Patents
Literature
413 results about "Protein engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein engineering is the process of developing useful or valuable proteins. It is a young discipline, with much research taking place into the understanding of protein folding and recognition for protein design principles. It is also a product and services market, with an estimated value of $168 billion by 2017.
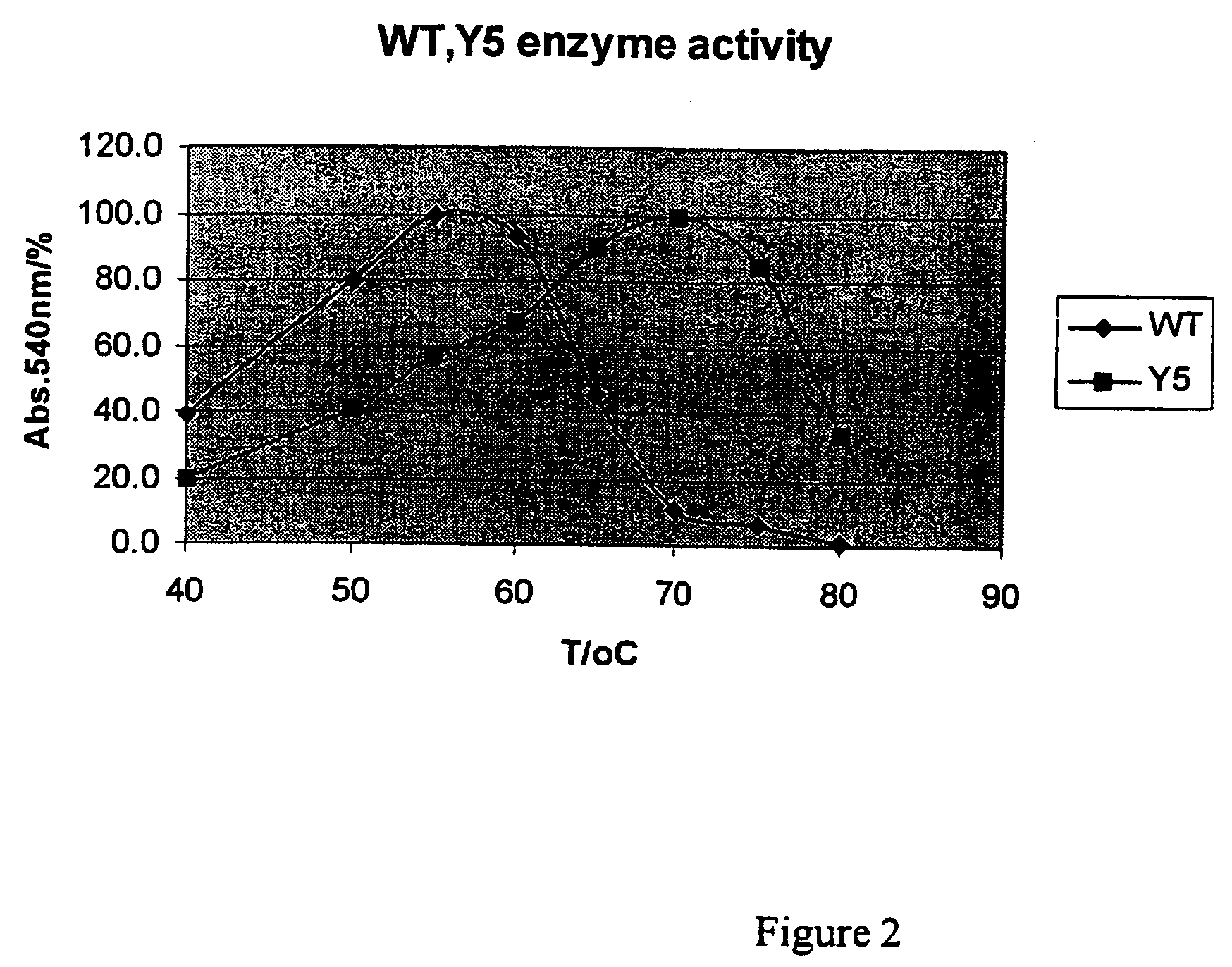
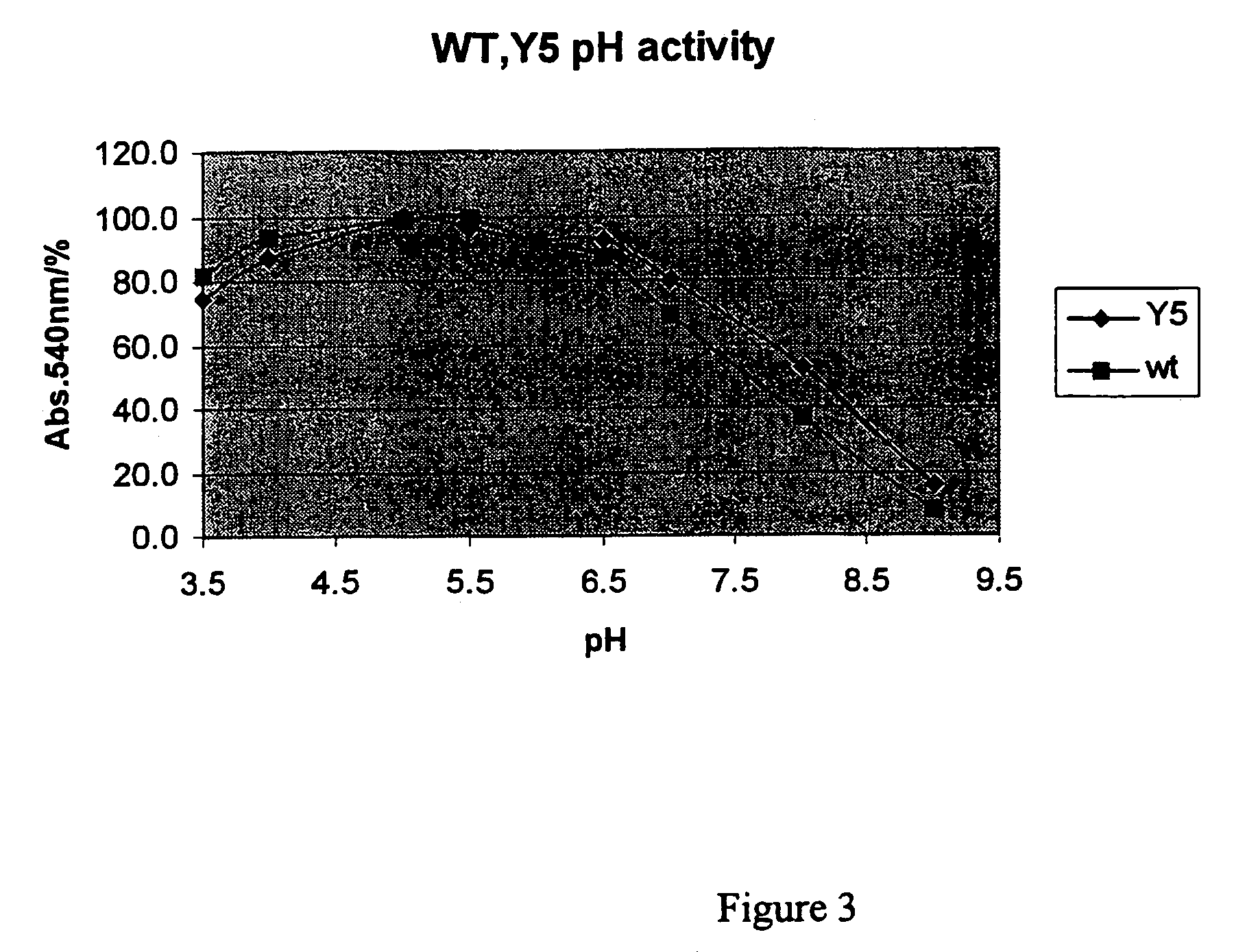
Compositions and methods comprising serine protease variants
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Genetic system and self-cleaving inteins derived therefrom, bioseparations and protein purification employing same, and methods for determining critical, generalizable amino acid residues for varying intein activity
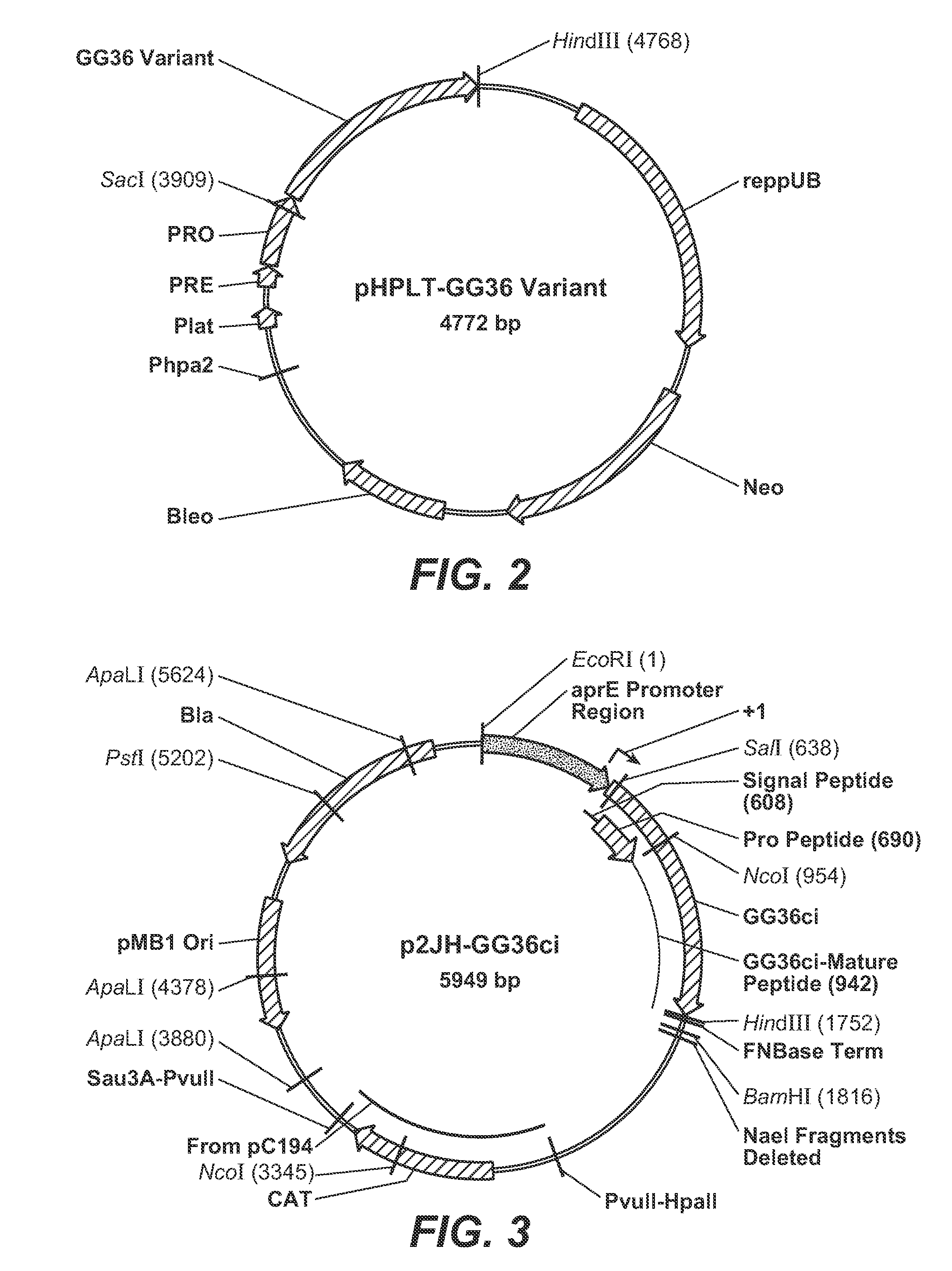
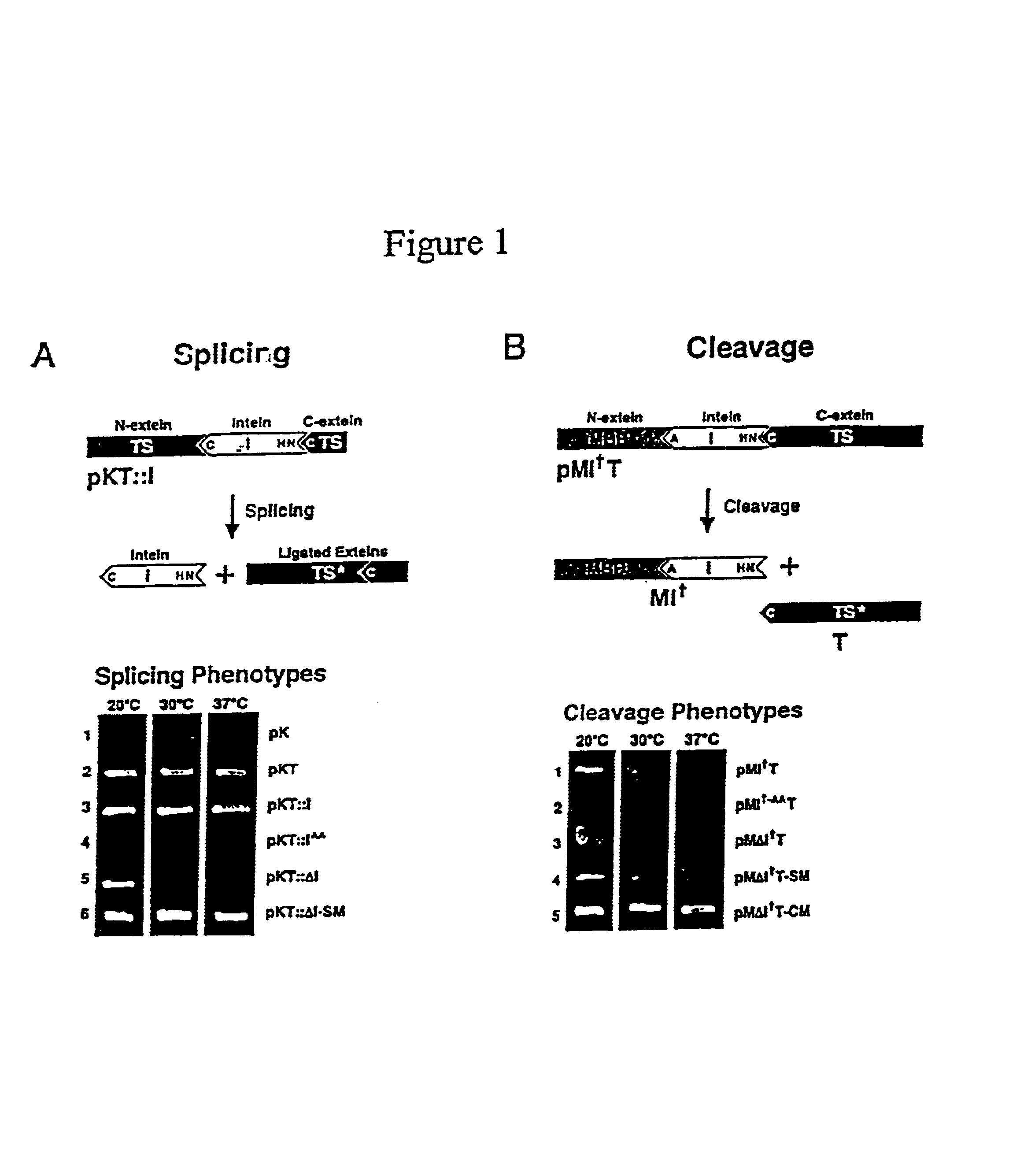
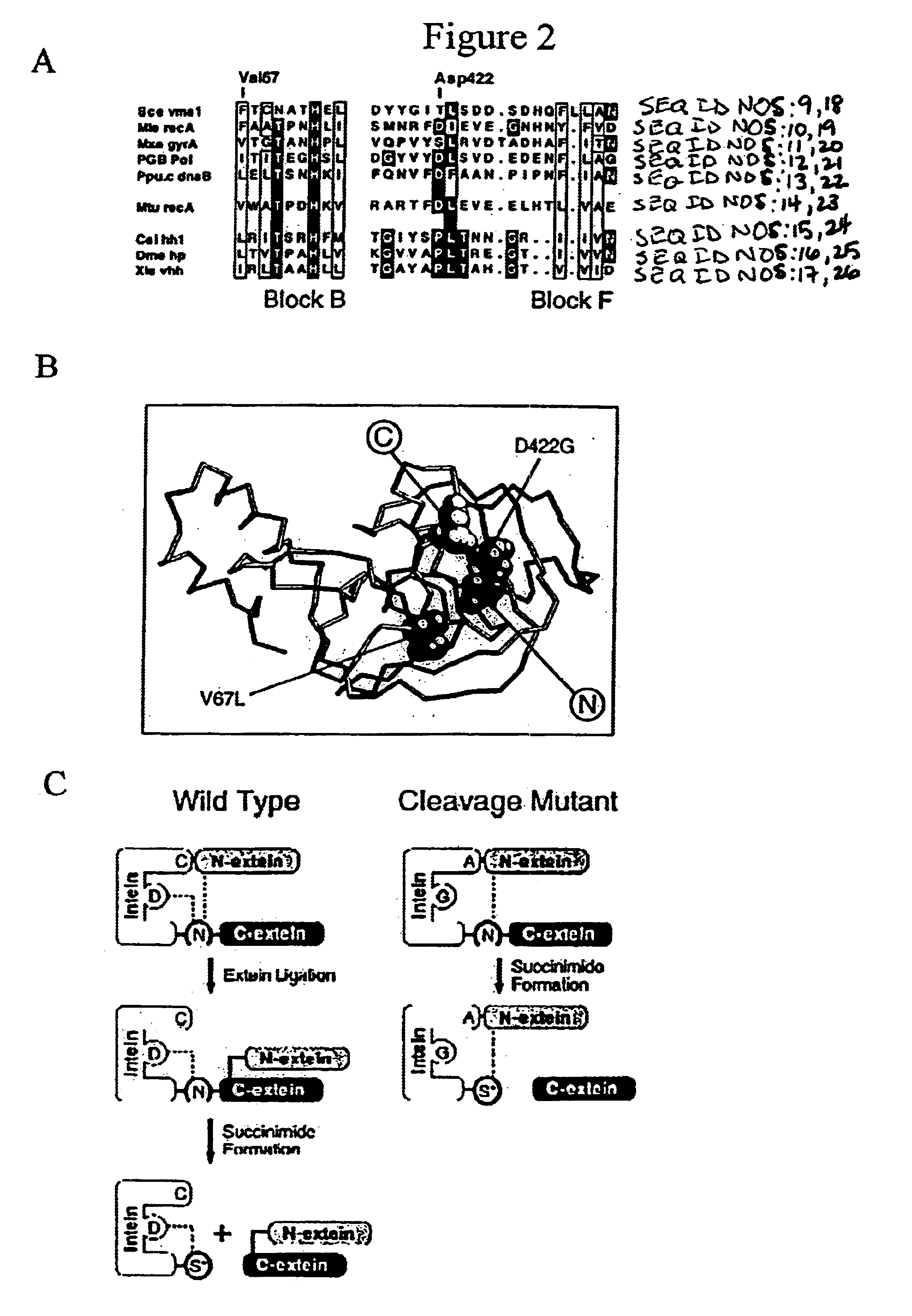
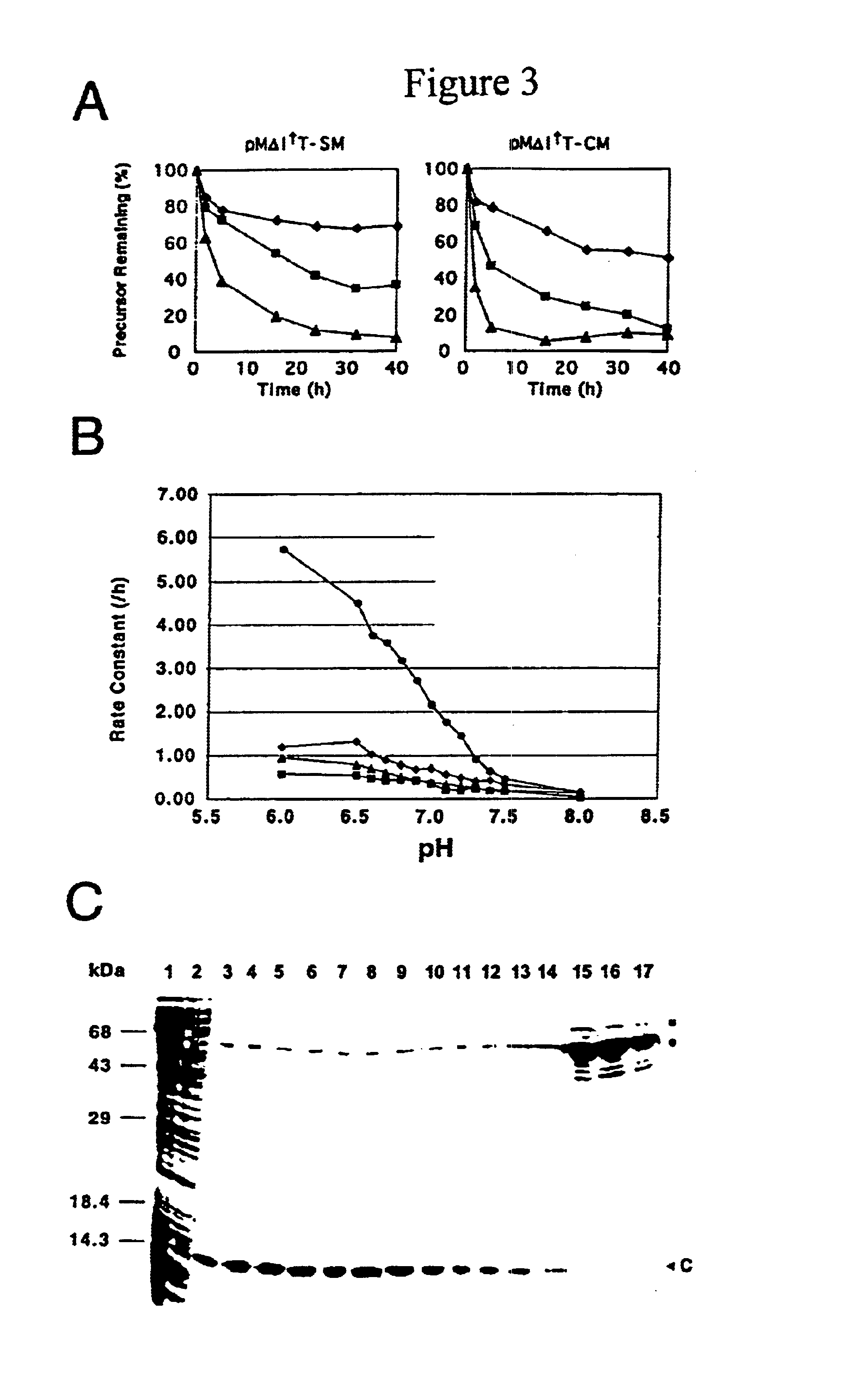
A self-cleaving element for use in bioseparations has been derived from a naturally occurring, 43 kDa protein splicing element (intein) through a combination of protein engineering and random mutagenesis. A mini-intein (18 kDa) previously engineered for reduced size had compromised activity and was therefore subjected to random mutagenesis and genetic selection. In one selection a mini-intein was isolated with restored splicing activity, while in another, a mutant was isolated with enhanced, pH-sensitive C-terminal cleavage activity. The enhanced cleavage mutant has utility in affinity fusion-based protein purification. The enhanced splicing mutant has utility in purification of proteins such as toxic proteins, for example, by inactivation with the intein in a specific region and controllable splicing. These mutants also provide new insights into the structural and functional roles of some conserved residues in protein splicing. Thus, disclosed and claimed are: a genetic system and self-cleaving inteins therefrom; bioseparations employing same; protein purification by inactivation with inteins in specific regions and controllable intein splicing; methods for determining critical, generalizable residues for varying intein activity; and products.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Protein engineering strategies to optimize activity of surface attached proteins
InactiveUS20100260465A1Without substantial loss of enzymatic activityHigh binding affinityHydrolasesTransferasesActive enzymeProtein isolate
Isolated and / or recombinant enzymes that include surface binding domains, surfaces with active enzymes bound to them and methods of coupling enzymes to surfaces are provided. Enzymes can include large and / or multiple surface coupling domains for surface coupling.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Prophylactic and therapeutic influenza vaccines, antigens, compositions and methods
The present invention relates to the intersection of the fields of immunology and protein engineering, and particularly to antigens and vaccines useful in prevention of infection by influenza virus. Provided are recombinant protein antigens, compositions, and methods for the production and use of such antigens and subunit vaccine compositions. In some embodiments, influenza antigens include hemagglutinin polypeptides neuraminidase polypeptides, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
Resonance driven changes in chain molecule structure
InactiveUS6060293AEfficient inductionPeptide preparation methodsElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentChemical industryDisease
