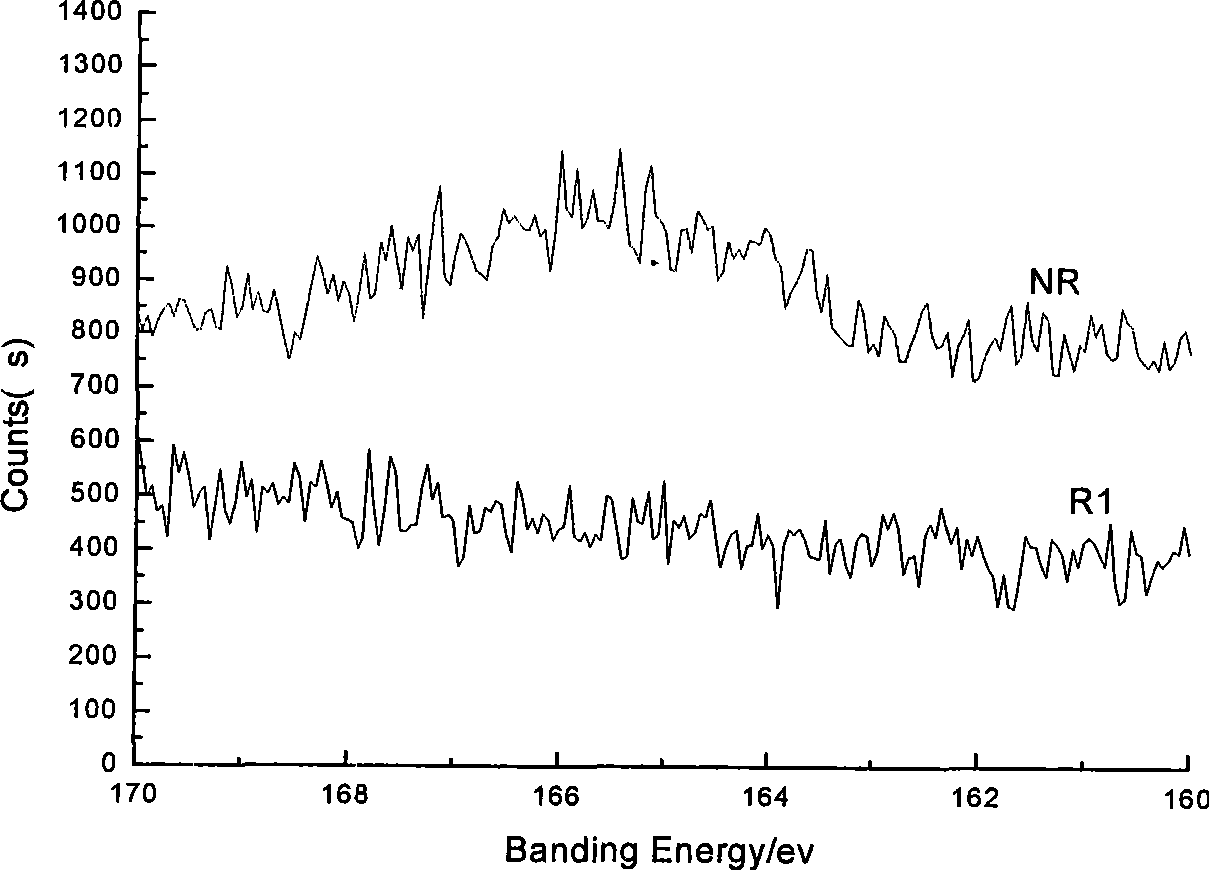
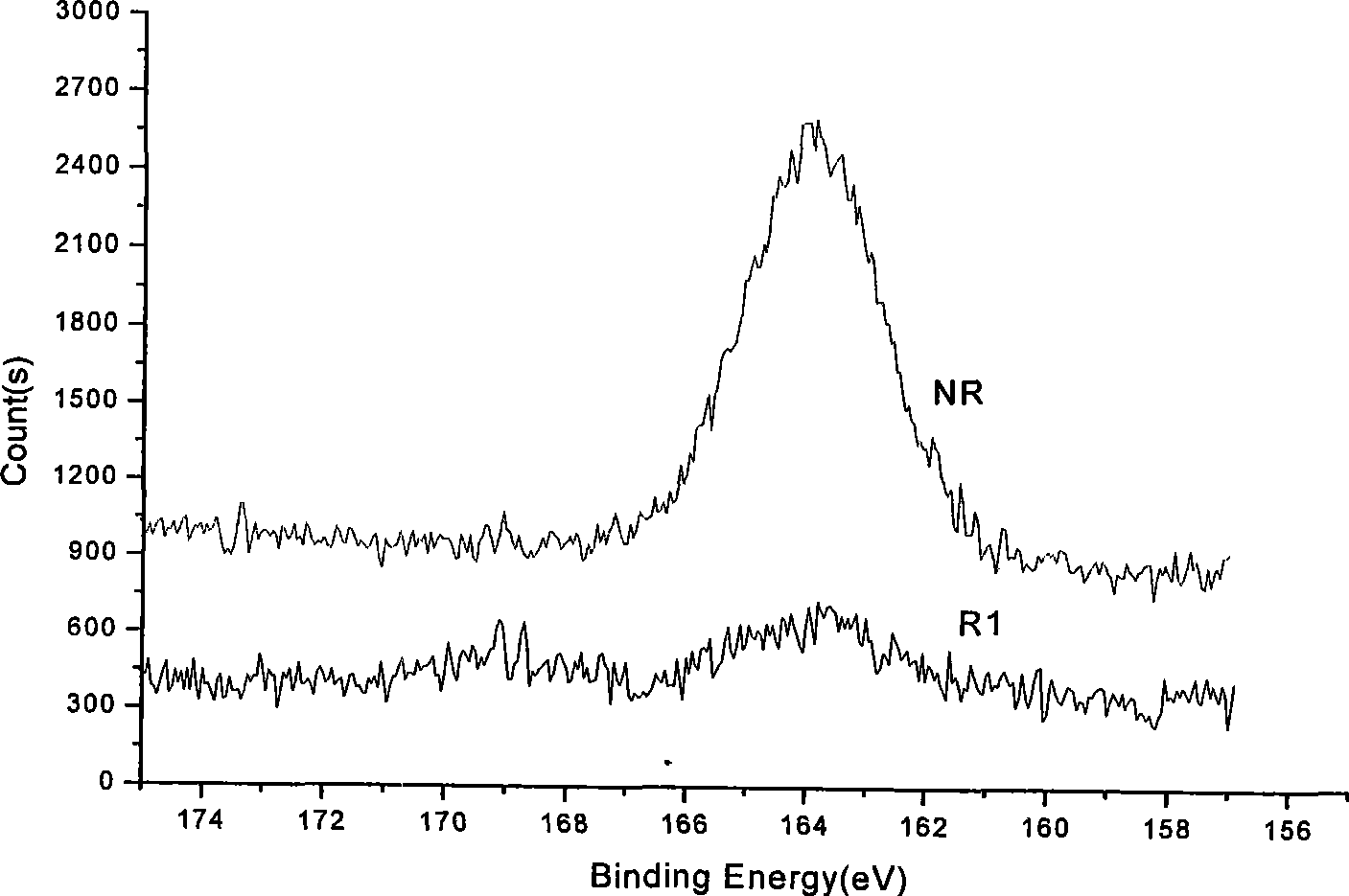
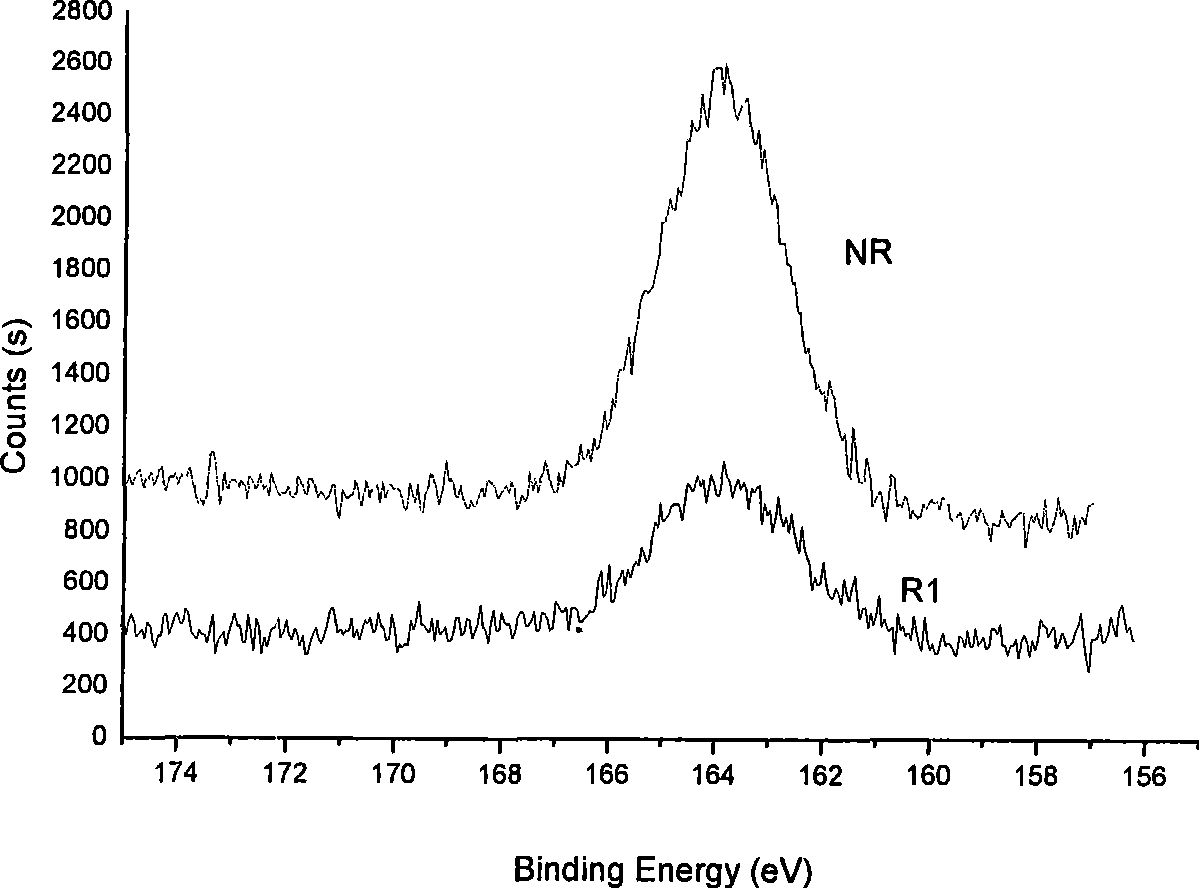
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Bond density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
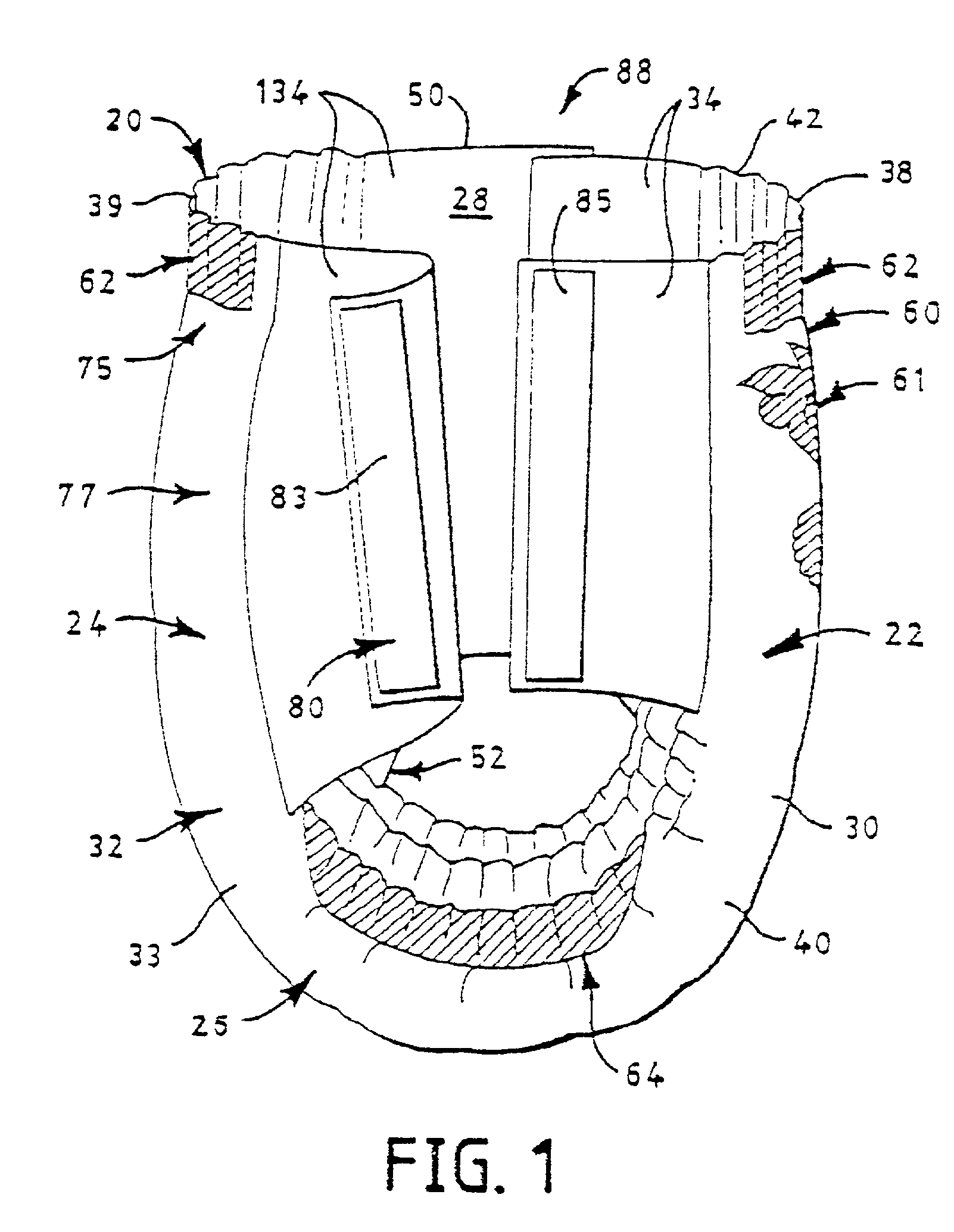
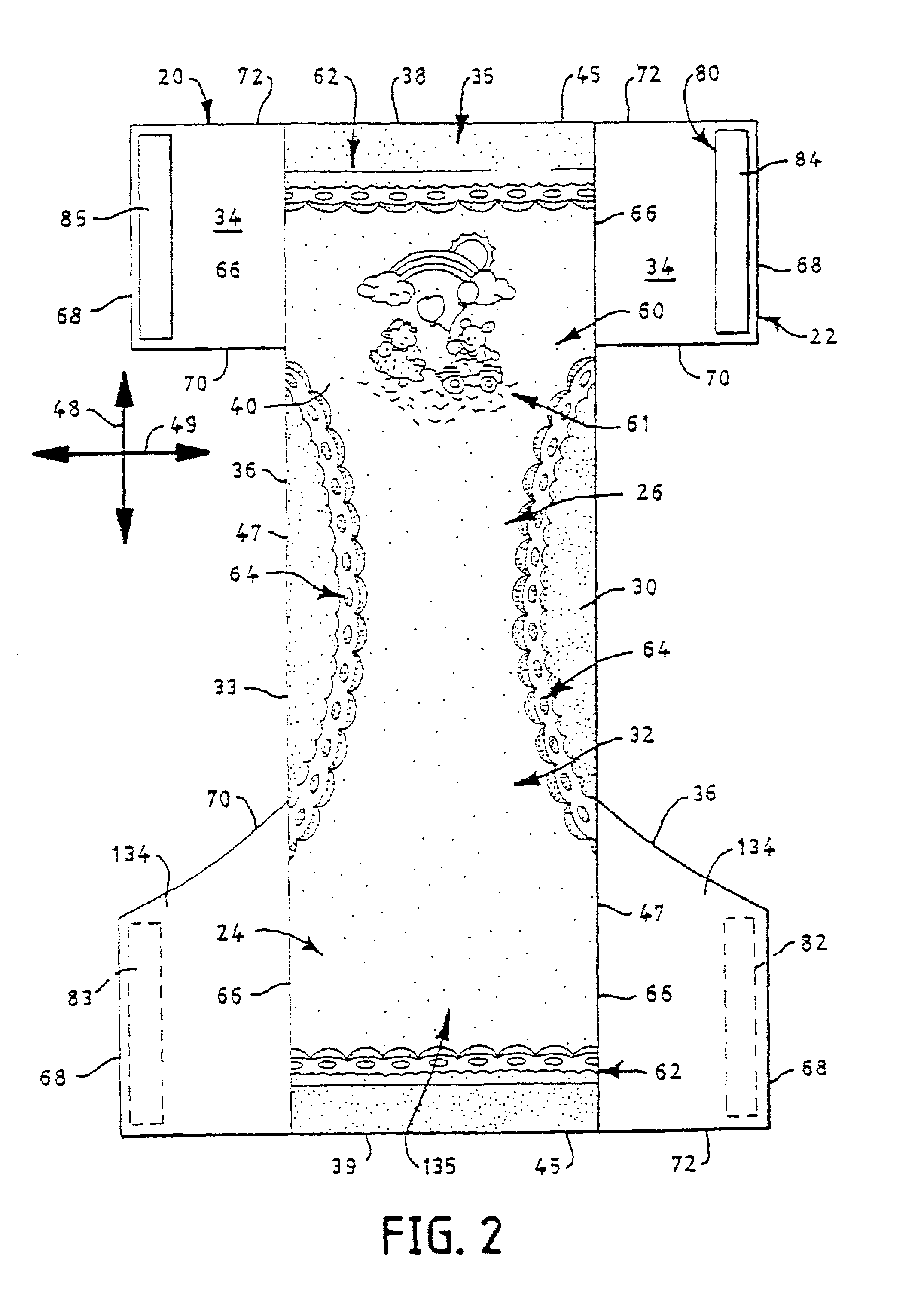
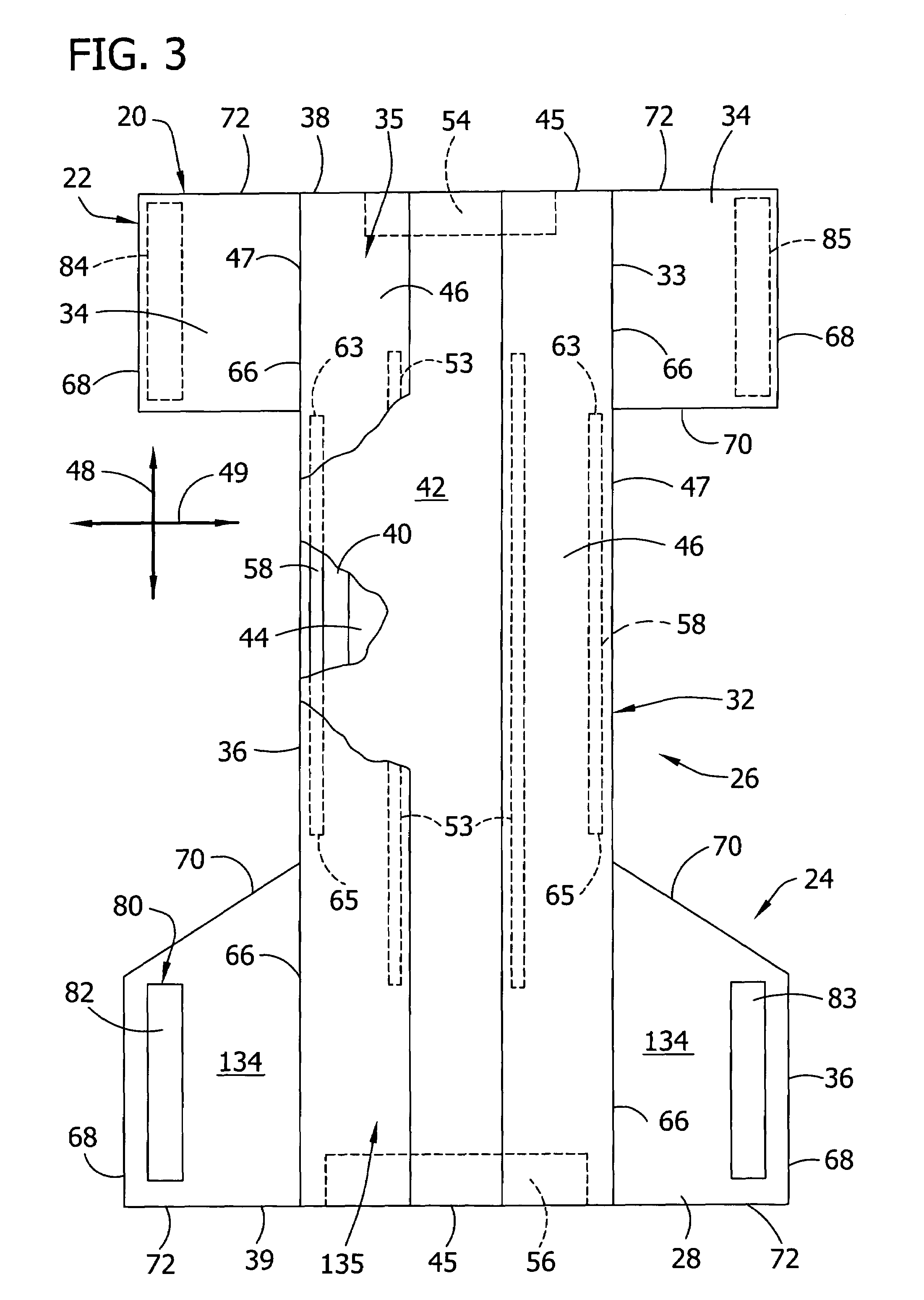
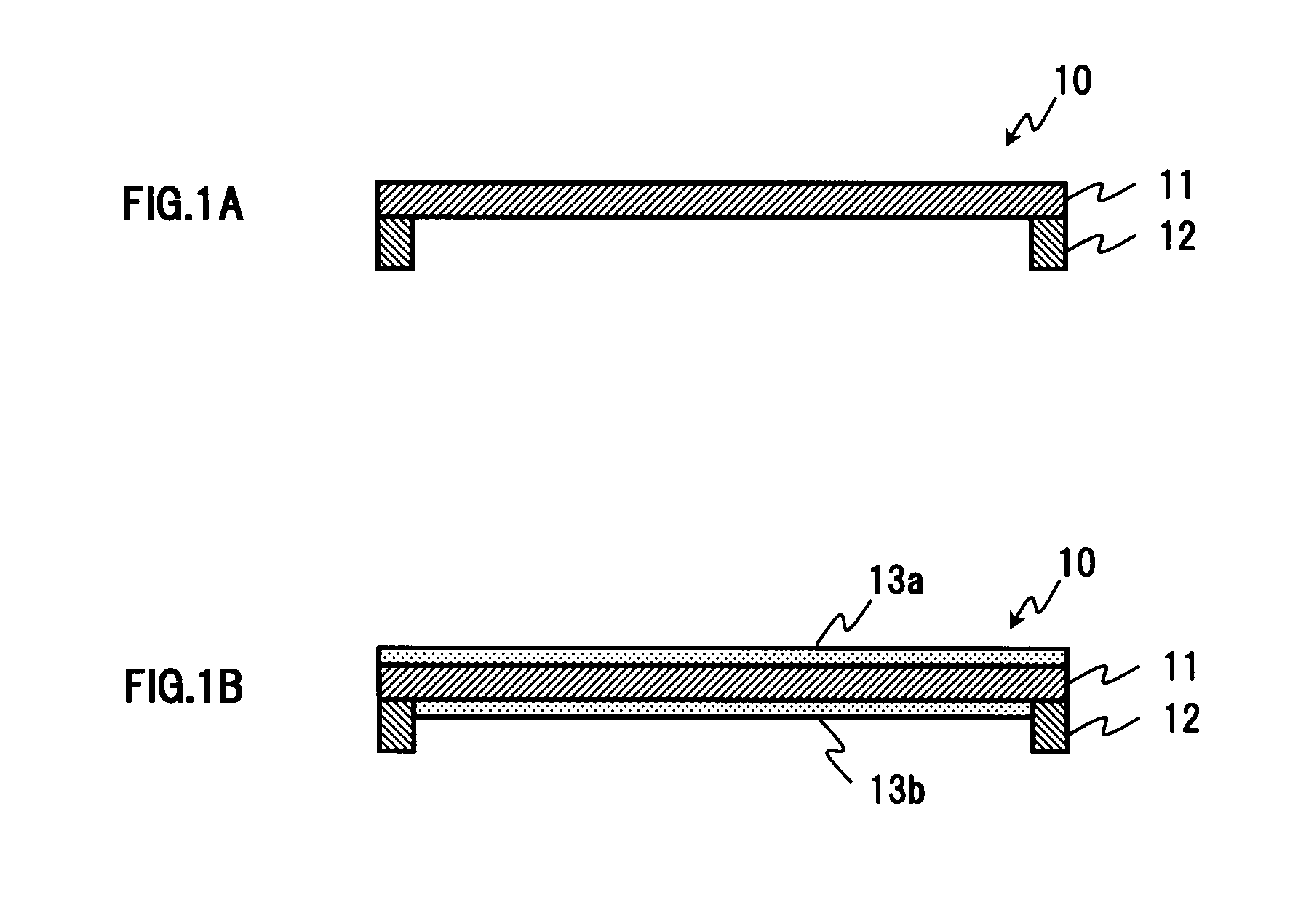
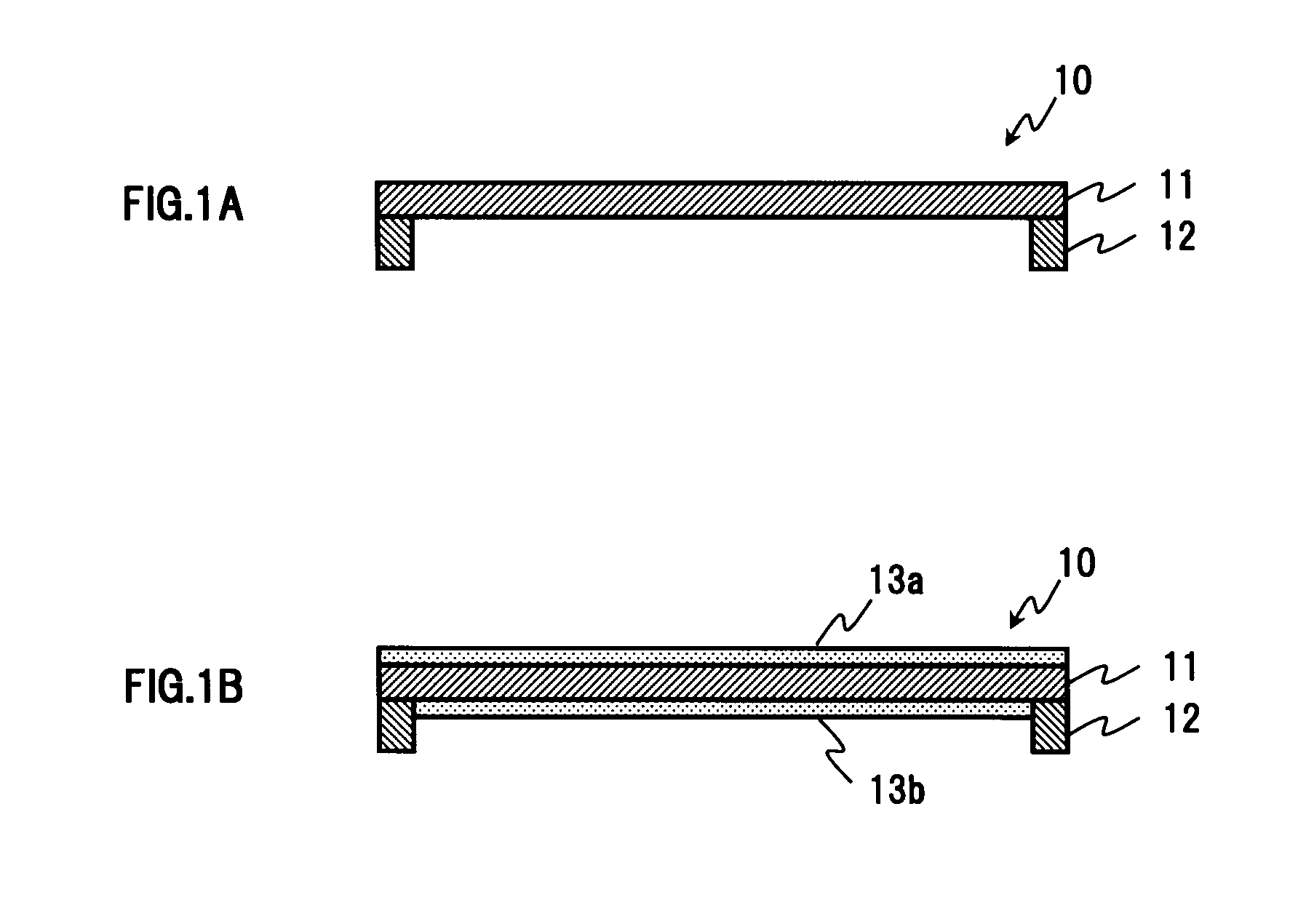
Mechanical fastening system for an absorbent article
An absorbent article such as infant training pants is provided with a mechanical hook-and-loop type fastening system in which at least the loop material is made of a laminate with a facing having a bond density of greater than 225 points per square inch.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
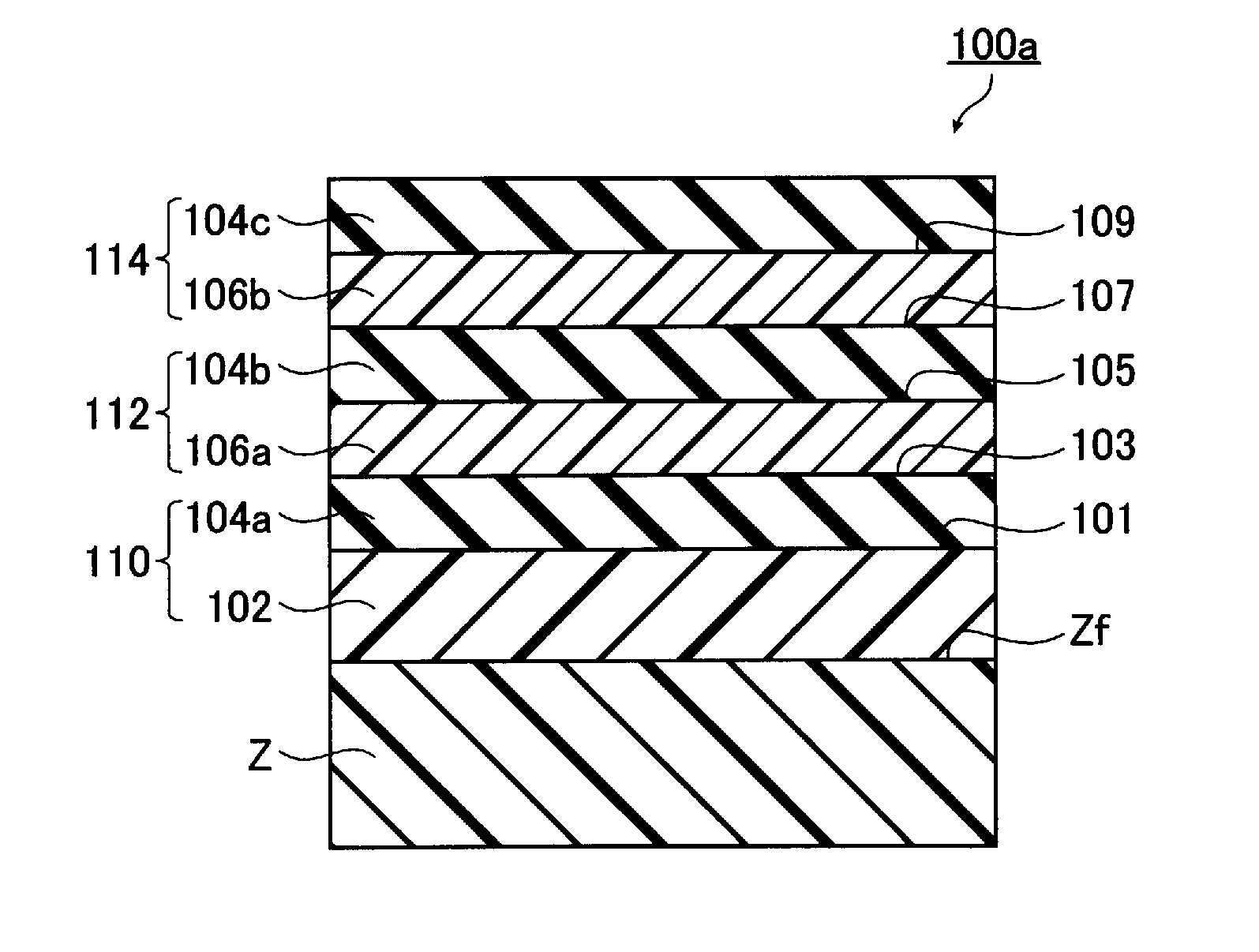
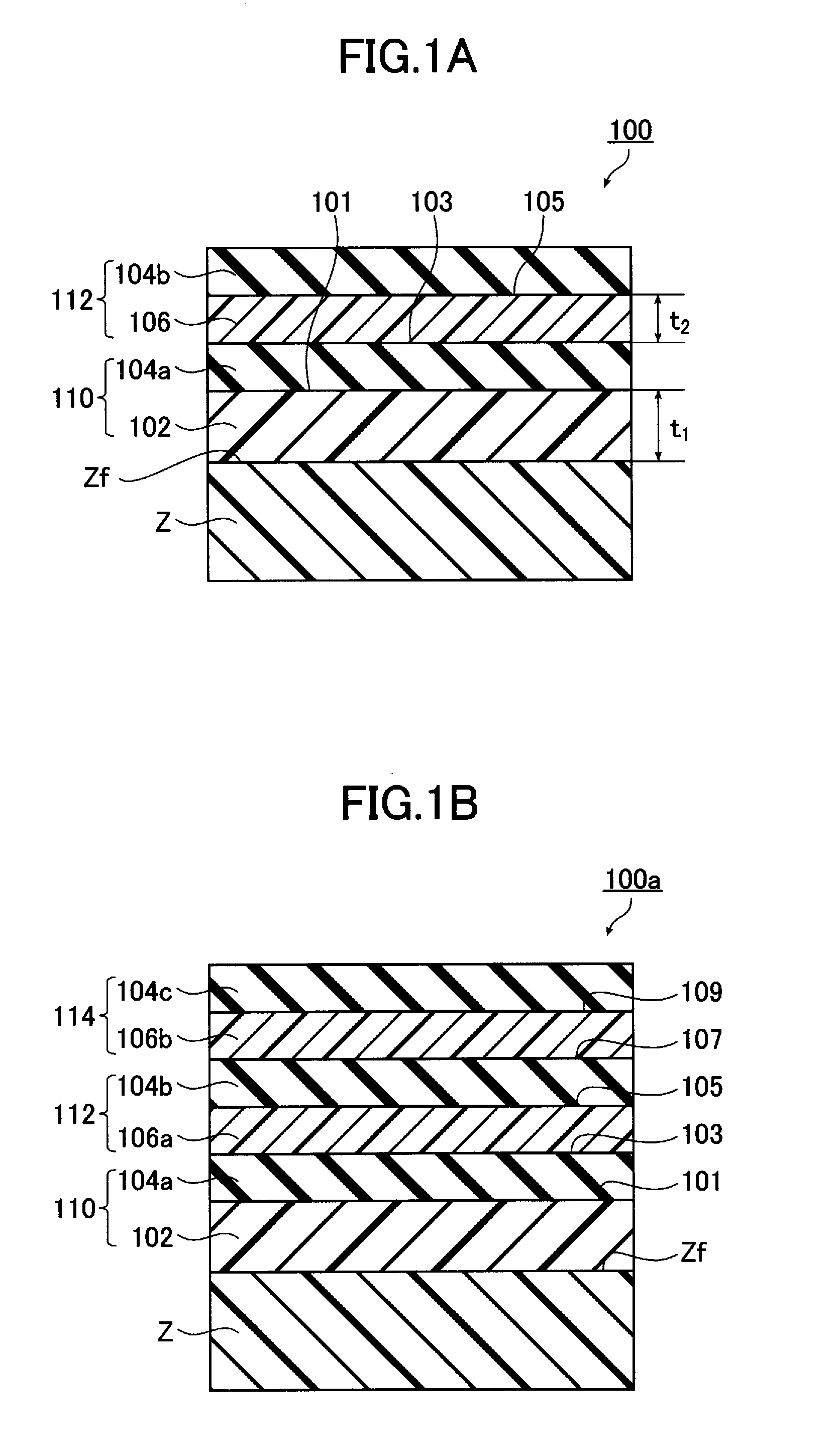
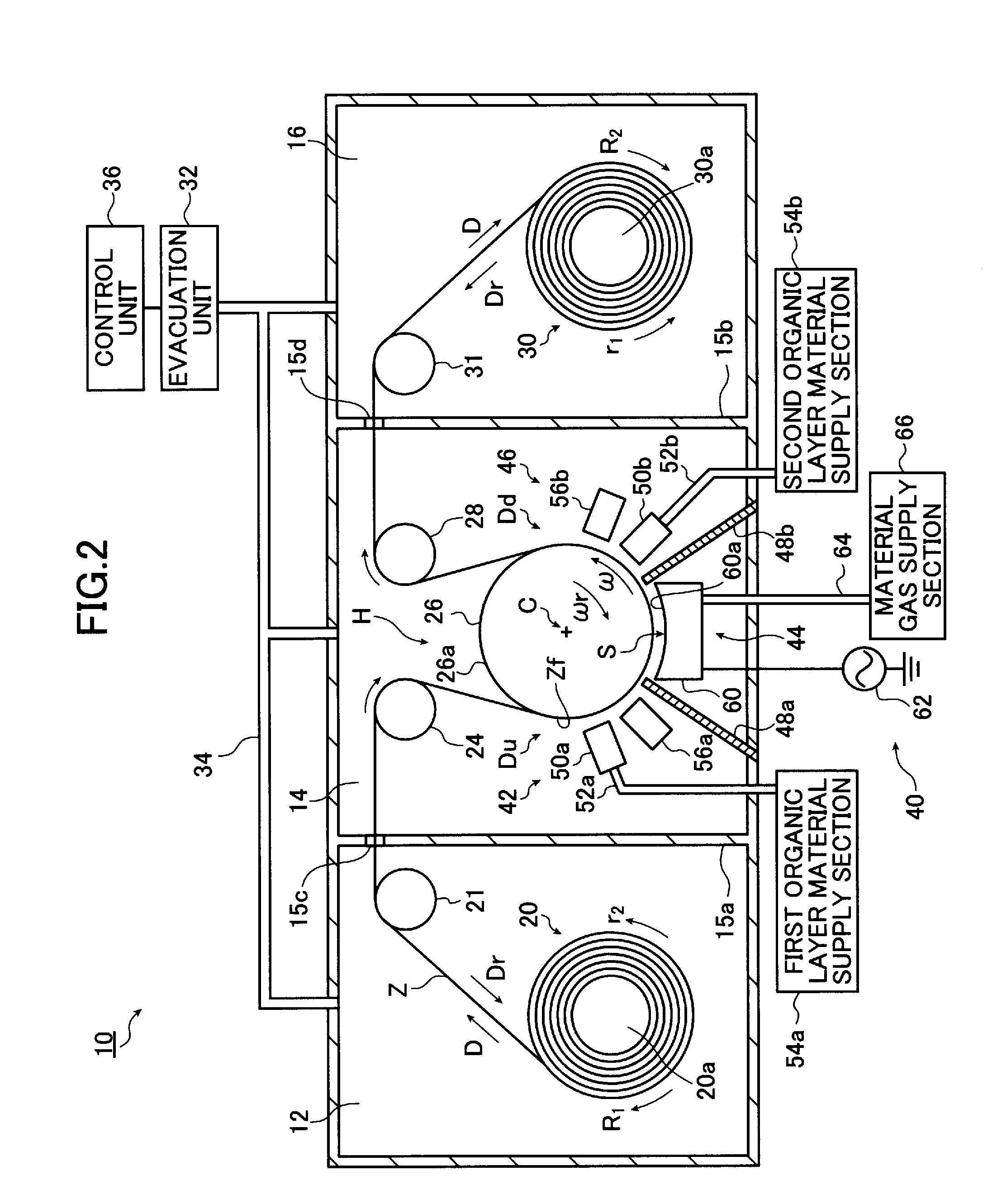
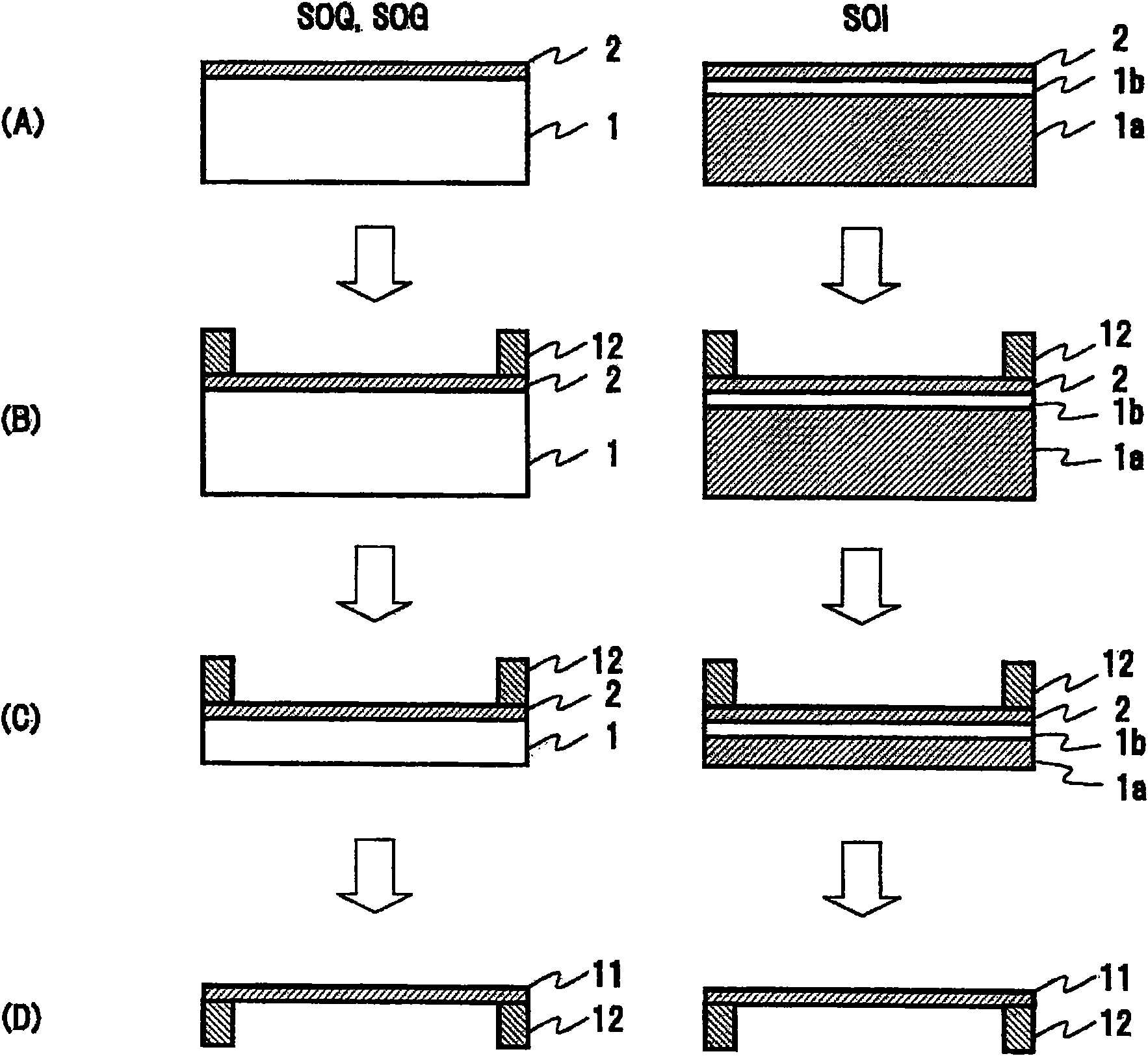
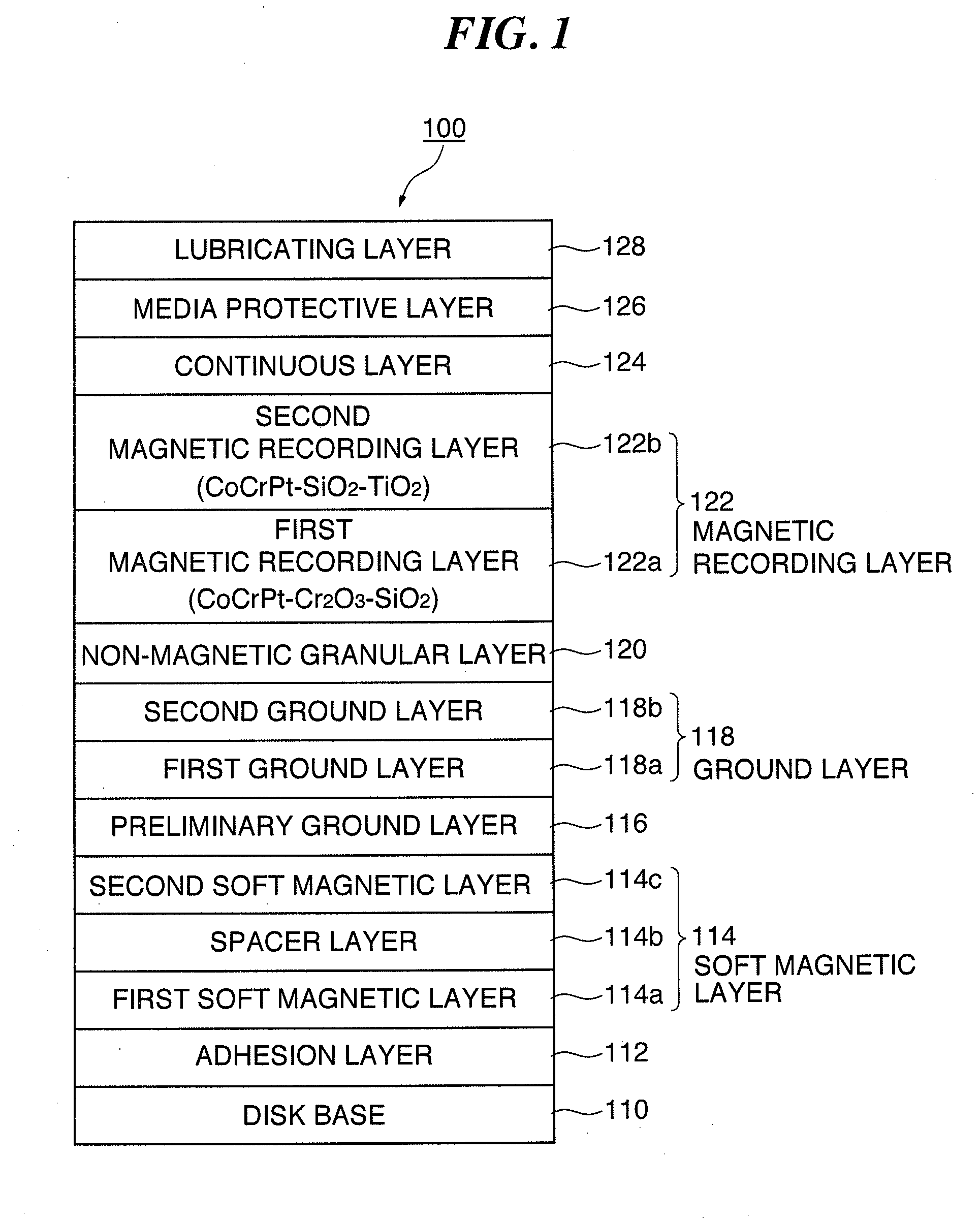
Method of producing a perpendicular magnetic recording medium and perpendicular magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20140011054A1Solve the lack of durabilitySolve the lack of resistanceProtective coatings for layersRecord information storageBond densityMoisture resistance
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
Method of producing a perpendicular magnetic recording medium and perpendicular magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS8623529B2Solve the lack of durabilitySolve the lack of resistanceMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageBond densityMoisture resistance
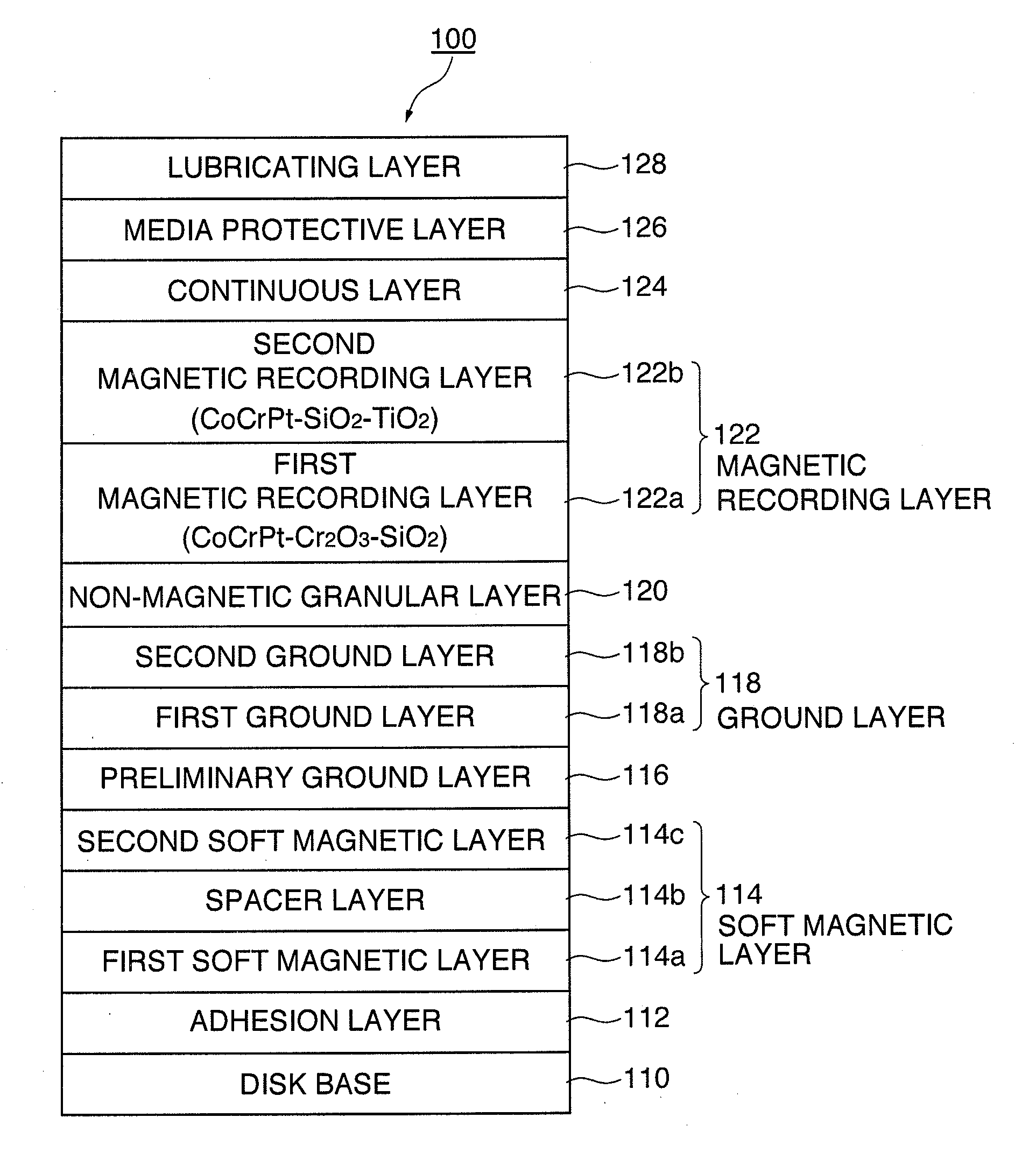
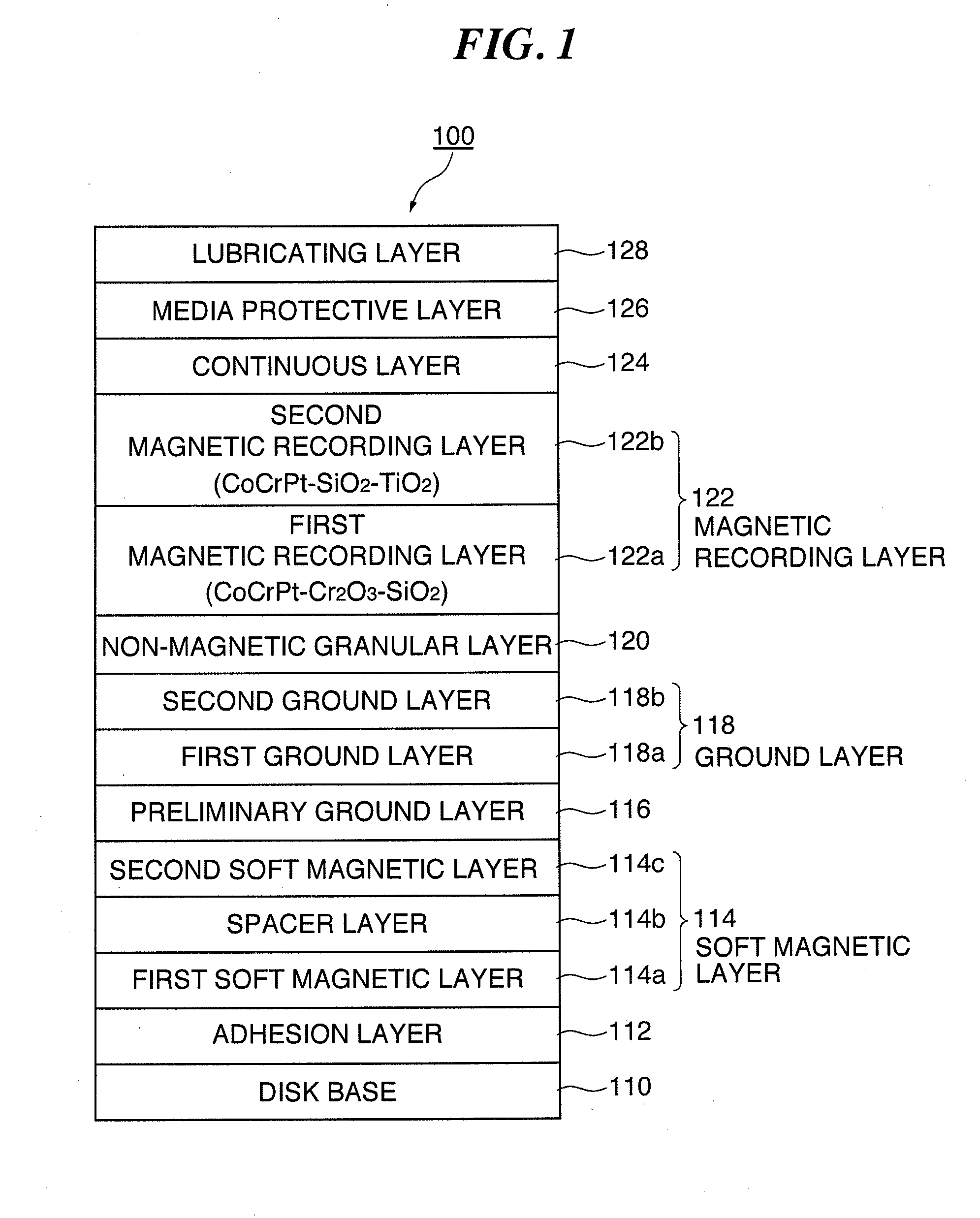
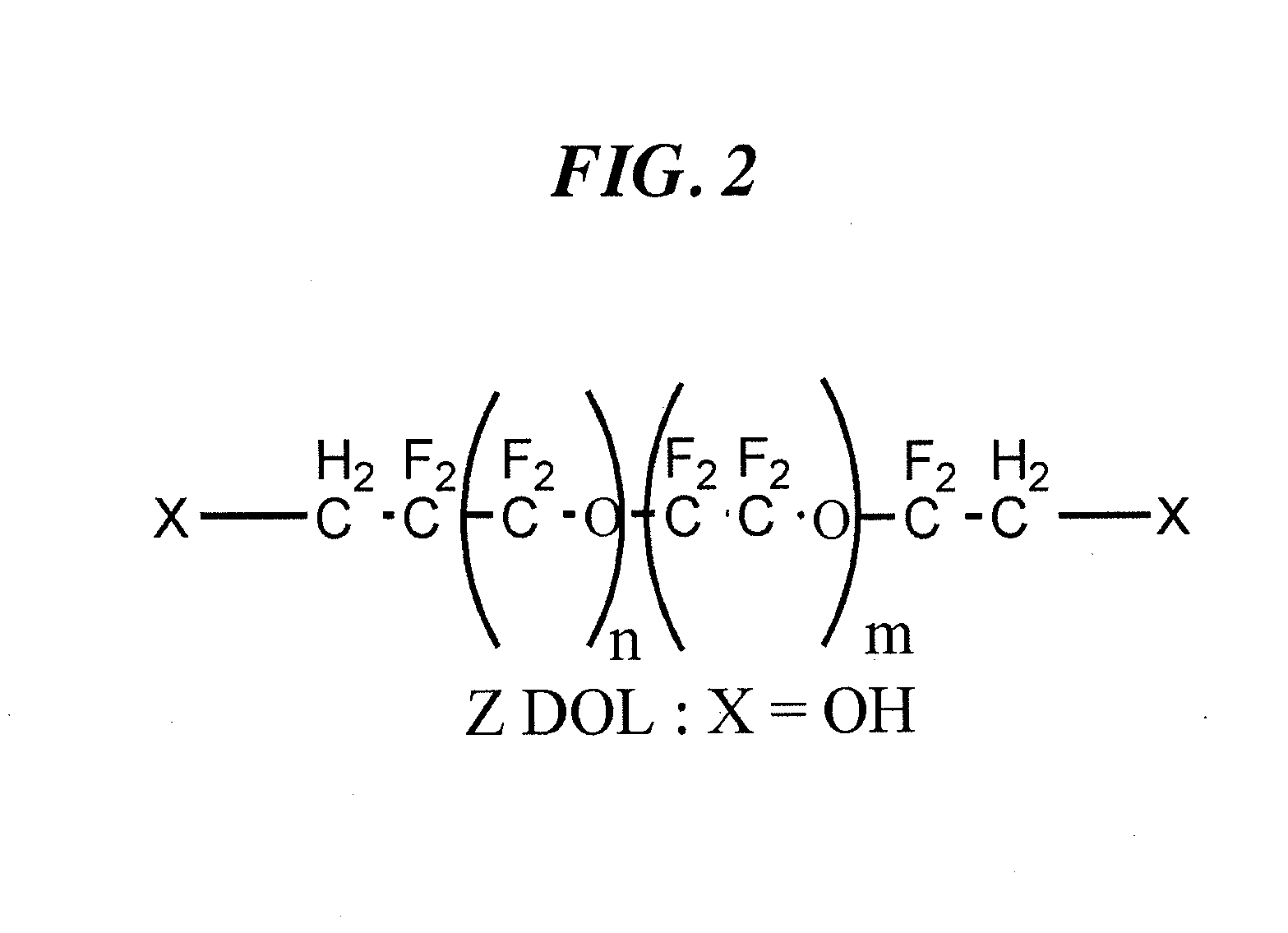
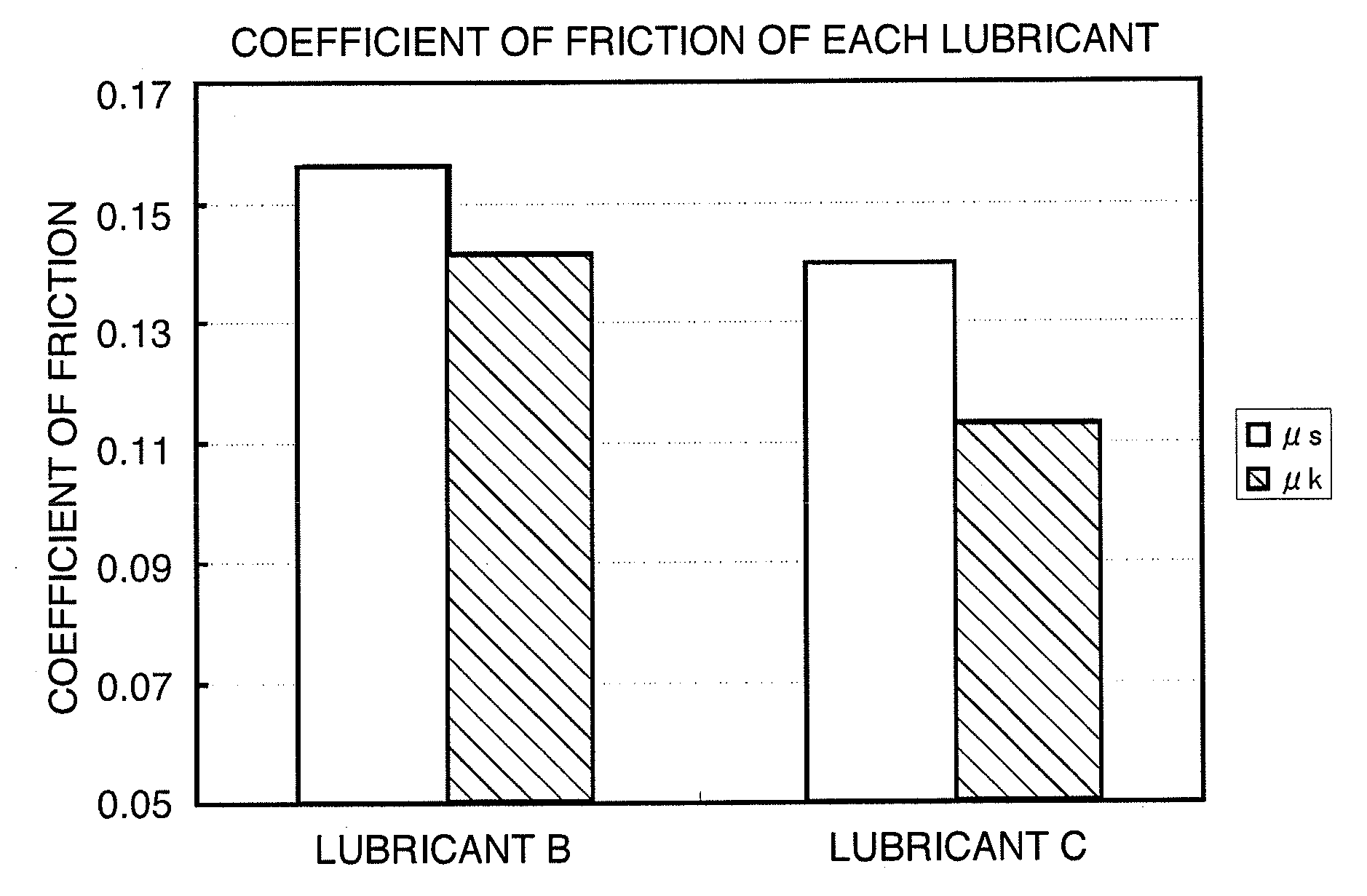
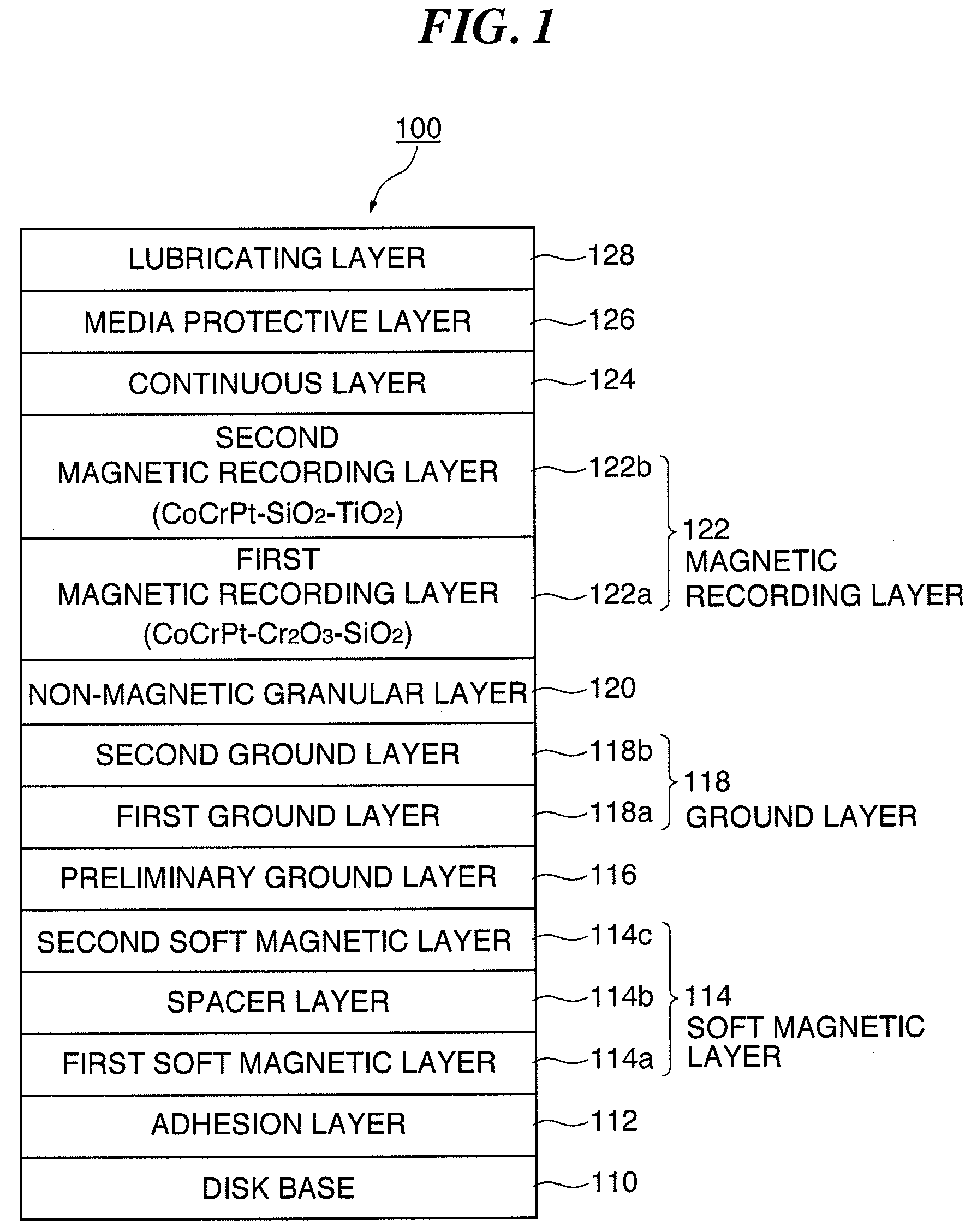
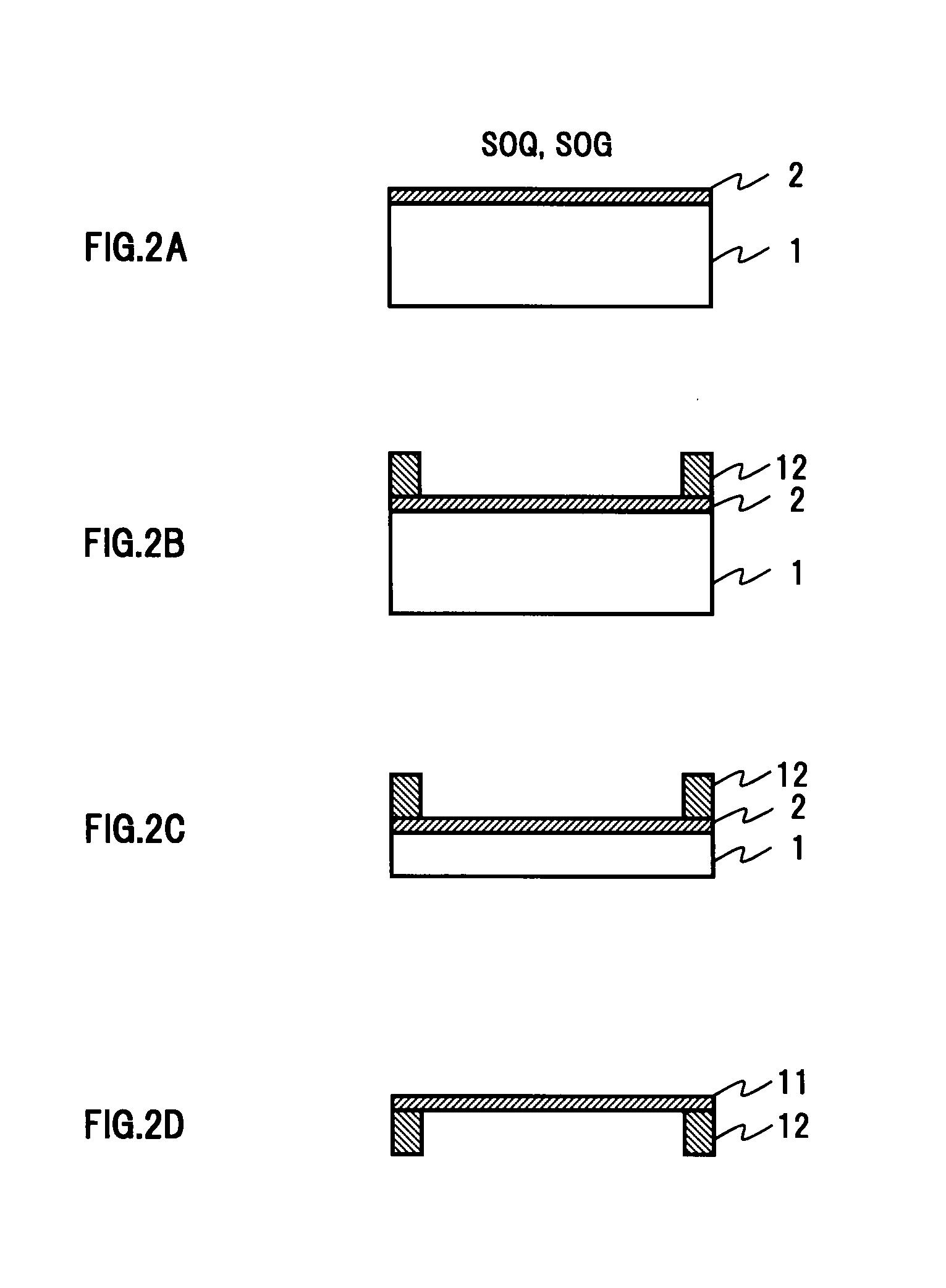
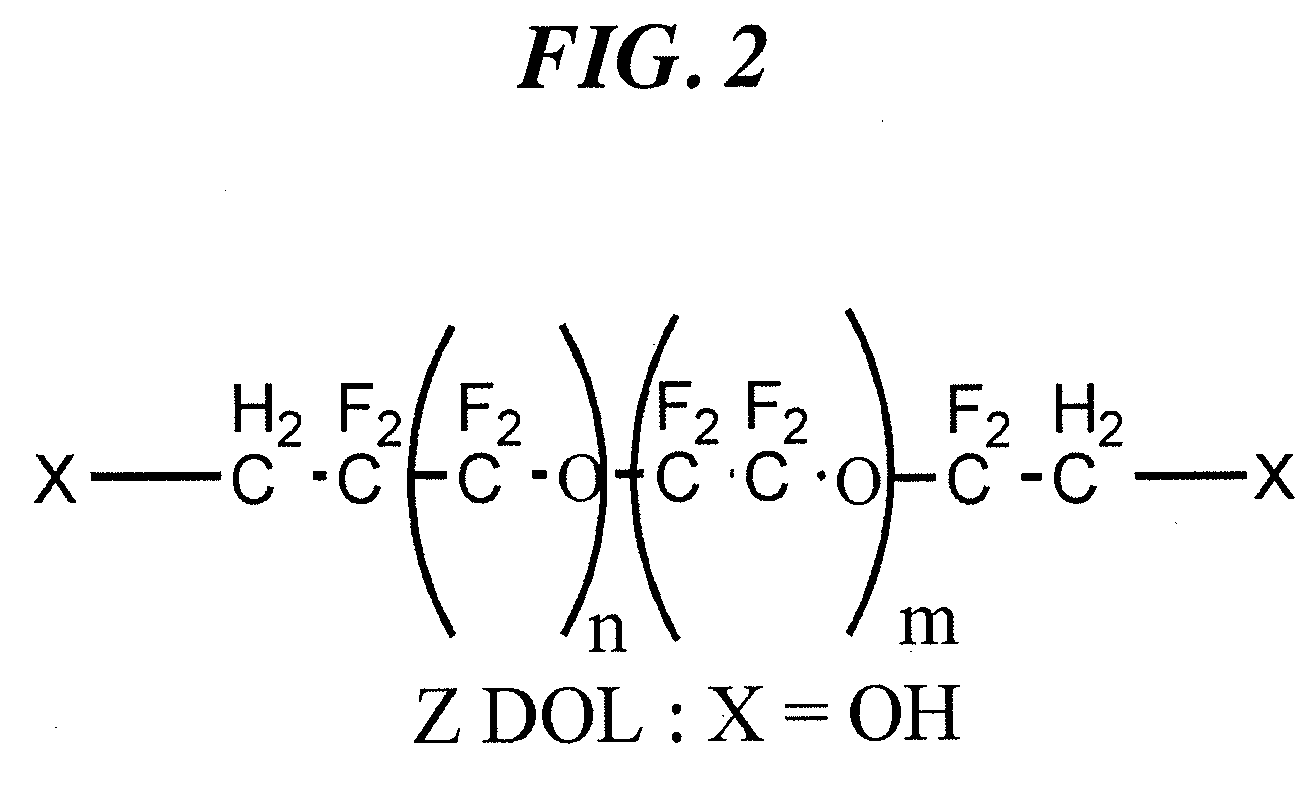
An object of the present invention is to provide a perpendicular magnetic recording medium including a suitable lubricating layer with sufficient durability, moisture resistance, and contamination resistance and also maintaining an R / W characteristic. In a typical structure of the present invention, a method of manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording medium 100 including a magnetic recording layer 122, a medium protective layer 126, and a lubricating layer 128 in this order on a base 110 includes: a CF bond density measuring step of measuring a CF bond density of a lubricant; and a lubricating layer forming step of forming a lubricating layer with the lubricant when the measured CF bond density is 2.0×1022 to 2.7×1022 atoms / cm3.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
Methods and apparatuses for assembling elastic laminates with different bond densities for absorbent articles
