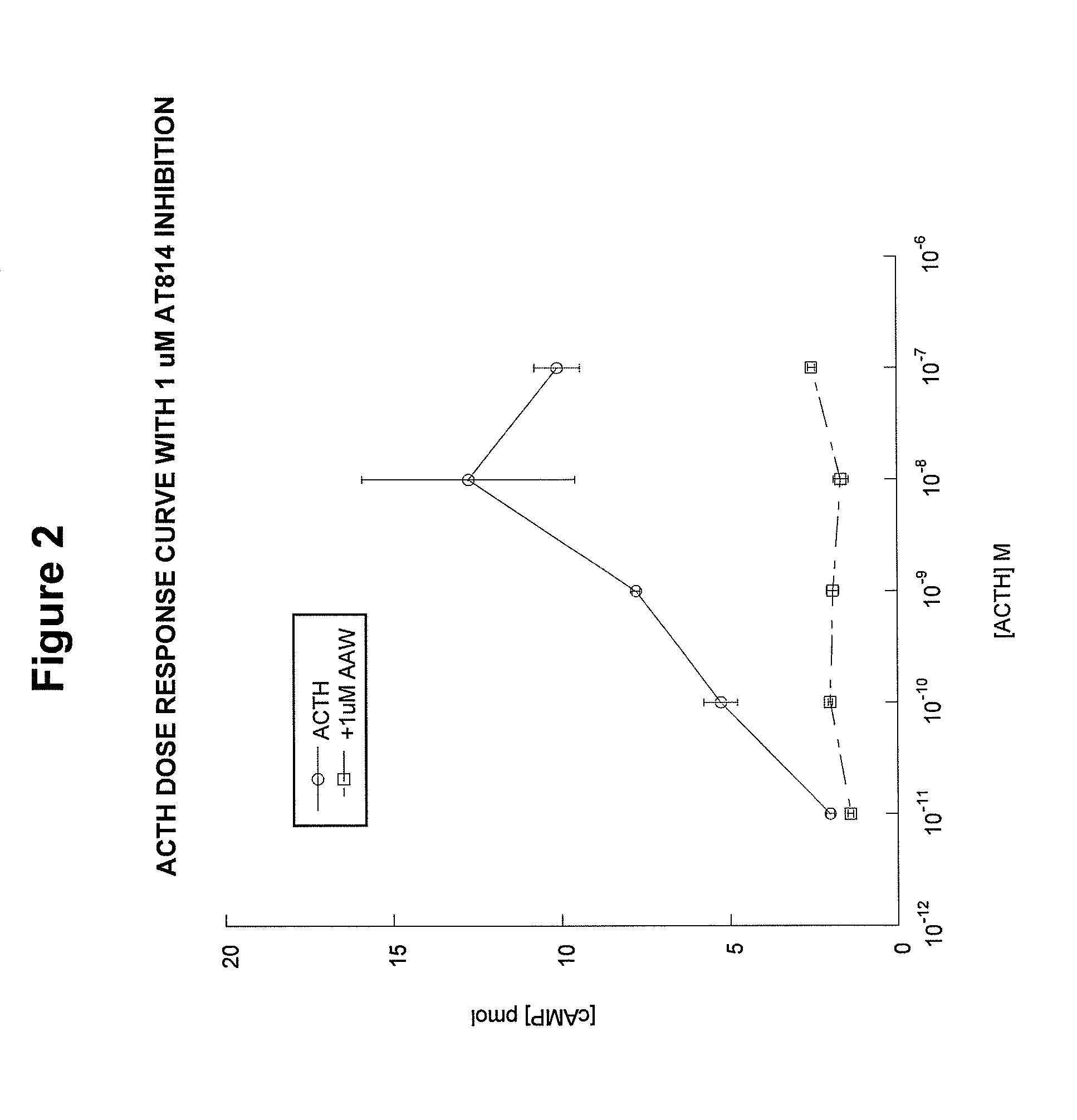
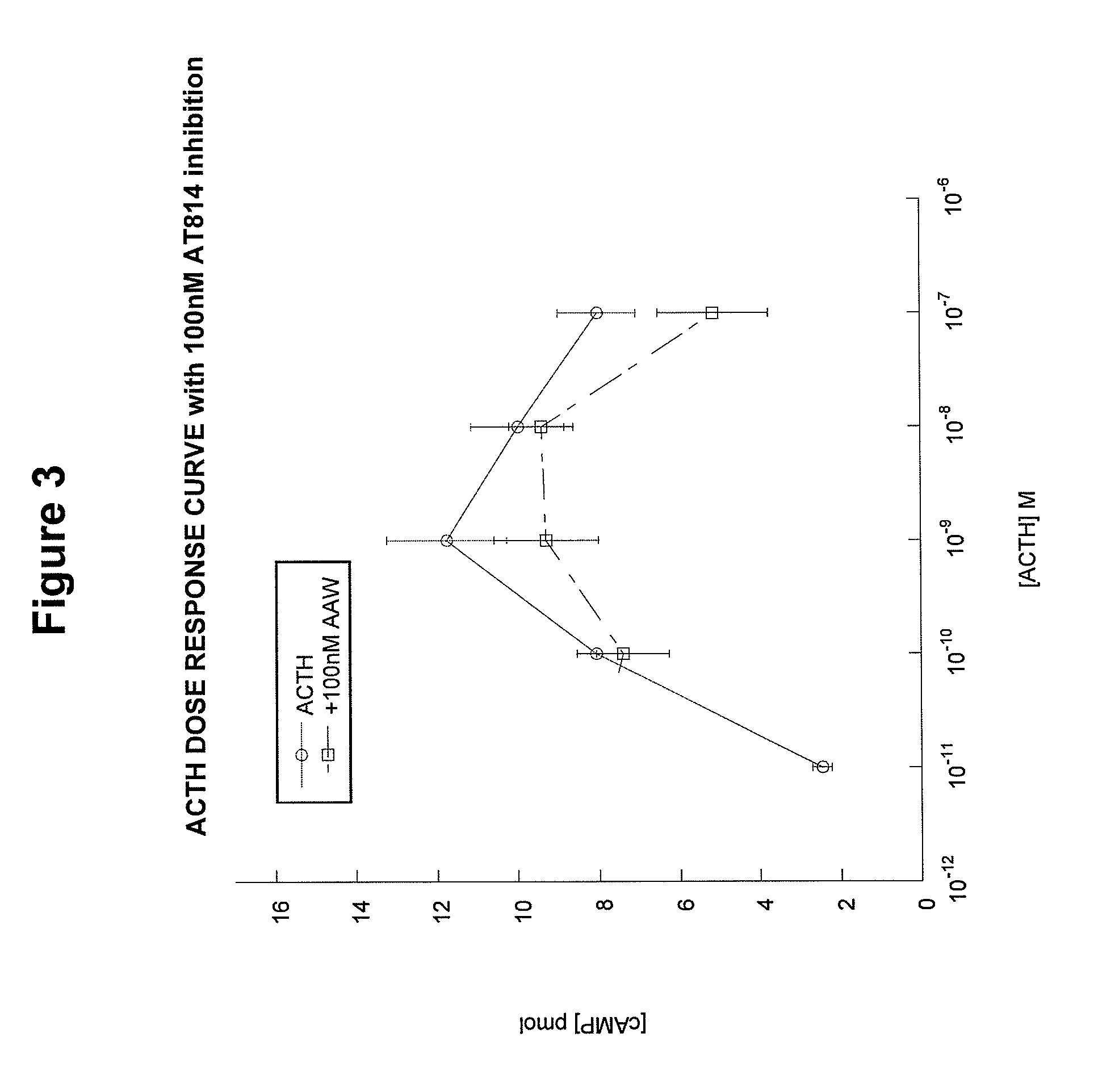
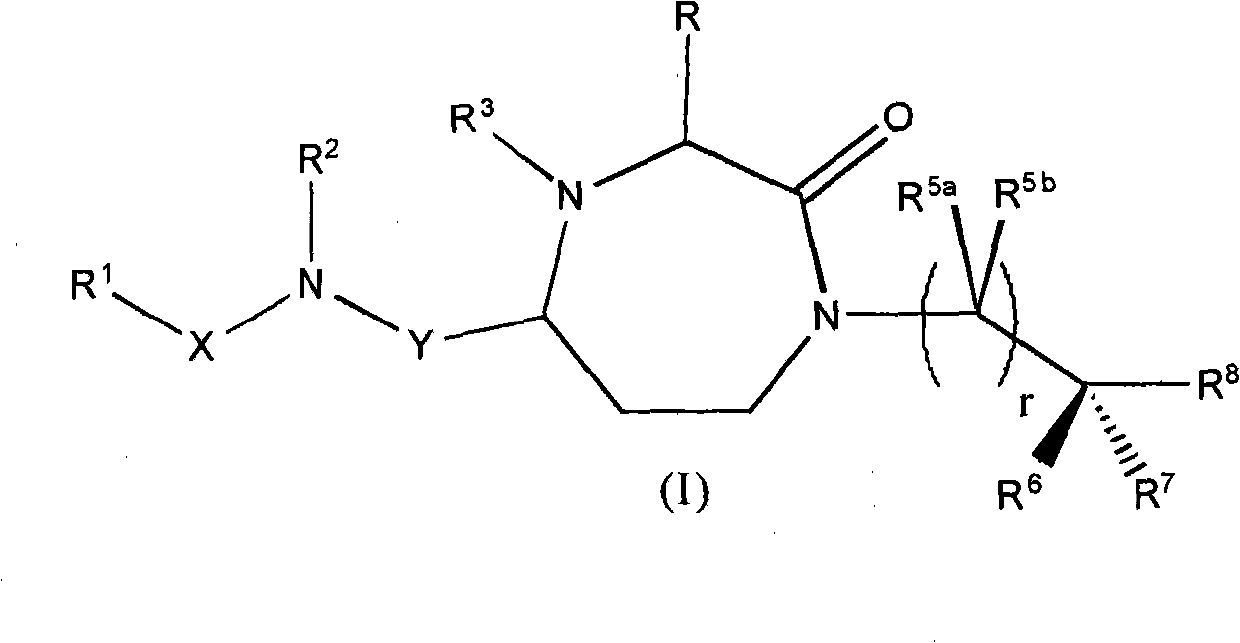
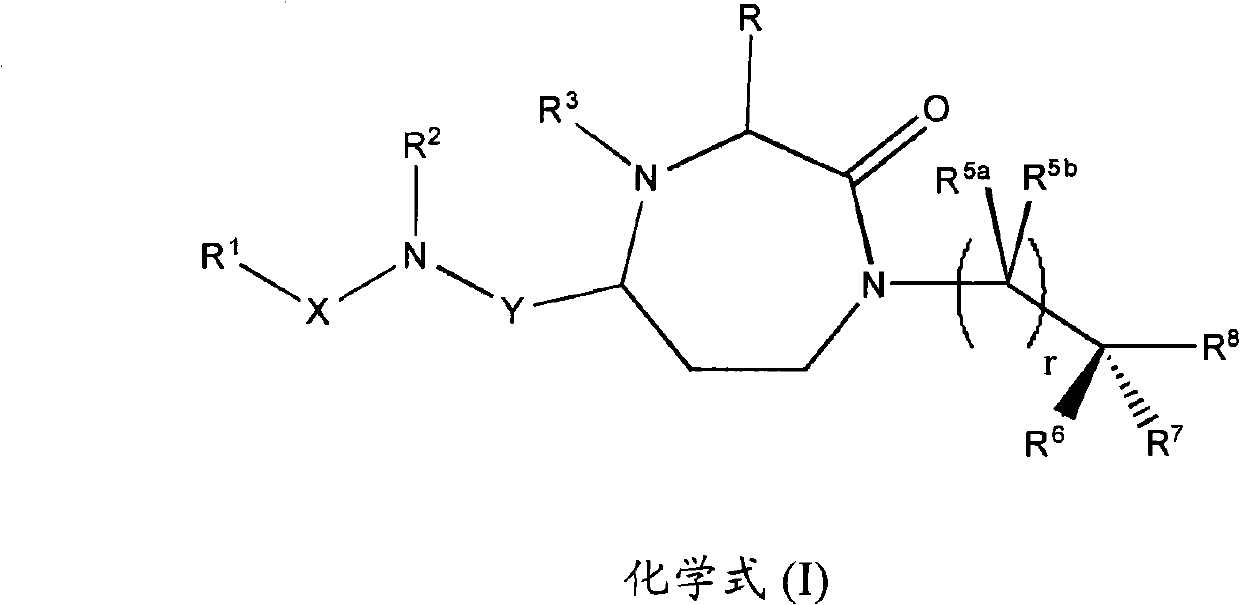
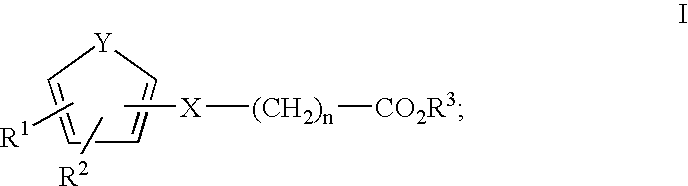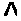Patents
Literature
40 results about "Melanocortin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The melanocortins are a group of peptide hormones which include adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and the different forms of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), and are derived from proopiomelanocortin (POMC) in the pituitary gland. The melanocortins exert their effects by binding to and activating the melanocortin receptors.
Multiple agent therapy for sexual dysfunction
InactiveUS20050222014A1Improve reliabilityIncreased temporal durationBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsSexual dysfunctionAgonist
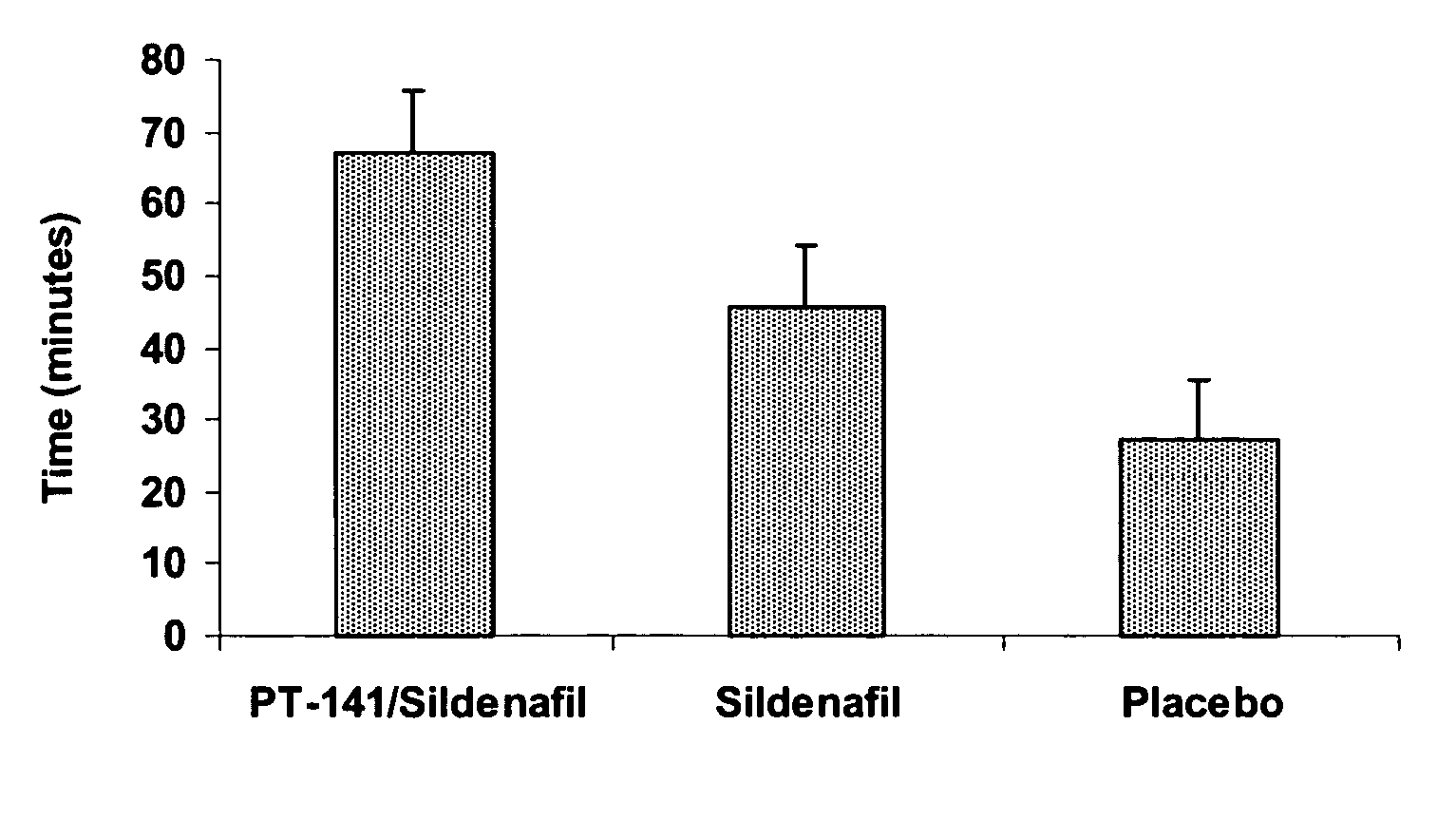
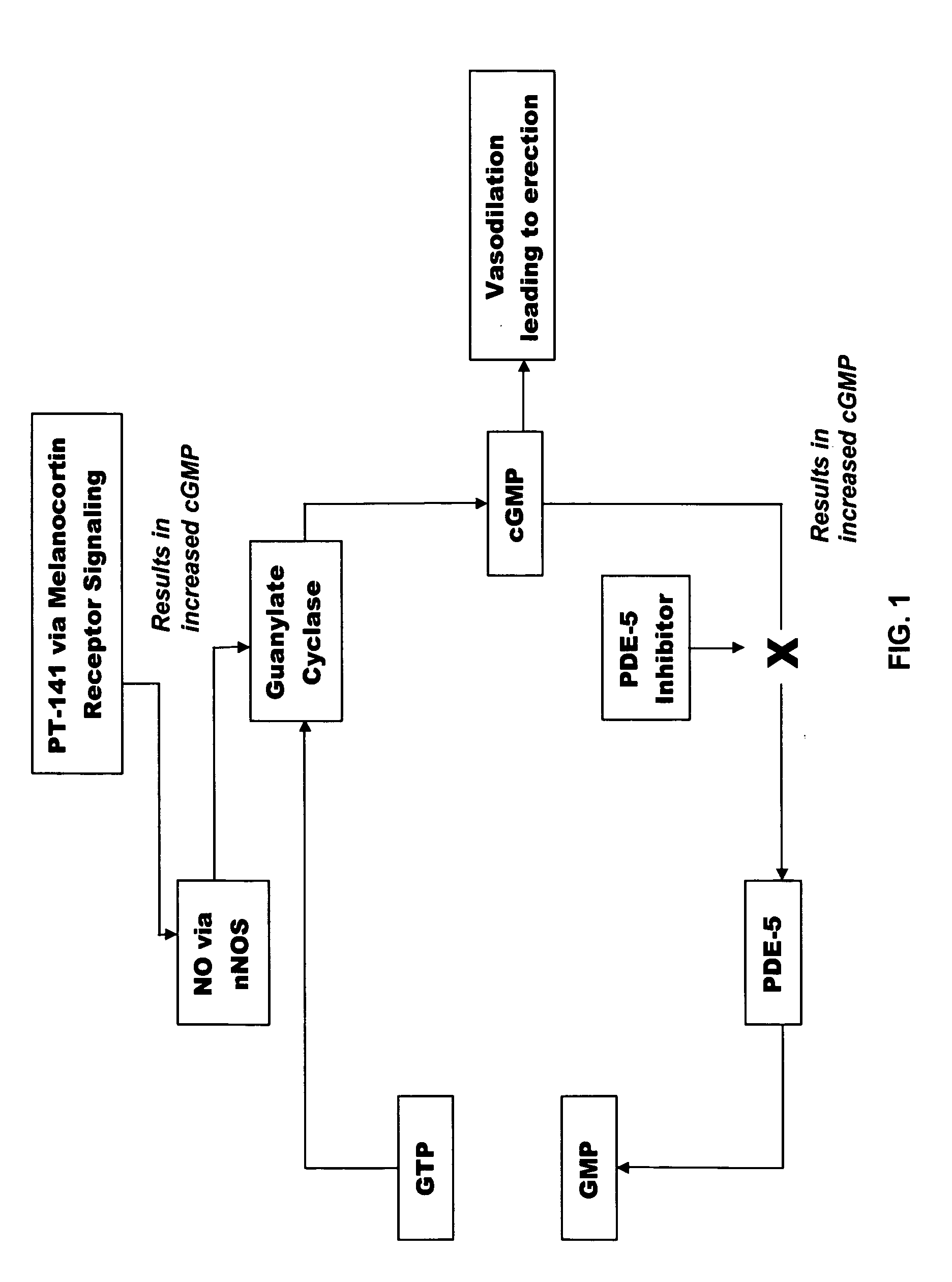
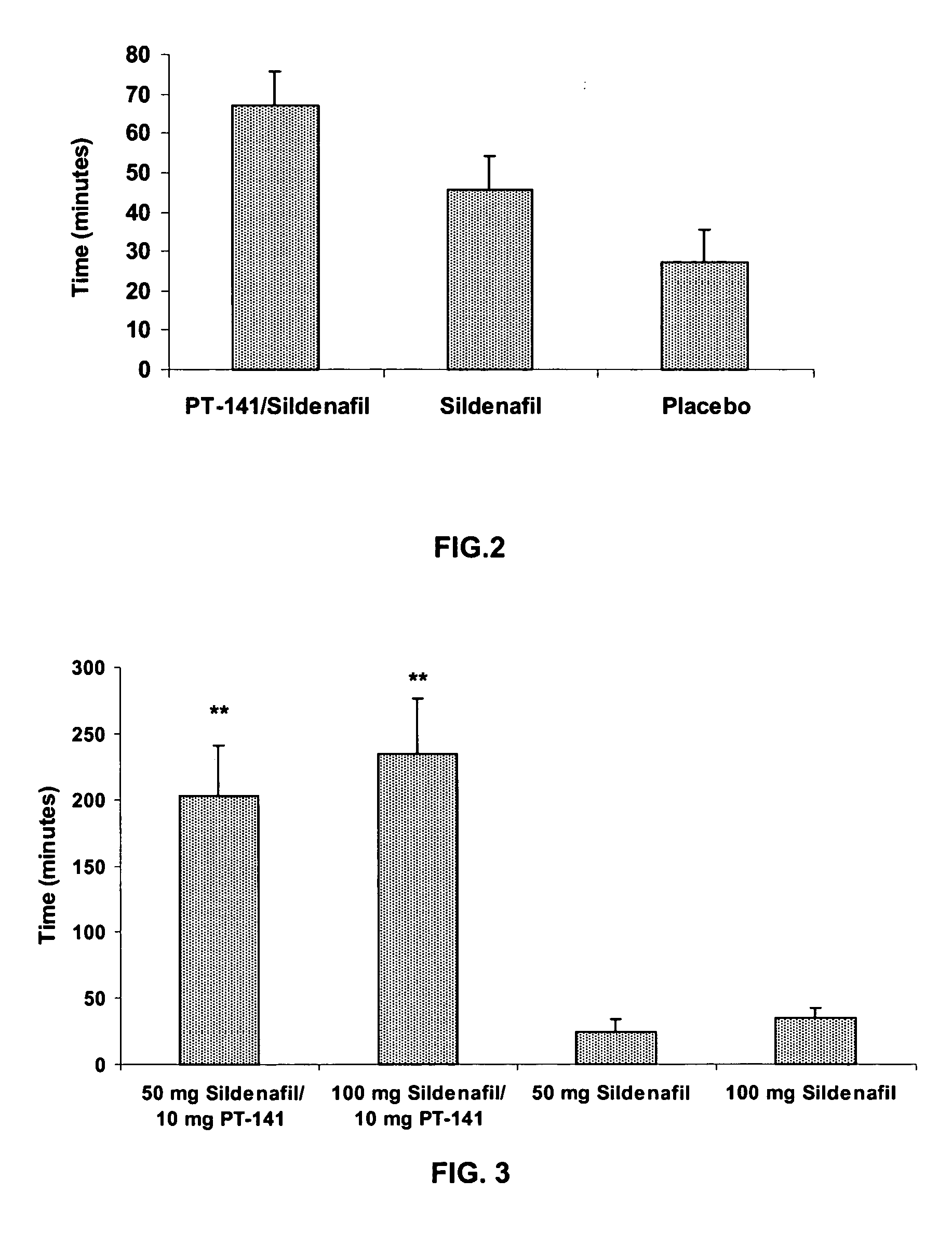
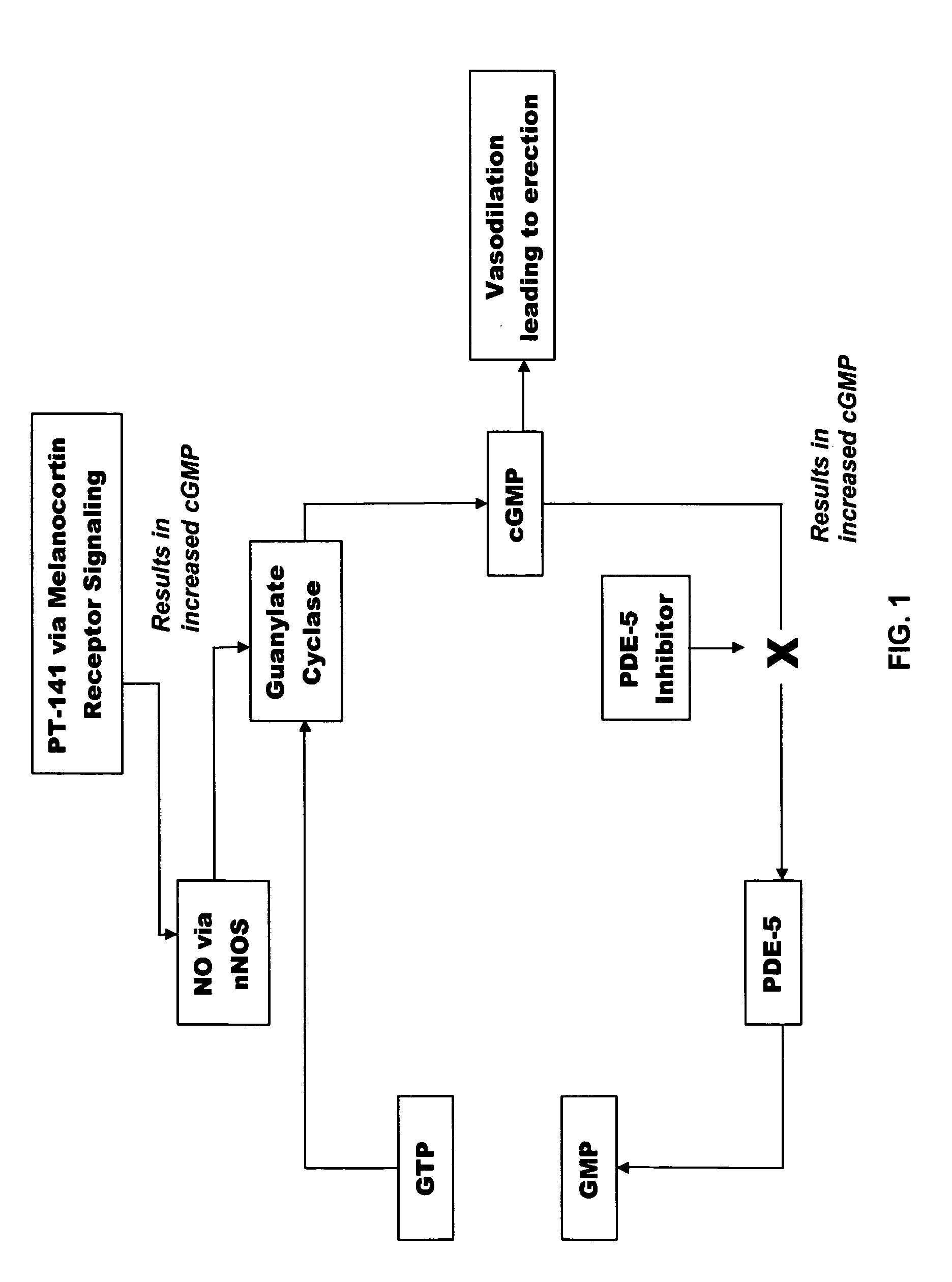
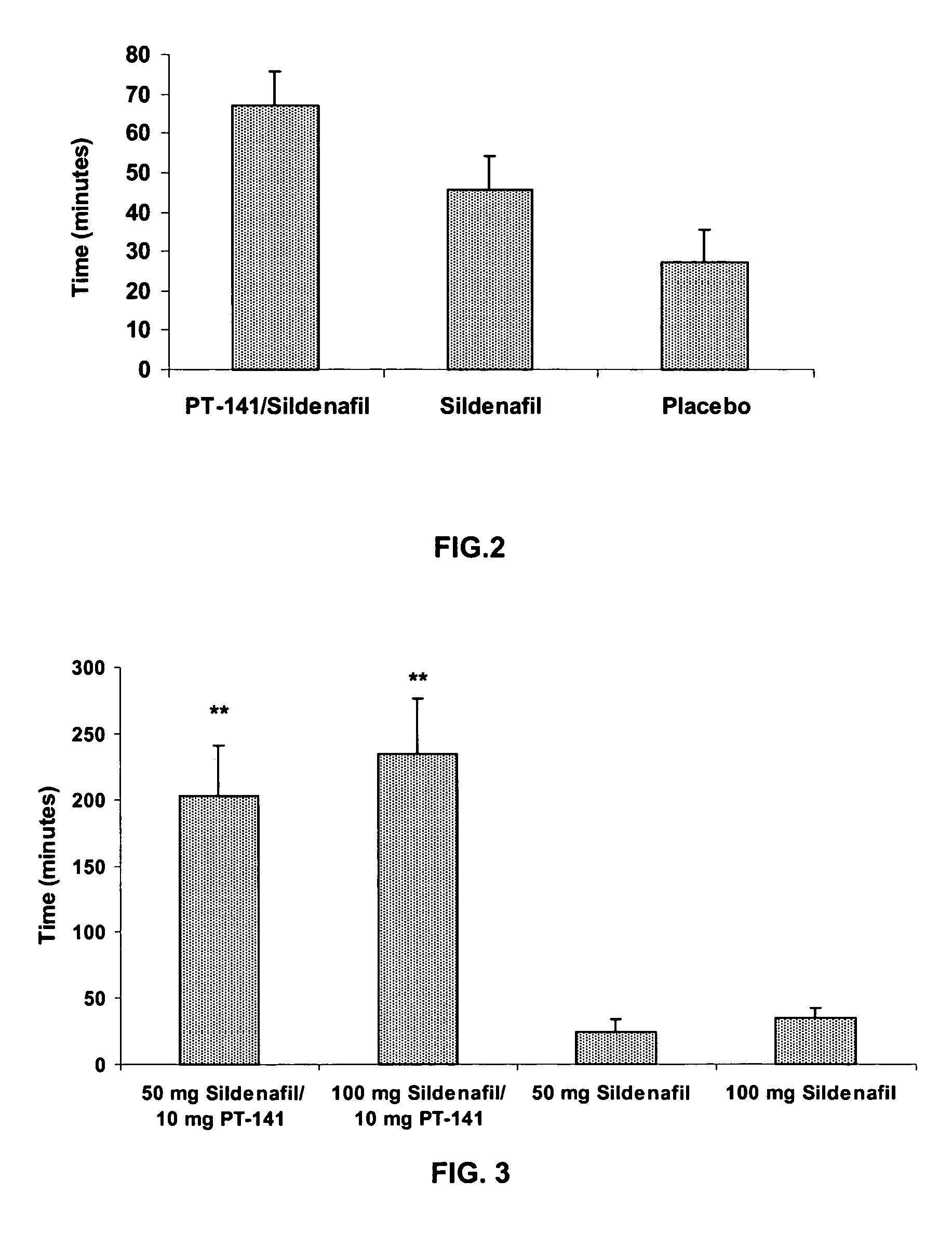
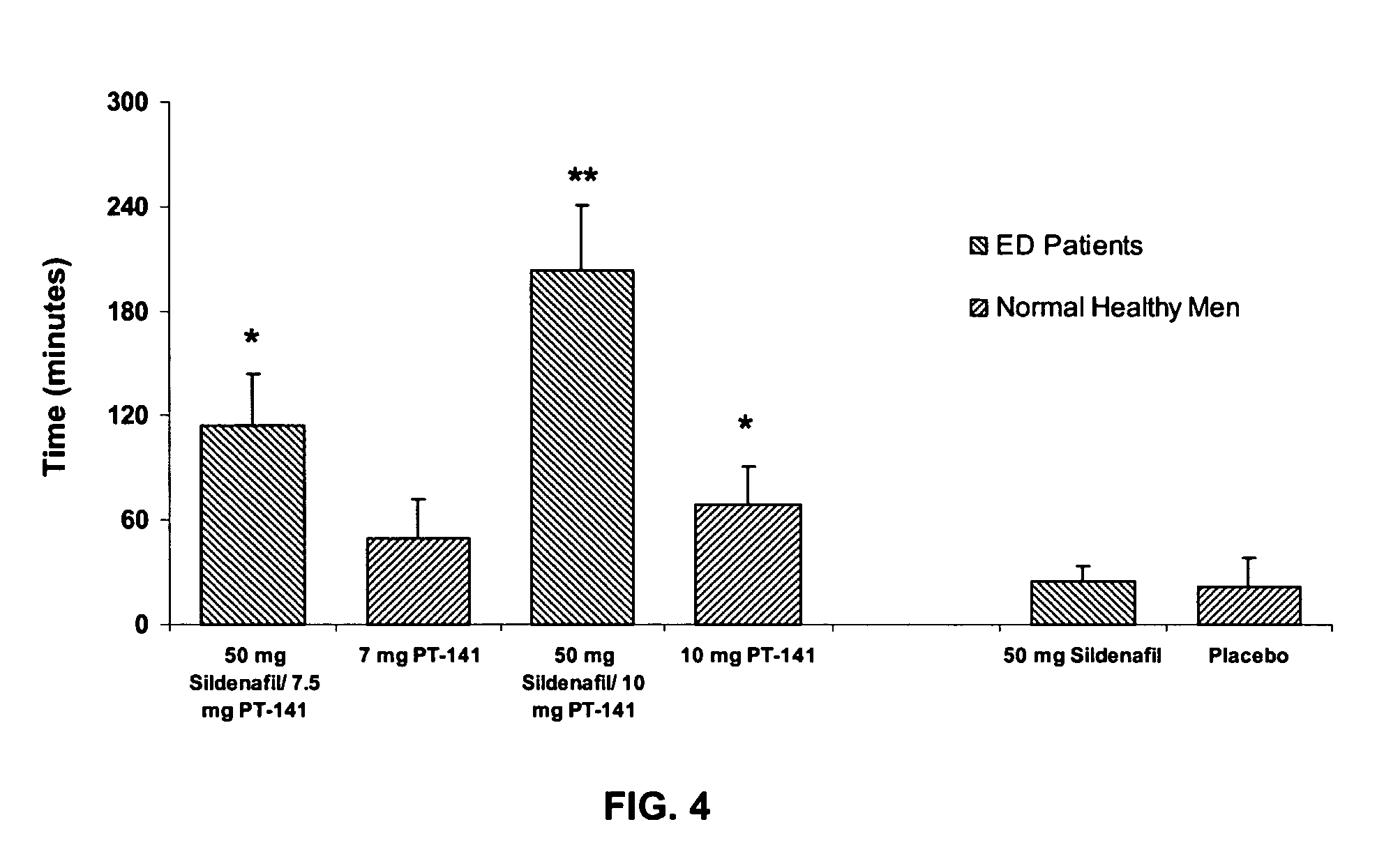
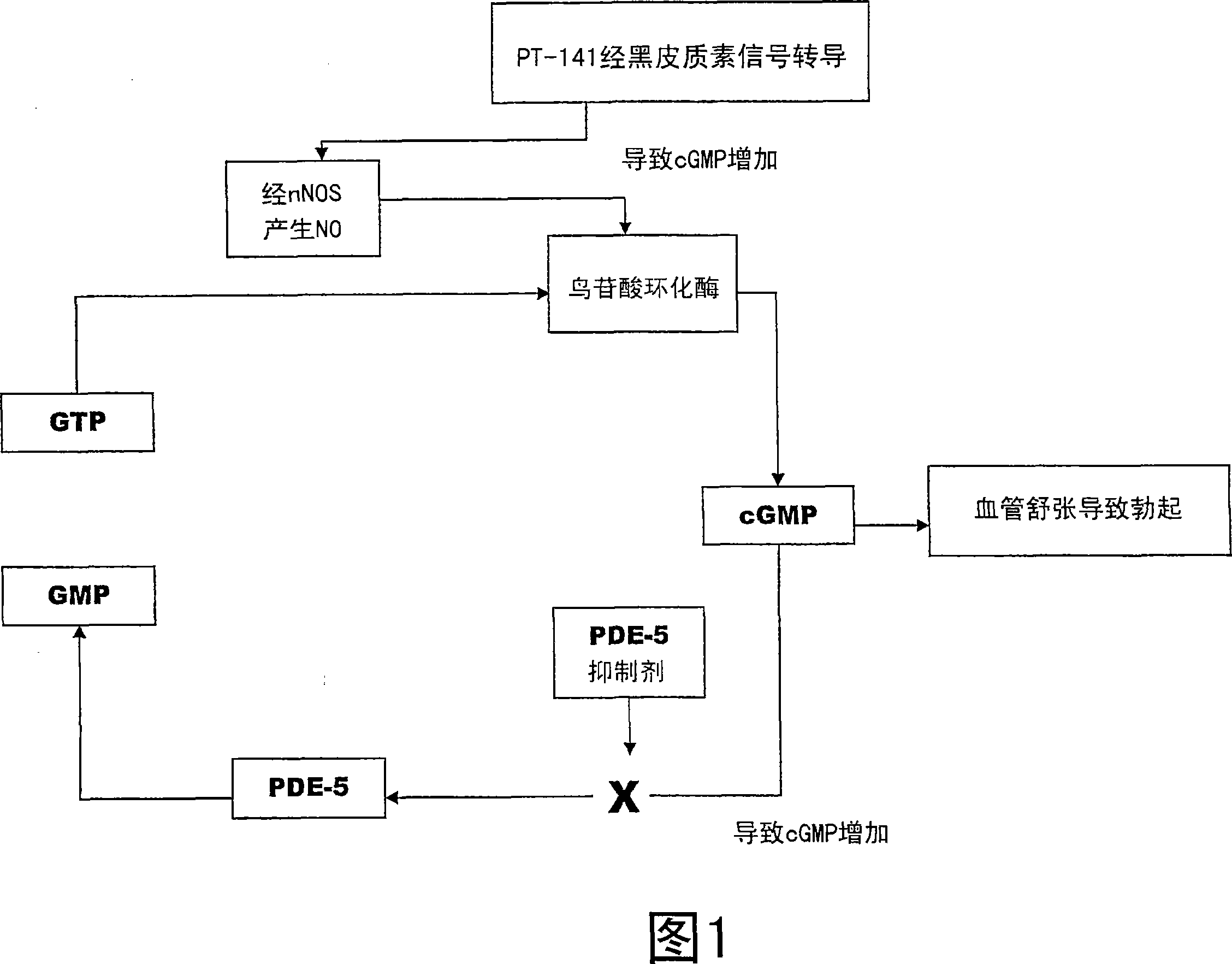
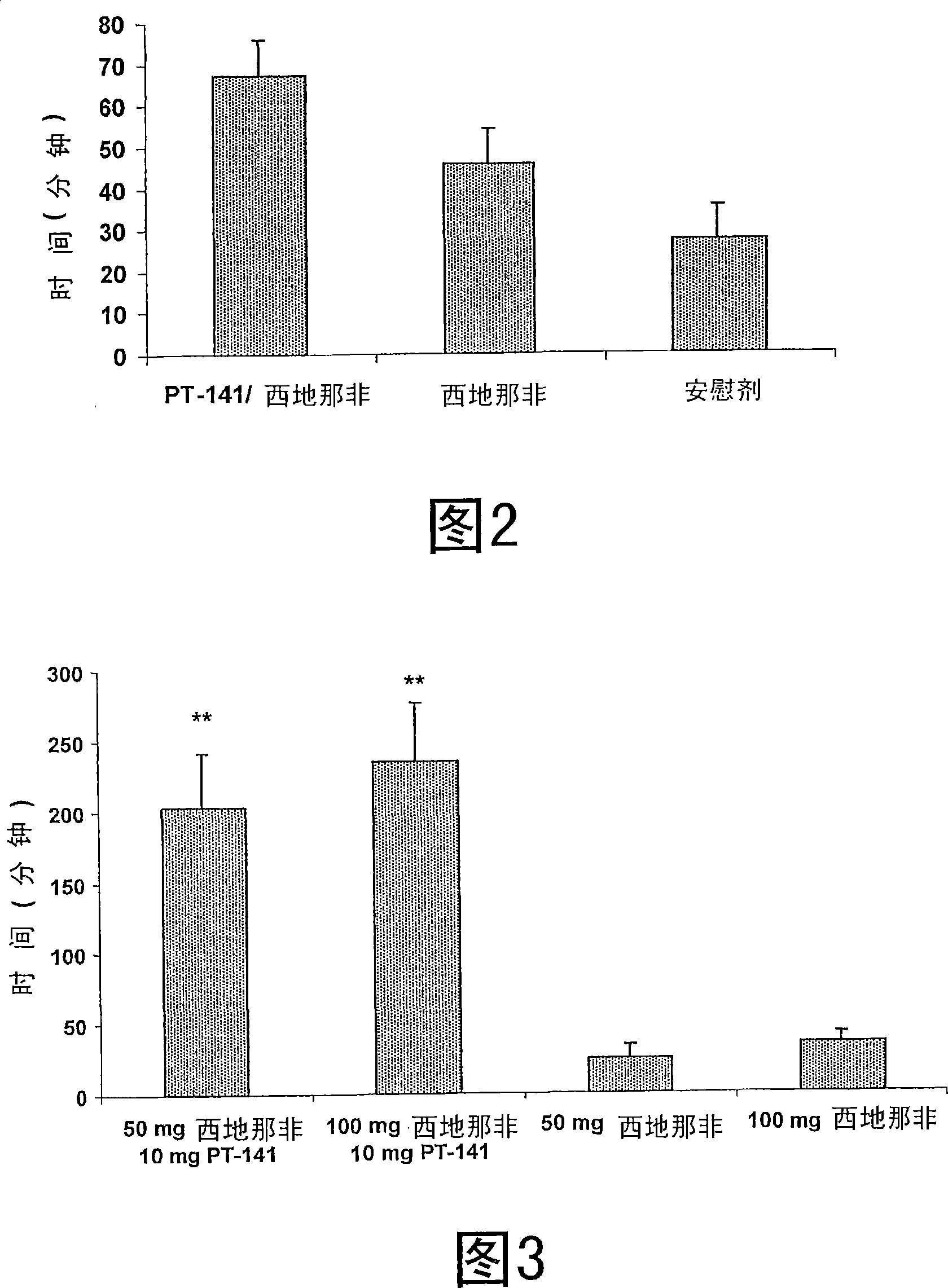
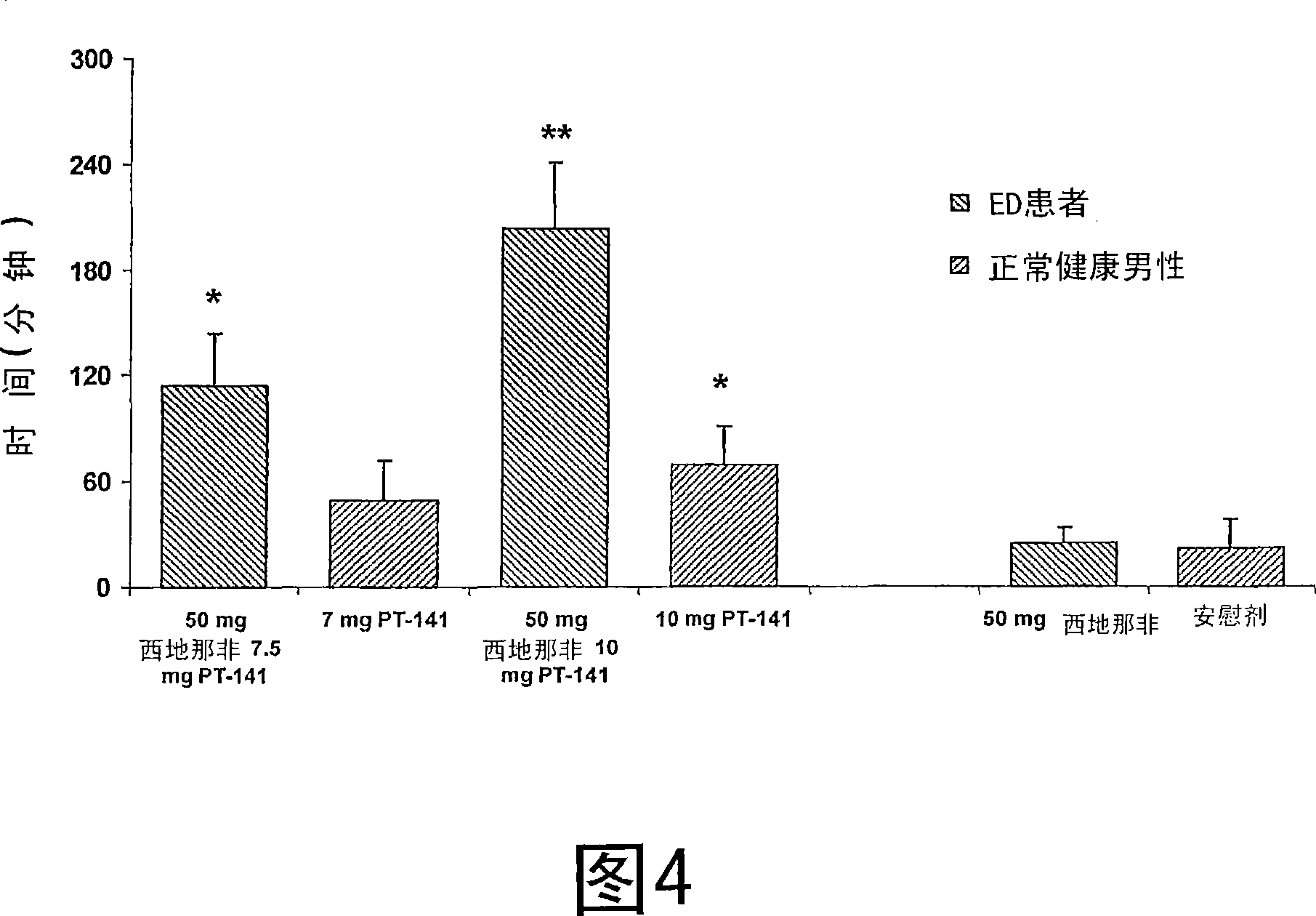
Multiple agent therapy for treatment of sexual dysfunction, including male erectile dysfunction, with sequential administration a type V phosphodiesterase inhibitor (PDE-5), such as sildenafil, preferably wherein the PDE-5 inhibitor is