Patents
Literature
31 results about "Cerebral amyloid angiopathy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
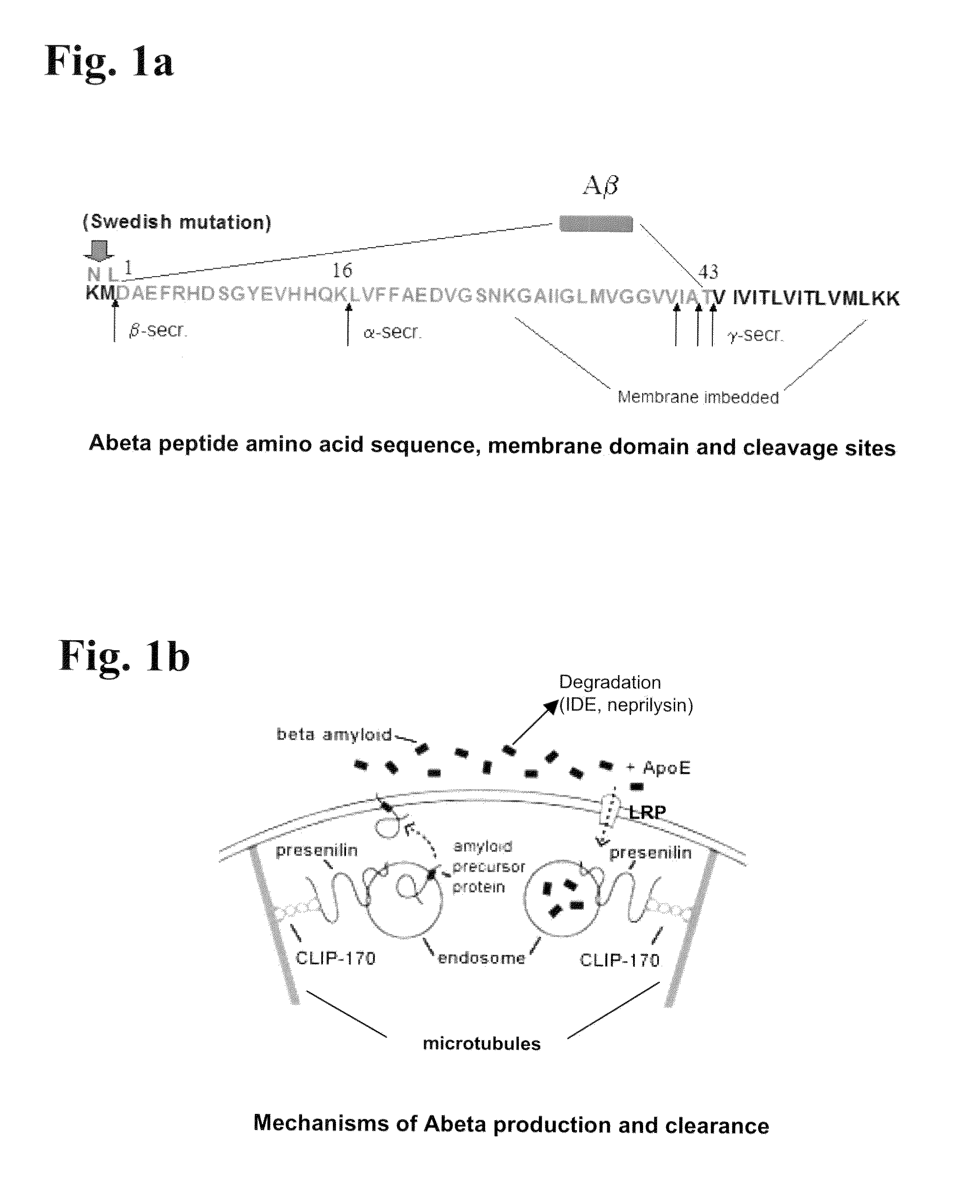
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), is a form of angiopathy in which amyloid beta peptide deposits in the walls of small to medium blood vessels of the central nervous system and meninges. The term congophilic is used because the presence of the abnormal aggregations of amyloid can be demonstrated by microscopic examination of brain tissue after application of a special stain called Congo red. The amyloid material is only found in the brain and as such the disease is not related to other forms of amyloidosis.
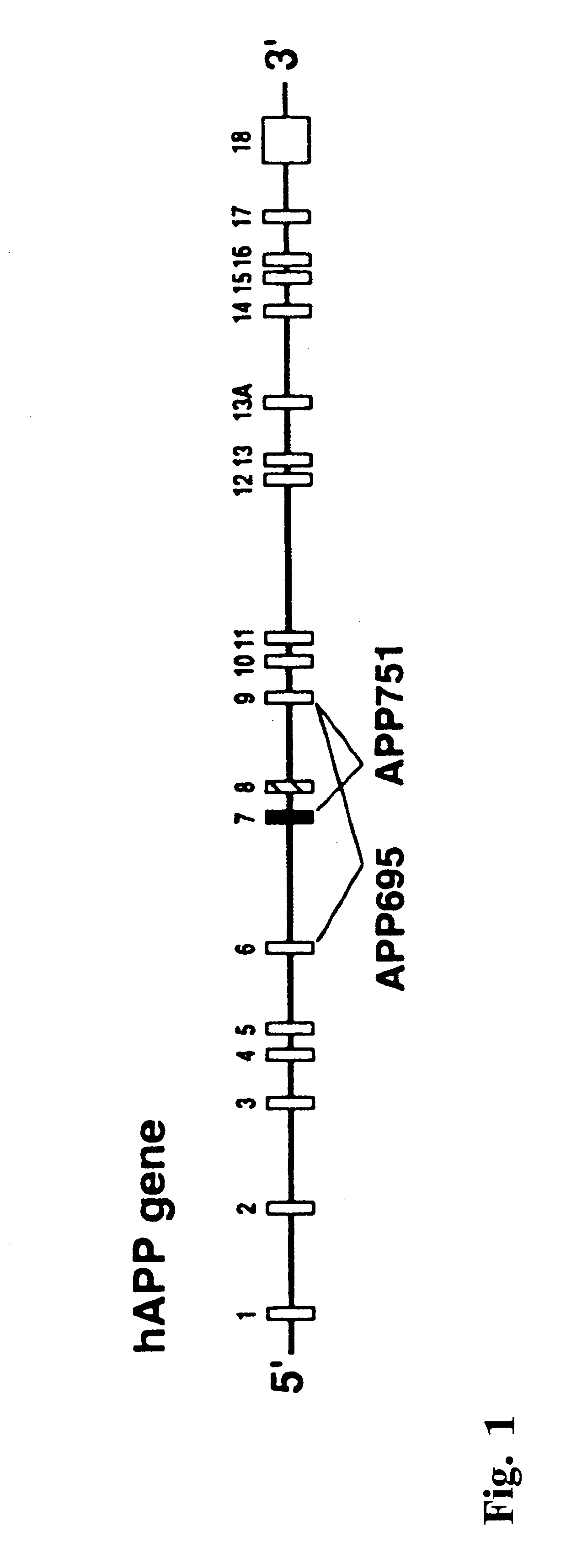
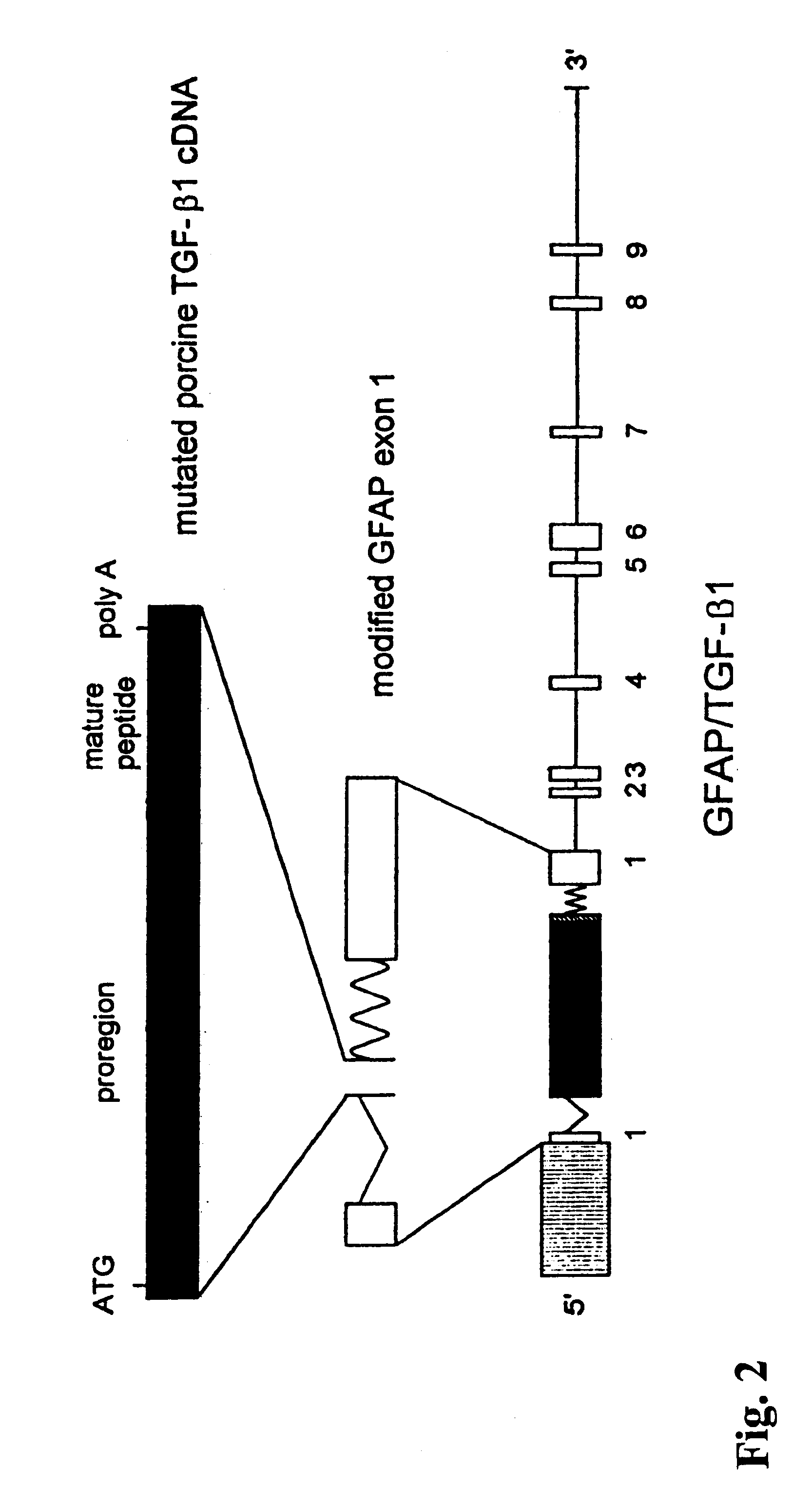
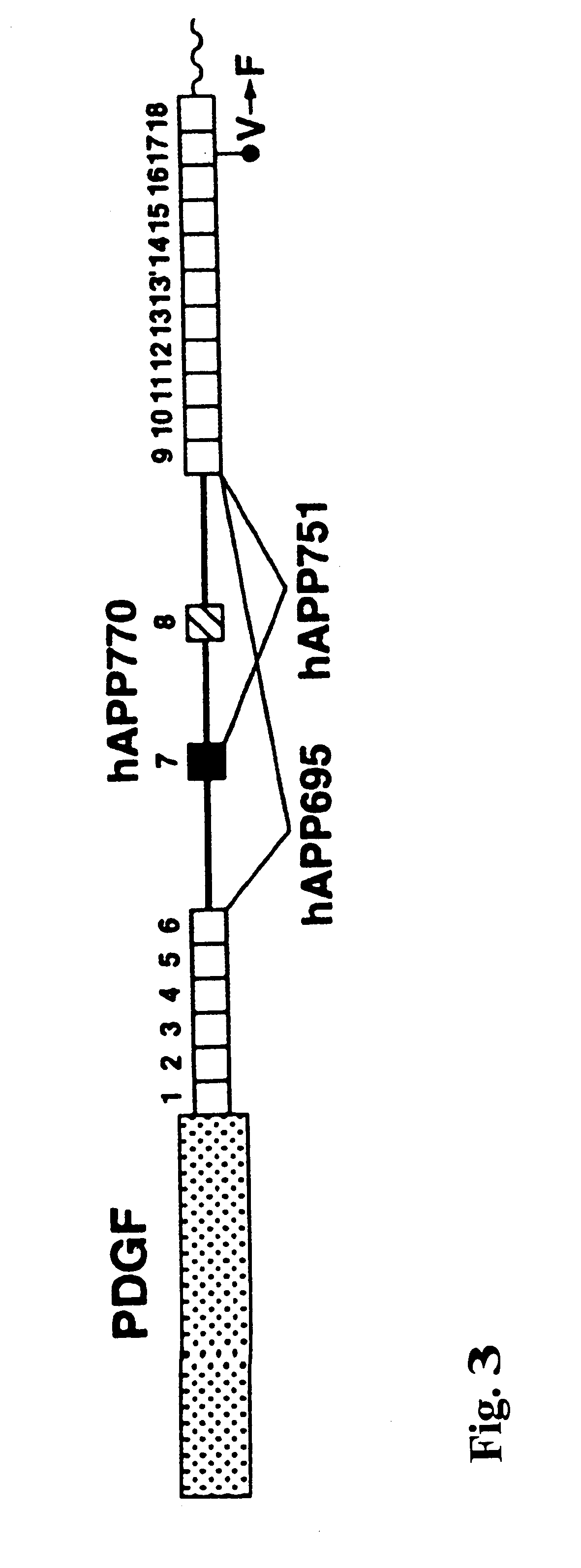
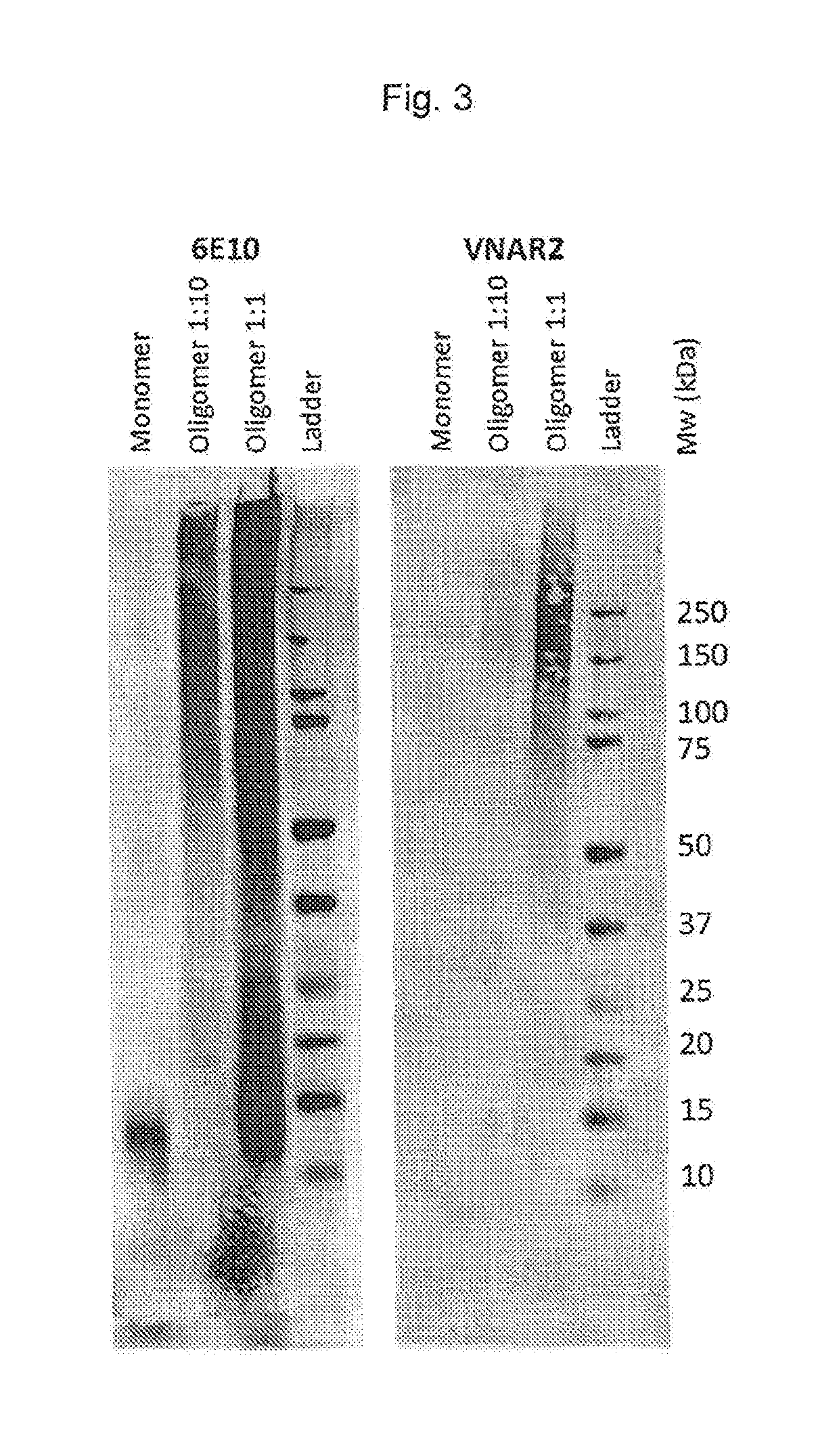
Transgenic mouse model of alzheimer's disease and cerebral amyloid angiopathy
InactiveUS6175057B1Lower Level RequirementsConvenient treatmentVectorsIn-vivo testing preparationsOrganismTgf beta1
The present invention features non-human transgenic animal models for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and CAA, wherein the transgenic animal is characterized by 1) overexpression of bioactive transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) or 2) both overexpression of bioactive TGF-beta1 and expression of a human amyloid beta precursor protein (APP) gene product. The transgenic animals may be either homozygous or heterozygous for these alterations. Bigenic animals are further characterized by development of AD-associated and / or CAA-associated pathology within about two to three months of age.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and methods for inhibiting and/or modulating effector t-cells involved in inflammatory neurodegenerative disease
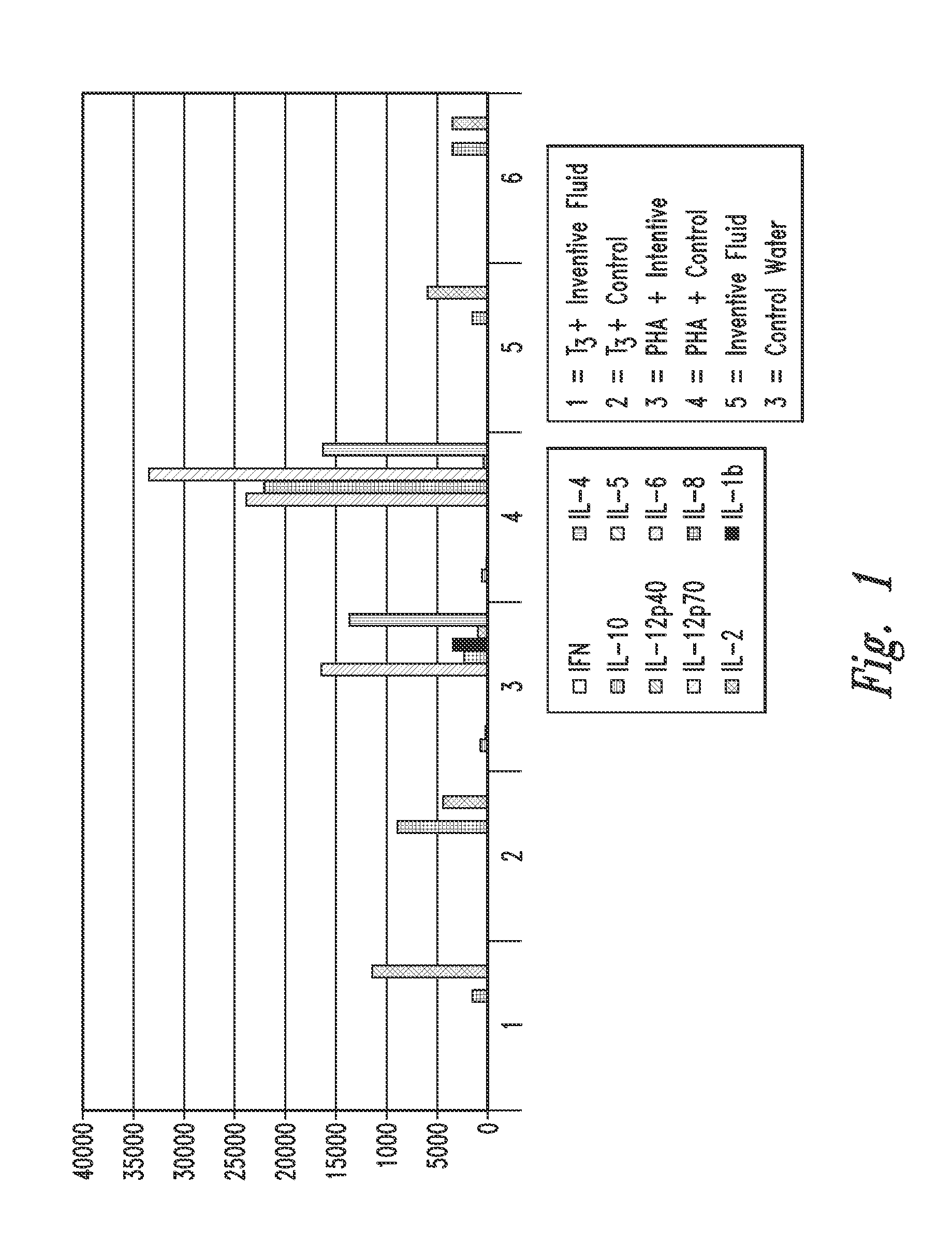
Provided are methods for treating inflammatory neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, stroke / cerebral ischemia, head trauma, spinal cord injury, Huntington's disease, migraine, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, inflammatory neurodegenerative condition associated with AIDS, age-related cognitive decline; mild cognitive impairment and prion diseases in a mammal), or at least one symptom thereof in a subject by administering a therapeutic composition comprising at least one electrokinetically-altered fluids (e.g., electrokinetically-generated oxygen-enriched fluids) of the present invention. Particular aspects provide methods for inhibiting and / or modulating the function and / or activity of effector T-cells, and / or for cell-based tolerogenic therapy (e.g., by modulating development and / or function and / or activity of TREG cells and / or dendritic cells (DCs) and / or TH17 cells (e.g., RORγt+ TH17 cells). In certain aspects such methods comprise ex vivo exposure of T-cells and / or APC (e.g., dendridic cells) to at least one electrokinetically-altered fluid as disclosed herein. Combination therapies are additionally provided.
Owner:REVALESIO CORP
Compounds and methods for treating protein folding disorders
InactiveUS20100144821A1Reduce rateGood effectBiocideNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaCell Aggregations
The invention is directed to compounds and methods for treating protein folder disorders. In certain embodiments the invention provides compounds and methods for treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, tauopathy, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, Lewy body disease, dementia, Huntington's disease and prion-based spongiform encelopathy. The invention further provides compounds, methods and pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting tau protein, Aβ protein or α-synuclein protein aggregation.
