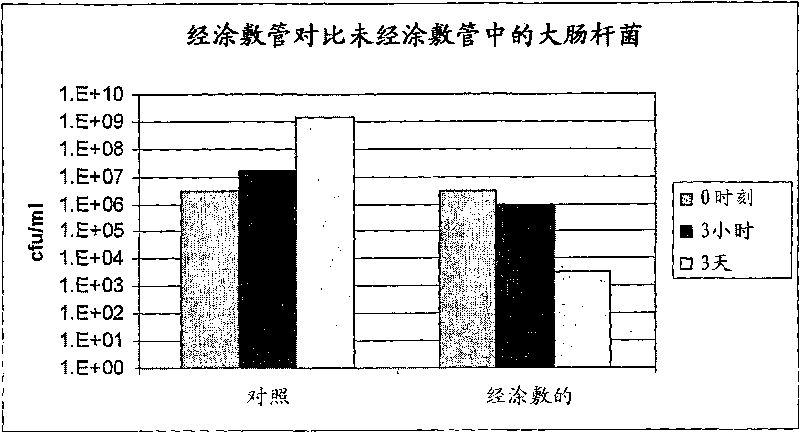
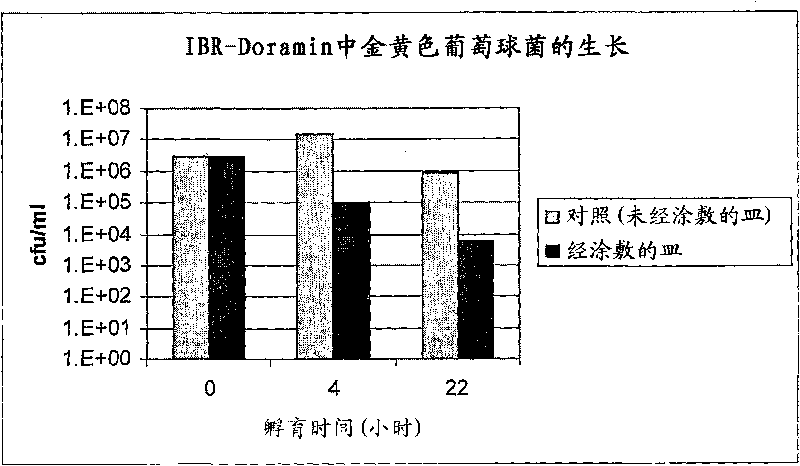
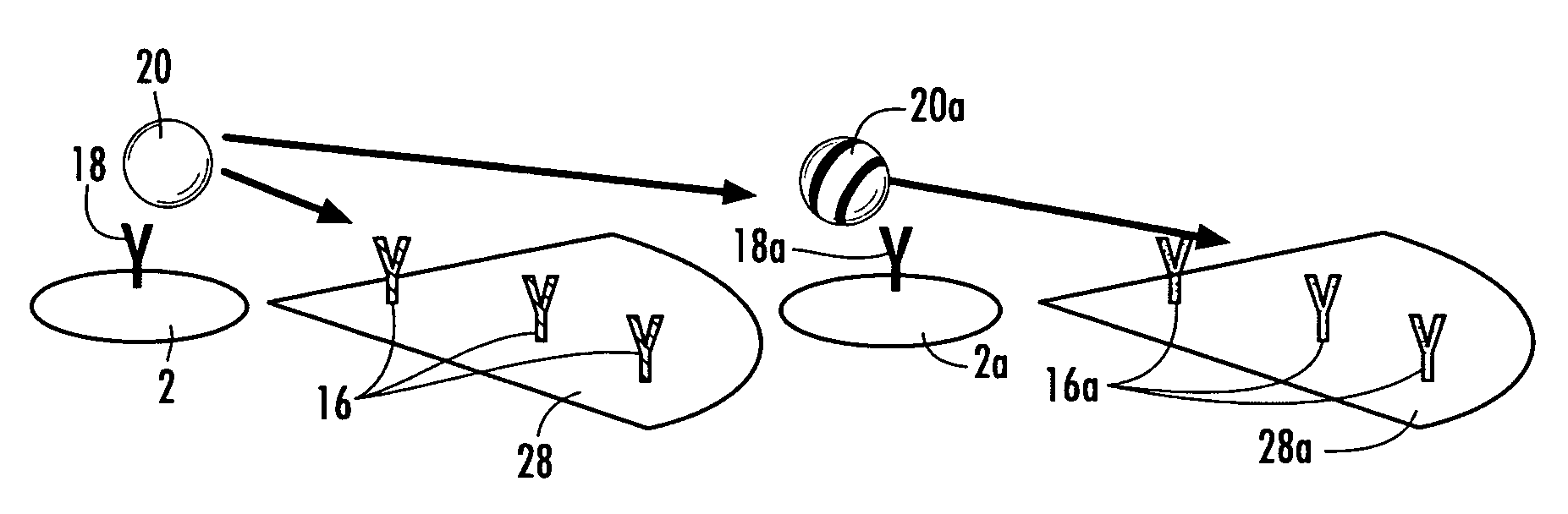
Patents
Literature
76 results about "Cell–cell interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell–cell interaction refers to the direct interactions between cell surfaces that play a crucial role in the development and function of multicellular organisms. These interactions allow cells to communicate with each other in response to changes in their microenvironment. This ability to send and receive signals is essential for the survival of the cell. Interactions between cells can be stable such as those made through cell junctions. These junctions are involved in the communication and organization of cells within a particular tissue. Others are transient or temporary such as those between cells of the immune system or the interactions involved in tissue inflammation. These types of intercellular interactions are distinguished from other types such as those between cells and the extracellular matrix. The loss of communication between cells can result in uncontrollable cell growth and cancer.
Multilayered microcultures
InactiveUS20060141617A1Accurate mimicFlexible and cost-effectiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningBiological bodyCell adhesion
A multilayer microculture capable of modeling complex in vitro structures such as mammalian tissues and organ structures is provided, along with methods for producing such a microculture and methods of using such microcultures for assaying for modulators of cell-cell interaction, cell migration, cell proliferation, cell adhesion or cellular or organismal physiology. Further provided are methods of identifying hazardous materials such as environmental toxins and pollutants (e.g., carcinogenic compounds), and methods of monitoring organismal physiology.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Molecular and functional profiling using a cellular microarray
InactiveUS20060019235A1Faster and efficient predictionReward for identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisCell–cell interactionFunctional profiling
Cells are profiled with respect to their expression of cell surface molecules, and ability to respond to external stimulus in the microenvironment. External stimuli include cell-cell interactions, response to factors, and the like. The cells are arrayed on a planar or three-dimensional substrate through binding to immobilized or partially diffused probes. Probes of interest include specific binding partners for cell surface molecules, signaling cues that act to regulate cell responses, differentiation factors, etc., which may be arrayed as one or a combination of molecules.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
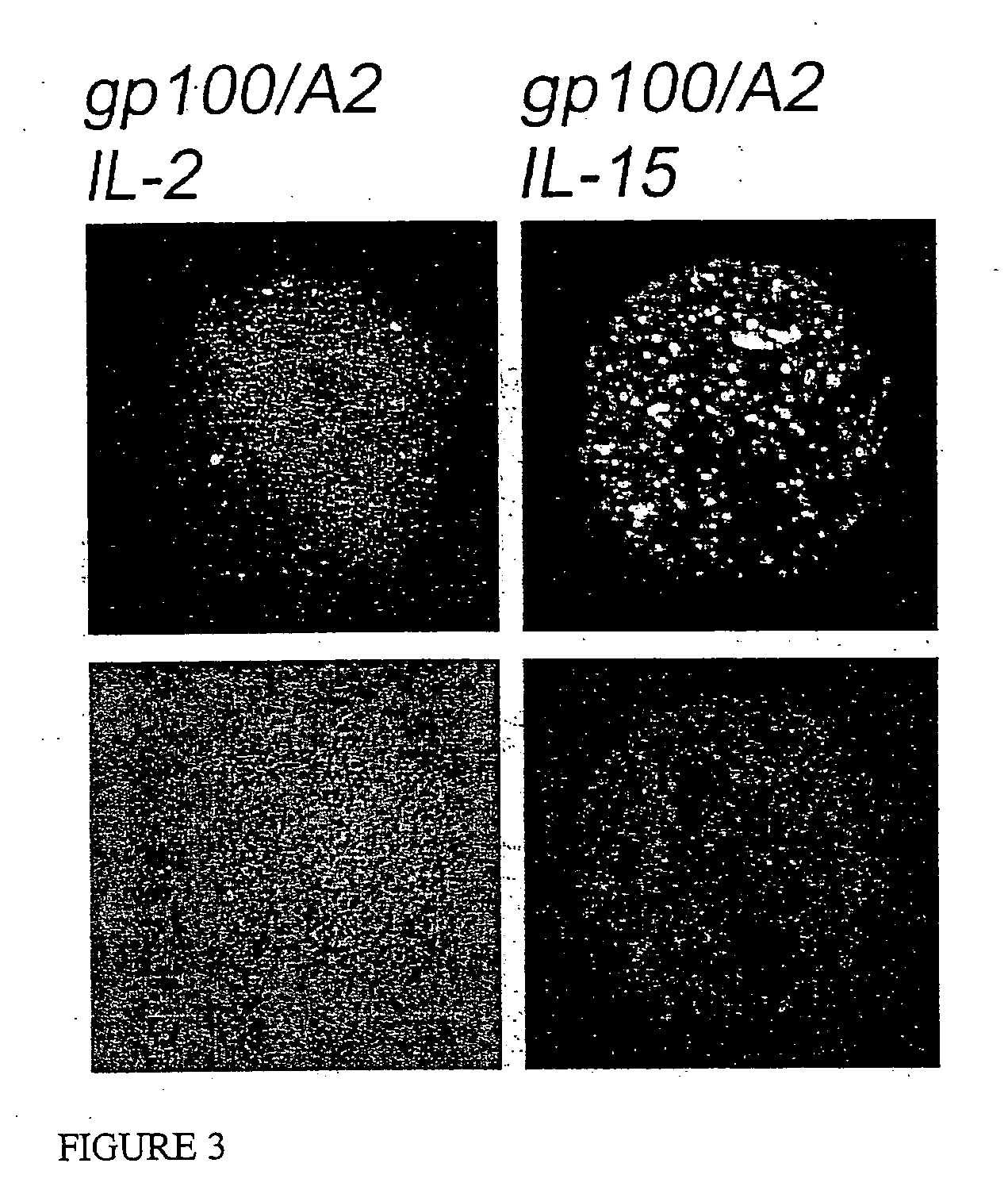
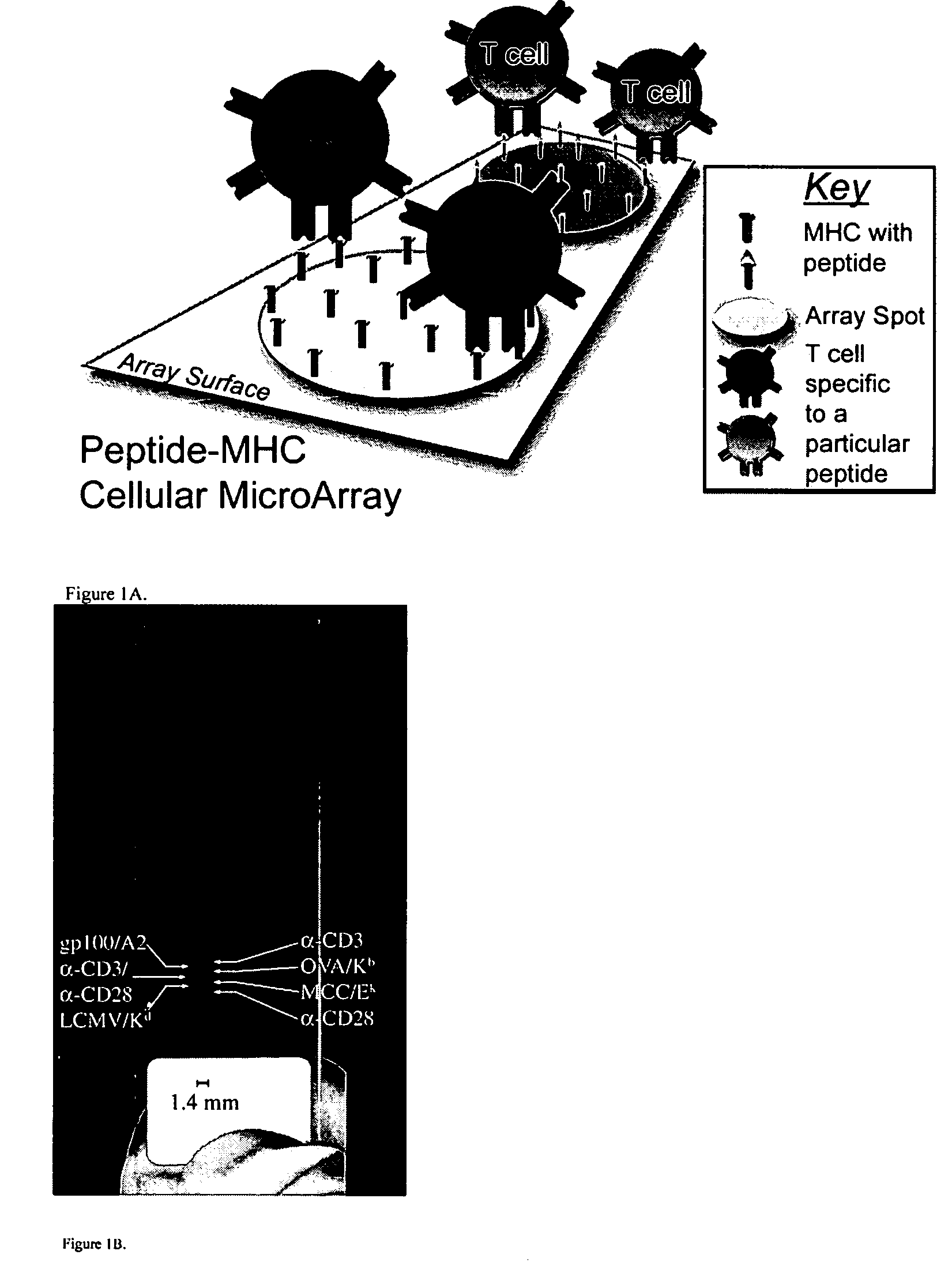