administered by oral dose means, and a melanocortin 3 and / or 4 receptor agonist, such as Ac-Nle-cyclo(-Asp-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Lys)-OH (PT-141) preferably wherein the PT-141 is formulated for and administered by intranasal means, and further preferably wherein the PDE-5 inhibitor is administered prior to PT-141.
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
Multiple agent therapy for sexual dysfunction
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
Compounds, Methods and Formulations for the Oral Delivery of a Glucagon-Like Peptide (Glp)-1 Compound or a Melanocortin-4 Receptor (Mc4) Agonist Peptide
Owner:EMISPHERE TECH INC
Pharmacological chaperones for treating obesity
InactiveUS20070021433A1High activityImprove scalabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideReticulum cellPharmacological chaperone
The invention relates to methods of enhancing normal melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) activity, and to enhancing activity of an MC4R having a mutation which affects protein folding and / or processing of the MC4R. The invention provides a method of treating an individual having a condition in which increased activity of an MC4R at the cell surface would be beneficial, for example in obesity, by administering an effective amount of a pharmacological chaperone for the MC4R. The invention provides MC4R pharmacological chaperones which enhance the activity of MC4R. The invention further provides a method of screening to identify pharmacological chaperones which enhance folding of an MC4R in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), in order to enhance the activity of the MC4R at the cell surface.