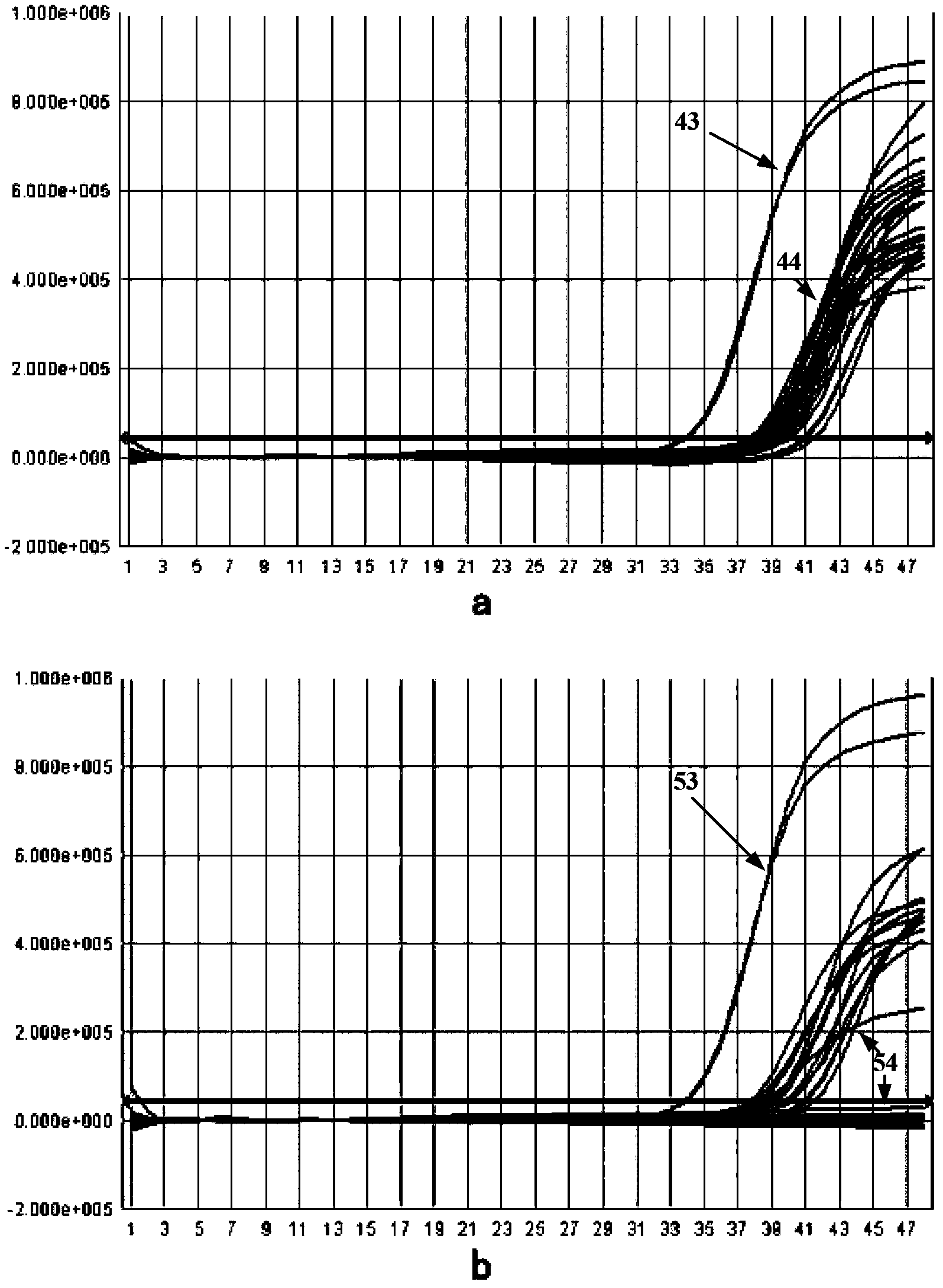
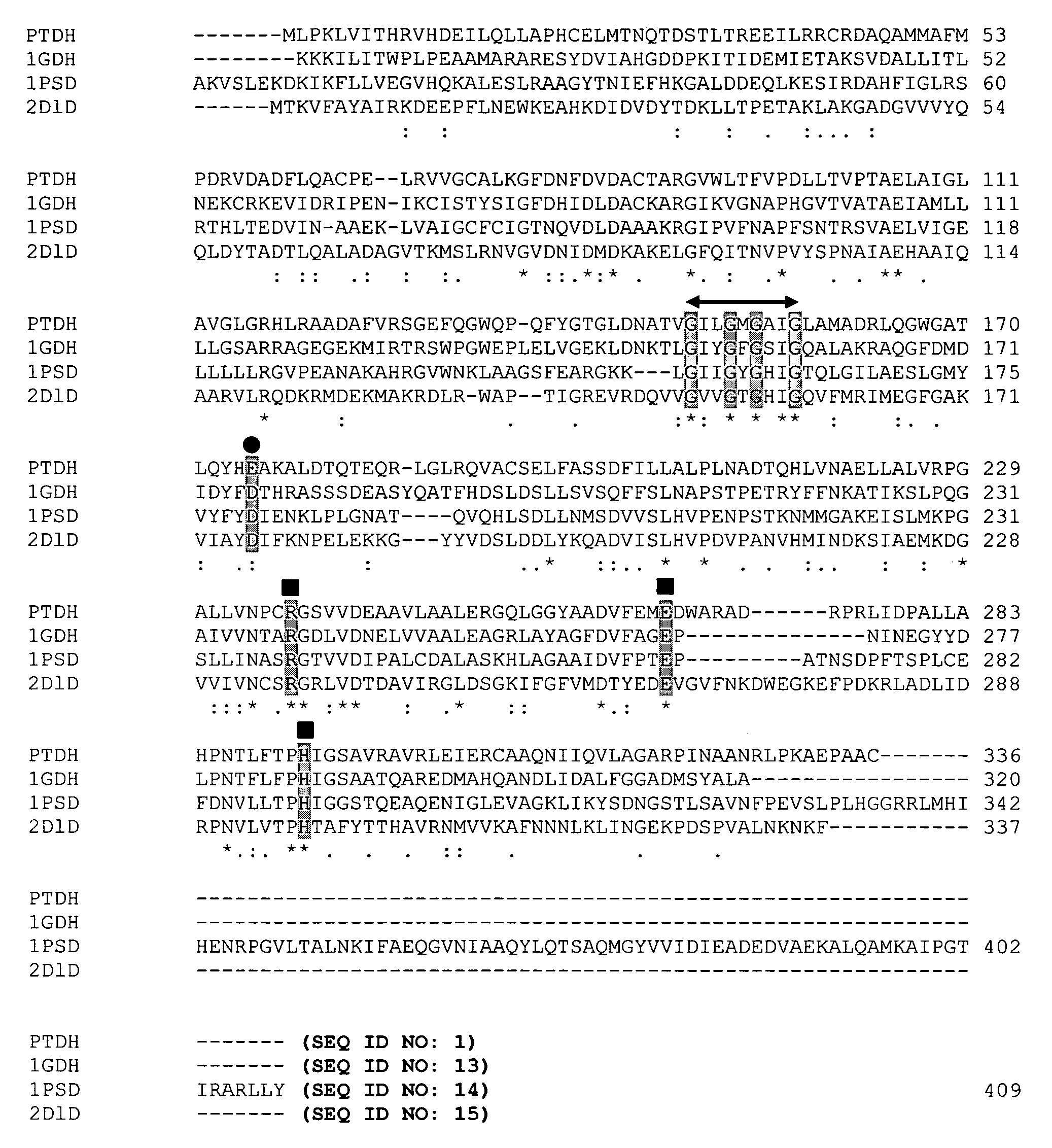
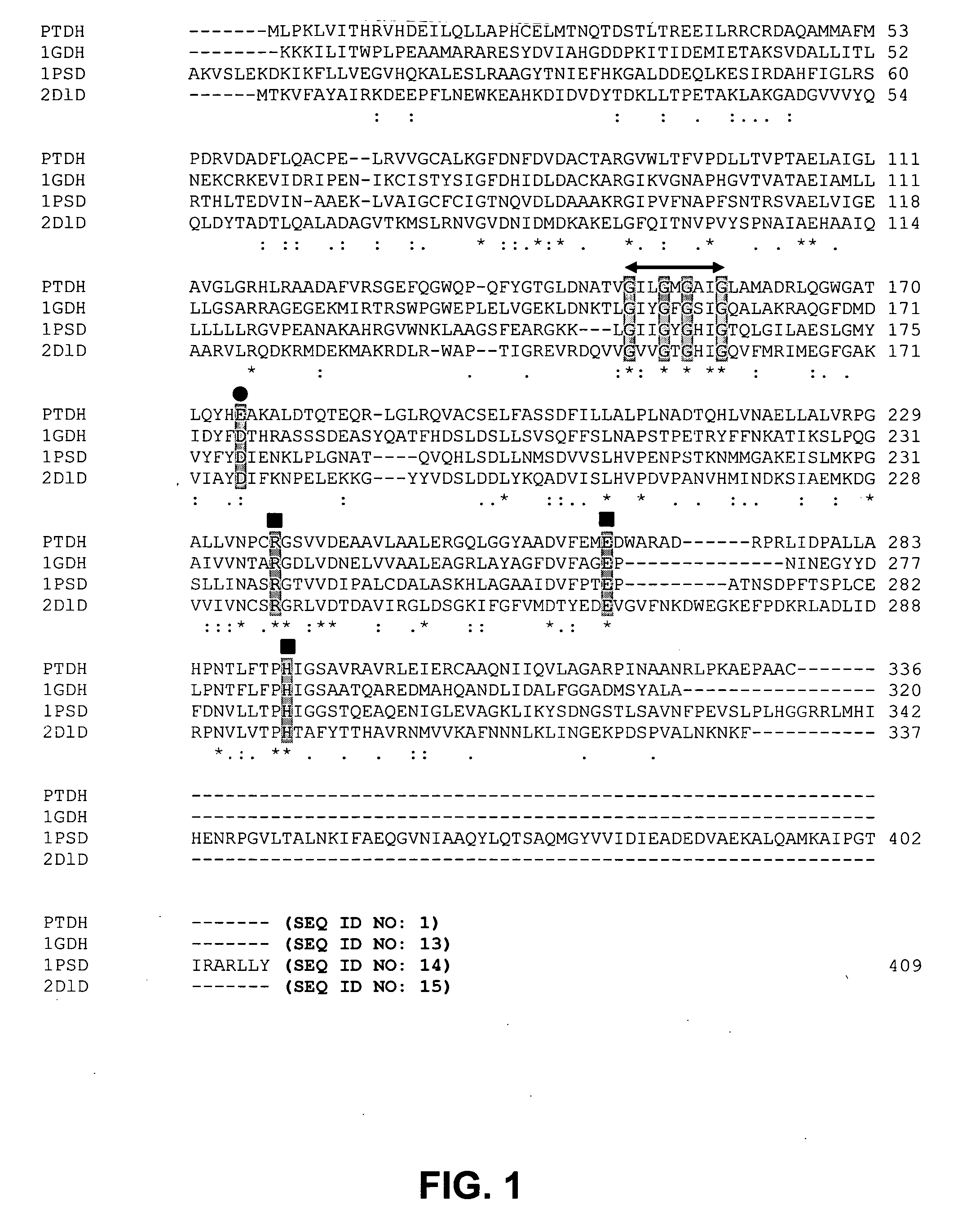
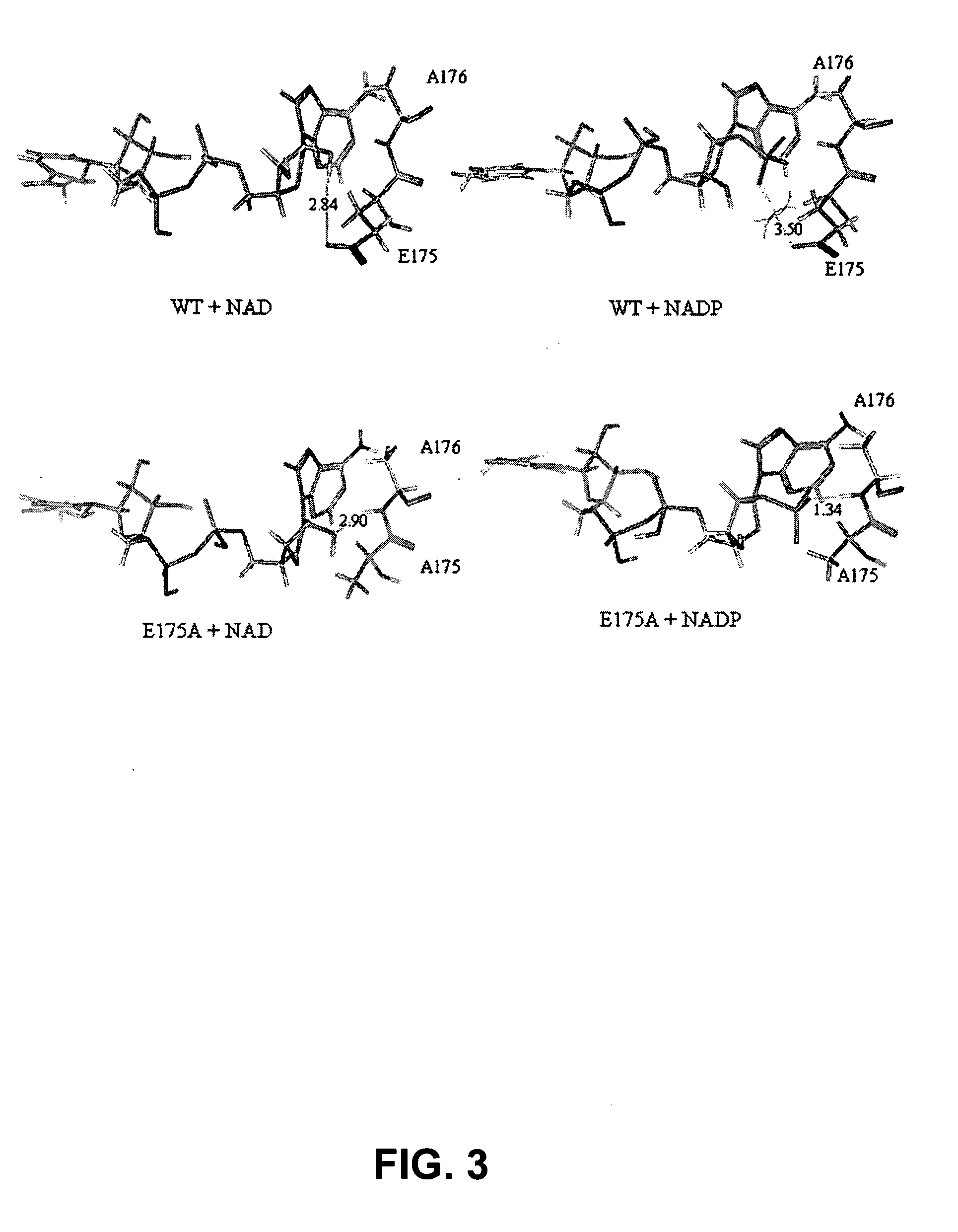
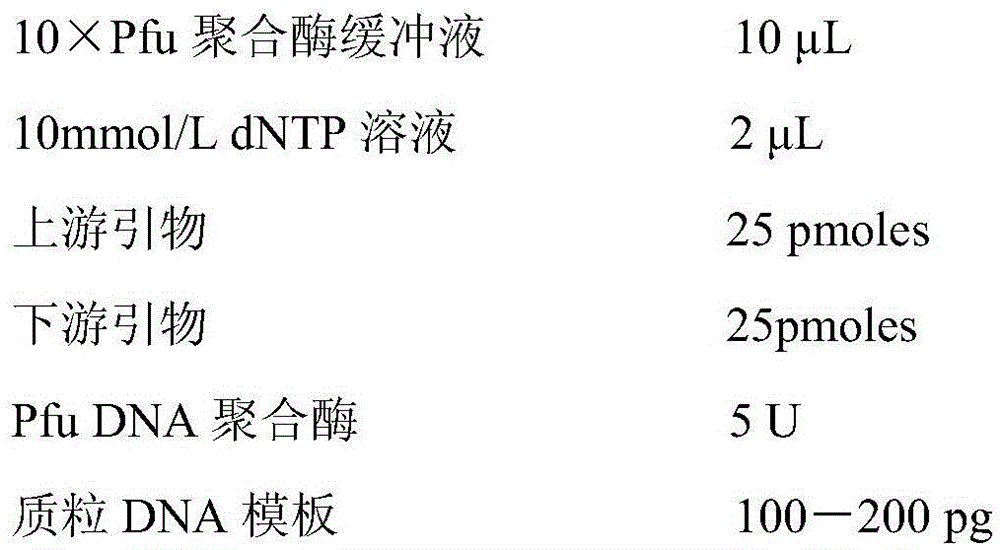
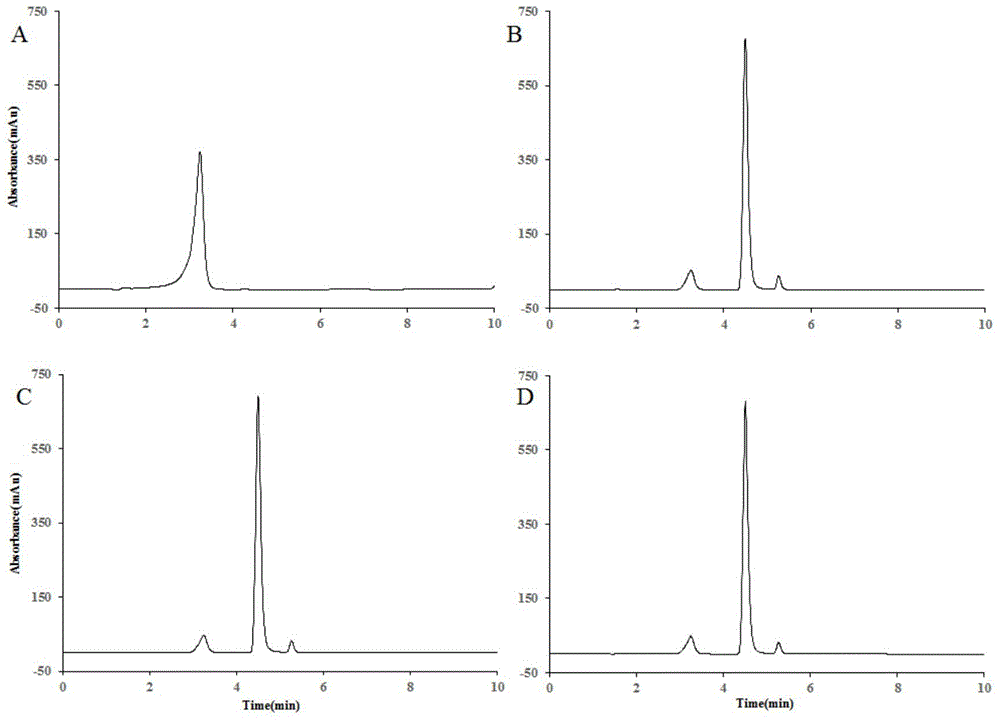
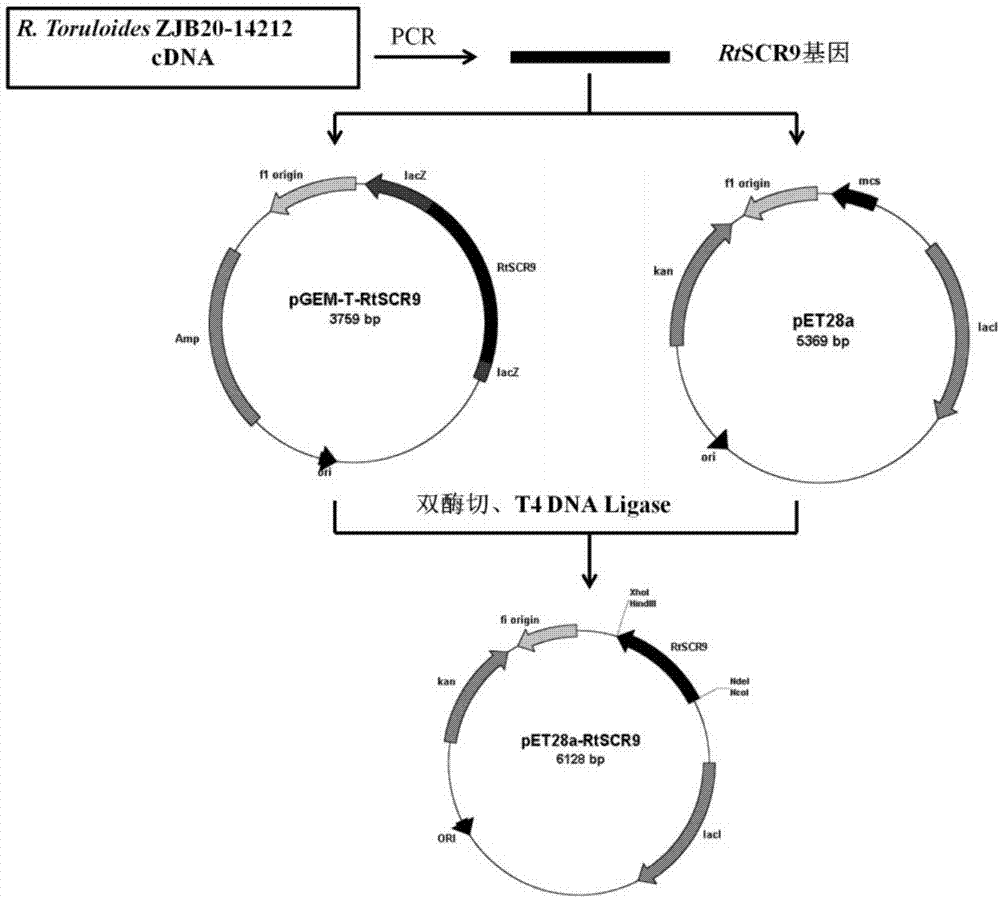
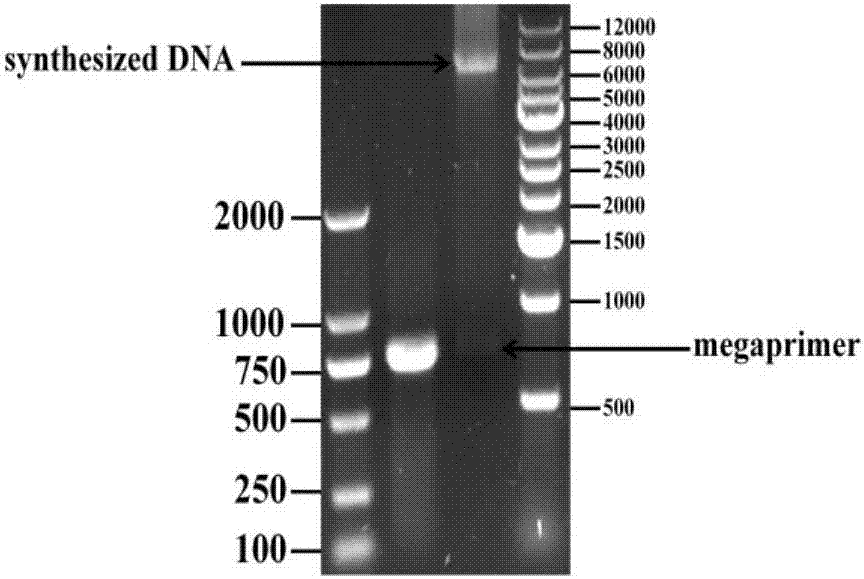
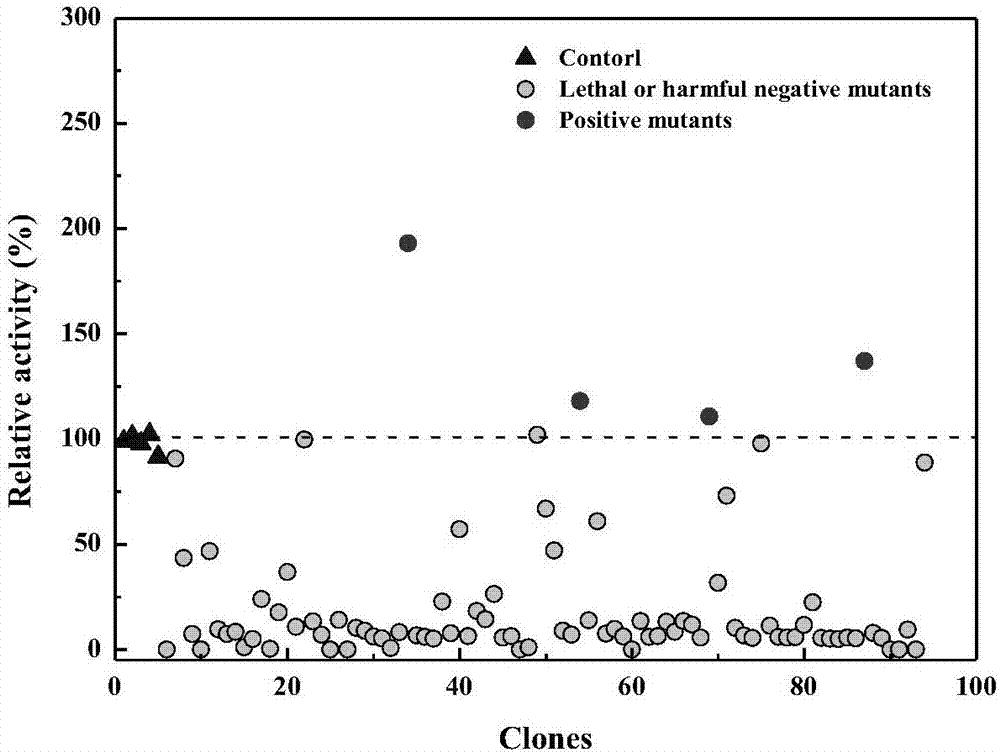
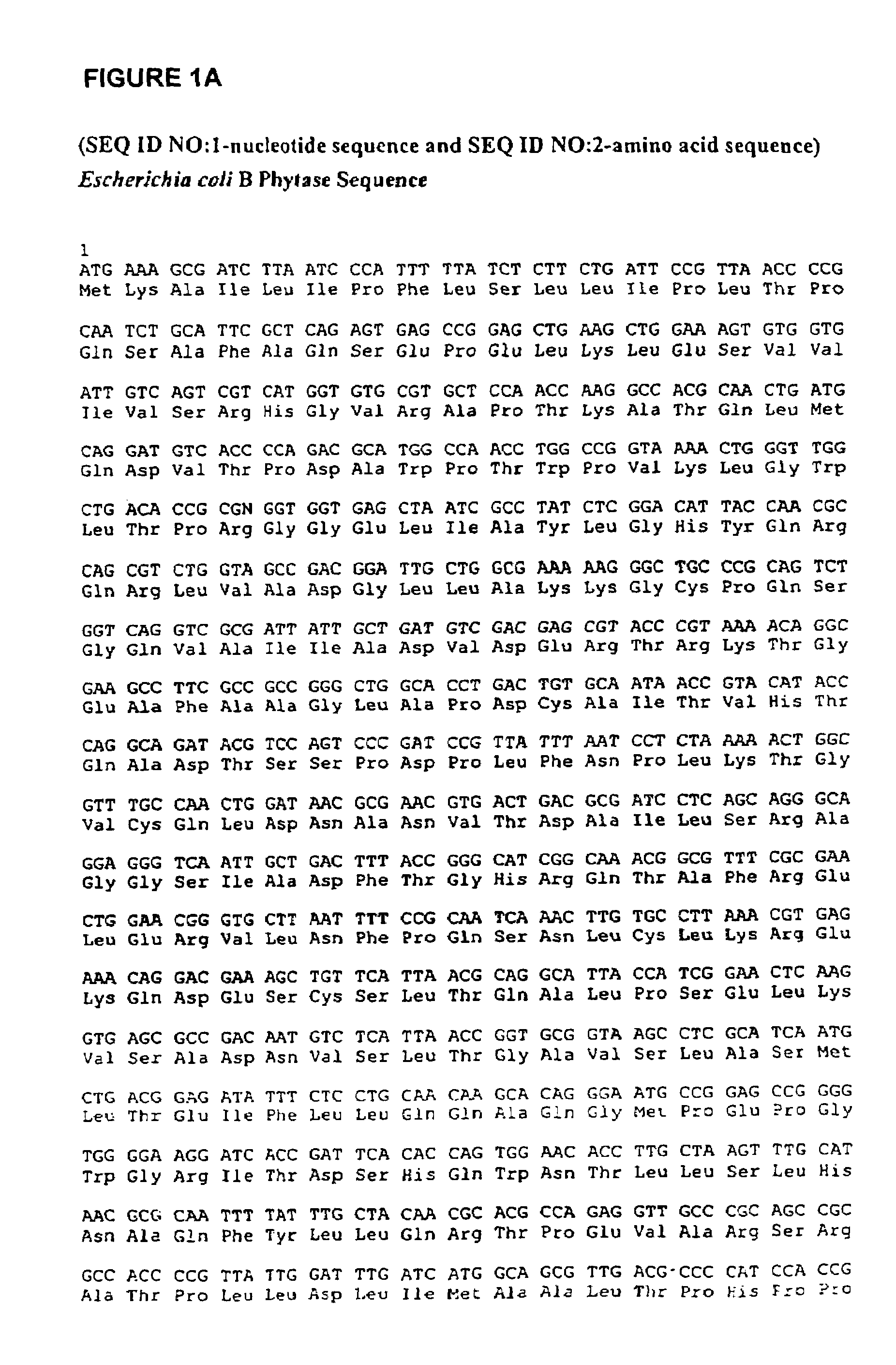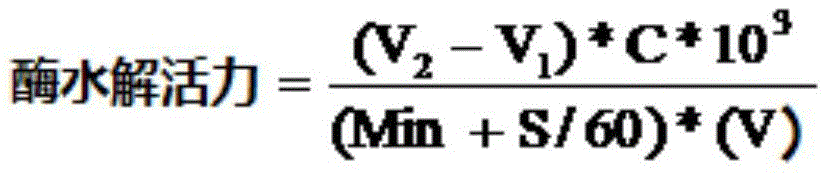Patents
Literature
209 results about "Wild type enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
