Patents
Literature
751 results about "Gas formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of forming insulation film using plasma treatment cycles
ActiveUS8647722B2Improve film qualityIncrease coverageChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueEngineeringMono layer
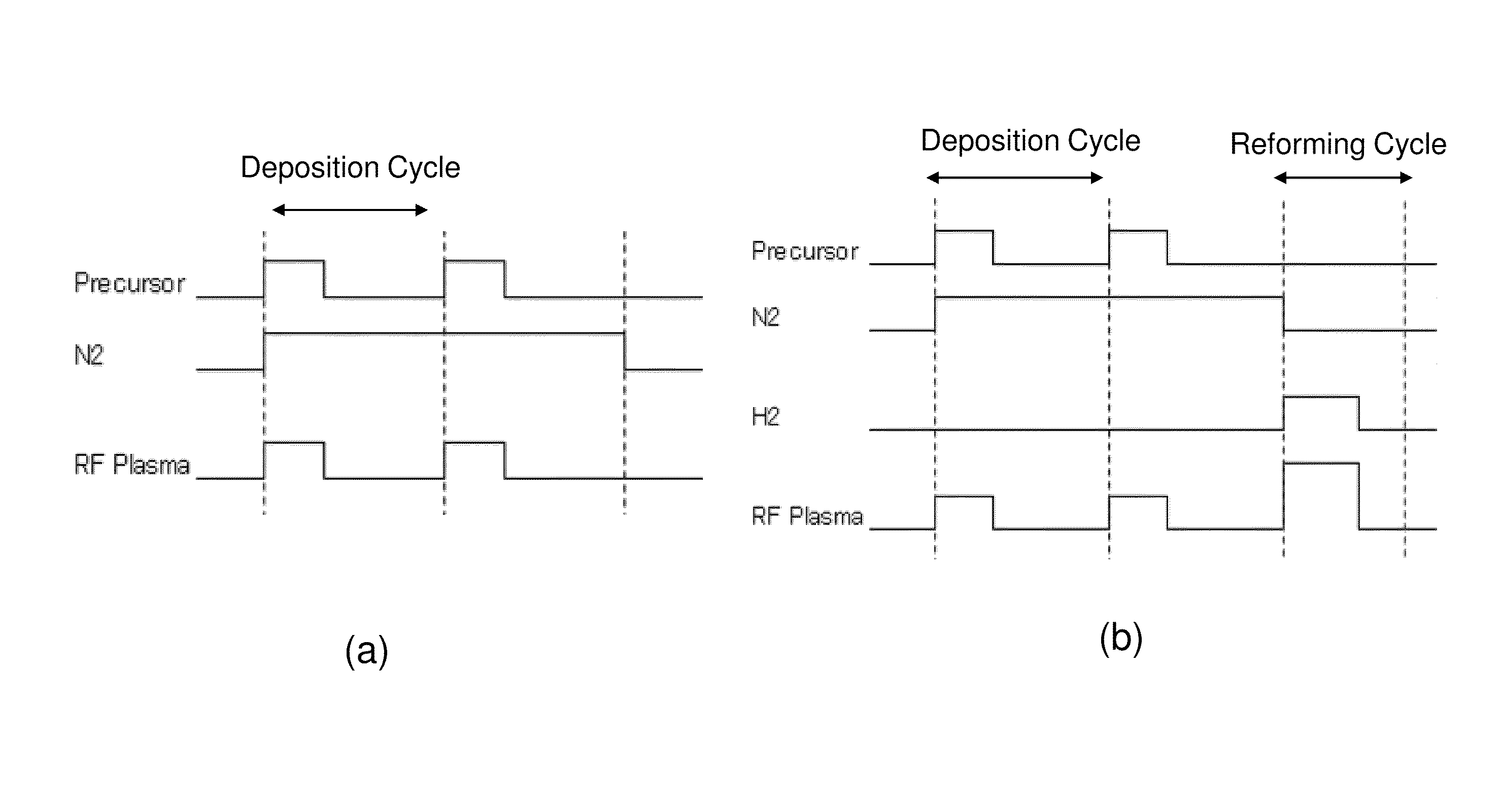
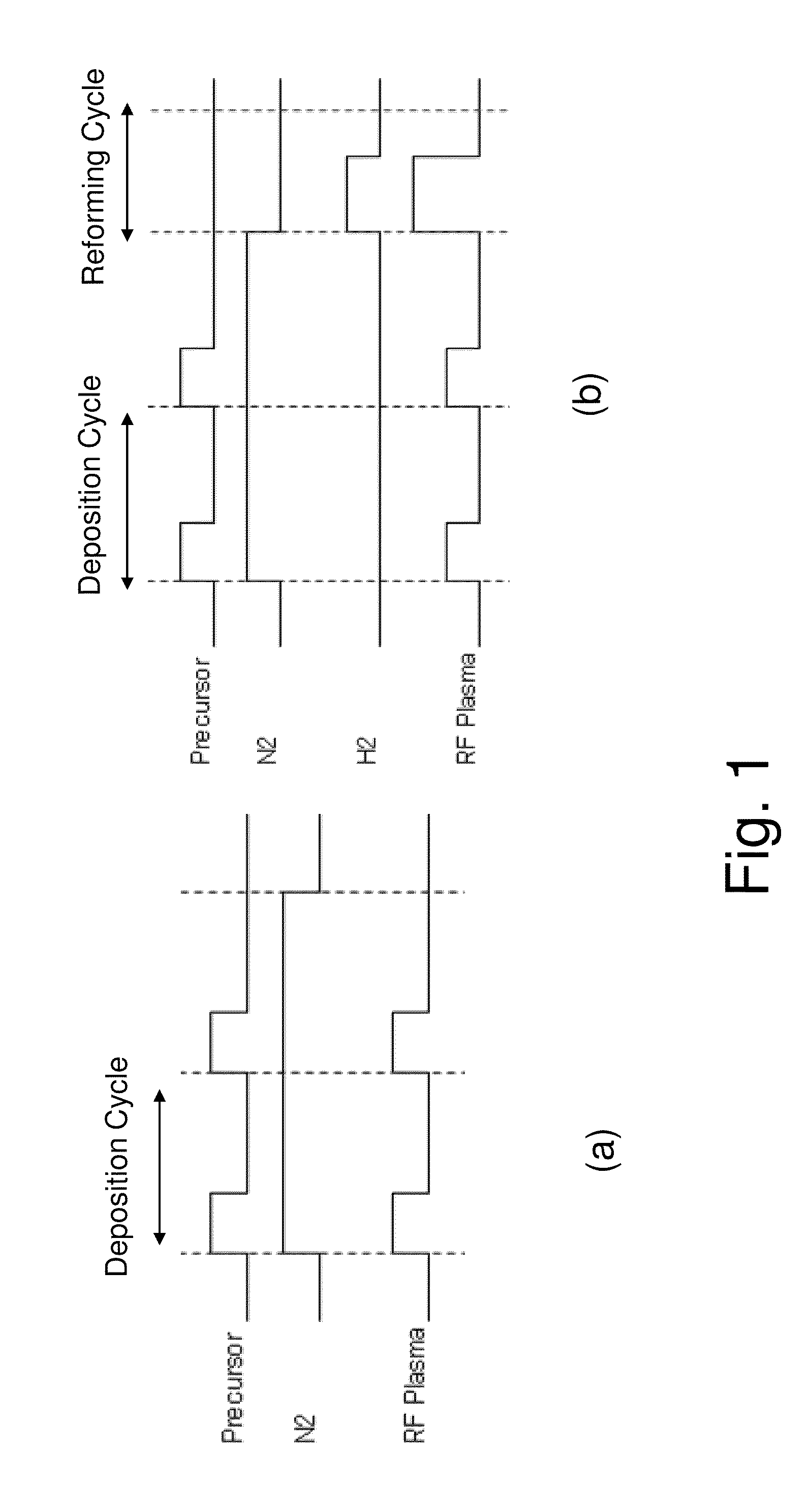
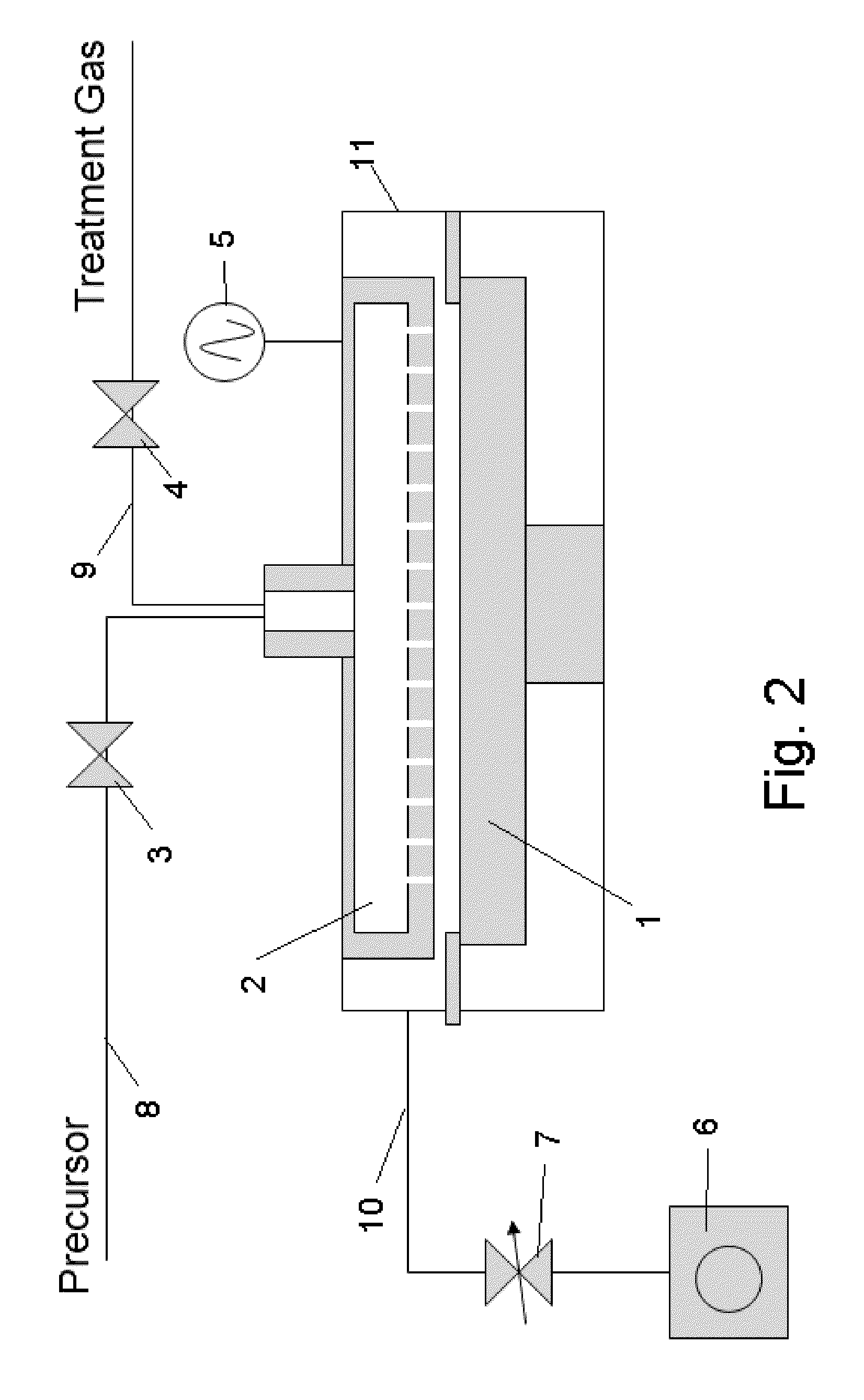
A film forming cycle based on pulse CVD or ALD is repeated multiple times to form a single layer of insulation film, while a reforming cycle is implemented in the aforementioned process, either once or multiple times per each film forming cycle, by treating the surface of formed film using a treating gas that has been activated by a plasma.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Lithium anodes for electrochemical cells
InactiveUS7247408B2Light weightFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsLithium metalReactive gas
Provided is an anode for use in electrochemical cells, wherein the anode active layer has a first layer comprising lithium metal and a multi-layer structure comprising single ion conducting layers and polymer layers in contact with the first layer comprising lithium metal or in contact with an intermediate protective layer, such as a temporary protective metal layer, on the surface of the lithium-containing first layer. Another aspect of the invention provides an anode active layer formed by the in-situ deposition of lithium vapor and a reactive gas. The anodes of the current invention are particularly useful in electrochemical cells comprising sulfur-containing cathode active materials, such as elemental sulfur.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Method for protecting layer by forming hydrocarbon-based extremely thin film
ActiveUS20170018477A1Improve concentrationGood chemical resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNoble gasProtection layer
A method for protecting a layer includes: providing a substrate having a target layer and forming a protective layer on the target layer, said protective layer contacting and covering the target layer and containing a hydrocarbon-based layer constituting at least an upper part of the protective layer, which hydrocarbon-based layer is formed by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) using an alkylaminosilane precursor and a noble gas without a reactant.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming dielectric film using porogen gas
ActiveUS7955650B2Low mechanical strengthIncrease equipment costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesDielectric permittivityGas formation
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Methods for controlling formation of deposits in a deposition system and deposition methods including the same
InactiveUS20060216416A1Avoid contactChemical vapor deposition coatingProcess engineeringReaction chamber
A method for controlling parasitic deposits in a deposition system for depositing a film on a substrate, the deposition system defining a reaction chamber for receiving the substrate and including a process gas in the reaction chamber and an interior surface contiguous with the reaction chamber, includes flowing a buffer gas between the interior surface and at least a portion of the process gas to form a gas barrier layer such that the gas barrier layer inhibits contact between the interior surface and components of the process gas.
Owner:CREE INC
Flexible Materials for Flexible Containers
ActiveUS20130294711A1Less-expensiveImprove the decorative effectDomestic containersCoatingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A flexible material for a flexible container can include a first laminate and a second laminate joined to at least a portion of the first laminate by at least one seal. The first laminate can include a first gas barrier layer disposed between first and second sealable layers, wherein the first and second sealable layers define opposed exterior layers of the first laminate. The second laminate can include a third sealable layer defining an exterior layer of the second laminate, and a second gas barrier layer. The at least one seal joins a portion of the third sealable layer to at least a portion of the second sealable layer.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Battery electrolytic solution with fluoride-ion-dissociating salt and battery using the same
InactiveUS6306540B1Improve stabilityAvoid conductivitySolid electrolyte cellsLi-accumulatorsSupporting electrolyteDecomposition
The present invention relates to an electrolytic solution excellent in stability, and also relates to a battery excellent in battery performance and having an outer structure having light weight. The electrolytic solution contains a supporting electrolyte and a gas formation inhibitor in the solvent. The gas formation inhibitor contains a decomposition product of the supporting electrolyte with formation of a gas in the solvent. It functions as controlling to solution equilibrium in the electrolytic solution participating in decomposition reaction of the supporting electrolyte. A battery is obtained by filling the electrolytic solution between a positive electrode and a negative electrode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Use of a composition made of mineral nutrients and optionally acetogenic and/or butyrogenic bacteria in order to avoid or reduce the formation of gas in the large intestine of a mammal and the resulting abdominal problems
InactiveUS20100247489A1Raise countSufficient supplyHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideAcetic acidMammal
The present invention relates to a composition comprising one or more minerals selected from the group consisting of selenium, molybdenum or tungsten, which is carried out galenically or chemically in a way that the mineral or minerals are released completely or in part, just before, during or shortly after arrival at the large intestine, and their use in the manufacture of a medicament for administering to a mammal for the prevention or reduction of gas formation in the colon thus conditioned abdominal complaints, particularly bloatings, meteorism or abdominal cramps. Furthermore, the invention relates to a procedure for the isolation of acetogenic and butyrogenic bacterial strains that are suitable for therapeutic purposes outlined above.
