Patents
Literature
704 results about "Gap filling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gap Filling. A process used when a contract fails to deal with some manner necessary for the contract to be performed. The court either interprets the contract in such a manner that there is no gap, or engages in gap filling where it deals with the gap in the contract by ascertaining what the parties intentions would have been at the time...
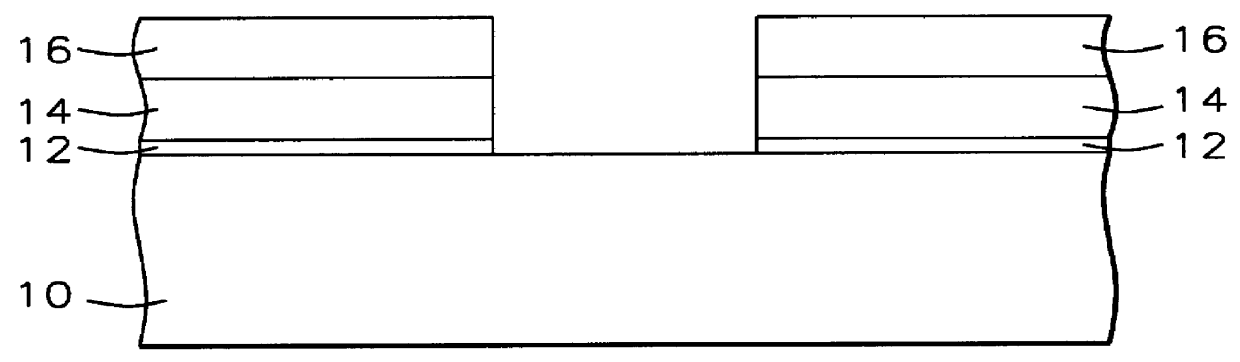
Stress management for tensile films
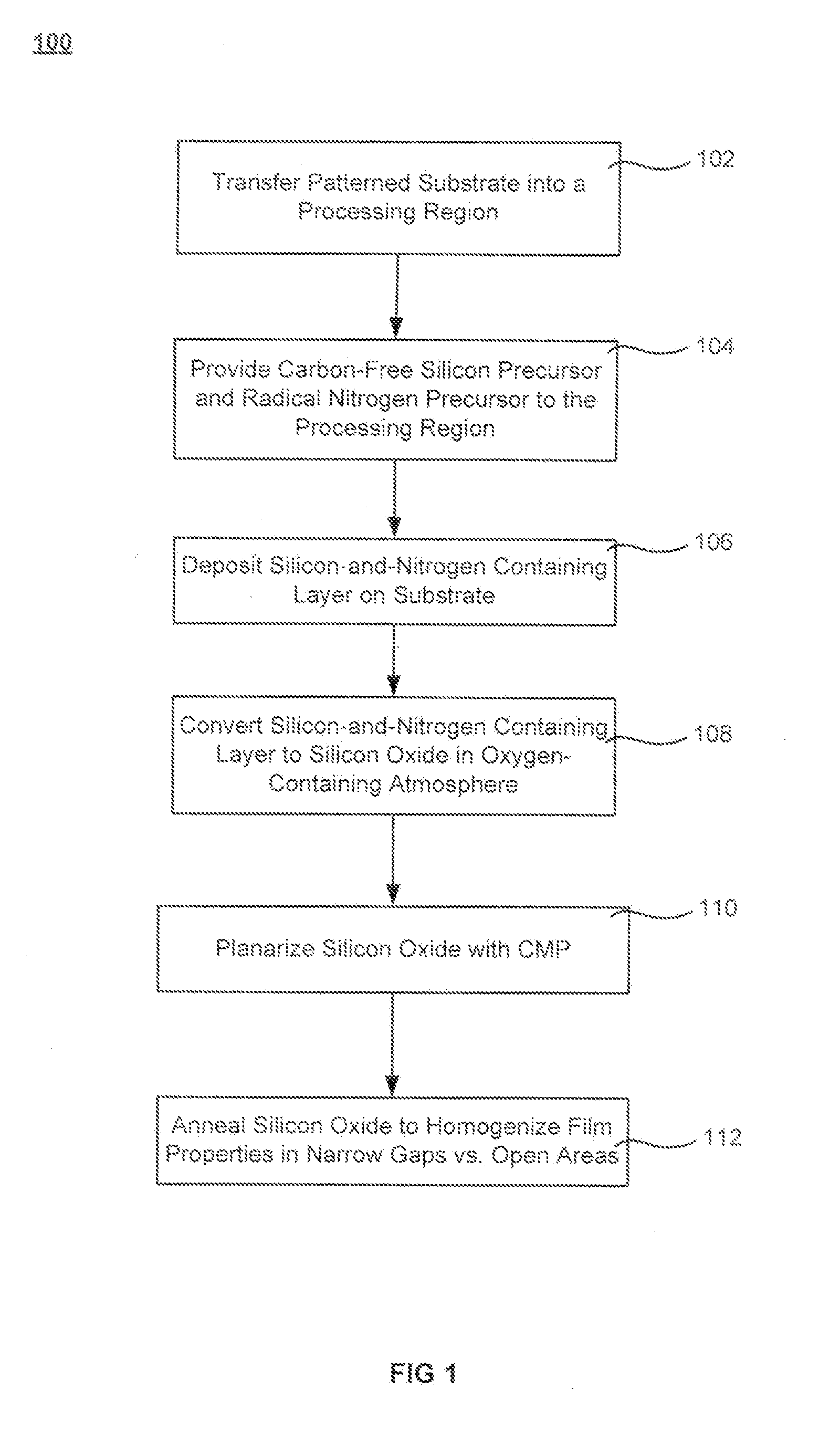
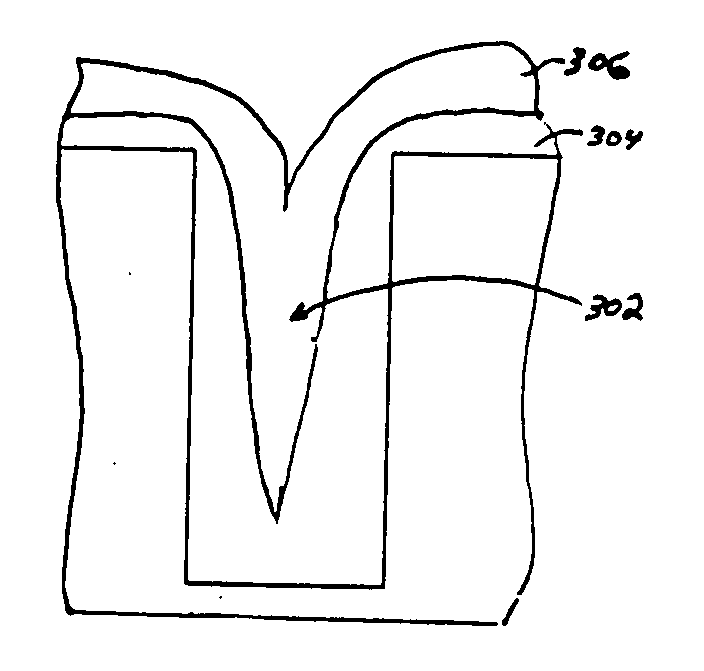
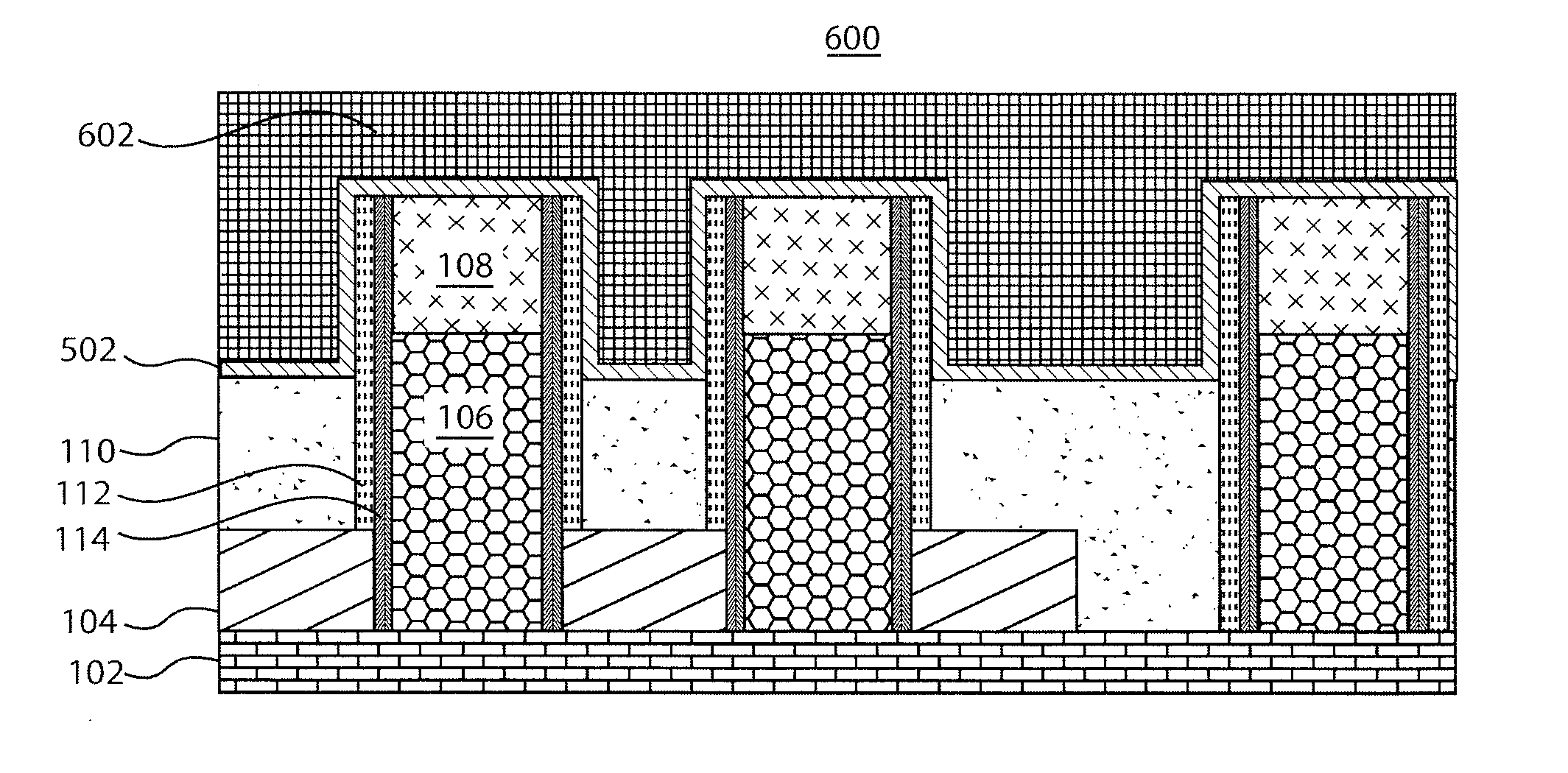
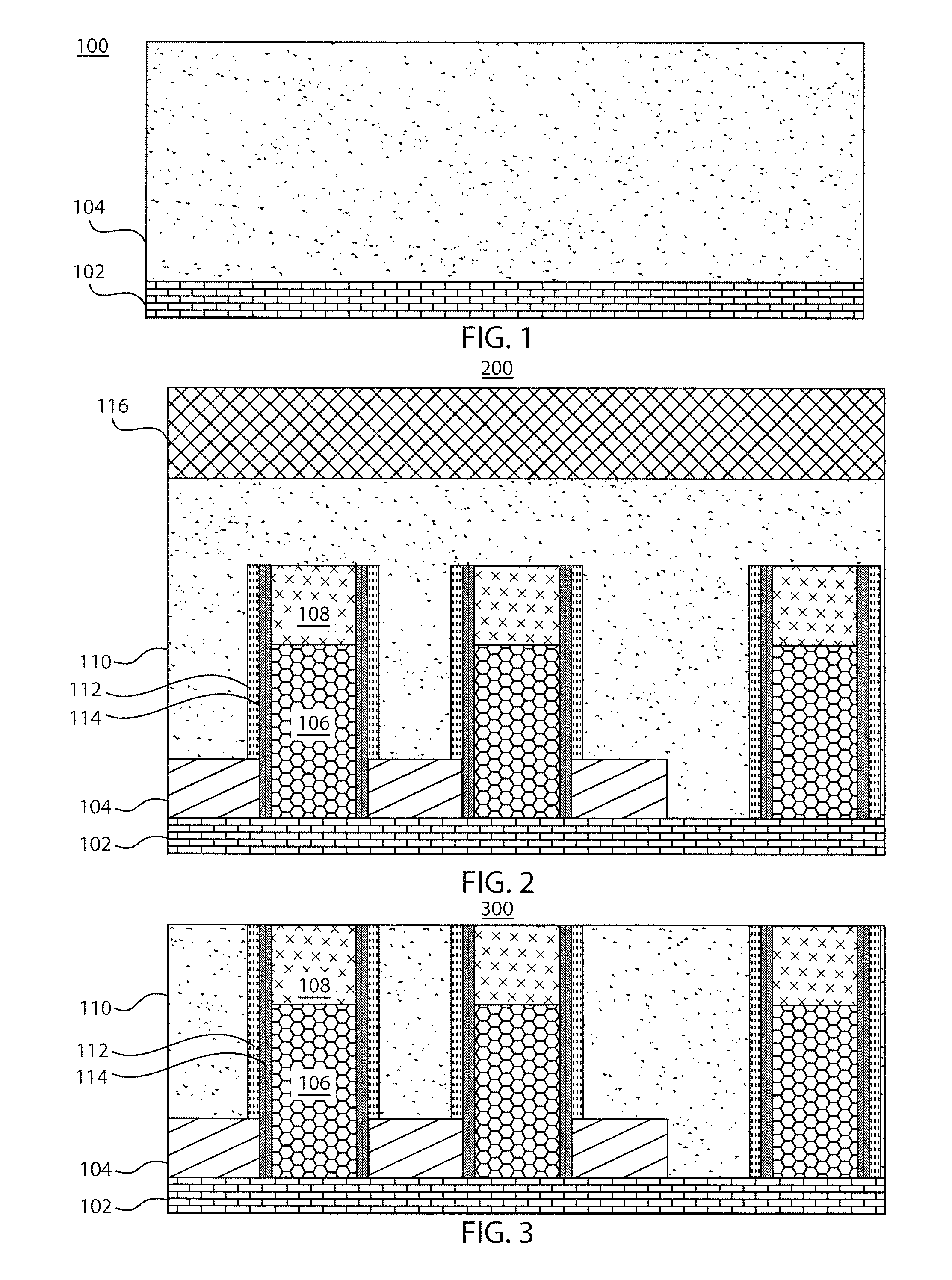
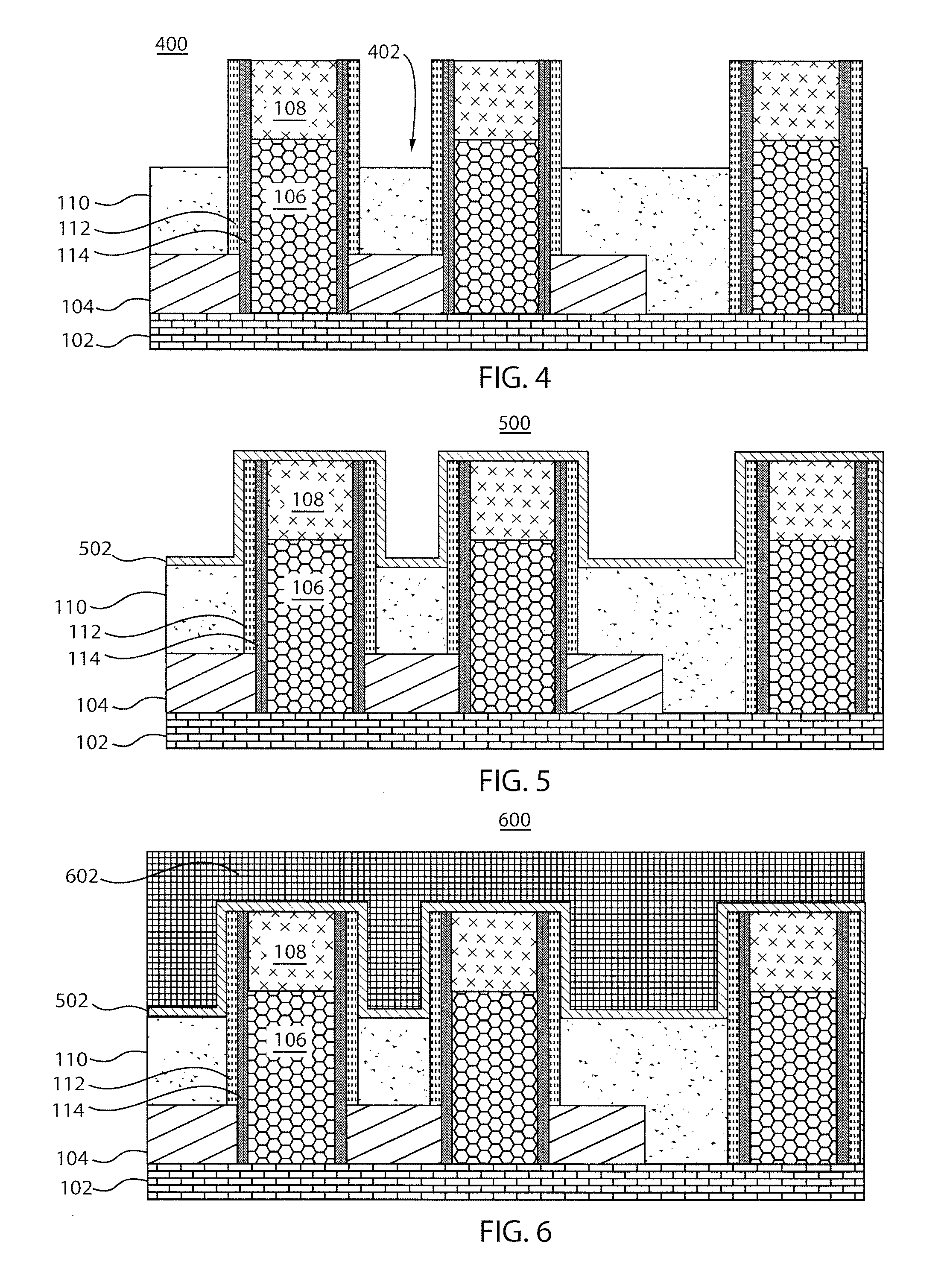
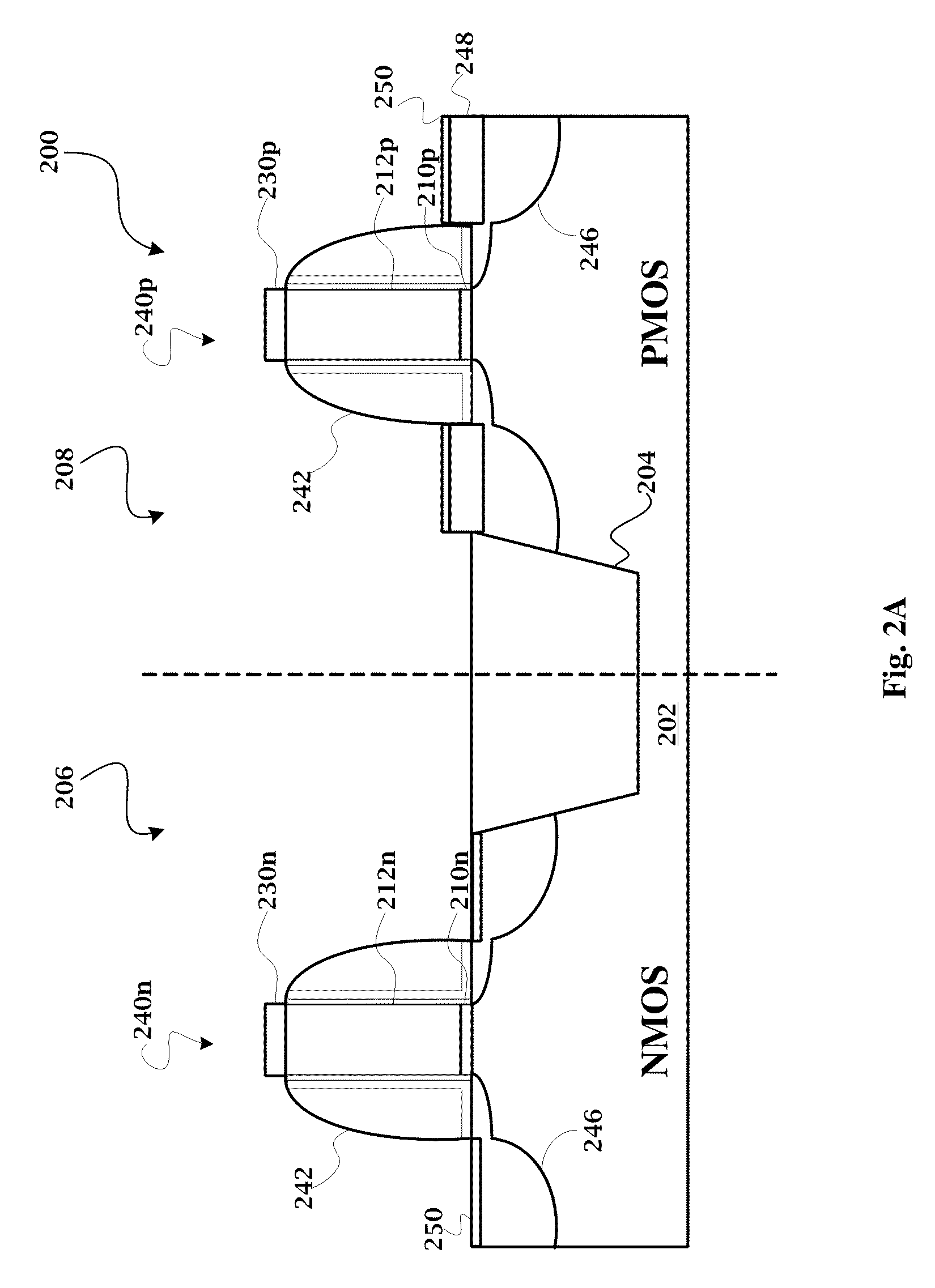
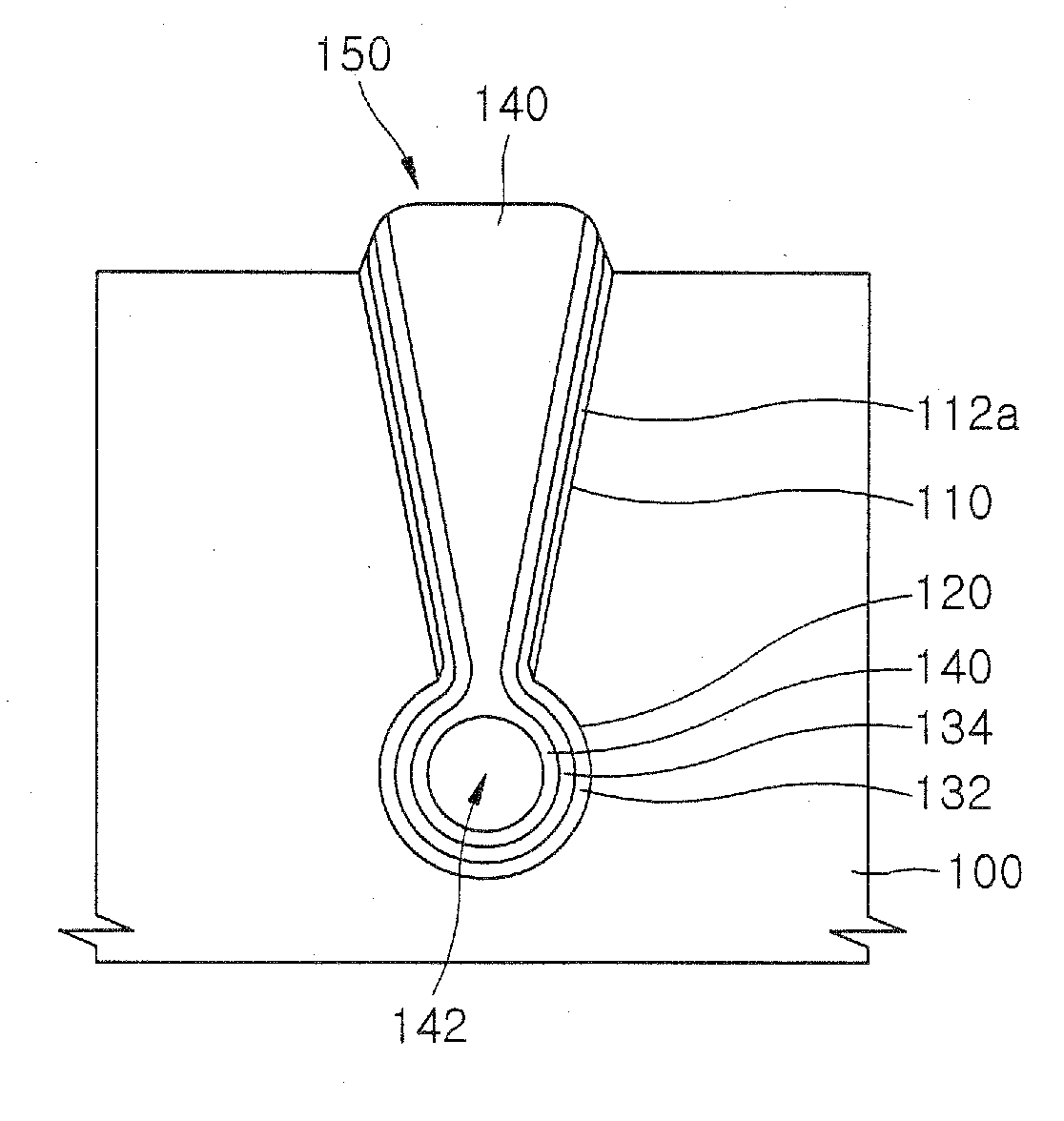
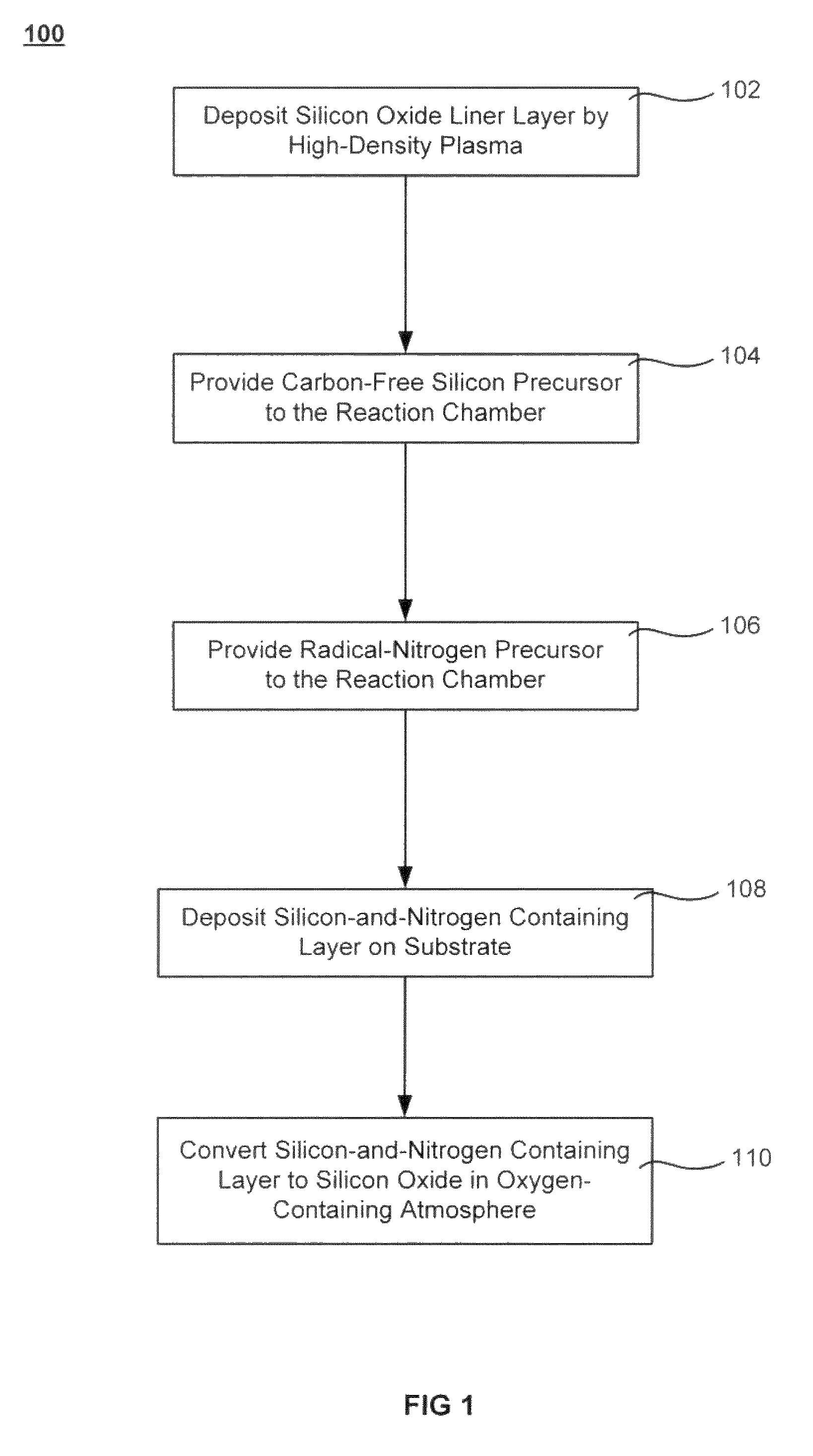
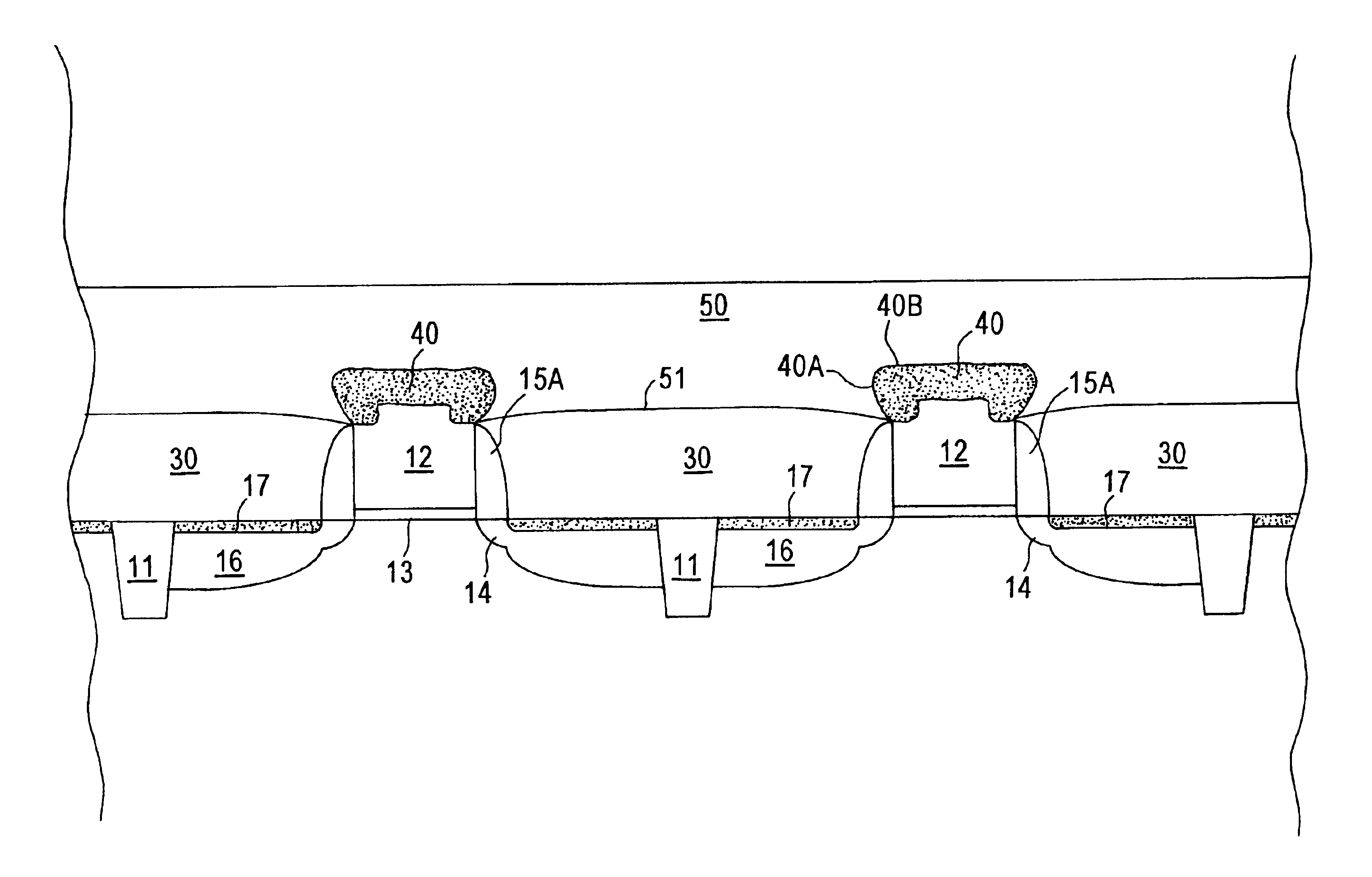
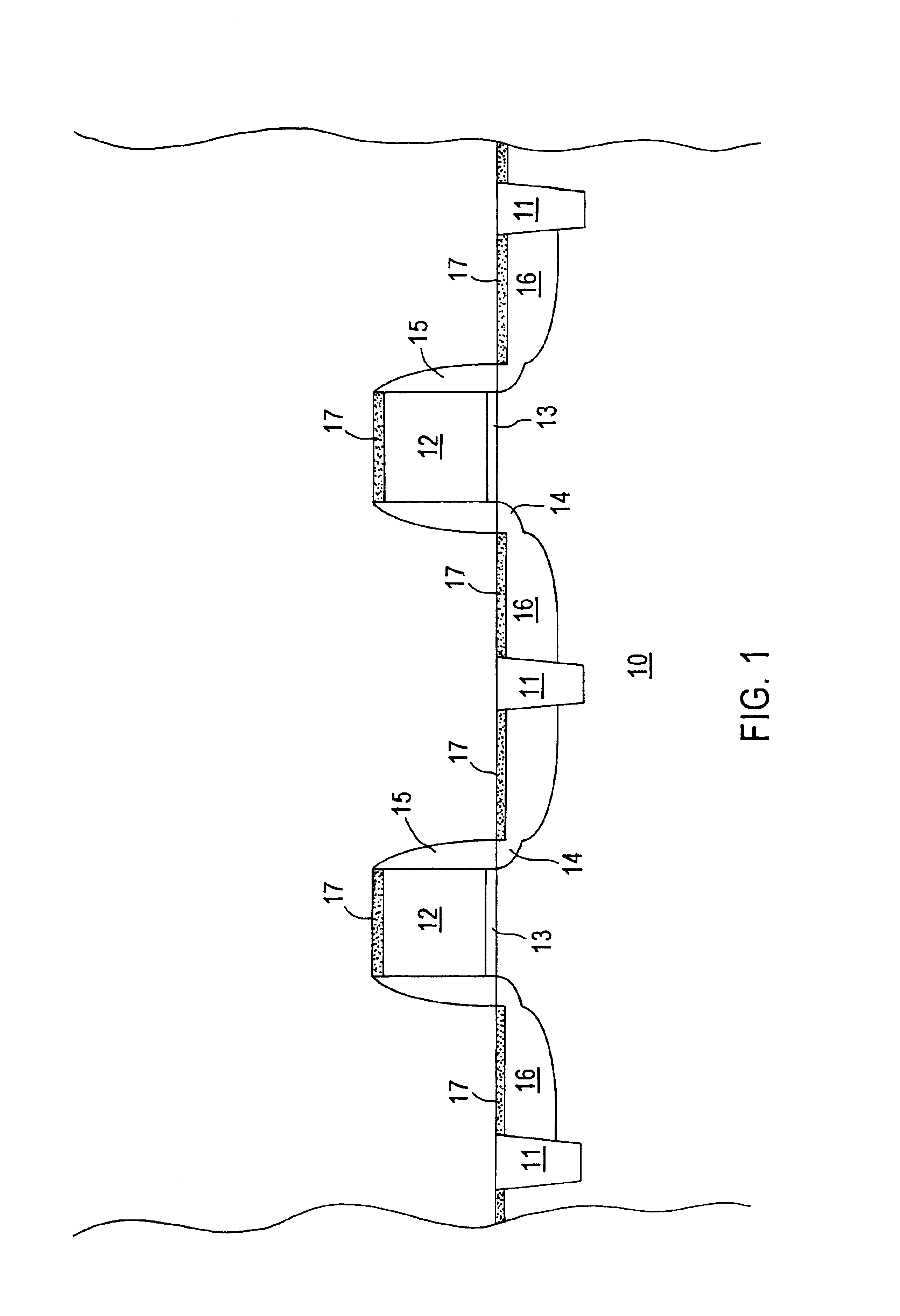
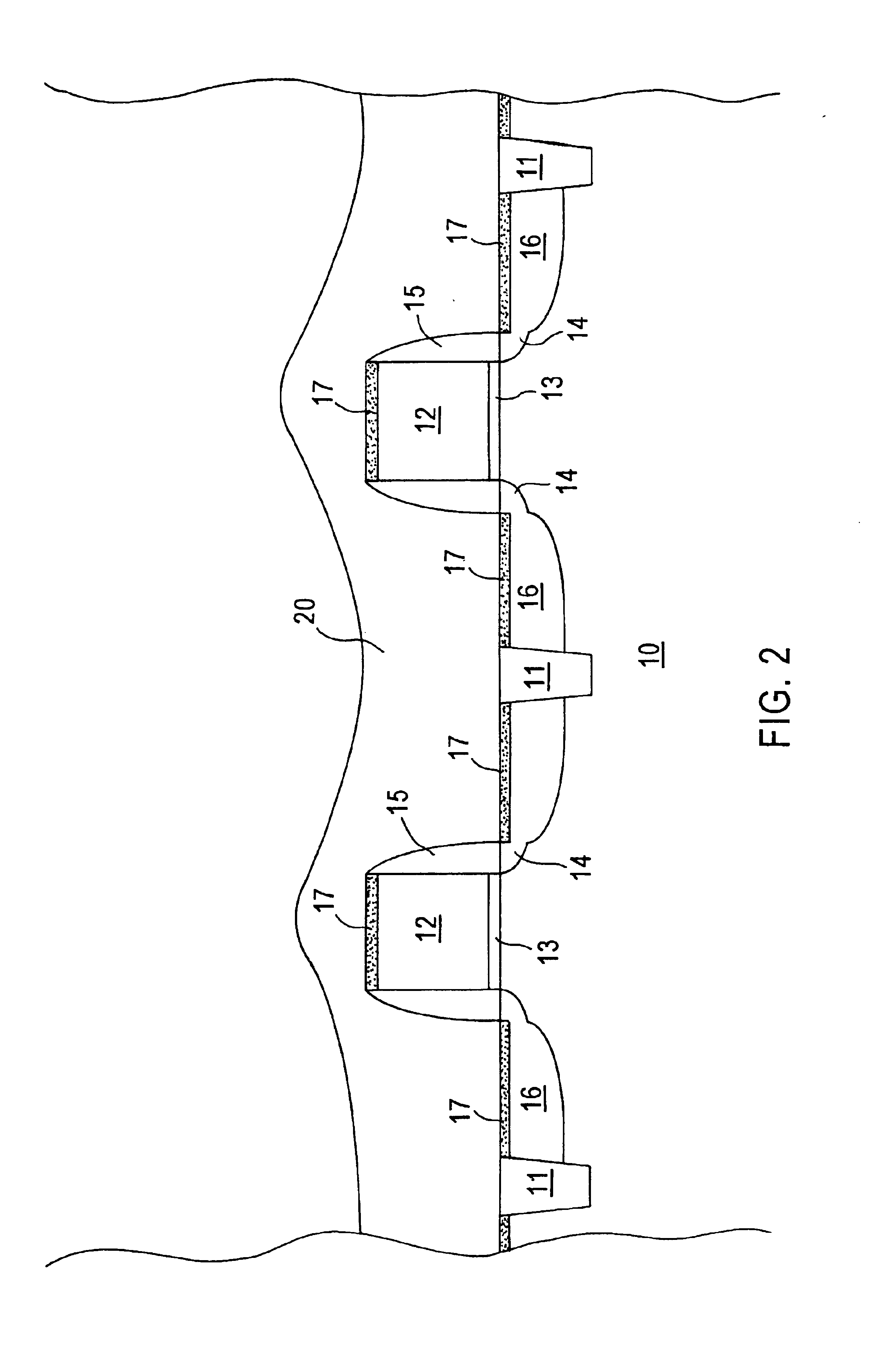
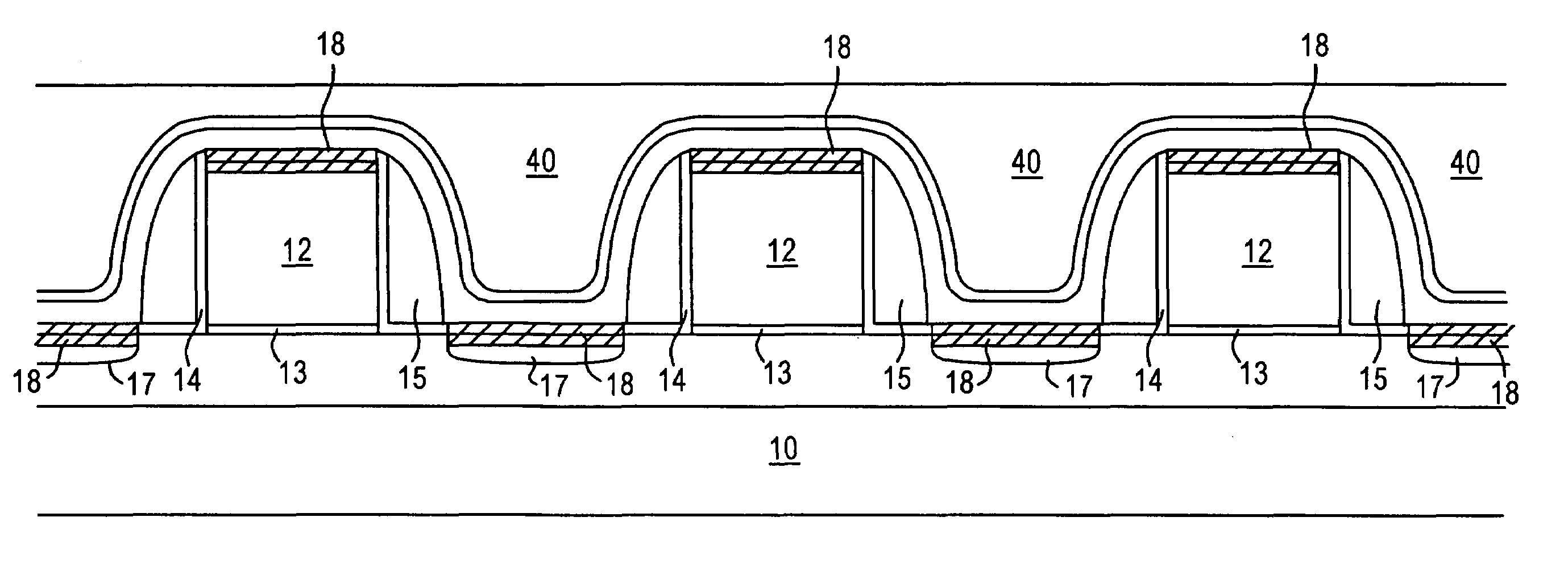
ActiveUS20110034035A1Reduced tendency towards crackingEasy to fillSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon oxideGap filling
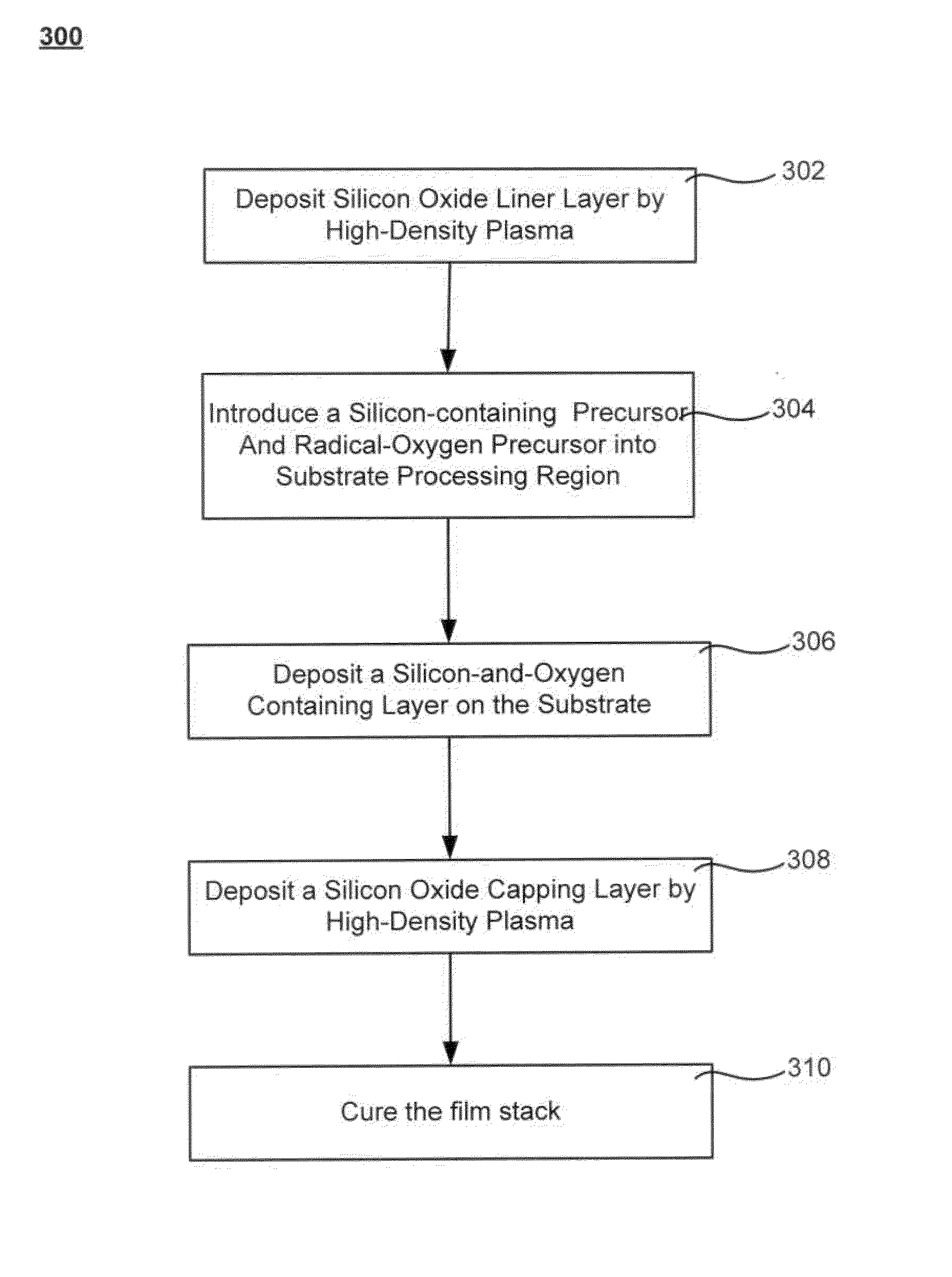
The formation of a gap-filling silicon oxide layer with reduced tendency towards cracking is described. The deposition involves the formation of a flowable silicon-containing layer which facilitates the filling of trenches. Subsequent processing at high substrate temperature causes less cracking in the dielectric film than flowable films formed in accordance with methods in the prior art. A compressive liner layer deposited prior to the formation of the gap-filling silicon oxide layer is described and reduces the tendency for the subsequently deposited film to crack. A compressive capping layer deposited after a flowable silicon-containing layer has also been determined to reduce cracking. Compressive liner layers and compressive capping layers can be used alone or in combination to reduce and often eliminate cracking. Compressive capping layers in disclosed embodiments have additionally been determined to enable an underlying layer of silicon nitride to be transformed into a silicon oxide layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Post-planarization densification
InactiveUS20110081782A1High densityReduce Pattern Loading EffectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHigh densitySilicon oxide
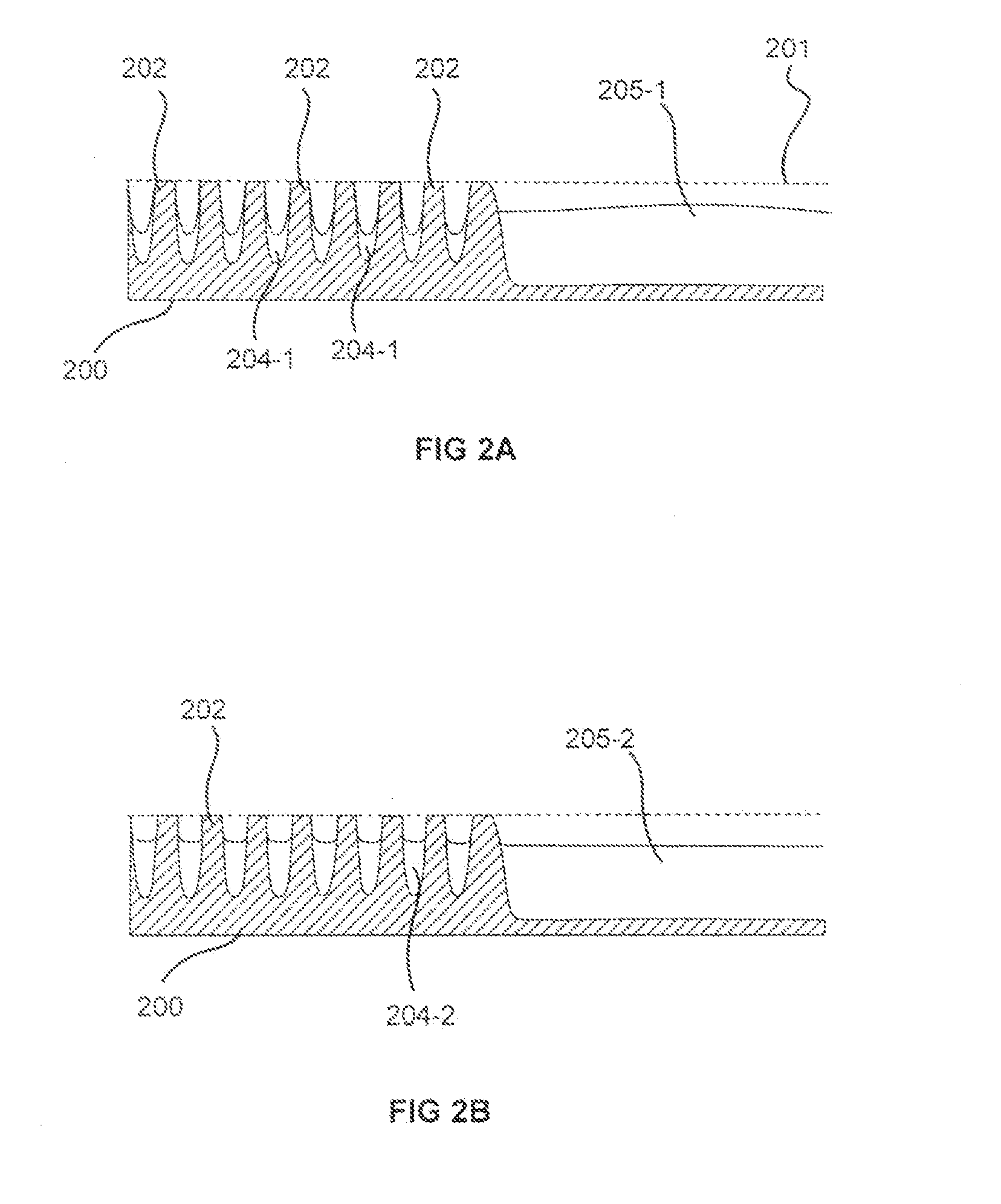
