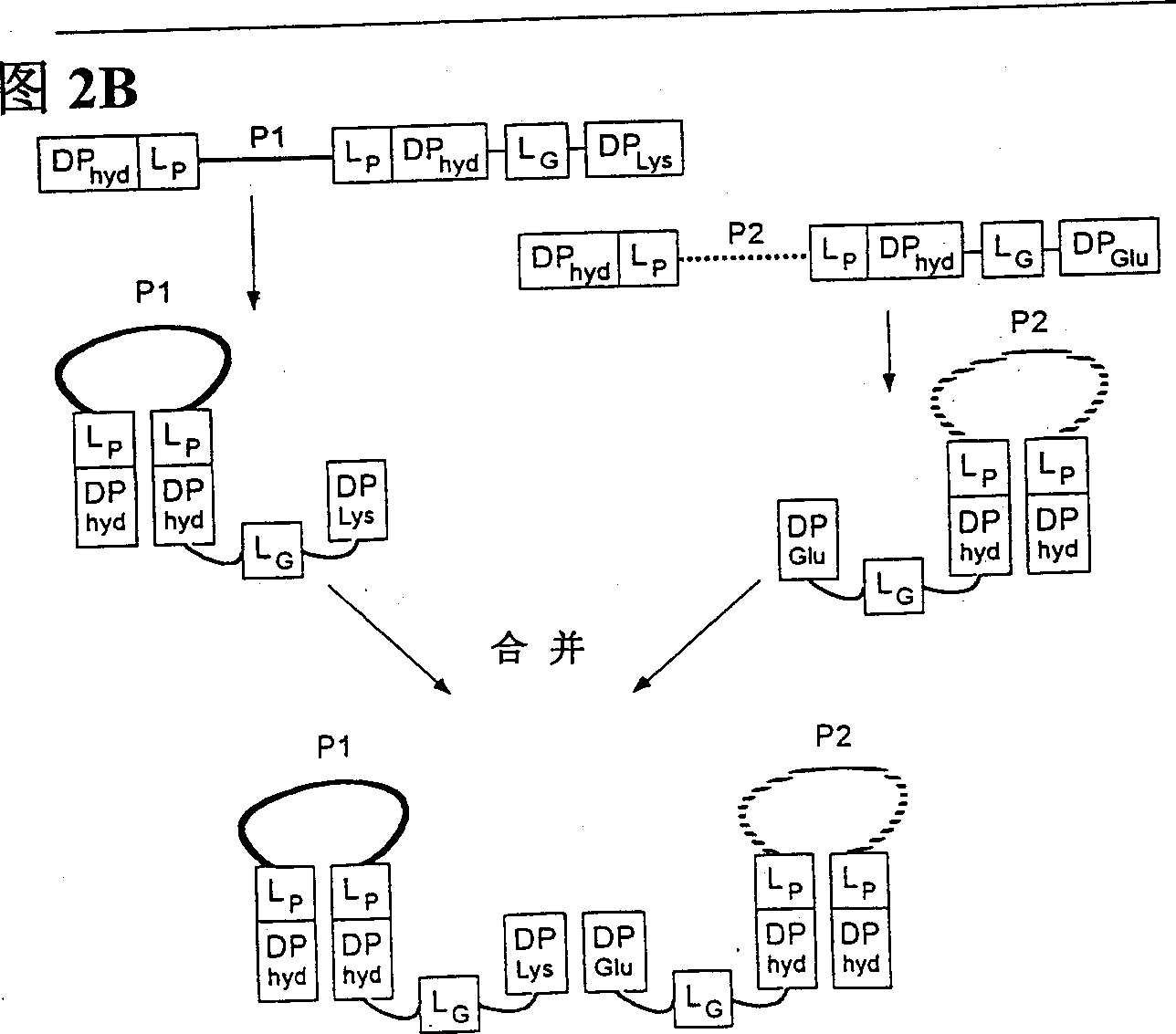
Peptides causing formation of compact structure
The present invention relates to compositions and methods comprising peptides with high mutual affinity that, when attached to a protein, assist the protein to fold into a compact structure. By virtue of its stability and binding, this scaffold extends the activity of any contained protein sequence in the presence of cellular and other proteases. This compact structure may have other included functional sequences, which are superior to linear and less constrained peptides for library screening, building structure-biased peptide libraries, and targeting specific intracellular and extracellular compartments. The compositions of the present invention can be displayed on viral, archaeal, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell surfaces for library screening, drug screening and display. The methods of the present invention are useful for in vivo screening of intracellular effector proteins that modulate signaling pathways, and for identification of interacting proteins in vitro. Therefore, the present invention can be used as a scaffold for gene therapy, for the isolation of new therapeutic drugs, and has potential utilization value for use as a therapeutic agent in physiological fluids.
Owner:RIGEL PHARMA
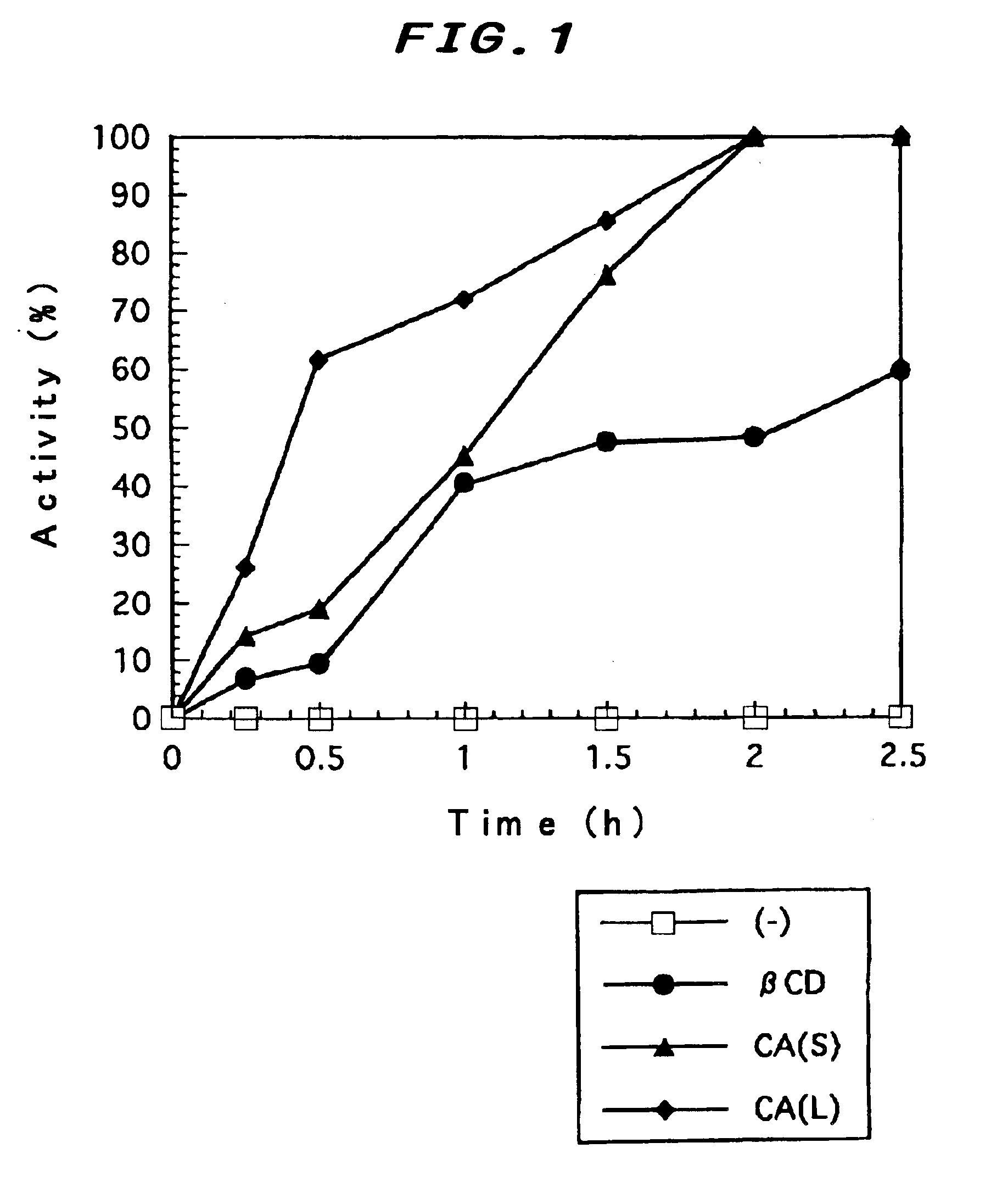
Artificial chaperon kit
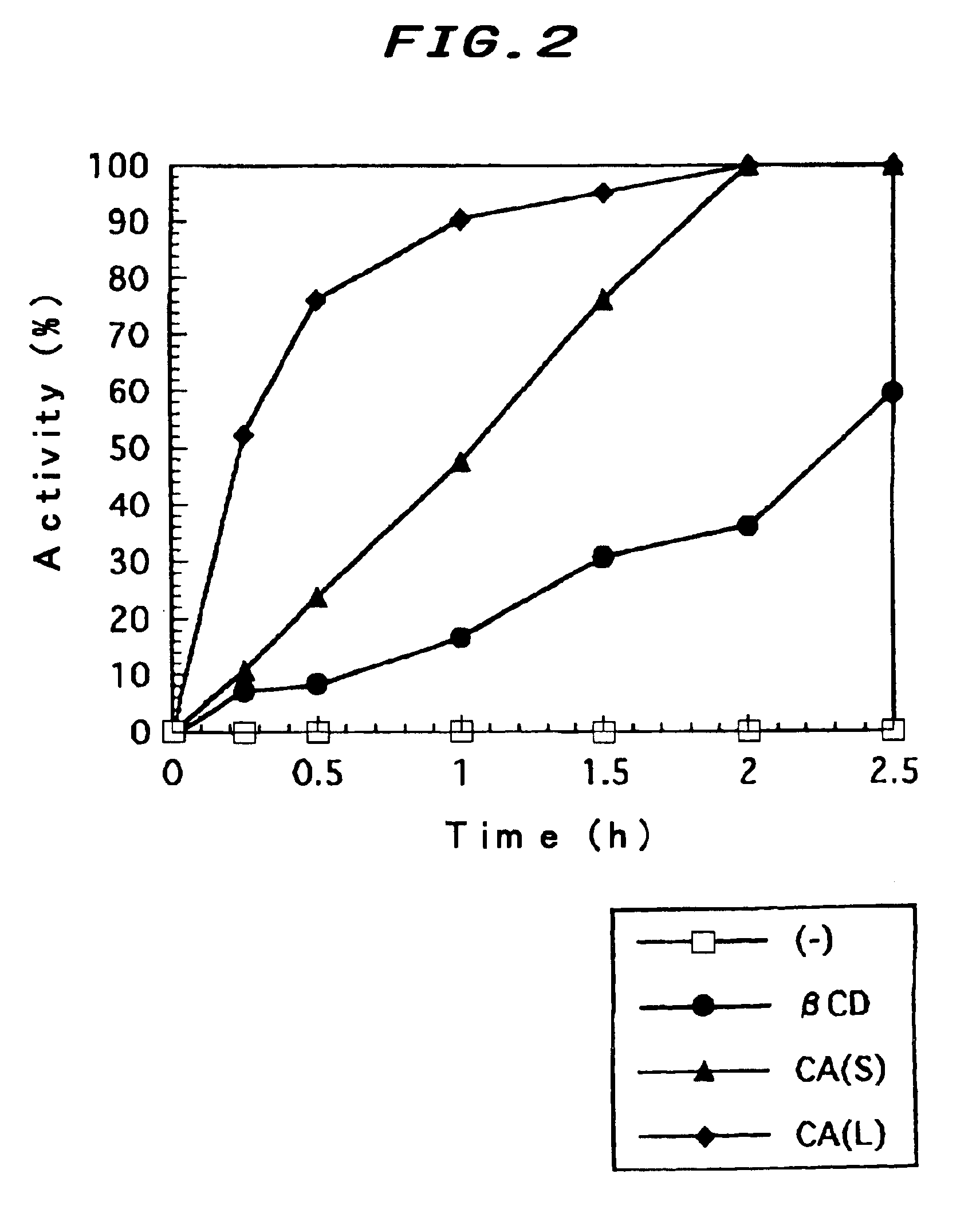
The present invention provides an artificial chaperon useful for refolding the proteins having low voluntary folding ability and being difficult or unable to be a native form without a second (or assistant) of a molecular chaperon in a short time, and folding said proteins as an active form. The present invention relates to an artificial chaperon kit characterized in that the kit comprises cyclic saccharide cycloamylose and polyoxyethylenic detergent or cyclic saccharide cycloamylose and ionic detergent. The present invention also relates to a method for diluting the denaturant making the protein a denatured state by adding a specific detergent to a denatured protein, and preventing protein molecules from aggregation, thereafter adding cyclic saccharide cycloamylose, utilizing the inclusion ability thereof to strip detergent, accelerating the proper folding of protein into a correct higher-order structure with activity.
