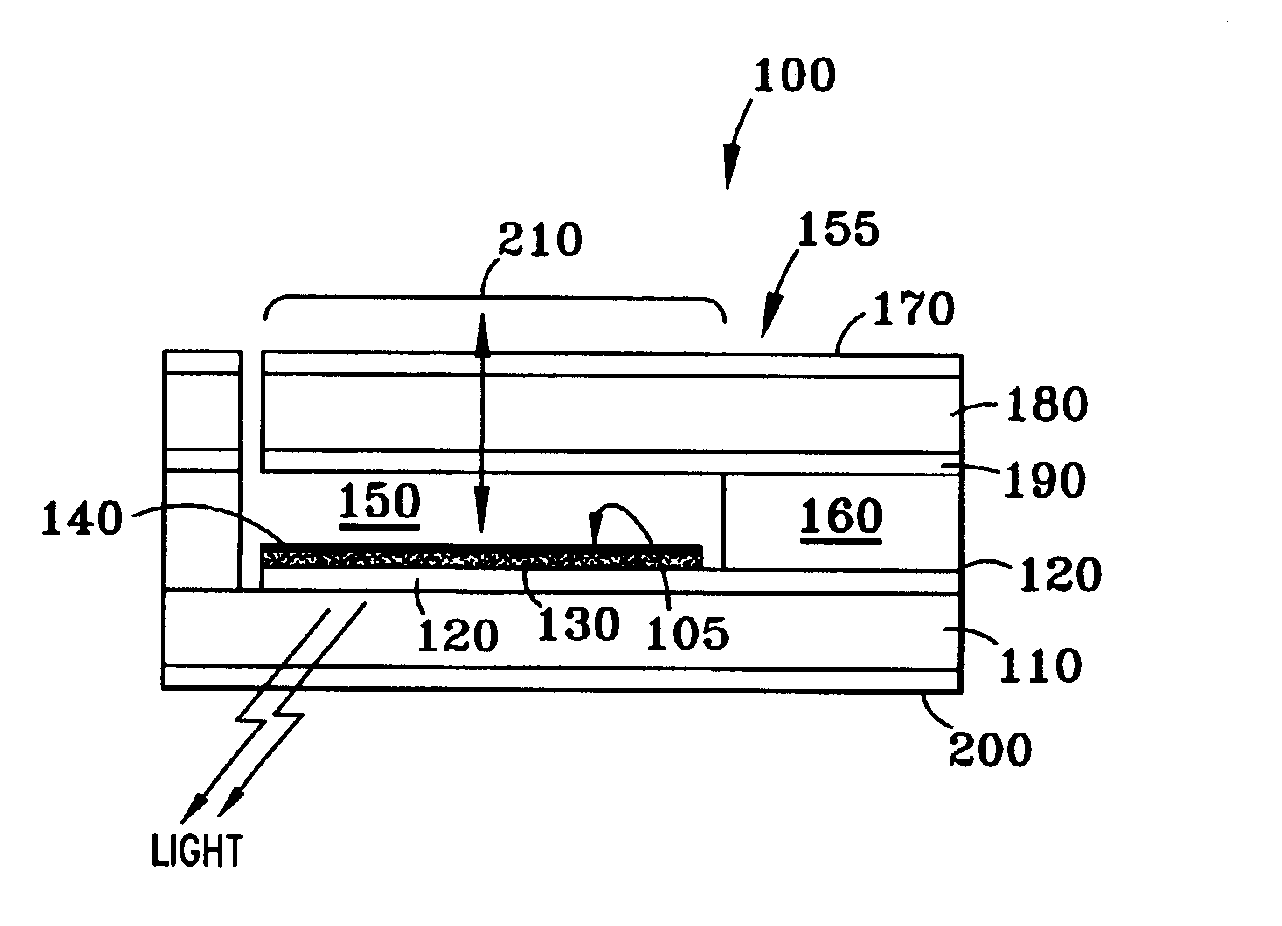
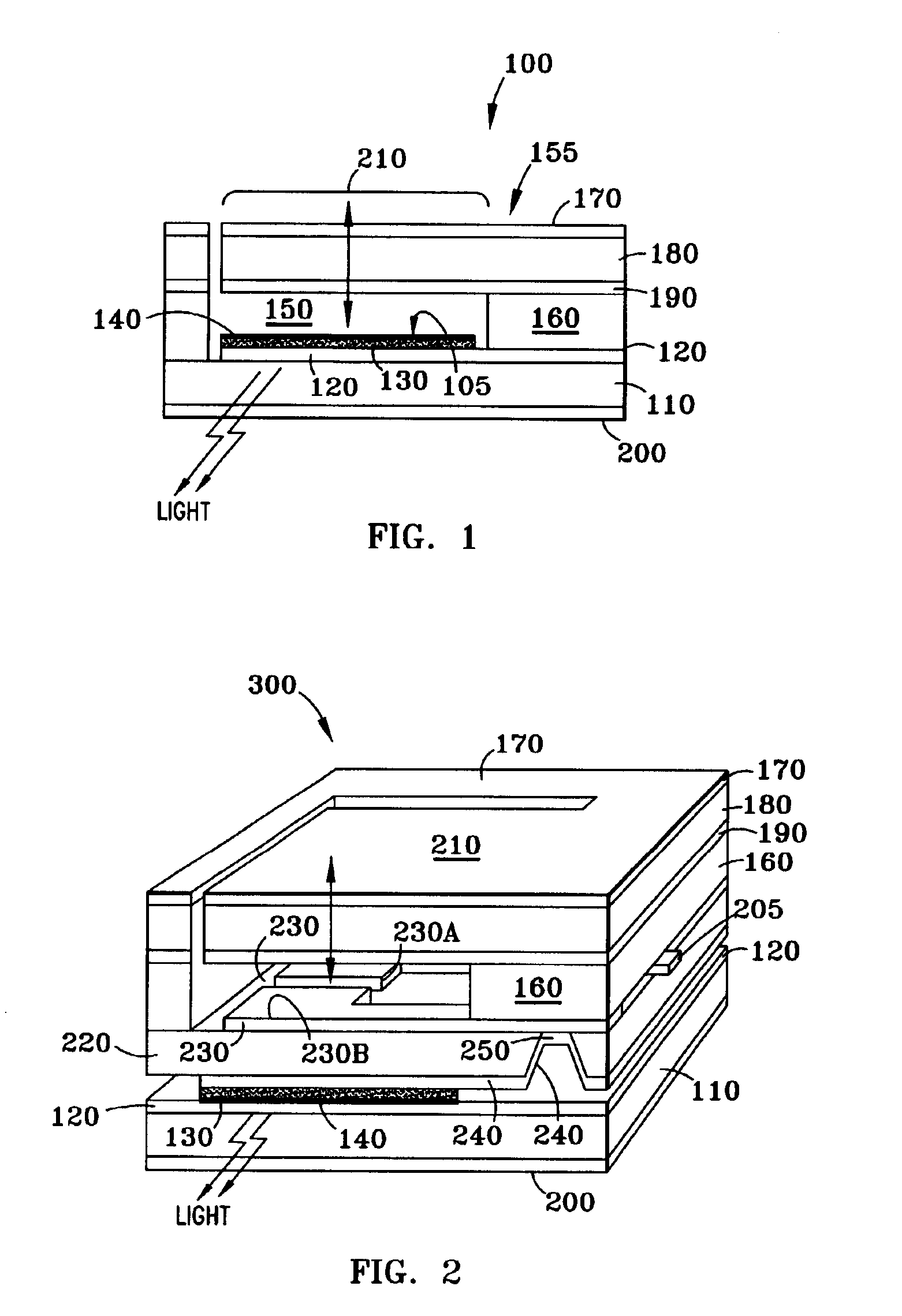
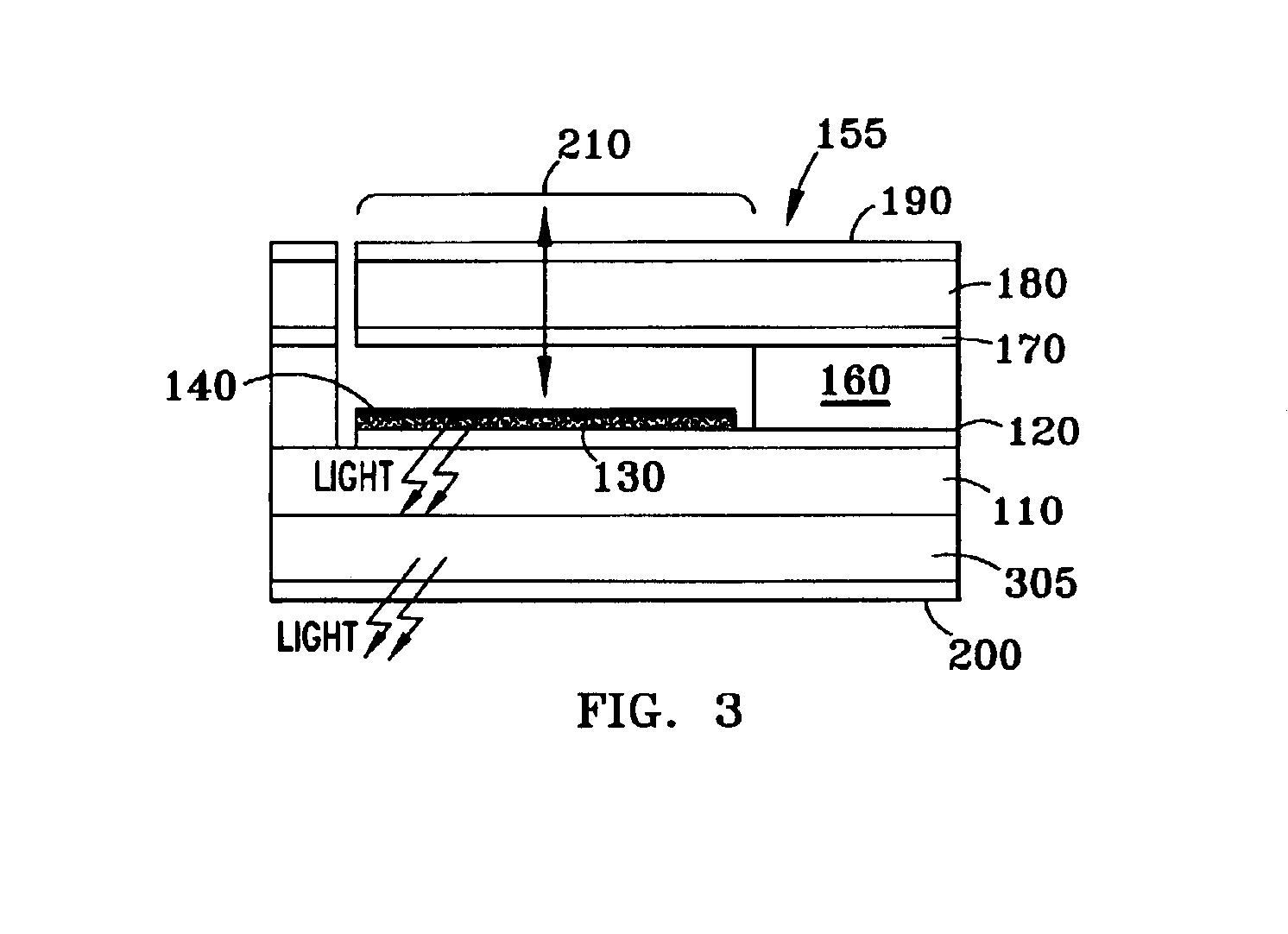
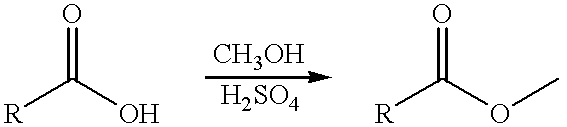Patents
Literature
408 results about "Large array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
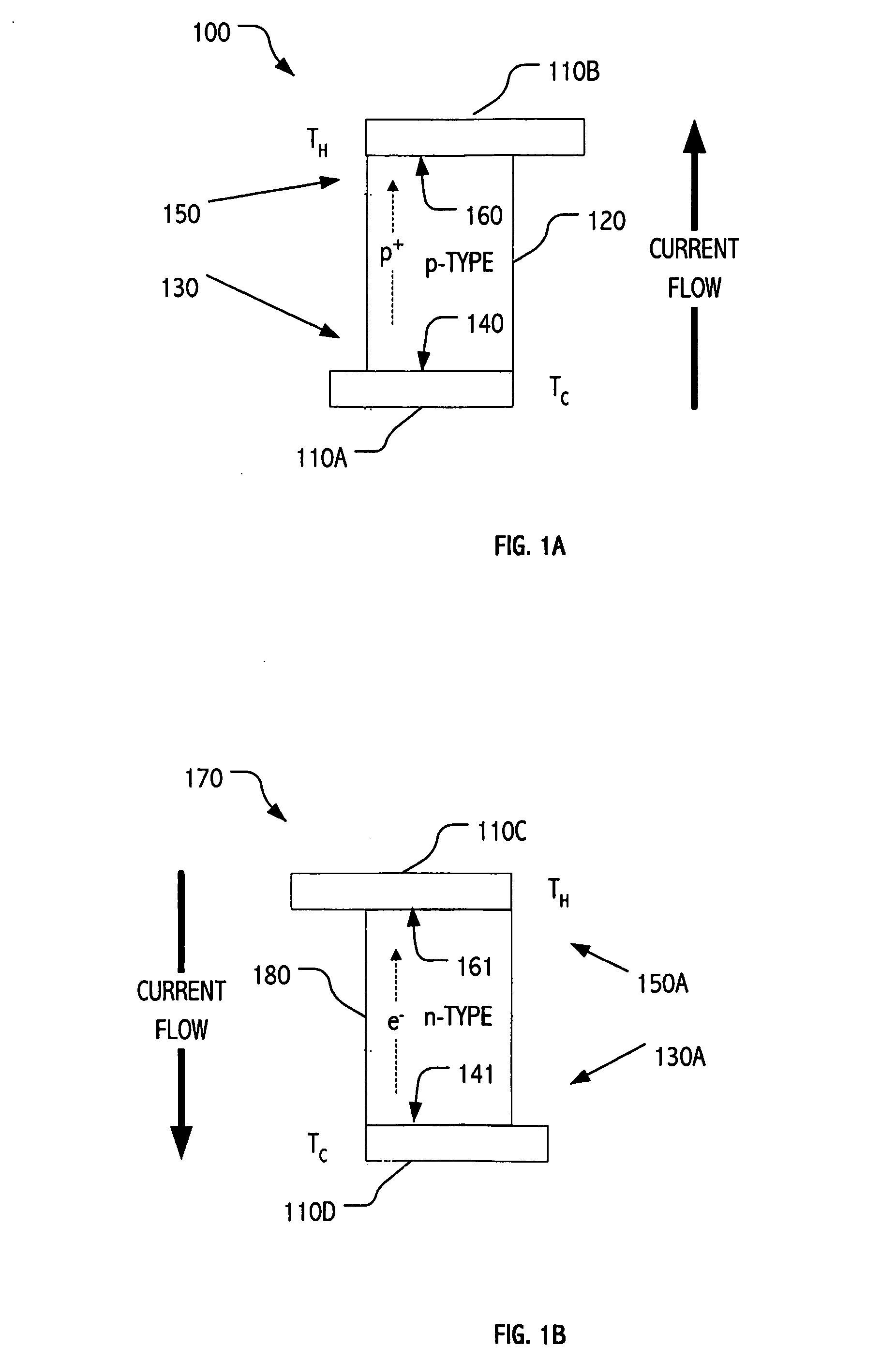
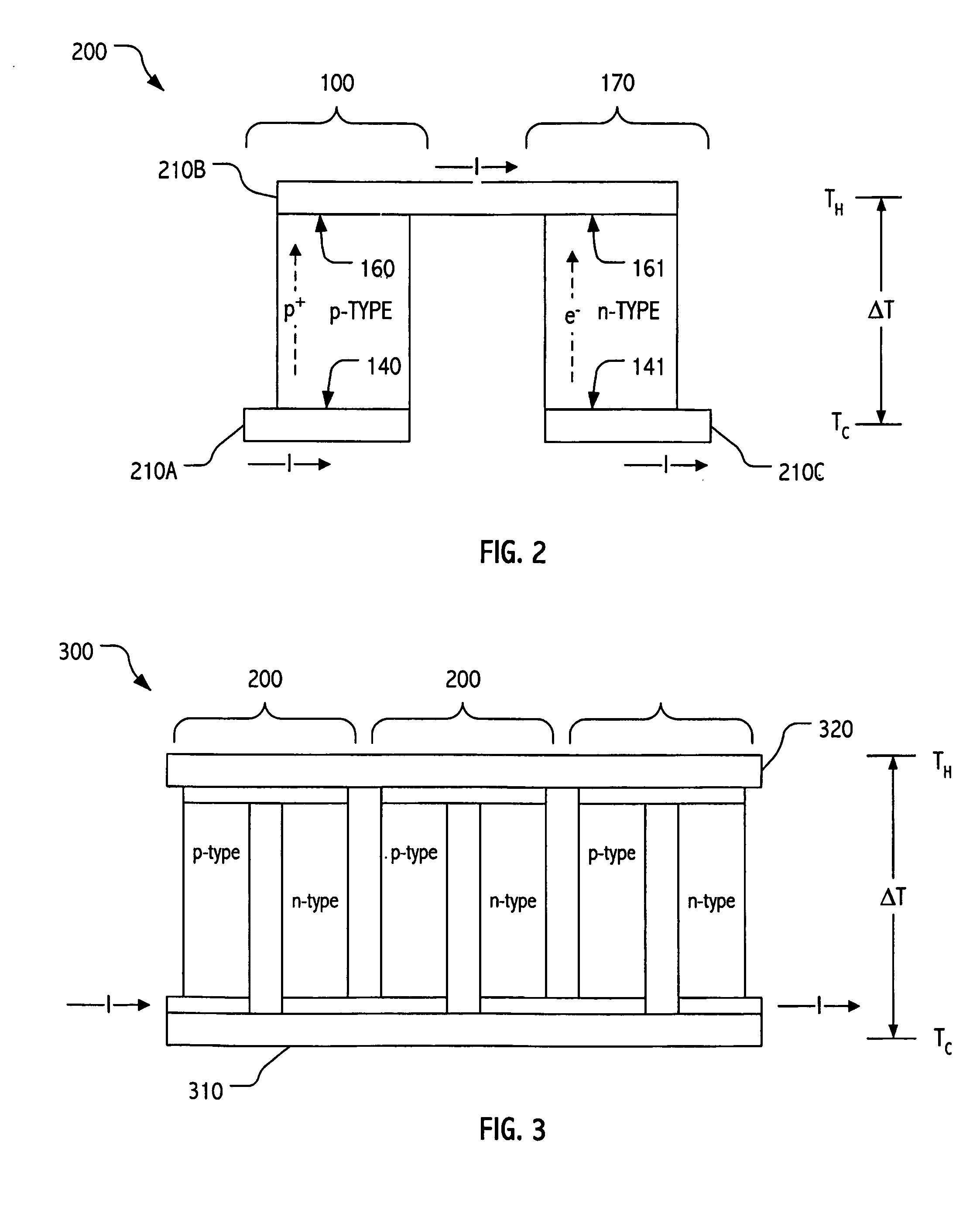
Method to form upward pointing p-i-n diodes having large and uniform current
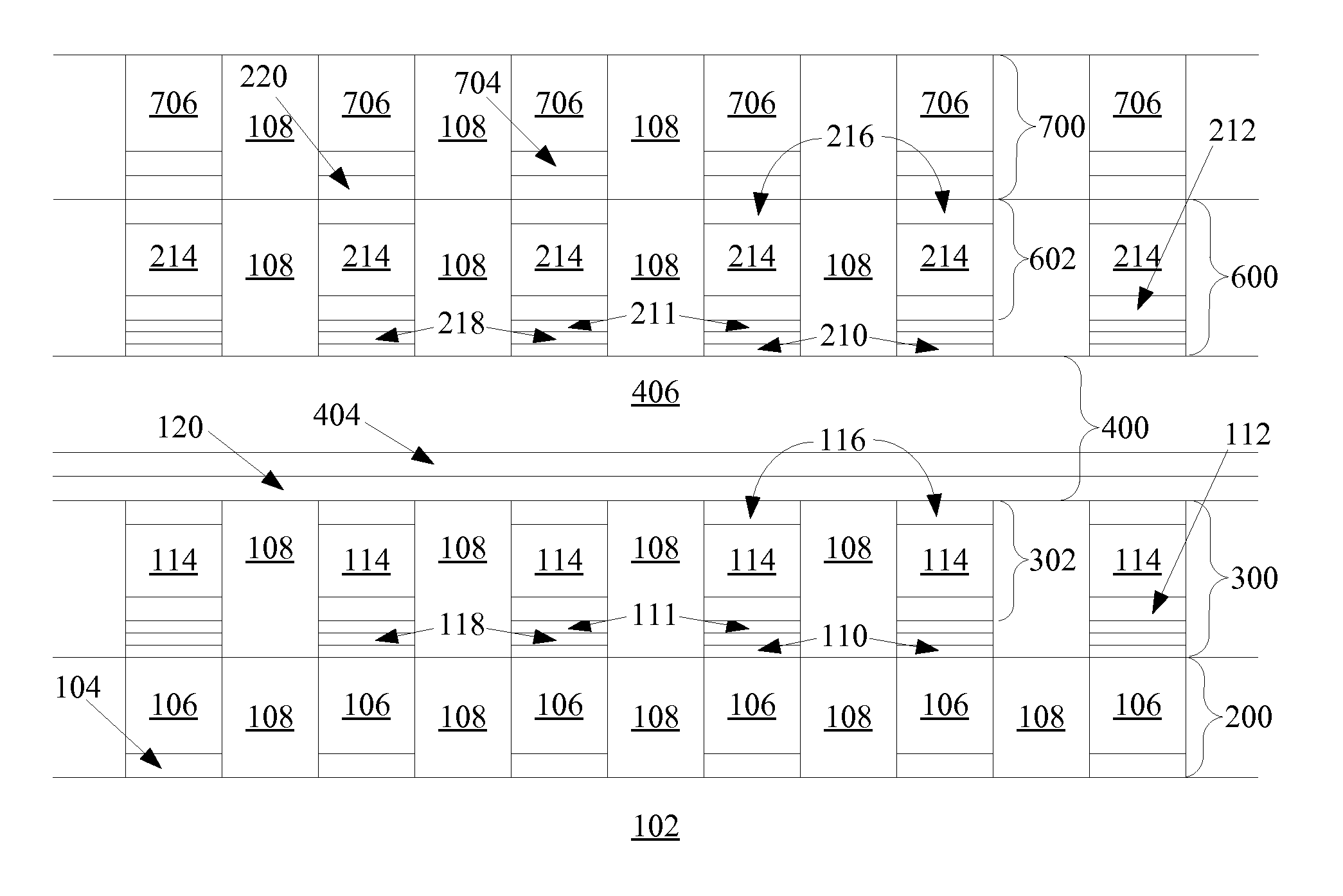
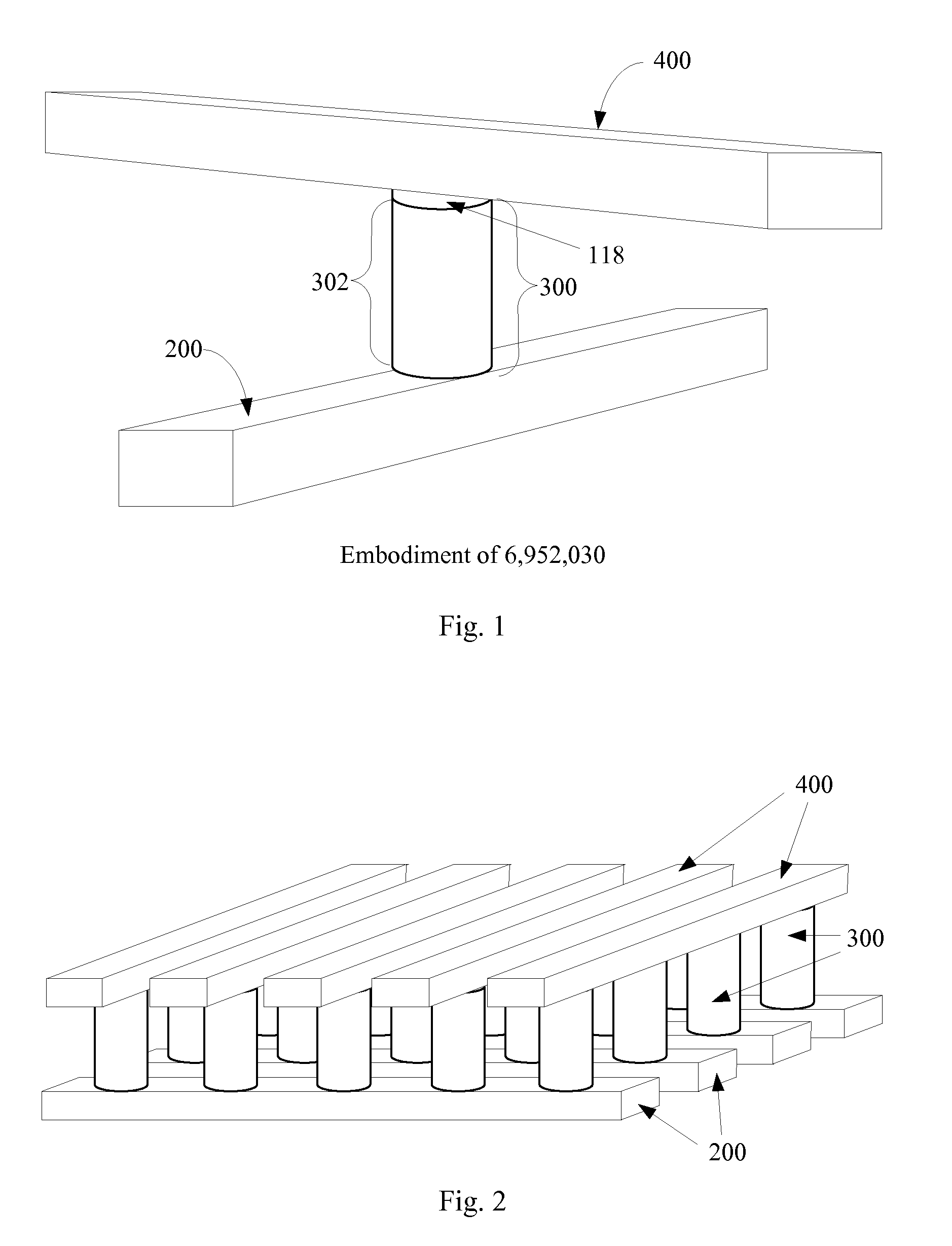
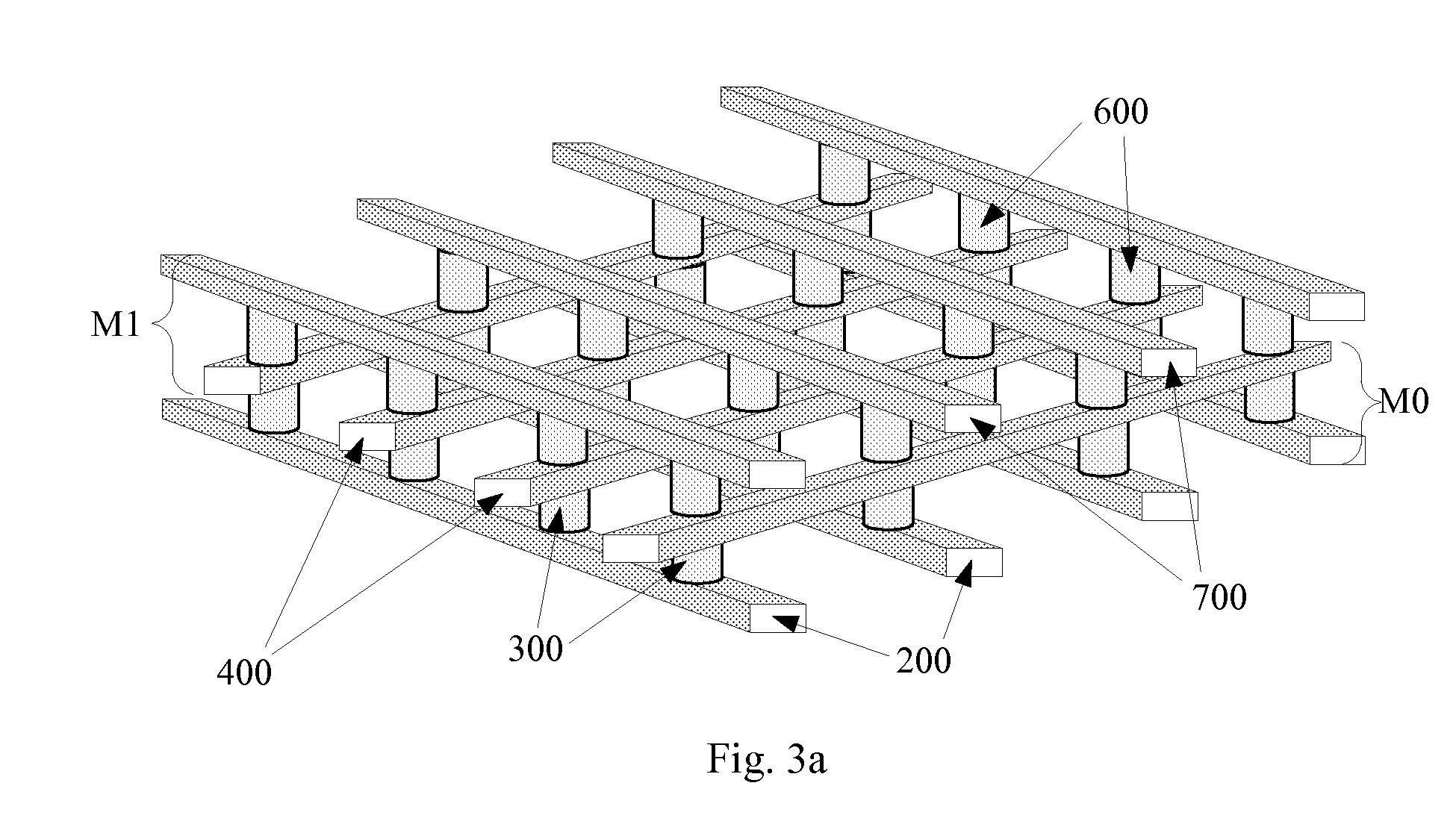
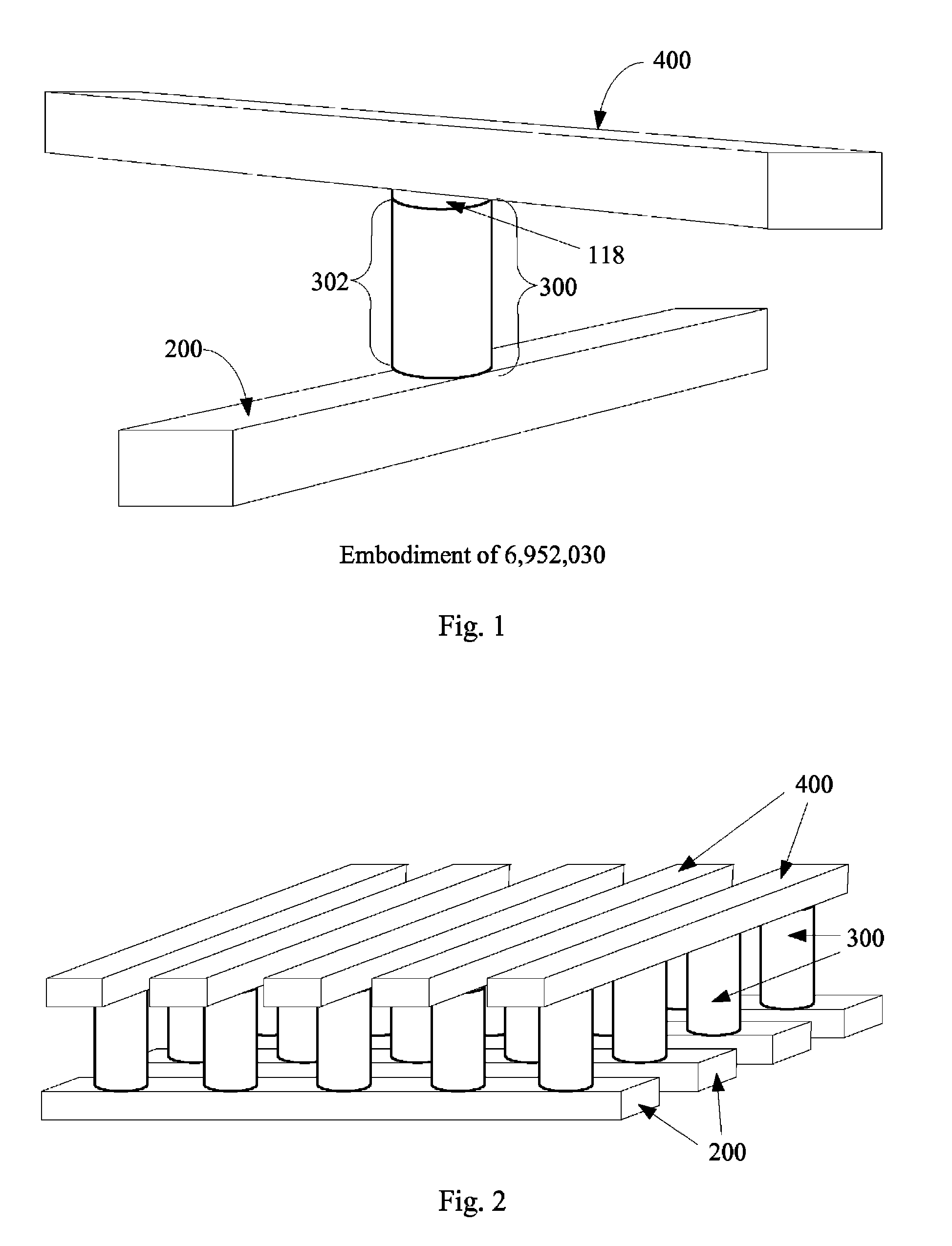
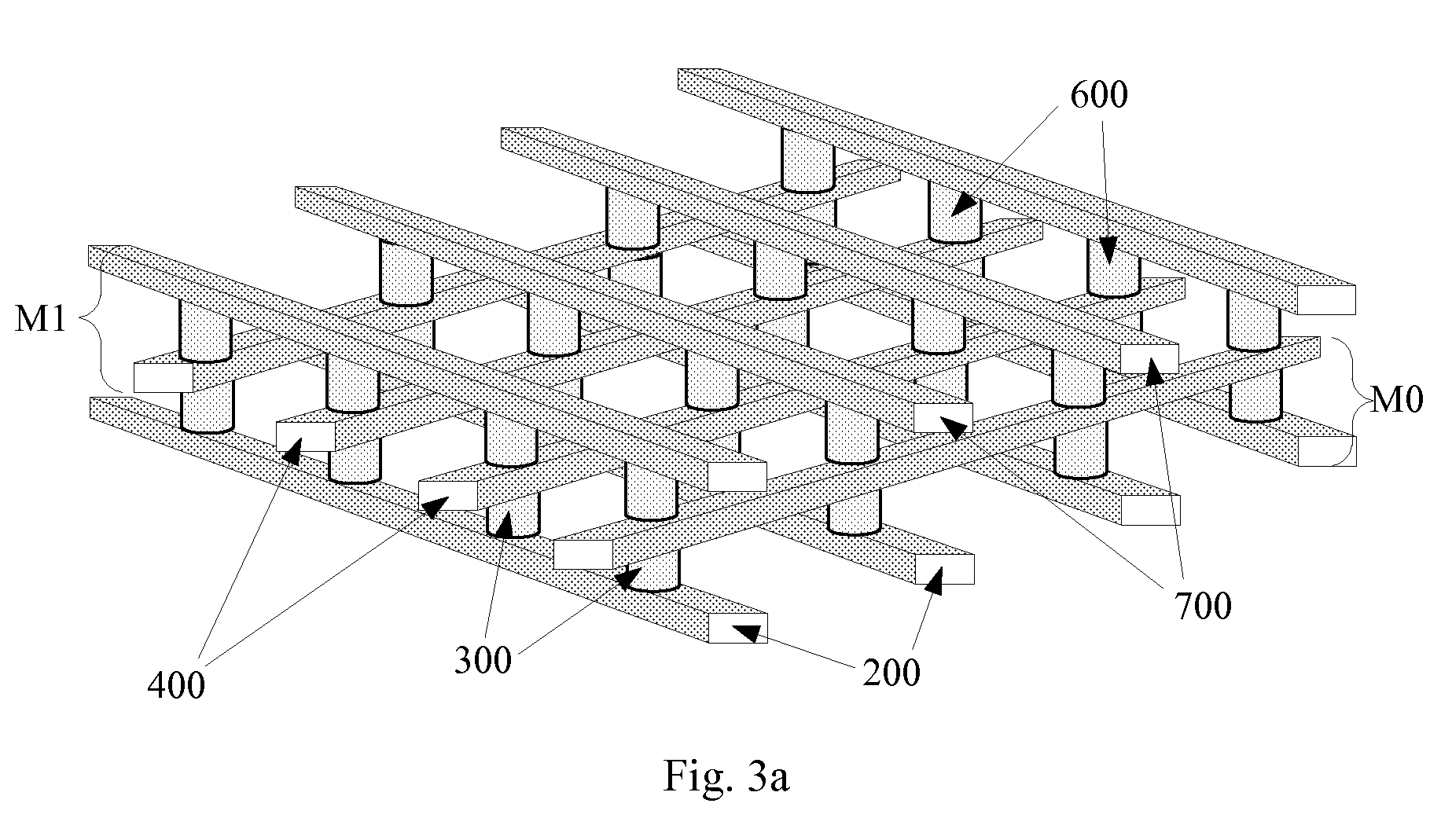
A method is disclosed to form an upward-pointing p-i-n diode formed of deposited silicon, germanium, or silicon-germanium. The diode has a bottom heavily doped p-type region, a middle intrinsic or lightly doped region, and a top heavily doped n-type region. The top heavily doped p-type region is doped with arsenic, and the semiconductor material of the diode is crystallized in contact with an appropriate silicide, germanide, or silicide-germanide. A large array of such upward-pointing diodes can be formed with excellent uniformity of current across the array when a voltage above the turn-on voltage of the diodes is applied. This diode is advantageously used in a monolithic three dimensional memory array.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
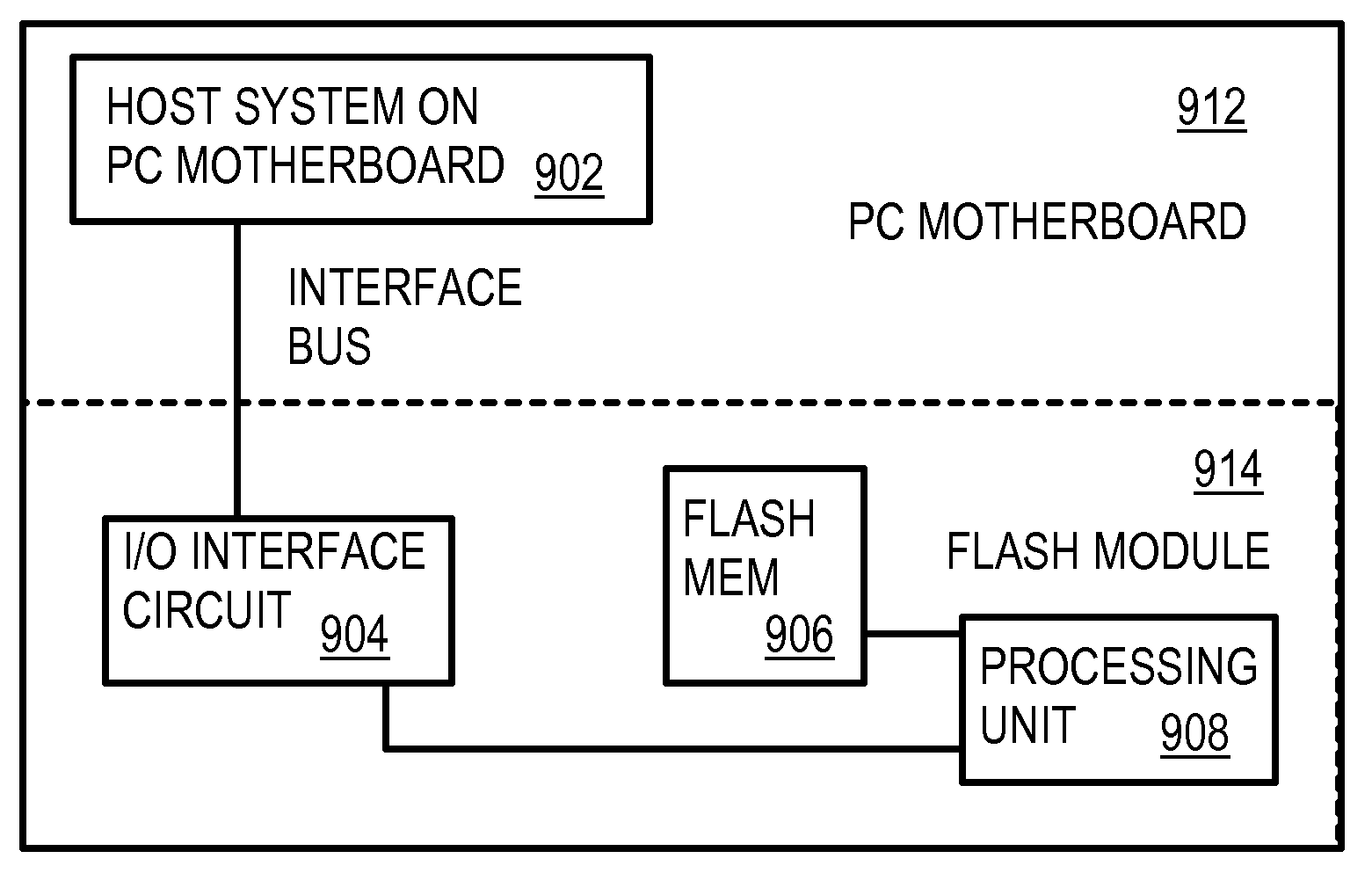
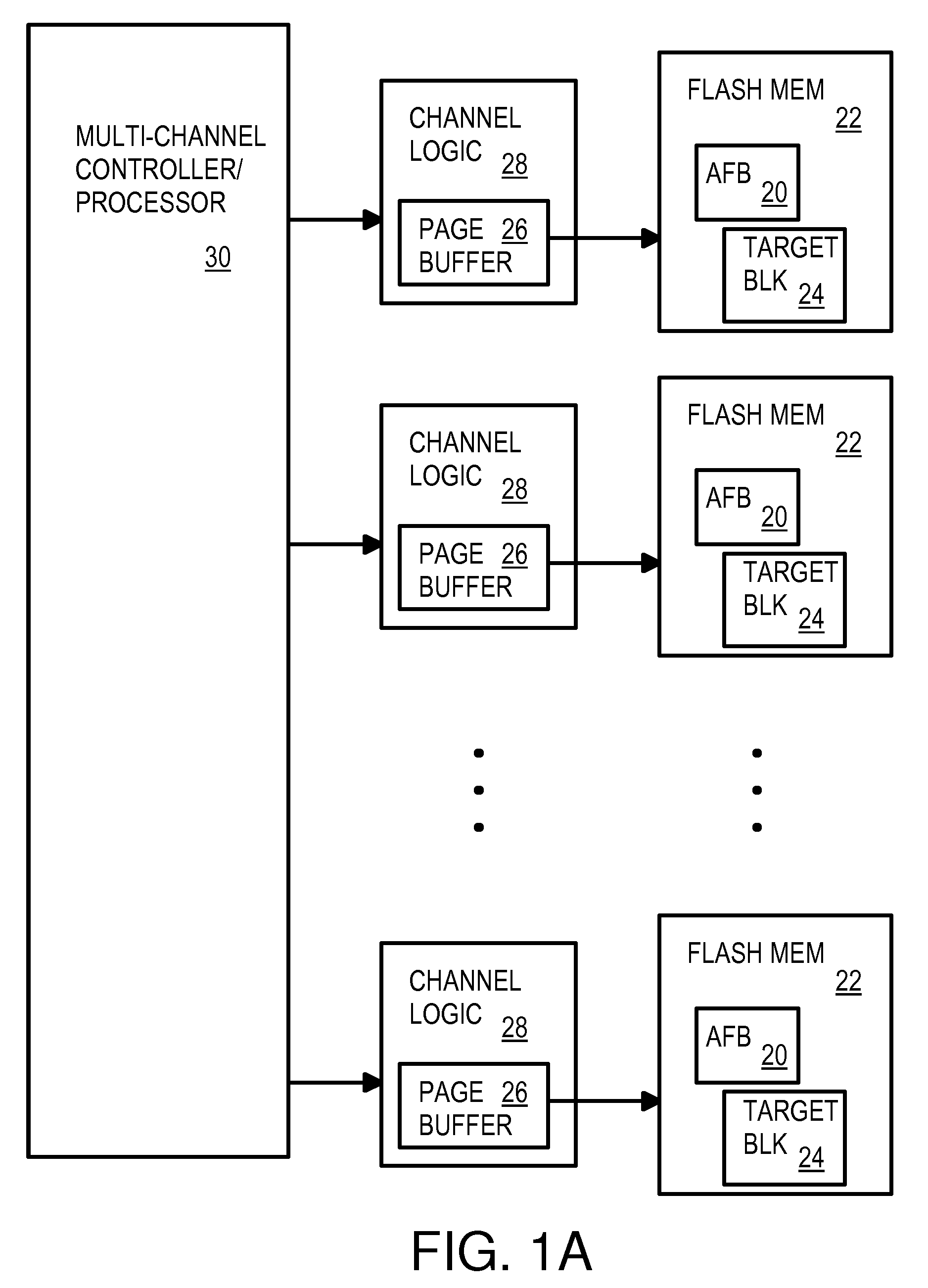
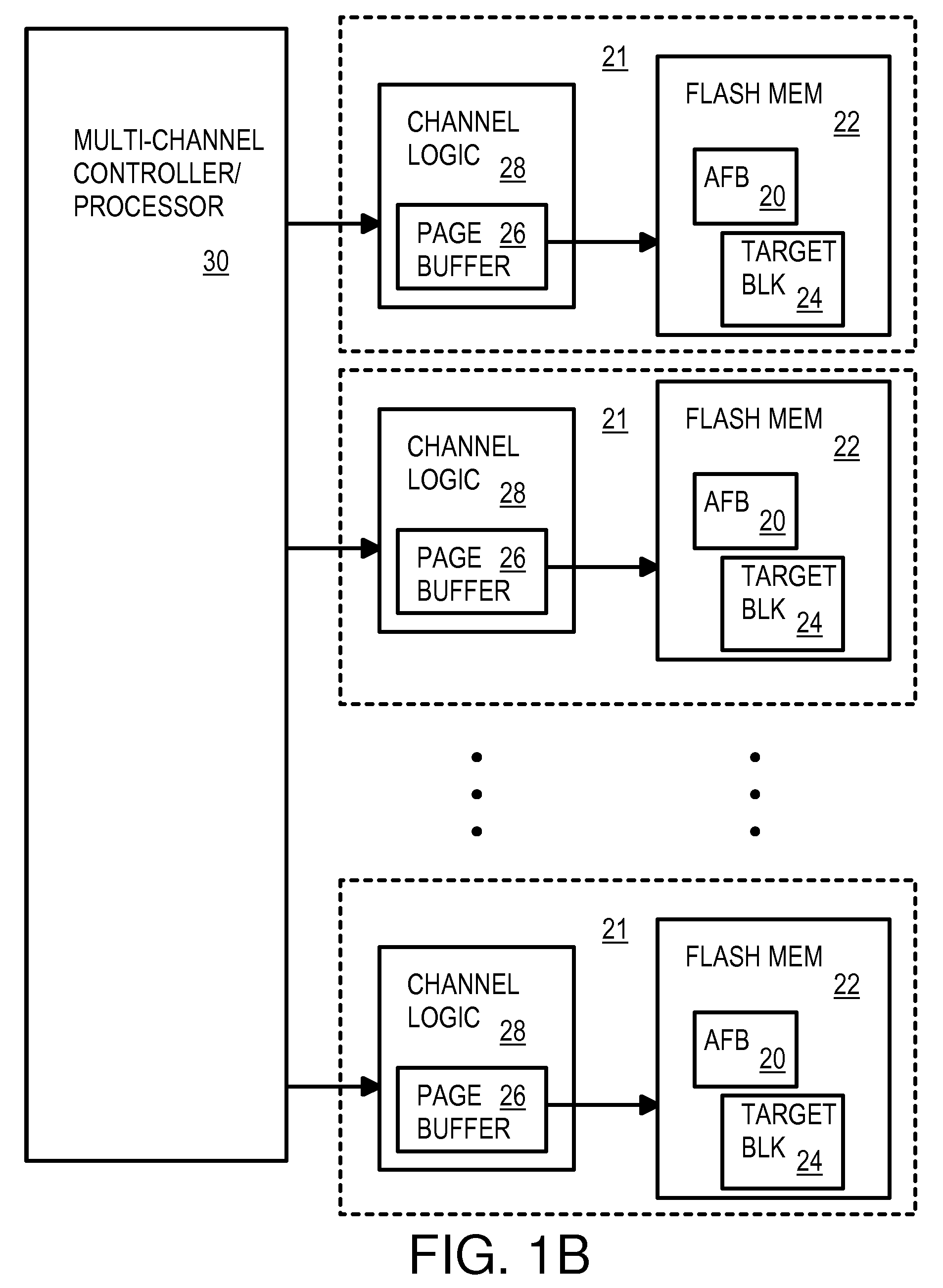
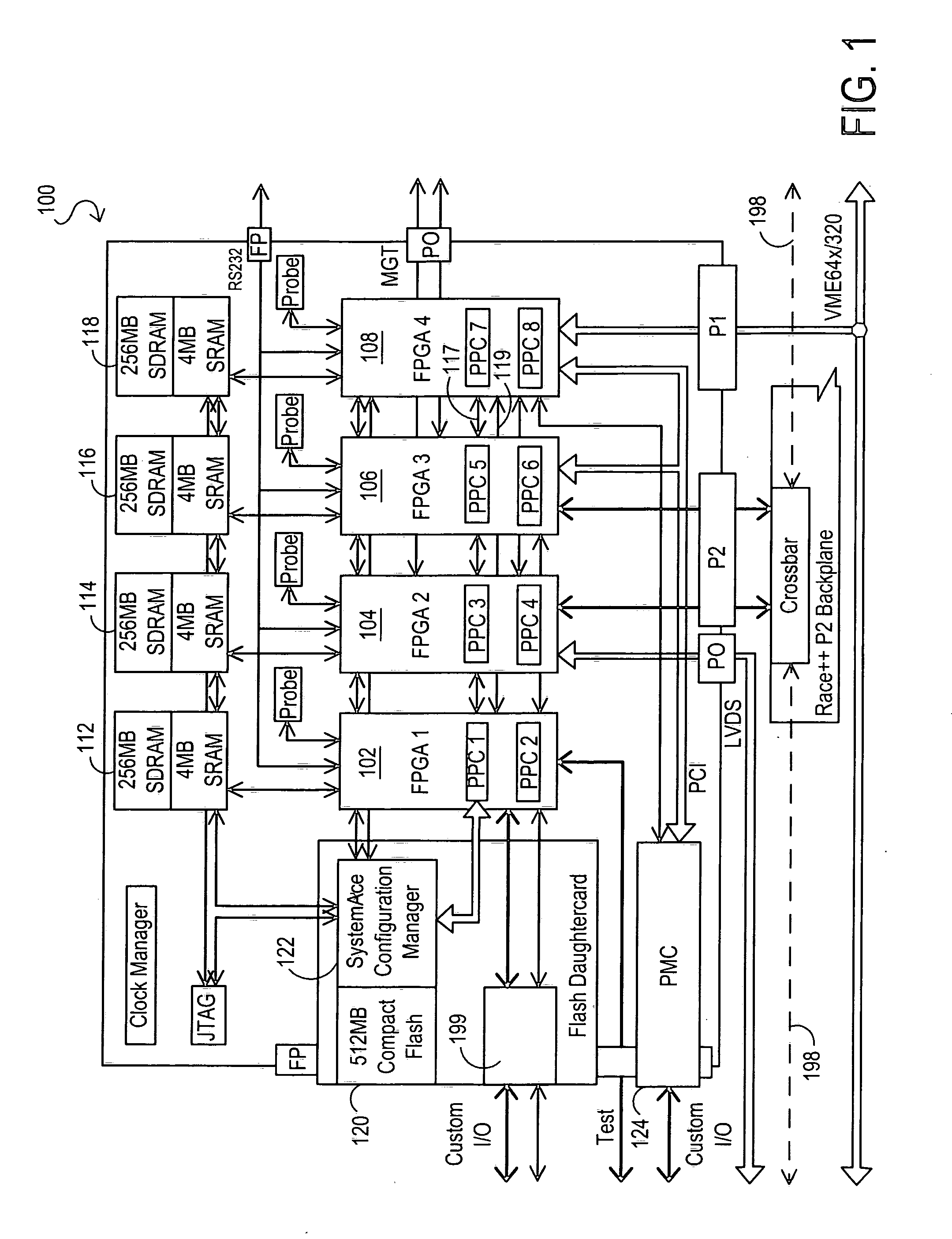
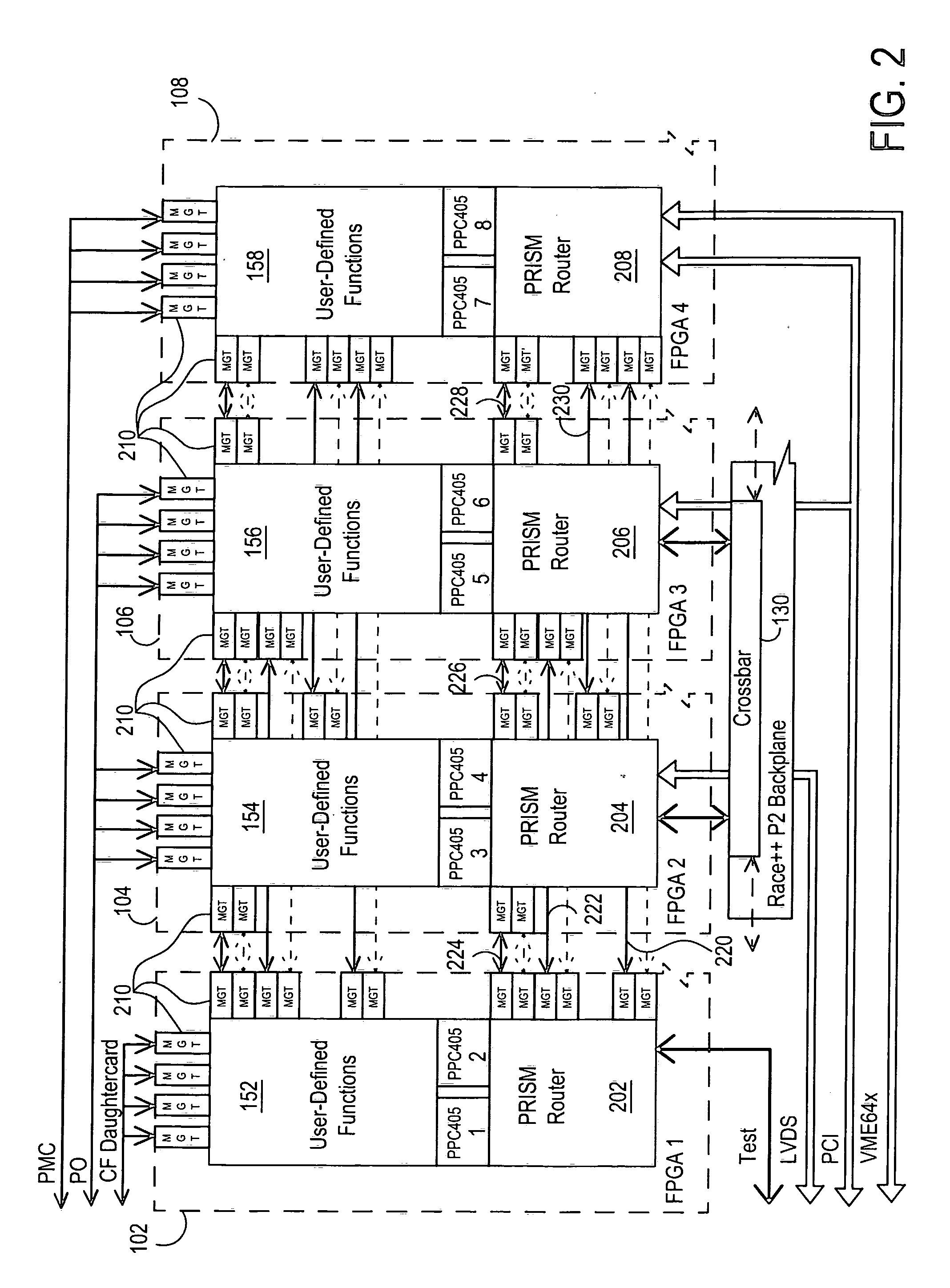