The methods herein relate to assembling an elastic laminate with a first elastic material and a second elastic material bonded between first and second substrates. During assembly, an elastic laminate may be formed by positioning the first and second substrates in contact with stretched central regions of the first and second elastic materials. The elastic laminates may include two or more bonding regions that may be defined by the various layers or components of the elastic laminate that are laminated or stacked relative to each other. In some configurations, a first plurality of ultrasonic bonds are applied to the elastic laminate to define a first bond density in the first bonding region, and a second plurality of ultrasonic bonds are applied to the elastic laminate to define a second bond density in the second bonding region, wherein the second bond density is not equal to the first bond density.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Gas barrier film and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20100261008A1Improve adhesionExcellent gas barrier performanceLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingVitrificationMeth-
A gas barrier film includes two or more laminates formed on a substrate. each laminate has a organic layer and a inorganic layer stacked in this order. The organic layer directly formed on the substrate includes a (meth)acrylic compound having a glass transition temperature of at least 200° C. and a C—C bond density in the monomer of at least 0.19, and has a thickness of at least 300 nm but less than 1000 nm, and the other organic layer includes a (meth)acrylic compound having a glass transition temperature of at least 105° C. and a C—C bond density in the monomer of at least 0.19, and has a thickness of at least 50 nm but less than 300 nm. The inorganic layers are formed by plasma-enhanced film deposition. A producing method produces the gas barrier film using the plasma-enhanced film deposition.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Pellicle and method for producing pellicle
ActiveUS20090274962A1Reduce generationImprove transmittancePicture framesNanoinformaticsBond densityLattice plane
A silicon single crystal film having a crystal plane as its principal plane, the crystal plane being inclined at 3 to 5° from any lattice plane belonging to {100} planes or {111} planes is used as a pellicle film. The silicon single crystal having such a crystal plane as its principal plane has effective bond density and Young's modulus thereof which are about 40% to about 50% higher than those of a silicon single crystal with <100> orientation, and therefore a cleavage and crack do not easily occur. Moreover, the silicon single crystal has a high chemical resistance such as hydrofluoric acid resistance, and hardly causes an etch pit and void. Accordingly, the present invention can provide a pellicle comprising a pellicle film for EUV having high transmission, and excellent mechanical and chemical stability, as well as having a high yield, and being practical also in cost.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Pellicle and method for producing pellicle