Processes for forming high density gap-filling silicon oxide on a patterned substrate are described. The processes increase the density of gap-filling silicon oxide particularly in narrow trenches. The density may also be increased in wide trenches and recessed open areas. The densities of the gap-filling silicon oxide in the narrow and wide trenches / open areas become more similar following the treatment which allows the etch rates to match more closely. This effect may also be described as a reduction in the pattern loading effect. The process involves forming then planarizing silicon oxide. Planarization exposes a new dielectric interface disposed closer to the narrow trenches. The newly exposed interface facilitates a densification treatment by annealing and / or exposing the planarized surface to a plasma.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
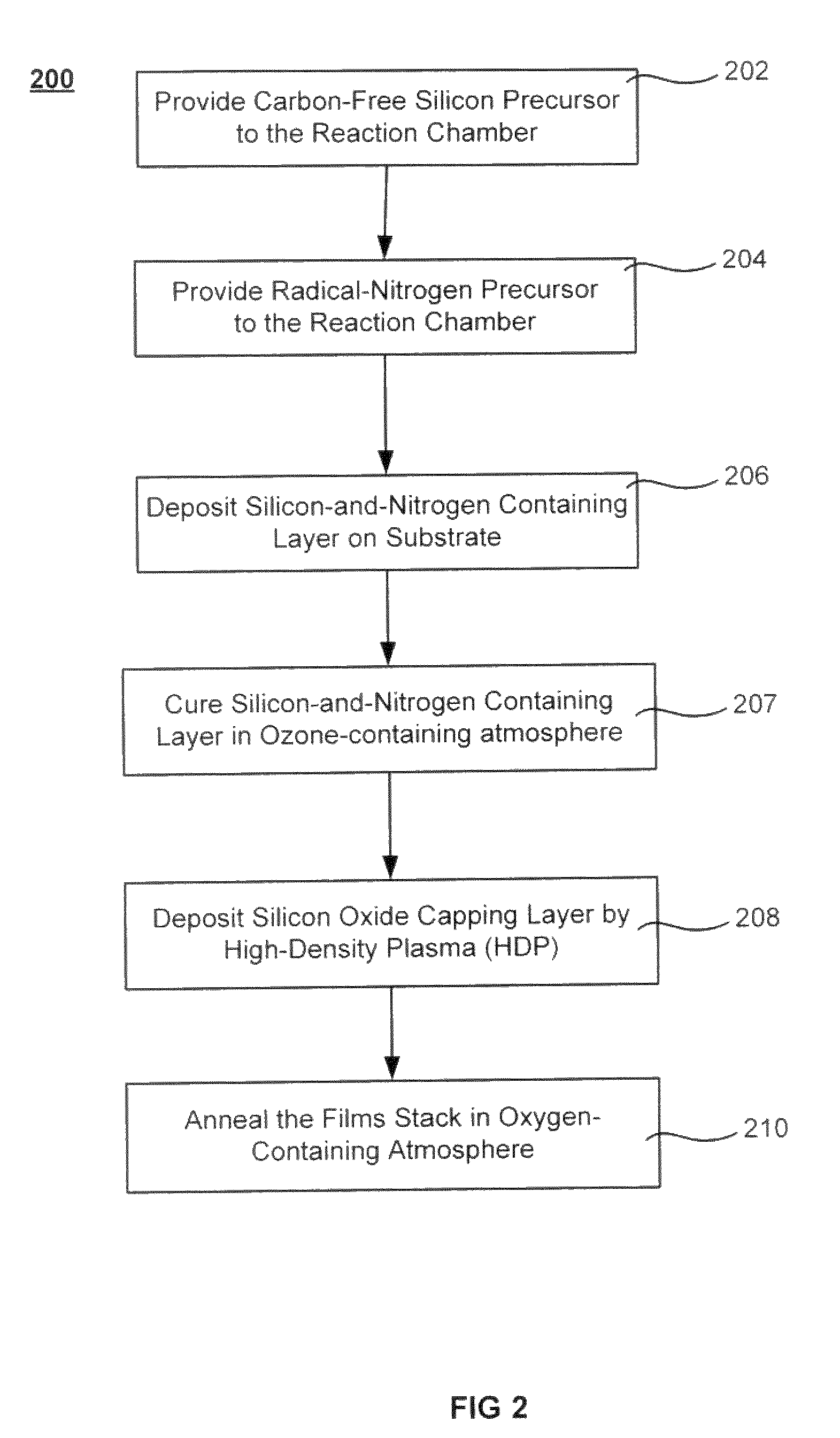
Oxide-rich liner layer for flowable CVD gapfill
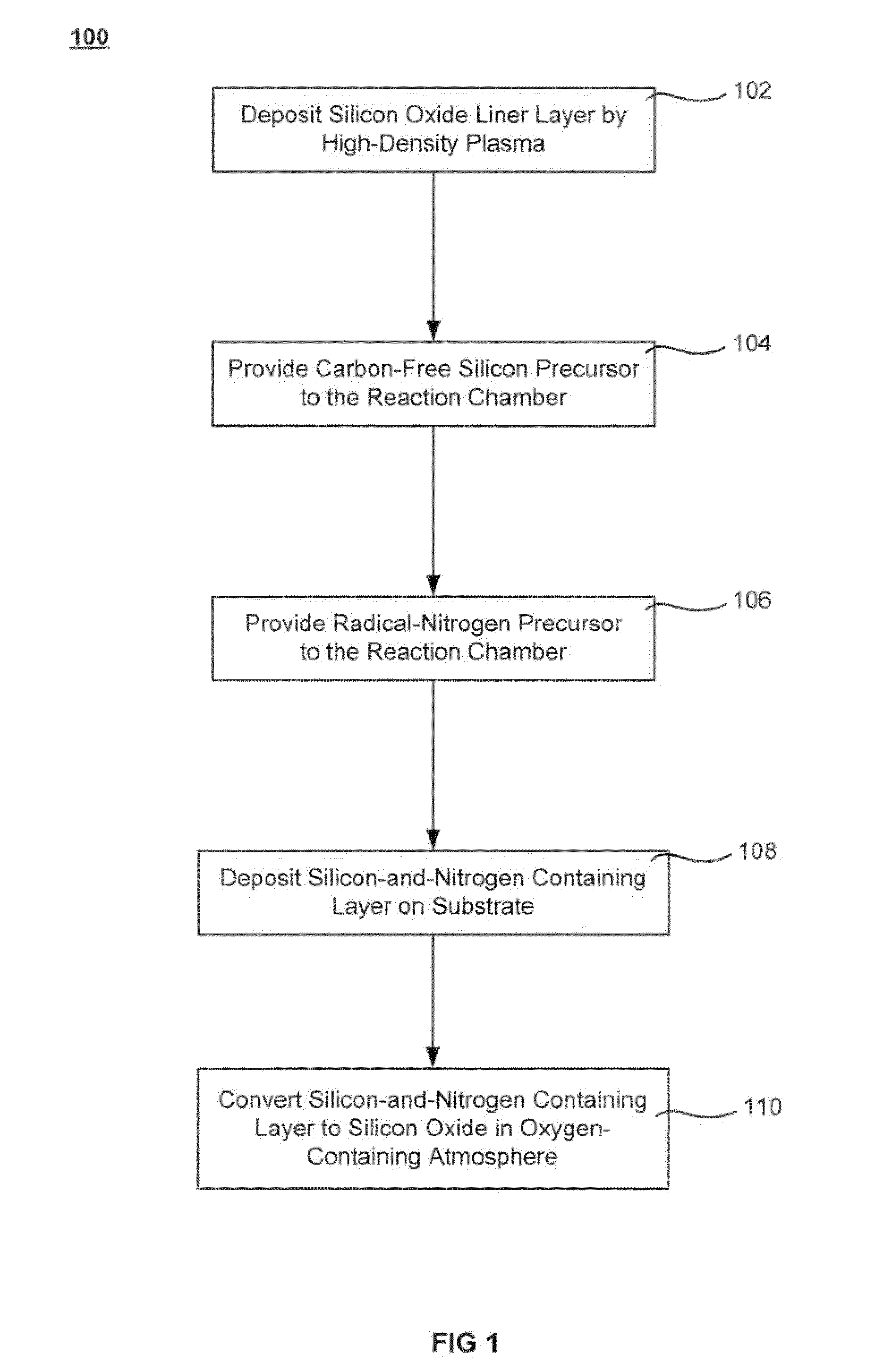
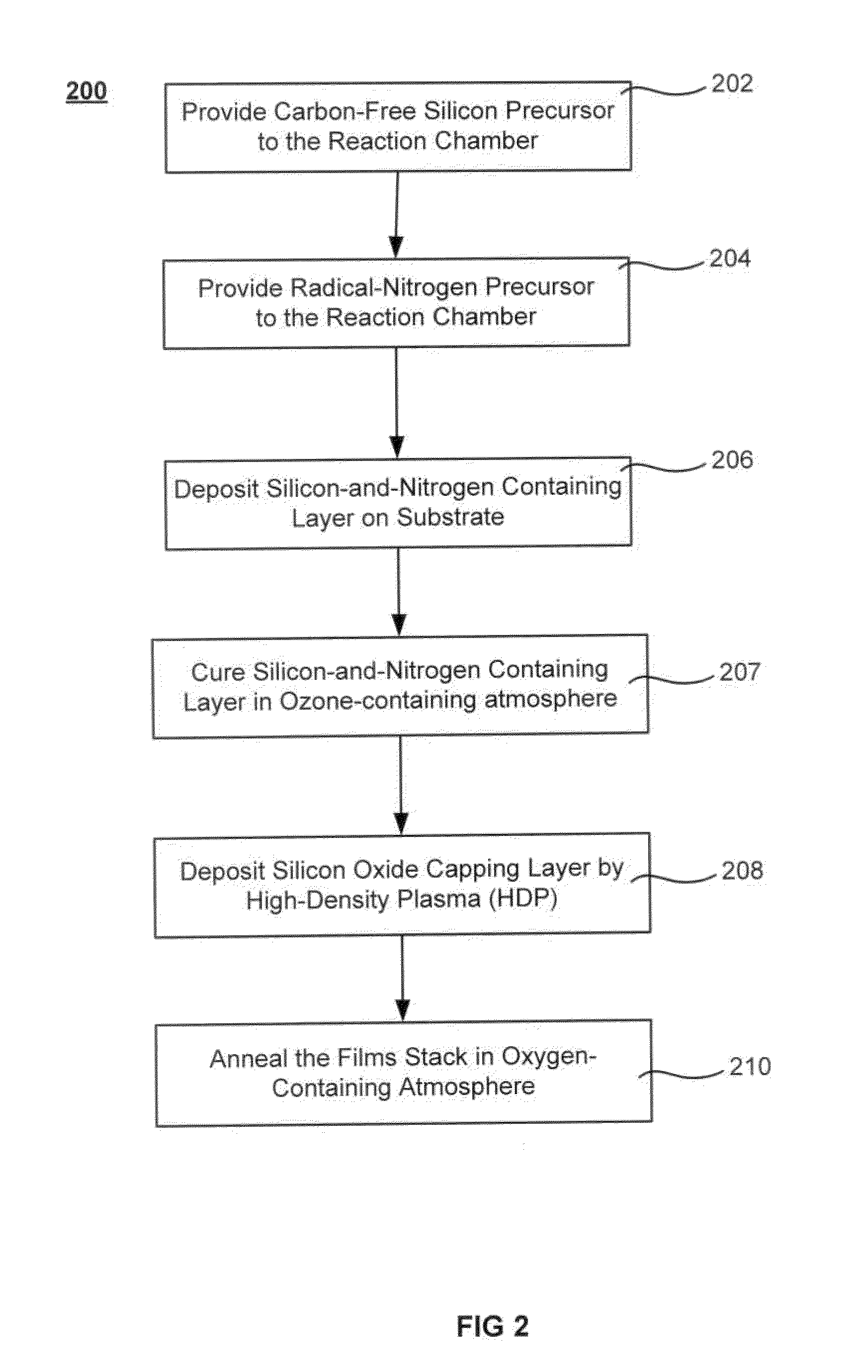
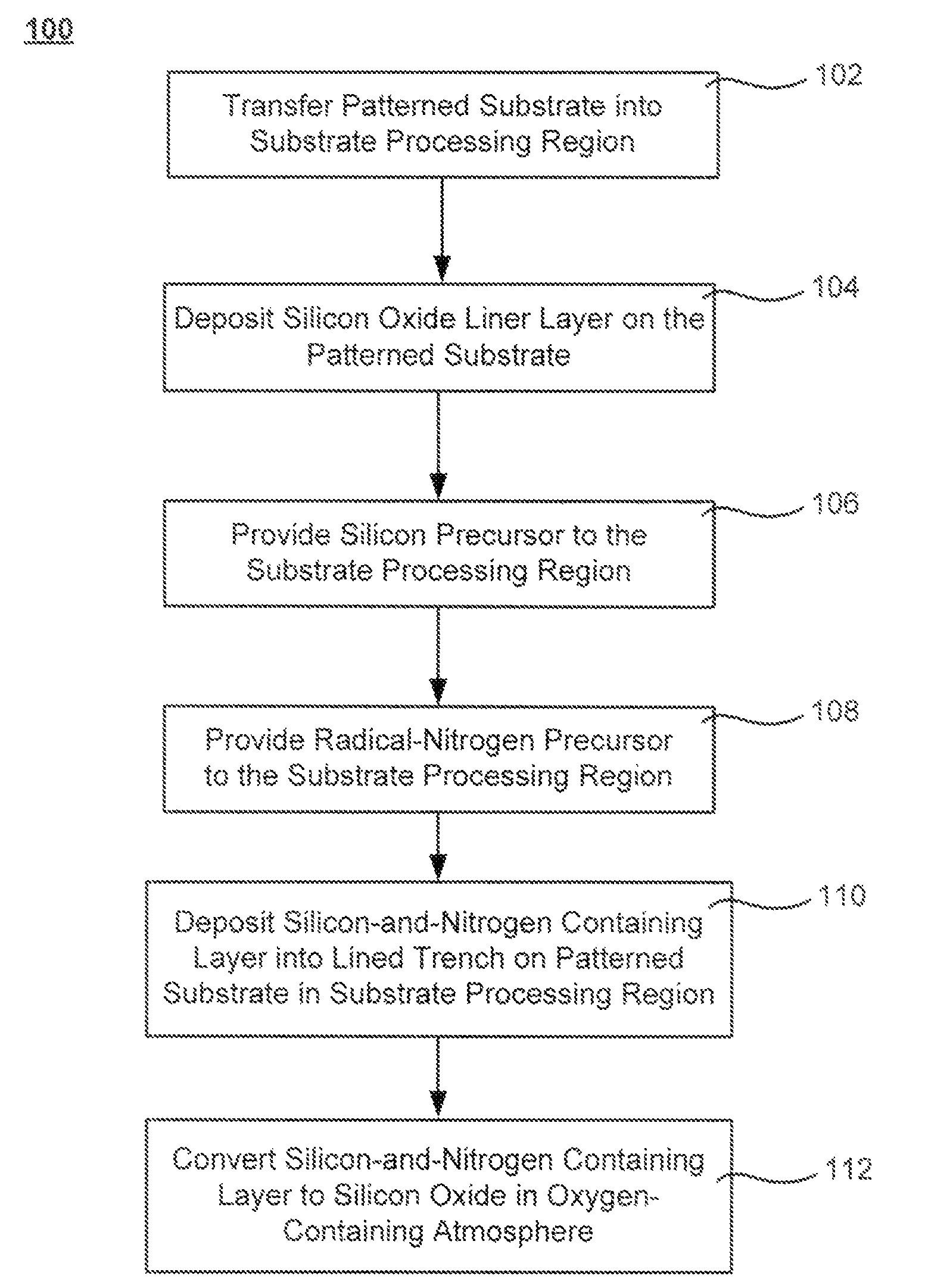
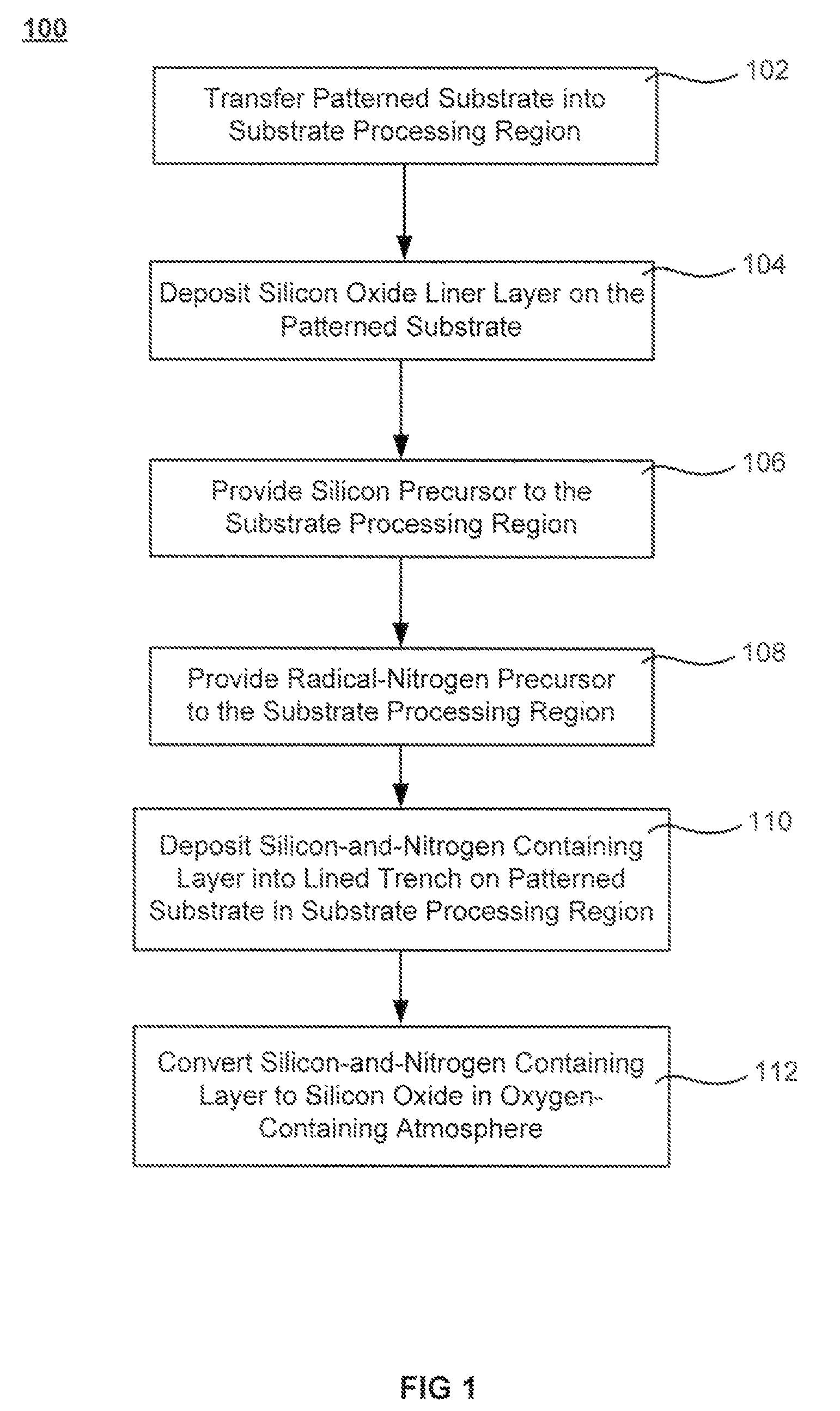
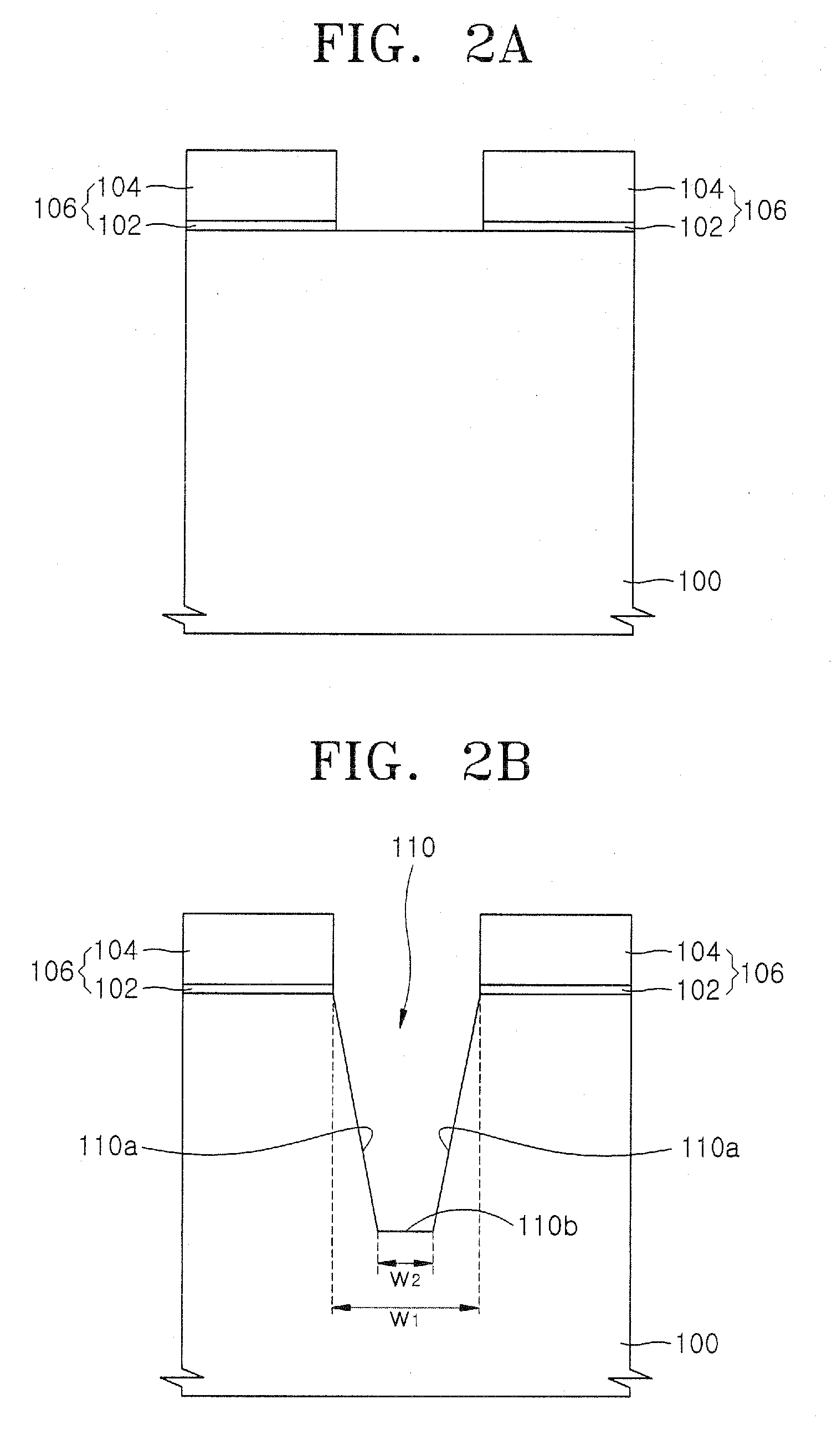
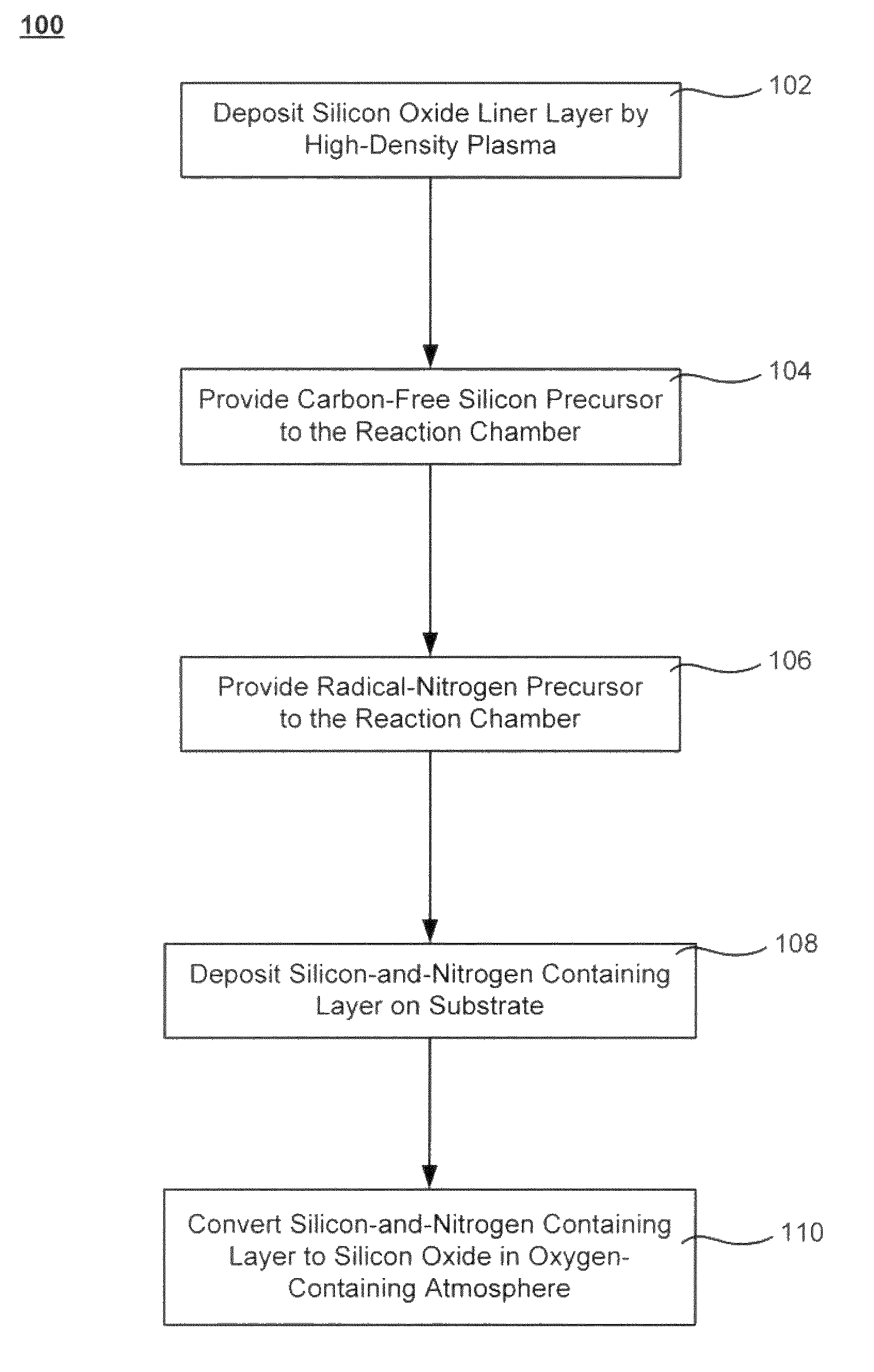
The formation of a gap-filling silicon oxide layer with reduced volume fraction of voids is described. The deposition involves the formation of an oxygen-rich less-flowable liner layer before an oxygen-poor more-flowable gapfill layer. However, the liner layer is deposited within the same chamber as the gapfill layer. The liner layer and the gapfill layer may both be formed by combining a radical component with an unexcited silicon-containing precursor (i.e. not directly excited by application of plasma power). The liner layer has more oxygen content than the gapfill layer and deposits more conformally. The deposition rate of the gapfill layer may be increased by the presence of the liner layer. The gapfill layer may contain silicon, oxygen and nitrogen and be converted at elevated temperature to contain more oxygen and less nitrogen. The presence of the gapfill liner provides a source of oxygen underneath the gapfill layer to augment the gas phase oxygen introduced during the conversion.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Inductively coupled plasma CVD
InactiveUS6184158B1Electric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringInductively coupled plasma
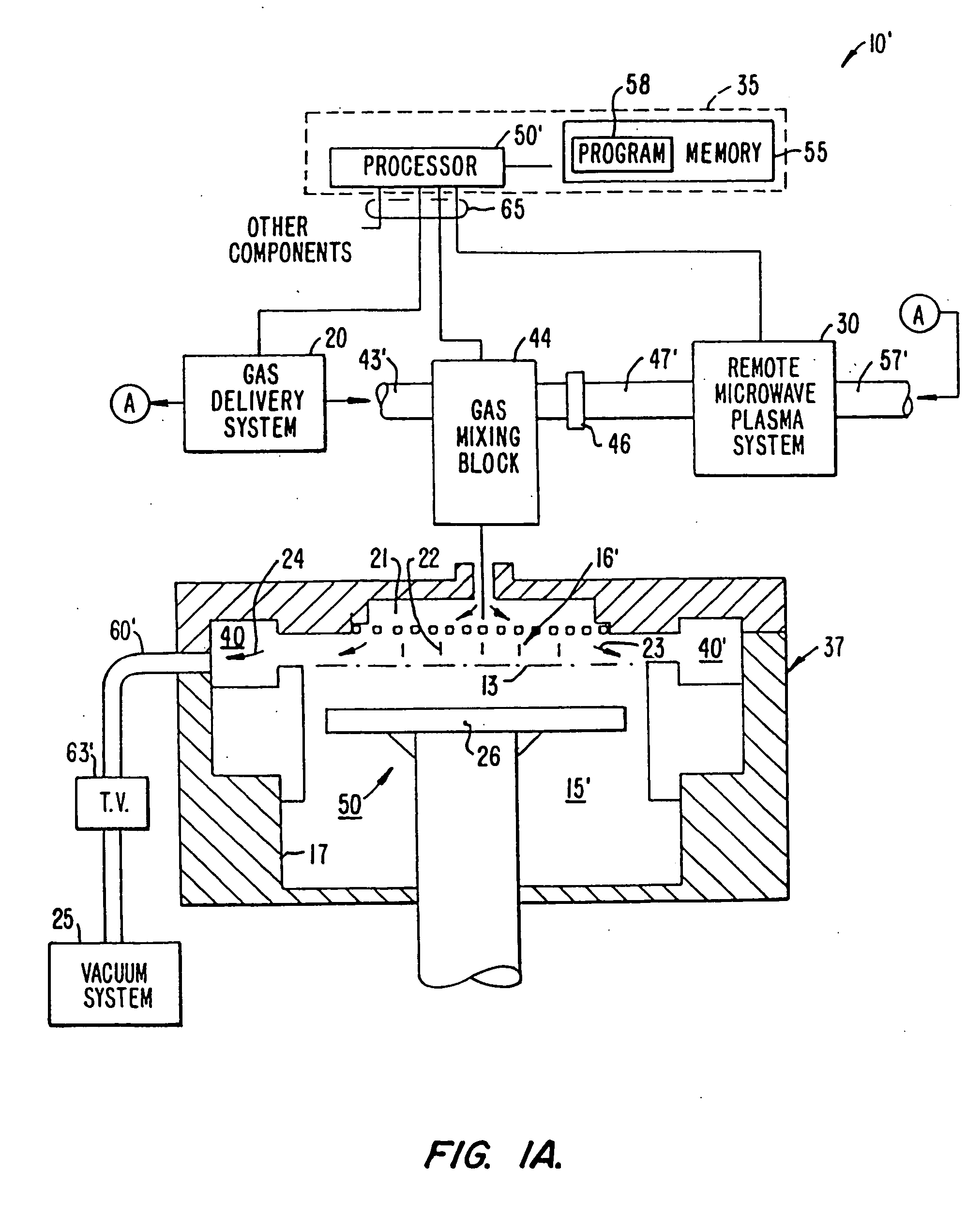
A method of depositing a dielectric film on a substrate in a process chamber of an inductively coupled plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition reactor. Gap filling between electrically conductive lines on a semiconductor substrate and depositing a cap layer are achieved. Films having significantly improved physical characteristics including reduced film stress are produced by heating the substrate holder on which the substrate is positioned in the process chamber.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
