Patents
Literature
286 results about "Cell response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellular response. The binding of chemical signals to their corresponding receptors induces events within the cell that ultimately change its behaviour. The nature of these intracellular events differs according to the type of receptor. Also, the same chemical signal can trigger different responses in different types of cell.
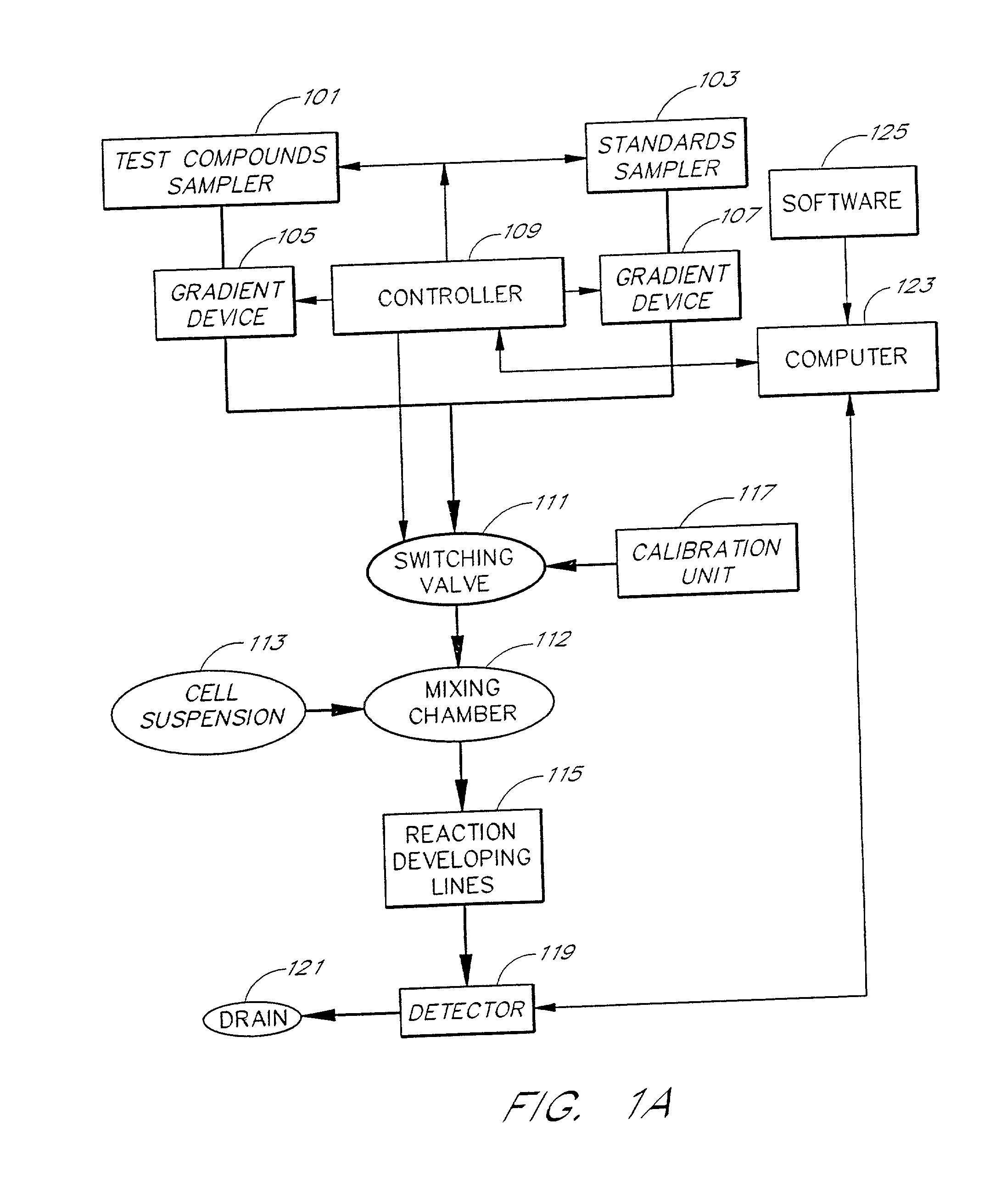
Cell flow apparatus and method for real-time of cellular responses
InactiveUS6280967B1Quick filterIncrease the number ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningMeasurement testCell type
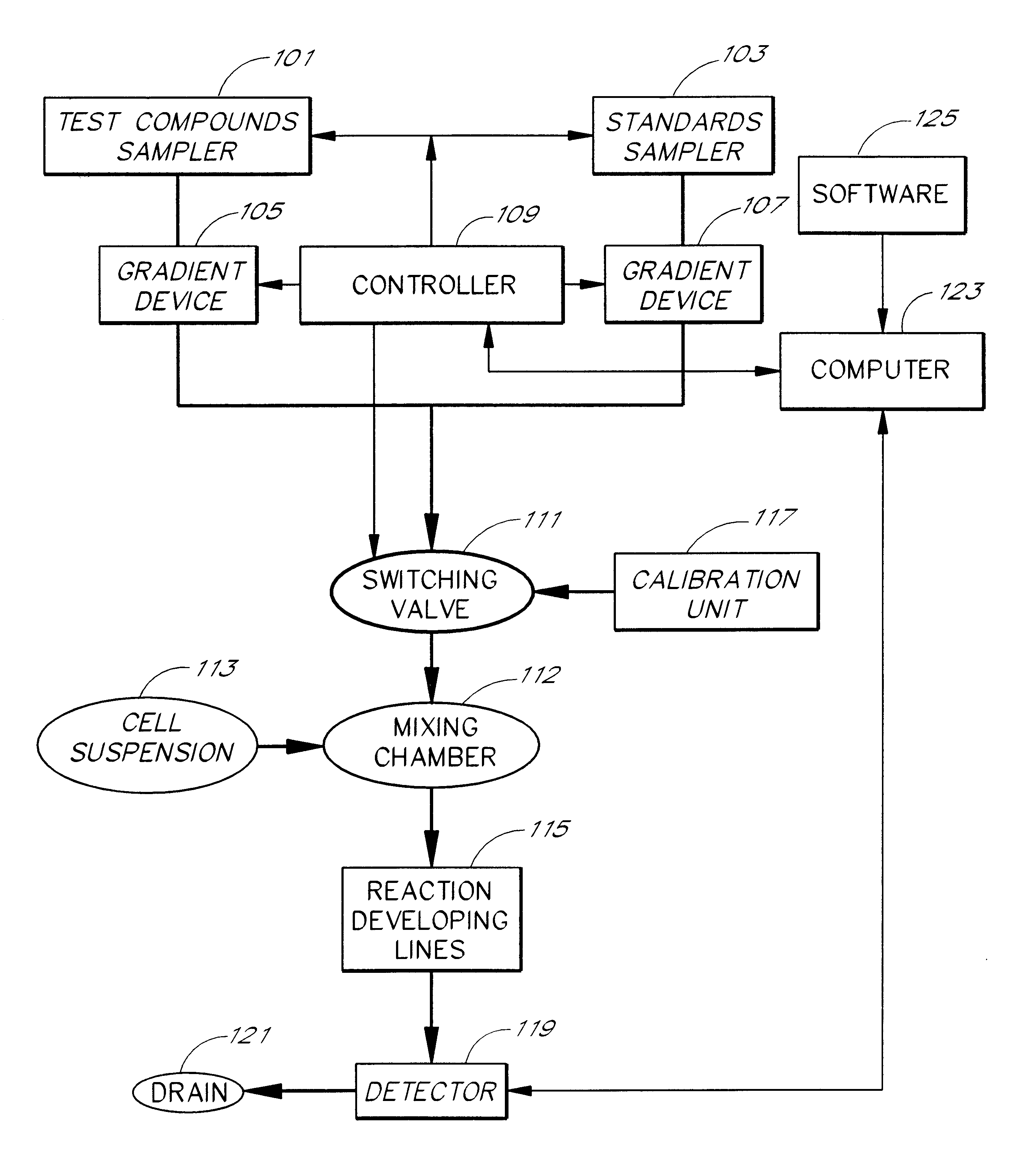
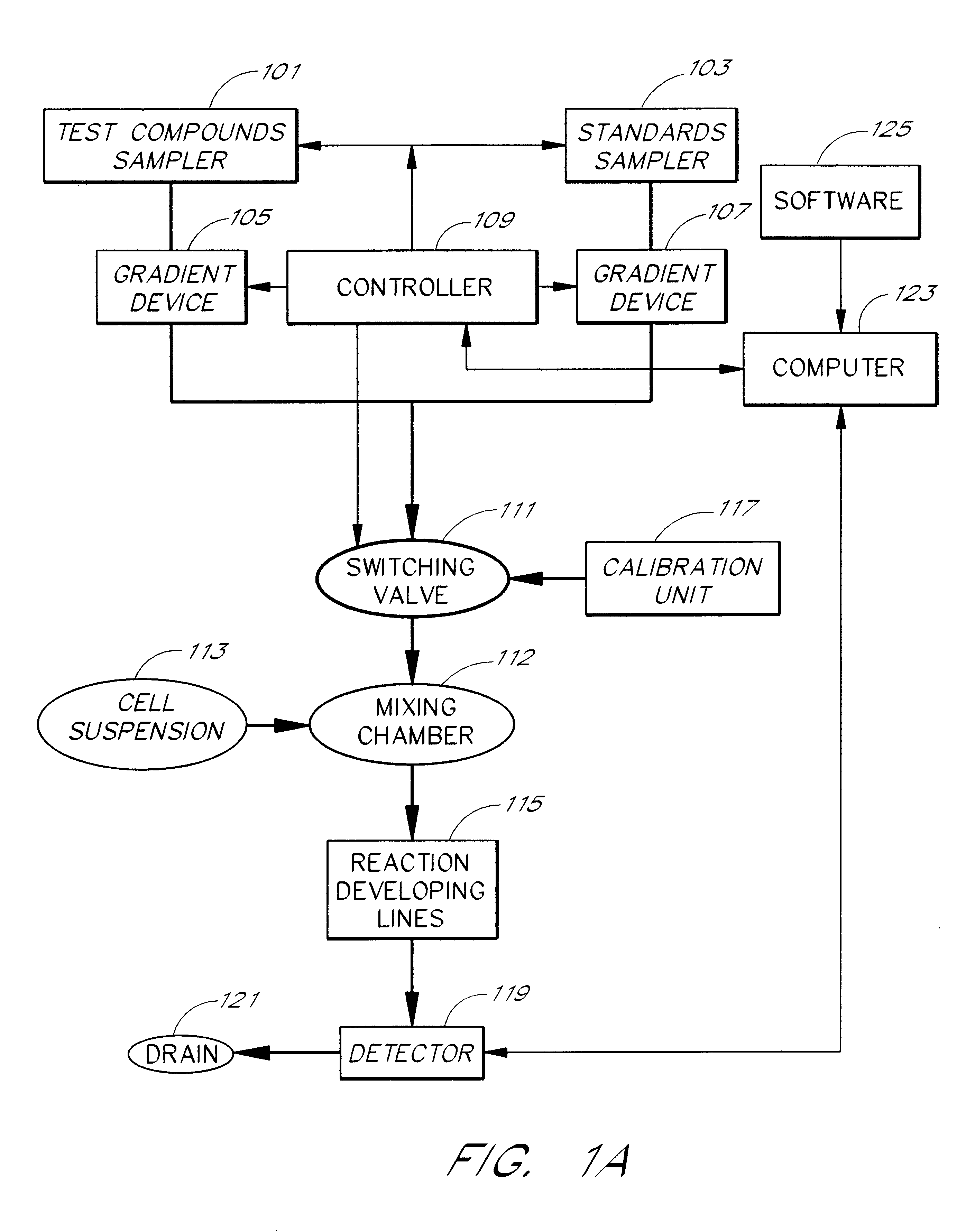
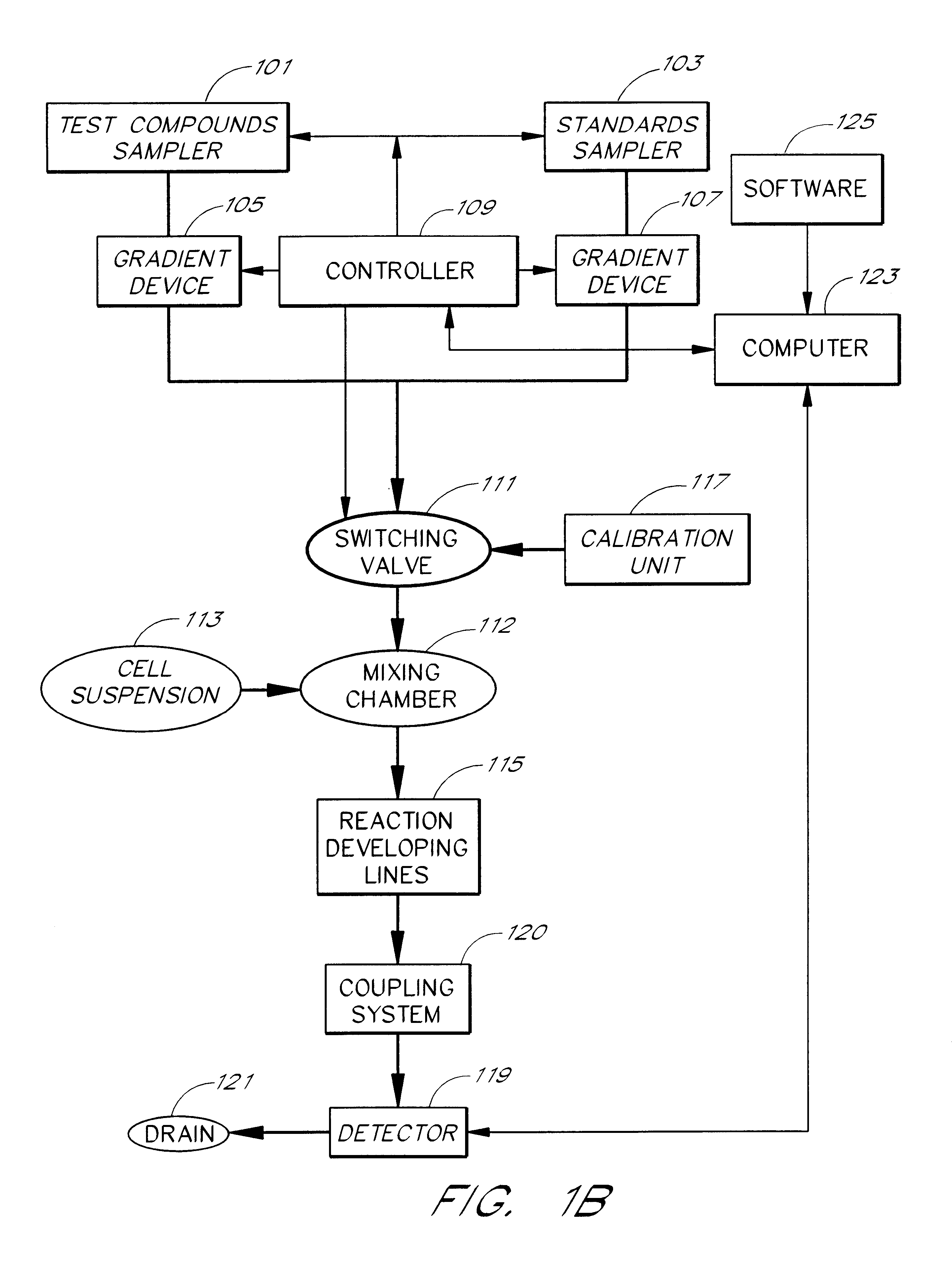
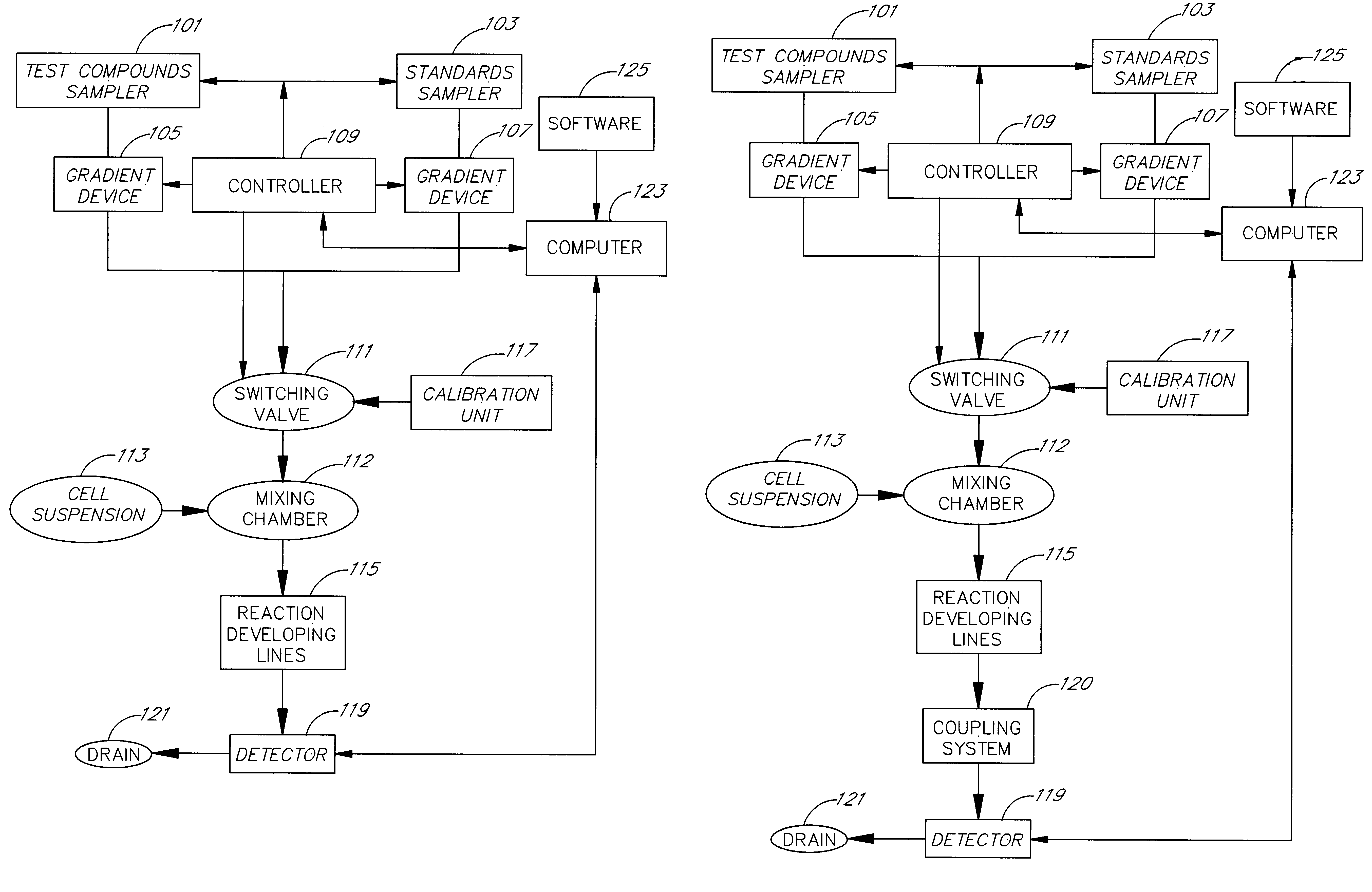
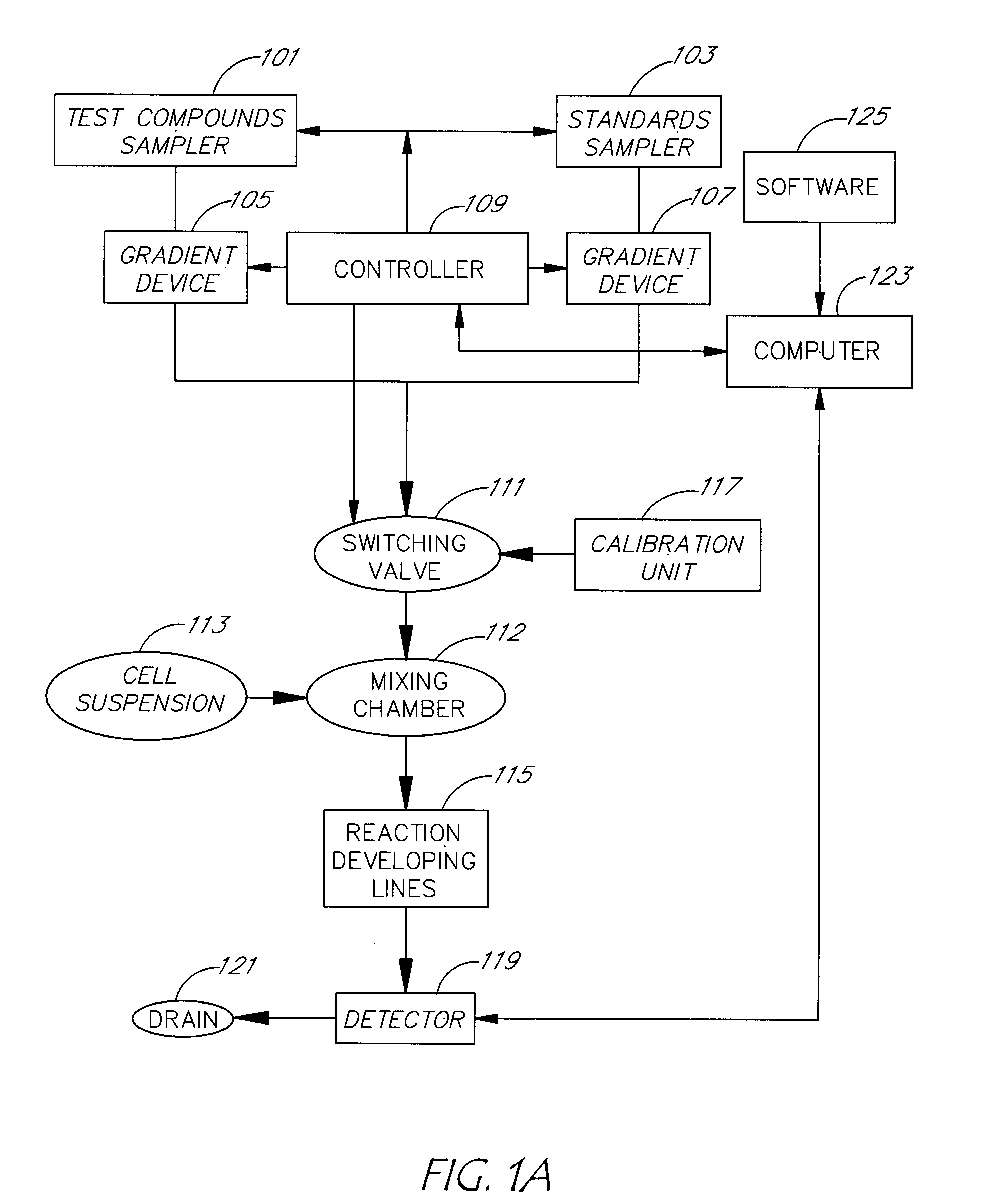
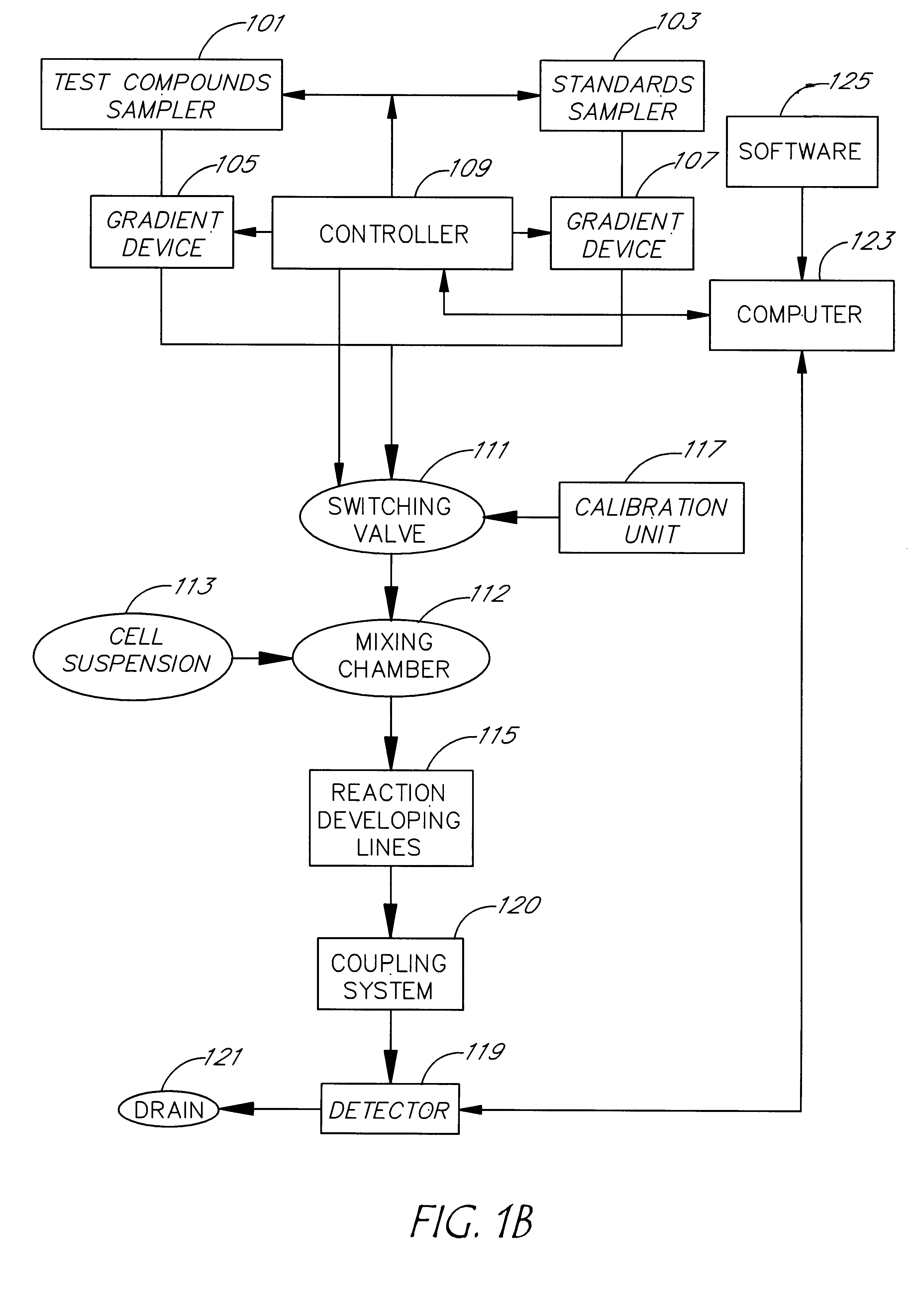
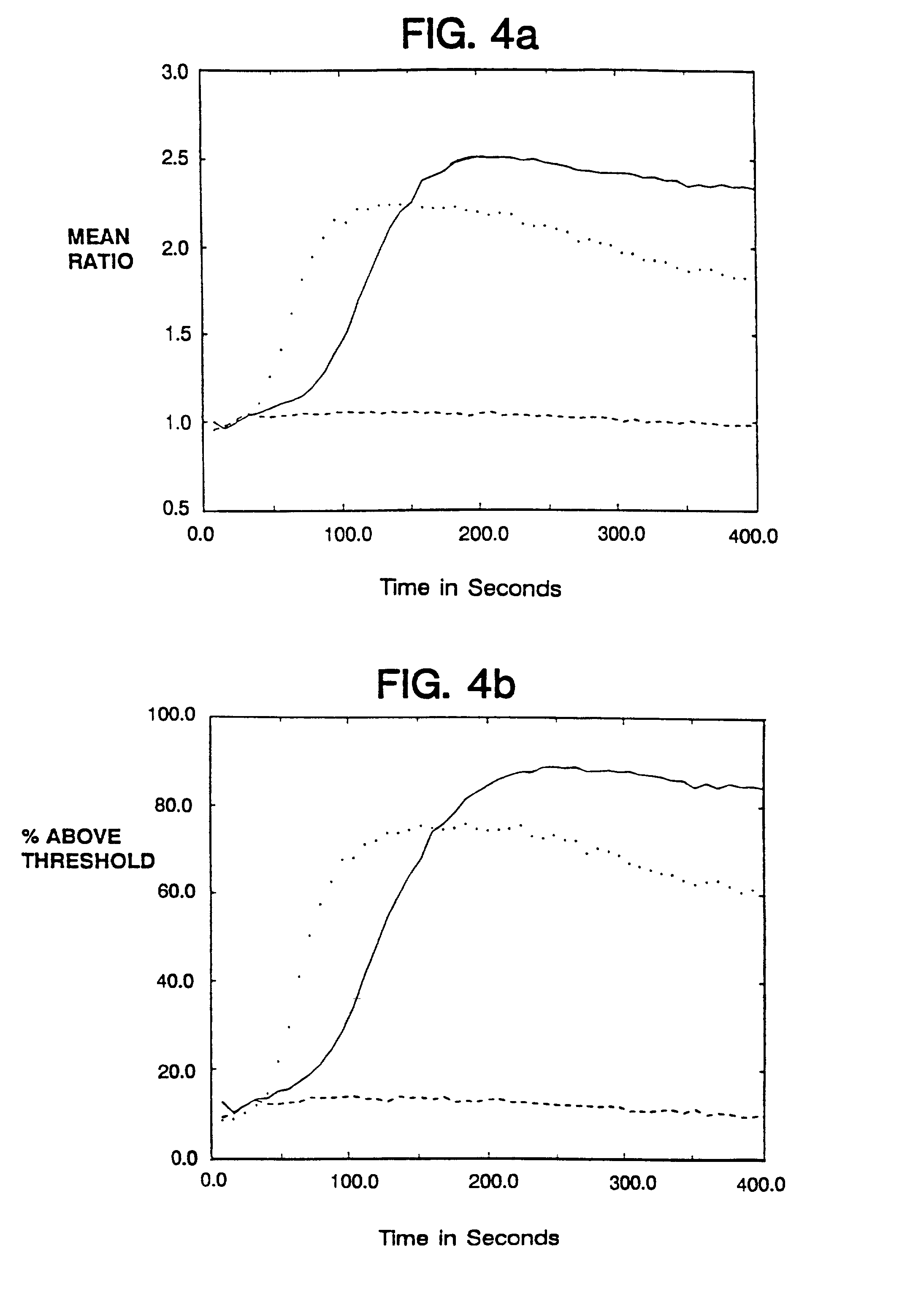
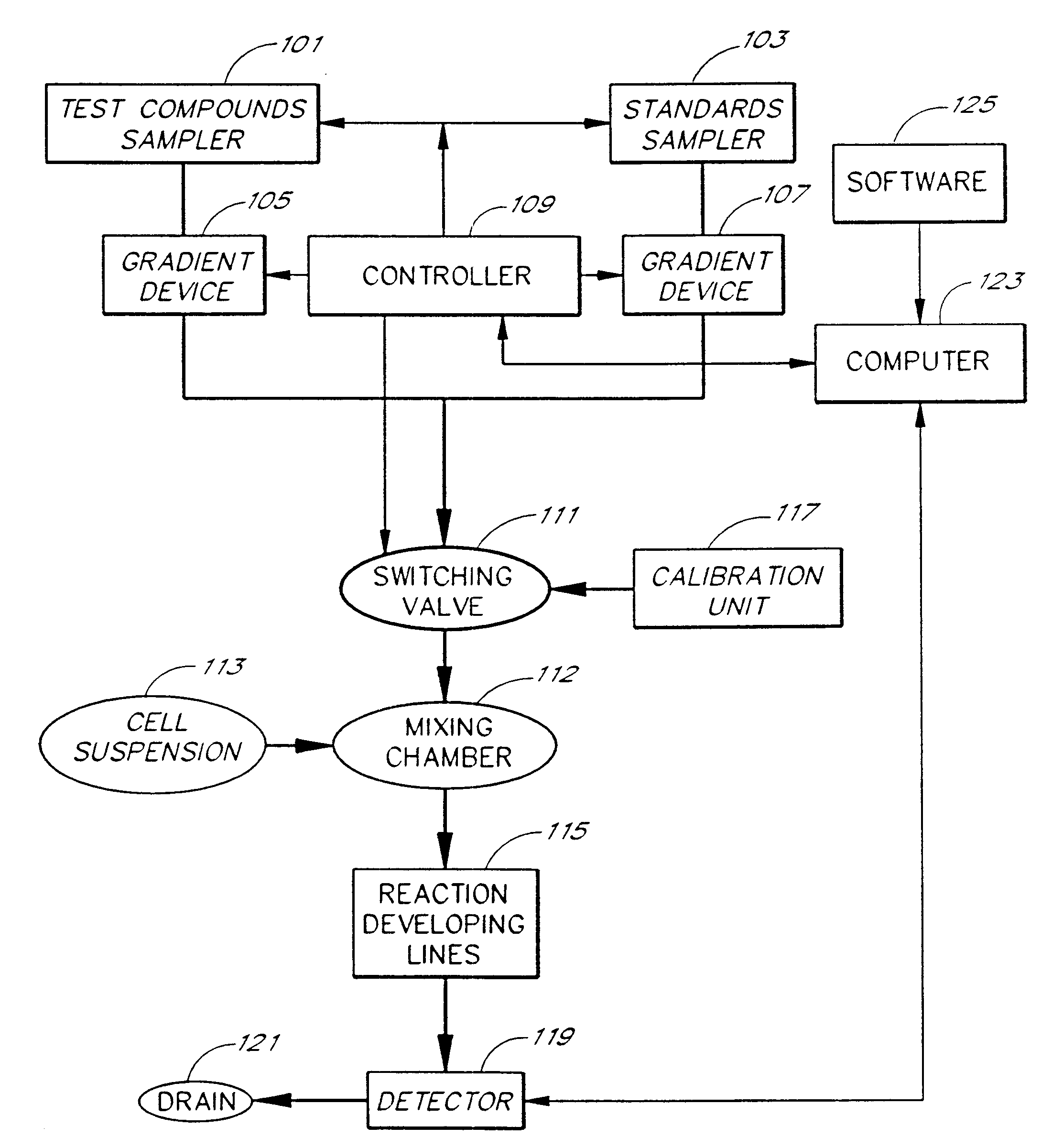
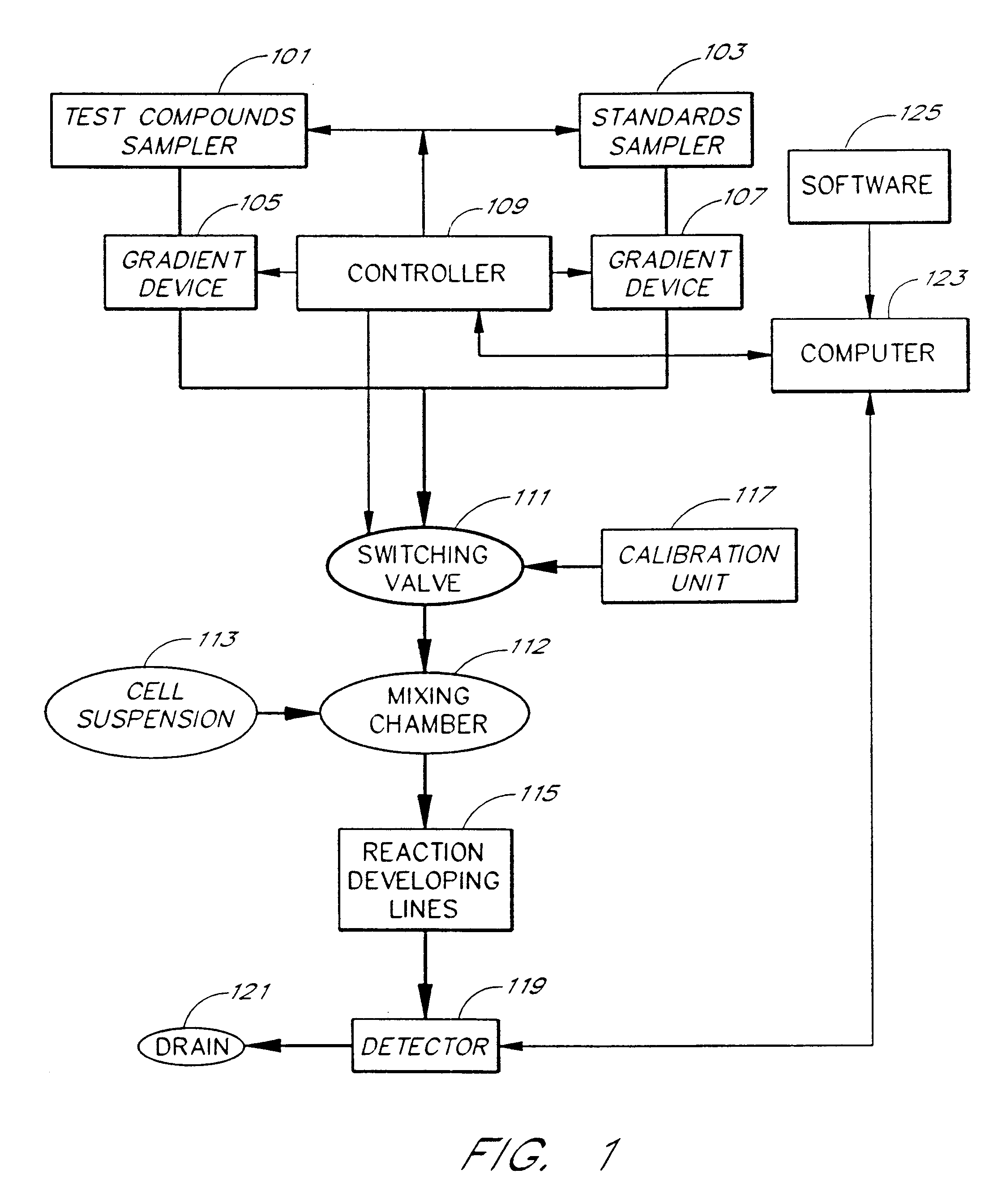
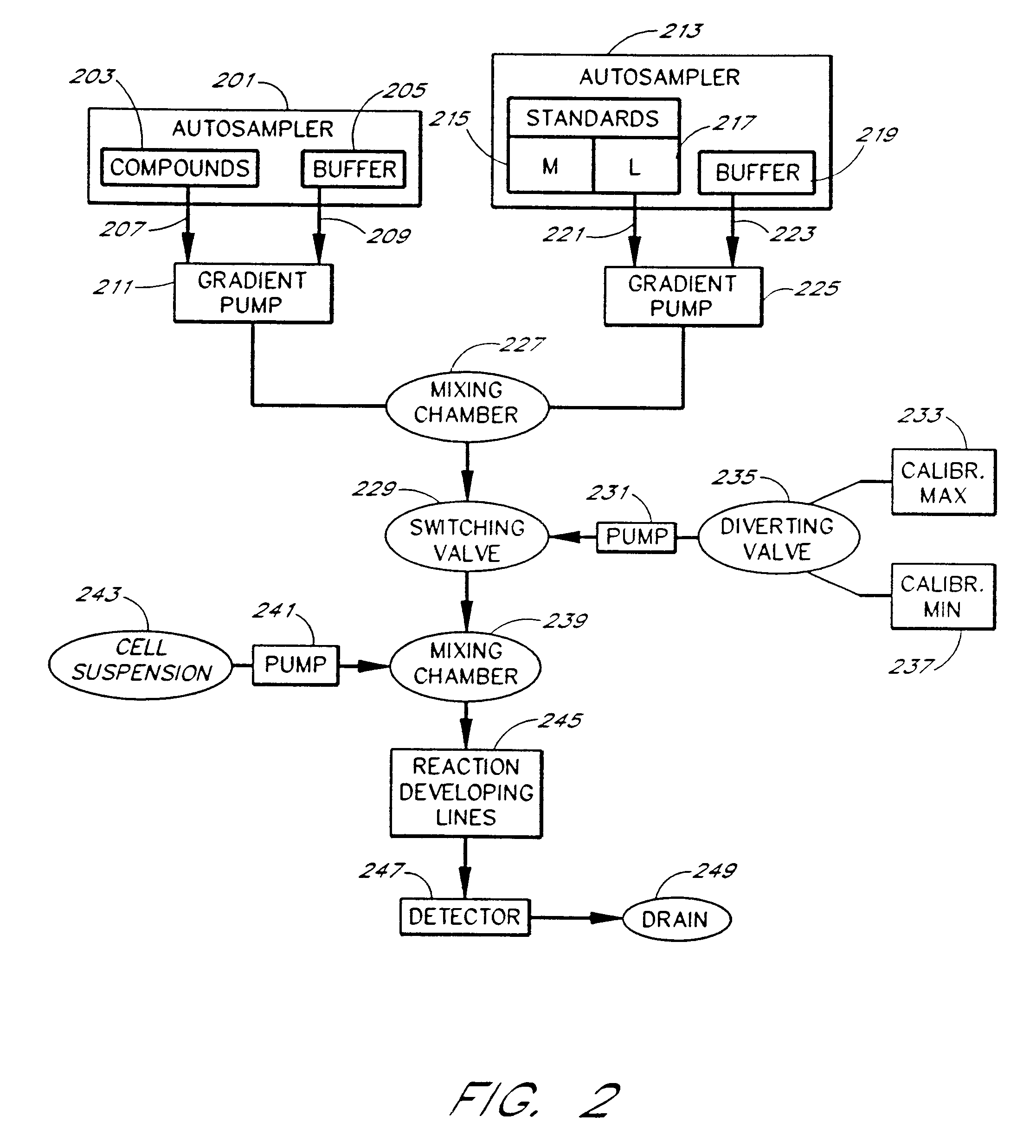
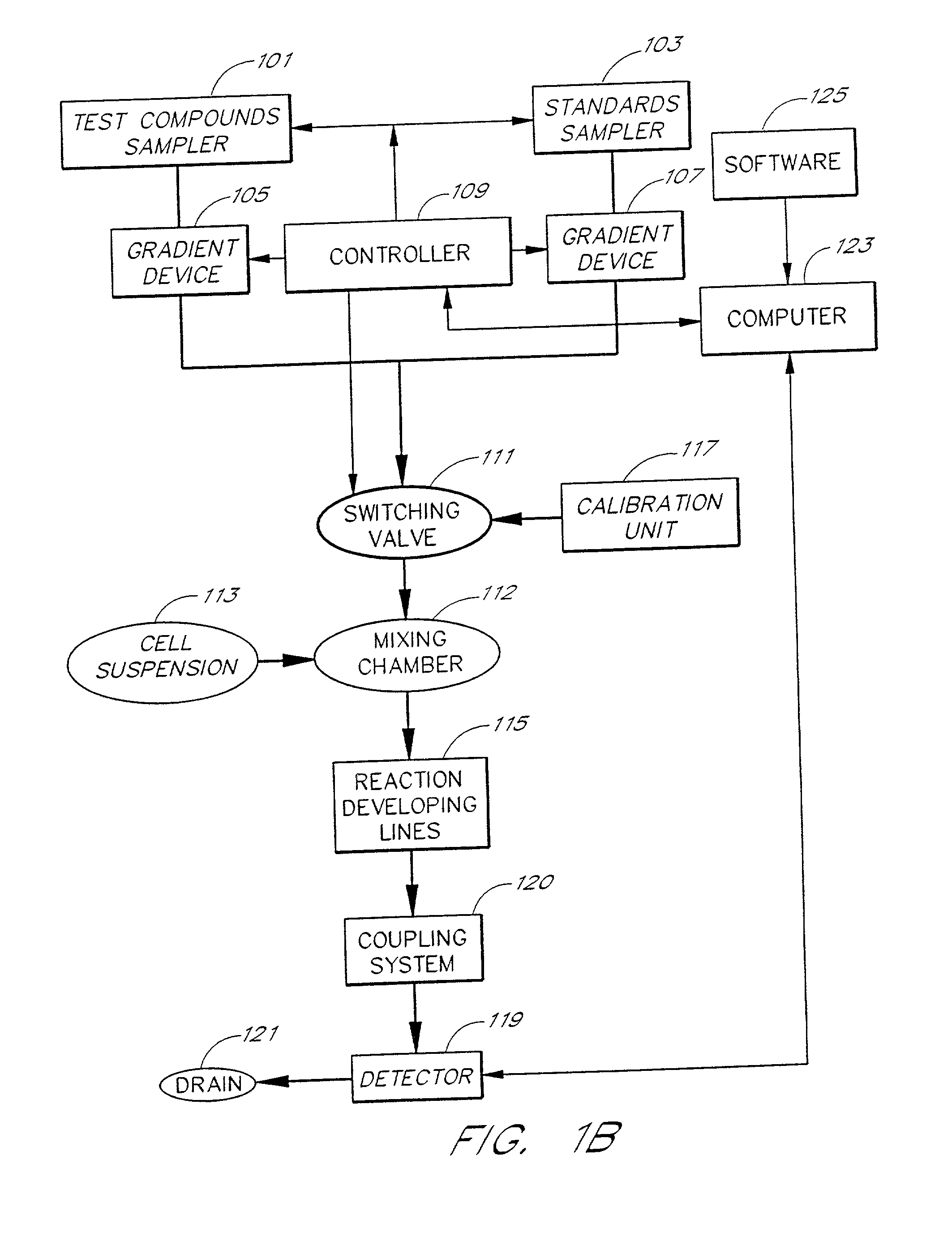
An apparatus and method for real-time measurement of a cellular response of a test compound or series of test compounds (303) on a flowing suspension of cells (349), in which a homogeneous suspension of each member of a series of cell types (349) is combined with a concentration of a test compound (303), directed through a detection zone (355), and a cellular response of the living cells is measured in real time as the cells in the test mixture are flowing through the detection zone (355). The apparatus may be used in automated screening of libraries of compounds, and is capable of real-time variation of concentrations of test and standard compounds and generation of dose / response profiles within a short time span.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Cell flow apparatus and method for real-time measurements of patient cellular responses
InactiveUS6558916B2Quick filterIncrease the number ofCompound screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTest agentBiology