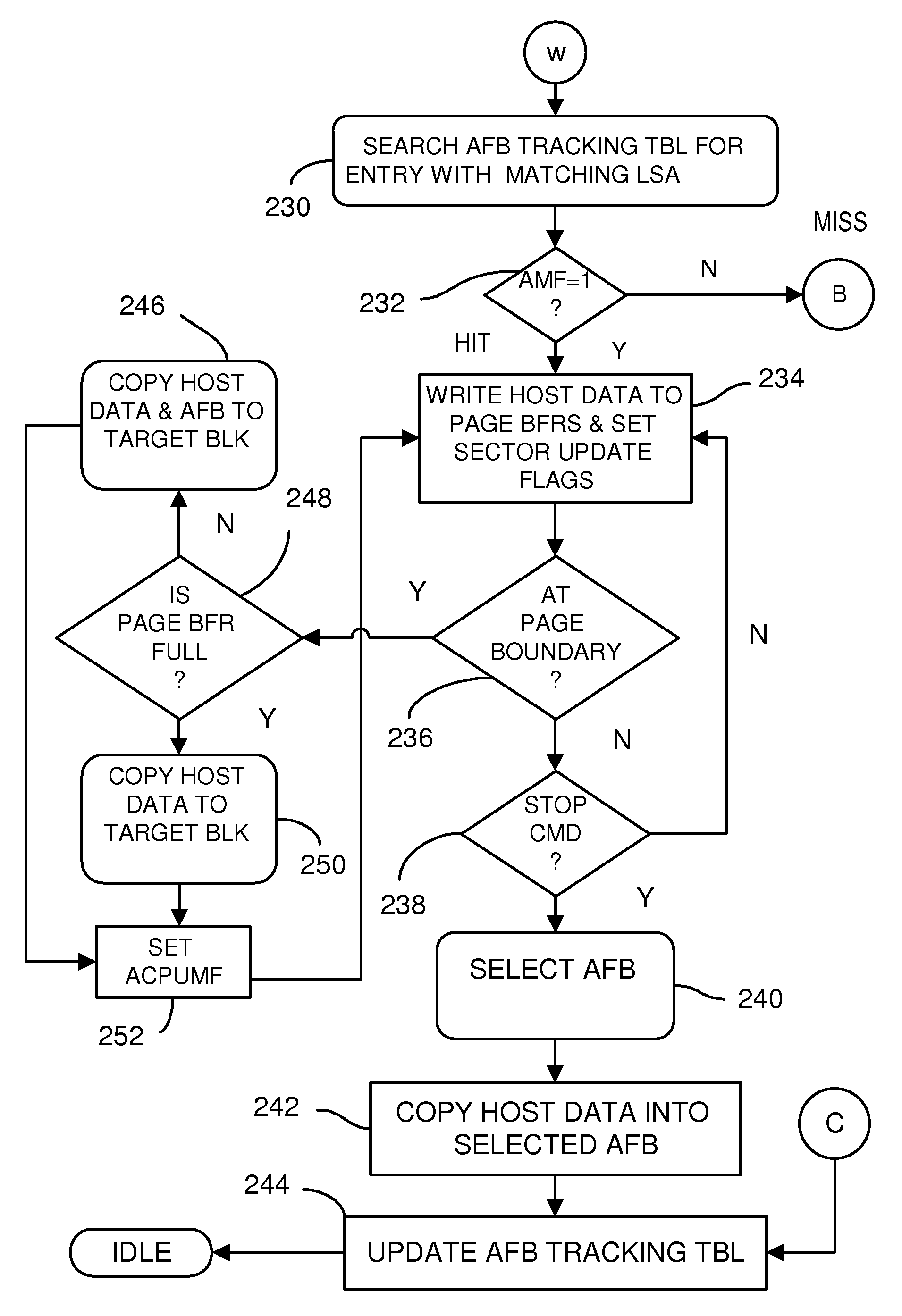
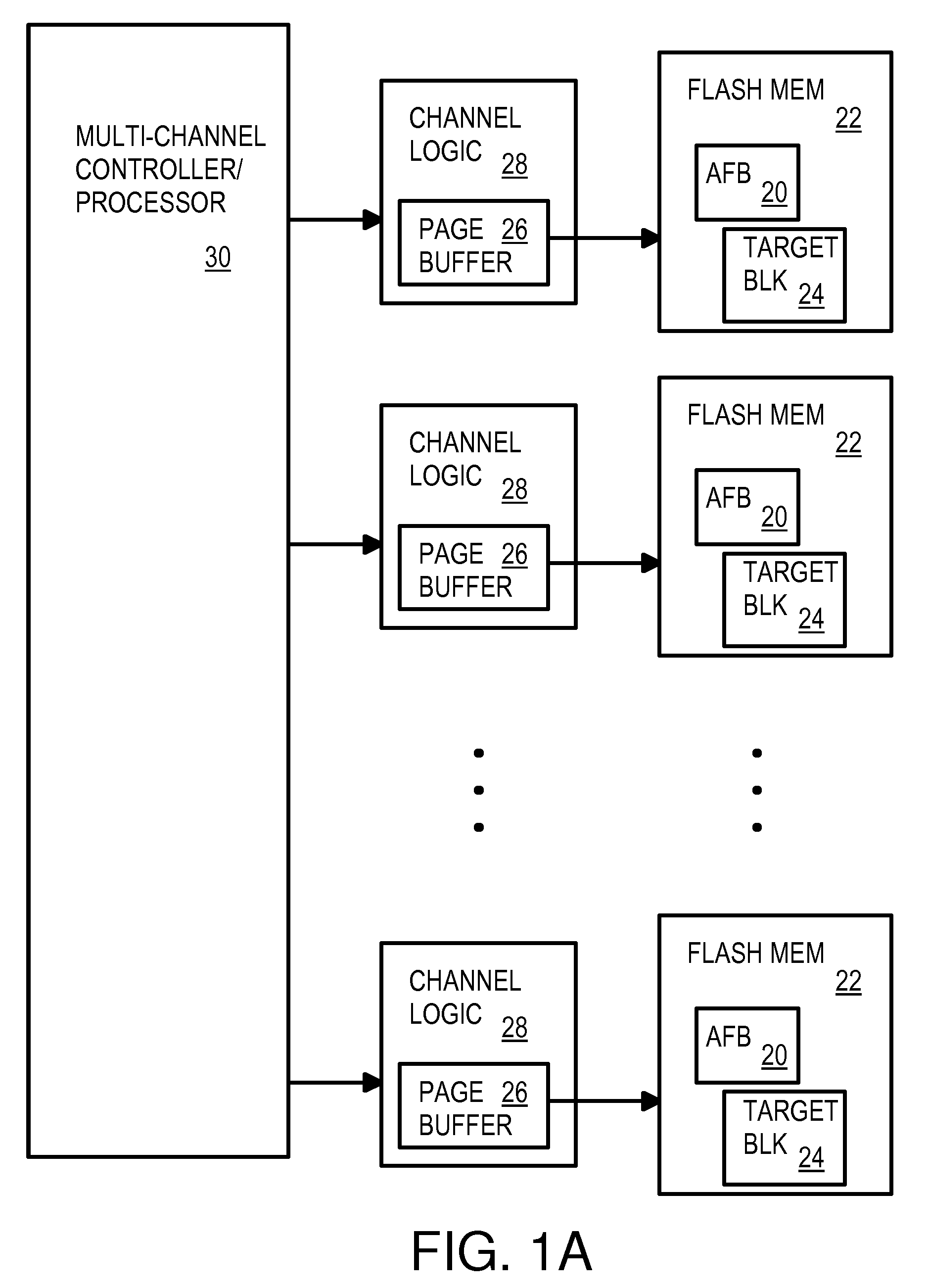
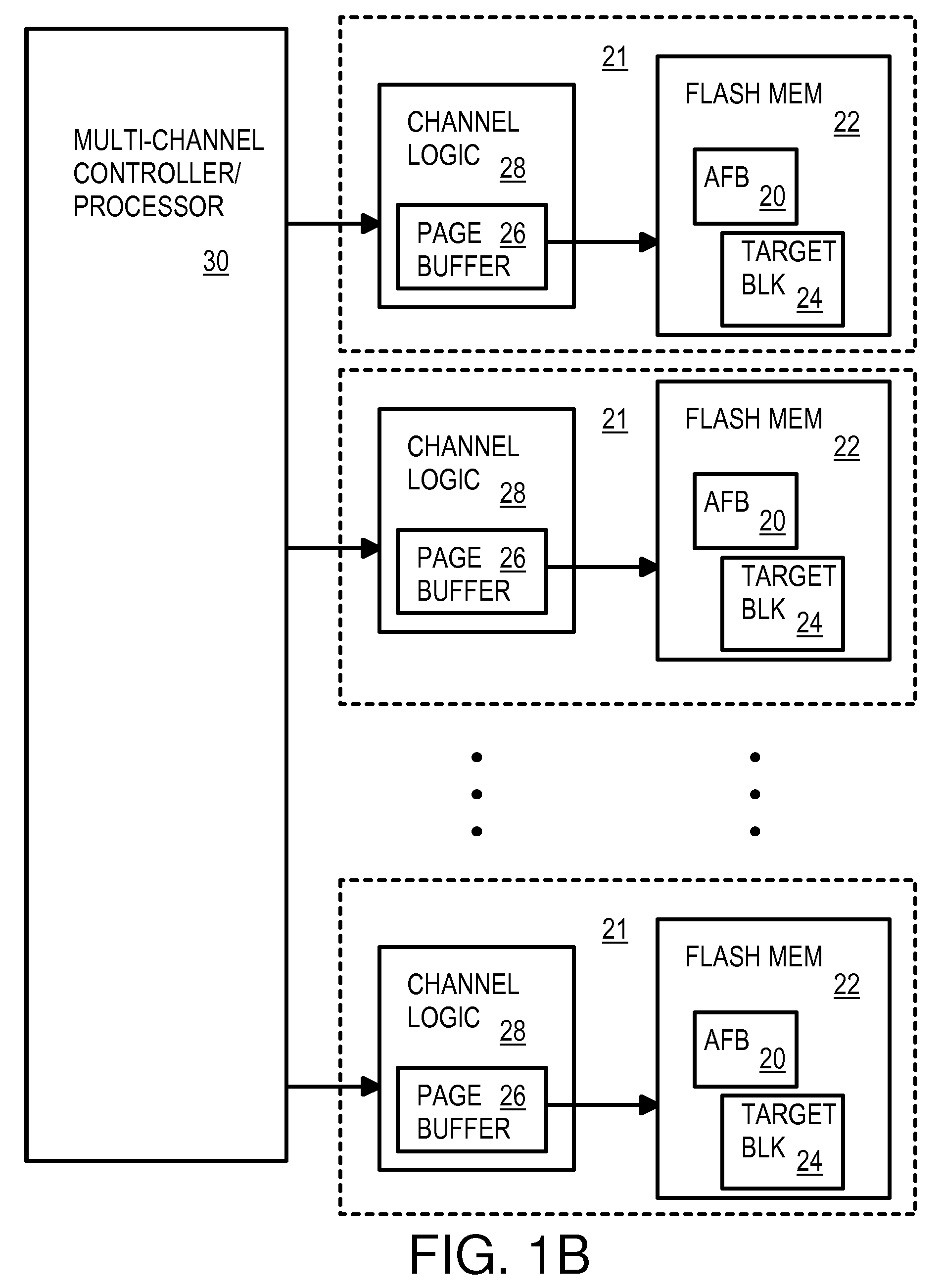
Multi-Operation Write Aggregator Using a Page Buffer and a Scratch Flash Block in Each of Multiple Channels of a Large Array of Flash Memory to Reduce Block Wear
InactiveUS20080250195A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSmall fragmentPage buffers
A flash system has multiple channels of flash memory chips that can be accessed in parallel. Host data is assigned to one of the channels by a multi-channel controller processor and accumulated in a multi-channel page buffer. When a page boundary in the page buffer is reached, the page buffer is written to a target physical block if full, or combined with old data fragments in an Aggregating Flash Block (AFB) when the logical-sector addresses (LSA's) match. Thus small fragments are aggregated using the AFB, reducing erases and wear of flash blocks. The page buffer is copied to the AFB when a STOP command occurs. Each channel has one or more AFB's, which are tracked by an AFB tracking table.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Array substrate for a liquid crystal display device and method for fabricating the same
A method of fabricating LCD devices from large array substrates having redundant pixels. Large array substrates without defects can be used to fabricate large LCD device and the redundant pixels can be disabled. Large array substrates with defects can be cut into smaller array substrates and then used to form small LCD devices. The pixels around the cutting lines of the large array substrate are redundant and can be covered or disabled.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
