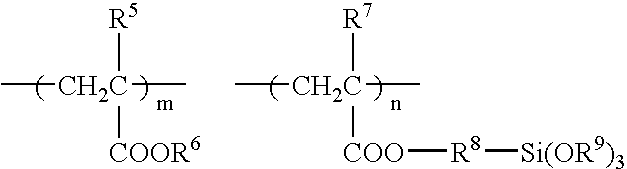Patents
Literature
826results about How to "Excellent gas barrier performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
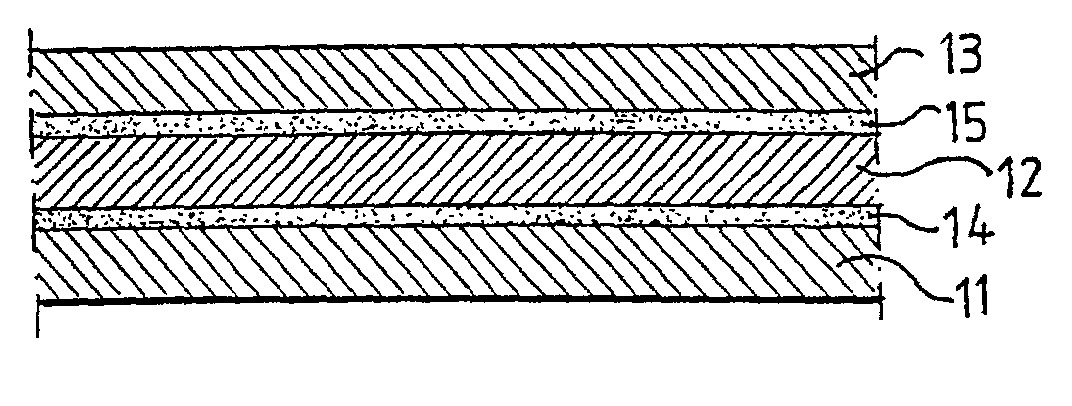
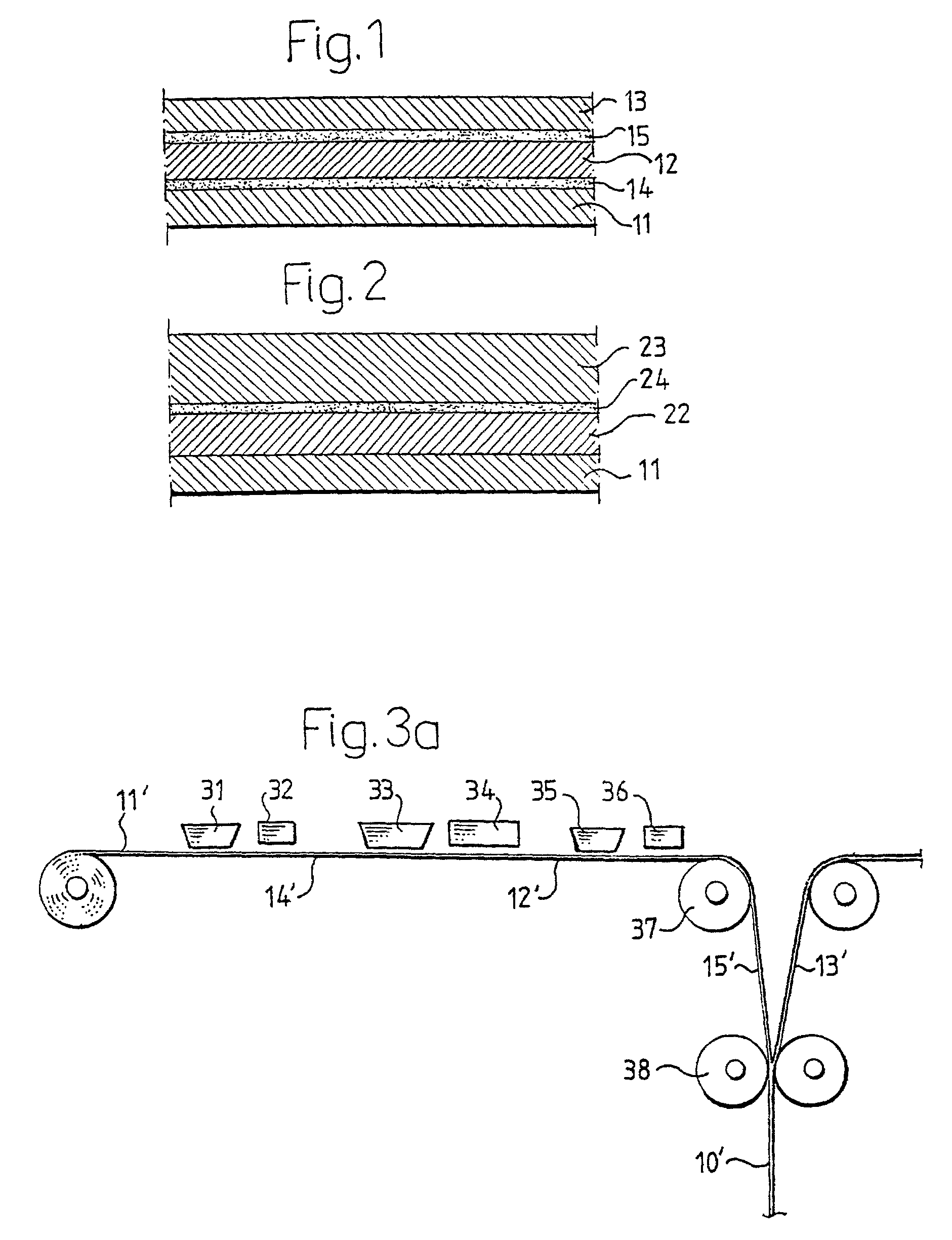
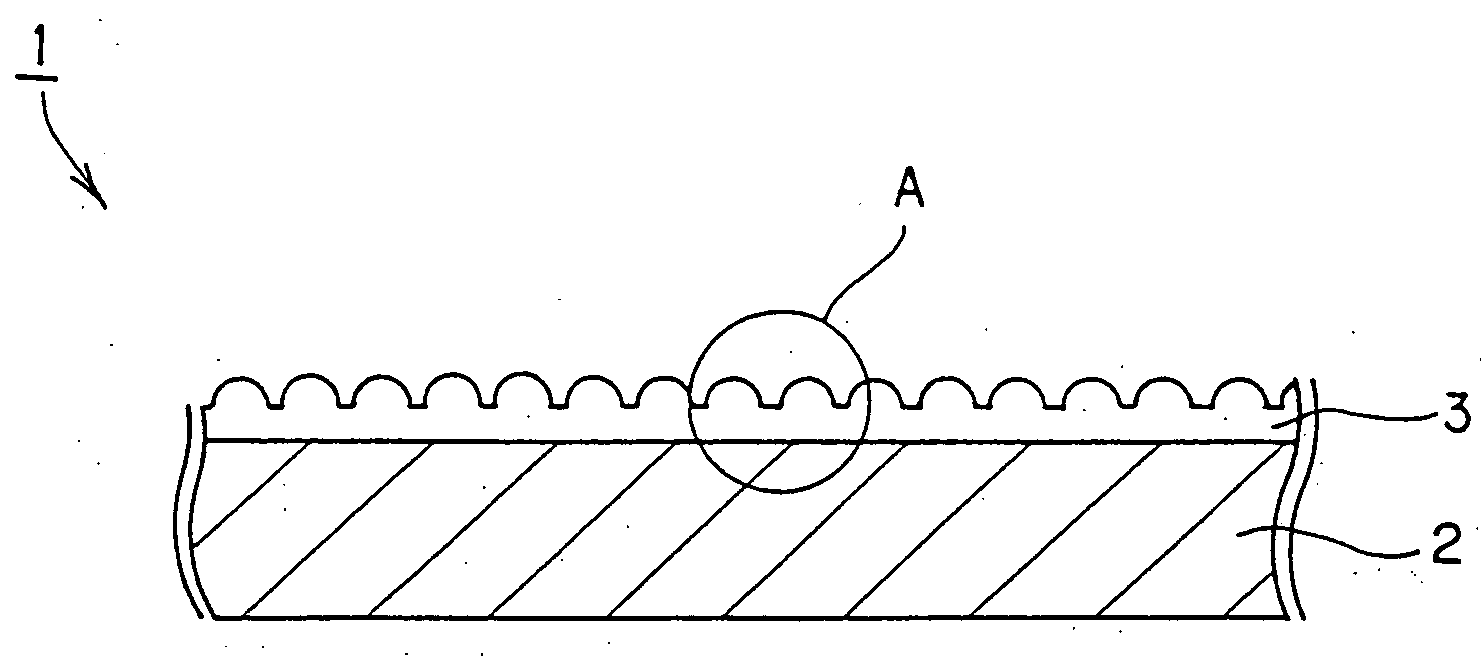
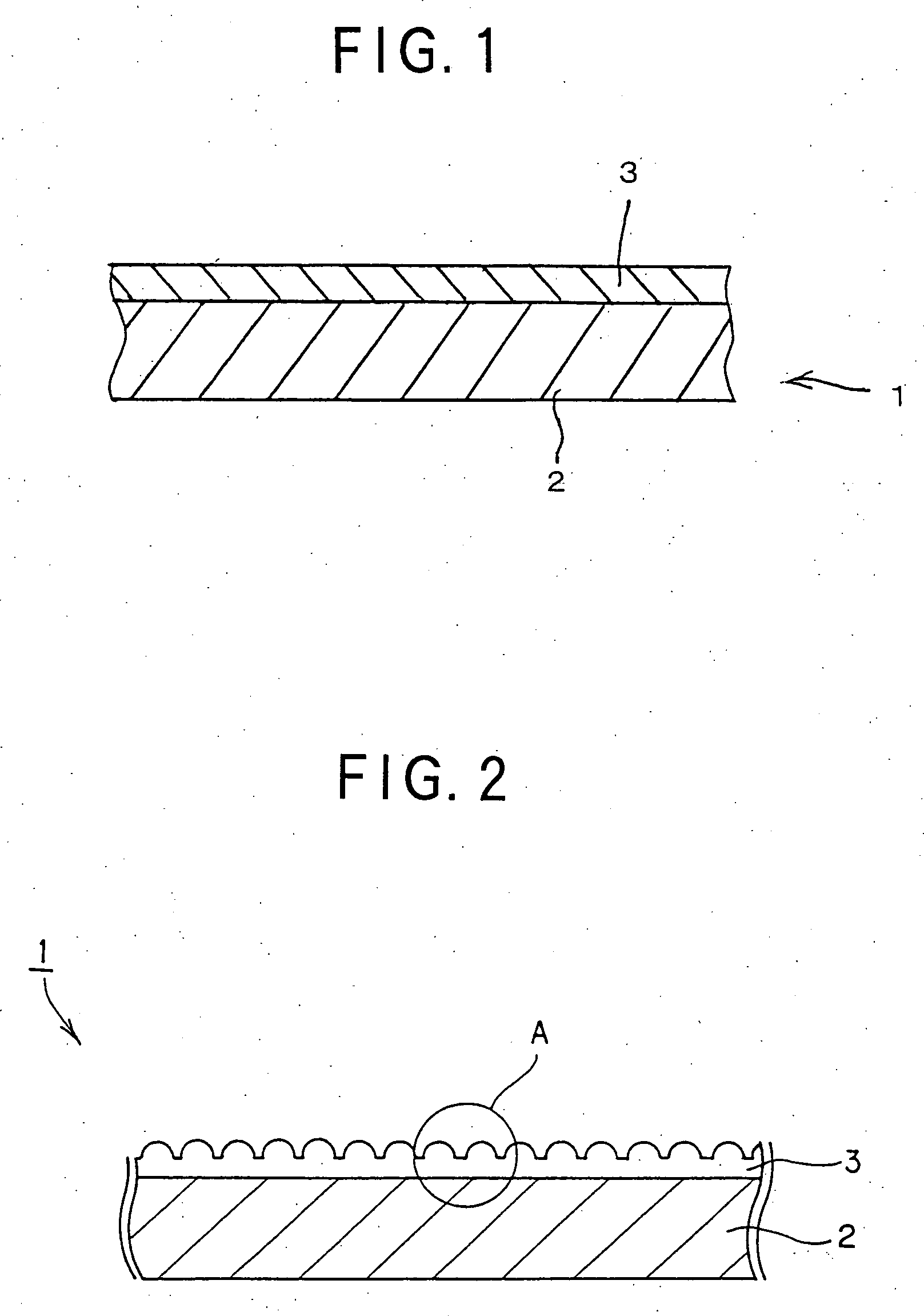
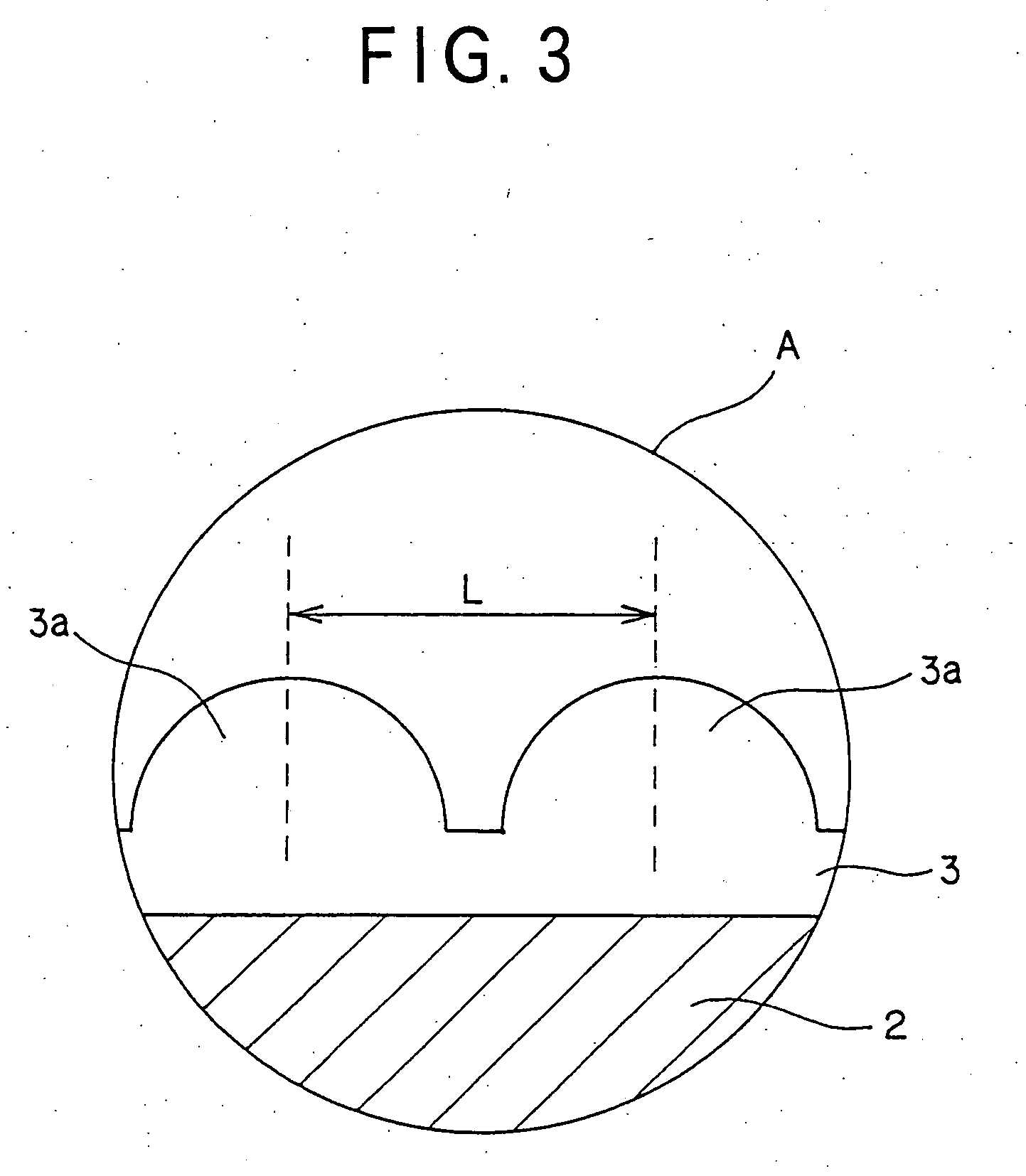
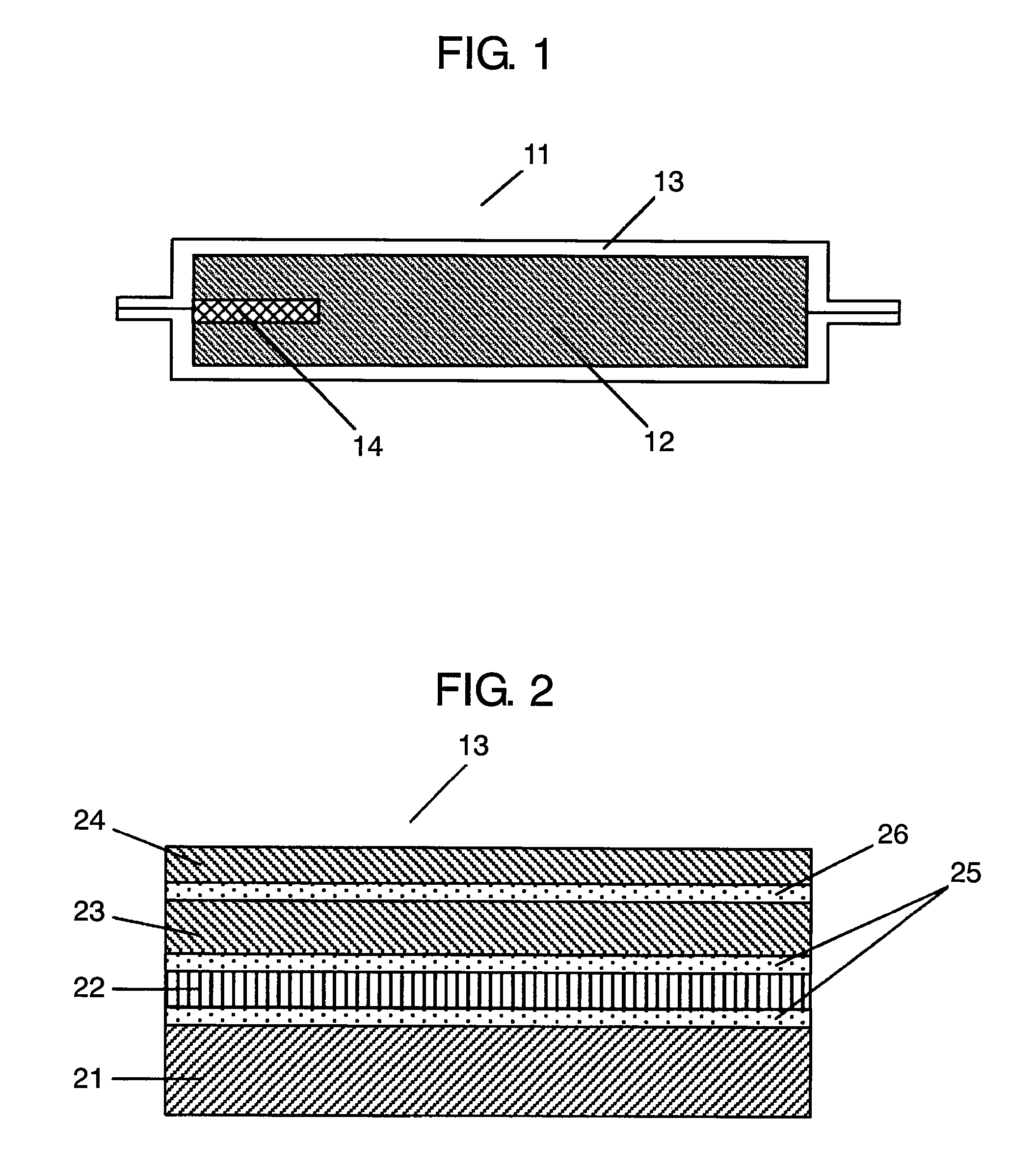
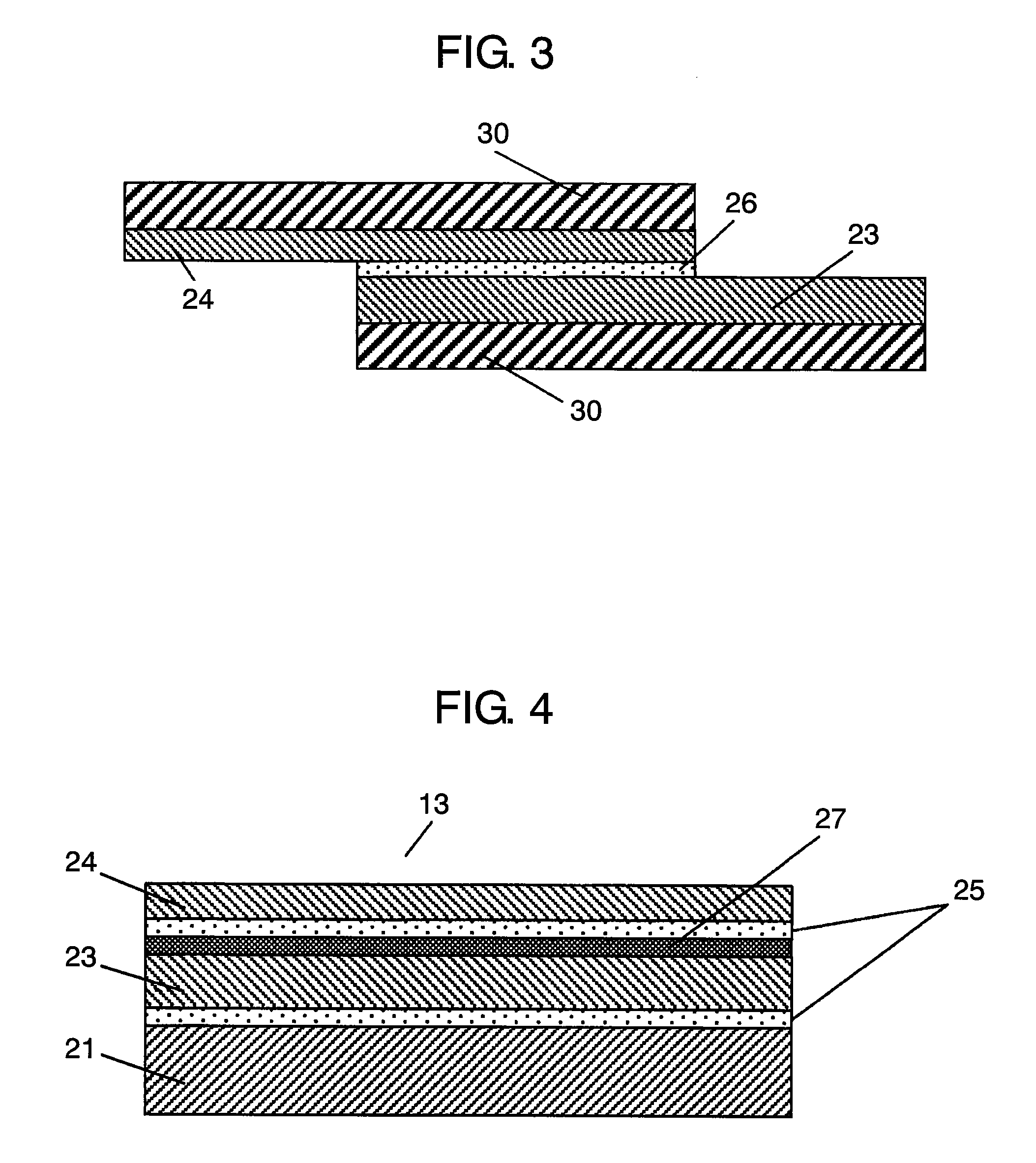
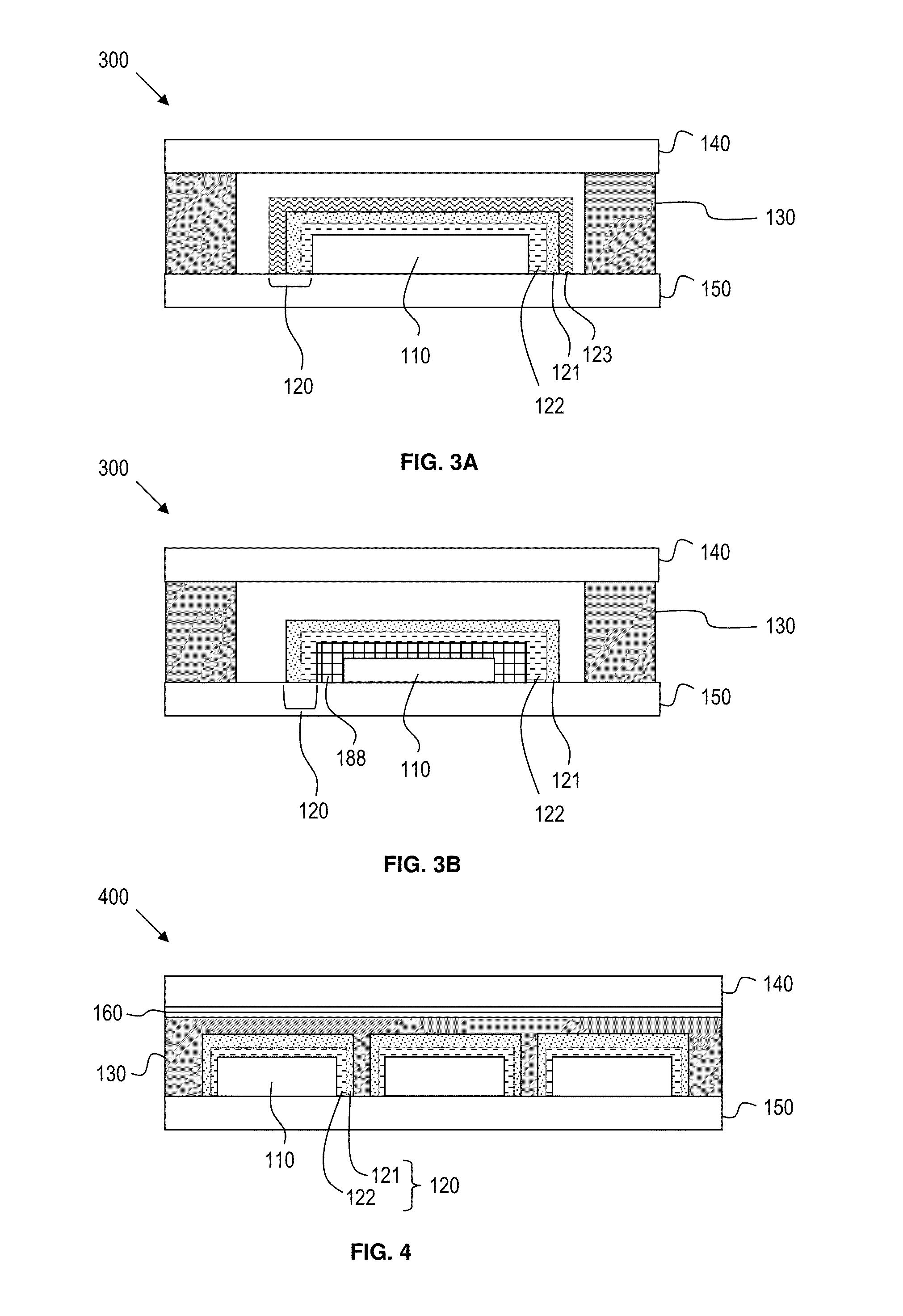
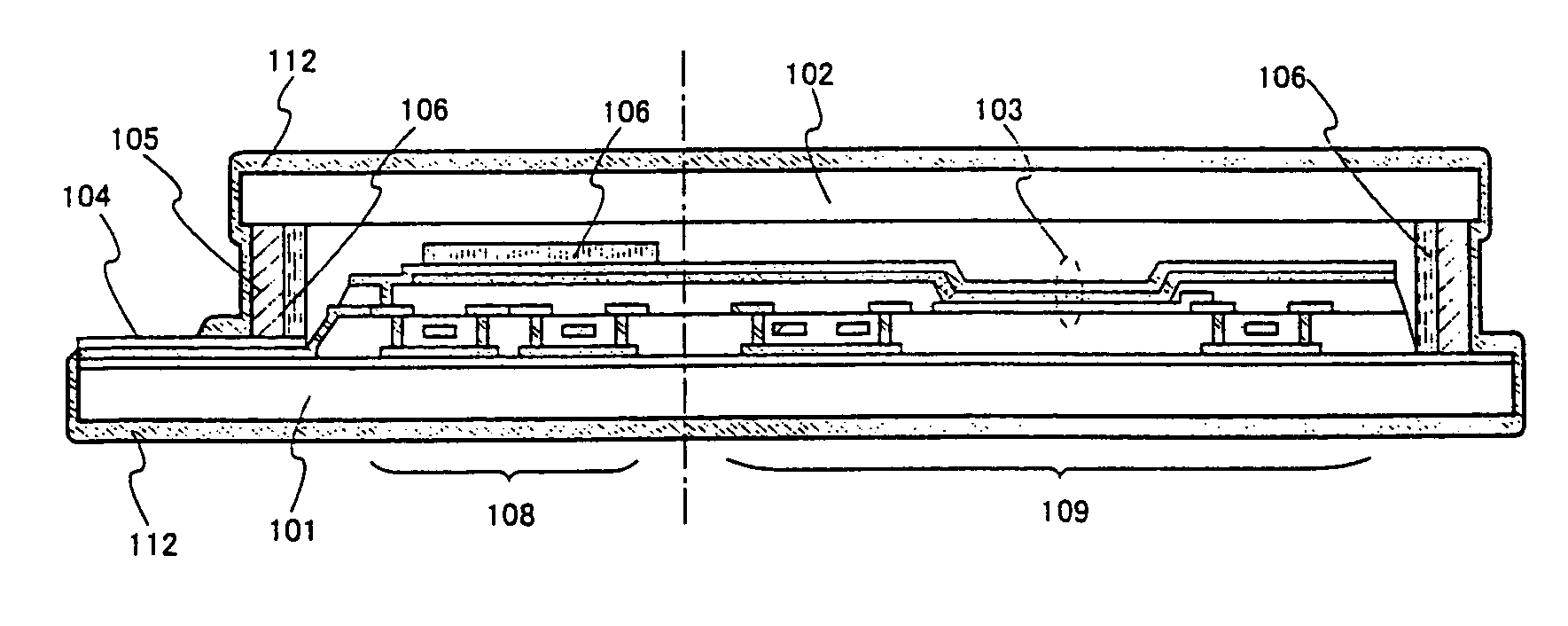
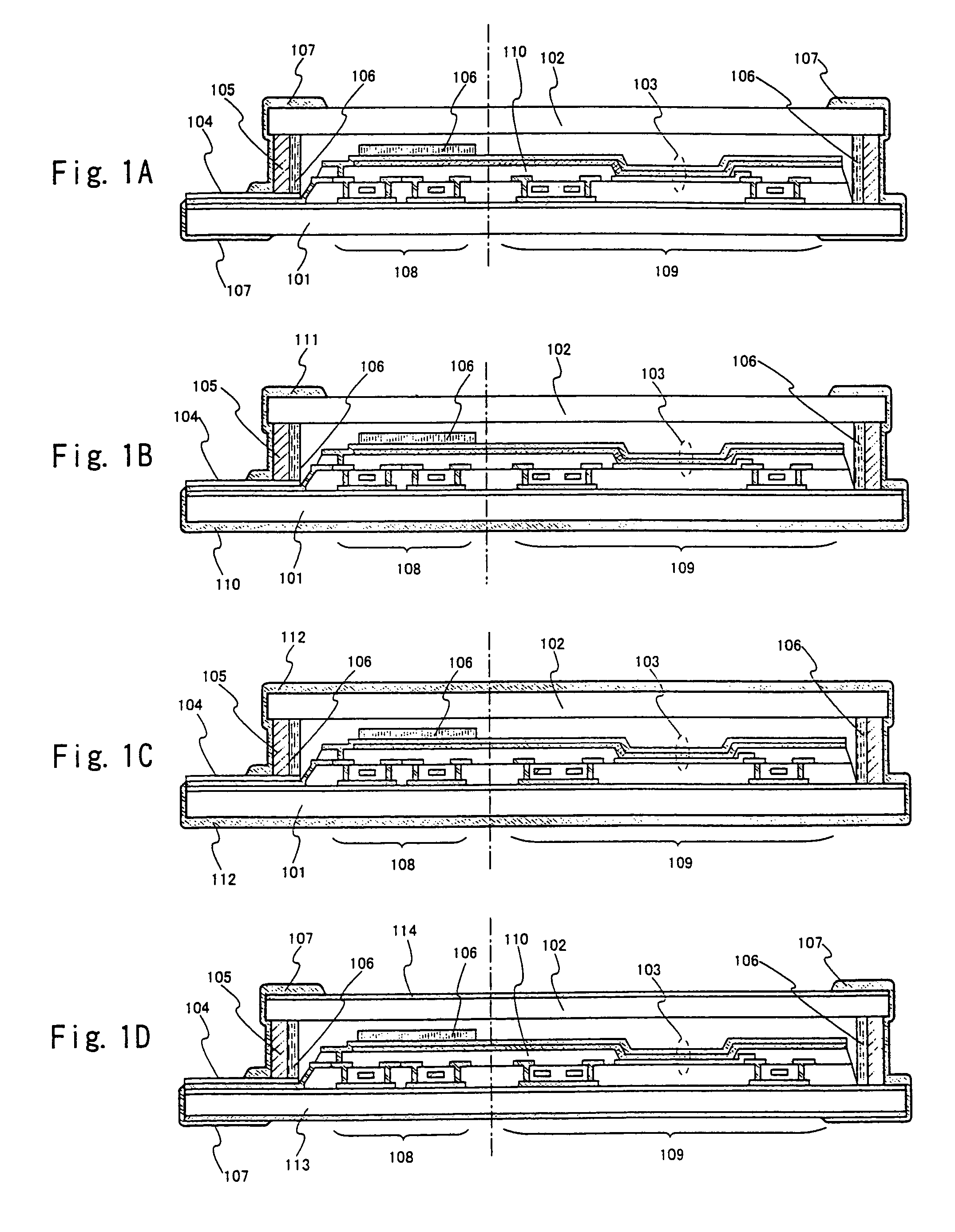
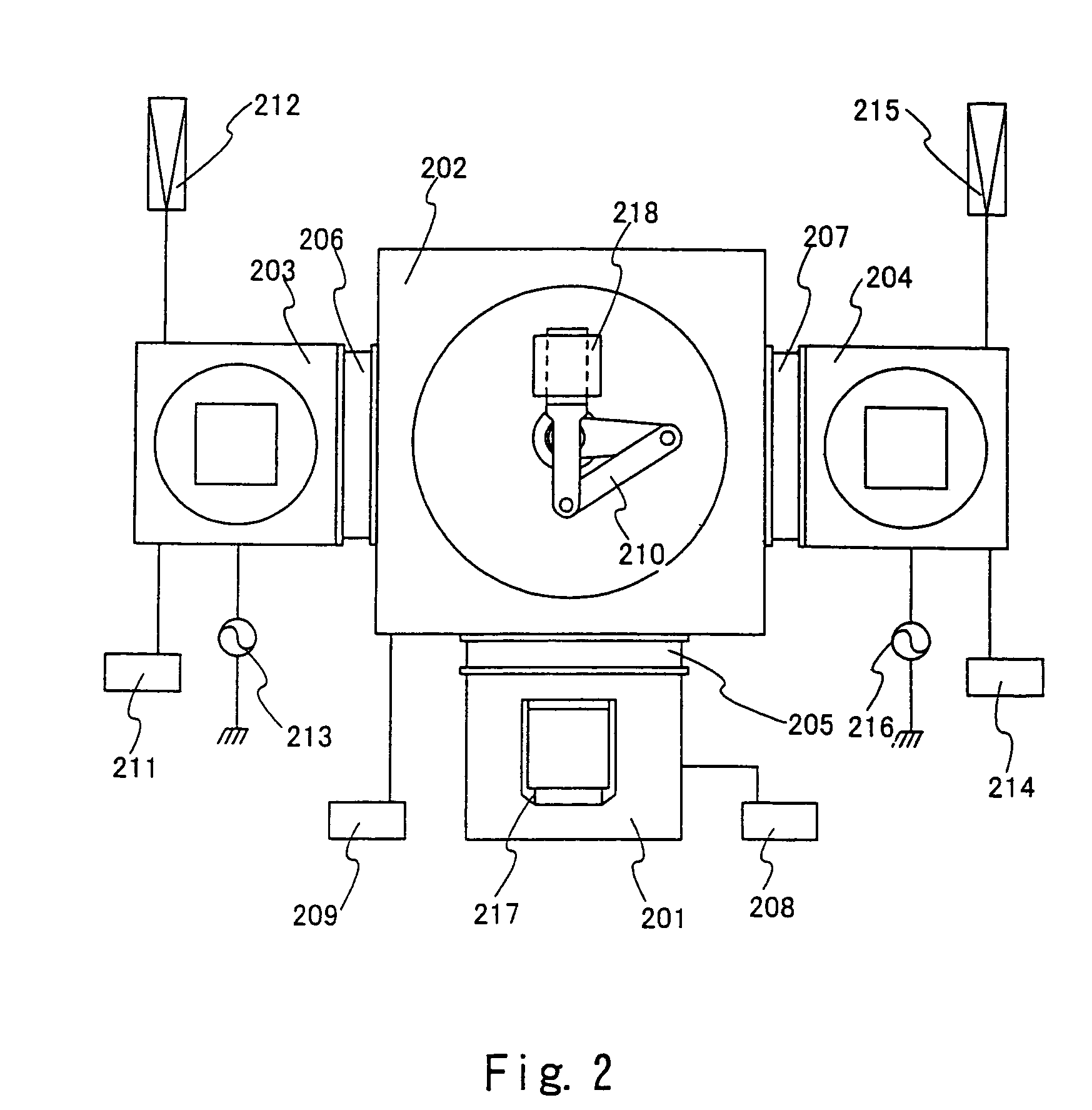
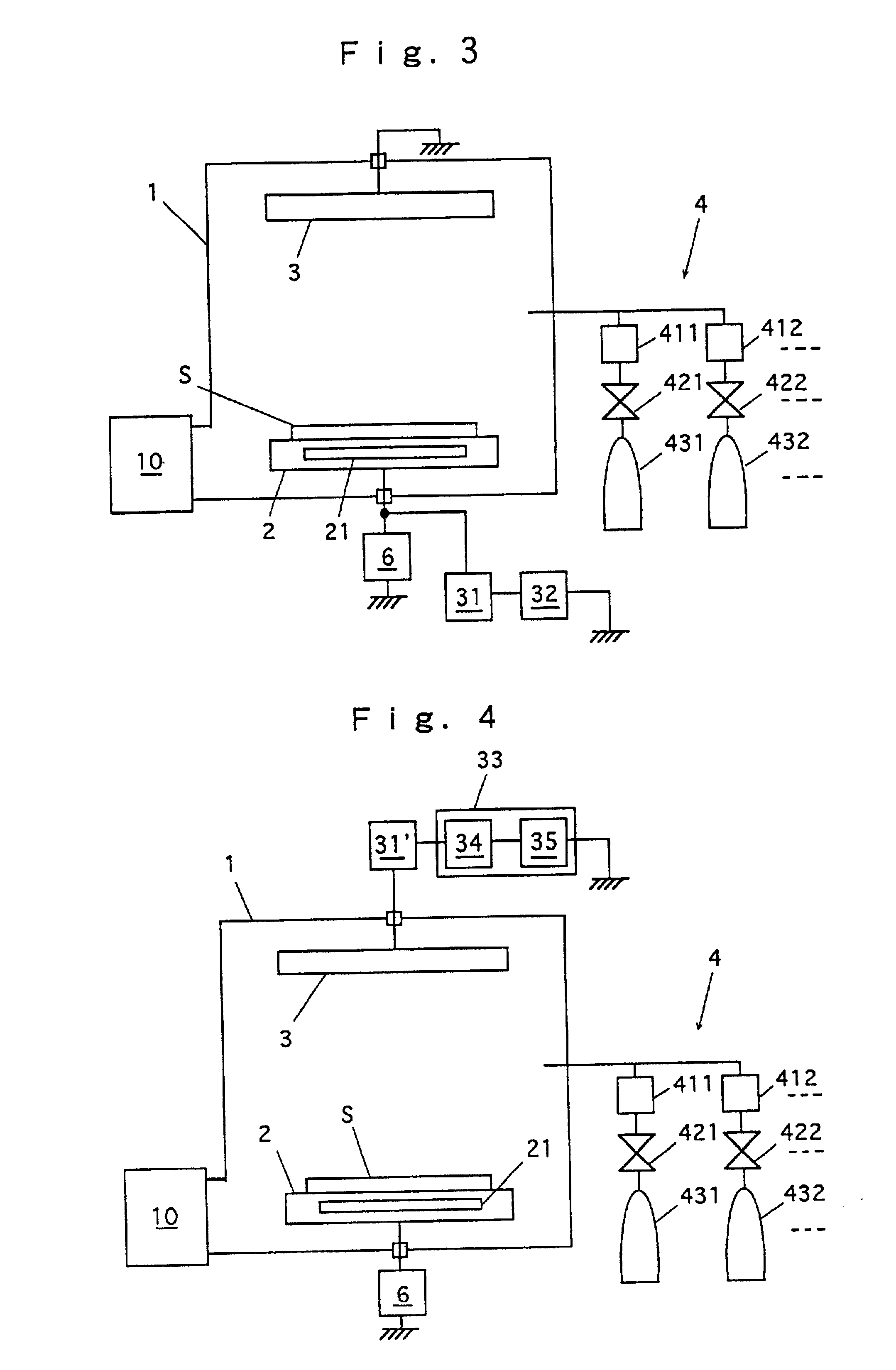
Process for producing multilayered gas-barrier film
InactiveUS20120003500A1Satisfactory productivityExcellent gas barrier performanceLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceThin membrane
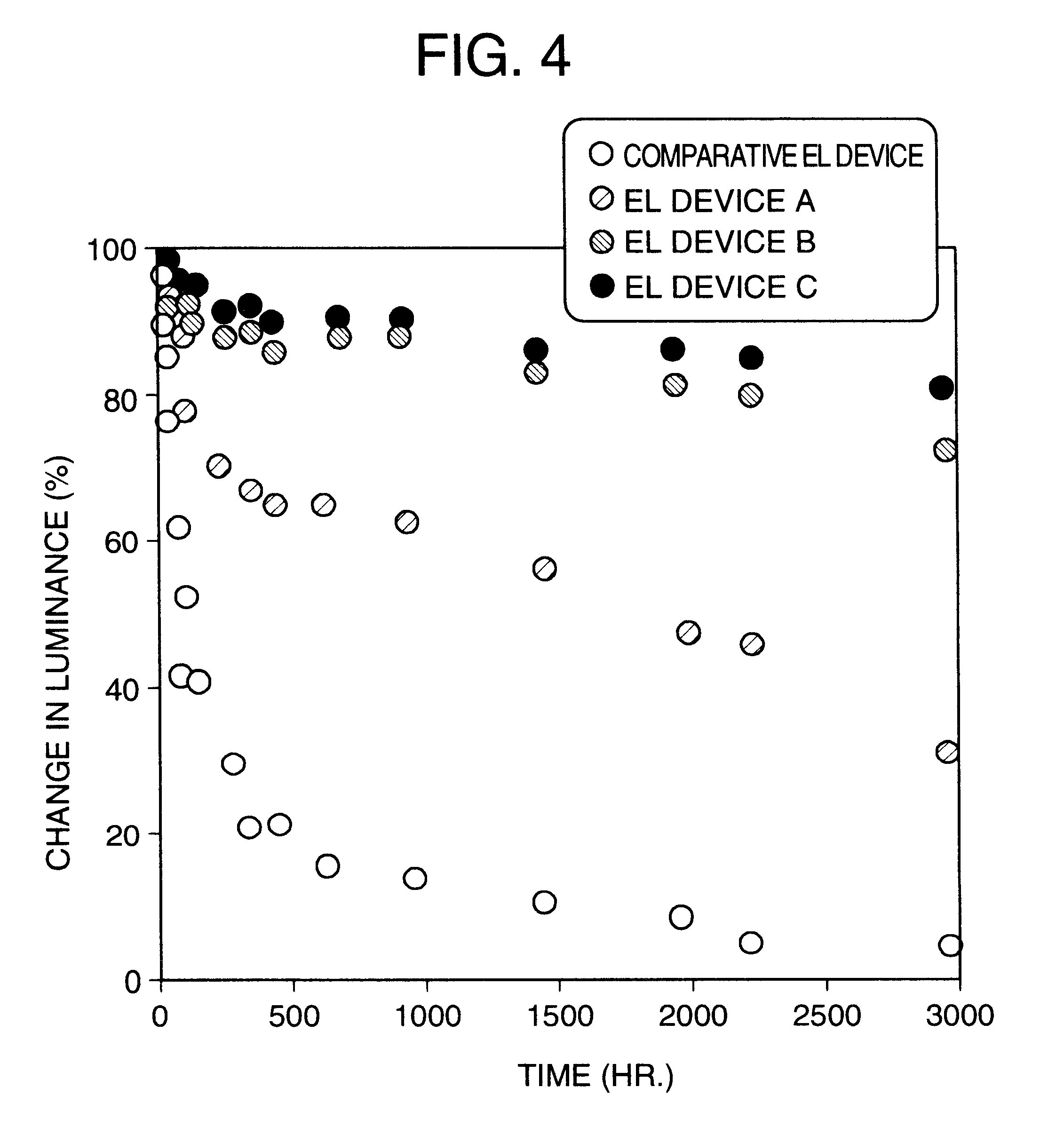
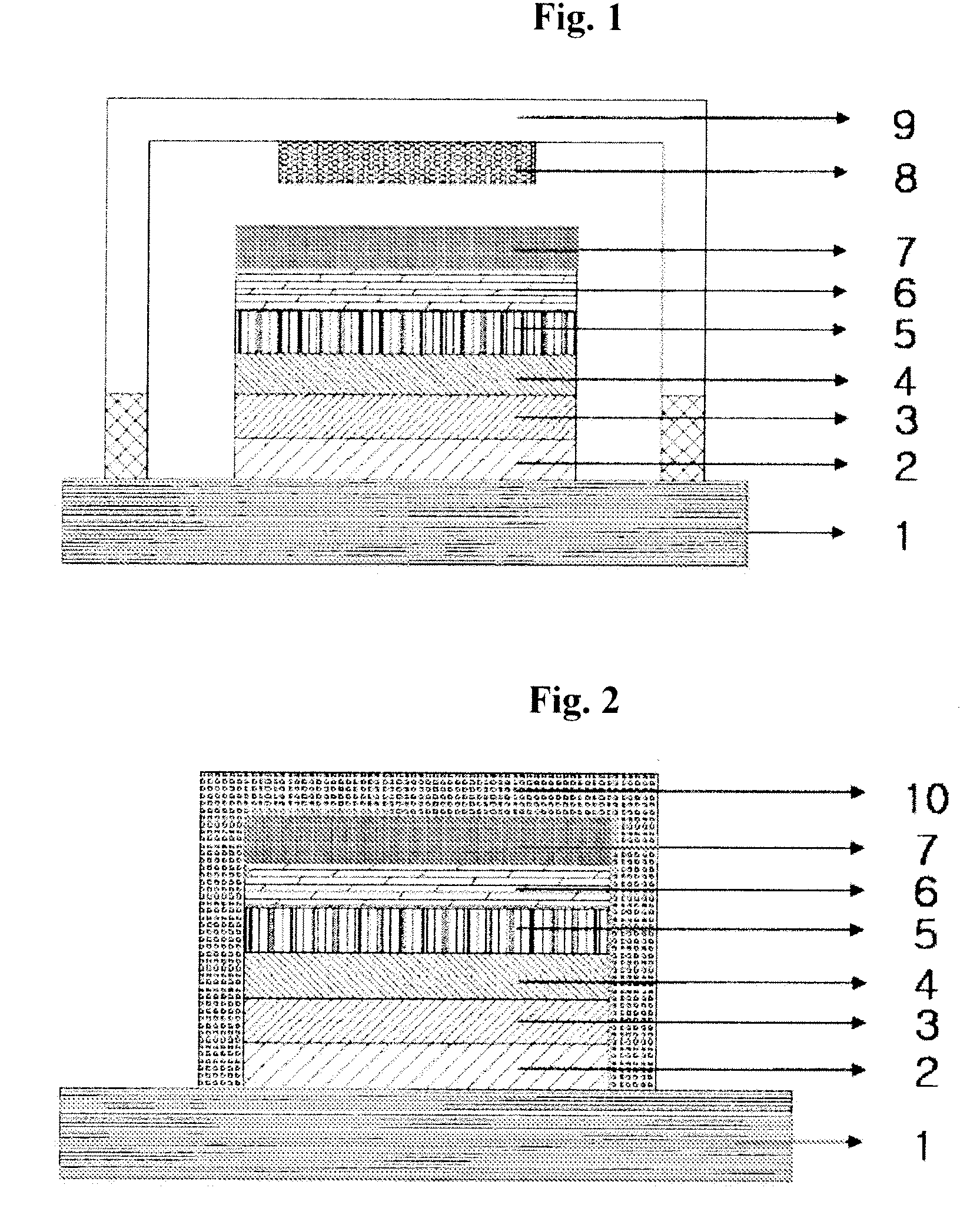
Provided are a method for producing a film, which is satisfactory in productivity, exhibits high gas-barrier property immediately after production, and has excellent adhesive strength between constituent layers while maintaining the excellent gas-barrier property, and a gas-barrier film, which is obtained by the method. The method for producing a gas-barrier film includes the steps of; (1) forming an inorganic thin film by a vacuum deposition method on at least one surface of a base film; (2) forming a thin film by a plasma CVD method on the inorganic thin film formed in the step (1); and (3) forming an inorganic thin film by the vacuum deposition method on the thin film formed in the step (2), in which each of the steps (1) and (3), and the step (2) are sequentially carried out at a pressure of 1×10−7 to 1 Pa, and at a pressure of 1×10−3 to 1×102 Pa, respectively.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PLASTICS INC
Method for fabrication of transparent gas barrier film using plasma surface treatment and transparent gas barrier film fabricated thereby
InactiveUS20100285319A1Excellent gas barrier performanceEconomical and simple methodSynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesOptoelectronicsInorganic layer
The present invention relates to a method of fabricating a transparent gas barrier film by using plasma surface treatment and a transparent gas barrier film fabricated according to such method which has an organic / inorganic gradient interface structure at the interface between an organic / inorganic hybrid layer and an inorganic layer. Since the method of the present invention is capable of fabricating a gas barrier film by plasma surface treatment instead of deposition under high vacuum, it can mass-produce a transparent gas barrier film with excellent gas barrier properties in an economical and simple manner. Further, since the transparent gas barrier film fabricated according to the method of the present invention shows excellent gas barrier properties and is free of crack formation and layer-peeling phenomenon, it can be effectively used in the manufacture of a variety of display panels.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
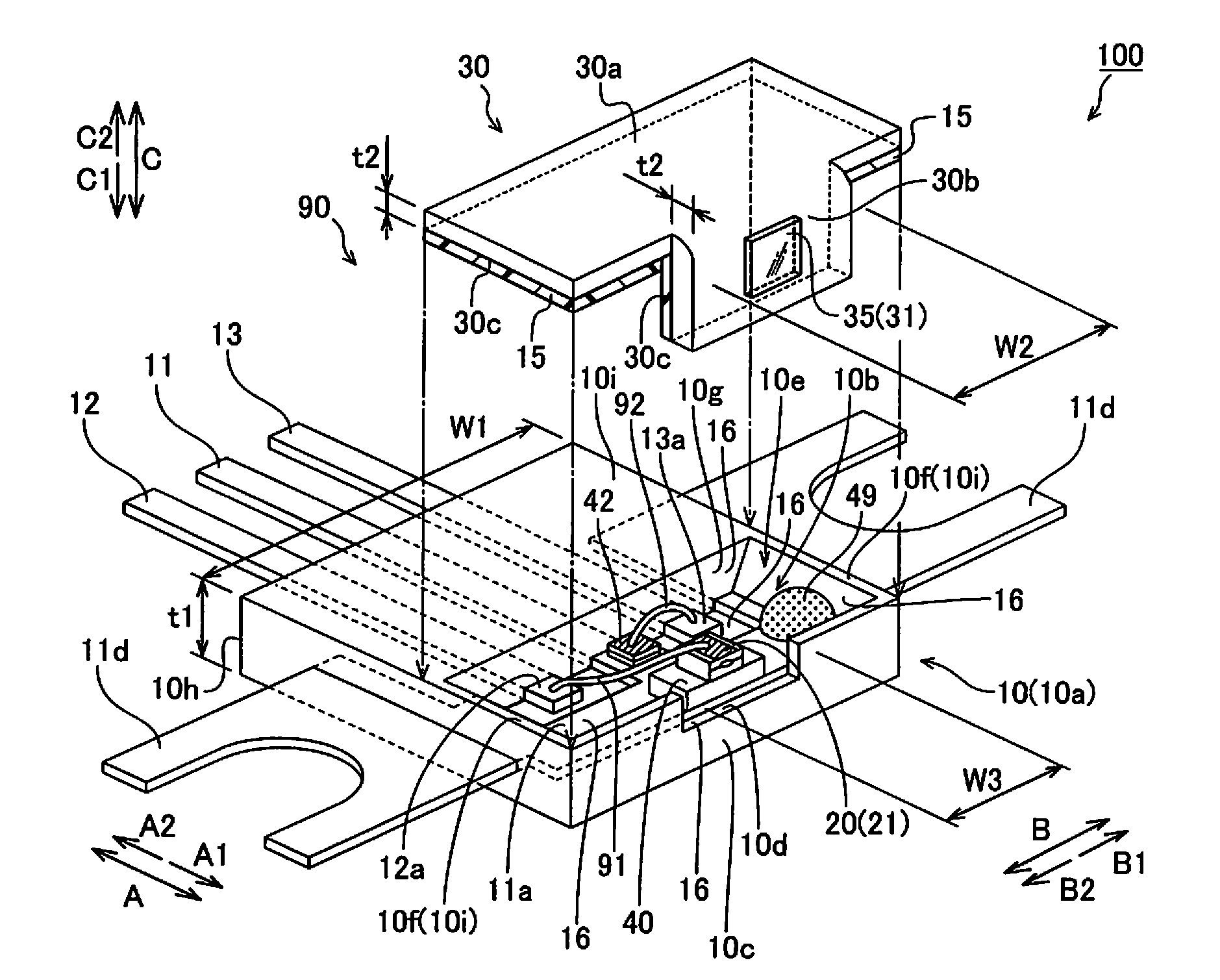
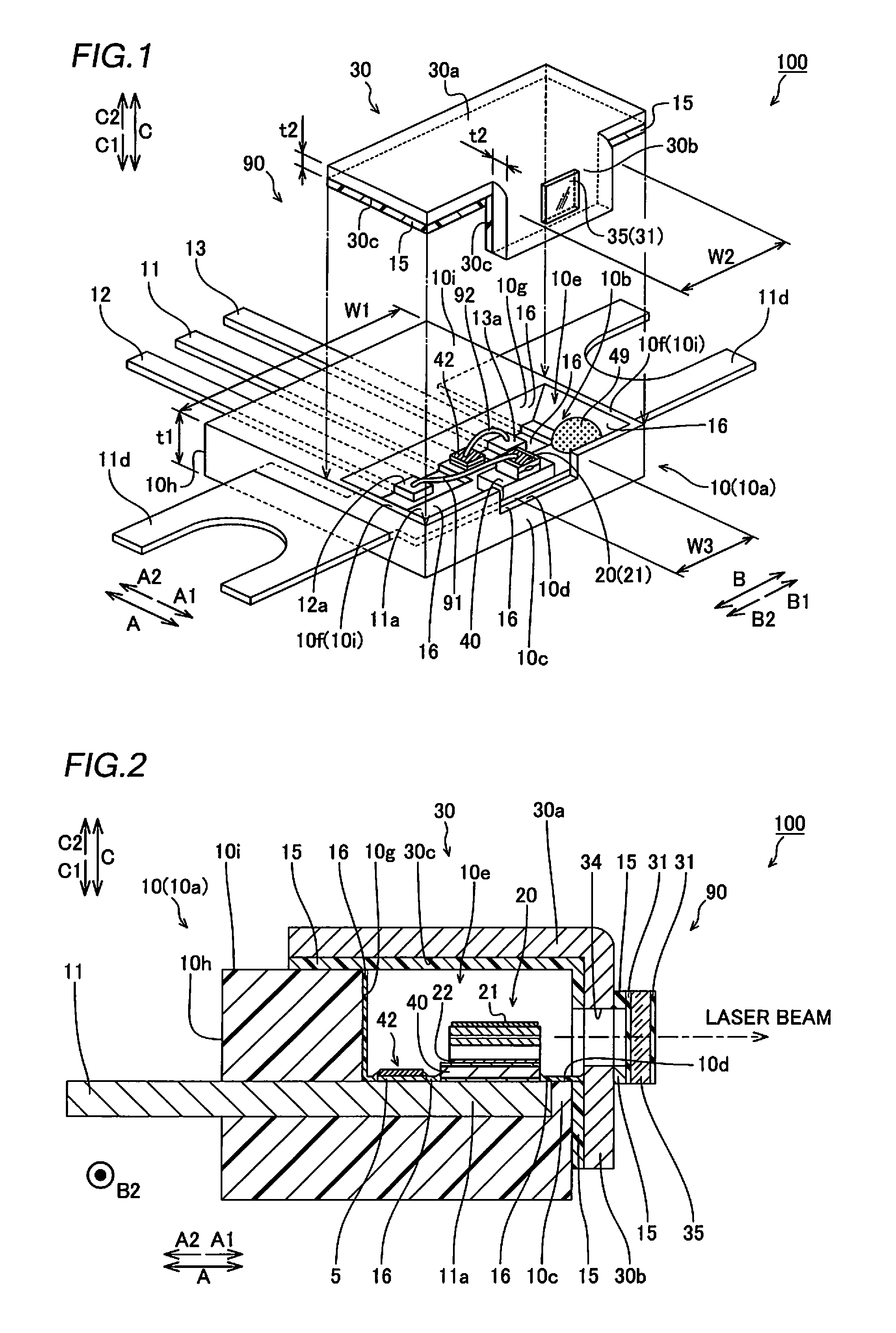
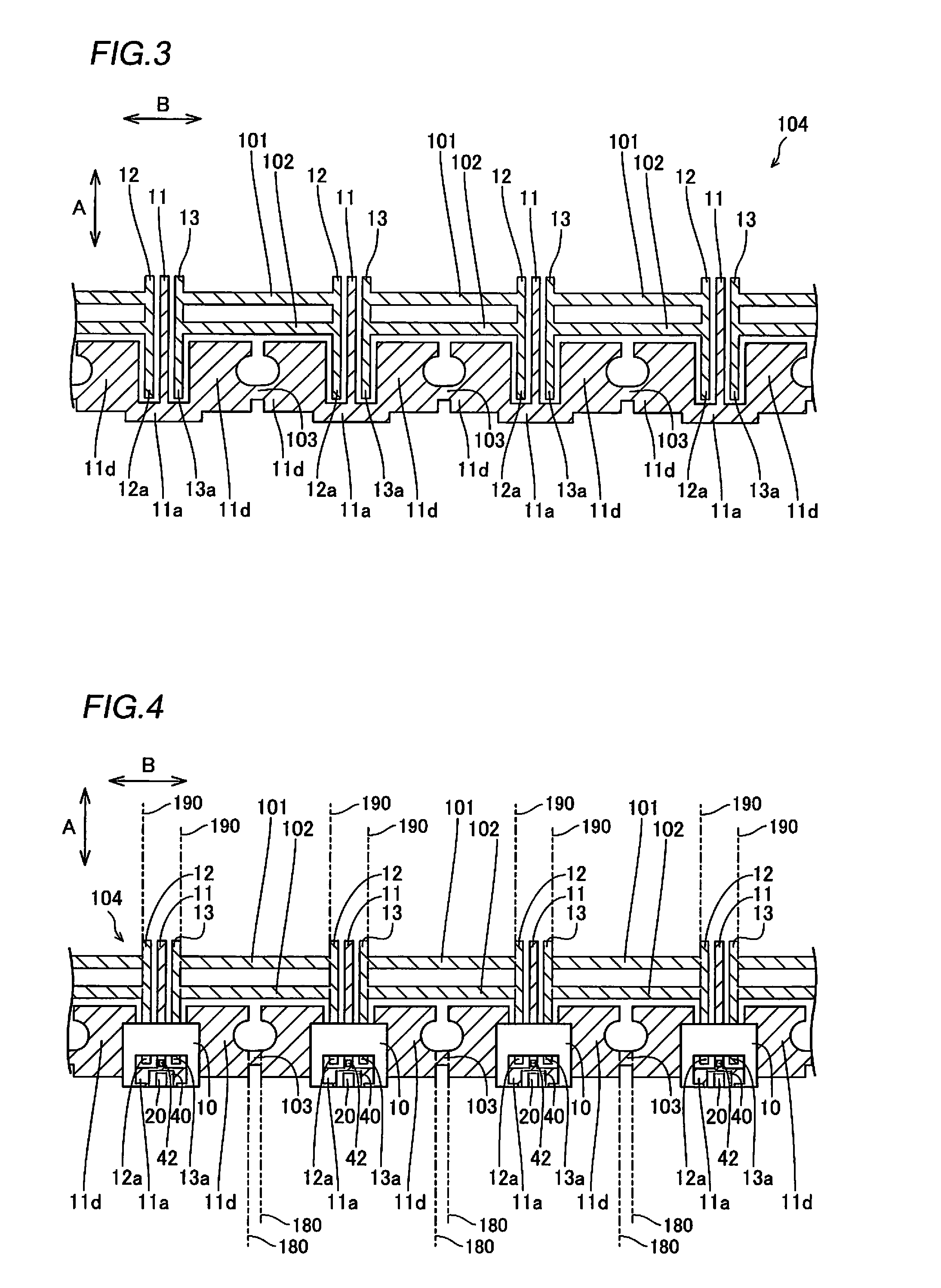
Semiconductor laser apparatus and optical apparatus
InactiveUS20120033695A1Improve sealingPromote absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor lasersPolyvinyl alcoholSemiconductor chip
This semiconductor laser apparatus includes a package constituted by a plurality of members, having sealed space inside and a semiconductor laser chip arranged in the sealed space, while surfaces of the members located in the sealed space are covered with a covering agent made of an ethylene-polyvinyl alcohol copolymer.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Functional graphene-polymer nanocomposites for gas barrier applications
InactiveUS20100096595A1Excellent gas barrier performanceImprove suppression propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNano compositesX-ray
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Multilayer film for encapsulating oxygen and/or moisture sensitive electronic devices
ActiveUS20110132449A1Excellent gas barrier performanceLow gas permeabilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleUltraviolet lights