Owner:NAT FOOD RES INST +1
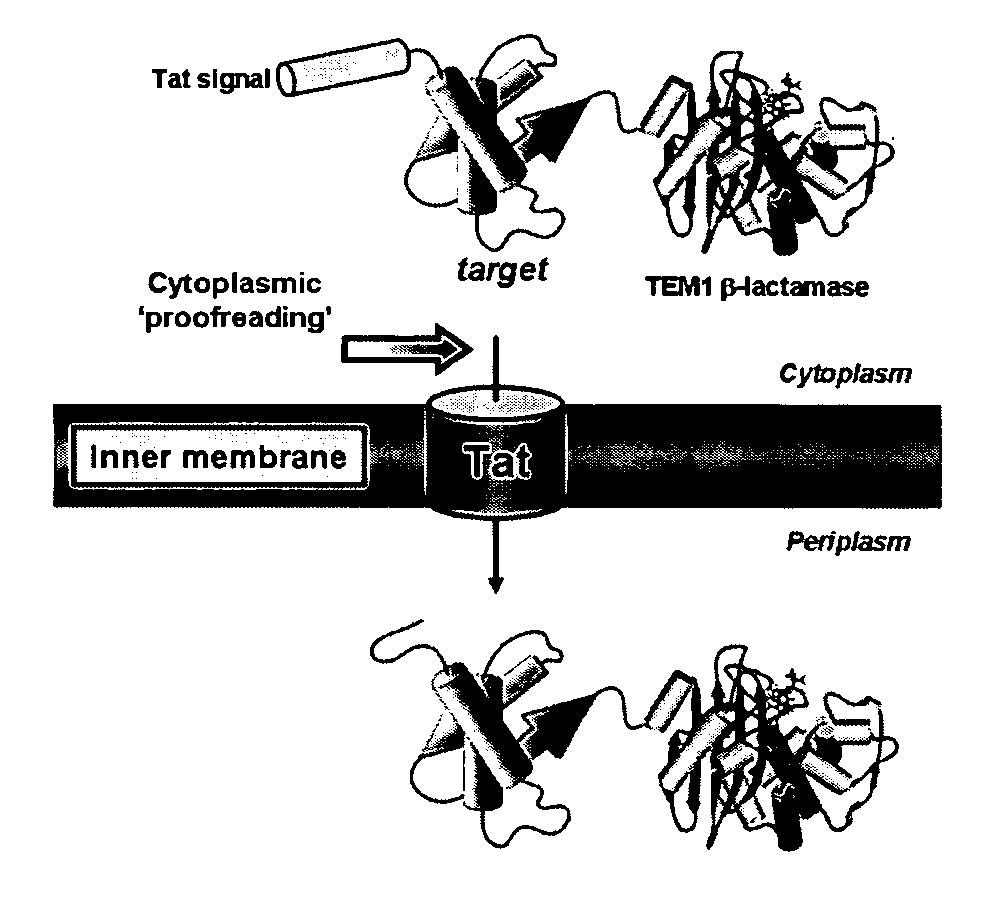
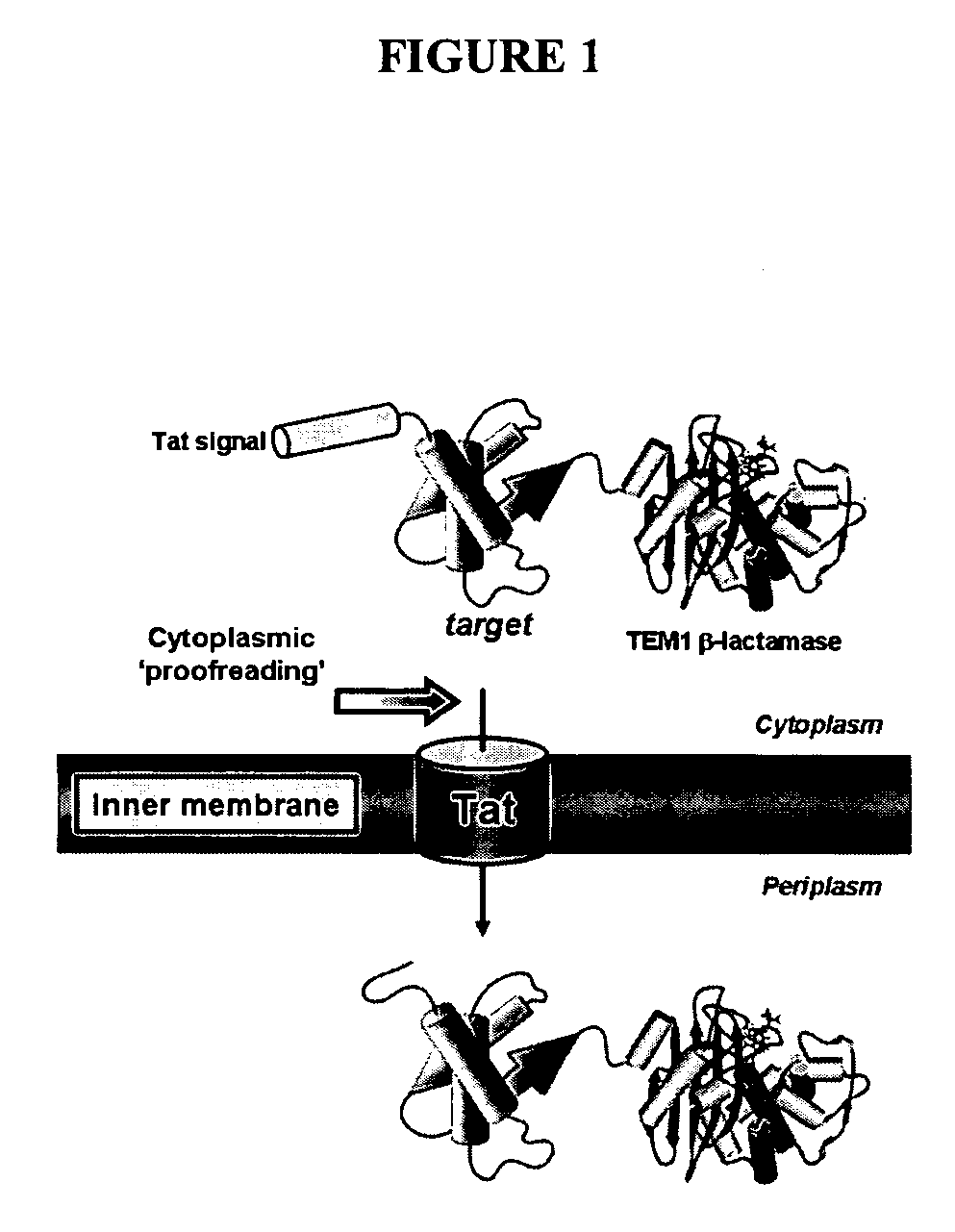
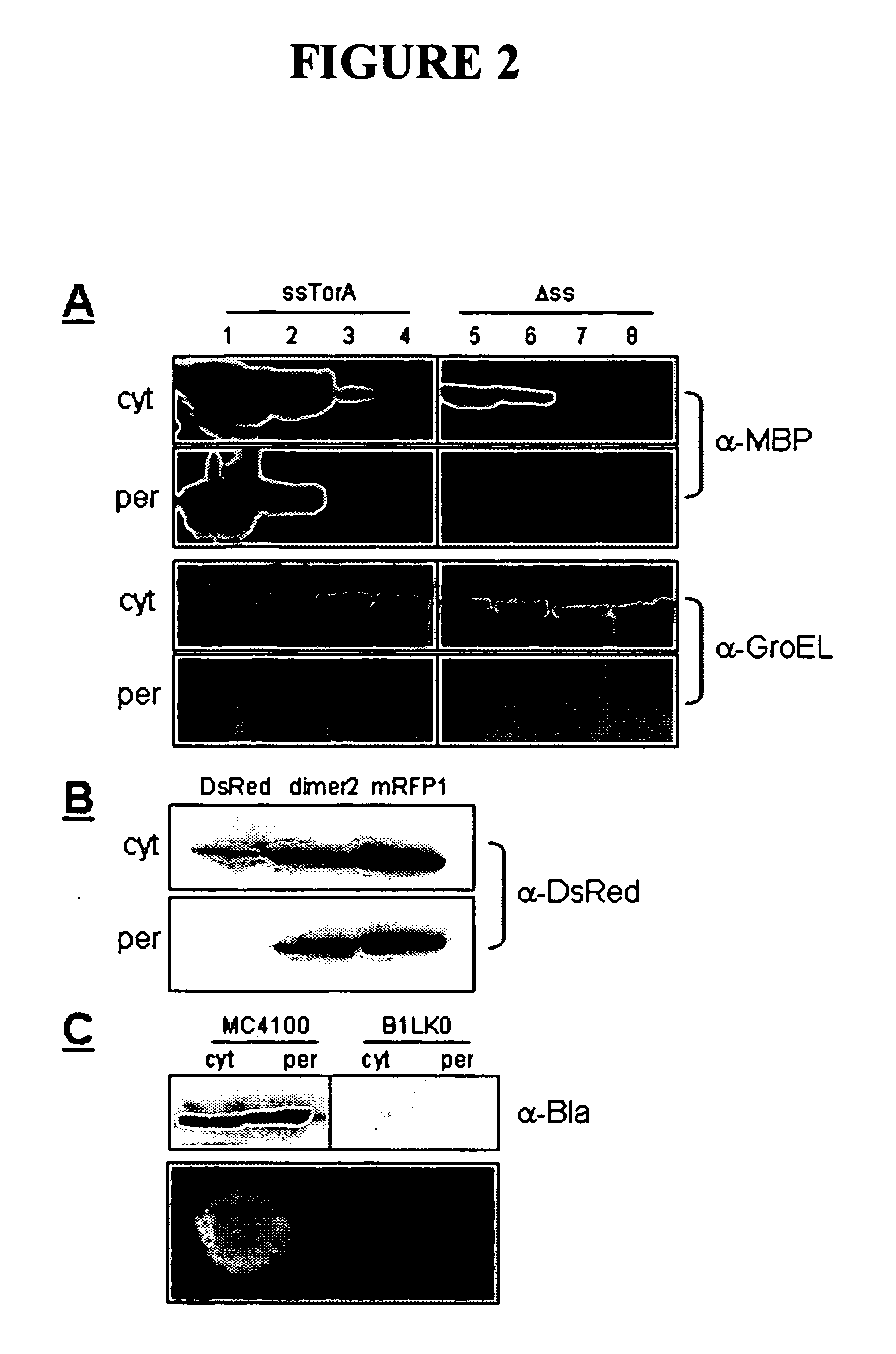
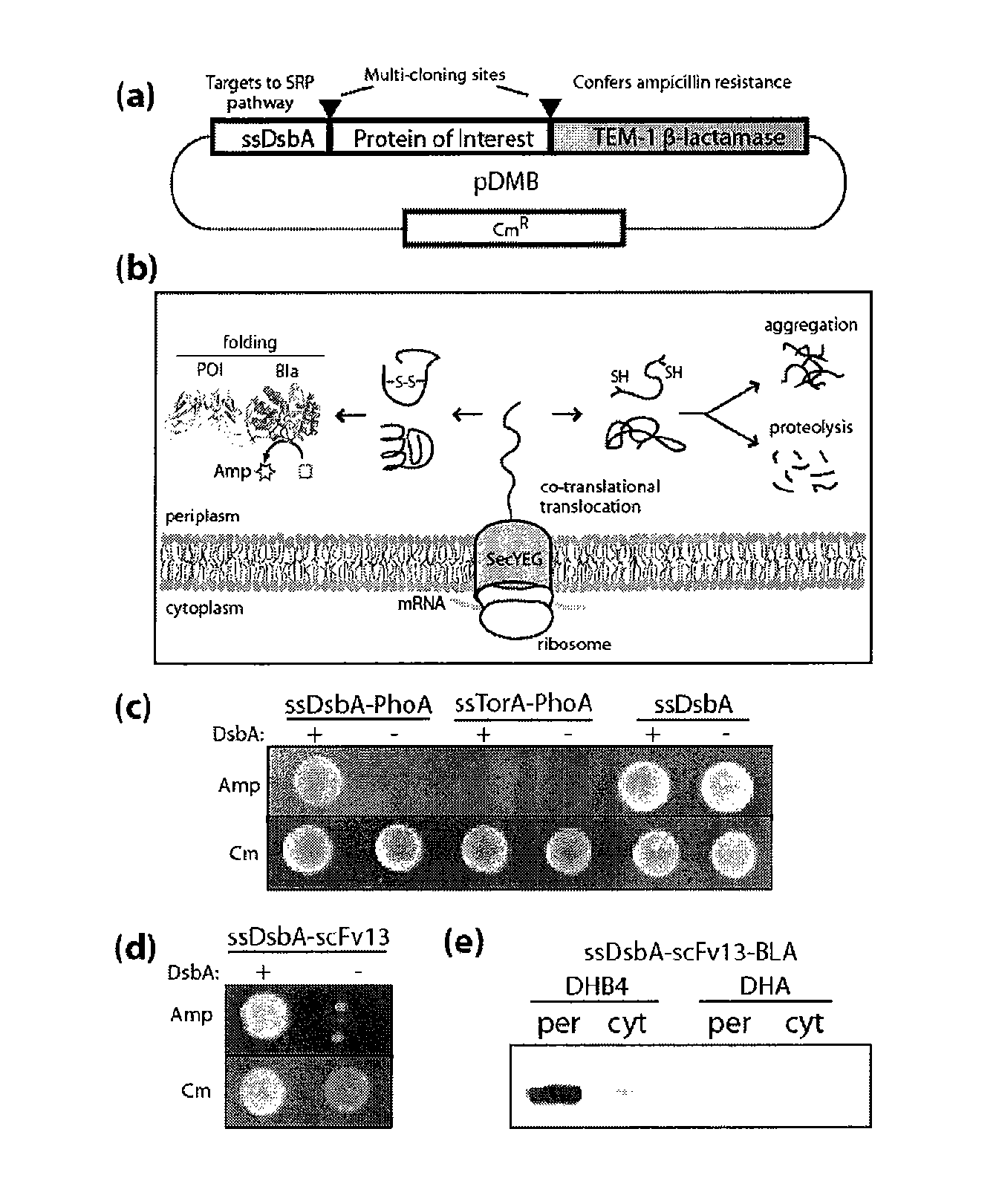
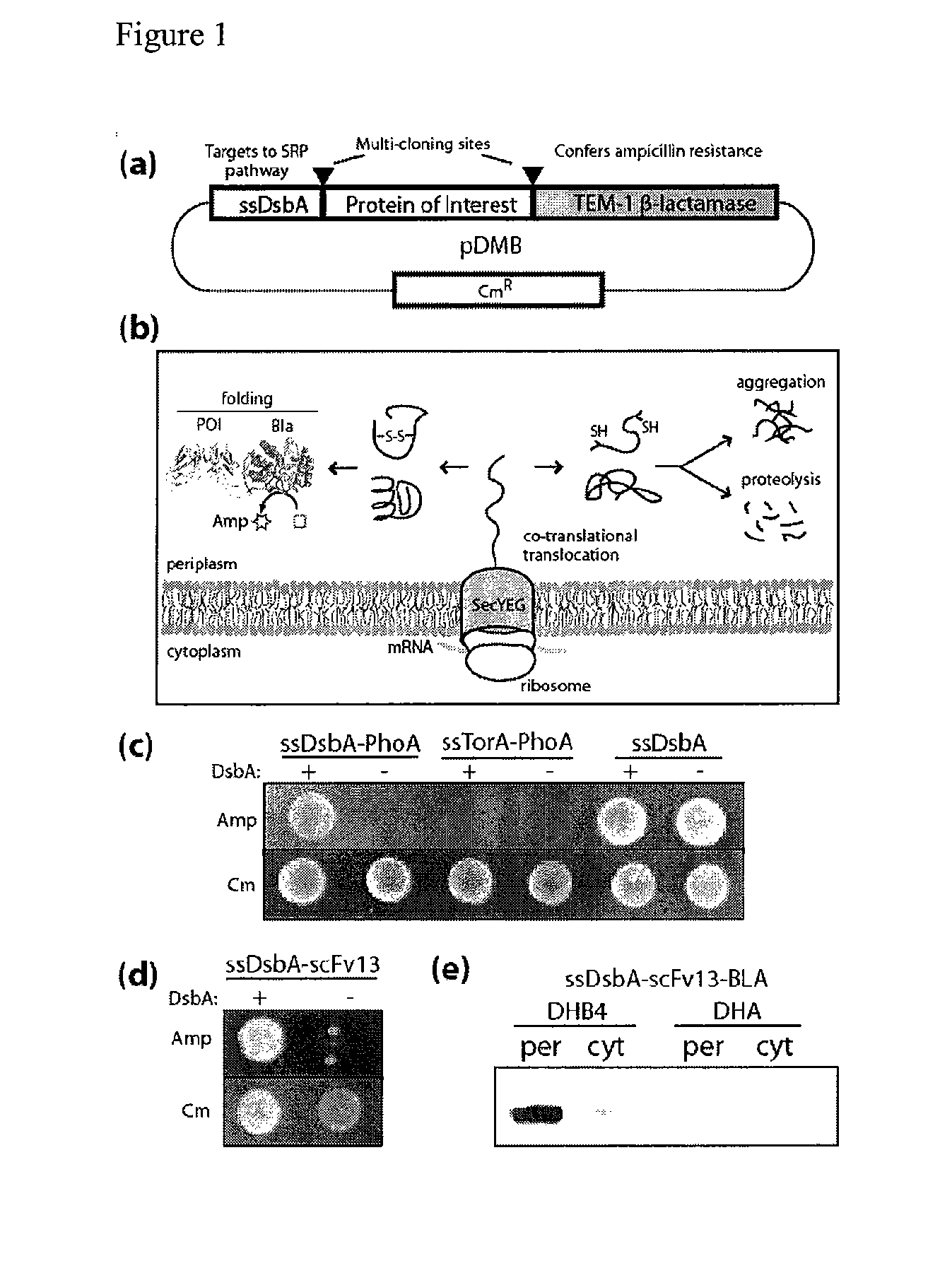
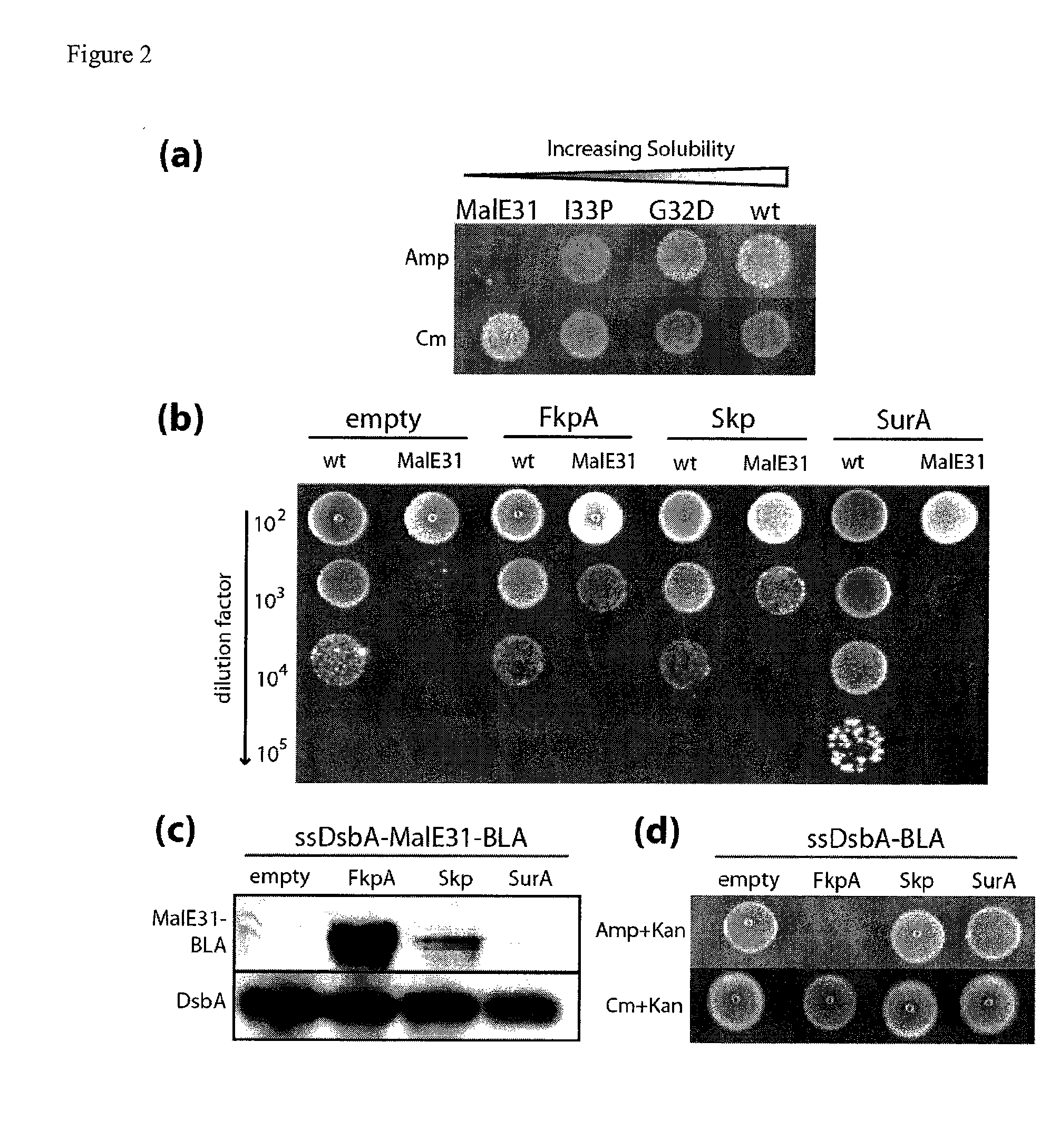
Genetic selection for protein folding and solubility in the bacterial periplasm
ActiveUS20100144546A1Sugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSignal recognition particleSolubility
The present invention relates to the fields of microbiology, molecular biology and protein biochemistry. More particularly, it relates to compositions and methods for analyzing and altering (e.g., enhancing or inhibiting) protein folding and solubility (e.g., within periplasm). The present invention provides an engineered assay for protein folding and solubility in the E. coli periplasm based on co-translational translocation of a chimera comprising a protein of interest fused to TEM-I β-lactamase that is targeted for export via the signal recognition particle (SRP)-dependent pathway. Using an array of native and heterologous proteins, it is demonstrated that periplasmic folding behavior of proteins is intimately