Owner:SAUR BROSCH ROLAND
Gas barrier substrate
InactiveUS20050029513A1Quality improvementExcellent gas barrier performanceSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingMetallurgyGas formation
The main object of the present invention is to provide a gas barrier substrate having a high gas barrier property without a ruggedness, a pin hole or the like in the gas barrier layer. The present invention solves the problem by providing a gas barrier substrate having a base material, a planarization layer formed on the base material, and a gas barrier layer comprising a deposition film formed on the planarization layer.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
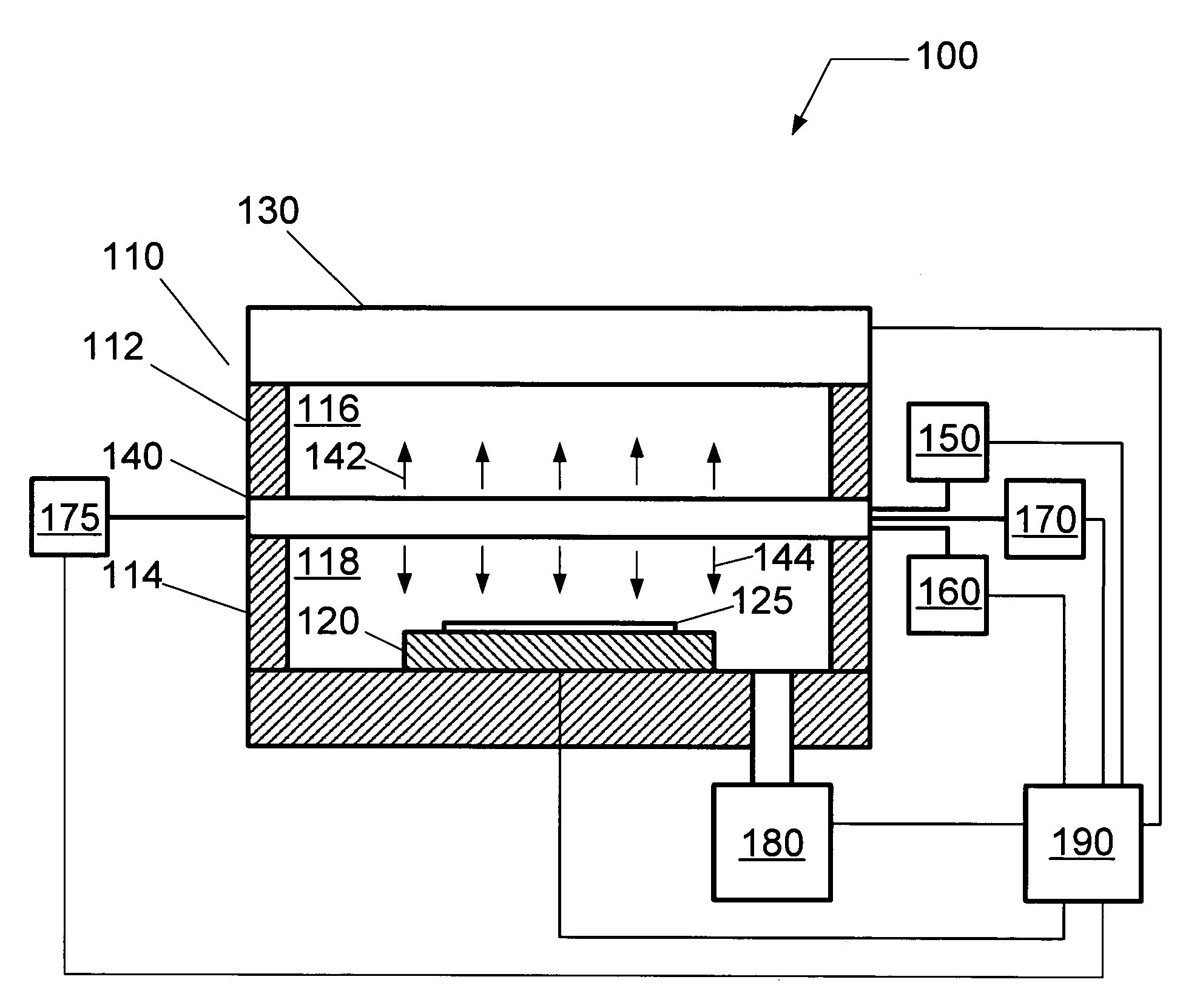
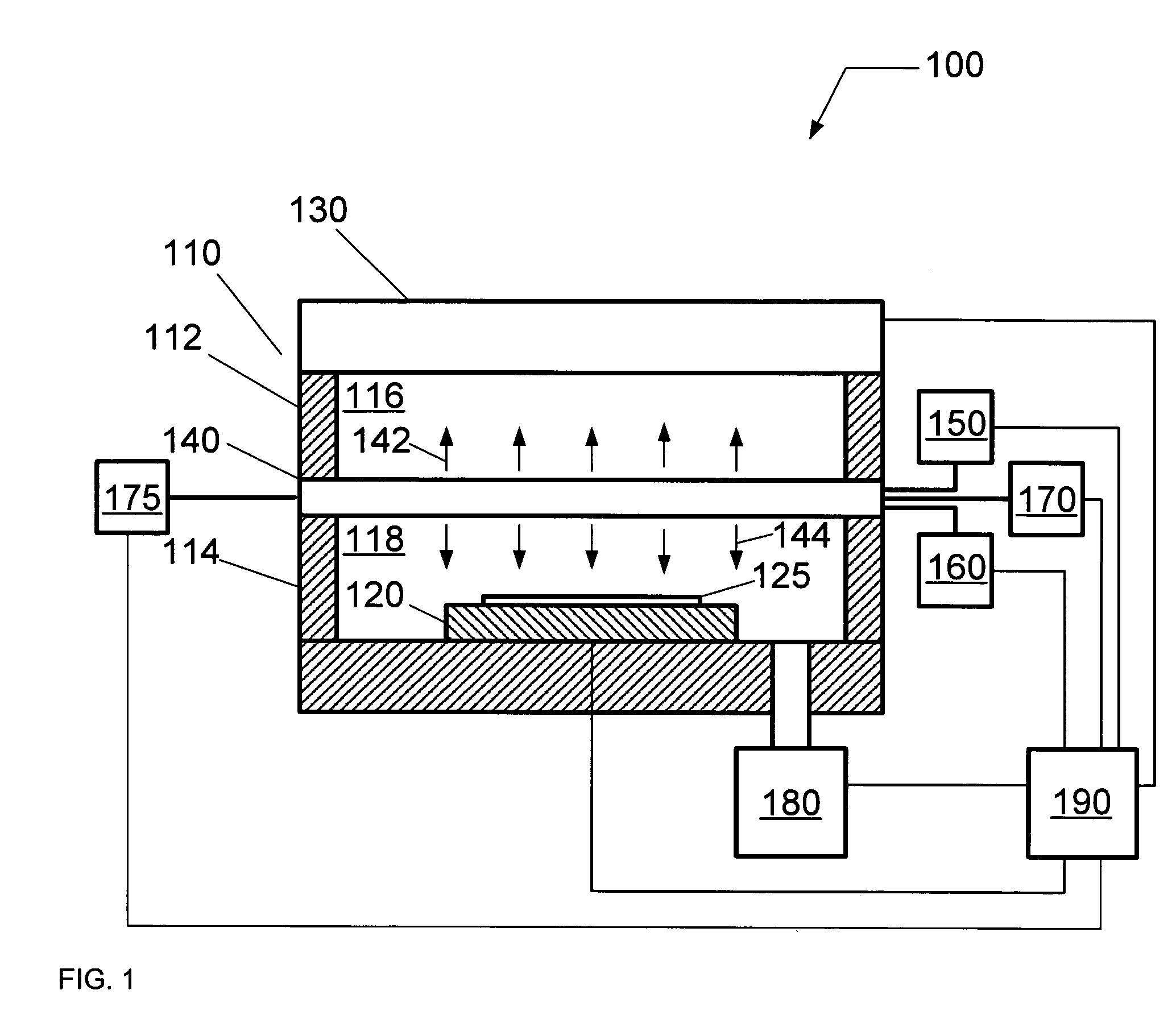
Method for treating a substrate
InactiveUS20060065629A1Reduce harmReduce the possibility of damageElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsProcess chemistryEngineering
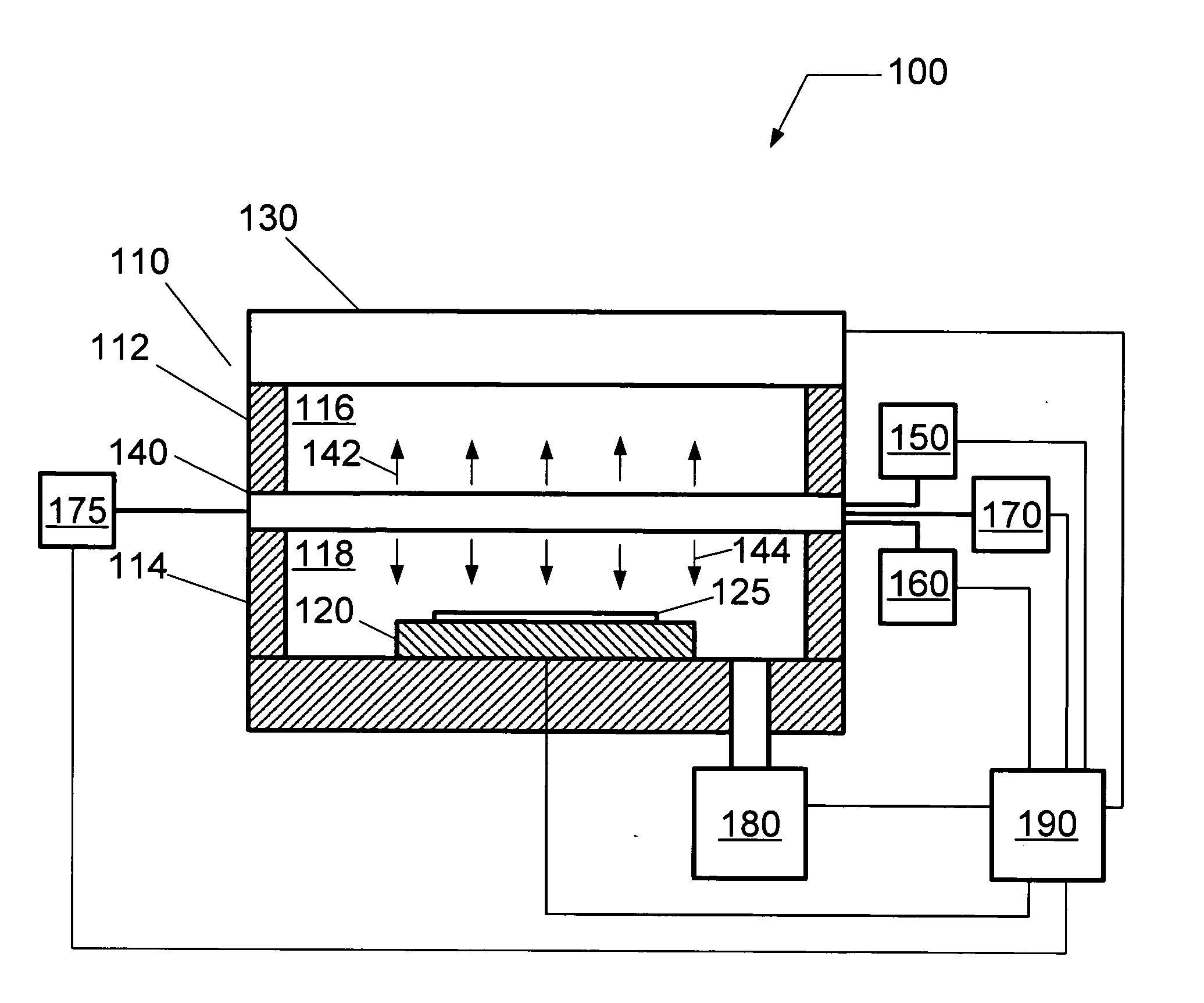
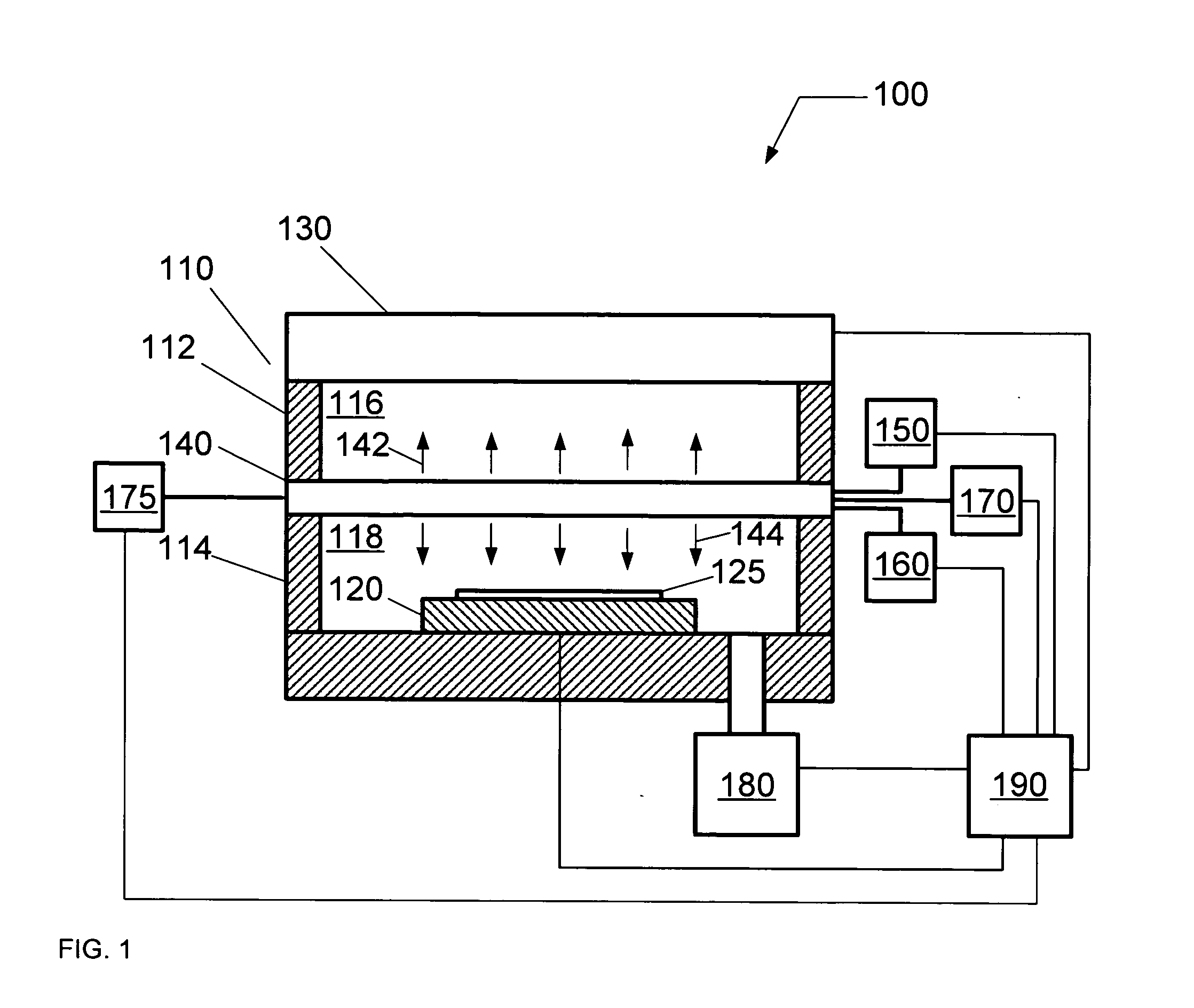
A method of treating a substrate includes disposing the substrate in a processing chamber having a first chamber portion configured to define a plasma space and a second chamber portion configured to define a process space, introducing a first gas to the plasma space and introducing a second gas to the process space. A plasma is formed in the plasma space from the first gas using a plasma source coupled to the upper chamber portion, and a process chemistry for treating the substrate is formed in the process space by providing a grid positioned between the first chamber portion and the second chamber portion such that the plasma can diffuse from the plasma space to the process space.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
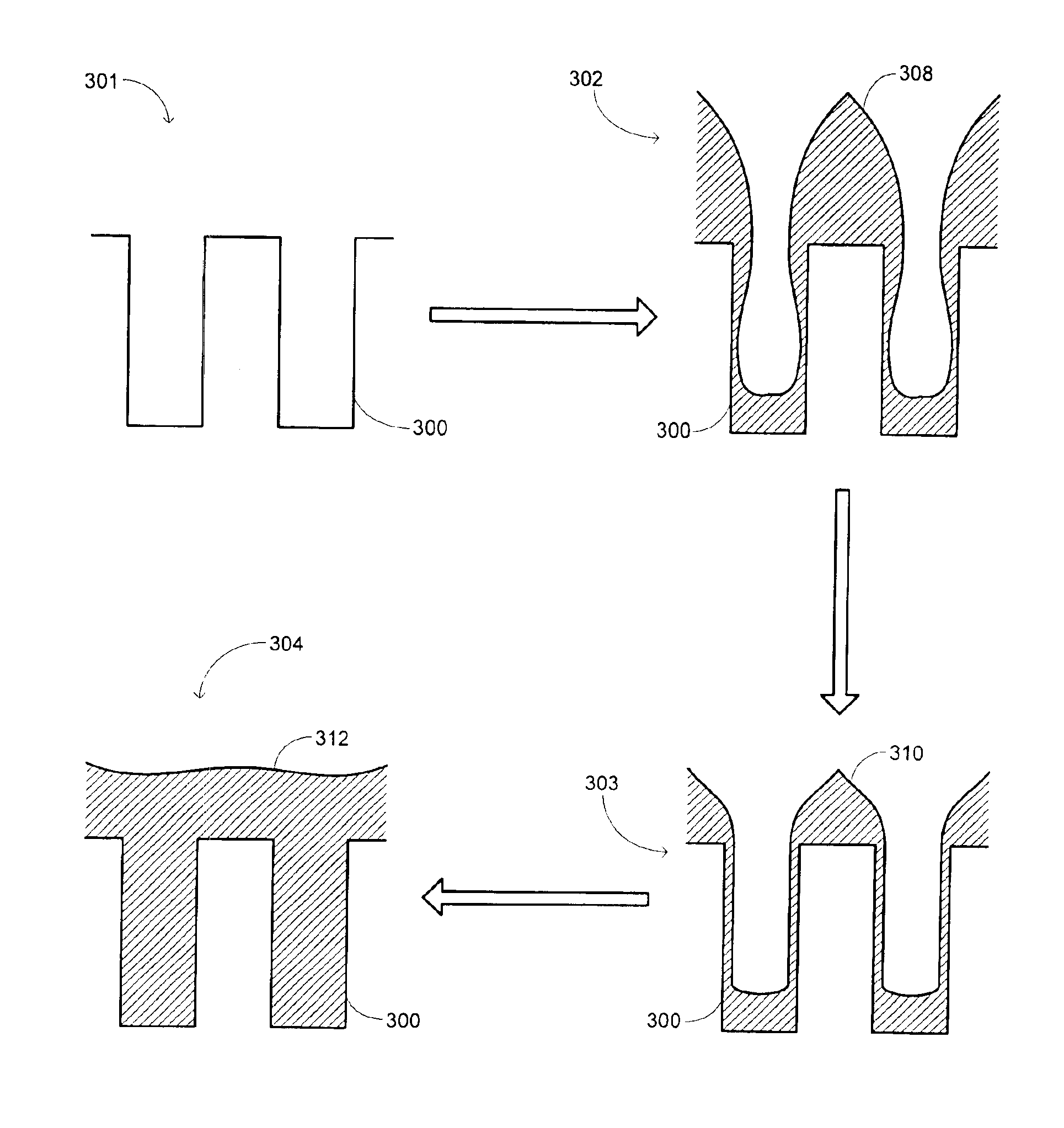
In-situ-etch-assisted HDP deposition using SiF4 and hydrogen
InactiveUS6903031B2Reduce concentrationImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenIon density
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
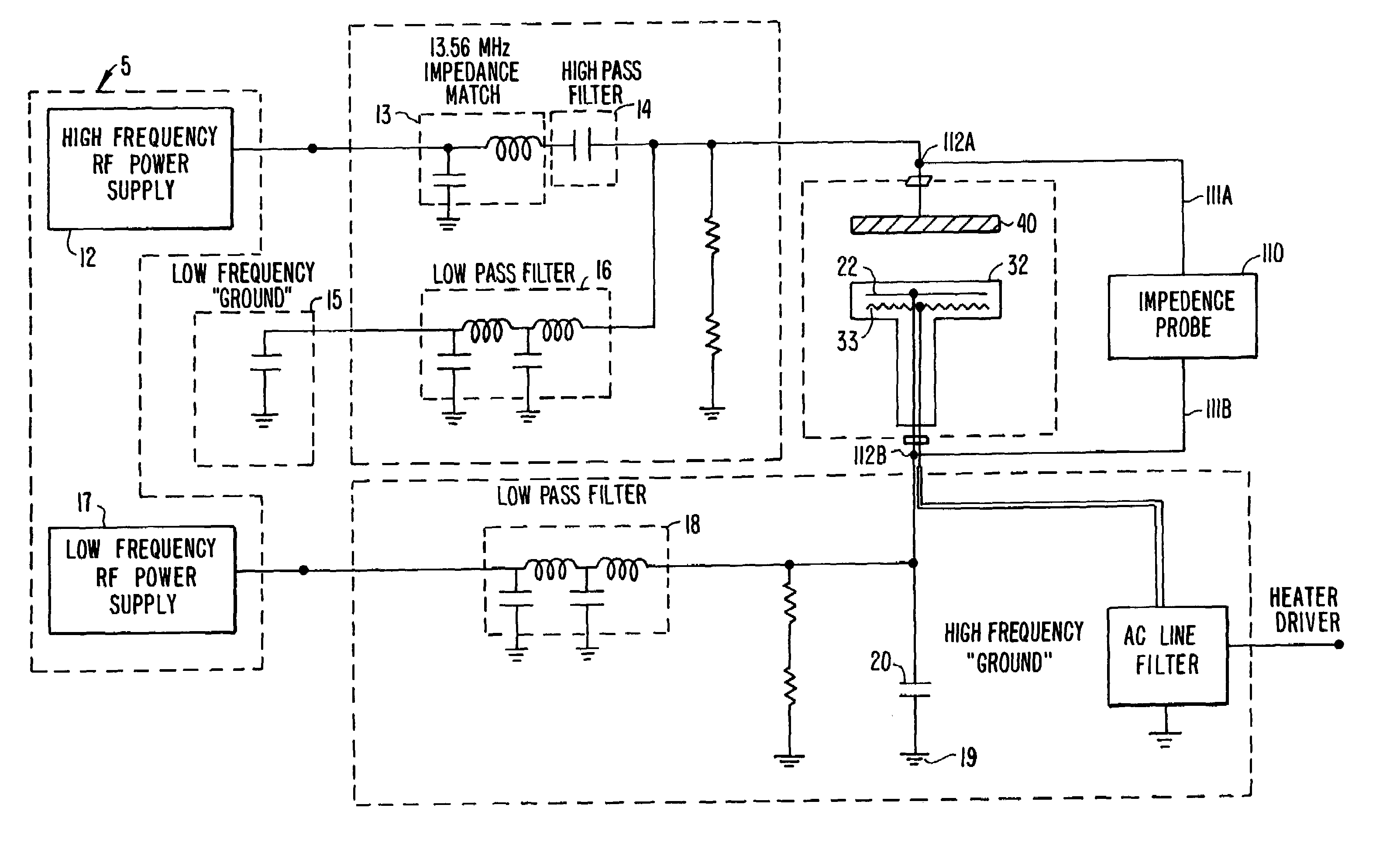
Method and apparatus for monitoring and adjusting chamber impedance
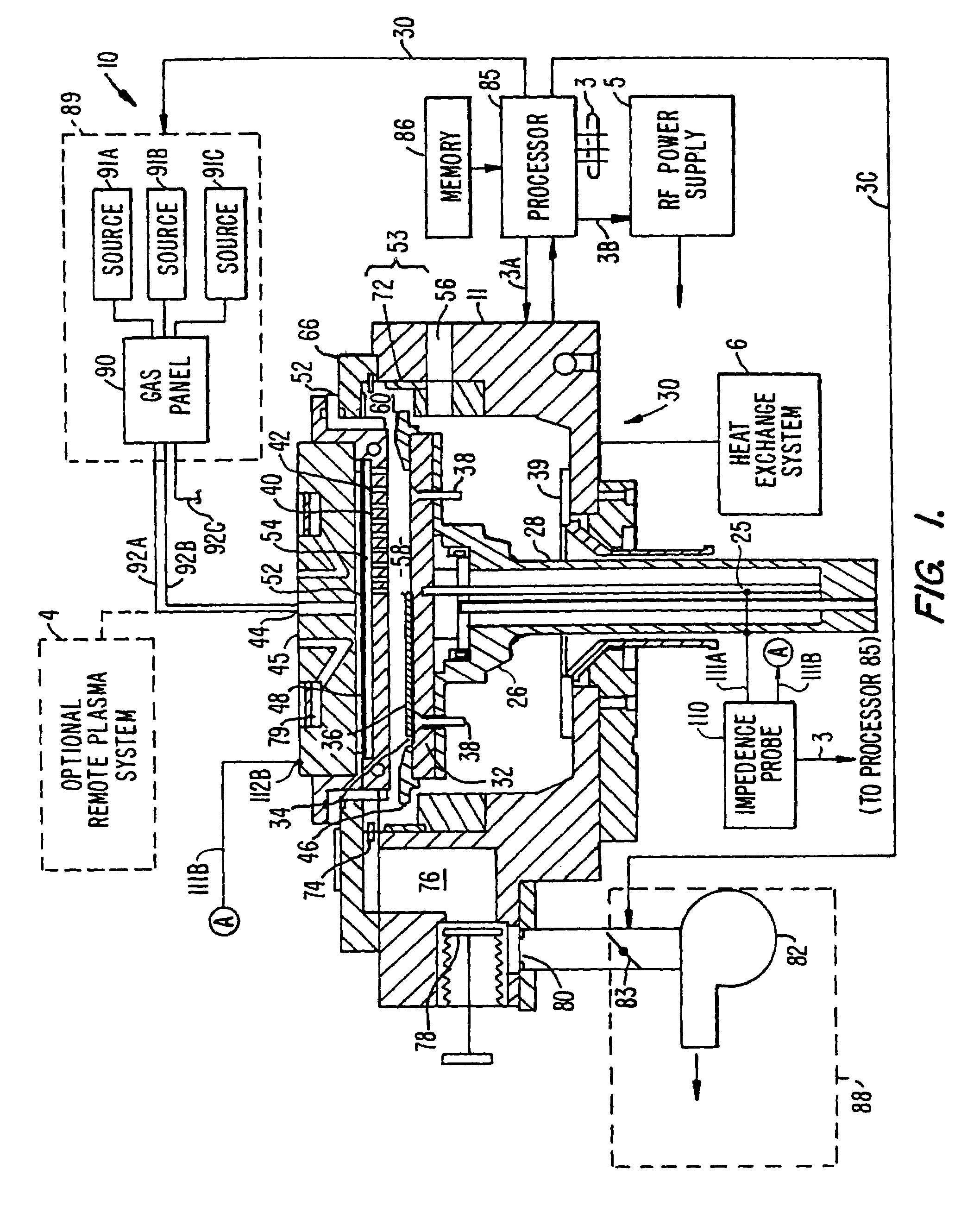
InactiveUS7004107B1Minimize phase interferencePotential for arcing is greatly reducedLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesElectricityControl system
A substrate processing system that includes a deposition chamber having a reaction zone, a substrate holder that positions a substrate in the reaction zone, a gas distribution system that includes a gas inlet manifold for supplying one or more process gases to said reaction zone, a plasma power source for forming a plasma from a process gas introduced into the reaction zone of the deposition chamber and an impedance monitor that is electrically coupled to the deposition chamber to measure an impedance level of the plasma. In a preferred embodiment, the substrate holder is a first electrode and the gas inlet manifold is a second electrode and RF power is supplied by the plasma power source to either the first or second electrodes to form the plasma. In another preferred embodiment, the processing system further includes a computer processor that is communicatively coupled to the impedance monitor and to other control systems of the processing system so that the computer processor can adjust the impedance of the deposition chamber during the course of an extended wafer run if the impedance drifts outside of a predetermined tolerance range.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Light-emitting device, method for manufacturing light-emitting device, and electronic apparatus
