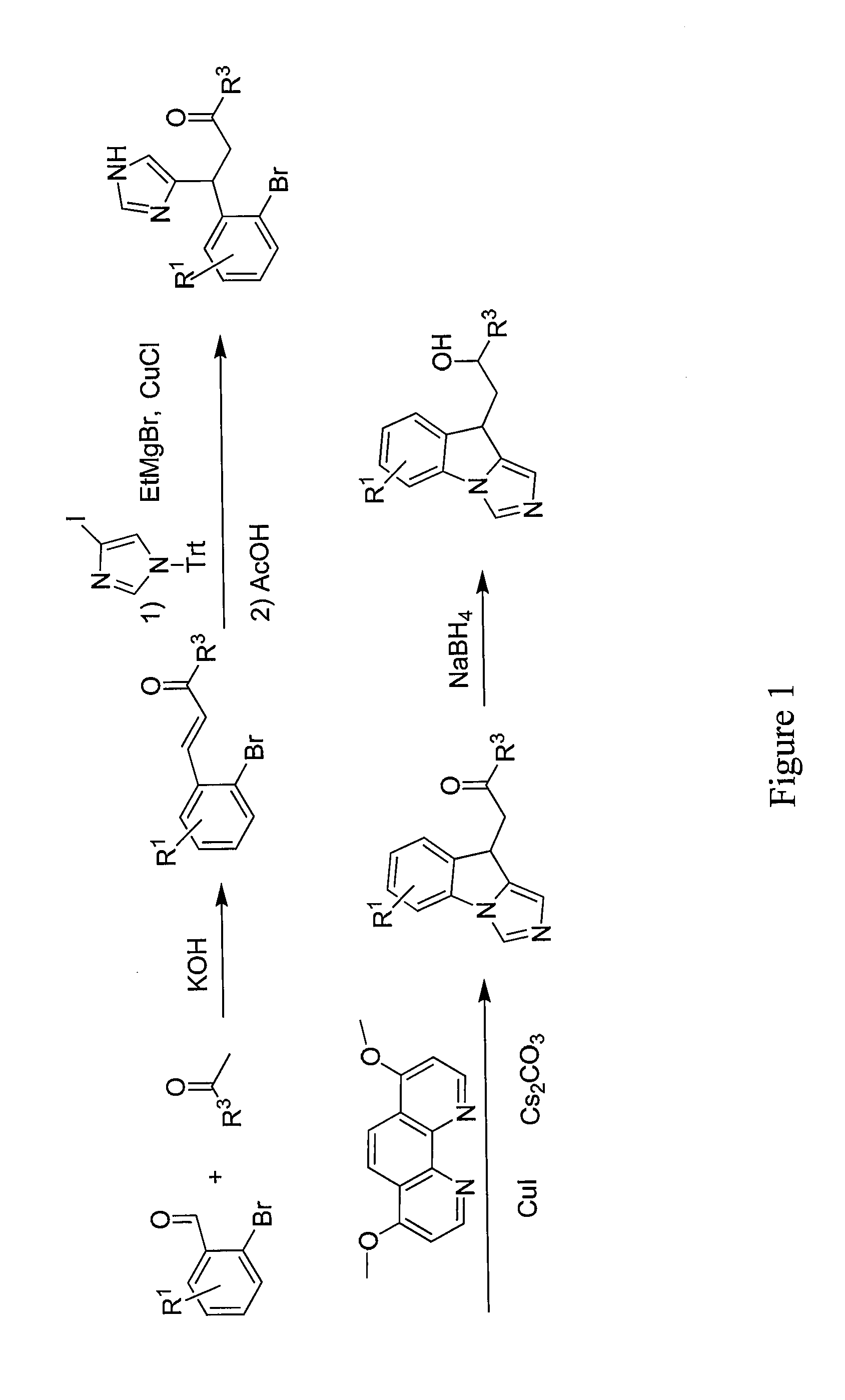
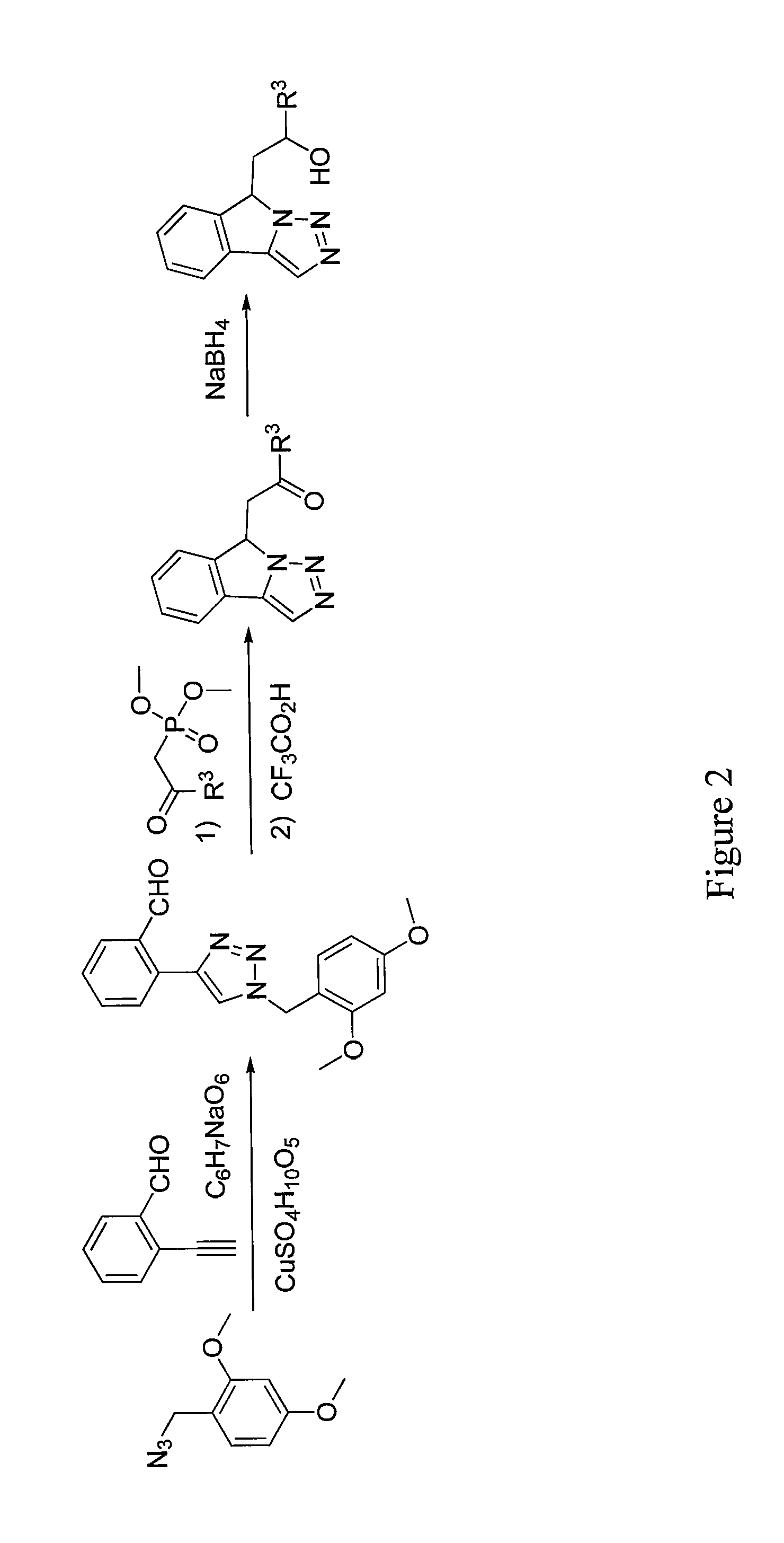
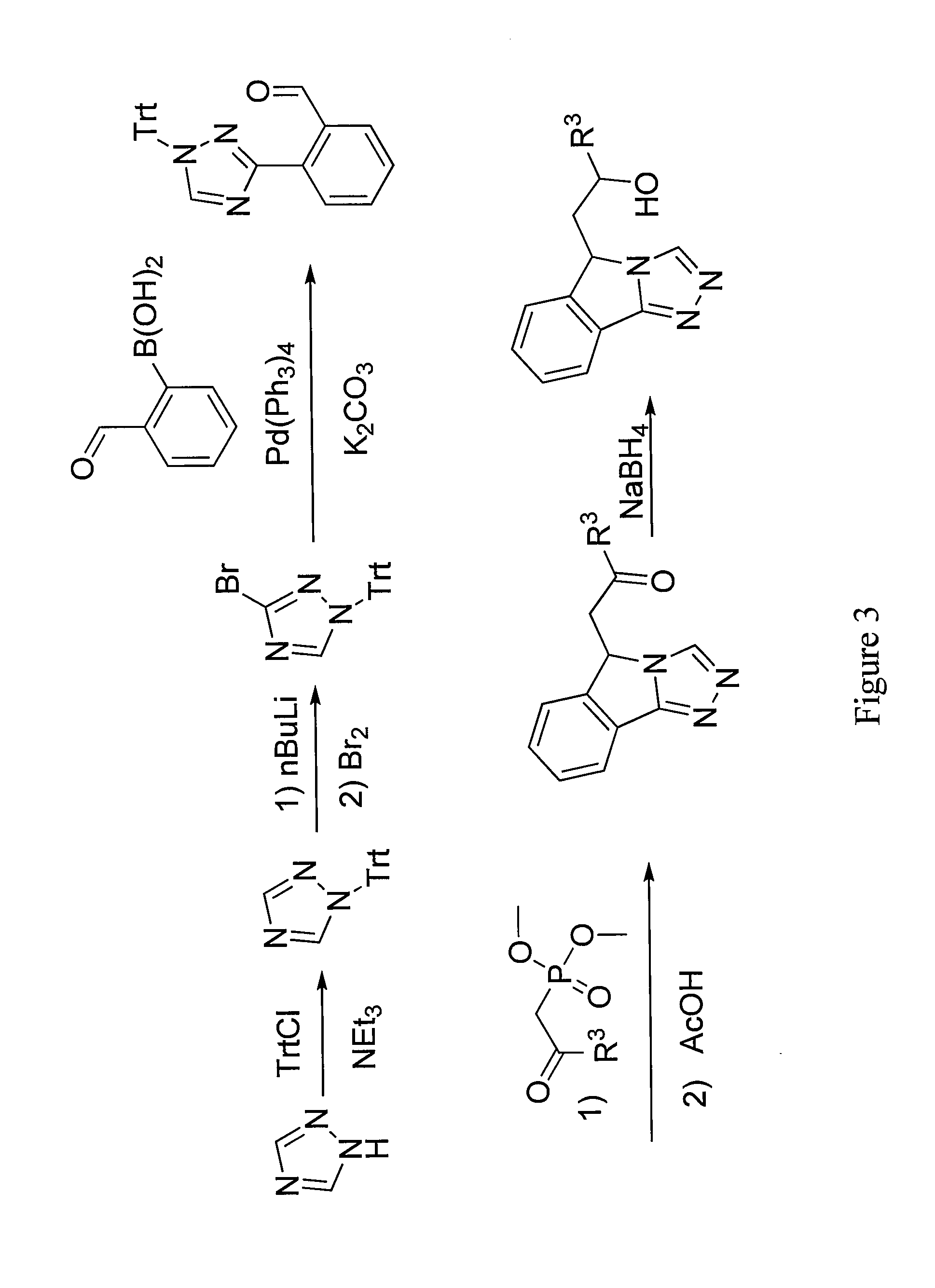
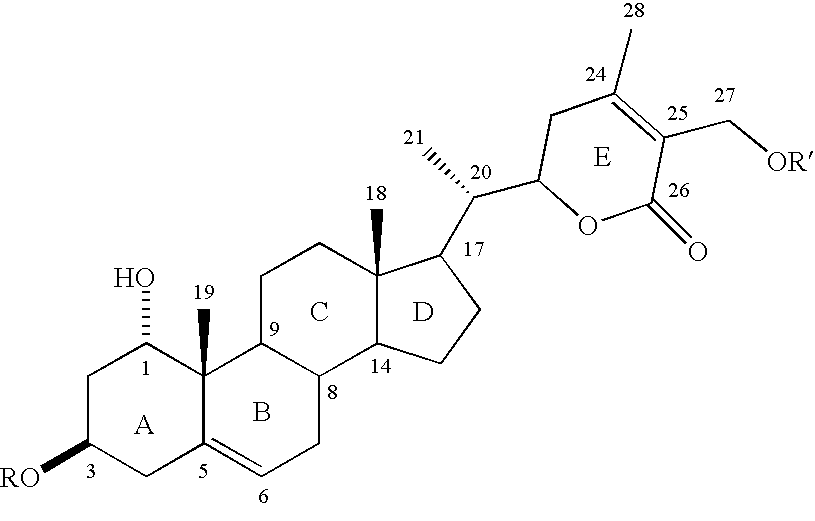
Patents
Literature
405 results about "Oxygenase" patented technology
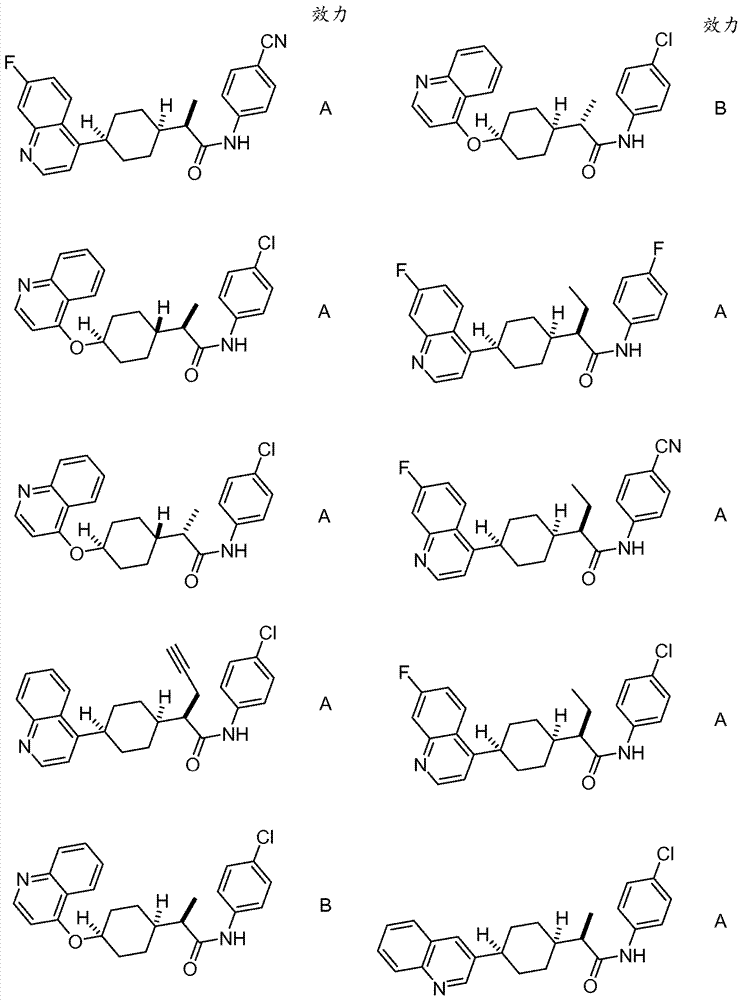
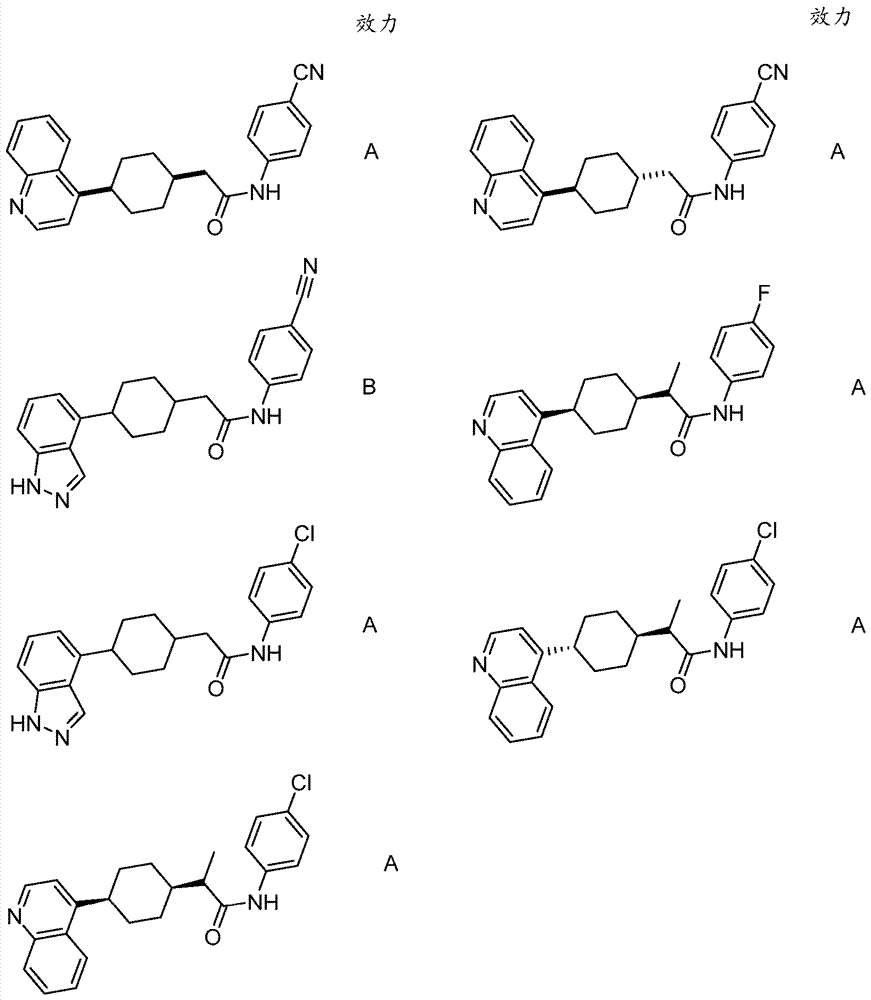
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An oxygenase is any enzyme that oxidizes a substrate by transferring the oxygen from molecular oxygen O₂ (as in air) to it. The oxygenases form a class of oxidoreductases; their EC number is EC 1.13 or EC 1.14.
