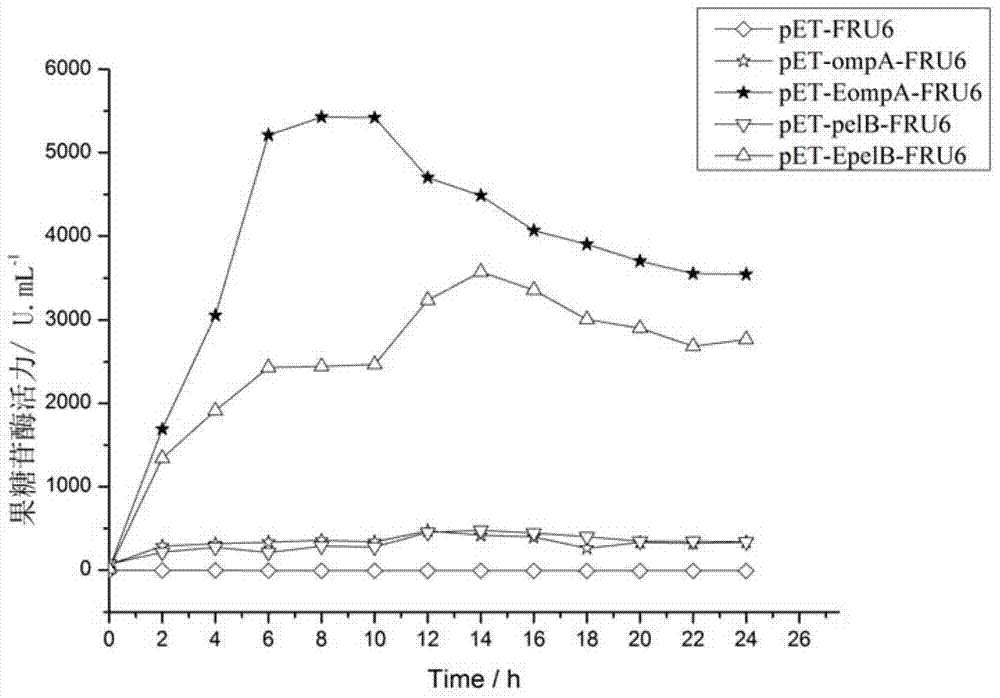
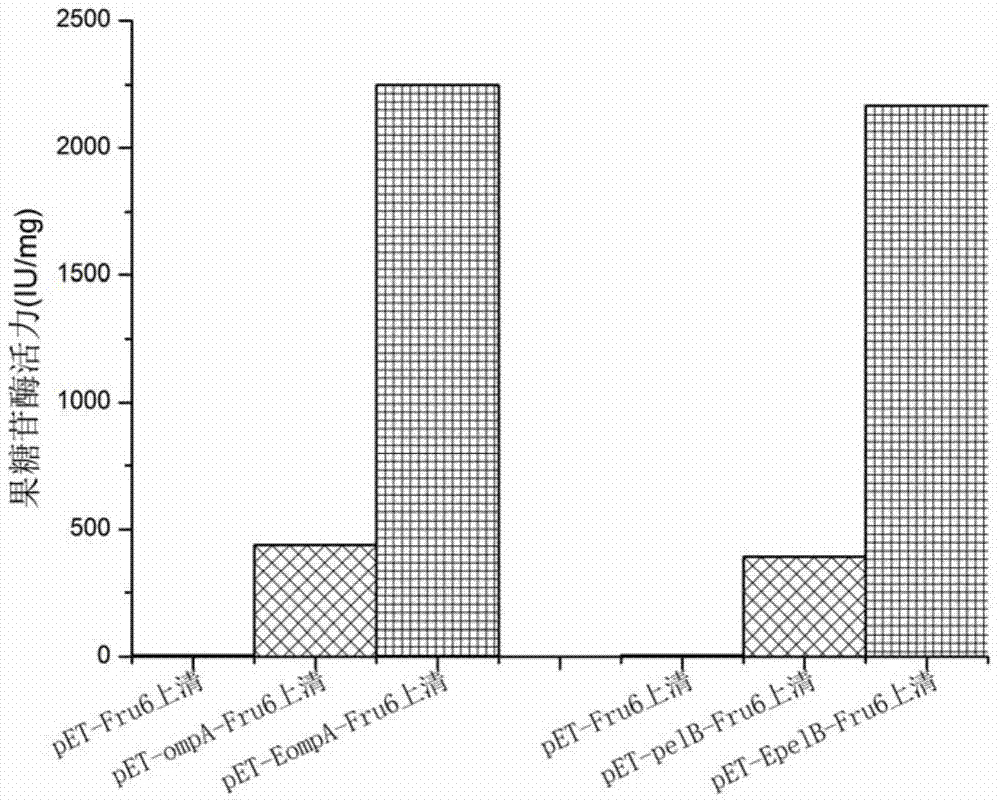
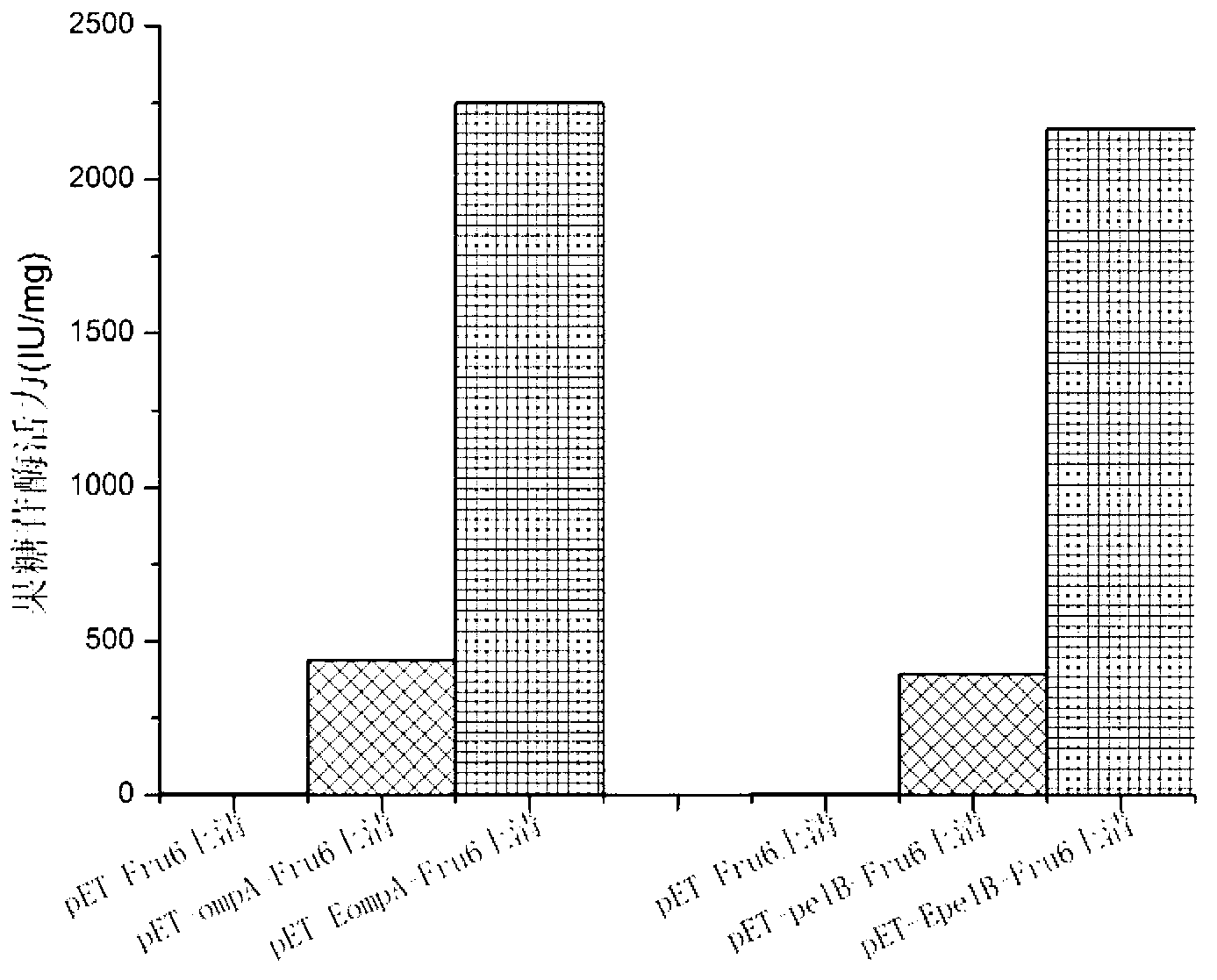Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Improve secretion efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
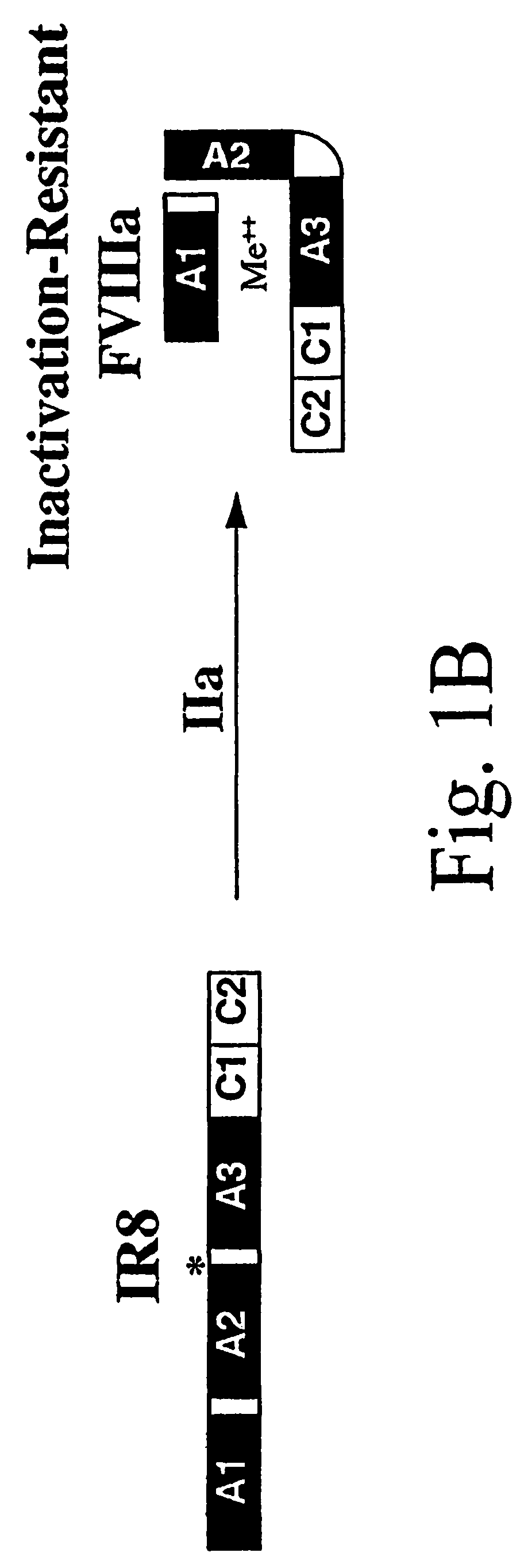
Inactivation resistant factor VIII
InactiveUS20060293238A1Increase secretionHigh expressionFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding siteENCODE
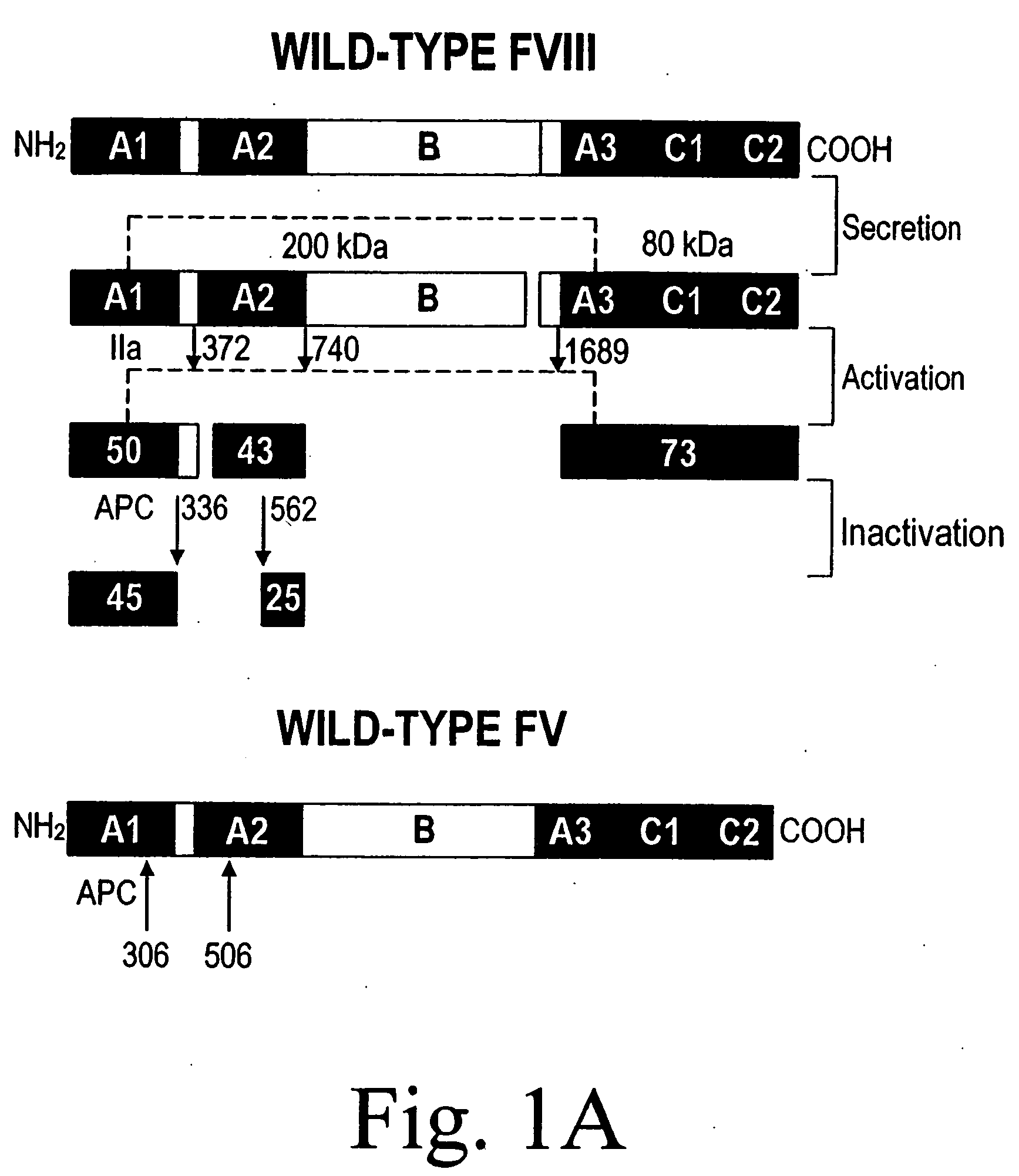
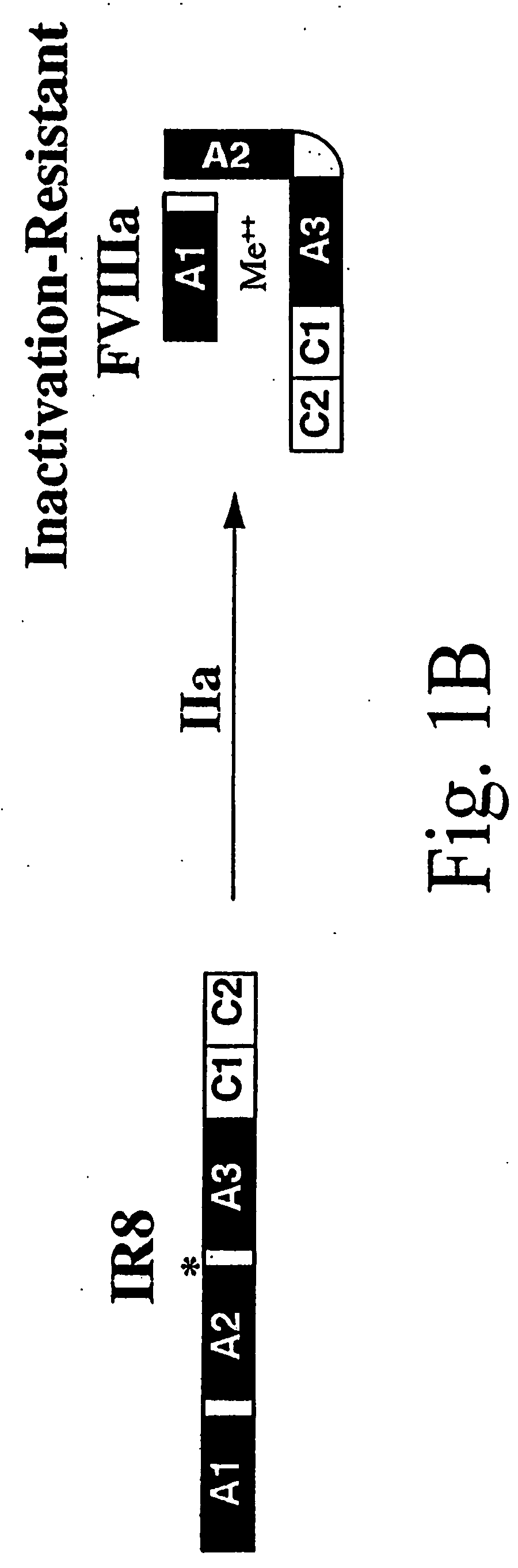
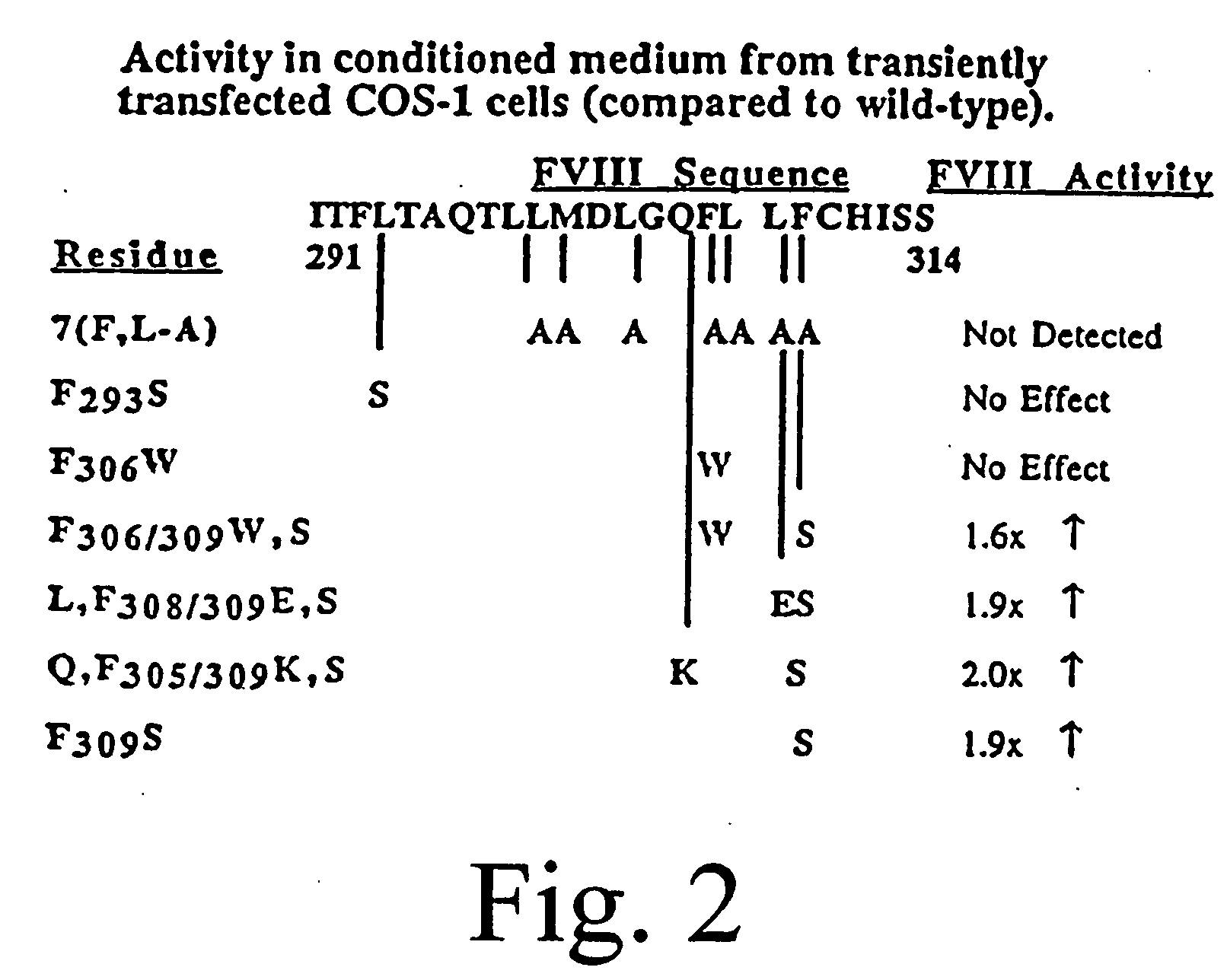
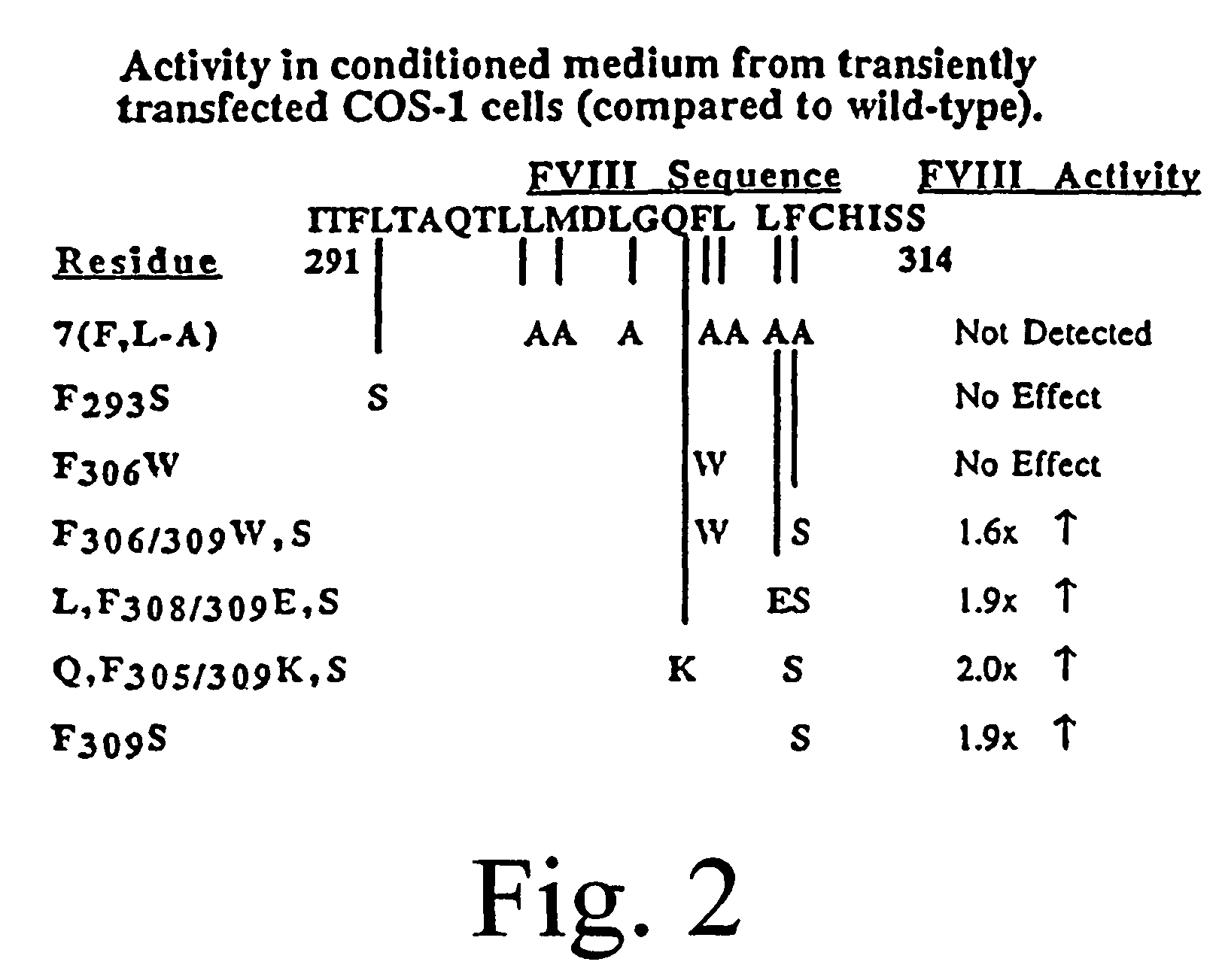
The present invention provides novel purified and isolated nucleic acid sequences encoding procoagulant-active FVIII proteins. The nucleic acid sequences of the present invention encode amino acid sequences corresponding to known human FVIII sequences, wherein residue Phe309 is mutated. The nucleic acid sequences of the present invention also encode amino acid sequences corresponding to known human FVIII sequences, wherein the APC cleavage sites, Arg336 and Ile562, are mutated. The nucleic acid sequences of the present invention further encode amino acid sequences corresponding to known human FVIII sequences, wherein the B-domain is deleted, the von Willebrand factor binding site is deleted, a thrombin cleavage site is mutated, an amino acid sequence spacer is inserted between the A2- and A3-domains. Methods of producing the FVIII proteins of the invention, nucleotide sequences encoding such proteins, pharmaceutical compositions containing the nucleotide sequences or proteins, as well as methods of treating patients suffering from hemophilia, are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
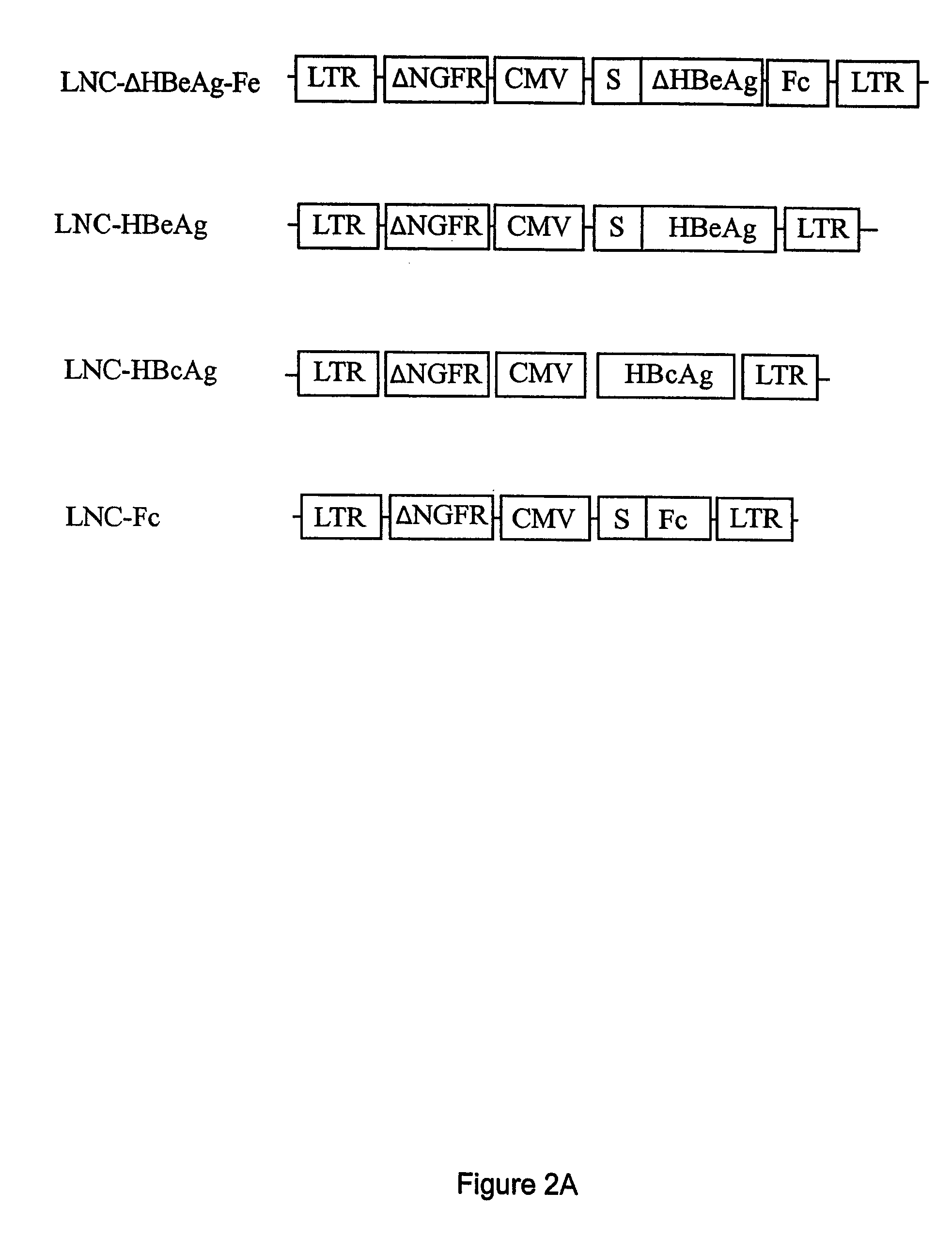
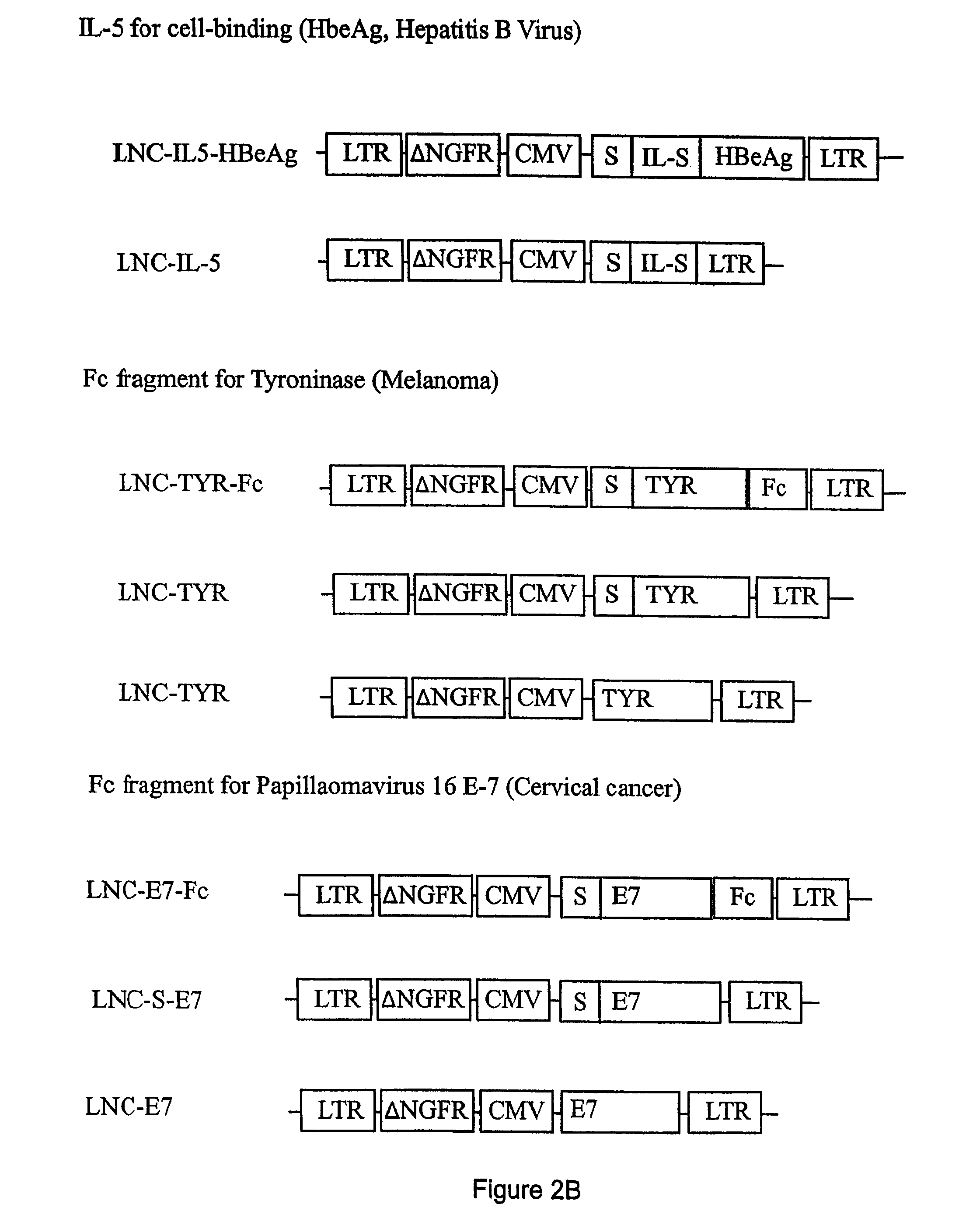
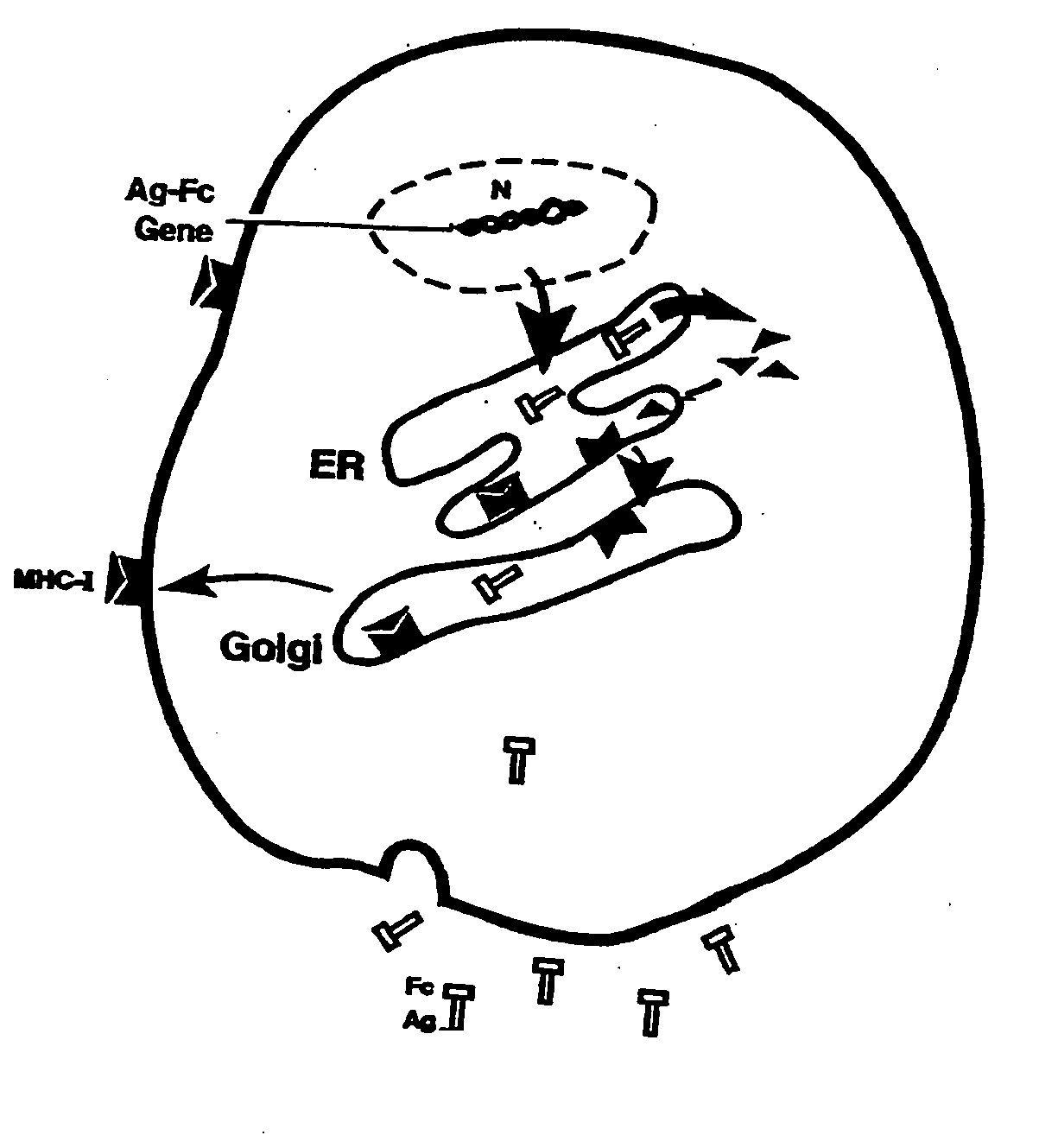
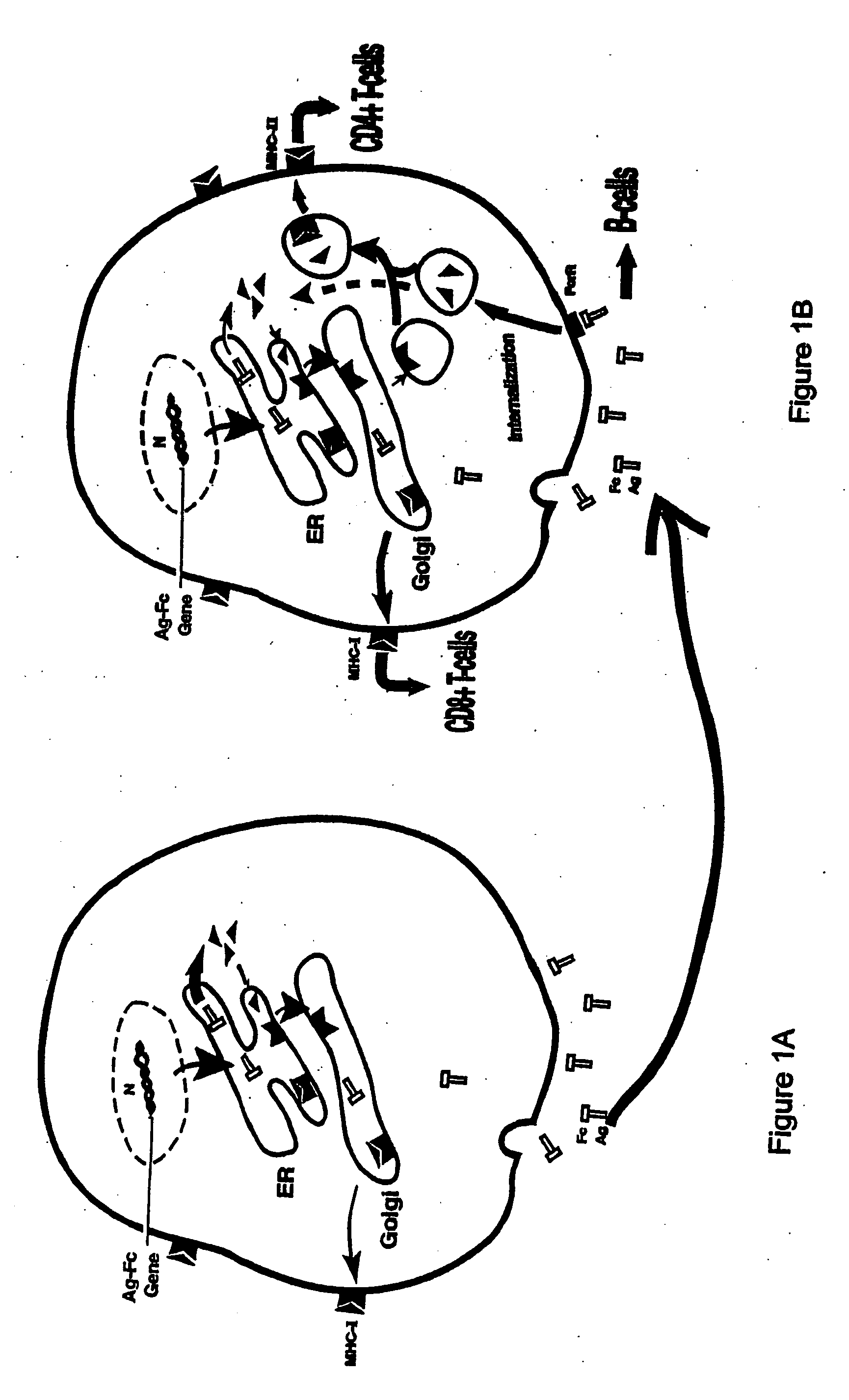
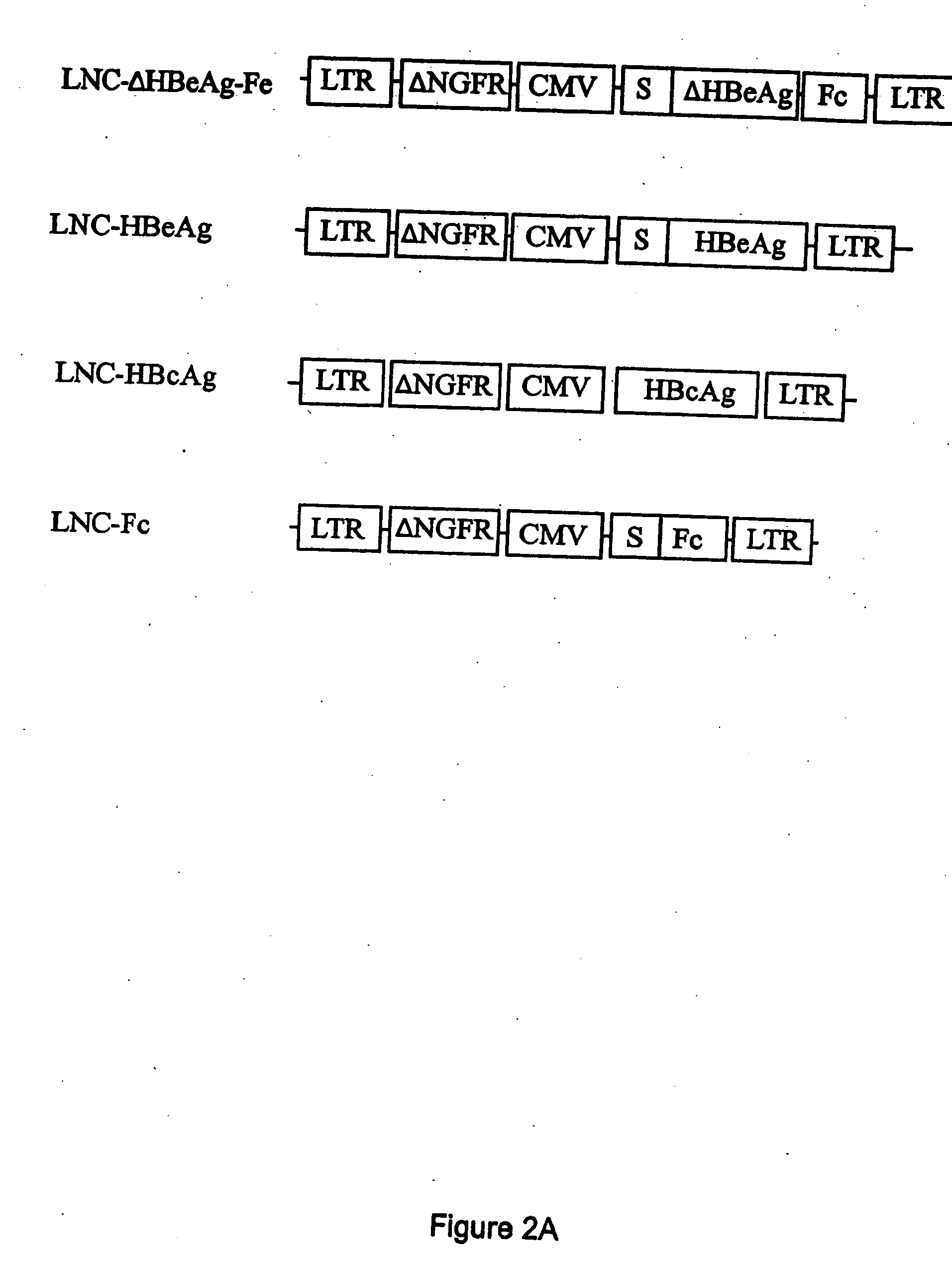
Compositions and methods for identifying antigens which elicit an immune response
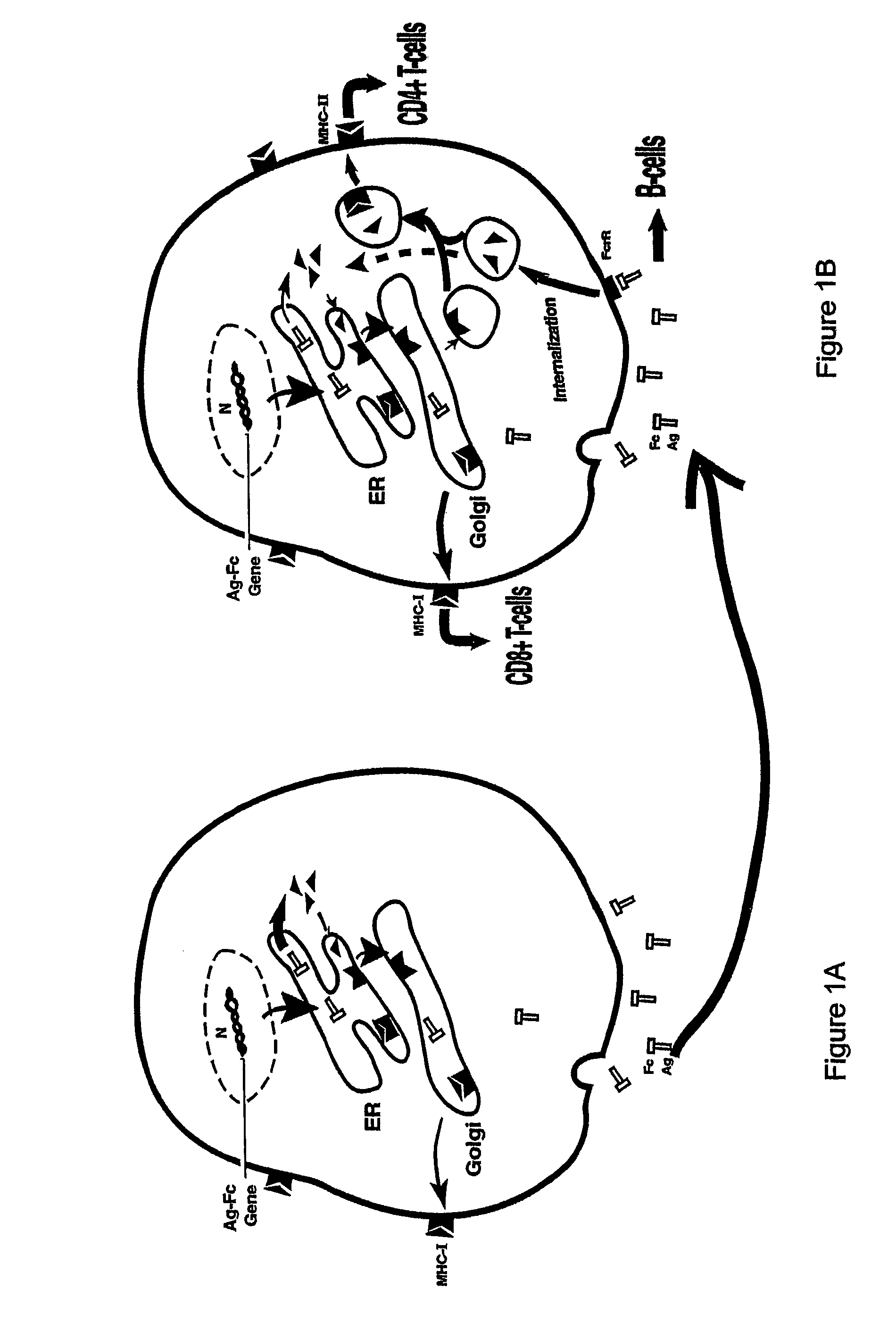
This invention relates to an expression vector wherein said expression vector comprises a polynucleotide promoter sequence, a polynucleotide encoding a signal sequence, a polynucleotide encoding an antigen protein or peptide, a polynucleotide encoding a cell binding element, and a polynucleotide polyadenylation sequence all operatively linked. More particularly, it relates to the method of eliciting an immune response directed against an antigen in a mammal comprising the steps of introducing the expression vector into a cell, expressing the vector to produce an antigen under conditions wherein the antigen is secreted from the cell, endocytosing the secreted antigen into the cell, processing the antigen, and presenting fragments to a receptor to elicit a T-cell response. In addition, this invention relates to a vaccine and a method of use. The invention also relates to the method of identifying MHC-II restricted epitopes.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
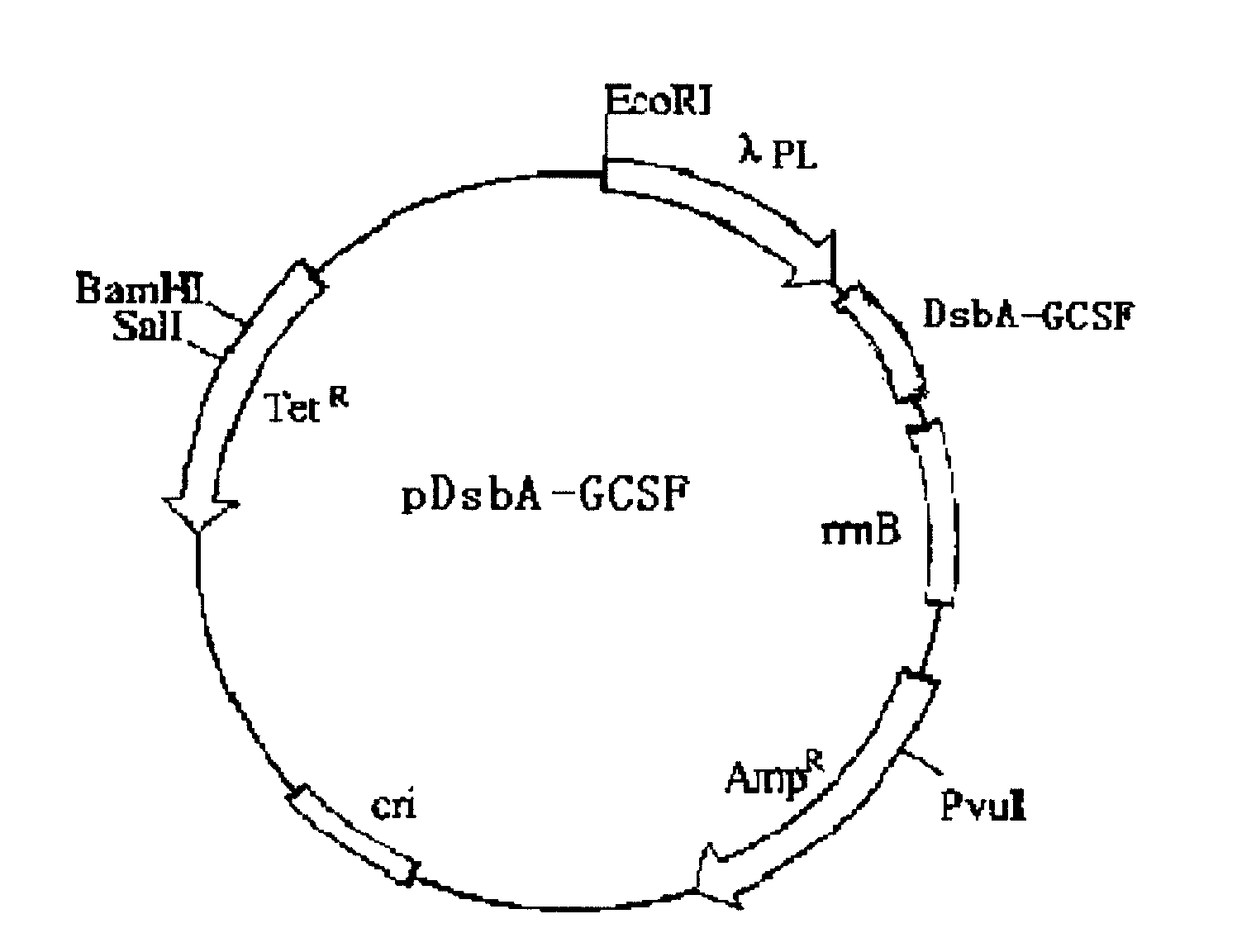
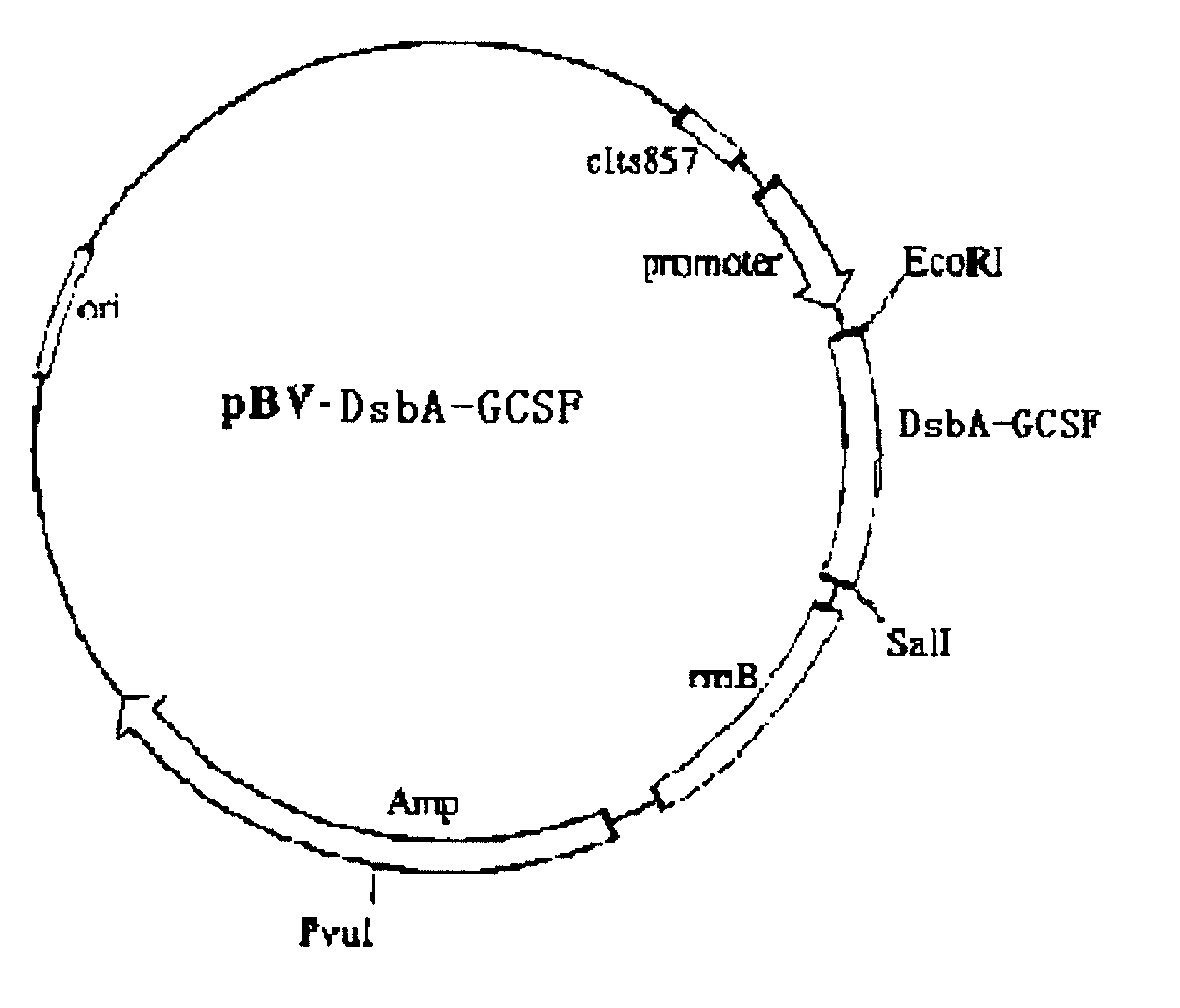
Method for excreting and expressing recombinant human granulocyte-colony factor in colon bacillus
InactiveCN101591660AImprove versatilityHigh expressionDepsipeptidesFermentationEscherichia coliCompetent cell
The invention relates to a method for the excretive expression of a recombinant human granulocyte-colony factor (rHG-CSF) in colon bacillus. In the invention, a carrier of periplasmic cavity excretive type expression recombinant proteins can be established by adding DsbA signal peptide (SEQ ID NO:1) at the N end of an exogenous protein and using an lambadaPL promoter, the DH5alpha competent cells of the colon bacillus are converted, and the expression of the exogenous protein in the periplasmic cavity of the colon bacillus is realized by temperature induction. The method has high expression quantity and high excreting efficiency, and is suitable for effectively and stably excreting and expressing various exogenous genes.