PCT No. PCT / DK96 / 00158 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 26, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 26, 1997 PCT Filed Apr. 1, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 30394 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 3, 1996The invention relates to the technical application of electromagnetic radiation such as microwaves and radiowaves and application of ultra sound to chain molecules. In particular, the present invention relates to the utilization of topological excitations such as wring, twist and torsional modes, e.g., for generating structure, such as in folding, refolding or renaturation, and denaturation or unfolding of peptides, polypeptides, proteins, and enzymes; for generating changes in molecular affinity; for stimulating drug receptor interactions; and for changing molecular communication, is described. The technique is based on a new understanding of the underlying physical phenomenon and can also be applied to other chain molecules and biologically active biomolecules and tailored polymers such as glucoproteins, antibodies, genomic chain molecules such as DNA and RNA as well as PNA, carbohydrates, and synthetic and natural organic polymers. The invention is especially applicable for solving problems related to inclusion bodies and aggregation when using recombinant DNA and protein engineering techniques. Furthermore, the invention can be utilized in therapeutic treatment and in development and production of pharmaceuticals. The area of applicability ranges from biotechnological industry, food industry, drug industry, pharmacological industry, chemical industry, and concerns, e.g., the treatment of conditions and diseases related to influenza, hepatitis, polio, malaria, borrelia, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, Creutzfeldt Jakob disease, other prion related diseases, multiple sclerosis, cataract, heart diseases, cancer, and aging.
Owner:PROKYON
7beta-hydroxyl sterol dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to preparation of ursodeoxycholic acid
ActiveCN108546691AEasy extractionEasy to manufactureOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringSterolProtein engineering
The invention discloses a 7beta-hydroxyl sterol dehydrogenase mutant which is obtained by protein engineering and of which coenzyme preference is changed, a coding gene of the 7beta-hydroxyl sterol dehydrogenase mutant, a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant expression transformant which contain a sequence of the gene, a preparation method of a recombinant mutant enzyme preparation, andapplication of the recombinant mutant enzyme preparation to preparation of ursodeoxycholic acid. By co-enzyme regeneration of enzymic coupling, the recombinant mutant enzyme preparation disclosed bythe invention can efficiently utilize relatively cheap oxidized coenzyme I (NAD+) instead of very expensive oxidized coenzyme II (NADP+); asymmetric reduction of catalytic 7-hydroxyl lithocholic acideffectively reduces production cost; moreover, the recombinant mutant enzyme preparation has the advantages of simplicity for operation, mild reaction condition, environmental-friendliness, high yieldand the like, and has a good application prospect in preparation of ursodeoxycholic acid by epimerization of chenodesoxycholic acid.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Influenza antibodies, compositions, and related methods
InactiveUS20080124272A1Inhibitory activityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsProtein engineeringProtein antigen
The present invention relates to the intersection of the fields of immunology and protein engineering, and particularly to antigens and vaccines useful in prevention of infection by influenza virus. Provided are recombinant protein antigens, compositions, and methods for the production and use of such antigens and vaccine compositions.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
POLYMER-BASED PROTEIN ENGINEERING METHODS TO RATIONALLY TUNE ENZYME ACTIVITY, pH-DEPENDENCE AND STABILITY
ActiveUS20160101190A1Improve biological activityHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzyme stabilisationStimuli responsiveChymotrypsin