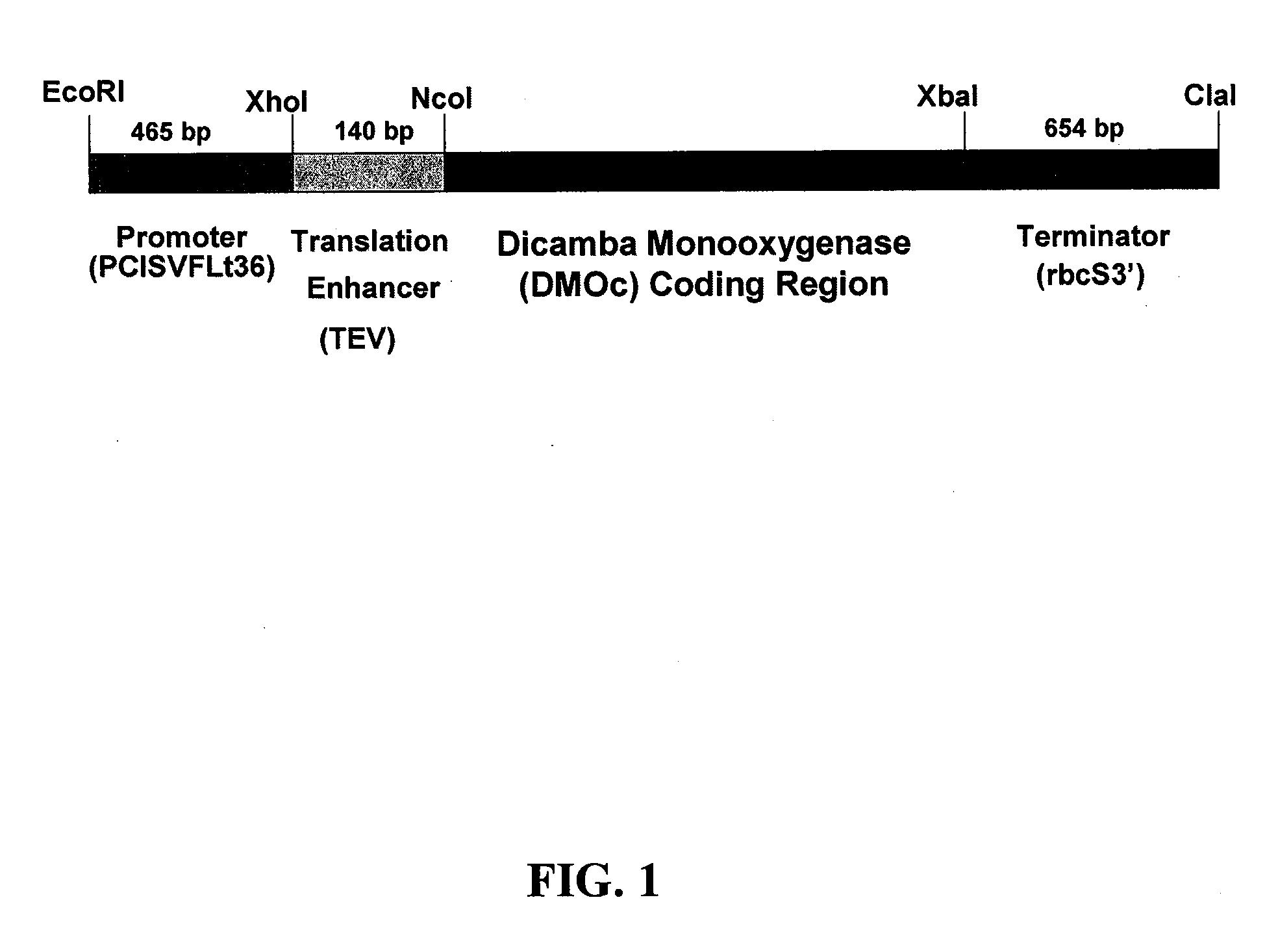
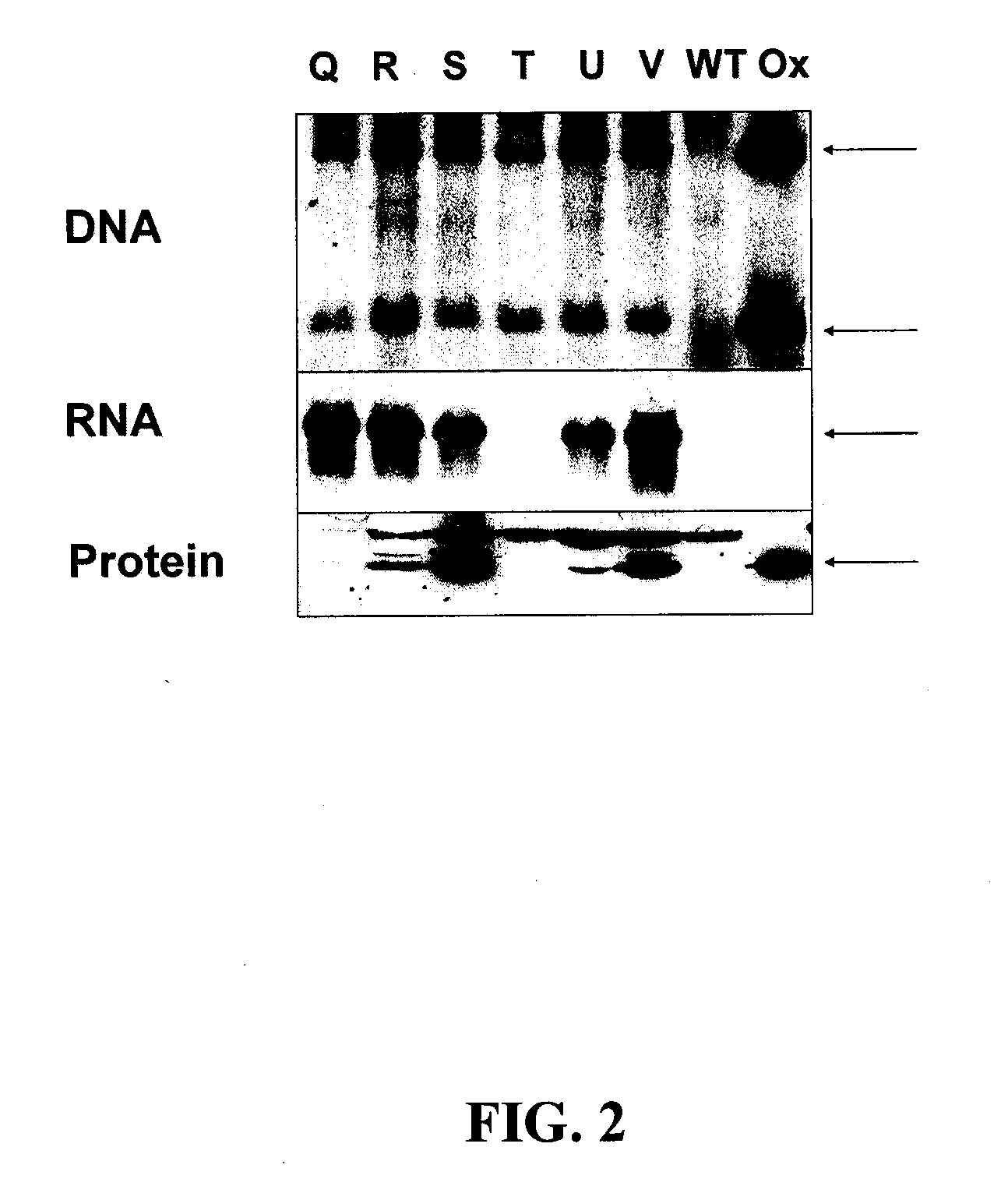
Modified dmo enzyme and methods of its use
The invention provides a modified variant of dicamba monooxygenase (DMO). The invention relates to the unexpected finding that cells expressing this DMO exhibit high levels of tolerance to the herbicide dicamba. Compositions comprising DMO-encoding nucleic acids and methods of use are provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC +1
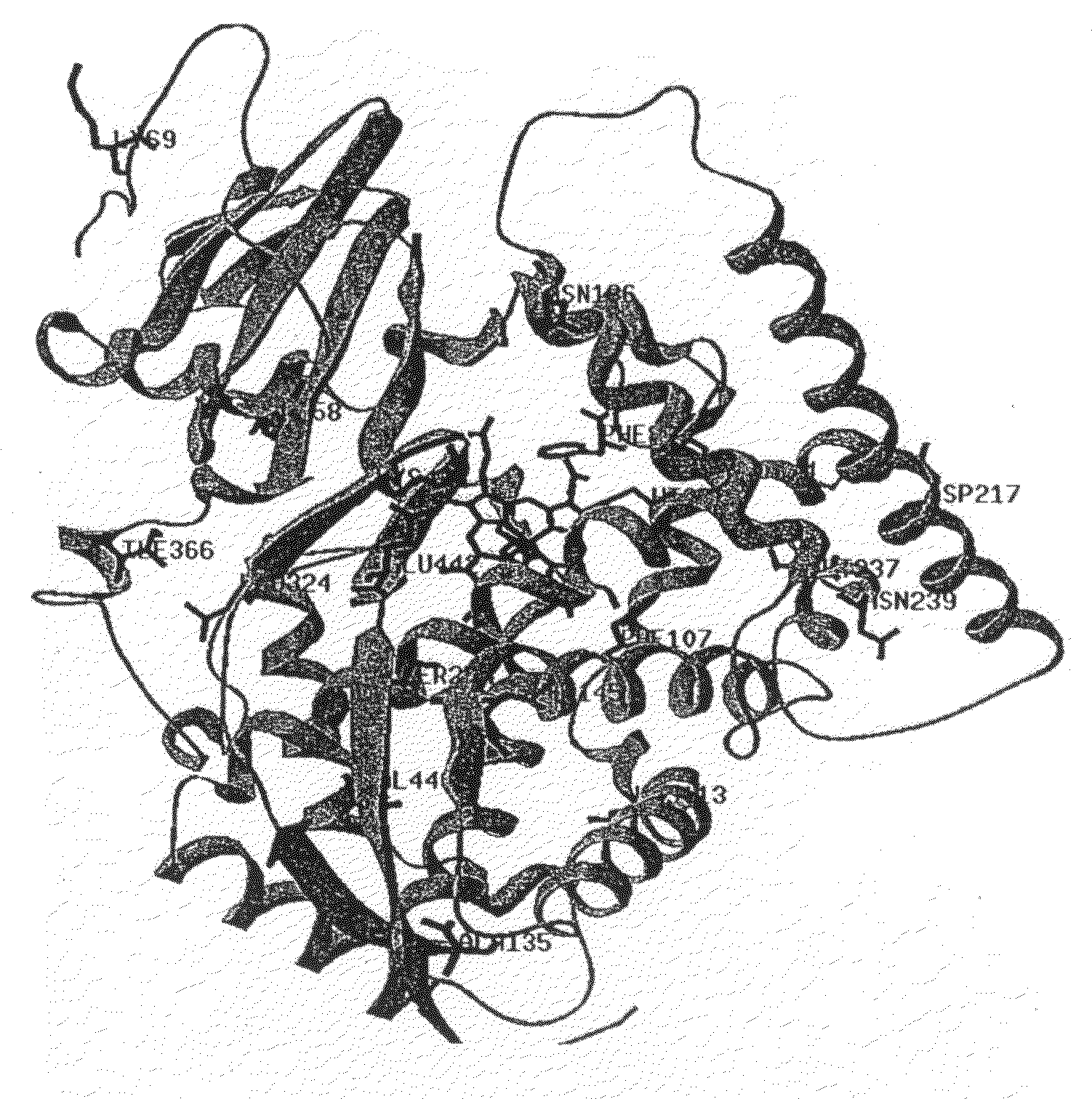
Peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants
InactiveUS20050202419A1Improve abilitiesImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesOxygenaseHeme
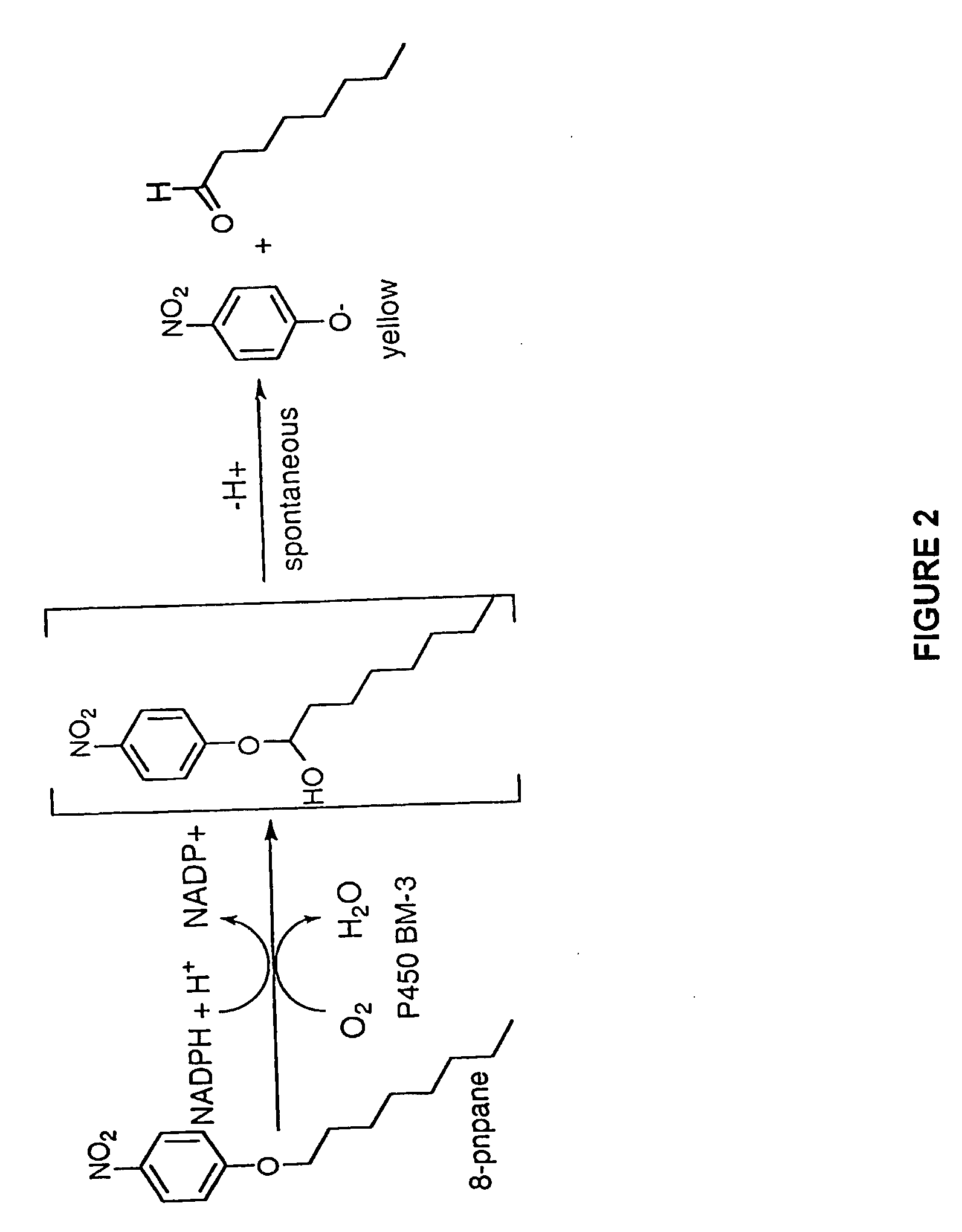
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have an improved ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. These variants also have an improved thermostability as compared to the cytochrome P450 BM-3 F87A mutant. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain mutants having I58V, F87A, H100R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, N239H, S274T, L324I, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Immunoregulatory agents
ActiveCN107427499ARaise countIncrease in opportunistic infectionsOrganic chemistryAntibody medical ingredientsDiseaseOxygenase
Compounds that modulate the oxidoreductase enzyme indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase, and compositions containing the compounds, are described herein. The use of such compounds and compositions for the treatment and / or prevention of a diverse array of diseases, disorders and conditions, including cancer- and immune-related disorders, that are mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is also provided.