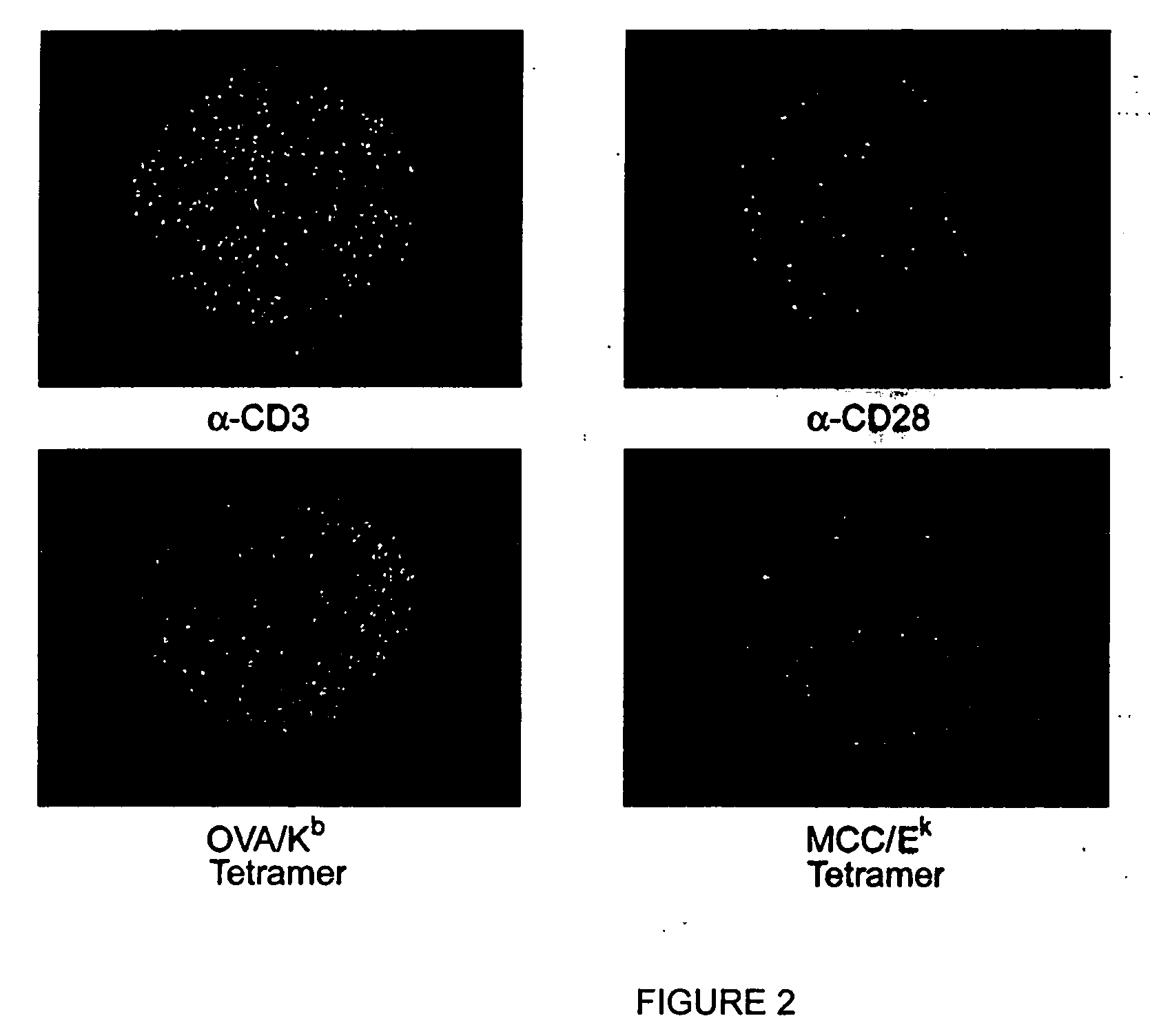
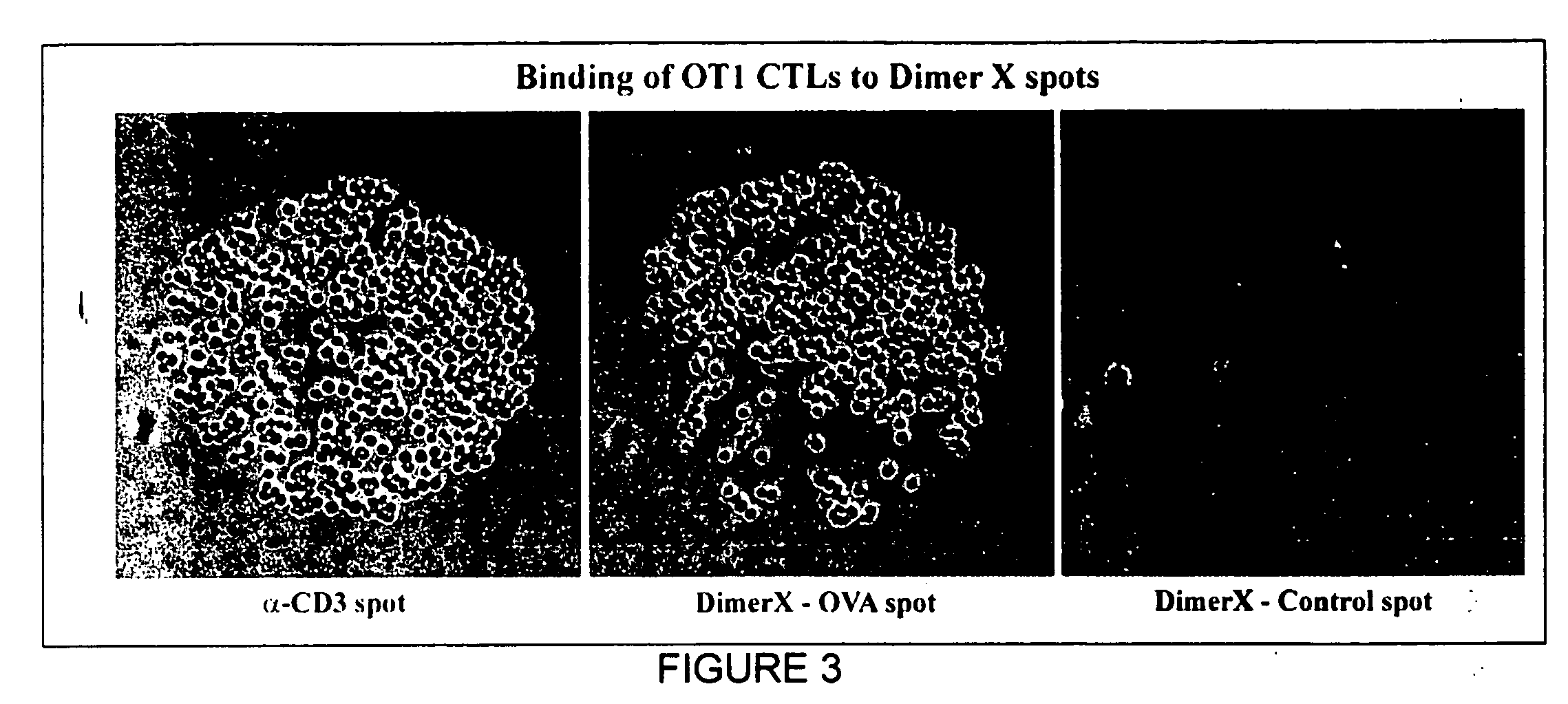
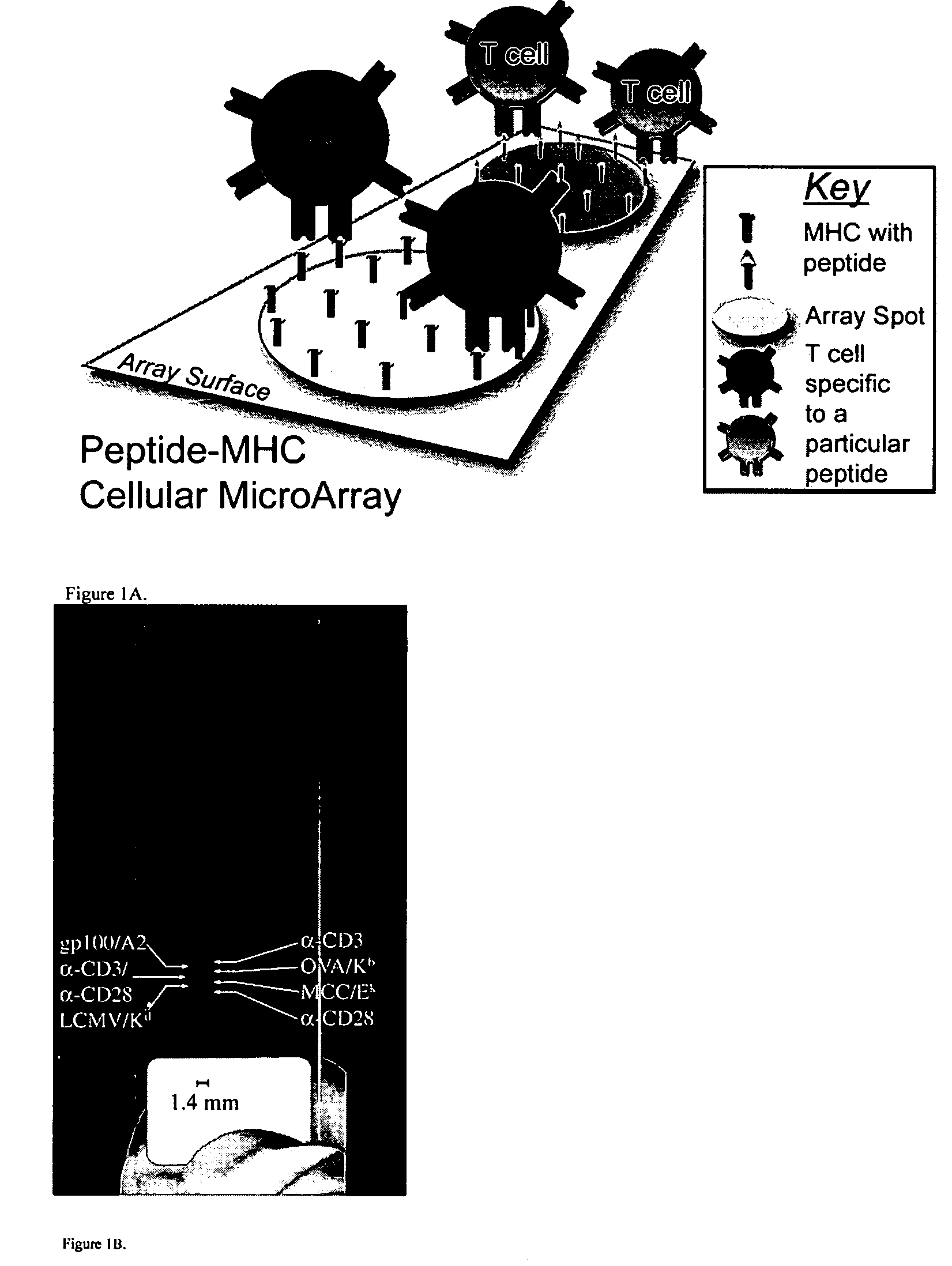
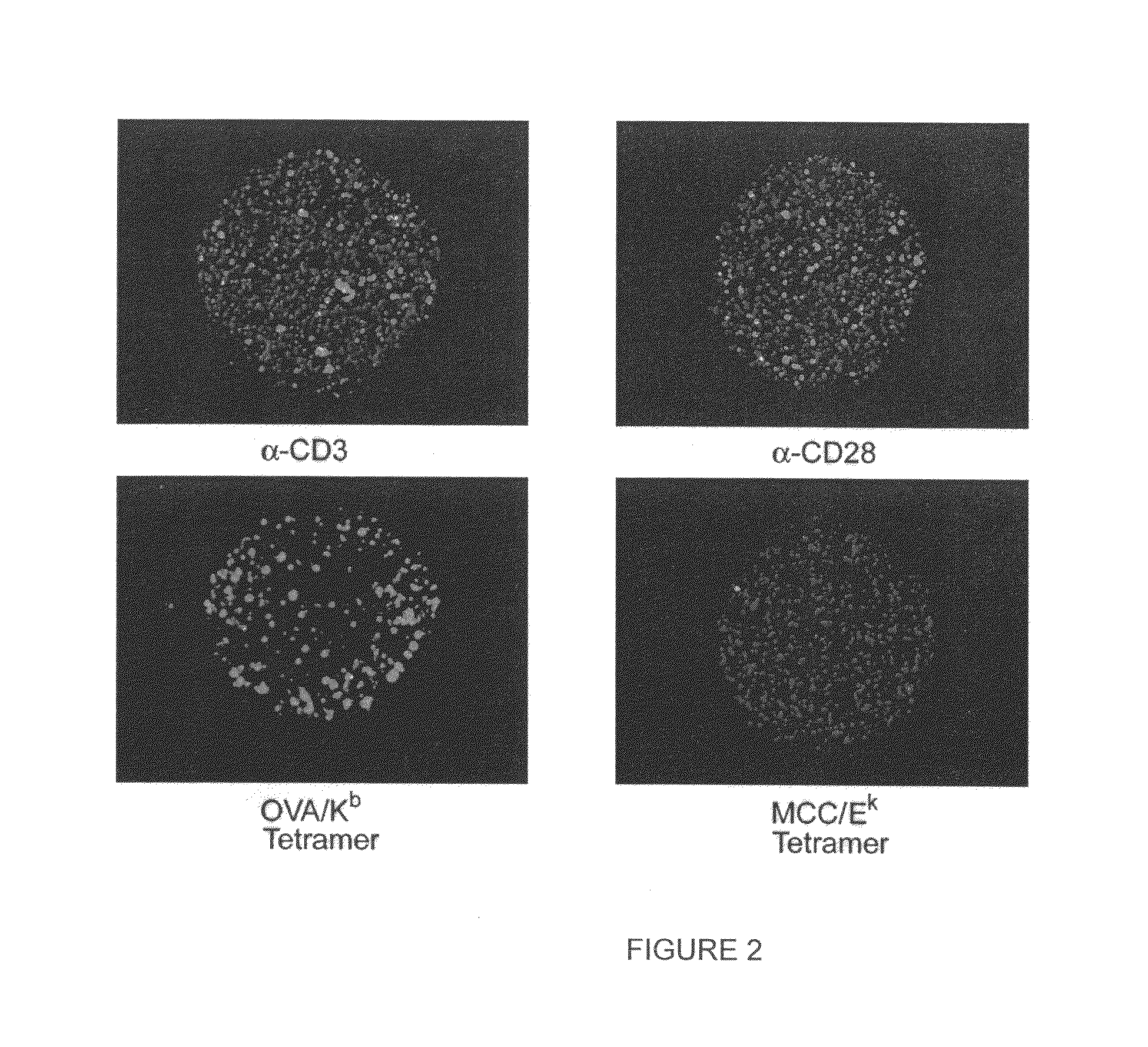
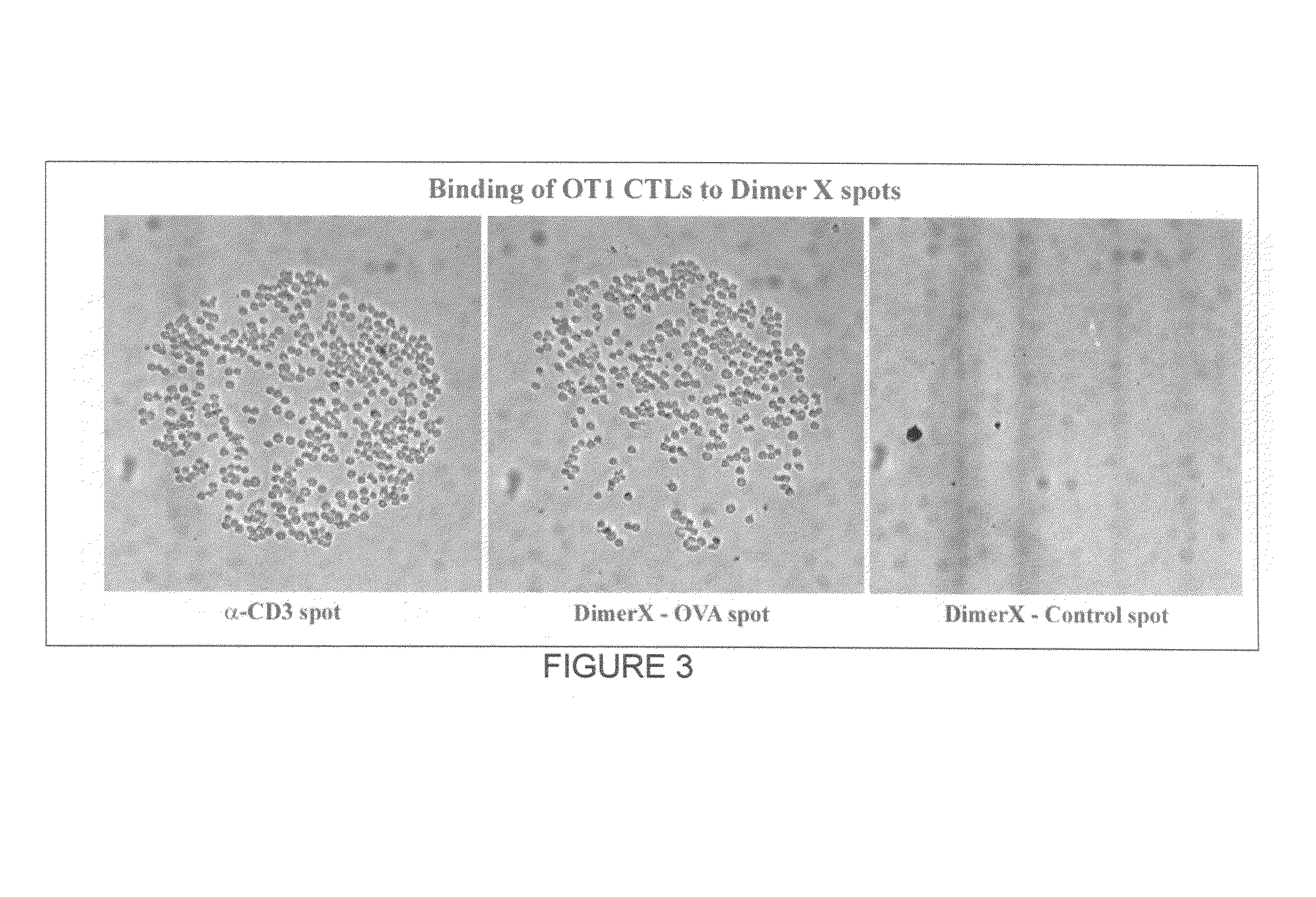
MHC-antigen arrays for detection and characterization of immune responses
InactiveUS20050019843A1High affinityBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAntigenCell–cell interaction
T cells are profiled with respect to their expression of antigen receptor. The cells are arrayed on a planar or three-dimensional substrate through binding to immobilized or partially diffused MHC-antigen complexes. The cells may further be characterized with respect to their ability to respond to external stimulus in the microenvironment. External stimuli include cell-cell interactions, response to factors, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Biocidic packaging for cosmetics and foodstuffs
InactiveUS20100178268A1Effective functionElectrical balance is disruptedBiocideFood preservationElectricityCell–cell interaction
The present invention presents a biocidic packaging for cosmetics and / or foodstuffs, comprises at least one insoluble proton sink or source (PSS). The packaging is provided useful for killing living target cells (LTCs), or otherwise disrupting vital intracellular processes and / or intercellular interactions of said LTC upon contact. The PSS comprises, inter alia, (i) proton source or sink providing a buffering capacity; and (ii) means providing proton conductivity and / or electrical potential. The PSS is effectively disrupting the pH homeostasis and / or electrical balance within the confined volume of the LTC and / or disrupting vital intercellular interactions of the LTCs while efficiently preserving the pH of said LTCs' environment. The present invention also discloses a method for killing living target cells (LTCs), or otherwise disrupting vital intracellular processes and / or intercellular interactions of said LTC being in a packaging, especially cosmetic or foodstuffs' packaging.
Owner:OPLON
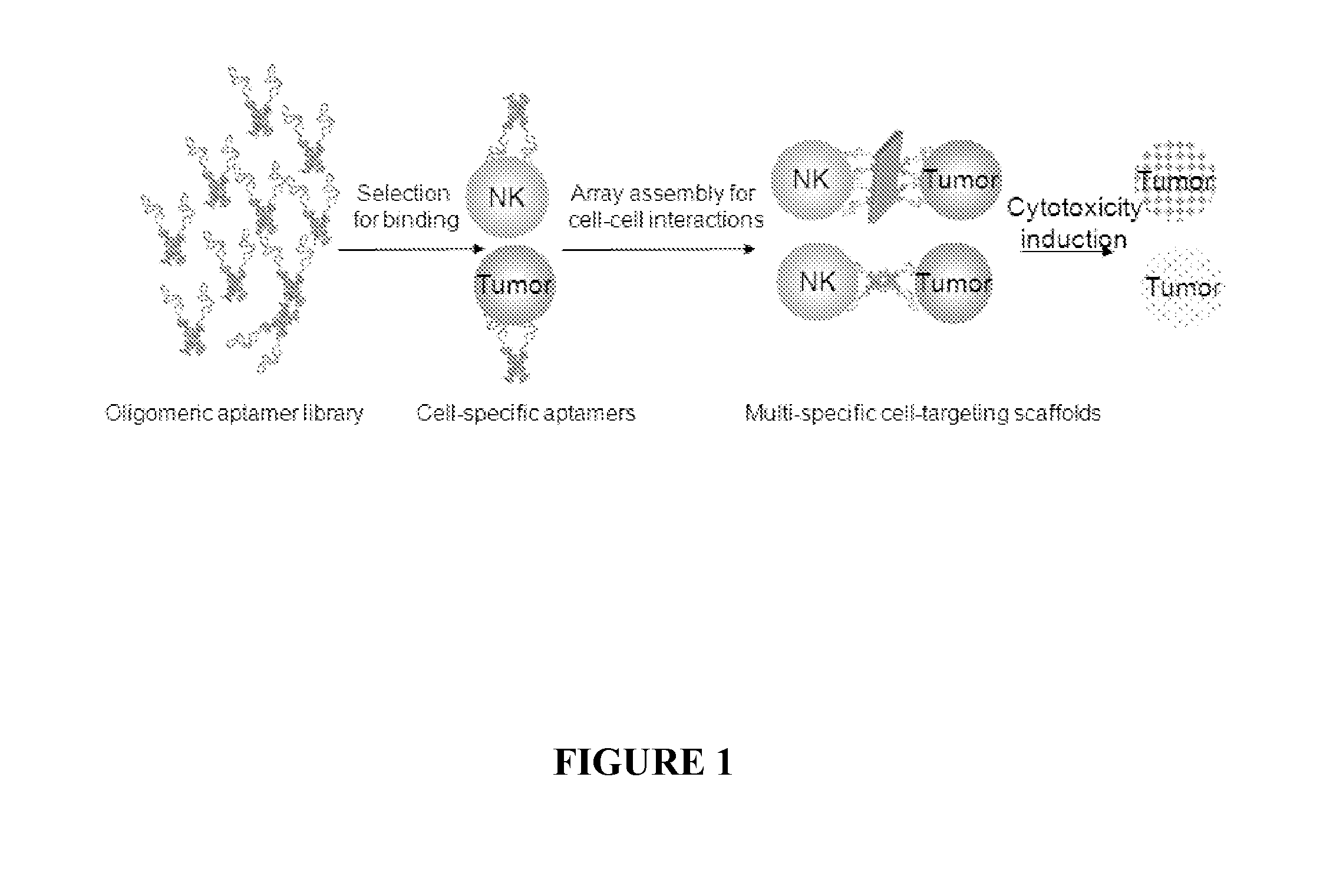
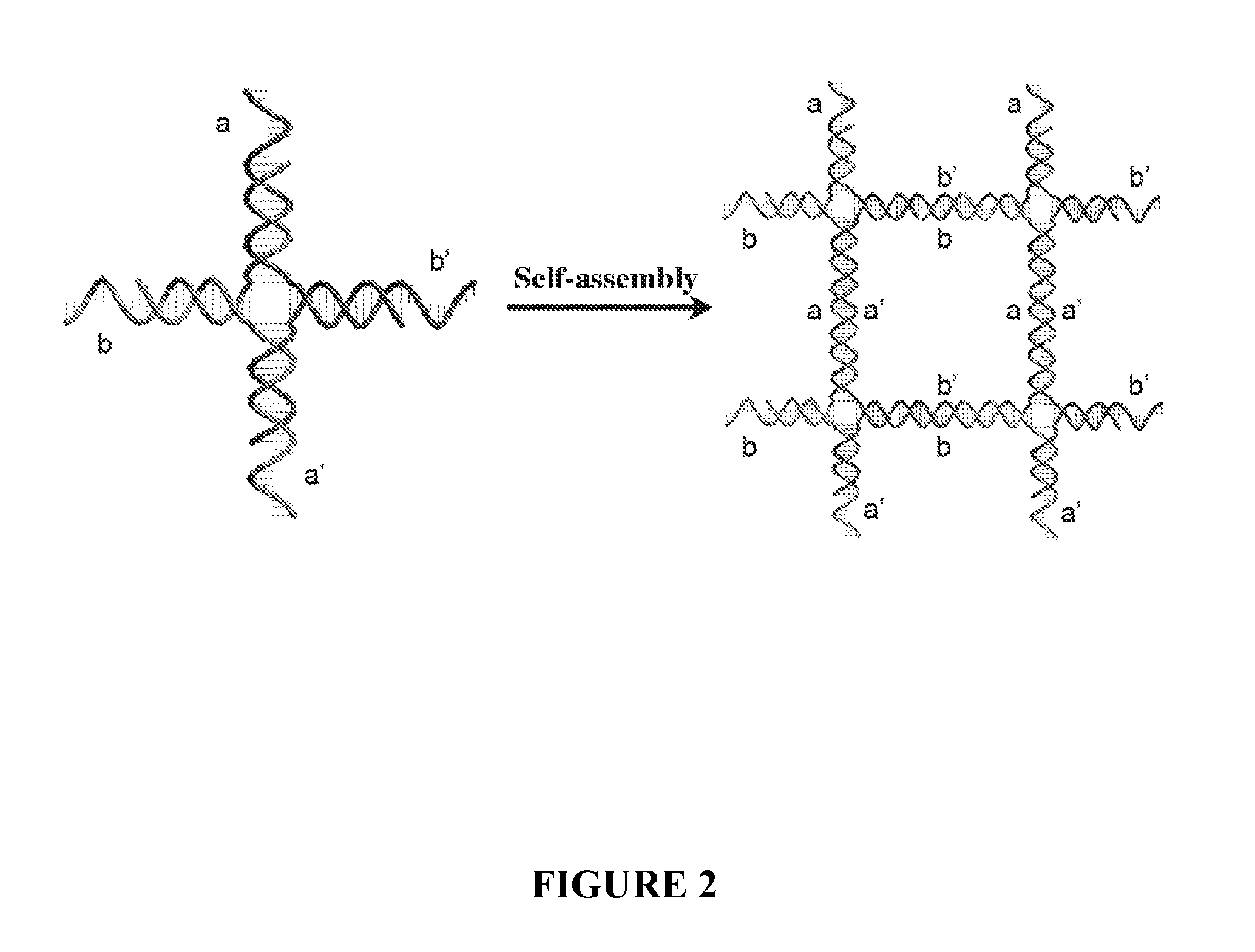
Novel DNA Nanostructures that Promote Cell-Cell Interaction and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20110275702A1Organic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCell–cell interactionDna nanostructure
The present invention provides a ligand-nucleic acid nanostructure that promotes cell-cell interaction. Specially, the invention provides a ligand-nucleic acid nanostructure for treating tumor in a mammal. The methods of using and making the composition comprising a ligand-nucleic acid nanostructure are also provided.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
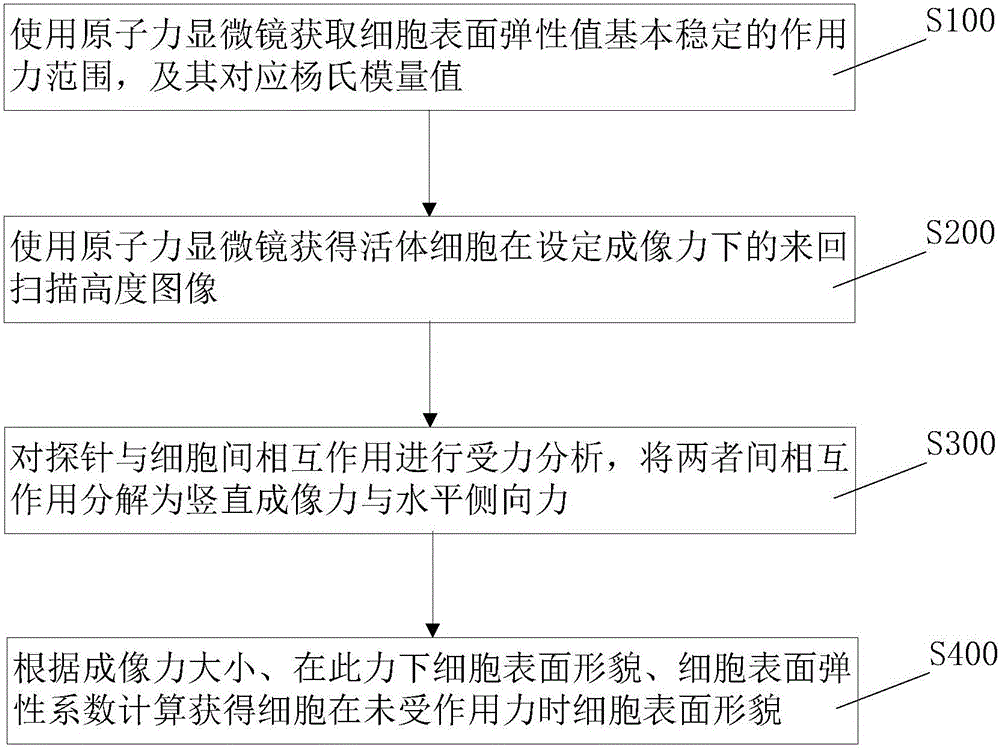
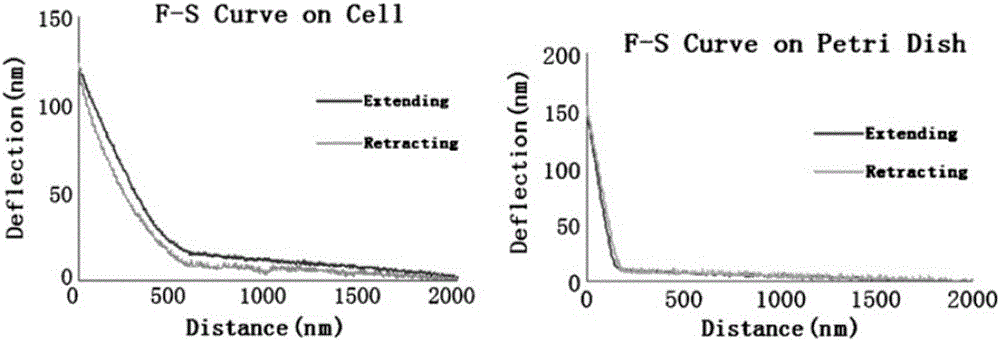
Fast and accurate characterization method for living cell surface morphology atomic force microscope
