Patents
Literature
137 results about "Osmolyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Osmolytes are low-molecular weight organic compounds that influence the properties of biological fluids. Their primary role is to maintain the integrity of cells by affecting the viscosity, melting point, and ionic strength of the aqueous solution. When a cell swells due to external osmotic pressure, membrane channels open and allow efflux of osmolytes which carry water with them, restoring normal cell volume. Osmolytes also interact with the constituents of the cell, e.g. they influence protein folding. Common osmolytes include amino acids, sugars and polyols, methylamines, methylsulfonium compounds, and urea.
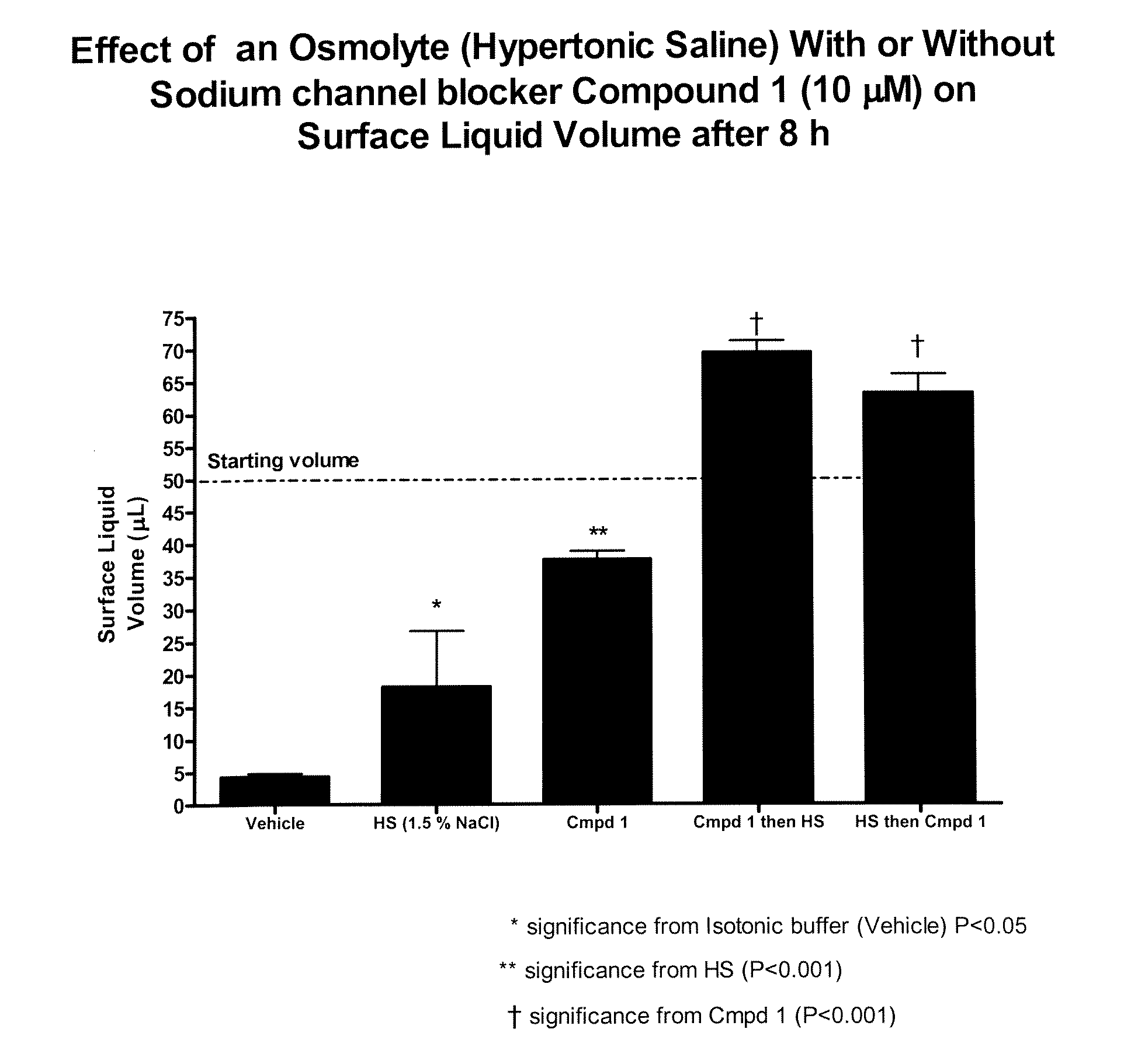
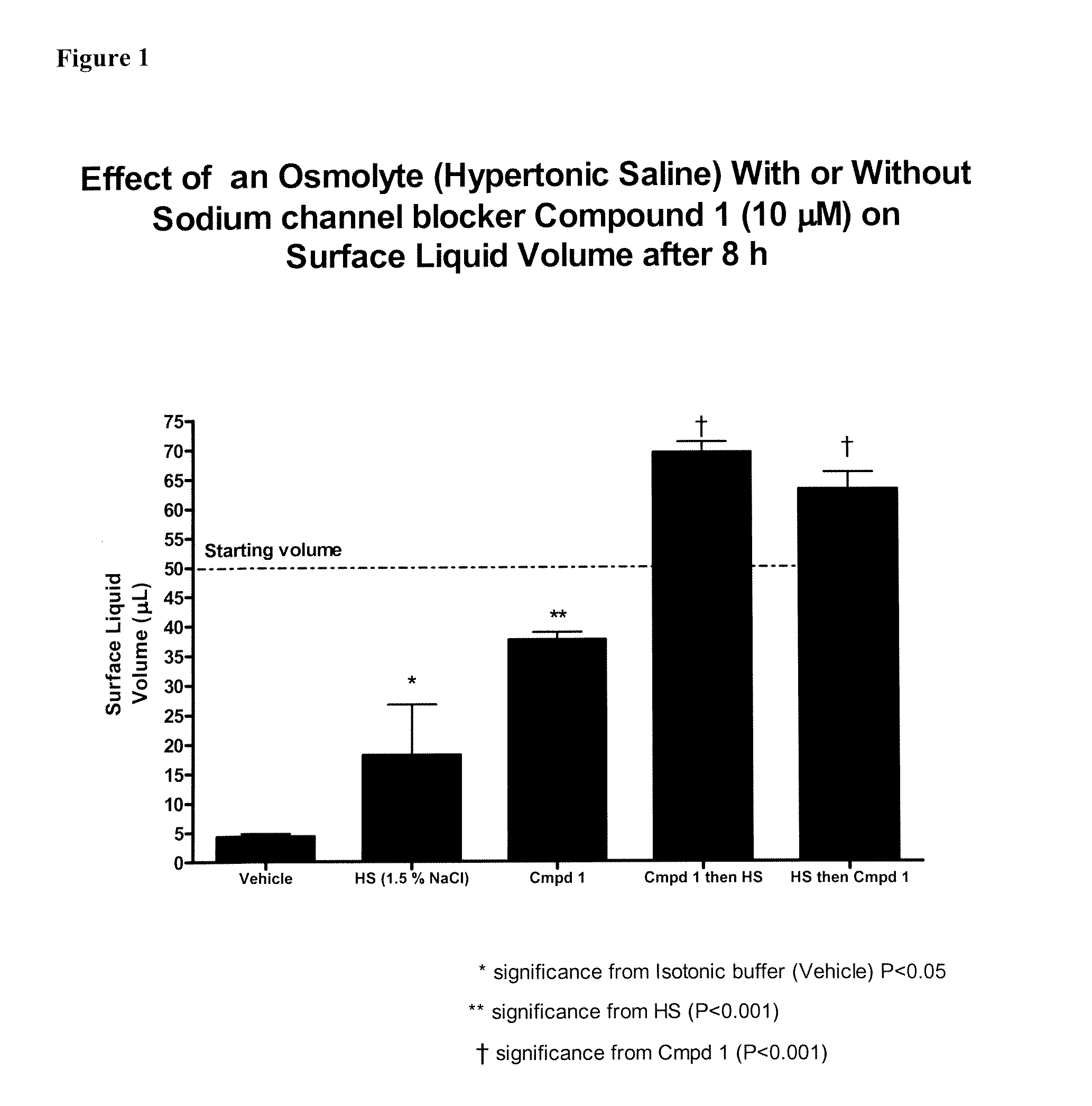
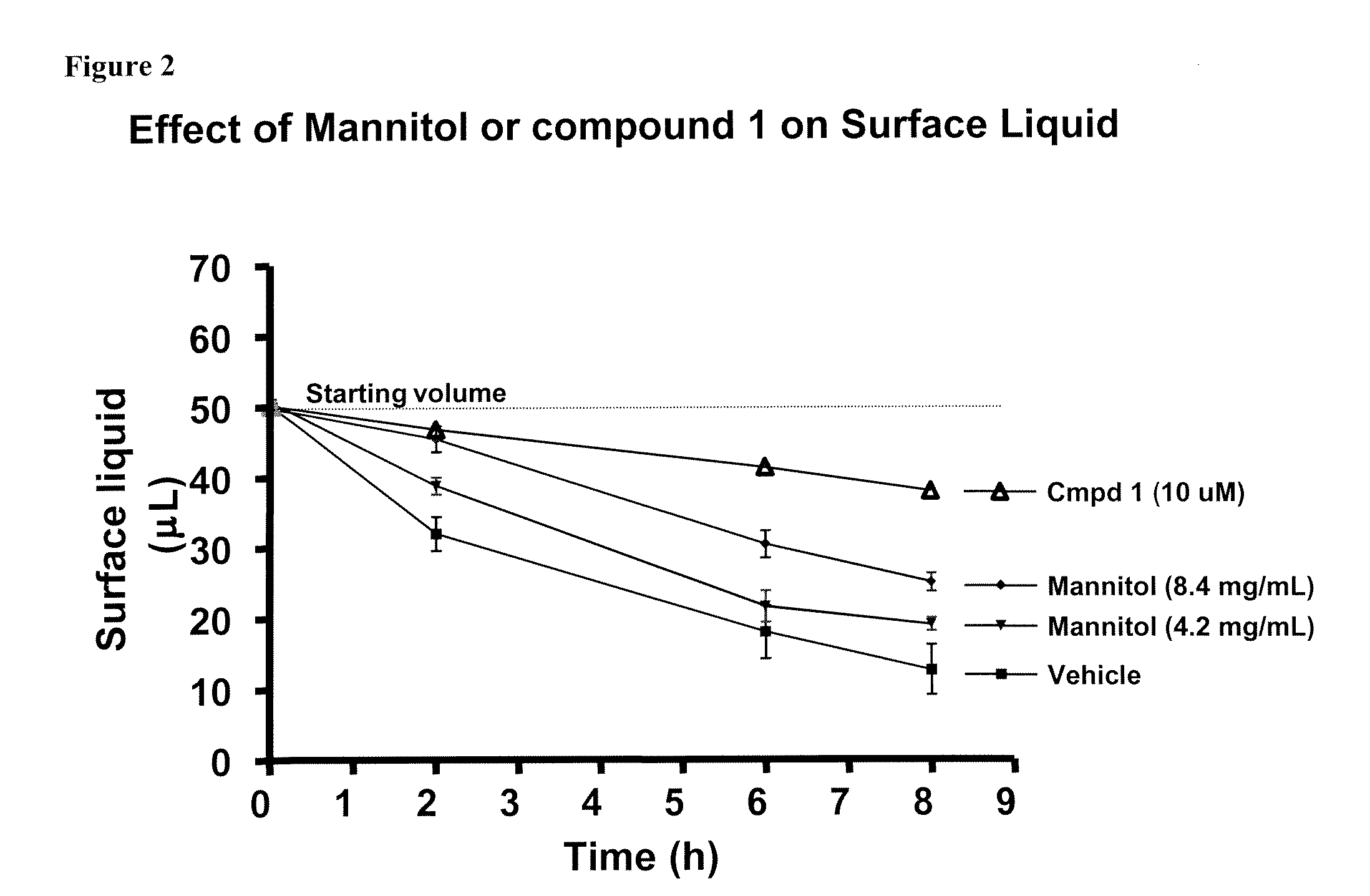
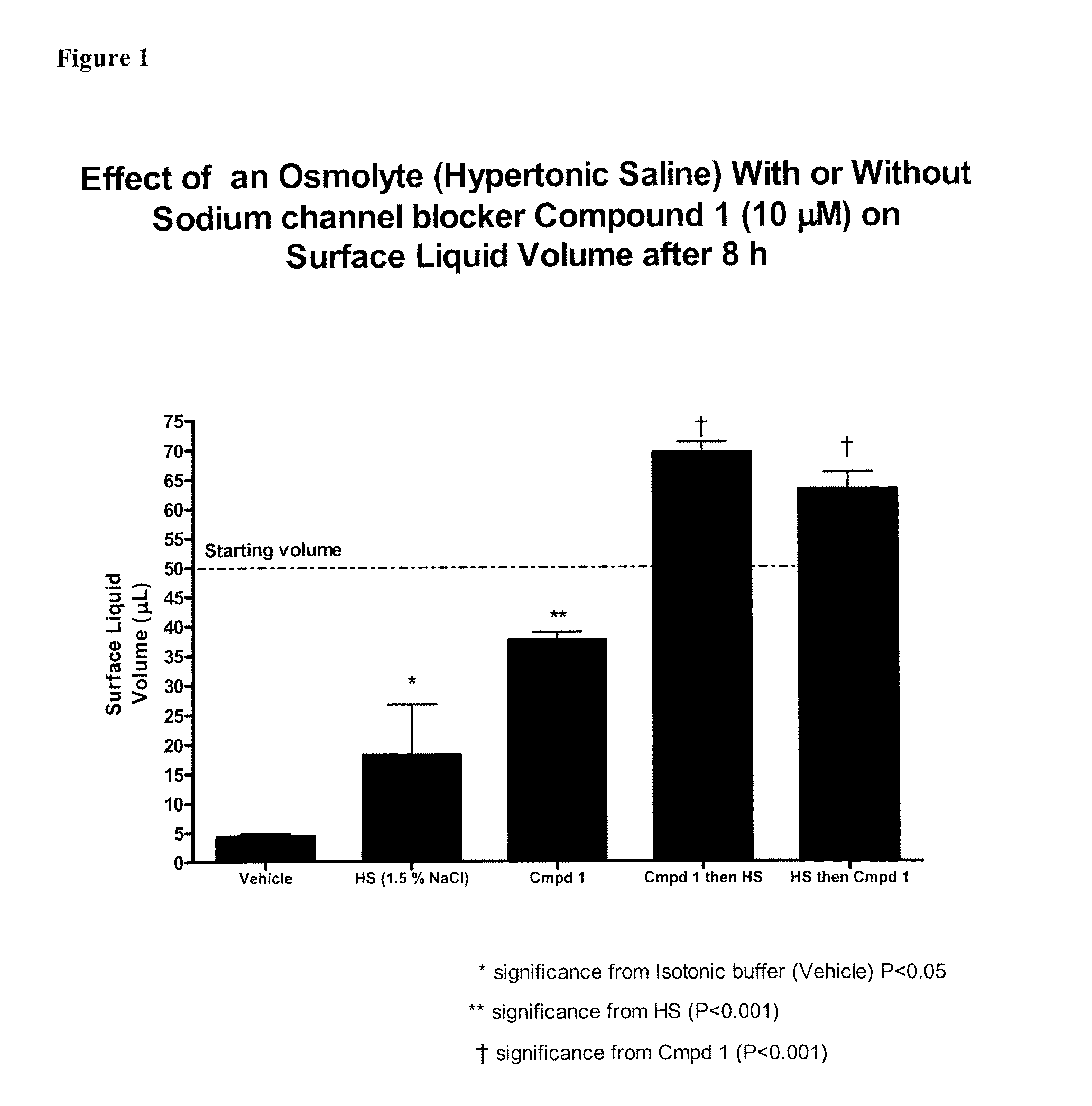
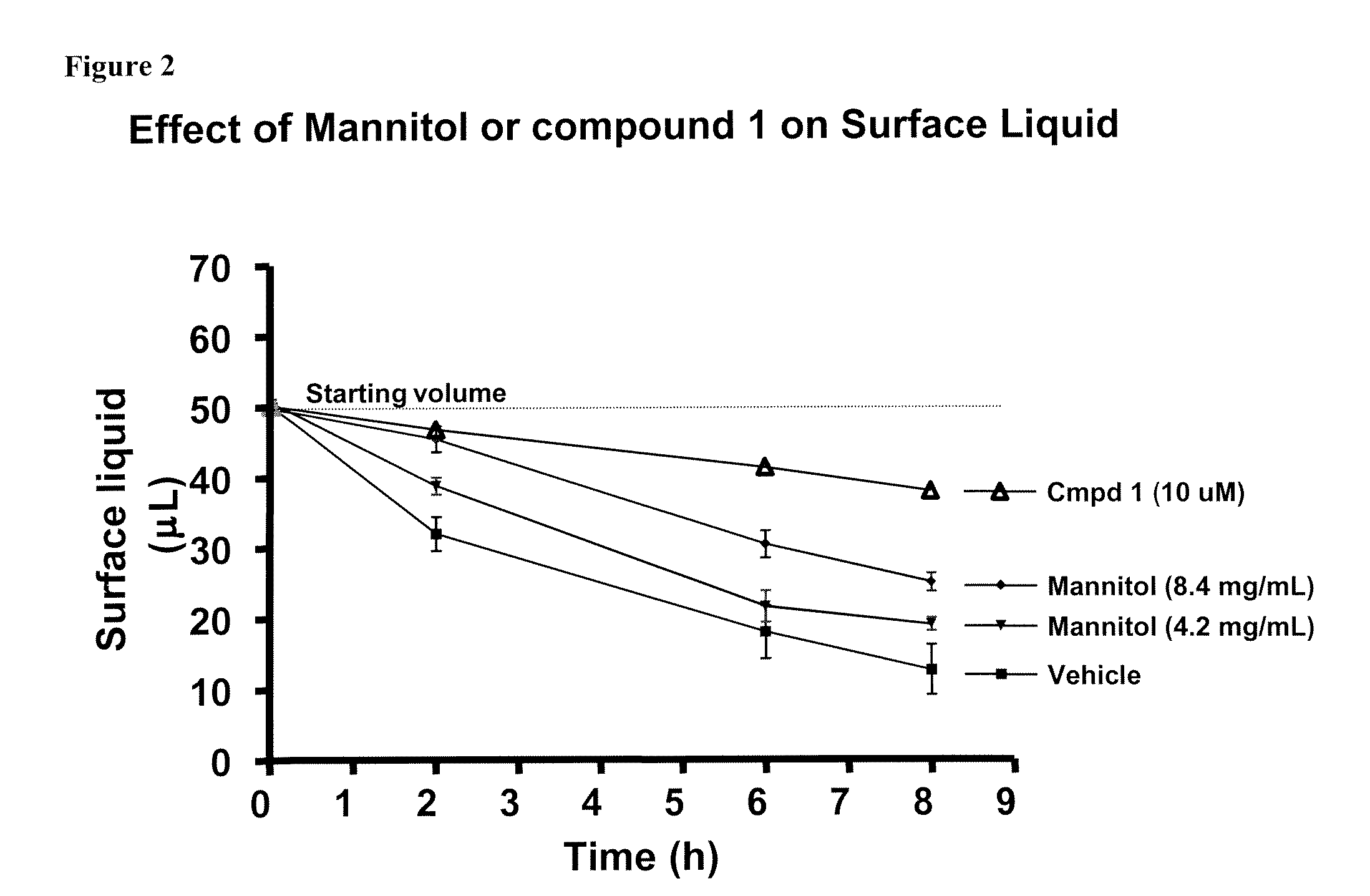
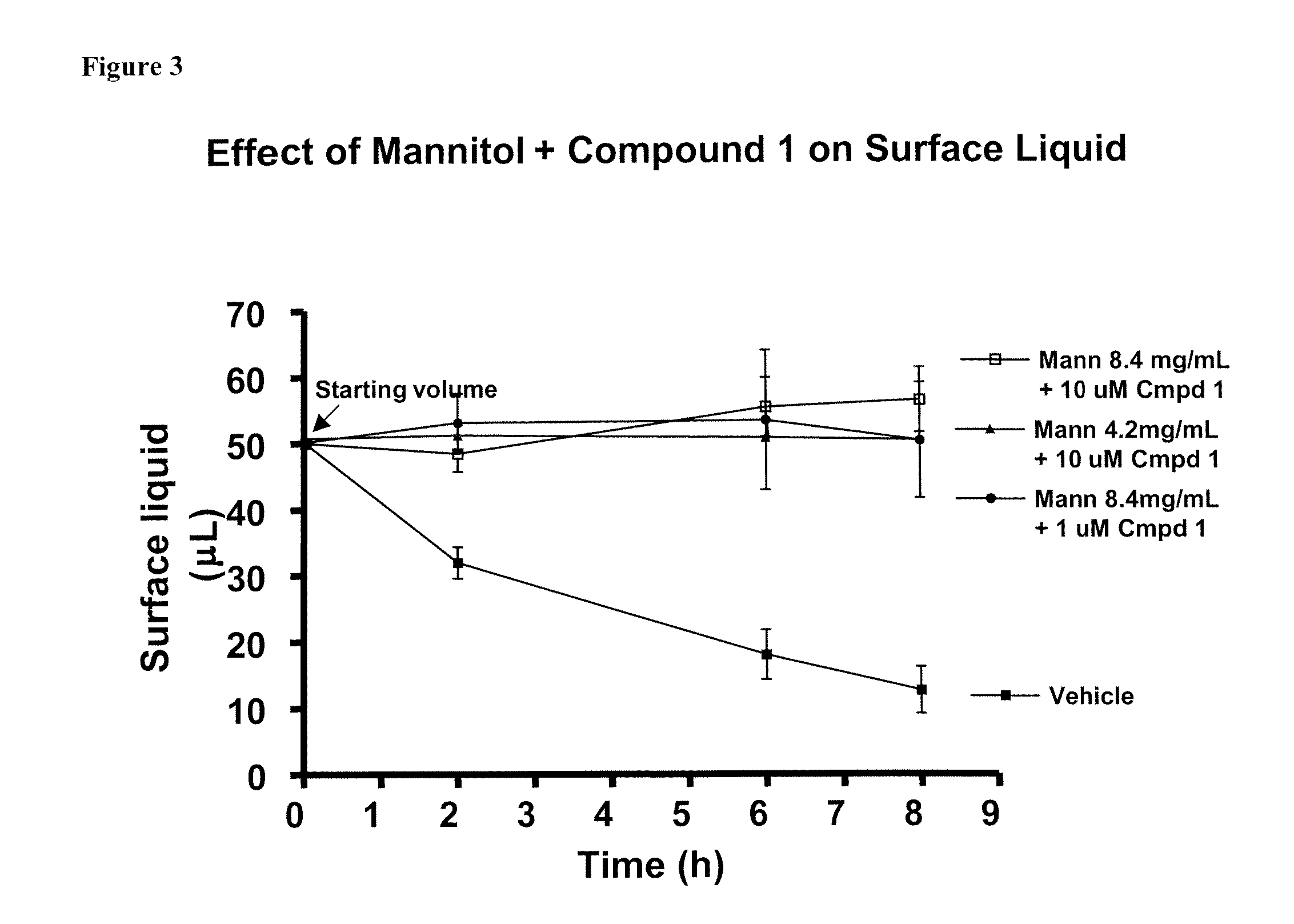
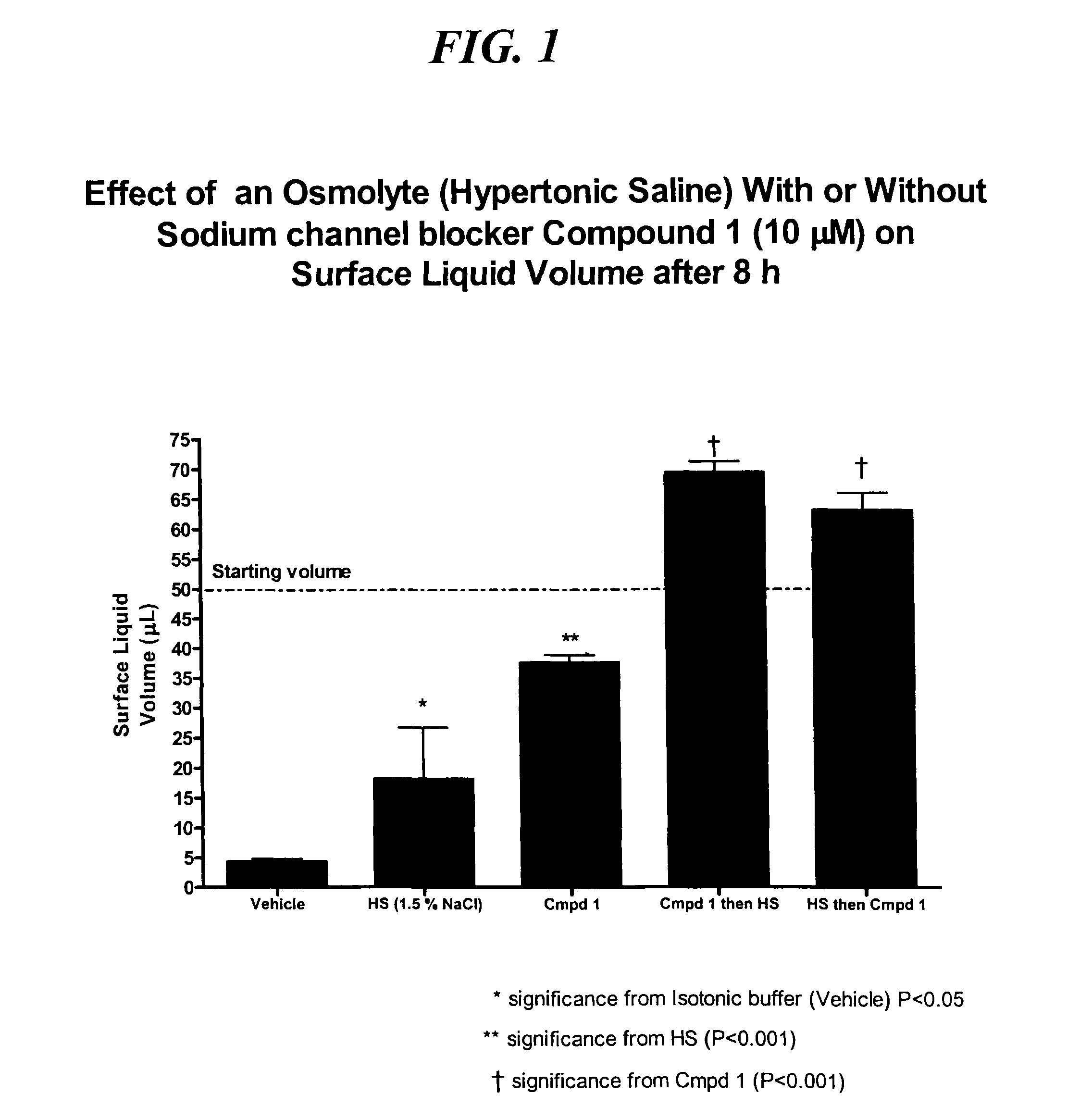
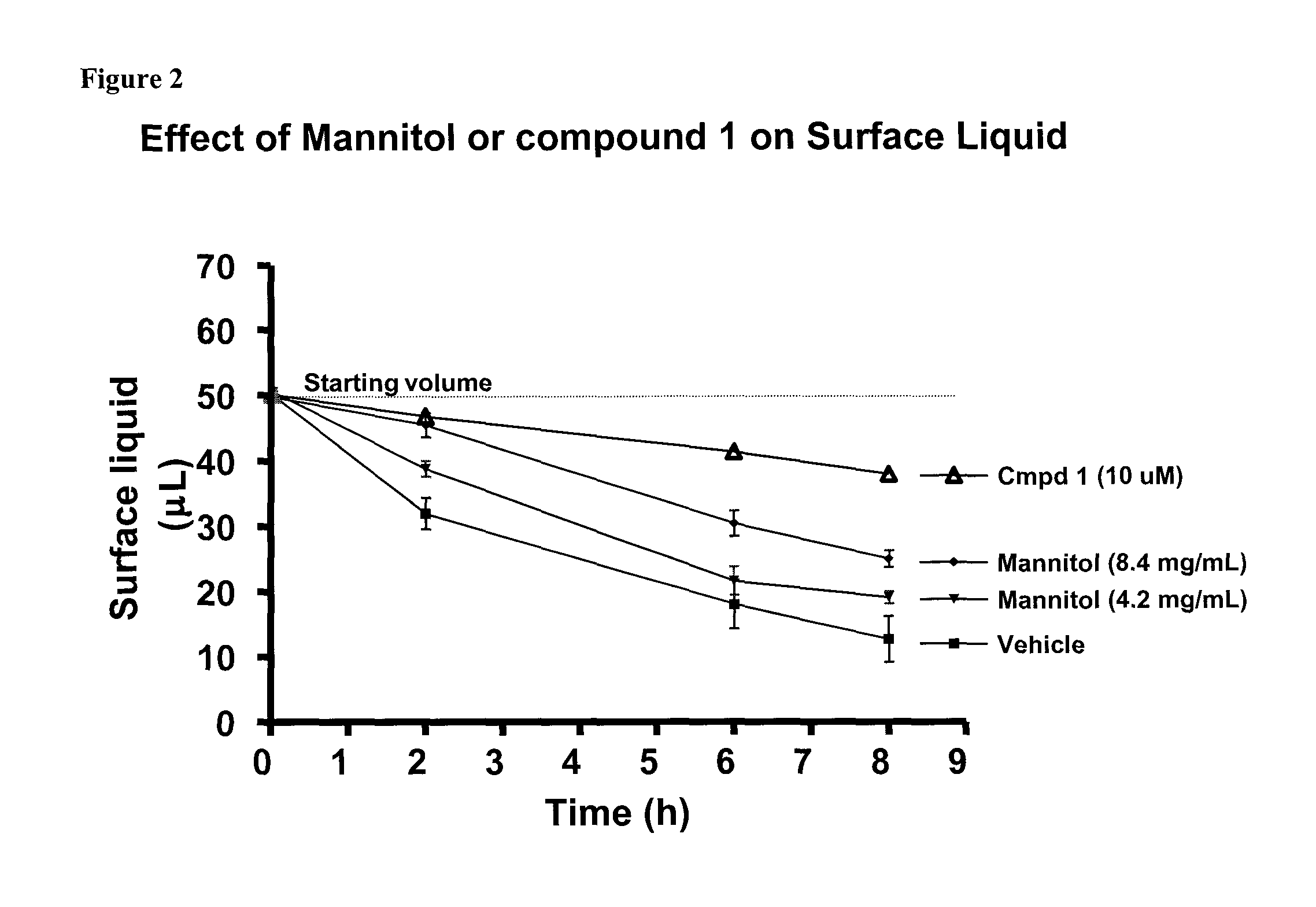
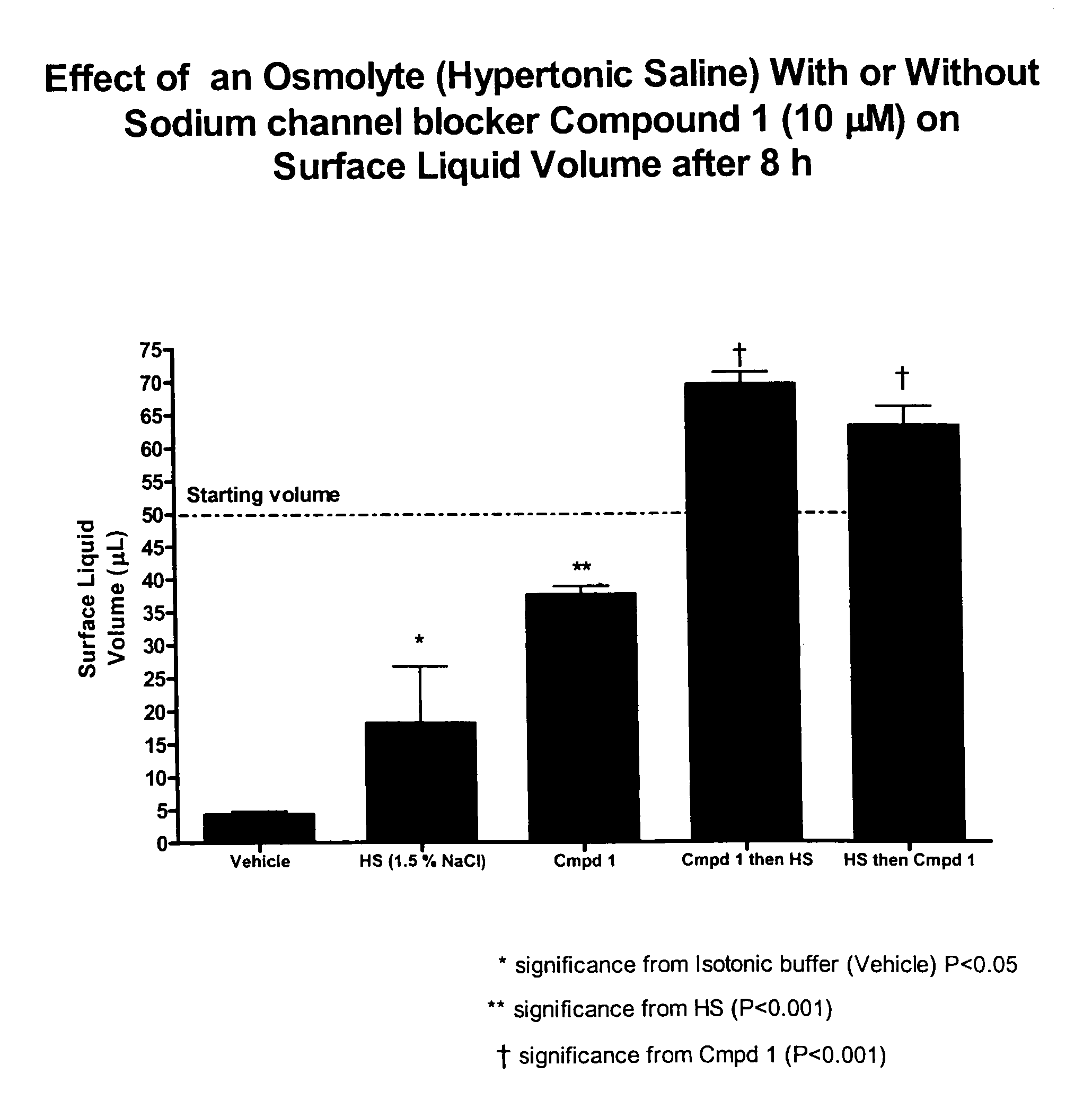
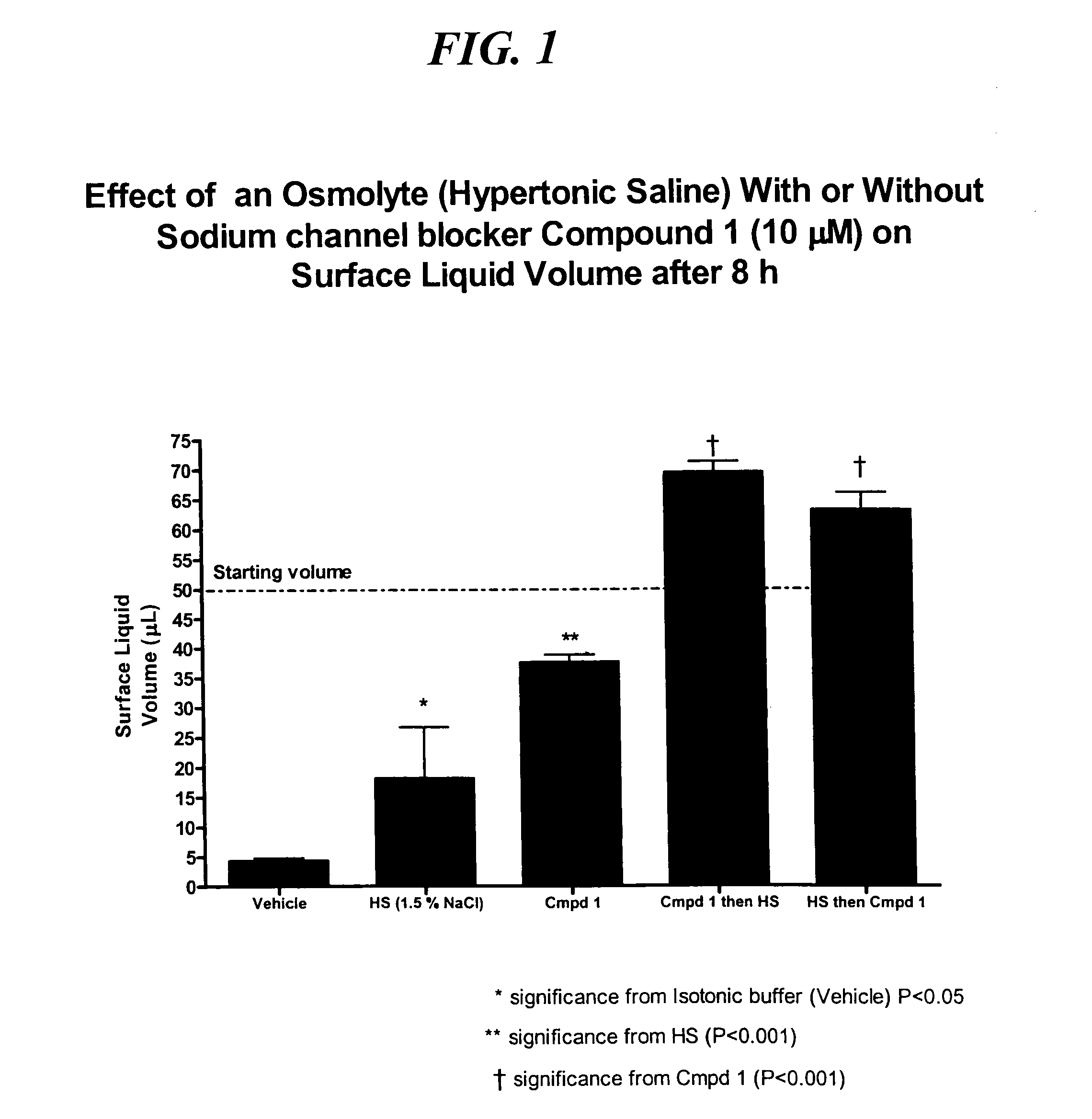
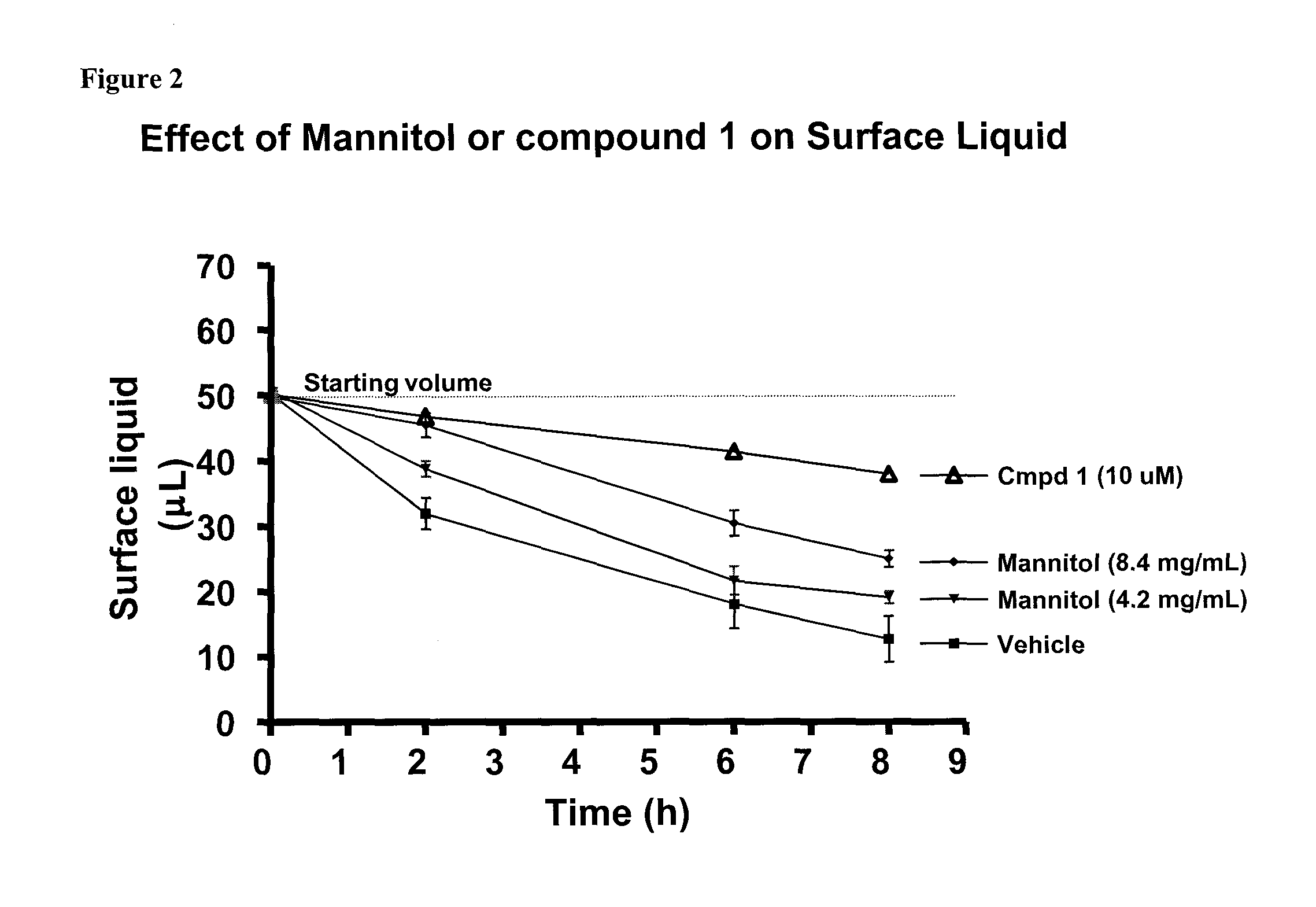
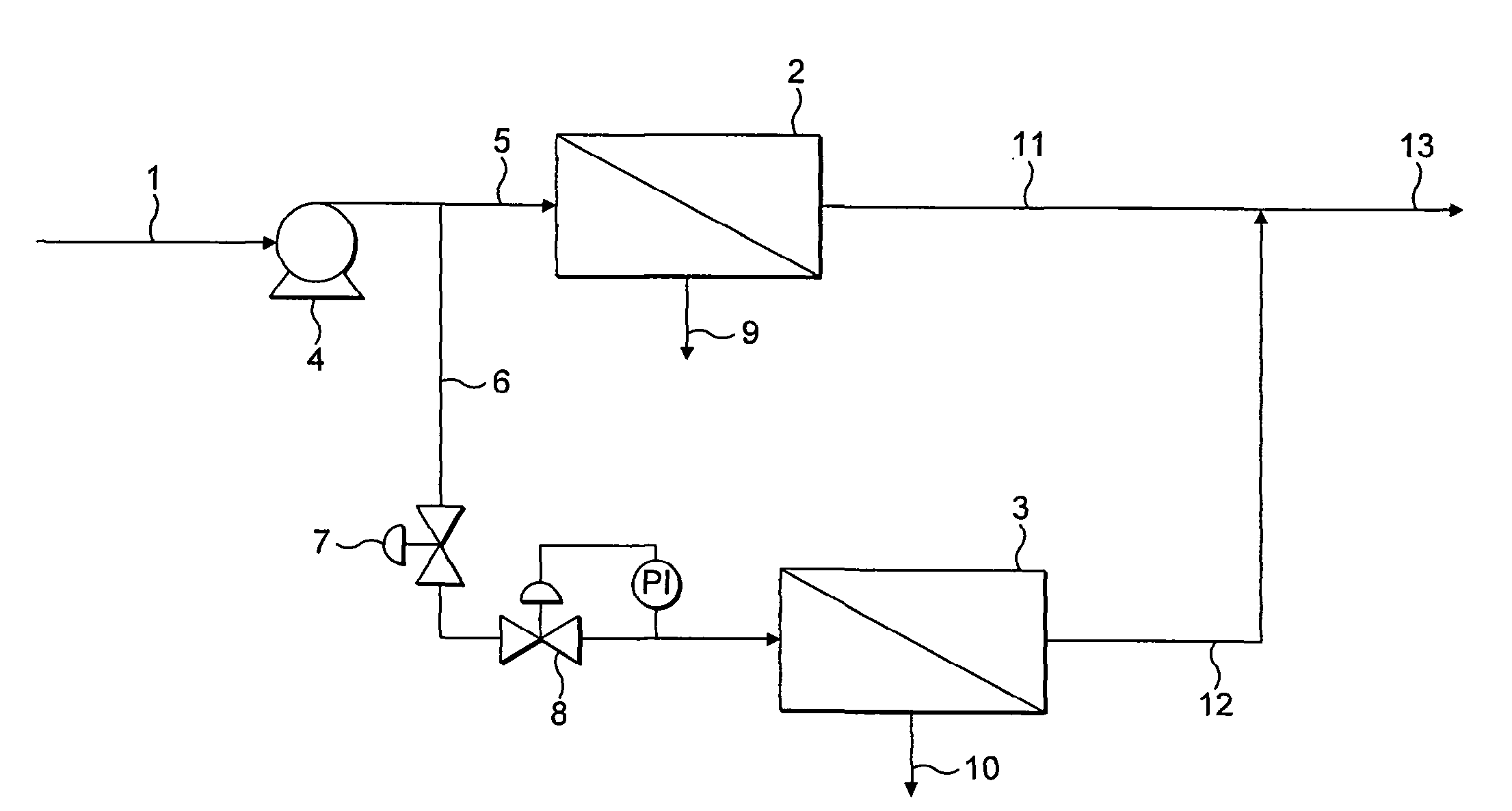
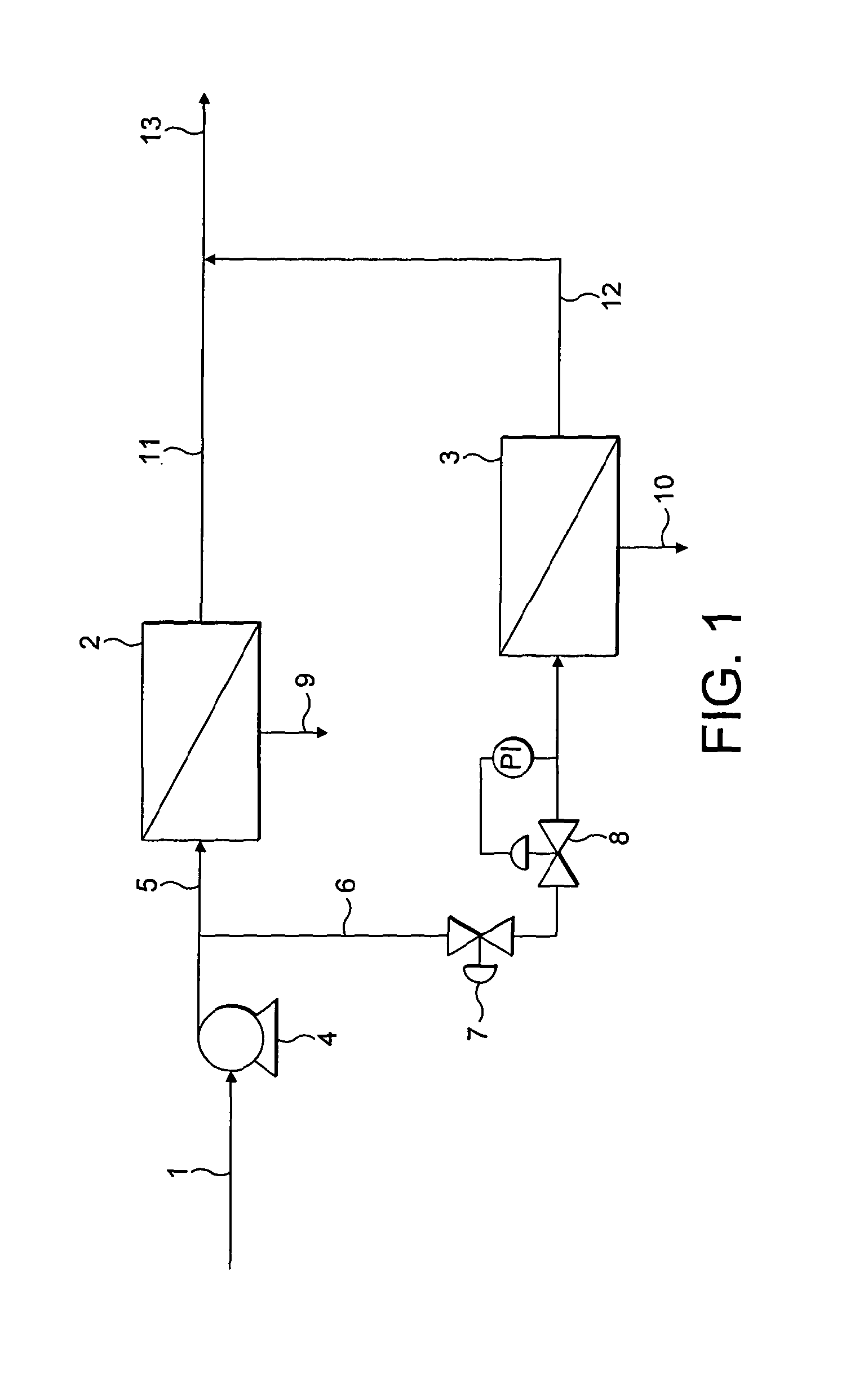
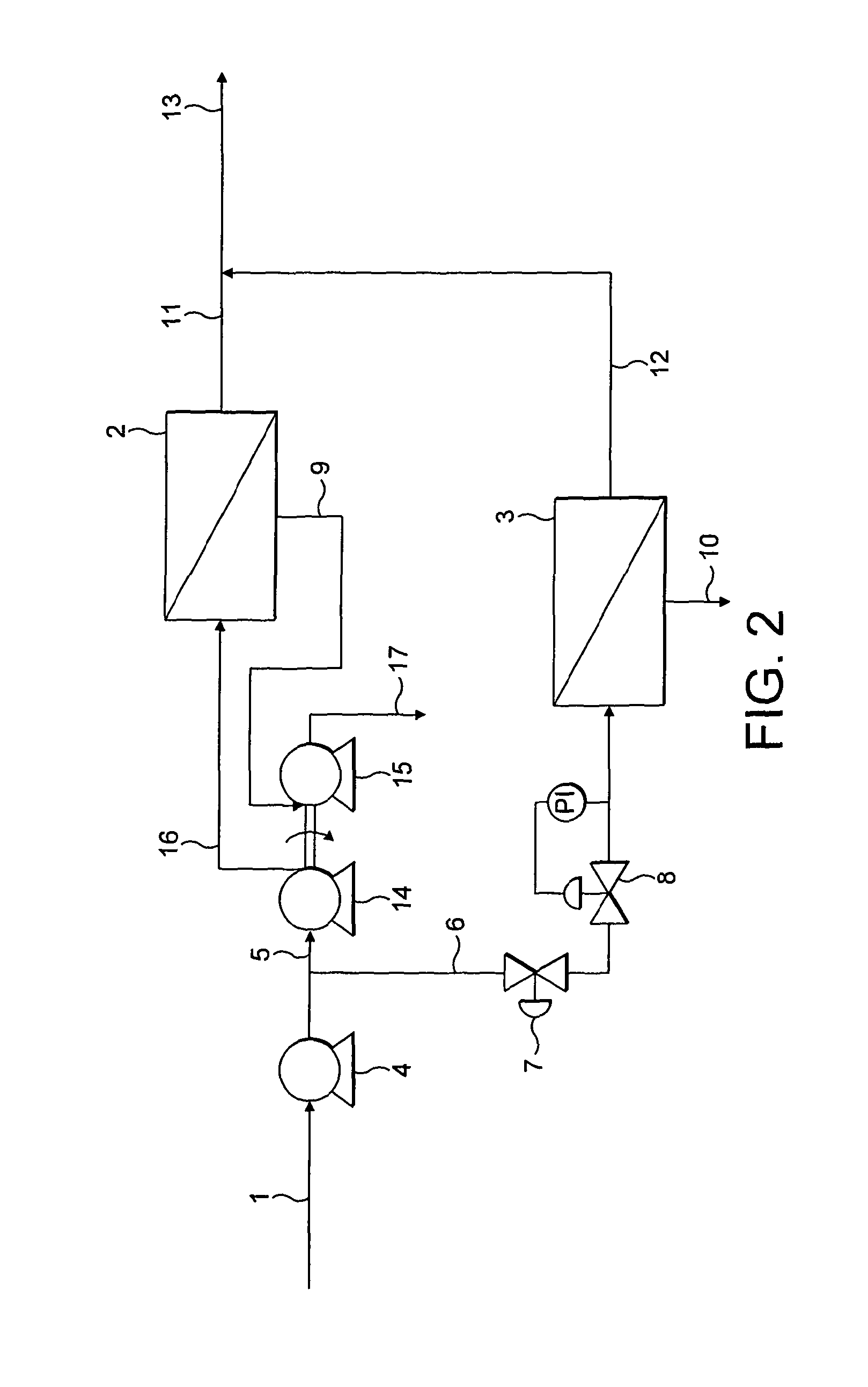
Methods of enhancing mucosal hydration and mucosal clearance by treatment with sodium channel blockers and osmolytes