ActiveUS7951513B2Improve transmittanceImprove stabilityPicture framesNanoinformaticsBond densityLattice plane
A silicon single crystal film having a crystal plane as its principal plane, the crystal plane being inclined at 3 to 5° from any lattice plane belonging to {100} planes or {111} planes is used as a pellicle film. The silicon single crystal having such a crystal plane as its principal plane has effective bond density and Young's modulus thereof which are about 40% to about 50% higher than those of a silicon single crystal with <100> orientation, and therefore a cleavage and crack do not easily occur. Moreover, the silicon single crystal has a high chemical resistance such as hydrofluoric acid resistance, and hardly causes an etch pit and void. Accordingly, the present invention can provide a pellicle comprising a pellicle film for EUV having high transmission, and excellent mechanical and chemical stability, as well as having a high yield, and being practical also in cost.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Cluster-Free Amorphous Silicon Film, and Method and Apparatus for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080008640A1Reduce probabilityFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingBond densityHydrogen
The intention is to clarify characteristics of a cluster-free amorphous silicon film which is practically produceable without incorporation of large clusters having a size of 1 nm or more, and provide a method and an apparatus for producing the amorphous silicon film. In the cluster-free amorphous silicone (a-Si:H) film, an in-film Si—H2 bond density is 10−2 atomic % or less, and an in-film volume fraction of the large clusters is 10−1% or less. The a-Si:H film is produced by depositing, on a substrate, a deposition material in a plasma flow of any one of a silane gas, a disilane gas and a gas obtained by diluting a silane or disilane gas with one or a combination of two or more selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, Ar, He, Ne and Xe. The a-Si:H film has prominent characteristics, such that: a light-induced defect density is reduced from 2×1016 cm−3 or more in conventional a-Si:H films to substantially zero; a stabilized efficiency (%), i.e., a light-energy conversion efficiency, is increased from 9% at the highest in existing a-Si:H films up to 14% or more; and a light-induced degradation rate, i.e., [(initial efficiency−stabilized efficiency) / initial efficiency]×100%, is reduced from 20% at the lowest in the existing a-Si:H films to substantially zero.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
Method for reproducing waste rubber by using microorganism
InactiveCN101456968ANo pollution in the processMild conditionsPlastic recyclingMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismBond density
