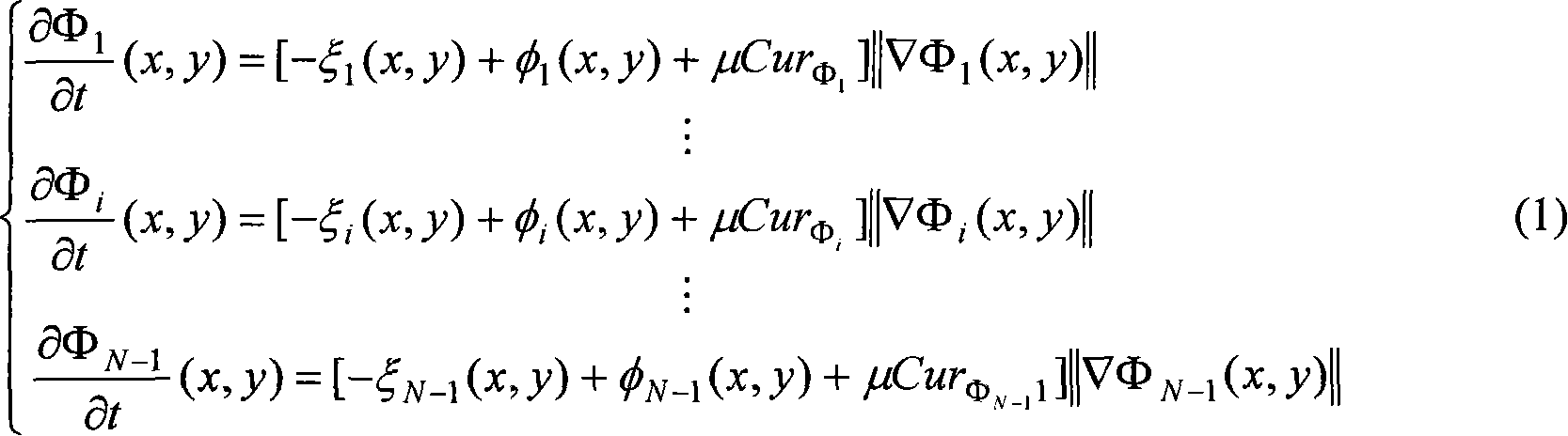Patents
Literature
780results about How to "Easy to divide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multi-scale image semantic segmentation method
ActiveCN110232394AIncrease profitEasy to handleCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSample imageMinutiae
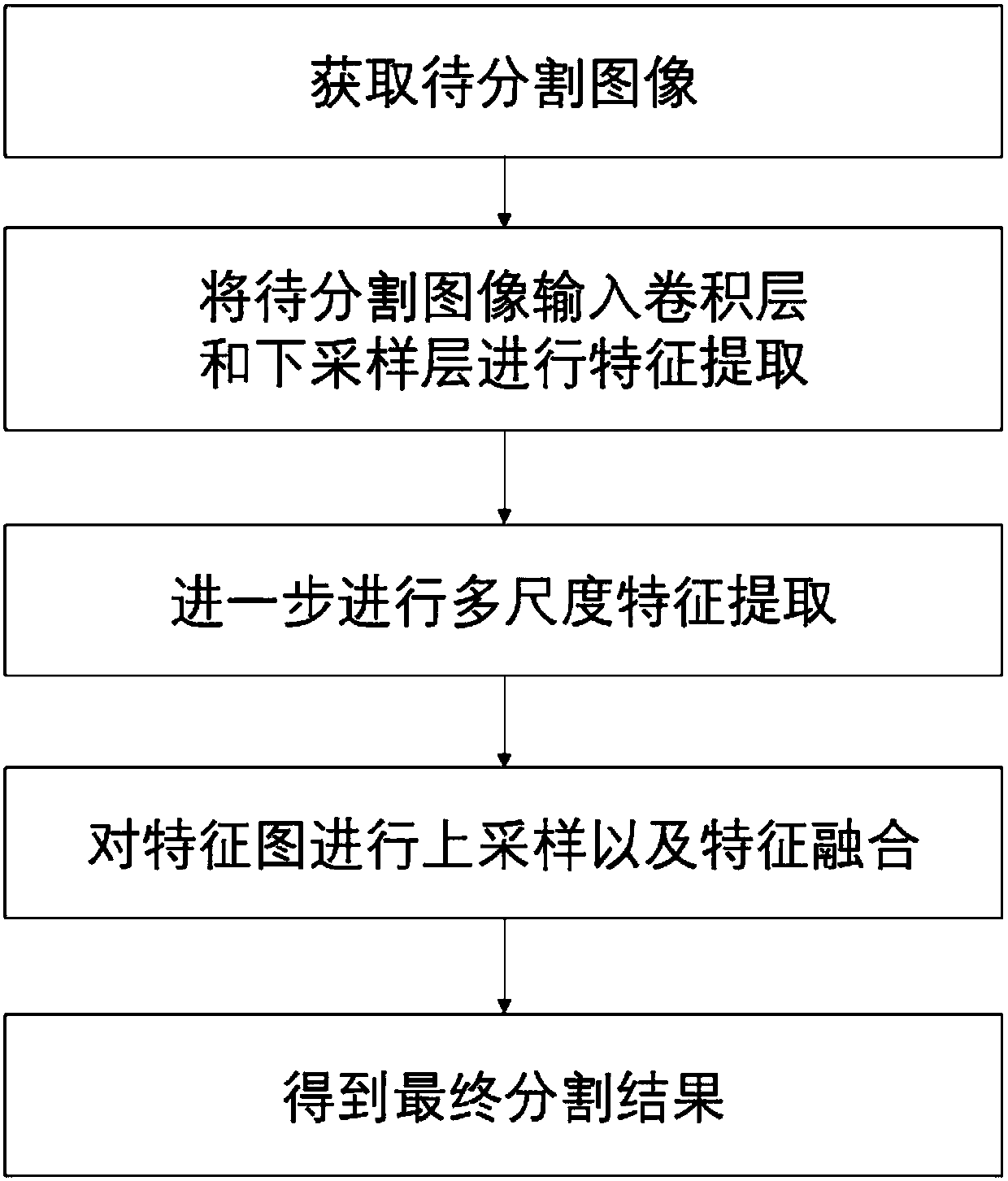
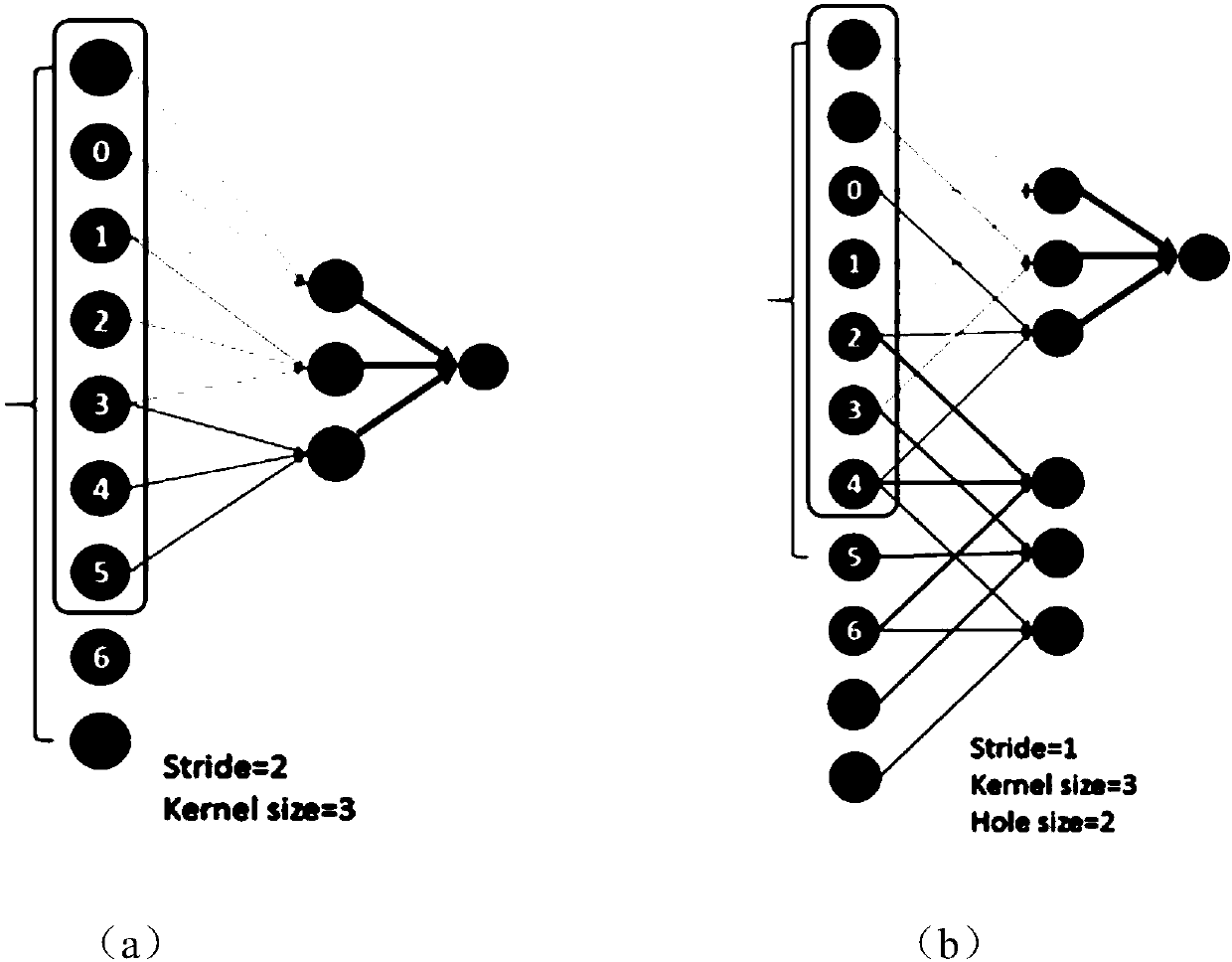
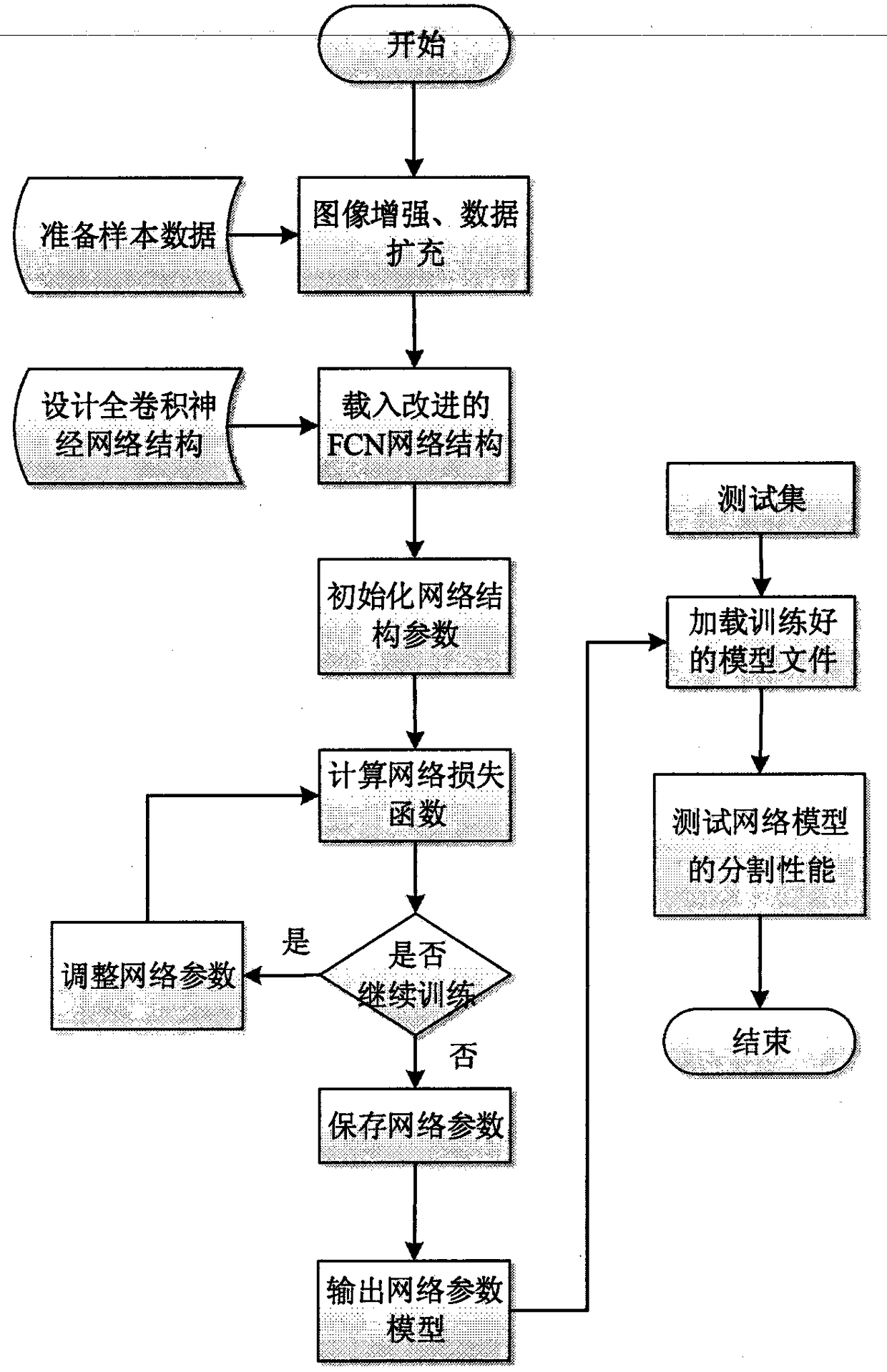
The invention discloses a multi-scale image semantic segmentation method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a to-be-segmented image and a corresponding label; constructing a full convolutional deep neural network, wherein the full convolutional deep neural network comprises a convolution module, a hole convolution module, a pyramid pooling module, a 1 * 1 * depth convolution layer and a deconvolution structure; setting hole convolution as channel-by-channel operation, and utilizing low-scale, medium-scale and high-scale characteristics in a targeted mode; training the full convolutional deep neural network, establishing a loss function, and determining parameters of the full convolutional deep neural network by training the sample image; and inputting the to-be-segmentedimage into the trained full convolutional deep neural network to obtain a semantic segmentation result. By means of the method, the image semantic segmentation problem with complex details, holes andlarge targets can be well solved while the calculated amount and the parameter number are reduced, and the consistency of category labels can be reserved while the target edges can be well segmented.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
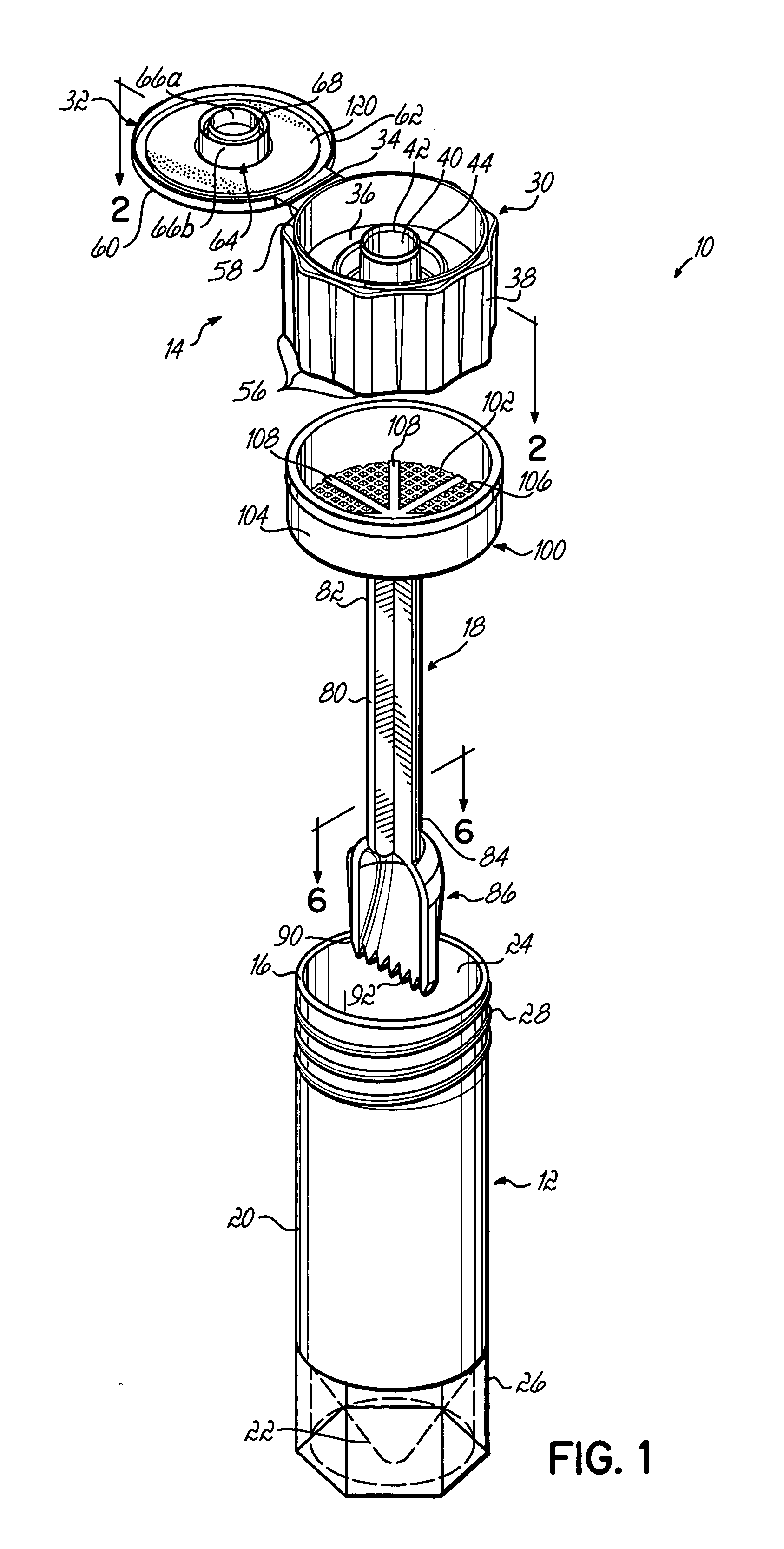
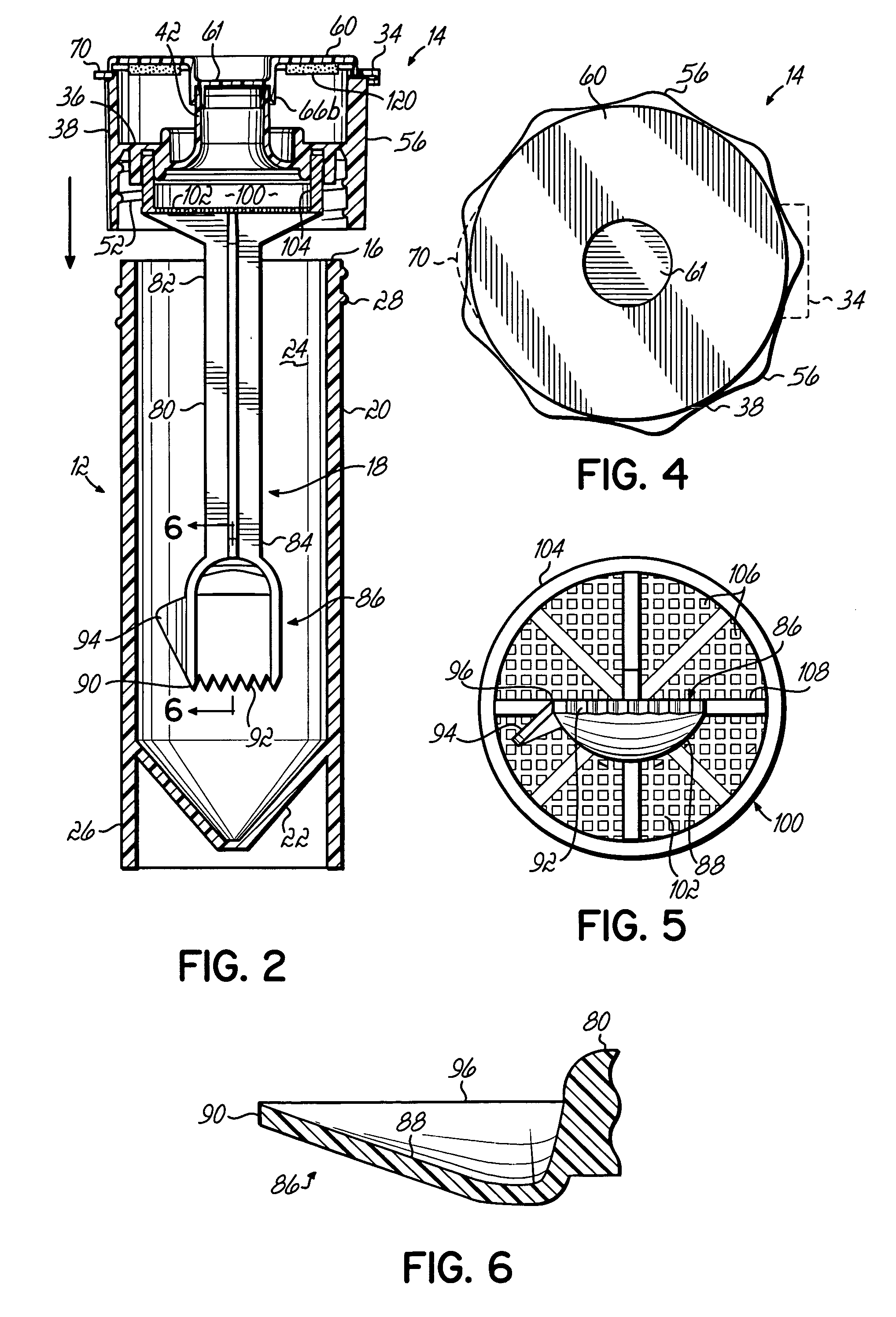
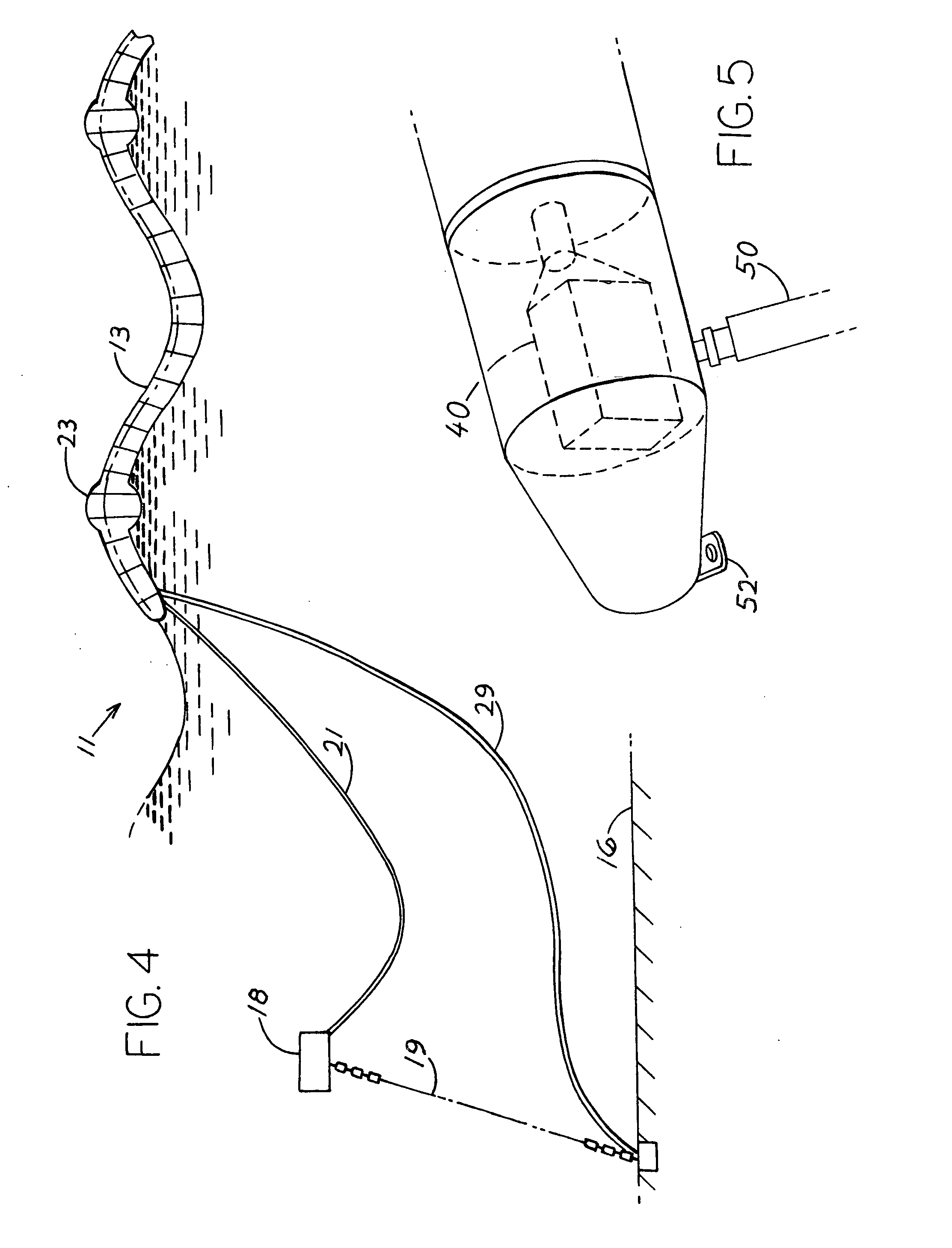