ActiveUS20080090841A1More specificLess reversibleAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsOtic AgentsOsmolyte
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for treating diseases ameliorated by increased mucociliary clearance and mucosal hydration by administering an effective amount of a sodium channel blocker as defined herein and an osmolyte to a subject to a subject in need of increased mucociliary clearance and mucosal hydration.
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
Methods of enhancing mucosal hydration and mucosal clearance by treatment with sodium channel blockers and osmolytes
InactiveUS8058278B2More specificAbsorbed less rapidlyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseOsmolyte
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for treating diseases ameliorated by increased mucociliary clearance and mucosal hydration by administering an effective amount of a sodium channel blocker as defined herein and an osmolyte to a subject to a subject in need of increased mucociliary clearance and mucosal hydration.
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
Methods of enhancing mucosal hydration and mucosal clearance by treatment with sodium channel blockers and osmolytes
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for treating diseases ameliorated by increased mucociliary clearance and mucosal hydration by administering an effective amount of a sodium channel blocker as defined herein and an osmolyte to a subject to a subject in need of increased mucociliary clearance and mucosal hydration.
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
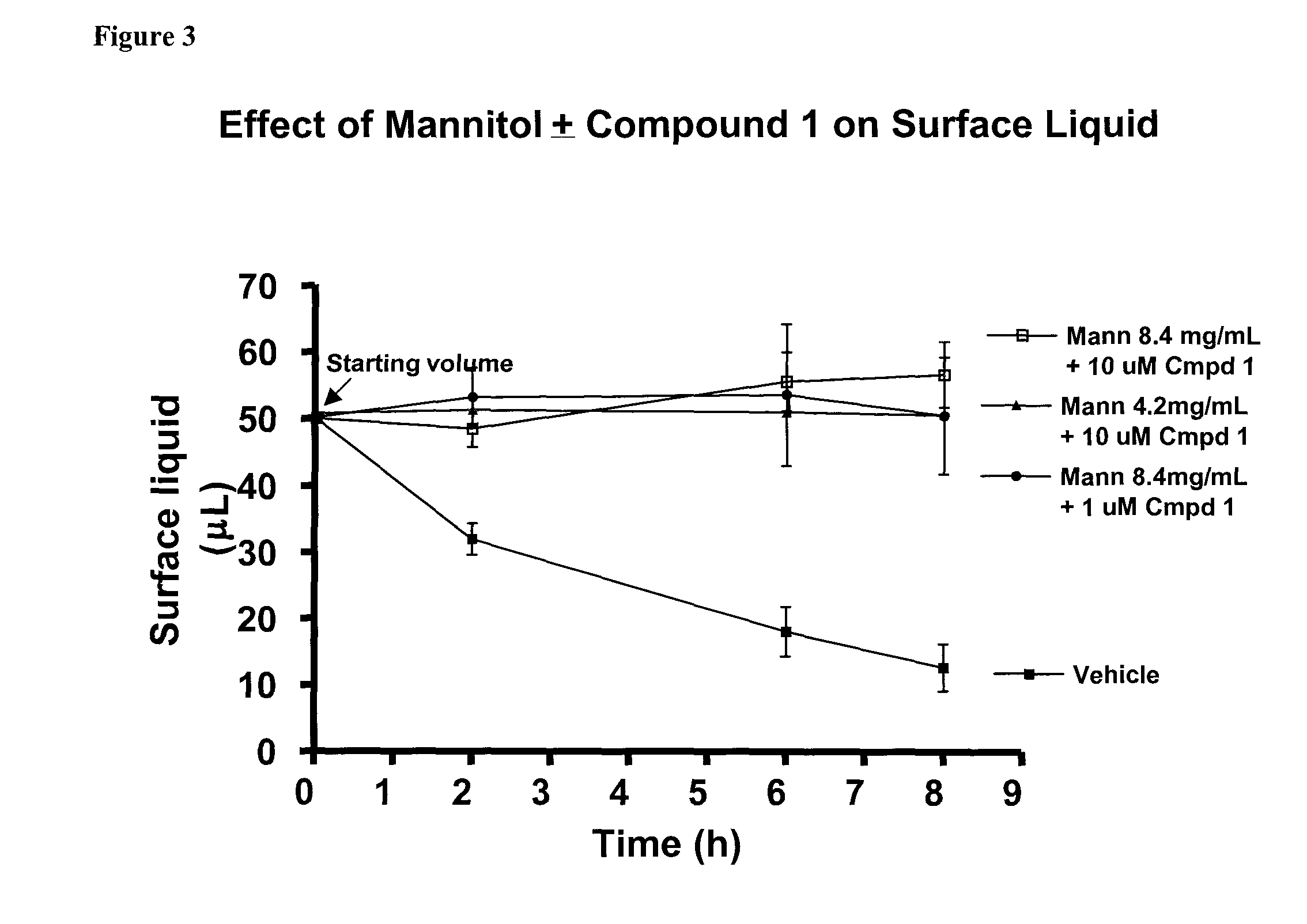
Transdermal Drug Delivery using an Osmolyte and Vasoactive Agent
ActiveUS20100076035A1Increase blood flowImprove permeabilityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsOtic AgentsActive agent
Owner:BIOCHEMICS +1
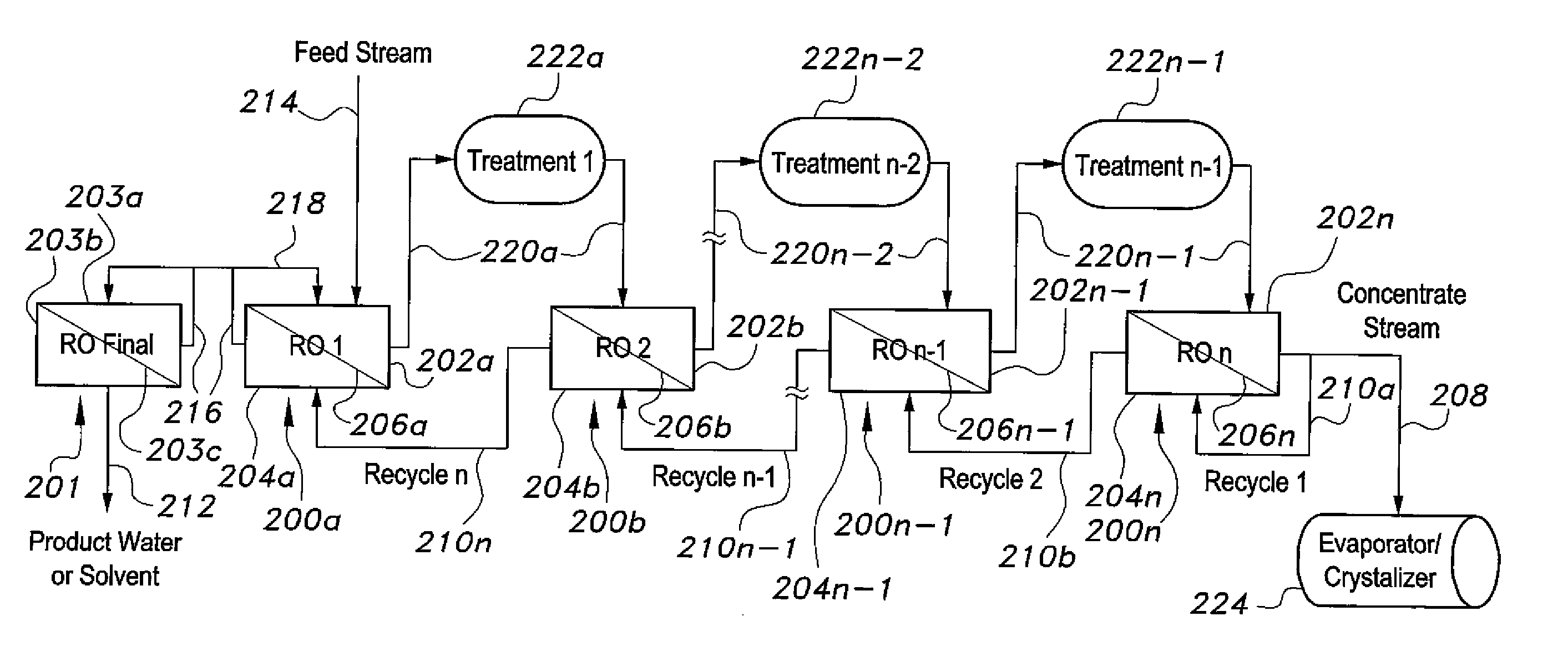
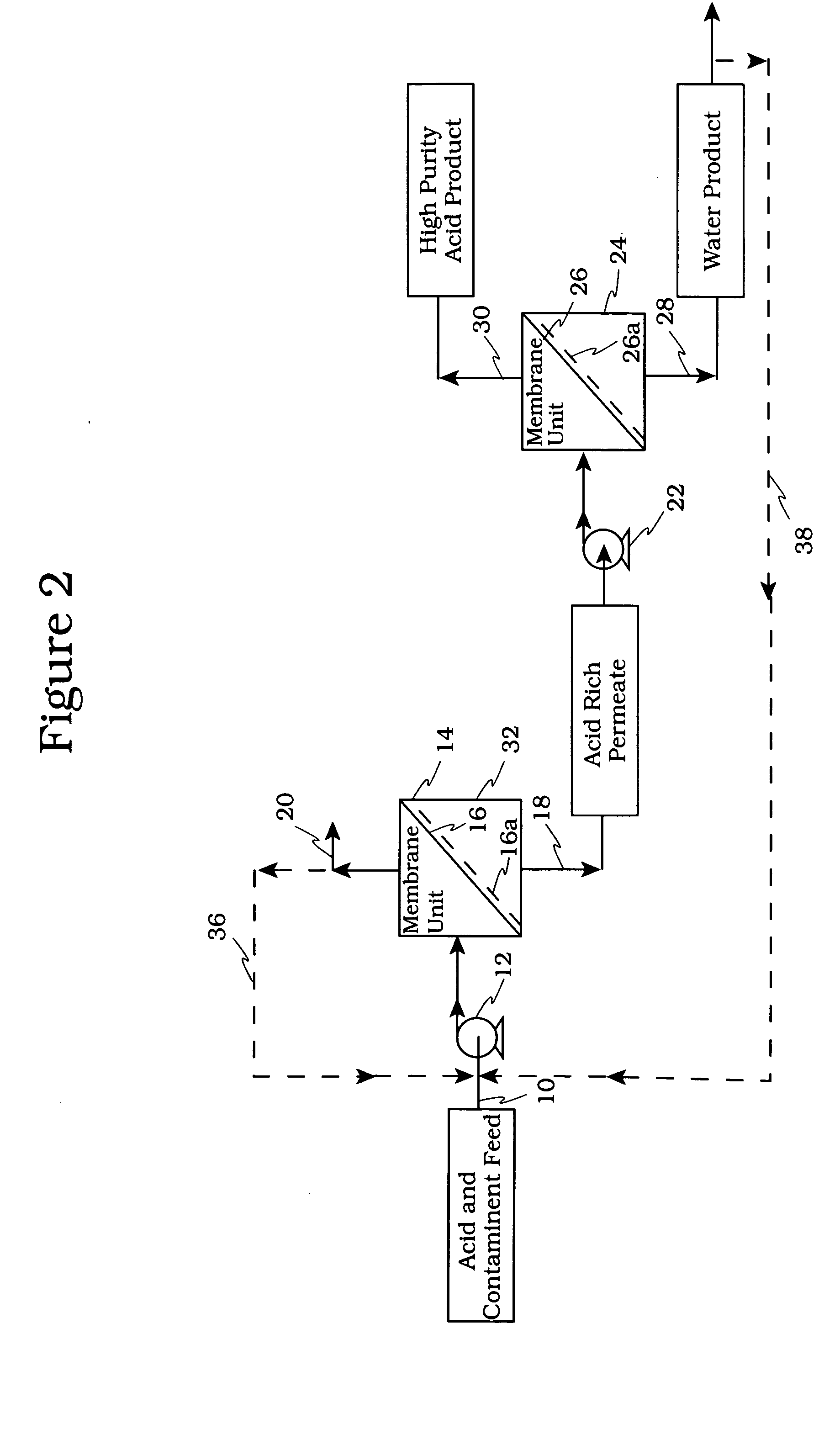
Method for purifying liquids
ActiveUS9206060B1Reduce gradientHigh rejectionMembranesGeneral water supply conservationSalt waterReverse osmosis
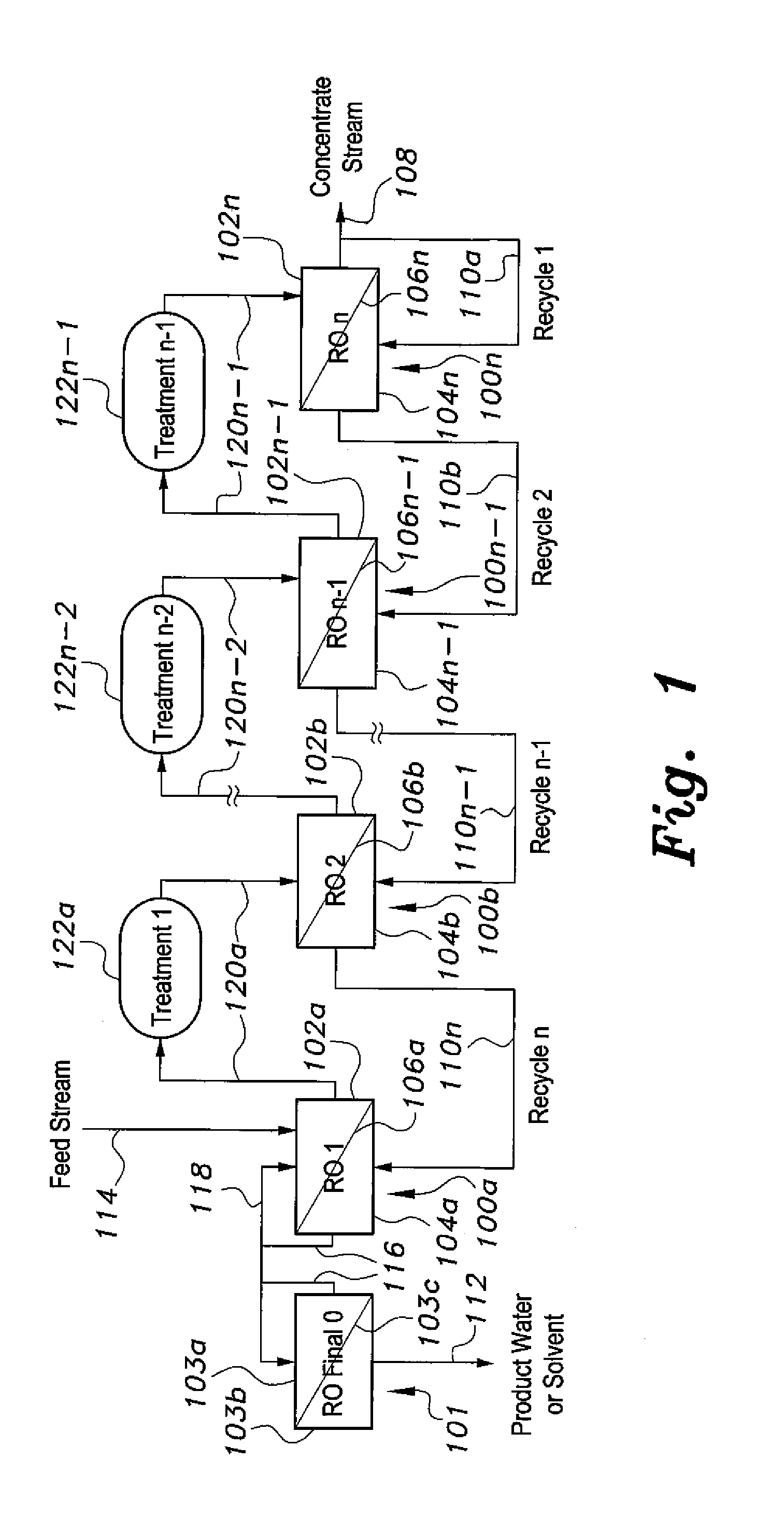
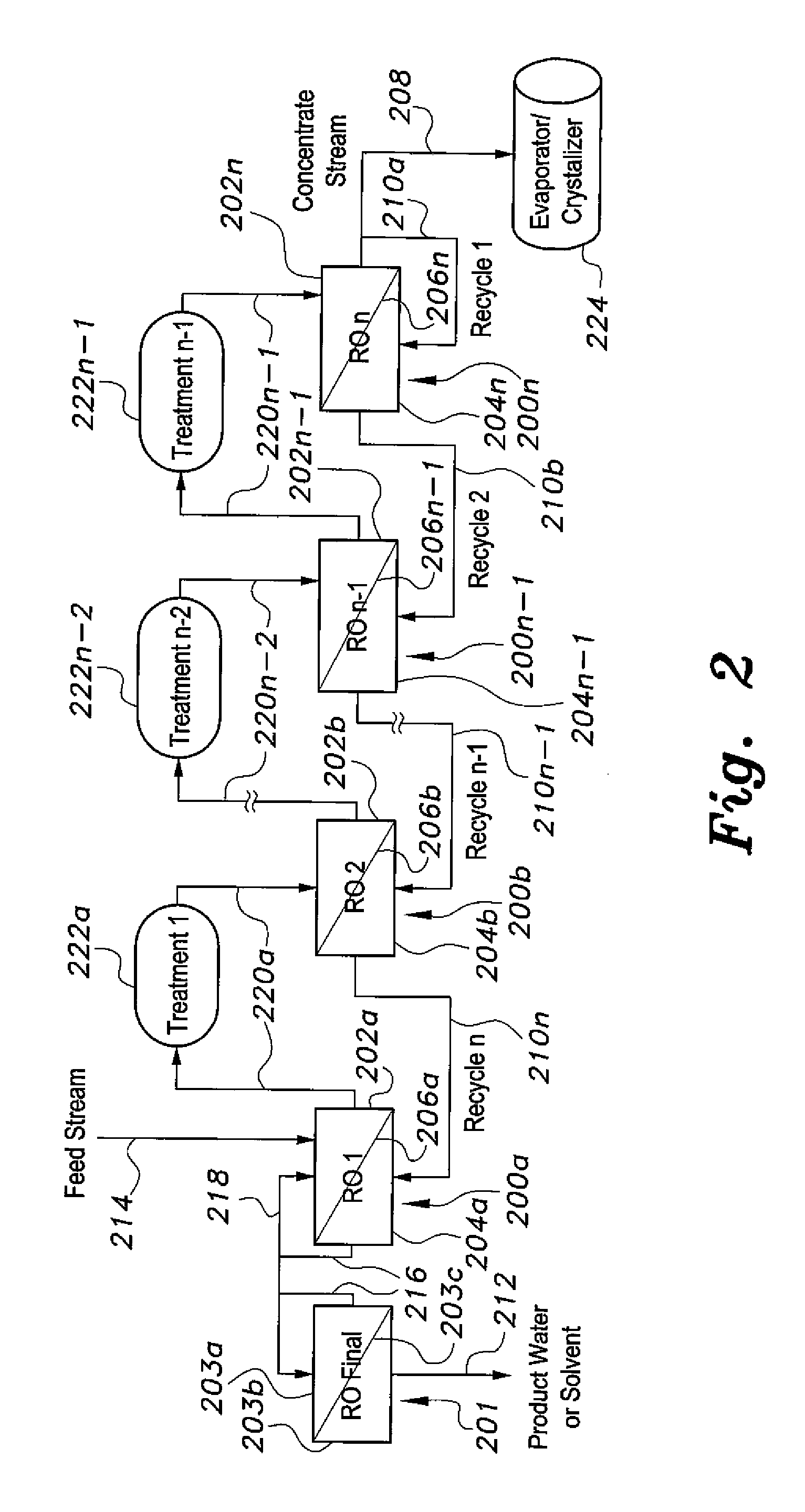
The method for purifying liquids purifies a saline liquid, e.g., salt water, using a plurality of first phase reverse osmosis (RO) units and at least one final phase reverse osmosis unit. The plurality of first phase reverse osmosis units are arranged in series. At least some of the concentrate in a last reverse osmosis unit of the series is recycled back to the permeate or output side of that unit to provide a mixed permeate. The mixed permeate is then passed successively to the permeate side of each preceding reverse osmosis unit in the series. This increases the salt content of the liquid in the permeate side of each phase, thus reducing the concentration differential across reverse osmosis membranes of the first phase reverse osmosis units.
