Patents
Literature
247 results about "Breast implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A breast implant is a prosthesis used to change the size, shape, and contour of a person's breast. In reconstructive plastic surgery, breast implants can be placed to restore a natural looking breast mound for post–mastectomy breast reconstruction patients or to correct congenital defects and deformities of the chest wall. They are also used cosmetically to enhance or enlarge the appearance of the breast through breast augmentation surgery.
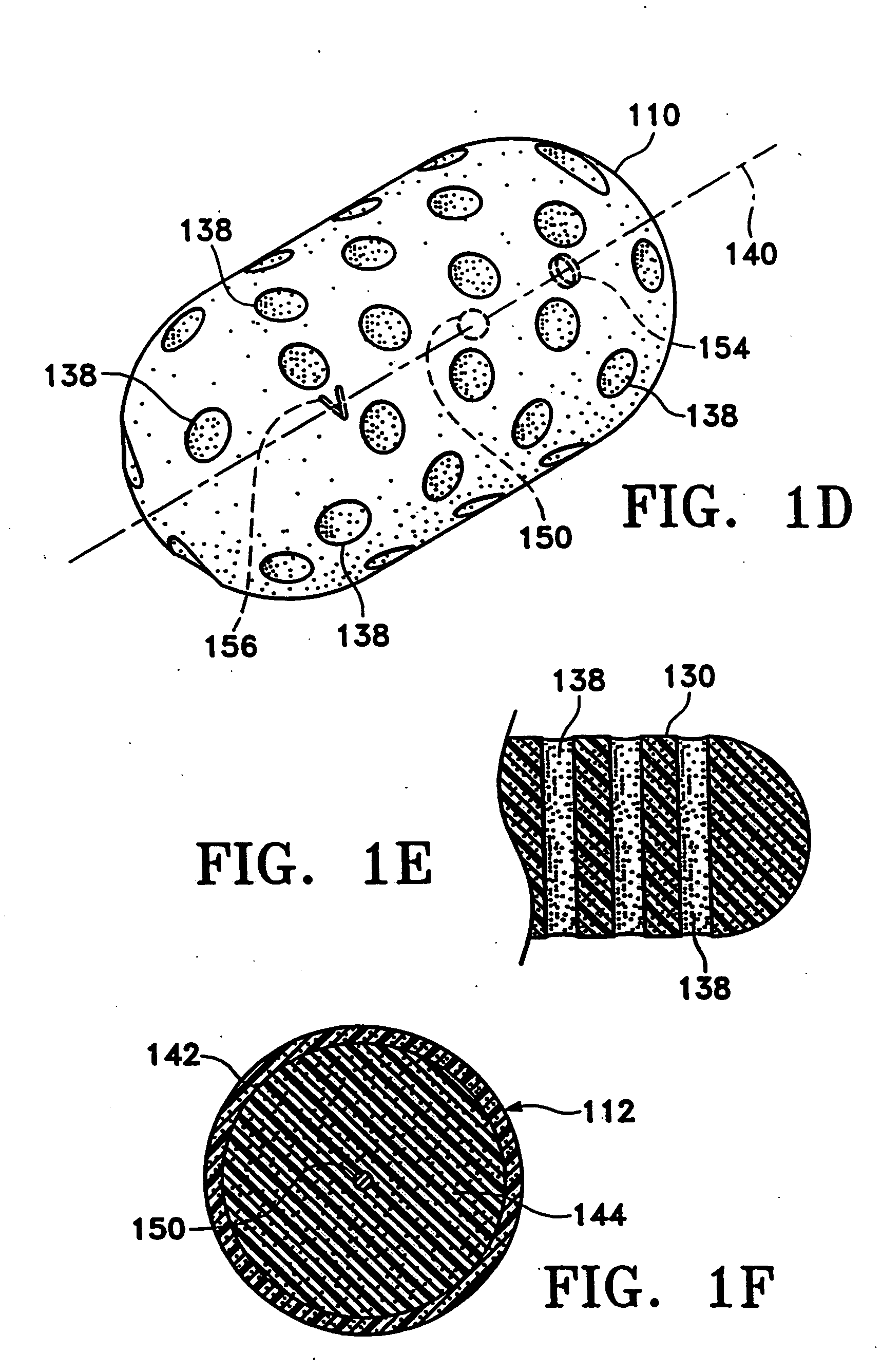
Fragmented polymeric compositions and methods for their use
InactiveUS6063061AImprove liquidityEasy to controlSurgical adhesivesSurgical drugsCross-linkBreast implant
Molecular cross-linked gels comprise a variety of biologic and non-biologic polymers, such as proteins, polysaccharides, and synthetic polymers. Such molecular gels may be applied to target sites in a patient's body by extruding the gel through an orifice at the target site. Alternatively, the gels may be mechanically disrupted and used in implantable articles, such as breast implants. When used in vivo, the compositions are useful for inhibiting post-surgical spinal and other tissue adhesions, for filling tissue divots, tissue tracts, body cavities, surgical defects, and the like.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Use of glucomannan hydrocolloid as filler material in prostheses
A prosthetic device for implantation into a mammalian body comprised of a non-absorbable biocompatible flexible material shell or sac filled with various biocompatible gel filler materials. The gel filler materials are comprised of biocompatible glucomannan obtained from konjac hydrocolloid flour and other biocompatible hydrocolloids, producing a natural look and feel for the prosthetic implants, especially reconstructive prostheses such as breast implants.
Owner:KONJAC TECH
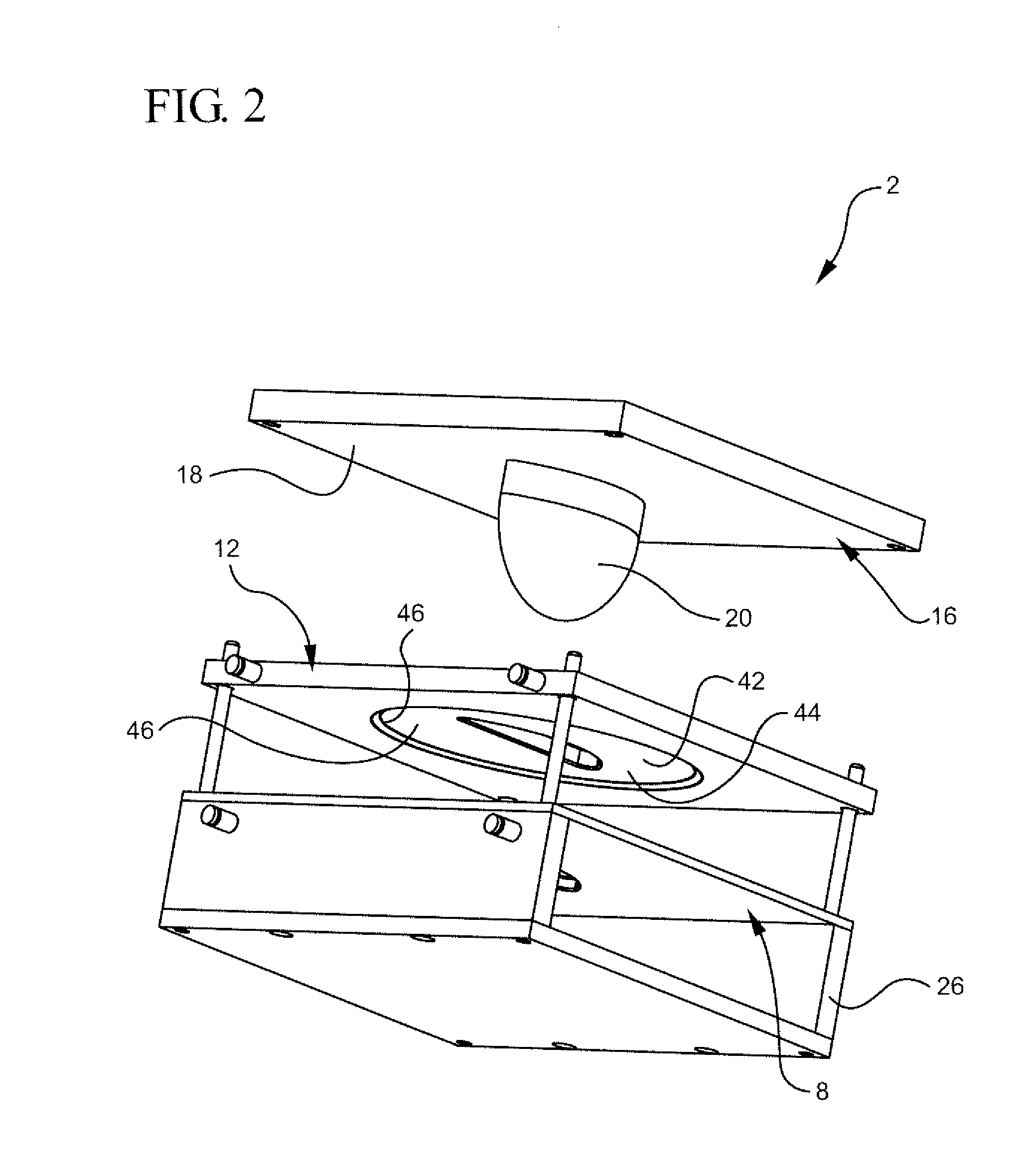
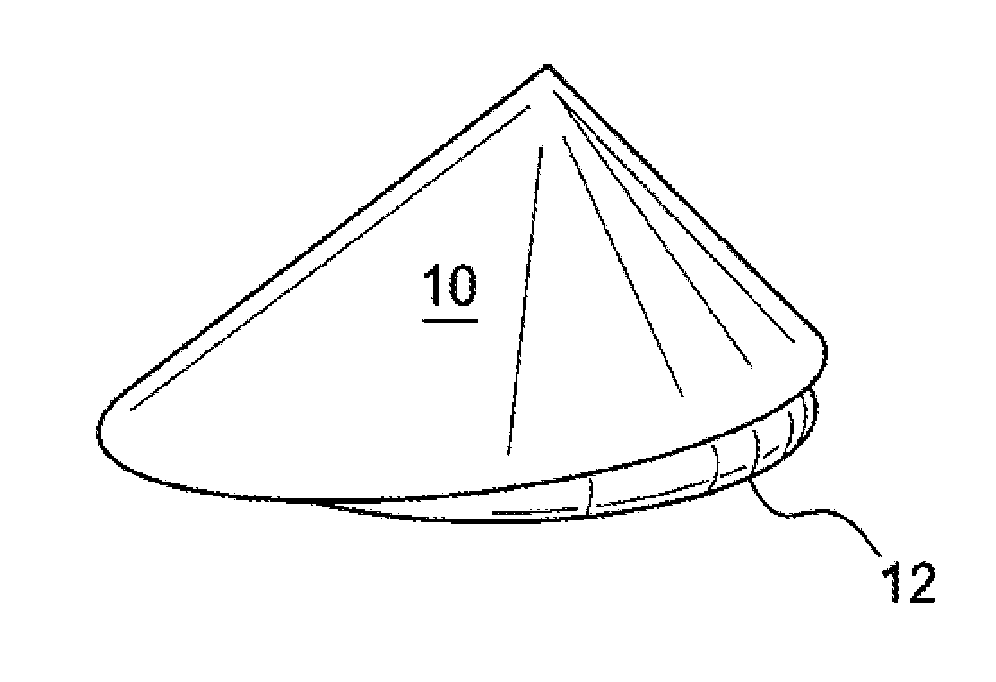
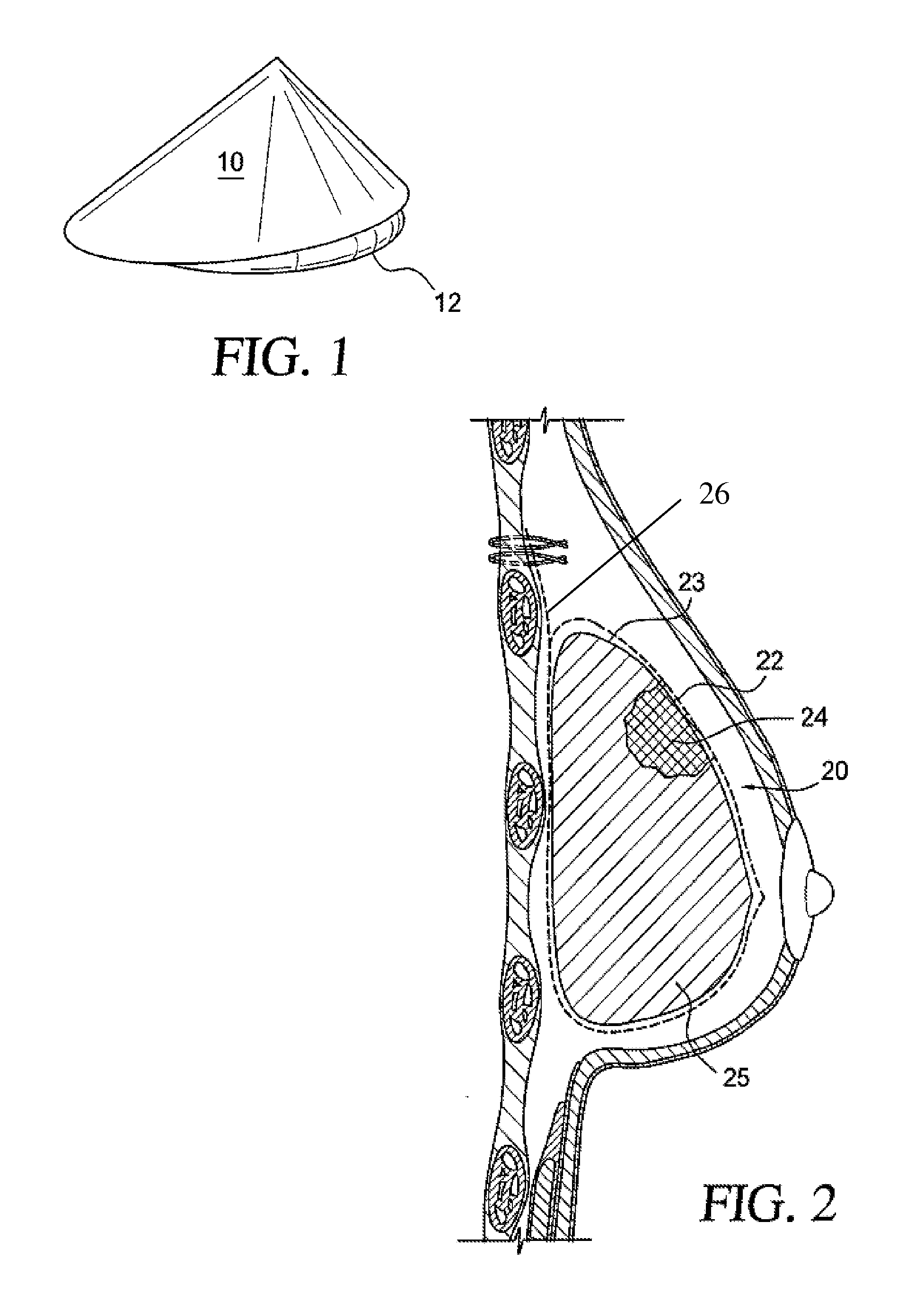
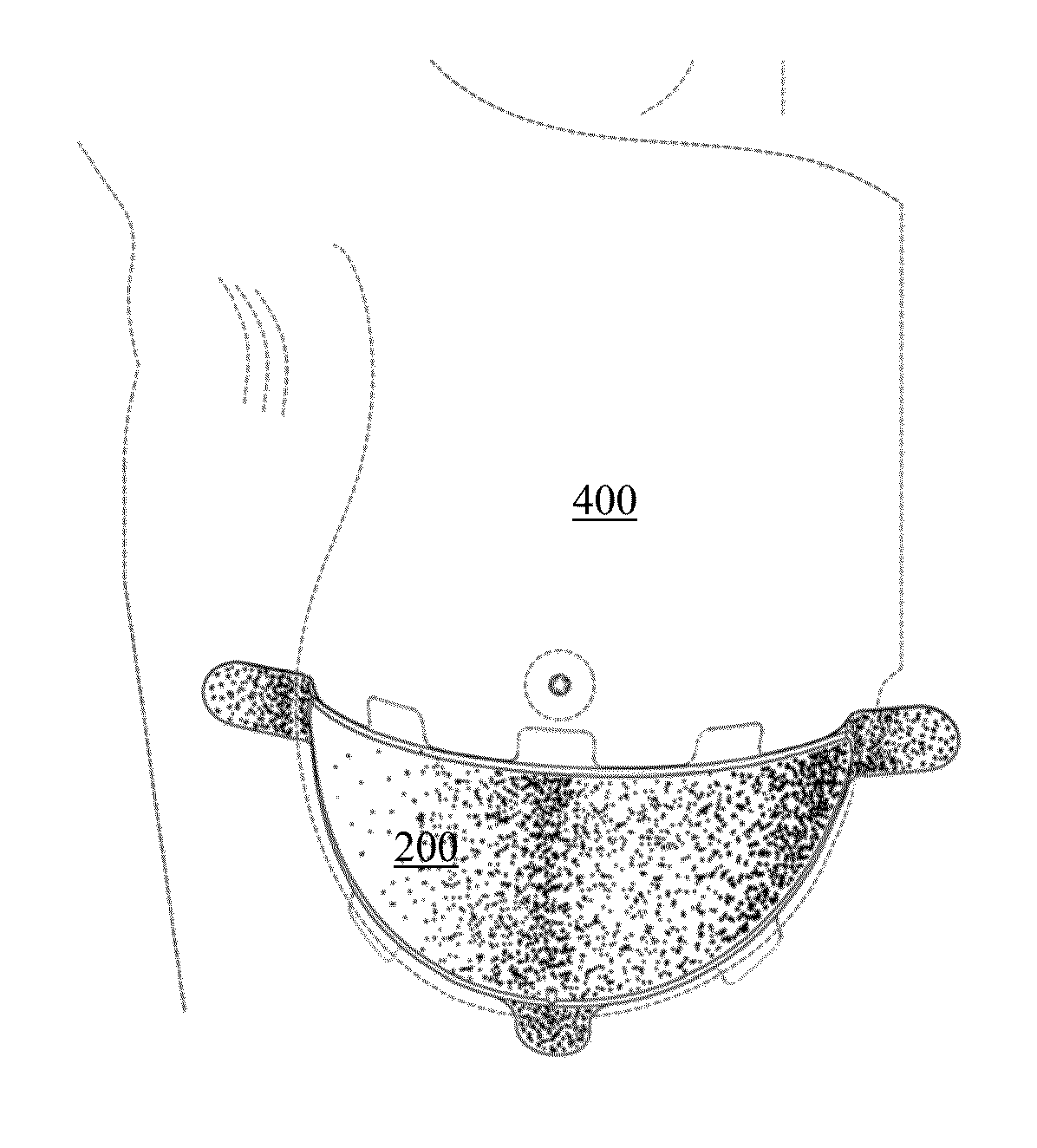
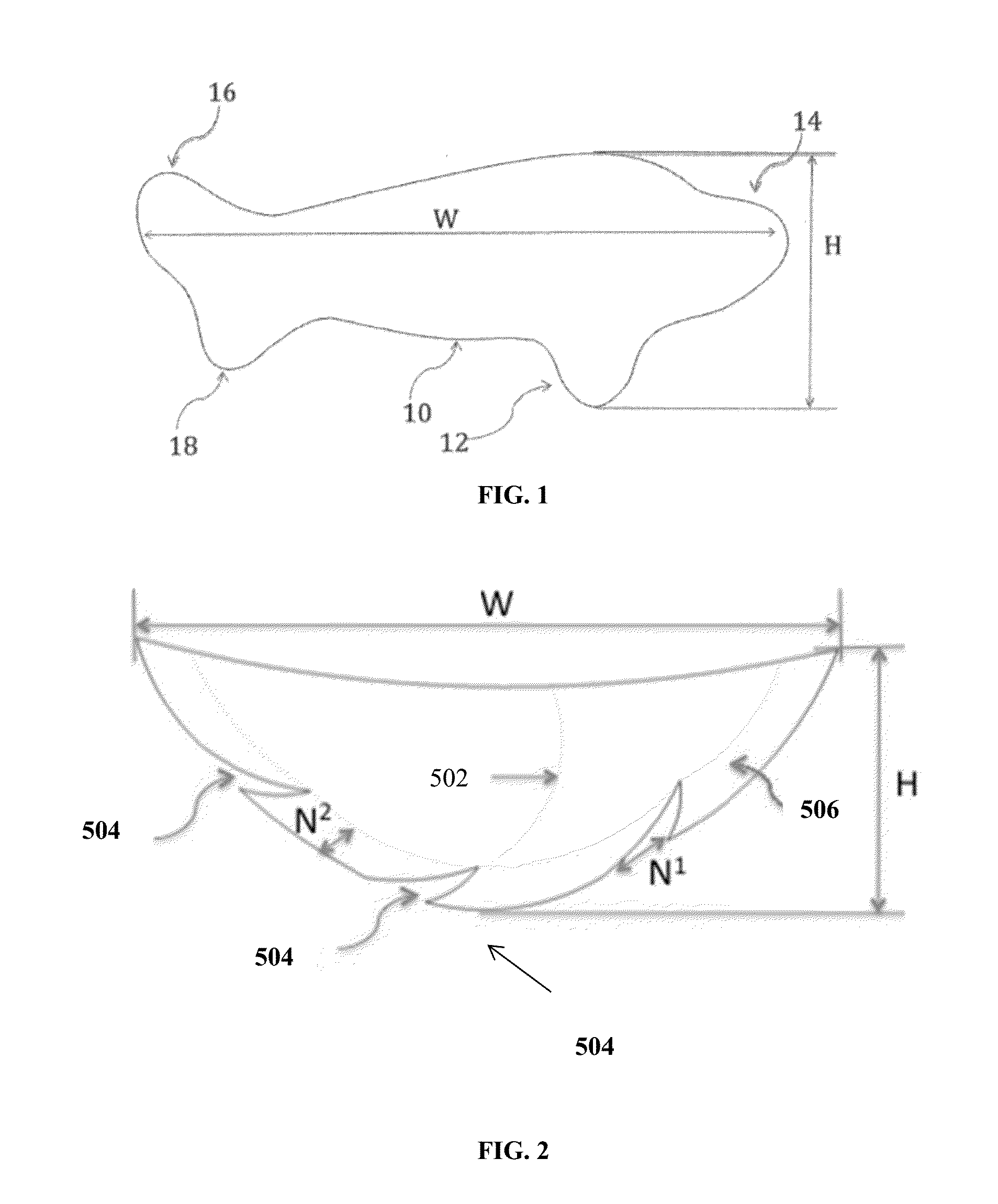
Naturally contoured, preformed, three dimensional mesh device for breast implant support
ActiveUS20090082864A1Easy to deployInherent disadvantageMammary implantsWound clampsWrinkle skinBreast implant
A preformed, seamless, three-dimensional, anatomically contoured prosthetic device for reinforcing breast tissue and supporting a breast implant includes a flat back wall, a concave front wall and a curved transitional region between the flat back wall and the front wall defining a smoothly curved bottom periphery. A concave receiving space is defined by the back wall and the front wall for at least partially receiving and supporting the breast implant therein. The three-dimensional prosthetic device is free of wrinkles, creases, folds or seams, which may have otherwise caused potential tissue irritation, bacteria hosting, infection and palpability problems.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Biodegradable, Polymer Coverings for Breast Implants
ActiveUS20080241212A1Inhibit and reduce formation of scar tissueInhibiting and reducingAntibacterial agentsBiocideBreast implantMedicine
A biodegradable, flexible covering for a breast implant is provided which comprises one or more biodegradable polymer layers dimensioned and shaped to cover at least a portion of the breast implant. The implant can be inserted into an opening of the covering immediately prior to surgery, but alternate configurations and times of insertion are contemplated as well as open or sheet type devices. The coverings can optionally contain one or more drugs for delivery at the surgical site, particularly for treating or preventing infection, pain, inflammation, capsular contracture, scarring or other complications associated with breast augmentation or breast reconstruction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Bioabsorbable breast implant