coupled to in vivo β-lactamase activity. As a result of this coupling, the reporter is useful for (1) facile discovery of extrinsic periplasmic factors that affect protein folding and solubility; and (2) genetic selection of solubility-enhanced proteins.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
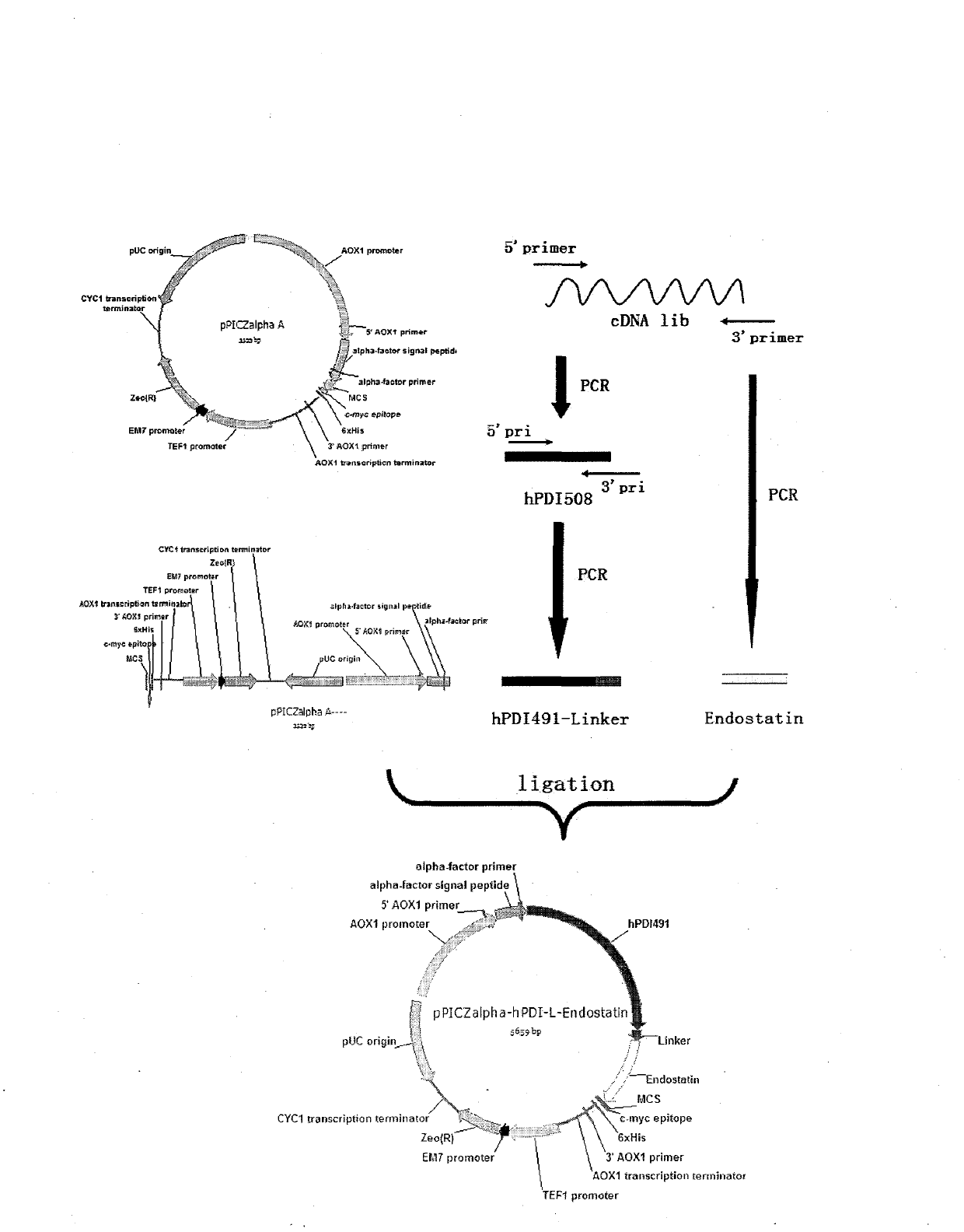
Method for performing fusion expression on protein containing disulfide bond
ActiveCN102533839AHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionPichia pastorisDisulfide bonding
The invention relates to a method for performing fusion expression on a protein containing a disulfide bond, in particular to a method for performing fusion expression on a recombinant protein, in particular a eukaryotic recombinant protein of which the activity is closely related with the forming of the (intrachain and interchain) disulfide bond in an eukaryotic host cell. An exogenous recombinant protein is expressed in a pichia pastoris expression system by a method for fusing human protein disulphide isomerase (hPDI) or a mutant of the hPDI. The method is suitable for expressing a eukaryotic exogenous protein of which protein activity or protein folding (comprising forms of a monomer, a dimmer or a polymer) are resistant to the disulphide bond. The protein expressed by the mode can be secreted out of a cell easily, and is high in yield, products cannot be gathered on a large scale and can be captured and purified easily, and the obtained target protein is uniform in N tail end, and high in activity. The recombinant protein expressed by the method can be industrially produced on a large scale.
Owner:SHANGHAI KAIYANG BIOTECH
Compositions and methods for treatment of disorders of protein aggregation
InactiveUS20070197453A1Sustained beneficial effectIncreased and restored long-term potentiationBiocideNervous disorderCell AggregationsProtein aggregation
The invention relates to compositions, methods and uses comprising an epi-inositol compound that provides beneficial effects in the treatment of a disorder and / or disease including a disorder in protein folding and / or aggregation, and / or amyloid formation, deposition, accumulation, or persistence. In aspects of the invention, the epi-inositol compounds provide beneficial effects in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and mild cognitive impairment.
