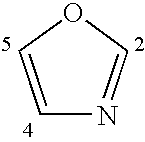
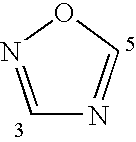
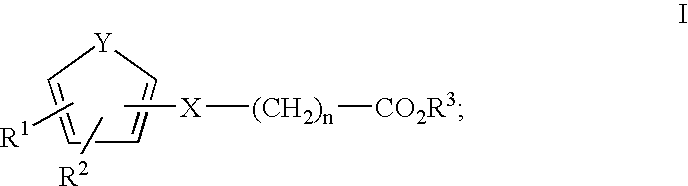Compounds, Methods and Formulations for the Oral Delivery of a Glucagon-Like Peptide (Glp)-1 Compound or a Melanocortin-4 Receptor (Mc4) Agonist Peptide
a technology of glucagon-like peptides and oral delivery methods, which is applied in the field of compoundes, methods and formulations for the oral delivery of glucagon-like peptides (glp)1 compounds or mc4 receptor agonist peptides, can solve the problems of ineffectiveness of agents, inability to effectively deliver active agents, and inability to rapidly render agents ineffective or destroyed in the gastrointestinal tra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation 1
6-Oxo-6-[N′-(pyridine-2-carbonyl)hydrazino]hexanoic Acid Methyl Ester
[0048]
[0049] Stir a solution of 2-picolinylhydrazide (8.05 g, 58.8 mmol) and adipic acid monomethyl chloride (10.5 g, 58.8 mmol) in DMF (117 mL) at room temperature under nitrogen for 12 hours. Remove the solvent under reduced pressure. Triturate the residue with diethyl ether (300 mL), collect the solids by filtration, dissolve in water (200 mL), and wash with ethyl acetate (200 mL). Adjust the pH to 8 with a saturated NaHCO3 solution and extract with ethyl acetate (2×200 mL). Dry the combined organic extracts over sodium sulfate and remove the solvent under reduced pressure to provide 6-oxo-6-[N′-(pyridine-2-carbonyl)hydrazino]hexanoic acid methyl ester (3.85 g, 59%).
example 1
5-(5-Pyridin-2-yl[1,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl)pentanoic Acid Methyl Ester
[0050]
[0051] Add triethylamine (14.4 mL, 104 mmol) to a mixture of 6-oxo-6-[N′-(pyridine-2-carbonyl)hydrazino]hexanoic octanoic acid methyl ester (9.63 g, 34 mmol), carbon tetrachloride (26.6 g, 172 mmol) and triphenylphosphine (20.3 g, 78 mmol) in acetonitrile (35 mL) at room temperature under nitrogen and stir for 30 minutes. Remove the solids by filtration and then remove the filtrate solvent under reduced pressure. Dilute the residue with water (500 mL) and extract with ethyl acetate (3×500 mL). Wash the combined organic extracts with brine (200 mL), dry over sodium sulfate and remove the solvent under reduced pressure. Triturate the residue with ethyl acetate and collect the solids by filtration to afford 5-(5-pyridin-2-yl[1,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl)pentanoic acid methyl ester (8.15 g, 91%).
example 2
5-(5-Pyridin-2-yl[1,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl)pentanoic Acid
[0052] Add 2 N sodium hydroxide (20 mL) to a solution of 5-(5-pyridin-2-yl[1,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl)pentanoic acid methyl ester (8.16 g, 31 mmol) in THF (60 mL) and methanol (20 mL) at room temperature under nitrogen and heat the mixture at reflux for 12 hours. Remove the solvent under reduced pressure, dilute the residue with water (500 mL), and wash with ethyl acetate (200 mL). Adjust the pH of the aqueous layer to pH 3 with concentrated HCl and extract with ethyl acetate (3×200 mL). Wash the combined organic extracts with brine (200 mL), dry over sodium sulfate, and remove the solvent under reduced pressure to afford 5-(5-pyridin-2-yl[1,3,4]oxadiazol-2-yl)pentanoic acid (2.05 g, 27%). APCI mass spectrum m / z 246 [C12H13N3O3+H]+.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com