Owner:TREVENTIS CORP
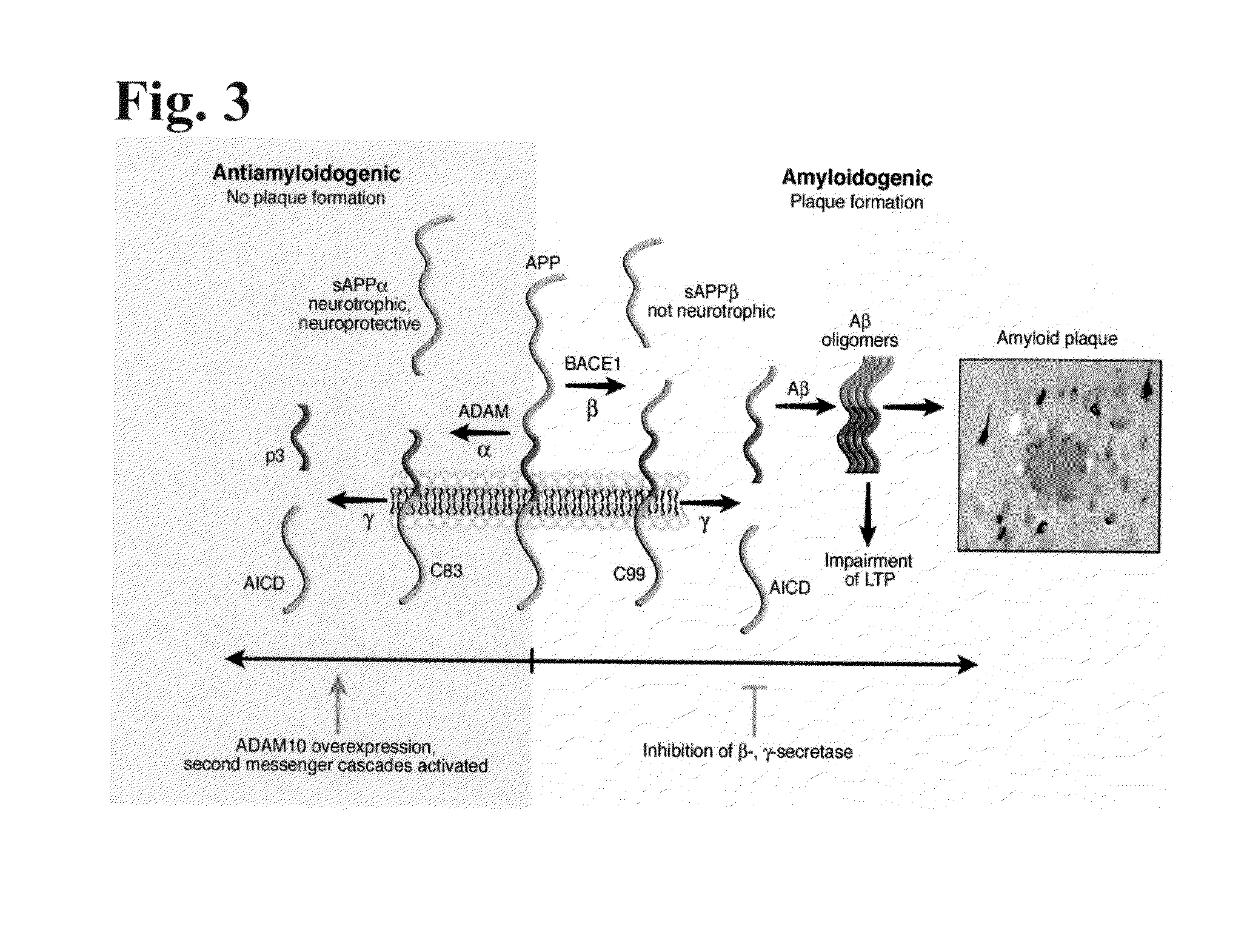
Selective inhibition of intracellular amyloid-beta neurotoxicity in human neurons
InactiveUS20040248766A1Reduce blockingAvoid accumulationCompound screeningNervous disorderParenchymaInclusion body myositis
While the extracellular accumulation of amyloid-beta in the brain parenchyma is a pathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease, its role as a cause or a consequence of AD is still debated. As described herein, intracellular Abeta1-42 is shown to be selectively toxic to neurons. The present invention provides methods of screening for compounds for the prevention and treatment of A amyloid associated diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Down's Syndrome, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, and inclusion body myositis.
Owner:LEBLANC ANDREA
2-aryl benzothiazole compound with high affinity with a(BETA) plaque and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103497217ALow initial brain uptakeNervous disorderIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCompetitive bindingBlood vessel
The invention provides a 2-aryl benzothiazole compound with high affinity with A(beta) plaque and a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the compound is shown by formula (I). In-vitro competitive binding experiments indicate that the kind of molecules have medium affinity with the A(beta) 1-42 aggregate; in-vitro autoradiography experiments indicate that the molecules marked by Tc-99m can be combined with the A(beta) plaque in blood vessels of the brain with specificity and high affinity; in-vivo bio-distribution experiments on a normal mice indicate that a developer partially marked by Tc-99m has the advantages of low initial brain extraction, fast blood removal and the like, and is expected to become a new single-photon A(beta) plaque developer for early-stage clinical diagnosis of CAA (cerebral amyloid angiopathy) or AD (Alzheimer's disease).
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
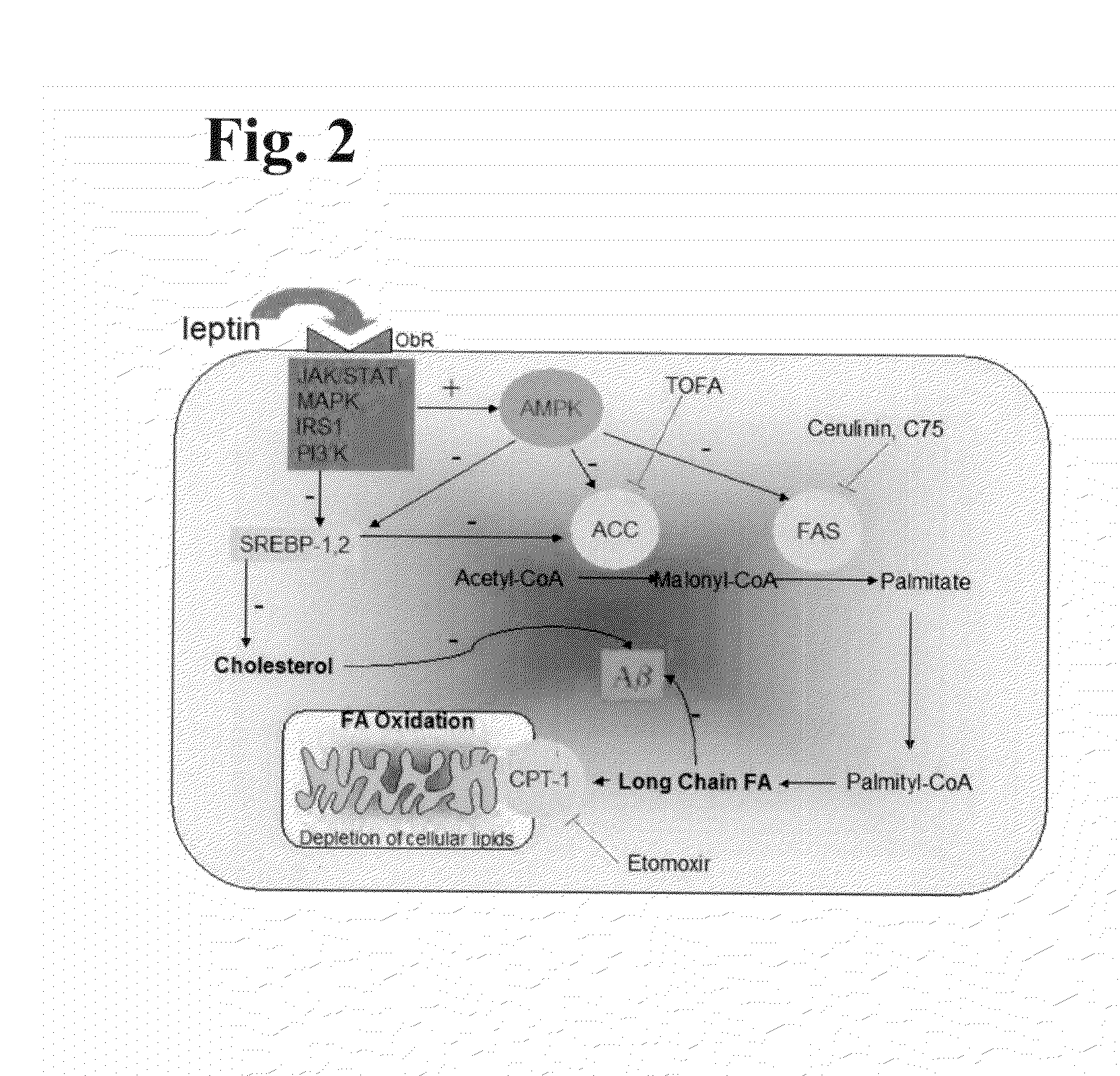
Fragments, Mutants and Chimeric Fusion Proteins of Leptin For Treating Alzheimer's Disease
InactiveUS20130183309A1Reduce productionIncrease elasticityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsPTK InhibitorsMutant
The described invention relates to methods for treating, preventing, or diagnosing the pathology of progressive cognitive disorders resulting from accumulation of an amyloid peptide, in particular, Alzheimer's disease, Down's syndrome and cerebral amyloid angiopathy, in mammalian subjects using a composition comprising therapeutically effective amount of a leptin, leptin mimic, leptin derivative, leptin agonist, or AMP-dependent protein kinase activator, alone, or in combination with, one or more lipolytic / antilipogenic compounds. It further relates to methods for improving cognitive function using a composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of leptin, a leptin mimic, a leptin derivative, an AMP-dependent protein kinase activator, a leptin agonist, a leptin blocker, a mimic of a leptin blocker, a leptin antagonist, an AMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:NEUROTEZ
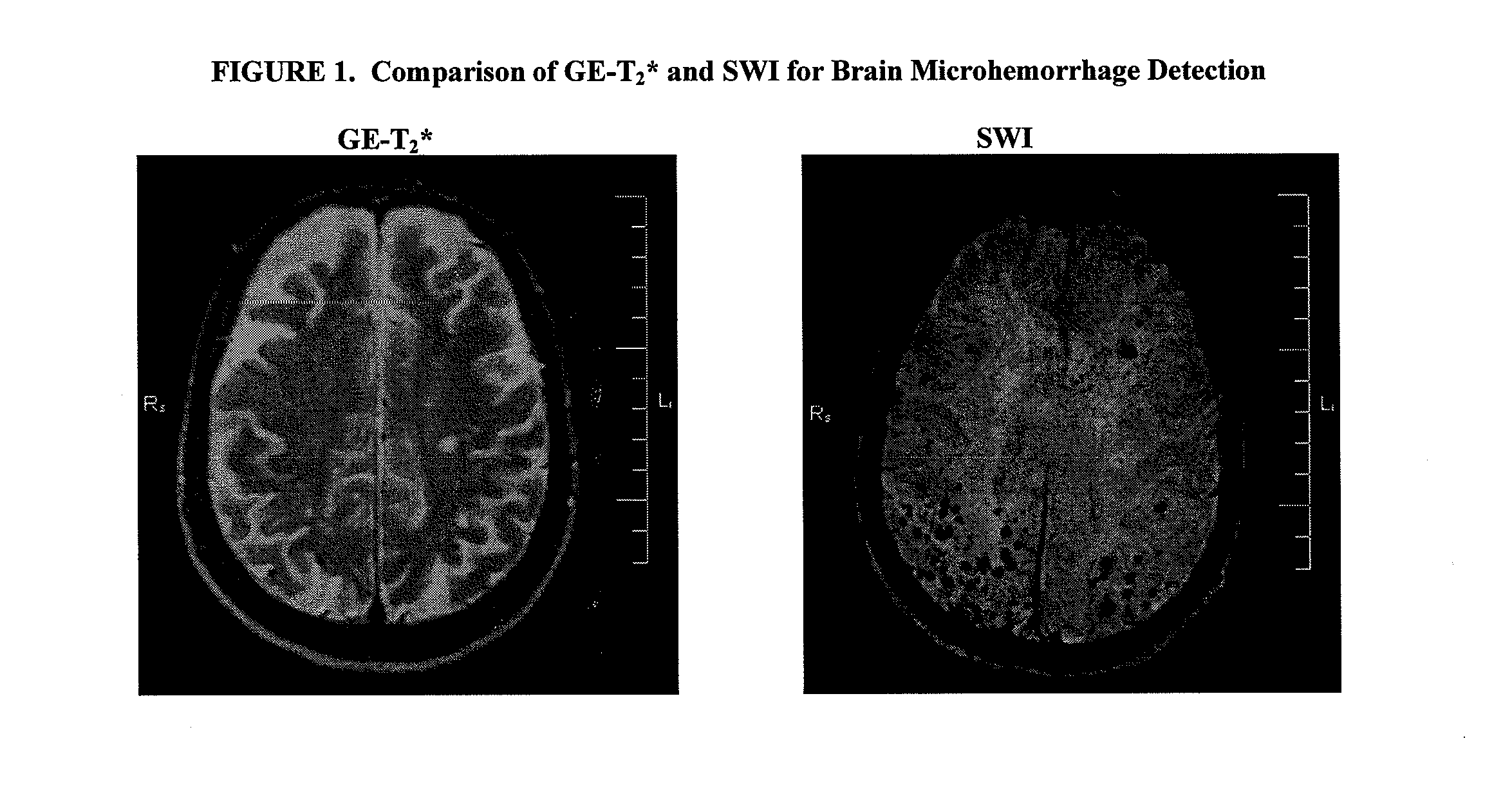
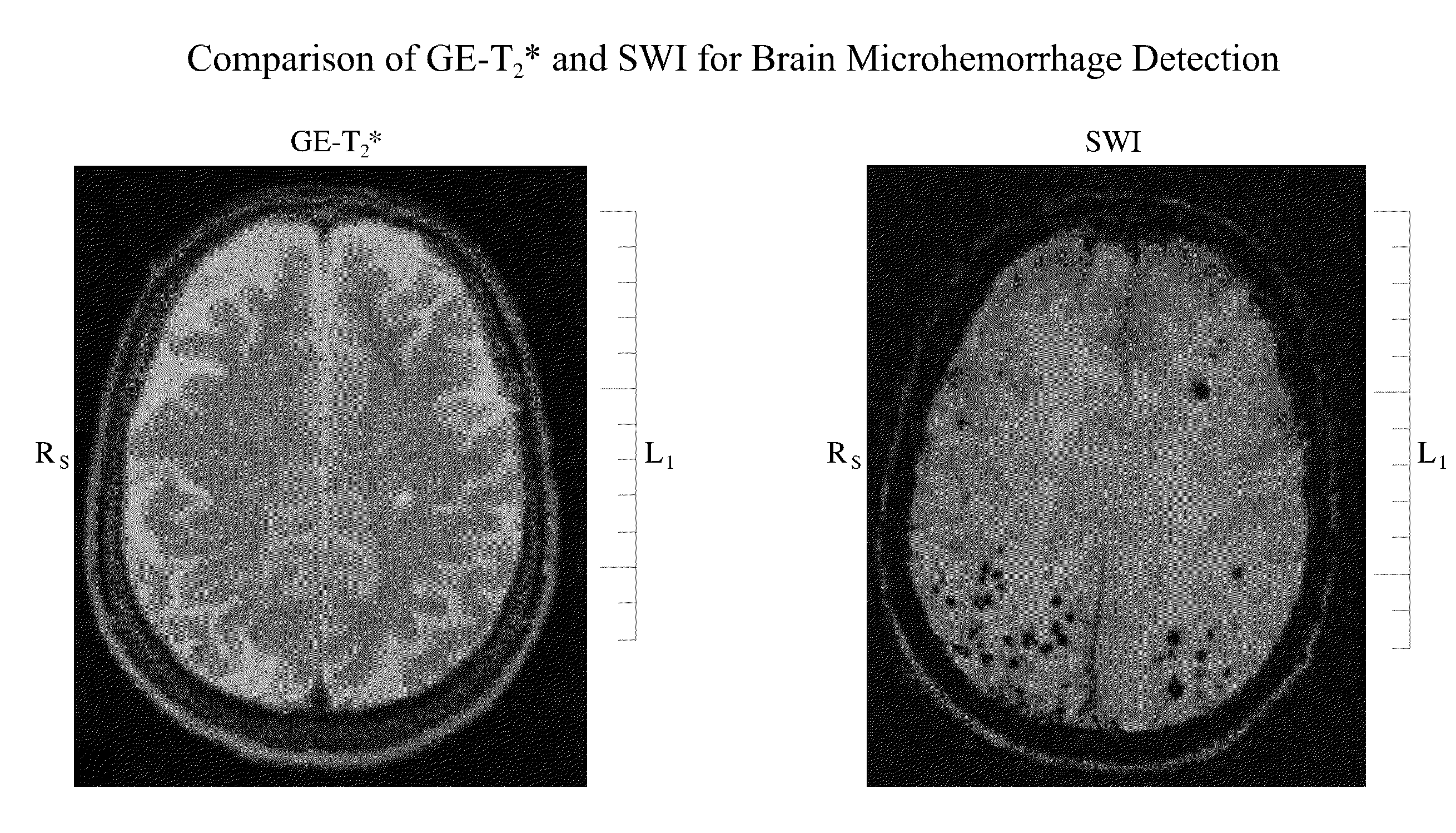
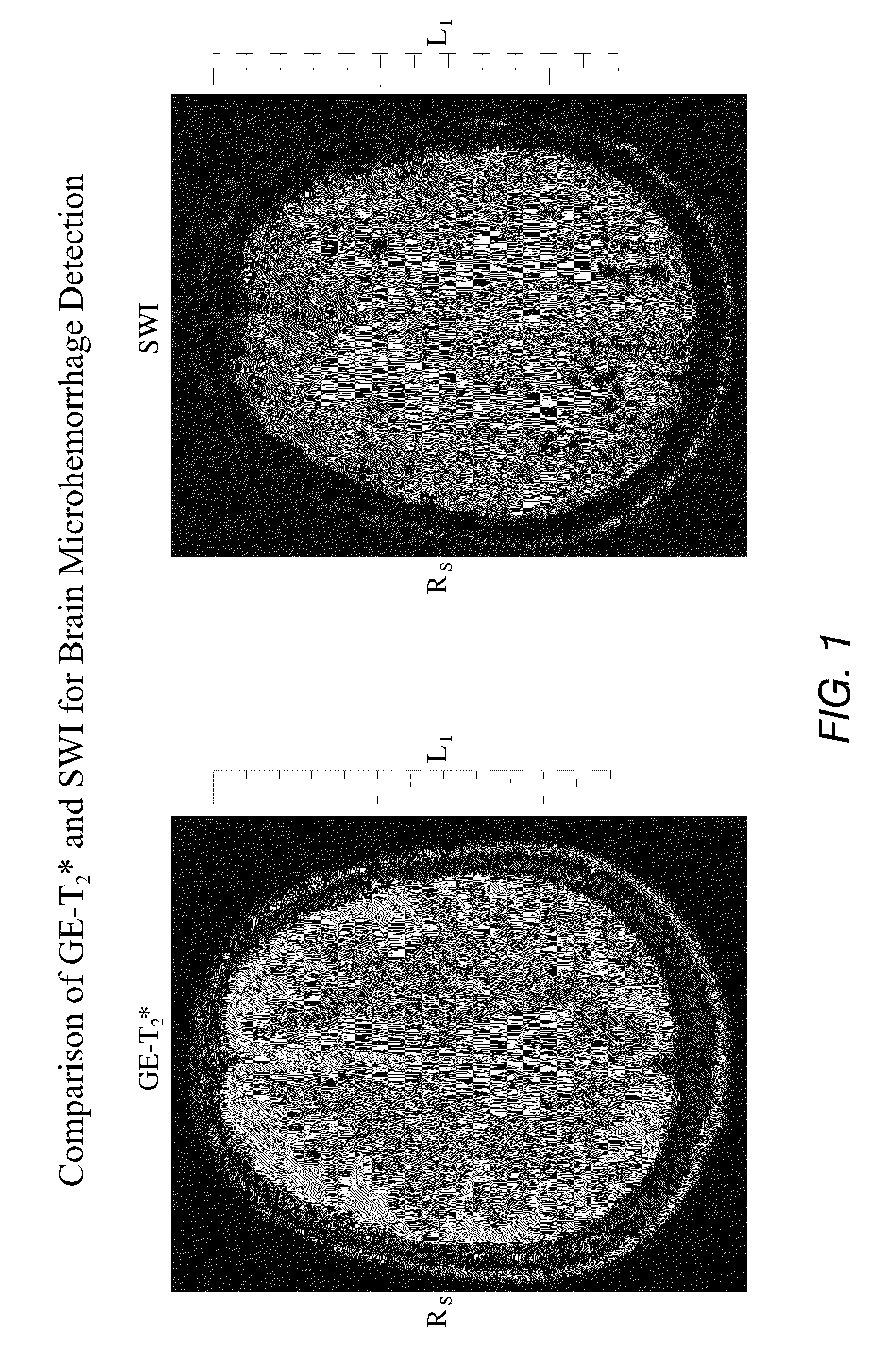
Inhibition of brain enzymes involved in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and macular degeneration
InactiveUS20090018094A1Avoid bleedingAvoid weakeningOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCaspase inhibitorsMammal
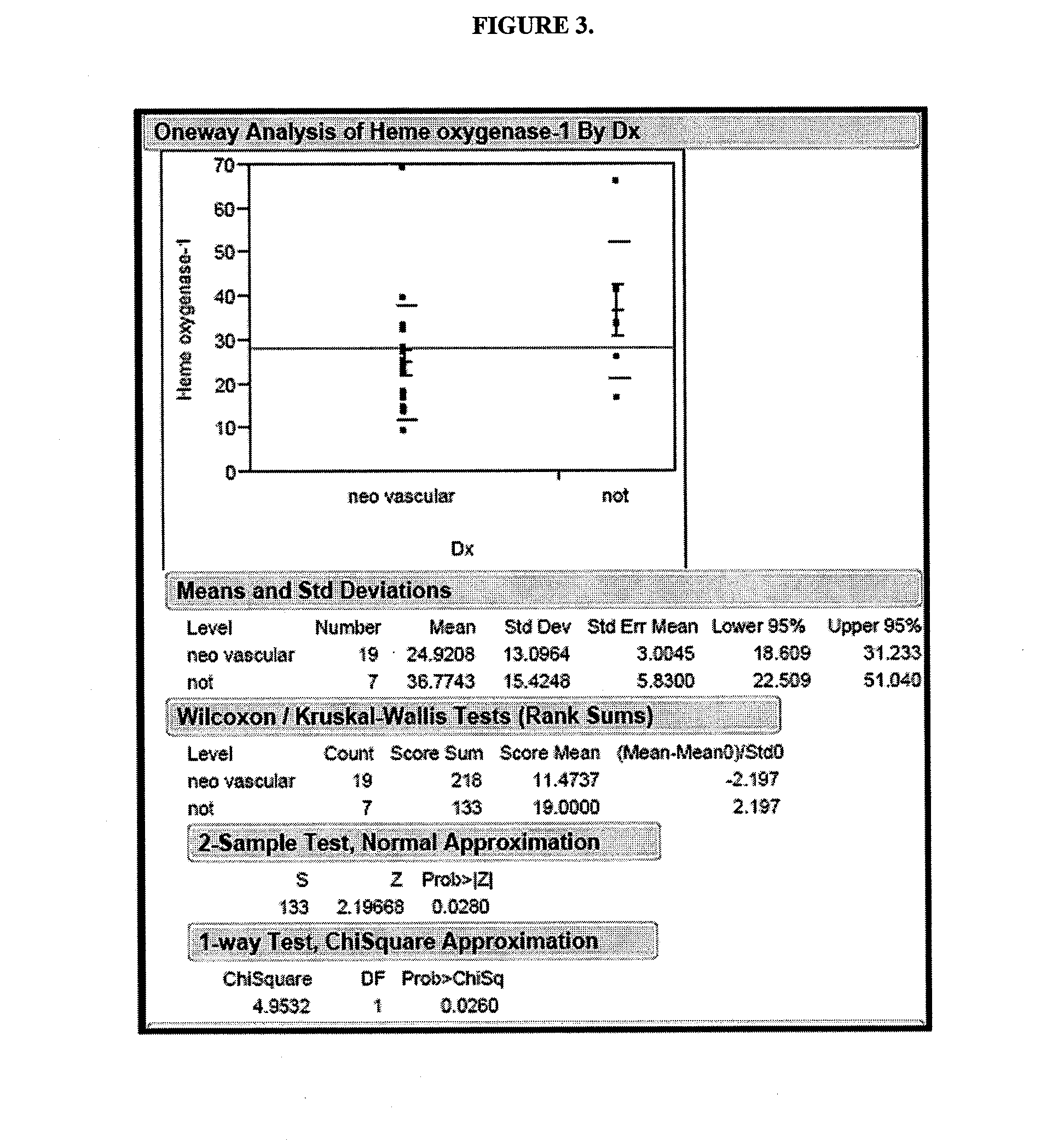
A method of treating or inhibiting progress of dementia and / or macular degeneration in a mammal involves administering compositions containing siRNA to heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) or heme oxygenase-2 (HO-2), a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor, a caspase inhibitor, or a metalloporphyrin in a manner that permits access to brain sites and / or the macula of the patient.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT +3
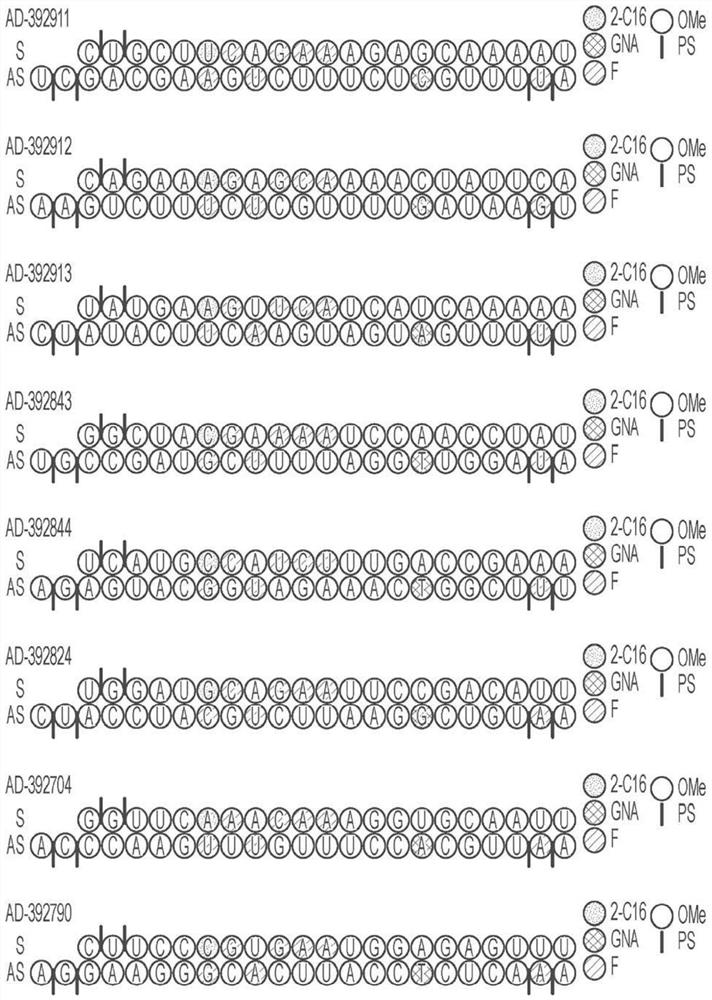
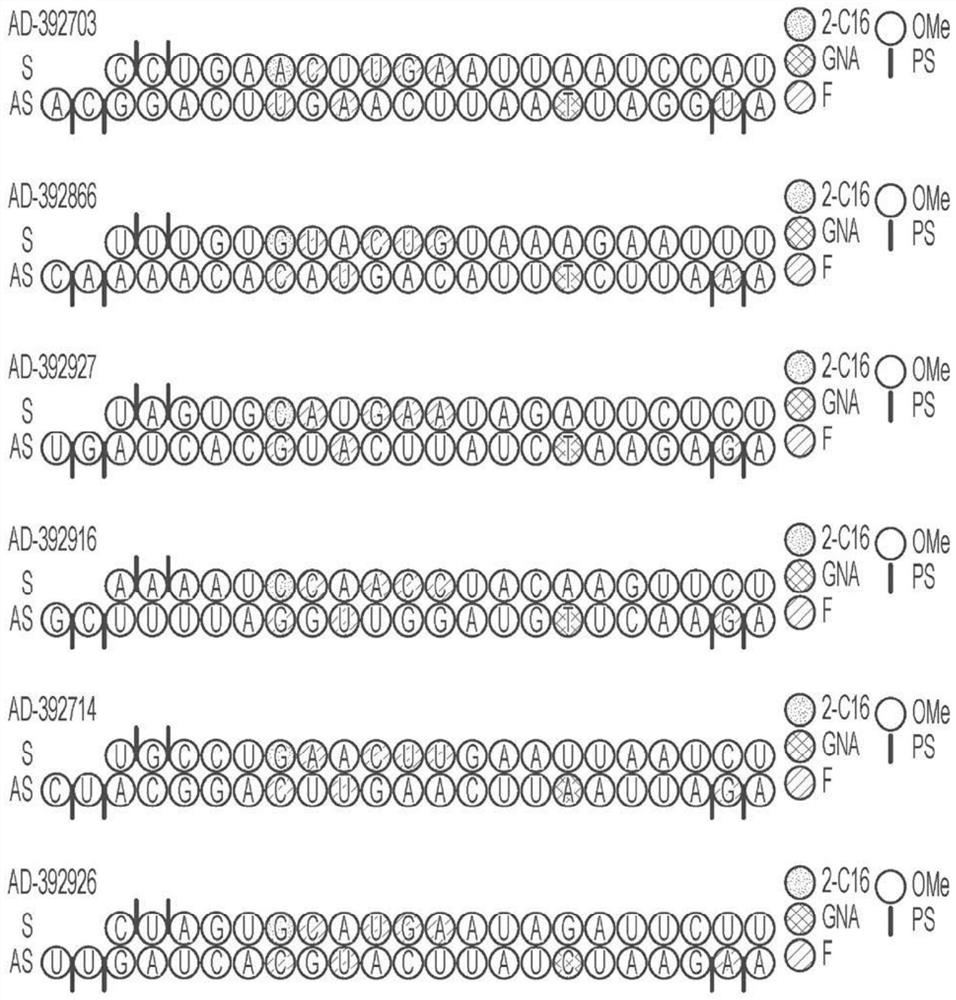
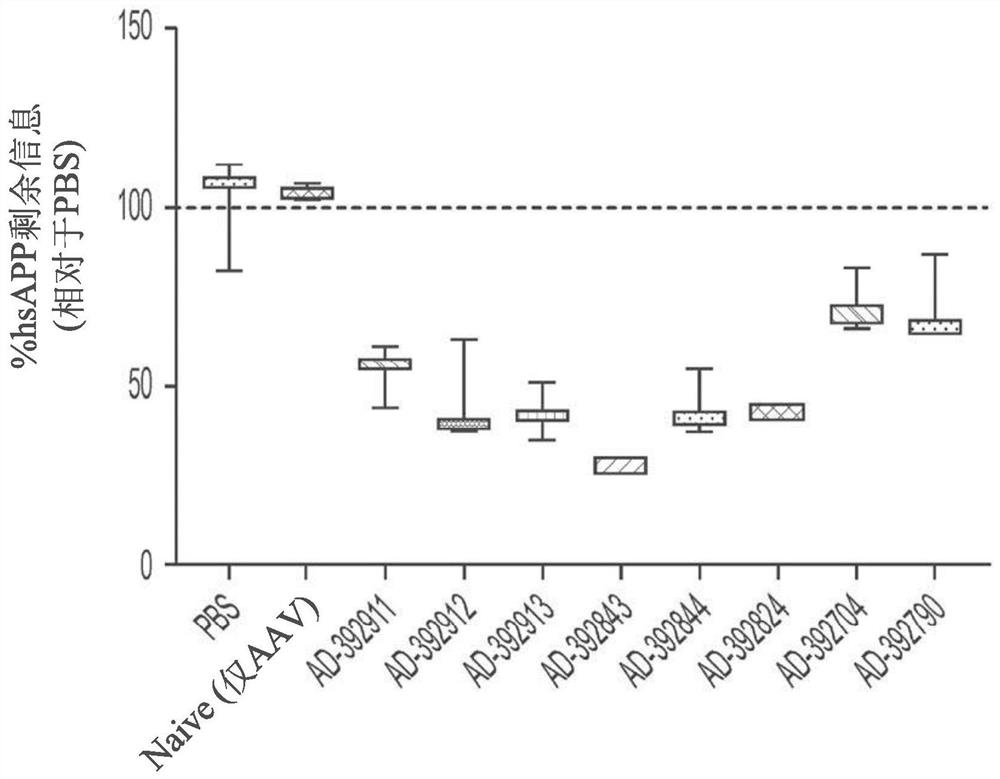
AMYLOID PRECURSOR PROTEIN (APP) RNAi AGENT COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF
ActiveUS20200339991A1Reduce expressionInhibit and reduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderRNA - Ribonucleic acidDouble strand
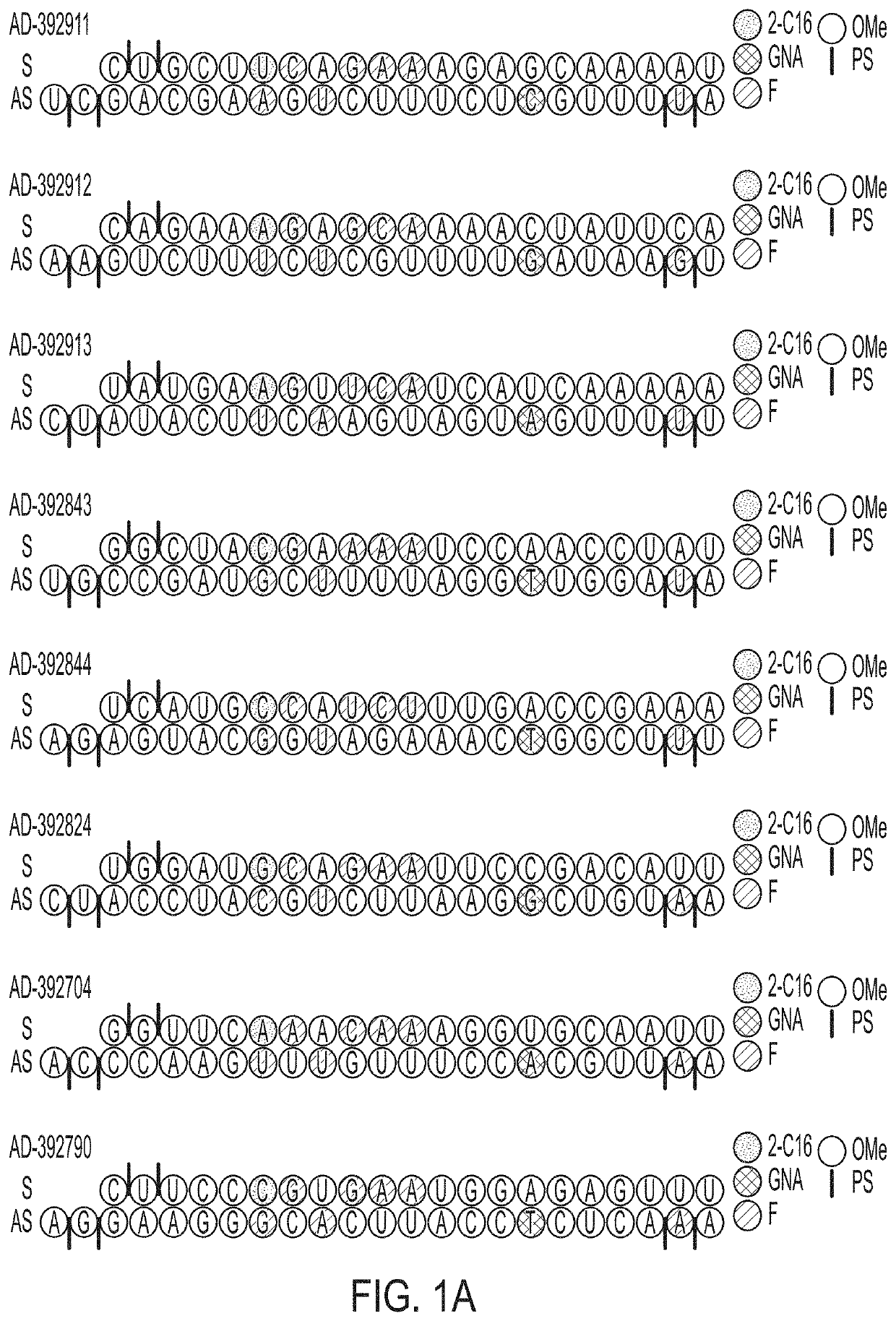
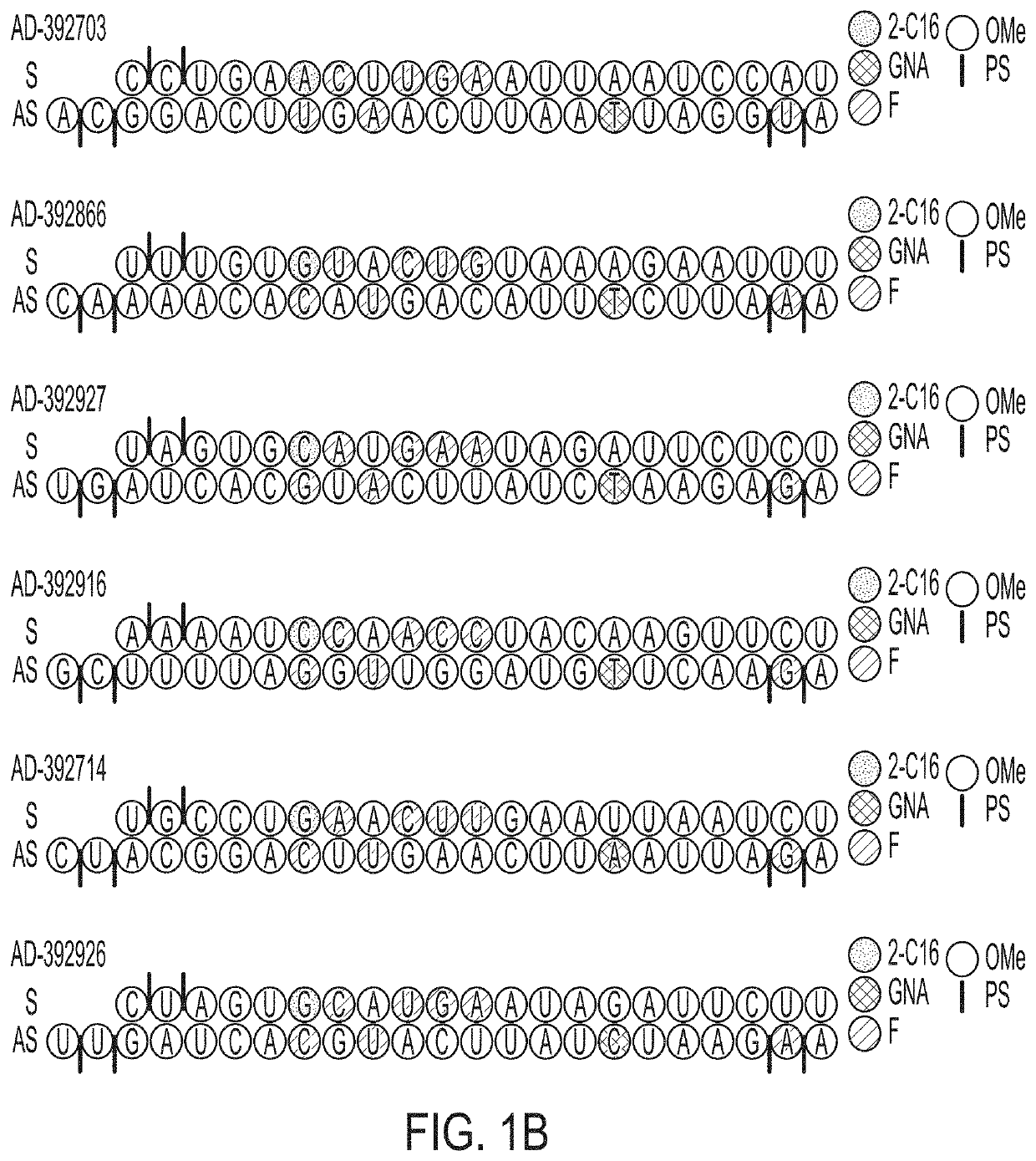
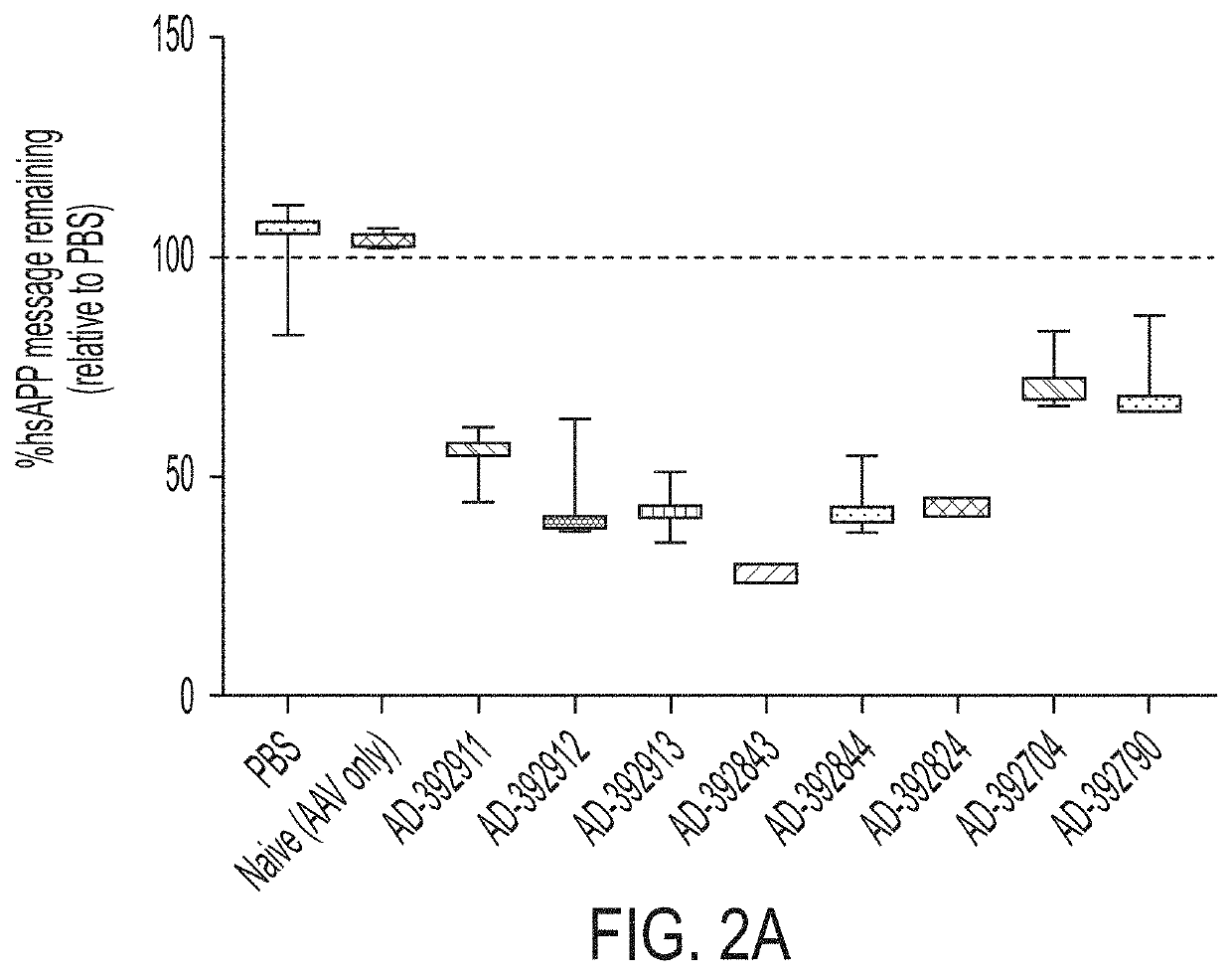
The disclosure relates to double stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNAi) agents and compositions targeting the APP gene, as well as methods of inhibiting expression of an APP gene and methods of treating subjects having an APP-associated disease or disorder, such as cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and early onset familial Alzheimer disease (EOFAD or eFAD), using such dsRNAi agents and compositions.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
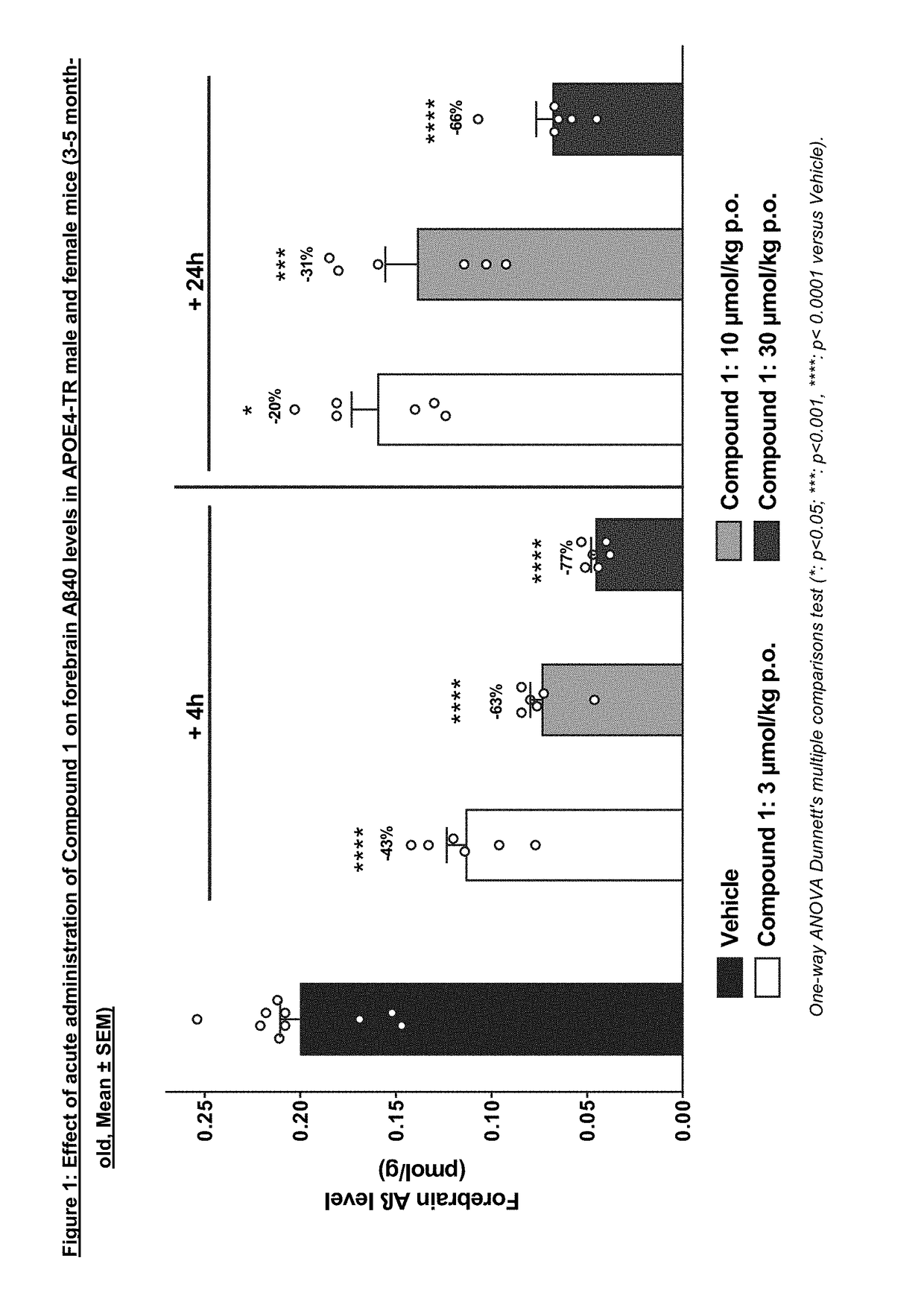
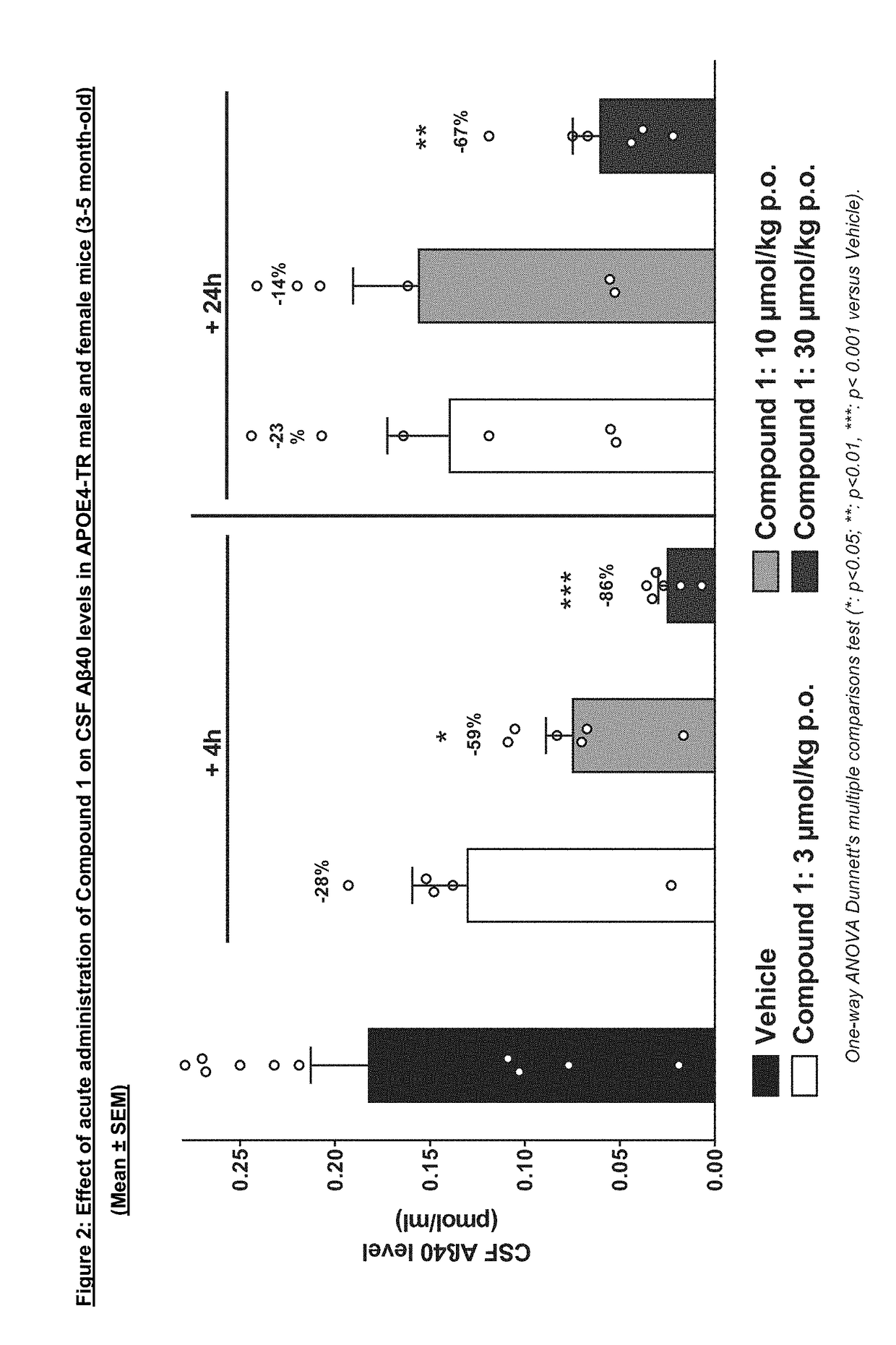
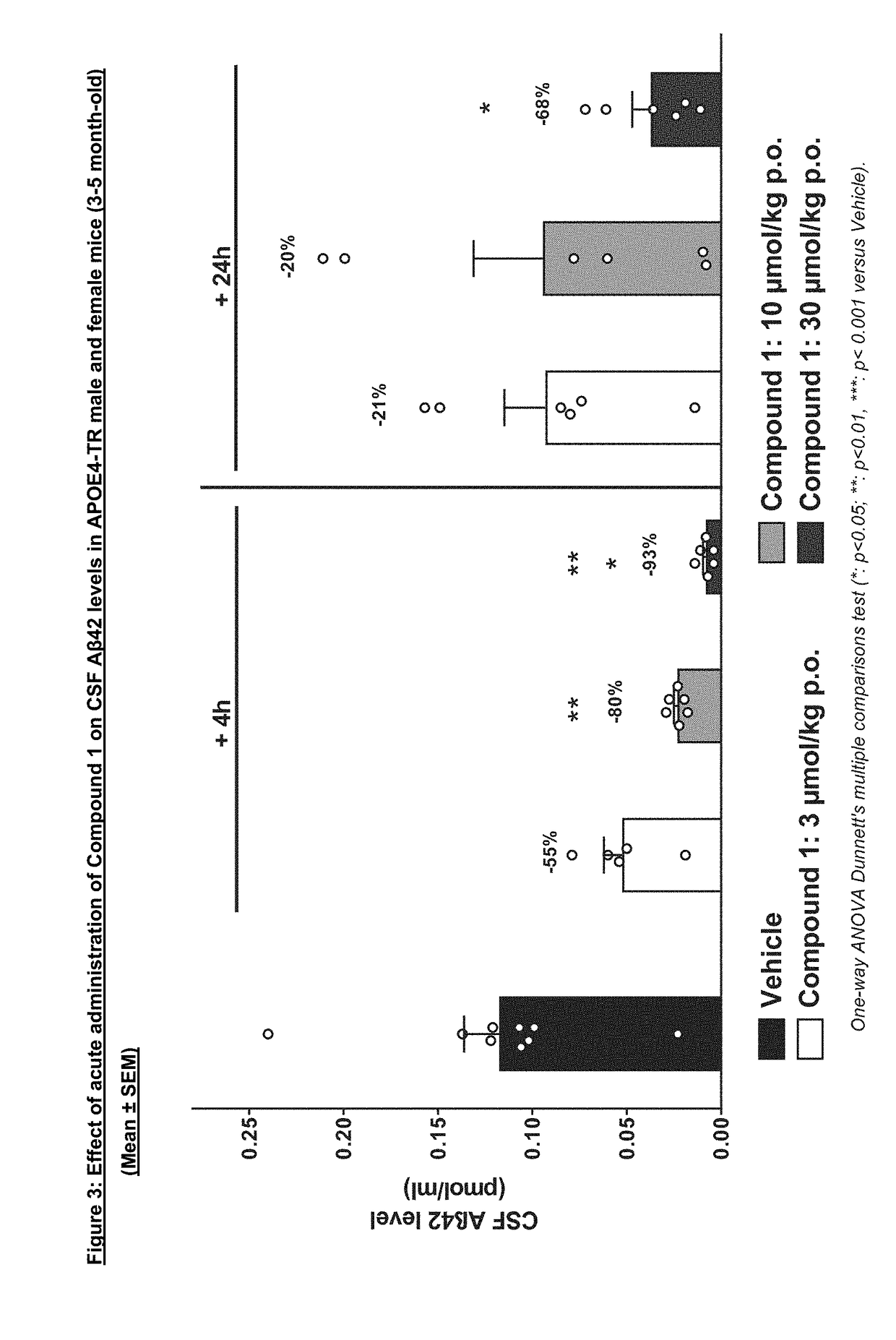
Oxazine derivative for use in the treatment or prevention of cerebral amyloid angiopathy