Owner:MCLAURIN JOANNE
Pharmacological chaperones for treating obesity
ActiveUS20090312345A1High activityImprove scalabilityBiocideMetabolism disorderReticulum cellMedicine
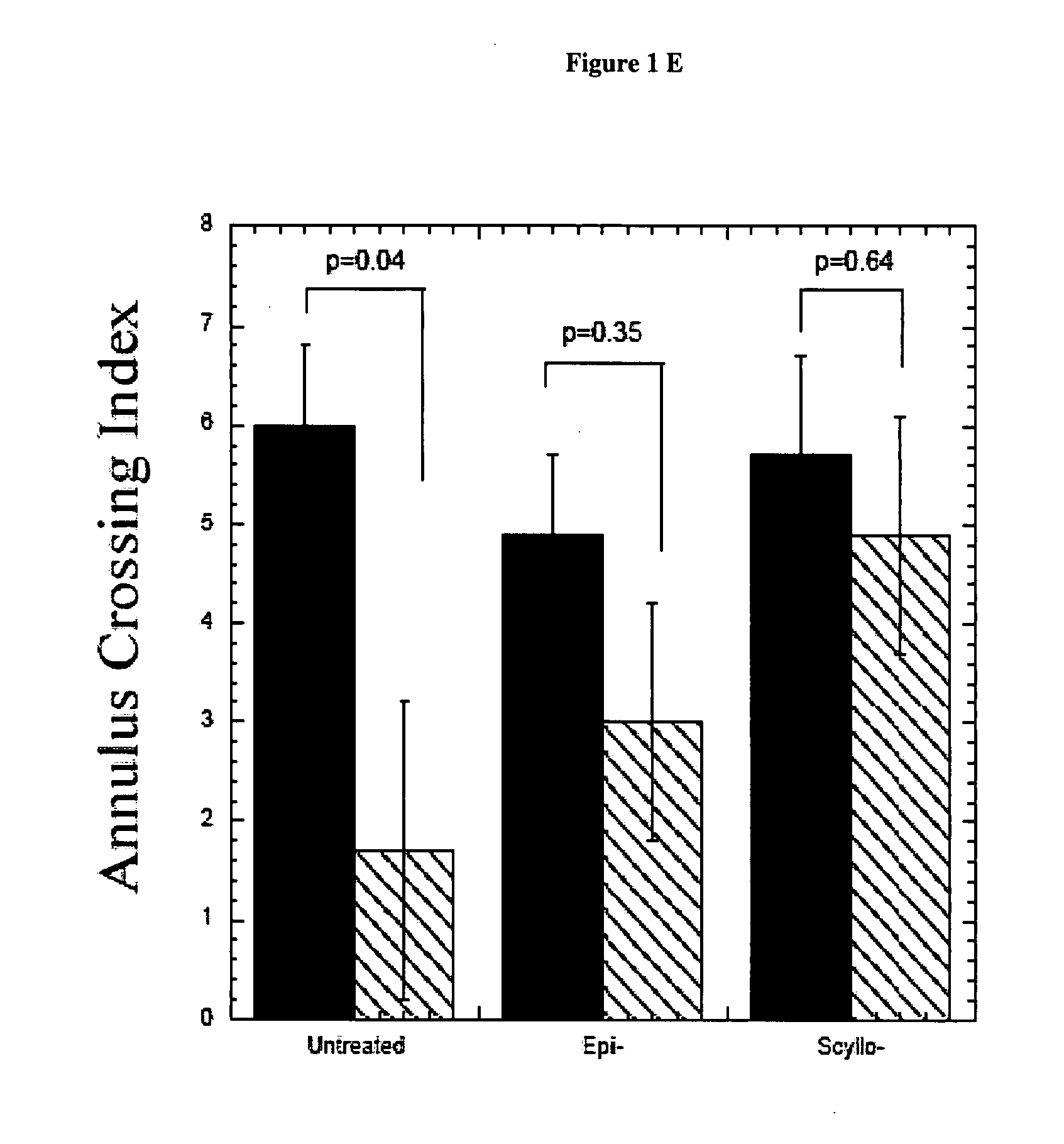
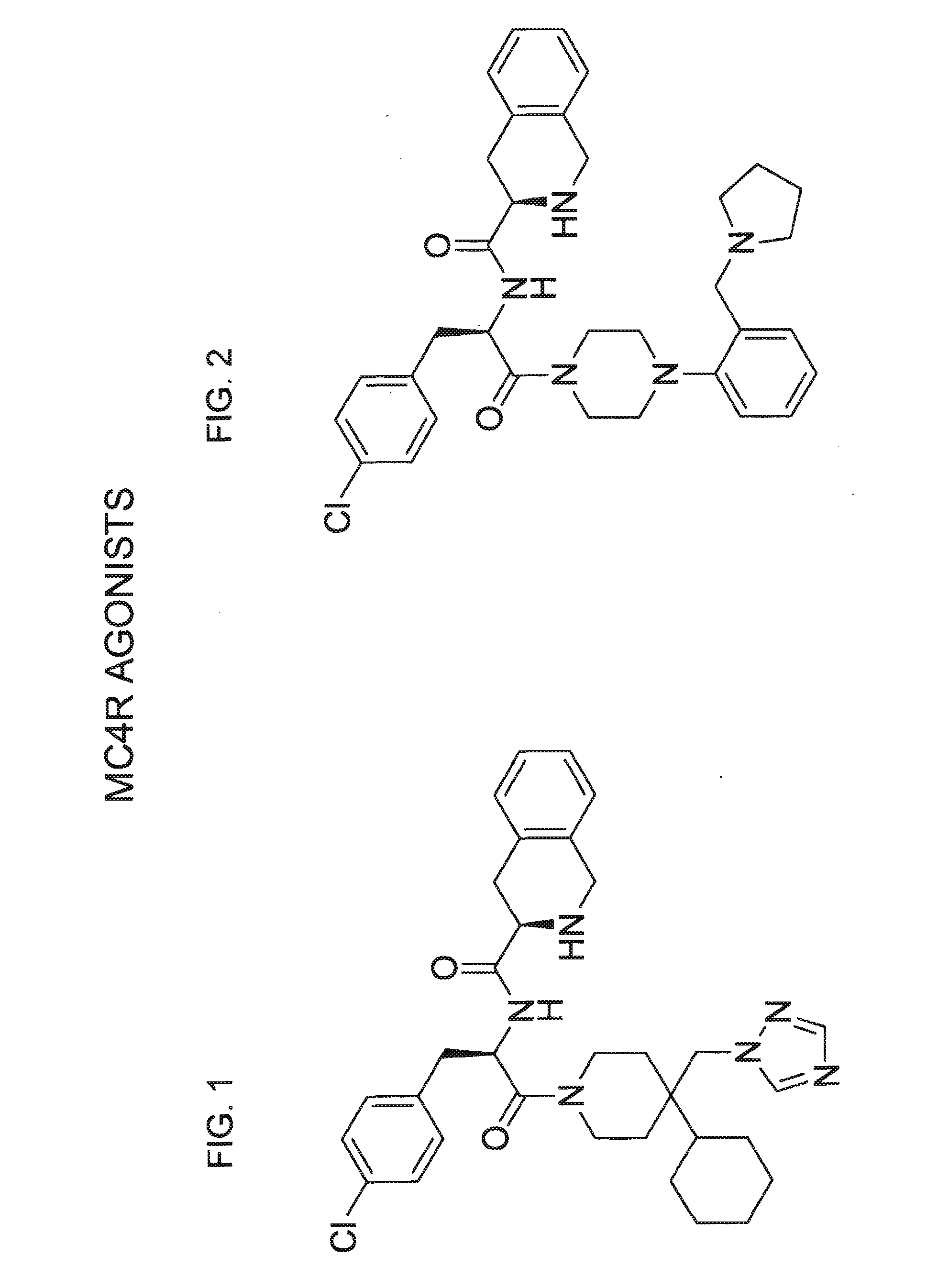
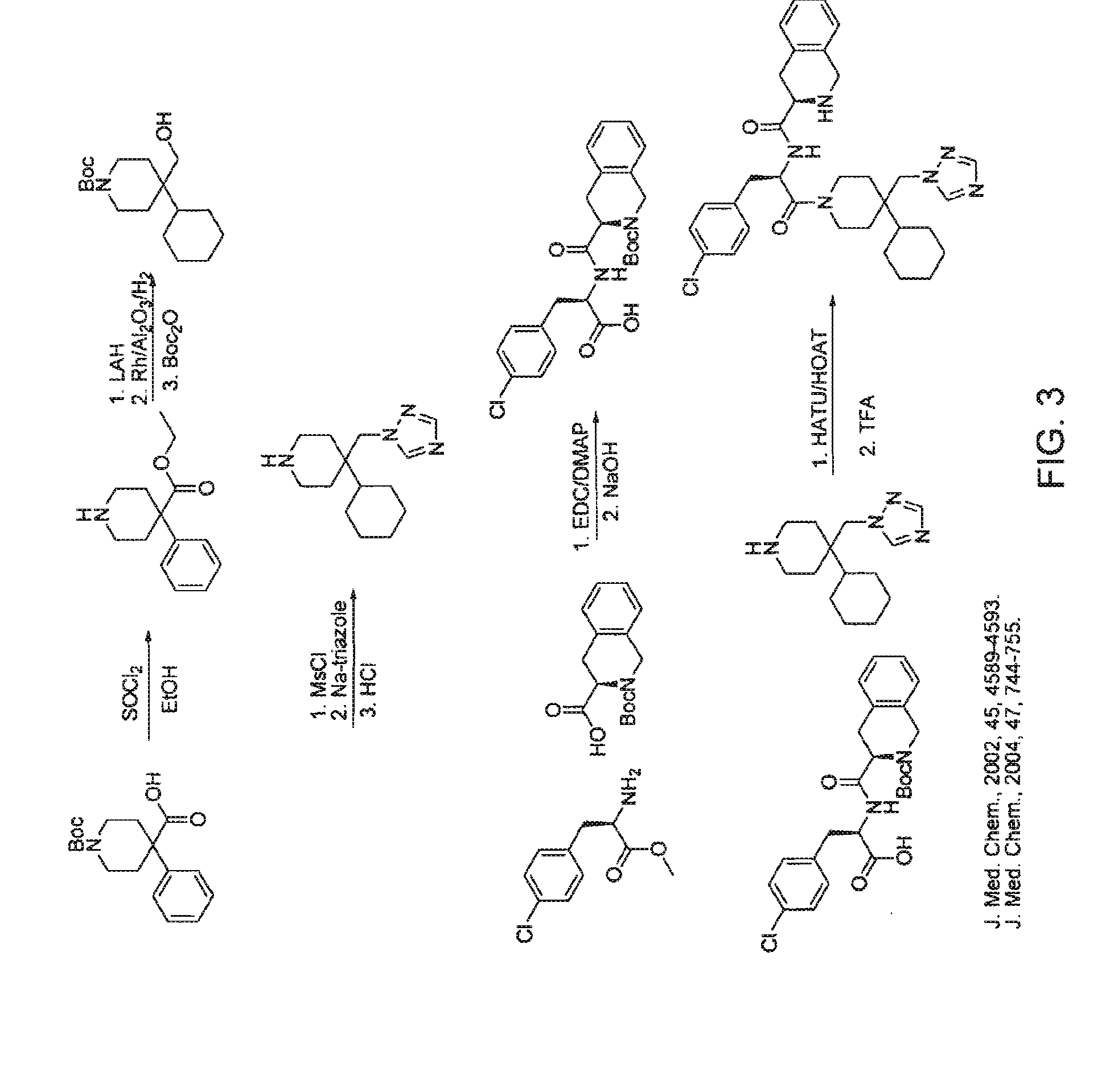
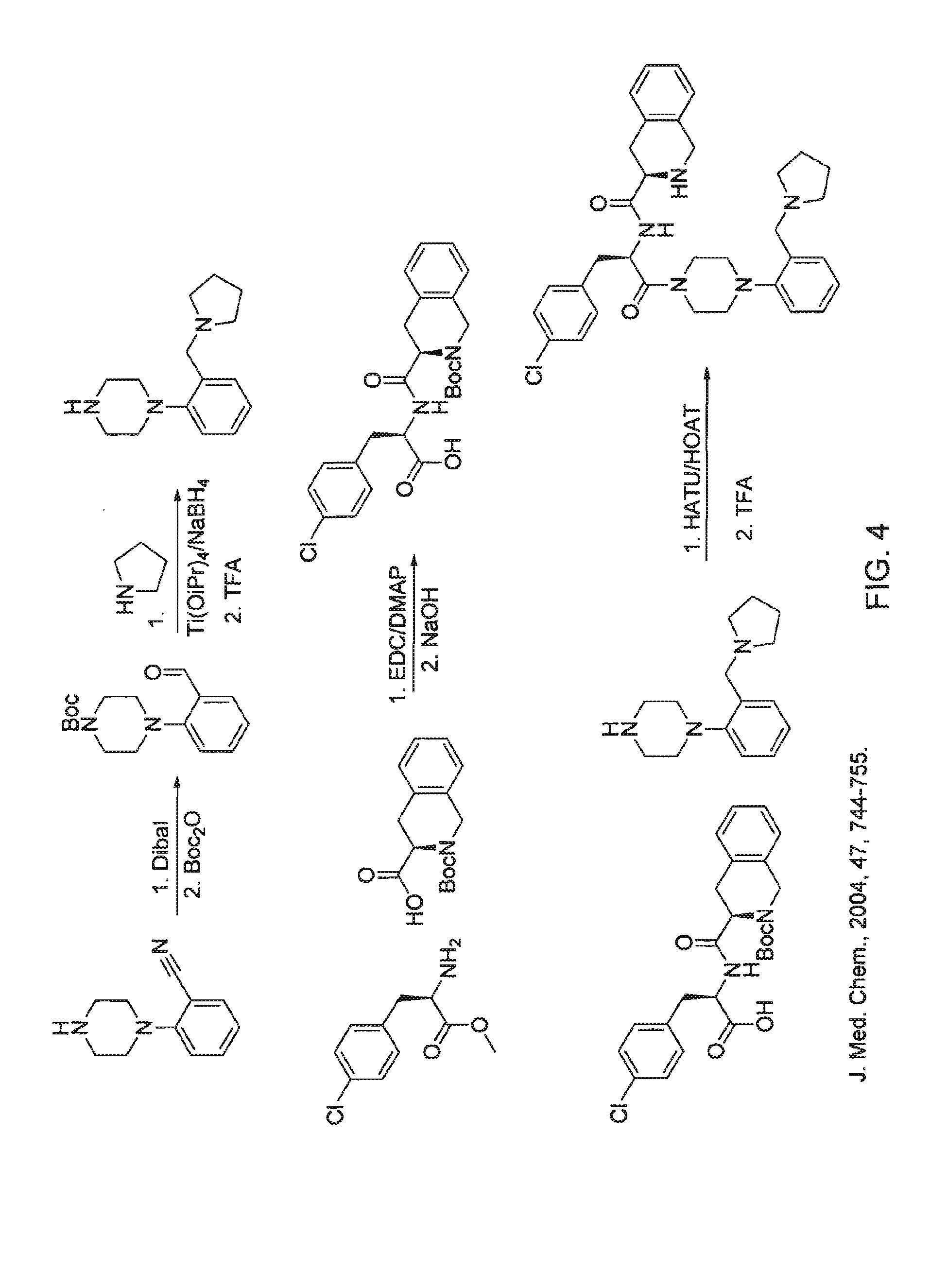
The invention relates to methods of enhancing normal melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) activity, and to enhancing activity of an MC4R having a mutation which affects protein folding and / or processing of the MC4R. The invention provides a method of treating an individual having a condition in which increased activity of an MC4R at the cell surface would be beneficial, for example in obesity, by administering an effective amount of a pharmacological chaperone for the MC4R. The invention provides MC4R pharmacological chaperones which enhance the activity of MC4R. The invention further provides a method of screening to identify pharmacological chaperones which enhance folding of an MC4R in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), in order to enhance the activity of the MC4R at the cell surface.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL
Fast computational methods for predicting protein structure from primary amino acid sequence
InactiveUS20080270094A1Analogue computers for chemical processesSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy minimizationProtein structure