Owner:BEIJING SL PHARMA
Compositions and methods for identifying antigens which elicit an immune response
This invention relates to an expression vector wherein said expression vector comprises a polynucleotide promoter sequence, a polynucleotide encoding a signal sequence, a polynucleotide encoding an antigen protein or peptide, a polynucleotide encoding a cell binding element, and a polynucleotide polyadenylation sequence all operatively linked. More particularly, it relates to the method of eliciting an immune response directed against an antigen in a mammal comprising the steps of introducing the expression vector into a cell, expressing the vector to produce an antigen under conditions wherein the antigen is secreted from the cell, endocytosing the secreted antigen into the cell, processing the antigen, and presenting fragments to a receptor to elicit a T-cell response. In addition, this invention relates to a vaccine and a method of use. The invention also relates to the method of identifying MHC-II restricted epitopes.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
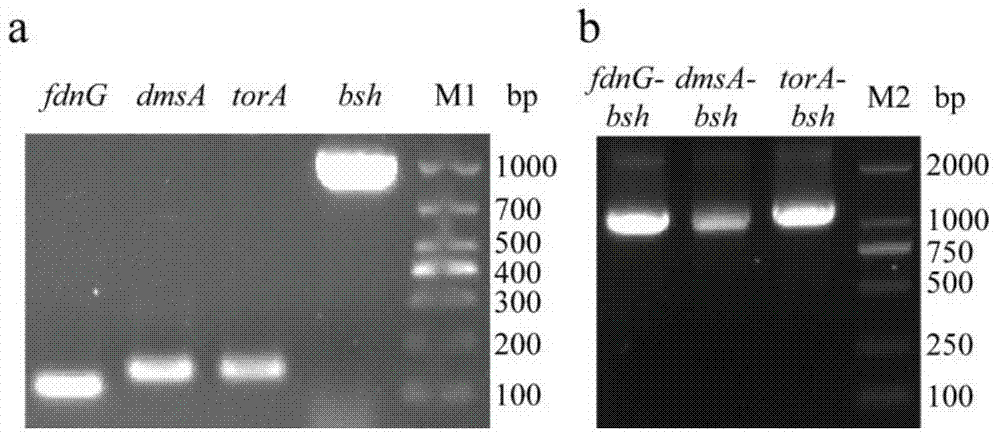
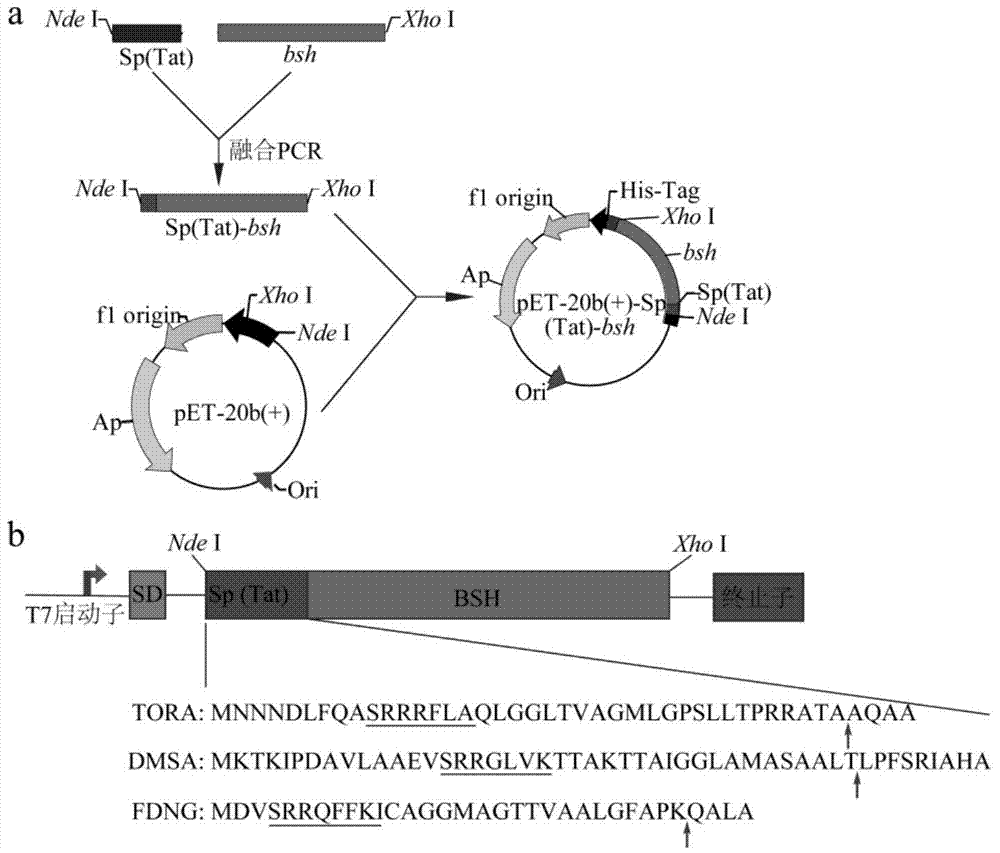
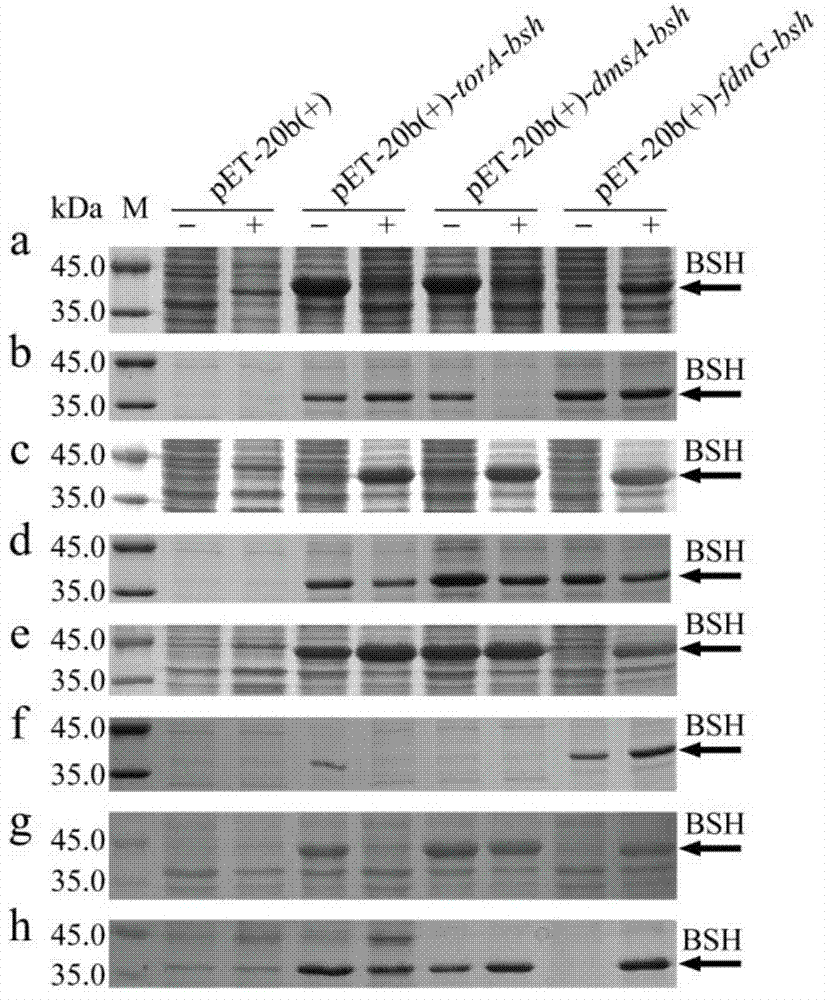
Method for producing bile salt hydrolase by fermentation of twin-arginine signal peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN103756989AImprove secretion efficiencyHigh extracellular BSH activityHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for producing bile salt hydrolase by fermentation of twin-arginine signal peptides and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to the method provided by the invention, a twin-arginine signal peptide gene and a bile salt hydrolase gene are fused, the fusion gene is transformed into the E.coli host to obtain recombinant bacteria, and recombinant bacteria is used for fermentation for producing bile salt hydrolase. The bile salt hydrolase is successfully secreted to the outside of the cells of the recombinant bacteria, and the extracellular BSH activity of the recombinant E.coli BL21 (DE3) pLysS (pET-20b (+)-dmsA-bsh) reaches the highest value of 0.72 + / - 0.05 U / mL. The invention lays foundation for the study on isolation and purification and enzymatic characteristics of BSH, and provides effective methods for secretion expression of other heterologous protein.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
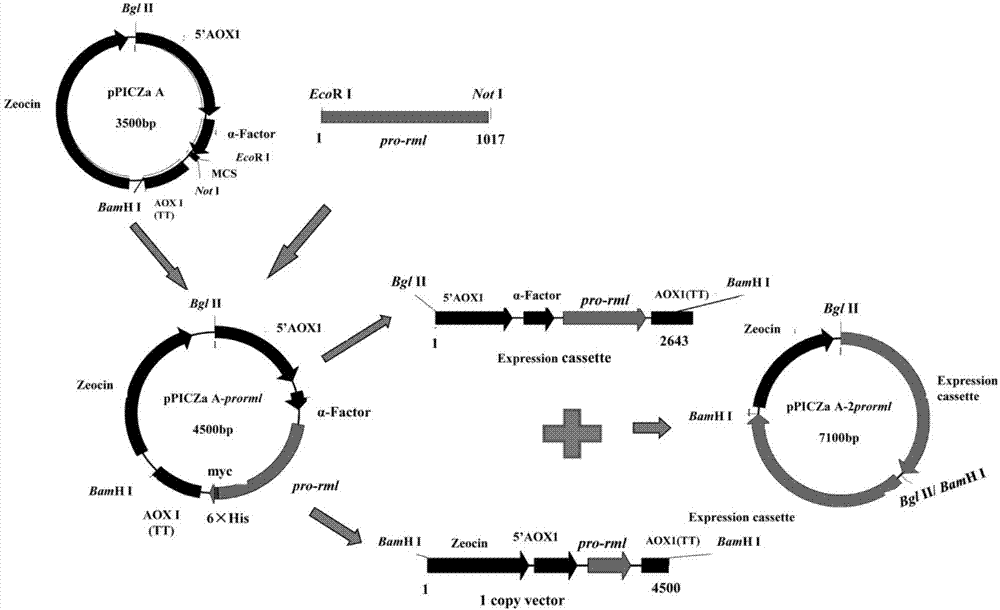
Recombinant pichia pastoris for heterologously and efficiently expressing rhizomucor miehei lipase and application of recombinant pichia pastoris
ActiveCN107043757APromote secretionImprove secretion efficiencyFungiHydrolasesHeterologousPichia pastoris
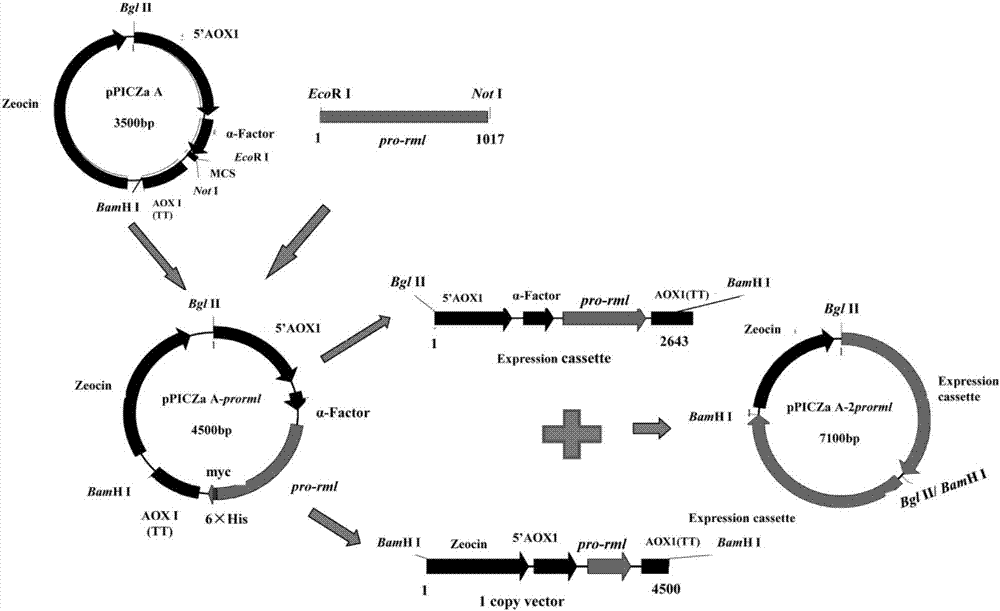
The invention discloses recombinant pichia pastoris for heterologously and efficiently expressing lipase and application of the recombinant pichia pastoris. The recombinant pichia pastoris is obtained through converting plasmid SEC31-pPIC3.5K overexpressing a gene SEC31 in recombinant pichia pastoris X-33, which contains a 4-copy number pro-rml gene and can express Pro-RML. According to the recombinant pichia pastoris and the application thereof, the expression of the rhizomucor miehei lipase is effectively promoted, the efficiency of secretion of the lipase is increased, the enzyme activity reaches 996U / mL after 144 hours of shake-flask fermentation, and the strain ectoenzyme activity secretion efficiency reaches 38U / OD600 and is higher than that (26U / OD600) of two recombinant pichia pastoris strains of rhizomucor miehei lipase copy numbers concerned in the patent CN103361327A.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant pichia pastoris for heterogenous efficient expression of lipase and application of recombinant pichia pastoris
ActiveCN107083373AImprove secretion efficiencyHigh expressionFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisHeterologous
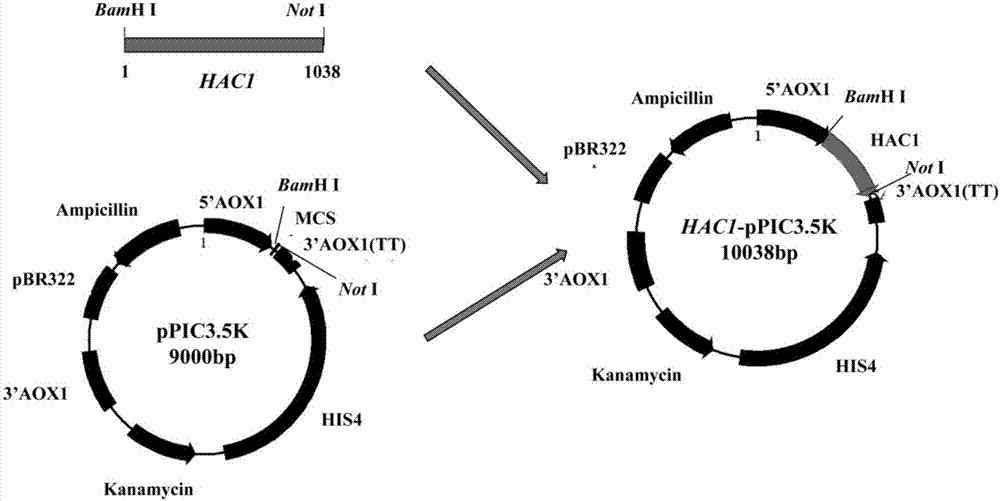