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
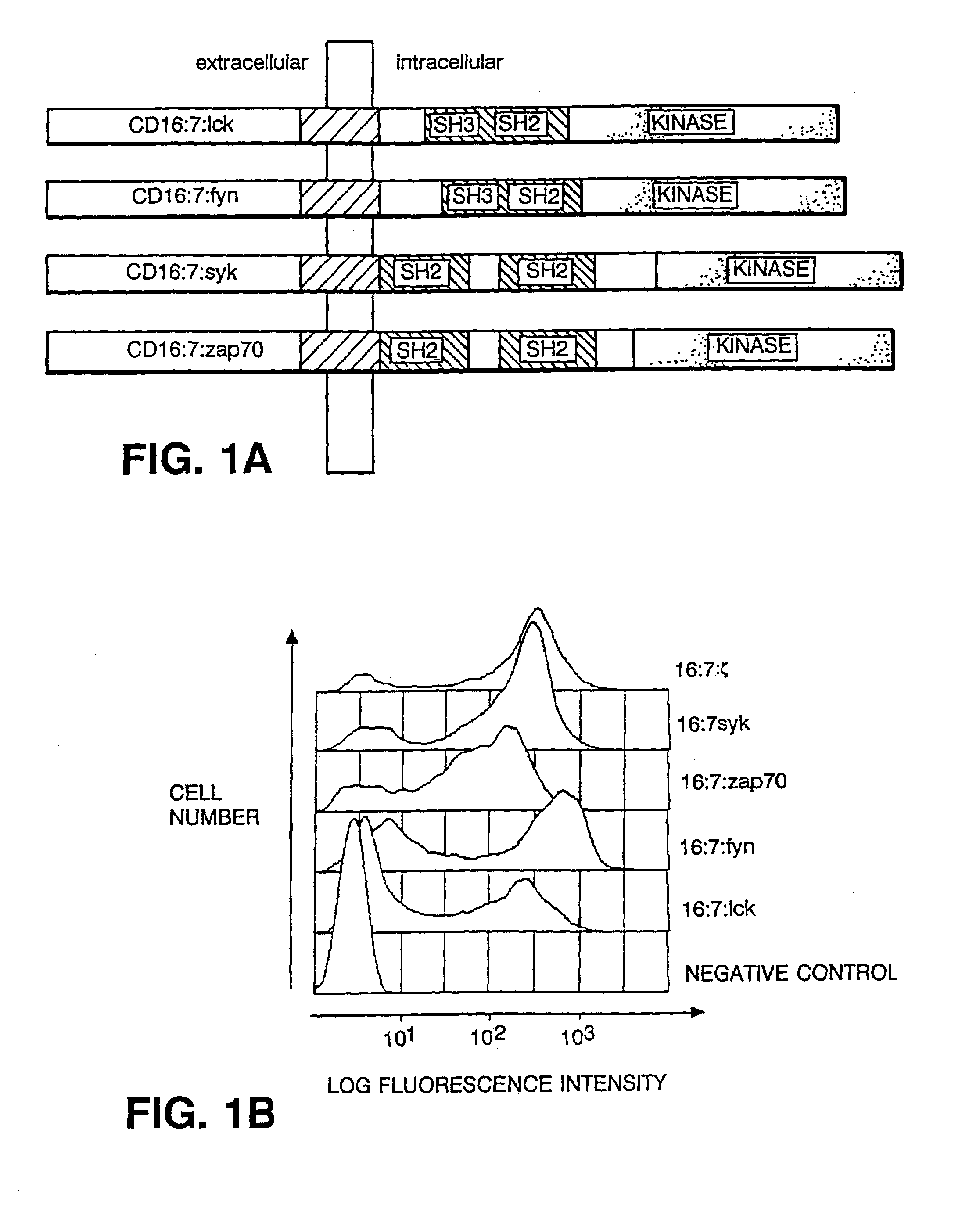
Redirection of cellular immunity by receptor chimeras
InactiveUS7049136B2Enhances immune system responseImprove responseVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
Disclosed is a method of directing a cellular response in a mammal by expressing in a cell of the mammal a chimeric receptor which causes the cells to specifically recognize and destroy an infective agent, a cell infected with an infective agent, a tumor or cancerous cell, or an autoimmune-generated cell. Also disclosed are cells which express the chimeric receptors and DNA encoding the chimeric receptors.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for real-time measurement of cellular response
InactiveUS6379917B1Quick filterBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMeasurement testCell type
An apparatus and method for real-time measurement of a cellular response of a test compound or series of test compounds (303) on a flowing suspension of cells (349), in which a homogenous suspension of each member of a series of cell types (349) is combined with a concentration of a test compound (303), directed through a detection zone (355), and a cellular response of the living cells is measured in real time as the cells in the test mixture are flowing through the detection zone (355). The apparatus may be used in automated screening of libraries of compounds, and is capable of real-time variation of concentrations of test and standard compounds and generation of dose / response profiles within a short timespan.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
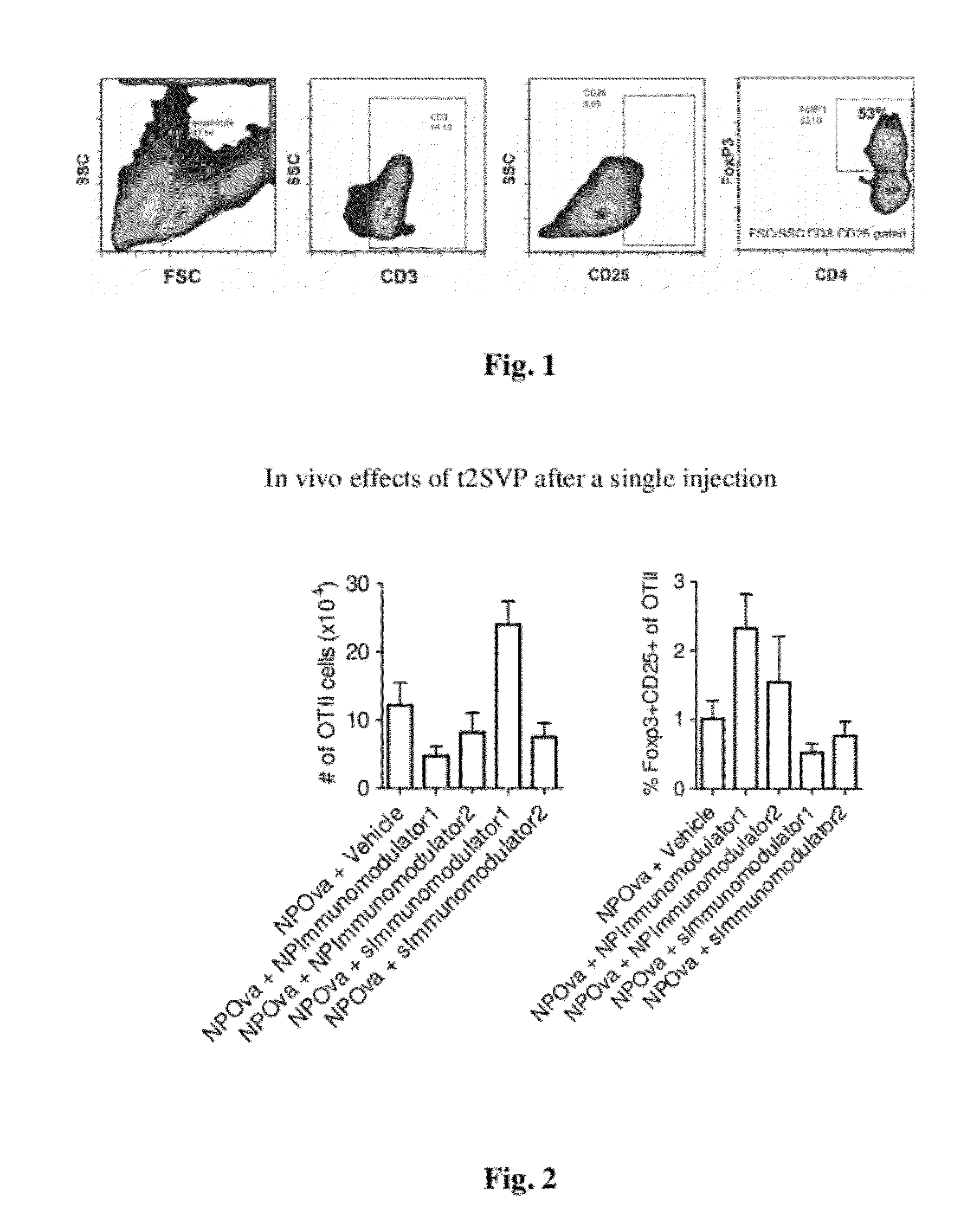
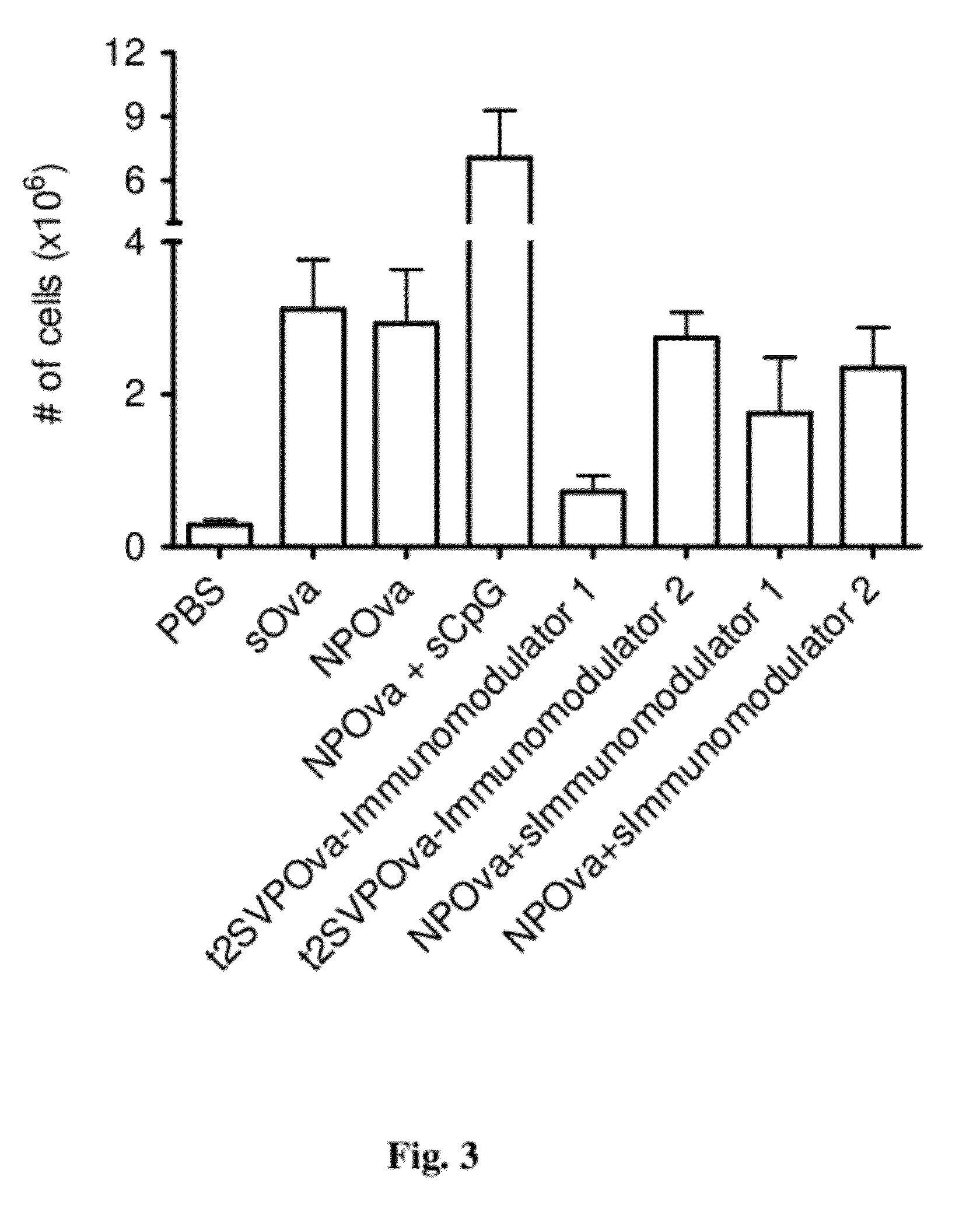
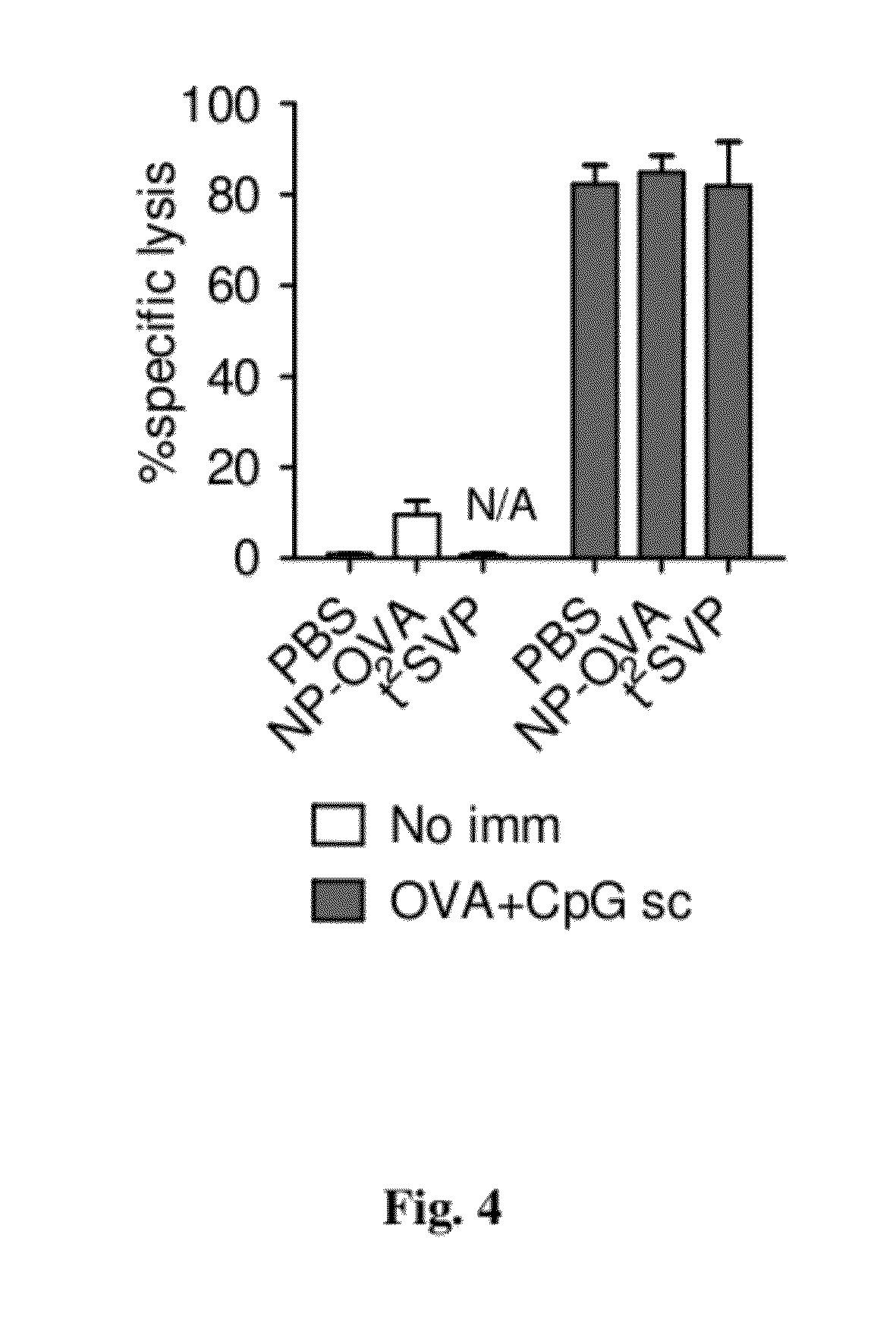
Tolerogenic synthetic nanocarriers to reduce cytotoxic t lymphocyte responses
Disclosed are synthetic nanocarrier compositions, and related methods, comprising MHC Class I-restricted and / or MHC Class II-restricted epitopes associated with undesired CD8+ T cell responses and immunosuppressants that provide tolerogenic immune responses against antigens that comprise the epitopes.