ActiveCN106199078AHigh precisionImprove time resolutionScanning probe microscopyAtomic force microscopyCell–cell interaction
The invention provides a fast and accurate characterization method for a living cell atomic force microscope. The method comprises the steps that the atomic force microscope is used to acquire the substantially stable applied force range of the cell surface elasticity value and the corresponding Young's modulus value; the atomic force microscope is used to acquire the back-and-forth scanning height image of a living cell under a set imaging force; force analysis is carried out on the interaction between a probe and the cell, and the interaction between the probe and the cell is decomposed into a vertical imaging force and a horizontal lateral force; and according to the imaging force magnitude, the cell surface topography under the force and the cell surface elasticity coefficient, the cell surface morphology of the cell without applied force is calculated. The fast and accurate characterization method for the living cell atomic force microscope has the advantages of high precision, high time resolution and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Device for controlling interaction of various cells as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102140422AInteraction effectAffect mobileBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAdhesion processCell adhesion
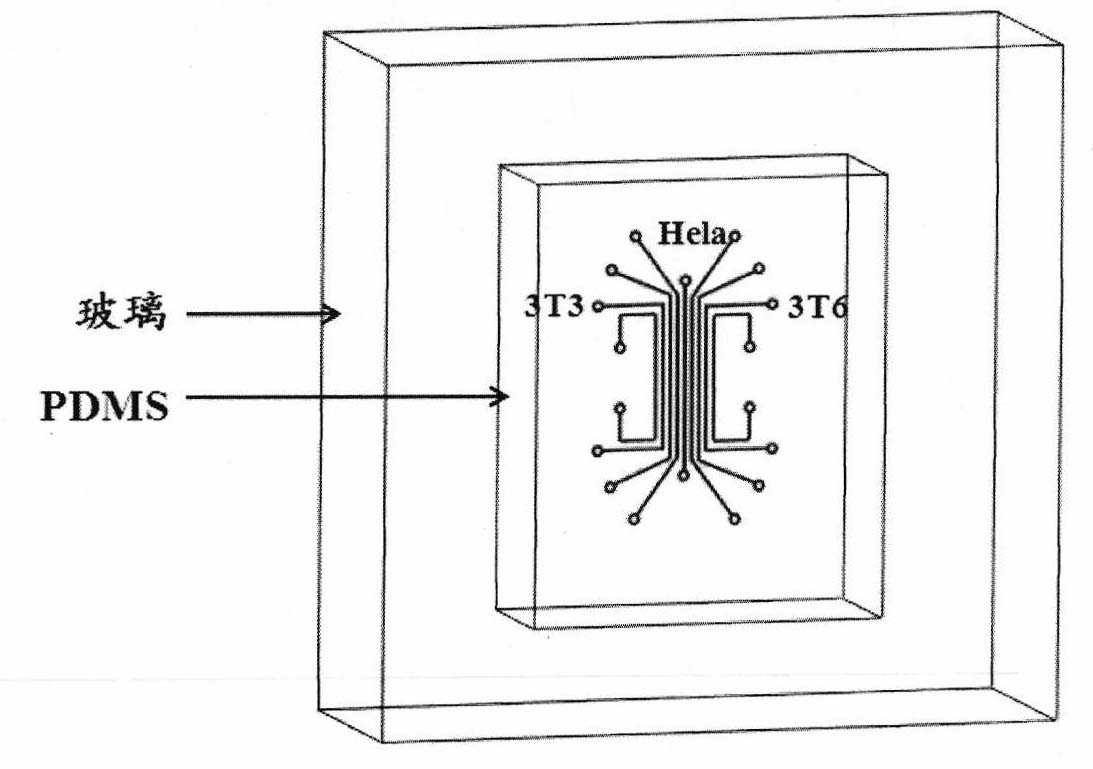
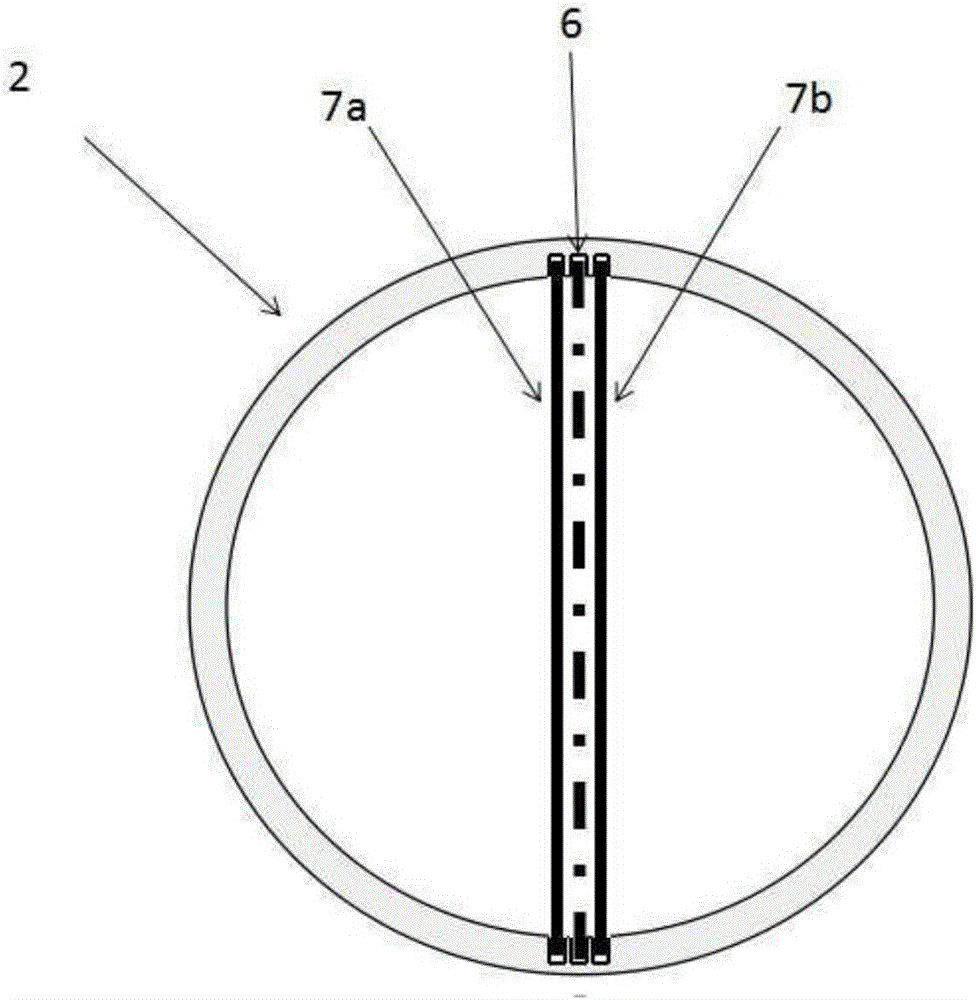
The invention provides a device for controlling interaction of various cells as well as a manufacturing method and application of the device. The device provided in the invention comprises a glass substrate (1) and a polydimethylsiloxane seal (2) with a plurality of grooves, wherein the polydimethylsiloxane seal is attached to the surface of the glass substrate to respectively form a plurality of micro-channels, the glass substrate in each micro-channel can be selectively modified to be a substrate for promoting cell adhesion by incubating extracellular matrix proteins or can be modified to be a cell adhesion-resistant substrate by assembling polyethylene glycol solution or is not modified. The device is simple and easy to operate, can control fixation, all movement and partial movement of various cells to achieve the purpose of arbitrarily controlling various cells, can be used for researching the interaction among various cells, the pathology or the cell biological development and can also be used for screening medicines.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
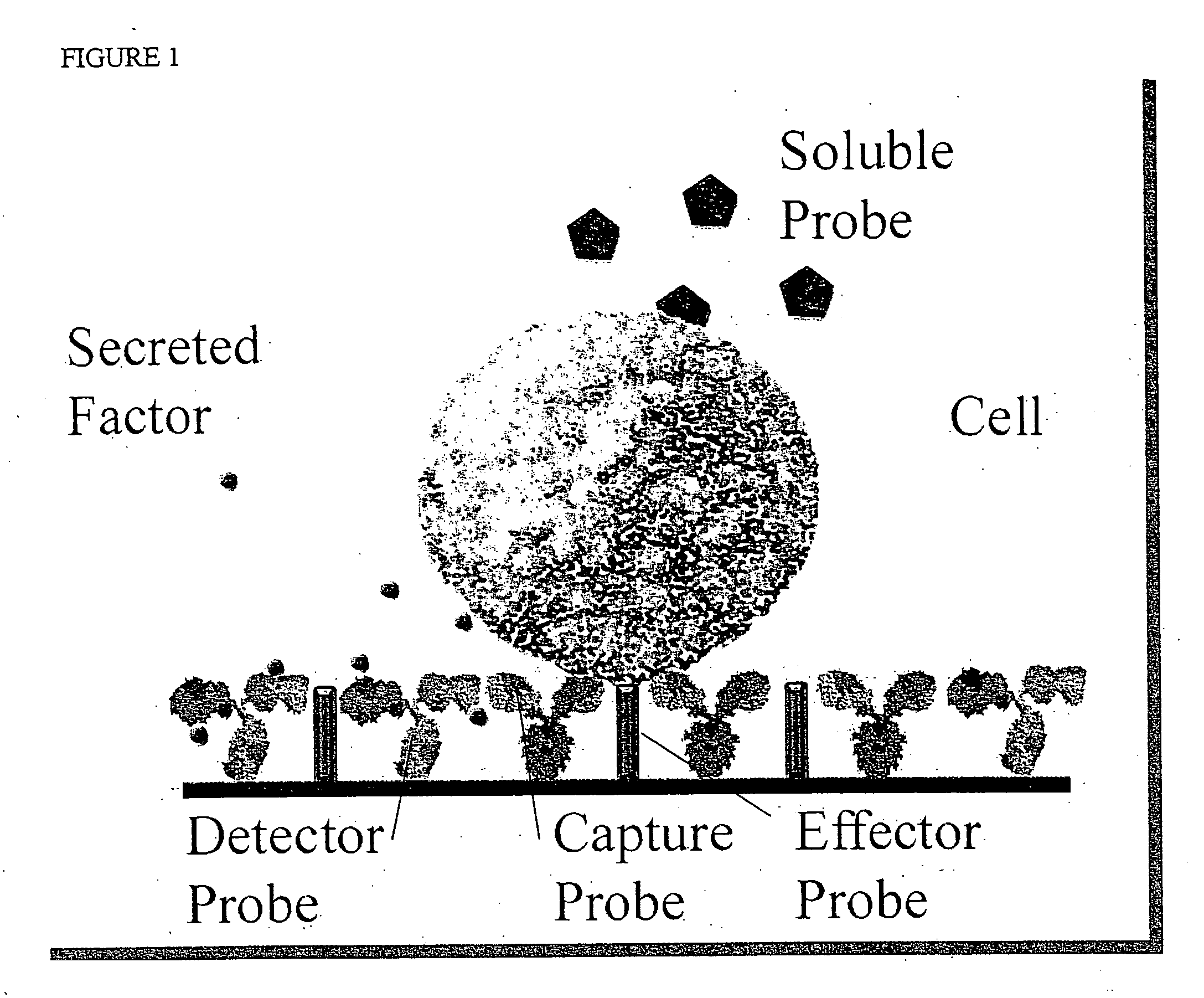
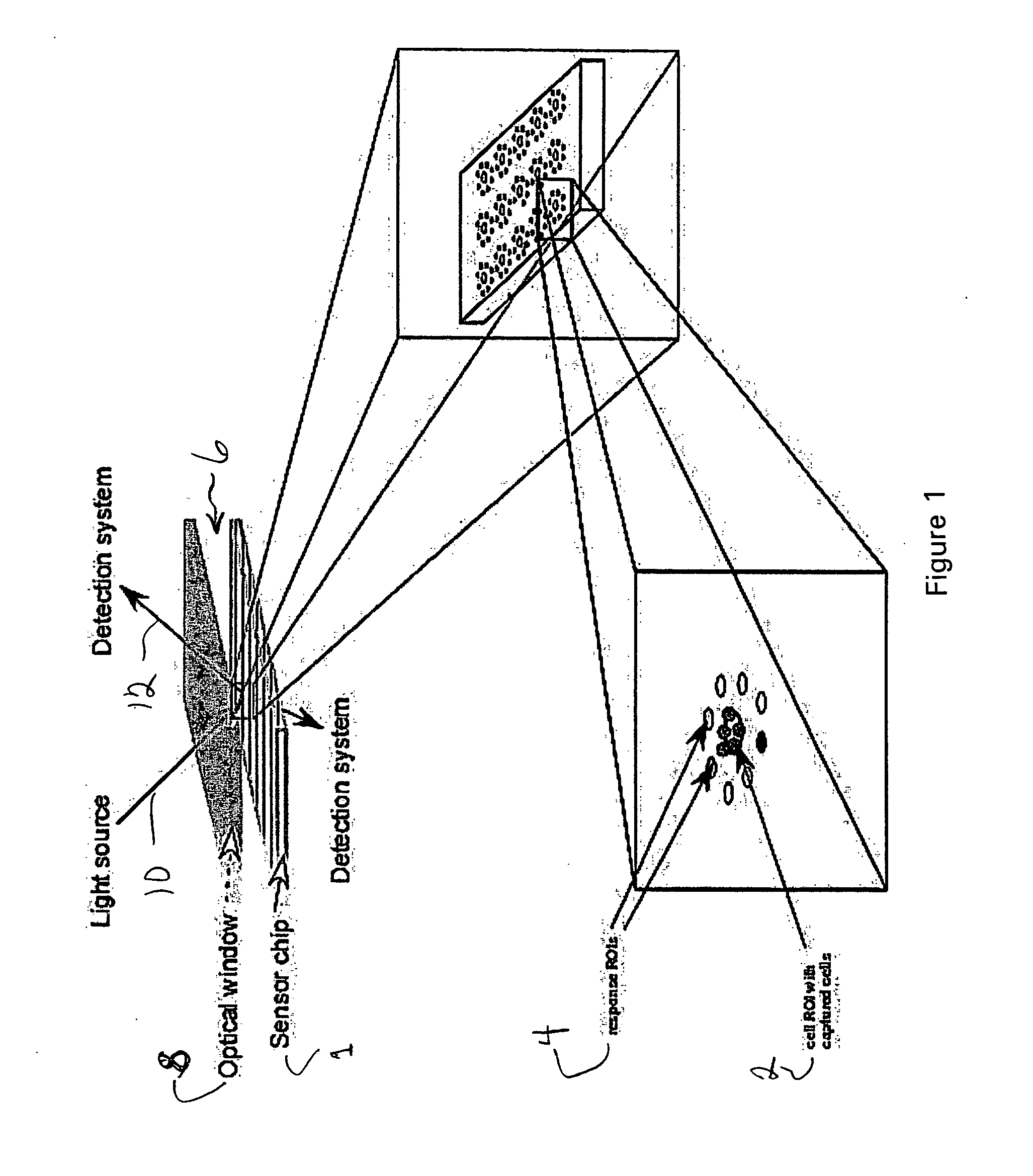
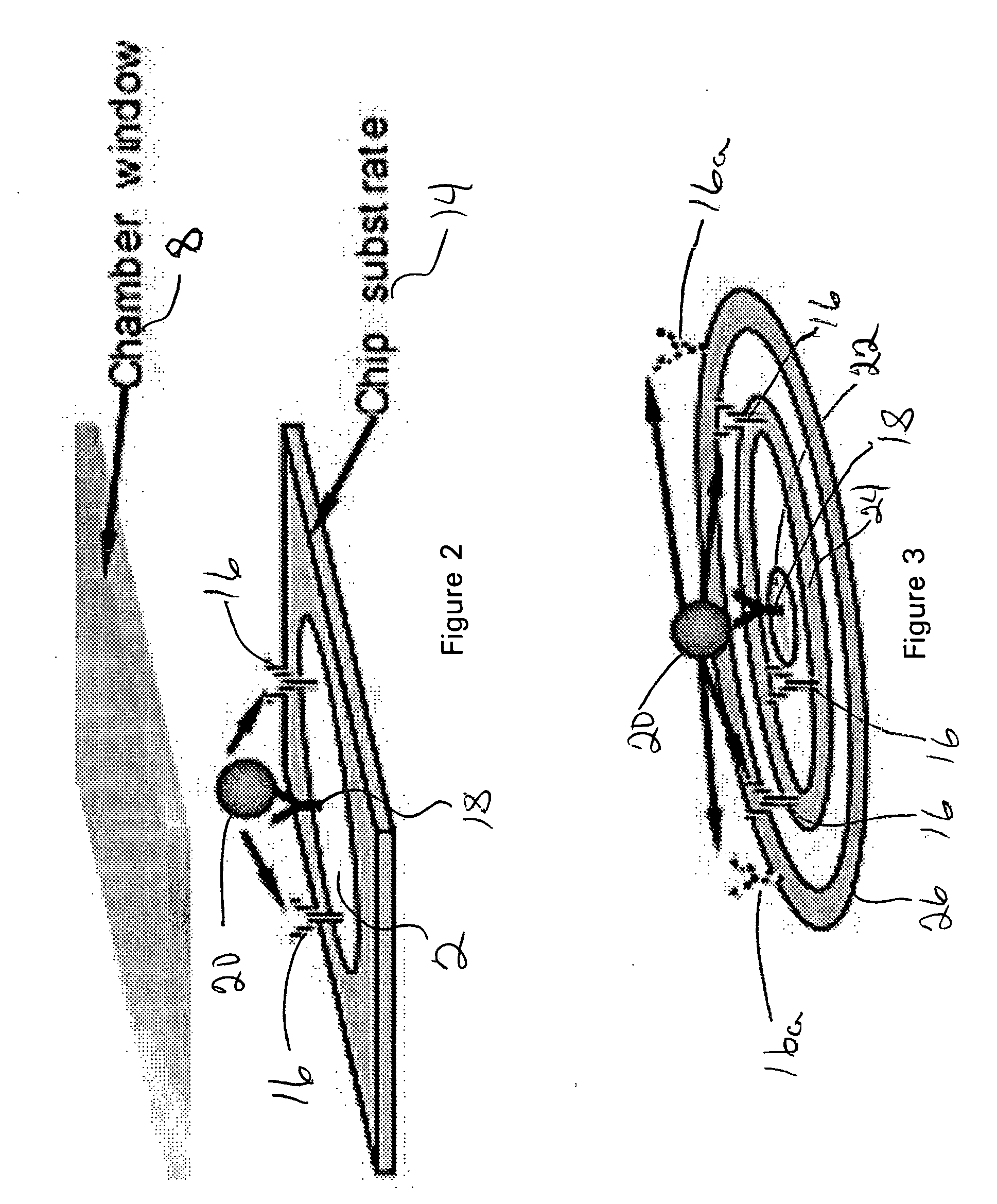
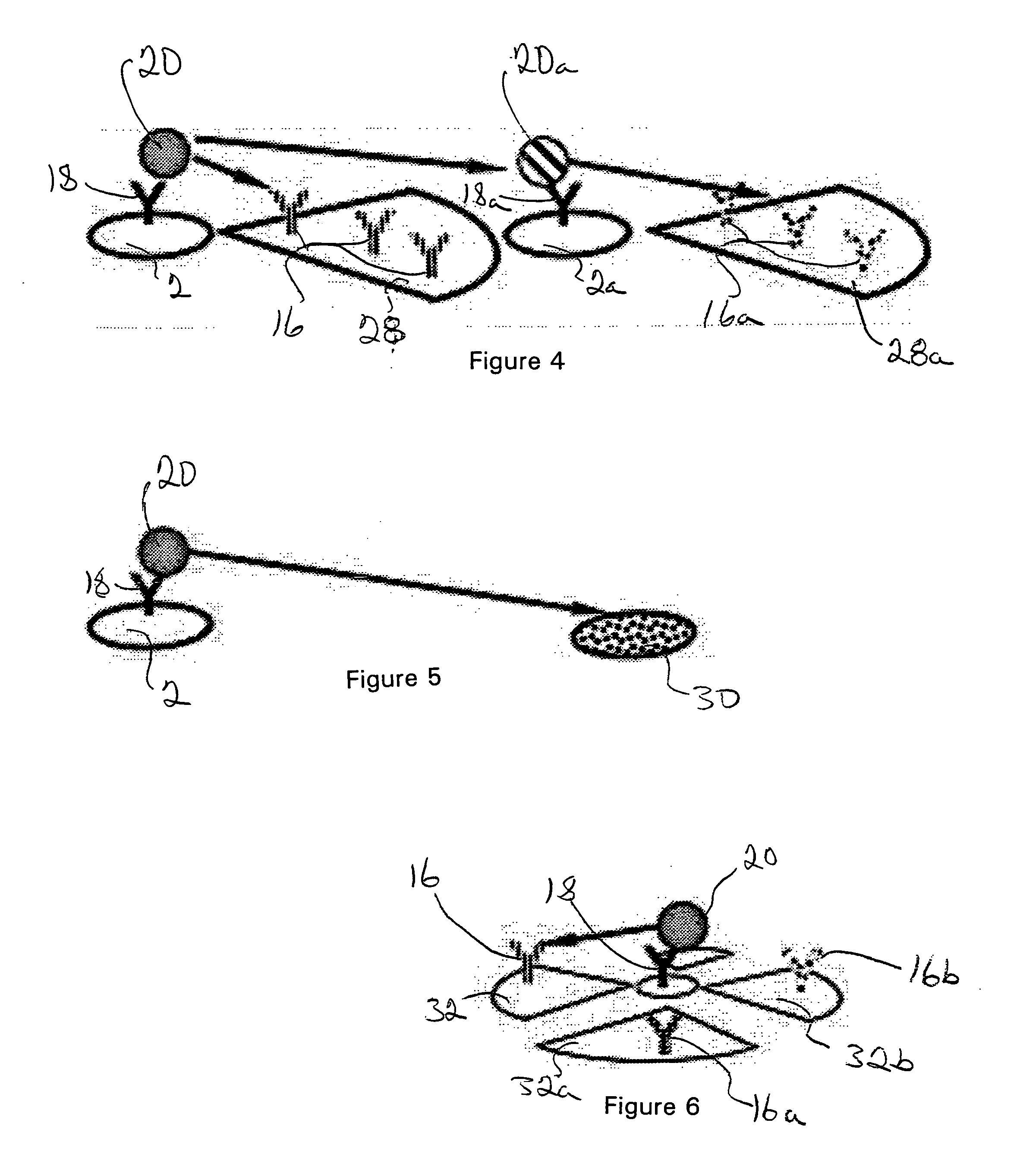
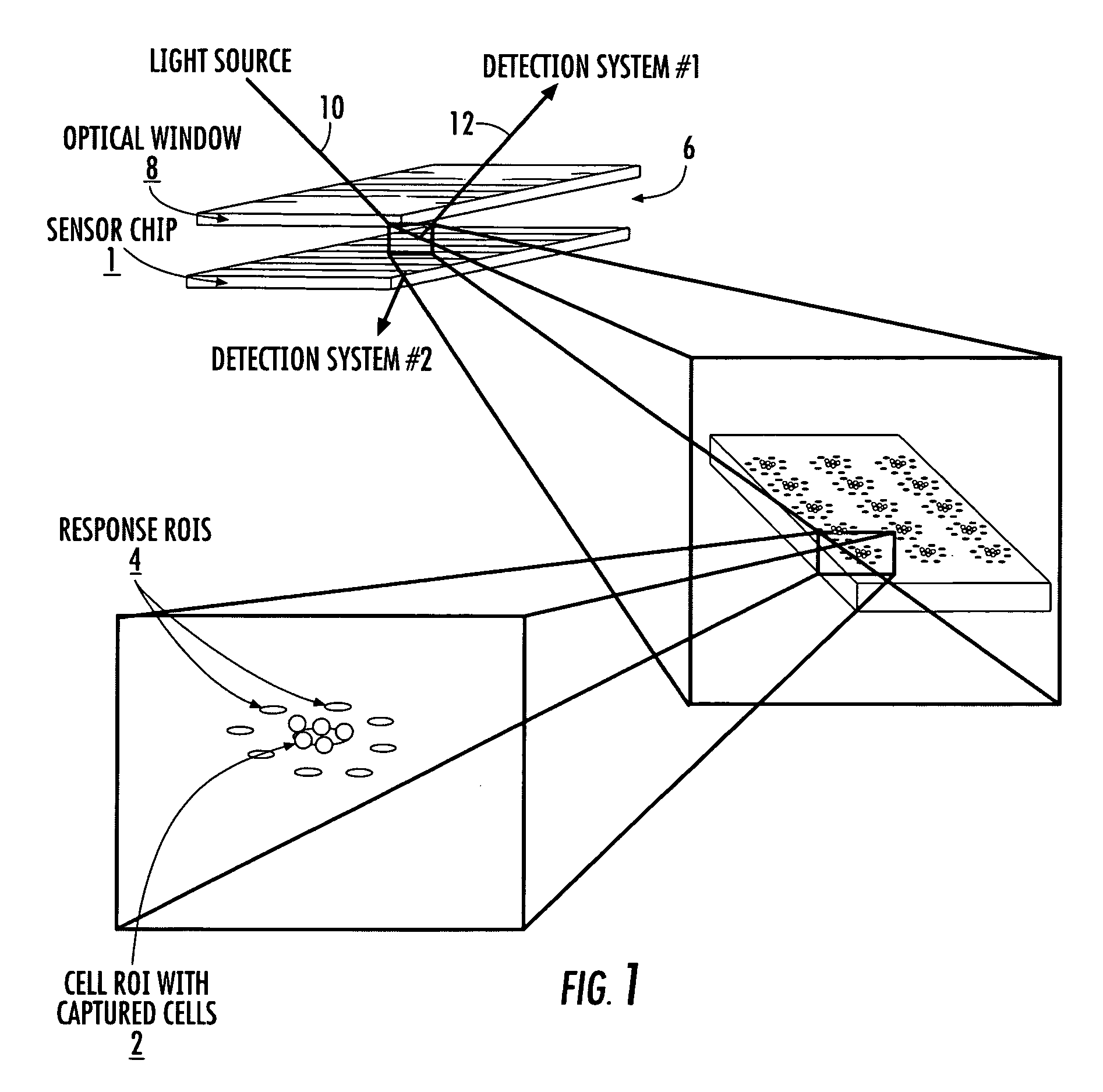
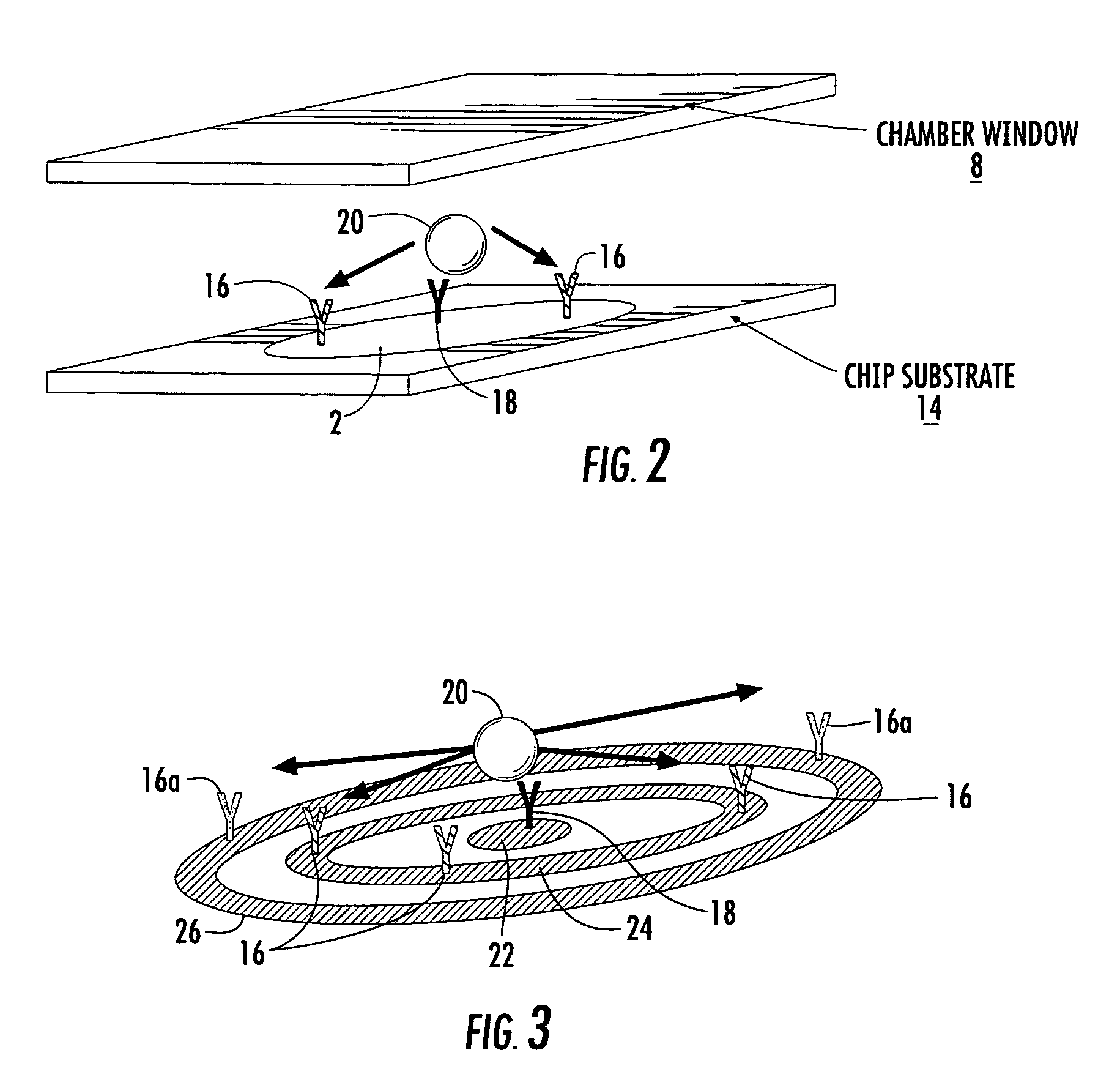