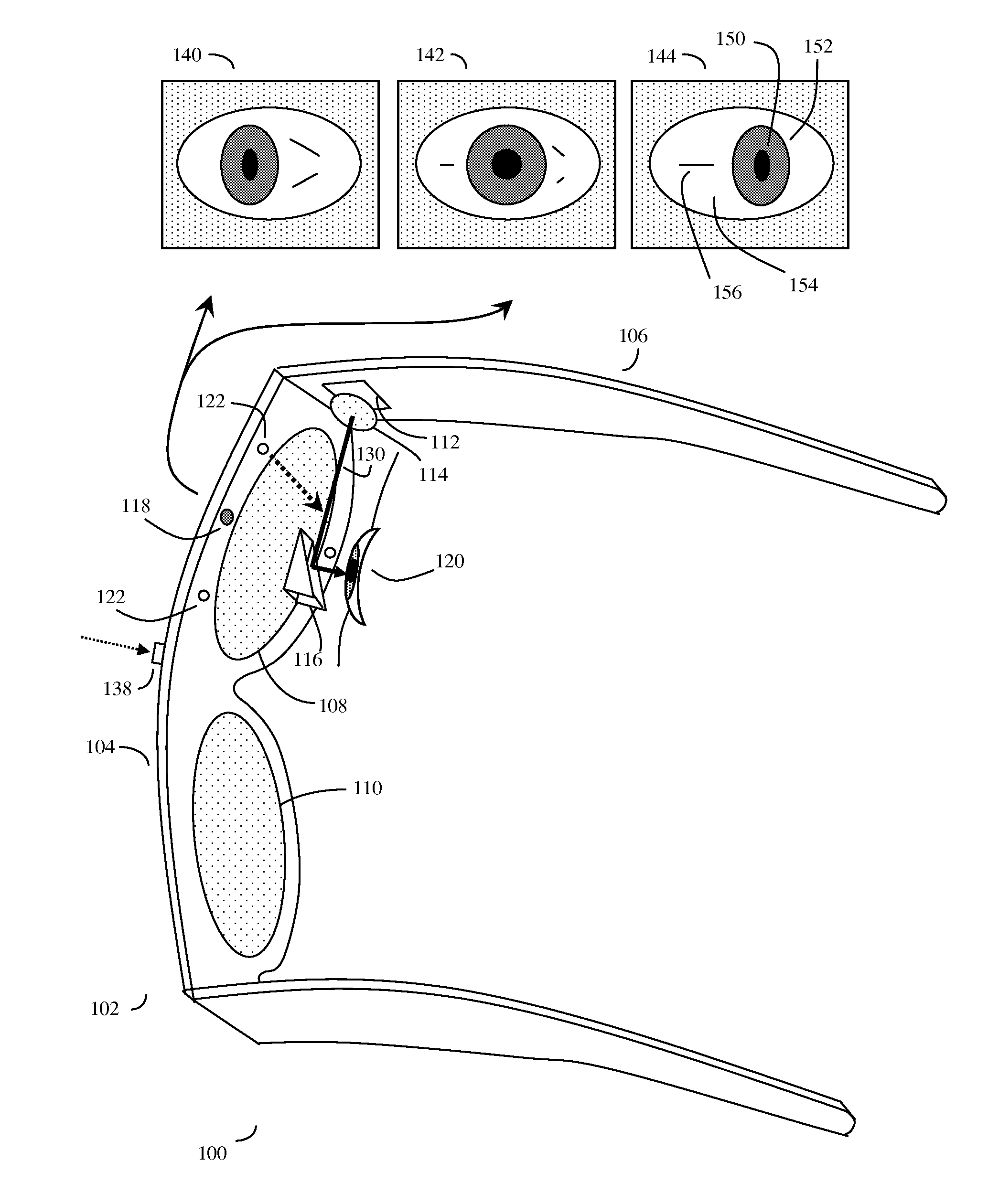
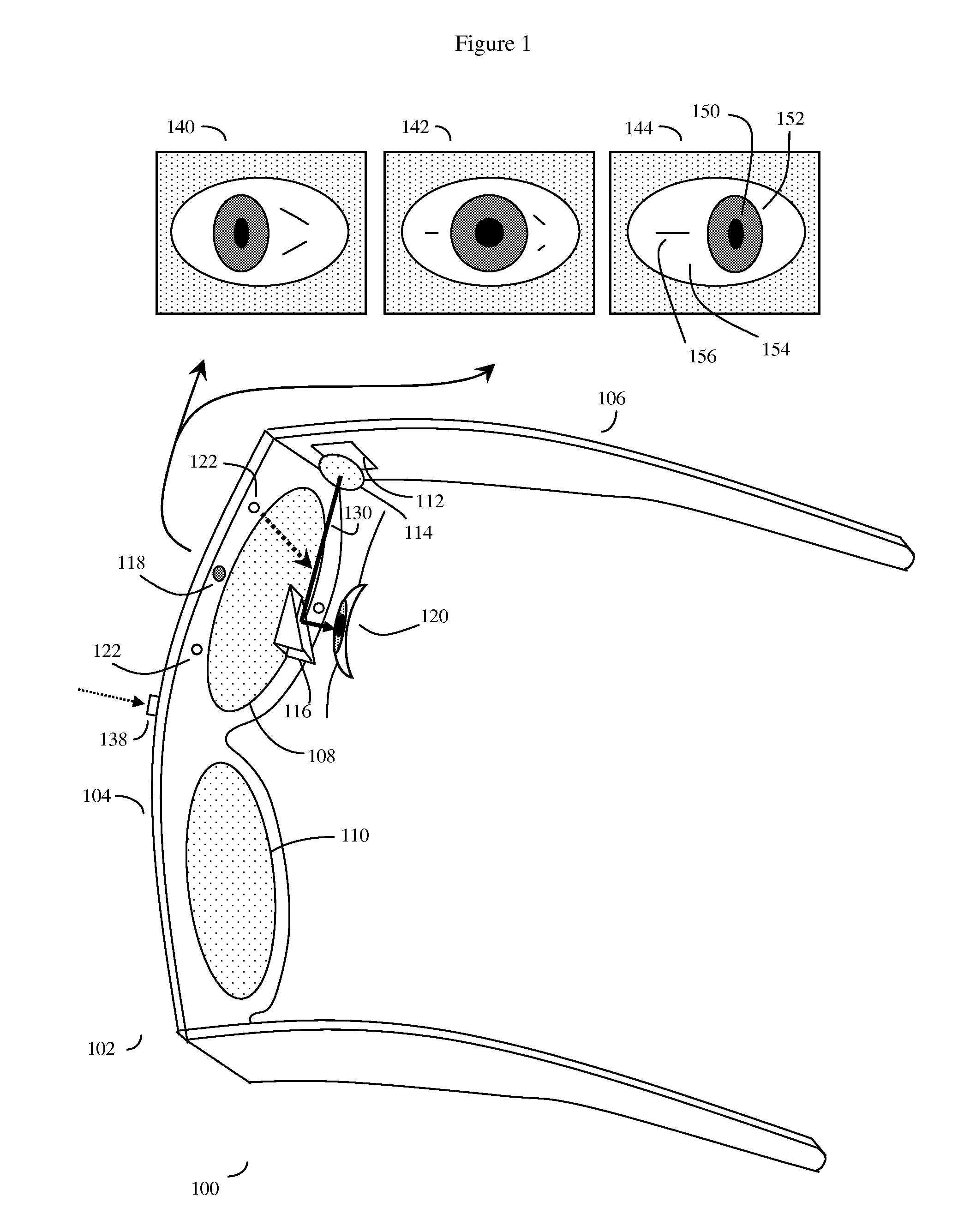
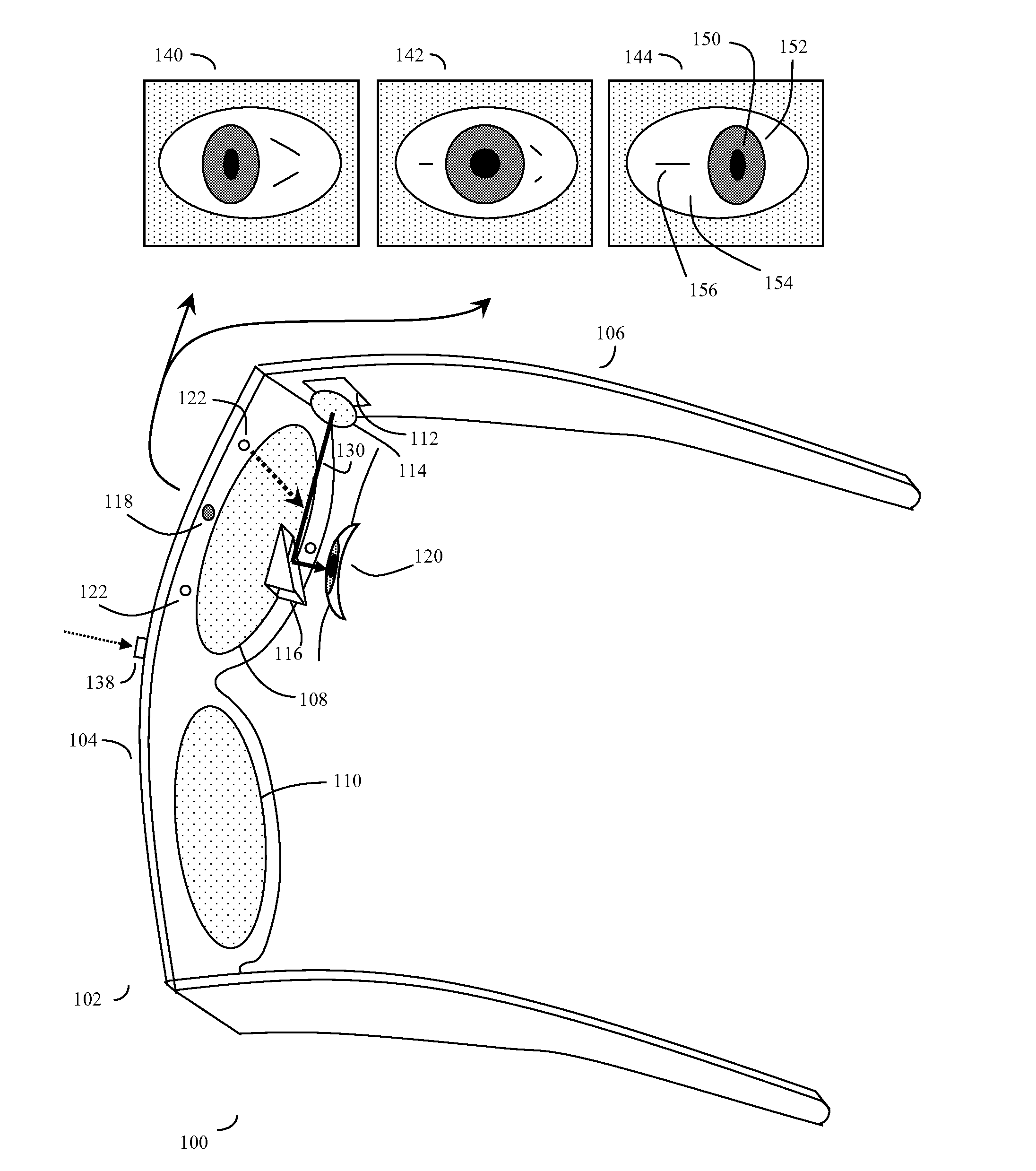
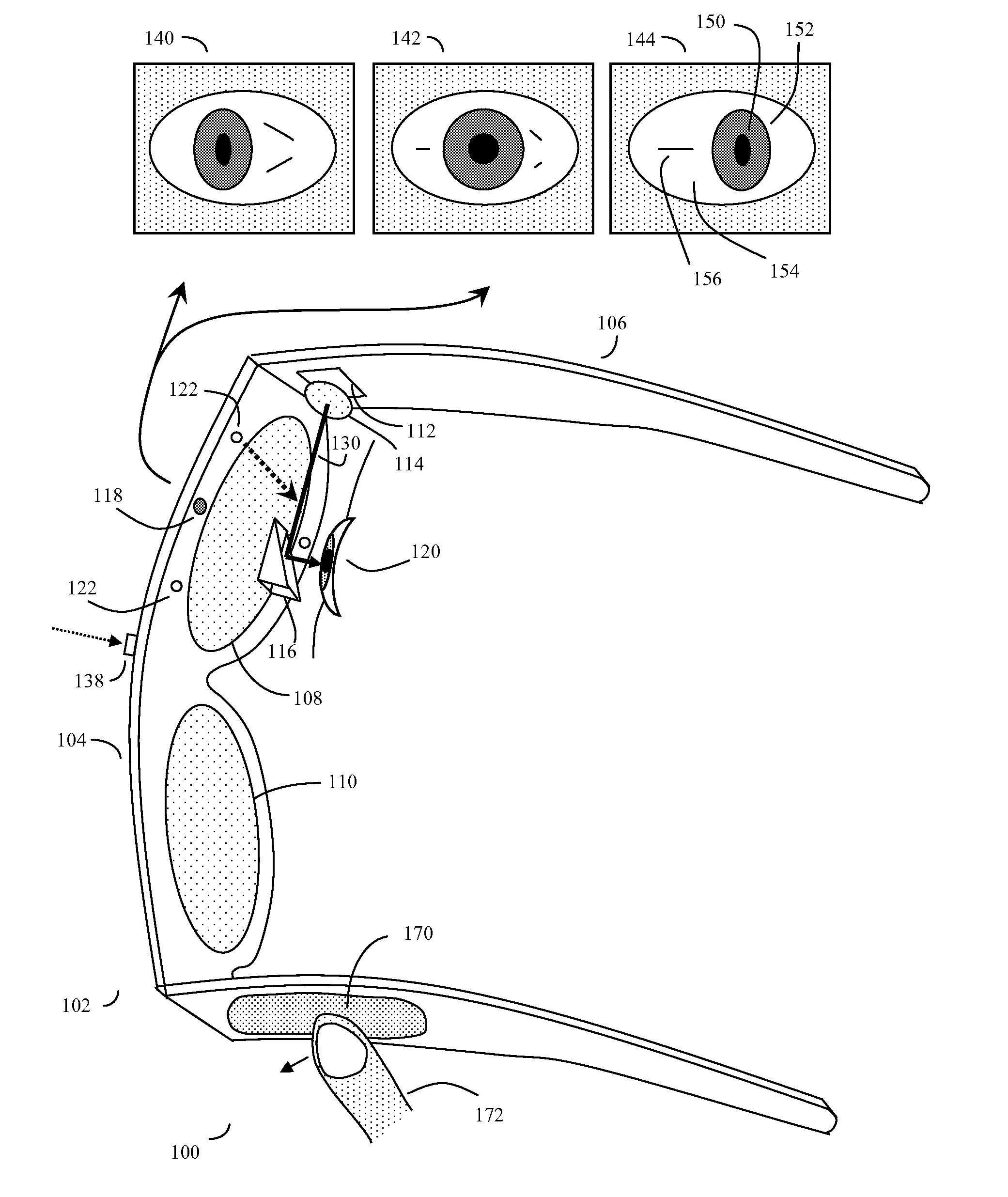
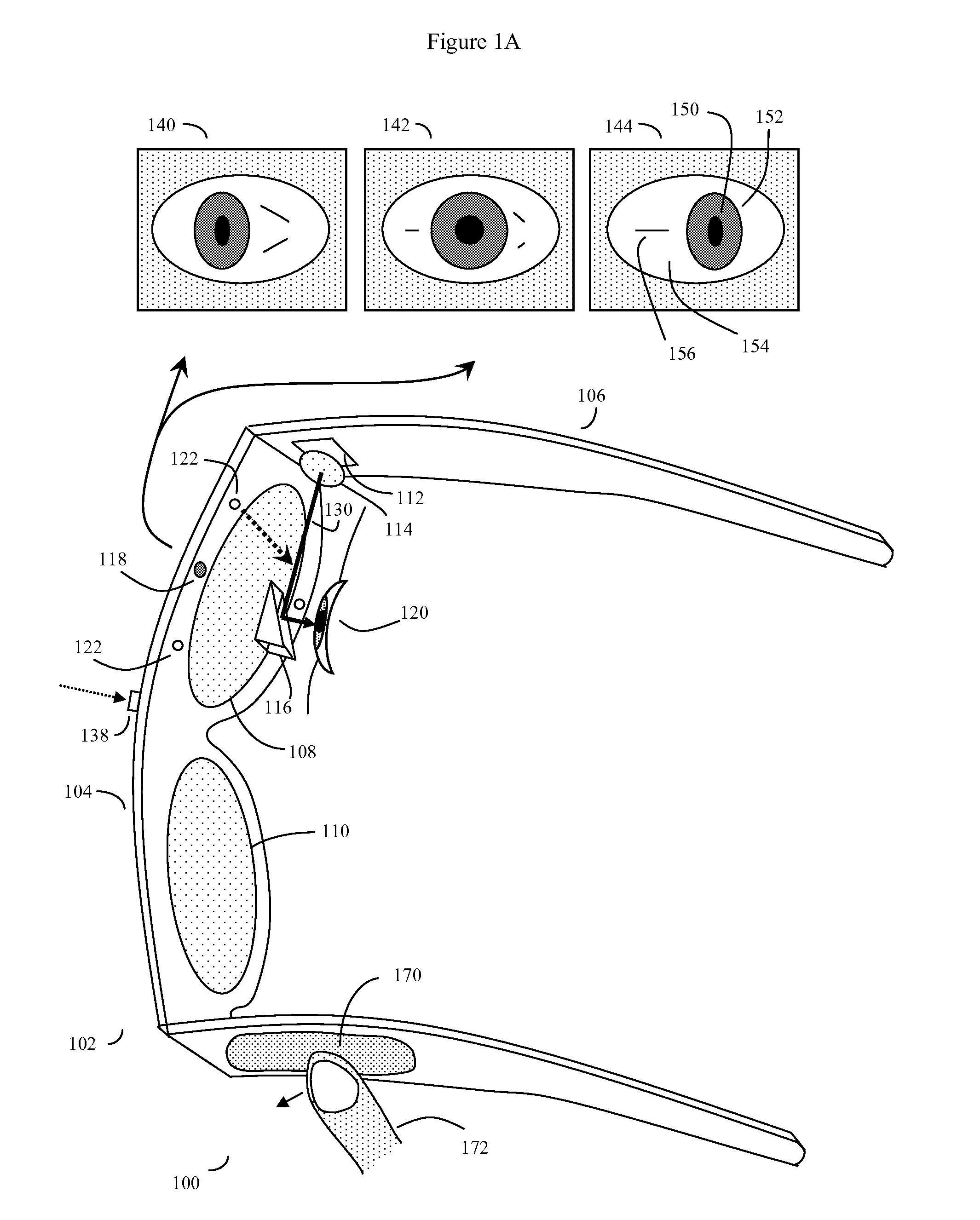
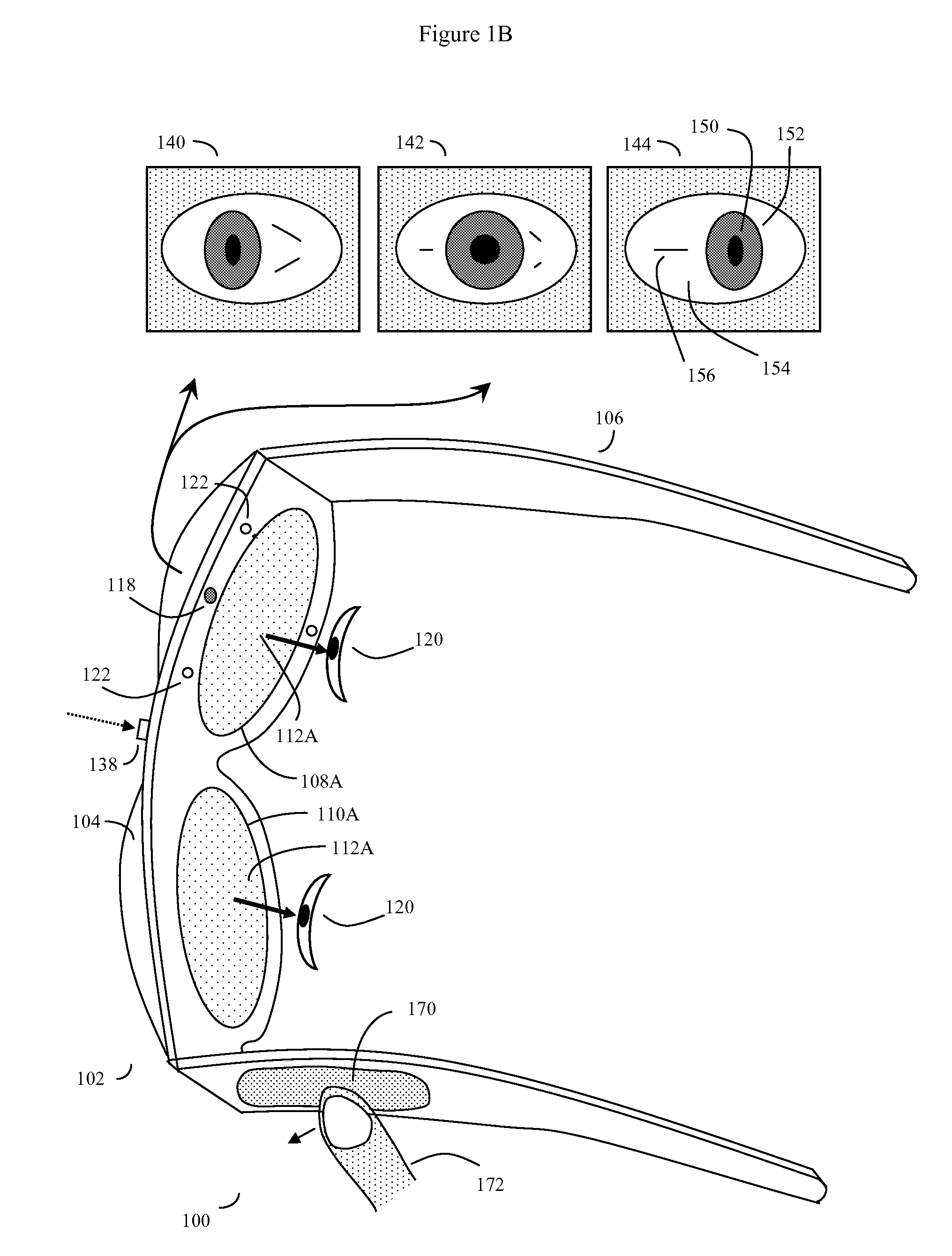
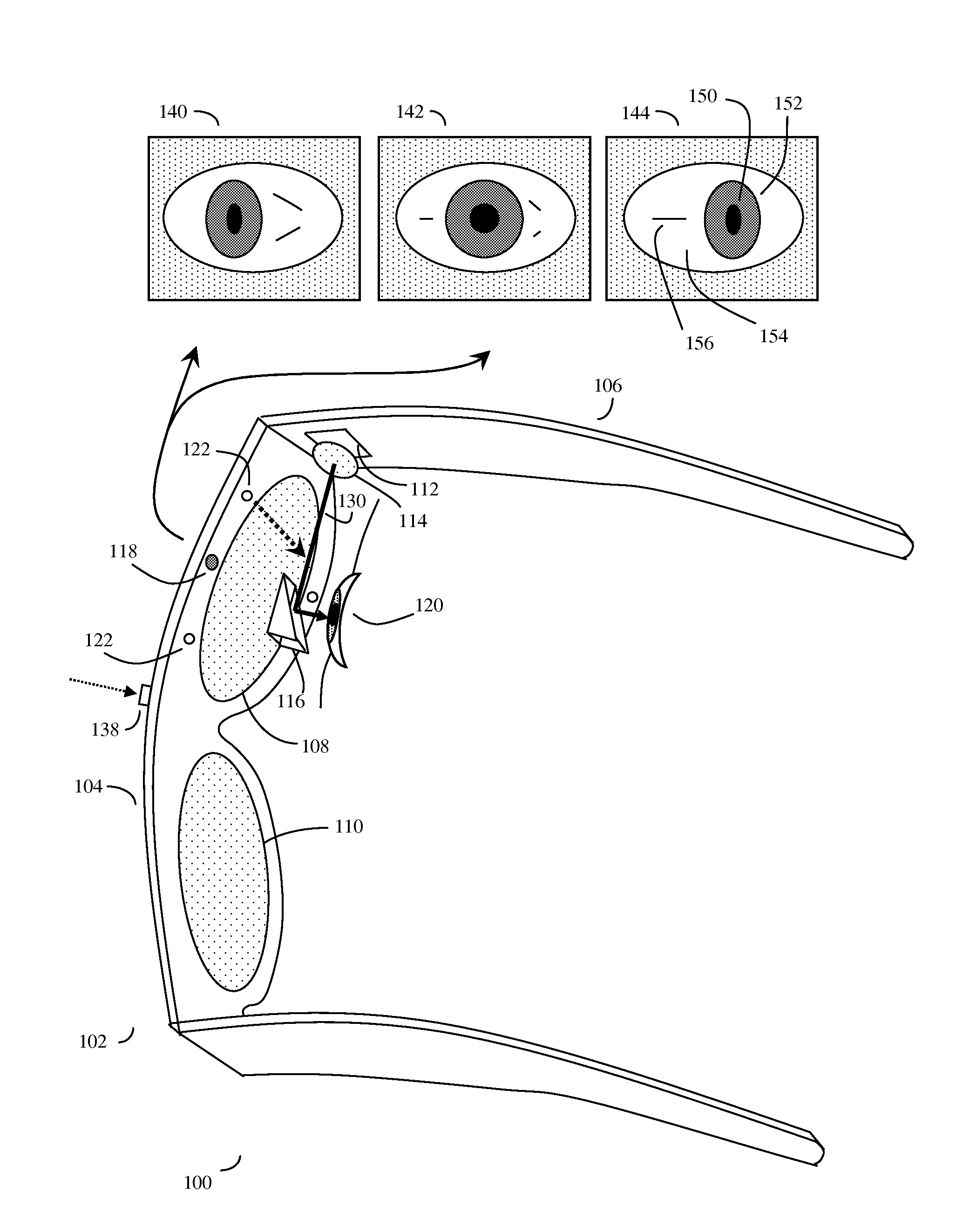
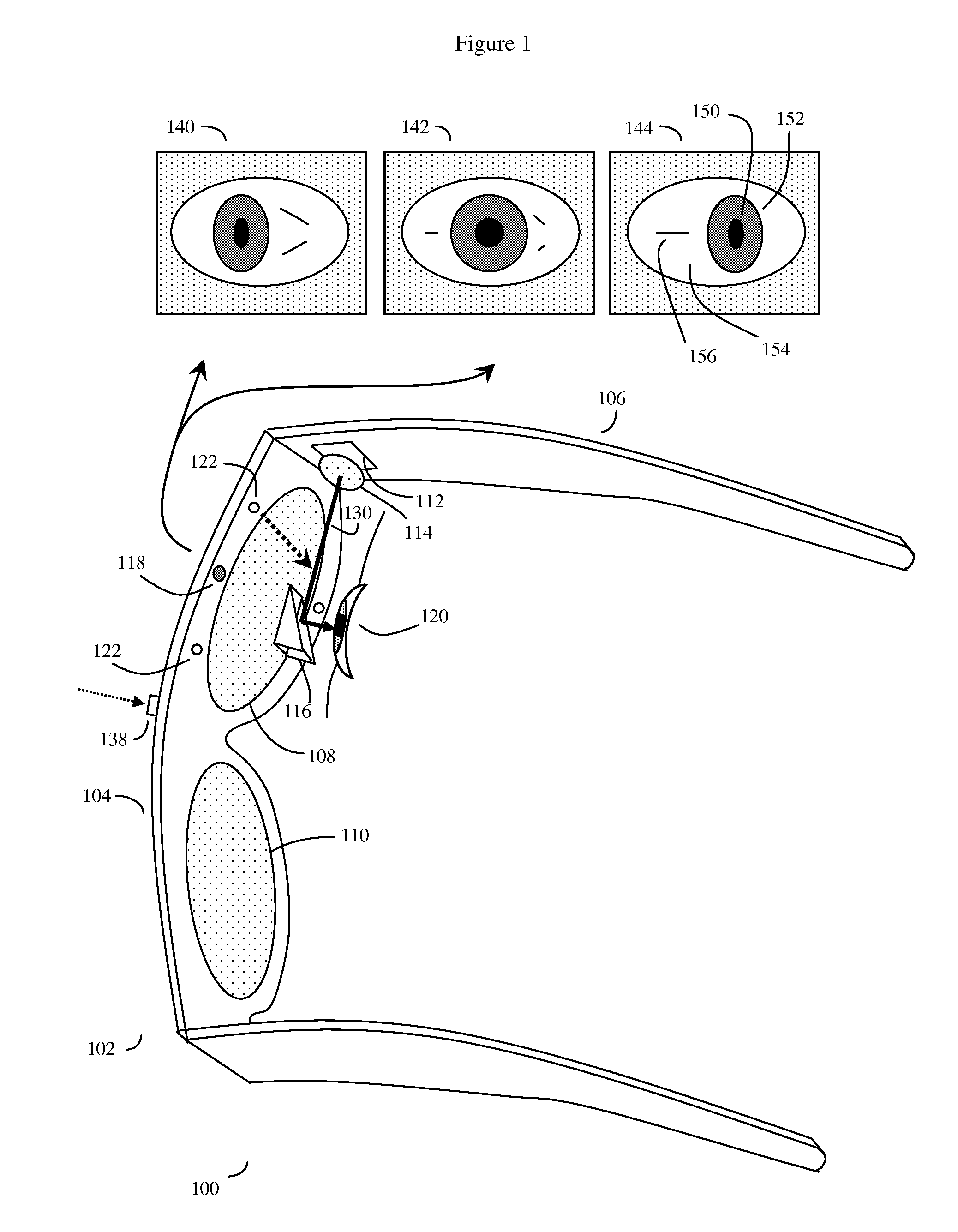
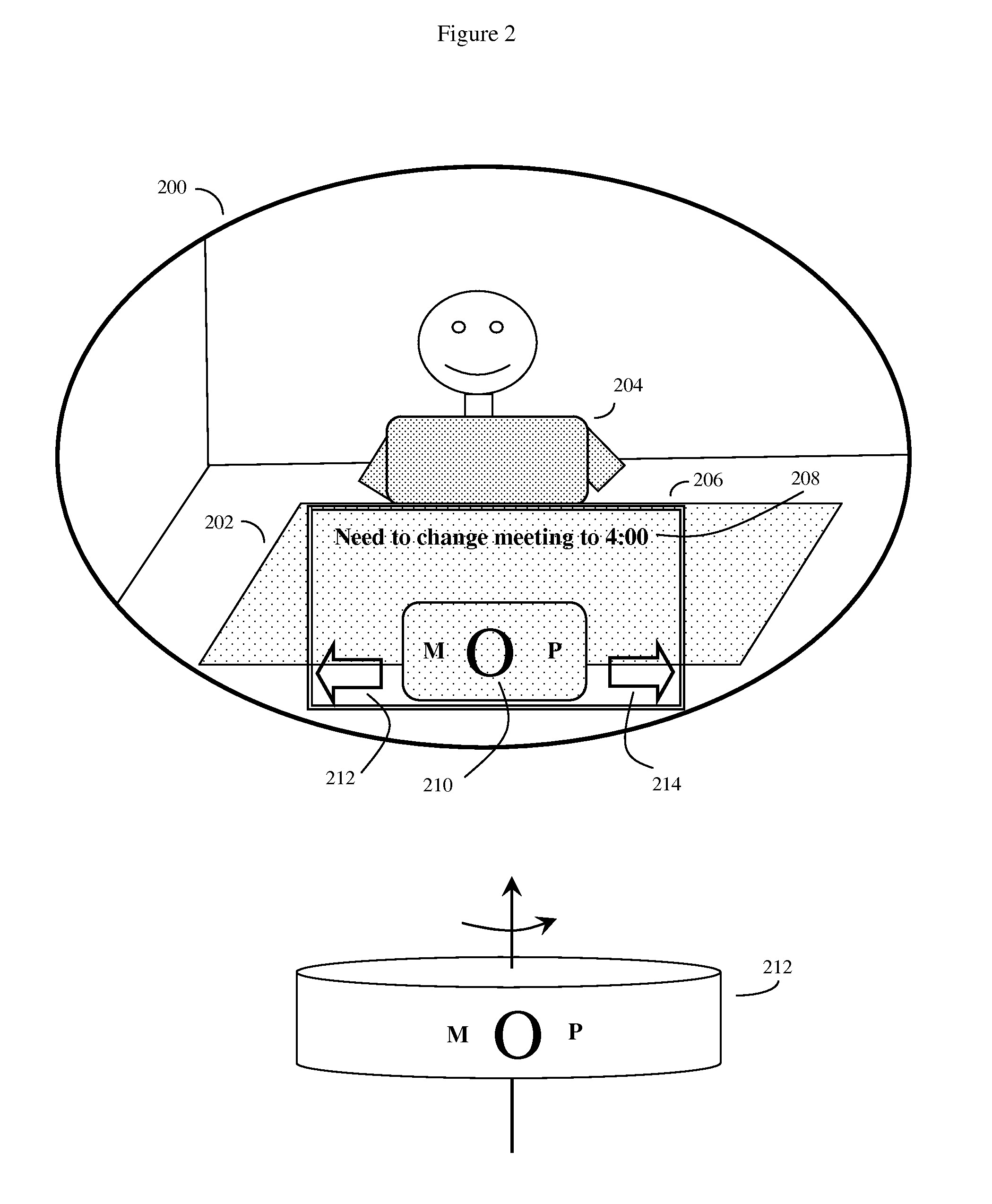
Eye gaze user interface and method
ActiveUS20120019662A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsClosed circuit television systemsGaze directionsVisual perception
A software controlled user interface and method for an eye gaze controlled device, designed to accommodate angular accuracy versus time averaging tradeoffs for eye gaze direction sensors. The method can scale between displaying a small to large number of different eye gaze target symbols at any given time, yet still transmit a large array of different symbols to outside devices with minimal user training. At least part of the method may be implemented by way of a virtual window onto the surface of a virtual cylinder, with eye gaze sensitive symbols that can be rotated by eye gaze thus bringing various groups of symbols into view, and then selected by continual gazing. Specific examples of use of this interface and method on an eyeglasses-like head-mountable, vision-controlled, device are disclosed, along with various operation examples including sending and receiving text messages, control of robotic devices and control of remote vehicles.
