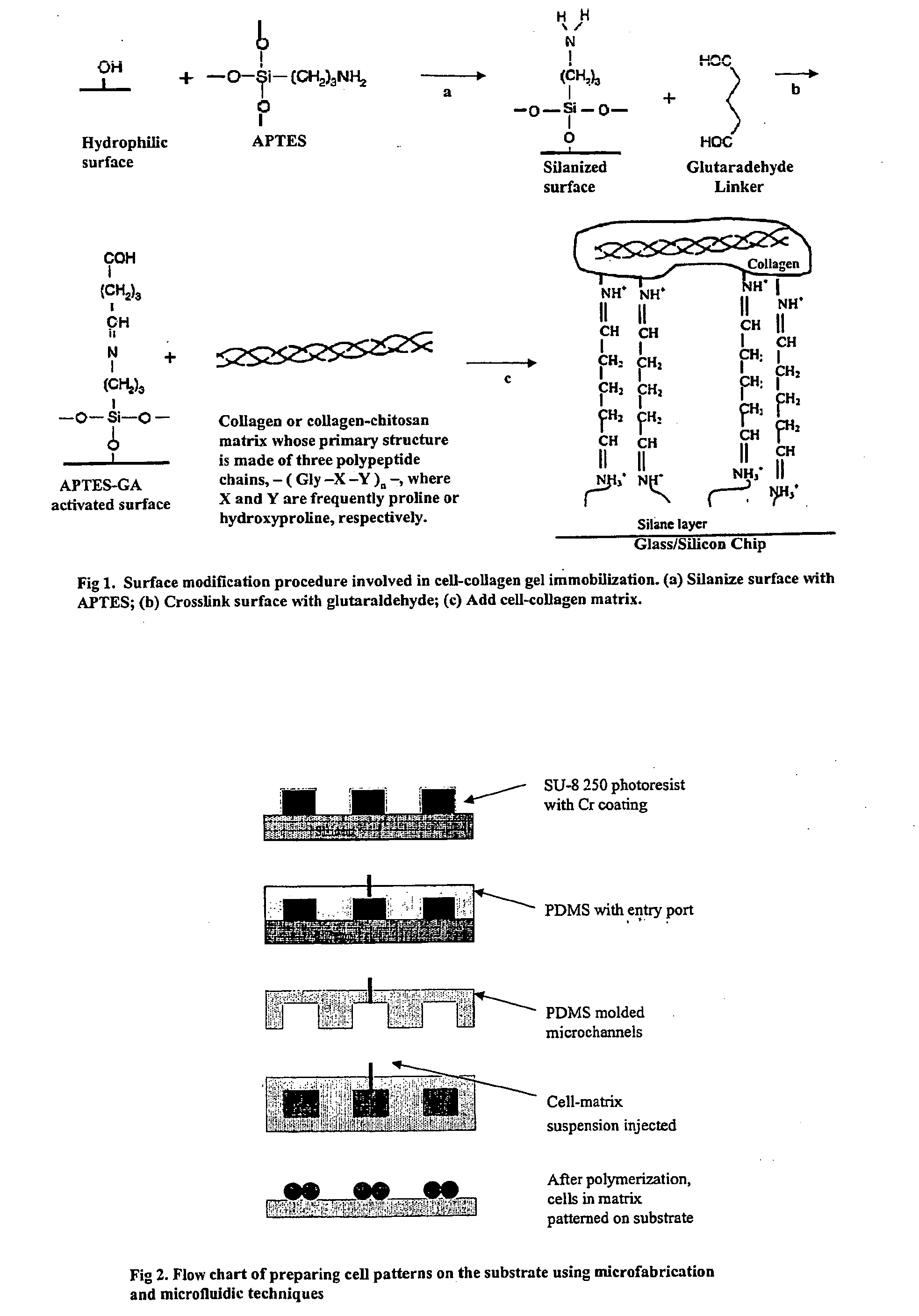
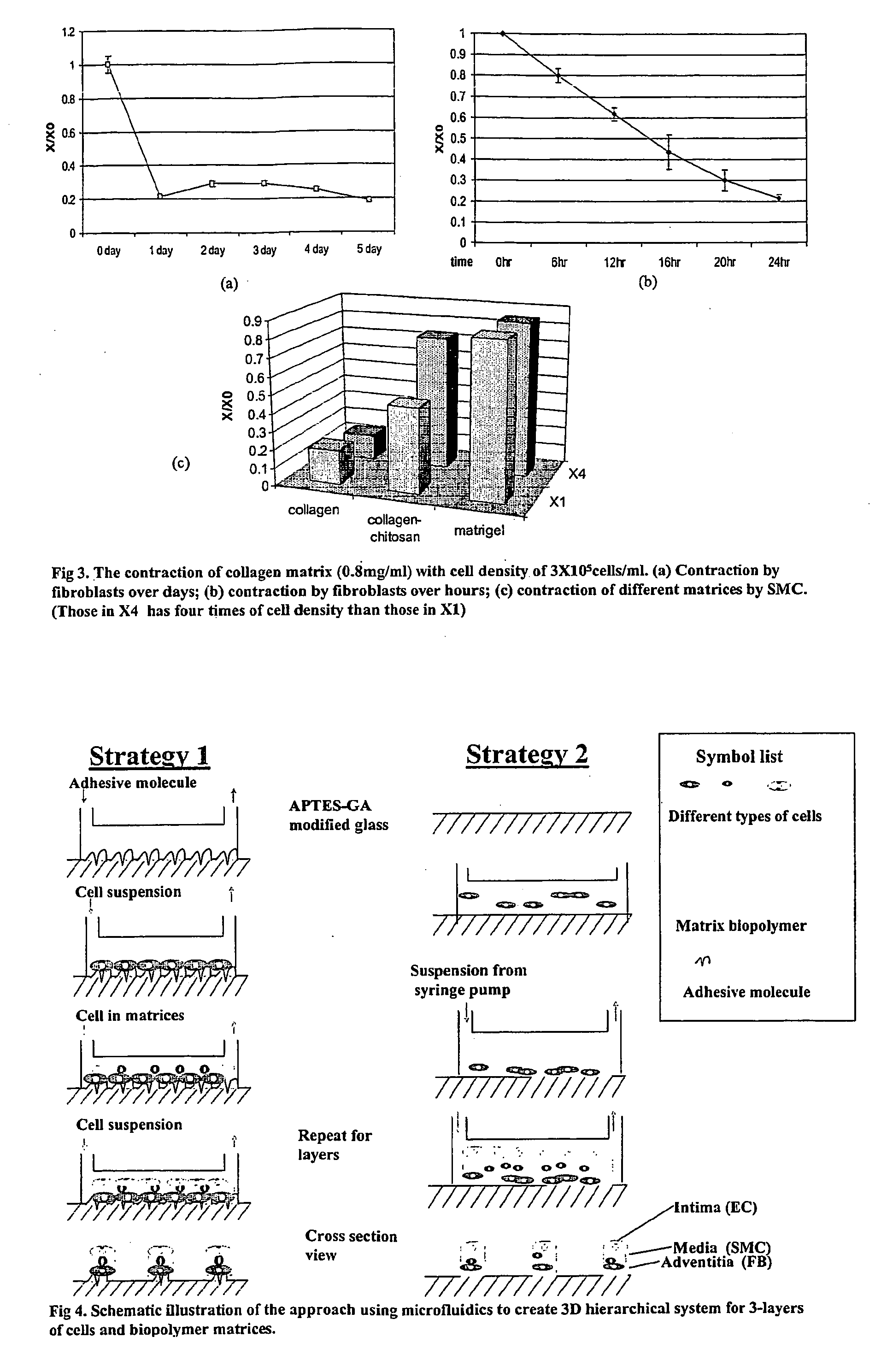
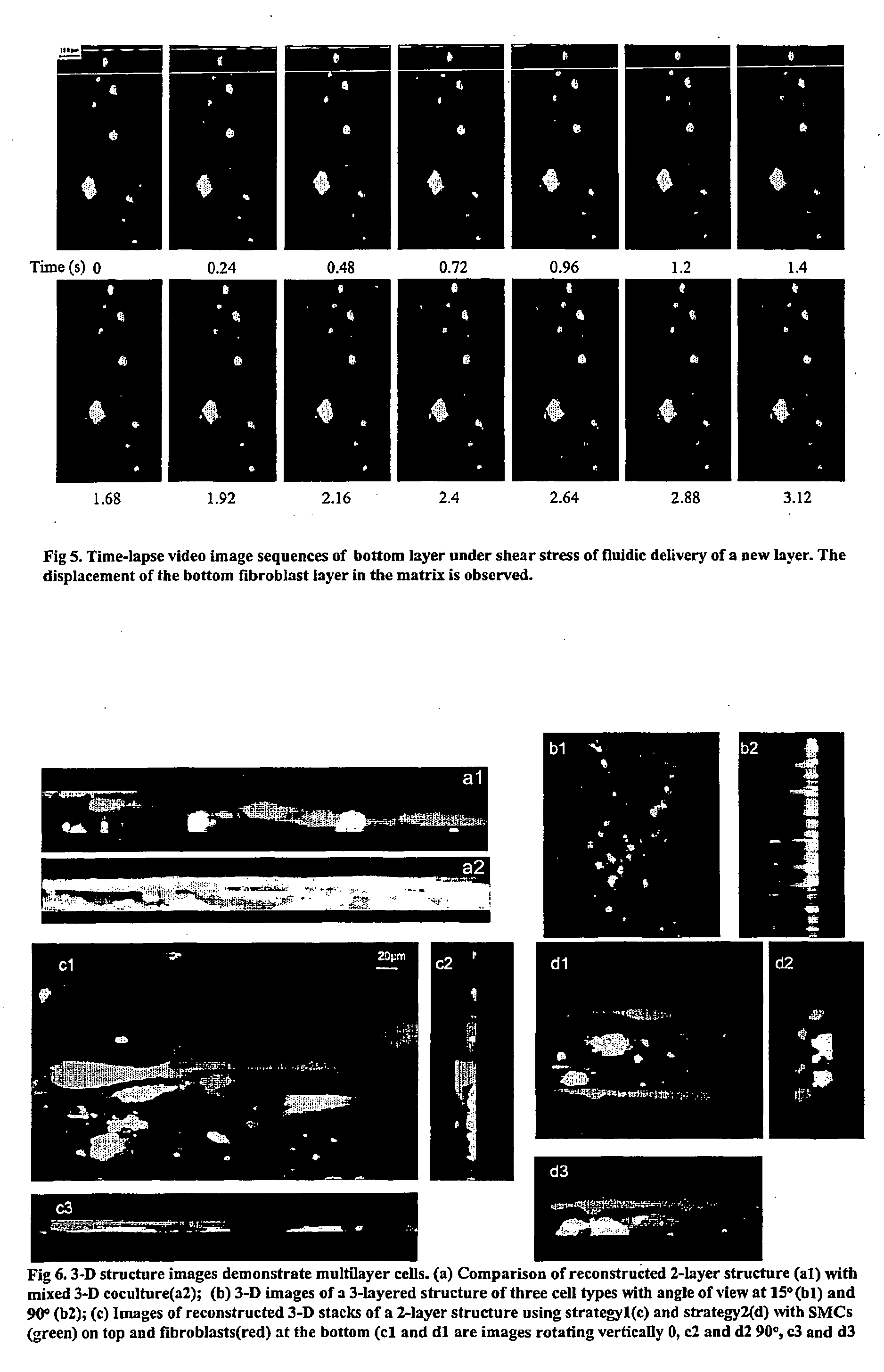
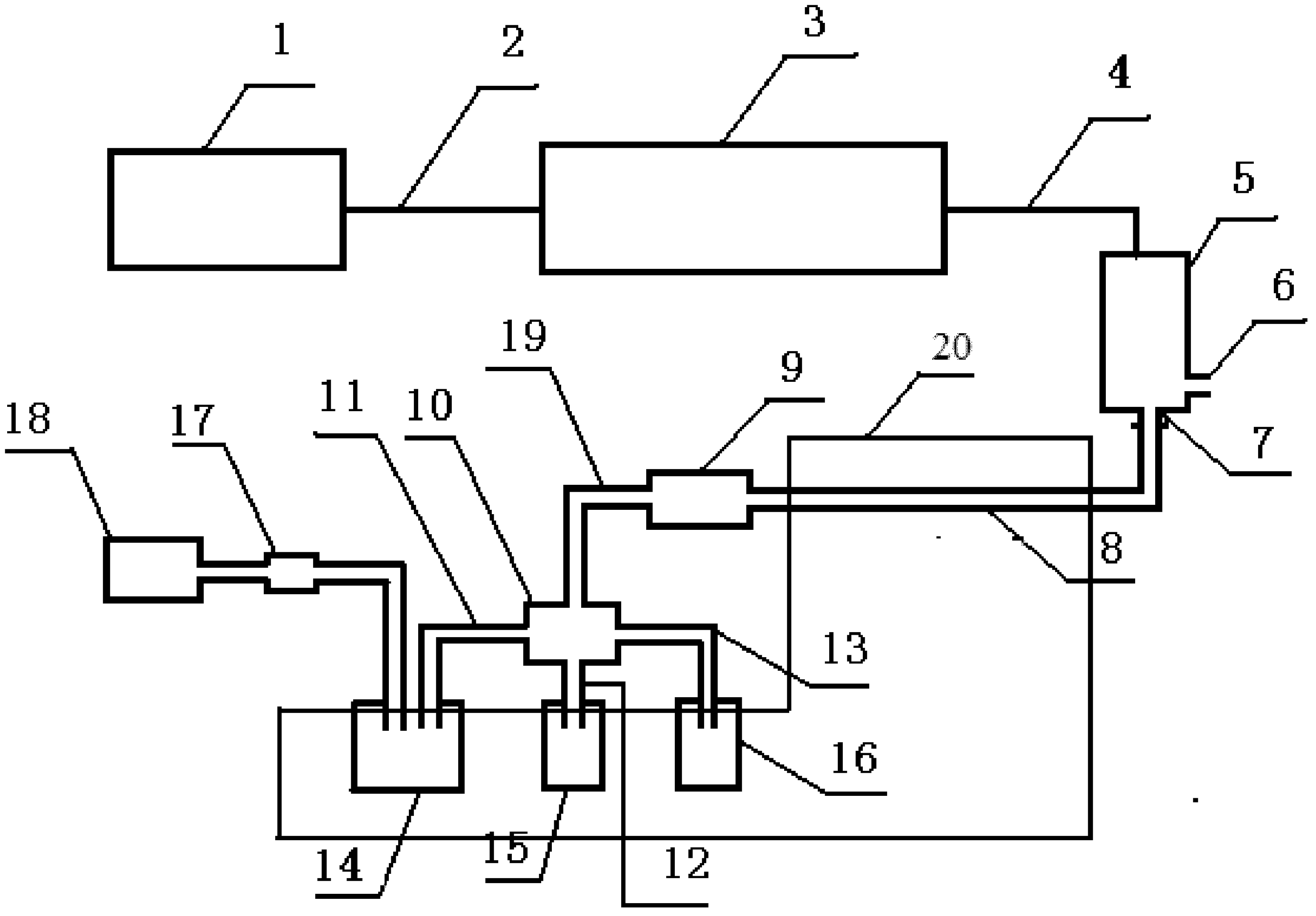
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Microculture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microculture refers to the specialised subgroups, marked with their own languages, ethos and rule expectations, that permeate differentiated industrial societies. A microculture depends on the smallest units of organization – dyads, groups, or local communities – as opposed to the broader subcultures of race or class, and the wider national/global culture, compared to which they tend also to be more short-lived, as well as voluntarily chosen. The study of kinesics – the nonverbal behavior of the small gathering – can be used to illuminate the dynamics of a given microculture.