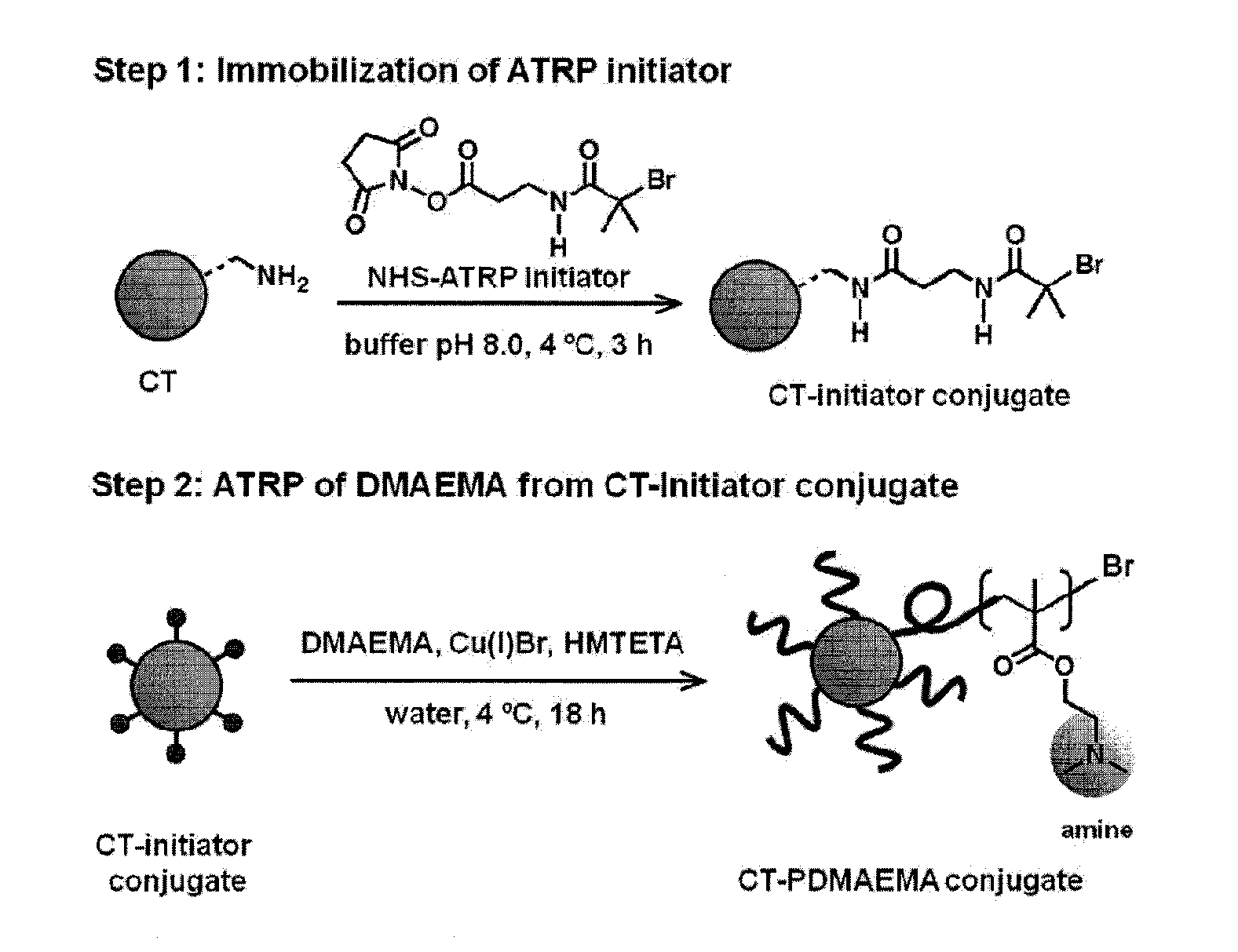
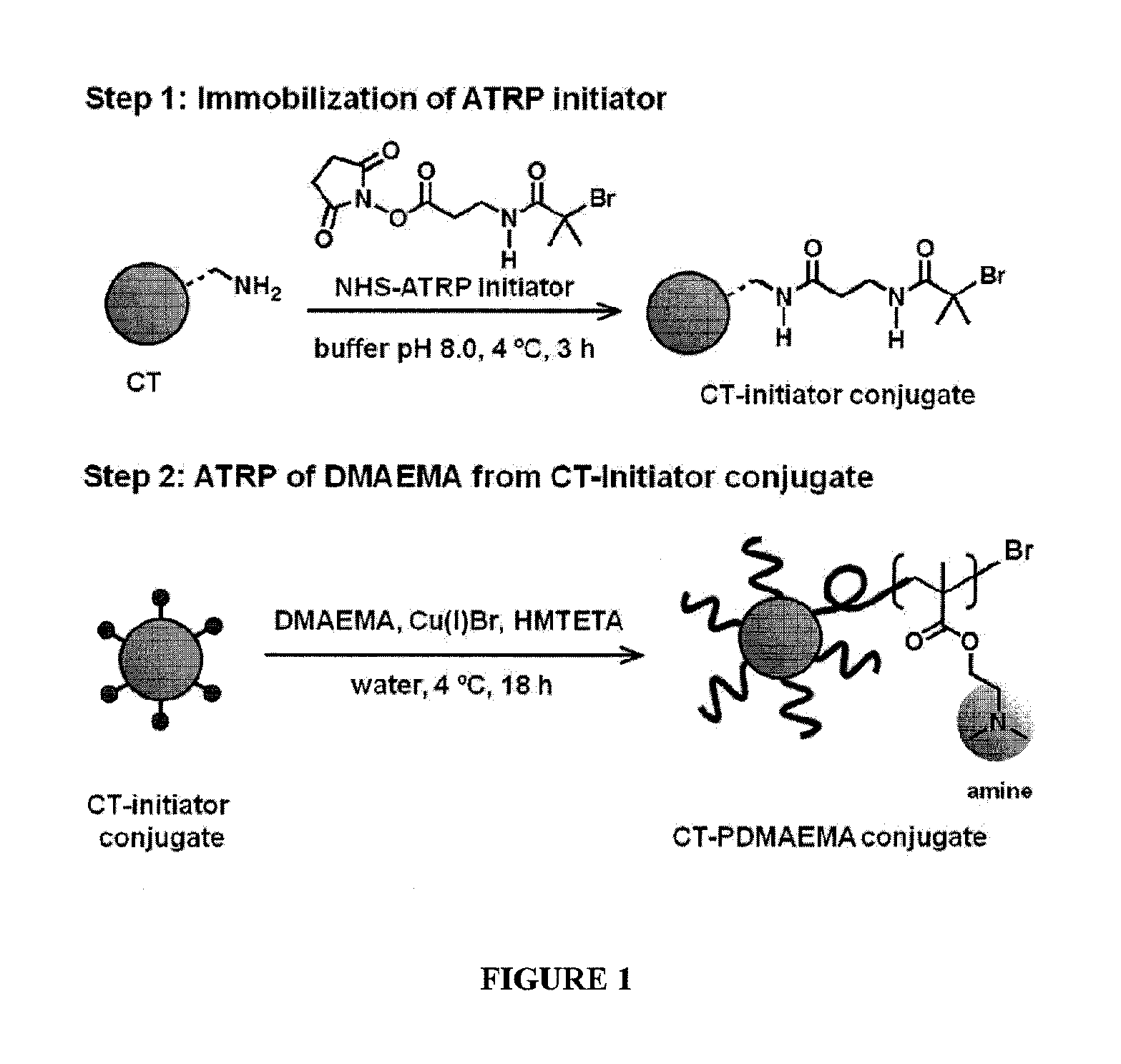
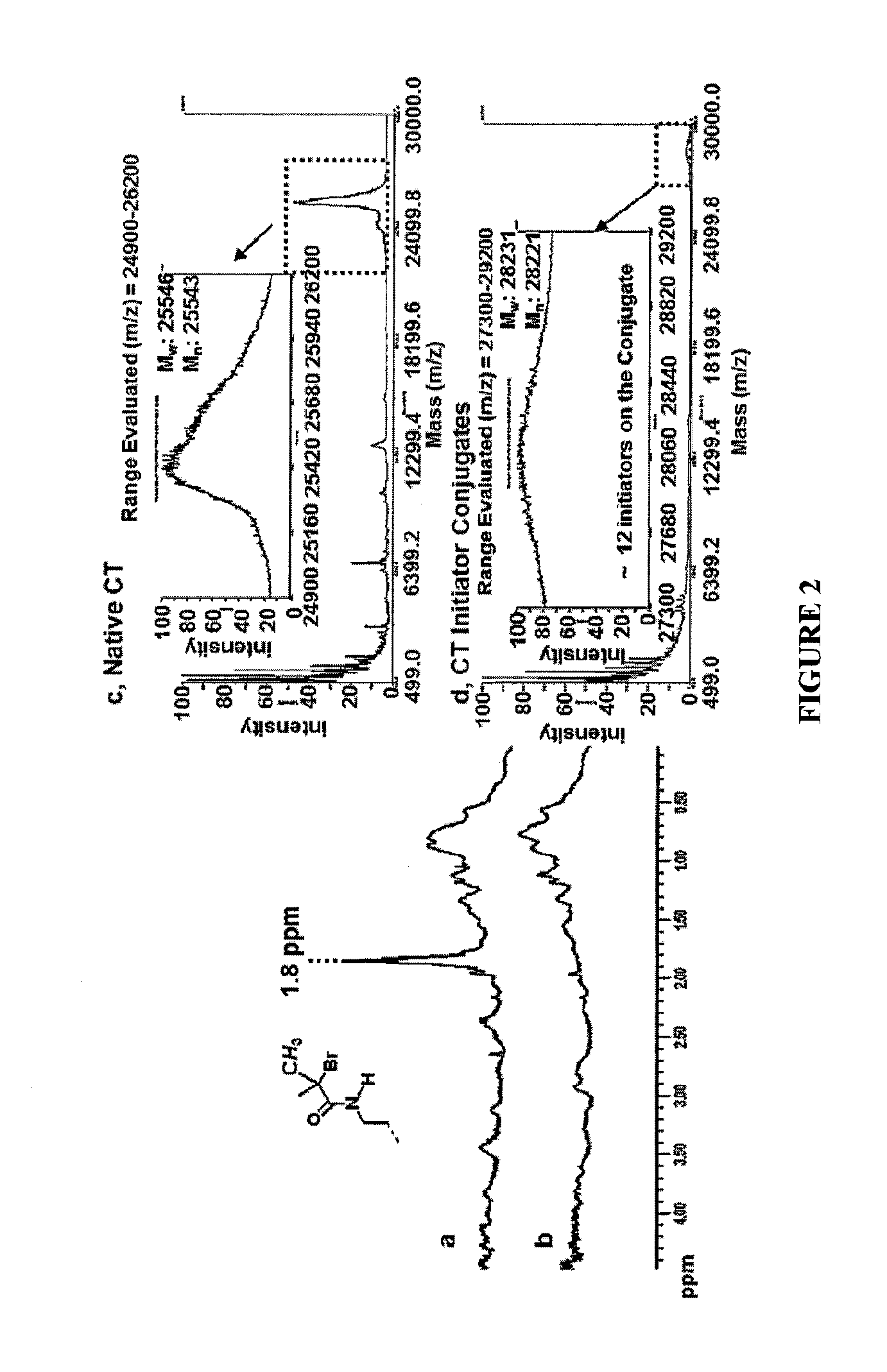
Using a novel water-soluble, active ester amide-containing functionalized controlled radical polymerization initiator, stimuli responsive polymers have been grown from the surface of a protein, exemplified by chymotrypsin or any protein having surface amino acids that will covalently bind to the active ester amide-containing functionalized initiator. It is shown that changes in temperature or pH can change the conformation of the polymer surrounding the enzyme, which in turn enabled the rational tailoring of enzyme activity and stability. This method has afforded an increase in the activity and stability of the enzyme by an order of magnitude at pH's where the enzyme is usually inactive or unstable. Multimodal temperature responsive protein-block copolymer conjugates are described.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
HPV antigens, vaccine compositions, and related methods
InactiveUS20080279877A1Reduces and eliminates riskLess considerationVirus peptidesAntiviralsHPV AntigenHuman papilloma virus infection
The present invention relates to the intersection of the fields of immunology and protein engineering, and particularly to antigens and vaccines useful in prevention of infection by human papilloma virus. Provided are recombinant protein antigens, compositions, and methods for the production and use of such antigens and vaccine compositions.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
Gene mutation type recombined protease K and industrialized production method thereof
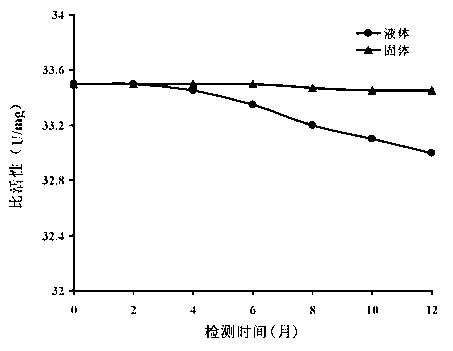
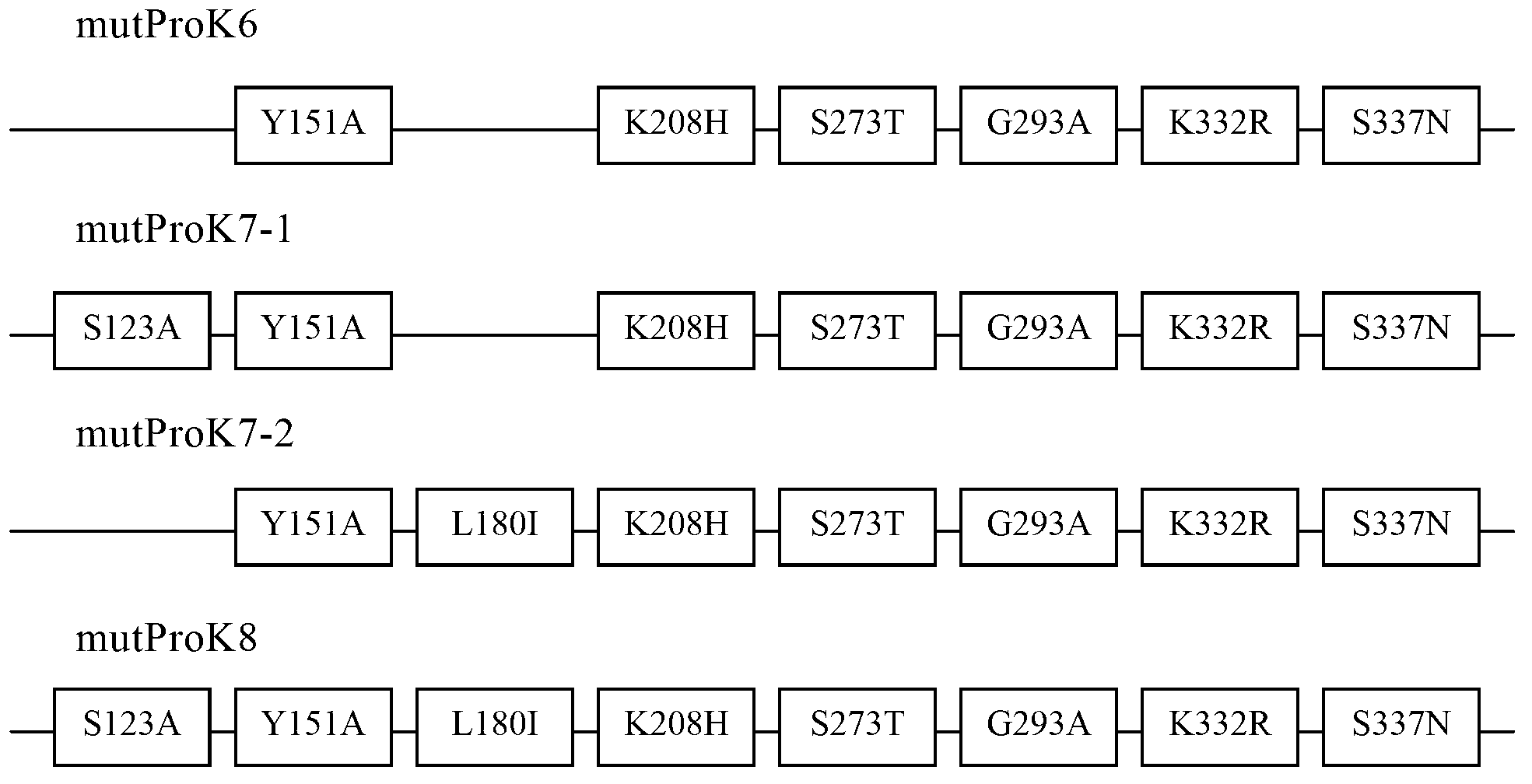
The invention relates to a gene mutation type recombined protease K and an industrialized production method thereof. Specifically, the invention relates to the gene mutation type recombined protease K which is obtained by performing gene reformation and protein engineering and has an enzymatic activity being more than two times of the enzymatic activity of the same natural protein, and further relates to the industrialized production method and a technical process for utilizing yeast cells to large-scale culture expressing foreign proteins and prepare the gene mutation type recombined protease K.
Owner:GPROAN BIOTECH (SUZHOU) INC
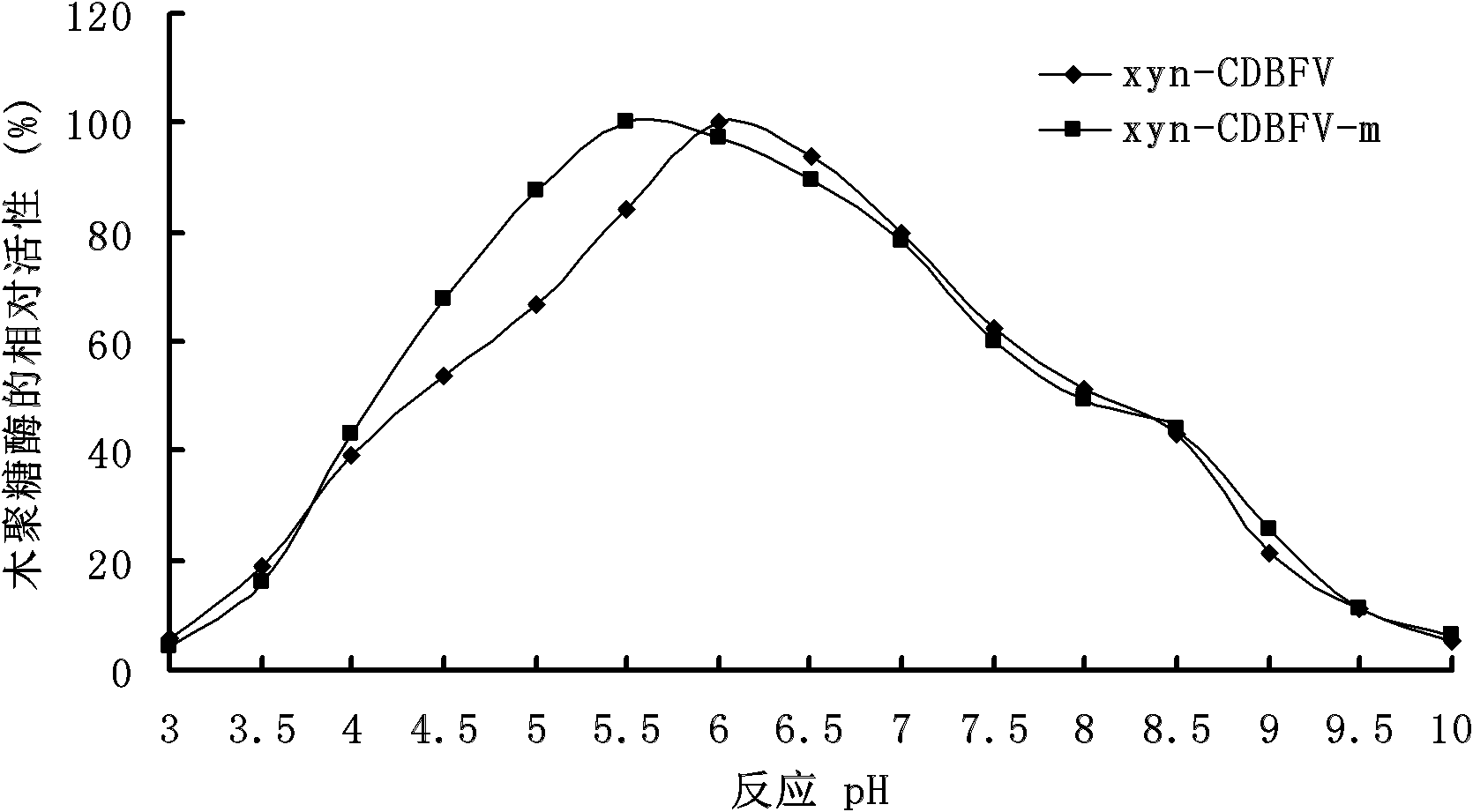
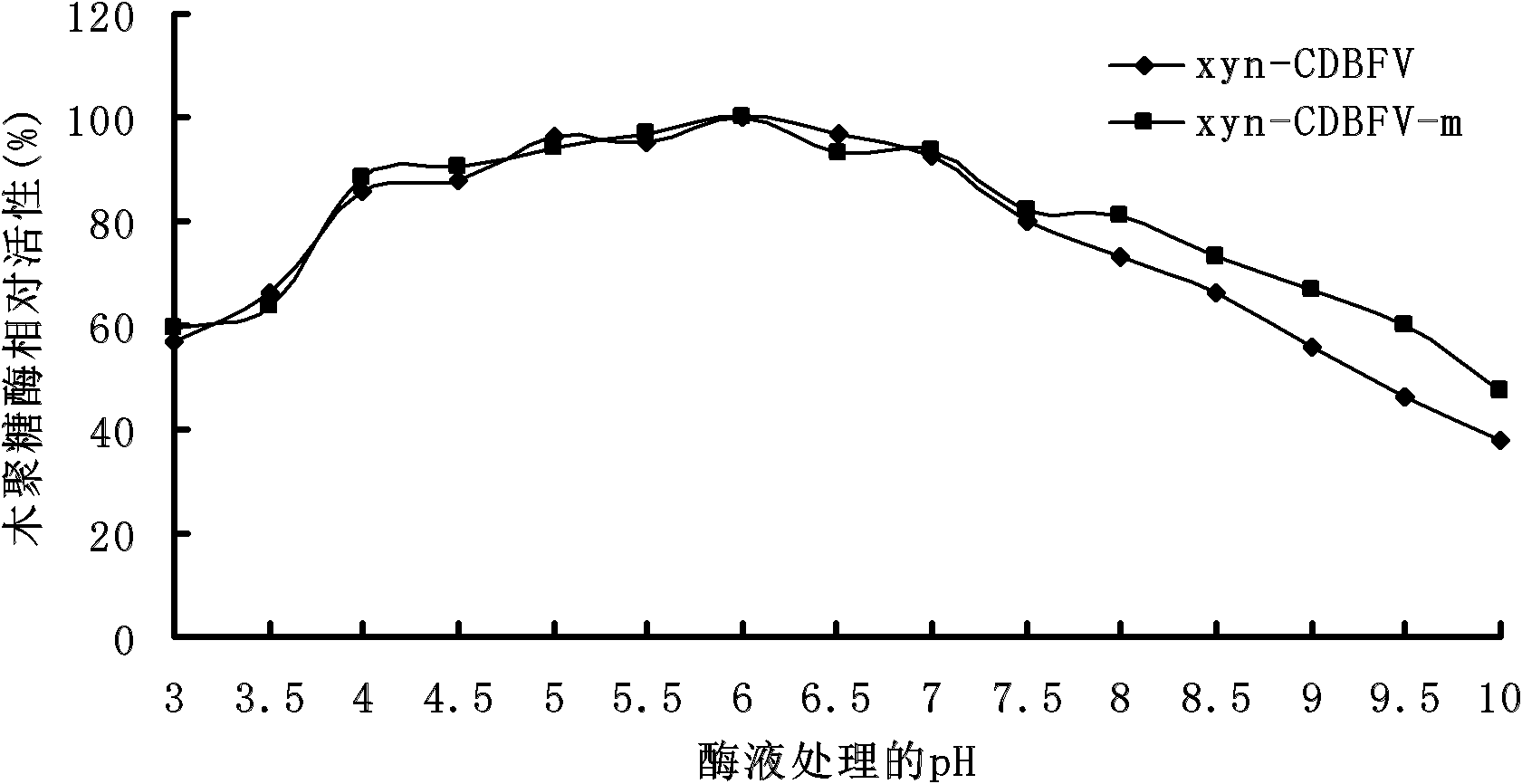
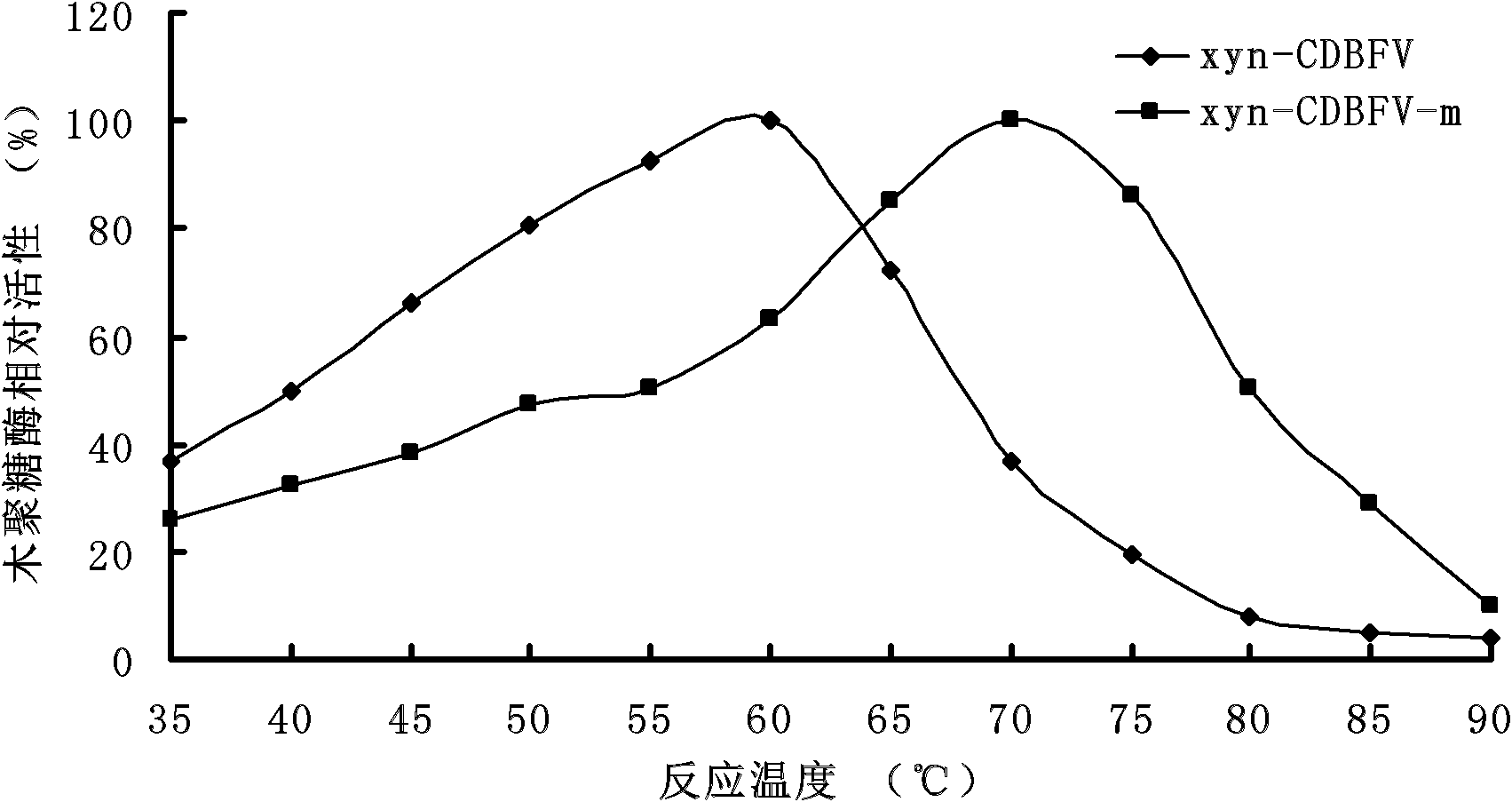
Xylanase xyn-CDBFV-m with modified thermal stability, gene thereof, and application thereof
ActiveCN102757947AMeet the requirements for using enzymesSolve the defect of excessive loss of enzyme activityFungiAnimal feeding stuffRumenProtein engineering
The invention relates to the filed of genetic engineering, and specifically relates to a xylanase xyn-CDBFV-m with modified thermal stability, a gene thereof, and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the xylanase is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. The invention aims at improving the thermal stability of the xylanase xyn-CDBFV of rumen fungi neocallimastix patriciarum, so that the xylanase can resist high temperature during a feestuff granulation process, and thereby the xylanase can be applied in feedstuffs. According to the invention, with a protein engineering approach, disulfide bond is introduced into an N terminal of the xylanase xyn-CDBFV; two relatively high regions of B-factor are eliminated; and salt bond is introduced into a molecular surface, so that a xylanase xyn-CDBFV-m with substantially improved thermal stability is obtained. According to the xylanase xyn-CDBFV-m provided by the invention, 56.7% of enzymatic activity is maintained after 4min of treatment under a temperature of 80 DEG C. Therefore, the xylanase can resist short high-temperature treatment during feedstuff granulation. The xylanase provided by the invention shows great application potential.
