Patents
Literature
117results about How to "Inhibiting and reducing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
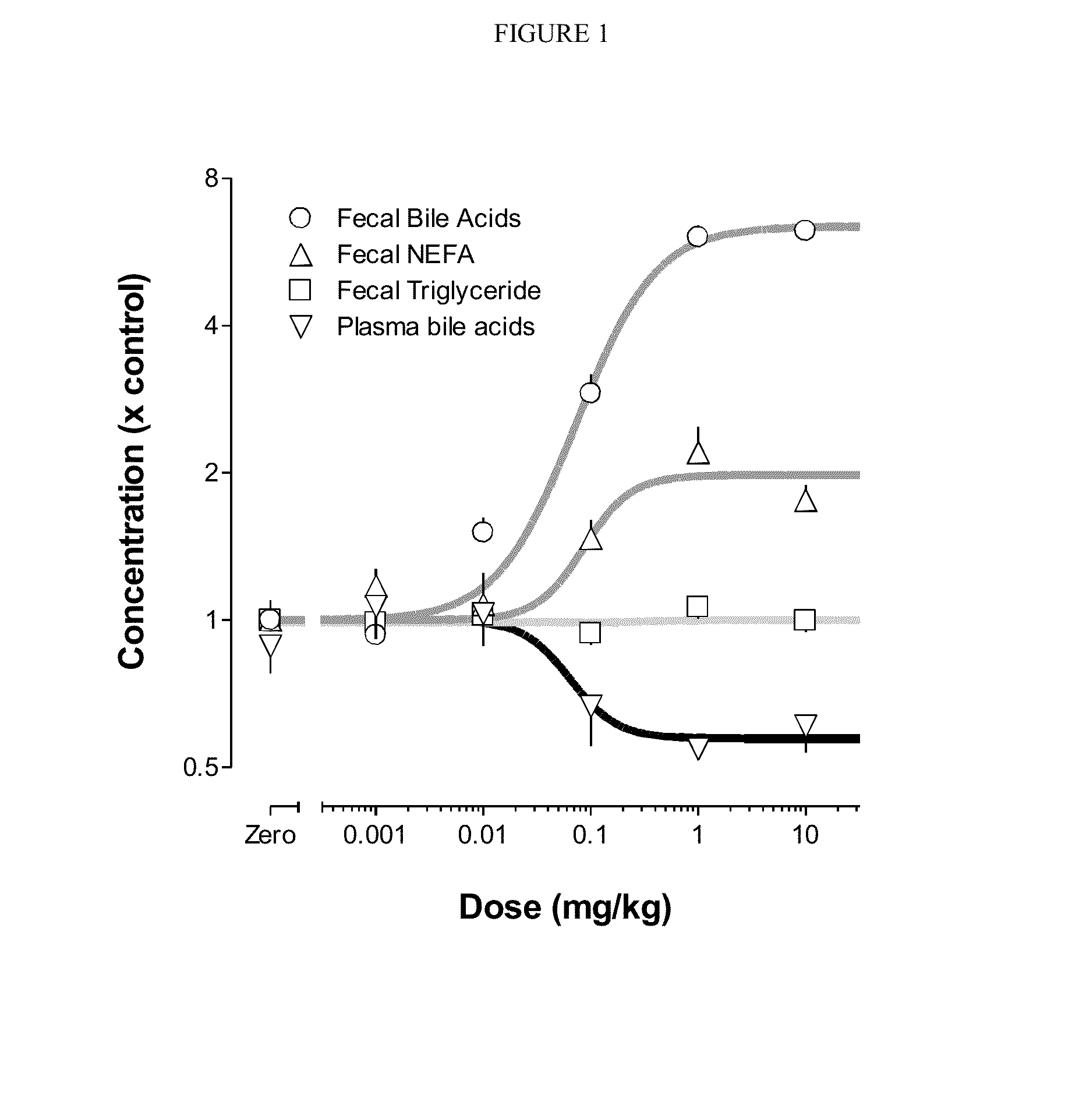
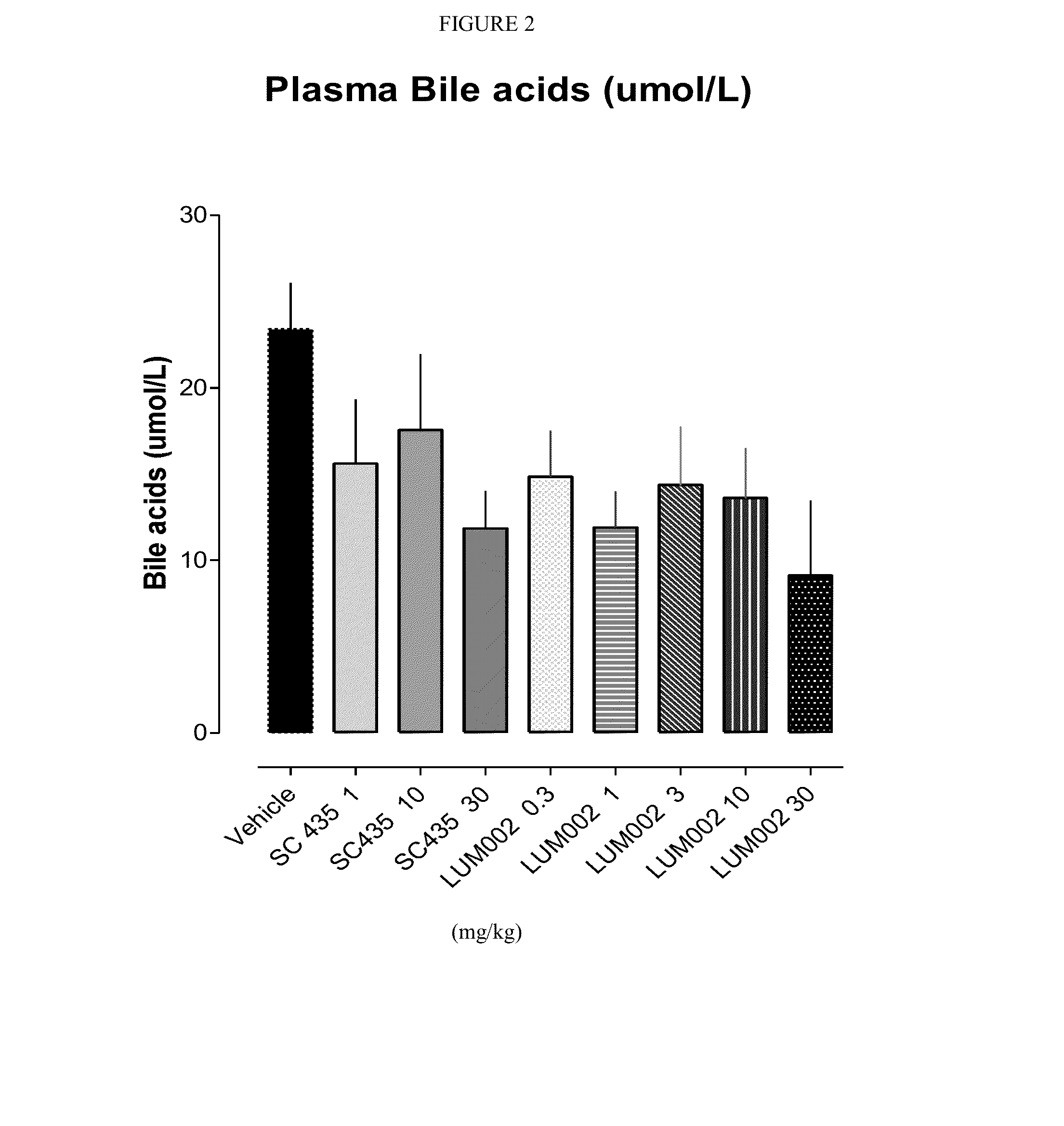
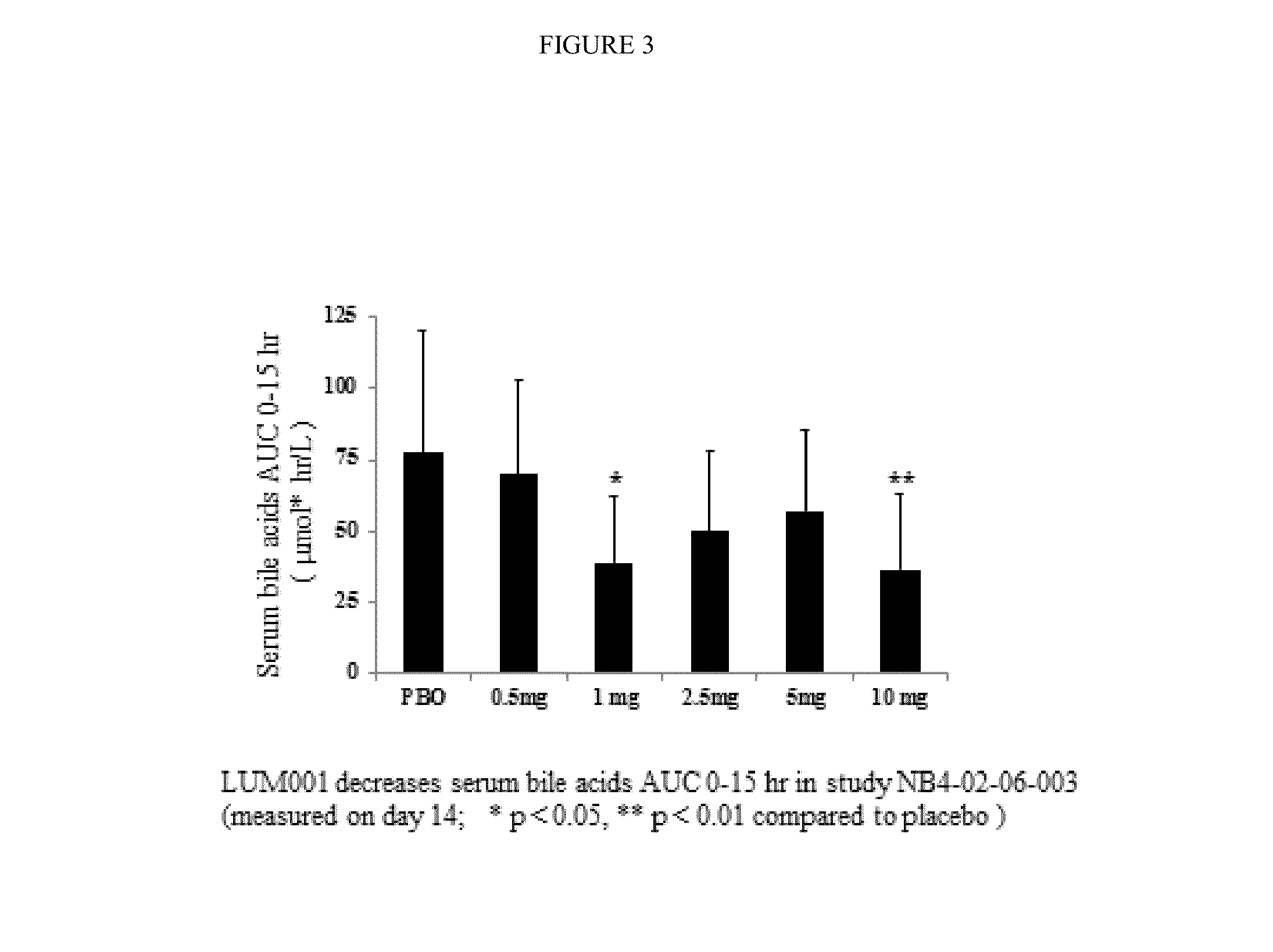
Bile Acid Recycling Inhibitors for Treatment of Hypercholemia and Cholestatic Liver Disease
InactiveUS20130108573A1Relieve symptomsReduce recurrenceBiocideCyclic peptide ingredientsDiseaseHepatic bile
Provided herein are methods of treating or ameliorating hypercholemia or a cholestatic liver disease by administering to an individual in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of an Apical Sodium-dependent Bile Acid Transporter Inhibitor (ASBTI) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. Also provided are methods for treating or ameliorating a liver disease, decreasing the levels of serum bile acids or hepatic bile acids, treating or ameliorating pruritis, reducing liver enzymes, or reducing bilirubin comprising administering to an individual in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of ASBTI or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:LUMENA PHARMA INC
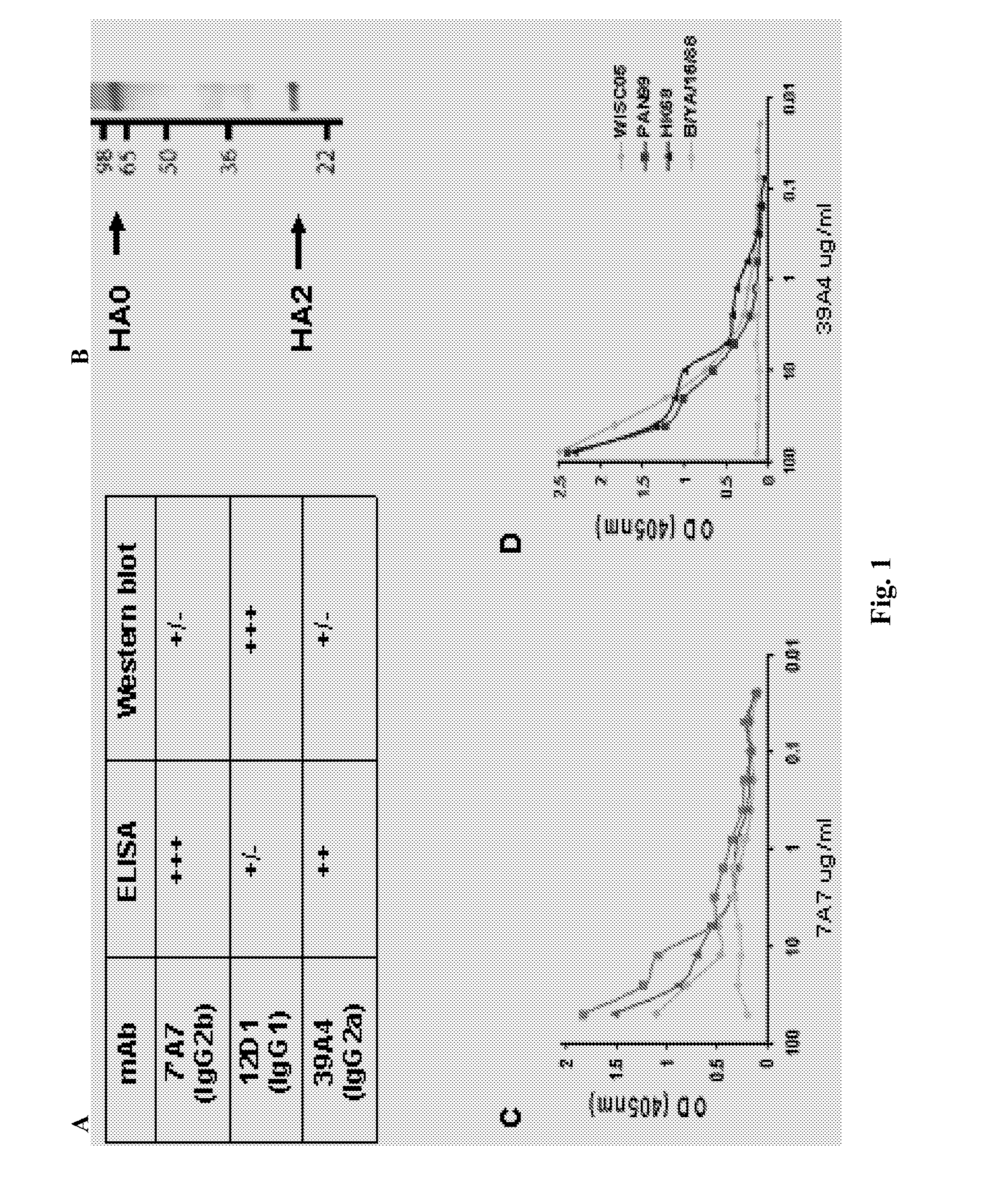
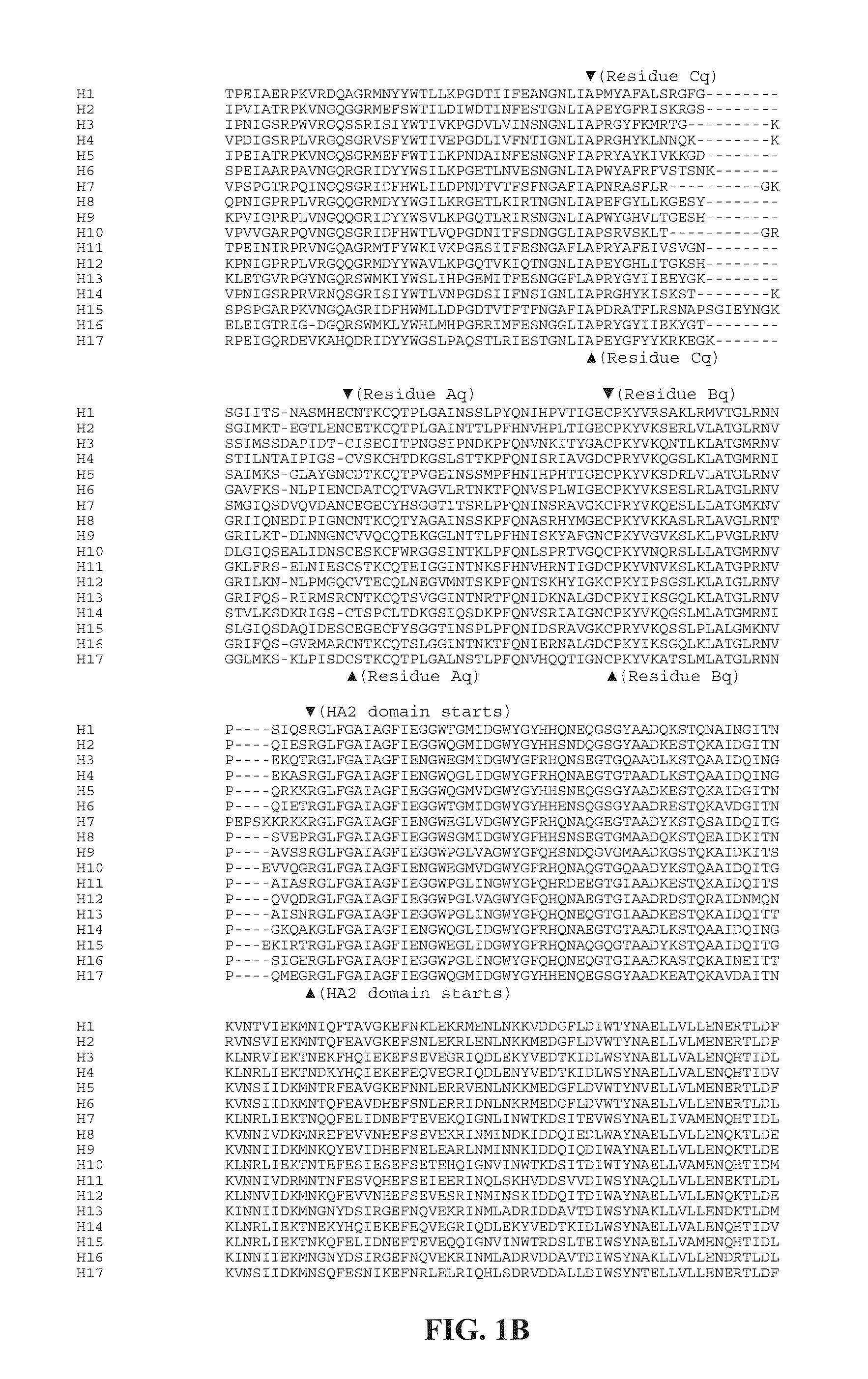