Owner:AL BAKRI SAMI ABDULRAHMAN
Inhaled hypertonic saline delivered by a heated nasal cannula
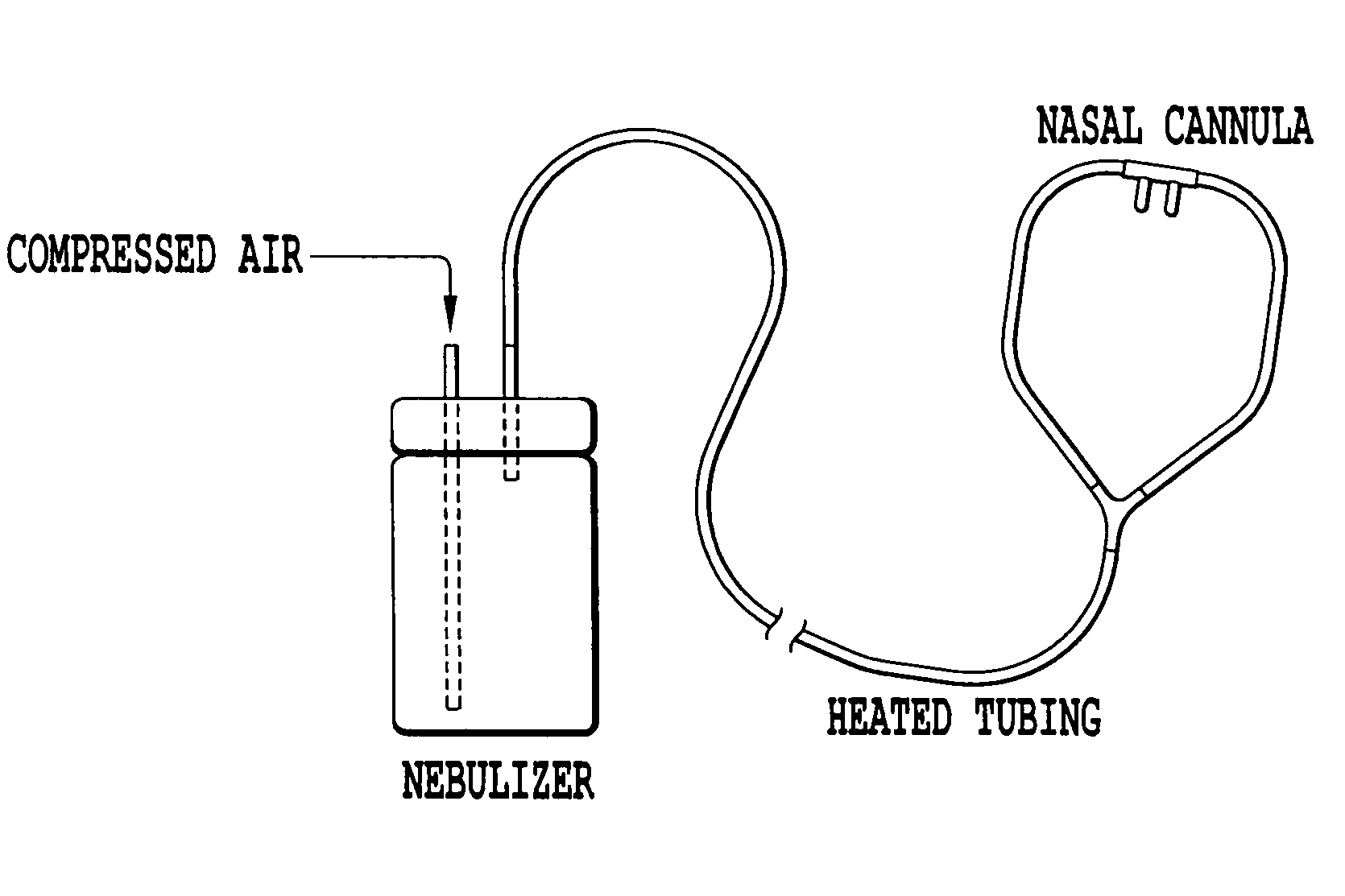
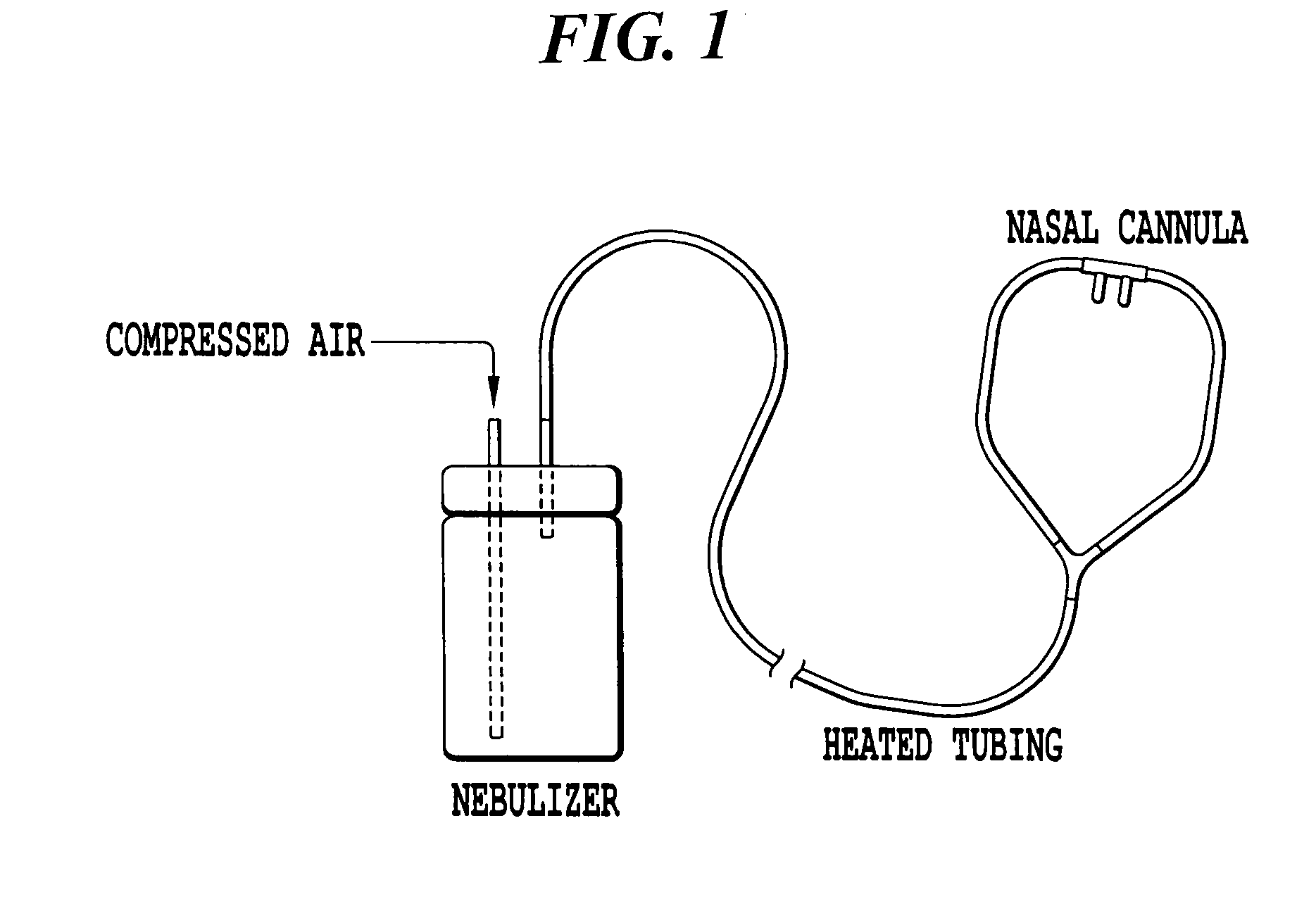
The invention described herein is directed to method of treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, comprising administering an effective amount of an osmolyte by at least one nasal cannula to a subject in need thereof. Also provided is a nasal cannula system for delivering an osmolyte, comprising a nebulizer and tubing having two ends, where the first end of the tubing is connected to the nebulizer and the second end of the tubing is tapered to fit in the nostril of a subject.
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
Methods of enhancing mucosal hydration and mucosal clearance by treatment with sodium channel blockers and osmolytes
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for treating diseases ameliorated by increased mucociliary clearance and mucosal hydration by administering an effective amount of a sodium channel blocker as defined herein and an osmolyte to a subject to a subject in need of increased mucociliary clearance and mucosal hydration.
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
Method for preparing potato crispy chips through osmotic dehydration and hot air and microwave combined drying
The invention discloses a method for preparing potato crispy chips through osmotic dehydration and hot air and microwave combined drying, and belongs to the technical field of fruit and vegetable processing. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: cleaning, peeling and slicing potatoes (the thickness of the slices is 4-8mm), blanching for deactivating enzyme (at the temperature of between 90 and 110DEG C), performing osmotic dehydration (penetrating fluid, namely a 40 mass percent sucrose solution is prepared, a mass ratio of the potato crispy chips to the penetrating fluid is 1:(10-12), the soaking temperature is 30-40DEG C, and the soaking time is 30 to 40 minutes), draining water, drying with hot air at the temperature of between 60 and 70DEG C at the air speed of 1-3m / s to obtain a semi-finished product of which the water content is 30 to 40 percent, and performing microwave drying (1-3W / g) finally to obtain the finished product of which the water content is 2 to 5 percent. A new process of assisting in dehydrating through osmotic soaking and performing normal-pressure hot air and vacuum microwave combined drying is adopted, the obtained potato product has nutrient components and color which are maintained well, has crispy texture and avoids defects of high oil content and greasy mouthfeel of a fried food, the production cost is far lower than that of a vacuum freeze-drying product, and the method has the characteristics of short production period, low cost, and good product quality.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Raw trichoderma asperellum strain, bactericide and application of raw trichoderma asperellum strain and bactericide in treatment of organic waste
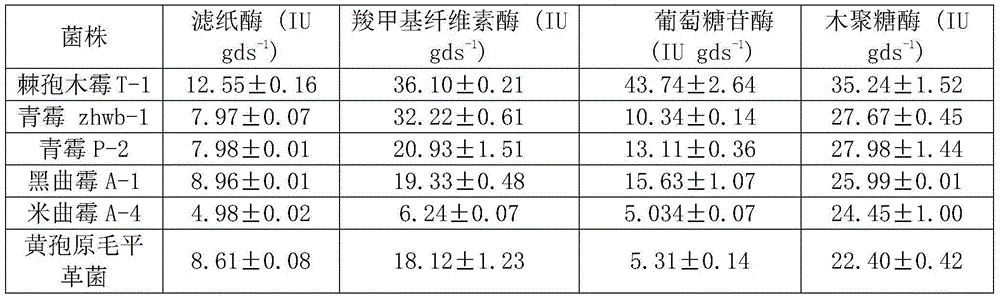