Owner:WUHAN SUNHY BIOLOGICAL
Prodrug activation in cancer cells using molecular switches
The present invention features a novel protein engineering strategy by combining the domains of two independent proteins into a molecular switch. The invention features polypeptides comprising a prodrug activating enzyme and a protein that binds a cancer specific marker, polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides, and molecular switches for converting a prodrug into a toxin, comprising the polypeptides. The invention also features methods for converting a prodrug into a toxin, methods for treating cancer, and methods for making the molecular switches, as well as kits.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Prepn of metallothionein
InactiveCN1348010AImprove compatibilityImprove production efficiencyFermentationEscherichia coliFusion Protein Expression
The present invention is one gene engineering process of preparing metallothionein in high yield. The process incldues constituting the expression plasmid or its mutant gene, transferring and fermentation culture in engineering colibacillus, induction and adding metal ion before further culture, collecting thallus; ultrasonic crushing thallus, centrifugation, static adsorption with affinity chromatographic column of glutathione-agarose gel 4B, incision with thrombase on the column, column chromatograhic desalting, gradient salt elution and collecting destination protein. The present inventioncan obtain destination protein with purity over 95 %. Using the said method to prepare 6 mutant proteins of monkey metallothionein I can obtain yield and purity similar to that in wild recombinant protein.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
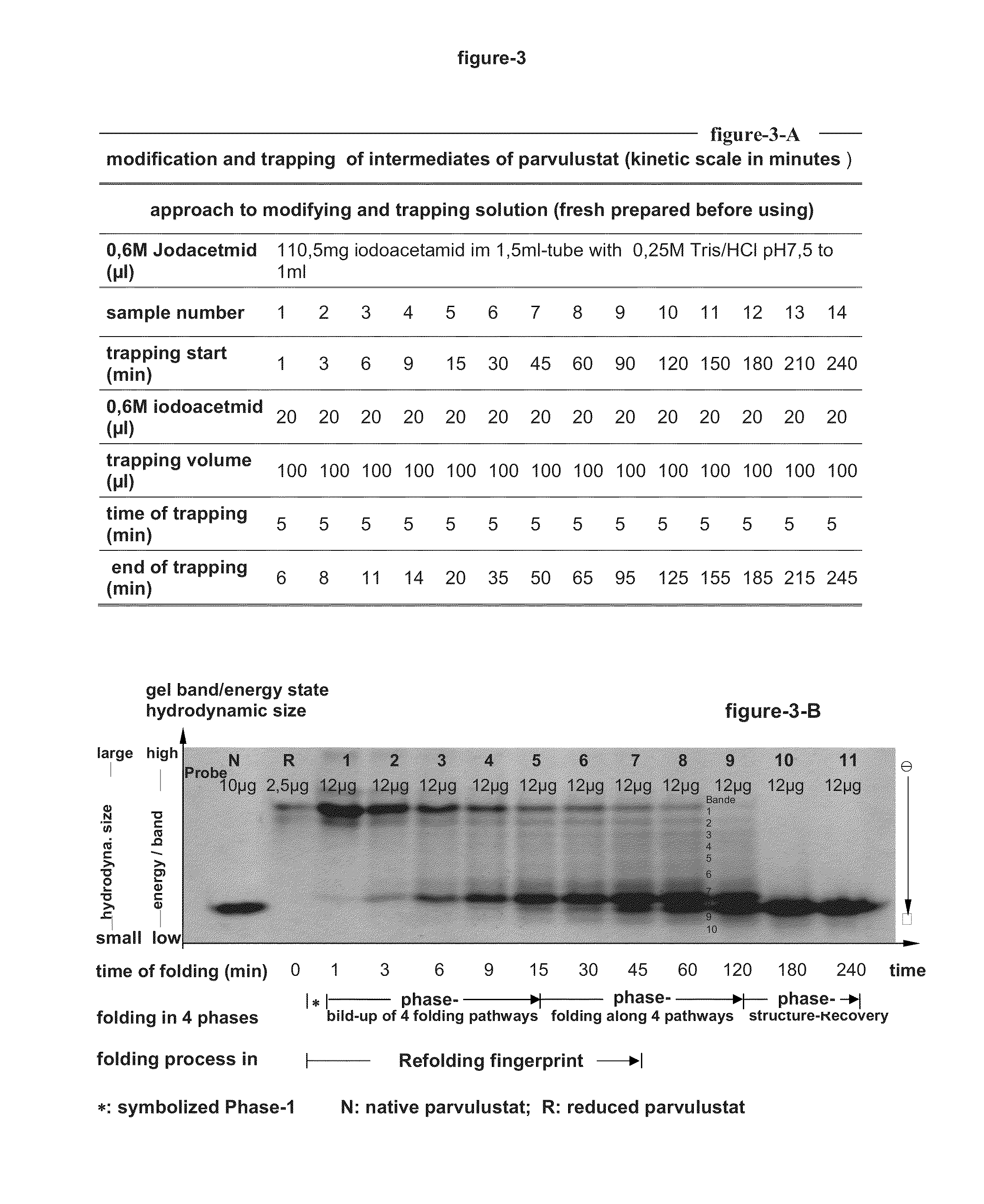
Novel method for characterizing and multi-dimensionally representing the folding process of proteins
InactiveUS20130130294A1Simple designHigh activityDiscounts/incentivesFinanceComputer-aidedComputer aid
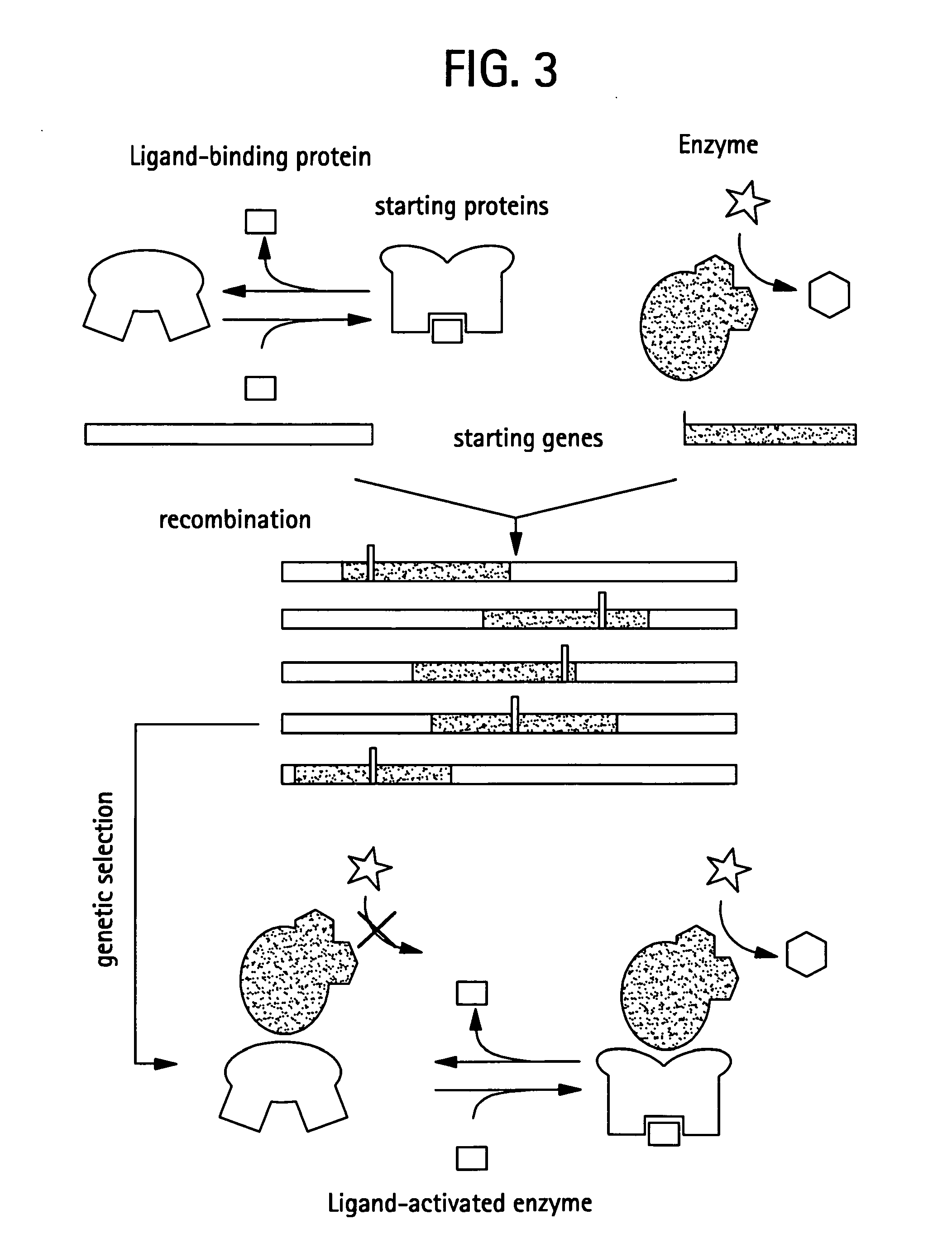
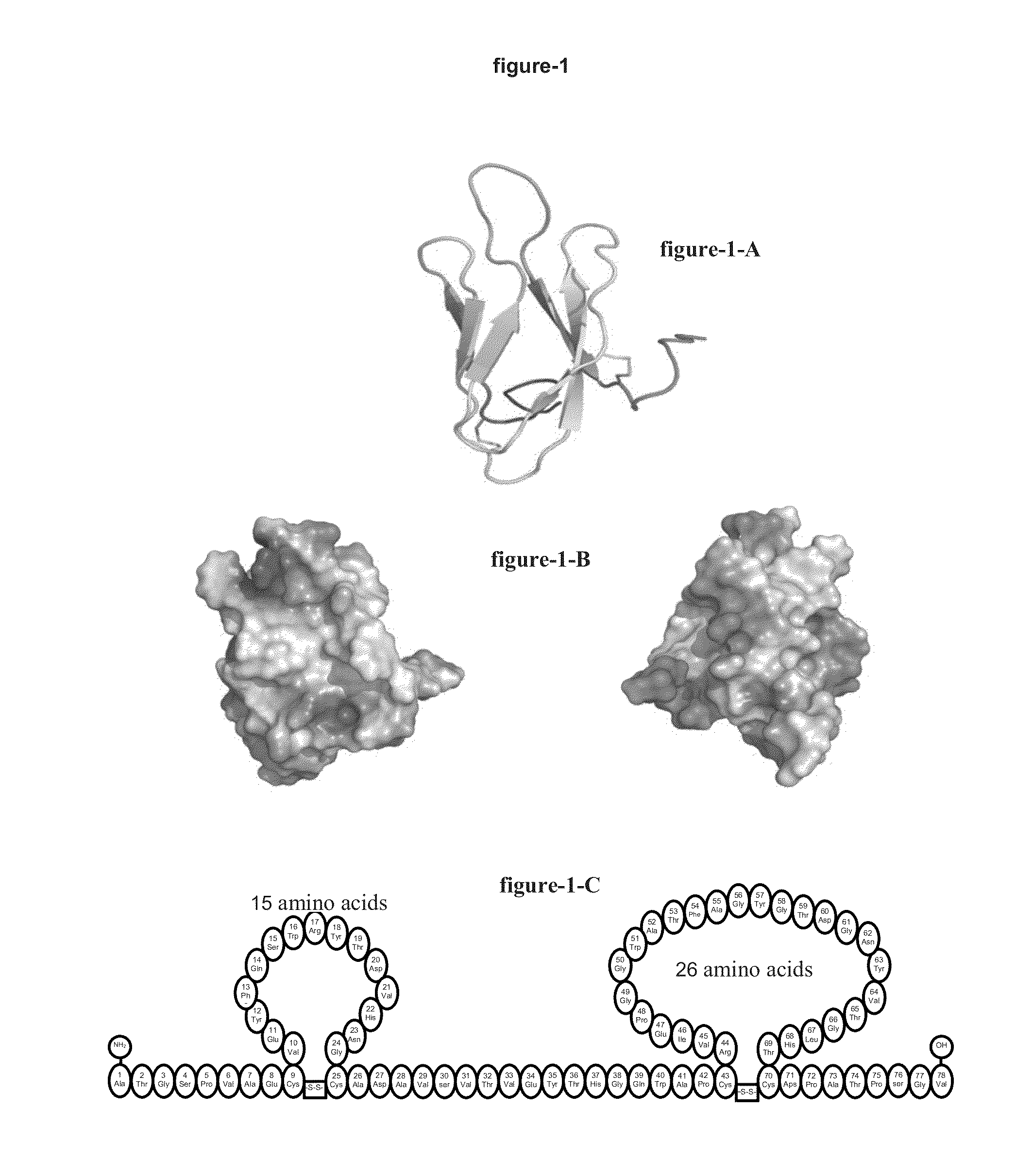
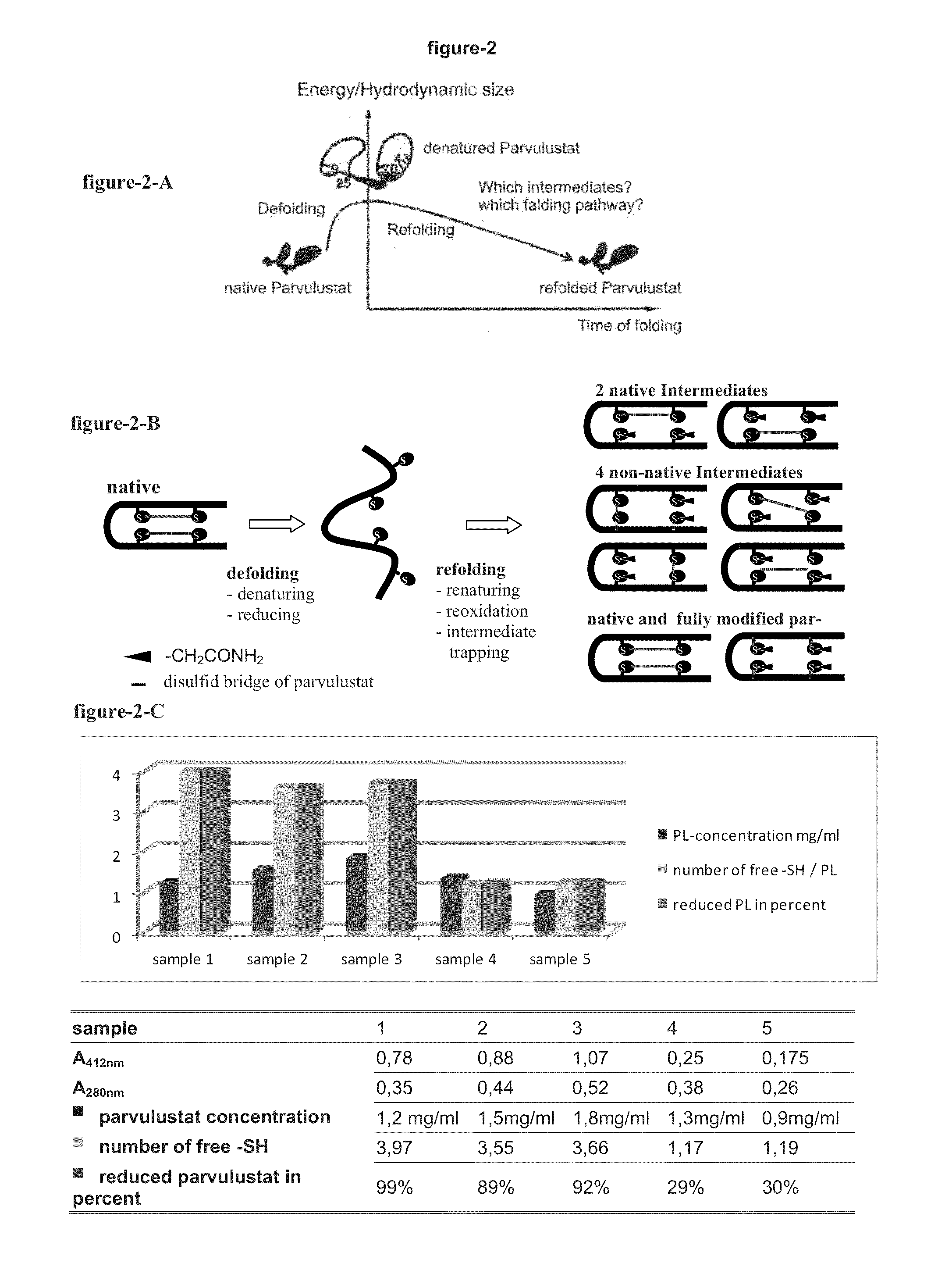
The invention relates to a novel method for characterizing and multi-dimensionally representing the folding process of proteins (FIG. 9). Said method comprises, in a methodically novel combination, kinetically arranging the hydrodynamic size of the refolding and thus modified protein, associating the proteolytically fragmented intermediates on the basis of the bioinformatic detection patterns, classifying the folding pathway association of the intermediates, characterizing the folding sequences, and multi-dimensionally visualizing the characterized folding process in a computer-aided manner. Said method is characterized in that all intermediates modified during the refolding and thus structurally blocked are identified and digitalized according to the four individual characteristics of said intermediates, namely the hydrodynamic size, the formation time, the folding pathway association, and amount. Said novel method has many applications in the field of research of protein folding and proteopathy, protein engineering, antibody engineering, molecular biology, therapeutic medicine, biotechnology, biotechnological production of protein pharmaceuticals, protein taxonomy, and nanotechnology for developing and producing novel functional protein materials. According to the invention, many and varied products in the form of different assay kits, devices, software, and machines can be produced and used to carry out said method.