The invention discloses recombinant pichia pastoris for heterogenous efficient expression of lipase and application of the recombinant pichia pastoris. The recombinant pichia pastoris is obtained by converting plasmid HAC1-pPIC3.5K of an overexpression HAC1 gene in recombinant pichia pastoris X-33 which contains a pro-rml gene of a copy number 4 and is capable of expressing Pro-RML. When the strain is subjected to 96 hours of flask shaking fermentation, the extracellular enzyme activity is up to 1078U / mL at most, and the enzyme activity secretion efficiency is up to 47U / OD600. 120 hours of fermentation is needed when pichia pastoris which is disclosed by patent CN103361327A and has a rhizomucor mieheilipase copy number of 2 meets the highest extracellular enzyme activity and enzyme secretion efficiency, the extracellular enzyme activity is 1038U / mL at most, and the enzyme activity secretion efficiency is only 25U / OD600. By adopting the recombinant pichia pastoris, expression of rhizomucor mieheilipase is effectively promoted, on the premise that the highest extracellular enzyme activity is not influenced, the secretion efficiency of the rhizomucor mieheilipase is increased by 1.9 times, and the fermentation time is shortened by 24 hours.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing protein A by utilizing recombinant pichia pastoris
InactiveCN103333911AImprove secretion efficiencyHigh expressionMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesIon exchangeYeast
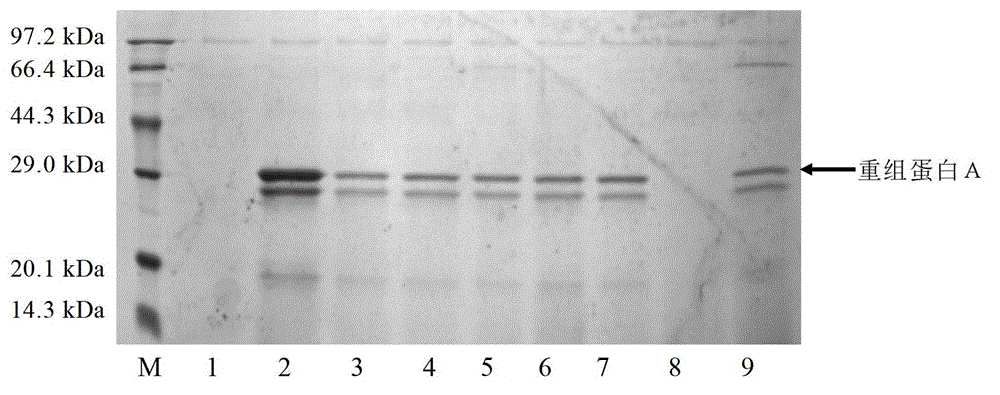
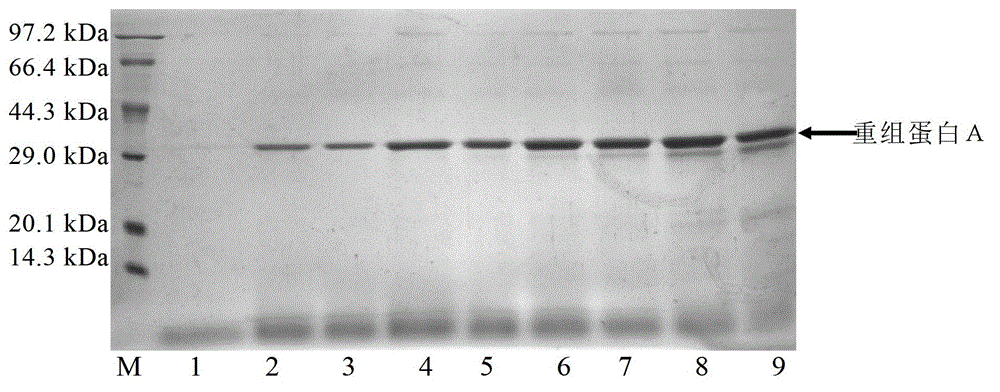
The invention relates to a process for producing staphylococcus aureus protein A by utilizing recombinant pichia pastoris. According to the production process, plasmid pPIC9K is utilized for integrating genes in a protein A antibody-binding fraction into a genome of the pichia pastoris GS115, and screening, expression and optimization of purification conditions are performed to get the active excretion protein A. The invention provides preparation and screening of a recombinant strain, as well as a culture and fermentation method by utilizing the strain to express the protein A, and a purification method of the expressed protein A. The strain is firstly cultured in a BMGY (buffered glycerol-complex medium) culture medium for about 17h and then expressed, screened and optimized in a culture medium BMMY (buffered methanol-complex medium) with the pH of 2.6-5.6 and the methanol content of 0.5%-2.0%. Then the expression of the recombinant protein A is further optimized in a fermentation tank, the expression level of the final protein A can achieve 8-10g per liter of bacterial liquid, accounting for about 80% of the secreted total protein. The high-purity protein A can be obtained by filtering through a desalting column and purifying by ion exchange chromatography, and the yield is about 80%. The process creates favorable conditions for low-cost and large-scale production of the high-purity protein A.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Small peptide strengthening mold sequence of strong secretory signal peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN103254277AEnhance secretory functionSignificant secretory functionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaNeutral Amino AcidsProtein engineering
The invention belongs to the field of protein engineering and genetic engineering, and relates to a small peptide strengthening mold sequence of a strong secretory signal peptide and an application thereof. The small peptide strengthening mold sequence comprises an amino acid sequence shown in the general formula: M(AlphaXBetaYGamma / AlphaYBetaXGamma)n, wherein the X represents an acidic amino acid; the Y represents a basic amino acid; the Alpha represents 0 to 2 neutral amino acids; the Beta represents 0 to 2 neutral amino acids; the Gamma represents 1 to 10 neutral amino acids; and the n represents 1 to 3. According to the application of the small peptide strengthening mold sequence, the small peptide strengthening mold sequence is use for constructing a carrier for strengthening the secretion capability of a common signal peptide, thereby being a method for improving the common signal peptide for the secretory expression of a foreign protein.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Method for improving secernment efficiency of recombined protein