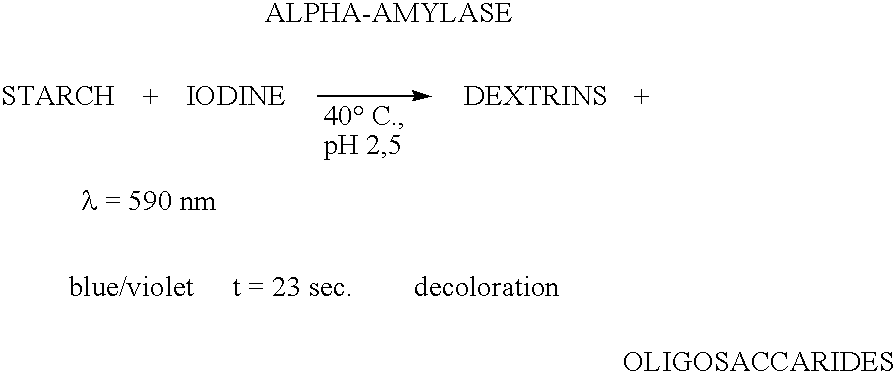
Enzymes for starch processing
InactiveUS20050054071A1Increased acid alpha-amylase activityImprove enzyme stabilitySugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyCarbohydrate-binding protein
The present invention relates to a hybrid enzyme comprising carbohydrate-binding module amino acid sequence and a fungal alpha-amylase amino acid sequence and to a variant of a fungal wild type enzyme comprising a carbohydrate-binding module and an alpha-amylase catalytic module. The invention also relates to the use of the hybrid enzyme or the variant in starch liquefaction.