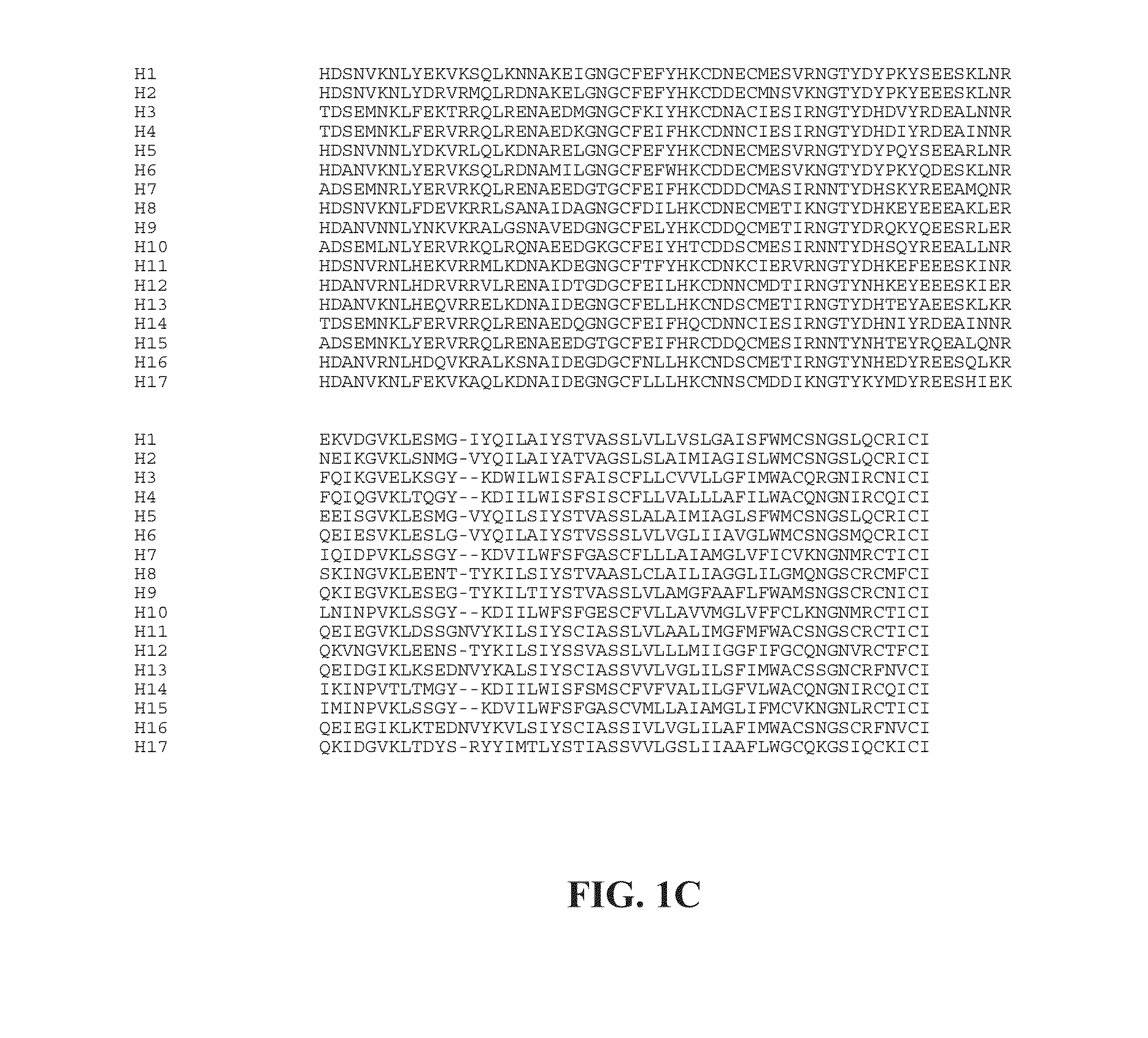
Influenza virus vaccines and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100297174A1Reduce severityImprove survivalSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHemagglutininInfluenza virus vaccine
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Treatment of lupus, fibrotic conditions, and inflammatory myopathies and other disorders using pi3 kinase inhibitors
ActiveUS20130344061A1Relieve symptomsPrevents mast cell degranulationBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseInflammatory myopathy
Owner:INFINITY PHARMA
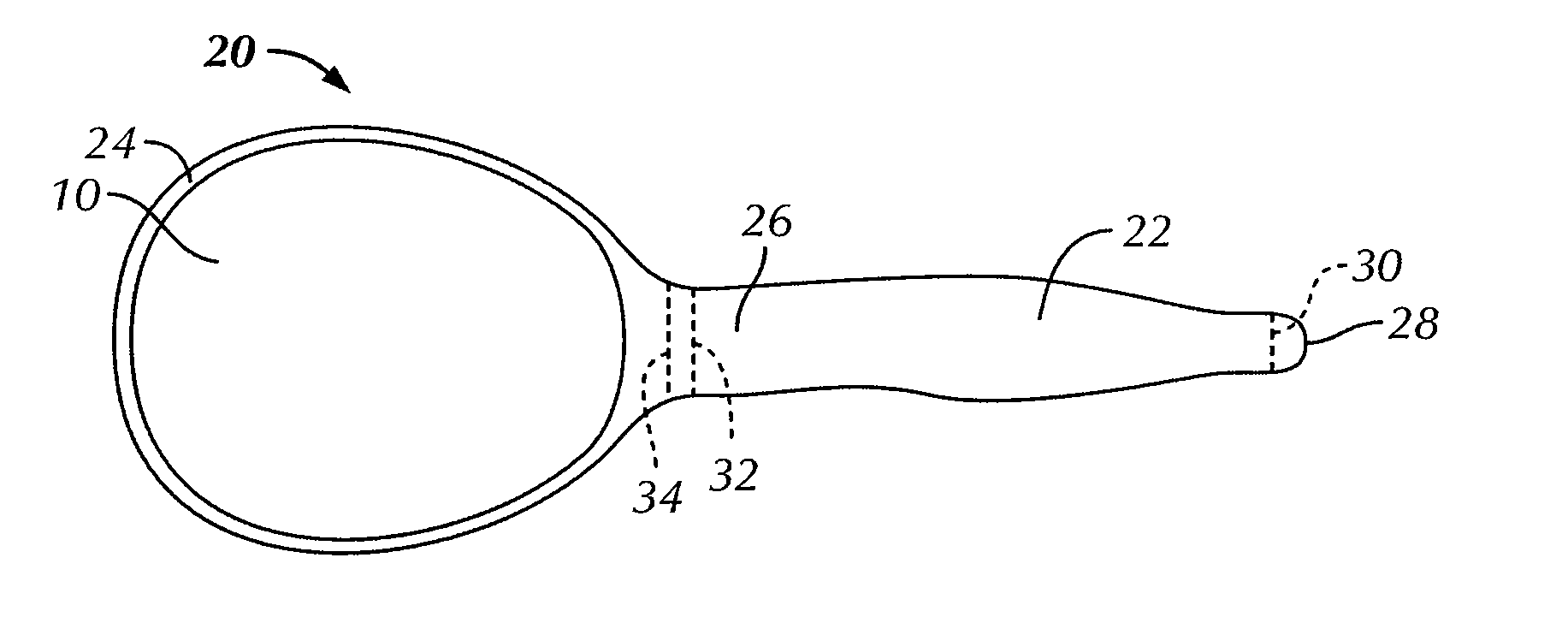
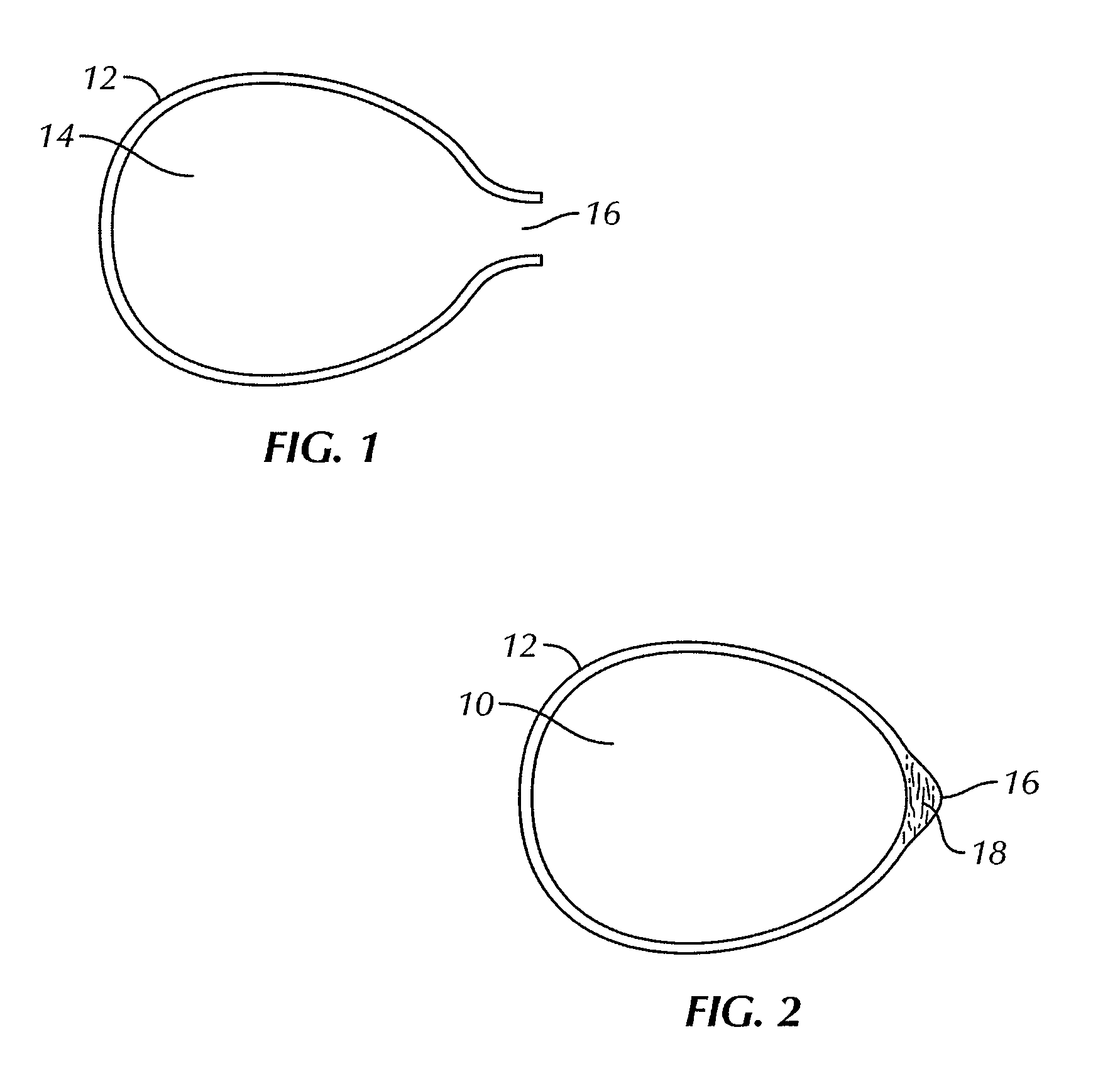
Breast implant implantation method and apparatus
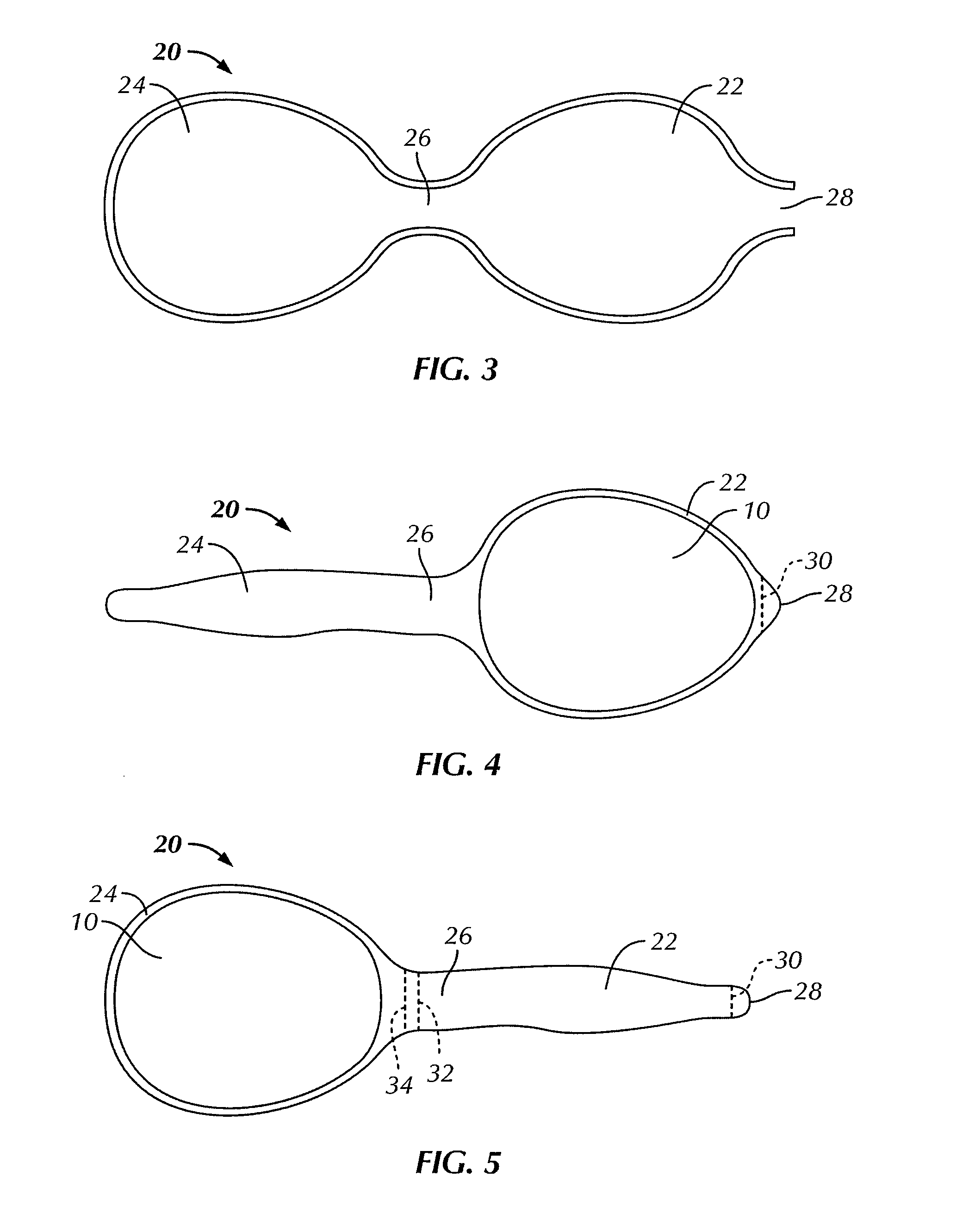
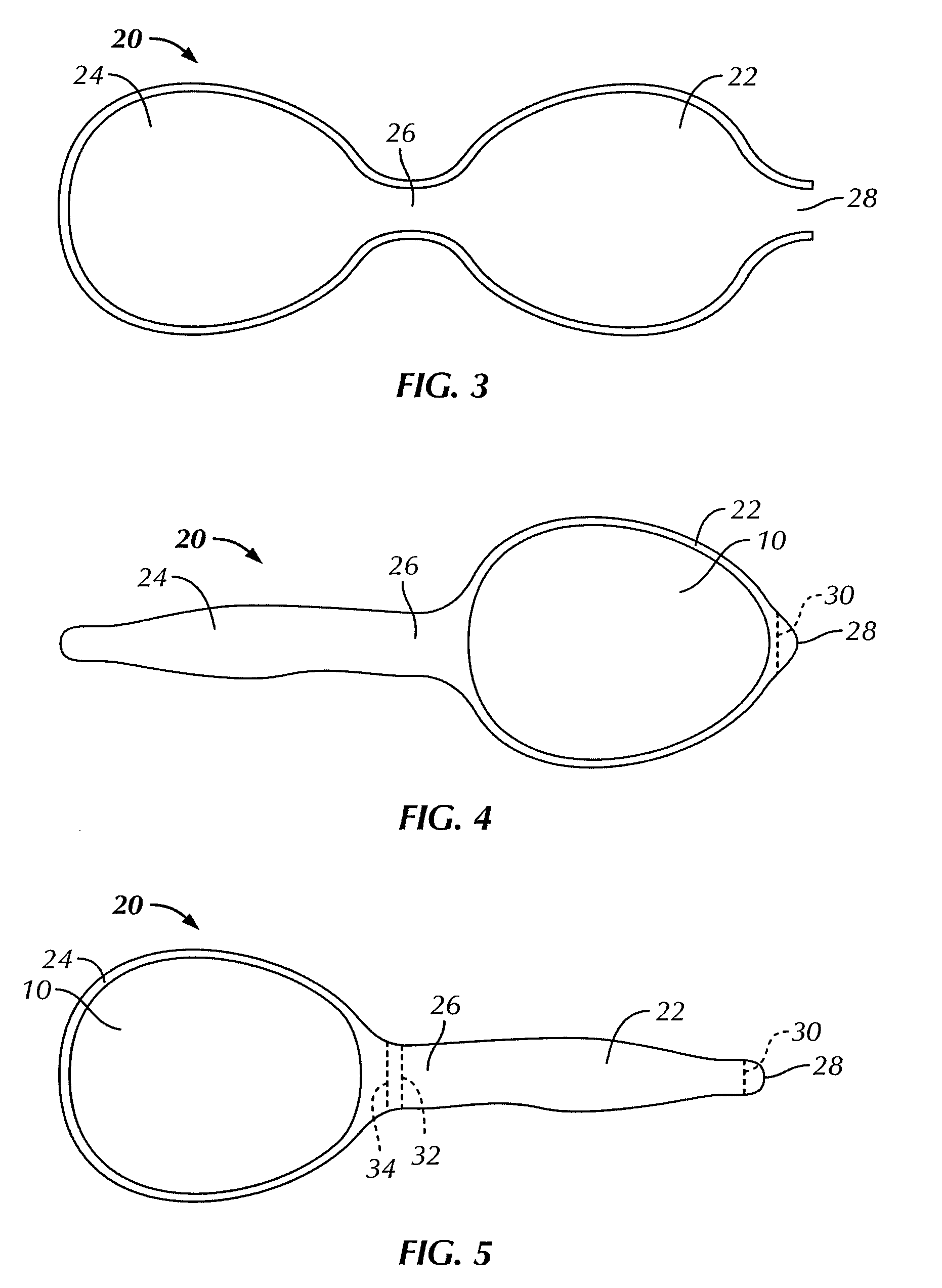
InactiveUS20110082546A1Inhibit and reduce formation of scar tissueInhibiting and reducingMammary implantsDiagnosticsAseptic processingDilator
A method for implanting a breast implant into a subject, the method includes: providing a sterile, flexible, elastic biodegradable bag sized to contain the breast implant; providing a sterile breast implant; inserting, using sterile handling, the sterile breast