Patents
Literature
3254 results about "Biological membrane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A biological membrane or biomembrane is an enclosing or separating membrane that acts as a selectively permeable barrier within living things. Biological membranes, in the form of eukaryotic cell membranes, consist of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded, integral and peripheral proteins used in communication and transportation of chemicals and ions. The bulk of lipid in a cell membrane provides a fluid matrix for proteins to rotate and laterally diffuse for physiological functioning. Proteins are adapted to high membrane fluidity environment of lipid bilayer with the presence of an annular lipid shell, consisting of lipid molecules bound tightly to surface of integral membrane proteins. The cell membranes are different from the isolating tissues formed by layers of cells, such as mucous membranes, basement membranes, and serous membranes.
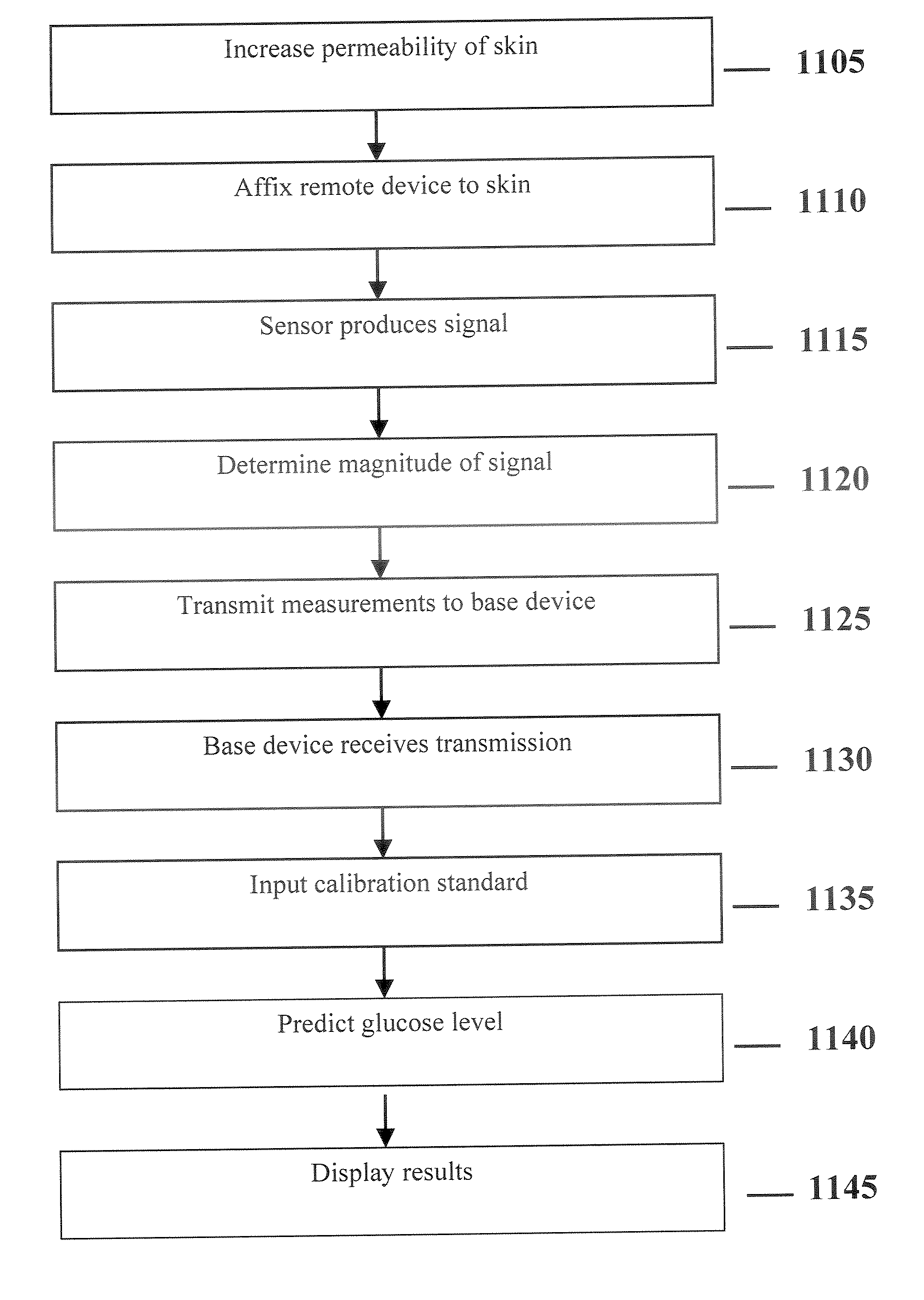
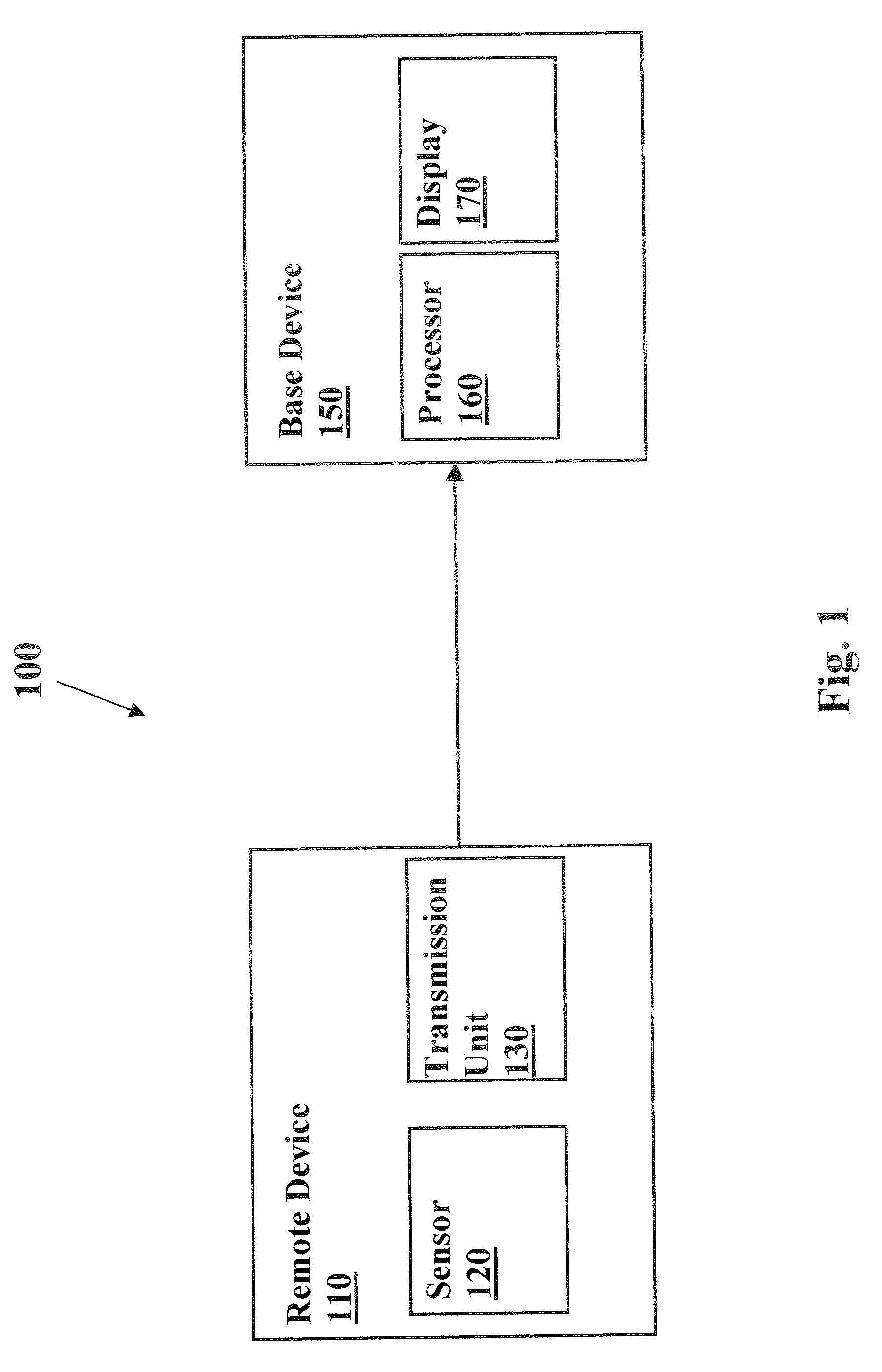
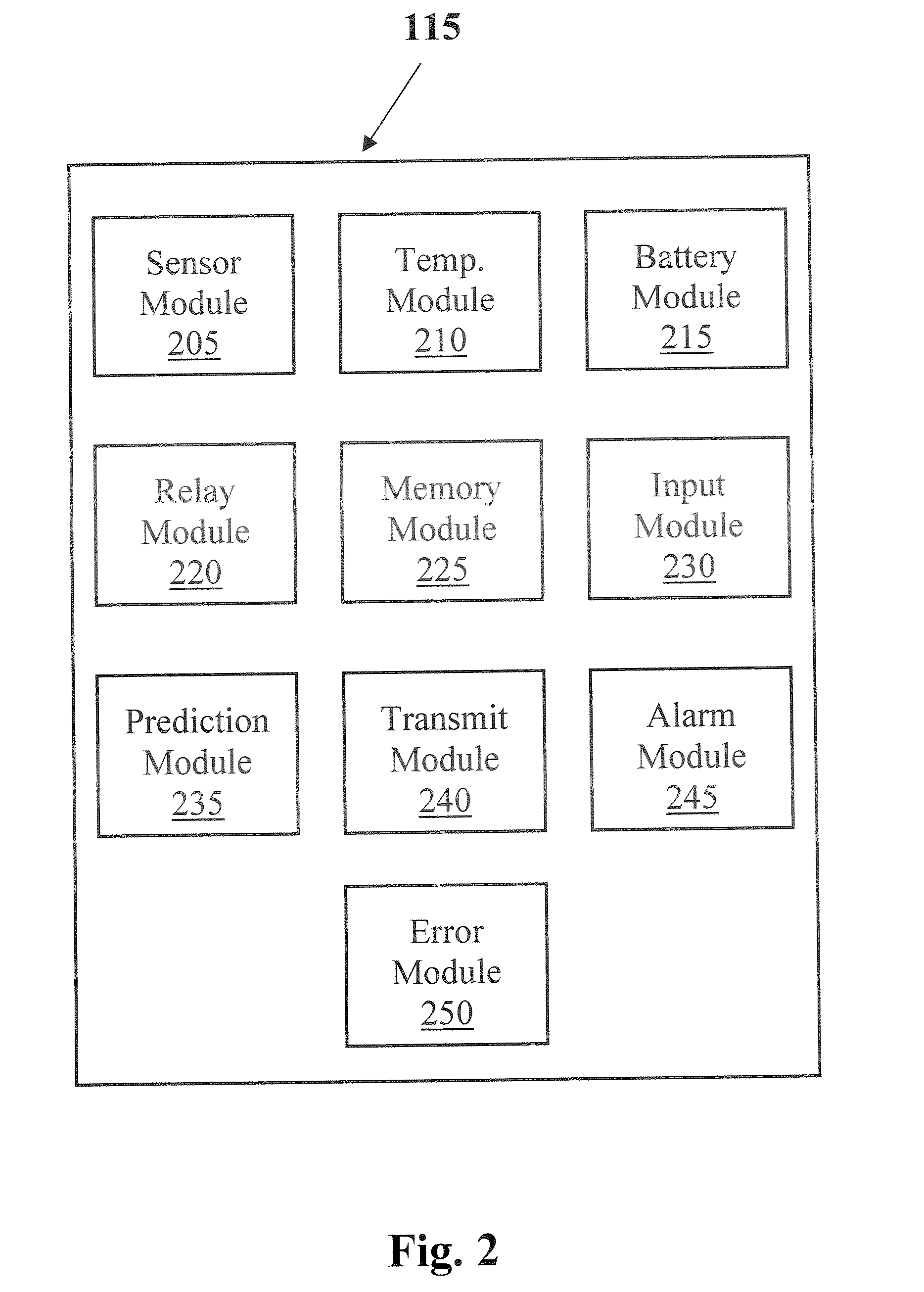
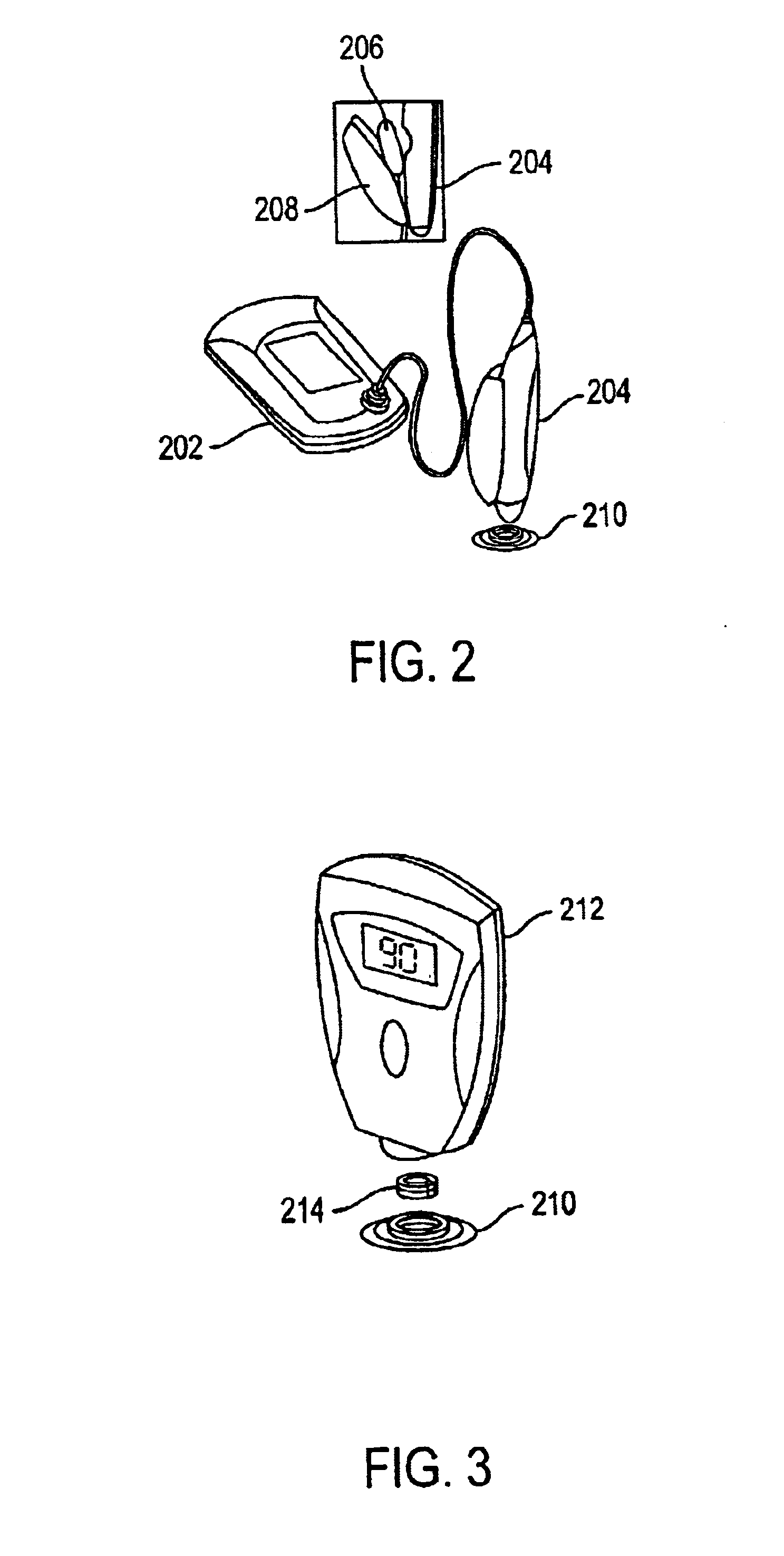
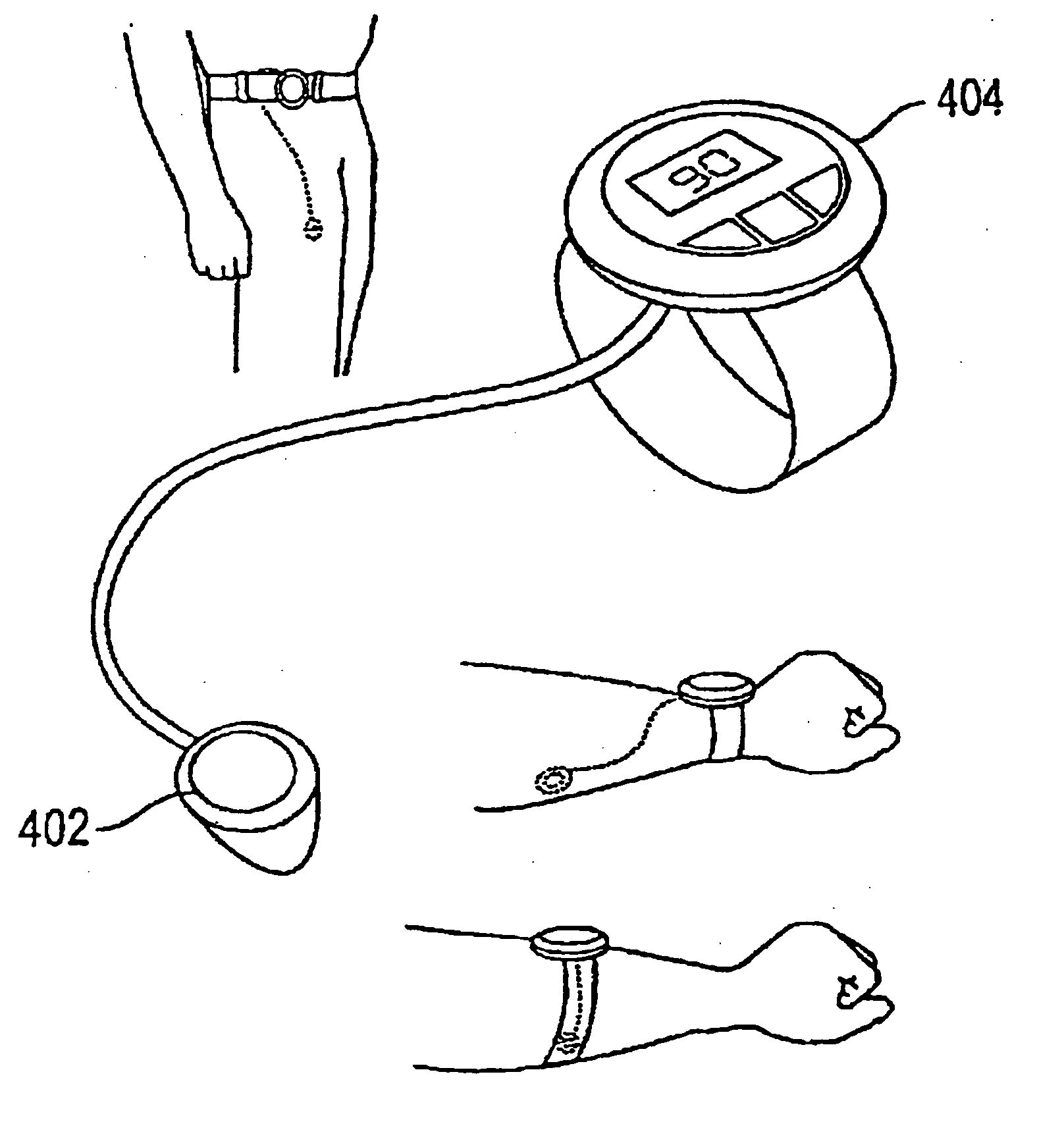
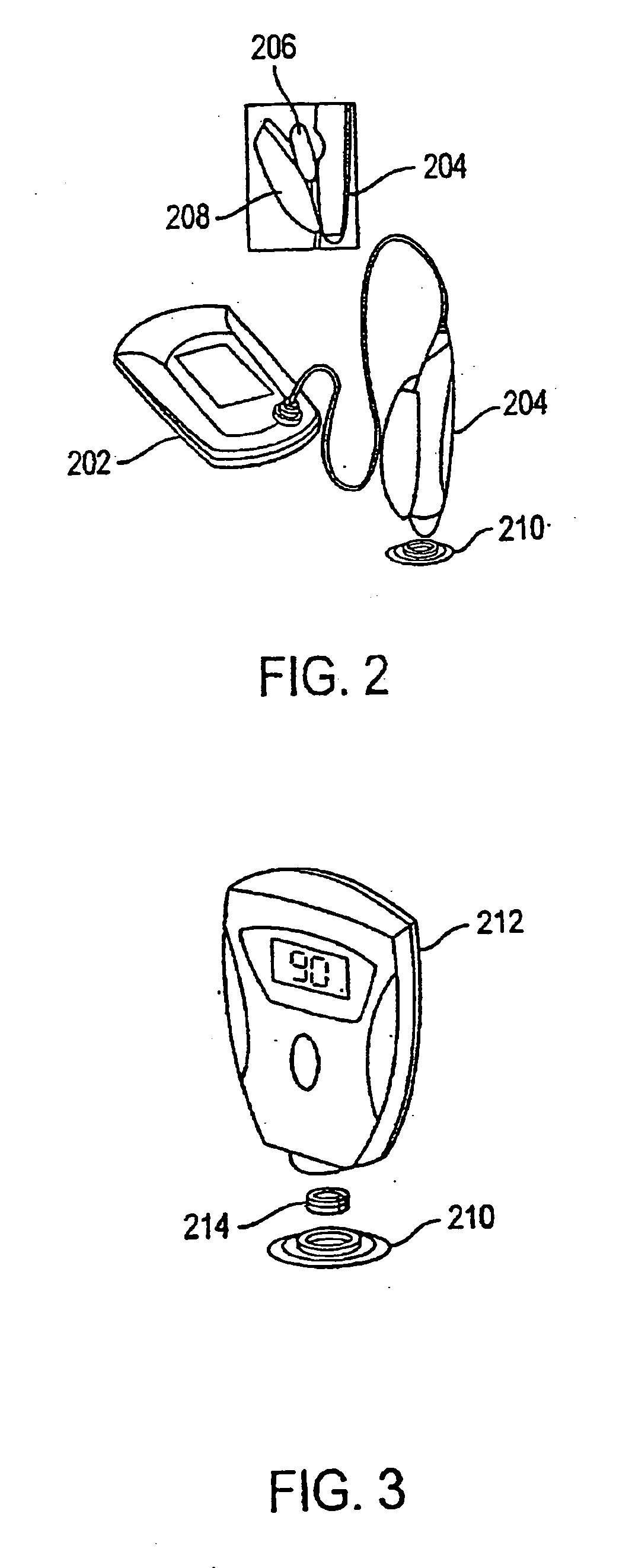
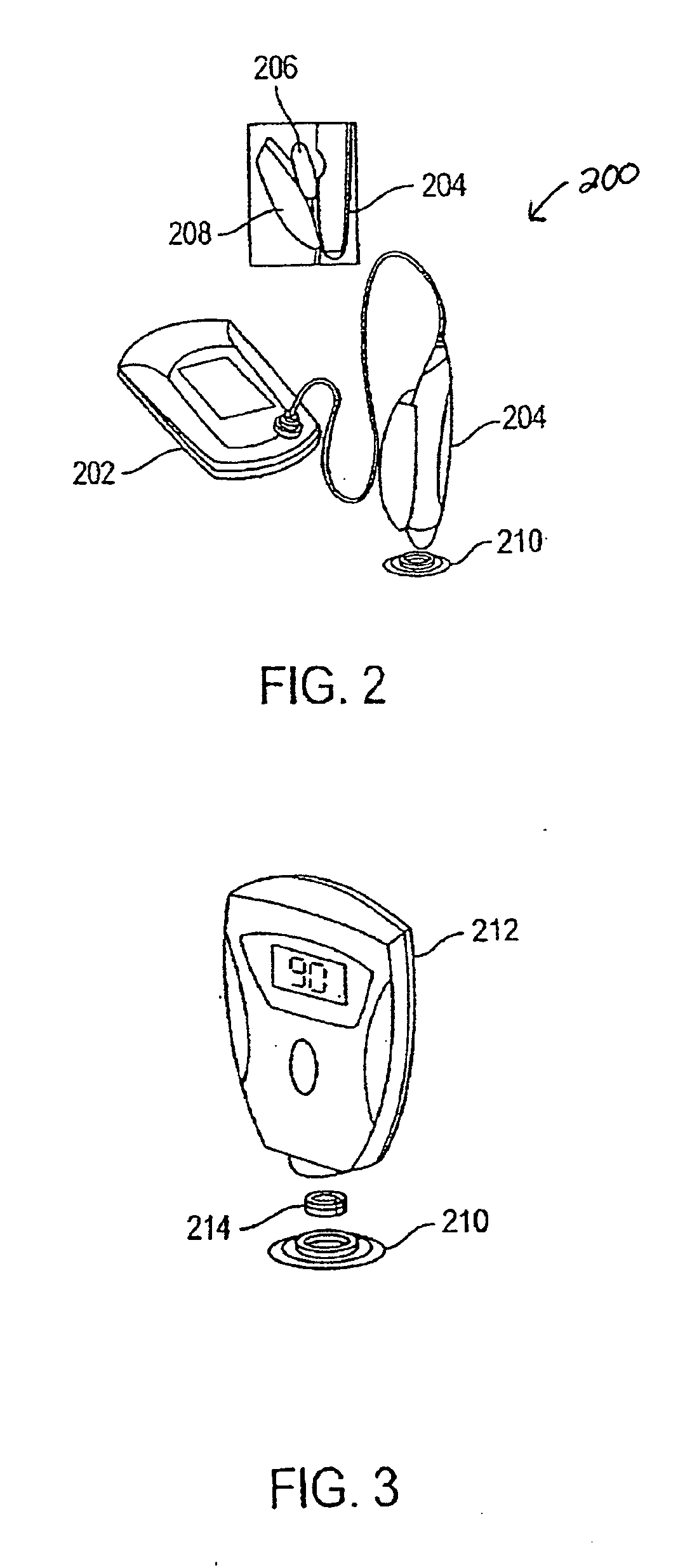
System and method for continuous non-invasive glucose monitoring
A system and method for continuous non-invasive glucose monitoring is disclosed. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the method includes the steps of (1) contacting a remote device to an area of biological membrane having a permeability level, the remote device comprising a sensor and a transmitter; (2) extracting the at least one analyte through and out of the area of biological membrane and into the sensor; (3) generating an electrical signal representative of a level of the at least one analyte; (4) transmitting the electrical signal to a base device; (5) processing the electrical signal to determine the level of the at least one analyte; and (6) displaying the level of the at least one analyte in real time. The system includes a remote device that includes a sensor that generates an electrical signal representative of the concentration of the at least one analyte; and a transmitter that transmits the electrical signal. The system further includes a base device that includes a receiver that receives the electrical signal; a processor that processes the electrical signal; and a display that displays the processed signal in real time.
