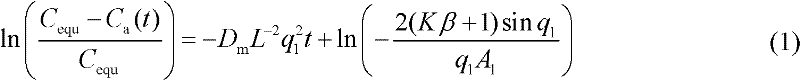Patents
Literature
502 results about "Partition coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the physical sciences, a partition coefficient (P) or distribution coefficient (D) is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in a mixture of two immiscible phases at equilibrium. This ratio is therefore a measure of the difference in solubility of the compound in these two phases. The partition coefficient generally refers to the concentration ratio of un-ionized species of compound, whereas the distribution coefficient refers to the concentration ratio of all species of the compound (ionized plus un-ionized).
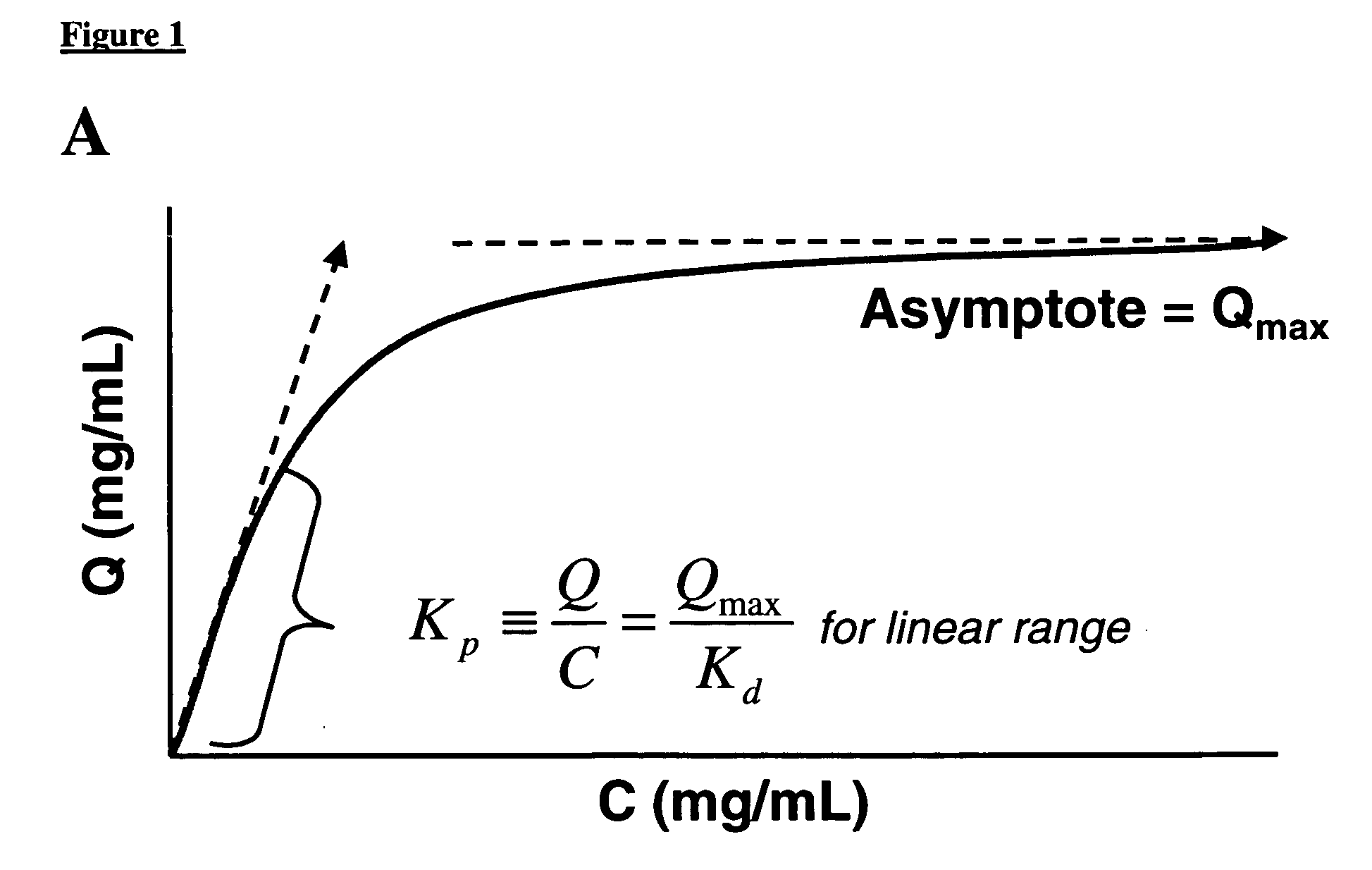
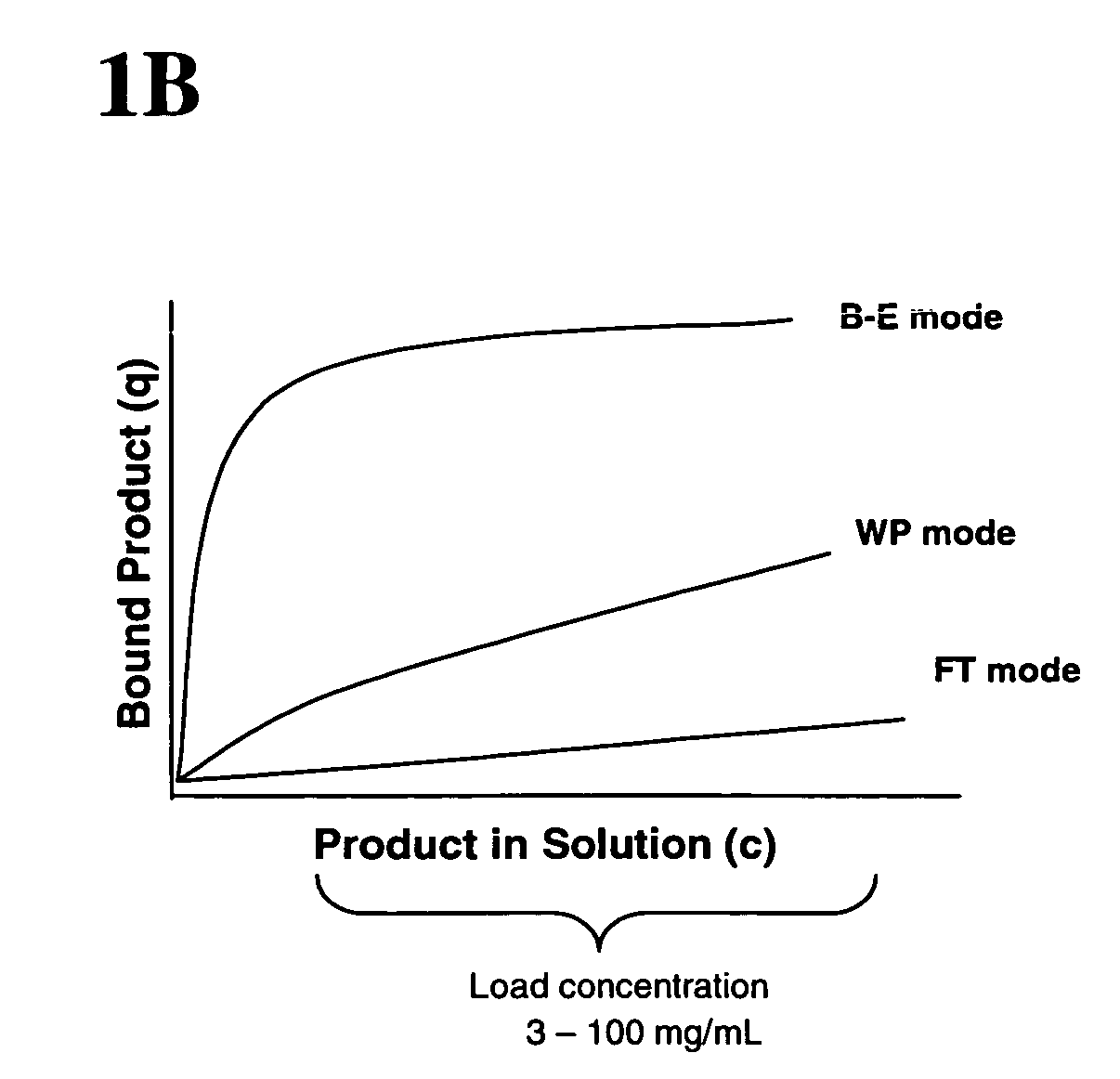
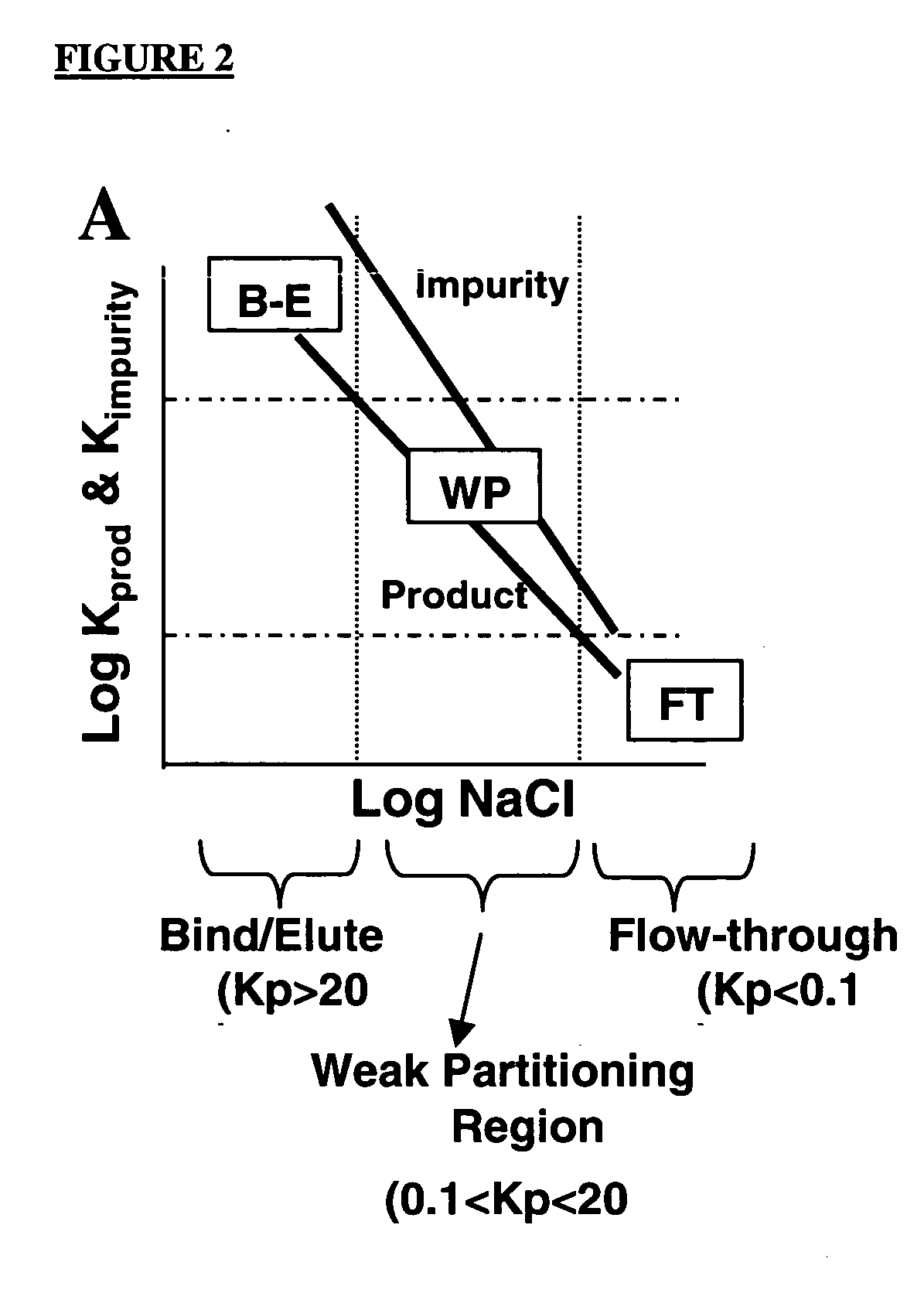
Method of weak partitioning chromatography
ActiveUS20070060741A1Solid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsOperant conditioningImpurity
Owner:WYETH LLC
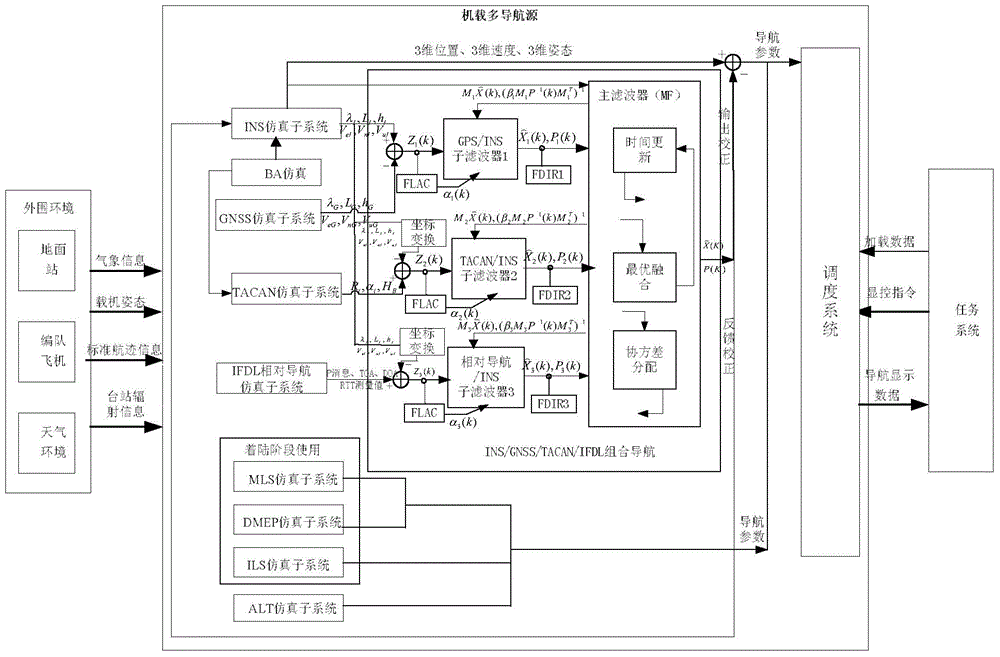
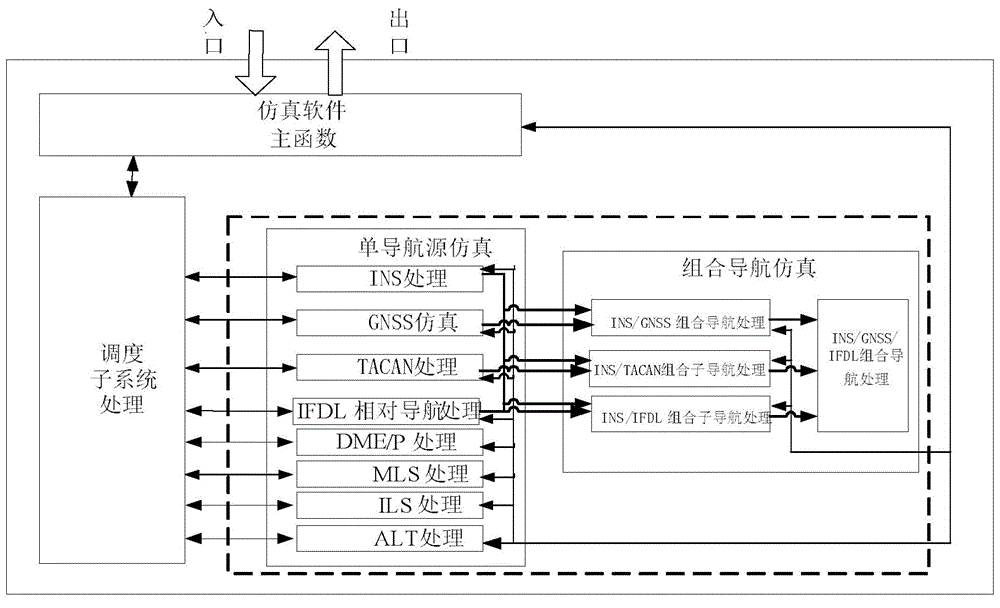
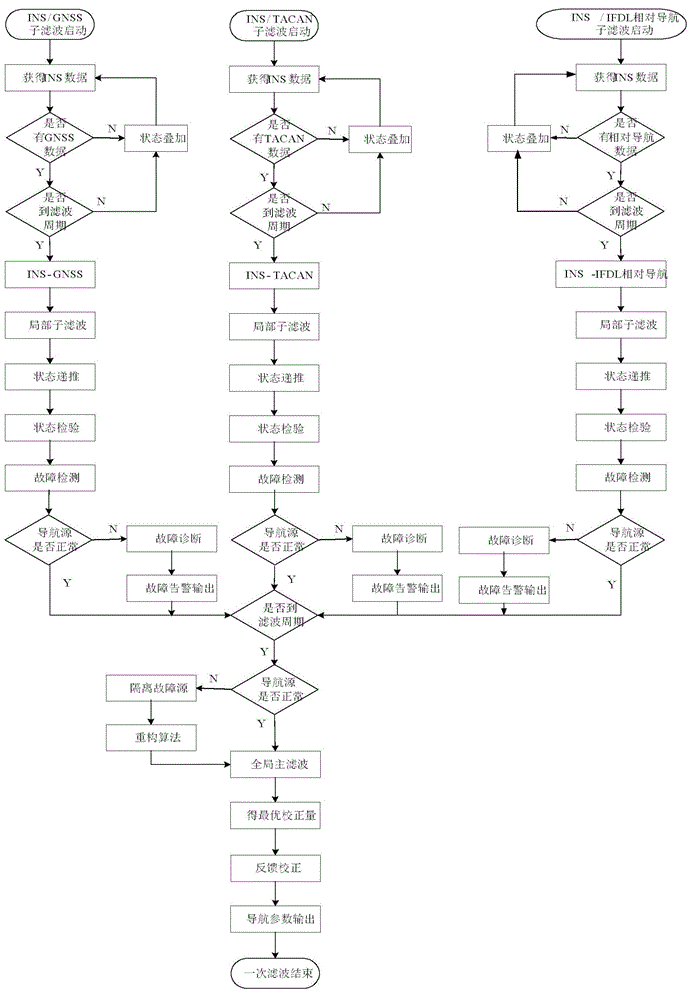
Aircraft-mounted multi-navigation-source comprehensive navigation simulation system
ActiveCN104406605AImprove adaptabilityImprove portabilitySatellite radio beaconingSelf navigationData information
The invention discloses an aircraft-mounted multi-navigation-source comprehensive navigation simulation system. In the system, each navigation simulation sub system really simulates functions, performances and interfaces which are same as those of a model according to a self-navigation principle. A scheduling system responds a display control command, a load command and load data information sent by a mission system, and drives the navigation simulation sub systems to perform simulation calculation with combination of environment simulation data. A combined navigation system, with an INS simulation sub system as a main navigation source, performs integrated navigation based on and fault detection federated Kalman filter with GNSS, TACAN and IFDL as auxiliary navigation sources. Information fusion is achieved through a generalized federated Kalman filter in