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
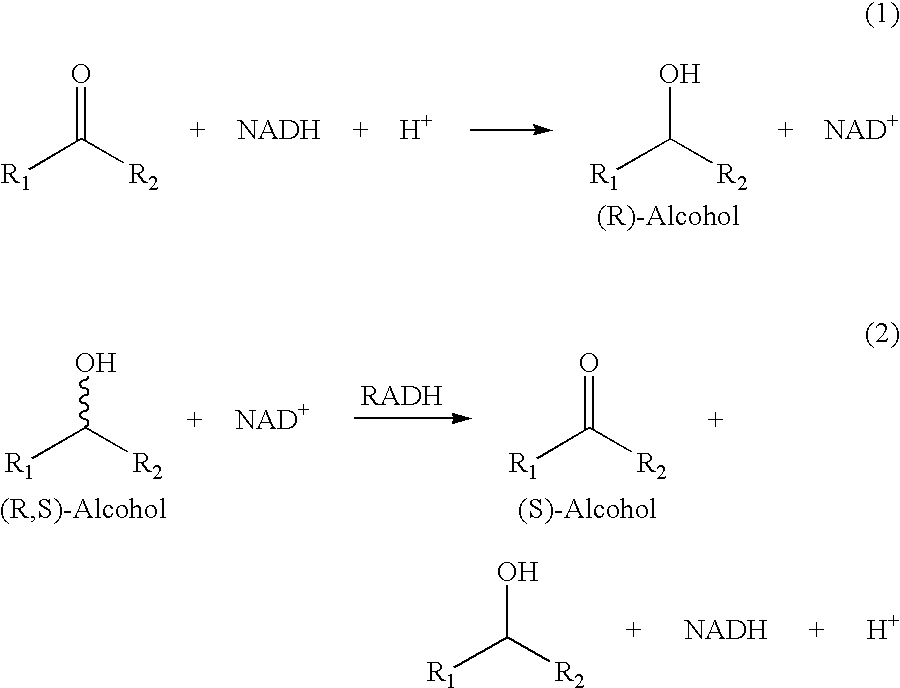
Recombinant enzymes having improved NAD (H) affinity
The present invention relates to recombinantly modified enzymes, which exhibit increased NAD(H) affinity compared to a unmodified or wildtype enzyme, gene sequences or polynucleotides that code for the recombinantly modified enzymes, plasmids and microorganisms that contain these gene sequences; as well as, methods of making and methods of using the enzymes of the present invention.