InactiveUS6881226B2Reduce scarsOvercome deficienciesMammary implantsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBreast implantBiomedical engineering
A breast implant has at least an outer shell which is composed of a resorbable material. The implant, which can be formed entirely of bioresorbable material such as a collagen foam, is sized and shaped to replace excised tissue. The implant supports surrounding tissue upon implantation, while allowing for in-growth of fibrous tissue to replace the implant. According to various alternative embodiments, the implant is elastically compressible, or can be formed from self-expanding foam or sponges, and can be implanted through a cannula or by injection, as well as by open procedures. The implant can carry therapeutic and diagnostic substances.
Owner:SENORX
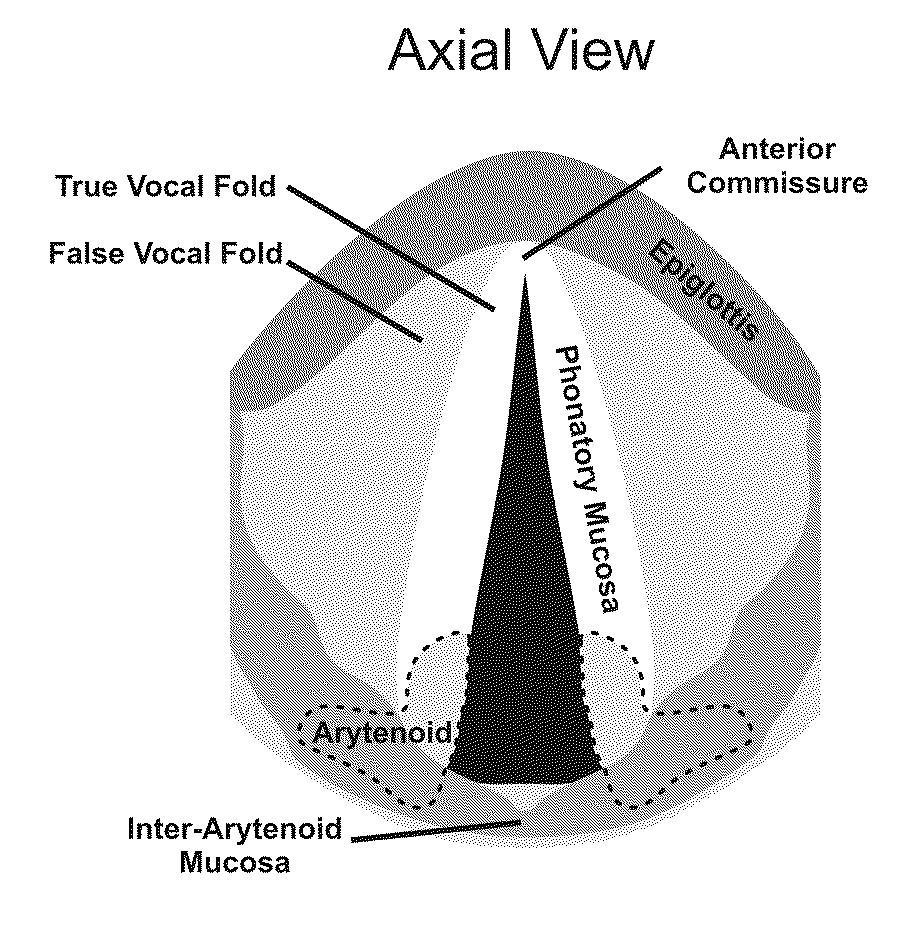
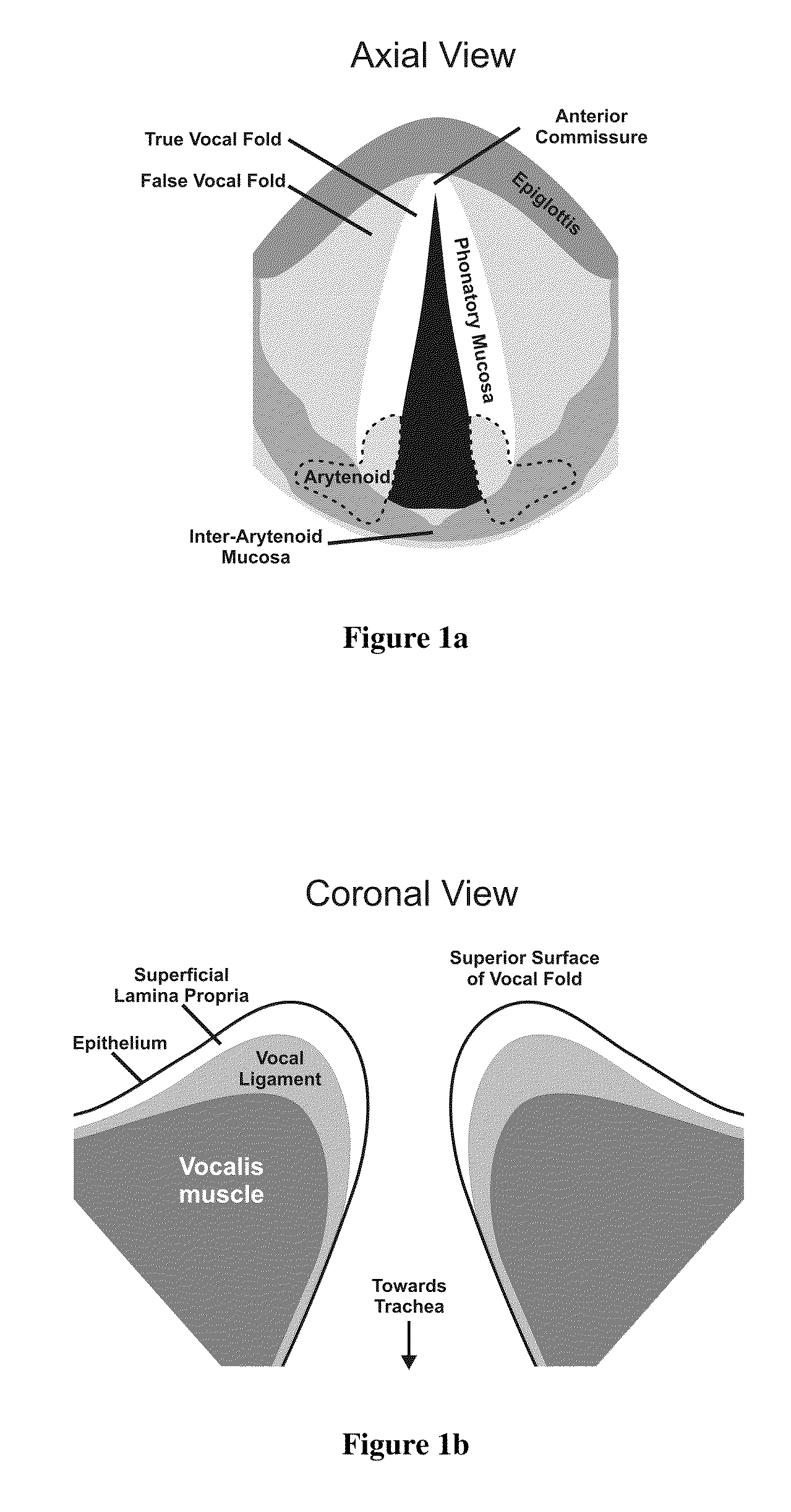
Hydrogels for vocal cord and soft tissue augmentation and repair
ActiveUS20100055184A1Repairing pliabilityDiminished functional vibratory capacityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsEpitheliumBreast implant
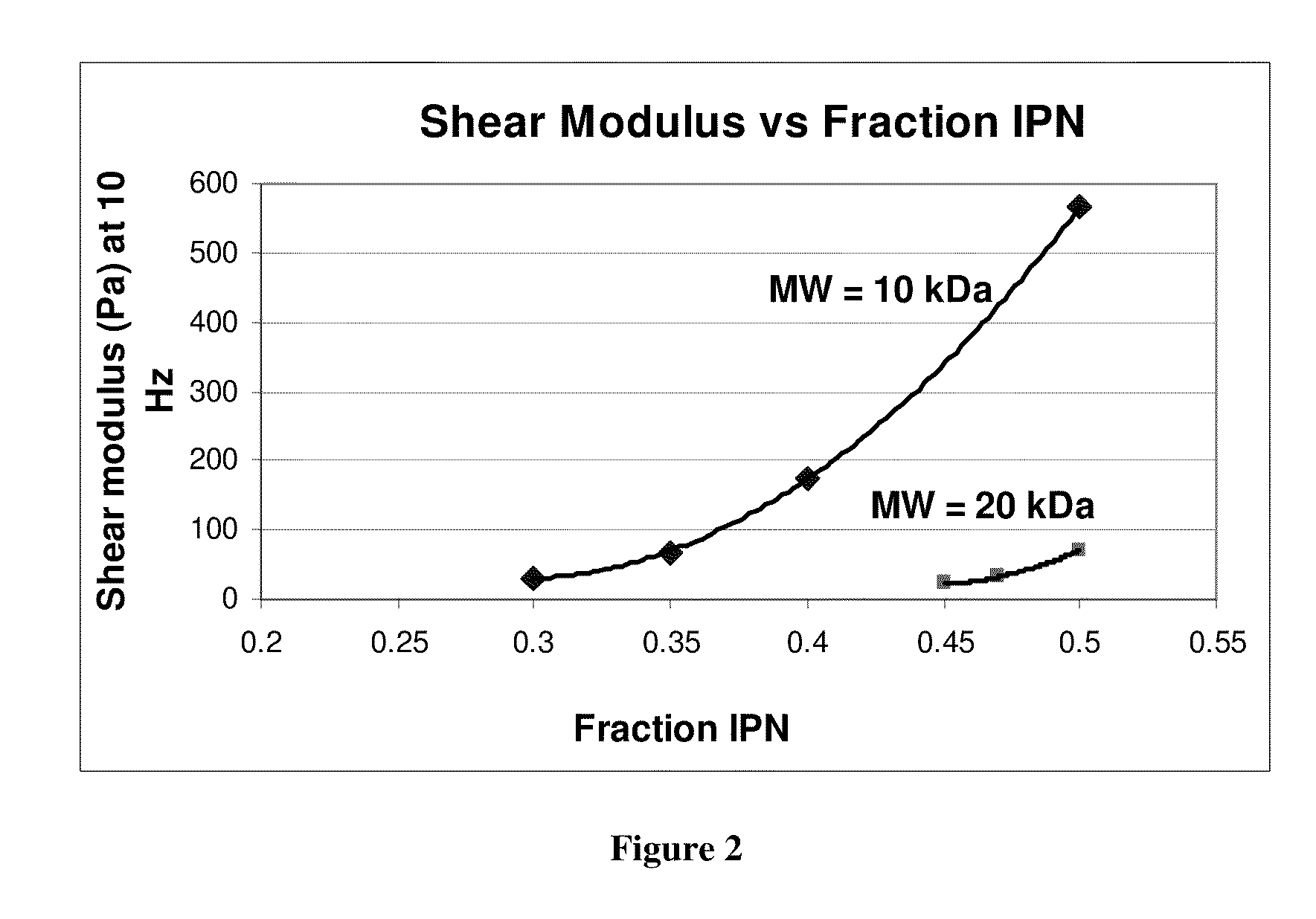
The present invention provides hydrogels and compositions thereof for vocal cord repair or augmentation, as well as other soft tissue repair or augmentation (e.g., bladder neck augmentation, dermal fillers, breast implants, intervertebral disks, muscle-mass). The hydrogels or compositions thereof are injected into the superficial lamina propria or phonatory epithelium to restore the phonatory mucosa of the vocal cords, thereby restoring a patient's voice. In particular, it has been discovered that hydrogels with an elastic shear modulus of approximately 25 Pa are useful in restoring the pliability of the phonatory mucosa. The invention also provides methods of preparing and using the inventive hydrogels.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
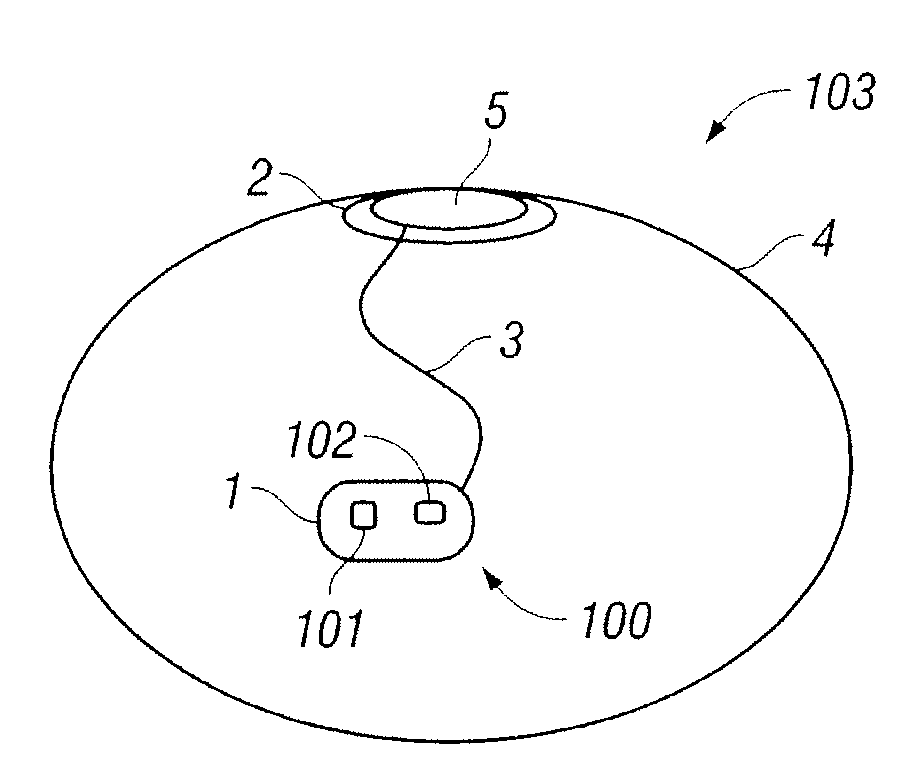
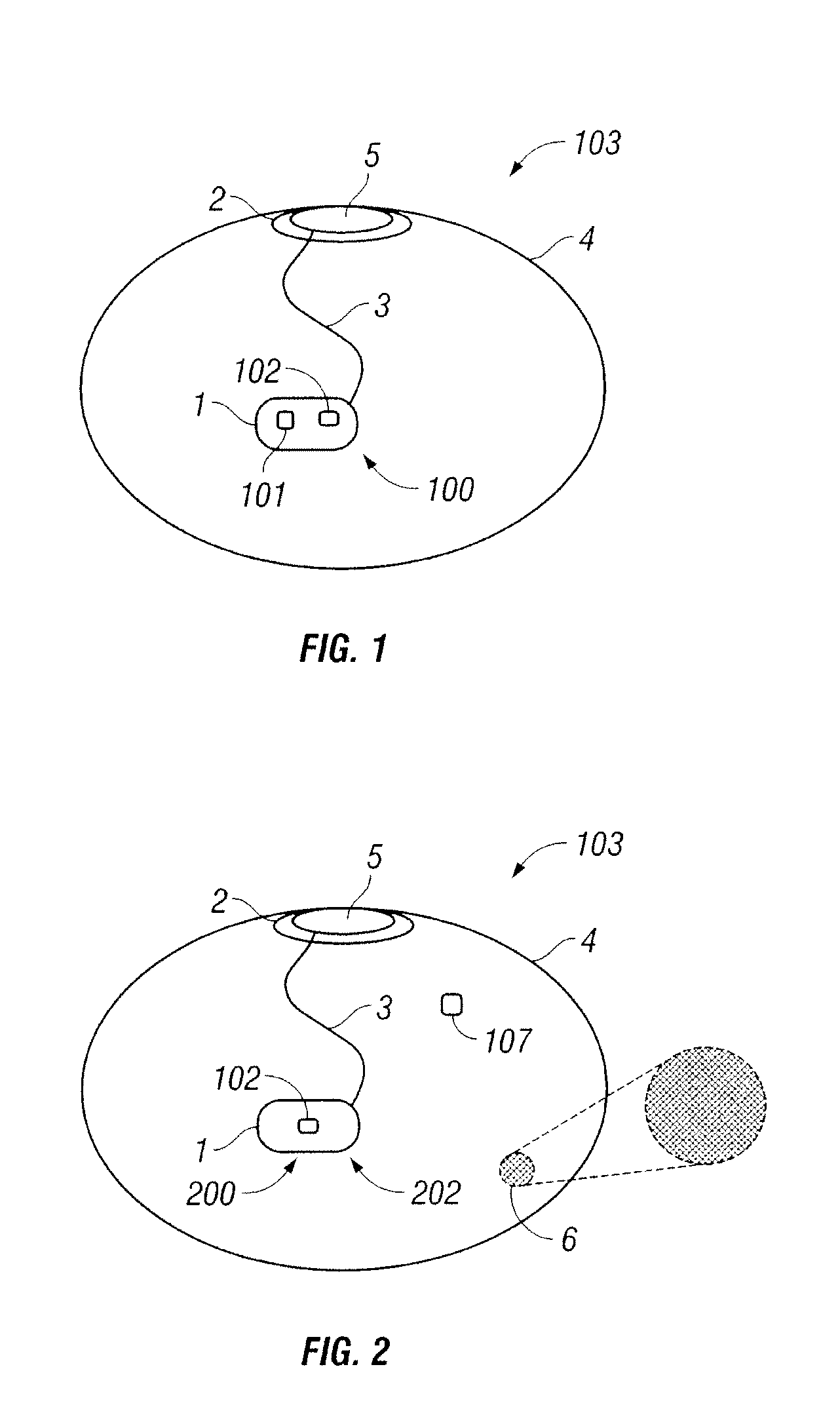
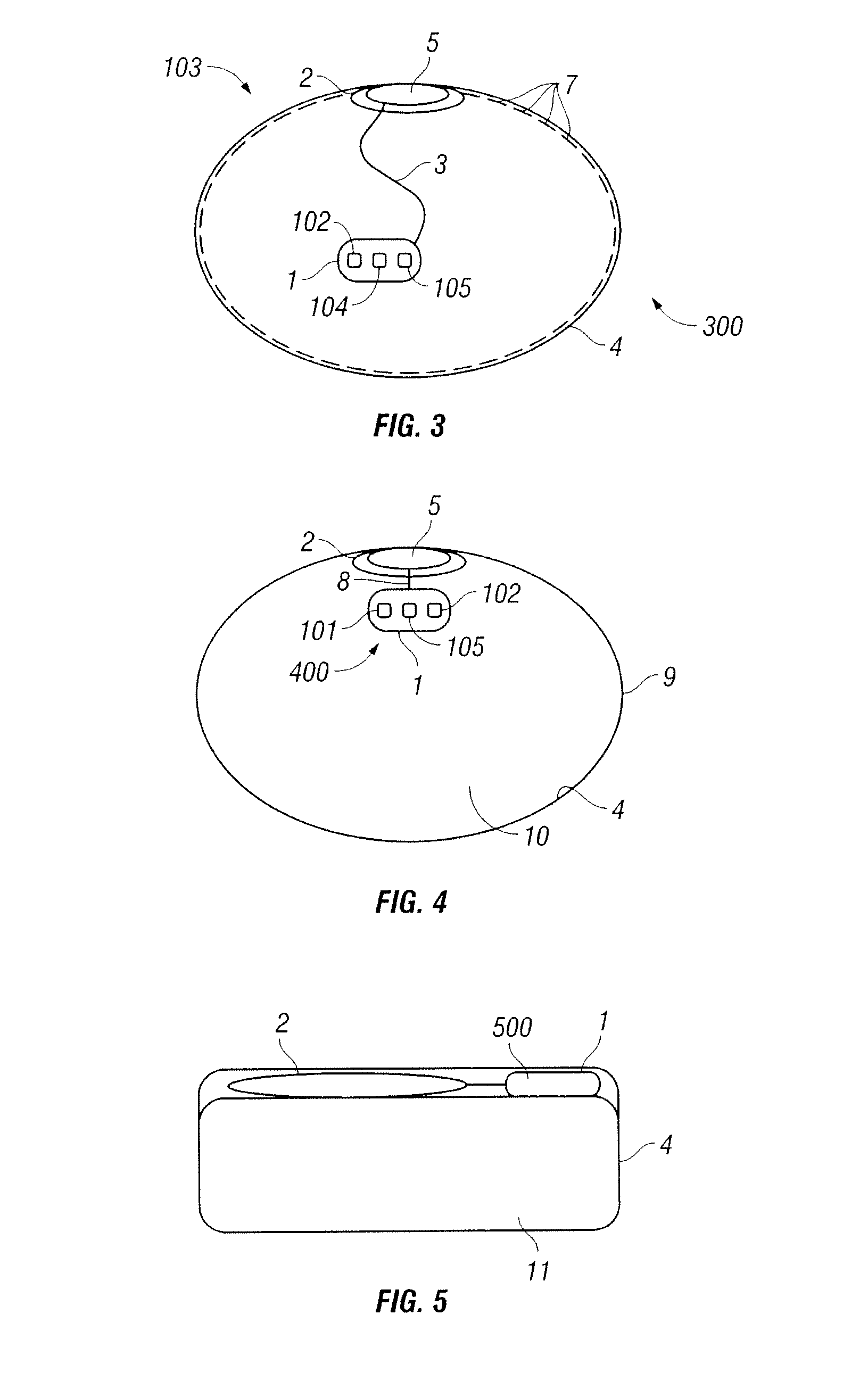
External sensing for implant rupture
InactiveUS20090012372A1The process is convenient and fastMammary implantsEndoradiosondesBreast implantOptical property
The present invention relates to a system and a method for sensing for the rupture of an implant (such as a breast implant) that has been implanted in body tissues or in an organ of a patient. In one embodiment, a system according to the present invention includes, among other possible things, a sensor coupled to an outer surface of the implant and configured to measure a property at the outer surface of the implant, for example, electrical conduction, chemical composition, or an optical property that is indicative of whether an implant rupture has occurred. The sensor is also configured to transmit a wireless signal to a device external to the body, which alerts the patient or a healthcare provider whether the measured property indicates that the implant rupture may have occurred.
Owner:NOVALERT
Tissue augmentation material and method
InactiveUS7060287B1Reduce deliveryImpression capsAnti-incontinence devicesUnilateral vocal cord paralysisSphincter