Specimen collection system
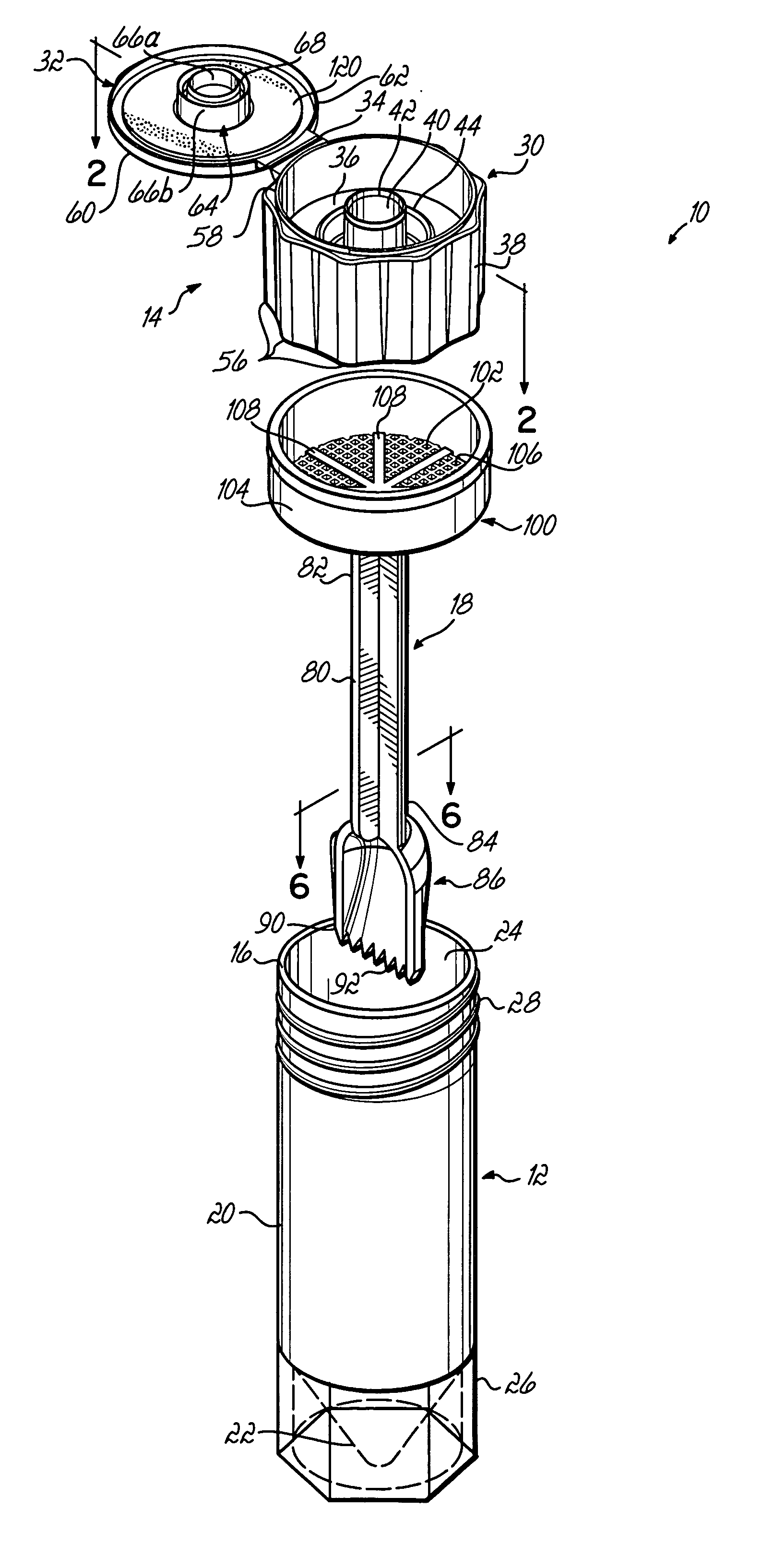
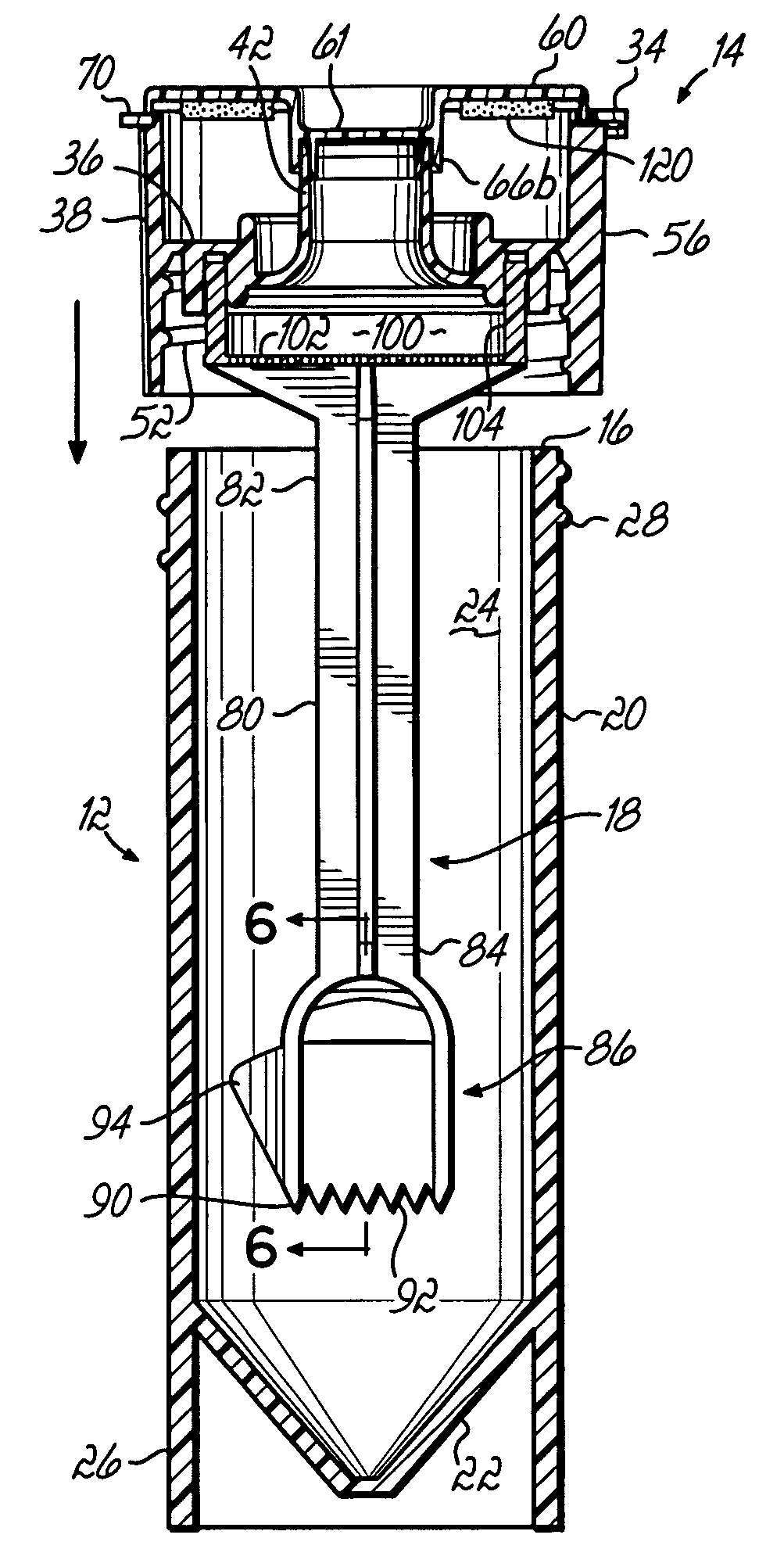
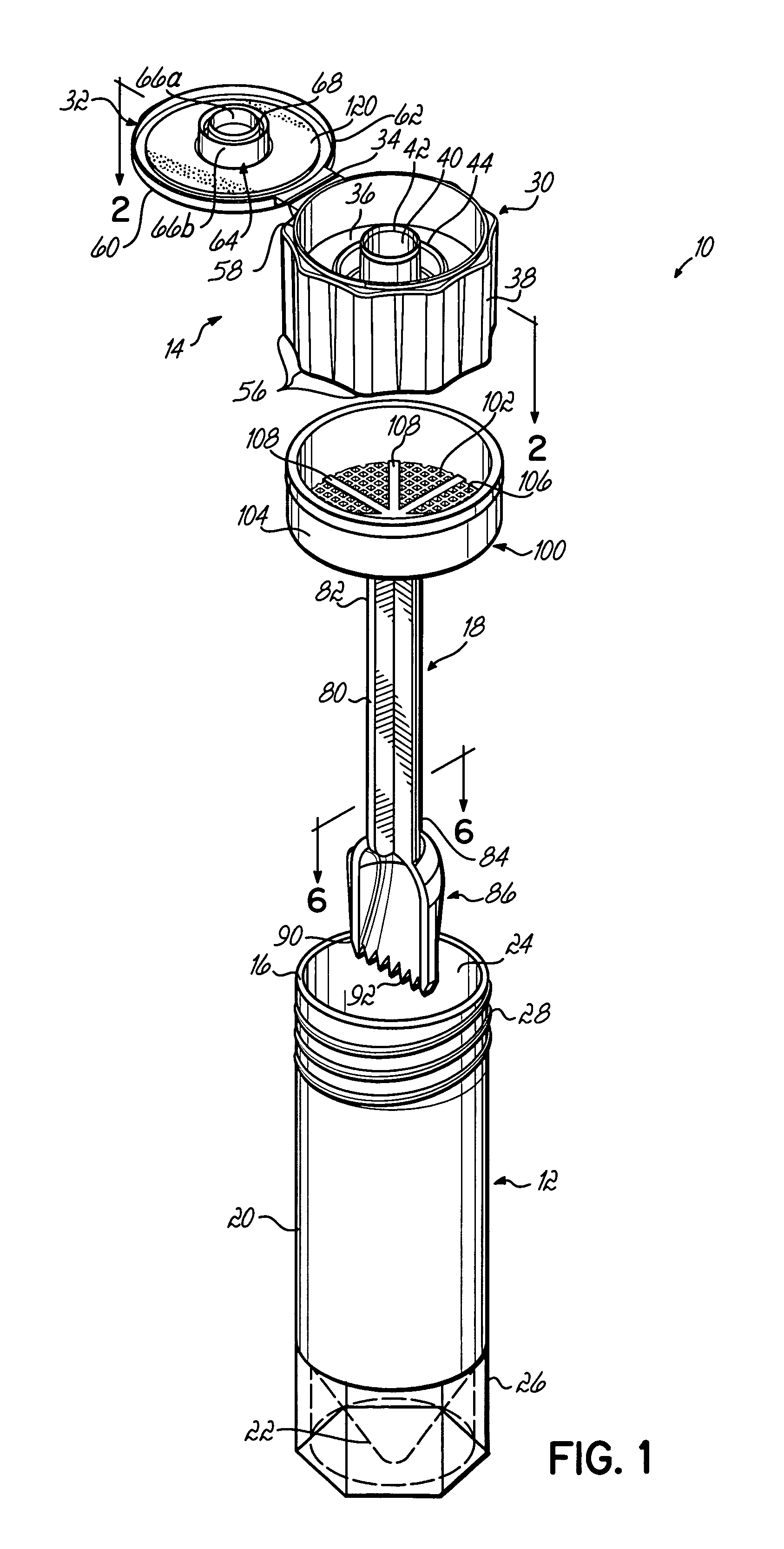
A system for collecting, transporting and preparing a fecal specimen for examination includes a container, a closure selectively secured over an open end of the container, and a sample collection member coupled to the closure and extending into the container when the closure is secured thereto. In one embodiment, the closure includes a base and a cap that are hingedly coupled together. The cap is selectively moveable between a closed position that seals an aperture in the base, and an open position wherein the aperture is exposed to permit expelling contents of the container through the aperture. In another embodiment, the closure comprises a base having a spout and an aperture, and a cap coupled to the base for axial movement along the spout between open and closed positions. The system may further include a deodorant to mask or absorb odors.
Owner:MERIDIAN BIOSCIENCE
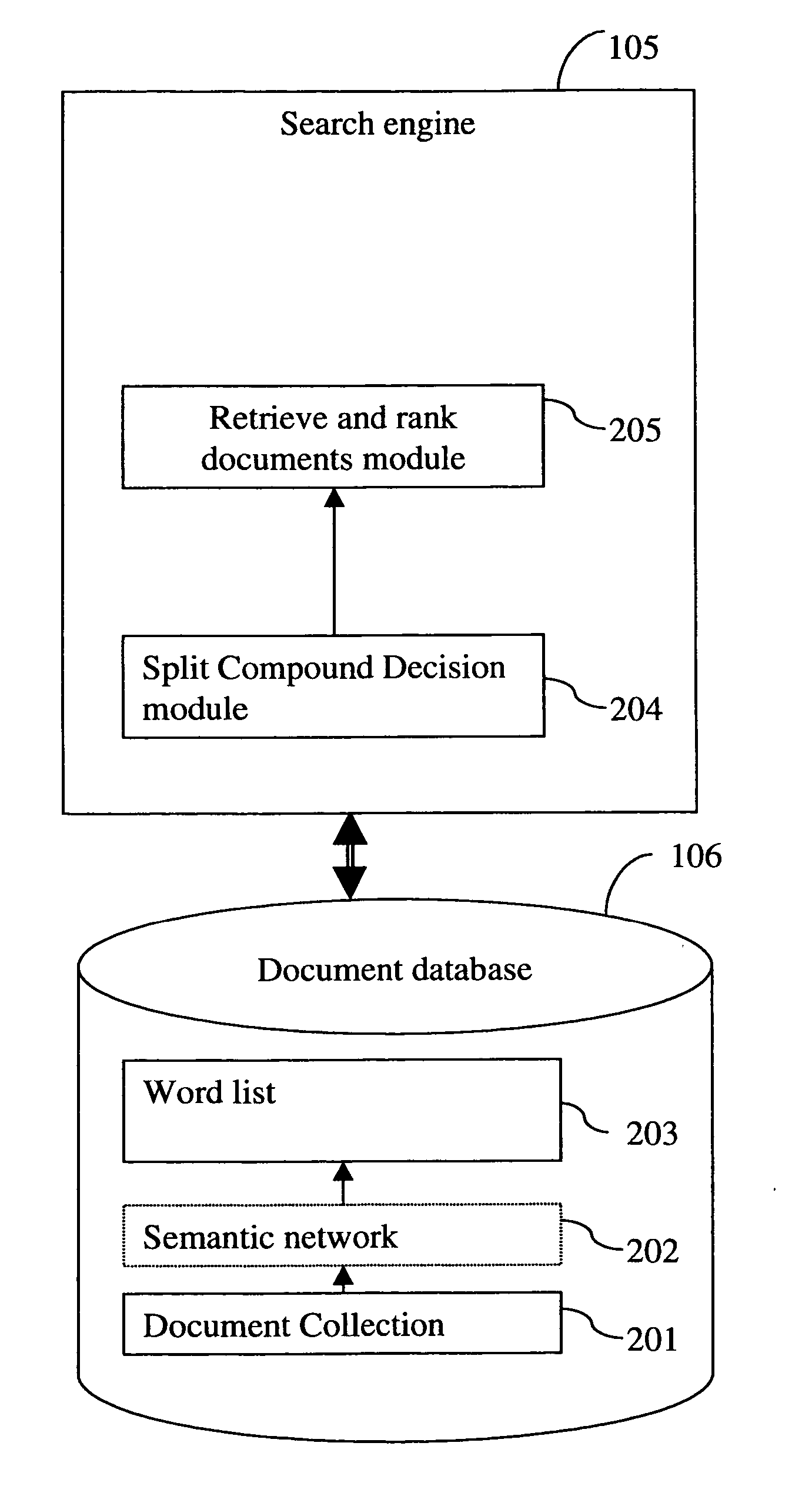
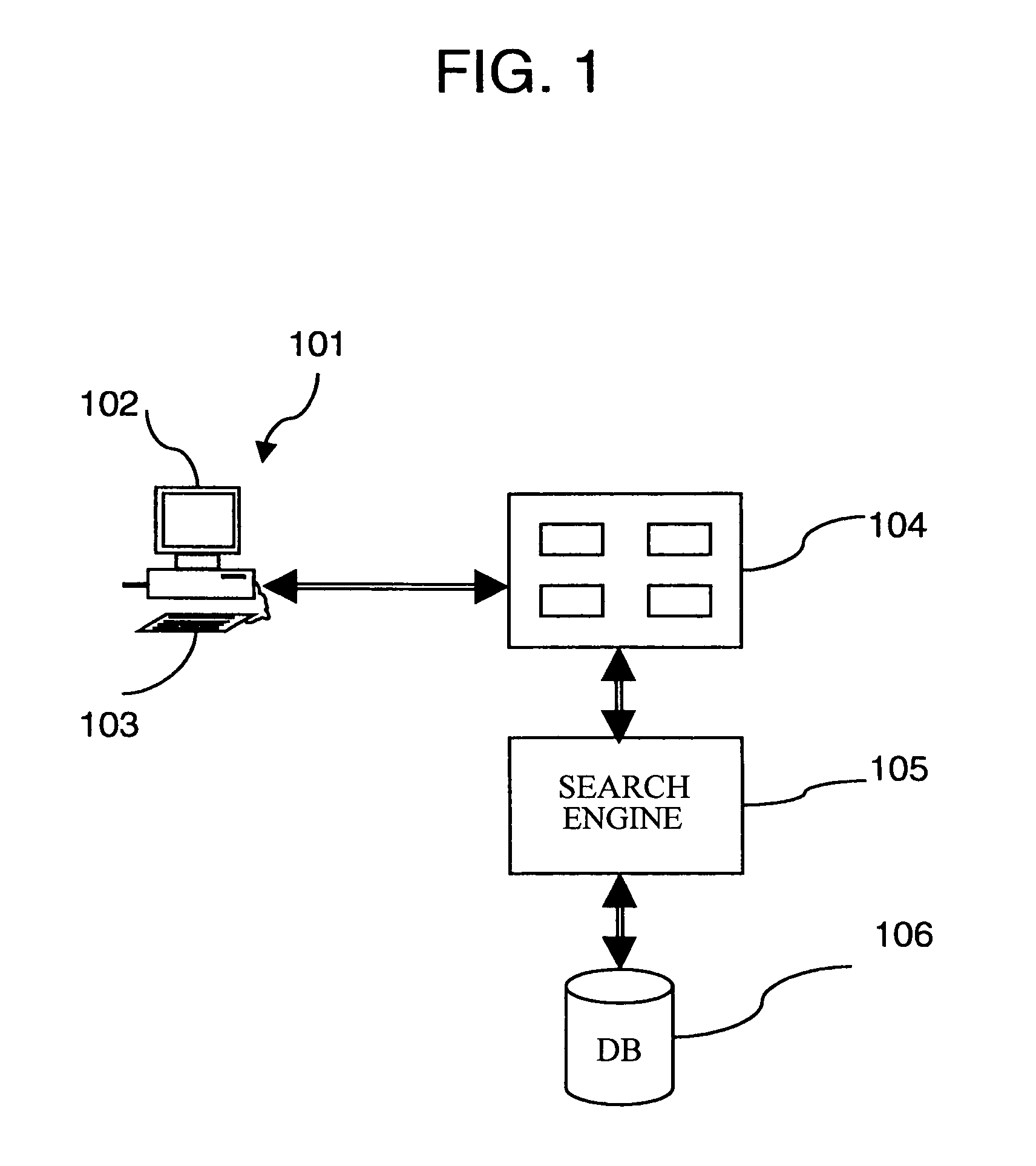
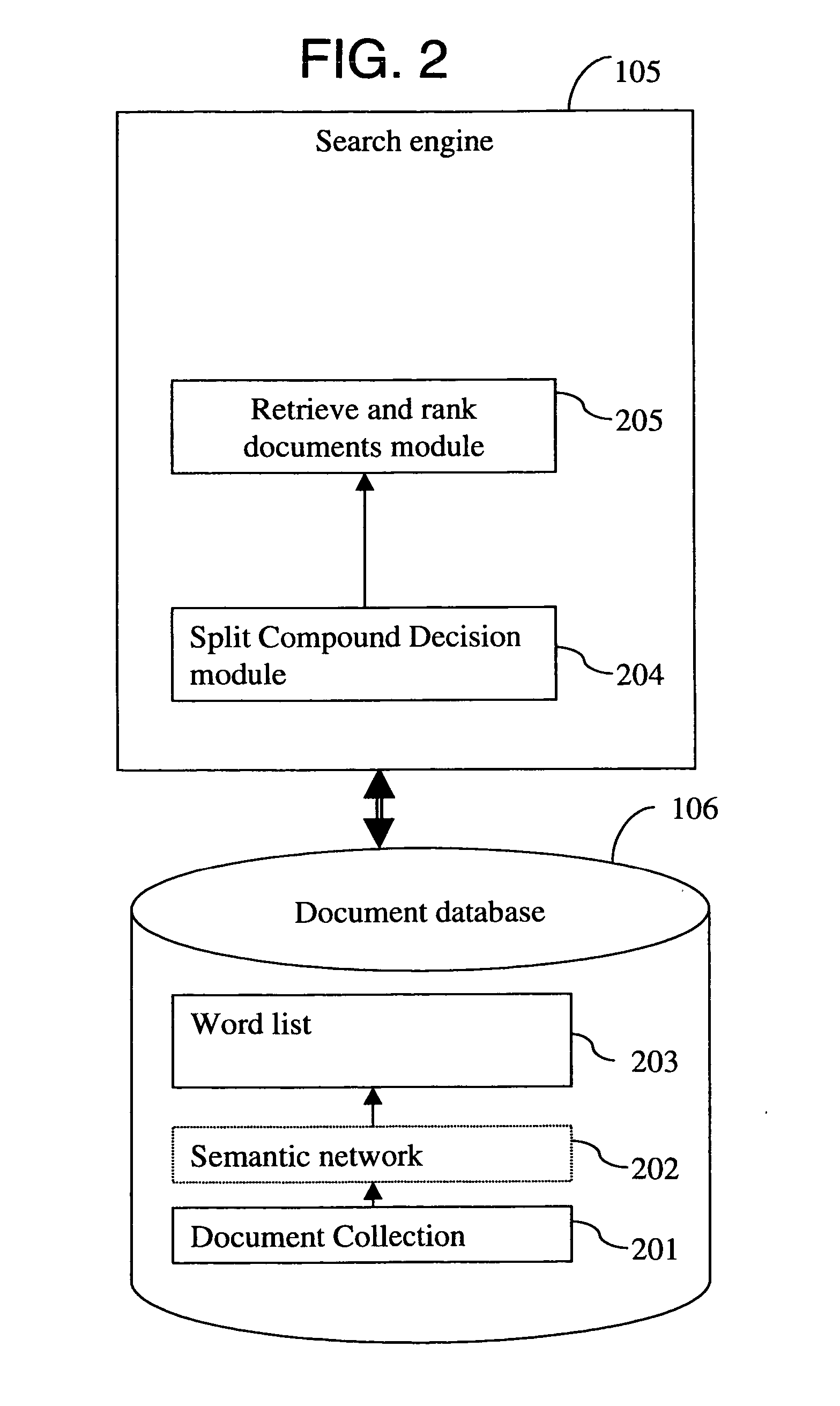
Apparatus and computerised method for determining constituent words of a compound word
InactiveUS20050222998A1Efficient detectionEasy to divideDigital data processing detailsNatural language data processingNatural language processingPaper document
An apparatus, a computer program and a computerized method for determining constituent words of a compound word are provided. Constituent words constitute a compound word. When the constituent words comply to split decision criteria then the constituent words can be used in a separate form. The separate form of the constituent words is used in the search to retrieve the related documents from the document collection.