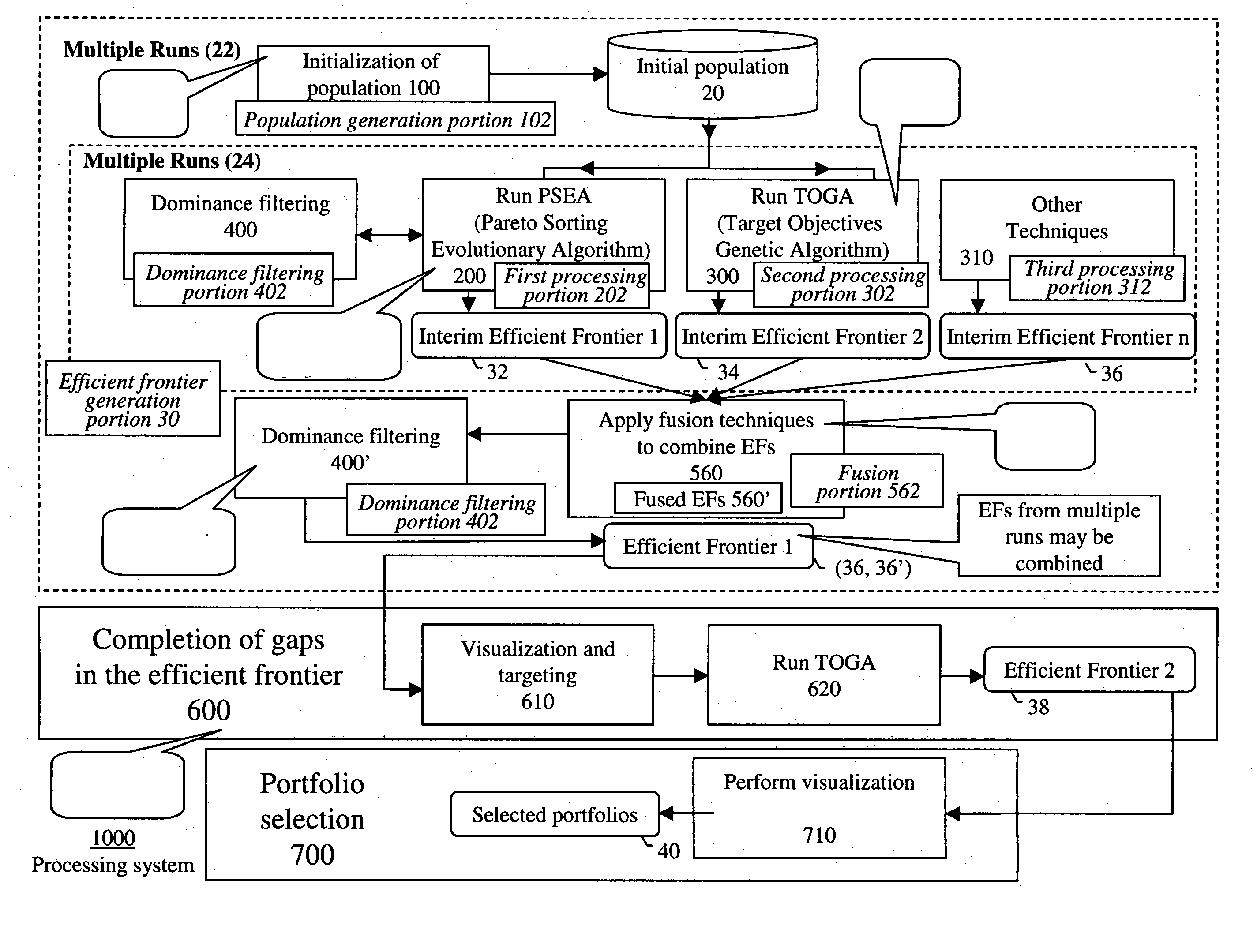
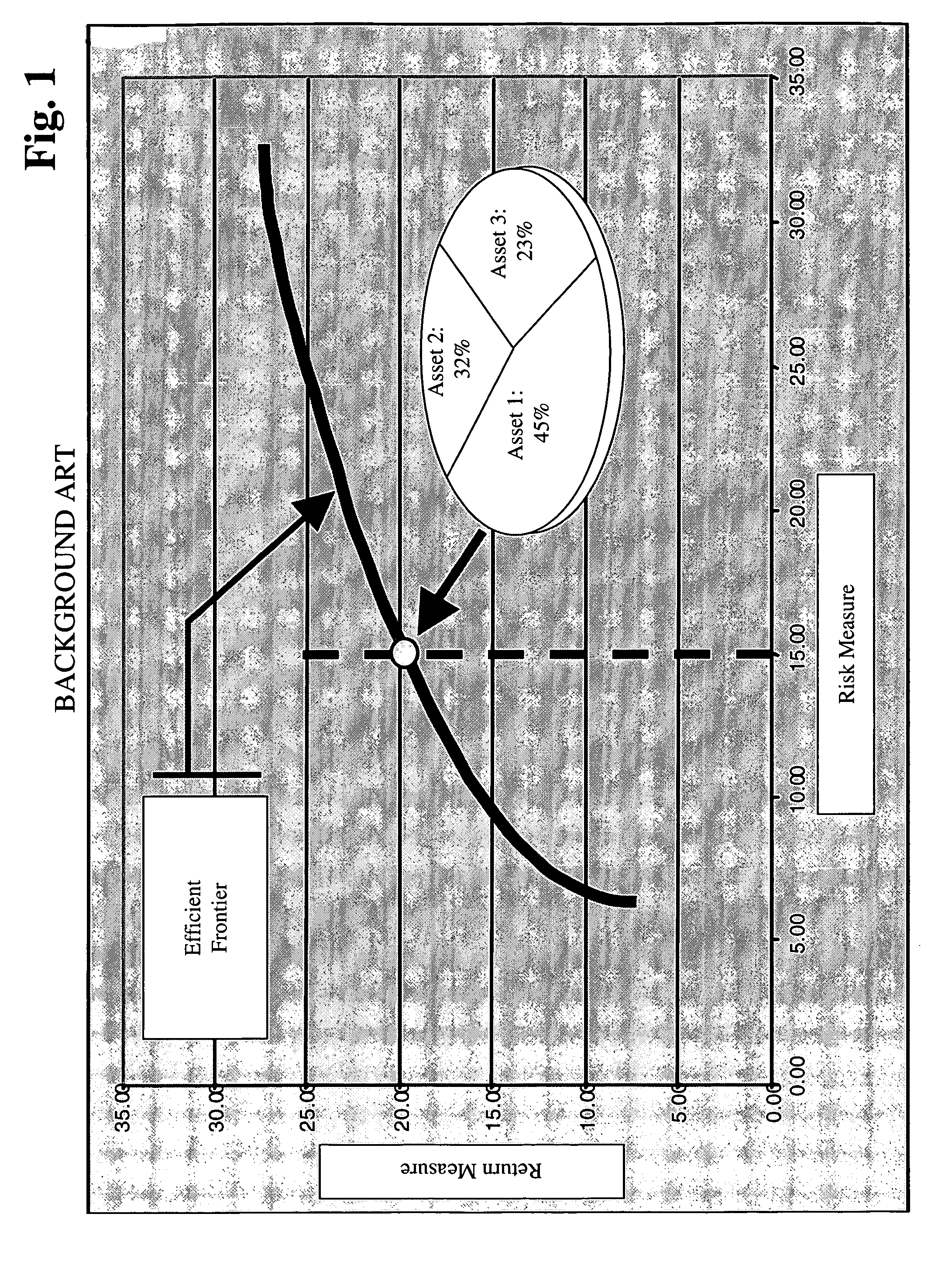
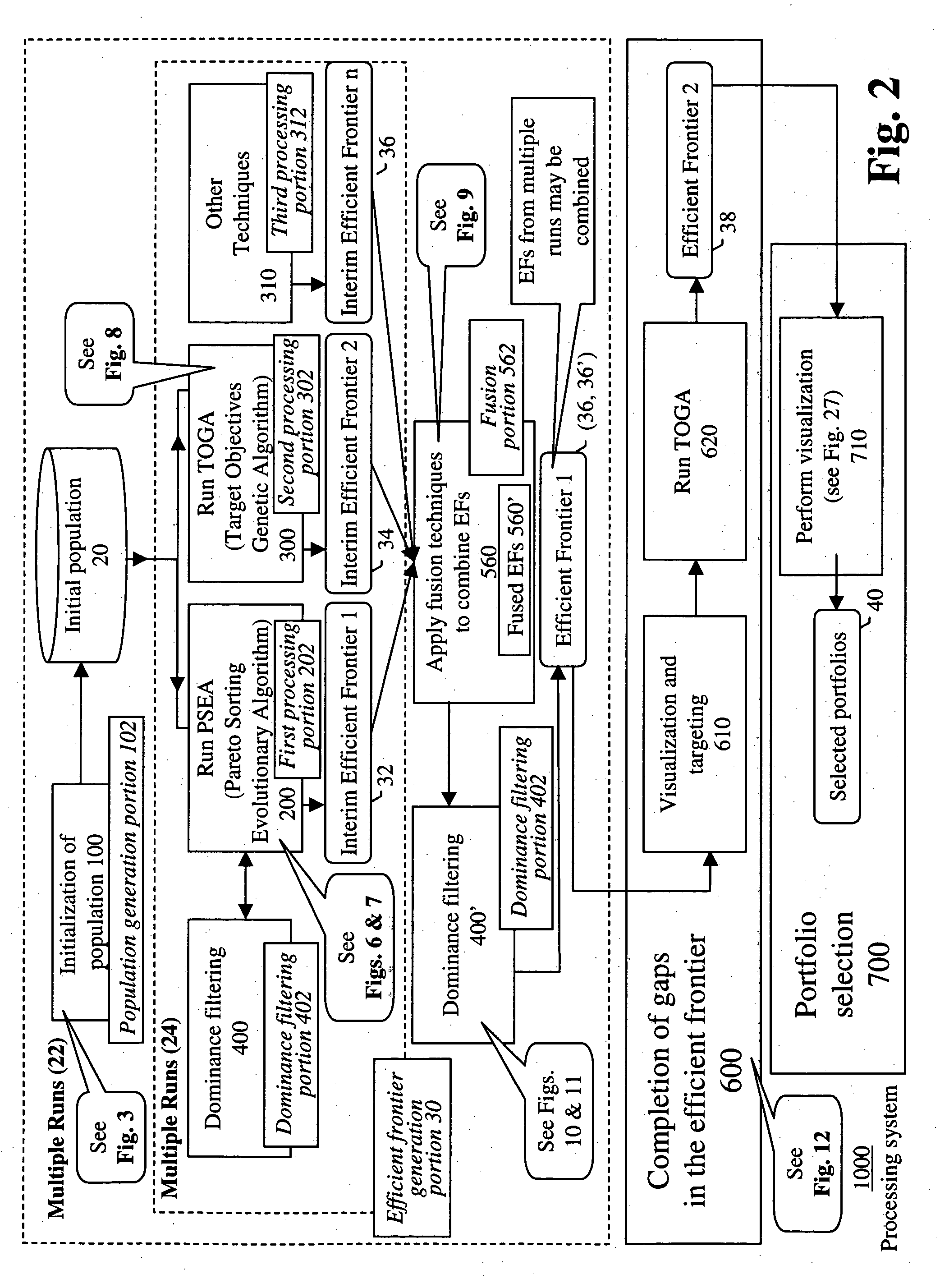
Systems and methods for efficient frontier supplementation in multi-objective portfolio analysis
InactiveUS20050187848A1FinanceSpecial data processing applicationsCombinatorial optimizationGap filling
The systems and methods of the invention are directed to portfolio optimization and related techniques. For example, the invention provides a method for multi-objective portfolio optimization for use in investment decisions based on competing objectives and a plurality of constraints constituting a portfolio problem, the method comprising: performing a first multi-objective optimization process, based on competing objectives, to generate an efficient frontier of possible solutions; observing the generated efficient frontier; based on the observing, identifying an area of the efficient frontier in which there is a gap; and effecting a gap filling process by which the efficient frontier is supplemented in the area of the gap, the efficient frontier being used in investment decisioning.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
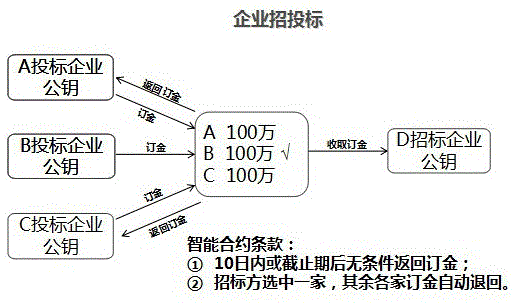
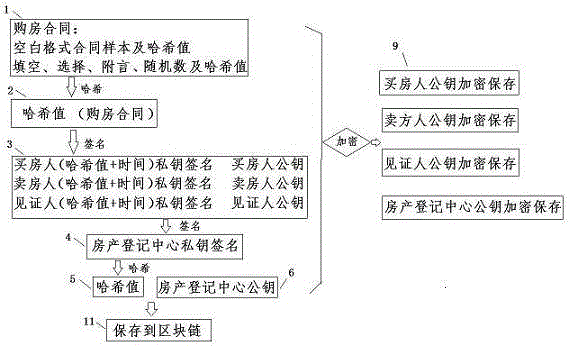
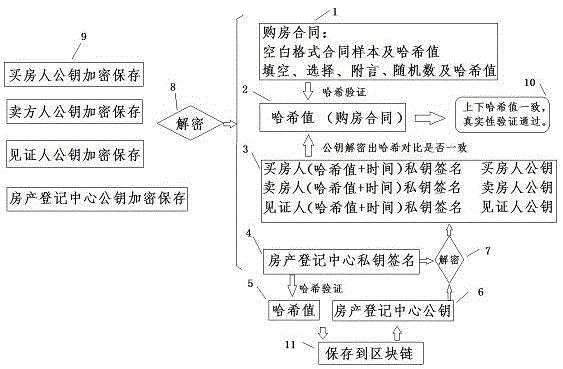
Block chain information archiving and privacy protection method
ActiveCN105610578APrevent tamperingEasy retrievalKey distribution for secure communicationThird partyPrivacy protection
The invention discloses a block chain information archiving and privacy protection method. The block chain information archiving and privacy protection method comprises the steps of adding random number generation Hash values to information needing archiving; then signing by an interest-related person or a eyewitness and generating Hash values; and finally recording at a block chain. Some information needing archiving is formatting and separable formatting information and self-filling information respectively stored and subjected to Hash verification, such as gap-filling information, selection information, postscript information, random number information (for preventing brute force attack). Data which are encrypted by using a public key only can be decrypted by a relevant person who knows the original information by using a private key; a third party verifies true and false of the information; and the encrypted information can be disclosed for a judicial institution if judiciary involvement is needed.