The present invention refers to a multilayer barrier film capable of encapsulating a moisture and / or oxygen sensitive electronic or optoelectronic device, the barrier film comprises at least one nanostructured layer comprising reactive nanoparticles capable of interacting with moisture and / or oxygen, the reactive nanoparticles being distributed within a polymeric binder, and at least one ultraviolet light neutralizing layer comprising a material capable of absorbing ultraviolet light, thereby limiting the transmission of ultraviolet light through the barrier film
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Gas barrier substrate
InactiveUS20050029513A1Quality improvementExcellent gas barrier performanceSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingMetallurgyGas formation
The main object of the present invention is to provide a gas barrier substrate having a high gas barrier property without a ruggedness, a pin hole or the like in the gas barrier layer. The present invention solves the problem by providing a gas barrier substrate having a base material, a planarization layer formed on the base material, and a gas barrier layer comprising a deposition film formed on the planarization layer.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Biodegradable packaging laminate, a method of producing the packaging laminate, and packaging containers produced from the packaging laminate
InactiveUS20020127358A1Improve adhesionExcellent gas barrier performanceAdhesive processesLiquid surface applicatorsLactideBiopolymer
Packaging laminate for packages for liquid foods having excellent liquid and oxygen gas barrier properties in which all included layers are biodegradable. The packaging laminate includes at least one liquidtight layer (11, 13) of homo or copolymers of monomers selected from a group consisting of lactic acid, glycol acid, lactide, glycolide, hydroxy butyric acid, hydroxy valeric acid, hydroxy caproic acid, valerolactone, butyrolactone and caprolactone, as well as an oxygen gas barrier layer (12) of ethylene vinyl alcohol, polyvinyl alcohol, starch or starch derivatives. The oxygen gas barrier layer is preferably applied by a dispersion coating process. The layers may be laminated directly to one another or indirectly by means of interjacent adhesive layers. The packaging laminate may also include a core layer of, for example, paper or paperboard, or a biopolymer. The invention also realises a method of producing the biodegradable packaging laminate according to the invention.