implant into the sterile bag to form a sterile breast implant assembly; closing the bag to fully enclose the implant within the bag; and implanting in a sterile manner the sterile breast implant assembly into the subject. A sterile bag, which may be provided in a kit, preferably for use with the method includes first and second chambers connected by a channel for moving a breast implant from the first chamber through the channel to the second chamber without directly touching the implant. An incision dilator may also be included with the kit or separately provided for use in a preferred embodiment of the method.
Owner:BREAST SHIELD MATERIALS
Antibody/drug conjugates and methods of use
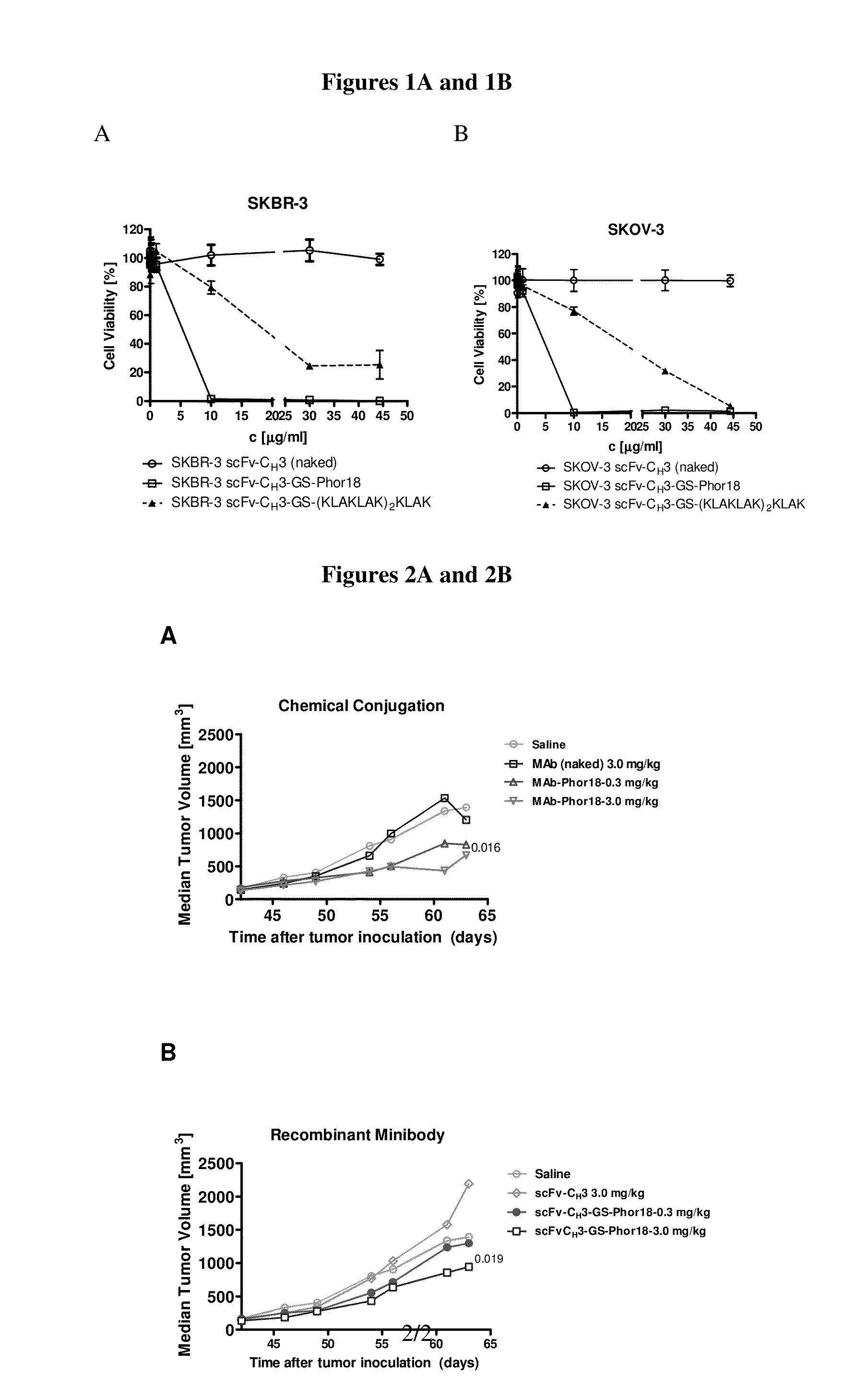
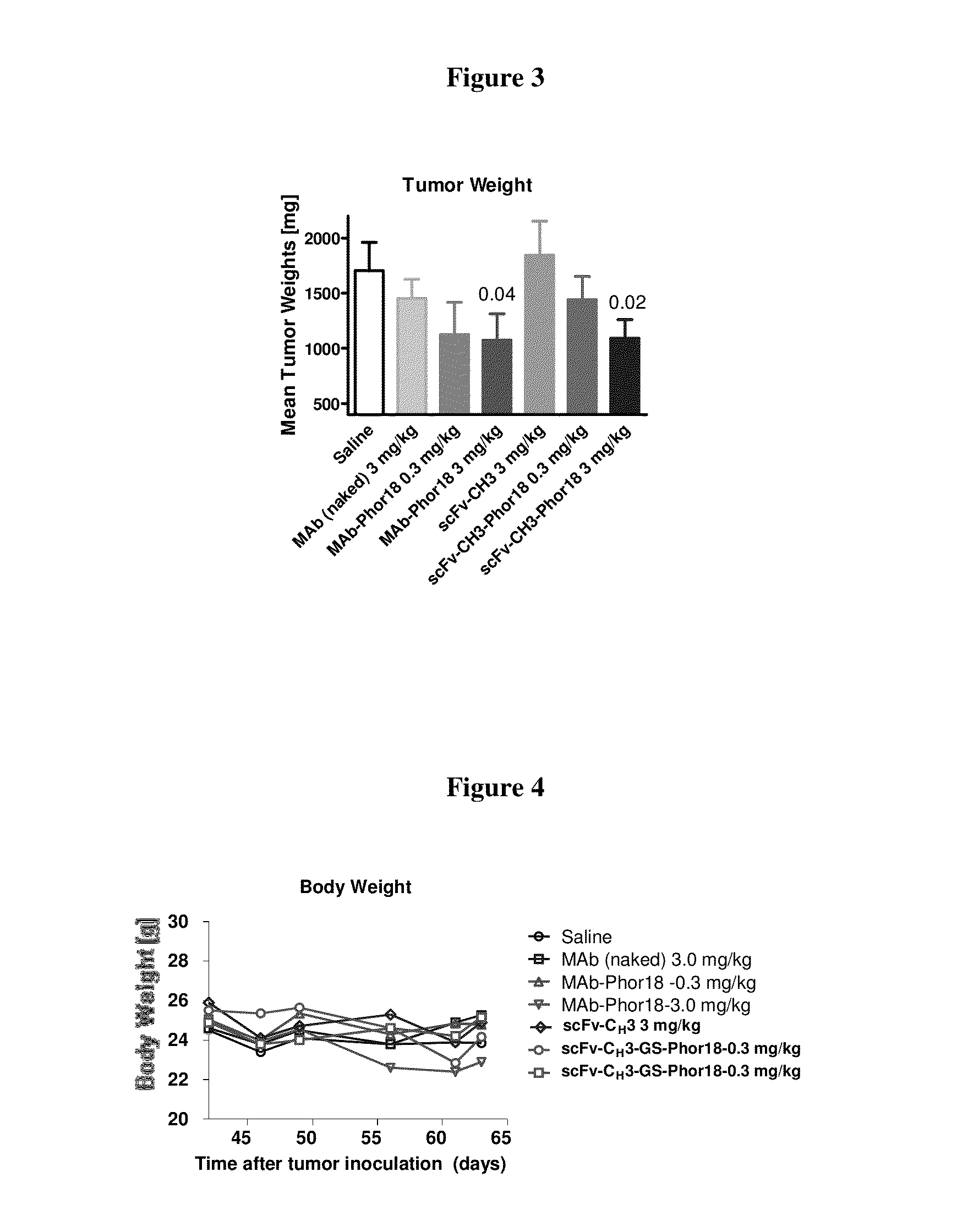
ActiveUS20140127241A1Reducing and inhibiting proliferationReducing and inhibiting and growthAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseDrug conjugation
The invention relates to conjugates that bind to targets, methods of using conjugates that bind to targets and methods of treating undesirable or aberrant cell proliferation or hyperproliferative disorders, such as tumors, cancers, neoplasia and malignancies that express a target.