ActiveCN104450530AGrow fastStrong sporulation abilityBiocideBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a biocontrol strain, namely trichoderma asperellum T-1, for highly producing composite cellulose degrading enzyme. The trichoderma asperellum T-1 is preserved at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on September 24, 2014; and the preservation number is CGMCC 9722. The invention also provides a waste composting bactericide prepared from the trichoderma asperellum T-1 and an application of the waste composting bactericide in treatment of the organic waste. The trichoderma asperellum T-1 provided by the invention is rapid in growth, high in spore-producing ability, and high pH tolerance; a plurality of cellulose materials can be taken as substrates; and the trichoderma asperellum T-1 is a member of biocontrol bacteria, and can be applied to planting of crops to prevent diseases. By adding the trichoderma asperellum T-1 provided by the invention to the organic waste, the penetrating fluid generated by waste composting can be reduced; the degradation efficiency of the cellulose materials in the waste can be improved; and the quality of the waste composting product is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Systemic plant conditioning composition
ActiveUS20070104751A1Improve availabilityFacilitate uptakeBiocideInorganic boron active ingredientsMedicineWhole body
This invention relates to compositions and methods facilitating availability, uptake and translocation of active ingredients in plants. More specifically, this invention relates to the surprising discovery that the application to the roots, such as administration to the soil surrounding plants, of two or more osmolytes in combination with an active ingredient, either simultaneously or within a short time of each other, results in an induction of translocation of active ingredient from the roots systemically into the plant.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
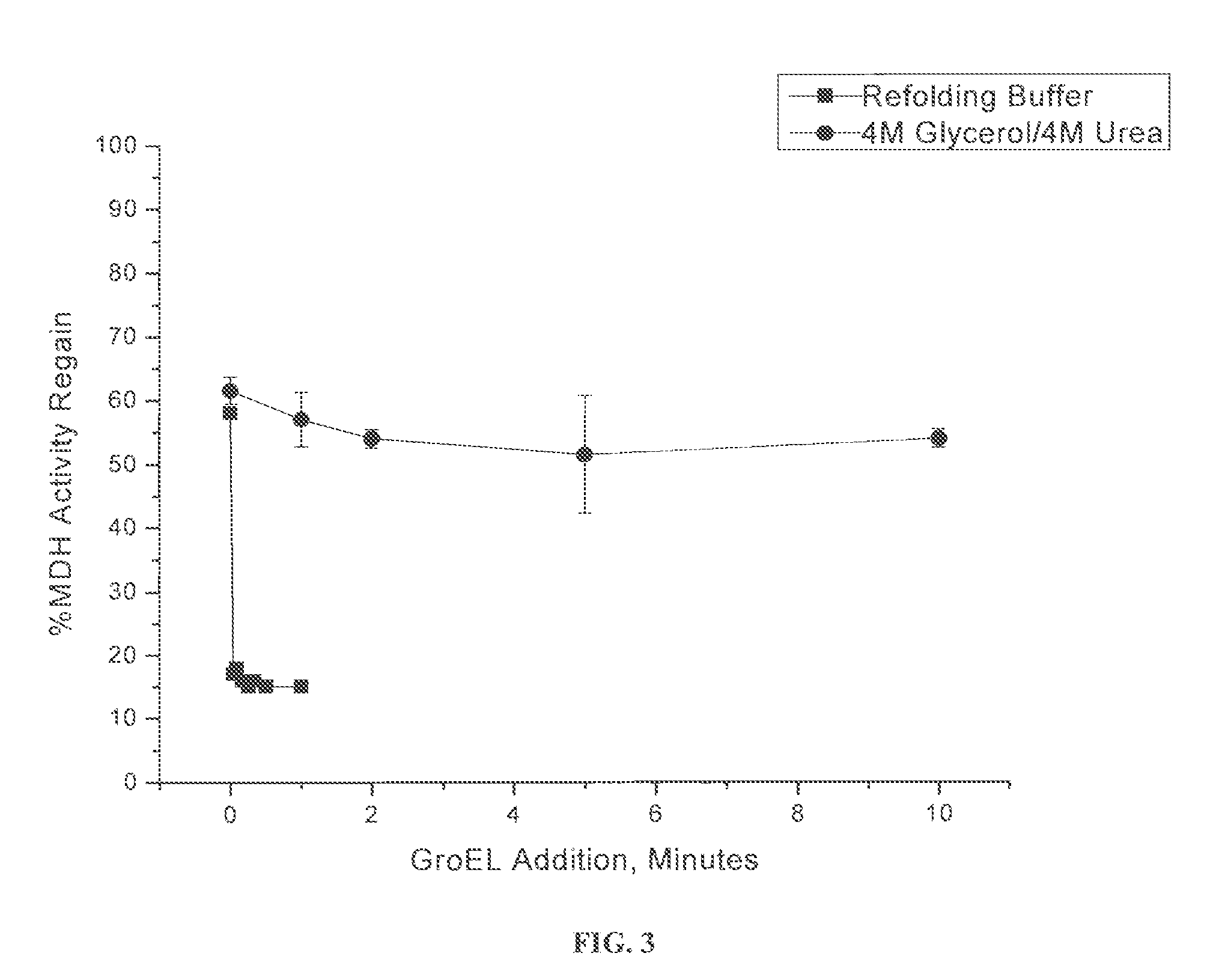
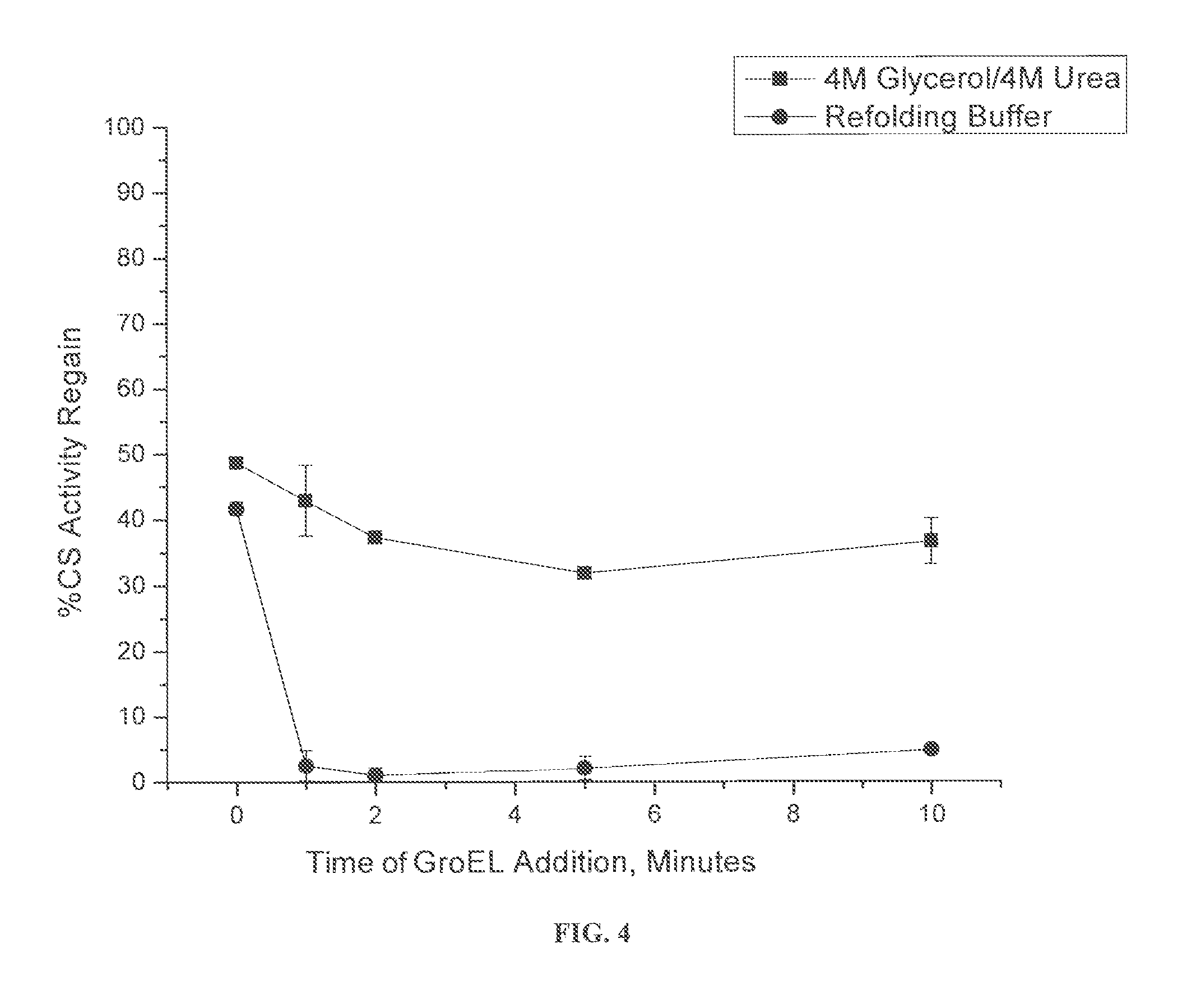
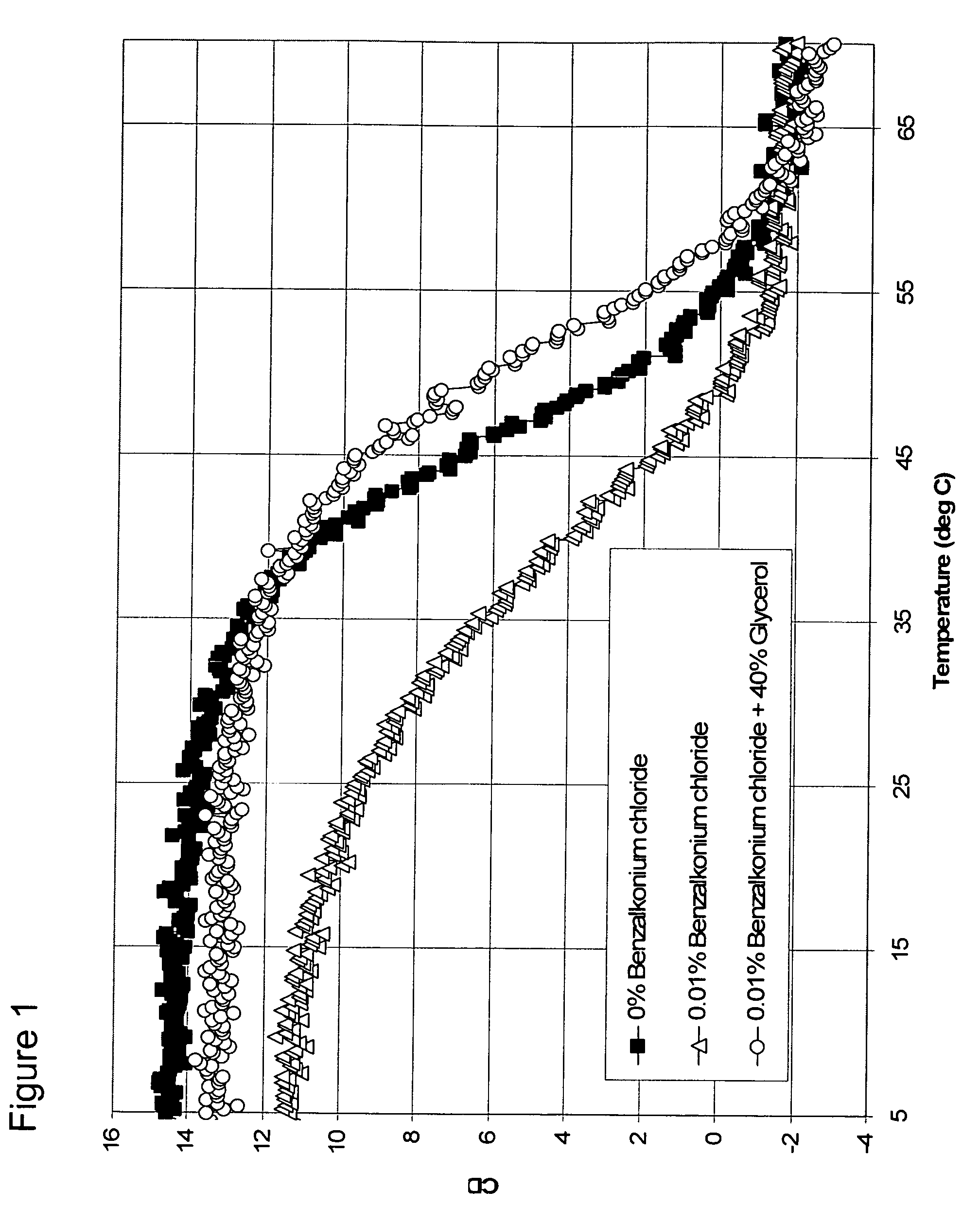
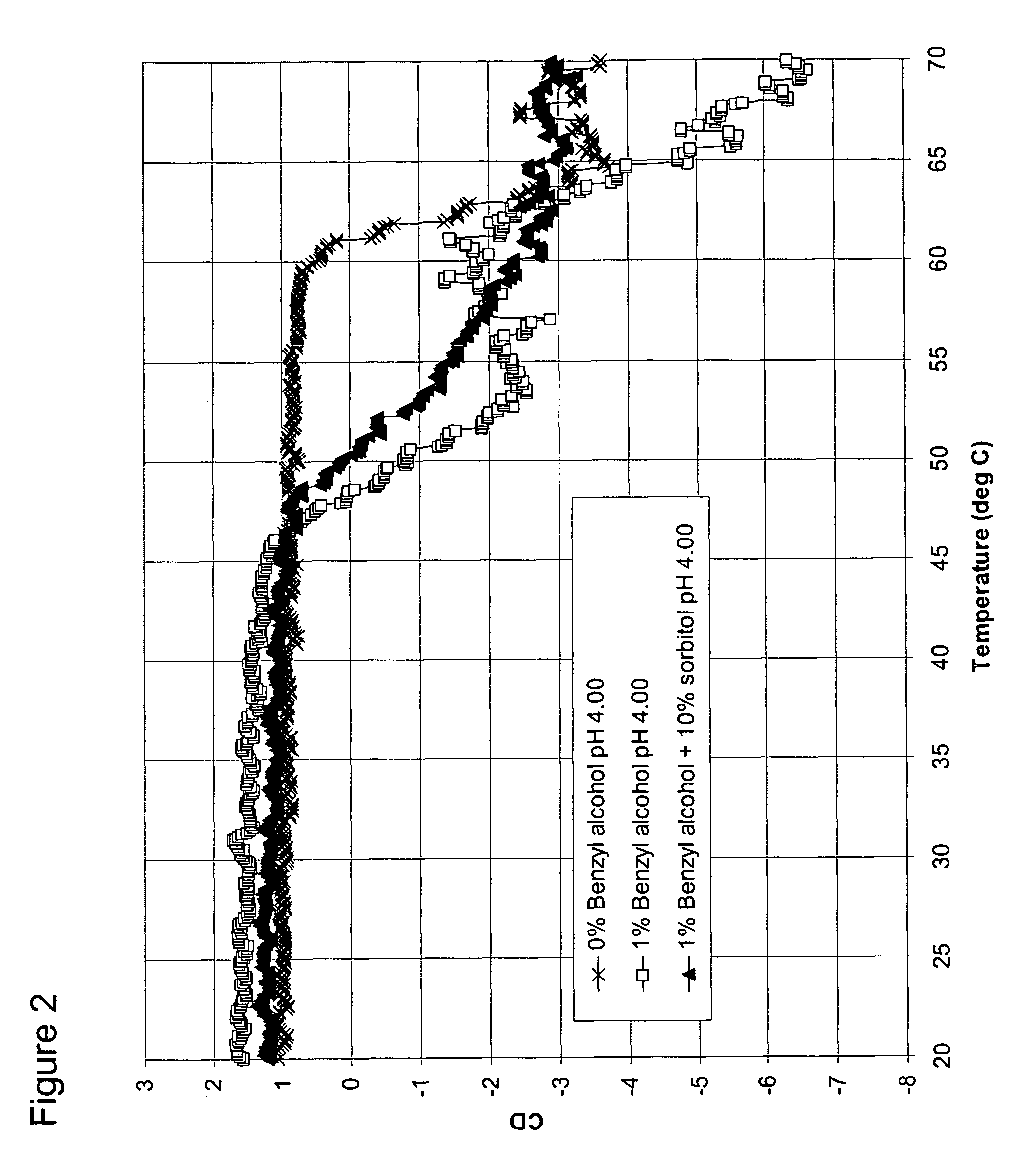
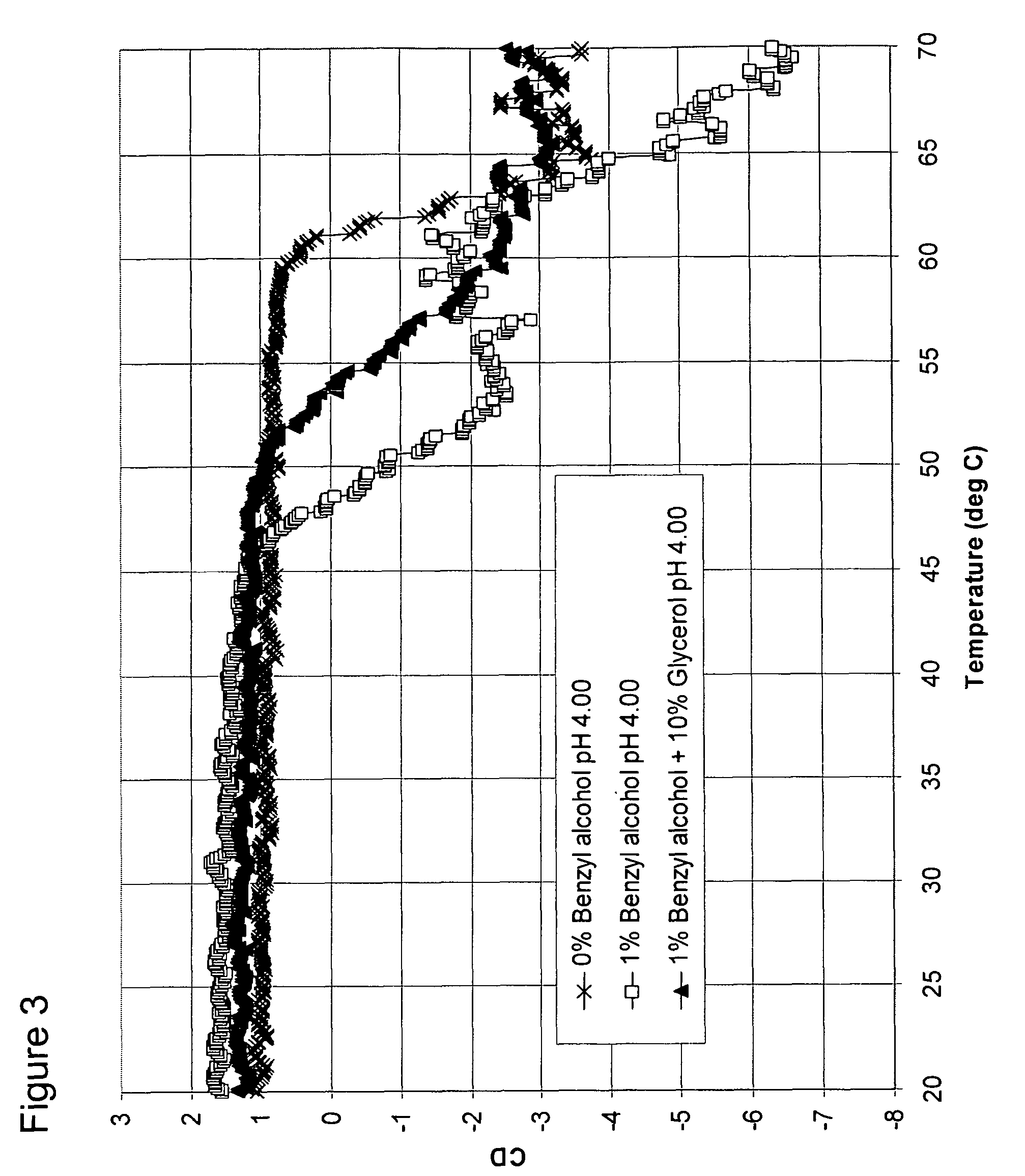
Osmolyte Mixture for Protein Stabilization
ActiveUS20110053795A1Speed up the processInhibit aggregationLibrary screeningEnzyme stabilisationProtein insertionOsmolyte
An osmolyte composition comprising 4 M glycerol and 4M urea for stabilizing previously transient protein folding intermediates as long-lived stable forms. A method to search for other possible stabilizing osmolyte mixtures using a screening array is also provided. These additional osmolyte mixtures may complement or augment the successful 4M glycerol / 4 M urea mixture.
Owner:UNIV KANSAS MEDICAL CENT
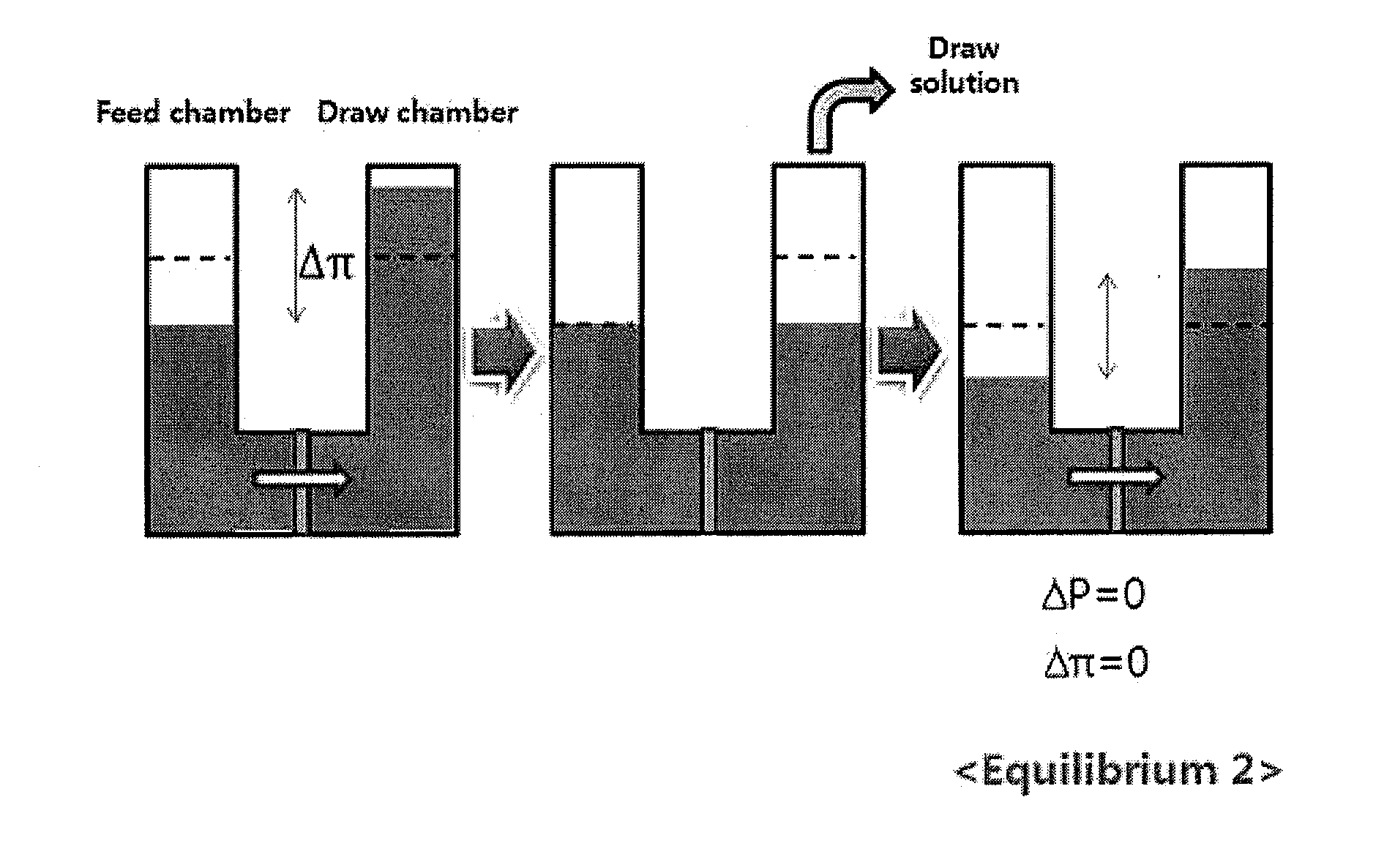
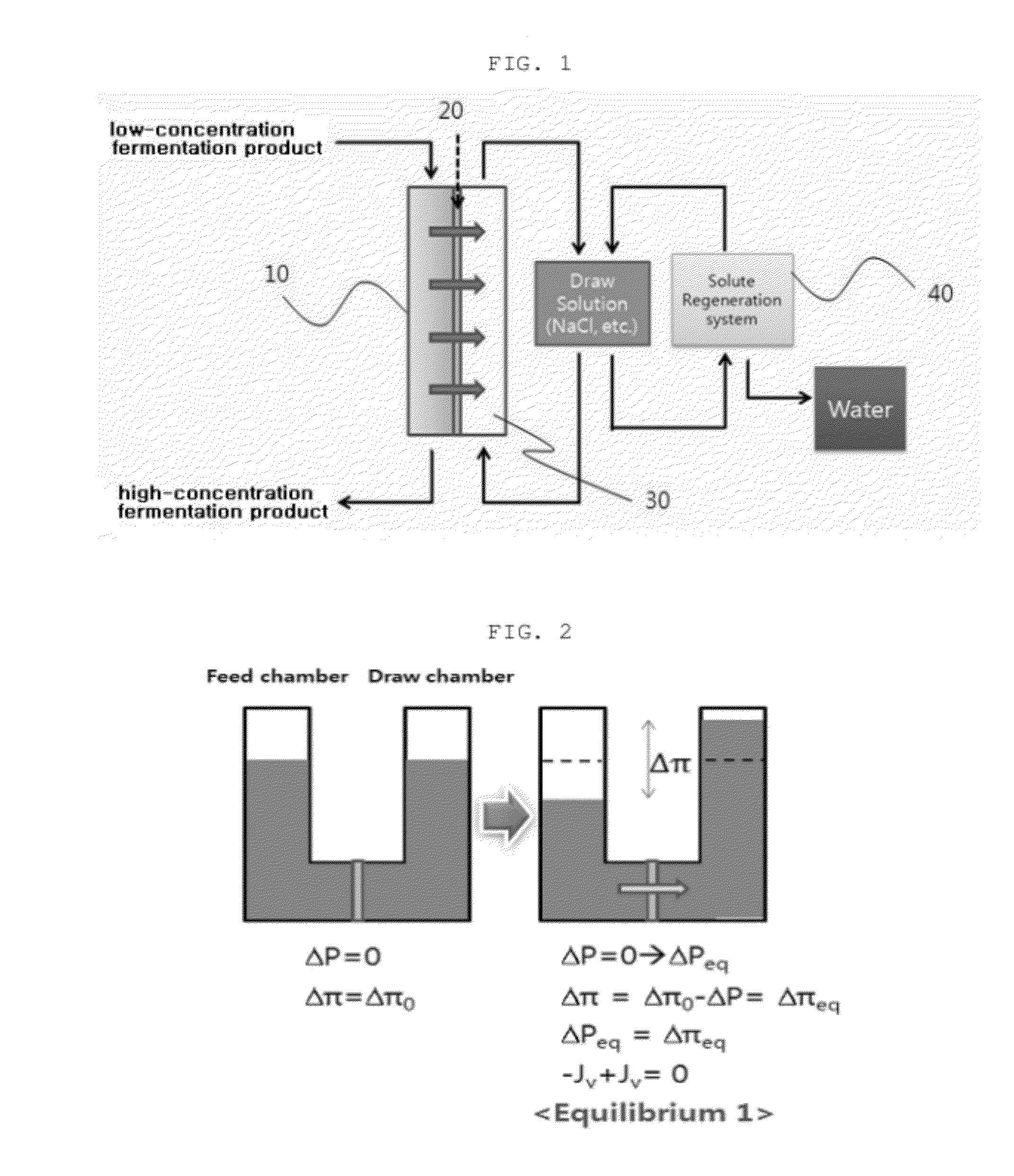
Method of concentrating low titer fermentation broths using forward osmosis
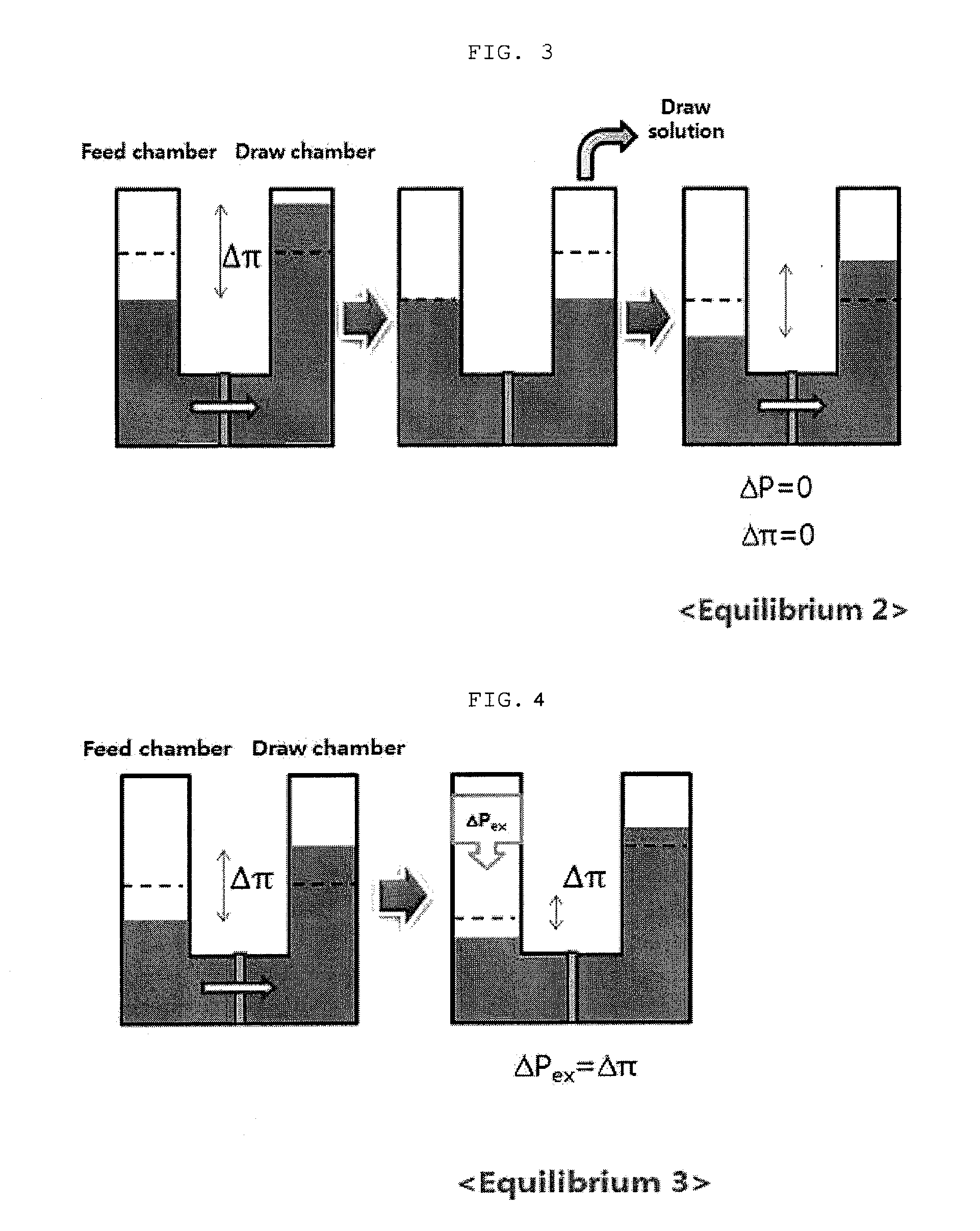
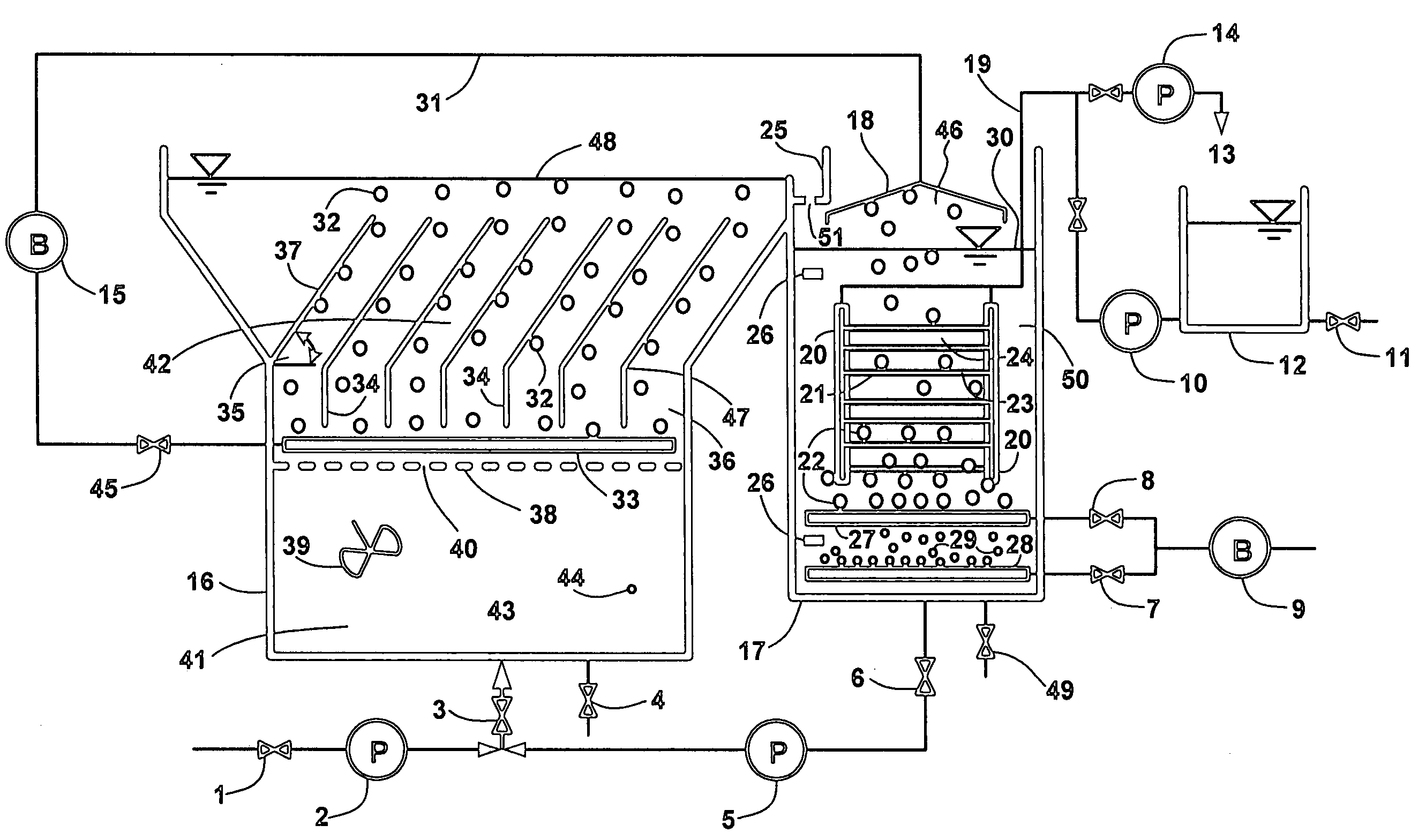
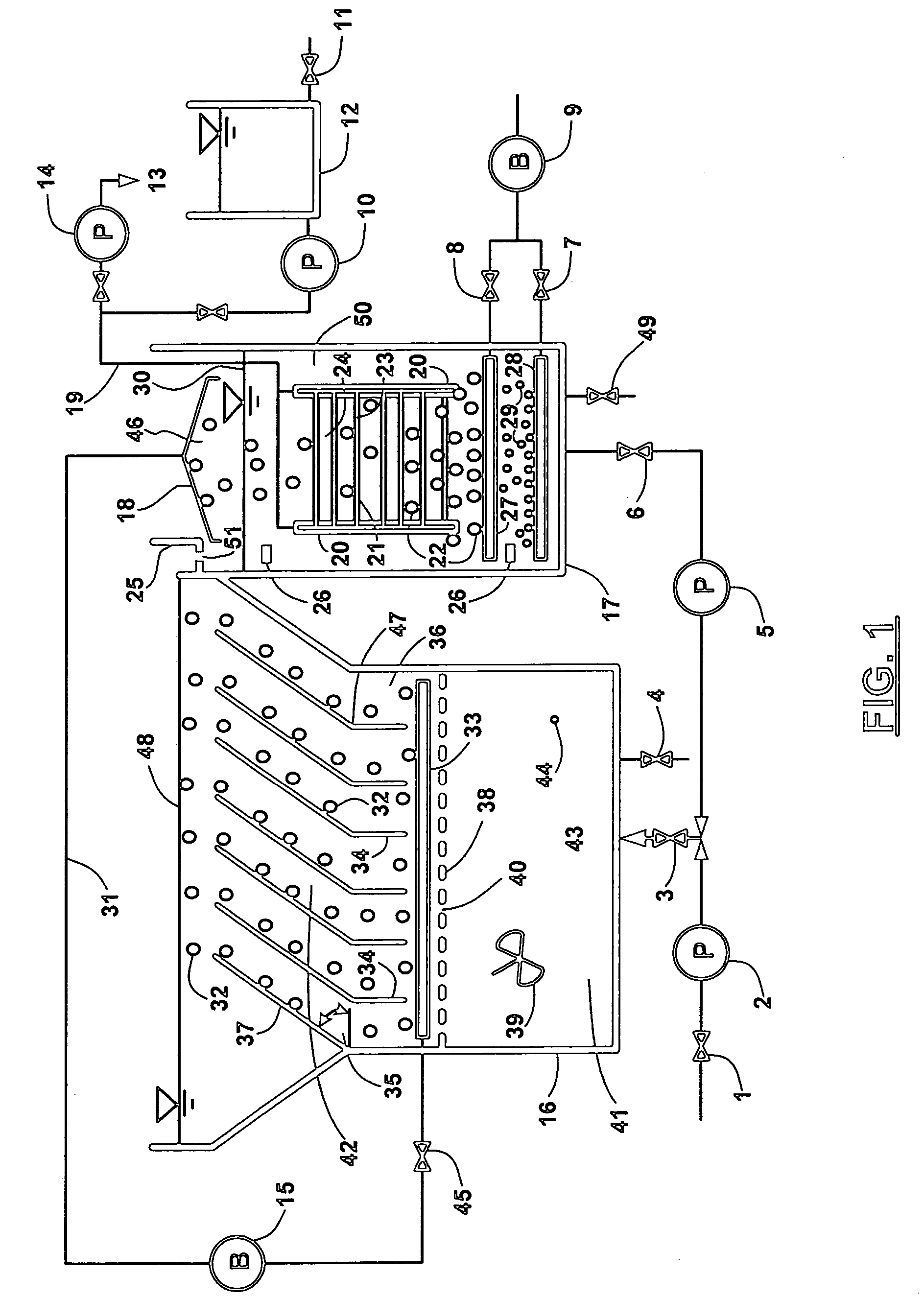
InactiveUS20120118827A1Concentration maximizationReduce energy consumption costsMembranesBiomass after-treatmentOsmolyteTiter