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
Redirection of cellular immunity by protein tyrosine kinase chimeras
InactiveUS7320787B2Facilitates specific recognitionFacilitates destructionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDna encodingProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
Disclosed is a method of directing a cellular response in a mammal by expressing in a cell of the mammal a chimeric receptor which causes the cells to specifically recognize and destroy an infective agent, a cell infected with an infective agent, a tumor or cancerous cell, or an autoimmune-generated cell. The chimeric receptor includes an extracellular portion which is capable of specifically recognizing and binding the target cell or target infective agent, and (b) an intracellular portion of a protein-tyrosine kinase which is capable of signalling the therapeutic cell to destroy a receptor-bound target cell or a receptor-bound target infective agent. Also disclosed are cells which express the chimeric receptors and DNA encoding the chimeric receptors.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
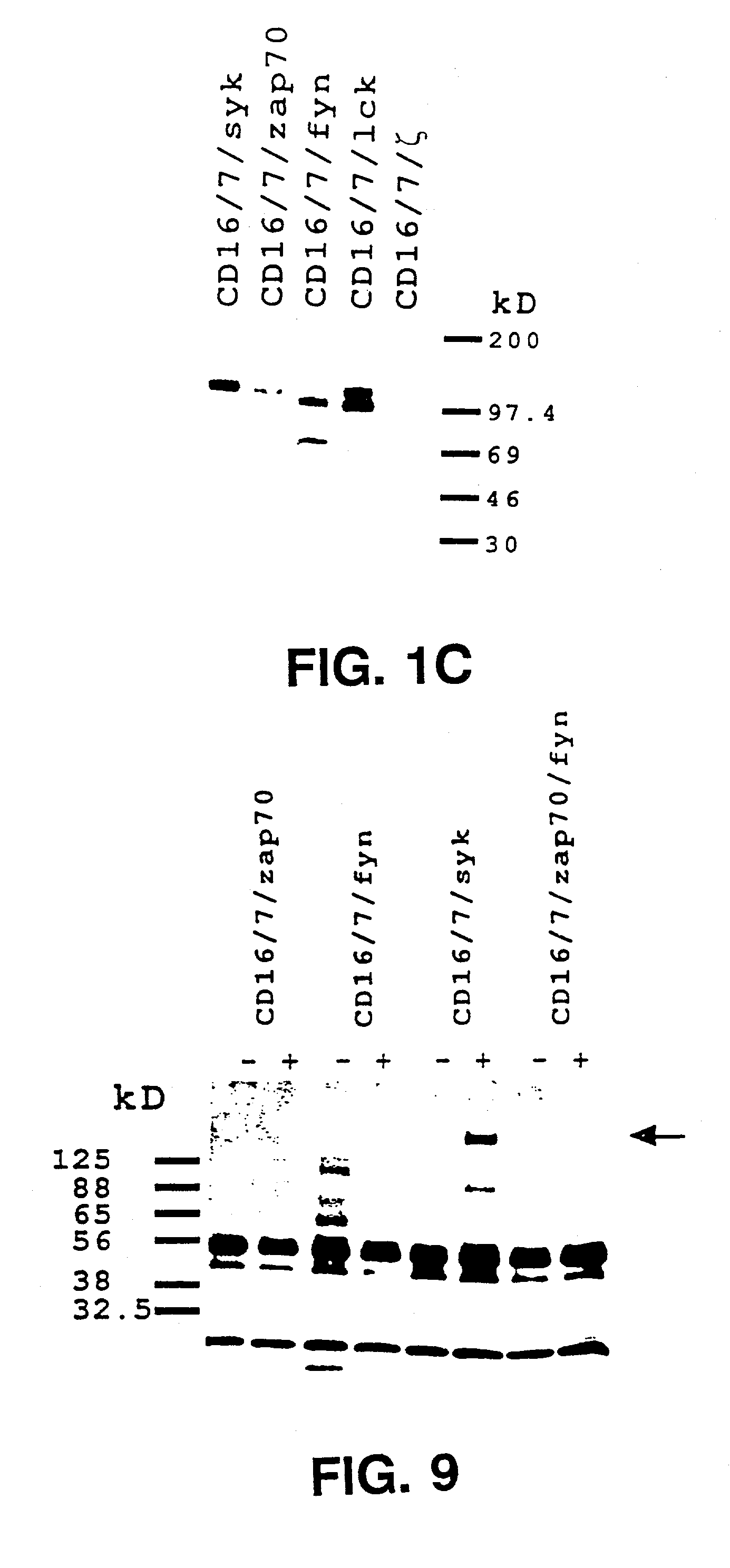
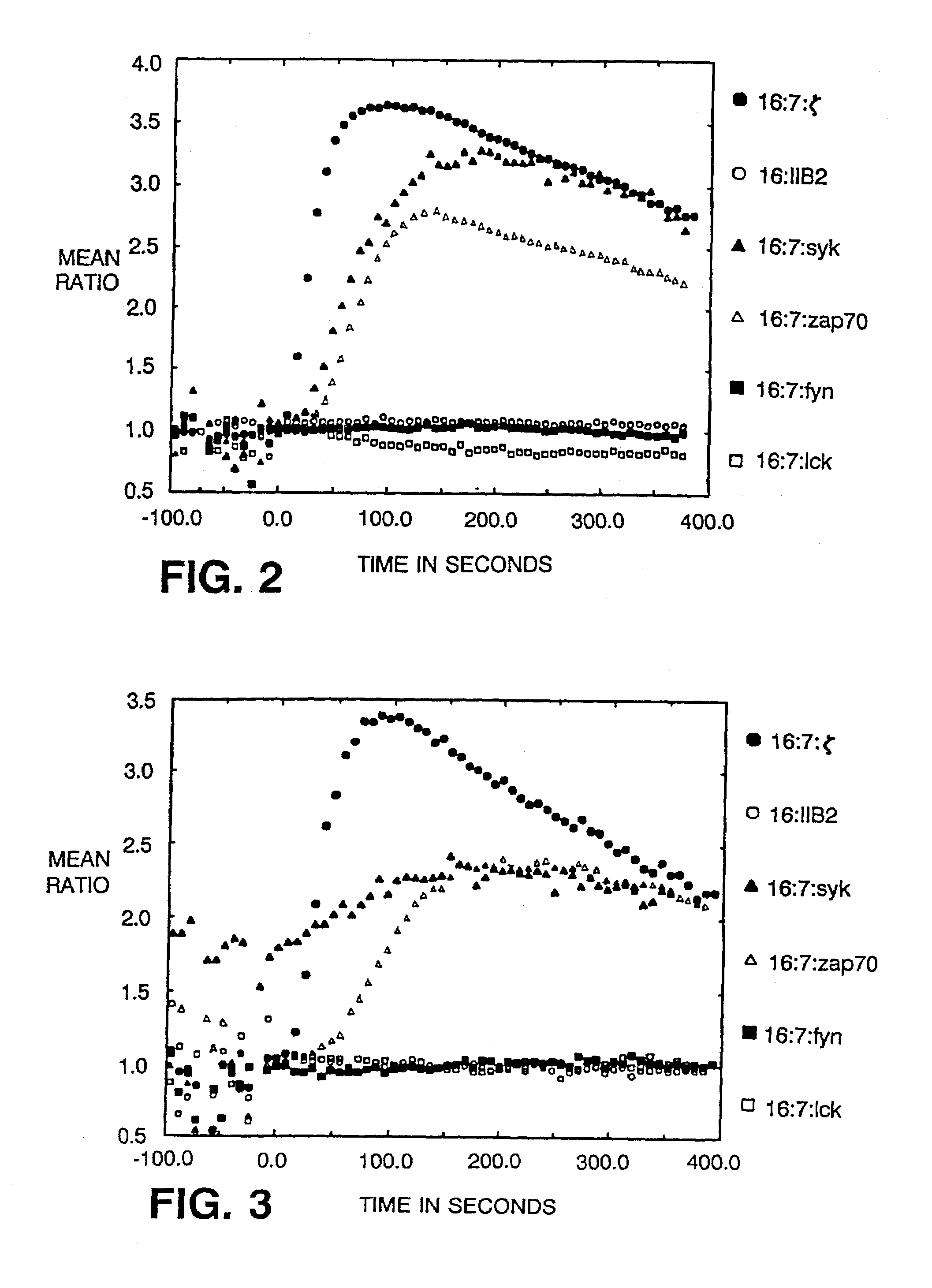
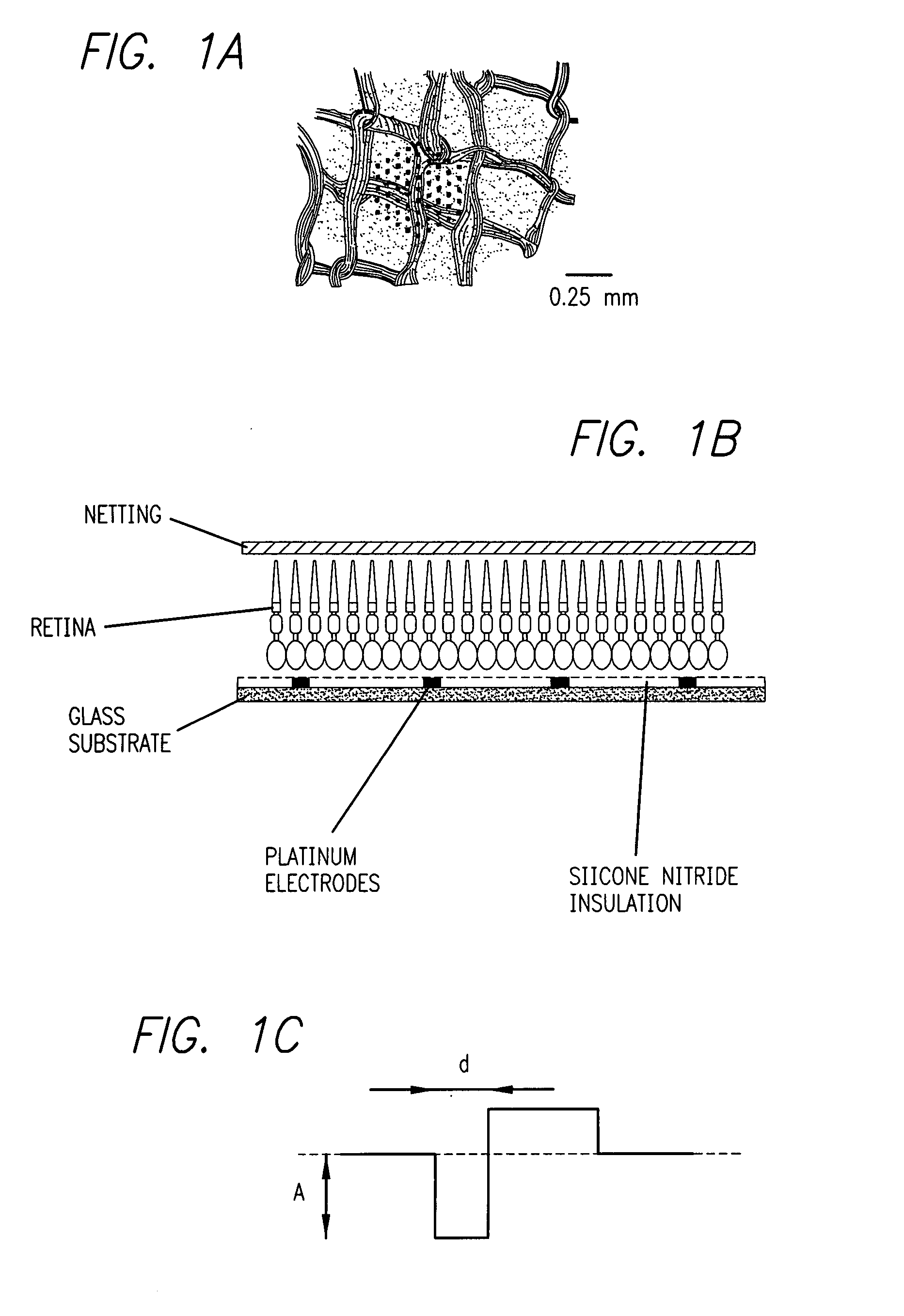
Method and apparatus for visual neural stimulation
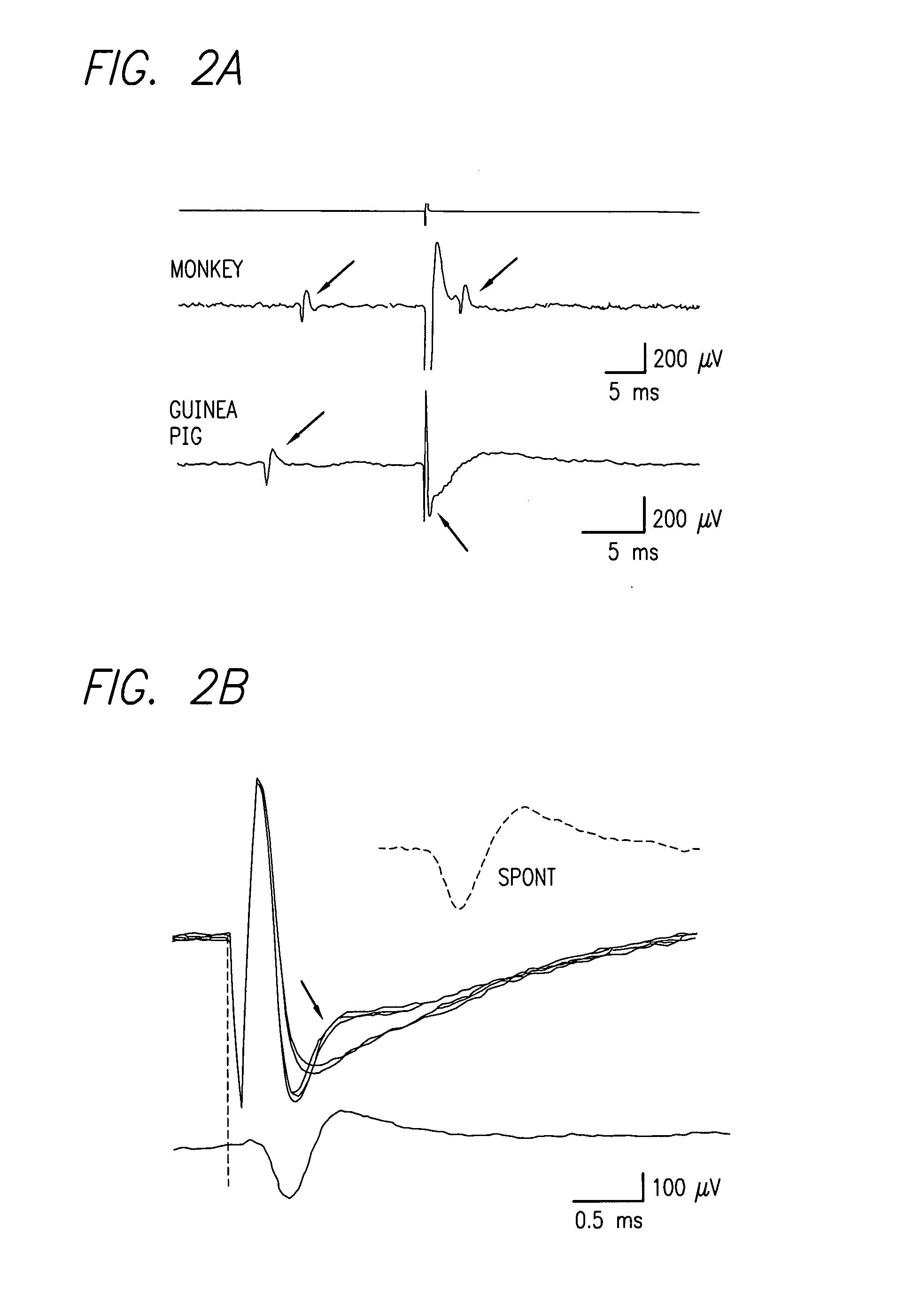
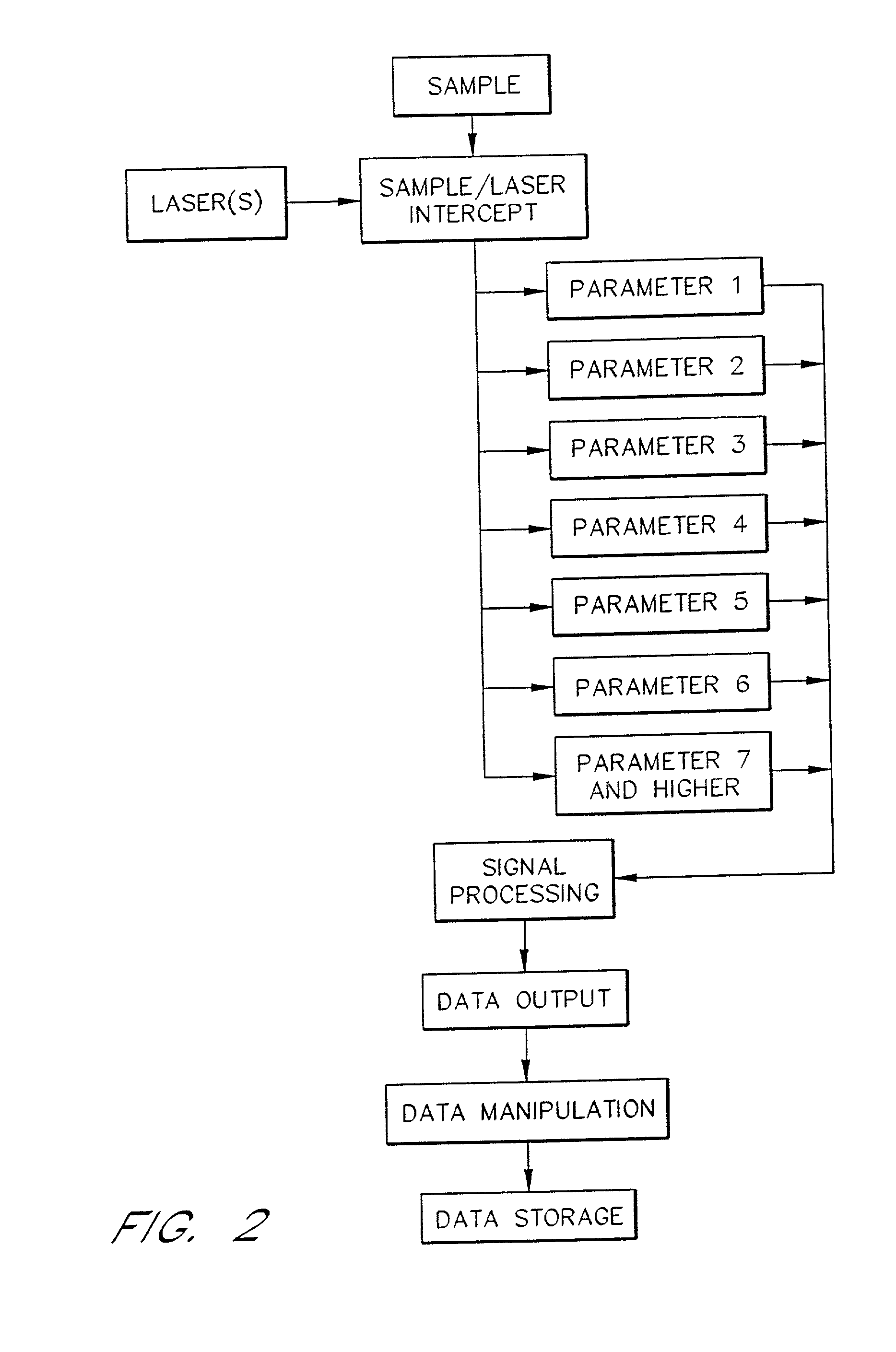
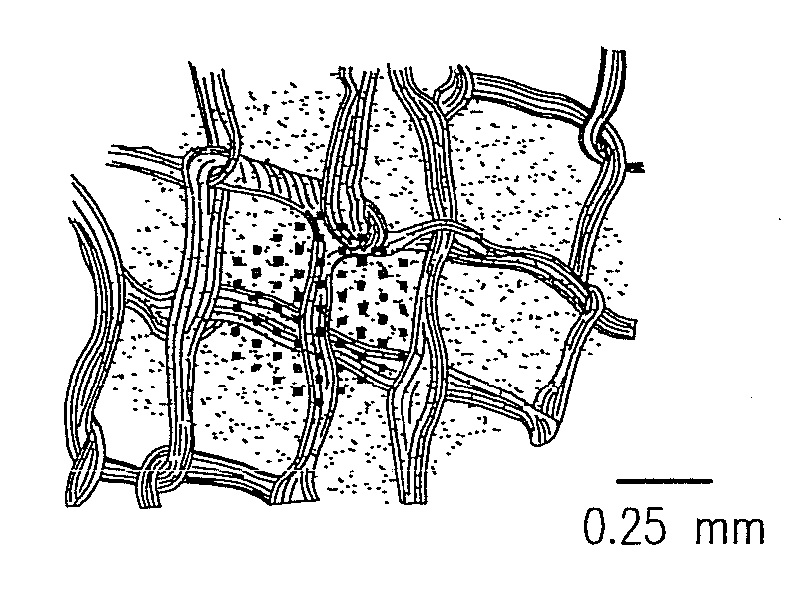
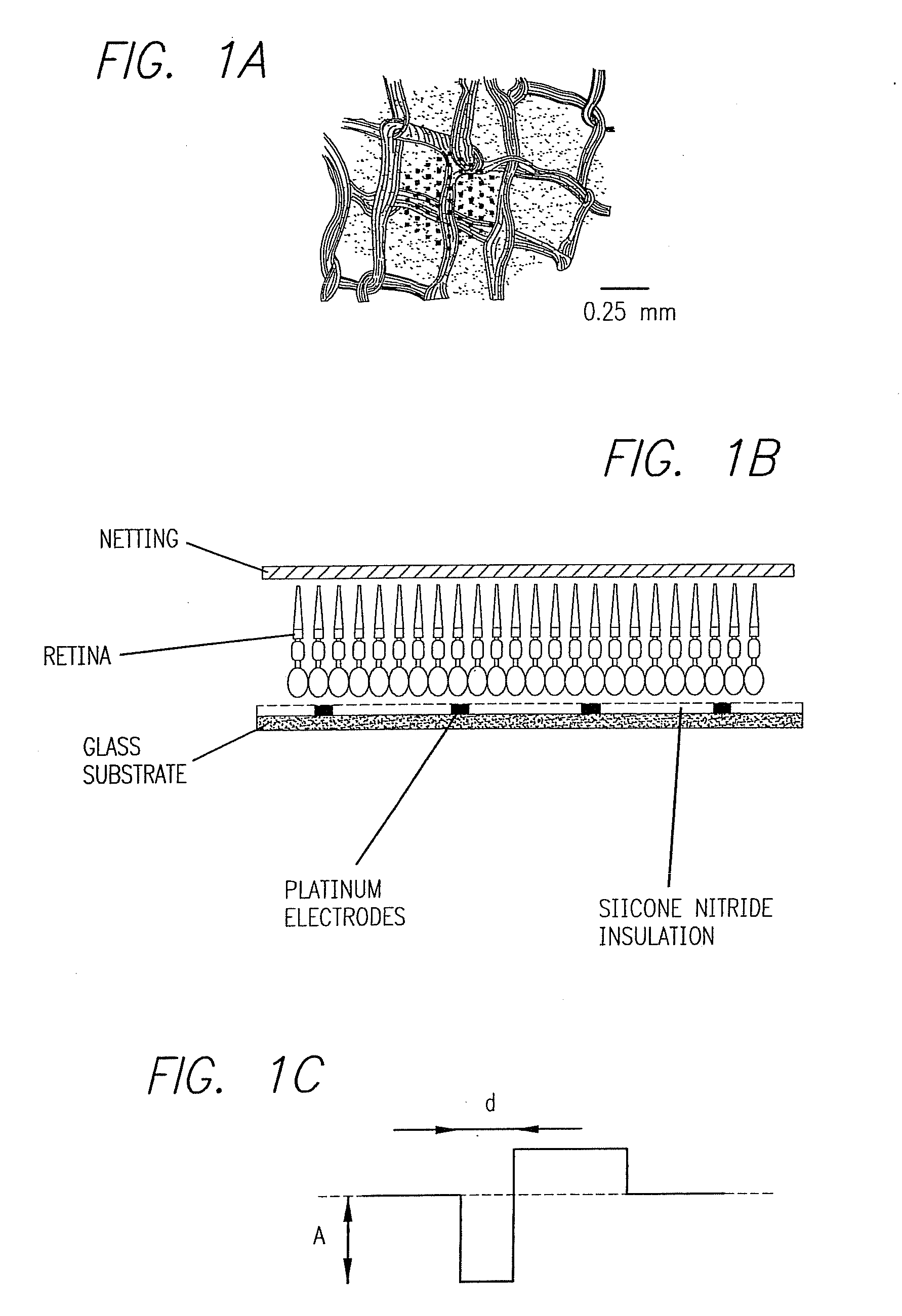
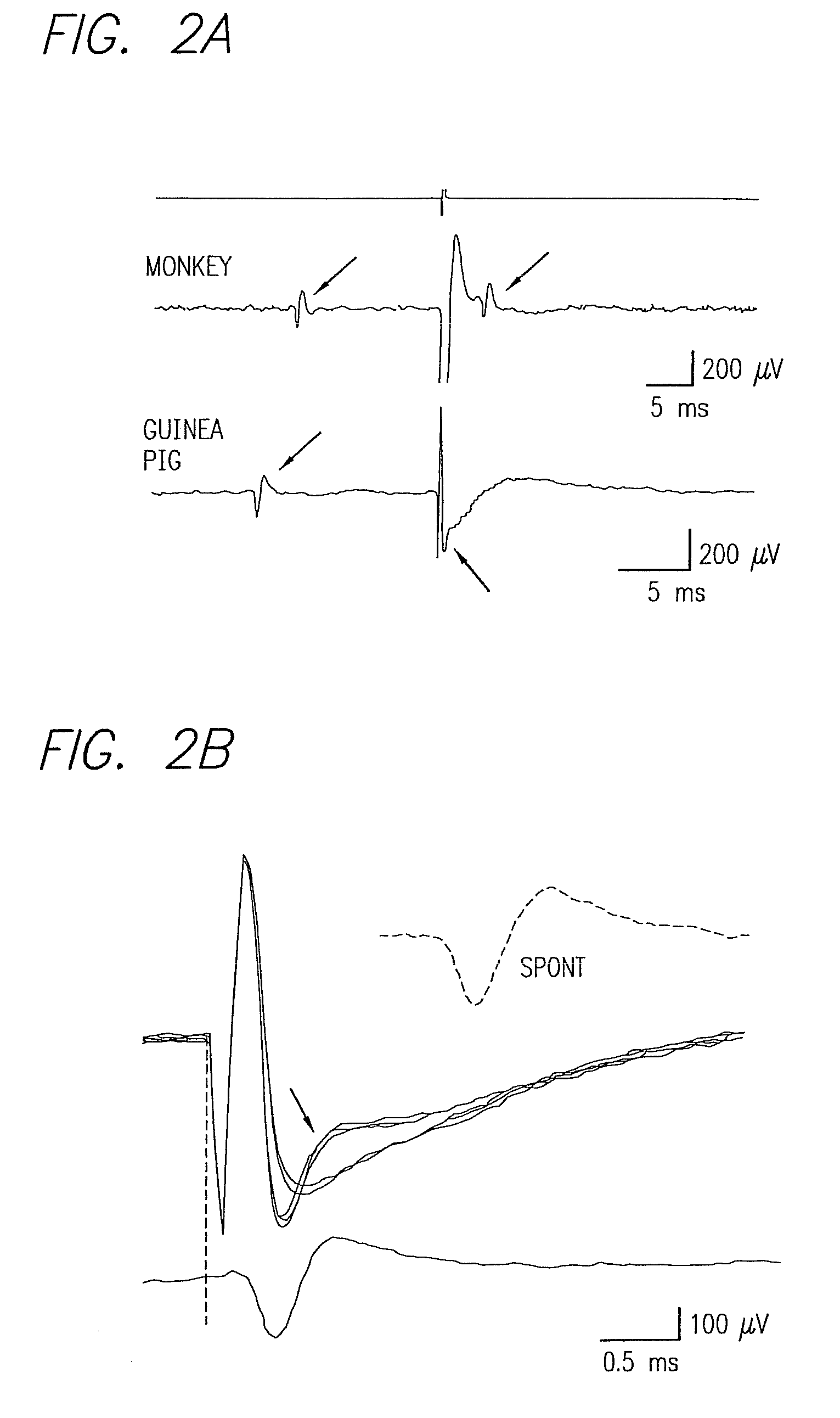
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES +1
Molecular and functional profiling using a cellular microarray
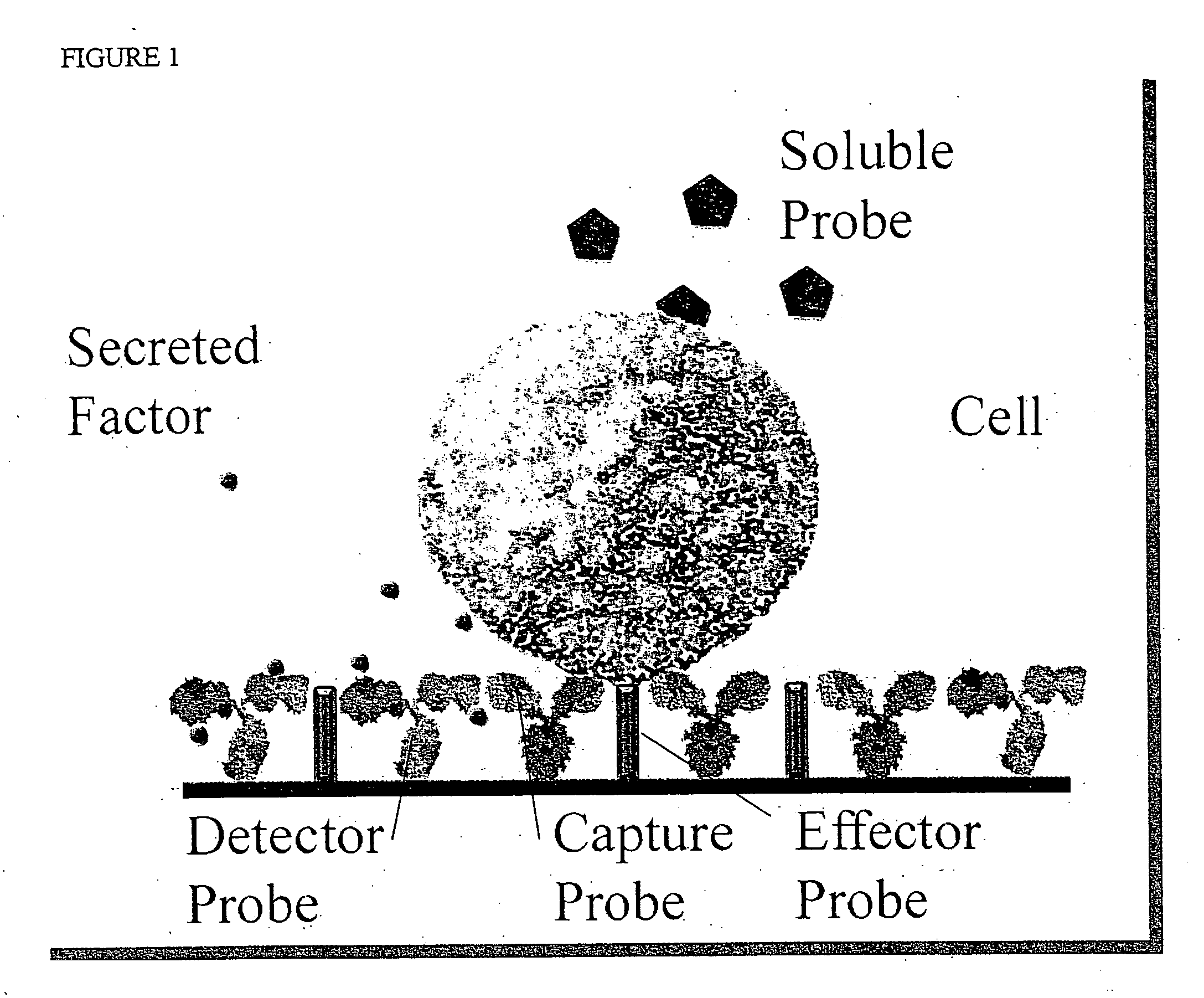
InactiveUS20060019235A1Faster and efficient predictionReward for identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisCell–cell interactionFunctional profiling
Cells are profiled with respect to their expression of cell surface molecules, and ability to respond to external stimulus in the microenvironment. External stimuli include cell-cell interactions, response to factors, and the like. The cells are arrayed on a planar or three-dimensional substrate through binding to immobilized or partially diffused probes. Probes of interest include specific binding partners for cell surface molecules, signaling cues that act to regulate cell responses, differentiation factors, etc., which may be arrayed as one or a combination of molecules.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods, systems and products for predicting response of tumor cells to a therapeutic agent and treating a patient according to the predicted response
InactiveUS20110027291A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsResponse treatmentsStatistical classification
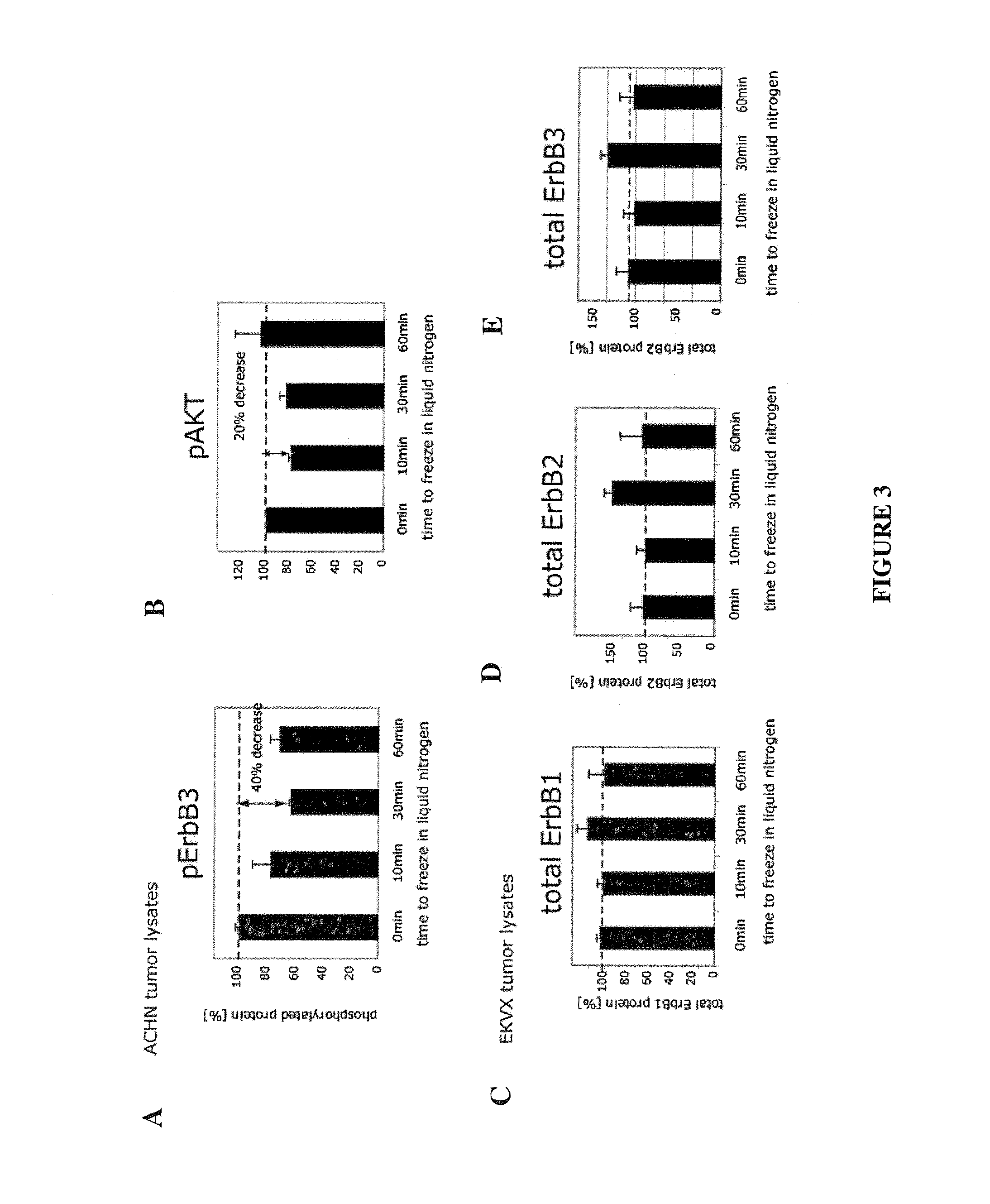
The invention provides methods for treating patients which methods comprise methods for predicting responses of cells, such as tumor cells, to treatment with therapeutic agents. These methods involve measuring, in a sample of the cells, levels of one or more components of a cellular network and then computing a Network Activation State (NAS) or a Network Inhibition State (NIS) for the cells using a computational model of the cellular network. The response of the cells to treatment is then predicted based on the NAS or NIS value that has been computed. The invention also comprises predictive methods for cellular responsiveness in which computation of a NAS or NIS value for the cells (e.g., tumor cells) is combined with use of a statistical classification algorithm. Biomarkers for predicting responsiveness to treatment with a therapeutic agent that targets a component within the ErbB signaling pathway are also provided.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Production of four carbon alcohols using improved strain