Owner:ECHO THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods of analyzing polymers using a spatial network of fluorophores and fluorescence resonance energy transfer
InactiveUS6263286B1Easy to analyze and useMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresEnergy transferResonance
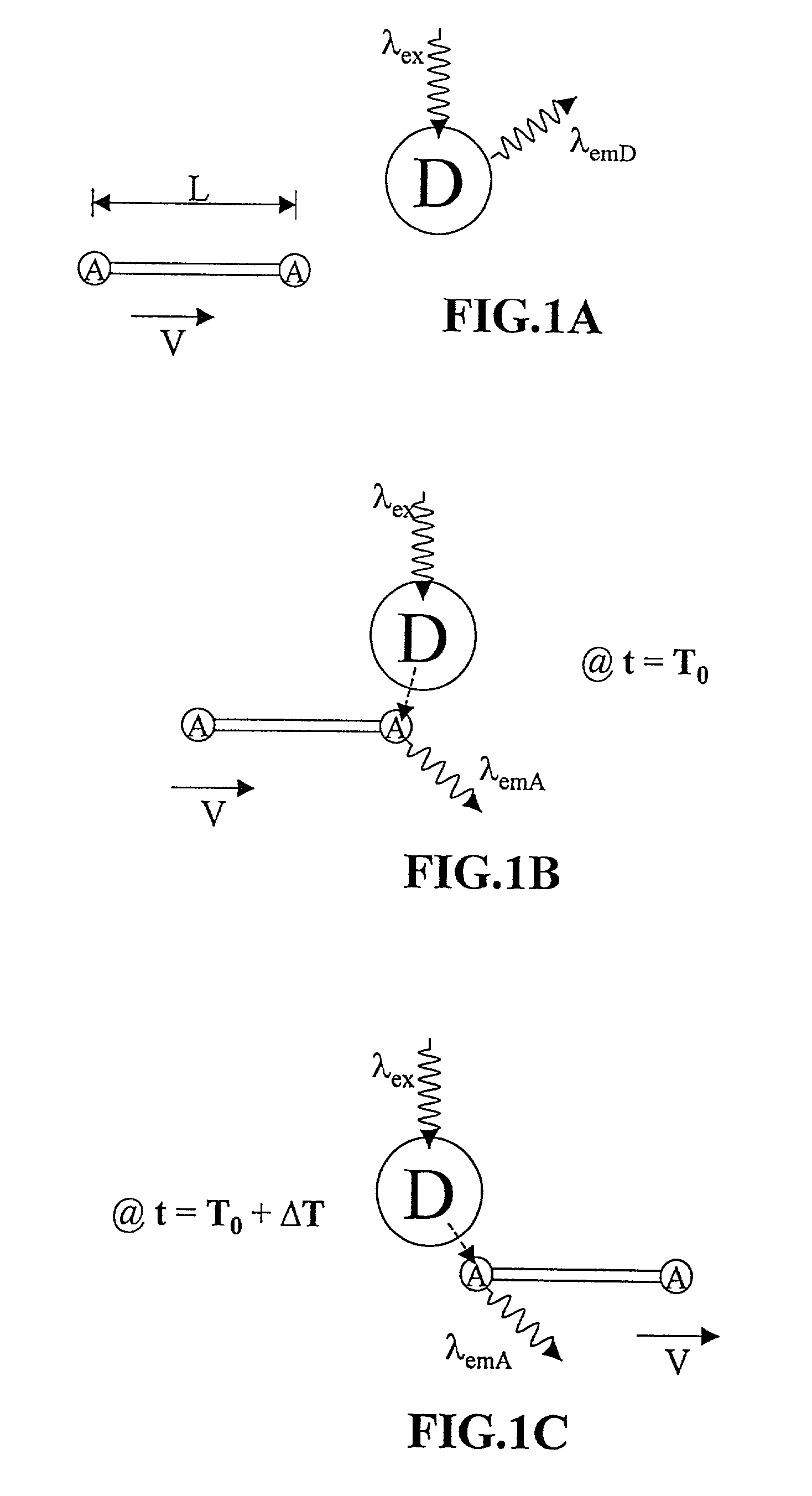
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for analyzing molecules, particularly polymers, and molecular complexes with extended or rod-like conformations. In particular, the methods and apparatuses are used to identify repetitive information in molecules or molecular ensembles, which is interpreted using an autocorrelation function in order to determine structural information about the molecules. The methods and apparatuses of the invention are used for, inter alia, determining the sequence of a nucleic acid, determining the degree of identity of two polymers, determining the spatial separation of specific sites within a polymer, determining the length of a polymer, and determining the velocity with which a molecule penetrates a biological membrane.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Microporation of tissue for delivery of bioactive agents