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
Gas barrier film
InactiveUS20050084686A1Maintain good propertiesPackaging material to expandSynthetic resin layered productsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsDiamineUrea
A gas barrier film exhibiting a superior gas barrier property and simultaneously provided with an excellent coating property, a polyurethane resin obtained by adding a polyisocyanate compound containing at least one of an aromatic, aromatic aliphatic, and alicyclic polyisocyanate in an amount of at least 30 wt % of the total polyisocyanate compound, a polyhydroxyalkane carboxylic acid, as necessary a polyol compound containing a C2 to C8 polyol ingredient in an amount of at least 90 wt % of the total polyol compound, a chain extender selected from the group comprised of at least one of ammonia, an ammonia derivative, diamine, hydrazine, and a hydrazine derivative, and a neutralization agent and having a total of a urethane group concentration and urea group concentration of 25 to 60 wt % and an acid value of 5 to 100 mgKOH·g−1, a swellable inorganic layer compound, and a polyamine compound having an amine value of 100 to 1900 mgKOH·g−1 formed on one side or both sides of a thermoplastic resin base.
Owner:FUTAMURA KAGAKU INDS
Gas barrier laminate film and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20050079380A1Excellent gas barrier performanceIncreased durabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesChemistryLiquid-crystal display
Disclosed is a gas barrier laminate film comprising at least one inorganic layer and at least one organic layer on a base material film, wherein the organic layer is a layer formed by ring opening polymerization of at least one kind of oxetanyl group-containing monomer. The gas barrier film can exhibit superior gas barrier property even if it is flexed and is preferably applicable in image display devices such as liquid crystal display devices and organic EL devices.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Functional graphene-polymer nanocomposites for gas barrier applications