Owner:SNAP INC
Monolayer and/or Few-Layer Graphene On Metal or Metal-Coated Substrates
InactiveUS20100255984A1Easy to disassembleMaterial nanotechnologyParticle separator tubesHigh concentrationIn plane
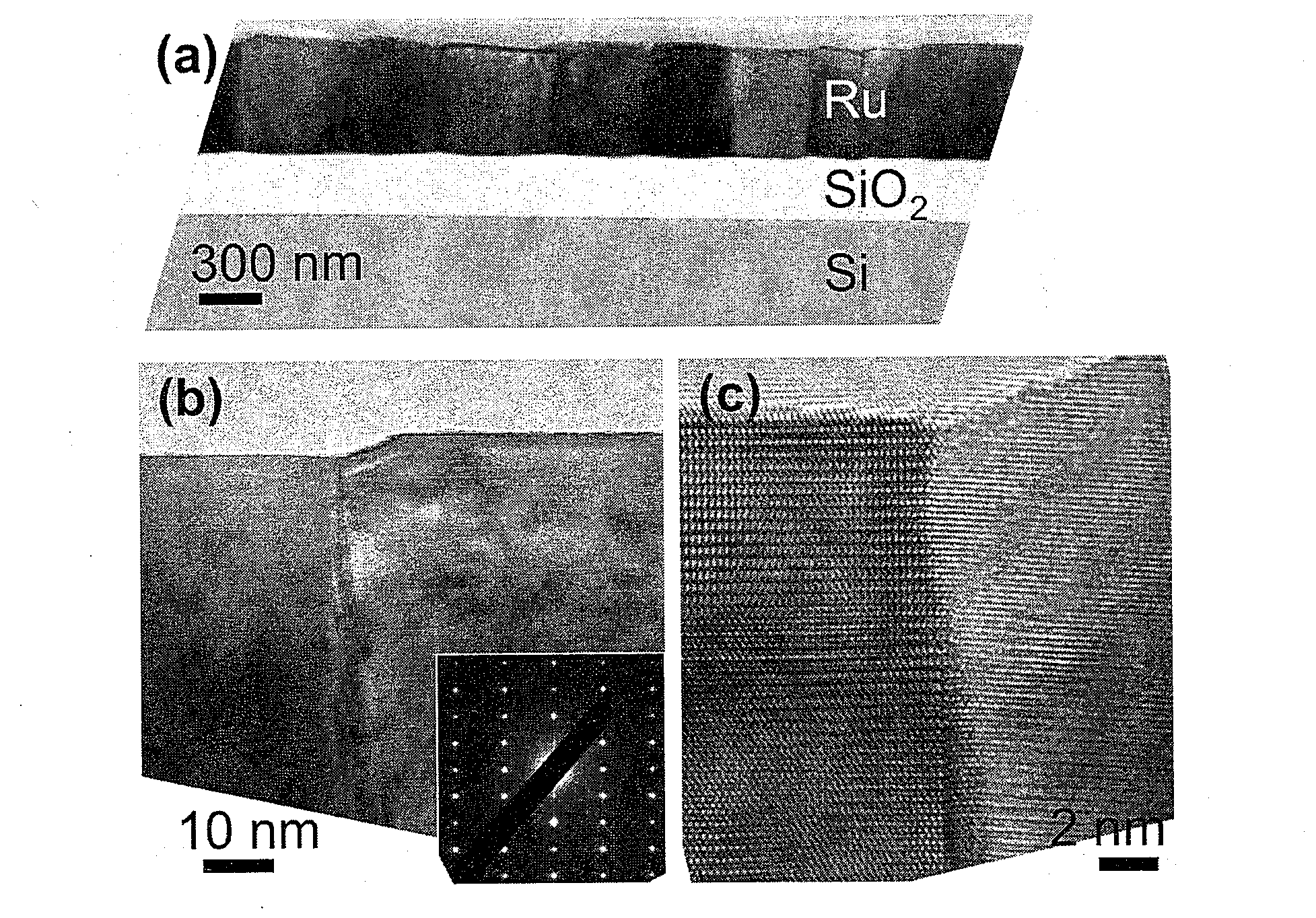
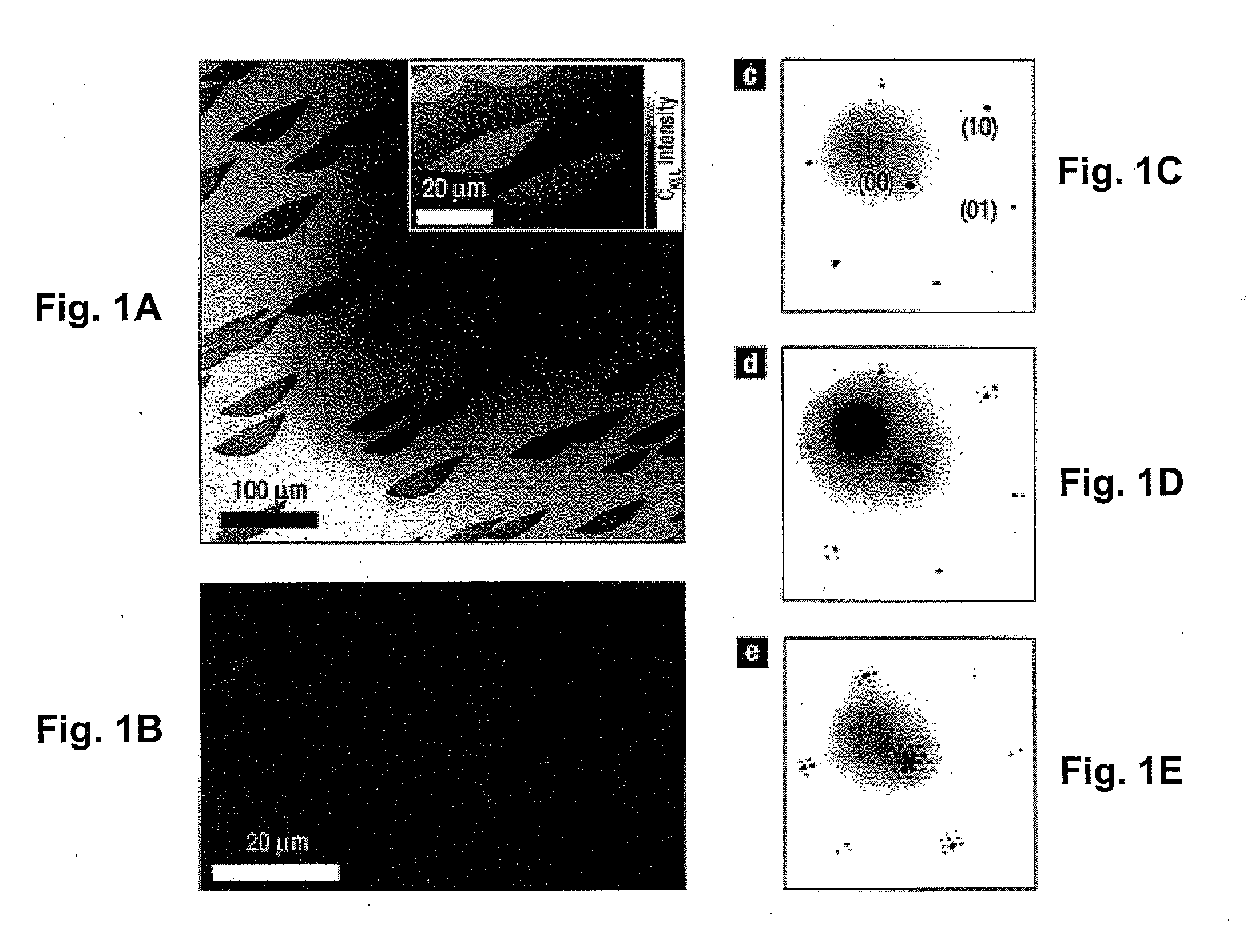
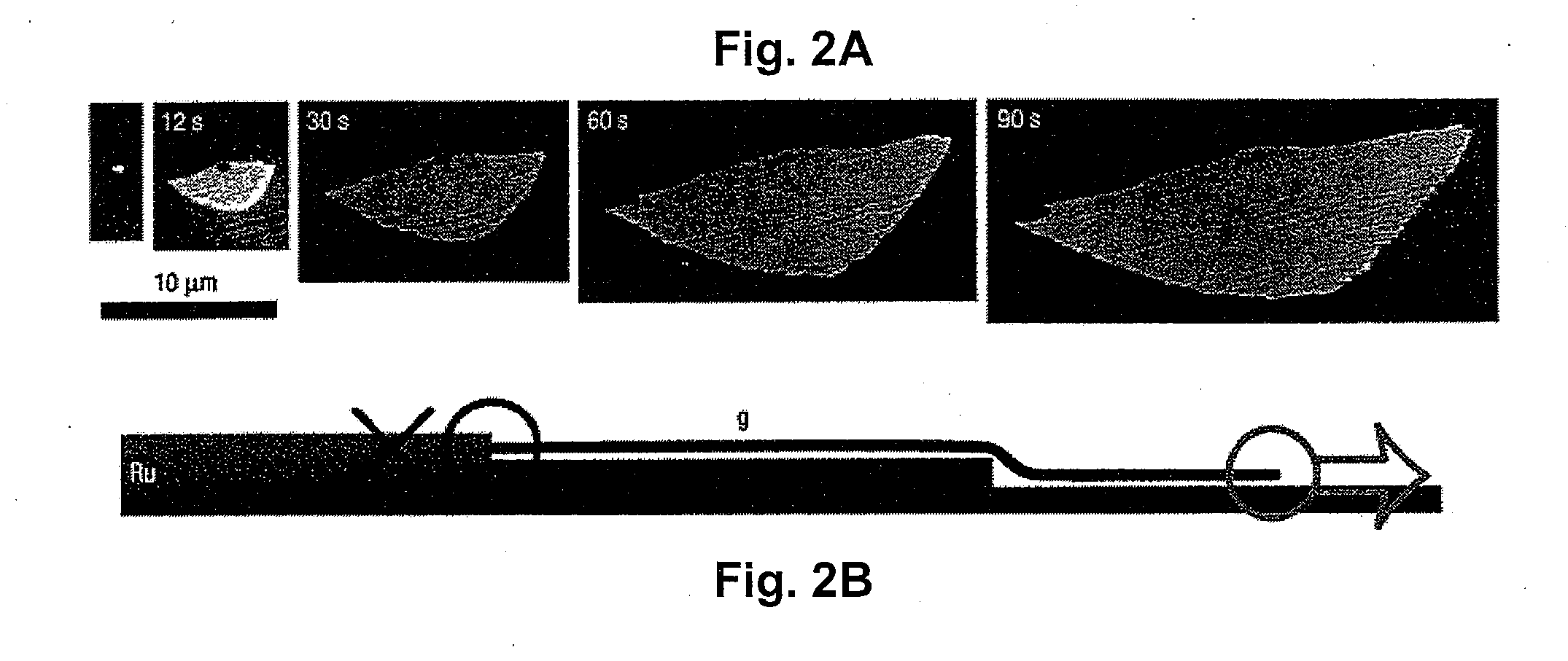
Graphene is a single atomic layer of sp2-bonded C atoms densely packed into a two-dimensional honeycomb crystal lattice. A method of forming structurally perfect and defect-free graphene films comprising individual mono crystalline domains with in-plane lateral dimensions of up to 200 μm or more is presented. This is accomplished by controlling the temperature-dependent solubility of interstitial C of a transition metal substrate having a suitable surface structure. At elevated temperatures, C is incorporated into the bulk at higher concentrations. As the substrate is cooled, a lowering of the interstitial C solubility drives a significant amount of C atoms to the surface where graphene islands nucleate and gradually increase in size with continued cooling. Ru(0001) is selected as a model system and electron microscopy is used to observe graphene growth during cooling from elevated temperatures. With controlled cooling, large arrays of macroscopic single-crystalline graphene domains covering the entire transition metal surface are produced. As the graphene domains coalesce to a complete layer, a second graphene layer is formed, etc. By controlling the interstitial C concentration and the cooling rate, graphene layers with thickness up to 10 atomic layers or more are formed in a controlled, layer-by-layer fashion.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
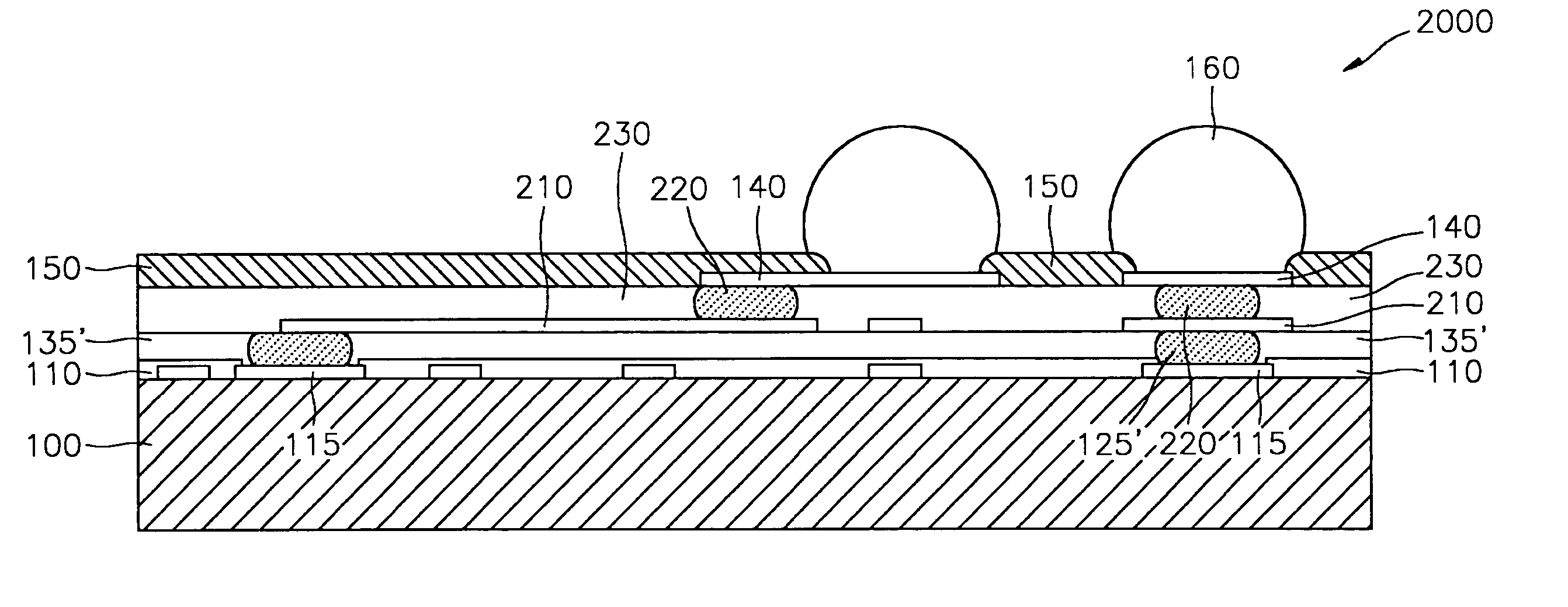
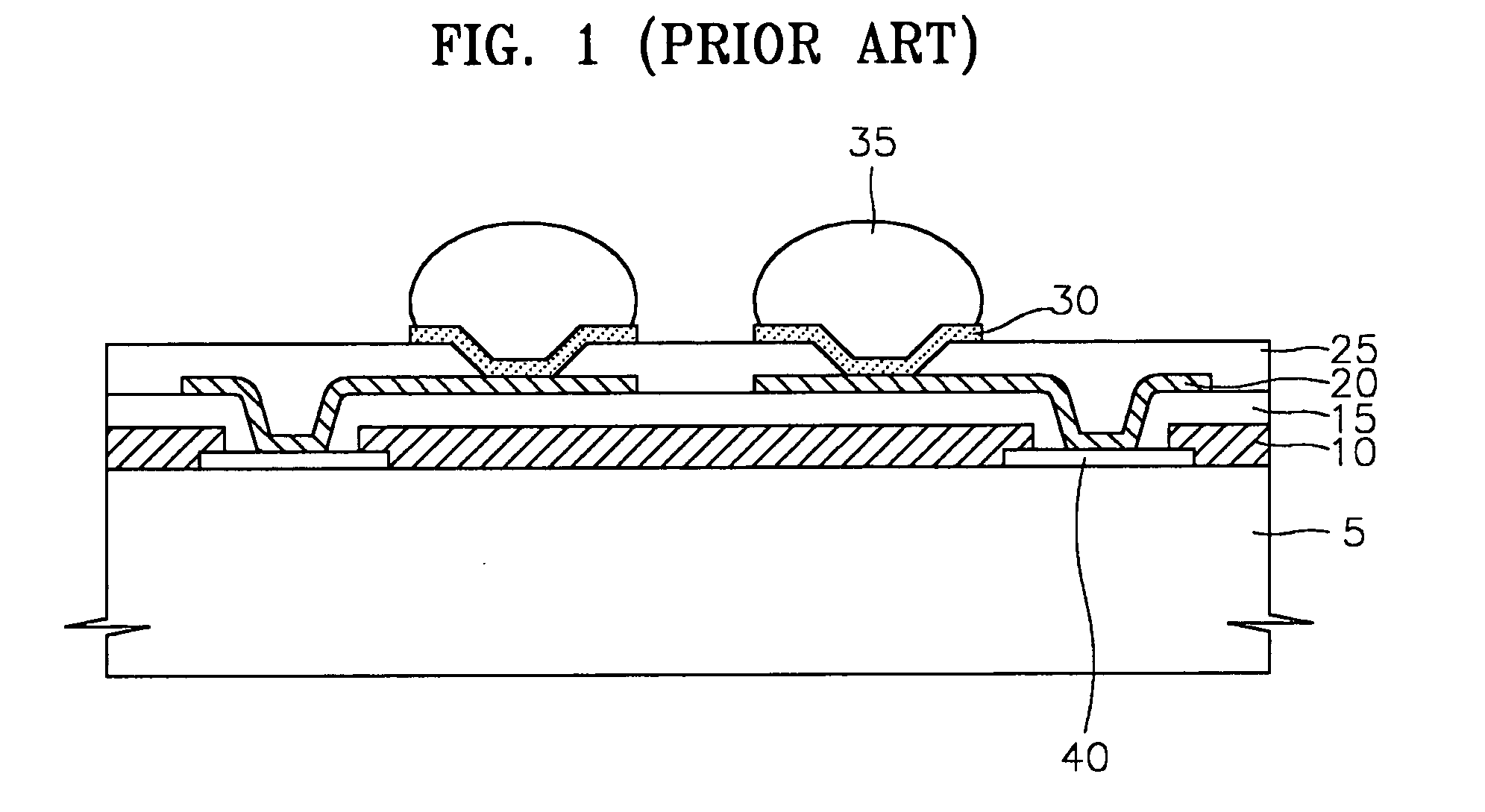
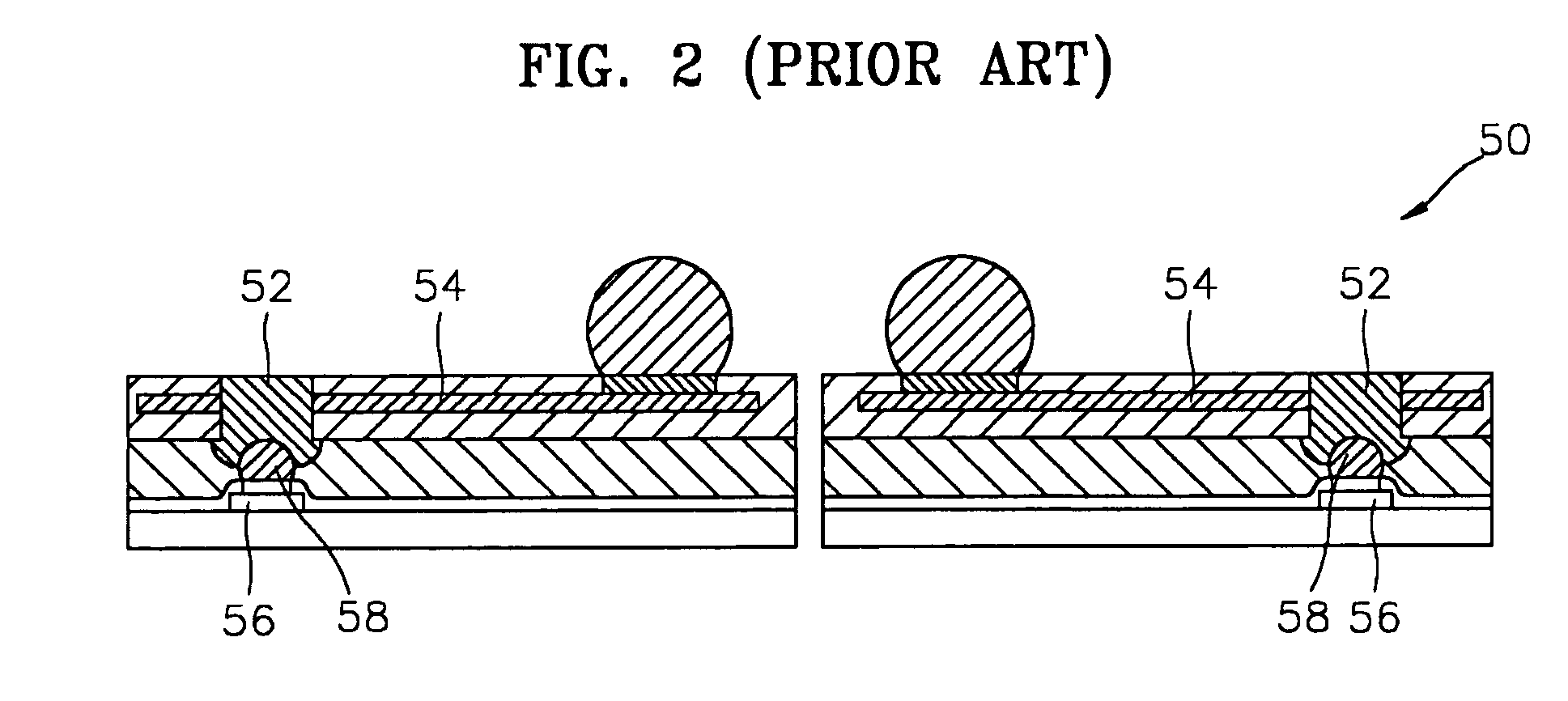
Wafer-level chip scale package and method for fabricating and using the same
InactiveUS20050012225A1Address rising pricesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRedistribution layerChip size
A packaged semiconductor device (a wafer-level chip scale package) containing a conductive adhesive material as an electrical interconnect route between the semiconductor die and a patterned conductive substrate is described. The patterned conductive substrate acts not only as a substrate, but also as a redistribution layer that converts the dense pad layout of the die to a larger array configuration of the solder balls in the circuit board. Using the invention allows the formation of a lower priced chip scale package that also overcomes the restriction of the die size used in die-sized chip packages and the input-output pattern that can be required by the printed circuit board. Thus, the invention can provide a familiar pitch (i.e.,interface) to the printed circuit board for any small die.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
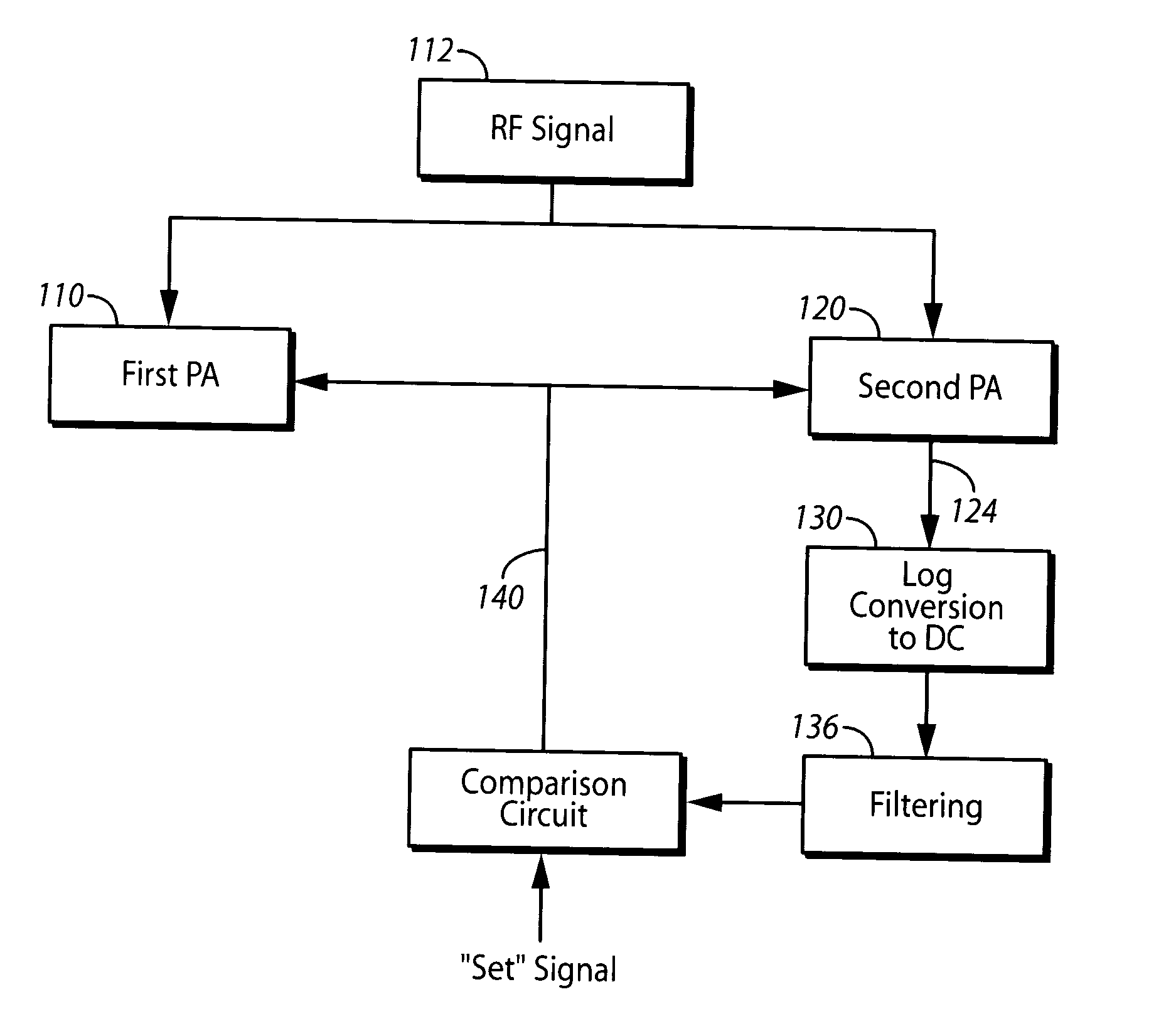
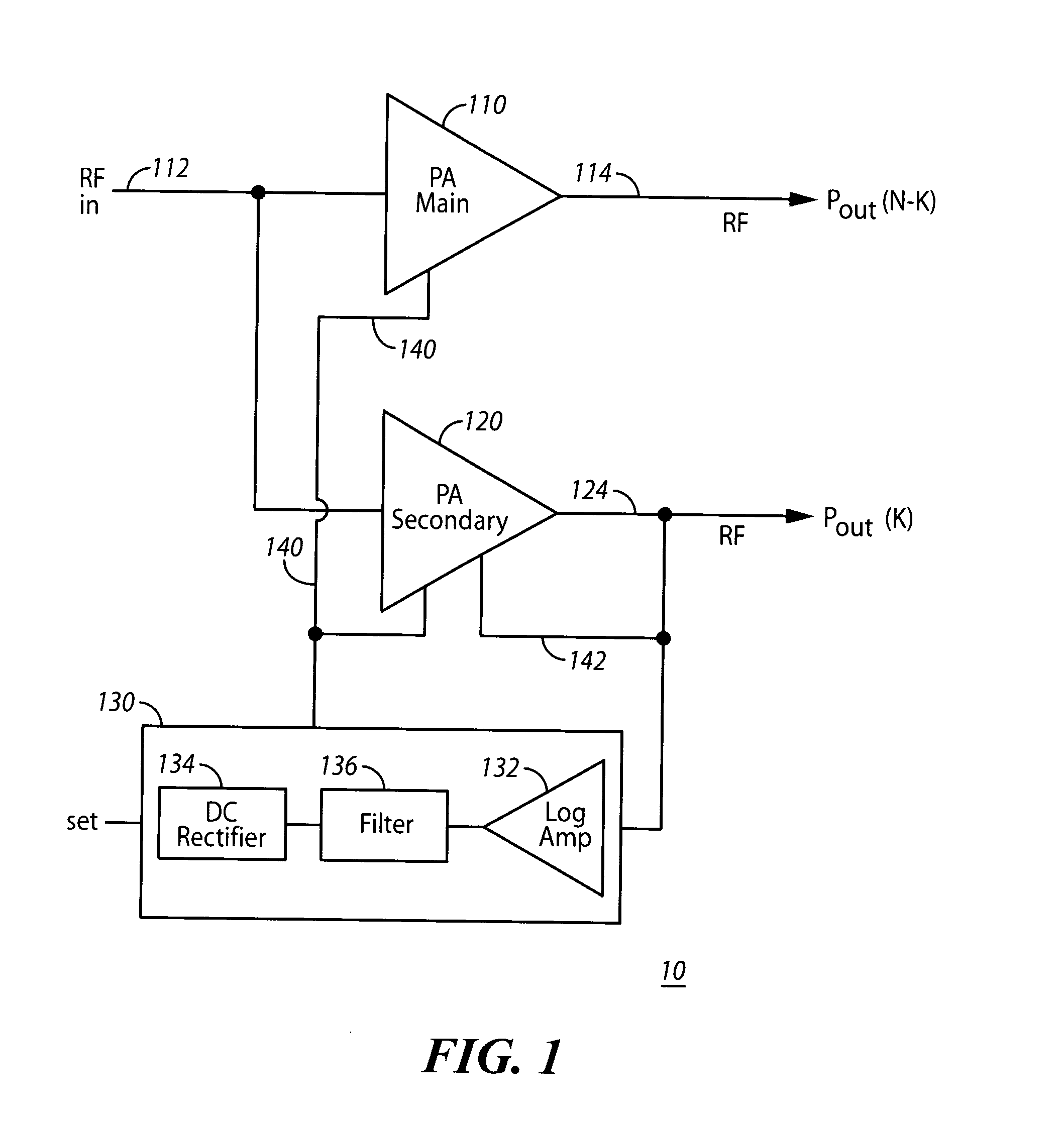
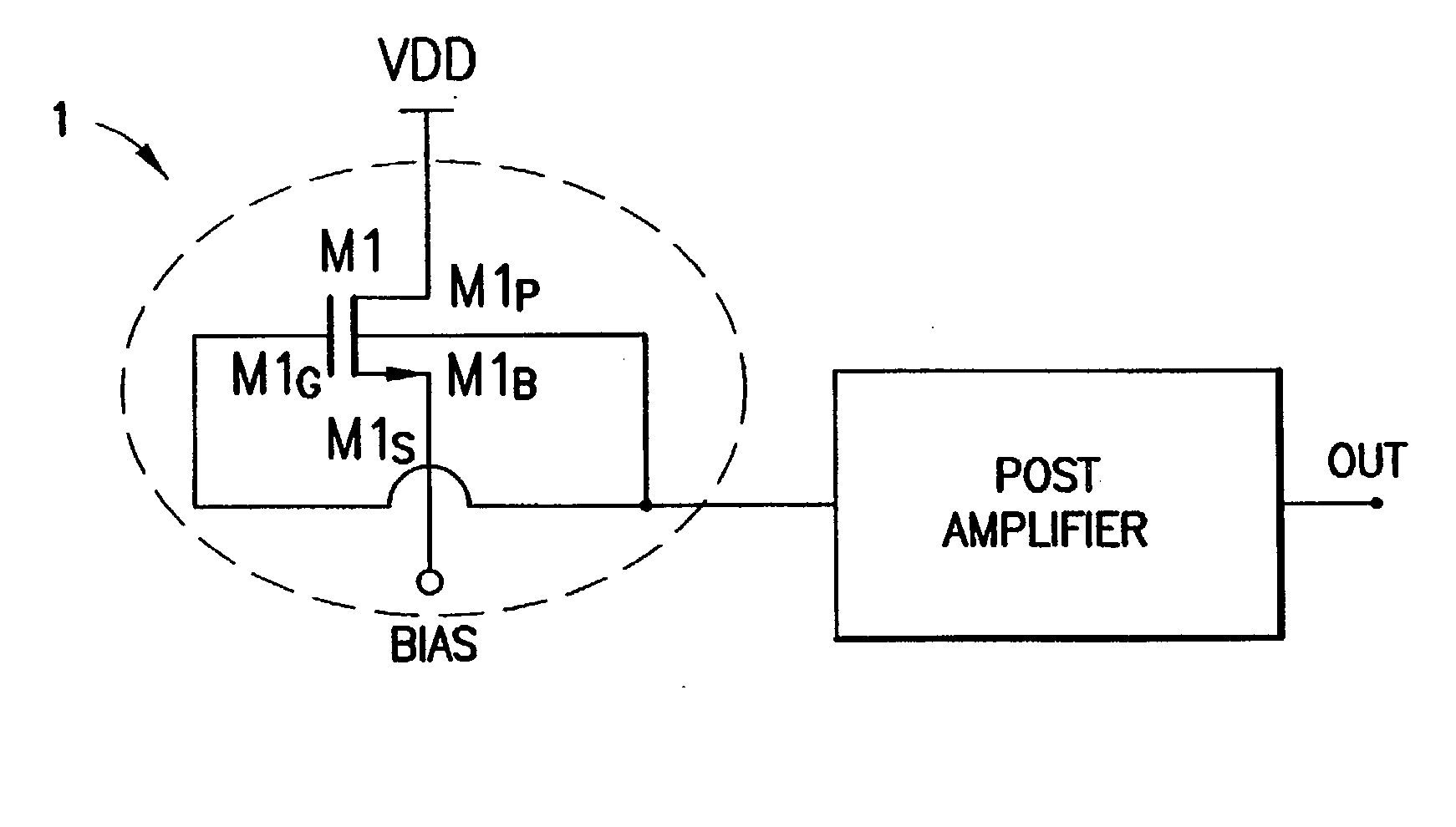
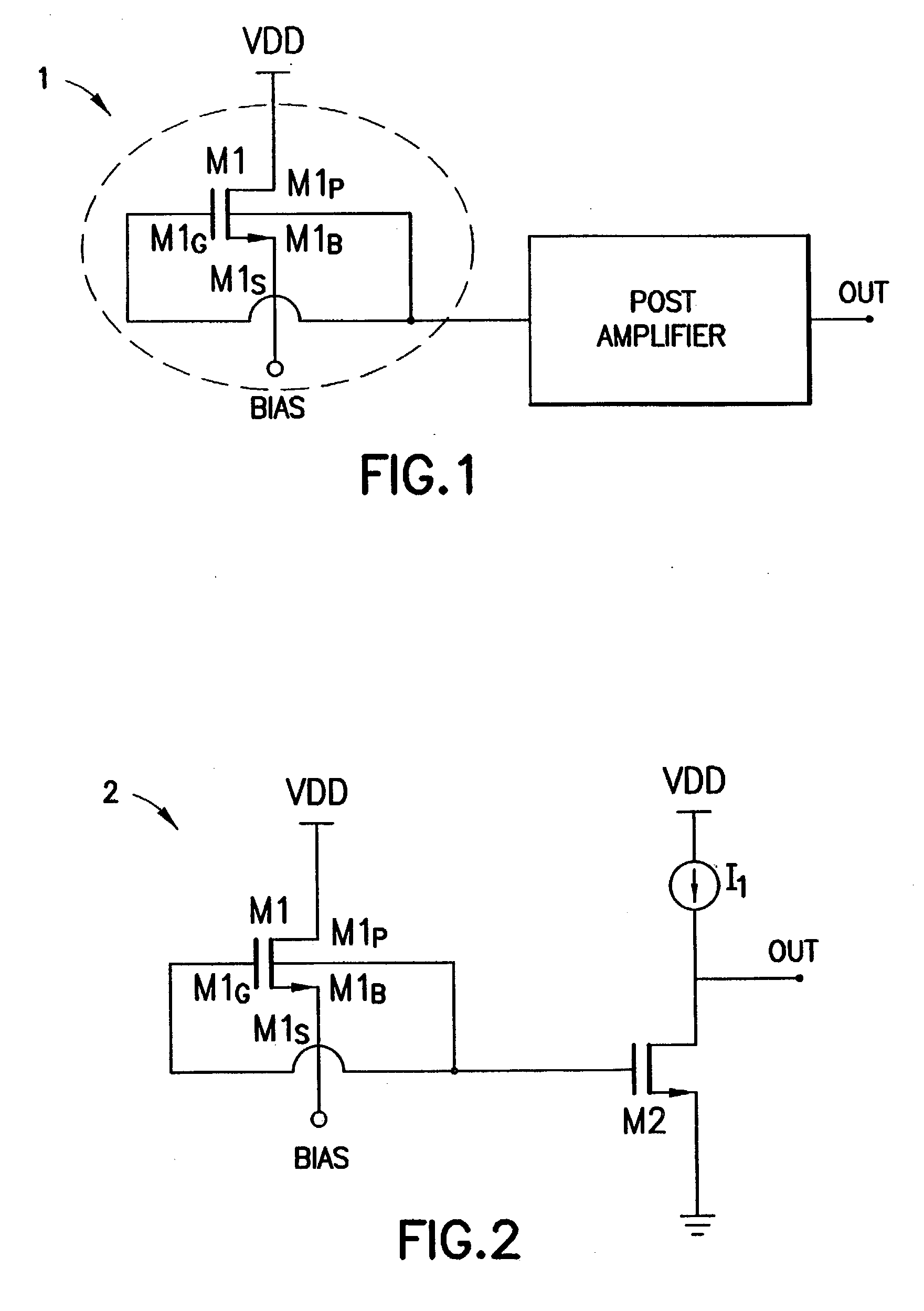
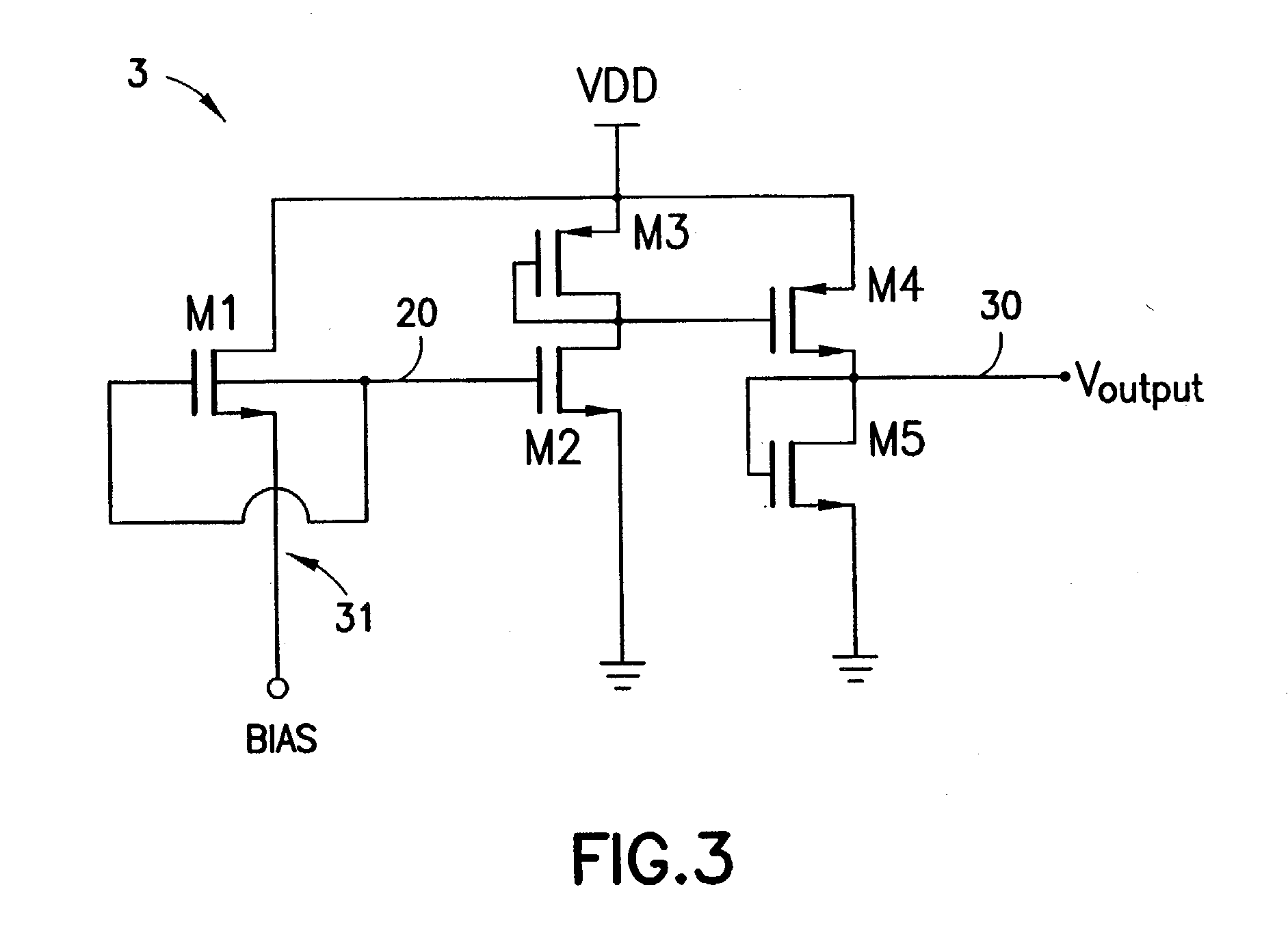
Radio frequency power detecting circuit and method therefor
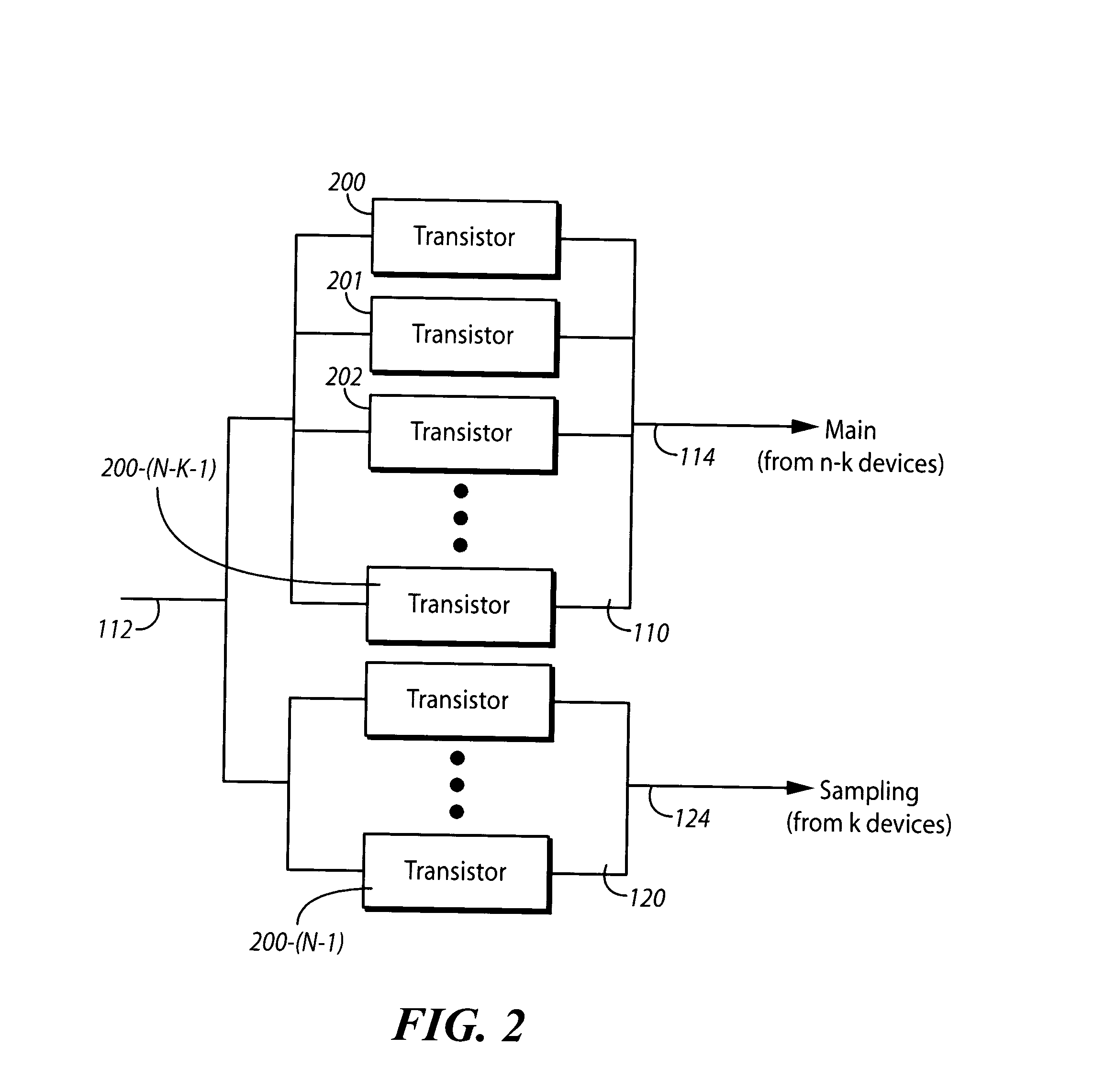
A circuit for detecting the amount of radio frequency power provided by an amplifier. The circuit contains an array of coupled transistors in two power amplifiers, and a log-detector circuit, all resident on a single semiconductor die. The main power amplifier contains the larger array of transistors to amplify the radio frequency signal for feeding to an antenna, and a secondary power amplifier contains a smaller array of transistors to provide a scaled output that is proportional to the amplified radio frequency signal and is used to control the main power amplifier. The log-detector circuit converts the signal from the secondary power amplifier to a full-wave rectified log-linear DC signal that is logarithmically proportional to the controlling signal. The DC signal output from the log-detector circuit is fed to the main power amp to control it.