Owner:HAN SIGENG
Bispecific antibody capable of resisting B cell lymphoma and application thereof
InactiveCN102250245AHighlighting the role of anti-B-cell lymphomaFungiHybrid immunoglobulinsAntiendomysial antibodiesT lymphocyte
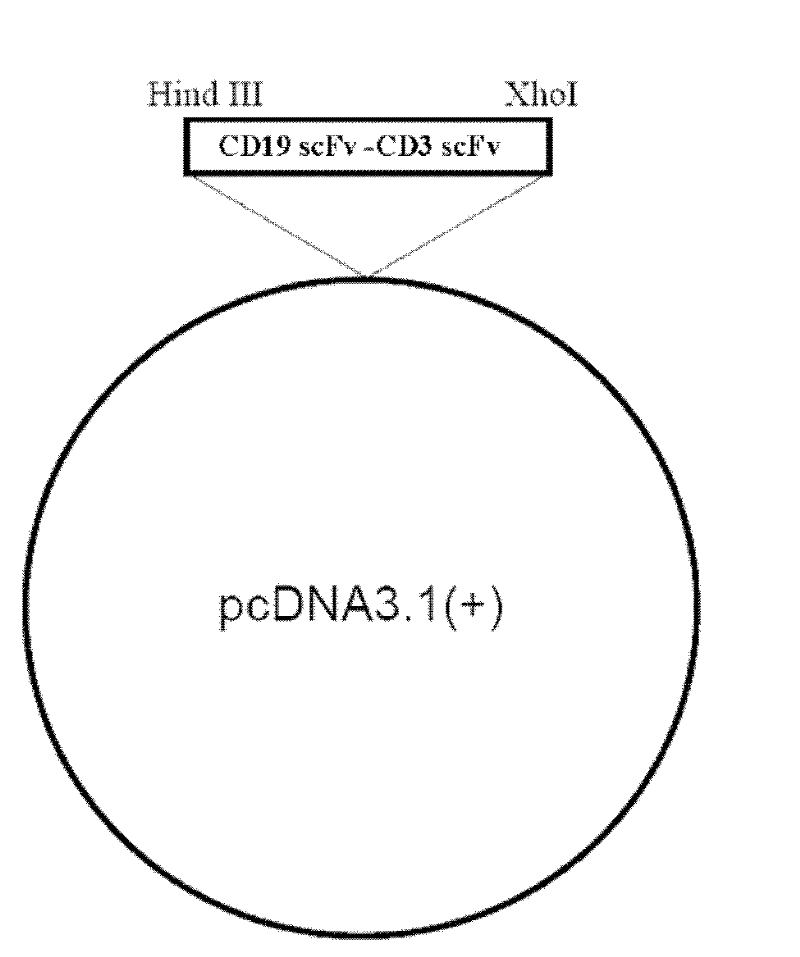
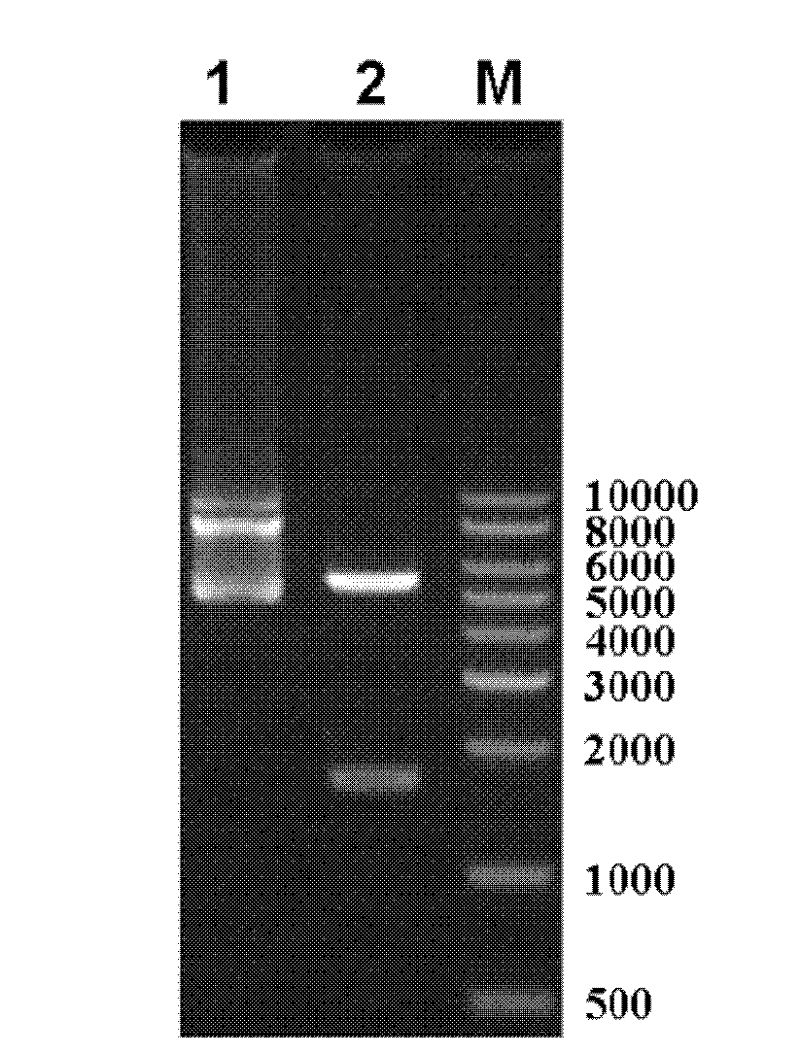
The invention relates to the technical fields of genetic engineering and protein engineering, in particular relates to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) for encoding recombinant fusion protein containing human CD19 antibody variable region and human CD3 antibody variable region fragments, fusion protein encoded by DNA, a production method of the fusion protein, pharmaceutical application of the fusion protein and a treatment method using the fusion protein. The invention provides bispecific antibody protein containing human CD19scFv and CD3scFv. The bispecific antibody protein can be combined with positive CD19 and CD3 positive cells, has good bioactivities in vivo and vitro, can activate human T lymphocyte, kill B lymphoma cells, and has good application prospects.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Mutant of cyclodextrin glucosyl transferase having highly beta-cyclodextrin yielding property and mutation method
InactiveCN101503680AEase of industrial productionStrong specificityTransferasesMicroorganism based processesWild typeSite-directed mutagenesis
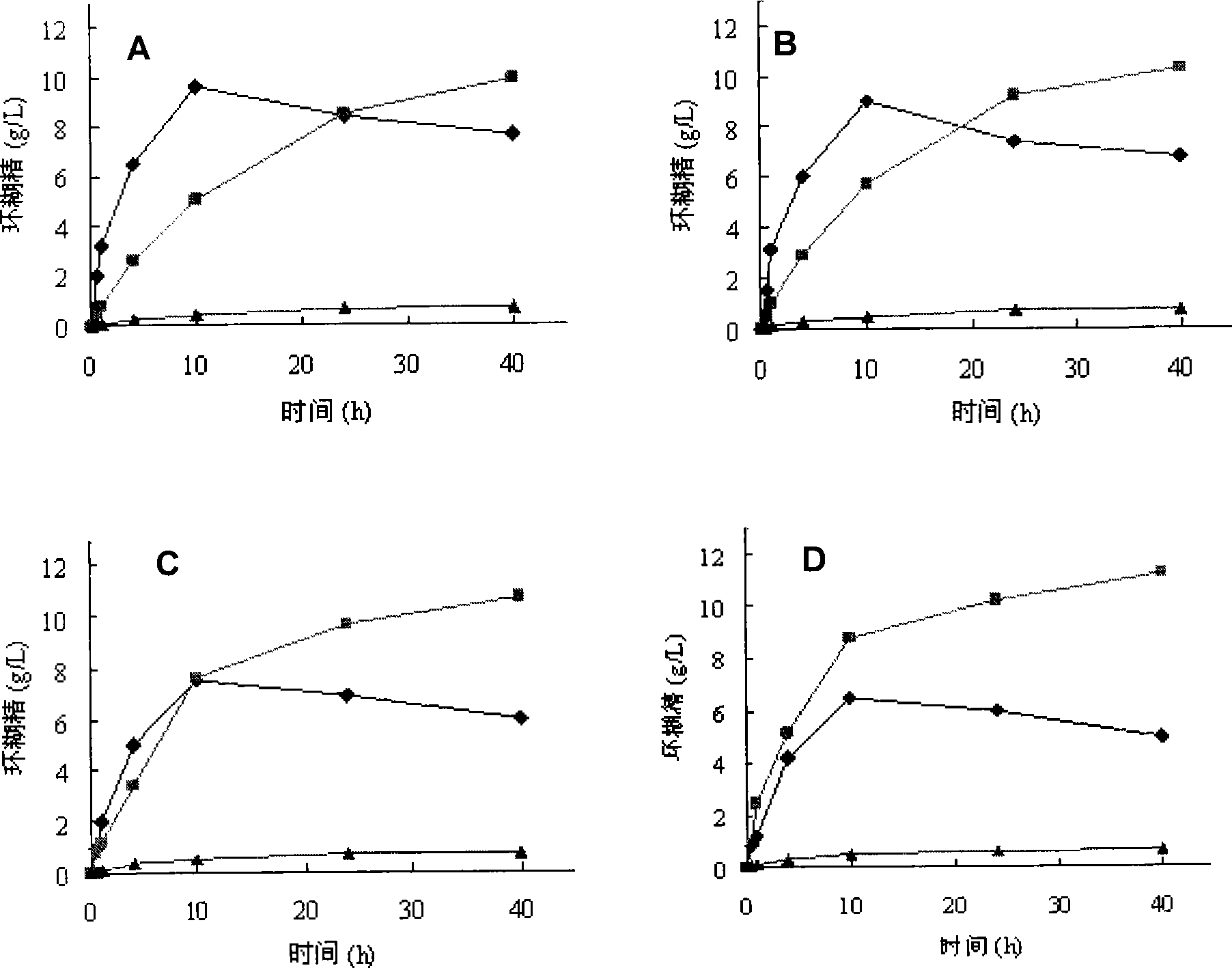
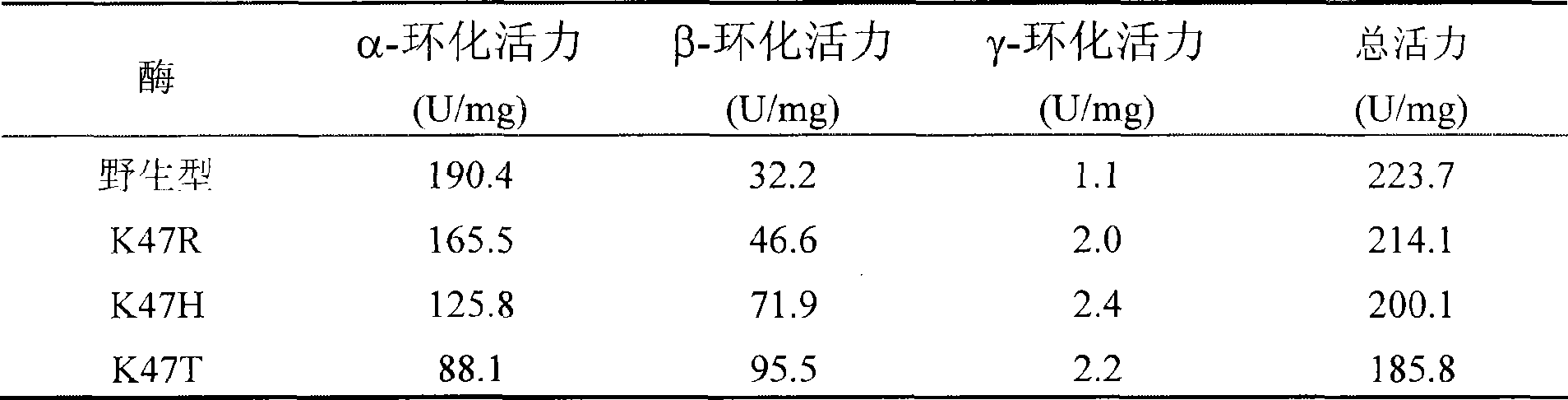
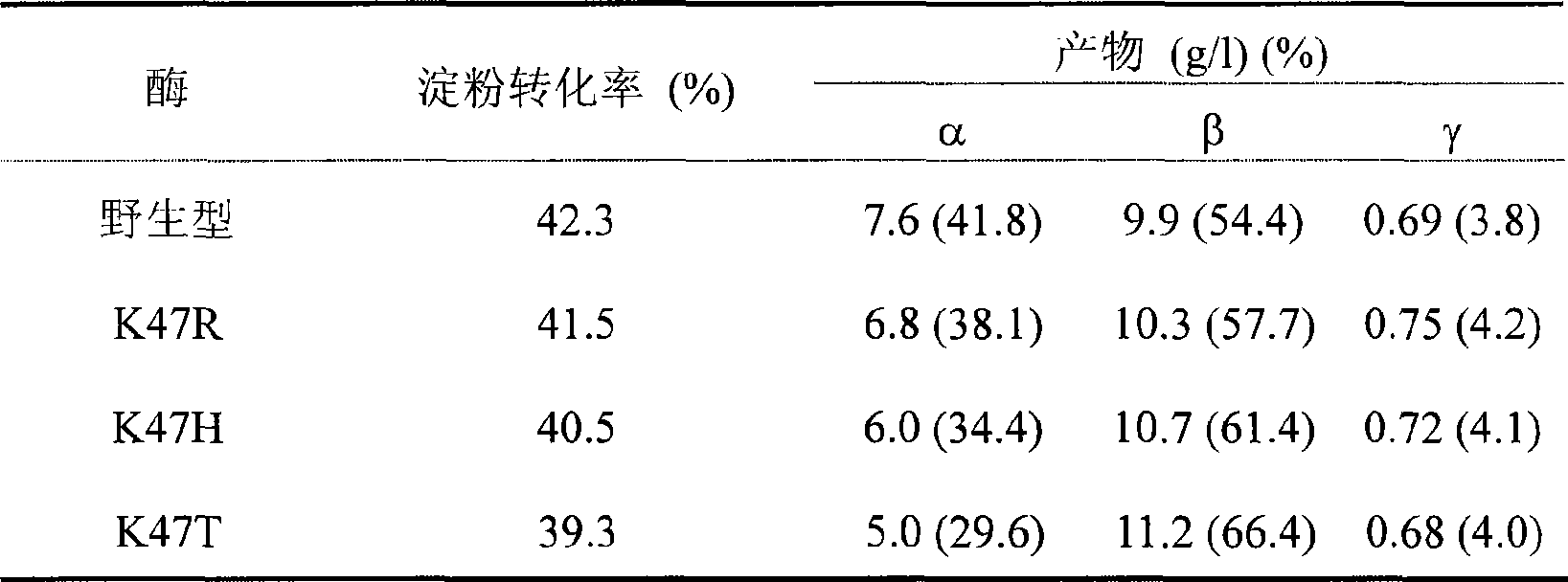
The invention relates to a mutant of a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with the capability of highly yielding beta-cyclodextrin and a mutation method, which belong to the fields of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The invention improves the capability of the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (CGT enzyme for short) for producing the beta-cyclodextrin by a rite-directed mutagenesis method, provides a mutant proposal for improving the capability of CGT enzyme from Peanibacillus macerans JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO: M 208063) for producing the beta-cyclodextrin, and substitutes Lys on the 47 position of the CGT enzyme for Arg, His and Thr respectively; the beta-cyclodextrin production capacity of the obtained three mutant enzyme of K47R, K47H and K47T is improved compared with wild type CGT enzymes, wherein the mutant enzyme K47T is particularly obvious. The mutant enzymes are more favorable for industrial production of the beta-cyclodextrin than the wild type CGT enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing CysC-paired monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN102321176AReduce workloadExpand the scope of the filterImmunoglobulins against protease inhibitorsAntigenPeroxidase
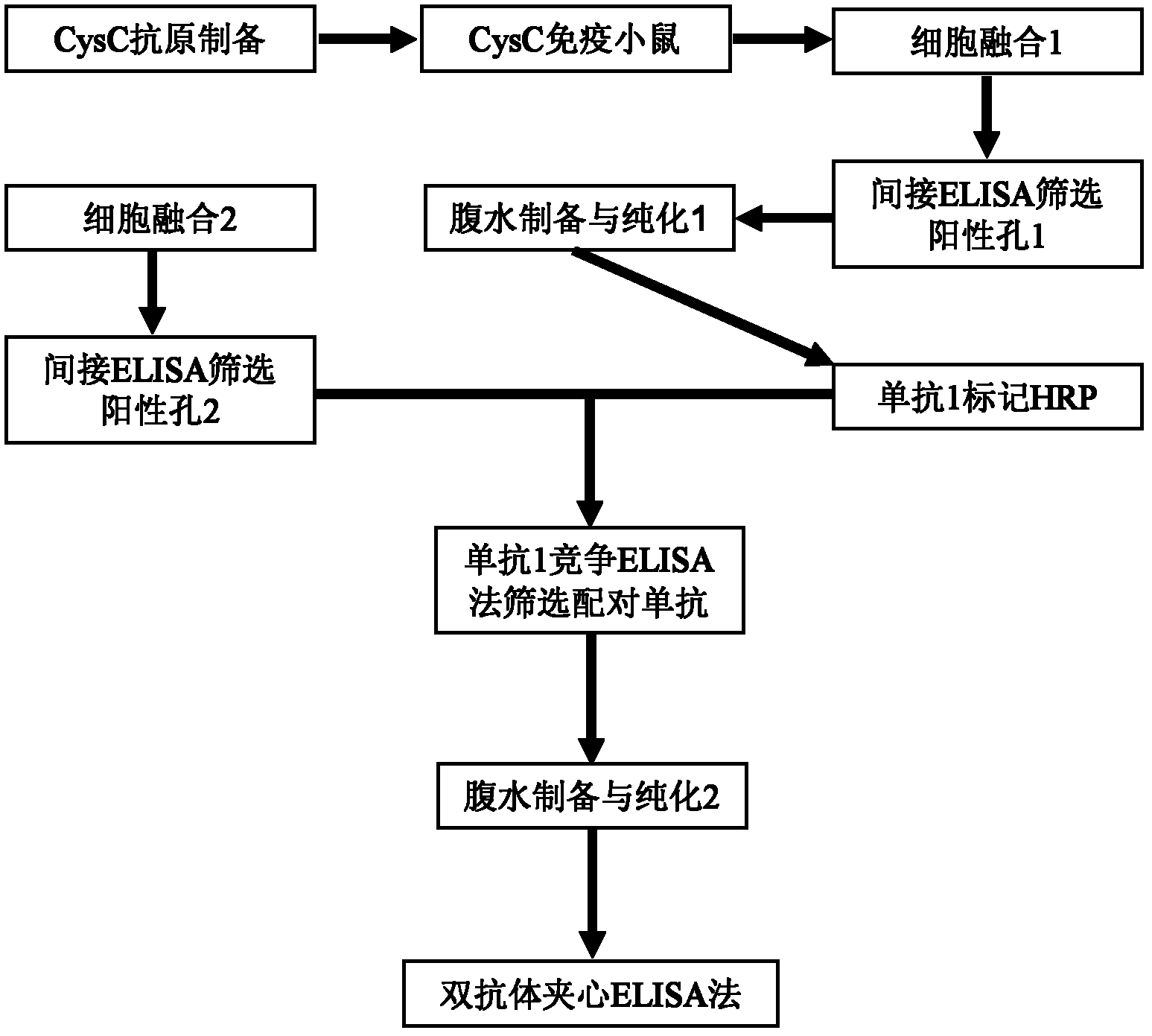
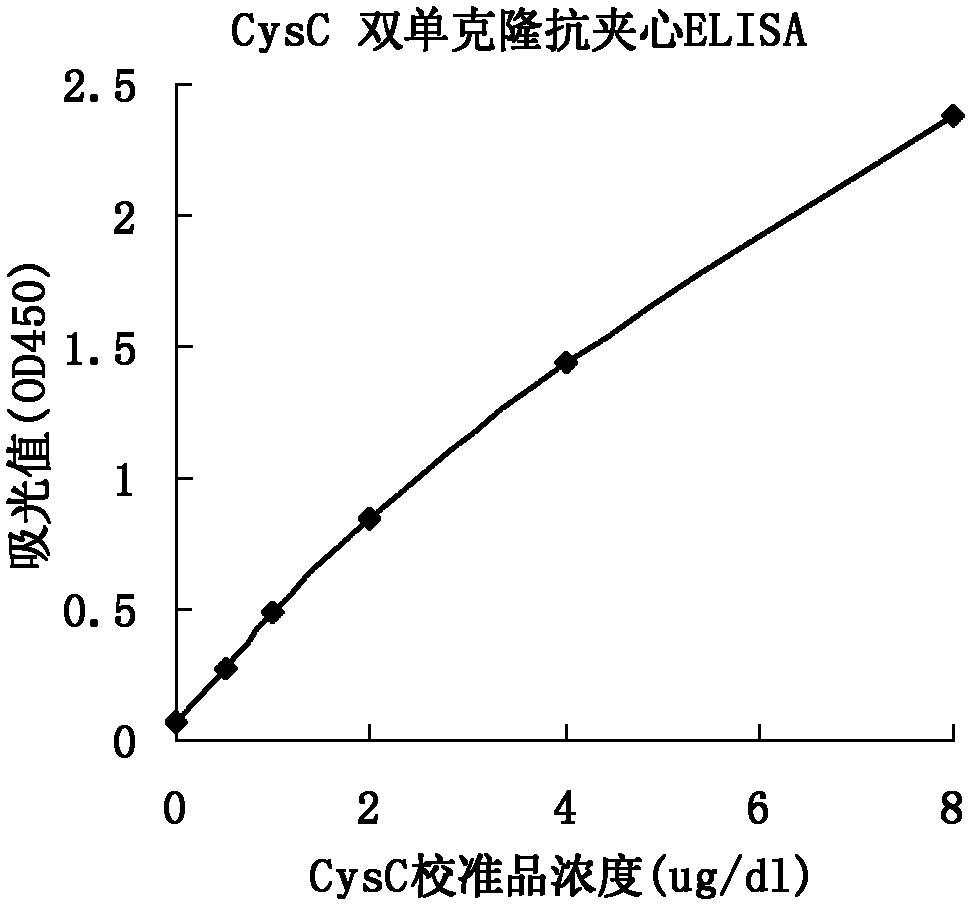