Owner:A28 THERAPEUTICS INC
Lipids, lipid compositions, and methods of using them
ActiveUS20140309277A1Inhibiting and reducingLower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLipidomeActive agent
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
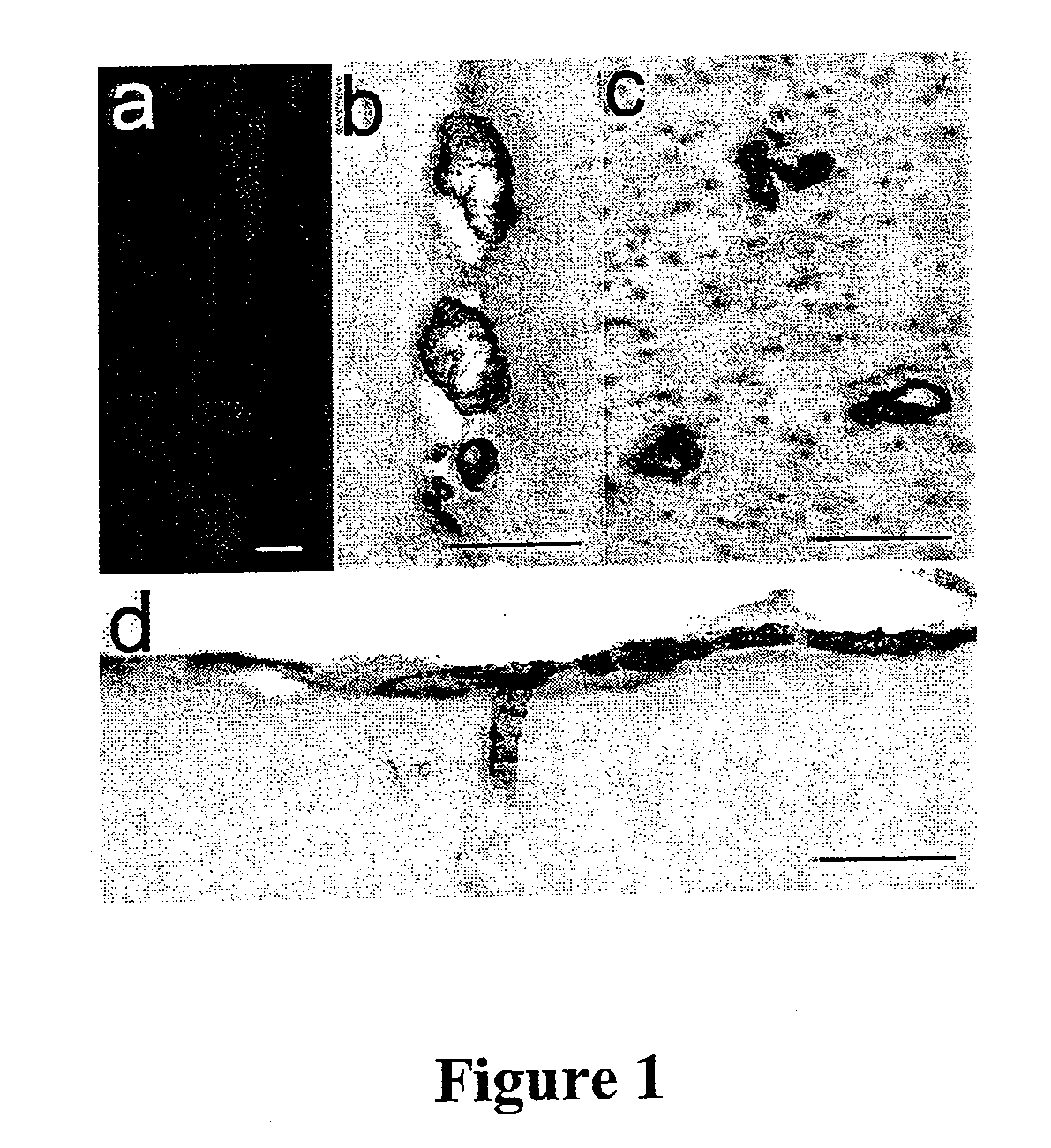
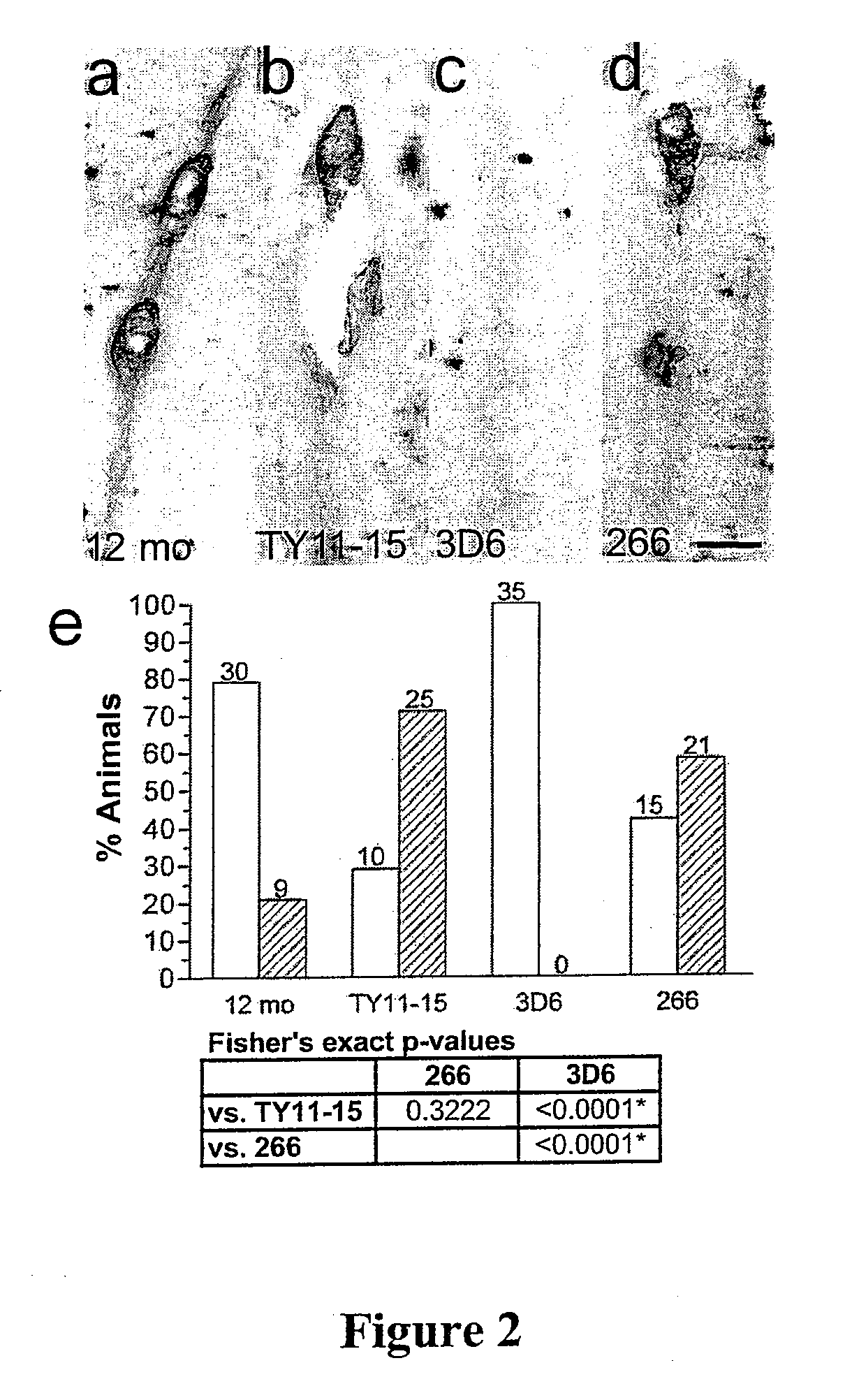
Prevention and treatment of cerebral amyloid angiopathy
InactiveUS20080292625A1Reduces and inhibits vascular amyloidogenic pathologyMinimizes microhemorrhageNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAmyloid angiopathyDisease cause
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and methods to effect prophylaxis of CAA. The methods can treat CAA concurrently with Alzheimer's disease or separately. The methods can effect prophylaxis of CAA concurrently with Alzheimer's disease or separately. The methods involve administering antibody that is specific for the N-terminus of Aβ or an agent that can induce such an antibody.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
Glucagon analogues
ActiveUS20140080757A1Avoid weight gainGood for weight lossBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsProviding materialObesity
The invention provides materials and methods for the treatment of obesity and excess weight, diabetes, and other associated metabolic disorders. In particular, the invention provides novel glucagon analogue peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Topical composition with skin lightening effect
ActiveUS7897184B1Inhibiting and reducingReduces and inhibits melanin productionCosmetic preparationsBiocideLarix sibiricaChemical composition
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Prevention and treatment of cerebral amyloid angiopathy
InactiveUS20090142270A1Reduces and inhibits development of vascularMinimizes microhemorrhageNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAmyloid angiopathyAntibody