Owner:GEVO INC
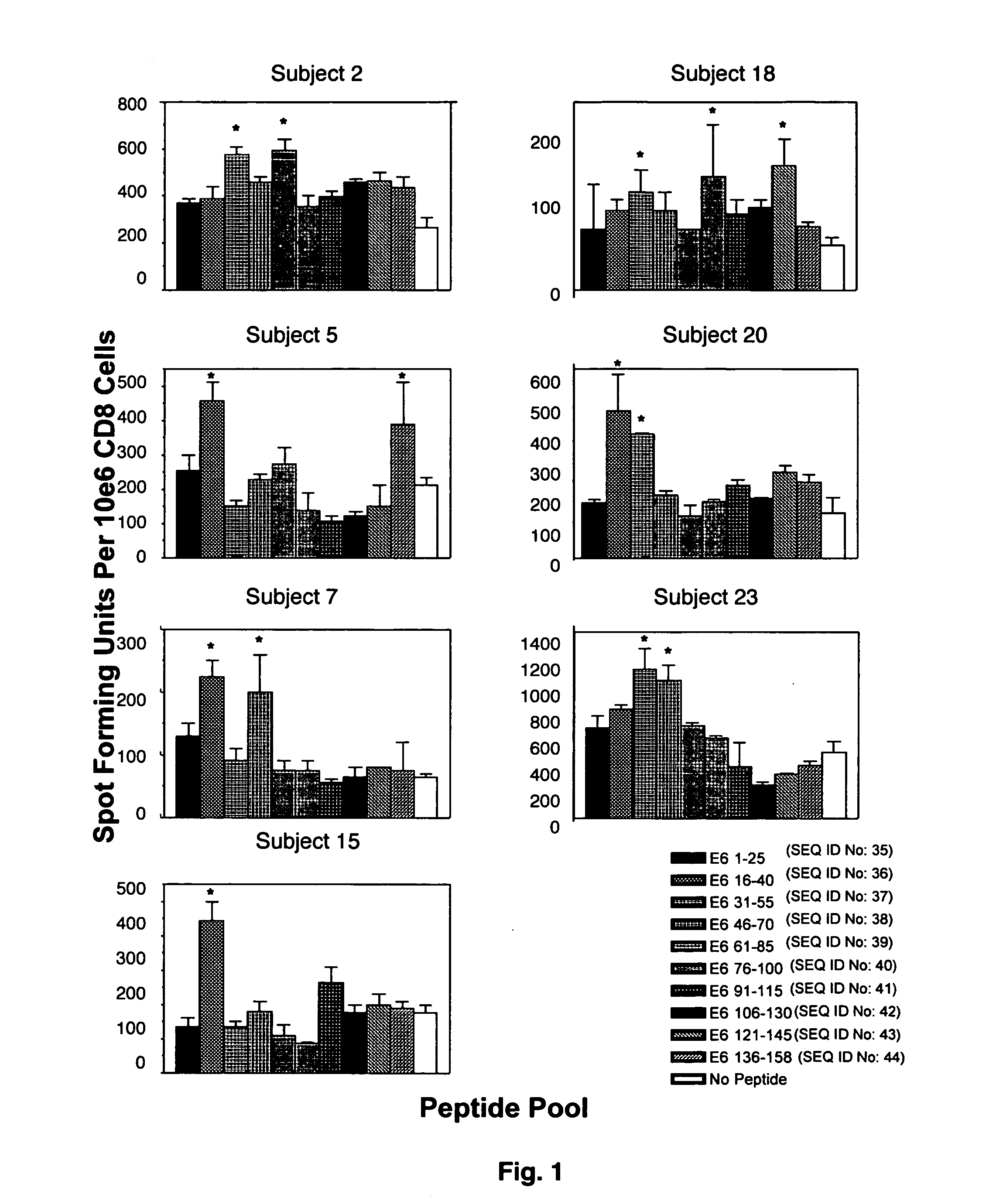
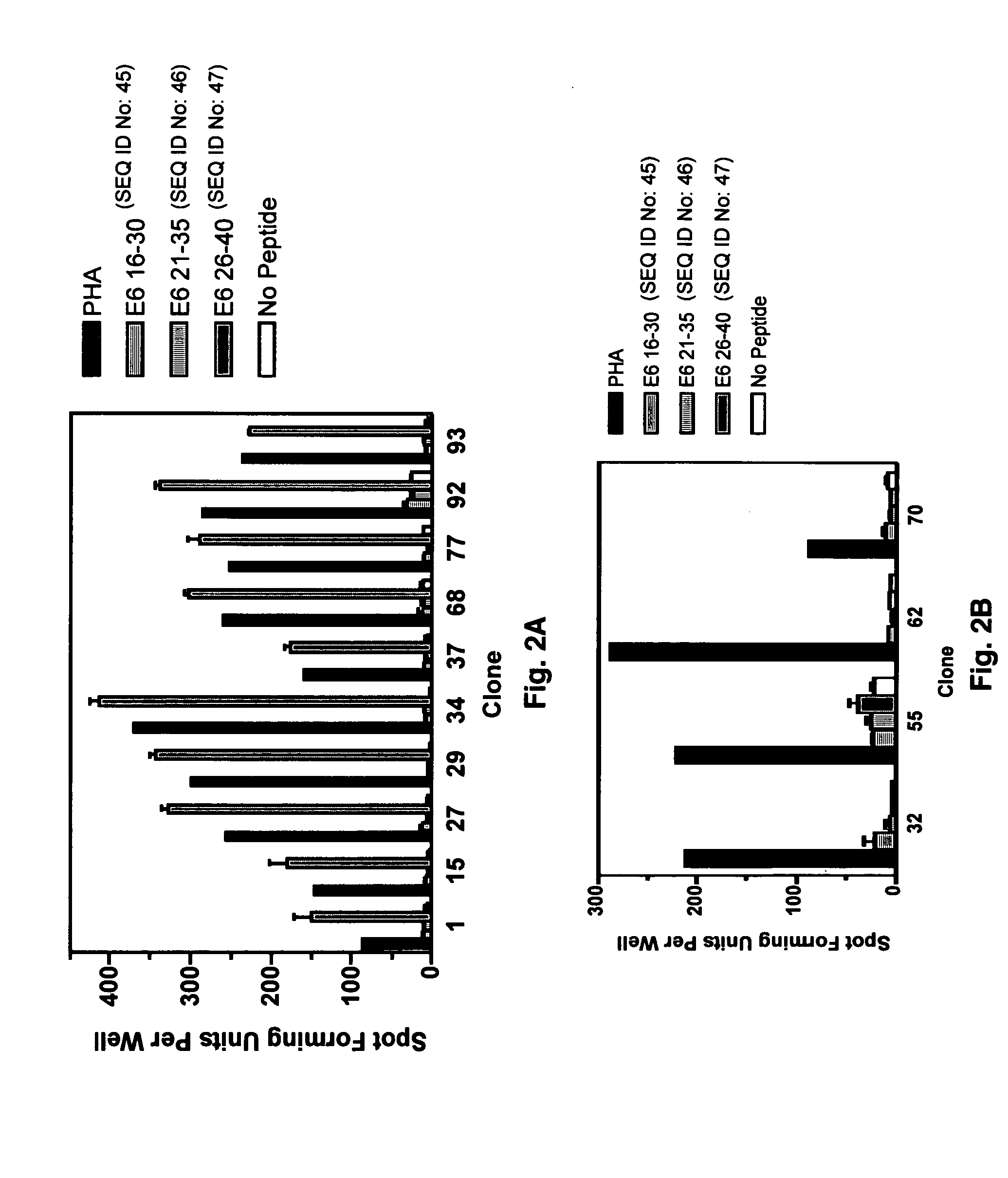
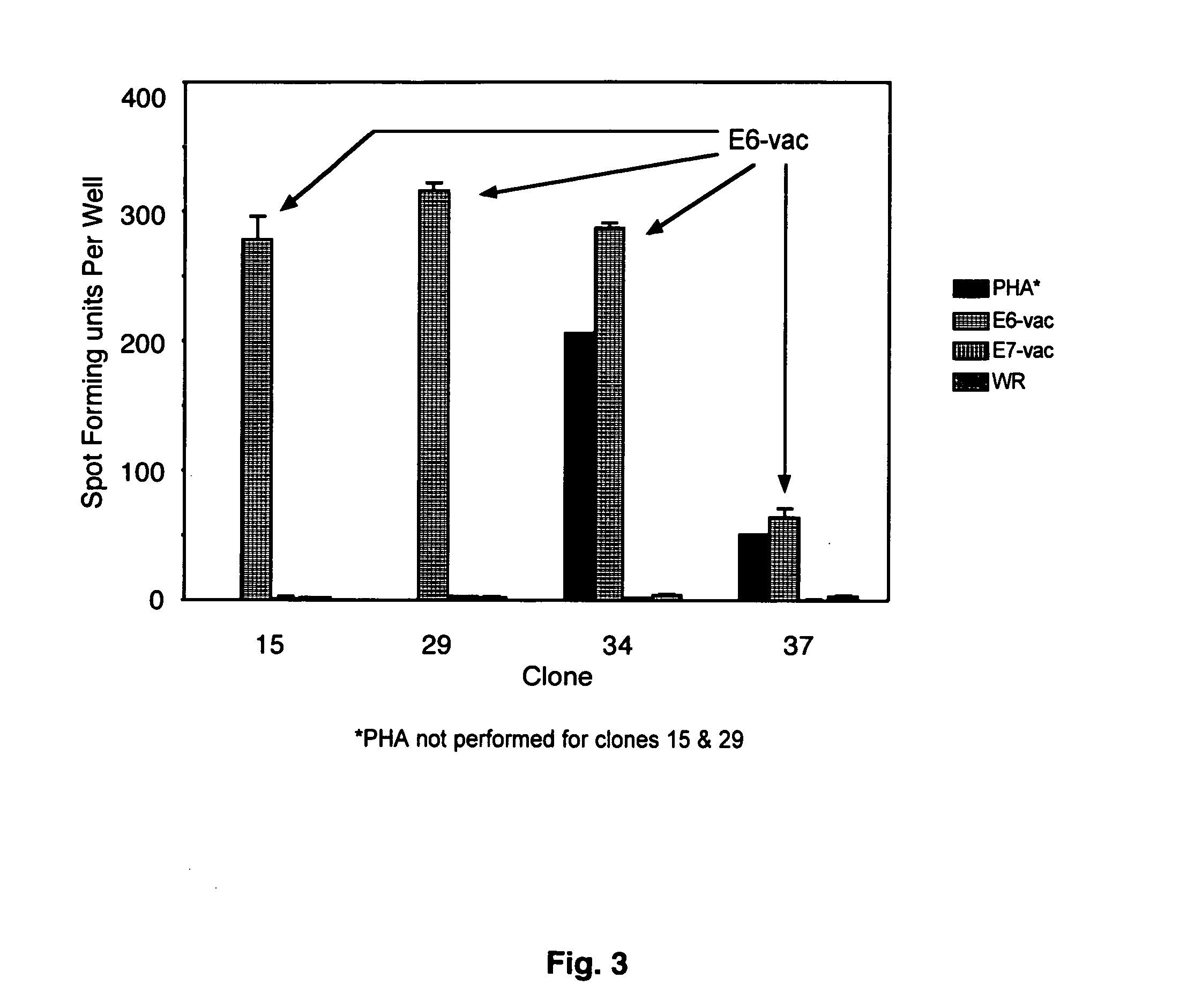
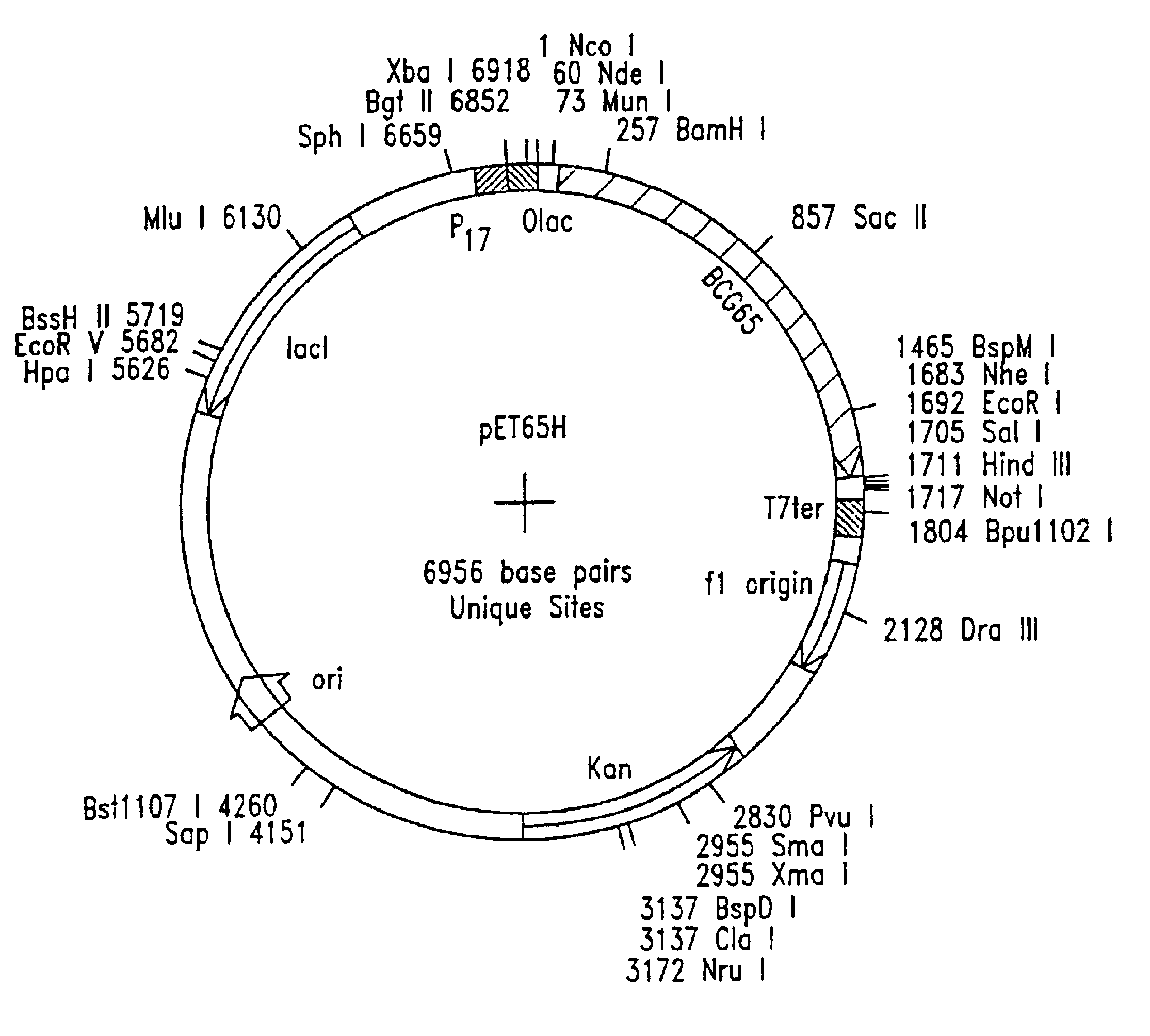
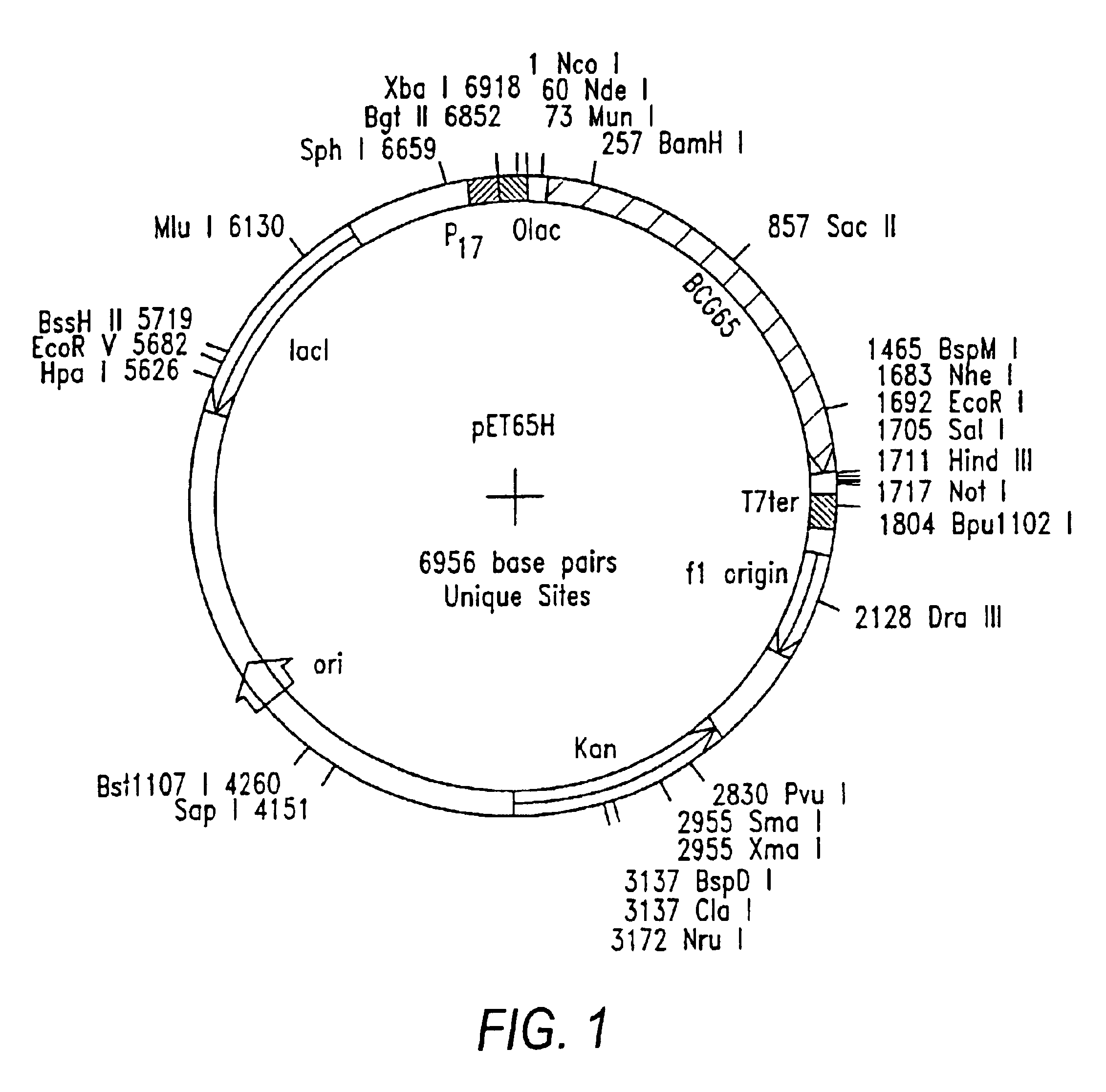
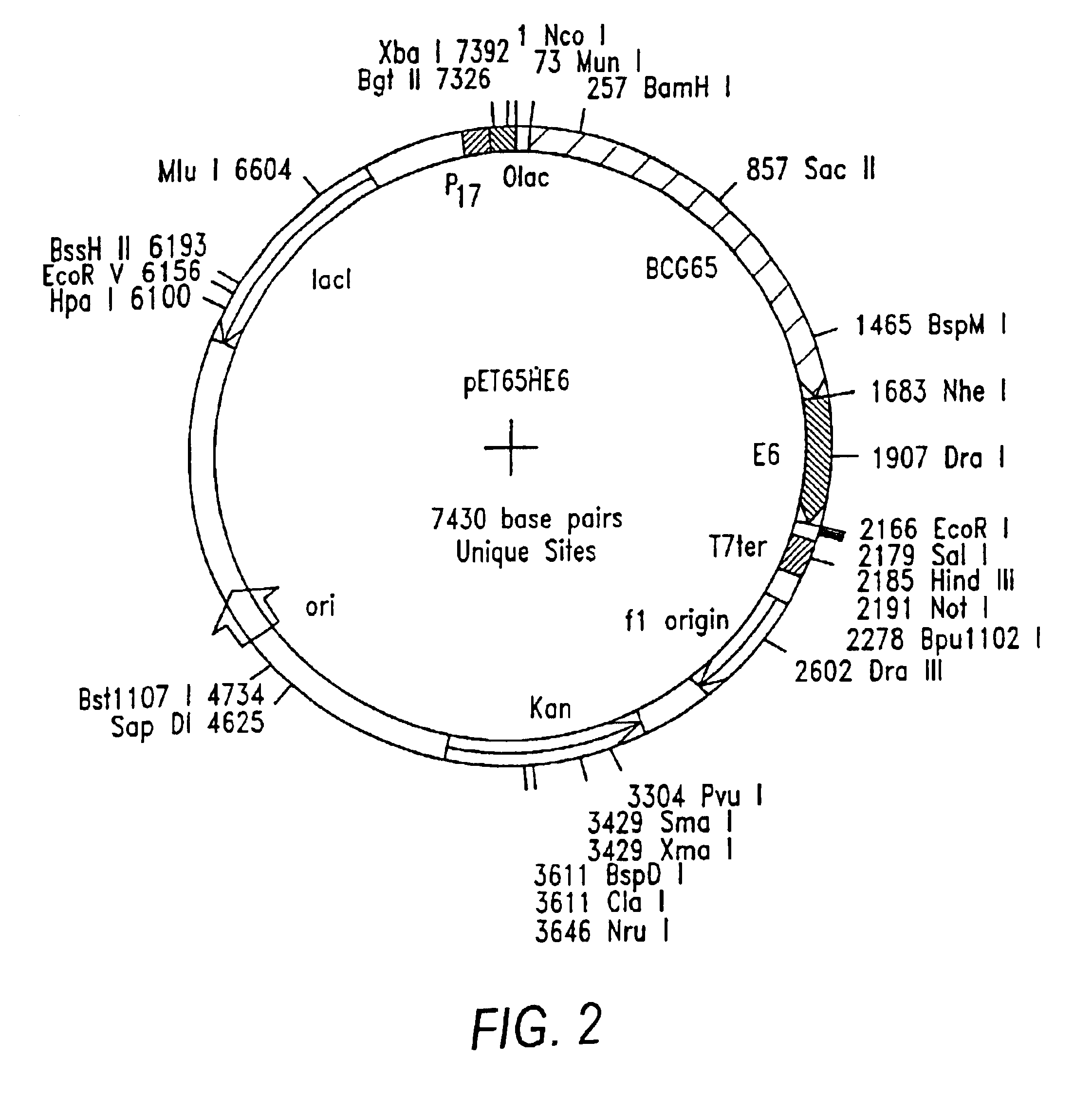
CD8 T cell epitopes in HPV 16 E6 and E7 proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060182763A1Peptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsHuman papillomavirusDendritic cell
The present invention is directed to the examination of the pattern of immunodominant CD8 T cell epitopes in the E6 and E7 protein of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and its further characterization in terms of its amino acid sequence and HLA restriction. These epitopes are identified based on their ability to induce strong CD8 T cell response and therefore, are important as sources of antigens for dendritic cell immunotherapy to treat cervical cancer. The present invention contemplates identifying a number of similar epitopes restricted by a wide variety of HLA types so that they can be used in concert to develop a preventative vaccine, which can be used for general population.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
Melan-A- carrier conjugates
InactiveUS7537767B2Improve responseMore immunogenicSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideDiseaseAllergy
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
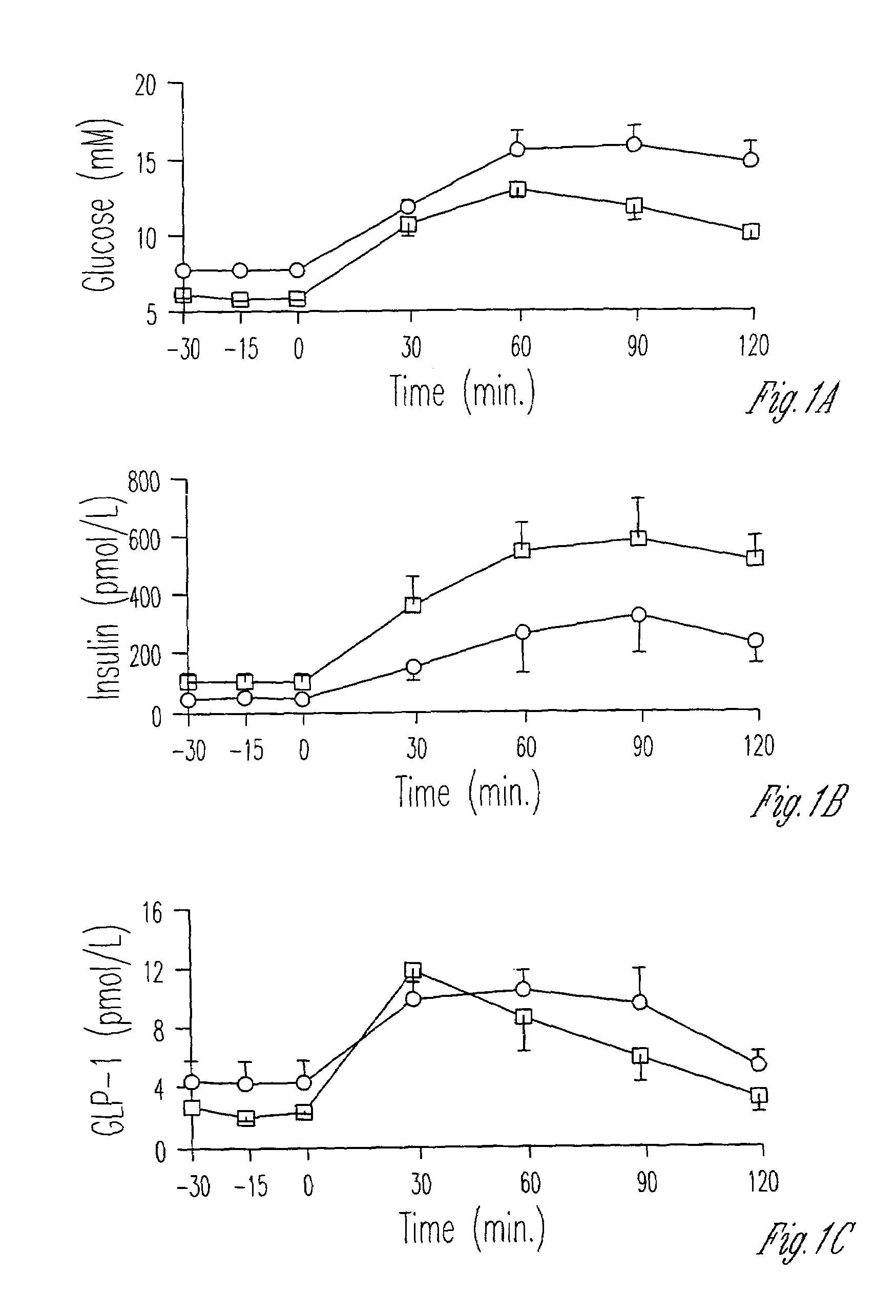
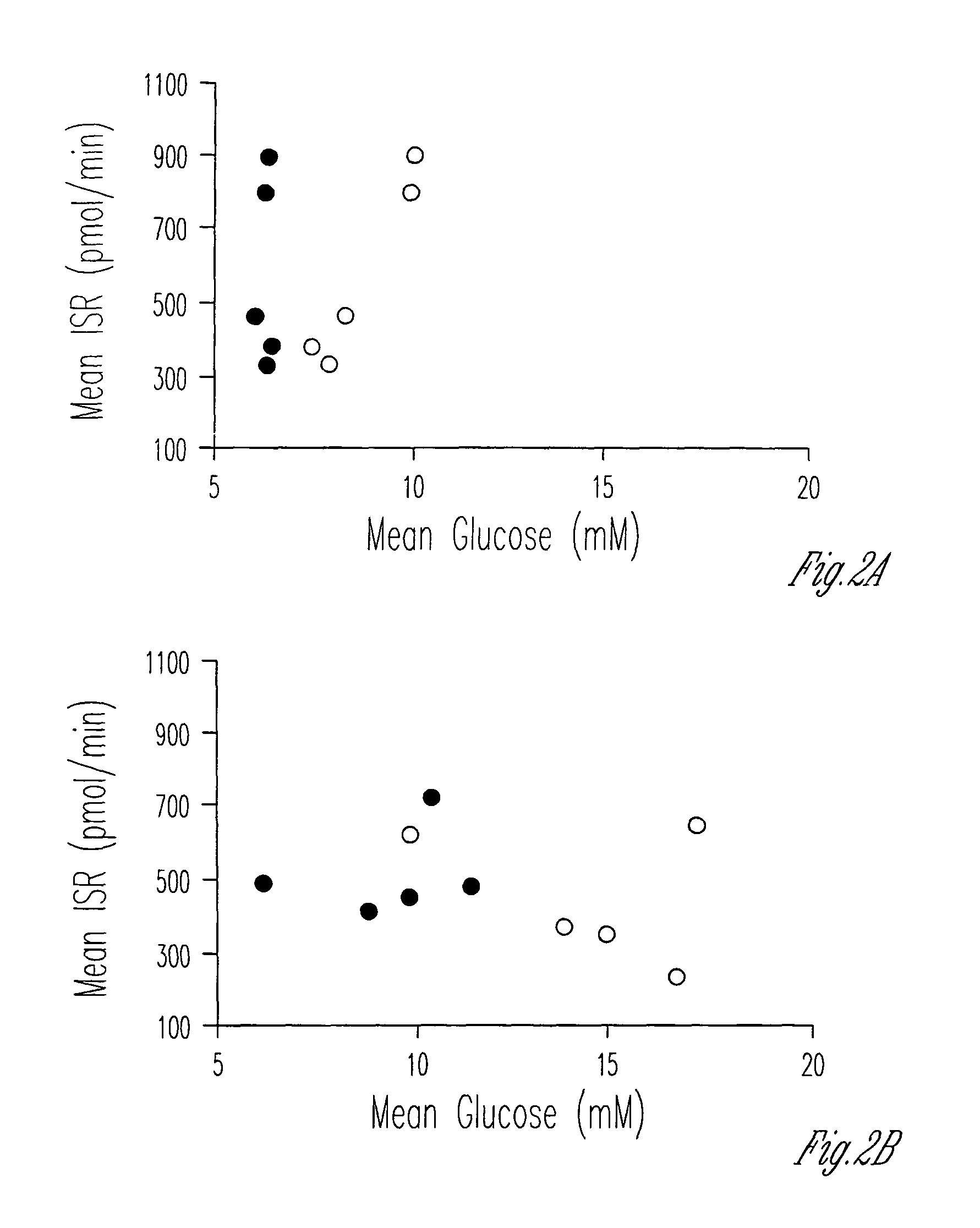
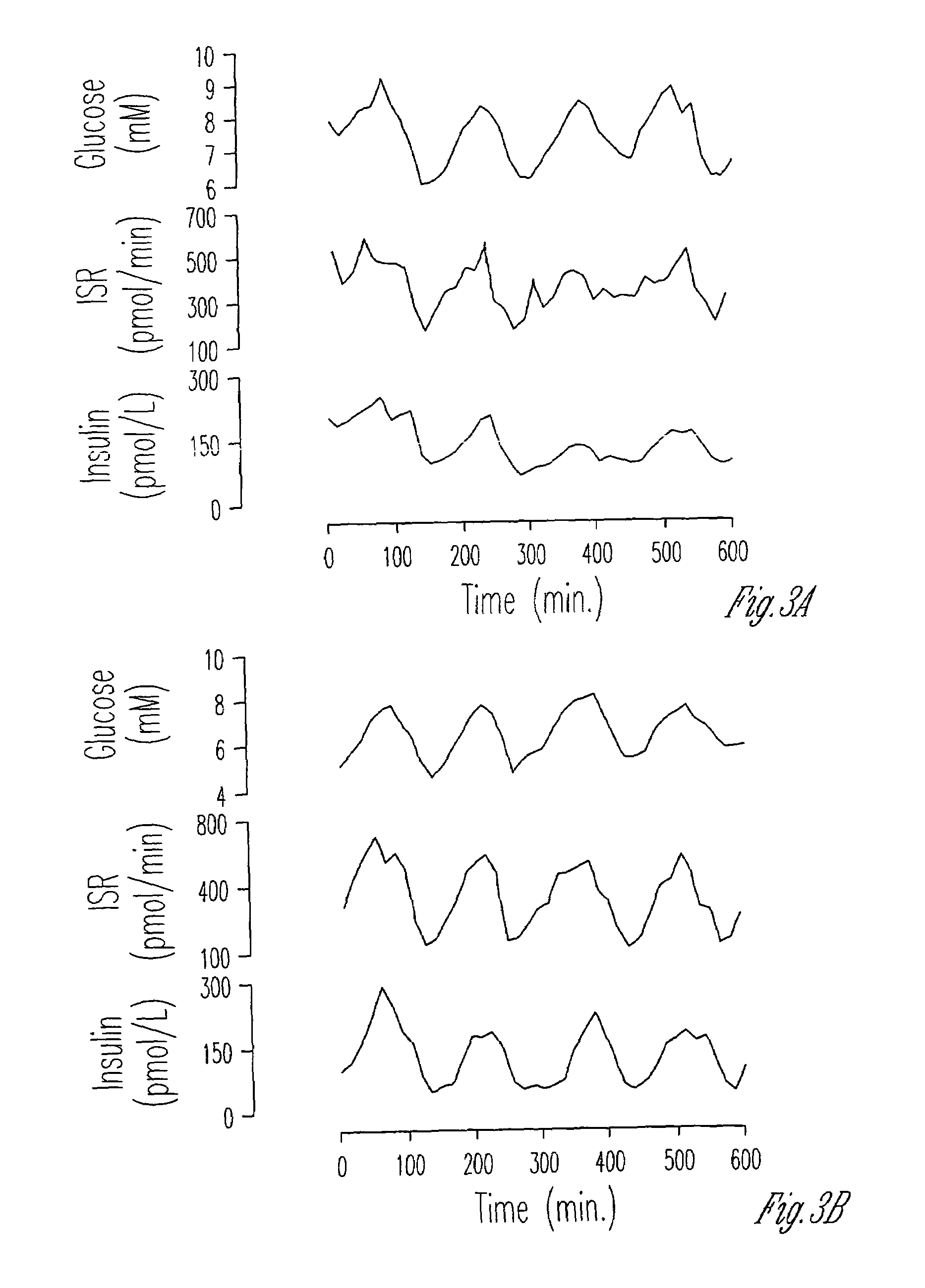
Exendin improves β-cell response in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance
InactiveUS7265087B1Restore responseLowering plasma insulin levelPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderCell sensitivityGlucagon-like peptide-1
A composition for the treatment of impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) including a compound which binds to a receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1, and a pharmaceutical carrier. The amount of the compound present is an effective amount to improve pancreatic β-cell sensitivity to blood glucose levels in a human with IGT. Also, a method for improving the pattern of insulin secretory responses in a human with IGT by administering to the human a composition comprising a compound which binds to a receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1 and a pharmaceutical carrier.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Immune responses against HPV antigens elicited by compositions comprising an HPV antigen and a stress protein or an expression vector capable of expression of these proteins
InactiveUS6900035B2Enhance immune responseVirusesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHPV AntigenInfected cell