The invention relates to the field of protein engineering, in particular to a method for preparing CysC-paired monoclonal antibodies, which comprises the following steps of: screening hybridoma cells having specific binding with CysC after fusing mouse splenic cells and myeloma cells capable of generating CysC antibodies, preparing cells for generating the monoclonal antibodies, finishing first-time cell fusion, further purifying out the monoclonal antibodies, and selecting one monoclonal antibody to be marked with horse radish peroxidase; then implementing the second-time fusion of the mouse splenic cells and the myeloma cells; finishing CysC-antigen coating on an elisa plate, adding a hybridoma-cell cultural supernatant obtained through the second-time cell fusion to elisa-plate holes, arranging a blank control hole, subsequently adding the monoclonal antibody marked with the horse radish peroxidase to the elisa-plate holes, incubating at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 30 minutes, adding a substrate to each hole for color rendering, and measuring a light absorption value under 450nm after stopping reaction through sulfuric acid; and selecting the uninhibited holes as the paired monoclonal antibodies.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
Trypanosoma Antigens, Vaccine Compositions, and Related Methods
ActiveUS20090324634A1Reduces and eliminates riskLess considerationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingProtozoaTrypanosoma antigen
The present invention relates to the intersection of the fields of immunology and protein engineering, and particularly to antigens and vaccines useful in prevention of infection by Trypanosoma protozoa. Provided are recombinant protein antigens, compositions, and methods for the production and use of such antigens and vaccine compositions.
Owner:IBIO
Xylanase mutants
ActiveCN109402091AImprove heat resistanceMicroorganism based processesFermentationHeat resistanceSite-directed mutagenesis
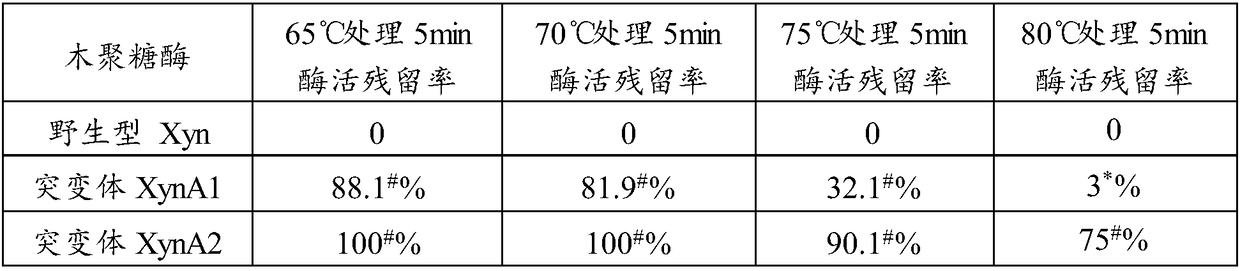
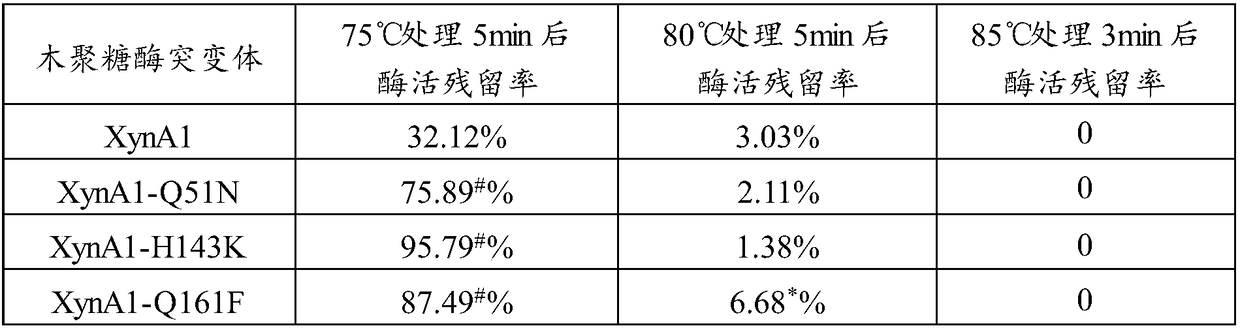
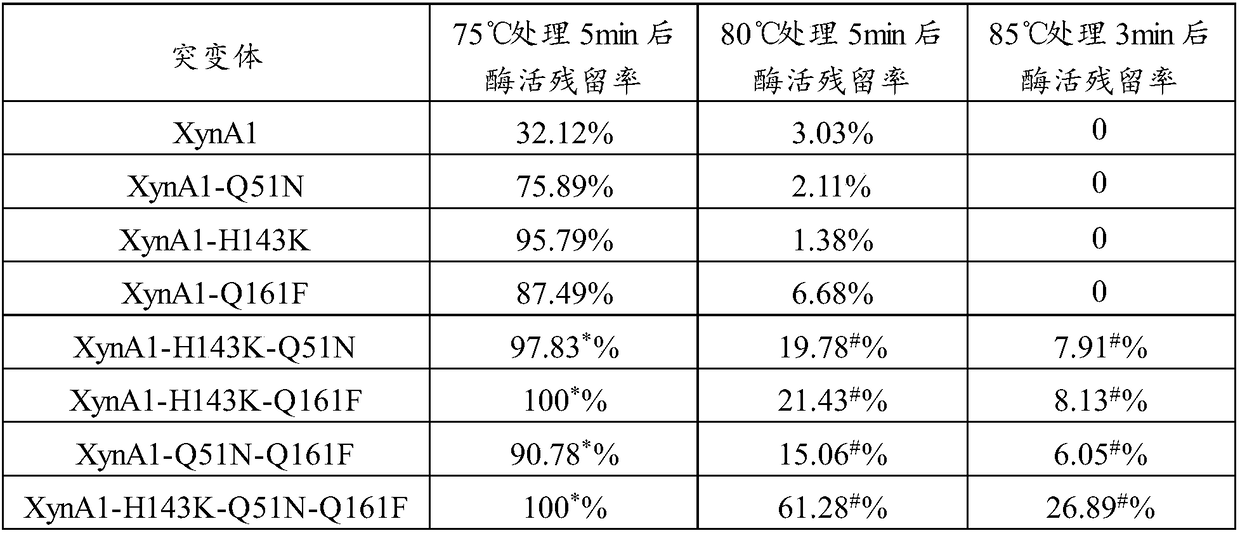
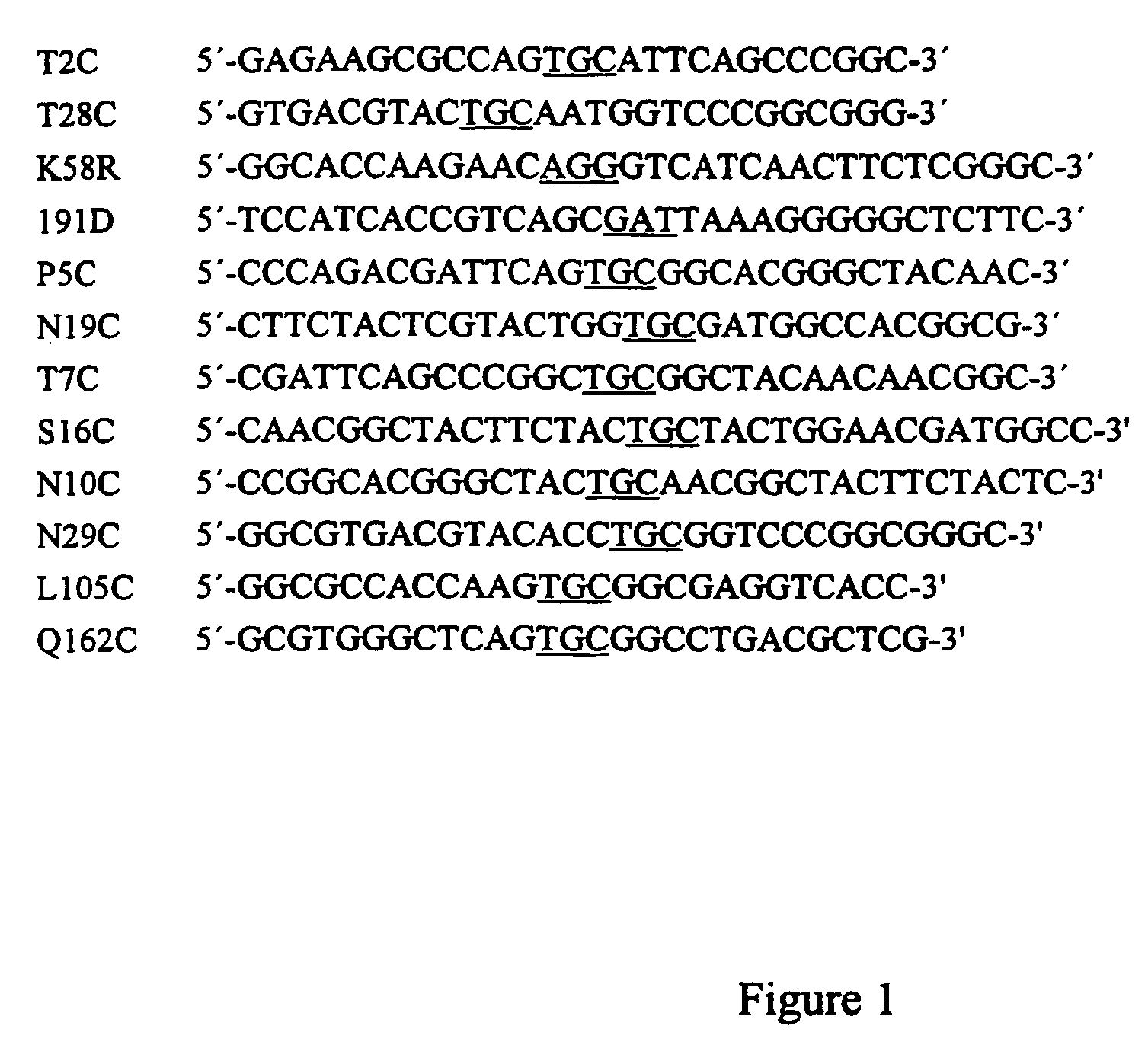
The invention relates to the technical field of protein engineering modification, in particular to xylanase mutants with improved heat resistance. Two or more unnatural disulfide bridges are manuallyintroduced into xylanase with a site-directed mutation method, the mutants XynA1 and XynA2 with improved heat resistance are obtained, and particularly, for the mutant XynA2 with three disulfide bridges introduced, enzyme activity residual rate of the mutant XynA2 after 5 min treatment at 80 DEG C is as high as 75% and is increased by 72% compared with that of the mutant XynA1. Three mutation sites Q51N, H143K and Q161F capable of improving heat resistance of the mutants remarkably are obtained by further screening, xylanase XynA1 and xylanase XynA2 are introduced into the mutation sites in amode of single-point, two-point combination or three-point combination, and heat resistance can be effectively improved.