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL +1
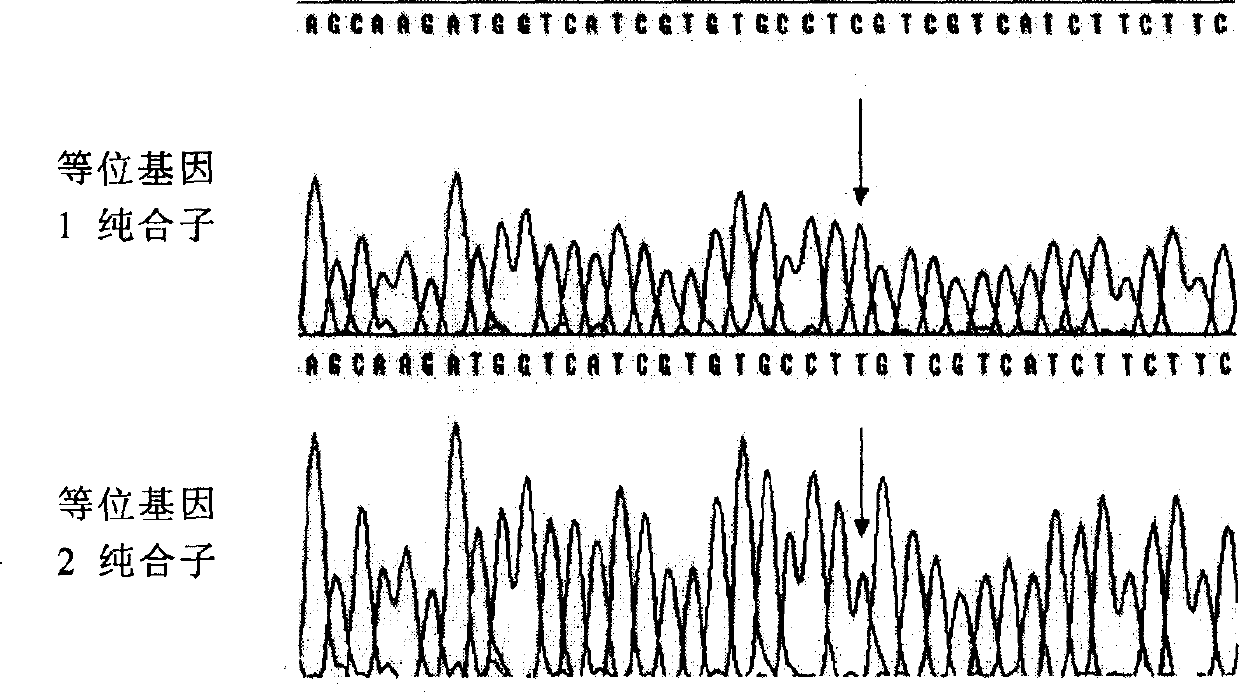
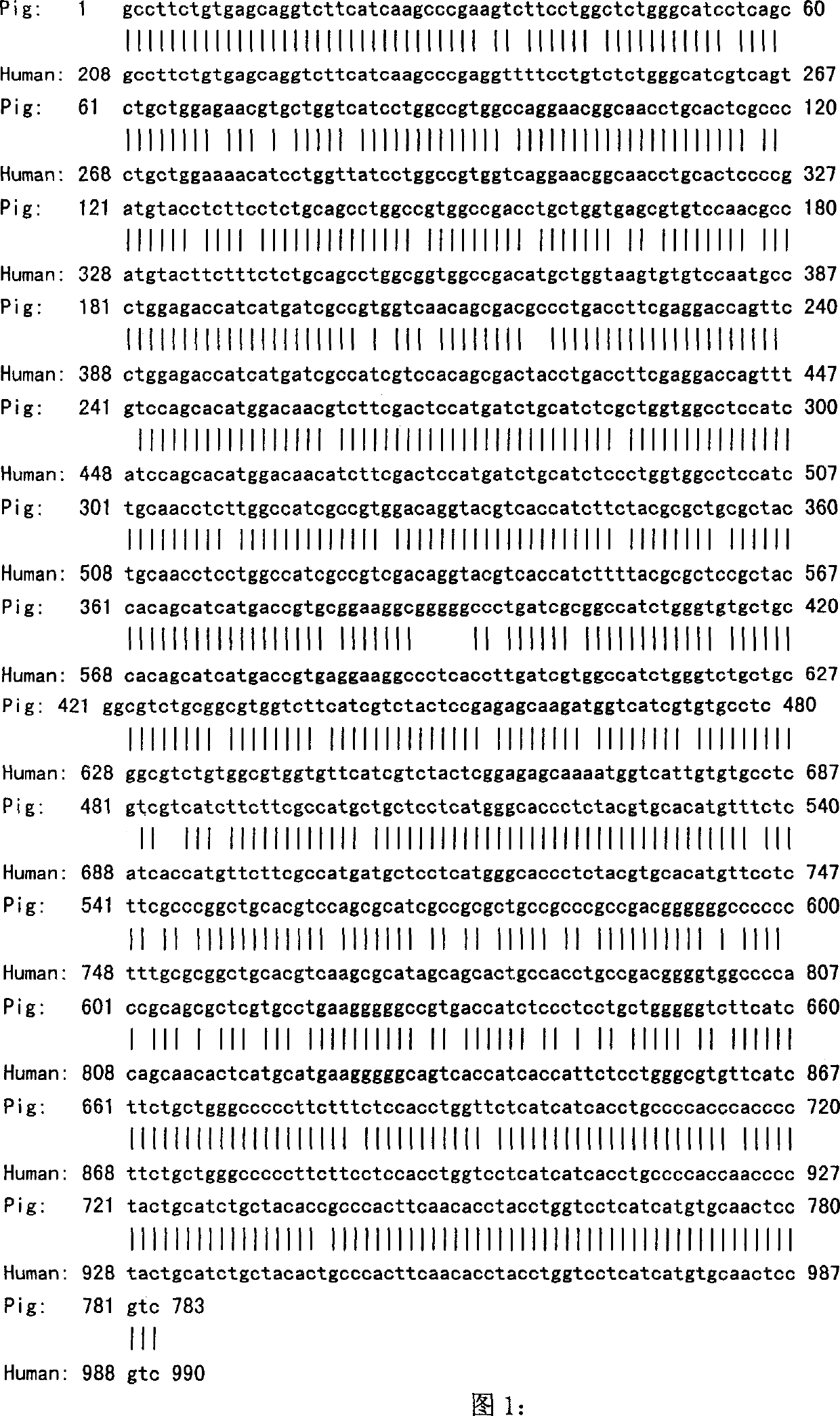
Gene of cortexin-3 receptor of pig melanin and method for detecting polymorphism of mononucleotide
InactiveCN1480532AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMelanocortin 3 receptorDirect sequencing
A process for detecting pig melanocortin-3 receptor (MC3R) gene and its single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) includes extracting DNA from pig blood genom, designing primer based on human and mouse MC3R gene conservative region, PCR amplification, directly sequencing the PCR product, comparing sequence, analyzing and detecting SNP.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
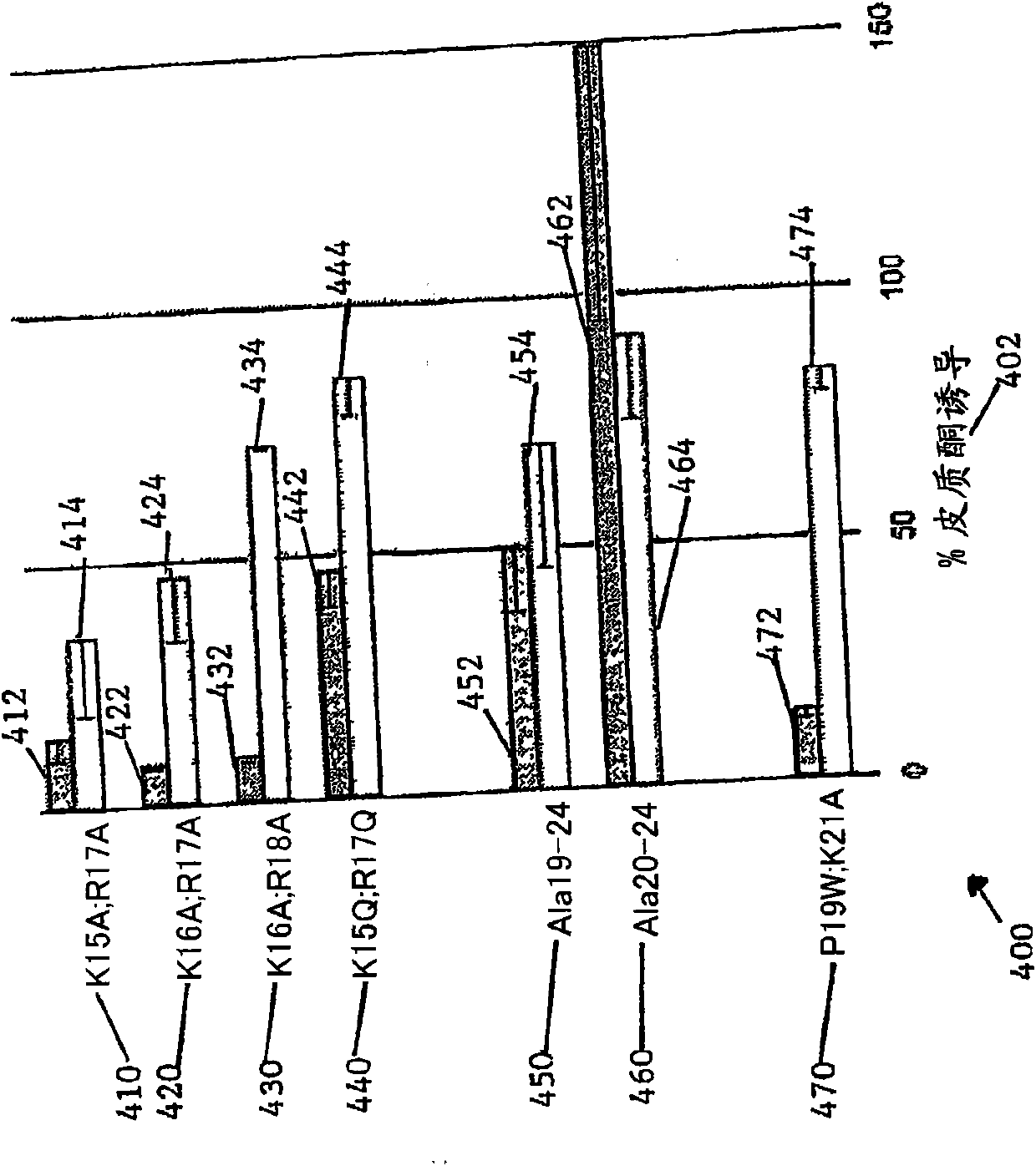
Stabilized melanocortin ligands
ActiveUS8541545B2Least riskEffectively producing chronic separationPeptide sourcesDepsipeptidesMelanocortinChemistry
Compositions and methods are disclosed for a non-naturally occurring melanocortin ligand comprised of a melanocortin analog coupled to a degradation-resistant C-terminal extension and, optionally, an N-terminal extension, to produce a stable melanocortin ligand having diminished or abolished cardiovascular activity while retaining desired melanocortin regulatory activity.