InactiveUS8110026B2Excellent gas barrier performanceImprove suppression propertiesMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesX-rayDiffusion barrier
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
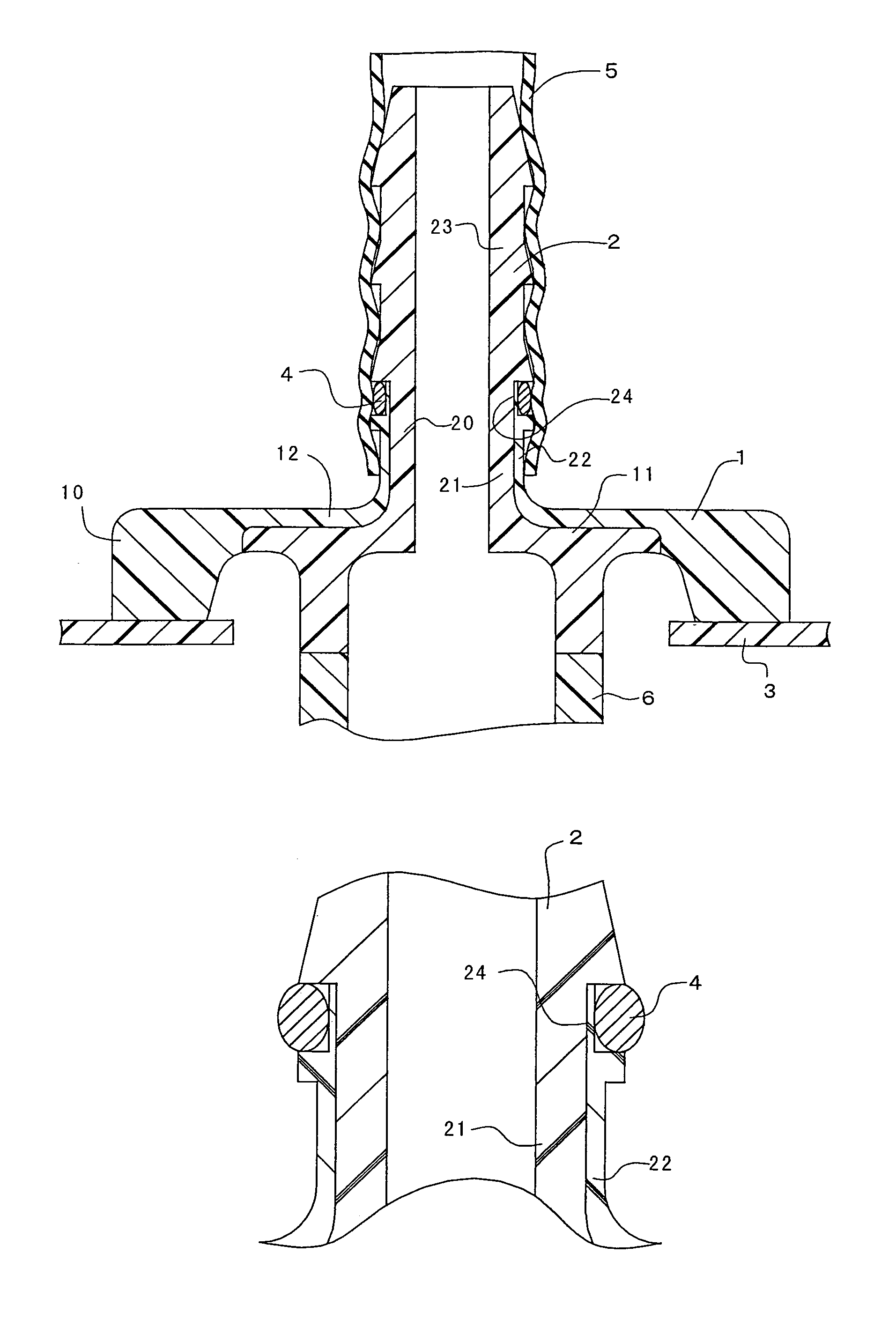
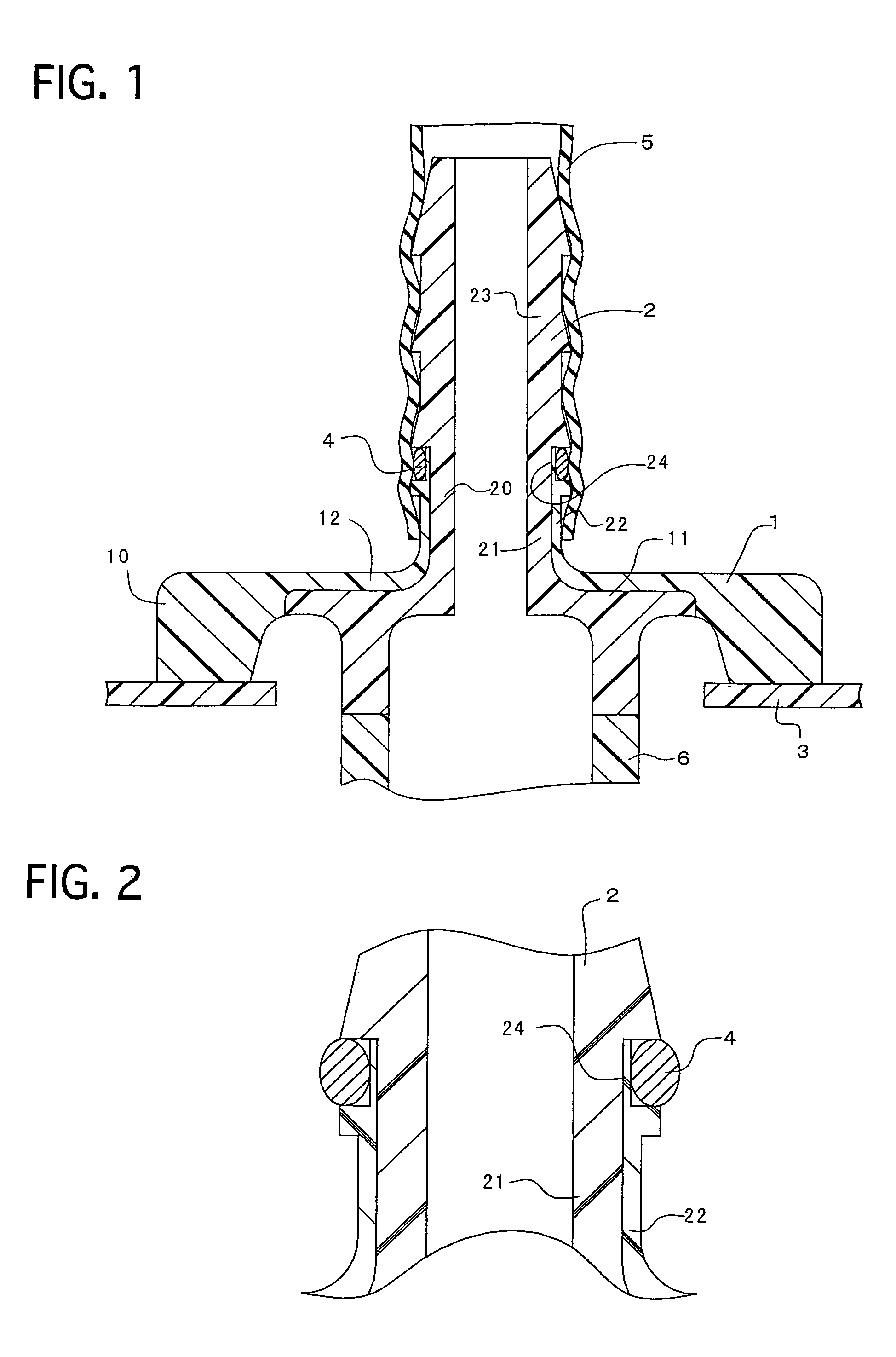
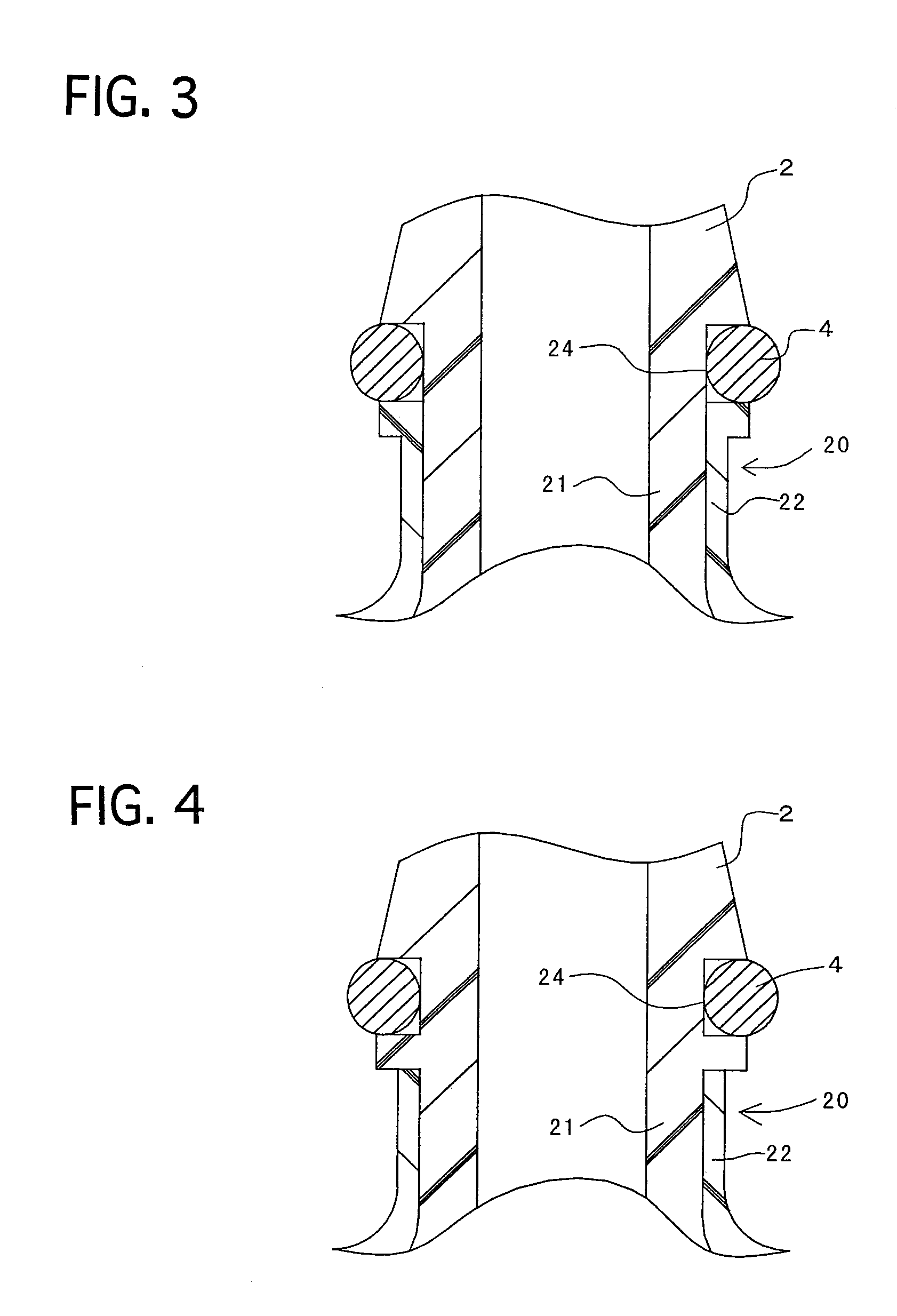
Resinous connector
A resinous connector includes a flange-shaped base, a nipple, an O-ring, and an O-ring groove. The nipple extends from the base, and has an outer peripheral surface and sealing projections disposed on the outer peripheral surface. The sealing projections have a substantially triangle-shaped cross section whose diameter reduces in the direction away from the base. The O-ring is disposed between the nipple and a hose. The O-ring groove is formed at a root of the nipple in the outer peripheral surface, and is disposed at a position closer to the base than the sealing projection disposed in most proximity to the base. The resinous connector can inhibit the O-ring from being twisted or bruised by the hose.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Gas barrier film
InactiveUS20050019503A1Excellent gas barrier performanceAvoid crackingSynthetic resin layered productsVacuum evaporation coatingCarbon atomSilicon oxide
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a gas barrier film having extremely excellent gas barrier property while retaining the film thickness at a predetermined thickness. A gas barrier film having a silicon oxide film formed by the plasma CVD method on the one side or both sides of a base material is provided, the silicon oxide film is characterized in that the film is comprised of the rate of components that the number of oxygen atoms is from 170 to 200 and the number of Carbon atoms is 30 or less to the number of Si atoms of 100, and that further the film has a peak position of IR absorption band based on the stretching vibration of Si—O—Si that exist between 1055 and 1065 cm−1.