InactiveUS20050165393A1Improve throughputImprove breathabilitySonopheresisUltrasound therapyBiological bodyThermal energy
A method of enhancing the permeability of a biological membrane, including the skin or mucosa of an animal or the outer layer of a plant to a permeant is described utilizing microporation of selected depth and optionally one or more of sonic, electromagnetic, mechanical and thermal energy and a chemical enhancer. Microporation is accomplished to form a micropore of selected depth in the biological membrane and the porated site is contacted with the permeant. Additional permeation enhancement measures may be applied to the site to enhance both the flux rate of the permeant into the organism through the micropores as well as into targeted tissues within the organism.
Owner:ALTEA THERAPEUTIC CORP +1
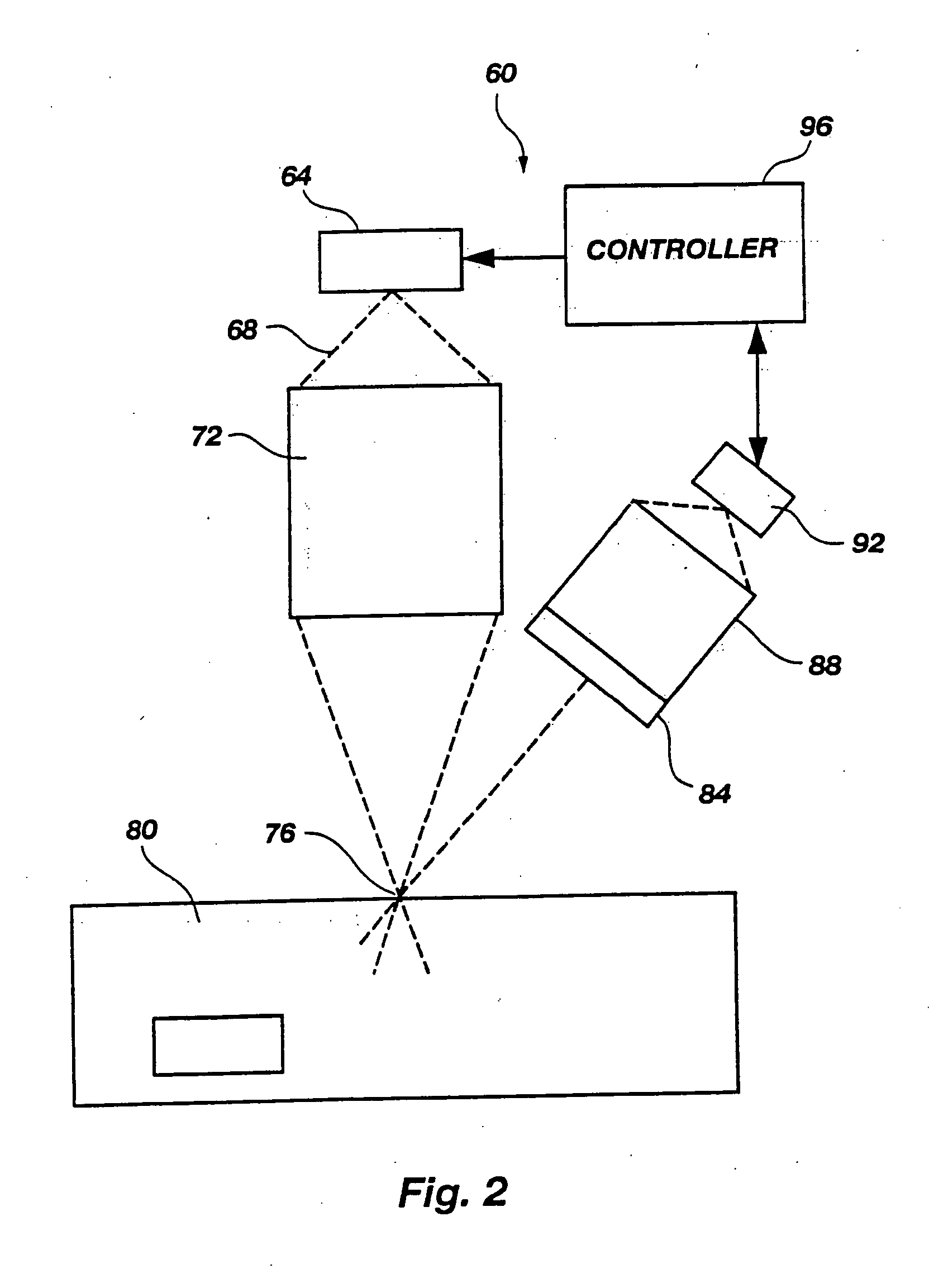
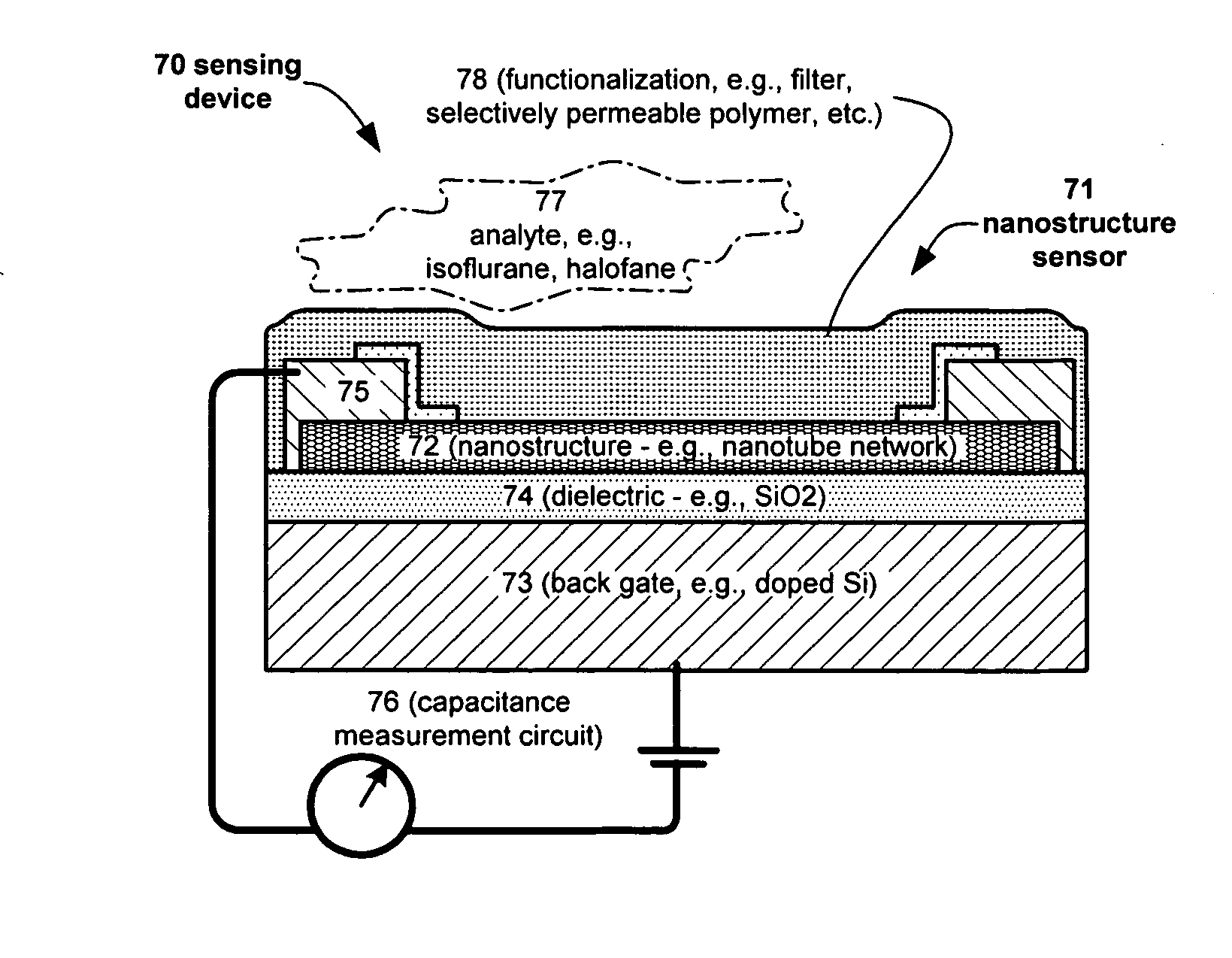
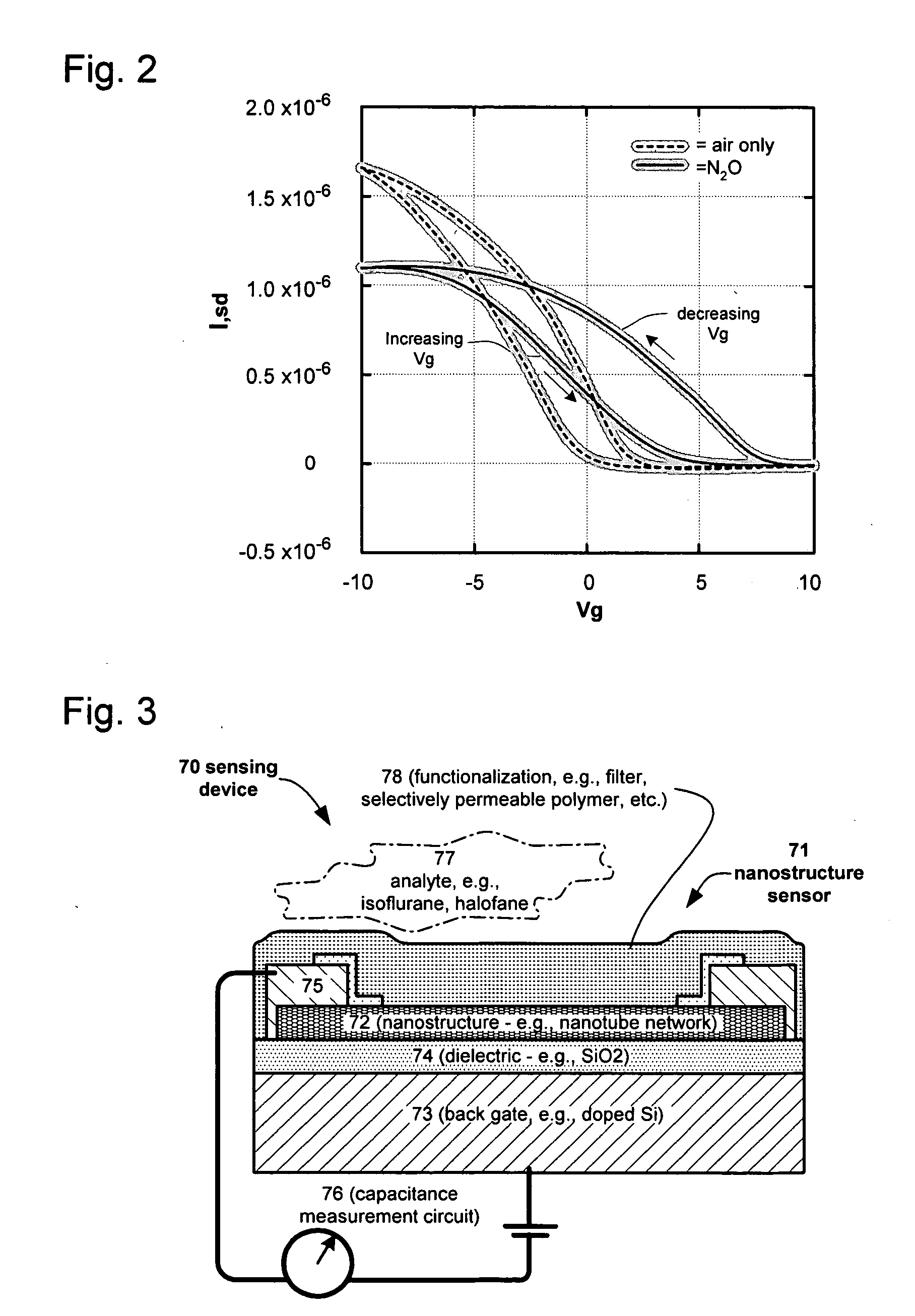
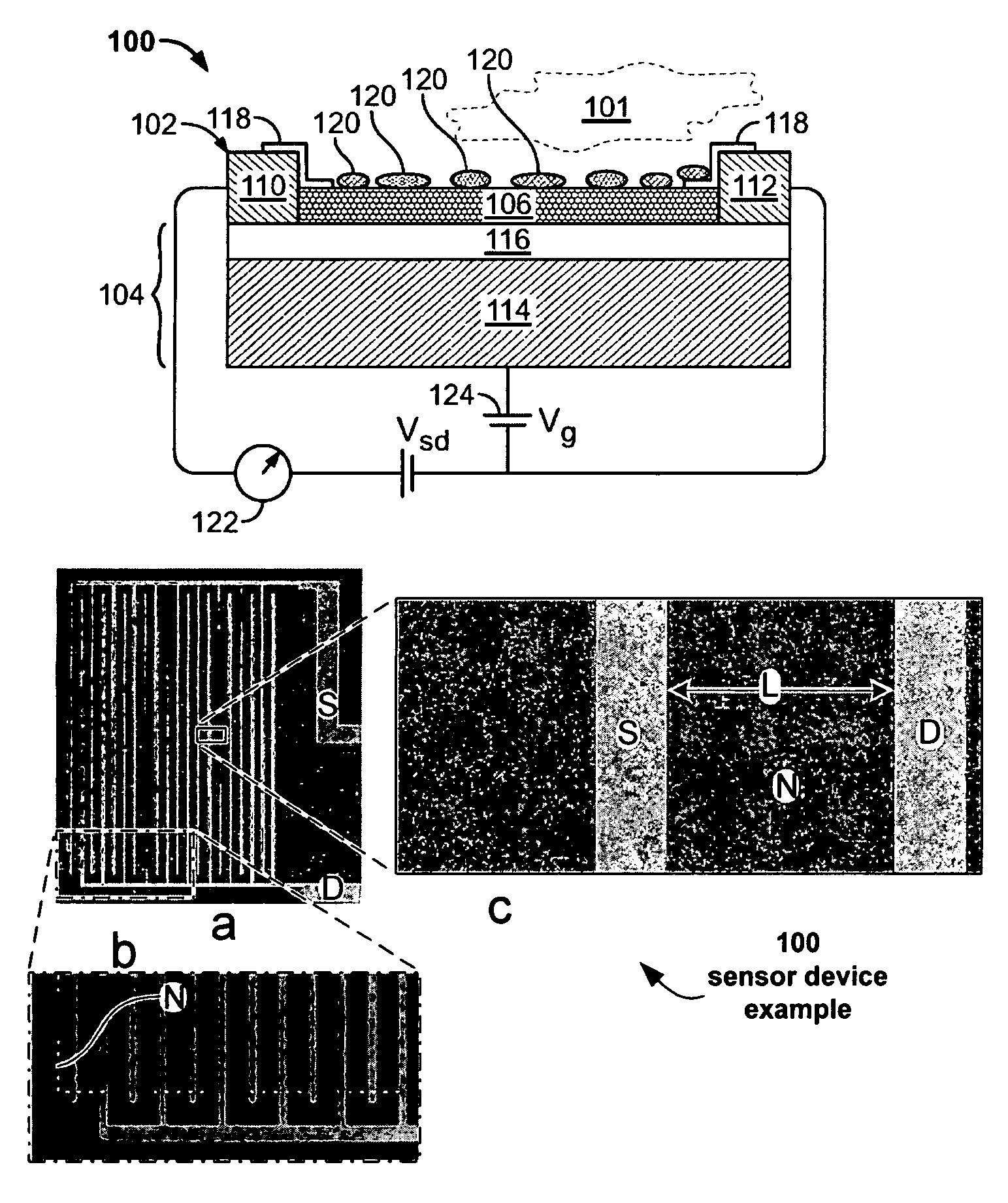
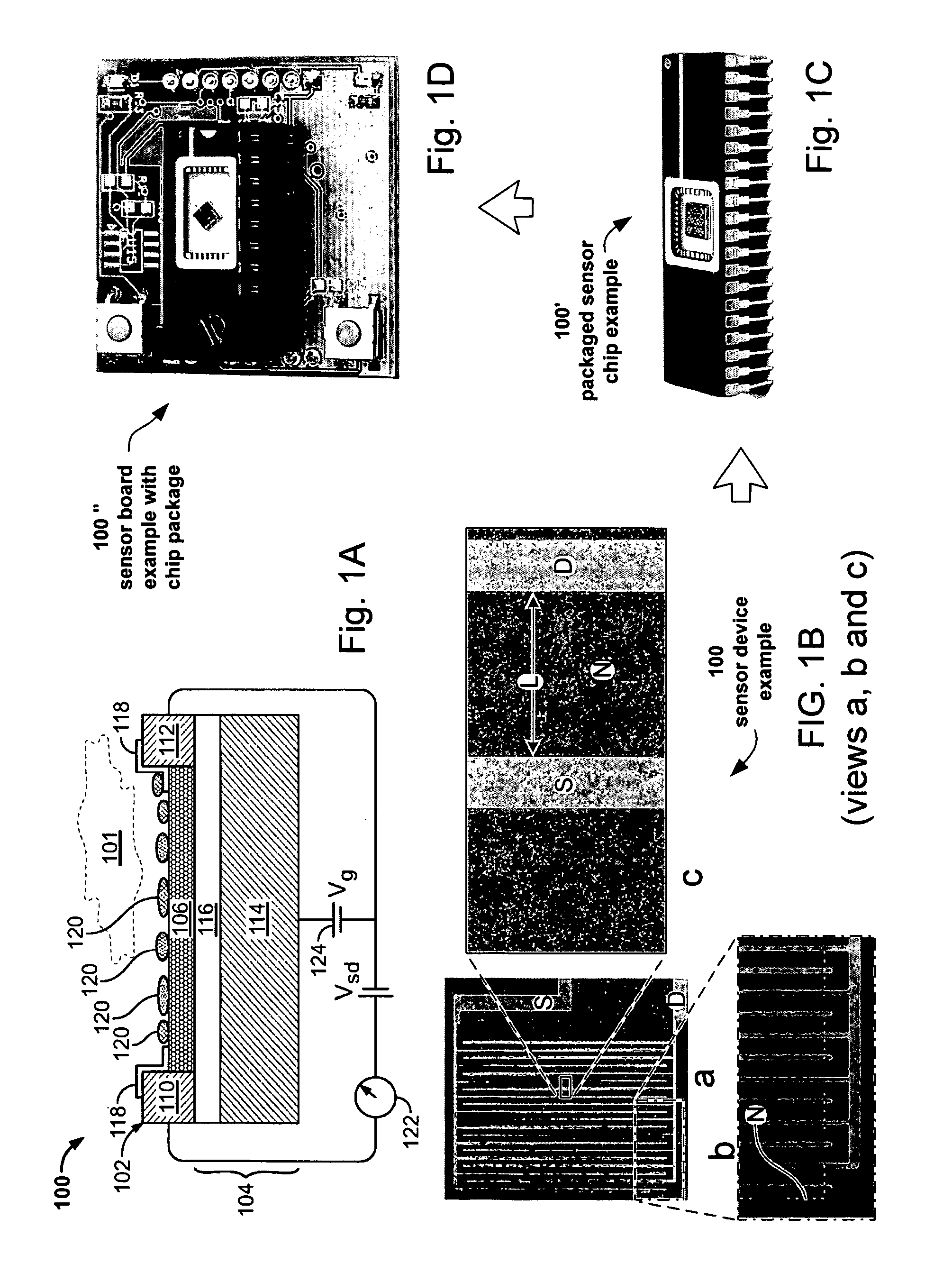
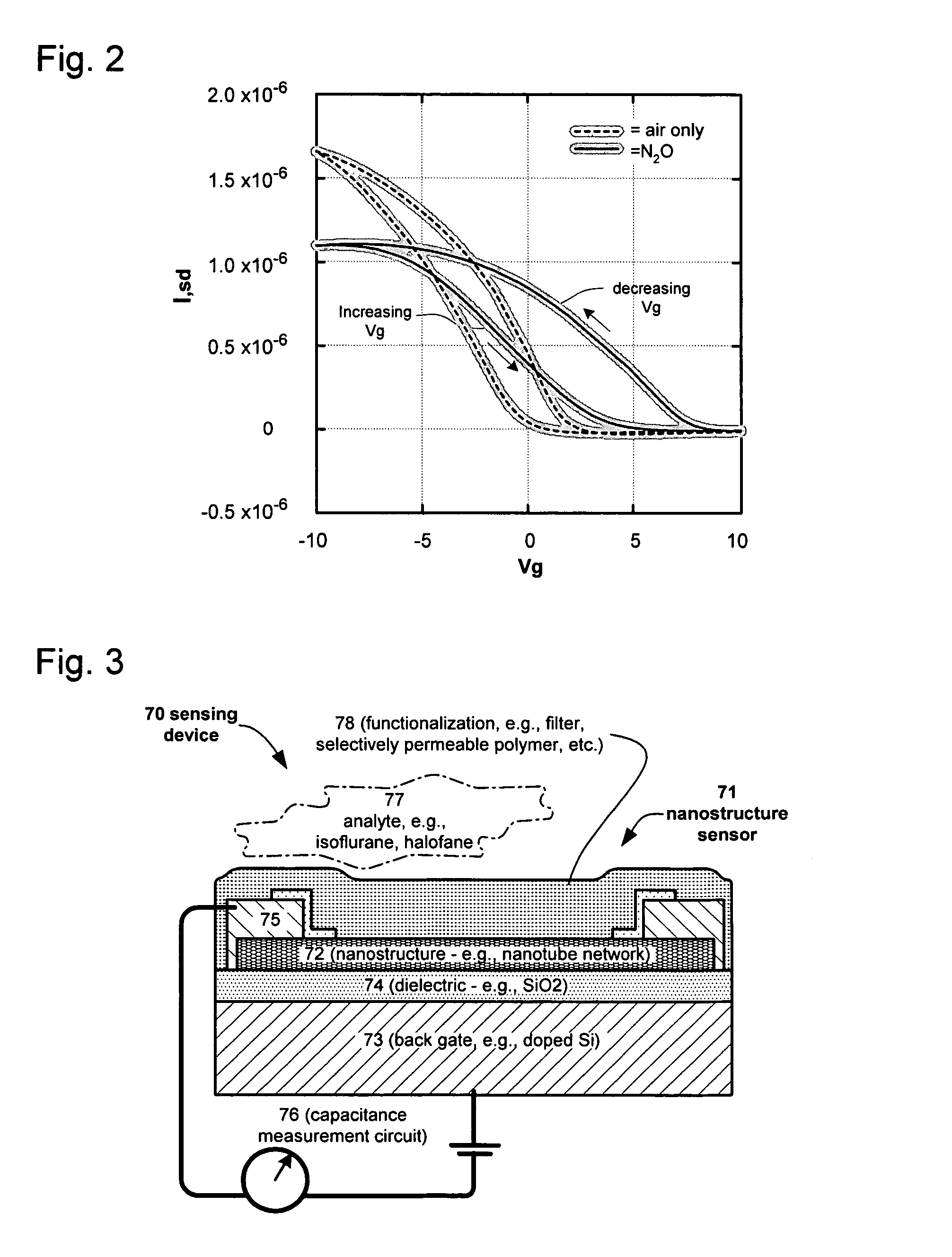
Nano-electronic sensors for chemical and biological analytes, including capacitance and bio-membrane devices
InactiveUS20070132043A1Enhanced signalSmall sizeNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesAnalyteCell membrane