This document describes compositions and methods for inducing an immune response (e.g., a cellular response such as a cell-mediated cytolytic immune response) to a human papillomavirus (HPV) antigen, which can be displayed by HPV or exhibited by infected cells (e.g., cells from cervical and other tumors). The HPV protein can be joined to a stress protein by chemical conjugation or noncovalently using linking moieties, or by fusion (e.g., a recombinant fusion protein). Also described are expression vectors containing sequences encoding HPV antigens and stress proteins, which can be introduced into cells of a subject or cells ex vivo. Also described are compositions that include a stress protein linked to an HPV antigen and another pharmacologically acceptable component and stress protein—HPV antigen fusions and conjugates. These compositions can be used to induce or enhance an immune response against HPV and cells that exhibit HPV antigens, including HPV-associated tumors.
Owner:NVENTA BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CORP
Human immune therapies using a cd27 agonist alone or in combination with other immune modulators
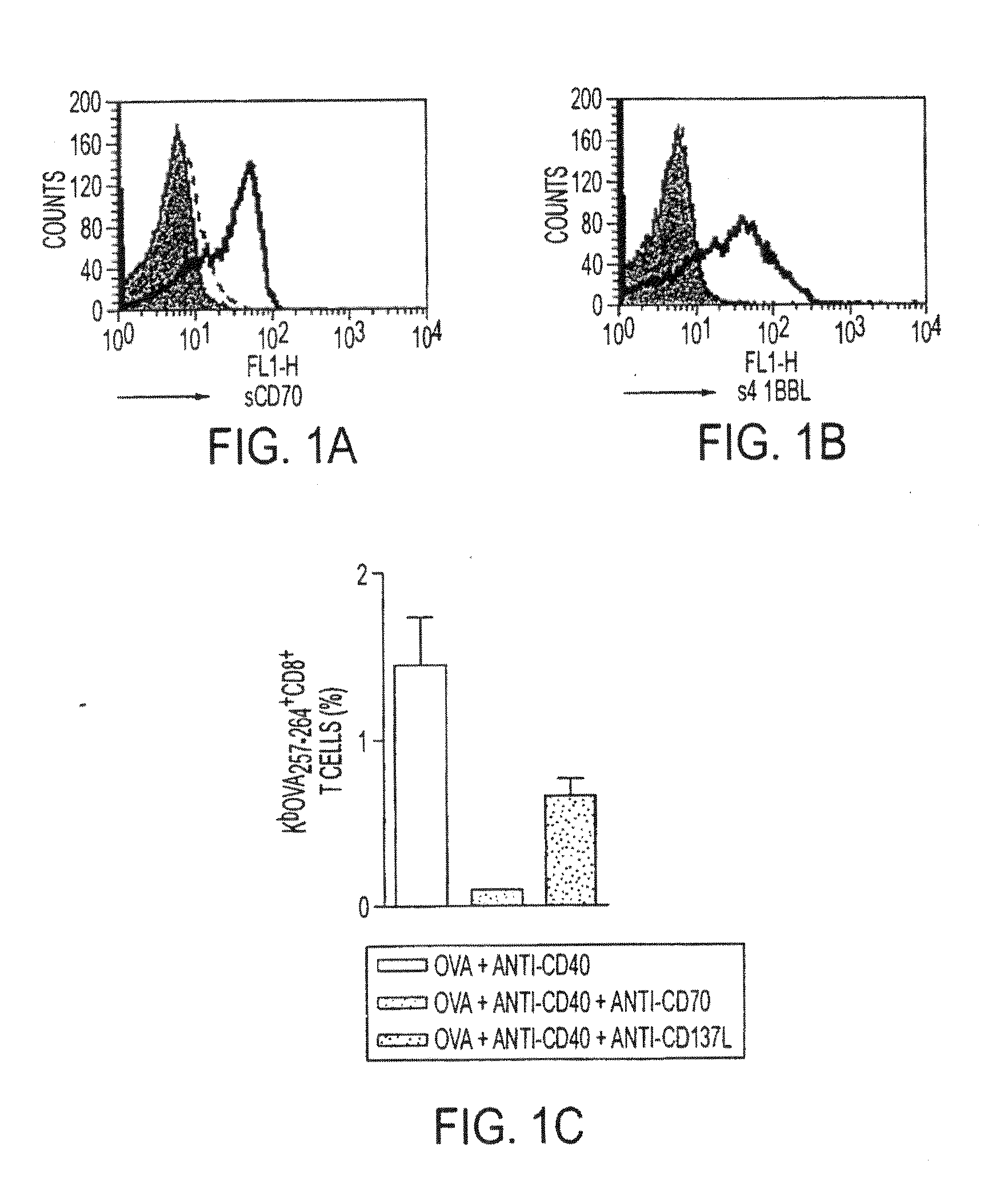
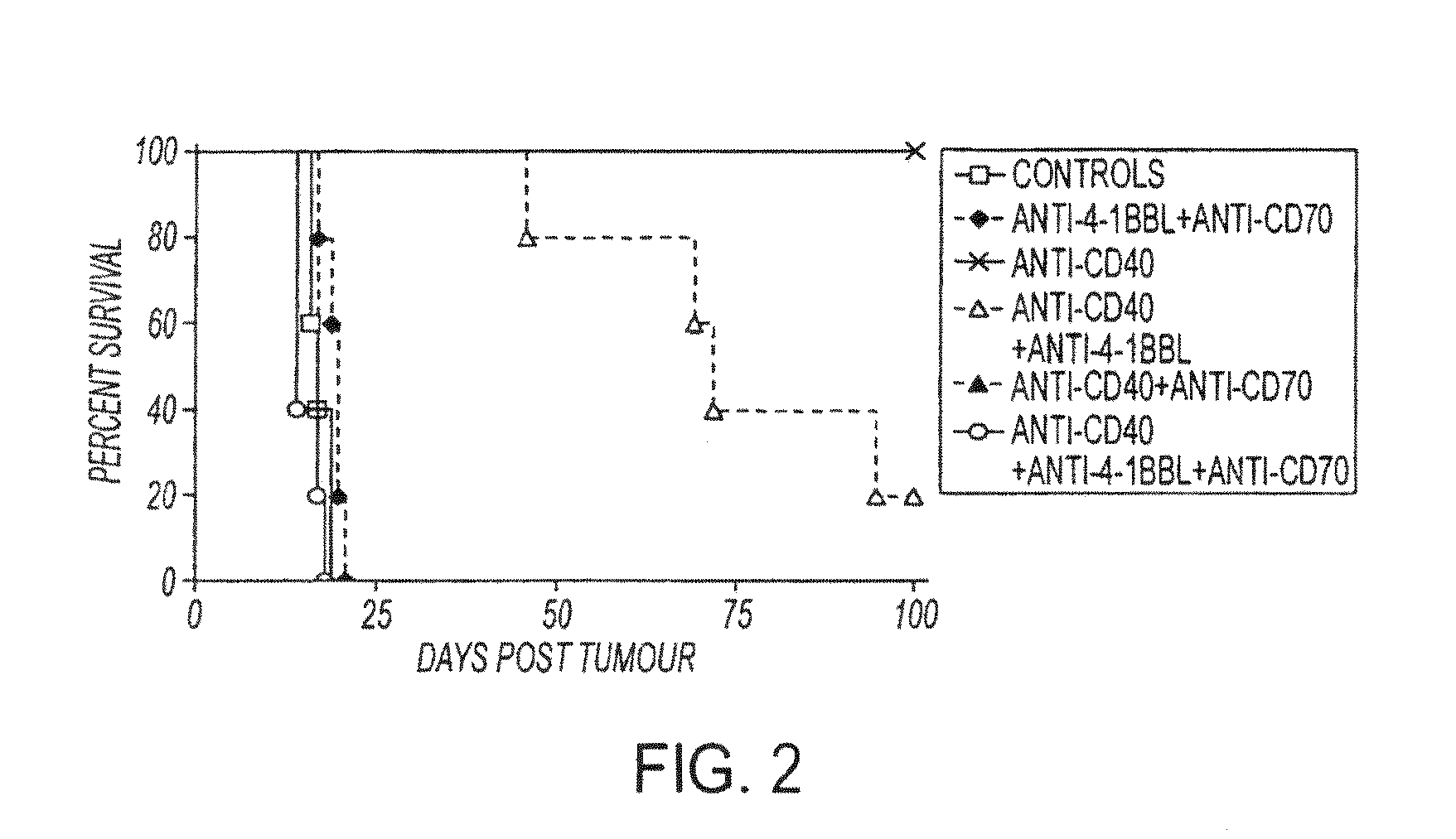
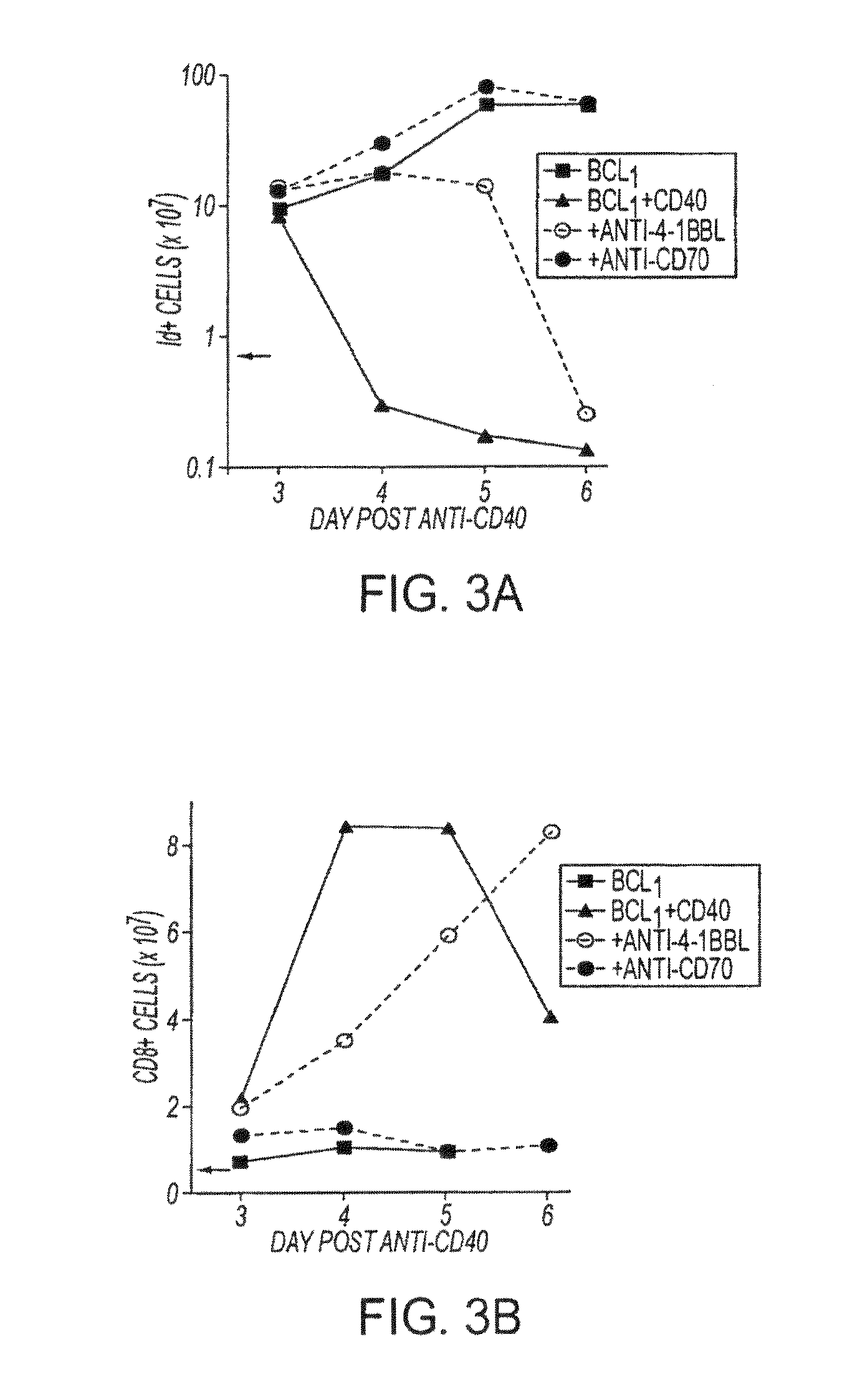
InactiveUS20130336976A1Promotes strong expression of 4-1BBImprove responseAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsIMMUNE STIMULANTSCD8
Methods of inducing T cell proliferation and expansion in vivo for treating conditions wherein antigen-specific T cell immune response are therapeutically desirable such as cancer, infection, inflammation, allergy and autoimmunity and for enhancing the efficacy of vaccines are provided. These methods comprise the administration of at least one CD27 agonist, preferably an agonistic CD27 antibody, alone or in association with another moiety such as immune stimulant or immune modulator such as an anti-CD40, OX-40, 4-1BB, or CTLA-4 antibody or an agent that depletes regulatory cells, or a cytokine. These mono and combination therapies may also optionally include the administration of a desired antigen such as a tumor antigen, an allergen, an autoantigen, or an antigen specific to an infectious agent or pathogen against which a T cell response (often CD8+) is desirably elicited.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Cell flow apparatus and method for real-time measurements of patient cellular responses
InactiveUS20020086340A1Quick filterIncrease the number ofCompound screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTest agentOn cells
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
System, device, and methods for real-time screening of live cells, biomarkers, and chemical signatures
InactiveUS7956328B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansMode of actionChemical species
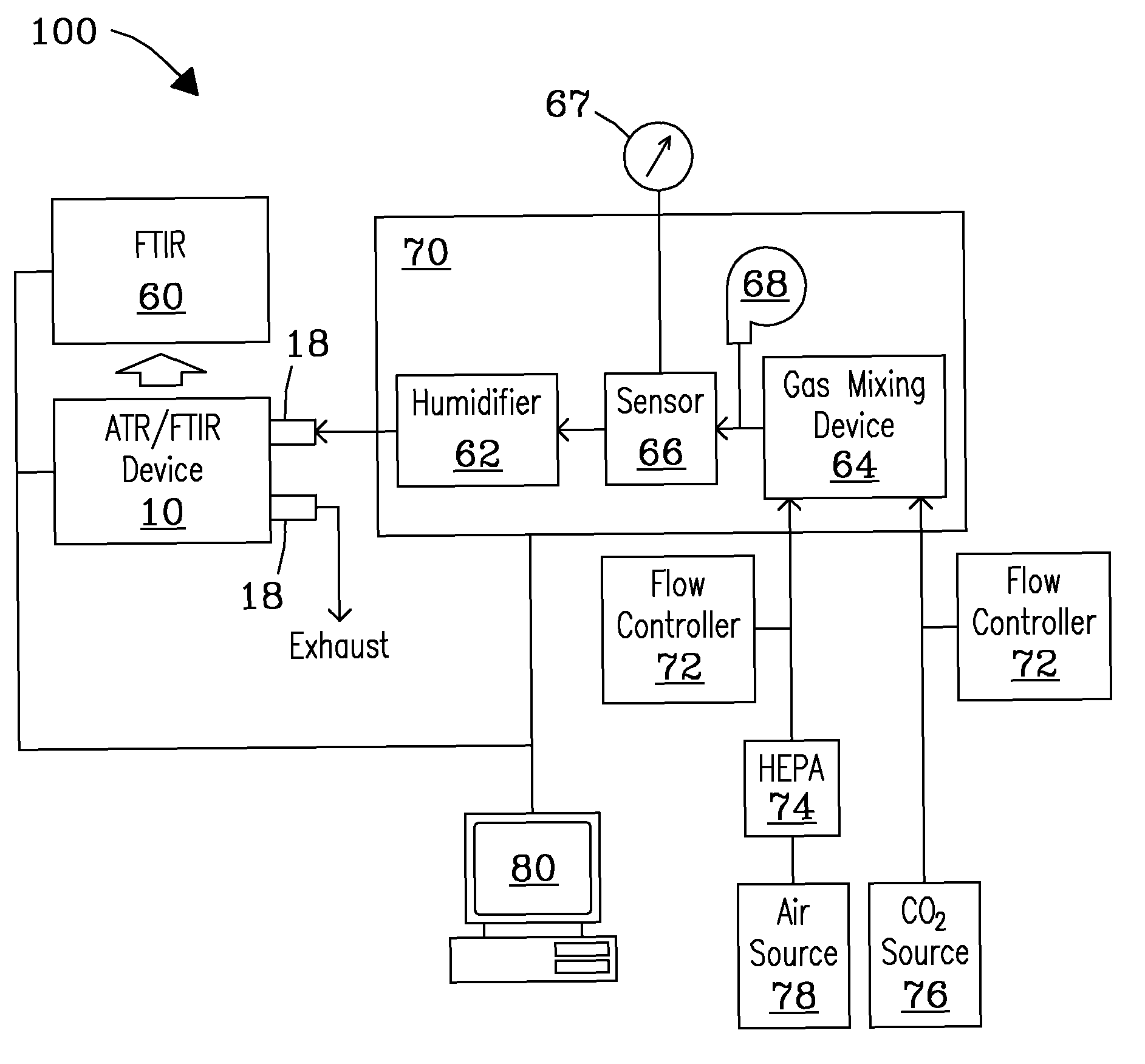
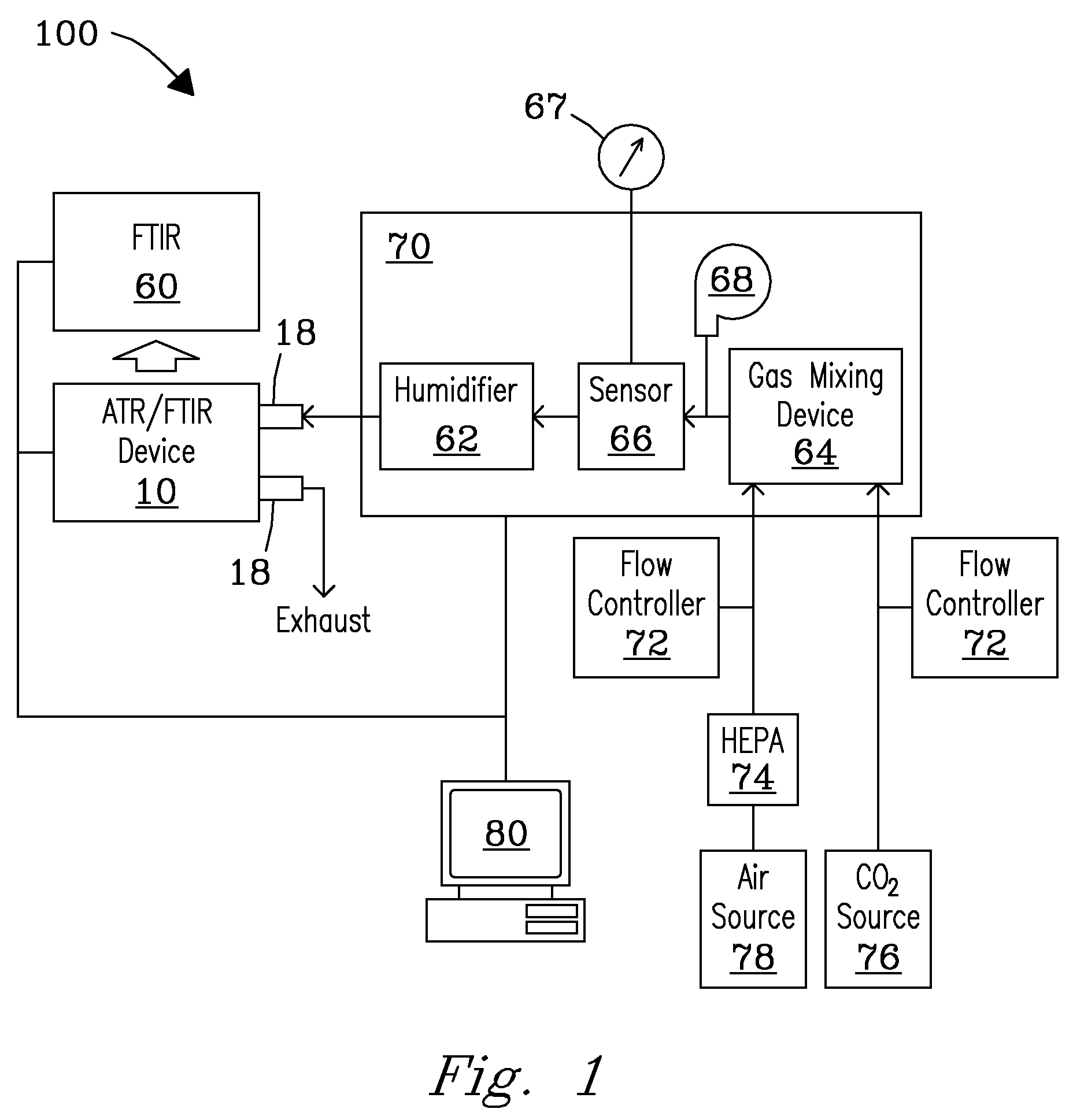
An ATR-FTIR device and system are described that defect live-cell responses to stimuli and perturbations in real-time. The system and device can monitor perturbations resulting from exposures to various physical, chemical, and biological materials in real-time, as well as those sustained over a long period of time, including those associated with stimuli having unknown modes-of-action (e.g. nanoparticles). The device and system can also be used to identify specific chemical species or substances that profile cellular responses to these perturbations.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
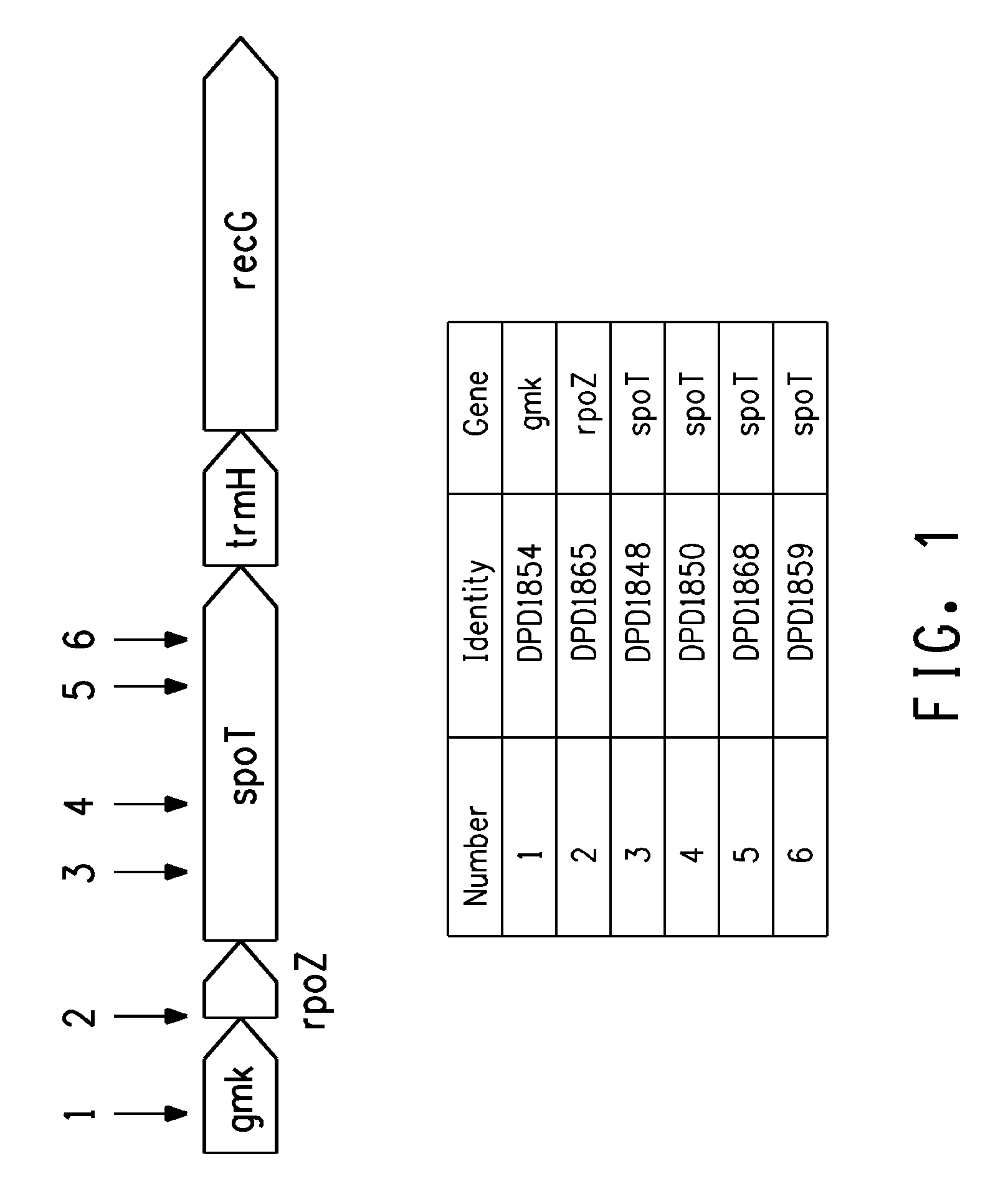
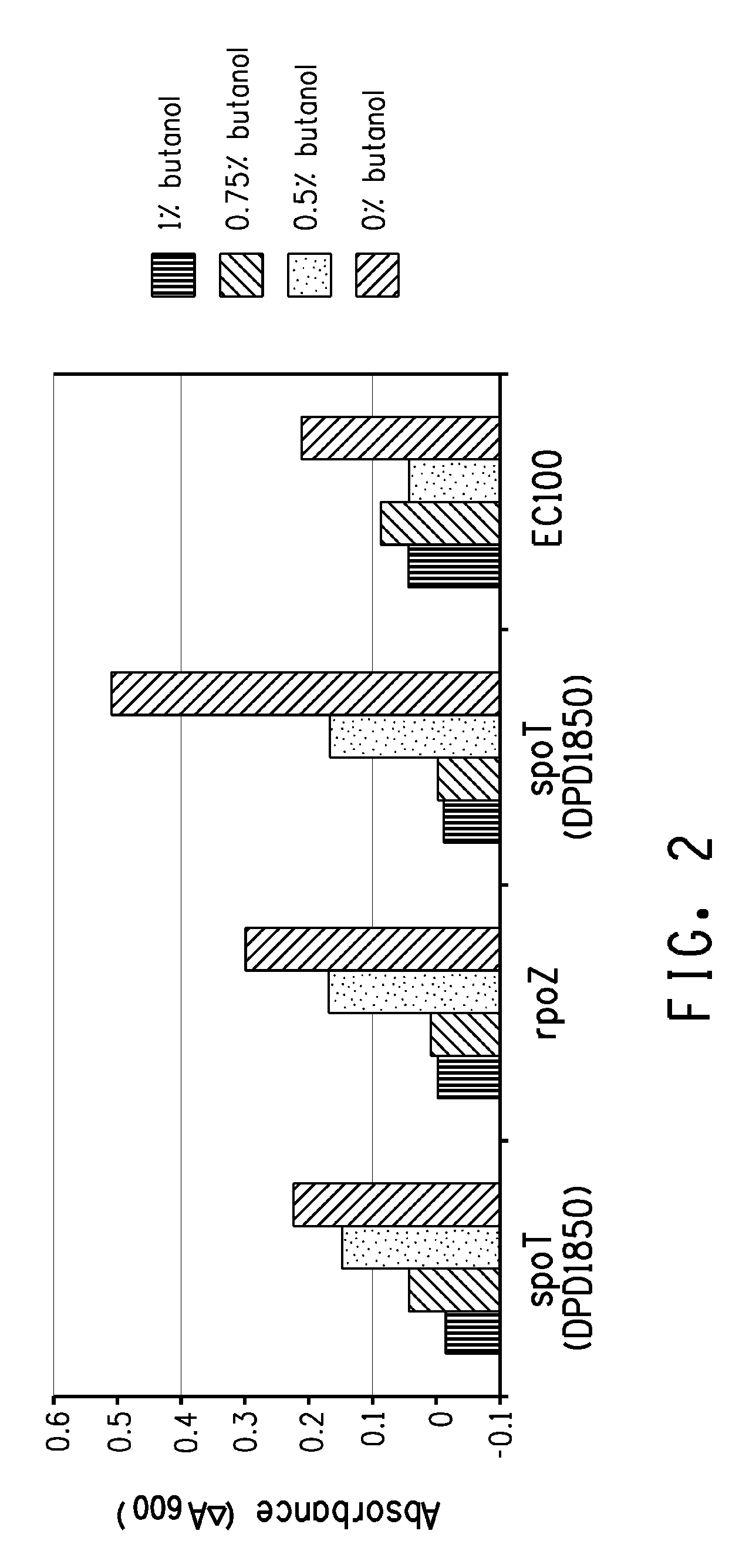
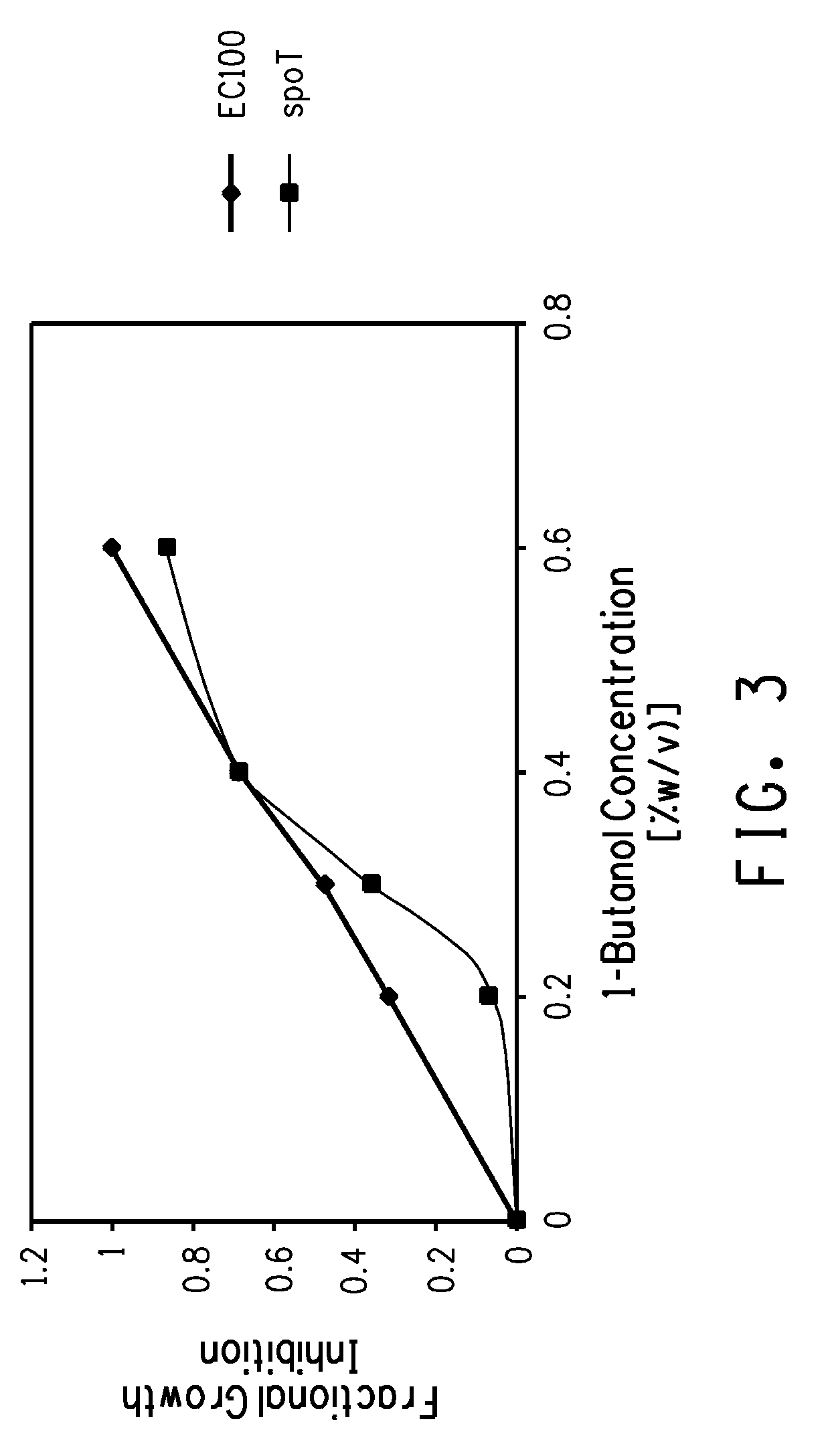
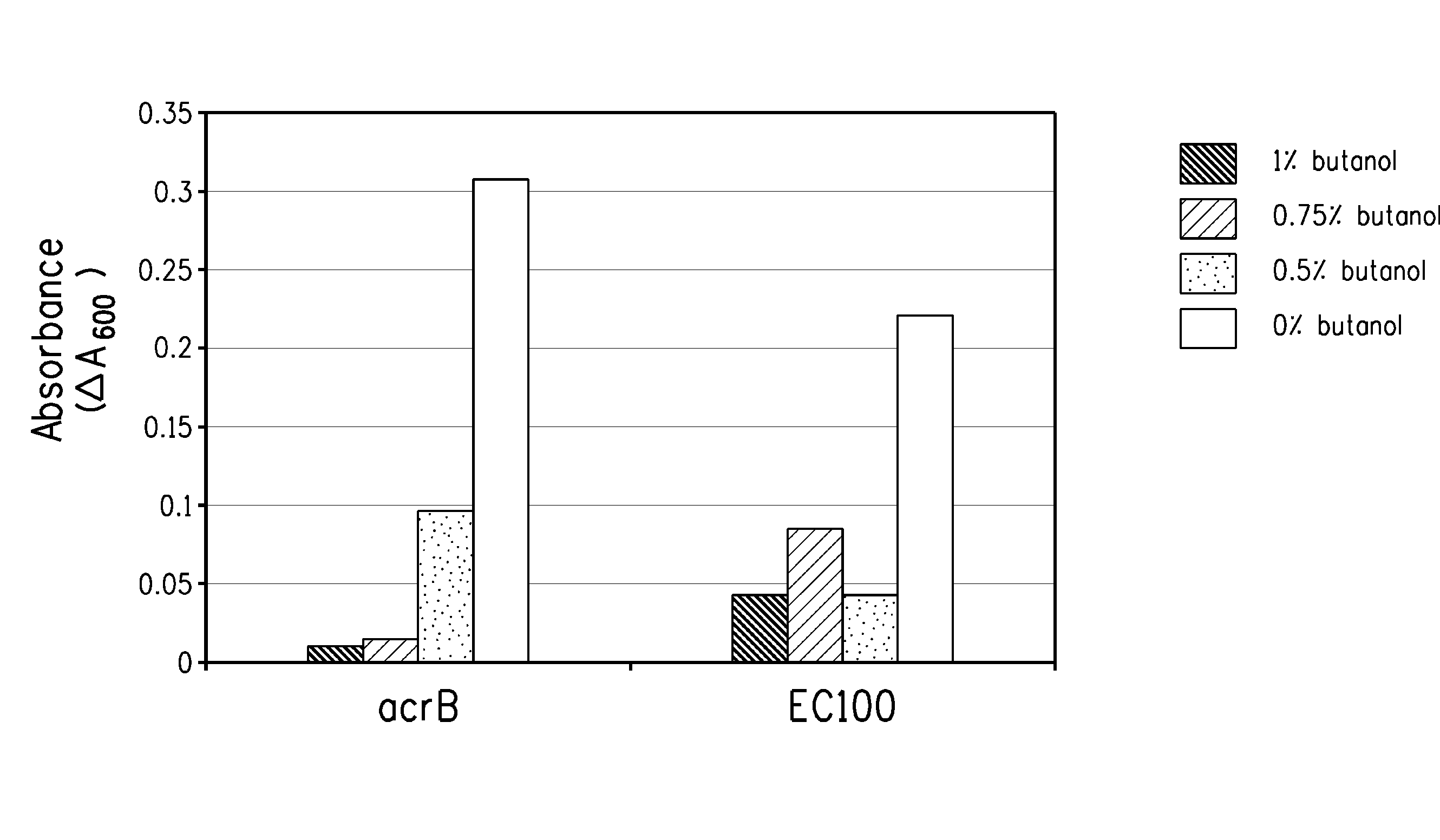
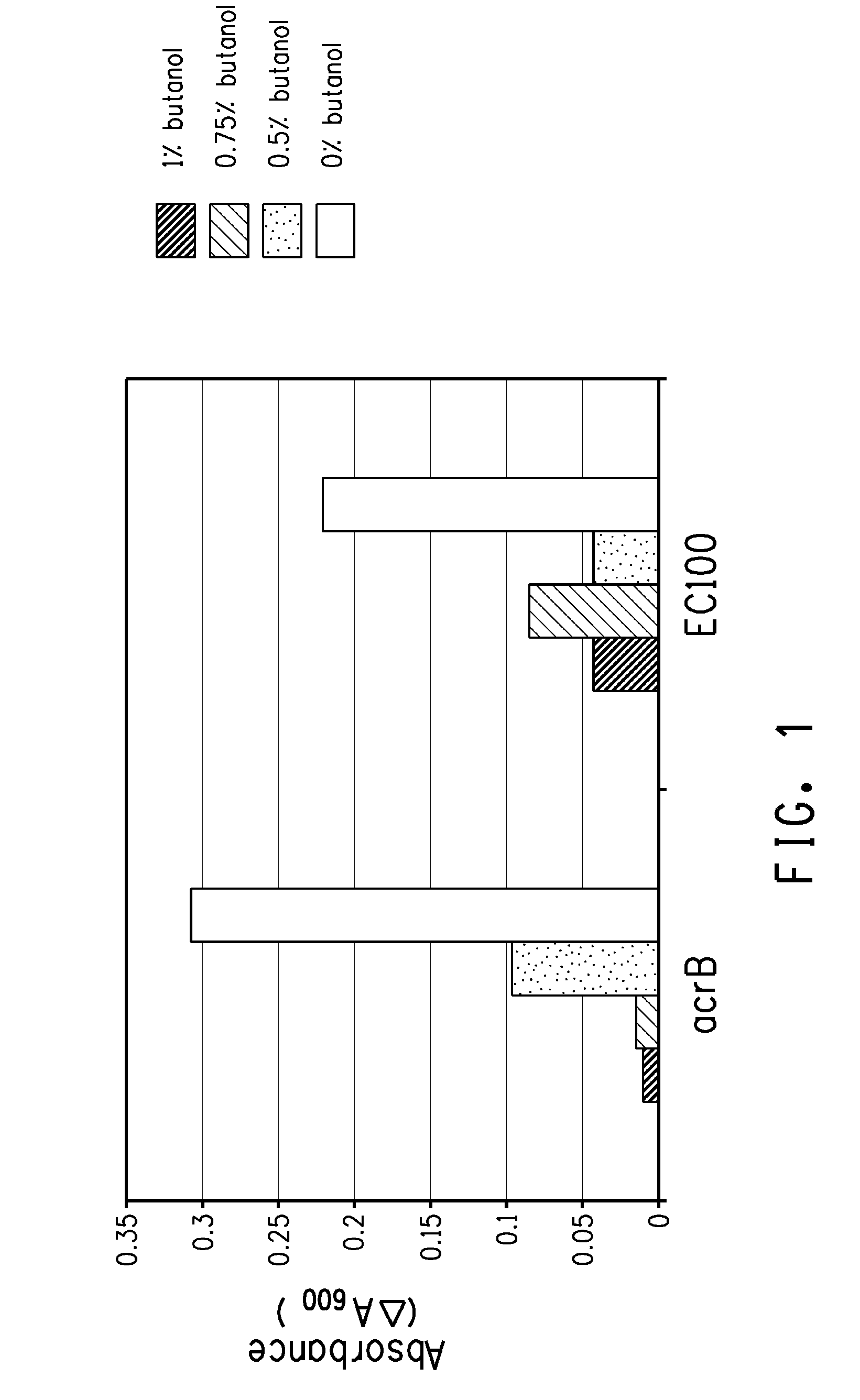