Owner:YUANTONIX
Single line bayer RGB bad pixel correction
InactiveUS20050248671A1Efficient detectionLow costTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionColor image
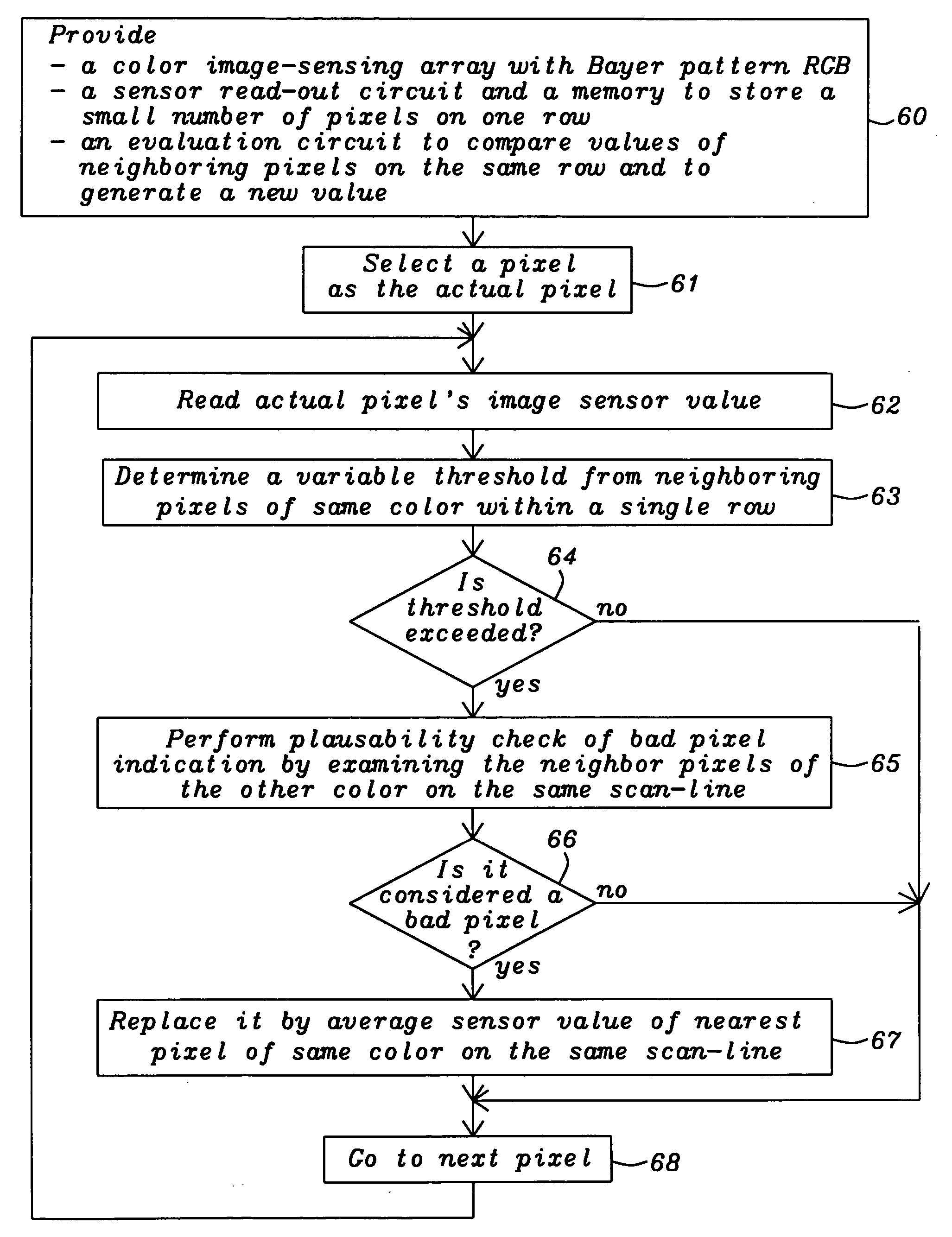
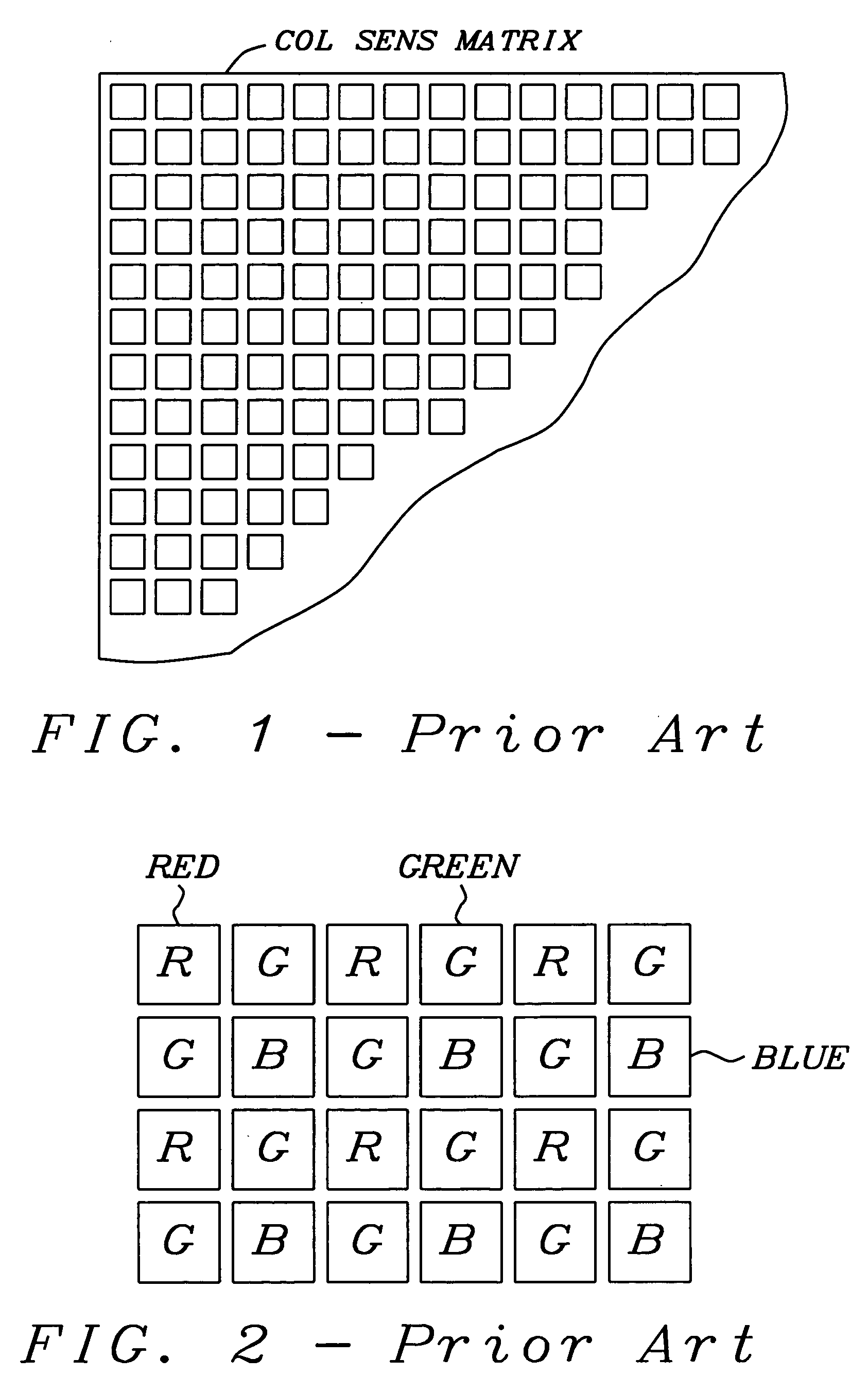
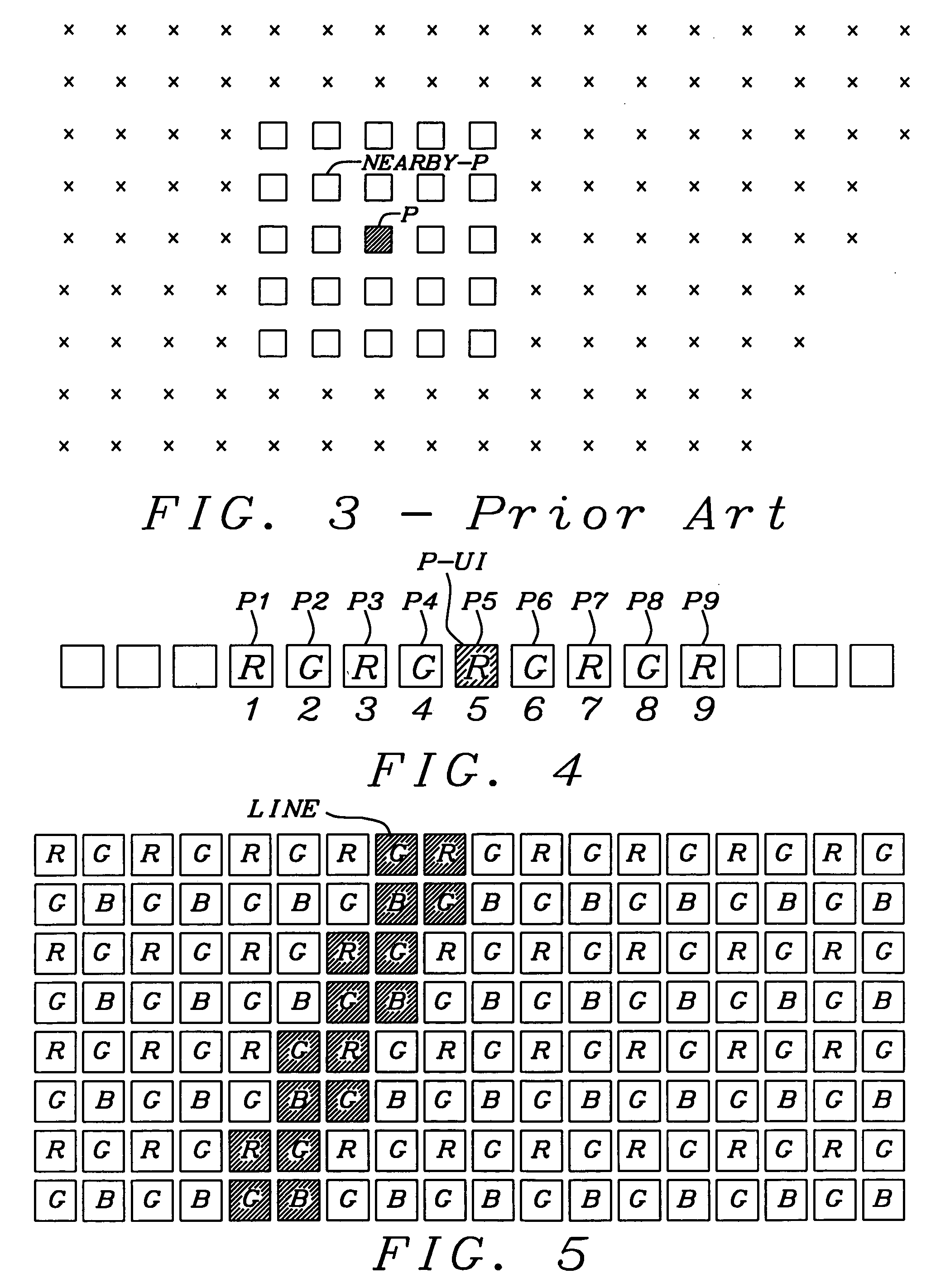
In large arrays of image sensing devices, like CCDs, a small number of defective image elements (pixels) must be tolerated and the resulting image degradation should be eliminated through bad pixel correction. The disclosed invention provides a mechanism to effectively detect defective pixels “on the fly” in a Bayer RGB type color image sensor, optimized for low cost applications. It calculates a variable threshold based on signal changes on nearby pixels of the same color within a single row and checks if the signal change of the pixel under test exceeds said variable threshold. It further performs a plausibility check using nearby pixels of an other color in the same row.
Owner:DIALOG IMAGING SYST
Eye gaze user interface and calibration method
ActiveUS20140049452A1Minimal user trainingInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsCylindromaGaze directions
A software controlled user interface and calibration method for an eye gaze controlled device, designed to accommodate angular accuracy versus time averaging tradeoffs for eye gaze direction sensors. The method can scale between displaying a small to large number of different eye gaze target symbols at any given time, yet still transmit a large array of different symbols to outside devices with minimal user training. At least part of the method may be implemented by way of a virtual window onto the surface of a virtual cylinder, with eye gaze sensitive symbols that can be rotated by eye gaze thus bringing various groups of symbols into view, and then selected by continual gazing. Specific examples of use of this interface and method on an eyeglasses-like head-mountable, vision-controlled, device are disclosed, along with various operation examples including sending and receiving text messages, control of robotic devices and control of remote vehicles.
Owner:SNAP INC
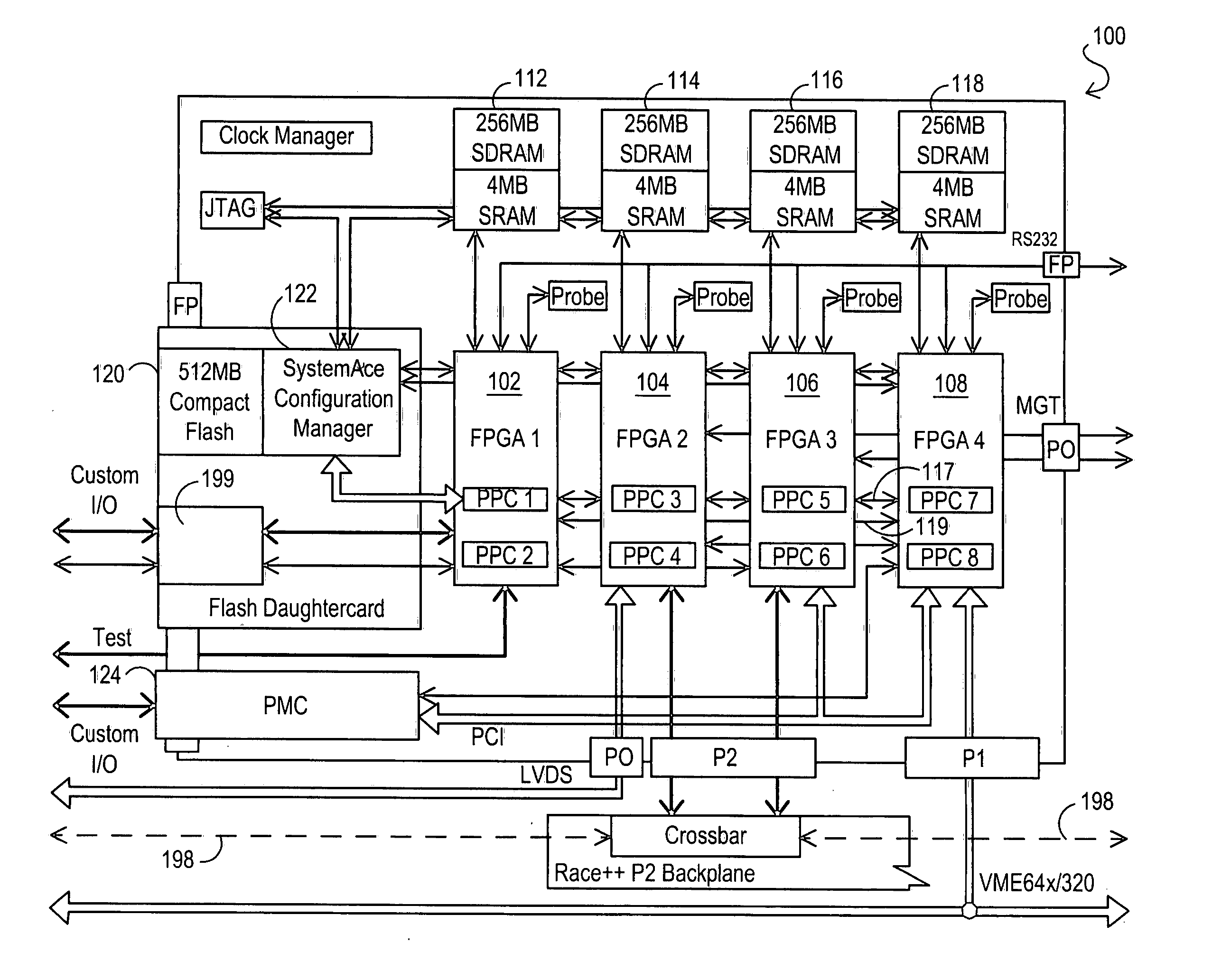
Reconfigurable communications infrastructure for ASIC networks
ActiveUS20070101242A1Increase network performance envelopeImprove performanceError detection/correctionCode conversionComputer hardwareHigh bandwidth
Reconfigurable communications infrastructures may be implemented to interconnect ASIC devices (e.g., FPGAs) and other computing and input / output devices using high bandwidth interconnection mediums. The computing and input / output devices may be positioned in locations that are physically segregated from each other, and / or may be provided to project a reconfigurable network across a wide area. The reconfigurable communications infrastructures may be implemented to allow such computing and input / output devices to be used in different arrangements and applications, e.g., for use in any application where a large array of ASIC devices may be usefully employed such as supercomputing, etc.
Owner:LIONRA TECH LTD +1
Multi-operation write aggregator using a page buffer and a scratch flash block in each of multiple channels of a large array of flash memory to reduce block wear
InactiveUS8108590B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSmall fragmentPage buffers
A flash system has multiple channels of flash memory chips that can be accessed in parallel. Host data is assigned to one of the channels by a multi-channel controller processor and accumulated in a multi-channel page buffer. When a page boundary in the page buffer is reached, the page buffer is written to a target physical block if full, or combined with old data fragments in an Aggregating Flash Block (AFB) when the logical-sector addresses (LSA's) match. Thus small fragments are aggregated using the AFB, reducing erases and wear of flash blocks. The page buffer is copied to the AFB when a STOP command occurs. Each channel has one or more AFB's, which are tracked by an AFB tracking table.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
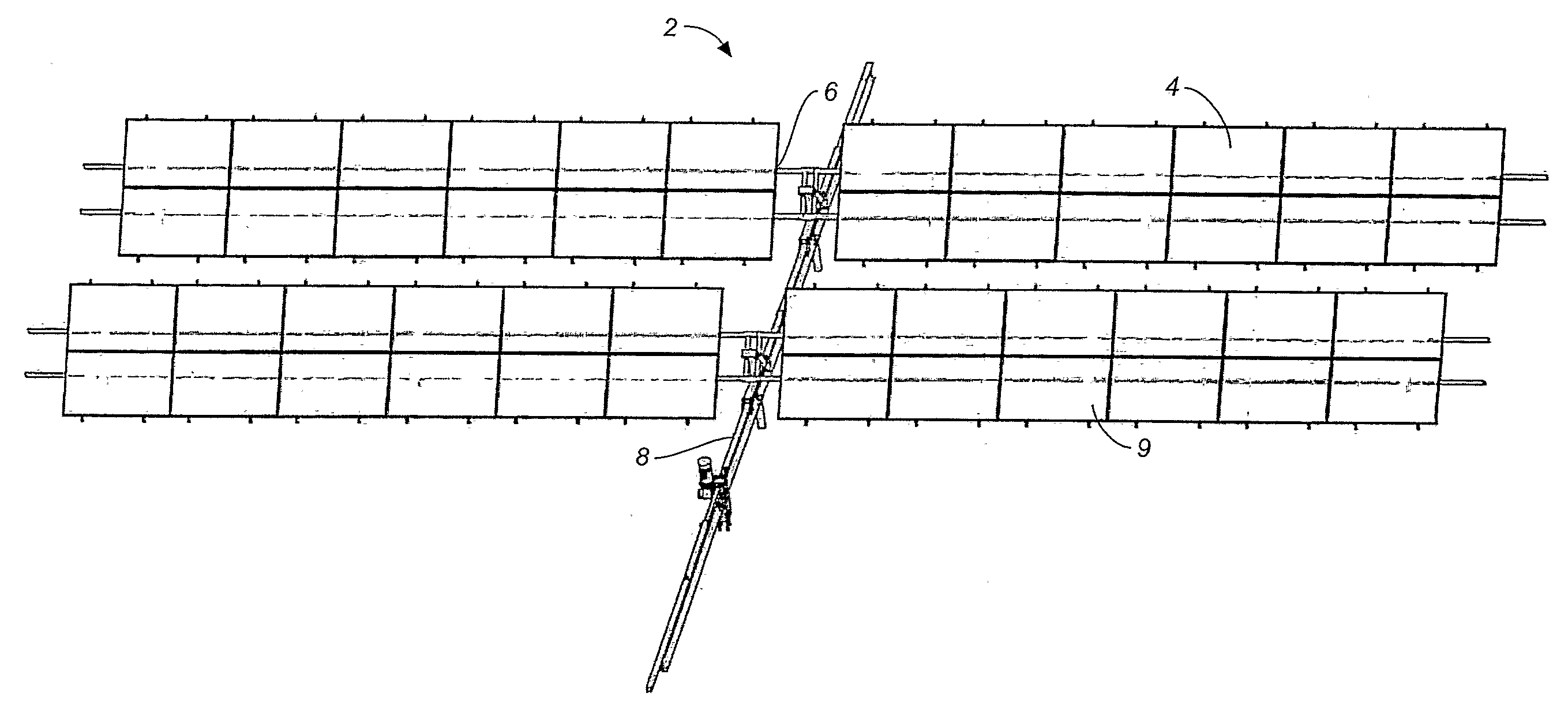
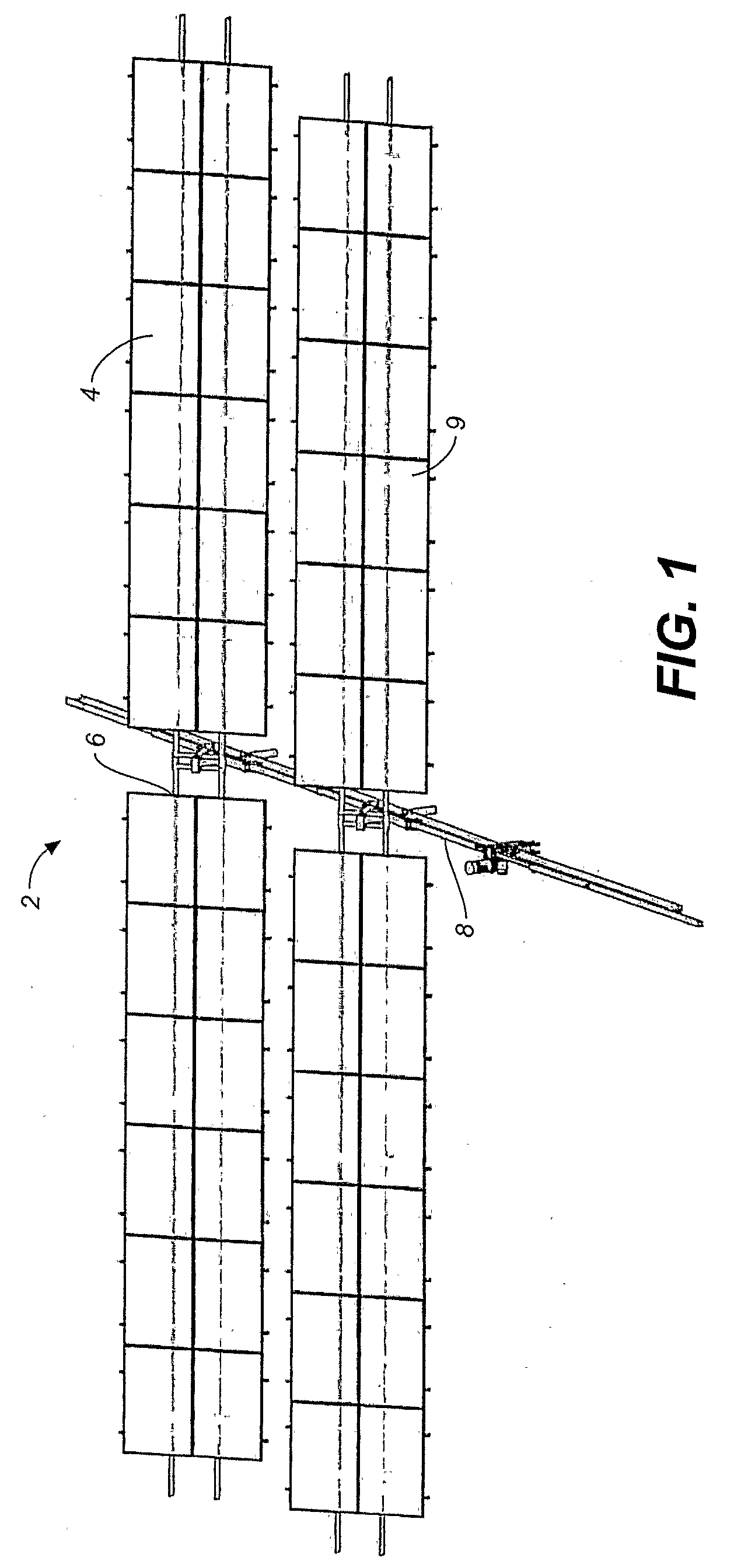
Solar Panel Array Sun Tracking System
InactiveUS20080251115A1Eliminates large side loadReduce the force requiredPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyDual beamEngineering
A solar panel tracking system that can simultaneously rotate large arrays of solar panels position in multiple rows utilizing a single drive system. The drive system comprises a single actuation device that drives multiple rotational translation stages at each solar array row for tilting the panels to the correct position. A dual beam structure within each row insure appropriate panel support during rotation and provide the framework for simplified installation and maintenance.
Owner:THOMPSON TECH IND
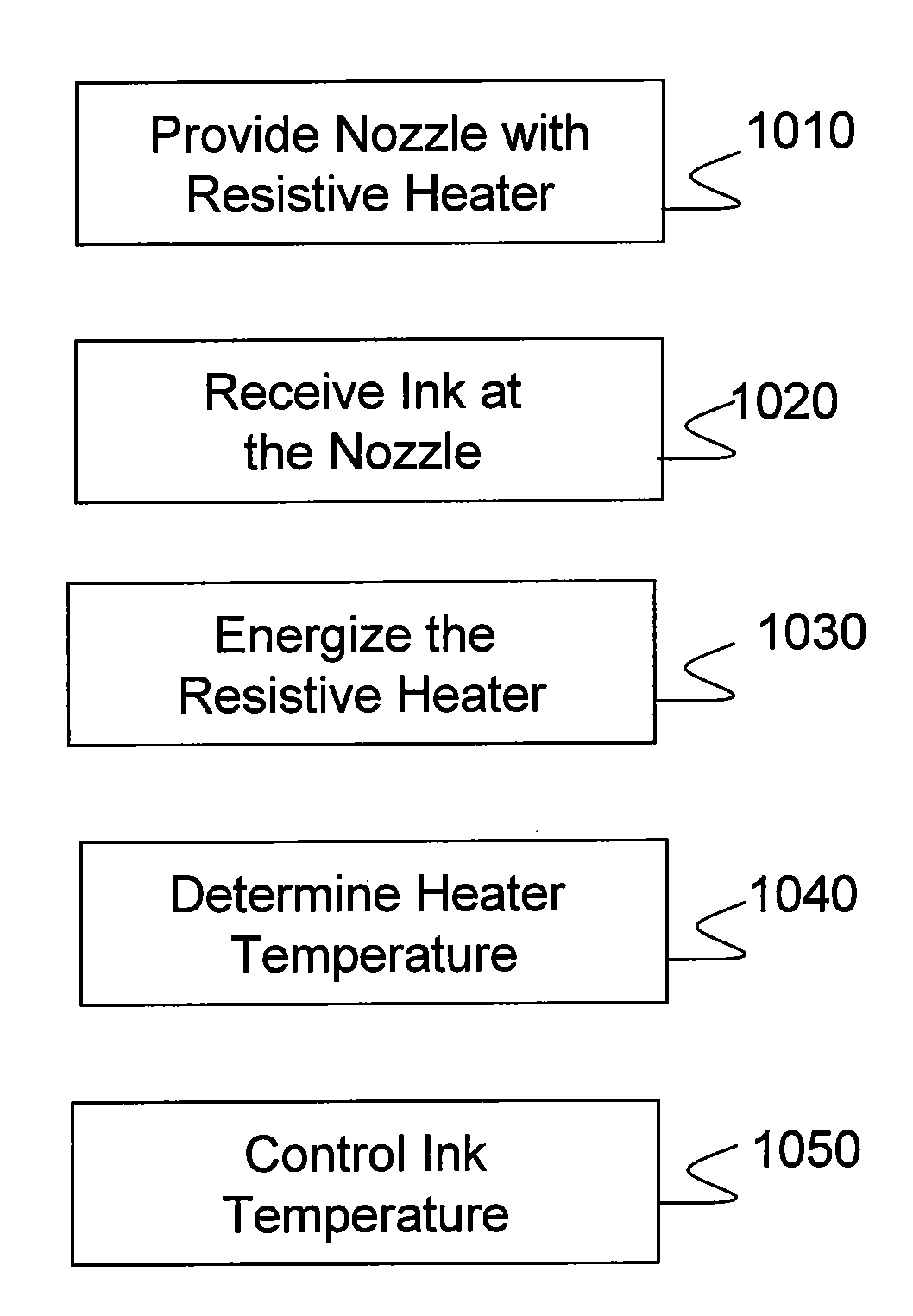
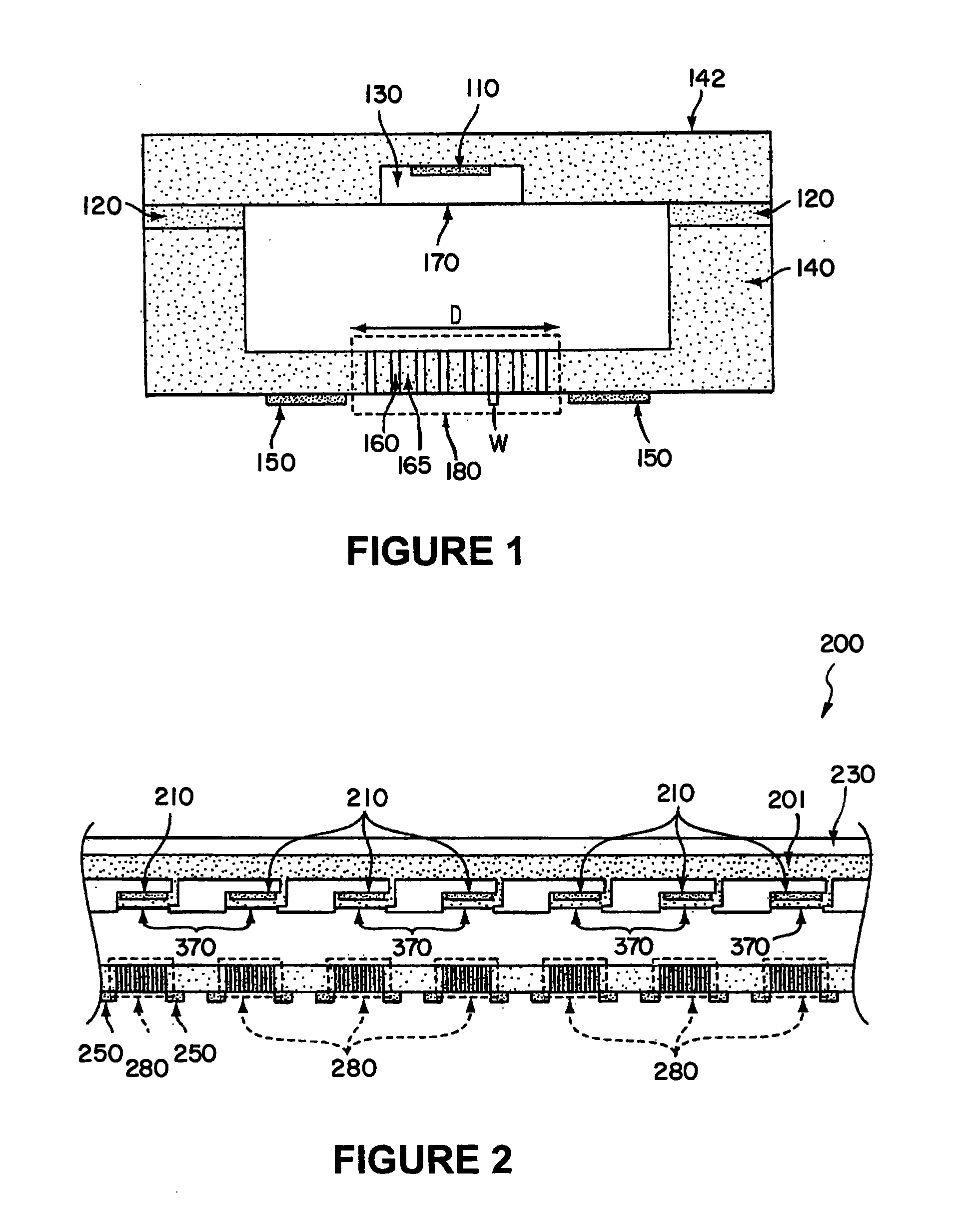
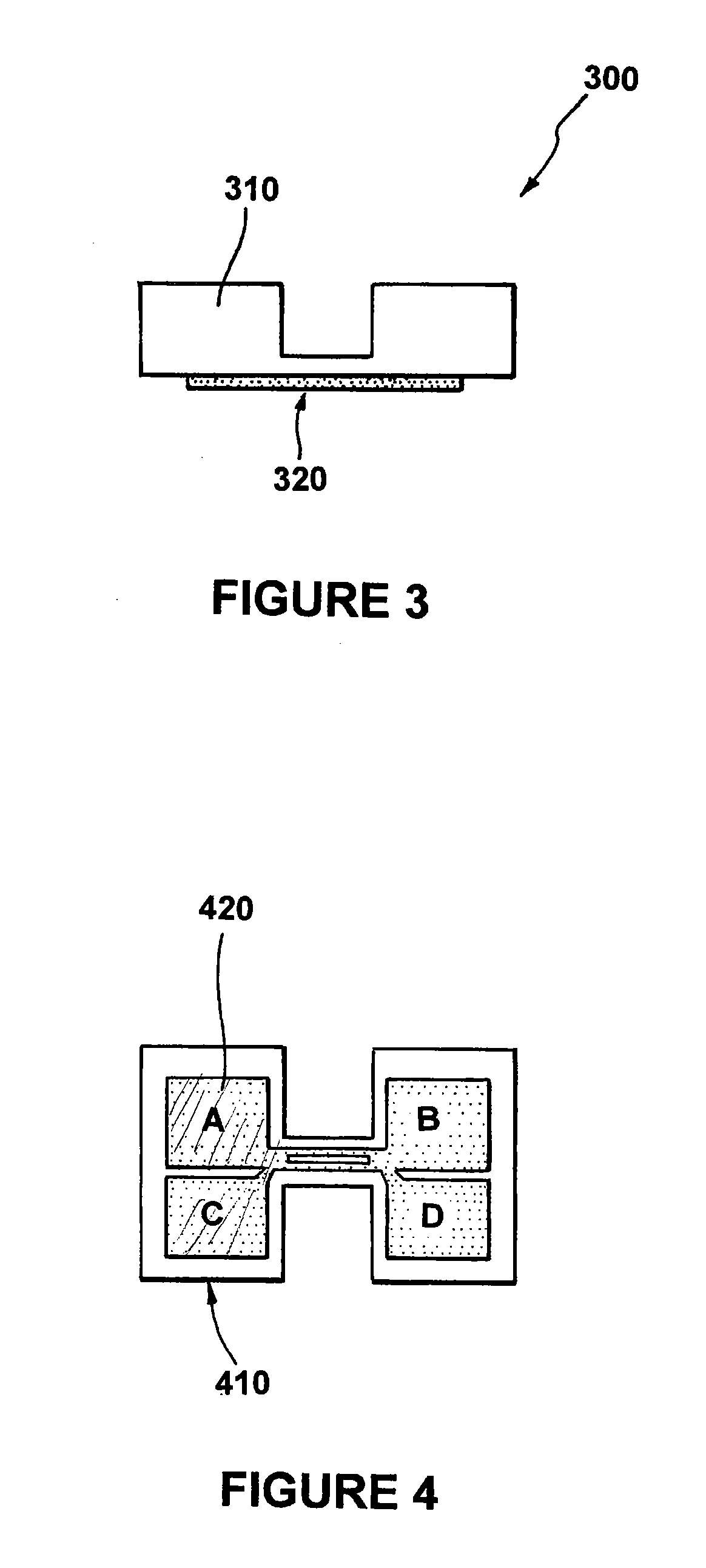
Method and apparatus for controlling the temperature of an electrically-heated discharge nozzle
InactiveUS20100188457A1Easy to identifySolid-state devicesMachines/enginesElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
In an embodiment, the disclosure relates to a method and apparatus for fault monitoring and controlling operation of a discharge nozzle in a large array of discharge nozzles. An exemplary apparatus includes a thin, thermally conductive membrane, with an integrated thin-film electrical heater. When a fixed voltage is applied to the heater, and as the heater heats, the resistance of the heater will increase which will cause a concomitant decrease in the electrical current flowing through the heater. By measuring the resistance of the heater it can readily be determined whether the device is functioning properly.