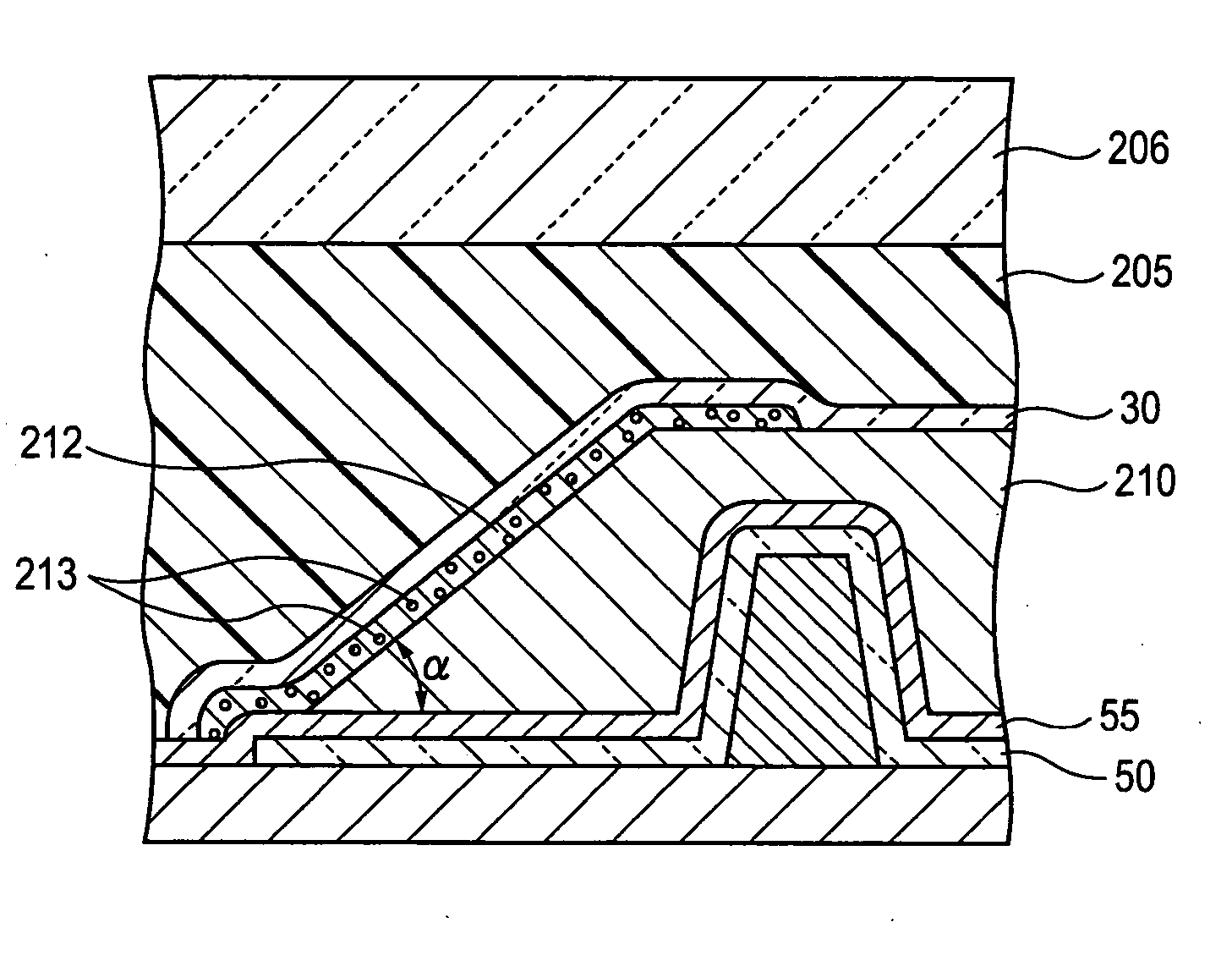
ActiveUS20060158111A1Prevent moisture penetrationPrevent penetrationDischarge tube luminescnet screensLayered productsEngineeringProtection layer
A light-emitting device includes a base; a plurality of first electrodes; a partition having a plurality of openings located at positions corresponding to the first electrodes; organic functional layers each arranged in the corresponding openings; a second electrode covering the partition and the organic functional layers; an organic buffer layer covering the second electrode; a gas barrier layer covering the organic buffer layer; and an intermediate protective layer, disposed between the organic buffer layer and the gas barrier layer, having an elasticity which is greater than that of the organic buffer layer and which is less than that of the gas barrier layer. These layers and electrodes are arranged on or above the base.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
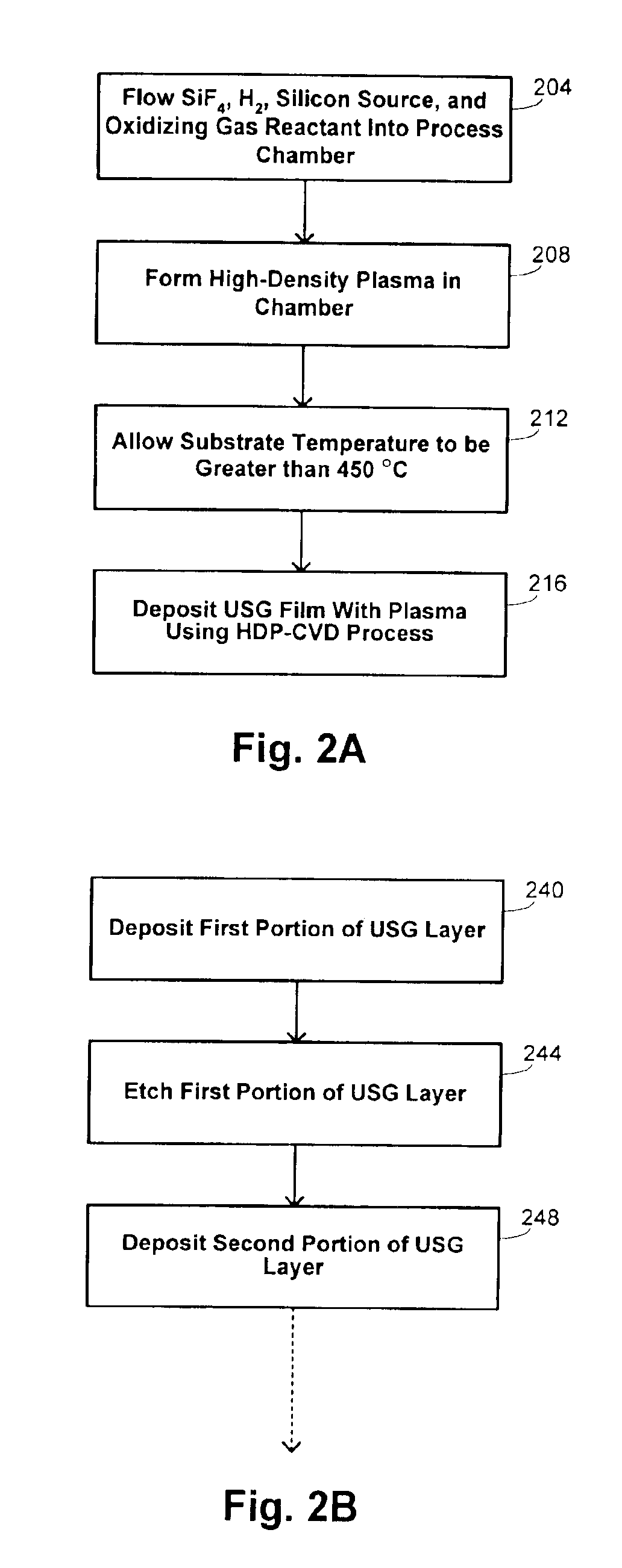
In-situ-etch-assisted HDP deposition using SiF4 and hydrogen
ActiveUS20050048801A1Good gapfill characteristicReduce fluorine concentrationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenIon density
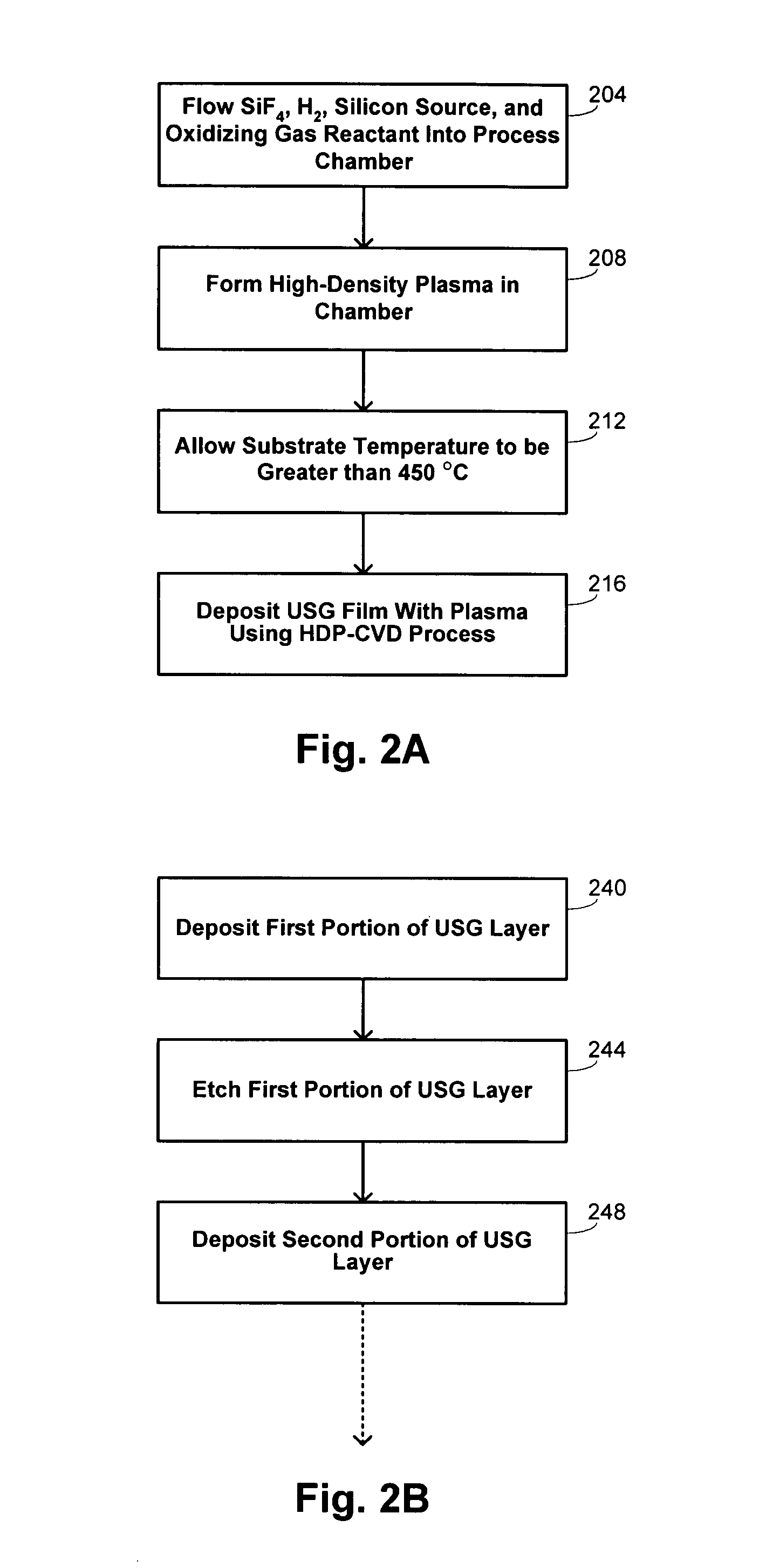
A process is provided for depositing an undoped silicon oxide film on a substrate disposed in a process chamber. A process gas that includes SiF4, H2, a silicon source, and an oxidizing gas reactant is flowed into the process chamber. A plasma having an ion density of at least 1011 ions / cm3 is formed from the process gas. The undoped silicon oxide film is deposited over the substrate with the plasma using a process that has simultaneous deposition and sputtering components. A temperature of the substrate during such depositing is greater than 450° C.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of cleaning an interior of a remote plasma generating tube and appartus and method for processing a substrate using the same
InactiveUS20050257890A1Efficient processingReduce throughputElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsRemote plasmaEngineering
A method of cleaning a remote plasma generating tube, and an apparatus and method for processing a substrate using the same, includes providing a cleaning gas into the remote plasma generating tube for generating a remote plasma, the remote plasma generating tube being connected to a processing chamber for processing a substrate using the remote plasma, forming a cleaning plasma from the cleaning gas, and removing particles formed inside the remote plasma generating tube using the cleaning plasma.
Owner:ULVAC INC +1
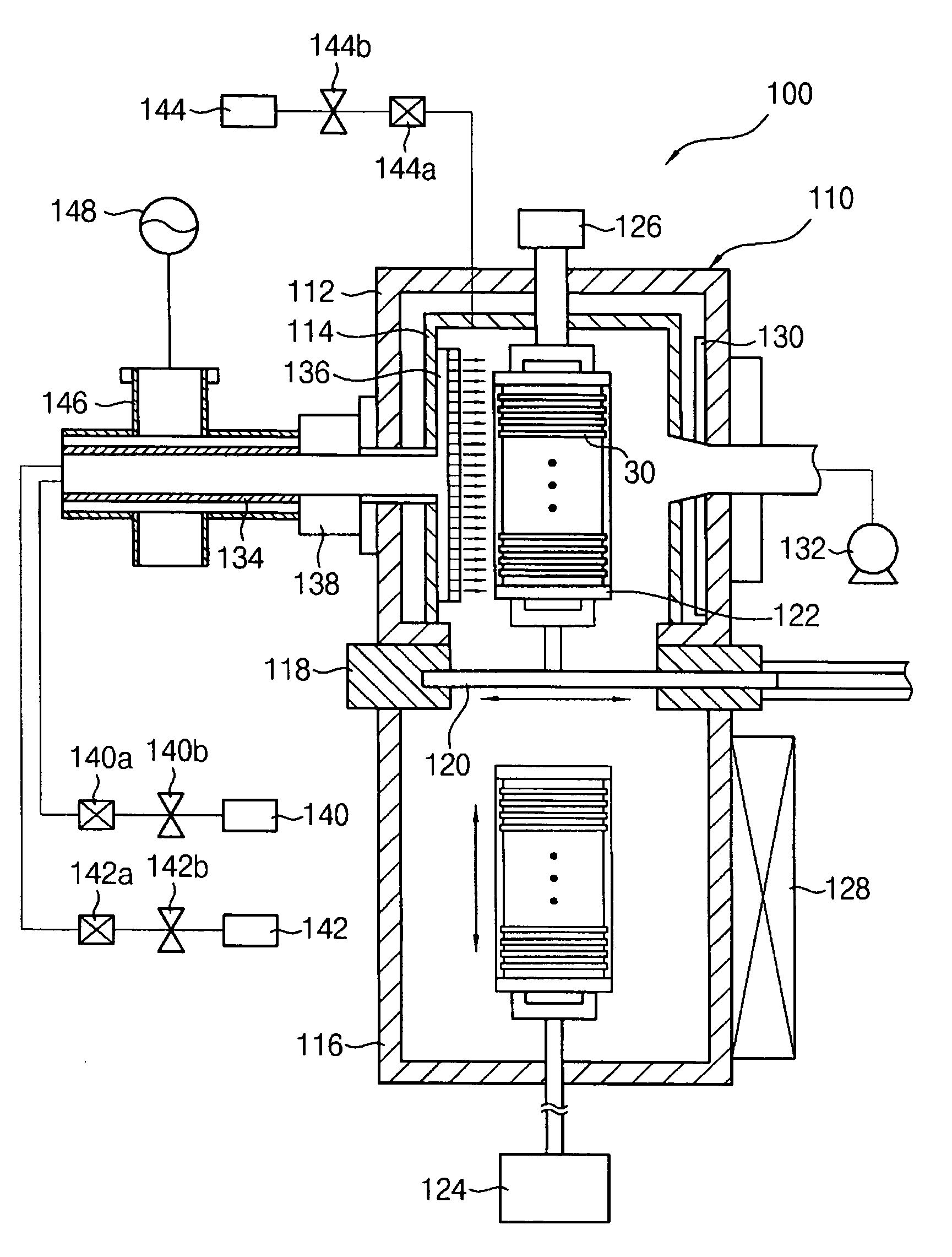
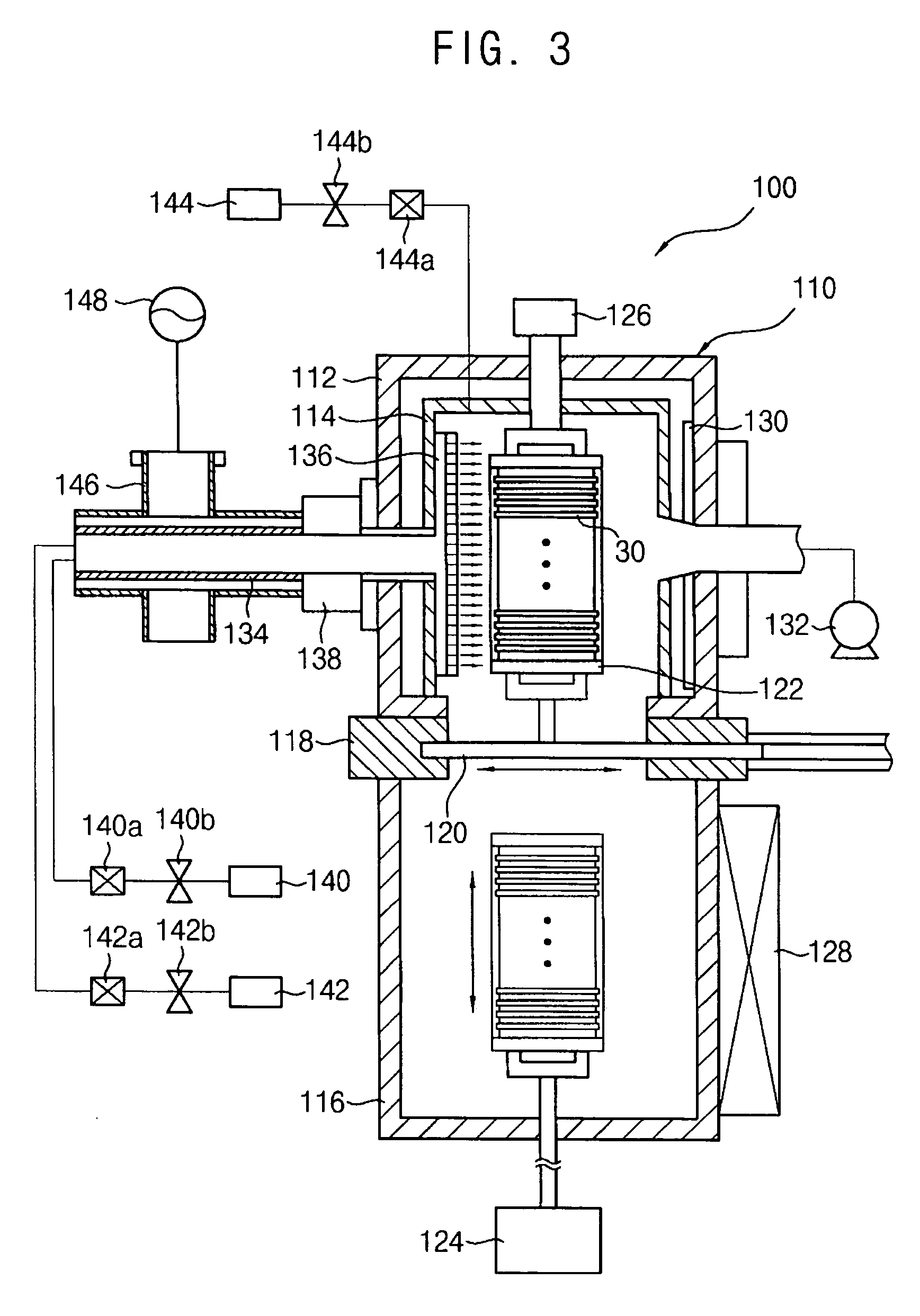
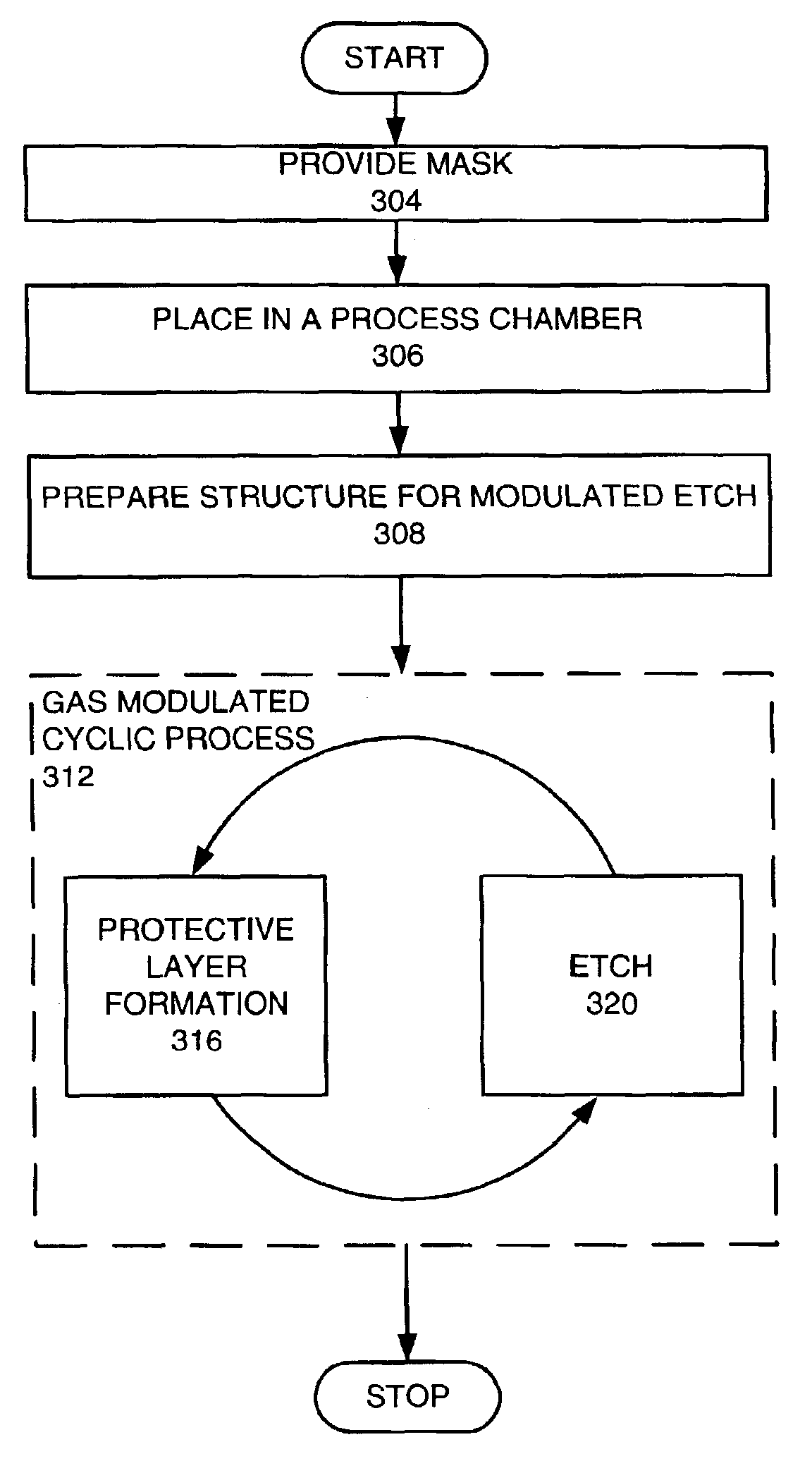
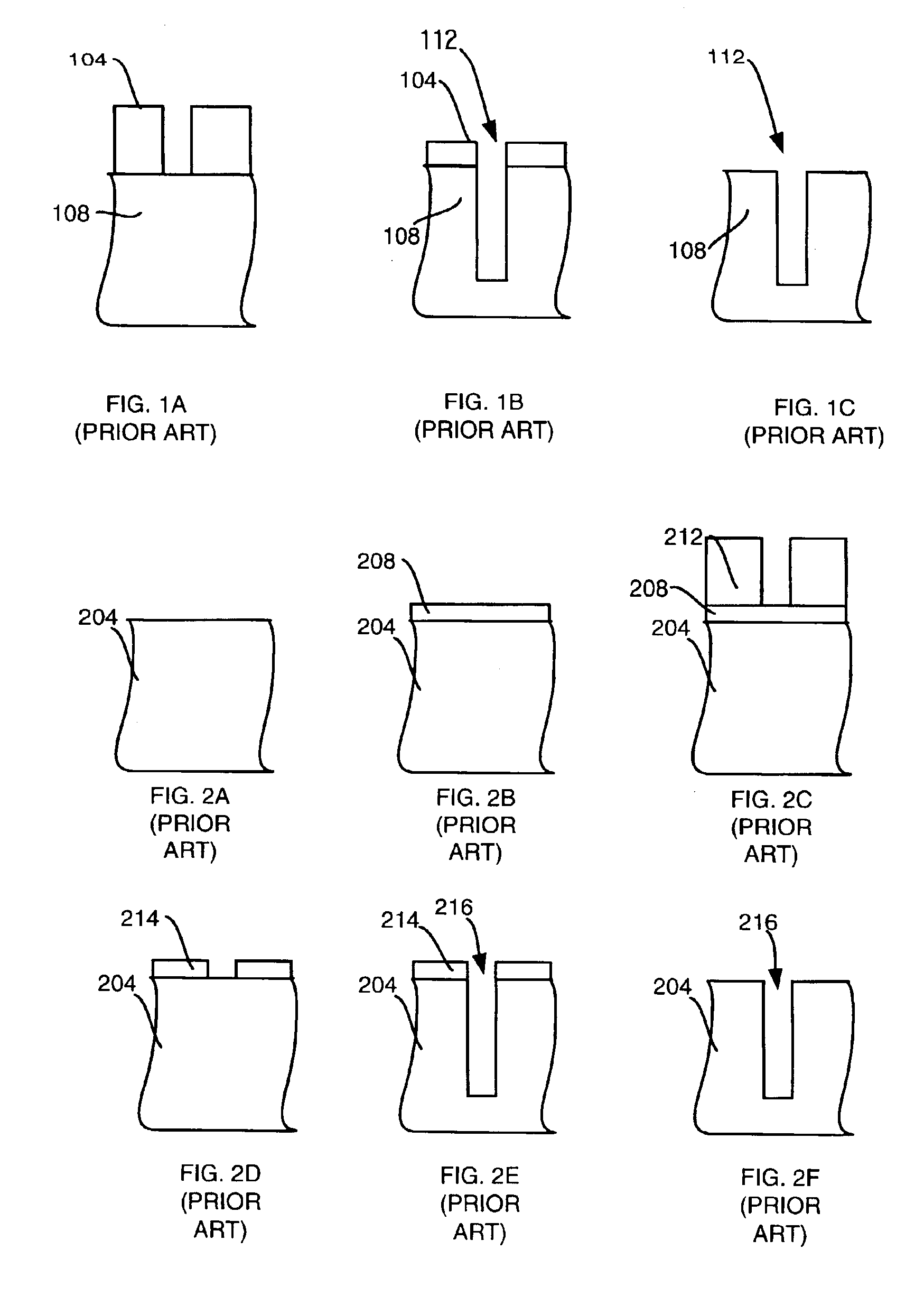
Method for plasma etching using periodic modulation of gas chemistry
InactiveUS6916746B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCyclic processGas chemistry