a two-stage structure constructed through a federated filter algorithm, wherein a main filter performs total information fusion and performs information distribution and information reset to each sub filter. Optimal estimation is carried out to a result of each sub filter through a dynamic information distribution coefficient. Meanwhile, the INS simulation sub system is subjected to closed-loop negative feedback correction through an estimated error by the system.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
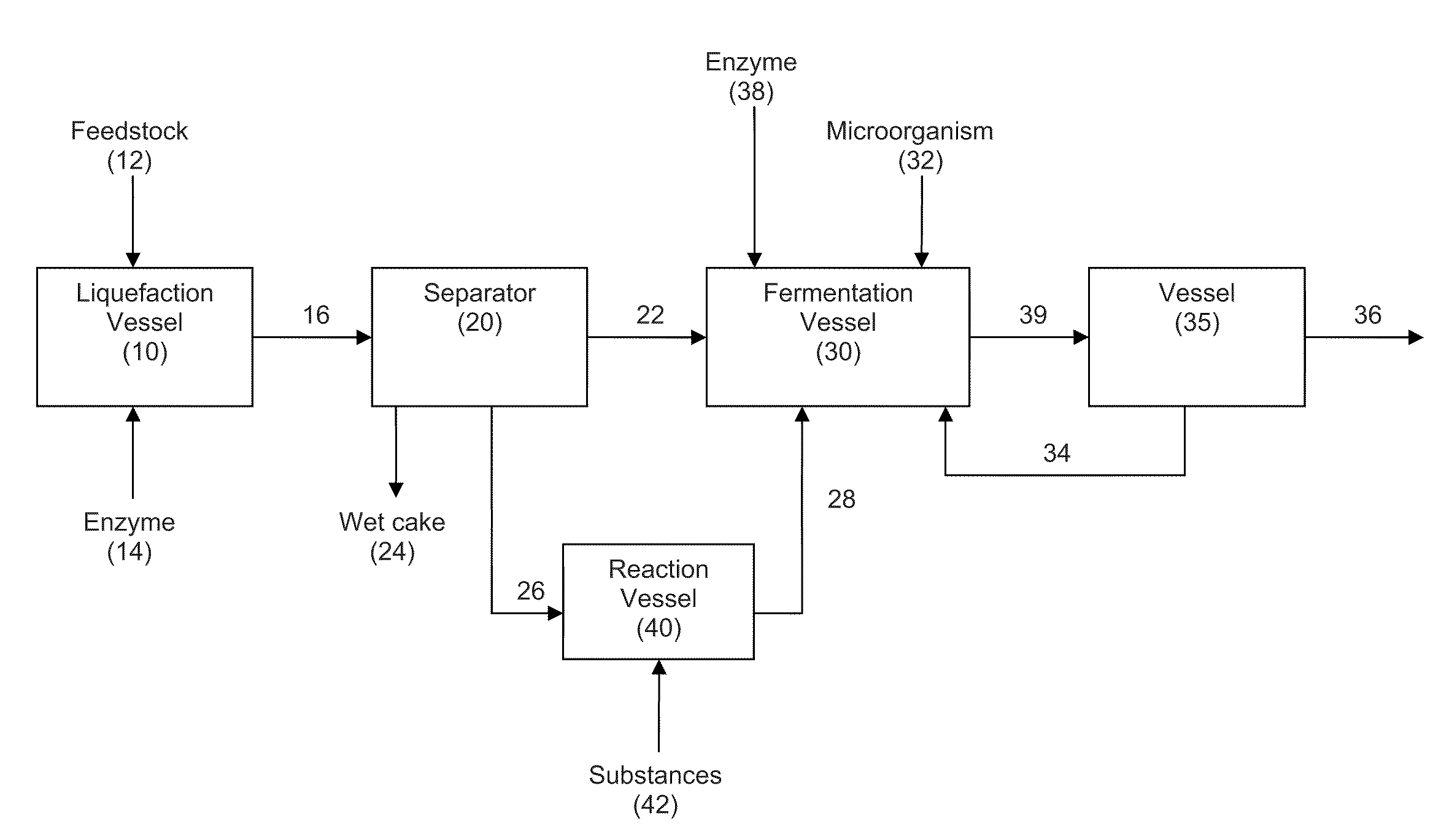
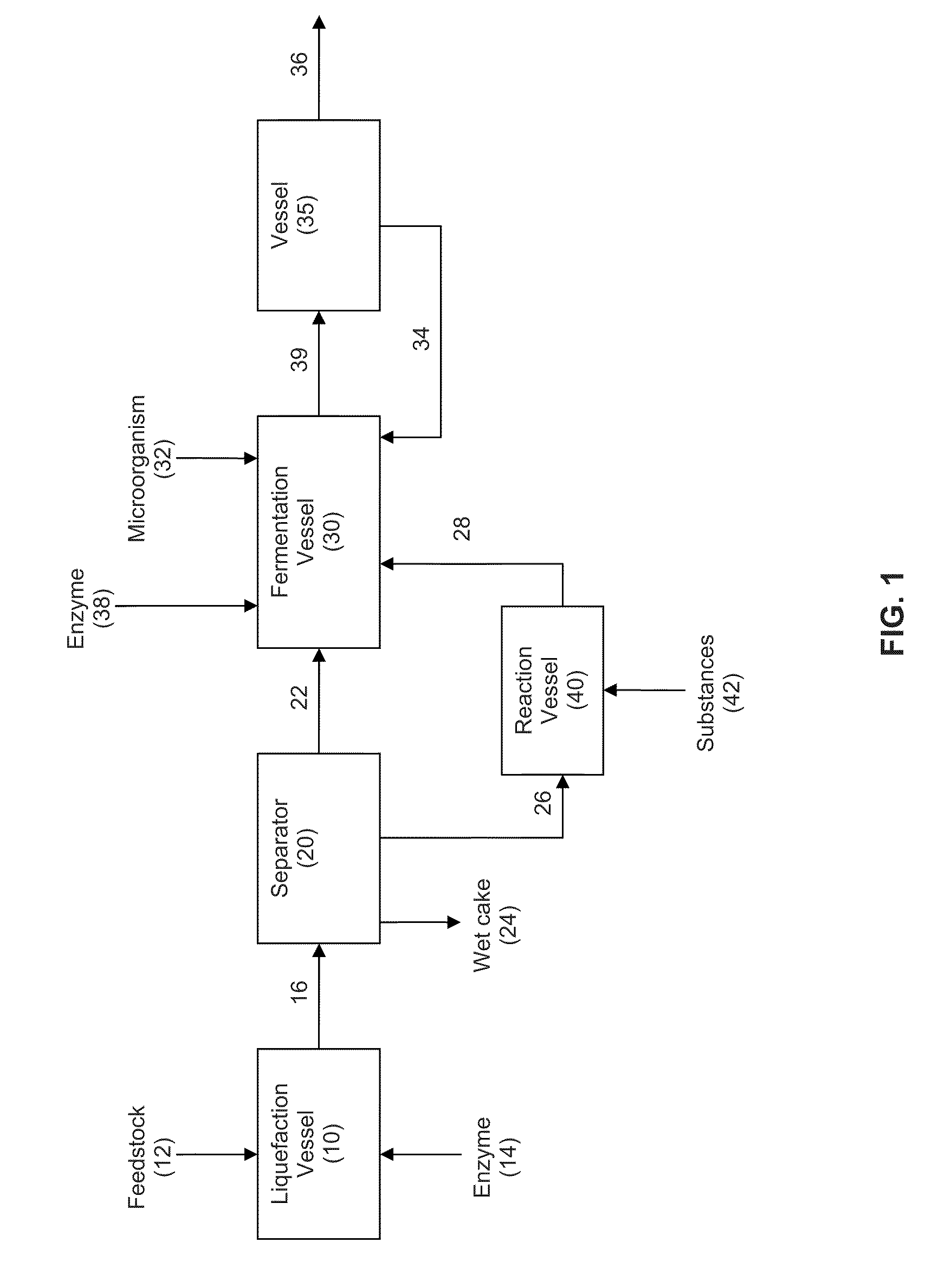
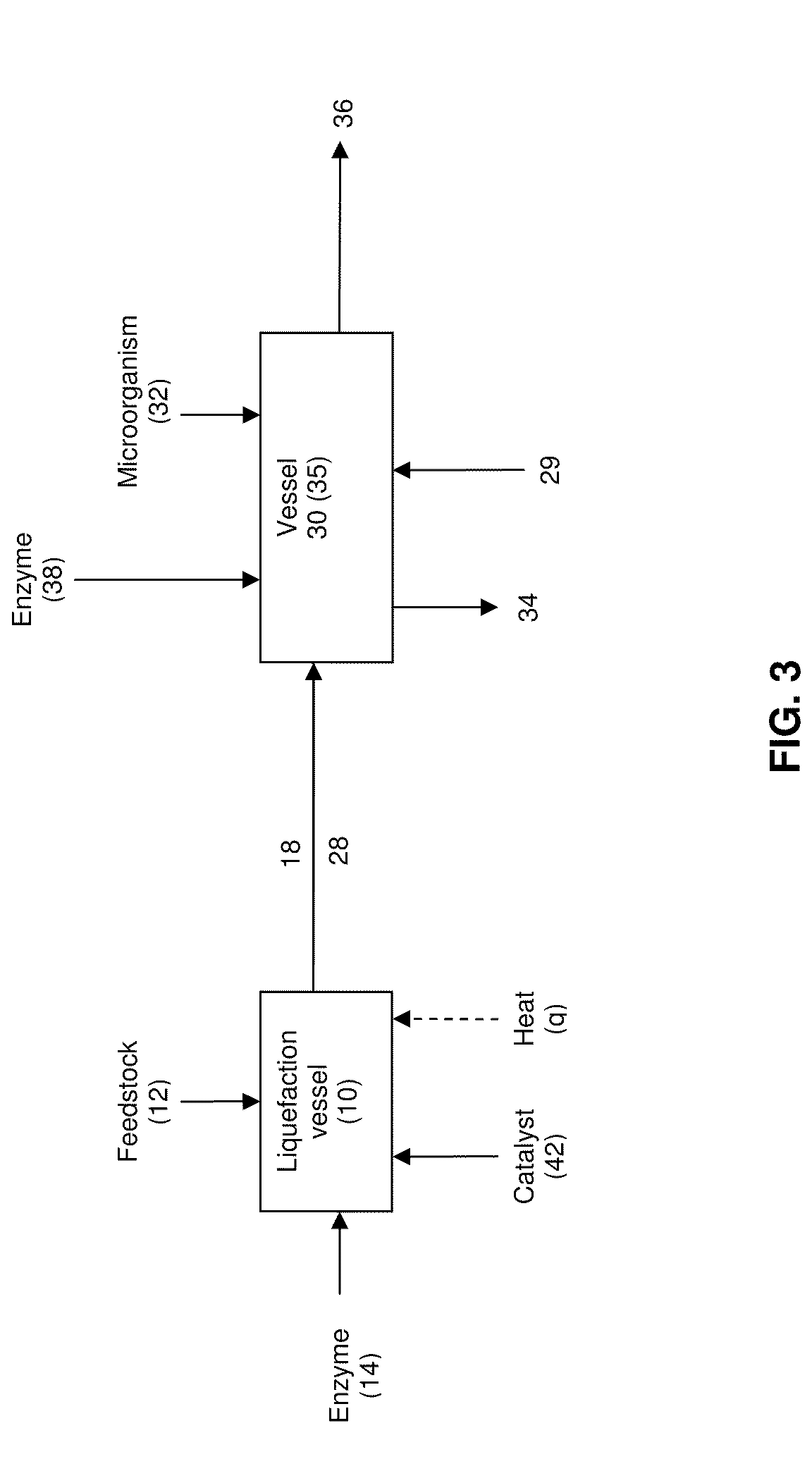
Extraction solvents derived from oil for alcohol removal in extractive fermentation
ActiveUS20110312044A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce decreaseFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOxygen-containing compound preparationSolventFatty alcohol
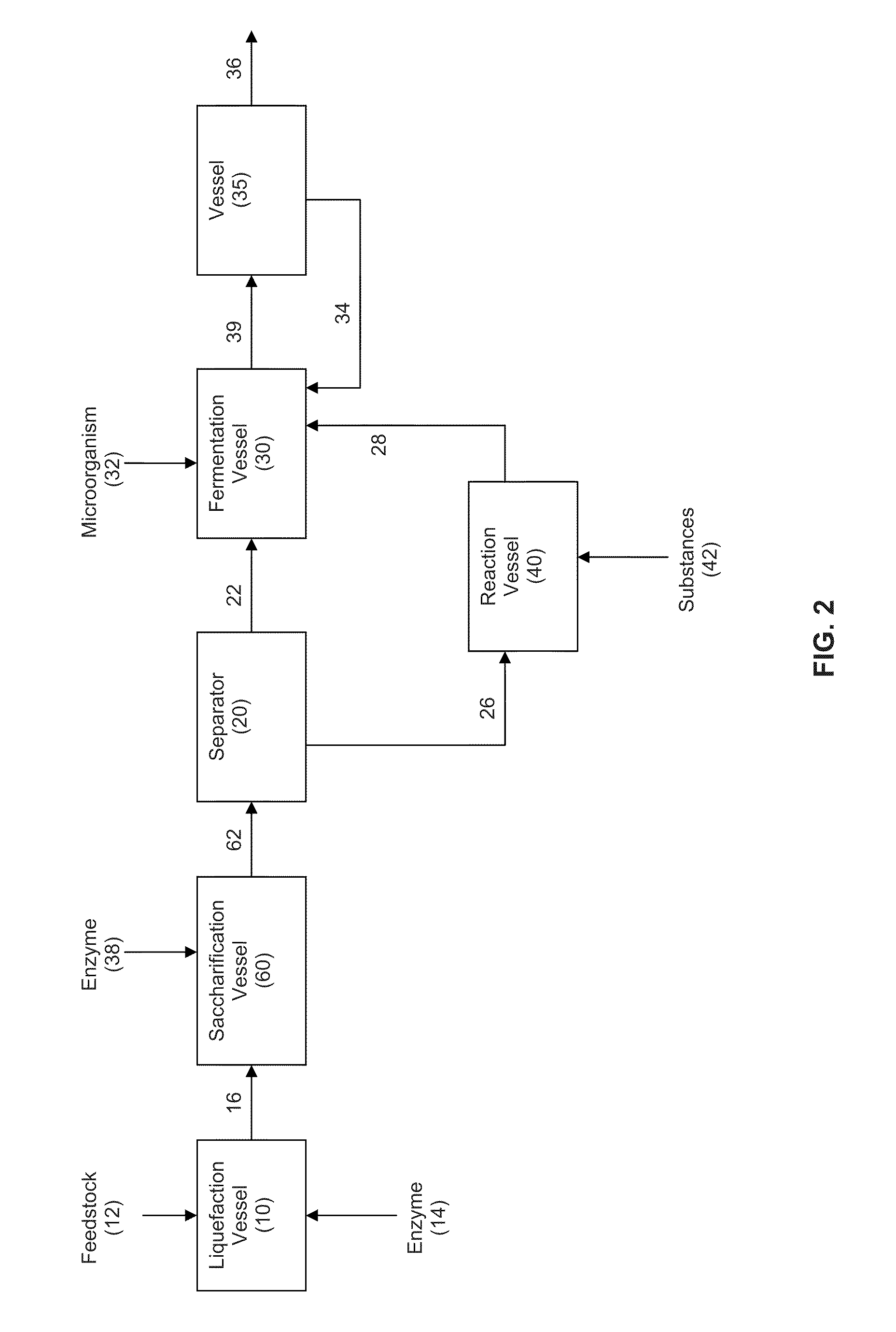
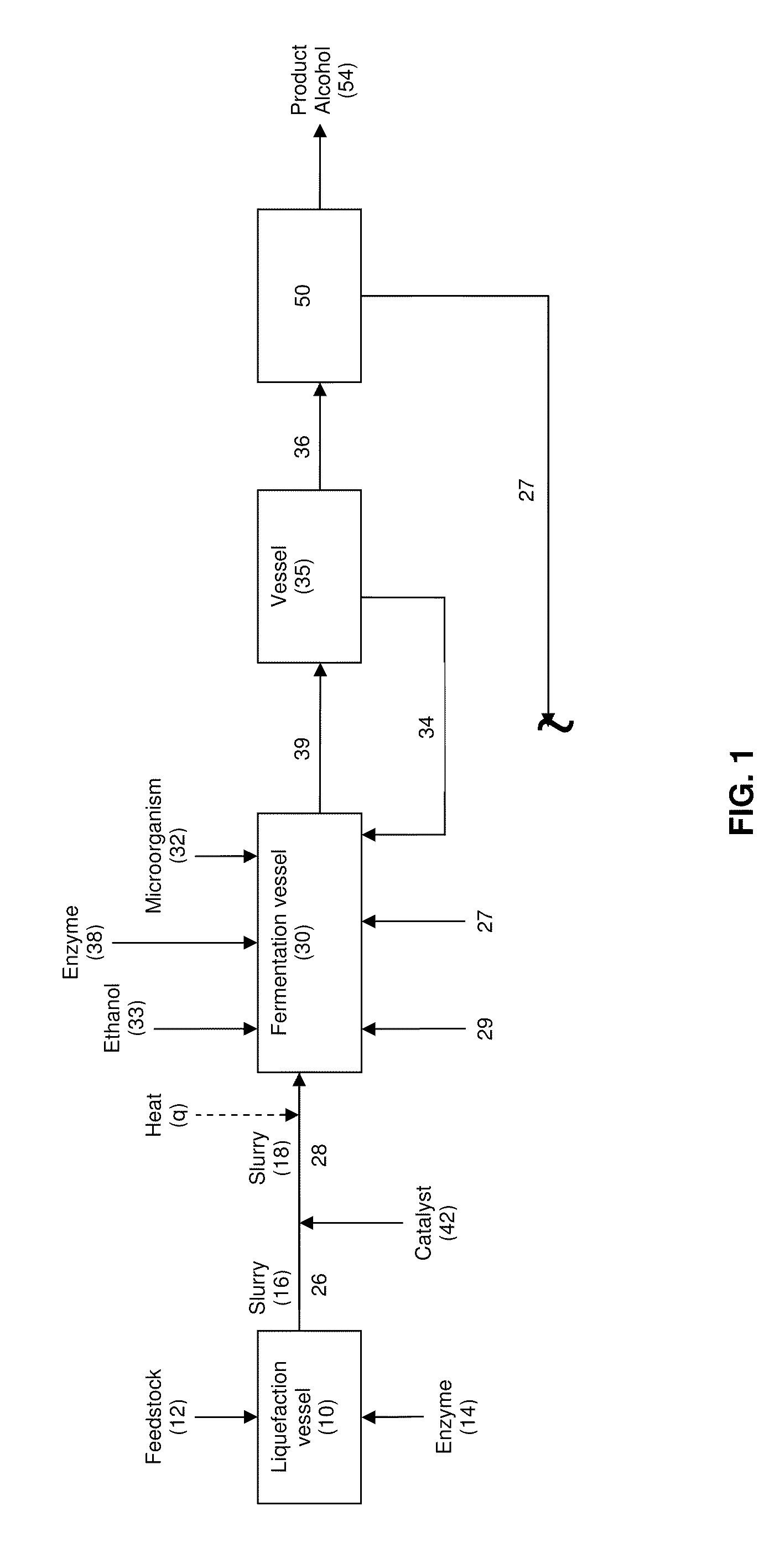
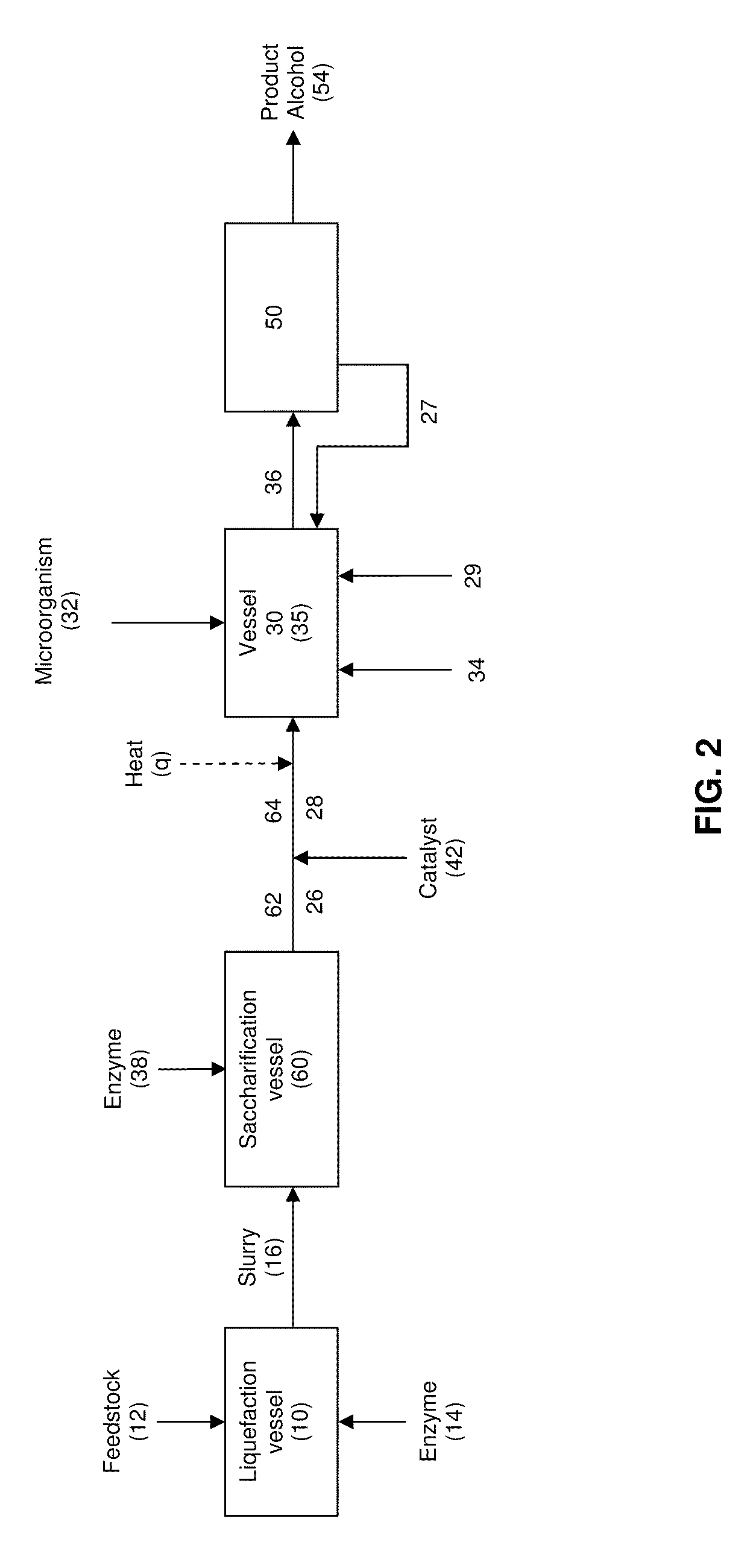
In an alcohol fermentation process, oil derived from biomass is chemically converted into an extractant available for in situ removal of a product alcohol such as butanol from a fermentation broth. The glycerides in the oil can be chemically converted into a reaction product, such as fatty acids, fatty alcohols, fatty amides, fatty acid methyl esters, fatty acid glycol esters, and hydroxylated triglycerides, and mixtures thereof, which forms a fermentation product extractant having a partition coefficient for a product alcohol greater than a partition coefficient of the oil of the biomass for the product alcohol. Oil derived from a feedstock of an alcohol fermentation process can be chemically converting into the fermentation product extractant. The oil can be separated from the feedstock prior to the feedstock being fed to a fermentation vessel, and the separated oil can be chemically converted to a fermentation product extractant, which can then contacted with a fermentation product comprising a product alcohol, whereby the product alcohol is separated from the fermentation product.