Owner:KOMADA MINORU
Vacuum heat insulation material and cold reserving apparatus with the same
ActiveUS7762634B2Long-lasting performanceExcellent pinhole resistanceThermal insulationSynthetic resin layered productsForeign matterMetal foil
A vacuum heat insulation material has a covering material which is a lamination body including a sealant layer, a metal foil layer, a first plastic film layer, and a second plastic film layer which are laminated in this order from inside to outside via adhesive layers. When a foreign body is pierced into the vacuum heat insulation material, the propagation of breakage caused by the piercing is blocked somewhere inside the lamination body, thereby preventing the formation of through-pinholes. This results in the provision of a high-quality vacuum heat insulation material with excellent long-term insulation performance by using a covering material excellent in gas barrier properties and pinhole resistance to the piercing of minute foreign bodies.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Gas barrier film laminate
ActiveUS20100015431A1Excellent gas barrier performanceImpurity is generatedLayered product treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsImpurityMaterials science
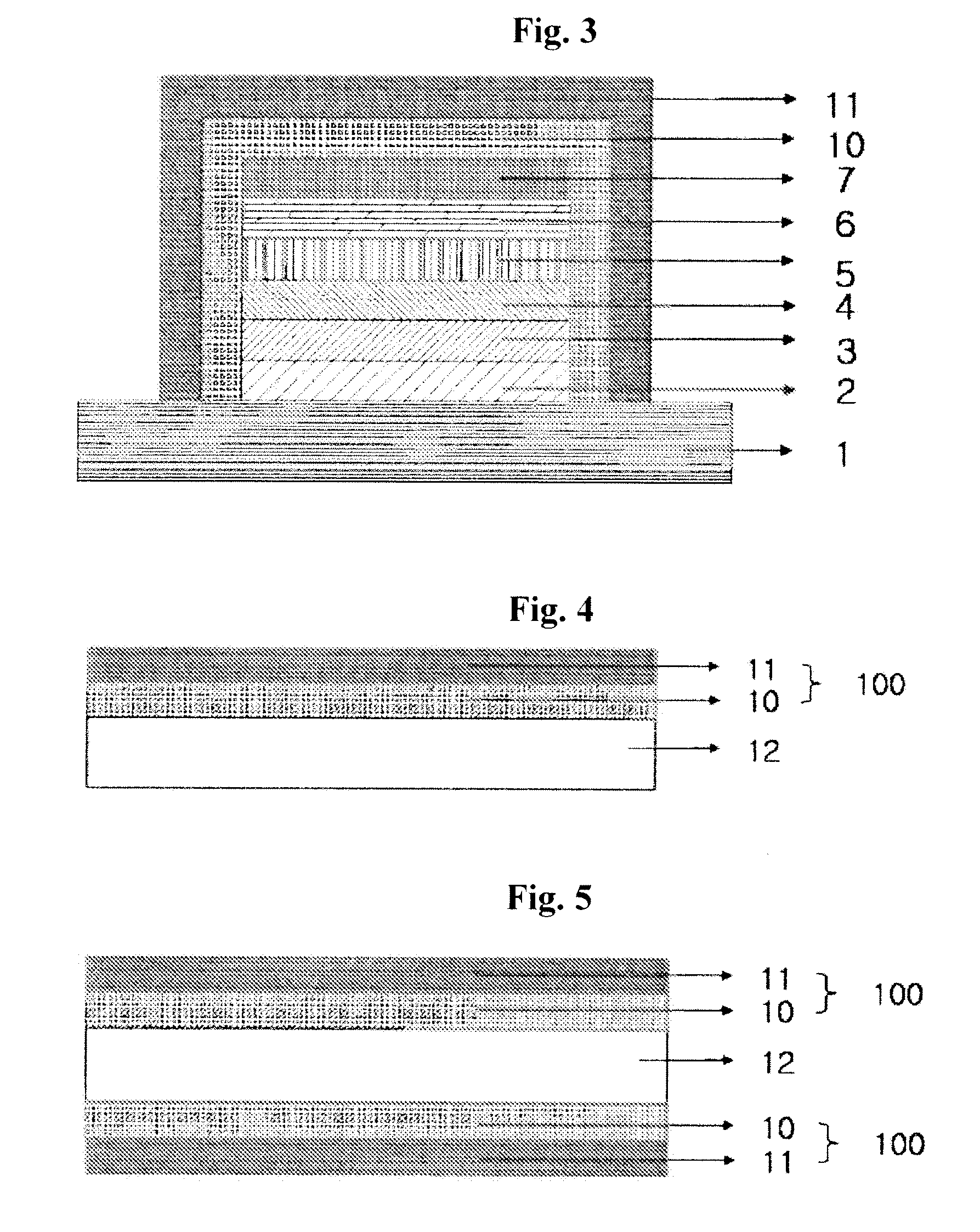
The present invention relates to a gas-barrier film laminate capable of greatly reducing the formation of bubbles and impurities between the gas-barrier film layers and having excellent gas-barrier property interlayer adhesiveness.The gas-barrier film laminate has at least two gas-barrier film layers laminated via an adhesive layer, wherein the gas-barrier film layer has a substrate film, and at least one constitutive unit layer comprising an anchor coat layer and an inorganic thin film layer formed on at least one surface of the substrate film in that order, and wherein the number of the bubbles having a diameter of at least 0.5 mm and the impurities having a diameter of at least 0.5 mm existing between the gas-barrier film layers is at most 3 in total per 100 cm2.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Film for organic EL device and an organic EL device using the film
InactiveUS6638645B2Excellent gas barrier performanceAvoid low lightDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesHybrid materialOrganic inorganic
The present invention provides a film for use in organic EL device, having a sufficient gas-barrier property for protection of organic EL device, and an organic EL device structure using such a film. That is, the present invention provides a film for use in organic EL device, made of an organic inorganic hybrid material whose molecules have an organic skeletal moiety and an inorganic skeletal moiety and contain fluorine group and siloxane group.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Organic-inorganic composite composition, plastic substrate, gas barrier laminate film, and image display device
InactiveUS20050214556A1Improve featuresImprove display qualitySynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingHeat resistanceInorganic compound
In a gas barrier laminate film comprising a base material film containing an inorganic compound and at least one set of inorganic layer and organic layer formed on the base material film, the base material film is formed with a resin having a glass transition temperature of 250° C. or higher. A gas barrier laminate film that has superior durability, heat resistance and gas barrier performance, shows a small difference in coefficient of linear expansion relative to an contiguous layer and can maintain superior gas barrier property even if it is bent is provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Glycolic acid copolymer and method for production thereof
A glycolic acid copolymer comprising (a) 80 to less than 95% by mole of glycolic acid monomer units, (b) 5.0 to 20.0% by mole of non-glycolic, hydroxycarboxylic acid monomer units, and (c) 0 to 0.10% by mole of diglycolic acid monomer units, the non-glycolic, hydroxycarboxylic acid monomer units (b) constituting a plurality of segments each independently consisting of at least one monomer unit (b), wherein the segments have an average chain length of from 1.00 to 1.50 in terms of the average number of monomer unit or units (b), the total of the components (a), (b) and (c) being 100% by mole, the glycolic acid copolymer having a weight average molecular weight of 50,000 or more.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
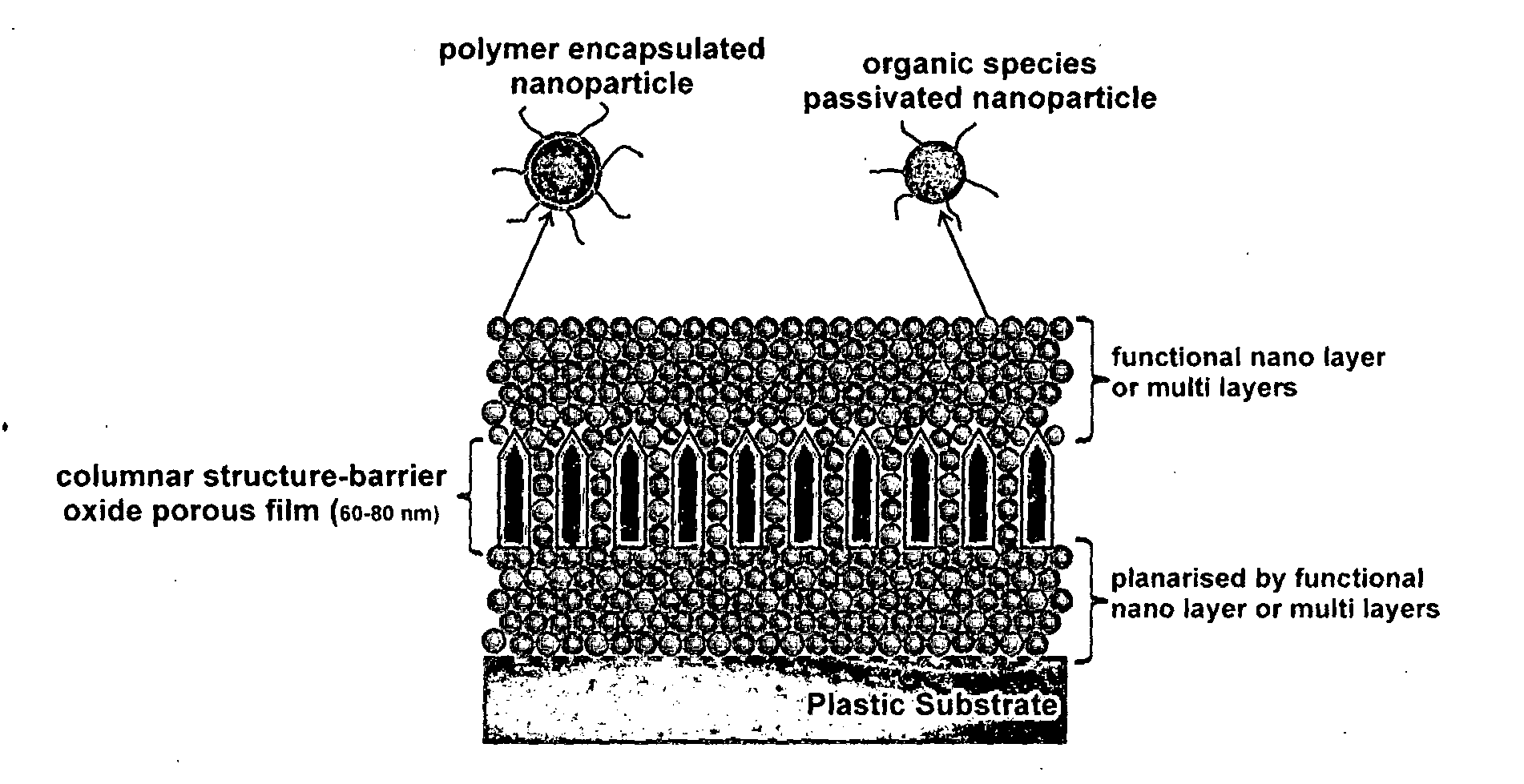
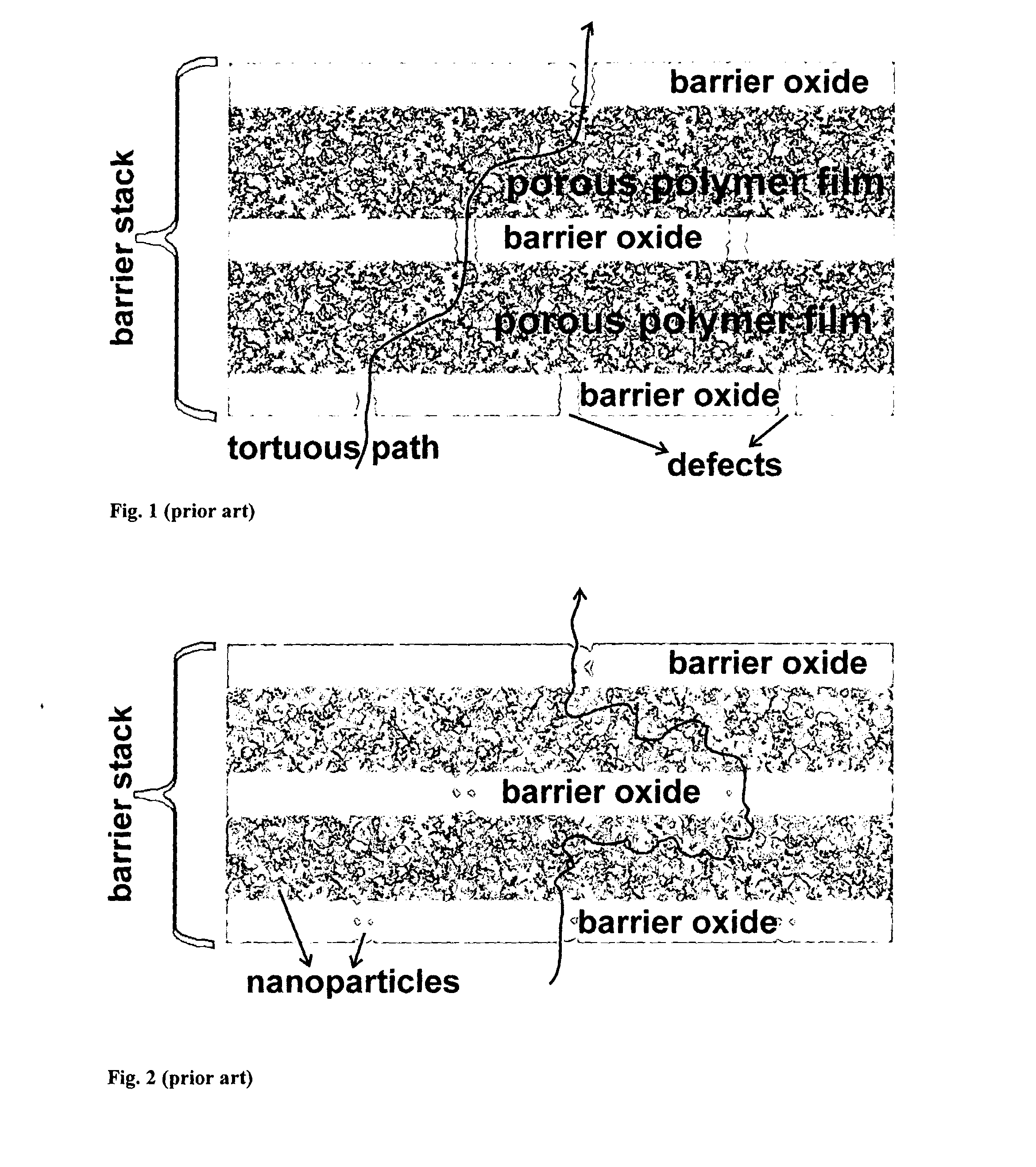
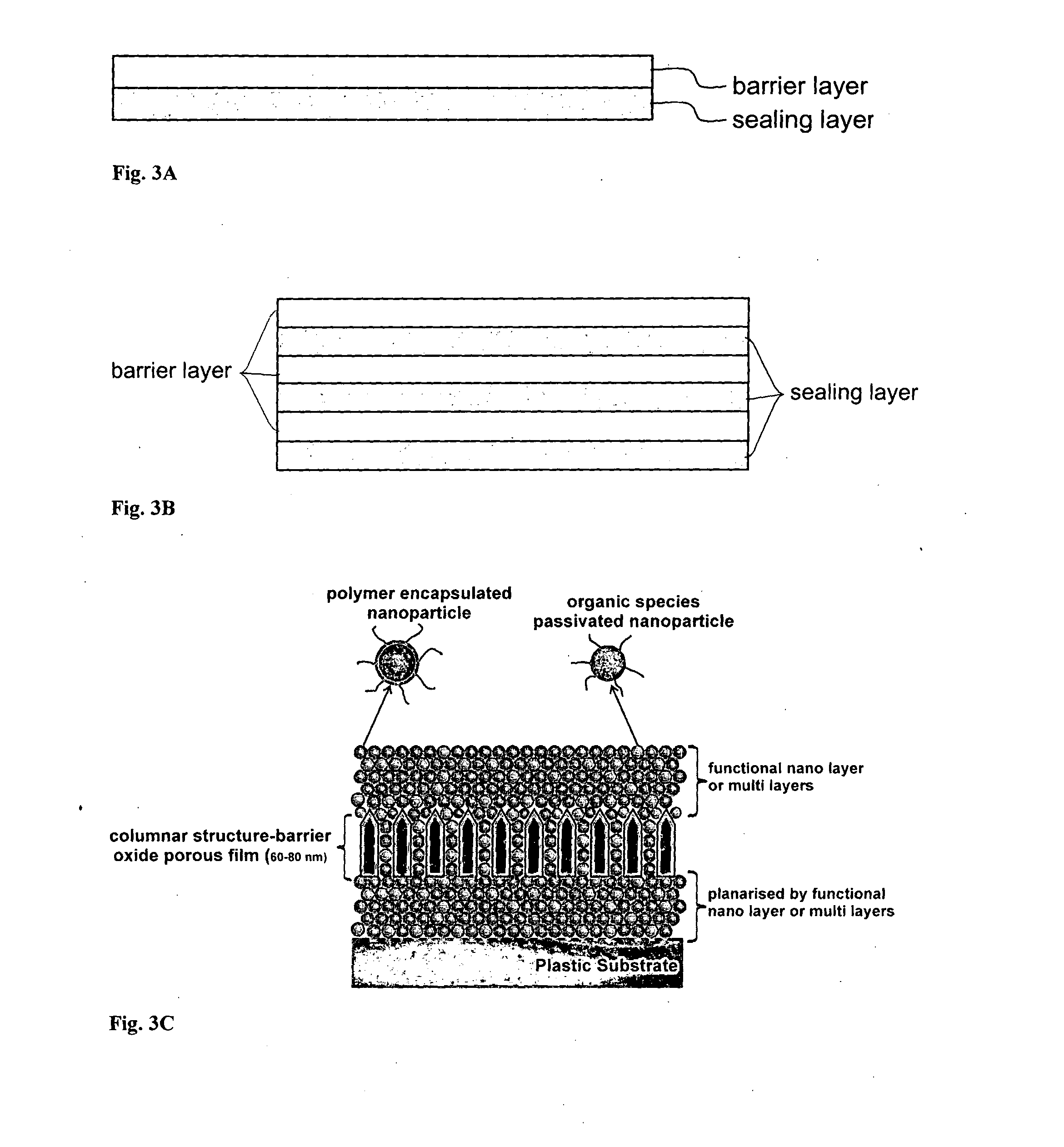
Encapsulation barrier stack
InactiveUS20140252342A1Minimise lateral diffusionImprove anti-reflection effectMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureCross-linkNanoparticle
Disclosed is an encapsulation barrier stack, capable of encapsulating a moisture and / or oxygen sensitive article and comprising a multilayer film, wherein the multilayer film comprises: one or more barrier layer(s) having low moisture and / or oxygen permeability, and one or more sealing layer(s) arranged to be in contact with a surface of the at least one barrier layer, thereby covering defects present in the barrier layer, wherein the one or more sealing layer(s) comprise(s) a plurality of encapsulated nano-particles, the nanoparticles being reactive in that they are capable of interacting with moisture and / or oxygen to retard the permeation of moisture and / or oxygen through the defects present in the barrier layer. The encapsulation of the particles can be obtained by polymerising a polymerisable compound (a monomeric or a polymeric compound with polymerisible groups or) cross-linking a cross-linkable compound on the surface of the reactive nanoparticles.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Multilayer film for encapsulating oxygen and/or moisture sensitive electronic devices