The present invention relates to a method for concentrating law titer fermentation broth, and more particularly to a method for concentrating a fermentation broth using forward osmosis. The method comprises: introducing the fermentation broth and an osmolyte into a feed chamber and a draw chamber, respectively, which are included in a concentration system and are divided from each other by a forward osmosis membrane, and subjecting the introduced fermentation broth to forward osmosis, thereby concentrating the fermentation broth in the feed chamber. The method can maximize the concentration of the low titer fermentation broth while minimizing energy consumption and operating cost, and thus can contribute to the industrialization of new technology.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Zero excess sludge membrane bioreactor
InactiveUS7311833B2High yieldCost-effectiveTreatment using aerobic processesDialysis systemsChemical oxygen demandMembrane fouling
Owner:YAMAMOTO KAZUO +1
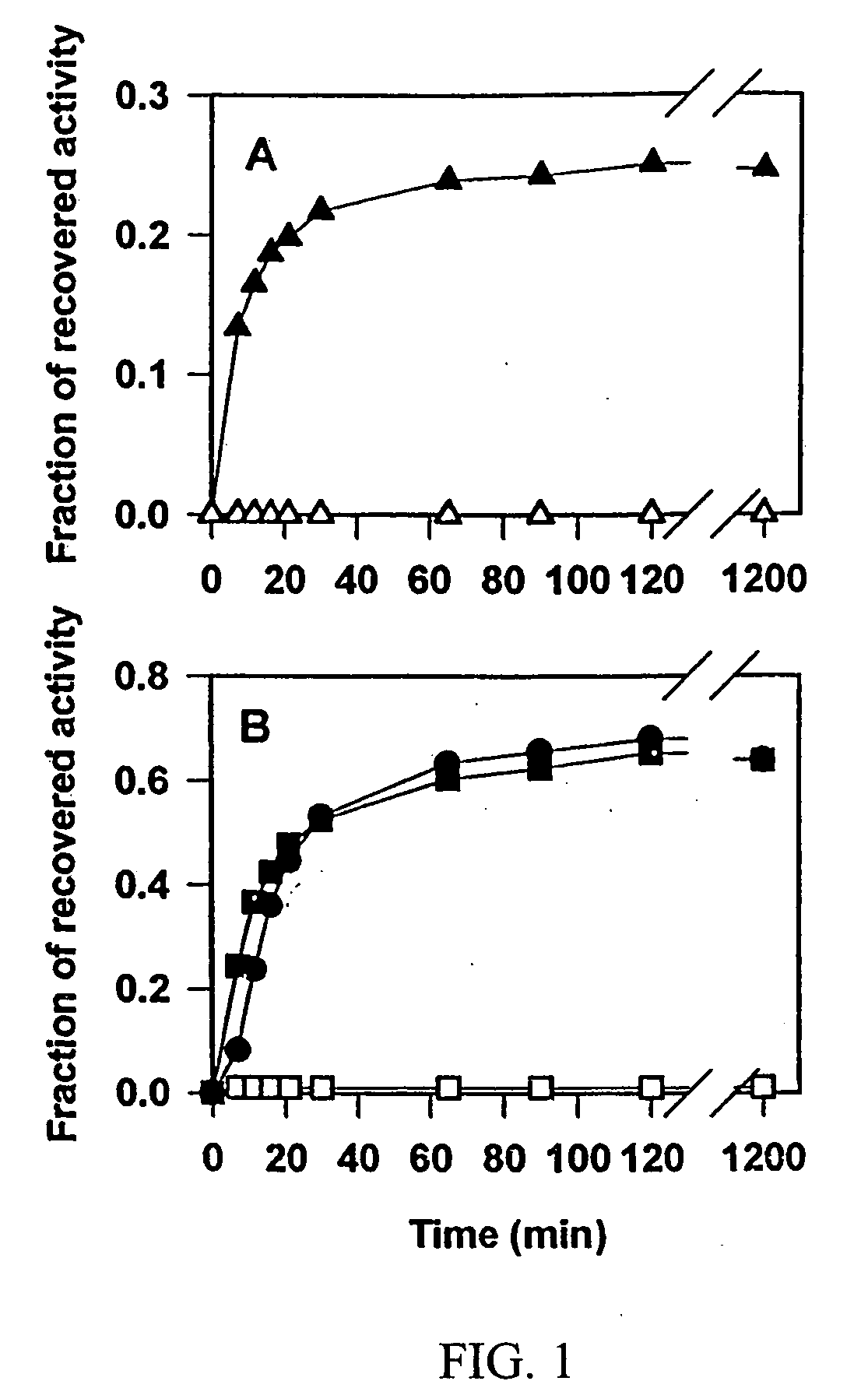
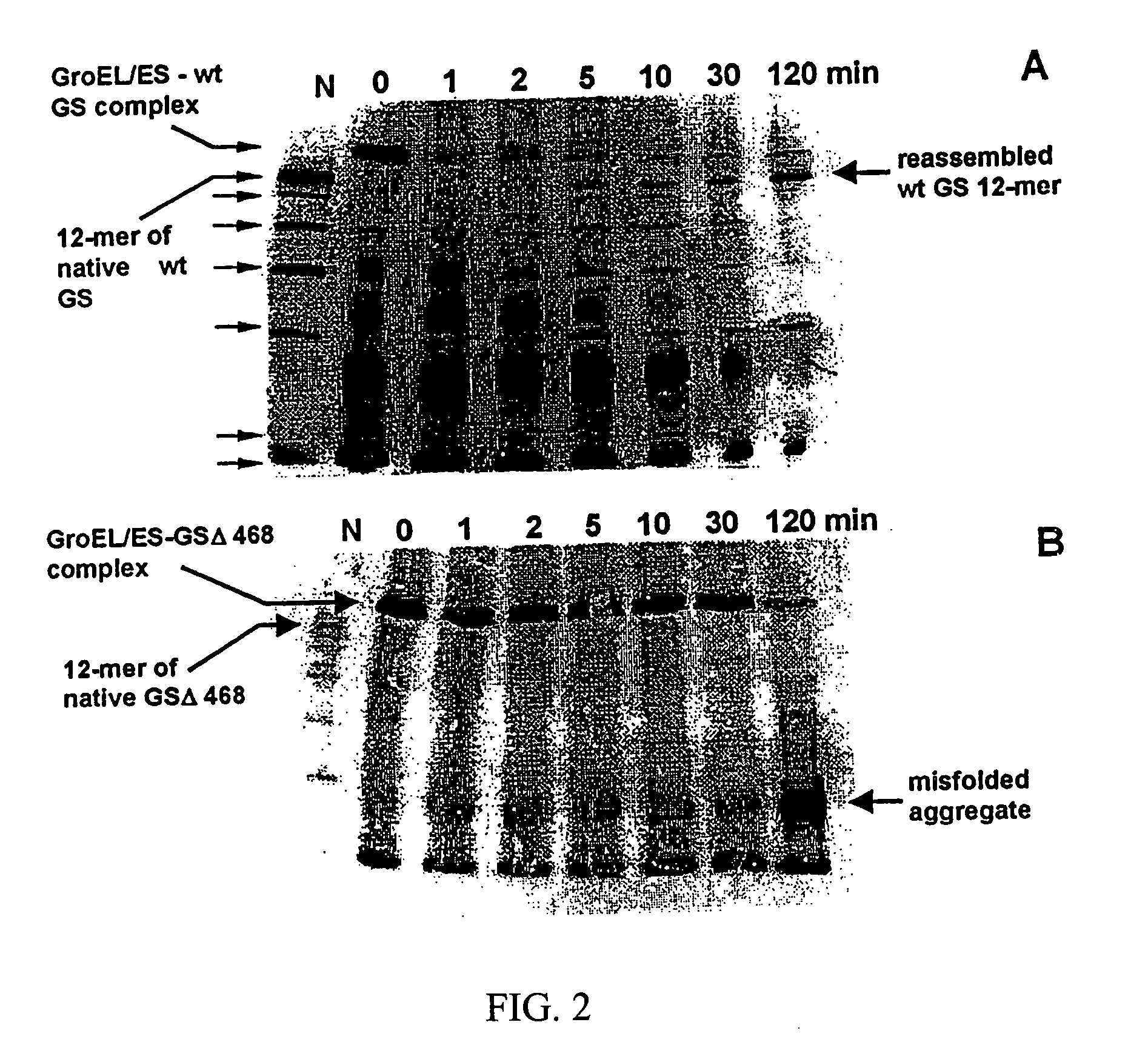
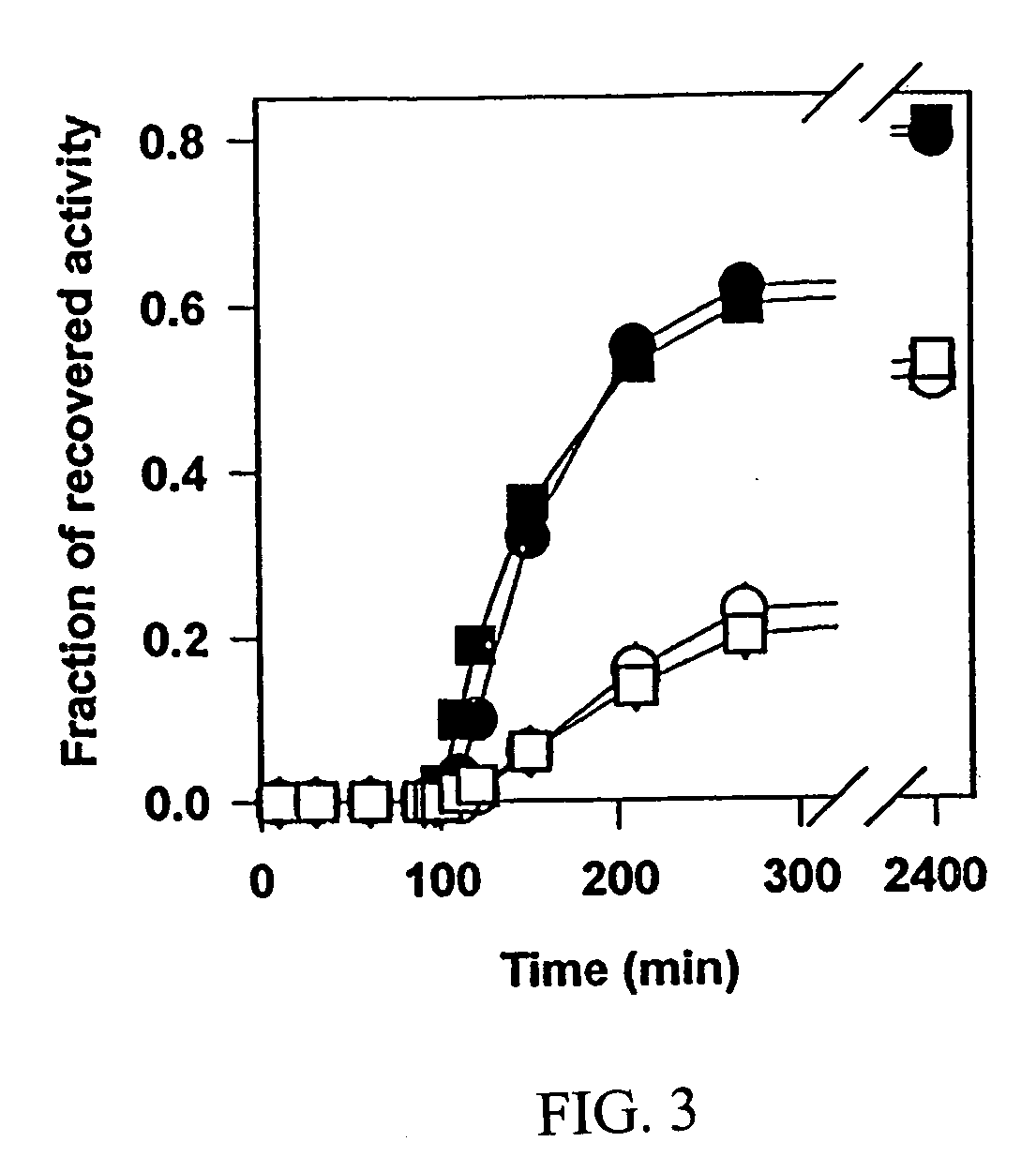
Chaperonin and osmolyte protein folding and related screening methods
InactiveUS20050196824A1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsIonic strengthOsmolyte
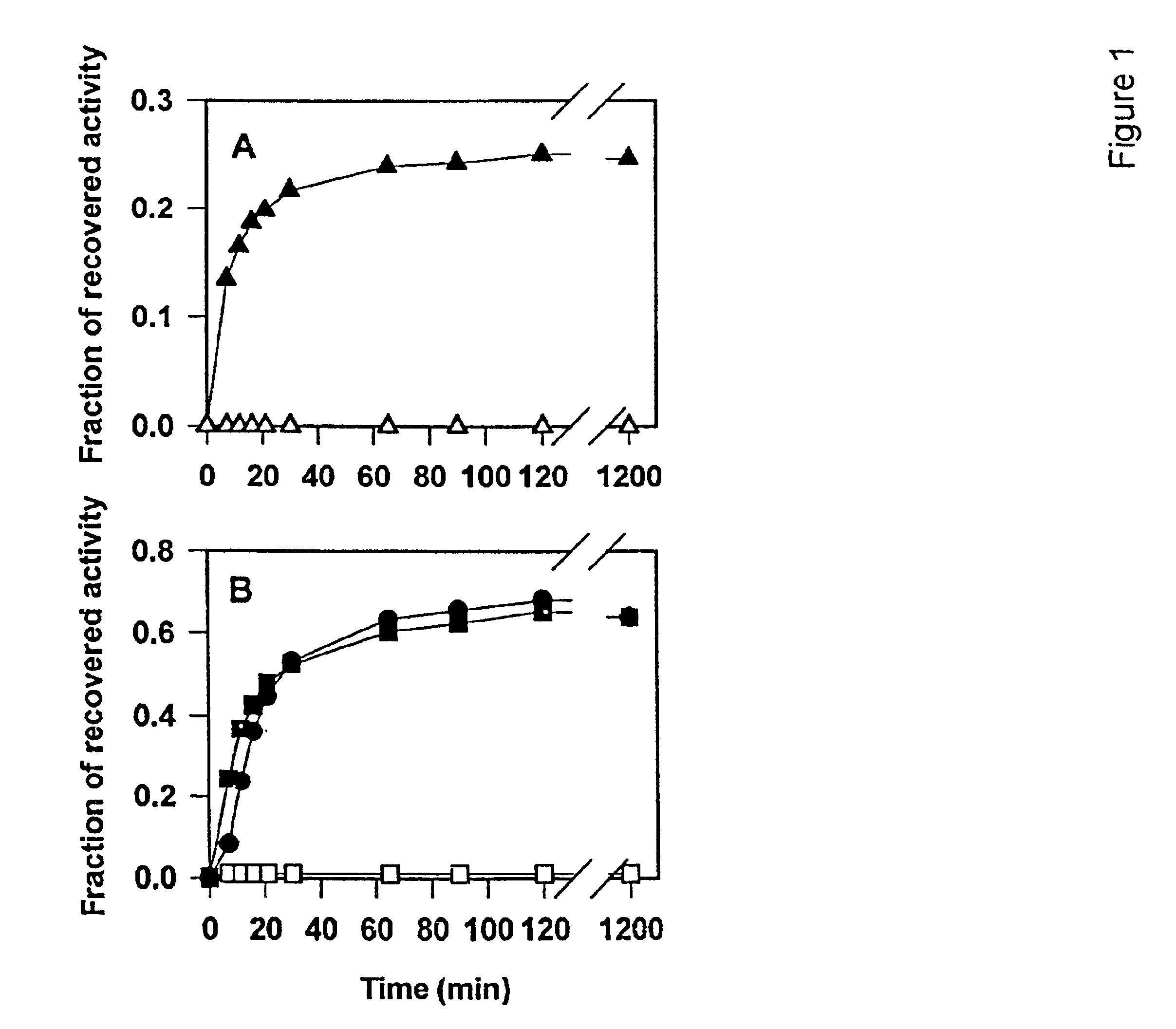
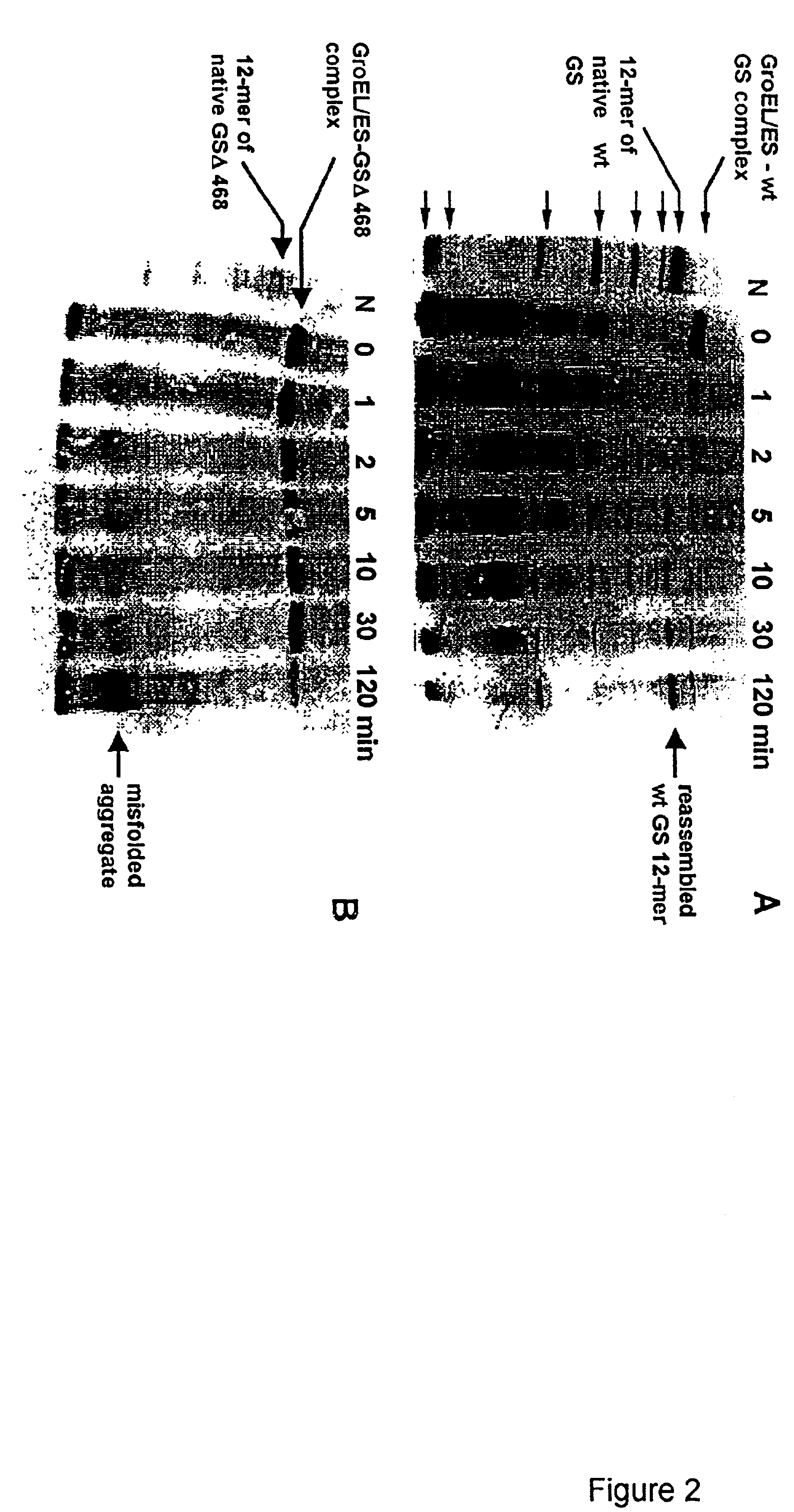
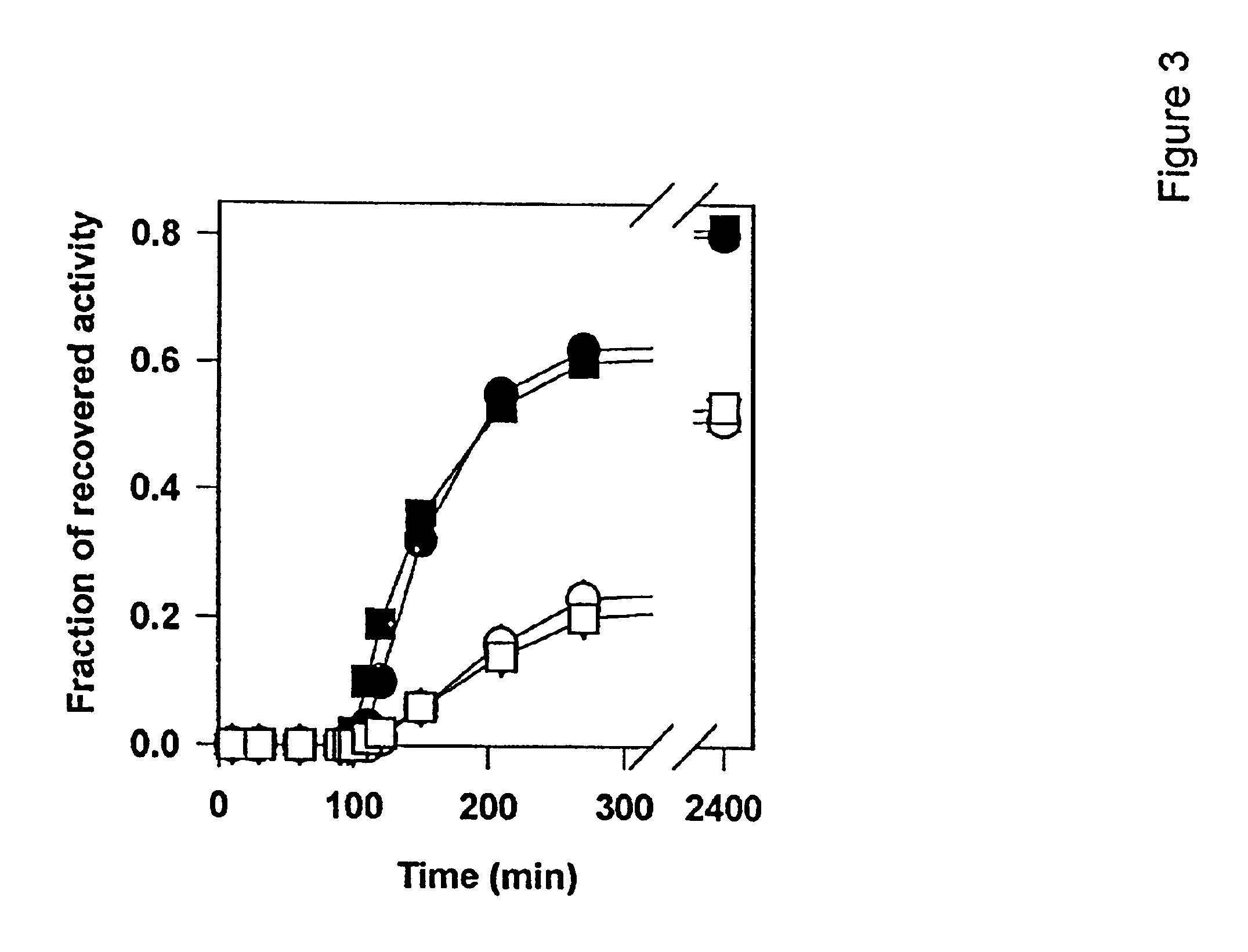
The invention describes an inexpensive in vitro protein folding process for preventing large scale protein misfolding and aggregation, for concentrating aggregation prone chaperonin-protein folding intermediates in a stable non-aggregating form, and for rapidly screening these stable concentrates for the best folding solution conditions. The process comprises: (1) the formation of a chaperone-substrate complex and (2) the release of the substrate using a broad array of folding solutions containing different osmolyte ions, detergents, gradients of ionic strength and pH or other commonly used folding additives. Specifically, when the chaperonin / osmolyte protein process was applied to identify and optimize GSΔ468 bacterial glutamine synthetase mutant refolding conditions that otherwise cannot be folded in vitro by commonly used techniques, 67% of the enzymatic activity was recovered.
Owner:UNIV KANSAS MEDICAL CENT
Method for purifying polysaccharide iron complex based on ultrafiltration membrane method
ActiveCN103224571AReduce salt concentrationIncrease concentrationMetabolism disorderChemical industrySeparation technologyOsmolyte
The present invention discloses a method for purifying polysaccharide iron complex, in particular to a method for desalination and concentration of the crude aqueous polysaccharide iron complex with the ultrafiltration membrane separation technology. Specific methods include the following steps of filtering the crude aqueous polysaccharide iron complex with ultrafiltration membrane components, whereby the pore diameter of ultrafiltration membrane components is between 2 and 50nm and molecular weight cutoff is between 5K and 150KDa; intercepting the polysaccharide iron complex by the ultrafiltration membrane, continuously discharging the sodium chloride and free iron ions in the crude aqueous solution through the osmotic solution to improve the purity and the concentration of polysaccharide iron complex in the ultrafiltration retentate liquid. The method for desalination and concentration of the crude aqueous polysaccharide iron complex with the ultrafiltration membrane provided by the invention has the following advantages of 1. simple operation process, safety and energy saving, mild condition and easy for continuous production; 2. reducing the salt concentration in the aqueous polysaccharide iron complex, and increasing the concentration of polysaccharide iron with recovery rate of more than 95%.