A permanent, biocompatible material for soft tissue augmentation. The biocompatible material comprises a matrix of smooth, round, finely divided, substantially spherical particles of a biocompatible ceramic material, close to or in contact with each other, which provide a scaffold or lattice for autogenous, three dimensional, randomly oriented, non-scar soft tissue growth at the augmentation site. The augmentation material can be homogeneously suspended in a biocompatible, resorbable lubricious gel carrier comprising a polysaccharide. This serves to improve the delivery of the augmentation material by injection to the tissue site where augmentation is desired. The augmentation material is especially suitable for urethral sphincter augmentation, for treatment of incontinence, for filling soft tissue voids, for creating soft tissue blebs, for the treatment of unilateral vocal cord paralysis, and for mammary implants. It can be injected intradermally, subcutaneously or can be implanted.
Owner:BIOFORM
Naturally contoured, preformed, three dimensional mesh device for breast implant support
ActiveUS7875074B2Shorten the construction periodOvercomes inherent disadvantageMammary implantsWound clampsWrinkle skinBreast implant
A preformed, seamless, three-dimensional, anatomically contoured prosthetic device for reinforcing breast tissue and supporting a breast implant includes a flat back wall, a concave front wall and a curved transitional region between the flat back wall and the front wall defining a smoothly curved bottom periphery. A concave receiving space is defined by the back wall and the front wall for at least partially receiving and supporting the breast implant therein. The three-dimensional prosthetic device is free of wrinkles, creases, folds or seams, which may have otherwise caused potential tissue irritation, bacteria hosting, infection and palpability problems.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Method for texturing the surface of a synthetic implant
InactiveUS20090198333A1Increase heightReducing capsular contractionMammary implantsDiagnosticsBreast implantAcellular Dermis
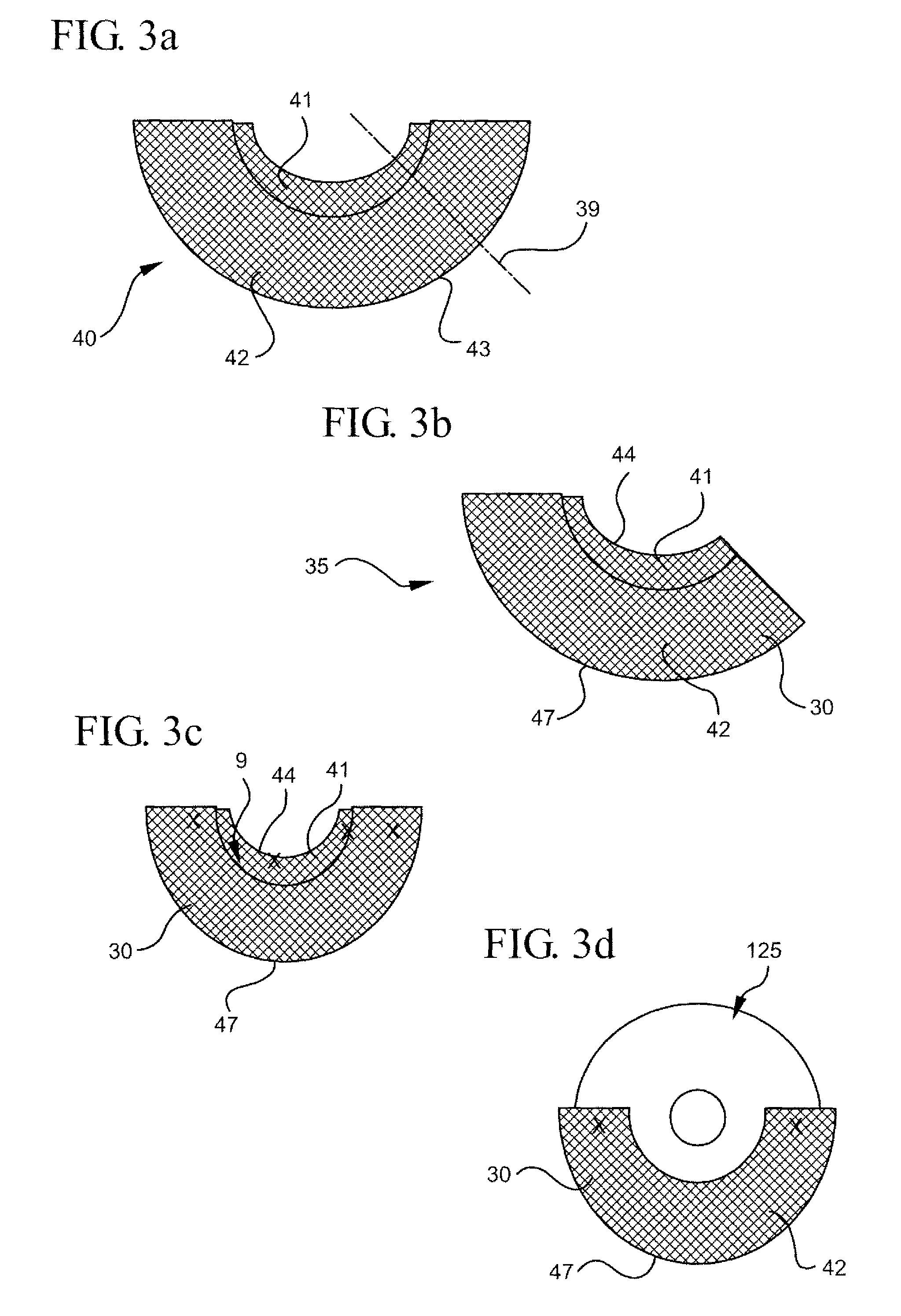
A method for texturing the surface of a breast implant includes the step of partially impregnating a silicone outer surface of the implant with particles of a biologically active material such as acellular dermis of human or animal origin impregnated with hyaluronic acid. The biologically active material promotes tissue ingrowth into a plurality of cavities filled with a biologically active material.
Owner:BECKER HILTON
Hinging breast implant
A hinging breast implant capable a being variably sized and that includes an exterior shell and an inner bladder is described. The exterior shell is typically a bellows having a plurality of pleats so that the outer size of the implant is variable so that different sizes and shapes can be obtained. The rear of the housing closest to the patient's interior is typically shaped in order to conform to the patient's rib cage and internal connective tissues. Conversely, the front of the housing is shaped to naturally conform to the outer shape of the patient. The inner bladder can be filled with a suitable filling material, liquid, gas or solid. As the bladder is filled, the exterior shell expands in a manner that creates a lifting effect and a ballooning effect. An appendage, used to fill the bladder external to the patient, is connected to both the exterior shell and the inner bladder.
Owner:TURNER MATTHEW LAMAR
Method for texturing the surface of a synthetic implant
InactiveUS20090198332A1Increase heightReducing capsular contractionMammary implantsCoatingsBreast implantAcellular Dermis
A method for texturing the surface of a breast implant includes the step of partially impregnating a silicone outer surface of the implant with particles of a biologically active material such as acellular dermis of human or animal origin impregnated with hyaluronic acid. The biologically active material promotes tissue ingrowth into a plurality of cavities filled with a biologically active material.