ActiveUS20140179040A1Excellent gas barrier performanceLow gas permeabilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleUltraviolet lights
The present invention relates to a multilayer barrier film capable of encapsulating a moisture and / or oxygen sensitive electronic or optoelectronic device, the barrier film including at least one nanostructured layer including reactive nanoparticles capable of interacting with moisture and / or oxygen, the reactive nanoparticles being distributed within a polymeric binder, and at least one ultraviolet light neutralizing layer comprising a material capable of absorbing ultraviolet light, thereby limiting the transmission of ultraviolet light through the barrier film.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
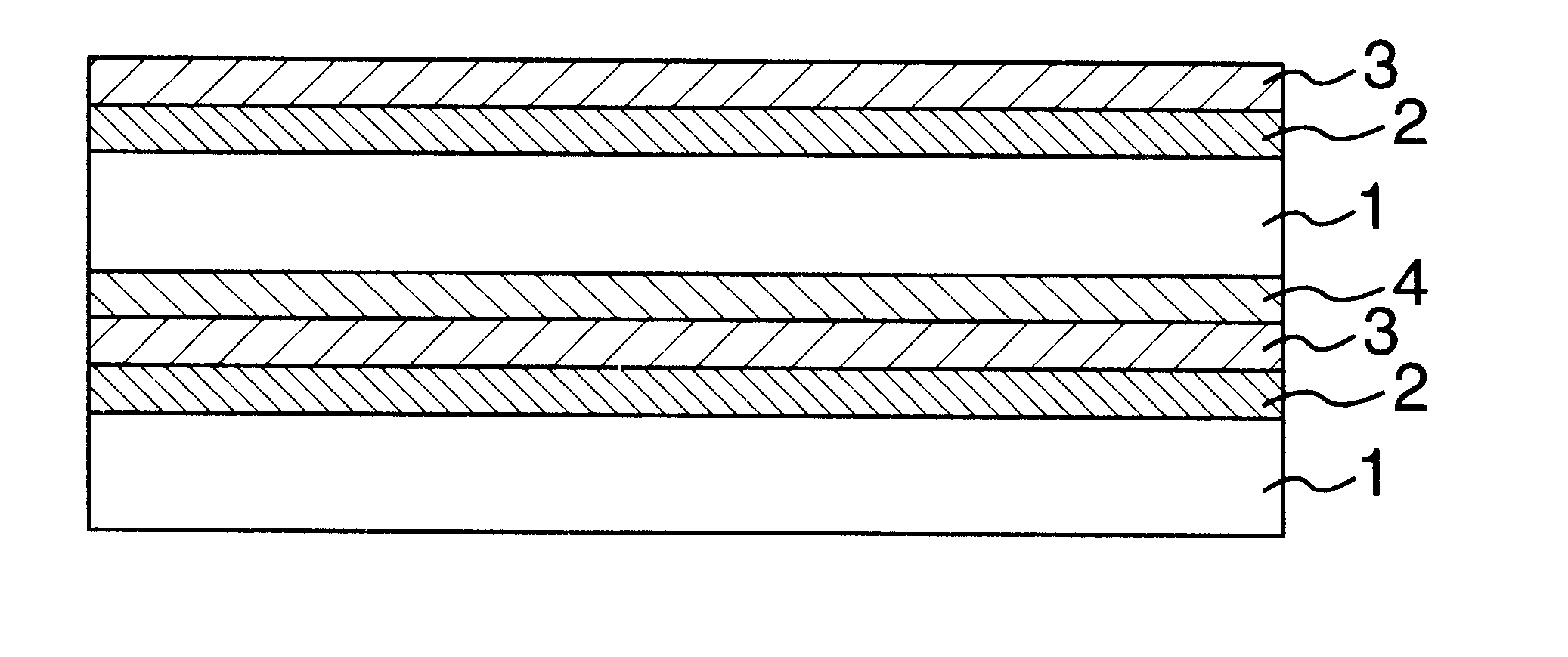
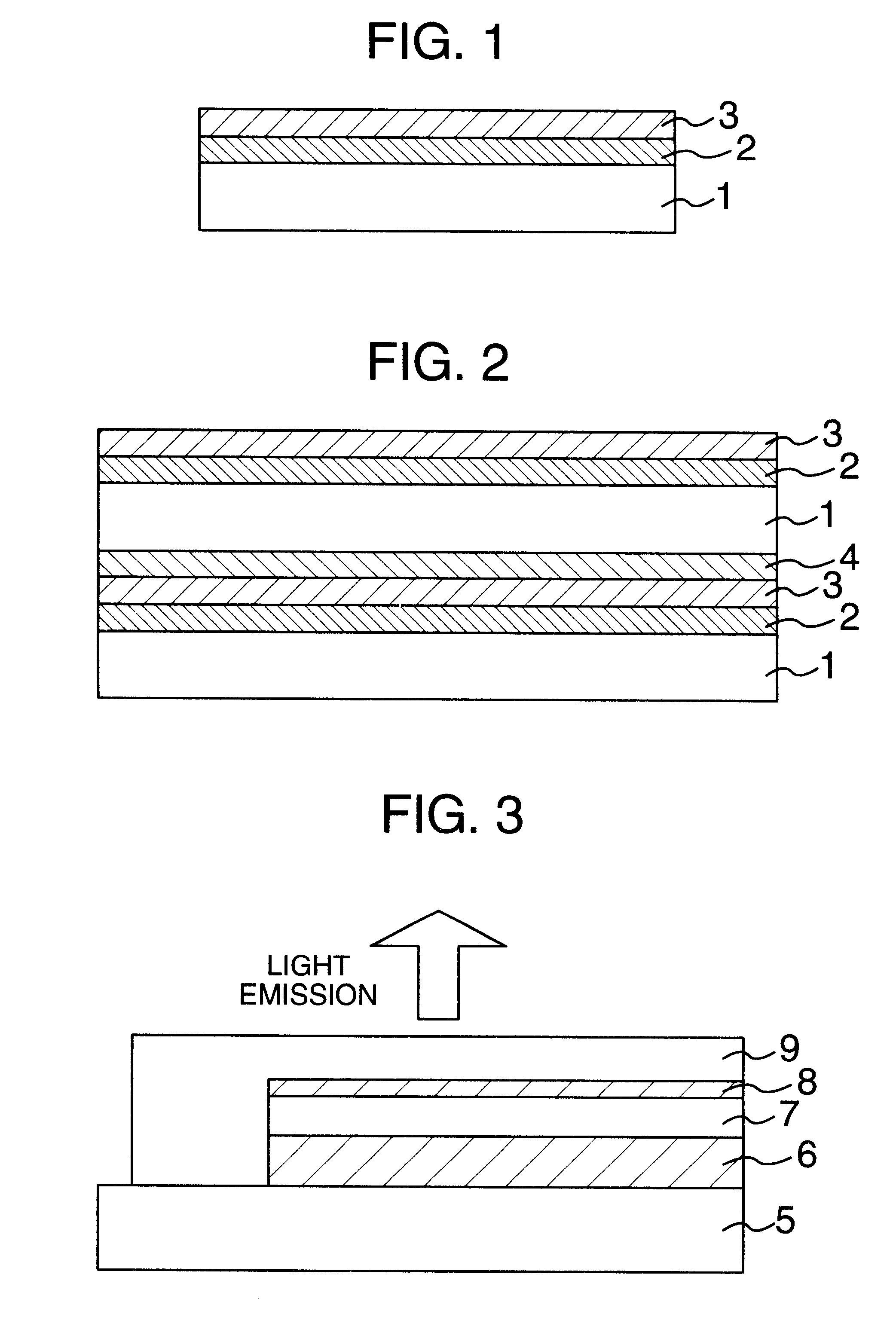
Gas barrier film and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20050112378A1Excellent gas barrier performanceImprove heat resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsGlass/slag layered productsVitrificationLiquid-crystal display
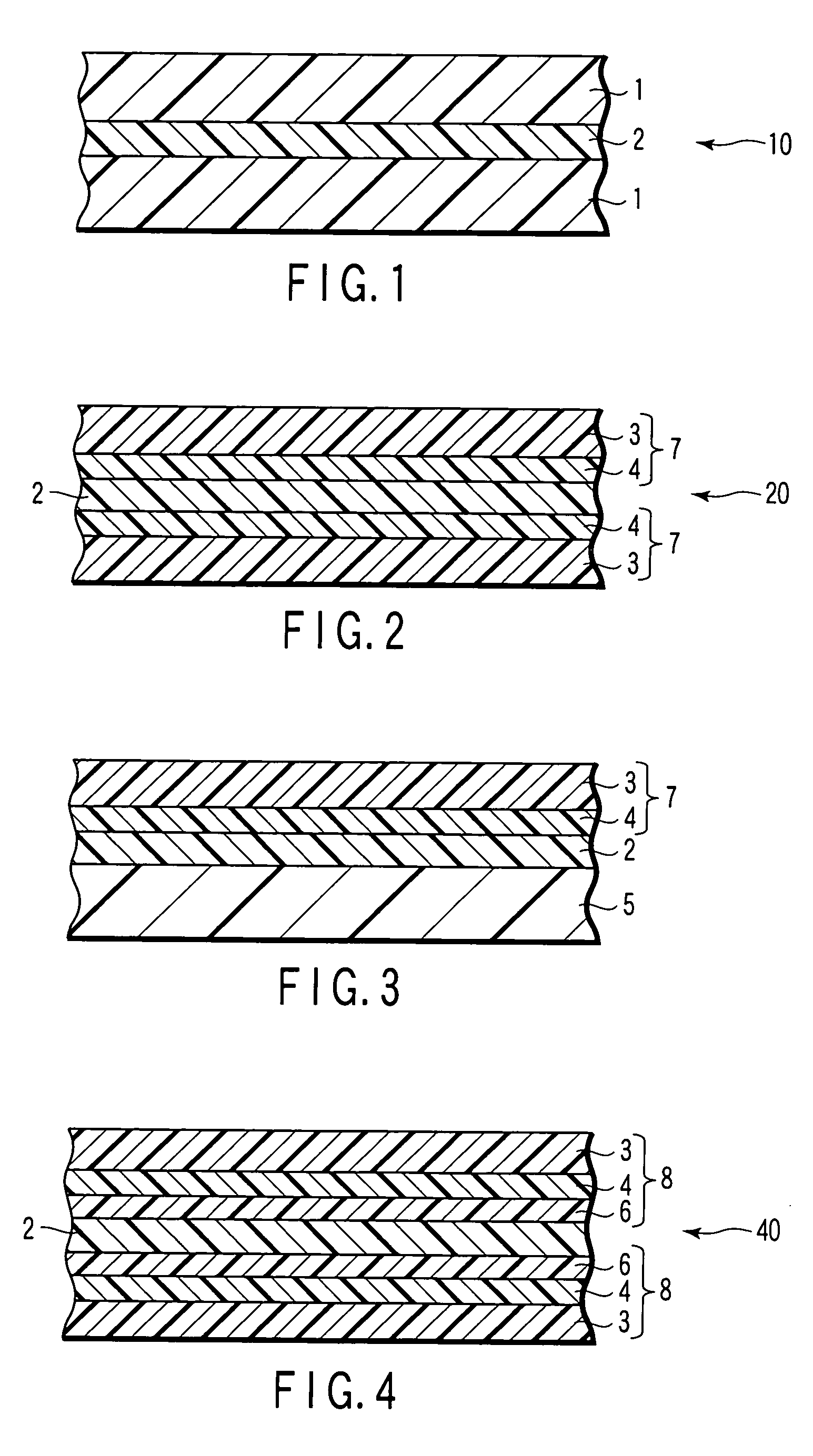
Disclosed is a gas barrier film alternately comprising at least one inorganic layer and at least one organic layer on a resin base material having a glass transition temperature of 250° C. or higher. The gas barrier film can exhibit superior gas barrier property when it is used in image display devices such as liquid crystal display devices and organic EL devices.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Light-emitting device with coating film on portions of substrates and sealing member
InactiveUS7189999B2Simple processAlters colorElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesCarbon filmDiamond-like carbon
Although an organic resin substrate is highly effective at reducing the weight and improving the shock resistance of a display device, it is required to improve the moisture resistance of the organic resin substrate for the sake of maintaining the reliability of an EL element. Hard carbon films are formed to cover a surface of the organic resin substrate and outer surfaces of a sealing member. Typically, DLC (Diamond like Carbon) films are used as the carbon films. The DLC films have a construction where carbon atoms are bonded into an SP3 bond in terms of a short-distance order, although the films have an amorphous construction from a macroscopic viewpoint. The DLC films contain 95 to 70 atomic % carbon and 5 to 30 atomic % hydrogen, so that the DLC films are very hard and minute and have a superior gas barrier property and insulation performance.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Gas barrier film
InactiveUS20040058157A1Maintain good propertiesIncrease resistanceLiquid crystal compositionsElectroluminescent light sourcesVitrificationHeat resistance
Disclosed is a gas barrier film having an inorganic coating layer formed by the sol-gel method or an organic-inorganic hybrid coating layer formed by the sol-gel method on a transparent base film having a glass transition temperature of 100° C. or higher and a linear thermal expansion coefficient of 40 ppm / ° C. or lower. There is provided a transparent plastic film showing superior heat resistance and gas barrier property.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Organic/inorganic hybrid thin film passivation layer for blocking moisture/oxygen transmission and improving gas barrier property
ActiveUS20090215279A1Avoid transmissionEnsure stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyElectroluminescent light sourcesLayer interfaceTransmittance
The present invention relates to an organic / inorganic hybrid thin film passivation layer comprising an organic polymer passivation layer prepared by a UV / ozone curing process and an inorganic thin film passivation layer for blocking moisture and oxygen transmission of an organic electronic device fabricated on a substrate and improving gas barrier property of a plastic substrate; and a fabrication method thereof. Since the organic / inorganic hybrid thin film passivation layer of the present invention converts the surface polarity of an organic polymer passivation layer into hydrophilic by using the UV / ozone curing process, it can improve the adhesion strength between the passivation layer interfaces, increase the light transmission rate due to surface planarization of the organic polymer passivation layer, and enhance gas barrier property by effectively blocking moisture and oxygen transmission.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Transparent gas barrier laminated film, and electroluminescent light-emitting element, electroluminescent display device, and electrophoretic display panel using the same
InactiveUS20060062995A1Excellent gas barrier performanceHigh transparencySolid-state devicesRecord information storageElectrophoresesEngineering
A transparent gas barrier laminated film includes at least two transparent gas barrier films, and a 1- to 30-μm-thick adhesive layer formed between the transparent gas barrier films.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Object coated with carbon film and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6893720B1Improve wear resistanceEasy to slideFlexible wall reciprocating enginesLayered productsCarbon filmMachine parts