Owner:OCE TECH
Lithology identification method
ActiveCN104989392ALithology Identification ContinuousMeet the evaluationBorehole/well accessoriesLithologyPorosity
The invention discloses a lithology identification method. The lithology identification method comprises the steps that firstly, conventional three-porosity (sound waves, density and neutrons) logging measured values of N rock core samples are obtained through the steps of thin section authentication, X-ray diffraction analysis, rock core true depth determination and the like; secondly, the relative distance between two parameters of conventional three-porosity logging is obtained, and the quantitative relation between the relative distance of the two parameters and primary mineral components obtained through X-ray diffraction total rock analysis is obtained according to the relative distance of the two parameters and the mineral components of the N rock core samples; thirdly, rock classification based on the relative distance of the two parameters is established and can be applied to lithology identification of fine grain sedimentary facies area logging, and continuous lithology identification can be carried out on well stratums without core sampled.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
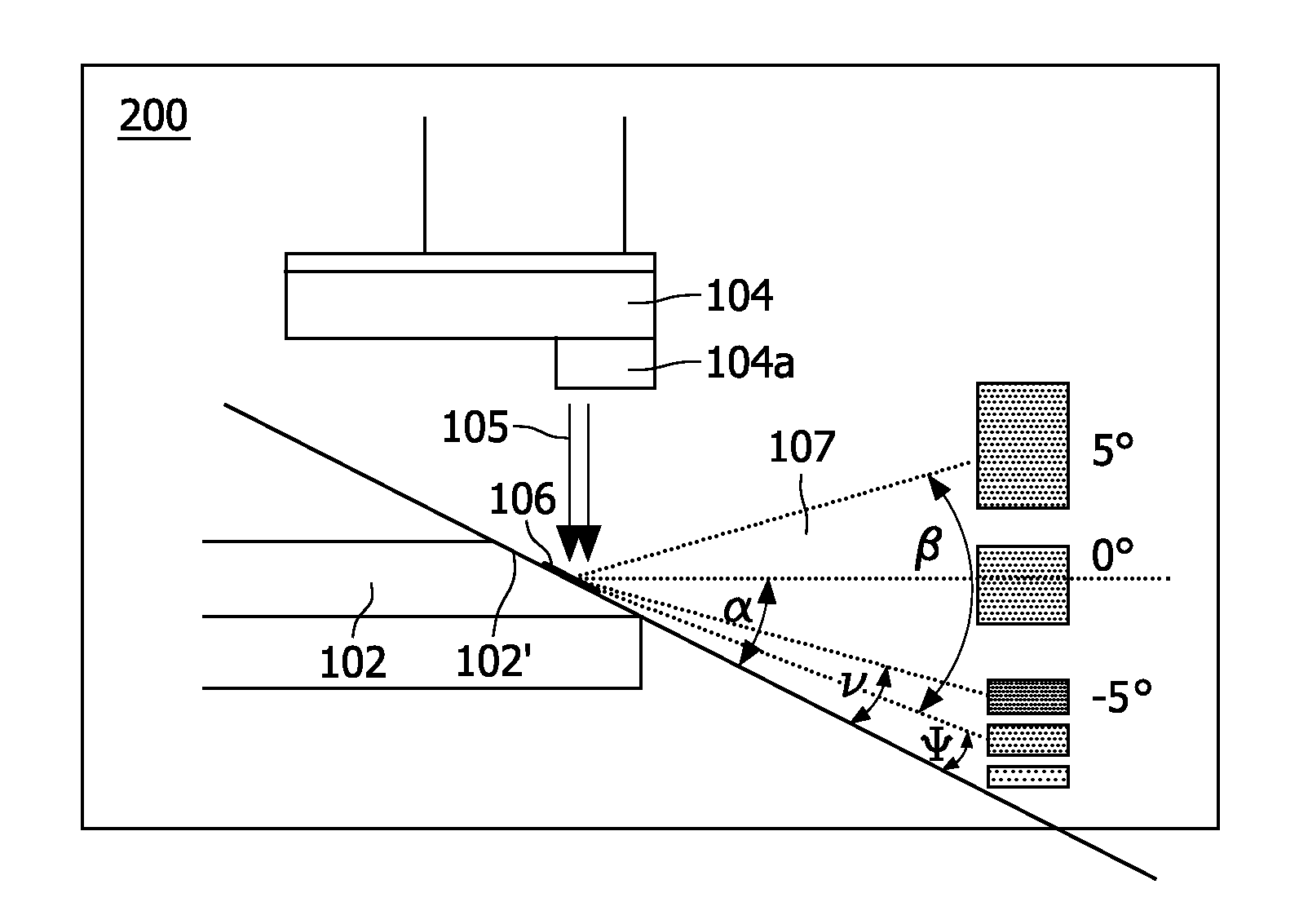
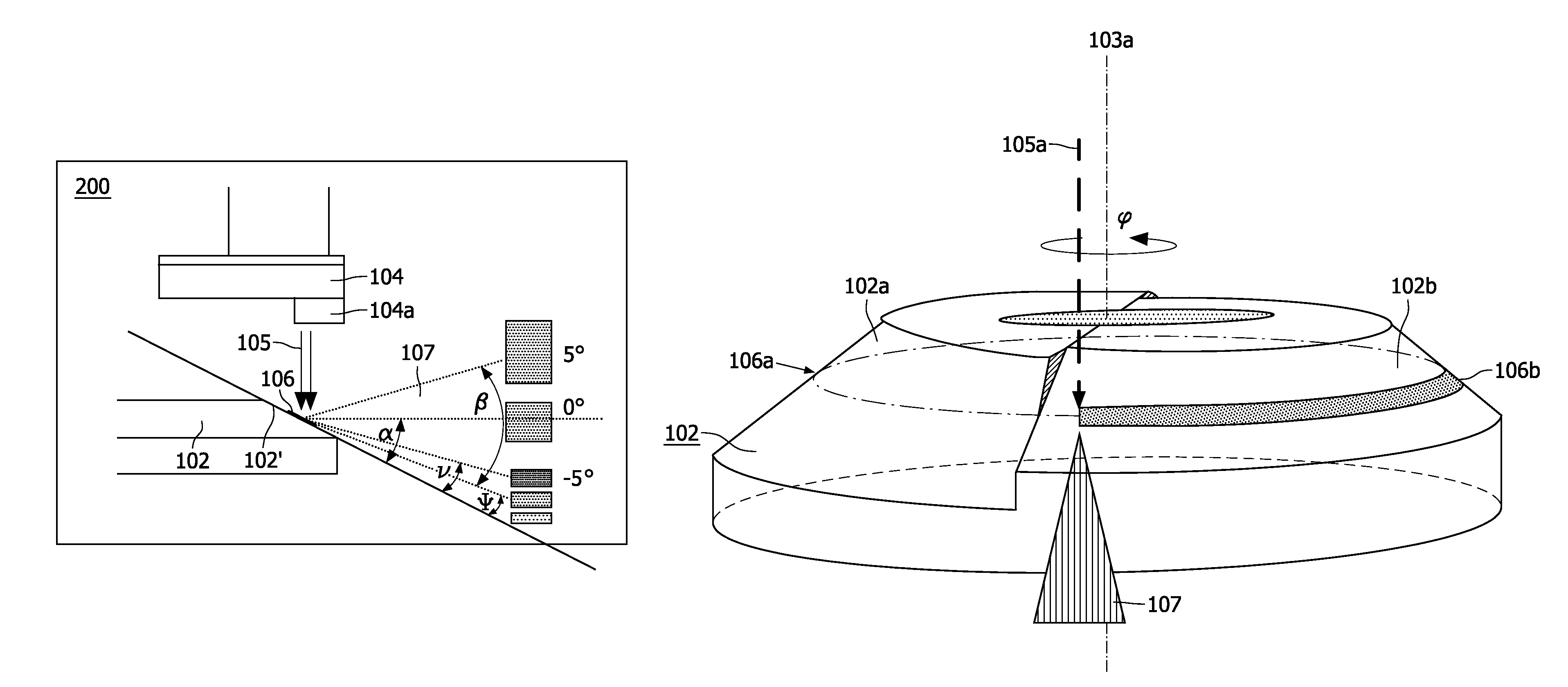
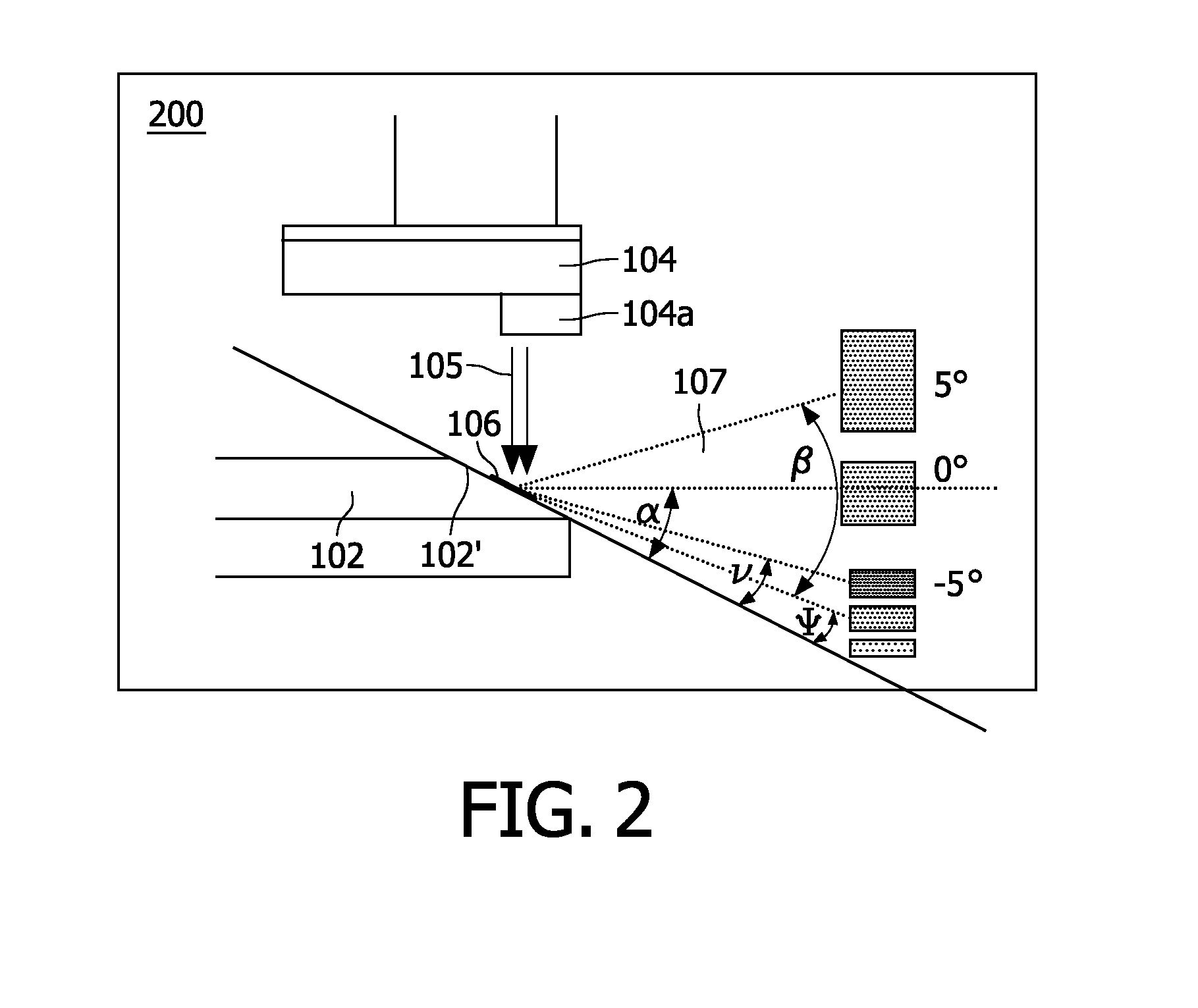
Multi-segment anode target for an x-ray tube of the rotary anode type with each anode disk segment having its own anode inclination angle with respect to a plane normal to the rotational axis of the rotary anode and x-ray tube comprising a rotary anode with such a multi-segment anode target
InactiveUS20110135066A1Compensation deviationMaximum brightnessX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingRotational axisAcute angle
The present invention refers to X-ray tubes for use in imaging applications with an improved power rating and, more particularly, to a multi-segment anode target (102′) for an X-ray based scanner system using an X-ray tube of the rotary anode type, said X-ray tube comprising a rotatably supported essentially disk-shaped rotary anode (102) with an anode target (102′) for emitting X-radiation when being exposed to an electron beam (105a) incident on a surface of said anode target (102′), wherein said rotary anode disk (102) is divided into at least two anode disk segments (102a and 102b) with each of said anode disk segments having a conical surface inclined by a distinct acute angle (α) with respect to a plane normal to the rotational axis (103a) of said rotary anode disk (102) and thus having its own focal track width. A control unit for pulsing the electron beam (105a) is provided which is adapted for pulsing the electron beam (105a) such that the electron beam has a duty cycle which takes on its switched on state only when incident on a selectable anode disk segment (102a or 102b) with an inclination angle (α) from a given angular range or on a anyone from a selectable set of these anode disk segments (102a or 102b). Controlling the electron beam's pulse sequence thereby allows to select the optimal segment of the focal spot track (106b) with the smallest possible inclination angle (α) dependent on the angular size (β) of a desired field of view and helps to achieve a maximum brightness of the focal spot (106) as well as a maximized power rating. An advantage of the invention consists in an enhanced image quality compared to conventional rotary anodes as known from the prior art.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
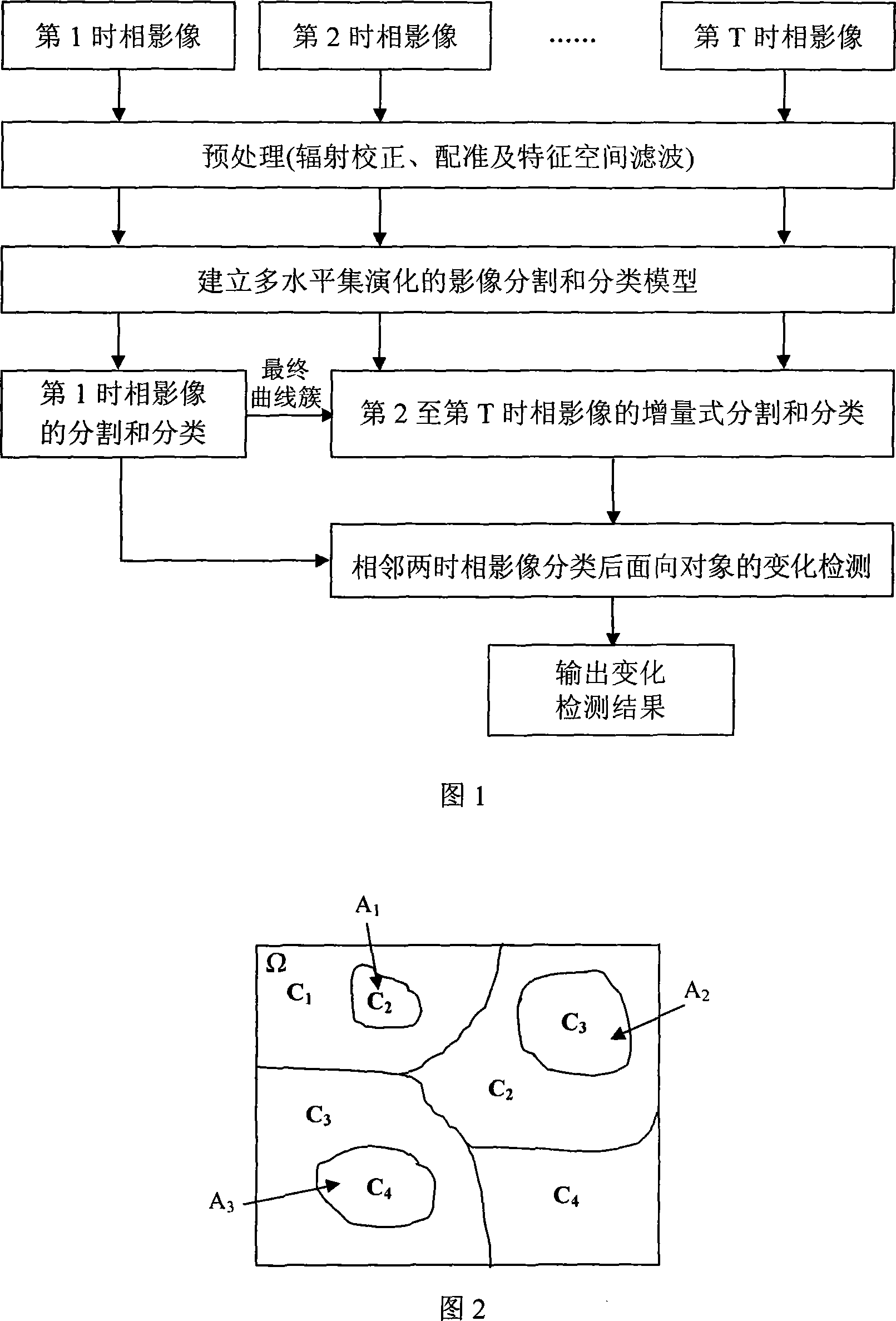
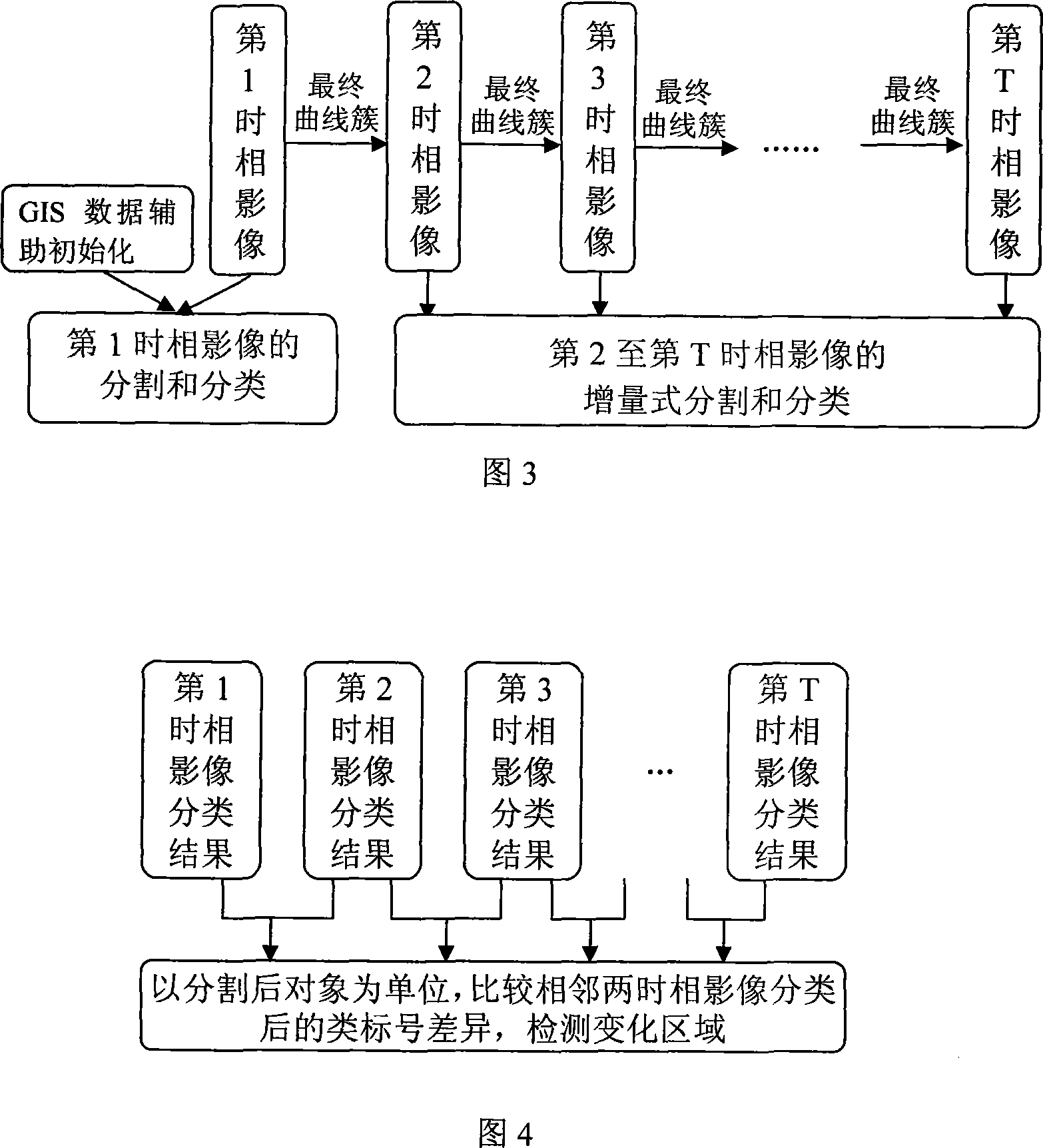
High resolution ratio remote-sensing image division and classification and variety detection integration method
InactiveCN101126812ASimple methodFew parametersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLand resourcesHazard monitoring