Owner:BECKER HILTON
Bioerodible matrix for tissue involvement
InactiveUS20100249924A1Improve efficiencyPromote wound healingBiocideMammary implantsPorosityBreast implant
Disclosed herein are polyurethane polymer matrices with a porosity of from about 20 microns to about 90 microns that are useful in promoting closure and protection of incision sites; supporting the lower pole position of breast implants; and providing a partial or complete covering of breast implants to provide a beneficial interface with host tissue and to reduce the potential for malpositioning or capsular contracture. The disclosed matrices can be seeded with mammalian cells.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
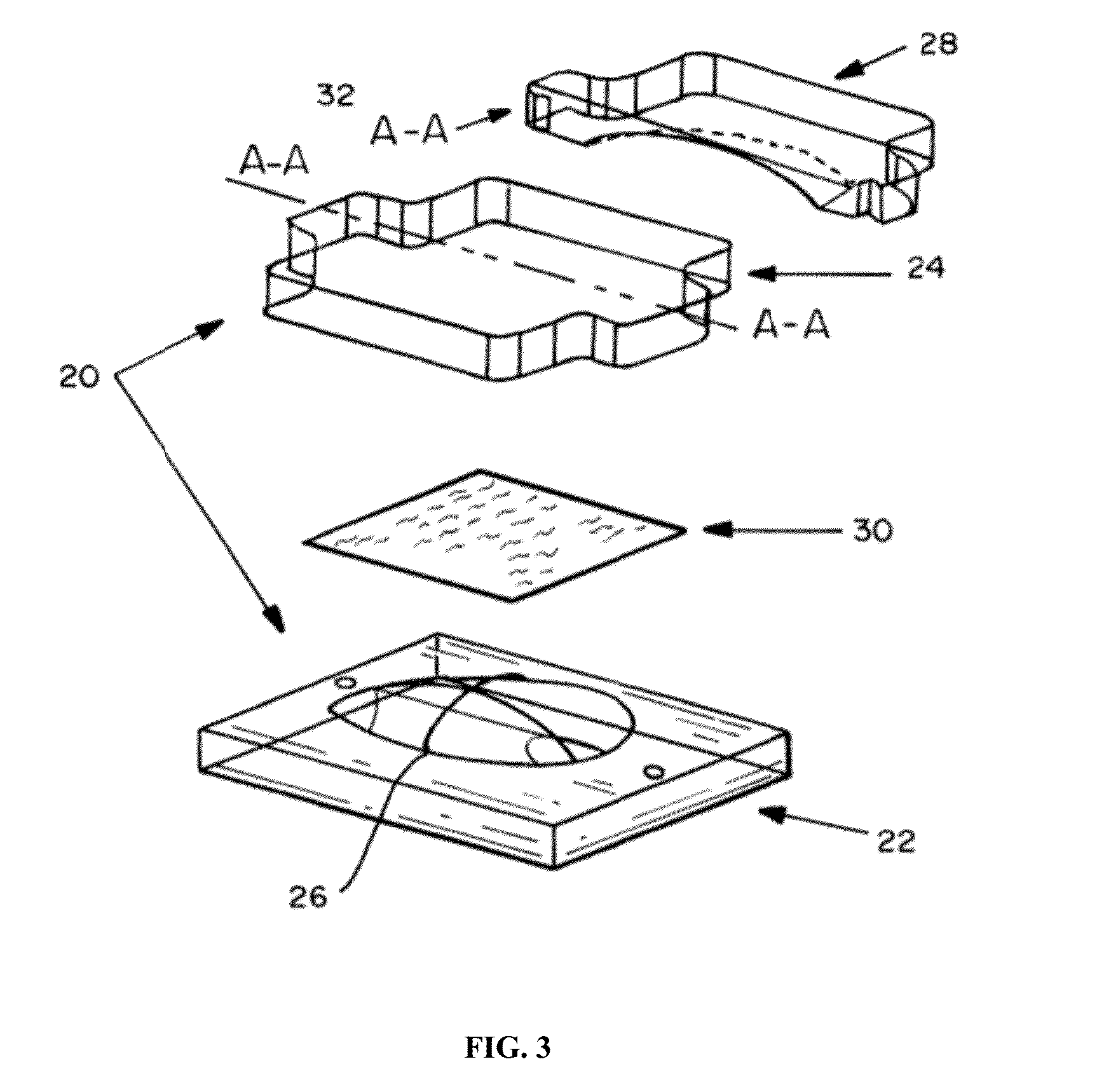
Preformed support device and method and apparatus for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090240342A1Increase the cross-sectional areaEliminate needConfectioneryWood working apparatusMammalian tissueEngineering
A device for making a seamless, anatomically contoured, prosthetic device for supporting or maintaining the position of mammalian tissue, organ or structure or a replacement thereof, such as a breast implant, includes a support plate, an ironing plate or a clamping plate and a core plate, each of which is made from a thermally conductive material. The support plate and the ironing or clamping plates have openings formed through the thickness thereof. The core plate has a core extending outwardly from a lower surface thereof which is received through the openings in the ironing or clamping plate and the support plate.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Self supporting and forming breast implant and method for forming and supporting an implant in a human body
InactiveUS20120226352A1Easy to optimizeEasy to anchorMammary implantsMetal working apparatusBreast implantBiomedical engineering
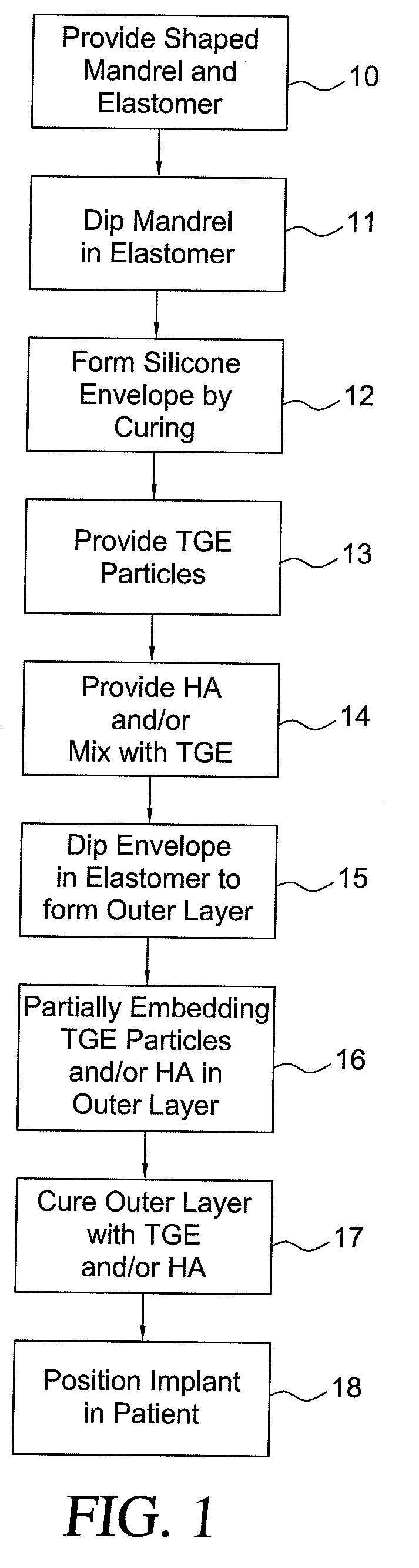
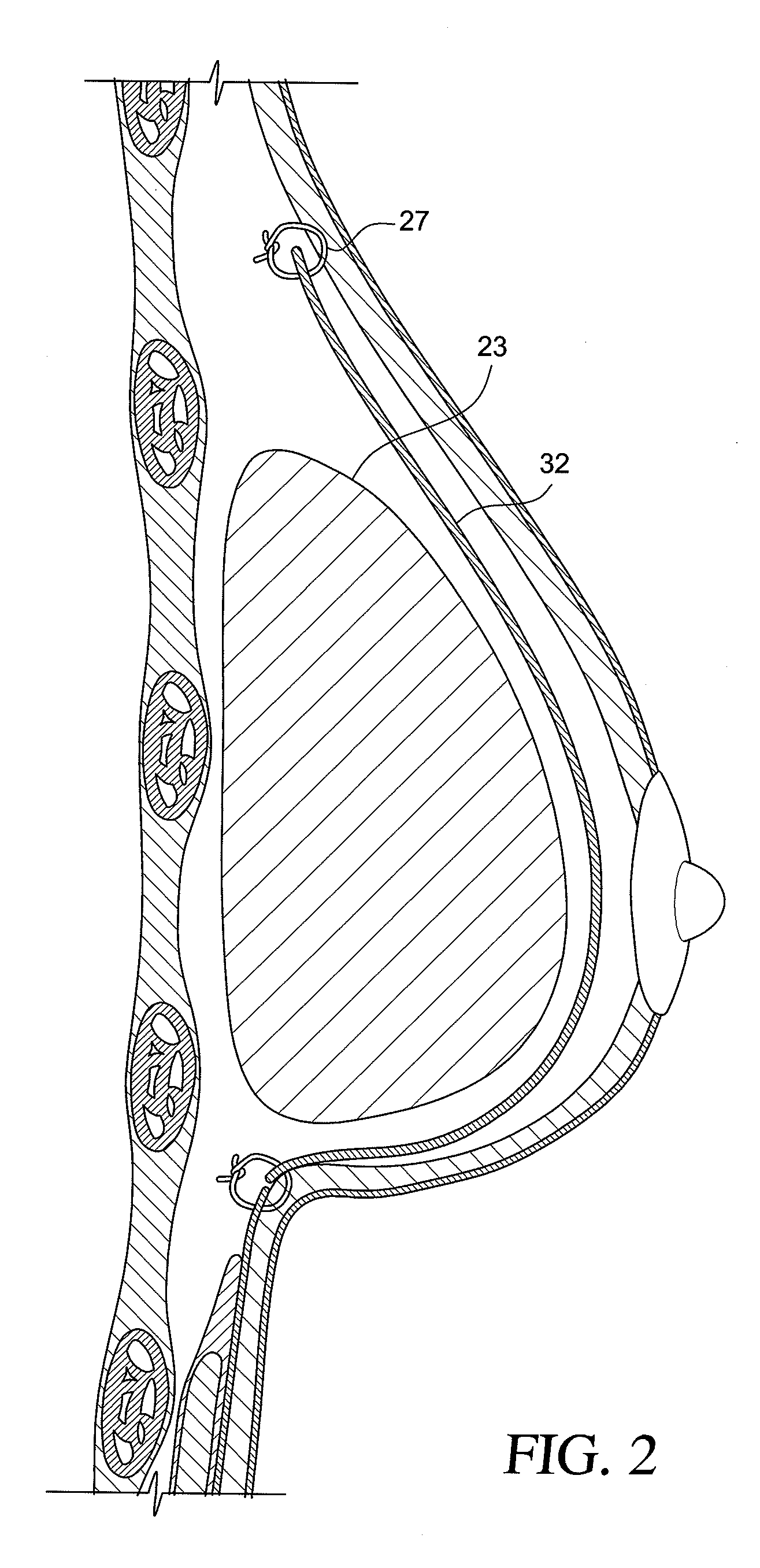
A breast implant includes an elastomer shell; a dermal matrix disposed on the implant shell; and a support interposed between the elastomer shell and dermal matrix to separate the elastomer shell and dermal matrix. A process for making a breast implant includes disposing an elastomer shell in a support; and disposing a dermal matrix on an outer surface of the support. A method of using the breast implant include disposing the breast implant in a subject and attaching the support to tissue of the subject.
Owner:TECHNO INVESTMENTS
Absorbable implants for plastic surgery
ActiveUS20150223928A1Solve the lack of mechanical propertiesMinimization requirementsMammary implantsDiagnosticsPullout strengthThree dimensional shape
Absorbable implants for breast surgery that conform to the breast parenchyma and surrounding chest wall have been developed. These implants support newly lifted breast parenchyma, and / or a breast implant. The implants have mechanical properties sufficient to support a reconstructed breast, and allow the in-growth of tissue into the implant as it degrades. The implants have a strength retention profile allowing the support of the breast to be transitioned from the implant to regenerated host tissue, without significant loss of support. Three-dimensional implants for use in minimally invasive mastopexy / breast reconstruction procedures are also described, that confer shape to a patient's breast. These implants are self-reinforced, can be temporarily deformed, implanted in a suitably dissected tissue plane, and resume their preformed three-dimensional shape. The implants are preferably made from poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB) and copolymers thereof. The implants have suture pullout strengths that can resist the mechanical loads exerted on the reconstructed breast.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Variable cohesive gel form-stable breast implant
ActiveUS20070135916A1Maintain formReduce and eliminate effectMammary implantsBreast implantSuperior pole
A variable cohesive gel form stabilizing implant is disclosed for augmentation or reconstruction of the breast. The prosthesis of this invention comprises an implantable shell or envelope (not limited to a single shell or envelope), filled with a biocompatible gel, or gels, having alterations in gel cohesiveness to maintain stable form, shape, and dimension after surgical implantation. The gel cohesiveness may increase, with increased volume or dimension of the prosthesis. The variable cohesiveness of the gel filler material may be altered by any means (i.e. chemical, fabrication, etc.). The variable cohesive gel form stabilizing implant has shape retention characteristics to maintain its form, thereby reducing or eliminating the undesirable effects of shell wrinkling, knuckling, scalloping or deformation, which can occur at the upper or lower pole of the prostheses, along the perimeter of the shell or at the base, post-implantation. Finally, the variable cohesive gel form stabilizing implant provides new control and possibilities for achieving and preserving the most natural breast shape.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Biopsy cavity marking device and method
InactiveUS20050080338A1Mark accuratelyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMammary implantsFiberBreast implant
These are breast implant devices and methods of use. The breast implants are made of a matrix of collagen material having a porous structure for supporting surrounding tissue of a breast. The implants are also configured to provide a framework for the in-growth of fibrous tissue into the matrix. The matrix can be resilient and / or self-expanding. The methods of use include the steps of forming a cavity having surrounding breast tissue and forming a resorbable implant made up of collagen that is sized to occupy the cavity. The implant is then implanted into the cavity, thereby supporting the surrounding tissue and allowing for in-growth of fibrous tissue into and replacing the resorbable material. The resorbable material may also be elastically compressible, such that the step of implanting includes the step of compressing the resorbable material. The implants may also contain a medicinal, therapeutic, or diagnostic substance.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
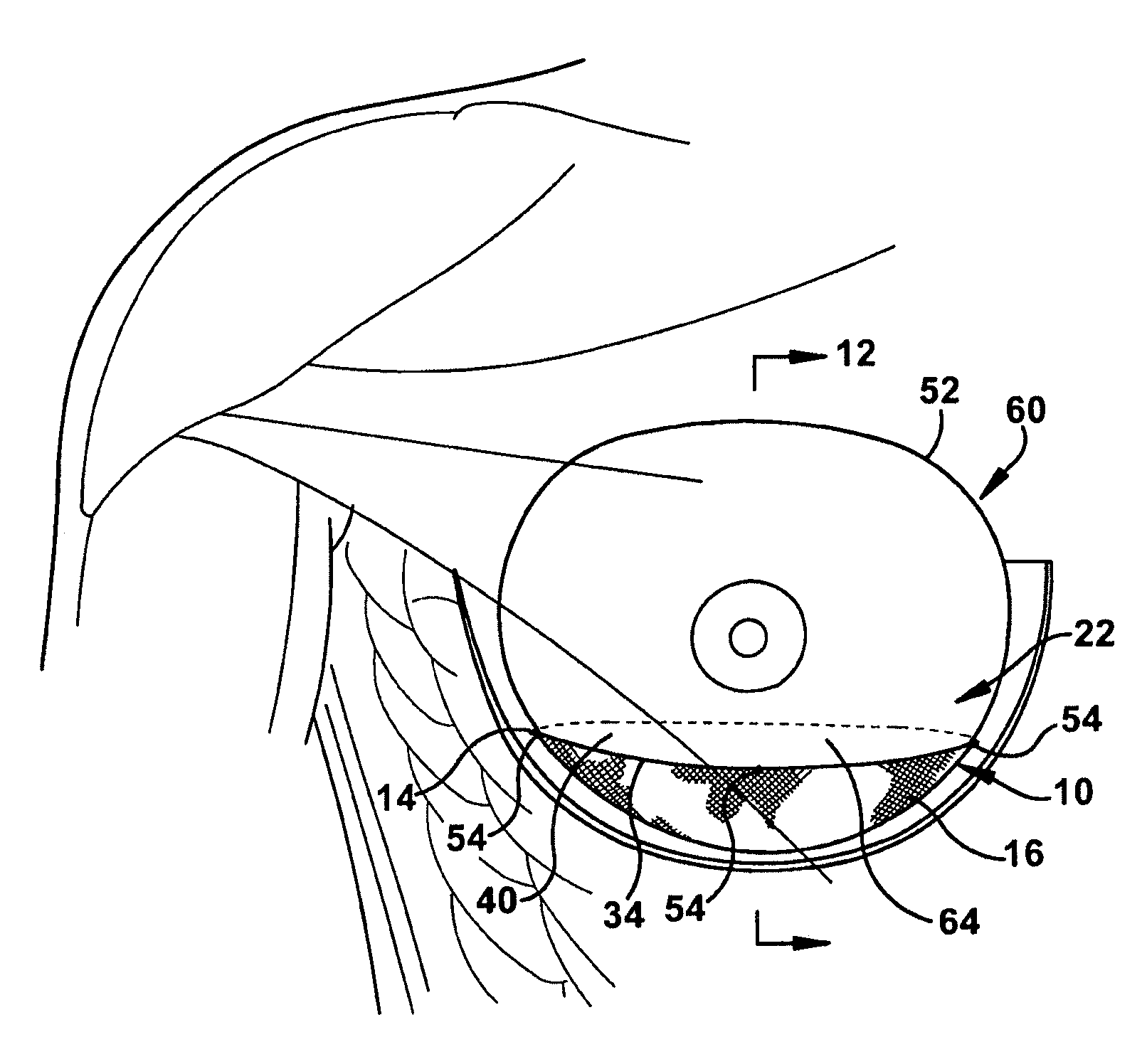
Implantable prosthesis for positioning and supporting a breast implant
An implantable prosthesis for use in positioning a breast implant comprising a sheet of a prosthetic material configured to form a sling-shaped receiving area for receiving and supporting the breast implant. The surface area of the implantable prosthesis contacting the breast implant comprises a biocompatible or chemically inert material to prevent abrasion of or reaction with the breast implant. The implantable prosthesis of the present invention can be used during corrective procedures to reposition and support a malpositioned breast implant or during reconstructive or cosmetic procedures at the time the implant is first positioned within the patient. The prosthesis is used with implants in the partial sub-muscular, completely sub-muscular, and sub-glandular position and is used to prevent medial, lateral and inferior displacement of the implant.