The present invention provides a method utilizing primary amino acid sequence of a protein, energy minimization, molecular dynamics and protein vibrational modes to predict three-dimensional structure of a protein. The present invention also determines possible intermediates in the protein folding pathway. The present invention has important applications to the design of novel drugs as well as protein engineering. The present invention predicts the three-dimensional structure of a protein independent of size of the protein, overcoming a significant limitation in the prior art.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method for Incorporating Internal Polar and Ionizable Groups in Proteins
ActiveUS20120258518A1High thermodynamic stabilityImprove accuracyHydrolasesPeptide preparation methodsElectricityCrystallography
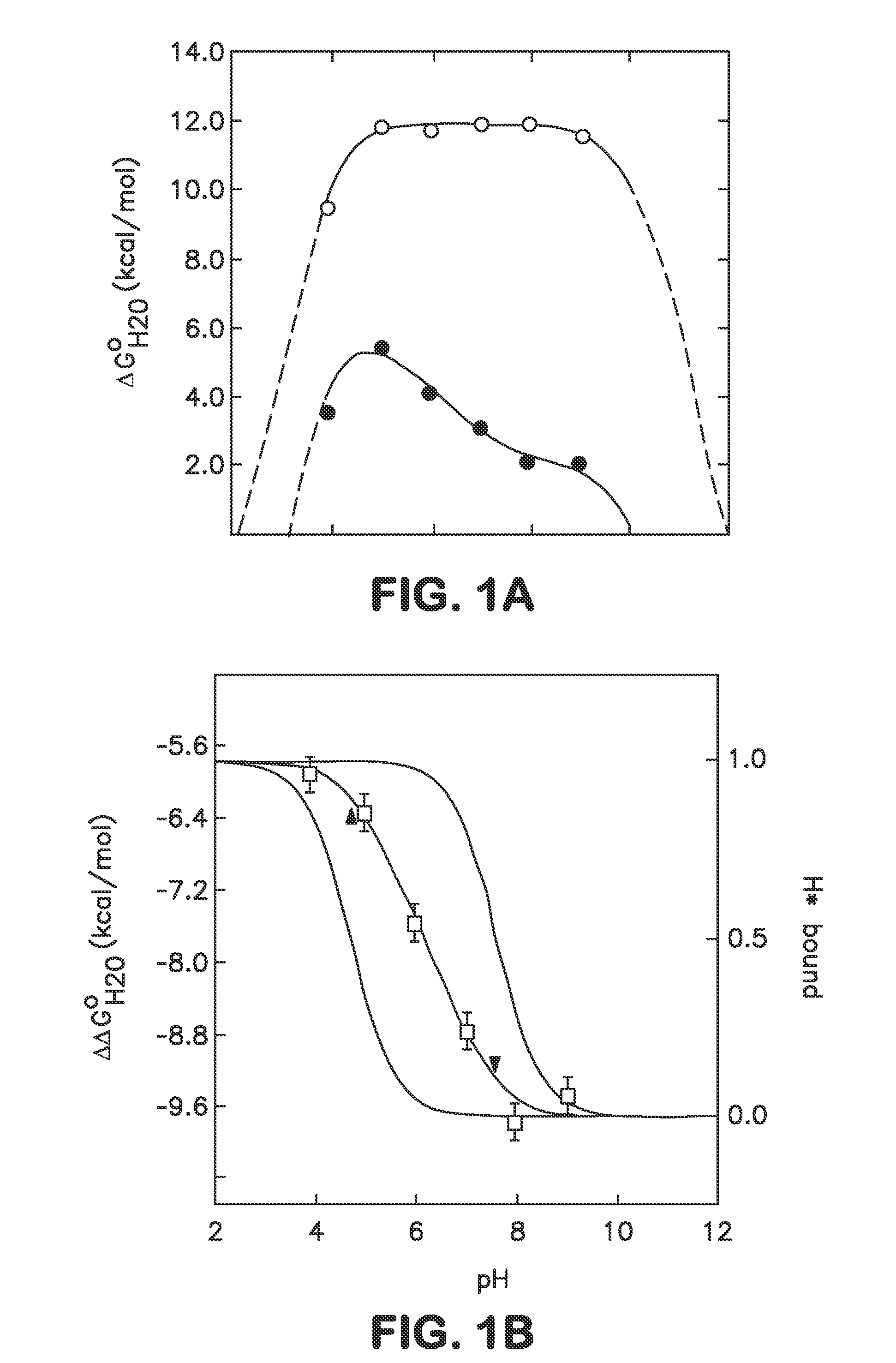
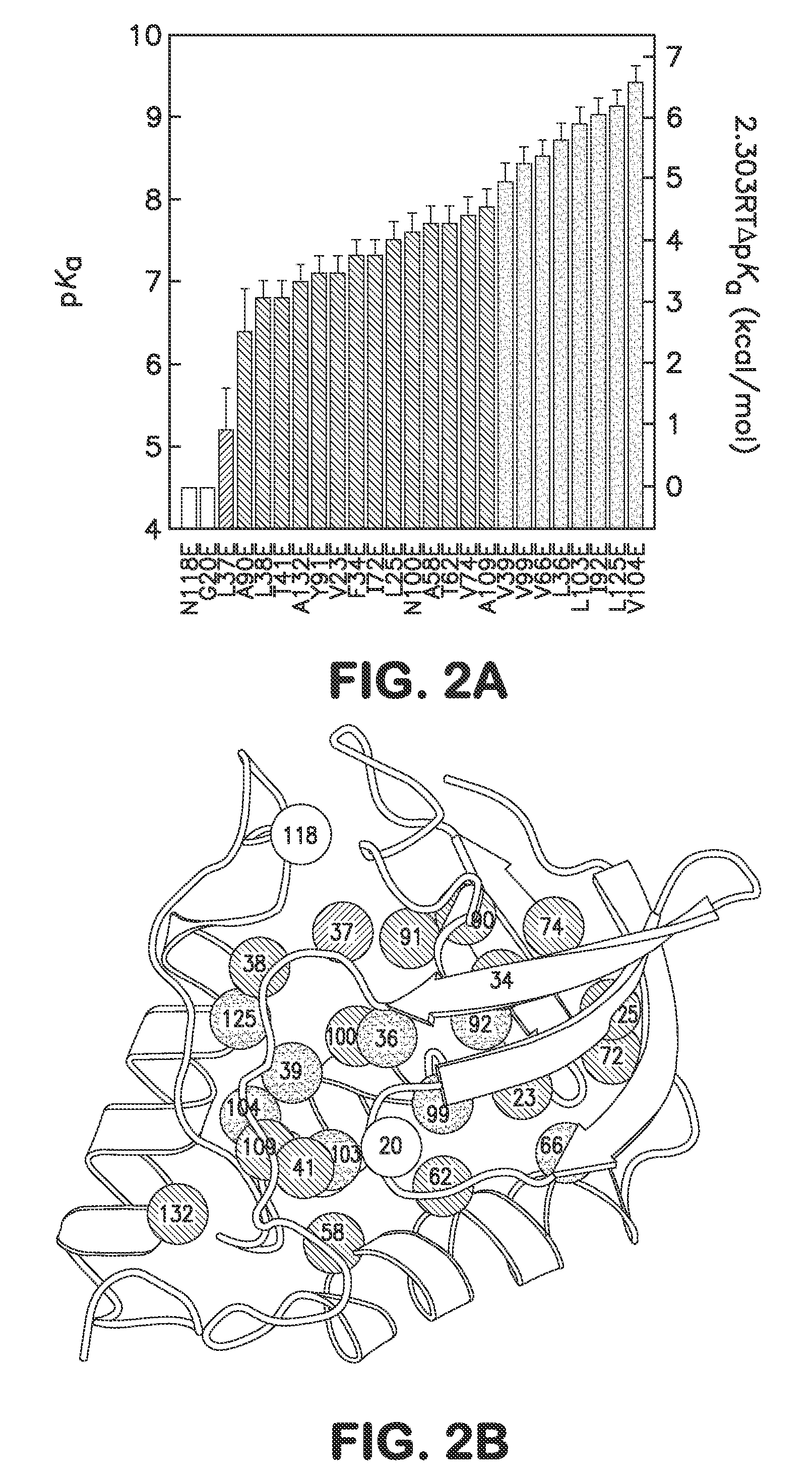
Internal polar and ionizable groups are essential for enzymatic catalysis, proton transport, redox reactions, and many other functional properties of proteins. To engineer novel enzymes or to modify the function of existing ones, and to build switches that can be used to modify the stability of proteins in response to changes in pH, it is necessary to introduce polar or ionizable groups or to modify the properties of existing ones. However, internal polar and ionizable groups usually destabilize proteins. The disclosure provides new methods that allow the introduction of polar and ionizable groups into the interior of proteins, as well as new methods for improving the accuracy of pKa of an internal amino acid of a protein, and methods for mapping the folding free energy landscape of a protein.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
