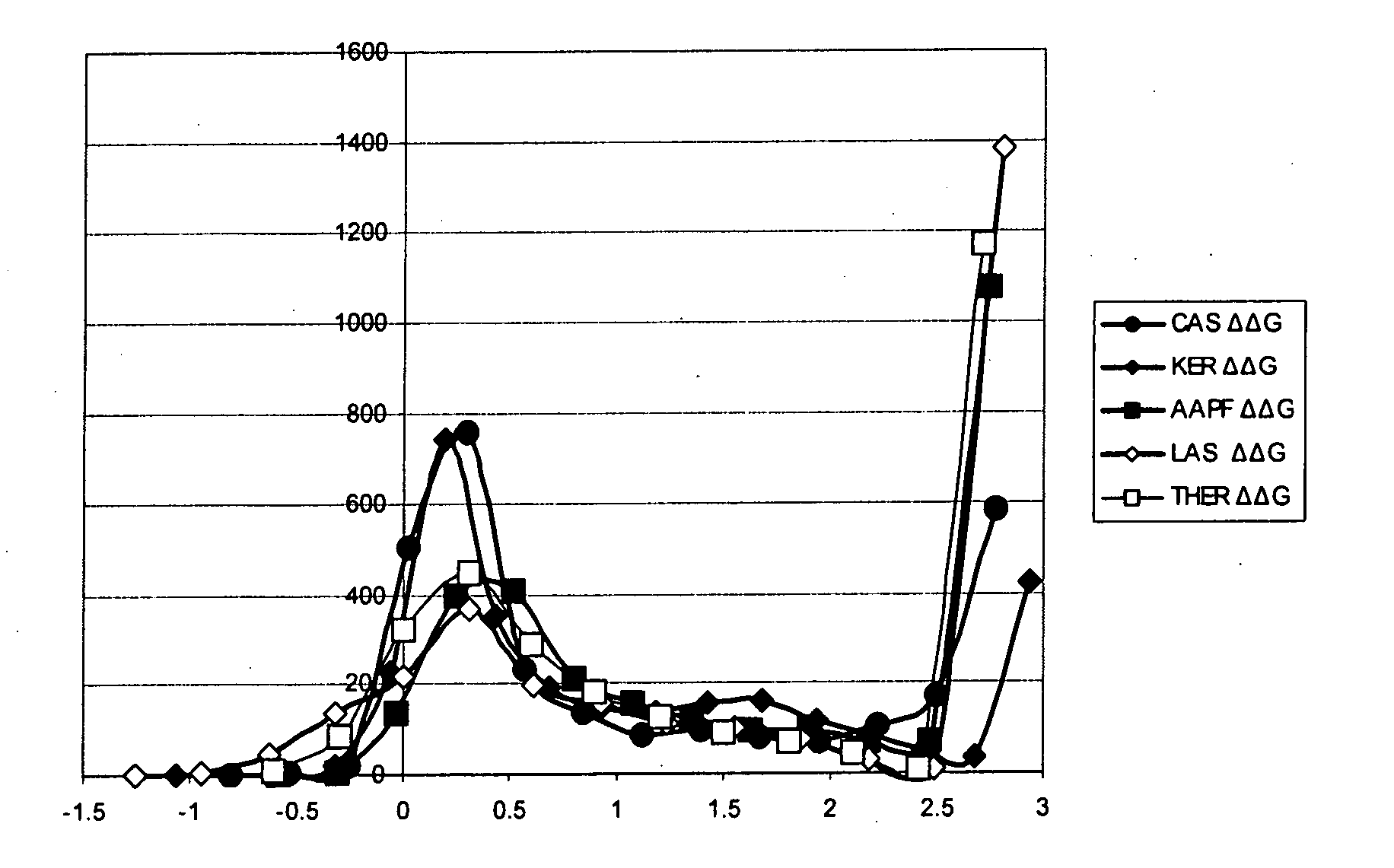
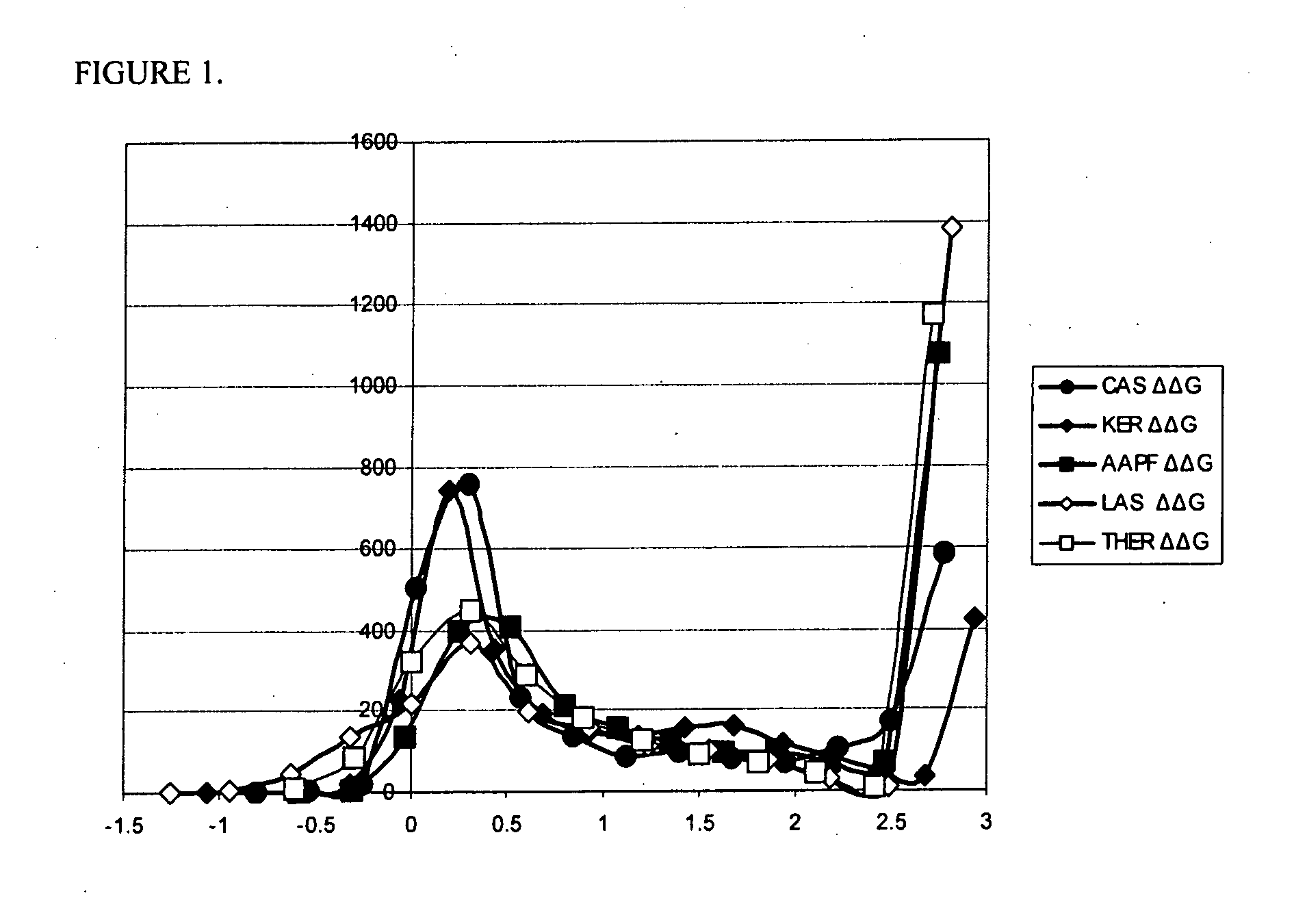
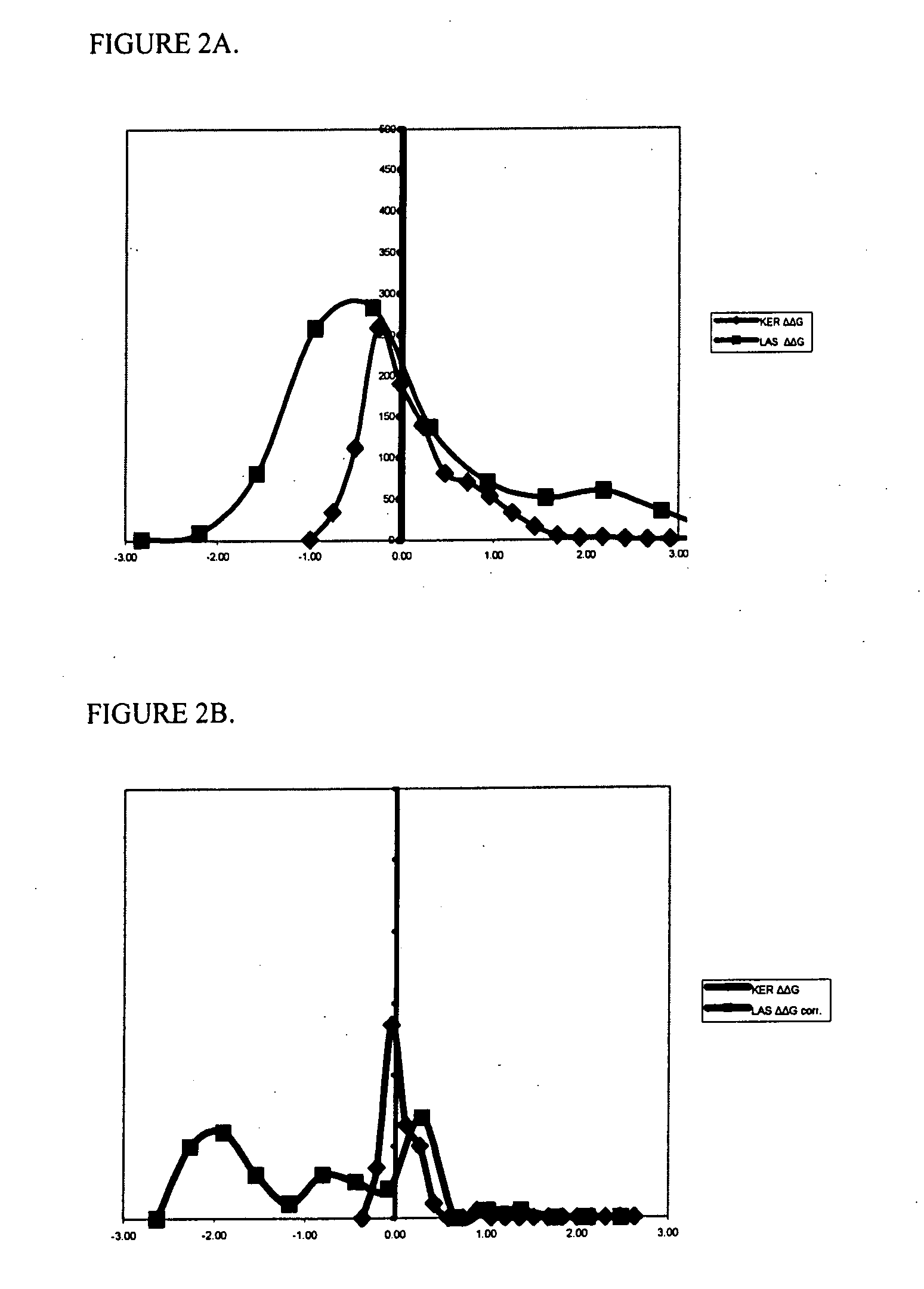
Systematic evaluation of sequence and activity relationships using site evaluation libraries for engineering multiple properties
a site evaluation and sequence-activity relationship technology, applied in the field of protein engineering, can solve the problems of laborious and time-consuming most methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Assays
[0149] In the following Examples, various assays were used, such as protein determinations, application-based tests, and stability-based tests. For ease in reading, the following assays are set forth below and referred to in the respective Examples. Any deviations from the protocols provided below in any of the experiments performed during the development of the present invention are indicated in the Examples.
A. TCA Assay for Protein Content Determination in 96-Well Microtiter Plates
[0150] This assay was started using filtered culture supernatant from microtiter plates grown 4 days at 33° C. with shaking at 230 RPM and humidified aeration. A fresh 96-well flat bottom plate was used for the assay. First, 100 μl / well of 0.25 N HCl were placed in the wells. Then, 50 μL filtered culture broth were added to the wells. The light scattering / absorbance at 405 nm (use 5 sec mixing mode in the plate reader) was then determined, in order to provide the “blank” reading.
[0151] For the...
example 2
Production of 69B4 Protease From the Gram-Positive Alkaliphilic Bacterium 69B4
[0189] This Example provides a description of the Cellulomonas strain 69B4 used to initially isolate the novel protease 69B4 provided by the present invention. The alkaliphilic micro-organism Cellulomonas strain 69B.4, (DSM 16035) was isolated at 37° C. on an alkaline casein medium containing (g L−1) (See e.g., Duckworth et al., FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 19:181-191 [1996]).
Glucose (Merck 1.08342)10Peptone (Difco 0118)5Yeast extract (Difco 0127)5K2HPO41MgSO4•7H2O0.2NaCl40Na2CO310Casein20Agar20
[0190] An additional alkaline cultivation medium (Grant Alkaliphile Medium) was also used to cultivate Cellulomonas strain 69B.4, as provided below:
Grant Alkaliphile Medium (“GAM”) solution A(g L−1)Glucose (Merck 1.08342)10Peptone (Difco 0118)5Yeast extract (Difco 0127)5K2HPO41MgSO4•7H2O0.2
[0191] Dissolved in 800 ml distilled water and sterilized by autoclaving
GAM solution B(g L1)NaCl40Na2CO310
[0192] Dissolved in 2...
example 3
ASP Protease Production in B. subtilis
[0197] Experiments conducted to produce 69B4 protease (also referred to herein as “ASP,”“Asp,” and “ASP protease,” and “Asp protease”) in B. subtilis are described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10 / 576,331, incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
[0198] The DNA sequence (synthetic ASP DNA sequence) is provided below, with codon usage adapted for Bacillus species, encodes the wild type ASP precursor protein:
(SEQ ID NO: 1)ATGACACCACGAACTGTCACAAGAGCTCTGGCTGTGGCAACAGCAGCTGCTACACTCTTGGCTGGGGGTATGGCAGCACAAGCTAACGAACCGGCTCCTC
[0199] In the above sequence, bold indicates the DNA that encodes the mature protease, standard font indicates the leader sequence, and the underline indicates the N-terminal and C-terminal prosequences.
Expression of the Synthetic ASP Gene
[0200] Expression of the synthetic ASP gene is described in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10 / 576,331, which is incorporated herein by reference, in its entirety.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com