Multilayered microcultures
InactiveUS20060141617A1Accurate mimicFlexible and cost-effectiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningBiological bodyCell adhesion
A multilayer microculture capable of modeling complex in vitro structures such as mammalian tissues and organ structures is provided, along with methods for producing such a microculture and methods of using such microcultures for assaying for modulators of cell-cell interaction, cell migration, cell proliferation, cell adhesion or cellular or organismal physiology. Further provided are methods of identifying hazardous materials such as environmental toxins and pollutants (e.g., carcinogenic compounds), and methods of monitoring organismal physiology.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
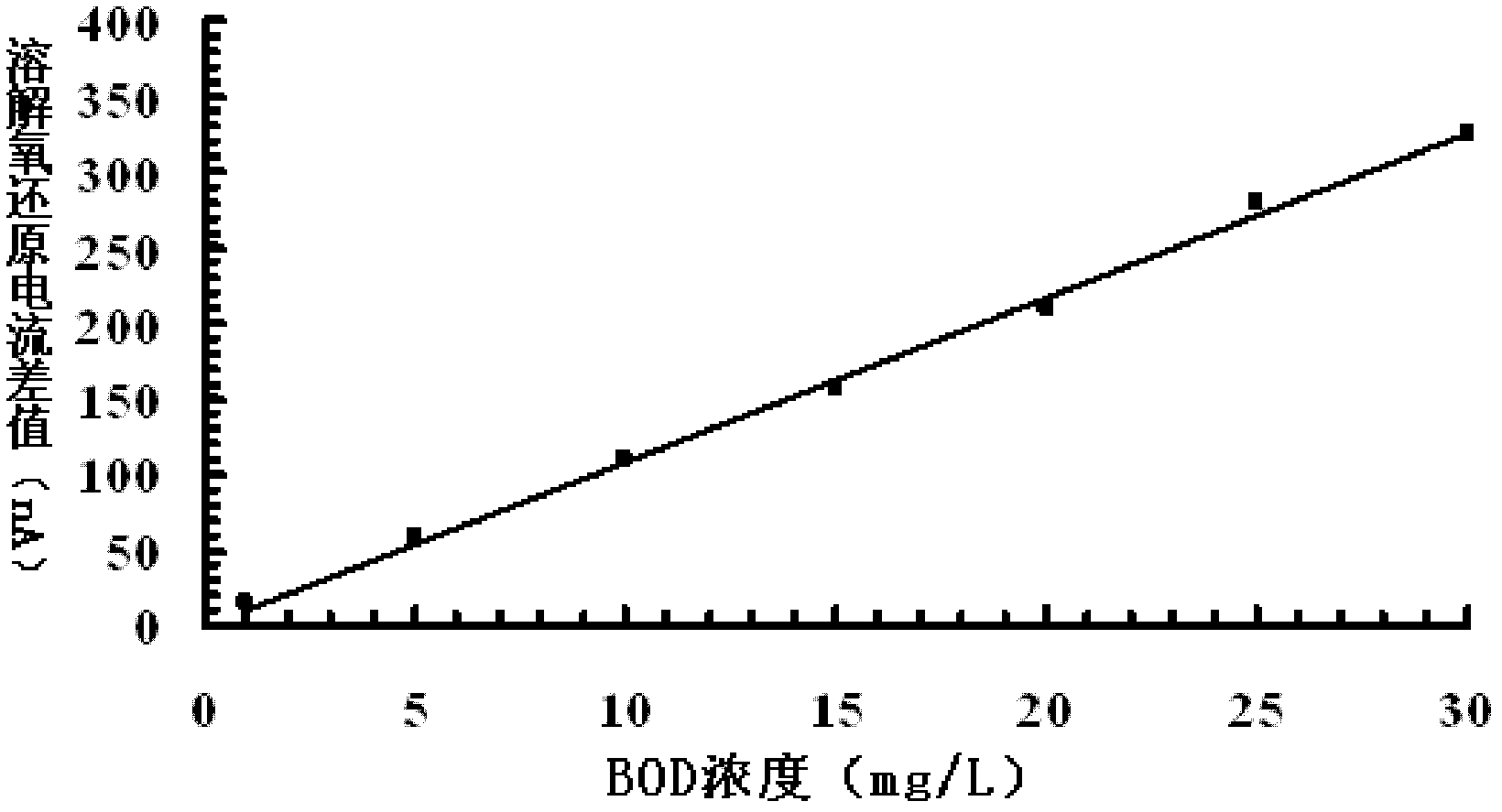
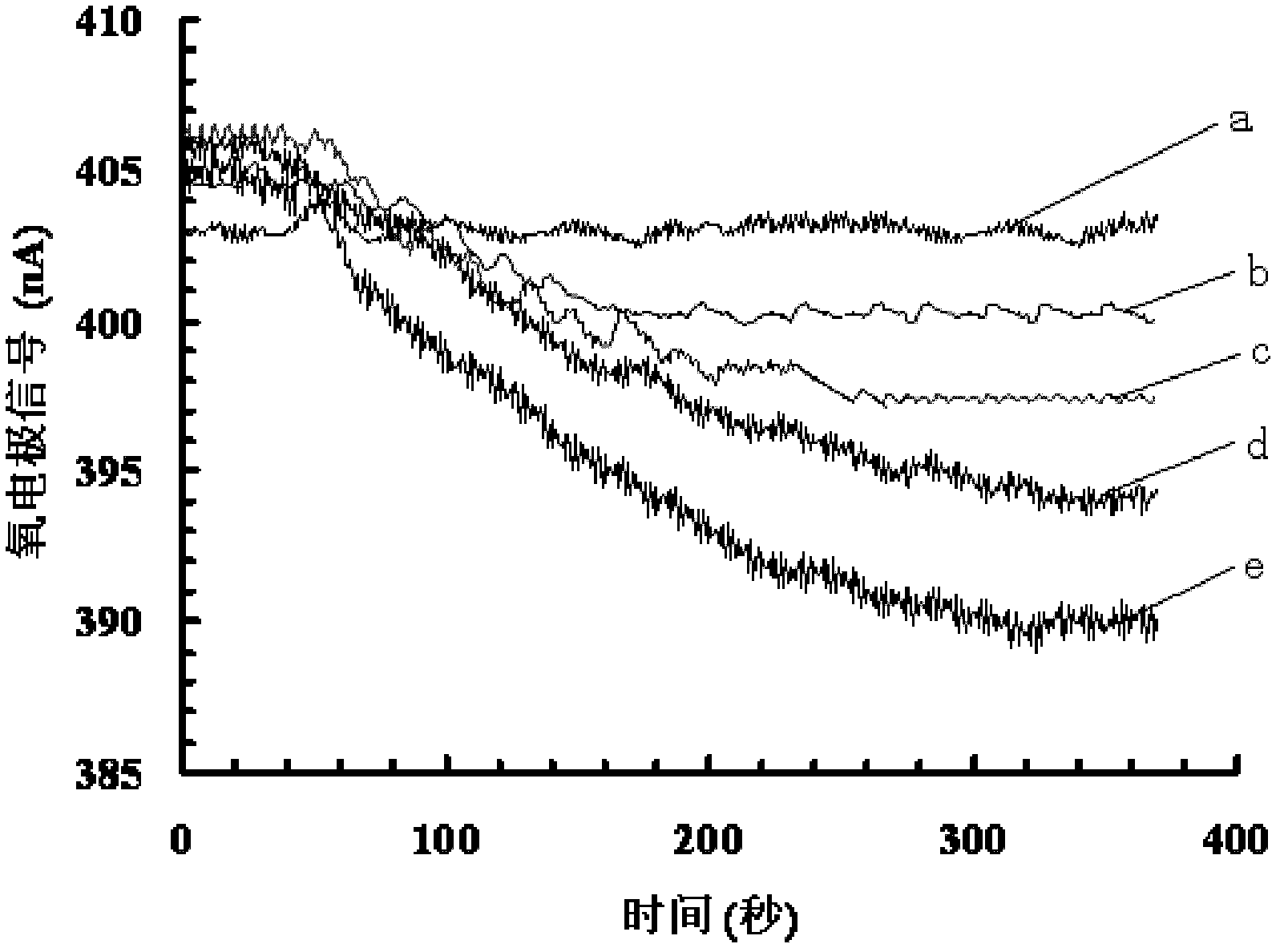
Method for detecting biochemical oxygen demand
ActiveCN102608181AHigh biodegradation rateImprove stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesIndustrial waste waterSludge
The invention provides a method for detecting a biochemical oxygen demand. The method comprises the following steps of performing microculture on a microbe containing water sample from active sludge, surface water, domestic sewage or microbe containing industrial waste water, thus obtaining a microbial film; enabling a blank water sample and a target water sample to pass through the microbial film respectively, detecting and obtaining dissolved oxygen reduction current of the blank water sample and the target water sample, thus obtaining a dissolved oxygen reduction current difference value between the target water sample and the blank water sample; and obtaining the biochemical oxygen demand of the target water sample according to the dissolved oxygen reduction current difference value and a preset standard curve. According to the method, since the microbial film obtained by culturing the microbe containing water sample from active sludge, surface water, domestic sewage or microbe containing industrial waste water has high environment adaptation capacity, a buffer solution system is not required and the physiological activity can be maintained by taking one or more then one of running water, well water, dropping water and underground water as a medium.
Owner:吉林市光大分析技术有限责任公司
Halimasch fermented tea and halimasch fermented tea composition, and preparation methods thereof
ActiveCN102613331AMaintain or improve healthEasy to brewPre-extraction tea treatmentMicroorganismBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention belongs to fermentation engineering of foods and drinks, and relates to a production process for fermenting tea by a microculture method, in particular to halimasch fermented tea and a production process thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing a culture medium; culturing first-stage seeds; performing amplification culture on second-stage seeds; inoculating and fermenting; and drying. The invention has the advantages that: halimasch is utilized to ferment tea, and the obtained fermented tea has double physiological effects, namely the pharmacological activity of tall gastrodia tuber and drinkability of tea, is easy to make and absorb, can fully integrate active ingredients of fermentation products, ensures that the resources of the fermentation products are fully utilized, and has good auxiliary and health-care effects in the aspect of improving human immunity.
Owner:西藏月王药诊生态藏药科技有限公司
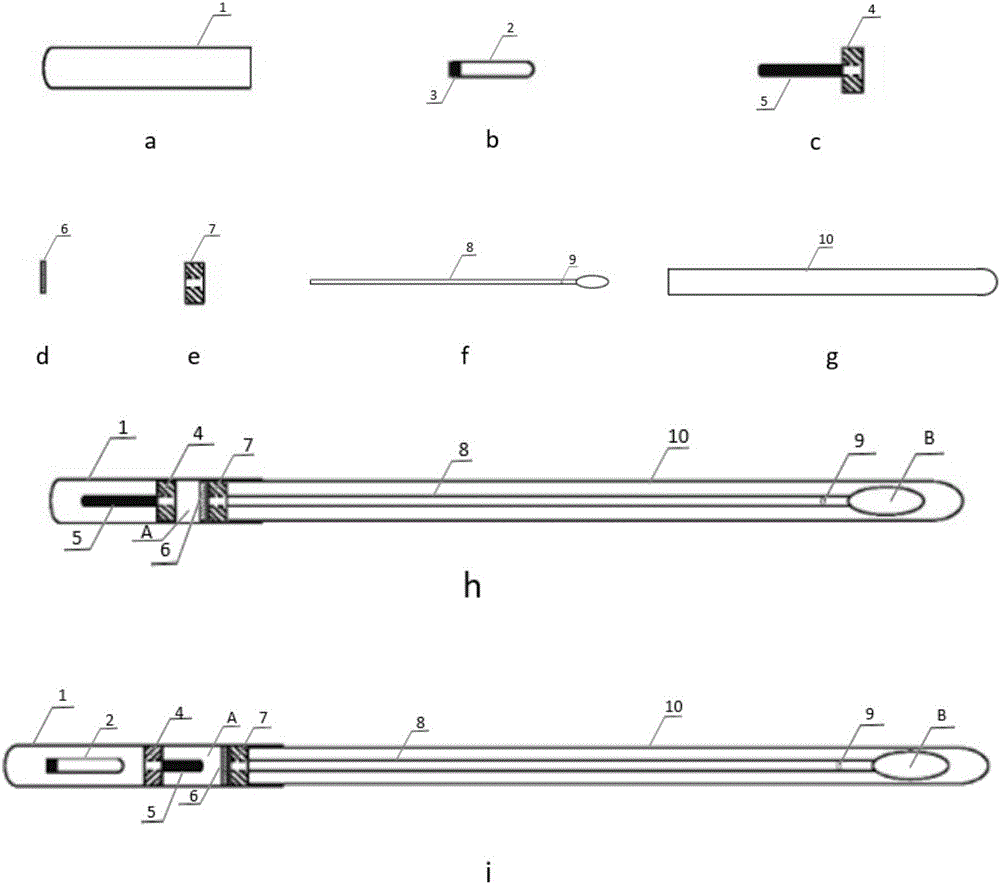
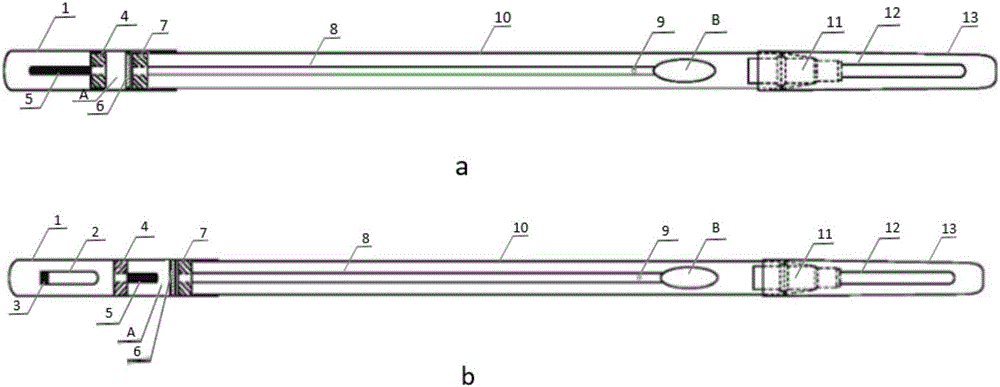
Device integrating sampling, reaction and detection
ActiveCN106053121AAvoid pollutionSimple structureMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorWithdrawing sample devicesEngineeringMicroculture
The invention discloses two devices integrating sampling, reaction and detection. A first device comprises a liquid storage tube, a liquid distribution valve, a fixing sheet, a sampling swab rod and a reaction tube, wherein a breakable valve needle is arranged on the liquid allocation valve; the fixing sheet is connected with the sampling swab rod; the liquid allocation valve is arranged inside the inner cavity of the liquid storage tube; the storage cavity formed by the liquid storage tube and the liquid distribution valve is filled with a solution; the valve needle of the liquid allocation valve is positioned inside the storage cavity; the fixing sheet is arranged inside the liquid storage tube; a gap is formed between the fixing sheet and the liquid distribution valve; the gap is filled with chemical substances; the opening end of the liquid storage tube is sleeved by the reaction tube; a second device contains all elements of the first device, and further contains a damageable ampoule tube; the valve needle of the liquid allocation valve is positioned outside the storage cavity. The devices are sample in structure, multiple reagents can be placed in different zones and are mixed to use before reaction, and steps of sampling, treatment, reaction and detection on samples can be continuously completed. The devices can be widely applied to pathogen detection, microculture, enzyme activity analysis, immunochemistry detection and the like of clinical samples.