A method for etching a layer over a substrate is provided. A gas-modulated cyclic process is performed for more than three cycles. Each cycle comprises performing a protective layer forming phase using first gas chemistry with a deposition gas chemistry, which is performed in about 0.0055 to 7 seconds for each cycle and performing an etching phase for the feature through the etch mask using a second gas chemistry using a reactive etching gas chemistry, which is performed in about 0.005 to 14 seconds for each cycle. The protective layer forming phase comprises providing the deposition gas and forming a plasma from the deposition gas. Each etching phase comprises providing a reactive etching gas and forming a plasma from the reactive etching gas.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
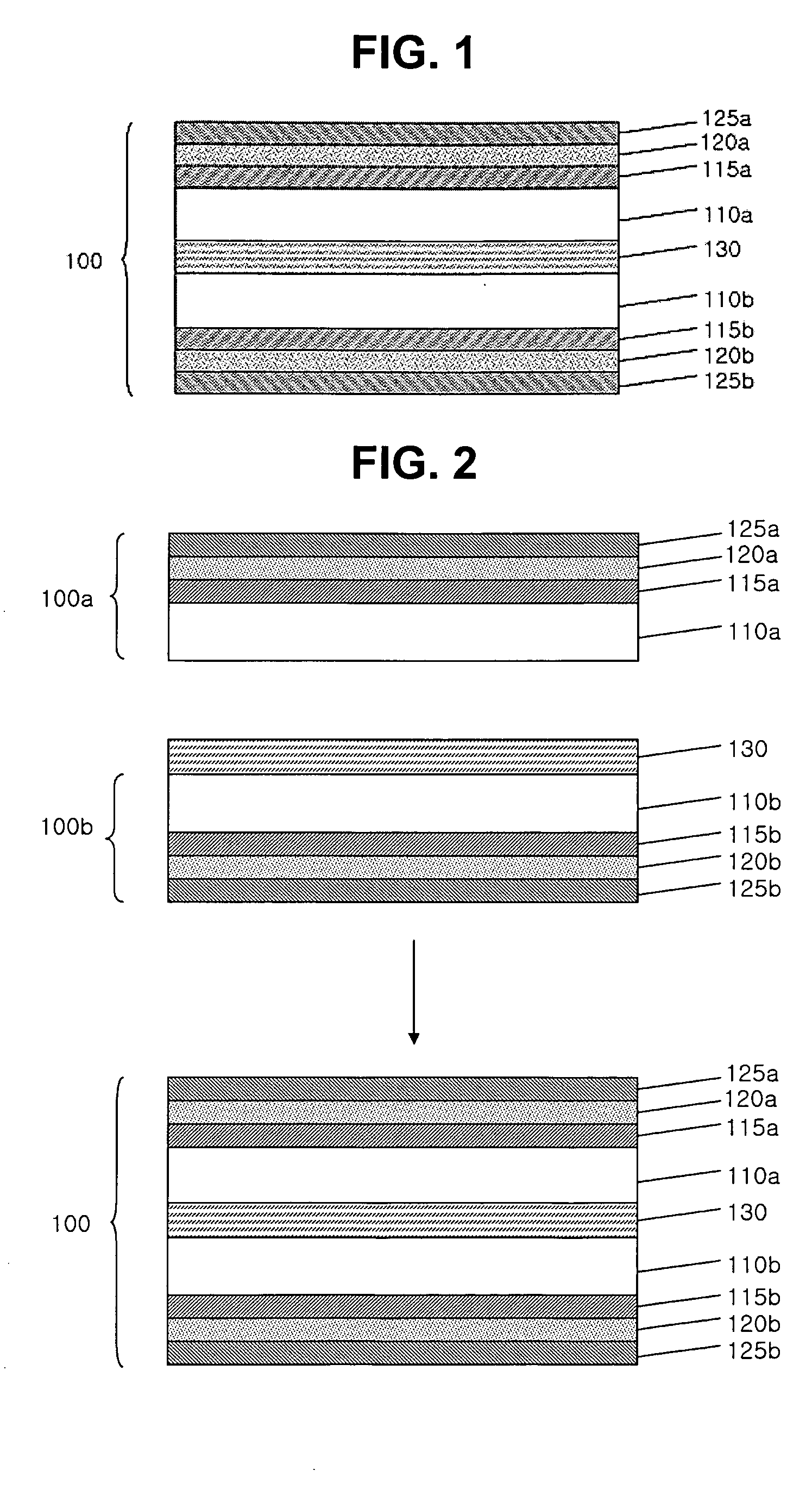
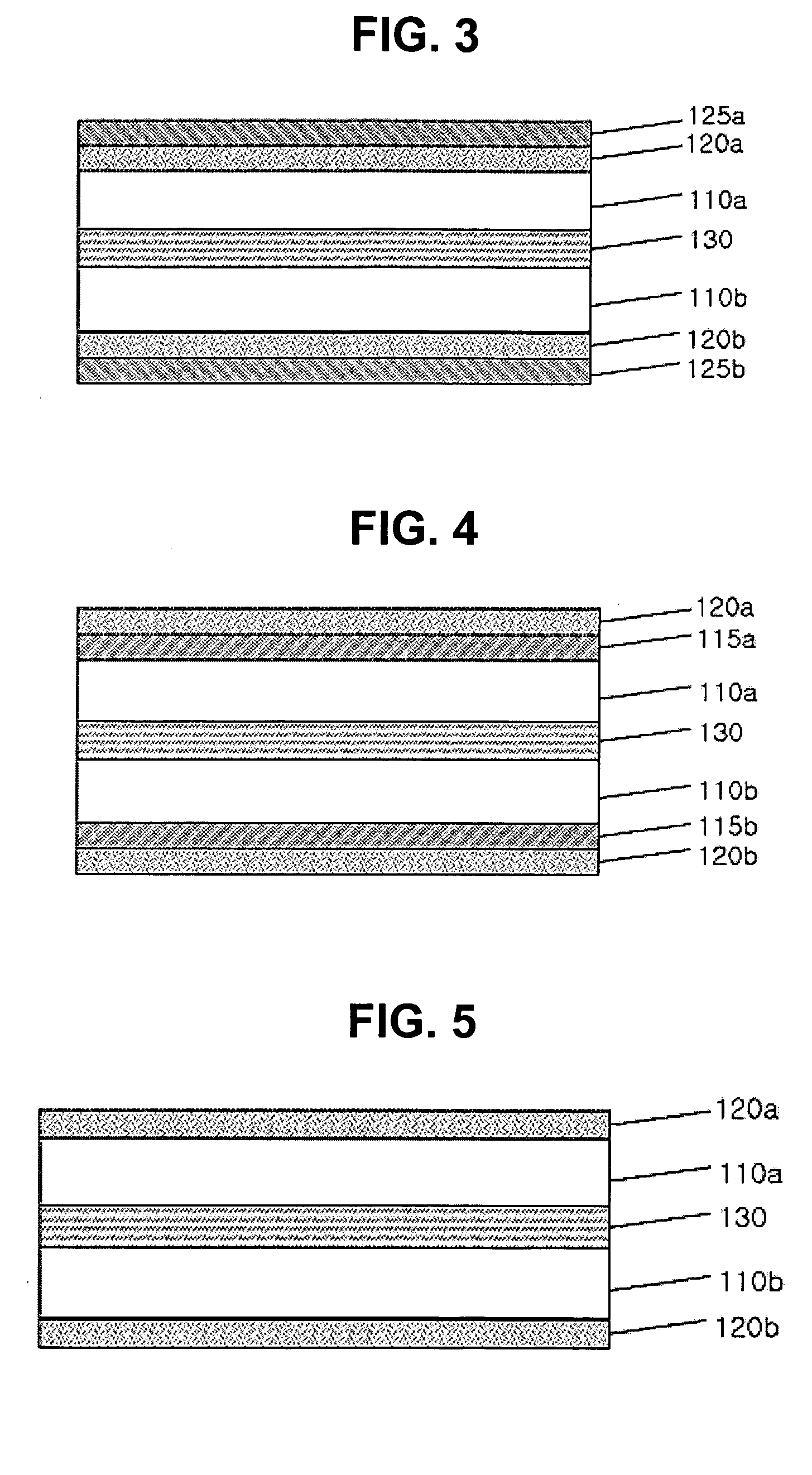
Plastic substrate having multi-layer structure and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20050175831A1Small coefficientGood dimensional stabilityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
The present invention relates to a plastic substrate having a multi-layer structure and a method for preparing the same. The plastic substrate of the present invention comprises plastic films attached to each other, and a first buffering layer of an organic-inorganic hybrid, a layer of gas barrier, and a second buffering layer of an organic-inorganic hybrid which are stacked on both sides of the plastic films in an orderly manner, each layer forming a symmetrical arrangement centering around the plastic films. Because the plastic substrate of the present invention has a small coefficient of thermal expansion, excellent dimensional stability, and superior gas barrier properties, it can replace the brittle and heavy glass substrate in display devices. Also, it can be used for a variety of packaging or container materials in applications requiring superior gas barrier properties.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Holey optical fiber with random pattern of holes and method for making same
ActiveUS20050094954A1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingSilicon dioxideAir bubble
A random array of holes is created in an optical fiber by gas generated during fiber drawing. The gas forms bubbles which are drawn into long, microscopic holes. The gas is created by a gas generating material such as silicon nitride. Silicon nitride oxidizes to produce nitrogen oxides when heated. The gas generating material can alternatively be silicon carbide or other nitrides or carbides. The random holes can provide cladding for optical confinement when located around a fiber core. The random holes can also be present in the fiber core. The fibers can be made of silica. The present random hole fibers are particularly useful as pressure sensors since they experience a large wavelength dependant increase in optical loss when pressure or force is applied.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
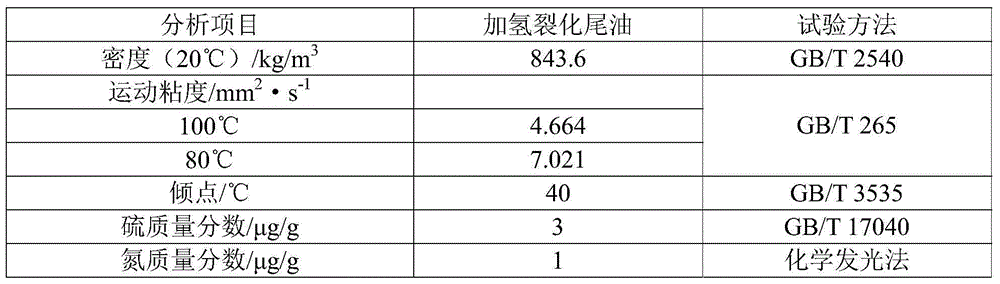
Hydroisomerization catalyst, preparation method and application thereof, and hydroisomerization method for hydrocracked tail oil
ActiveCN105582992AHigh catalytic activityHigh isomerization reaction selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon oils refiningMolecular sieveHalogen