Cytometer on a chip
ActiveUS20070026382A1Highly multiplexed label-free mannerHighly parallel detectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell–cell interactionBiology
An assay technique for label-free, highly parallel, qualitative and quantitative detection of specific cell populations in a sample and for assessing cell functional status, cell-cell interactions and cellular responses to drugs, environmental toxins, bacteria, viruses and other factors that may affect cell function. The technique includes a) creating a first array of binding regions in a predetermined spatial pattern on a sensor surface capable of specifically binding the cells to be assayed; b) creating a second set of binding regions in specific spatial patterns relative to the first set designed to efficiently capture potential secreted or released products from cells captured on the first set of binding regions; c) contacting the sensor surface with the sample, and d) simultaneously monitoring the optical properties of all the binding regions of the sensor surface to determine the presence and concentration of specific cell populations in the sample and their functional status by detecting released or secreted bioproducts.
Owner:CIENCIA
MHC-antigen arrays for detection and characterization of immune responses
T cells are profiled with respect to their expression of antigen receptor. The cells are arrayed on a planar or three-dimensional substrate through binding to immobilized or partially diffused MHC-antigen complexes. The cells may further be characterized with respect to their ability to respond to external stimulus in the microenvironment. External stimuli include cell-cell interactions, response to factors, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for synergistic growth of multiple cells
ActiveCN102965330AAchieve growthEasy to recycleAnimal cellsOn/in organic carrierCell–cell interactionPhysiological condition
The invention relates to a method for synergistic growth of multiple cells. The method is characterized by: using a hydrogel carrier prepared under physiological conditions to culture different cells in different carriers by means of embedding small carriers in large carriers, thus studying intercellular chemical signal transmission and interaction. The biggest advantages of the method lie in that: the carrier can contain one or over two different types of cells or tissues; non-direct contact spaces of different cells are provided; the growth of different cells or tissues in a three-dimensional environment is realized; biological effects are generated by chemical signal transmission among different cells; intercellular interaction generated effects can be investigated by crushing each carrier respectively to obtain different cells successively; and during actual application, the method is easy to realize recovery and scale-up.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