Owner:ENDEVICA BIO INC
Adrenocorticotropic hormone analogs and related methods
InactiveCN101947310AMaintain healthPromote healthy growthPeptide/protein ingredientsCorticotropinAdrenal glandPeptide sequence
ACTH analog compounds of the present invention include compounds comprising an ACTH peptide sequence with one or more structural modifications that can have one or more of the following preferred ACTH analog biological functions: (1) reduction of corticosteroid secretion by adrenal membrane in the presence of the ACTH analog compared to unmodified ACTH, (2) reduction of corticosteroid secretion by adrenal membrane in the presence of endogenous ACTH and (3) increased MC-2R binding affinity with reduced activation of the MC-2R receptor compared to unmodified ACTH binding to the MC-2R melanocortin. The ACTH analog compounds of the present invention are therefore useful for treatment or prevention of diseases and disorders related to ACTH, ACTH receptors or corticosteroid secretion, such as premature labor and Cushing's Disease.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DENVER +2
Melanocortin analogs with antimicrobial activity
The present invention finds application in the therapeutic fields. In particular, it concerns new synthetic melanocortin peptides having improved antimicrobial activity.
Owner:FOND IRCCS CA GRANDA OSPEDALE MAGGIORE POLICLINICO
Multiple agent therapy for sexual dysfunction
Multiple agent therapy for treatment of sexual dysfunction, including male erectile dysfunction, with sequential administration a type V phosphodiesterase inhibitor (PDE-5), such as sildenafil, preferably wherein the PDE-5 inhibitor is administered by oral dose means, and a melanocortin 3 and / or 4 receptor agonist, such as Ac-Nle-cyclo(-Asp-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Lys)-OH (PT-141) preferably wherein the PT-141 is formulated for and administered by intranasal means, and further preferably wherein the PDE-5 inhibitor is administered prior to PT-141.
Owner:PALATIN TECH INC
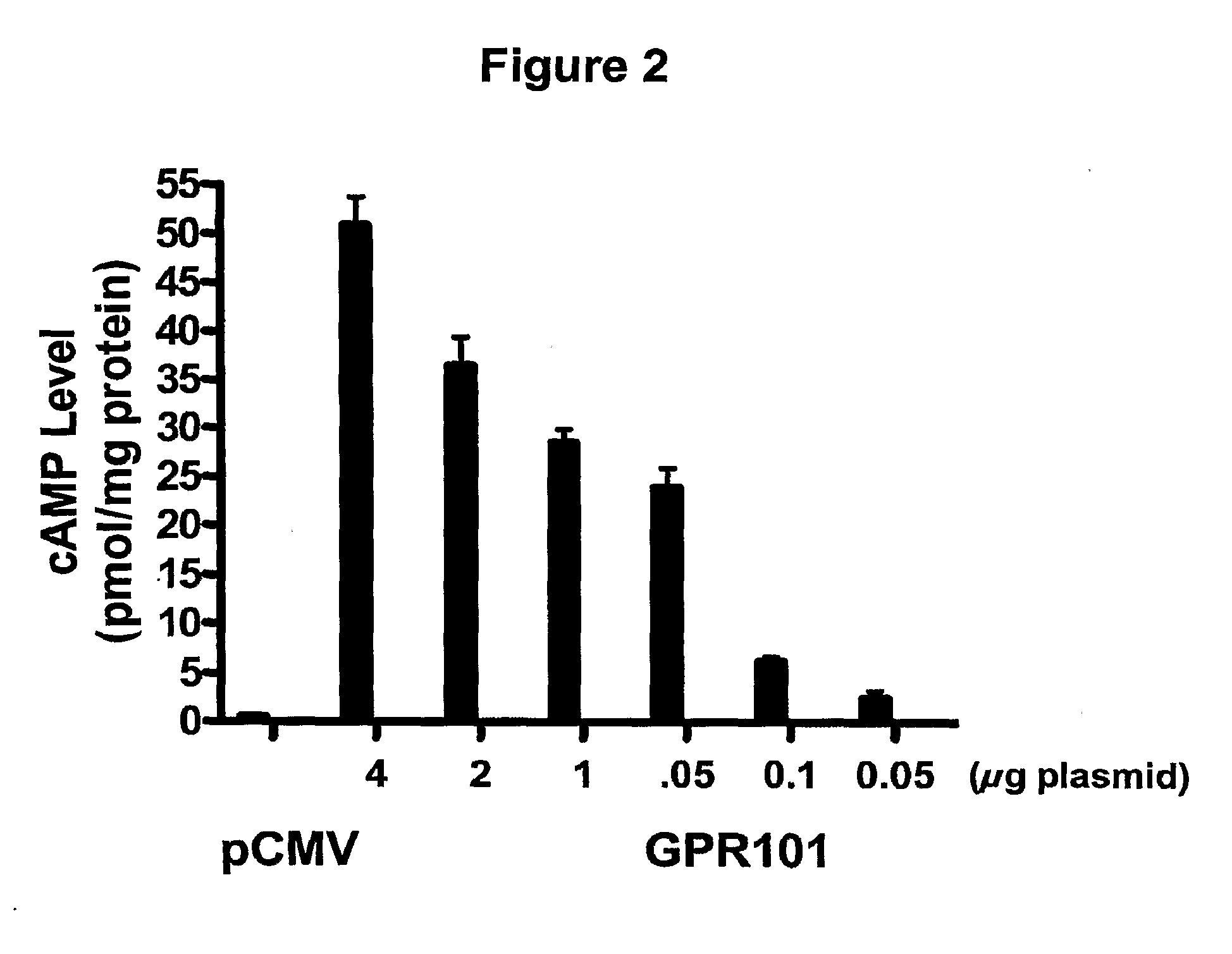
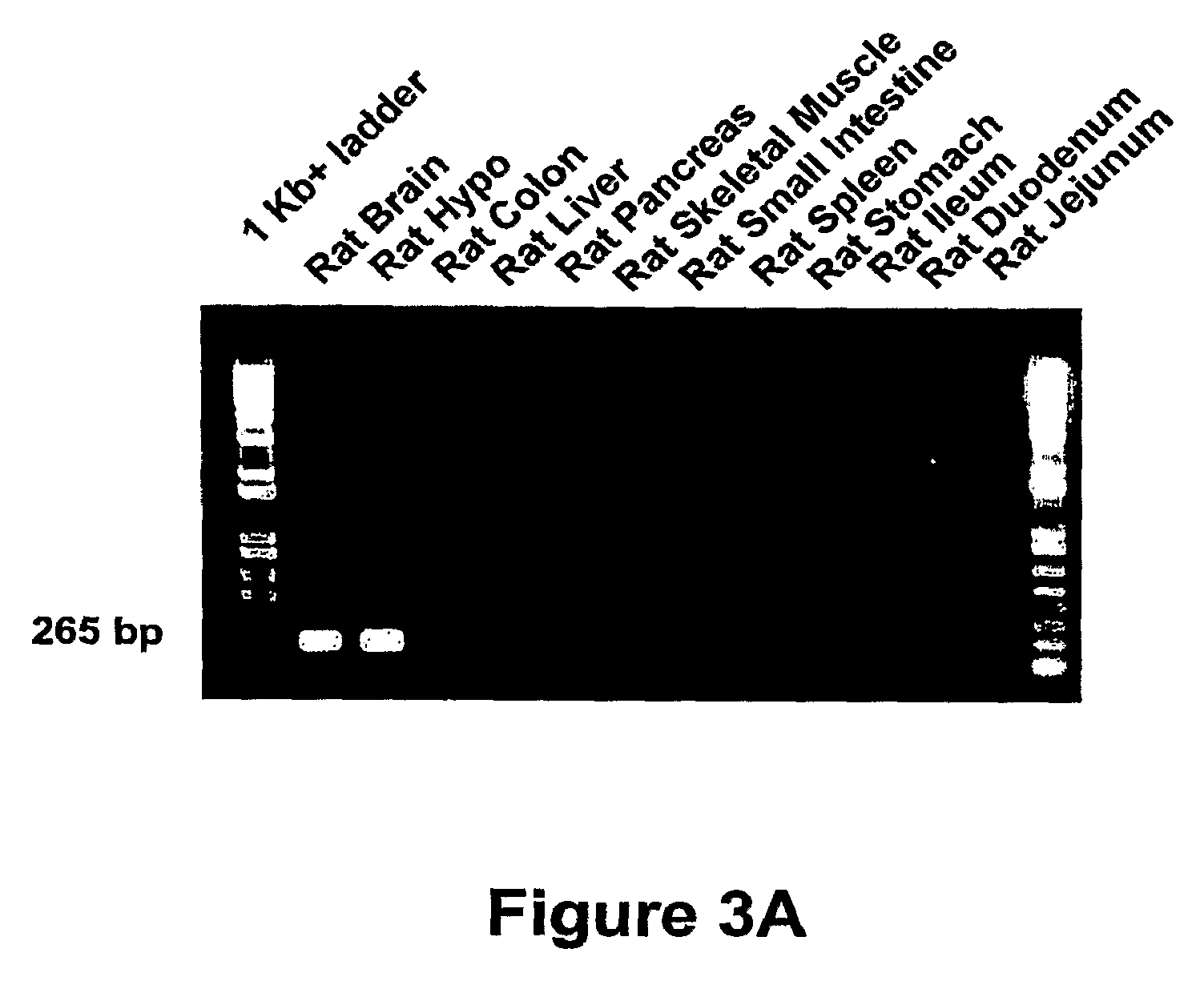
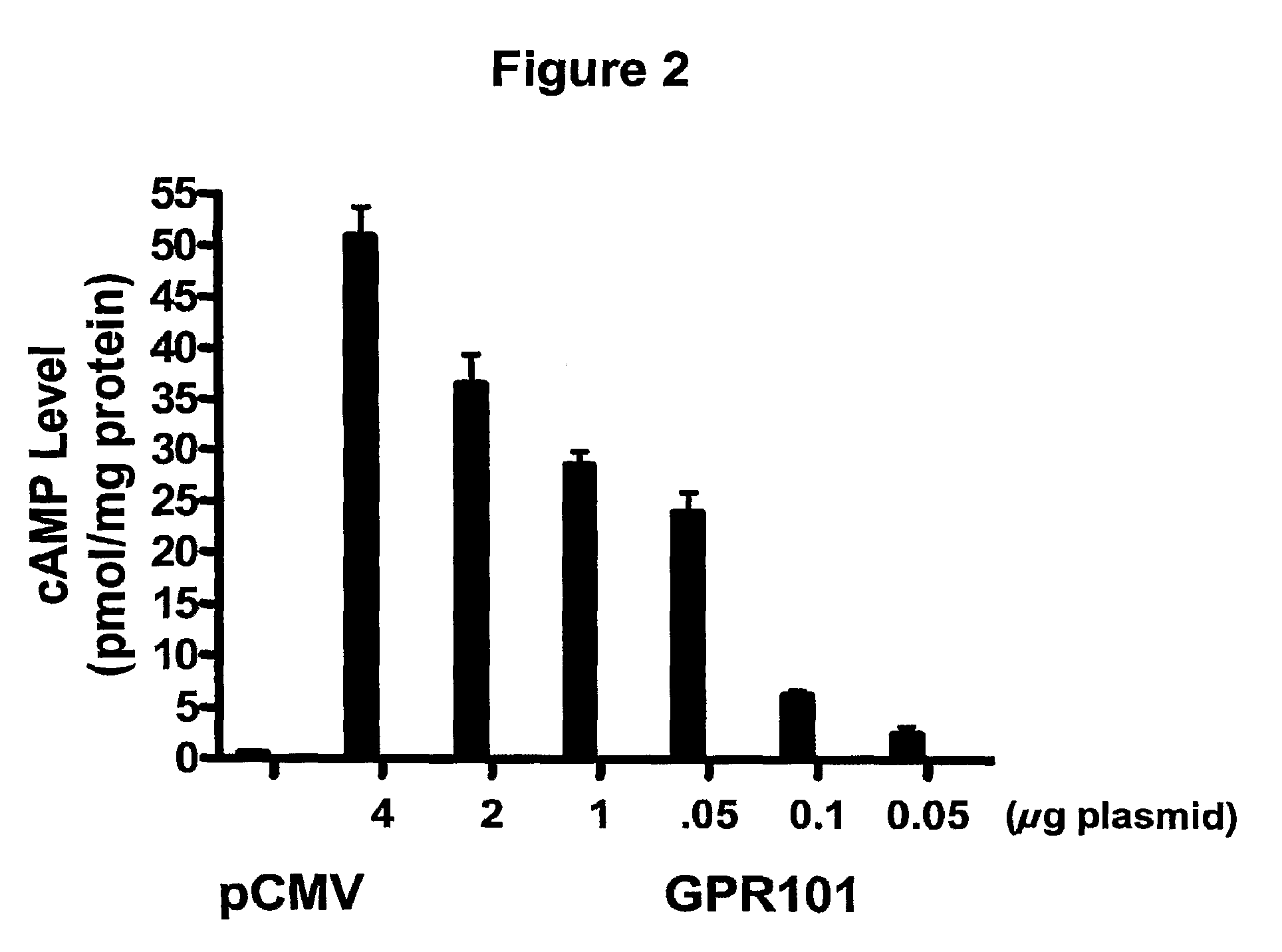
Use of gpr101 receptor in methods to identify modulators of hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin (POMC)-derived biologically active peptide secretion useful in the treatment of pomc-derived biologically
InactiveUS20100056442A1Promote and stabilizeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMelanophore-dispersing hormone
The present invention relates to methods of using GPR101 G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) to screen candidate compounds as modulators of hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin (POMC)-derived biologically active peptide secretion. Modulators of GPR101 receptor modulate hypothalamic POMC-derived biologically active peptide secretion and are useful in the treatment of POMC-derived biologically active peptide-related disorders. POMC-derived biologically active peptides include, but are not limited to, α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH), β-melanocyte stimulating hormone (β-MSH) and γ-melanocyte stimulating hormone (γ-MSH). Agonists and partial agonists of GPR101 receptor stimulate hypothalamic α-MSH, β-MSH and γ-MSH secretion and are useful, for example, in the treatment and prevention of obesity and conditions related thereto (including but not limited to Type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome), inflammation-associated disorders, and pyrexia. Inverse agonists and antagonists of GPR101 receptor inhibit α-MSH, β-MSH and γ-MSH secretion and are useful, for example, in the treatment and prevention of disorders such as cachexia.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Methods of using GPR101 receptors to identify modulators of hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin (POMC)-derived biologically active peptide secretion
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Purification method for domestic rabbits with Belgian hair color based on genotype selection