Embodiments of nanoelectronic sensors are described, including sensors for detecting analytes inorganic gases, organic vapors, biomolecules, viruses and the like. A number of embodiments of capacitive sensors having alternative architectures are described. Particular examples include integrated cell membranes and membrane-like structures in nanoelectronic sensors.
Owner:NANOMIX
Methods and compositions for the inhibition of biofilms on medical devices
Embodiments of the invention provide compositions which are effective to inhibit the development of biofilms on a surface of a medical device having the composition applied thereto, to medical devices having the composition applied to a surface thereof and to methods for using the compositions to coat medical devices.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
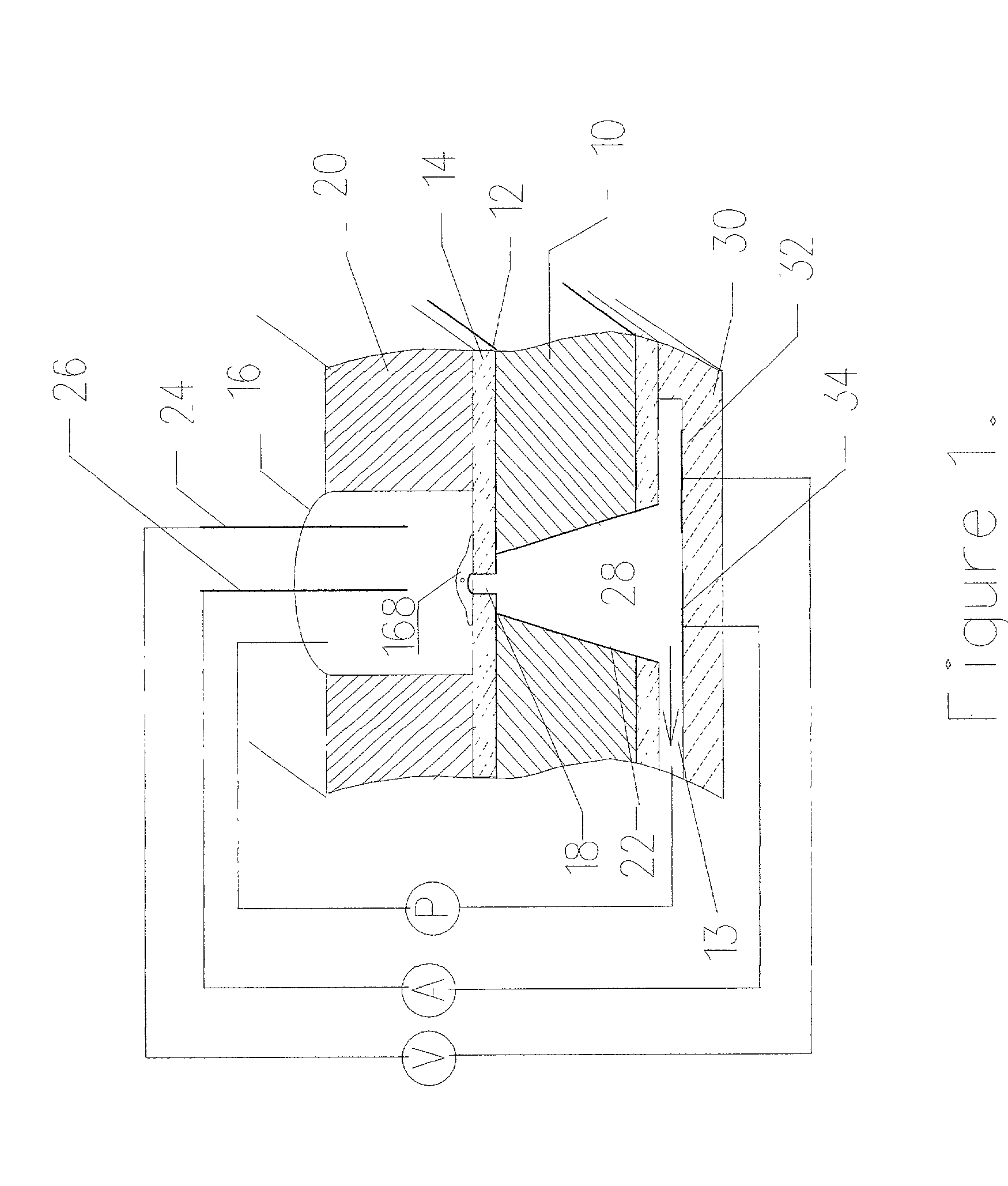
Tissue interface device
InactiveUS7041057B1Simpler basic array designImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiological bodyEngineering
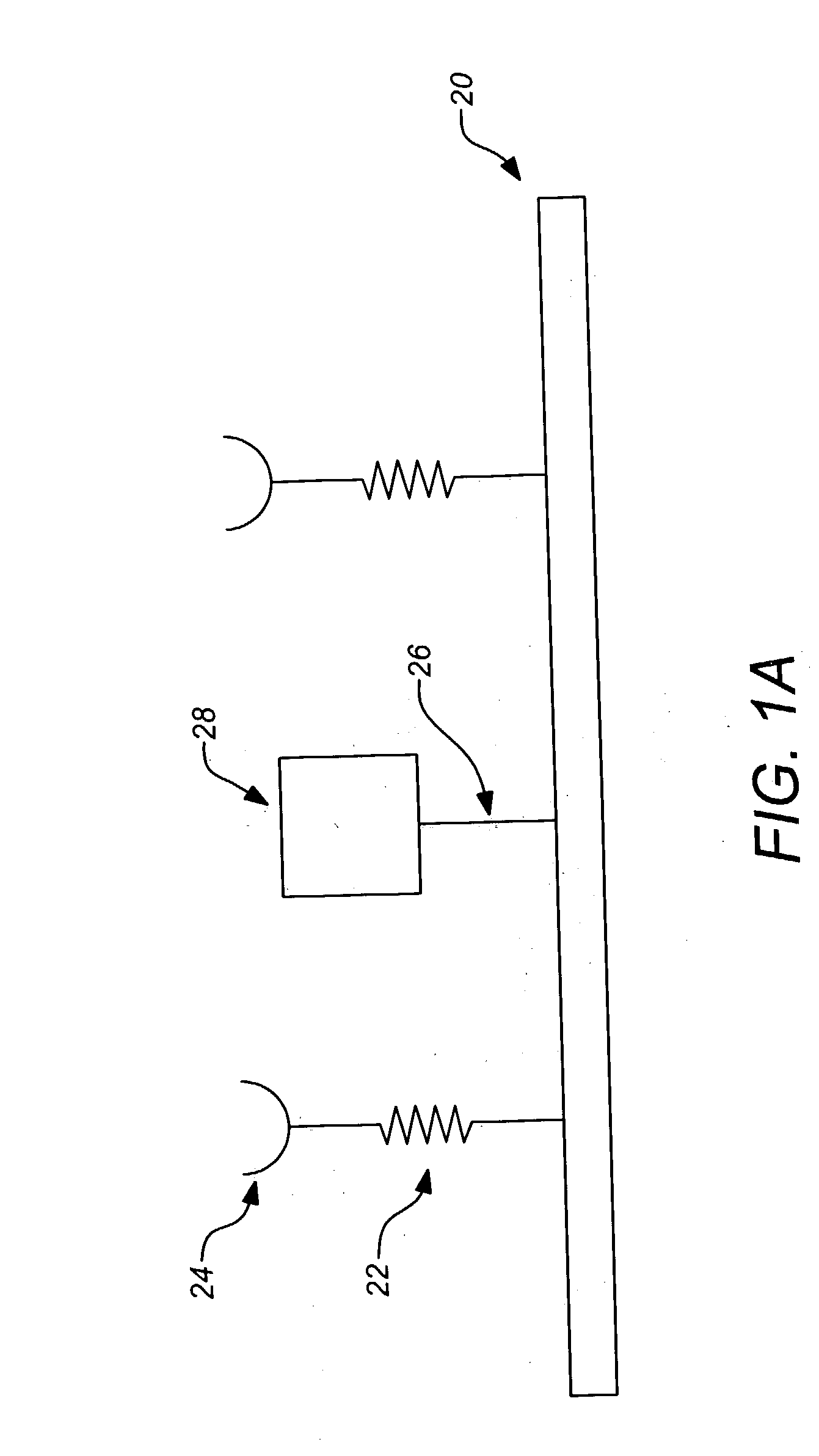
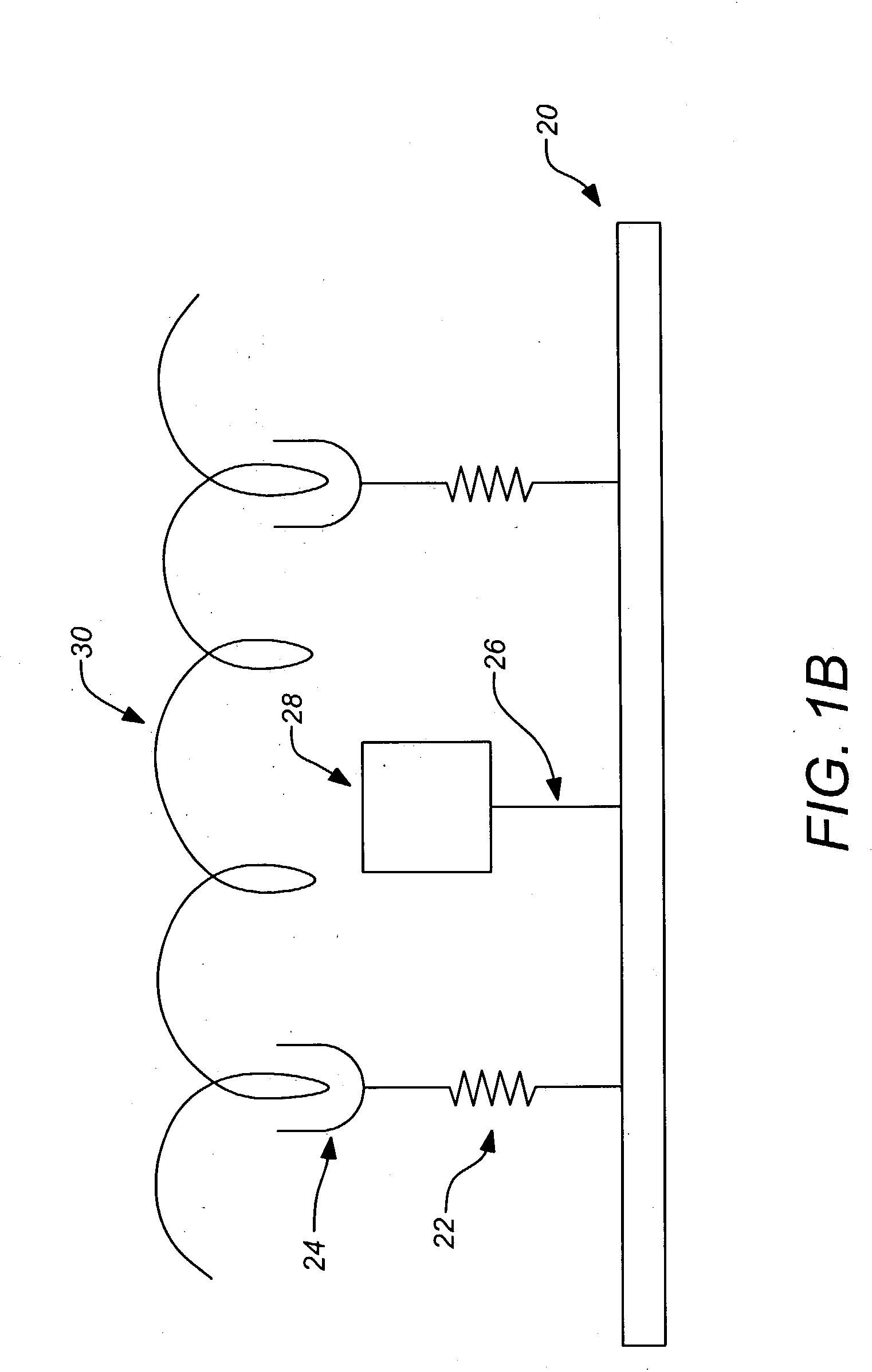
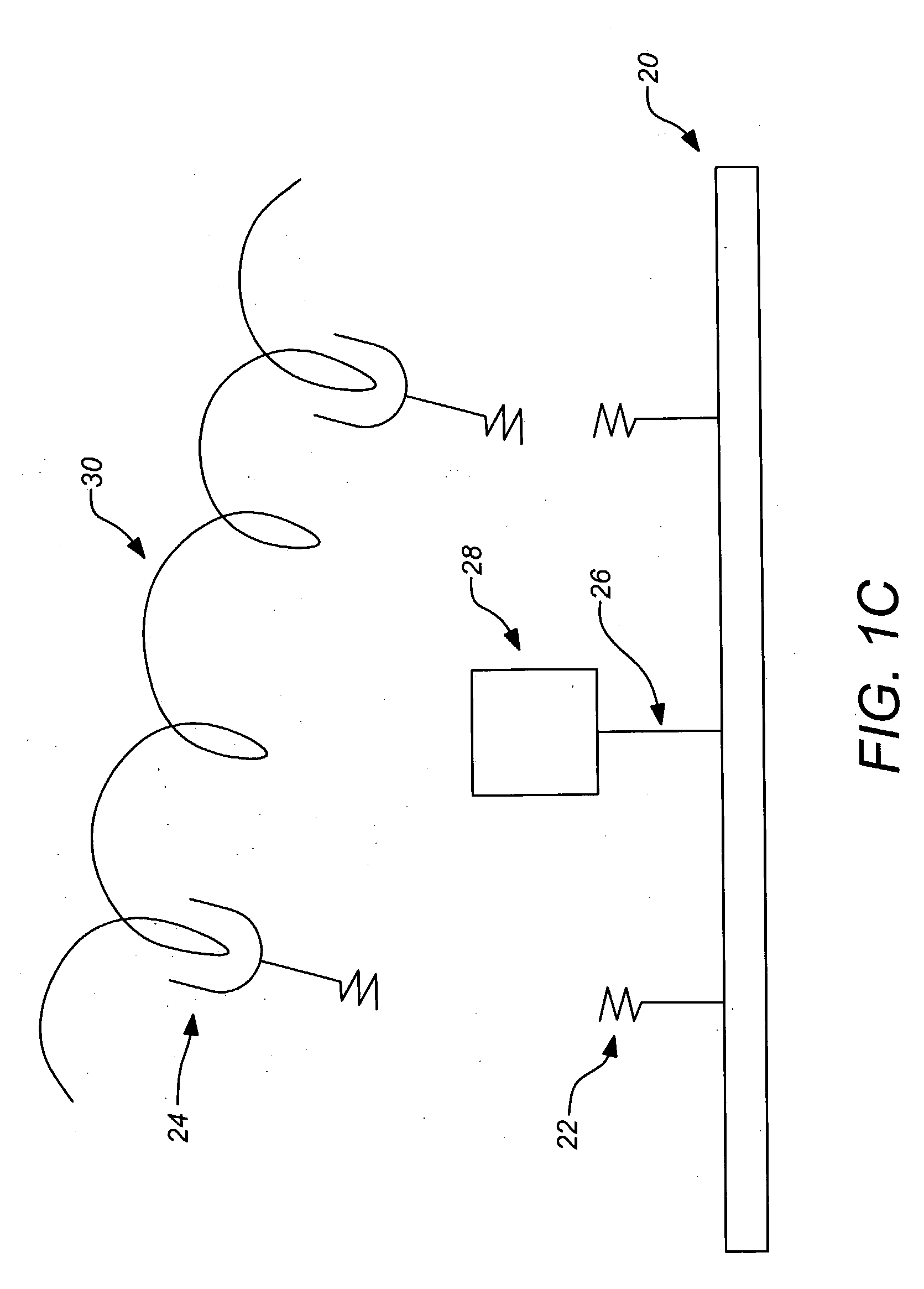
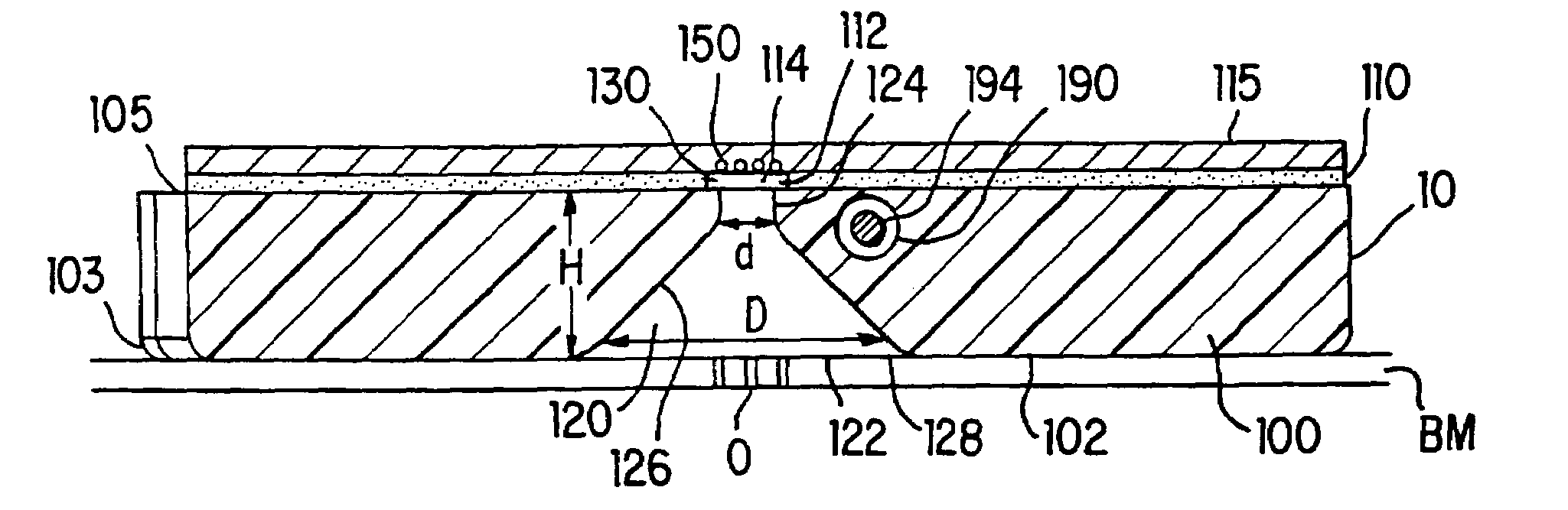
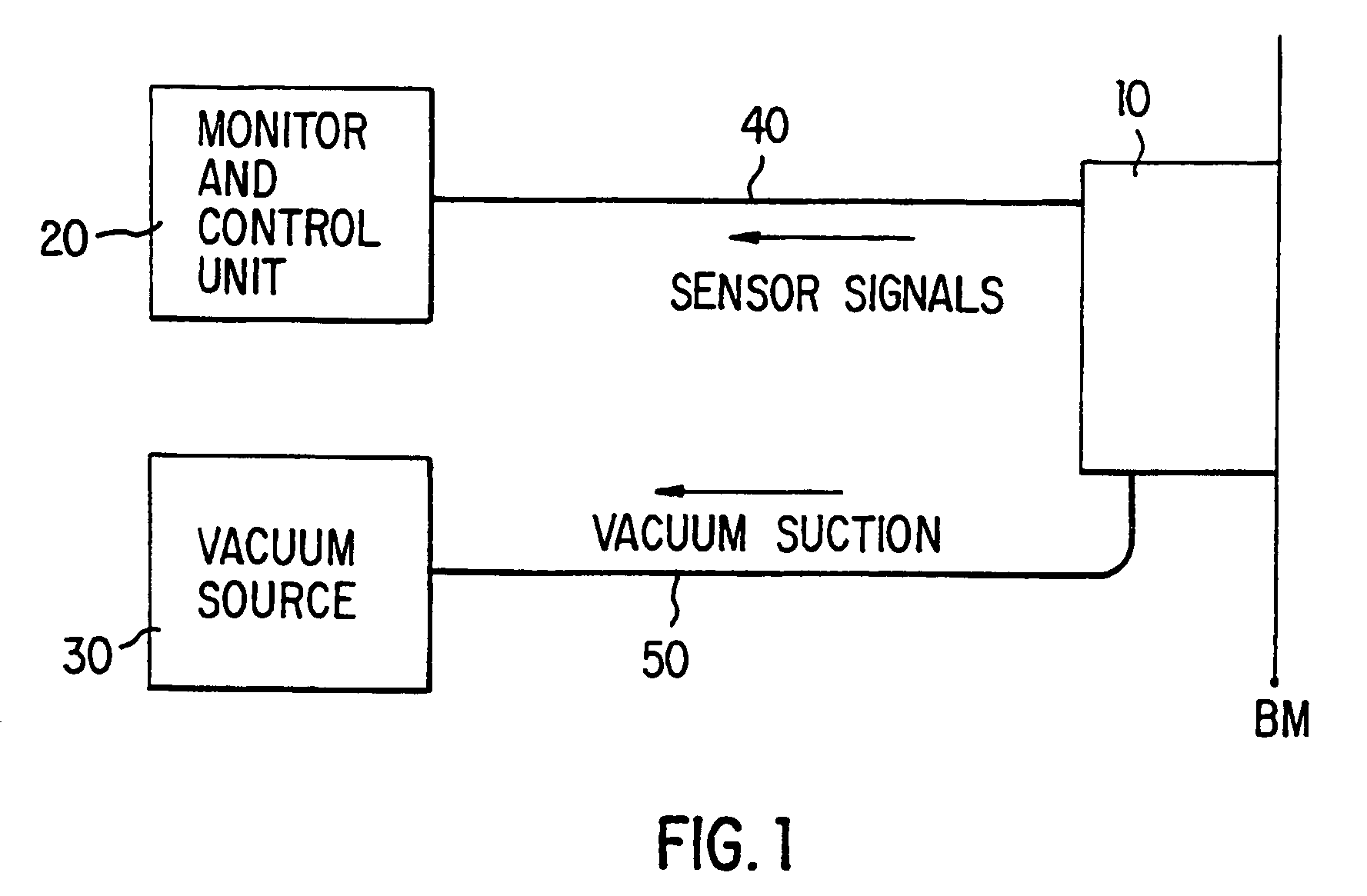
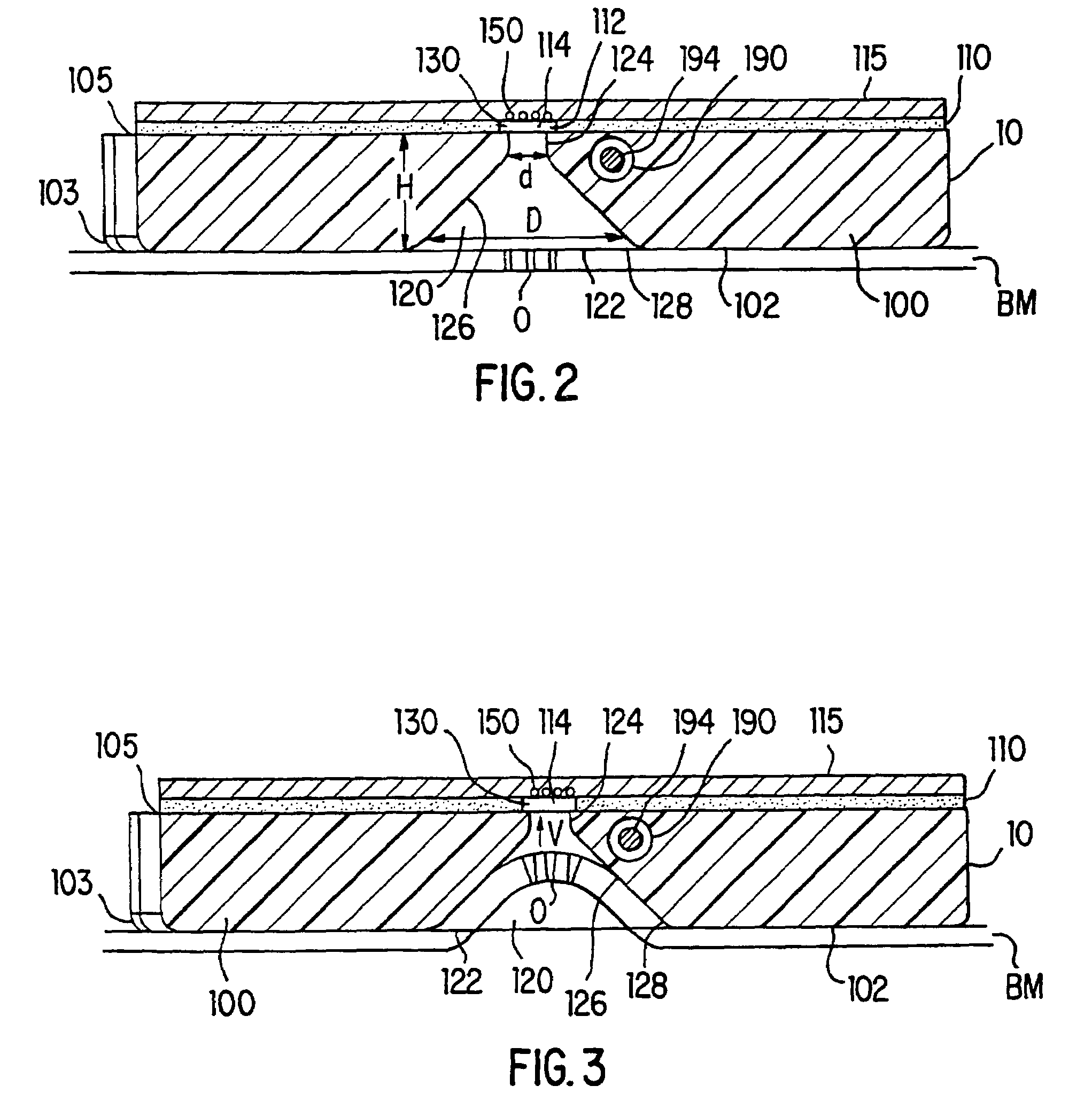
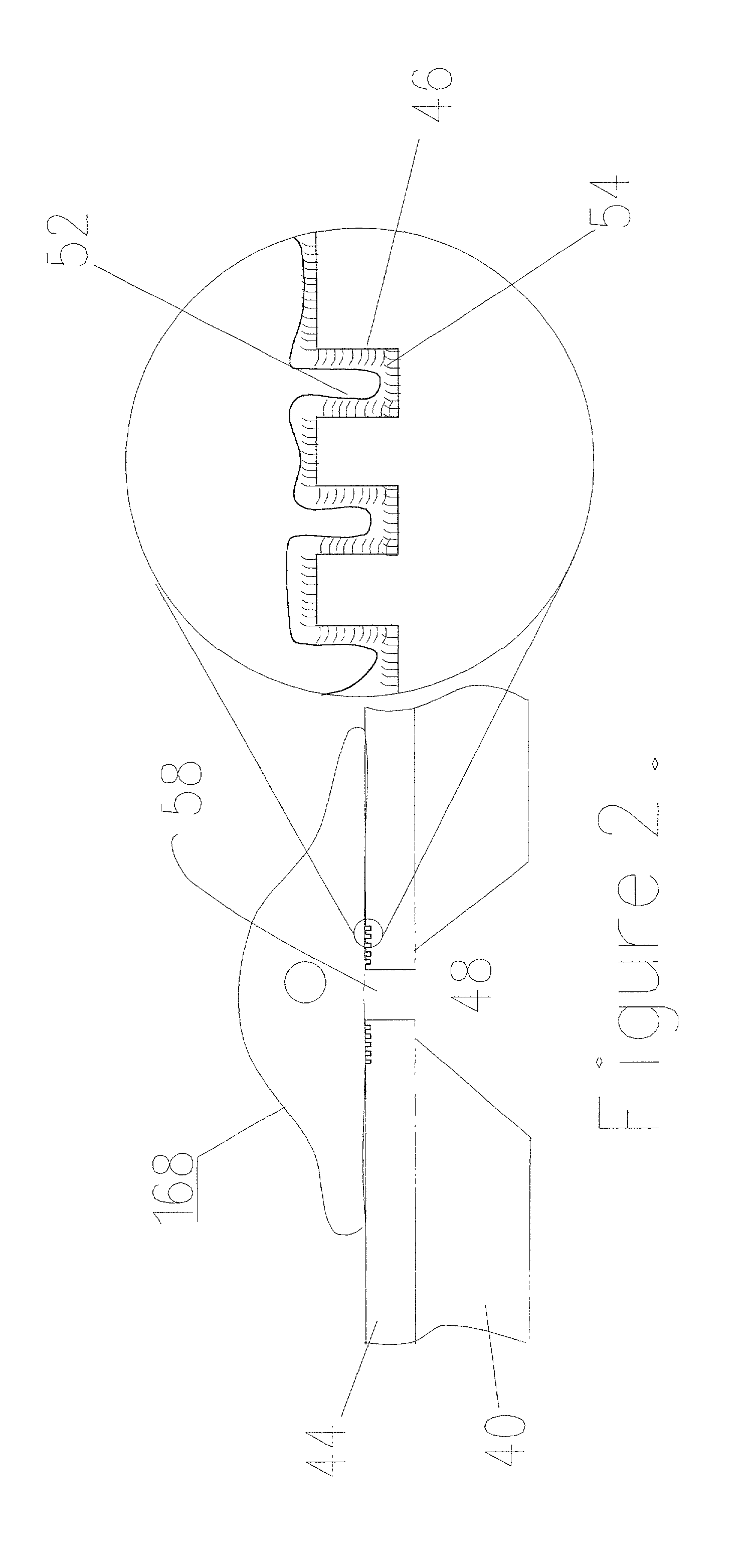