InactiveCN101173270AImprove secretion efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationSecreted substanceSecretion
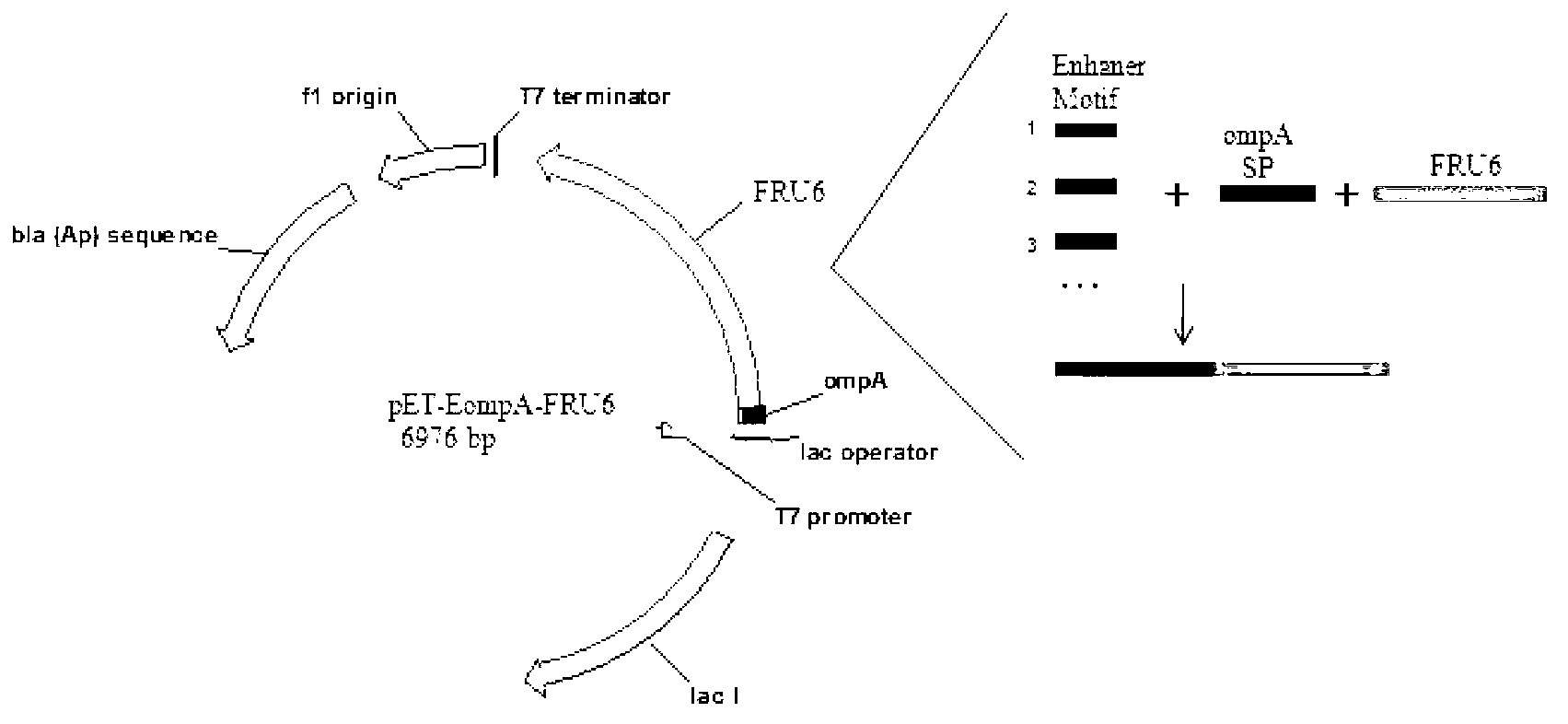
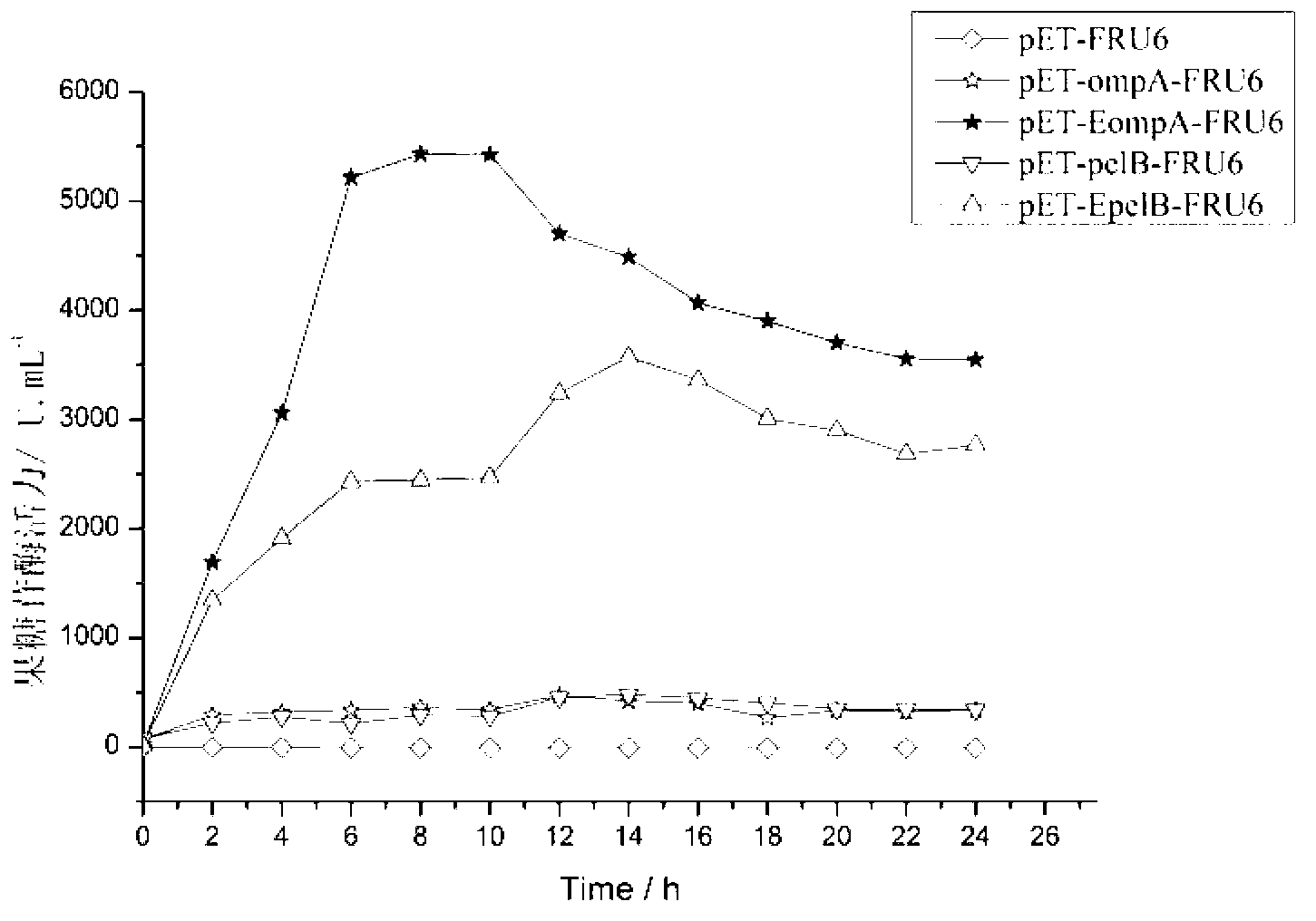
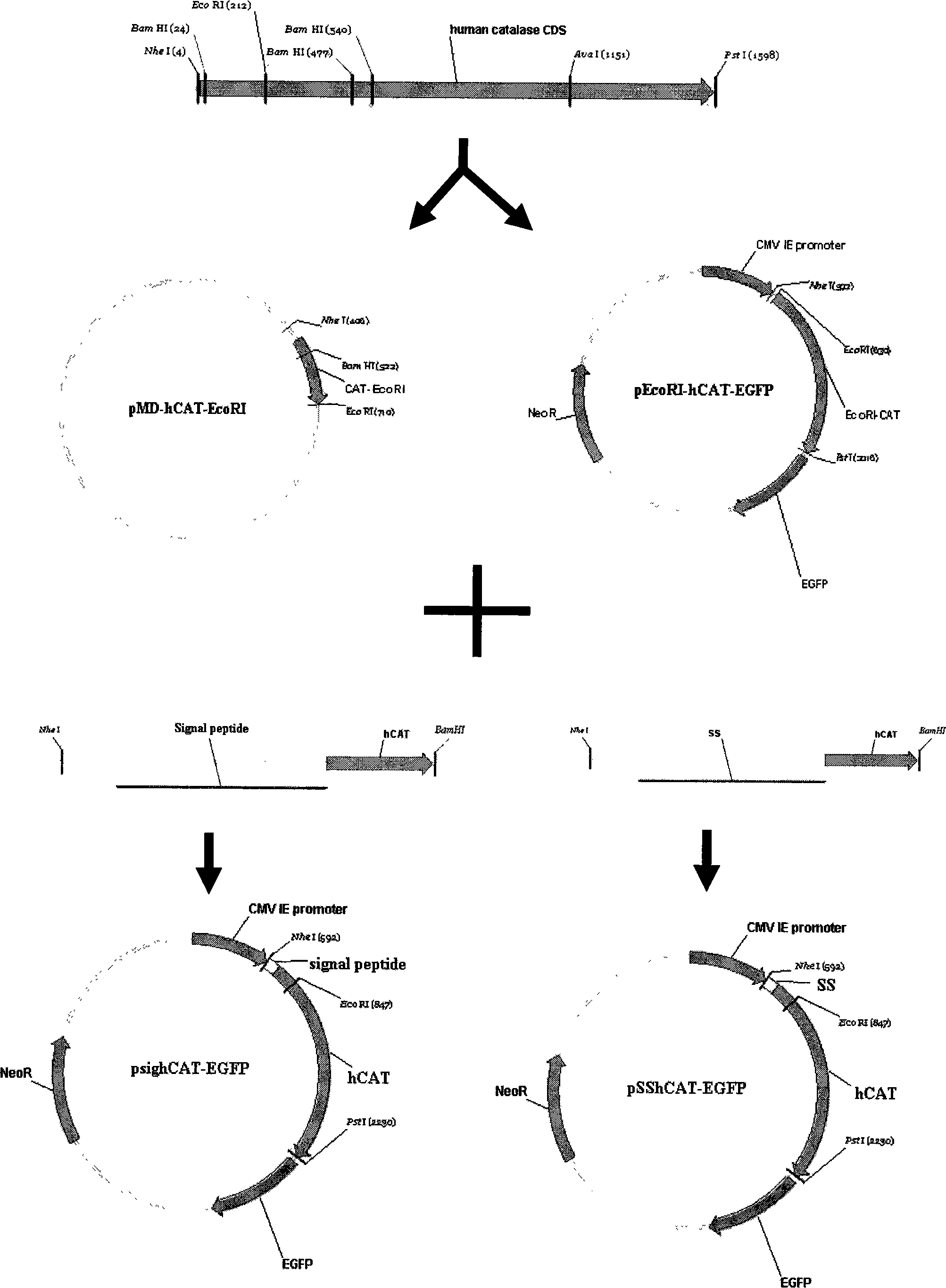
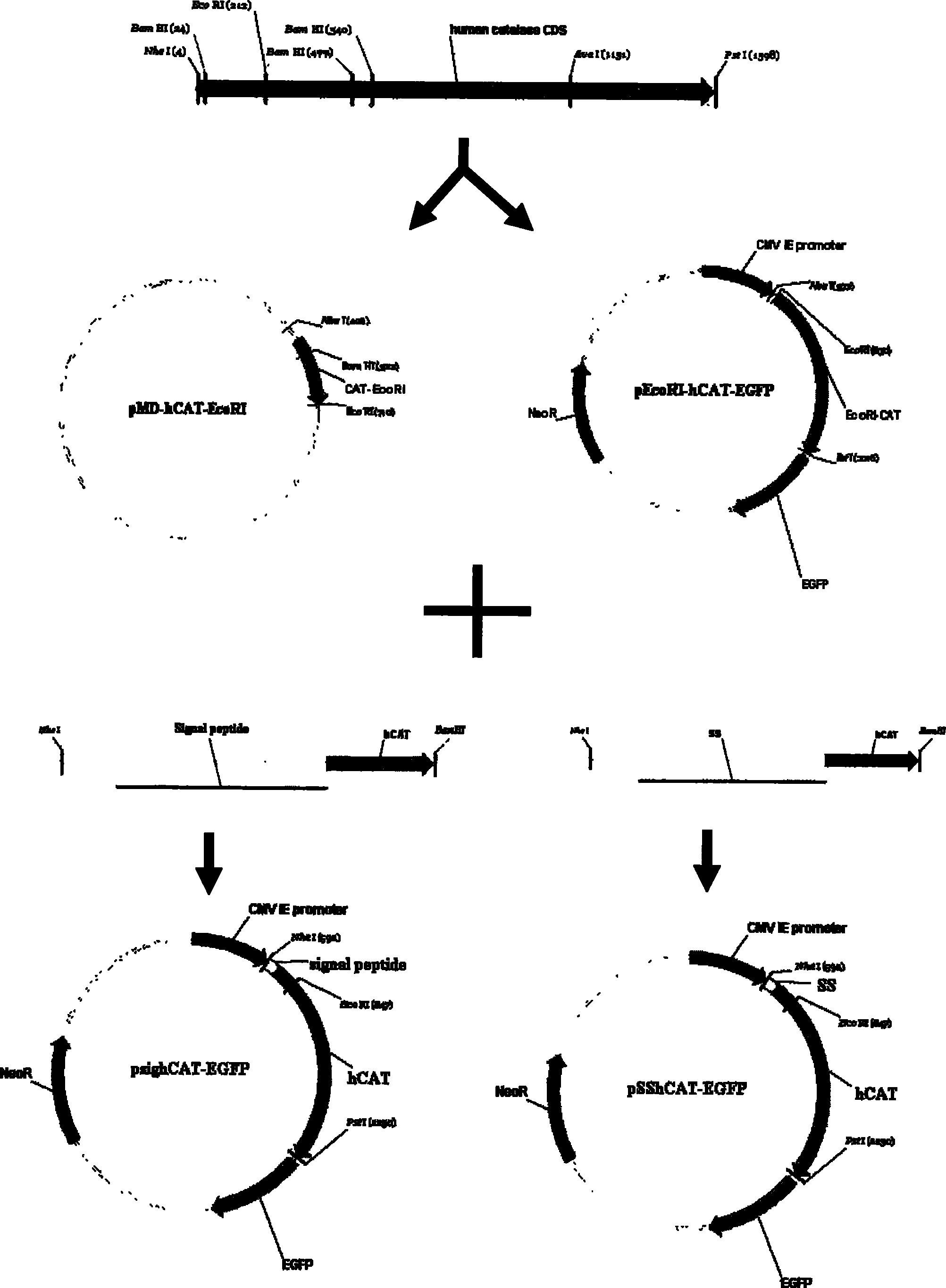
The invention provides a method for improving the secretion efficiency of recombinant protein, which is to fuse the secretory sequence SS in the homeotic domain of mouse transcription factor Engrailed 2 to the N-terminal of the recombinant protein, the amino acid sequence of the secretory sequence SS For: Ala Gln Glu Leu Ser Leu Asn Glu Ser Gln. The secretion efficiency of the human catalase obtained by the method of the invention is 2.3 times higher than that of the classic secretion guided by the signal peptide of bovine beta casein, which provides an effective solution for improving the secretion efficiency of the recombinant protein in industrial production.
Owner:WUXI KINGENEW BIOTECHNOLOGY LIMITED COMPANY
Inactivation resistant factor VIII
InactiveUS8183344B2Increase secretionHigh expressionFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIII vWFBinding site
The present invention provides novel purified and isolated nucleic acid sequences encoding procoagulant-active FVIII proteins. The nucleic acid sequences of the present invention encode amino acid sequences corresponding to known human FVIII sequences, wherein residue Phe309 is mutated. The nucleic acid sequences of the present invention also encode amino acid sequences corresponding to known human FVIII sequences, wherein the APC cleavage sites, Arg336 and Ile562, are mutated. The nucleic acid sequences of the present invention further encode amino acid sequences corresponding to known human FVIII sequences, wherein the B-domain is deleted, the von Willebrand factor binding site is deleted, a thrombin cleavage site is mutated, an amino acid sequence spacer is inserted between the A2- and A3-domains. Methods of producing the FVIII proteins of the invention, nucleotide sequences encoding such proteins, pharmaceutical compositions containing the nucleotide sequences or proteins, as well as methods of treating patients suffering from hemophilia, are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Heat-resistant neutral pullulanase mutant and application thereof
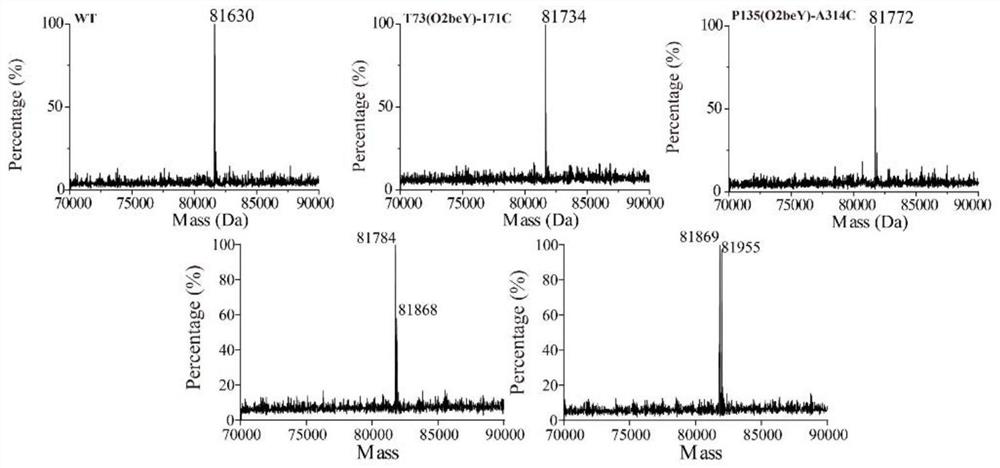
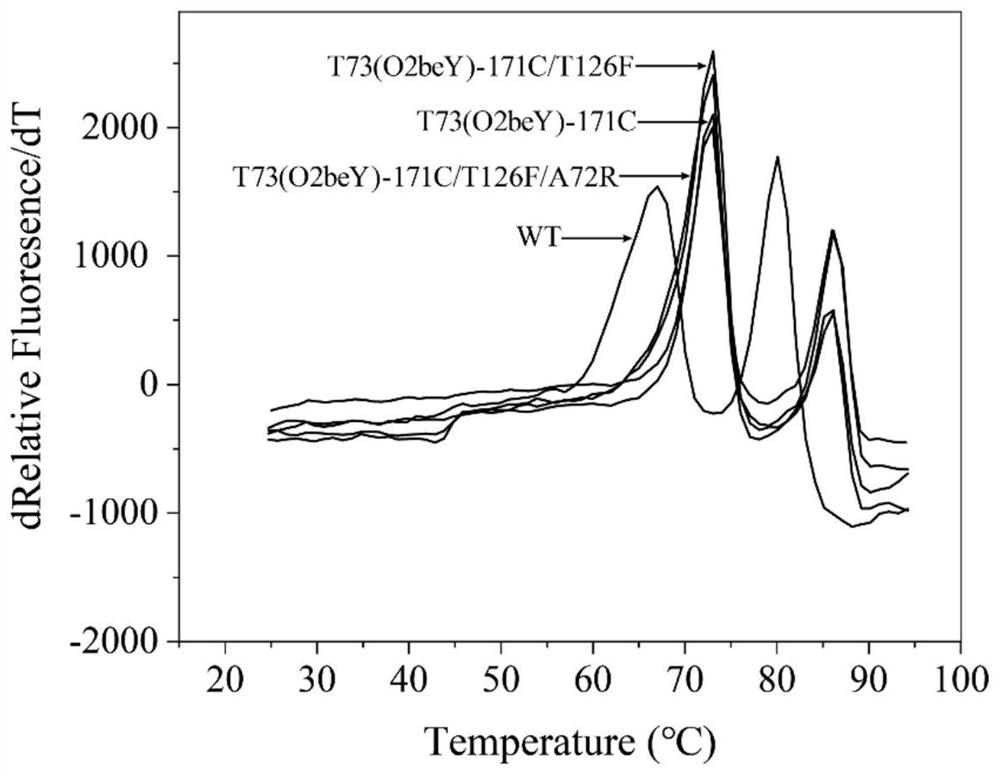
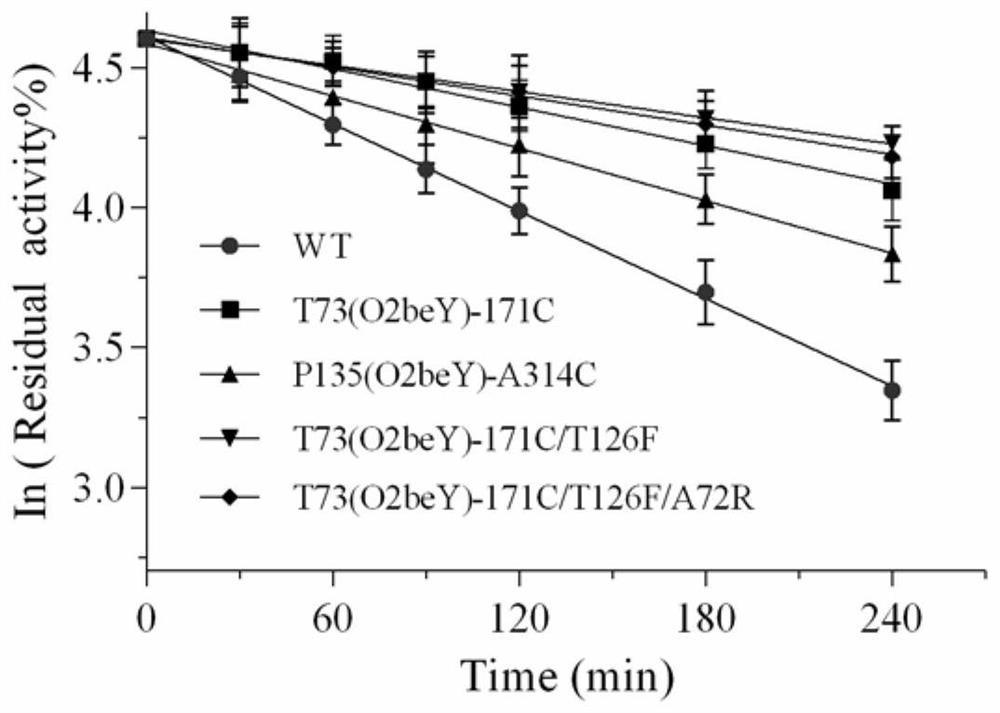
ActiveCN113265386AImprove thermal stabilityImprove secretion efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiExtracellularSecretion expression
The invention discloses a heat-resistant neutral pullulanase mutant and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, amino acids at the 73th site, the 135th / 314th site, the 135th / 314th / 126th site and the 135th / 314th / 126th / 72nd site of pullulanase are respectively mutated, so that four pullulanase mutants with improved thermal stability and unchanged or improved catalytic efficiency are obtained. At the temperature of 70 DEG C, the half-life periods of the four mutants are respectively 2.6, 1.9, 3.3 and 3.1 times that of a wild type; and the Tm values are respectively increased by 7.0 DEG C, 6.5 DEG C, 6.7 DEG C and 6.9 DEG C. The extracellular enzyme activity of pullulanase reaches 9.7 U / mL by fusing OptPelB at the N terminal of the high-temperature-resistant neutral pullulanase mutant, and is 4.9 times that of a wild type. The heat-resistant neutral pullulanase mutant capable of secreting and expressing has the application potential of high-value utilization of starch raw materials.