Owner:MADIGAN CONNOR F +2
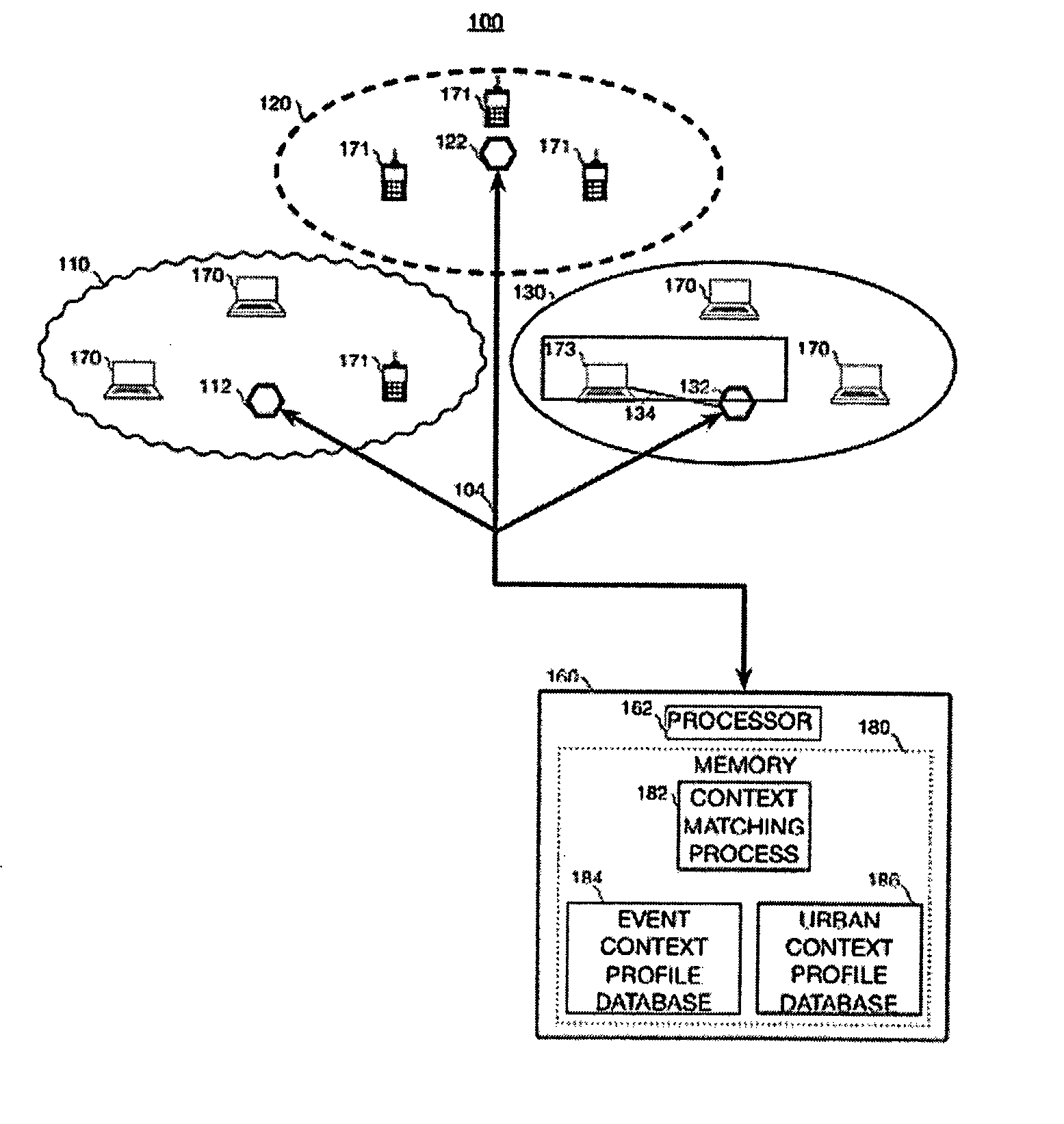
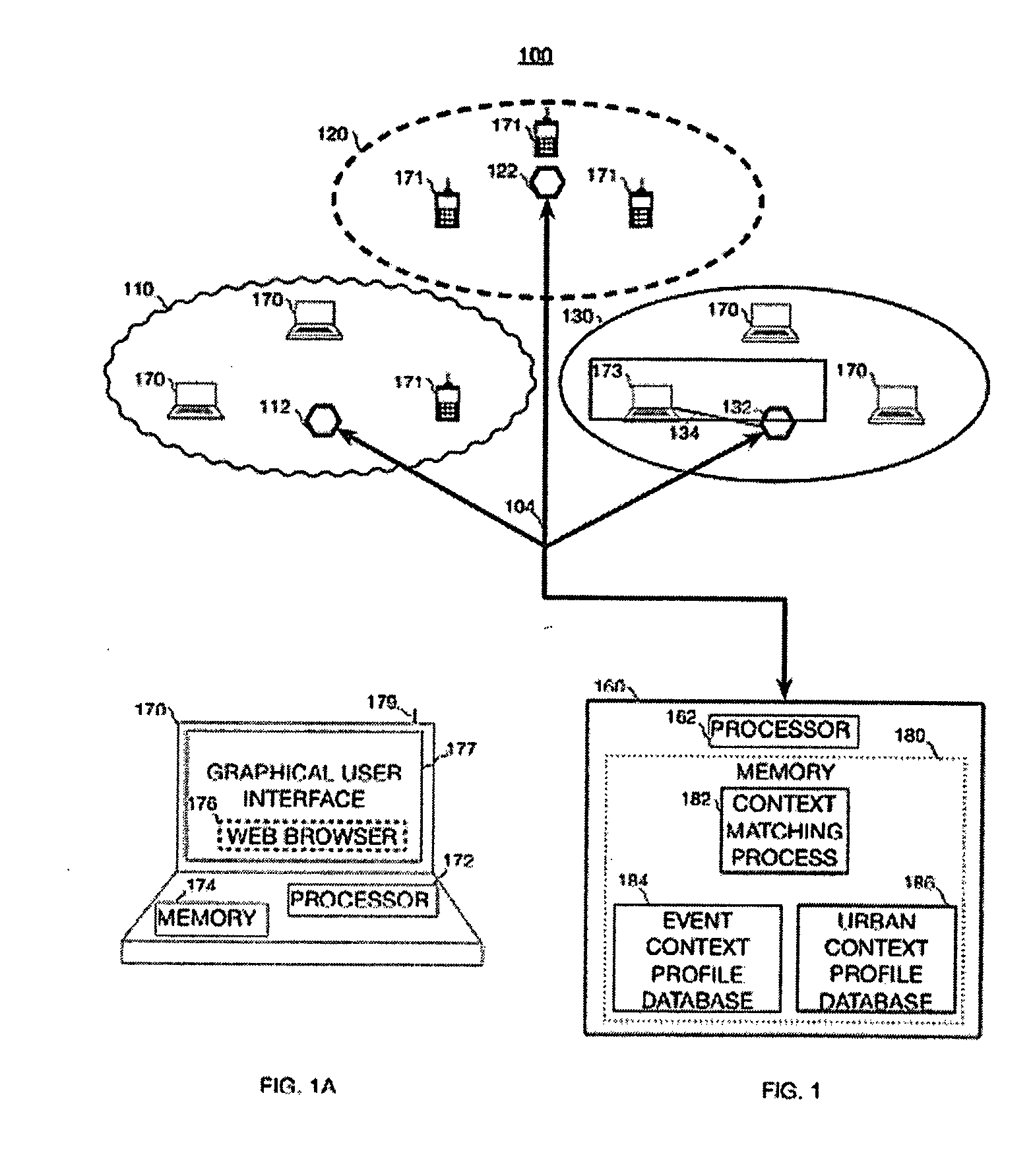
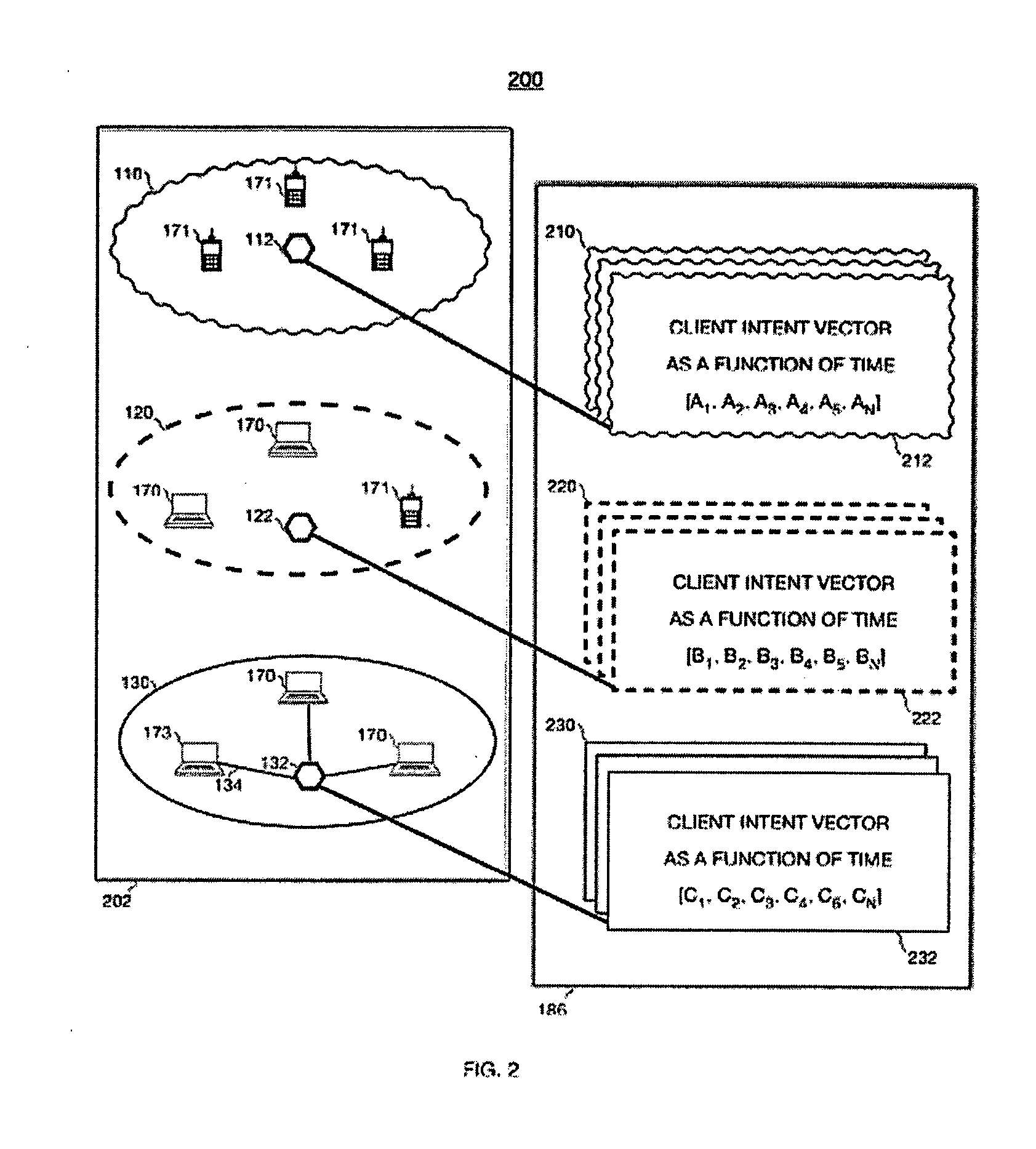
Context-based search engine residing on a network
InactiveUS20070198505A1Easy to operateDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsInformation resourceCellular telephone
This invention provides a context-aware search engine that communicates with users having a particular location at a particular time within a tessellated network of geographically spaced-apart communication nodes, typically wireless nodes / access points (APs). Based upon the user's location and time, the search engine delivers relevant site-specific information germane to that user's place and time. In an illustrative embodiment, the search engine correlates the address of the node within which the user is located when making a query to the engine via a wireless device such as a laptop computer, PDA or cellular telephone. The time of the query is also accounted for. The query causes the search engine to focus its database search (from a large array of information resources indexed by the search engine and accessible thereby) on those informational items / web sites that fit the appropriate place and time of the user. In particular wireless nodes are viewed as spatial aggregation units (such as polygons) of demarcation in an urban or other densely settled environment (e.g. a university campus, institution, etc.) to identify and characterize the physical environment of the information-seeker.
Owner:PANTHAEN INFORMATICS
Integrated photodetector for VCSEL feedback control
InactiveUS20030109142A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling light guidesDriver circuitPhotovoltaic detectors
An integrated photodetector means for controlling the output of a light source, where the control means is a photodetector formed on a silicon-on-insulator substrate. The integrated photodetector senses the optical power from the light source and provides an electrical feedback signal which can be used to adjust the DC bias levels of the light source control driver circuit. The approach readily lends itself to large arrays of light sources bonded to silicon-on-sapphire driver circuits and is especially suitable for controlling light sources such as VCSELs in arrays such as are found in communications systems.
Owner:PEREGRINE SEMICONDUCTOR
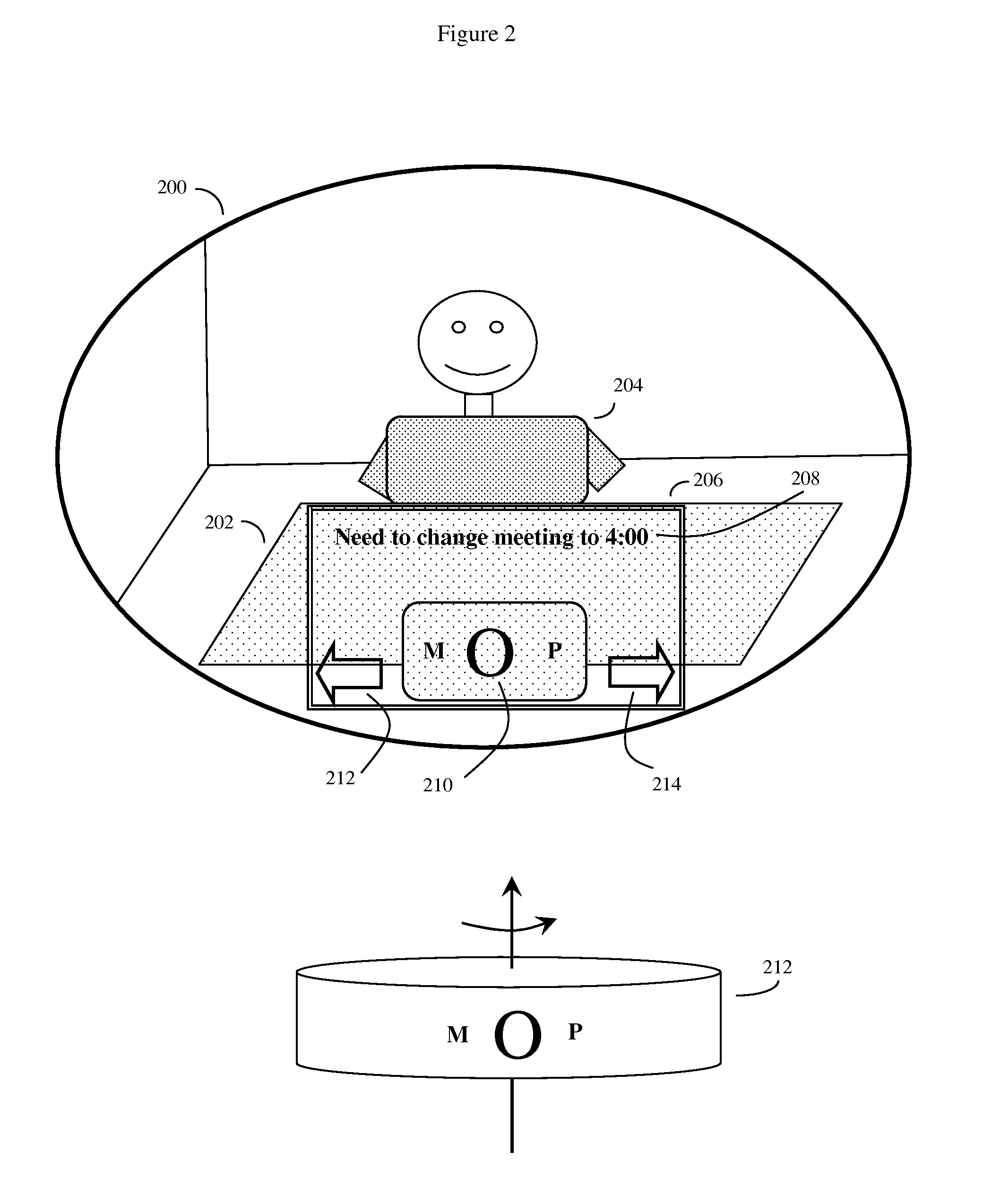
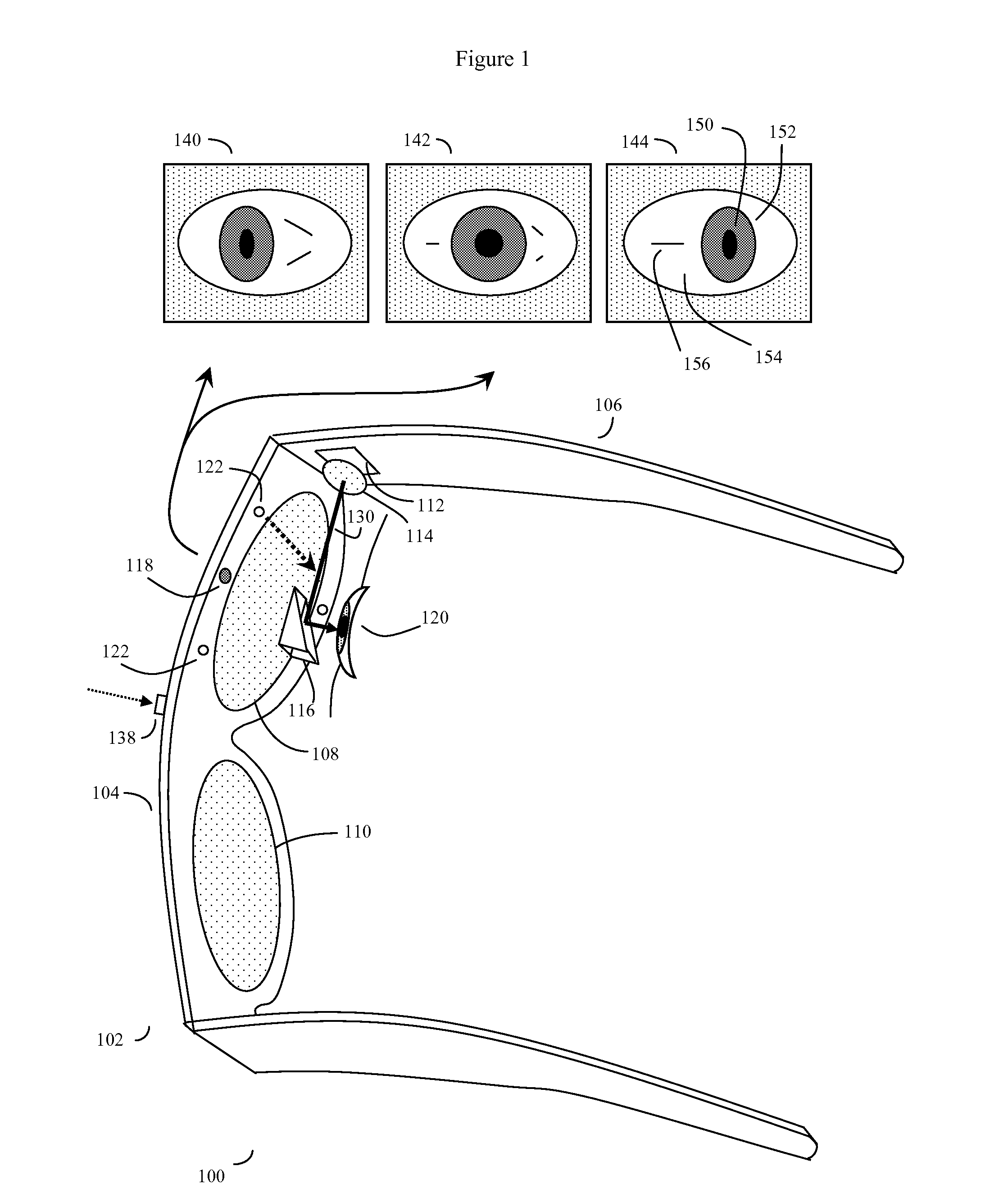
Eye-wearable device user interface and augmented reality method
ActiveUS20160004306A1Minimal user trainingIncrease the number ofInput/output for user-computer interactionStatic indicating devicesTouchpadDisplay device
A software controlled user interface and method for a head-mountable device equipped with at least one display or connectivity to at least one touch pad. The method can scale between displaying a small to large number of different eye gaze target symbols at any given time, yet still transmit a large array of different symbols to outside devices. At least part of the method may be implemented by way of a virtual window onto the surface of a virtual cylinder, with touchpad or eye gaze sensitive symbols that can be rotated by touchpad touch or eye gaze thus bringing various groups of symbols into view, and then selected. Specific examples of use of this interface and method on a head-mountable device are disclosed, along with various operation examples including transmitting data including text, functionality in virtual or augmented reality, control of robotic devices and control of remote vehicles.
Owner:SNAP INC
Controller architecture for combination touch, handwriting and fingerprint sensor
InactiveUS20120092293A1Reduce power consumptionInternal/peripheral component protectionDigital data authenticationController architectureHandwriting
A separate control system may be configured for a combined sensor device. Alternatively, at least part of the control system may be included in another device, such as a processor of a mobile device. Software for handwriting, touch and fingerprint detection may be included in the control system. Low, medium and high resolution may be obtained with a single combined sensor device by scanning a subset of the sensels, or by aggregating lines or columns. Power consumption may be reduced by aggregating sensor pixels (or rows or columns) electrically using the controller, so that they perform as a low power small array until higher resolution with a larger array is needed. Power consumption may be reduced by turning off portions or all of the sensor device, turning off parts of the control system, and / or employing first-level screening at a reduced frame rate.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Method to form upward pointing p-i-n diodes having large and uniform current
A method is disclosed to form an upward-pointing p-i-n diode formed of deposited silicon, germanium, or silicon-germanium. The diode has a bottom heavily doped p-type region, a middle intrinsic or lightly doped region, and a top heavily doped n-type region. The top heavily doped p-type region is doped with arsenic, and the semiconductor material of the diode is crystallized in contact with an appropriate silicide, germanide, or silicide-germanide. A large array of such upward-pointing diodes can be formed with excellent uniformity of current across the array when a voltage above the turn-on voltage of the diodes is applied. This diode is advantageously used in a monolithic three dimensional memory array.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
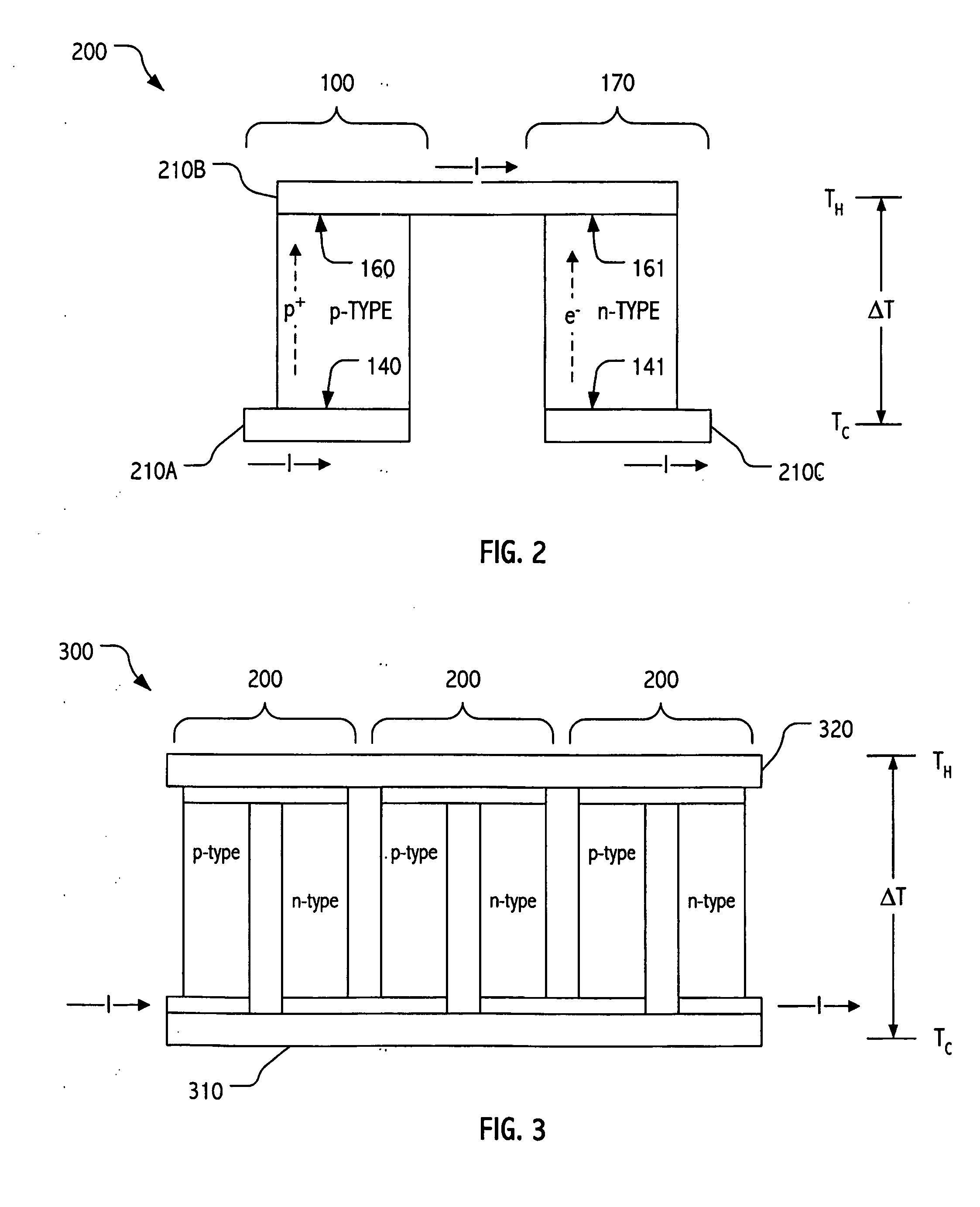
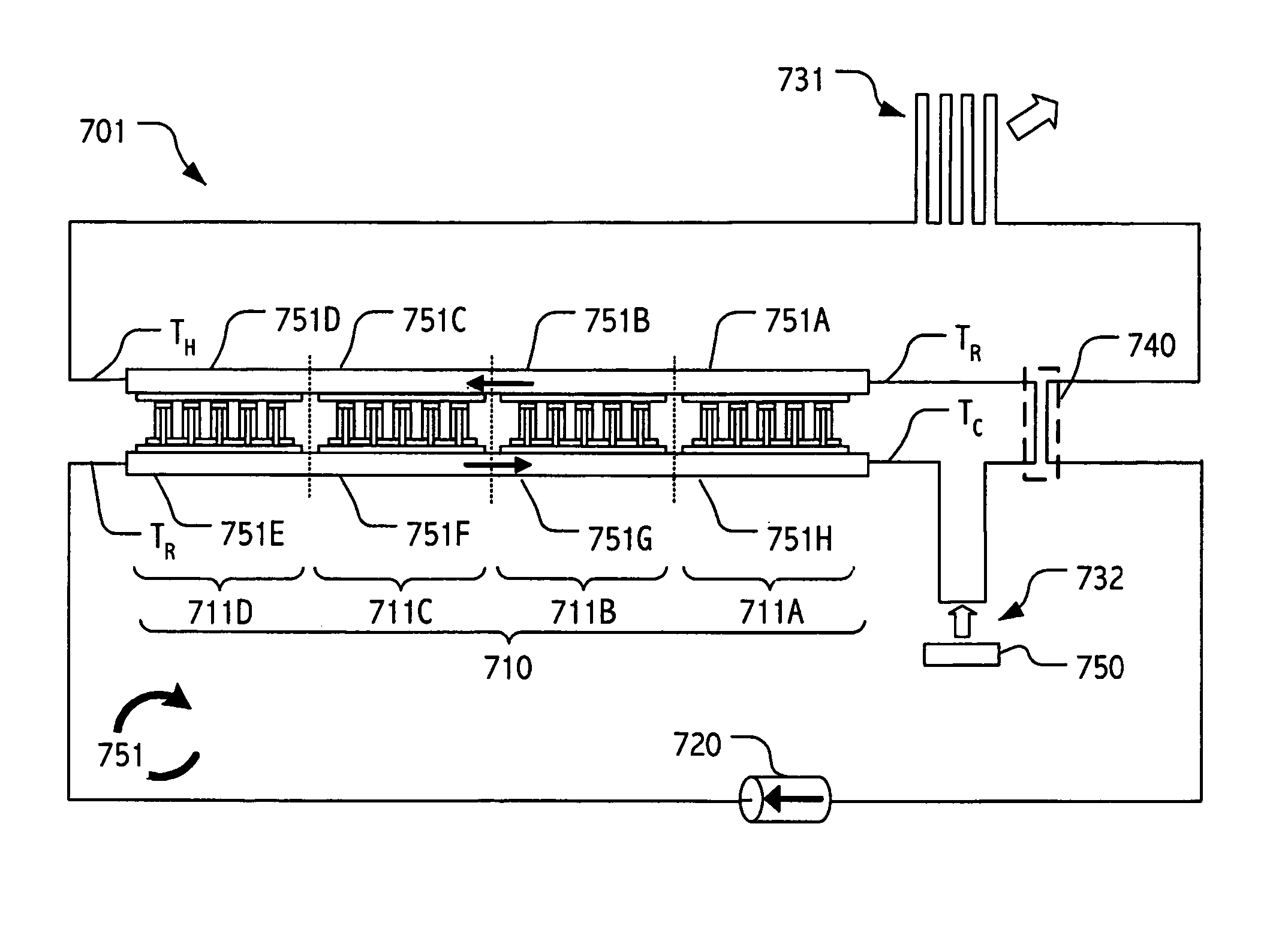
Counterflow thermoelectric configuration employing thermal transfer fluid in closed cycle
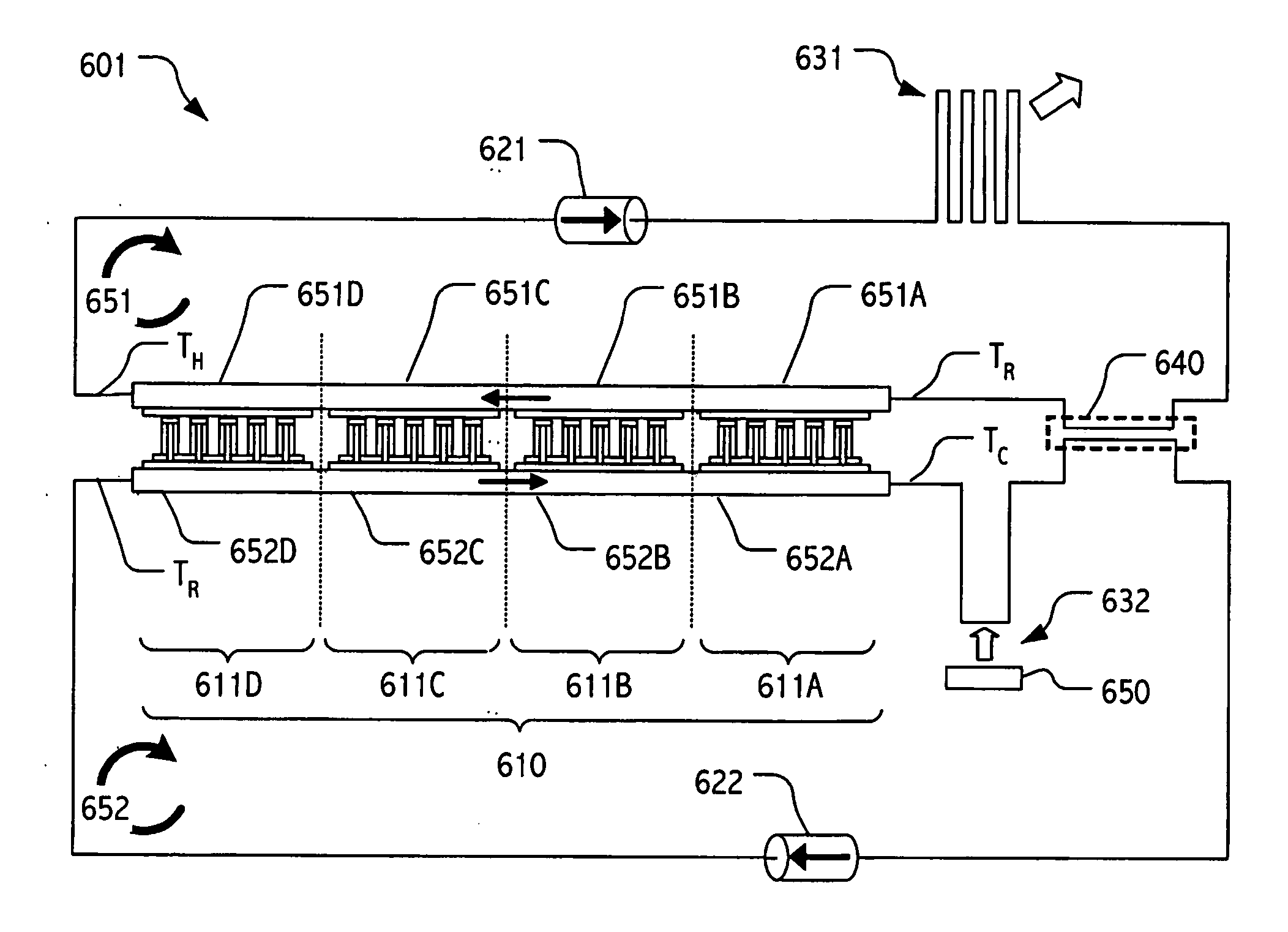
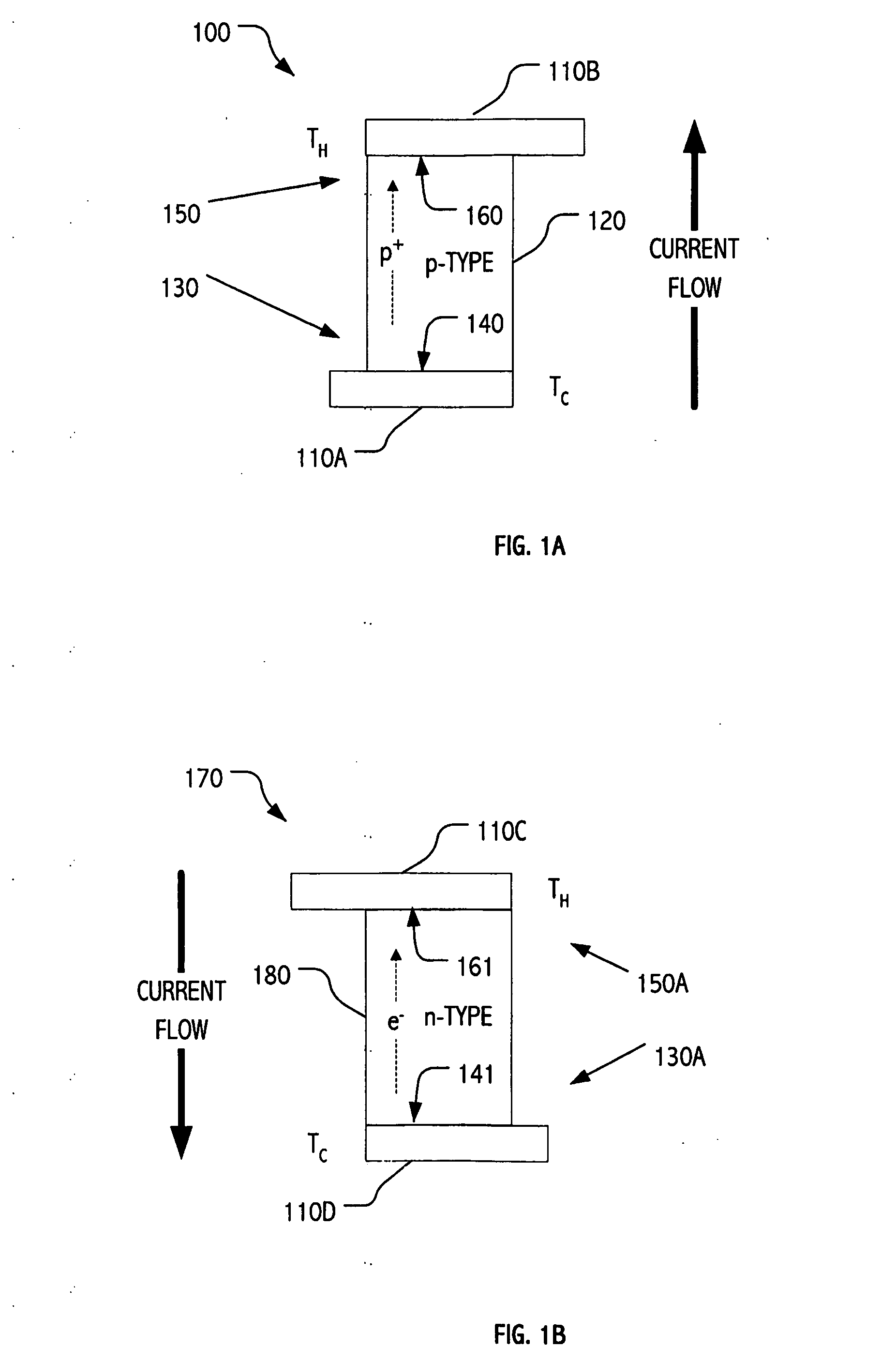
ActiveUS20060137359A1Cost-effectively employedCost-effectively configuredThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectMachines using electric/magnetic effectsNuclear engineeringActive cooling
Active cooling technologies such as thermoelectrics can be used to introduce thermal “gain” into a cooling system and, when employed in combination with forced flow liquid metal cooling loops, can provide an attractive solution for cooling high heat flux density devices and / or components. Total cooling power can be increased by employing multiple thermoelectric elements. Indeed, by employing modern semiconductor technologies, including e.g., thin-film technologies, thermoelectric elements may be cost-effectively employed and configured in large arrays.