The invention provides a method for using microorganism to regenerate scrap rubber. The microorganism used is saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme and metabolin containing hydrosulphonyl produced in the process of growth of cells of saccharomyces cerevisiae reacts with the scrap rubber, and sulfur cross bond of the rubber is fractured and decoking regeneration is carried on, thus reaching the aim of targeted decoking. The decoking is carried on by using co-cultivating the rubber powder and saccharomyces cerevisiae germs and the scrap rubber decoking regeneration effects are strengthened by combining thermal cracking broken wall reaction of the saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, a phase transfer agent and an addition agent of the phase transfer agent. The excellent technical conditions of the decoking regeneration are confirmed: temperature, pH, rotation speed, reaction time, doze of the phase transfer agent and the addition agent of the phase transfer agent, etc. By checking the cross bond density and the degree of swelling and showing the detection of X ray electron spectrum (XPS), after the function of saccharomyces cerevisiae, the cross bond density of the decoking regeneration rubber is obviously reduced, and the degree of swelling is obviously improved, sulfur element contents on the regeneration rubber surface is decreased, thus showing that the decoking regeneration effects of the saccharomyces cerevisiae is applied to the rubber surface.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Pellicle and method for fabrication thereof
InactiveCN101571671AStrong mechanical propertiesGood chemical propertiesNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusBond densityLattice plane
A silicon single crystal film having a crystal plane as its principal plane, the crystal plane being inclined at 3 to 5 DEG from any lattice plane belonging to {100} planes or {111} planes is used as a pellicle film (11). The silicon single crystal having such a crystal plane as its principal plane has effective bond density and Young's modulus thereof which are about 40% to about 50% higher than those of a silicon single crystal with orientation, and therefore a cleavage and crack do not easily occur. Moreover, the silicon single crystal has a high chemical resistance such as hydrofluoric acid resistance, and hardly causes an etch pit and void. Accordingly, the present invention can provide a pellicle comprising a pellicle film for EUV having high transmission, and excellent mechanical and chemical stability, as well as having a high yield, and being practical also in cost.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
A flowable chemical vapor deposition method of a silicon oxide film
ActiveCN109166787AReduced Si-H bond densityReduce wet etch rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBond densityGas phase
The invention provides a flowable chemical vapor deposition method of a silicon oxide film with a lower etching rate, wherein a cyclosilane with a ring molecular structure is used as a precursor, andthe cyclosilane is reacted with a nitrogen-containing compound to deposit on a substrate to form a flowable silicon nitride film, and the silicon oxide film is obtained by oxidation of oxidizing gas.The Si-H bond density and wet etch rate are significantly reduced. Aft high temperature annealing or ultraviolet curing, bottom-up, seamless gap filling can be realized on that patterned silicon wafer; High quality silicon oxide film can be formed on the blank silicon wafer. Good uniformity and good covering performance.