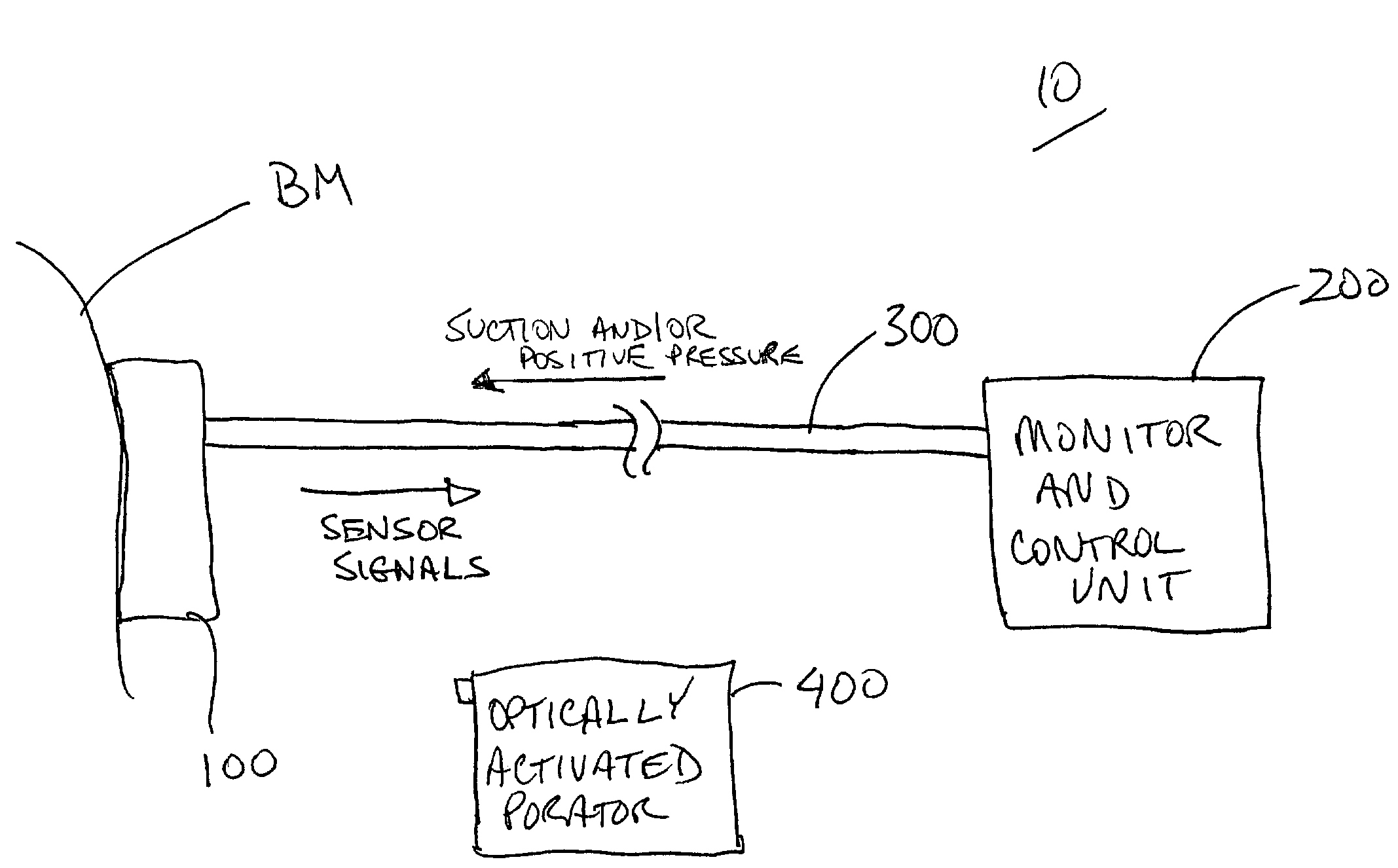
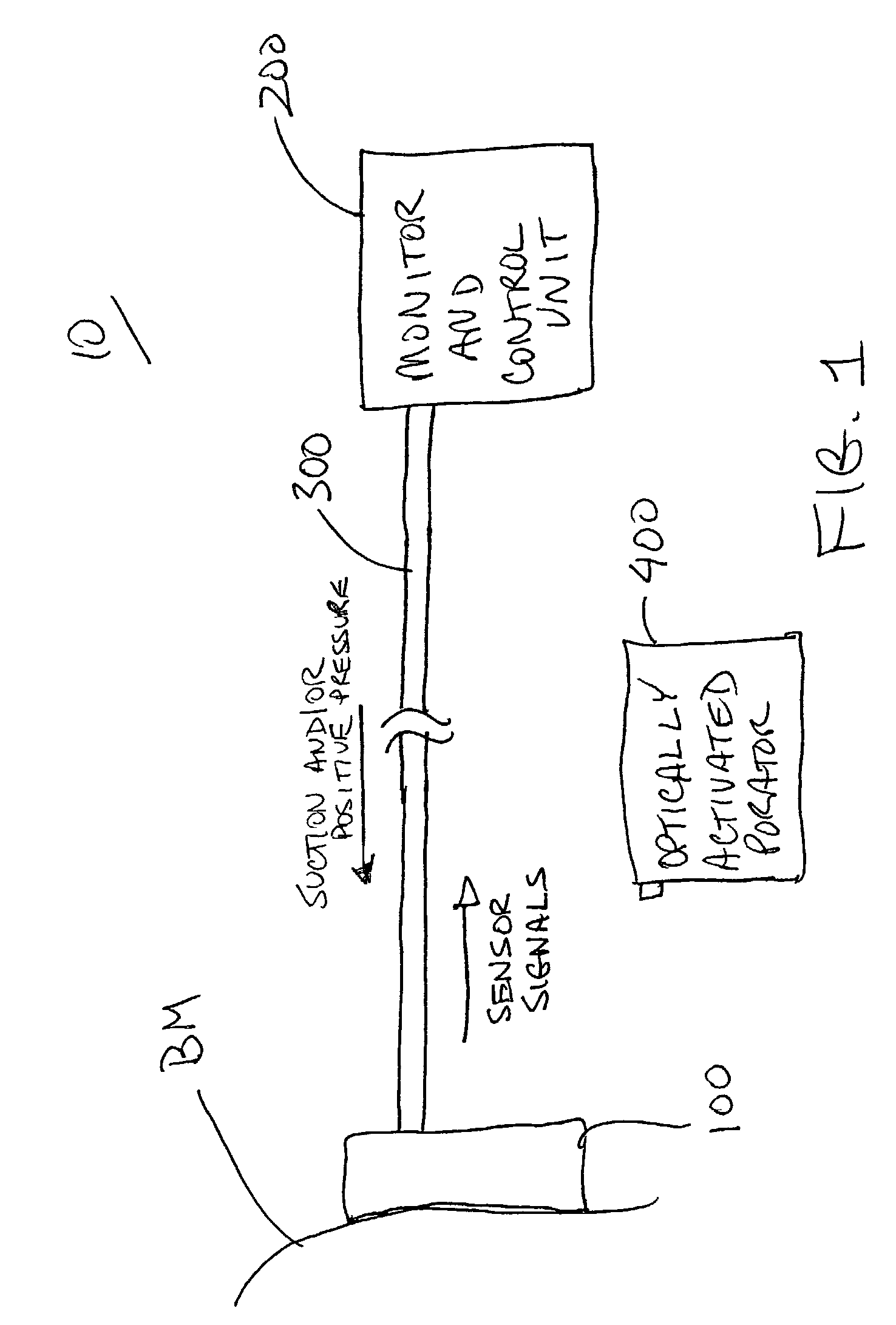
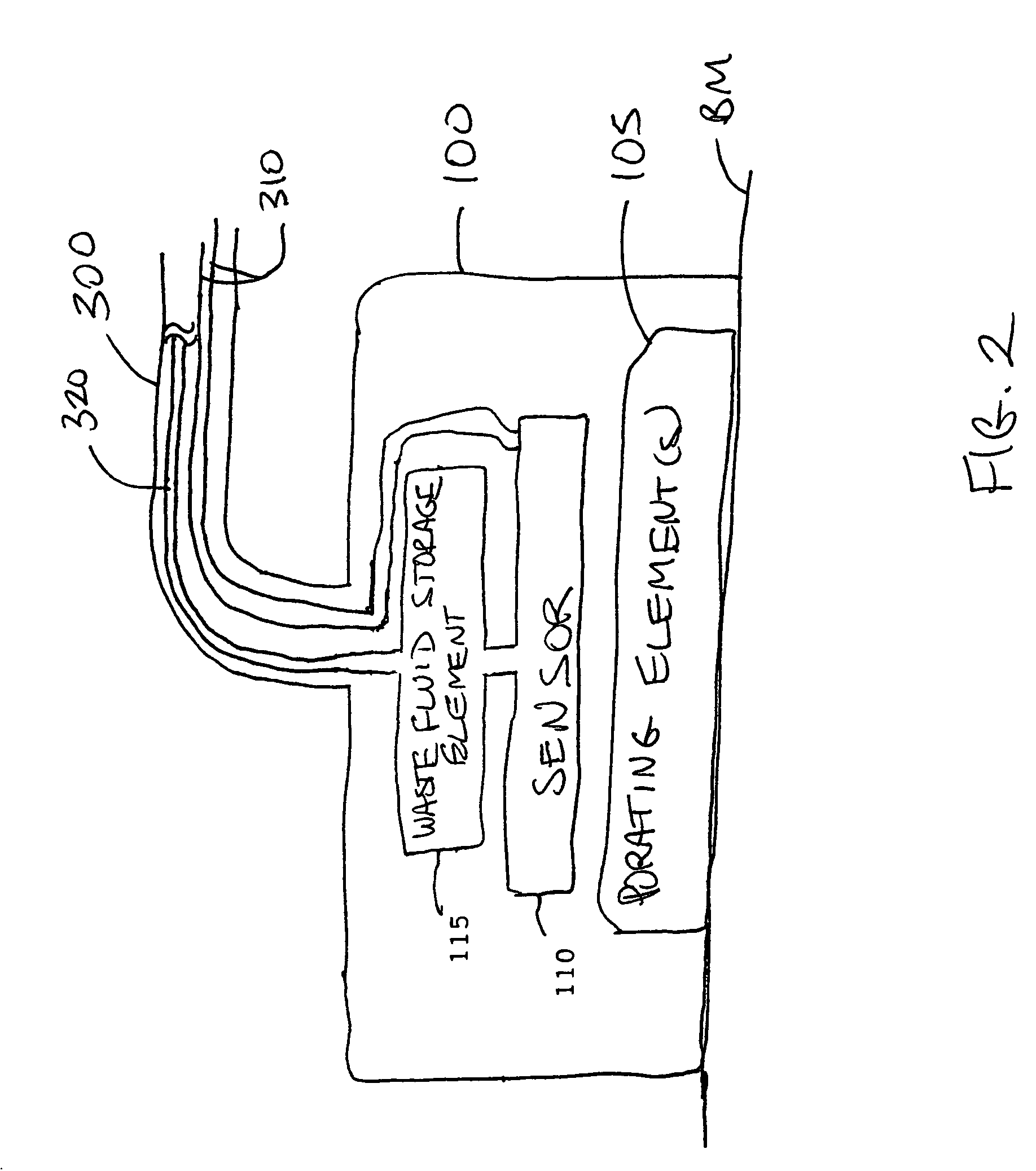
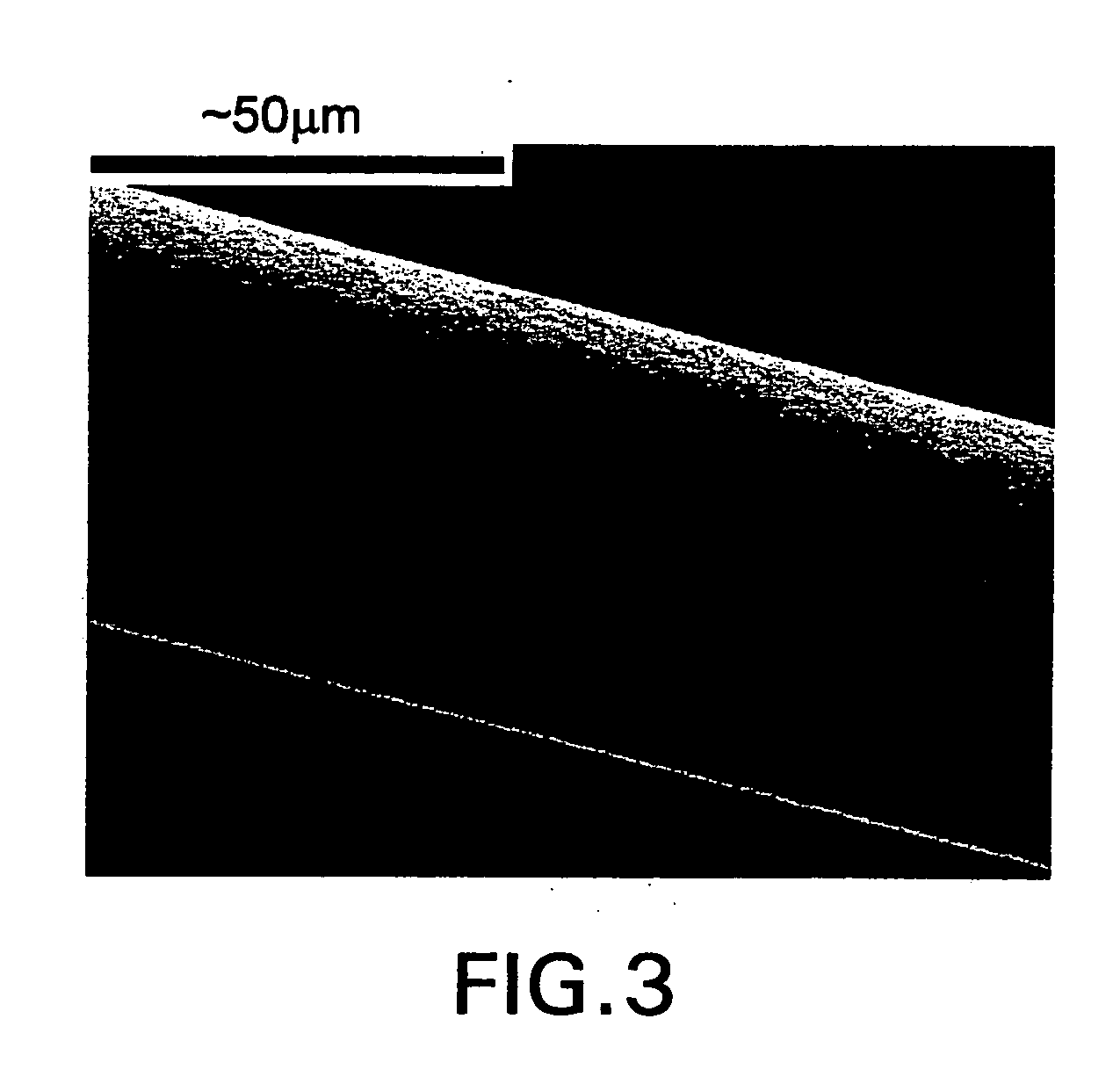
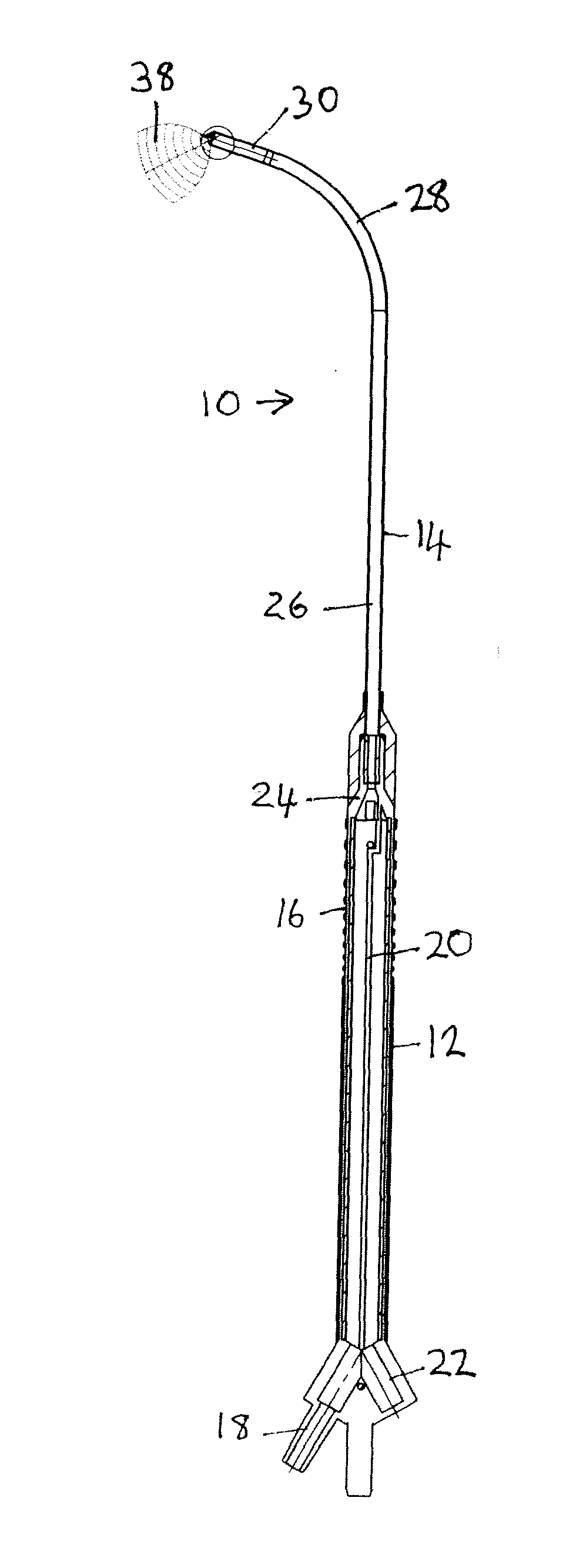
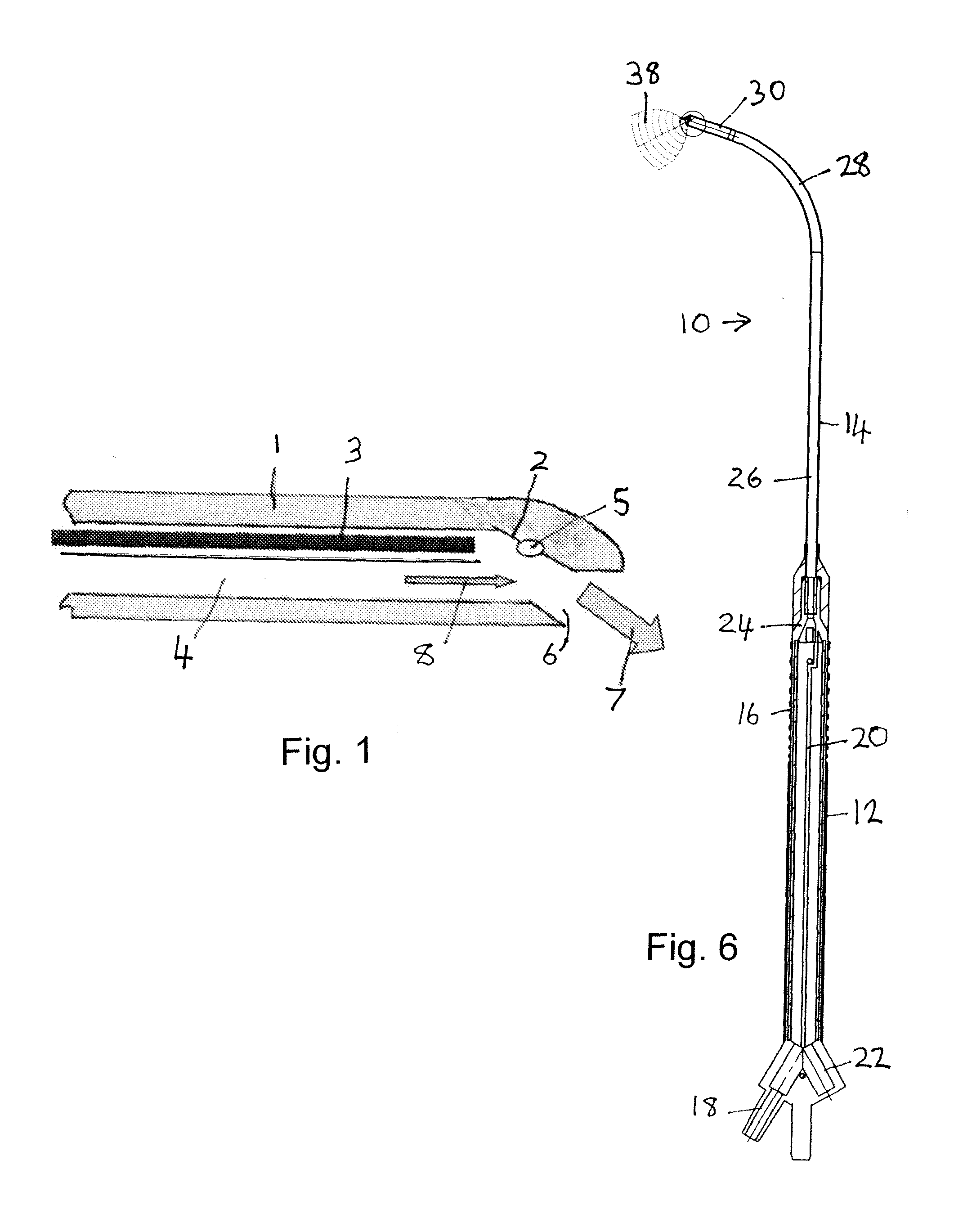
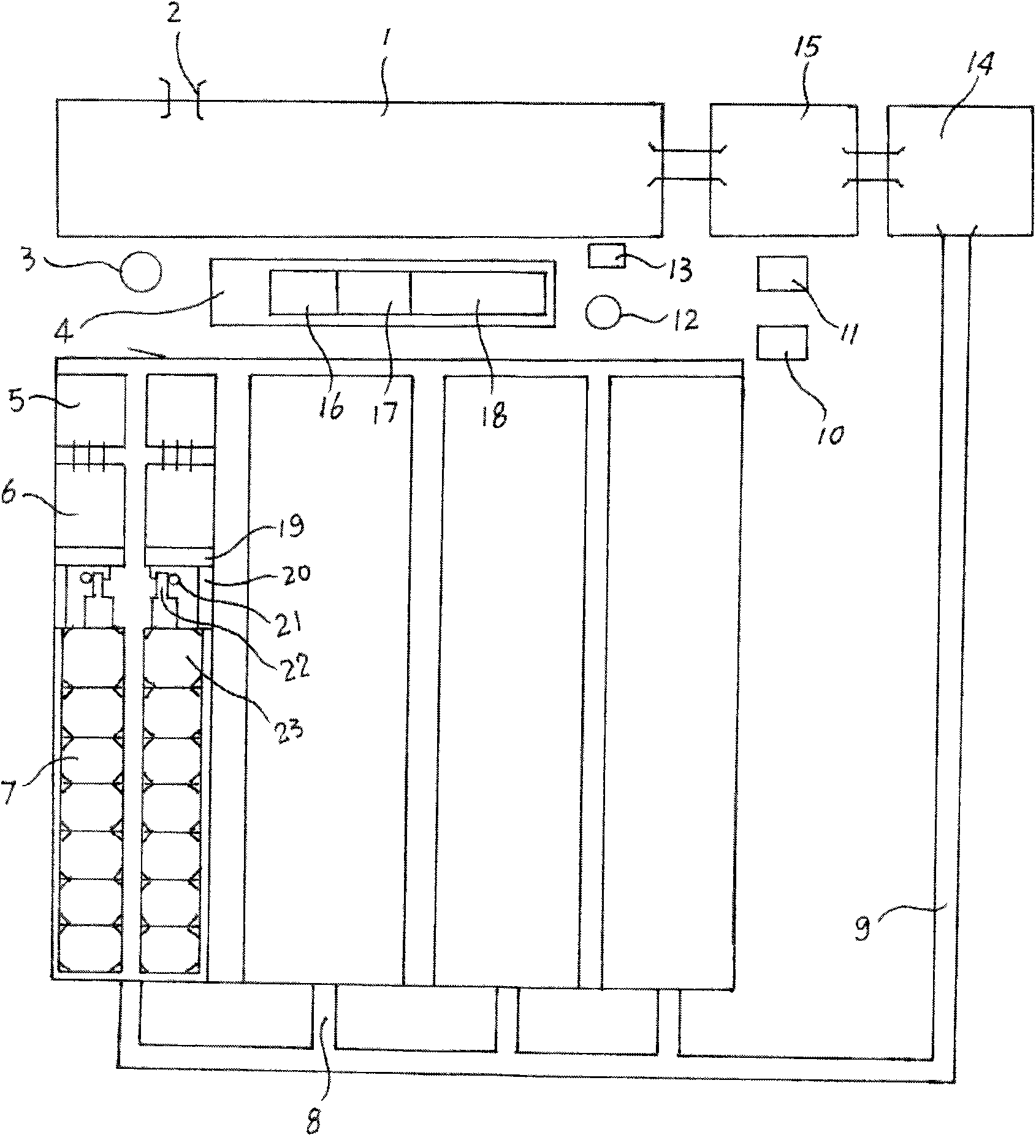
A tissue interface device (10) suitable for positioning on or about one or more artificial openings in a biological membrane of an organism and for coupling to a monitor and control unit and a vacuum source. The tissue interface device (10) comprises a housing (100), a sensor channel (130), and a sensor (150). The housing (100) defines an orifice (120), the orifice (120) having an open inlet port (122) on the bottom end (102) of the housing (100) and a distal end (124) that is in fluid communication with the sensor channel (130). The orifice (120) is in fluid communication with fluid that flows from the artificial opening formed in the biological membranes. The sensor channel (130) is for coupling to, and fluid communication therewith, the vacuum source. The sensor (150) is positioned in the sensor channel (130) in a flow path of the fluid for sensing a characteristic of the fluid as it flows out from the artificial opening. The sensor generates a sensor signal representative thereof.