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and methods to effect prophylaxis of CAA. The methods can treat CAA concurrently with Alzheimer's disease or separately. The methods can effect prophylaxis of CAA concurrently with Alzheimer's disease or separately. The methods involve administering antibody that is specific for the N-terminus of Aβ or an agent that can induce such an antibody.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC +1
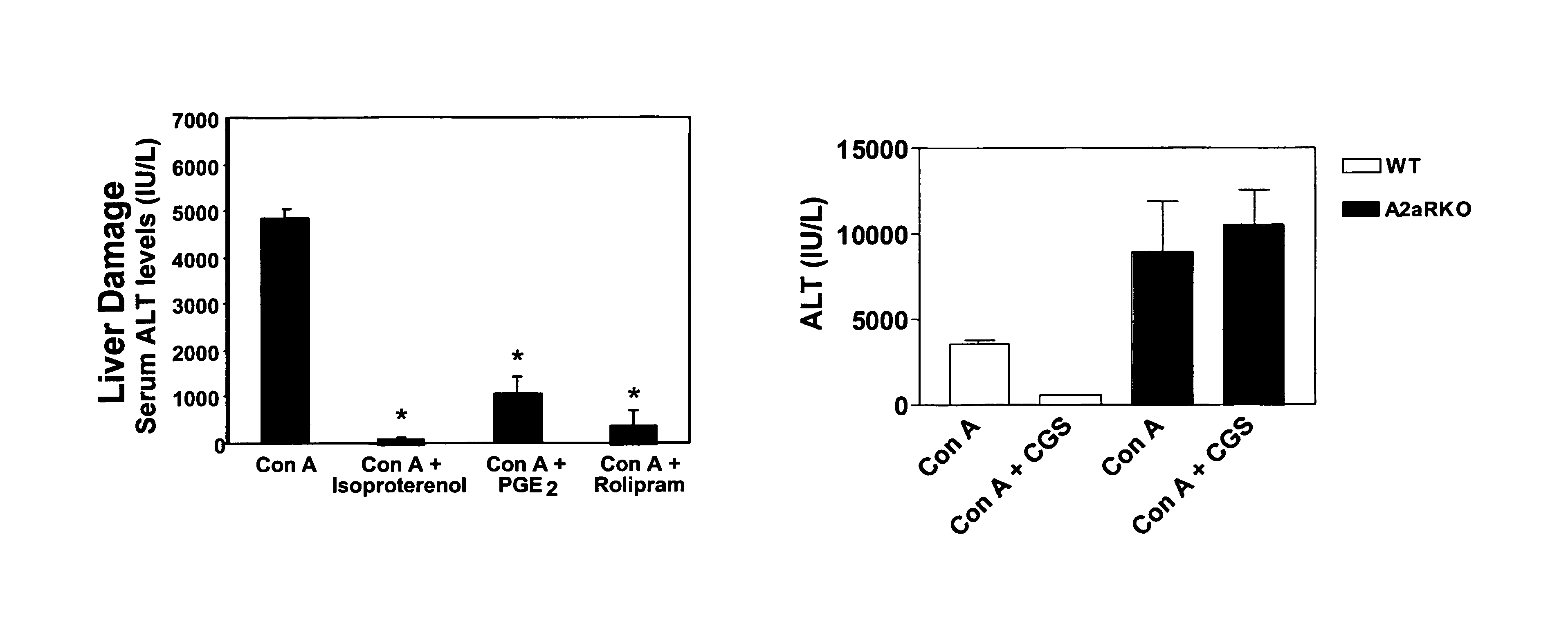
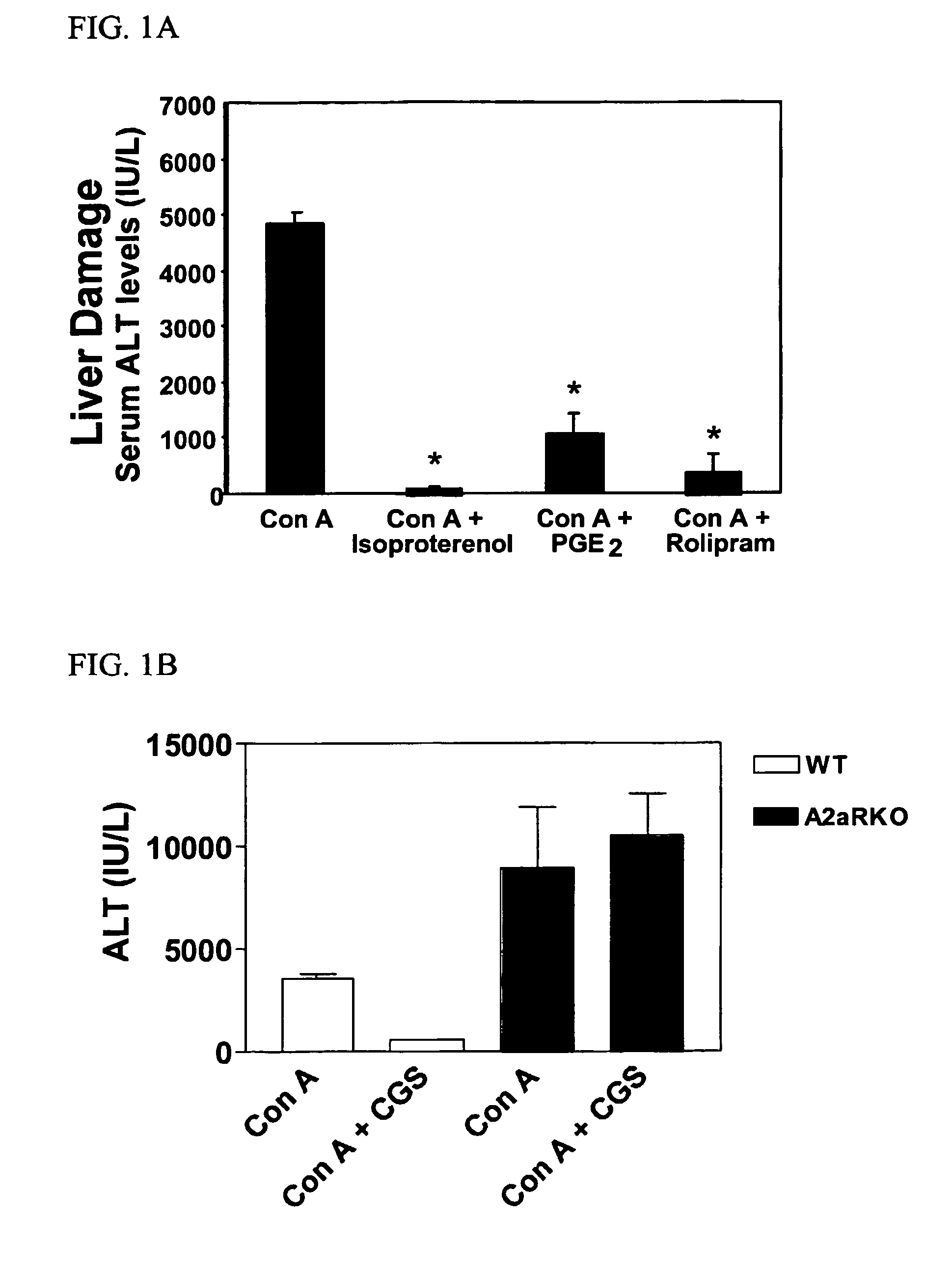
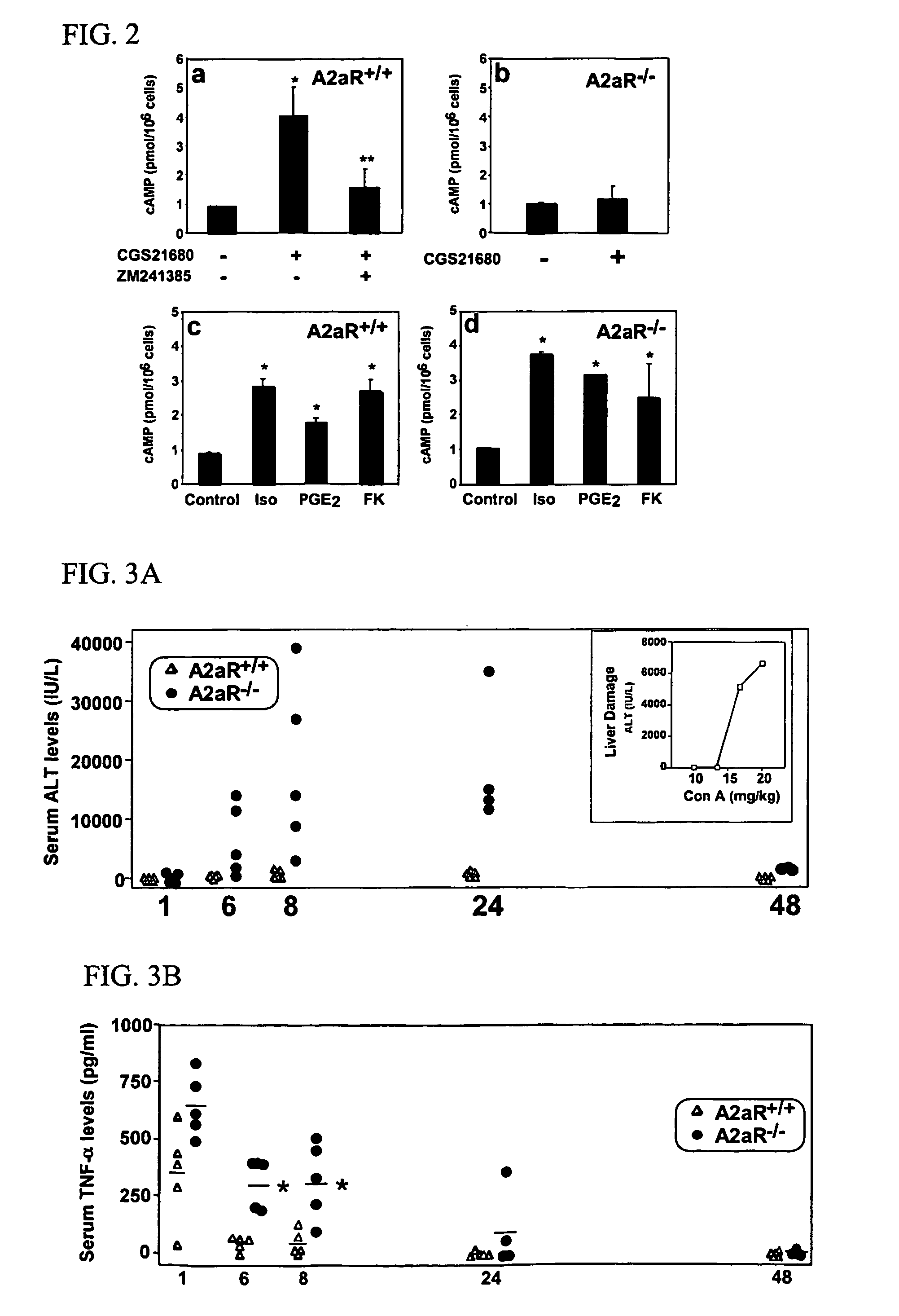
Methods for using extracellular adenosine inhibitors and adenosine receptor inhibitors to enhance immune response and inflammation
ActiveUS8080554B2Suppress immune responseEnhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsBiocideVaccine PotencyTumor destruction
A method is provided herein to increase an immune response to an antigen. The method includes administering an agent that inhibits extracellular adenosine or inhibits adenosine receptors. Also disclosed are methods to increase the efficacy of a vaccine and to increase an immune response to a tumor antigen or immune cell-mediated tumor destruction.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF
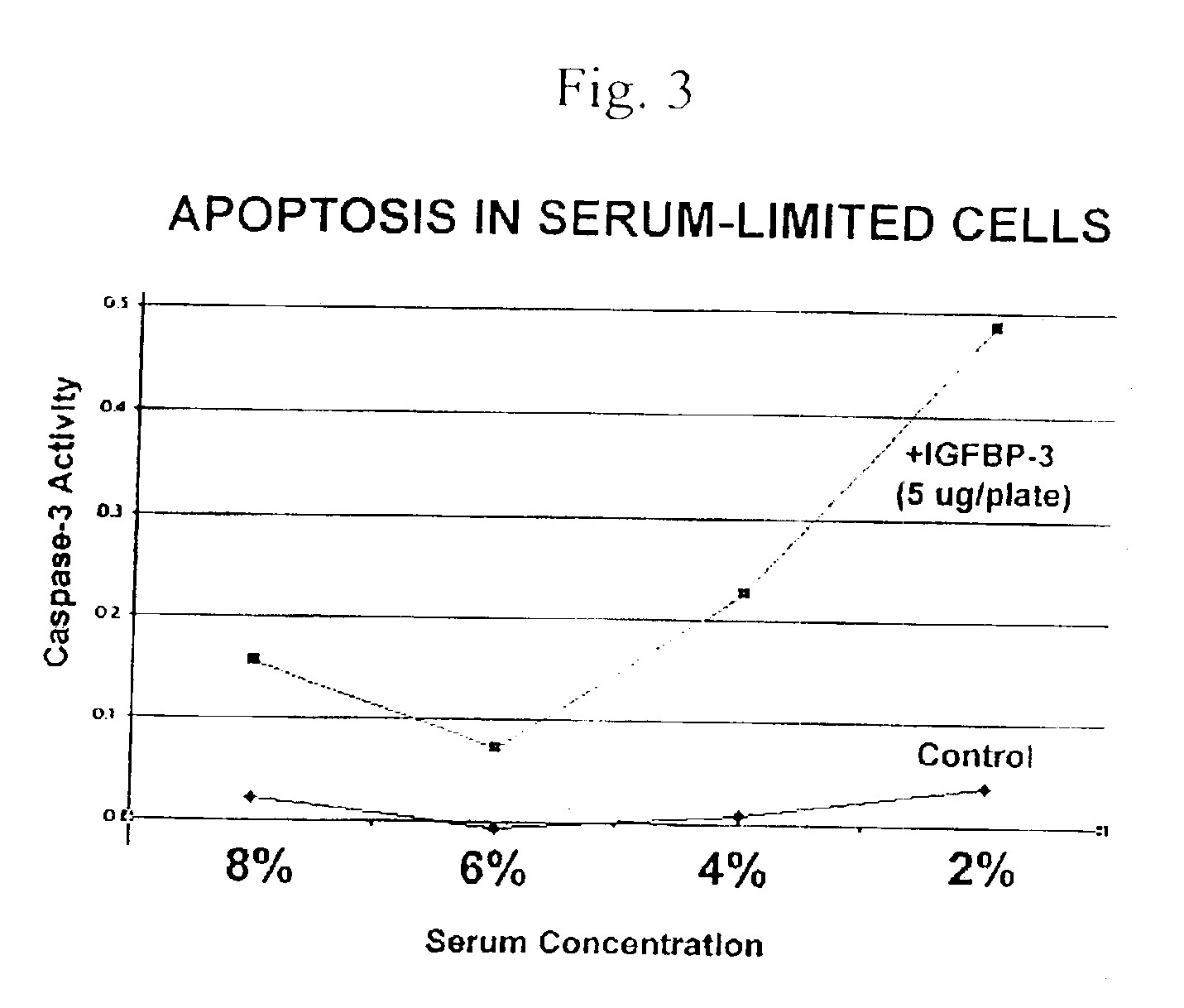
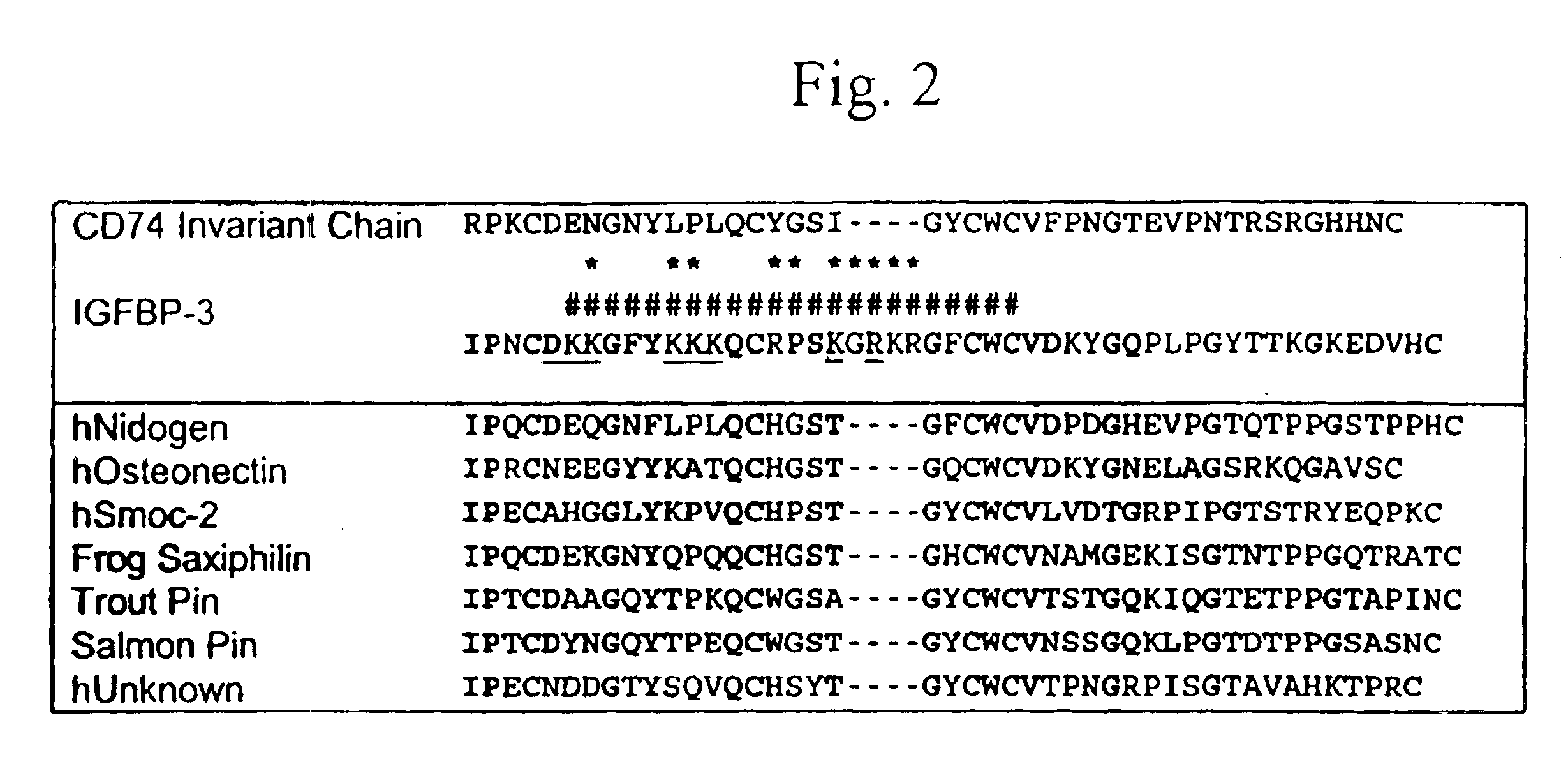
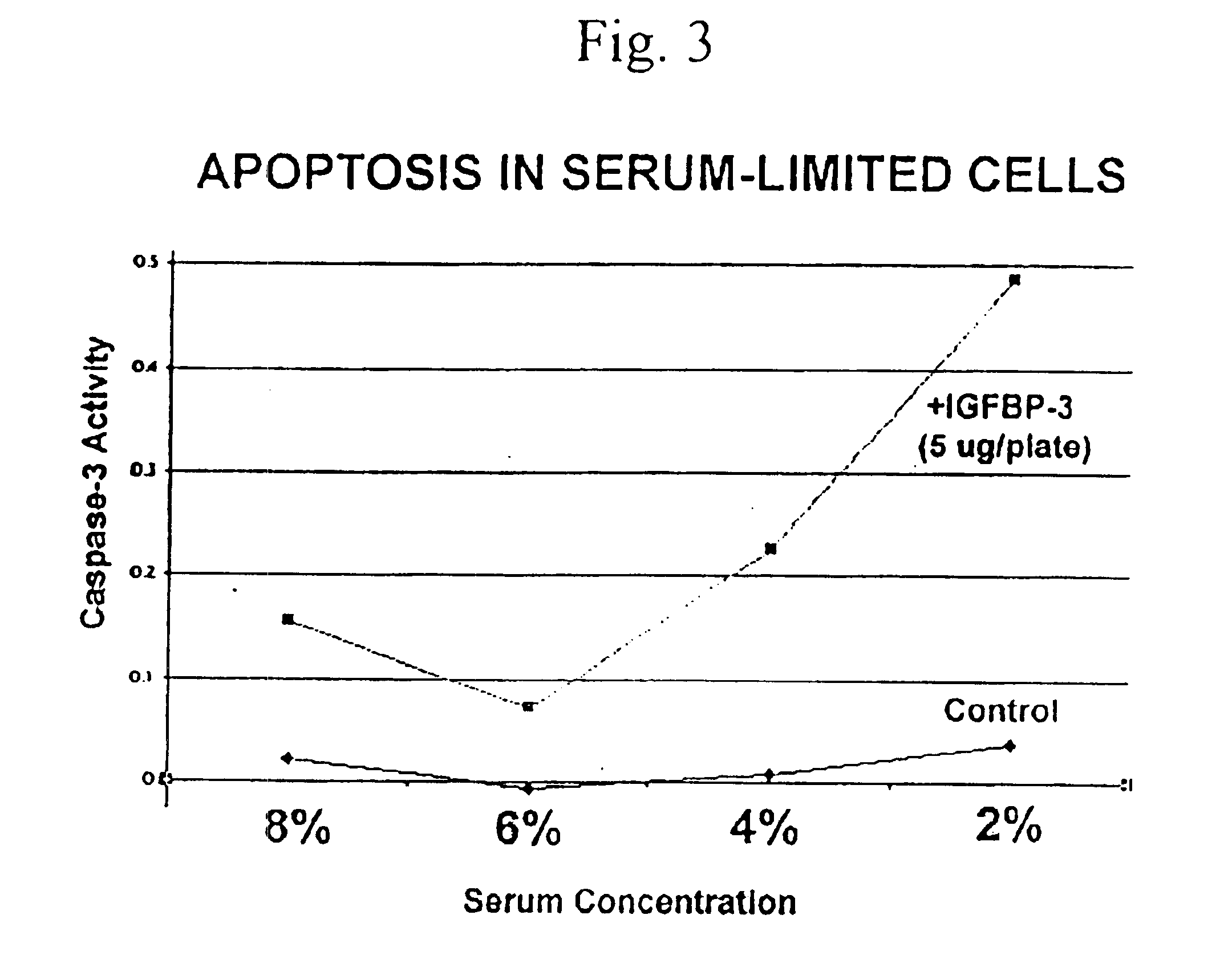
IGF-binding protein-derived peptide or small molecule
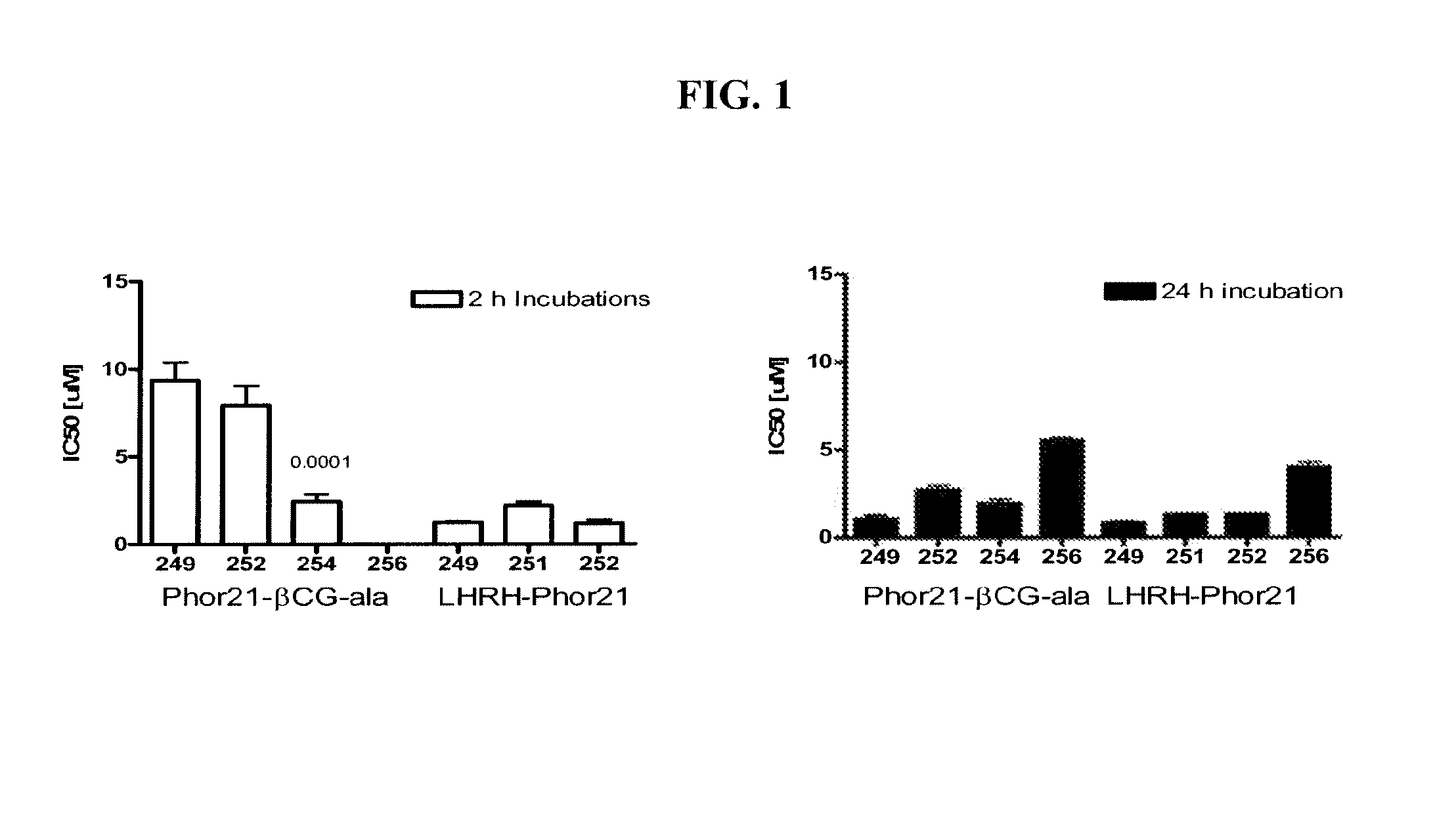
InactiveUS6914049B2Reducing tumor invasivenessReducing and inhibiting vascular restenosisSenses disorderNervous disorderPeptideSmall molecule
New compositions based on IGF-binding protein sequences are provided. New tools for high-throughput research are provided. New methods for the treatment of human disease are provided. IGFBP-3-derived peptide or small molecule is administered to subjects having disease, thereby alleviating the symptoms of the disease.