Owner:JIANGSU JIUWU HITECH
Pharmaceutical formulations
Owner:AMGEN INC
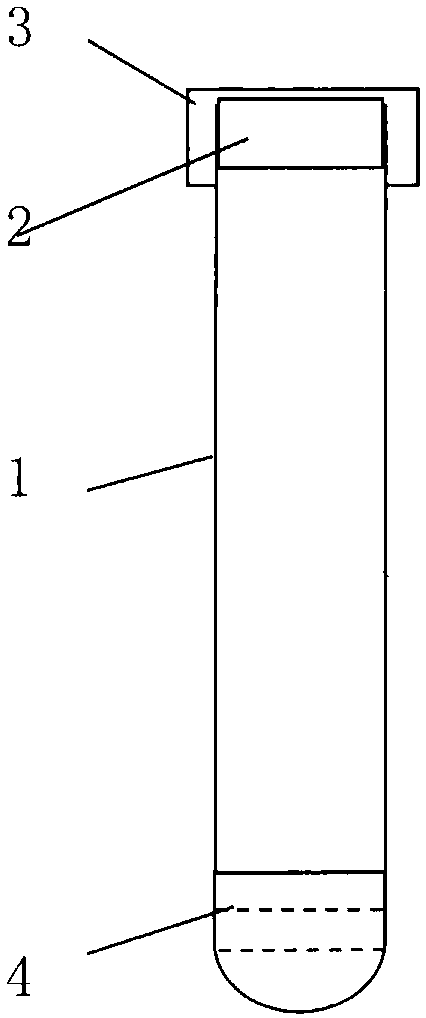
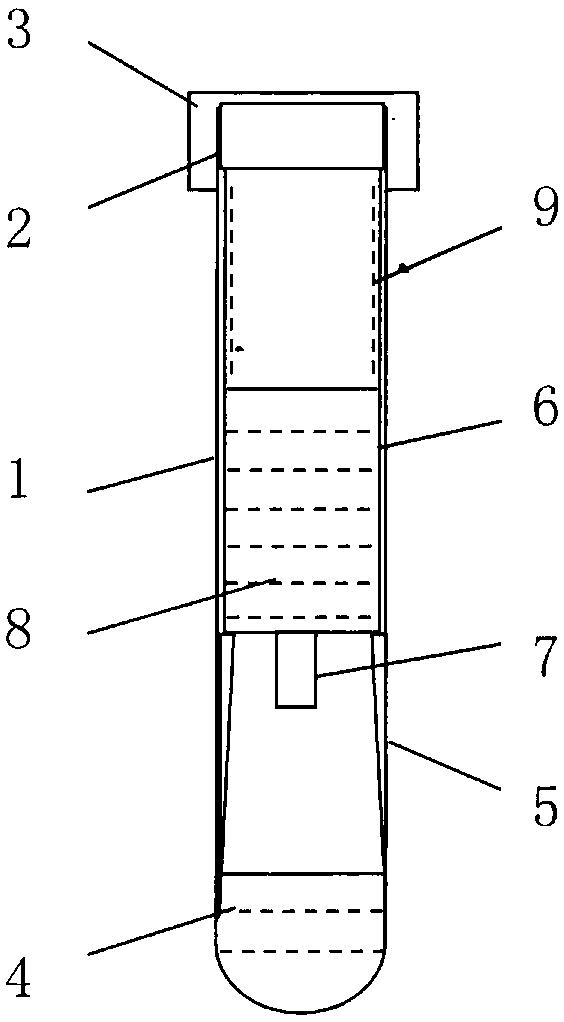
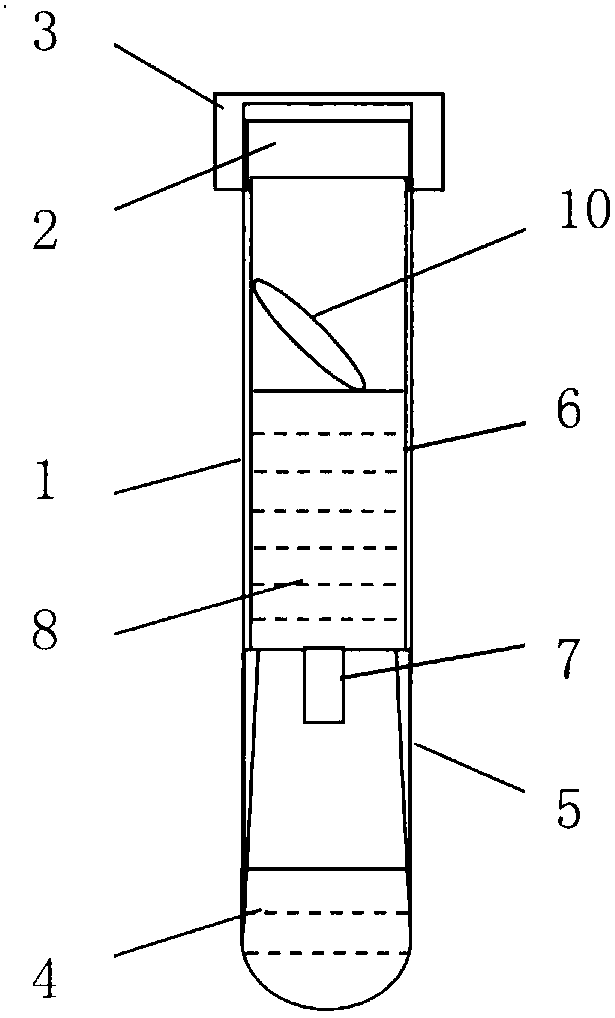
Vacuum blood collection tube for storing and transporting circulating nucleic acid sample
InactiveCN107760593AGuaranteed not to degradeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material testing proceduresBlood Collection TubeCross-link
The invention discloses a vacuum blood collection tube, particularly a vacuum blood collection tube for storing and transporting a circulating nucleic acid sample. The vacuum blood collection tube comprises an original tube, a rubber plug and a protective cap, wherein the original tube is vacuumized; the rubber plug seals the original tube; a composite additive is arranged inside the original tube; the composite additive is obtained by mixing a chelating agent, an enzyme inhibitor, an osmotic agent, an antioxidant, an apoptosis inhibitor, a cell membrane stabilizer and a buffer solution. The invention can enable a collected sample to keep a whole-blood initial state under a room-temperature condition for 7-14 days without deterioration, and also can ensure that circulating nucleic acids inplasma or serum of whole blood are not degraded and whole blood cells are free of apoptosis and rupture, so that the circulating nucleic acids existing in the plasma or the serum are prevented from being contaminated by genomic nucleic acids, and adverse effects of a cross-linking action of a formaldehyde slow release agent-based preservation solution on subsequent experiments are avoided.
Owner:付士明
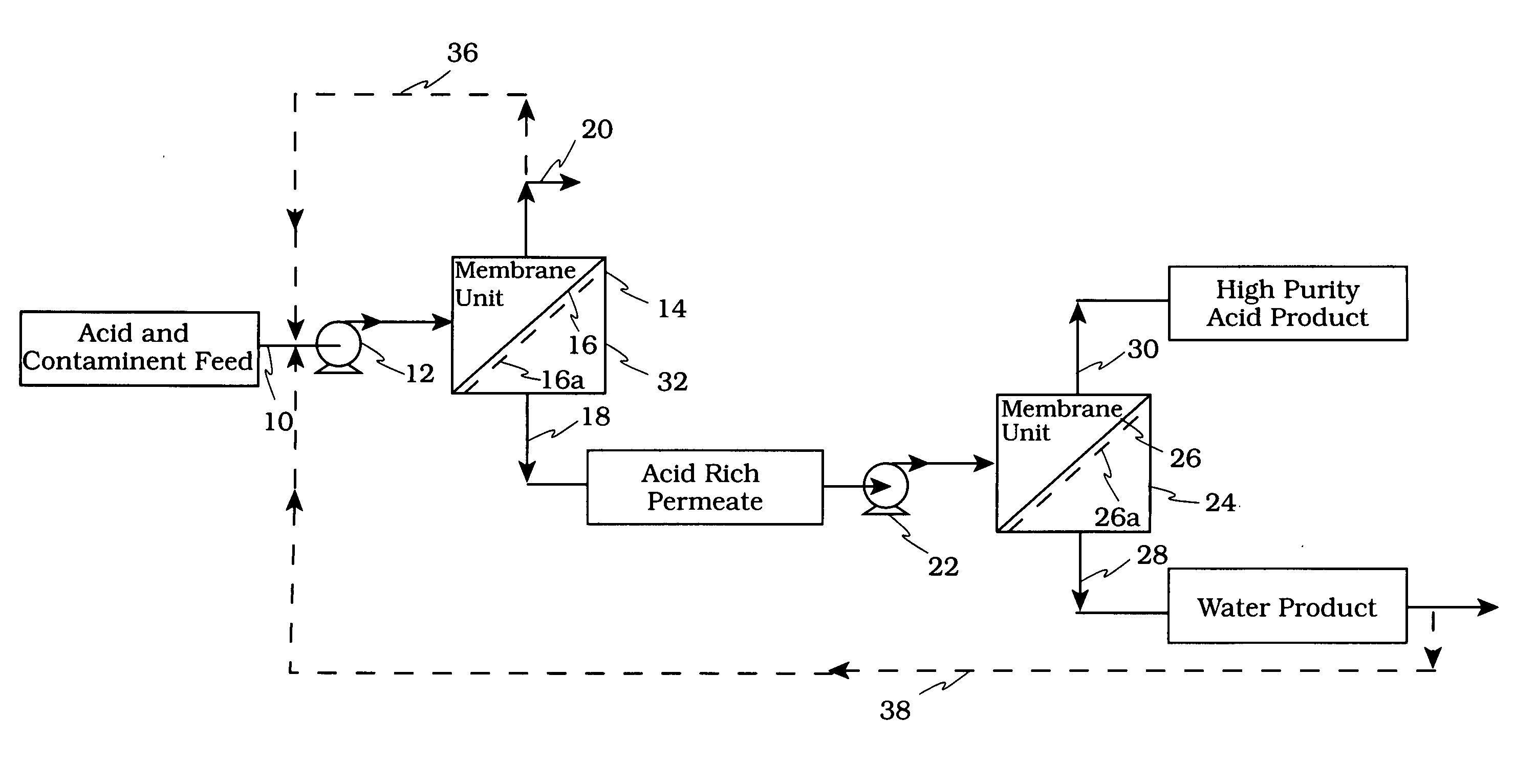
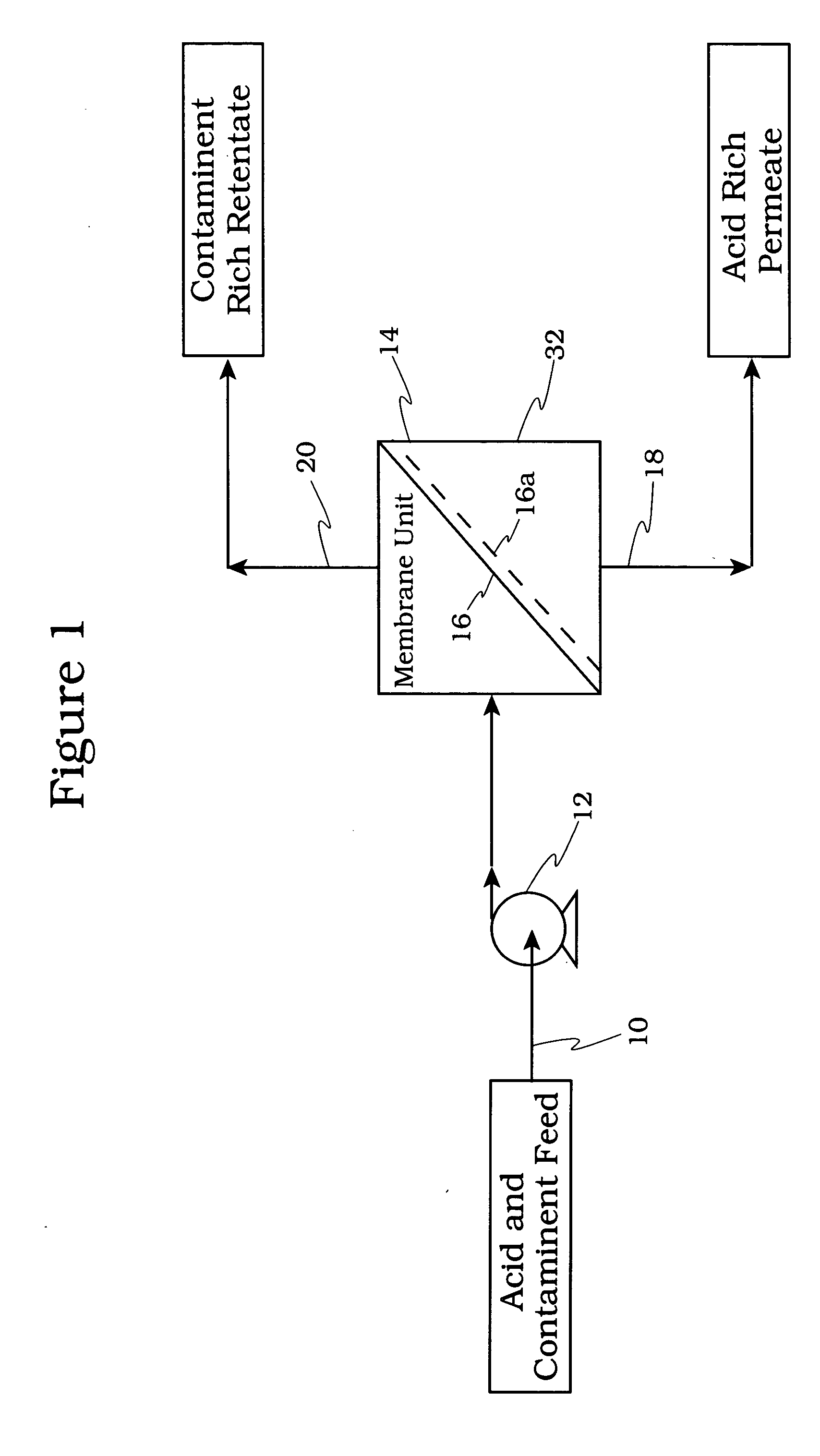
Acid tolerant polymeric membrane and process for the recovery of acid using polymeric membranes
InactiveUS20050173345A1Speed up the processReduced strengthMembranesDialysisPolyvinyl alcoholHydrocotyle bowlesioides
A crosslinked polymeric polyvinyl sulfate membrane or crosslinked copolymer polyvinyl sulfate and polyvinyl alcohol membrane, suitable for use in an acid environment, and its use for recovering acid from a feed mixture comprising acid, hydrocarbons and water, the method comprising: processing said mixture using a first polymeric membrane to form a first retentate containing a substantially greater concentration of hydrocarbons than said feed mixture and a first permeate containing a substantially greater concentration of acid and water than said mixture, said first polymeric membrane being selectively permeable to the acid and water over the hydrocarbons found in the mixture, and recovering the first permeate; said first permeate can be processed further using a second water reduction mean to form a first stream containing a substantially greater concentration of acid than said first permeate and a second stream containing a substantially greater concentration of water than said first permeate, said water reduction step may be a second polymeric membrane being selectively permeable to the water over the acid in said first permeate; and recovering said second stream or retentate.