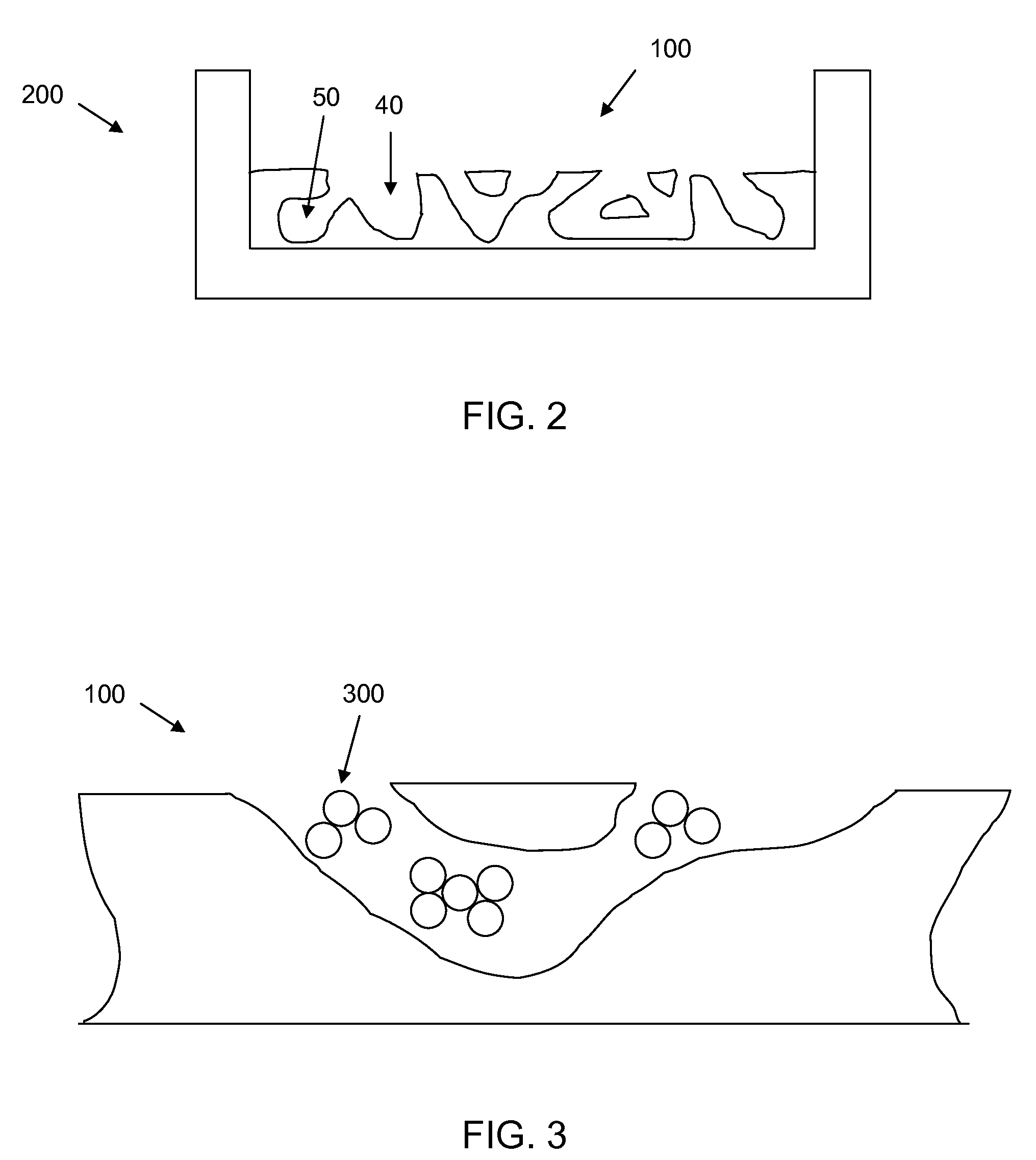
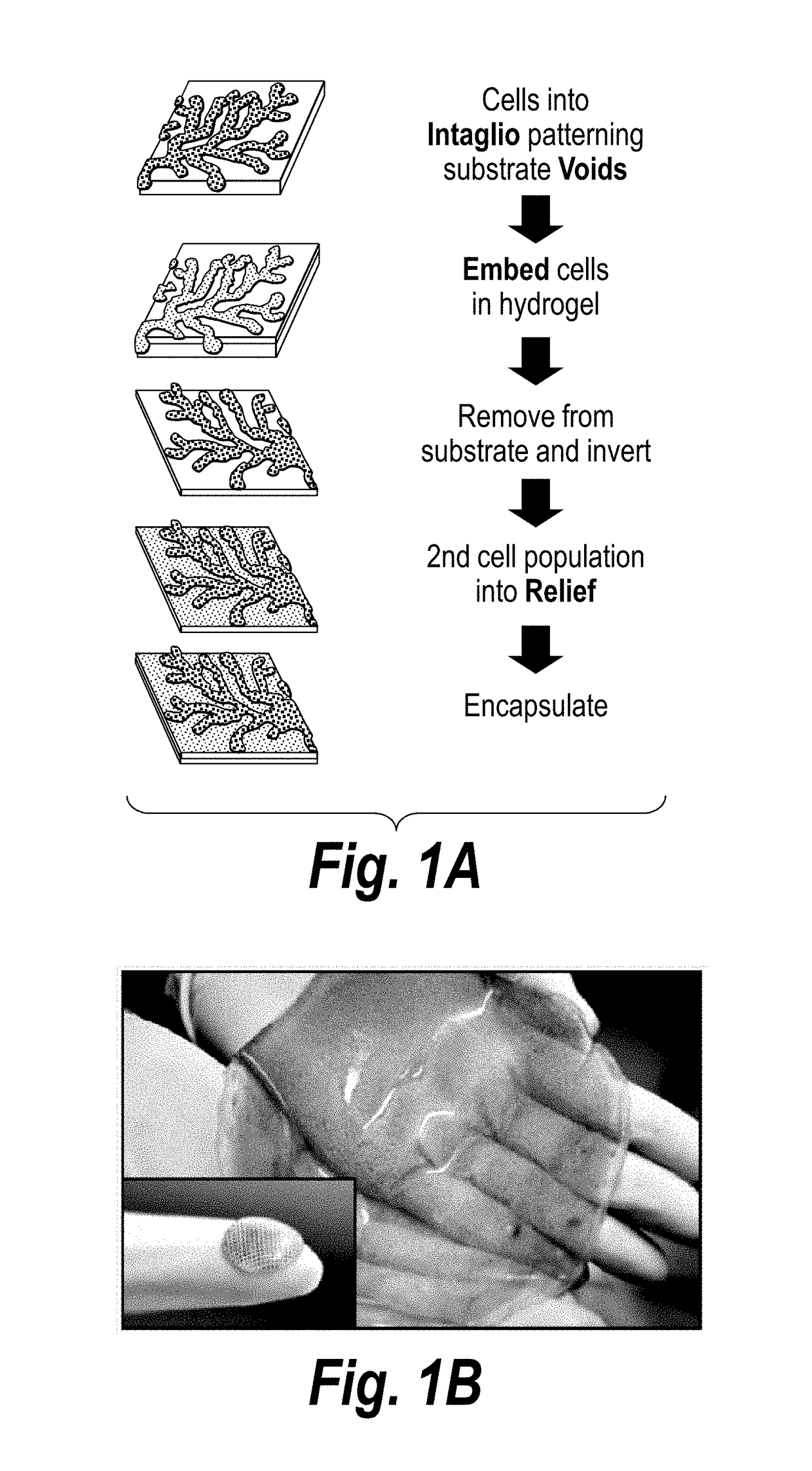
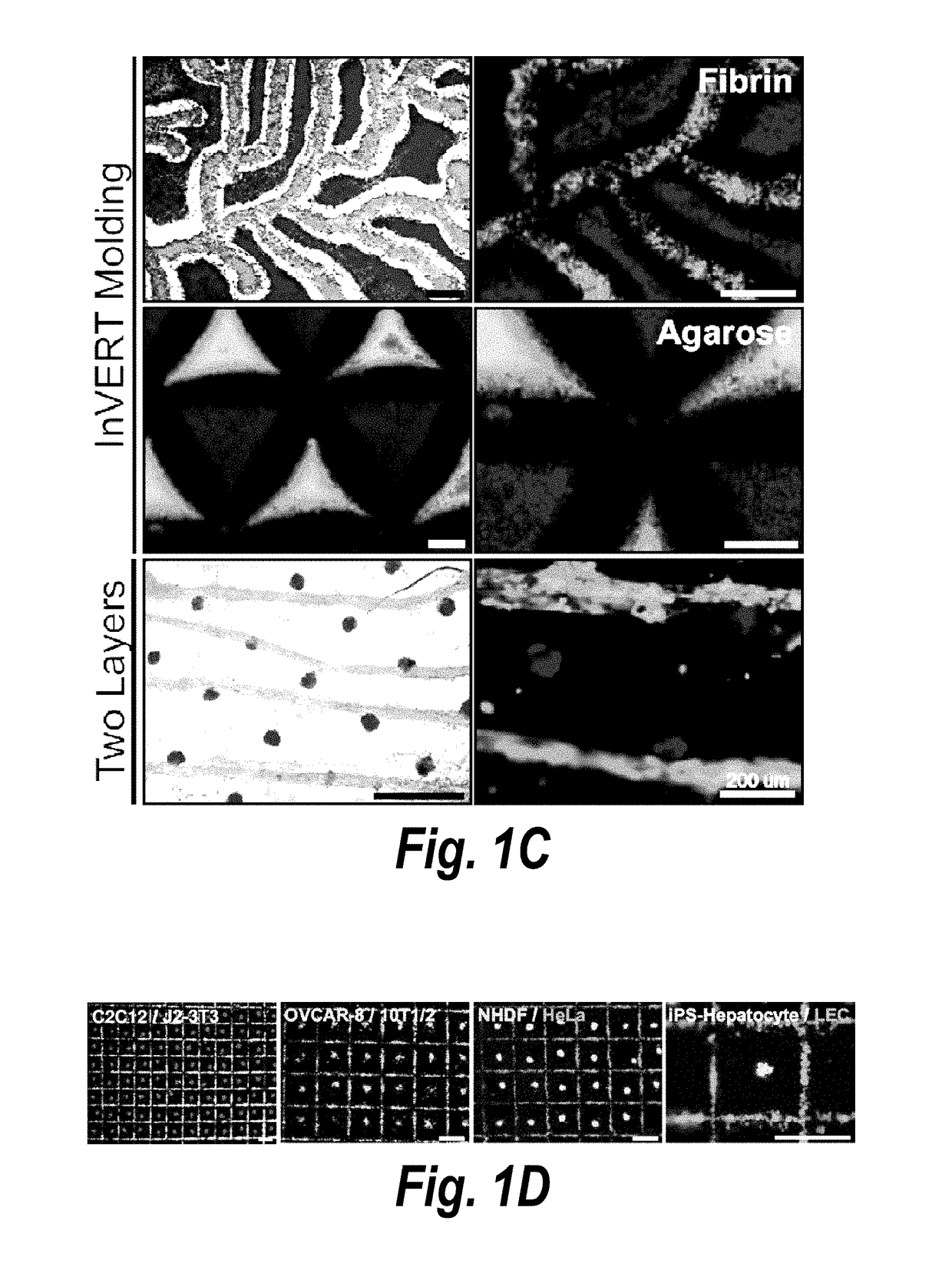
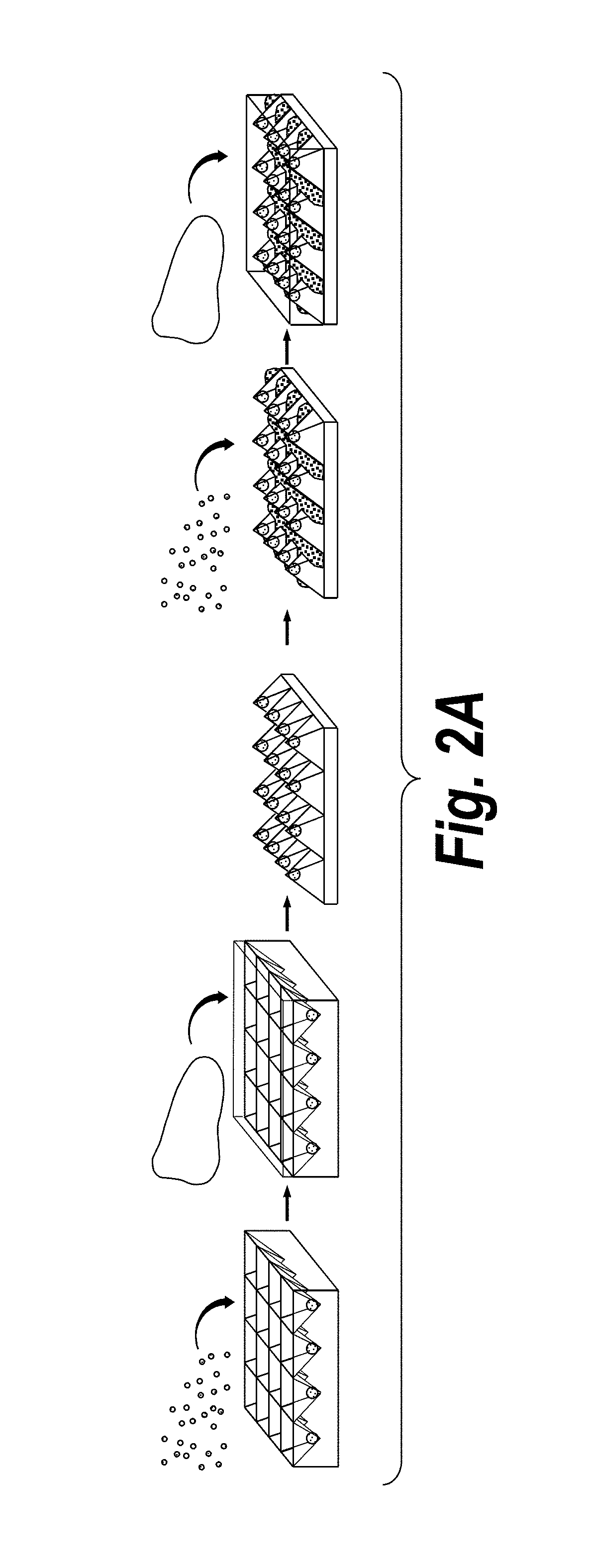
Inverse patterning process for three-dimensional multi-compartmental micro-organization of multiple cell types
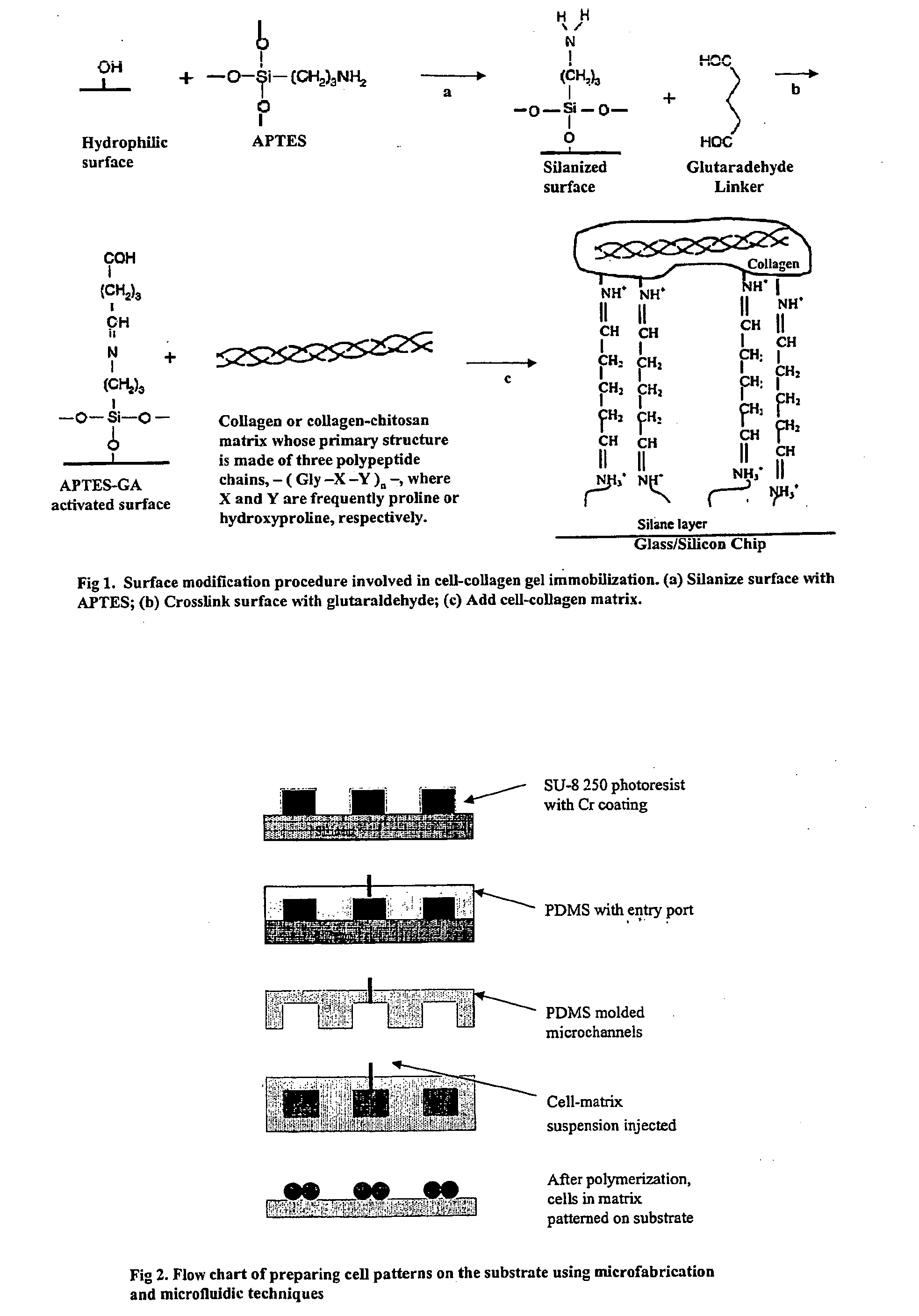
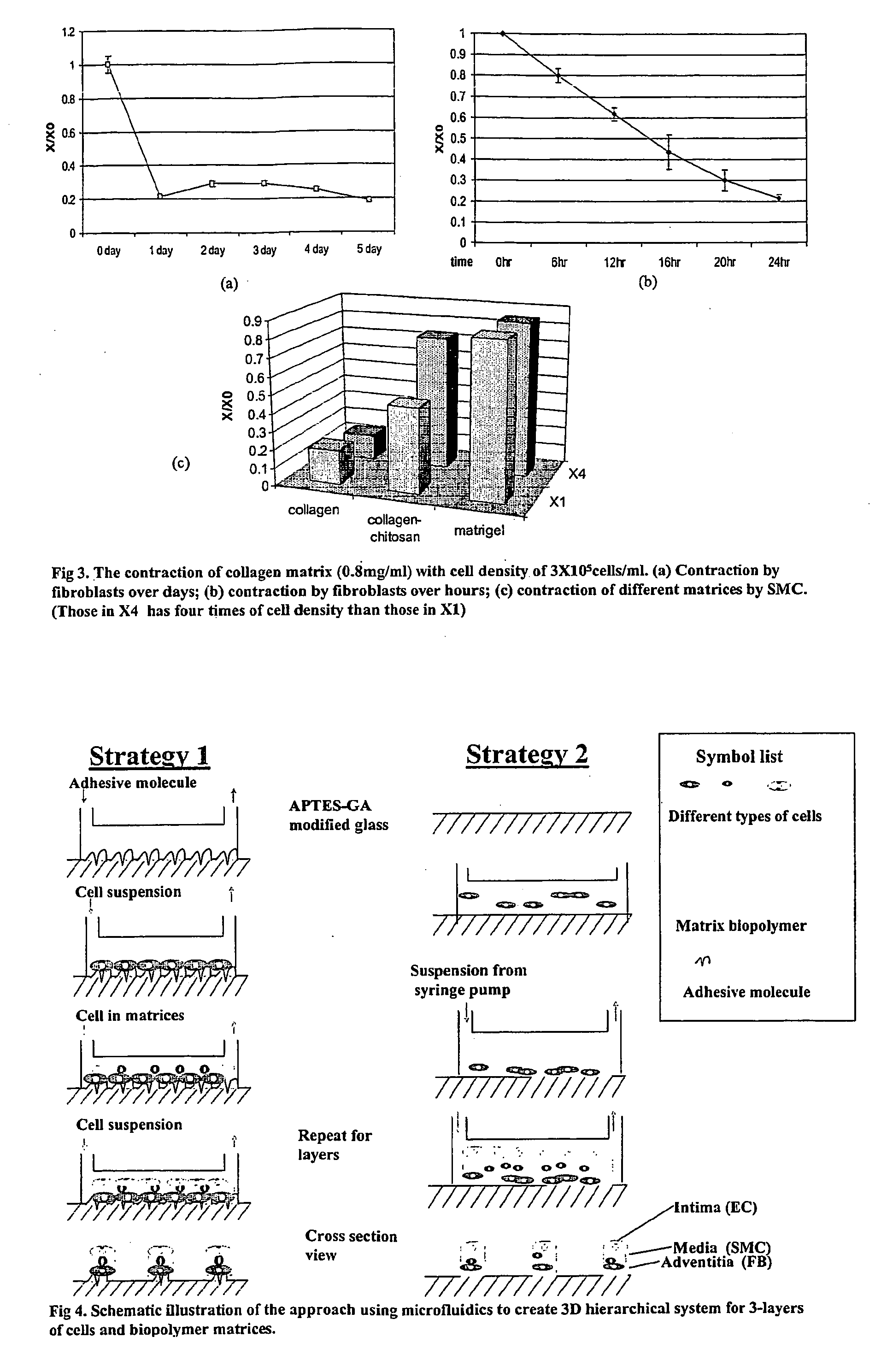
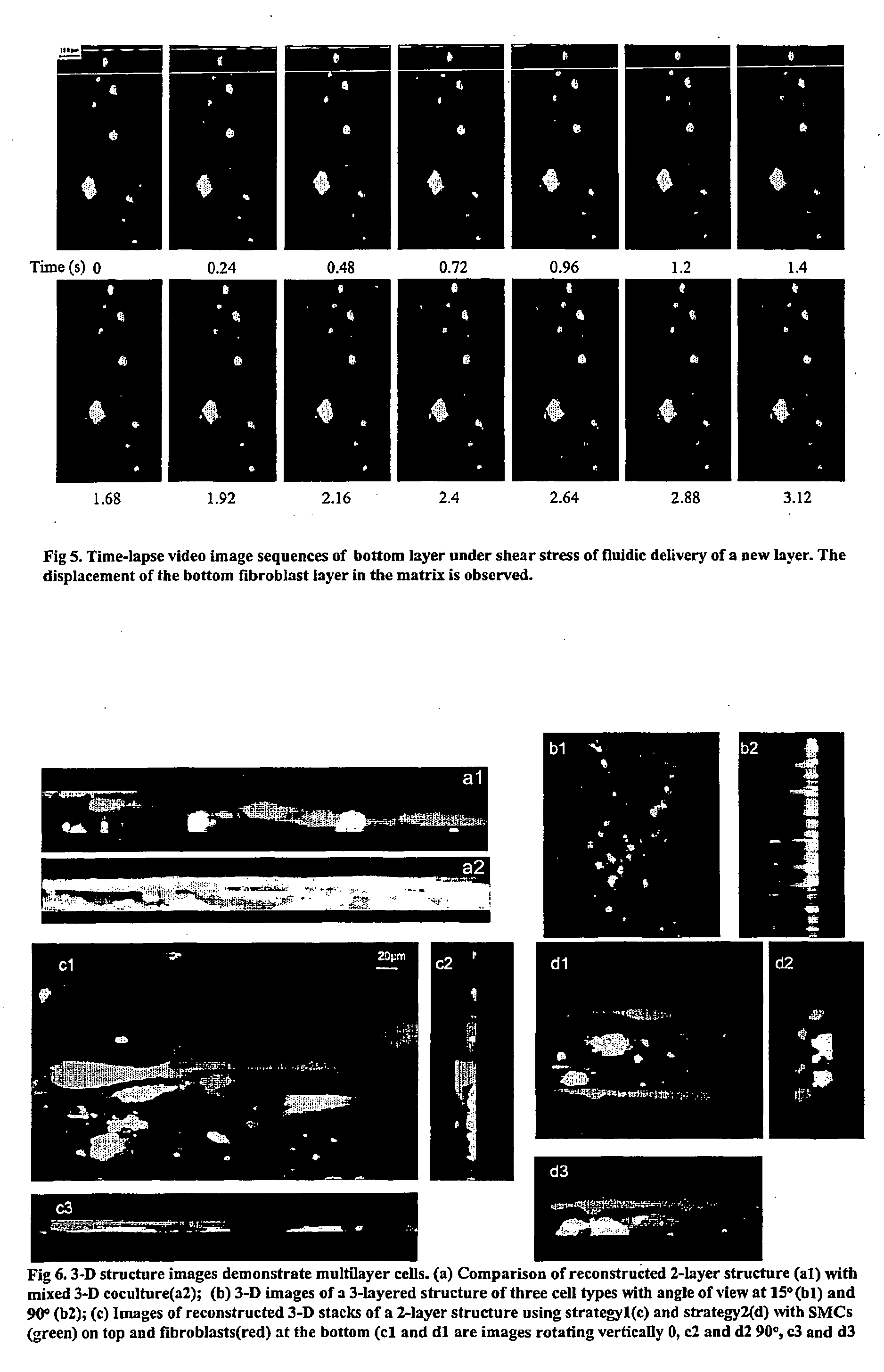
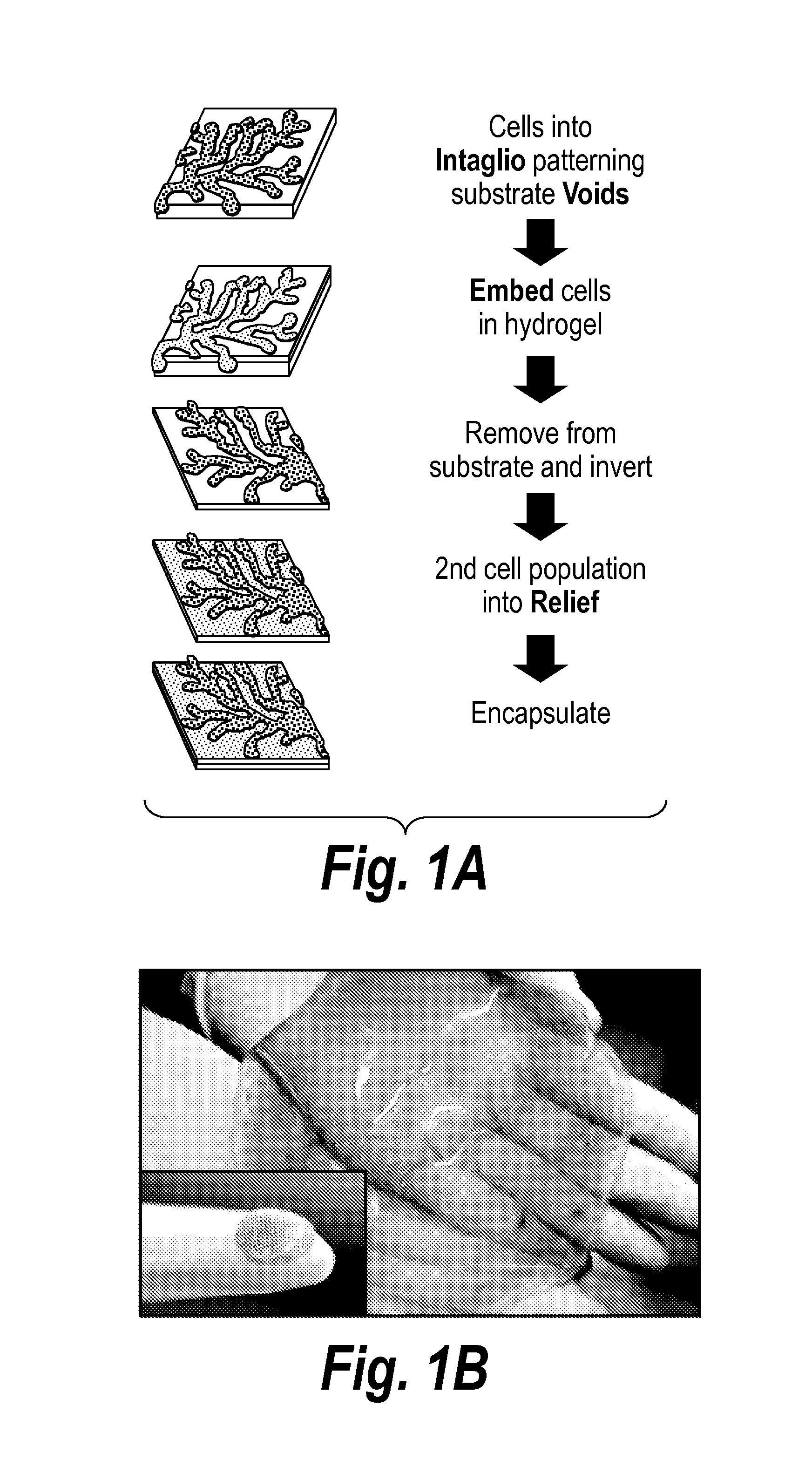
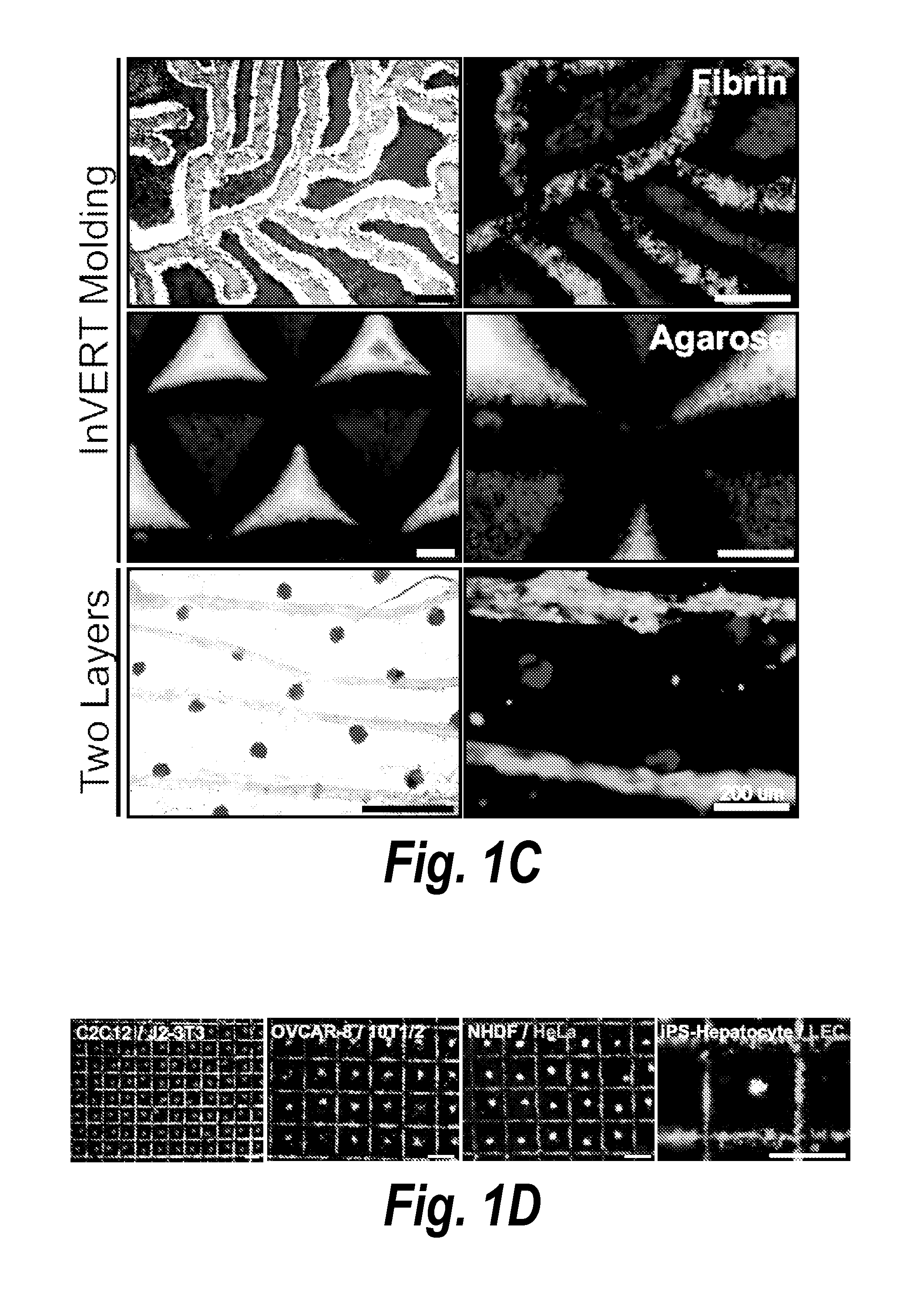
The invention features an “inverse patterning” or “Intaglio-Void / Embed-Relief Topographic (In VERT) molding” manufacturing process for generating high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) multi-cellular microstructures in distinct cellular compartments of a single hydrogel. The platform has general utility in the development of engineered tissues for human therapies, drug testing, and disease models. Additionally, the platform can serve as a model system for studying 3D cell-cell interactions in fields as diverse as stem cell biology to the development of cancer therapeutics.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Disintegrin homologs, ZSNK10, ZSNK11, and ZSNK12
InactiveUS20020081685A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesProteinase activityNucleotide
The present invention relates to polynucleotide and polypeptide molecules, and variants thereof, for ZSNK10, ZSNK11, and ZSNK12, novel members of the Disintegrin Proteases. The polypeptides, and polynucleotides encoding them, are cell-cell interaction modulating and may be used for delivery and therapeutics. The present invention also includes antibodies to the ZSNK10, ZSNK11, and ZSNK12 polypeptides.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
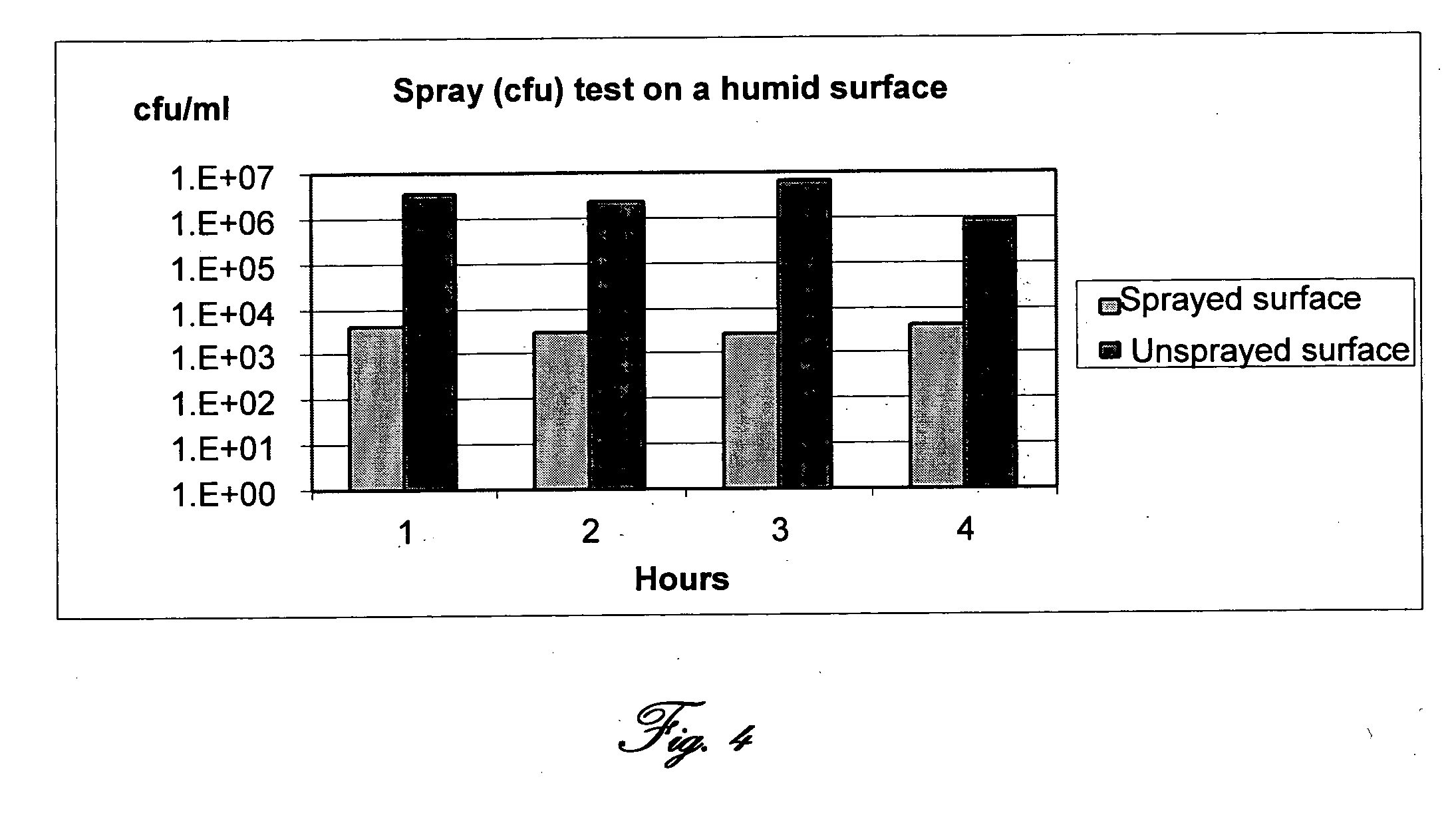
Biocidic household cleansing materials
InactiveUS20100136077A1Effective preservationMinimize changesBiocideWarp knittingElectricityCell–cell interaction
The present invention discloses household cleaning materials comprising at least one insoluble proton sink or source (PSS) and to method for utilizing the PSS as a biocidic agent. The household cleaning materials are provided useful for killing living target cells (LTCs) or otherwise inhibiting LTCs growth, disrupting vital intracellular processes and / or intercellular interactions of the LTC upon contact. The household cleaning materials consisting of at least one PSS, comprises, inter alia, (i) proton source or sink providing a buffering capacity; and (ii) means providing proton conductivity and / or electrical potential. The PSS is effectively disrupting the pH homeostasis and / or electrical balance within the confined volume of said LTC and / or disrupting vital intercellular interactions of said LTCs while efficiently preserving the pH of said LTCs' environment.