Owner:FLEXUS BIOSCI
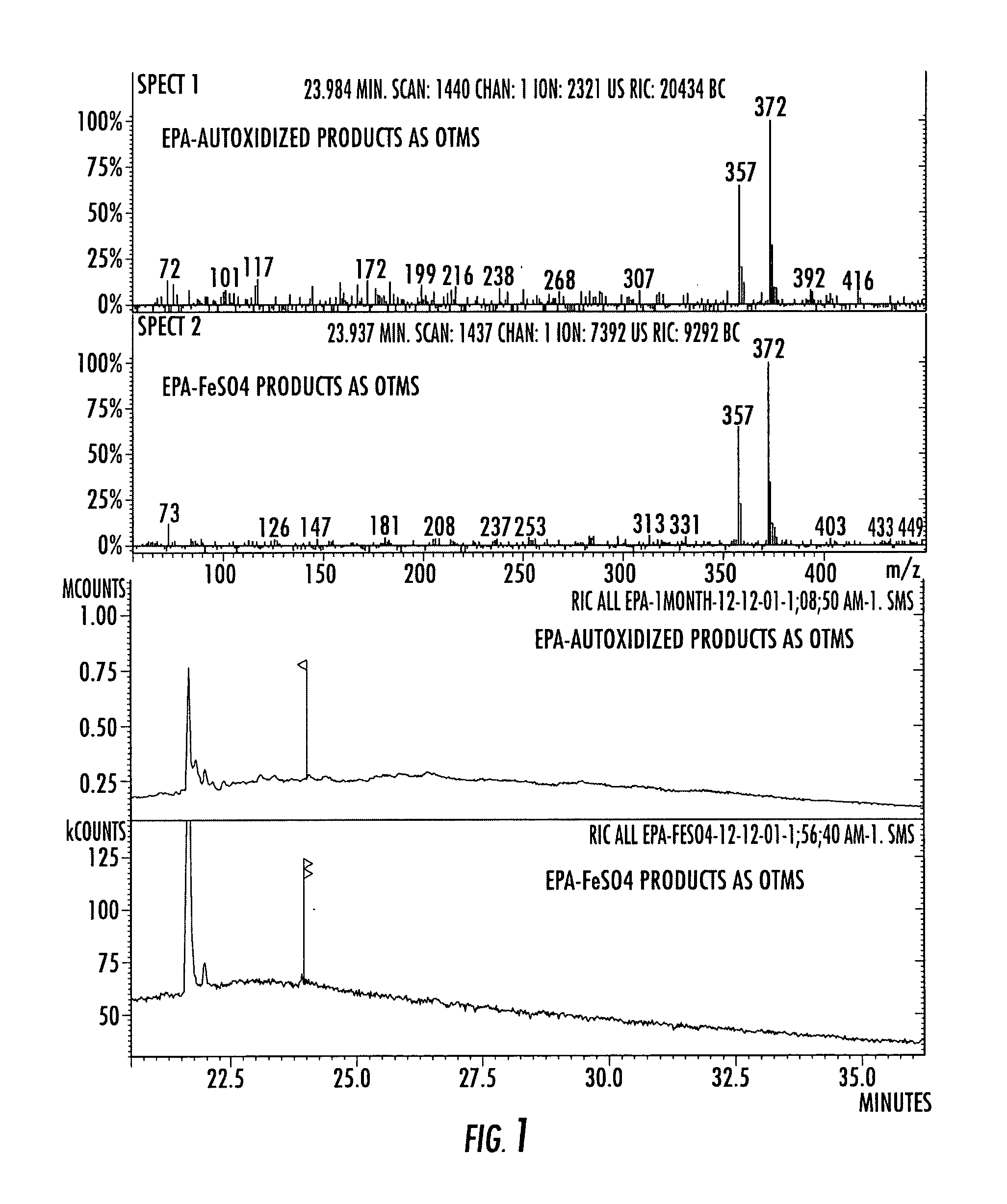
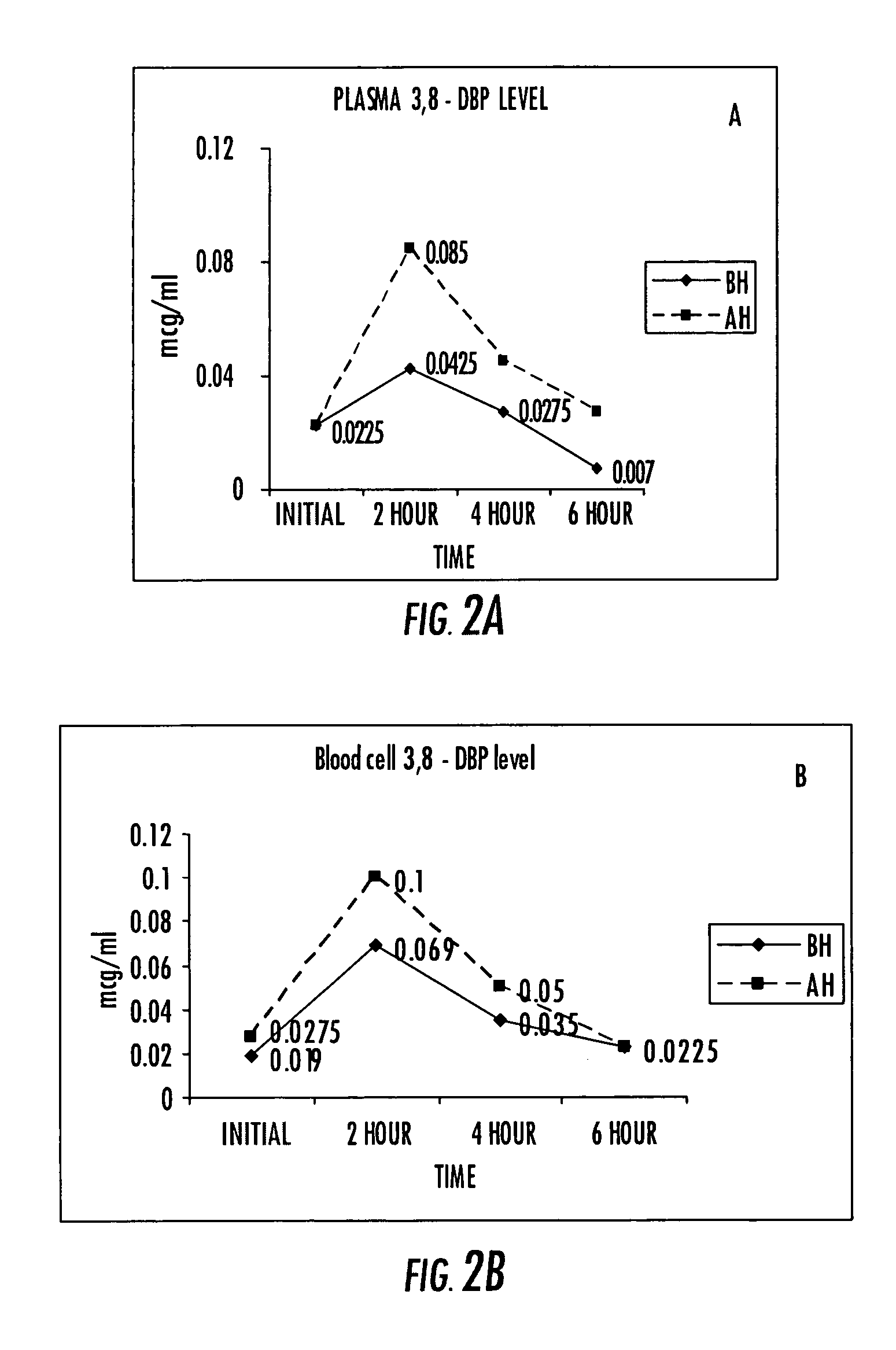
Compositions of stable bioactive metabolites of docosahexaenoic (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic (EPA) acids
InactiveUS20050282781A1Affect rate of absorptionOptimal moisture rangeBiocideNervous disorderMetaboliteBenzopyrone
An invention that adduces cogent evidence to establish that oxygenated dibenzo-α-pyrones (DBPs and their conjugates), the major bioactives of shilajit (Ayurvedic vitalizer), have their origin, at least partly, in EPA and DHA. Earlier research has shown that, in mammals, C-20 PUFAs are metabolized by oxygenases and other enzymes to produce short-lived prostaglandins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes that bind to specific G-protein-coupled receptors and signal cellular responses, e.g., inflammation, vasodilation, blood pressure, pain etc. But never before it was suggested / shown that C20:5n-3 (and C22:6 n-3) PUFAs, e.g., EPA (and DHA), are transformed into stable aromatic metabolites, DBPs, which elicit a large array of bioactivities in the producer organisms and also control the synthesis and metabolism of arachidonate-derived prostaglandins. The major beneficial effects attributed to EPA and DHA are now found to be largely contributed by DBPs and their aminoacyl conjugates and the dibenzo-α-pyrone-chromoproteins (DCPs). Because of the highly unstable nature of EPA and DHA, when administered, they are metabolized into a large array of uncontrolled products, several of which are systemically undesirable. By contrast, DBPs, because of their stability, perform the biological response modifier (BRM) functions in a directed and sustained way. Many of the biological effects of DBPs described in this invention, were earlier attributed to EPA and DHA,—the precursors of DBPs.