Owner:益思美诠生物科技(上海)有限公司
Nanogel inclined plane culture medium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107034140AShorten the setting timeSlow down the speed of solidificationMicroorganismsBiotechnologyEngineering
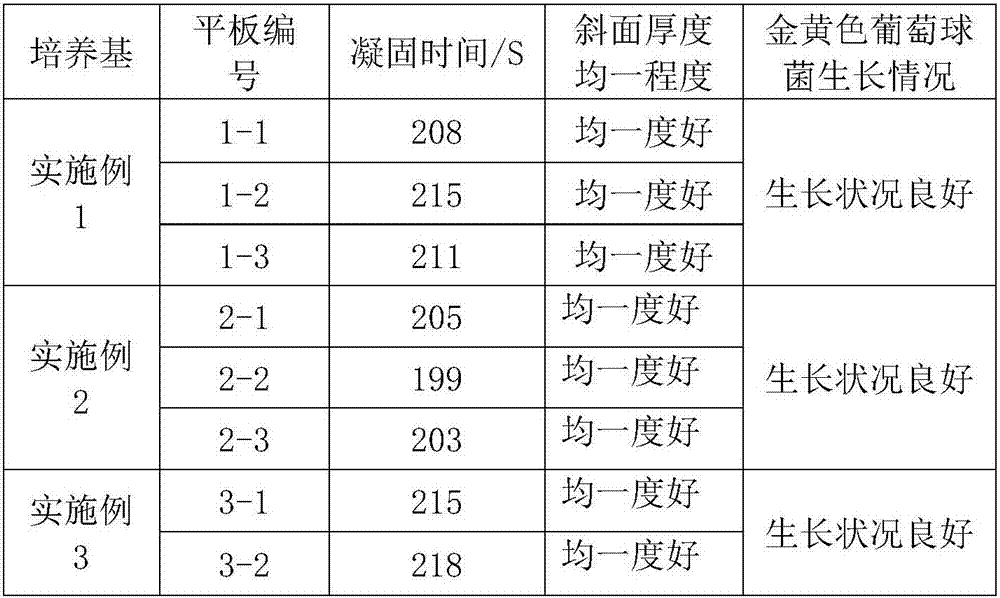
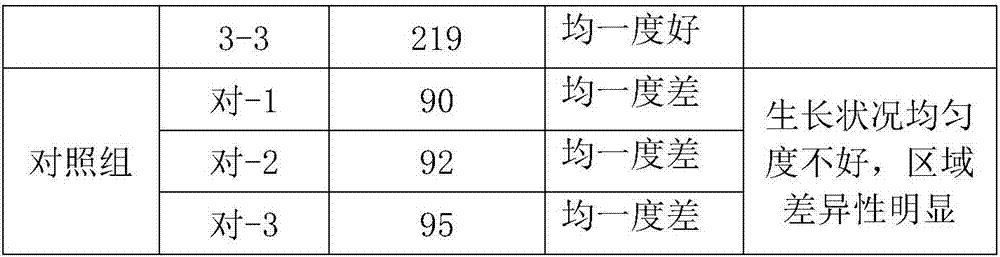
The invention discloses a nanogel inclined plane culture medium and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of microculture. Part of agar powder is replaced with part of nanogel particles and agarose gel on the basis of an ordinary inclined plane culture medium. Concretely, by mass percentage, first nanogel particles are used to replace 20-30% of agar powder, and then the agarose gel is used to replace 25%-35% of agar powder. The setting time and setting rate of the culture medium are effectively delayed, the thickness uniformity degree during inclined plane culture medium preparation is improved, the uniform distribution degree of culture medium nutrient substances is also improved, and thus accuracy of culture and subsequent test results is effectively ensured. Repeated testing is avoided, testing time is shortened, errors are reduced, and the precision degree of tests is improved. In addition, the preparation method is reasonable in design and simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:句容亿格纳米材料厂
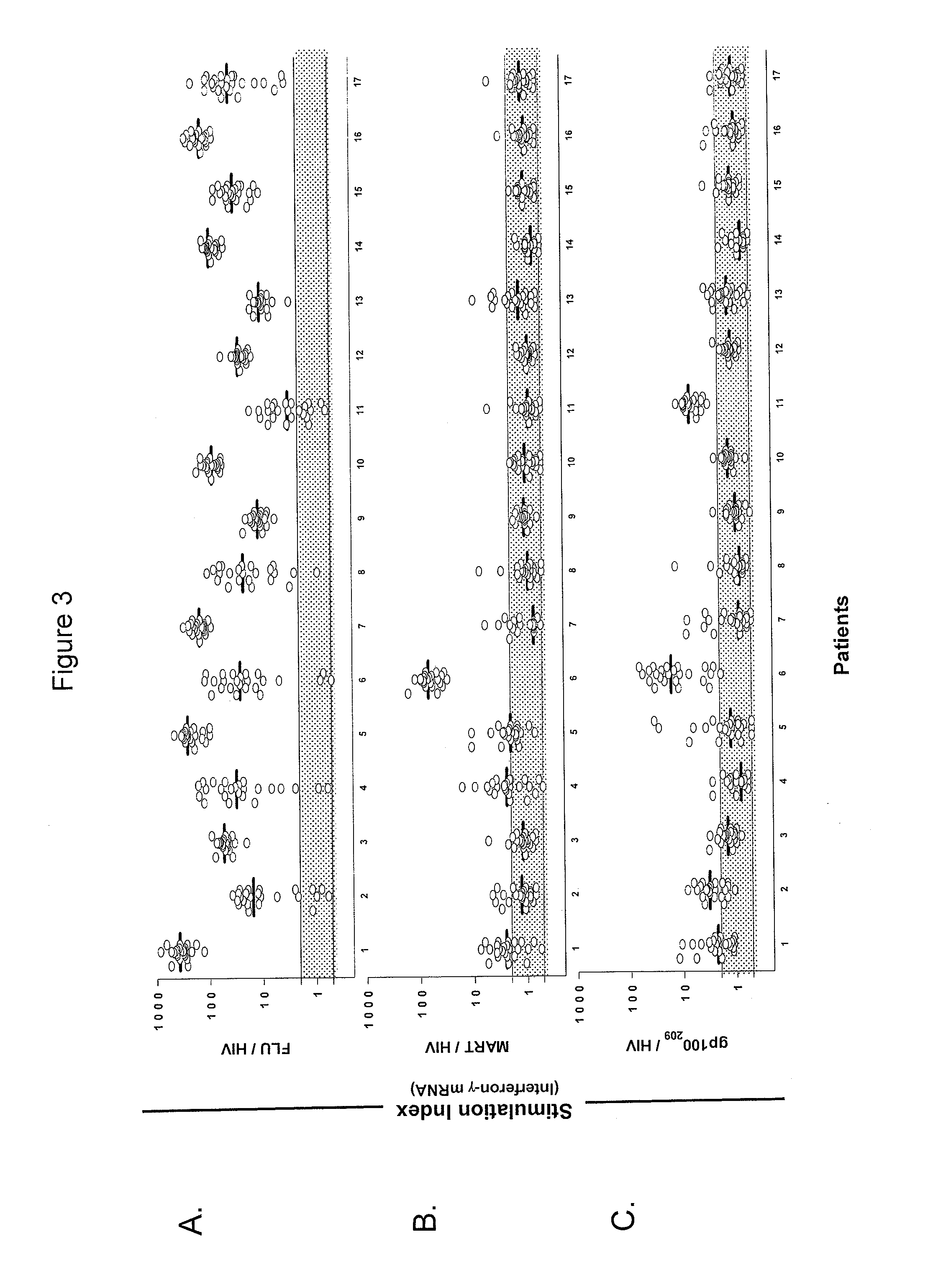
Methods of obtaining antigen-specific T cell populations
InactiveUS8759014B2Fast wayImprove throughputBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseSub populations
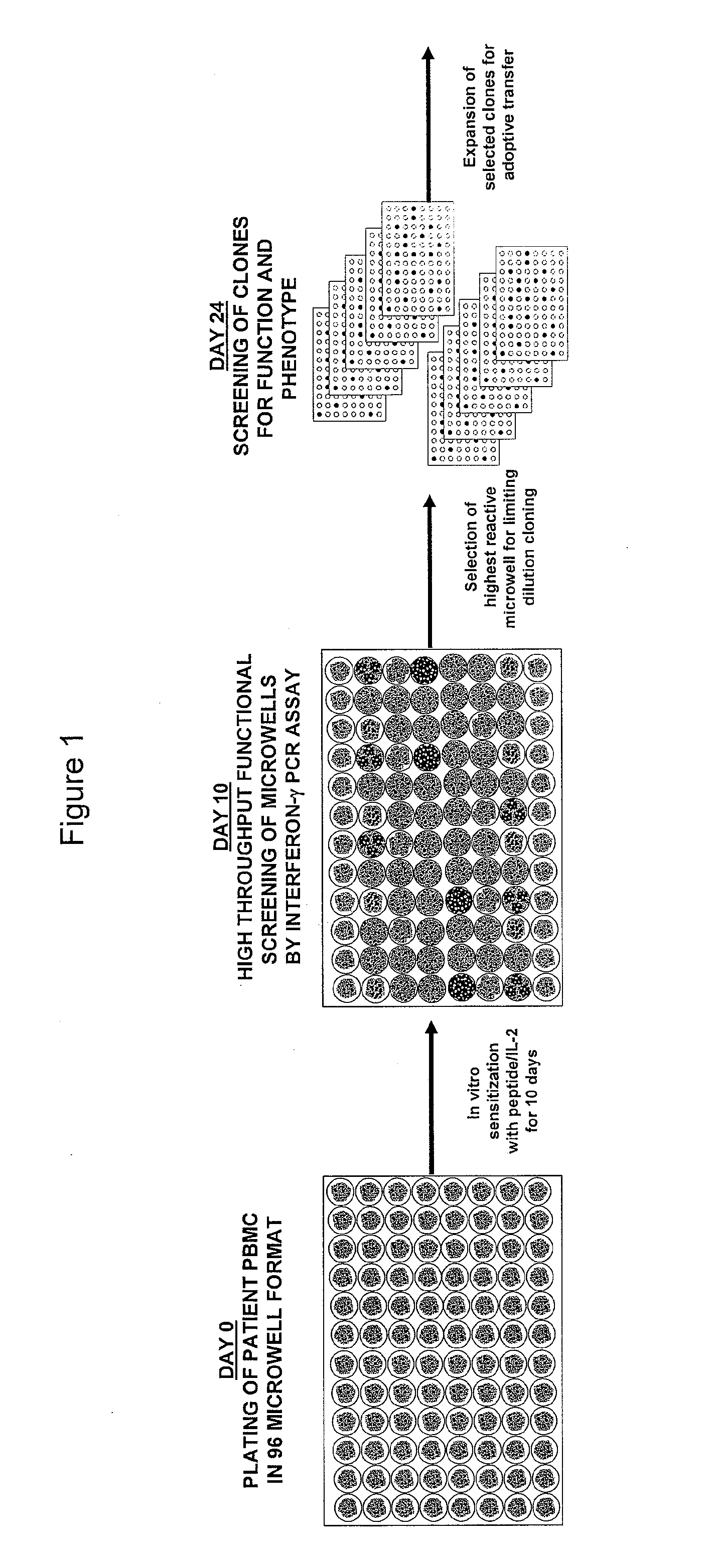
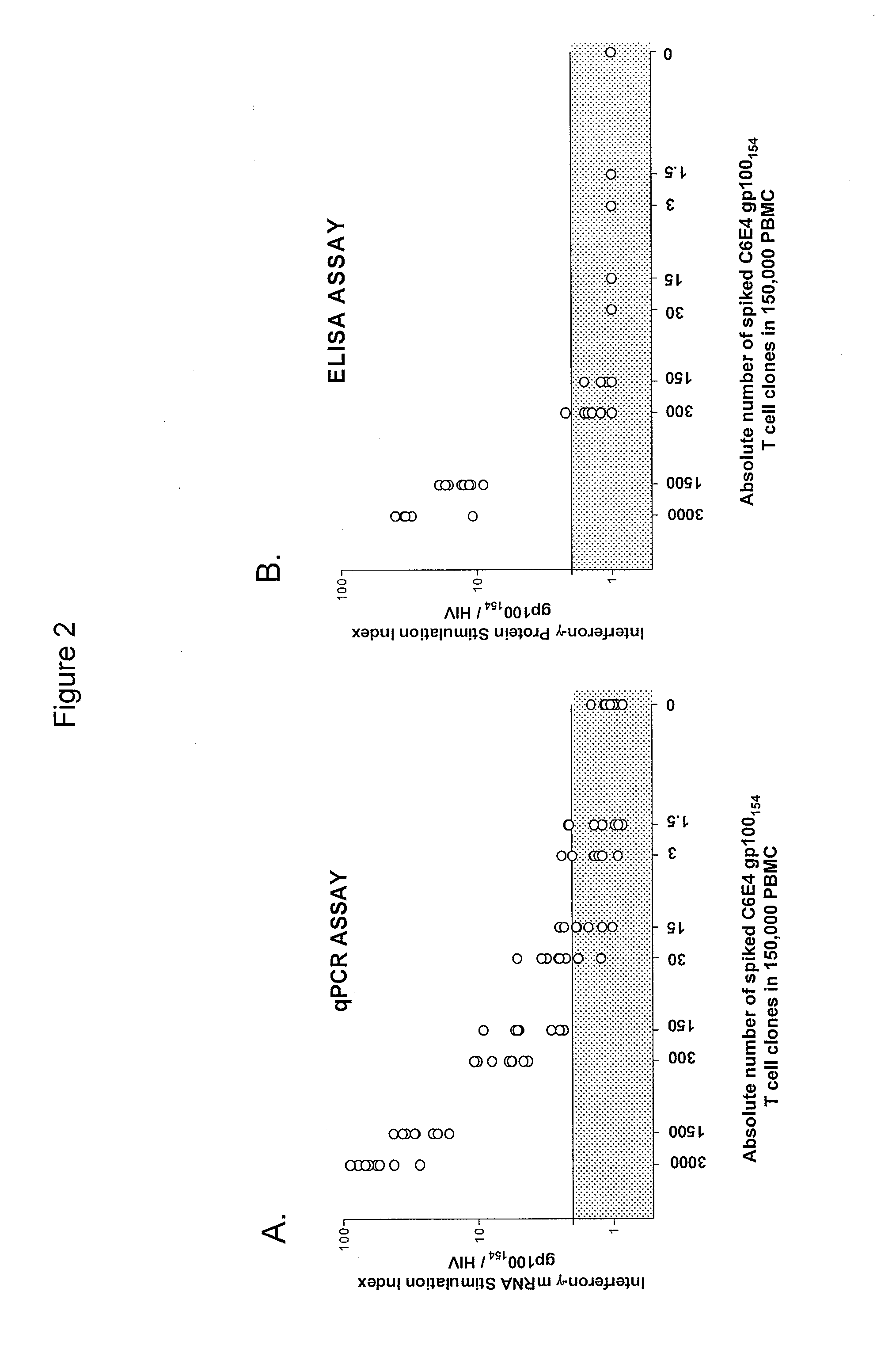
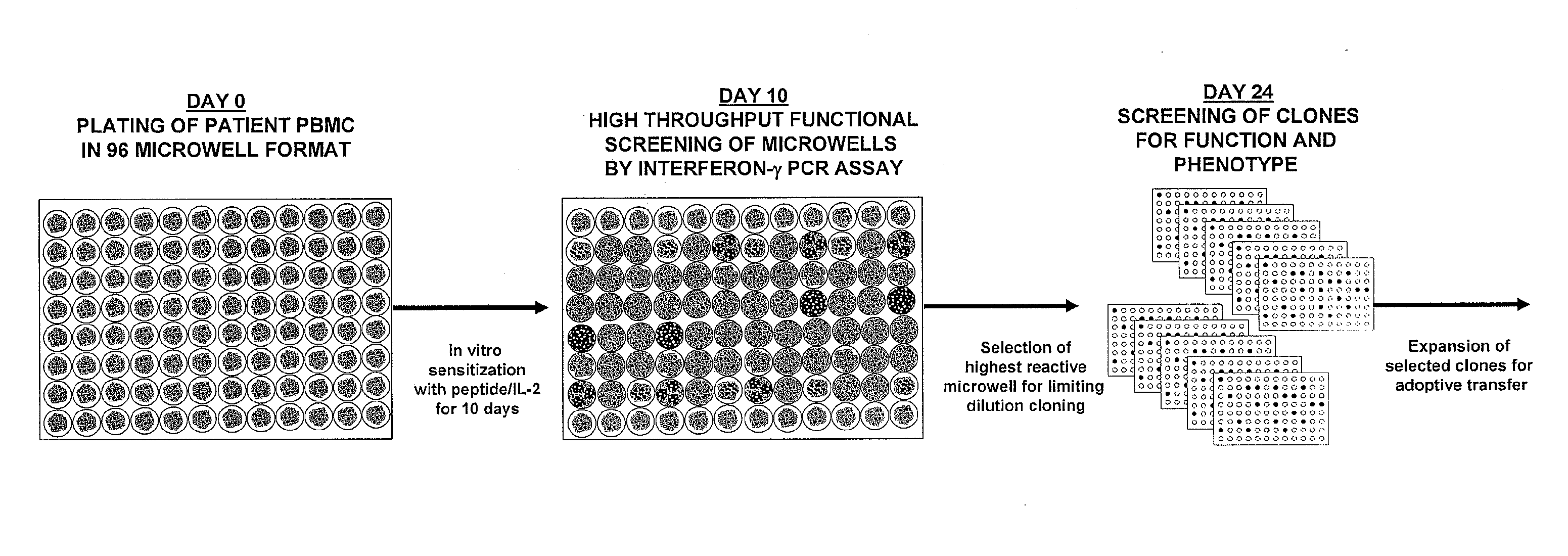
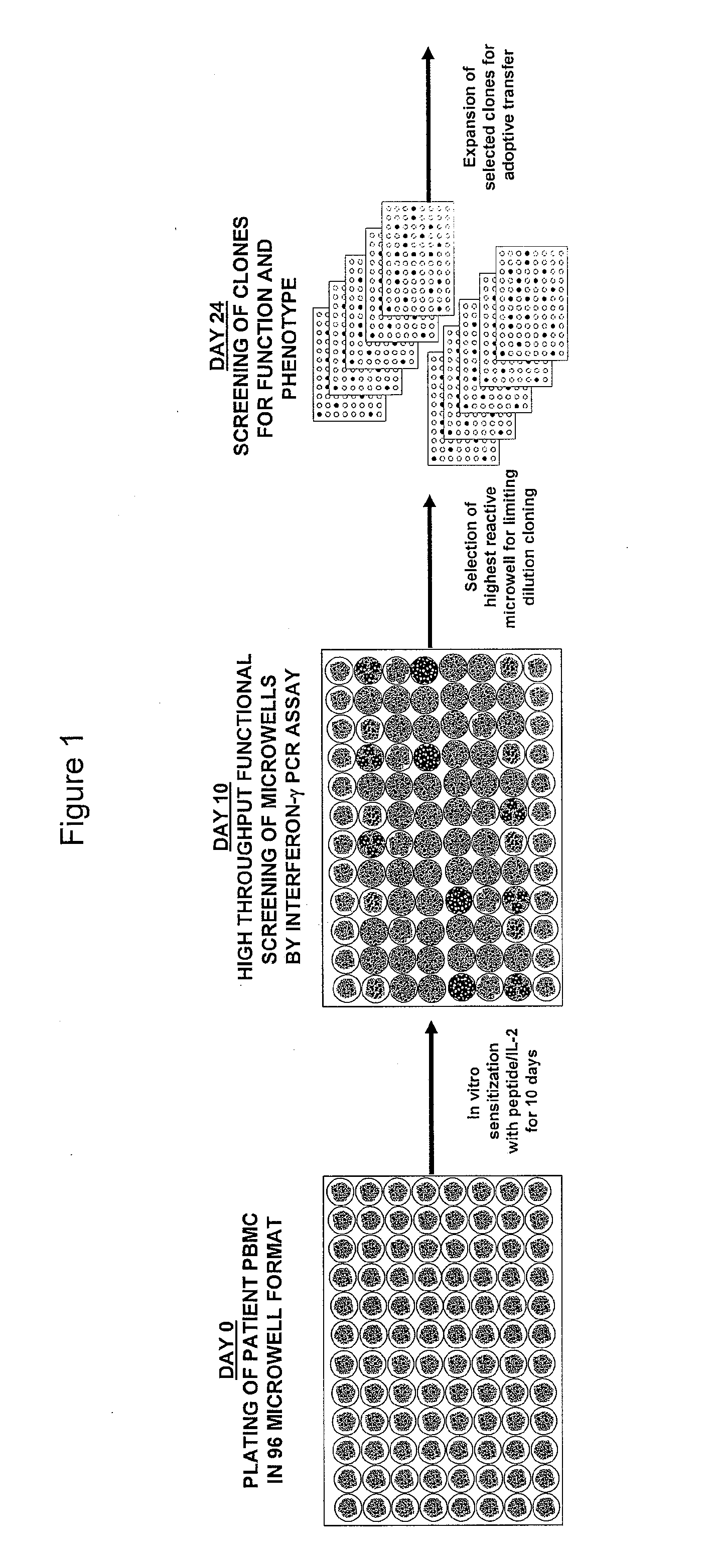
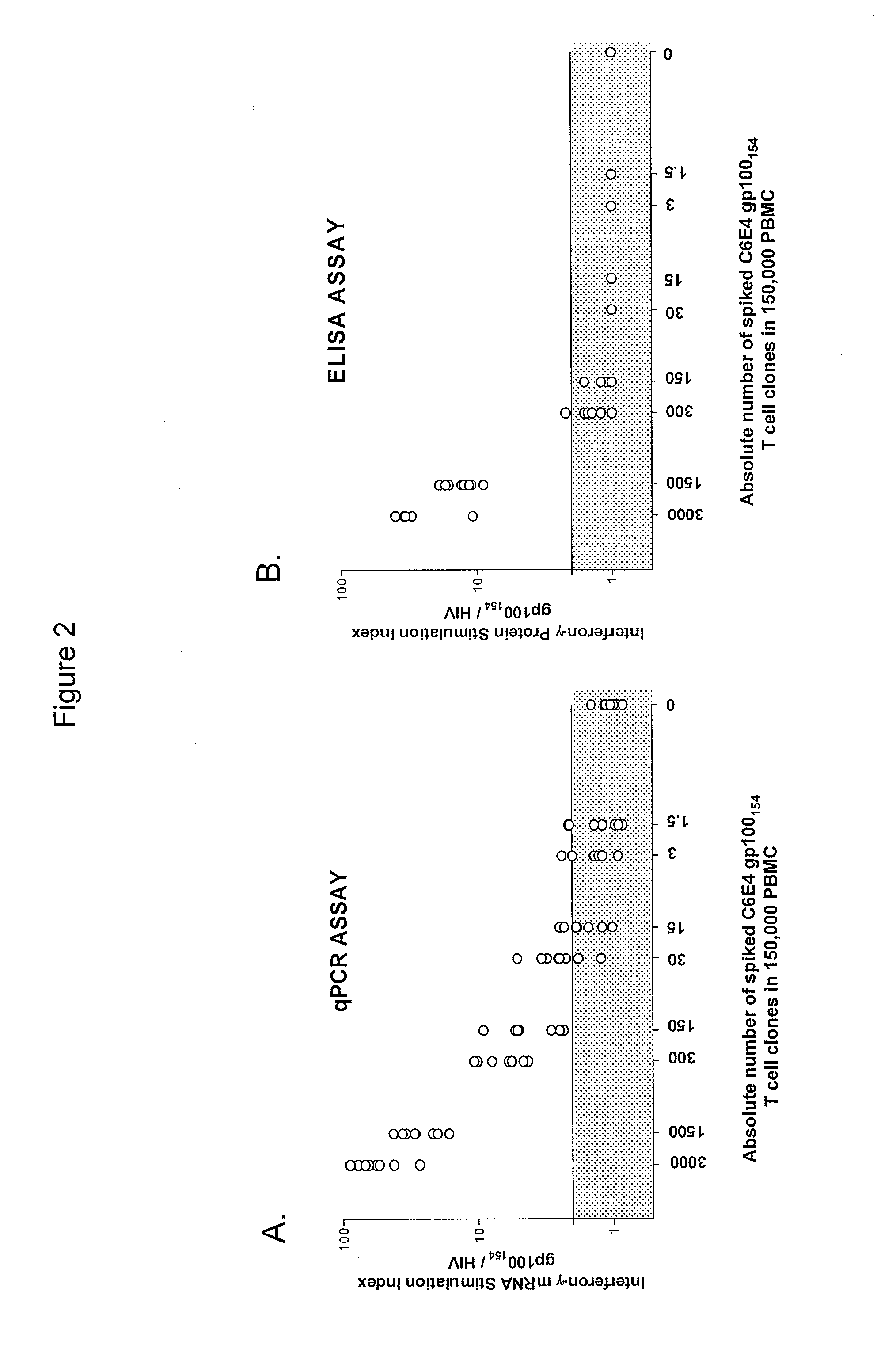