Owner:宿迁市江南大学产业技术研究院
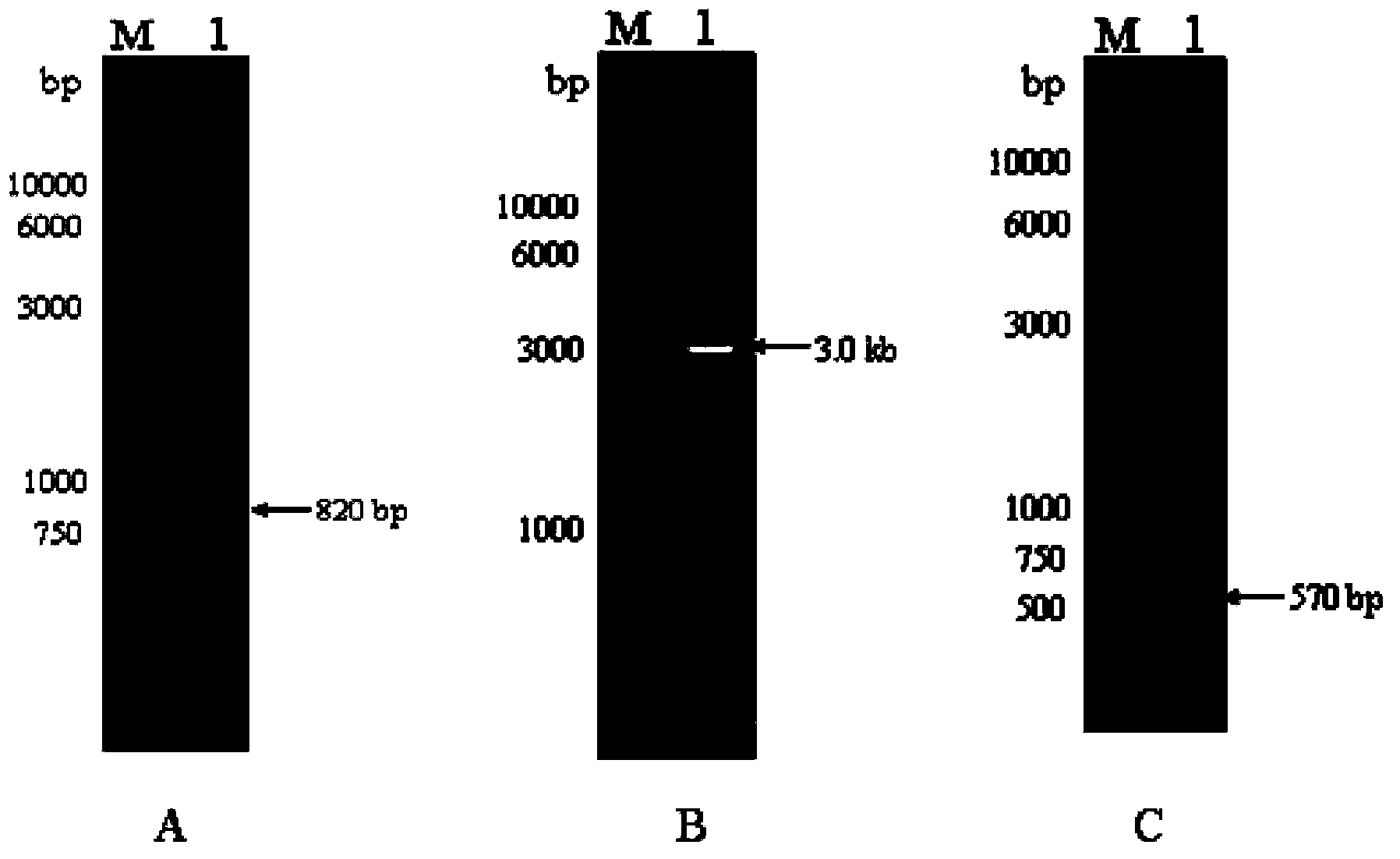
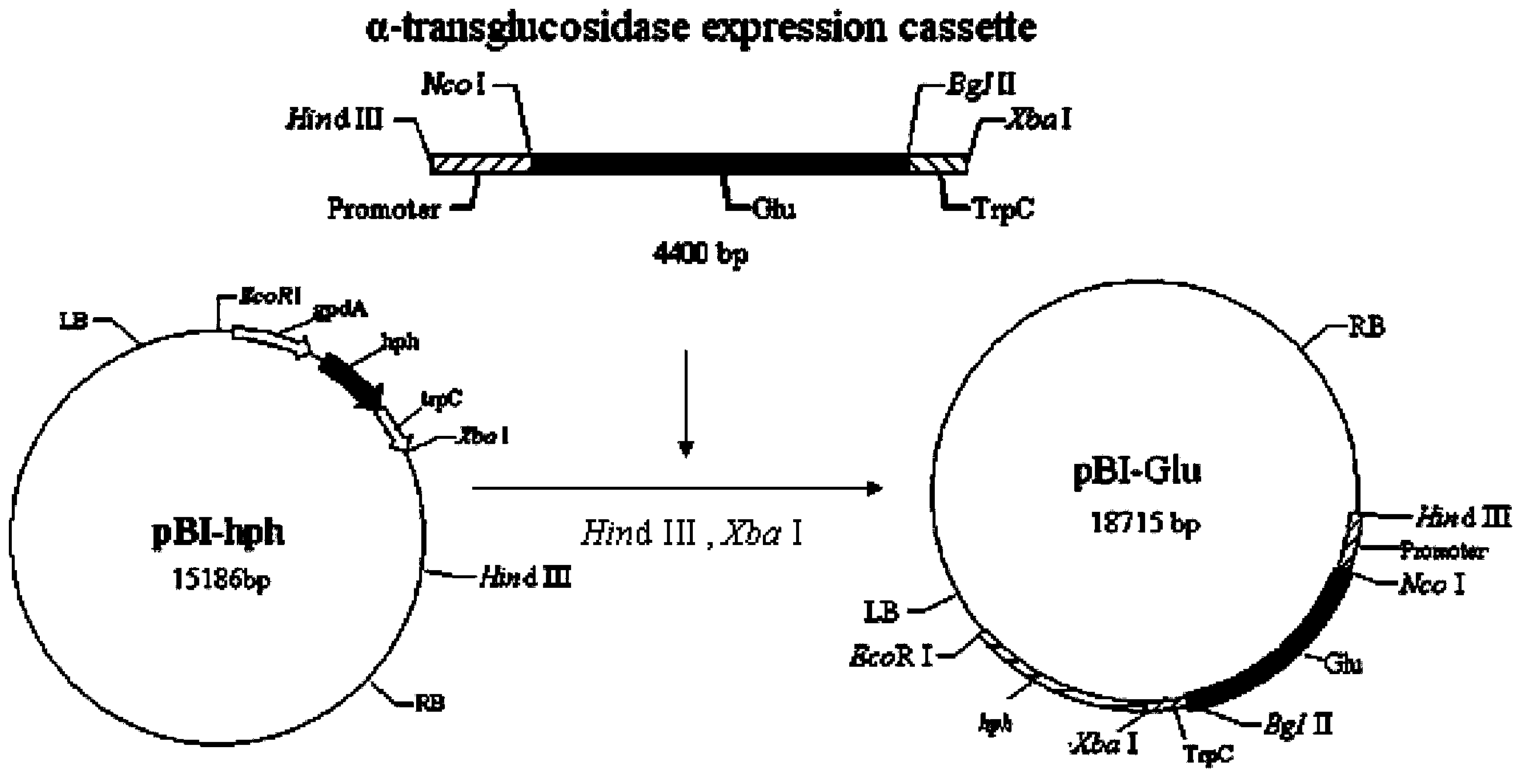
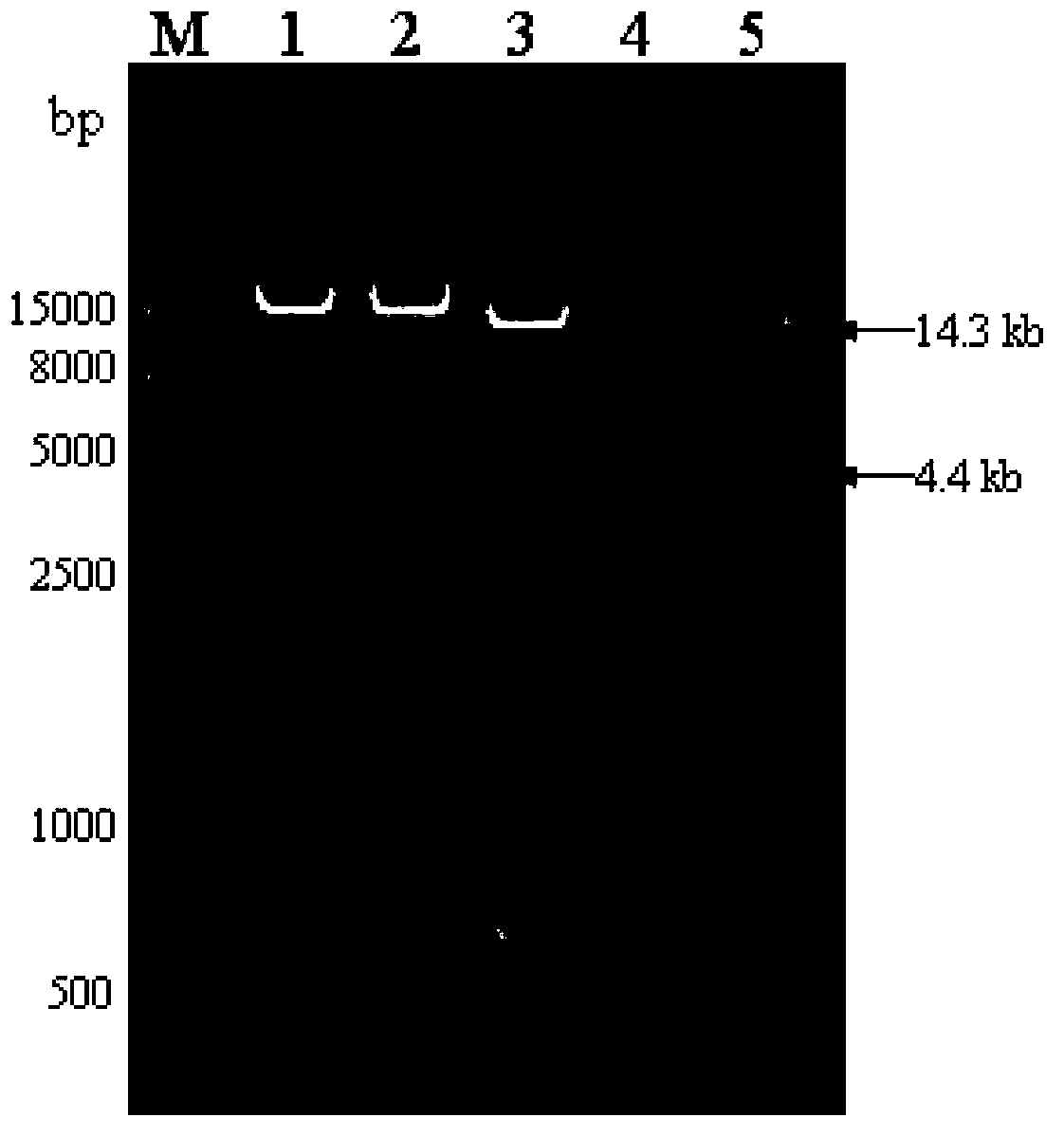
Genetically engineered bacterium capable of efficiently expressing alpha-transglucosidase, and construction method of genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN103436454AImprove secretion efficiencyReduce the cost of extraction and purificationFungiMicroorganism based processesGene expressionEnzyme
The invention relates to a genetically engineered strain efficiently expressing alpha-transglucosidase. A host bacterium of the genetically engineered strain is aspergillus niger, and the genetically engineered strain comprises an alpha-transglucosidase gene expression cassette. A genetically engineered bacterium can efficiently express alpha-transglucosidase, and improves the secretion efficiency of alpha-transglucosidase. In addition, alpha-transglucosidase is secreted to the outside of a cell, so that the cost of alpha-transglucosidase extraction purification is lowered, industrial materials are saved, the production cost is lowered, and the genetically engineered strain has an obvious social benefit. The enzyme activity of a crude enzyme obtained after the strain is fermented is improved by 4.0-12.1 times in comparison to a starting strain; a foundation is laid for an application of alpha-transglucosidase in the food industry and industrial production; a bottleneck that alpha-transglucosidase depends on import is broken; and the genetically engineered strain has huge economic and social benefits, and has a broad market development prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for increasing secretion efficiency of bile salt hydrolase
The invention discloses a method for increasing the secretion efficiency of bile salt hydrolase, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. In the invention, by adopting the recombinant DNA technology, the bile salt hydrolase gene bsh from lactobacillus plantarum is fused with signal peptide alpha-MF and connected with a carrier pPIC9K and transformed into pichia pastoris GS115 to obtain bile salt hydrolase producing recombinant pichia pastoris. By exogenously adding castanospermine and Fe<2+>, the secretion efficiency of pichia pastoris bile salt hydrolase is increased, the activity of the fermentation 3d bile salt hydrolase reaches 14.96U / mL which is 1.74 times higher than that without exogenous substance.
Owner:曹书华
Method for reinforcing secretion efficiency of recombination exogenous protein in sprout fungi expression system
InactiveCN101473035AImprove secretion efficiencyHigh yieldHybrid cell preparationEnzymesBiotechnologyProtein C
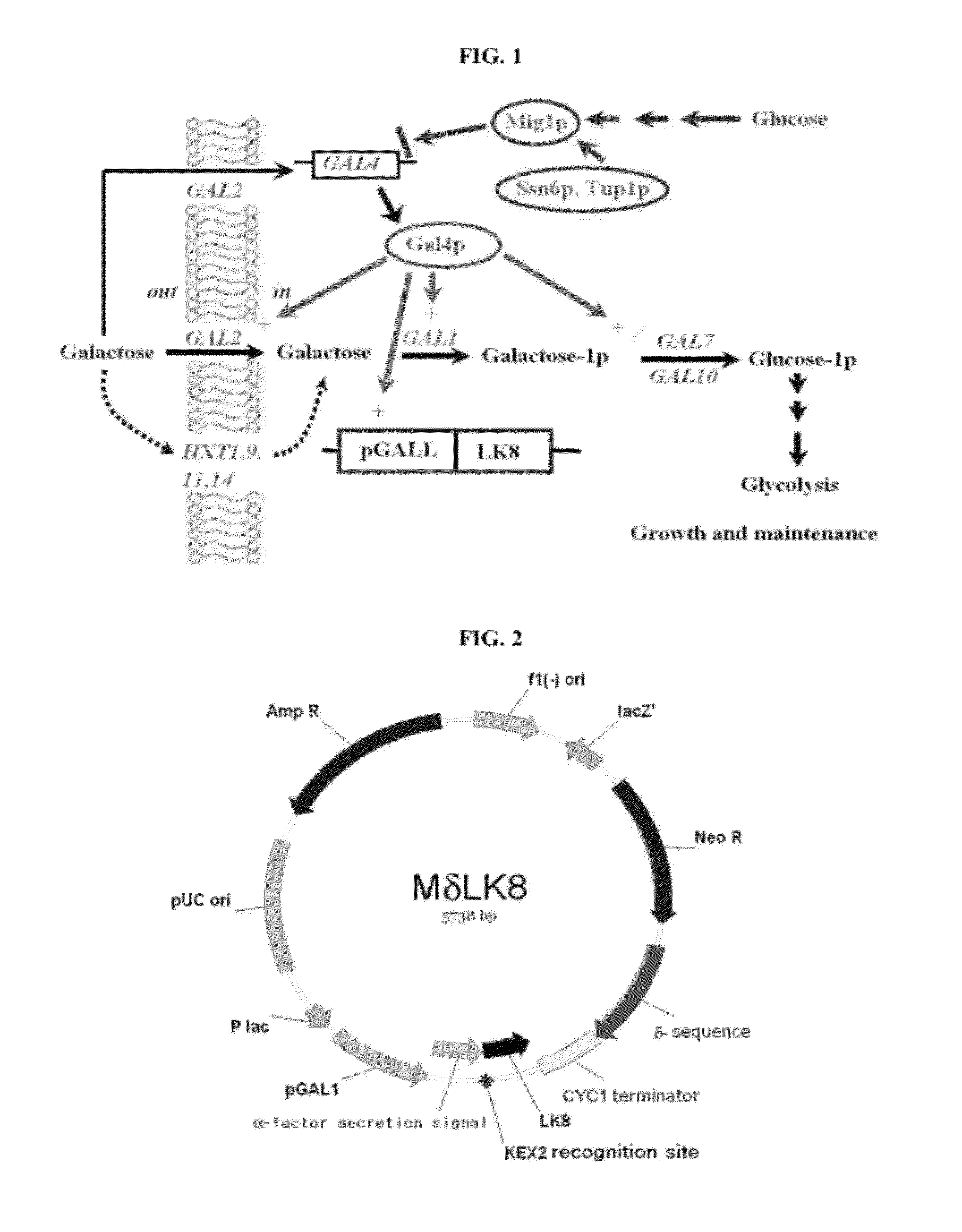
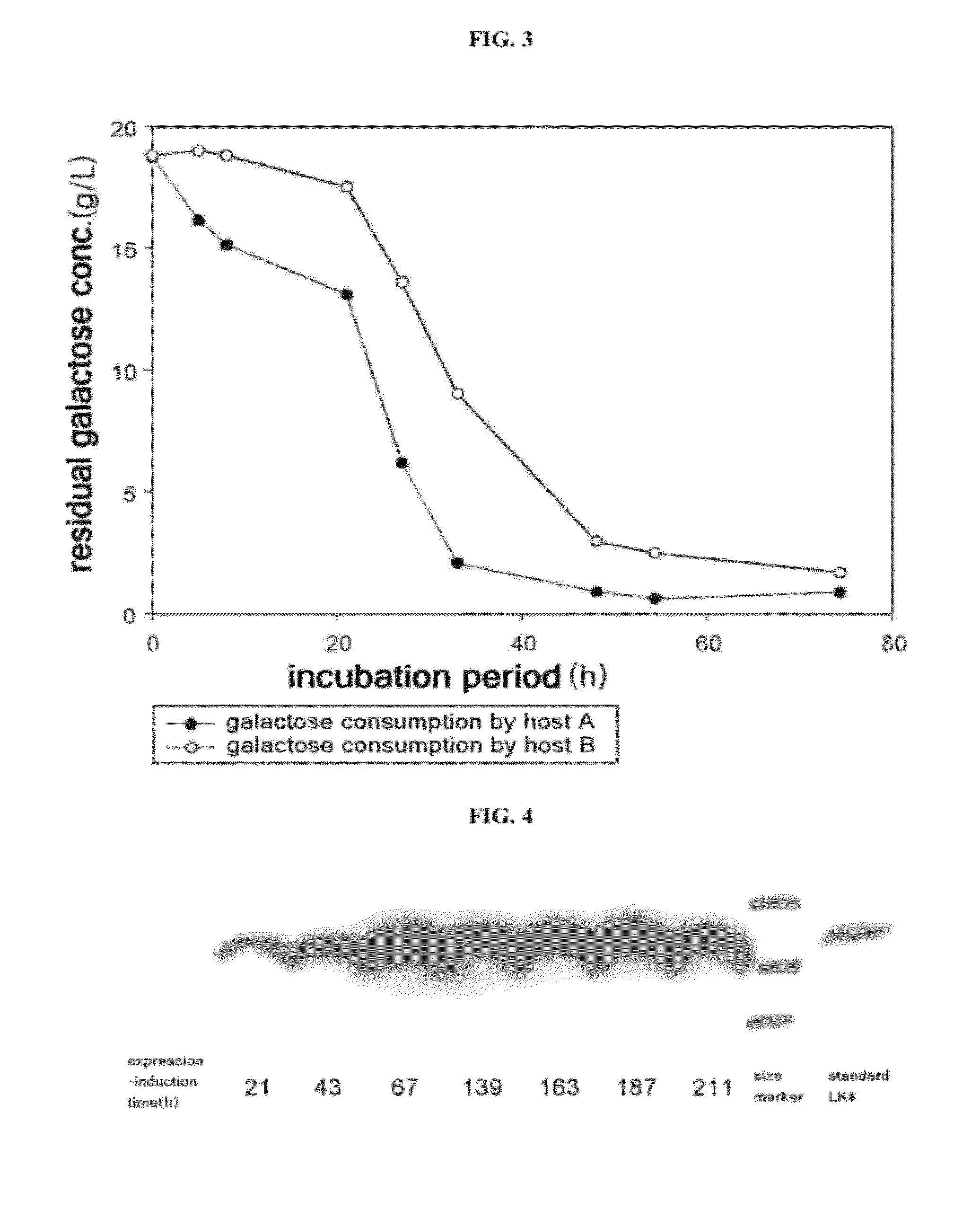
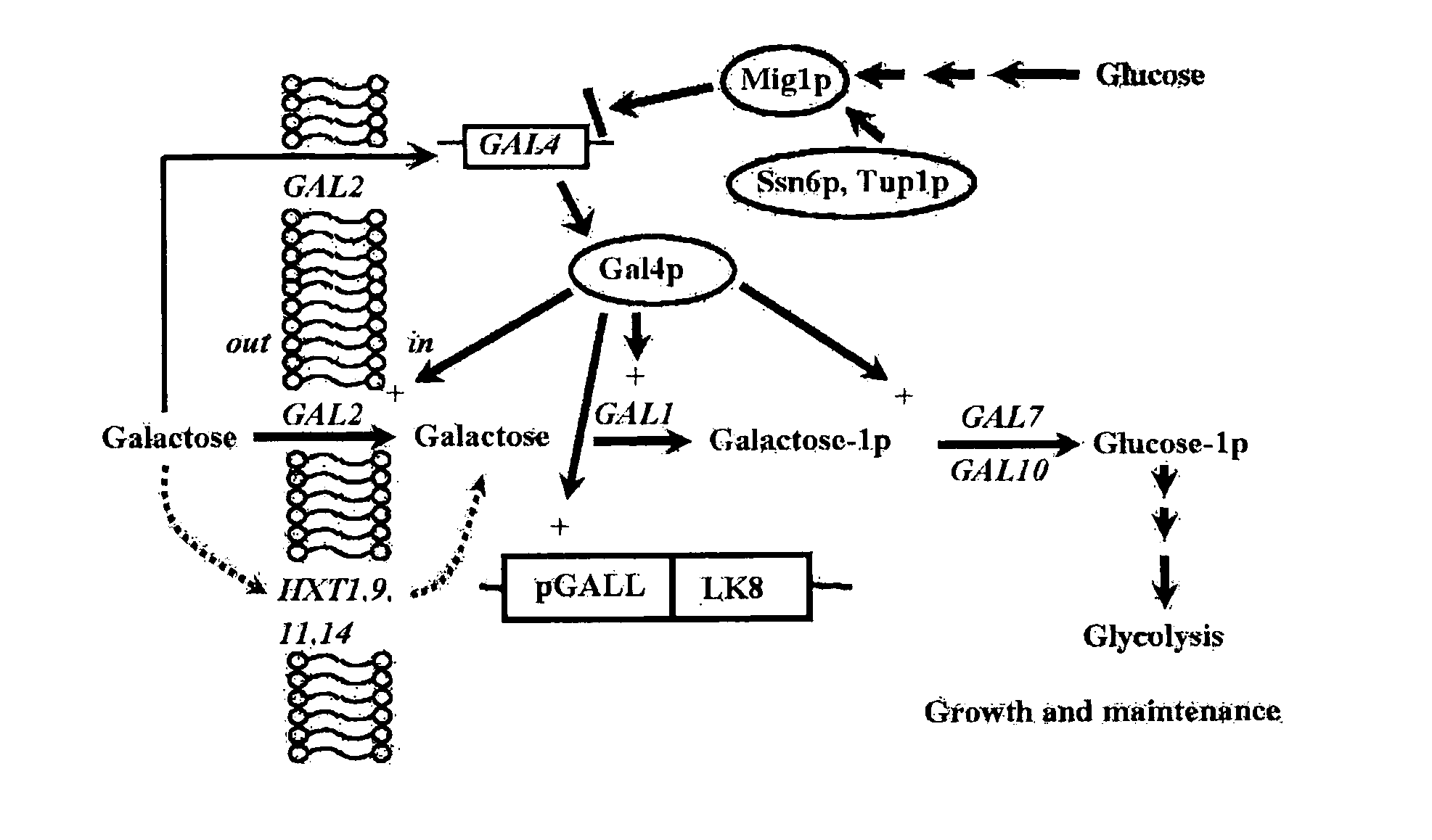
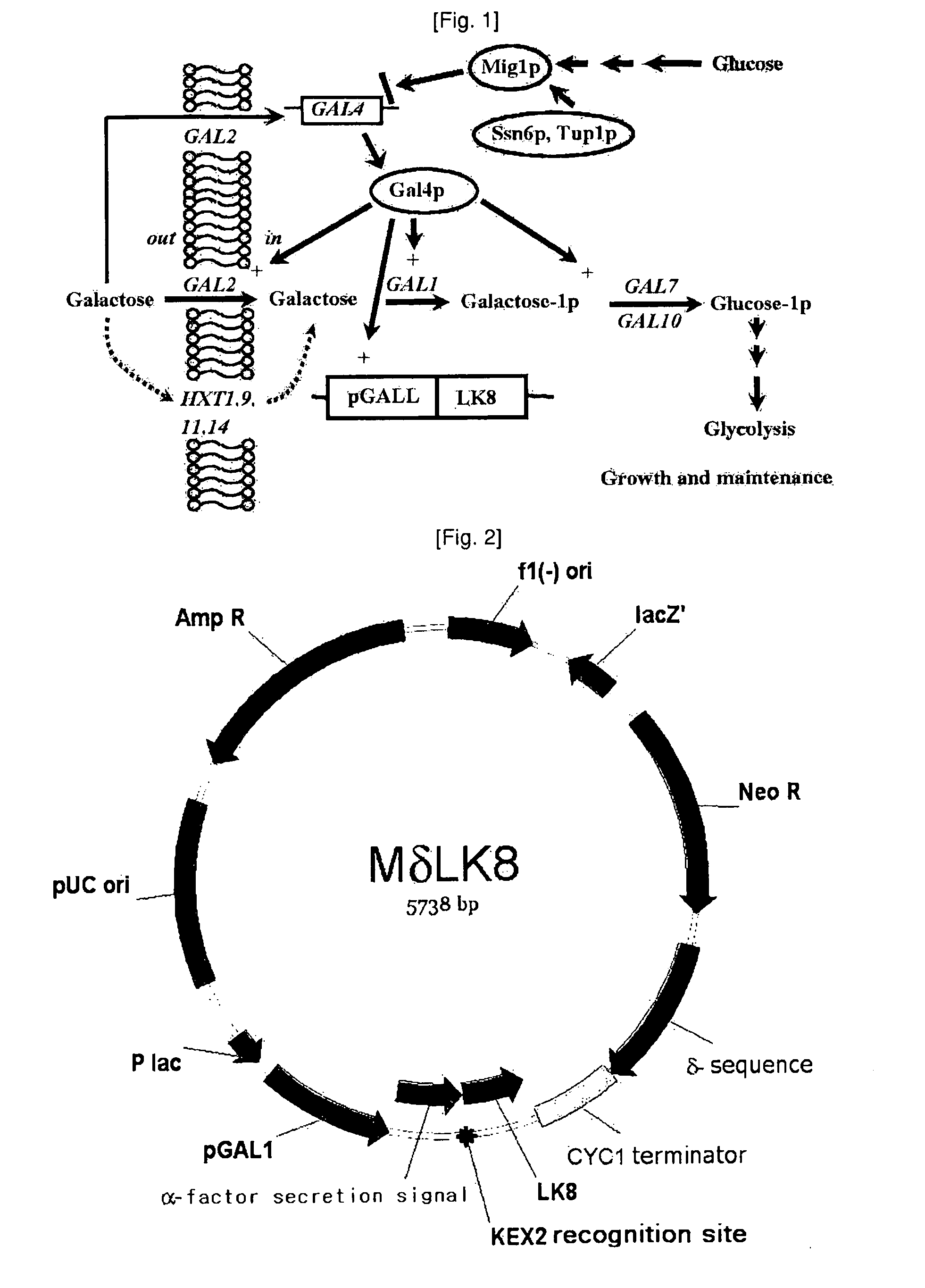
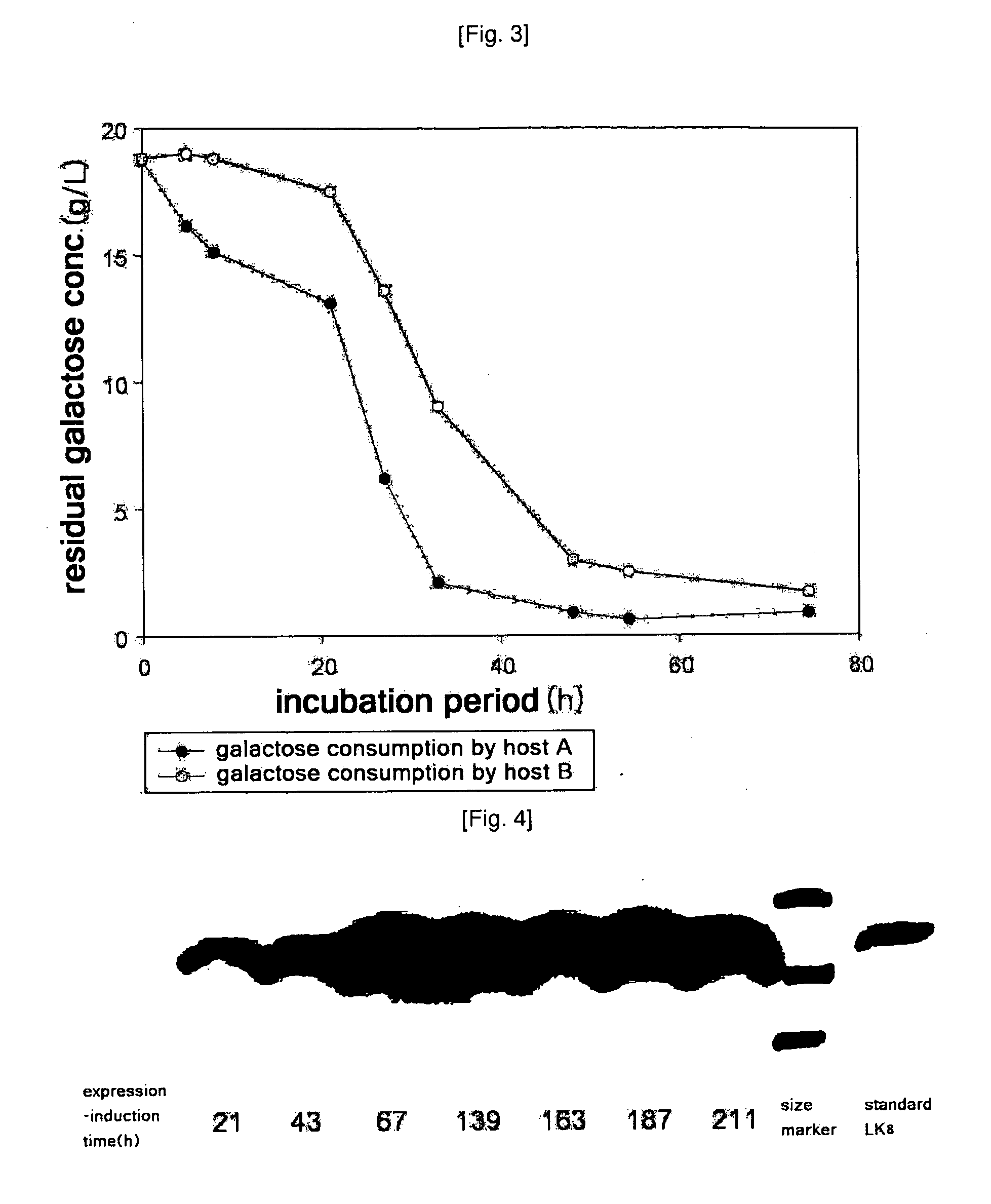