Owner:NATREON INC
Octahedral nanometer alloy, porous octahedral nanometer alloy as well as preparation method and purpose thereof
InactiveCN106493386AEasy to prepareSimple methodMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingOctahedronAlloy
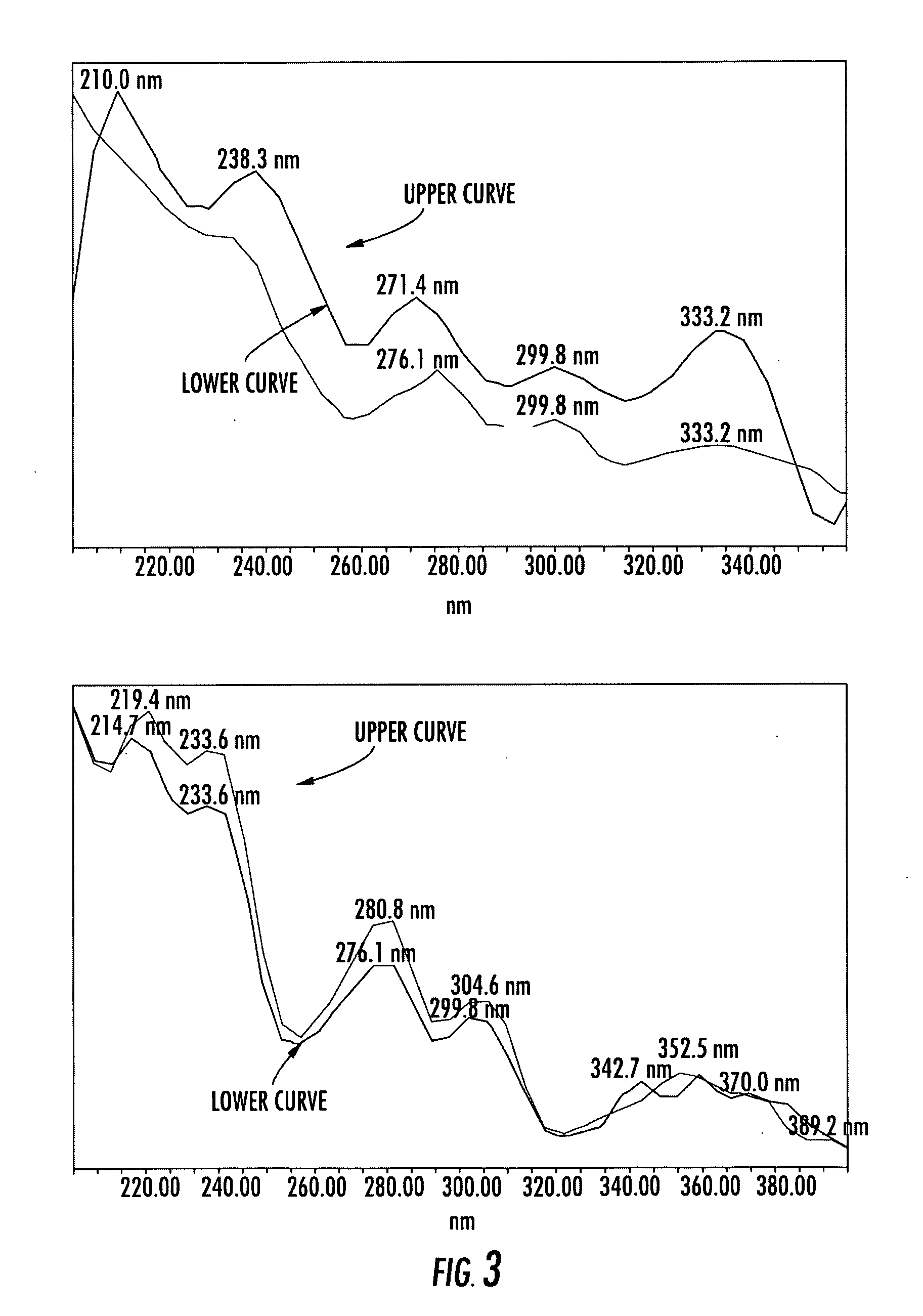
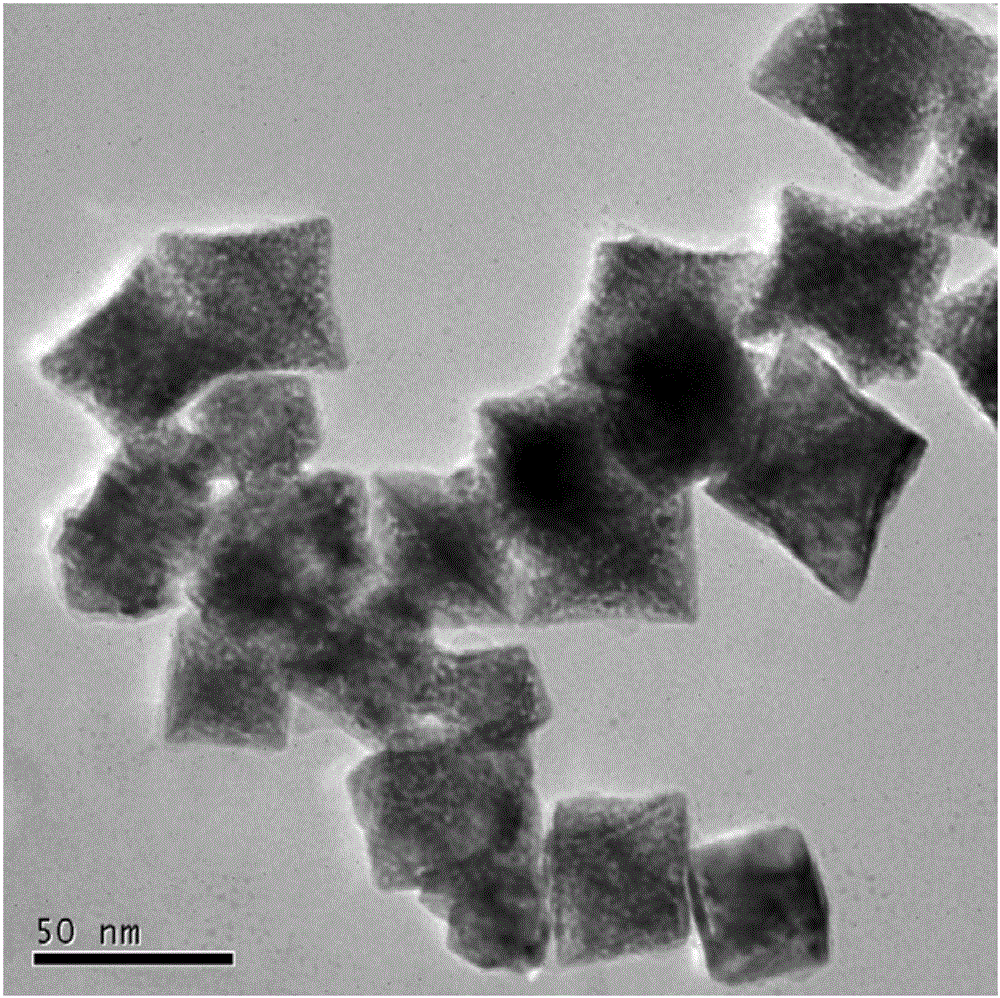
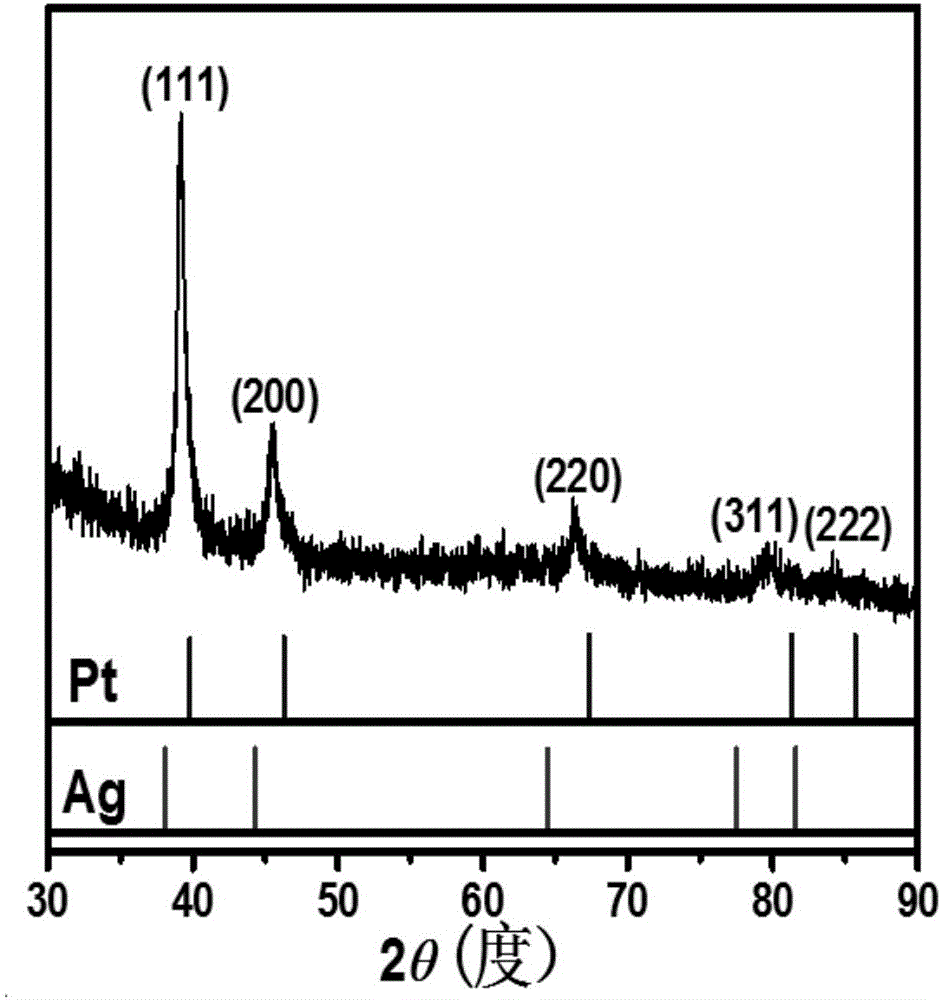
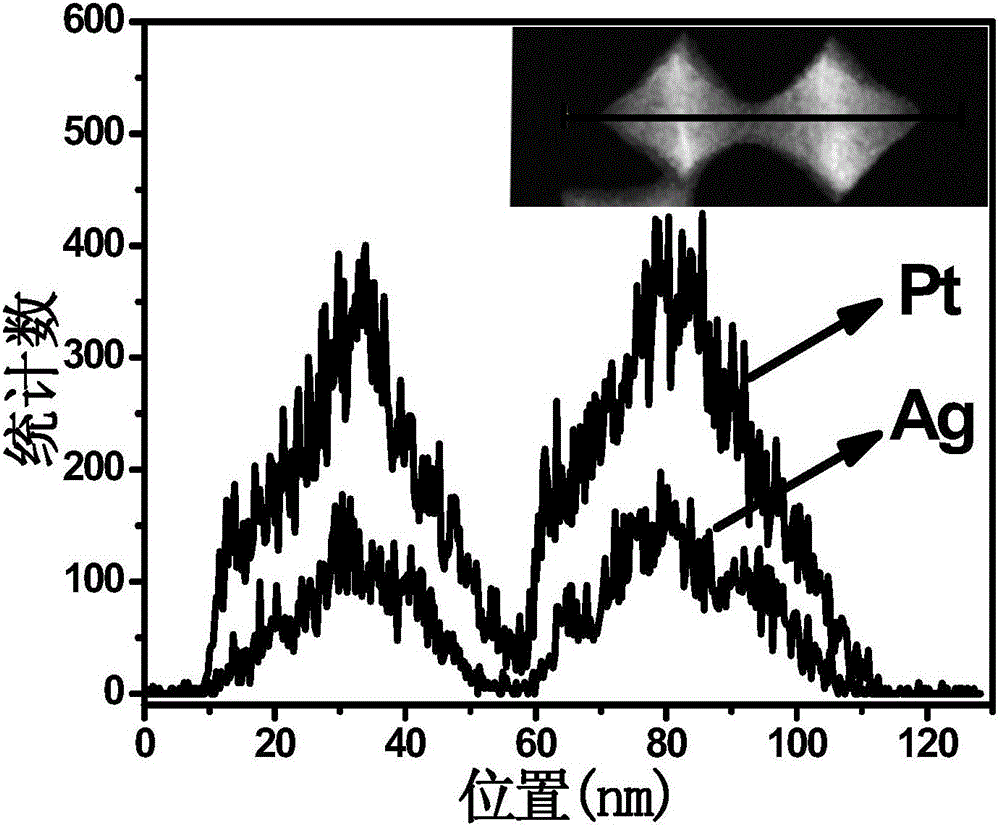
The invention relates to octahedral nanometer alloy, porous octahedral nanometer alloy as well as a preparation method and a purpose thereof. The octahedral nanometer alloy is prepared by mixing a metal salt precursor, a surfactant, a reducer and a solvent together and carrying out reaction for a certain time at a proper temperature. A crystal structure of the octahedral nanometer alloy has high symmetry, and a lattice structure of octahedral nanometer particles which form the nanometer alloy is face-centered cubic. The preparation method is simple, is simple and convenient to operate and does not need complex equipment and process; the obtained octahedral nanometer alloy is further dealloyed to obtain the porous octahedral nanometer alloy which also has very high structural symmetry and is large in specific surface area and good in structure stability; as a novel class of high-activity oxygenase mimetic enzyme and peroxidase mimetic enzyme, the octahedral nanometer alloy and the porous octahedral nanometer alloy can be applied to catalysis, immunoassay, biological detection and clinical diagnosis by replacing oxygenase and peroxidase.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Cytochrome P450 oxygenases
ActiveUS7226768B2High activityImprove stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesCytochrome p450 enzymeAmino acid
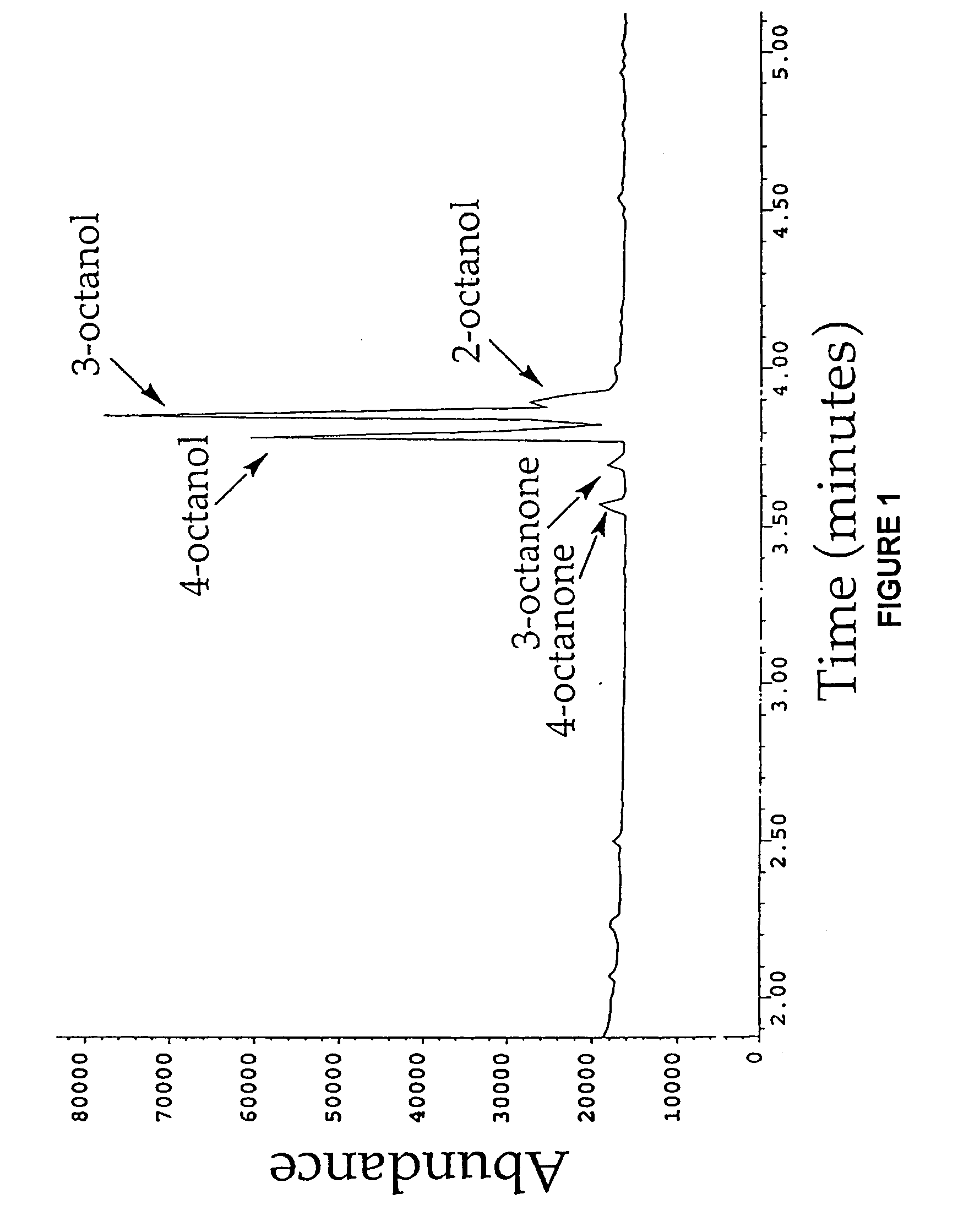
Nucleic acids encoding cytochrome P450 variants are provided. The cytochrome P450 variants of have a higher alkane-oxidation capability, alkene-oxidation capability, and / or a higher organic-solvent resistance than the corresponding wild-type or parent cytochrome P450 enzyme. A preferred wild-type cytochrome P450 is cytochrome P450 BM-3. Preferred cytochrome P450 variants include those having an improved capability to hydroxylate alkanes and epoxidate alkenes comprising less than 8 carbons, and have amino acid substitutions corresponding to V78A, H236Q, and E252G of cytochrome P450 BM-3. Preferred cytochrome P450 variants also include those having an improved hydroxylation activity in solutions comprising co-solvents such as DMSO and THF, and have amino acid substitutions corresponding to T235A, R471A, E494K, and S1024E of cytochrome P450 BM-3.