Owner:WEIFANG KANGDIEN BIOTECH +1
Trichoderma reesei G/11 xylanases with improved stability
ActiveUS7718411B1Improve enzyme stabilityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesGlycosylasesBiotechnologySite-directed mutagenesis
The present invention relates to protein engineering, and concerns especially family G / 11 xylanases, and genes encoding said enzymes. In specific, the invention concerns Trichoderma reesei XYNII gene, which codes for endo-1,4-β-xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8). The invention describes how site-directed mutagenesis can be used to improve the properties of an enzyme to match the industrial conditions where it is used. Protein engineering can be used to improve thermoactivity and thermostability of xylanases, as well as to broaden their pH range.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
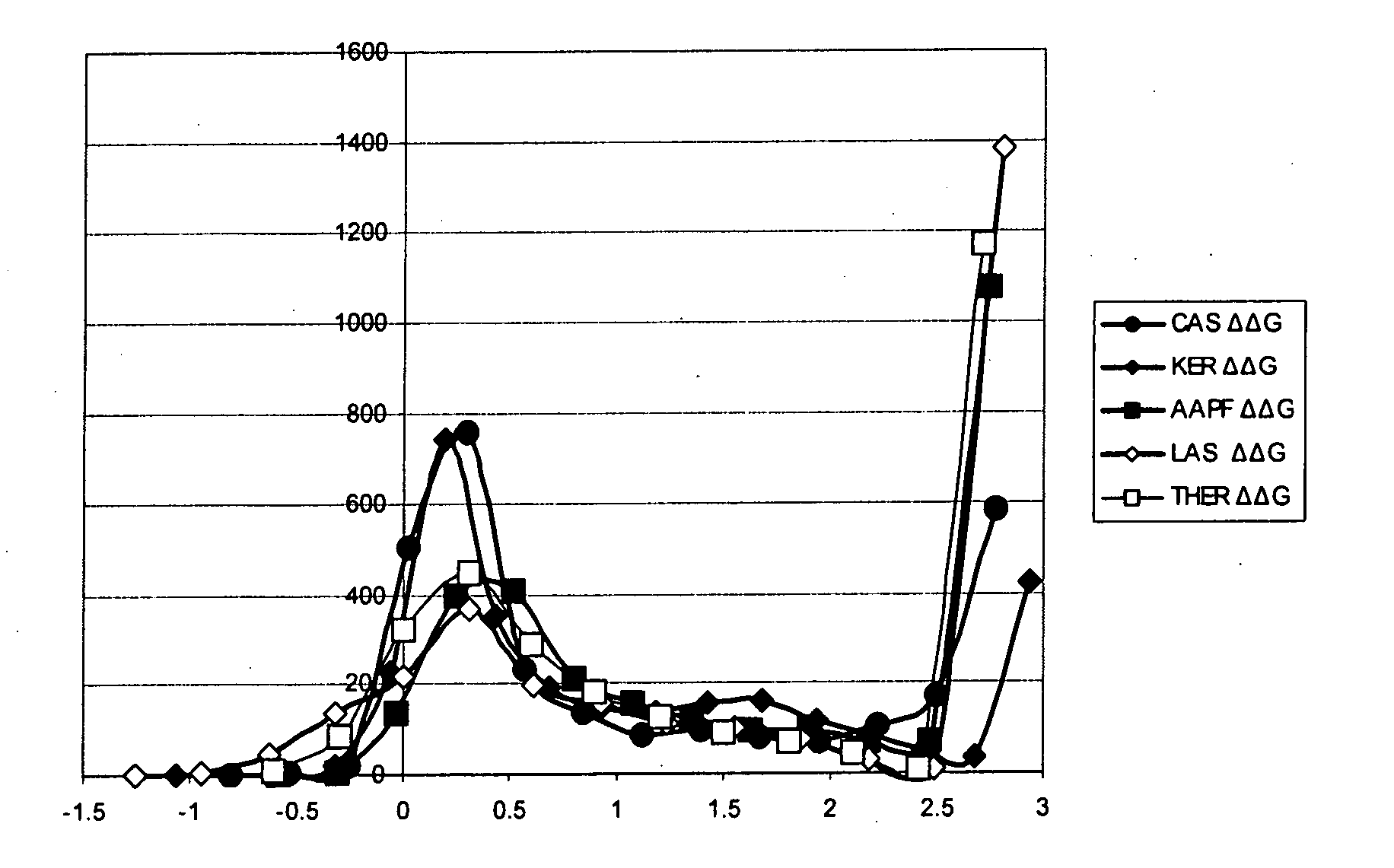
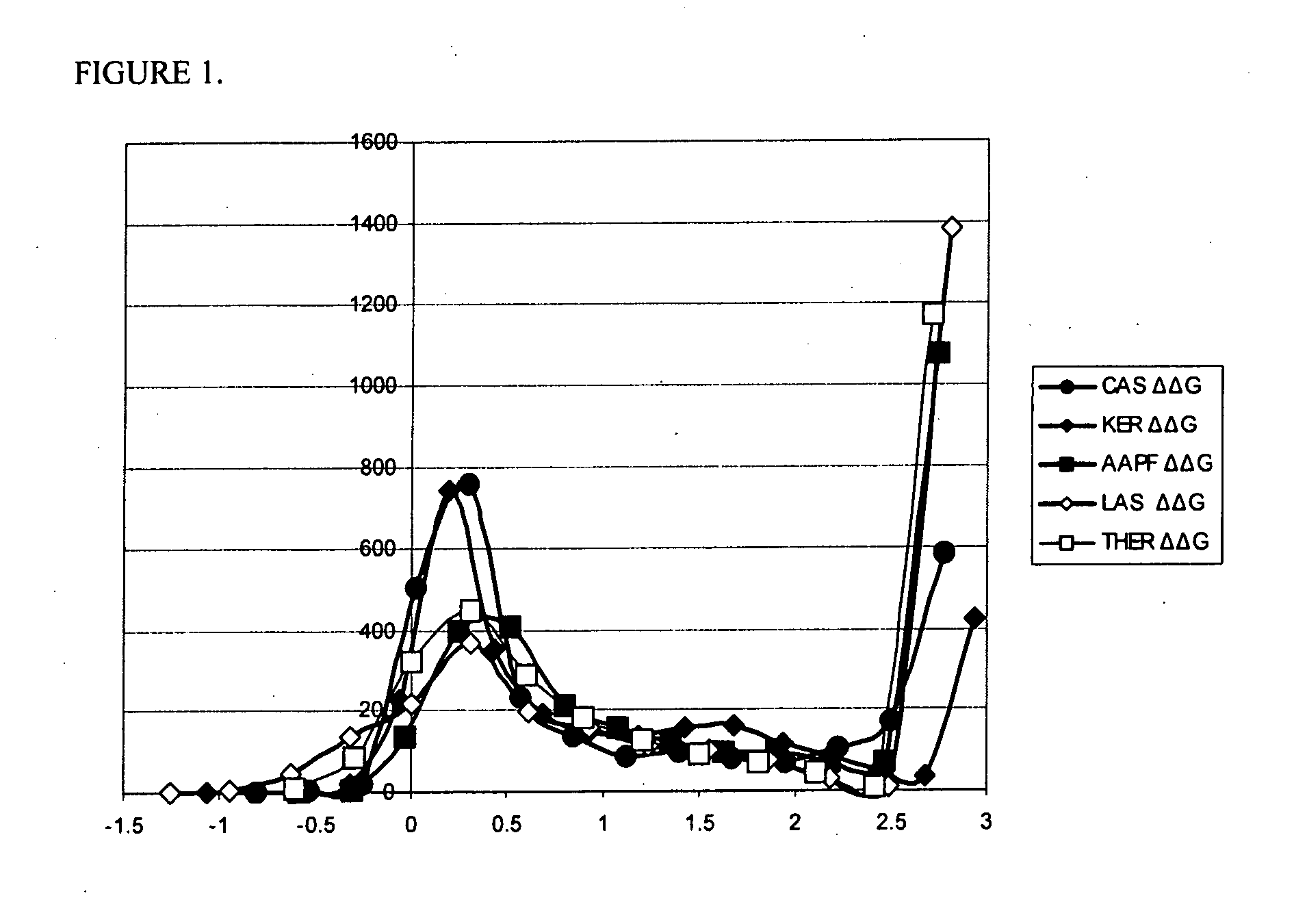
Systematic evaluation of sequence and activity relationships using site evaluation libraries for engineering multiple properties
InactiveUS20080004186A1Improve propertiesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein engineeringSite evaluation
The present invention provides methods for protein engineering. Specifically, the invention provides methods utilizing site evaluation libraries to design libraries that optimize two or more properties of a protein.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
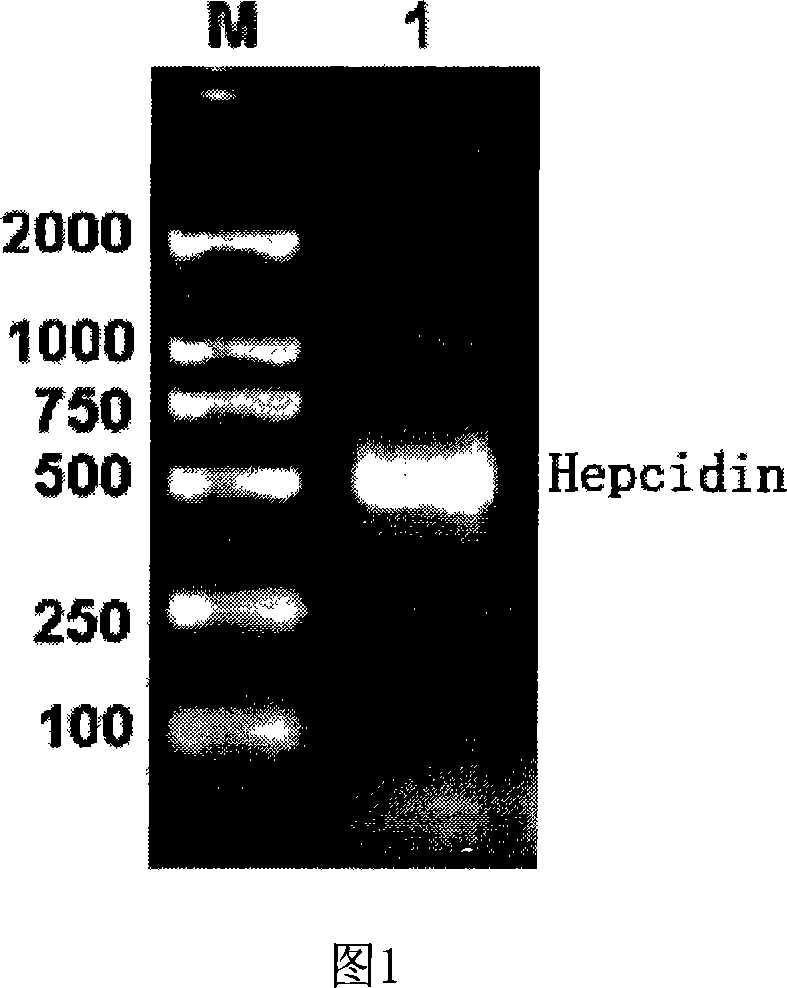
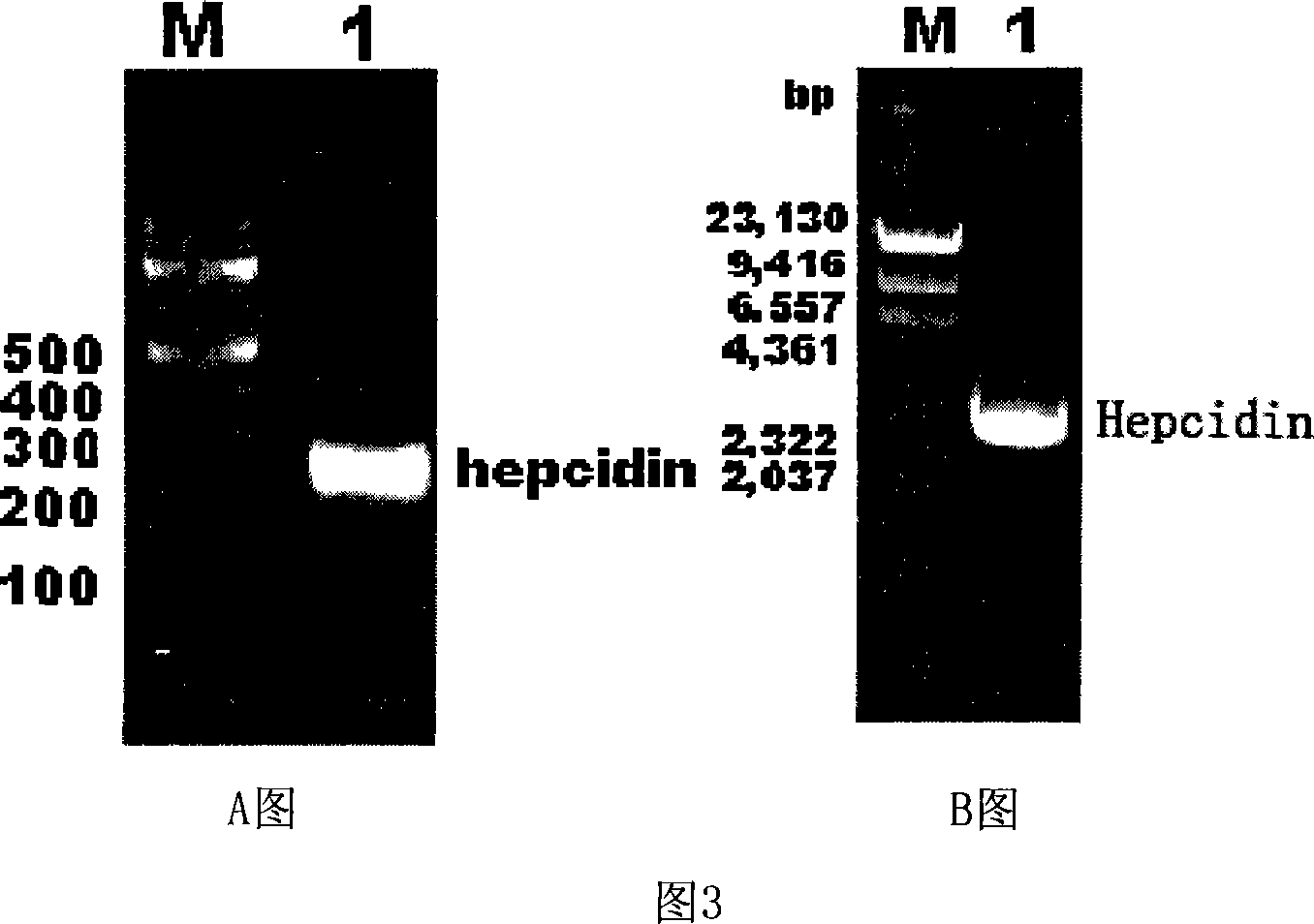
Expression carrier for black porgy antibiotic peptide Hepcidin and expression product and constructing preparation method
The invention discloses an expressing carrier of black porgy antibiotic peptide Hepcidin, expressing product and preparing method, which is characterized by the following: incorporating E. coliTrc promoter, protein project improving CKS gene and procaryotic expressing carrier pTrc-CKS of histidine tag (His-Tag); connecting to black porgy Hepcidin gene; constructing pTrc-CKS / hepcidin expressing plasmid; possessing P3C enzyme cutting site; fusing six histidine on C end; getting CKS-hepcidin; purifying through C end His-Tag affinity chromatography; getting the purified product; cutting CKS with P3C enzyme in fuse protein; getting the purified Hepcidin.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Fluorescent labeling of specific protein targets in vitro and in vivo
InactiveUS20060147948A1High sensitivityReduced flexibilityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceIn vivo
New methods are provided for the post-genomic era that will permit the analysis of the dynamic expression and localization of gene products in living cells. Herein we propose the development of such a method from a bioorganic approach involving organic synthesis and protein engineering. Specifically, novel compounds bearing two maleimide groups attached directly to fluorescent cores will be prepared, whose latent fluorescence is quenched until their maleimide groups undergo a specific thiol addition reaction. Complementary a-helical proteins are designed bearing two cysteine residues appropriately positioned to react with our novel fluorogens. Genetically fusing our helical probe peptides to test proteins of interest, we can selectively label the target sequence in living cells with our small synthetic fluorogenic molecules. The scope of this technique is described in the context of studying protein localization and protein-protein interactions in living cells.