Owner:LIFECELL
Biocompatible implant system and method
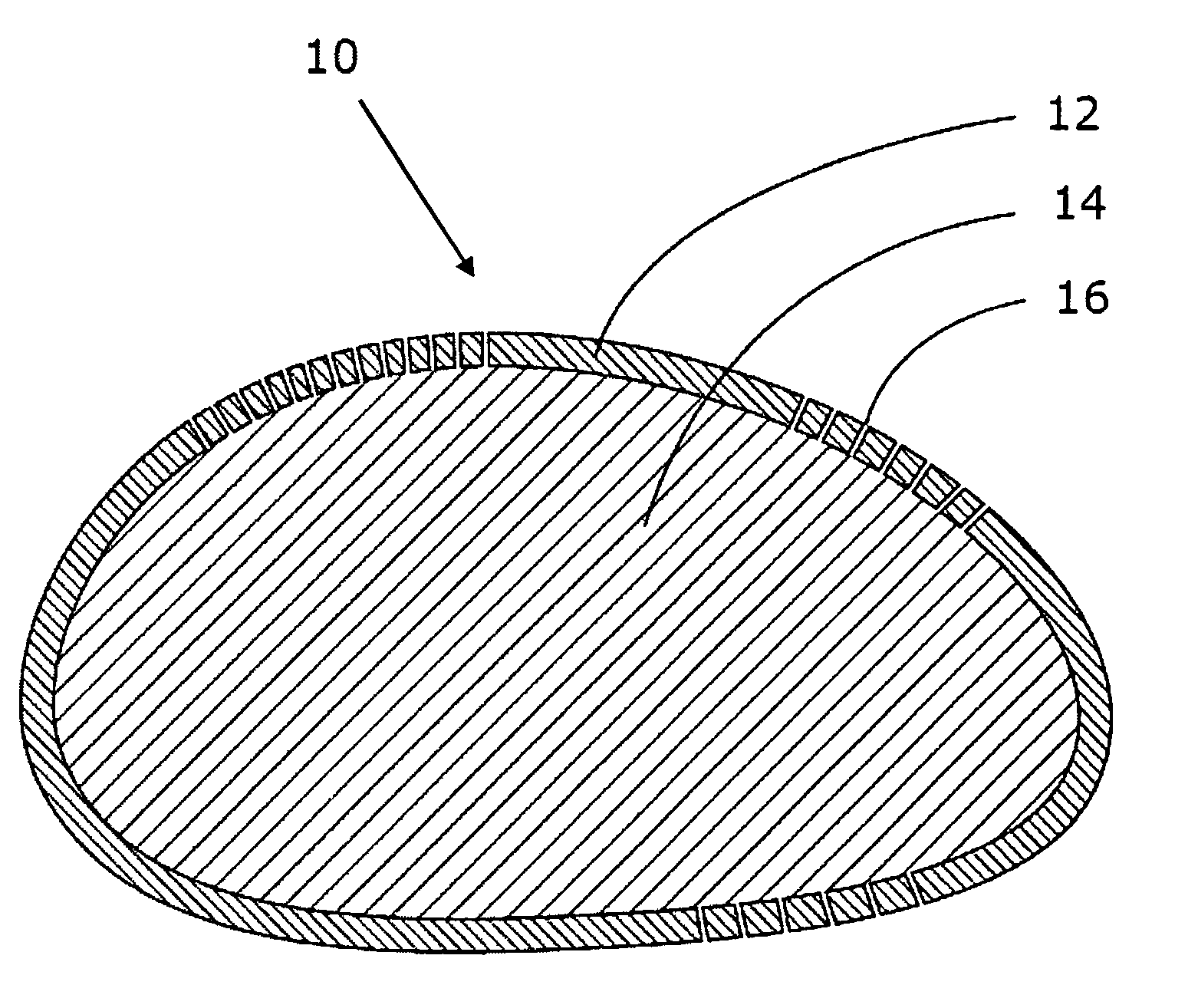
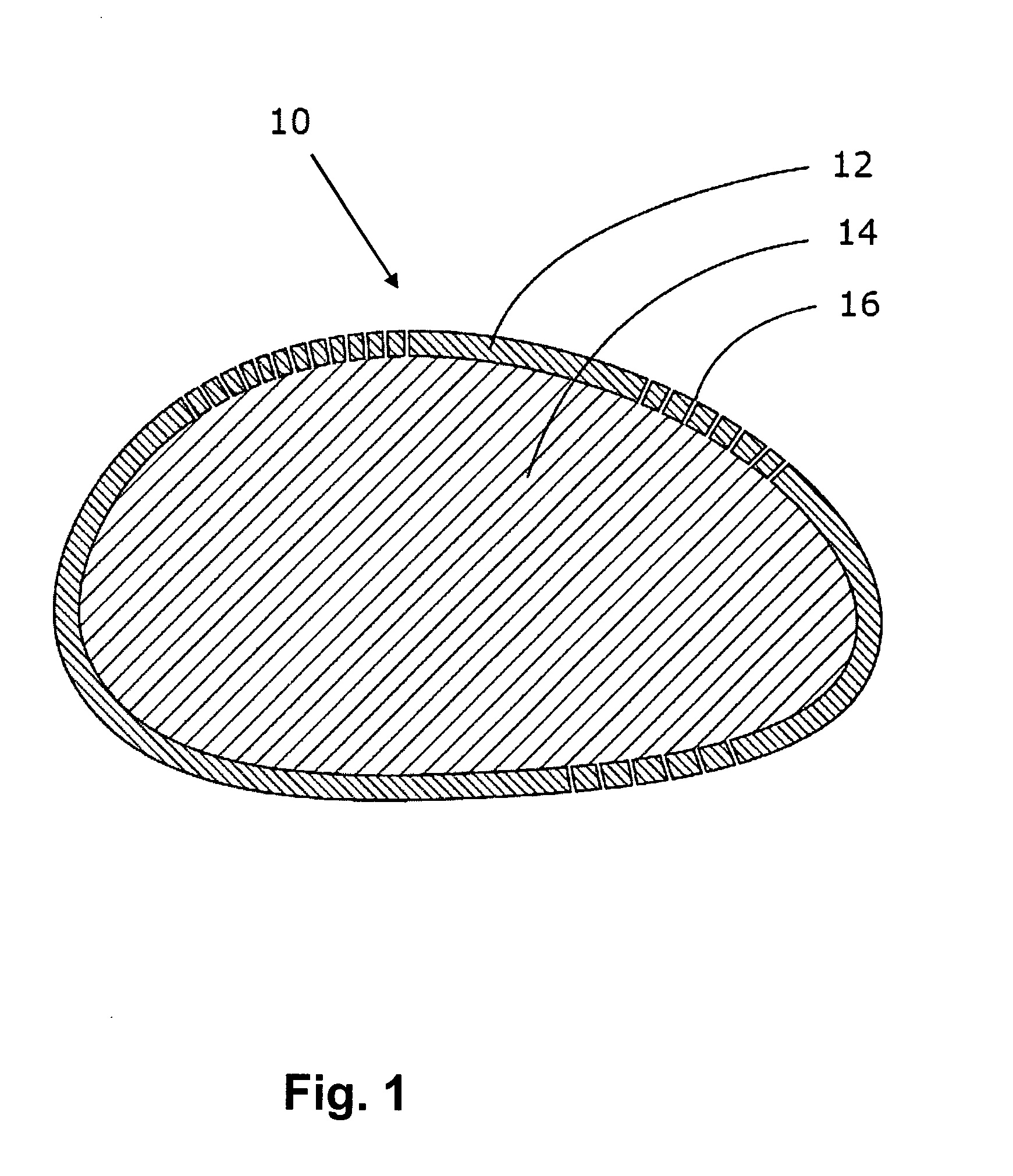
The invention relates to an implantable combination comprising a barrier (12), and a macromolecular bio-compatible material (14). The barrier (12) is porous to allow moieties of the macromolecular bio-compatible material (14), when implanted, to be exposed through the barrier, whereby the surface of the barrier is experienced by the body as an essentially non-foreign object. It also relates to an implant made from a barrier material and a bio-compatible material, the implant being suitable as e.g. a breast implant.
Owner:Q MED AB
Apparatus and method for preventing adhesions between an implant and surrounding tissues
An anti-adhesion membrane is placed onto an implant introduced into a surgical site of a patient to prevent post-surgical adhesions between the implant and surrounding tissue. The implant may comprise either biological material, such as a transplanted organ, or non-biological material such as a medical device. The membrane may be applied in a variety of ways. In one example, a membrane according to the present invention is shrink-wrapped around a pace-maker. In another example, a breast implant is spray-coated or dipped with the membrane material.
Owner:MAST BIOSURGERY
Implantable prosthetic or tissue expanding device
InactiveUS6849092B2Reduce incidenceSmall incisionMammary implantsCosmetic implantsBreast implantTissue Expansion Devices
A keratin hydrogel-filled implantable prosthetic device. One device is a breast implant for augmenting or reconstructing a human breast including an envelope containing a keratin hydrogel. One keratin hydrogel is formed from a solid precursor which forms a keratin hydrogel upon addition of water. One source of keratin is human hair. In one method, an envelope suitable for implantation and a solid keratin hydrogel precursor are provided. The solid can be in fibrous or powder form. The solid precursor can be inserted into the envelope interior. A small incision near the breast can be made and the envelope inserted into the incision. After insertion, water can be injected into the envelope interior, preferably through the incision and through a self-sealing port in the envelope. In one method, the implant is provided as a kit, with the envelope and keratin hydrogel provided. The hydrogel can be injected into the envelope either before or after insertion into the breast area. One kit has a powdered, keratin hydrogel precursor disposed within the envelope interior, awaiting the addition of water, preferably after insertion of the implant into the body.
Owner:KERAPLAST TECH LTD
Apparatus and process for delivering a silicone prosthesis into a surgical pocket