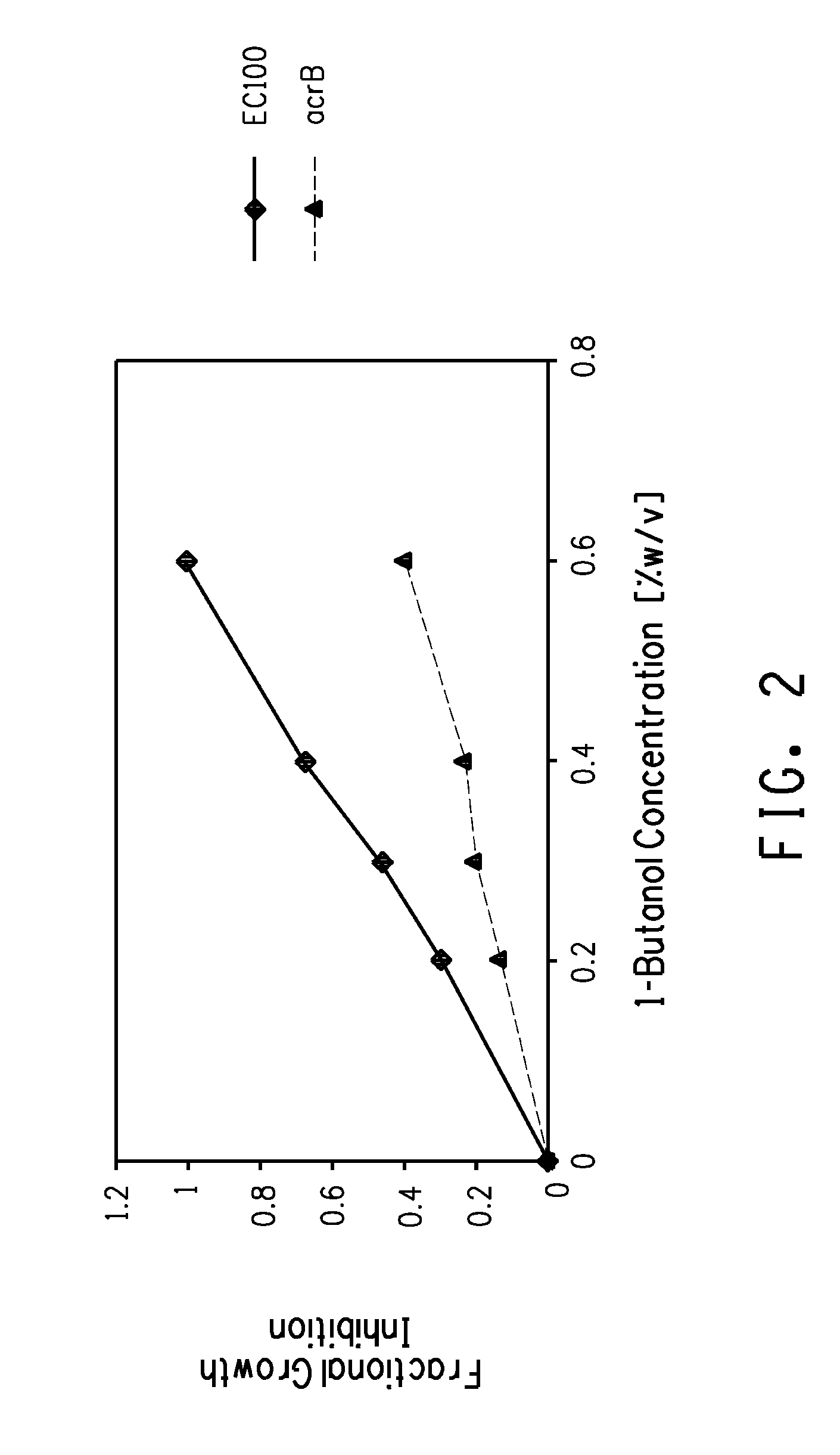
Strain for butanol production
Using screening of transposon random insertion mutants, genes involved in a complex that is a three-component proton motive force-dependent multidrug efflux system were found to be involved in E. coli cell response to butanol. Reduced production of the AcrA and / or AcrB proteins of the complex confers increased butanol tolerance. E. coli strains with reduced AcrA or AcrB production and having a butanol or 2-butanone biosynthetic pathway are useful for production of butanol or 2-butanone.
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
Method and Apparatus for Visual Neural Stimulation
Existing epiretinal implants for the blind are designed to electrically stimulate large groups of surviving retinal neurons using a small number of electrodes with diameters of several hundred μm. To increase the spatial resolution of artificial sight, electrodes much smaller than those currently in use are desirable. In this study we stimulated and recorded ganglion cells in isolated pieces of rat, guinea pig, and monkey retina. We utilized micro-fabricated hexagonal arrays of 61 platinum disk electrodes with diameters between 6 and 25 μm, spaced 60 μm apart. Charge-balanced current pulses evoked one or two spikes at latencies as short as 0.2 ms, and typically only one or a few recorded ganglion cells were stimulated. Application of several synaptic blockers did not abolish the evoked responses, implying direct activation of ganglion cells. Threshold charge densities were typically below 0.1 mC / cm2 for a pulse duration of 100 μs, corresponding to charge thresholds of less than 100 pC. Stimulation remained effective after several hours and at high frequencies. To demonstrate that closely spaced electrodes can elicit independent ganglion cell responses, we utilized the multi-electrode array to stimulate several nearby ganglion cells simultaneously. From these data we conclude that electrical stimulation of mammalian retina with small-diameter electrode arrays is achievable and can provide high temporal and spatial precision at low charge densities. We review previous epiretinal stimulation studies and discuss our results in the context of 32 other publications, comparing threshold parameters and safety limits.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +1
Compositions and methods for the detection, diagnosis and therapy of hematological malignancies
Disclosed are methods and compositions for the detection, diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of hematological malignancies, and in particular, B cell leukemias, lymphomas and multiple myelomas. Disclosed are compositions, methods and kits for eliciting immune and T cell responses to specific malignancy-related antigenic polypeptides and antigenic polypeptide fragments thereof in an animal. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for use in the identification of cells and biological samples containing one or more hematological malignancy-related compositions, and methods for the detection and diagnosis of such diseases and affected cell types. Also disclosed are diagnostic and therapeutic kits, as well as methods for the diagnosis, therapy and / or prevention of a variety of leukemias and lymphomas.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Anti-il13 receptor alpha1 neutralizing antibody
InactiveUS20050154192A1High expressionEffective therapyAnimal cellsBiological material analysisNeutralizing antibodyAmino acid