Owner:ALTEA THERAPEUTIC CORP +1
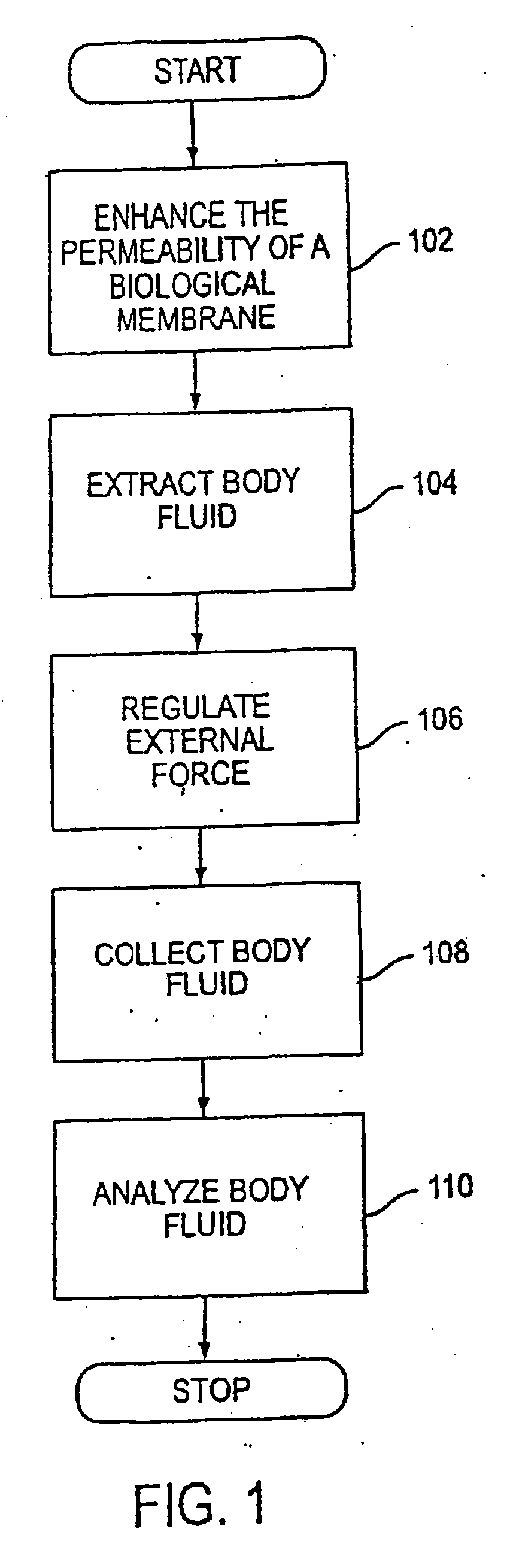
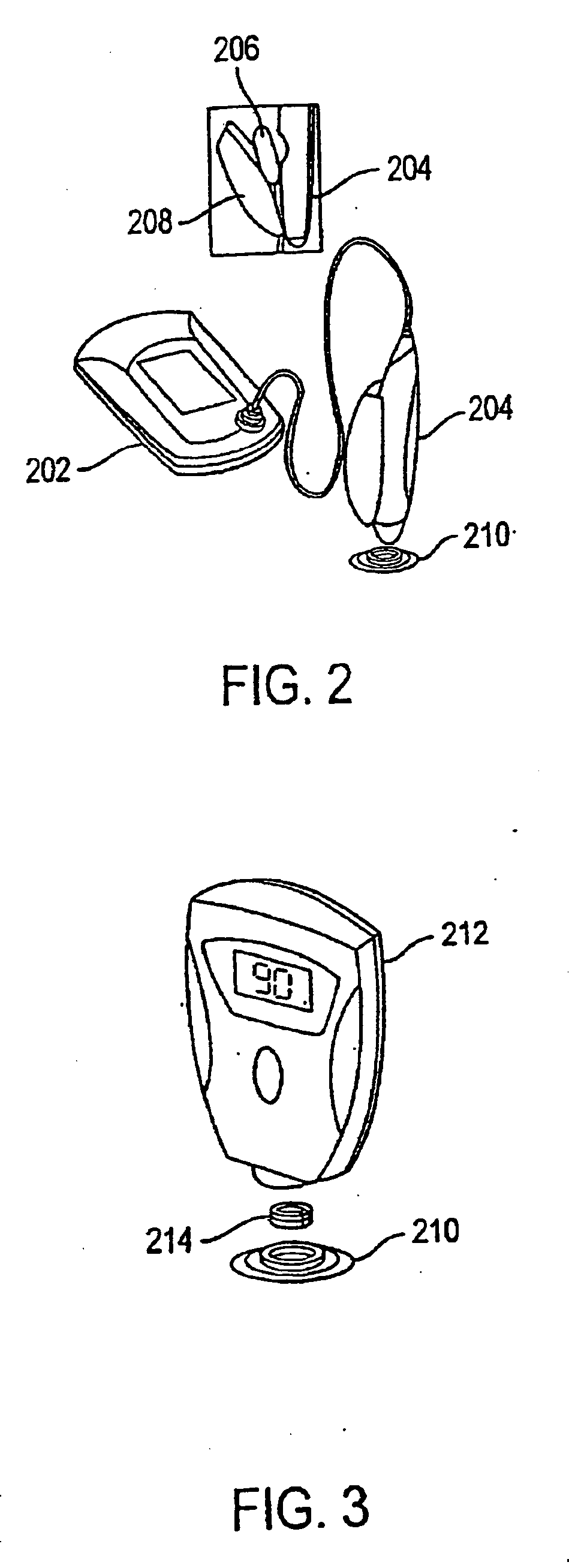
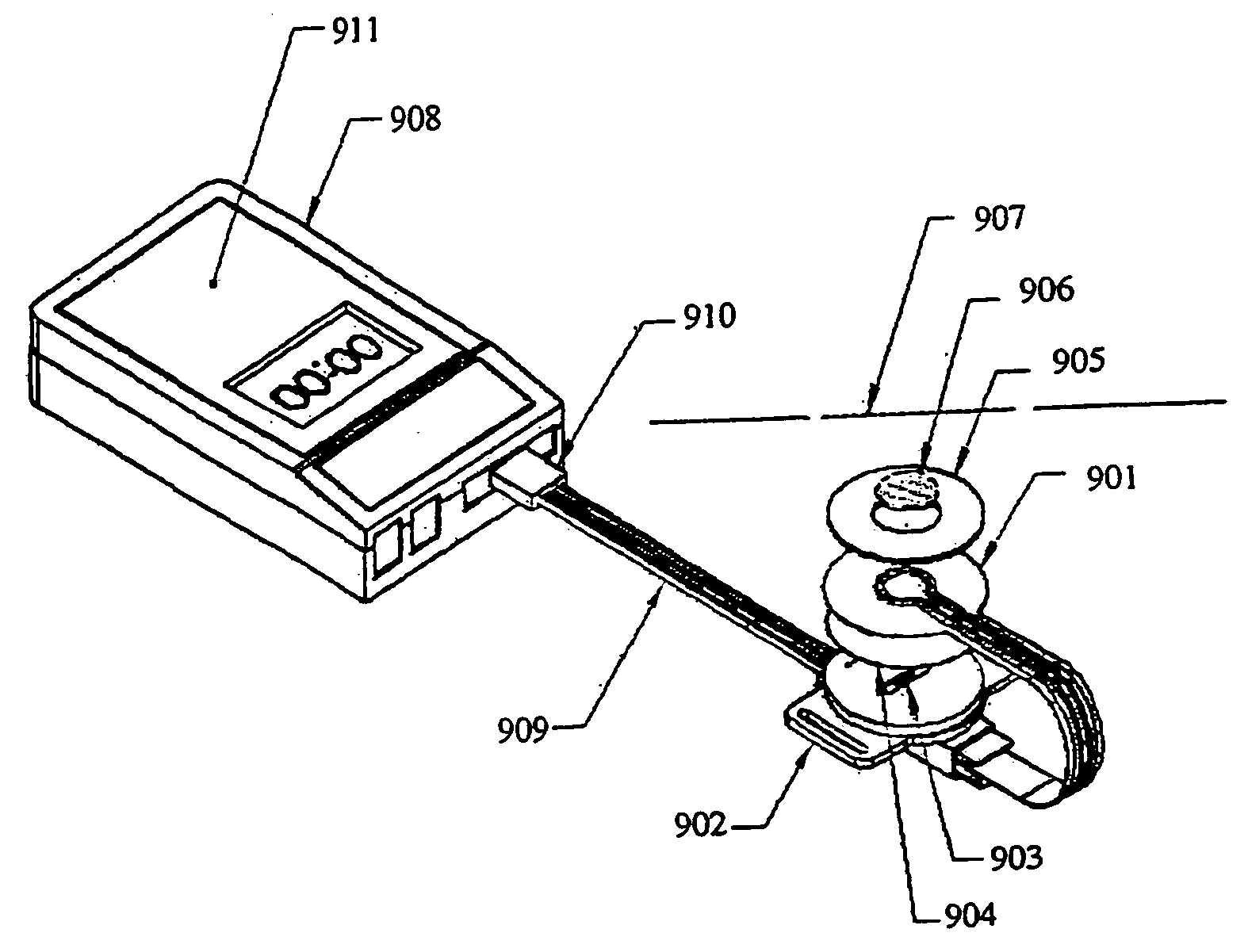
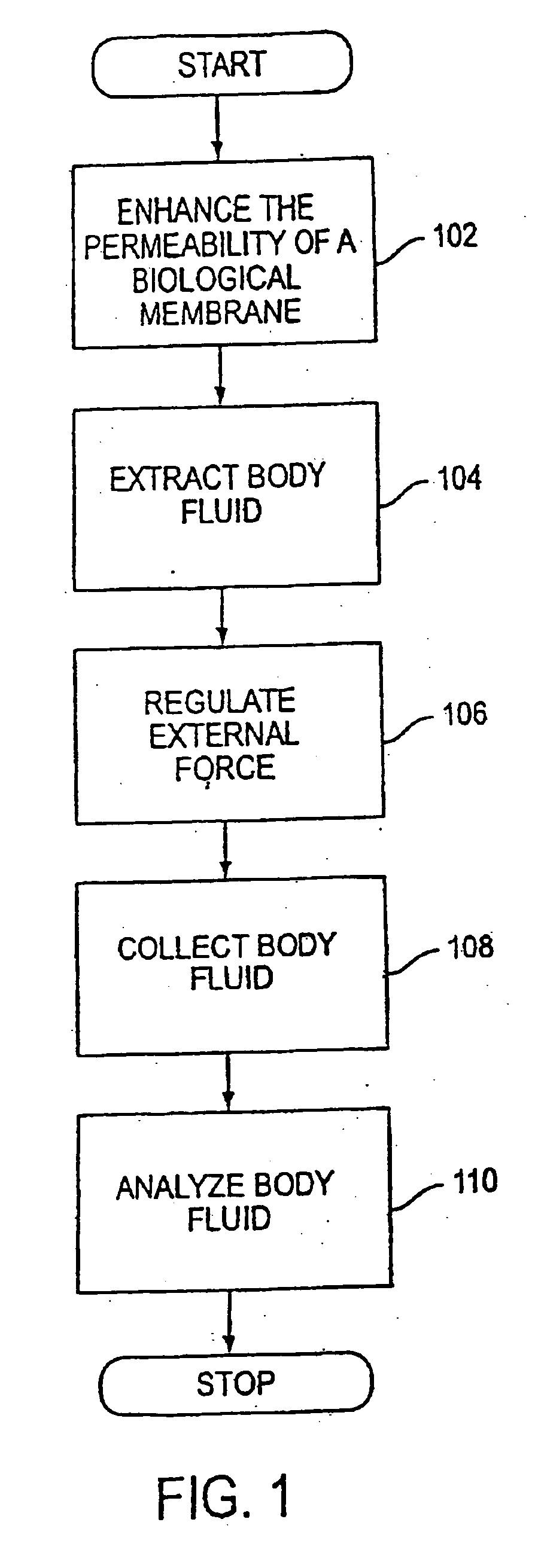
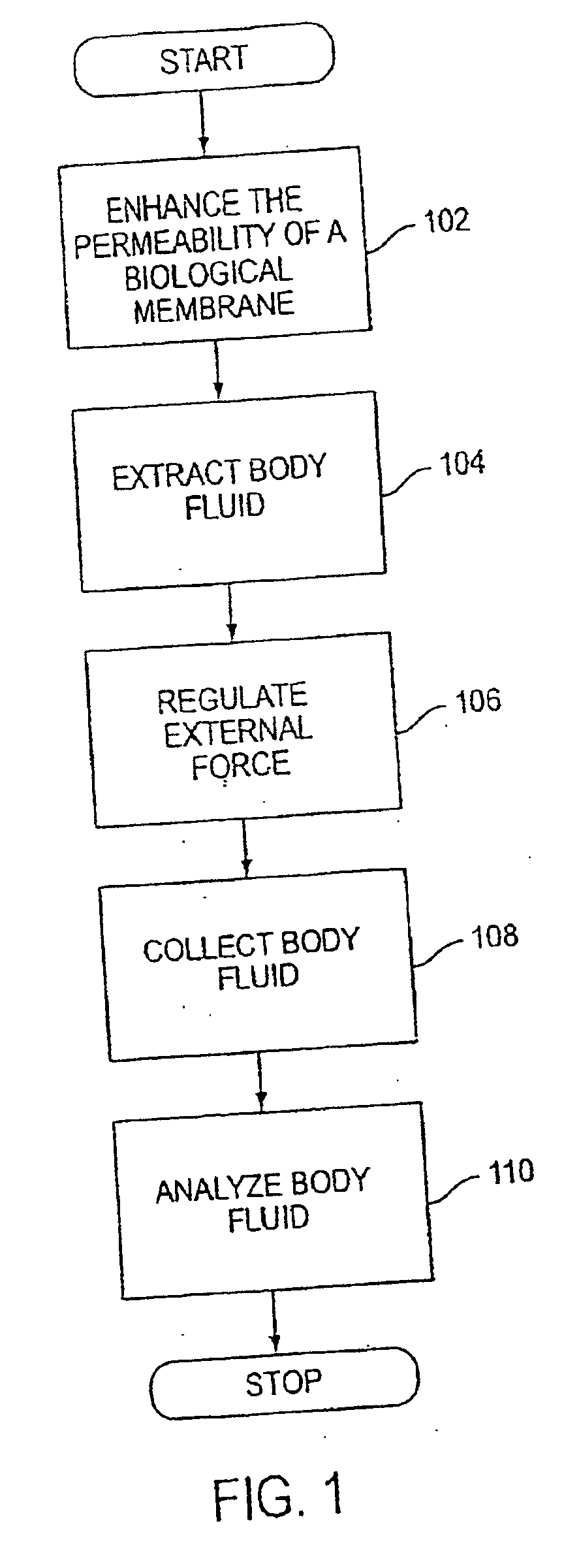
System, method, and device for non-invasive body fluid sampling and analysis
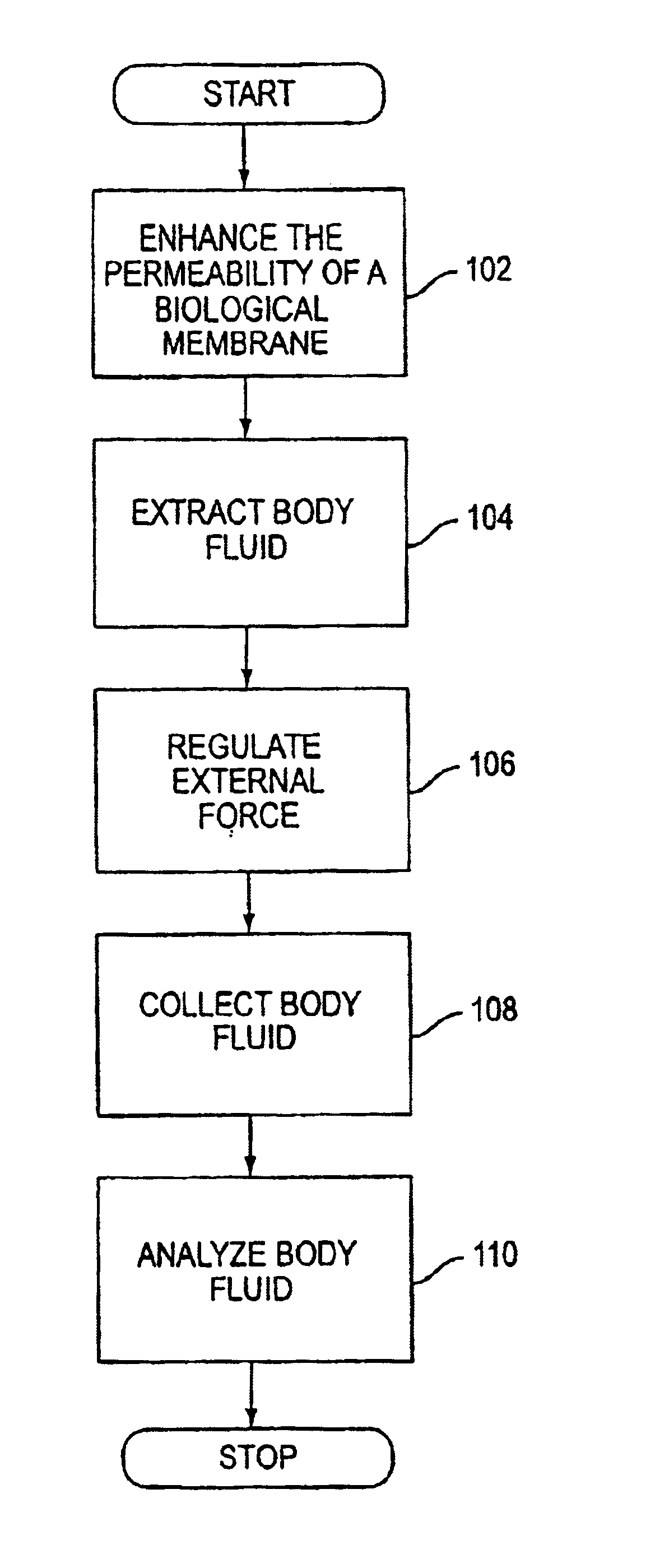
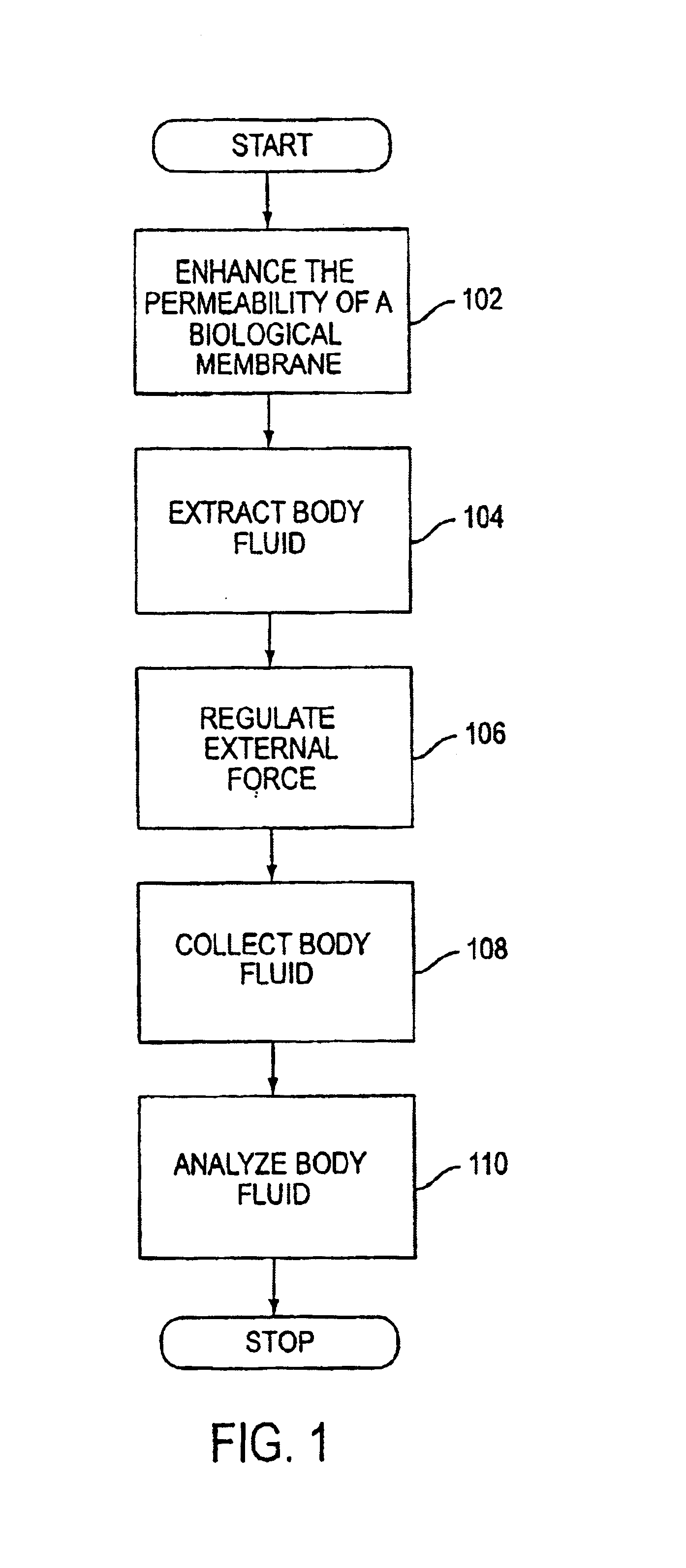
A system, method, and device for non-invasive body fluid sampling is provided. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the system includes a controller that controls the generation of ultrasound; an ultrasonic applicator that applies the ultrasound to an area of biological membrane; a receiver that contacts the area of biological membrane and receives body fluid through and out of the area of biological membrane; and a meter that interacts with the receiver and detects the presence of at least one analyte in the body fluid in the receiver. The receiver may include a membrane and a medium, such as a hydrogel, a fluid, or a liquid, that is contained in the membrane. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the method includes the steps of (1) identifying an area of biological membrane having a permeability level; (2) increasing the permeability level of the area of biological membrane; (3) contacting the area of biological membrane with a receiver; (4) extracting body fluid through and out of the area of biological membrane; (5) providing an external force to enhance the body fluid extraction; (6) collecting the body fluid in the receiver; (7) analyzing the collected body fluid for the presence of at least one analyte; and (8) providing the results of the step of analyzing the body fluid.
Owner:ECHO THERAPEUTICS INC
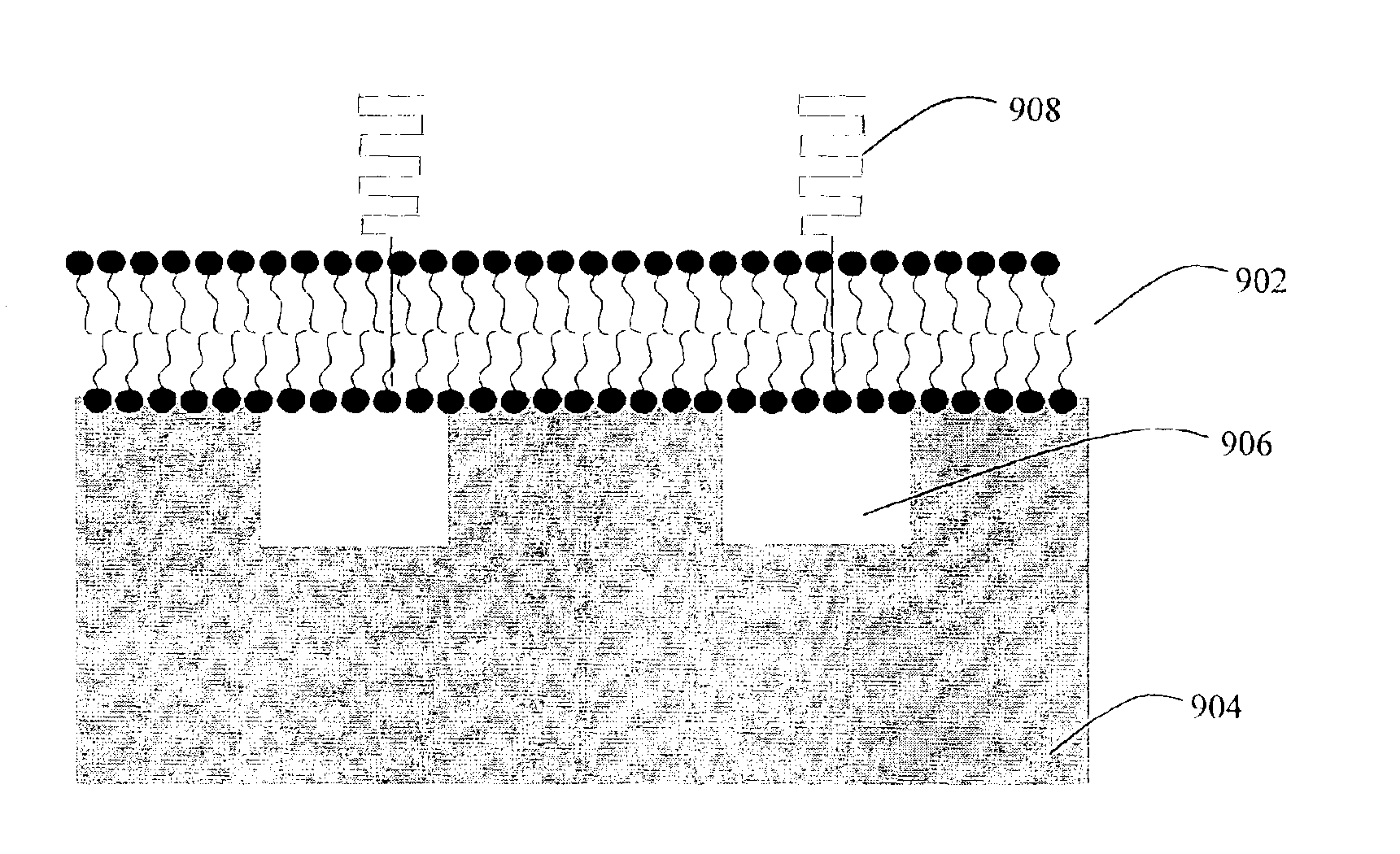
Nanostructured separation and analysis devices for biological membranes
InactiveUS6913697B2Ion-exchanger regenerationVolume/mass flow measurementBiological membraneNanostructure
The present invention provides a nanostructured device comprising a substrate including nanotroughs therein; and a lipid bilayer suspended on or supported in the substrate. A separation method is also provided comprising the steps of supporting or suspending a lipid bilayer on a substrate; wherein the substrate comprises nanostructures and wherein the lipid bilayer comprises at least one membrane associated biomolecule; and applying a driving force to the lipid bilayer to separate the membrane associated biomolecule from the lipid bilayer and to drive the membrane associated biomolecule into the nanostructures.
Owner:STC UNM
System and method for analyte sampling and analysis with hydrogel
InactiveUS20060094946A1Microbiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementPolyethylene glycolCorrection method
The invention relates to a transdermal analyte monitoring system comprising a medium adapted to interface with a biological membrane and to receive an analyte from the biological membrane and an electrode assembly comprising a plurality of electrodes, wherein the medium is adapted to react continuously with the analyte, an electrical signal is detected by the electrode assembly, and the electrical signal correlates to an analyte value. The analyte value may be the flux of the analyte through the biological membrane or the concentration of the analyte in a body fluid of a subject. The medium may comprise a vinyl acetate based hydrogel, an agarose based hydrogel, or a polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEG-DA) based hydrogel, for example. The surface region of the electrode may comprise pure platinum. The system may include an interference filter located between the biological membrane and the electrode assembly for reducing interference in the system. The system may comprise a processor programmed to implement an error correction method that corrects for sensor drift.