The utility model discloses a integrated method based on multi-level set evolution and high resolution remote sensing image partition, classification and change inspection, which is characterized in that (1) image preprocessing (radiation, registration and filtering); (2) the multi-level set evolutional partition and classification model, after registration, the GIS data determines the initial profile of each level set function and performs the partition and classification to the first phase image; (3) the model described in the (2) is still adopted, and the initial profile of each level set function is optimized, increment type partition and classification is adopted for the second to T phase; (4) the objective after partition is used as unit, the ith and (i+1)th two adjacent phase image classification results are compared to determine the change area; (5) return back to (3) until the partition, classification and change inspection of all T phase image are finished. The utility model has the advantages that: compared with the traditional pixel-oriented K value method, the classification and inspection precision are improved, The utility model is applicable for the change inspection of sequence remote sensing image and has wide application in hazard monitoring and land resource investigation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
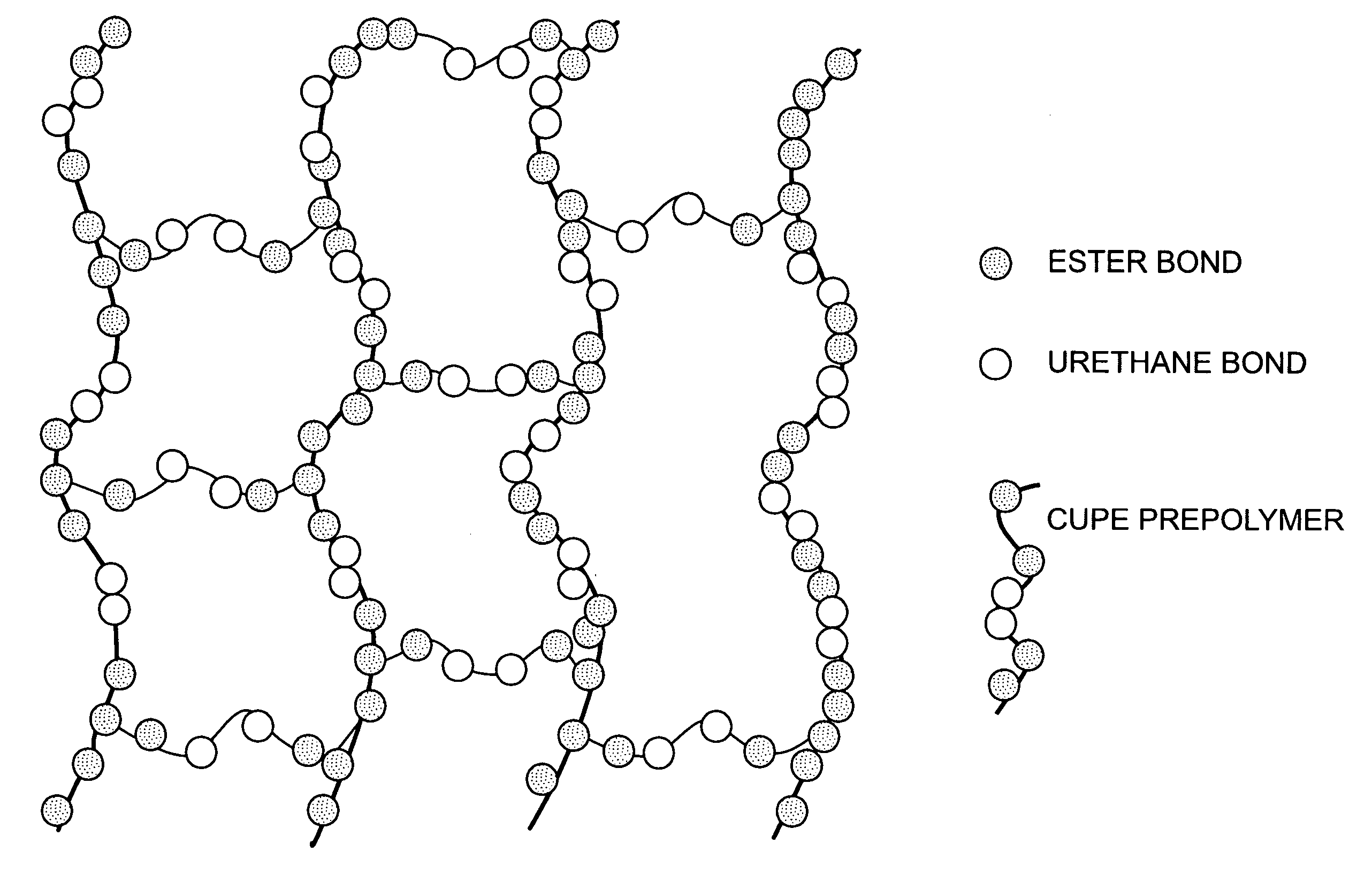
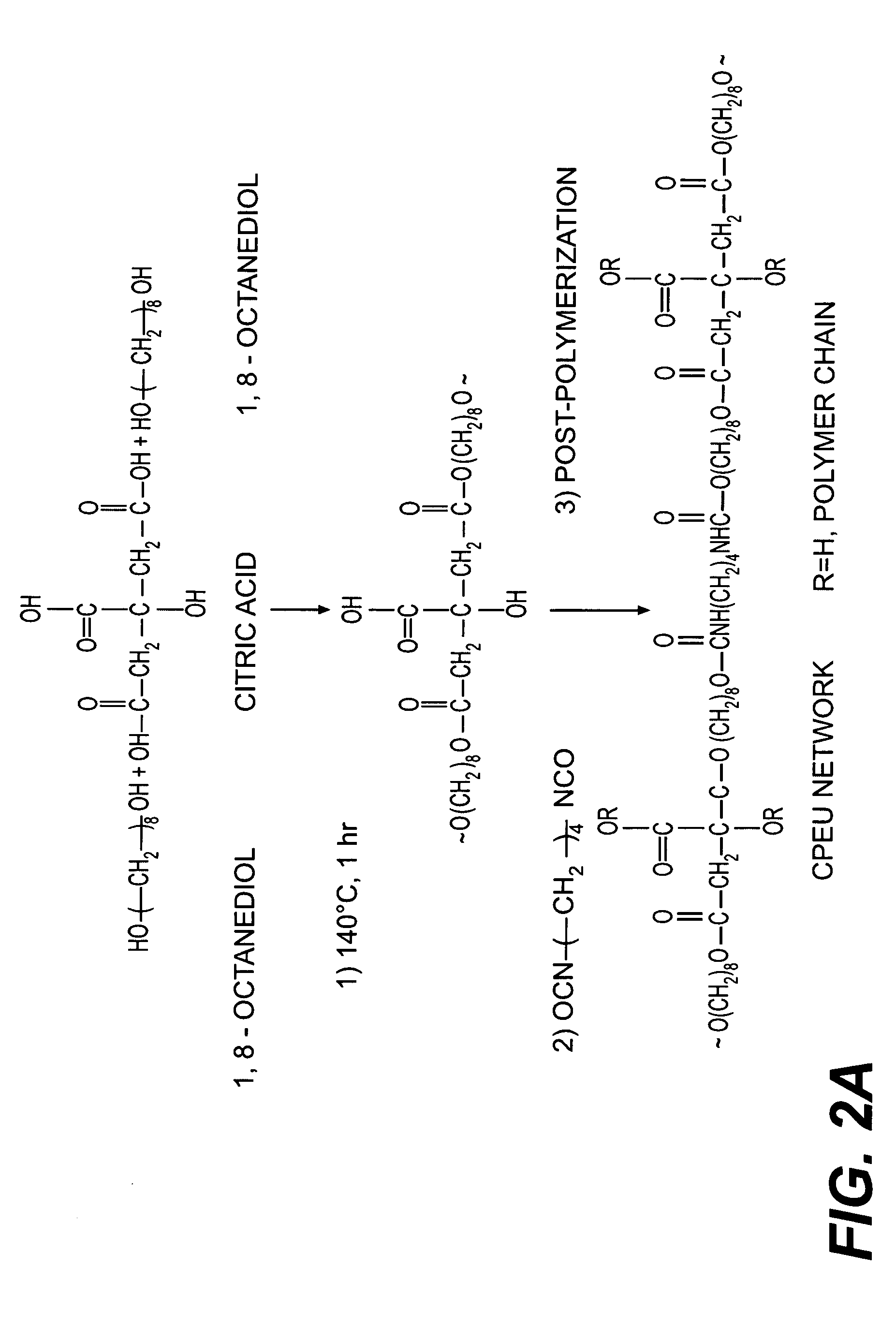
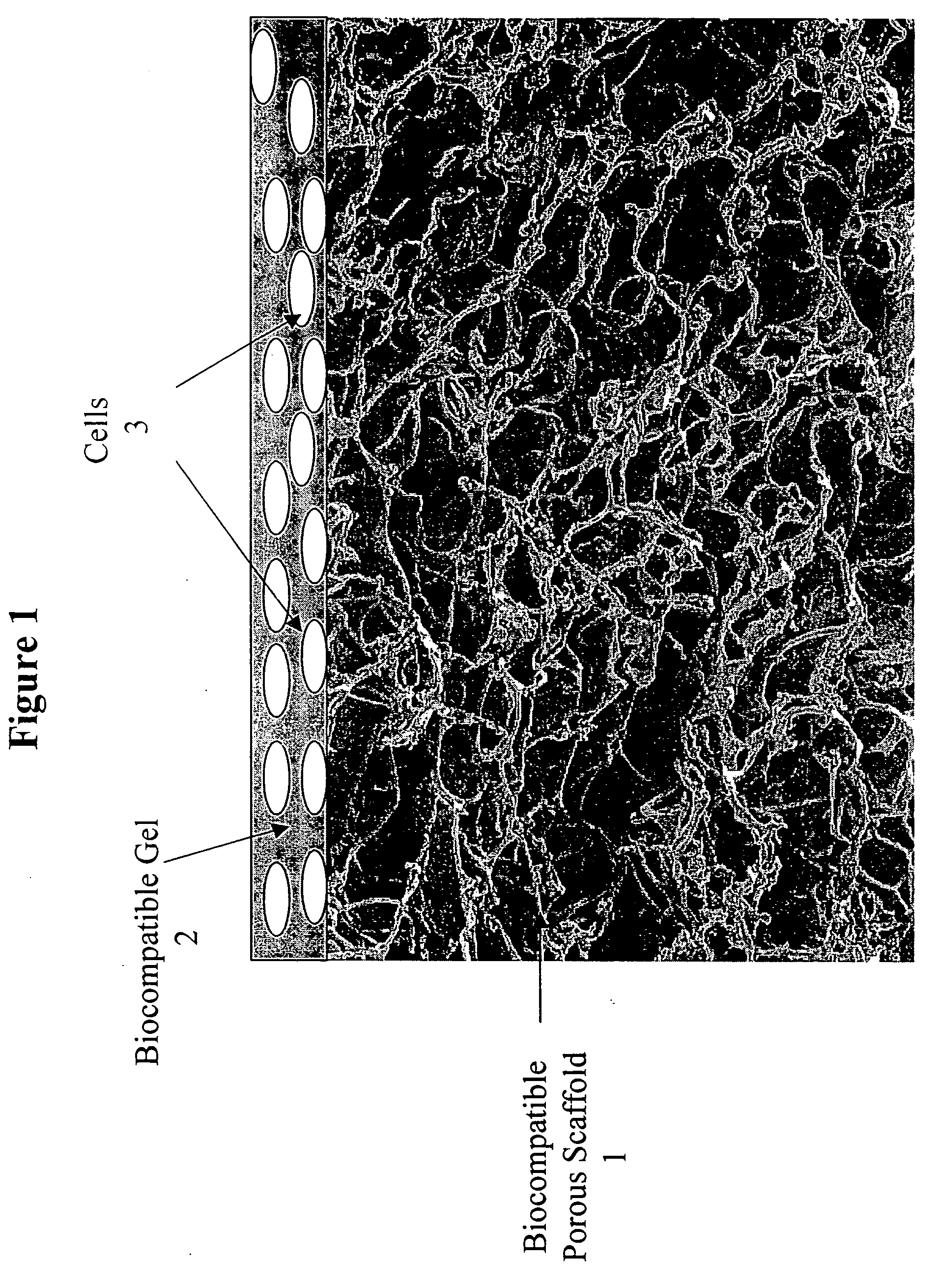
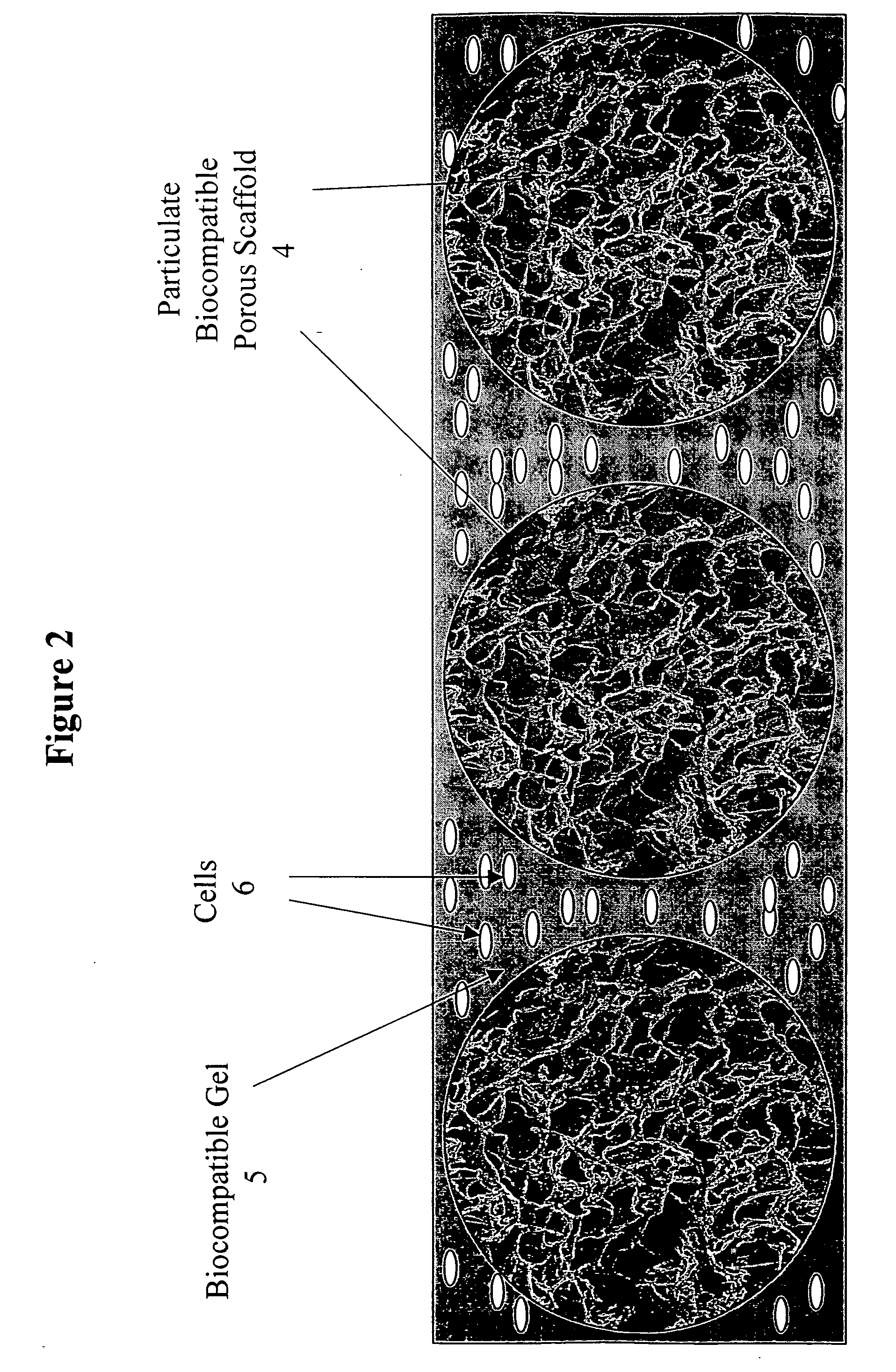
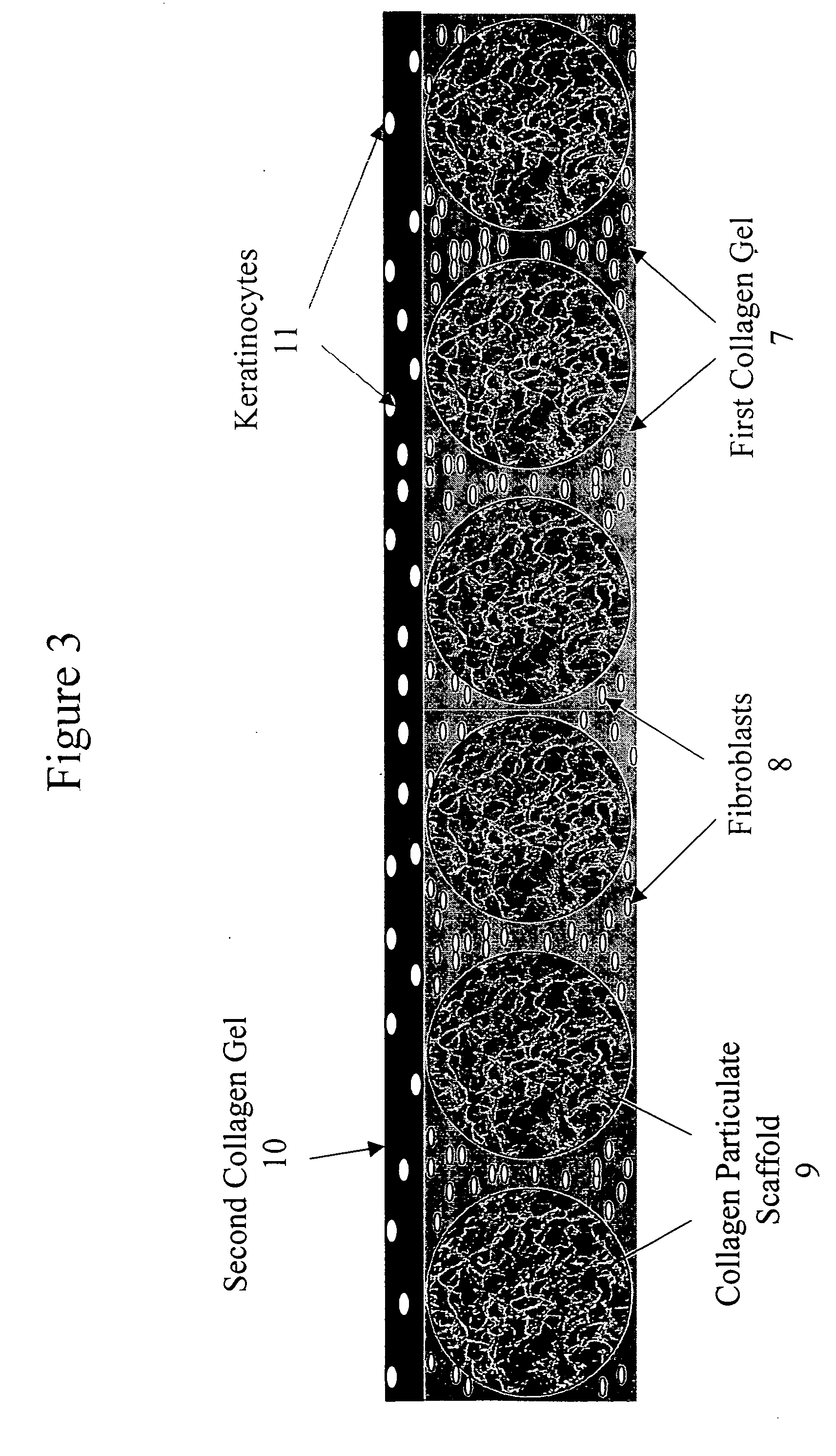
Bio-polymer and scaffold-sheet method for tissue engineering
ActiveUS20090093565A1Easy to divideAvoid communicationAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical adhesivesElastomerPolyester
A method of making a new type of biomaterials, biodegrable crosslinked urethane-containing polyester (CUPE) elastomers and a scaffold-sheet engineering method for tissue engineering applications is provided. CUPEs can be synthesized by forming a linear pre-polymer, which is a polyester, introducing the urethane bonds into polyester using a diisocyanate as a linker, and crosslinking the resulting urethane containing linear polymers to form CUPEs via post-polymerization. This family of polymers, CUPEs, exhibit excellent biocompatibility with desired degradation. Tissue engineering scaffolds made of CUPEs are soft and elastic, and have good mechanical strength. Complex tissue grafts can be constructed by a novel layer-by-layer (LBL) scaffold-sheet engineering design using CUPE sheets. CUPE scaffolds can provide openings for cell to cell communication across scaffold layers and angiogenesis into the depth of the construct. Biomolecules, such as anticoagulants, can be incorporated into the CUPE polymers, increasing their viability as vascular graft scaffolds.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
System and method for bladder detection using harmonic imaging
ActiveUS20090264757A1Improve Segmentation AccuracyEasy to divideUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsTransceiverHarmonic analysis
Systems, methods, and ultrasound transceivers equipped and configured to execute harmonic analysis and extract harmonic information related to a targeted organ of a subject are described. The methods utilize neural network algorithms to establish improved segmentation accuracy of the targeted organ or structures within a region-of-interest. The neural network algorithms, refined for detection of the bladder and to ascertain the presence or absence of a uterus, is optimally applied to better segment and thus confer the capability to optimize measurement of bladder geometry, area, and volumes.
Owner:VERATHON
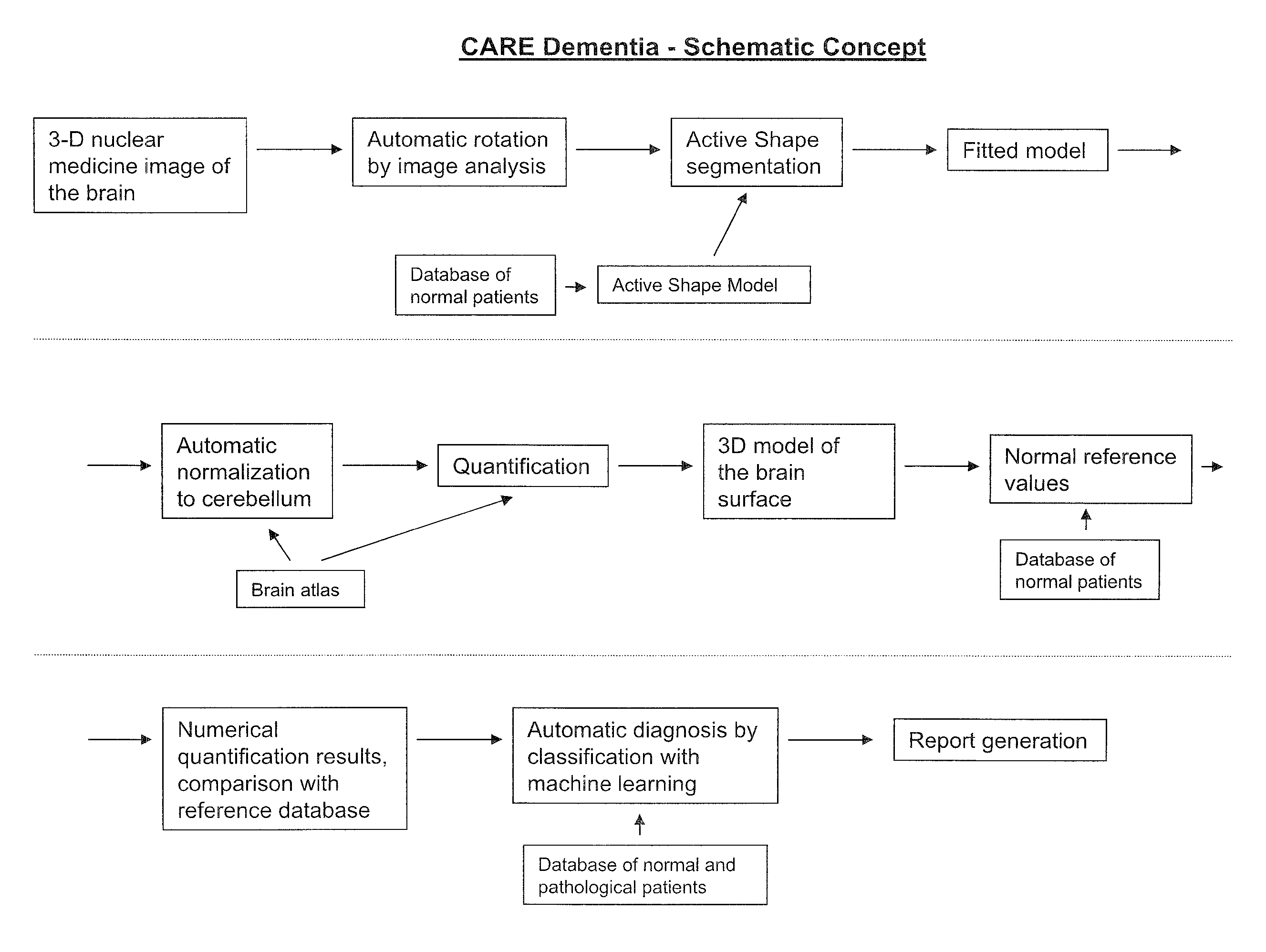
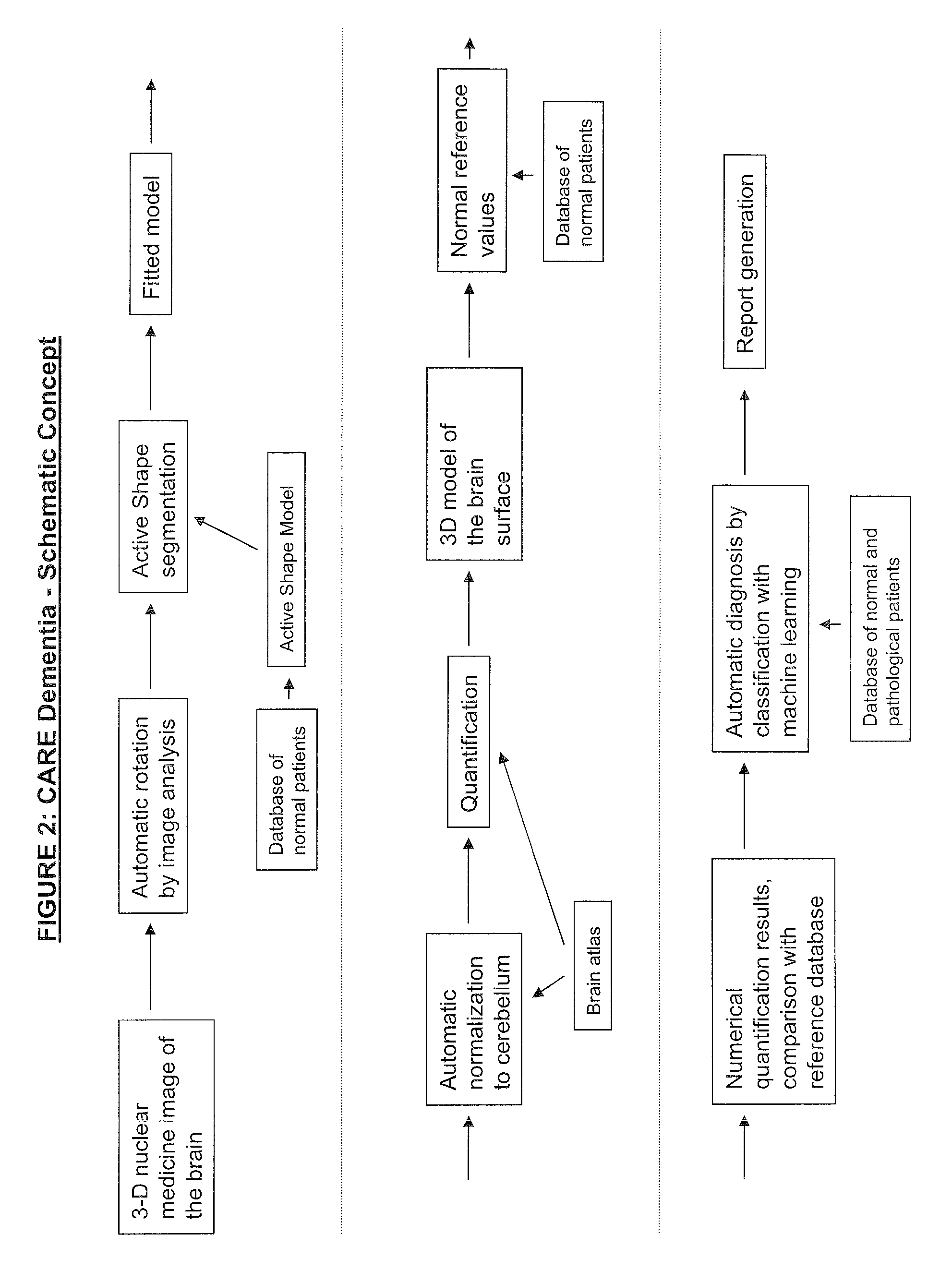
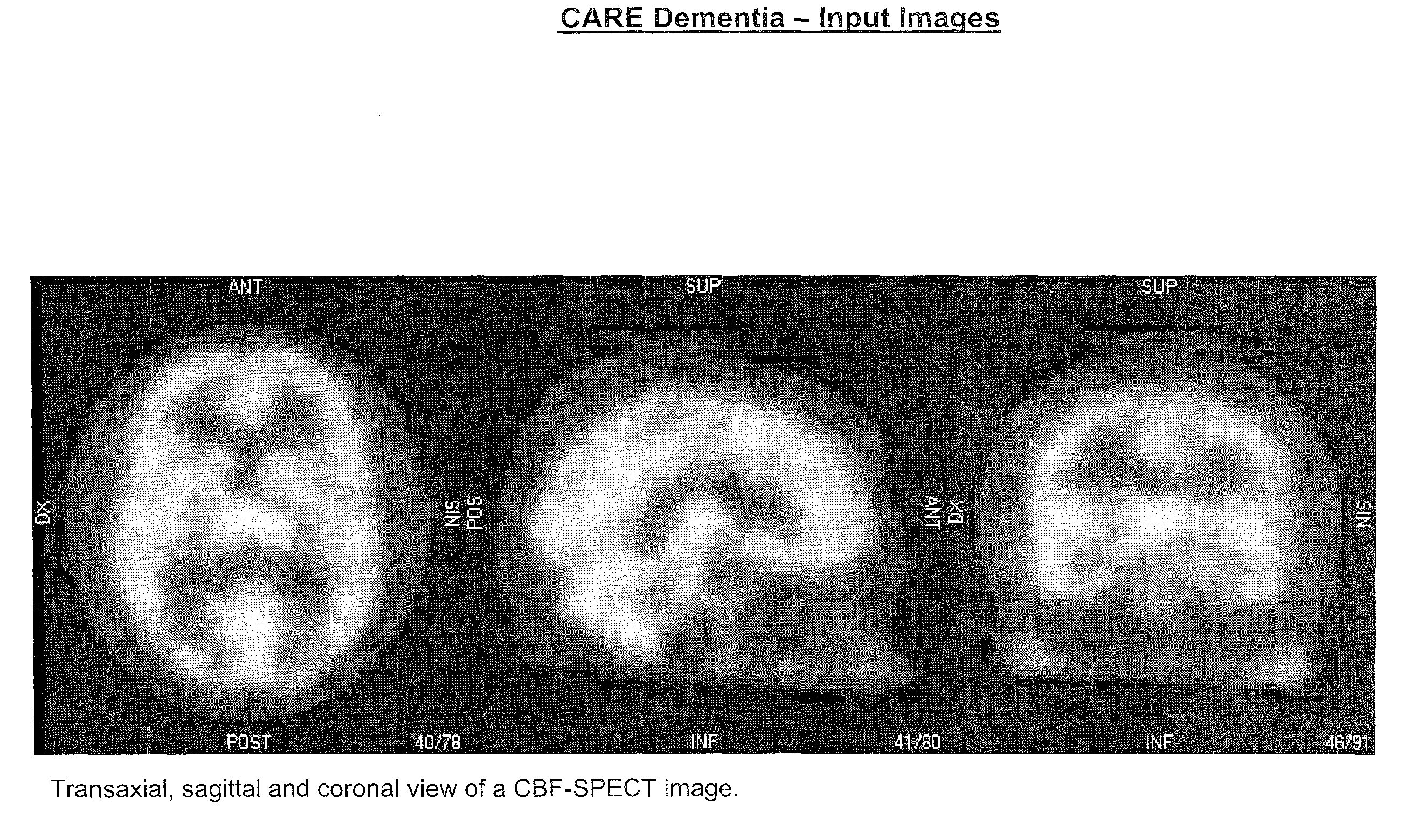
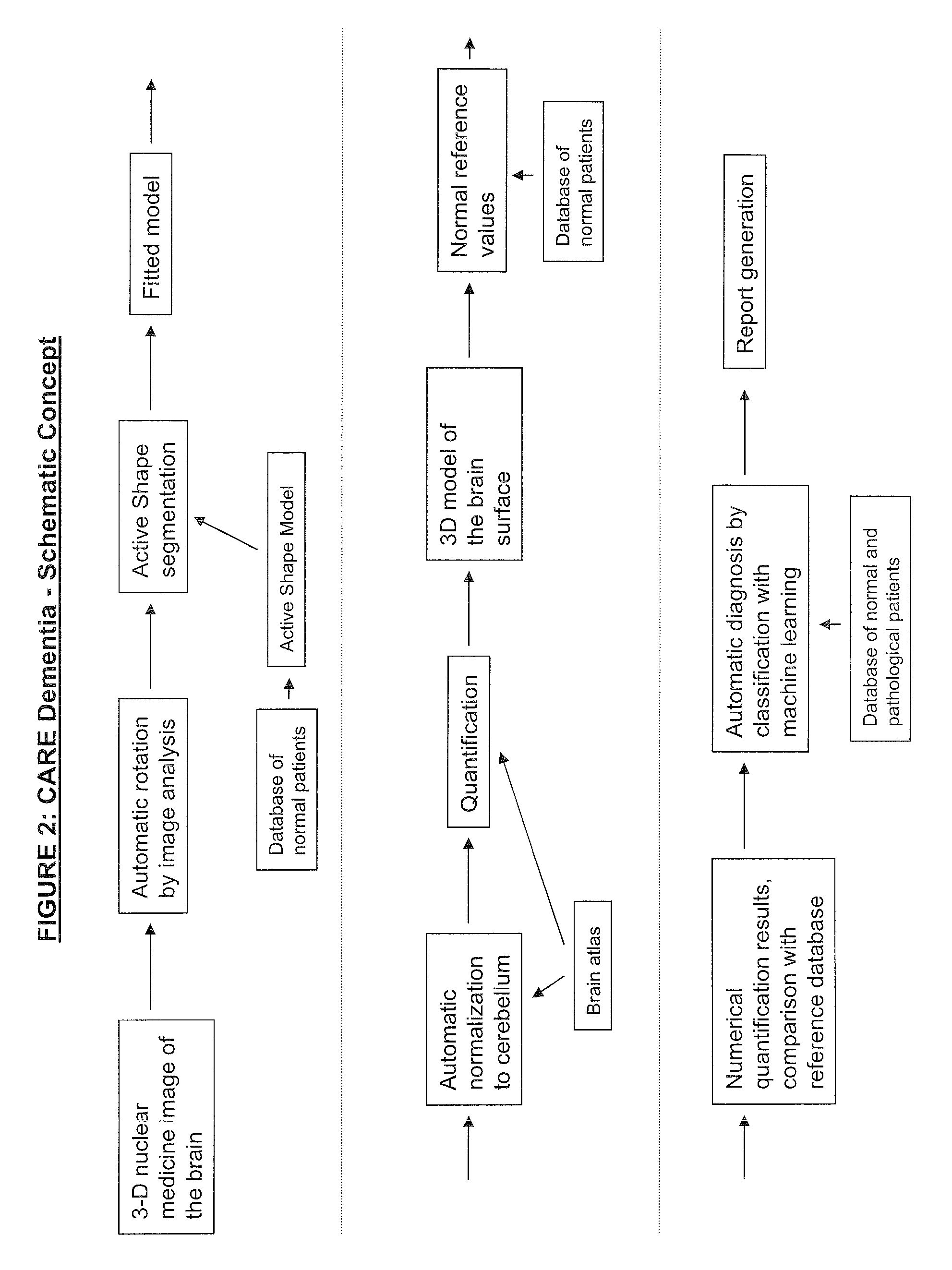
Automatic interpretation of 3-D medicine images of the brain and methods for producing intermediate results
ActiveUS8199985B2Shorten the timeAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFully automatic
Methods for fully automatic quantification and interpretation of three dimensional images of the brain or other organs. A system for Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of diseases affecting cerebral cortex from SPECT images of the brain, where said images may represent cerebral blood flow (CBF). The methods include image processing, statistical shape models, a virtual brain atlas, reference databases and machine learning.
Owner:EXINI DIAGNOSTICS
Tissue composites and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050129730A1Shorten the timeFacilitate cell compartmentalizationBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsTissue repairBiomedical engineering
The invention is directed to improved tissue composites, e.g., biocompatible composites, that overcome or minimize the problems associated with existing tissue repair systems, which can be easily prepared and maintained in a sufficient quantity, and suitable shapes, to enable a convenient treatment of tissues requiring repair. Additionally, the invention is directed to methods of preparation of these tissue composites and methods of use thereof.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