Owner:DEGUSSA AG
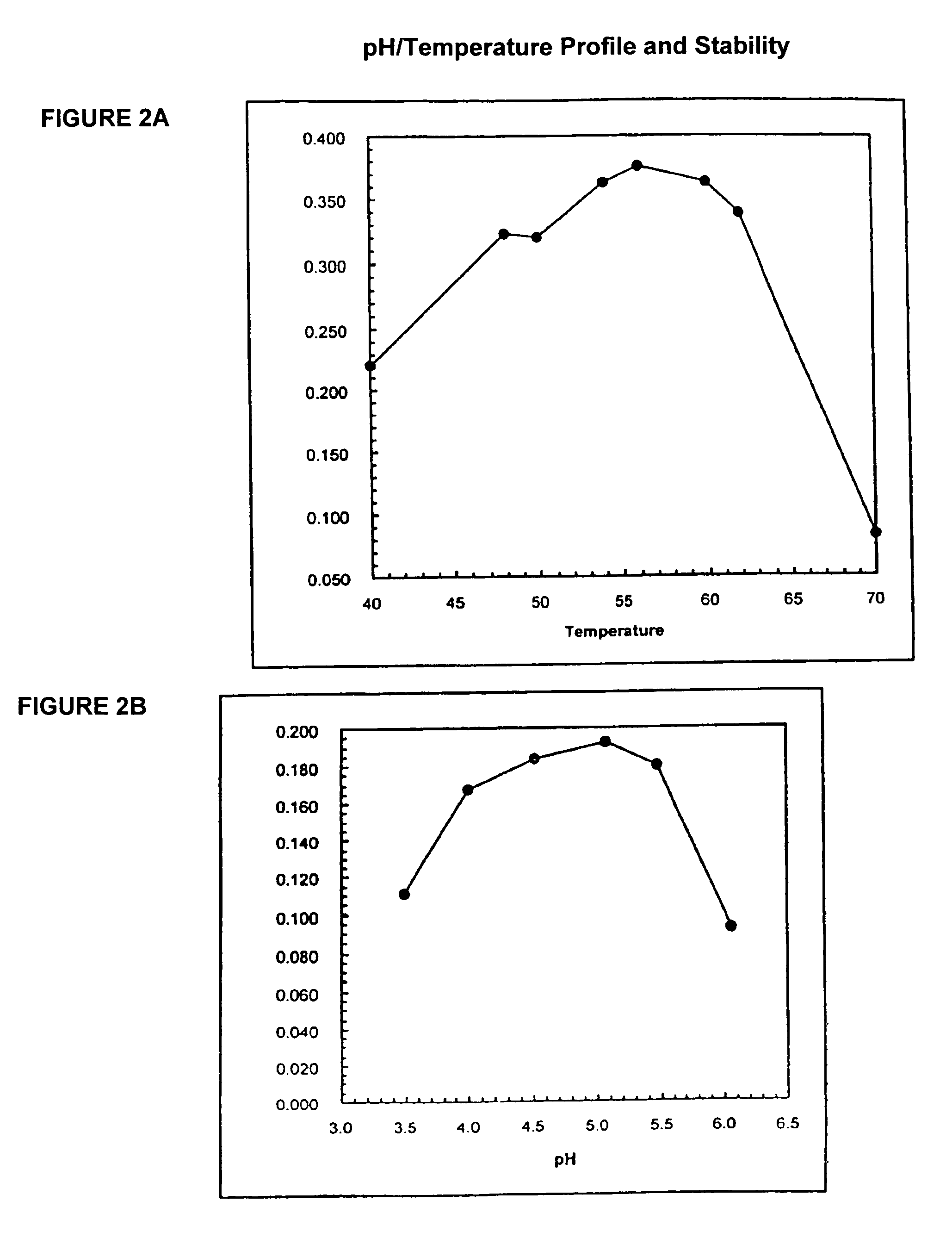
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods of making and using them
InactiveUS20050281792A1Improve publishing efficiencyHigh nutritional valueImmobilised enzymesBacteriaEscherichia coliAdditive ingredient
In one aspect, the invention provides a purified and modified phytase enzyme from Escherichia coli K12 appA phytase. The enzyme has phytase activity and improved thermal tolerance as compared with the wild-type enzyme. In addition, the enzyme has improved protease stability at low pH. Glycosylation of the modified phytase provided a further improved enzyme having improved thermal tolerance and protease stability. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells and can be used to aid in the digestion of phytate where desired. In one aspect, the phytase of the present invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants
InactiveUS20050202419A1Improve abilitiesImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesOxygenaseHeme
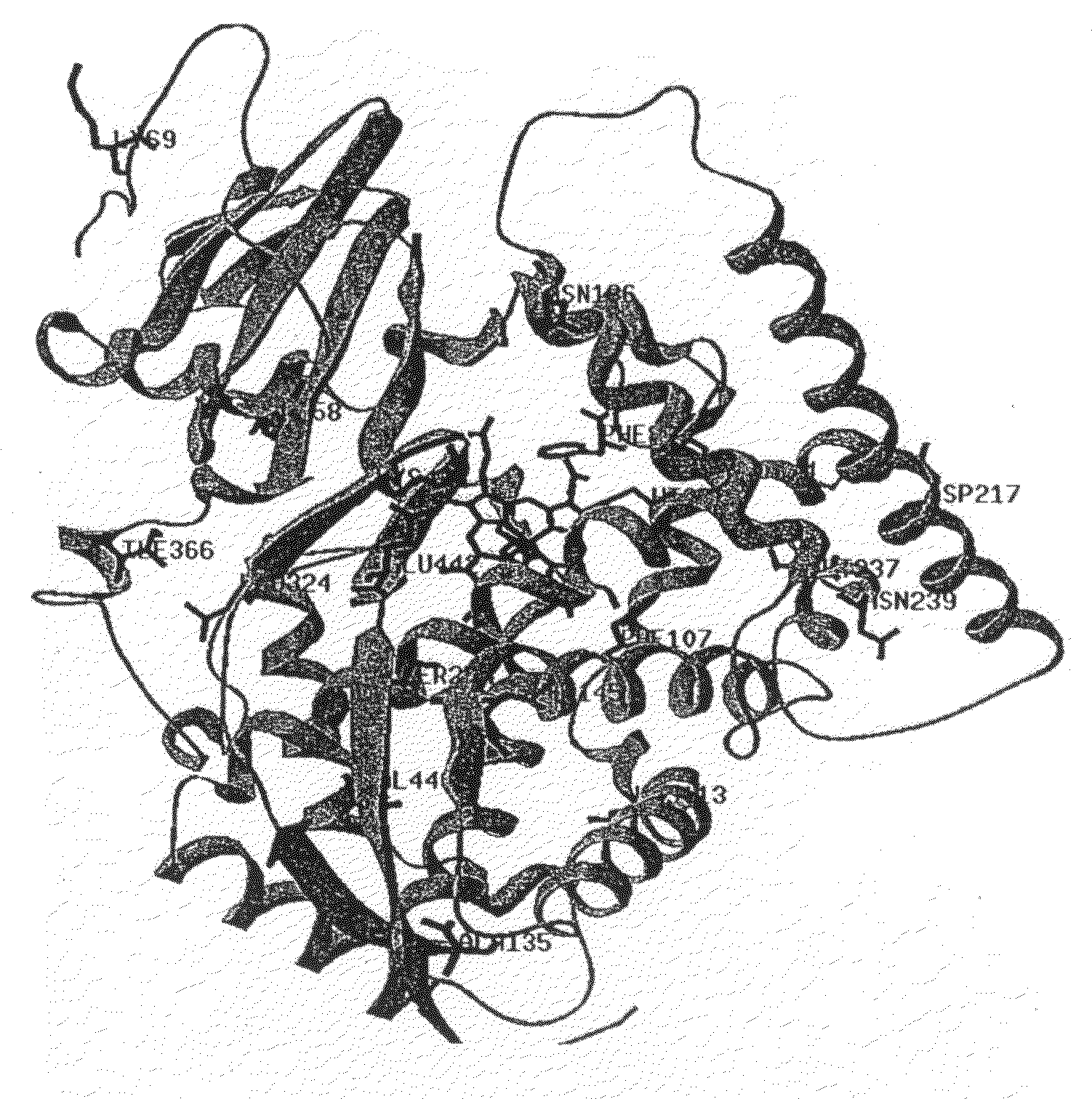
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have an improved ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. These variants also have an improved thermostability as compared to the cytochrome P450 BM-3 F87A mutant. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain mutants having I58V, F87A, H100R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, N239H, S274T, L324I, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for production of isoprenoids
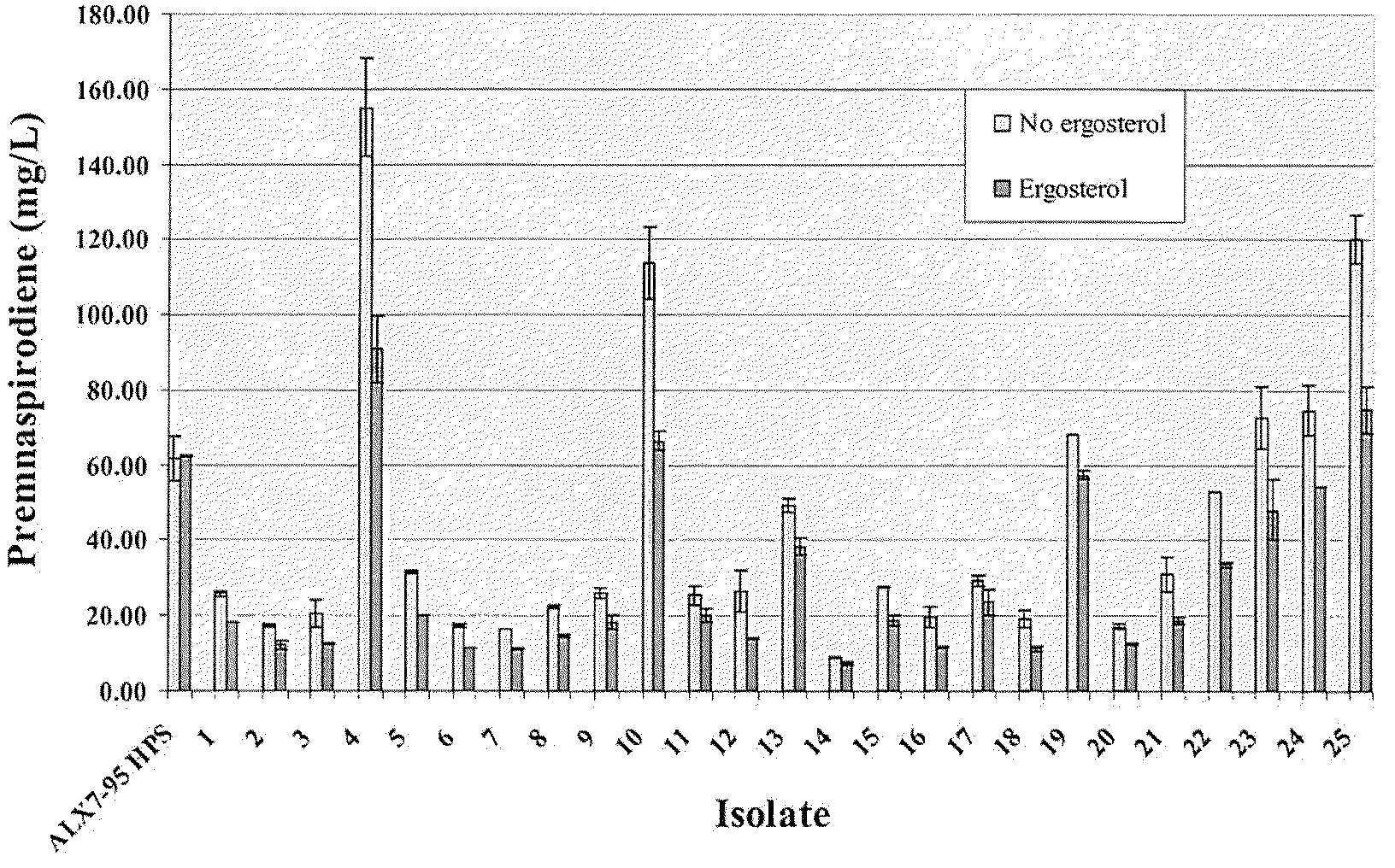
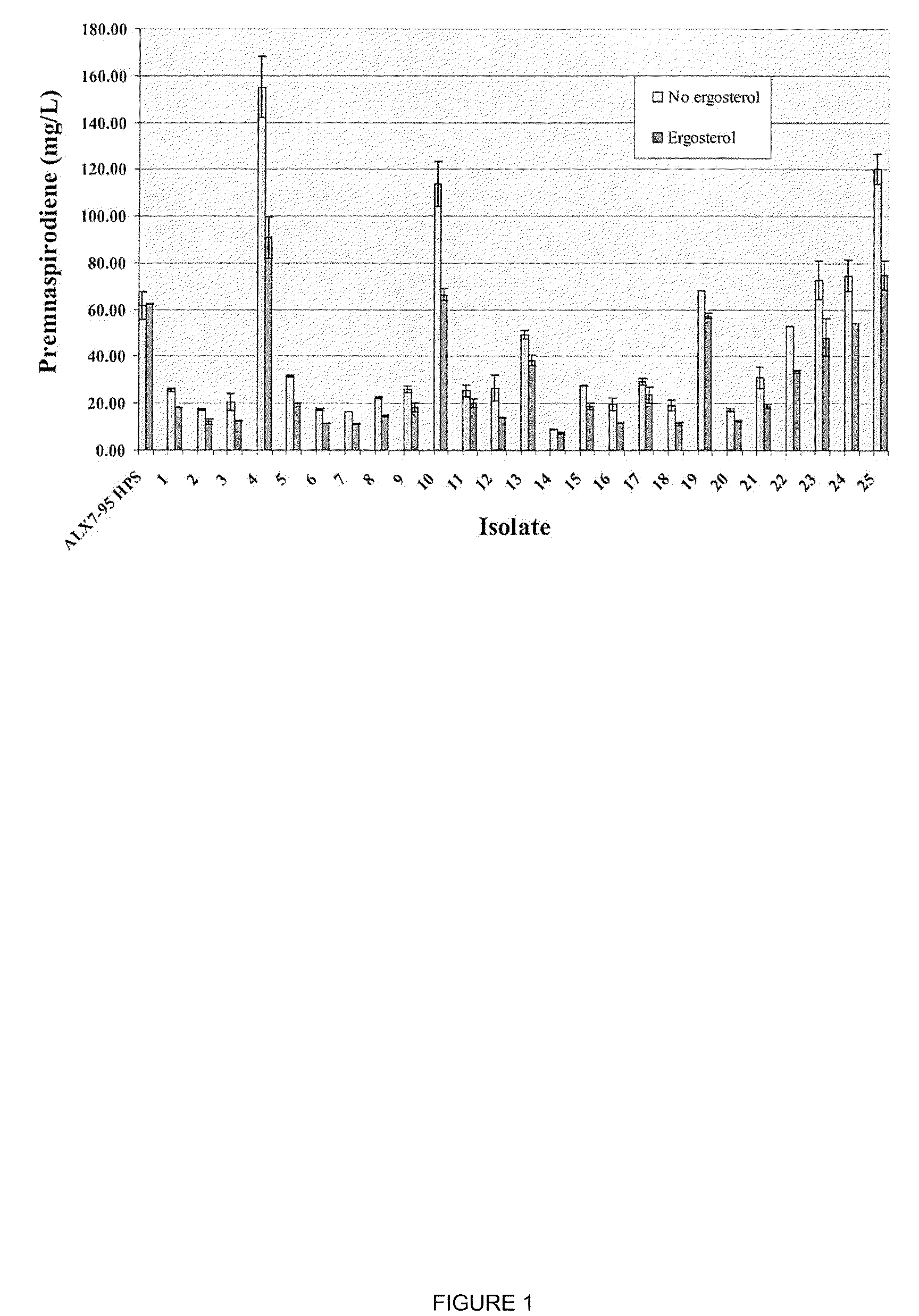
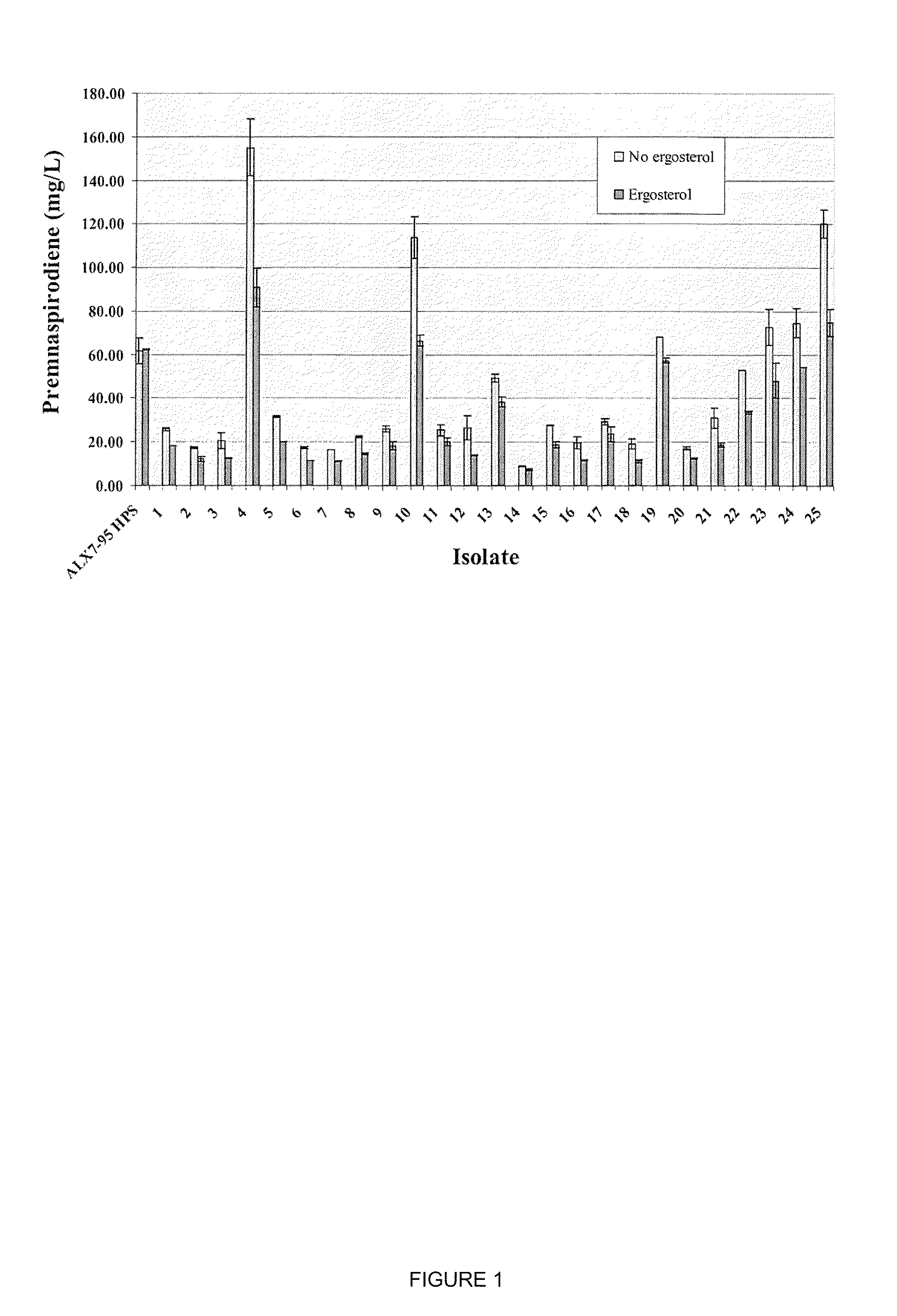
The present invention is directed to variant squalene synthase enzymes, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae squalene synthase enzymes, and to nucleic acid molecules encoding these variant enzymes. These variant enzymes produce squalene at a lower rate than the wild-type enzyme, allowing more farnesyl pyrophosphate to be utilized for production of isoprenoid compounds, while still producing sufficient squalene to allow the S. cerevisiae cells to grow without the requirement for supplementation by sterols such as ergosterol. These variant enzymes, therefore, are highly suitable for the efficient production of isoprenoids.
Owner:EVOLVA INC
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods of making and using them
InactiveUS7432097B2High nutritional valueImprove publishing efficiencyImmobilised enzymesBacteriaEscherichia coliAdditive ingredient
In one aspect, the invention provides a purified and modified phytase enzyme from Escherichia coli K12 appA phytase. The enzyme has phytase activity and improved thermal tolerance as compared with the wild-type enzyme. In addition, the enzyme has improved protease stability at low pH. Glycosylation of the modified phytase provided a further improved enzyme having improved thermal tolerance and protease stability. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells and can be used to aid in the digestion of phytate where desired. In one aspect, the phytase of the present invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Isoprenoid compounds
The present invention is directed to variant squalene synthase enzymes, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae squalene synthase enzymes, and to nucleic acid molecules encoding these variant enzymes. These variant enzymes produce squalene at a lower rate than the wild-type enzyme, allowing more farnesyl pyrophosphate to be utilized for production of isoprenoid compounds, while still producing sufficient squalene to allow the S. cerevisiae cells to grow without the requirement for supplementation by sterols such as ergosterol. These variant enzymes, therefore, are highly suitable for the efficient production of isoprenoids.
Owner:EVOLVA INC
Thermostable peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants and methods of use
InactiveUS20090264311A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove abilitiesSugar derivativesLibrary screeningOxygenaseHeme