Owner:SHEETAK INC
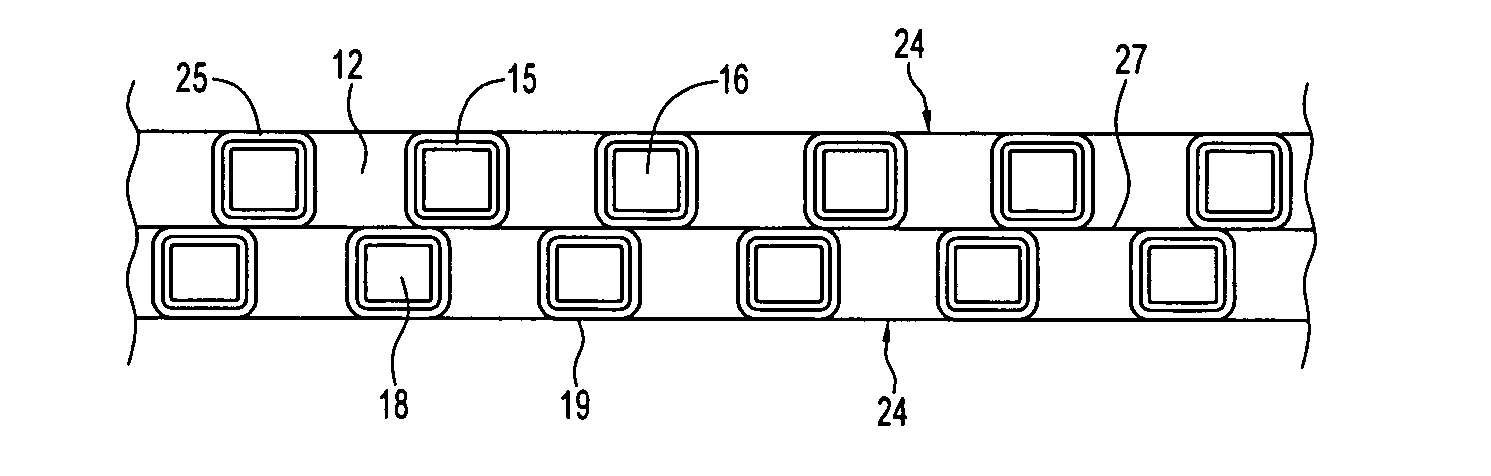
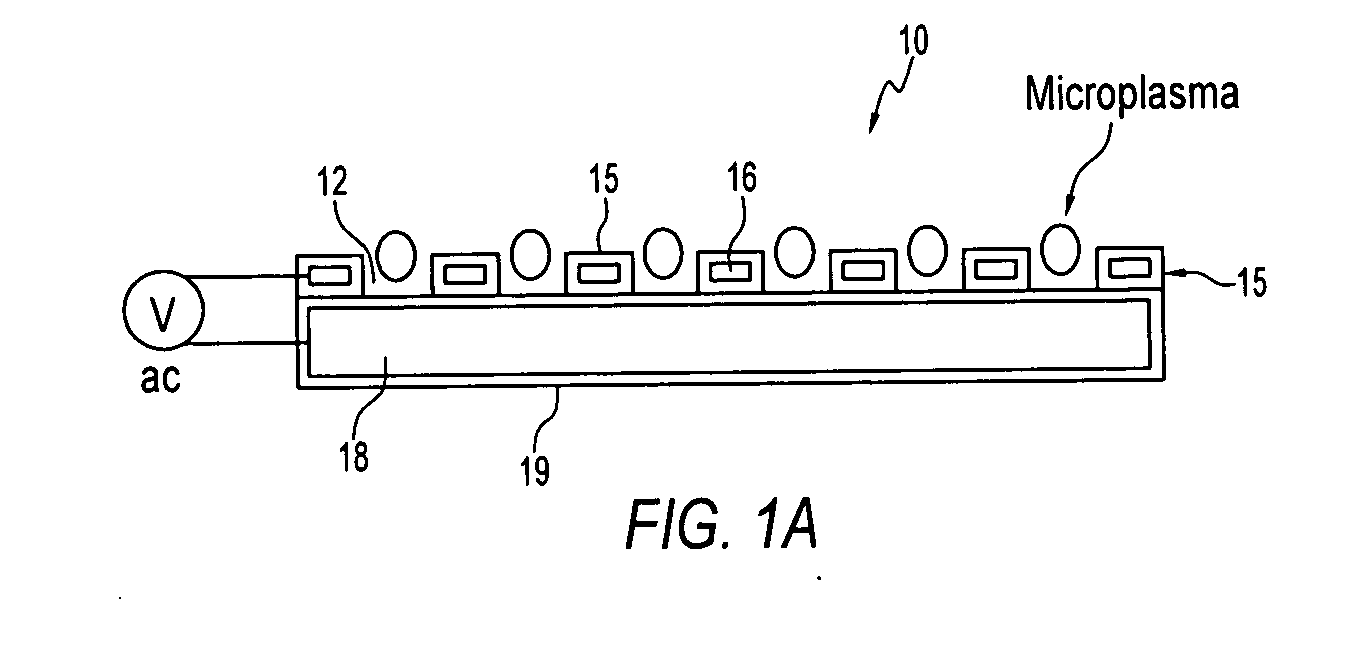
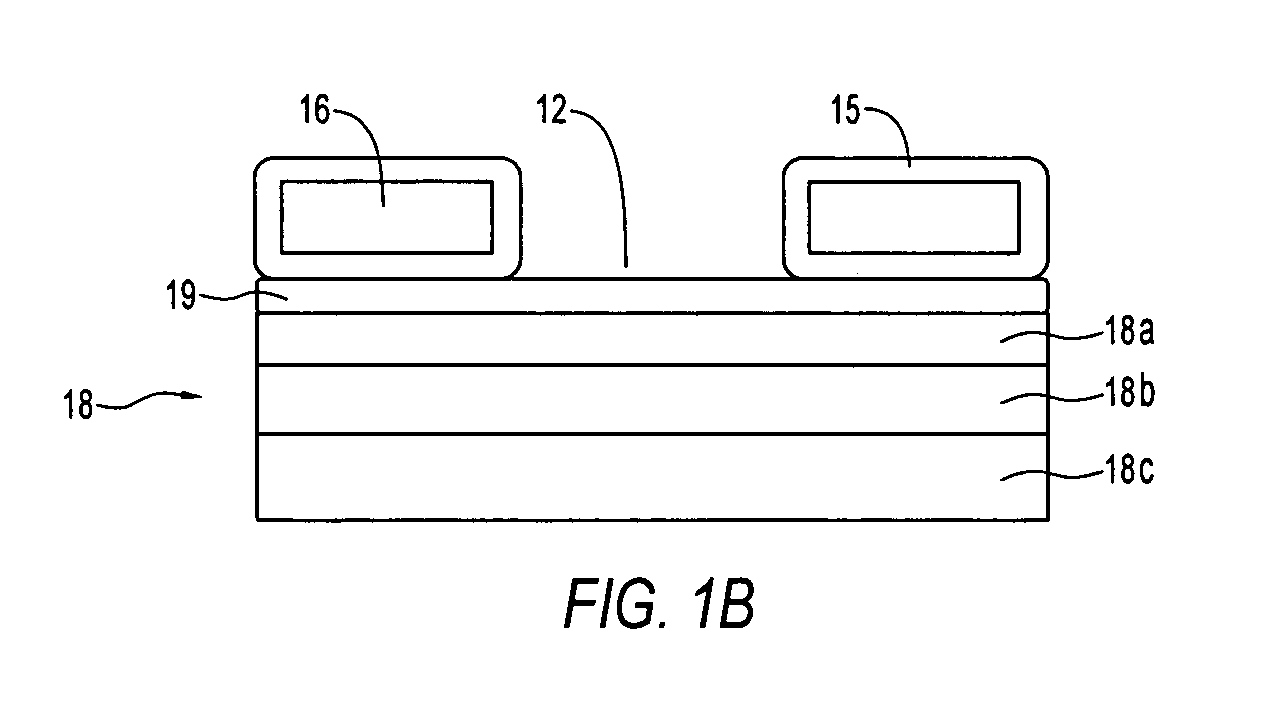
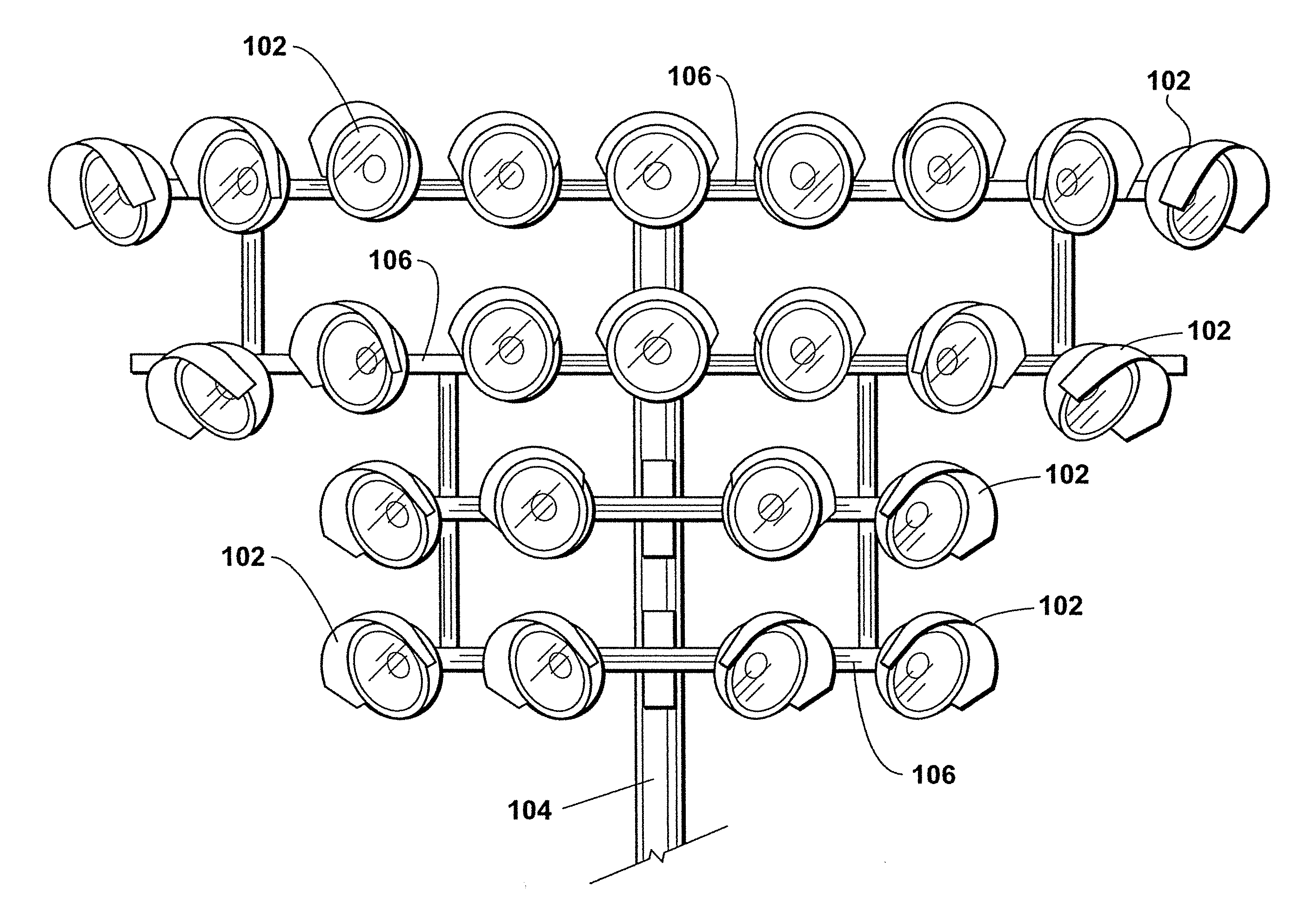
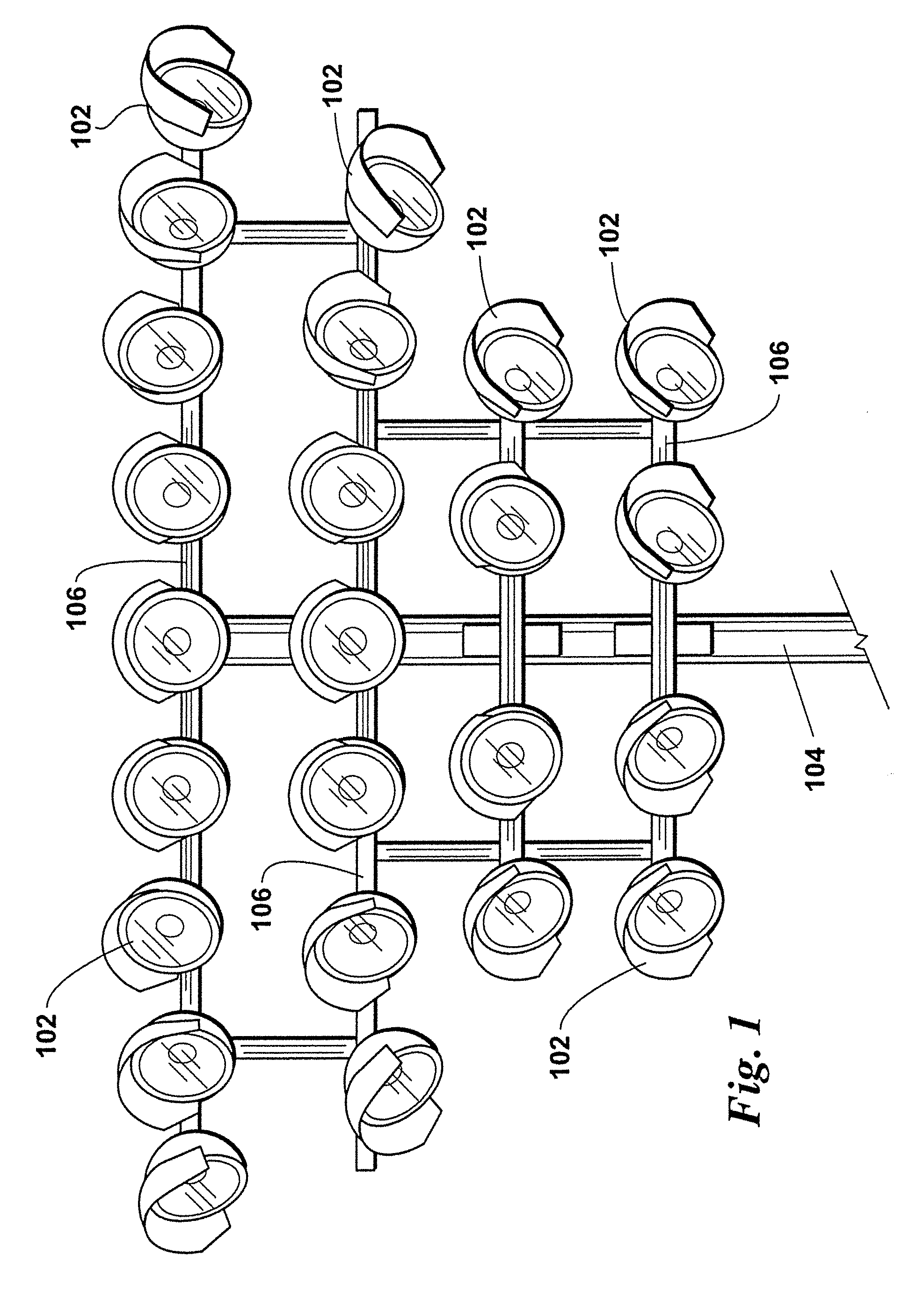
Arrays of microcavity plasma devices with dielectric encapsulated electrodes
ActiveUS20070170866A1Cheap to makeAlternating current plasma display panelsShieldingDielectricRoll-to-roll processing
The invention concerns microcavity plasma devices and arrays with thin foil metal electrodes protected by metal oxide dielectric. Devices of the invention are amenable to mass production techniques, and may, for example, be fabricated by roll to roll processing. Exemplary devices of the invention are flexible. Embodiments of the invention provide for large arrays of microcavity plasma devices that can be made inexpensively. The structure of preferred embodiment microcavity plasma devices of the invention is based upon thin foils of metal that are available or can be produced in arbitrary lengths, such as on rolls. In a device of the invention, a pattern of microcavities is produced in a metal foil. Oxide is subsequently grown on the foil and within the microcavities (where plasma is to be produced) to protect the microcavity and electrically isolate the foil. A second metal foil is also encapsulated with oxide and is bonded to the first encapsulated foil. For preferred embodiment microcavity plasma device arrays of the invention, no particular alignment is necessary during bonding of the two encapsulated foils. A thin glass layer or vacuum packaging, for example, is able to seal the discharge medium into the array.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Micro electro mechanical system controlled organic LED and pixel arrays and method of using and of manufacturing same
InactiveUS6943495B2Wide choiceOvercome limitationsTelevision system detailsContact surface shape/structureOrganic light emitting deviceInorganic materials
Organic light emitting devices are disclosed that use a micro electromechanical system (MEMS) structure to enable a pixel and pixel array wherein each pixel contains a MEMS and an OLED element. A MEMS structure is used for switching the OLED element. These OLED / MEMS pixels can be fabricated on flex circuit, silicon, as well as other inorganic materials. They can be fabricated in a large array for developing a 2-dimensional display application and each pixel can be addressed through conventional matrix scanning addressing scheme. The ability of fabricating these OLED / MEMS pixels on flexible organic substrates as well as other rigid substrates enables wider selection of substrate materials for use with different applications.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method used in multiple, simultaneous synthesis of general compounds
InactiveUS6258323B1Damage and harmEasy accessPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsInorganic compoundSolvent
The apparatus and method of the present invention provides for conducting simultaneous multiple synthesis of general compounds, which often takes place under varied uneven conditions requiring heating, cooling, agitation, reagent / solvent additions to the reactor contents at each reaction vessel location, supply and maintenance of inert atmosphere and means to facilitate the reflux of the reactor contents. Thus, it becomes necessary to monitor and control the reaction conditions during the simultaneous multiple synthesis of general compounds. The apparatus allows the user to connect various independently controlling and conveying means to each reaction vessel through multiple ports provided on a stopper mounted on each reaction vessel. The apparatus of the present invention permits user to readily access the reaction vessels without interrupting the reactions occurring in the adjacent reaction vessels. The unique geometry and shape of the stopper allows positioning of multiple ports, while still providing the stopper with a compact size. As a result, a large array of reaction vessels can be accommodated in the device of the present invention without significantly increasing the overall size of the apparatus. Some of the general compounds that can be readily synthesized by the apparatus and the method of the present invention include inorganic compounds as well as organic compounds, such as oligomers, polymers, agricultural chemicals, drugs, peptides and oligonucleotides.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
LED venue lighting system and method
ActiveUS20150308655A1Increase heatMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceOutdoor areaEngineering
An outdoor area LED lighting system including: a housing containing a large array of LEDs mounted to an aluminum direct thermal path printed circuit board and a single lens. The large array of LEDs are capable of producing light rays directed through the single lens to produce a beam of light to illuminate the outdoor area. The single lens is preferably a Fresnel lens. The housing is preferably capable of being sealed in a weather-tight manner. A second housing may at least partially surround the first housing such that at least one air passage is provided between the first housing and the second housing. A heat sink including a heat block in thermal communication with a plurality of heat tubes and fin assemblies may be in partial thermal contact with the LED module and in fluid communication with the at least one air passage. At least one fan may be provided in or in fluid communication with said at least one air passage to cool the heat sink. A digital interface may connect the LED module to a host computer to monitor and track information and trending for statistical process control.
Owner:SPORTSBEAMS LIGHTING INC
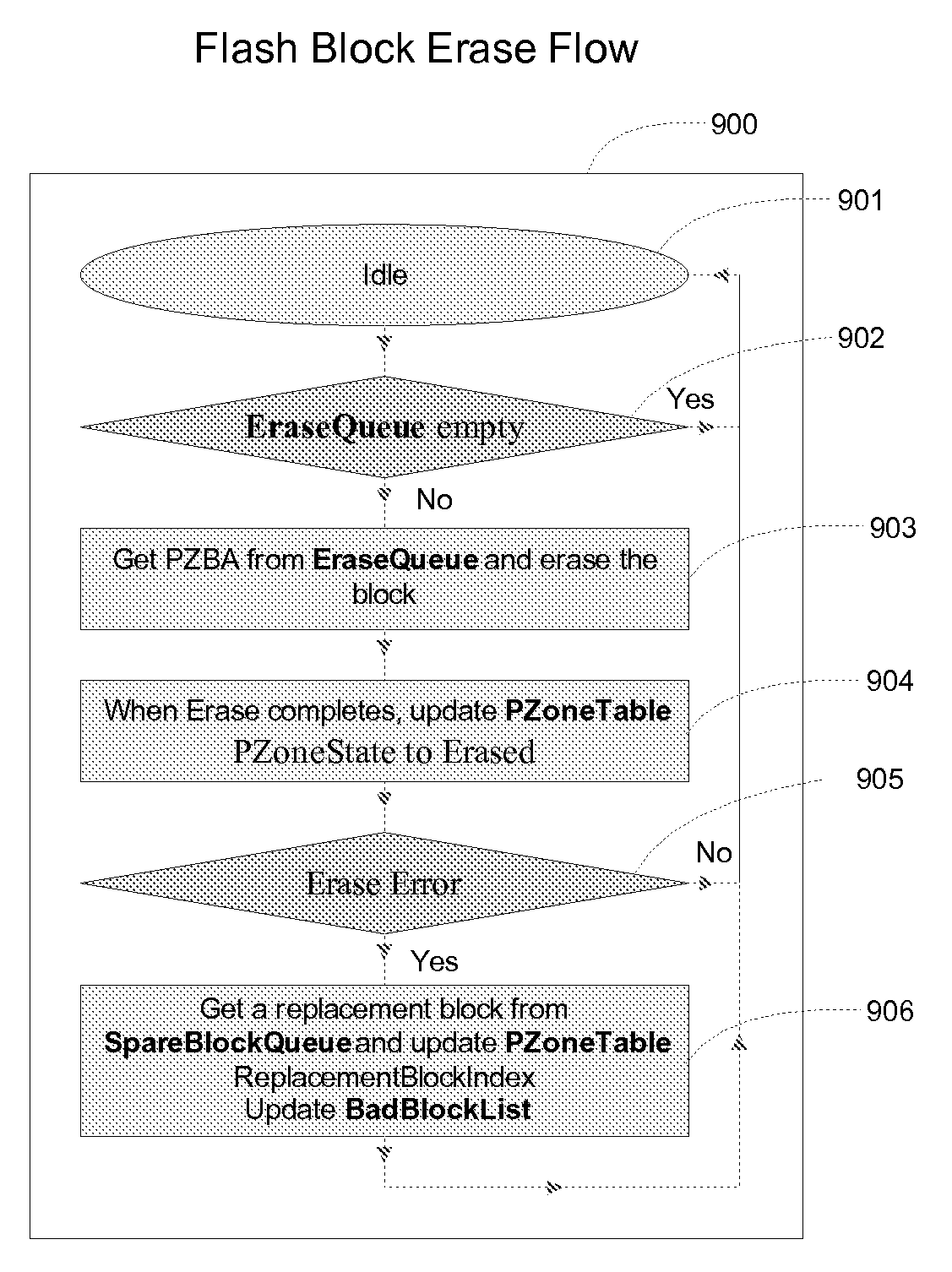
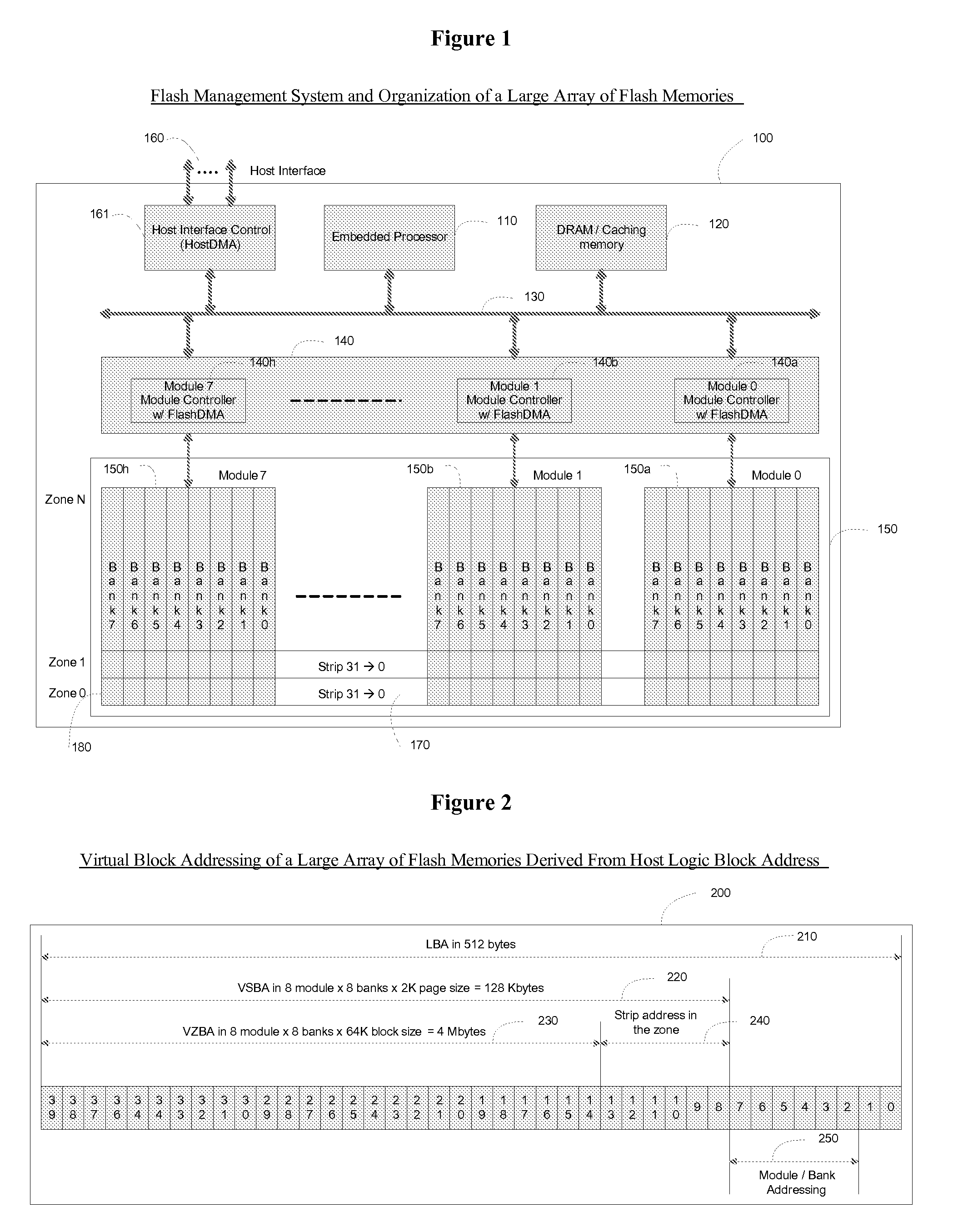
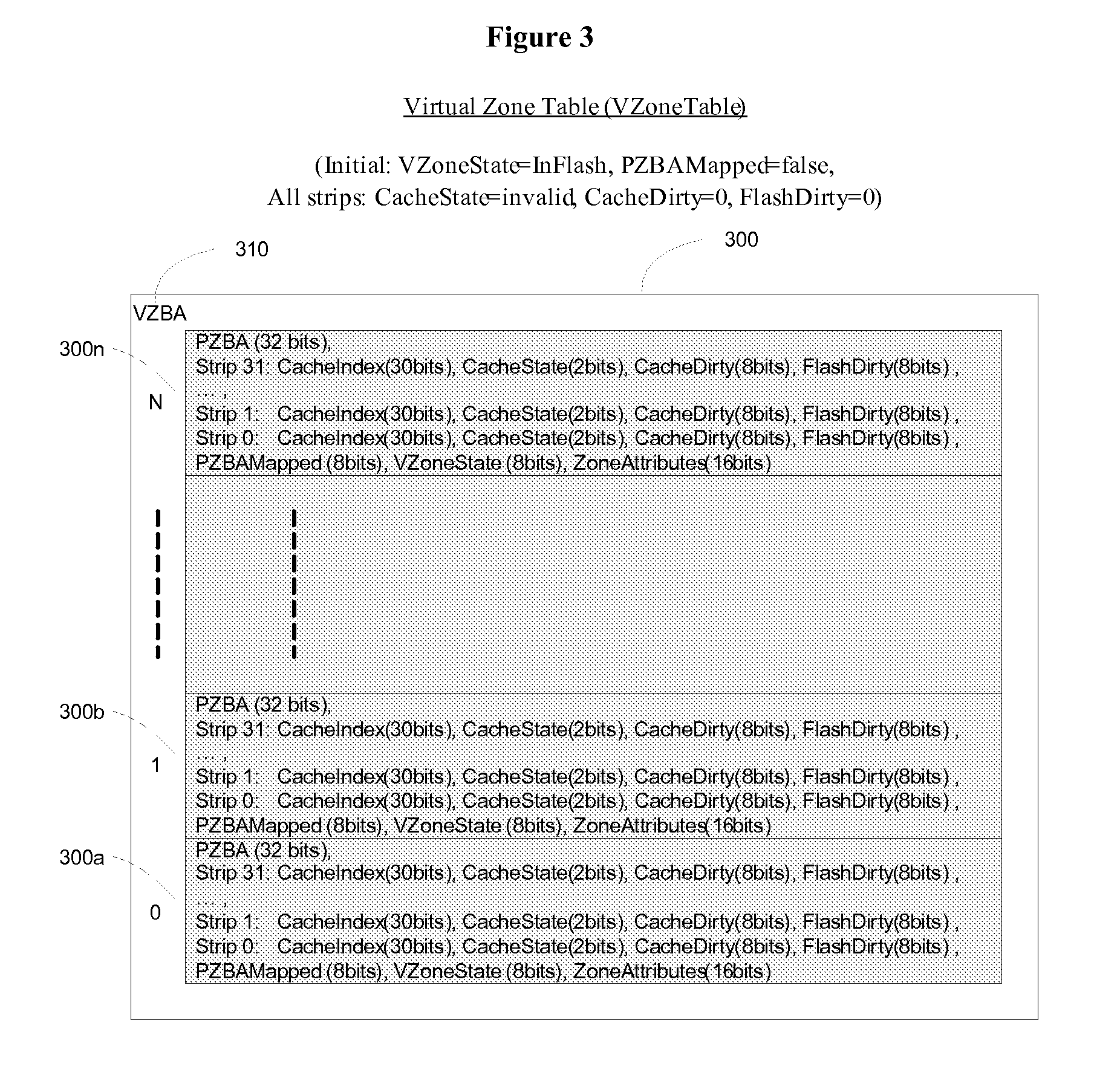
Method of managing a large array of non-volatile memories
InactiveUS20080155183A1Efficient managementIncreased longevityMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsParallel computingModularity
The present invention provides a non-volatile flash memory management system and method that provides the ability to efficiently manage a large array of flash devices and allocate flash memory use in a way that improves reliability and longevity, while maintaining excellent performance. The invention mainly comprises of a processor, an array of flash memories that are modularly organized, an array of module flash controllers and DRAM caching. The processor manages the above mention large array of flash devices with caching memory through mainly two tables: Virtual Zone Table and Physical Zone Table, a number of queues: Cache Line Queue, Evict Queue, Erase Queue, Free Block Queue, and a number of lists: Spare Block List and Bad Block List.