Owner:BIOEXPERTISE +1
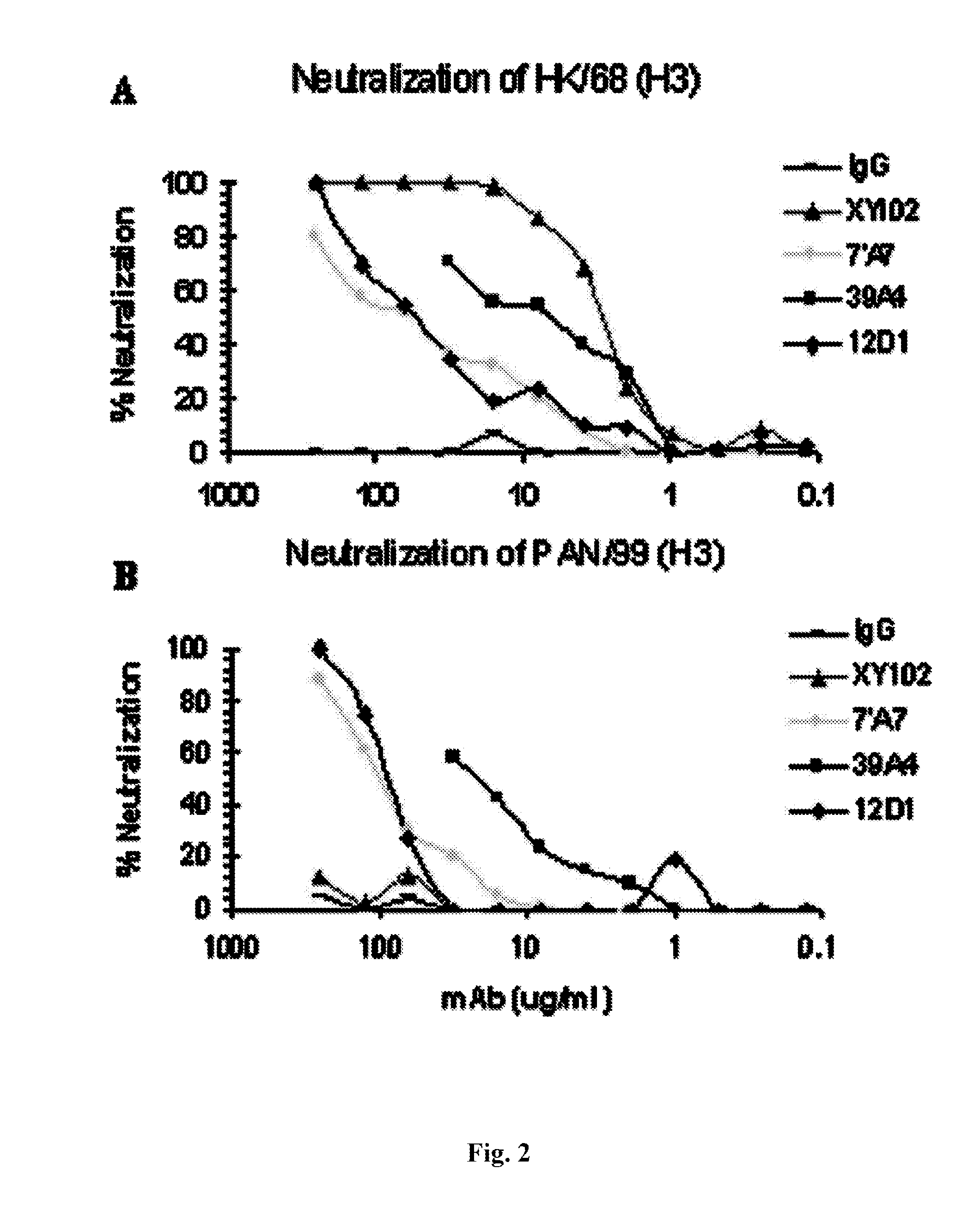
Monoclonal antibodies against influenza virus generated by cyclical administration and uses thereof
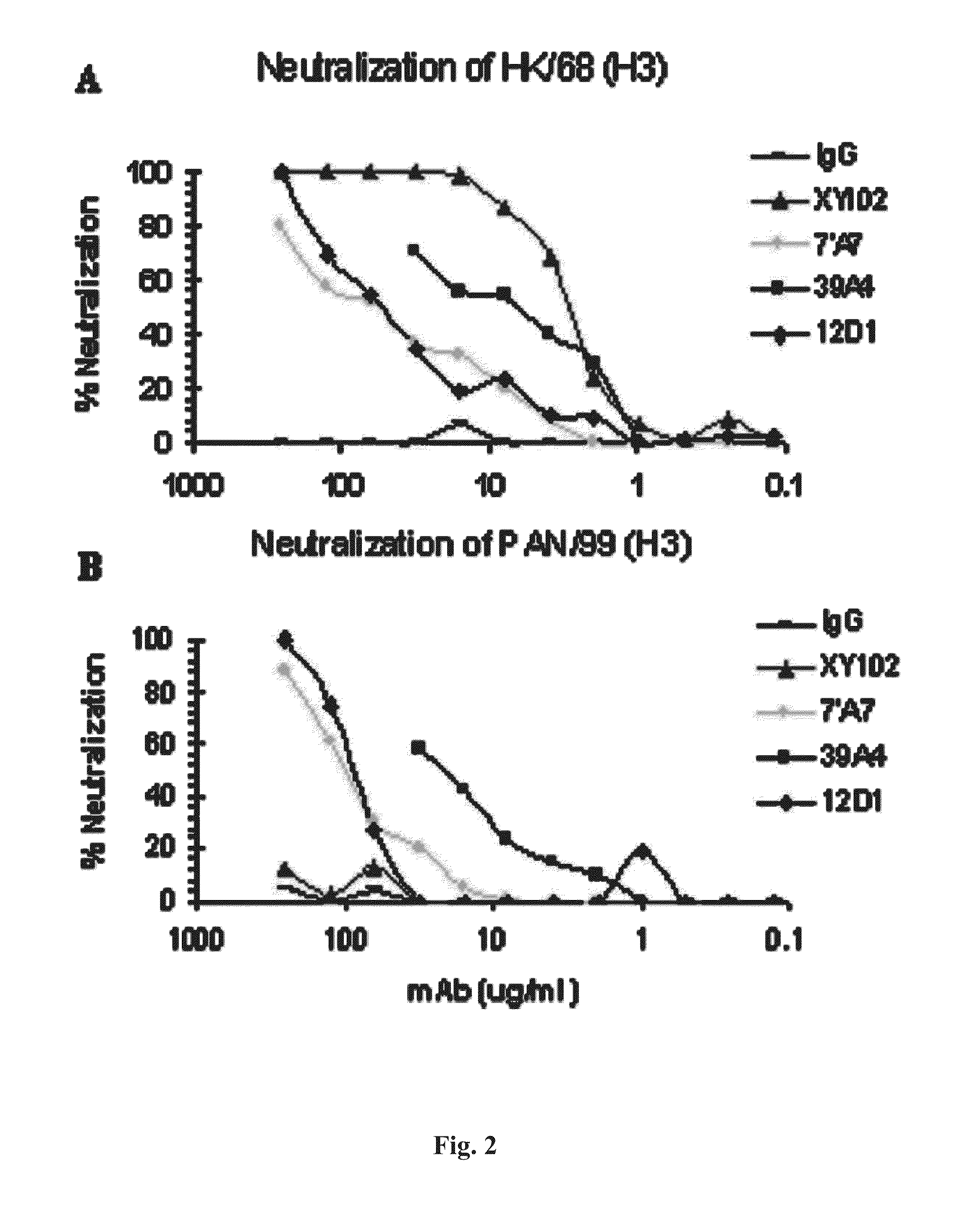
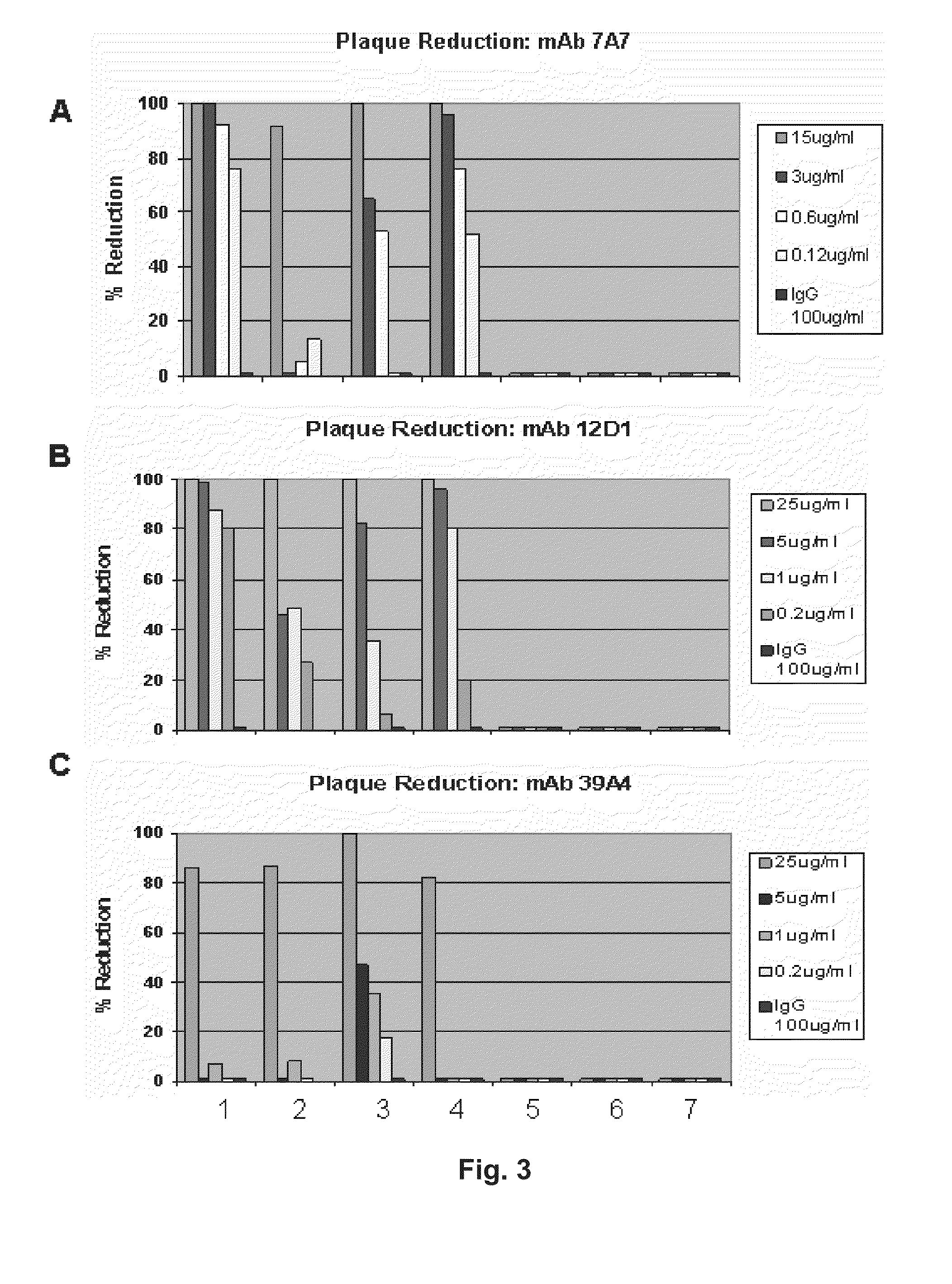
ActiveUS20110027270A1Reduce in quantityLower titerSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesMonoclonal antibodyVirus diseases
Provided herein are methods of producing neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, by cyclical immunization, that cross-react with strains of Influenza virus of the same subtype or different subtypes. Also provided herein are compositions comprising such antibodies and methods of using such antibodies to diagnose, prevent or treat Influenza virus disease.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Acylated glucagon analogues
ActiveUS20150111826A1Avoid weight gainGood for weight lossOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseReceptor
The invention provides materials and methods for the treatment of obesity and excess weight, diabetes, and other associated metabolic disorders. In particular, the invention provides novel acylated glucagon analogue peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Oral immunotherapy of bacterial overgrowth
InactiveUS6096310AInhibiting and reducingReduce acidityBacterial antigen ingredientsSerum immunoglobulinsDiseaseBacteroides
The object of the present invention is the oral administration of animal immunoglobulins for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders caused by bacterial and / or yeast overgrowth. Immunoglobulins derived from the blood, plasma or serum of animals, such as cow, goats, sheep and pigs, contain a broad spectrum of antibodies to bacteria and yeast that afflict the gastrointestinal tract of human patients.