The invention discloses a hydroisomerization catalyst, a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a) providing a catalyst precursor containing a carrier, and a compound containing noble metals in the VIII group and a compound containing a second metal which are both supported on the carrier, wherein the two compounds hereinabove are both non-oxides, the second metal is one or more than two selected from the metal in the VB group, the metal in the VIB group, non-noble metal in the VIII group and lanthanum-series metals, the carrier containing mesoporous molecular sieve; and b) roasting the catalyst precursor in an atmosphere formed by a gas containing an oxidizing gas and a halogen-containing compound. The invention also discloses a hydroisomerization method for hydrocracked tail oil with the hydroisomerization catalyst. The hydroisomerization catalyst, when being used in the hydroisomerization for the hydrocracked tail oil, can be used for producing an isomerized product having high viscosity index and low pour point, which is suitable for being used as lubricant basic oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Emissive device, process for producing emissive device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20070132381A1Avoid crackingIncrease productivityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOptoelectronicsElectron
An emissive device includes a substrate; a plurality of first electrodes; pixel banks having a plurality of openings each corresponding to the position of a corresponding one of the first electrodes; organic function layers disposed in at least the openings; a second electrode disposed so as to cover the pixel banks and the organic function layers; a first inorganic layer disposed over the second electrode; a second inorganic layer disposed over the first inorganic layer; an organic buffer layer disposed over the second inorganic layer; and a gas barrier layer disposed over the organic buffer layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Two-component on-site foam system and its use for foaming openings for the purpose of fire protection
InactiveUS20020020827A1High foaming rateIncreased fire resistance enduranceOther chemical processesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPolyesterVolumetric Mass Density
A two-component on-site foam system for producing an intumescing fire protection foam is described with a density of less than 200 kg / m3 and an increased fire resistance endurance, with a polyol component (A), which contains at least one polyol, one catalyst for the reaction between the polyol and the polyisocyanate, water or a blowing agent based on a compressed or liquefied gas as foam-forming agent and at least one intumescing material based on an acid-forming agent, a carbon-supplying compound and a gas-forming agent, and a polyisocyanate component (B), which contains at least one polyisocyanate, wherein the polyol component (A) contains at least one polyester polyol, at least one aminopolyol, at least one halogen-containing polyol, at least one acidforming agent, expanding graphite and at least one ash crust stabilizer, the quantitative ratios of the polyols to the polyisocyanate or polyisocyanates being matched so that, when the polyol component (A) is mixed with the polyisocyanate component (B) as specified, the molar ratio of isocyanate groups of the polyisocyanate to the hydroxyl groups of the polyol (NCO: OH ratio) is larger than 1: 1, as well as to the use of this system for filling openings, cable and pipe leadthroughs in walls, floors and / or ceilings of buildings with foam for the purpose of fire protection.