ActiveUS20090204107A1Reduce deliveryEasy to installBronchoscopesMammary implantsBreast implantProsthesis
A tapered sleeve is provided that includes a lubricating coating on an inner surface. An implant (e.g., a pre-filled silicon breast implant) is introduced into a large end of the sleeve and extruded into a surgical pocket of minimal access incision size through a small-sized end of the apparatus.
Owner:KELLER MEDICAL
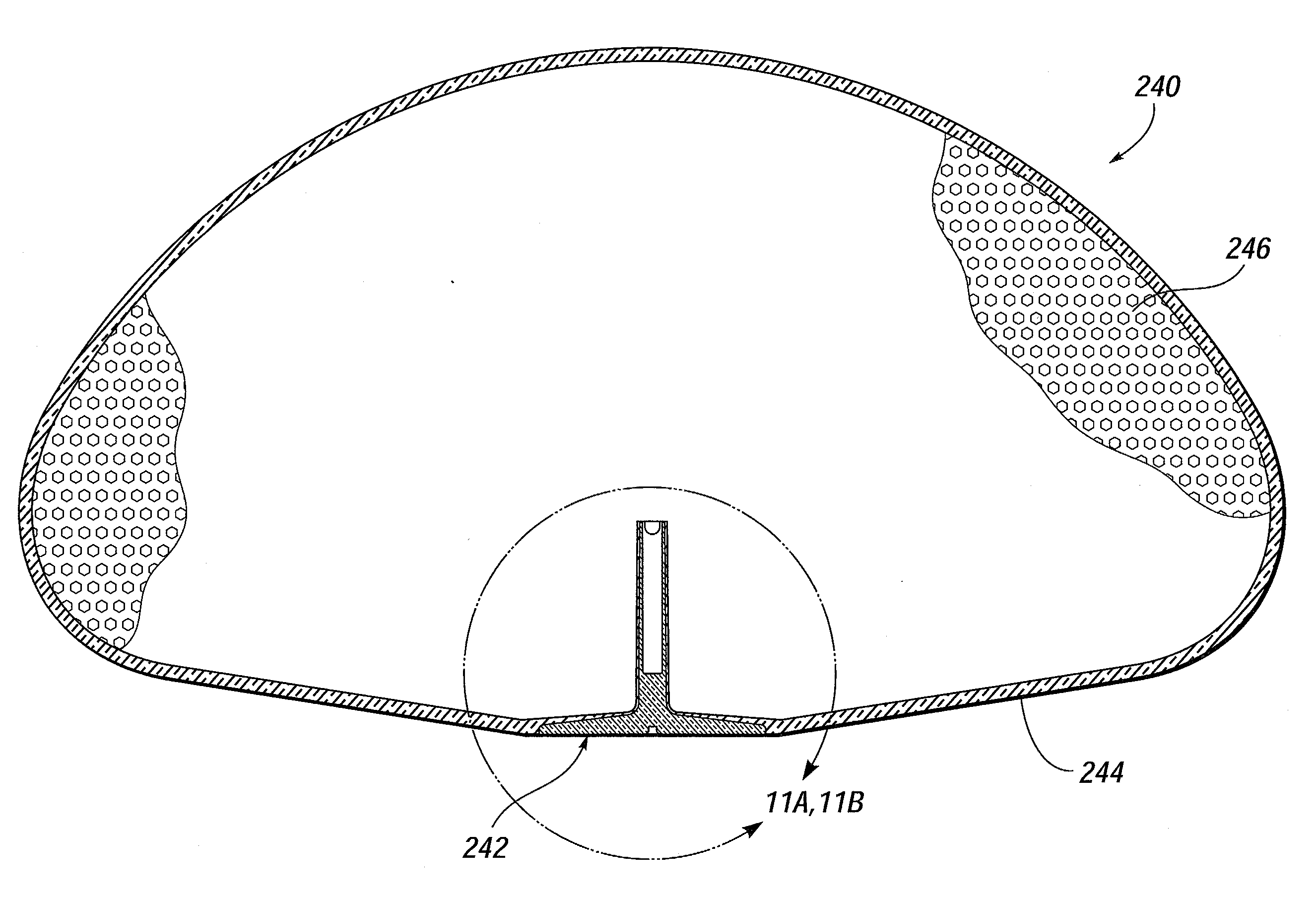
Flush Patch For Elastomeric Implant Shell
InactiveUS20090270985A1Facilitate inflationEqually distributedMammary implantsObesity treatmentSilicone GelsBreast implant
An elastomeric prosthetic implant having a shell and a patch providing a reinforced access region on the shell for introduction of manufacturing implements, such as a gel-filling tool. The shell may cover the entire inner face of the patch, or a substantial part thereof, and a peripheral edge of the patch and the shell cooperate to form a flush interface with no sudden surface steps on both interior and exterior surfaces of the implant. The removal of any surface steps eliminates undesirable tactile discontinuities and stress points that may cause the shell wall to wear or may irritate the surrounding tissues. The prosthetic implant may be a breast implant formed of a silicone elastomer. The patch may be the same material or a liquid silicone rubber, but at least has similar material properties such as elastic modulus, durometer and elongation. The patch may include a channel used for introducing silicone to the mold to form the shell, for venting the mold cavity during the mold process, and / or for introducing the silicone gel into the hollow prosthesis.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
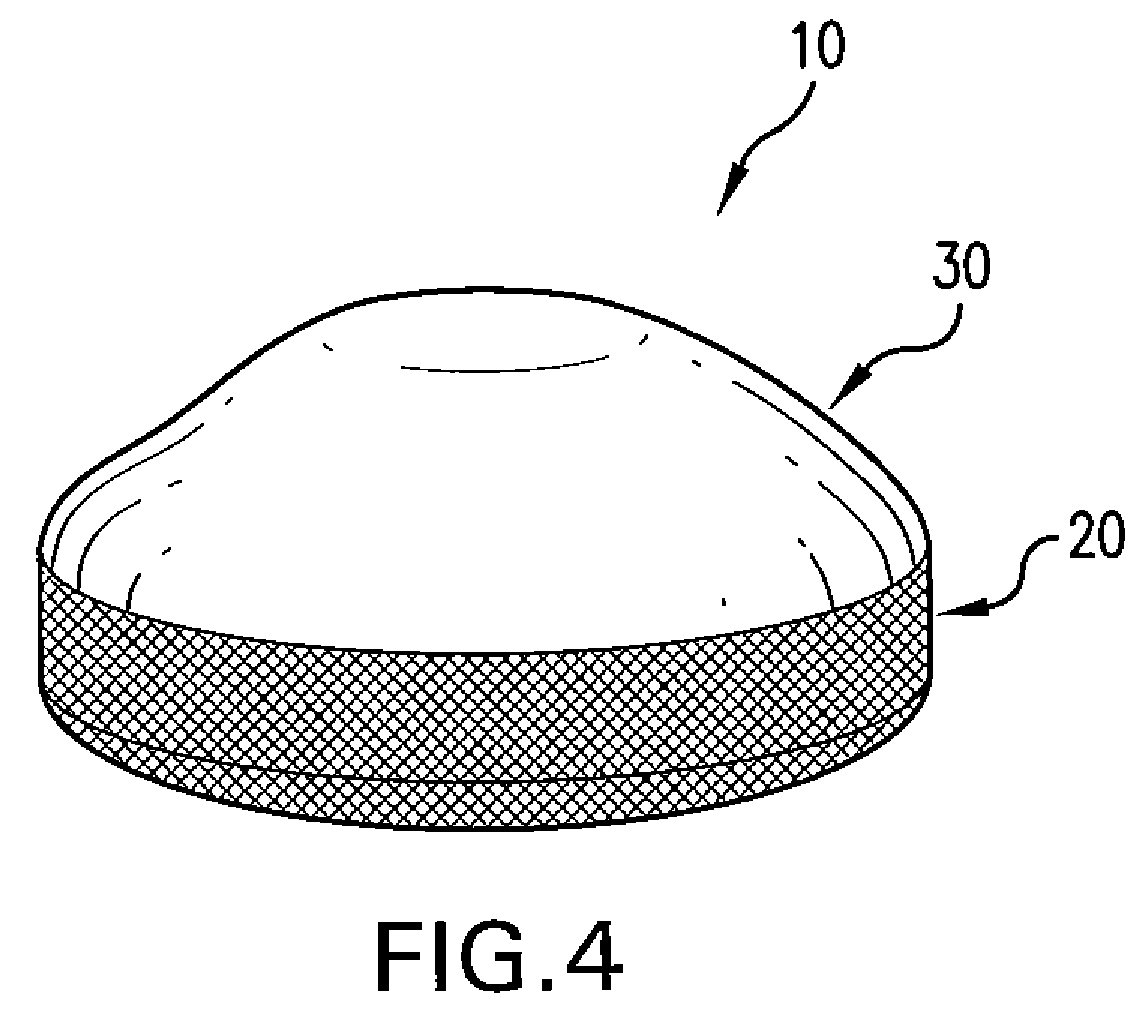
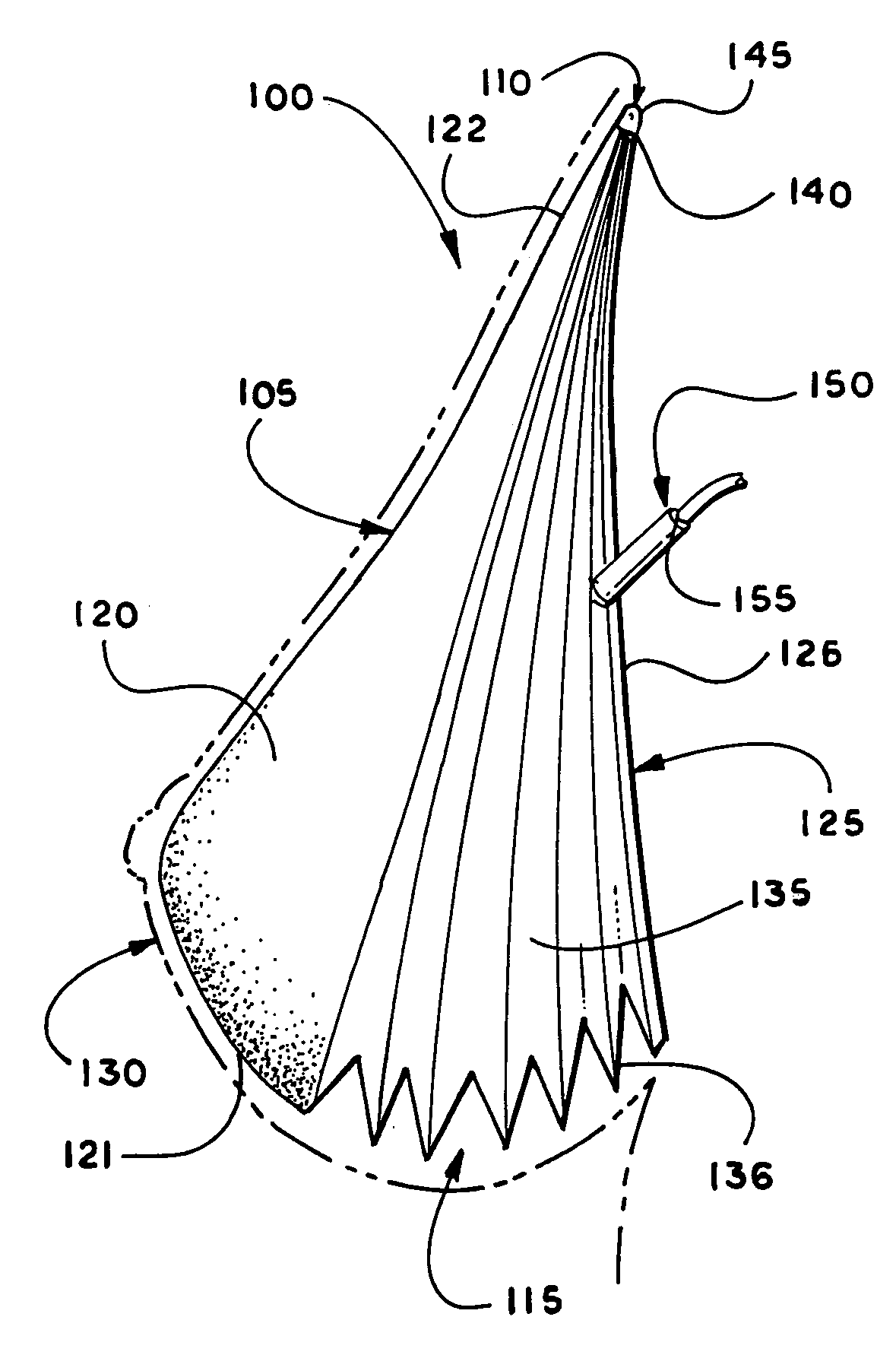
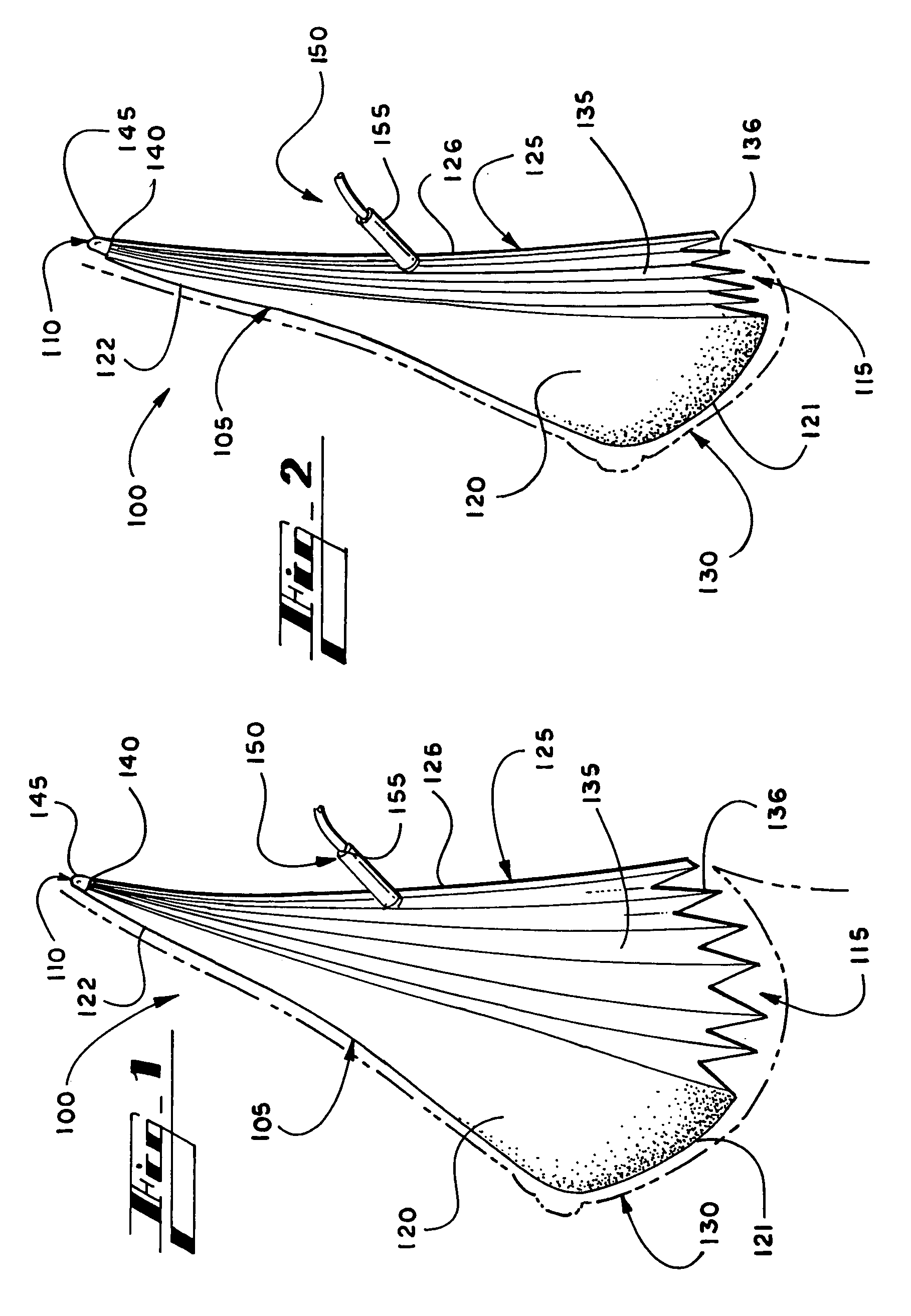
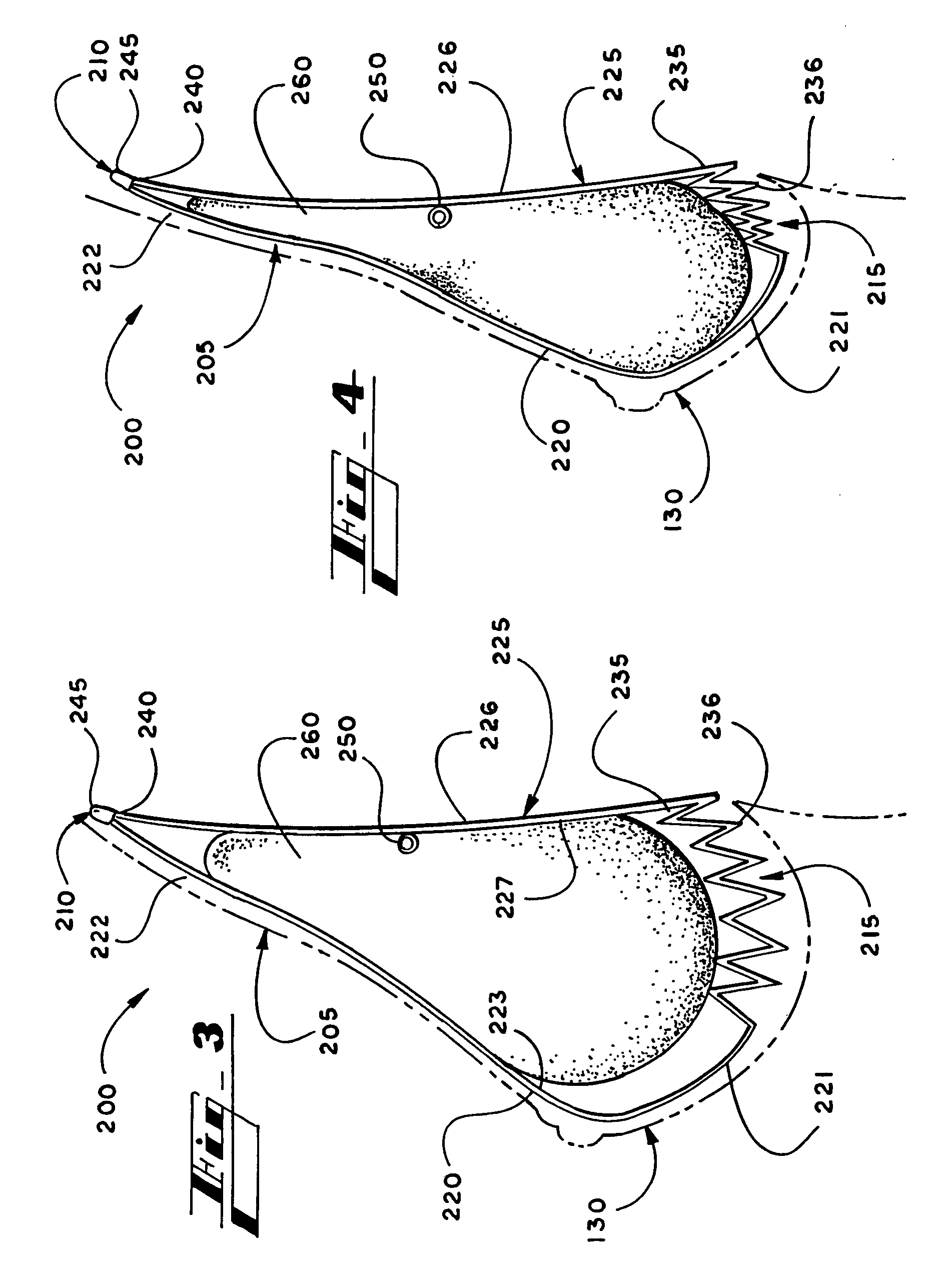
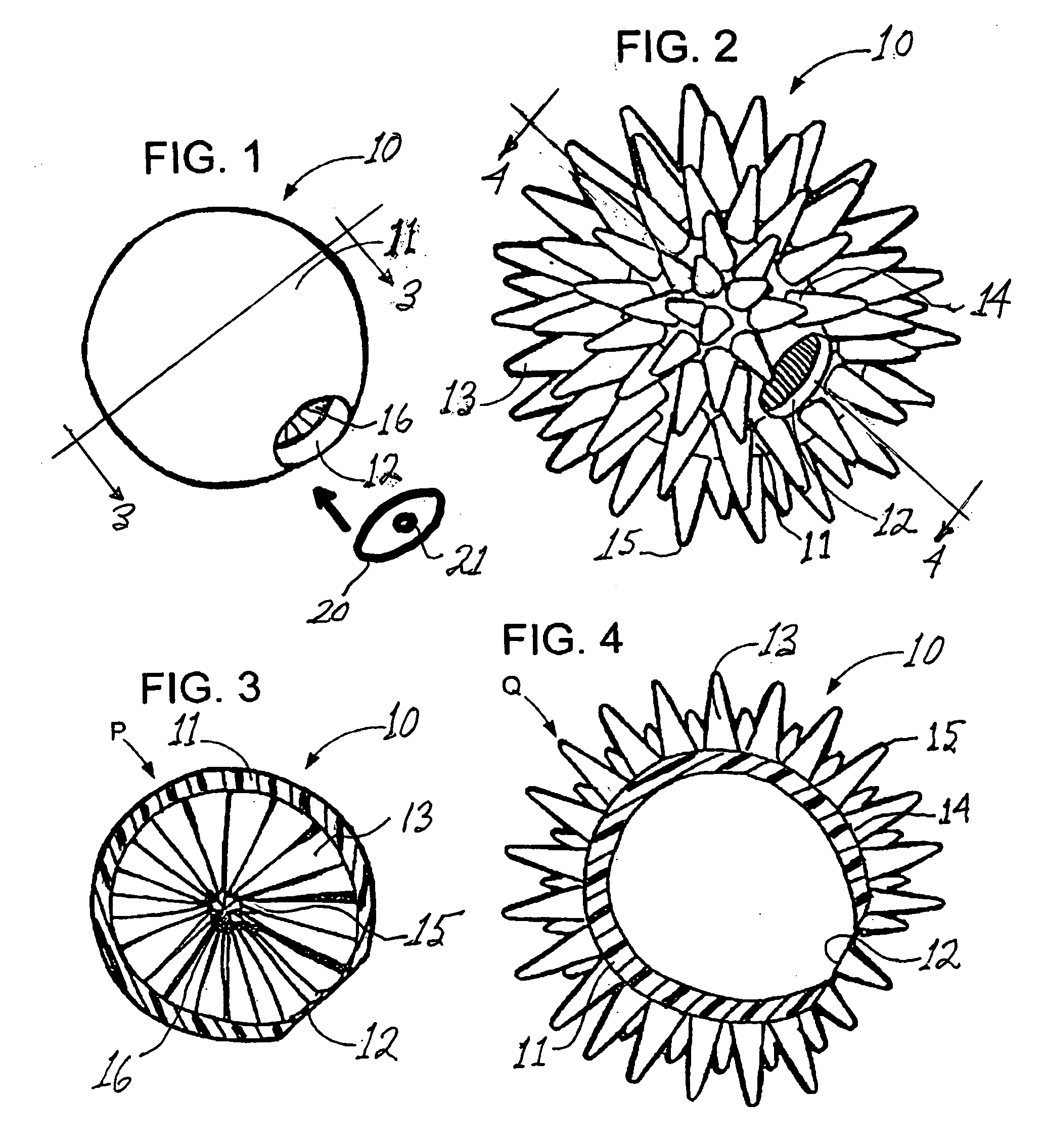
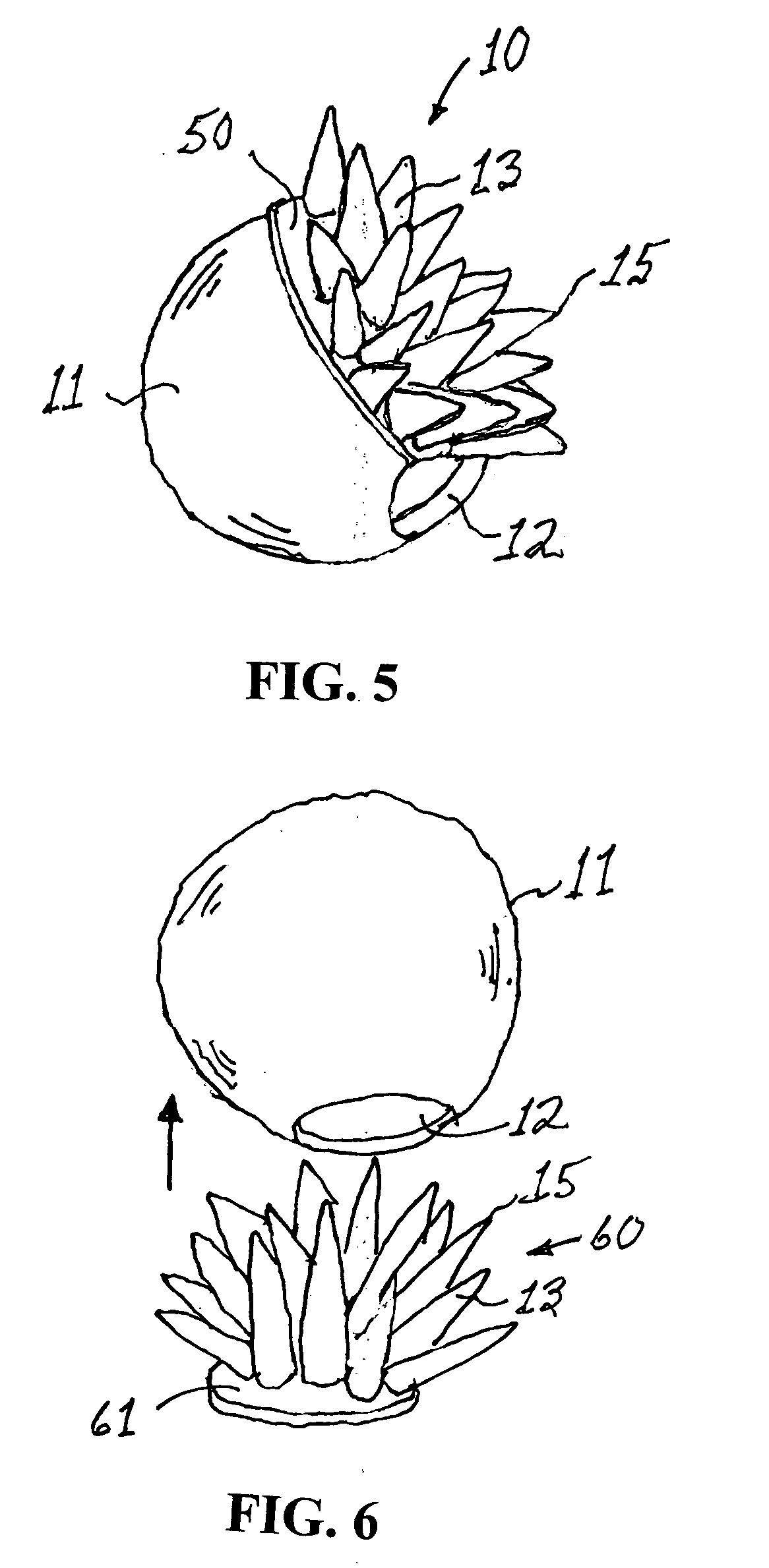
Breast implant
A breast prosthesis has a flexible shell surrounding an interior compartment. An inner surface of the shell has a plurality of flexible protuberances or struts integral therewith that extend inwardly into the interior compartment. The opposing outer surface of the shell of the breast prosthesis is preferably textured to promote tissue ingrowth. A hole in the flexible shell allows the breast prosthesis to be made in an everted configuration, then everted to provide the prosthesis. In a preferred embodiment, the prosthesis does not contain a fluid filler material and is leak and rupture-proof. The breast prosthesis may be encased in a biocompatible elastomeric shell for implantation or be made from a suitable and inexpensive elastomer and worn as an explant. The prosthesis can be made in a variety of shapes for other types of soft tissue implants.