Owner:BIER MILAN
IGF-binding protein-derived peptide
InactiveUS6887851B2Reducing tumor invasivenessReducing and inhibiting vascular restenosisBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSmall moleculePeptide
New compositions based on IGF-binding protein sequences are provided. New tools for high-throughput research are provided. New methods for the treatment of human disease are provided. IGFBP-3-derived peptide or small molecule is administered to subjects having disease, thereby alleviating the symptoms of the disease.
Owner:ENMODULIN INC +1
Glucagon analogues
InactiveUS20130157935A1Effect on cholesterol levelAvoid weight gainPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderWeight gain preventionProviding material
The invention provides materials and methods for promoting weight loss or preventing weight gain without affecting glycemic control. In particular, the invention provides novel glucagon analogue peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Glucagon analogues
ActiveUS20150111817A1Avoid weight gainGood for weight lossNervous disorderBacteriaProviding materialObesity
The invention provides materials and methods for the treatment of obesity and excess weight, diabetes, and other associated metabolic disorders. In particular, the invention provides novel glucagon analogue peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Combination therapy for the treatment of influenza
InactiveUS20090298797A1Increase survivabilityInhibiting or reduceBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsNeuraminidase inhibitorInflammation
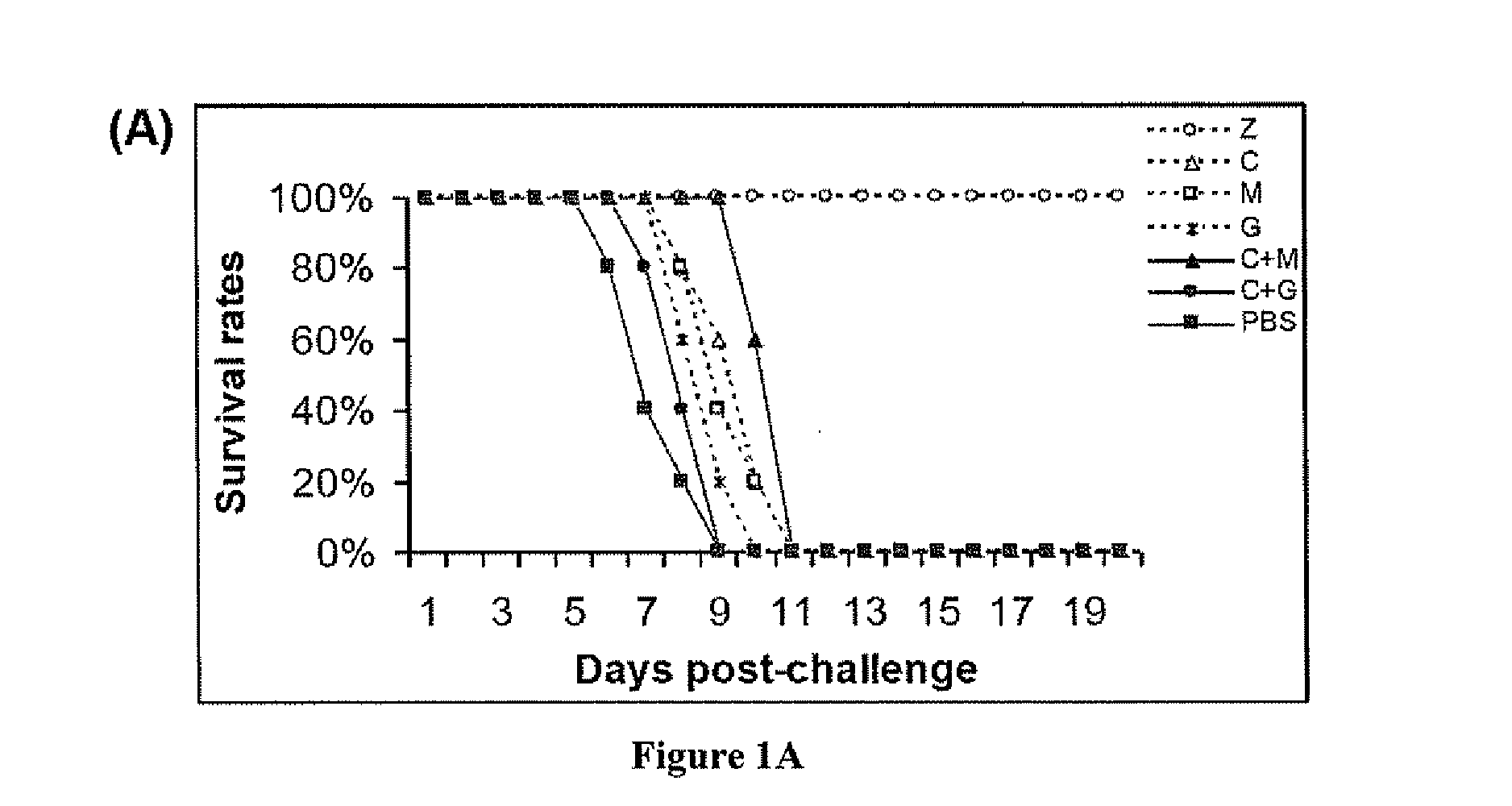
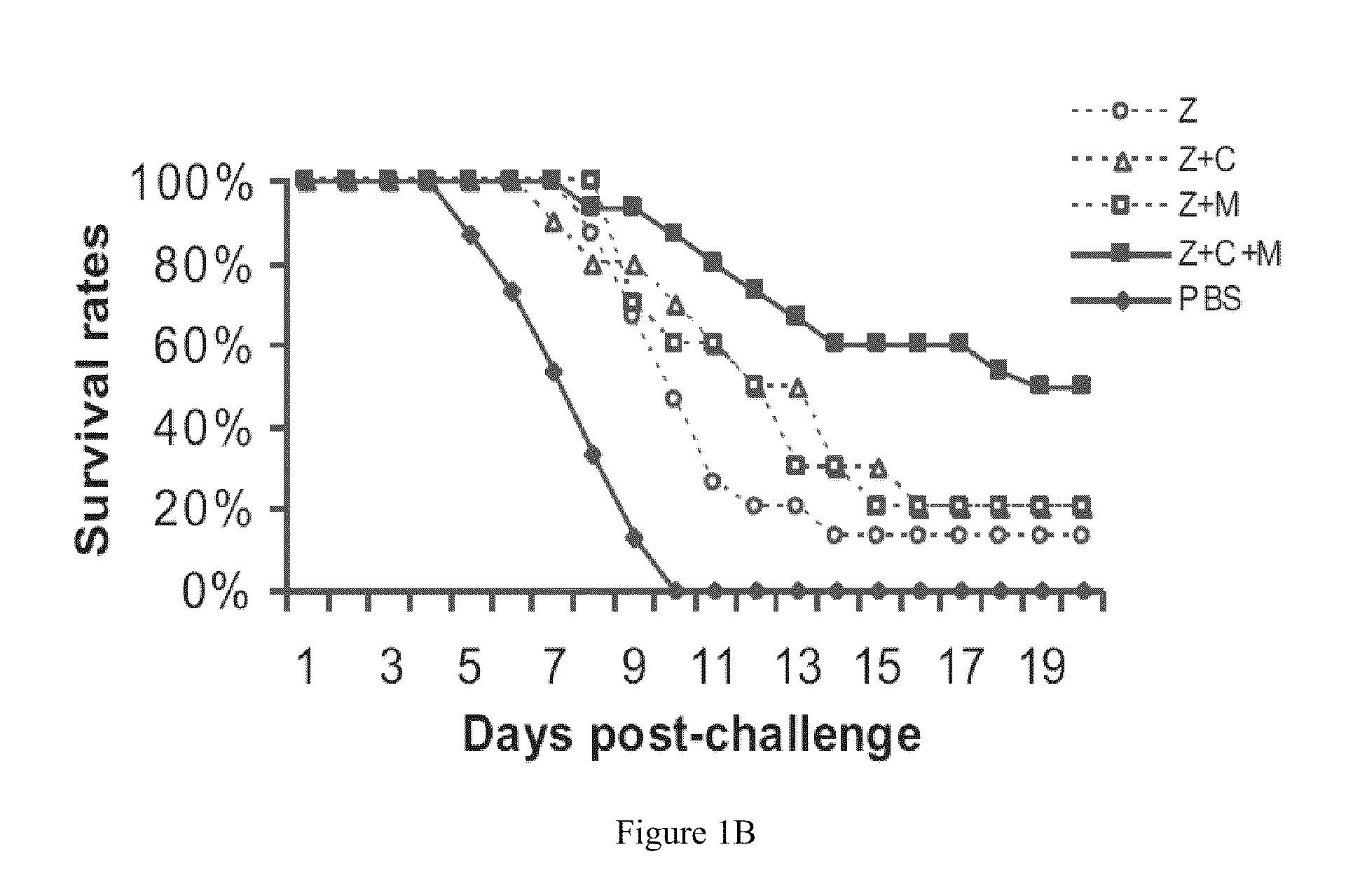
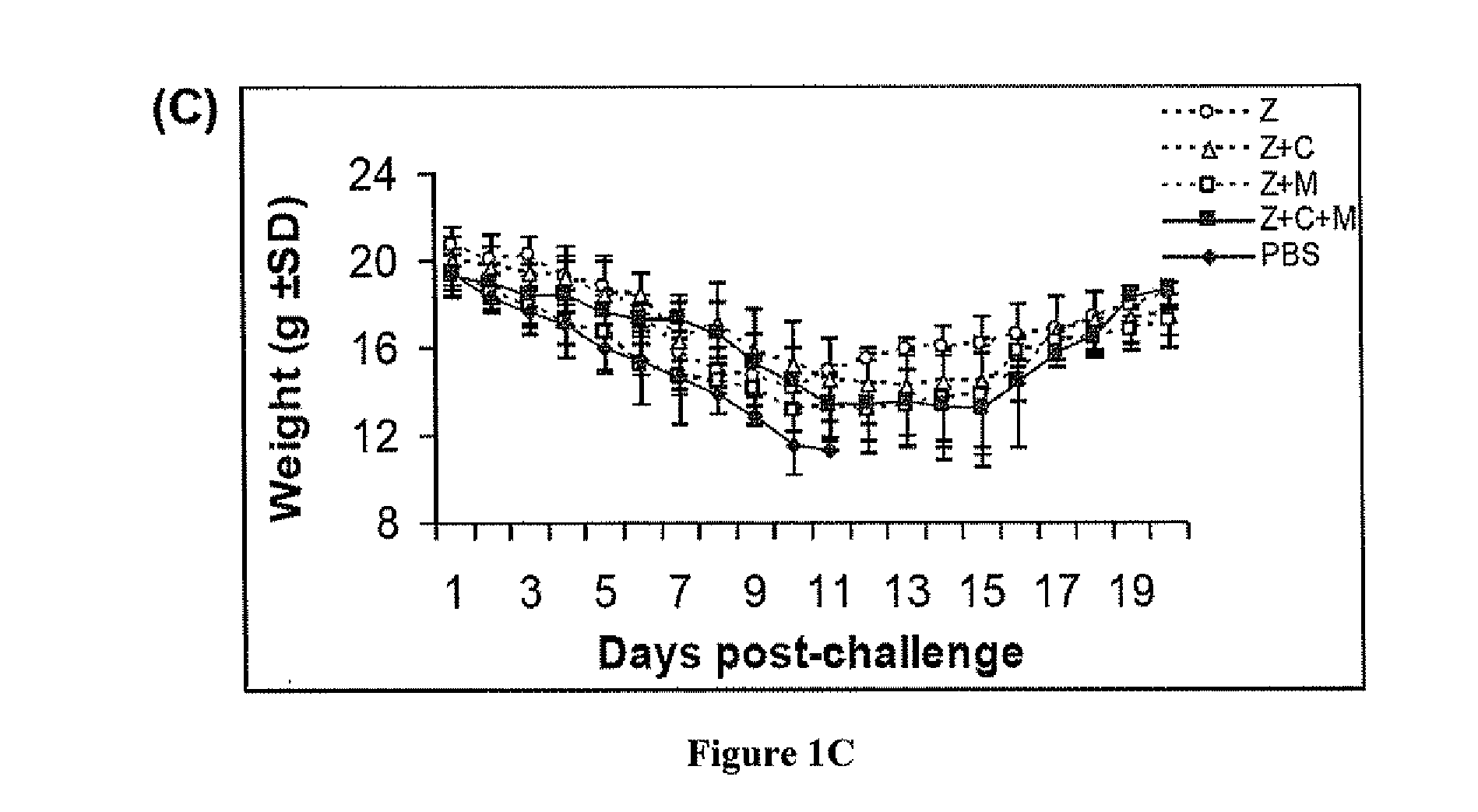
Compositions and methods for treating one or more symptoms of influenza, preferably influenza due to infection with influenza A (H5N1) are provided. It has been discovered that administration of a combination of a neuraminidase inhibitor with two immunomodulators increases survivability in subjects 24, 48, or even 72 hours post infection compared to administration of the neuraminidase inhibitor alone. A preferred neuraminidase inhibitor is zanamivir. Preferred immunomodulators include, but are not limited to celecoxib and mesalazine. Another embodiment provides a method for treating influenza, preferably, influenza due to infection with avian influenza A (H5N1) by administering to subject infected with the influenza virus, an effective amount of a neuraminidase inhibitor to inhibit or reduce budding of the influenza virus from infected cells of the subject, and an effective amount of at least two immunomodulators effective to reduce or inhibit one or more symptoms of inflammation in the subject.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP +1
Treatment of cerebral amyloid angiopathy
InactiveUS8003097B2Reduces and inhibits development of vascularMinimizes microhemorrhageNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAmyloid angiopathyAntibody
The invention provides improved agents and methods for treatment of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and methods to effect prophylaxis of CAA. The methods can treat CAA concurrently with Alzheimer's disease or separately. The methods can effect prophylaxis of CAA concurrently with Alzheimer's disease or separately. The methods involve administering antibody that is specific for the N-terminus of Aβ or an agent that can induce such an antibody.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC +1
Biodegradable, polymer coverings for breast implants
ActiveUS8911765B2Inhibit and reduce formation of scar tissueInhibiting and reducingAntibacterial agentsBiocideBreast implantBreast augmentation
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Redox flow battery and method for operating the battery continuously in a long period of time
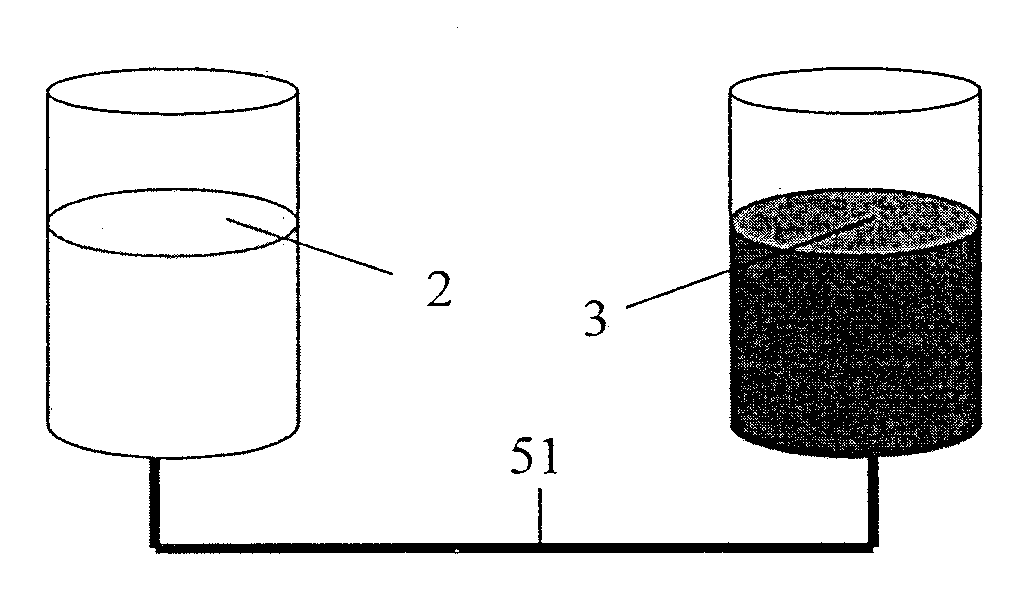
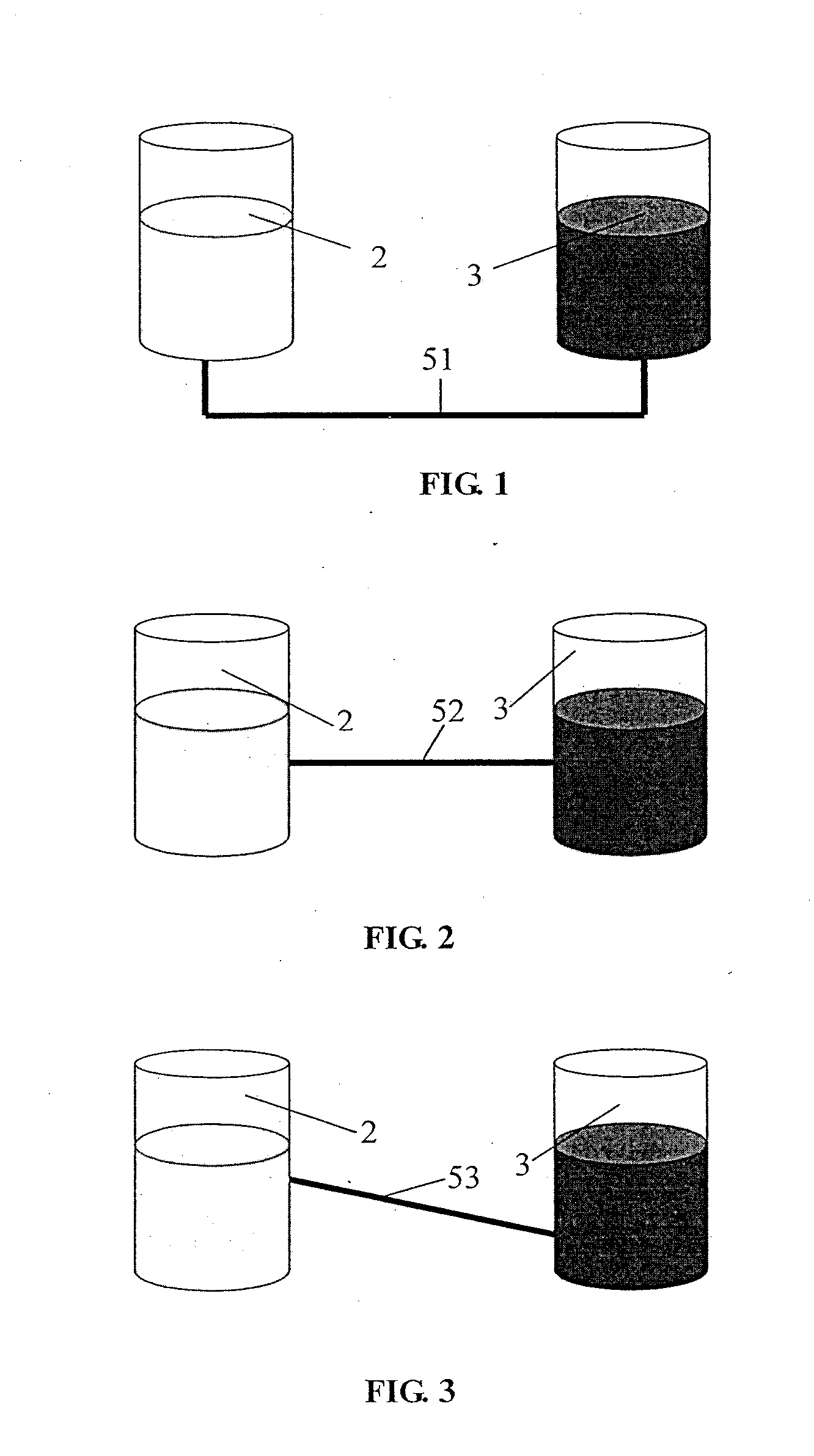
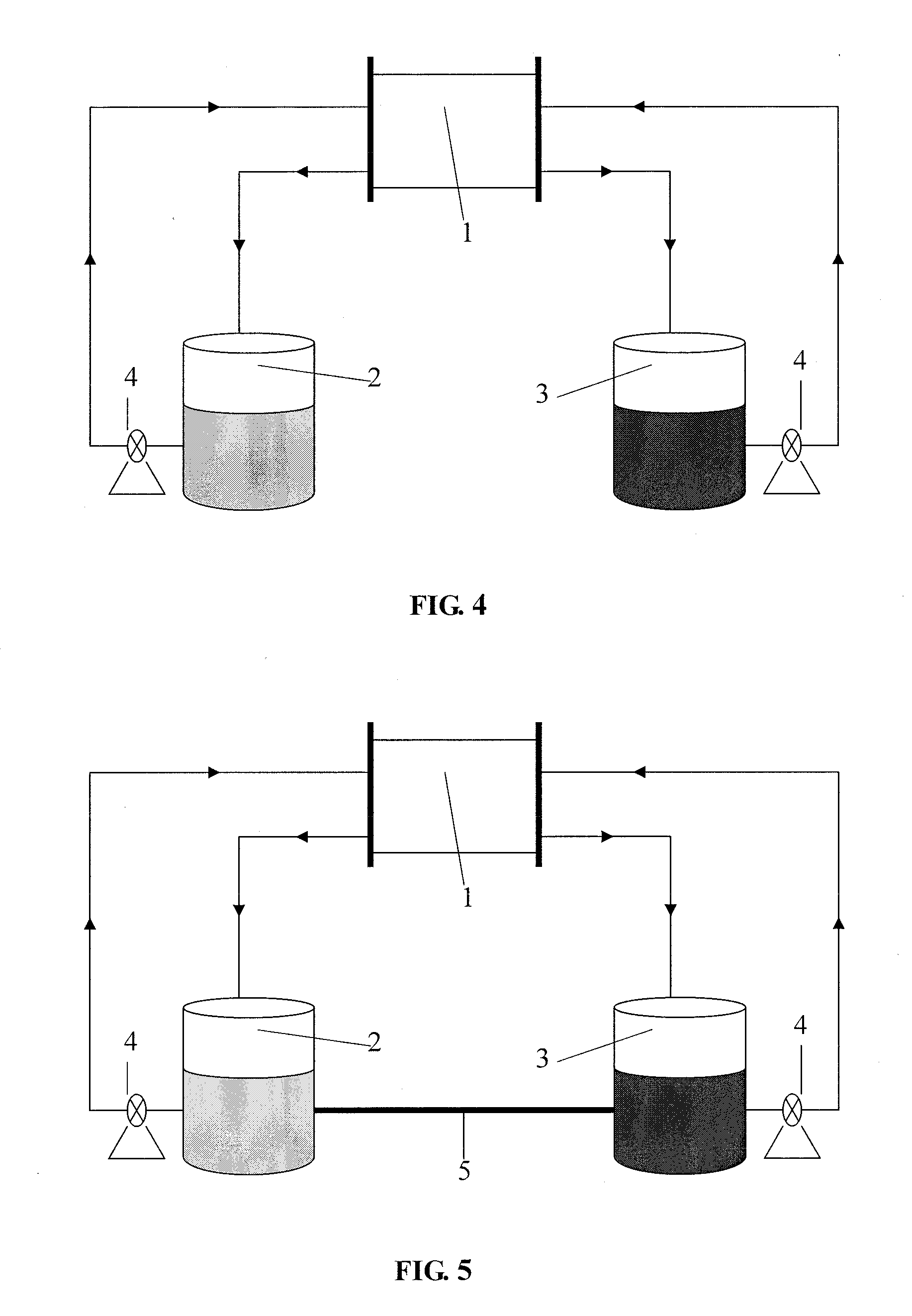
ActiveUS20110300417A1Inhibition of capacity fadingReduce frequencyReactant parameters controlElectrolyte stream managementElectrical batteryDiameter ratio
The present invention provides a redox flow battery comprising a positive electrolyte storage tank and a negative electrolyte storage tank, wherein the positive electrolyte storage tank and the negative electrolyte storage tank is kept to be in liquid communication through a pipe, wherein the length-to-diameter ratio of the pipe for the liquid communication is not less than about 10. The present invention also provides a method for operating the redox flow battery continuously in a long period of time.
Owner:BEIJING PRUDENT CENTURY TECH CO LTD
Glucagon analogues
ActiveUS9180169B2Avoid weight gainGood for weight lossPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderProviding materialObesity
The invention provides materials and methods for the treatment of obesity and excess weight, diabetes, and other associated metabolic disorders. In particular, the invention provides novel glucagon analog peptides effective in such methods. The peptides may mediate their effect by having increased selectivity for the GLP-1 receptor as compared to human glucagon.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Breast implant implantation method and apparatus
InactiveUS8409279B2Inhibiting and reducingInhibit migrationMammary implantsDiagnosticsBreast implantBiodegradable bag