Owner:ECHO THERAPEUTICS INC
Biosensors for single cell and multi cell analysis
InactiveUS20030104512A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingElectricityBiological cell
The present invention relates to a structure comprising a biological membrane and substrate with fluidic network, an array of membranes and an array of fluidic networks in substrate, a high throughput screen, methods for production of the membrane, substrate structure, and a method for interconnected array of substrate structures and a method for attaching membranes to structure, a method to electrically record events from the membranes and a method to screen large compound library using the array. More particularly, it relates to biological cells and artificial cell membranes adhered to the substrate with a high electrical resistivity seal, a method to manufacture array configuration of such substrates, and a method to screen compounds using the membrane receptors such as ion-channels, ion pumps, & receptors.
Owner:CYTOPLEX BIOSCI
Intracellular delivery of biological effectors
InactiveUS6960648B2Improve concentrationTo promote metabolismOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell typeBiological membrane
Owner:XIGEN
System and method for analyte sampling and analysis with error correction
InactiveUS20060094944A1SurgeryMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPolyethylene glycolCorrection method
The invention relates to a transdermal analyte monitoring system comprising a medium adapted to interface with a biological membrane and to receive an analyte from the biological membrane and an electrode assembly comprising a plurality of electrodes, wherein the medium is adapted to react continuously with the analyte, an electrical signal is detected by the electrode assembly, and the electrical signal correlates to an analyte value. The analyte value may be the flux of the analyte through the biological membrane or the concentration of the analyte in a body fluid of a subject. The medium may comprise a vinyl acetate based hydrogel, an agarose based hydrogel, or a polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEG-DA) based hydrogel, for example. The surface region of the electrode may comprise pure platinum. The system may include an interference filter located between the biological membrane and the electrode assembly for reducing interference in the system. The system may comprise a processor programmed to implement an error correction method that corrects for sensor drift.
Owner:SONTRA MEDICAL CORP
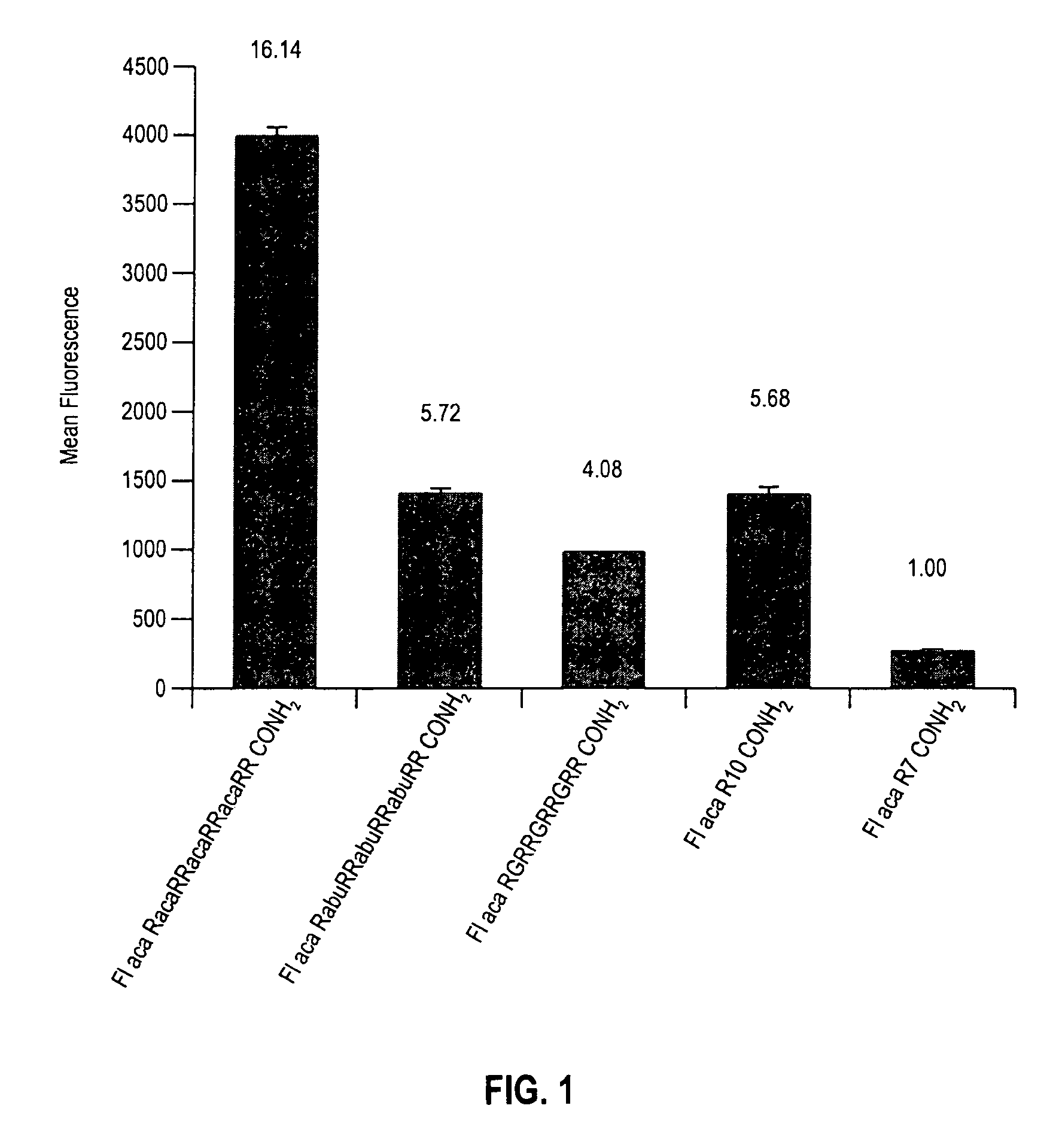
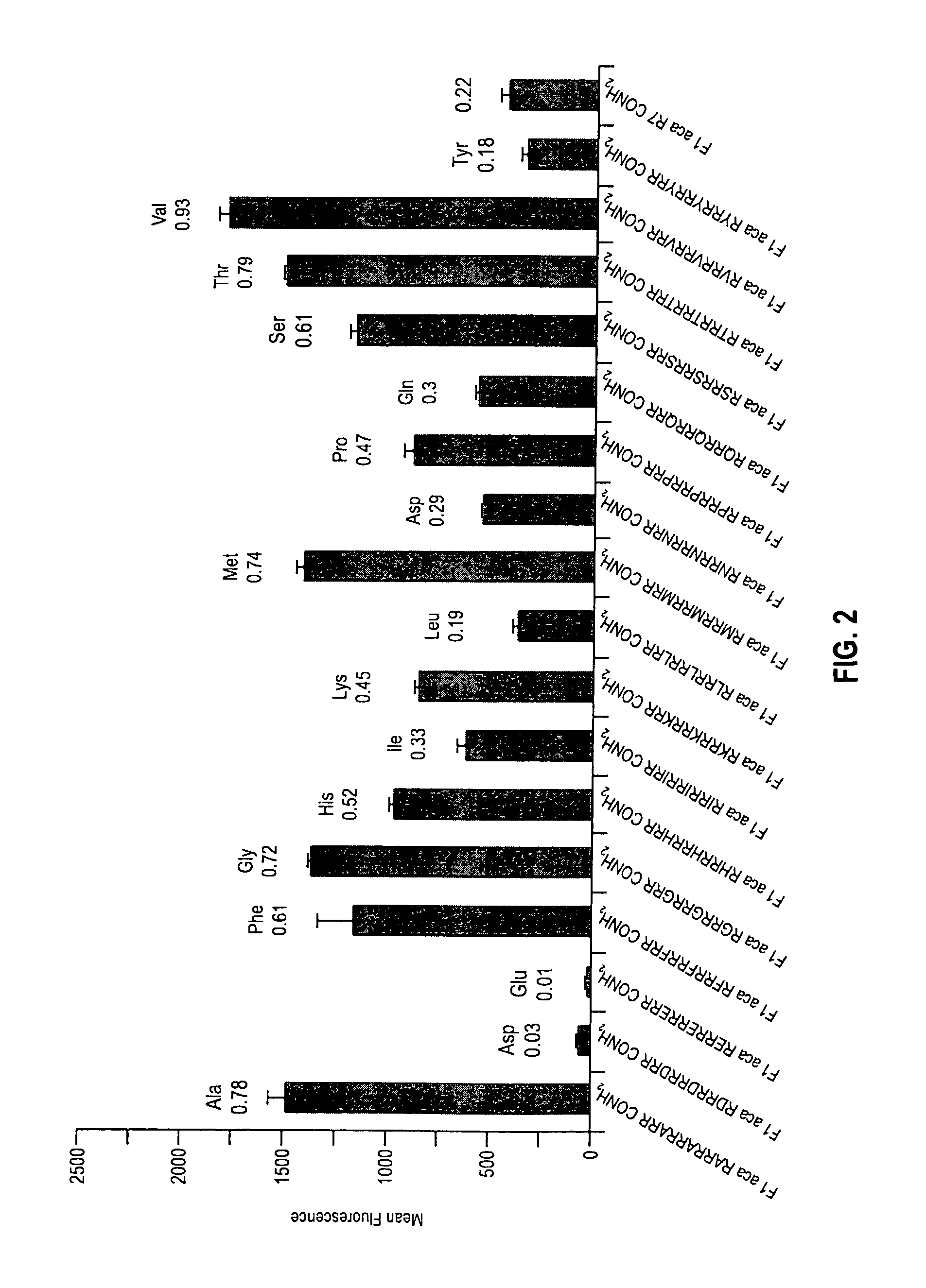
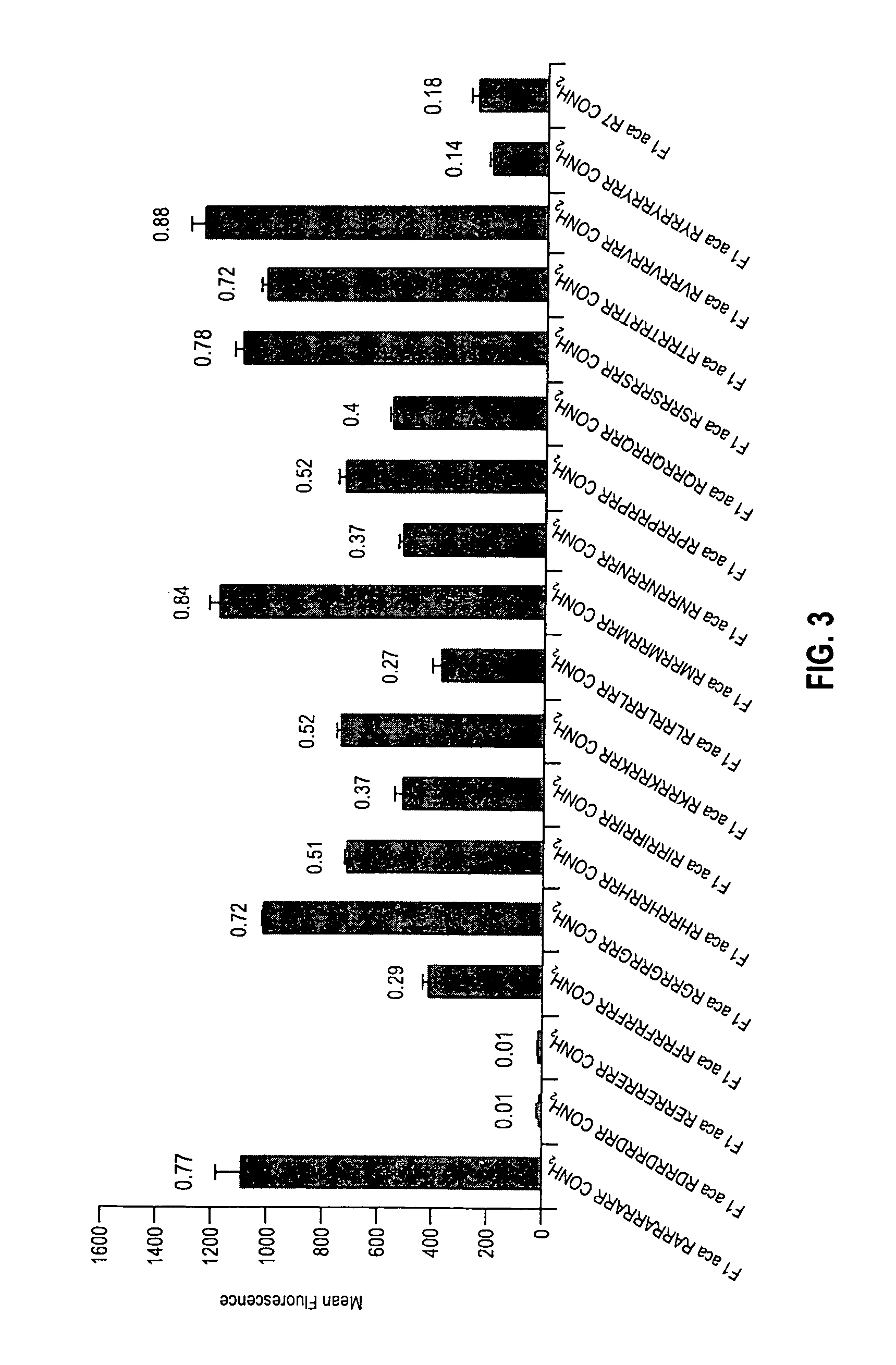
Transporters comprising spaced arginine moieties
The present invention provides compositions and methods for enhancing transport of biologically active compounds across biological membranes and across and into animal epithelial or endothelial tissues. The composition includes a biologically active agent and a transport moiety. The transport moiety includes a structure selected from the group consisting of (ZYZ)nZ, (ZY)nZ, (ZYY)nZ and (ZYYY)nZ. Subunit “Z” is L-arginine or D-arginine, and subunit “Y” is an amino acid that does not comprise an amidino or guanidino moiety. Subscript “n” is an integer ranging from 2 to 10. The method for enhancing transport involves the administration of the aforementioned composition.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Drug delivery compositions
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Process and system for treating a vascular occlusion or other endoluminal structure
A process and instruments for diminishing an undesired endoluminal structure present at a treatment site in a mammalian treatment subject. The endoluminal can be or include a vascular occlusion, a biofilm or another undesired biological structure. The process can include applying mechanical shockwaves to the endoluminal structure and the endoluminal structure absorbing the applied mechanical shockwaves and becoming diminished, dispersed or weakened. The shockwaves can be generated by pulsed laser energy delivered to an ionizable target via an optical fiber.
Owner:KRESPI YOSEF
Drug delivery compositions
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
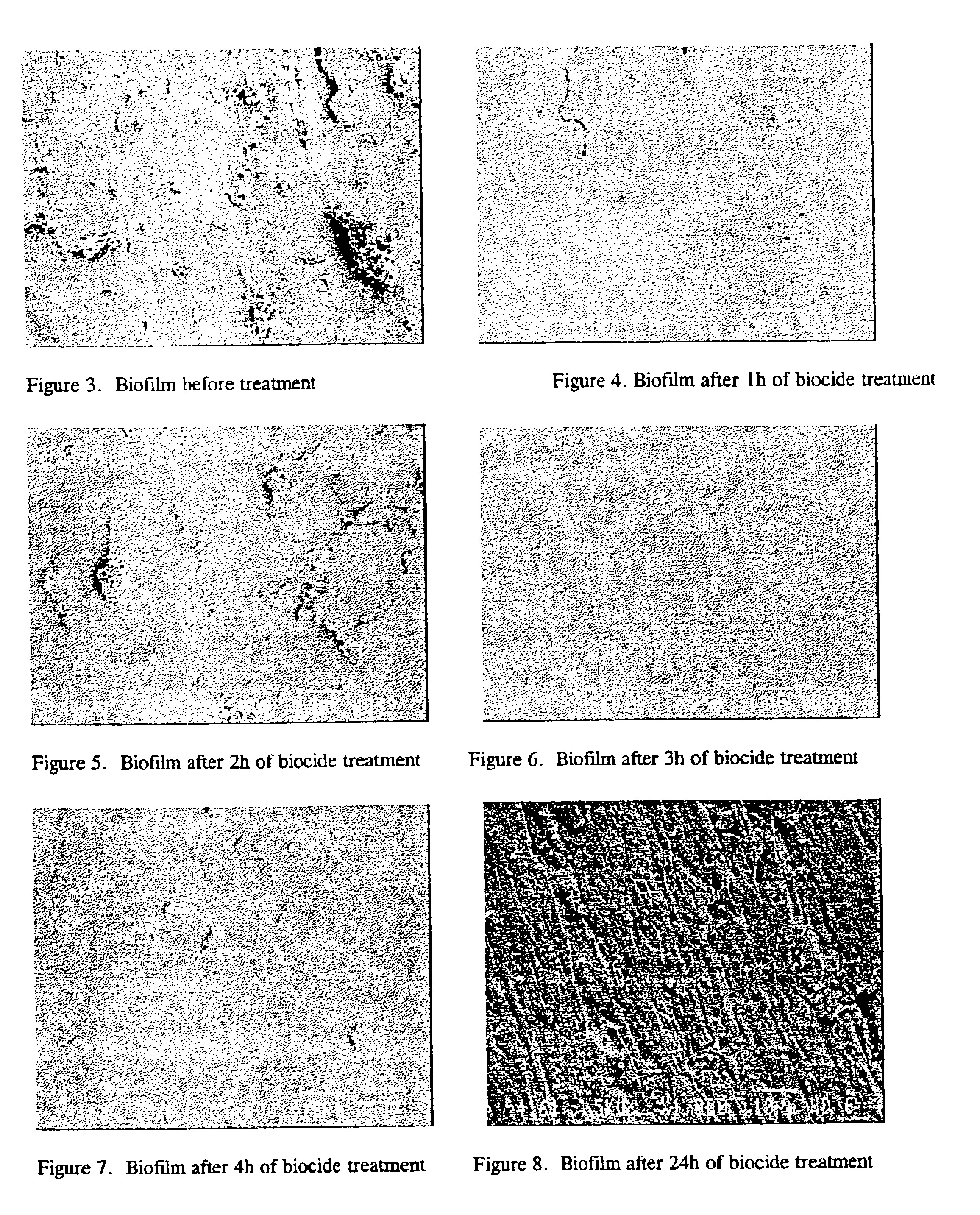
Method of removing a biofilm
The present invention relates to a method of removing a biofilm, which comprises at least the following steps, carried out simultaneously or consecutively: a) a solution comprising an enzyme mixture containing at least one enzyme chosen from the group of proteases, at least one enzyme chosen from the group of esterases and an amylase is prepared; b) a solution comprising a detergent with an alkaline pH is prepared; and c) said solutions are applied, by washing or by circulation, to the surface to be treated. It also relates to a kit intended for removing a biofilm, which comprises the solutions defined above and the compositions comprising the said solutions.
Owner:KARINE MARION +1
Agents and methods for enhancement of transdermal transport
InactiveUS20060015058A1Enhance transdermal transportImproved transdermal transportElectrotherapySurgeryAnalyteBiological membrane
The invention according to an exemplary embodiment relates to a method for transporting a substance across a biological membrane comprising the steps of applying a delipidation agent to a portion of the biological membrane, applying a hydration agent to the portion of the biological membrane, sonicating the portion of the biological membrane, and transporting the substance across the biological membrane. The step of applying the delipidation agent may be carried out prior to or simultaneously with the step of applying the hydration agent. The hydration agent may be applied before, during, or after the sonication step. The methods according to exemplary embodiments of the invention can provide improved transdermal transport in applications such as continuous analyte extraction and analysis and transdermal delivery of drugs and vaccines.
Owner:KELLOGG SCOTT C +7
System and method for continuous analyte monitoring
InactiveUS7384396B2Simpler basic assay designImprove signal-to-noise ratioSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsElectricityBiological body
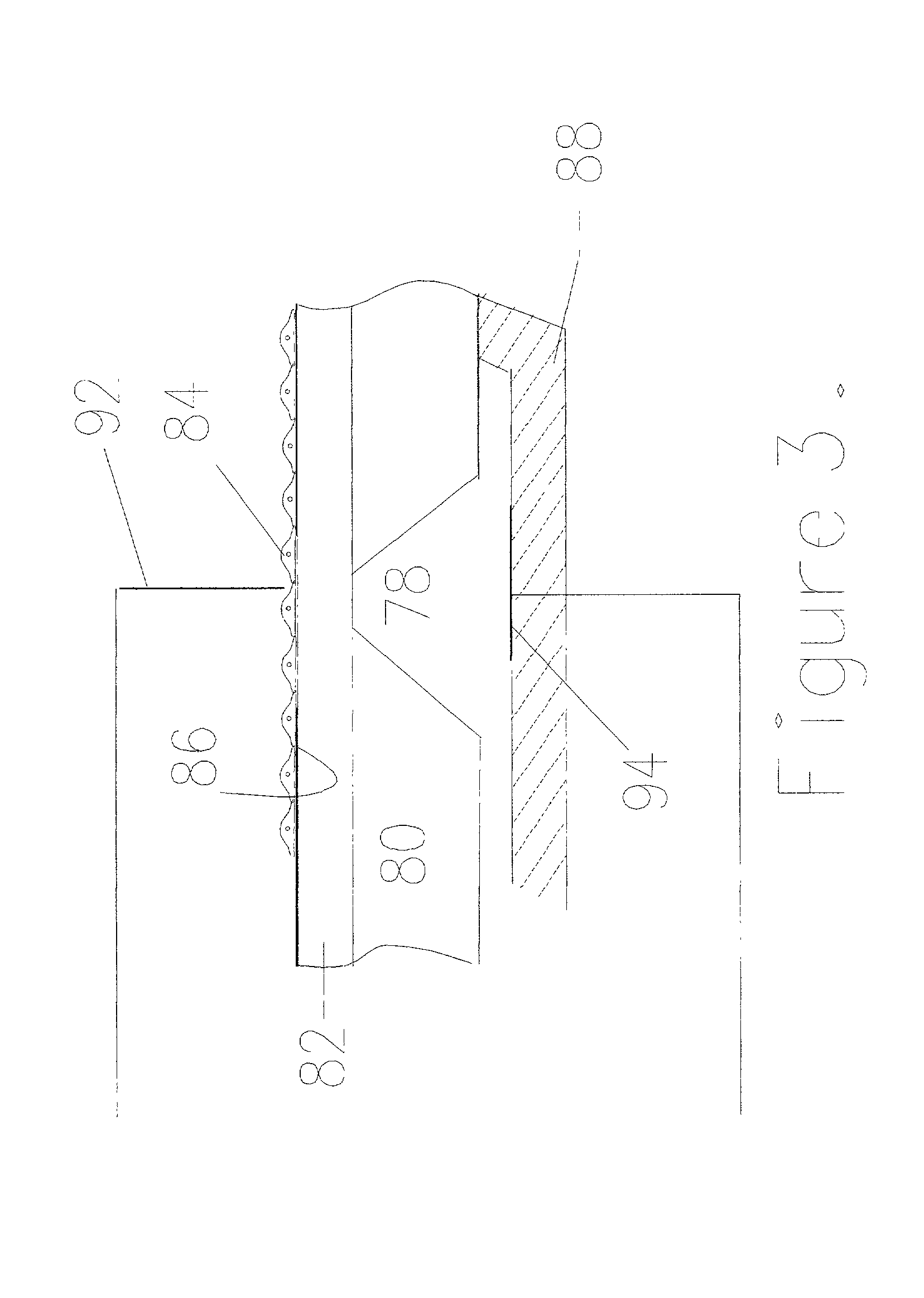
A system and method for extracting a biological fluid from an organism and continuously monitoring its characteristics. The system includes a tissue interface device suitable for positioning on or about the surface of the biological membrane of the organism and a monitor and control unit coupled to the tissue interface device. The tissue interface device includes a sensor positioned in a flow path of the fluid for continuously sensing a characteristic of the biological fluid as it flows out from the one or more artificial openings formed in the biological membrane. The sensor generates a sensor signal representative thereof. The monitor and control unit electrically or optically reads the sensor to obtain a measurement of a characteristic, such as concentration of a particular analyte, of the biological fluid on a continuous basis.