Owner:GEVO INC
Method and apparatus for charging multiple energy storage devices
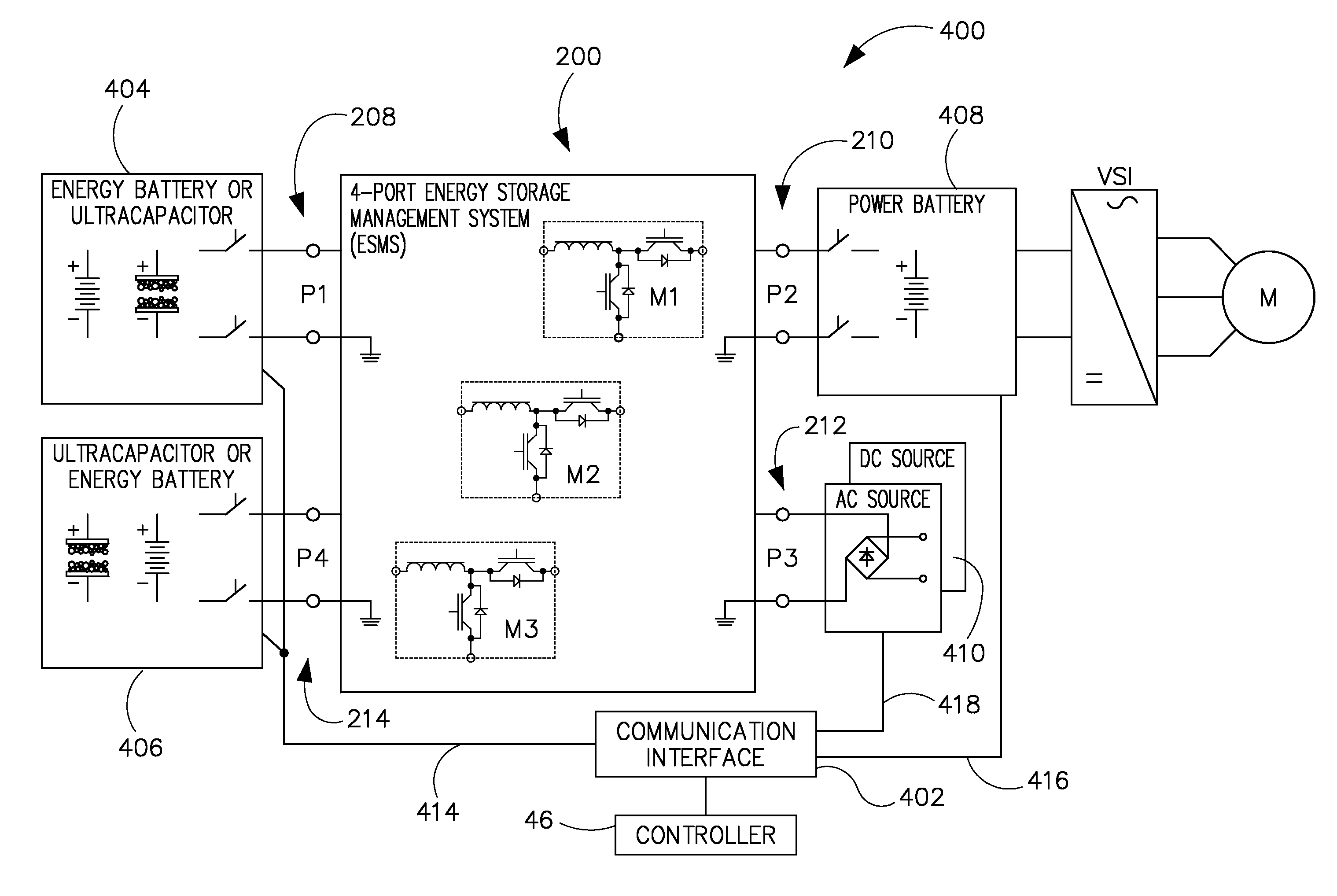
ActiveUS8981727B2Vehicular energy storageArrangements for several simultaneous batteriesPower splitCharge current
An electric vehicle includes a controller configured to receive sensor feedback from a high voltage storage device and from a low voltage storage device, compare the sensor feedback to operating limits of the respective high and low voltage storage device, determine, based on the comparison a total charging current to the high voltage storage device and to the low voltage storage device and a power split factor of the total charging current to the high voltage device and to the low voltage device, and regulate the total power to the low voltage storage device and the high voltage storage device based on the determination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method, apparatus, and program product for clustering entities in a persistent virtual environment
ActiveUS20070149288A1Apparatus for meter-controlled dispensingProgram controlWeight coefficientComputer compatibility
Apparatus, methods, and computer program products are disclosed that accesses coefficient vectors each of which represent an entity within a persistent virtual environment. Each accessed coefficient vector includes coefficients having coefficient values related to the represented entity. The coefficients represent a temporal profile of the entity in the persistent virtual environment. This aspect assigns a coefficient weight to at least one of the coefficients. and partitions the coefficient vectors responsive to the coefficient weight and at least one of the coefficients of each of the coefficient vectors into clusters. Finally, the technology presents a recommendation responsive to the clusters. Furthermore, a compatibility metric can be determined by comparing weighted coefficient vectors of two entities, and the compatibility metric can also be presented.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Method of separating sound signal
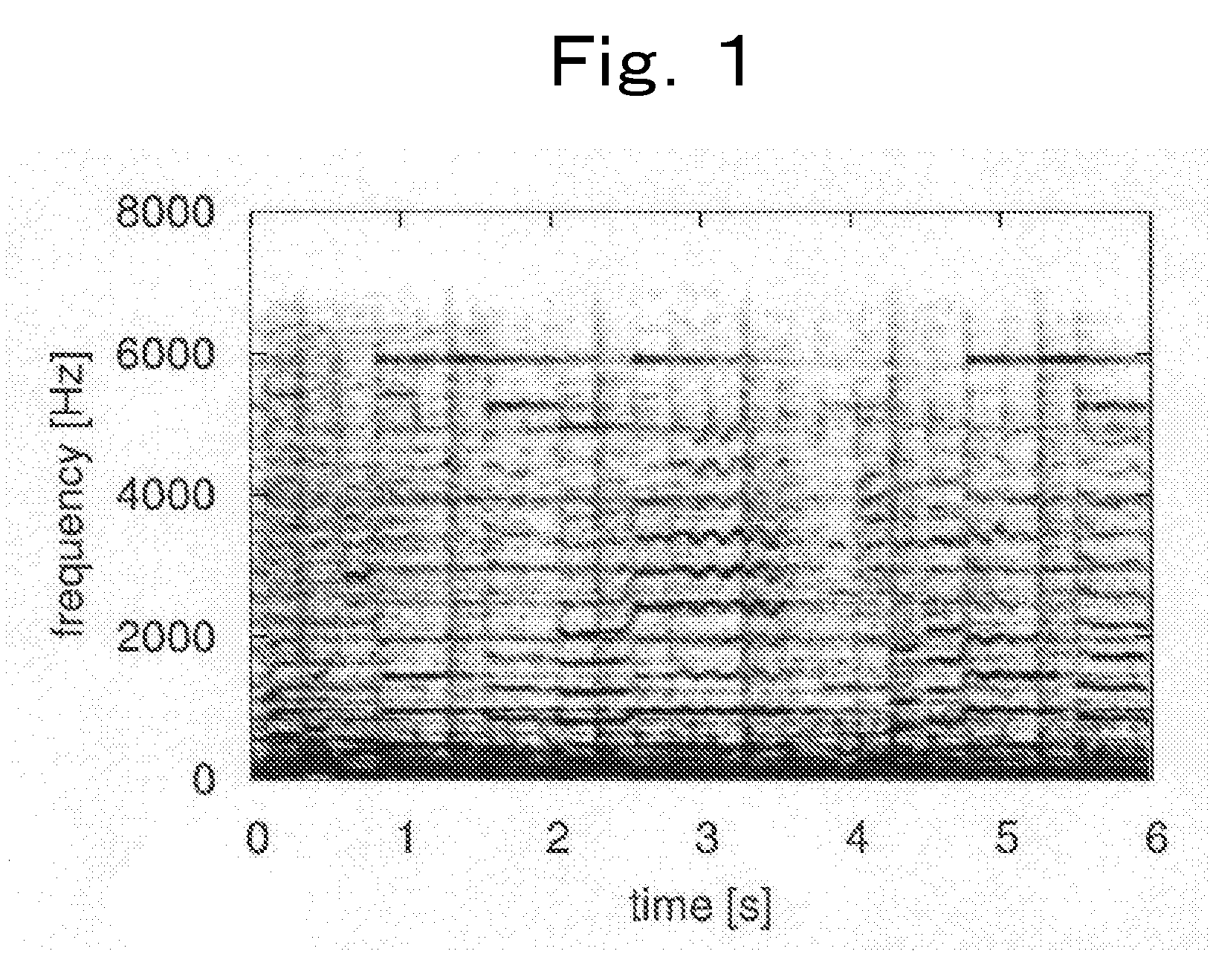
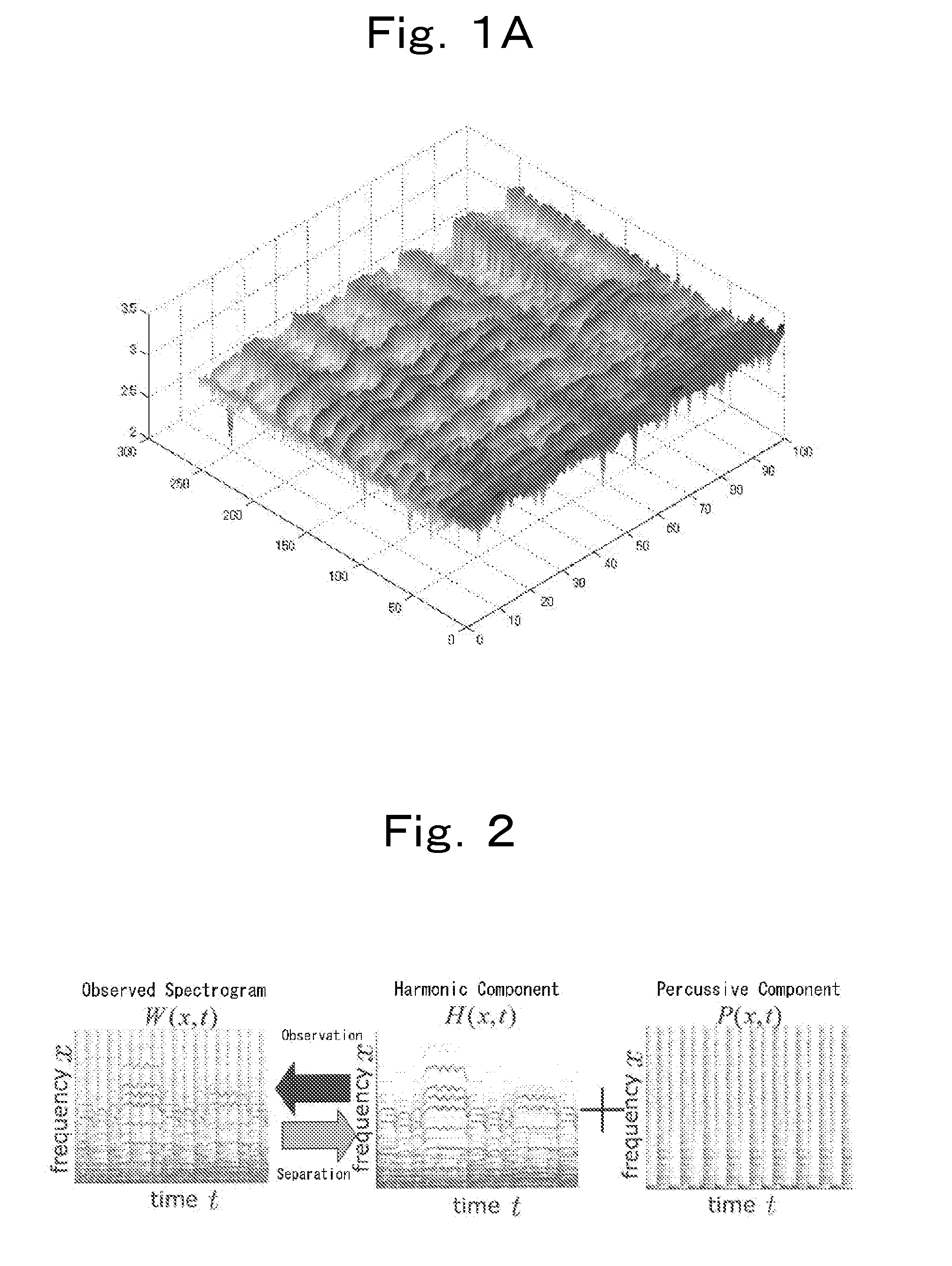
InactiveUS20110058685A1Easy to getMinimizing smoothnessSpeech analysisTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsFrequency spectrumAudio frequency
The present invention obtains a separated signal from an audio signal based on the anisotropy of smoothness of spectral elements in the time-frequency domain. A spectrogram of the audio signal is assumed to be a sum of a plurality of sub-spectrograms, and smoothness of spectral elements of each sub-spectrogram in the time-frequency domain has directionality on the time-frequency plane. The method comprises obtaining a distribution coefficient for distributing spectral elements of said audio signal in the time-frequency domain to at least one sub-spectrogram based on the directionality of the smoothness of each sub-spectrogram on the time-frequency plane, and separating at least one sub-spectrogram from said spectral elements of said audio signal using said distribution coefficient.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Extraction solvents derived from oil for alcohol removal in extractive fermentation
ActiveUS20110312043A1Reduce capacityPreventing lowering of partition coefficientFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFungiAlcoholSolvent
In an alcohol fermentation process, oil derived from biomass is hydrolyzed into an extractant available for in situ removal of a product alcohol such as butanol from a fermentation broth. The glycerides in the oil can be catalytically (e.g., enzymatically) hydrolyzed into free fatty acids, which form a fermentation product extractant having a partition coefficient for a product alcohol greater than a partition coefficient of the oil of the biomass for the product alcohol. Oil derived from a feedstock of an alcohol fermentation process can be hydrolyzed by contacting the feedstock including the oil with one or more enzymes whereby at least a portion of the oil is hydrolyzed into free fatty acids forming a fermentation product extractant, or the oil can be separated from the feedstock prior to the feedstock being fed to a fermentation vessel, and the separated oil can be contacted with the enzymes to form the fermentation product extractant. The fermentation product extractant can be contacted with a fermentation broth for in situ removal of a product alcohol.
Owner:GEVO INC
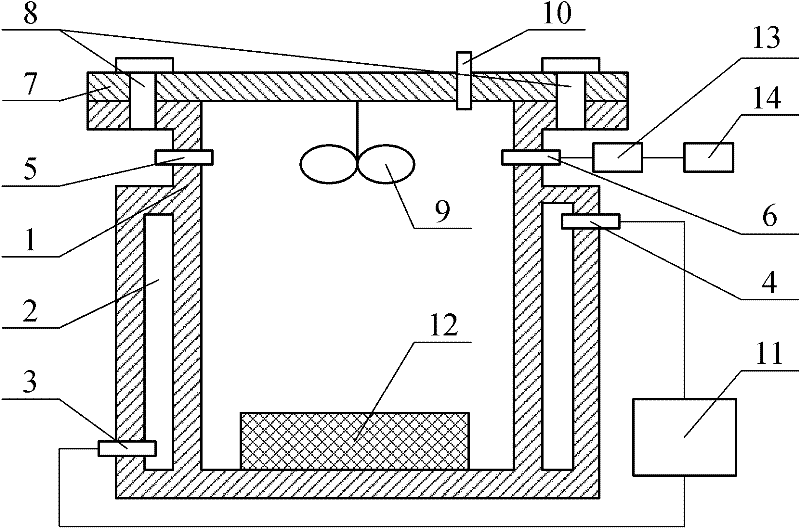
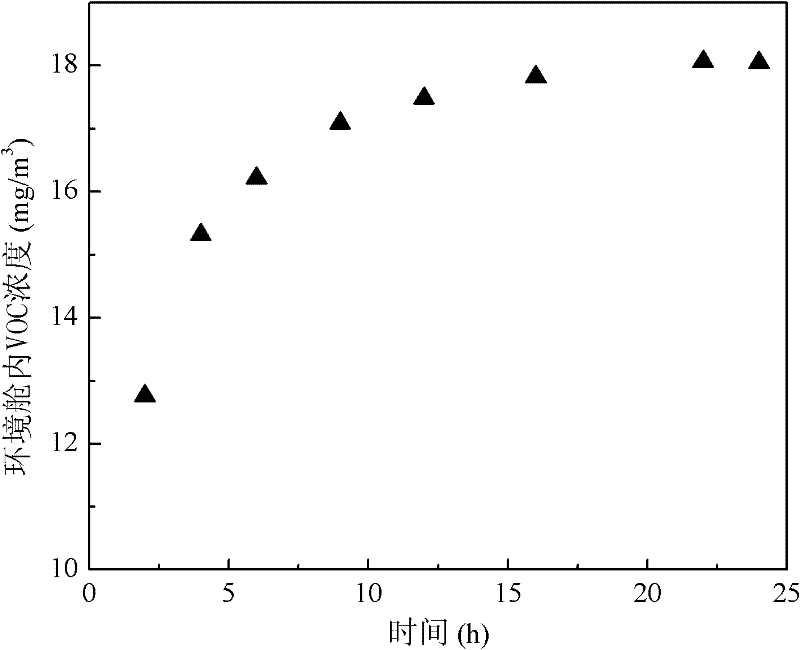
Method and device for quickly measuring building material emission key parameter
The invention relates to a method and device for quickly measuring a building material emission key parameter, belonging to the field of indoor environmental tests. The method comprises the following steps: building an effect model for concentration in the measuring device in the building material VOC (volatile organic compounds) emission process; controlling the temperature of the measuring device to be always kept at a set value by a temperature controlling device (such as a constant-temperature water bath); putting a building material to be measured into the measuring device, and sealing the measuring device; in the building material emission process, measuring the concentration of target VOC in the measuring device for several times; finally, taking the average value of the concentration results of the last 2-3 times as a balanced concentration, and taking other concentration results as a hourly concentration; tidying into the mode of logarithm; and then, carrying out linear fit for emission time to obtain a slope and an intercept so as to obtain three key parameters, i.e. initial concentration, diffusion coefficient and distribution coefficient in the building material emission process. The environmental chamber system and the measuring method are simple, have the advantages of short test time and higher precision and are convenient for engineering application.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
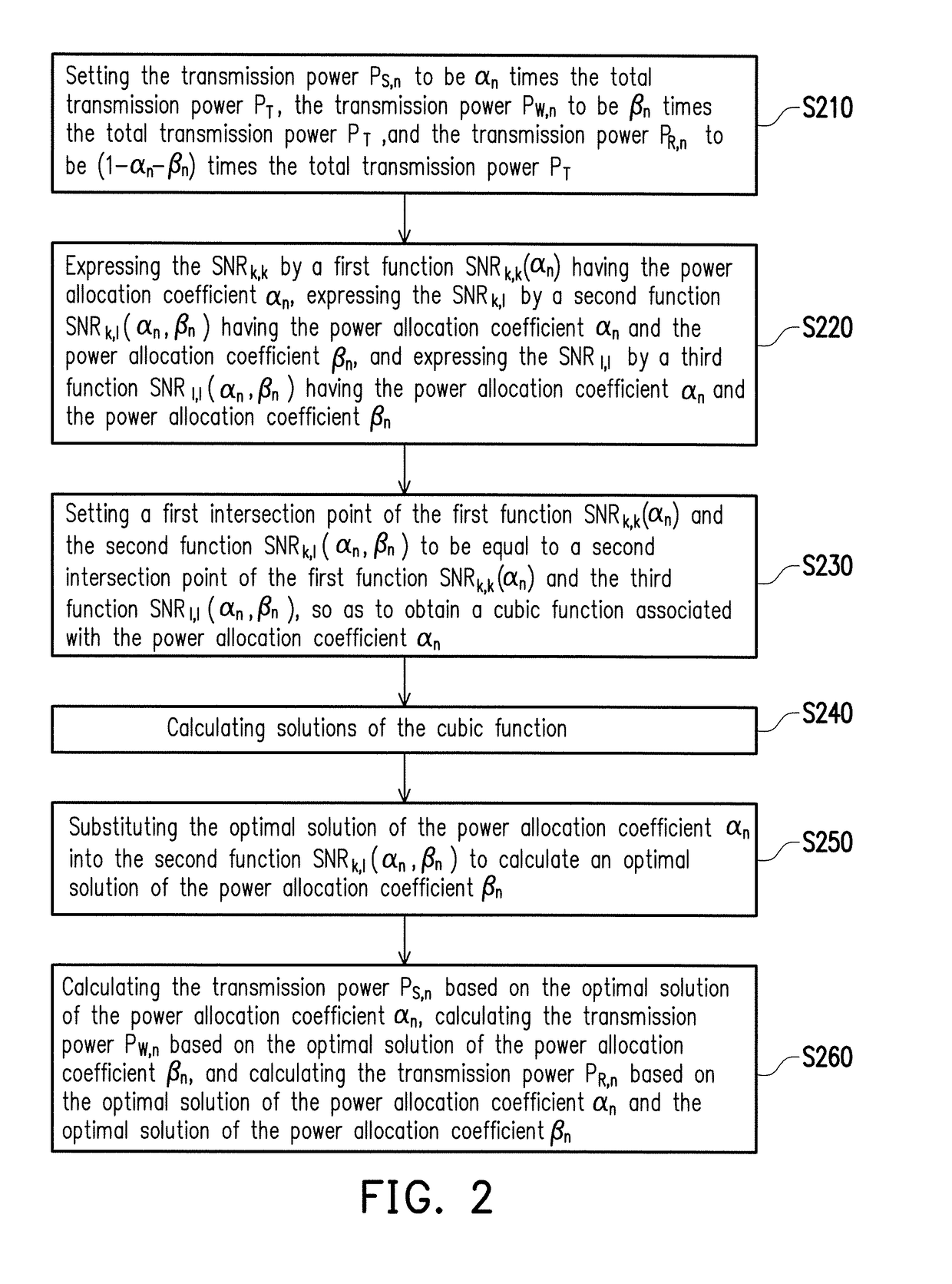
Joint user clustering and power allocation method and base station using the same
ActiveUS20180234867A1Method is fastReduce complexityPower managementCriteria allocationNon orthogonalUser equipment