ActiveCN109680075AGuaranteed uniformityEnsure consistencyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention provides a purification method for domestic rabbits with a Belgian hair color based on genotype selection. The purification method is applicable to purification of various domestic rabbits with the Belgian hair color, such as meat rabbits, rex rabbits, long hair rabbits and ornamental rabbits. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting thedomestic rabbits with a hair color phenotype which is the Belgian hair color; then detecting an ASIP (Agouti Signaling Protein) gene, an MC1R (Melanocortin 1-Receptor) gene and a TYR (Tyrosinase) geneat the same time by utilizing a first primer group, a second primer group and a third primer group; screening the domestic rabbits with genotypes of AA (corresponding to the ASIP gene), EE (corresponding to the MC1R gene) and CC (corresponding to the TYR gene). The domestic rabbits with the genotype of AAEECC, which are obtained by the purification method, are Belgian hair color homozygotes and recessive white genes are eliminated. According to a domestic rabbit specialized line with the Belgian hair color, which is cultivated by the purification method, germplasm materials of breeding enterprises can be protected very well on the basis of ensuring that the hair colors of commercial rabbits are consistent.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods of treating overproduction of cortisol using ACTH antagonist peptides
Owner:COLORADO SEMINARY
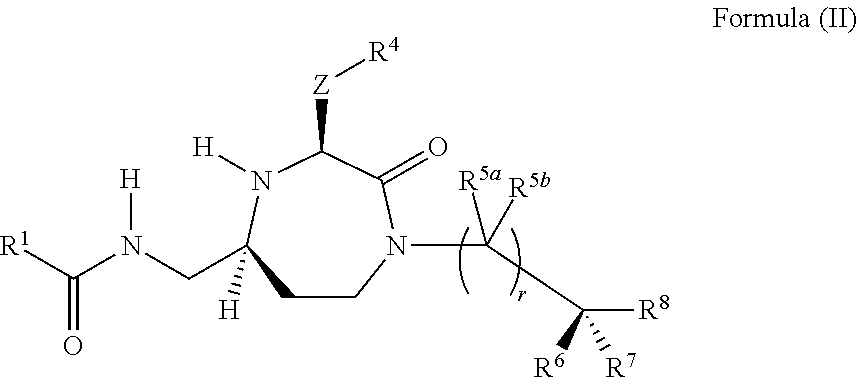
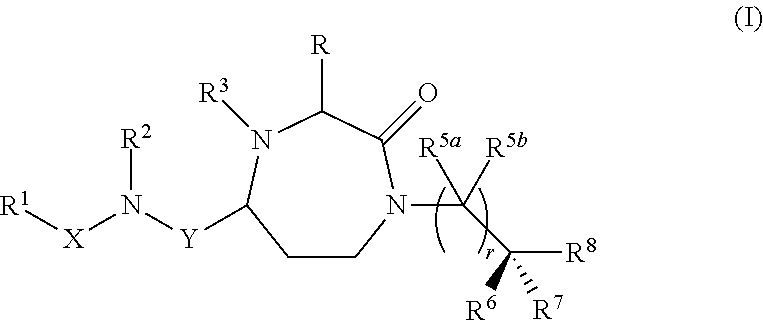
Methods of modulating the activity of the mc5 receptor and treatment of conditions related to this receptor
ActiveCN102006873AOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsSeborrheic dermatitisMelanocortin 5 receptor
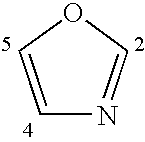
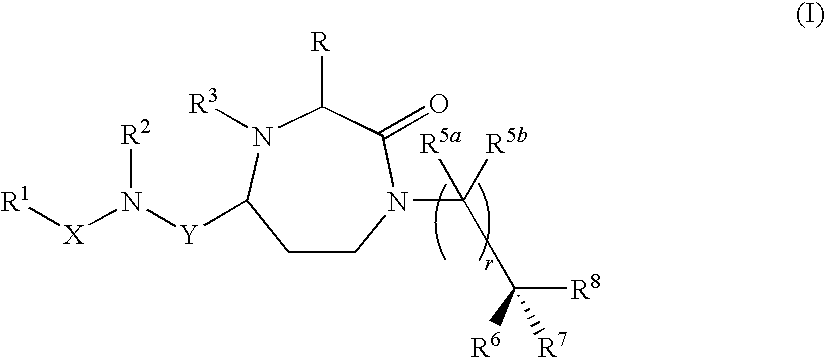
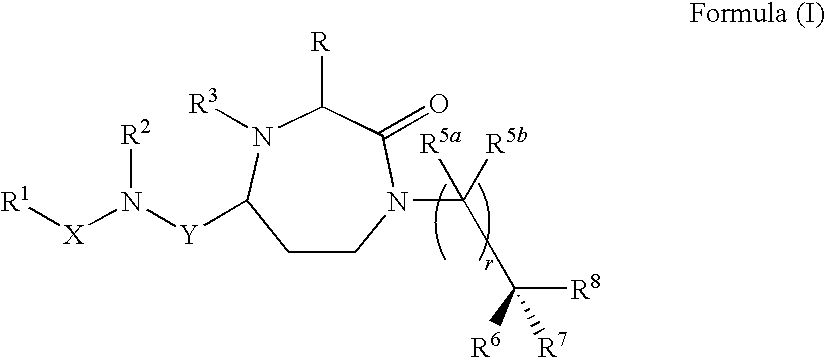
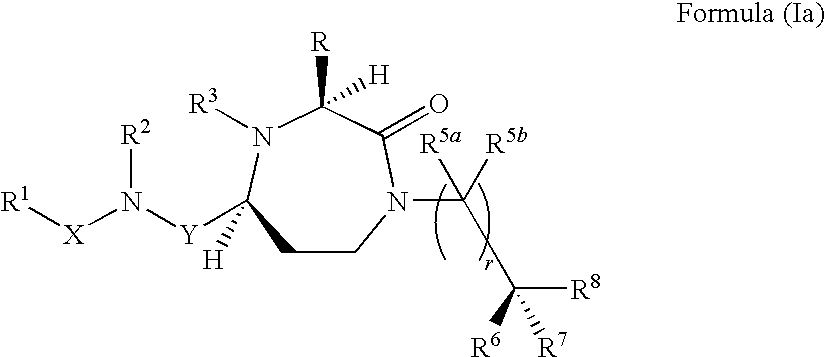
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) that are useful for modulating the biological activity of the melanocortin-5 receptor (MC5R). Compounds of this invention can be used to treat diseases and / or conditions in which downregulation of MC5R is beneficial. Such diseases and / or conditions include, but are not limited to, acne, seborrhea, seborrheic dermatitis, cancer, and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:马普治疗私人有限公司
Melanocortin ligands and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20170342107A1Lower blood pressureInduce weight lossHormone peptidesTetrapeptide ingredientsMelanocortinStereochemistry
Owner:TORREY PINES INST FOR MOLECULAR STUDIES +1
Chimeric melanocortin ligands and methods of use thereof
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
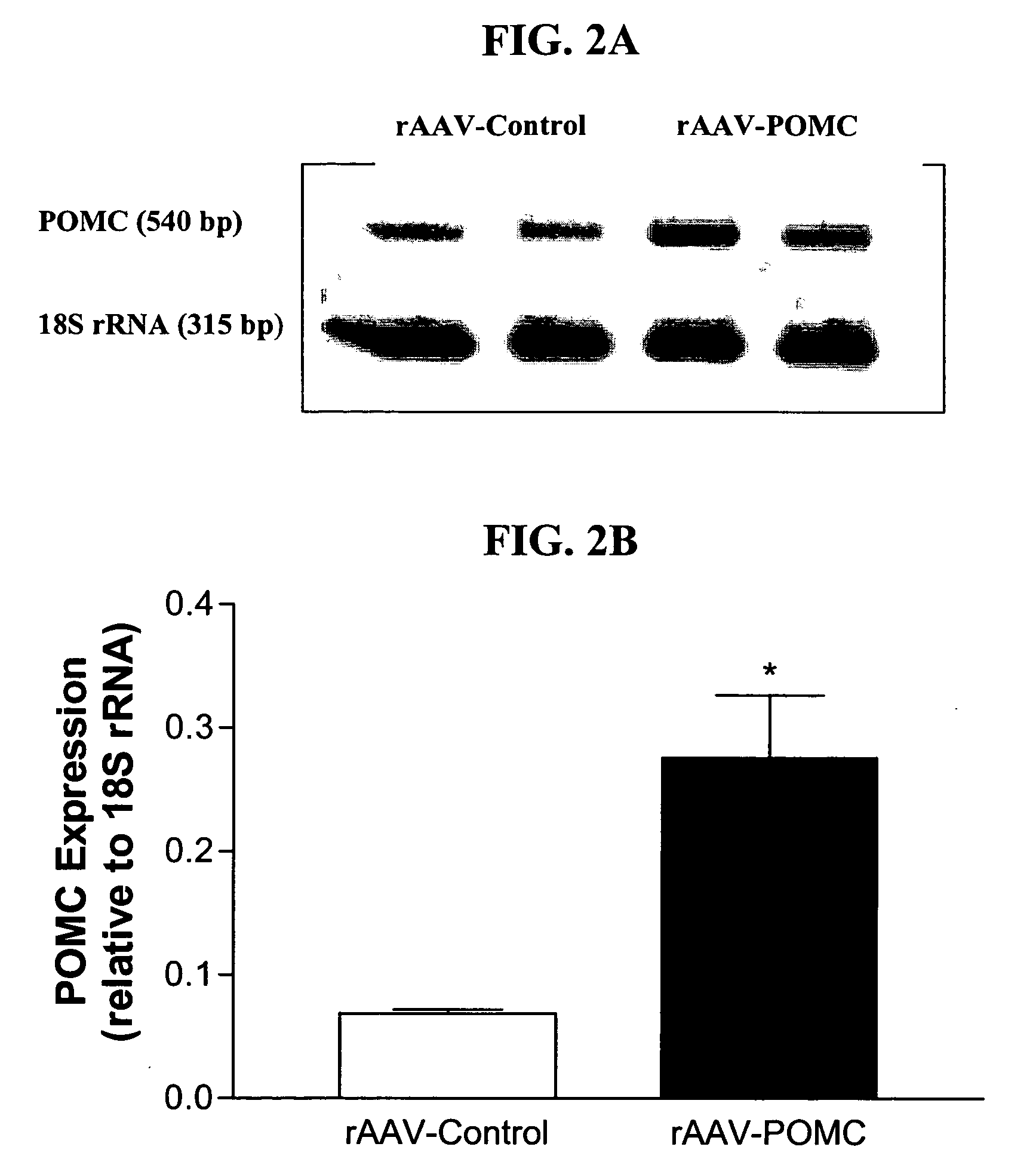
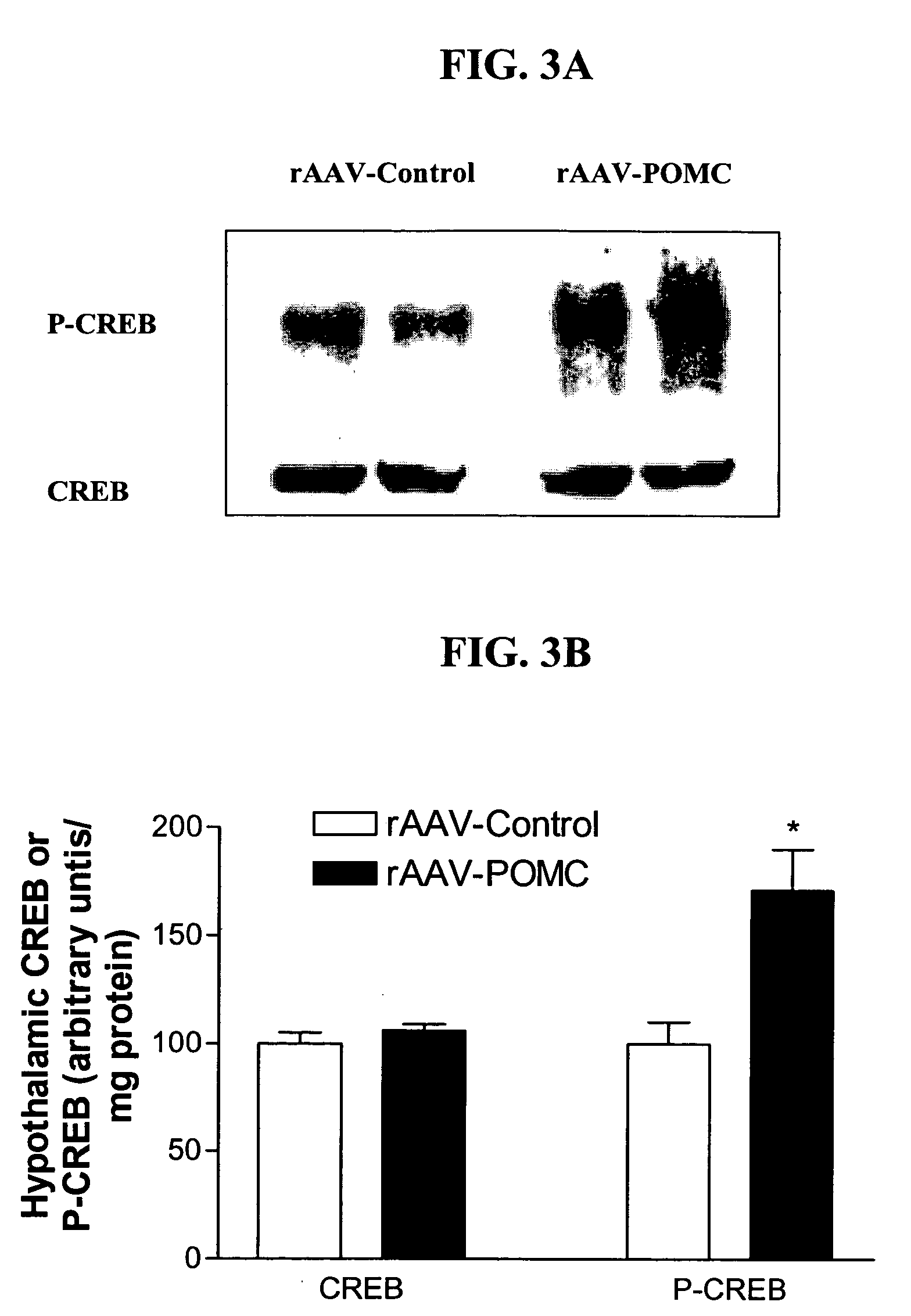
RAAV vector-based pro-opiomelanocortin compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20050002905A1Reduce risk factorOvercome limitationsBiocideMetabolism disorderHyperinsulinemiaNucleotide
Disclosed are methods for the use of pro-opiomelanocortin-encoding polynucleotides in the creation of transformed host cells and transgenic animals. In particular, the use of recombinant adeno-associated viral (rAAV) vector compositions, virions, and pluralities of virus particles that comprise a nucleic acid segment that expresses one or more mammalian pro-opiomelanocortin polypeptides in suitably transformed host cells is described. Also disclosed are methods for the treatment and amelioration of symptoms of a variety of conditions and disorders in an animal, including hyperinsulinemia, obesity, adiposity, overeating, and related eating disorders.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
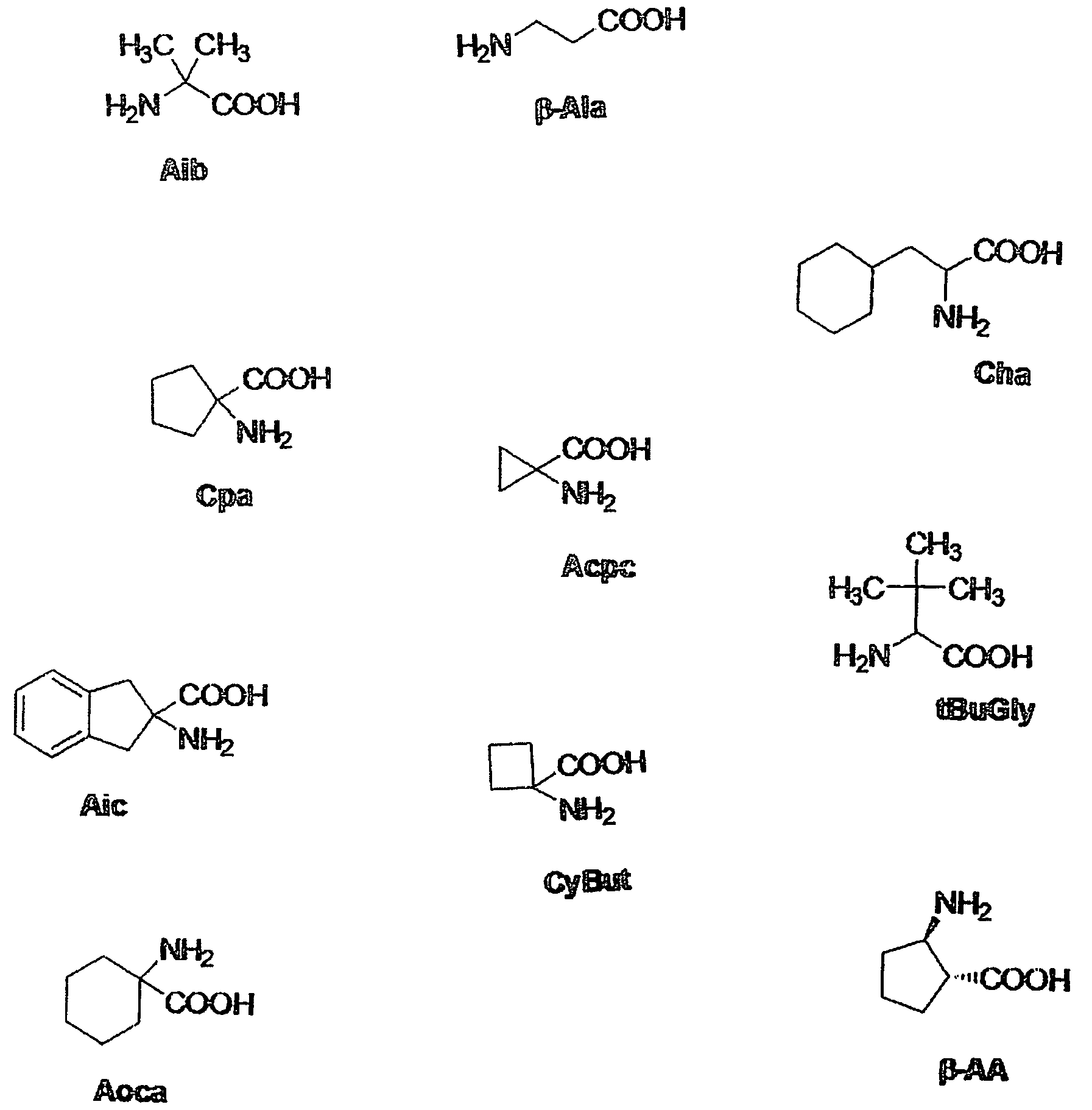
Melanocortin analogue as well as preparation method and application thereof
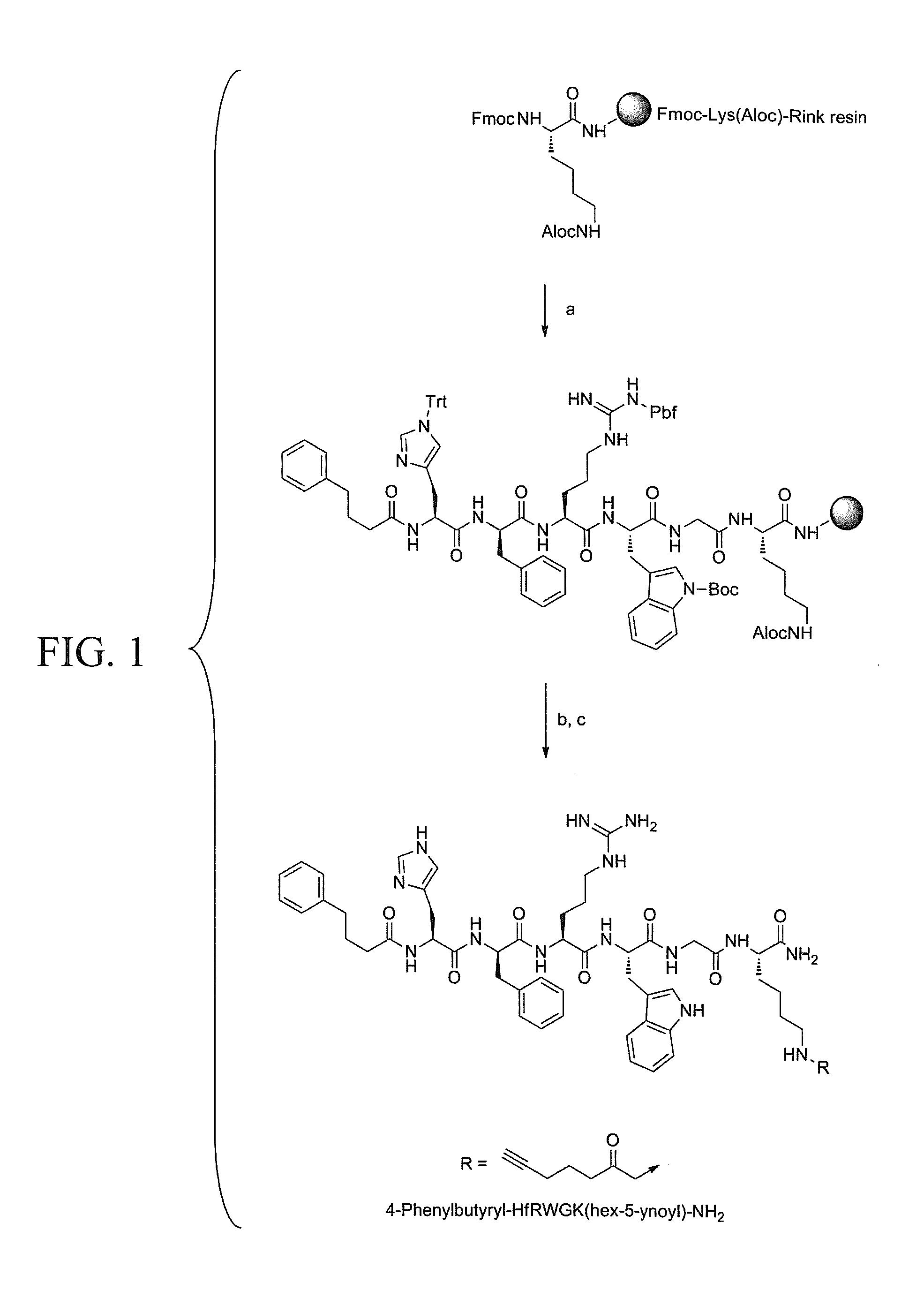
The invention discloses melanocortin analogue as well as preparation method and application thereof. A polypeptide structure of the melanocortin analogue consists of a functional amino acid sequence and a load amino acid sequence, wherein the functional amino acid sequence is an annular melanocortin analogue consisting of heptamers, and the load amino acid sequence consists of a plurality of polypeptide segments in 47th-60th segments of HIV-1 (human immunodeficiency virus type 1)TAT (trans-activator of transcription) protein. The melanocortin analogue can be absorbed through mucous membranes or skin and used for treating male and female sexual dysfunctions, obesities and pigmentation deficiencies.