The present invention relates to an oxazine derivative BACE-1 inhibitor and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such oxazine derivative for use in the treatment or prevention of cerebral amyloid angiopathy and, in particular, wherein the patient carries one or two copies of the ApoE4 allele.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
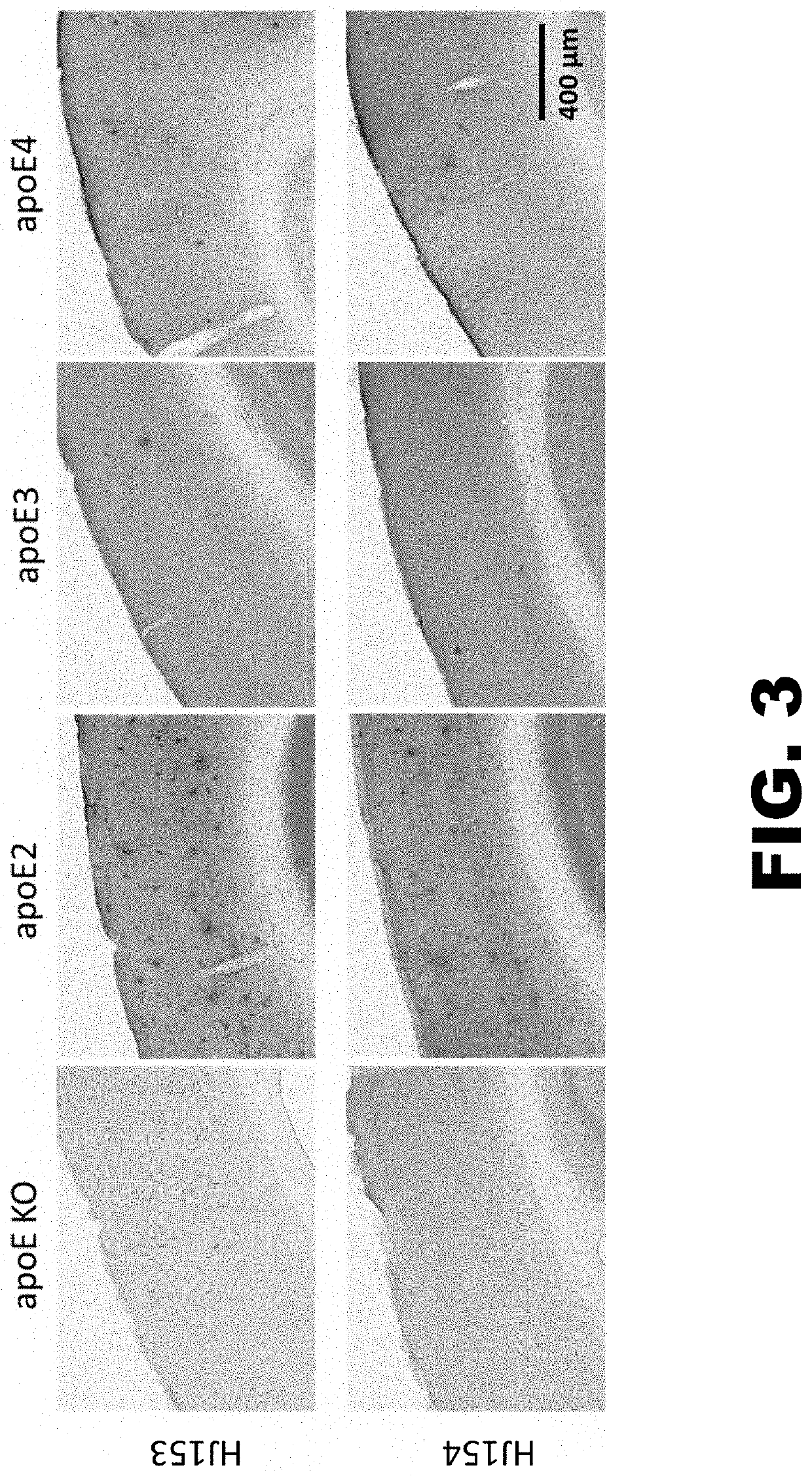
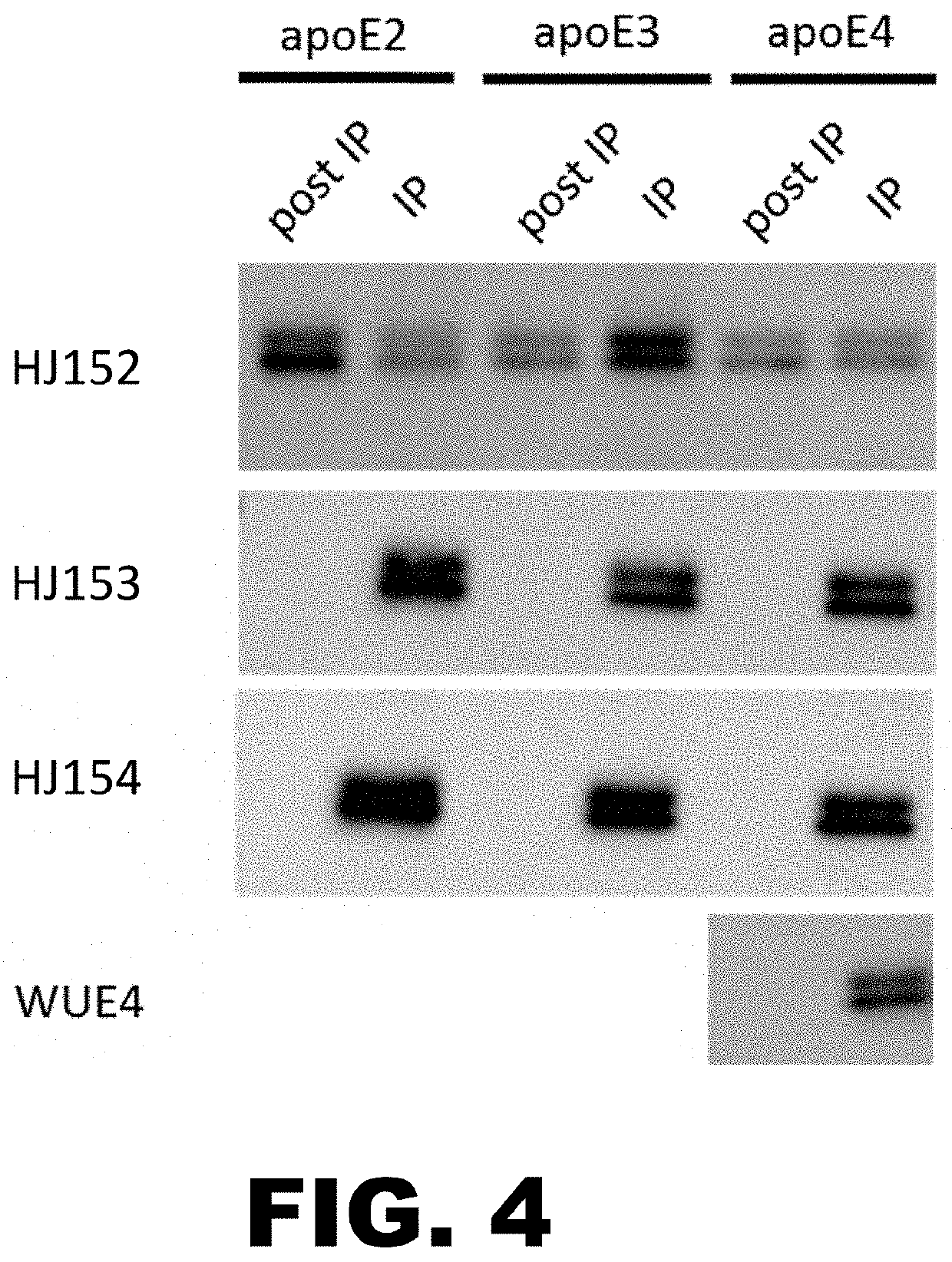
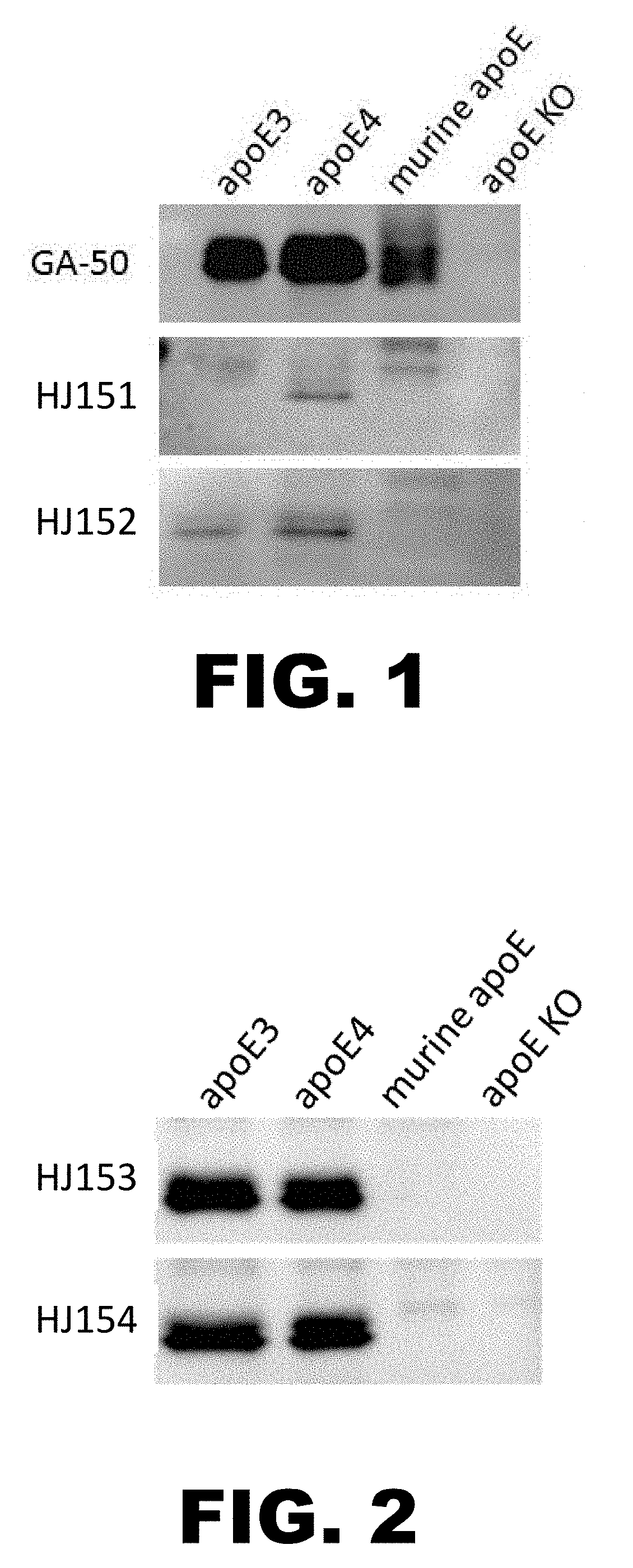
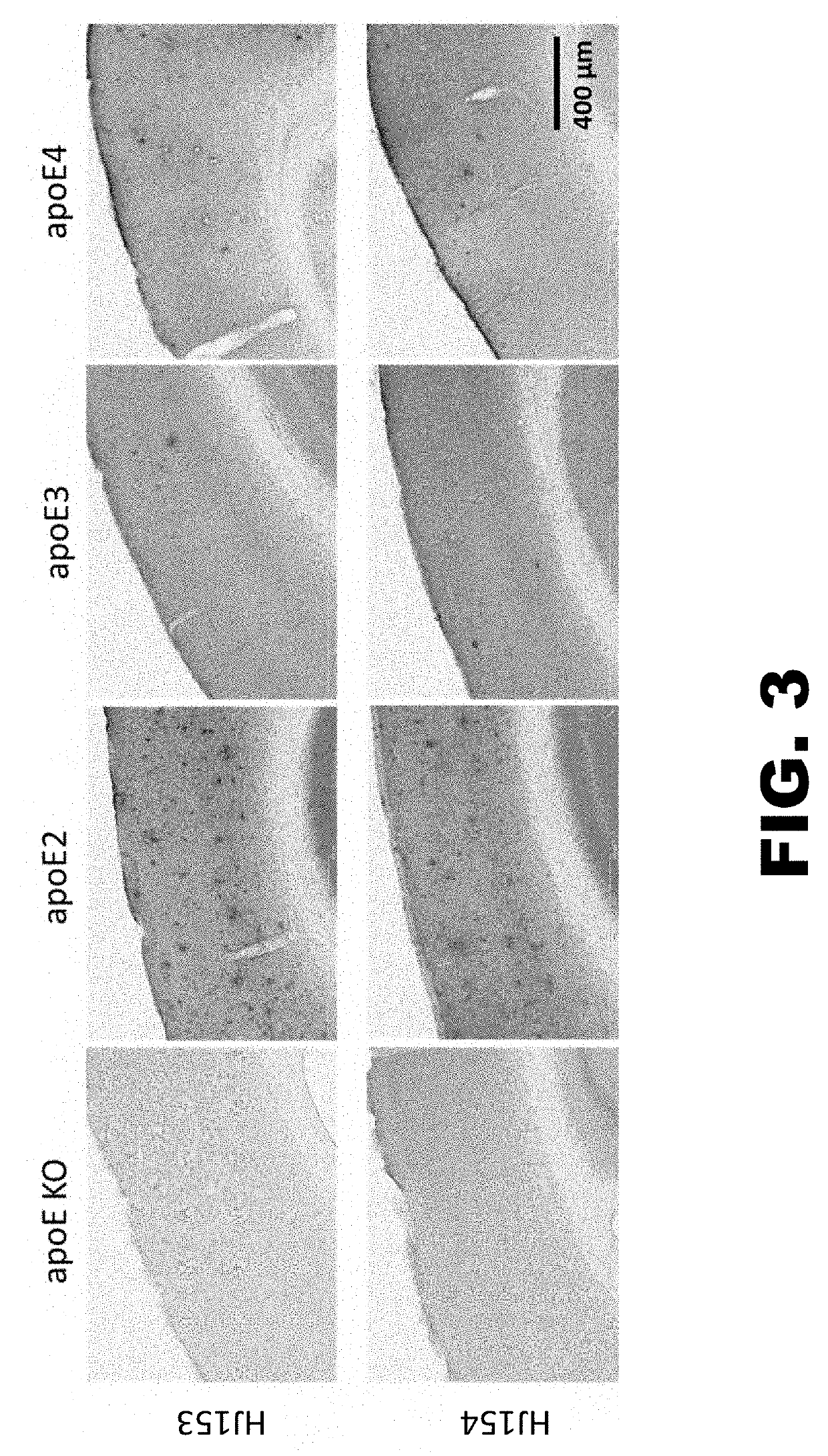
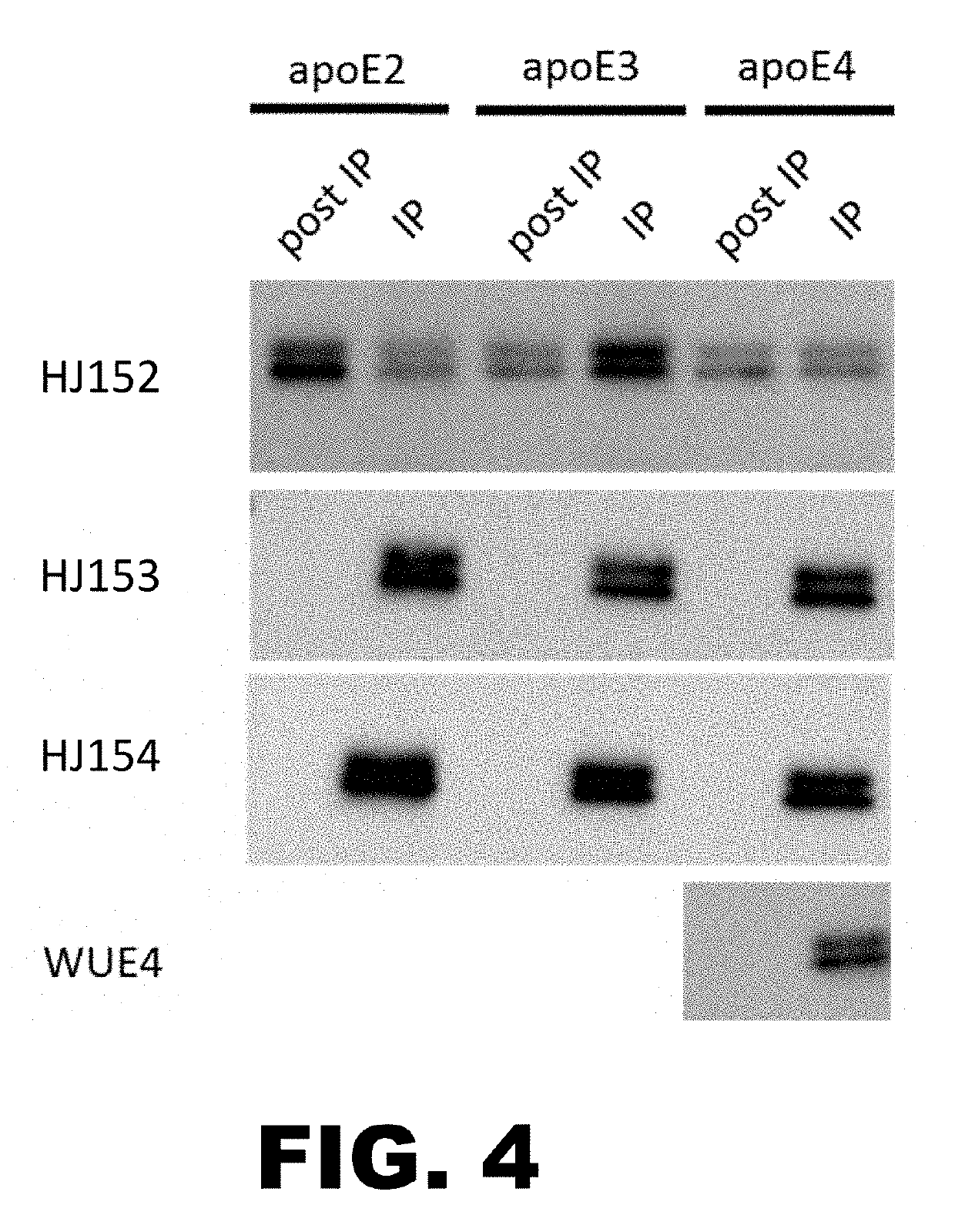
Anti-ApoE antibodies
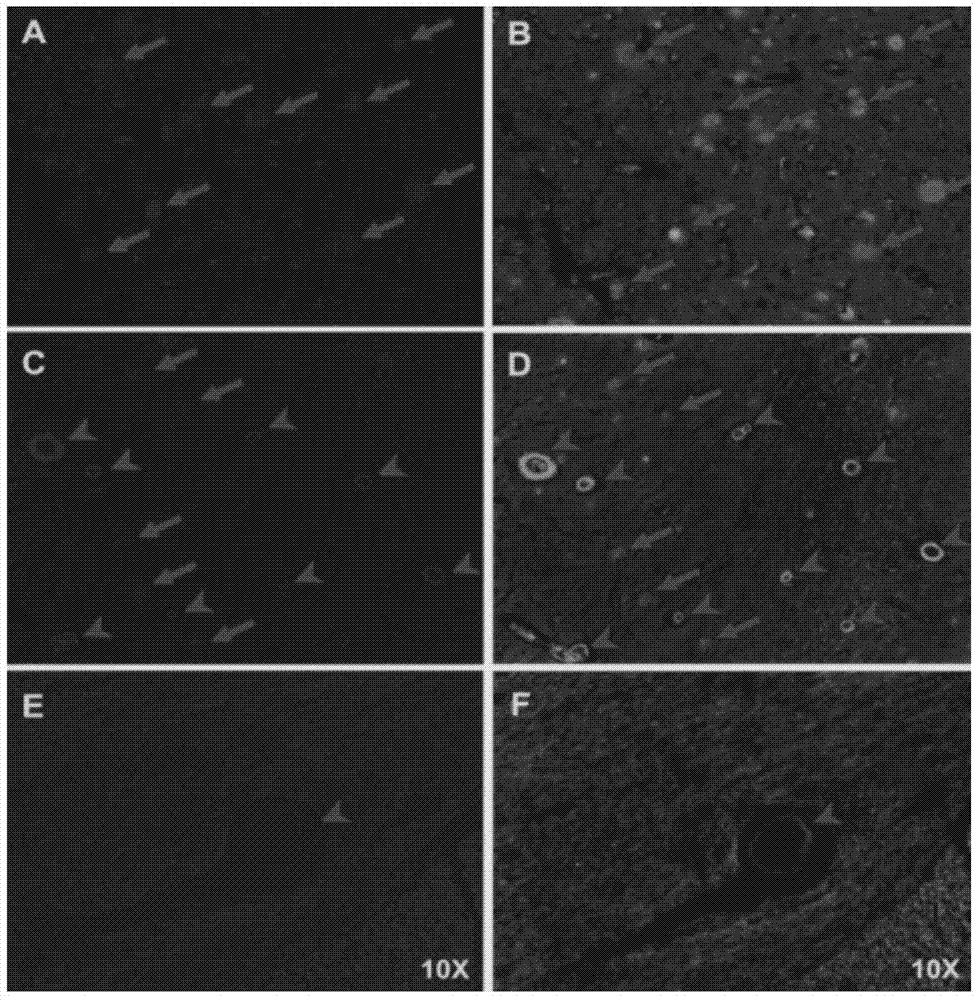
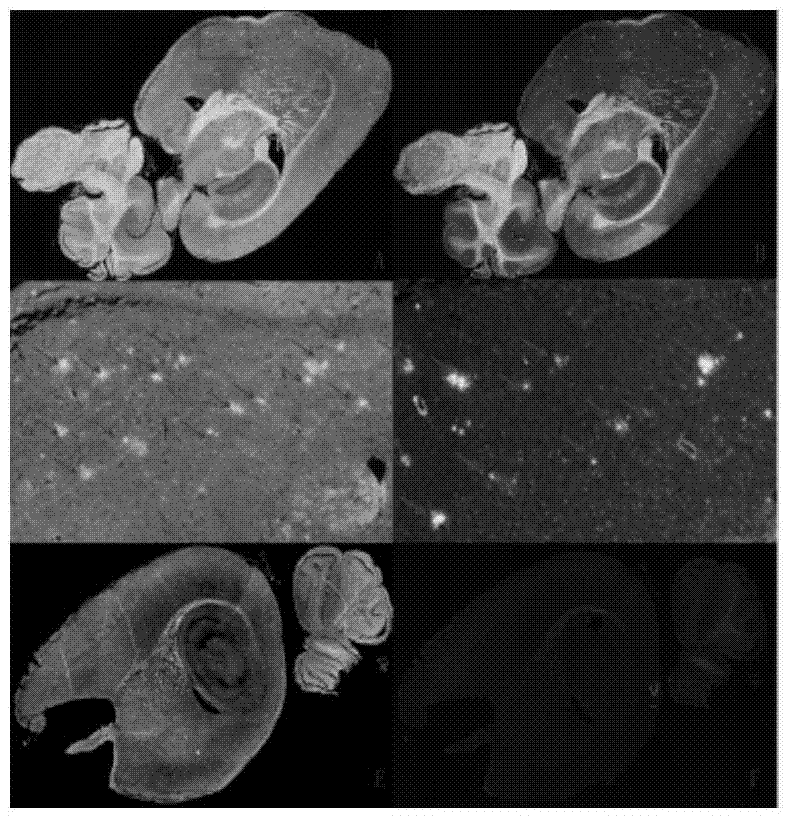
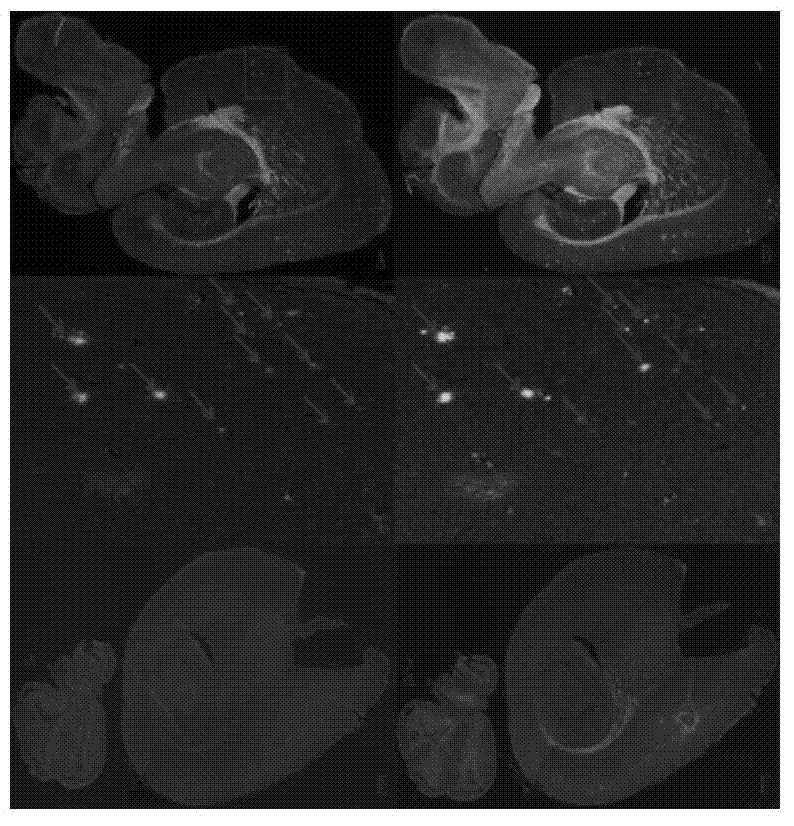
The present disclosure encompasses compositions and methods for effectively treating at least one symptom or sign of A plaque or cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) associated symptoms, or for decreasing amyloid plaque load or CAA load. The method comprises administering an effective amount of an anti-ApoE antibody to a mammalian subject, such as to a human.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Anti-apoe antibodies
ActiveUS20190270794A1Signs improvedEffective treatmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAntibodyProtein C
The present disclosure encompasses compositions and methods for effectively treating at least one symptom or sign of A plaque or cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) associated symptoms, or for decreasing amyloid plaque load or CAA load. The method comprises administering an effective amount of an anti-ApoE antibody to a mammalian subject, such as to a human.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
AMYLOID PRECURSOR PROTEIN (APP) RNAi AGENT COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF
The disclosure relates to double stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNAi) agents and compositions targeting the APP gene, as well as methods of inhibiting expression of an APP gene and methods of treating subjects having an APP-associated disease or disorder, such as cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and early onset familial Alzheimer disease (EOFAD or eFAD), using such dsRNAi agents and compositions.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Prevention or treatment agent for cerebral amyloid-beta storage diseases
InactiveCN106102736AReduce accumulationStop progressOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAmyloid betaIguratimod
Owner:FUJIFILM RI PHARMA
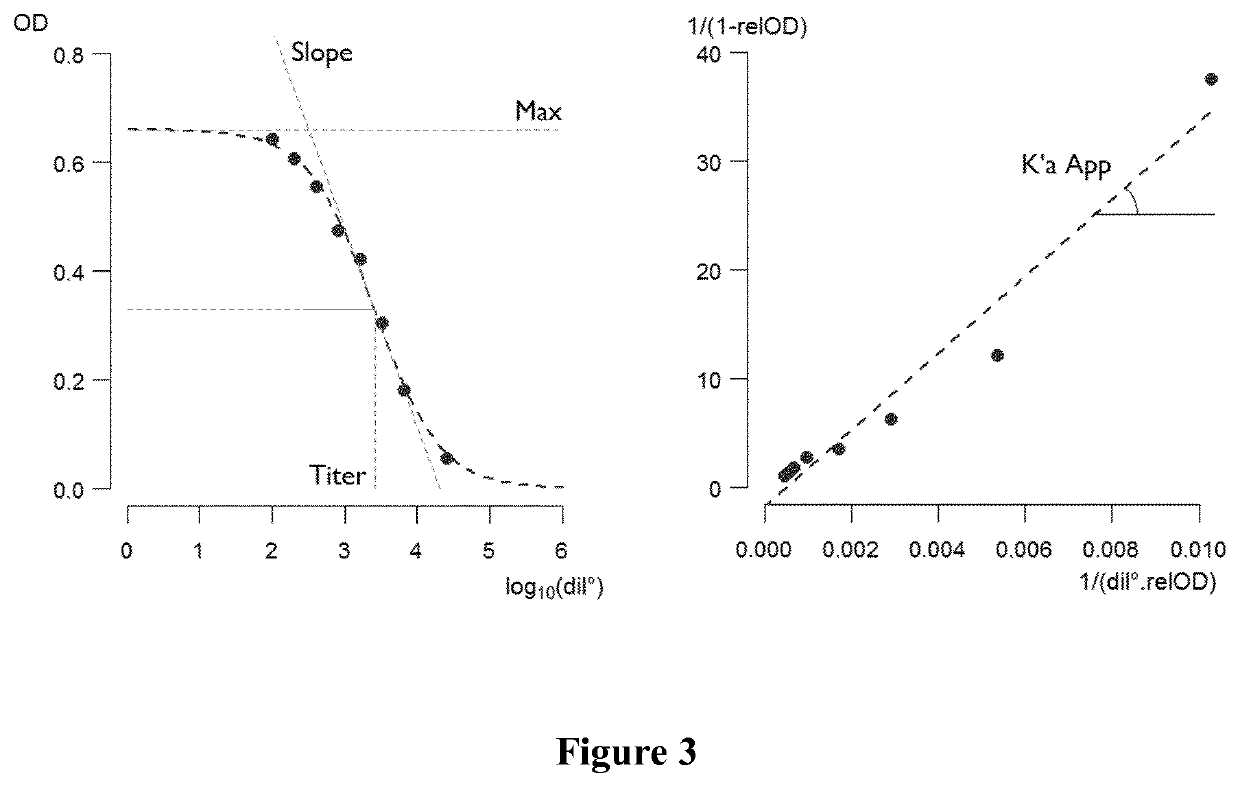
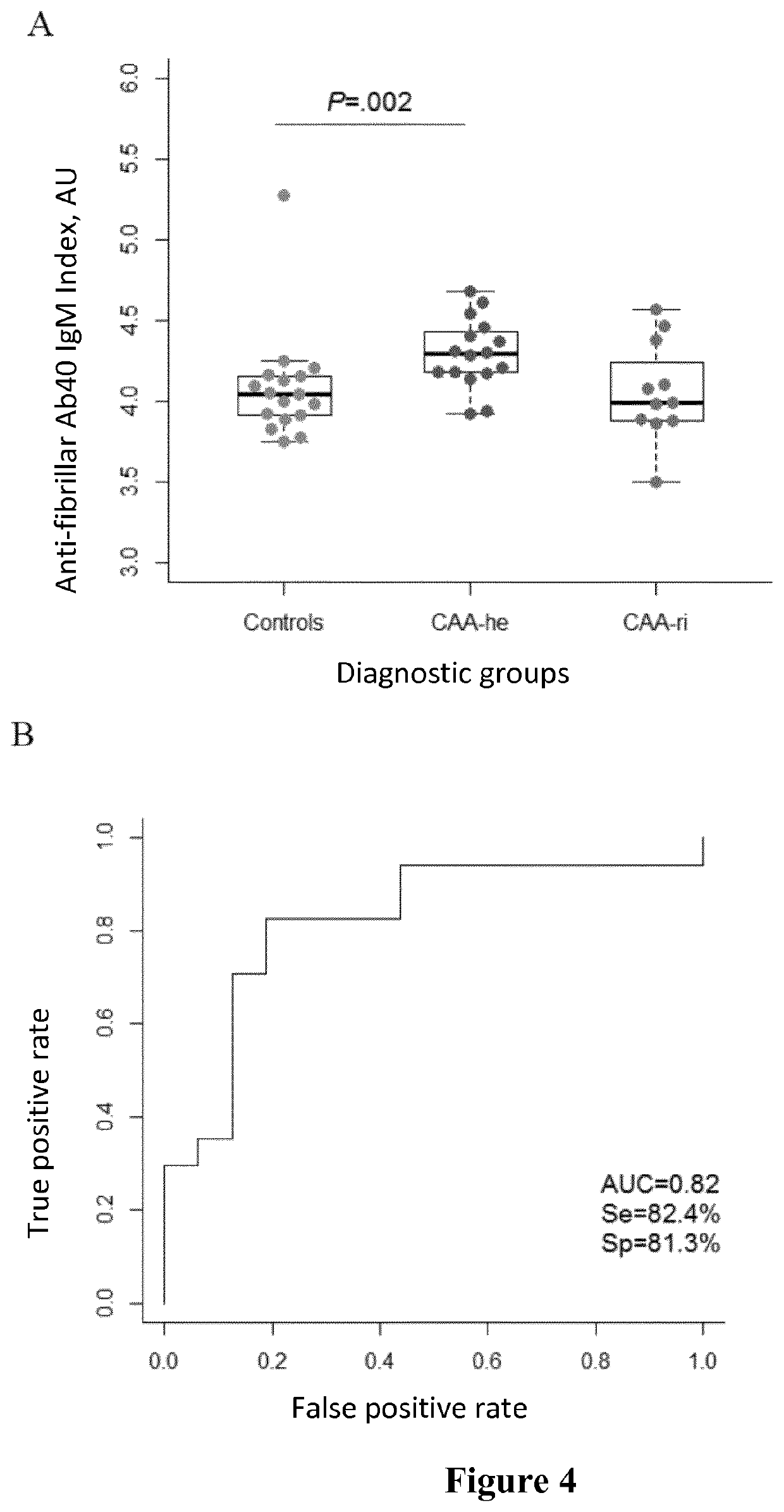
Methods for diagnosing a cerebral amyloid angiopathy
PendingUS20210285969A1Possible to detectBiological material analysisBiological testingAntiendomysial antibodiesSerum samples