Owner:铜陵安德科铭电子材料科技有限公司
Method of producing a perpendicular magnetic recording medium and perpendicular magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20110102944A1Solve the lack of durabilityAvoid insufficient moisture resistanceRecord information storageDisk carriersBond densityElectrical and Electronics engineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a perpendicular magnetic recording medium including a suitable lubricating layer with sufficient durability, moisture resistance, and contamination resistance and also maintaining an R / W characteristic. In a typical structure of the present invention, a method of manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording medium 100 including a magnetic recording layer 122, a medium protective layer 126, and a lubricating layer 128 in this order on a base 110 includes: a CF bond density measuring step of measuring a CF bond density of a lubricant; and a lubricating layer forming step of forming a lubricating layer with the lubricant when the measured CF bond density is 2.0×1022 to 2.7×1022 atoms / cm3.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
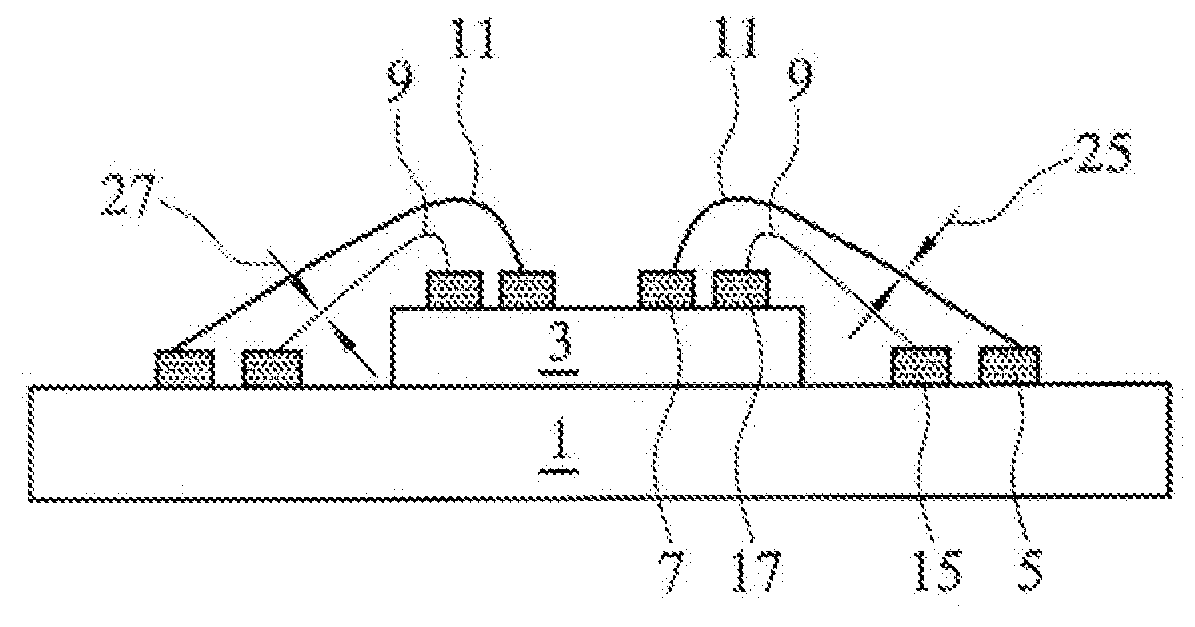
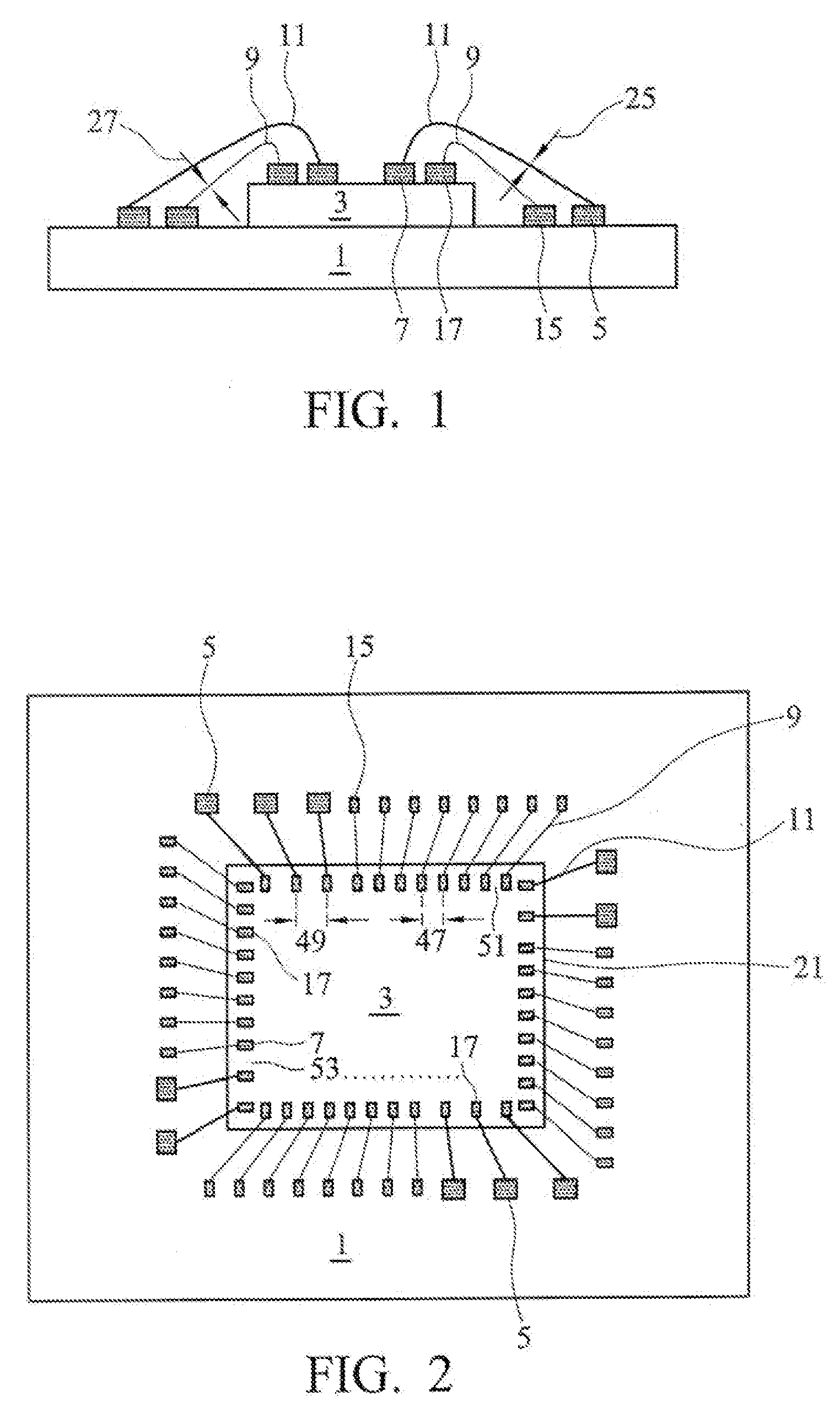
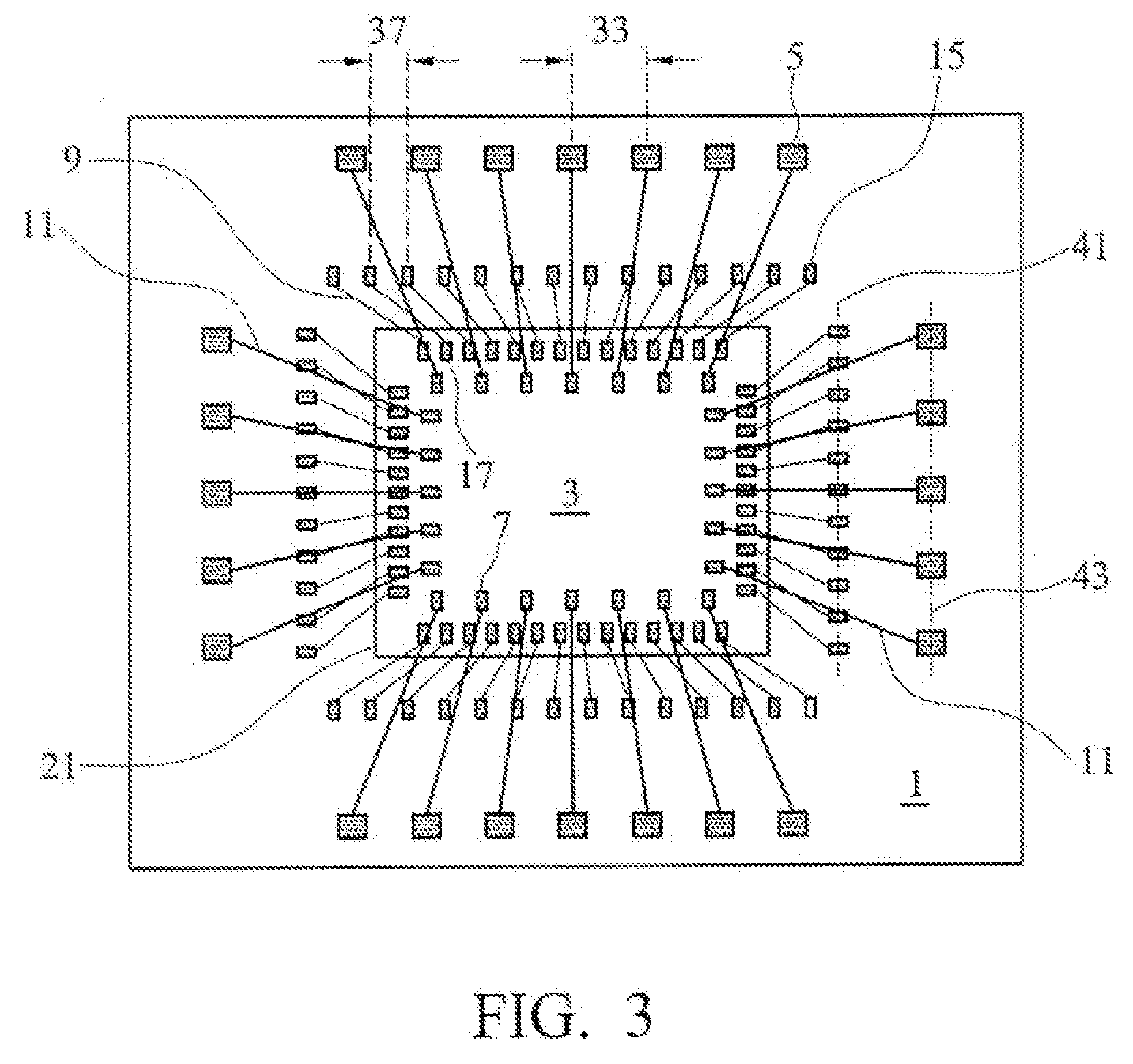
Method and structure for increased wire bond density in packages for semiconductor chips
ActiveUS20090057902A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGround contactContact pad
A semiconductor package provides an IC chip on at least one package substrate and including signal bond pads, ground bond pads and power bond pads. The package substrate includes signal contact pads, ground contact pads and power contact pads which are respectively coupled to signal bond pads, ground bond pads and power bond pads formed on the IC chip. The contact pads are coupled to the associated bond pads by a bonding wire. The bonding wires that connect the power and ground pads have a thickness that is greater than the thickness of the bonding wires that couple the signal pads. The various bond pads on the IC chip may be staggered to provide for enhanced compactness and integration. The package substrates may be a plurality of stacked package substrates.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Mesoporous silica nano-drug carrier and preparation method thereof
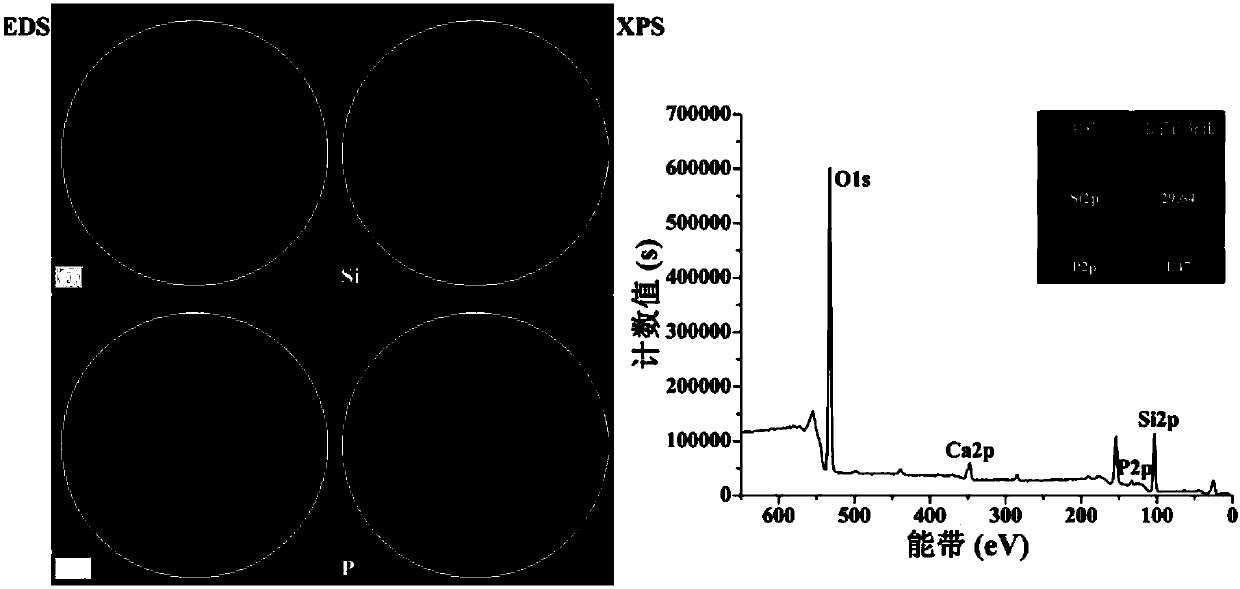
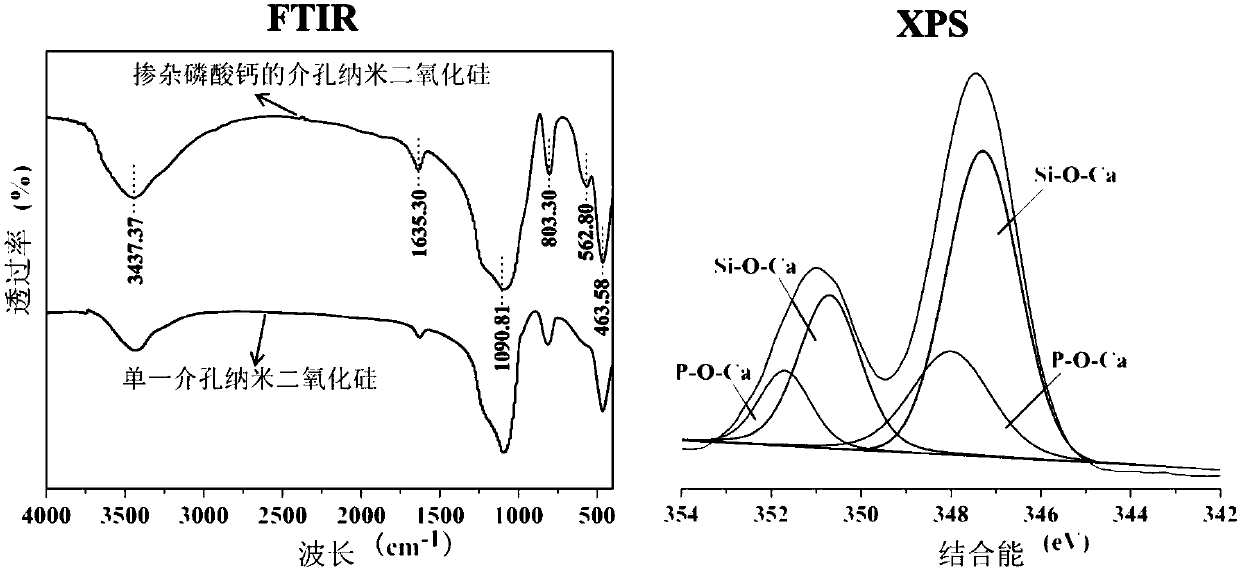
InactiveCN107684546APromote degradationLow densityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryBond densityMesoporous silica