Owner:OPLON
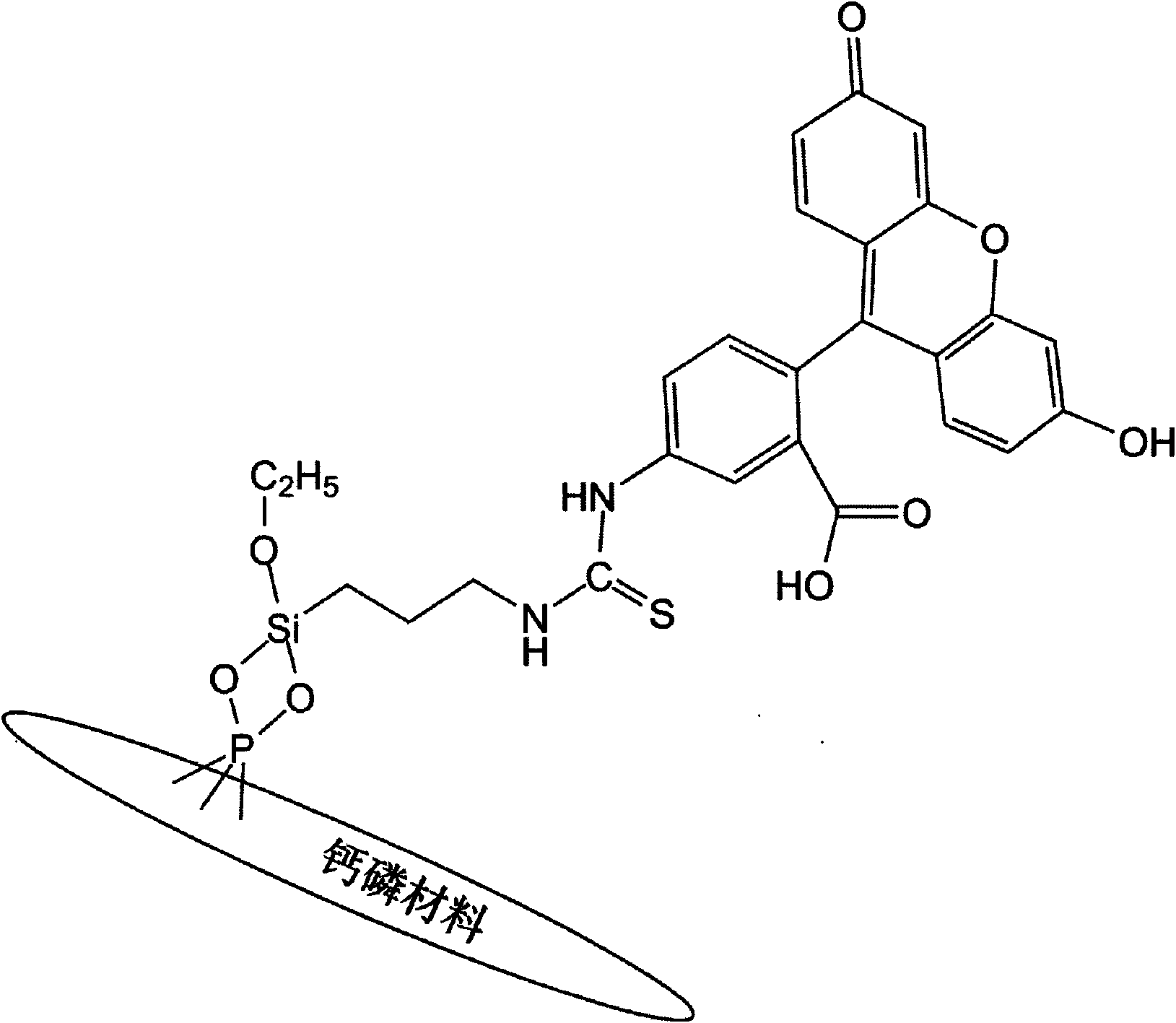
Calcium phosphate material marked by fluorescein isothiocyanate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101643645AHigh fluorescence intensityClear imagingMicrobiological testing/measurementIn-vivo testing preparationsCell–cell interactionSilicon oxygen
The invention discloses a calcium phosphate material marked by fluorescein isothiocyanate and a preparation method thereof. In the invention, an amino-silane coupling agent is firstly adopted to carry out surface modification on the calcium phosphate material, silicon-oxygen-phosphorus (Si-O-P) covalent bond is formed on the surface of the calcium phosphate material, an amino group in the coupling agent is then utilized to covalently combine with iso-thiocyanate in fluorescein, and the stable covalence-type calcium phosphate material can be marked by fluorescein. The compounded material has high fluorescence intensity, stable chemical property and good biocompatibility, and is suitable for tracing the calcium phosphate material in cells in complex internal and external body environment. The calcium phosphate material marked by fluorescein isothiocyanate has important application in the aspects of material biocompatibility evaluation and material-cell interaction, and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
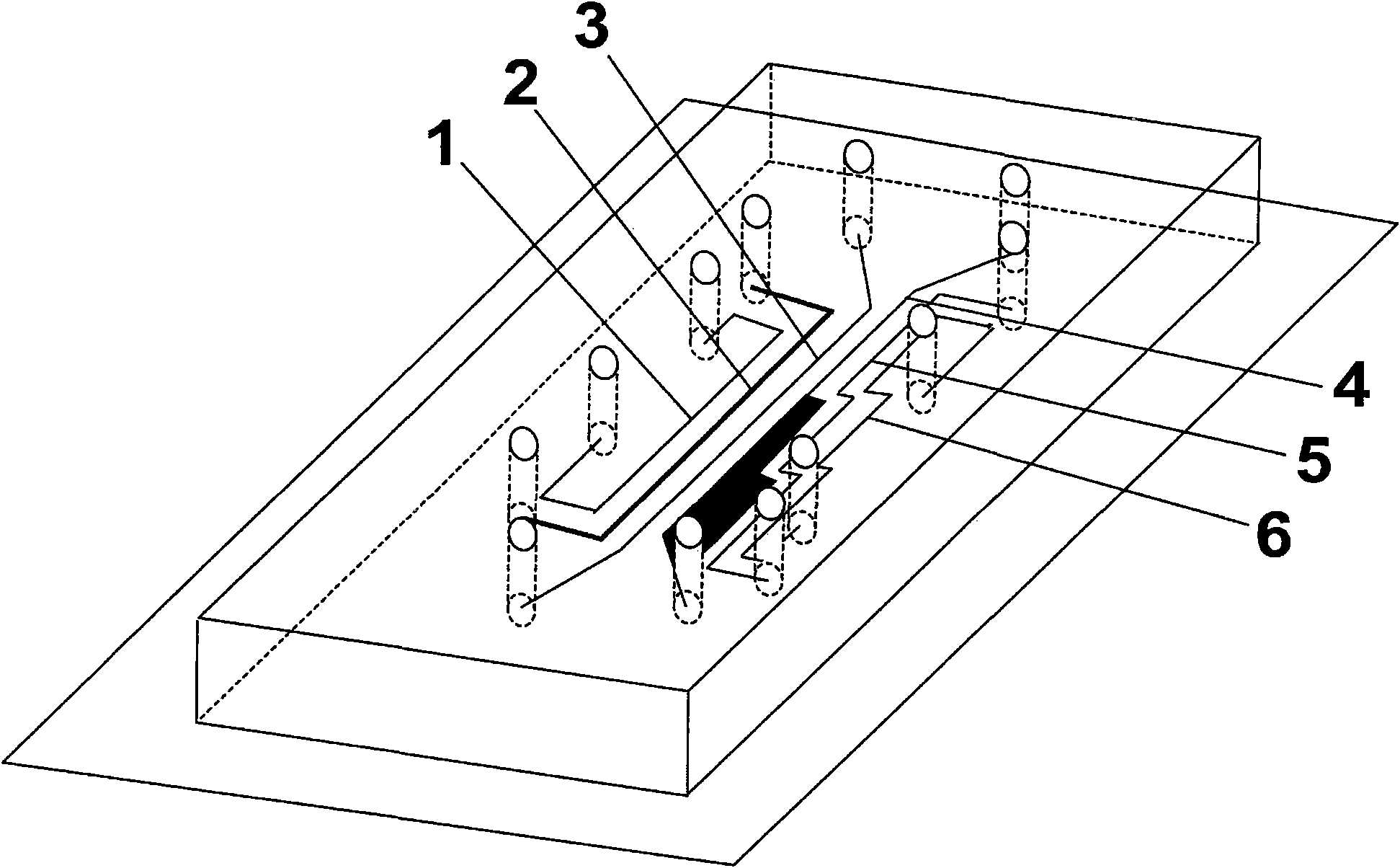
Device and method for operating multiple adherent cells on same substrate
InactiveCN101624569AOrderly growthOrdered AdhesionTissue cultureTissue/virus culture apparatusCell–cell interactionEngineering
The invention relates to a device and a method for adhering multiple cells to the same substrate and operating the cells, which divide a gold surface of the substrate into a modifiable region and an unmodifiable region by using a microflow pipeline of PDMS. The method comprises the following steps: introducing different molecular modifications to different pipeline regions to ensure that the substrate is divided into a cell adhesive region and a cell nonadhesive region; inoculating different cells in different adhesive regions, taking away the PDMS, and adhering multiple cells to the surface in sequence; electrochemically desorbing to destroy combination of molecules and gold in the nonadhesive region to ensure that all kinds of cells can move freely; and selectively modifying two sides of one or more cells as the nonadhesive region, separating other cells by using PBS, removing PDMS, and fixing the selected cells to lead other cells to move freely. The method and the device have simple and easy operation, can control fixation, complete motion or partial motion of different cells to achieve the aim of operating multiple cells at will, and can be used for studying interaction among multiple cells and medicinal screening.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
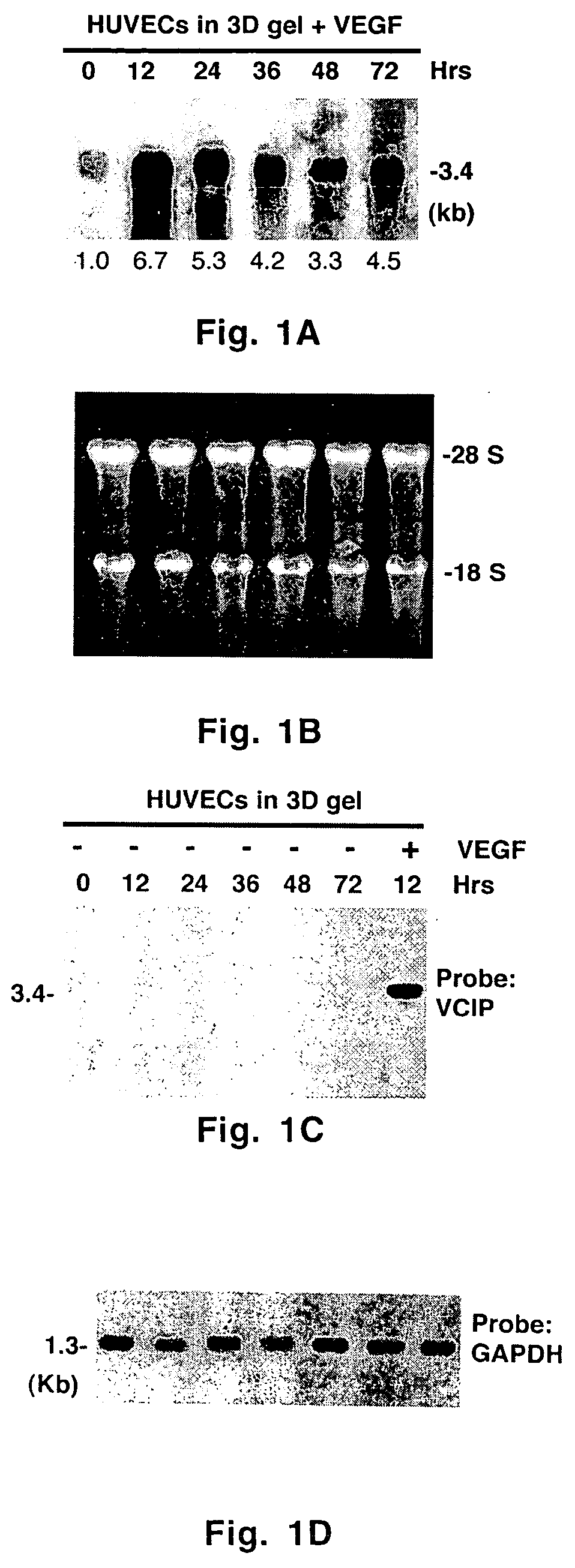
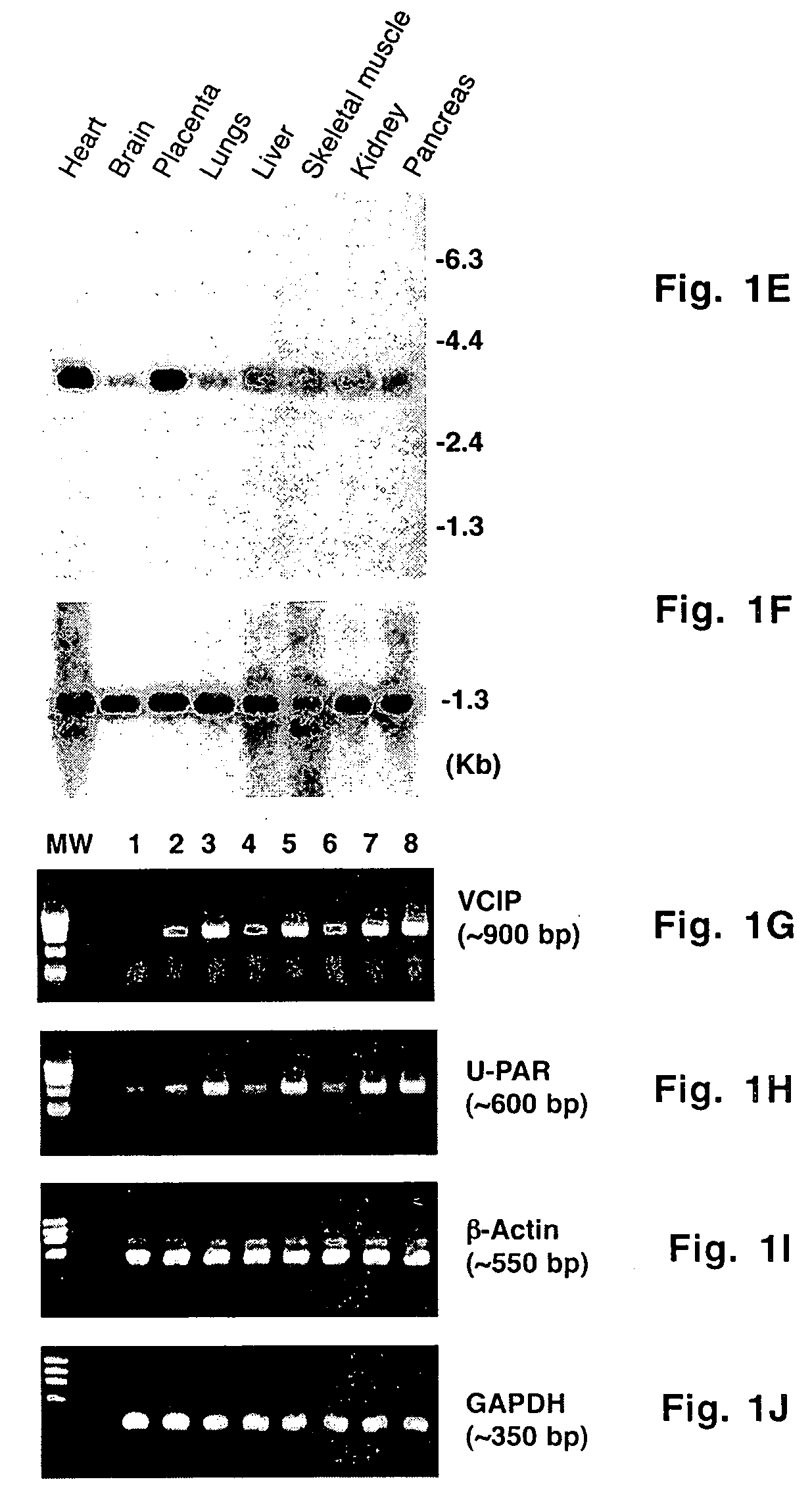
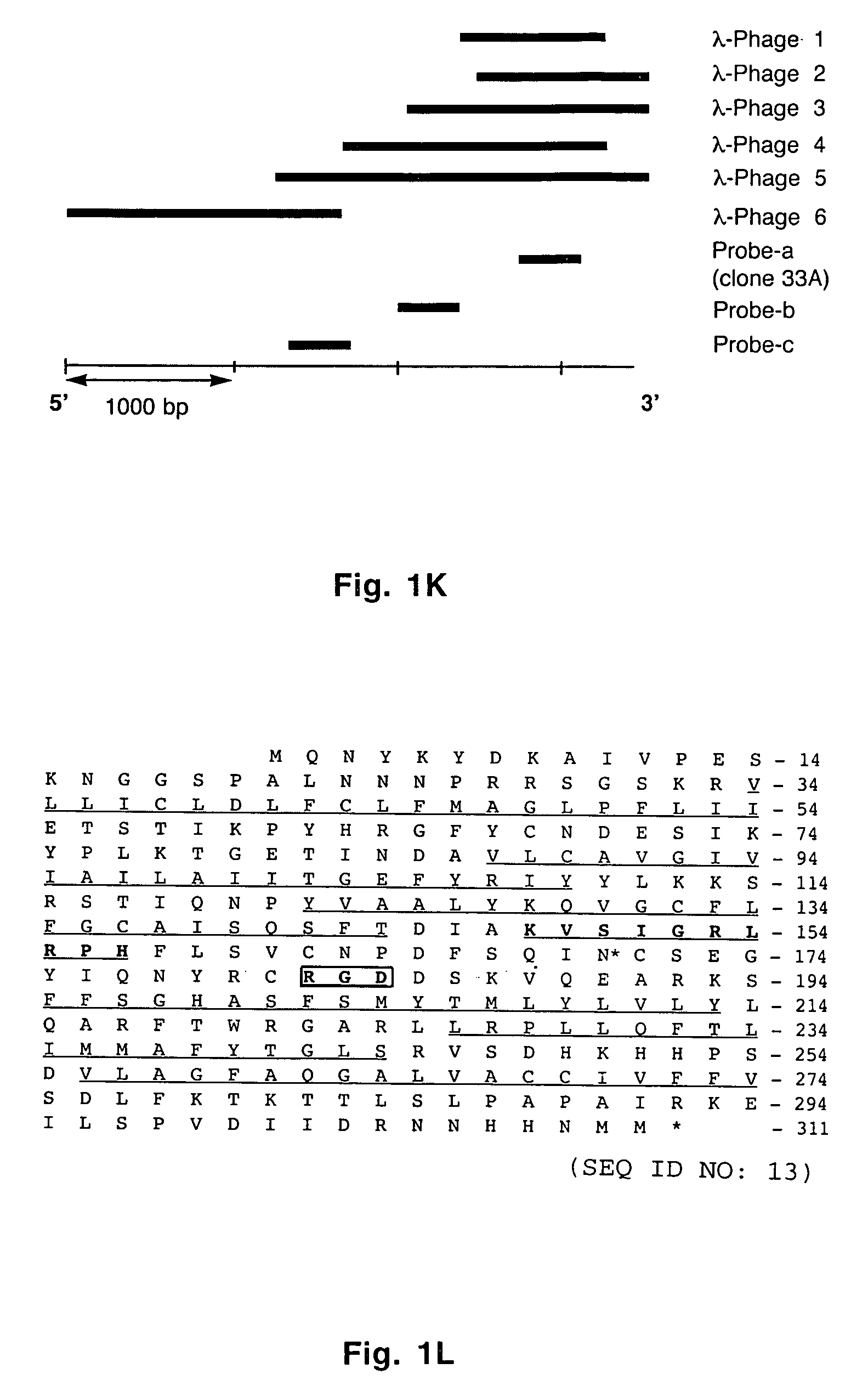
Uses of vascular endothelial growth factor and type I collagen inducible protein (VCIP)
InactiveUS20050002904A1Easy adhesionEasy to spreadBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCell–cell interactionIntegrin ligand
Vascular endothelial growth factor and type I collagen inducible protein (VCIP), also known as phosphatidic acid phosphatase 2b (PAP2b), was identified in a functional assay of angiogenesis. Previously, VCIP was not known to function as an integrin ligand. The present invention discloses VCIP-derived peptides and proteins act as integrin ligands. Since VCIP-derived peptides or proteins are capable of inhibiting specific cell-cell interactions, such inhibitors of cell-cell interactions would be useful for developing novel therapeutic approaches to treat diseases where these interactions have clear pathological consequences. For example, VCIP / PAP2b can be a novel target for anti-angiogenic, anti-cancer and anti-metastatic therapy.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
DNA nanostructures that promote cell-cell interaction and use thereof
The present invention provides a ligand-nucleic acid nanostructure that promotes cell-cell interaction. Specially, the invention provides a ligand-nucleic acid nanostructure for treating tumor in a mammal. The methods of using and making the composition comprising a ligand-nucleic acid nanostructure are also provided.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Biocidic medical devices, implants and wound dressings
InactiveUS20100087769A1Effectively electrical balanceEffective preservationAntibacterial agentsSurgeryElectricityWound dressing
The present invention discloses a medical device selected from a group consisting of medical devices, implants wound dressings, comprises at least one insoluble proton sink or source (PSS). The medical device is provided useful for killing living target cells (LTCs), or otherwise disrupting vital intracellular processes and / or intercellular interactions of the LTC upon contact. The PSS comprises, inter alia, (i) proton source or sink providing a buffering capacity; and (ii) means providing proton conductivity and / or electrical potential. The PSS is effectively disrupting the pH homeostasis and / or electrical balance within the confined volume of the LTC and / or disrupting vital intercellular interactions of the LTCs while efficiently preserving the pH of the LTCs' environment.