This invention provides a joint user clustering and power allocation method and a base station using the same. They are applicable to cooperative non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) systems. The method includes: sorting K user equipment devices (UEs) according to the K channel gains between the base station and the K UEs, and then establishing a strong user candidate group of K / 2 UEs and a weak user candidate group of K / 2 UEs; pairing each of the UEs in the strong user candidate group with each of the UEs in the weak user candidate group so as to divide the K UEs into K / 2 clusters, where the power allocation coefficients for each pair of UEs are also calculated during the paring process; and transmitting messages to the K UEs based on the calculated power allocation coefficients of the K / 2 clusters.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
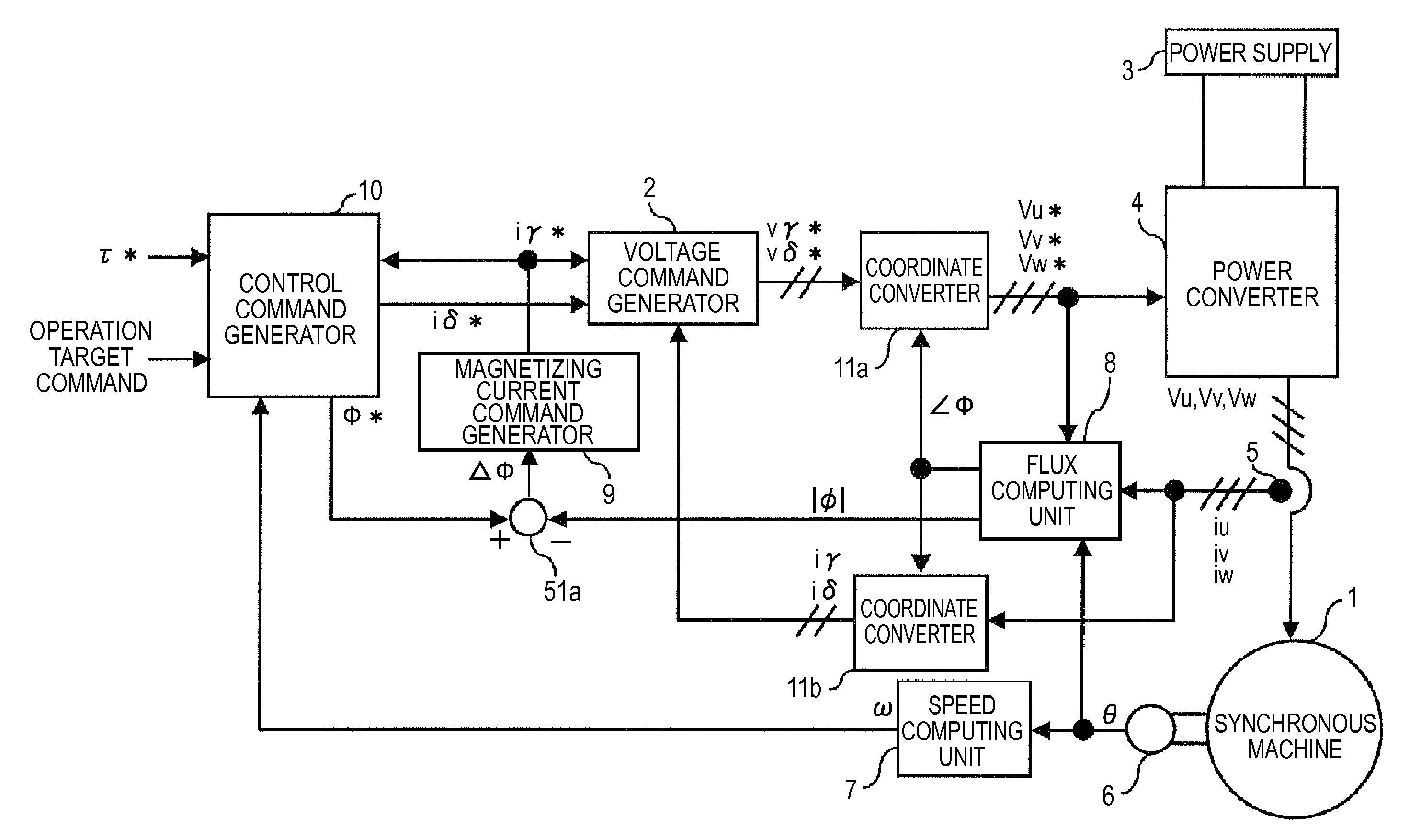
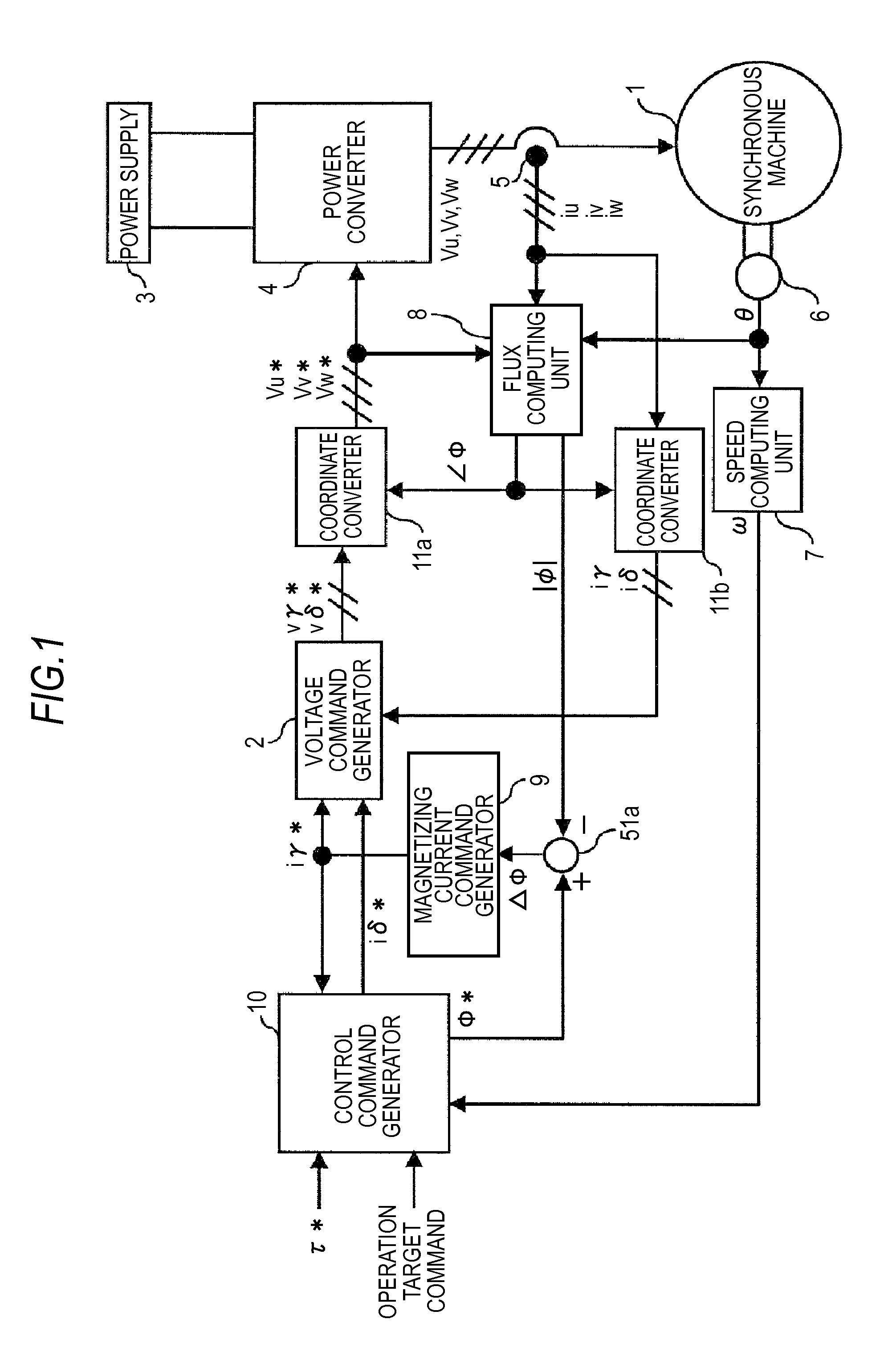
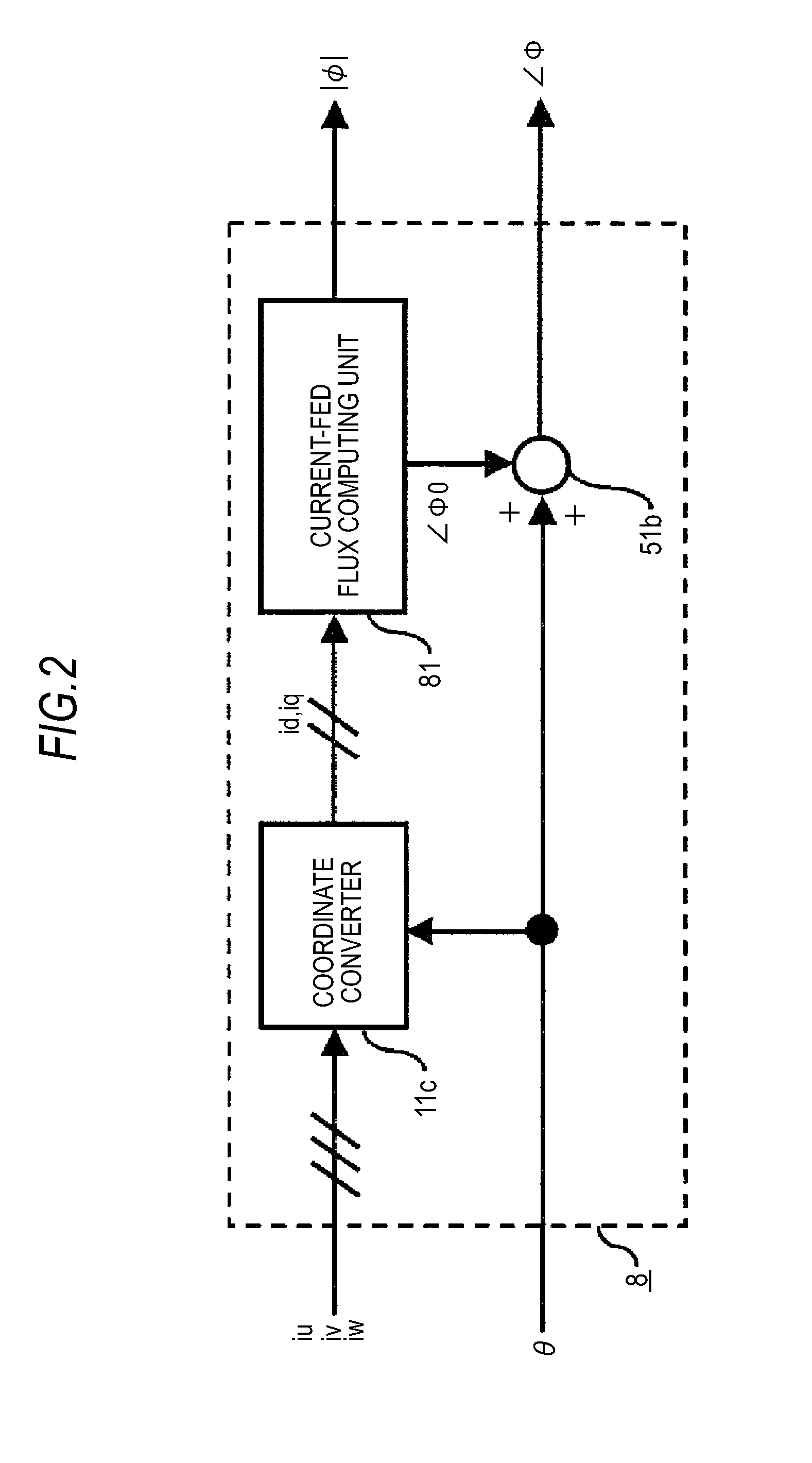
Synchronous machine control apparatus
InactiveUS20130088179A1Loss and heat generatedElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersMachine controlControl theory
A control command generator that generates an armature interlinkage flux command and a torque current command by a torque command, a rotation speed, and an operation target command, includes a first flux command generator generating a first flux command by the toque command or the torque current command, a second flux generator generating a second flux command by the torque command or the torque current command and the rotation speed of the synchronous machine, a command allocation setting unit setting an allocation coefficient equivalent to an allocation ratio of the two first and second flux commands by the operation target command, a flux command adjuster outputting an armature interlinkage flux command by the two flux commands and the allocation coefficient, and a torque current command generator generating the torque current command by the torque command and the armature interlinkage flux command.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
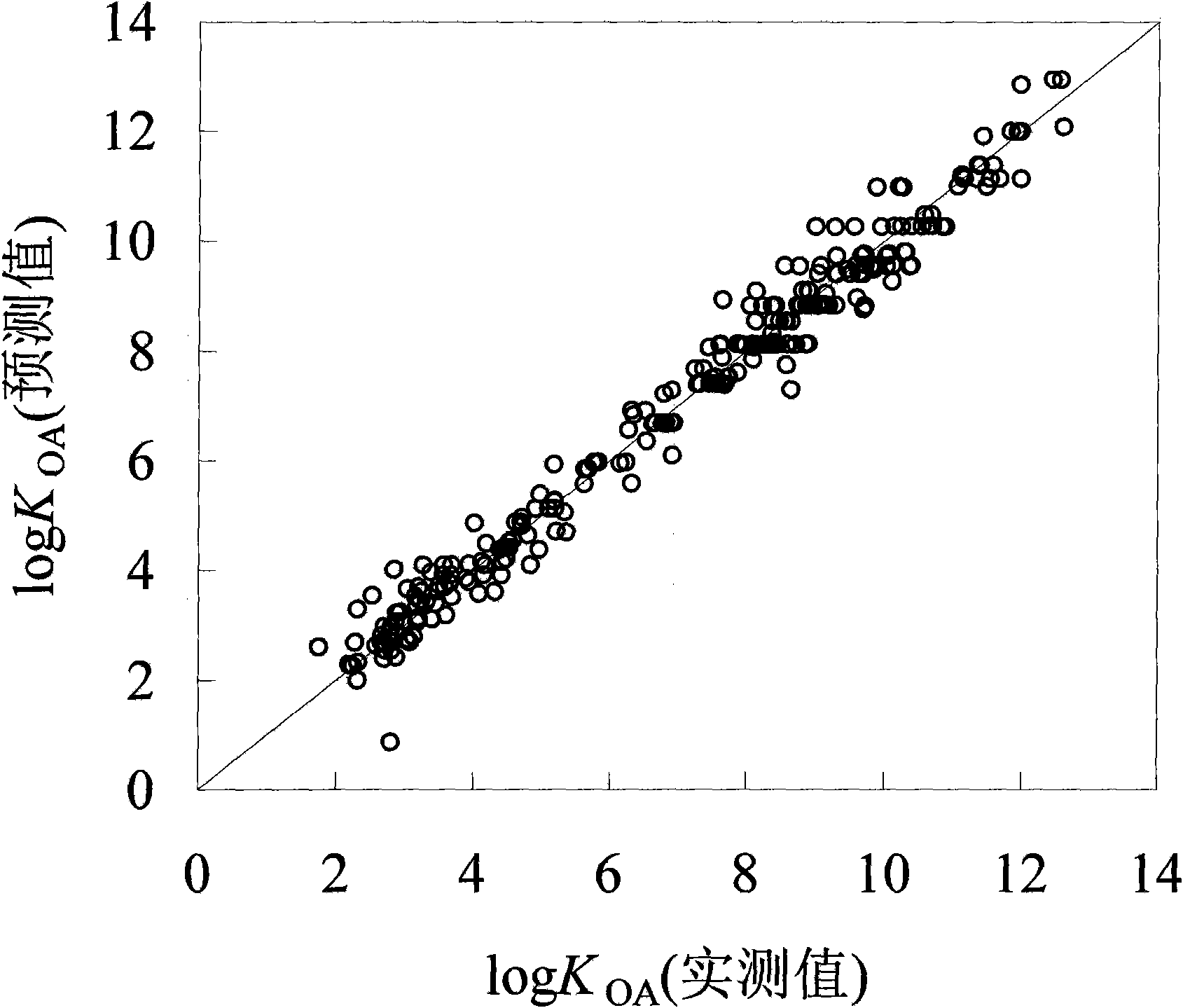
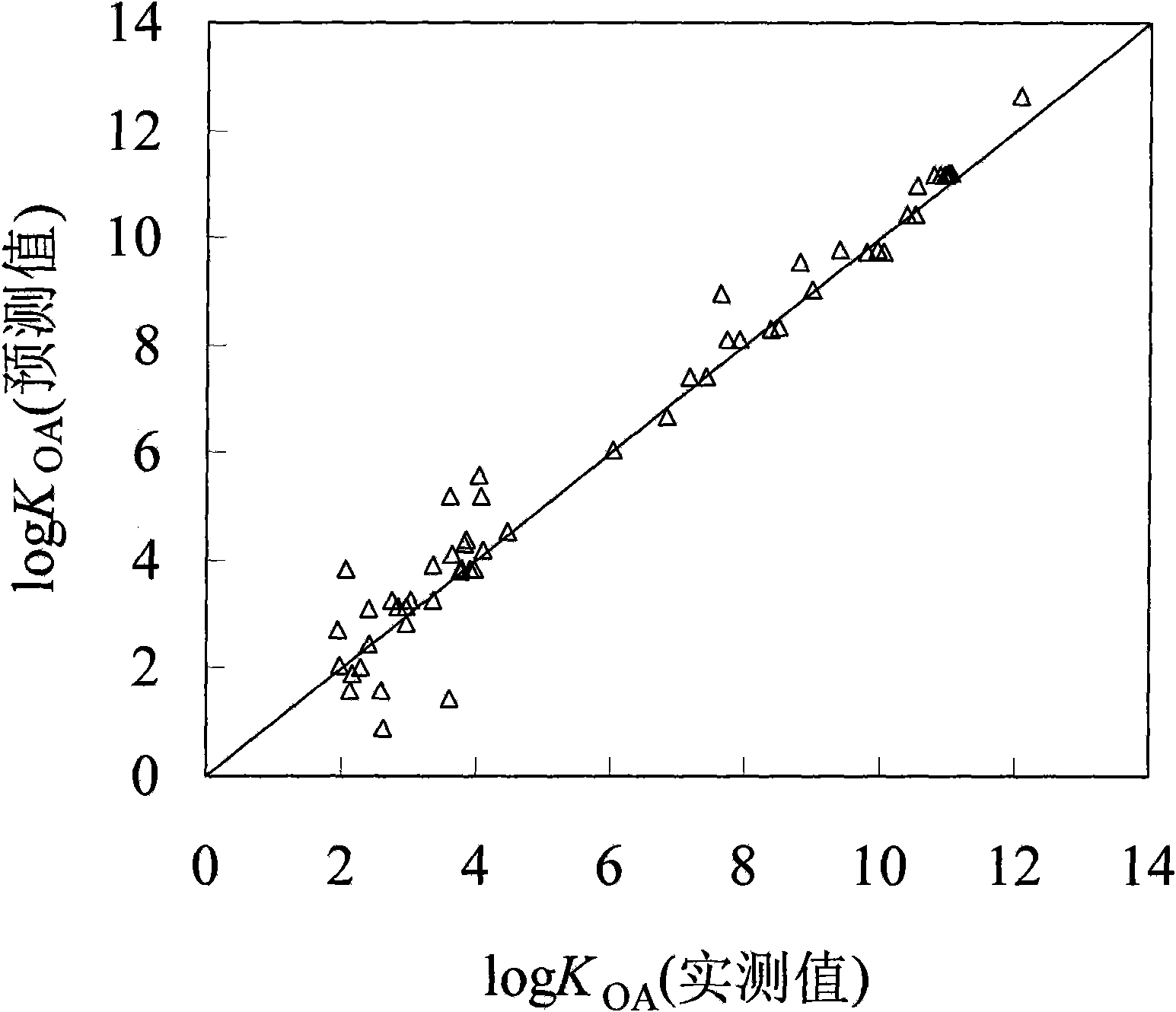
Method for fast predicting organic pollutant n-caprylic alcohol/air distribution coefficient based on molecular structure
InactiveCN101673321AEasy to divideQuick divisionSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive methodsExternal validation
The invention discloses a method for fast predicting organic pollutant n-caprylic alcohol / air distribution coefficient based on molecular structure, belonging to the technical field of quantifying structure / active relationship (QSAR) facing to the environmental risk evaluation. The method is characterized of comprising the steps of: adopting the molecular structure of atomic center fragment characterization compound; and screening the atomic center fragment combination by means of stepwise regression and partial least-squares regression, to build a group contribution model for predicting KOA.The internal authentication and the external authentication improves that the built KOA group contribution model has stability and predicting capability, and a range and distance method and a probability density method express the application domain of the group contribution model, thereby defining the application range of the model and guaranteeing the predict accuracy. The method has the effectsand benefits of being capable of fast predicting the KOA of the high flux compound, obtaining the KOA with low cost, being helpful for obtaining the high flux KOA data, and having a significant meaning for the environment supervision and the risk evaluation of chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
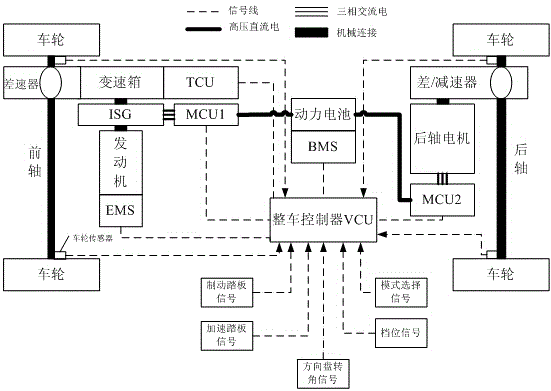
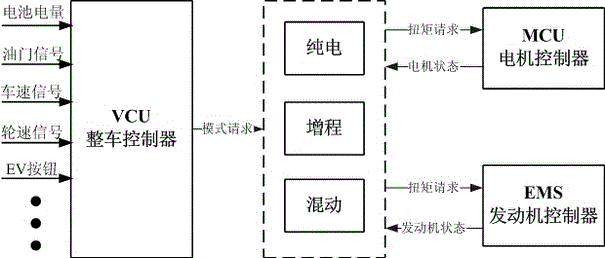
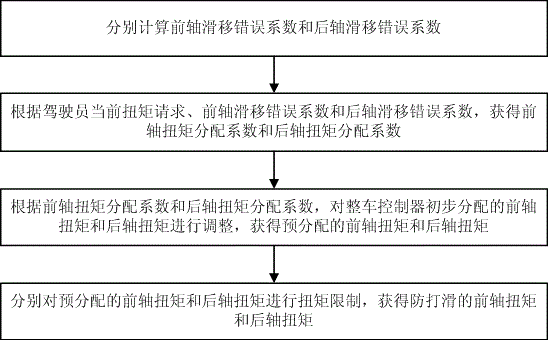
Method and device for anti-slip control over four-wheel drive hybrid power system
ActiveCN106740820AGood road adhesionImprove driving stabilityHybrid vehiclesFour-wheel drivePartition coefficient
The invention provides a method and device for anti-slip control over a four-wheel drive hybrid power system. The method for anti-slip control comprises the steps of respectively calculating a front axle slip error coefficient and a rear axle slip error coefficient; according to a current torque request of a driver, the front axle slip error coefficient and the rear axle slip error coefficient, obtaining a front axle torque distribution coefficient and a rear axle torque distribution coefficient; according to the front axle torque distribution coefficient and the rear axle torque distribution coefficient, adjusting front axle torque and rear axle torque which are preliminarily distributed by a vehicle control unit, and obtaining pre-distributed front axle torque and rear axle torque; respectively performing torque limitation on the pre-distributed front axle torque and rear axle torque, and obtaining anti-slip front axle torque and rear axle torque. The method and the device have the advantages that when a vehicle slips, the anti-slip front axle torque and the rear axle torque can be distributed intelligently, an optimal vehicle road adhesive force and an optimal off-the-hook capability are achieved, and driving stability and passing capability of the vehicle are effectively improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
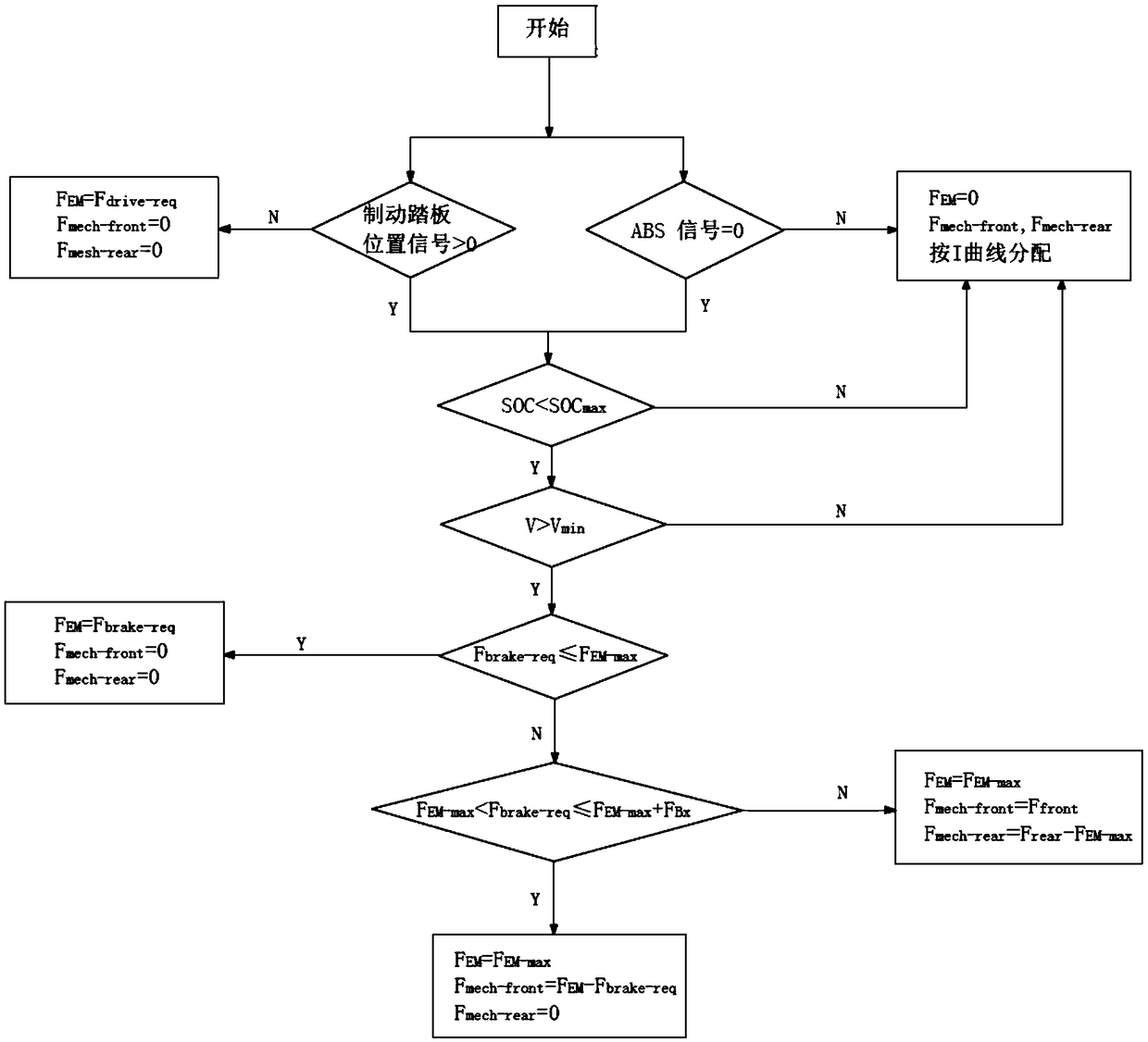
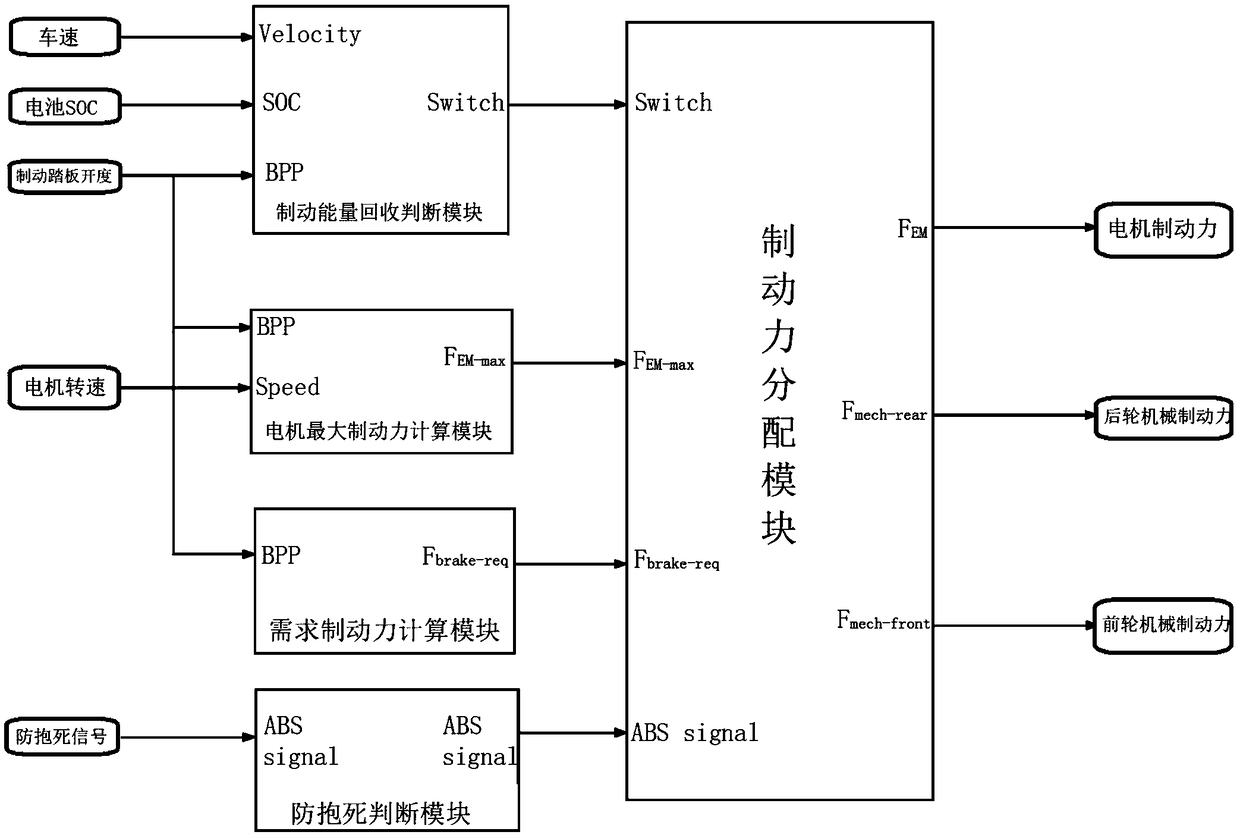
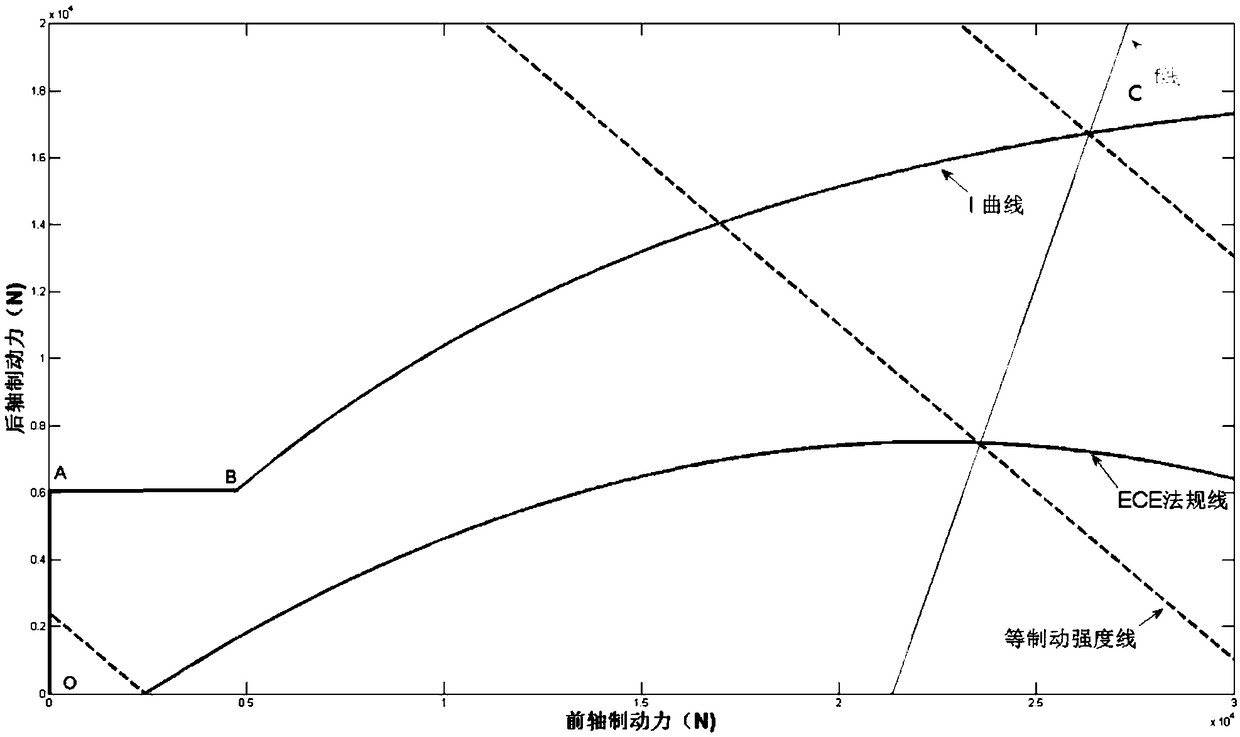
Braking energy recovery control method and device of rear wheel drive pure electric vehicle
ActiveCN109278566AImprove recycling efficiencyIncrease mileageElectrodynamic brake systemsControl devicesPower batteryRegenerative brake
The invention relates to the technical field of electric vehicles, specifically to a braking energy recovery control method and device of a rear wheel drive pure electric vehicle. The braking energy recovery control method of the rear wheel drive pure electric vehicle comprises the steps of a braking energy recovery mode judging step, a maximum regenerative braking force calculating step, a demandbraking force calculating step, a braking force distributing step and an anti-lock judging step; in the automobile braking process, distribution of a mechanical braking force and a regenerative braking force is controlled; on the basis of guaranteeing braking safety and braking efficiency, a regenerative braking force distribution coefficient is furthest increased; wasted energy in the braking process is sufficiently recovered by using the feeding capacity of a motor to charge a power battery; the braking energy recovery efficiency is enhanced; the braking energy loss is reduced; and the running range of the vehicle is optimized.