Owner:NORO MOSELEY PARTNERS V +2
Immunoregulatory agents
ActiveCN106999450AReduce loadRaise countImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAmide active ingredientsOxygenaseBiochemistry
Compounds that modulate the oxidoreductase enzyme indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase, and compositions containing the compounds, are described herein. The use of such compounds and compositions for the treatment and / or prevention of a diverse array of diseases, disorders and conditions, including cancer- and immune-related disorders, that are mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is also provided.
Owner:FLEXUS BIOSCI
Method for producing alcohol by using microorganism
The present invention describes a recombinant of a microorganism that does not inherently utilize an alkane, and an alcohol, whereby the recombinant has acquired an ability to convert the alkane into the alcohol due to transformation with a DNA encoding a methane oxygenase. The present invention describes a method for producing alcohol by culturing the recombinant, and allowing the obtained culture, cells isolated from the culture or processed product of the cells to exist with the alkane to produce the alcohol.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Use of novel lipid mediators to inhibit angiogenesis
The present invention is generally drawn to novel isolated therapeutic agents, termed lipoxins, generated from the interaction between a dietary omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) such as arachidonic acid (AA), oxygenases and the analgesic aspirin (ASA). Surprisingly, careful isolation of compounds generated from the combination of components in an appropriate environment provide di- and tri-hydroxy containing derivatives of AA containing compounds having unique structural and physiological properties. The present invention therefore provides for many new useful therapeutic di- and tri-hydroxy derivatives of AA (lipoxins, aspirin-triggered epi-lipoxins) that diminish, prevent, or eliminate NV, hemangiogenesis and / or angiogenic condition(s) of corneal tissue. The present invention also provides methods of use, methods of preparation, and packaged pharmaceuticals for use as medicaments for the compounds disclosed throughout the specification.
Owner:THE SCHEPENS EYE RES INST +1
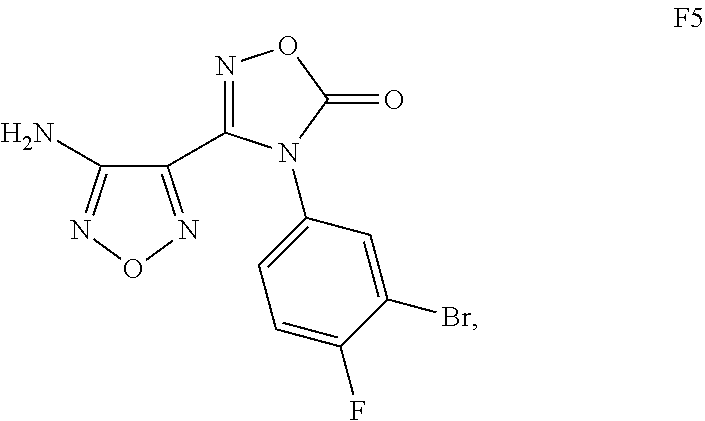
Process for the synthesis of an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor
ActiveUS20150133674A1Organic active ingredientsCarbamic acid derivatives preparationDioxygenaseStereochemistry
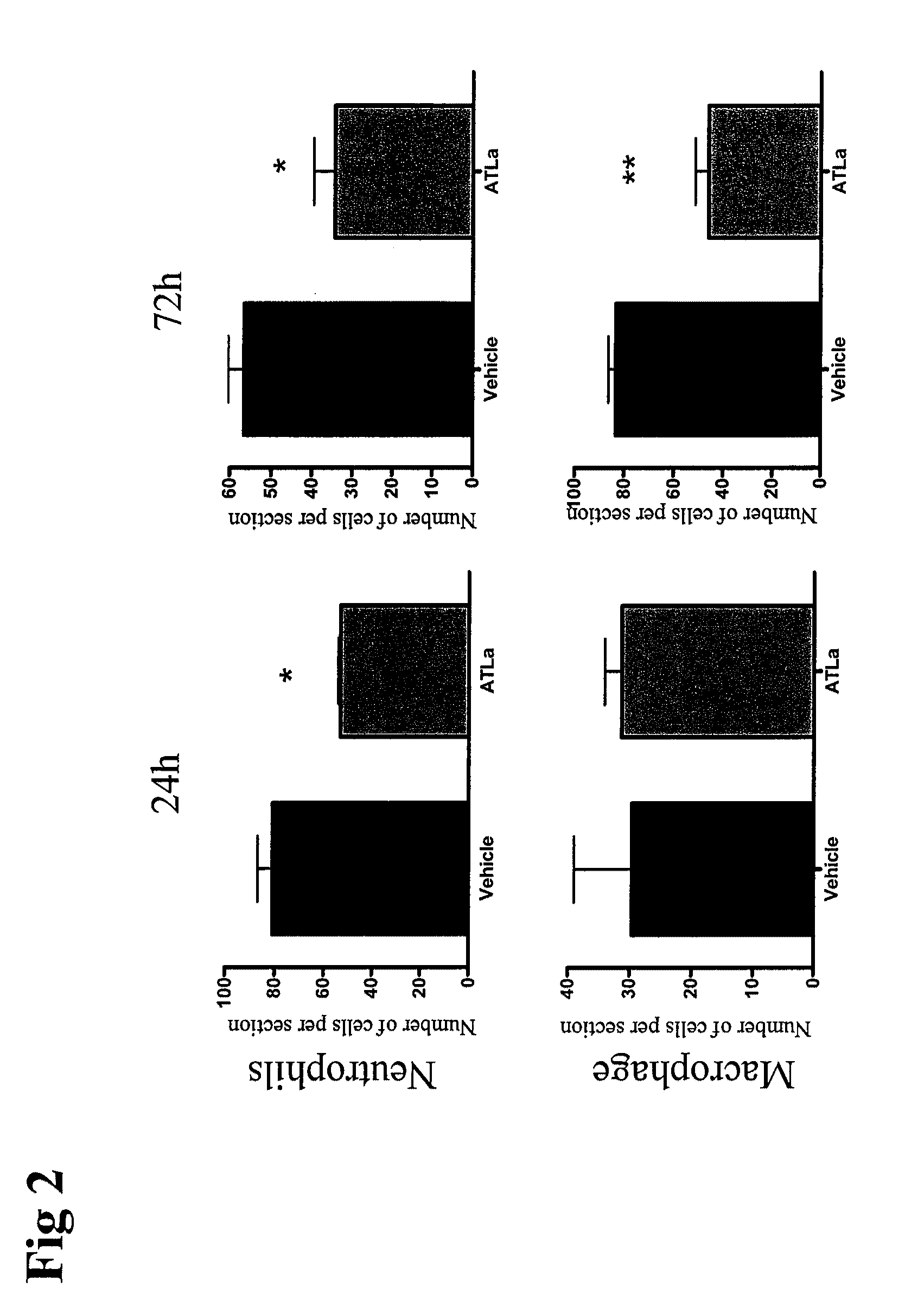
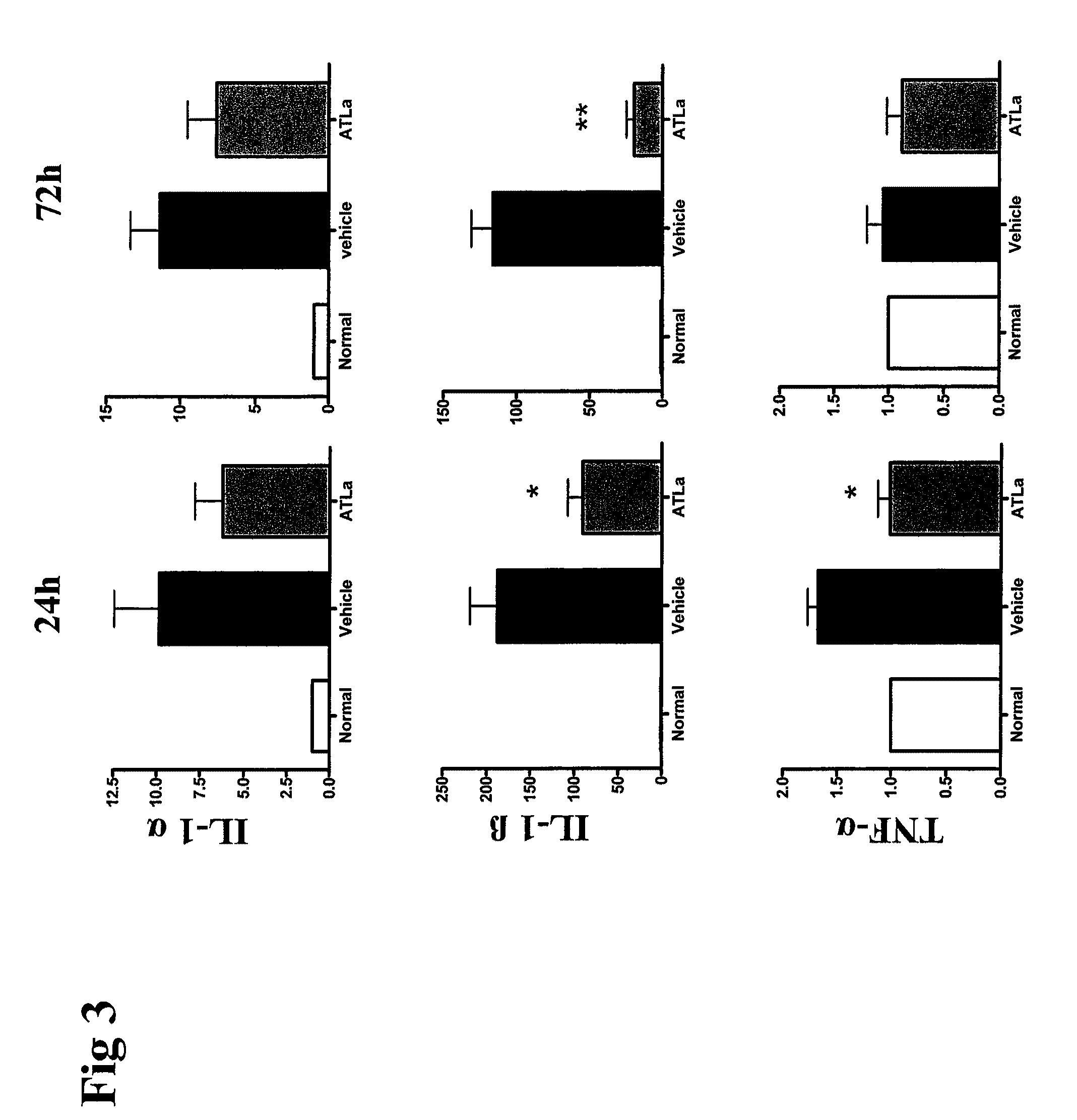
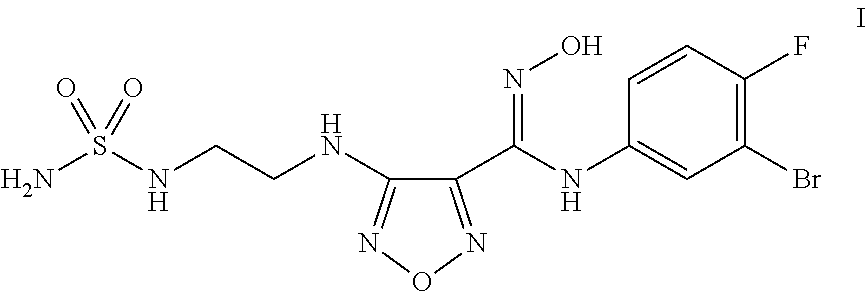
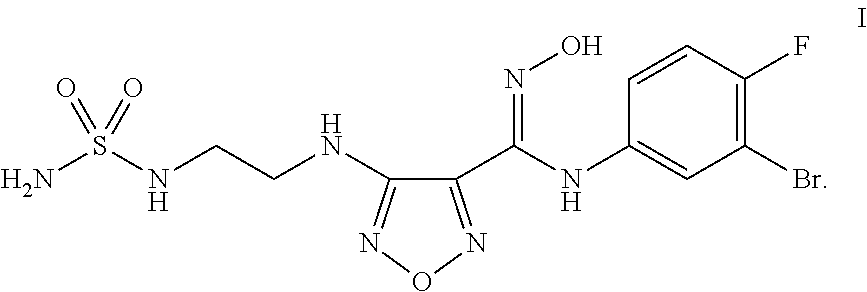
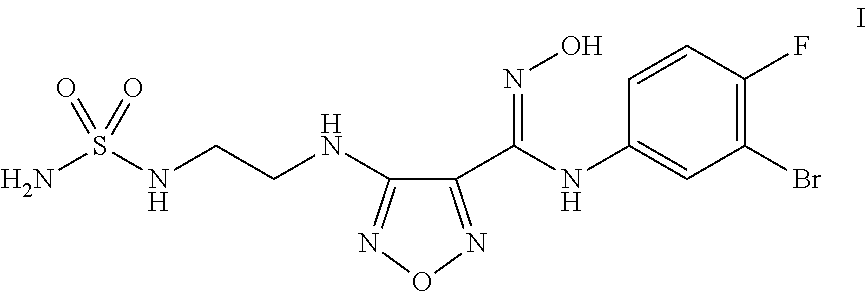
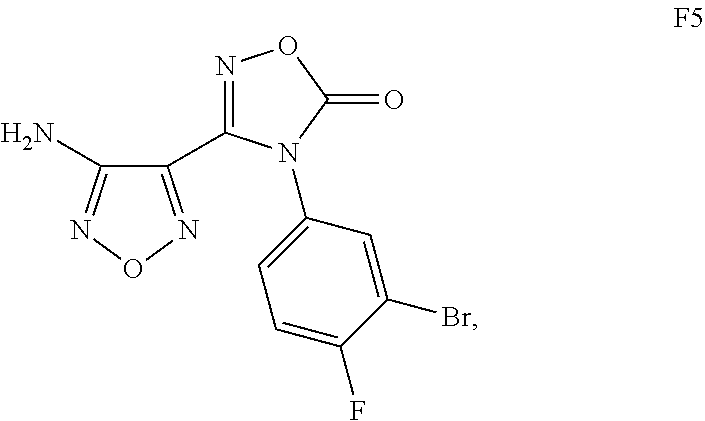
The present application is directed to processes and intermediates for making 4-({2-[(aminosulfonyl)amino]ethyl}amino)-N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N′-hydroxy-1,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide, which is an inhibitor of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, useful in the treatment of cancer and other disorders.