Owner:OPLON
Biofilm deterrence in water supply systems
InactiveUS20100133114A1Effective preservationMinimize changesBiocideSpecific water treatment objectivesCell–cell interactionBiological membrane
Means and methods for deterring biofilm in water supply systems, comprising at least one insoluble proton sink or source (PSS). The means and methods for deterring biofilm is provided useful for killing living target cells (LTCs), or otherwise disrupting vital intracellular processes and / or intercellular interactions of the LTC upon contact. The PSS comprises, inter alia, (i) proton source or sink providing a buffering capacity; and (ii) means providing proton conductivity and / or electrical potential. The PSS is effectively disrupting the pH homeostasis and / or electrical balance within the confined volume of the LTC and / or disrupting vital intercellular interactions of the LTCs while efficiently preserving the pH of the LTCs' environment.
Owner:OPLON
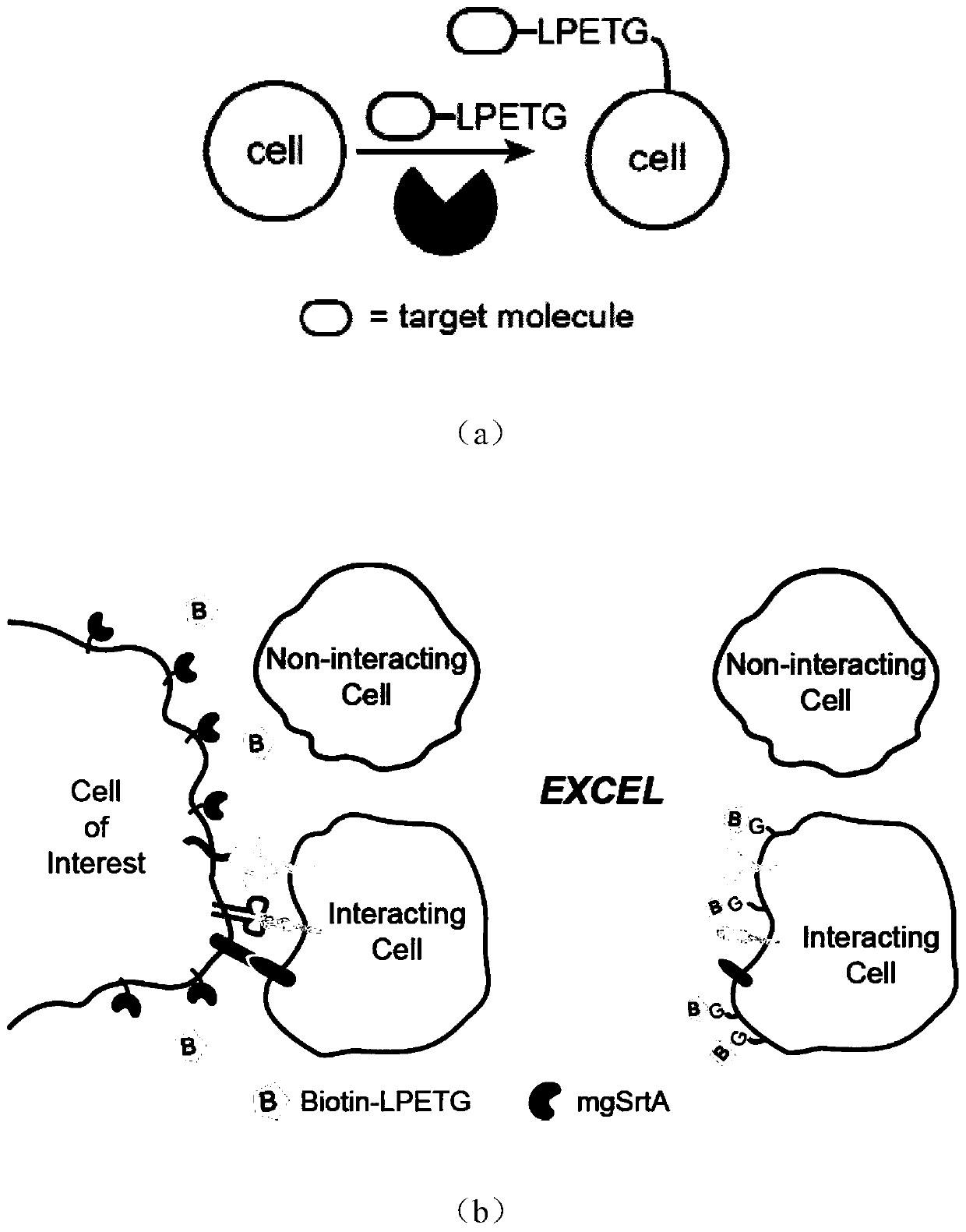
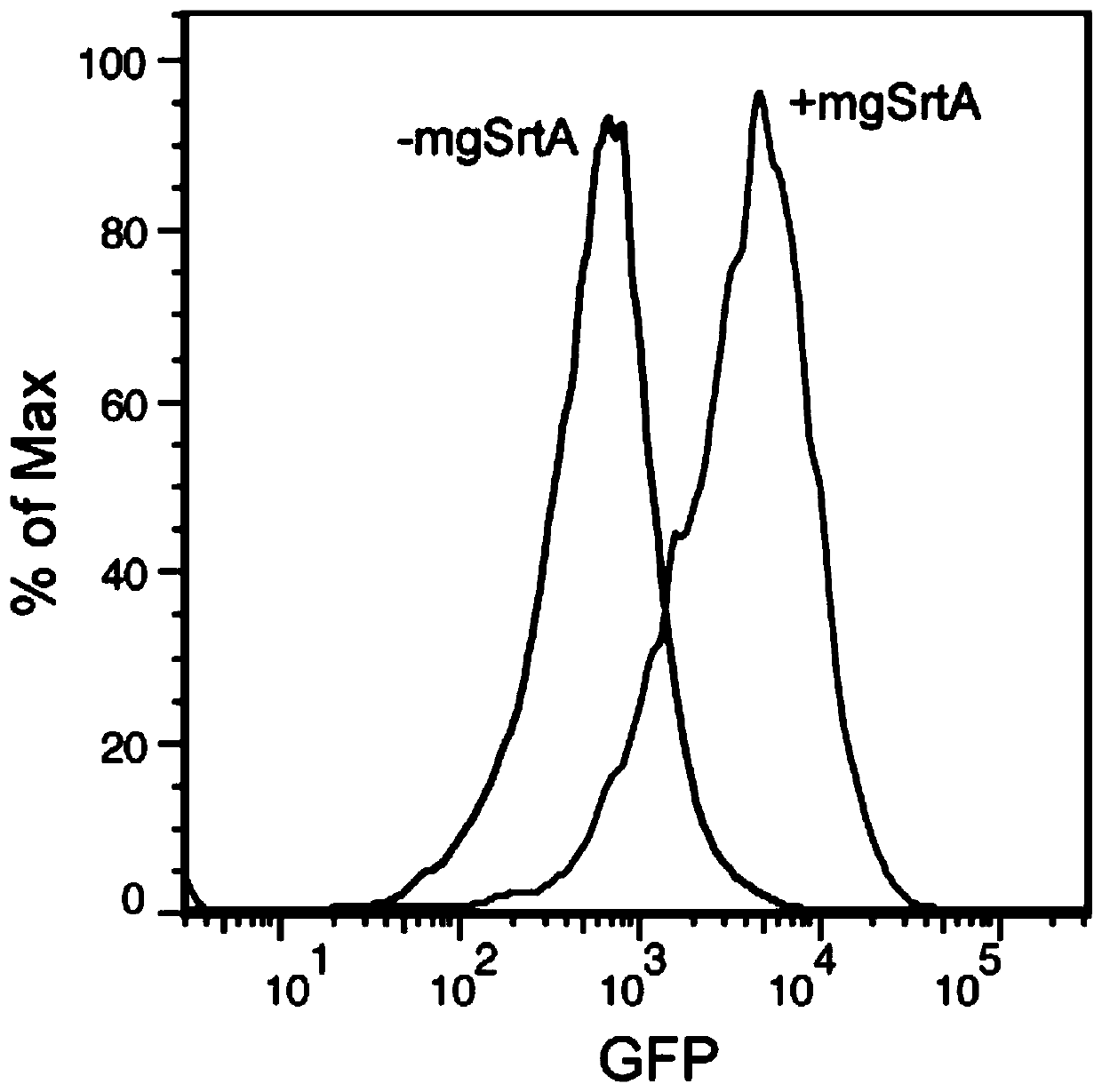
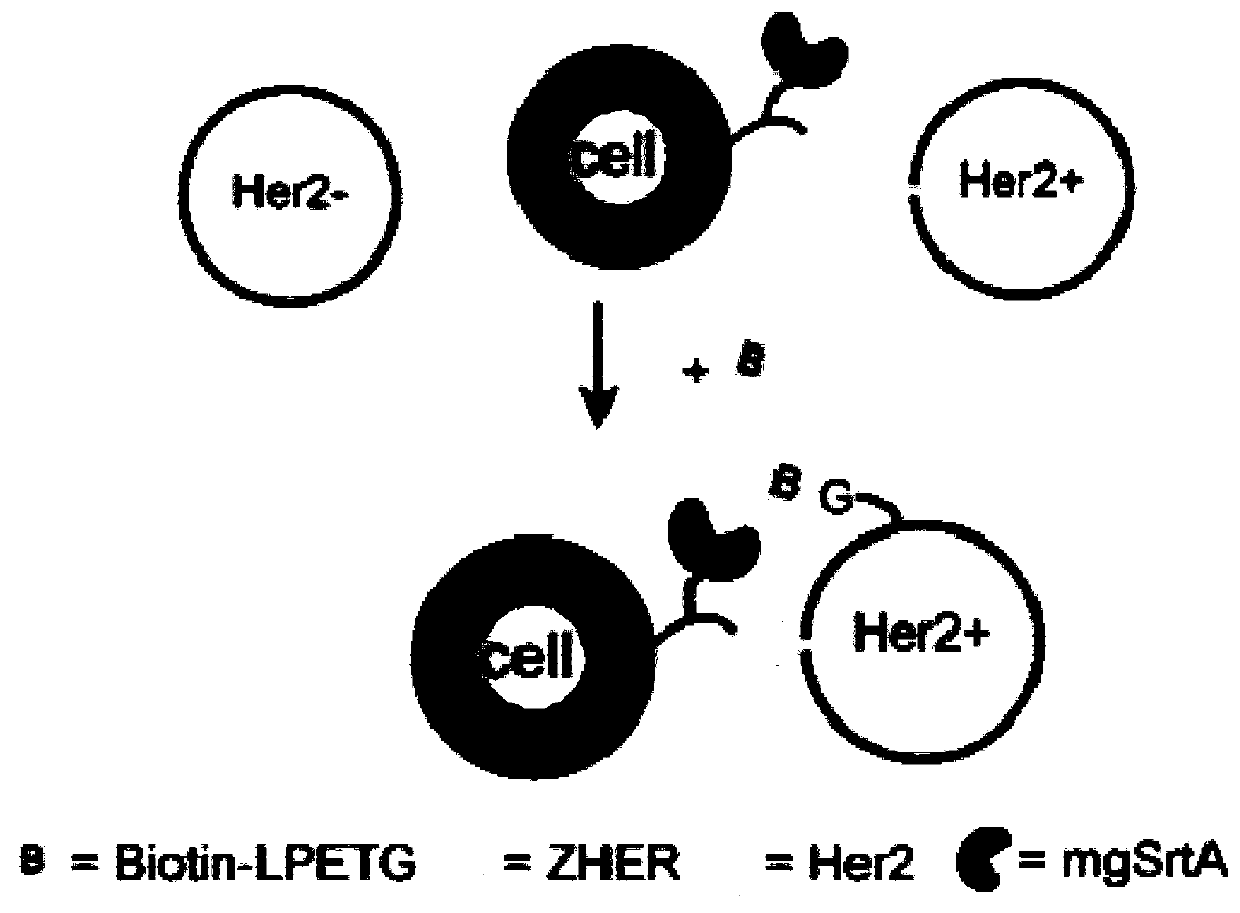
Enzyme and method for marking cell membrane surfaces and researching cell-cell interaction
ActiveCN109797194AImprove labeling efficiencyTag implementationMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesCell–cell interactionCell membrane
The invention discloses an enzyme and a method for marking cell membrane surfaces and researching cell-cell interaction, and relates to a staphylococcus aureus sortase A mutant evolved by gene engineering. The mutant can realize proximity effect-mediated marking reaction, the cell membrane surfaces not subjected to gene modification can be marked on the basis, and cell-cell interaction can be accurately caught and marked in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Substrate and method for culturing breast cells
InactiveUS20100297675A1Easy to handleImprove the bactericidal effectEpidermal cells/skin cellsDrug screeningPorous substrateNon malignant
A cell culture article includes a porous substrate having a plurality of pores and a plurality of interstices in communication with the pores. At least some of the plurality of pores and interstices are sufficiently large for two or more mammary epithelial cells to cluster within the pores or interstices. Non-malignant mammary epithelial cells or breast cancer cells may not attach strongly to the substrate surface, which may encourage cell-cell interaction. In many cases, the article is desirably free of components of unknown origin. The articles may be capable of maintaining culture of malignant and non-malignant mammary epithelial cells and allowing for development of in vivo-like morphologies or characteristics of such cells.
Owner:CORNING INC
Inverse patterning process for three-dimensional multi-compartmental micro-organization of multiple cell types
ActiveUS10072257B2Rapid cell patternsMinimal damageHepatocytesMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCell–cell interaction
The invention features an “inverse patterning” or “Intaglio-Void / Embed-Relief Topographic (In VERT) molding” manufacturing process for generating high-resolution three-dimensional (3D) multi-cellular microstructures in distinct cellular compartments of a single hydrogel. The platform has general utility in the development of engineered tissues for human therapies, drug testing, and disease models. Additionally, the platform can serve as a model system for studying 3D cell-cell interactions in fields as diverse as stem cell biology to the development of cancer therapeutics.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for cell killing
The present invention presents a biocidic packaging for cosmetics and / or foodstuffs, comprises at least one insoluble proton sink or source (PSS). The ackaging is provided useful for killing living target cells (LTCs), or otherwise disrupting vital intracellular processes and / or intercellular interactions of said LTC upon contact. The PSS comprises, inter alia, (i) proton source or sink providing a buffering capacity; and (ii) means providing proton conductivity and / or electrical potential. The PSS is effectively disrupting the pH homeostasis and / or electrical balance within the confined volume of the LTC and / or disrupting vital intercellular interactions of the LTCs while efficiently preserving the pH of said LTCs' environment. The present invention also discloses a method for killing living target cells (LTCs), or otherwise disrupting vital intracellular processes and / or intercellular interactions of said LTC being in a packaging, especially cosmetic or foodstuffs' packaging.
Owner:OPLON
Cytometer on a chip
ActiveUS7655421B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell–cell interactionBiology
An assay technique for label-free, highly parallel, qualitative and quantitative detection of specific cell populations in a sample and for assessing cell functional status, cell-cell interactions and cellular responses to drugs, environmental toxins, bacteria, viruses and other factors that may affect cell function. The technique includes a) creating a first array of binding regions in a predetermined spatial pattern on a sensor surface capable of specifically binding the cells to be assayed; b) creating a second set of binding regions in specific spatial patterns relative to the first set designed to efficiently capture potential secreted or released products from cells captured on the first set of binding regions; c) contacting the sensor surface with the sample, and d) simultaneously monitoring the optical properties of all the binding regions of the sensor surface to determine the presence and concentration of specific cell populations in the sample and their functional status by detecting released or secreted bioproducts.
Owner:CIENCIA
Co-culture device for cell culture and cell-cell interaction and using method of co-culture device
InactiveCN105695328ASimple structureEasy to operateApparatus sterilizationTissue/virus culture apparatus3D cell cultureCell–cell interaction
The invention discloses a co-culture device for cell culture and cell-cell interaction and a using method of the co-culture device. The device comprises a culture plate, wherein the culture plate is provided with at least one culture hole, at least one detachable semipermeable membrane spacing block and detachable spacing blocks; each detachable semipermeable membrane spacing block divides the corresponding culture hole into a plurality of cell culture rooms; and the detachable spacing blocks are positioned on two sides of each detachable semipermeable membrane spacing block. The using method of the device comprises the following steps: inserting the detachable semipermeable membrane spacing blocks and the detachable spacing blocks in the culture holes after sterilization; culturing tumor cells in a segmented cell culture room; culturing adherent cells in another cell culture room; detaching the detachable spacing blocks, and enabling the tumor cells and the adherent cells to be in co-culture; and continuing co-culture, observing a tumor cell balling condition and a migration condition of the balled tumor cells from one cell culture room to the other cell culture room. The co-culture device for cell culture and cell-cell interaction is simple in structure, simple and practical in operation, and visual and clear in effect.
Owner:张姝 +1
Biocidic textiles and fabrics
InactiveUS20100136074A1Minimize changesEffective preservationBiocideBiochemical fibre treatmentCell–cell interactionBiotextile
It is in the scope of the invention to disclose a biocidic textiles and fabrics, comprising at least one insoluble proton sink or source (PSS). The textiles and fabrics is provided useful for killing living target cells (LTCs), or otherwise disrupting vital intracellular processes and / or intercellular interactions of the LTC upon contact; the PSS comprising (i) proton source or sink providing a buffering capacity; and (ii) means providing proton conductivity and / or electrical potential; wherein the PSS is effectively disrupting the pH homeostasis and / or electrical balance within the confined volume of the LTC and / or disrupting vital intercellular interactions of the LTCs while efficiently preserving the pH of the LTCs' environment.