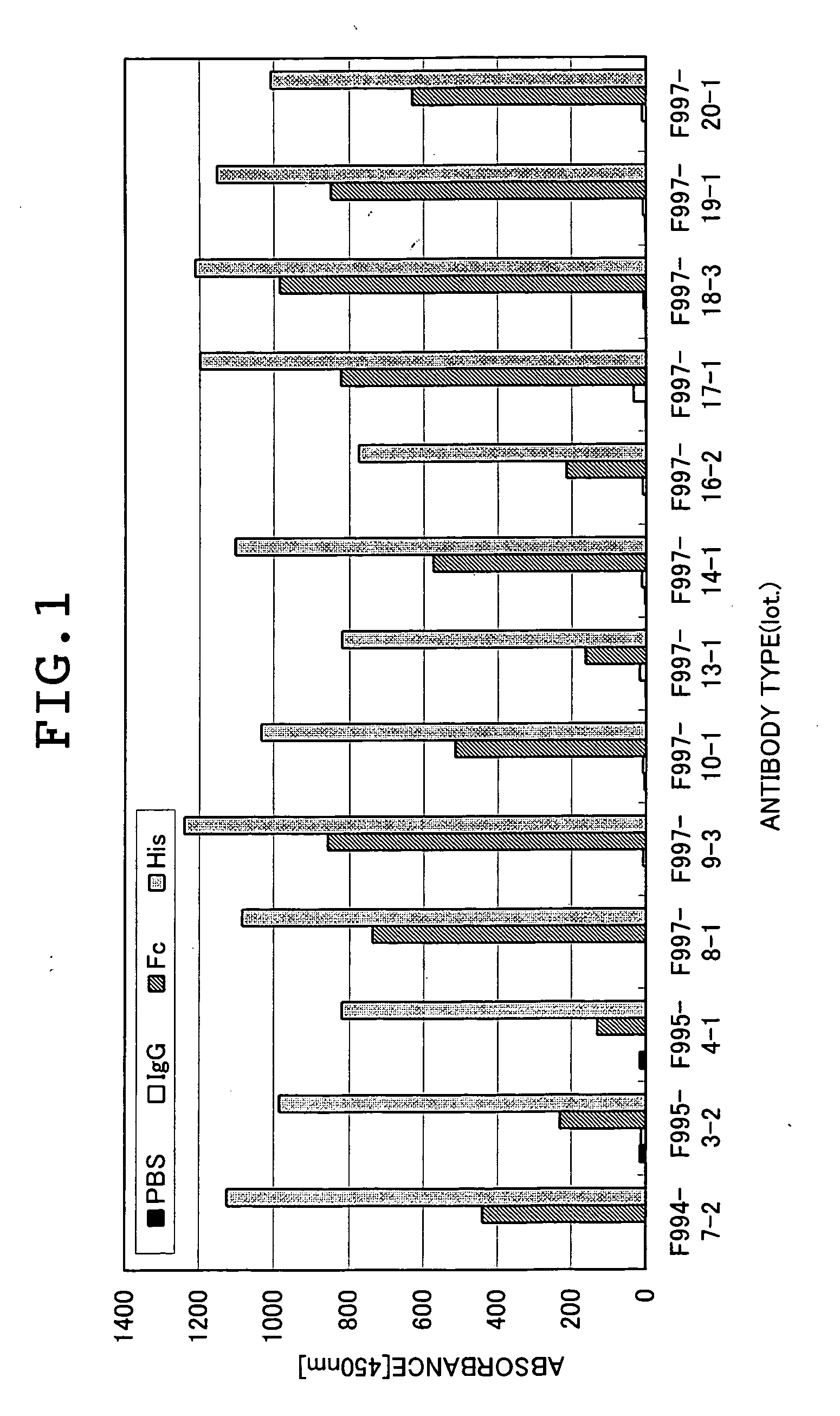
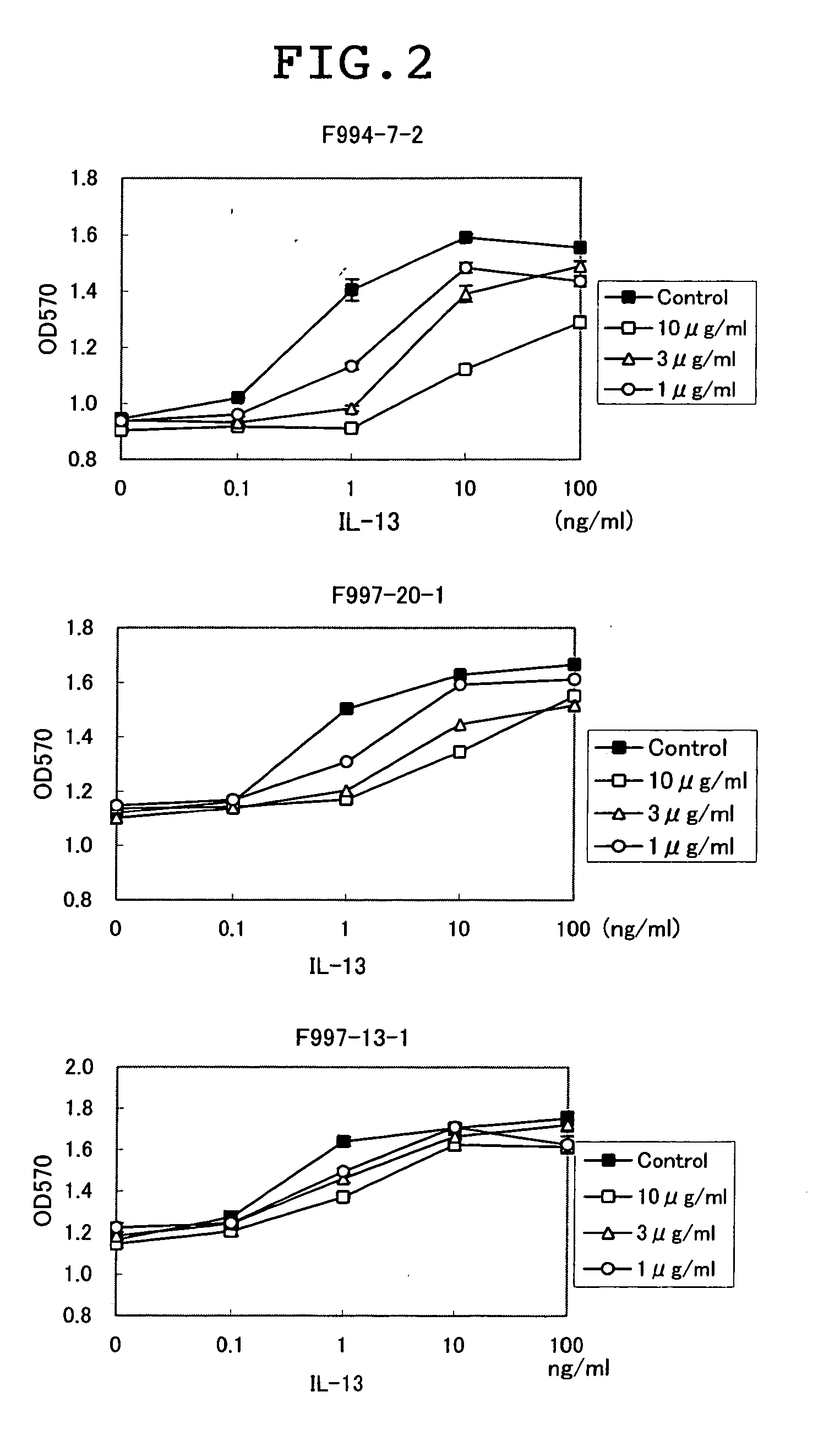
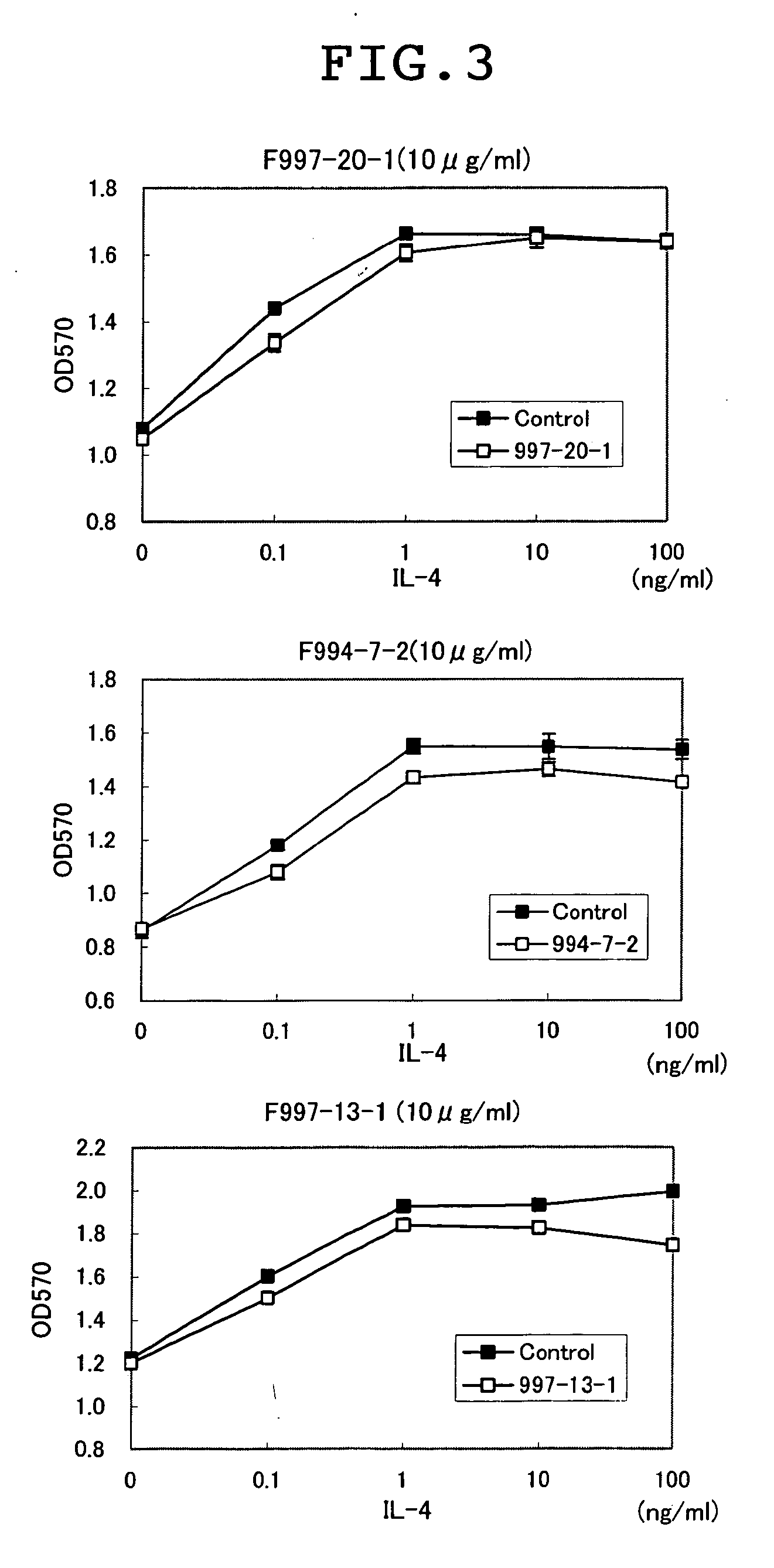
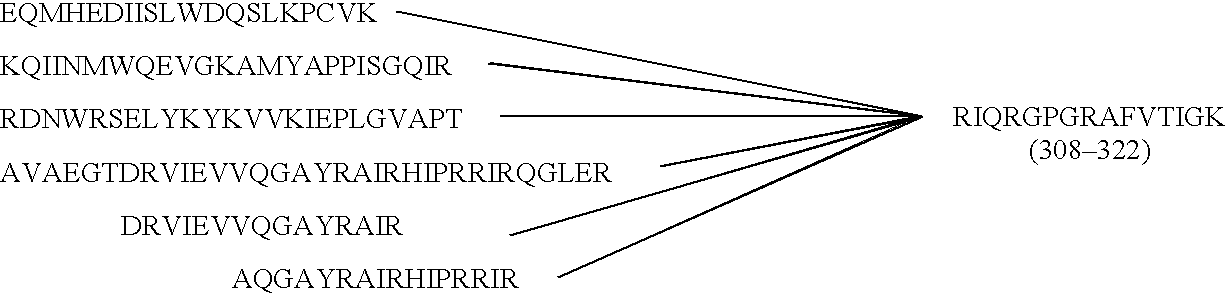
A novel anti-IL13 receptor α1 antibody having an activity of inhibiting a cell response by IL13, in particular, having an activity of inhibiting the cell response by IL13 but not inhibiting the cell response by IL4, a characteristic amino acid sequence in a variable region thereof, and a method of detecting IL13 receptor α1 in a sample using the same are provided.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
Peptides which elicit a high neutralizing antibody titer, cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and T helper cell response in a broad range of MHC type recipients
InactiveUS7094405B1High titerHigh titer of neutralizing antibodyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsV3 loopT helper cell
Peptide constructs comprised of multideterminant T helper peptides from the envelope glycoprotein of HIV previously identified to induce proliferative responses in four different haplotypes of mice and IL-2 responses in 52-73% of HIV positive, flu positive patients (cluster peptides), were co-linearly synthesized with the peptide 18 of the V3 loop of HIV-1 gp 160, corresponding to the principal neutralizing determinant of HIV-IIIB and also shown to contain a dominant CTL epitope. Cognate help for peptide 18 antibody was elicited following a single immunization in all strains of mice which had previously responded to a T cell epitope encompassed by the peptides. In two strains of mice, the level of neutralizing antibody achieved was comparable to levels adequate for protection from homologous viral challenge in chimpanzees. After a single boost, much higher antibody titers for 90% neutralization in the range of 1:1000 to 1:16,000 were achieved. Spleen cells from mice of three distinct MHC haplotypes sharing the Dd class I MHC molecule but with different class II molecules, immunized with the compound peptides, exhibited enhanced gp160-specific CTL activity.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
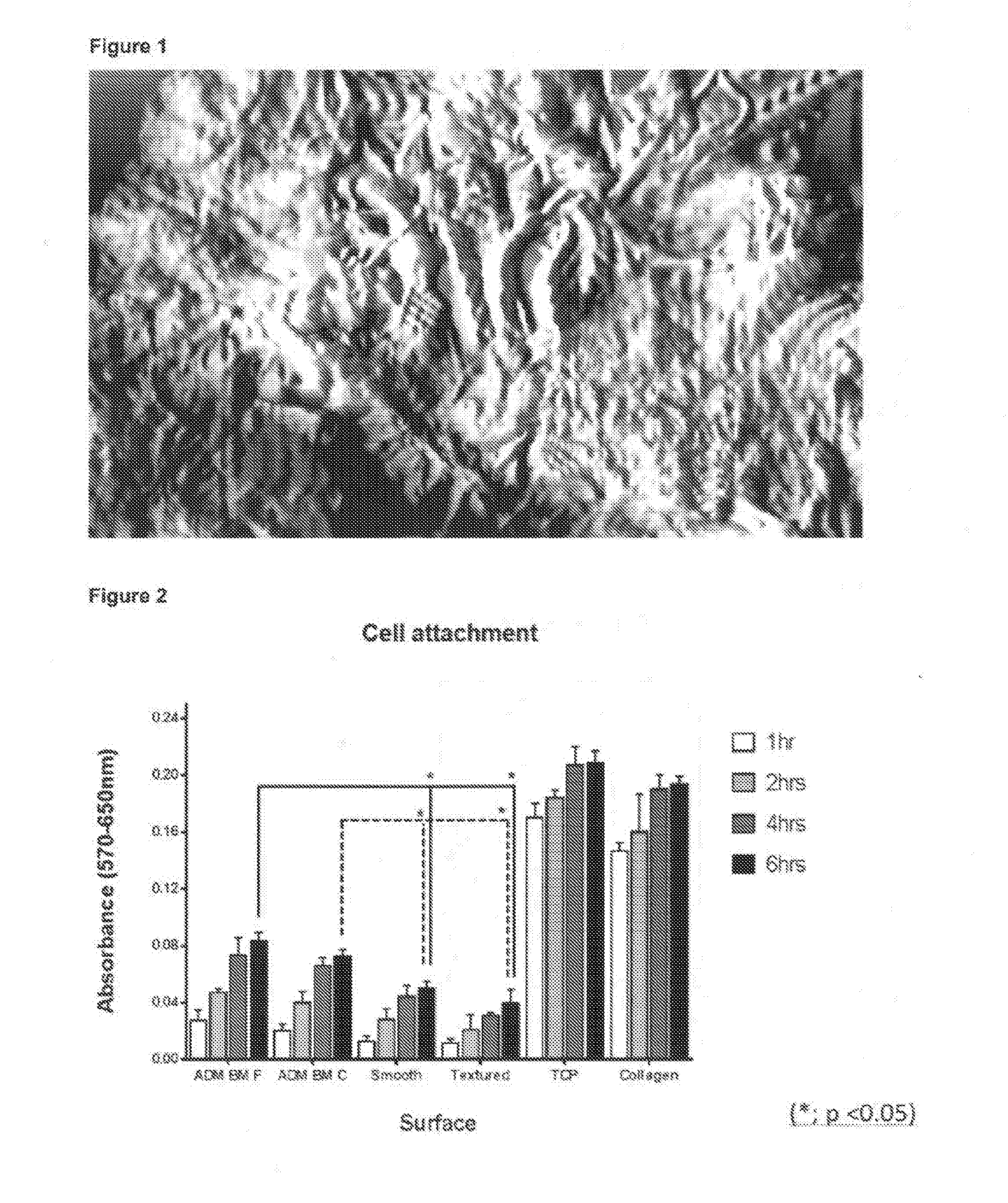
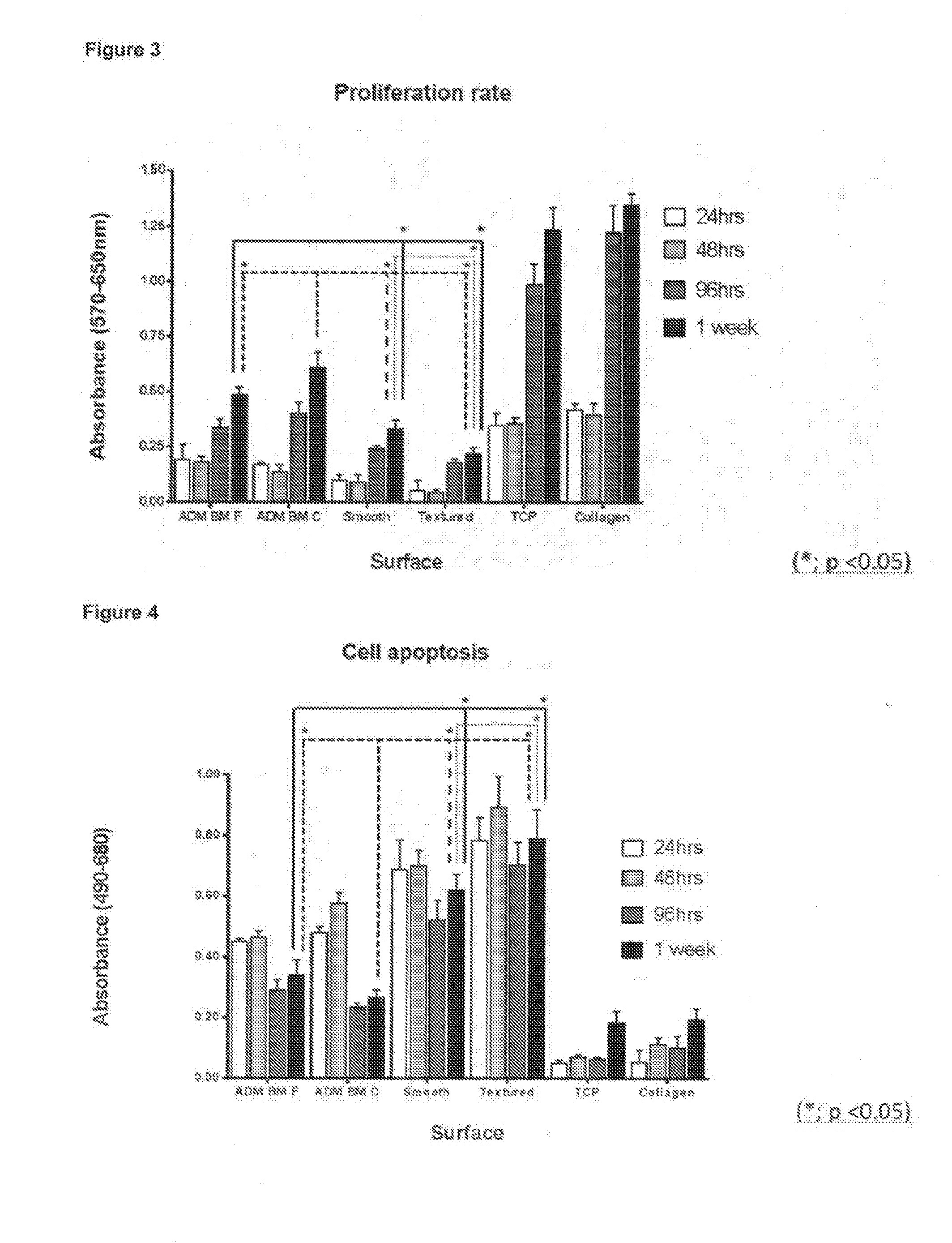
Textured surfaces for breast implants
ActiveUS20170049549A1Improve responseReduce contractionMammary implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatusBreast implantBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides new devices for implantation in a patient having irregular textured surfaces, which devices show significantly improved cellular response compared to conventional smooth and textured implants, indicating that significantly improved biocompatibility would be achieved in vivo. Methods for making such new devices and surface textures are also disclosed.
Owner:ESTAB LABS
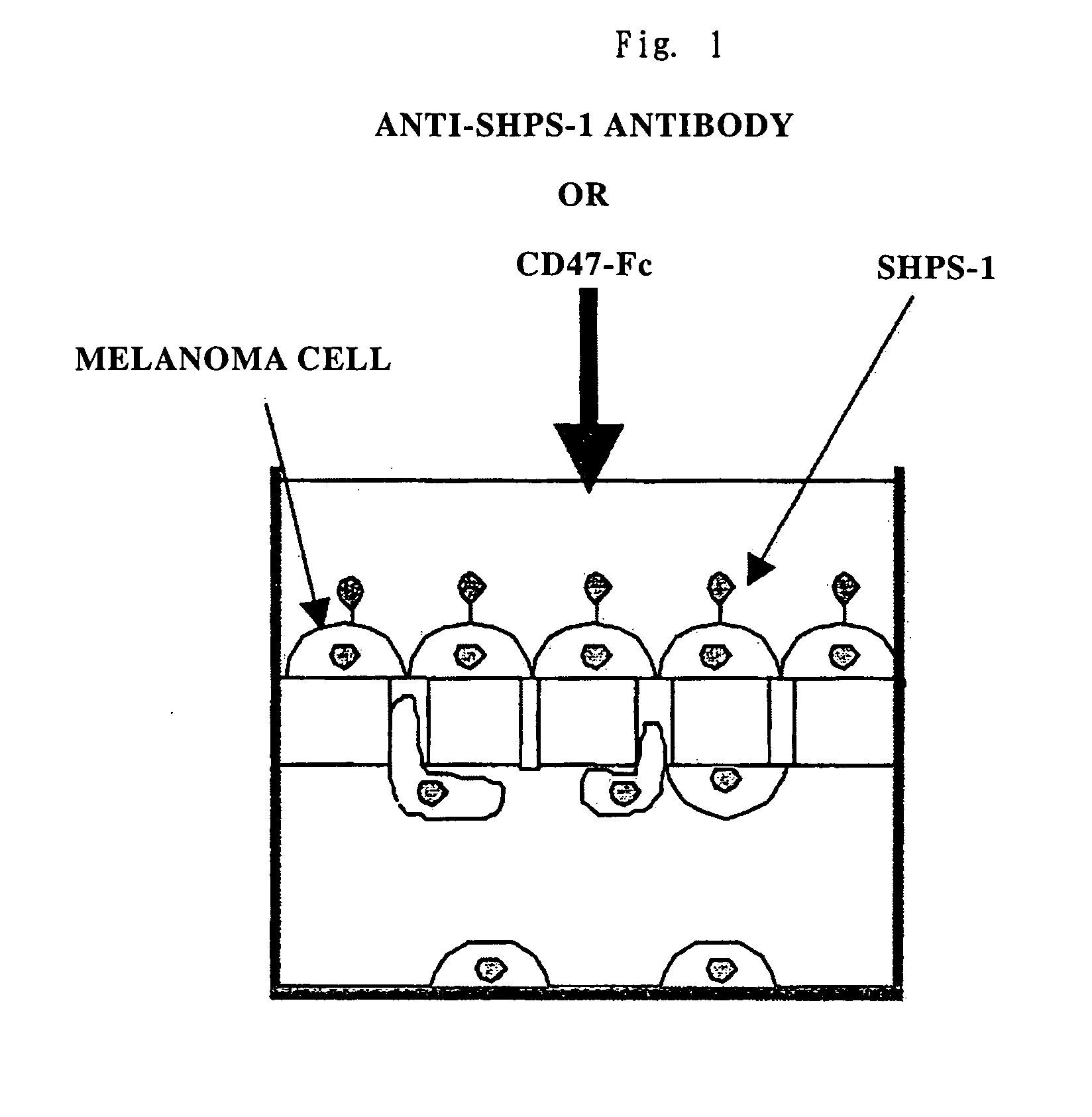
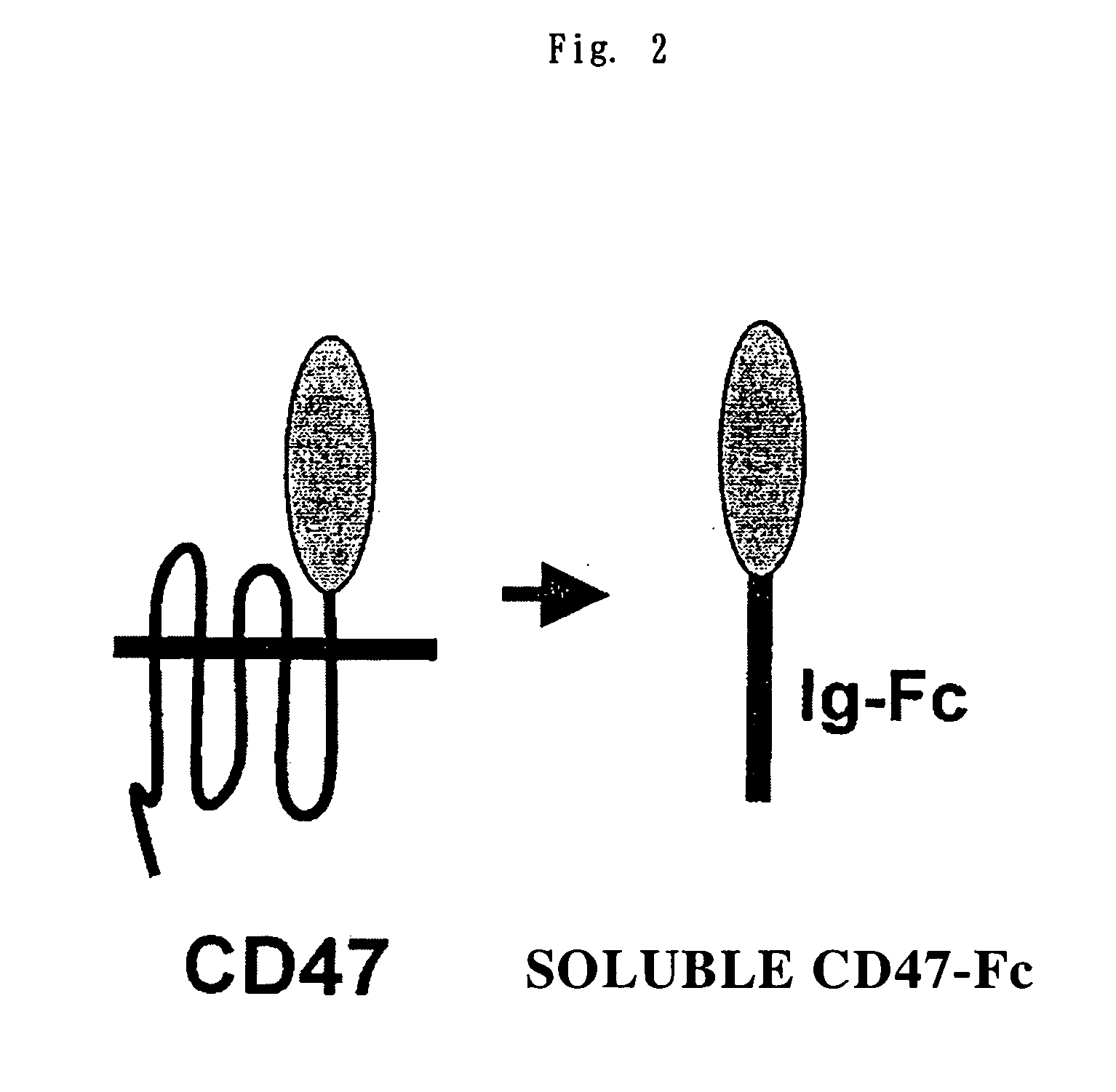
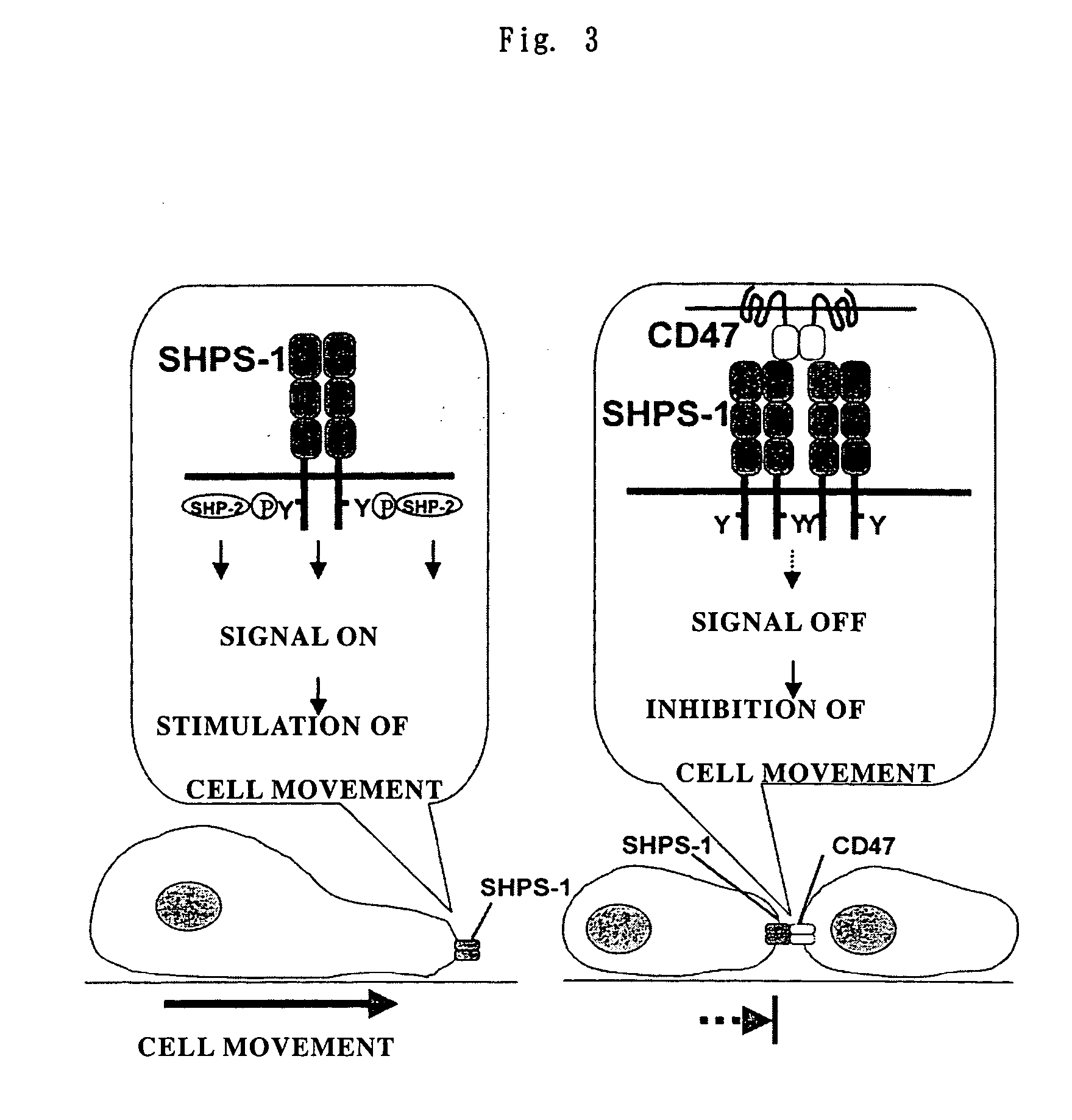
Cd47 partal peptdie and anti-shps-1 monoclonal antibody
A CD47 partial peptide which has an amino acid sequence constituting an extracellular region having an immunoglobulin-like structure of a CD47 protein, which is specifically bound to an N-terminal immunoglobulin-like structure of a dephosphorylation substrate protein SHPS-1 of an SH2 domain-containing protein, and which can act on a function of cell response mediated by SHPS-1, and an anti-SHPS-1 monoclonal antibody.