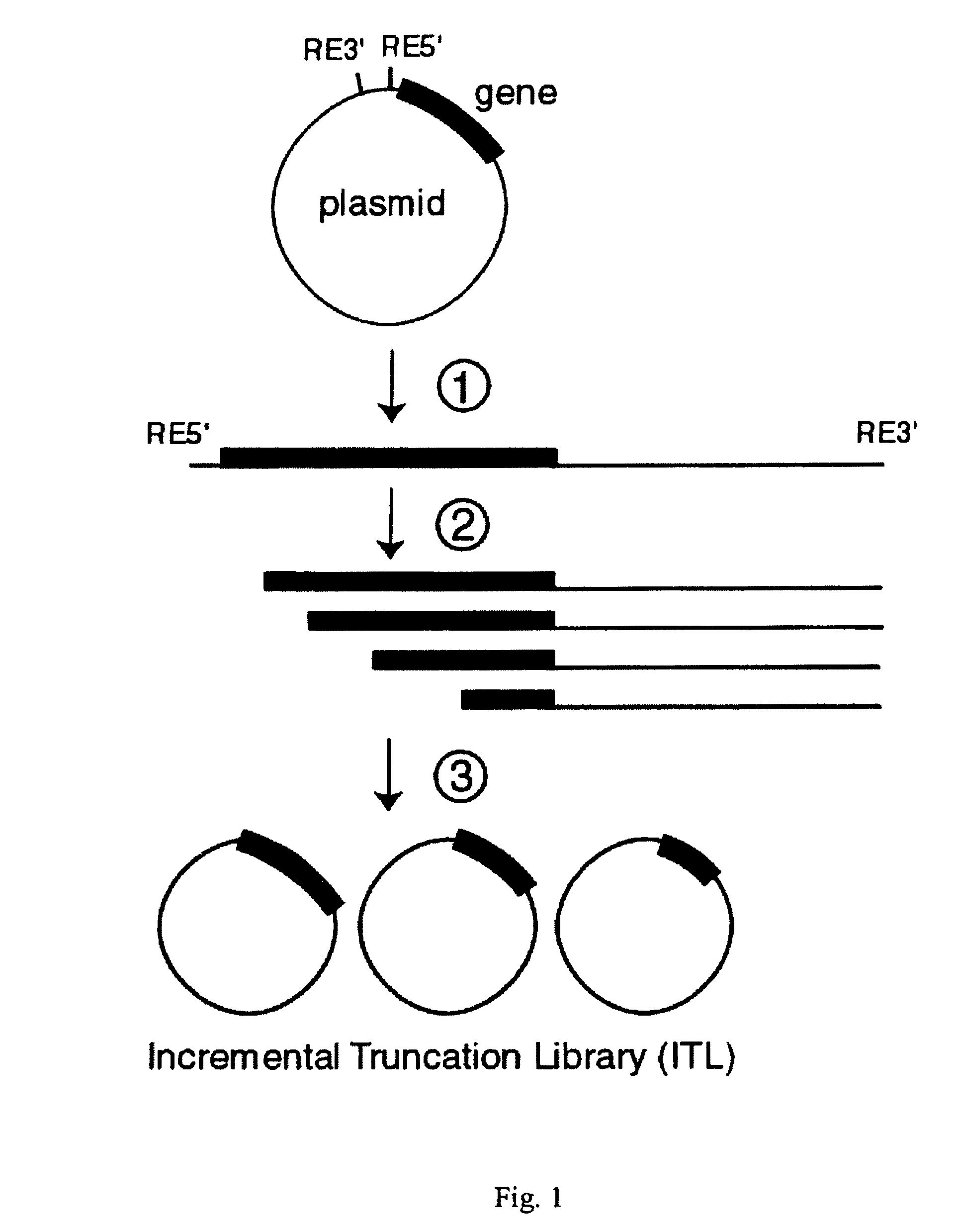
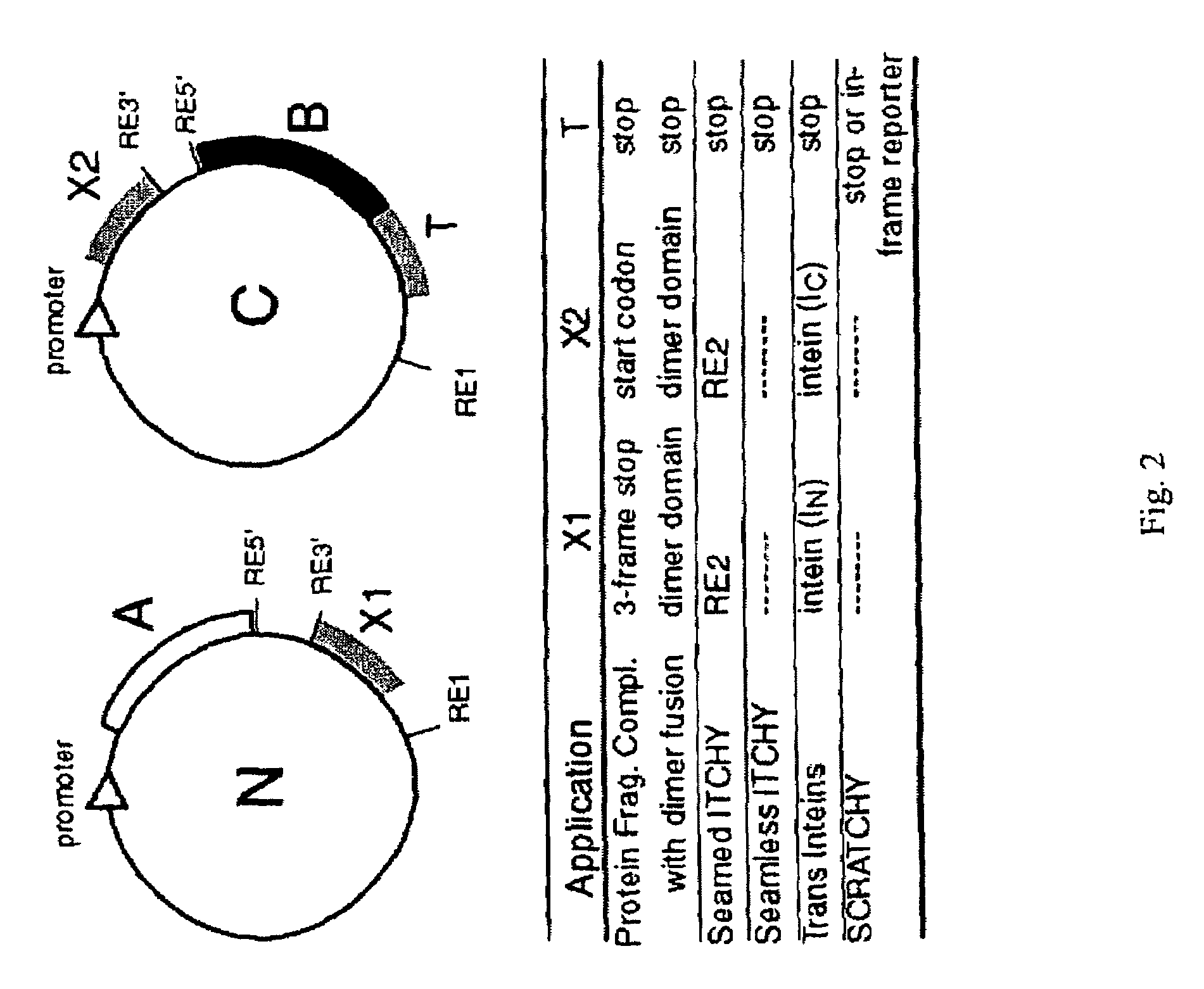
Incrementally truncated nucleic acids and methods of making same
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Substituted benzoyl urea compound and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101880246AMild reaction conditionsAbundant and easy to get raw materialsUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationImmunosuppressive drugAutoimmune responses
The invention relates to a novel substituted benzoyl urea compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has the structure general formula disclosed in (I), wherein definitions of R1, R2, and R3 are described in the specification, and the compound can be used as a micromolecule inhibitor of Cyclophilin A (CypA); the CypA is a protein with the activity of Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase), and is related to the in vivo protein folding, assembly and transfer. The current research shows that the CrpA takes part in various physiology approaches, such as autoimmunity depression, HIV-1 invasion infection and the like. Therefore, the compound of the invention can become a novel immunosuppressive drug or anti-HIV-1 drug.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
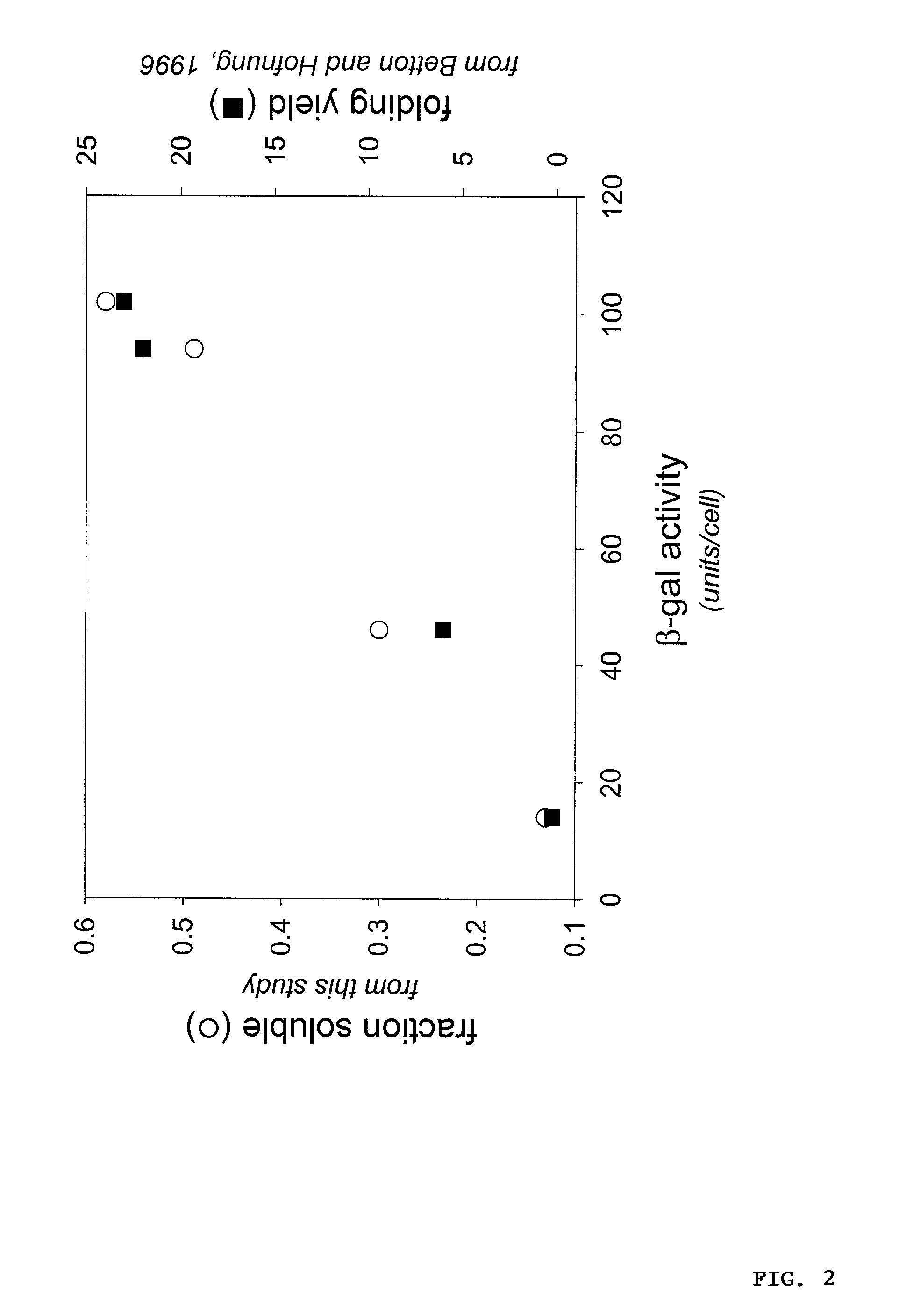
Protein/solubility folding assessed by structural complementation
Many proteins, when produced recombinantly, suffer from improper processing, folding and lack normal solubility. Modified proteins, including those indicative of disease states, also can have such defects. The present invention is directed to methods of identifying proper and