The invention provides a method of obtaining a population of antigen-specific T cells from peripheral blood of a host. An embodiment of the method of the invention comprises (i) dividing PBMCs from peripheral blood of a host into more than one sub-population; (ii) contacting the PBMCs with an antigen and IL-2; (iii) obtaining a sample of PBMCs from each sub-population; (iv) identifying an antigen-reactive sub-population by determining by high throughput quantitative PCR the expression of a factor produced by the PBMCs of each sample; (v) dividing the antigen-reactive sub-population into microcultures; (vi) identifying the antigen-reactive microculture; and (vii) expanding the microculture, thereby obtaining a population of T cells specific for the antigen. The invention also provides a population of T cells obtained by the inventive method, a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, and a method of treating a disease in a host using the pharmaceutical composition. Related isolating and screening methods are further provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
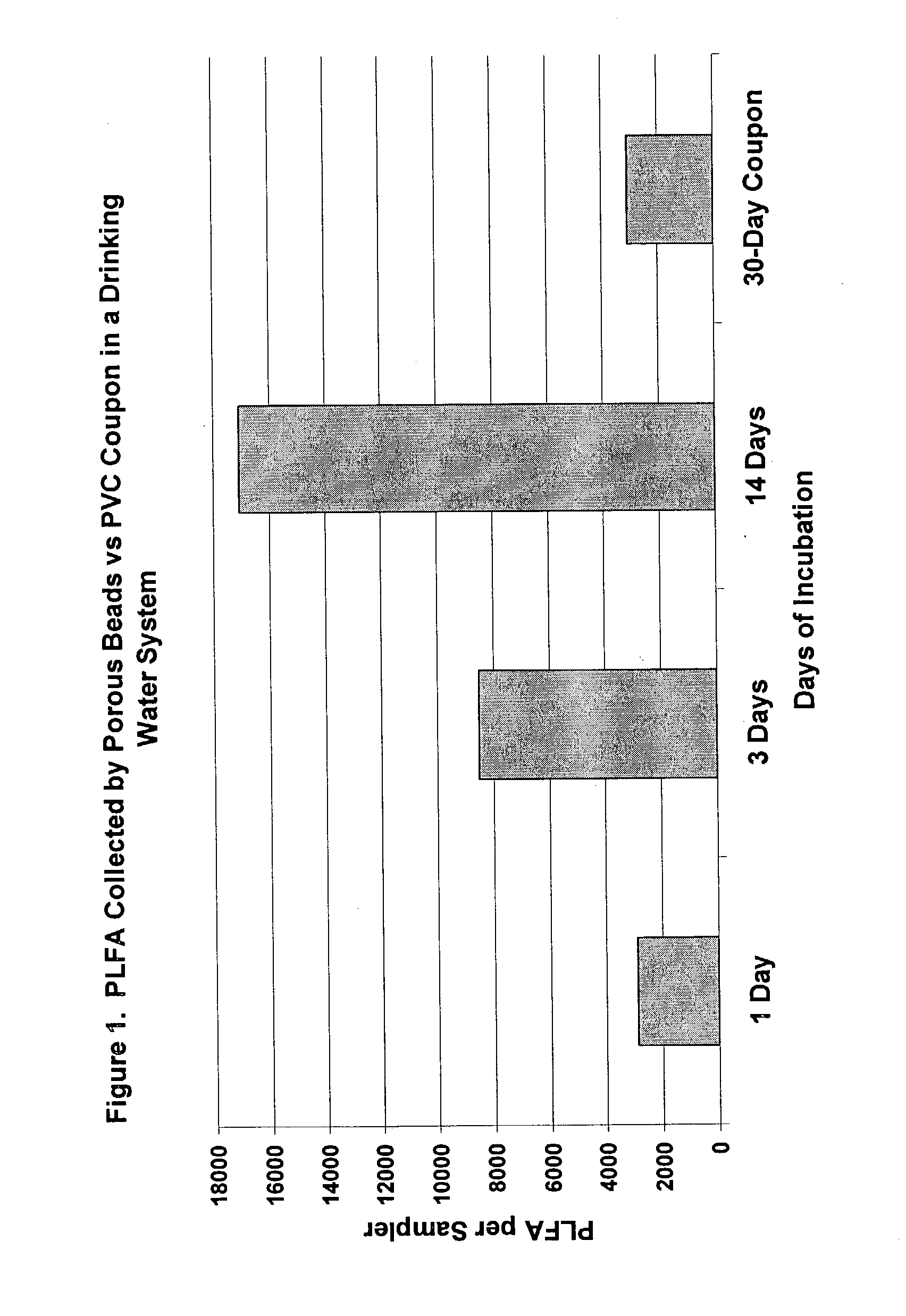
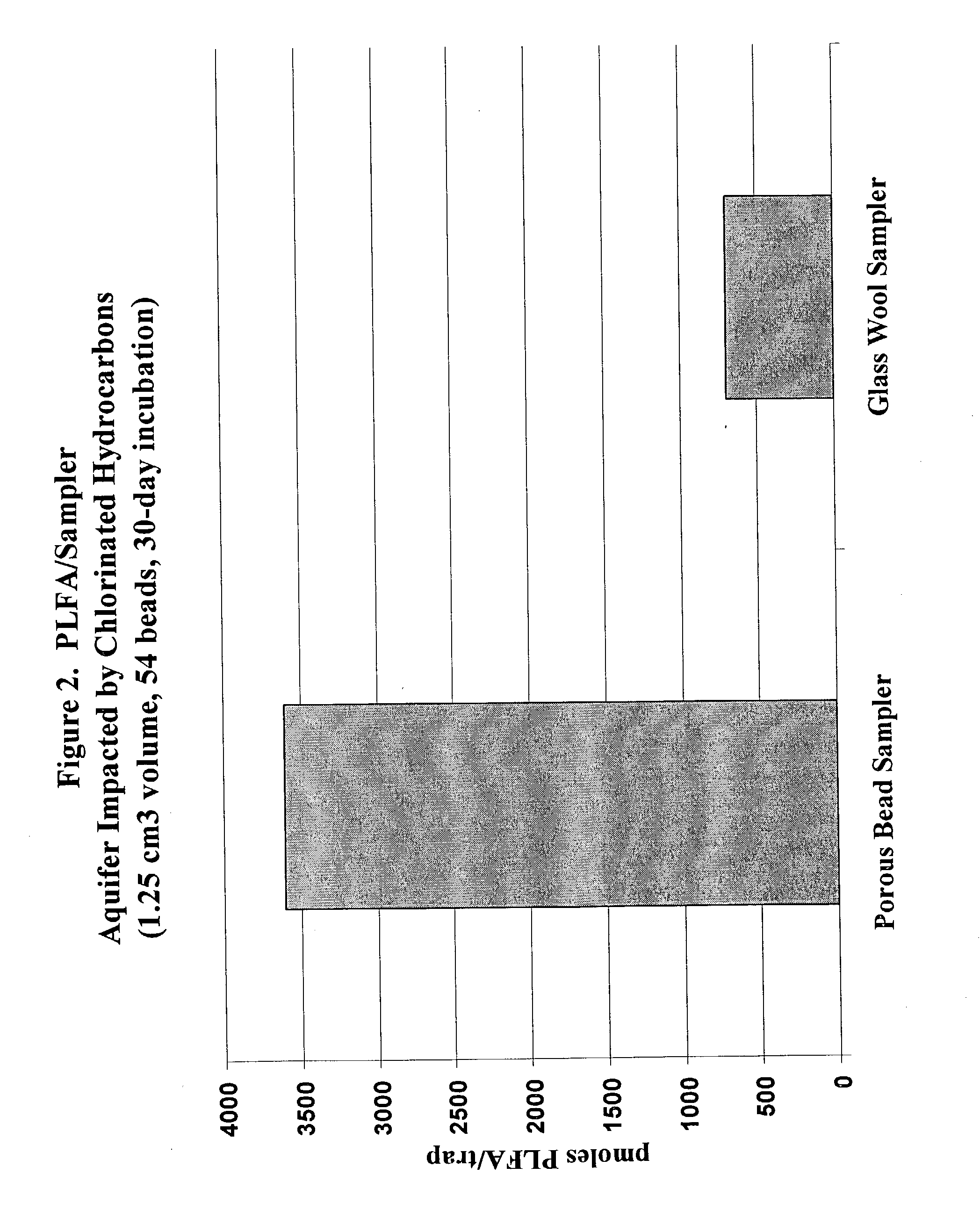
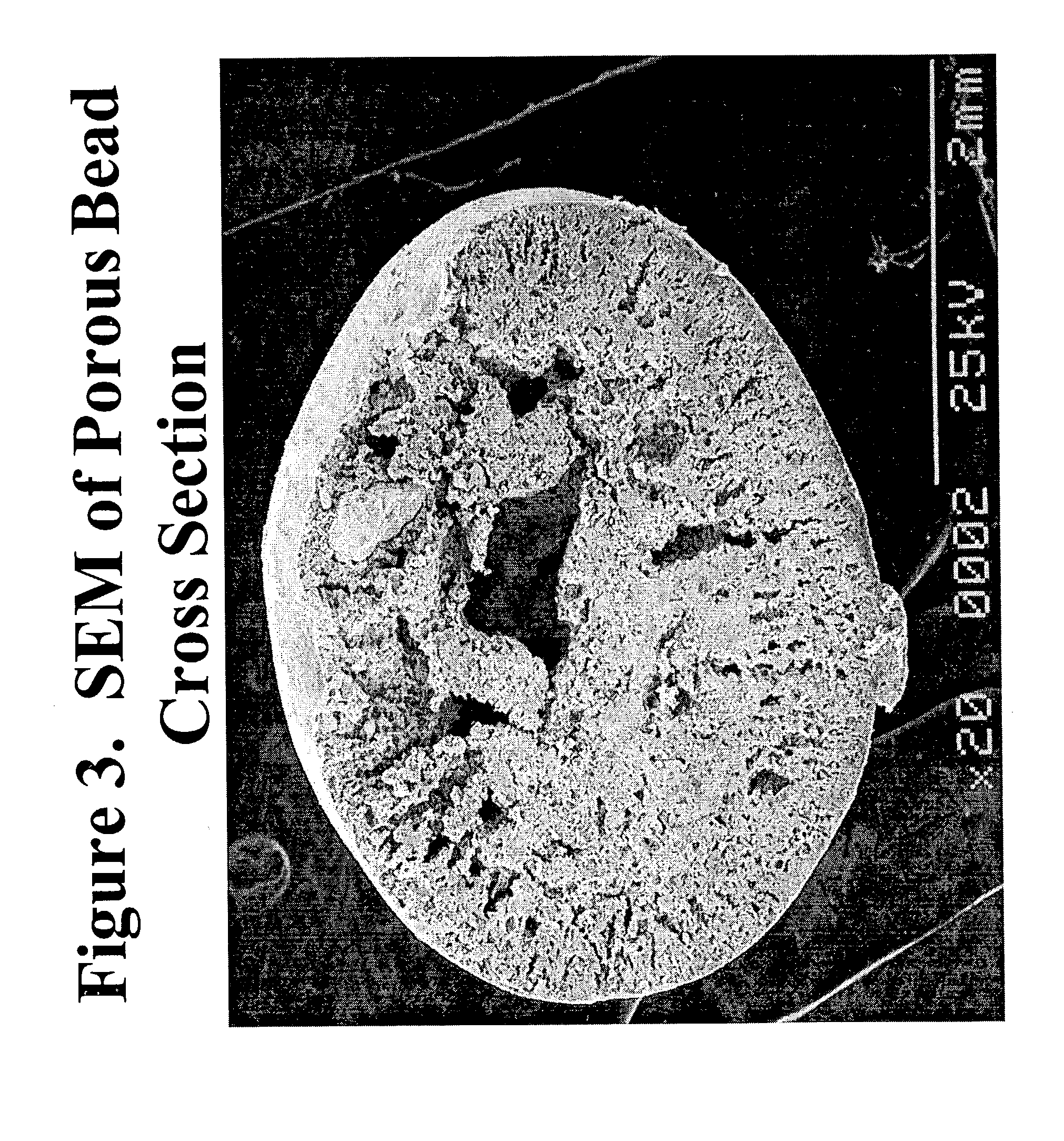
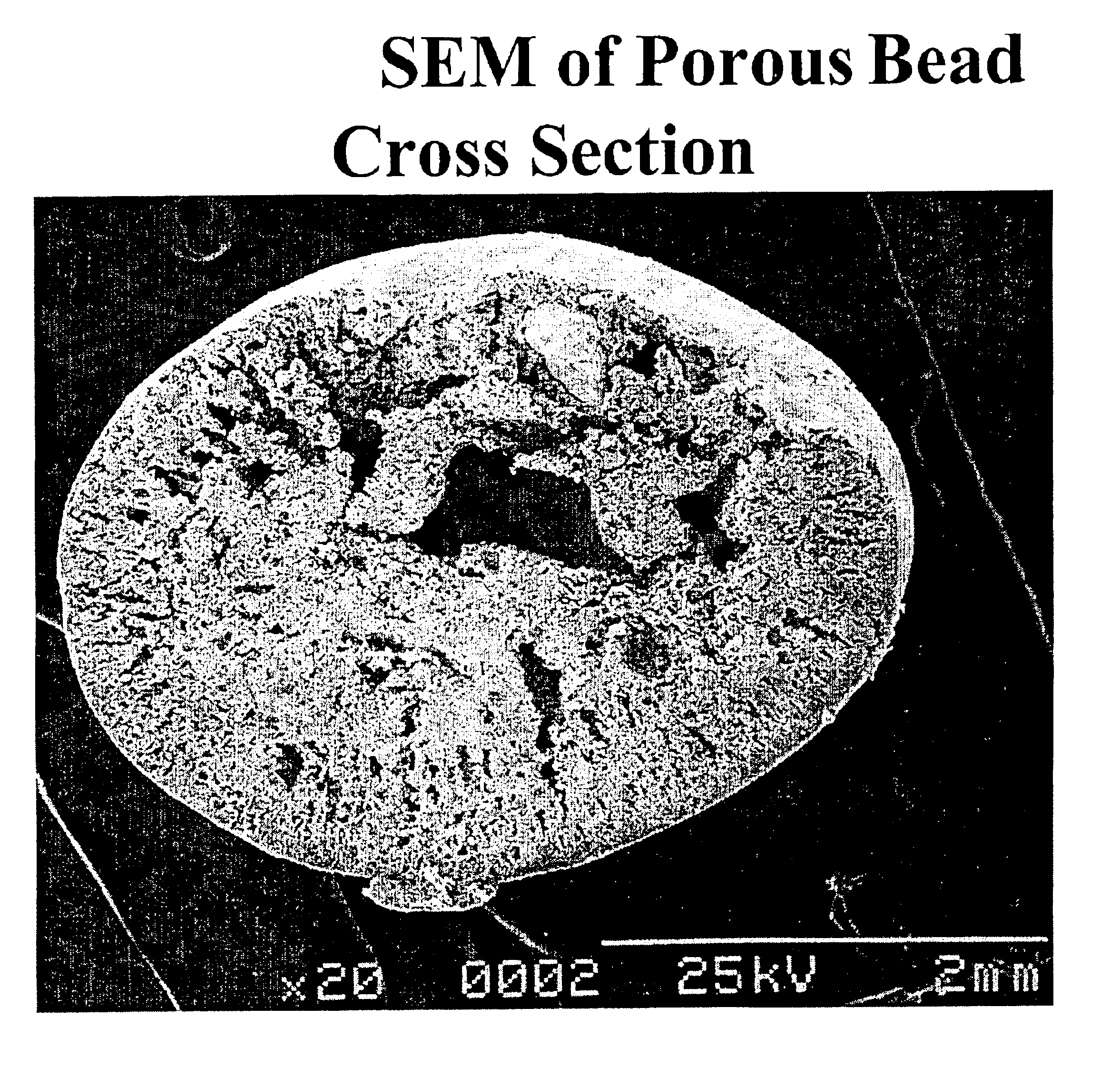
Apparatus and methods for forming microcultures within porous media
Highly porous, beads are comprised of a polymer and a second compound mixed into it. The second compound, an amendment, is either a nutrient or a compound having high affinity to one or more nutrients. A plurality of these beads may be exposed to an aqueous environment, usually a body of water. Bacteria and other microorganisms rapidly enter and remain within the nutrient filled interior space of the beads. Any of a number of various detection methods may then be used to characterize, detect and / or identify the microorganisms.