The invention discloses a mesoporous silica nano-drug carrier and a preparation method thereof. The mesoporous silica nano-drug carrier mainly comprises calcium phosphate and silicon dioxide of whichthe mass percent ratio is 1-1.2 to 2.9-25.8. As calcium phosphate is doped with a mesoporous silica skeleton, the -Si-O-Si-bond density is reduced, and the biodegradability of mesoporous silica is improved; besides, the characteristic that calcium phosphate is stable under a neutral condition and easily soluble under an acid condition is utilized, so that drug release has the pH response characteristic, and drug targeted therapy is realized; on the other hand, dissolution of calcium phosphate enables pyrolysis of silica carrier, and degradation and excretion of the carrier are more facilitated.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
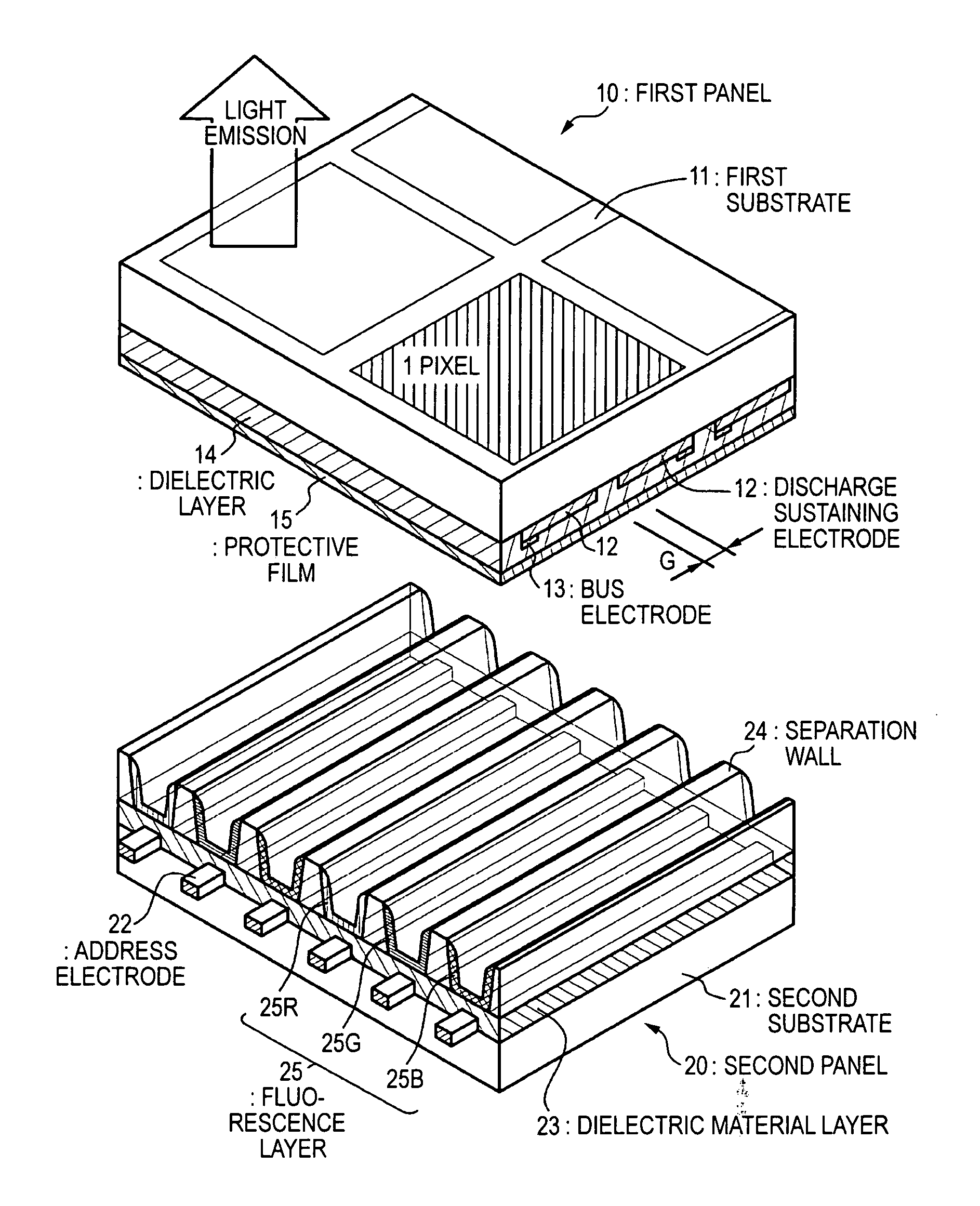
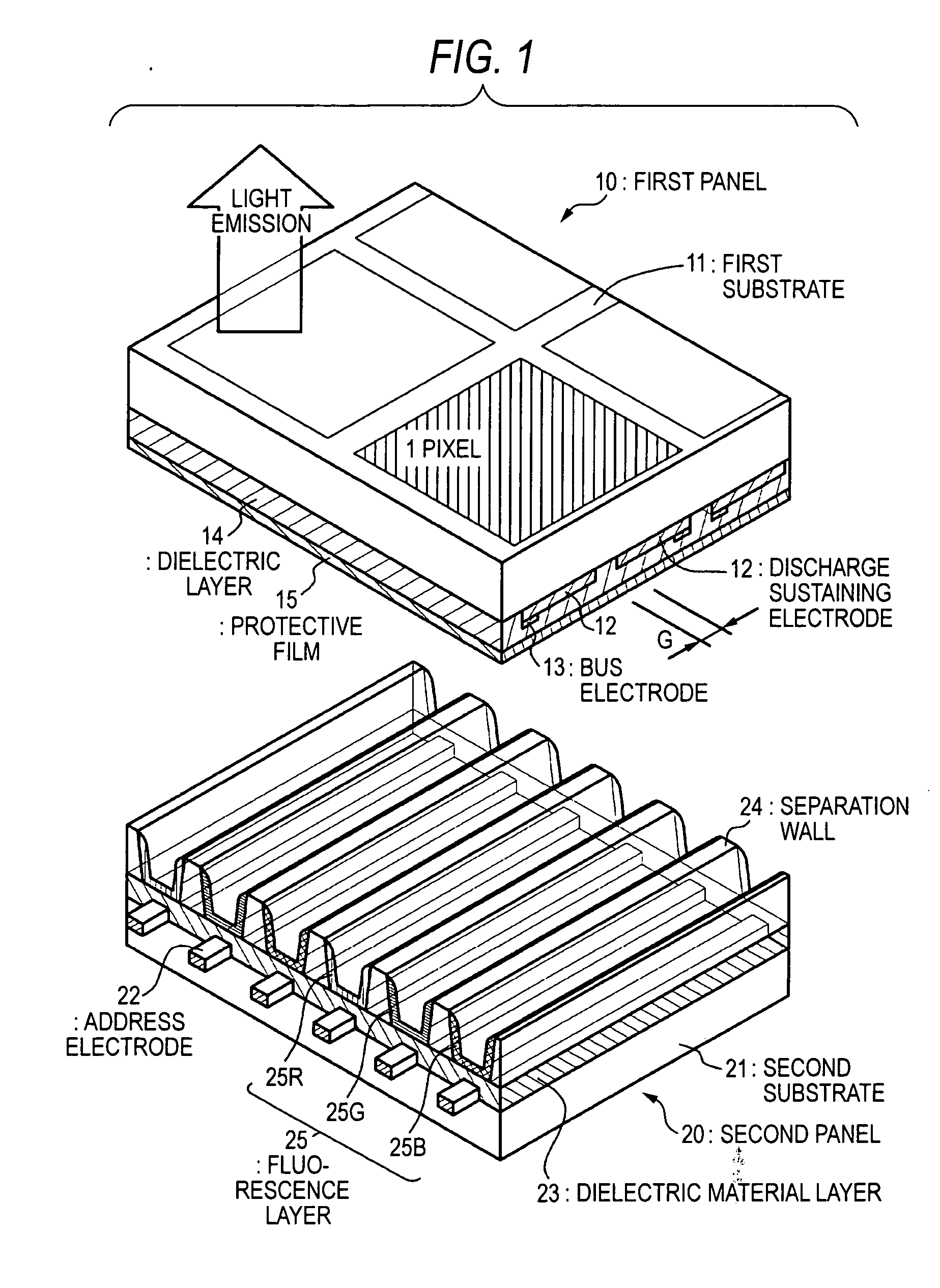
Alternating current driven type plasma display device and production method therefor
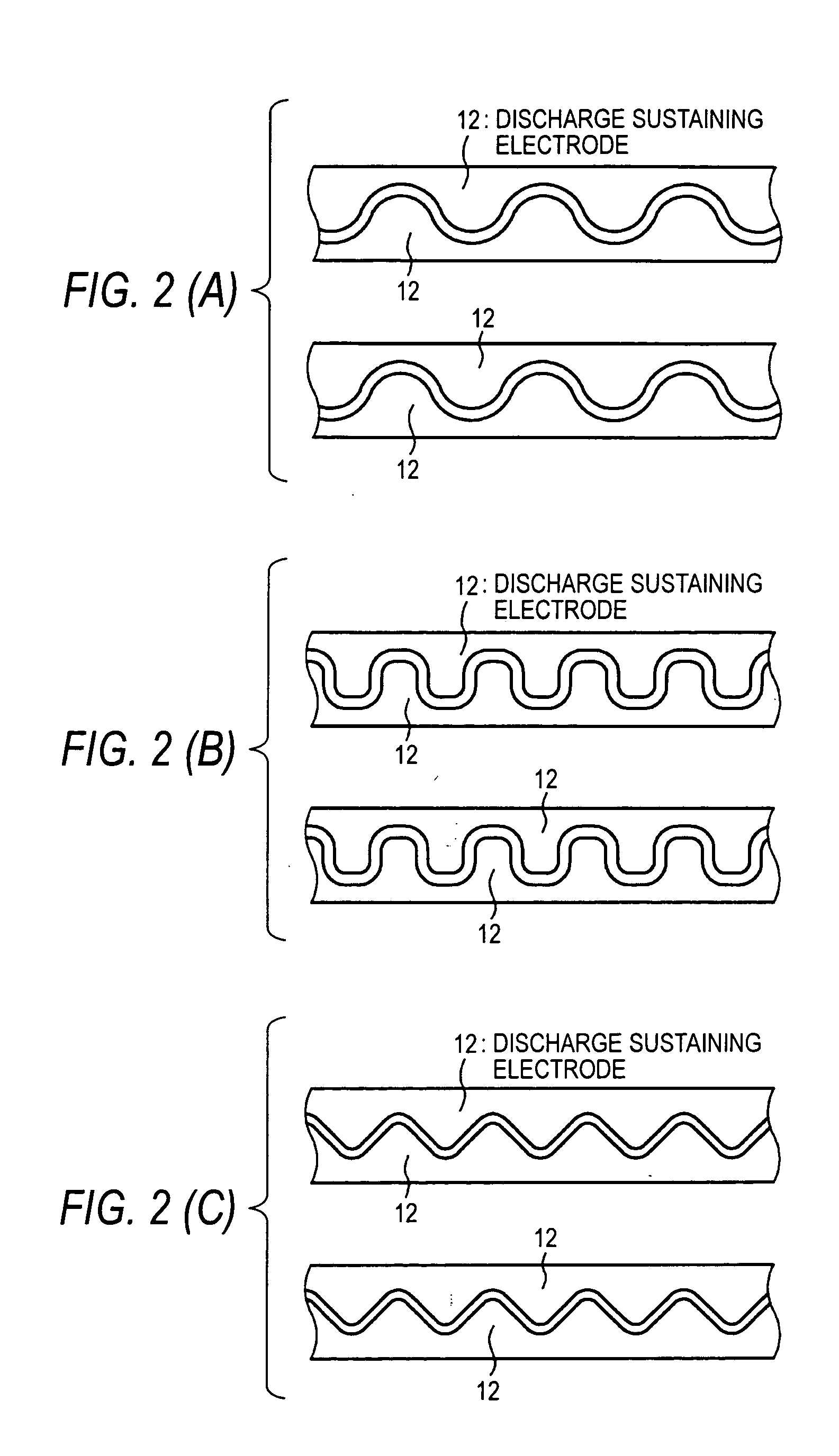
InactiveUS20050275350A1Improve efficiencyReduce power consumptionGas discharge electrodesAlternating current plasma display panelsBond densityEngineering
An alternating current driven type plasma display device which does not increase a driving voltage (discharge voltage) and does not increase a time delay of discharge is provided. The alternating current driven type plasma display device contains a first panel having a plurality of first electrodes formed on a fist substrate and a dielectric layer formed on the first substrate and the first electrodes and a second panel, in which the first panel and the second panel are bonded to each other in circumferential portions thereof, the dielectric layer is constituted by SiOX, and bonding density of H2O contained in SiOX is 3.0×1020 Bonds / cm3 or more.
Owner:SONY CORP
Preparation method of epoxy resin composite material with electric tree resistance characteristic
The invention discloses a preparation method of an epoxy resin composite material with an electric tree resistance characteristic. The method comprises the steps that nano-scale alumina and micro-scale alumina are compounded to serve as an inorganic filler; inorganic particles have a function of preventing electric tree growth, so that an electric tree channel is blocked by the inorganic particles, thereby enhancing the ability of epoxy resin to inhibit the electric branch growth; the cooperative use of fillers with different particle sizes can effectively reduce the generation of air gaps between filler particles and an epoxy polymer, and after coupling agent-low temperature plasma synergistic treatment is carried out on the inorganic filler, the bonding between the fillers with differentparticle sizes and an epoxy resin matrix is promoted, thereby effectively improving the bonding density between the filler and the resin matrix; during the curing of the epoxy resin composite material, intermittent ultrasonic treatment and vacuum degassing treatment reduce the generation of the air gaps in an epoxy system, thereby achieving the purpose of inhibiting the generation of a secondaryelectric tree structure.