Owner:TIAHRT LEIF K
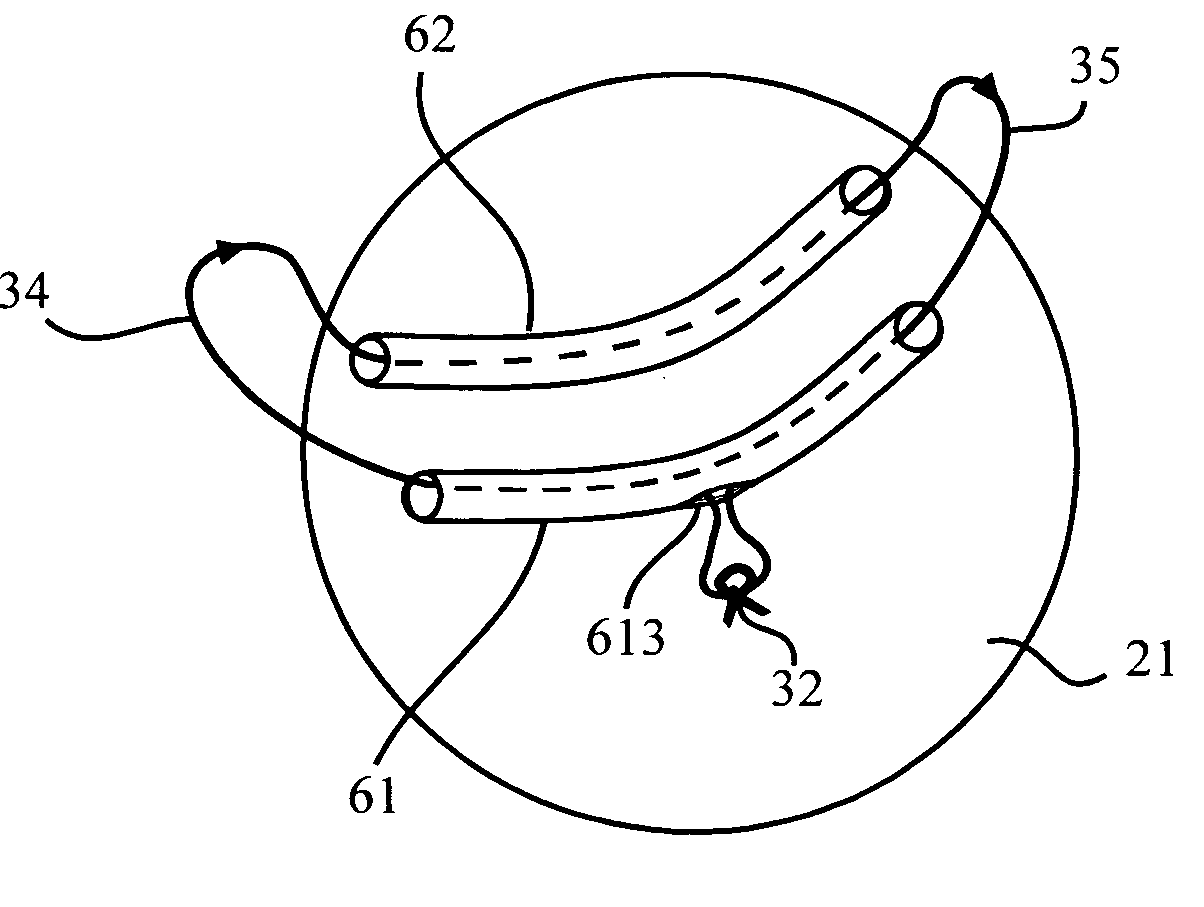
Implant device and method
InactiveUS20060136056A1Prevent slippingExtended service lifeMammary implantsBreast implantImplanted device
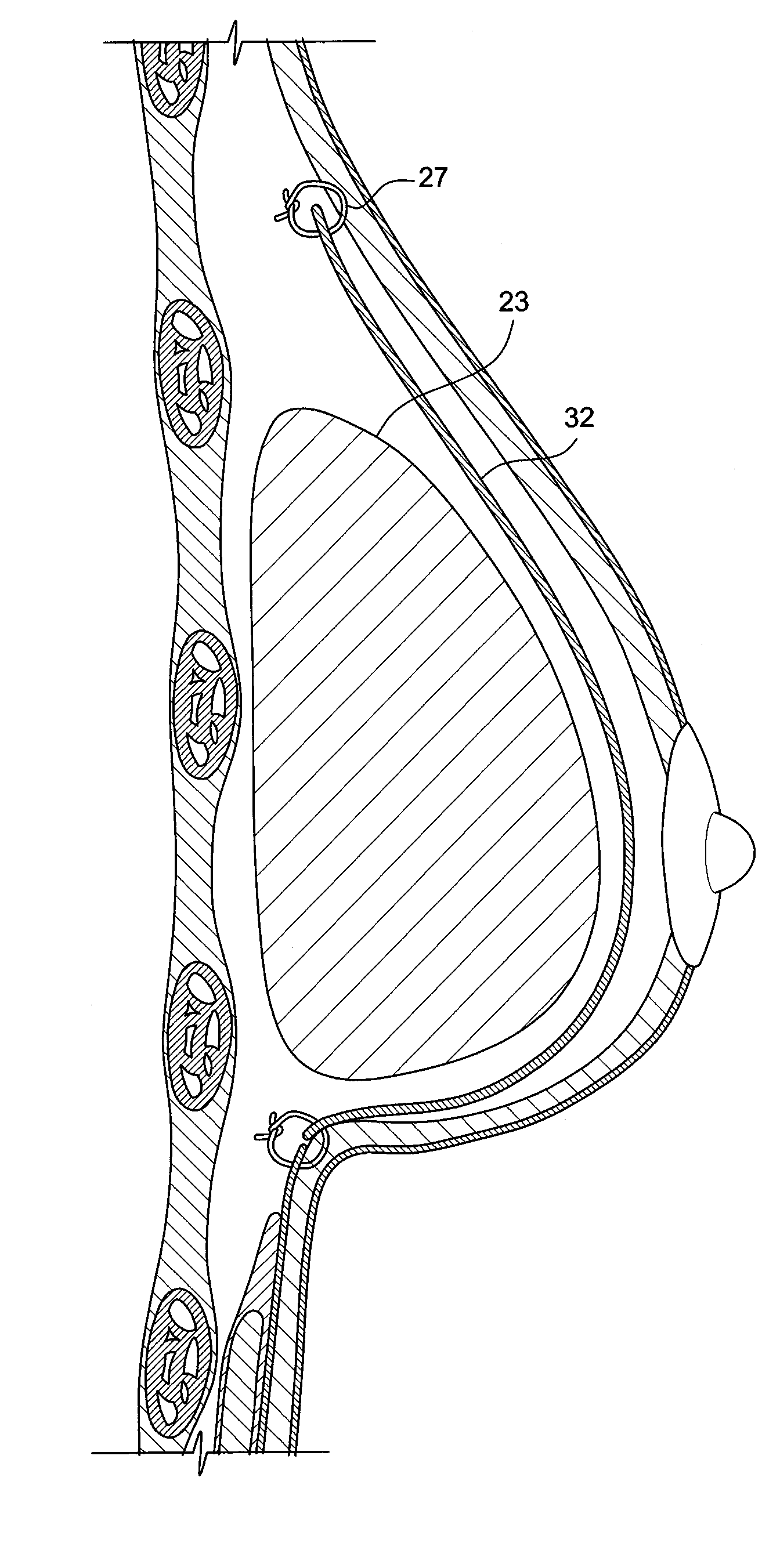
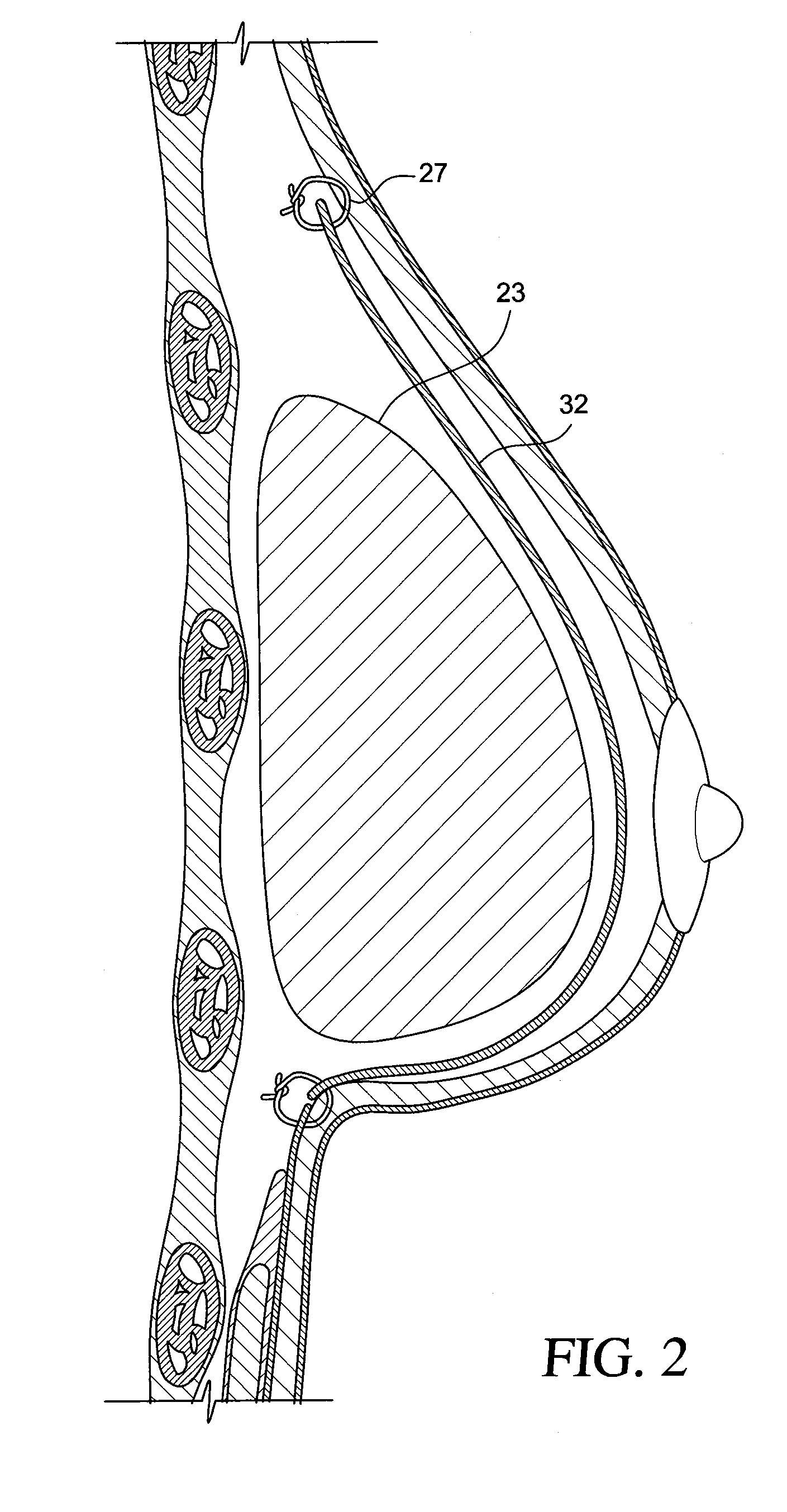
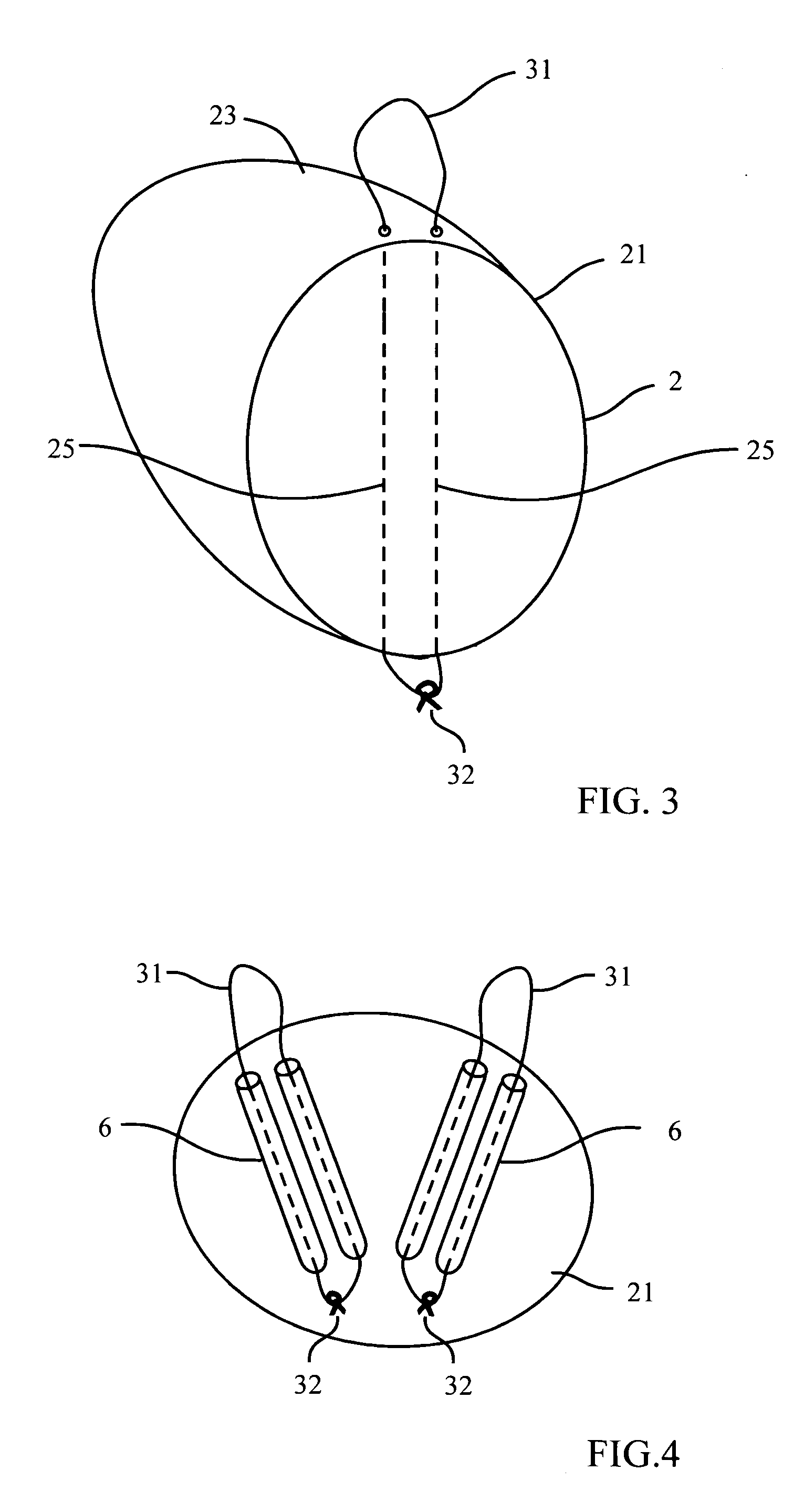
A breast implant includes means for attaching to a patient's body at an attaching point located at the upper part of the implant using surgical wire, and for allowing to secure the wire at a securing point located on the lower part of the implant. The means for attaching to a patient's body further include two flexible noncompressible tubes for passing the surgical wire up to the attaching point, and back down to the wire securing point. The means for attaching to a patient's body further include two pairs of flexible noncompressible tubes for passing the surgical wire up to the attaching point, and back down to the wire securing point.