Provided is a method for improving secretion efficiency of a recombinant foreign protein in a yeast expression system. The method comprises transforming a yeast host with a recombinant foreign gene construct comprising a galactose-inducible promoter, a secretion signal sequence and a gene encoding the foreign protein to construct a transformed yeast strain; and culturing the transformed yeast strain under the condition that the activity of the galactose-inducible promoter is controlled. Improved secretion efficiency of the foreign protein can be achieved by decreasing over-expression-induced insoluble precipitation of the recombinant foreign protein suffered by a conventional galactose-inducible promoter-based yeast expression system, via appropriate control of a level of galactose functioning as an inducer of the galactose-inducible promoter in cells. Due to improved secretion efficiency of the recombinant foreign protein, present invention makes a contribution to improvement in productivity of recombinant foreign proteins in the yeast expression system and reduction in production costs.
Owner:MOGAM BIOTECH RES INST
Method of producing secretable antibodies by expression in saccharomyces cerevisiae
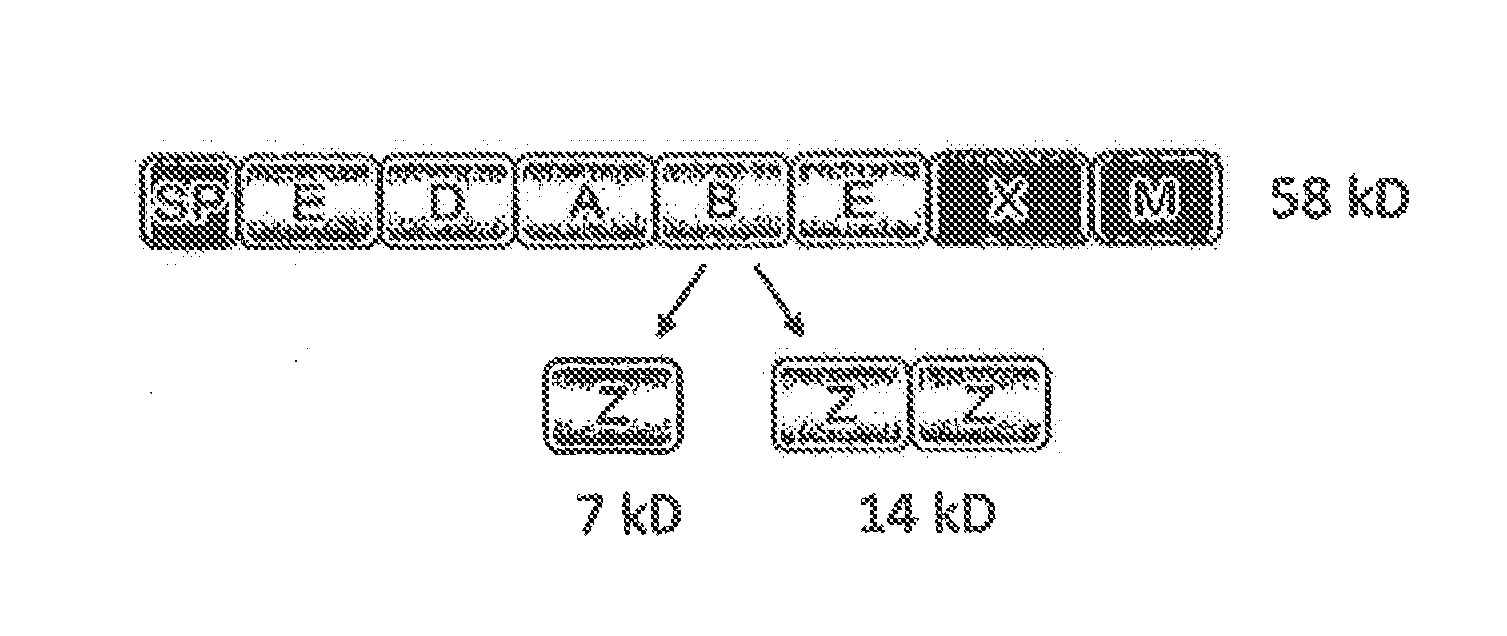
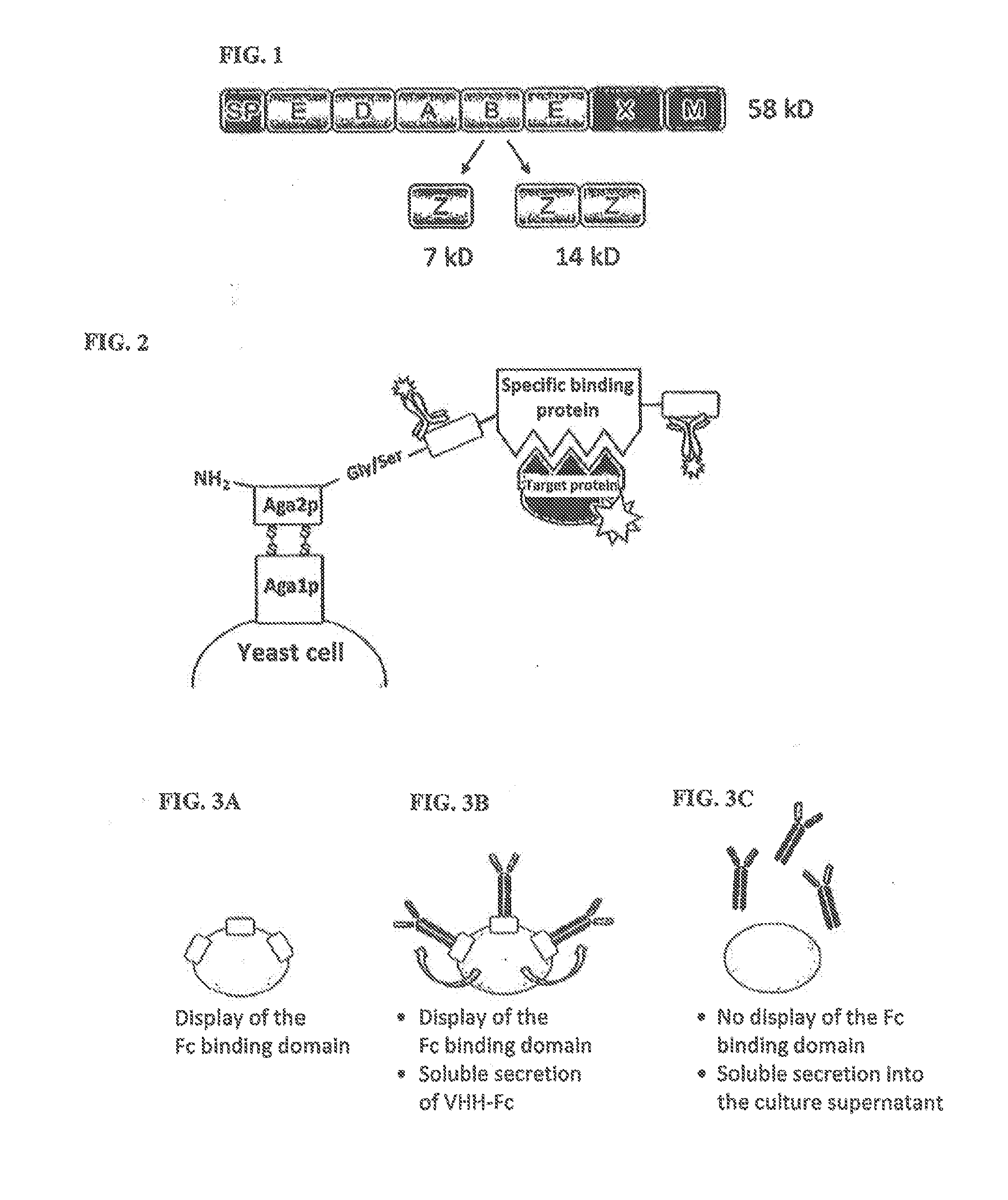
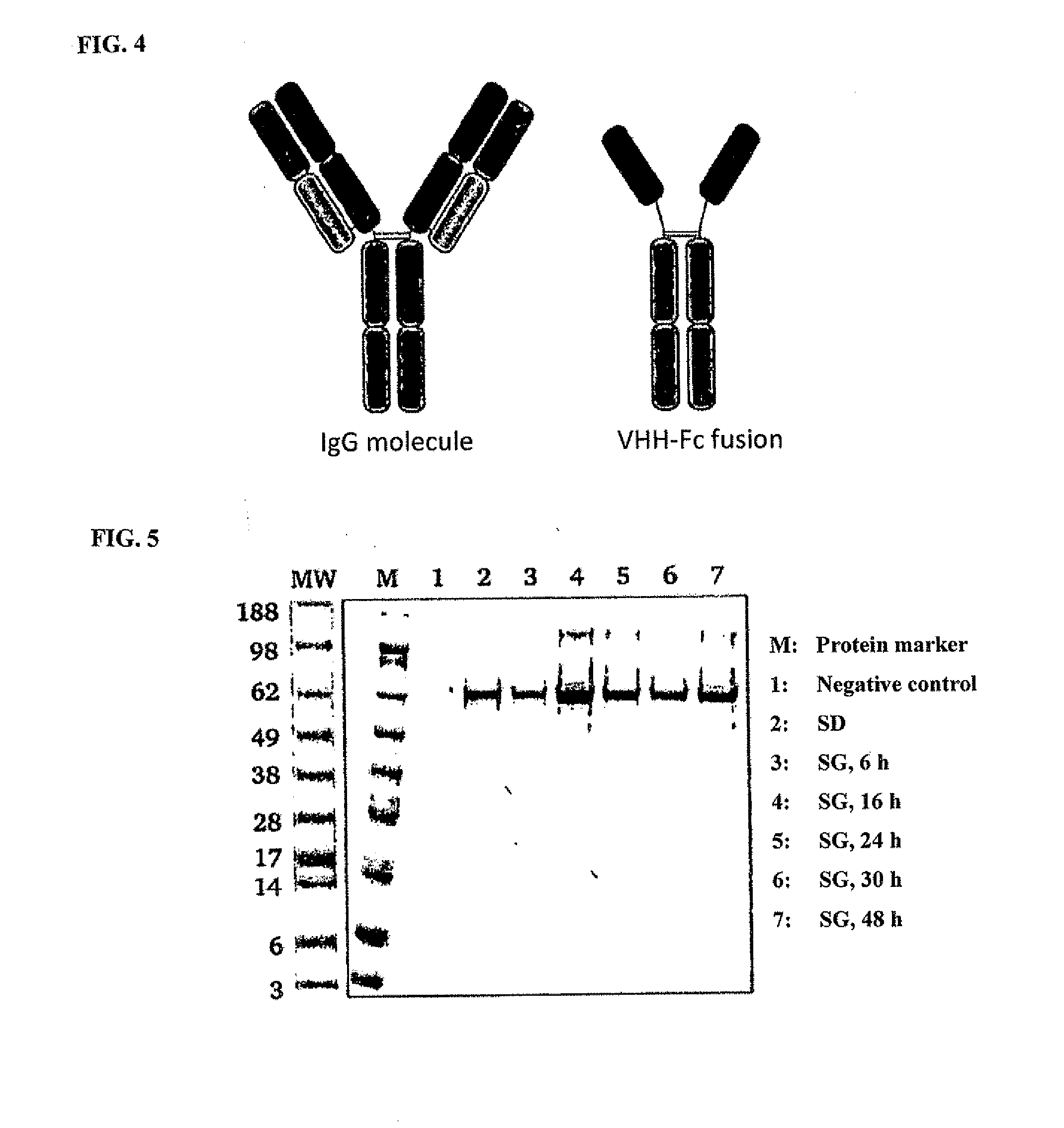
ActiveUS20150337292A1Simplification and accelerationPromote generationImmunoglobulinsLibrary creationHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSecretion
The invention relates to a method for the production and non-covalent surface display of antibodies and derived fragments as well as molecule libraries based thereon on the surface of S. cerevisiae cells. The non-covalent manner of the surface display renders possible the selection of specific variants by means of high throughput screening and the subsequent switchable secretion of the selected binding molecule into the culture supernatant for biochemical characterisation.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Method of isolating secretion signals in lactic acid bacteria and novel secretion signals isolated from lactococcus lactis
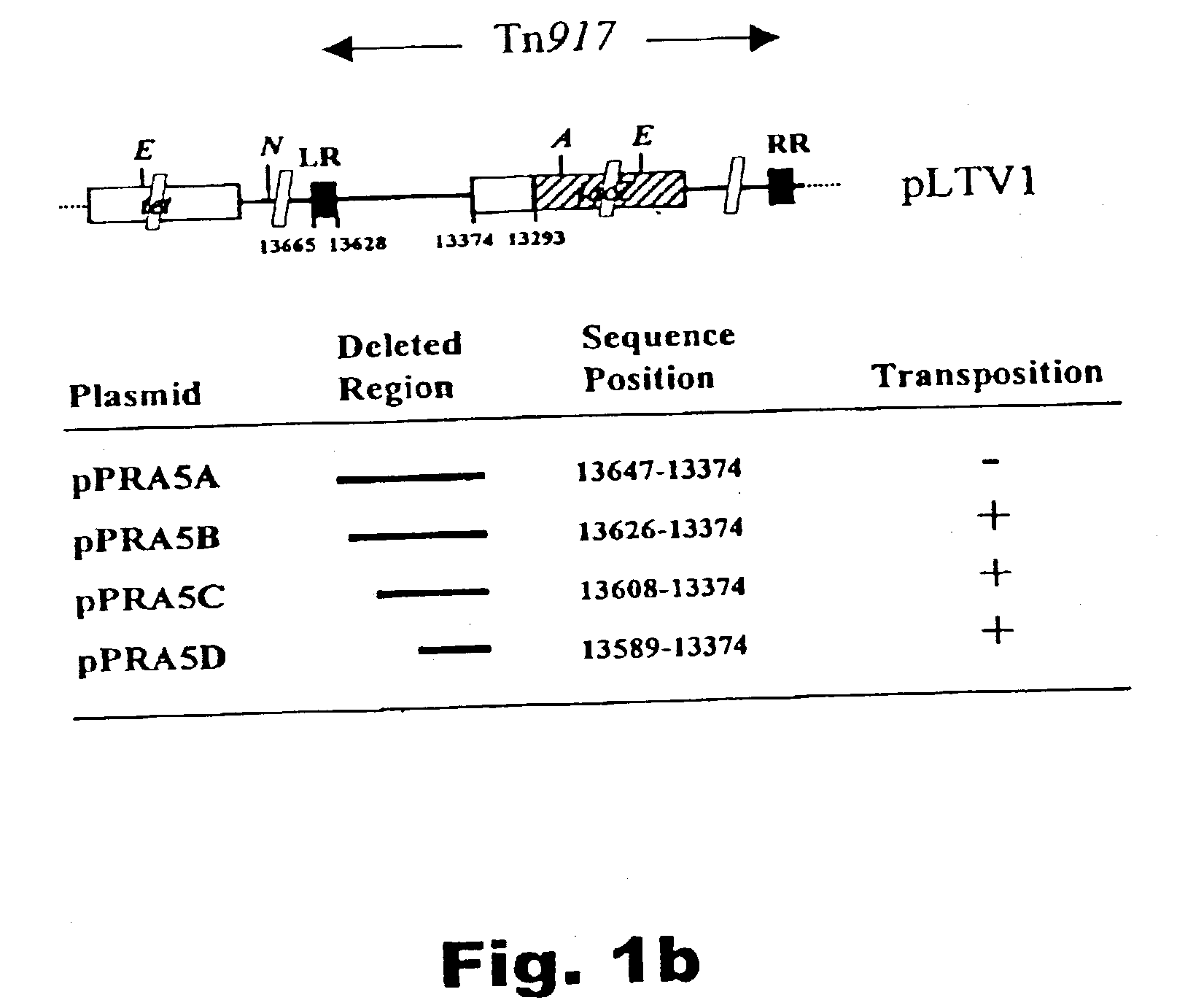
InactiveUS20040038263A1Improve secretion efficiencyReserved functionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesLactobacillusNucleotide
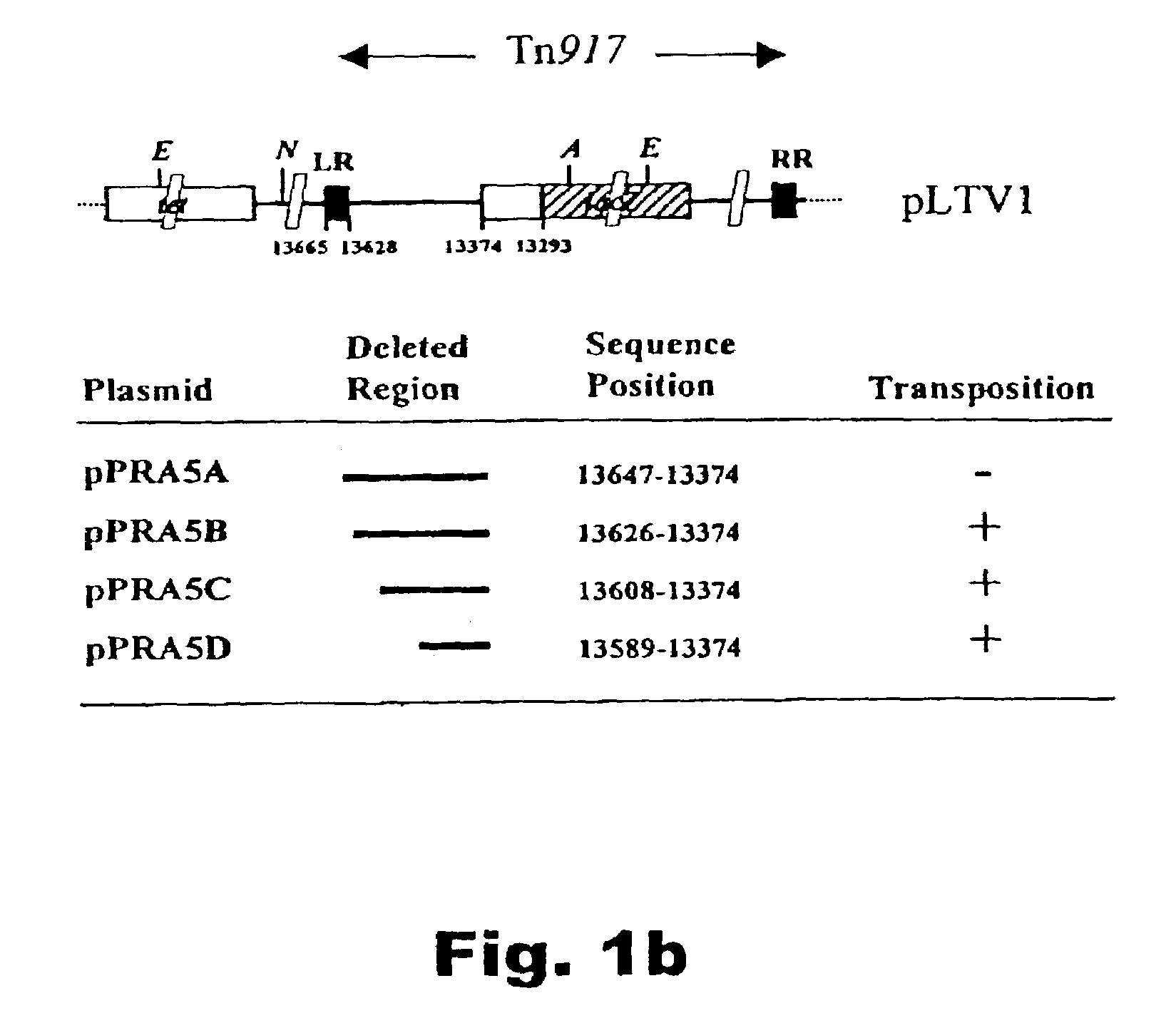
A method of identifying nucleotide sequences coding for signal peptides in lactic acid bacteria, using a DNA molecule comprising a transposon including a promoterless reporter gene from which DNA molecule a region between the LR and the reporter gene is deleted and the DNA molecule comprises a DNA sequence coding for a secretion reporter molecule. By deleting the region between the LR and the reporter gene, stop codons in-frame with the secretion reporter molecule is removed which upon transposition permits translational fusions from upstream the LR.