Owner:苏州交链科技有限公司 +1
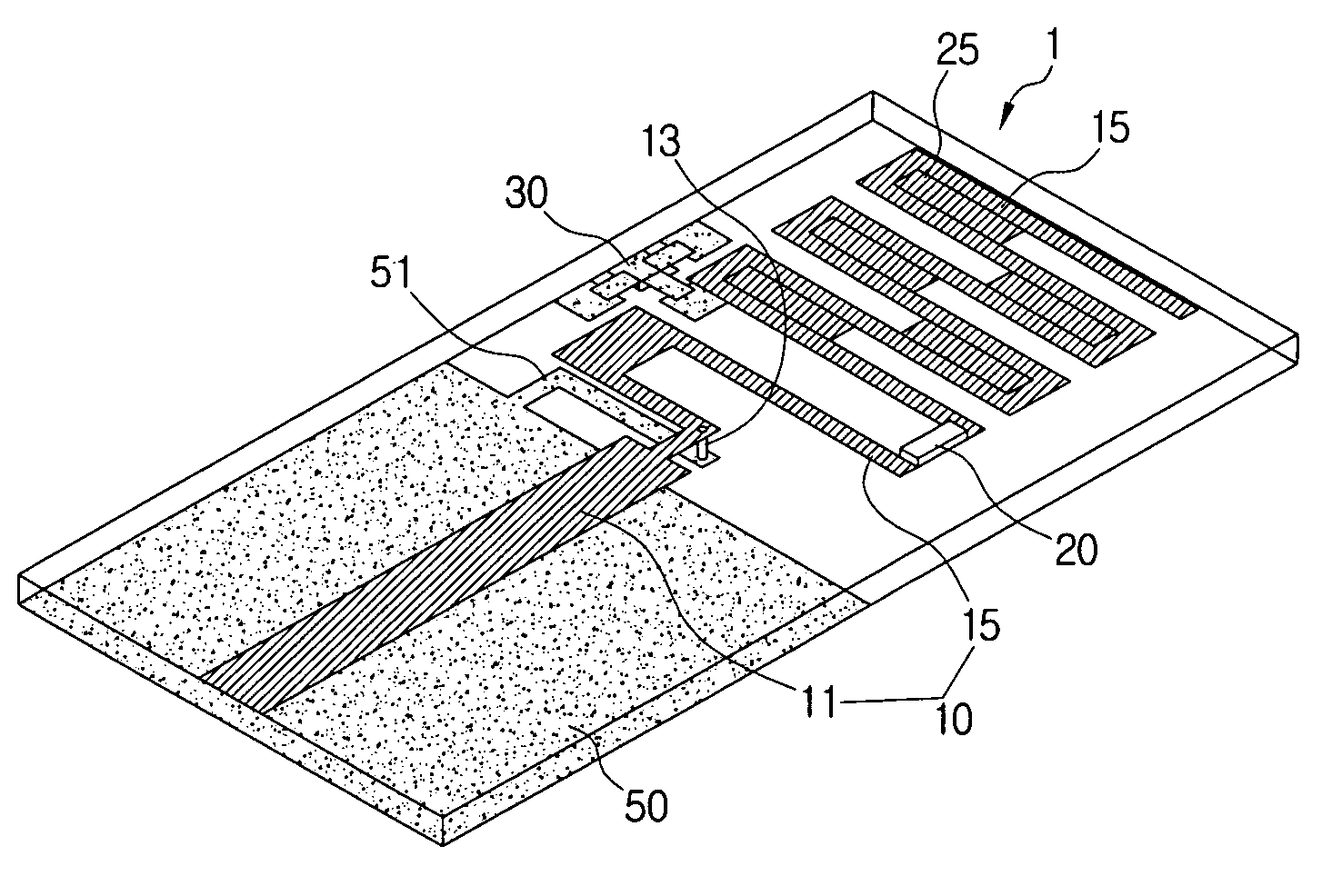
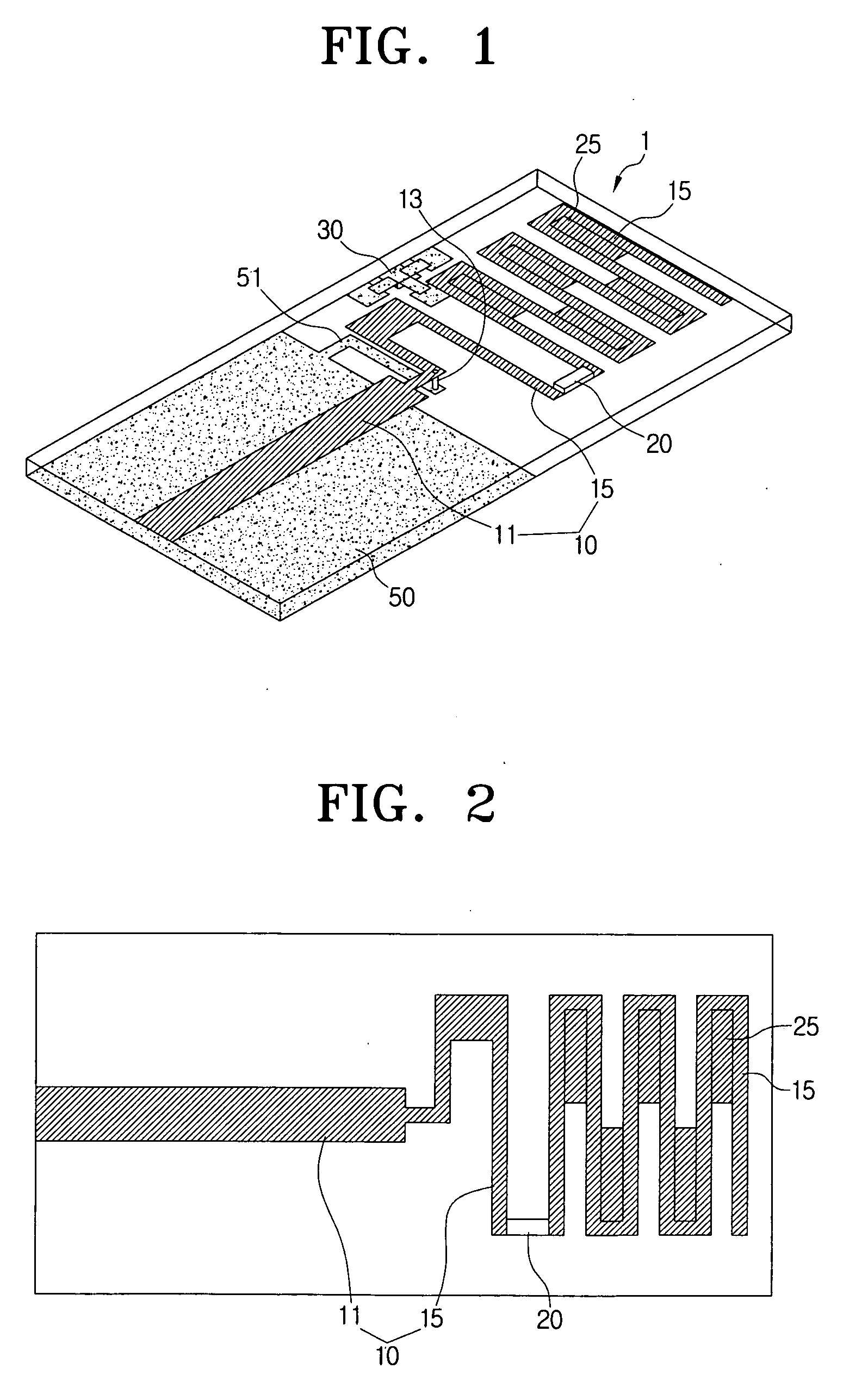
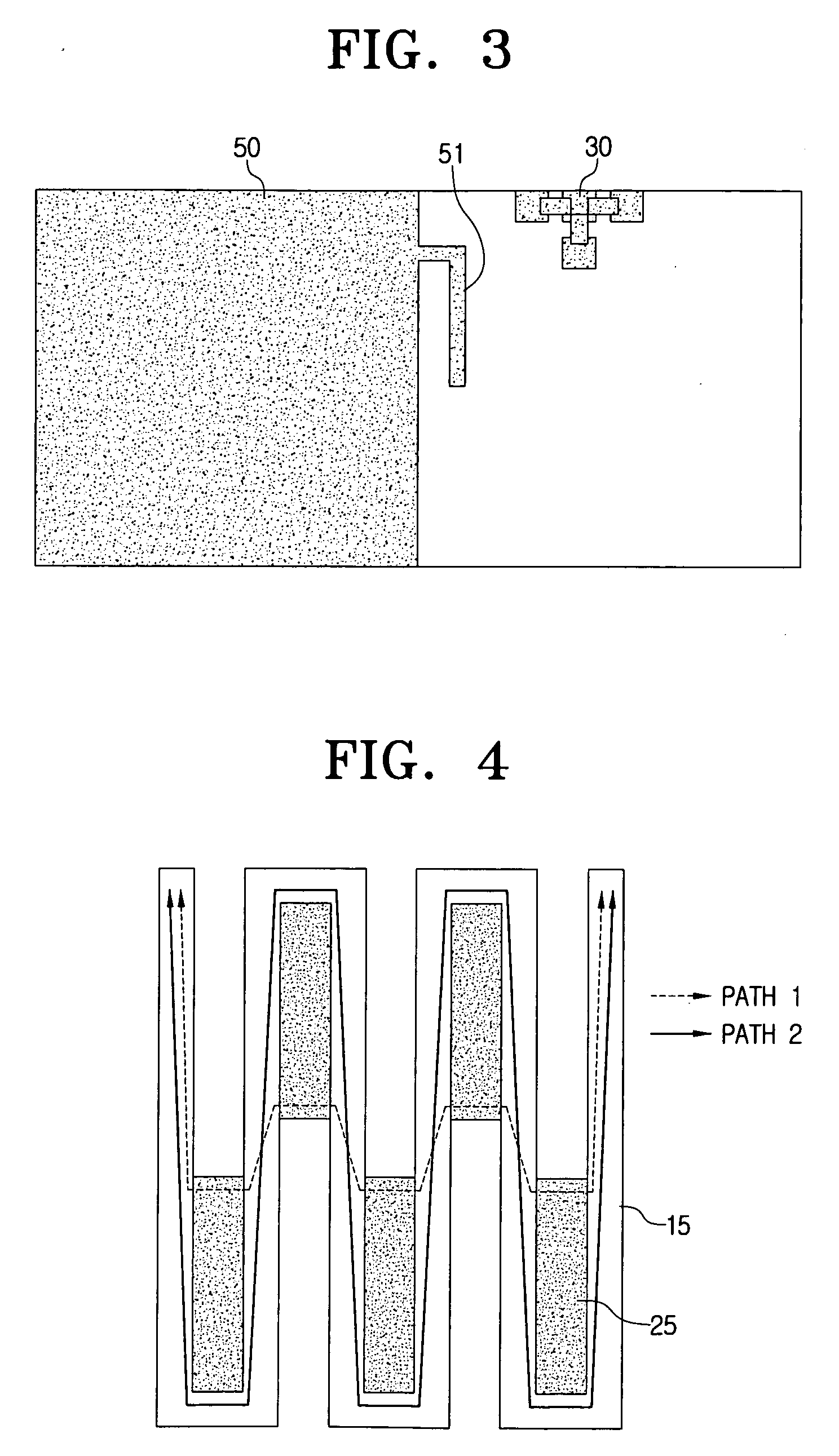
Multiband antenna with removed coupling
A multiband antenna with removed coupling includes a radiator formed as a meander line bent zigzag several times and having a gap filling part in at least one area between neighboring meander lines. The gap filling part interconnects the neighboring meander lines. The multiband antenna further includes a ground connected with the radiator and at least one switch element mounted in an area along the longitudinal direction of the radiator and configured to alternately short or open an area of the radiator. Accordingly, two different resonance frequencies can be tuned using the single antenna, and the antenna efficiency can be enhanced by removing the coupling between the resonant frequencies that are tuned through the gap filling.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Gap-fill techniques
InactiveUS20050136684A1Excellent dielectric propertiesPlasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingRemote plasmaHigh density
A variety of techniques may be employed, separately or in combination, to improve the gap-filling performance of a dielectric material formed by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). In one approach, a first dielectric layer is deposited using sub-atmospheric chemical vapor deposition (SACVD), followed by a second dielectric layer deposited by high density plasma chemical vapor deposition (HDP-CVD) or plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD). In another approach, a SACVD dielectric layer is deposited in the presence of reactive ionic species flowed from a remote plasma chamber into the processing chamber, which performs etching during the deposition process. In still another approach, high aspect trenches may be filled utilizing SACVD in combination with oxide layers deposited at high temperatures.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plating of a thin metal seed layer
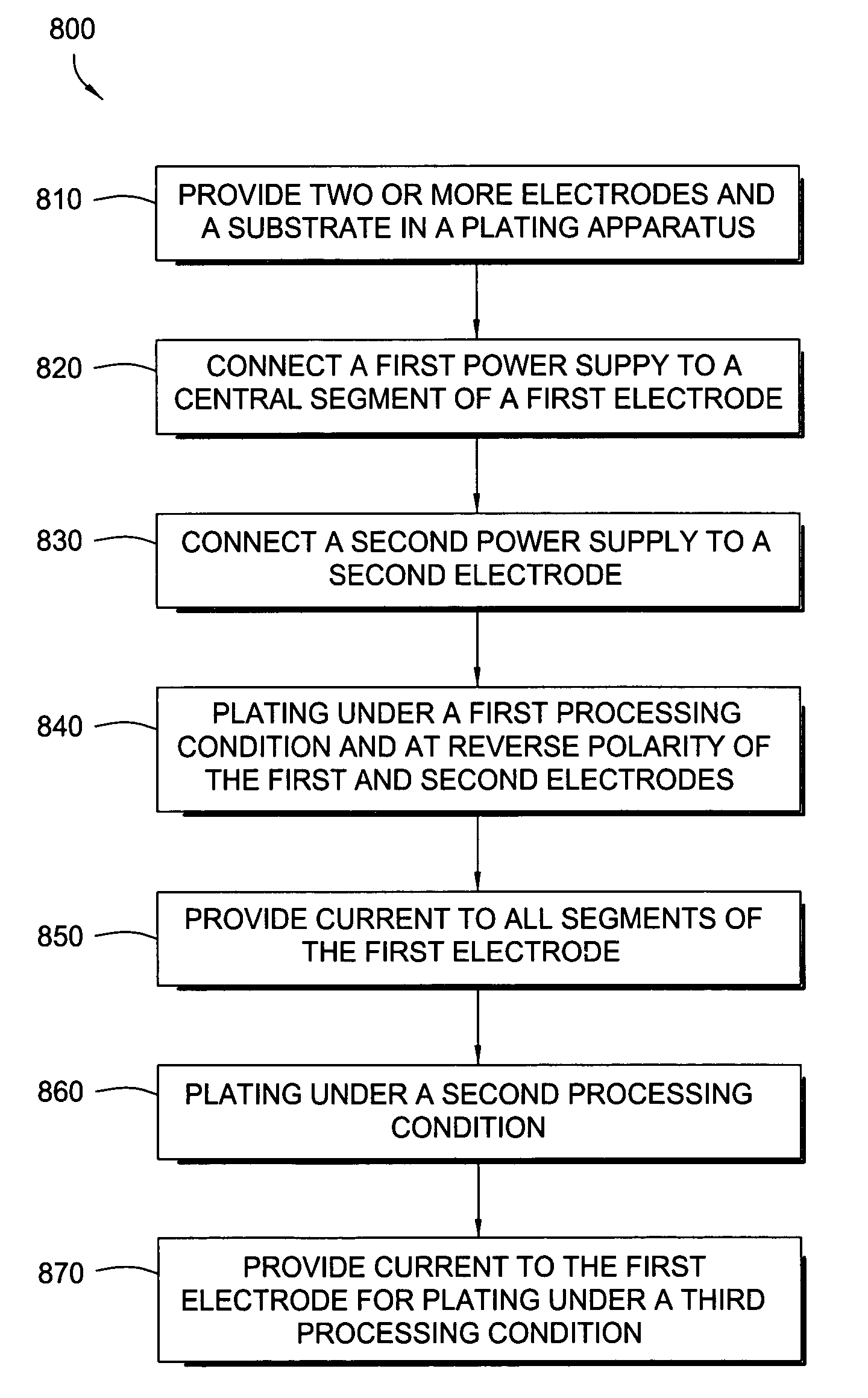
InactiveUS20050145499A1CellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin metalAuxiliary electrode
A method and apparatus for plating a metal layer onto a substrate is provided. The plating apparatus includes two or more segments of an anode and an auxiliary electrode. The plating method includes a first stage of plating a thin metal seed uniformly in the center of the substrate and near the edges of the substrate before metal gap filling and bulk metal plating are performed. The thin metal seed is plated on the substrate surface by applying a current pulse provided by a first power supply and a second power supply which are in electrical communication in reverse polarity with one segment of the anode and the auxiliary electrode. Thereafter, gap filling of features is performed by applying a second current pulse where current is provided to all segments of the anode.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
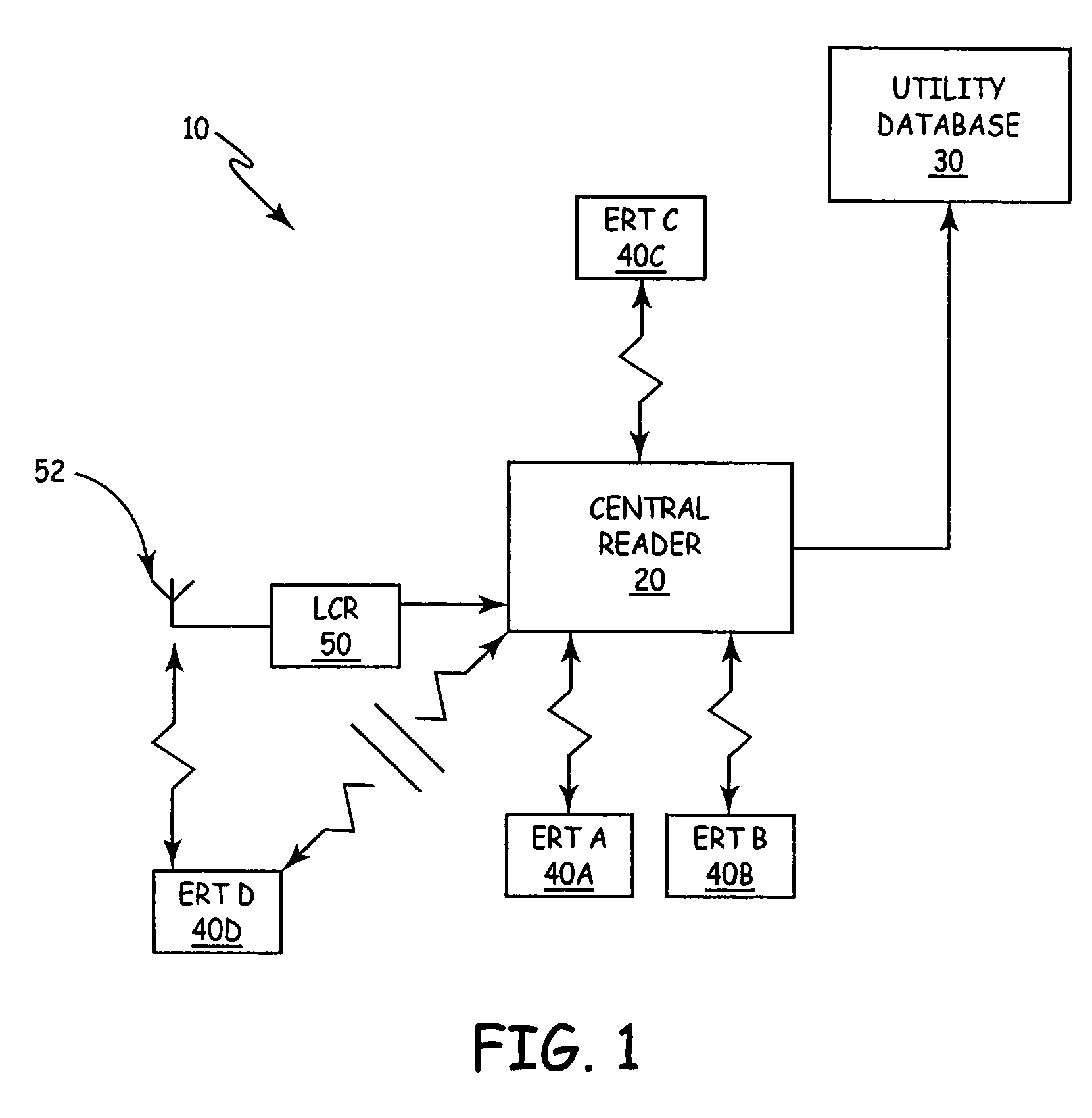
Applications for a low cost receiver in an automatic meter reading system
ActiveUS7417557B2Expand coverageLow costElectric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusTransceiverCentral database
Owner:ITRON
Apparatus, method for depositing thin film on wafer and method for gap-filling trench using the same
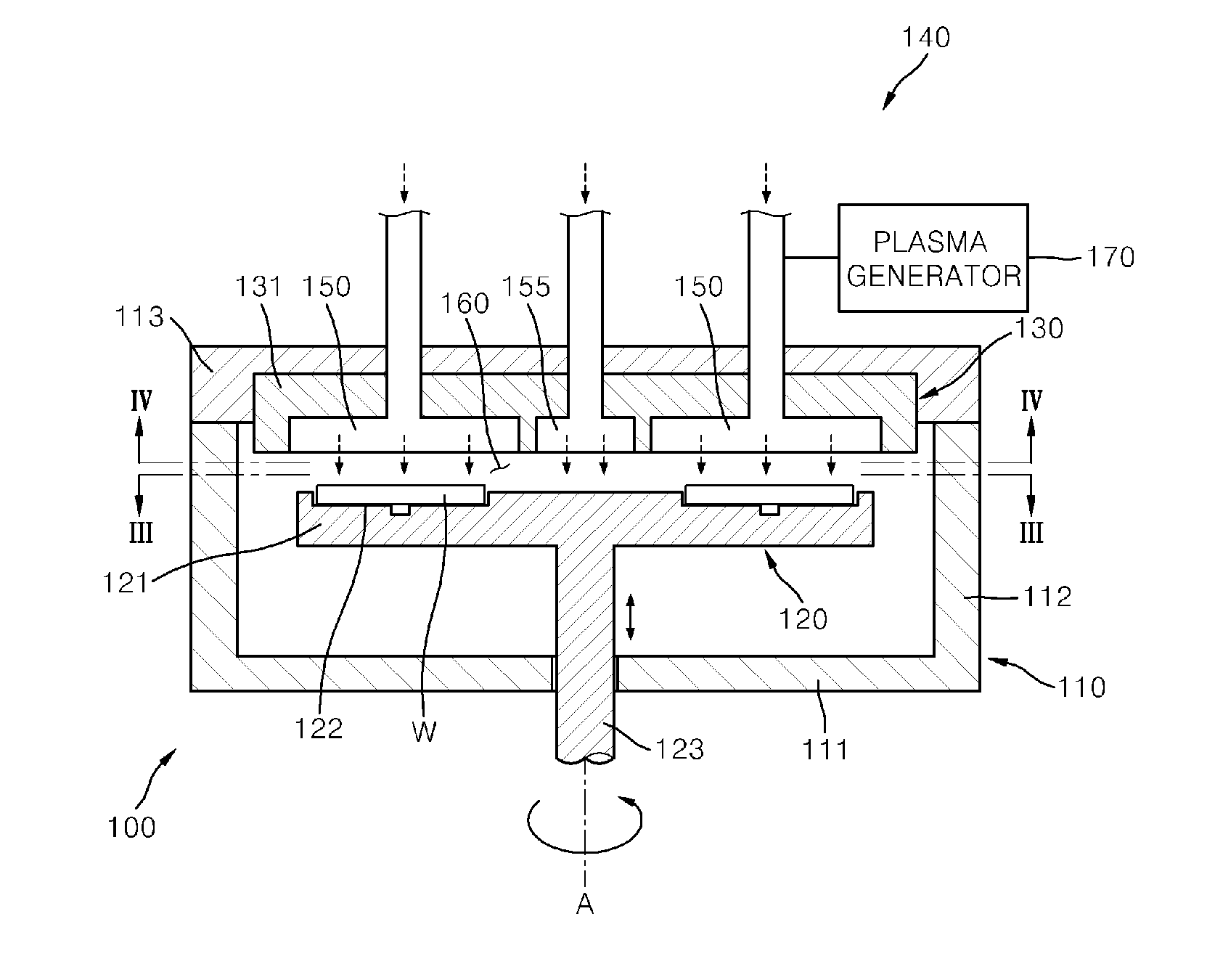
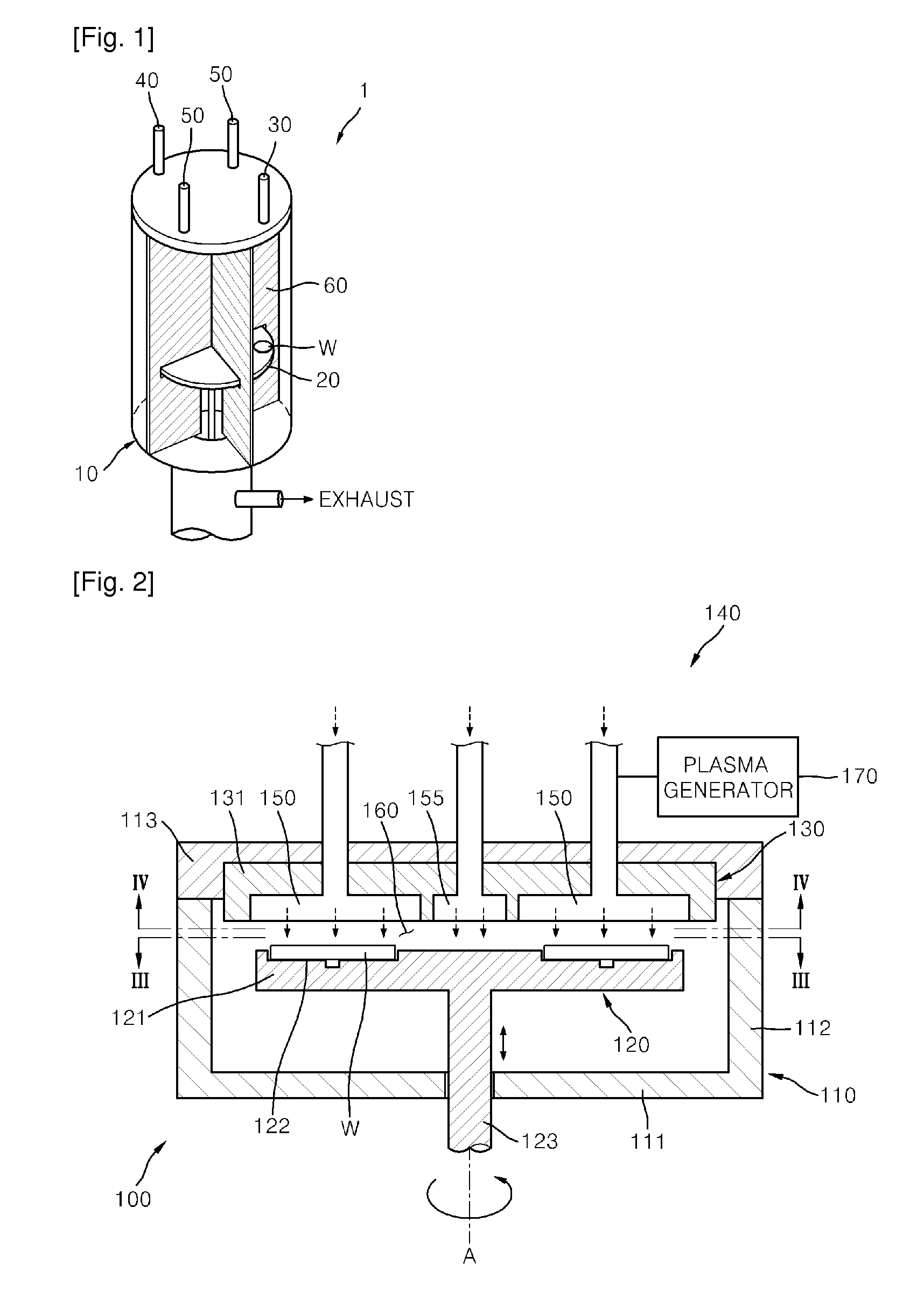
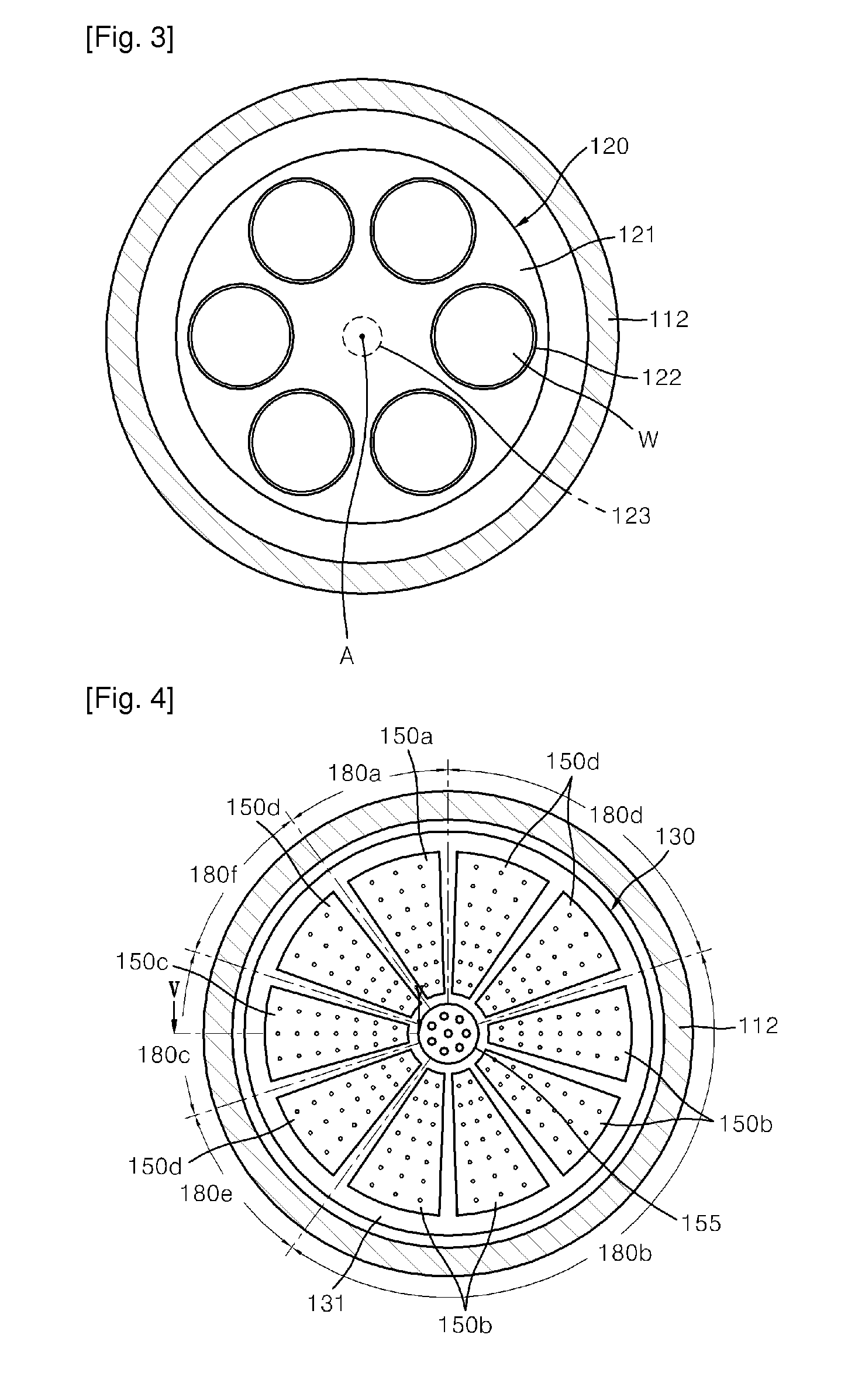
InactiveUS20100190341A1Excellent gap fillingReduce wasteElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingEngineering
Provided are an apparatus and method for depositing a thin film, and a method for gap-filling a trench in a semiconductor device. The thin film depositing apparatus includes a plurality of substrates provided on the same space inside a reactor, wherein deposition of the thin film and partial etching of the deposited thin film are repeated to form the thin film on the plurality of substrates by exposing the substrates to two or more source gases and an etching gas supplied together at predetermined time intervals while rotating the substrates. According to exemplary embodiments, it is possible to concurrently or alternatively perform deposition and etching of a thin film, so that a thin film with good gap-fill capability can be deposited.