Owner:TULSA THE UNIV OF +1
Methods for forming microcultures within porous media
InactiveUS6908556B2Rapidly and readily performedAccurate detectionWater cleaningByproduct vaporizationInterior spacePorous medium
Highly porous, beads are comprised of a polymer and a second compound mixed into it. The second compound, an amendment, is either a nutrient or a compound having high affinity to one or more nutrients. A plurality of these beads may be exposed to an aqueous environment, usually a body of water. Bacteria and other microorganisms rapidly enter and remain within the nutrient filled interior space of the beads. Any of a number of various detection methods may then be used to characterize, detect and / or identify the microorganisms.
Owner:TULSA THE UNIV OF +1
Streptomycete fermentation medium
InactiveCN106086120AReduce utilizationImprove leaching rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydrolysateDipotassium phosphate
The invention belongs to the technical field of microculture, and discloses a streptomycete fermentation medium. The streptomycete fermentation medium is prepared from, by weight, 7.3-9.2% of straw zymolyte, 4.2-6.8% of potato diffusion juice, 3.3-5.5% of bean pulp hydrolysate, 2.6-4.7% of fishbone meal hydrolysate, 2.3-3.7% of wheat bran, 1.5-2.6% of glucose, 0.1-0.2% of dipotassium phosphate, 0.05-0.08% of magnesium sulfate, 0.02-0.03% of sodium chloride and the balance water. The streptomycete fermentation medium is low in cost and increases enterprise profits.
Owner:FUYANG HUAIBANG MACHINERY
Identifying genes involved in antibiotic resistance and sensitivity in bacteria using microcultures
InactiveUS20170342407A1Increase probabilityLoss of fitnessMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein nucleotide librariesTransposon mutagenesisAntibiotic sensitivity
Described is a method for identifying a gene which mediates antibiotic sensitivity or resistance in a target bacterium, the method comprising the steps of: (a) generating a pool of mutant target bacteria by transposon mutagenesis with an activating transposon (TnA), wherein the TnA comprises an outward-facing promoter (TnAP) capable of increasing transcription of a gene at or near its insertion site in the DNA of said target cells; (b) generating a control microdroplet library by encapsulating individual members of the pool of step (a) in microdroplets, the microdroplets comprising a volume of aqueous growth media suspended in an immiscible carrier liquid, each microdroplet comprising a single mutant target cell; (c)generating a test microdroplet library by encapsulating individual members of the pool of step (a) in microdroplets, the microdroplets comprising a volume of aqueous growth media containing the antibiotic and suspended in an immiscible carrier liquid, each microdroplet comprising a single mutant target cell; (d) incubating the control and test microdroplet libraries to produce control and test microcultures; and (e) comparing the distribution of TnA insertions between control and test microcultures to identify a gene which mediates antibiotic sensitivity or resistance in said target bacterium.
Owner:DISCUVA
Microfluid device and three-dimensional microculture method for cell
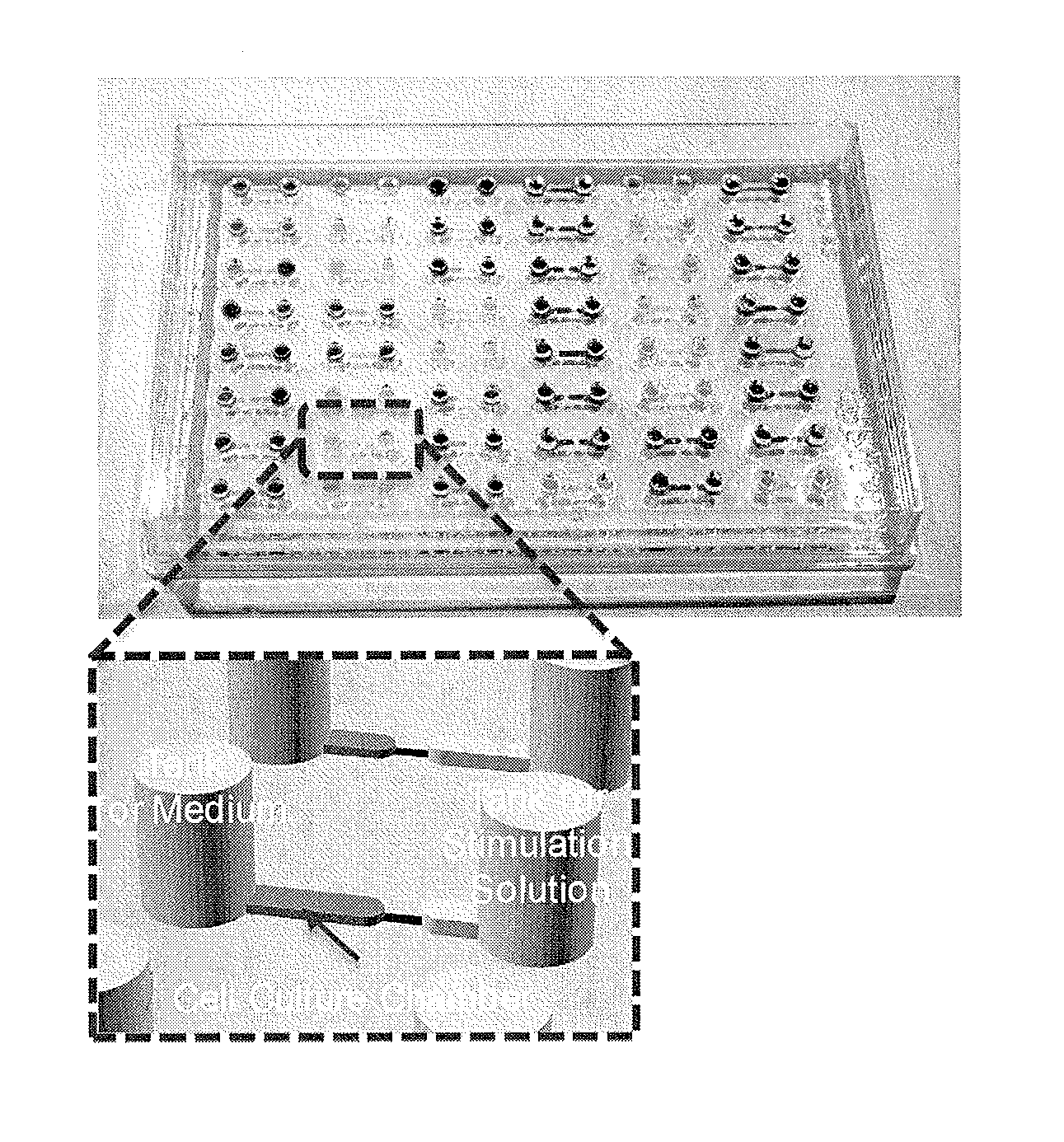
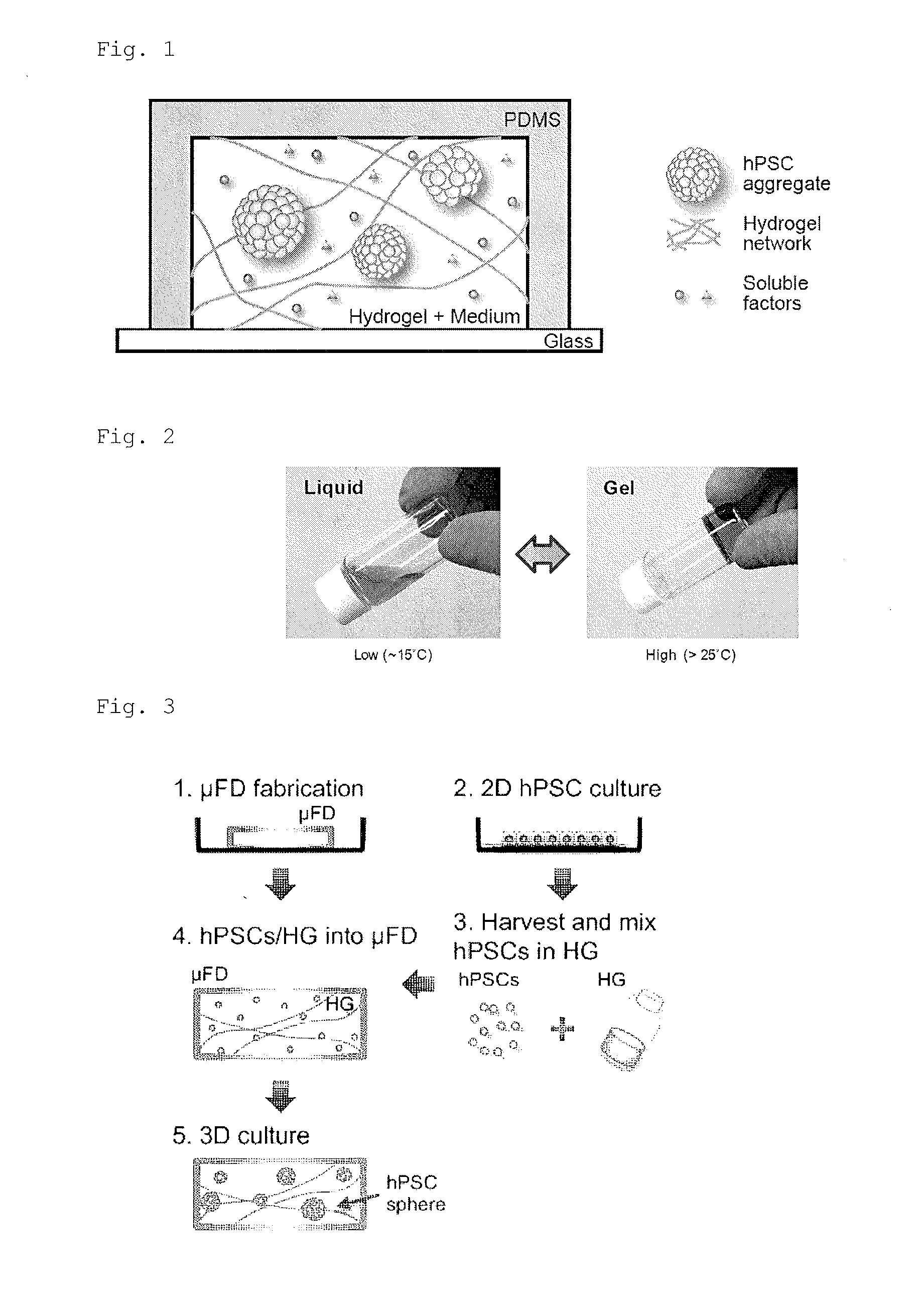
ActiveUS20160369218A1Easy to buildImprove throughputAdditive manufacturing apparatusApparatus sterilizationConcentration gradientMicroculture
The present invention provides a microfluidic device comprising at least one cell culture chamber, the or each chamber being connected to at least two openings, the device being configured to supply at least one physiologically active substance from at least one of the openings to the or each cell culture chamber in such a manner as to form a concentration gradient or concentration gradients in the or each chamber when cells and a hydrogel are introduced into the or each chamber to culture the cells in a 3D-gel medium.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Protein culture medium for fast propagating biological bacteria
The invention relates to the field of microculture, in particular to a protein culture medium for fast propagating biological bacteria. The protein culture medium is prepared from, by weight, 0.1-0.3part of growth factors, 20-25 parts of a coagulator, 18-28 parts of a protein additive, 0.5-1.5 parts of a PH modifier, 1.3-2.9 parts of microelements, 9-15 parts of saccharide and 30-40 parts of water. According to the culture medium, absorption of microorganisms to nutrient substances and conduction of related metabolic processes can be promoted, and stable growth and propagation of microorganisms can be stimulated. In addition, by adding vitamin, the protein additive and thelike, enough energy can be provided for the microorganisms to take, and fast propagation and metabolism of the microorganisms are promoted. Compared with a culture medium in the prior art, the culture medium is high in microorganism culture speed and microorganism propagating speed, balanced in nutrition and long innutrition holding time.
Owner:天适立农生态农业发展(广州)股份有限公司
Method for screening for bioactive natural products
InactiveUS20170342460A1Guaranteed detection effectIncrease probabilityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsTransposon mutagenesisExtinction
Describe is a method for screening mutant prokaryotic cells to identify producers of a cytotoxic agent active against a target cell, the method comprising the steps of: (a) providing cells of a producer prokaryotic species; (b) generating a pool of mutant producer cells by transposon mutagenesis of the cells of step (a) with an activating transposon (TnA), wherein the TnA comprises an outward-facing promoter (TnAP) capable of increasing transcription of a gene at or near its insertion site in the DNA of said producer cells; (c) co-encapsulating individual members of the pool of step (b) with one or more target cells in microdroplets, the microdroplets comprising a volume of aqueous growth media suspended in an immiscible carrier liquid, thereby generating a library of microdroplets each comprising a single mutant producer cell and one or more target cell(s); (d) incubating the microdroplet library of step (c) under conditions suitable for co-culture of the single mutant producer cell and target cell(s) to produce a library of microcultures, whereby mutant producer cells producing a cytotoxic agent active against the target cell(s) outgrow target cells in each microculture; and (e) screening the library of microcultures of step (d) for microcultures in which target cells have been outgrown or overgrown to extinction by mutant producer cells.
Owner:NANNA THERAPEUTICS LTD
Identifying genes involved in antibiotic resistance and sensitivity in bacteria using microcultures
InactiveUS20180179518A9Increase probabilityLoss of fitnessMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein nucleotide librariesBacteroidesAntibiotic sensitivity
Described is a method for identifying a gene which mediates antibiotic sensitivity or resistance in a target bacterium, the method comprising the steps of: (a) generating a pool of mutant target bacteria by transposon mutagenesis with an activating transposon (TnA), wherein the TnA comprises an outward-facing promoter (TnAP) capable of increasing transcription of a gene at or near its insertion site in the DNA of said target cells; (b) generating a control microdroplet library by encapsulating individual members of the pool of step (a) in microdroplets, the microdroplets comprising a volume of aqueous growth media suspended in an immiscible carrier liquid, each microdroplet comprising a single mutant target cell; (c)generating a test microdroplet library by encapsulating individual members of the pool of step (a) in microdroplets, the microdroplets comprising a volume of aqueous growth media containing the antibiotic and suspended in an immiscible carrier liquid, each microdroplet comprising a single mutant target cell; (d) incubating the control and test microdroplet libraries to produce control and test microcultures; and (e) comparing the distribution of TnA insertions between control and test microcultures to identify a gene which mediates antibiotic sensitivity or resistance in said target bacterium.
Owner:DISCUVA
Culture medium for culturing fat stem cells and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107828724AImprove securityGrowth inhibitionCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAdditive ingredientNutrition
The invention relates to the technical field of microculture, in particular to a culture medium for culturing fat stem cells and a preparation method thereof. The culture medium comprises a basic culture medium and additives, and the additives include peptone, sodium chloride, glucose, lactose, phosphorus source, pig gall salt, mannitol, sodium pyruvate, amino acid, vitamin, antibiotic, metal salt, plant polysaccharide and distilled water. The culture medium contains the plant polysaccharide, thereby being capable of inhibiting growth of other cells except for fat stem cells and promoting proliferation of the fat stem cells and conducive to increasing concentration of the fat stem cells in the culture medium and shortening culture time; through synergism among ingredients, sufficient nutrition and good environment needed for cell growth and proliferation can be provided, cell growth can be promoted, albumin synthesis can be promoted, and cell activity can be maintained for a long time.
Owner:沈国青
Portable refrigerated storage and transportation box
InactiveCN106742750AAct as low temperature protectionImprove protectionLiving organism packagingMachines using electric/magnetic effectsMicroorganismEvaporation
A portable refrigerated storage and transportation box is composed of a box body, a box cover, a box belt, a semiconductor refrigeration chip, magnets, a gas filling device and a power socket. A water tank made of a metal material is arranged in the middle of the box body. A gas guide pipe is arranged on the portion, on the rear portion of the left side of the water tank, of the box body. The gas filling device is mounted on an open hole which is provided with an inner thread and located on the portion, on the front portion of the left side of the water tank, of the box body. The semiconductor refrigeration chip is mounted on the portion, at the lower end of the water tank, of the box body. The power socket is mounted on an open hole in the rear end of the left side of the lower portion of the box body. The left side and the right side of the lower portion of the box body are each provided with an opening. The lower end of the rear portion of the box cover is mounted at the upper end of the rear portion of the box body through two hinges. One magnet is mounted at the lower end of the front portion of the box cover, the other magnet is mounted at the upper end of the front portion of the box body, and the box belt is mounted on the upper portions of the left side and the right side of the box body. By the adoption of the portable refrigerated storage and transportation box, the semiconductor refrigeration chip is powered and refrigerated through a storage battery in an automobile, the manner of butagas evaporation, heating and refrigeration is adopted, the low temperature is provided in the whole transportation process of cultures and microorganism samples, and the good protection function on the cultures and the microculture samples is achieved.