Owner:ZHUANG ZHIQING +1
Method of managing a large array of non-volatile memories
InactiveUS20100115175A9Efficient managementIncreased longevityMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsParallel computingModularity
The present invention provides a non-volatile flash memory management system and method that provides the ability to efficiently manage a large array of flash devices and allocate flash memory use in a way that improves reliability and longevity, while maintaining excellent performance. The invention mainly comprises of a processor, an array of flash memories that are modularly organized, an array of module flash controllers and DRAM caching. The processor manages the above mention large array of flash devices with caching memory through mainly two tables: Virtual Zone Table and Physical Zone Table, a number of queues: Cache Line Queue, Evict Queue, Erase Queue, Free Block Queue, and a number of lists: Spare Block List and Bad Block List.
Owner:ZHUANG ZHIQING +1
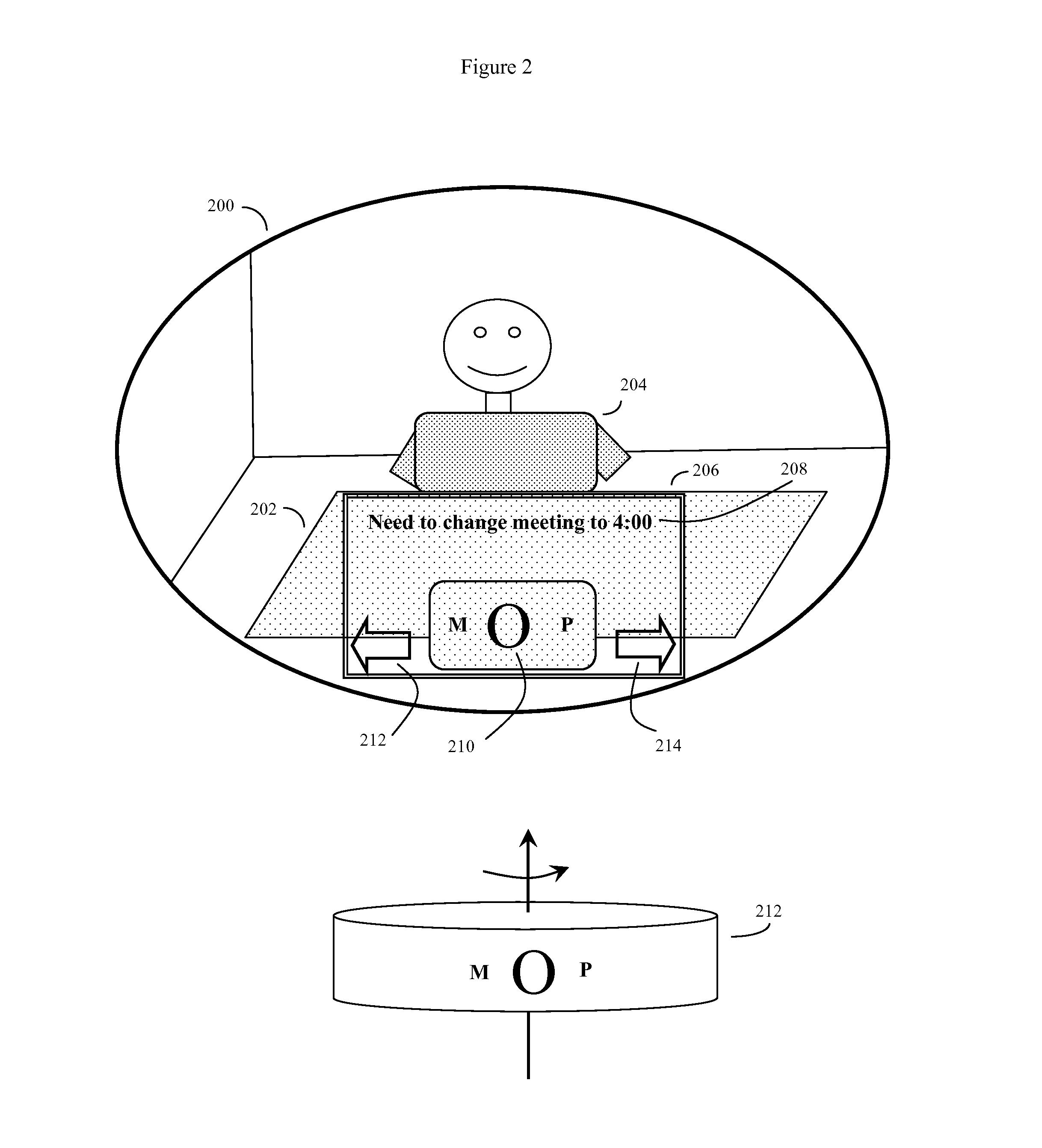
Eye gaze user interface and method
ActiveUS8593375B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsClosed circuit television systemsGaze directionsVisual perception
A software controlled user interface and method for an eye gaze controlled device, designed to accommodate angular accuracy versus time averaging tradeoffs for eye gaze direction sensors. The method can scale between displaying a small to large number of different eye gaze target symbols at any given time, yet still transmit a large array of different symbols to outside devices with minimal user training. At least part of the method may be implemented by way of a virtual window onto the surface of a virtual cylinder, with eye gaze sensitive symbols that can be rotated by eye gaze thus bringing various groups of symbols into view, and then selected by continual gazing. Specific examples of use of this interface and method on an eyeglasses-like head-mountable, vision-controlled, device are disclosed, along with various operation examples including sending and receiving text messages, control of robotic devices and control of remote vehicles.
Owner:SNAP INC
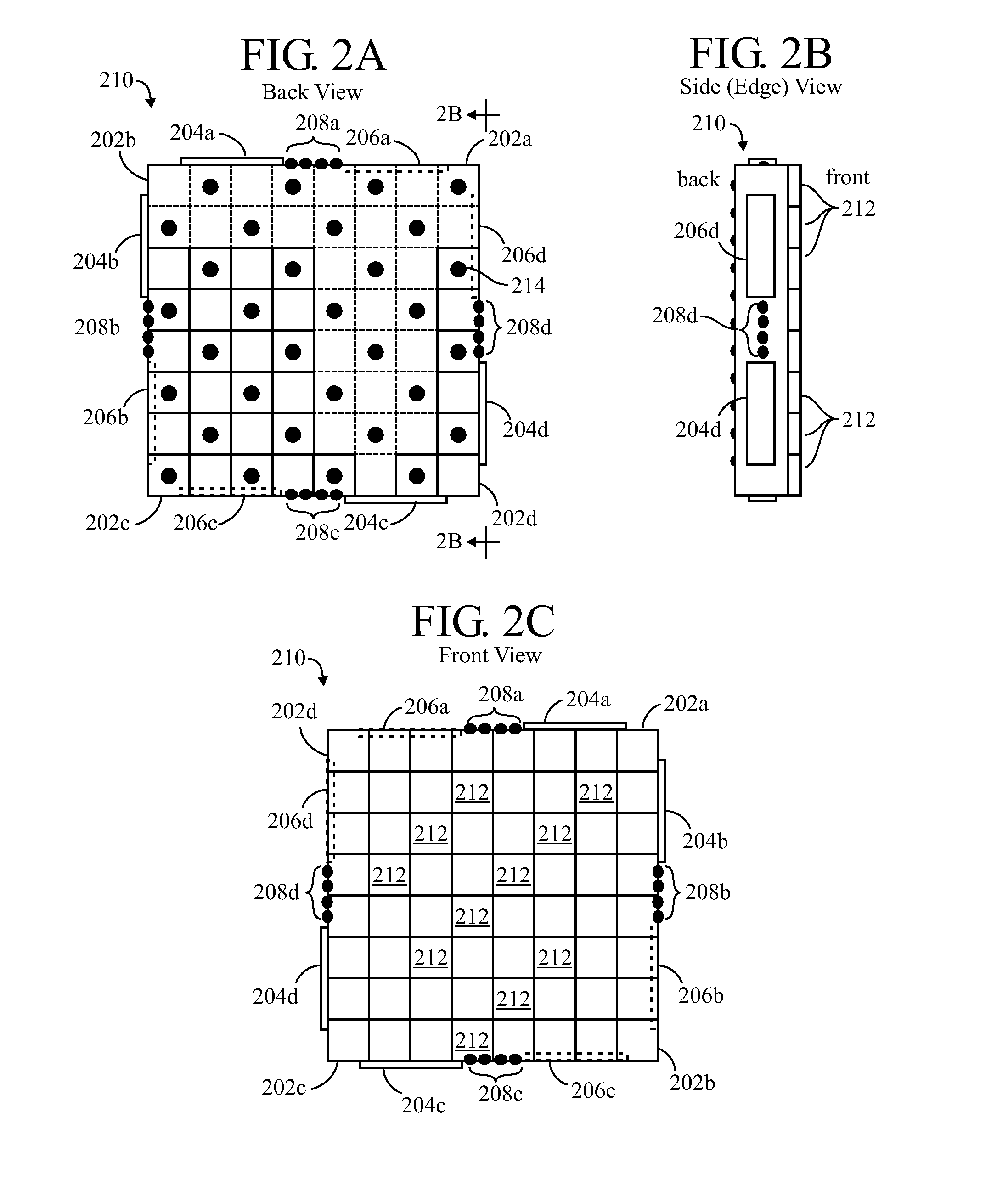
Techniques for Tiling Arrays of Pixel Elements
ActiveUS20140138543A1Remove complexitySimple technologyLine/current collector detailsWave amplification devicesMicrobolometerDamage tolerance
Sub-arrays such as tiles or chips having pixel elements arranged on a routing layer or carrier to form a larger array. Through-chip vias or the like to the backside of the chip are used for connecting with the pixel elements. Edge features of the tiles may provide for physical alignment, mechanical attachment and chip-to-chip communication. Edge damage tolerance with minimal loss of function may be achieved by moving unit cell circuitry and the electrically active portions of a pixel element away from the tile edge(s) while leaving the optically active portion closer to the edge(s) if minor damage will not cause a complete failure of the pixel. The pixel elements may be thermal emitter elements for IR image projectors, thermal detector elements for microbolometers, LED-based emitters, or quantum photon detectors such as those found in visible, infrared and ultraviolet FPAs (focal plane arrays), and the like. Various architectures are disclosed.
Owner:SANTA BARBARA INFRARED +2
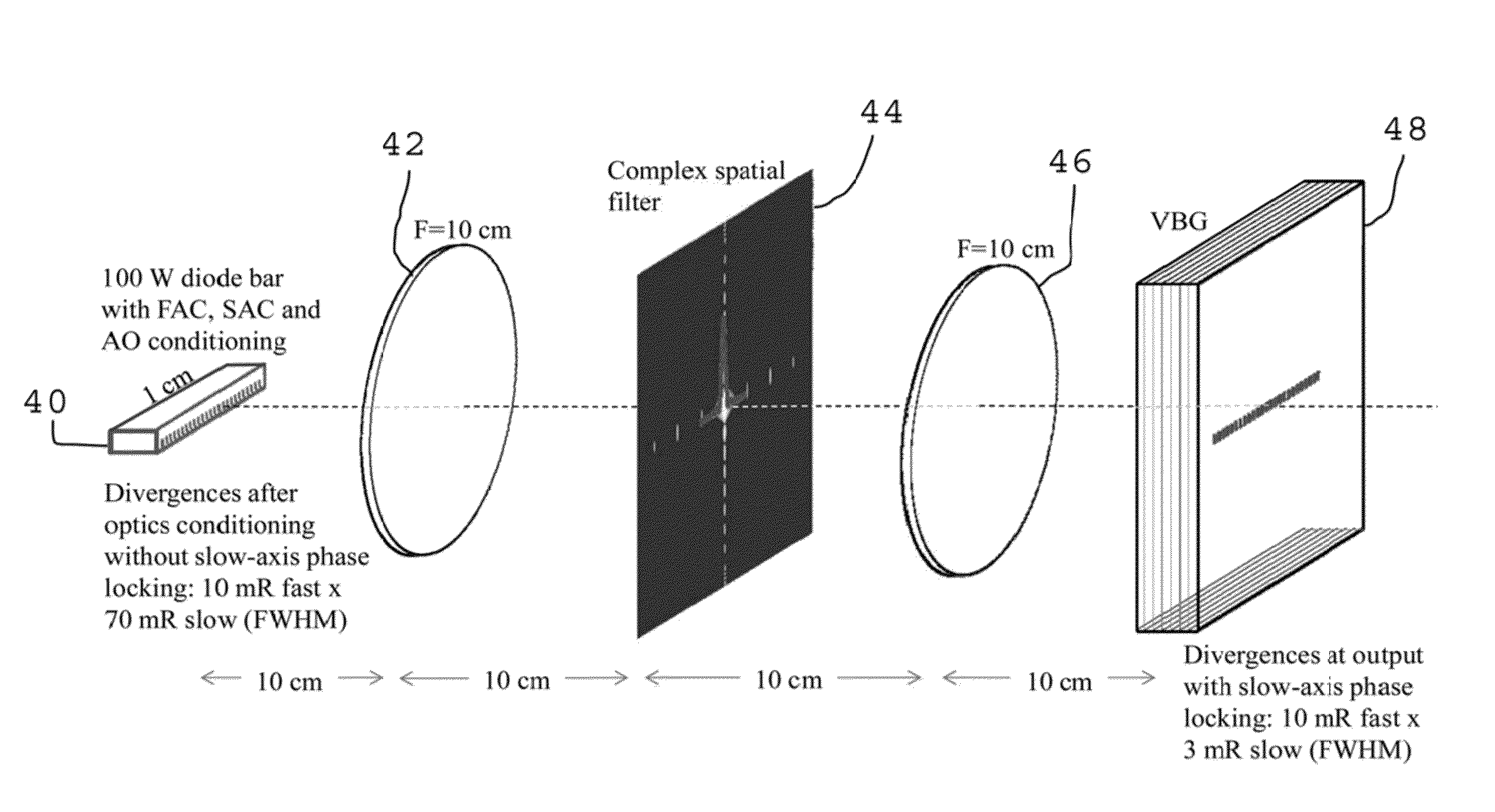
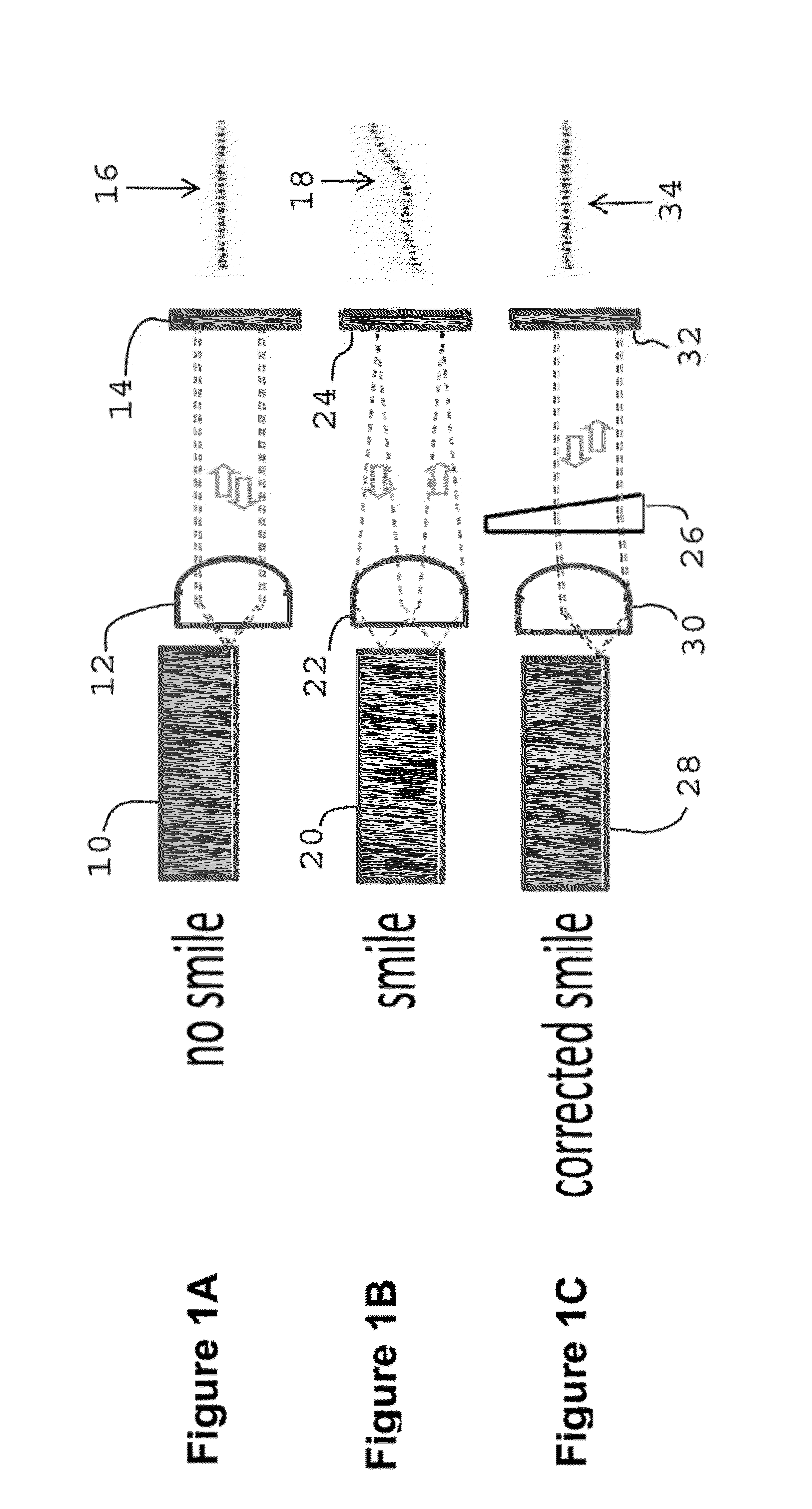
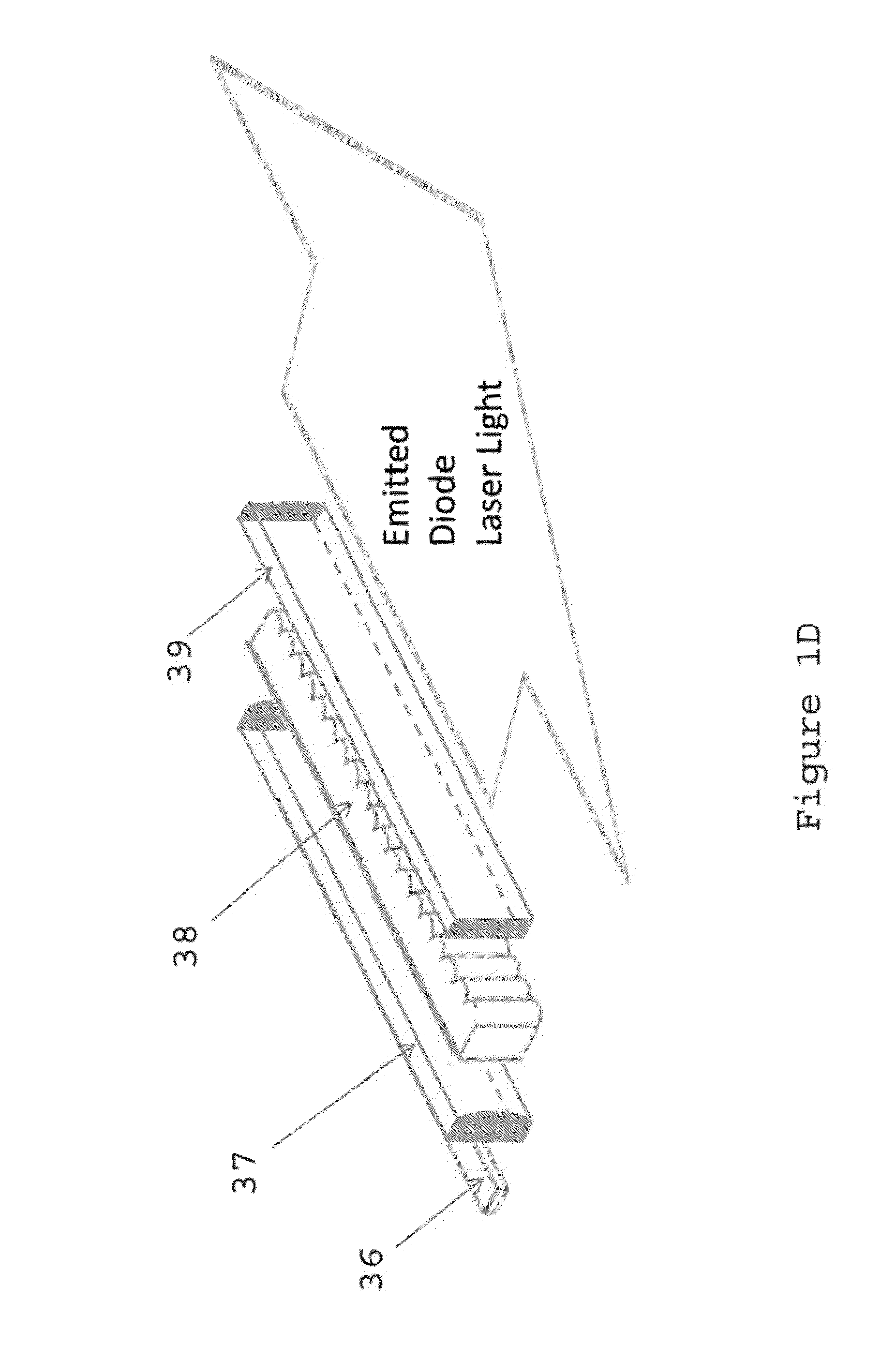
Increasing the spatial and spectral brightness of laser diode arrays
InactiveUS20160094016A1Increasing laser radiancePotential simplicitySemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser optical deviceWavefrontLaser array
Techniques for increasing the spatial and spectral brightness of laser arrays such as laser diode arrays are provided. Passive cavity designs are described that produce wavefront phase locking across the face of large arrays. These designs enable both spatial and spectral selectivity in order to coherently link the individual emitters that make up the diode array. Arrays of customized micro-optics correct aberrations of the individual apertures of the arrays while highly spectrally selective partial reflectors overcome the deleterious effects of inhomogeneities in local thermal environments of the individual emitters that are being phase locked together. Using these two technologies, along with intracavity diffractive beam coupling, solves two long standing problems that have prevented effective and robust phase locking of laser diode arrays.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Counterflow thermoelectric configuration employing thermal transfer fluid in closed cycle
ActiveUS7293416B2Cost-effectively employedCost-effectively configuredThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectMachines using electric/magnetic effectsNuclear engineeringActive cooling
Active cooling technologies such as thermoelectrics can be used to introduce thermal “gain” into a cooling system and, when employed in combination with forced flow liquid metal cooling loops, can provide an attractive solution for cooling high heat flux density devices and / or components. Total cooling power can be increased by employing multiple thermoelectric elements. Indeed, by employing modern semiconductor technologies, including e.g., thin-film technologies, thermoelectric elements may be cost-effectively employed and configured in large arrays.
Owner:SHEETAK INC
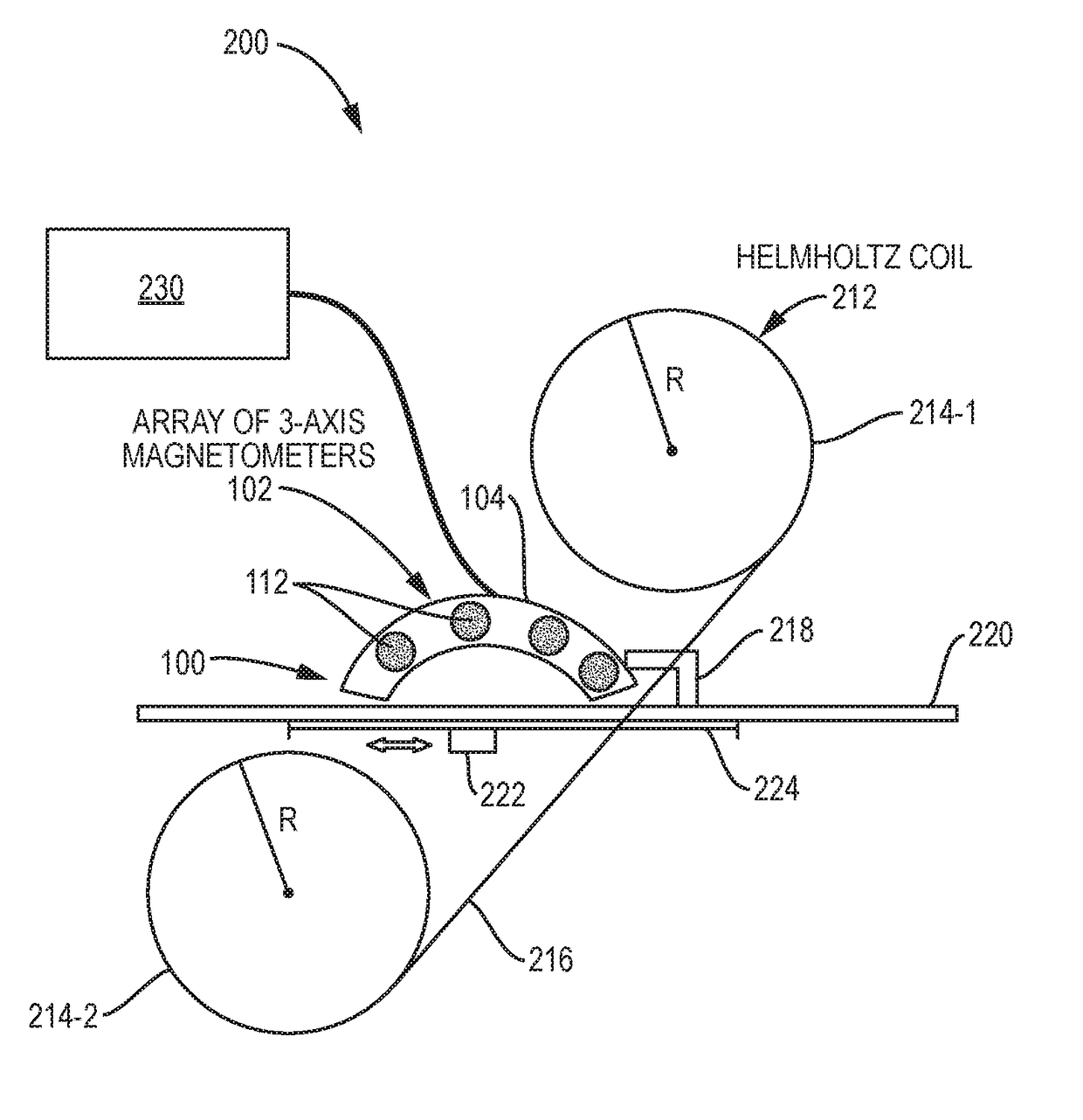
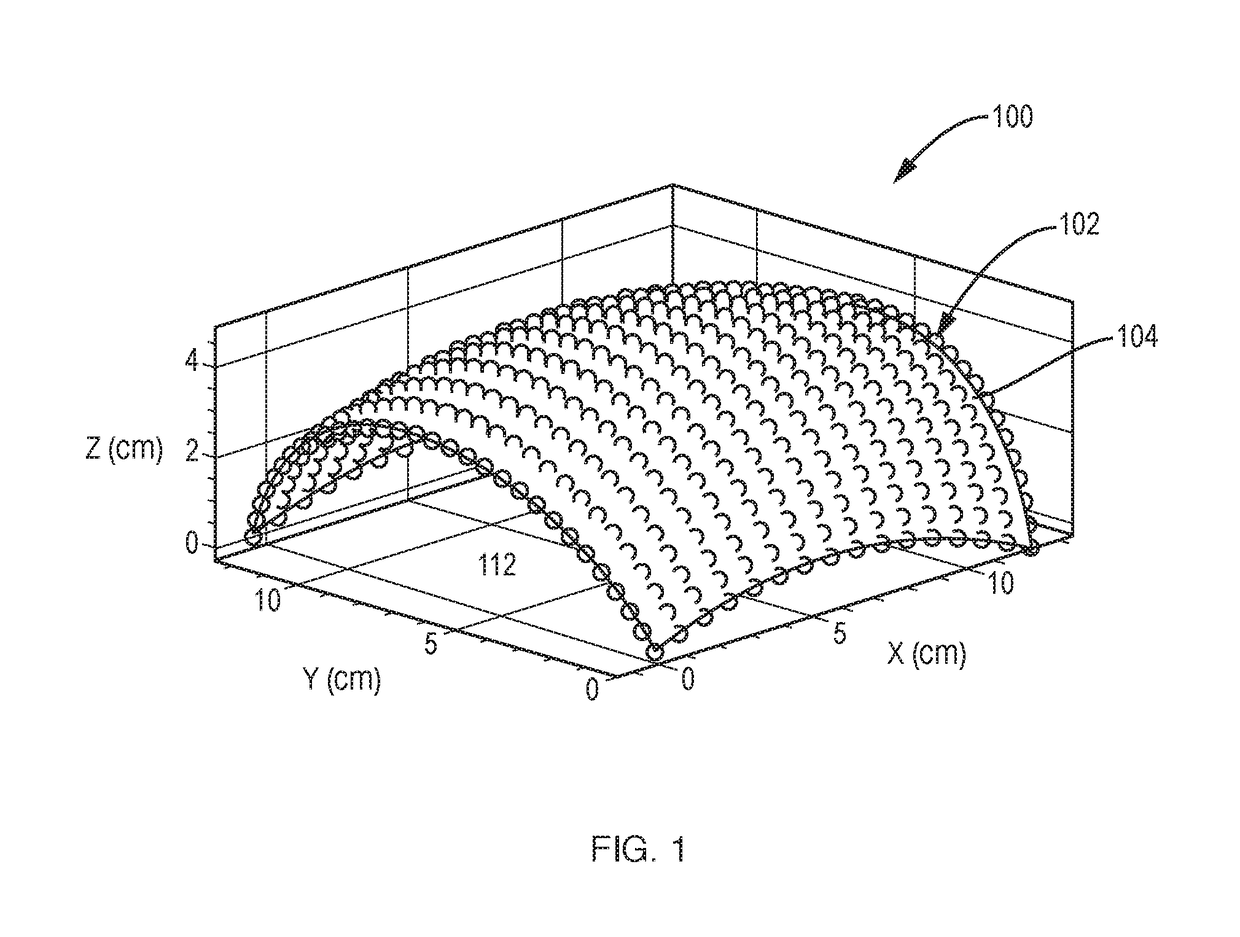
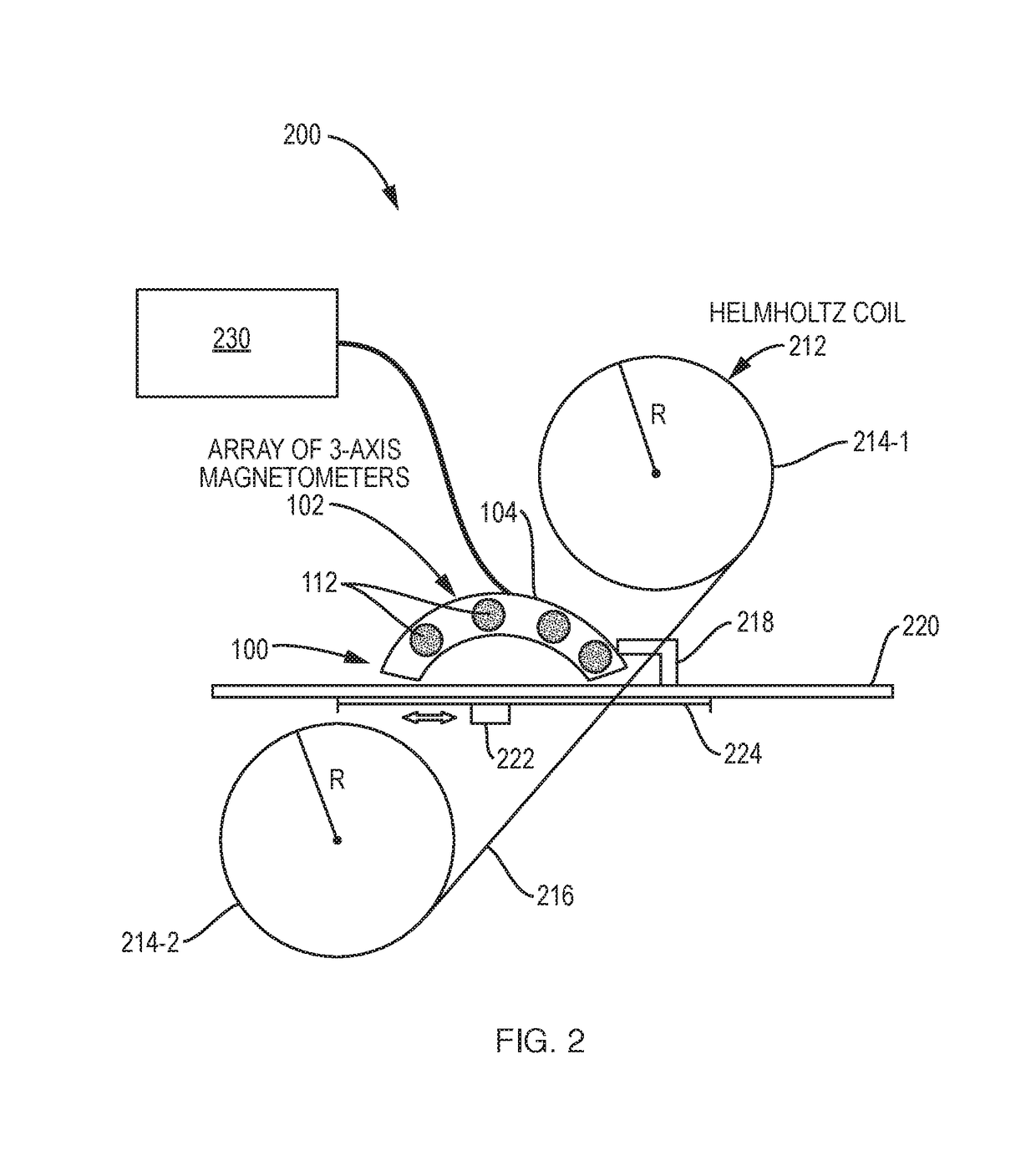
Calibration and Monitoring for 3-Axis Magnetometer Arrays of Arbitrary Geometry
ActiveUS20180003777A1Good reproducibilityShorten the timeElectrical measurementsThree-component magnetometersMagnetic tension forceMagnetometer
A system and method for calibrating rigid and non-rigid arrays of 3-axis magnetometers as disclosed. Such arrays might be used to analyze structures containing ferromagnetic material. The calibration determines scale factor and bias parameters of each magnetometer in the array, and the relative orientation and position of each magnetometer in the array. Once the parameters are determined, the actual magnetic field value at the magnetometer location can be simply related to magnetometer measurements. The method and system can be used to calibrate an array of 3-axis magnetometers in aggregate as opposed to individual magnetometers. This is critical in large arrays to increasing reproducibility of the calibration procedure and decreasing time required to complete calibration procedure.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com