Owner:SHAANXI AUTOMOBILE GROUP
Method for dyeing textile by dye liquor prepared by mutually dissolving organic solvent and water
The invention relates to a method for dyeing textile by dye liquor prepared by mutually dissolving organic solvent and water and belongs to the technical field of textile printing and dyeing processing. The dye liquor applies organic solvent soluble in water and lower than water in boiling point, and dye is soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvent, so that effective liquor ratio is lowered, distribution coefficient of dye on fiber is changed, and dye uptake is of dye is increased. Adding the organic solvent allows boiling point of the dye liquor to reduce, energy is saved, water consumption in dyeing process is greatly reduced, the organic solvent can be recycled and reused, and discharge of waste liquor is reduced. The dyeing process includes performing twice-soaking and twice-rolling accelerant solution to textile, and solid accelerant is prevented from being precipitated out at a great amount by being added in dyeing process. The method is low in water consumption, utilization rate of dye is increased, energy consumption is low, the organic solvent can be recycled and reused, and cleaning and dyeing are achieved simultaneously.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
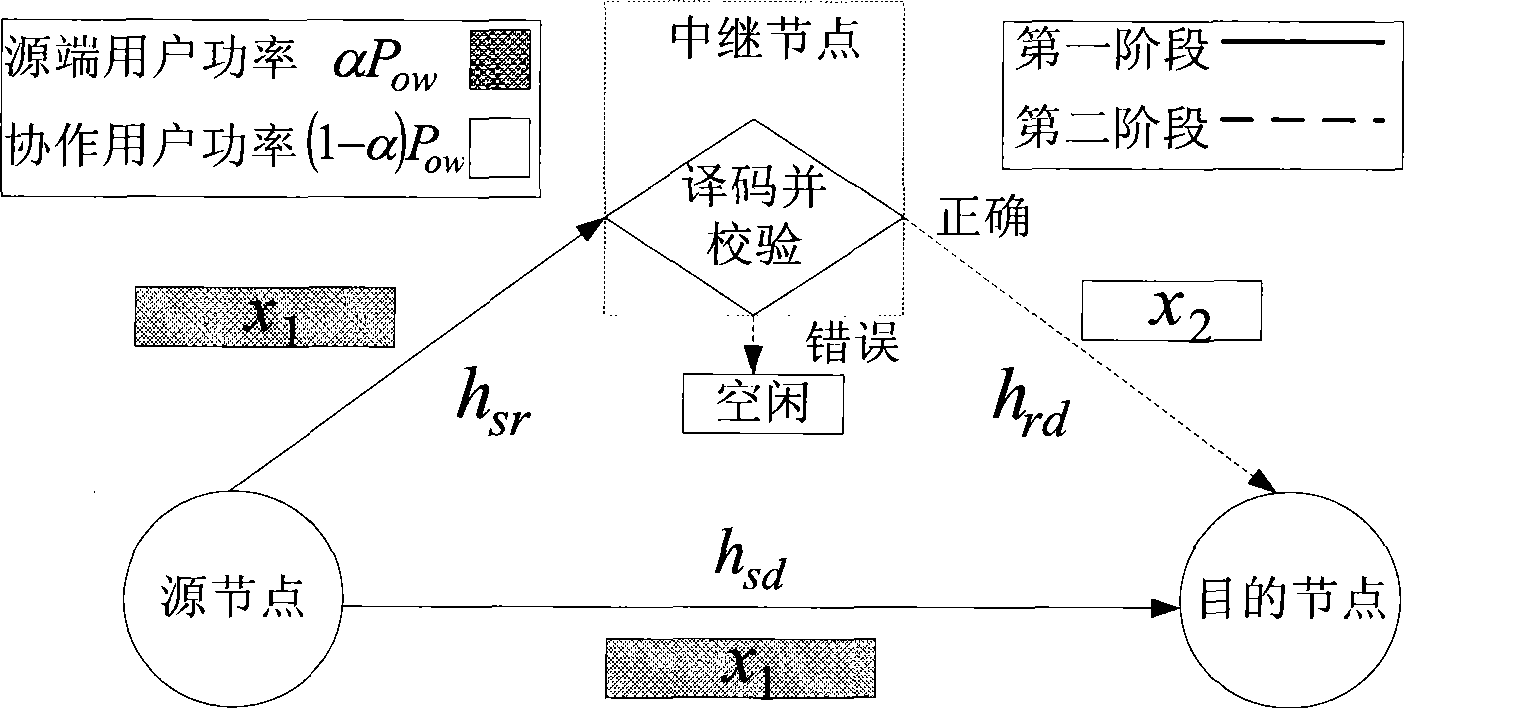
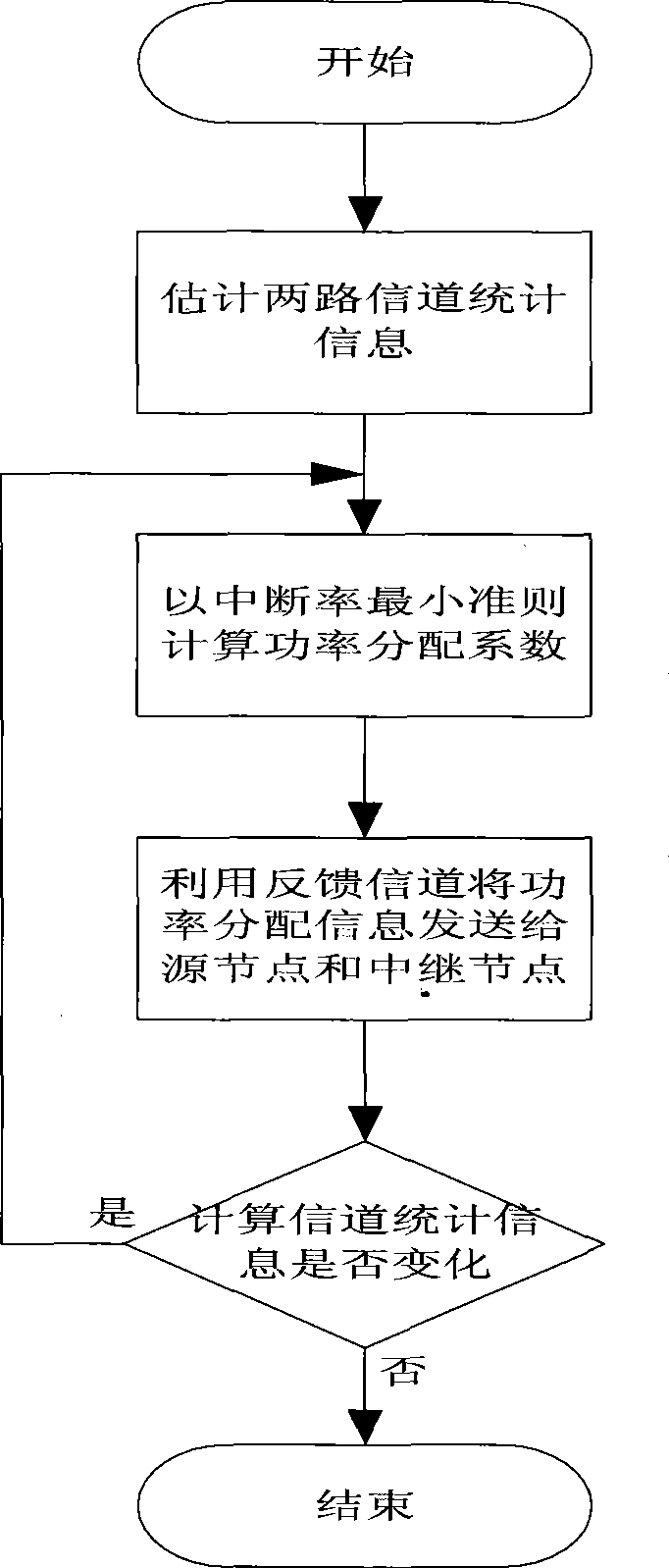
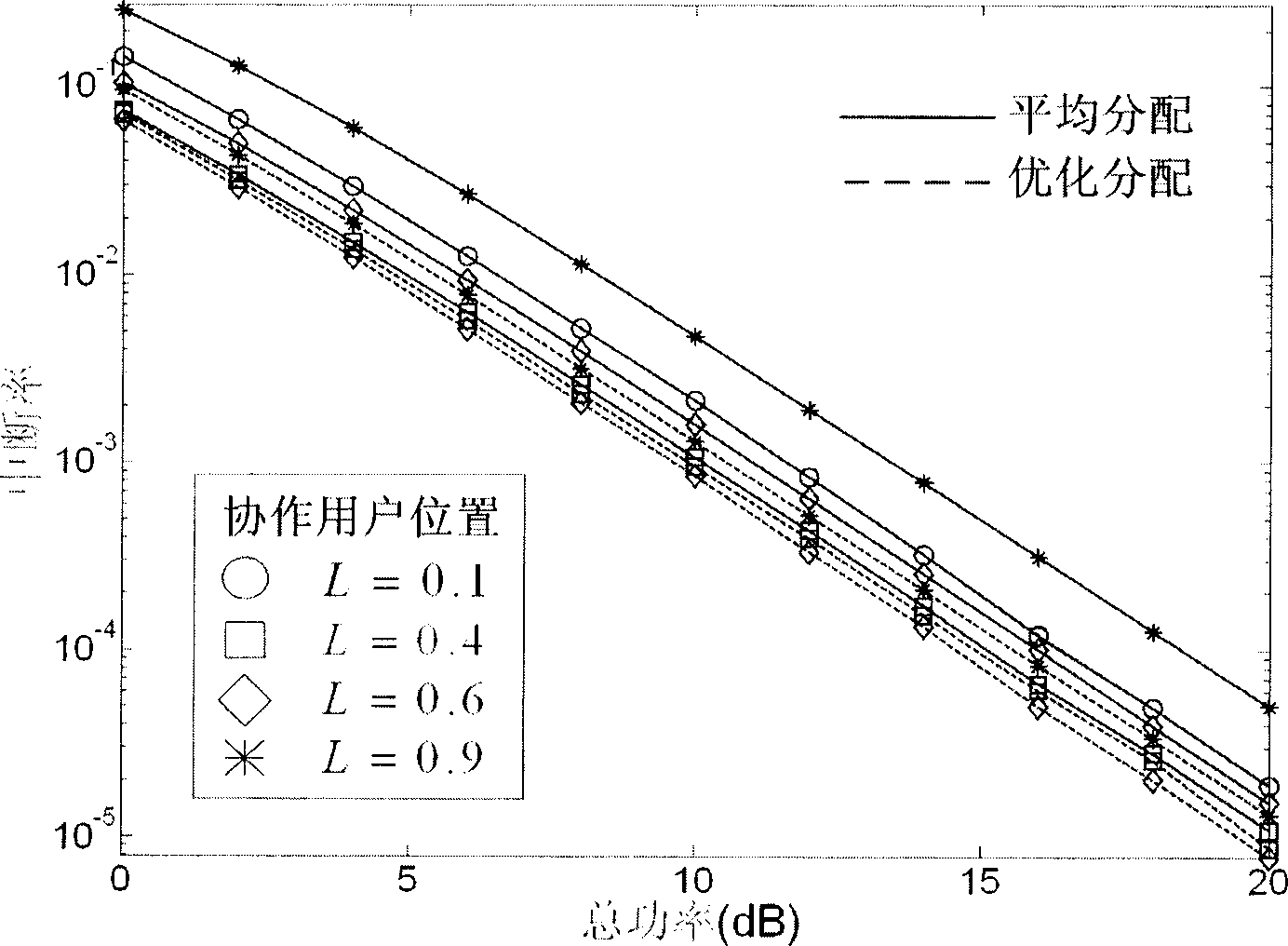
Optimized power allocation method reducing interruption rate in encoded collaboration communication
InactiveCN101394253AReduced probability of outageA simple expression for an upper bound on the outage rate and lowered by the outage rateBaseband system detailsTransmission control/equalisingPartition coefficientDistribution method
The invention discloses an optimal power allocation method for reducing the outage probability in the coding cooperation communication of the wireless communication field, and mainly solves the problem of higher outage probability in the system based on the prior average power allocation method. The optimal power method comprises the following steps: the channel statistical information of an original node to a relay node and a target node as well as the relay node to the target node are respectively estimated after the information from the original node and the relay node is received by the target node; subsequently, the lowest outage probability is taken as a target by the target node, an optimal power allocation coefficient is calculated based on an optimal power allocation formula according to the estimated channel statistical information, and the power allocation information is sent to the original node and the relay node by utilizing a feedback channel; the feedback information is received by the original node and the relay node which send the information at the allocated power respectively. The optimal power allocation method can remarkably reduce the outage probability of the coding cooperation communication, and ensure the lower complexity for the calculating method of the power allocation coefficient, therefore, the method can be used for reducing the outage probability of the coding cooperation communication system and ensuring the communication quality.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for producing butanol using extractive fermentation with electrolyte addition
ActiveUS20110159558A1Increase butanol partition coefficientLess corrosiveOxygen-containing compound preparationBacteriaFermentationButanol
A method for producing butanol through microbial fermentation, in which the butanol product is removed during the fermentation by extraction into a water-immiscible organic extractant in the presence of at least one electrolyte at a concentration at least sufficient to increase the butanol partition coefficient relative to that in the presence of the salt concentration of the basal fermentation medium, is provided. The electrolyte may comprise a salt which dissociates in the fermentation medium, or in the aqueous phase of a biphasic fermentation medium, to form free ions. Also provided is a method and composition for recovering butanol from a fermentation medium.
Owner:GEVO INC
Method for dynamically setting tandem rolling schedule of hot rolling strip
InactiveCN101733289ASave iterative stepsSimple algorithmRoll mill control devicesSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringLoad distribution