Owner:VALORISATION RECH LLP +1
Method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid with high yield
ActiveCN108467860AIncreased enzyme activityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus megateriumGlutamate decarboxylase
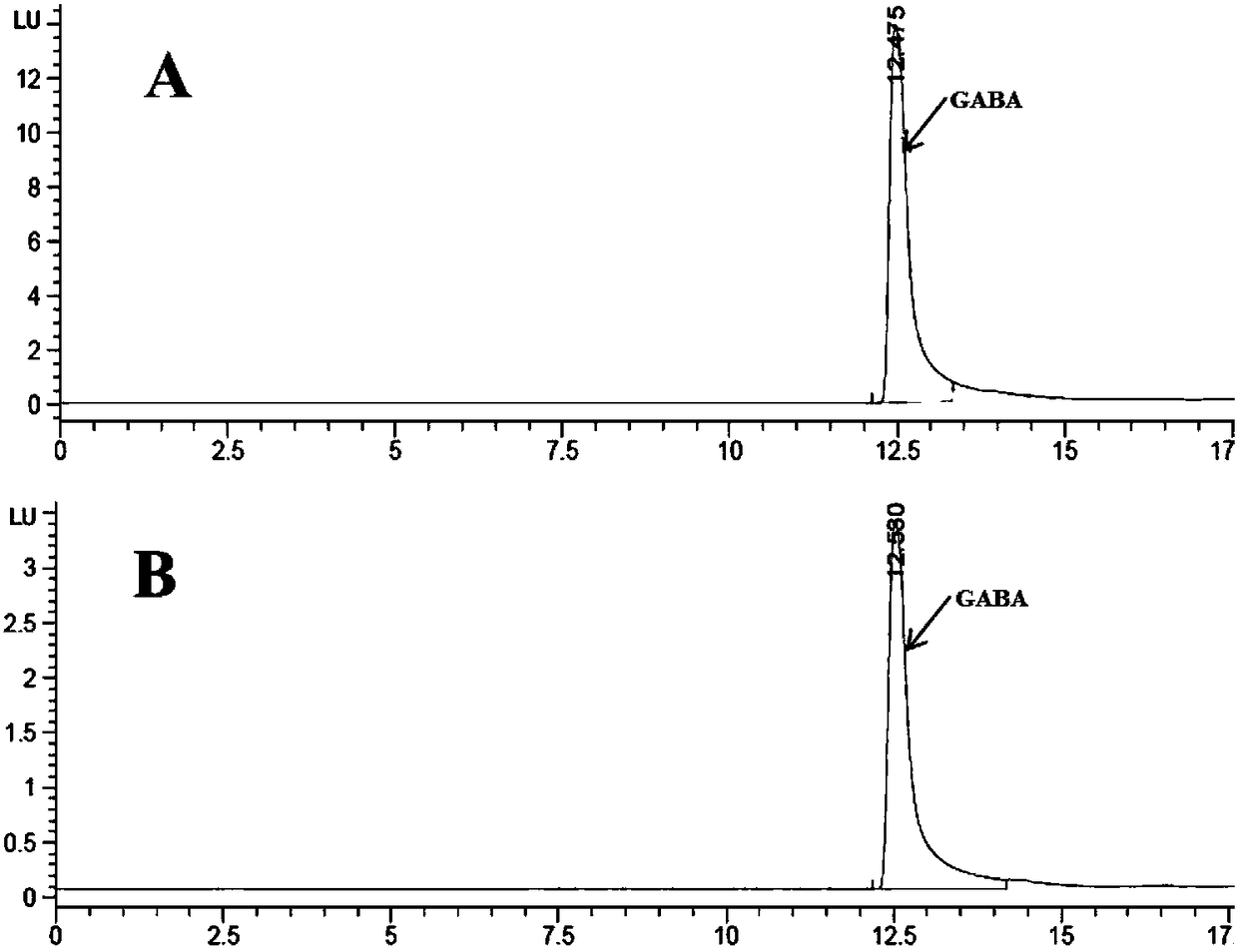
The invention discloses a method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid with a high yield, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Glutamic acid decarboxylase derived from Bacillus megaterium is modified by protein engineering, and a modified glutamic acid decarboxylase gene is linked to a pET24a vector, and is epressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3). A recombinant strain is cultured in a fermenter for transforming glutamic acid to produce the gamma-aminobutyric acid, the wet cell addition amount is 7.0g / L, the transformation period is 8h, the yield can reach 425.0g / L, and the glutamic acid molar conversion rate is up to 99%, the space time yield of the gamma-aminobutyric acid is 53.1 g / L / h.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
ELISA detection kit for bovine Brucella
ActiveCN105445473AEasy to operateReduce use costBiological material analysisBiological testingSerum igeElisa kit
The invention provides an ELISA detection kit for bovine Brucella, belonging to the technical field of protein engineering. In the kit provided by the invention, the mixed antigen of the outer membrane proteins OMP19, OMP22 and OMP28 of bovine Brucella is used as an envelope antigen of the ELISA kit; the concentration of each antigen is 1mu g / ml, and the antigens are mixed in a volume ratio of 1:1:1 to obtain the mixed antigen; the serum dilution is 1:200, and the dilution of the enzyme-labeled secondary antibody is 1:20,000; and the bovine Brucella is detected through an indirect ELISA method. The kit provided by the invention has the characteristics of high specificity, high sensitivity, high accuracy, easiness in operation and good reproducibility while the market application prospect is good.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Influenza antigens, vaccine compositions, and related methods
ActiveUS8124103B2Reduces and eliminates riskLess considerationSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesProtein antigenProtein engineering
Owner:IBIO
Signal peptide capable of effectively improving protein secretion expression efficiency and application of signal peptide
ActiveCN105601720ASmooth transmembrane transportImprove secretion efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesSequence signalProtein target
The invention discloses a signal peptide for mediating protein secretion expression and belongs to the field of protein engineering and gene engineering. By modifying known signal peptides PelB and OmpA, the N terminal of the signal peptide contains the first three amino acid residues MKK of the signal peptide OmpA, the C terminal of the signal peptide contains the last three amino acid residues AQA of the signal peptide OmpA, and a middle hydrophobic structure is the hydrophobic sequence LLPTAAAGLLLLAAQP of the signal peptide PelB. After the signal peptide capable of effectively improving protein secretion efficiency is used, the secretion expression capability of a strain on target protein is obviously improved; the extracellular enzyme activity of phospholipase D of target protein can be improved by 2 times, the extracellular enzyme production capability of the modified strain is significantly improved, and industrialized application is better facilitated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
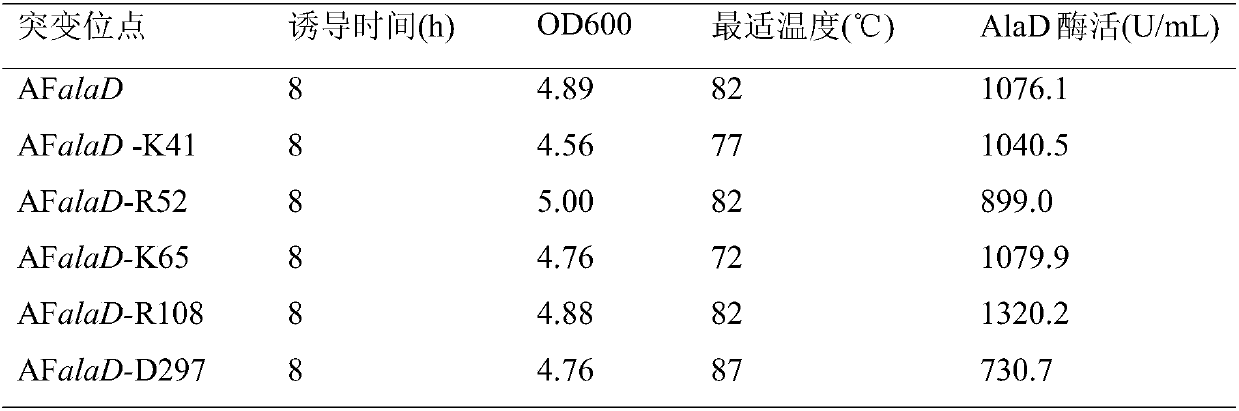
Alanine dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN107937361AChange flexibilityEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBacteroides
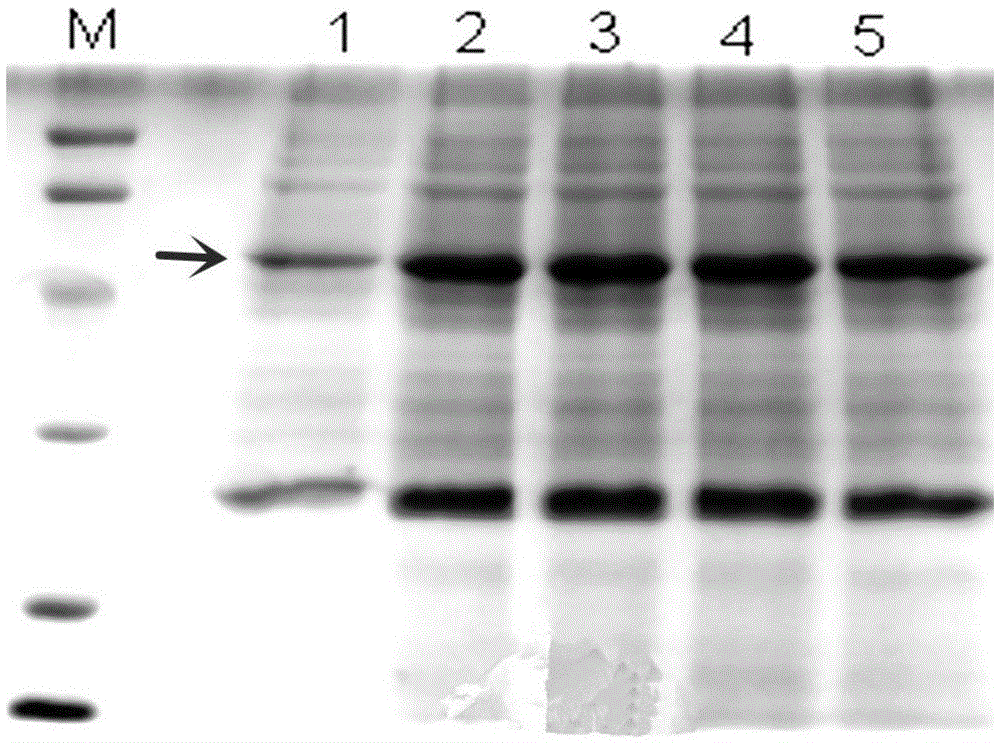
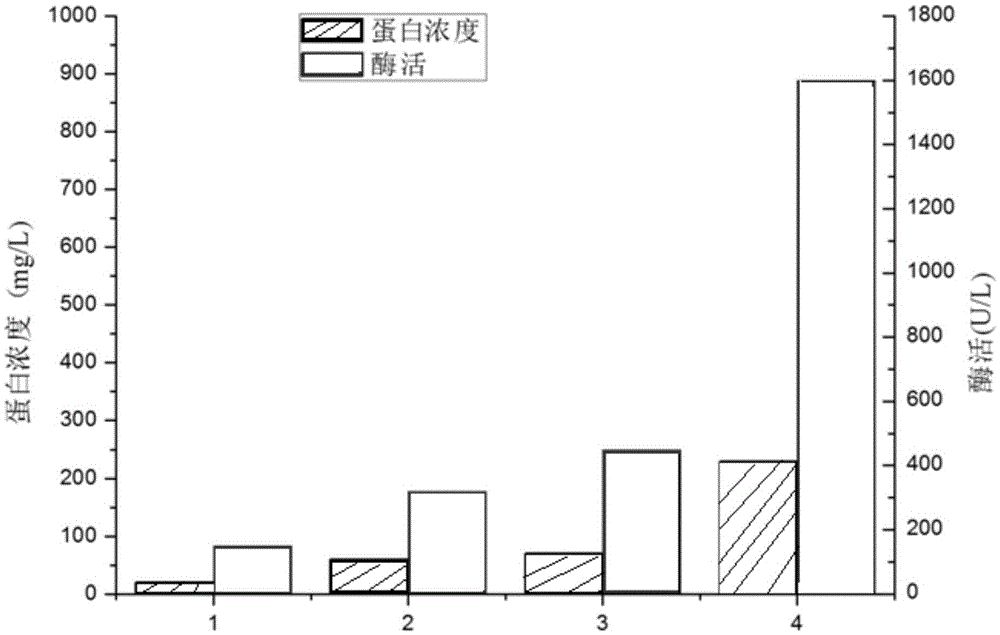
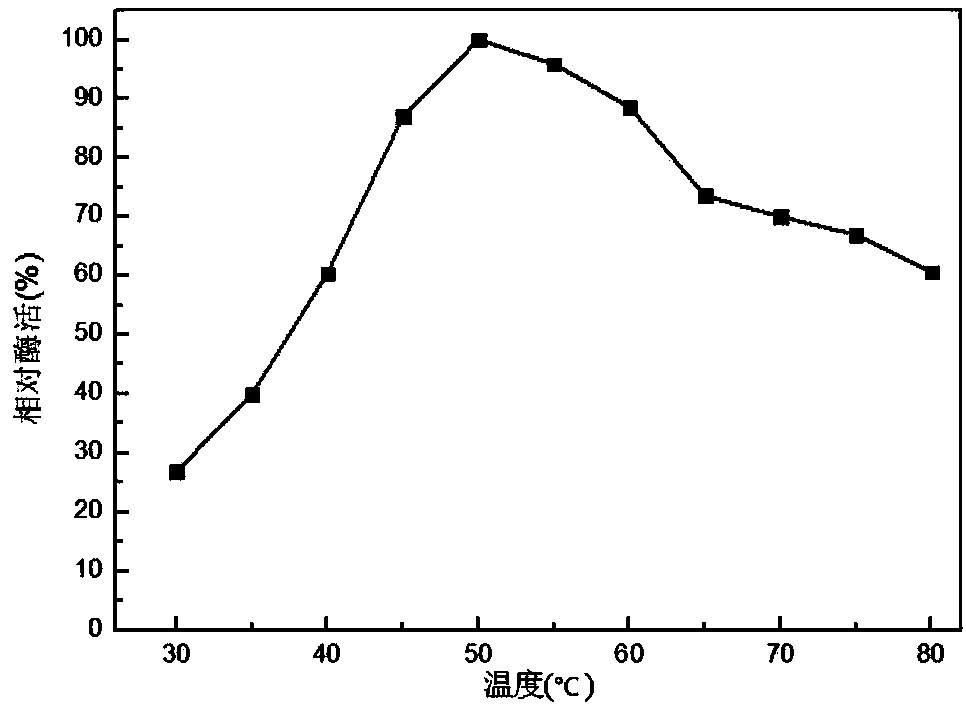
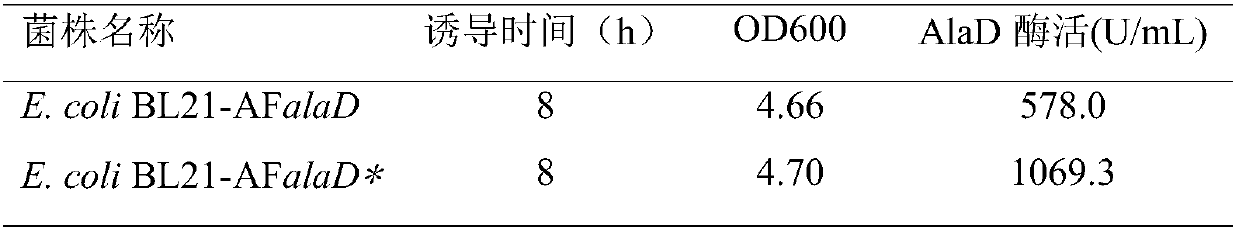
The invention discloses an alanine dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. According to the alanine dehydrogenase mutant, archaeoglobus fulgidus derived alanine dehydrogenase is modified through protein engineering; an optimal enzyme-activity temperature of the alanine dehydrogenase is decreased from 82 DEG C to 50 DEG C; a key gene on a synthetic competitive route of L-alanine is cancelled in bacillus coli K12; the generation of by-products is reduced; an alaD gene and an alanine racemase dadX gene for coding the L-alanine dehydrogenase in a recombinant strain are replaced with modified archaeoglobus fulgidus derived alanine dehydrogenase genes; the two-stage fermentation is carried out by utilizing the recombinant strain; the fermentation is carried out for 42h; a yield of the L-alanine reaches 153.9g / L, and a sugar-acid conversion ratio is 81.0 percent.
Owner:金华利家园生物工程有限公司 +1
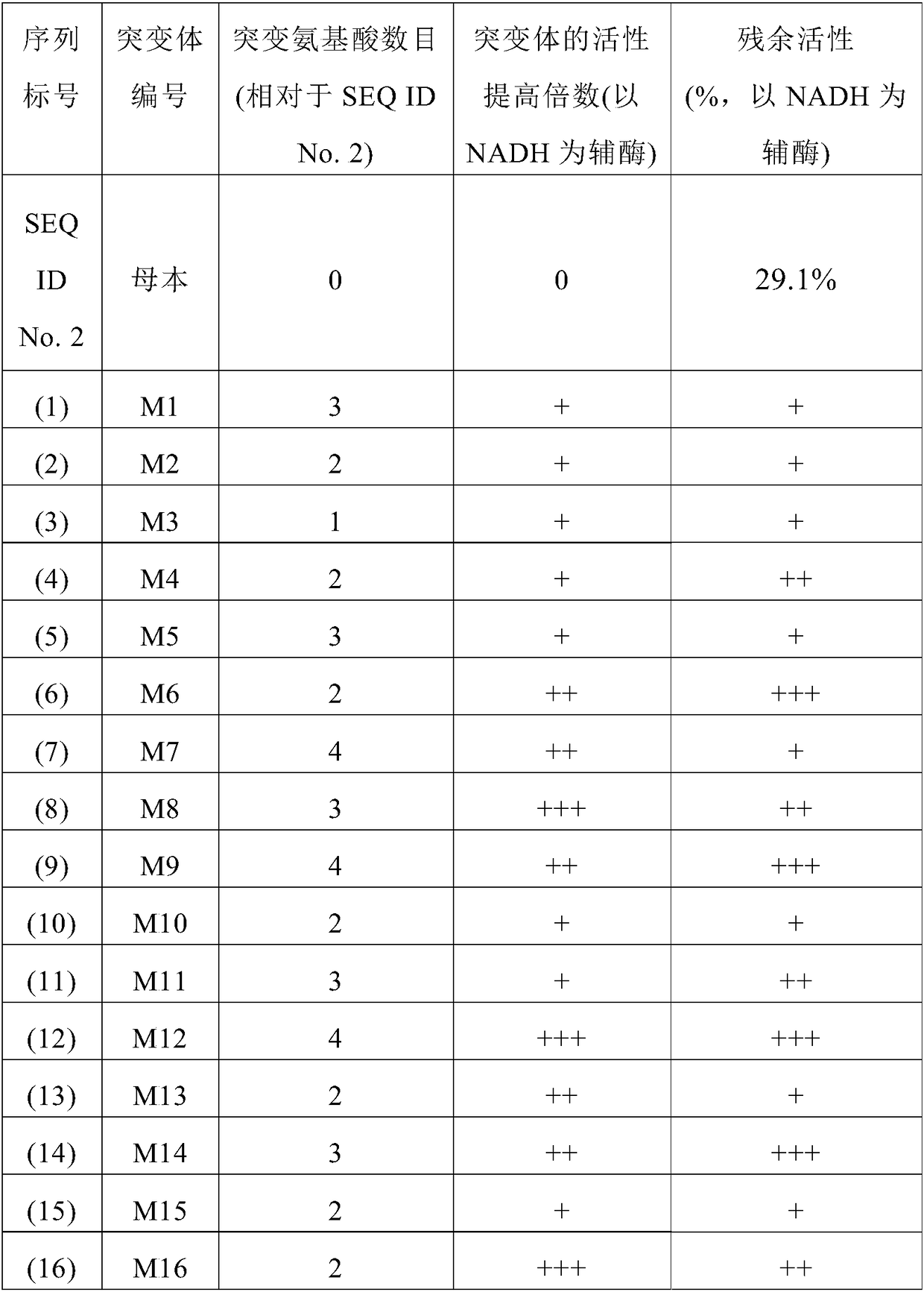
NADH oxidase mutant having improved stability and use thereof
Water-forming NADH oxidase derived from Streptococcus mutans should be further improved in terms of stability for practical use in industrial production. An object of the present invention is to provide an enzyme that is obtained through modification of a water-forming NADH oxidase, which is useful as an NAD+ regeneration system for stereoselective oxidation catalyzed by an oxidoreductase, by protein engineering techniques so that the enzyme can withstand long-term use without exhibiting a reduction of its activity for the regeneration of NAD+, that is, an enzyme having improved stability, and to provide a method for efficiently producing a useful substance such as an optically active alcohol or amino acid. The present invention relates to an enzyme modification method that can improve the stability of water-forming NADH oxidase derived from Streptococcus mutans by appropriately introducing mutation.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Improved broad-spectrum endonuclease and industrial production method thereof
ActiveCN105985968AIntermediate processing steps are safeAvoid digestionFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyFreeze-drying
The invention relates to DNA which achieves efficient expression in yeast cells and is used for coding improved broad-spectrum endonuclease, the improved broad-spectrum endonuclease which is coded by the DNA, and a method for constructing the DNA and the broad-spectrum endonuclease by virtue of genetic engineering technology and protein engineering technology; and the invention also relates to an industrial fermentation method for producing the improved broad-spectrum endonuclease. By virtue of the industrial fermentation method, the DNA, which is used for coding the improved broad-spectrum endonuclease, is expressed in eukaryotic host yeast cells, and the produced improved broad-spectrum endonuclease is high in specific activity and yield; therefore, the problems of the prior art that yield is low and an operation of conducting purifying is difficult. In addition, the improved broad-spectrum endonuclease disclosed by the invention, which is free from bacterial endotoxin, is conducive to application of medical and bio-engineering fields. Meanwhile, the improved broad-spectrum endonuclease disclosed by the invention can be also prepared into a dosage form of freeze-dried powder, so that the broad-spectrum endonuclease, as a finished product, is more convenient for transportation, preservation and industrial application.
Owner:GPROAN BIOTECH (SUZHOU) INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com