Owner:BIONEER
Methods for enhancing a secretion efficiency of recombinant foreign protein in yeast expression system
ActiveUS8298787B2Improve secretion efficiencyReduce precipitationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPromoter activity
Provided is a method for improving secretion efficiency of a recombinant foreign protein in a yeast expression system. The method includes transforming a yeast host with a recombinant foreign gene construct containing a galactose-inducible promoter, a secretion signal sequence and a gene encoding the foreign protein to construct a transformed yeast strain; and culturing the transformed yeast strain under the condition that the activity of the galactose-inducible promoter is controlled. Improved secretion efficiency of the foreign protein can be achieved by decreasing overexpression-induced insoluble precipitation of the recombinant foreign protein suffered by a conventional galactose-inducible promoter-based yeast expression system, via appropriate control of a level of galactose functioning as an inducer of the galactose-inducible promoter in cells. Due to improved secretion efficiency of the recombinant foreign protein, present invention makes a contribution to improvement in productivity of recombinant foreign proteins in the yeast expression system and reduction in production costs.
Owner:MOGAM BIOTECH RES INST
Recombinant human dyad stem cell factor and preparing thereof
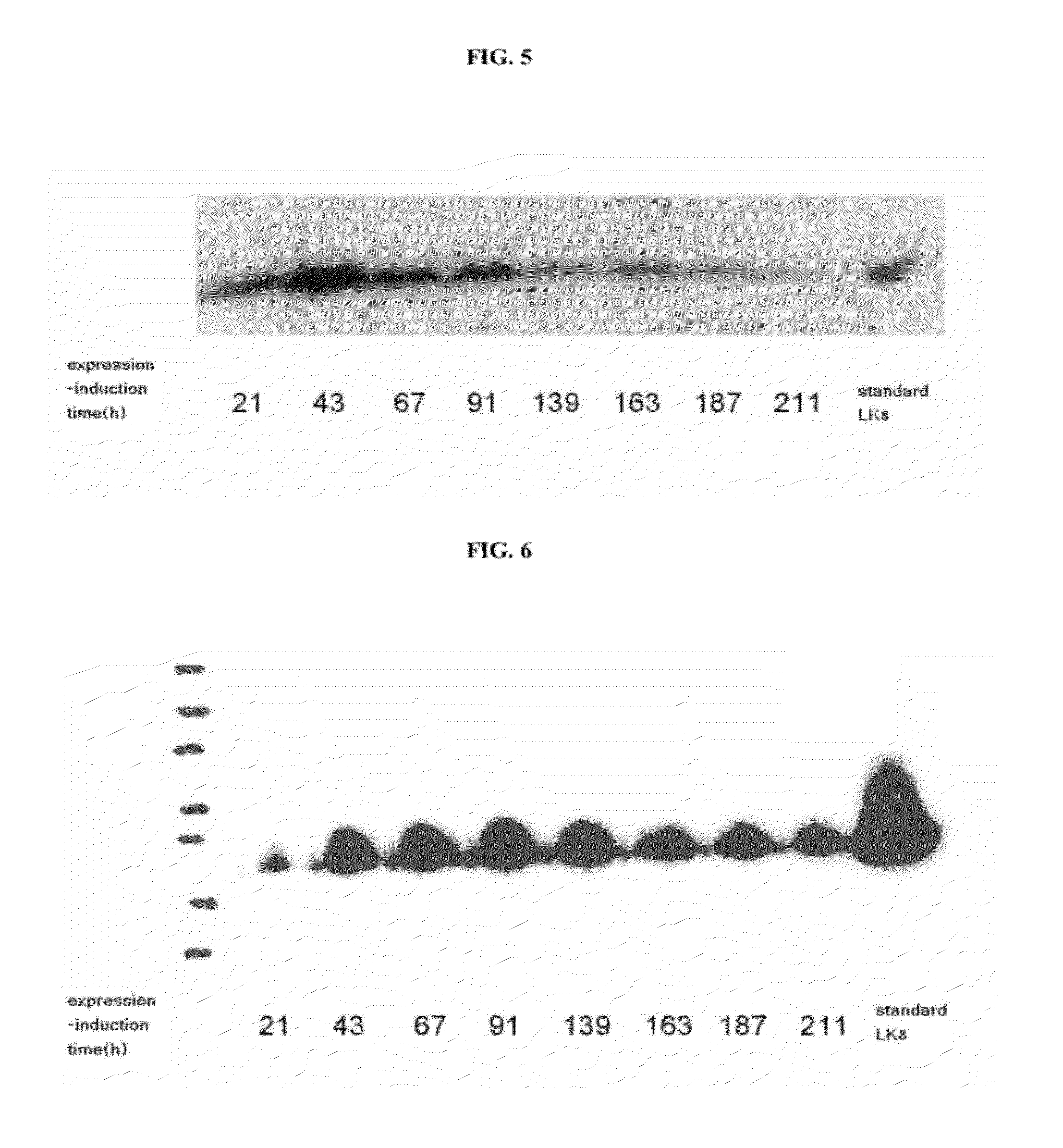
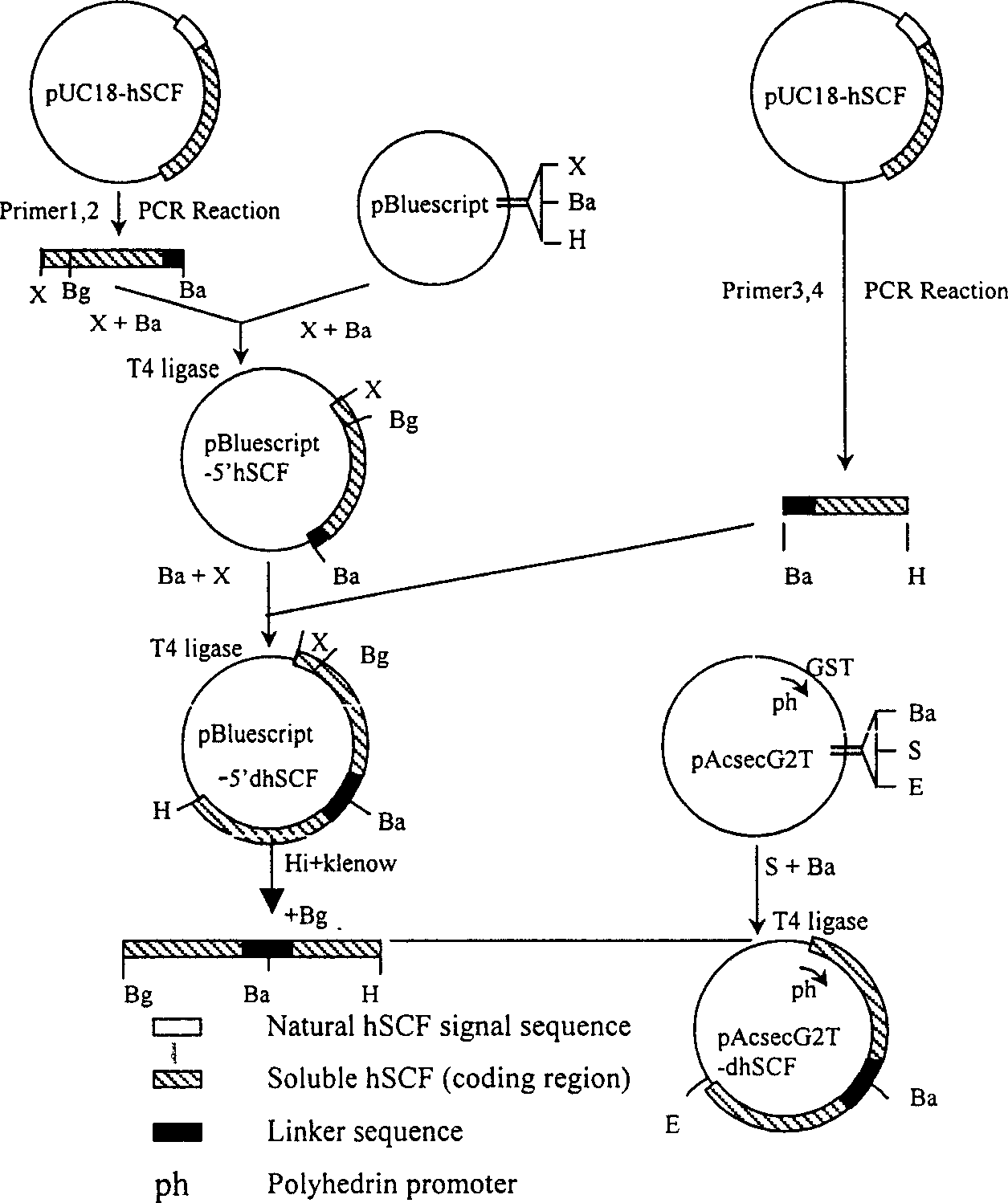
InactiveCN1435426AEasy to separate and purifyImprove secretion efficiencySugar derivativesFermentationFactor iiLinker peptide
A recombinant human diad stem cell factor (rhdSCF) used for radiotherapy, chemicotherapy and recreating and restoring the hematognesis and immune function after bone marrow transplantation is disclosed. It sequentially contains amino acid codons No1-165 of human SCF, 12 amino acid linker peptides, codons No1-145 of human SCF and DNA fragment of termination codon. Its advantage is high specific activity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Production of soluble recombinant protein by pi value control of n-terminal
InactiveUS20100305040A1PreventionIncrease secretionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic proteinBiology
The present invention relates to a method for improving secretion efficiency of a recombinant foreign protein using a polypeptide fragment containing N-region of a signal sequence (directional signal) or variants thereof with the controlled pI value and / or a secretional enhancer composed of a hydrophilic polypeptide with the controlled pI value. The method of the present invention can be not only useful for the production of a recombinant foreign protein by preventing precipitation of an insoluble precipitate and by increasing extracellular or extra-periplasmic secretion efficiency of a recombinant protein but also useful for the transduction of an effective therapeutic protein by increasing membrane permeability using a strong secretional enhancer.
Owner:REPUBLIC OF KOREA (NAT FISHERIES RES & DEV INST)
Method of isolating secretion signals in lactic acid bacteria and novel secretion signals isolated from Lactococcus lactis
InactiveUS7186815B2Improve secretion efficiencyReserved functionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaLactobacillusNucleotide
A method of identifying nucleotide sequences coding for signal peptides in lactic acid bacteria, using a DNA molecule comprising a transposon including a promoterless reporter gene from which DNA molecule a region between the LR and the reporter gene is deleted and the DNA molecule comprises a DNA sequence coding for a secretion reporter molecule. By deleting the region between the LR and the reporter gene, stop codons in-frame with the secretion reporter molecule is removed which upon transposition permits translational fusions from upstream the LR.
Owner:BIONEER
A method for improving the secretion rate of exogenous protein expressed by silkworm cells
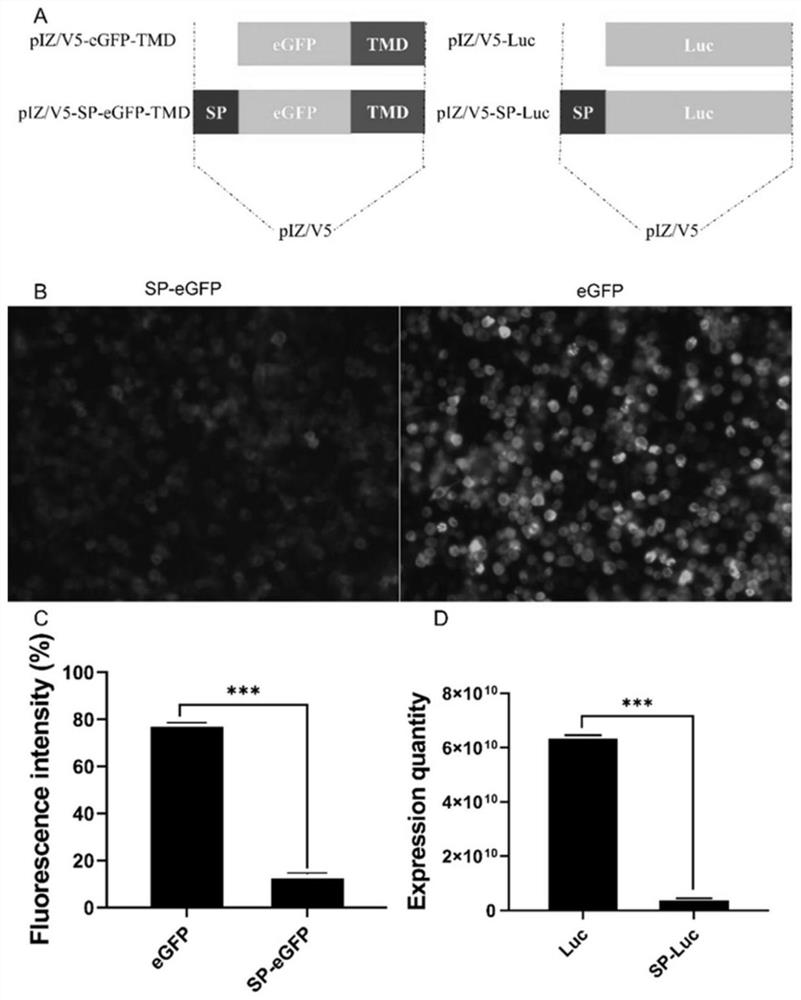
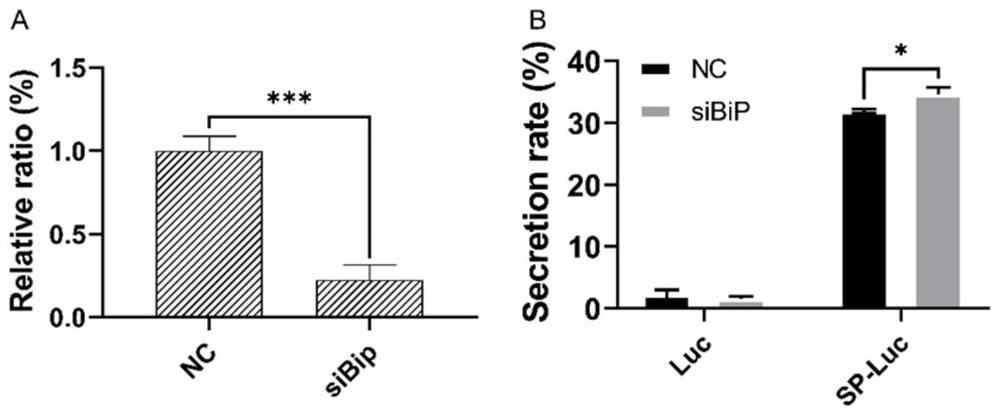
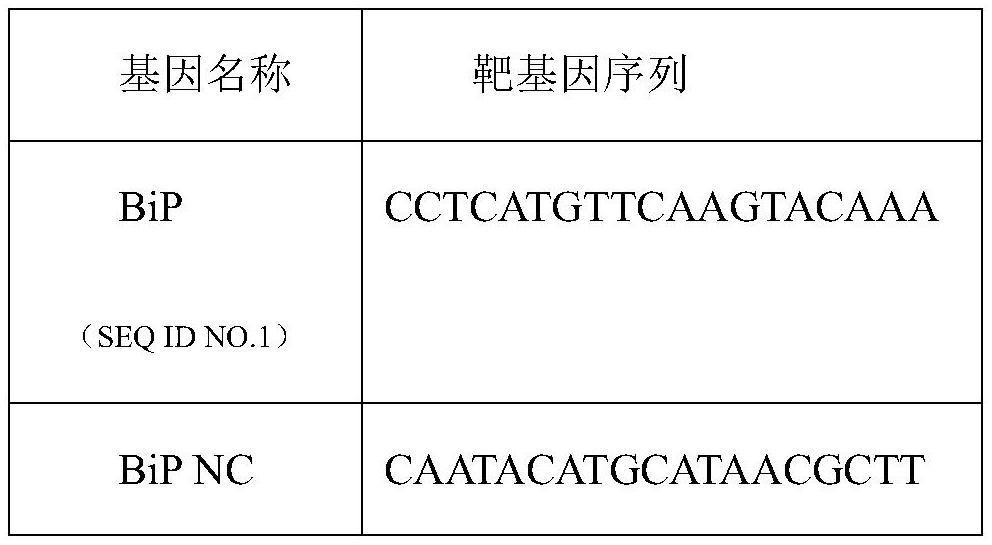
ActiveCN112342247BIncrease secretion rateImprove secretion efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorSecretion rateBaculovirus expression
A method for improving the secretion rate of exogenous protein expressed by silkworm cells, designing and synthesizing an RNAi interference fragment for interfering with the BiP gene in silkworm BmN cells, transfecting BmN cells for 24 hours and then continuing to transfect the expression vector carrying the foreign gene, after 72 hours That is, the secretion rate of the foreign protein can be significantly increased. This method is simple and easy to operate, and can effectively improve the secretion efficiency of exogenous proteins expressed in silkworm cells. It can provide a new idea to improve the expression of membrane proteins by using BiP etc. as molecular targets, and is conducive to in-depth understanding of baculovirus Expression system, and provide a reference for the mechanism research of signal peptide involved in protein secretion.
Owner:上海五心医疗科技集团股份有限公司
Method for improving secernment efficiency of recombined protein
InactiveCN101173270BImprove secretion efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsDermatological disorderAllotypeBovine casein
The invention provides a method for improving recombinant protein secretion efficiency, which is characterized in that a secretion signal sequence SS in the homeotic allotype domain of the mouse transcription factor Engrailed 2 is fused to the N-terminal of the recombinant protein; wherein the amino acid sequence of the secretion signal sequence SS is that: Ala Gln Glu Leu Ser Leu Asn Glu Ser Gln. The invention has the advantages that: the secretion efficiency of human catalase using the invention is improved to 2.3 times than the normal secretion efficiency guided by bovine Beta-casein signal peptide and provides an effective solution for improving recombinant protein secretion efficiency in industrial production.