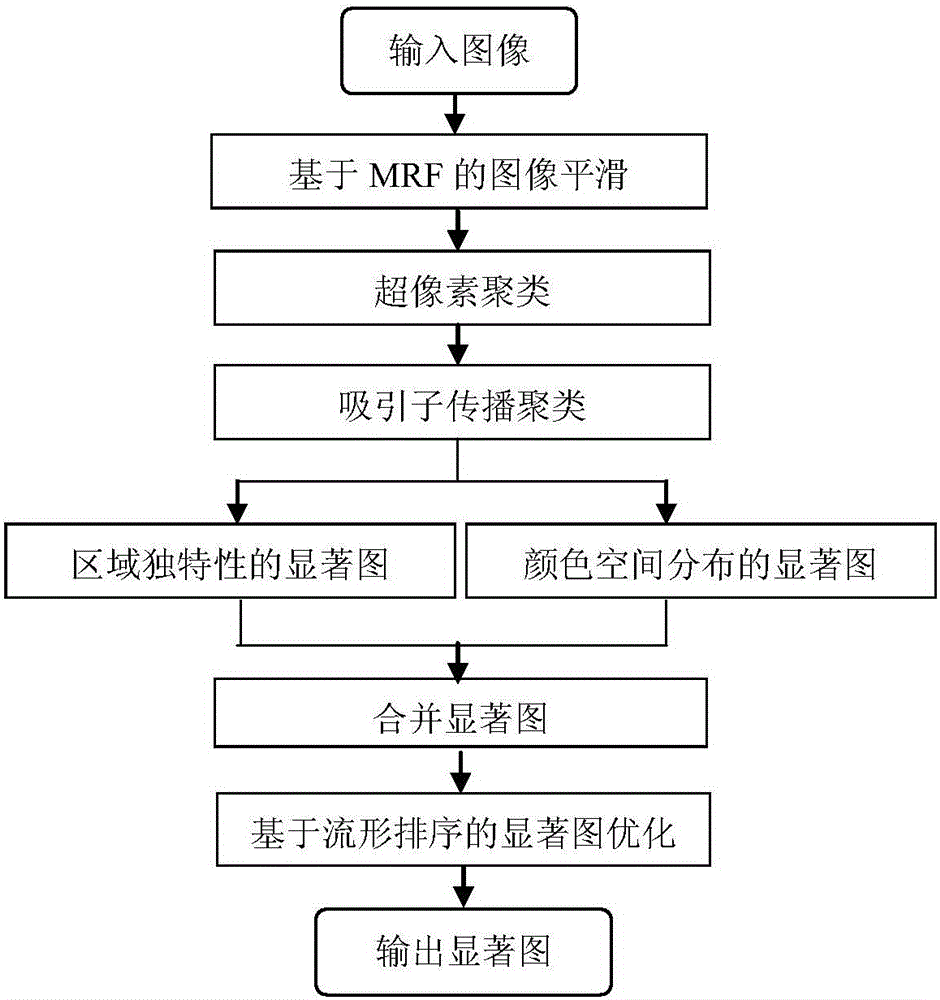
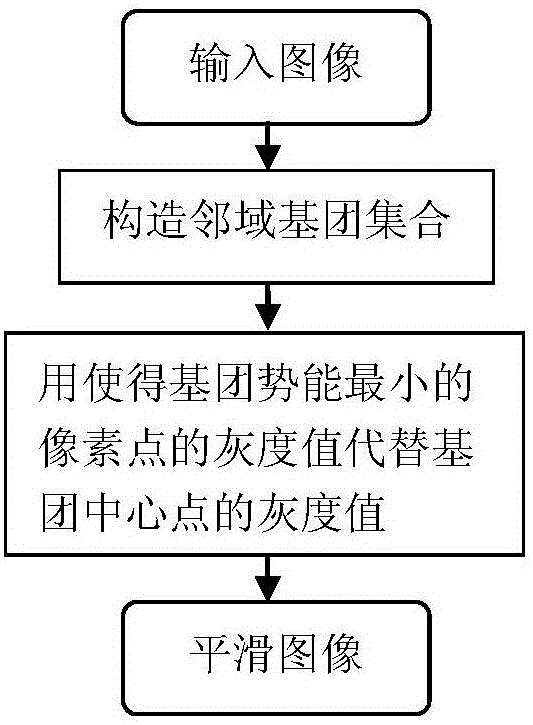
Graph model based saliency target detection method
ActiveCN105976378AImprove accuracyImprove clustering effectImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage segmentation
The invention relates to a graph model based saliency target detection method. First, the method includes improving the clustering effect of an HAIC (Hexagon Arrangement Iteration Clustering) algorithm by using MRF overall potential energy minimization image smoothing; dynamically setting a threshold value so as to enable areas similar in color while communicating with each other in space to be divided into the same area by utilizing an improvement-based graph model for image division; combining areas with rich borders and improving excess division of image borders by using an attractor propagation clustering method. Second, the method includes optimizing a saliency graph by adopting a manifold ranking algorithm according to a manifold structure among super pixels so as to highlight the whole saliency area in the final saliency graph further.
Owner:重庆诺思达医疗器械有限公司
Contact network failure detection and diagnosis method based on unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN102129564ASave storage spaceReduce computationBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionContact networkDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses a contact network failure detection and diagnosis method based on an unmanned aerial vehicle, which comprises the following steps: (1) image acquisition: carrying a video camera to shoot along a contact network by an unmanned aerial vehicle so as to respectively acquire contact network images under visible light and infrared light; (2) image graying; (3) image enhancement; (4) image segmentation; (5) image dissection; (6) image fusion: fusing Laplacian pyramid layers under visible light with corresponding Laplacian pyramid layers under infrared light, and carrying out image reconstruction on the fused Laplacian pyramid to obtain a contact network component image after the visible light image and the infrared light image are fused; and (7) carrying out image identification and failure judgment by a BP (back-propagation) neural network. The method can be used for effectively acquiring a contact network image in the operation process of a locomotive in a multidirectional multiangular real-time mode, automatically identifying the contact network component in the image, and judging whether the contact network fails and the type of the failure; and the judgment result is more accurate and reliable, and can better ensure the safety of railway transportation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Automatic interpretation of 3-d medicine images of the brain and methods for producing intermediate results
ActiveUS20100067761A1Shorten the timeAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFully automatic
Methods for fully automatic quantification and interpretation of three dimensional images of the brain or other organs. A system for Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) of diseases affecting cerebral cortex from SPECT images of the brain, where said images may represent cerebral blood flow (CBF). The methods include image processing, statistical shape models, a virtual brain atlas, reference databases and machine learning.
Owner:EXINI DIAGNOSTICS
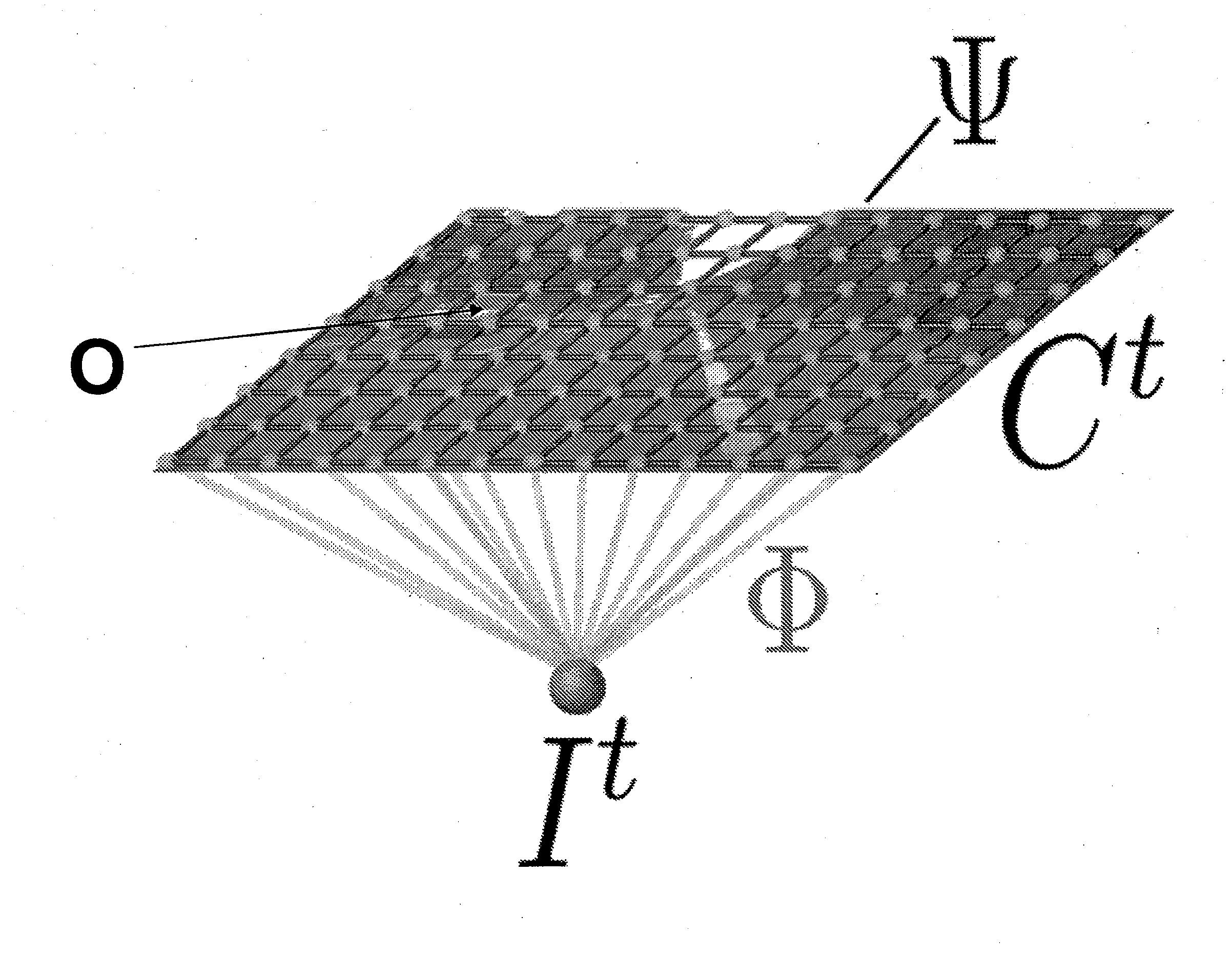
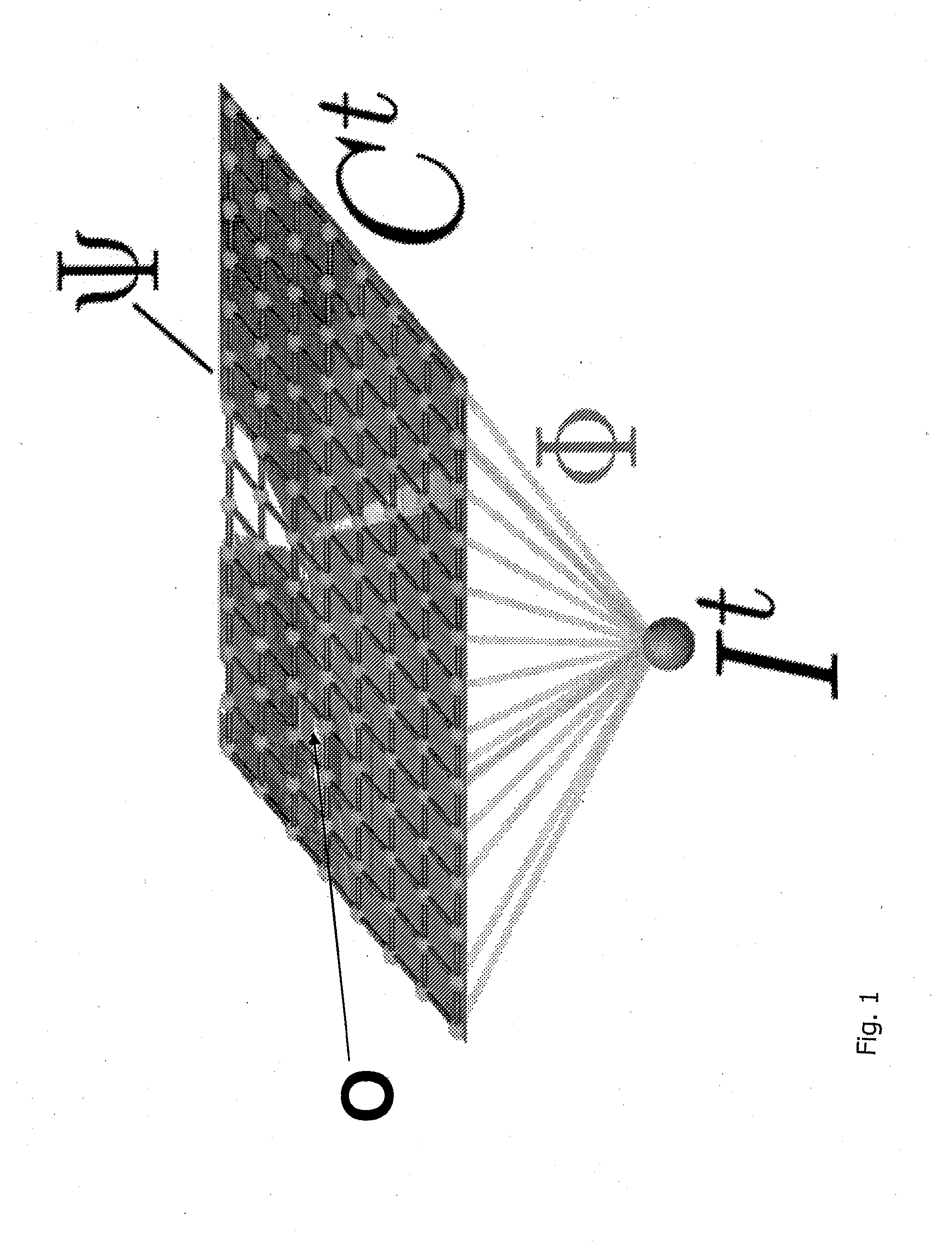
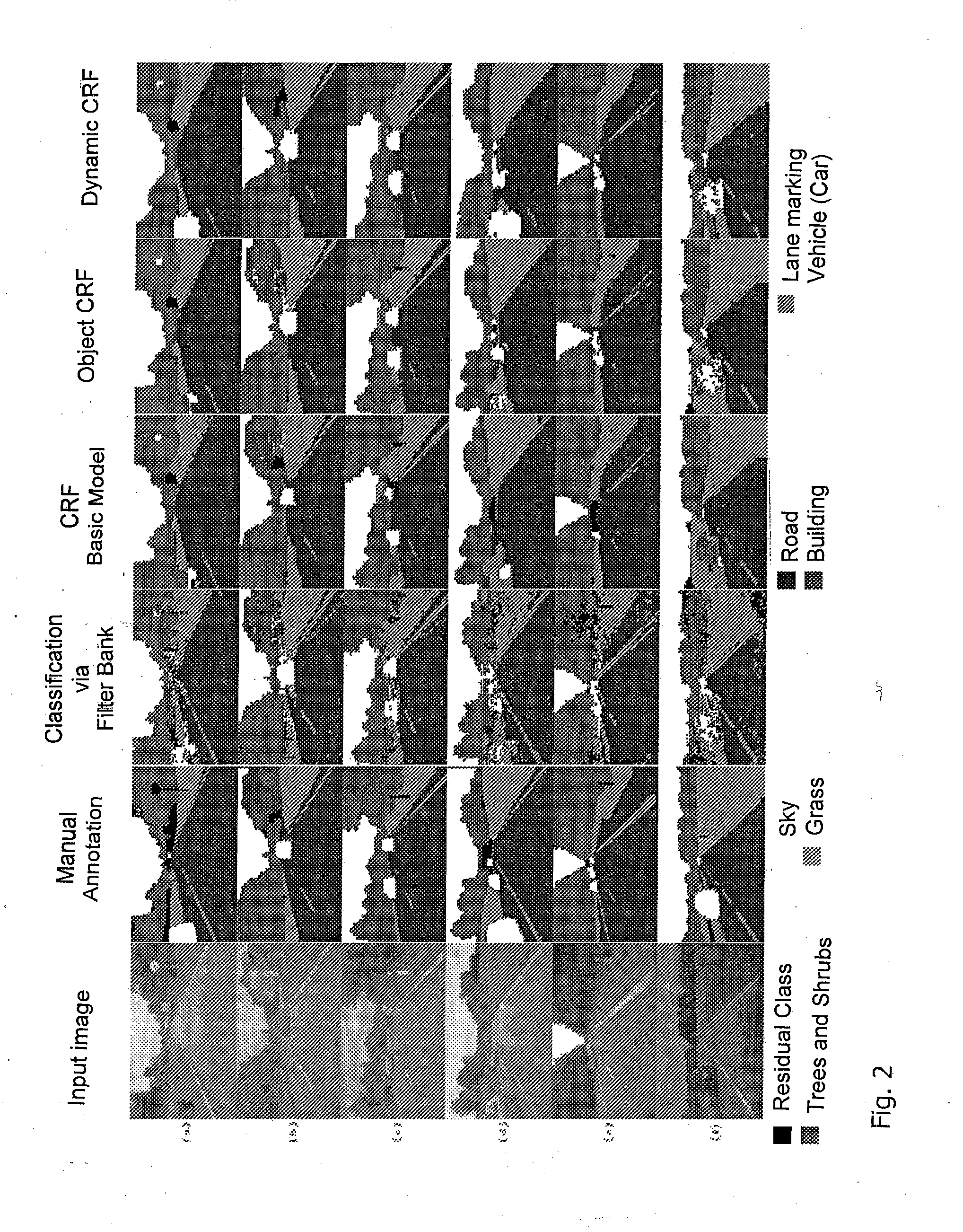
Method and device for analyzing surrounding objects and/or surrounding scenes, such as for object and scene class segmenting
ActiveUS20110200230A1Easy to divideImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionConditional random fieldObject detector
The invention relates to a method and an object detection device for analysing objects in the environment and / or scenes in the environment. The object detection device includes a data processing and / or evaluation device. In the data processing and / or evaluation device, image data (xt) is evaluated on the basis of a Conditional Random Field (CRF) model and the CRF model provides additional object nodes (otn) which take into account information from an object detector.