Owner:PASSPORT TECH +1
Methods of analyzing polymers using a spatial network of fluorophores and fluorescence resonance energy transfer
InactiveUS20010014850A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresChemical physicsFluorophore
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for analyzing molecules, particularly polymers, and molecular complexes with extended or rod-like conformations. In particular, the methods and apparatuses are used to identify repetitive information in molecules or molecular ensembles, which is interpreted using an autocorrelation function in order to determine structural information about the molecules. The methods and apparatuses of the invention are used for, inter alia, determining the sequence of a nucleic acid, determining the degree of identity of two polymers, determining the spatial separation of specific sites within a polymer, determining the length of a polymer, and determining the velocity with which a molecule penetrates a biological membrane.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Methods and apparatus for spinning spider silk protein
InactiveUS20050054830A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentBiotechnologySpider Proteins
The invention features methods and apparatuses for spinning silk protein fibers (biofilaments) from recombinant biofilament proteins. The methods are particularly useful for spinning fibers of spider silk or silkworm silk proteins from recombinant mammalian cells and may be used to spin such fibers for use in the manufacture of industrial and commercial products.
Owner:NEXIA BIOTECH
Two step mammalian biofilm treatment processes and systems
ActiveUS20100160838A1Reduce probabilityTime period is limitedUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyMicrobiologyBiological membrane
A two-step mammalian biofilm treatment process can have a first step of disrupting or dispersing an undesired biofilm present at a treatment site in or on a mammalian host by suitable mechanical action for example, by applying irrigation fluid, sonic or other vibration, a mechanical instrument or laser-generated mechanical shockwaves to the biofilm. The treatment can also have a second step comprising applying an antimicrobial treatment to the mammalian host to control possible infection related to biofilm dispersed in the first step or to residual biofilm at the treatment site. Usefully, the second step can be performed within a limited time period after the first step. The process can also include additional steps The antimicrobial treatment can employ light or an antibiotic material. Included are implants cleaned of biofilm by a described process.
Owner:VALENT MEDICAL INC
Genes encoding biofilm formation inhibitory proteins and a method for producing L-lysine using a bacterial strain with the inactivated genes
The present invention relates to a novel isolated gene (polynucleotide) which encodes a protein having a biofilm formation inhibitory activity derived from Coryneform bacteria, a L-lysine-producing strain in which the polynucleotide is inactivated, and a method for producing L-lysine using the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Reversed liquid crystalline phases with non-paraffin hydrophobes
Compounds which are otherwise difficult to solubilize, such as, for example, pharmaceutical actives difficult for the body to absorb, are solubilized into a composition using a solvent system that is a structured fluid. The structured fluid is a reversed cubic phase or reversed hexagonal phase material, or a combination thereof, which includes a polar solvent, a surfactant and a non-paraffinic liquid with a high octanol-water partition coefficient which does not qualify as a surfactant. The compositions thus formed are able to enhance absorption of drugs by the induction of local, transient nanopores in biomembrane absorption barriers and particularly those in which efflux mechanisms, such as those associated with P-glycoprotein and / or cytochrome 3A4, are active. The compositions and methods that are used for solubilizing pharmaceutical actives in structured fluids can simultaneously accomplish solubilization of difficultly soluble drugs and enhancement of absorption.
Owner:LYOTROPICS THERAPEUTICS INC
Method of and equipment for washing, disinfecting and/or sterilizing health care devices
InactiveUS20040037737A1Inexpensive, but effectiveLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsPathogenic microorganismBiological membrane
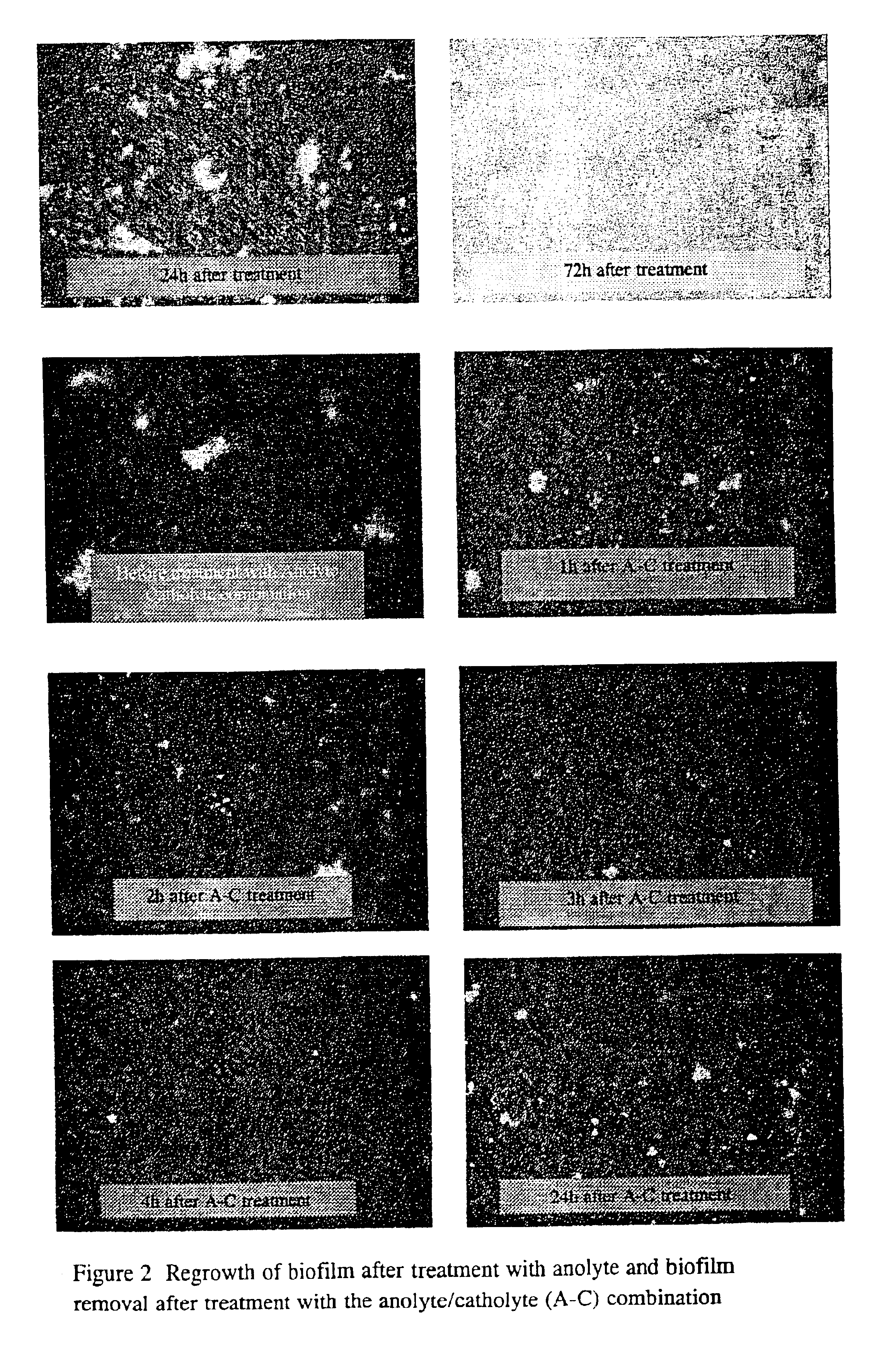
The invention provides a method for automatically washing, disinfecting and / or sterilizing health care equipment and / or cooking and catering utensils. The method includes the steps of placing the equipment to be washed in an enclosure; introducing a first electrochemically activated aqueous solution into the enclosure; and either sequentially or simultaneously introducing a second electrochemically activated aqueous solution into the enclosure. The first solution is characterised therein that it has dispersing or surfactant characteristics for at least partially dispersing a biofilm, pathogenic microorganisms, contamination or the like. The second solution is characterised therein that it has biocidal characteristics for killing microorganisms and disinfecting and / or sterilizing the equipment. The invention also extends to an apparatus for use in the above method.
Owner:RADICAL WATERS IP
Nano-electronic sensors for chemical and biological analytes, including capacitance and bio-membrane devices
Embodiments of nanoelectronic sensors are described, including sensors for detecting analytes inorganic gases, organic vapors, biomolecules, viruses and the like. A number of embodiments of capacitive sensors having alternative architectures are described. Particular examples include integrated cell membranes and membrane-like structures in nanoelectronic sensors.
Owner:NANOMIX INC
Ecological closed cycle water fish-cultivating method
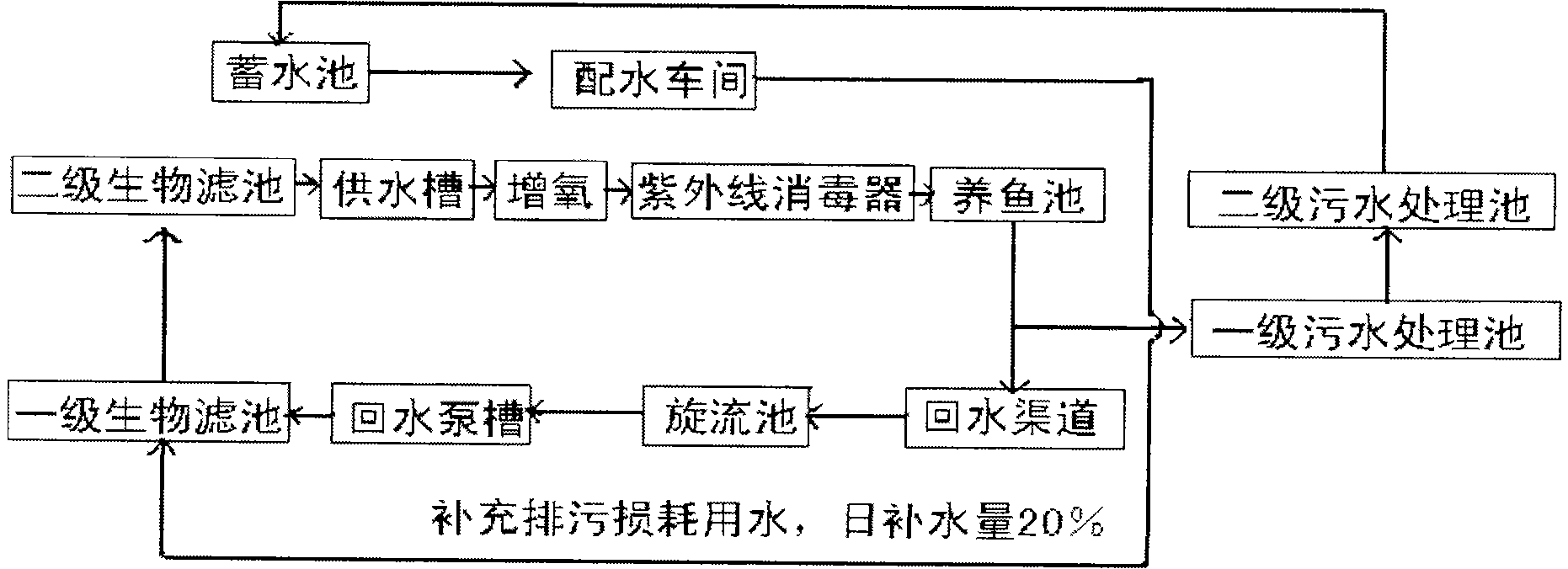
InactiveCN101548655AClean up sediment pollutionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationClimate change adaptationDiseaseParticulates
The present invention belongs to an industrialization aquiculture field, particularly relates to a closed cycle water industrialized fish cultivating system. The system separates solid and liquid in a storage sedimentation basin and a backwater channel sedimentation and rotational flow pool sedimentation, the tiny particulate matter is separated and purified by a sandrock filtering bed of a one level biological filter based on the water particulate matter separation, the water purified by the one level biological filter is feed into a two stage biological filter, the biological film of biologic filling material in the one level and the two stage biological filters is degraded with ammonia nitrogen and azote nitrous acid, the total purifying rate of the water particulate matter reaches more than 99%, the culturing water is added with oxygen mechanically or by liquid oxygen, finally the water is disinfected and sterilized through a ultraviolet ray sterilizer, and the clean ecological water is feed into a fish pool, thus the waste water of the fish pool may be purified and used in repeat. The fish-cultivating system implements completely closed cycle water industrialized fish cultivation, the fish is out of a disease or less, and the fish survival is more than 80%.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for delivery of monomeric or dimeric insulin complexed to diketopiperazine microparticles
InactiveUS7648960B2Rapid increase in blood agent concentrationEasy to transportPowder deliverySpray deliveryBlood insulinBlood agent
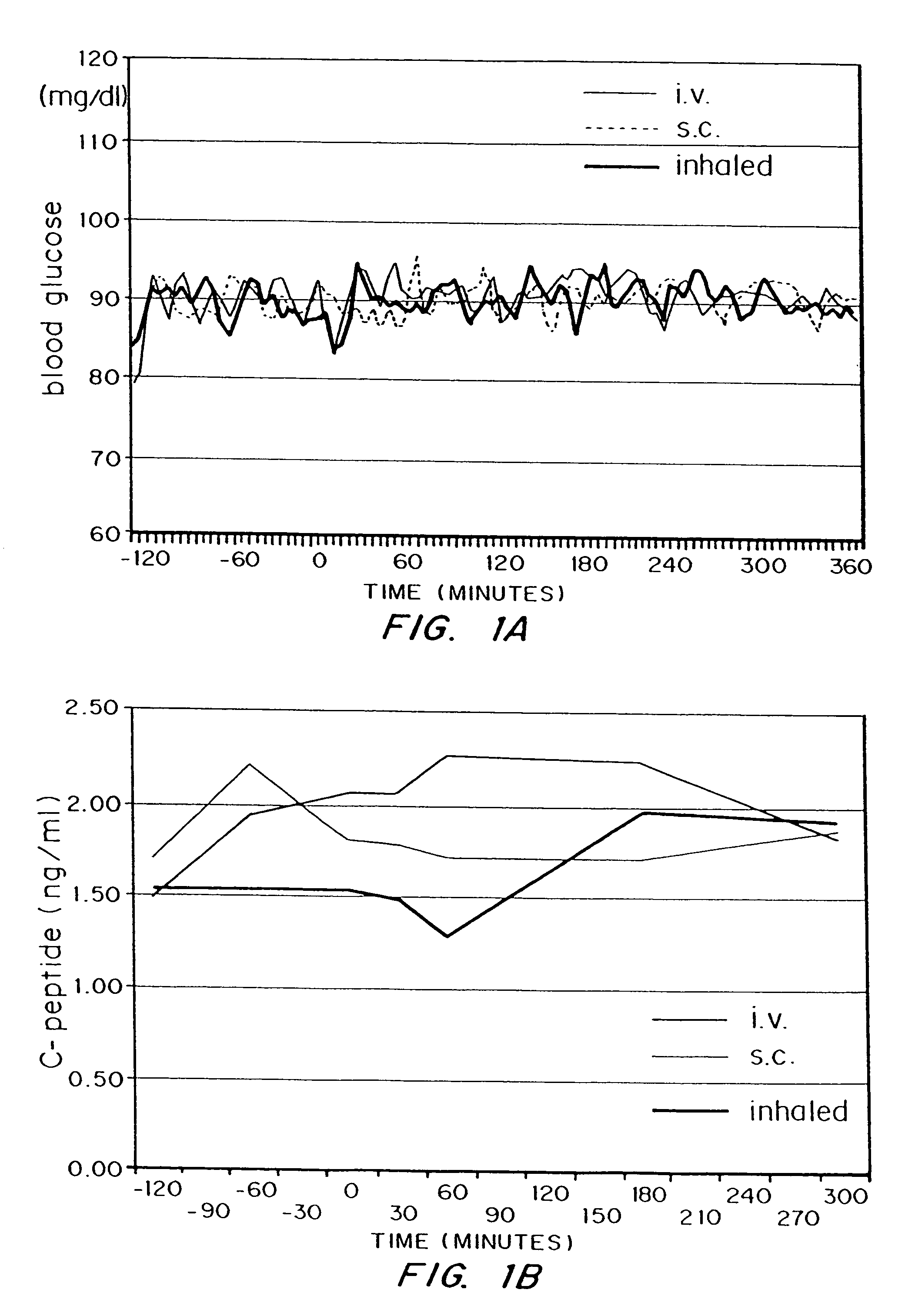
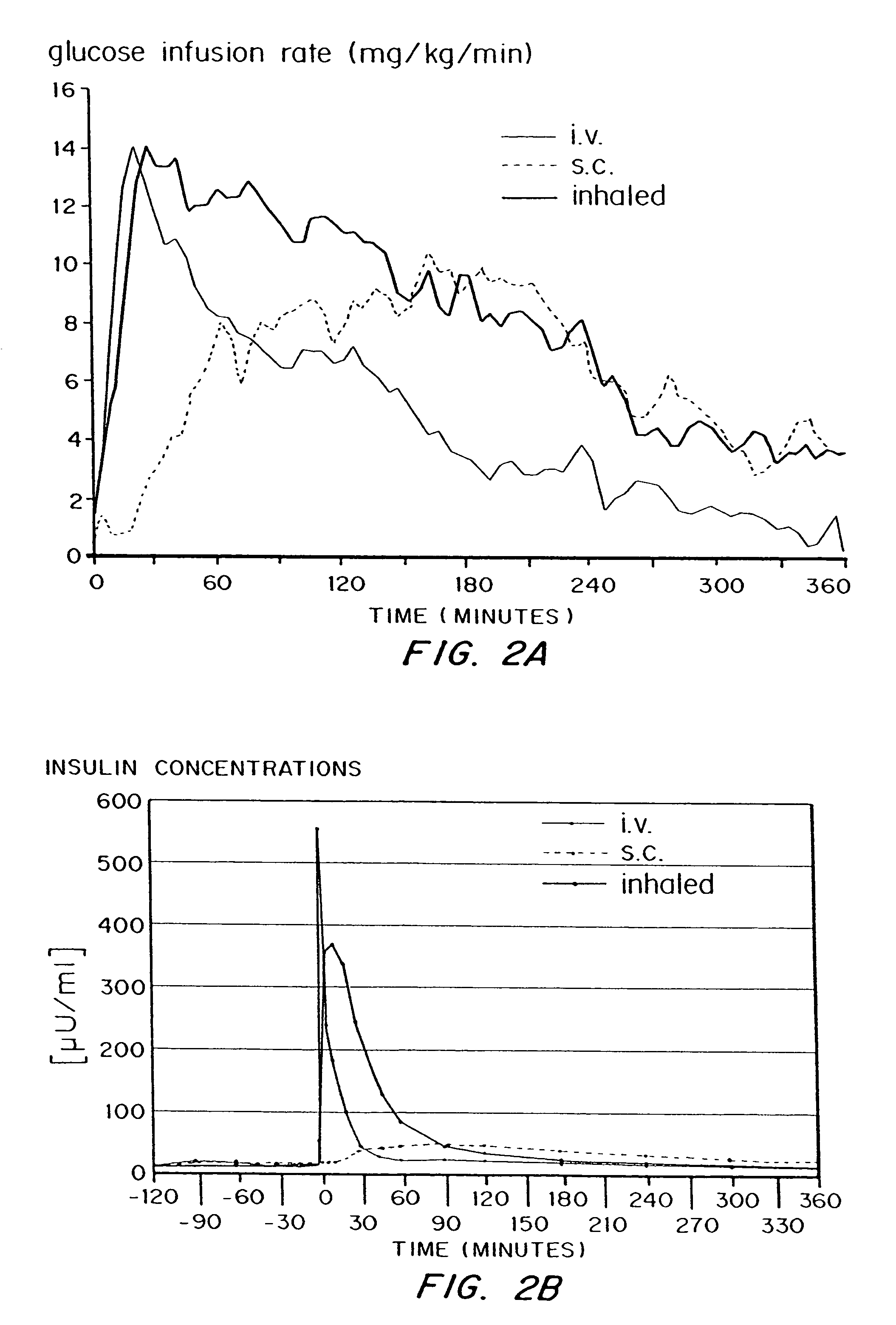
Methods are provided for purifying peptides and proteins by incorporating the peptide or protein into a diketopiperazine or competitive complexing agent to facilitate removal of one or more impurities from the peptide or protein. Formulations and methods also are provided for the improved transport of active agents across biological membranes, resulting for example in a rapid increase in blood agent concentration. The formulations include microparticles formed of (i) the active agent, which may be charged or neutral, and (ii) a transport enhancer that masks the charge of the agent and / or that forms hydrogen bonds with the target biological membrane in order to facilitate transport. In one embodiment insulin is administered via the pulmonary delivery of microparticles comprising fumaryl diketopiperazine and insulin in its biologically active form. This method of delivering insulin results in a rapid increase in blood insulin concentration that is comparable to the increase resulting from intravenous delivery.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Dental equipment and method of operating such equipment
InactiveUS6878287B1Suitable for useEliminate biofilmElectrostatic separatorsElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisDental Equipment
An electrolytically activated, microcidal aqueous solution is disclosed which is used in the elimination and control of biofilm in dental unit water lines. The solution has a pH between 6.75 and 10 with microcidal as well as anti-oxidising, dispersing and surfactant properties, rendering the solution bio-compatible and non-corrosive, as well as capable of eliminating biofilm in dental unit water lines, while simultaneously dispersing and dislodging the biofilm from the water lines so as reduce the micro-organisms in the dental water to a predetermined level. The aqueous solution is produced using an electrolytic device that allows the independent manipulation of specific individual properties of two separate product streams (a cation-rich stream and an anion-rich stream), the manipulation being performed by separate and independent recirculation through the same electrode chamber or counter-electrode chamber of the electrolytic device to modulate the respective properties of the anion-containing and the cation-containing solutions.
Owner:RADICAL WATERS IP
Pharmaceutical compositions based on a microemulsion
InactiveUS20100034880A1Efficient deliveryIncrease concentrationOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPropylene carbonateBiological membrane
The invention provides a transdermal, transmucosal pharmaceutical composition suitable for substantially extra-vascular application of at least one biologically active substance to biological membranes of a mammal, comprising a pharmaceutical or cosmetic composition comprising propylene carbonate at least one oil or source of fatty acid or surfactant; and water; in combination with the at least one biologically active substance wherein the propylene carbonate is adapted to enhance the bioavailability of the at least one biologically active substance.
Owner:NANODERMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com