Owner:上海瀚鸿科技股份有限公司
Melanocortin 1 receptor ligands and methods of use
ActiveUS9441013B2Dispersion deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide ligandMelanocortin 1 receptor
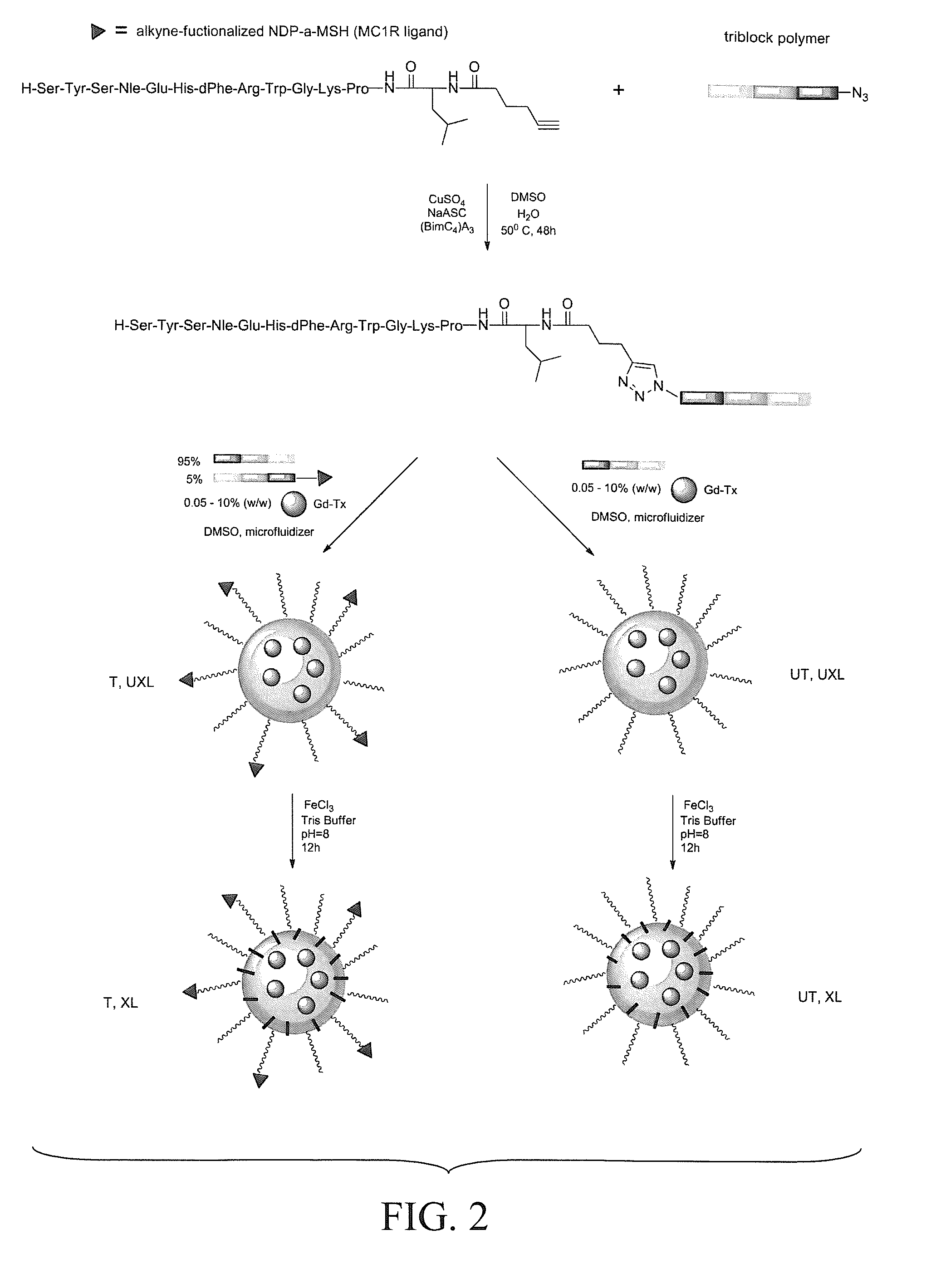
The subject invention pertains to a modified MC1R peptide ligand comprising a peptide that is a melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) ligand and a functionality or linker, such as a click functionality, for conjugation to a surface or agent. The modified MC1R peptide ligand can be coupled, e.g., via a click reaction with a complementary click functionality attached, to a moiety to form an MC1R-targeted agent. Drugs, contrast agents, polymers, particles, micelles, surfaces of larger structures, or other moieties can be targeted to the MC1R. The subject invention also pertains to a MC1R peptide ligand-micelle complex comprising a peptide that is a melanocortin 1 receptor ligand connected via a click reaction product to a micelle. The micelle is stable in vivo and can target melanoma tumor cells by association of the peptide ligand with the MC1R or the tumor and selectively provide a detectable and / or therapeutic agent (such as an imageable contrast agent and / or anti-cancer agent) selectively to the tumor cell.
Owner:INTEZYNE TECH INC +3
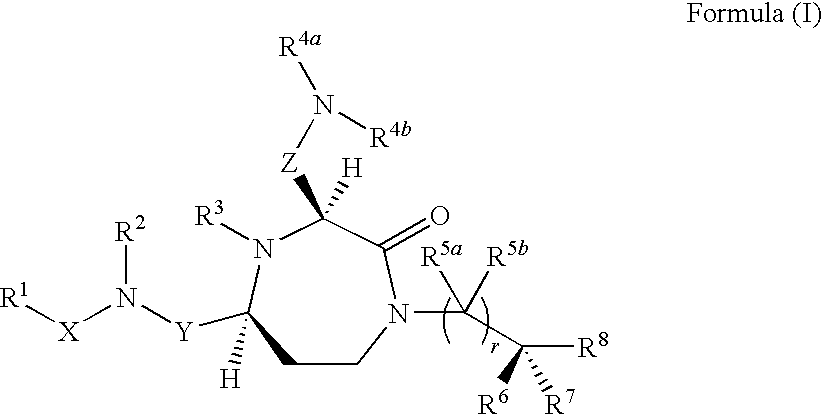
Methods of modulating the activity of the MC5 receptor and treatment of conditions related to this receptor
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) that are useful for modulating the biological activity of the melanocortin-5 receptor (MC5R). Compounds of this invention can be used to treat diseases and / or conditions in which downregulation of MC5R is beneficial. Such diseases and / or conditions include, but are not limited to, acne, seborrhea, seborrheic dermatitis, cancer, and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:MARP THERAPEUTICS PTY LTD
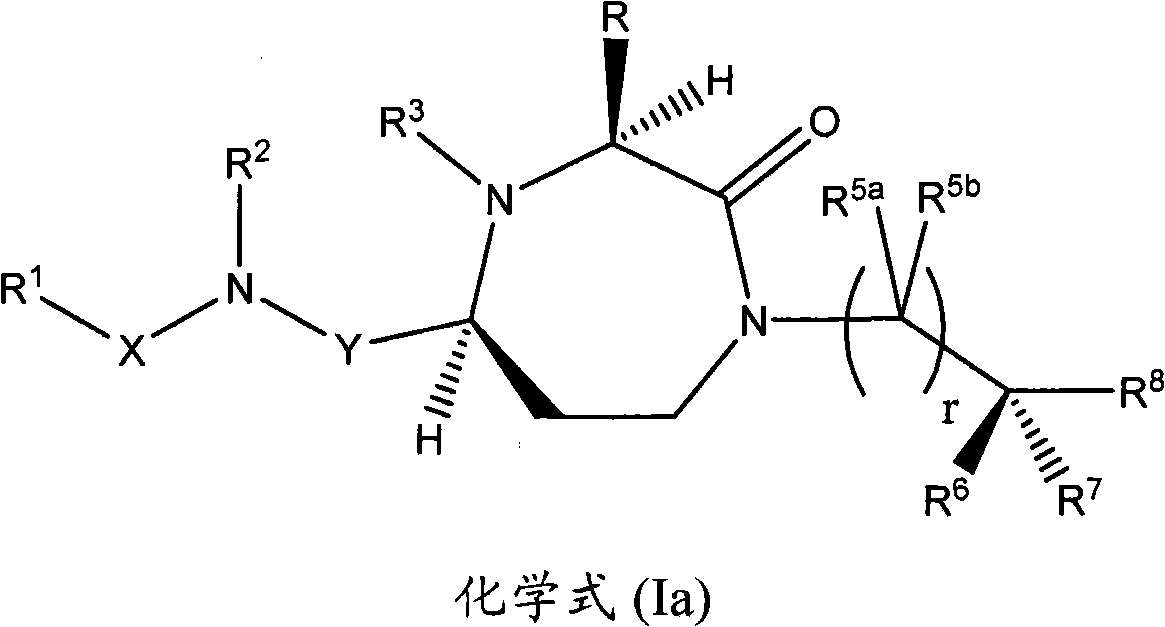
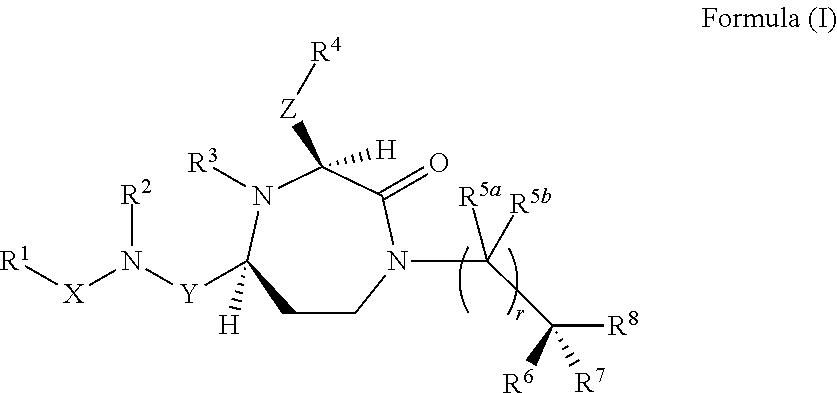
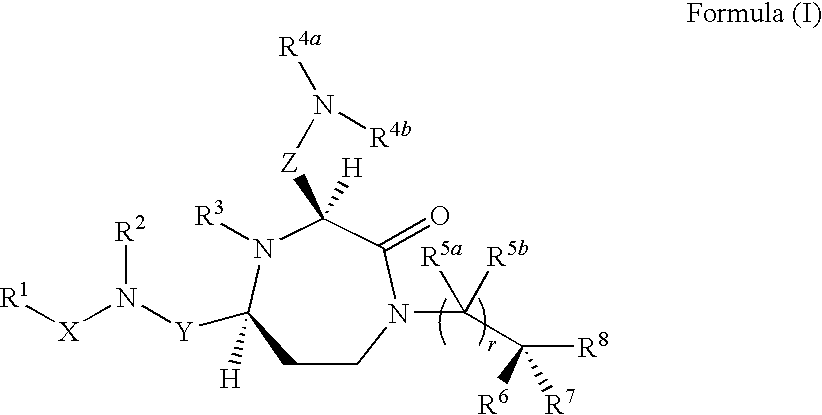
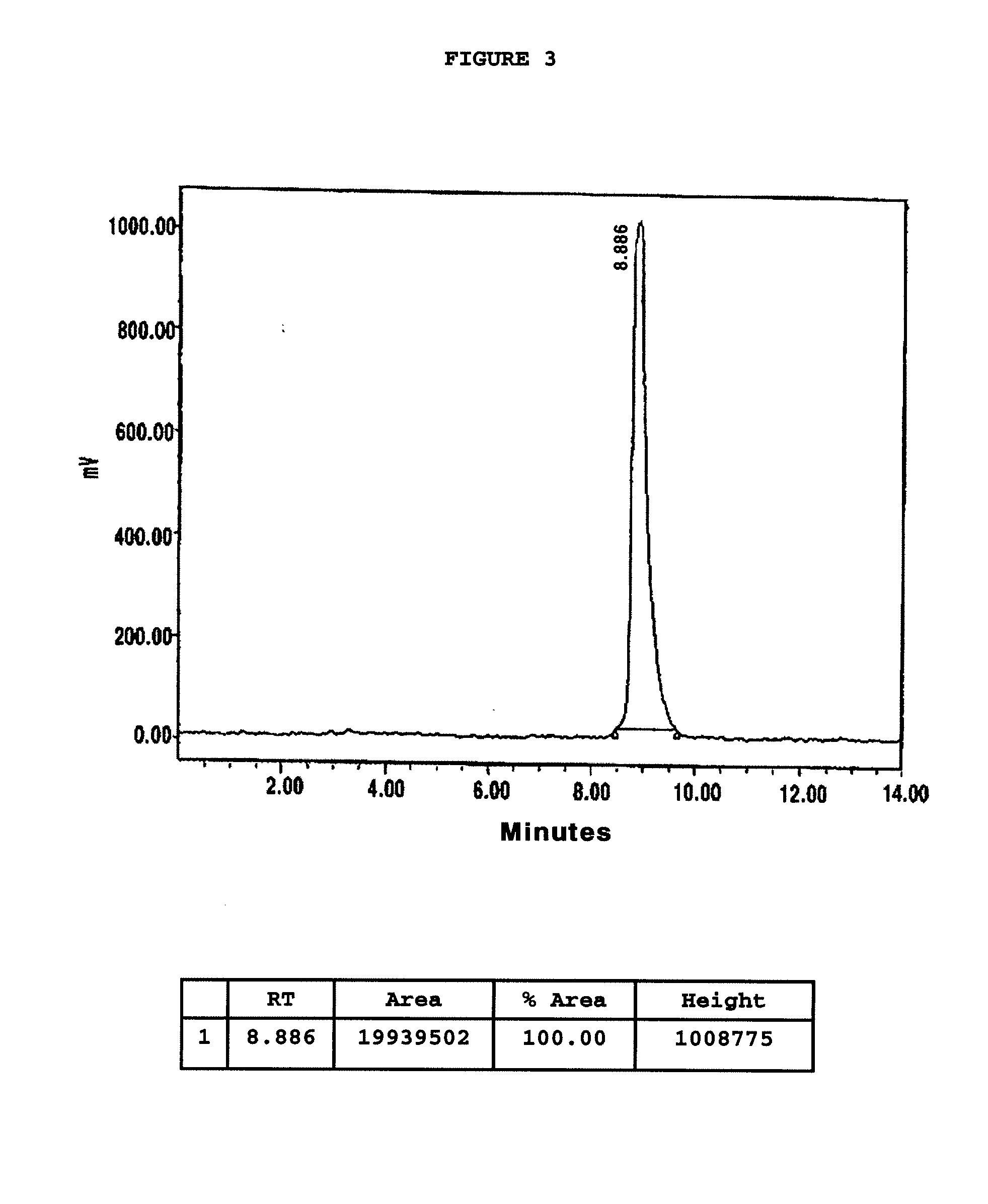
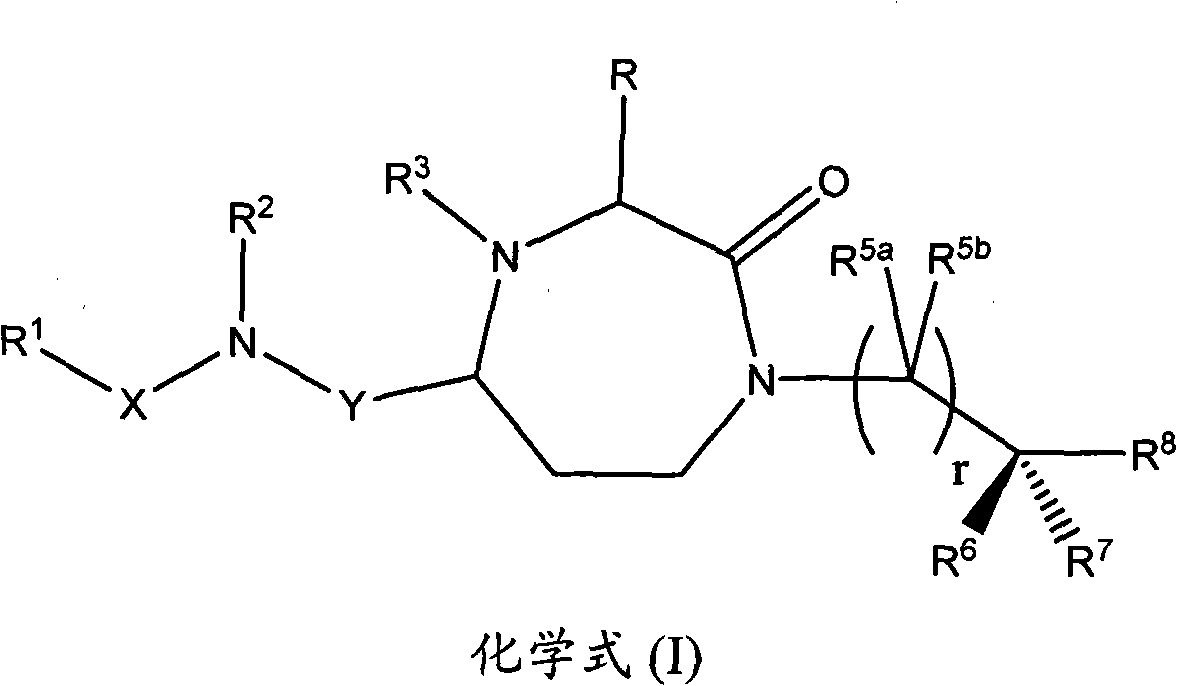
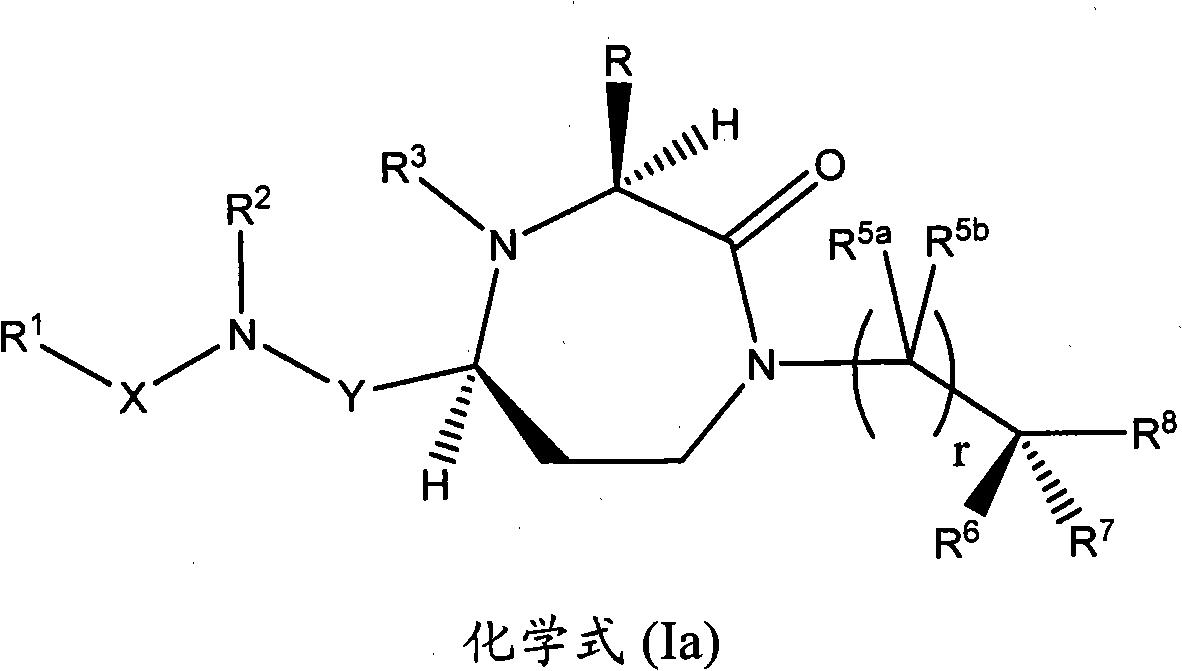
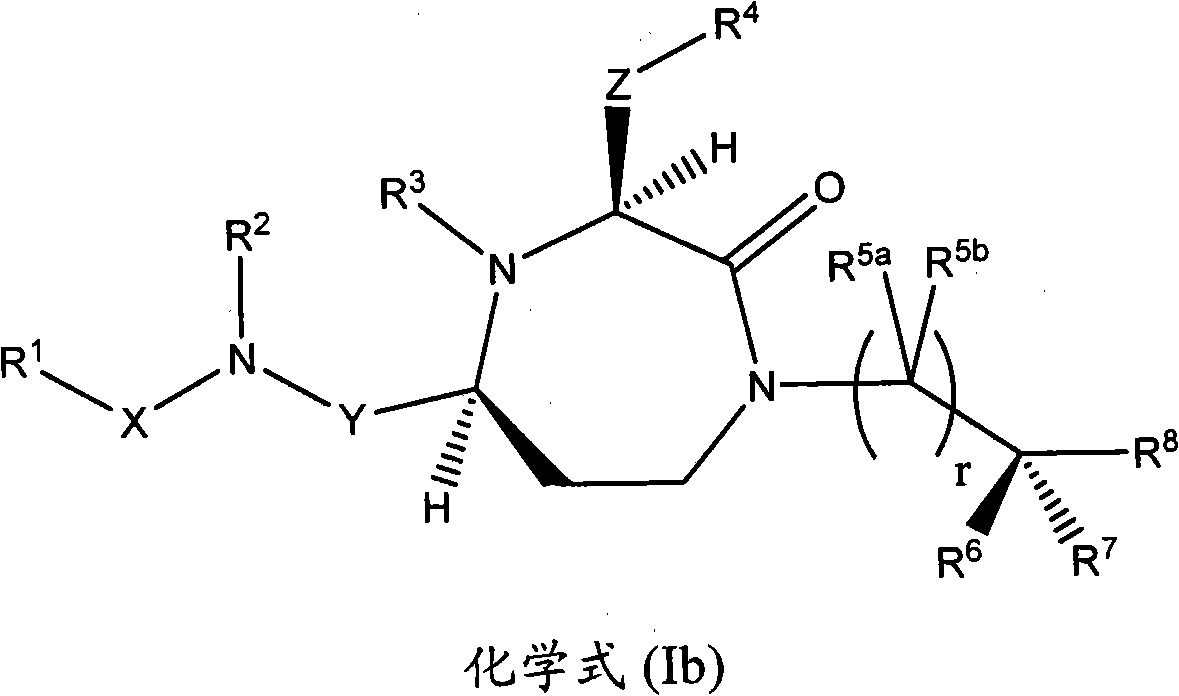
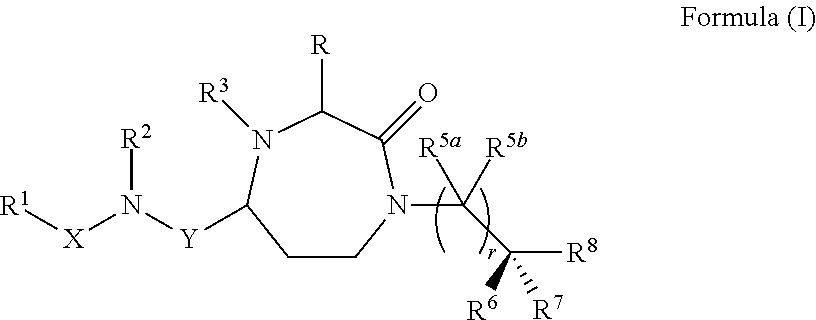