Owner:OPLON
Method for modifying probe of atomic force microscope by using magnetic nano-particles
ActiveCN108398578AImprove adhesionImprove adhesion strengthScanning probe microscopyAdhesion forceMagnetic force microscope
The invention belongs to the atomic force microscope measurement technical field and provides a method for modifying the probe of an atomic force microscope by using magnetic nano-particles. With themethod adopted, the direct test of interaction between nano-particles and cells can be realized. According to the method, nano-scale magnetic particles and micro-scale carbon sphere particles are adopted; the V-shaped micro-cantilever and flat plate probe of the atomic force microscope are placed under the microscope; a particle mixed dispersion liquid is added dropwise, washing, drying and otherprocesses are performed, and therefore, a magnetic nano-particle-modified V-shaped cone-like tip probe can be obtained. The micro-scale carbon spheres are adopted as the carriers of the magnetic nano-particles, and therefore, experimental operation can be simplified, modification efficiency can be improved, a modification effect can be optimized, the direct test of the interaction between the nano-particles and the cells can be realized, and further experimental verification is provided for the uptake of the particles by the cells, adhesion forces between the particles and the cells, the survival ability of the cells and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for Micromanipulation of Cells
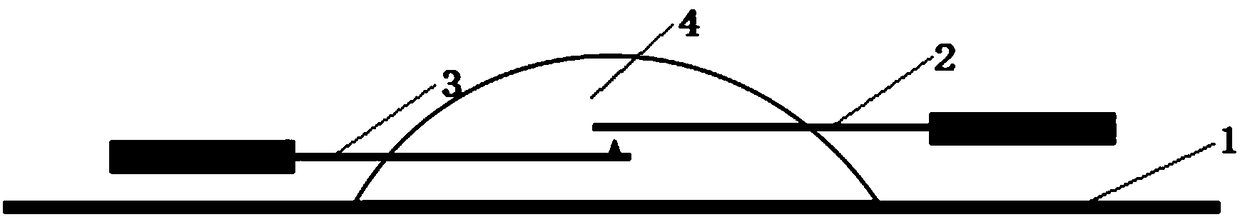
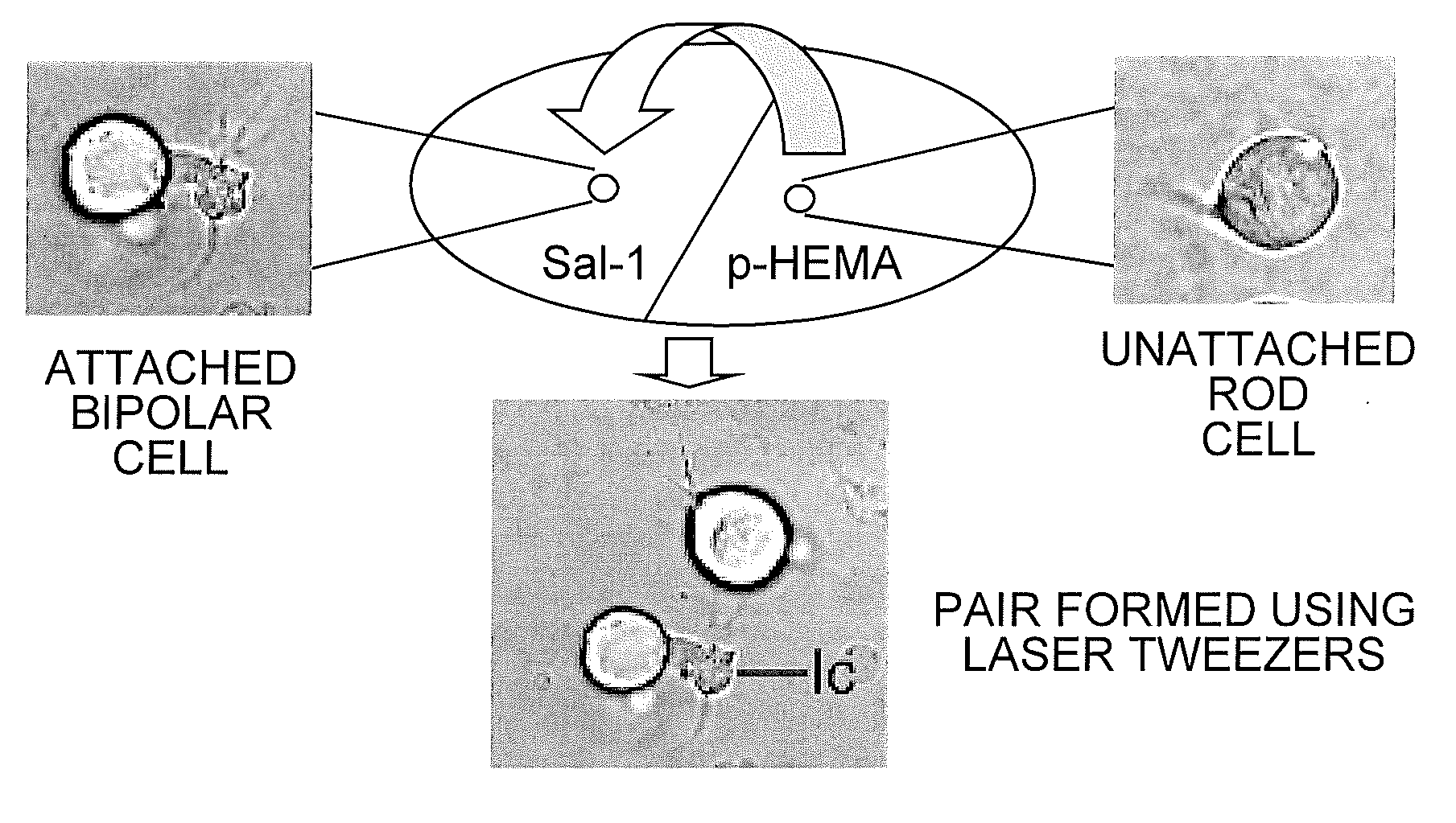
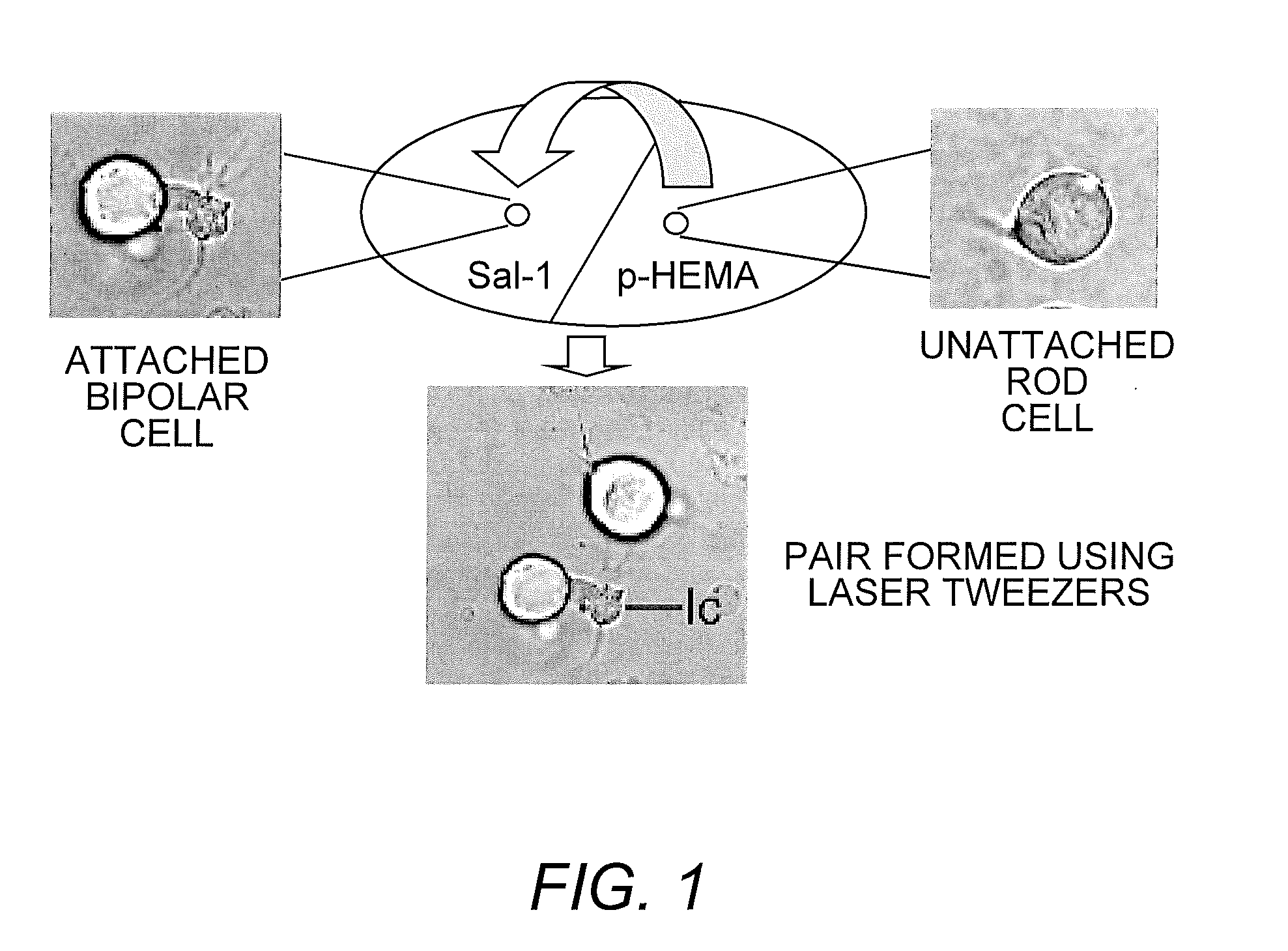
InactiveUS20100267105A1Laboratory glasswaresElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentCoated surfaceCell–cell interaction
The present invention is a method for manipulating living cells in vitro using poly-2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate-coated surfaces and optical tweezers to obtain cells in isolation or to create specific cell-cell interactions.
Owner:UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW JERSEY
Isolated mucins and different microorganisms, and methods of use
ActiveUS20160228507A1Decreasing competitive natureReduce microbial pathogenicityCompound screeningBiocideCell–cell interactionGrowth cell
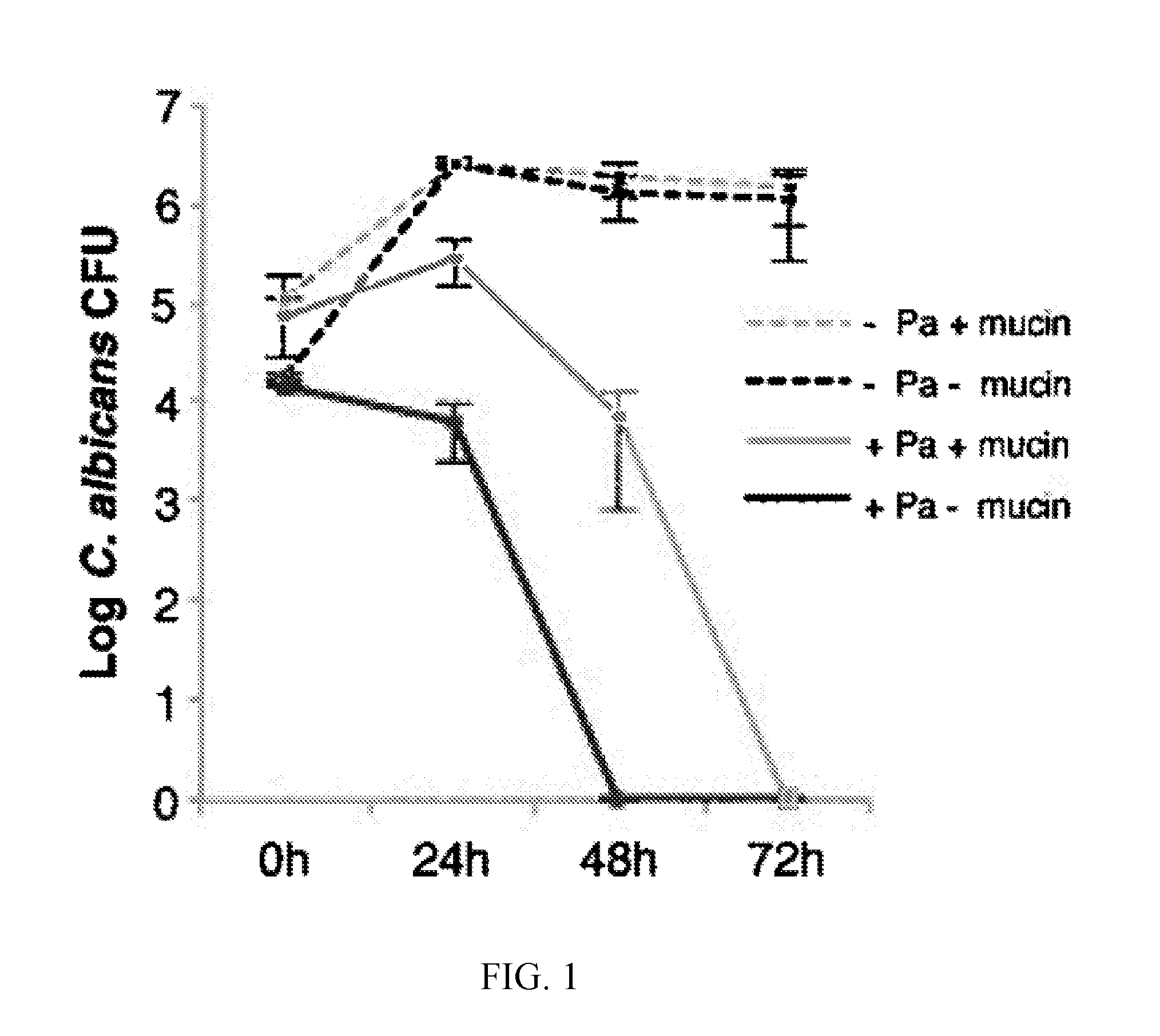
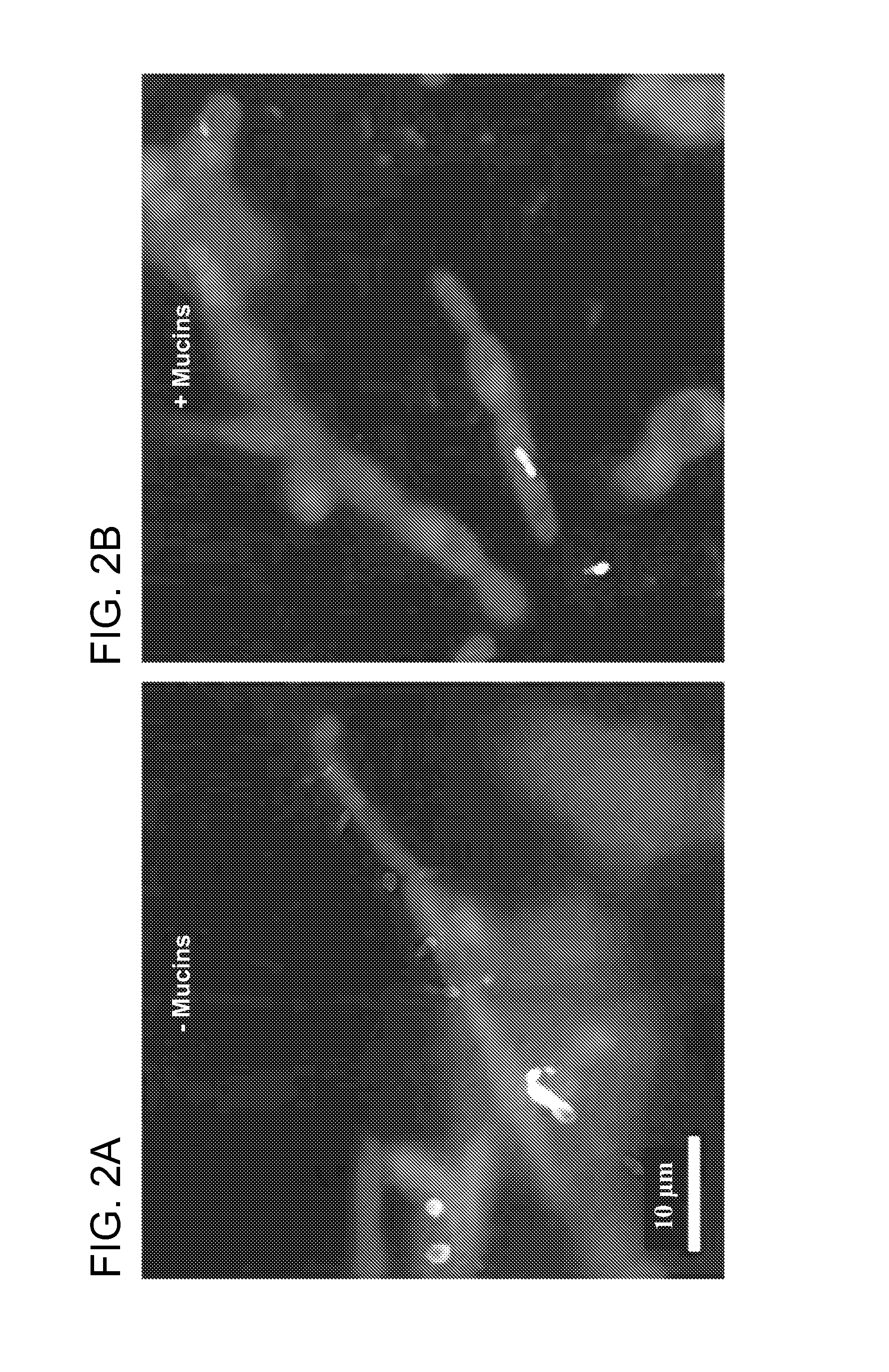
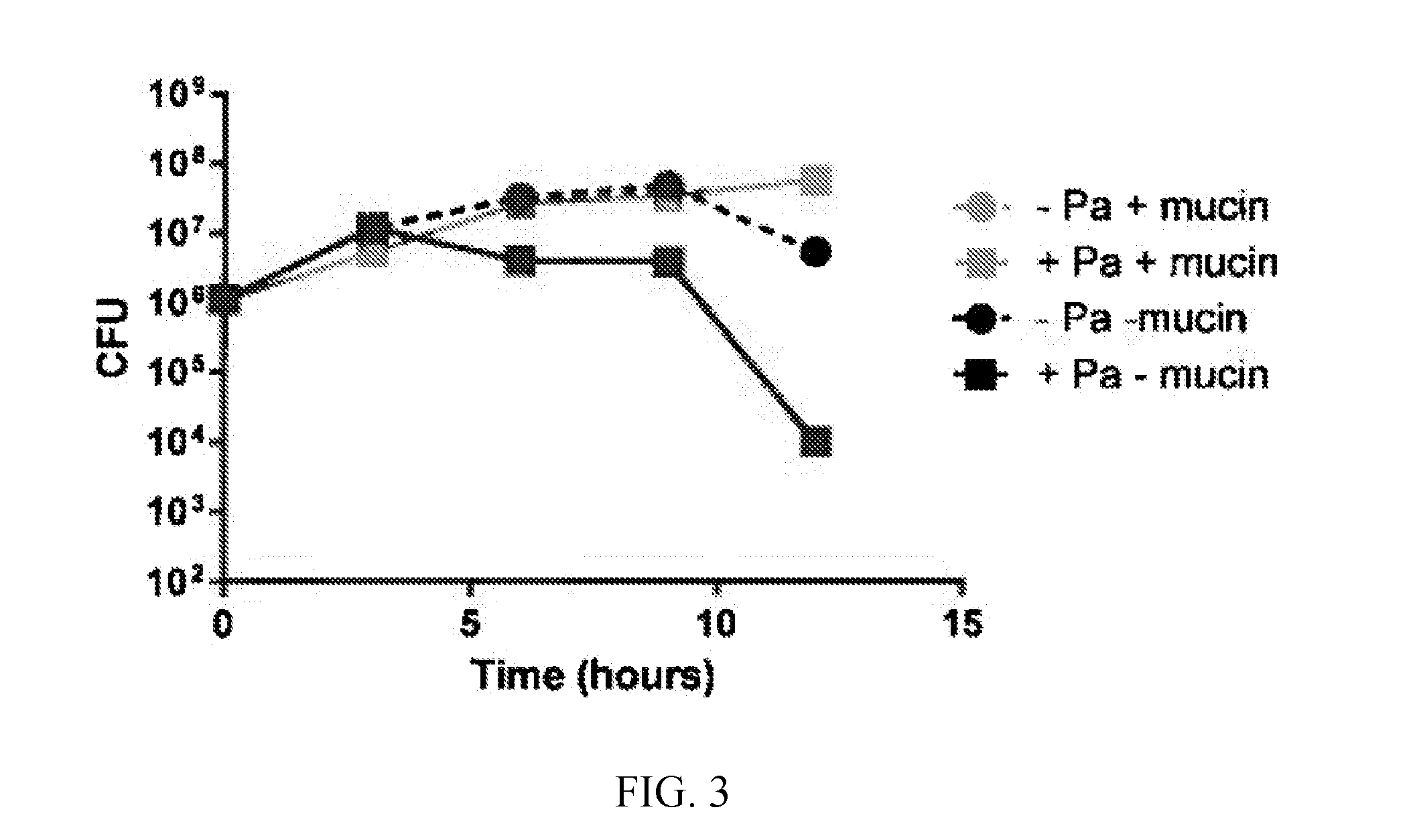
A method of altering intercellular interactions between a combination of microorganisms includes contacting a combination of different species of microorganisms with at least one mucin. Isolated compositions include a combination of microorganisms and at least one mucin. One microorganism of the combination inhibits cell growth or promotes cell death of at least one other microorganism of a different species in the combination. The combination of microorganisms with the mucin results an increase in cell growth or a reduction in cell death, respectively, of the at least one other microorganism.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Gold nanoparticle serial compound with surface diversity
ActiveCN106892896AGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic chemistry methodsDiseaseSpatial structure
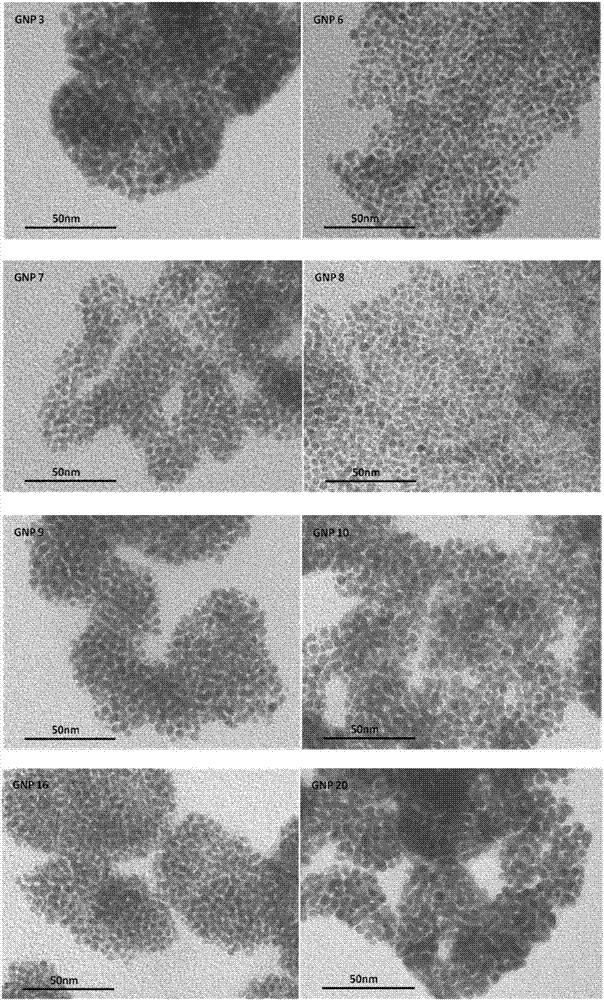
The invention discloses a gold nanoparticle serial compound with surface diversity. Four groups based on pi-bond density and space structure difference selection and seven groups based on hydrophilic-hydrophobic property difference selection are connected on a parent nucleus of a lysine-amide compound in pairs by changing a structure of a ligand of the lysine-amide compound, and molecules of the ligand are connected with gold nanoparticles, so as to obtain the gold nanoparticle serial compound. The invention also discloses a differentiated surface property of the gold nanoparticle serial compound and potential application of the differentiated surface property in research on interaction between nanoparticle materials and cells, so that a design that the gold nanoparticle serial compound serving as a targeted carrying drug, a biological developer, a disease diagnosis drug, a gene therapy drug and the like is applied to a carrier of the bio-medical field can be guided by utilizing a result of an interactive relationship.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com