Owner:HILTI AG
Method and apparatus for controlling a gas cluster ion beam formed from a gas mixture
ActiveUS20090140165A1Scattering properties measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas analysisGas cluster ion beam
Methods and apparatus for controlling a gas cluster ion beam formed from a plurality of process gases in a gas mixture. The methods and apparatus involve measuring gas analysis data relating to the composition of the gas mixture and modifying the irradiation of the workpiece in response to the detected parameter. The gas analysis data can be derived from samples of the composition of the gas mixture flowing from a gas source to the gas cluster ion beam apparatus or samples of the residual gases inside the vacuum vessel of the gas cluster ion beam apparatus.
Owner:TEL EPION
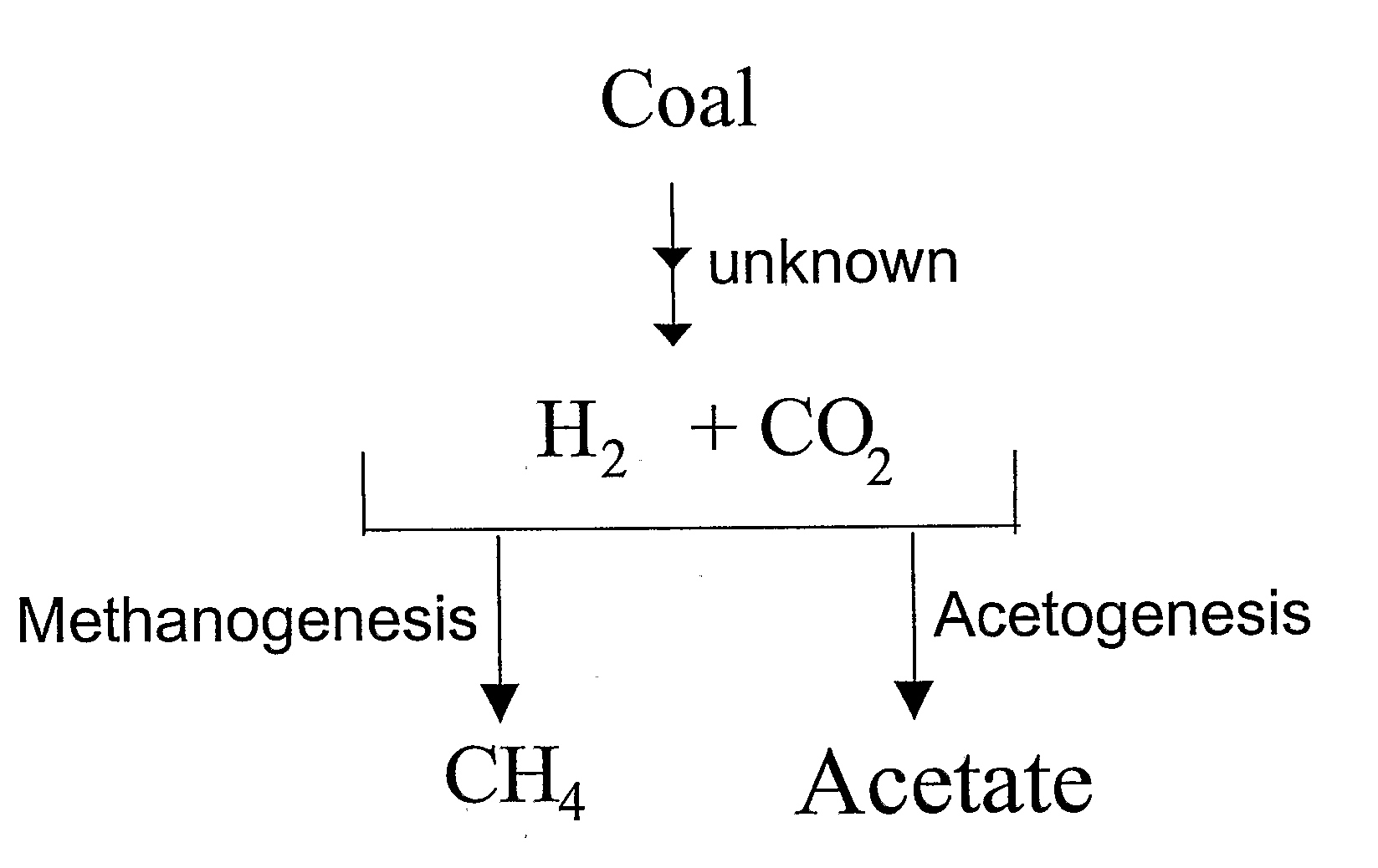
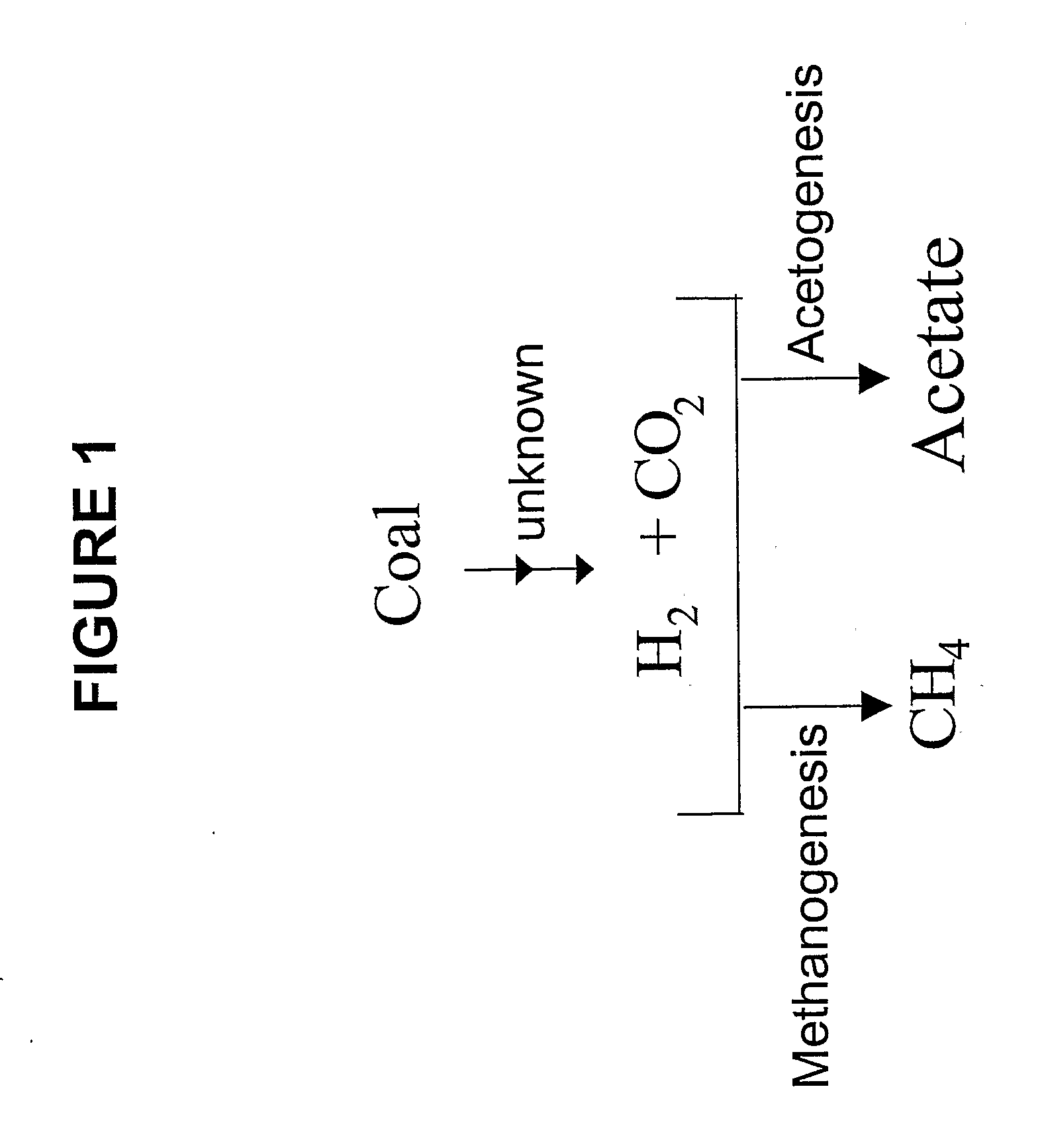
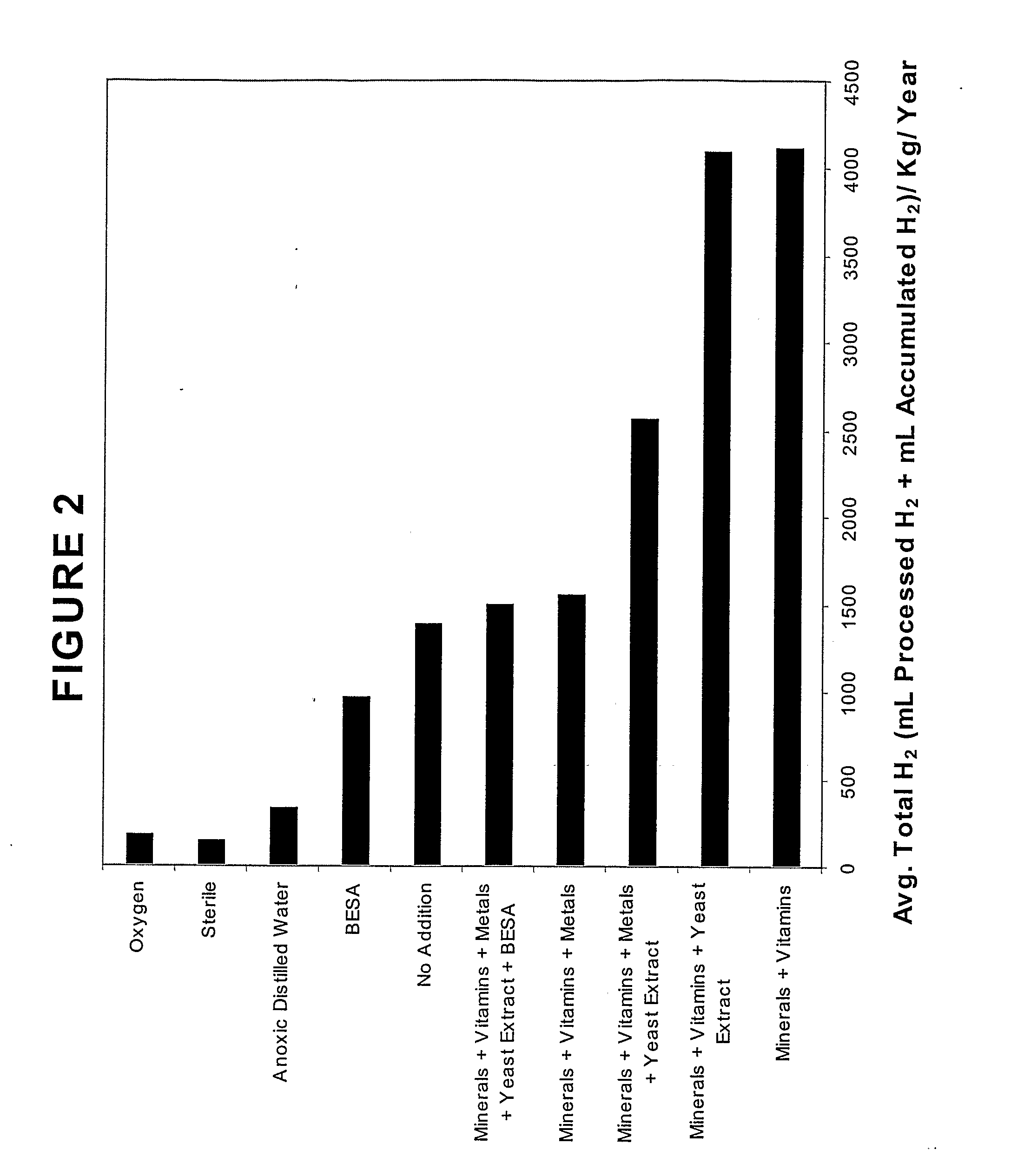
Generation of Hydrogen from Hydrocarbon Bearing Materials
ActiveUS20070248531A1Enhanced methanogenesisIncreased hydrogen productionHydrogenWaste based fuelHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSand granules
Disclosed are strategies for the economical microbial generation of hydrogen, useful as an alternative energy source, from hydrocarbon-rich deposits such as coal, oil and / or gas formations, oil shale, bitumen, tar sands, carbonaceous shale, peat deposits and sediments rich in organic matter through the management of the metabolism of microbial consortia.