Owner:WOHL ISHAY
Non-rotating breast implant
InactiveUS7105116B2Precise positioningNatural appearanceMammary implantsMouldsWrinkly skinWrinkle skin
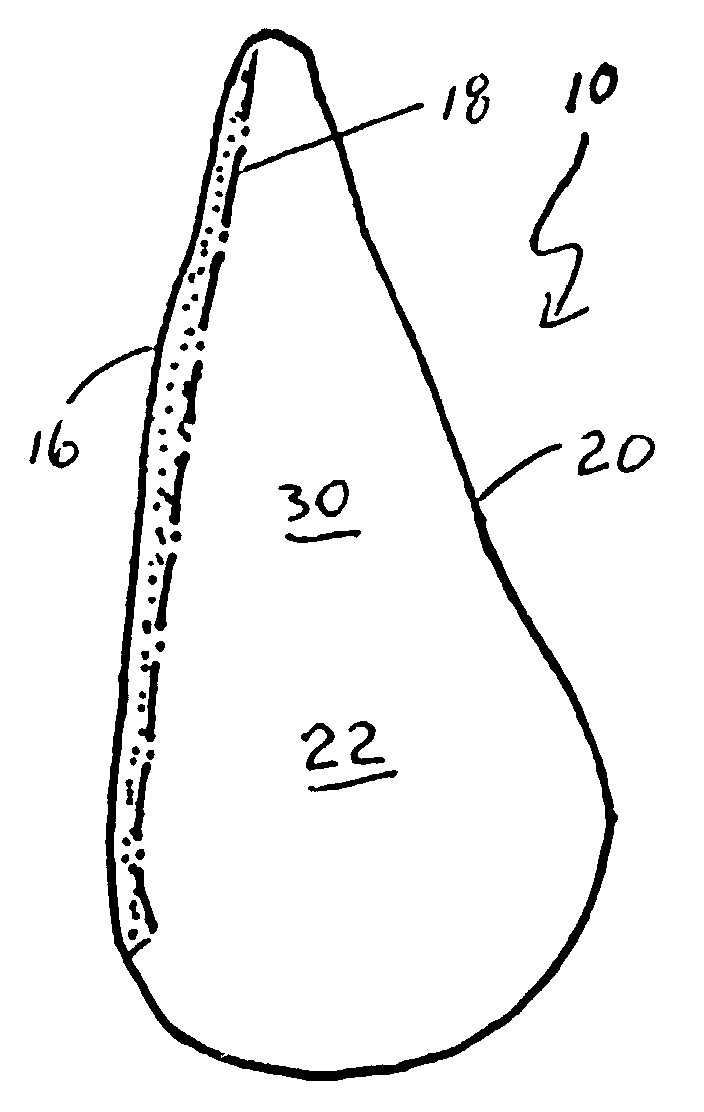
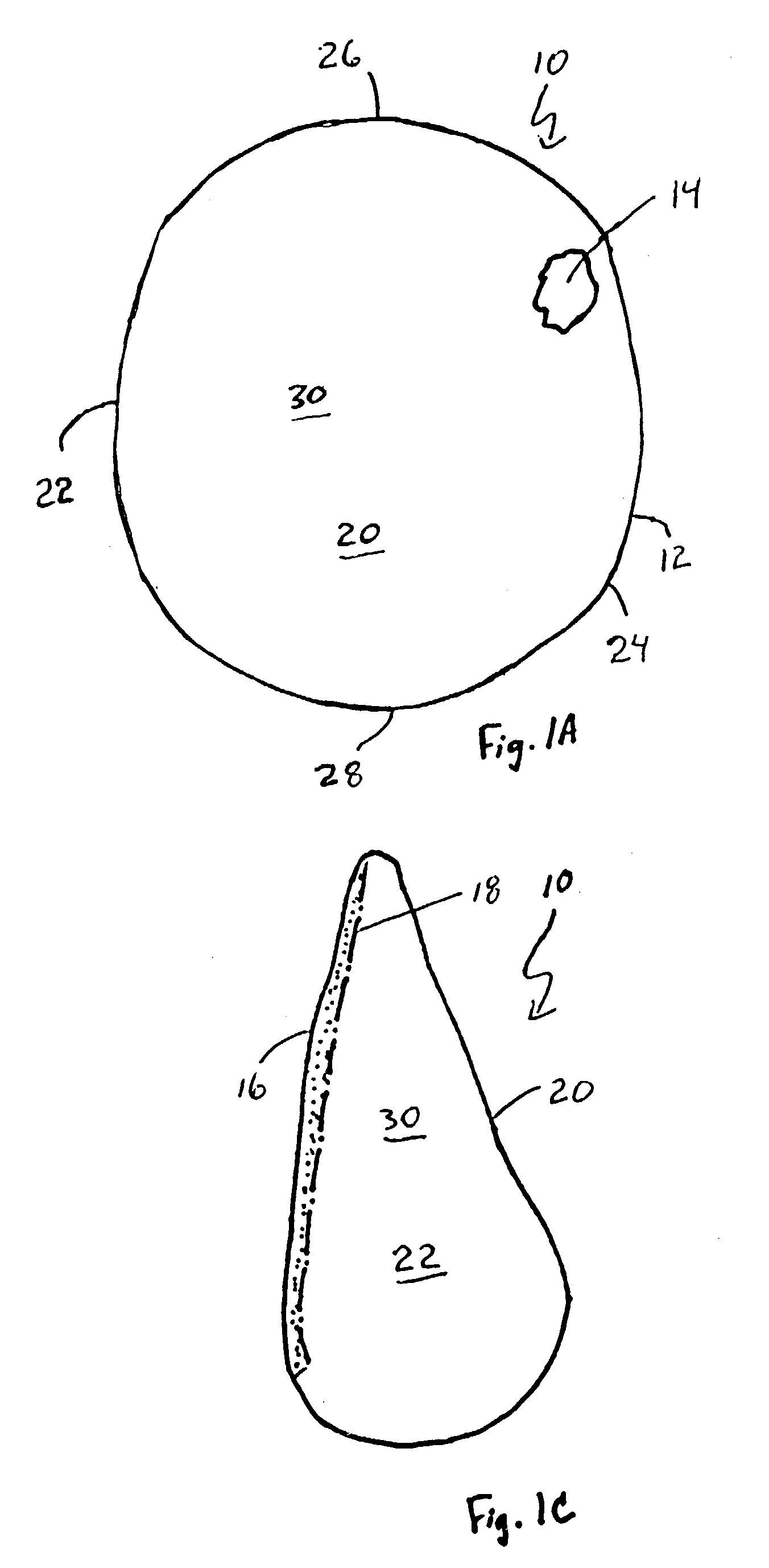
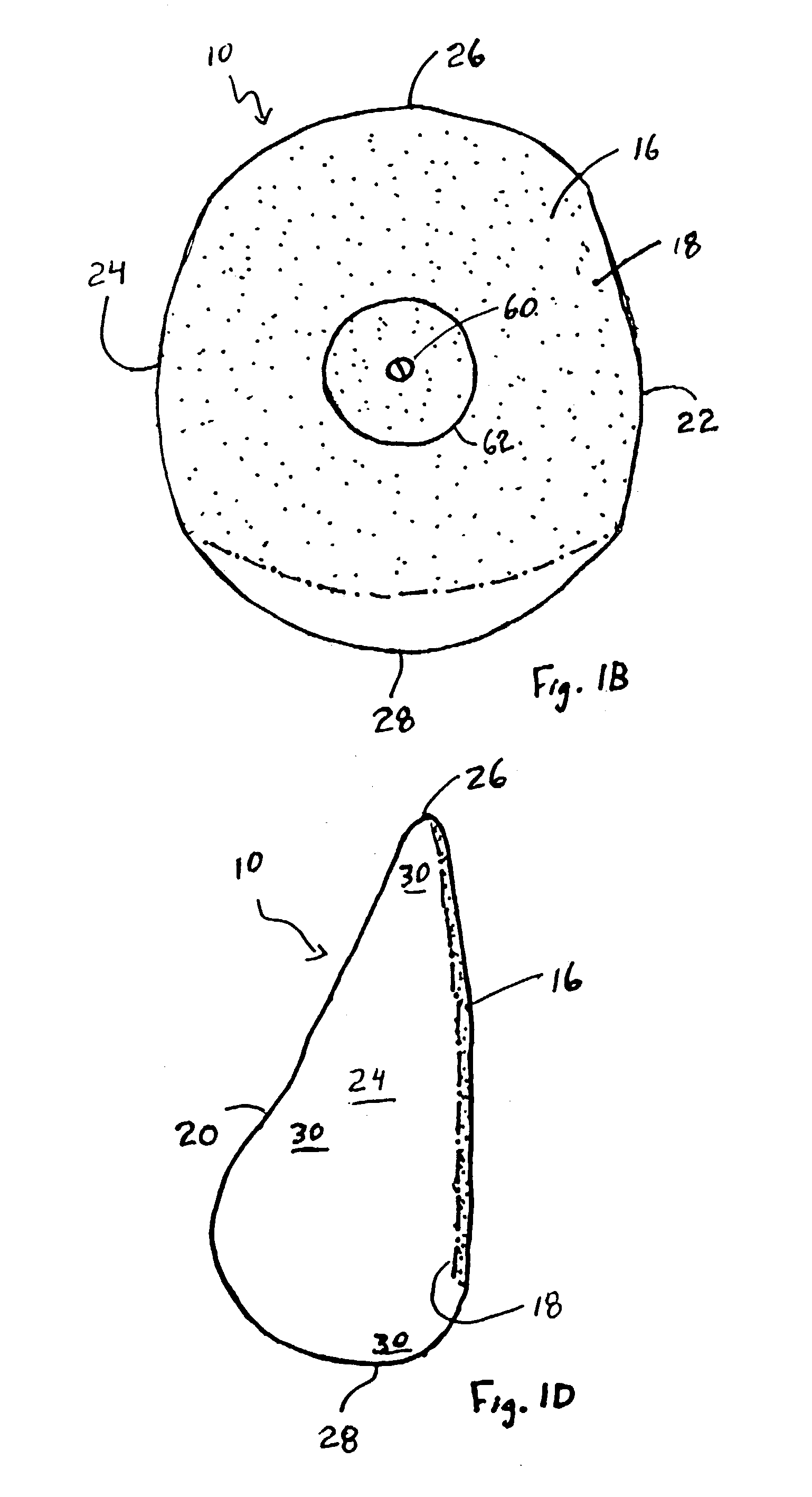
A non-rotating anatomical-shaped breast implant having a front side with a smooth surface and a rear side with a textured surface. A smooth surface ripples or wrinkles little, if at all. Rippling or wrinkling of the implant may undesirably produce a visible or palpable waviness on the skin of the breast. A smooth surface is more likely to produce the look and feel of a natural breast. A rear side with a textured surface is desirable because tissue growth of the body, after the implant has been implanted, engages the textured surface to anchor the implant in place such that the front side with the smooth surface remains matched with the front side of the body and such that the anatomical-shaped breast implant with its tear drop shaped fullness remains at a natural position within the breast. The disclosure further includes a method for minimizing the rotation of an implant within the body and a method for making an implant envelope that has different thicknesses.
Owner:BELLIN HOWARD T
Fragmented polymeric compositions and methods for their use
InactiveUS8357378B2Improve liquidityHydration can be adjusted very simplyPowder deliverySurgical adhesivesBiopolymerIn vivo
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
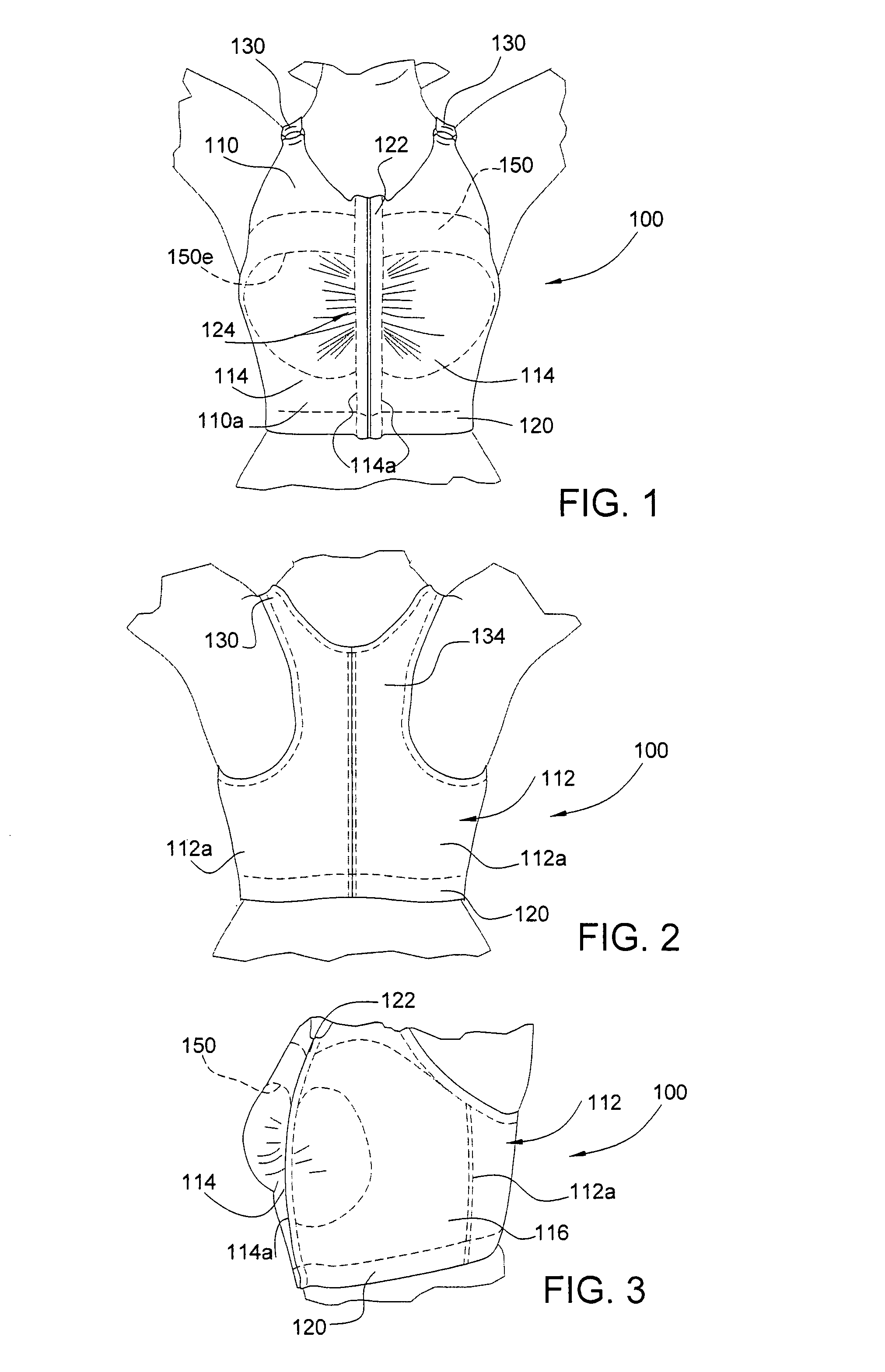
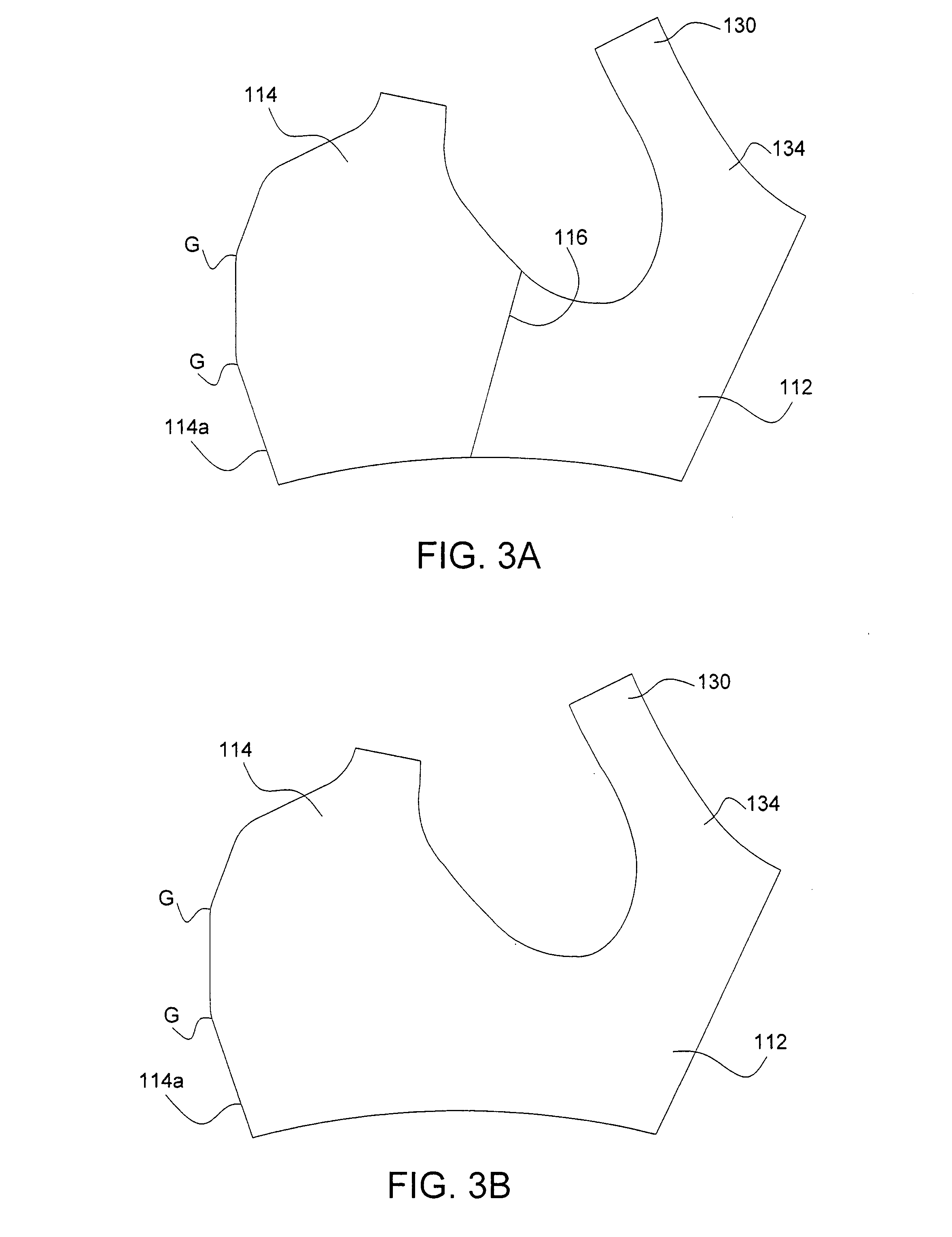
Garment with breast implant stabilizers
InactiveUS7909675B1Achieve stabilityAid in healing transformationBreast bandagesBrassieresBreast implantAreola
A breast garment for stabilizing breast implants includes a body surrounding the wearer's mid to upper torso, left and right built-in implant stabilizers positioned at the front of the body for applying medium to firm downward and lateral pressure on a wearer's breasts, and an adjustable front closure provided at the front edges of the body for making the body tighter or loose for adjusting the amount of downward and lateral pressure. The implant stabilizers have top, bottom, front, and back edges, with a cut-out in the front edge shaped to permit the areole and surrounding area of the breast to protrude therethrough. The body and the implant stabilizers are made of a stretch compressive fabric.
Owner:RAINEY APPAREL MFG
Apparatus and method for preventing adhesions between an implant and surrounding tissues
An anti-adhesion membrane is placed onto an implant introduced into a surgical site of a patient to prevent post-surgical adhesions between the implant and surrounding tissue. The implant may comprise either biological material, such as a transplanted organ, or non-biological material such as a medical device. The membrane may be applied in a variety of ways. In one example, a membrane according to the present invention is shrink-wrapped around a pace-maker. In another example, a breast implant is spray-coated or dipped with the membrane material.
Owner:MAST BIOSURGERY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com