The invention provides an in vitro method for diagnosing cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), or for diagnosing or determining the risk of developing a complication of CAA, in a human subject, which method comprises analyzing serial dilutions of a plasma or serum sample of the subject, for determining at least one binding parameter of antibodies present therein, wherein said antibodies are anti-Aβ amyloid peptide(s) antibodies.
Owner:SORBONNE UNIV +2
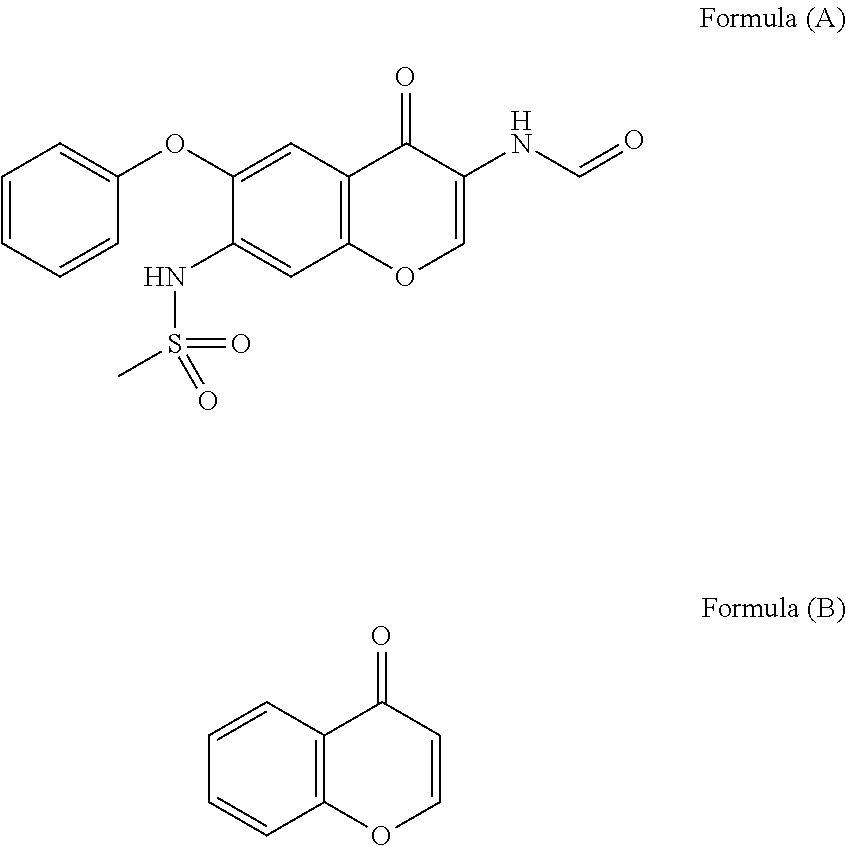
Process for the preparation of exo-tert-butyl n-(3-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)carbamate
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of a compound (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, which is useful as the key intermediate for the synthesis of compounds for prophylaxis and treatment of a disease associated with the deposition of β-amyloid in the brain, in particular Alzheimer's disease, and other diseases such as cerebral amyloid angiopathy, hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis, Dutch-type (HCHWA-D), multi-infarct dementia, dementia pugilistica and Down syndrome.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
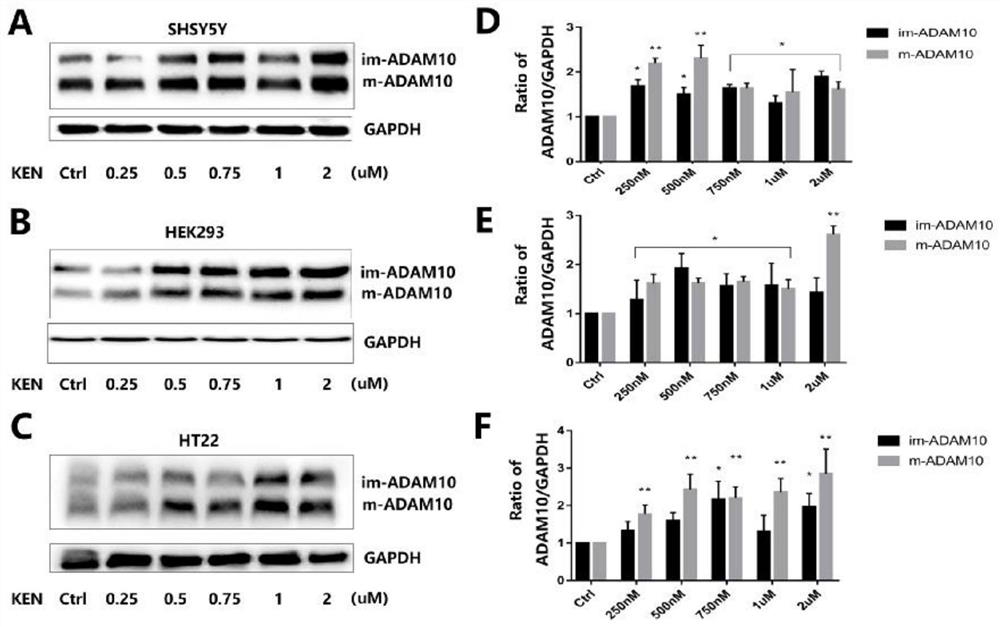
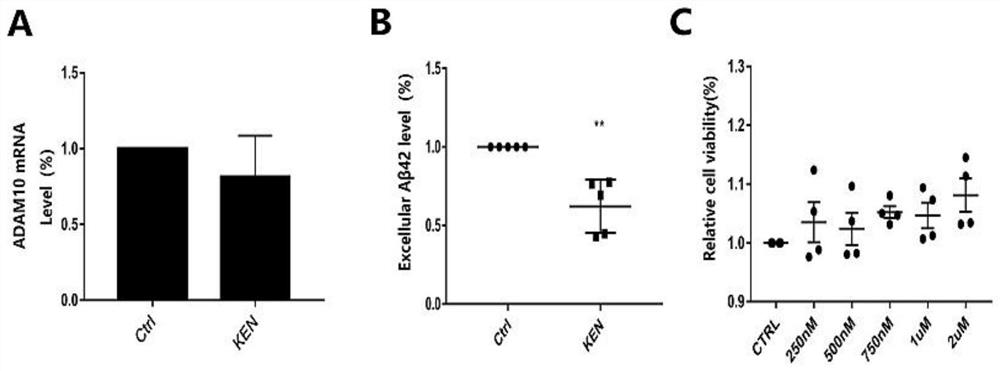
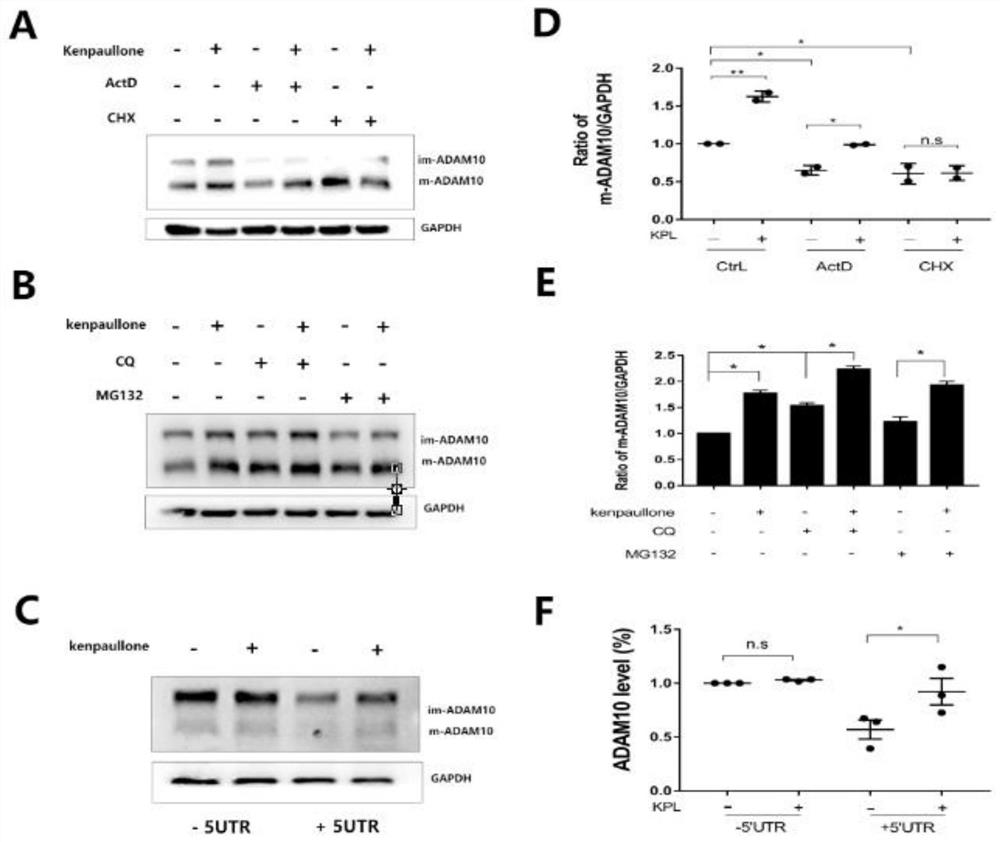
Application of Kenpaullone in preparation of medicine capable of preventing or treating cerebral amyloid angiopathy
InactiveCN112336729AHigh expressionReduce generationNervous disorderBlood disorderAlsterpaulloneKenpaullone
The invention provides application of Kenpaullone in preparation of a medicine capable of preventing or treating cerebral amyloid angiopathy. An experiment discovers that the Kenpaullone can increaseexpression of ADAM10 on a cell level but does not accelerate the expression of mRNA. In a further animal experiment APP / PS1 mouse model, a result discovers that the Kenpaullone obviously lightens cerebral vessel amyloid precipitation. An experiment proves for the first time that the Kenpaullone can increase the expression of the ADAM10, the amyloid metabolic pathway of APP can be converted into anon-amyloid metabolic pathway, and the generation of A[beta] which can be gathered and can precipitate is reduced. Research discovers that a Kenpaullone derivative Alsterpaullone(ALS) accelerates theprotein expression of the ADAM10 in SH-SY5Y cells; and AT7519 which is also CDK inhibitor does not affect the expression of the ADAM10 in SYSY5Y cells. All above research provides a clinical experiment guidance meaning for treatment of cerebral vessel amyloid degeneration and further medicine research and development.