The invention relates to a method for dynamically setting tandem rolling schedule of hot rolled plate, belonging to the control technical filed in the process of steel plate rolling. In the invention, the method combing a depressing distribution coefficient with a load distribution coefficient is utilized to set rolling schedule, comprising the following steps: utilizing the depressing distribution coefficient as the optimizing initial point, calculating corresponding load at the moment, comparing with a target load distribution coefficient, and regulating depressing amount of each channel according to difference values; therefore, the purpose that set load distribution is approximate to the target load distribution after multiple times of comparison and regulation. In the invention, standard depressing distribution coefficient is used as an initial calculation point, thus saving iteration steps as the distance from the initial point to the optimized value is not too far; and load is calculated by depressing amount which is regulated through the difference between the set load distribution obtained by calculation and the target load distribution, namely the positive calculation of depressing amount to load, the algorithm is relatively simple, and the calculation time is greatly saved, thereby ensuring that the method can meet the requirement of dynamic application of production field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
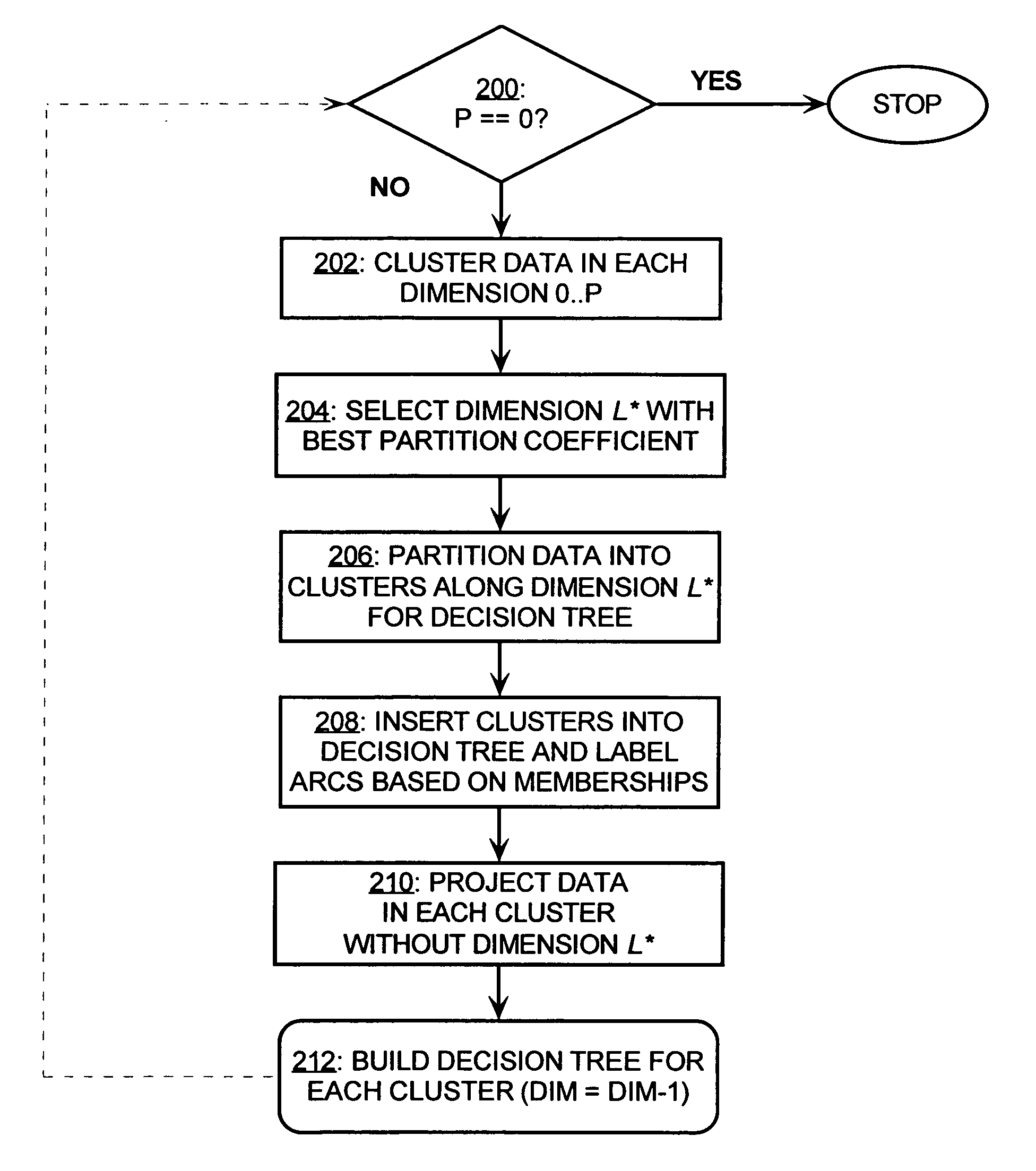
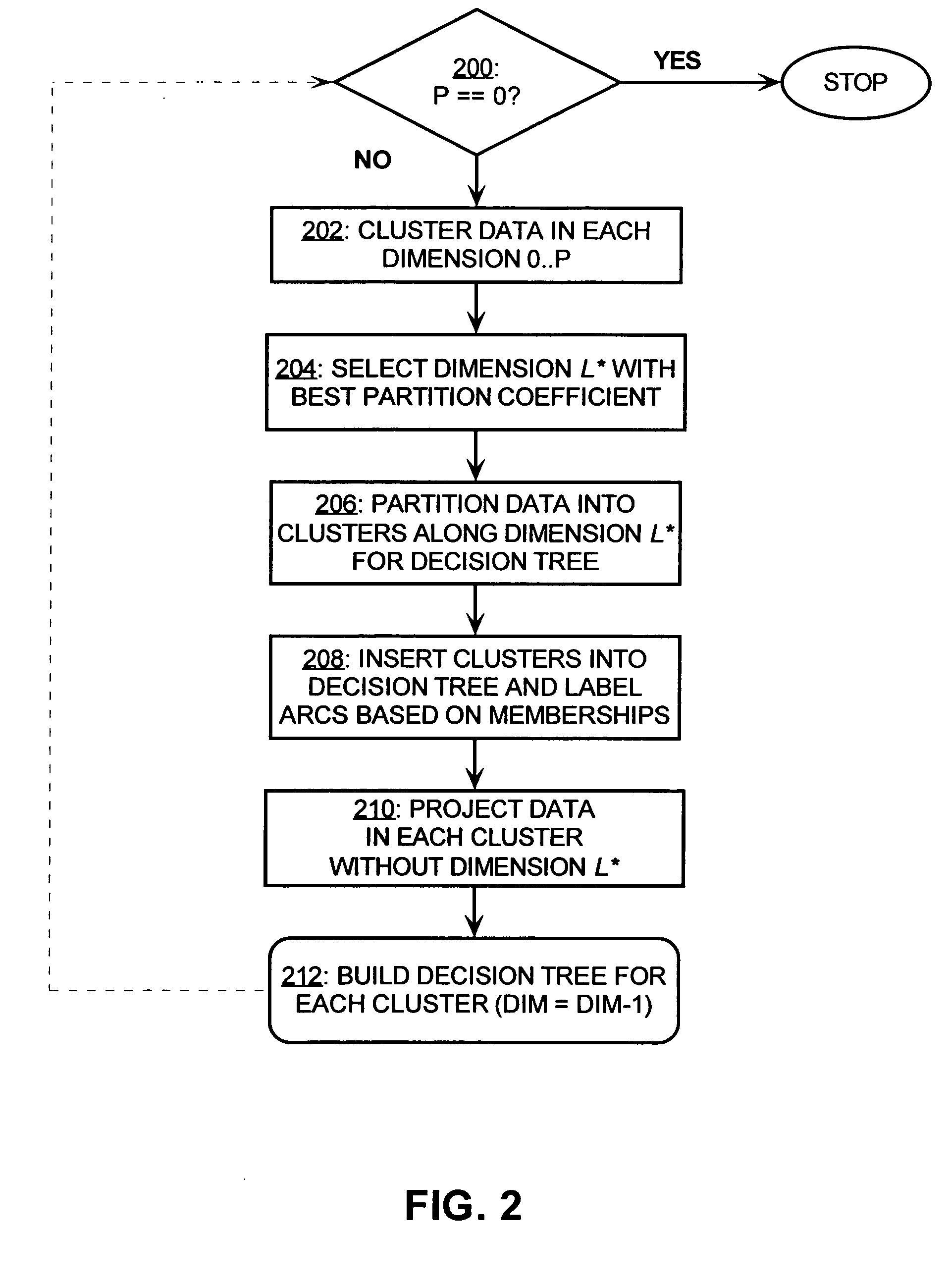
System and method for generating decision trees
InactiveUS7197504B1Medical data miningData processing applicationsDecision treePartition coefficient
A decision tree clustering procedure is provided which employs a unified approach to extracting both the decision tree and (preferably fuzzy) clusters. The decision tree is built by subsequent clustering of single dimensions or features, and the choice of the winning separation is based on cluster validity. In one embodiment, the clustering employs a fuzzy c-means (FCM) model and the partition coefficient (PC) to determine the selected separations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for leveling strip produced by secondary cold rolling unit
ActiveCN101513647AEasy to shapeQuality improvementTension/compression control deviceProfile control deviceHorizontal distributionWork roll
The invention provides a method for leveling a strip produced by a secondary cold rolling unit, which controls the surface roughness of the strip by reasonably setting the partition coefficients of the roughness and elongation of the working rolls of first and second machine frames and controls the shapes of finished strips other possible surface defects by reasonably setting a bending-roller force, a roll shifting rate and the tension of the front, middle and rear sections of the machine frames to achieve uniform front tension of finished strips and uniform horizontal distribution of a rolling force, thereby establishing effectively improved technology for leveling high-brightness micro plates produced by a secondary cold rolling unit. The principle of the method is clear, a secondary cold rolling process is carried out smoothly according to obtained rolling process set values, the quality of the shape and surface of leveled strips is high, the calculation is quick, and the method issuitable for online use.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
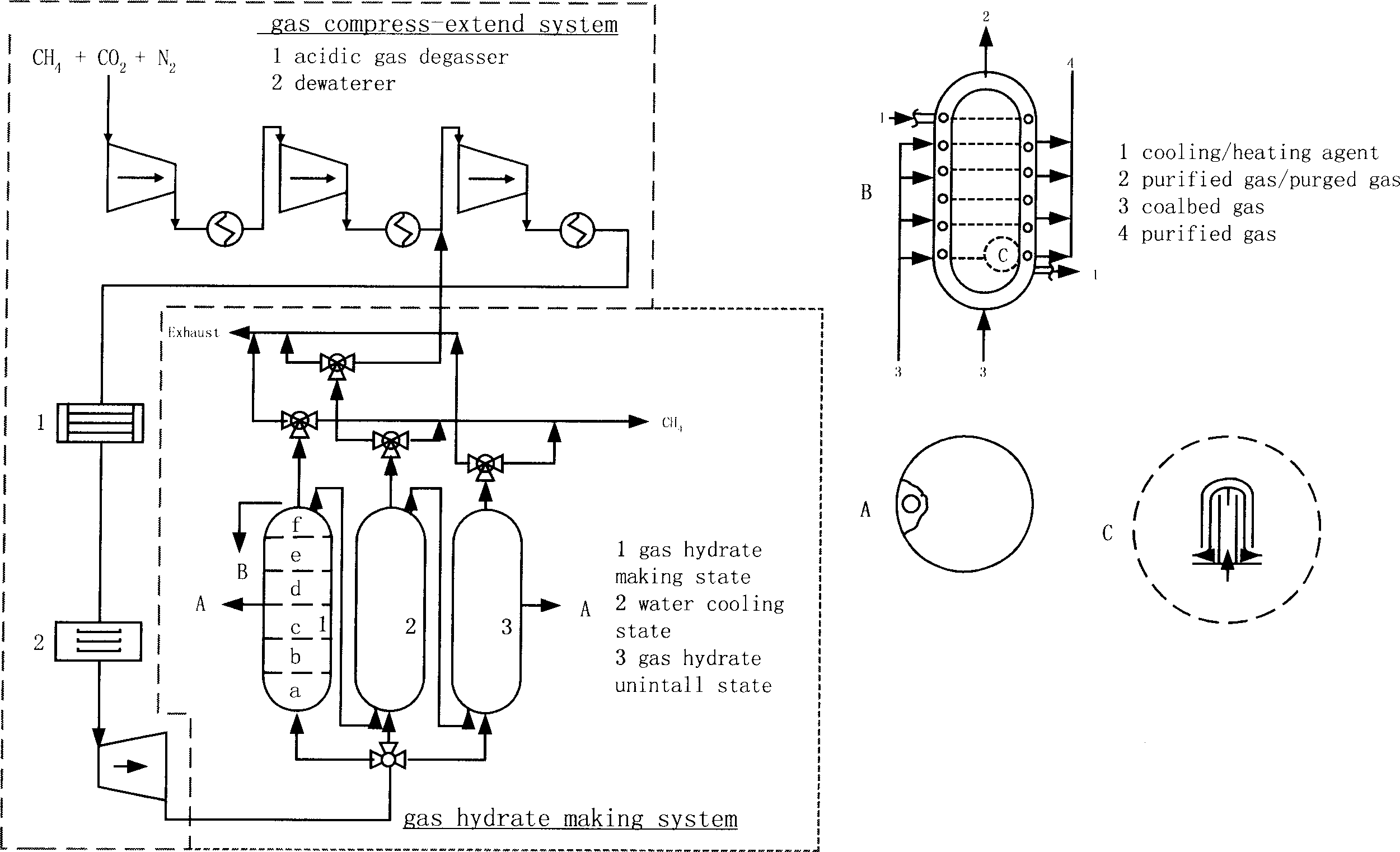
Method and equipment for enriching and storing and transporting coalbed gas by using hydrate
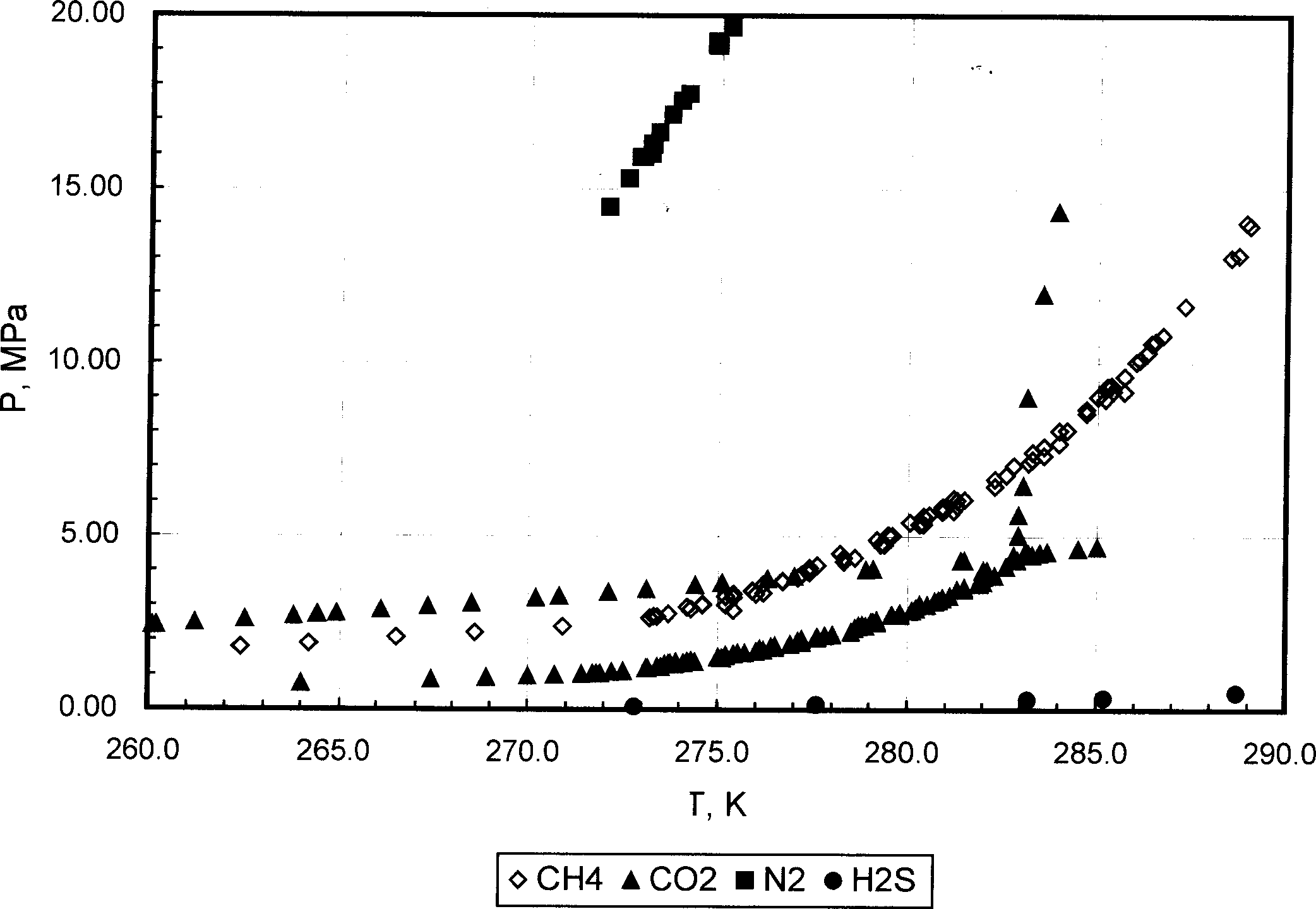
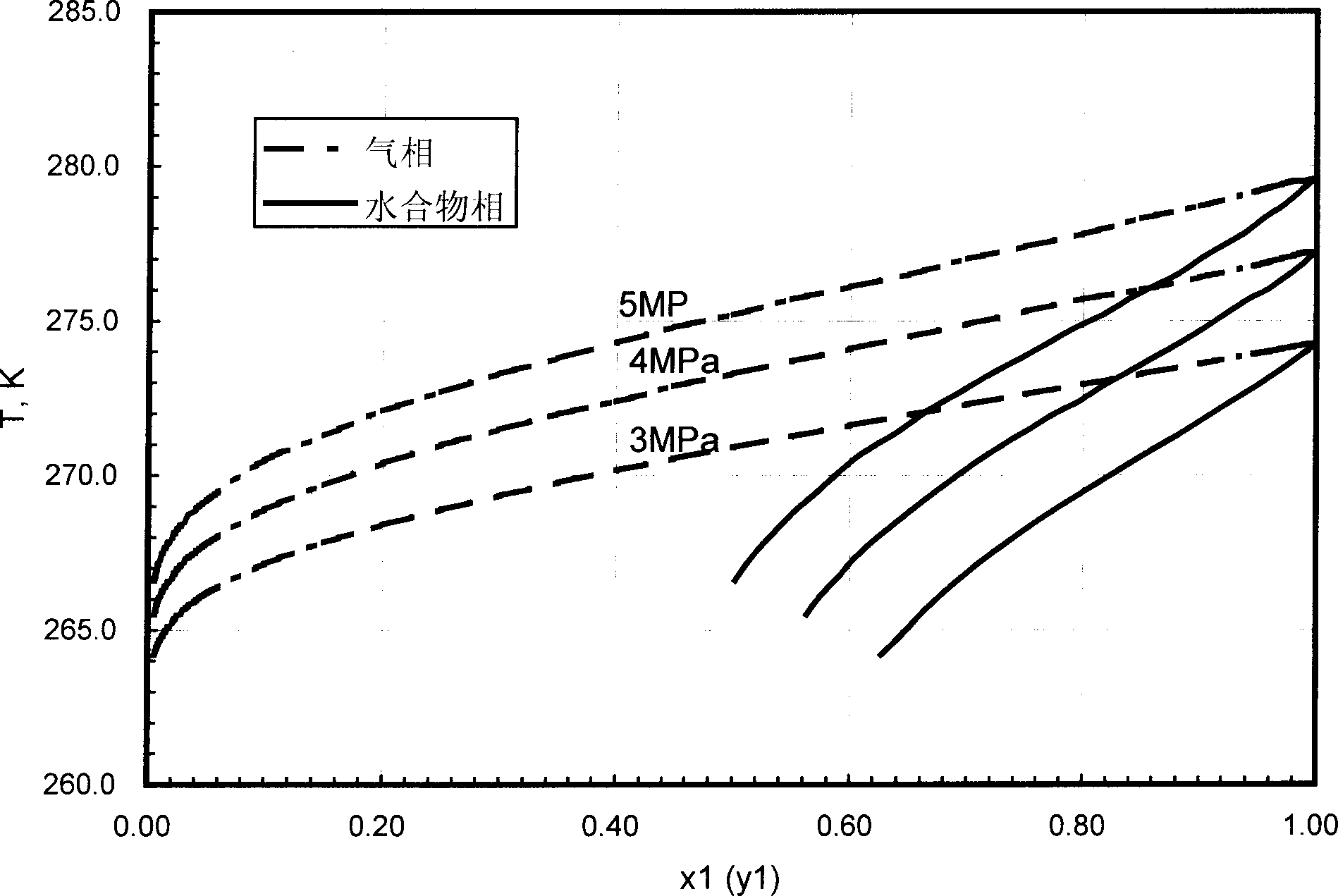
The present invention provides a method capable of utilizing hydrate to make concentration, storage of utilizing hydrate to make concentration, storage and transportation of coal-bed gas and its equipment. Said method is characterized by that it utilizes the difference of distribution coefficient of methane (CH4) and other component in the coal-bed gas in gas phase and hydrate phase, and utilizes the control of generation condition of hydrate to make the methane (CH4) in coal-bed gas be concentrated in hydrate phase, then the generated pasty or solid hydrate can be directly used for storage and transportation of coal-bed gas, also can be decomposed, then it adopts the form of compressed gas to make storage and transportion.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Parallel processing for decoding and cyclic redundancy checking for the reception of mobile radio signals
InactiveUS20050229075A1Reduce complexityShorten the timeError preventionCode conversionMobile radioLinearity
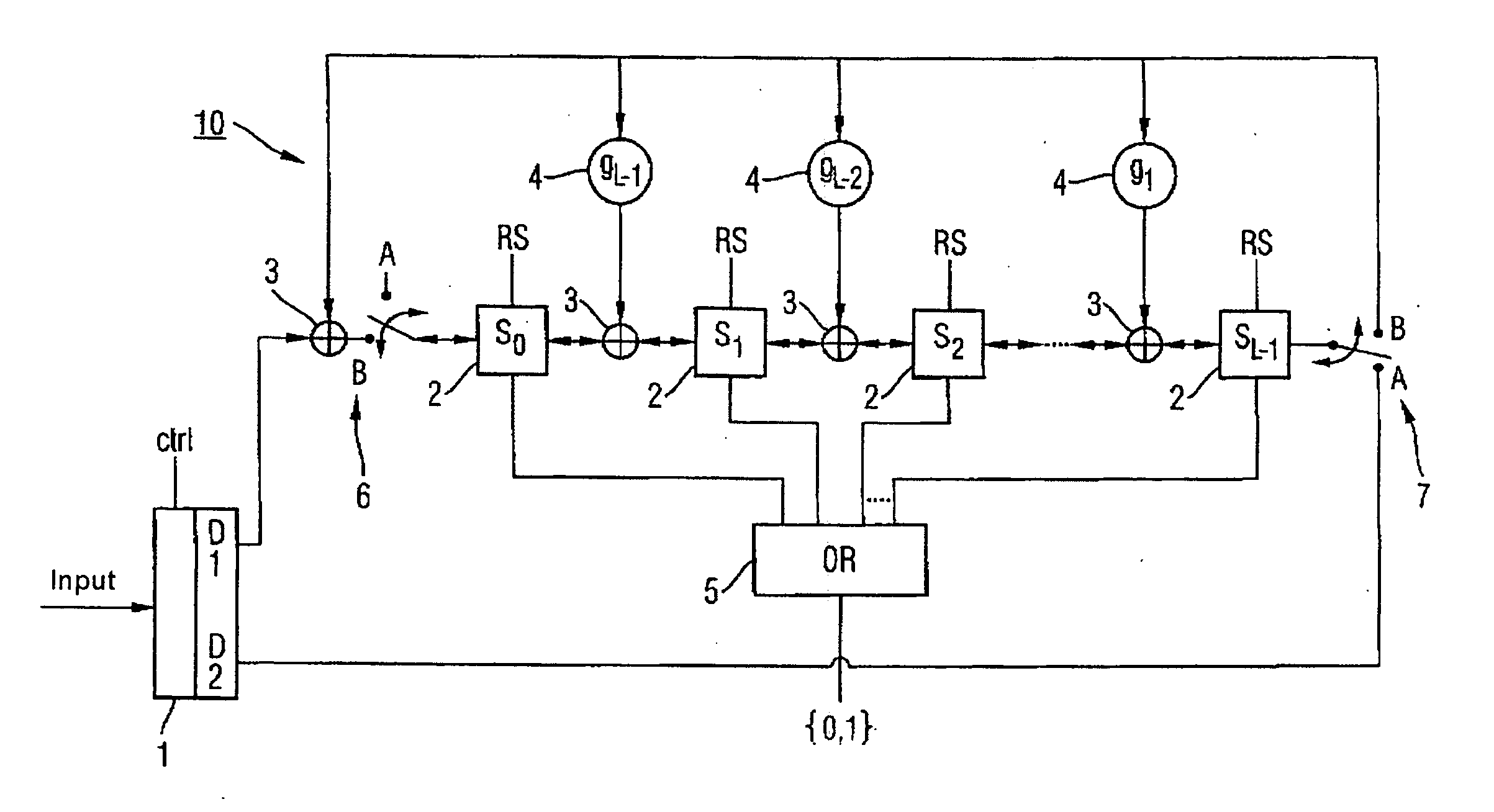
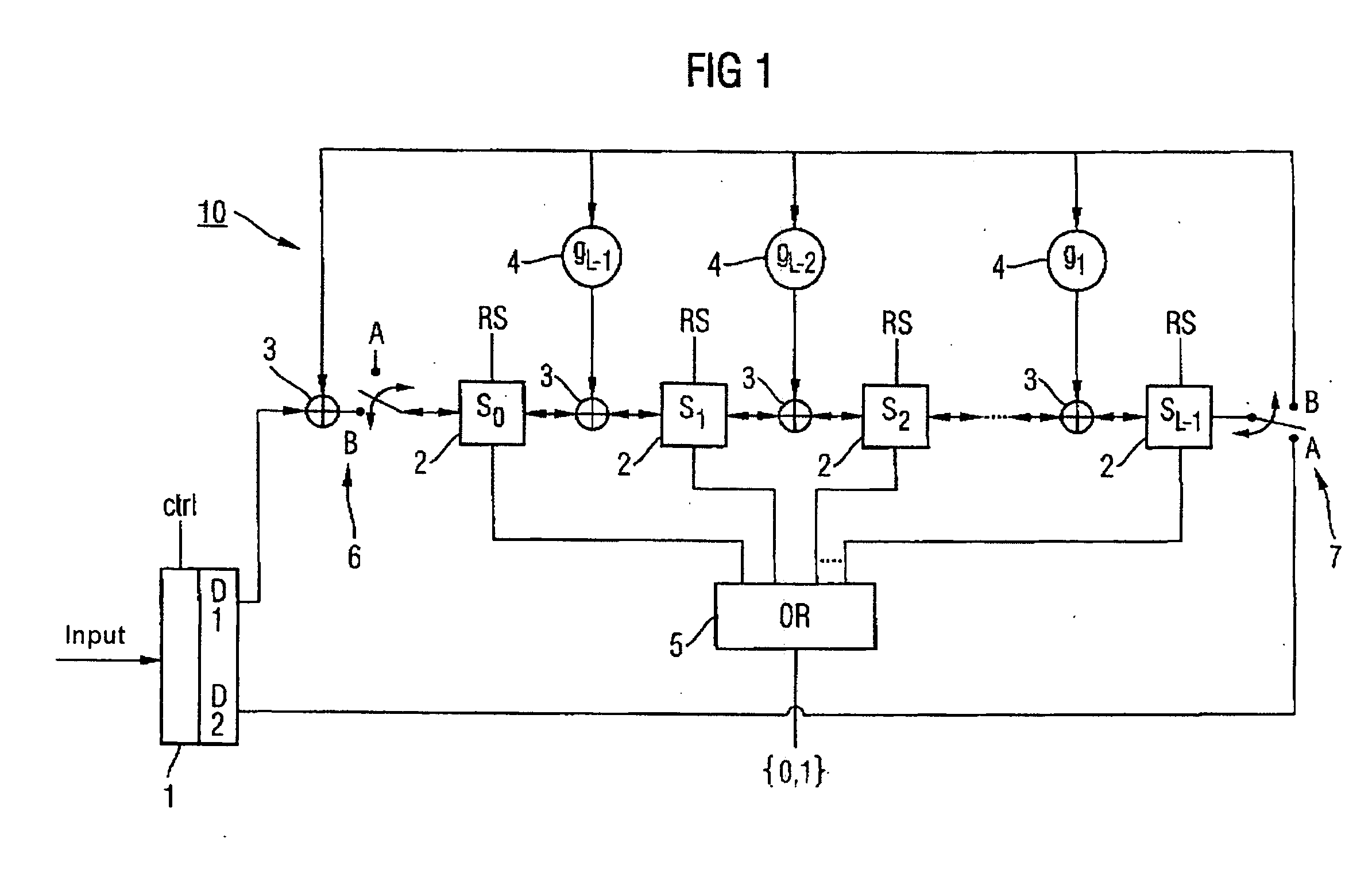
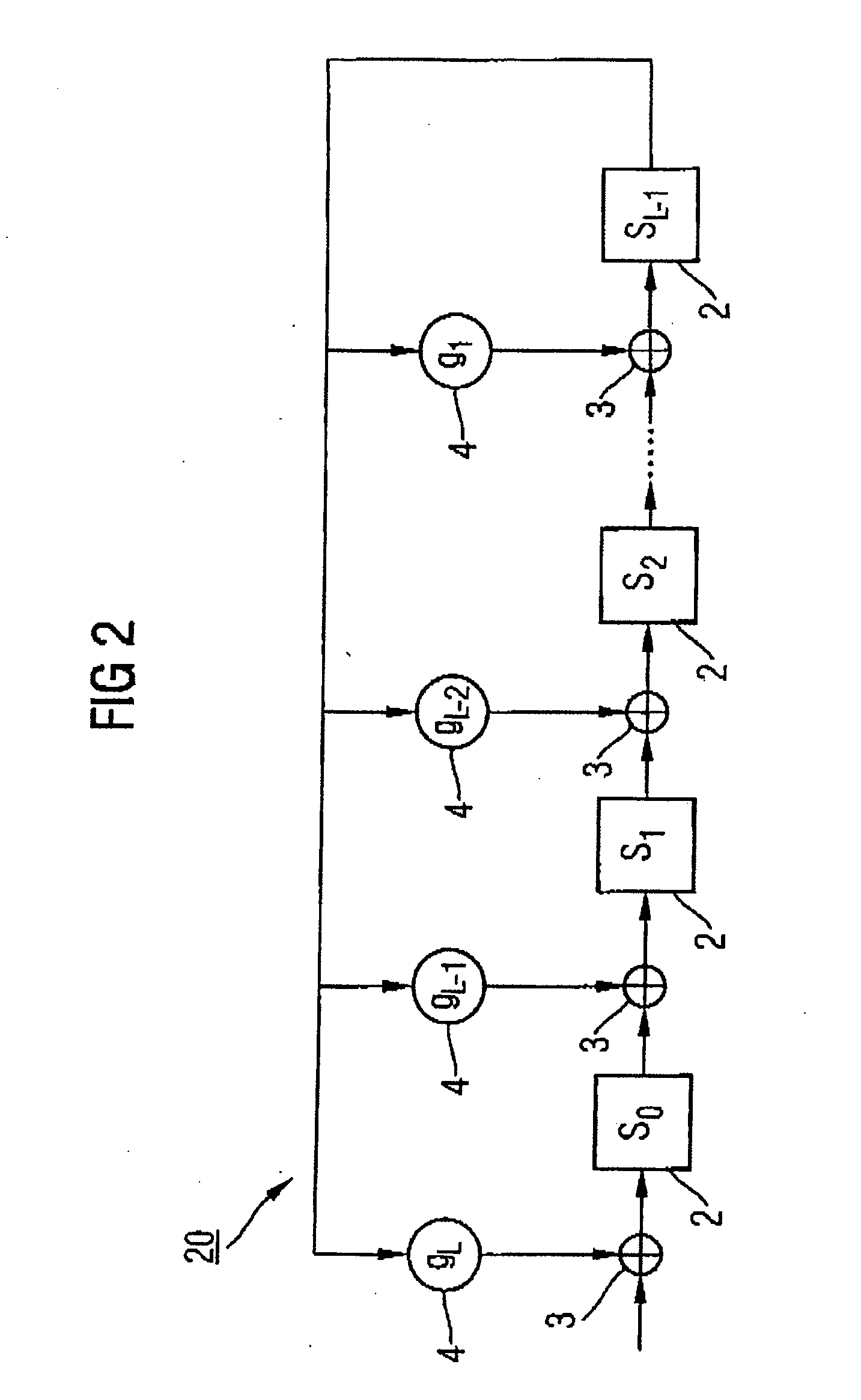
Depending on the sequence of the decoded payload signal bits (am1, . . . , amA) and redundancy checking bits (pm1, . . . , pmL) which are produced by the Viterbi traceback, either some of these bits are inserted by means of a distribution device (1) from the front into a linear feedback shift register (10), or some of these bits are inserted by means of the distribution device (1) from the rear into a linear feedback shift register (10), or all of them are inserted into a linear feedback shift register (20) from the rear with the allocated coefficients being unchanged, or all of them are inserted into a shift register from the front with the allocated coefficients being inverted. This allows a redundancy checking process to be carried out on a transmitted data block in the shift register (10; 20) without temporary storage of the bits produced by the decoding process.