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have at least one mutation improving their ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. The variants also have at least one mutation improving thermostability as compared to the parent enzyme or corresponding wild-type enzyme. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain variants having L52I, I58V, F87A, H100R, S106R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, A184V, N239H, S274T, L324I, V340M, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Cell-wall degrading enzyme variants
InactiveUS20050250181A1Process can be usedImprove performanceBacteriaSugar derivativesEnzyme variantBiology
The present invention relates to variants of a cell-wall degrading enzyme having a beta-helix structure, which variant has at least one substituent in a position determined by identifying all residues potentially belonging to a stack; characterizing the stack as interior or exterior; characterizing the stack as polar, hydrophobic or aromatic / heteroaromatic based on the dominating characteristics of the parent or wild-type enzyme stack residues and / or its orientation relative to the beta-helix (interior or exterior); optimizing all stack positions of a stack either to hydrophobic aliphatic amino acids, hydrophobic aromatic or polar amino acids by allowing mutations within one or all positions to amino acids belonging to one of these groups; measuring thermostability of the variants by DSC or an application-related assay such as a Pad-Steam application test; and selecting the stabilized variants. Variants of a wild-type parent pectate lyase (EC 4.2.2.2) having the conserved amino acid residues D111, D141 or E141, D145, K165, R194 and R199 when aligned with the pectate lyase comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 are preferred.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have an improved ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. These variants also have an improved thermostability as compared to the cytochrome P450 BM-3 F87A mutant. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain mutants having I58V, F87A, H100R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, N239H, S274T, L324I, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for production of isoprenoid compounds
The present invention is directed to variant squalene synthase enzymes, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae squalene synthase enzymes, and to nucleic acid molecules encoding these variant enzymes. These variant enzymes produce squalene at a lower rate than the wild-type enzyme, allowing more farnesyl pyrophosphate to be utilized for production of isoprenoid compounds, while still producing sufficient squalene to allow the S. cerevisiae cells to grow without the requirement for supplementation by sterols such as ergosterol. These variant enzymes, therefore, are highly suitable for the efficient production of isoprenoids.
Owner:EVOLVA INC
Thermostable Alcohol Dehydrogenase Derived From Thermococcus Guaymasensis
An alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) from hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus guaymasensis was purified to homogeneity and was found to be a homotetramer with a subunit size of 40±1 kDa. The gene encoding the enzyme was cloned and sequenced, and found to have significant sequence homology to known zinc-containing ADHs and L-threonine dehydrogenases with both binding motifs of catalytic zinc and NADP+. The wild-type enzyme is a primary-secondary ADH that exhibits a substrate preference for secondary alcohols and corresponding ketones, and exhibits unusual stereoselectivity. The wild-type enzyme was found to have outstanding thermostability, demonstrating 60% activity after incubation at 80° C. for 40 hours. Site-directed mutagenesis was used to substitute the cyteine residue at position 56 with a serine, to provide the TgADH(C56S) mutant. In the assays that we carried out, we found virtually no difference in enzyme activity and oxygen-sensitivity between the mutant TgADH (C56S) and wild type TgADH.