Owner:WONIK IPS CO LTD
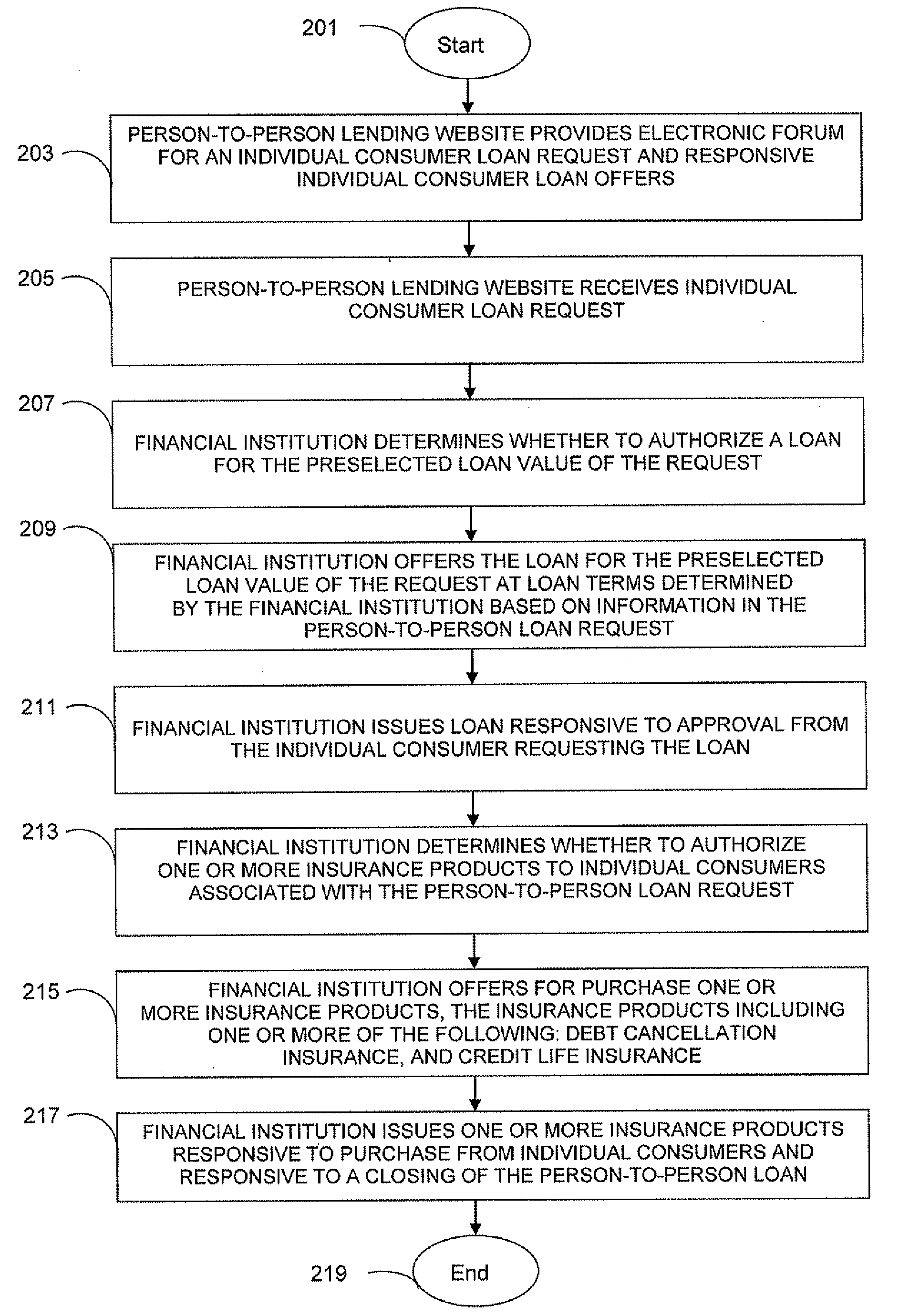
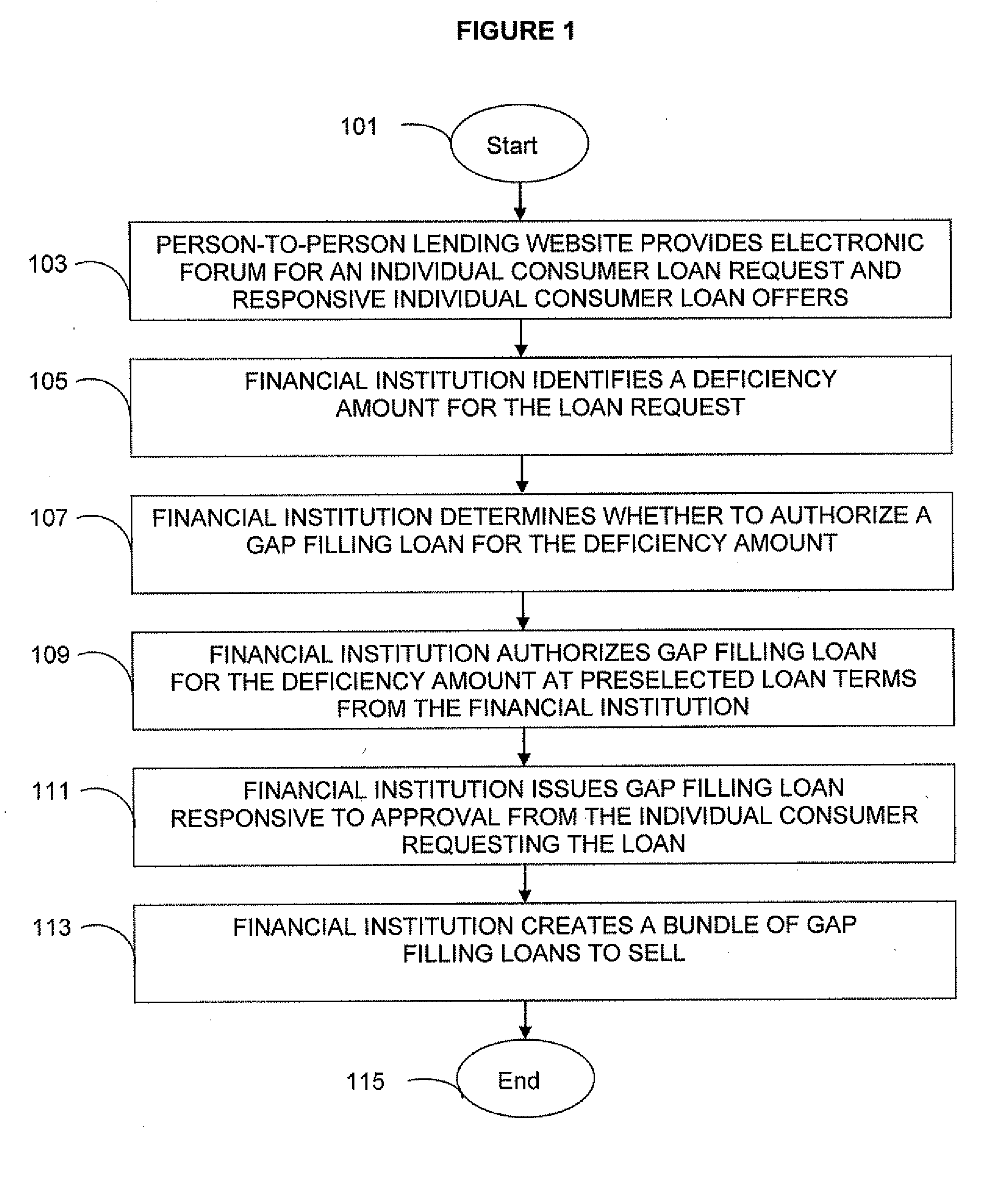
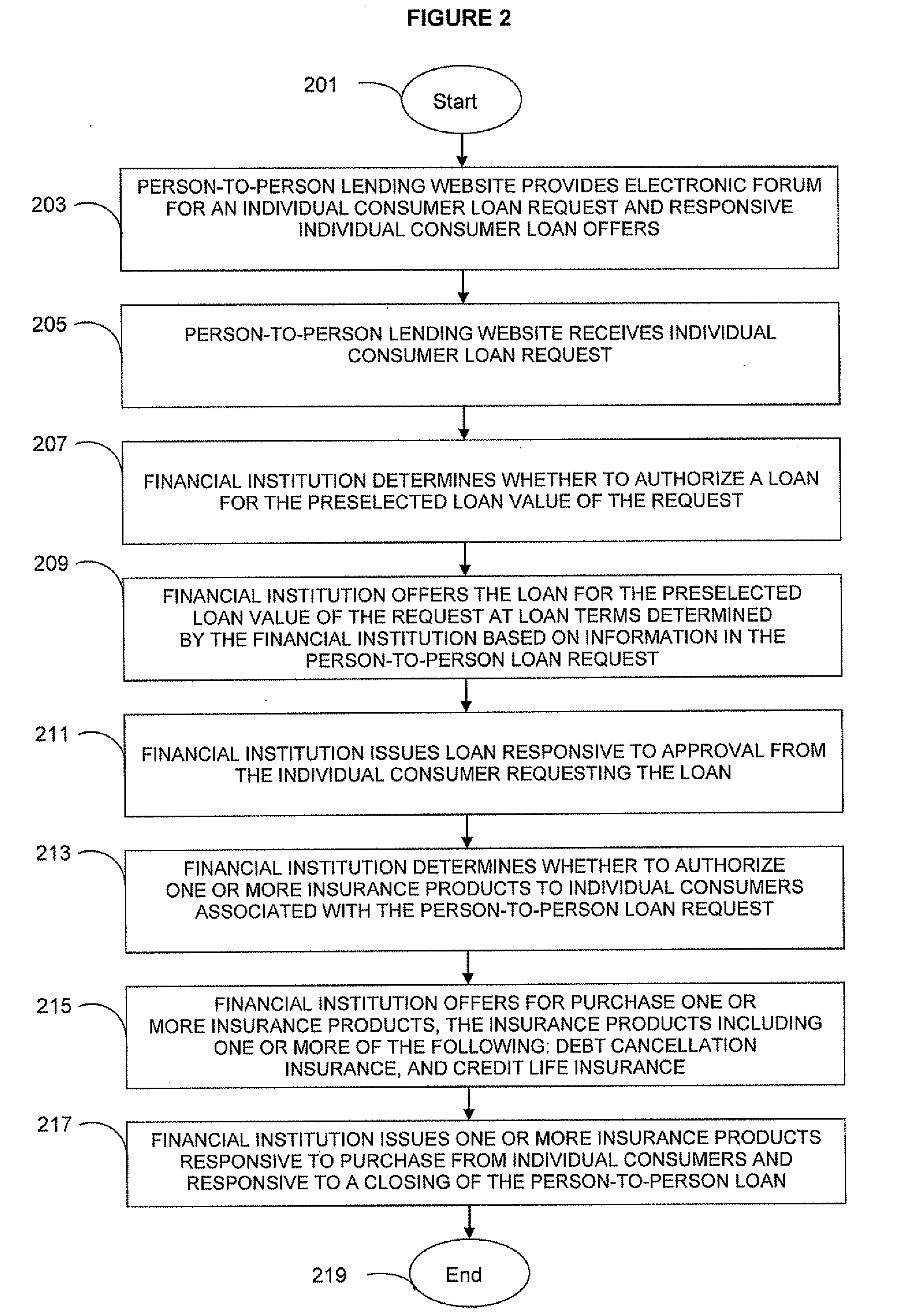
Person-To-Person Lending Program Product, System, And Associated Computer-Implemented Methods
An individual consumer borrower accessing a person-to-person lending website is provided an opportunity to have a loan request wholly or partially satisfied by a financial institution at loan terms from the financial institution. The financial institution, for example, can receive information about a person-to-person loan request, determine whether to authorize a financial institutional loan, offer a loan to the individual on terms determined by the financial institution, and issue the loan to an individual consumer borrower responsive to approval of the terms. Prior to an auction, the individual consumer can choose an immediate loan offer having financial institution terms or choose to solicit individual consumer loan offers with more favorable terms through the person-to-person lending website. The financial institution can also offer a gap filling loan for a deficiency amount so that the loan request can be partially satisfied by individual consumer loan offers.
Owner:PATHWARD NAT ASSOC
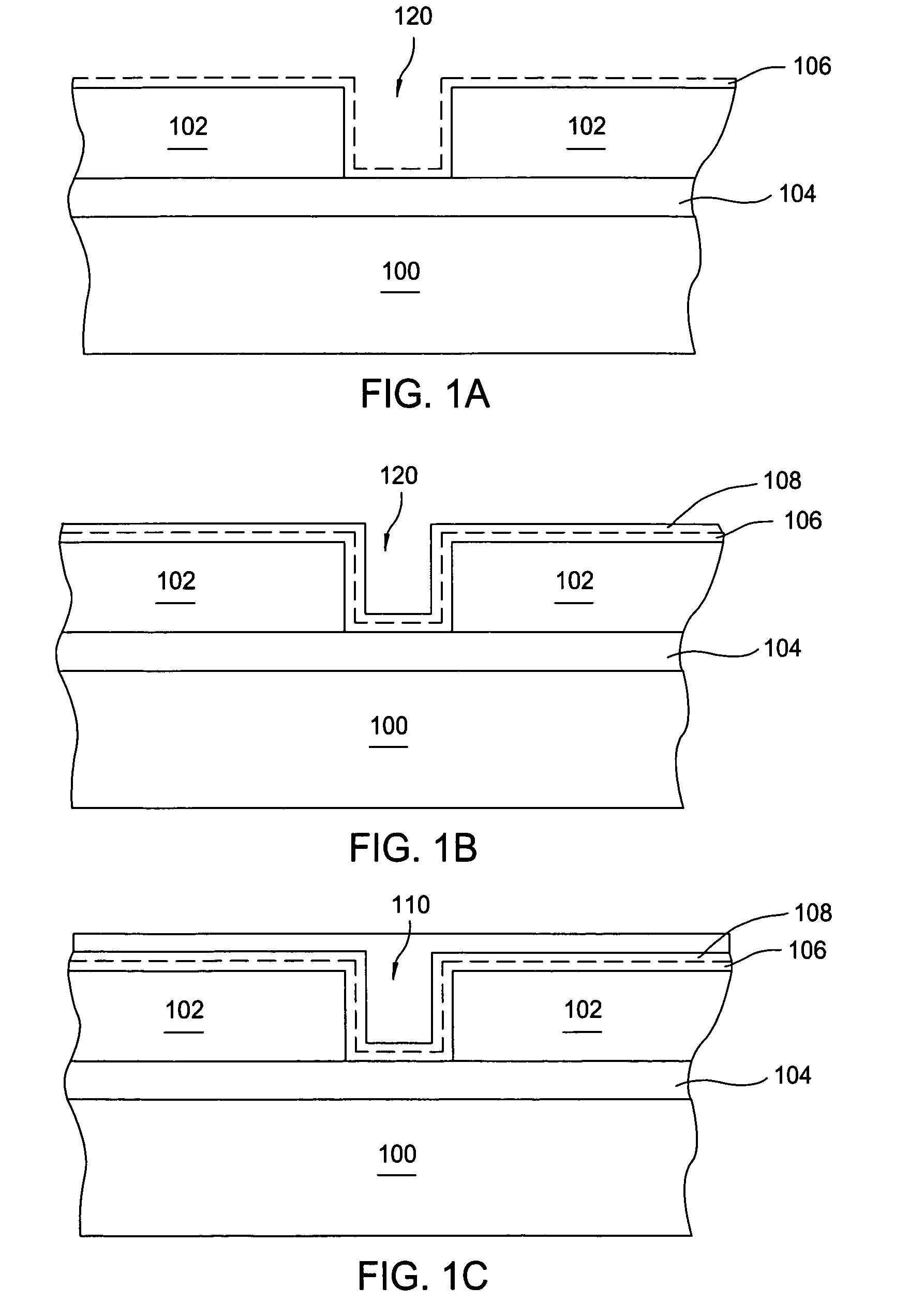
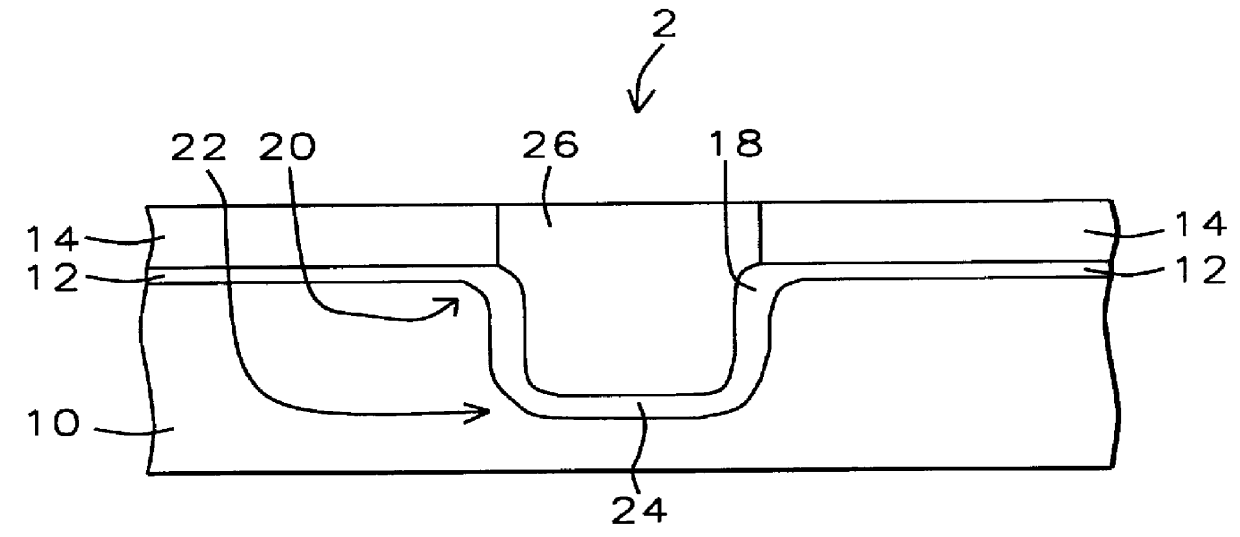
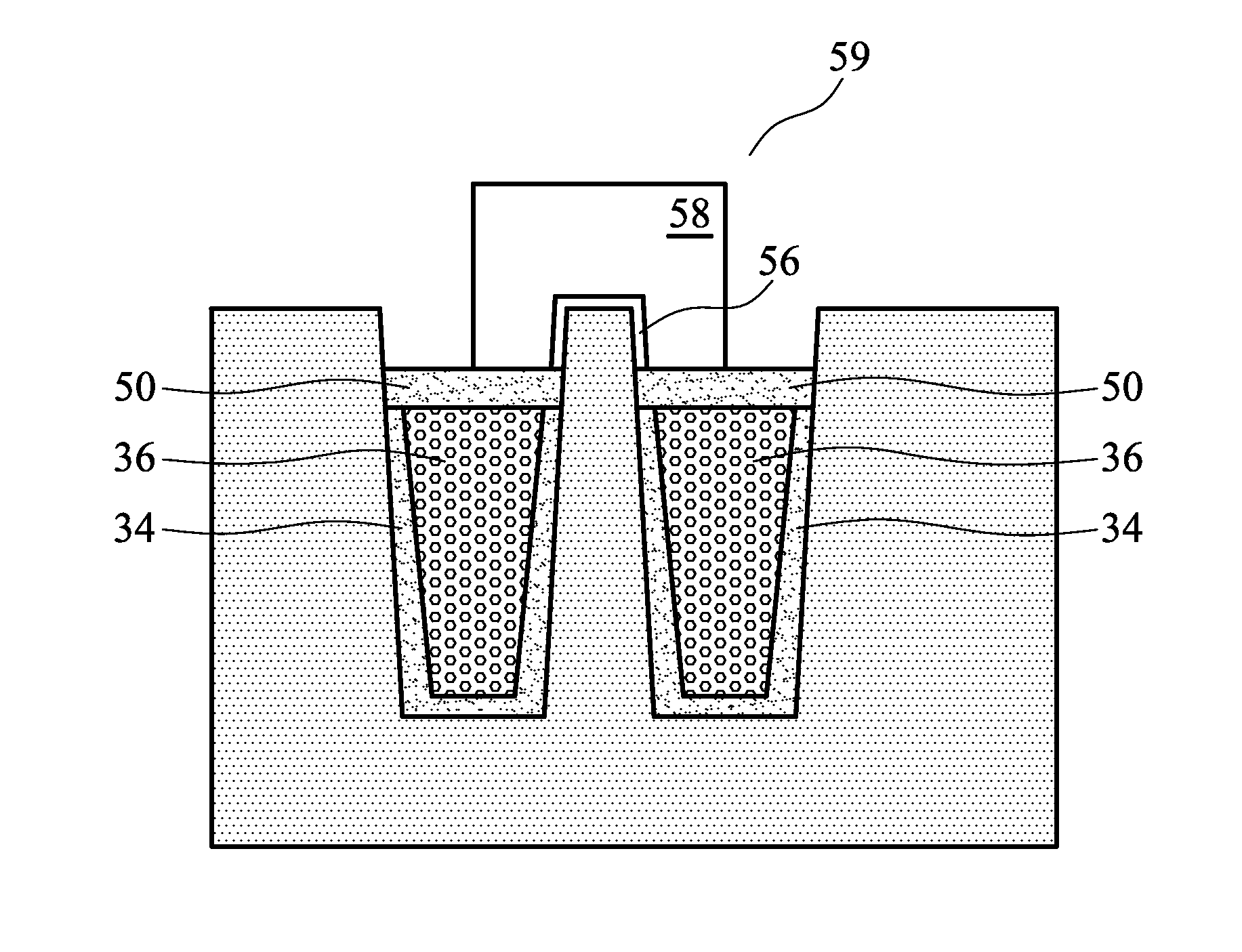
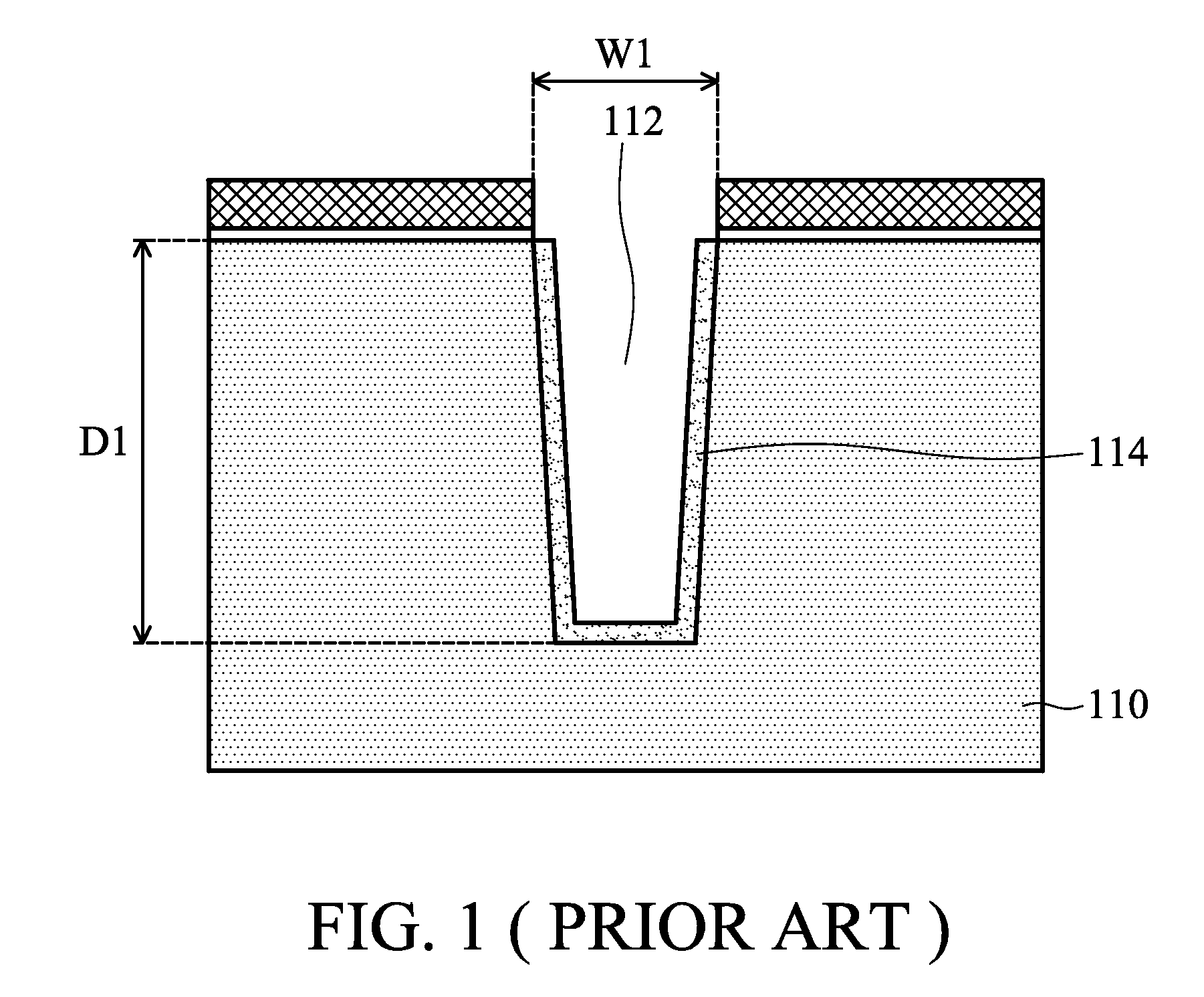
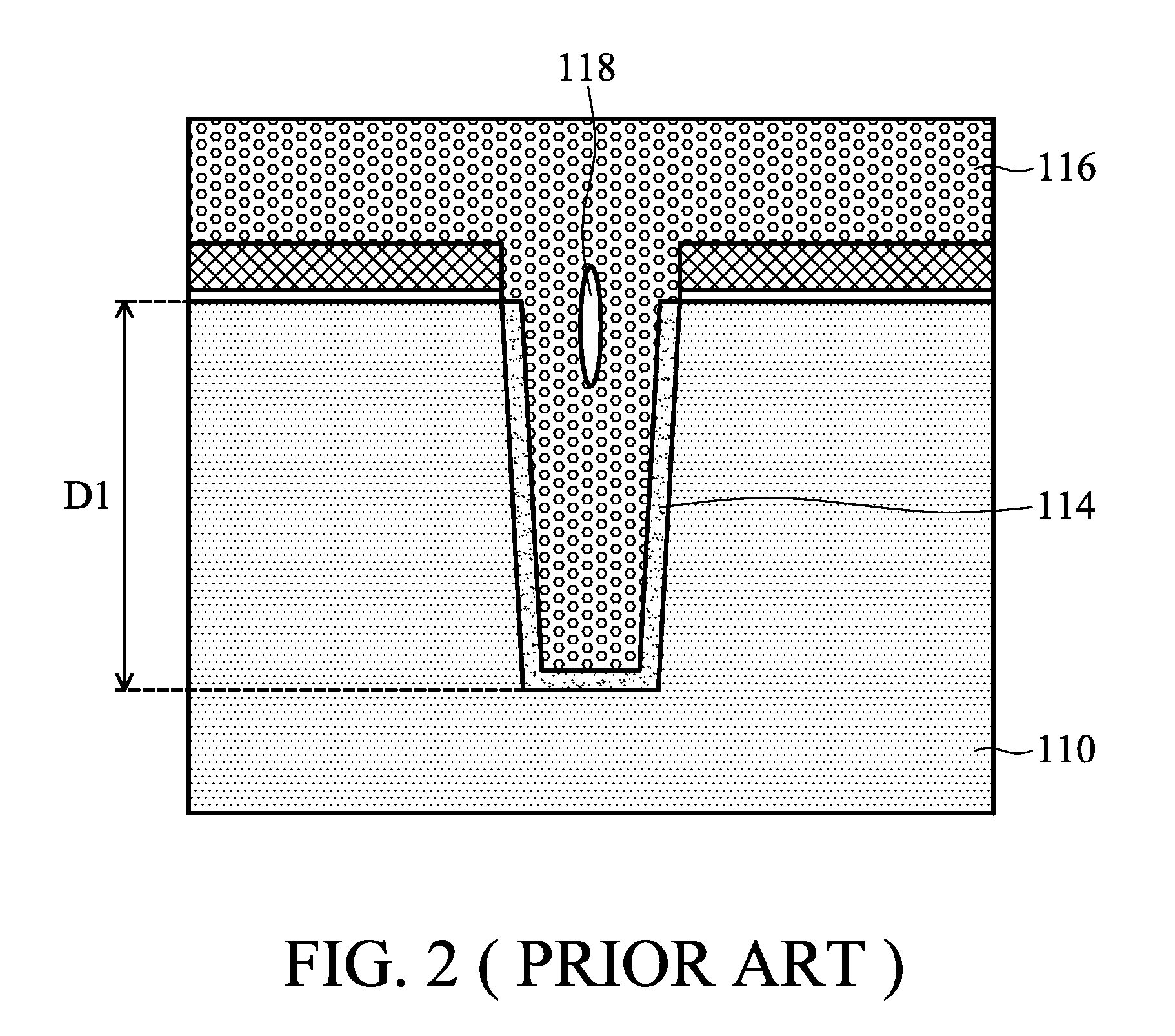
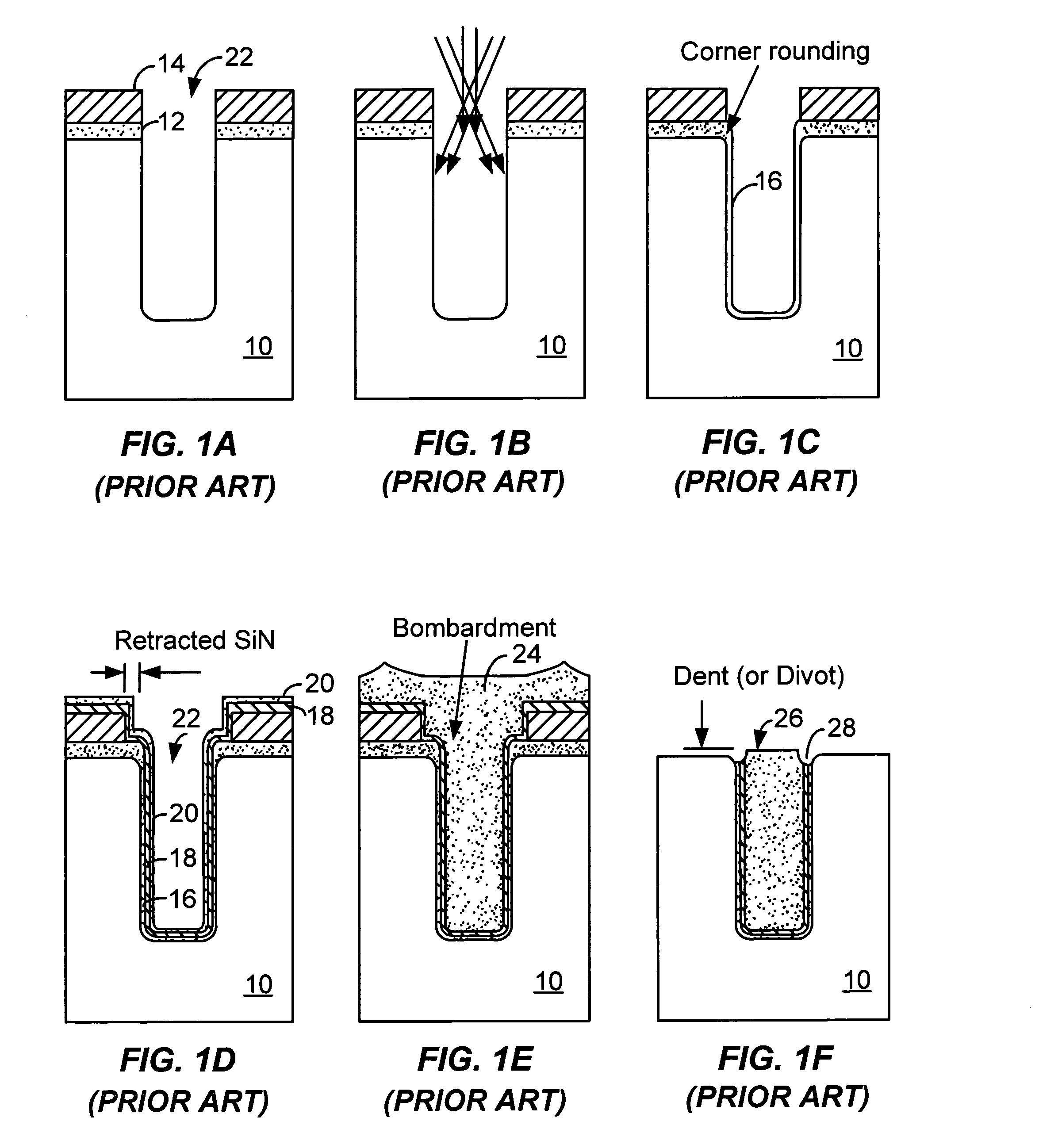
Method for making a trench isolation having a conformal liner oxide and top and bottom rounded corners for integrated circuits
A method for forming an improved trench isolation having a conformal liner oxide and rounded top and bottom corners in the trench was achieved. The conformal liner oxide improves the CVD gap-filling capabilities for these deep submicron wide trenches, and the rounded corners improve the electrical characteristics of the devices in the adjacent device areas. After etching trenches with vertical sidewalls in the silicon substrate, a two-step oxidation process is used to form the conformal liner oxide. A first oxidation step using a low-oxygen flow rate and a low temperature (about 850 to 920 DEG C.) is used to achieve rounded bottom corners. A second oxidation step at a low-oxygen flow rate and a higher temperature (about 1000 to 1150 DEG C.) is used to achieve rounded top corners. The two-step process also results in a more conformal liner oxide. The trenches are then filled with a CVD oxide and polished or etched back to an oxidation-barrier layer / etch-stop layer over the device areas to complete the trench isolation.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Nitride micro light emitting diode with high brightness and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060208273A1Maximize the light emitting areaImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFilling materialsPolyamide