Owner:A D C AUTOMOTIVE DISTANCE CONT
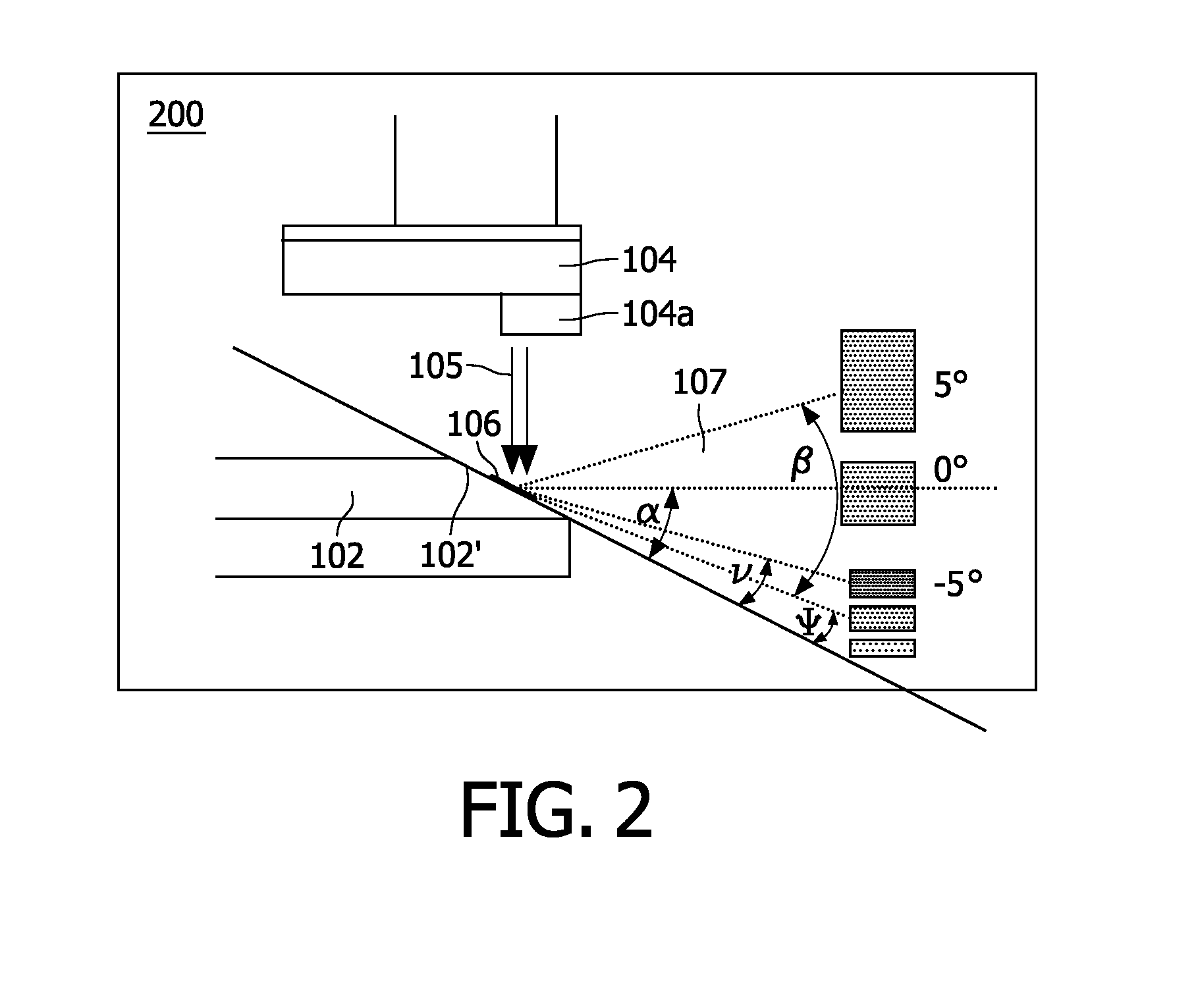
Multi-segment anode target for an X-ray tube of the rotary anode type with each anode disk segment having its own anode inclination angle with respect to a plane normal to the rotational axis of the rotary anode and X-ray tube comprising a rotary anode with such a multi-segment anode target
InactiveUS8520803B2Maximum brightnessMaximized power ratingX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingRotational axisImaging quality
The present invention refers to X-ray tubes for use in imaging applications with an improved power rating and more particularly, to a multi-segment anode target (102′) for an X-ray based scanner system using an X-ray tube of the rotary anode type; the X-ray tube including a rotatably supported essentially disk-shaped rotary anode (102) with an anode target (102′) for emitting X-radiation when being exposed to an electron beam (105a) incident on a surface of the anode target (102′), wherein the rotary anode disk (102) is divided into at least two anode disk segments (102a and 102b) having a conical surface inclined by a distinct acute angle (α) with respect to a plane normal to the rotational axis (103) of the rotary anode disk (102), thus having its own focal track width. An advantage of the invention consists in an enhanced image quality compared to conventional rotary anodes as known from the prior art.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Fast object recognition algorithm
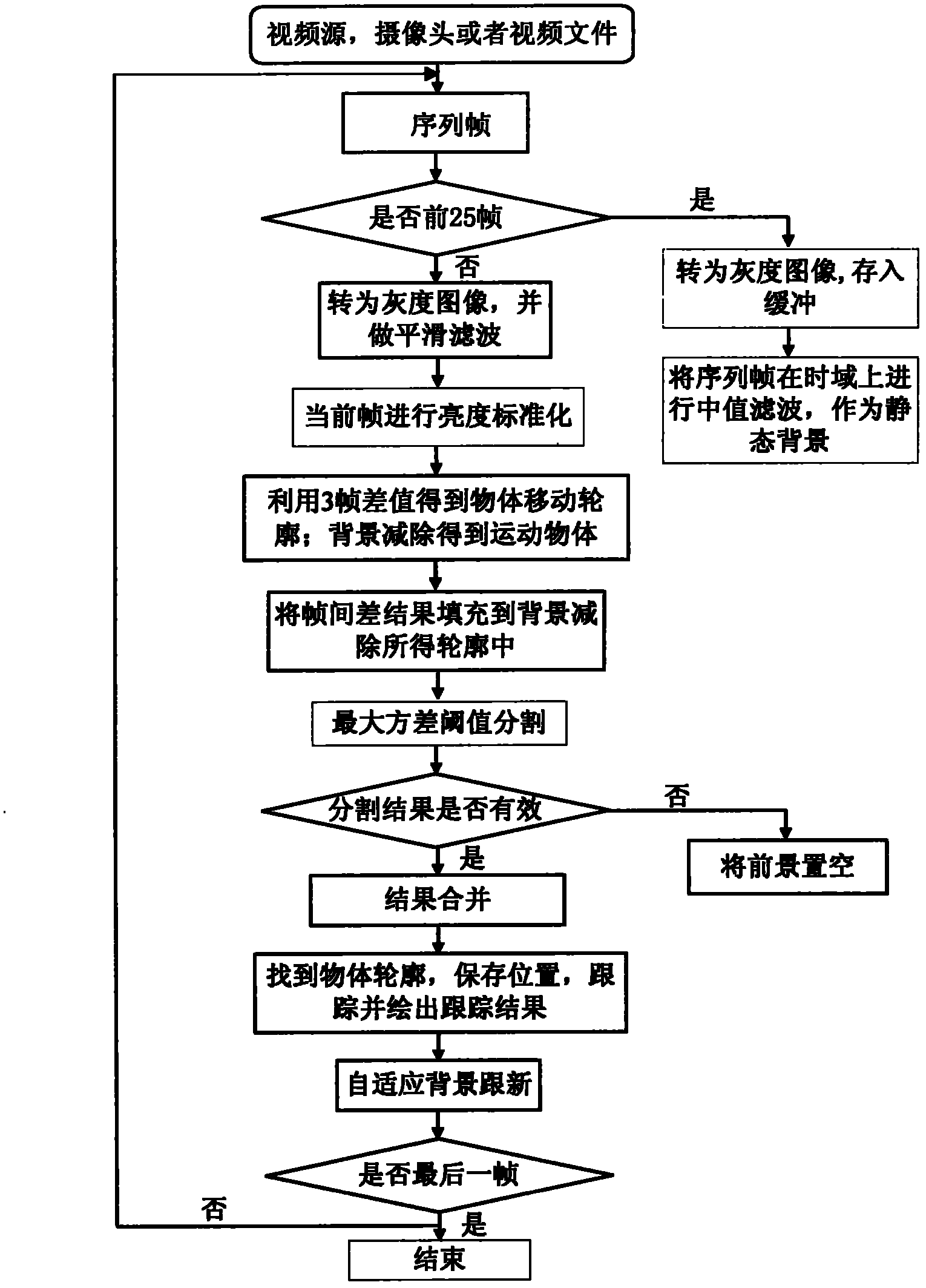
InactiveCN102222214AImprove robustnessEasy to divideImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainRecognition algorithm
The invention relates to a fast object recognition algorithm comprising the following steps of: firstly, carrying out median filtering on approximately one second sequence frame in time domain so as to be taken as a static background; secondly, determining a moving object by utilizing the fusion algorithm of background subtraction and interframe difference; thirdly, carrying out binaryzation on the obtained result by utilizing maximum variance threshold segmentation, and simultaneously analyzing the effectiveness of the segmentation; and finally, merging the results of the effective segmentation, and tracking by utilizing Kalman filtering. The intelligent video object-tracking method has good tracking effect and high robustness, dispenses with manual intervention and effectively avoids the phenomena of tracking and alarming by mistake.
Owner:SUZHOU YISIKANG INFORMATION TECH
Environmental electrical generator
An electricity generator having variable capacitors that each includes a repeatedly stretched and relaxed sheet (20, FIG. 3) of SM (stretchable material) and electrodes (22, 24) lying against opposite faces of the sheet, which includes a power extraction unit (110, FIG. 9) coupled to the electrodes of at least a pair of capacitors that are activated out of phase with each other. The unit directs an electrical charge (current) from a first pair of electrodes that have a higher voltage, to one or more second pairs of electrodes that have a lower voltage, to recharge the second pairs of electrodes. During the current flow electrical power is extracted by the drop in voltage of current passing through the unit. The power extraction unit can be provided with a control unit that has voltage detectors (54) and that selectively connect capacitors, based on their voltages, for maximum efficiency in generating power output.
Owner:SINGLE BUOY MOORINGS INC
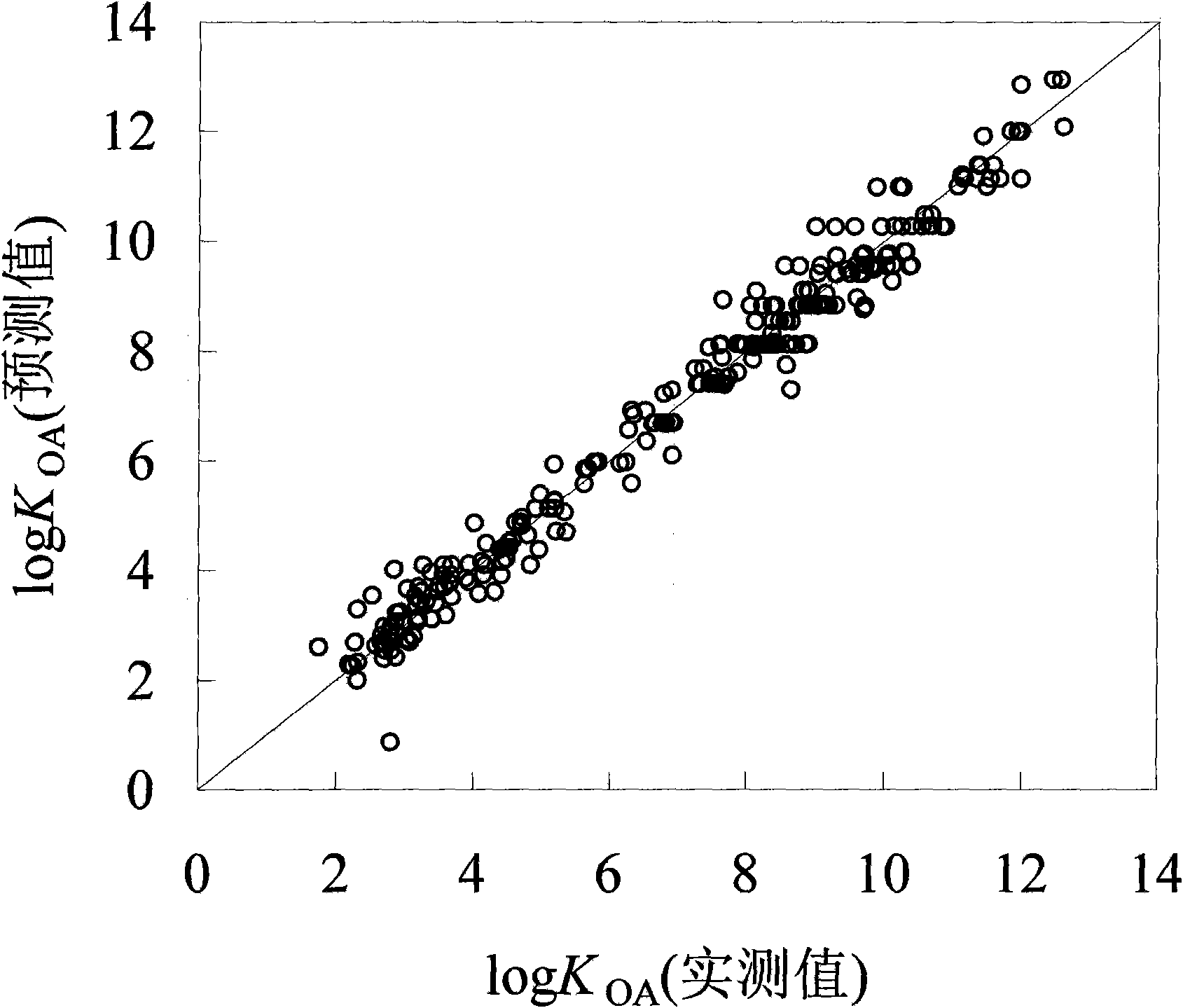
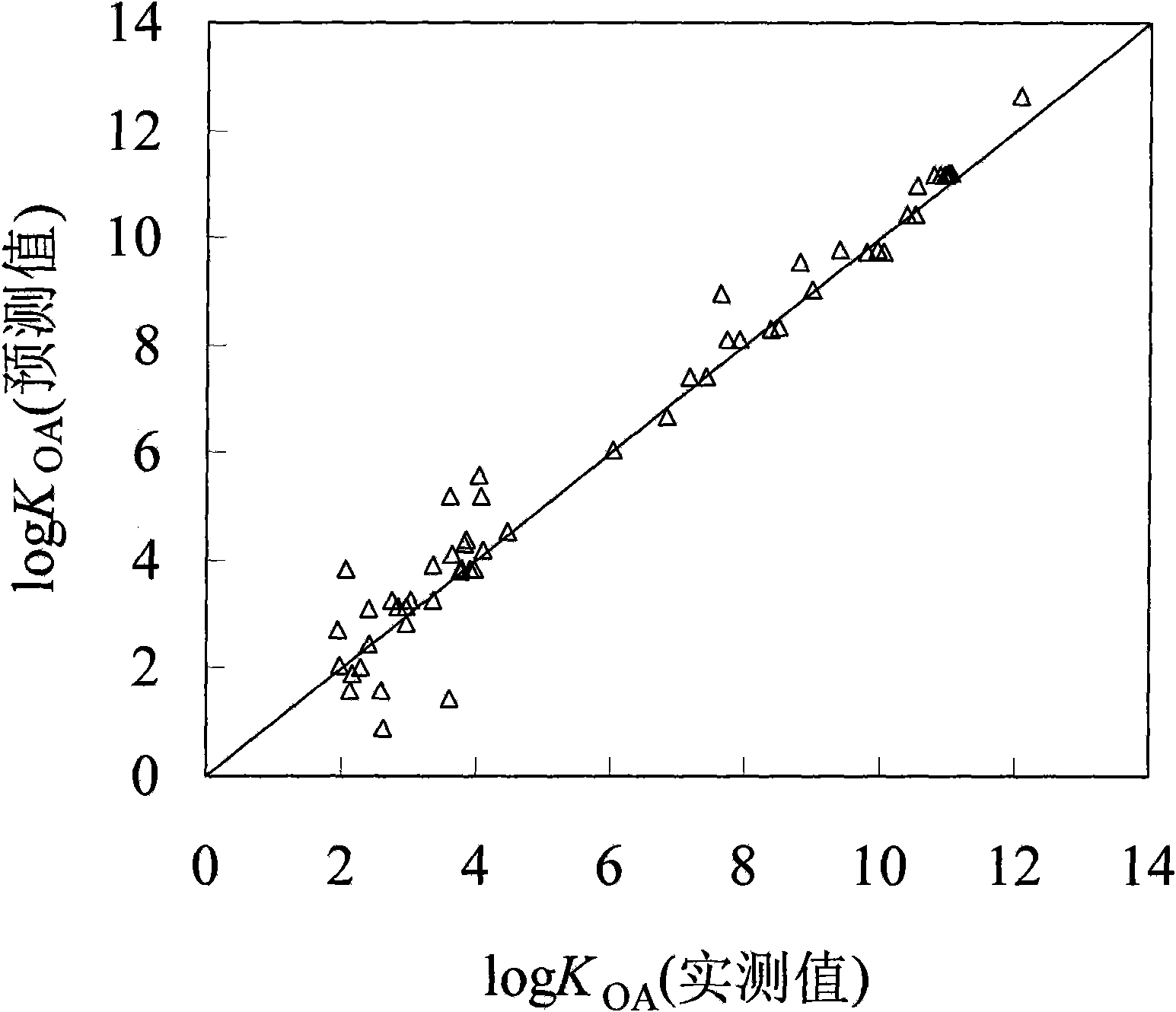
Method for fast predicting organic pollutant n-caprylic alcohol/air distribution coefficient based on molecular structure
InactiveCN101673321AEasy to divideQuick divisionSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive methodsExternal validation
The invention discloses a method for fast predicting organic pollutant n-caprylic alcohol / air distribution coefficient based on molecular structure, belonging to the technical field of quantifying structure / active relationship (QSAR) facing to the environmental risk evaluation. The method is characterized of comprising the steps of: adopting the molecular structure of atomic center fragment characterization compound; and screening the atomic center fragment combination by means of stepwise regression and partial least-squares regression, to build a group contribution model for predicting KOA.The internal authentication and the external authentication improves that the built KOA group contribution model has stability and predicting capability, and a range and distance method and a probability density method express the application domain of the group contribution model, thereby defining the application range of the model and guaranteeing the predict accuracy. The method has the effectsand benefits of being capable of fast predicting the KOA of the high flux compound, obtaining the KOA with low cost, being helpful for obtaining the high flux KOA data, and having a significant meaning for the environment supervision and the risk evaluation of chemicals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
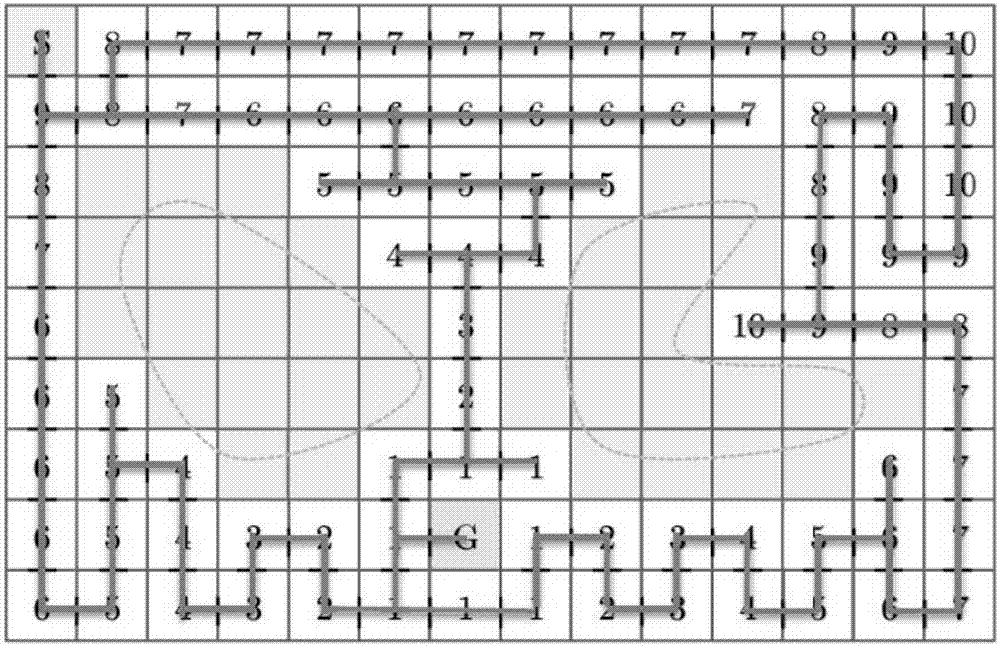
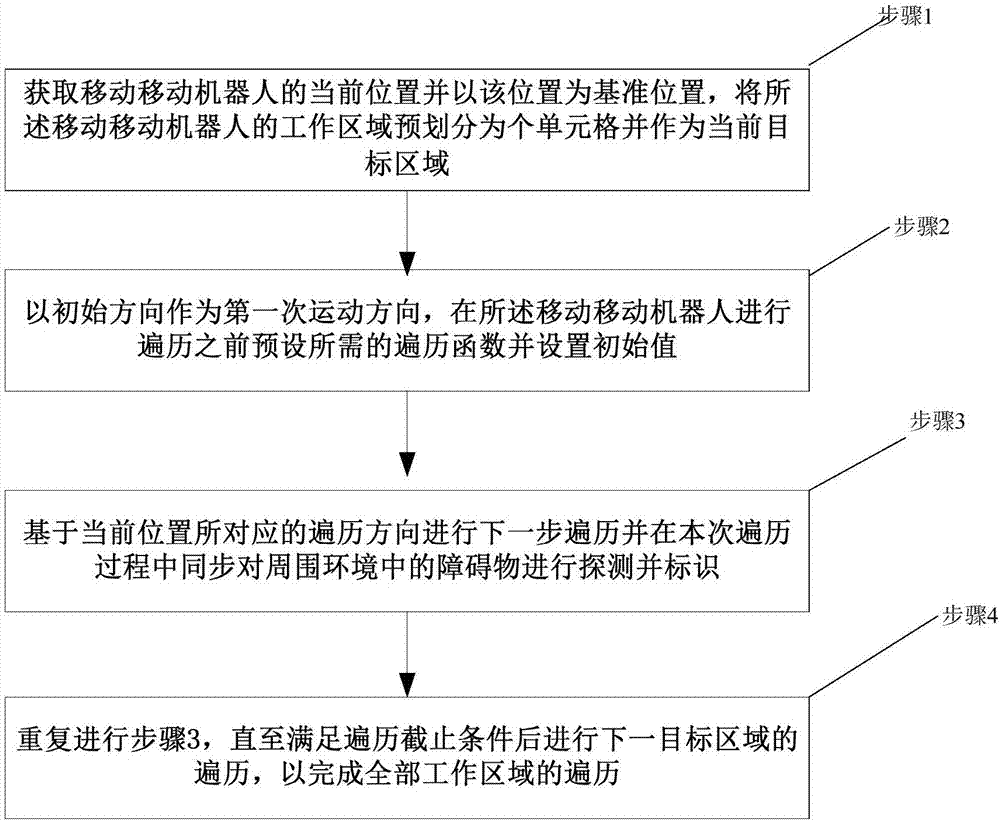
Full coverage path planning method of mobile robot
ActiveCN107505939AImprove traversal efficiencyShorten the planning pathPosition/course control in two dimensionsPlanning approachEngineering
The invention discloses a full coverage path planning method of a mobile robot. The method comprises: step one, a current position of a mobile robot is obtained and with the position as a reference position, a working area of the mobile robot is divided into a plurality of unit cells in advance to form current target regions; step two, with an initial direction as a first movement direction, a needed traversal function is preset before traversing by the mobile robot and an initial value is set; step three, next traversing is carried out based on a traversing direction corresponding to a current position and an obstacle in an environment is detected and identified synchronously during the traversing process; and step four, the step three is repeated and traversing of a next target region is carried out until a traversing cut-off condition is met, so that traversing of all working areas is completed. The method has advantages of high coverage rate, low repetition coverage rate and short consumption time.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
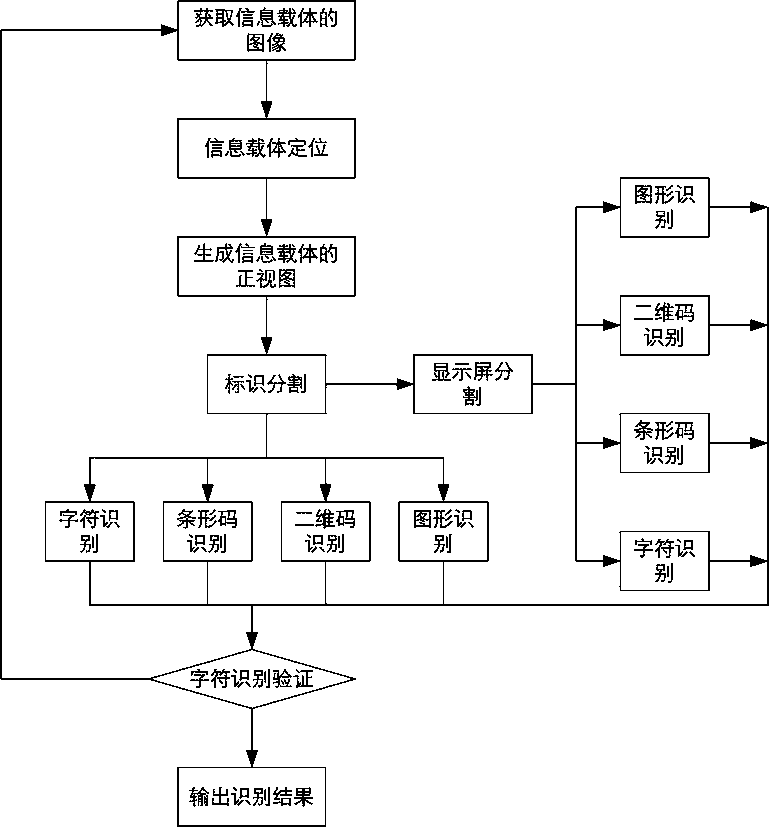
Identification method for information carrier comprising multi-type identifications
ActiveCN104392238AAccurate Segmentation MarkEasy to divideCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationGraphicsAlgorithm
The invention brings forward an identification method for an information carrier comprising multi-type identifications. The information carrier can be a product label. By use of auxiliary positioning identification and a corresponding positioning identification detection identification algorithm, auxiliary positioning identifications on the information carrier are automatically identified, such that automatic positioning of multi-type data is realized. By use of an image identification algorithm, such information as characters, bar codes, display contents of display screens, two-dimensional codes, images and the like can be simultaneously identified, and the electronic display screens can display such contents as the characters, the bar codes, the two-dimensional codes, the images and the like, such that the information carrier has abundant information, and the identification results are accurate and reliable. Compared to bar code identification, two-dimensional code identification and image identification, character identification is smaller in characters and high in character segmentation and character identification difficulty. In order to ensure the accuracy of the character identification, the identification results are verified for the character identification by use of already known character lengths.