Owner:MA KESEN +1
Feedback-resistant homoserine transsuccinylases
The invention concerns a homoserine transsuccinylase having at least one mutation compared to a wild-type homoserine transsuccinylase and reduced sensitivity towards a L-methionine or SAM, compared to the wild-type enzyme. The latter comprises an amino acid sequence including a partial AspGlyXaaXaaXaaThrGlyAlaPro sequence between position 90 and position 115 and a partial TyrGlnXaaThrPro sequence between position 285 and position 310, position 1 of the amino acid sequence corresponding to the initial methionine. The invention is characterized in that the mutation is a substitution of the aspartate in the partial AspGlyXaaXaaXaaThrGlyAlaPro sequence, or a substitution of the tyrosine in the partial TyrGlnXaaThrPro sequence.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Variant reverse transcriptase
ActiveUS8900814B2Maintain good propertiesHigh general versatilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseThermal stability
The present invention provides a versatile mutant reverse transcriptase with high thermal stability, a nucleic acid thereof and a method for producing a mutant reverse transcriptase, a versatile kits for reverse transcription and detection, a method for improving thermal stability of a nucleic acid-related enzyme, which significantly improves thermal stability of a nucleic acid-related enzyme, and a reverse transcription method, which efficiently performs a reverse transcription. An amino acid residue in a nucleic acid interaction region of a wild-type enzyme is substituted with a positively-charged amino acid residue or a nonpolar amino acid residue, to form a nucleic acid interaction region having a positive effective charge larger than the nucleic acid interaction region of a wild-type enzyme.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
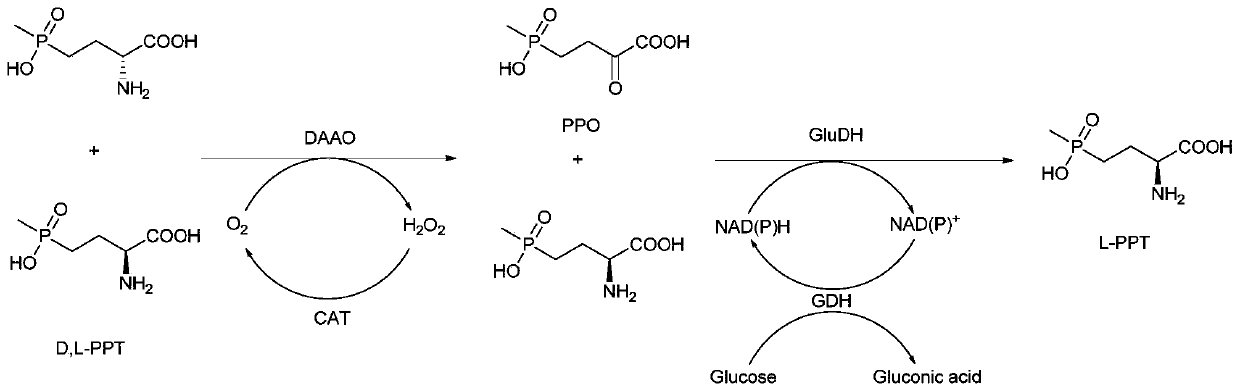
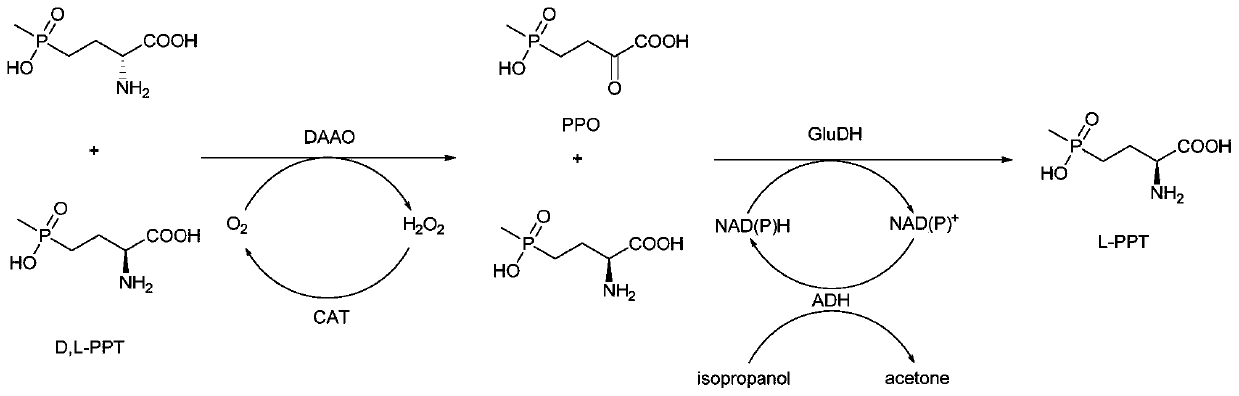
Redox asymmetrical method for preparing L-phosphinothricin by biological multi-enzyme coupling
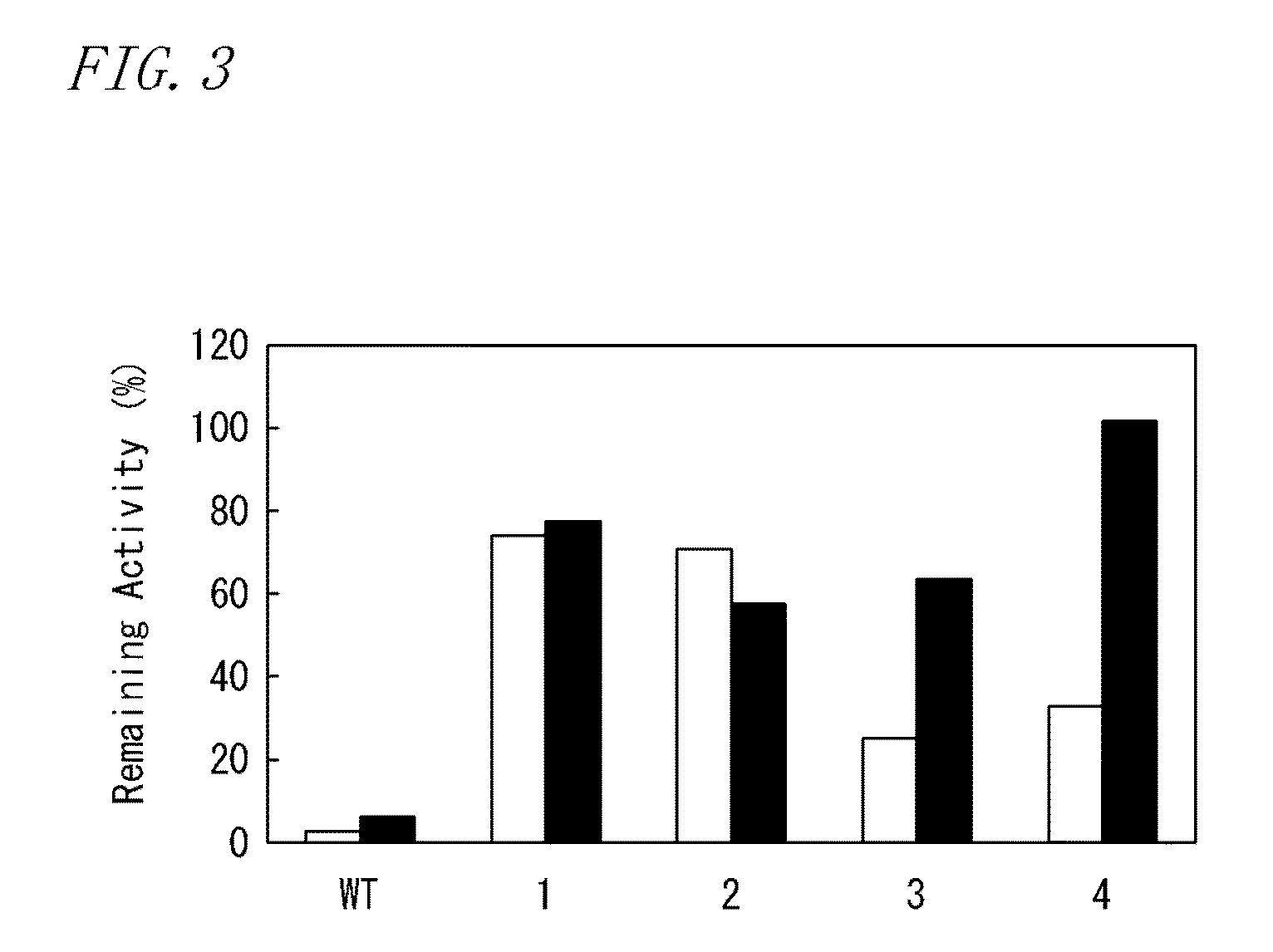
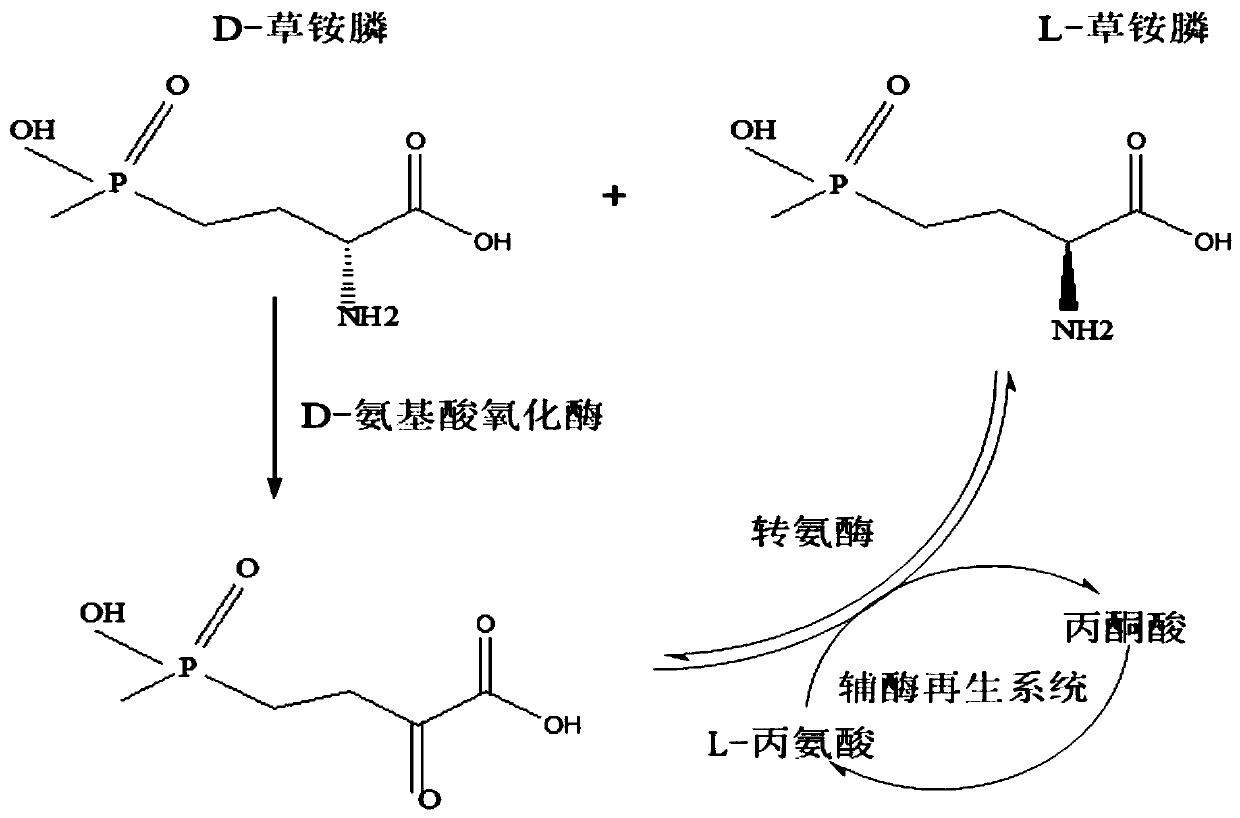
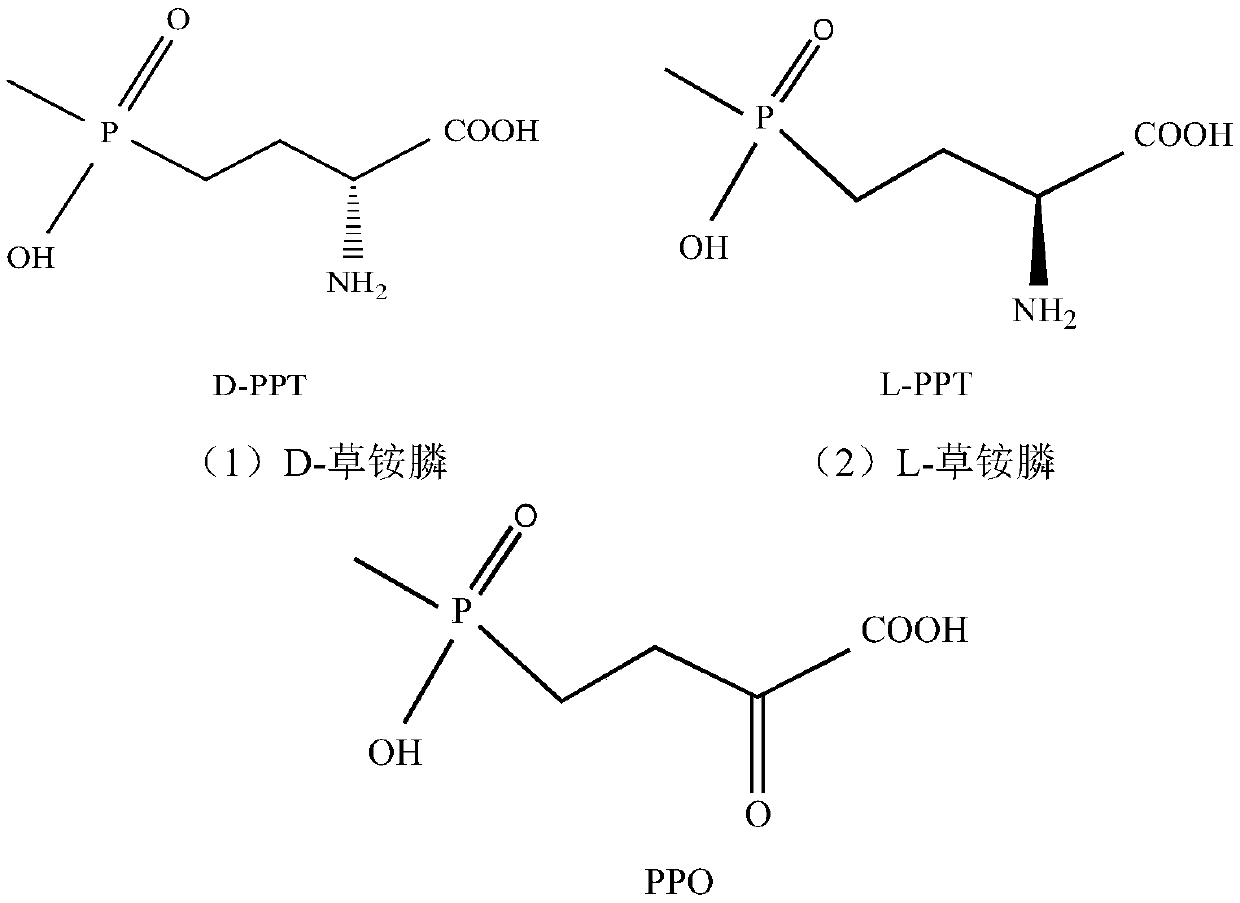
The present invention discloses a redox asymmetrical method for preparing L-phosphinothricin by biological multi-enzyme coupling. D, L-phosphinothricin is used as a raw material, the L-phosphinothricin is obtained through catalysis of an enzyme catalysis system, the enzyme catalysis system comprises a D-amino acid oxidase mutant for catalyzing D-phosphinothricin in the D, L-phosphinothricin into 2-carbonyl-4-[hydroxy (methyl) phosphonyl] butyric acid and a transaminase for catalyzing and reducing the 2-carbonyl-4-[hydroxy (methyl) phosphonyl ] butyric acid into the L-phosphinothricin, the D-amino acid oxidase mutant is obtained by mutation of D-amino acid oxidase in wild rhodotorula taiwanensis, and mutation sites are selected from one of the following four types: (1) M213S; (2) M213S-N54V-F58E; (3) M213S-N54V-F58E-D207A; and (4) M213S-N54V-F58E-D207A-S60T. The D-amino acid oxidase mutant has better catalytic efficiency, a conversion rate is far higher than that of wild enzyme when theracemic D, L-phosphinothricin is used as a substrate, and yield of PPO is also greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
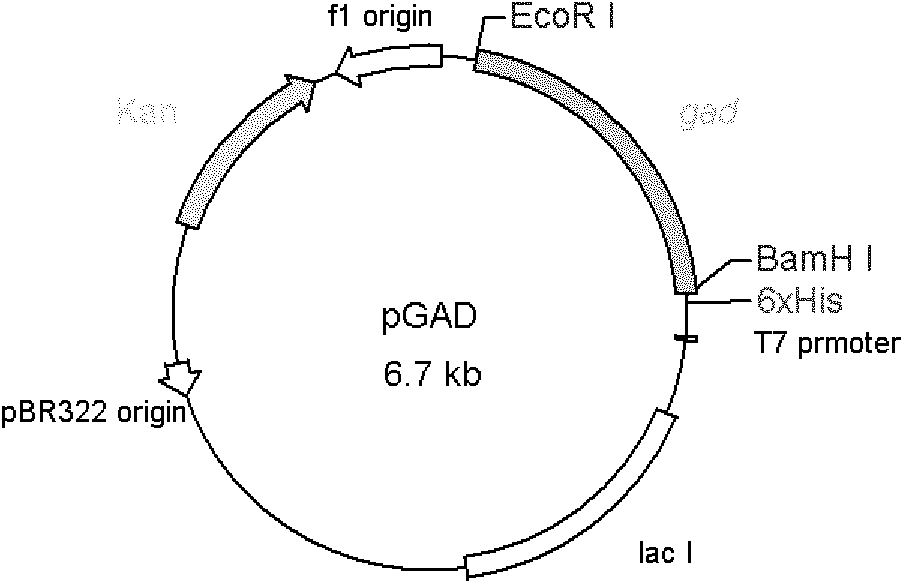
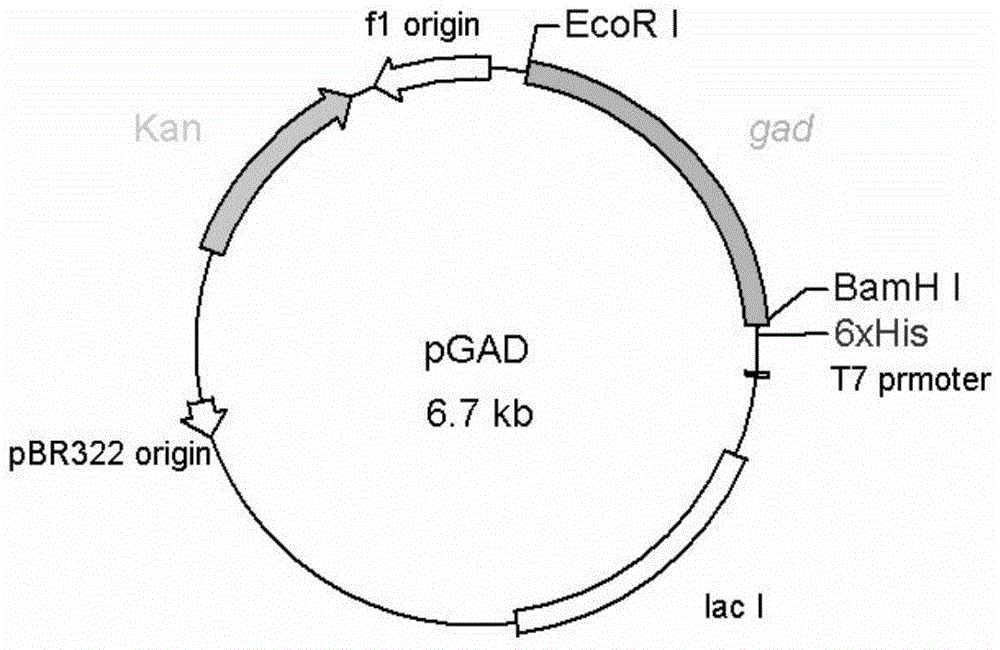
Variant gene of glutamate decarboxylase and purpose thereof