Owner:TRANSWORLD TECH
Coatings for lithium titanate to suppress gas generation in lithium-ion batteries and methods for making and use thereof
ActiveUS20140113197A1Reduced and suppressed gas generationLess hydrogenMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode manufacturing processesElectrical batteryElectrochemical cell
An electroactive material for use in an electrochemical cell, like a lithium-ion battery, is provided. The electroactive material comprises lithium titanate oxide (LTO) and has a surface coating with a thickness of less than or equal to about 30 nm that suppresses formation of gases within the electrochemical cell. Methods for making such materials and using such materials to suppress gas formation in electrochemical cells are likewise provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Plasma processing system for treating a substrate
ActiveUS7396431B2Reduce harmReduce the possibility of damageElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess chemistryEngineering
A plasma processing system for treating a substrate includes a processing chamber including a first chamber portion configured to receive a first gas for providing a plasma space, and a second chamber portion configured to receive a second gas for providing a process space having process chemistry to treat the substrate. A substrate holder is coupled to the second chamber portion of the processing chamber, and configured to support the substrate proximate the process space, and a plasma source is coupled to the first chamber portion of the processing chamber, and configured to form a plasma in the plasma space. A grid is located between the plasma space and the process space, and configured to permit the diffusion of the plasma between the plasma space and the process space in order to form the process chemistry from the process gas.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
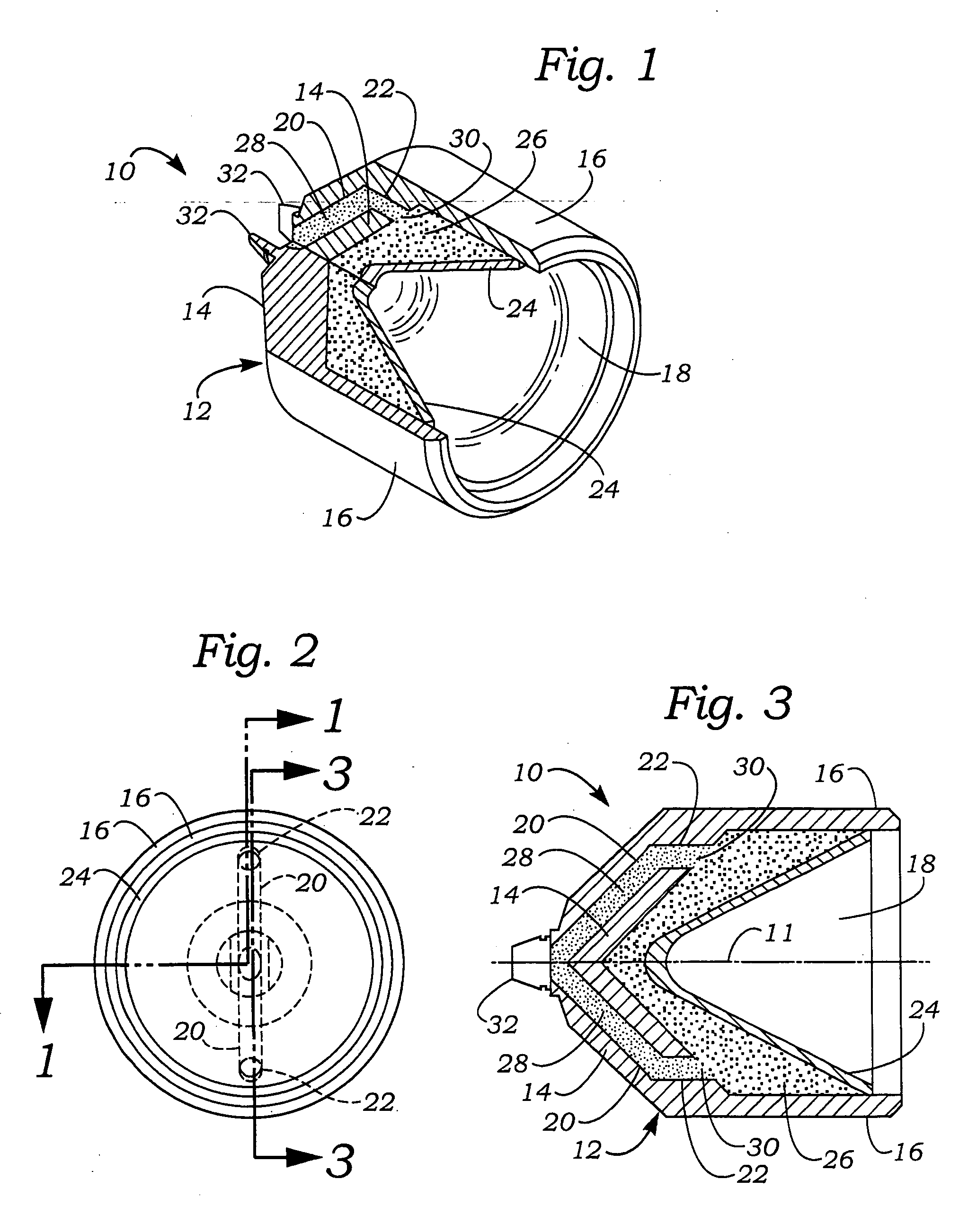
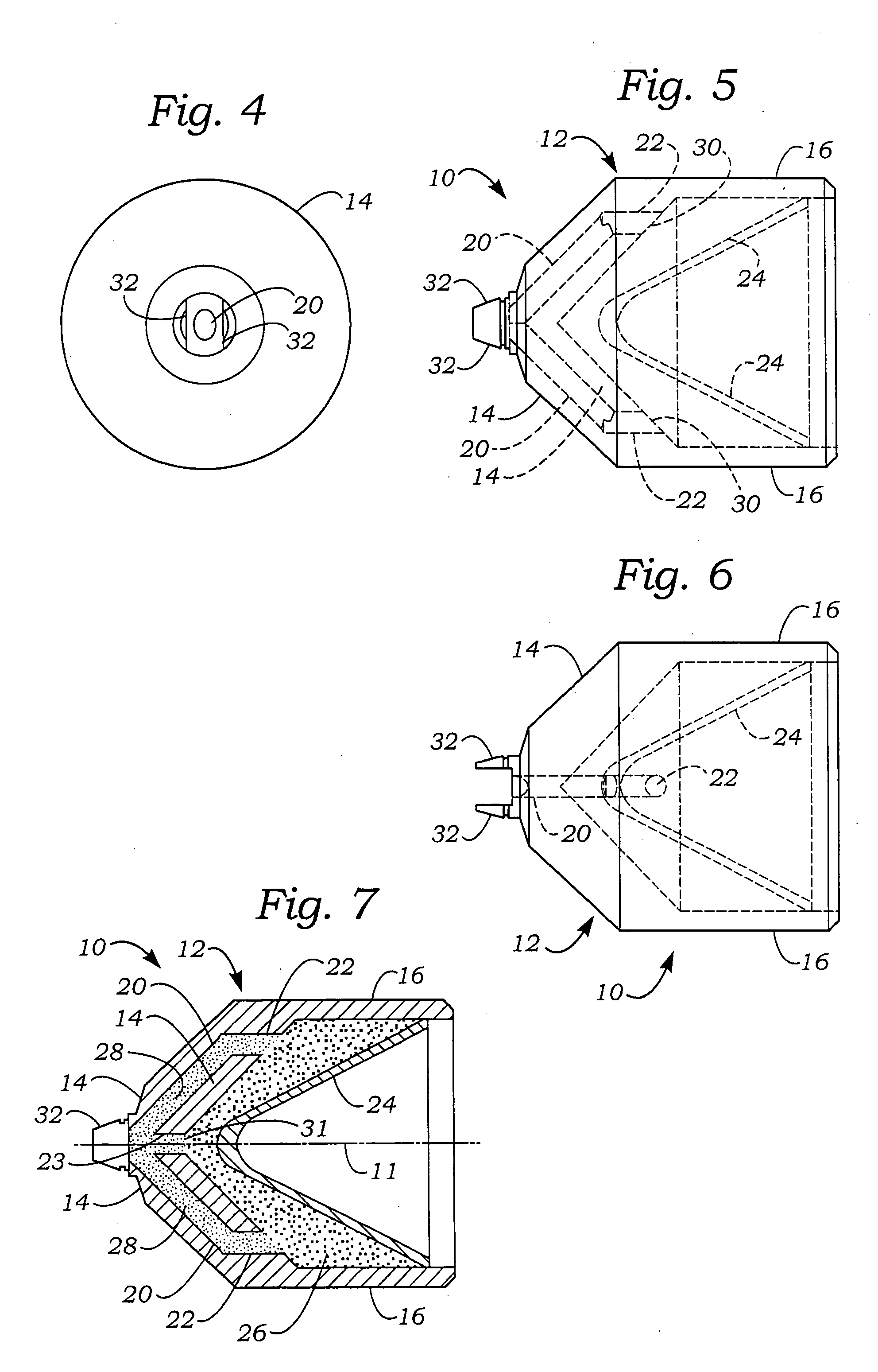
Unique multiple point initiated shaped charge perforator and method for its use
InactiveUS20050188878A1Minimize potentialImprove effectivenessAmmunition projectilesExplosive chargesInitiation pointShaped charge
A non-linear shaped charge perforator for use in perforating an oil and gas formation into which a wellbore has been drilled comprises a monolithic, axisymmetric metal case in which is disposed a main explosive charge between the front of the case, which is closed with a concave metal liner, and the closed back end of the case. The main explosive charge contains multiple initiation points, preferably two initiation points located about 180° apart on the outside surface of the charge, so that when the perforator is detonated the main charge is initiated such that the metal liner is collapsed into a non-circular jet, preferably a fan-shaped jet, that pierces the casing of the wellbore and forms non-circular perforations, preferably slot-shaped perforations, in the surrounding formation.
Owner:BAKER ERNEST L +5
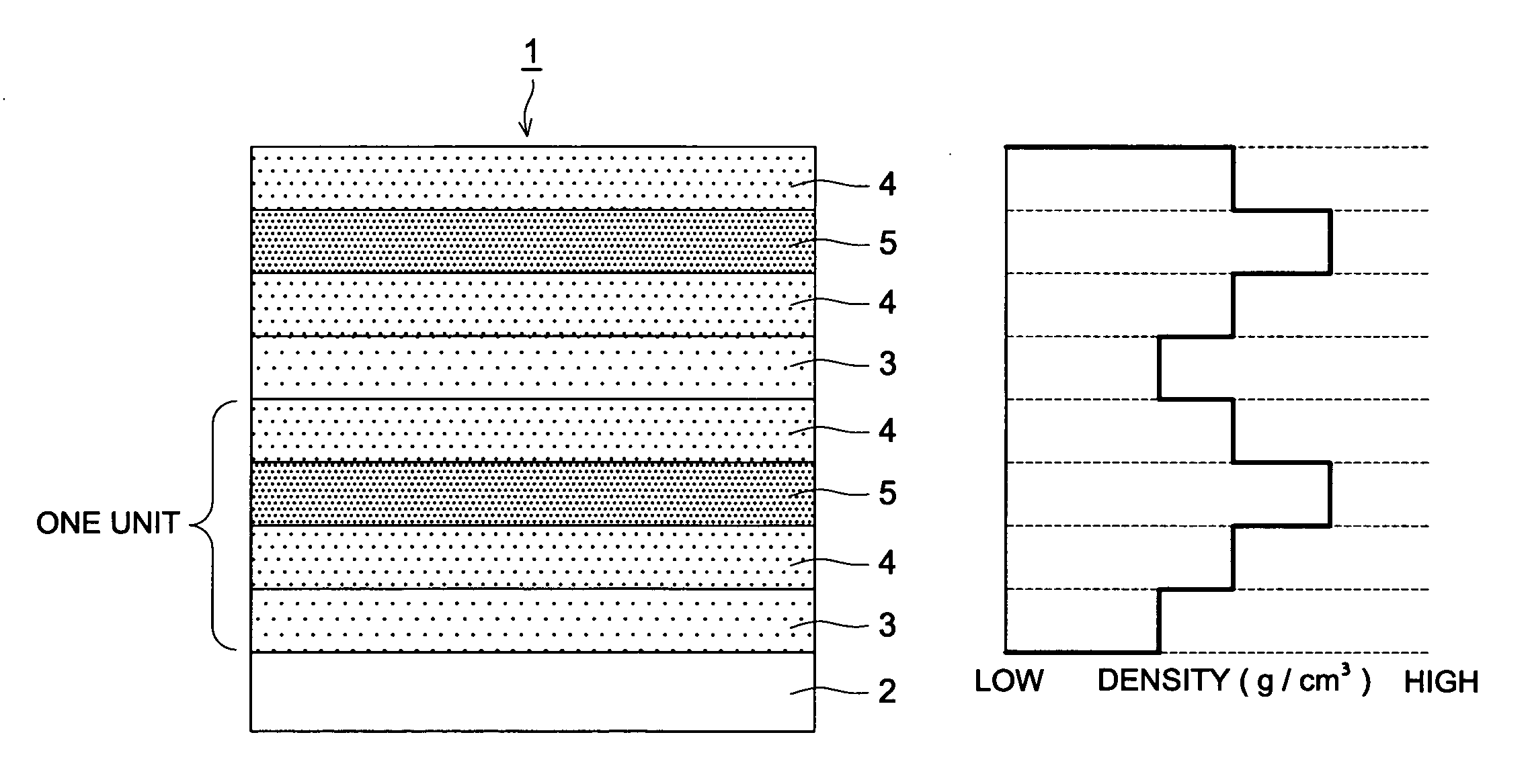
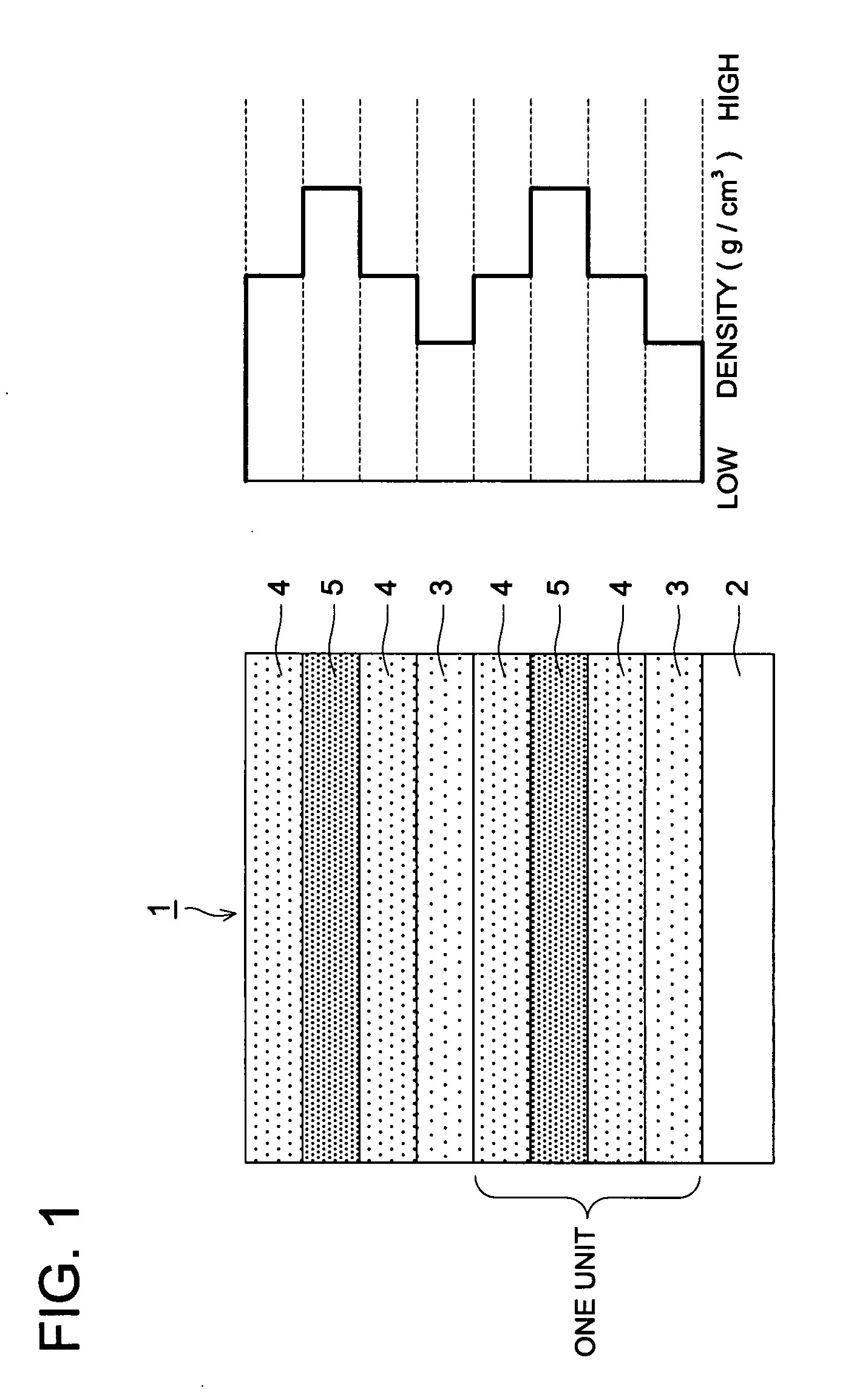
Transparent Gas Barrier Film
ActiveUS20080085418A1Improve adhesionHigh transparencySynthetic resin layered productsSolid-state devicesHigh densityLow density
A transparent gas barrier film comprising a substrate having thereon a gas barrier layer comprising at least a low density layer and a high density layer, wherein one or more intermediate density layers are sandwiched between the low density layer and the high density layer.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
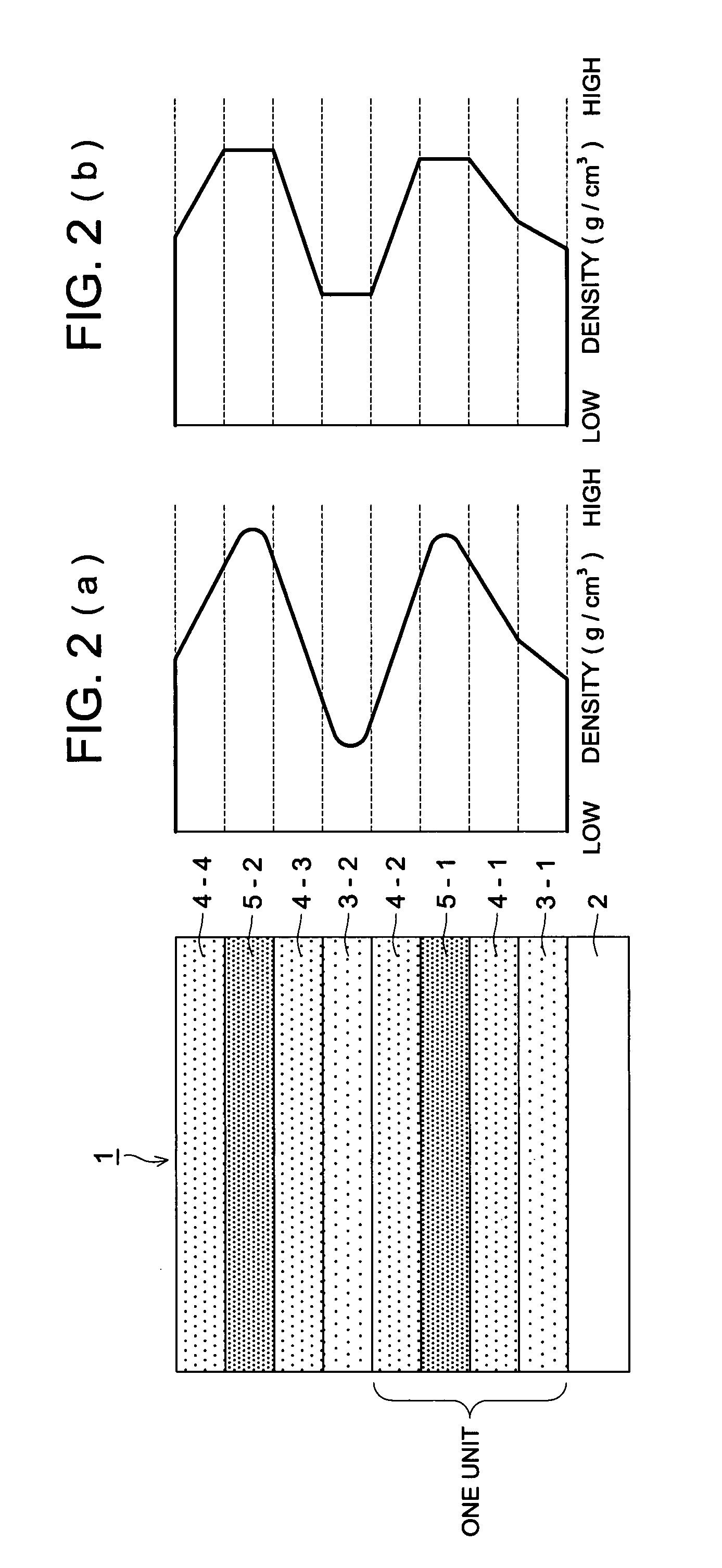
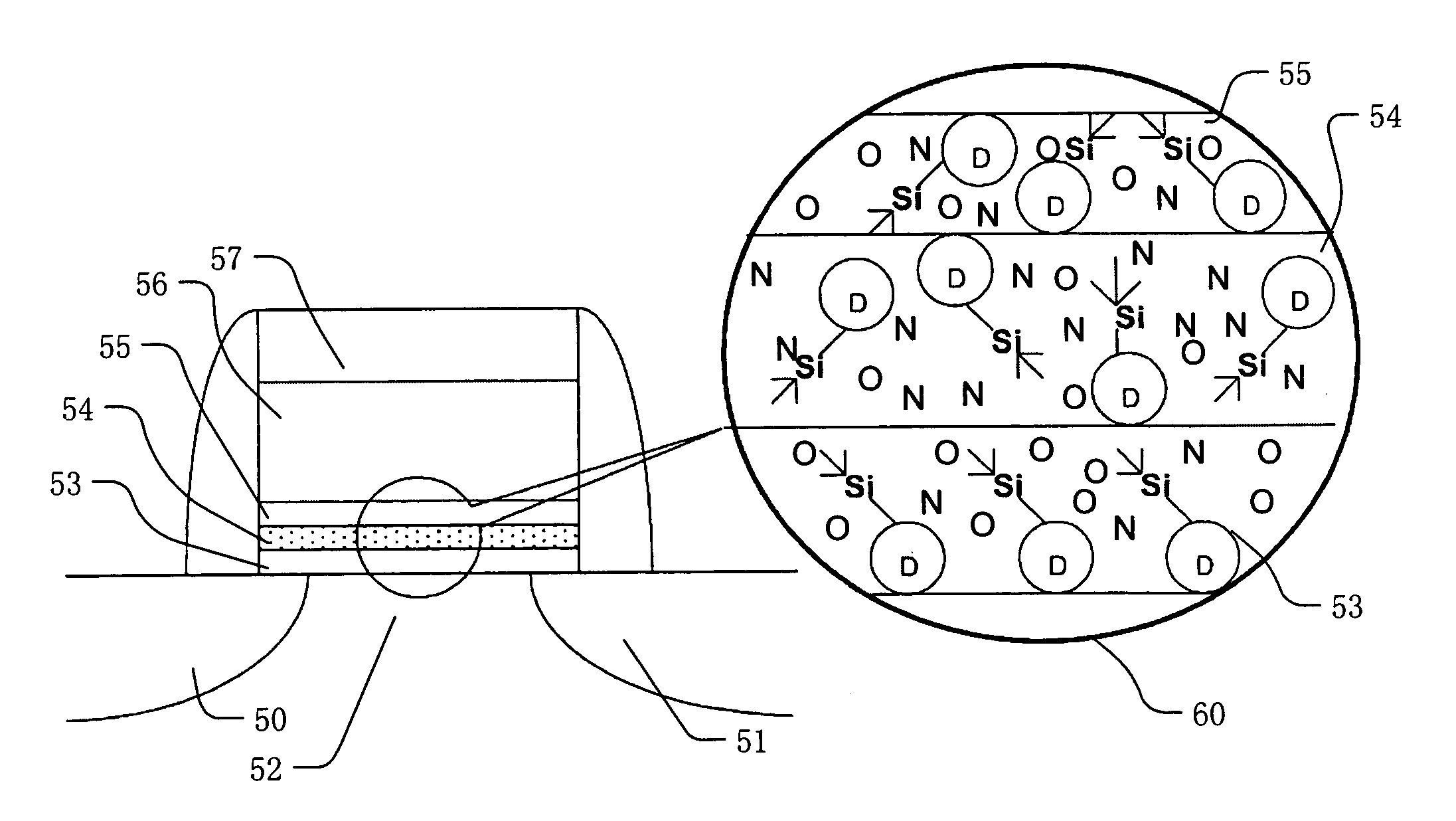
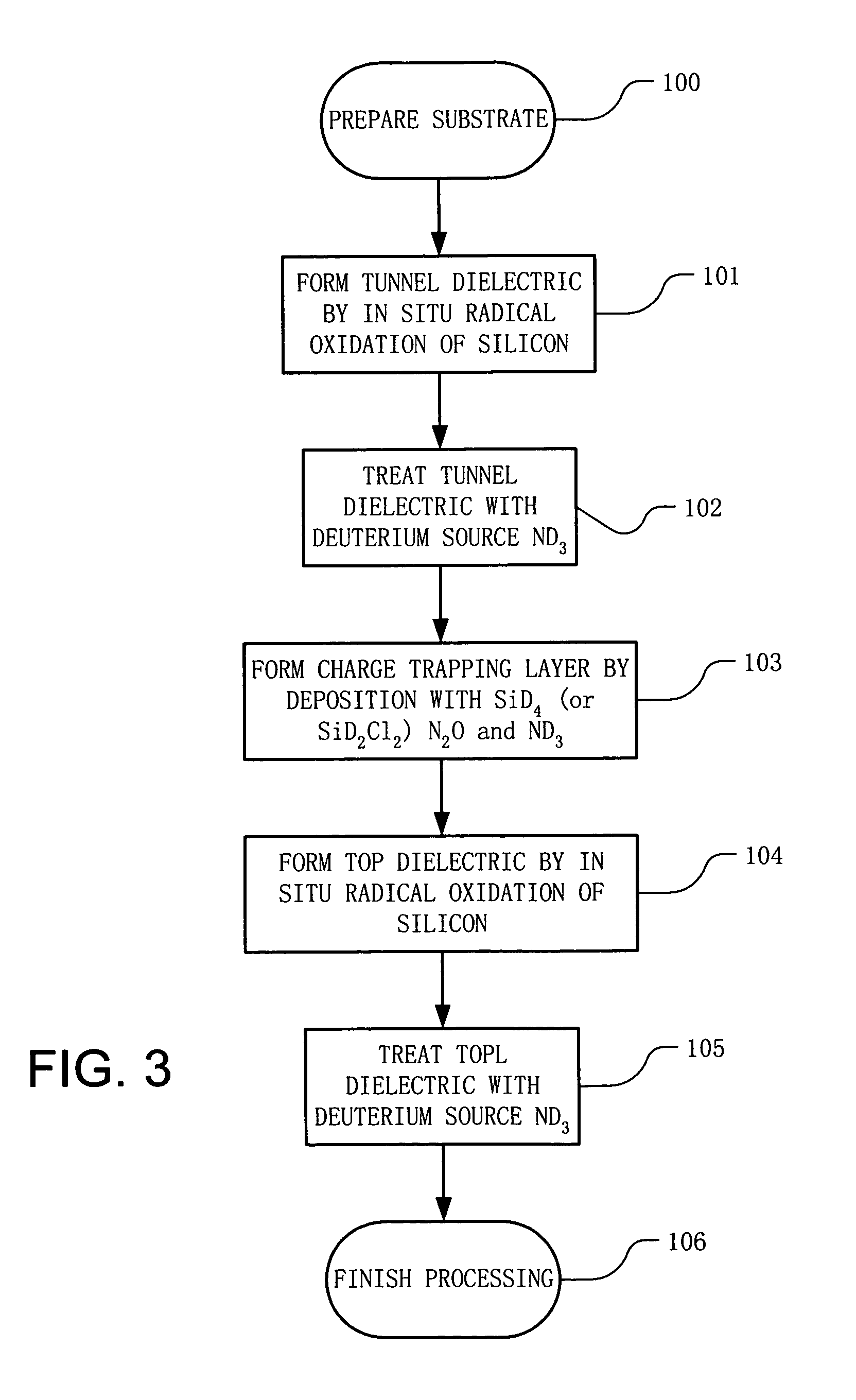
Memory device and method of manufacturing including deuterated oxynitride charge trapping structure
ActiveUS7060594B2Improved data retention characteristicReduce in quantitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrappingIsotope
A method for manufacturing a charge storage stack including a bottom dielectric layer, a charge trapping structure on the bottom dielectric layer, and a top dielectric layer, each comprising silicon oxynitride, are formed using reactant gases that comprise hydrogen, where the hydrogen comprises at least 90 percent deuterium isotope. The bottom dielectric layer, charge trapping structure, and top dielectric layer each have respective relative concentrations of oxygen and nitrogen. The relative concentration of nitrogen in the charge trapping structure is high enough for the material to act as a charge trapping structure with an energy gap that is lower than the energy gaps in the bottom dielectric layer and the top dielectric layer. The presence of oxygen in the charge trapping structure reduces the number of available dangling bonding sites, and thereby reduces the number of hydrogen inclusions in the structure.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD +1
Integrated process modulation (IPM) a novel solution for gapfill with hdp-cvd
InactiveUS20070243693A1Reduce moistureAvoid attackSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectric discharge tubesHalogenIon density
A process is provided for depositing an silicon oxide film on a substrate disposed in a process chamber. A process gas that includes a halogen source, a fluent gas, a silicon source, and an oxidizing gas reactant is flowed into the process chamber. A plasma having an ion density of at least 1011 ions / cm3 is formed from the process gas. The silicon oxide film is deposited over the substrate with a halogen concentration less than 1.0%. The silicon oxide film is deposited with the plasma using a process that has simultaneous deposition and sputtering components. The flow rate of the halogen source to the process chamber to the flow rate of the silicon source to the process chamber is substantially between 0.5 and 3.0.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Shale organic porosity detection method
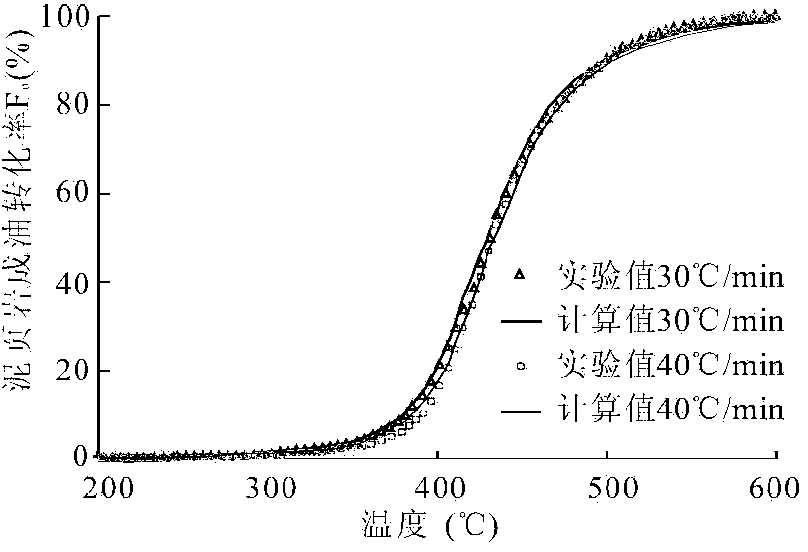
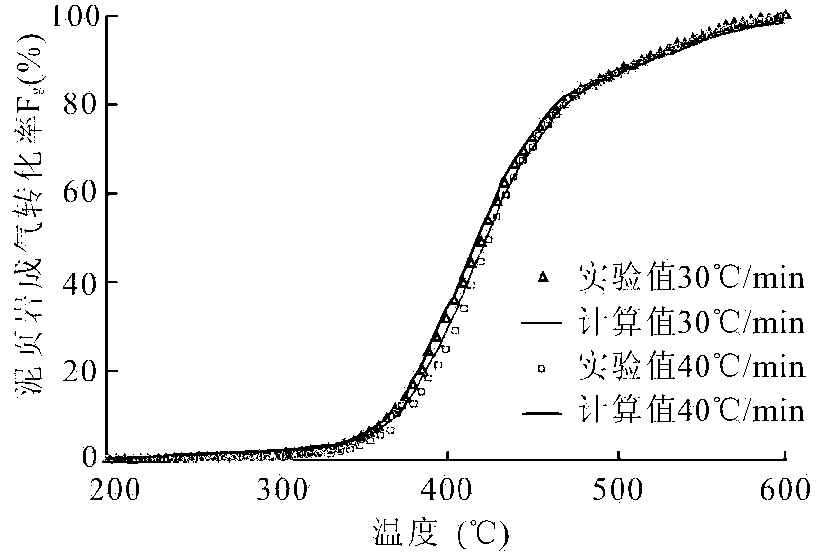
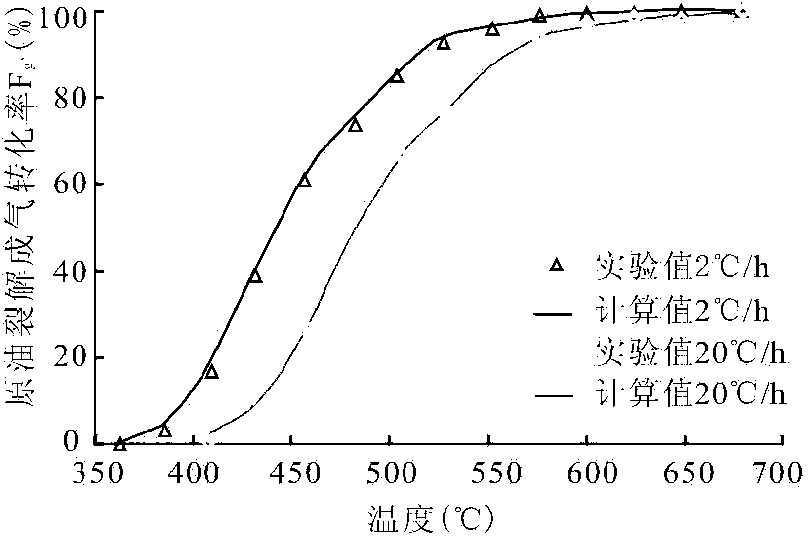
InactiveCN103454198ARealize computingLow costPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityHydrogen index
The invention discloses a shale organic porosity detection method, and belongs to the technical field of petroleum, geology and mining exploration and development. The shale organic porosity detection method comprises the steps of calculating chemical kinetic parameters of petroleum formation from kerogen, gas formation from kerogen and gas formation from crude oil pyrolysis by utilizing a chemical kinetic method based on the thermal simulation experiment of a shale sample and a crude oil sample with representativeness, and determining the conversion rate of the petroleum formation from kerogen, gas formation from kerogen and gas formation from crude oil pyrolysis of shale at the study layer section by combining with the burial history and thermal history of a target layer; recovering the original hydrogen index and the original organic carbon of shale of the target layer by utilizing residual hydrogen index and data of residual organic carbon of shale of the target layer and combining with the conversion rate of the petroleum formation from kerogen, gas formation from kerogen and gas formation from crude oil pyrolysis; analyzing the organic pore compressibility of shale by utilizing a Ar ion polishing thin sheet of a shale sample of the target layer; calculating the organic porosity of the shale sample of the target layer section. The shale organic porosity detection method has the effects that the organic porosity of the reservoir of shale can be calculated, and the shale organic porosity detection method is high in calculation accuracy, and is easy to operate.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com