Owner:樊晓莉
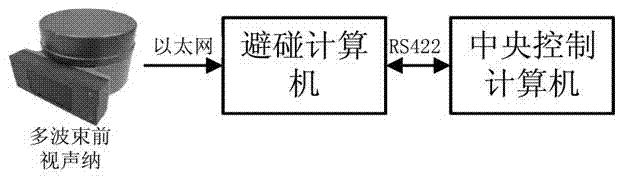
Obstruction automatic recognition system for collision preventing of large-scale autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV)
InactiveCN103033817AEasy to divideGood segmentation resultCharacter and pattern recognitionAcoustic wave reradiationSonarNetwork communication
The invention discloses an obstruction automatic recognition system for collision preventing of a large-scale autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) and belongs to the technical field of digital image processing. The system comprises a multi-beam foresight sonar, a sonar computer and a central control computer. Network communication passes between the foresight sonar and the sonar computer. The sonar computer is connected with the central control computer through RS 422. The multi-beam foresight sonar collects information of an obstruction. The information is converted to an image and is sent to the sonar computer. The sonar computer receives the image and figures out information about distance, location, size of the obstruction in real time and sends the information to the central control computer. The obstruction automatic recognition system for the collision preventing of the large-scale AUV is strong in real-time judging of the obstruction, free of prior knowledge and suitable for the large-scale AUV.
Owner:710TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Method for segmenting an image and an image transmission system and image transmission unit therefore
InactiveUS20070003138A1Easy to operateRobust algorithmImage enhancementImage analysisImage transferImage segmentation
A method (500) for segmenting an image comprises the step of identifying (502) one or more regions in the image. The method further comprises the steps of applying a single embedded surface for a Level Sets representation of said image; and performing region control logic (504) to enable said Level Sets, representation to manipulate one or more region boundaries in order to segment said image. This provides a method by which unsupervised image segmentation can be performed on an arbitrary number of classes / objects in the image.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
FCN retina image blood vessel segmentation through combination of depth separable convolution and channel weighing
InactiveCN108510473AAvoid image processingHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionRetina
The present invention relates to an FCN retina image blood vessel segmentation through combination of depth separable convolution and channel weighing. The method comprises the steps of: 1) performingCLAHE and Gamma correction to enhance a contrast ratio of a green channel of an eye bottom image; 2) in order to adapt network training, performing partitioning of the enhanced image to expand data;and 3) replacing a standard convolution mode with depth separable convolution to increase the width of the network, and introducing a channel weighing module to explicitly perform modeling of a dependency relation of a feature channel so as to improve the separability of the features. The depth separable convolution and the channel weighing are combined to be applied into the FCN network, an expert manual identification result is taken as supervision to perform experiment in a DRIVE database. The result shows that: the method can accurately perform segmentation of the retina image blood vessels and has high robustness.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Biological sequence data-base searching multilayered accelerating method based on flow process
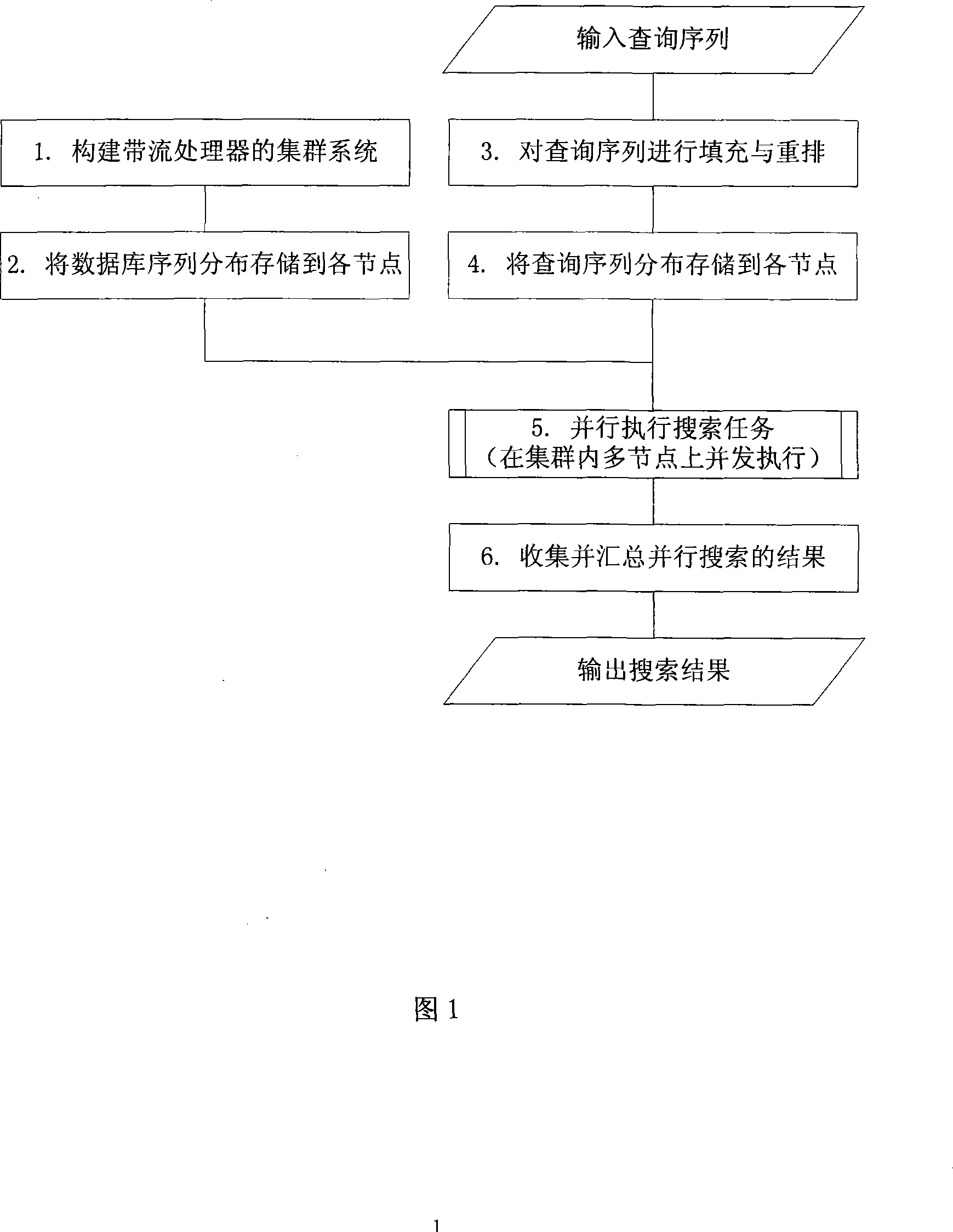
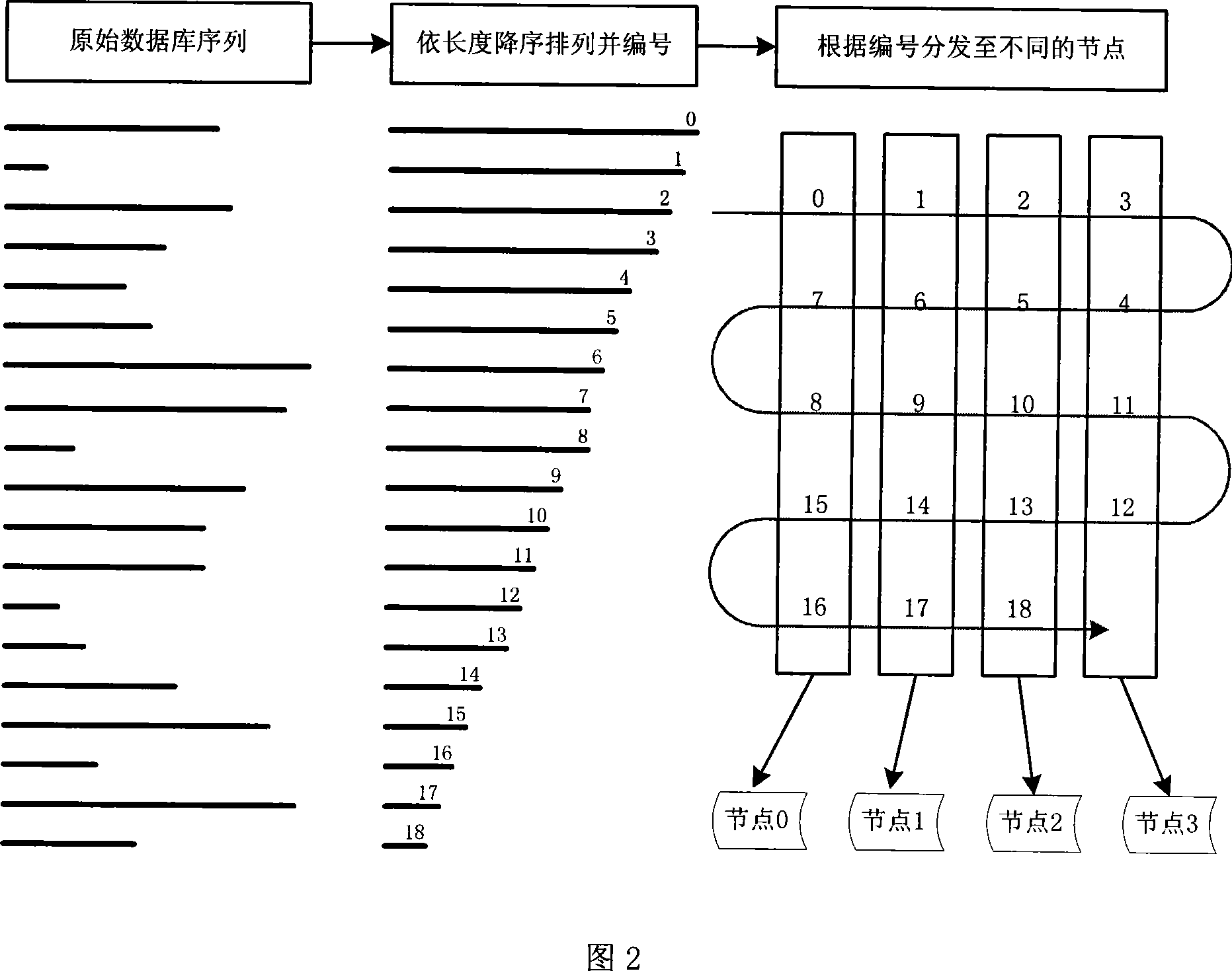
InactiveCN101158952AImprove search speedIncrease computing speedSpecial data processing applicationsCluster systemsSequence database
The invention discloses a multi-level acceleration method of flow-based biological sequence database search, which is to accelerate the search speed of a biological sequence database on the premise of ensuring search accuracy and relatively low cost. The technical proposal is that a cluster system composed of a plurality of personal computers shall be created firstly, and a master control node machine is assigned; the master control node machine distributes the database sequence and stores into each node machine in the cluster system, so as to fill and rearrange an inquiry sequence, and distribute the inquiry sequence to all the node machines in the cluster system; each node machine executes the search task in parallel, so as to be responsible for the completion of search tasks of the inquiry sequence in a local database sequence; the master control node machine collects, summarizes and outputs the results of parallel search tasks on all the node machines. The invention makes the search tasks be executed in parallel between the n node machines of the cluster, each node machine distributes the comparative calculation task of two sequences to p hardware calculation clusters to be conducted in parallel, thereby realizing the multi-level acceleration objective in parallel of three layers including a cluster node layer, a flow-level calculation layer, as well as a flow inner core command layer.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Specimen collection system
Owner:MERIDIAN BIOSCIENCE
Spiral static mixer