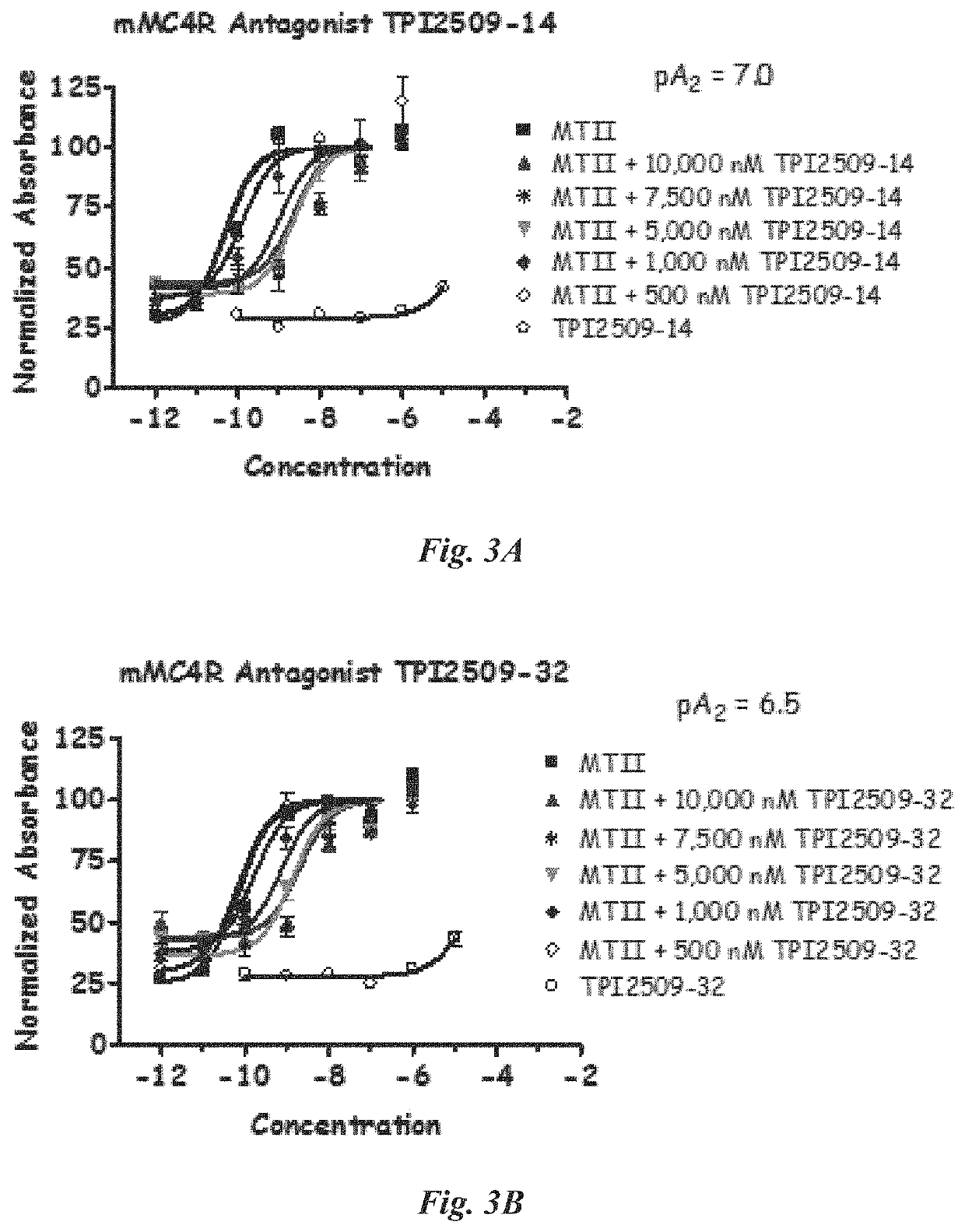
3-substituted-1,4-diazepan-2-one melanocortin-5 receptor antagonists
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) that are useful for modulating the biological activity of the melanocortin-5 receptor (MC5R). Compounds of this invention can be used to treat diseases and / or conditions in which downregulation of MC5R is beneficial. Such diseases and / or conditions include, but are not limited to, acne, seborrhea, seborrheic dermatitis, cancer, and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:MIMETICA PTY LTD
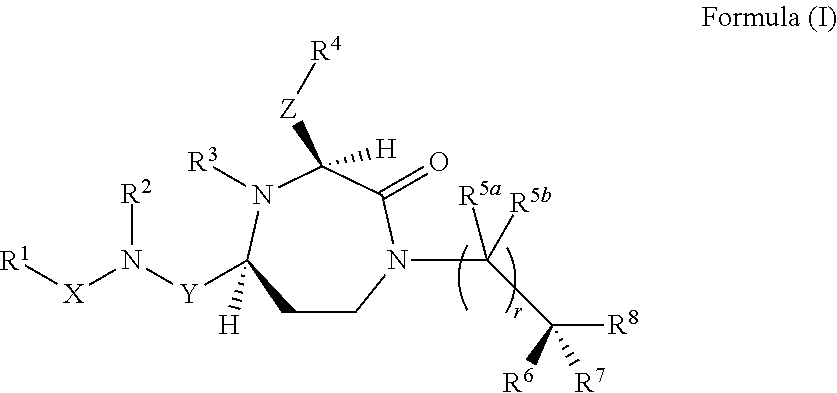
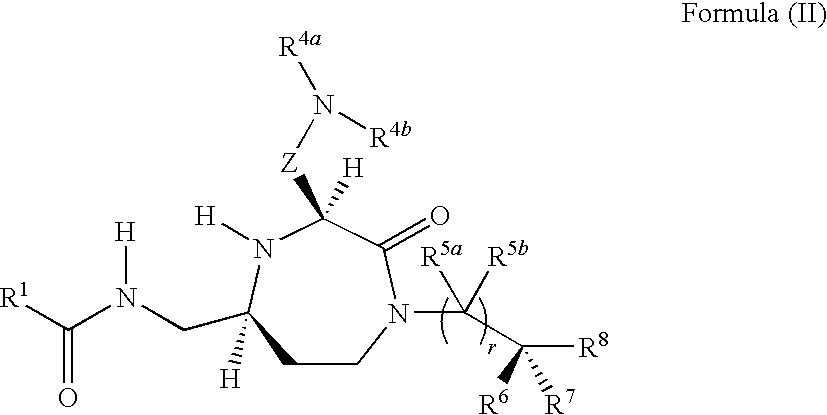
3-aminoalkyl-1,4-diazepan-2-one melanocortin-5 receptor antagonists
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) that are useful for modulating the biological activity of the melanocortin-5 receptor (MC5R). Compounds of this invention can be used to treat diseases and / or conditions in which downregulation of MC5R is beneficial. Such diseases and / or conditions include, but are not limited to, acne, seborrhea, seborrheic dermatitis, cancer, and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:MARP THERAPEUTICS PTY LTD
Chelating Agent Conjugated Alpha-MSH Peptide Derivatives, Preparation Method Thereof and Composition for Diagnosis and Treatment of Melanoma Comprising the Same as an Active Ingredient
ActiveUS20090304586A1High yieldHigh tumor uptakePeptide/protein ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersIsotopeBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Disclosed are chelating agent-conjugated α-MSH peptide derivatives, preparation methods thereof, and compositions for use in a diagnosis or treatment of a melanoma tumor containing the same as an active ingredient. The novel α-MSH peptide derivatives conjugated with chelating agent according to the present invention are highly selective to the melanocortin-1 receptor which is α-MSH receptor expressing in melanoma tumor and their labeling rate of a radioactive isotope is high. Also, they remain in kidney shortly and have high taking rate of the melanoma tumor. Therefore, with the aforesaid reasons, they may be effectively used for early diagnosis or treatment of melanoma tumor.