Owner:MINHAS BHUPENDER S +2
Method for preparing hollow blade inner chamber diffusion layer with high temperature resistance, oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance
ActiveCN102485934AImprove resistance to high temperature oxidationAccelerated corrosionBlade accessoriesSolid state diffusion coatingOsmolyteNichrome
Owner:SHENYANG LIMING AERO-ENGINE GROUP CORPORATION
Systemic plant conditioning composition
ActiveUS8492312B2Improve availabilityFacilitate uptakeBiocideInorganic boron active ingredientsBiotechnologyOsmolyte
This invention relates to compositions and methods facilitating availability, uptake and translocation of active ingredients in plants. More specifically, this invention relates to the surprising discovery that the application to the roots, such as administration to the soil surrounding plants, of two or more osmolytes in combination with an active ingredient, either simultaneously or within a short time of each other, results in an induction of translocation of active ingredient from the roots systemically into the plant.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
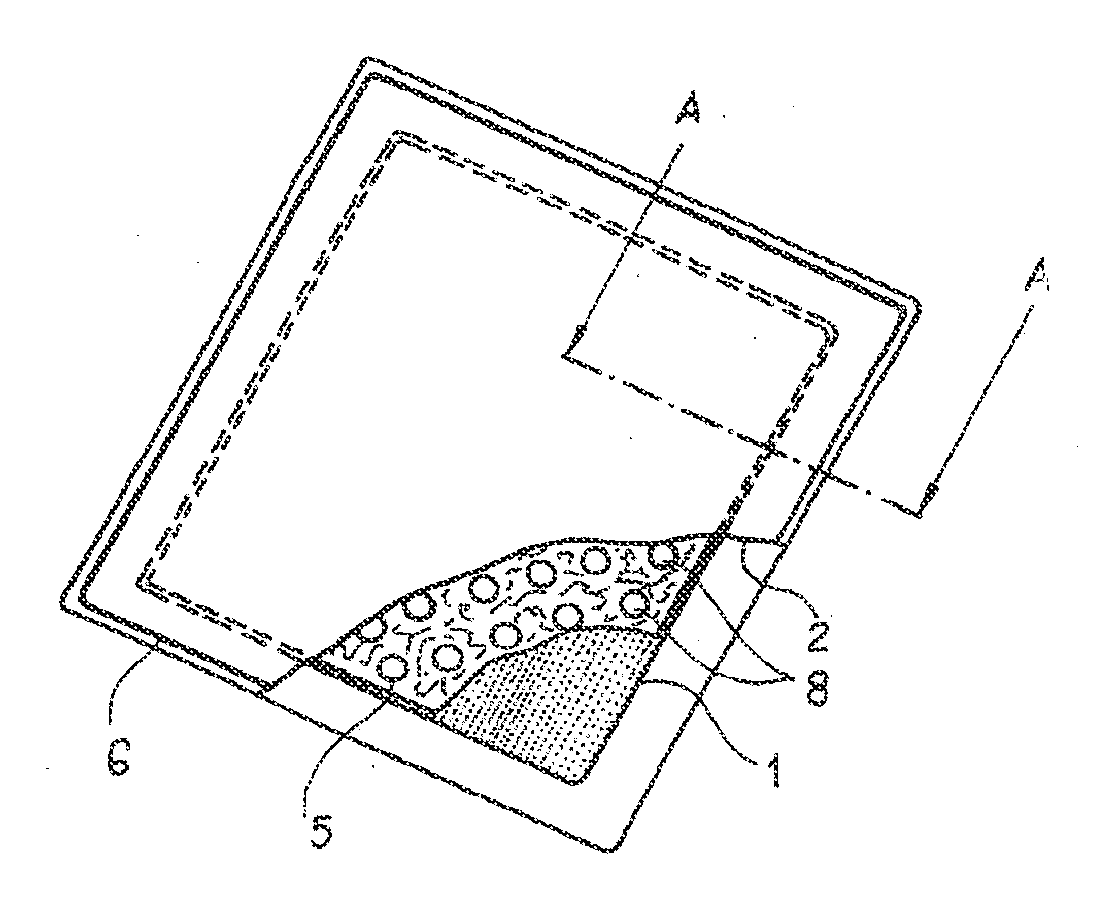
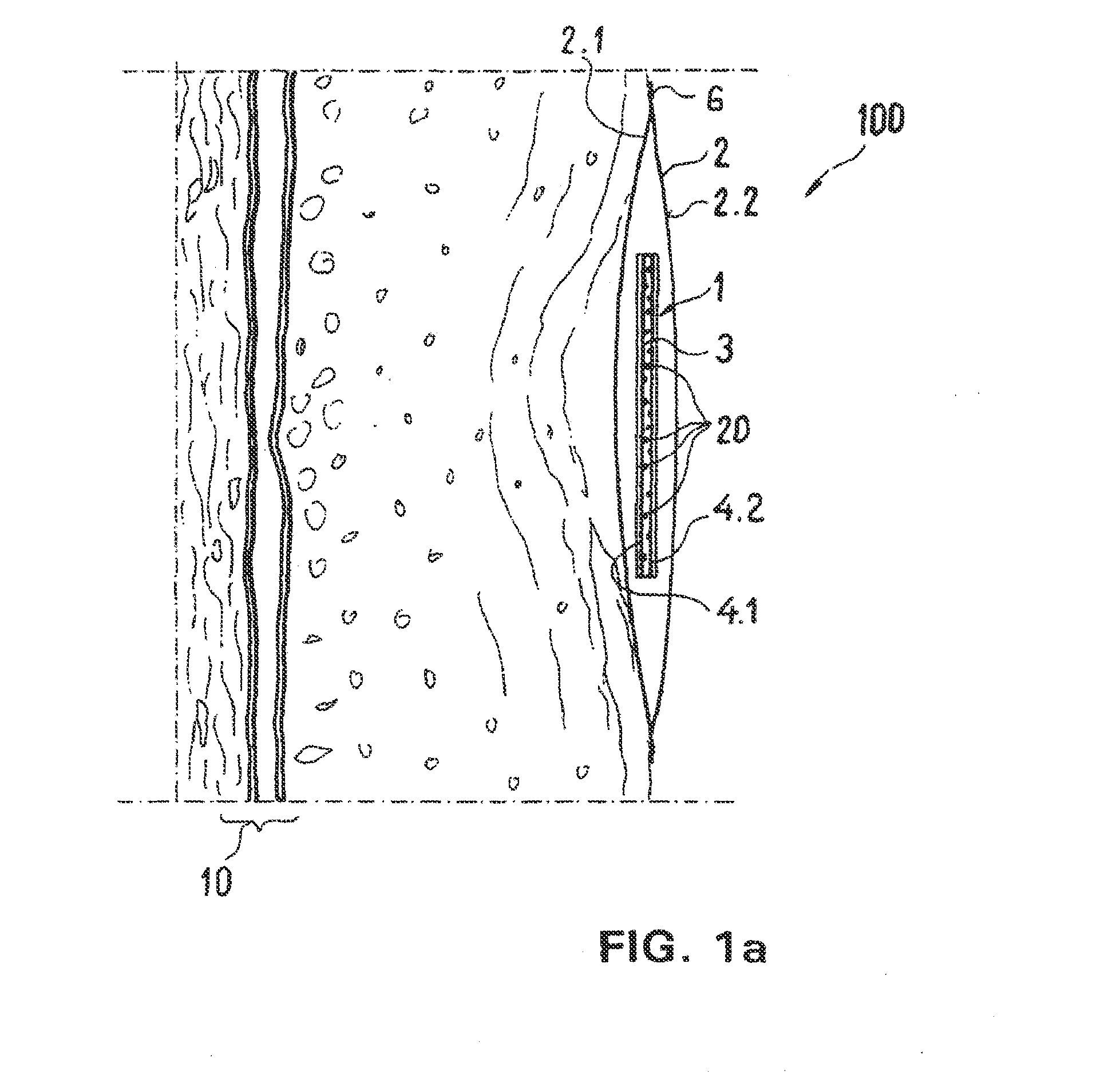
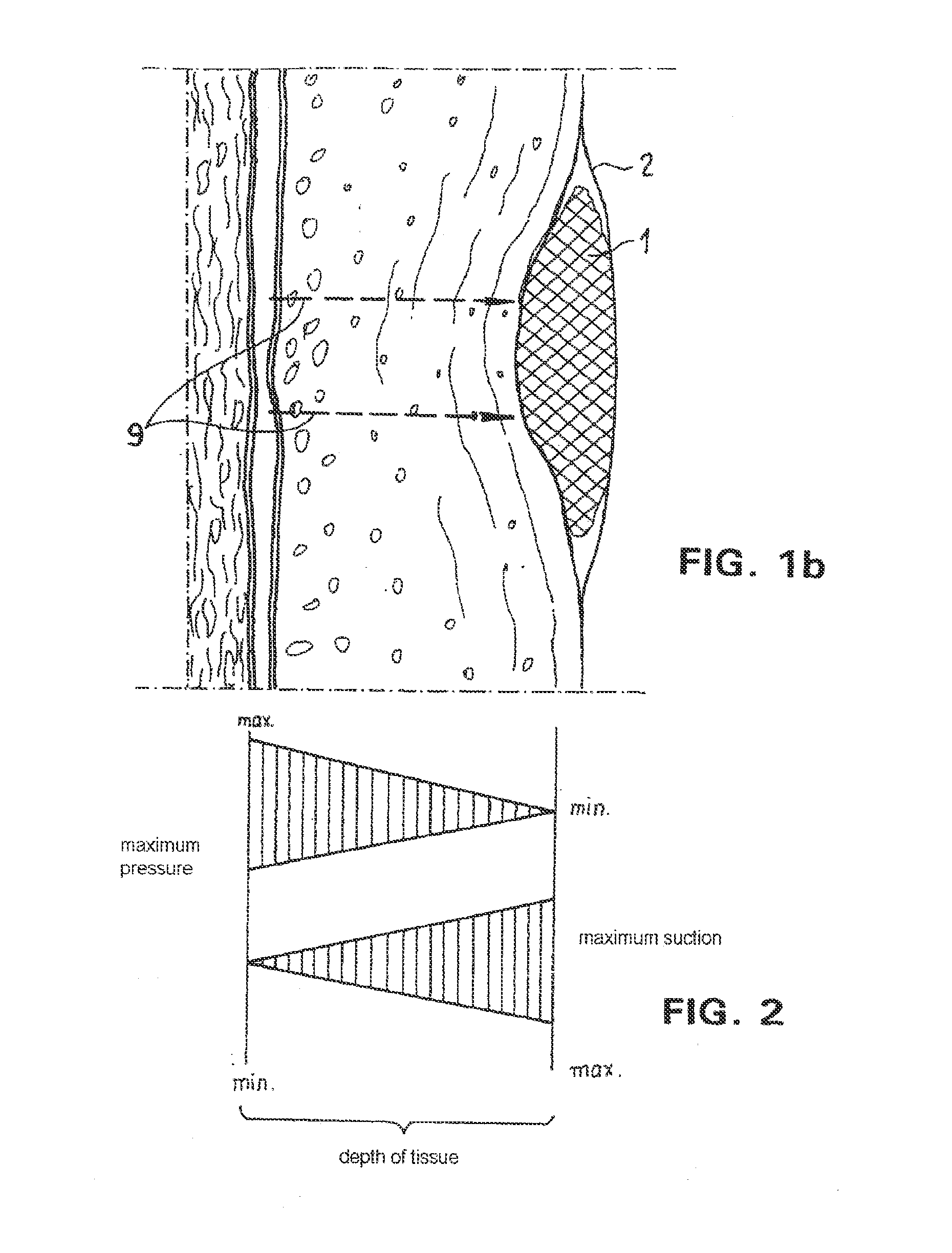
Absorbent article for application to human or animal skin surfaces
The invention relates to an absorbent article for application to human or animal skin surfaces in the region of wounds, consisting of an outer covering (2) which is permeable for liquid substances, and of an inner layer (1) which is surrounded by the covering (2) and which consists essentially of a mixture of an amount of strongly osmotically active substances with an amount of osmotically comparatively weak or osmotically inactive substances, such as cellulose. The inner layer (1) is filled with osmotically active substances in such a way that it is possible to exert on a wound, with the wound fluids contained therein, an osmotic pressure via which the wound fluid can be removed from the organism to be treated, and thus it is possible to assist both in the surfaced wound region and in the depth of the tissue a normal interstitial hydration of tissue by directing endogenous fluids in their direction of flow to the patient's skin surface into the absorbent article, and keeping them there.
Owner:BSN MEDICAL GMBH & CO KG
Dynamic evaluation method of scale inhibition performance of reverse osmosis scale inhibitor
ActiveCN102507359AScale inhibition performance evaluationGuaranteed stabilityMaterial weighingOsmolyteReverse osmosis
Owner:STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST +2
Remediation agent and remediation method for heavy metal contaminated soil
InactiveCN111362746ALow toxicityPromote growthAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersSodium phosphatesOsmolyte
The invention relates to the technical field of soil remediation, in particular to a remediation agent and remediation method for heavy metal contaminated soil. The remediation agent for the heavy metal contaminated soil comprises 2-16 parts of humic acid, 5-10 parts of succinic acid, 5-20 parts of sawdust, 2-10 parts of bentonite, 10-20 parts of sodium polyacrylate, 5-10 parts of honeycomb briquette ash, 5-20 parts of seaweed residues, 2-10 parts of zeolite, 5-10 parts of nano hydrogel, 10-30 parts of charcoal, 10-20 parts of Fe-Mn binary oxide, 5-10 parts of sodium pyrophosphate and 2-10 parts of microorganism mixed bacteria. The remediation agent is good in repairing effect and low in cost. The remediation method for remediating the heavy metal contaminated soil through the remediationagent is simple, heavy metal in the soil can be efficiently solidified, and the water quality grade of the soil penetrating fluid is improved.
Owner:WEIFANG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process of supplying water of controlled salinity
ActiveUS9492790B2Reduce riskReduce salinityWaste water treatment from quariesMembranesSingle stageSulfate
Process for producing an injection water for an oil reservoir by pressurizing water having a total dissolved solids content of 20,000 to 45,000 ppm and a sulfate concentration of 1,000 to 4,000 ppm to 350 to 1250 psi absolute; and dividing the water into first and second feeds for reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration (NF) units respectively. The units are operated in single-pass, single-stage mode or single-pass, two-stage mode, the NF permeate has a pressure at least 5 psi higher than the RO permeate, and the recoveries of the RO and NF permeates are 35 to 75% and 35 to 60% by volume respectively. RO permeate and NF permeate are mixed in a ratio of 2:1 to 40:1 to provide injection water having a TDS content of 500 to 5,000 ppm, and a sulfate concentration of less than 7.5 ppm.
Owner:BP EXPLORATION OPERATING CO LTD
Chaperonin and osmolyte protein folding and related screening methods
The invention describes an inexpensive in vitro protein folding process for preventing large scale protein misfolding and aggregation, for concentrating aggregation prone chaperonin-protein folding intermediates in a stable non-aggregating form, and for rapidly screening these stable concentrates for the best folding solution conditions. The process comprises: (1) the formation of a chaperone-substrate complex and (2) the release of the substrate using a broad array of folding solutions containing different osmolyte ions, detergents, gradients of ionic strength and pH or other commonly used folding additives. Specifically, when the chaperonin / osmolyte protein process was applied to identify and optimize GSΔ468 bacterial glutamine synthetase mutant refolding conditions that otherwise cannot be folded in vitro by commonly used techniques, 67% of the enzymatic activity was recovered.
Owner:KANSAS MEDICAL CENT UNIV OF
Stabilized bio-available soluble silicate solution
InactiveCN102892292AHigh yieldImprove quality parametersMagnesium silicatesBiocideBiological bodyOsmolyte
The present invention relates to dissolved silicate compositions in which the dissolved silicate is stabilized by at least two selected osmolytes and is therefore bioavailable. The composition and its dilutions are stable over a long period of time and are used in a wide field of applications for the benefit of living organisms such as plants, animals and humans.
Owner:TAMINCO NV
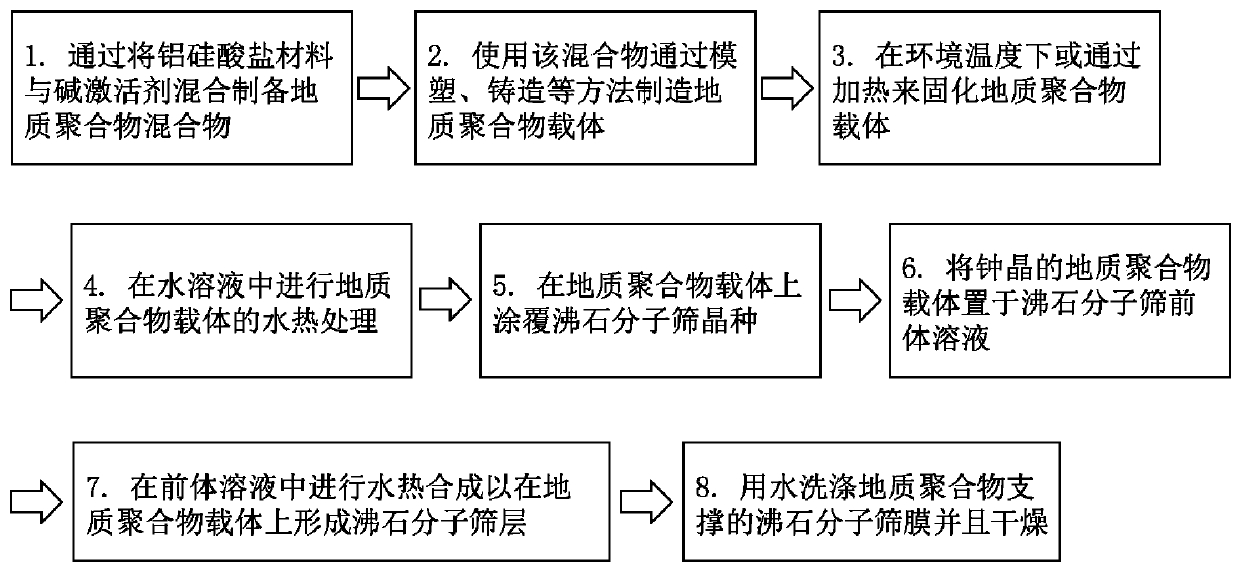
Supported zeolite membranes
ActiveCN110913979AIncrease the effective permeable areaFlexible Design ConfigurationMembranesDistillationOsmolyteAlcohol ethyl
An asymmetric membrane having a layer containing a zeolite supported on a geopolymer substrate and methods for making an asymmetric membrane having a layer containing a zeolite supported on a geopolymer substrate. A cross-flow membrane separation method for increasing the concentration of ethanol from a feed mixture comprising water and ethanol, comprising: cross-flowing a feed mixture comprisingwater and ethanol across the layer comprising a zeolite of the asymmetric membrane of the instant invention to produce a permeate having an ethanol concentration less than the ethanol concentration ofthe feed mixture and a retentate having an ethanol concentration greater than the ethanol concentration of the feed mixture, the pressure of the feed mixture being greater than the pressure of the permeate.
Owner:NOVO RUICHI TECH CO LTD
Process for the treatment of a stream of substances
InactiveUS20100038246A1Improve reverse osmosis efficiencyImprove efficiencySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementInorganic saltsReverse osmosis
A process for a stream of substances containing at least one valuable substance including (A) amino acids, (B) carboxylic acids, and (C) inorganic salts includes: (1) treating the stream by nanofiltration to obtain a retentate enriched with valuable substance (A); (2) treating the permeate of step (1) by electrodialysis in order to obtain a concentrate enriched with valuable substance (C); (3) treating the diluate of step (2) using a system (3) of two stages (4) and (5) which are directly or indirectly interconnected, wherein (4) one treatment is performed by reverse osmosis and (5) one treatment is performed by electrodialysis, whereby a concentrate enriched with valuable substance (B) is obtained, (6) at least a portion of the retentate of step (4) is directly or indirectly supplied to step (5) and (7) at least a portion of the diluate of step (5) is directly or indirectly supplied to step (4).
Owner:GRUENE BIORAFFINERIE AT
Colorless transparent penetrating agent
ActiveCN102585761AOther chemical processesOptically investigating flaws/contaminationAdditive ingredientMicro fracture
The invention relates to engineering flaw detection which is related with micro-fractures on the surface of a metal workpiece, in particular to reaction-type coloring flaw detection penetrating fluid. The invention also relates to an engineering flaw detection method, in particular to a nondestructive flaw detection method which is simple and is simple and convenient to operate. The invention aims to provide a colorless transparent penetrating agent which is really colorless, transparent, pollution-free and natural and does not need to react for the second time. In order to achieve the goal of the invention, the invention is realized in such a mode as follow: the colorless transparent penetrating agent is characterized by consisting of polyalcohol, surface active agent and water, wherein the polyalcohol accounts for 30-60 percent, the surface active agent accounts for 8-15 percent, and the balance is a dissolving agent. By adopting the scheme, the complicated formula in the past is not needed. A detection effect can be achieved only by mixing three ingredients which are the most natural and simplest.
Owner:归锦华 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com