improper protein folding, aberrant processing and / or insolubility. The method relies on the use of two components: a specialized fusion protein and structural complementation. The fusion protein contains sequences from the protein of interest and one portion of a marker protein that, by itself, is not active. A host cell then provides the remainder of the marker protein that serves to "complement" the function of the fused marker protein such that their association restores activity, permitting detection.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Systems and methods for protein production
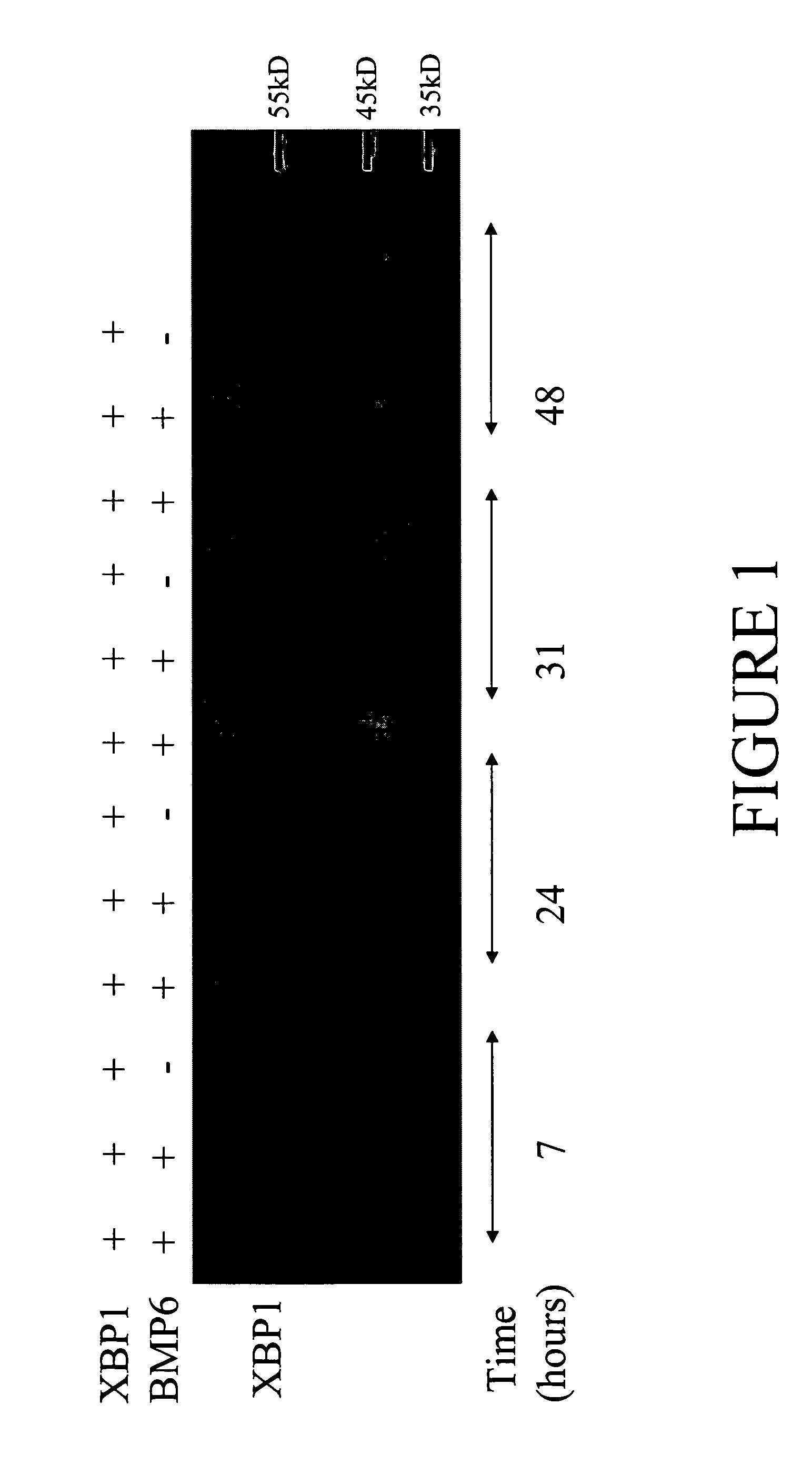
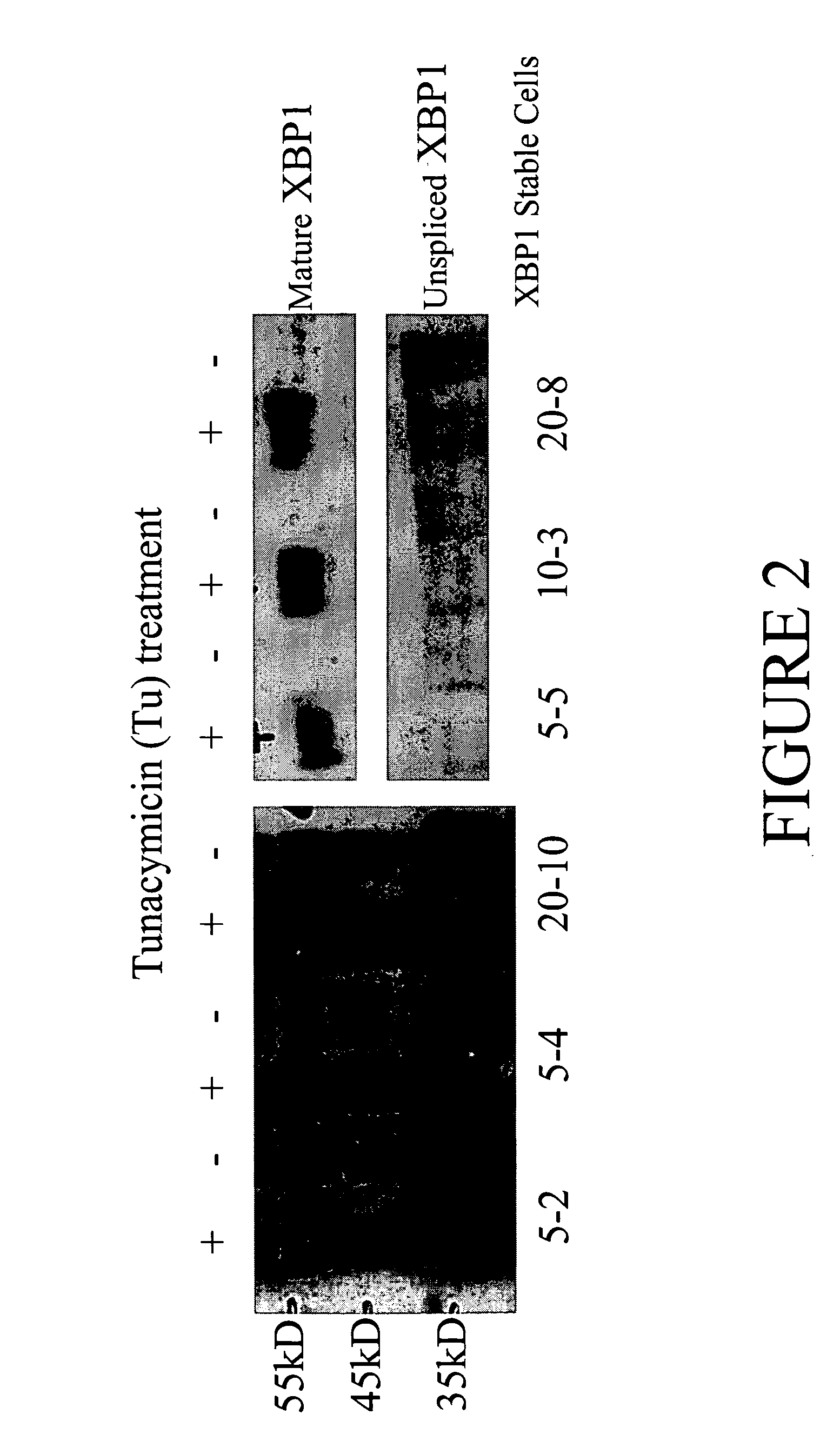
ActiveUS20060053502A1Improve production yieldEnhanced protein foldingBacteriaHydrolasesXBP1Plant cell
The invention relates to systems and methods for producing proteins of interest. The invention employs genetically-engineered animal or plant cells that have modified protein folding or processing capacities. In one aspect, the invention features genetically-engineered cells comprising one or more recombinant expression cassettes which encode (1) a protein of interest and (2) a polypeptide that is functional in the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway of the cells. Co-expression of the polypeptide significantly increases the yield of the protein of interest in the genetically-engineered cells. In one example, the genetically-engineered cells are animal cells, and the co-expressed polypeptide is a component or modulator of an XBP1- or ATF6-mediated UPR pathway.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com