Owner:云南坤发环境科技有限公司
Methods of obtaining antigen-specific t cell populations
InactiveUS20100322910A1High throughput screeningSensitive highBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a method of obtaining a population of antigen-specific T cells from peripheral blood of a host. An embodiment of the method of the invention comprises (i) dividing PBMCs from peripheral blood of a host into more than one sub-population; (ii) contacting the PBMCs with an antigen and IL-2; (iii) obtaining a sample of PBMCs from each sub-population; (iv) identifying an antigen-reactive sub-population by determining by high throughput quantitative PCR the expression of a factor produced by the PBMCs of each sample; (v) dividing the antigen-reactive sub-population into microcultures; (vi) identifying the antigen-reactive microculture; and (vii) expanding the microculture, thereby obtaining a population of T cells specific for the antigen. The invention also provides a population of T cells obtained by the inventive method, a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, and a method of treating a disease in a host using the pharmaceutical composition. Related isolating and screening methods are further provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
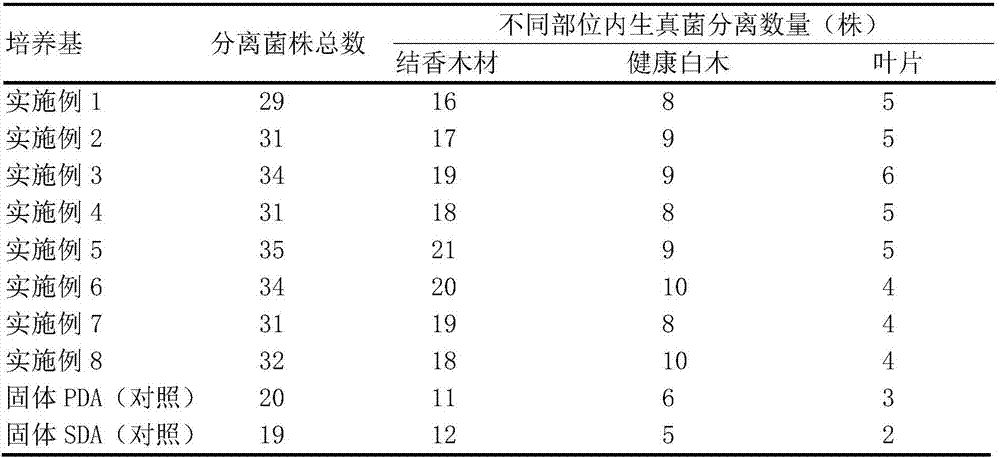
Culture medium for endophytic fungi separation and rapid propagation of agilawood edgeworthia chrysantha
InactiveCN106967617ANutritious and comprehensiveRich and full growthFungiMicroorganism separationMicrobial culture techniqueEdgeworthia chrysantha
The invention belongs to the technical field of microculture, and provides a culture medium for endophytic fungi separation and rapid propagation of agilawood edgeworthia chrysantha, wherein the culture medium is prepared from potato, chenopodium quinoa, glucose, agar and distilled water. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a preparation method of the culture medium. The test result shows that the agilawood endophytic fungi quantity separated by the culture medium is obviously increased, and the agilawood endophytic fungi in fluid fungi shaking culture can reach the maximum growth within a short time, thereby greatly shortening the fungi shaking time. Moreover, all nutrition components of the culture medium are originated from the natural food materials (potato and chenopodium quinoa) and glucose; there is no any other additive; the culture of agilawood edgeworthia chrysantha fungi used as the edible treatment drugs is very important; the culture medium is green and environment-friendly, and the preparation is simple, economic and practicable.
Owner:伍亭亦
Listeria monocytogenes selective medium
InactiveCN105506054AImprove separation rateReliable detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementArginineGluconic acid
The invention discloses a listeria monocytogenes selective medium, and belongs to the field of detection of microculture. The listeria monocytogenes selective medium is characterized in that the prepared 1000 ml culture medium comprises the following components: yeast extract powder, beef powder, casein peptone, agar, glucose, sodium chloride, zinc gluconate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, optical, polymyxin,bacitracin, gamma-arginine hydroxy and sterile horse blood protein, and distilled water is added into the components to 1000 ml. Compared with the prior art, the selective medium has the characteristics of being reliable in detection result, and high in listeria monocytogenes separation rate.
Owner:夏淑平
Fusobacterium necrophorum selective medium
InactiveCN104894214AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMagnesium saltThermal deformation
The invention discloses a fusobacterium necrophorum selective medium and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of microculture examination. The fusobacterium necrophorum selective medium is characterized in that 1000 ml of culture medium comprises casein tryptone, glucose, yeast powder, sodium chloride, agar, bile salt, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid dipotassium magnesium salt, gamma-aminobutyric acid, sterile thermal-deformation calf serum and the balance of distilled water. Compared with the prior art, the fusobacterium necrophorum selective medium has the advantages of reliability in examination and high separation rate of fusobacterium necrophorum.
Owner:鲁莉
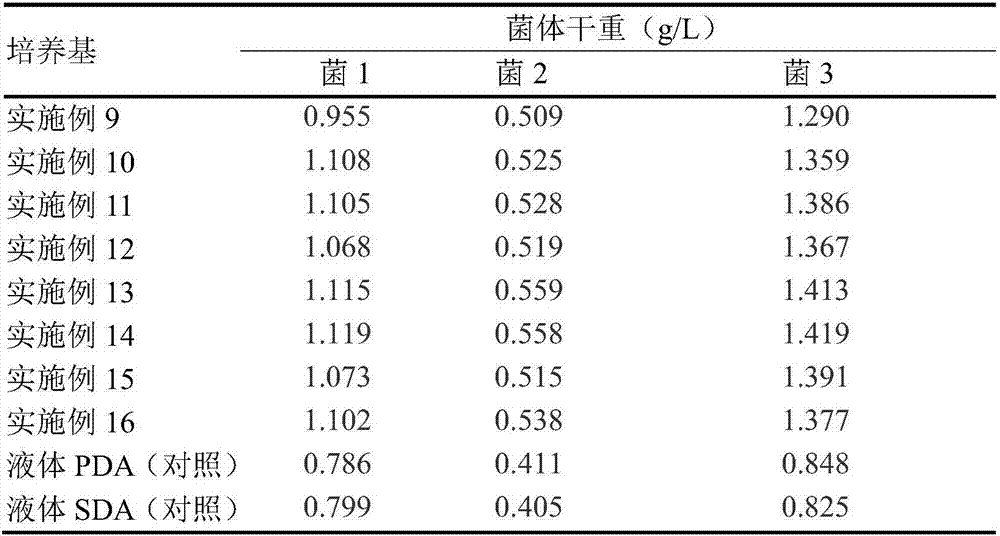
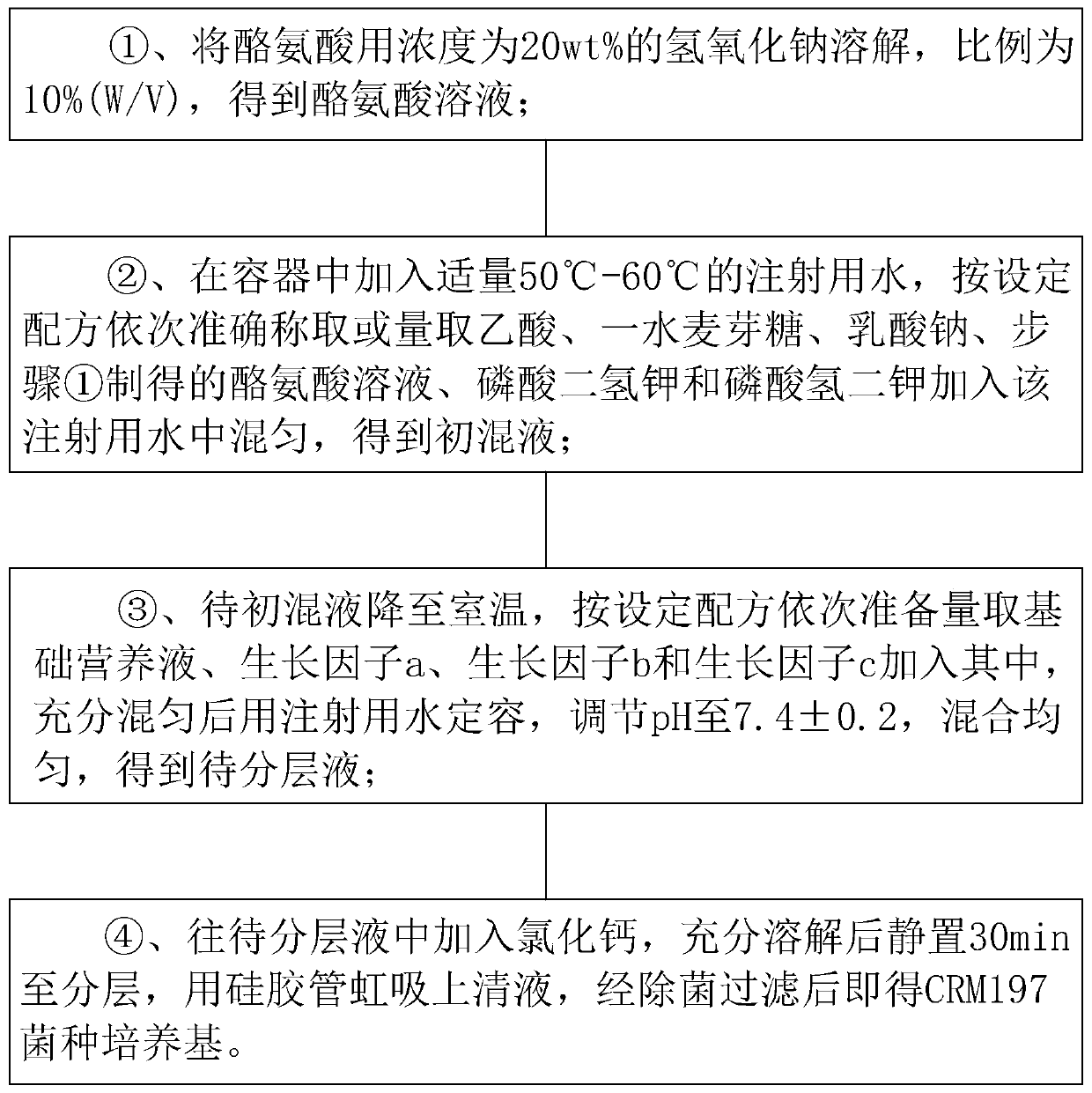
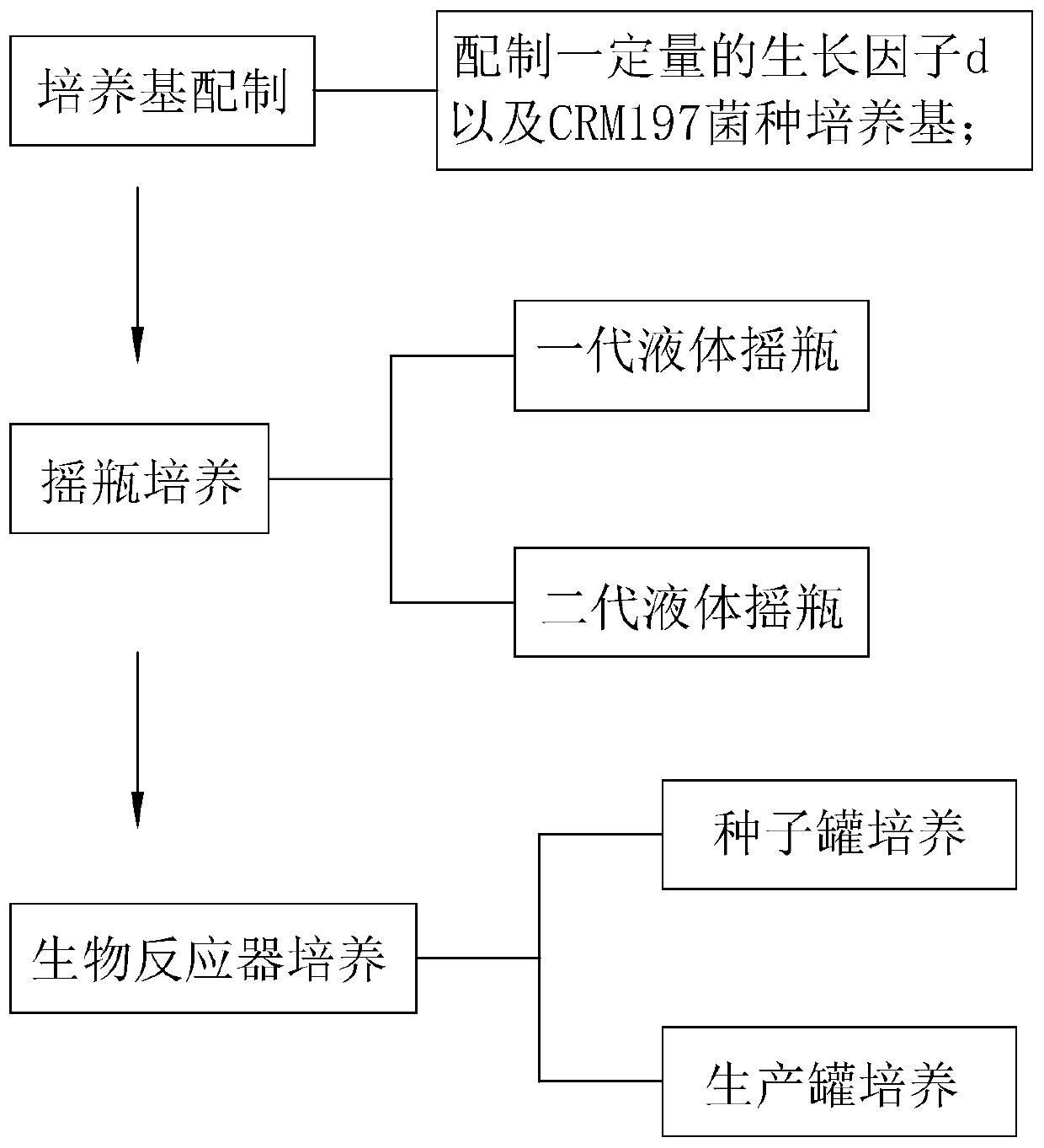
CRM197 strain culture medium, preparing method and fermentation culture method
ActiveCN110452838AFacilitate large-scale expansionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSodium lactateDipotassium phosphate
The invention relates to the technical field of bio-pharmaceuticals and microculture, in particular to a CRM197 strain culture medium, a preparing method and a fermentation culture method. The CRM197strain culture medium is a liquid culture medium. Each L of culture medium comprises 250 mL of a basic nutrient solution, 7.2 mL of acetic acid, 30 g of maltulose monohydrate, 2 mL of sodium lactate,0.5 g of tyrosine, 1.96 g of monopotassium phosphate, 5.1 g of dipotassium phosphate, 6.13 mL of a growth factor a, 8 mL of a growth factor b, 8 mL of a growth factor c and 1.3 g of calcium chloride.All the components can be rapidly dissolved when the culture medium is prepared, and the uniformity of the culture medium is ensured. By means of the step-by-step amplification fermentation culture amplification mode, the CRM197 strain fermentation culture method has the advantages of being rapid, convenient to implement, low in cost and high in efficiency, the large-scale amplification of a CRM197 strain is facilitated, and therefore a high-expression-amount fermentation bacteria liquid is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG VACIN BIO PHARMA LTD
Microculture method
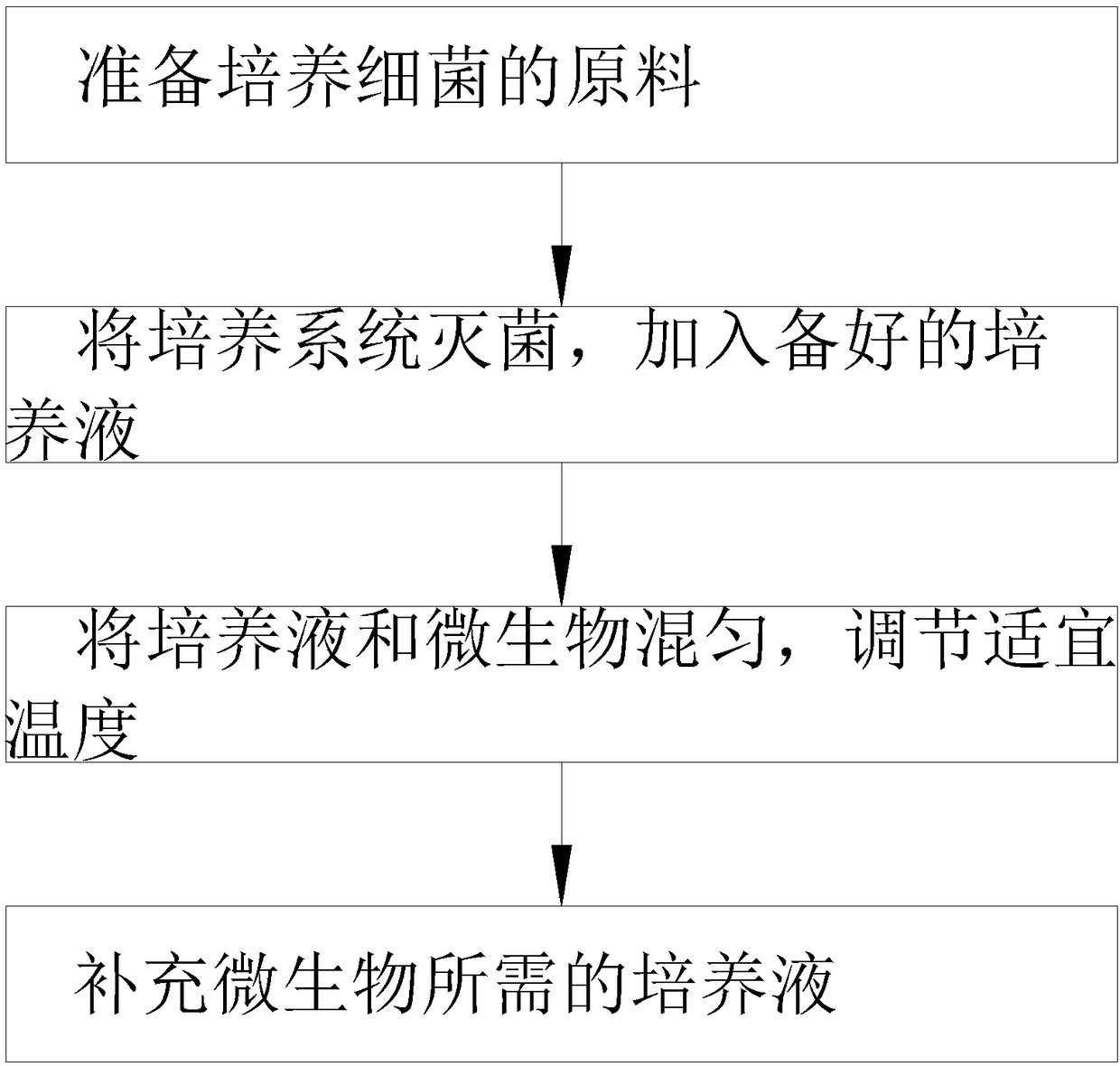
PendingCN108410736AEasy to trainReproduce fastBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCulture fluid
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a microculture method. An incubator is adopted in the method and comprises a box, three culture tanks, a motor, ultraviolet lamps and culture liquid delivery pipes, the box is cylindrical, the culture tanks are positioned inside the box and used for culturing microorganisms, the motor is mounted at the bottom of the culture tank in the middle, the ultraviolet lamps are mounted on the inner wall of the box, and the culture liquid delivery pipes penetrate the box and are positioned inside the culture tanks and used for supplementing culture liquid for the culture tanks. The microculture method is mainly used for mass culture of microorganisms; the culture liquid delivery pipes are utilized to timely supplement the culture liquid in the culture tanks, and breeding and growing of the microorganisms are improved to greatest content. Power generated by stirring rods is utilized to provide proper temperature in the culture tanks.