InactiveCN101914560ASolve the problem of low catalytic activityBroaden the optimum pH rangeFungiBacteriaSolubilityEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a variant gene of glutamate decarboxylase. DNA sequence of the gene is SEQ ID: No.1. By site-directed mutagenesis on the basis of coded wild GAD enzyme gene, the variant gene according to the invention enhances catalytic activity of the corresponding variant enzyme thereof in neutral pH value and widens the most proper scope of pH value of enzyme, so that the GABA generation ability of the corresponding variant enzyme through the catalysis of glutamic acid on condition of pH=6.0 is twice as much as that of wild-type enzyme. As the most proper scope of pH value of enzyme is widened, catalysis reaction can be conducted on condition that pH is higher than 5.0, thus the problem that the solubility of substrate, i.e. glutamic acid, is low on condition of pH from 4.0 to 5.0 is solved, and conditions are created for GABA production by biotransformation of enzyme.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Mutant Taq enzyme and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103509767AImprove thermal stabilityMeet the needs of industrial and research applicationsBacteriaTransferasesGenetic engineeringMutagenic Process
The invention discloses a mutant Taq enzyme and a preparation method thereof. A modern genetic engineering technology is adopted, amino acids on a plurality of sites in an amino acid sequence of a natural Taq enzyme are mutated and recombined to obtain the mutant Taq enzyme, and specifically, a glutamic acid on the 626th site of the natural Taq enzyme is mutated into lysine, alanine on the 661st site of the natural Taq enzyme is mutated into a glutamic acid, isoleucine on the 665th site of the natural Taq enzyme is mutated into threonine, phenylalanine on the 667th site of the natural Taq enzyme is mutated into leucine, and isoleucine on the 707th site of the natural Taq enzyme is mutated into leucine. Compared with an unmodified wild-type Taq enzyme, the mutant Taq enzyme has the advantages that the activity and thermal stability of the enzyme are greatly improved by site-specific mutagenesis, and the requirements of industrial production and scientific research application can be better met.
Owner:GUANGDONG FAPON BIOTECH CO LTD +1
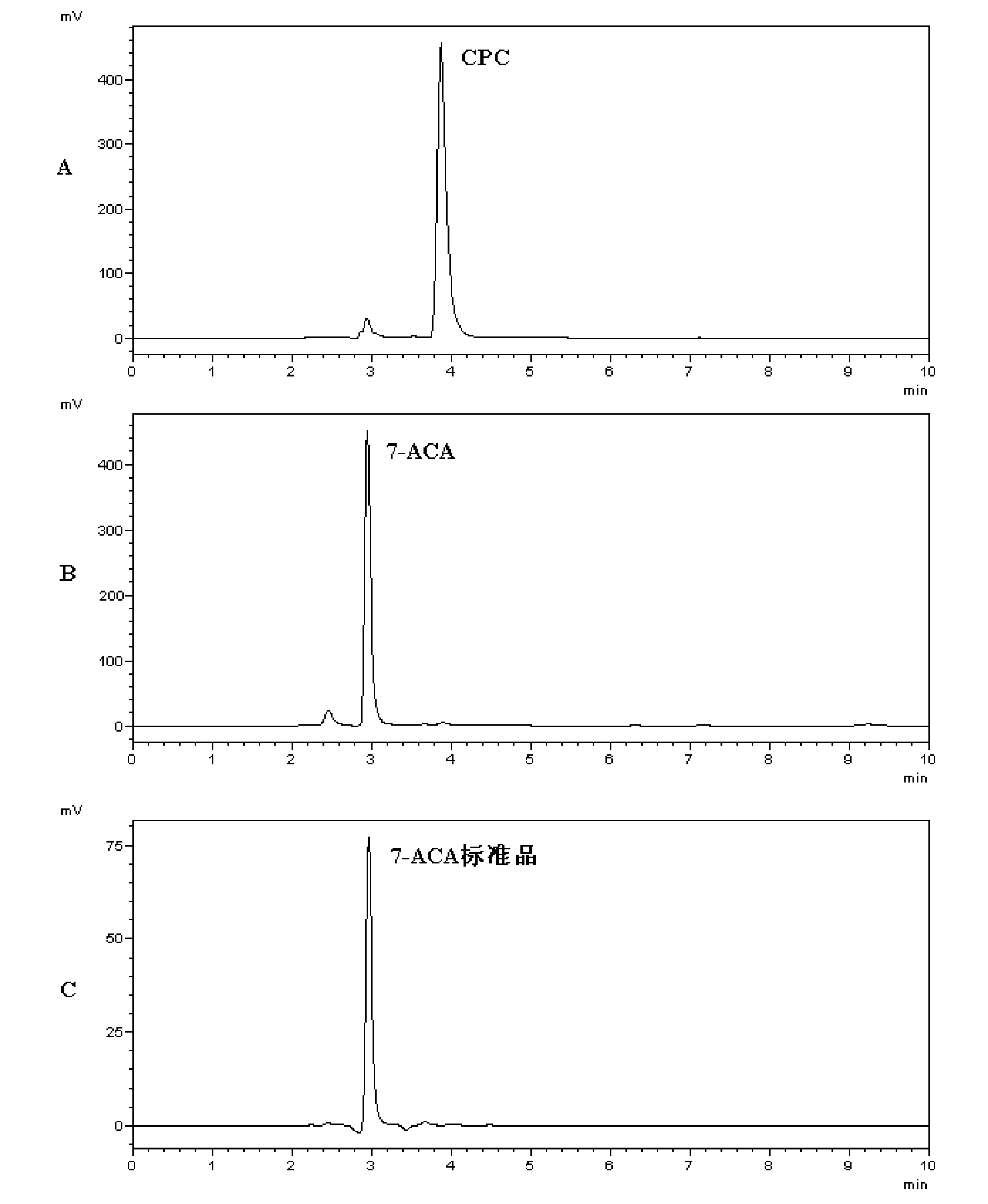
Cephalosporin acylase mutant and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a cephalosporin acylase mutant and an encoding gene and an application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is any one of the following 1)-3): 1) protein formed by an amino acid sequence shown as sequence 4 in the sequence table; 2) protein formed by an amino acid sequence shown as sequence 3 in the sequence table; 3) protein which is obtained by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or several amino acid residues in the amino acid residue sequence of sequence 3 or sequence 4 in the sequence table, has the functions of cephalosporin acylase, andis derived from 1). Experiment of the invention shows that the invention provides a wild-type CPC acylase mutant; HPLC results show that the specific activity for CPC of the wild-type CPC acylase mutant of the invention is increased by 6.5 times when compared with that of wild-type enzymes. In one-step conversion, the conversion rate is up to above 98% within 3 hours.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
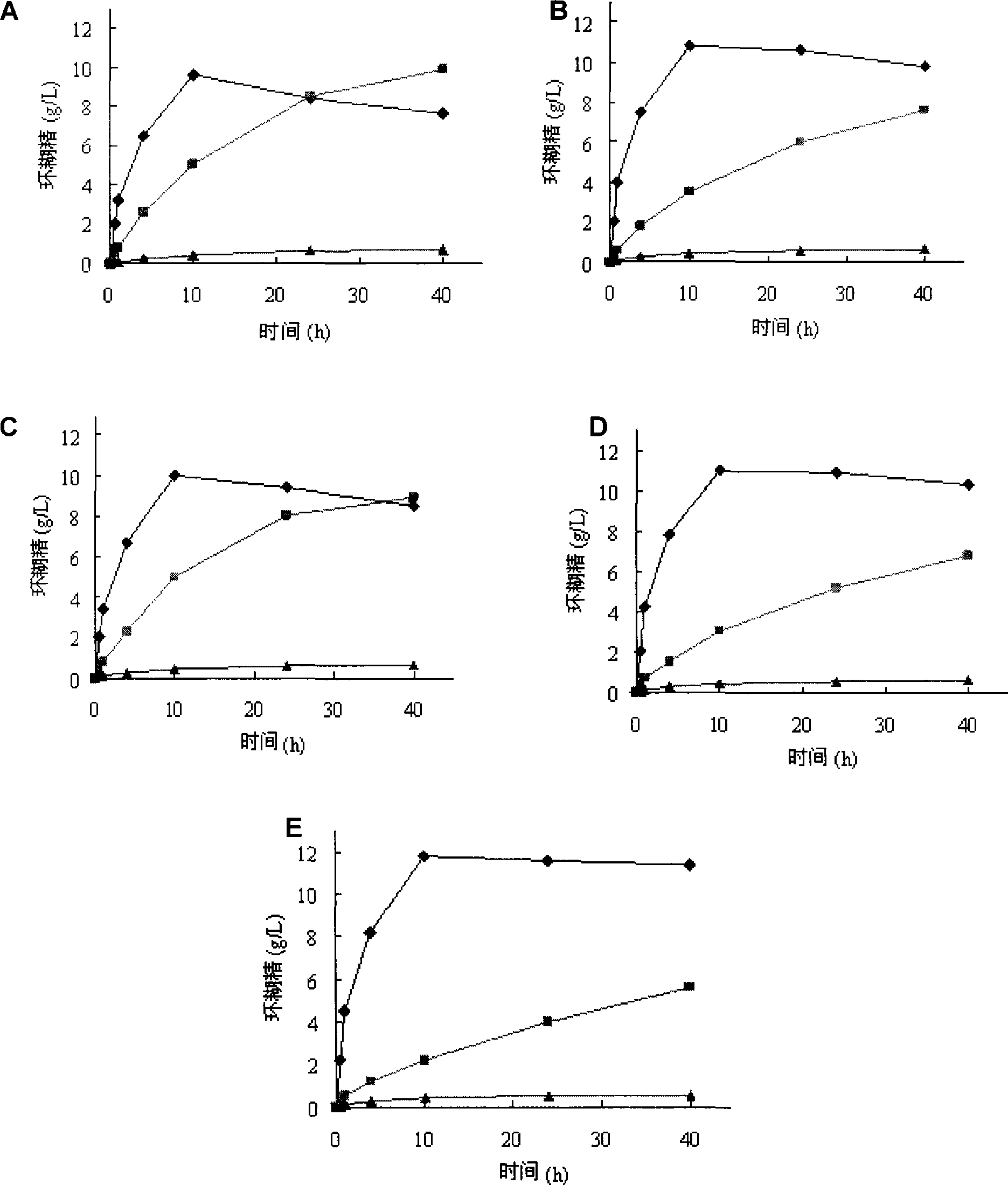
Mutant of cyclodextrin glucosyl transferase having highly alpha-cyclodextrin yielding property and mutation method