Owner:INCYTE
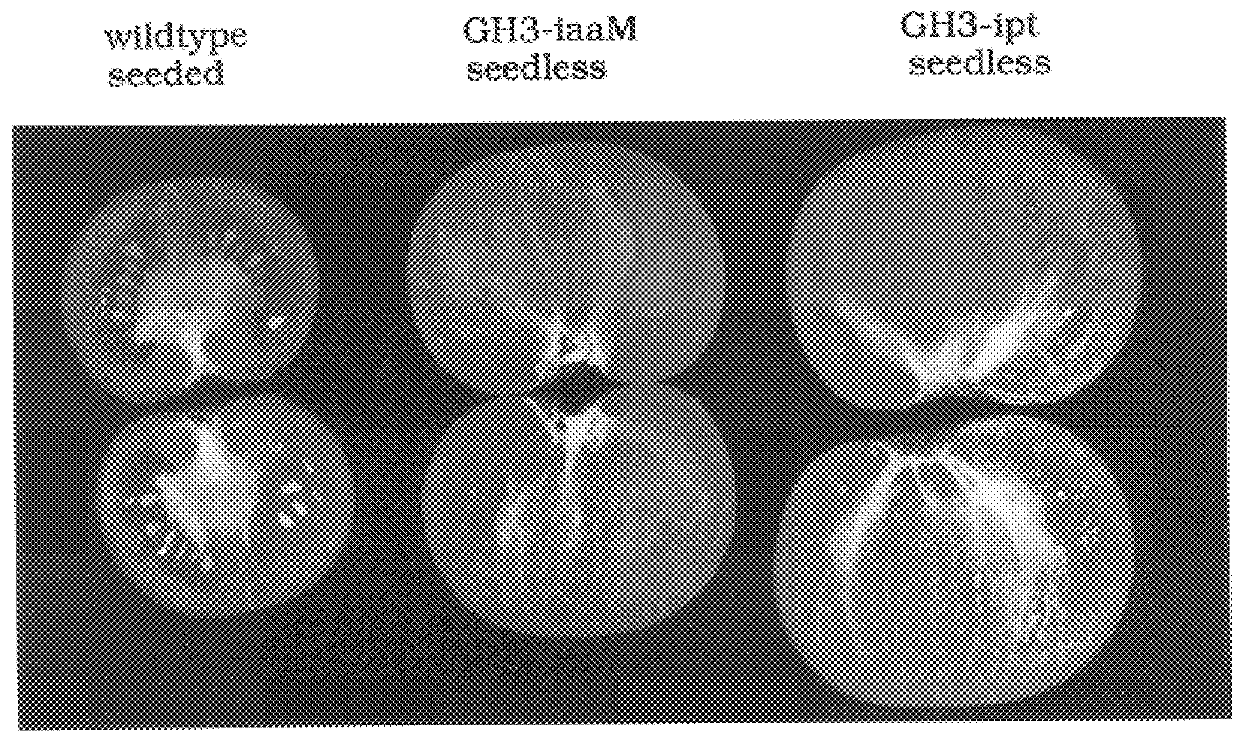
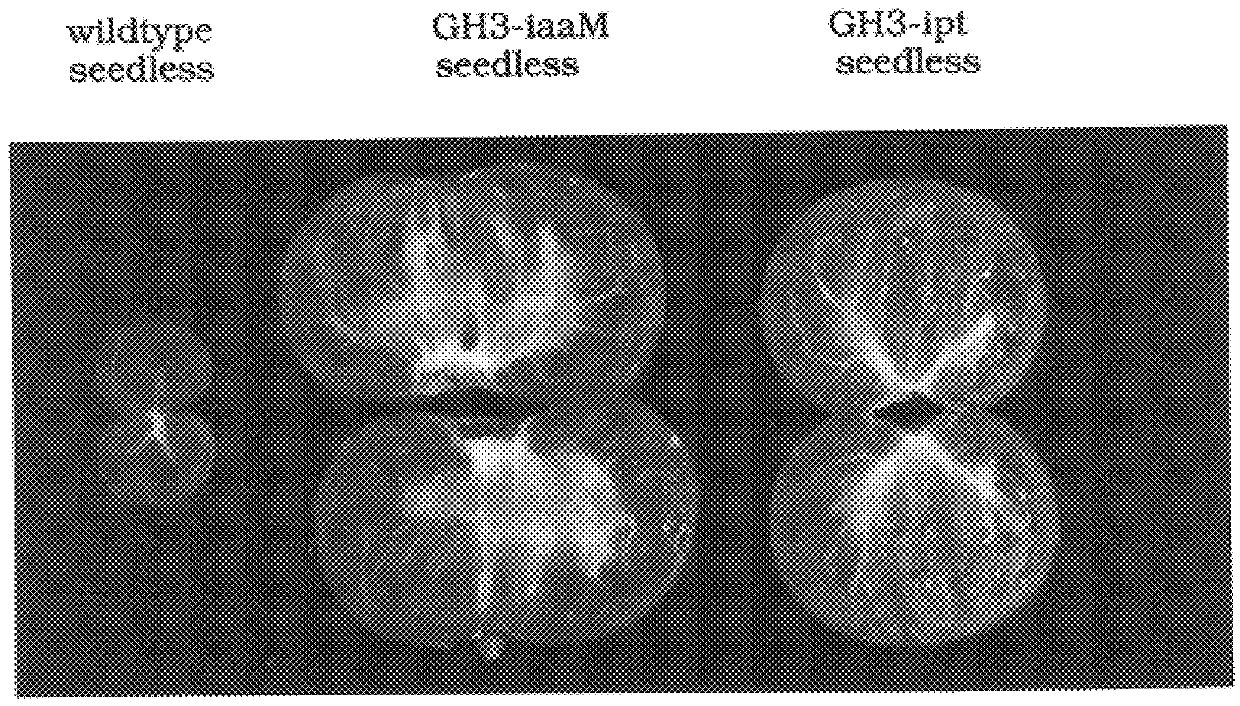
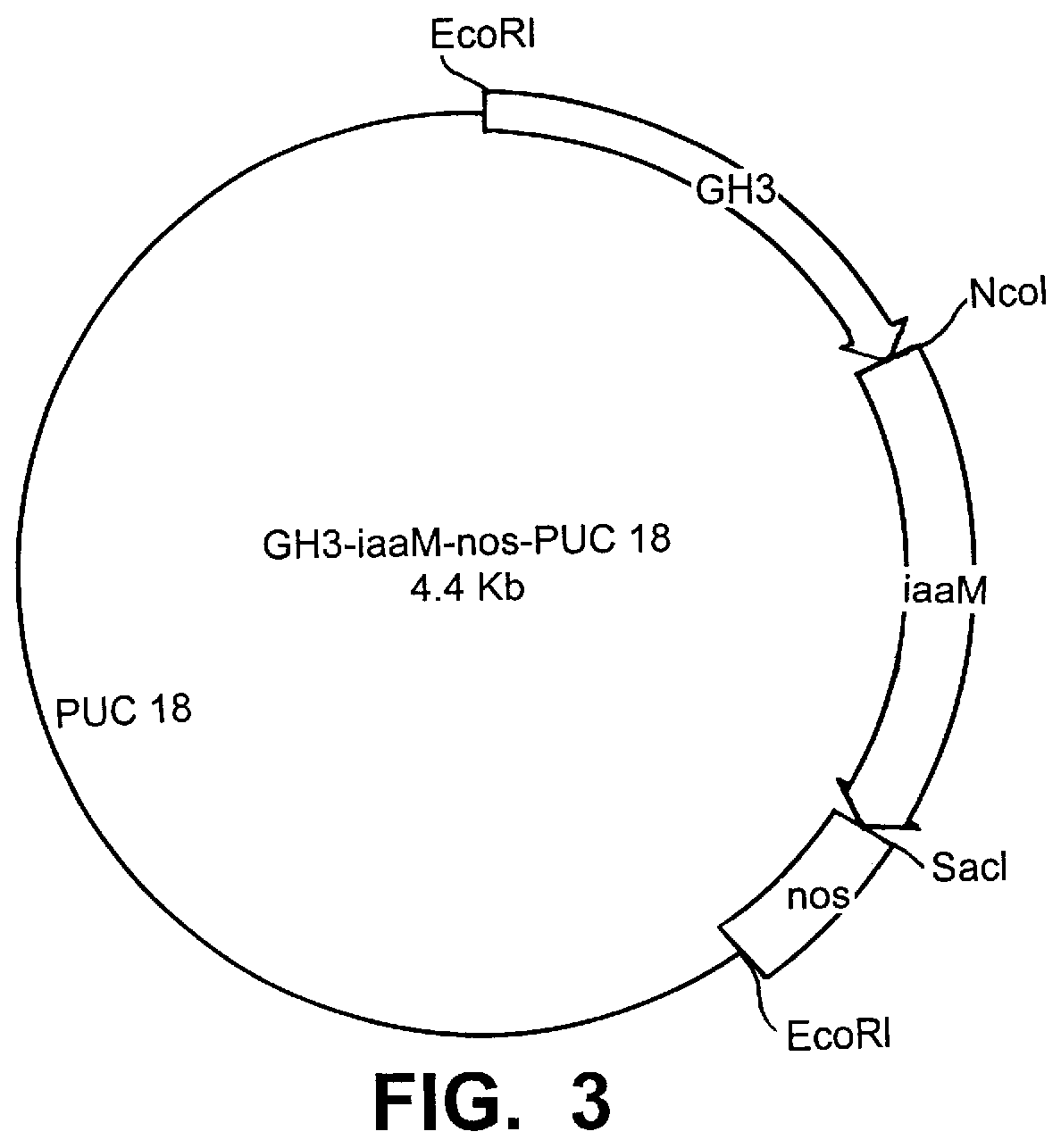
Transgenic seedless fruit comprising AGL or GH3 promoter operably linked to isopentenyl transferase or tryptophan monooxygenase coding DNA
InactiveUS6268552B1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesBiosynthetic genesDNA construct
The present invention provides methods and DNA constructs for the genetic engineering of plant cells to produce plants which produce substantially seedless fruit in the absence of exogenous growth factors (auxins or cytokinins) and in the absence of pollination. The substantially seedless fruits produced by the methods described herein are about the size of wildtype seeded fruit (or somewhat larger) and these fruits are equal to or superior to the wildtype seeded fruit with respect to solid content and flavor. The seedless fruits of the present invention are produced in transgenic plants which contain and express auxin or cytokinin biosynthetic genes, e.g., tryptophan oxygenase or isopentenyl transferase coding sequences expressed under the regulatory control of GH3 or AGL promoter sequences directing preferential or tissue specific expression of a downstream gene in the ovaries or developing fruit.
Owner:LI YI
Thermostable peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants and methods of use
InactiveUS20090264311A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove abilitiesSugar derivativesLibrary screeningOxygenaseHeme
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have at least one mutation improving their ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. The variants also have at least one mutation improving thermostability as compared to the parent enzyme or corresponding wild-type enzyme. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain variants having L52I, I58V, F87A, H100R, S106R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, A184V, N239H, S274T, L324I, V340M, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
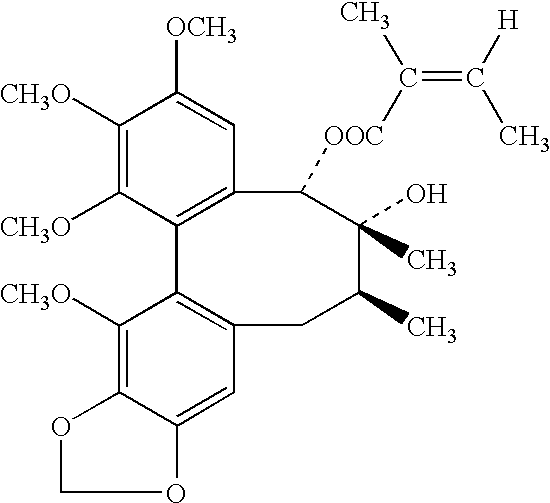
Plant drug for treatment of liver disease
The present invention related to safe plant drug for treatment of liver disease, specifically, this invention proves a safe plant drug Schisandrin and its preparation. Schisandrin has the following pharmaceutical functions: increasing tumor suppresson genes express activity, decreasing activity of oncogenes, increasing immune function, increasing liver DNA synthesis, decreasing serum alamine aminotransferase activity, increasing glutathione level, increasing glutathione reductase activity, decreasing lipid peroxidation of liver, increasing hepatic microsomal monooxygenases activity, increasing ATP content in liver, increasing energy metabolism activity, decreasing density lipoprotein oxidation, protecting gastrointestinal function, increasing killer cell activity, increasing complement activity, decreasing induced liver cancer activity and decreasing grown of cancer cells.
Owner:ZHAO XINXIAN
Directed evolution of recombinant monooxygenase nucleic acids and related polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20060051782A1Improve abilitiesIncrease rangeBacteriaLibrary screeningNitrobenzeneMonooxygenase
The present invention relates to novel monooxygenase nucleic acids and polypeptides created using mutagenesis, DNA shuffling, or both, in a single iteration or multiple iterations, and methods for their creation and use. The monooxygenase enzymes of the present disclosure have particular utility as biocatalysts in industrial chemical redox reactions, such as the oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons, for example, toluene, benzene, or nitrobenzene, into industrially desirable products. The systems and processes of the present invention are especially useful for the coupled synthesis and recovery of catechols, methylcatechols, resorcinols, methylresorcinols, hydroquinones, methylhydroquinones, hydroxybenzenes, cresols, nitrobenzenes, and nitrohydroxyquinones.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Process for the synthesis of an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor
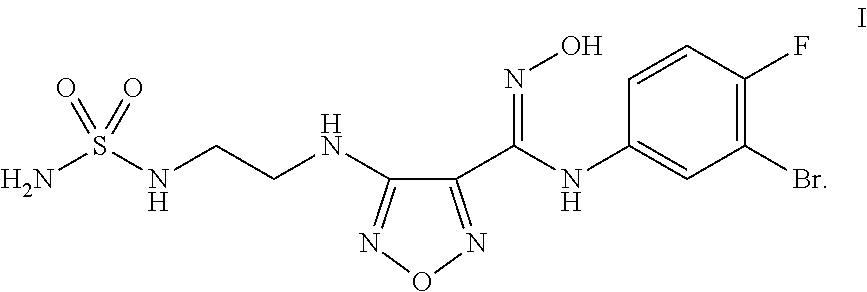
The present application is directed to processes and intermediates for making 4-({2-[(aminosulfonyl)amino]ethyl}amino)-N-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-N′-hydroxy-1,2,5-oxadiazole-3-carboximidamide, which is an inhibitor of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, useful in the treatment of cancer and other disorders.