Owner:KAIBIOTECH
Methods of modulating the activity of the mc5 receptor and treatment of conditions related to this receptor
Owner:马普治疗私人有限公司
Application of Ipsen17 in preparing medicaments for treating obesity caused by melanocortin-4 receptor
InactiveCN104147009ARecovery capacityRestore expressivenessOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSignalling moleculesMorbid obesity
The invention relates to an application of Ipsen17 in preparing medicaments for treating obesity caused by melanocortin-4 receptor. Obesity means early-onset morbid obesity. 10 different kinds of cell membrane expression deficient human melanocortin-4 receptors can be rescued by functions of the Ipsen17 in human embryonic kidney cell HEK293, the EC 50 (effective concentration 50) expressed by the cell membrane of the melanocortin-4 receptor mutant rescued by the micro-molecular pharmaceutical molecular chaperone is less than 10-7M, wherein the EC50 of two mutants achieves the level of less than 10-8M. The EC50 of the signal molecule producing ability of the rescued melanocortin-4 receptor mutant is less than 10-7M, wherein the EC50 of a mutation receptor achieves the level less than 10-8M.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Methods of modulating the activity of the mc5 receptor and treatment of conditions related to this receptor
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) that are useful for modulating the biological activity of the melanocortin-5 receptor (MC5R). Compounds of this invention can be used to treat diseases and / or conditions in which downregulation of MC5R is beneficial. Such diseases and / or conditions include, but are not limited to, acne, seborrhea, seborrheic dermatitis, cancer, and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:MARP THERAPEUTICS PTY LTD
Selective small molecule peptidomimetic melanocortin ligands
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
Melanocortin 1 receptor ligands and methods of use
The subject invention pertains to a modified MC1R peptide ligand comprising a peptide that is a melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) ligand and a functionality or linker, such as a click functionality, for conjugation to a surface or agent. The modified MC1R peptide ligand can be coupled, e.g., via a click reaction with a complementary click functionality attached, to a moiety to form an MC1R-targeted agent. Drugs, contrast agents, polymers, particles, micelles, surfaces of larger structures, or other moieties can be targeted to the MC1R. The subject invention also pertains to a MC1R peptide ligand-micelle complex comprising a peptide that is a melanocortin 1 receptor ligand connected via a click reaction product to a micelle. The micelle is stable in vivo and can target melanoma tumor cells by association of the peptide ligand with the MC1R or the tumor and selectively provide a detectable and / or therapeutic agent (such as an imageable contrast agent and / or anti-cancer agent) selectively to the tumor cell.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +3
Transgenic mouse models for mc4r
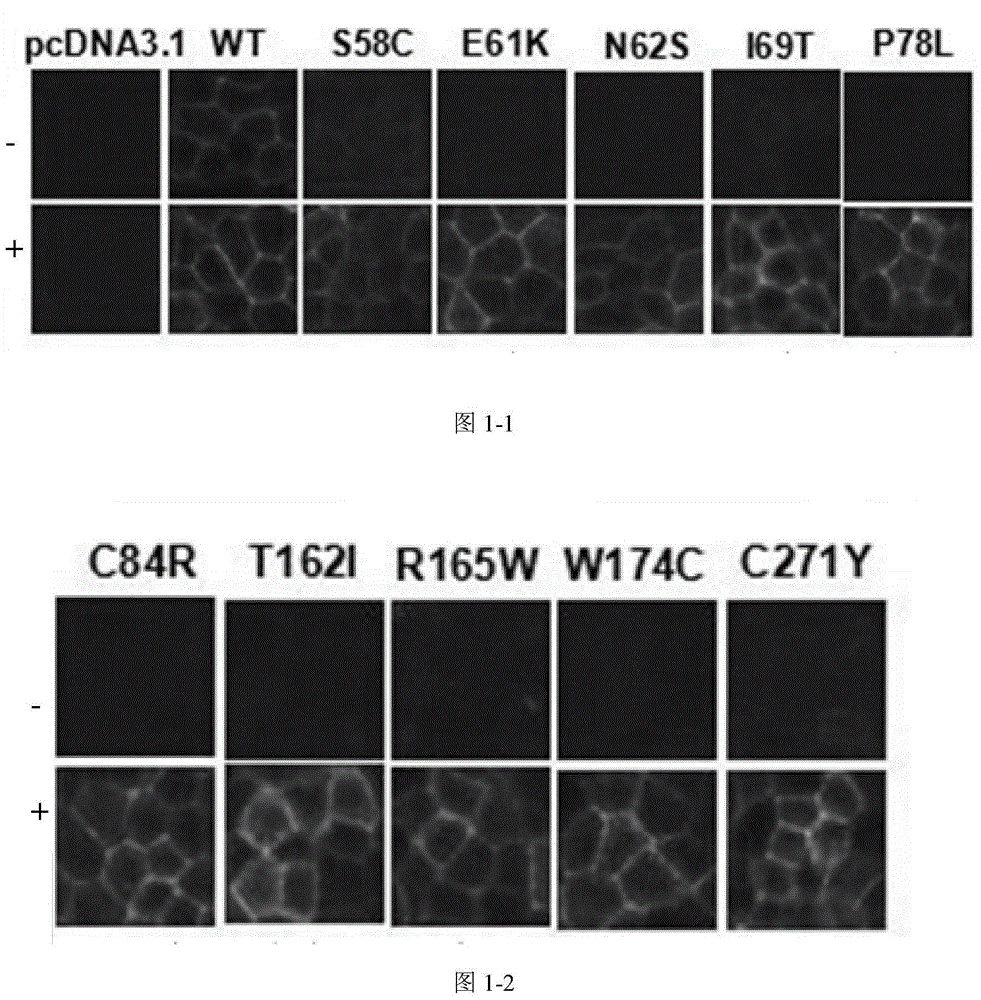
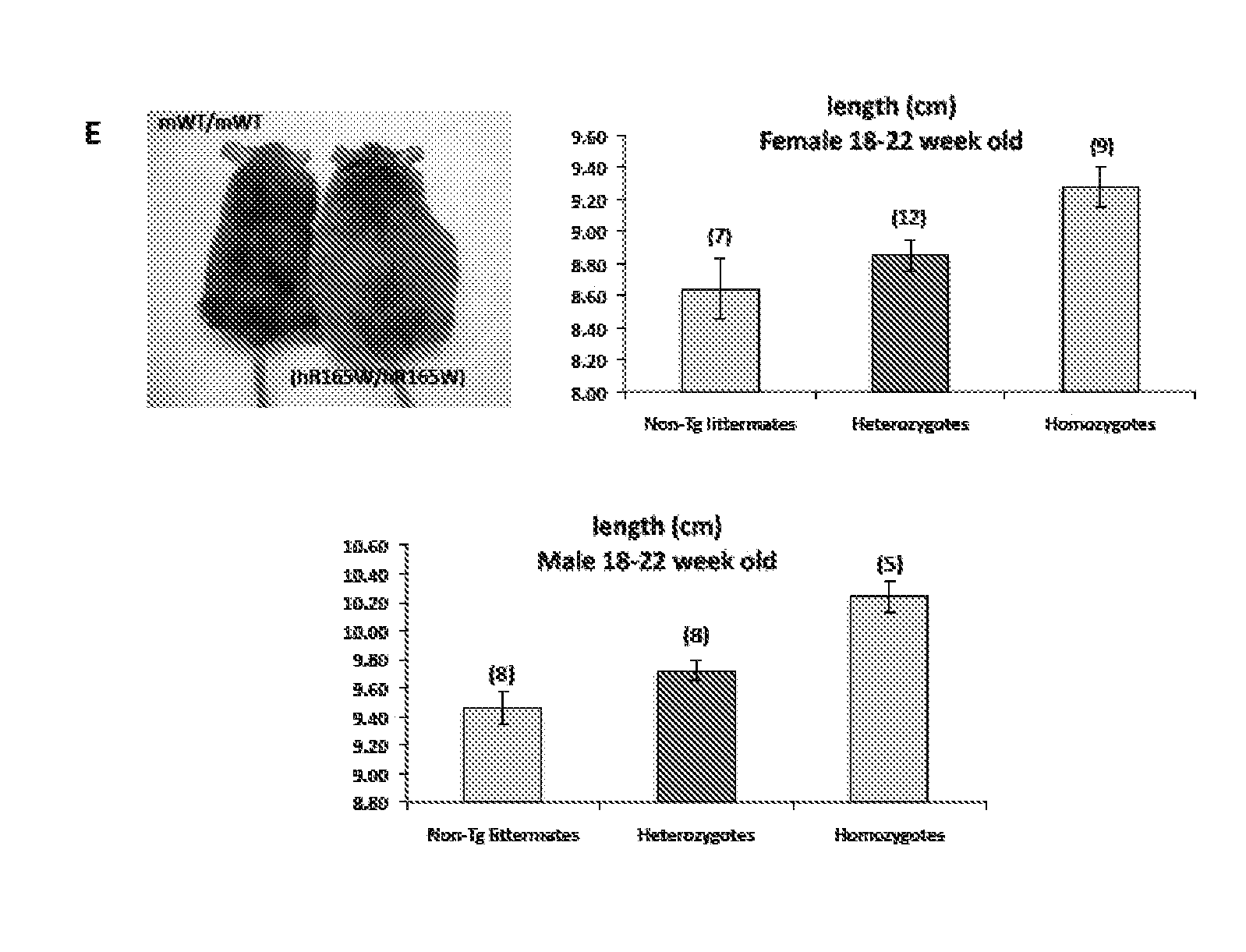
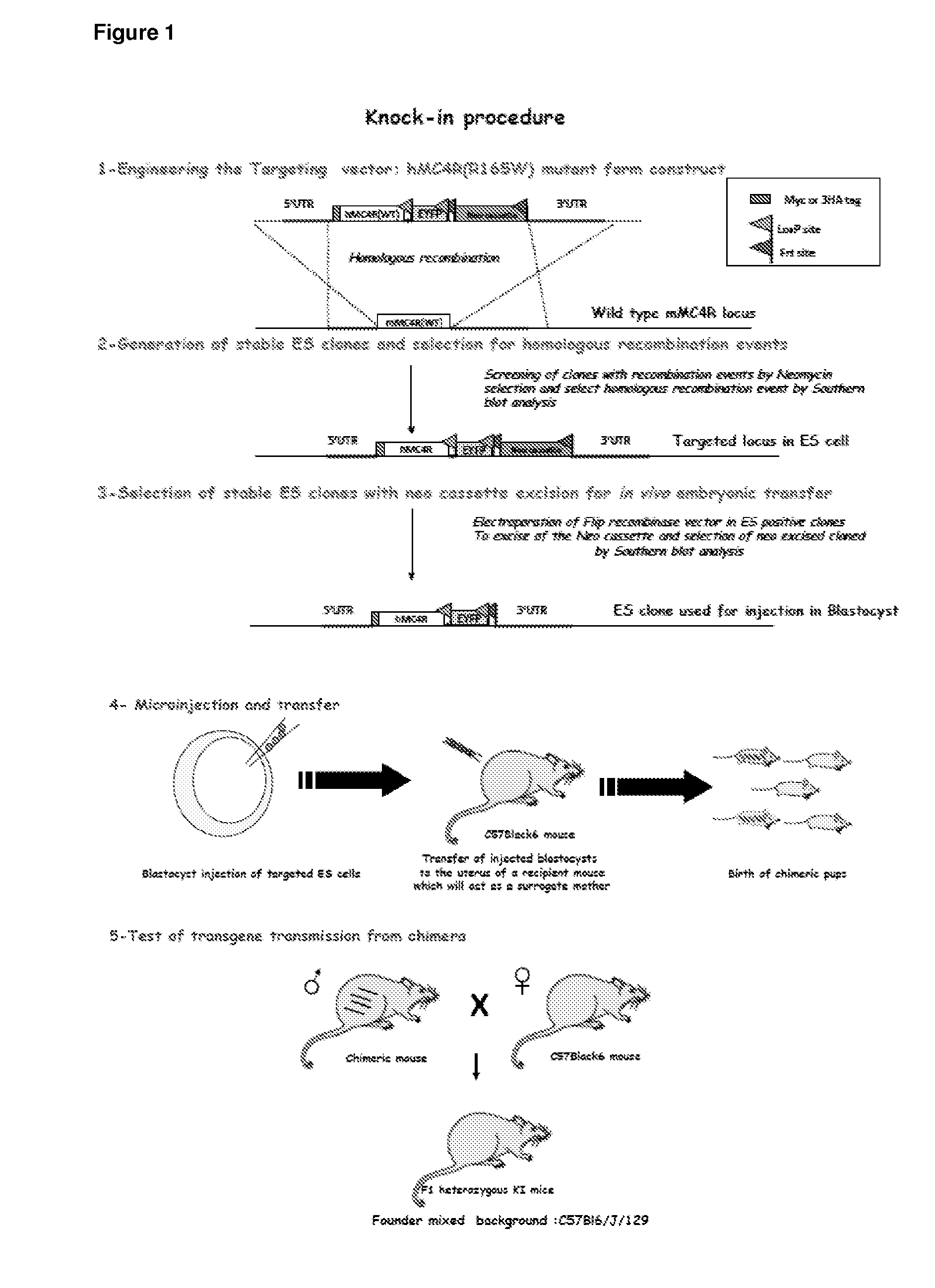
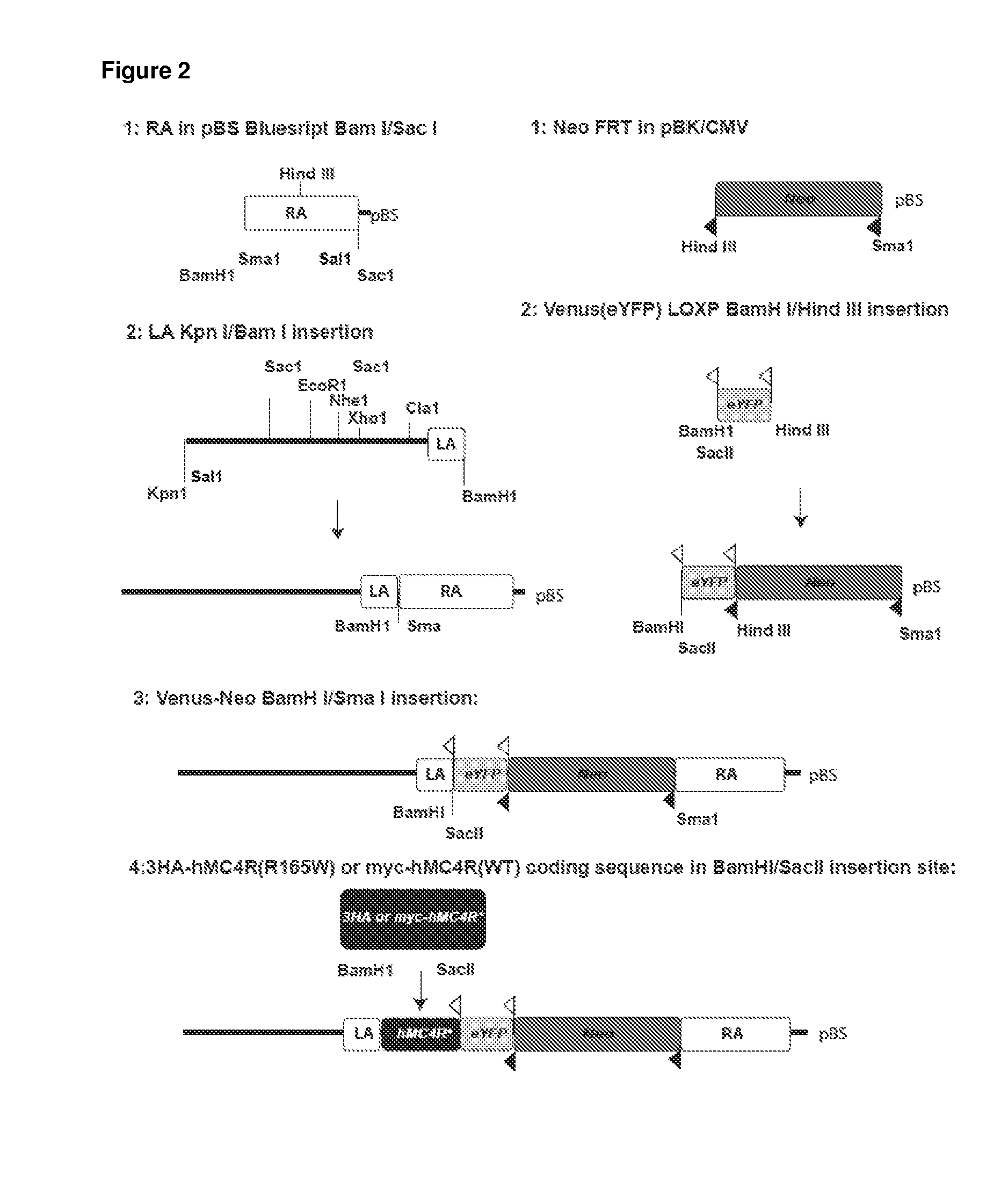
InactiveUS20150150224A1Abolishing receptor functionPrevent surfaceCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningMutated proteinWild type
There are provided herein transgenic non-human animals and cells comprising a transgene encoding either a mutated human melanocortin type-4 receptor (hMC4R) protein, wherein the mutated protein is misfolded and retained intracellularly, or a wild-type human melanocortin type-4 receptor (hMC4R) protein. Transgenes and targeting constructs used to produce such transgenic animals and cells are also provided, as well as methods for using the transgenic animals in pharmaceutical screening and as commercial research animals for modeling obesity.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL
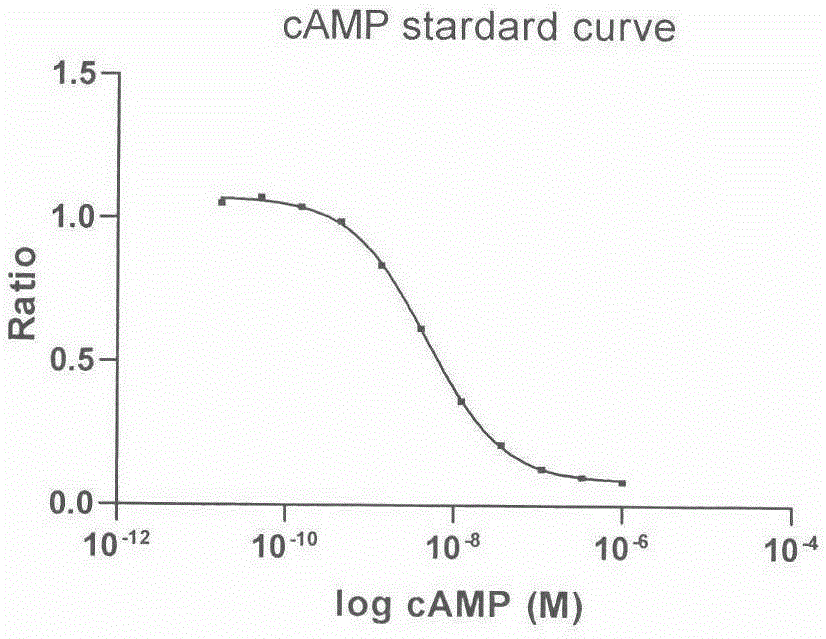
Melanocortin receptor 1 drug screening model based on fluorescence resonance energy transferring technology
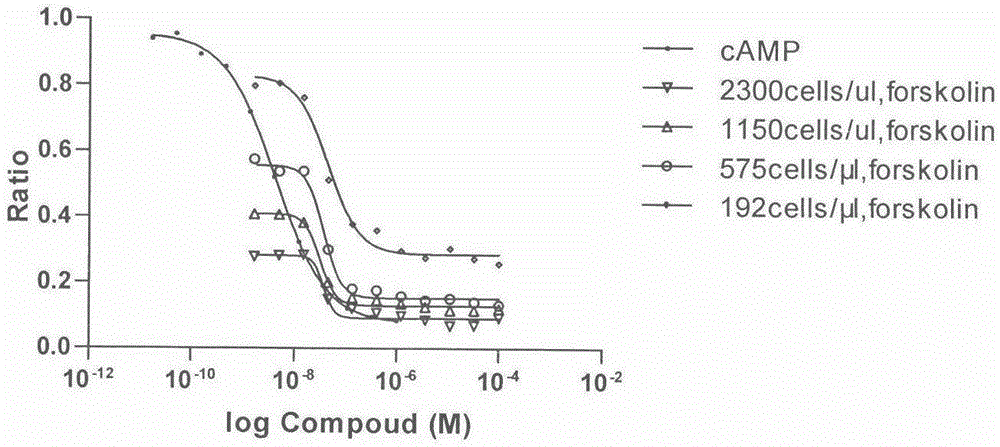
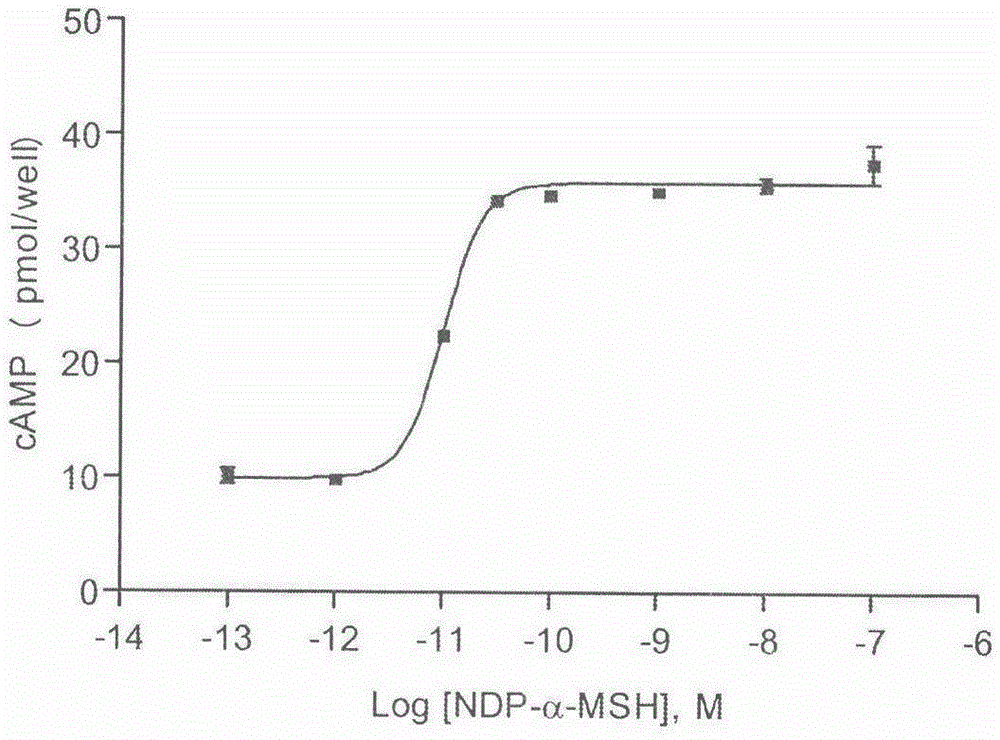
The invention provides a drug screening method for screening a melanocortin receptor 1 agonist. Based on a fluorescence resonance energy transferring principle, cAMP produced by complete cells and cAMP (b-cAMP) marked by biotins in a reaction system are competitively combined with an anti-cAMP antibody and a fluorescence resonance energy transferring process is interrupted to cause weakening of fluorescence signals, so that whether a compound has an excitement effect of a melanocortin receptor 1 or not is reflected. The drug screening method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing cells; (2) determining a standard curve; and (3) identifying a model: identifying that a positive drug IC50 is consistent to references. The method is simple and rapid; a fluorescence detection value has high sensitivity and the detection accuracy is improved; and the result is stable and reliable and the reproducibility is good.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com