Owner:郭庆
Temperature-controlled microculture instrument and using method thereof
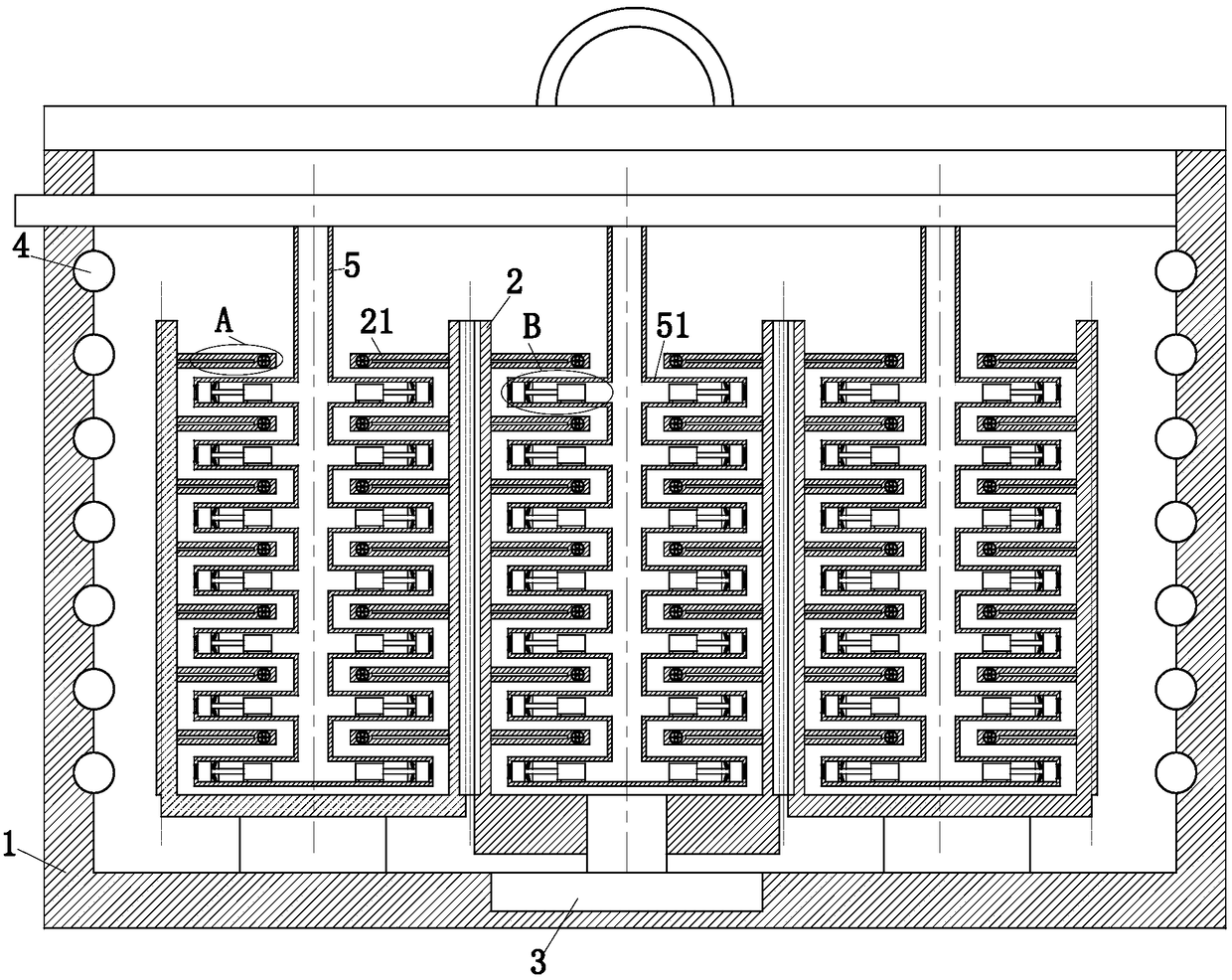
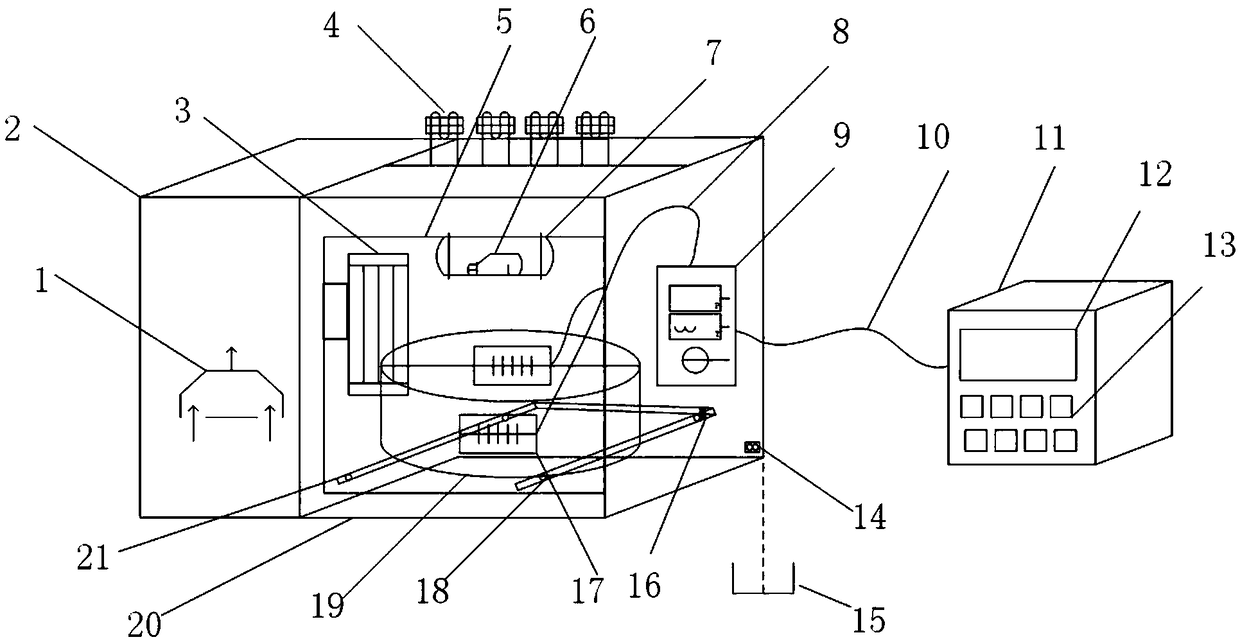
InactiveCN108913537AIncrease flexibilityImprove convenienceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl lineEngineering
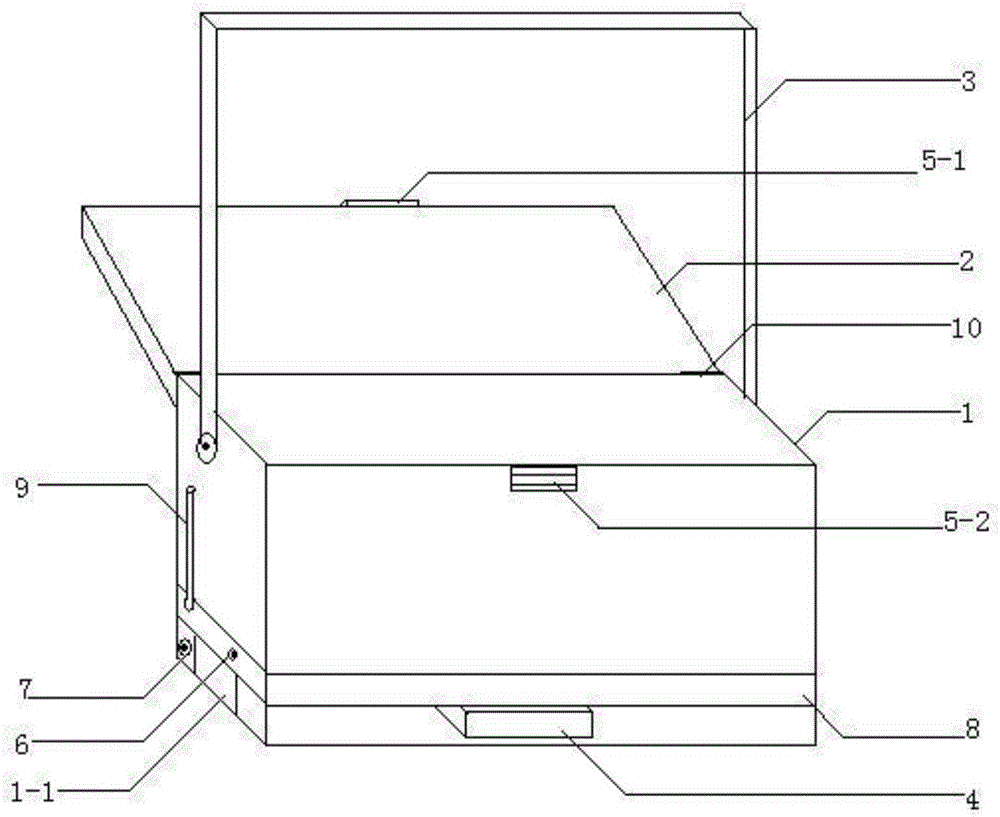
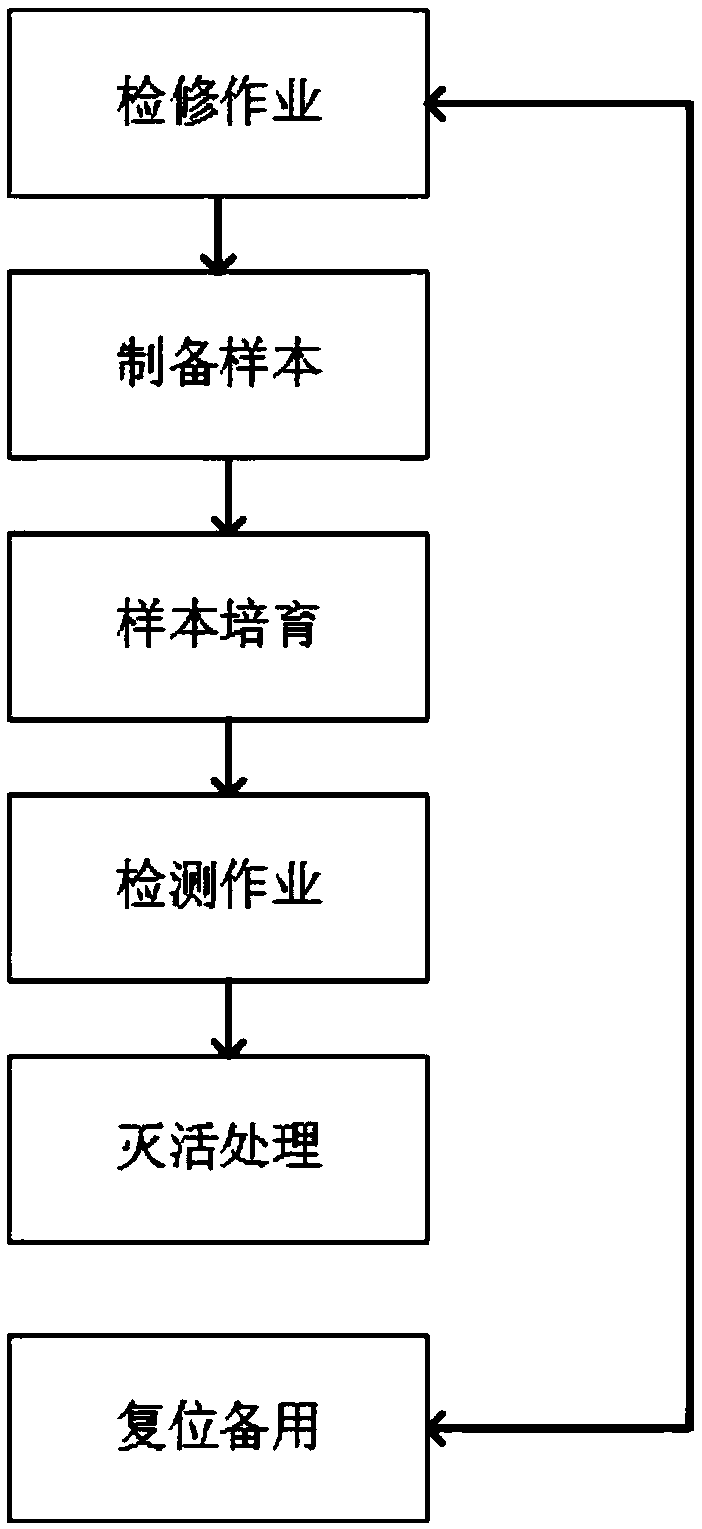
The invention relates to a temperature-controlled microculture instrument and a culture method. The temperature-controlled microculture instrument includes a ventilating fan, a fan cabinet, a ventilating opening, ultraviolet lampshades, a cabinet door, a CCD camera, a radiation lampshade, a signal line, an instrument panel, a control line, a control cabinet, a display screen, control buttons, a charging port, a dirt discharging tube, a limiting block, a temperature and humidity sensor, pulley, a carrying box, an incubator and a guide rail. A using method of the instrument includes the following six steps: maintenance work, sample preparation, sample cultivation, detection work, inactivation treatment and resetting for later use. The instrument has the advantages of simple system formationstructure, high integration and high running automation degree, effective improvement of the flexibility, convenience and working efficiency of microculture work, effective improvement of the workingefficiency and precision of the detection operation, effective avoiding of harms and pollution of a detection sample to an operator and the surrounding environment, and improvement of the safety and reliability of the operation.
Owner:李桂云 +3
Nocardia asteroid selective medium for sputum samples
InactiveCN104830955AImprove separation rateReliable detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementNalidixic acidKetone
The invention discloses a nocardia asteroid selective medium for sputum samples and belongs to the field of detection of microculture. The nocardia asteroid selective medium is characterized in that 1000 ml of culture medium comprises ox liver powder, malt extract powder, yeast extract powder, sodium chloride, agar, ferroporphyrin, calcium lactate, nalidixic acid, Incarvillea argute ketone, vitamin K1, casein phosphopeptides and sterile defiber sheep blood and the balance of distilled water. Compared with the prior art, the nocardia asteroid selective medium has the advantages of reliability in detection and high separation efficiency of nocardia asteroid.
Owner:王均梅
Oscillation appliance for improving dissolved oxygen level of microculture process
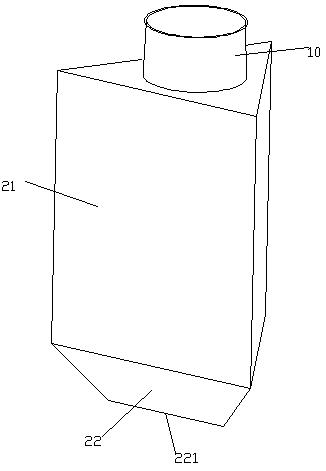
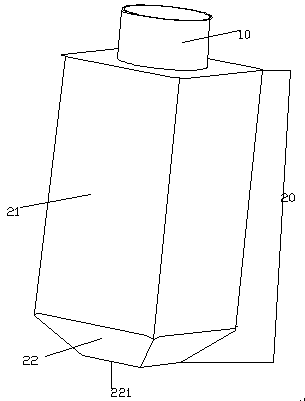
InactiveCN104212709AIncrease contentIncrease the wet weight of bacteriaBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnvironmental engineeringMicroculture
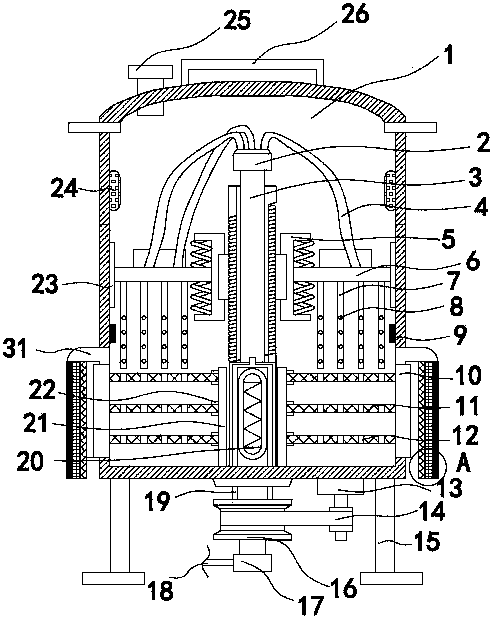
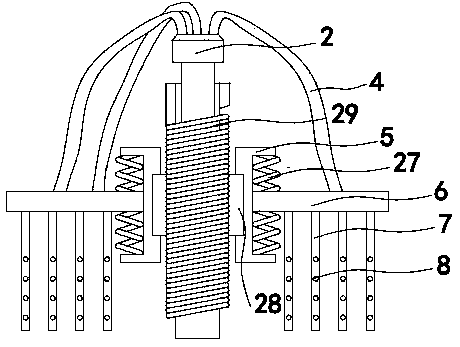
The invention relates to a microculture appliance, in particular to an oscillation appliance for improving the dissolved oxygen level of a microculture process. The oscillation appliance comprises an opening portion 10 and an appliance body 20, the opening portion 10 is located above the appliance body 20, the opening portion is a hollow body A, the appliance body 20 is composed of an appliance body upper portion 21 and an appliance body lower portion 22, the appliance body upper portion 21 is a hollow body B with an included angle on the inner side, an opening is designed in a surface portion of the upper end of the appliance body upper portion 21, the opening is in sealed connection with the lower end of the opening portion 10, the appliance body lower portion 22 is a big-end-up inner hollow cavity with an included angle on the inner side, the bottom of the big-end-up inner hollow cavity is sealed by a sealing plane 221, and the hollow body B of the appliance body upper portion 21 is in sealed connection with the inner hollow cavity of the appliance body lower portion 22. The oscillation appliance for improving the dissolved oxygen level of the microculture process has the advantages that the application range is wide, the dissolved oxygen level of the microculture process can be improved, and thereby, microbial metabolism target product content and thallus wet weight can be increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENGHUA BIOK BIOLOGY
Microculture device capable of controlling illumination brightness
InactiveCN109593649AEasy to trainGuaranteed training effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlMicrobial culture technique
The invention provides a microculture device capable of controlling illumination brightness and belongs to the technical field of microculture. The microorganism culture device comprises a culture tank, vibrating pins, a threaded rod and shading assemblies, wherein a handle is arranged at the top of the culture tank, the shading assemblies are connected to two sides of the culture tank, the bottomof the culture tank is supported by support legs, a drive mechanism is mounted between the support legs, the threaded rod is arranged in the culture tank and sleeved with a U-shaped clamp ring, the vibrating pins are connected with two sides of the U-shaped snap ring, and clamp plates are arranged below the vibrating pins. The temperature control force of the culture device can be kept, the solarenergy utilization rate of the culture device can be increased, and energy consumption of microorganisms in the culture process is greatly reduced.