Owner:INCYTE HLDG CORP
Cytochrom P450 oxygenases
InactiveUS20080293928A1High activityImprove stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesCytochrome p450 enzymeAmino acid
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for producing glucaric acid by constructing recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and fermenting
ActiveCN107164255AAvoid non-selectiveImprove energy performanceFungiHydrolasesHigh energyInositol monophosphatase
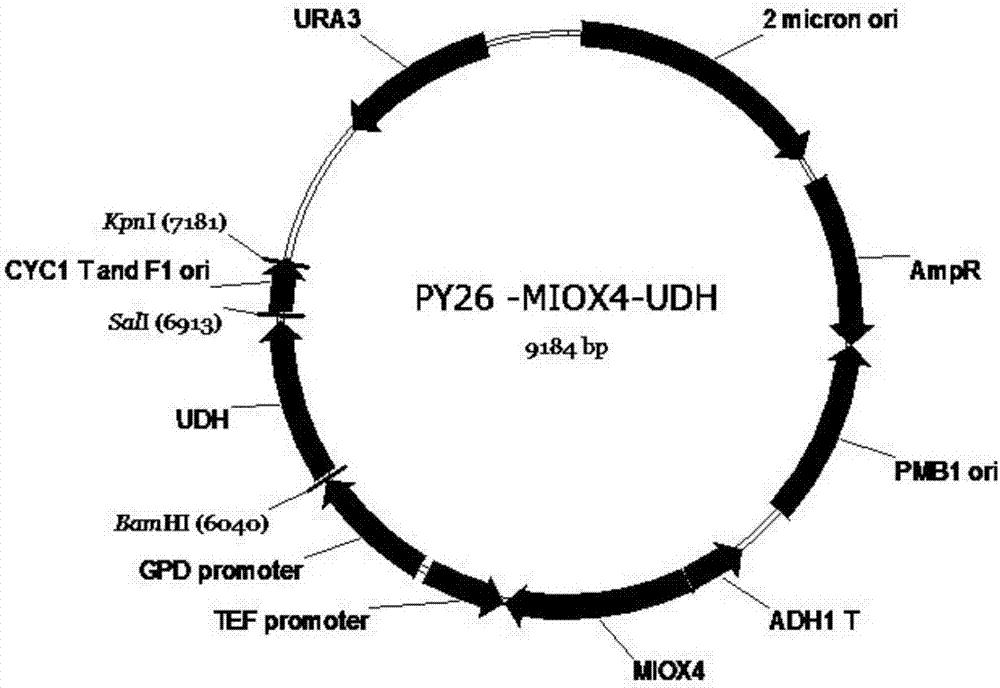
The invention discloses a method for producing glucaric acid by constructing recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and fermenting and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: knocking out an OPI gene of saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741; introducing myo inositol-1-phosphate synthase and inositol monophosphatase from the saccharomyces cerevisiae, inositol from arabidopsis thaliana and uronic acid dehydrogenase from pseudomonas syringae into the saccharomyces cerevisiae through constitutive plasmid pY26-GPD-TEF, and realizing approach construction of the saccharomyces cerevisiae from glucose to the glucaric acid. According to the method disclosed by the invention, by use of a constructed metabolic pathway, non-selectivity, high energy consumption property and high cost performance of a chemical oxidation method are avoided; the low-priced glucose is directly transformed into D-glucaric acid with high added value by fermentation culture of engineering bacteria; the method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, high transformation rate and fewer byproducts; production cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have an improved ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. These variants also have an improved thermostability as compared to the cytochrome P450 BM-3 F87A mutant. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain mutants having I58V, F87A, H100R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, N239H, S274T, L324I, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Oxygenase-bath alkali-free desizing process for polyester/cotton high-count and high-density fabric
InactiveCN102011298AQuality improvementFeel goodDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesBleaching apparatusPolyesterAlkali free
The invention relates to an oxygenase-bath alkali-free desizing process for a polyester / cotton high-count and high-density fabric. The process sequentially comprises the following steps of: sewing and singeing the fabric; washing the fabric with three-grid hot water; washing the fabric with two-grid coldwater; padding oxidation bleaching working solution; steaming at the temperature of 102 DEG C for 50 minutes; washing the fabric with four-grid hot water; drying; and shaping, wherein in the step of padding oxidation bleaching working solution, the formula of the oxidation bleaching working solution comprises 10g / L of high-efficient scouring agent HS-120B, 65g / L of 288 dispersing agent, 5g / L of scouring enzyme 188, 5g / L of wax regent WR, 10g / L of hydrogen peroxide stabilizing agent P and 14.0 to 15.0g / L of hydrogen peroxide (wherein the concentration is 33 percent). Compared with the prior art, the desized fabric has greatly improved quality, namely the handfeel is plump; the fabric surface loss ratio is low; the fabric surface whiteness is good; and the fabric has no cotton, multiple nodes and no alkaline spots.
Owner:HUAFANG
Method of Isolating P450 Gene
InactiveUS20080220419A1Effective isolationHigh throughput screeningAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganismsElectron transferMicroorganism resource
The present invention provides a method for preparing a hybrid gene. The method includes a step of amplifying a P450 gene fragment contained in a sample using primers designed on the basis of regions of a plurality of P450 in which amino acid sequences are highly conserved and a step of preparing the hybrid gene using the amplified fragments and a known P450 gene. The method includes no culturing step or a step of normalizing extracted DNAs and is useful in isolating a P450 gene from various microbial resources.The present invention further provides a fused cytochrome P450 monooxygenase containing a peptide which is linked to the C-terminus of a P450 protein with a linker portion disposed therebetween and which has the same function as that of a reductase domain contained in a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase originating from Rhodococcus sp. strain NCIMB 9784. This enables the construction of a high-efficiency electron transfer system useful for various P450 proteins and also enables the production of an active P450 monooxygenase.
Owner:KNC LAB
Tricyclic Compounds as Inhibitors of Immunosuppression Mediated By Tryptophan Metabolization
InactiveUS20160060266A1Improve efficiencyEffective inhibiting amountOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryOxygenaseAnticarcinogen
Presently provided are inhibitors of IDO and TDO and pharmaceutical compositions thereof, useful for modulating an activity of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophan 2,3 dioxygenase; treating immunosuppression; treating a medical conditions that benefit from the inhibition of tryptophan degradation; enhancing the effectiveness of an anti-cancer treatment comprising administering an anti-cancer agent; treating tumor-specific immunosuppression associated with cancer; and treating immunosuppression associated with an infectious disease.
Owner:NEWLINK GENETICS
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory withanolide compositions and method
Cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme inhibiting withanolides are described. In particular, compounds from Withania somnifera are the preferred source of the withanolides, although they can be from other plant sources. The COX-2 inhibition is selective over COX-1.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Decreasing RUBISCO content of algae and cyanobacteria cultivated in high carbon dioxide
InactiveUS20100081177A1Increase storage capacityImprove capacity utilizationBacteriaHydrolasesPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
Algae and cyanobacteria are genetically engineered to have lower RUBISCO (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase) content in order to grow more efficiently at elevated carbon dioxide levels while recycling industrial CO2 emissions back to products, and so as not to be able to grow outside of cultivation.
Owner:TRANSALGAE
Flavin monooxygenase mutant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107384880AIncreased specific enzyme activityEasy to produceFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastRandom mutation
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering and particularly relates to a flavin monooxygenase mutant and a preparation method thereof. The error-prone PCR technology is used to conduct random mutation on wild type flavin monooxygenase to obtain the flavin monooxygenase mutant. The specific enzyme activity of the flavin monooxygenase mutant is improved by 35% compared with that of the wild type flavin monooxygenase. Meanwhile, a yeast expression system is adopted, when the flavin monooxygenase is displayed on the surface of yeasts, yeast cells can serve as enzyme producers and can also serve as carriers in immobilized enzymes, operation of purification, fixation and the like of the enzymes are omitted, the production link is simplified, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Cyclohexanone monooxygenase and application thereof
ActiveCN108118035AHigh yieldLow priceBacteriaOxidoreductasesHigh concentrationCyclohexanone monooxygenase
The invention discloses cyclohexanone monooxygenase and an application thereof, in particular cyclohexanone monooxygenase obtained by site-specific mutagenesis and an application thereof. Compared with a SEQ ID NO: 1, the amino acid sequence of the cyclohexanone monooxygenase has gene mutation in at least one site as follows: serine Ser at the 386th site is mutated to asparagines Asn, and serine Ser at the 435th is mutated to threonine Thr. Experiments show that the cyclohexanone monooxygenase disclosed by the invention can catalytically convert a high concentration omeprazole thioether primerinto esomeprazole.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINGXIN PHARMA +1
Tricyclic compounds as inhibitors of immunosuppression mediated by tryptophan metabolization
InactiveUS9617272B2Improve efficiencyEffective inhibiting amountOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAnticarcinogenOxygenase
Presently provided are inhibitors of IDO and TDO and pharmaceutical compositions thereof, useful for modulating an activity of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophan 2,3 dioxygenase; treating immunosuppression; treating a medical conditions that benefit from the inhibition of tryptophan degradation; enhancing the effectiveness of an anti-cancer treatment comprising administering an anti-cancer agent; treating tumor-specific immunosuppression associated with cancer; and treating immunosuppression associated with an infectious disease.
Owner:NEWLINK GENETICS
Oxidizing enzymes in the manufacture of paper materials
InactiveCN1575363AHave a bleaching effectWith deinking effectNon-fibrous pulp additionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpAmylaseAdjuvant
The use of fatty acid oxidizing enzymes in the manufacture of paper materials, such as paper, linerboard, corrugated paperboard, tissue, towels, corrugated containers and boxes. Examples of fatty acid oxidizing enzymes are oxygenases classified as EC 1.13.11. including any of the sub-classes thereof, such as lipoxygenase, EC 1.13.11.12. The effect of these enzymes is that the deposition of pitch is reduced, and bleaching and de-inking effects are also observed on the paper pulp and the resulting paper material. The fatty acid oxidizing enzyme can be used in combination with a substrate, with proteases, lipases, xylanases, cutinases, oxidoreductases, cellulases, endoglucanases amylases, mannanases, steryl esterases, and / or cholesterol esterases; or with surfactants and other adjuvants.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
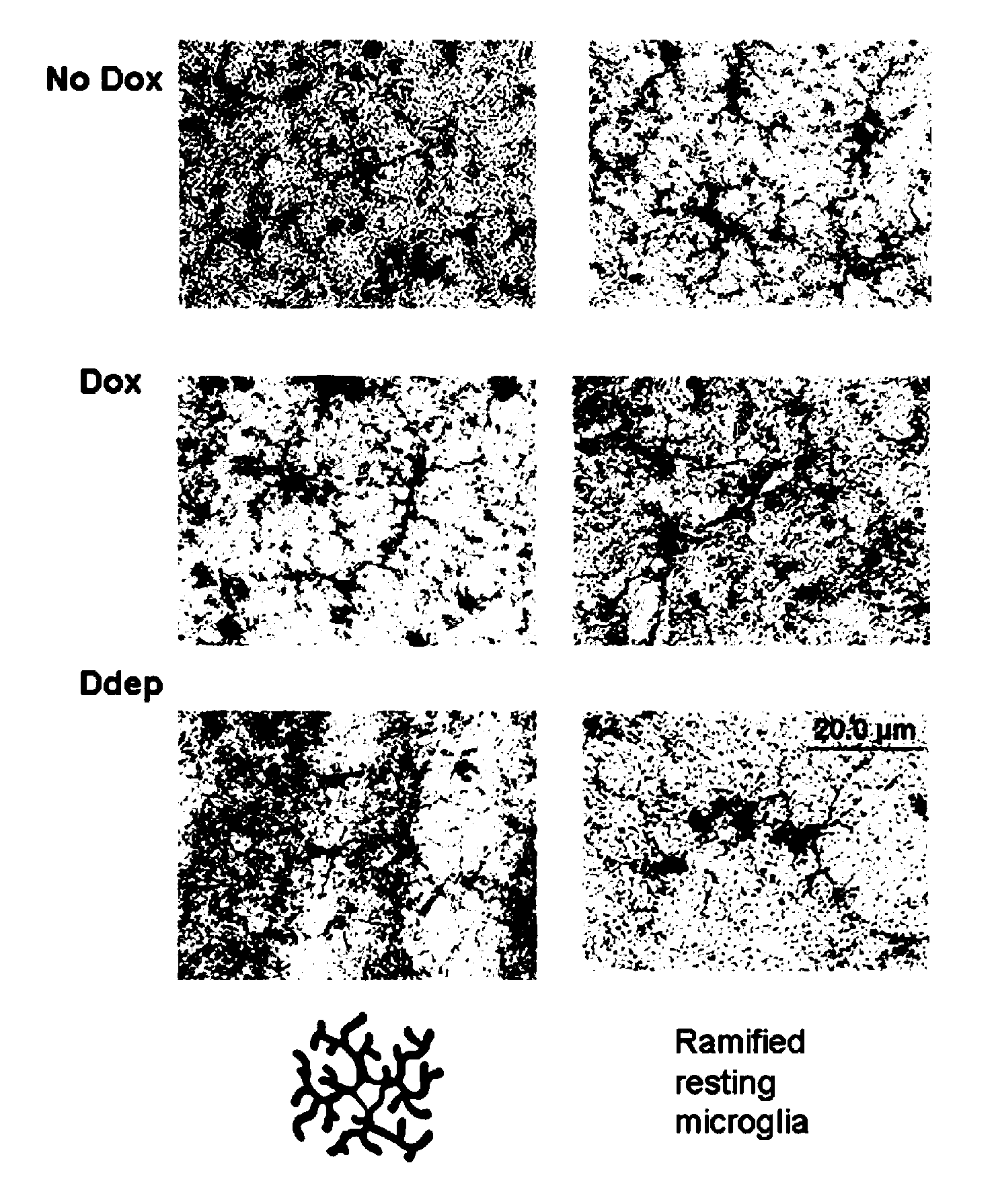
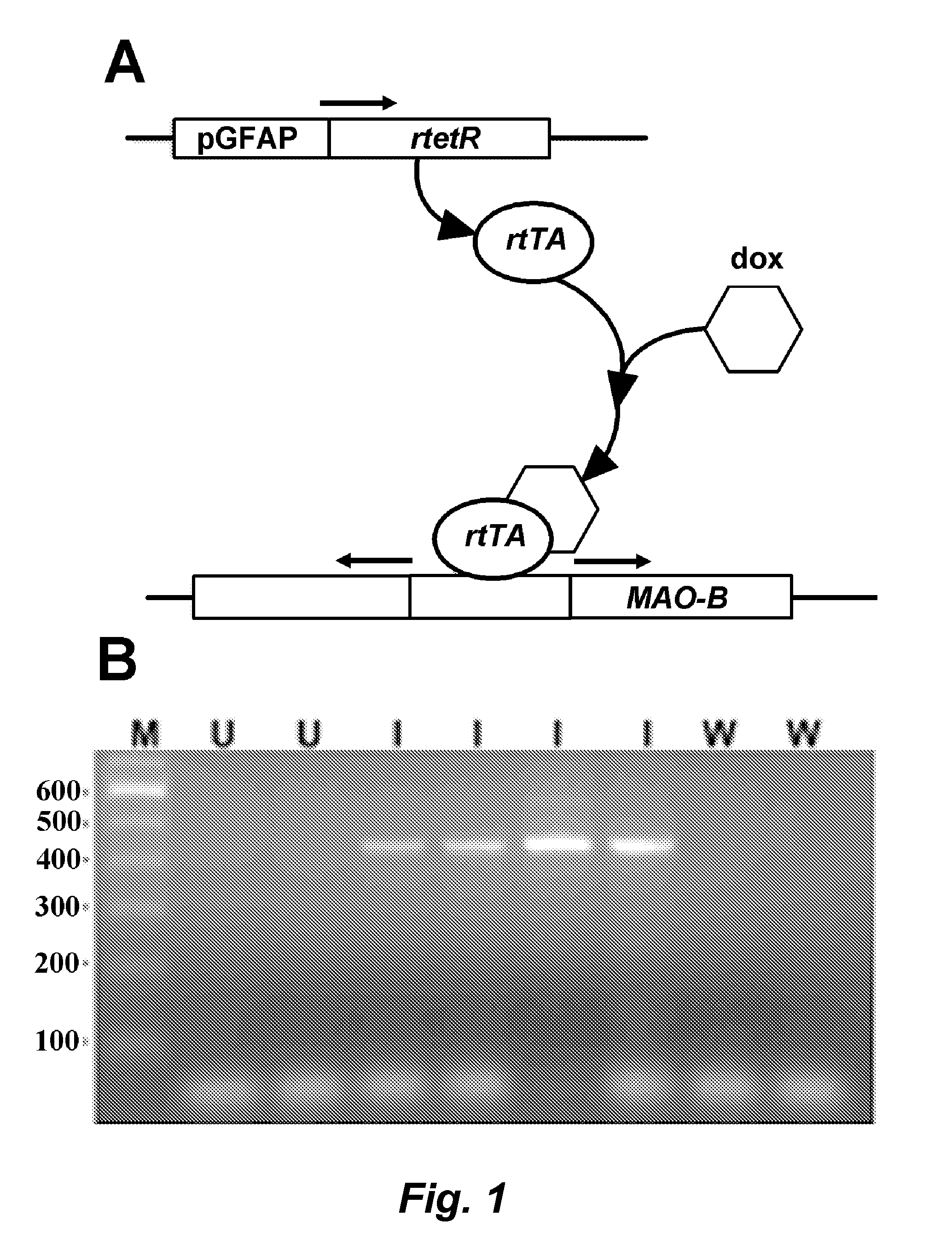
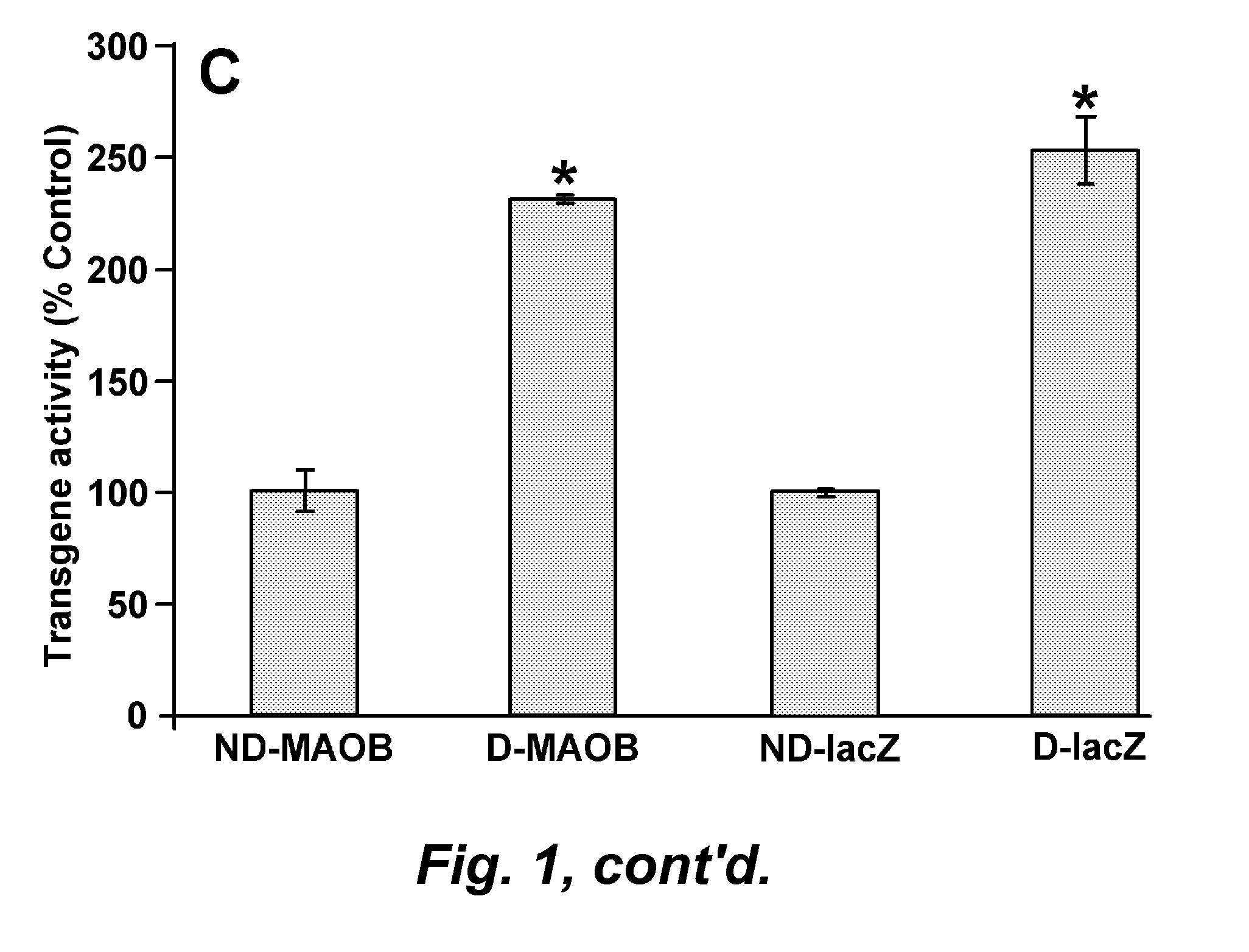
Mao-b elevation as an early parkinson's disease biomarker
InactiveUS20110067123A1Eliminate the effects ofBiocideCompound screeningMonoamine Oxidase Type BOxygenase
This invention pertains to development of a new animal model for Parkinson's Disease (PD) and to the discovery that elevated monoamine oxygenase B (MOA-B) expression and / or activity is a strong prognostic indicator for the disease. Accordingly, in certain embodiments, methods are provided for identifying a mammal at risk for Parkinson's disease. The methods typically involve determining level of expression or activity of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) in a sample from the mammal wherein an elevated level of MAO-B expression and / or activity as compared to a control (reference) is an indicator that the mammal has an increased likelihood of developing Parkinson's disease.