The invention discloses a spiral static mixer which is applied to mixing of multiple materials and particularly mixing of high-viscosity materials. The spiral static mixer comprises a shell, mounting flanges, left rotating blades and right rotating blades and is characterized in that the mounting flanges are respectively arranged at the two ends of the shell, the left rotating blades and the right rotating blades are in multiple-spiral blade structures and sequentially and alternately arranged from an inlet of the shell to an outlet of the shell, the adjacent left rotating blades and right rotating blades are fixedly connected at the periphery in a staggering manner, and a washing lifting ring is connected at one end of a blade group formed by the left rotating blades and the right rotating blades. The spiral static mixer provided by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, high mixing efficiency, convenience and fastness in installation, low cost, convenience in washing and suitability for long-time working; a mixed blade unit can be replaced; and the spiral static mixer is more widely applied to mixing of the high-viscosity materials in the chemical engineering industry.
Owner:MECHANICS RES & DESIGN ACAD SICHUAN PROV
Motive target imaging method of synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN1769925AEasy to divideRealize separate detectionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInverse synthetic aperture radarFrequency domain
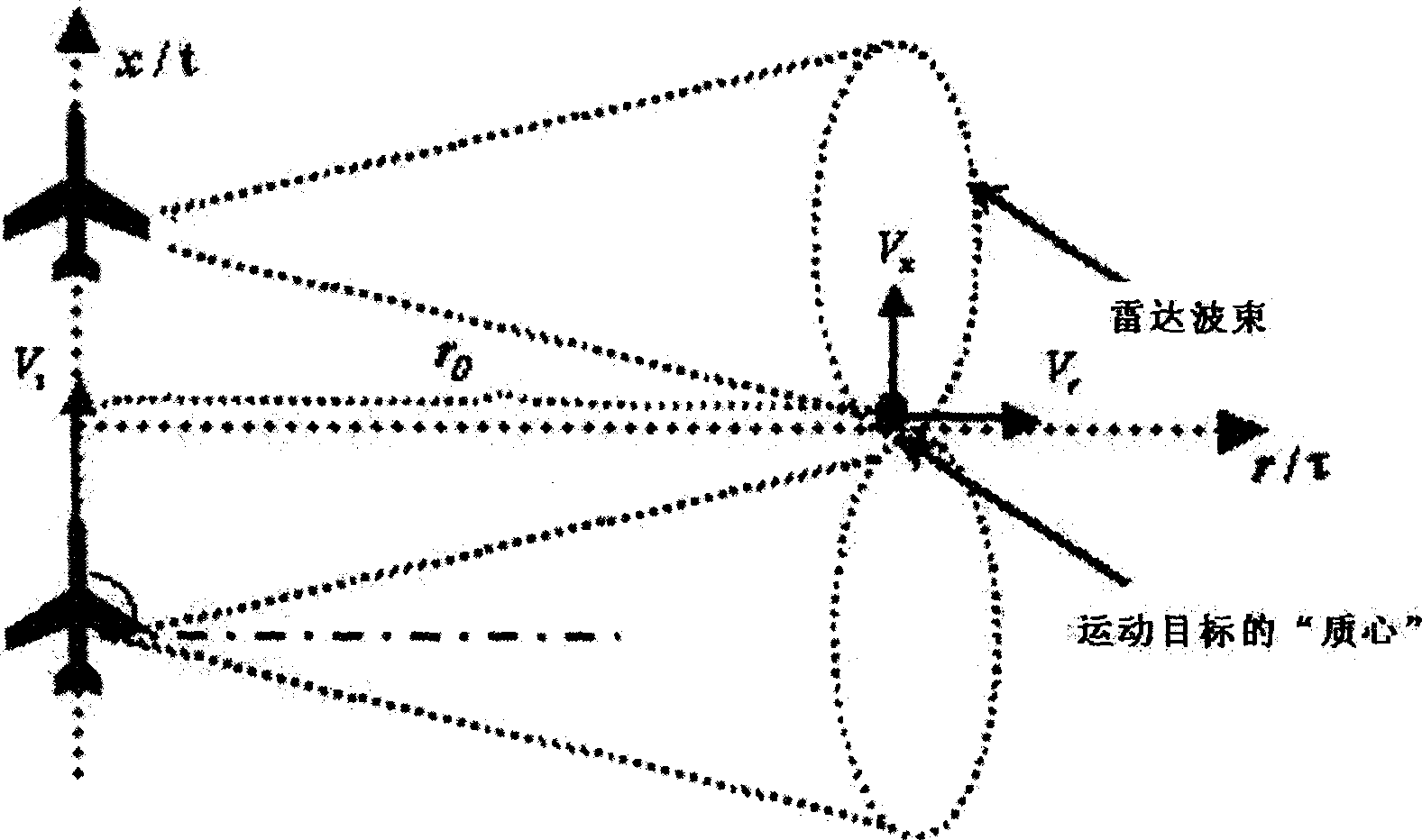
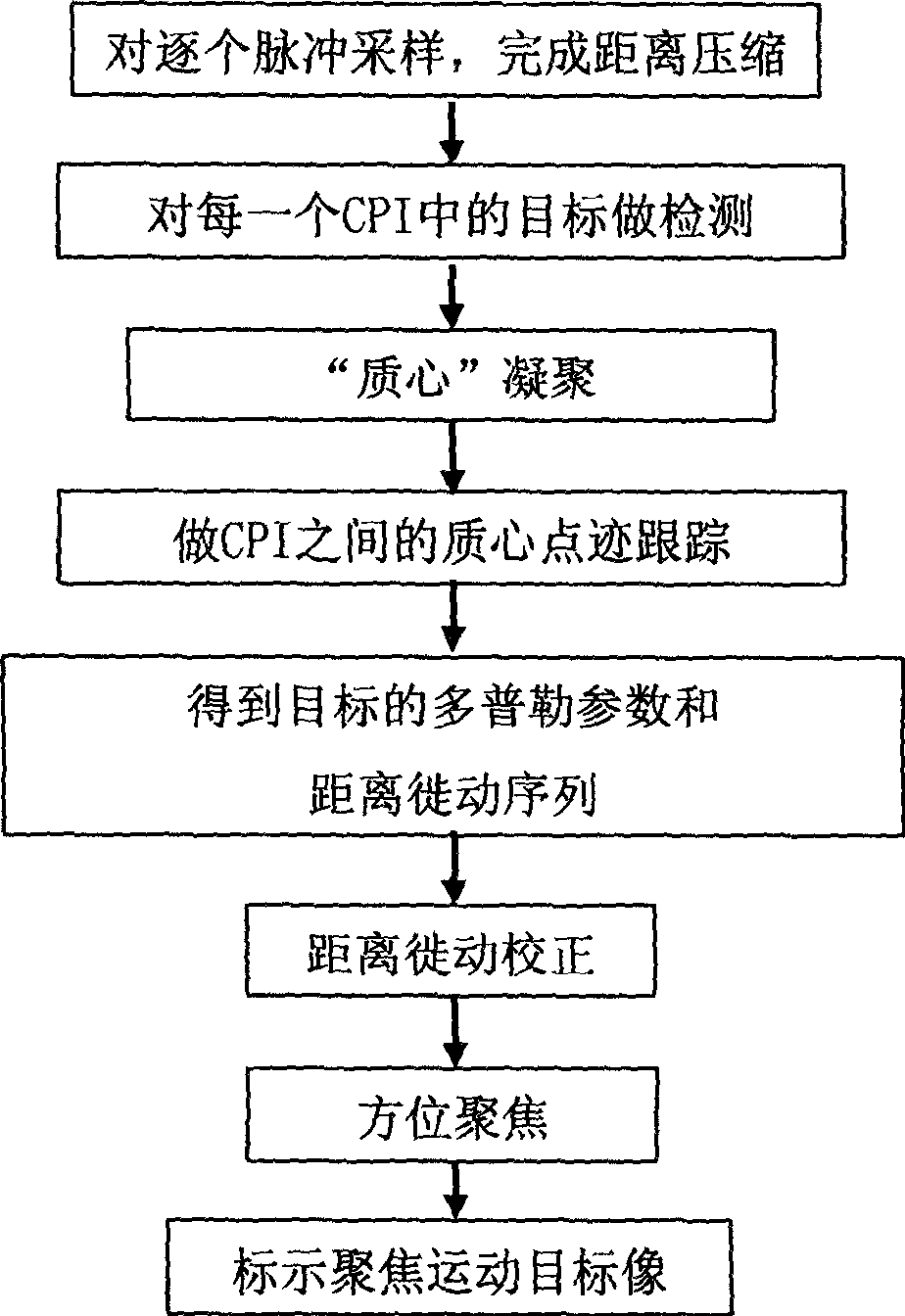
The invention relates to a synthetic aperture radar motion object imaging method which comprises steps of: 1. impulse sampling for each impulse to compress distance; 2. performing FFT on each impulse sampling between coherent treating spaces and make them enter into orientation frequency domain, judging output of each frequency channel to get instantaneous amplitude, slant range and Doppler frequency shift as the properties set of motion objects; 3. aggregating mass center; 4. tracking mass center dot trace; 5. getting Doppler parameters and distance migration sequence of motion object; 6. correcting distance migration; 7. orientation focus; 8. accurately indicating focusing motion object image. The invention has the advantages of being able to take advantages of detecting dot trace information to realize motion object data block in the division of whole data block, and of being able to realize the separately detecting, tracing and imaging for multiple motion objects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
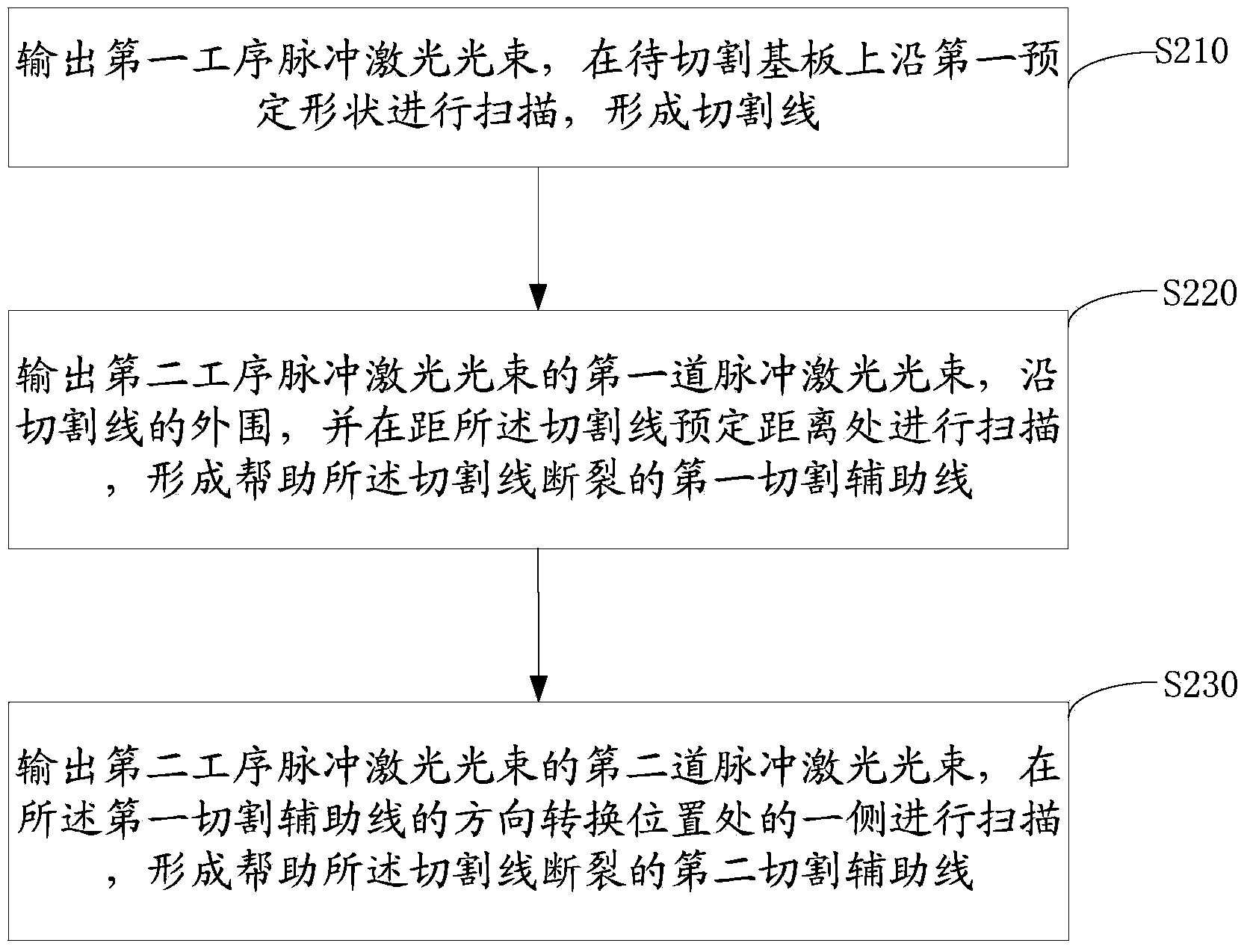
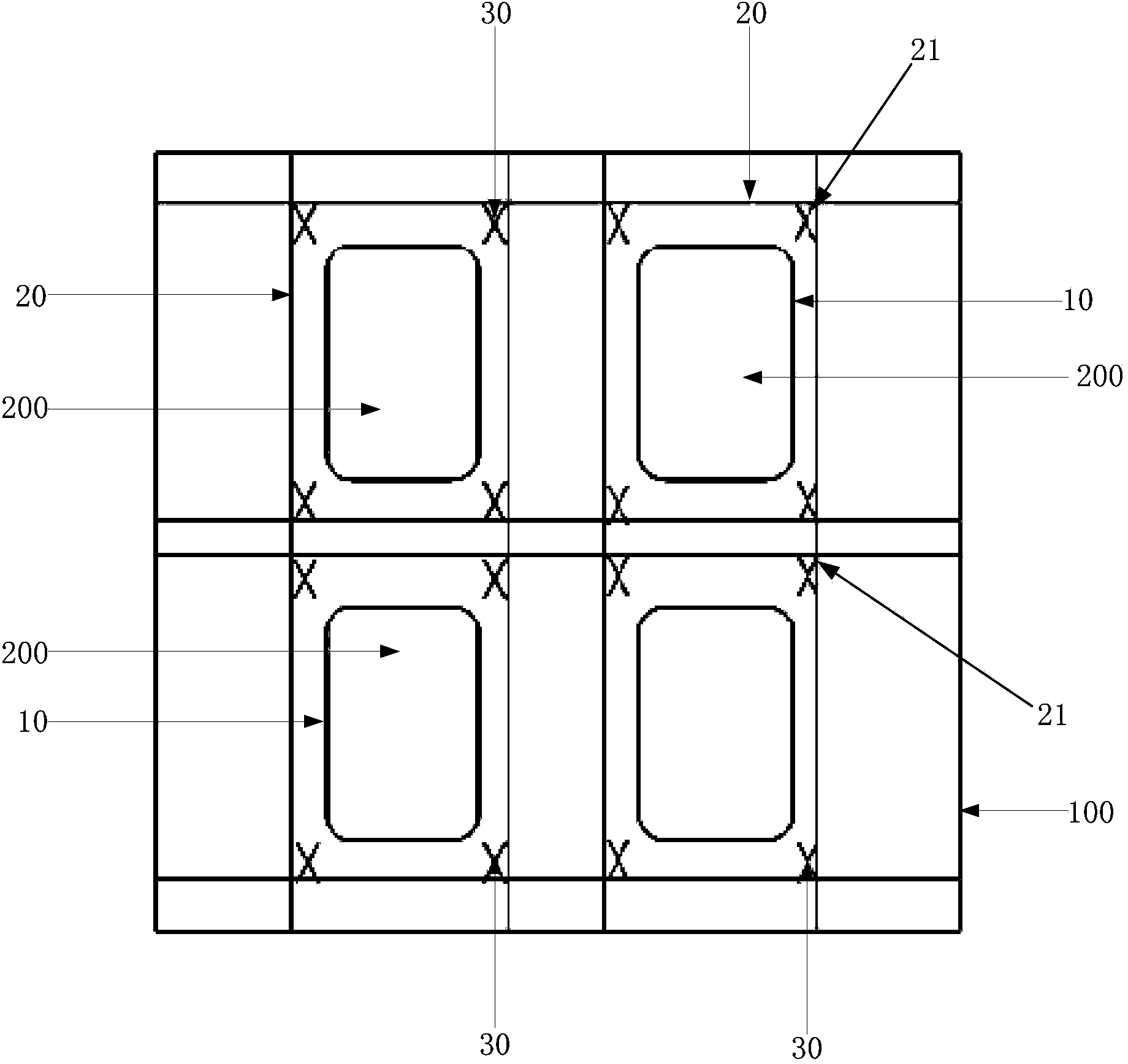
Laser cutting method and laser cutting system
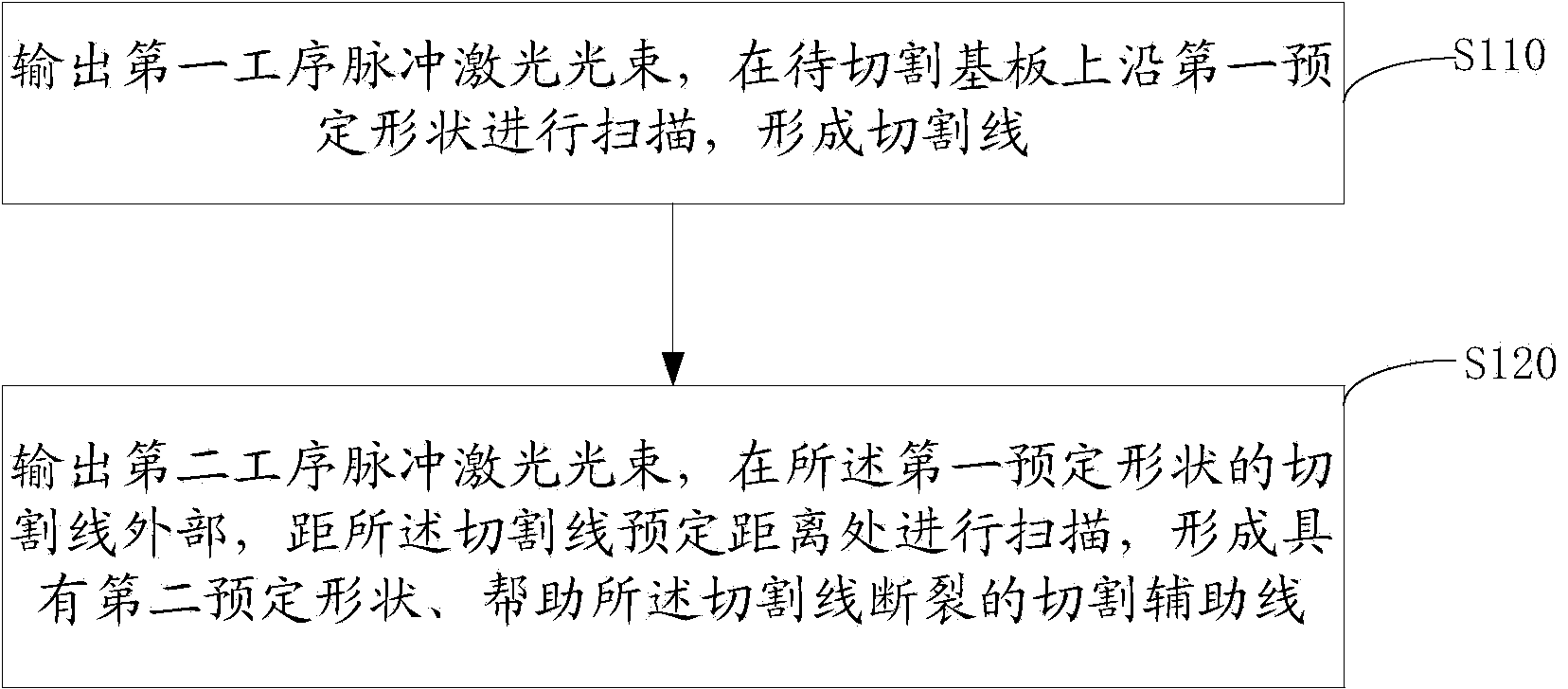
ActiveCN103771694AIncrease stress failure pointEasy to divideGlass severing apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusLaser cuttingMechanical engineering
The invention provides a laser cutting method and a laser cutting system. The laser cutting method comprises the following steps: forming a cutting line of a first preset shape on a base plate to be cut, wherein the first preset shape is a shape to be cut; forming an auxiliary cutting line of a second preset shape on the base plate to be cut, wherein the auxiliary cutting line is used for prompting the cutting line to break off and is positioned outside the cutting line of the first reset shape. By adopting the mode that the auxiliary cutting line is formed outside the cutting line, stress damage points for the base plate are increased when the cutting line is formed through laser cutting, and the base plate can be conveniently cut and separated, and therefore, when the power of pulse laser cutting or laser cutting is relatively low and the base plate cannot be separated through the formed cutting line, the base plate can be successfully separated by further applying the auxiliary cutting line to form the stress damage points.
Owner:HEFEI XINSHENG OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD +1
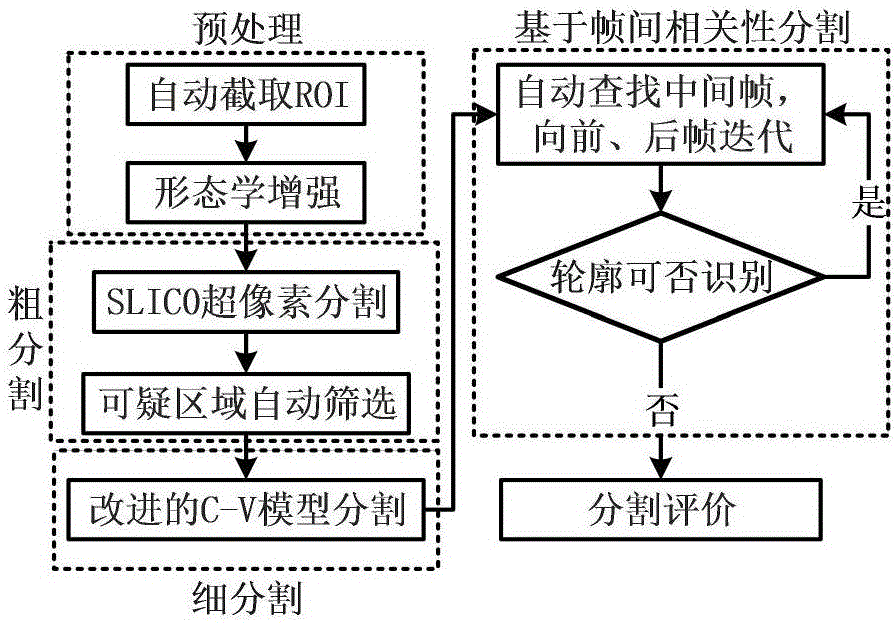
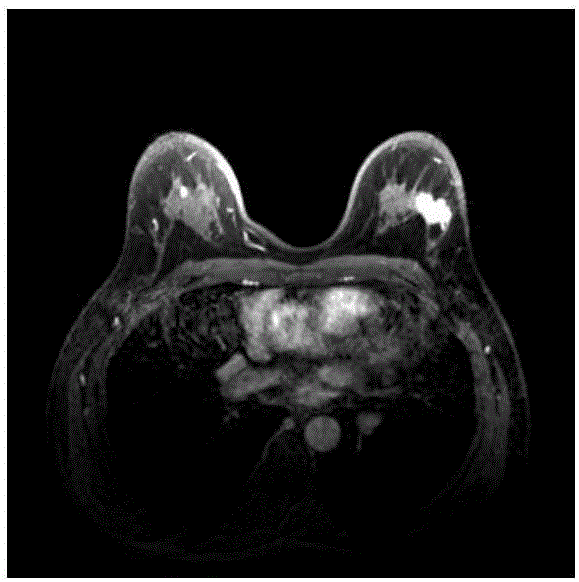
Automatic segmentation method for breast MRI focus based on Inter-frame correlation
InactiveCN106447682AEasy to divideImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationModel method
The present invention relates to an automatic segmentation method for a breast MRI focus based on inter-frame correlation. The method comprises: reading an MRI image; preprocessing the image, and performing coarse segmentation on the preprocessed image to determine an initial contour of a focus; and by adopting an improved C- V level set model method, performing fine segmentation on a coarsely segmented image that is obtained in the prior step, further refining the tumor contour on the basis of a coarsely segmented contour, and optimizing an obtained finely segmented result by combining inter-frame correlation. The method provided by the present invention has higher accuracy and can better segment the focus.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
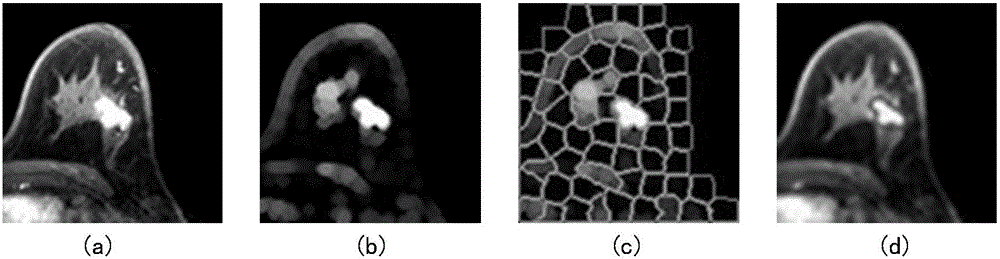
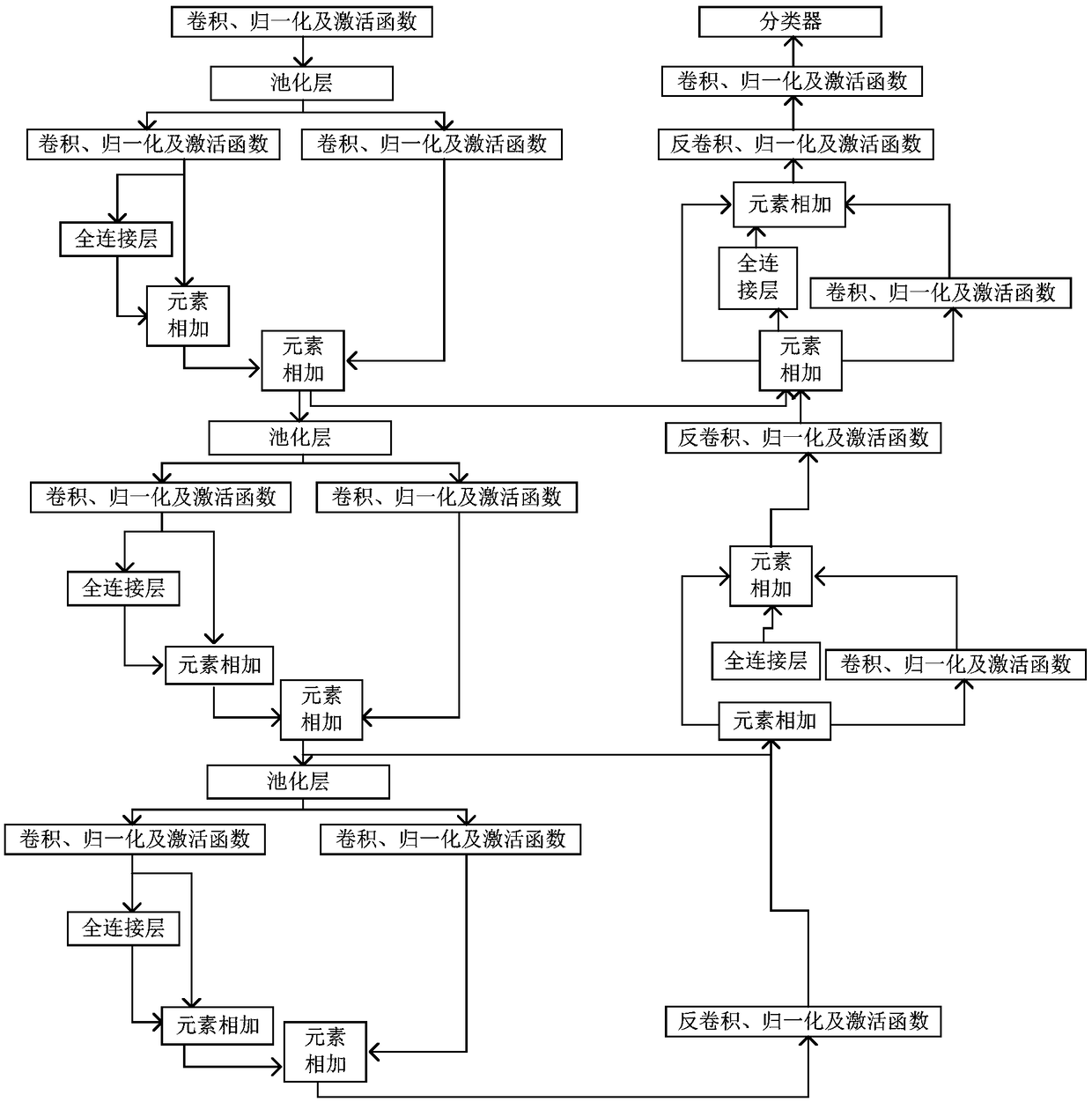
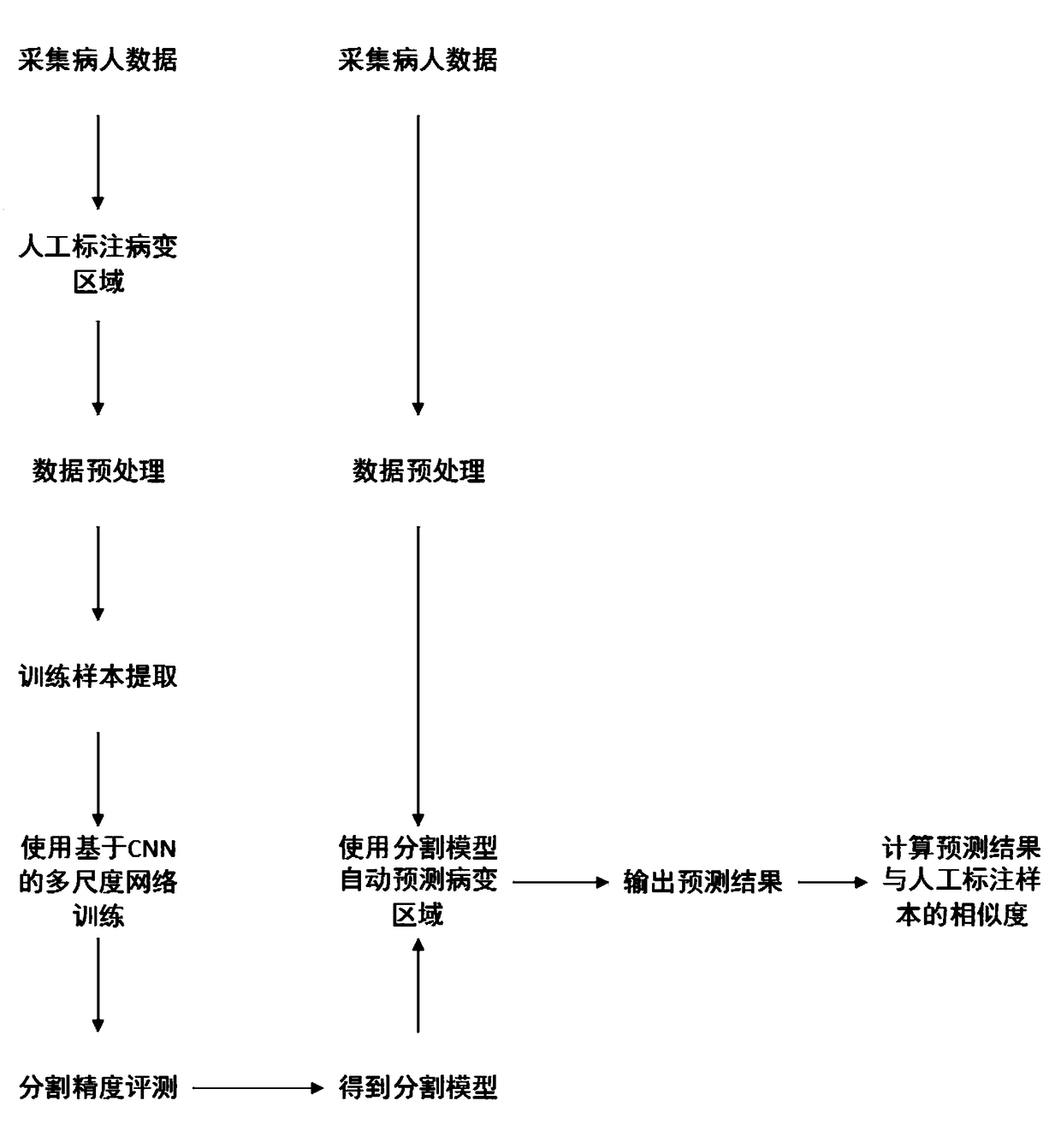
Multi-scale nasopharyngeal tumor segmentation based on CNN
InactiveCN109389584ARealize automatic segmentationHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationData set
The invention relates to a multi-scale nasopharyngeal tumor segmentation method based on CNN. Includes collecting MRI image data of nasopharyngeal region of several cases with nasopharyngeal tumor; Performing artificial edge labeling on the lesion area of the MRI image data collected in the previous step as label data layer by layer; Performing standardized preprocessing on the label data obtainedin the previous step and converting the label data into a two-dimensional data set; A CNN-based multi-layer two-dimensional convolution neural network is constructed and trained by using the two-dimensional data set in the previous step. For the MRI image data of nasopharyngeal region to be segmented, medical images of the same region and the same mode are collected, and the collected images arestandardized. The MRI image data of nasopharyngeal region to be segmented is segmented automatically by the network model. The invention can realize automatic segmentation of nasopharyngeal tumor, andcan obtain higher precision compared with mainstream network.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com