The present invention relates to a nitride micro light emitting diode (LED) with high brightness and a method of manufacturing the same. The present invention provides a nitride micro LED with high brightness and a method of manufacturing the same, wherein a plurality of micro-sized luminous pillars 10 are formed in a substrates, a gap filling material such as SiO2, Si3N4, DBR(ZrO2 / SiO2 HfO2 / SiO2), polyamide or the like is filled in gaps between the micro-sized luminous pillars, a top surface 11 of the luminous pillar array and the gap filling material is planarized through a CMP processing, and then a transparent electrode 6 having a large area is formed thereon, so that all the luminous pillars can be driven at the same time. In addition, the present invention provides a nitride micro LED with high brightness in which uniformity in formation of electrodes on the micro-sized luminous pillars array is enhanced by employing a flip-chip structure.
Owner:KANG DA
Applications for a low cost receiver in an automatic meter reading system
ActiveUS20050179561A1Improving AMR system coverageLow costElectric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusTransceiverCentral database
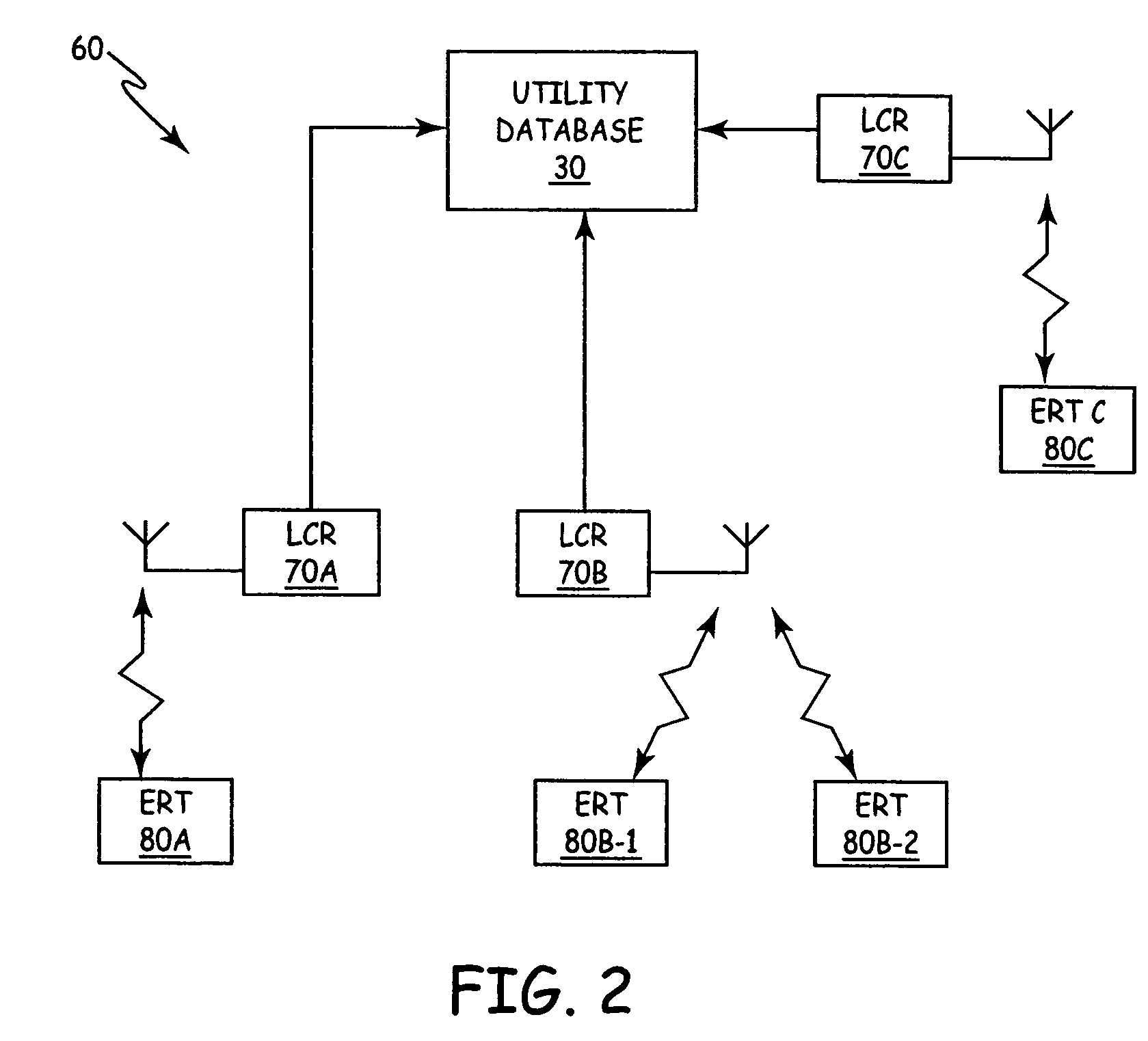
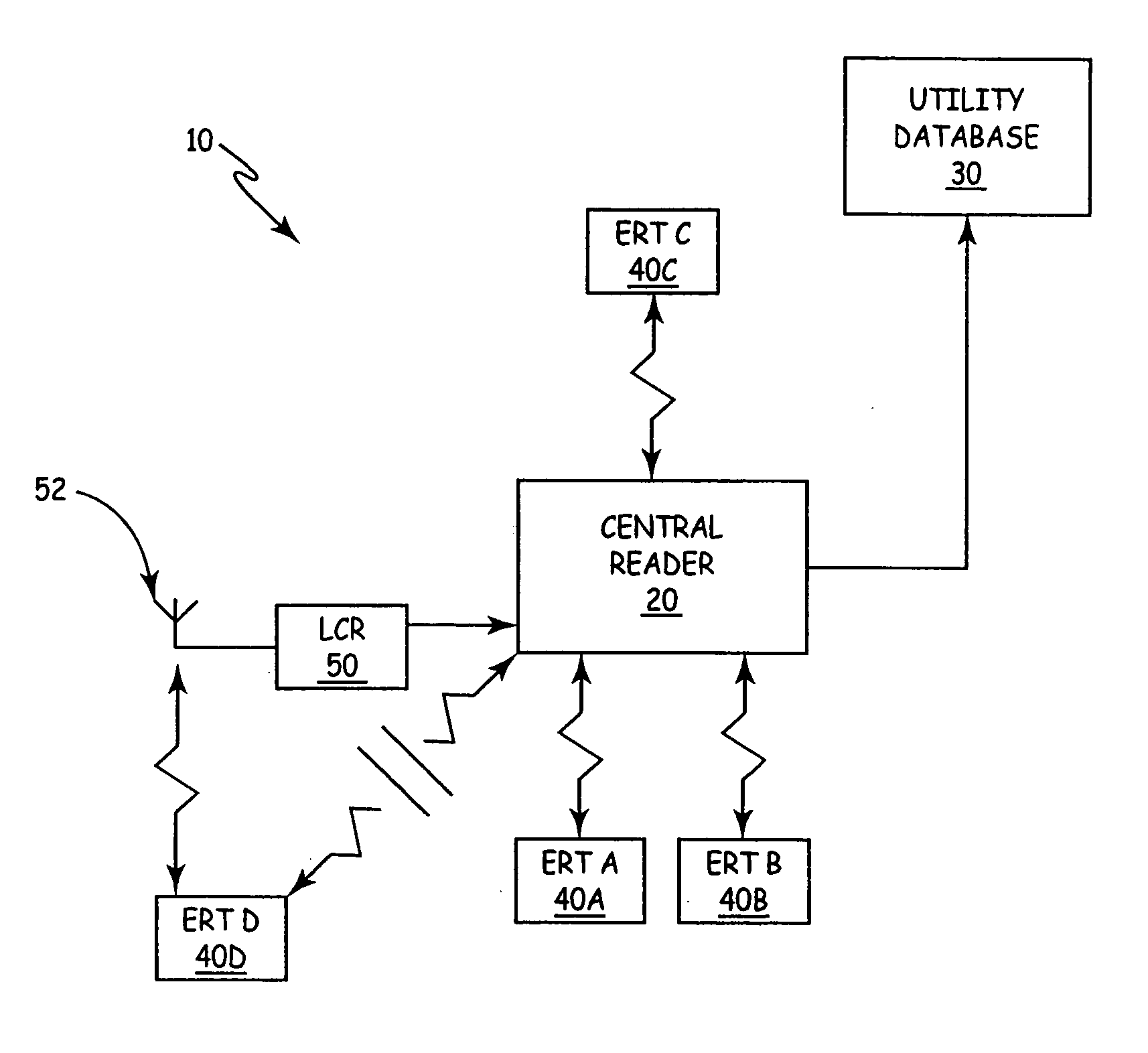
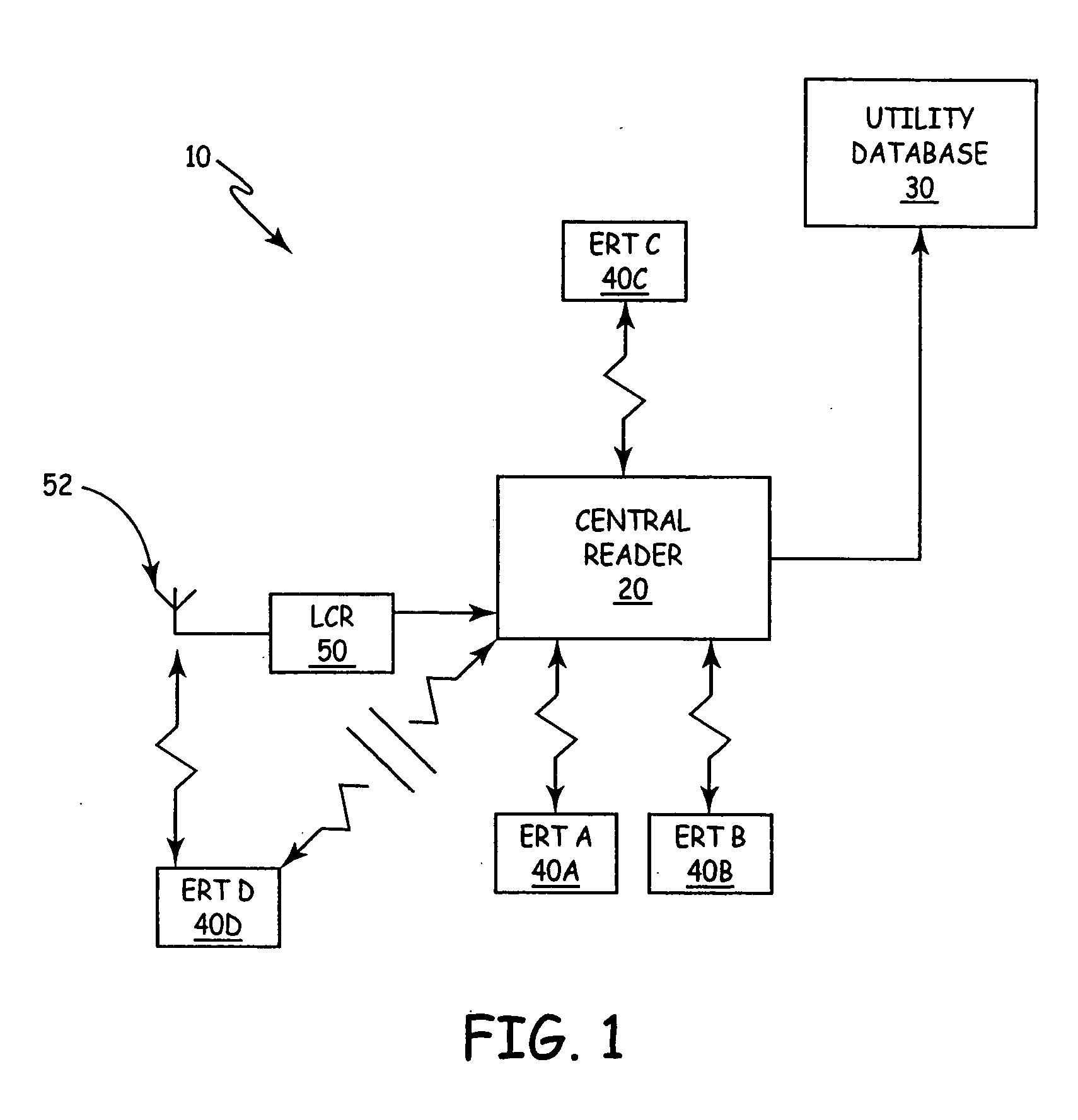
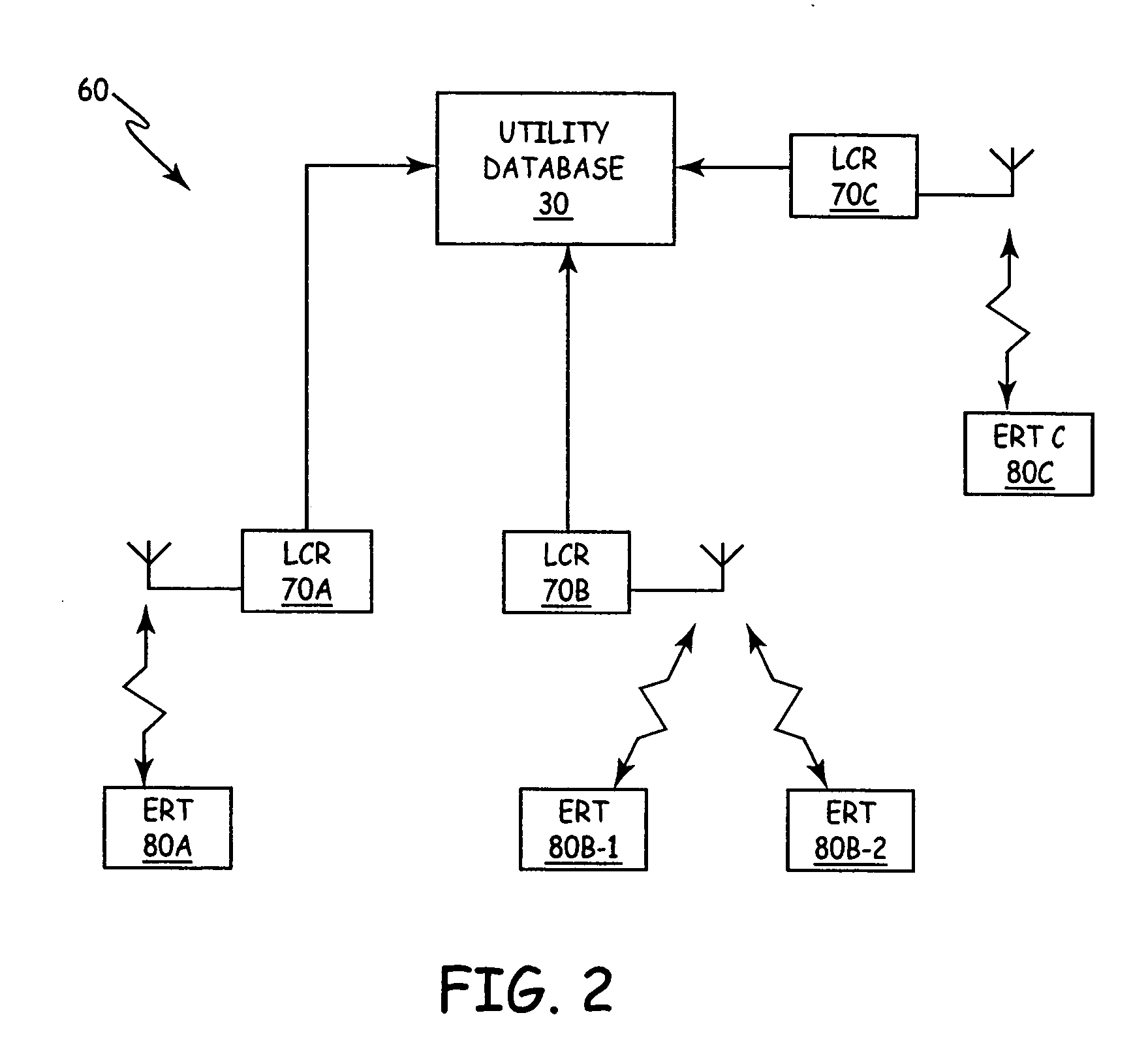
An automatic meter reading (AMR) system includes a plurality of utility meter endpoints, each of which includes a radio-frequency (RF) transmitter adapted for transmitting endpoint information. A plurality of transceivers are adapted to read endpoints located throughout a designated coverage area, and each transceiver adapted to receive endpoint information from utility meter endpoints located within a corresponding portion of the designated coverage area. A central storage arrangement is adapted to communicate with each of the transceivers and to store endpoint information in a central database. The AMR system also includes a low cost receiver (LCR) having a communications range that defines a gap-filling coverage area. The LCR is adapted to automatically forward received endpoint information to the central storage arrangement.