Owner:INTEL CORP
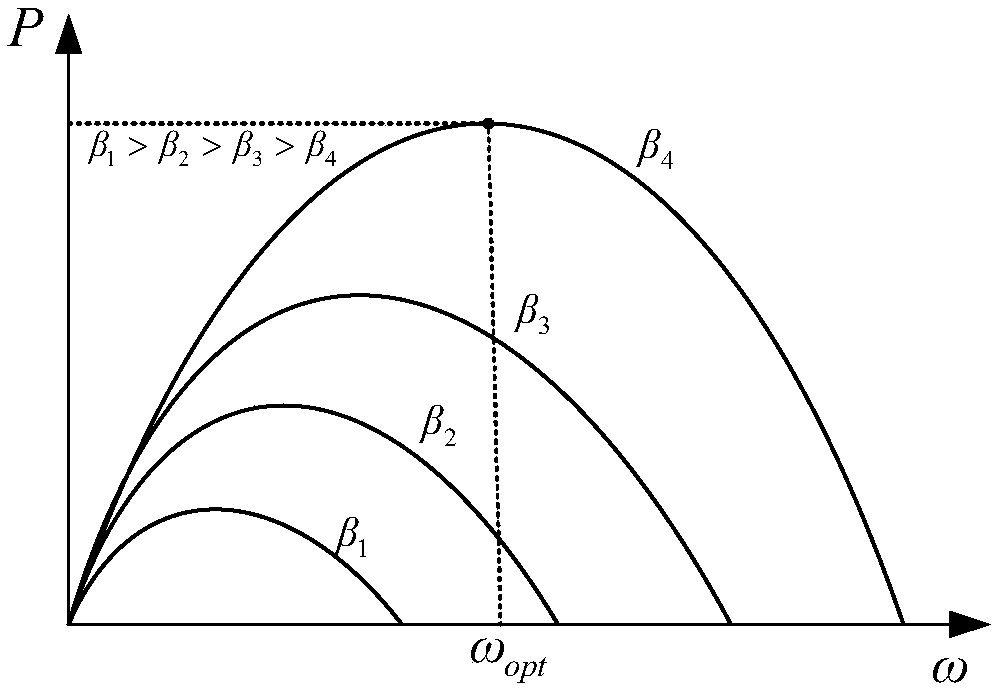
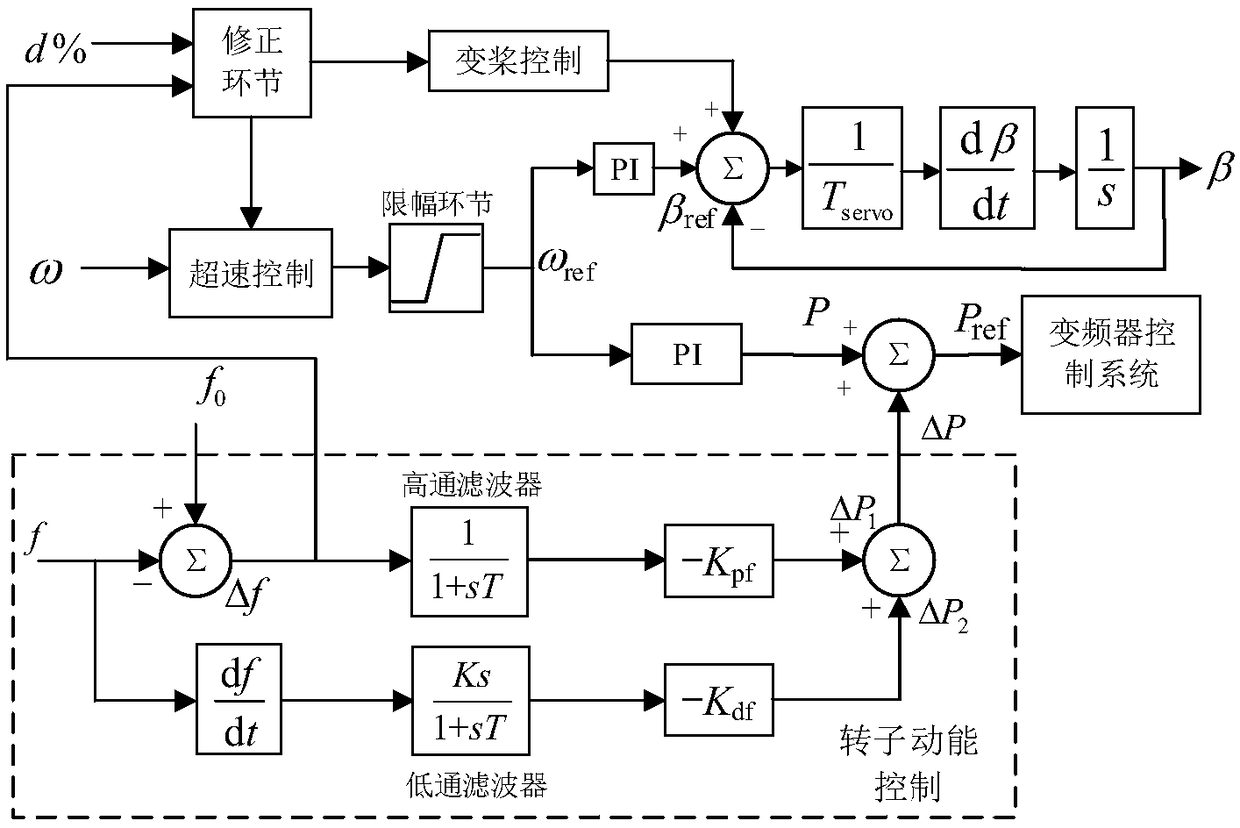
Wind field participation frequency modulation method and system
ActiveCN109494769AFull use of FM capabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectricityPeaking power plant
The embodiment of the invention provides a wind field participation frequency modulation method and system. The method comprises the steps: performing the control of kinetic energy of a wind power generator set rotor and the power standby frequency modulation control; building a comprehensive frequency modulation control strategy of each wind motor under different wind speeds; building a quantified calculation relation among wind speed, wind power field deloading total power and each wind motor deloading power based on a variable parameter deloading power coordinative distribution coefficientof the wind speed; and obtaining the output of each wind power generator set after deloading distribution. According to the embodiment of the invention, the method gives full consideration to the impact on the frequency modulation capability of the whole wind power plant from the internal deloading power distribution of the wind field, achieves the coordinative distribution of the output of each wind motor, is suitable for the wind speed distribution difference between the wind power generator sets in a cluster wind power plant, and gives full play to the frequency modulation capability of thewind power plant.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Sample pretreatment method for detection of organochlorine pesticide residue in food
The invention discloses a sample pretreatment method for detection of organochlorine pesticide residue in food and is characterized by comprising the following steps: water is added to a food sample, sample solution is swirled, and then inorganic salt and hydrophilic organic solvent are added to the sample solution, the sample solution is swirled and shaken uniformly, the sample solution undergoes phase splitting after centrifugation at room temperature, the upper-phase liquid is purified through dispersion solid-phase extraction method, the extraction temperature is 20-30 DEG C, and finally the upper-phase liquid is detected by gas chromatography; and the mass percent of the inorganic salt accounts for 5%-35% of the total mass of the system, the mass percent of the hydrophilic organic solvent accounts for 10%-50% of the total mass of the system, and water is of the residual amount, and the total mass of the system is the mass sum of water contained in the sample, the added water, the inorganic salt and the hydrophilic organic solvent. According to the sample pretreatment method, a dual-water-phase system consisting of the hydrophilic organic solvent, the organic salt and water is utilized, the partition coefficient is increased by means of changing the types and concentrations of the organic solvent and the inorganic salt, and the organochlorine pesticide residue in the sample can be directly extracted at room temperature.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
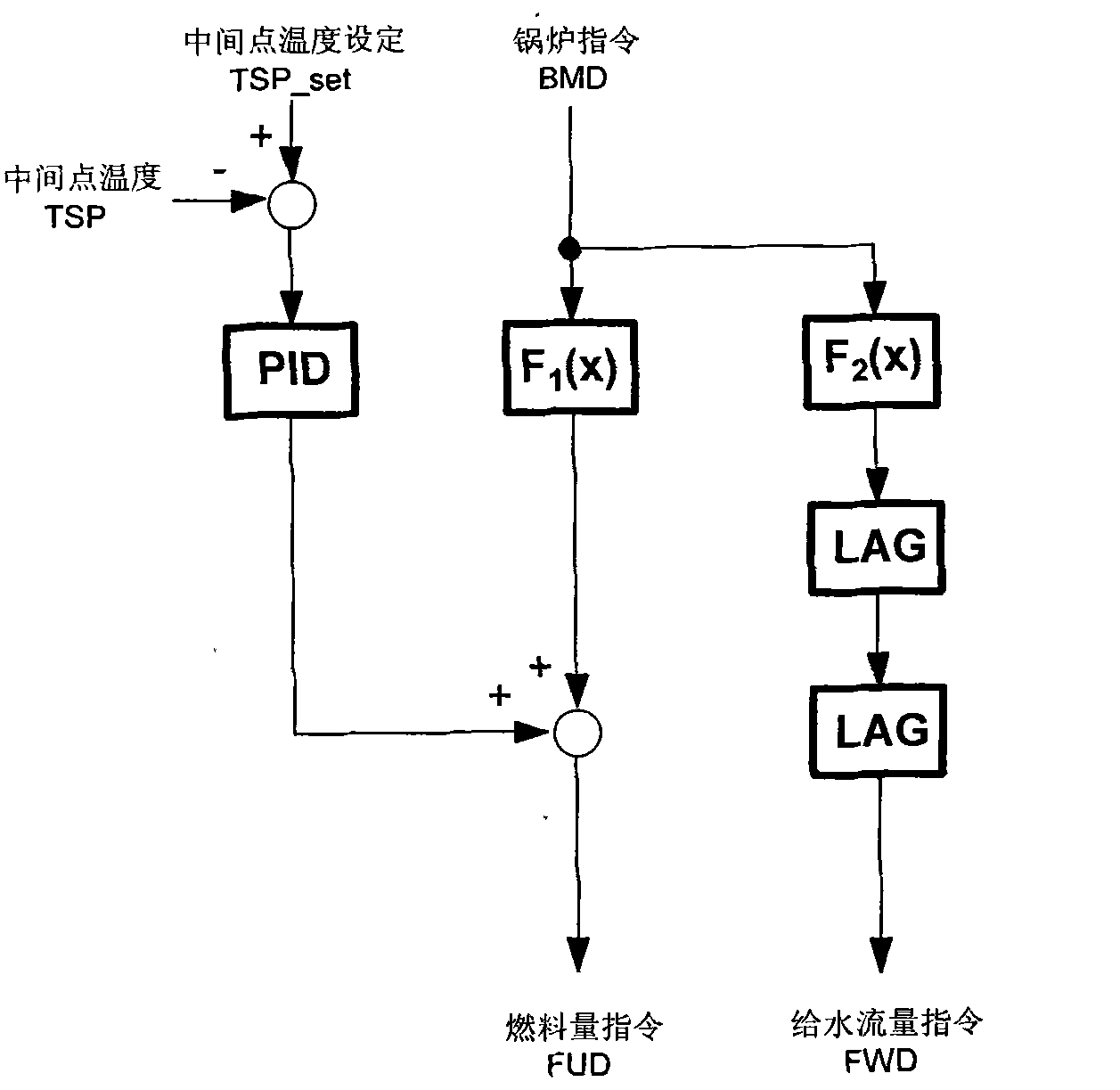
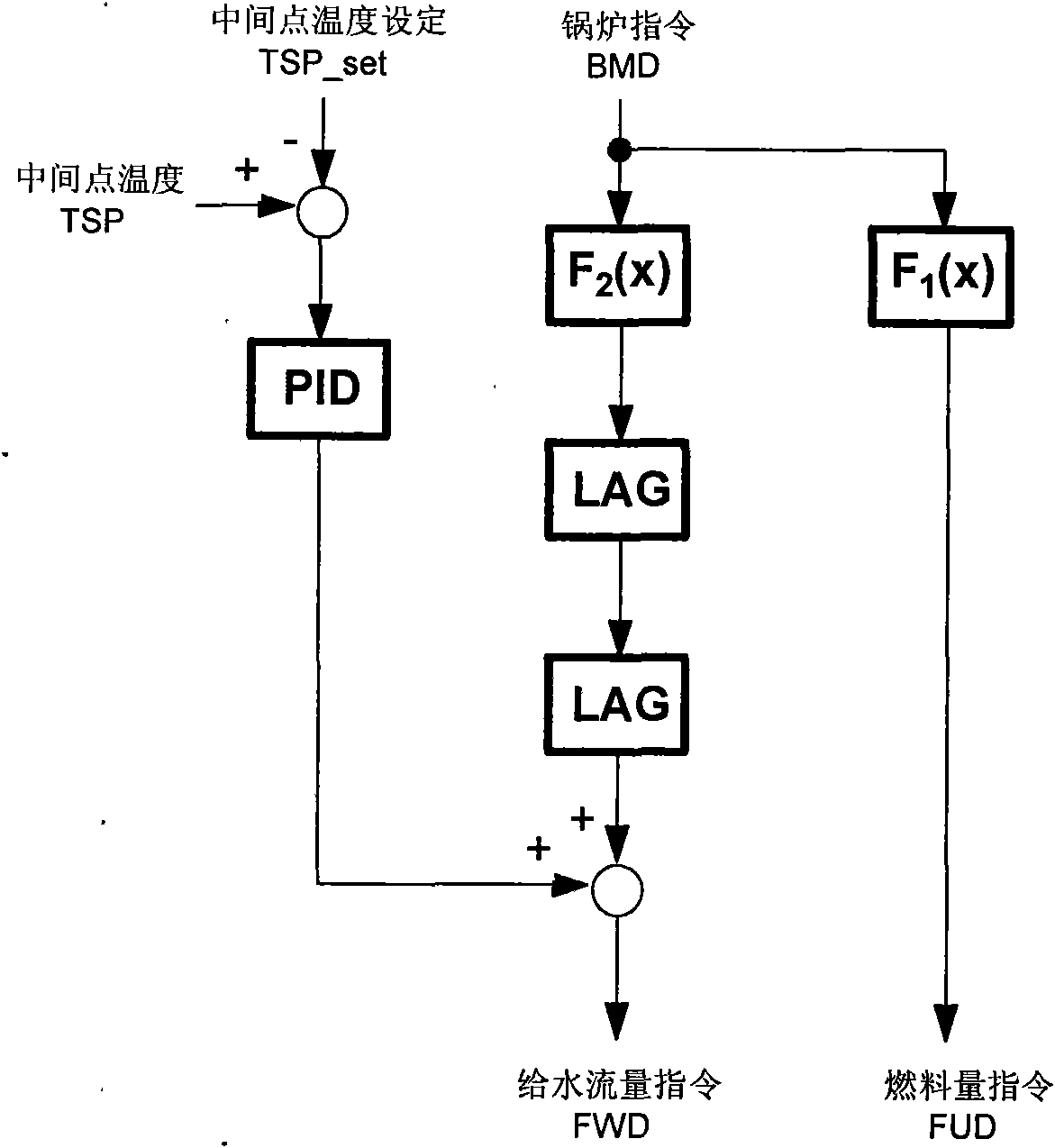
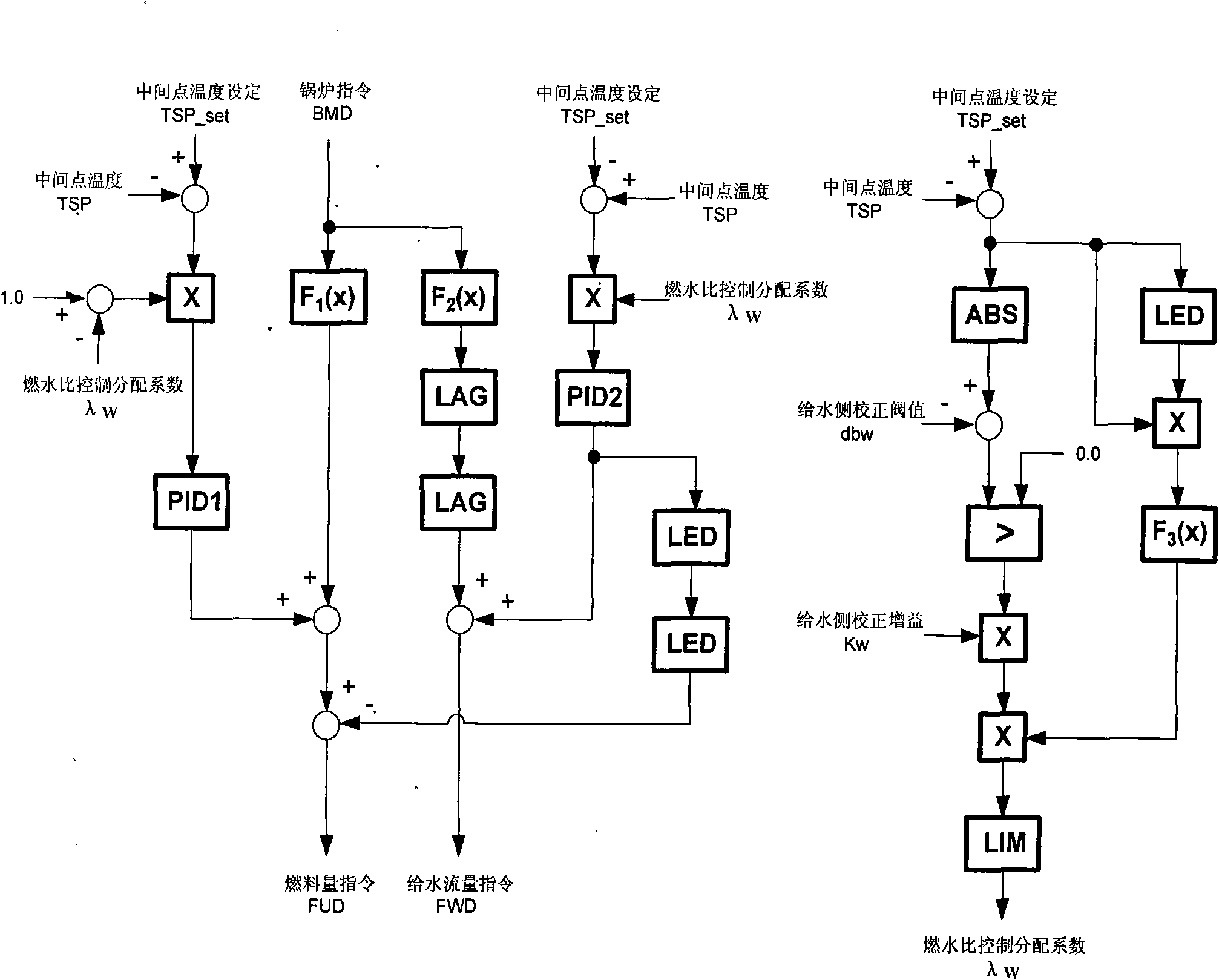
Fuel-water ratio control method for supercritical and ultra supercritical unit
InactiveCN102109172AThe total gain of the control remains unchangedEliminate disturbanceFuel supply regulationSteam pressureWater flow
The invention discloses a fuel-water ratio control method for a supercritical and ultra supercritical unit, and provides a novel fuel-water ratio control method in which fuel quantity and feed water flow simultaneously play parts in intermediate point temperature correction. The method comprises the following steps of: defining a fuel-water ratio distribution coefficient; correspondingly adjusting the magnitude of the fuel-water ratio distribution coefficient according to intermediate point temperature difference and deviation variation of the temperature difference; and determining instruction values of the fuel quantity and the feed water flow to keep control overall gain of an entire fuel-water ratio adjusting system unchanged and keep the system stability not influenced. Meanwhile, a decoupling loop from a water feed side correcting value to a fuel side is further added in a control logic, so that the load on the unit and the disturbance of steam pressure brought by adjustment of the fuel-water ratio by the feed water flow can be greatly eliminated. Actual system application shows that the supercritical (ultra supercritical) unit using the control method can more effectively adjust the fuel-water ratio during running of the unit, and has more stable variation in main steam temperature and main steam pressure while loading rate quickly varies.