A method for implanting a breast implant into a subject, the method includes: providing a sterile, flexible, elastic biodegradable bag sized to contain the breast implant; providing a sterile breast implant; inserting, using sterile handling, the sterile breast implant into the sterile bag to form a sterile breast implant assembly; closing the bag to fully enclose the implant within the bag; and implanting in a sterile manner the sterile breast implant assembly into the subject. A sterile bag, which may be provided in a kit, preferably for use with the method includes first and second chambers connected by a channel for moving a breast implant from the first chamber through the channel to the second chamber without directly touching the implant. An incision dilator may also be included with the kit or separately provided for use in a preferred embodiment of the method.
Owner:BREAST SHIELD MATERIALS
Influenza virus vaccines and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140328875A1Highly potent and broadly neutralizing antibodiesStimulate immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaHemagglutininInfluenza virus vaccine
Provided herein are chimeric influenza hemagglutinin (HA) polypeptides, compositions comprising the same, vaccines comprising the same, and methods of their use.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Lytic domain fusion constructs and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS20090269341A1Reducing and inhibiting and growthReducing and inhibiting proliferationNervous disorderFollicle-stimulating hormoneAbnormal tissue growthAberrant cell
The invention relates to fusion constructs, methods of using fusion constructs and methods of treating undesirable or aberrant cell proliferation or hyperproliferative disorders, such as tumors, cancers, neoplasia and malignancies.
Owner:A28 THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Listeria-induced immunorecruitment and activation, and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070190029A1Improve survivalInhibiting and reducingAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellReagent
Provided are reagents and methods for administering an attenuated bacterium for use in treating a cancerous or infectious condition. Reagents and methods for administering an attenuated bacterium for use in inducing an immune response against a tumor, cancer cell, or infective agent are further provided. Also provided are methods of diagnosis and kits.
Owner:ANZA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Methods for detecting and inhibiting angiogenesis
InactiveUS7056506B2Reducing and inhibiting angiogenesisReduce severityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsΑ5β1 integrinAngiogenesis growth factor
The present invention provides methods for reducing or inhibiting angiogenesis in a tissue, by contacting α5β1 integrin in the tissue with an agent that interferes with specific binding of the α5β1 integrin to a ligand expressed in the tissue; and methods of identifying angiogenesis in a tissue, by contacting the tissue with an agent that specifically binds α5β1 integrin, and detecting specific binding of the agent to α5β1 integrin associated with a blood vessel in the tissue. Also provided are methods of diagnosing a pathological condition characterized by angiogenesis in a tissue in an individual. The invention further provides methods of reducing or inhibiting angiogenesis in a tissue in an individual, by administering to the individual an agent that interferes with the specific binding of α5β1 integrin to a ligand expressed in the tissue; and methods of reducing the severity of a pathological condition associated with angiogenesis in an individual, by administering to the individual an agent that interferes with specific binding of α5β1 integrin to a ligand in a tissue associated with the pathological condition. The invention also provides methods of identifying an agent that reduces or inhibits angiogenesis associated with α5β1 integrin expression in a tissue by contacting a tissue exhibiting angiogenesis associated with α5β1 integrin expression with an agent, and detecting a reduction or inhibition of angiogenesis in the tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Influenza virus vaccines and uses thereof
ActiveUS9051359B2Elimination of glycosylationReduce severitySsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHemagglutininInfluenza virus vaccine
Provided herein are influenza hemagglutinin stem domain polypeptides, compositions comprising the same, vaccines comprising the same and methods of their use.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Monoclonal antibodies against influenza virus generated by cyclical administration and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140170163A1Reduce in quantityLower titerSsRNA viruses negative-senseAnimal cellsMonoclonal antibodyVirus diseases
Provided herein are methods of producing neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, by cyclical immunization, that cross-react with strains of Influenza virus of the same subtype or different subtypes. Also provided herein are compositions comprising such antibodies and methods of using such antibodies to diagnose, prevent or treat Influenza virus disease.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com