Owner:ITRON
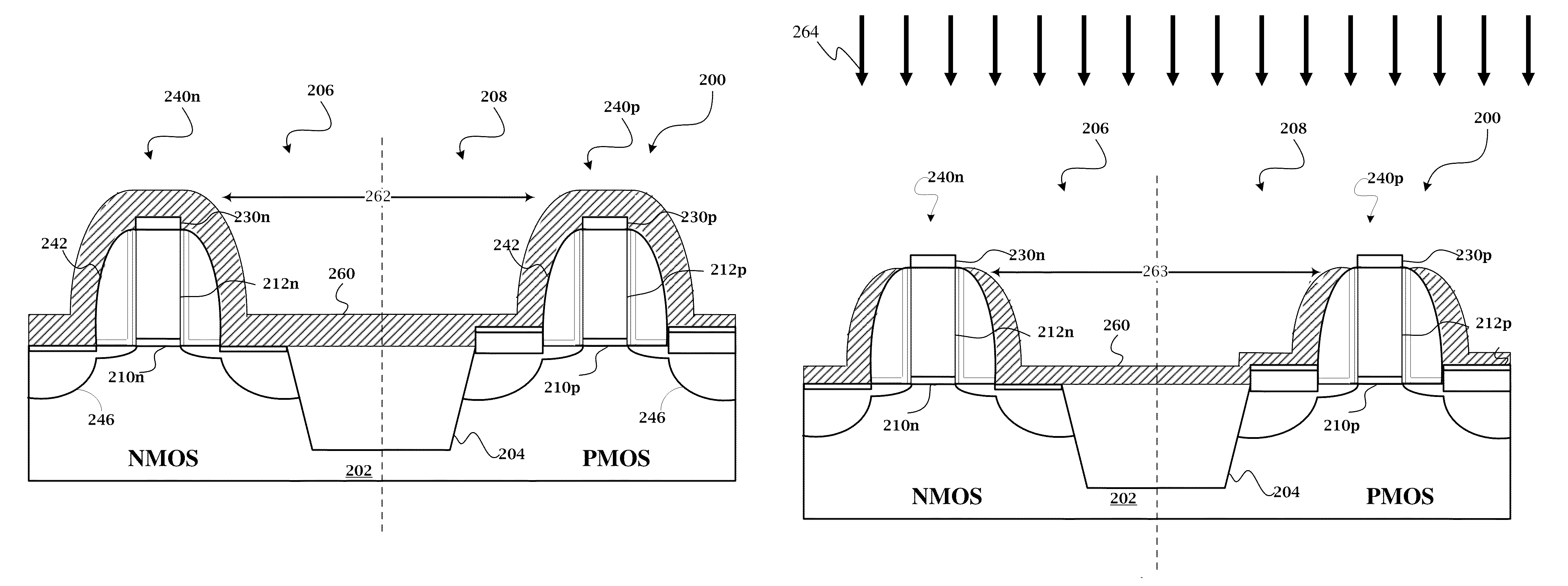
Etch resistant barrier for replacement gate integration
InactiveUS20130309856A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFilling materialsNitride
Semiconductor devices and methods of their fabrication are disclosed. One method includes forming a semiconductor device structure including a plurality of dummy gates and a dielectric gap filling material with a pre-determined aspect ratio that is between the dummy gates. An etch resistant nitride layer is applied above the dielectric gap filling material to maintain the aspect ratio of the gap filling material. In addition, the dummy gates are removed by implementing an etching process. Further, replacement gates are formed in regions of the device structure previously occupied by the dummy gates.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hybrid STI Gap-Filling Approach
ActiveUS20100230757A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricEngineering
A method of forming an integrated circuit structure includes providing a semiconductor substrate including a top surface; forming an opening extending from the top surface into the semiconductor substrate; and performing a first deposition step to fill a first dielectric material into the opening. The first dielectric material is then recessed. A second deposition step is performed to fill a remaining portion of the opening with a second dielectric material. The second dielectric material is denser than the first dielectric material. The second dielectric material is recessed until a top surface of the second dielectric material is lower than the top surface of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
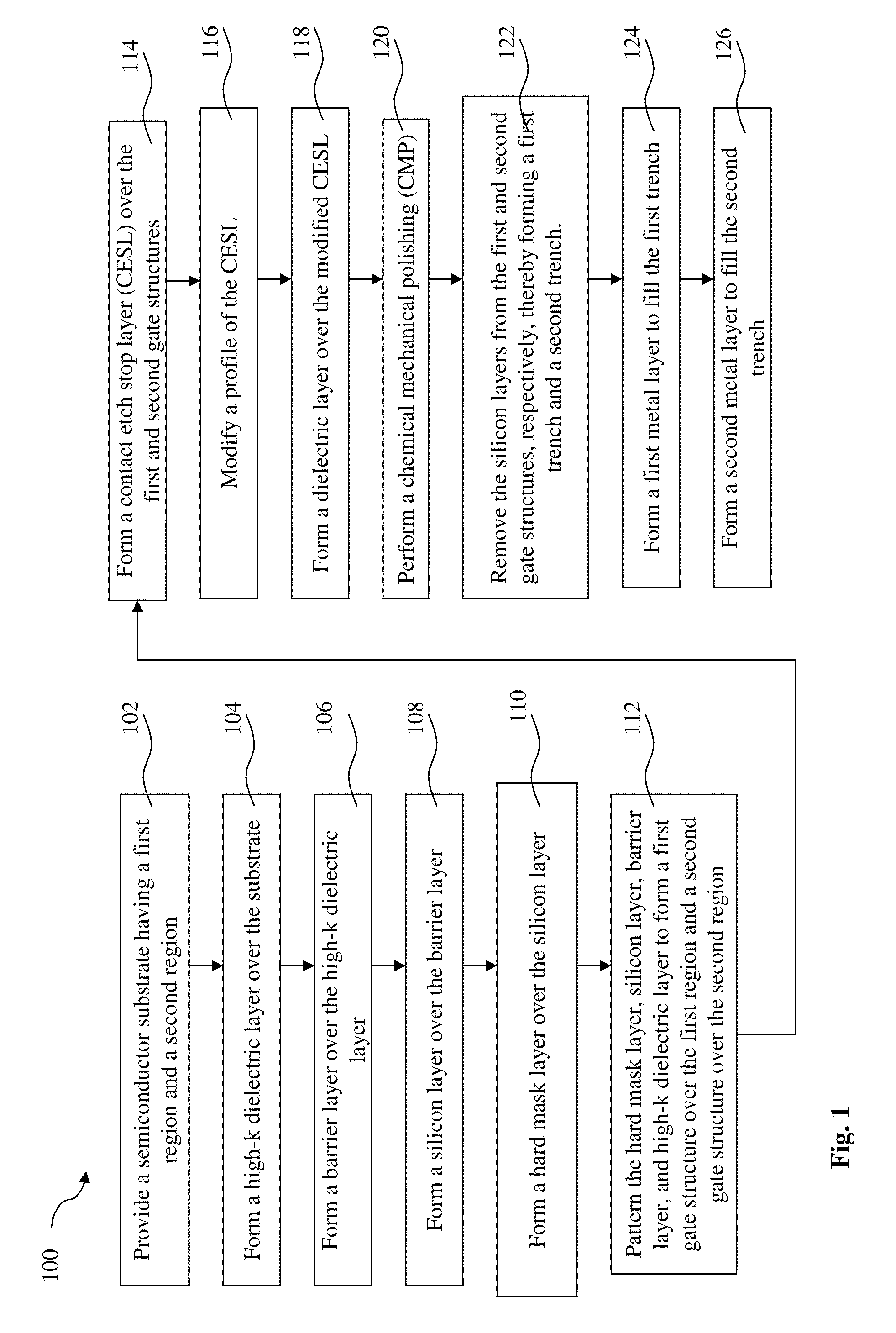
Method for gap filling in a gate last process
ActiveUS7923321B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesInter layerGate dielectric
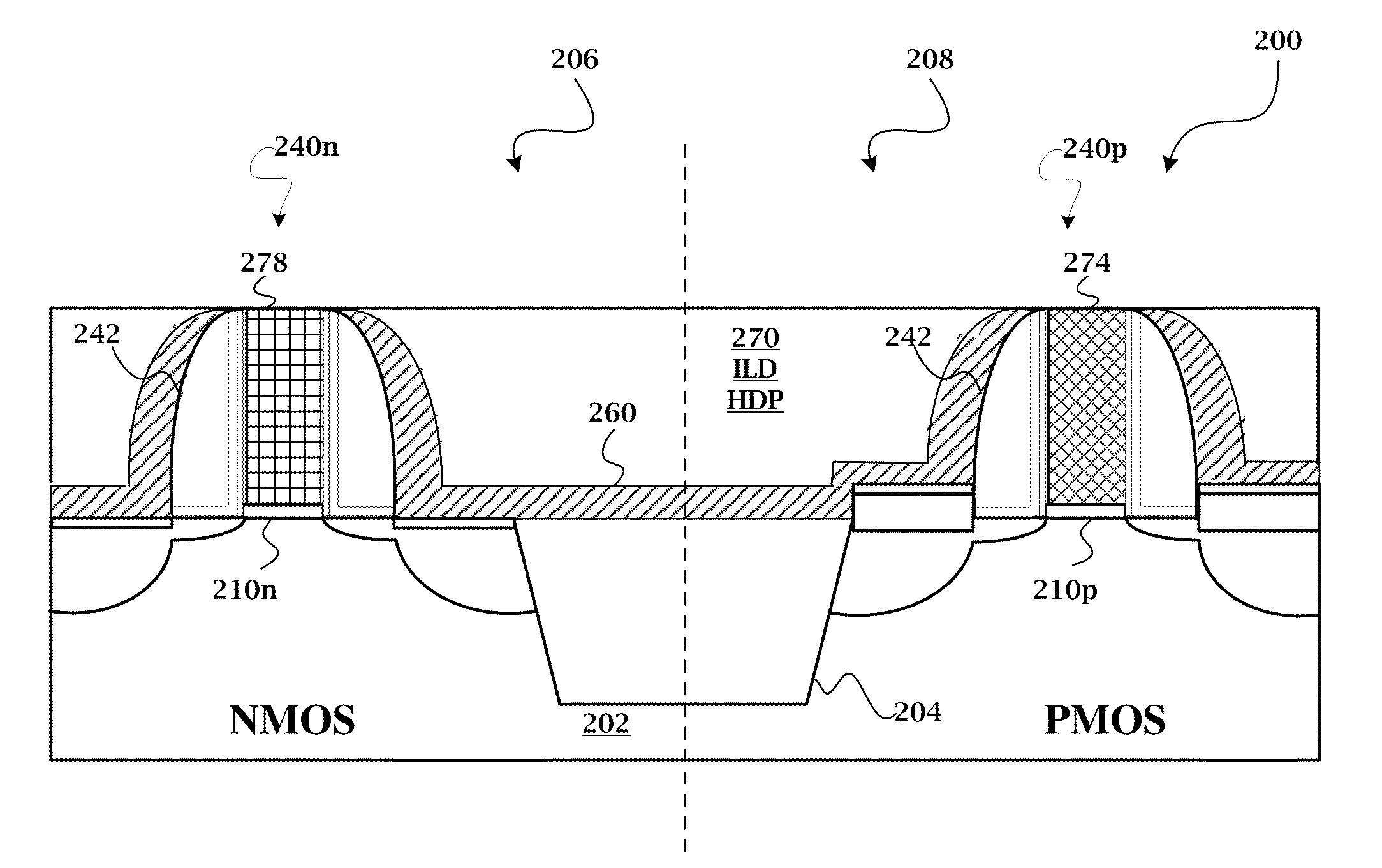
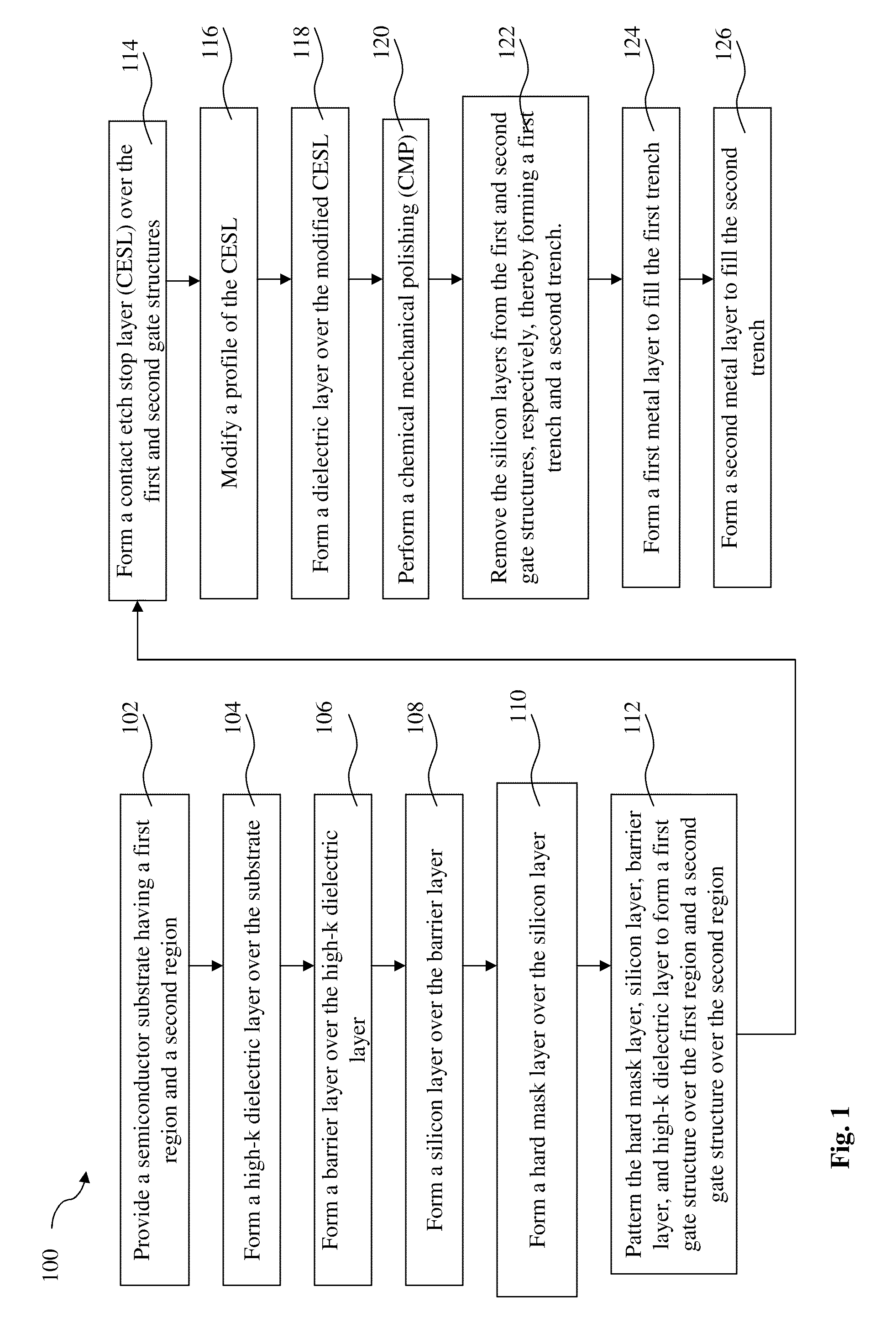
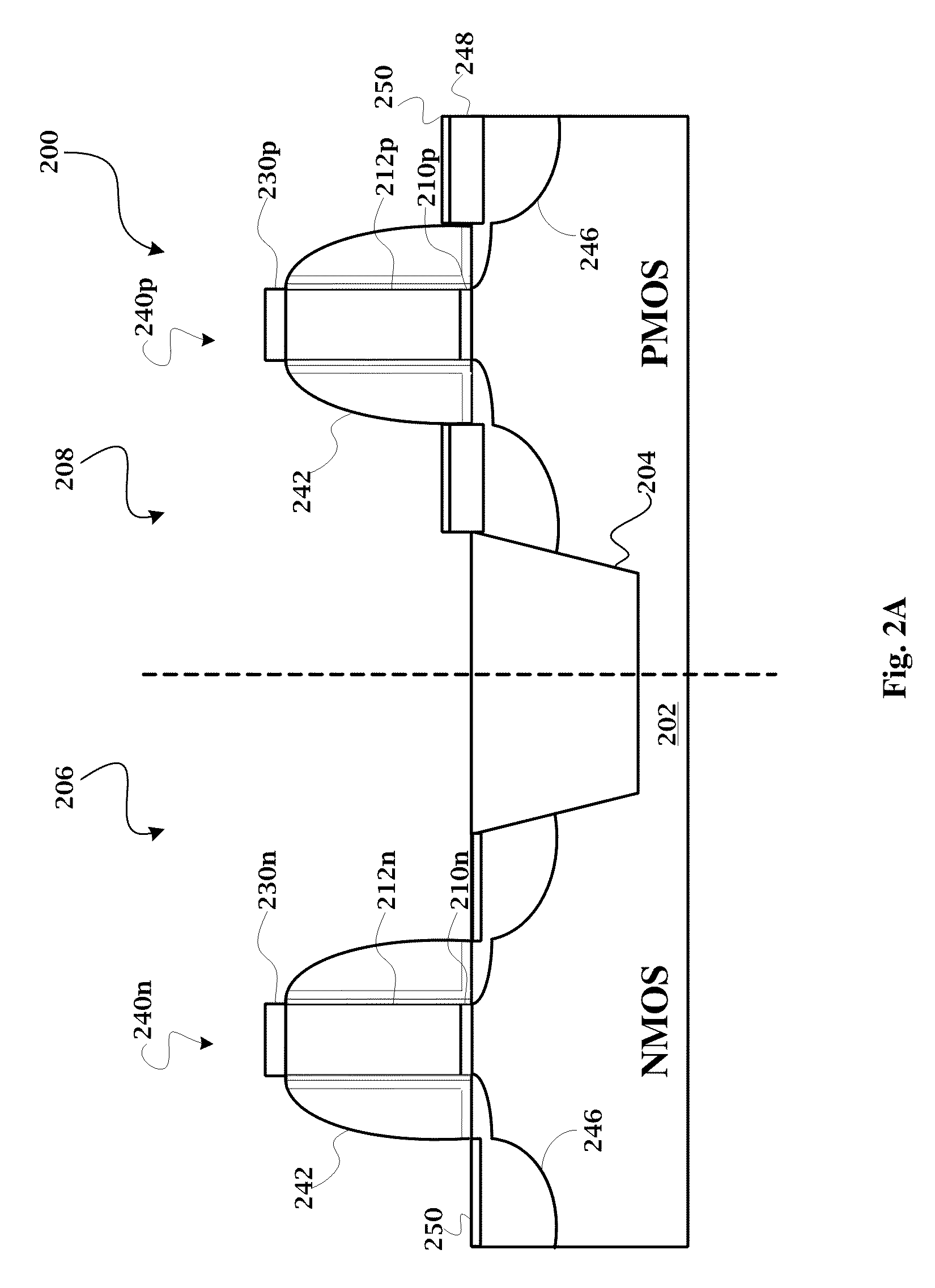
A method is provided for fabricating a semiconductor device that includes providing a semiconductor substrate having a first region and a second region, forming a high-k dielectric layer over the substrate, forming a silicon layer over the high-k dielectric layer, forming a hard mask layer over the silicon layer, patterning the hard mask layer, silicon layer, and high-k dielectric layer to form first and second gate structures over the first and second regions, respectively, forming a contact etch stop layer (CESL) over the first and second gate structures, modifying a profile of the CESL by an etching process, forming an inter-layer dielectric (ILD) over the modified CESL, performing a chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) on the ILD to expose the silicon layer of the first and second gate structures, respectively, and removing the silicon layer from the first and second gate structures, respectively, and replacing it with metal gate structures.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Optoelectronic device encapsulant
InactiveUS6356686B1Preventing interfering accumulationAvoid wear and tearCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideEpoxyParticulates
An optically clear encapsulant for optoelectronic packages exhibits a suitably high viscosity both to replace a silicon nitride passivation layer required on a VCSEL die and to fill a gap between the die and an optical coupler, preventing light signal degradation. The encapsulant exhibits optical transparency to light having a wavelength of about 850 nanometers (nm) with substantially no Mie scattering since particulate fillers are not required to modulate viscosity in the encapsulant. Also, the encapsulant further seals wire bonds between the die and a cable header to prevent abrasive wear. The gap-filling encapsulant is particularly suitable for use with vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) technology. The encapsulant includes prior to curing, a difunctional acrylate epoxy resin exhibiting pseudoplastic flow and a viscosity of greater than about 0.7x106 centipoise. Accordingly, a method of manufacturing an optical subassembly may eliminate a separate passivation step and instead fill the gap between the die and optical coupler with an optically clear encapsulant.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for gap filling in a gate last process
ActiveUS20100112798A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricInter layer
A method is provided for fabricating a semiconductor device that includes providing a semiconductor substrate having a first region and a second region, forming a high-k dielectric layer over the substrate, forming a silicon layer over the high-k dielectric layer, forming a hard mask layer over the silicon layer, patterning the hard mask layer, silicon layer, and high-k dielectric layer to form first and second gate structures over the first and second regions, respectively, forming a contact etch stop layer (CESL) over the first and second gate structures, modifying a profile of the CESL by an etching process, forming an inter-layer dielectric (ILD) over the modified CESL, performing a chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) on the ILD to expose the silicon layer of the first and second gate structures, respectively, and removing the silicon layer from the first and second gate structures, respectively, and replacing it with metal gate structures.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
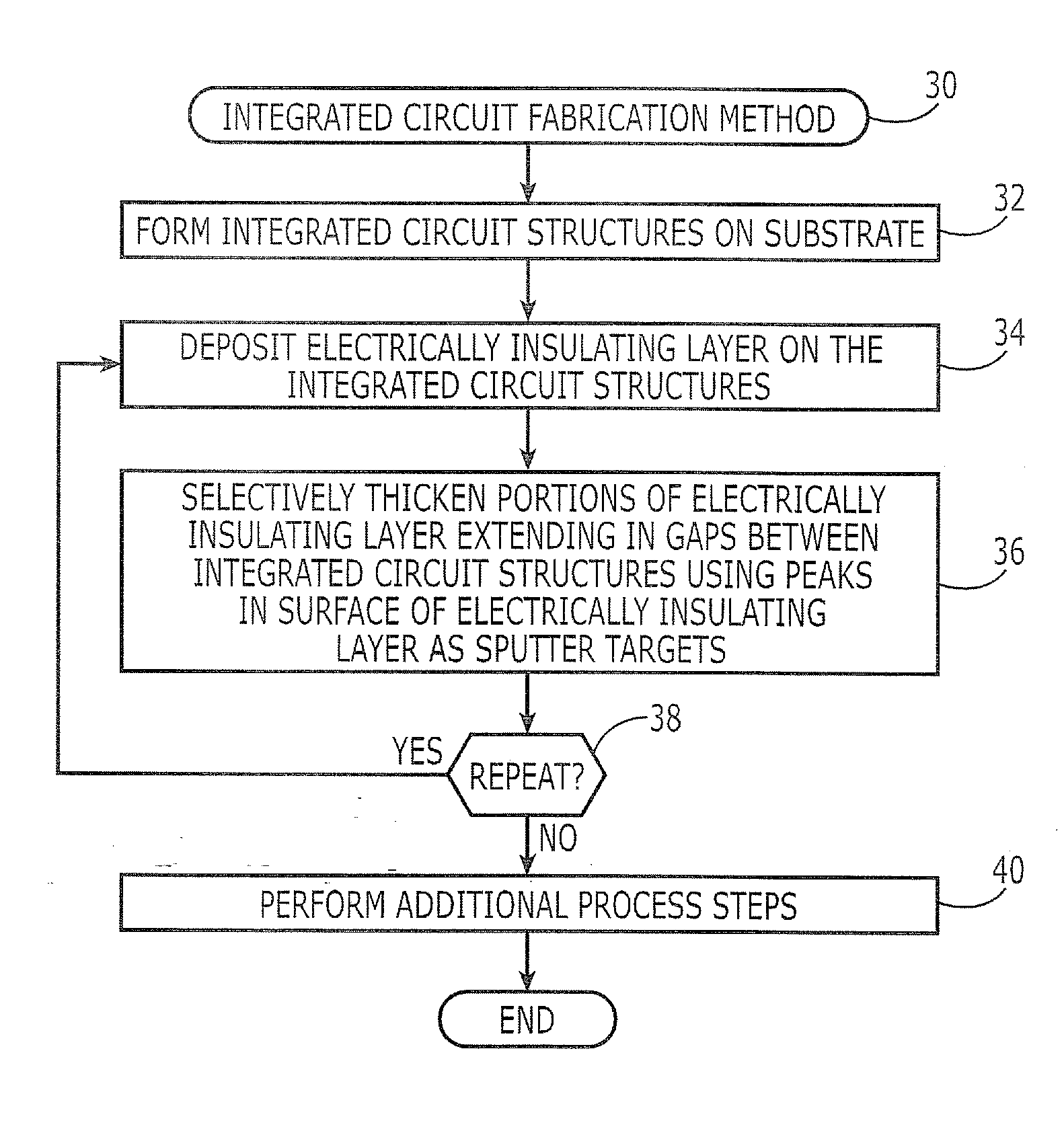
Methods of Forming Integrated Circuit Structures Using Insulator Deposition and Insulator Gap Filling Techniques
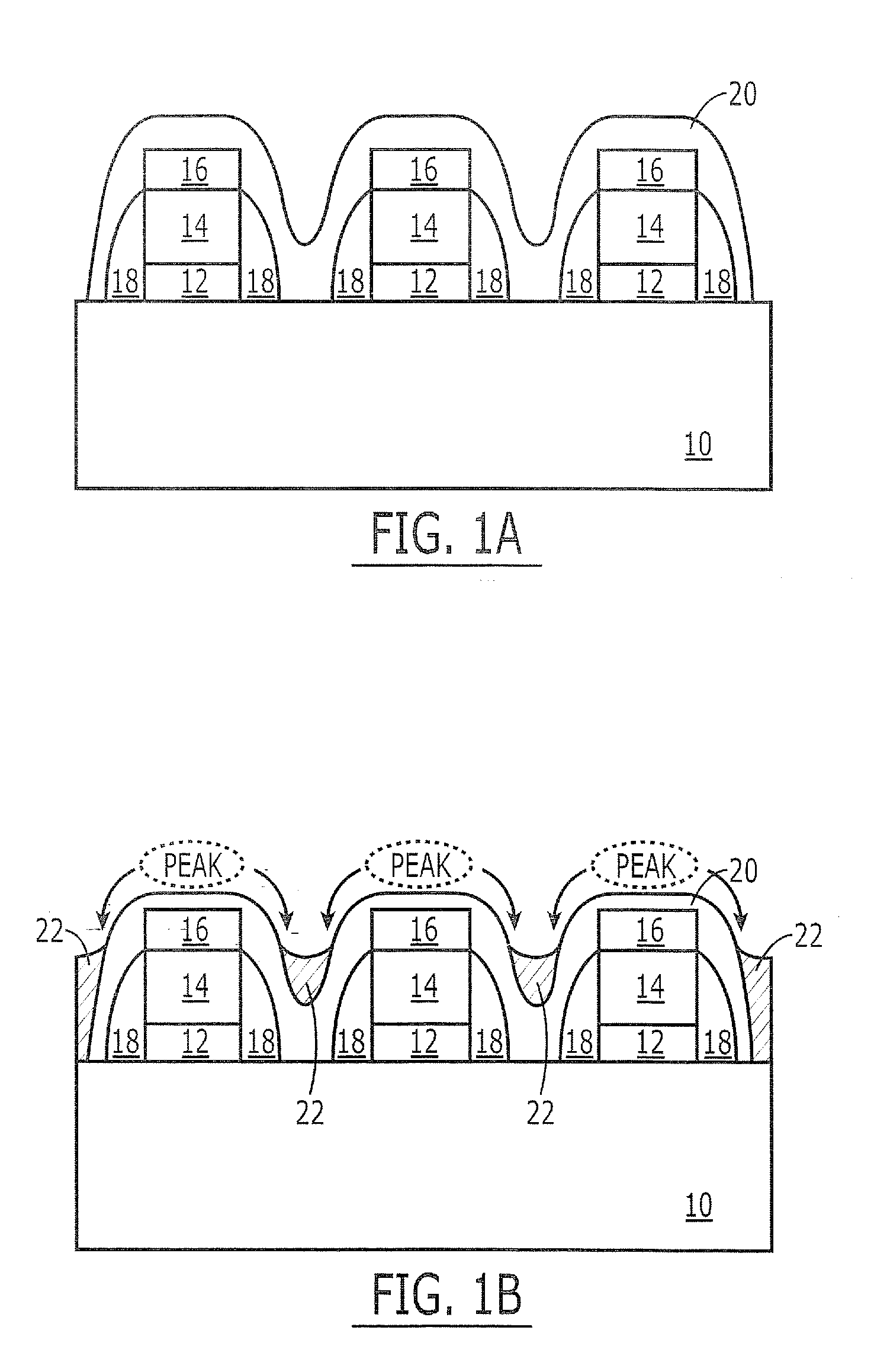
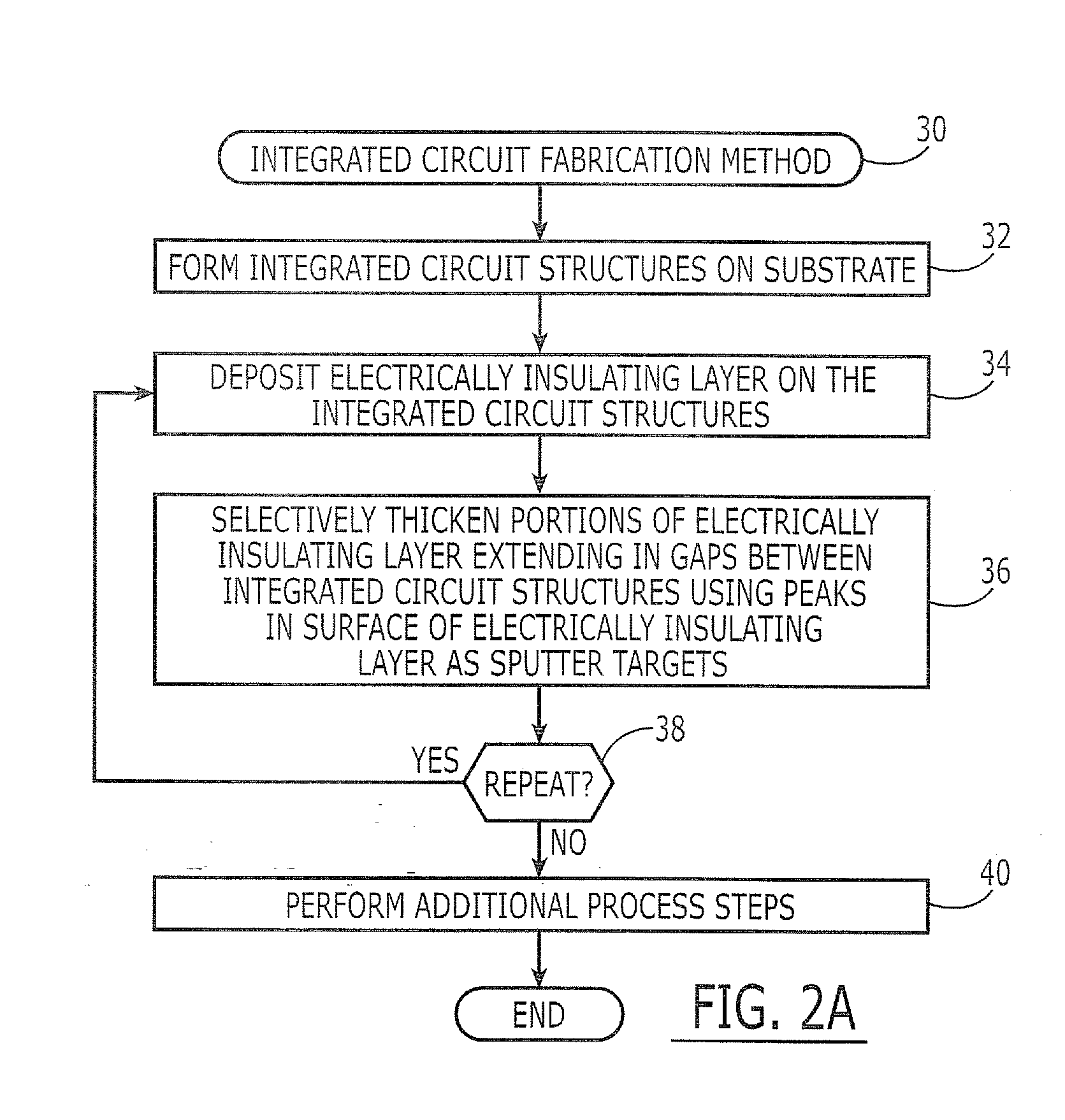
ActiveUS20080220584A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringSputter deposition
Methods of forming integrated circuit devices include depositing an electrically insulating layer onto an integrated circuit substrate having integrated circuit structures thereon. This deposition step results in the formation of an electrically insulating layer having an undulating surface profile, which includes at least one peak and at least on valley adjacent to the at least one peak. A non-uniform thickening step is then performed. This non-uniform thickening step includes thickening a portion of the electrically insulating layer by redepositing portions of the electrically insulating layer from the least one peak to the at least one valley. This redeposition occurs using a sputter deposition technique that utilizes the electrically insulating layer as a sputter target.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +2
Inductively coupled plasma CVD
InactiveUS20010019903A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringInductively coupled plasma
A method of depositing a dielectric film on a substrate in a process chamber of an inductively coupled plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition reactor. Gap filling between electrically conductive lines on a semiconductor substrate and depositing a cap layer are achieved. Films having significantly improved physical characteristics including reduced film stress are produced by heating the substrate holder on which the substrate is positioned in the process chamber.