Owner:JIANGSU FRONTIER ELECTRIC TECH +4
Control method of miniature photovoltaic inverter having three-phase unbalance management function
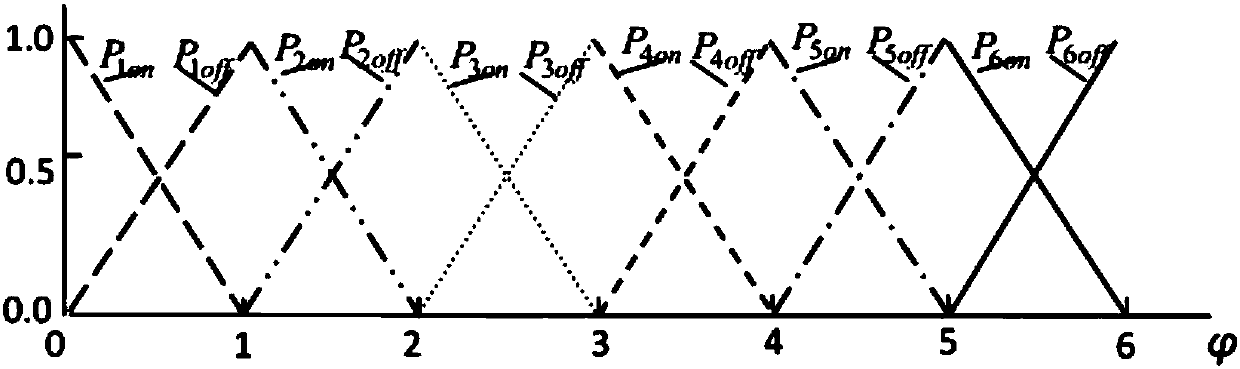
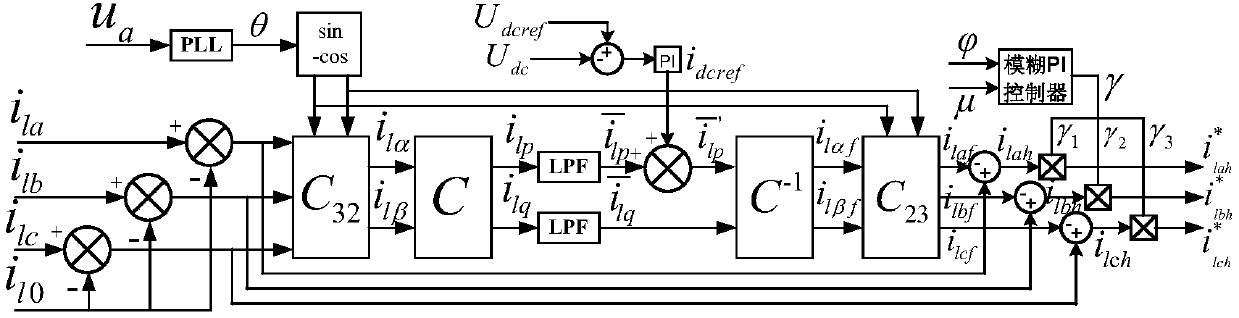
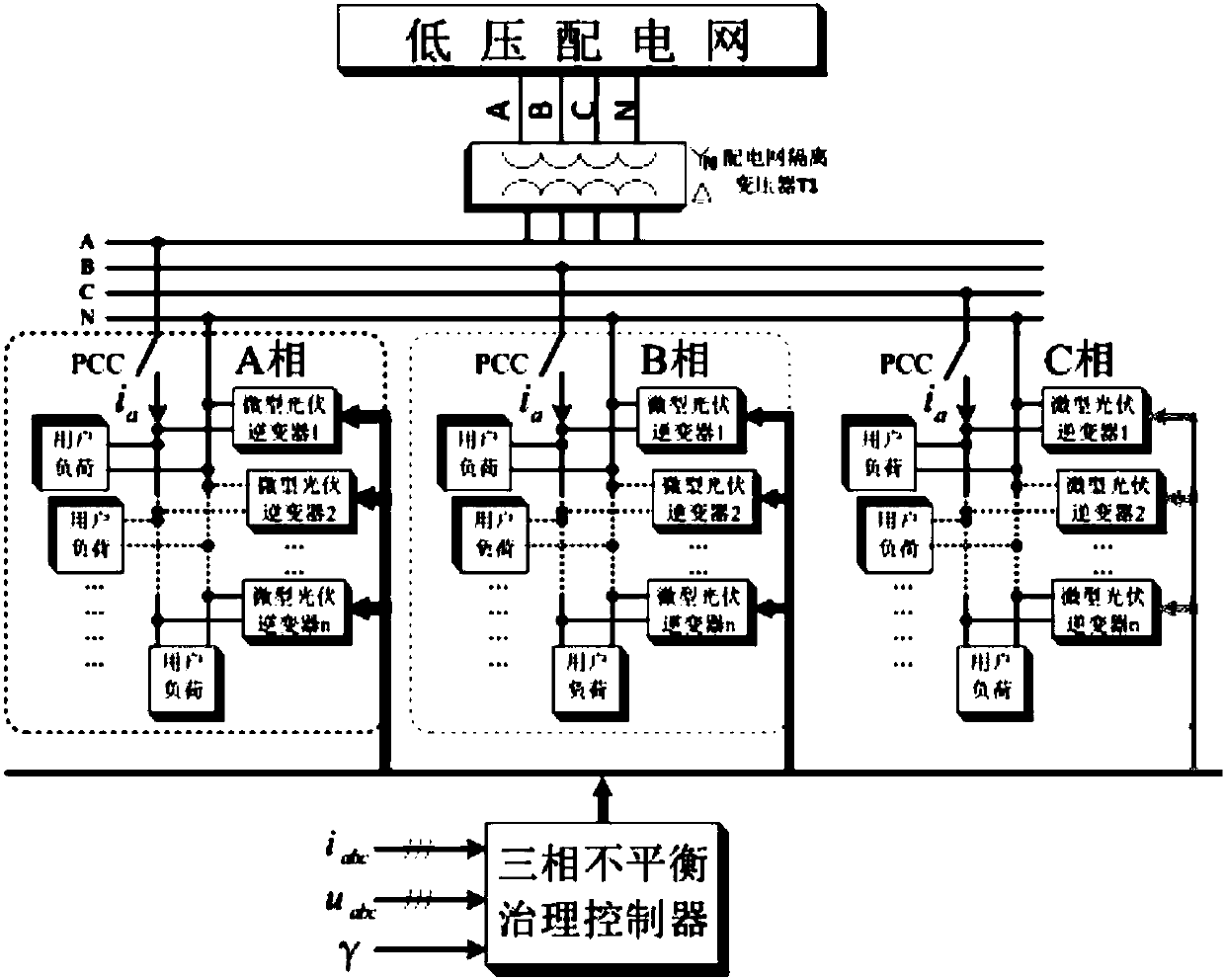
ActiveCN107317352ARealize Harmonic Current ControlRealize the loadSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionMicrogridEngineering
The invention provides a control method of a miniature photovoltaic inverter having a three-phase unbalance management function. The control method comprises the steps of performing real-time detection to obtain an illumination intensity coefficient Phi of a microgrid photovoltaic panel and current / voltage values of a plurality of single-phase miniature photovoltaic inverters to which a three-phase power grid is connected, calculating three-phase unbalance degree Mu, determining a power allocation efficient Gamma of a photovoltaic cell module by simultaneously combining the coefficient Phi and the unbalance degree Mu and by employing a fuzzy proportional integral (PI) control algorithm, and building an output power allocation scheme of the cell module; and building an i-i<q> instruction current solution model, subtracting load current from the solved fundamental positive-sequence component to obtain a compensation current containing harmonic, a fundamental wave negative-sequence current and a fundamental wave active power transmission current in the compensation current, and finally, adjusting the size of an injected power to a microgrid from the battery module according to the allocation coefficient Gamma. The illumination intensity coefficient, the three-phase current unbalance degree, the fuzzy PI control algorithm and the i-i<q> model are combined, and harmonic current suppression, load reactive power compensation and three-phase unbalance management are adaptively achieved.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
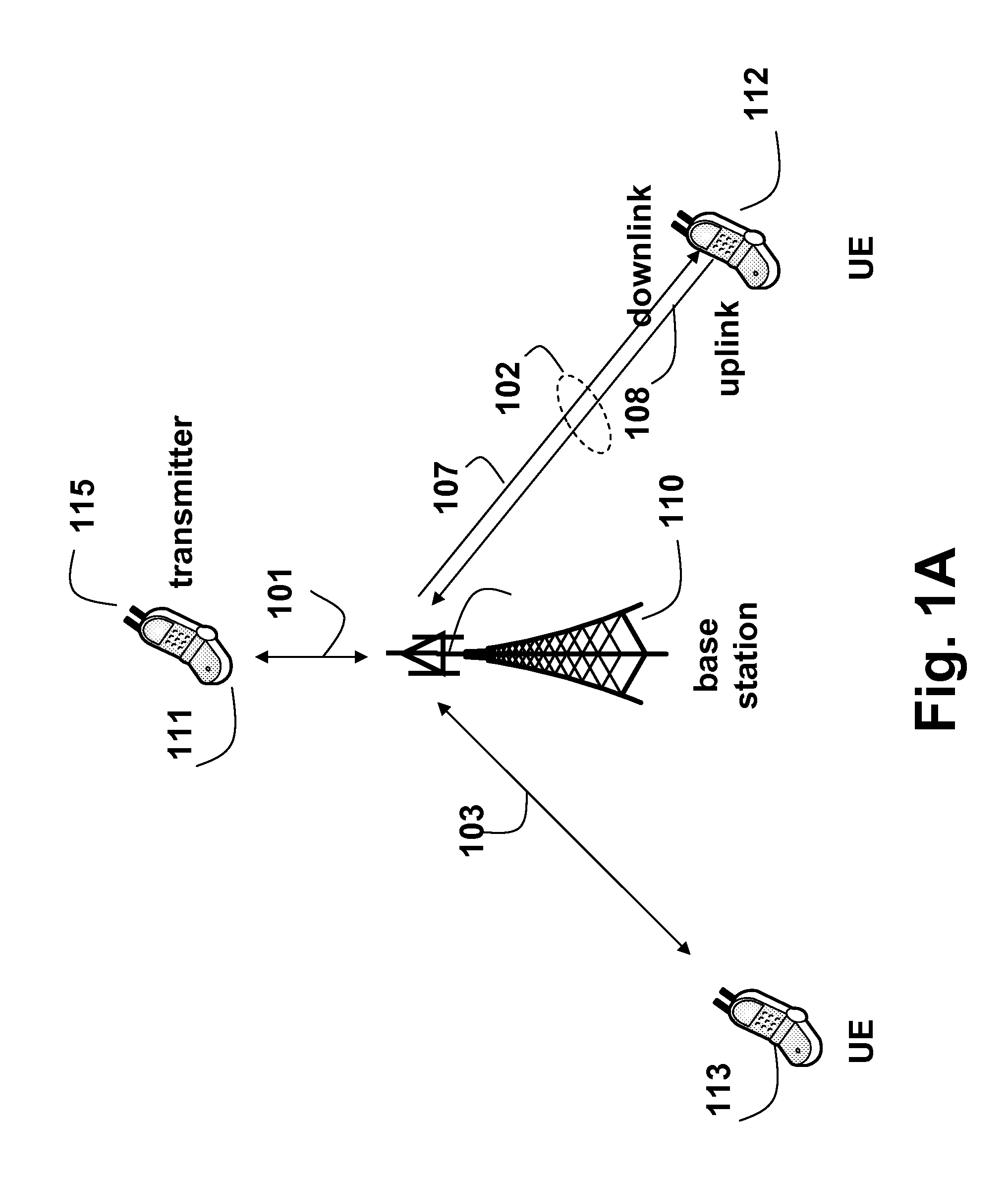
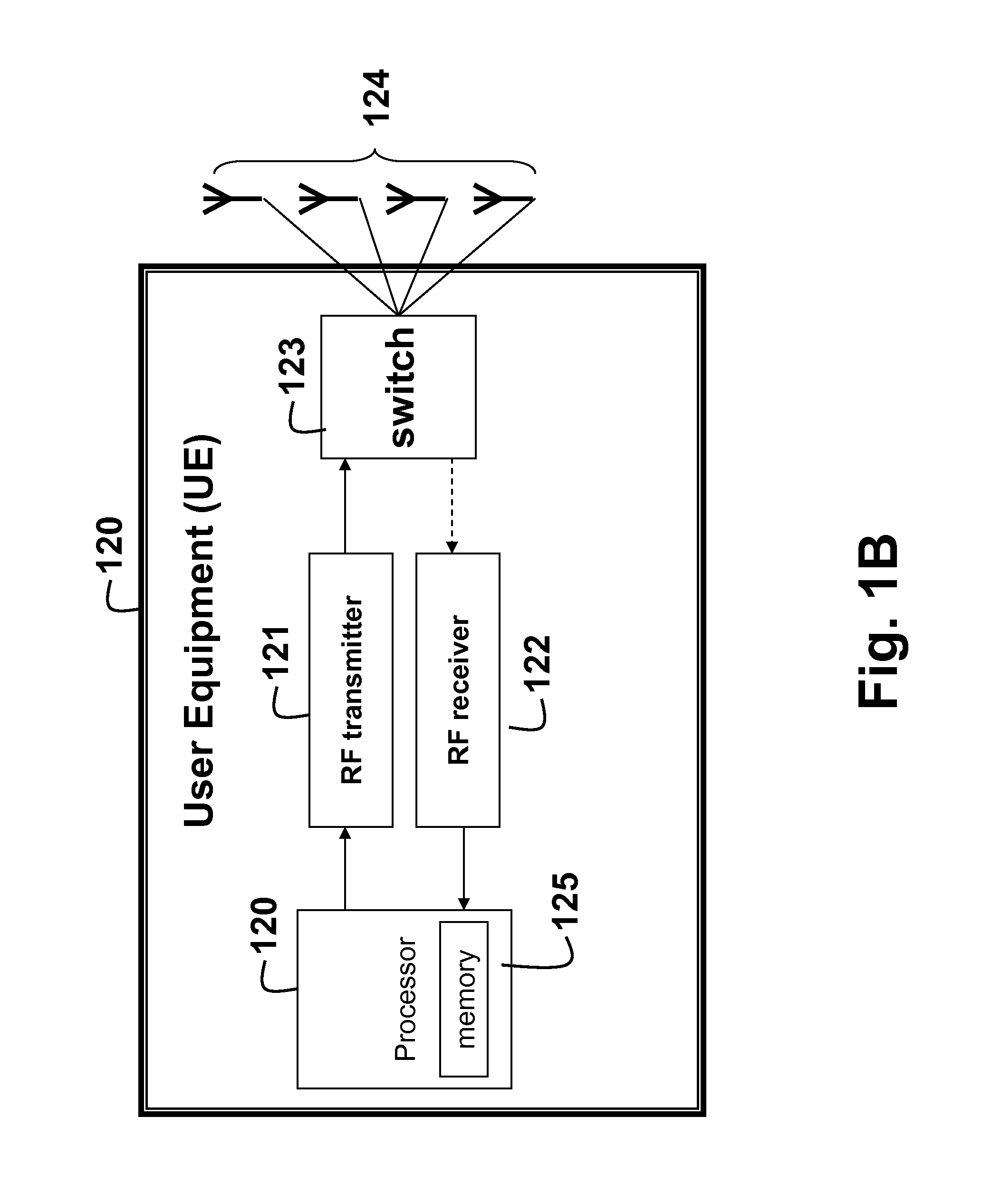
Antenna Selection with Frequency-Hopped Sounding Reference Signals
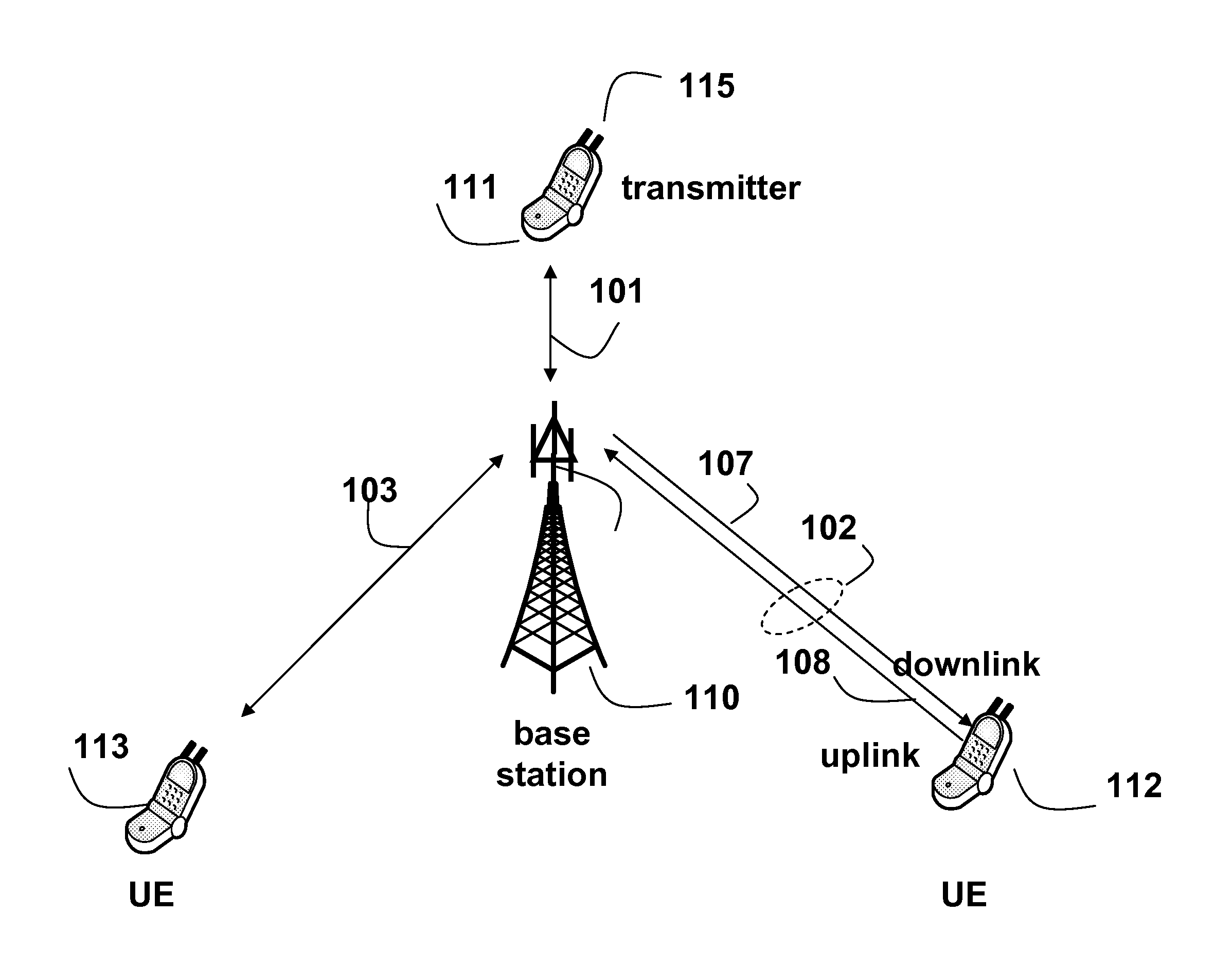
ActiveUS20110310931A1Network traffic/resource managementSignal allocationSounding reference signalEngineering
The embodiments of the invention provide a method for selecting antennas for date transmission in a wireless communication network including user equipment (UE). The network is assigned a band of frequencies, wherein the band is partitioned into at least one set of subbands of the band according to a sounding reference signal (SRS) band-width configuration in a form of a code-tree having a plurality levels and each level is associated with a partition coefficient. The UE is configured to transmit frequency-hopped SRS on the set of sub-bands using subsets of the set of antennas. First, the method determines if a number of subbands in the set of the sub-bands is odd or even based on the SRS bandwidth configuration, and selects a particular subset of the antennas according to whether the number is odd or even. Then, the SRS is transmitted from the particular subset of the antennas.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Simulation method for finite element of laser welding temperature field based on BP neural network and genetic algorithm GA
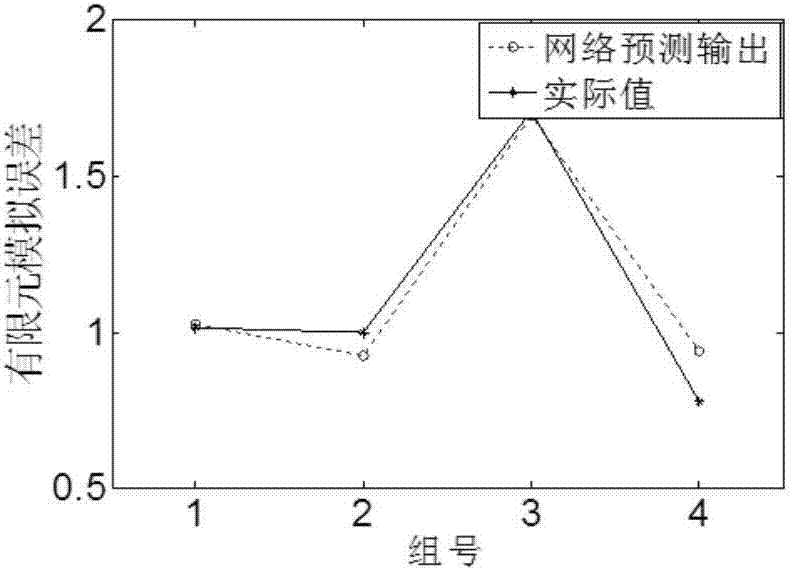
ActiveCN106909727AImprove forecast accuracyEfficient and accurate simulationDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesEffective radiusEngineering
The invention discloses a simulation method for a finite element of a laser welding temperature field based on a BP neural network and a genetic algorithm GA, which includes the following steps. Step 1 is a simulation of the finite element of the laser welding in which a heat source model with a surface body combination consisting of a gauss surface heat source and a cylinder heat source is selected, a thermal distribution coefficient of a surface heat source, an effective radius of the surface heat source, and an effective thermal power coefficient are selected to be design variables. Moreover, an orthogonal experiment table is designed and simulation errors of the finite element of the heat source model with a surface body combination under different parameters are calculated. Step 2, the BP neural network is established, trained and tested. Step 3, the solution of a optimum parameter is found and the feasibility of optimization results is determined. Then the BP neural network is re-established and the optimization solution of the genetic algorithm is found again when there are big errors. The simulation method for the finite element of the laser welding temperature field based on the BP neural network and the genetic algorithm GA achieves the improved efficiency and precision of the traditional welding temperature field, thereby being easy to find the optimal solution of the simulation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
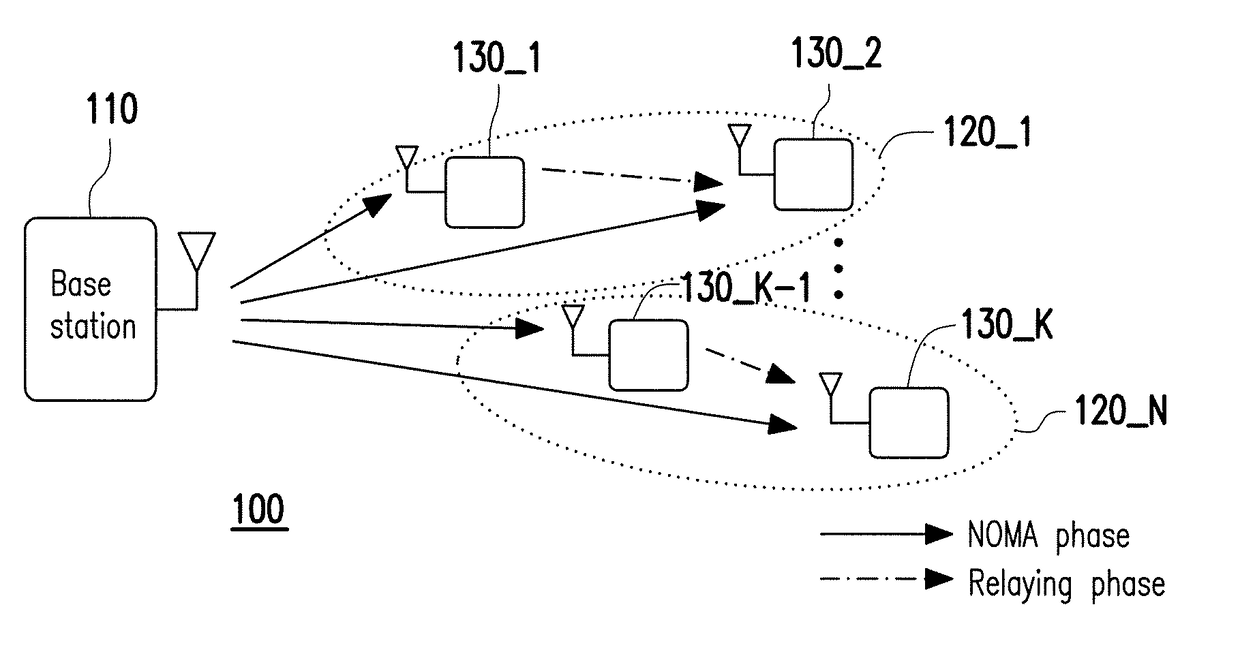
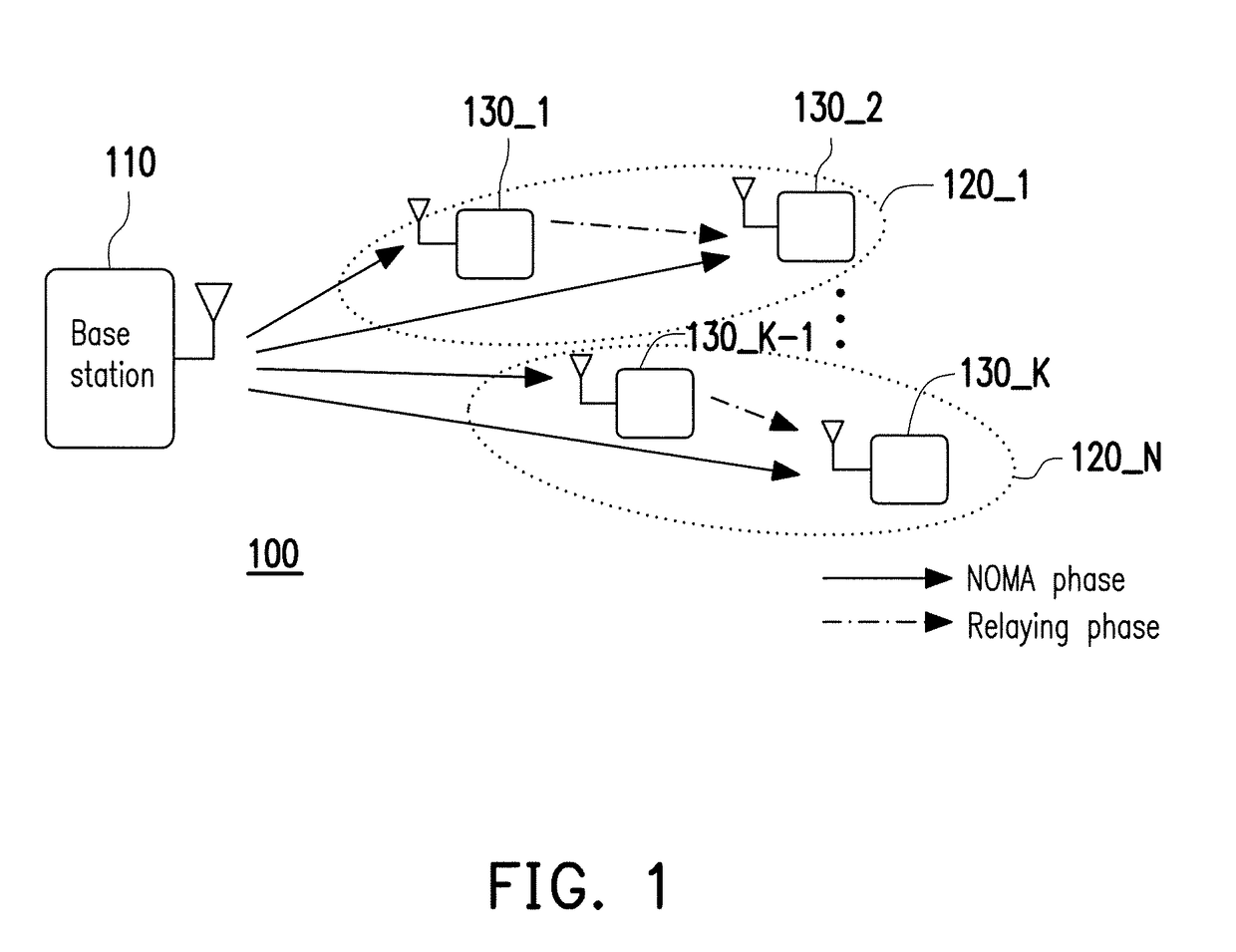
Dynamic-SWIPT-based cooperative transmission method in downlink NOMA communication system
ActiveCN109347609ATotal data rateBalance data rate differences in real timeCriteria allocationAllocation timingEngineeringTime distribution
The invention discloses a dynamic-SWIPT-based cooperative transmission method in a downlink NOMA communication system. A system transmission period T is divided into two phases, time of a first phaseis (1-alpha)T, and time of a second phase is alphaT; in the first phase, a near-end user receives a radio frequency signal of a base station, the radio frequency signal is divided into two parts, power of a first part accounts for beta and the first part is used for performing energy harvesting by a near-end user, power of a second part accounts for 1-beta and the second part is used for performing user information decoding by the near-end user and receiving a base station signal by a far-end user; and in the second phase, the near-end user is taken as a relay and transmits information to thefar-end user, and the far-end user decodes a signal by virtue of a selection combination technology, wherein a time distribution coefficient alpha and a power distribution coefficient beta are determined by solving an optimization problem. The method disclosed by the invention performs dynamic adjustment on the time distribution coefficient and the power distribution coefficient, balances a data rate difference between the near-end user and the far-end user in real time and also realizes maximum total data rate of the communication system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Chemiresistor for use in conducting electrolyte solution
ActiveUS20100276302A1Effective capacitanceImproving impedanceWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The present invention provides a chemiresistor-based sensor for measuring the presence or amount of analyte in an electrolyte solution; said chemiresistor comprising (i) a chemiresistor film wherein the impedance of said nanoparticle film changes in the presence of an analyte; and (ii) two electrically conducting electrodes in electrical contact with said nanoparticle film; wherein said electrically conducting electrodes are adapted to be connected to a device for measuring the impedance of said chemiresistor film under a voltage signal and wherein the impedance of the double layer capacitor formed by the two electrically conducting electrodes in the presence of the electrolyte solution, is larger than the impedance of the chemiresistor film either before or after exposure of the chemiresistor film to the analyte. A method of using said chemiresistor-based sensor to measure the presence or amount of analyte is also provided. Further provided is a method of determining the partition coefficient of an analyte using said chemiresistor-based sensor.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com