Owner:陈国俊 +1
Oxazine derivative for use in the treatment or prevention of cerebral amyloid angiopathy
The present invention relates to an oxazine derivative BACE-1 inhibitor and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such oxazine derivative for use in the treatment or prevention of cerebral amyloid angiopathy and, in particular, wherein the patient carries one or two copies of the ApoE4 allele.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Inhibition of brain enzymes involved in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and macular degeneration
InactiveUS20100047336A1Avoid bleedingAvoid weakeningOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCaspase inhibitorsMammal
A method of treating or inhibiting progress of dementia and / or macular degeneration in a mammal involves administering compositions containing siRNA to heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) or heme oxygenase-2 (HO-2), a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor, a caspase inhibitor, or a metalloporphyrin in a manner that permits access to brain sites and / or the macula of the patient.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT +3
Prevention or treatment agent for cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases
ActiveUS9968585B2Inhibit progressImprove the quality of lifeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAmyloid betaAlzheimer type dementia
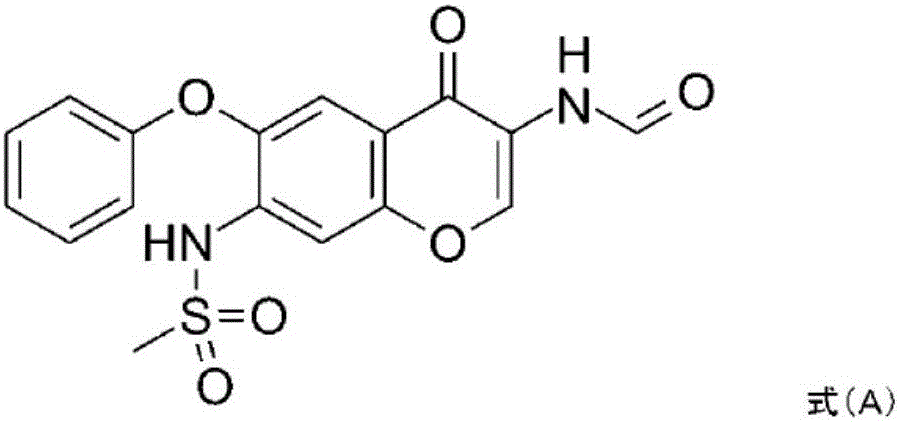
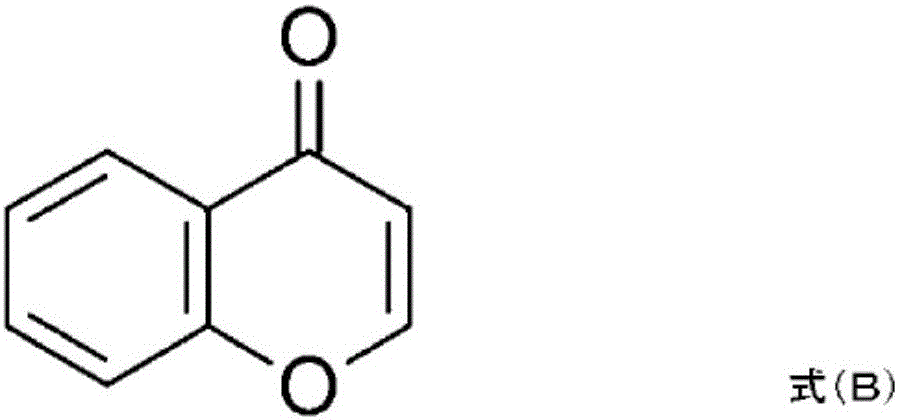
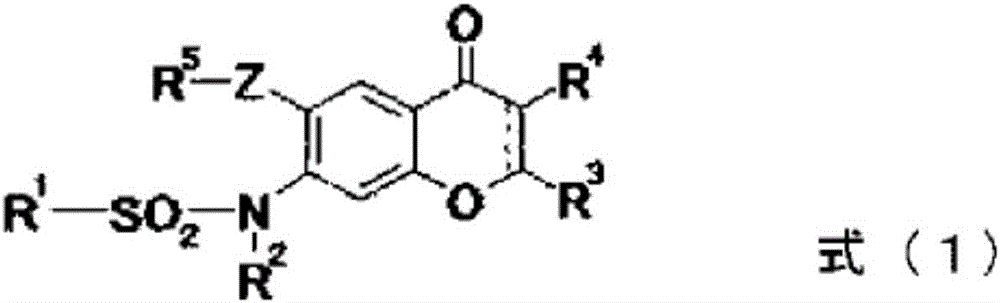
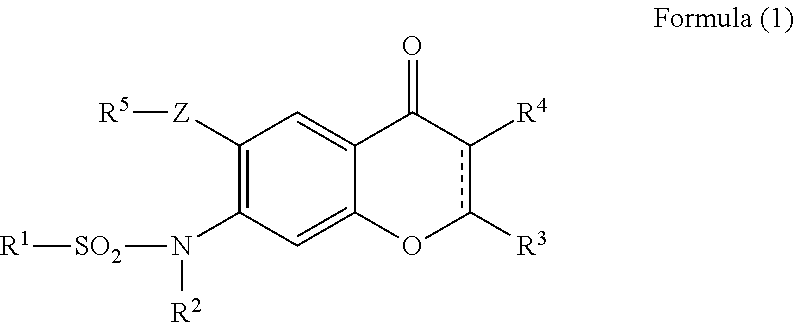
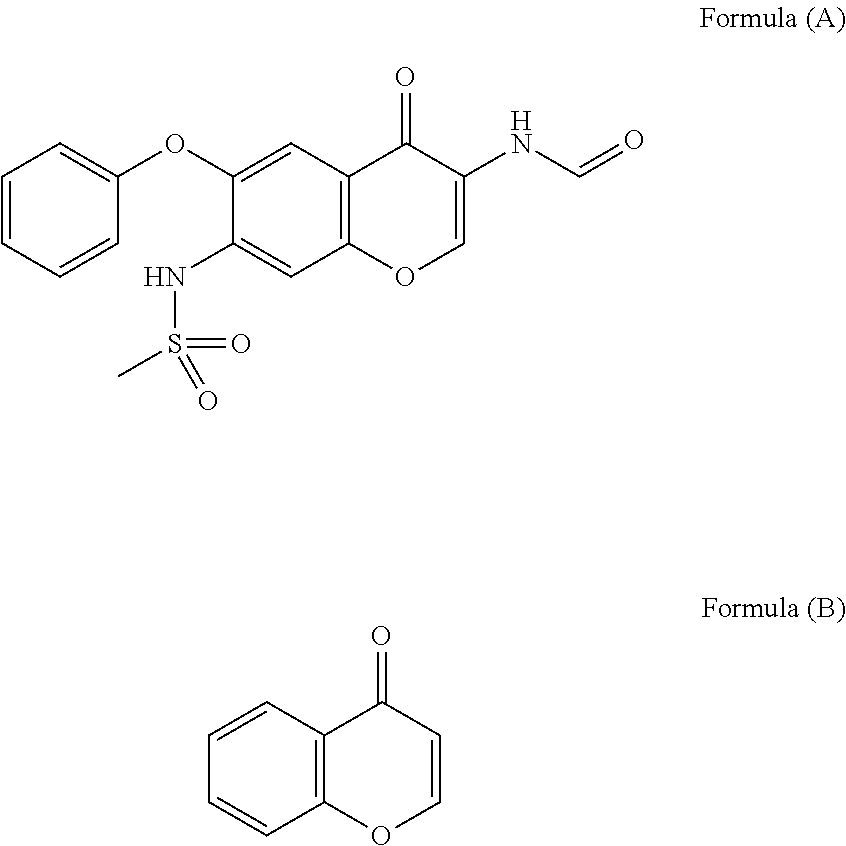
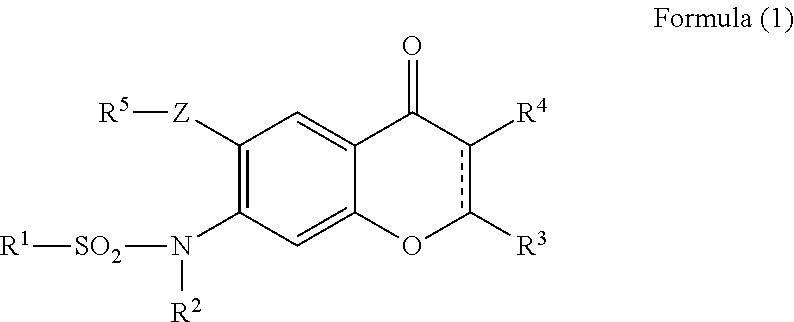
Provided is a prevention or treatment agent for cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases, that contains a substance capable of suppressing the progression, alleviating the symptoms, and improving cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases. This prevention or treatment agent for cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases has as an effective component thereof a compound (e.g., Iguratimod) indicated by formula (1) or a salt thereof and, as a result, is capable of preventing or treating cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases such as Alzheimer-type dementia or cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Owner:TOYAMA CHEM CO LTD
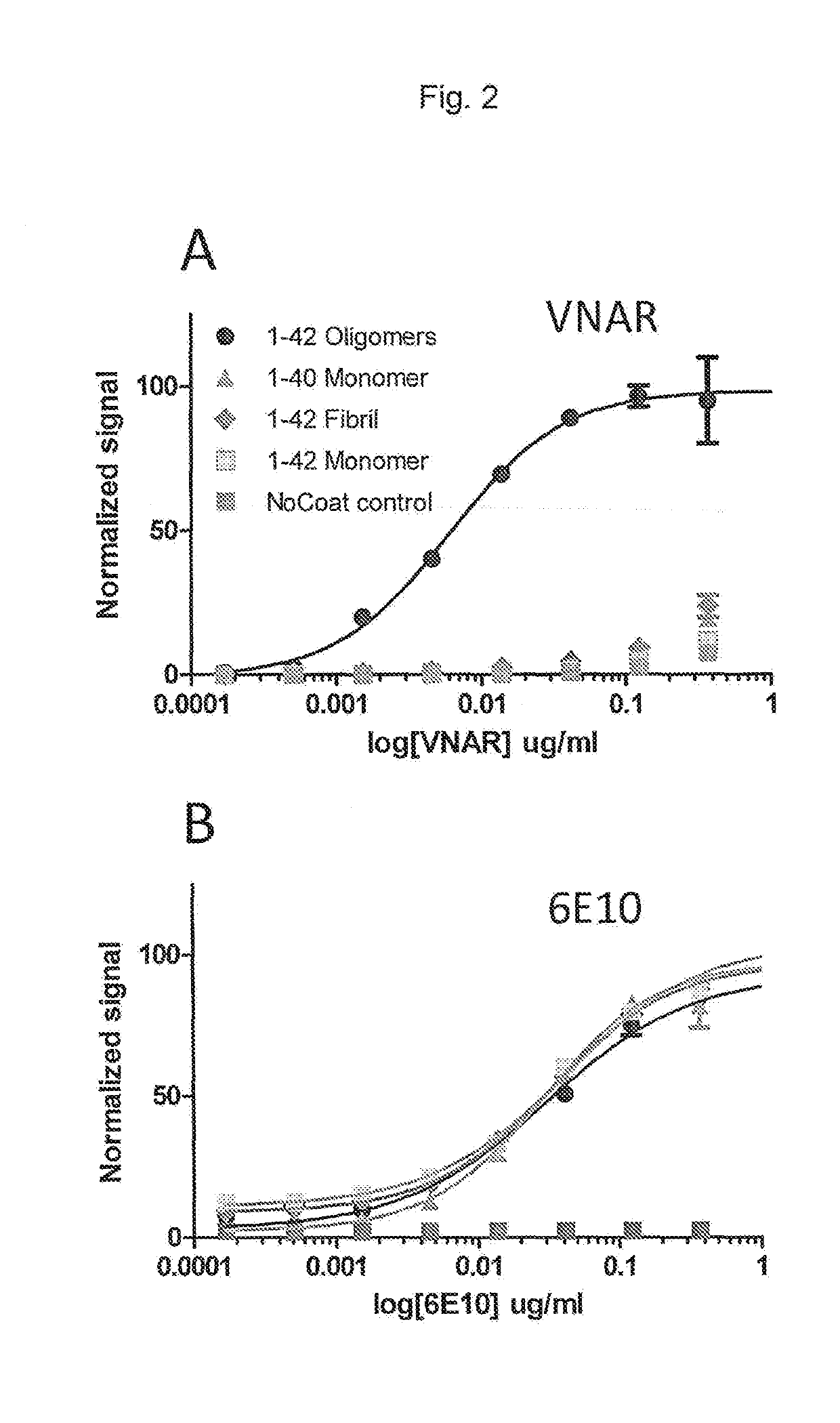
Novel amyloid beta oligomer specific binding molecule
ActiveUS20190292247A1Reduced level of bindingLower Level RequirementsNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDementia with Lewy bodiesHuntingtons chorea
This disclosure relates to an amyloid beta peptide (Aβ)-oligomer-specific antigen binding molecule and the use thereof as a diagnostic agent or as a therapeutic agent for the treatment or prevention of Alzheimer's Disease, Down's syndrome, mild cognitive impairment, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, vascular dementia, multi-infarct dementia, Parkinson's disease, Dementia with Lewy Bodies, Huntington's disease, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, cystic fibrosis, or Gaucher's disease.
Owner:DEGENRX BV
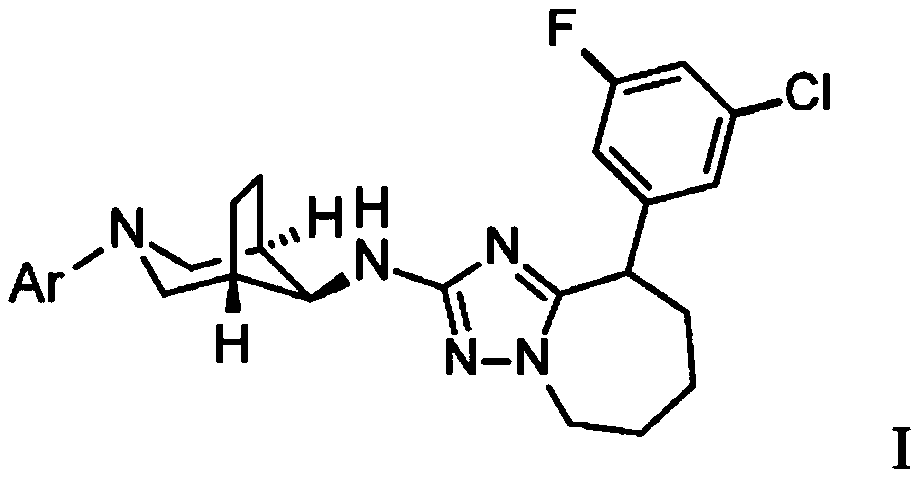
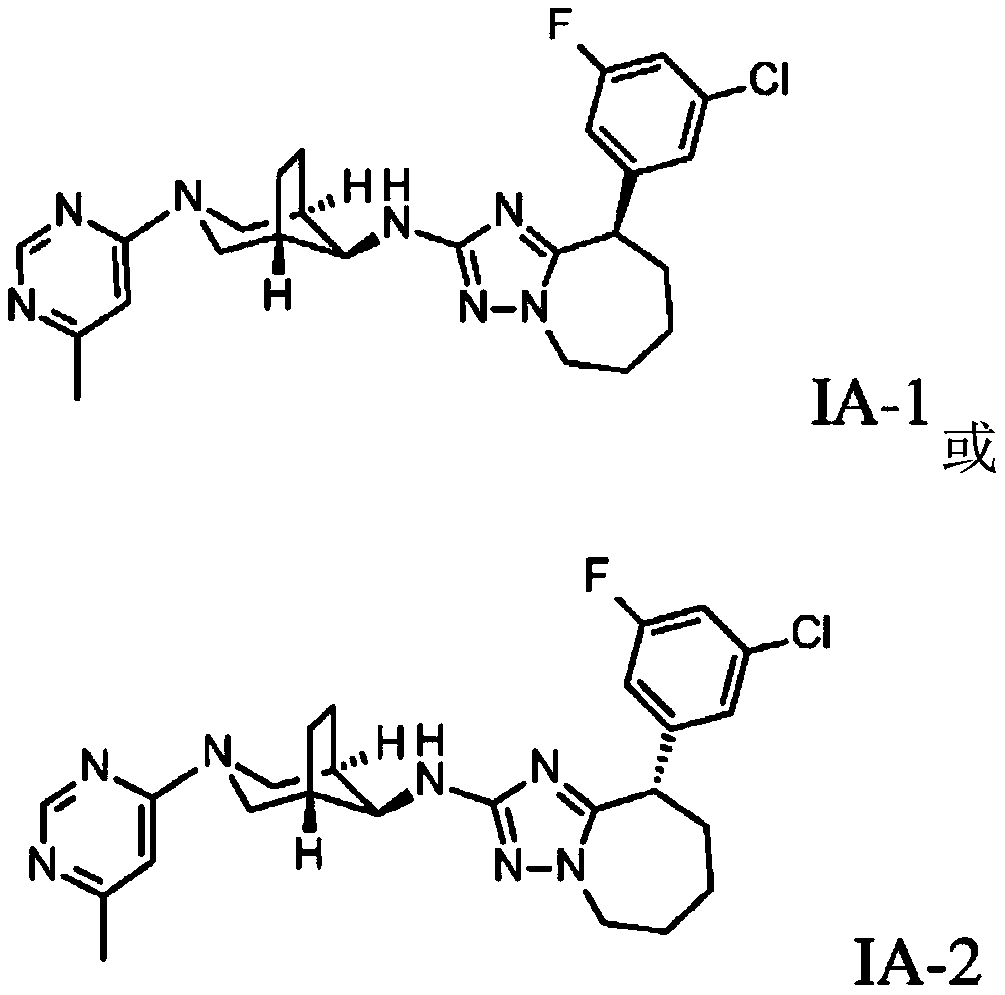
Triazolo-azepine derivatives
The present invention relates to a compound of formula (I) wherein Ar is (II) or (III); R is CH3or OCH3; or a pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salt or a corresponding enantiomer thereof. Thecompounds are modulators of gamma-secretase (A[BETA)42) and may be useful for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis-Dutch type (HCHWA-D), multi-infarct dementia, dementia pugilistica or Down syndrome.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
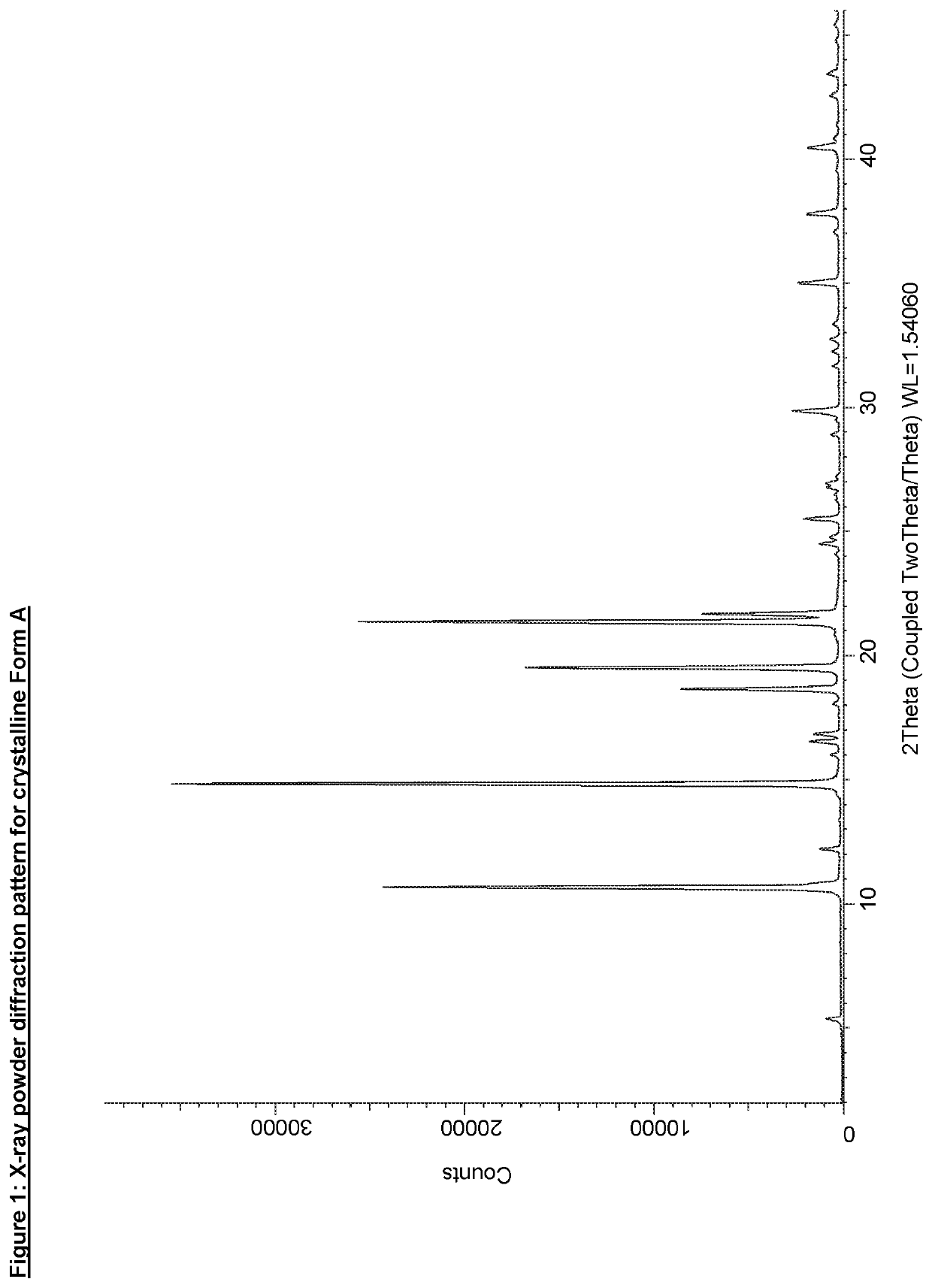
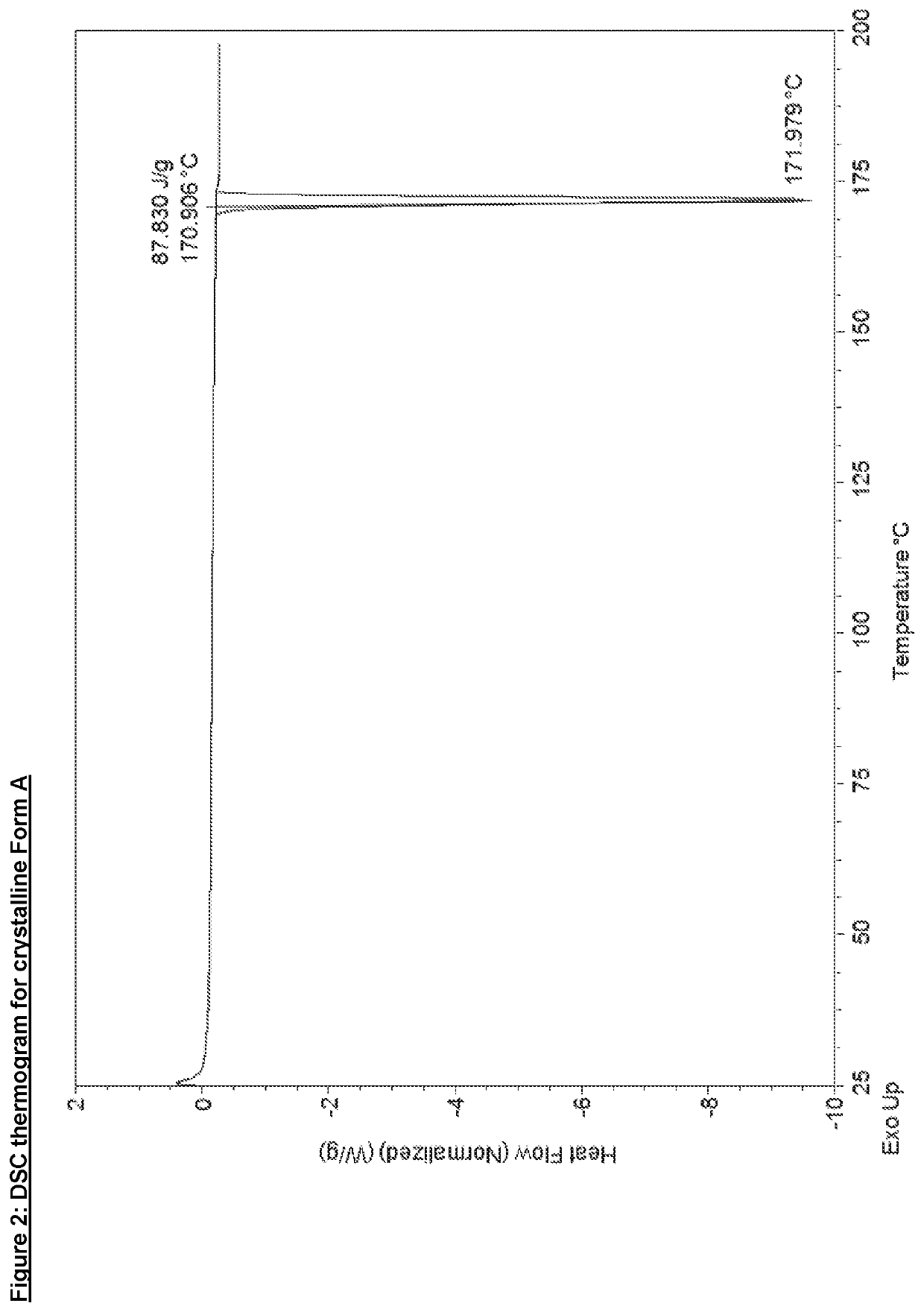
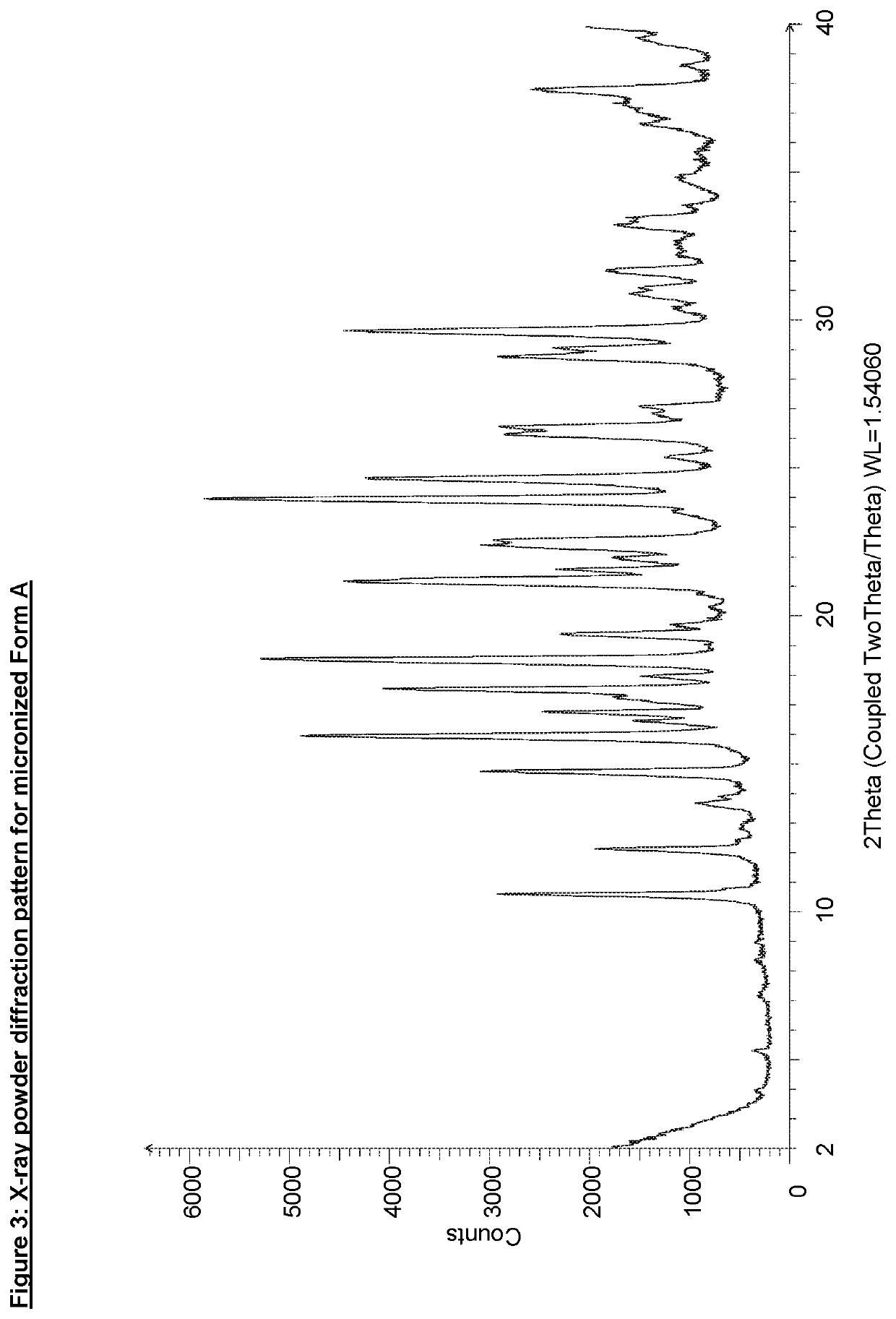
A Free Base Oxazine Derivative in Crystalline Form
InactiveUS20200048237A1Improve propertiesPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical drugPerylene derivatives
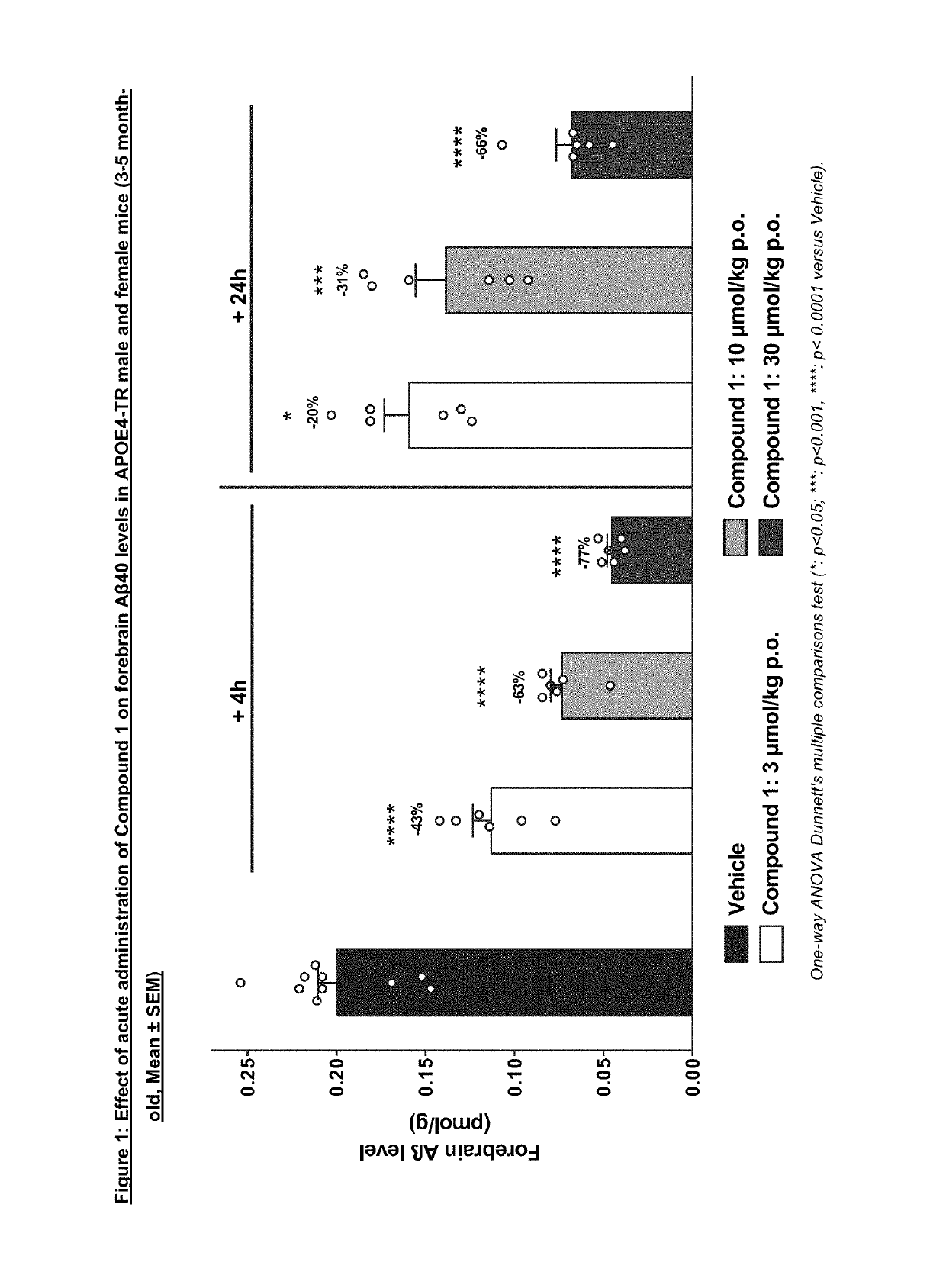
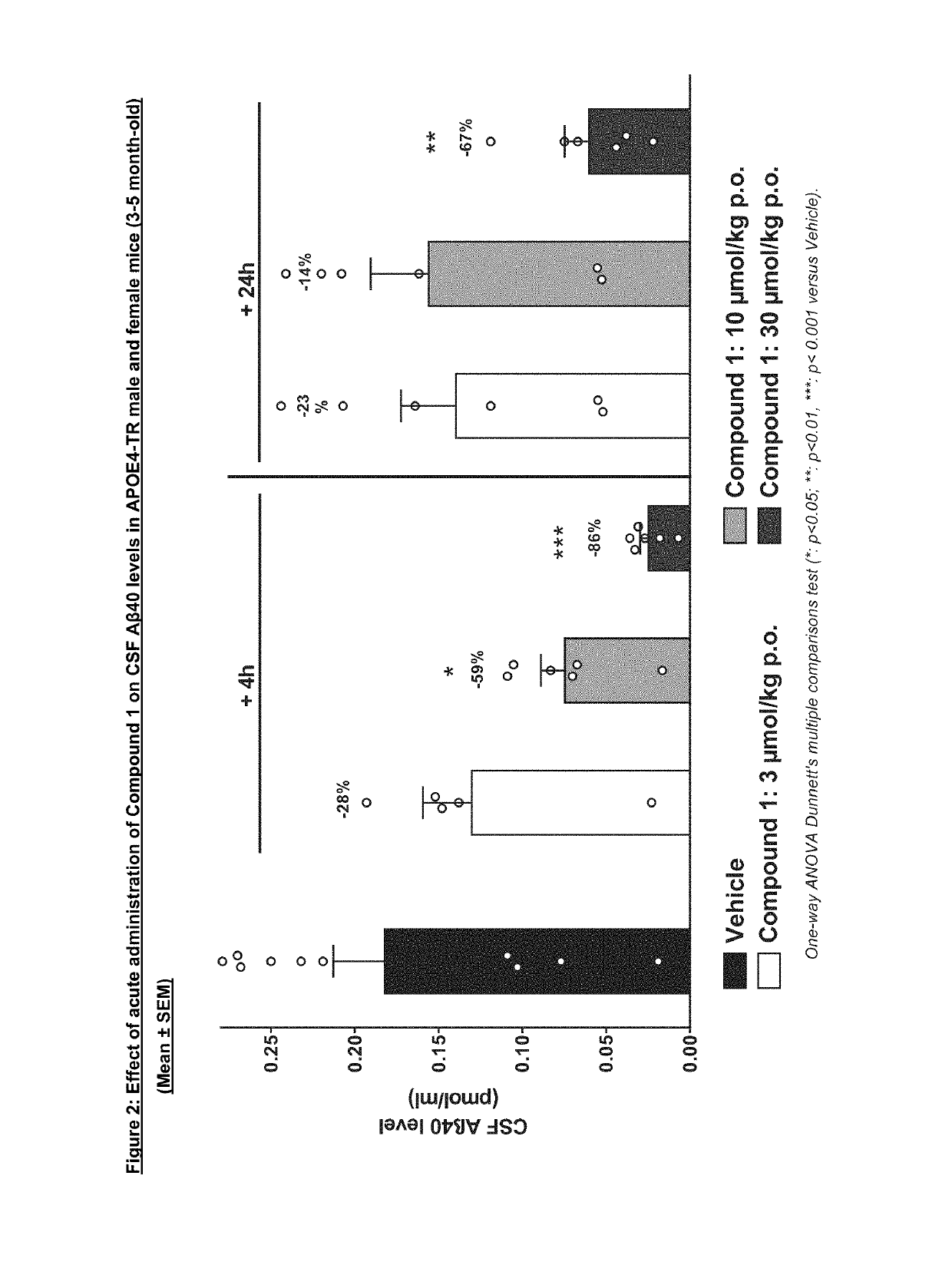
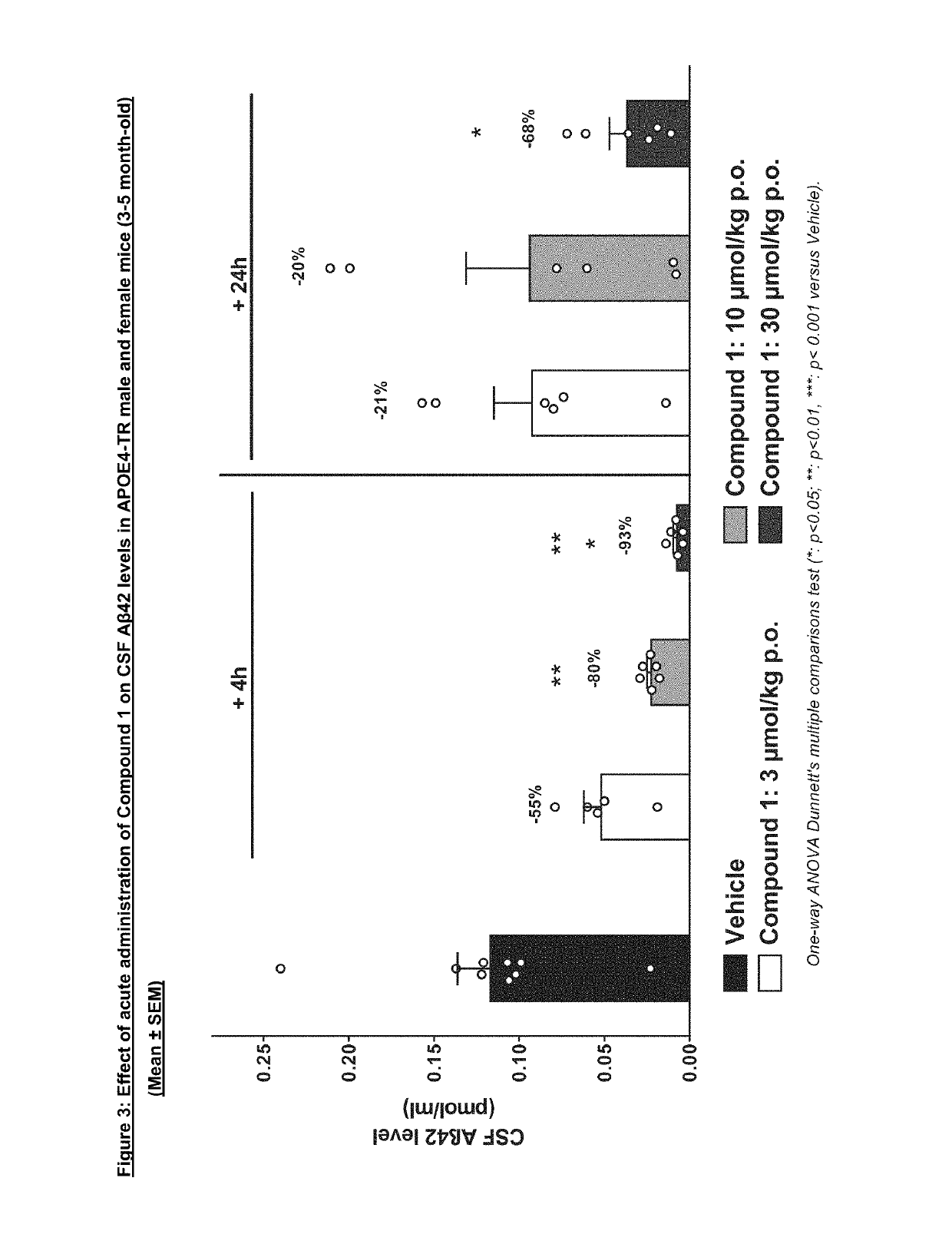
The invention relates to a solid form, namely crystalline Form A, of Compound 1, (1) and discloses the process for making said solid form of Compound 1. Also disclosed are further solid forms of Compound 1, including its hydrate and amorphous form. The present invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising crystalline Form A of Compound 1, and methods of using said form and pharmaceutical composition in the treatment or prevention of Alzheimer's disease or cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
6-difluoromethyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives
The invention relates to novel 6-difluoromethyl-5,6-dihydro-2H-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives as inhibitors of beta-secretase, also known as beta-site amyloid cleaving enzyme, BACE, BACE1, Asp2, or memapsin2. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, to processes for preparing such compounds and compositions, and to the use of such compounds and compositions for the prevention and treatment of disorders in which beta-secretase is involved, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment, senility, dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, multi-infarct dementia, Down's syndrome, dementia associated with stroke, dementia associated with Parkinson's disease and dementia associated with beta-amyloid.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
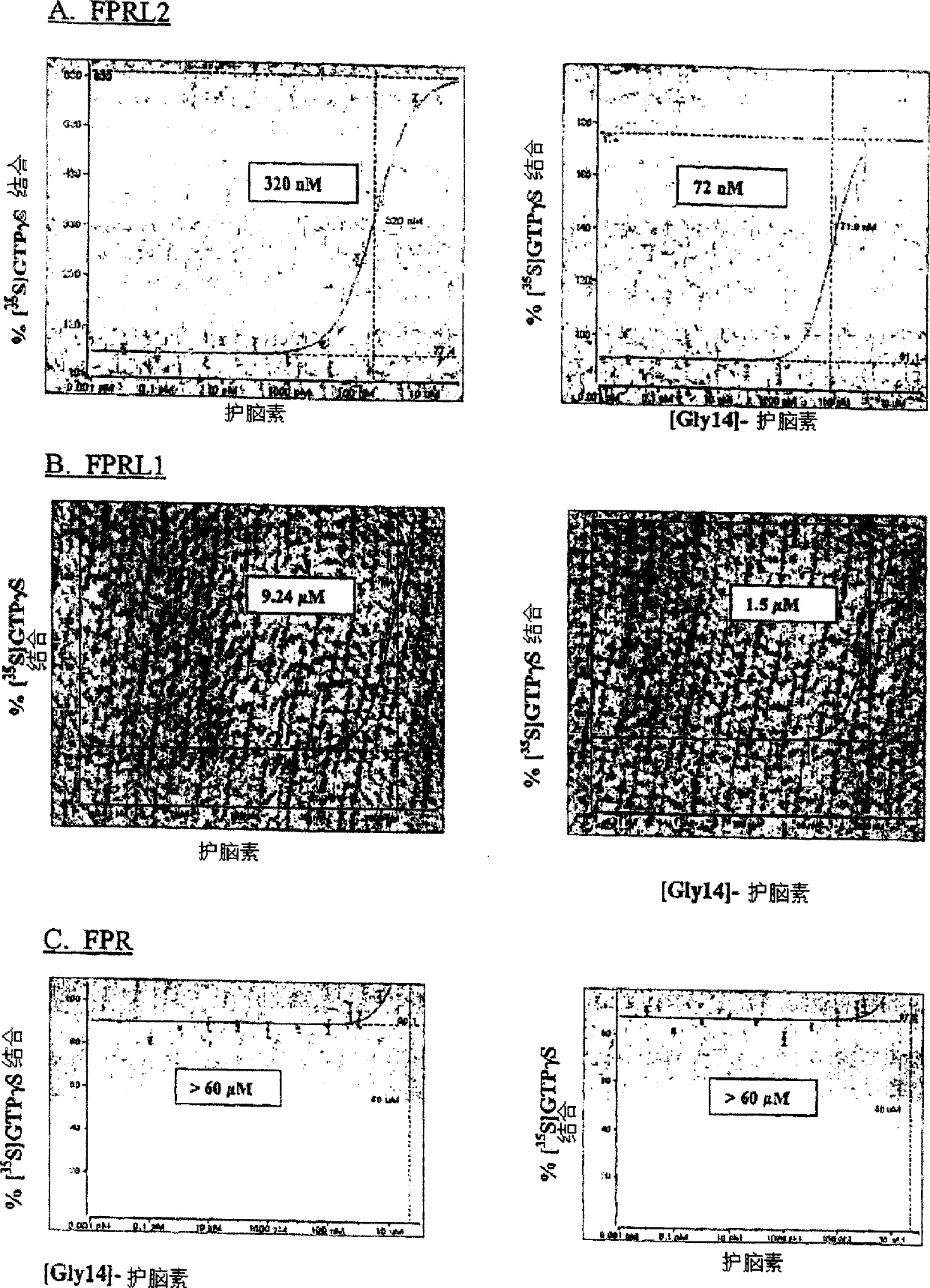
Modulators of the G protein-coupled formyl peptide receptor-like 2 and their therapeutic use against cell death-related disorders
The present invention relates to methods of identifying whether a candidate compound is a modulator of a G protein coupled receptor (GPCR). In certain embodiments, the GPCR is human. In certain embodiments, the GPCR is endogenously expressed by nerve cells or muscle cells. In certain embodiments, the GPCR is neuroprotective or myoprotective. In certain embodiments, the GPCR is a Humanin receptor. The invention also relates to methods of using said modulators of GPCRs. A preferred modulator is an agonist. The agonists of the present invention are generally used as therapeutic agents to prevent or treat neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, prions Associated diseases, stroke and motor neurone disease, especially peripheral neuropathy, cerebral amyloid beta-protein angiopathy and ischemic heart disease, including myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
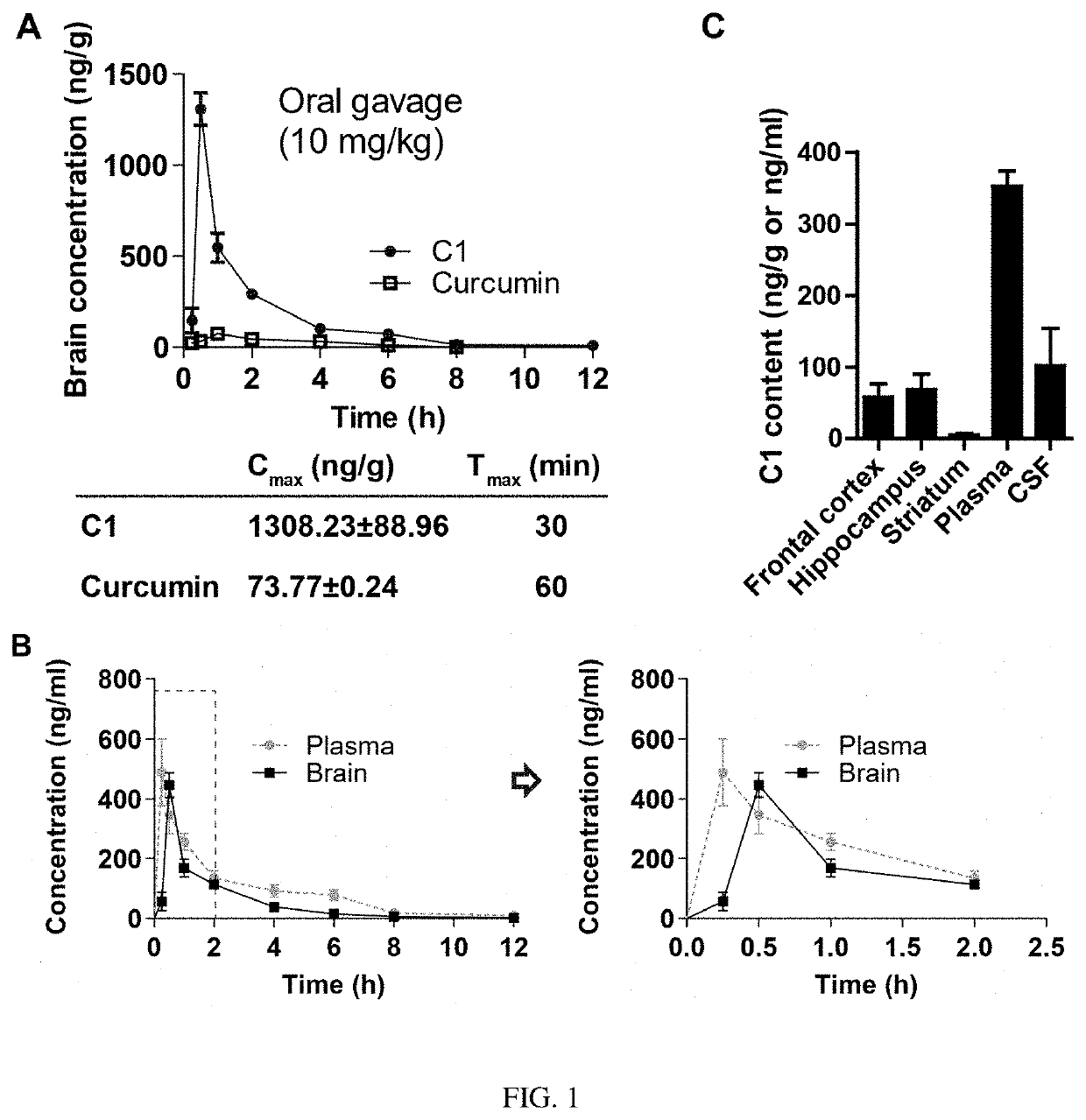
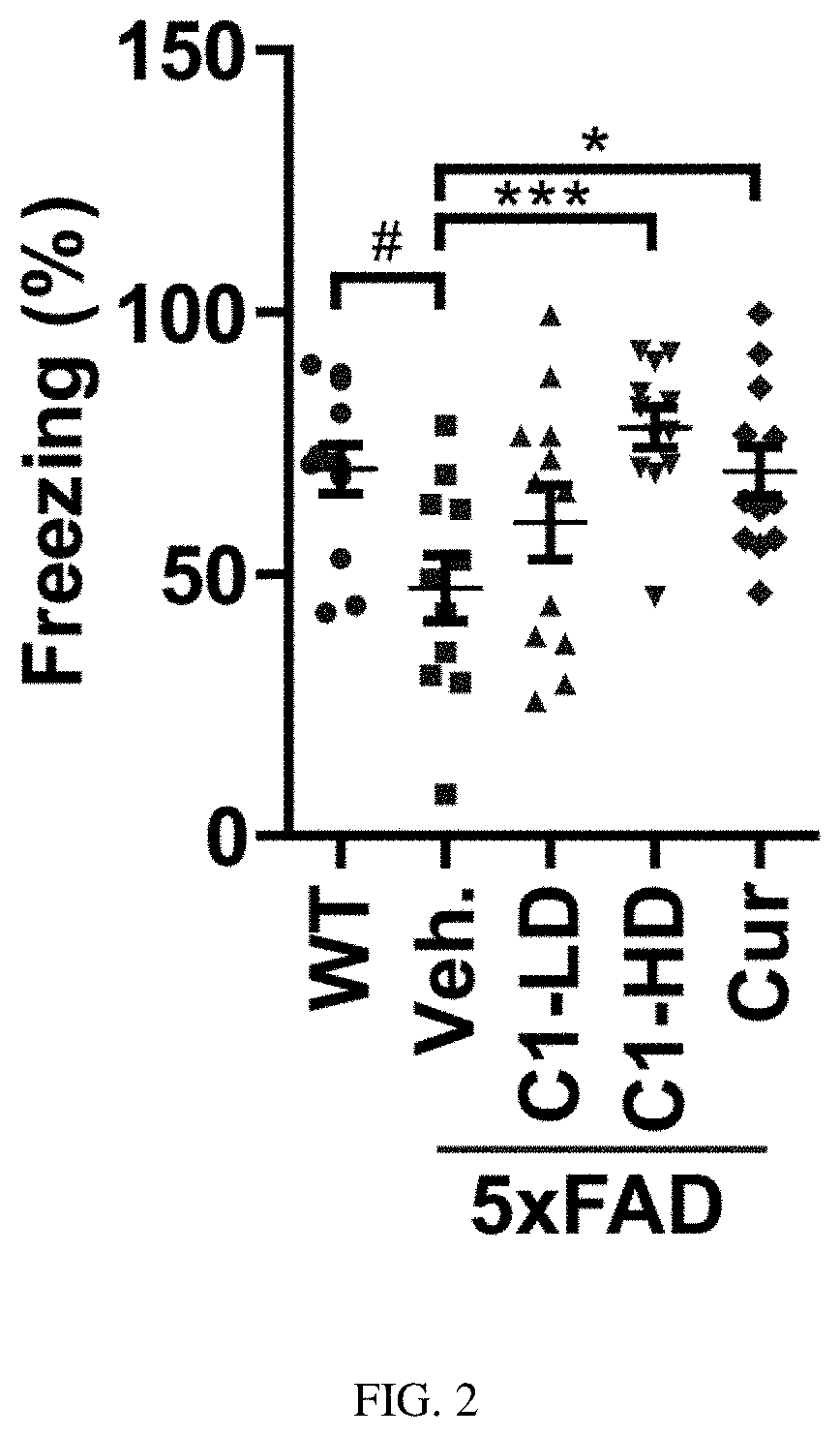
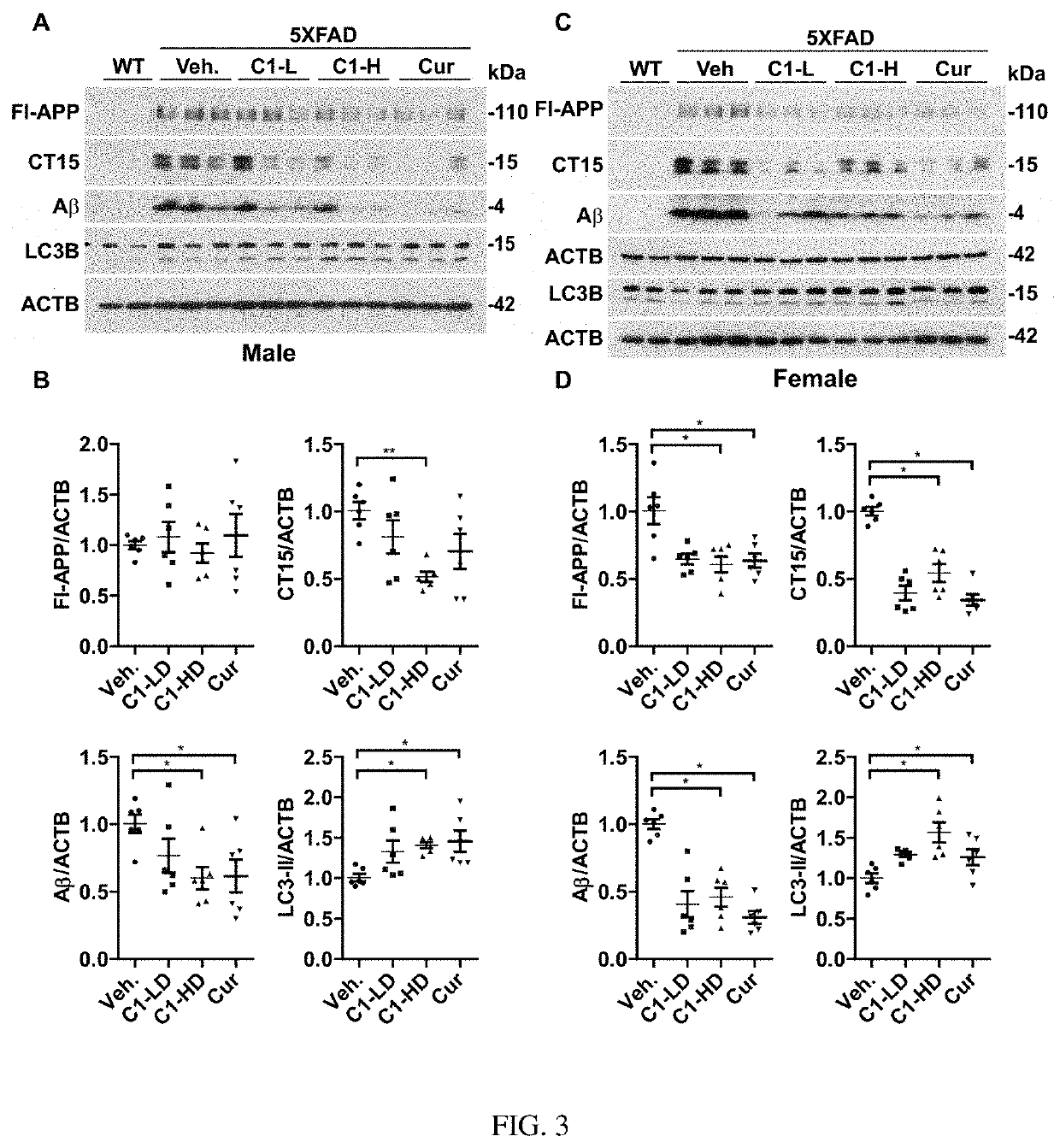
TFEB activator C1 ameliorates app and tau pathology and rescues cognitive deficits in neurodegenerative diseases
ActiveUS10987319B2Improve permeabilityPotent TFEB-activating effectNervous disorderKetone active ingredientsHuntingtons choreaNeuro-degenerative disease
The present invention relates to a method of use of a composition comprising an autophagy enhancement compound for treating neurodegenerative diseases. In particular, the said composition is used to treat the neural condition of synaptic dysfunction. Such neurodegenerative diseases include Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, Frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism-17 (FTDP-17), Pick disease (PiD), Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), Corticobasal degeneration (CBD) and Cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
Prevention or treatment agent for cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases
ActiveUS20170049744A1Inhibit progressImprove the quality of lifeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAmyloid betaIguratimod
Provided is a prevention or treatment agent for cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases, that contains a substance capable of suppressing the progression, alleviating the symptoms, and improving cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases. This prevention or treatment agent for cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases has as an effective component thereof a compound (e.g., Iguratimod) indicated by formula (1) or a salt thereof and, as a result, is capable of preventing or treating cerebral amyloid beta storage diseases such as Alzheimer-type dementia or cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Owner:TOYAMA CHEM CO LTD
Application of macrophage migration body as cerebral amyloid vascular disease treatment target
PendingCN114854815AWide range of contrast effectsSmall hemorrhagic transformationNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTSSide effect
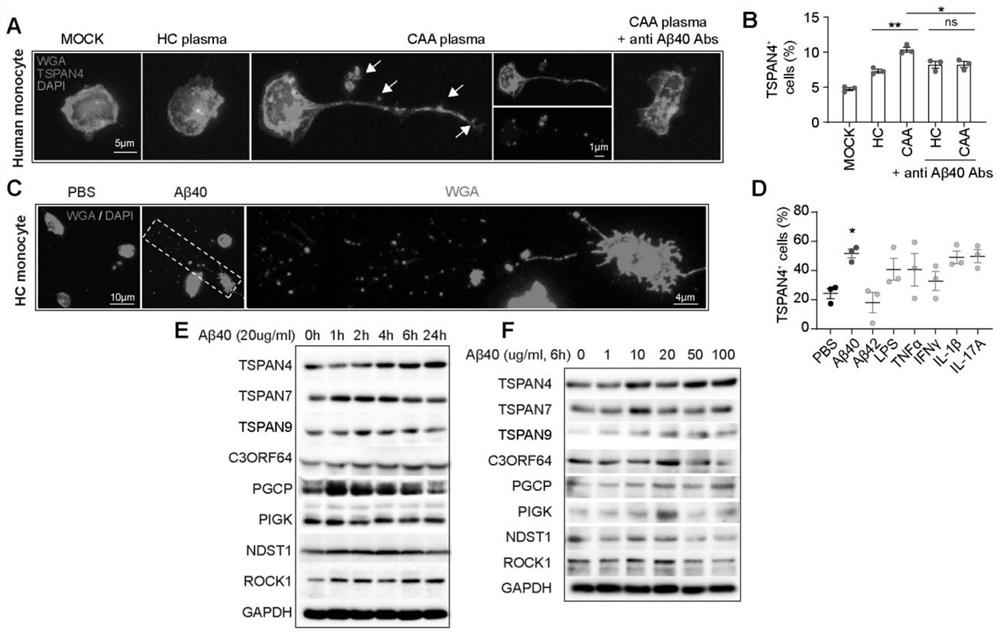
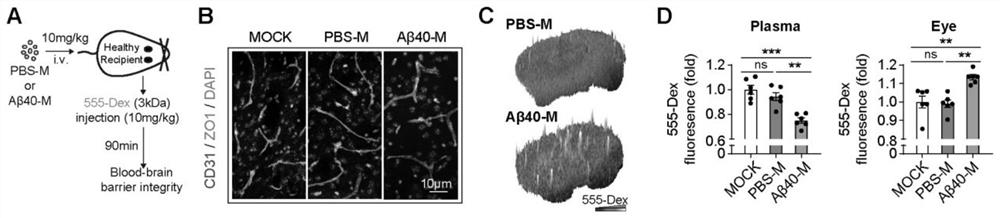
The invention discloses an application of a macrophage migration body as a cerebral amyloid vascular disease treatment target. According to the application disclosed by the invention, it is found for the first time that migratory bodies generated by A beta40-induced macrophages are related to pathophysiological processes of CAA, the migratory bodies derived from the macrophages damage blood-brain barriers in the CAA through complement-dependent cytotoxic effects, and macrophage apoptosis inhibition factors CD5L stop on blood vessel walls through the migratory bodies derived from the macrophages; the macrophage cell apoptosis inhibition factor CD5L can be used for promoting complement-dependent cytotoxic effect in CAA, so that the macrophage-derived migration body and the macrophage apoptosis inhibition factor CD5L can be used as new targets for CAA treatment. A reagent for inhibiting formation of macrophage migration bodies and expression of macrophage apoptosis inhibiting factors CD5L is developed to prepare a medicine for preventing and treating CAA, and compared with an immunosuppressor and glucocorticoid which are wide in action range, the reagent has the advantage of being high in targeting performance and small in side effects such as bleeding transformation, hepatorenal toxicity and A beta deposition.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