Owner:SHUFFLEBOTHAM PAUL KEVIN +5
Semiconductor device having shallow trench isolation structure and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060263991A1Maintain stable propertiesIncrease region of active regionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialIsolation layer
In one embodiment, a semiconductor device has an active region defined by an isolation layer formed inside an STI trench that includes an upper trench and a lower trench having a substantially curved cross-sectional profile under the upper trench so that the lower trench is in communication with the upper trench. Since the upper trench has a sidewall tapered with a positive slope, a good gap filling property can be obtained when filling the upper trench with an insulating layer. By forming a void in the lower trench, a dielectric constant at the bottom of the isolation layer is lower than a dielectric constant at an oxide layer, thereby improving the isolation property. The isolation layer includes a first insulating layer formed inside only the upper trench and covering an inner wall of the upper trench in the form of a spacer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stress management for tensile films
ActiveUS7935643B2Reduced tendency towards crackingEasy to fillSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon oxideGap filling
The formation of a gap-filling silicon oxide layer with reduced tendency towards cracking is described. The deposition involves the formation of a flowable silicon-containing layer which facilitates the filling of trenches. Subsequent processing at high substrate temperature causes less cracking in the dielectric film than flowable films formed in accordance with methods in the prior art. A compressive liner layer deposited prior to the formation of the gap-filling silicon oxide layer is described and reduces the tendency for the subsequently deposited film to crack. A compressive capping layer deposited after a flowable silicon-containing layer has also been determined to reduce cracking. Compressive liner layers and compressive capping layers can be used alone or in combination to reduce and often eliminate cracking. Compressive capping layers in disclosed embodiments have additionally been determined to enable an underlying layer of silicon nitride to be transformed into a silicon oxide layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
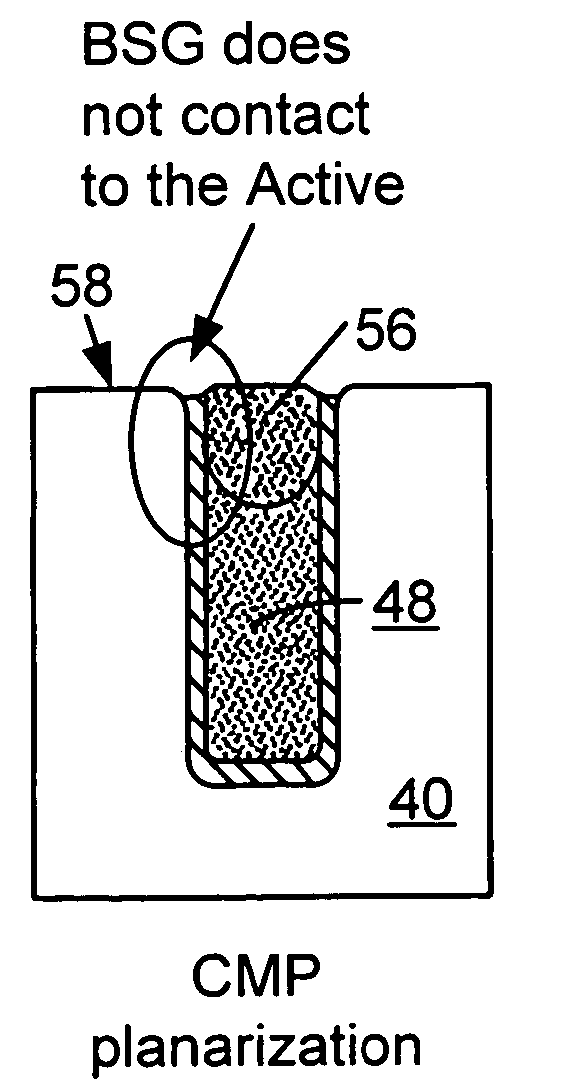
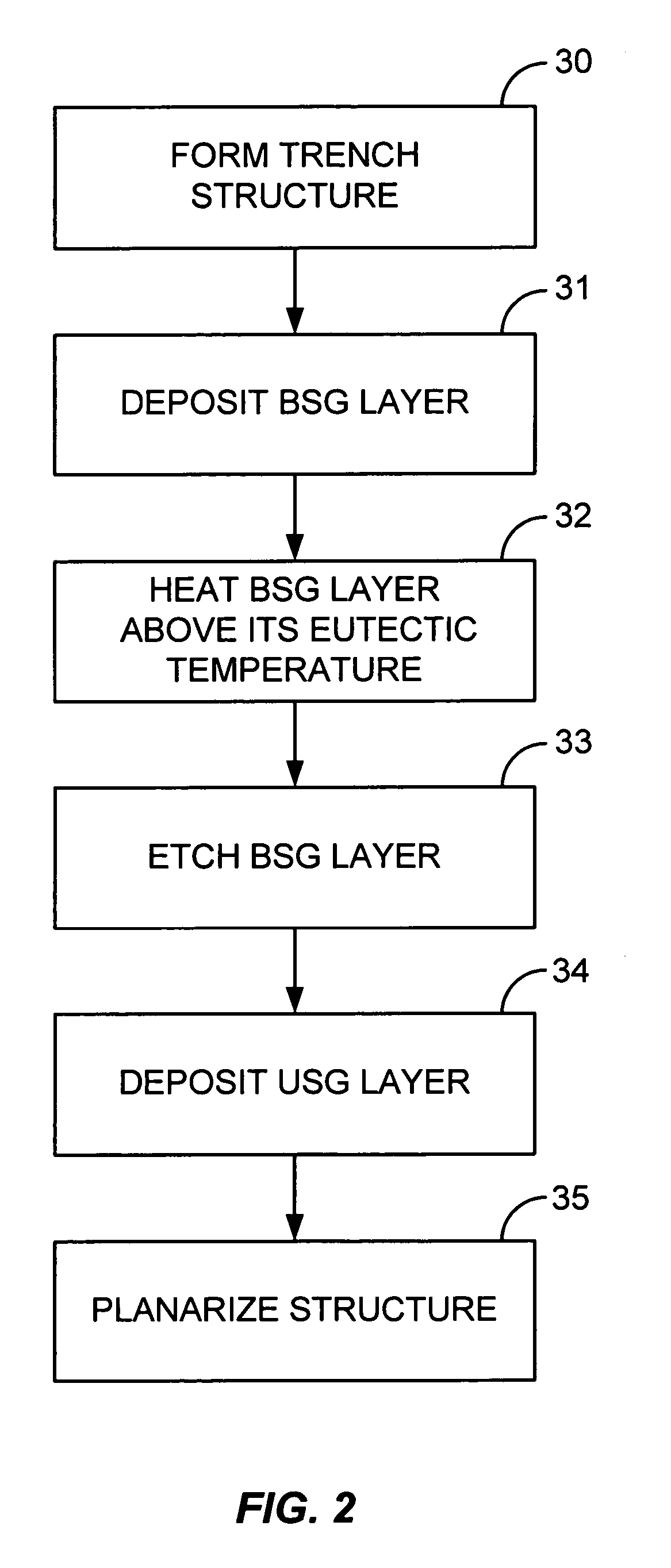
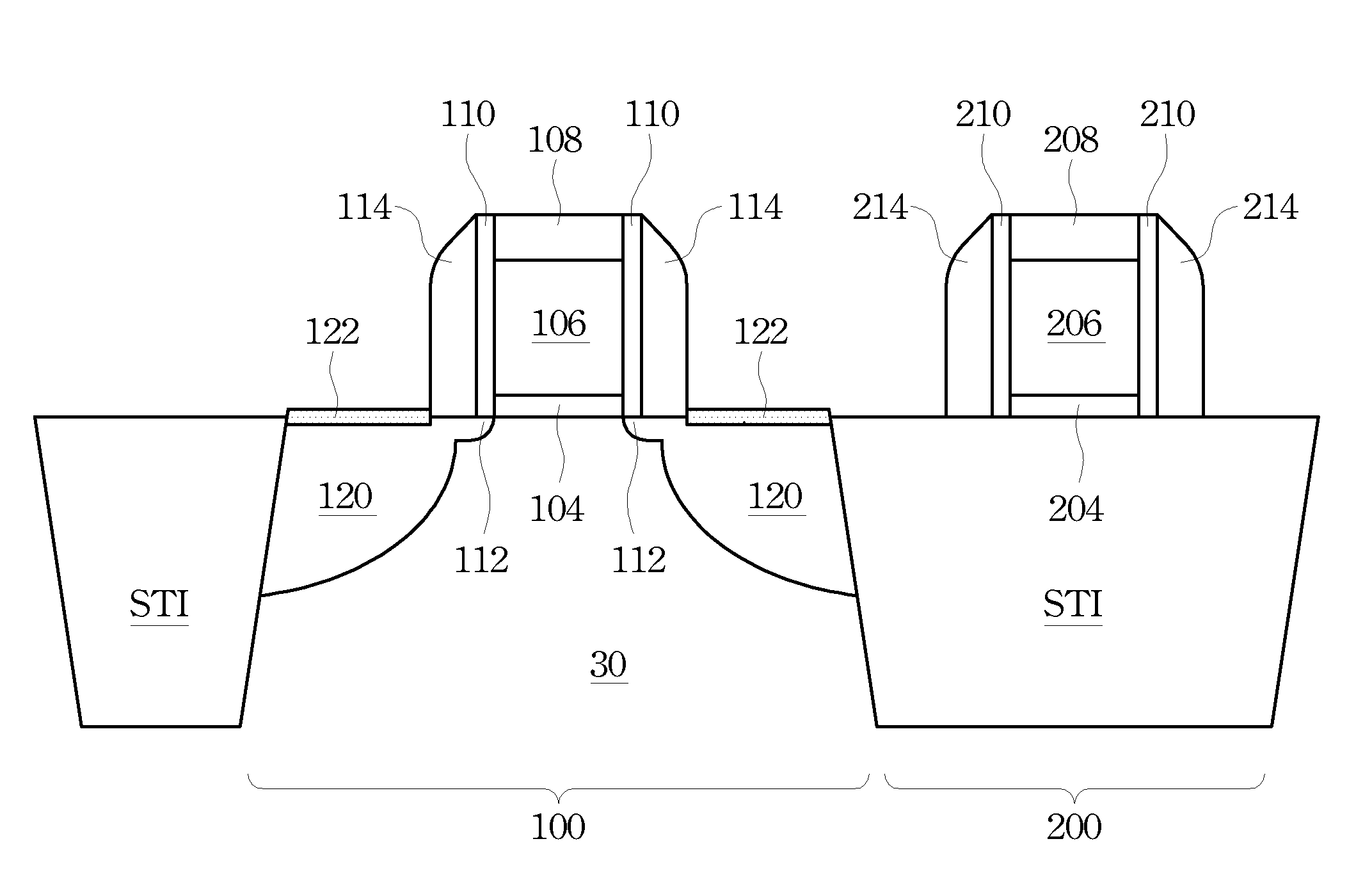
Gap filling with a composite layer
A method of filling a gap formed between adjacent raised surfaces on a substrate. In one embodiment the method comprises depositing a boron-doped silica glass (BSG) layer over the substrate to partially fill the gap using a thermal CVD process; exposing the BSG layer to a steam ambient at a temperature above the BSG layer's Eutectic temperature; removing an upper portion of the BSG layer by exposing the layer to a fluorine-containing etchant; and depositing an undoped silica glass (USG) layer over the BSG layer to fill the remainder of the gap.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Spacer Shape Engineering for Void-Free Gap-Filling Process
ActiveUS20100022061A1Improve gap fillingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringGate stack
A method of forming a semiconductor device includes providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a gate stack on the semiconductor substrate; forming a gate spacer adjacent to a sidewall of the gate stack; thinning the gate spacer; and forming a secondary gate spacer on a sidewall of the gate spacer after the step of thinning the gate spacer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Enhanced silicidation of polysilicon gate electrodes
InactiveUS6867130B1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPlasma depositionMetal silicide
Semiconductor devices exhibiting reduced gate resistance and reduced silicide spiking in source / drain regions are fabricated by forming thin metal silicide layers on the gate electrode and source / drain regions and then selectively resilicidizing the gate electrodes. Embodiments include forming the thin metal silicide layers on the polysilicon gate electrodes and source / drain regions, depositing a dielectric gap filling layer, as by high density plasma deposition, etching back to selectively expose the silicidized polysilicon gate electrodes and resilicidizing the polysilicon gate electrodes to increase the thickness of the metal silicide layers thereon. Embodiments further include resilicidizing the polysilicon gate electrodes including a portion of the upper side surfaces forming mushroom shaped metal silicide layers.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
In-situ nitride/oxynitride processing with reduced deposition surface pattern sensitivity
ActiveUS7009226B1Increase drive currentReduced oxide deposition surface pattern sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSurface patternPattern sensitivity
Carrier mobility in transistor channel regions is increased by depositing a conformal stressed liner. Embodiments include forming a silicon oxynitride layer on the stressed liner to reduce or eliminate deposition surface pattern sensitivity during gap filling, and in-situ SACVD of silicon oxide gap fill directly on the stressed liner with reduced pattern sensitivity. Embodiments also include the use of Si—Ge substrates.
Owner:INNOVATIVE FOUNDRY TECH LLC
Titanium-based amorphous brazing alloy foil strip for brazing and preparation method for foil strip
InactiveCN102430874ABright surfaceNeat edgesWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSurface brightnessBraze alloy
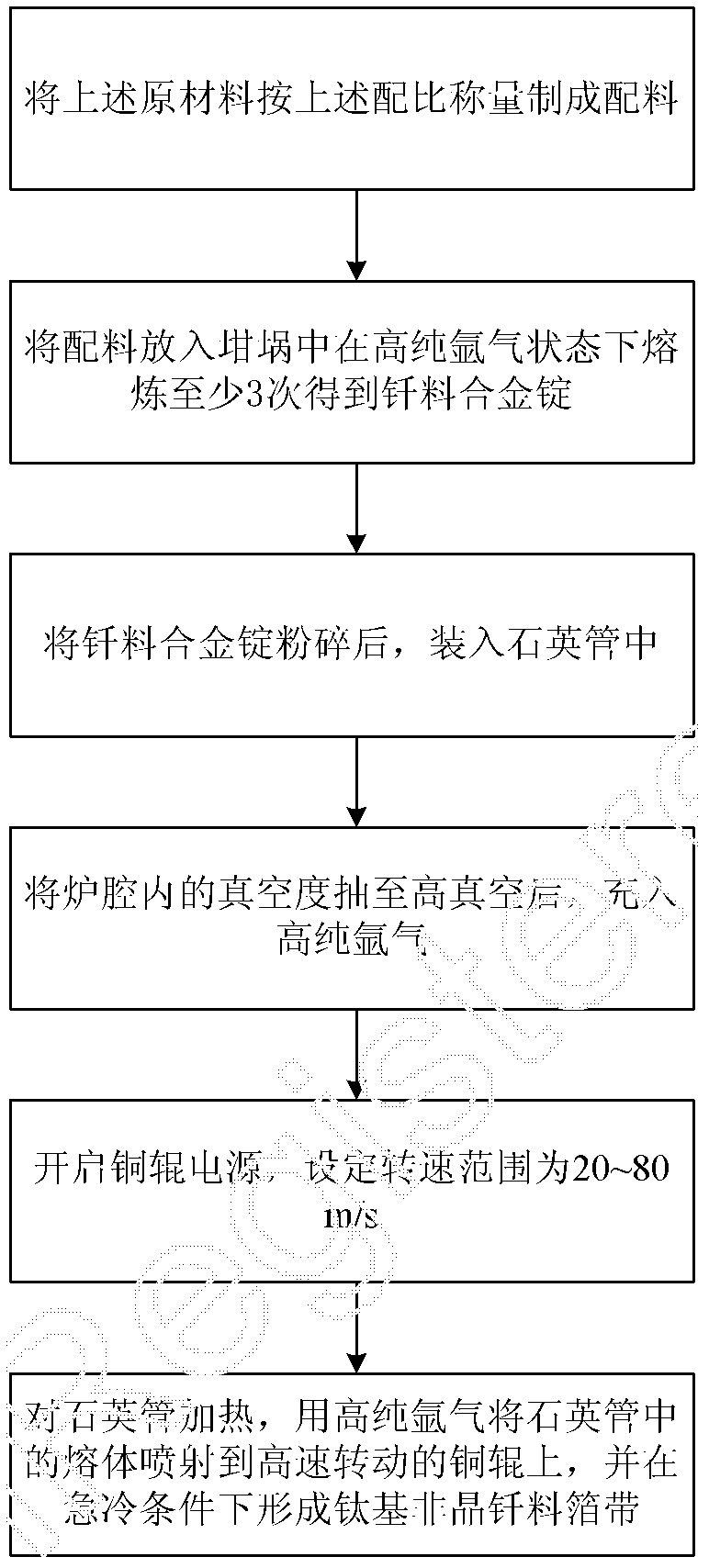
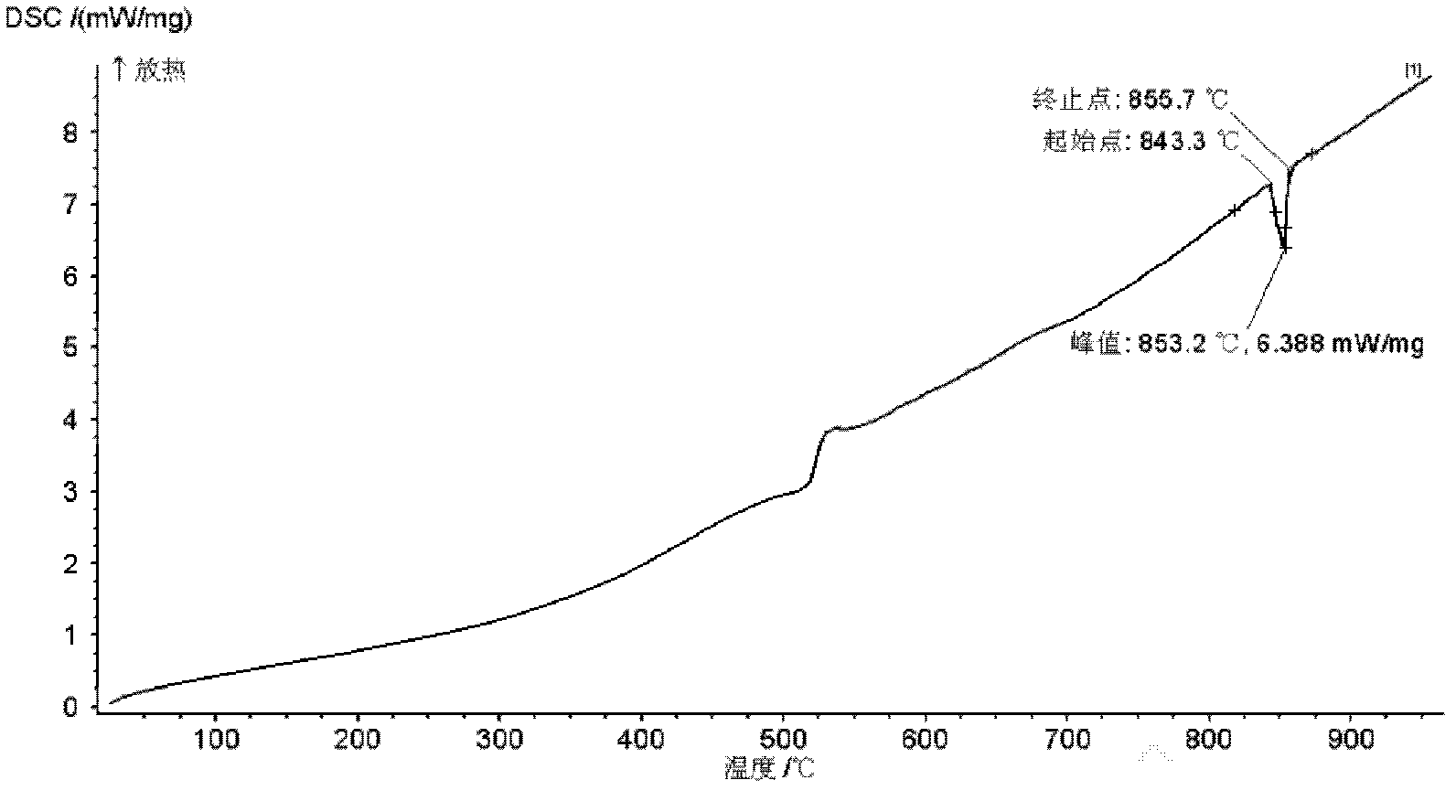
The invention provides a titanium-based amorphous brazing alloy foil strip for brazing and a preparation method for the foil strip. Components of the brazing alloy foil strip by percentage include 35-50% of Ti (titanium), 25-35% of Zr (zirconium), 10-24% of Cu (copper), 5-15% of Ni (nickel) and 0.5-8% of Co (cobalt). The method for preparing the brazing alloy foil strip includes the steps: weighing raw materials according to the proportion to prepare ingredients; placing the ingredients into a crucible and smelting the ingredients for at least three times in a high-purity argon state to obtain brazing alloy ingots; crushing the brazing alloy ingots and then placing the crushed brazing alloy ingots into a quartz tube; pumping a furnace chamber into high vacuum and then charging high-purity argon; turning on a copper roller power supply and setting the range of rotating speeds; and heating the quartz tube, spraying melts in the quartz tube onto a copper roller rotating at a high speed and forming the titanium-based amorphous brazing alloy foil strip under the condition of quenching. The brazing alloy foil strip has the advantages of surface brightness, uniformity of composition and the like, the negative effects of eutectic composition brazing alloy brittleness and over-high welding temperature on base metal can be avoided, and assembly and gap filling are easier when complex structural components are brazed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor devices having a support structure for an active layer pattern and methods of forming the same
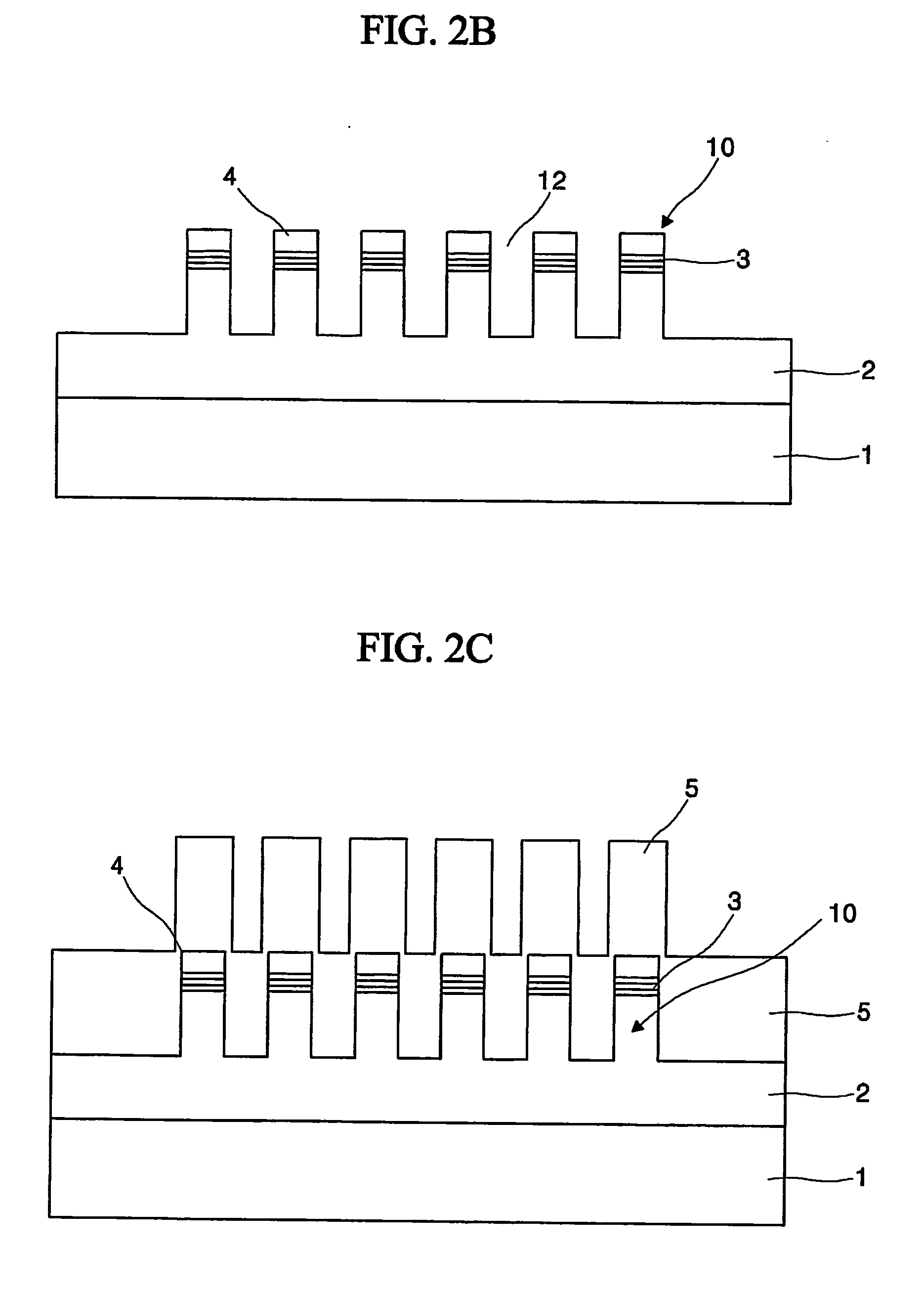
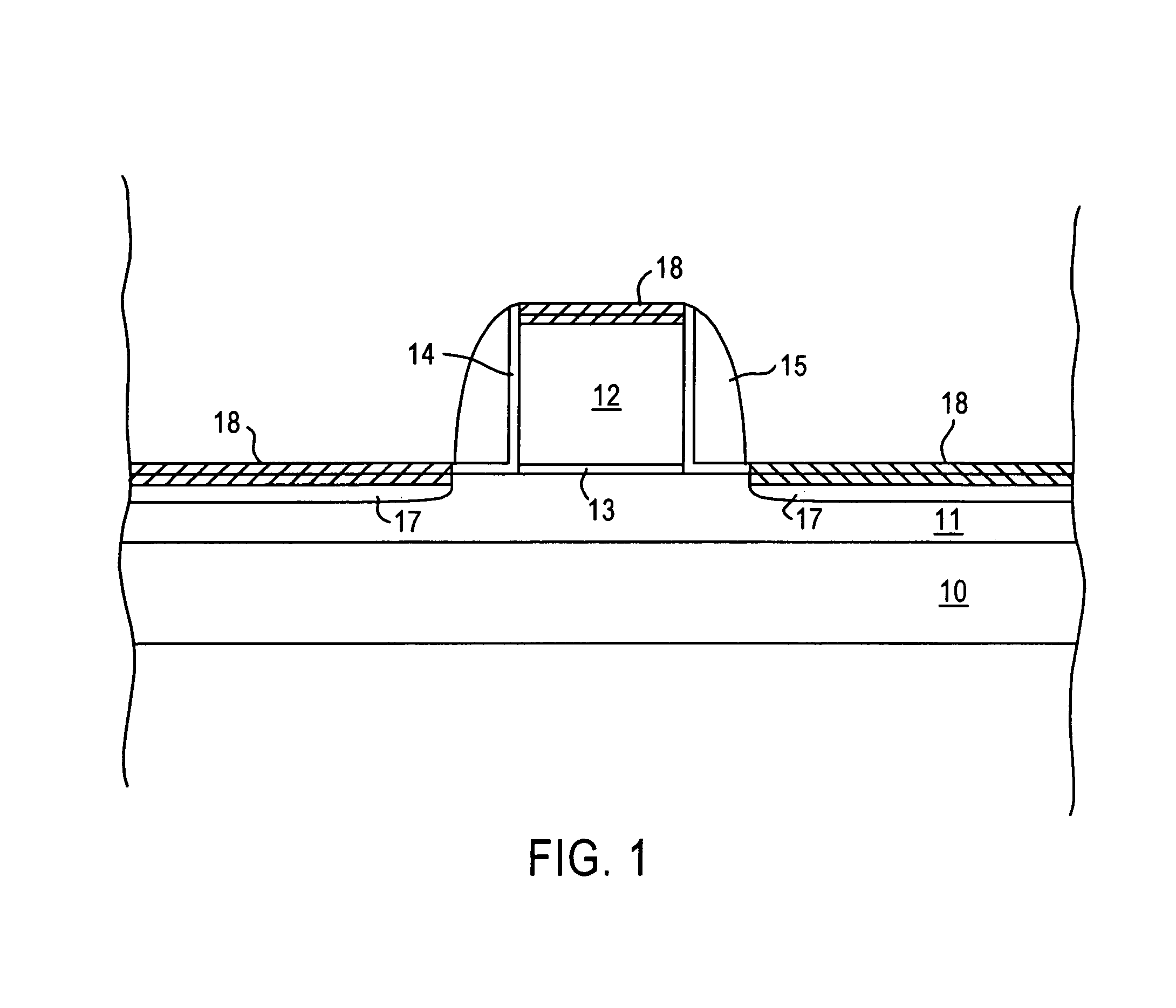
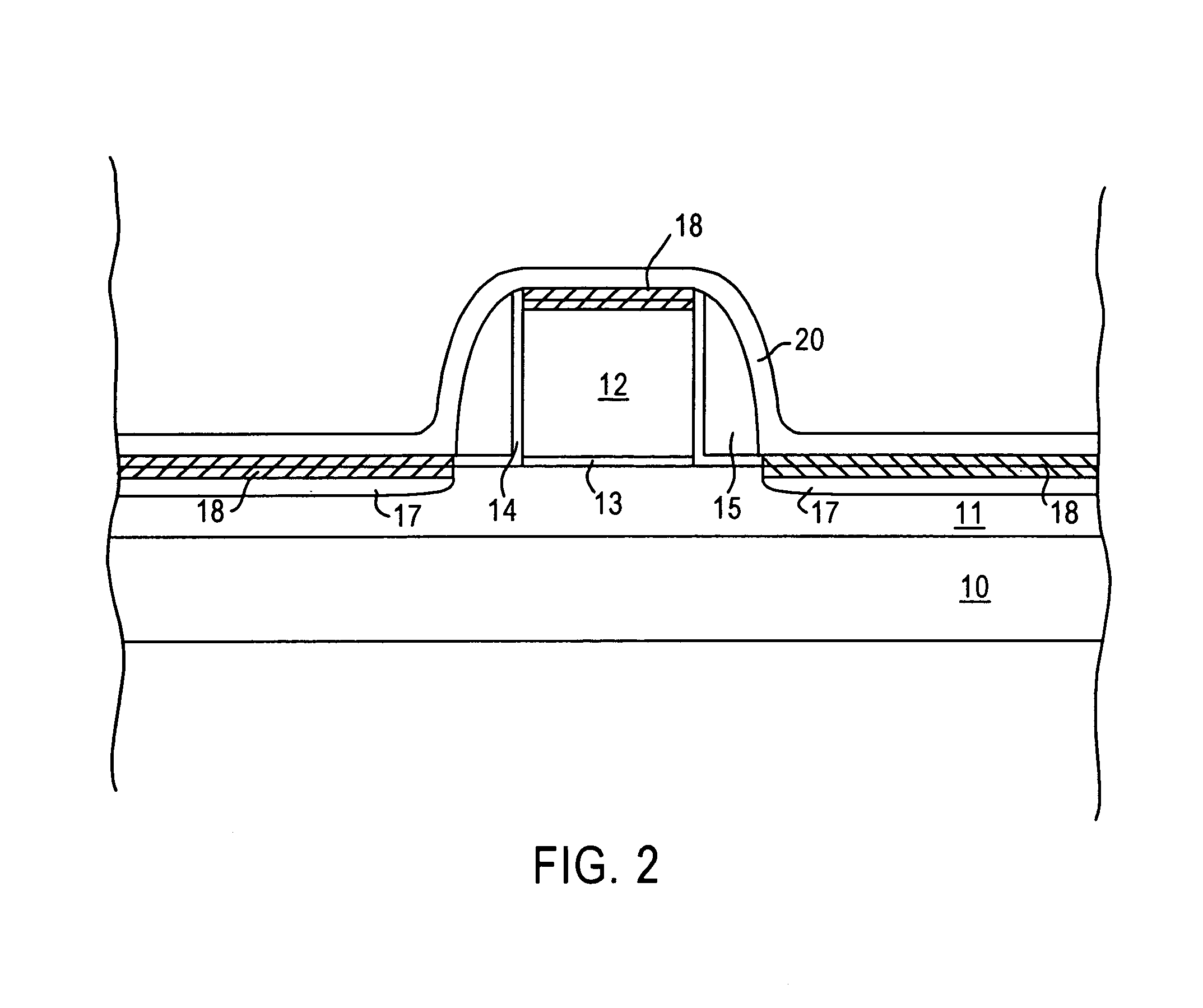
ActiveUS20060029887A1Prevent crashSolid-state devicesPhotomechanical apparatusDevice materialDevice form
Semiconductor devices include a semiconductor substrate with a stack structure protruding from the semiconductor substrate and surrounded by an isolation structure. The stack structure includes an active layer pattern and a gap-filling insulation layer between the semiconductor substrate and the active layer pattern. A gate electrode extends from the isolation structure around the stack structure. The gate electrode is configured to provide a support structure for the active layer pattern. The gate electrode may be a gate electrode of a silicon on insulator (SOI) device formed on the semiconductor wafer and the semiconductor device may further include a bulk silicon device formed on the semiconductor substrate in a region of the semiconductor substrate not including the gap-filing insulation layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com