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
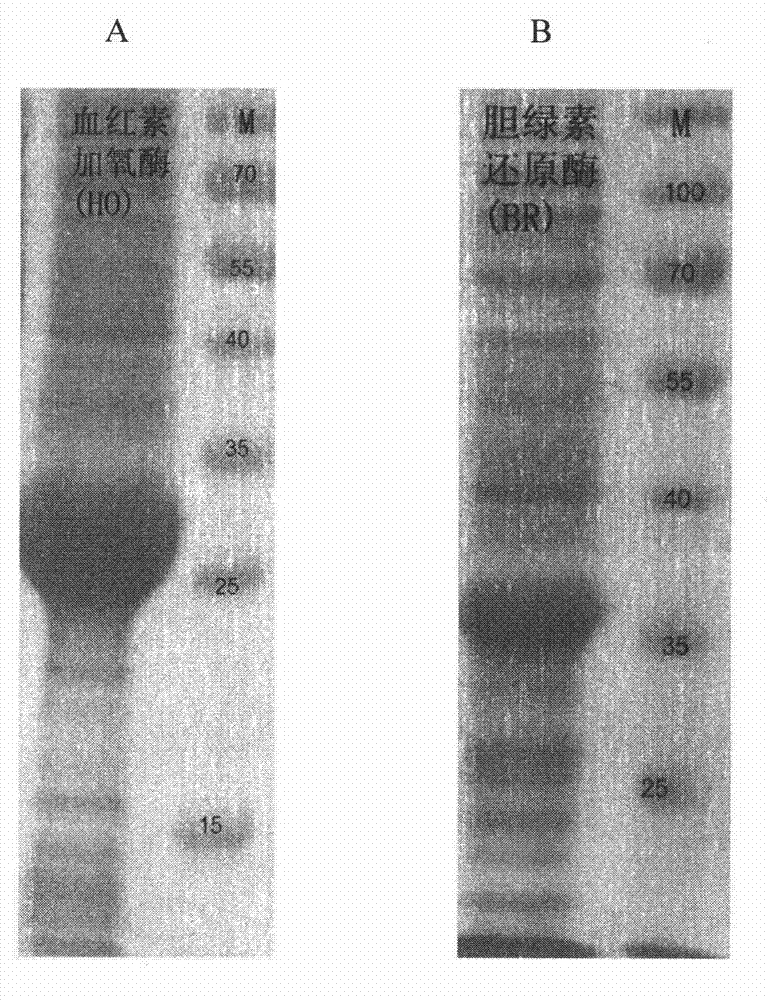
Method for synthesizing bilirubin by utilizing immobilized enzyme
The invention relates to the technical field of bilirubin production methods and discloses a method for synthesizing bilirubin by utilizing an immobilized enzyme. The method comprises the following steps of: a) respectively cloning haem oxygenase genes and biliverdin reductase genes; b) respectively expressing the recombinant haem oxygenase and biliverdin reductase in escherichia coli; c) extracting a crude extract or pure enzyme of haem oxygenase and a crude extract or pure enzyme of biliverdin reductase; d) immobilizing the crude extract or pure enzyme of haem oxygenase and the crude extract or pure enzyme of biliverdin reductase; and e) preparing bilirubin in the assistance of an oxidized coenzyme II by catalyzing with the immobilized haem oxygenase and the immobilized biliverdin reductase and taking haem and oxygen as substrates.
Owner:BONTAC BIO ENG SHENZHEN
Screening and function verification of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase encoding gene participating in synthesis of gardenia jasminoides ellis crocin
InactiveCN107502614ASignificant application valueMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesOpen reading frameAmino acid
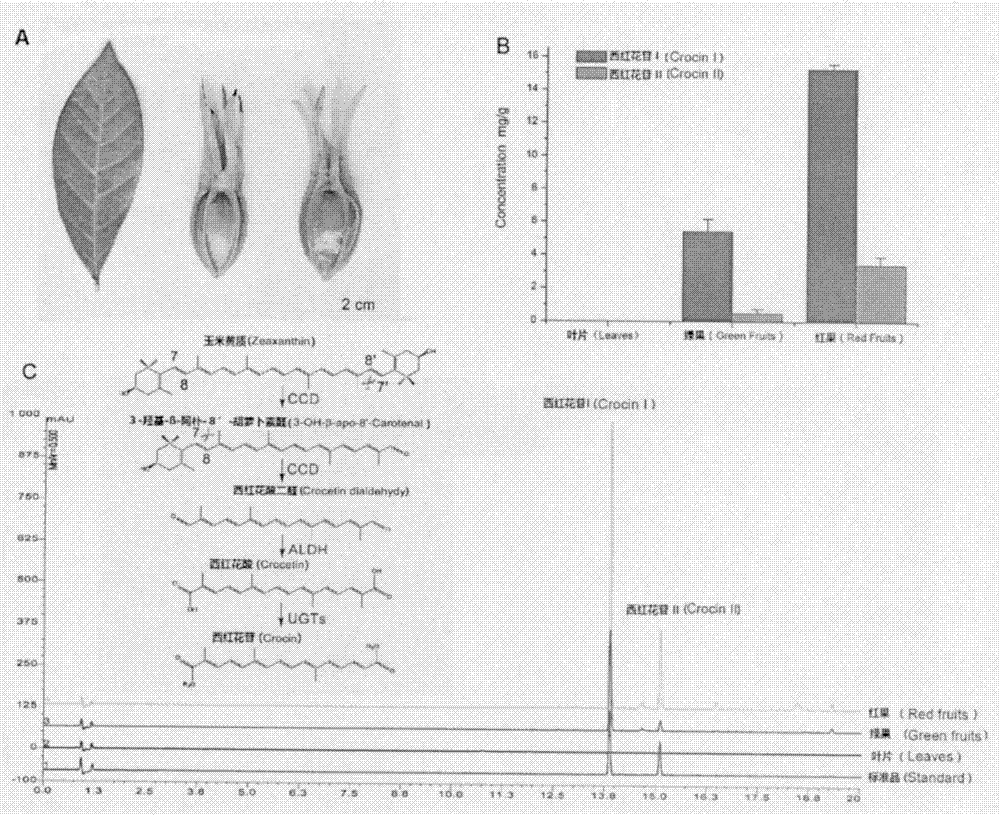
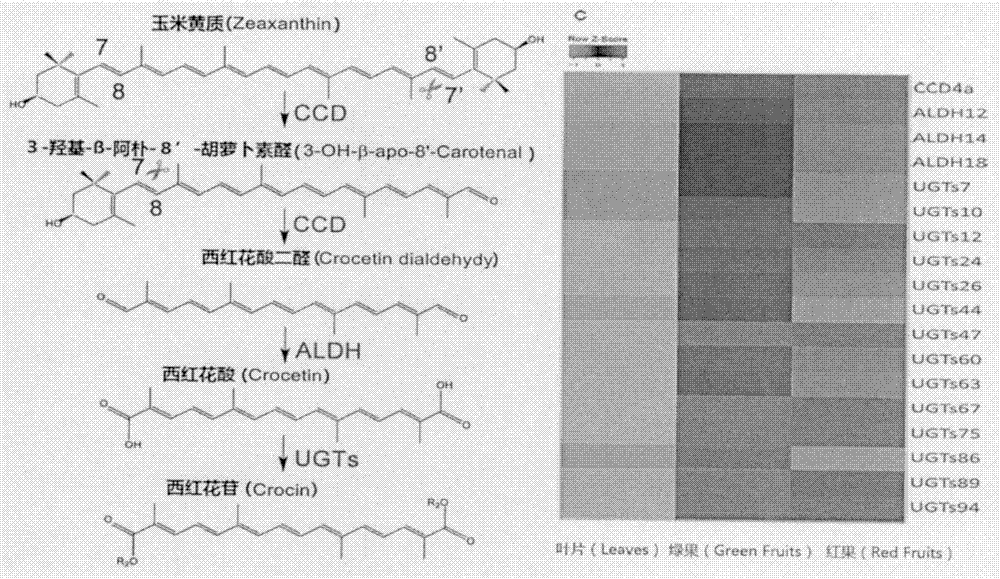
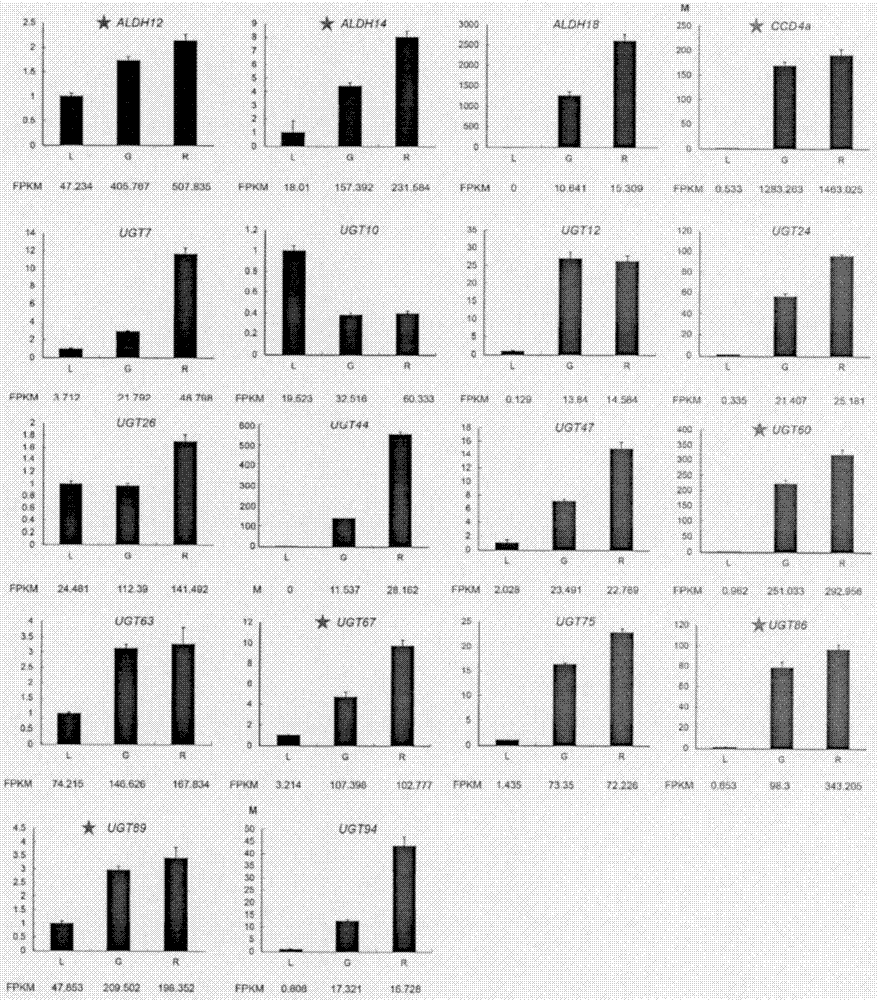
The present invention relates to a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase CCD4a involved in the synthesis of gardenia jasminoides ellis crocin, an encoding gene and functions thereof, belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and discloses the open reading frame sequence of a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase CCD4a gene and the amino acid sequence encoded by the carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase CCD4a gene. According to the present invention, the CCD4a gene is screened based on transcriptomics, the functions of CCD4a are verified in vitro by using zeaxanthin as the substrate and constructing the pET28a-CCD4a prokaryotic expression vector, and the results prove that CCD4a has the functions of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase so as to establish the foundation for the analysis and biosynthetic research of the crocin source pathway.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com