Owner:GUNMA UNIVERSITY
Whole cell assays and methods
Owner:CELCUITY INC
Microfluidic System Having Monolithic Nanoplasmonic Structures
ActiveUS20140004507A1Simple and robust and cost-effectiveLow costMaterial nanotechnologyServomotor componentsPolymer substrateEngineering
A microfluidic system, particularly suited as a cell culture system, is provided having a single monolithic biocompatible substrate with both a surface having an ordered array of nano-scale elements required for plasmonic response monitoring and a network of microchannels for precisely controlling cellular environment. The system has the additional advantages of low-volume consumption, rapid low-cost fabrication of molds with easily interchangeable microfluidic channel layouts, amenability to mass production, and in situ label-free real-time detection of cellular response, viability, behavior and biomolecular binding using plasmonic techniques. A ratio of greater than 0.2 between the cross-sectional dimension and the spacing distance of the nano-scale elements is useful for plasmonic response monitoring. A process for producing such a system involves fabrication of a master mold containing the nano-scale elements etched into a hard substrate, and the micro-scale and meso-scale features, such as channels and chambers, provided in a soft membrane bonded to the hard substrate. A stamp may be created by setting a settable liquid polymer or metal placed in the master mold and then the features of the intended device transferred to a polymeric substrate using the stamp.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Totally-integrated high-flux cell level micro-fluidic chip medicine evaluating system
ActiveCN103257213ARealize real-time tracking analysisReduce consumptionLaboratory glasswaresTesting medicinal preparationsHigh fluxComputer module
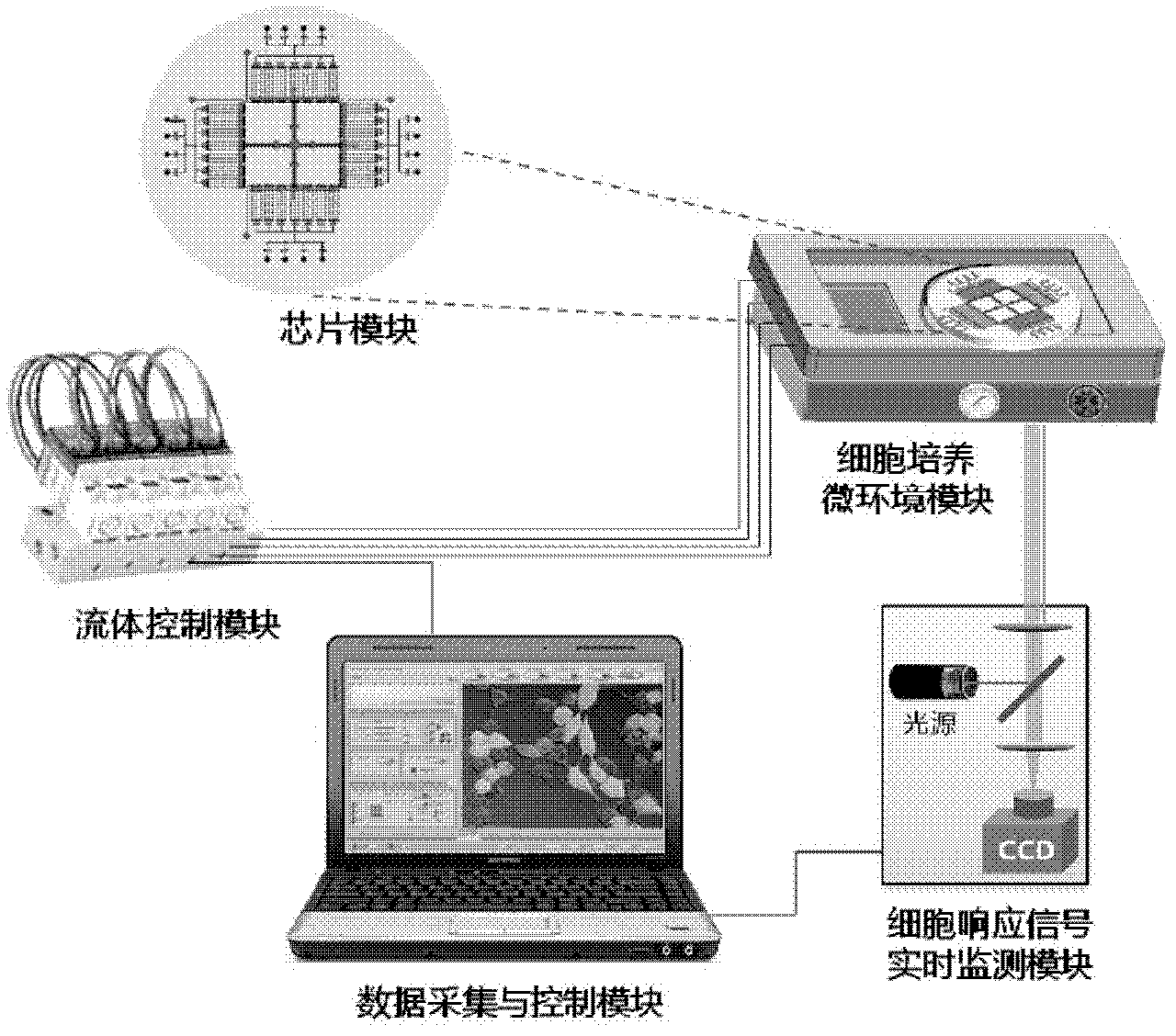
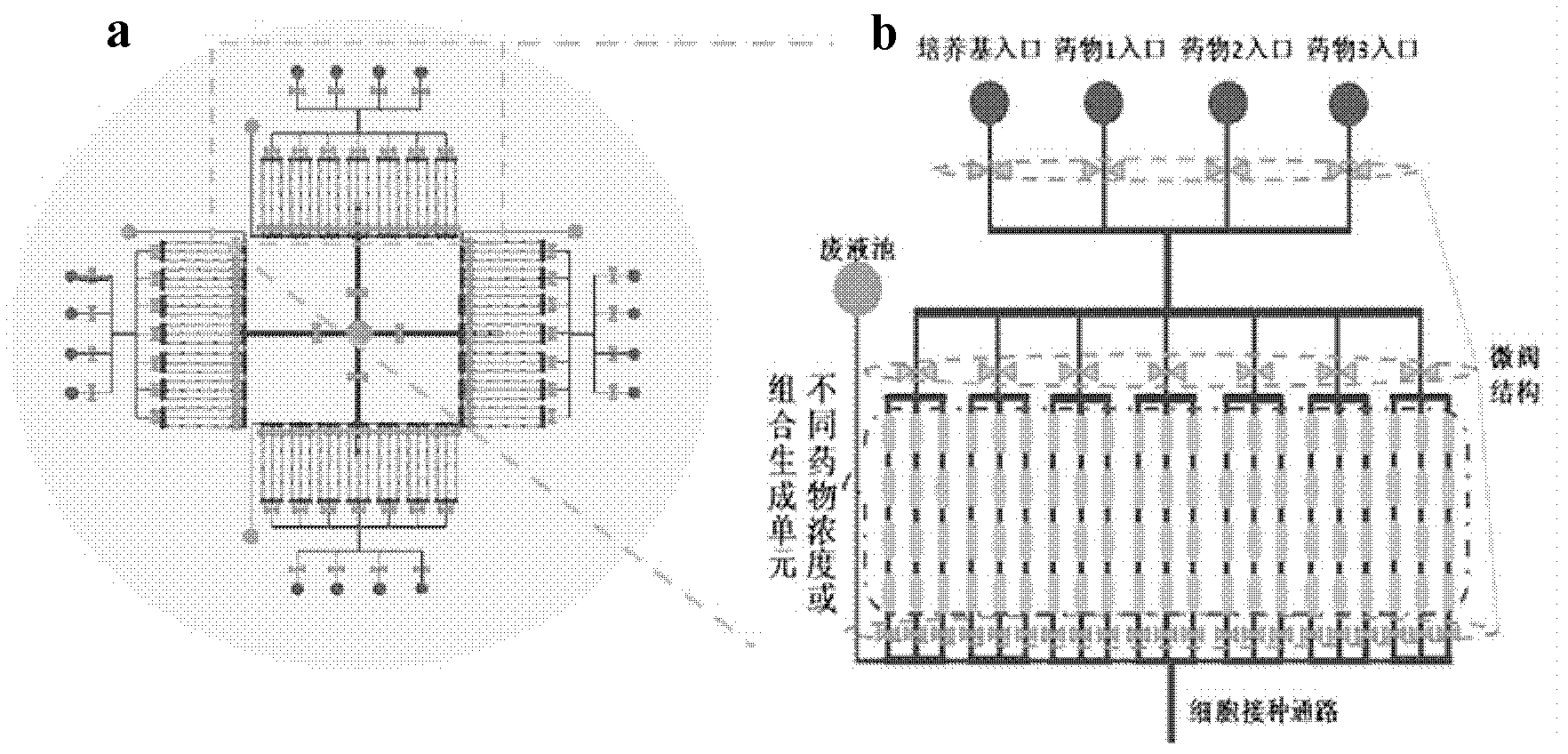
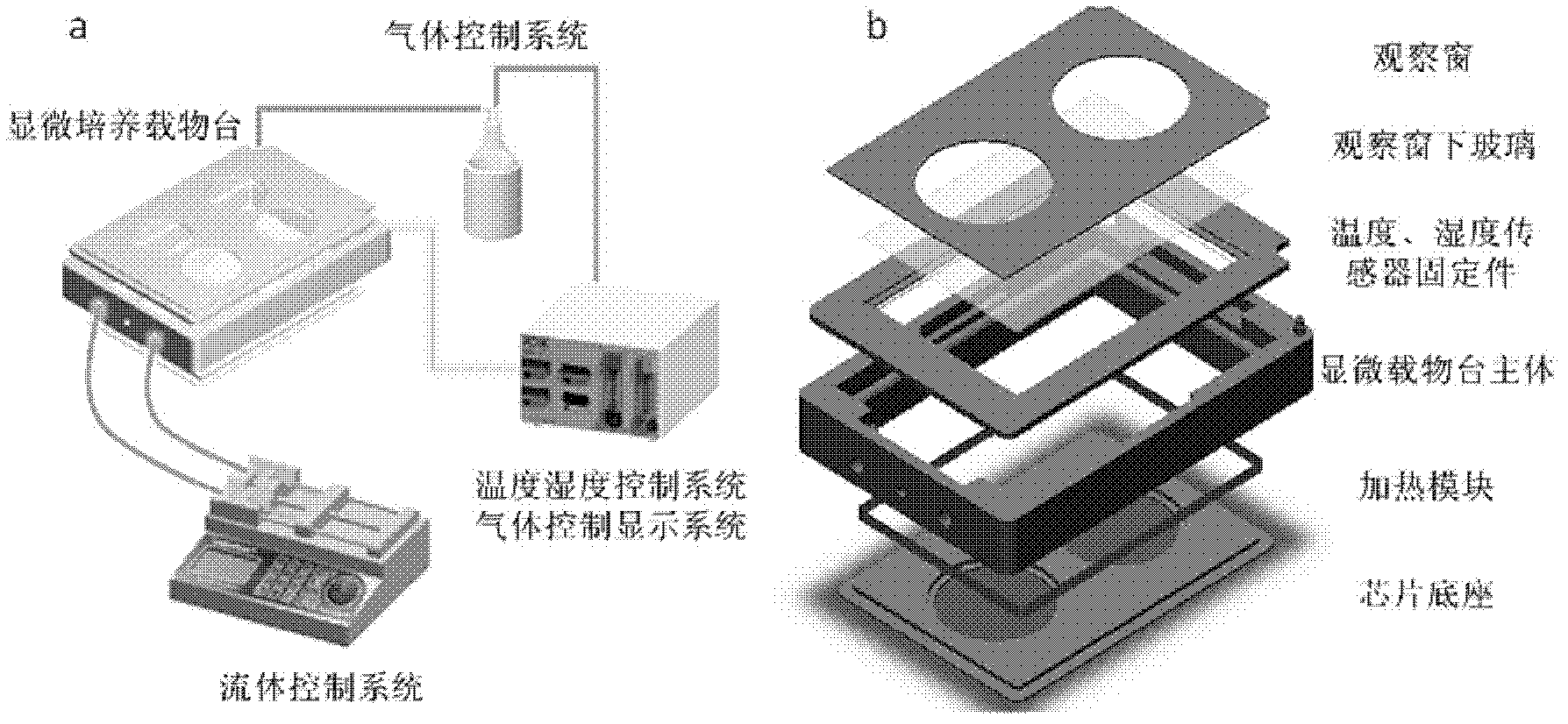
A totally-integrated high-flux cell level micro-fluidic chip medicine evaluating system is a multifunctional cell level medicine evaluating system treating a micro-fluidic chip as a core technology, starting from the total design of an integrated high-flux automatic micro-fluidic chip system and integrating a cell function chip module, a flow path control module, a cell culture microenvironment module and a cell response signal real-time monitoring module. The totally-integrated high-flux cell level micro-fluidic chip medicine evaluating system has the characteristics of total integration, high flux, less sample consumption, totally-closed operation, realization of multi-parameter real time monitoring, and the like, has a very strong original innovativeness, and is of great significance to the large-scale medicine research and development.
Owner:苏州纳米大健康研究院有限公司
Cell-based kinase assay
InactiveUS20060141549A1Simple and sensitive high-throughput assayQuick identificationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionKinase activityAssay
The present invention relates to improved systems and strategies for the investigation of kinase activity in cells. More specifically, cell-based assay methods are provided that allow the phosphorylating activity of a kinase to be determined inside a cell. The invention also provides cell-based screening assays for identifying compounds that have the ability to modulate the phosphorylating activity of protein kinases. Modulators of kinase activity identified by the screening methods are also described, as are pharmaceutical compositions comprising these modulators and methods of using them for inhibiting or enhancing cellular responses triggered by kinase-mediated events.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Antagonist of th-1 immunerresponse inducing cytokine for the treatment of autoimmune diseases
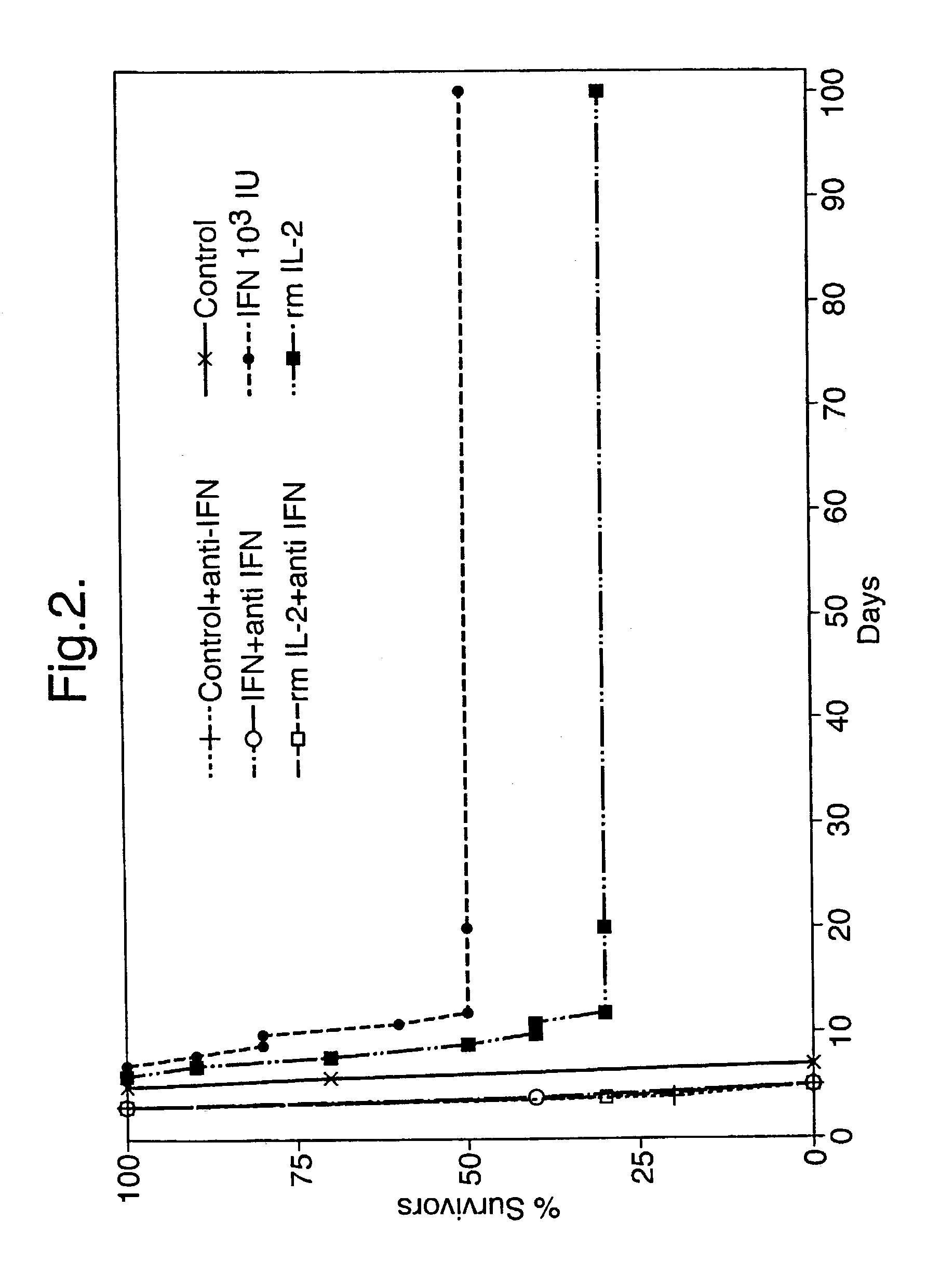
Oromucosal administration of antagonists of cytokines associated with stimulation or enhancement of T helper 1 cell responses, preferably for example a Type 1-interferon antibody, is disclosed for inhibition of prevention of autoimmune diseases.
Owner:PHARM PACIFIC PTY LTD
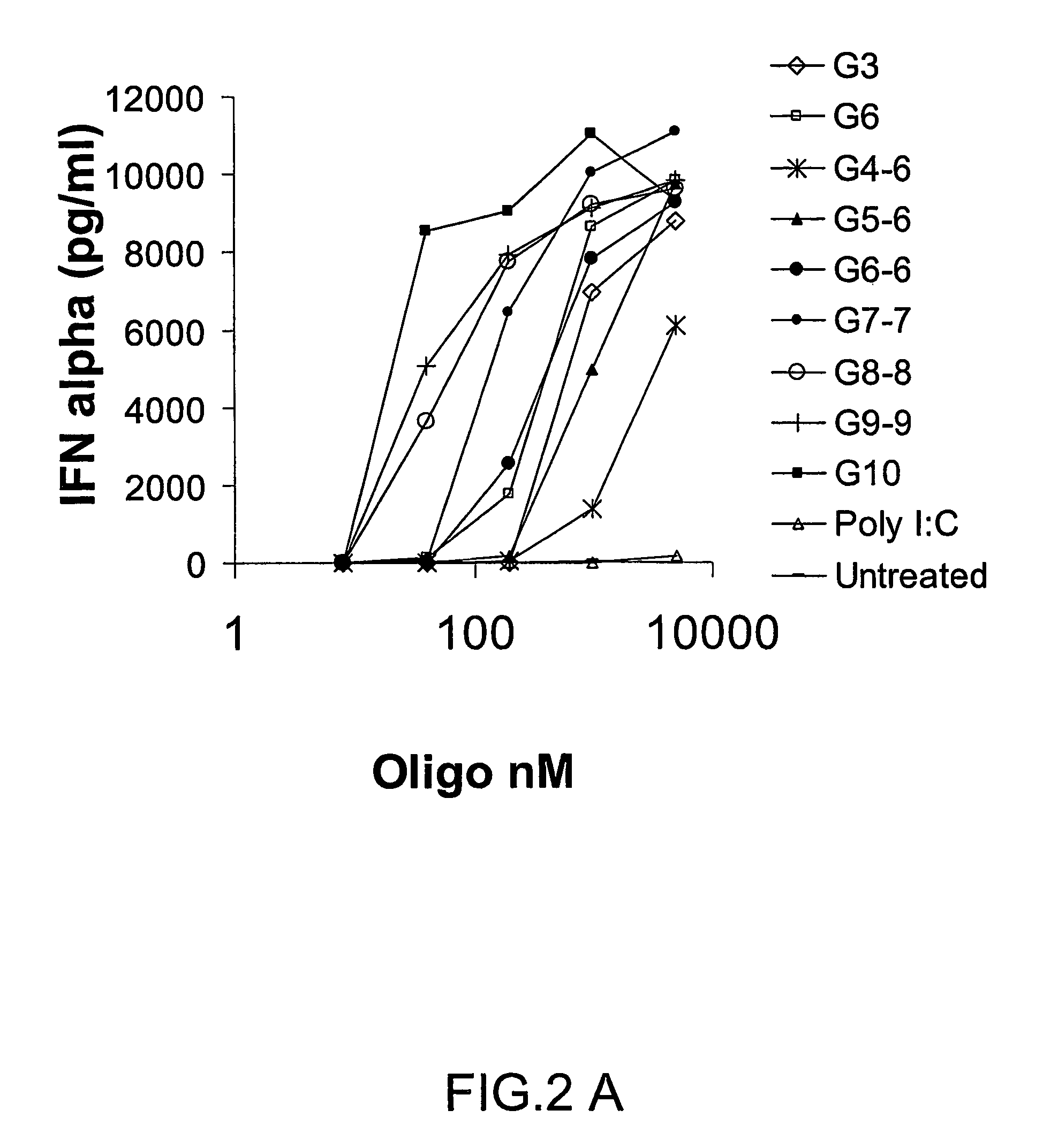
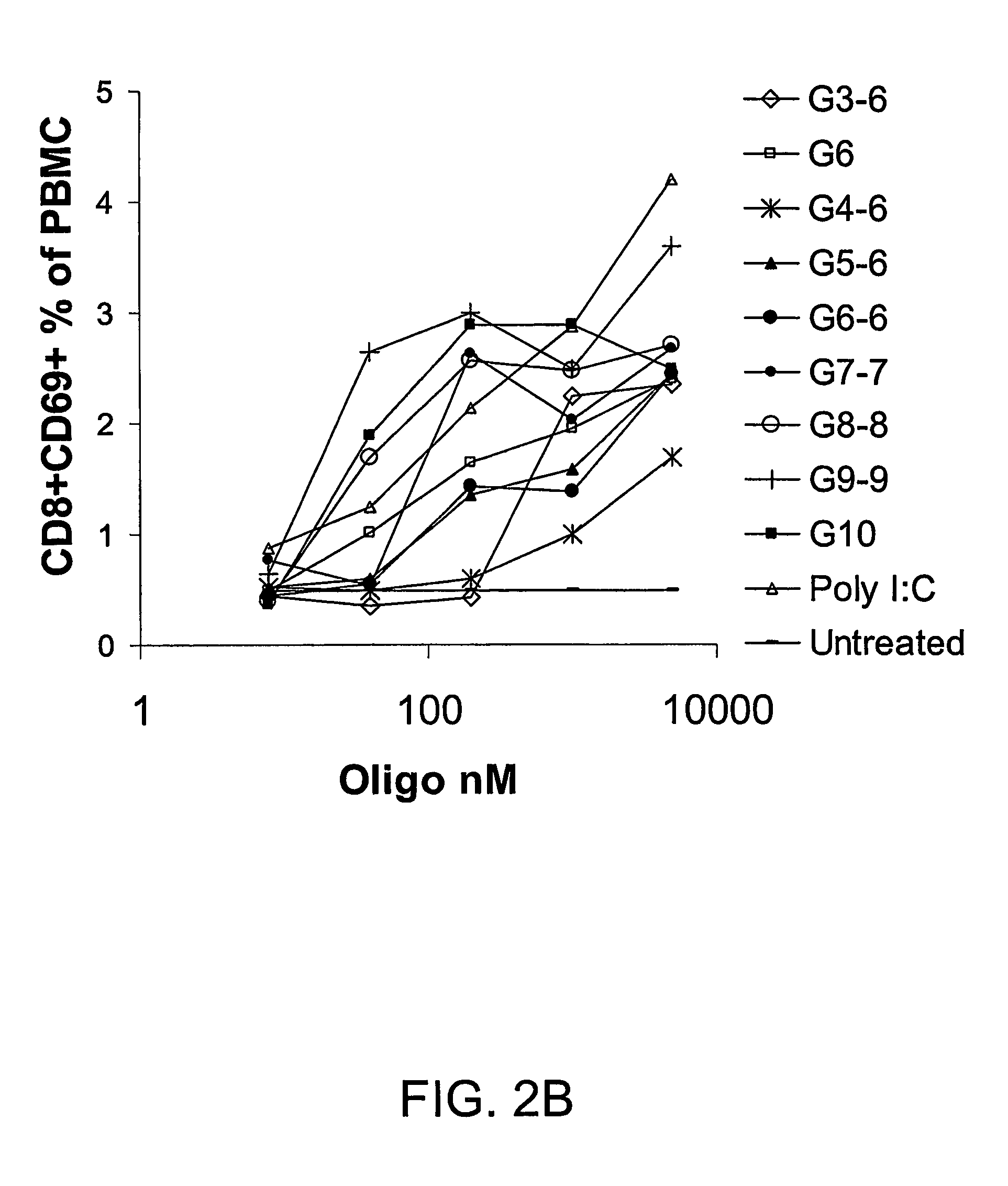
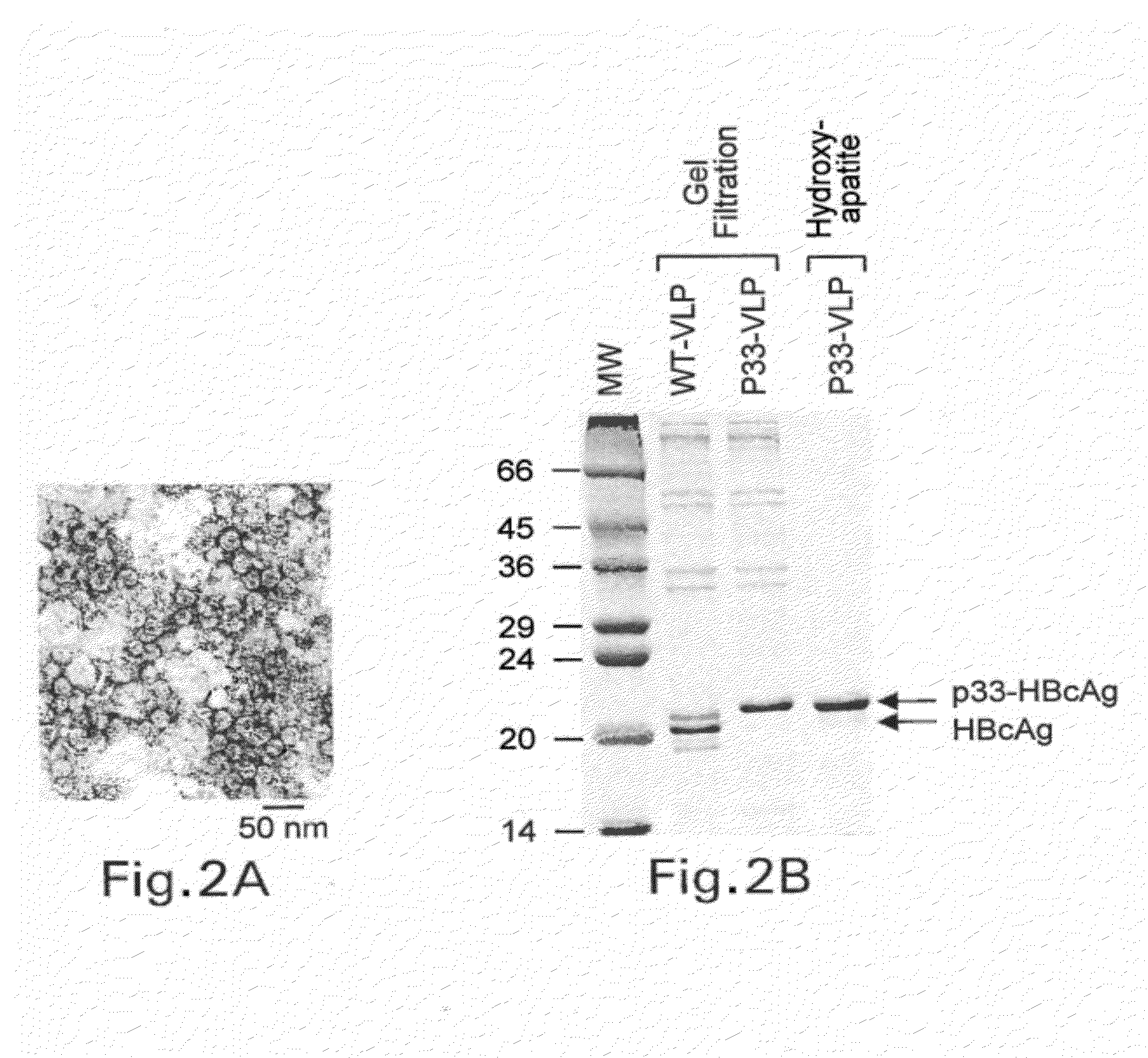
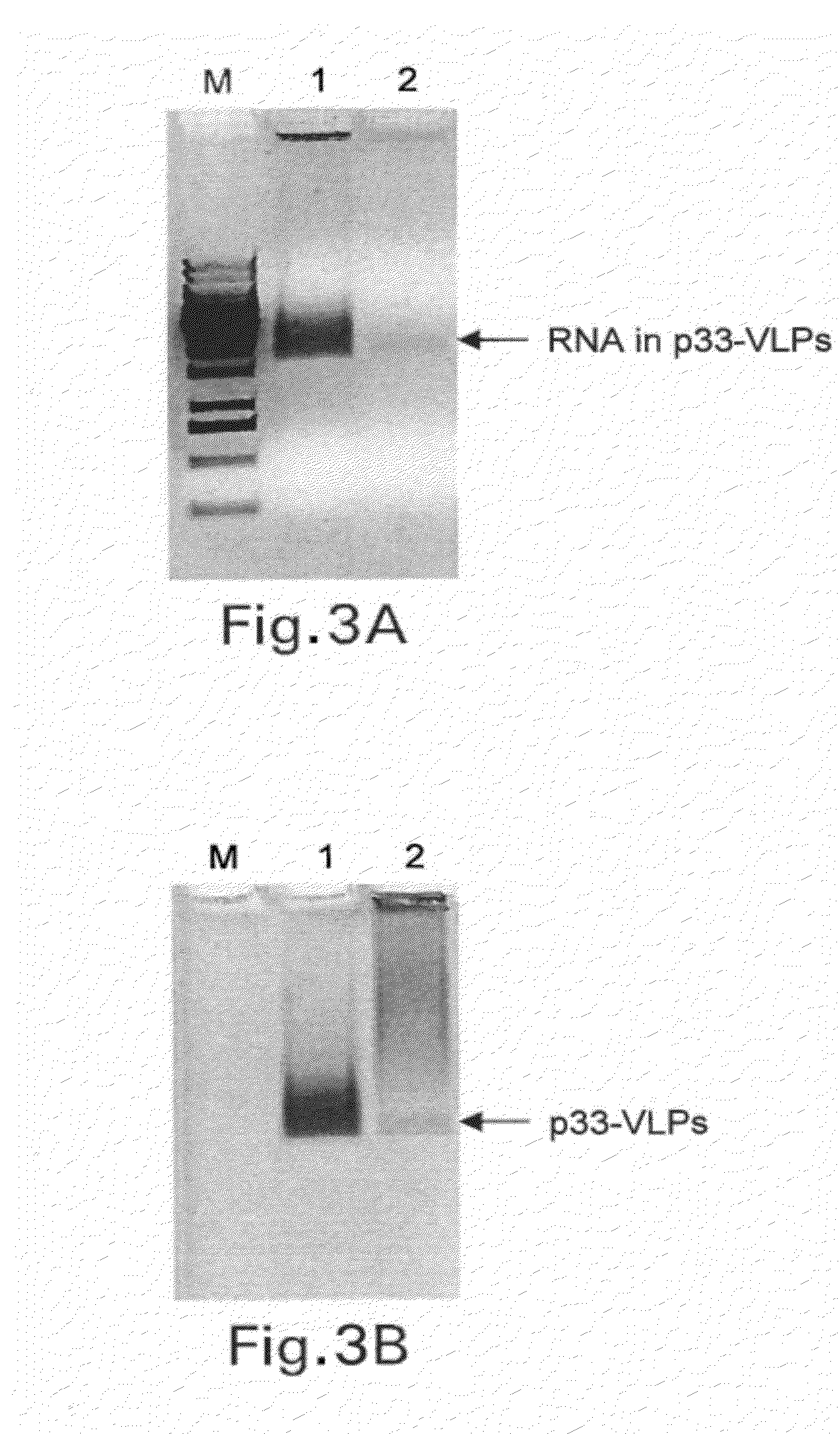
Packaging of Immunostimulatory Substances into Virus-Like Particles: Method of Preparation and Use
InactiveUS20120301499A1More immunogenicEnhance immune responseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesVaccinationViral disease
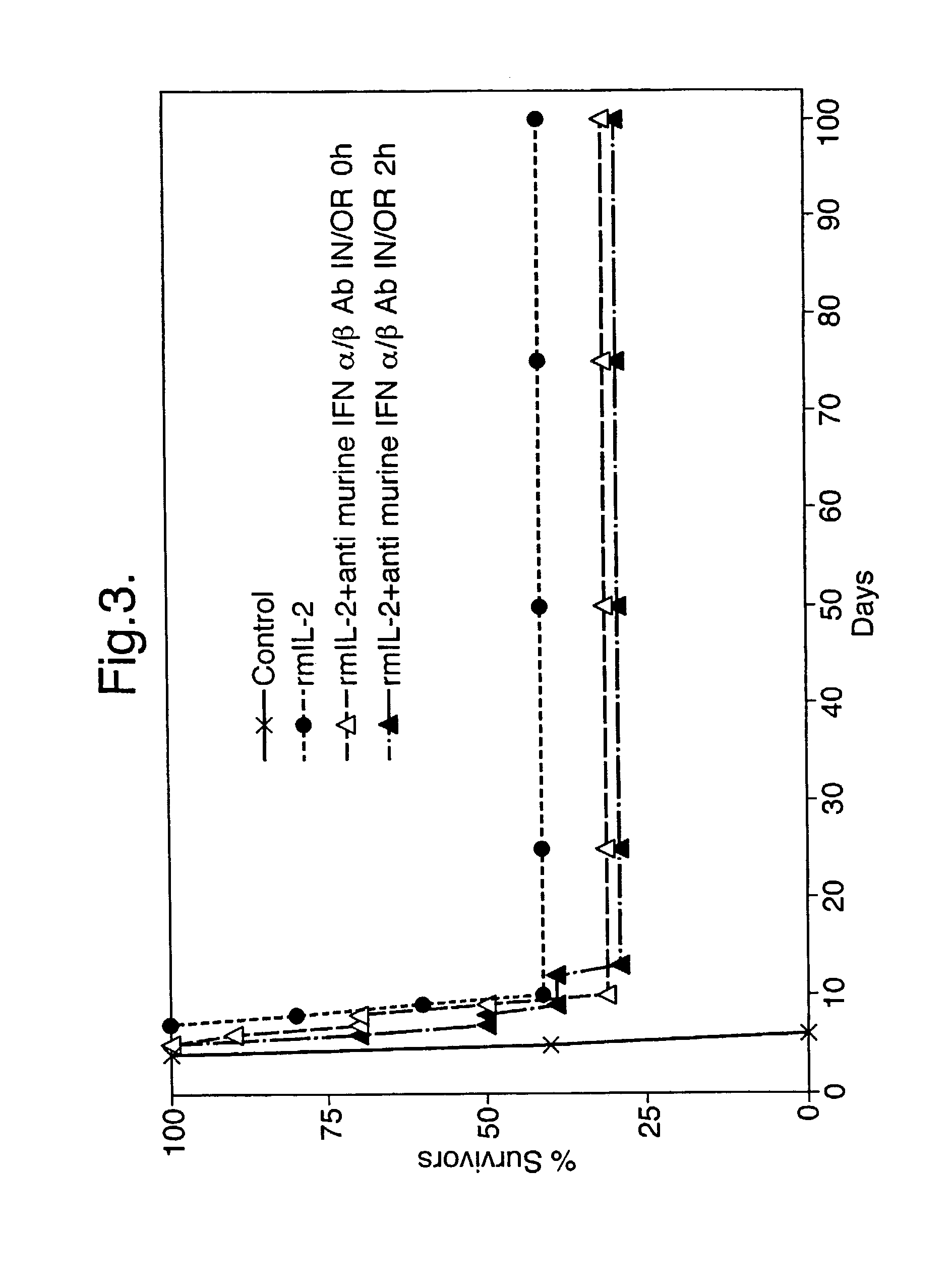
The invention relates to the finding that virus like particles (VLPs) can be loaded with immunostimulatory substances, in particular with DNA oligonucleotides containing non-methylated C and G (CpGs). Such CpG-VLPs are dramatically more immunogenic than their CpG-free counterparts and induce enhanced B and T cell responses. The immune response against antigens optionally coupled, fused or attached otherwise to the VLPs is similarly enhanced as the immune response against the VLP itself. In addition, the T cell responses against both the VLPs and antigens are especially directed to the Th1 type. Antigens attached to CpG-loaded VLPs may therefore be ideal vaccines for prophylactic or therapeutic vaccination against allergies, tumors and other self-molecules and chronic viral diseases.
Owner:KUROS US LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com