Owner:嘉兴市爵拓科技有限公司
Microbiological detection device and microbiological detection method
InactiveCN104502427ARapid Indicator ChangesQuick detection of indicator changesMaterial electrochemical variablesProblem of timeCulture fluid
The invention relates to the field of microculture and detection, and provides a microbiological detection device and a microbiological detection method, aiming at solving the problems of time consuming, high cost and poor biocompatibility and the like in the existing microbiological detection method. The microbiological detection device comprises a reaction chamber used for containing nutrient solution, a sensitive element and an organic thin-film field effect transistor, wherein the sensitive element is communicated with the reaction chamber, is contacted with the nutrient solution and is used for sensing pH value variation of the nutrient solution and producing an electric charge according to the pH value variation; and the organic thin-film field effect transistor is electrically communicated with the sensitive element and is used for determining whether microorganisms exist or not according to charge of the sensitive element, and kinds of the microorganisms are also determined. The organic thin-film field effect transistor is adopted as a detecting element, so that microorganism growth condition in the nutrient solution can be detected in real time according to variation of channel current of the transistor, a detection result can be rapidly obtained, and the microbiological detection method has the advantages that the cost is low and biocompatibility is good compared with the existing detection method.
Owner:融智生物科技(青岛)有限公司
Methods of identifying central memory t cells and obtaining antigen-specific t cell populations
InactiveUS20130164272A1BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementCentral Memory T-CellSub populations
The invention provides a method of obtaining a population of antigen-specific T cells comprising: (i) dividing PBMCs from peripheral blood of a host into more than one sub-population; (ii) contacting the PBMCs of each sub-population with an antigen; (iii) obtaining a sample of the contacted PBMCs from each sub-population; (iv) measuring the quantity of 1) IL-2 mRNA and 2) IFN-γ mRNA expressed by the PBMCs of each sample; (v) determining the IL-2 index of each sample; (vi) identifying one or more samples with an IL-2 index determined in (v) of greater than or equal to about 10 to identify one or more antigen-reactive, central memory T cell sub-populations; (vii) dividing the antigen-reactive, central memory T cell sub-population(s) identified in (vi) into microcultures; (viii) identifying one or more antigen-reactive microcultures; and (ix) expanding the microculture(s).
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Culture medium for culturing lysurus mokusin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108795776AFast growthEasy to getFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrocultureCulture fungus
The invention provides a culture medium for culturing lysurus mokusin, and belongs to the field of the microculture. Research shows that the lysurus mokusin has good pesticide development prospect. According to a plurality of current lysurus mokusin culture mediums for culturing fungi, the growth of mycelium is slow, a form of the mycelium is sparse and distorted, and cannot satisfy the requirements of an experiment. The invention provides the culture medium for culturing lysurus mokusin mycelium. A preparation method for the culture medium comprises the following steps: collecting raw materials of silver birch branches in two years old, fallen leaves of dahurian larch, fallen leaves of silver birch and the like, after treatment of smashing, an ultrasonic wave and the like, preparing an agar culture medium, sub-packaging in a culture dish, and enabling the lysurus mokusin mycelium to be inoculated on the culture medium for culturing. The culture medium is capable of accelerating a growth rate of the lysurus mokusin mycelium, wherein time of overgrowing in 9 mm of the culture dish is shortened from 14 days of a common fungus culture medium to 9 days. The culture medium is also suitable for isolating a tissue of a lysurus mokusin sporophore and culturing ysurus mokusin spores.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
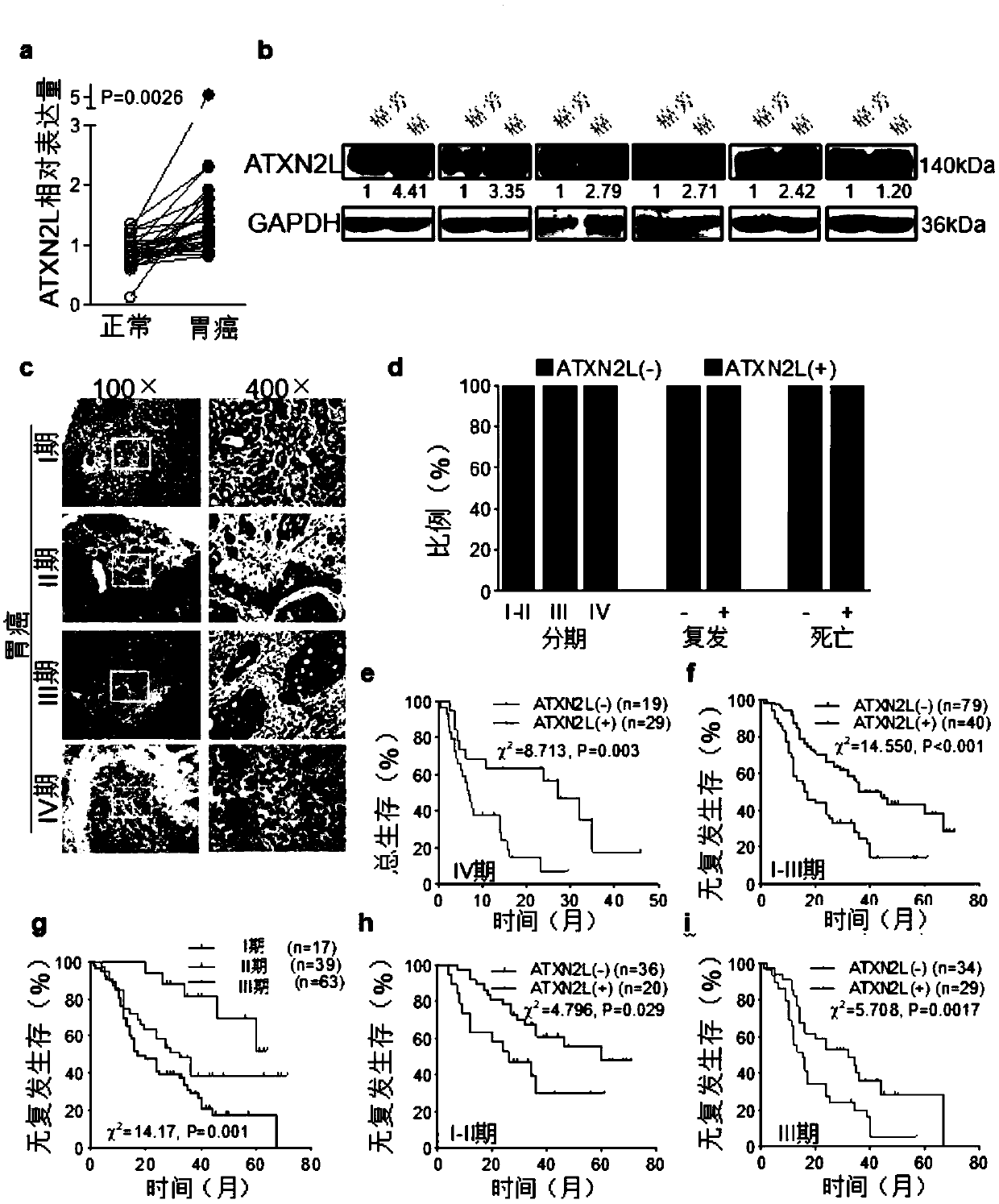
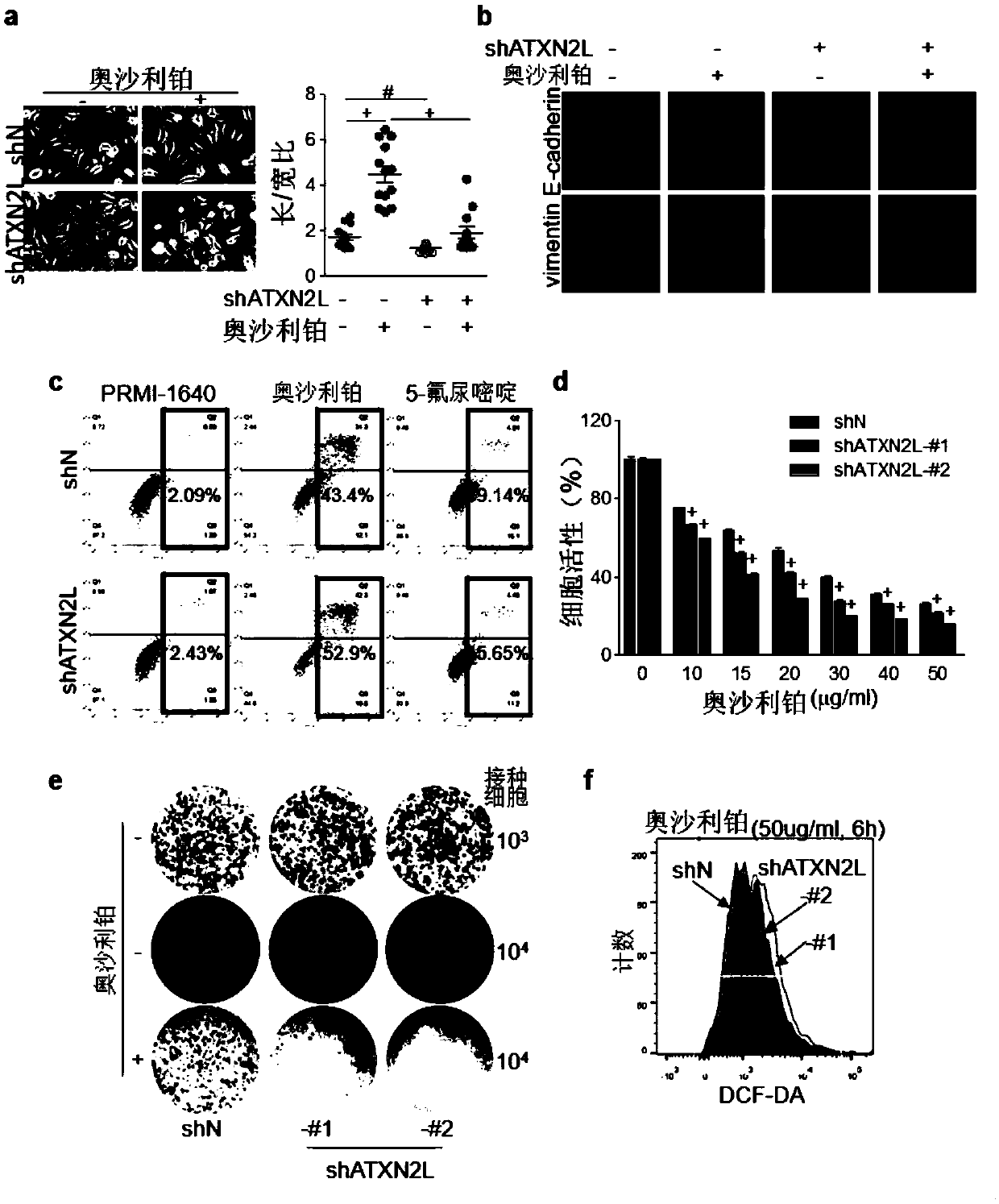
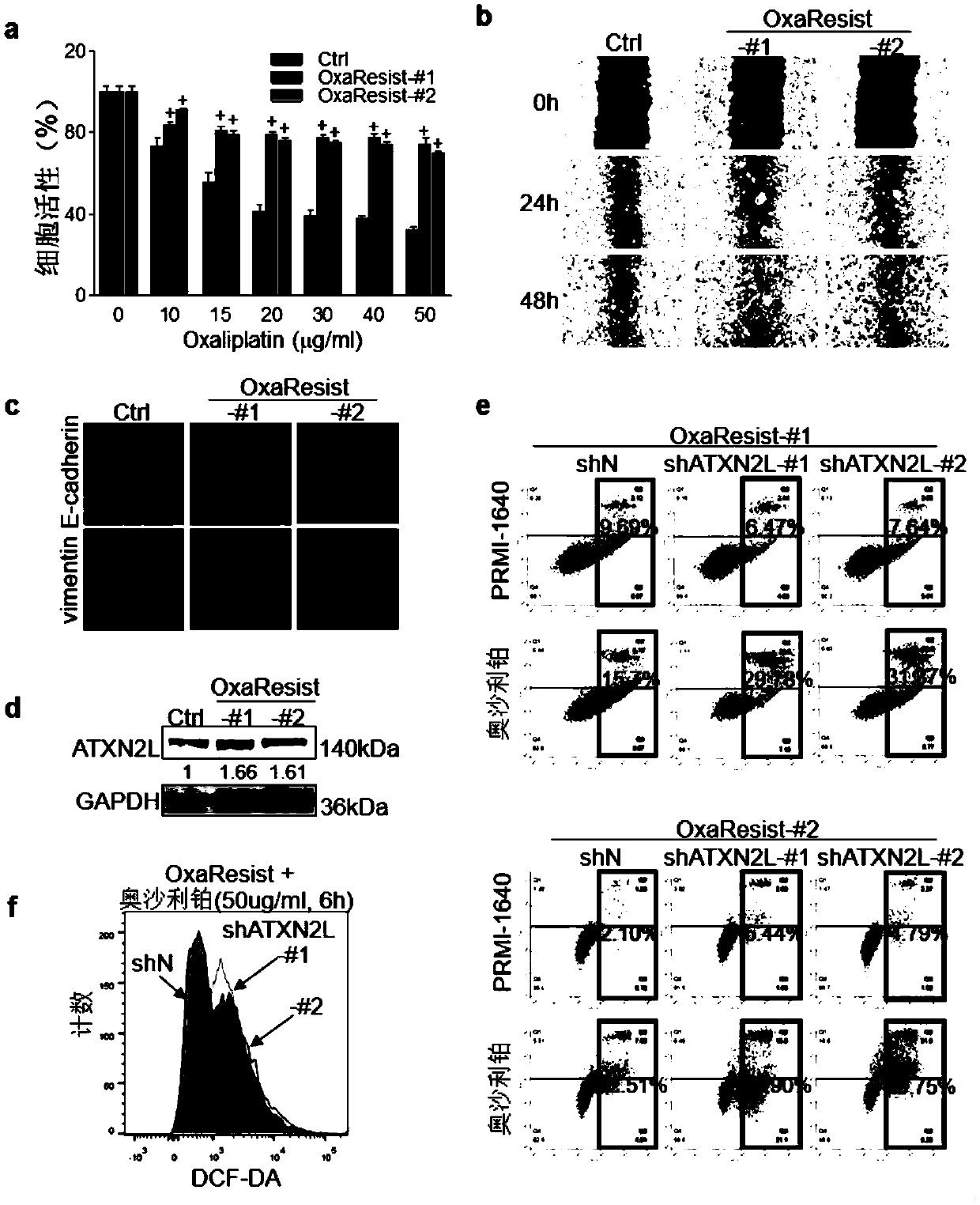
Application of ATXN2L (Ataxin-2like) as marker capable of assisting in evaluating gastric carcinoma oxaliplatin secondary drug resistance
ActiveCN109557317AHigh degree of malignancyIncreased sensitivityBiological testingMedicineWestern blot
The invention belongs to the field of the function and the application of genes and proteins, and relates to a new application of ATXN2L (Ataxin-2like) as a marker capable of assisting in evaluating gastric carcinoma oxaliplatin secondary drug resistance. Through a clinic specimen, a gastric carcinoma patient with high ATXN2L expression is proved to have bad prognosis. After the ATXN2L is silenced, the sensitivity of a gastric carcinoma cell for the oxaliplatin is enhanced. Through an in vitro induction method, an oxaliplatin drug-resistant strain is obtained, and an MTT (microculture tetrozolium) experiment proves that the oxaliplatin drug-resistant strain resists the oxaliplatin and a malignance degree is higher. Western blot detection finds that the expression of the ATXN2L in the oxaliplatin drug-resistant strain is higher than expression in a sensitive strain. In a flow type detection apoptosis experiment, after the ATXN2L is silenced, the sensitivity of the oxaliplatin drug-resistant strain for the oxaliplatin is increased. Therefore, the ATXN2L can be used as the marker capable of assisting in evaluating gastric carcinoma oxaliplatin secondary drug resistance, and therefore,an existing preparation technology for a kit can be used for providing a kit capable of assisting in evaluating gastric carcinoma oxaliplatin secondary drug resistance.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com