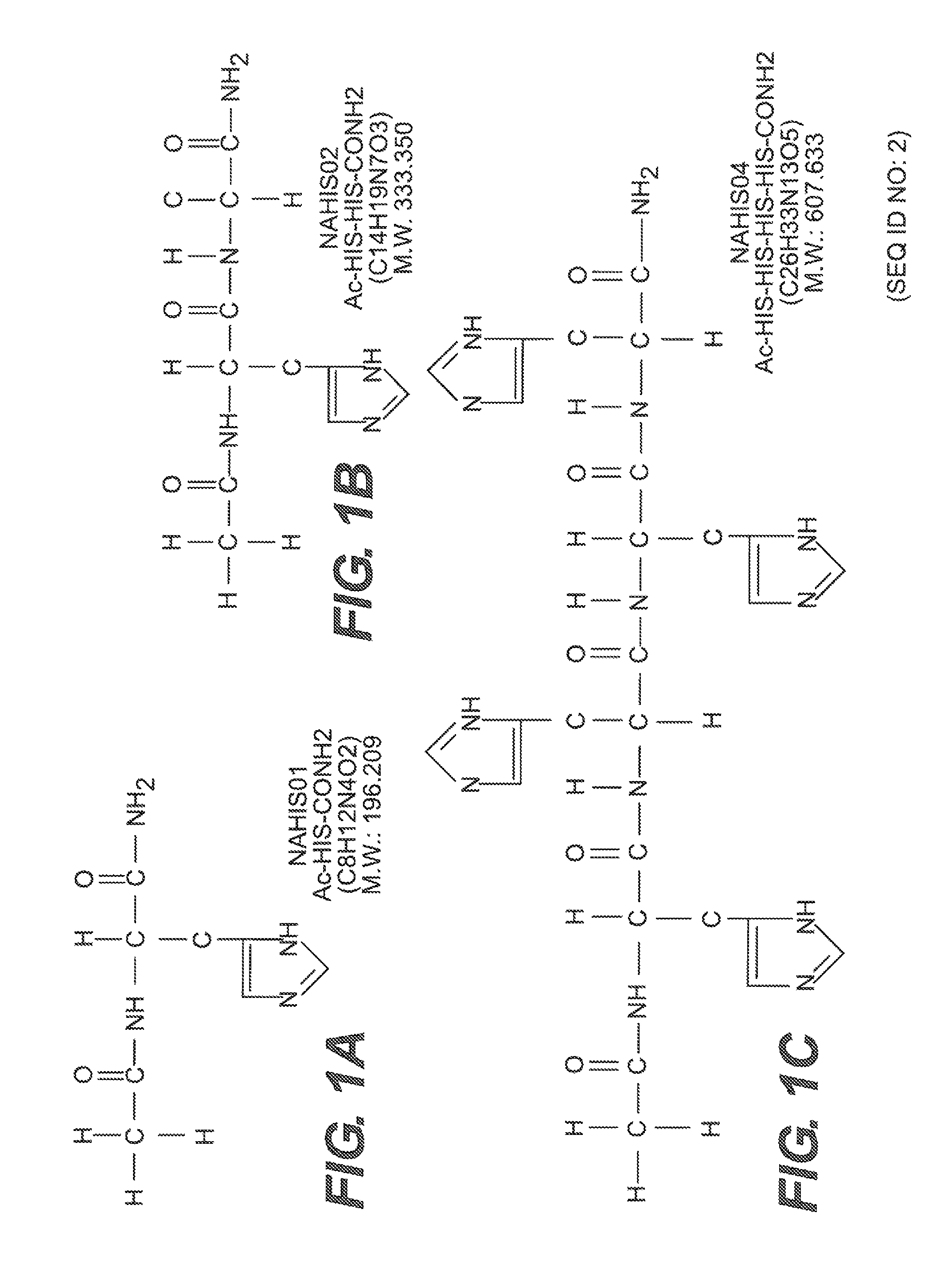
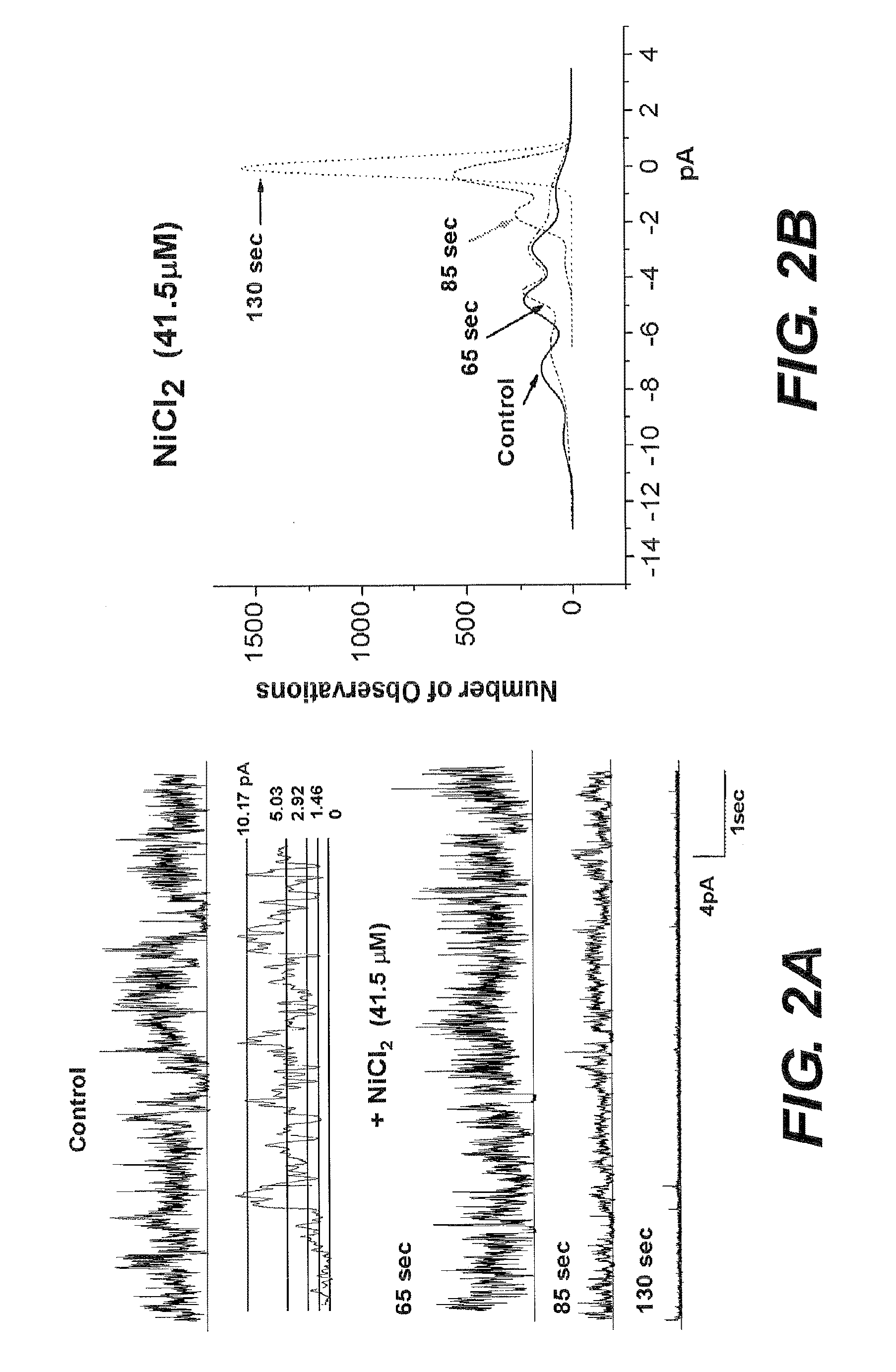
Histidine related compounds for identifying and blocking amyloid beta ion channels
InactiveUS8476240B2Prolong lifeInhibition formationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAmyloid betaInclusion body myositis
The present disclosure relates to amyloid beta (Aβ) channels and the diseases and disorders caused by abnormal activity in these channels, such as Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body dementia, inclusion body myositis, or cerebral amyloid angiopathy. The disclosure provides compositions and methods that block Aβ channel activity and / or reduce Aβ-induced toxicity in a cell. Compositions comprised of compounds having histidine coordinating capacity are used in methods to prevent, reduce, or eliminate damage caused by Aβ ion channels.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC
Compounds and methods for the treatment of alzheimer's disease and/or cerebral amyloid angiopathy
ActiveUS9994589B2Preventing and/or treating cerebral amyloidosesSpeed up the processNervous disorderOrganic chemistryMedicineCerebral amyloid angiopathy
Described herein are novel compounds and methods for the treatment and / or prevention of cerebral amyloidoses such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and / or cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA).
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
5-(3-aminophenyl)-5-alkyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives
The present invention relates to novel 5-(3-aminophenyl)-5-alkyl-5,6-dihydro-2H-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives as inhibitors of beta-secretase, also known as beta-site amyloid cleaving enzyme, BACE, BACE1, Asp2, or memapsin2. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, to processes for preparing such compounds and compositions, and to the use of such compounds and compositions for the prevention and treatment of disorders in which beta-secretase is involved, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment, senility, dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, multi-infarct dementia, Down's syndrome, dementia associated with stroke, dementia associated with Parkinson's disease and dementia associated with beta-amyloid.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Process for the preparation of exo-tert-butyl n-(3-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)carbamate Process for the preparation of exo-tert-butyl n-(3-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)carbamate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/58040593-aa7f-4b97-8e87-53bb57d2e204/US20220073469A1-C00001.png)
![Process for the preparation of exo-tert-butyl n-(3-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)carbamate Process for the preparation of exo-tert-butyl n-(3-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)carbamate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/58040593-aa7f-4b97-8e87-53bb57d2e204/US20220073469A1-C00002.png)
![Process for the preparation of exo-tert-butyl n-(3-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)carbamate Process for the preparation of exo-tert-butyl n-(3-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl)carbamate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/58040593-aa7f-4b97-8e87-53bb57d2e204/US20220073469A1-C00003.png)
![6-difluoromethyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives 6-difluoromethyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/bc92e17d-7662-417d-9264-d12fb3ca6090/US20140343048A1-20141120-C00001.png)
![6-difluoromethyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives 6-difluoromethyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/bc92e17d-7662-417d-9264-d12fb3ca6090/US20140343048A1-20141120-C00002.png)
![6-difluoromethyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives 6-difluoromethyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/bc92e17d-7662-417d-9264-d12fb3ca6090/US20140343048A1-20141120-C00003.png)

![5-(3-aminophenyl)-5-alkyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives 5-(3-aminophenyl)-5-alkyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f3b93ce9-5dff-458a-bb7d-07d97fb57de7/US20140364428A1-20141211-C00001.png)
![5-(3-aminophenyl)-5-alkyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives 5-(3-aminophenyl)-5-alkyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f3b93ce9-5dff-458a-bb7d-07d97fb57de7/US20140364428A1-20141211-C00002.png)
![5-(3-aminophenyl)-5-alkyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives 5-(3-aminophenyl)-5-alkyl-5,6-dihydro-2h-[1,4]oxazin-3-amine derivatives](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f3b93ce9-5dff-458a-bb7d-07d97fb57de7/US20140364428A1-20141211-C00003.png)