Owner:WUHU BAOYI AMUSEMENT EQUIP
Method and structure for increased wire bond density in packages for semiconductor chips
ActiveUS7884473B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGround contactContact pad
A semiconductor package provides an IC chip on at least one package substrate and including signal bond pads, ground bond pads and power bond pads. The package substrate includes signal contact pads, ground contact pads and power contact pads which are respectively coupled to signal bond pads, ground bond pads and power bond pads formed on the IC chip. The contact pads are coupled to the associated bond pads by a bonding wire. The bonding wires that connect the power and ground pads have a thickness that is greater than the thickness of the bonding wires that couple the signal pads. The various bond pads on the IC chip may be staggered to provide for enhanced compactness and integration. The package substrates may be a plurality of stacked package substrates.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
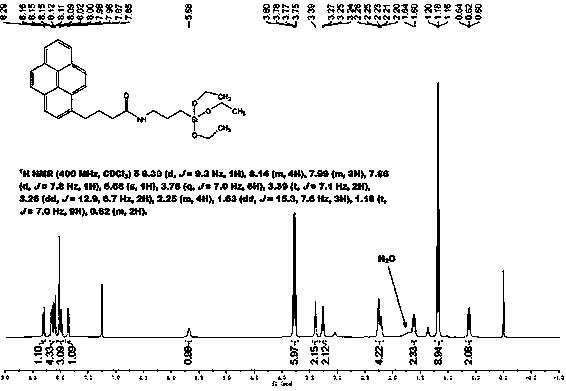
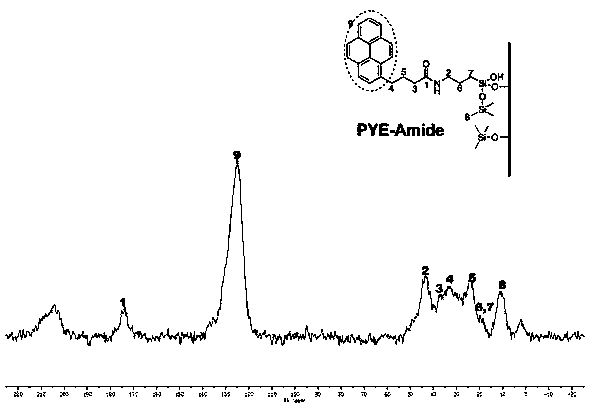
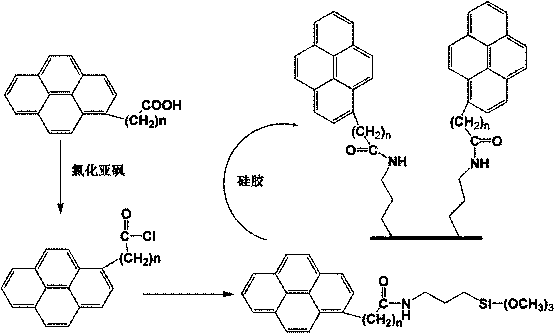
Condensed ring aromatic hydrocarbon based amide embedded type liquid chromatography stationary phase synthesis method
ActiveCN109704985AAvoid time costLow raw material costGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationBond densitySynthesis methods
The invention relates to a novel condensed ring aromatic hydrocarbon based amide embedded type liquid chromatography stationary phase synthesis method. According to the condensed ring aromatic hydrocarbon based amide embedded type liquid chromatography stationary phase synthesis method, condensed ring aromatic hydrocarbon based carboxylic acids and isocyanate silane reagents are taken as raw materials, amide type silane reagents are synthesized, simple purification is adopted, modification onto stationary phase matrix surfaces is realized so as to synthesize a condensed ring aromatic hydrocarbon based amide embedded type liquid chromatography stationary phase. The properties such as bonding density, aromatic and hydrophobic compound separation effect, charge transfer capacity, and isomer selectivity are tested, it is shown that better aromatic compound selectivity and shape selectivity are achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU HANBON SCI & TECH CO
Thermally insulating sheet formed from a down core structure and method of fabrication
A thermally insulating sheet formed by a down core structure which is comprised solely of down feather material mixed with binding material which is heat fused together to form a homogeneous sheet core. The method of fabricating the homogeneous thermally insulating sheet to form the down core structure is described. This novel method restrains the down clusters and binding material during the process of mixing, depositing, conveying and heat fusing to form a homogeneous down core sheet. The down core structure is subjected to two separate heat treatments which produces a down core sheet having at least some of its outer surfaces being of higher bond density than the inside of the core.
Owner:REUBEN RONIE
Chiral medicine resolution medium based on polypeptide combined chiral recognition base and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102688750AStrong specificityBroad chiral resolution rangeOther chemical processesBond densitySilica gel
A chiral medicine resolution medium based on a polypeptide combined recognition base is obtained by bonding the polypeptide combined base with different chiral recognition capabilities onto the surface of porous silica gel with its pore size being 8-12nm and particle size being 5-30mm through chemical modification. According to a preparation method of the above chiral medicine resolution medium, one or some medicine-related proteins undergo enzymatic hydrolysis at 25-37 DEG C by the use of trypsin or papain or elastase or one or some enzymes thereof; zymoprotein is removed from the polypeptide combined base obtained after enzymatic hydrolysis by denaturation and adsorption or dialysis, and then the polypeptide combined base is bonded onto the porous silica gel surface by chemical modification so as to obtain the required chiral medicine resolution medium. The prepared chiral medicine resolution medium has wide chiral resolution range and uniform surface distribution, and its bonding density is higher than the bonding density of a protein stationary phase. The chiral medicine resolution medium has the combined chiral recognition base which can be used for resolution and analysis of a plurality of chiral medicines and provides a foundation for developing chiral resolution materials with a wider resolution range and chiral medicines with better specificity.
Owner:WUHAN HUISHITONG BIO ENG
Bond pattern
A composite includes a first substrate and a second substrate joined in a bonding region, wherein the first substrate comprises a first Peak Force Tensile Strength and the second Peak Force Tensile Strength. The first Peak Force Tensile Strength is greater than or equal to the second Peak Force Tensile Strength. The bonding region has a Bond Density of about 10% to about 22%; and a Composite Tensile Strength at Peak Force that is within about 15% of the second Peak Force Tensile Strength.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
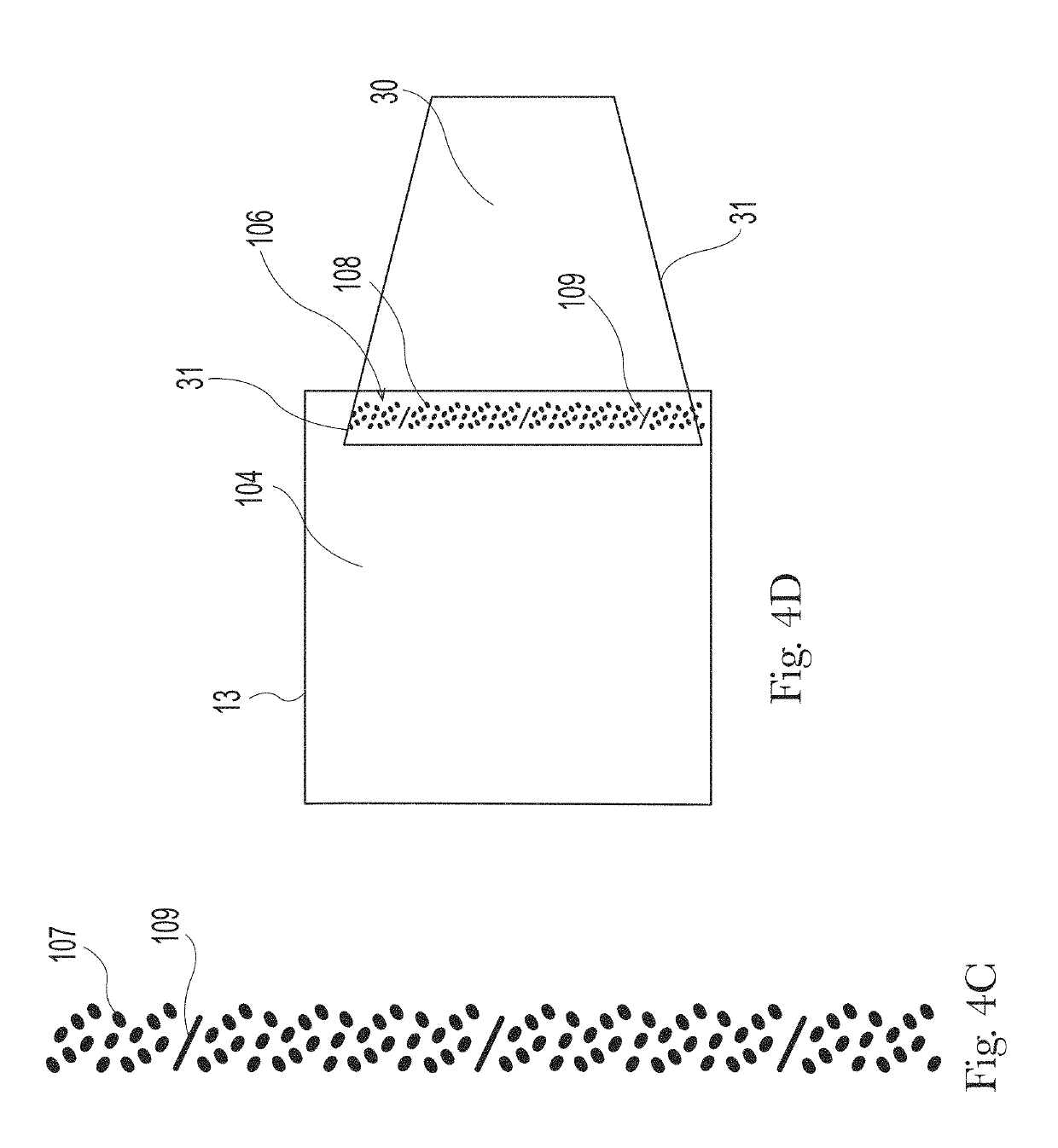
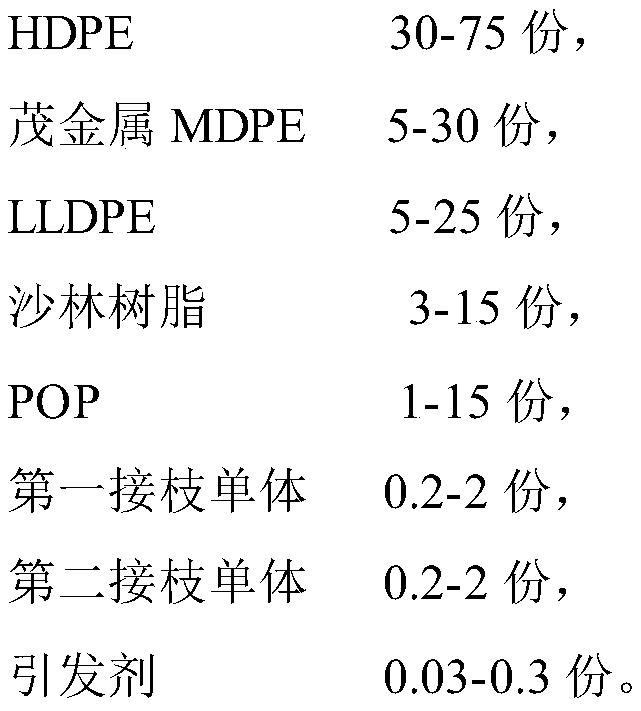
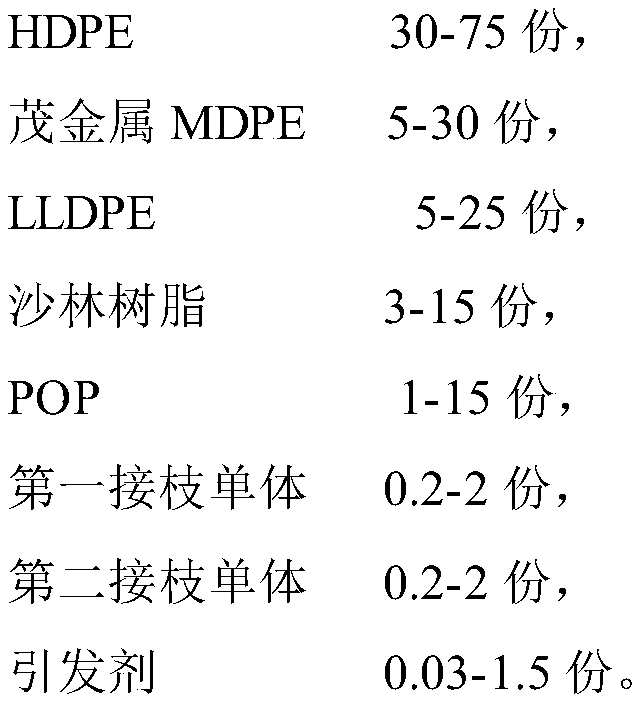
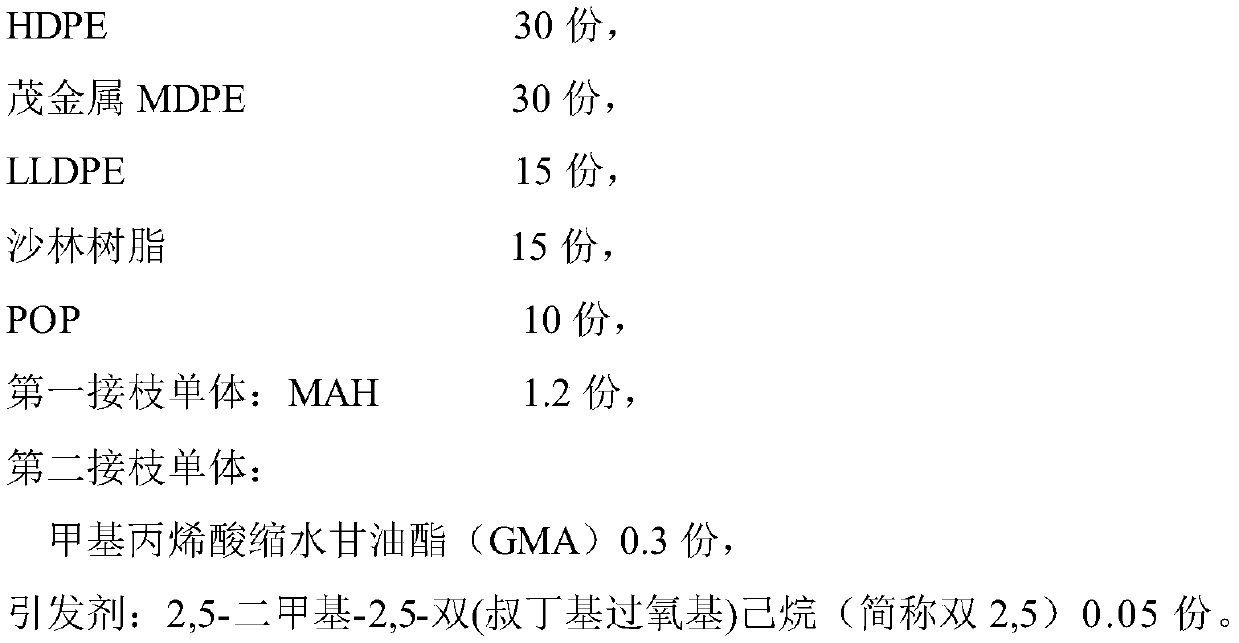
Polyethylene pipe bonding material and preparation method thereof
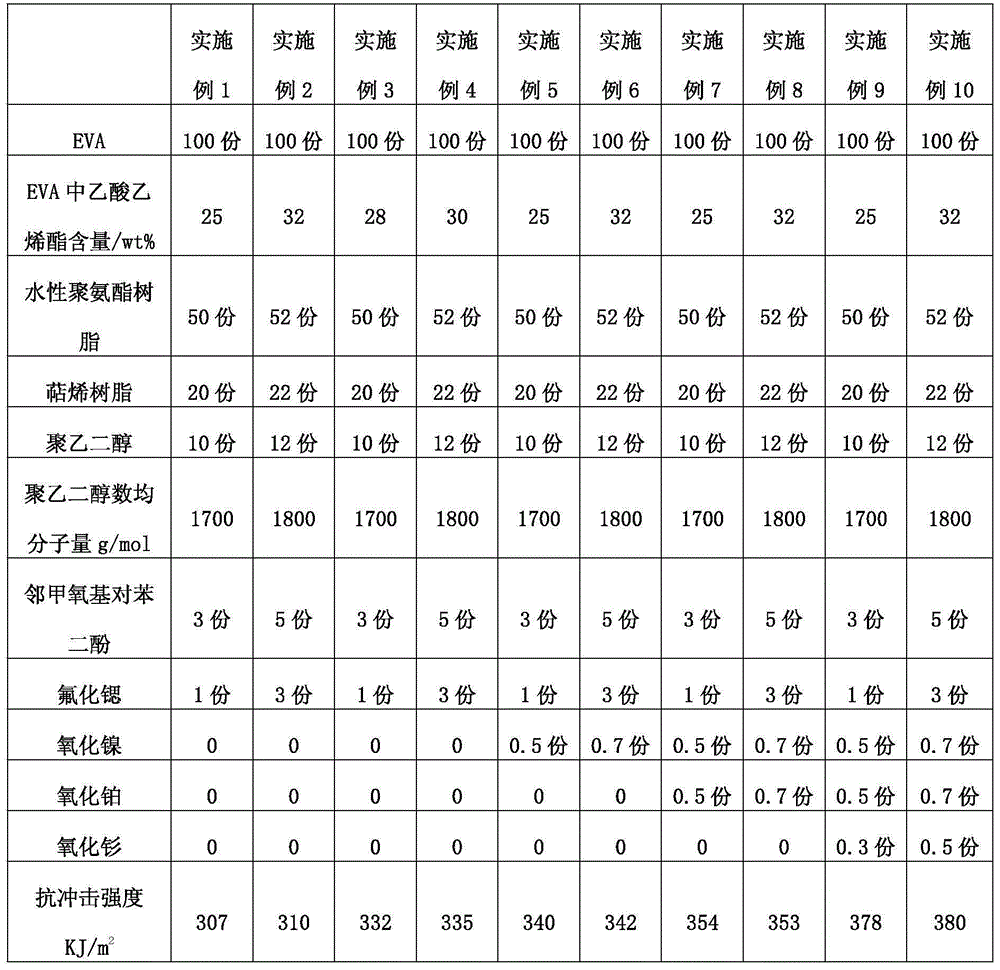
ActiveCN110295019AHigh tensile strengthGood wetting and coating effectGraft polymer adhesivesEpoxyBond density
The invention relates to a polyethylene pipe bonding material and a preparation method thereof. By selecting metallocene MDPE and HDPE for blending and LLDPE, sarin resin and POP for supplementing toperform maleic anhydride grafting reaction on a polyethylene polymer chain during melt blending, the polyethylene pipe bonding material is prepared, and the polyethylene pipe bonding material has tensile strength greater than 25 MPa, impact strength greater than 32 kJ / m<2>, melt flow rate less than 3.8 g / 10 min and peel strength greater than 13.8 N / mm, while the higher peel strength greatly increases the bonding density of the polyethylene pipe bonding material with steel wires or steel pipes; the polyethylene pipe bonding material is applied to high-speed plastic coating of a steel wire meshin a steel wire reinforced polyethylene pipe, and can also be applied to bonding a steel pipe coated with epoxy powder and outer layer PE in a 3PE anticorrosive pipe; the bonding material has better bonding performance with the steel wires or steel pipes.
Owner:江苏鸿硕工程塑料科技股份有限公司
Manufacturing method of anti-impact soft no-woven cloth
ActiveCN104999748AHigh bonding strengthHigh densitySynthetic resin layered productsLaminationBond densityAdhesive
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of anti-impact soft no-woven cloth. The method comprises the steps that 1, fiber adhesive dipping is conducted, and hot-pressing is conducted on single-fiber layers; 2, hot-pressing is conducted on two-layer composite fiber layers; 3, hot-pressing is conducted on two-layer composite fiber layers with two to four rolls to prepare the anti-impact soft no-woven cloth with four to eight composite fiber layers, wherein adhesives used in the method comprises ethylene vinyl acetate copolymers, waterborne polyurethane resin, terpene resin, polyethylene glycol, o-methoxyhydroquinone and strontium fluoride. According to the manufacturing method of the anti-impact soft no-woven cloth, the adhesives are improved, a multi-component composite formula is adopted, the bonding strength and the bonding density of the adhesives on fibers are effectively improved, and the tenacity and the anti-impact property of the no-woven cloth are improved; freezing and unfreezing are conducted on the fibers which are dipped in the adhesives, the internal stress and the surface tension of the adhesives are effectively decreased, and hot-pressed composite fiber layers have higher strength and anti-impact capacity.