Owner:WUXI KINGENEW BIOTECHNOLOGY LIMITED COMPANY
Signal peptide capable of improving secretion efficiency, and applications thereof
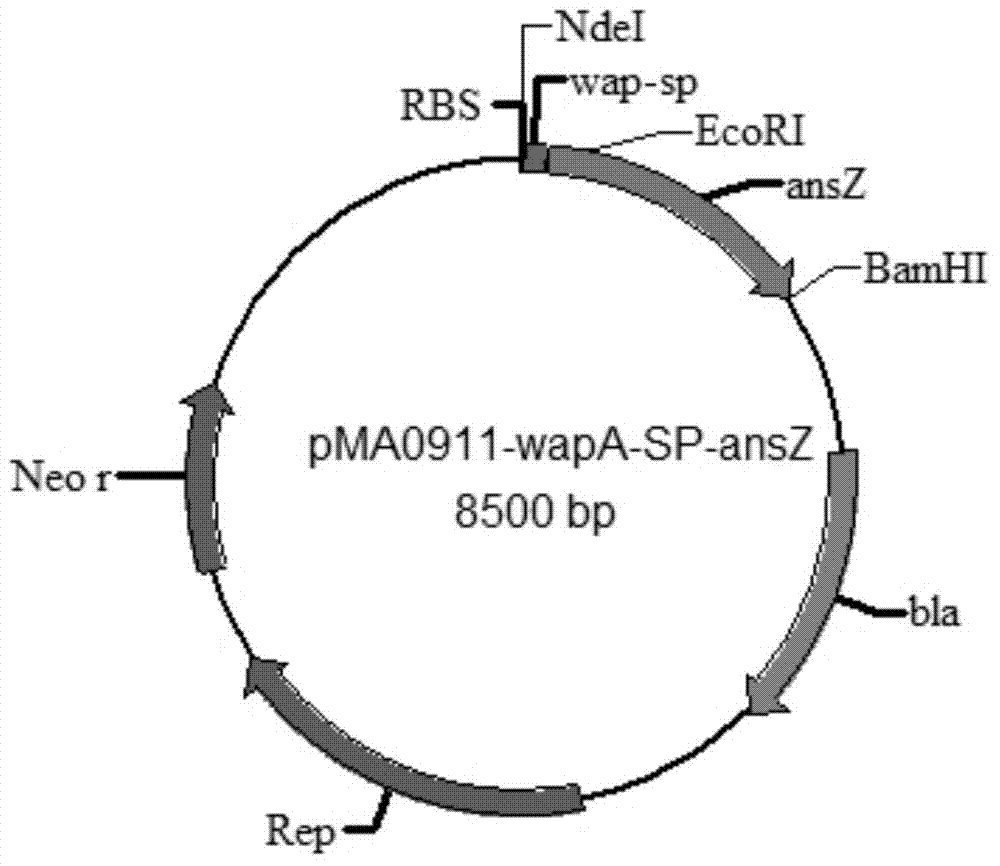
ActiveCN103709236BImprove secretion efficiencyImprove enzyme production capacityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyNucleotide
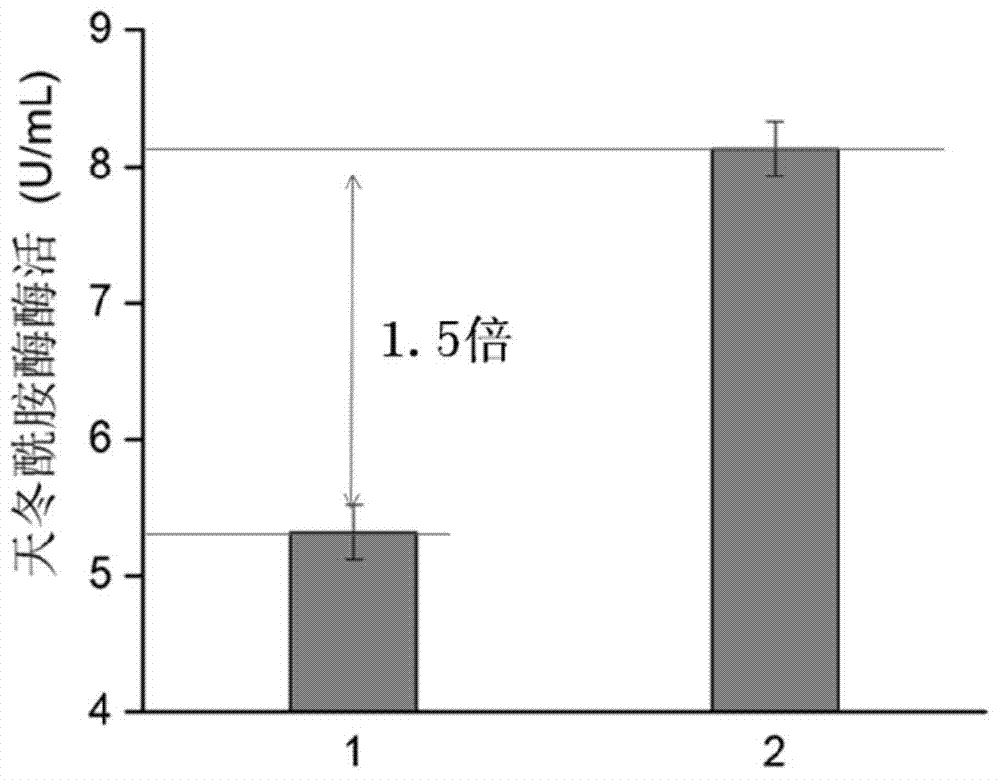
The invention discloses a signal peptide capable of improving secretion efficiency. A nucleotide sequence is shown in 1) or 2): 1) the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1; 2) after transforming the SEQ ID NO.1 sequence, the nucleotide sequence still performs the function of signal peptide and the secretion efficiency of the nucleotide sequence does not have fundamental change. The invention provides a signal peptide capable of improving the secretion efficiency, the secretion capability of strains can be remarkably improved after the signal peptide is used, and the enzyme activity of asparaginase can be improved by 1.5 times. The enzyme production capability of the transformed strains is remarkably improved, and the transformed strains are more suitable for industrial application, the production cost can be lowered, and the production efficiency can be improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of producing secretable antibodies by expression in saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveUS10138477B2Simplification and accelerationPromote generationImmunoglobulinsDNA preparationSurface displaySecretion
The invention relates to a method for the production and non-covalent surface display of antibodies and derived fragments as well as molecule libraries based thereon on the surface of S. cerevisiae cells. The non-covalent manner of the surface display renders possible the selection of specific variants by means of high throughput screening and the subsequent switchable secretion of the selected binding molecule into the culture supernatant for biochemical characterization.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Methods For Enhancing A Secretion Efficiency Of Recombinant Foreign Protein In Yeast Expression System
ActiveUS20100184136A1Improve secretion efficiencyReduce precipitationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPromoter activity
Provided is a method for improving secretion efficiency of a recombinant foreign protein in a yeast expression system. The method comprises transforming a yeast host with a recombinant foreign gene construct comprising a galactose-inducible promoter, a secretion signal sequence and a gene encoding the foreign protein to construct a transformed yeast strain; and culturing the transformed yeast strain under the condition that the activity of the galactose-inducible promoter is controlled. Improved secretion efficiency of the foreign protein can be achieved by decreasing over-expression-induced insoluble precipitation of the recombinant foreign protein suffered by a conventional galactose-inducible promoter-based yeast expression system, via appropriate control of a level of galactose functioning as an inducer of the galactose-inducible promoter in cells. Due to improved secretion efficiency of the recombinant foreign protein, present invention makes a contribution to improvement in productivity of recombinant foreign proteins in the yeast expression system and reduction in production costs.
Owner:MOGAM BIOTECH RES INST
Modified i(E.coli) enterotoxin II signal peptide and microorganism expressing fusion protein of said peptide and heterologous protein
InactiveCN1318070AImprove secretion efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaHeterologousProtein
A heterologous protein is produced by: (i) culturing a microorganism transformed with an expression vector comprising a gene encoding a modified E. coli enterotoxin II signal peptide fused with the heterologous protein to produce and secrete the heterologous protein to periplasm, the modified E. coli enterotoxin II signal peptide being obtained by replacing at least one of the 2nd, 4th, 5th, 12th, 20th, and 22nd amino acids of E. coli enterotoxin II signal peptide of the following amino acid sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1) with another amino acid, with the proviso that at least one of the 2nd and 4th amino acid of the modified peptide is lysine; and (ii) recovering the heterologous protein from the periplasm.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
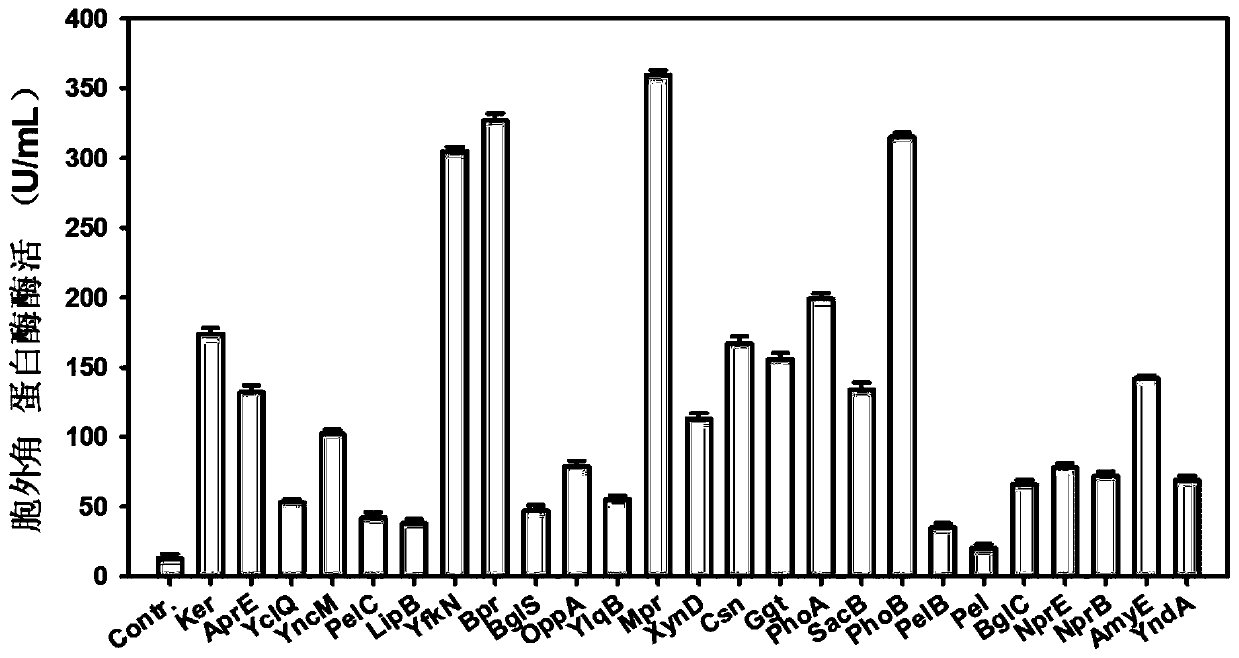
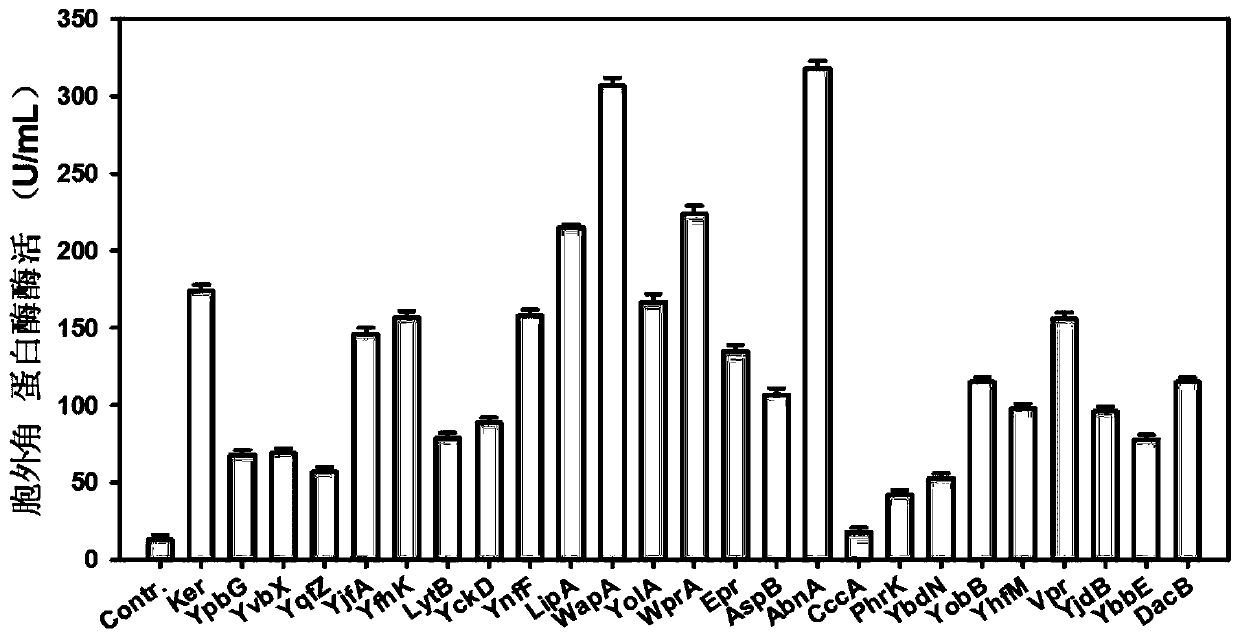
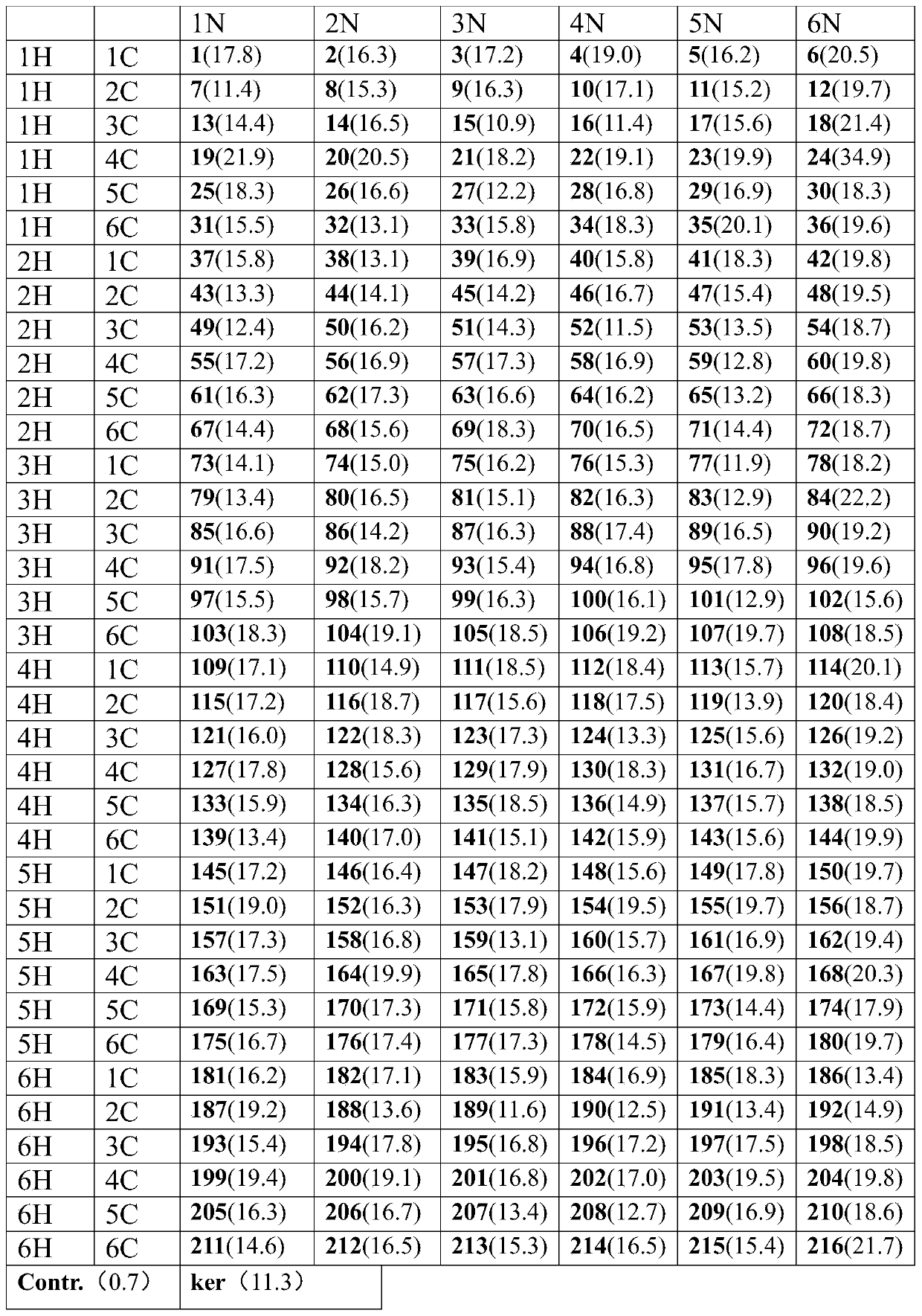
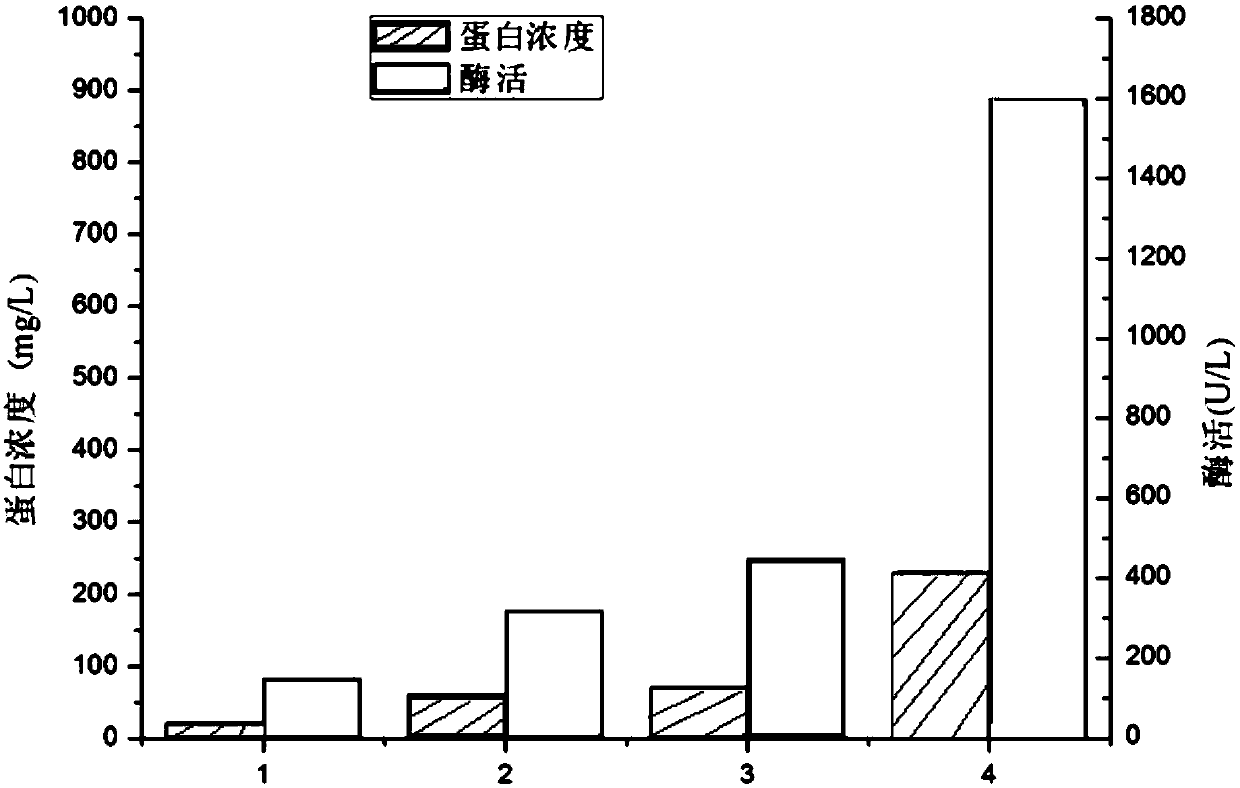
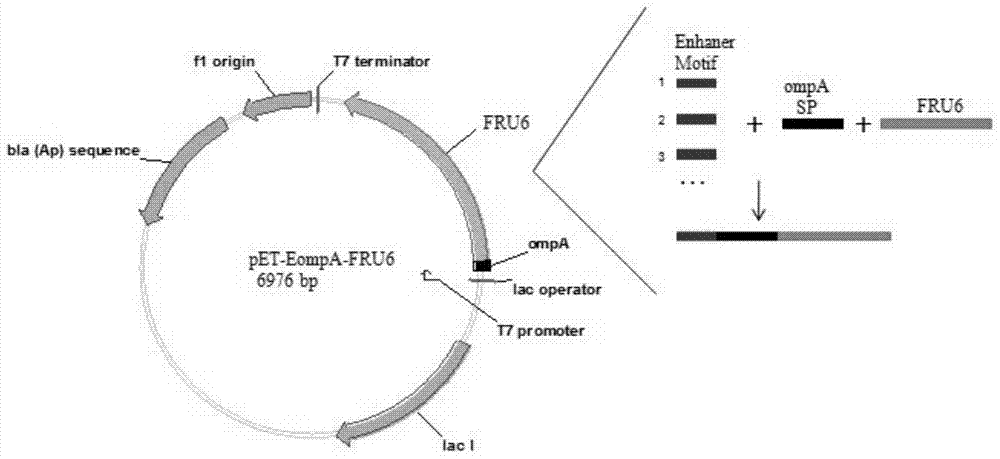
A signal peptide for optimizing the high-efficiency secretion and expression of keratinase keratinase and its application
ActiveCN107200772BIncrease secretionImprove secretion efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesSecretion expressionSecretion
The invention discloses a signal peptide for optimizing high-level secretory expression of keratinase Ker and application of the signal peptide and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The signal peptide is characterized in that 46 secretory signal peptides from bacillus subtilis are preliminarily screened and 6 secretory signal peptides capable of obviously improving the secretion volume of the keratinase in the 46 secretory signal peptides are directionally transformed, so the signal peptide for optimizing the high-level secretory expression of keratinase is obtained. An N terminal of the signal peptide is provided with first nine amino acid residues of a signal peptide AbnA; an H terminal of the signal peptide is provided with a hydrophobic sequence of a signal peptide YfkN, and a C terminal of the signal peptide is provided with last four amino acid residues of a signal peptide PhoB. The signal peptide disclosed by the invention is fused at the N terminal of the keratinase Ker, so the secretion efficiency of the keratinase of recombinant bacillus subtilis is remarkably improved, and the enzyme activity of extracellular keratinase of the bacillus subtilis is improved by 3.39 times. The extracellular keratinase producing capability of a transformed strain is remarkably improved, the industrial application is better facilitated, the production cost can be reduced, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI +1
A signal peptide that can effectively improve the efficiency of protein secretion and expression and its application
ActiveCN105601720BSmooth transmembrane transportImprove secretion efficiencyBacteriaHydrolasesPhospholipaseProtein target
The invention discloses a signal peptide for mediating protein secretion expression and belongs to the field of protein engineering and gene engineering. By modifying known signal peptides PelB and OmpA, the N terminal of the signal peptide contains the first three amino acid residues MKK of the signal peptide OmpA, the C terminal of the signal peptide contains the last three amino acid residues AQA of the signal peptide OmpA, and a middle hydrophobic structure is the hydrophobic sequence LLPTAAAGLLLLAAQP of the signal peptide PelB. After the signal peptide capable of effectively improving protein secretion efficiency is used, the secretion expression capability of a strain on target protein is obviously improved; the extracellular enzyme activity of phospholipase D of target protein can be improved by 2 times, the extracellular enzyme production capability of the modified strain is significantly improved, and industrialized application is better facilitated.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Strong Secretory Signal Peptide Enhancing Small Peptide Motif and Its Application
ActiveCN104211776BEnhance secretory functionSignificant secretory functionBacteriaPeptidesNeutral Amino AcidsADAMTS Proteins
The invention belongs to the field of protein engineering and genetic engineering, and relates to a class of strongly secreted signal peptide enhancing small peptide modules and applications thereof. The strong secretory signal peptide enhancing small peptide motif of the present invention has an amino acid sequence of the following general formula: M(αXβYγ / αYβXγ)n, wherein X represents an acidic amino acid; Y represents a basic amino acid; α is 0-2 β represents 0-2 neutral amino acids; γ represents 1-10 neutral amino acids; n is 1-3. The application of the strong secretory signal peptide enhancing small peptide motif of the present invention is to use the strong secretory signal peptide enhancing small peptide motif of the present invention to construct a carrier that enhances the secretory ability of ordinary signal peptides, so as to improve It secretes a method of expressing a foreign protein.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com