An object such as an automobile part, an image forming apparatus part, a bicycle part, other machine parts, a sport article or its part, a toy or its part, or a rain article or its part has a portion to be in contact with a contact object. The contact portion is made of at least one kind of material selected from a group including polymer material such as resin or rubber as well as glass, and the contact portion has a surface entirely or partially coated with a carbon film (typically, a DLC film) having a wear resistance as well as at least one of a lubricity, a water repellency and a gas barrier property. The carbon film is formed on the object with a good adhesion.
Owner:NISSIN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Tie-layer for polyolefin films
ActiveUS20060257652A1Improve barrier propertiesExcellent gas barrier performanceSynthetic resin layered productsBagsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
A laminate film including a first polyolefin layer comprising of a blend of 50-95% ethylene-propylene copolymer and 50-5% ethylene polar terpolymer with a polar polymer layer on one side of said first polyolefin resin-containing layer is disclosed. The laminate film could further have additional layers such as a second polyolefin resin-containing layer, a metal layer, or combinations thereof.
Owner:TORAY PLASTICS AMERICA
Multi-layer high moisture barrier polylactic acid film
ActiveUS20110171489A1Excellent gas barrier performanceImprove moisture resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMoisture barrierMetal
A laminate film including a first polylactic acid layer; a second metal-receiving layer including PVOH, EVOH, or a blend thereof on a side of the first polylactic acid layer; and a metal layer deposited on a side of the metal-receiving layer opposite the polylactic acid layer. The metal-receiving layer may be coextruded with the polylactic acid first layer or may be a coating applied to one side of the polylactic acid first layer. This laminate film exhibits excellent gas and moisture barrier properties, appearance, and metal adhesion. It may also include a heat sealable or winding improving layer on the side opposite the metal receiving-layer of the first polylactic acid layer.
Owner:TORAY PLASTICS AMERICA
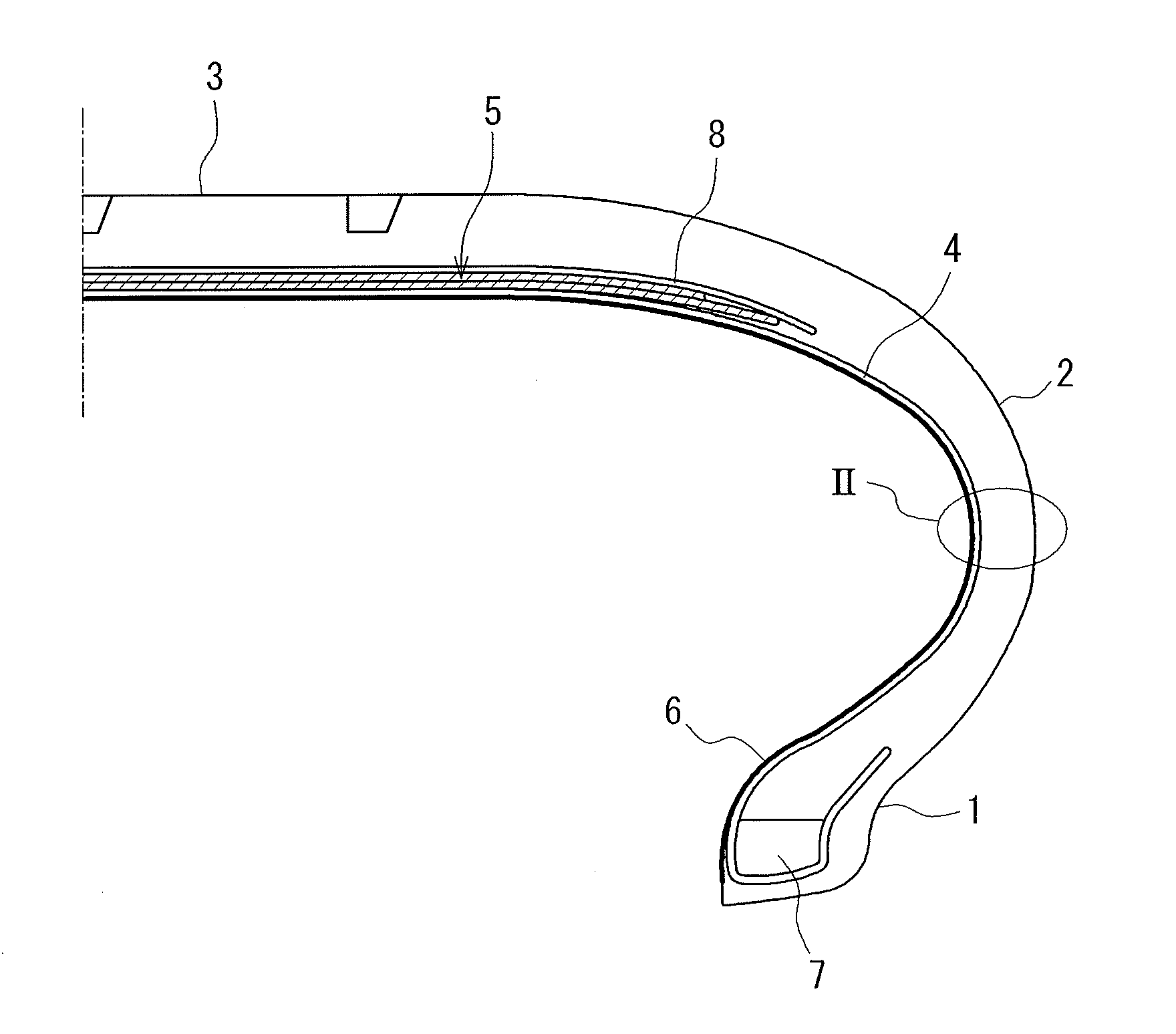
Film, inner liner for tire, and tire using the same
InactiveUS20110024015A1Excellent gas barrier propertiesImprove bending resistanceWithout separate inflatable insertsWith separate inflatable insertsInternal pressureEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide: a film which is applicable to a tire, has excellent gas barrier properties and bending resistance, allows weight of a tire to be reduced with improving internal pressure retainability of the tire at both the brand-new stage and the used stage thereof, and is capable of demonstrating good gas barrier properties without breaking especially in a running condition at a relatively low temperature in winter time or the like; an inner liner for tire, using the film; and a tire provided with the inner liner for tire. The film of the present invention comprises at least a layer composed of resin composition (D) produced by dispersing viscoelastic substance (C) in a resin containing modified ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (B) obtained by subjecting ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (A) to a reaction, wherein 100% modulus at −30° C. of the viscoelastic substance (C) is smaller than 6 MPa. The inner liner for tire, and the tire, of the present invention are an inner liner for tire, using said film, and a tire provided with said inner liner for tire, respectively.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP +1
Gas-barrier laminate
ActiveUS20070059541A1Good printabilityHigh industrial valueSynthetic resin layered productsCoatingsPolyesterVitrification
A gas-barrier laminate comprises a plastic substrate (A), an inorganic thin film (B) formed on at least one surface of the plastic substrate (A), and a polyester-based resin layer (C) formed by applying a coating material containing a polyester-based resin on a surface of the inorganic thin film (B), wherein the polyester-based resin has a glass transition temperature of 50 to 70° C., a molecular weight of 1500 to 15000 and a hydroxyl value of 10 to 60 mg KOH / g, and the gas-barrier laminate has an oxygen permeability of not more than 5 cc / m2 / day / atm and a water vapor permeability of not more than 5 g / m2 / day. The gas-barrier laminate of the present invention is excellent in printability (in particular, gradation printability), is free from deterioration in gas-barrier property, namely is excellent in gas-barrier property, even after providing a printed layer thereon, and further exhibits an excellent adhesion between the plastic substrate (A) and the inorganic thin film (B) even after being subjected to retort treatments.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Organic electroluminescence display panel and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20050116637A1Highly reliable gas barrierExcellent gas barrier performanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensFinal product manufactureOrganic electroluminescencePolymer
An organic electroluminescence display panel includes an organic electroluminescence element and a resin substrate that supports the organic electroluminescence element. A gas barrier laminate is formed between the resin substrate and the organic electroluminescence element. The gas barrier laminate includes two or more inorganic barrier layers and one or more polymer compound layers each provided between the inorganic barrier layers. The exposed parts of the polymer compound layer that are not covered by the inorganic barrier layers are subjected to plasma processing. The exposed parts may be covered by a cover layer or a sealing layer that affords gas barrier properties.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com