Owner:CHANGSHU YONGLIJIAN NEW MATERIALS
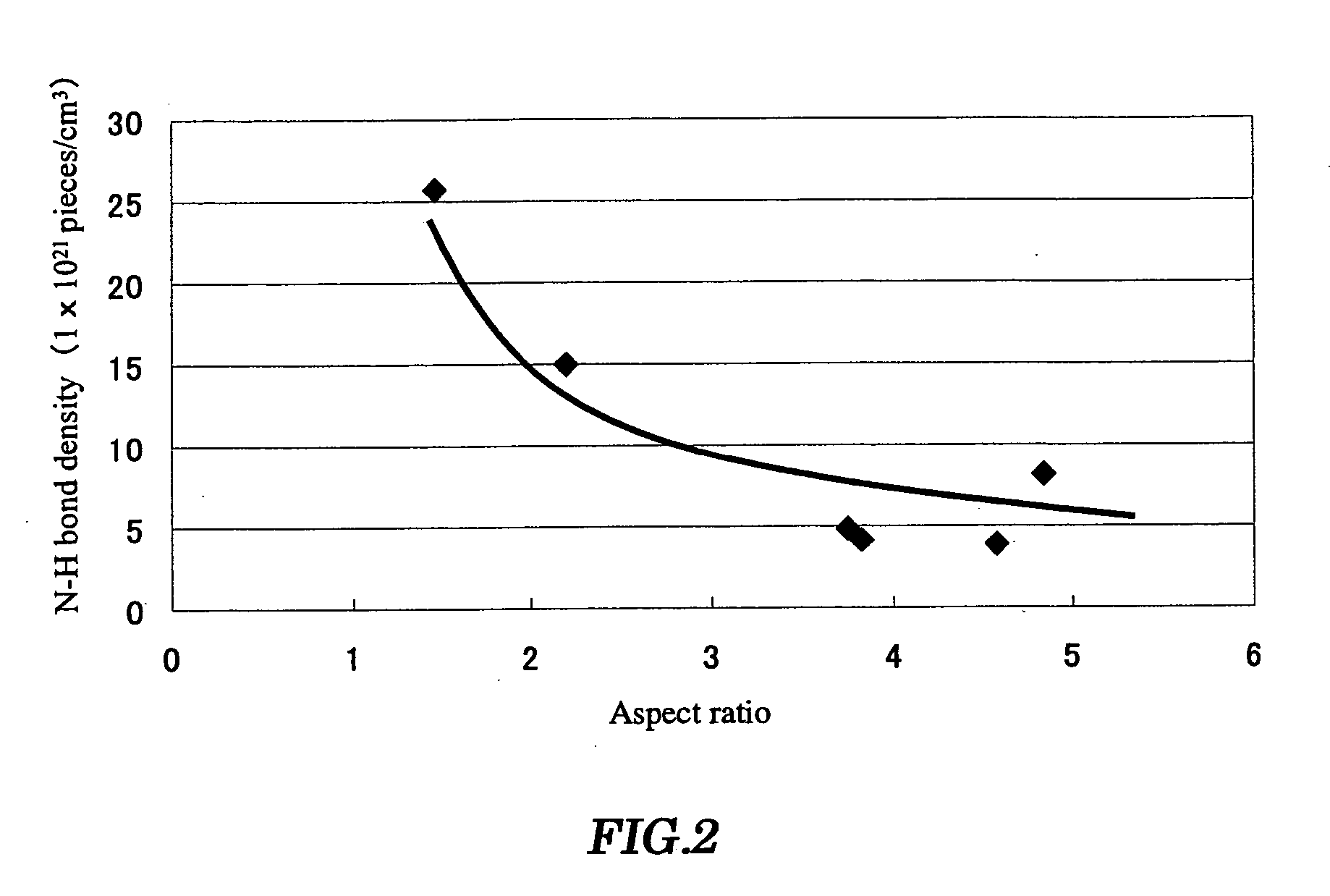
Method for forming interlayer insulation film
ActiveUS20050159015A1Short timeReduce harmSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBond densitySemiconductor
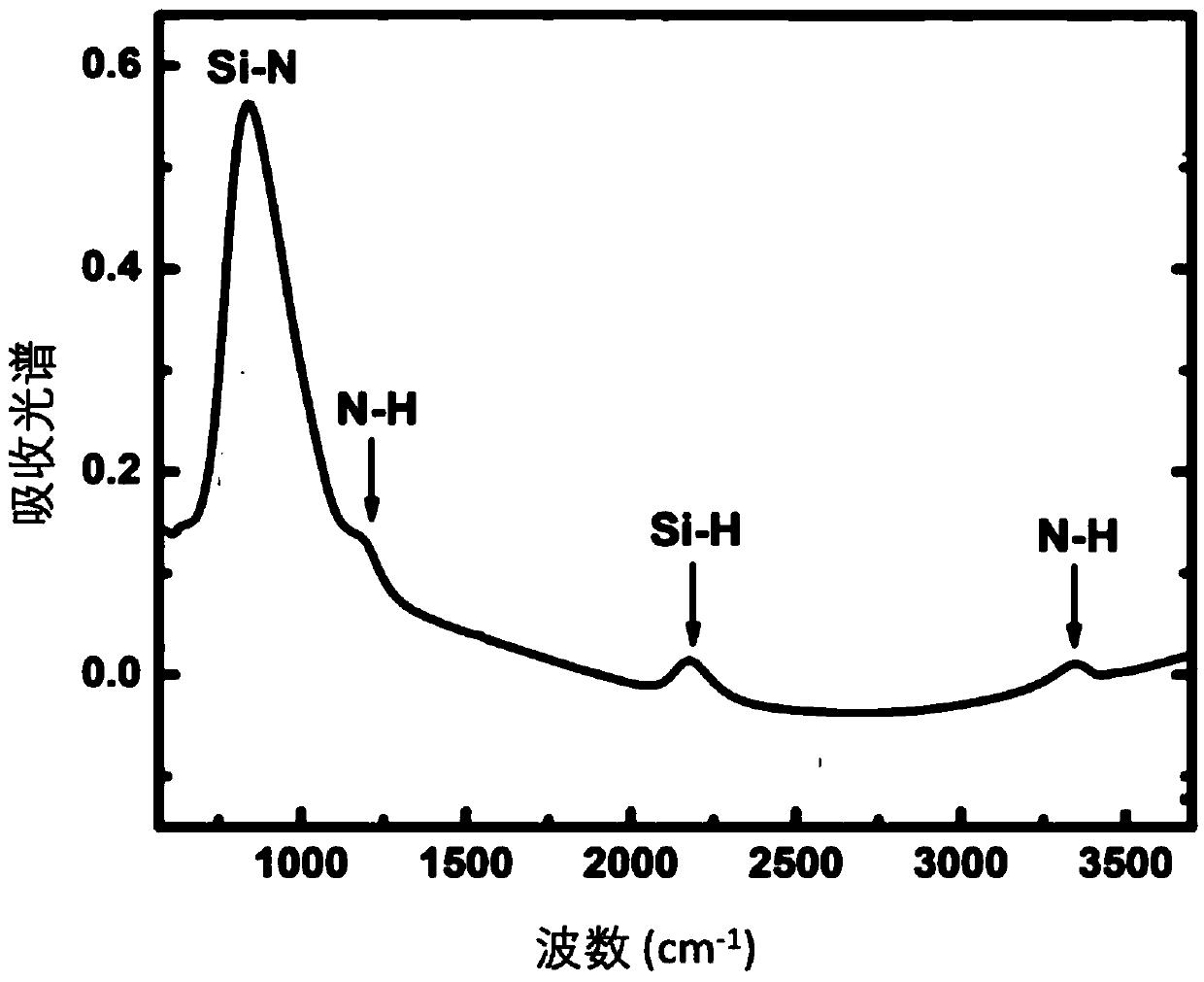
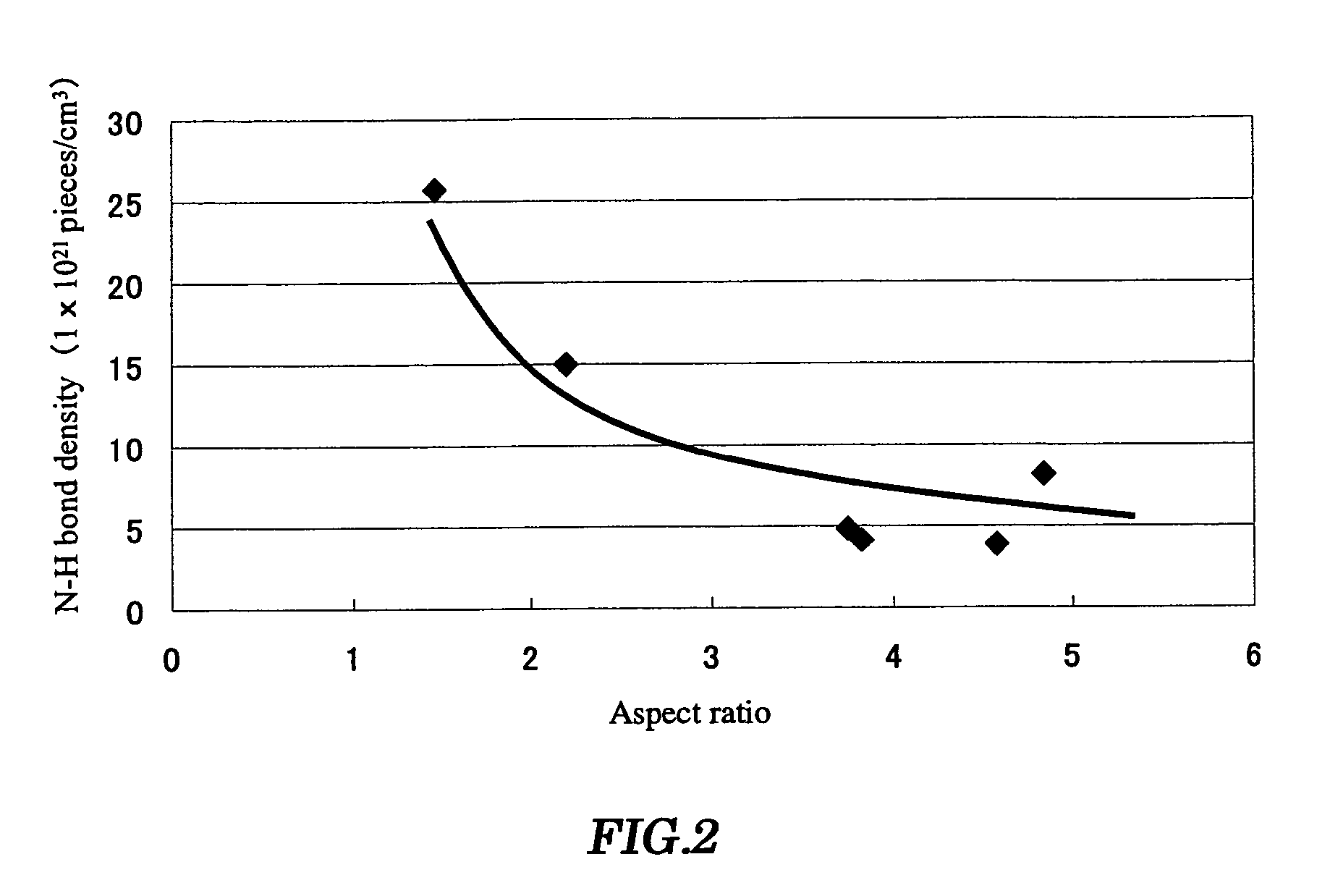
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for forming an interlayer insulation film suppressing the occurrence of voids in the interlayer insulation film. A method for forming an interlayer insulation film of the present invention, comprising the steps of: (1) forming an etching stopper film of a silicon nitride film on an entire surface including a step part on a semiconductor substrate having the step part with an aspect ratio of ≧3; (2) forming an interlayer insulation film of an impurity-doped silicate film on the silicon nitride film; and (3) performing reflow of the interlayer insulation film by a heat treatment, wherein the formation of the silicon nitride film is controlled such that the N—H bond density of the silicon nitride film is 1.0×1022 pieces / cm3 or less. According to the method for forming the interlayer insulation film of the present invention, the occurrence of the voids can be suppressed in the interlayer insulation film even if the aspect ratio of the step part formed on the semiconductor substrate is 3 or more. Also, the damage applied to the semiconductor device by reflow can be reduced.
Owner:SHARP KK
Movable chemical vapor deposition method of silicon nitride thin film
ActiveCN109585264AReduced Si-H bond densityReduce wet etch rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBond densityWafering
The invention provides a movable chemical vapor deposition method of a silicon nitride thin film with relatively low etching rate. Cyclosilane with an annular molecule structure is used as a precursor, the cyclosilane and a nitrogen-containing compound are deposited on a substrate by a deposition-curing periodic circulation mode to form the movable silicon nitride thin film until a groove of the substrate is filled. The Si-H bond density of the silicon nitride thin film is remarkably reduced, the etching speed is also greatly reduced, and seamless gap filling in a silicon wafer with a patterncan be achieved from bottom to top, the high-quality silicon nitride thin film can be formed on a blank silicon wafer, the method is more suitable for filling of a new-generation semiconductor component with high depth-to-width ratio gap, and the silicon nitride thin film is good in uniformity, good in compactness and high in convergence rate.
Owner:合肥安德科铭半导体科技有限公司
Method for forming interlayer insulation film
ActiveUS7402513B2Reduce harmSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBond densityThermal treatment
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method for forming an interlayer insulation film suppressing the occurrence of voids in the interlayer insulation film.A method for forming an interlayer insulation film of the present invention, comprising the steps of: (1) forming an etching stopper film of a silicon nitride film on an entire surface including a step part on a semiconductor substrate having the step part with an aspect ratio of ≧3; (2) forming an interlayer insulation film of an impurity-doped silicate film on the silicon nitride film; and (3) performing reflow of the interlayer insulation film by a heat treatment, wherein the formation of the silicon nitride film is controlled such that the N—H bond density of the silicon nitride film is 1.0×1022 pieces / cm3 or less.According to the method for forming the interlayer insulation film of the present invention, the occurrence of the voids can be suppressed in the interlayer insulation film even if the aspect ratio of the step part formed on the semiconductor substrate is 3 or more. Also, the damage applied to the semiconductor device by reflow can be reduced.
Owner:SHARP KK
A flowable chemical vapor deposition method for silicon oxide films
ActiveCN109166787BReduced Si-H bond densityReduce wet etch rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBond densityGas phase
The invention provides a flowable chemical vapor deposition method of a silicon oxide film with a lower etching rate, wherein a cyclosilane with a ring molecular structure is used as a precursor, andthe cyclosilane is reacted with a nitrogen-containing compound to deposit on a substrate to form a flowable silicon nitride film, and the silicon oxide film is obtained by oxidation of oxidizing gas.The Si-H bond density and wet etch rate are significantly reduced. Aft high temperature annealing or ultraviolet curing, bottom-up, seamless gap filling can be realized on that patterned silicon wafer; High quality silicon oxide film can be formed on the blank silicon wafer. Good uniformity and good covering performance.
Owner:铜陵安德科铭电子材料科技有限公司
Method for reproducing waste rubber by using microorganism
InactiveCN101456968BNo pollution in the processMild conditionsPlastic recyclingMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismBond density
The invention provides a method for using microorganism to regenerate scrap rubber. The microorganism used is saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme and metabolin containing hydrosulphonyl produced in the process of growth of cells of saccharomyces cerevisiae reacts with the scrap rubber, and sulfur cross bond of the rubber is fractured and decoking regeneration is carried on, thus reaching the aim of targeted decoking. The decoking is carried on by using co-cultivating the rubber powder and saccharomyces cerevisiae germs and the scrap rubber decoking regeneration effects are strengthened by combining thermal cracking broken wall reaction of the saccharomyces cerevisiae cells, a phase transfer agent and an addition agent of the phase transfer agent. The excellent technical conditions of the decoking regeneration are confirmed: temperature, pH, rotation speed, reaction time, doze of the phase transfer agent and the addition agent of the phase transfer agent, etc. By checking the cross bond density and the degree of swelling and showing the detection of X ray electron spectrum (XPS), after the function of saccharomyces cerevisiae, the cross bond density of the decoking regeneration rubberis obviously reduced, and the degree of swelling is obviously improved, sulfur element contents on the regeneration rubber surface is decreased, thus showing that the decoking regeneration effects ofthe saccharomyces cerevisiae is applied to the rubber surface.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Chromatographic cake fillers and application thereof
InactiveCN103623794AUniform particlesHigh bonding densityComponent separationOther chemical processesMethacrylateBond density
The invention relates to chromatographic cake fillers and an application thereof. One kind of chromatographic cake fillers are epoxypropyl methacrylate microspheres with grain sizes not more than 2mu m. A preparation method of the fillers comprises the steps of preparing a polystyrene seed solution with a grain size less than 1mu m and preparing the epoxypropyl methacrylate microspheres with grain sizes not more than 2mu m. The other kind of chromatographic cake fillers are modified epoxypropyl methacrylate microspheres with grain sizes not more than 2mu m. The chromatographic cake fillers are uniform in grains. The modified chromatographic cake fillers have high bond density and loading capacities. The modified fillers are applied to polypeptide and protein biomacromolecules with molecular weights more than 5000.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
A high-performance polycrystalline diamond sintered body
ActiveCN104942280BIncrease the volume ratioImprove wear resistanceUltra-high pressure processesBond densityPolycrystalline diamond
The invention discloses a high-performance polycrystalline diamond sintered body with the characteristics of high wear resistance, high impact resistance and good thermal stability and a preparation method thereof, and simultaneously provides a nanometer metal bond used in the sintered body. Its nano-metal binder is composed of Co powder, Ni powder, Si powder, Ti powder, Ta powder, Hf powder and B powder according to a specific ratio. It has a good sintering promotion effect under high temperature and high pressure, and is helpful for sintering The bonding density between diamonds (D-D bonds) is conducive to the formation of a strong sintered body, which enhances the wear resistance, high heat resistance and high impact toughness of the sintered body, and prolongs the service life of the sintered body. Compared with the existing diamond sintered body, the prepared polycrystalline diamond sintered body: the wear ratio is increased from 200,000 to 250,000 to 350,000 to 400,000; the impact toughness is increased from 40 to 50 joules to 60 to 70 joules, and the thermal stability: in After roasting at 800°C for 5 minutes, the wear ratio of the product is 320,000 to 380,000, the impact toughness is 57 to 67 Joules, and the thermal stability is good.
Owner:ZHONGNAN DIAMOND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com