InactiveCN101503681AEase of industrial productionStrong specificityTransferasesMicroorganism based processesWild typeGene engineering
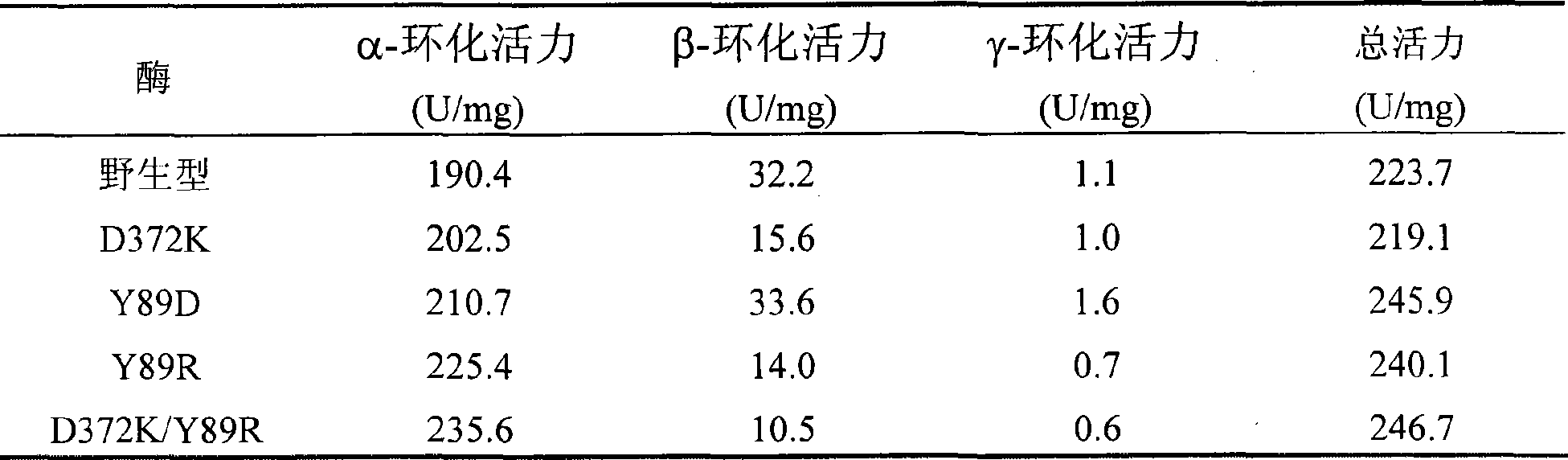
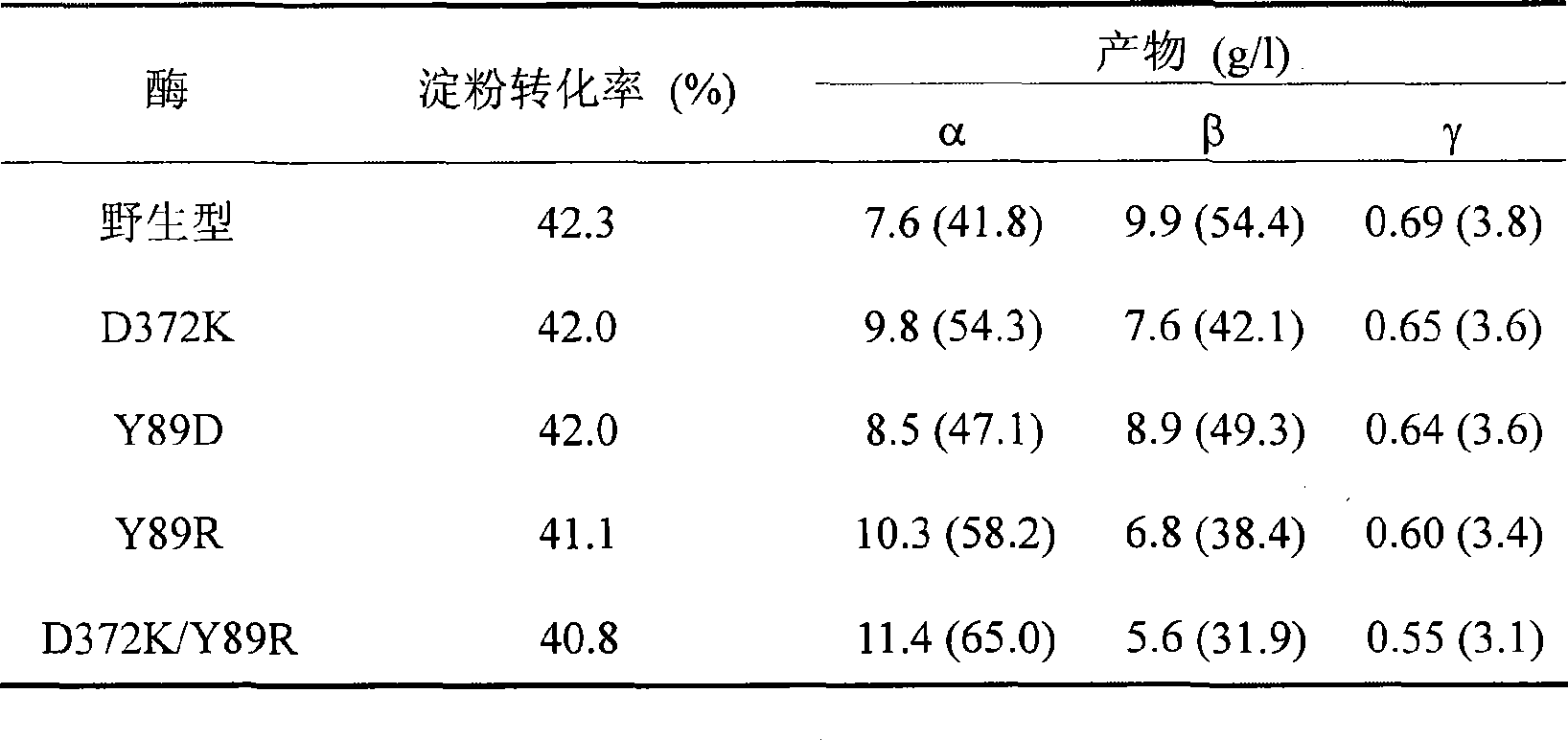
The invention relates to a mutant of a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with the capability of highly yielding alpha-cyclodextrin and a mutation method, which belong to the fields of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The invention improves the specificity of products of the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (CGT enzyme for short), provides a mutant proposal for improving the capability of CGT enzyme from Peanibacillus macerans JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO: M 208063) for producing the alpha-cyclodextrin, and substitutes Asp on the 372 position of the CGT enzyme for Lys, and Tyr on the 89 position as Asp and Arg to respectively obtain single mutant enzyme D372K, Y89D and Y89R; the alpha-cyclodextrin production capacity of the obtained mutant enzyme is improved compared with wild type CGT enzymes; genetic fragments of the CGT enzyme with Lys 372 are substituted by corresponding genetic fragments of Y89R so as to obtain double mutant enzyme D372K / Y89R; and the yield of the alpha-cyclodextrin of the ouble mutant enzyme D372K / Y89R is improved by 1.5 times compared with the wild type CGT enzyme, while the yield of the beta-cyclodextrin is reduced by 57 percent. The mutants are more favorable for industrial production of the beta-cyclodextrin than the wild type CGT enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
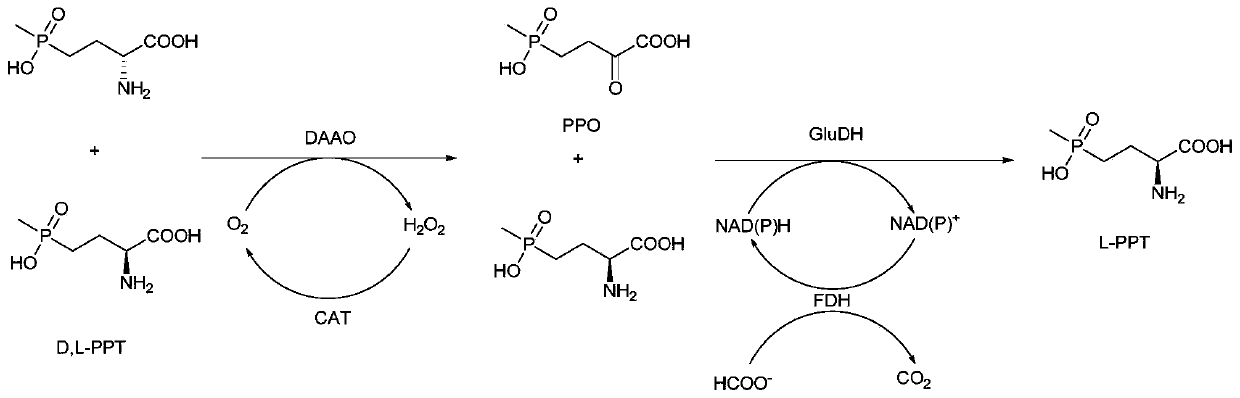
Method for preparing L-phosphinothricin through de-racemization by biological enzyme method, phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant and application
ActiveCN111363775AHigh catalytic efficiencyImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesAntibodiesAcid catalysisOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-phosphinothricin through de-racemization by a biological enzyme method, a phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant and an application. According to the method for preparing L-phosphinothricin through de-racemization by a biological enzyme method, D,L-phosphinothricin is used as a raw material, through catalysis with a multienzyme catalysis system, theL-phosphinothricin is obtained, wherein the enzyme catalysis system comprises D-amino acid oxidase which is used for catalyzing D-phosphinothricin in the D,L-phosphinothricin into 4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-2-oxobutanoic, and the phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant which is used for performing catalytic reduction on the 4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-2-oxobutanoic to obtain the L-phosphinothricin,the phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant is obtained through mutation of phosphinothricin dehydrogenase in wild mushrooms Thiopseudomonas denitrificans, and a mutation site is V377S. The phosphinothricin dehydrogenase mutant disclosed by the invention has better catalysis efficiency, when a catalytic reaction is performed by using racemation D,L-phosphinothricin as a substrate, the conversion rate is far higher than that of a catalytic reaction performed by using a wild type enzyme as a substrate, and the PPO yield is also substantially increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
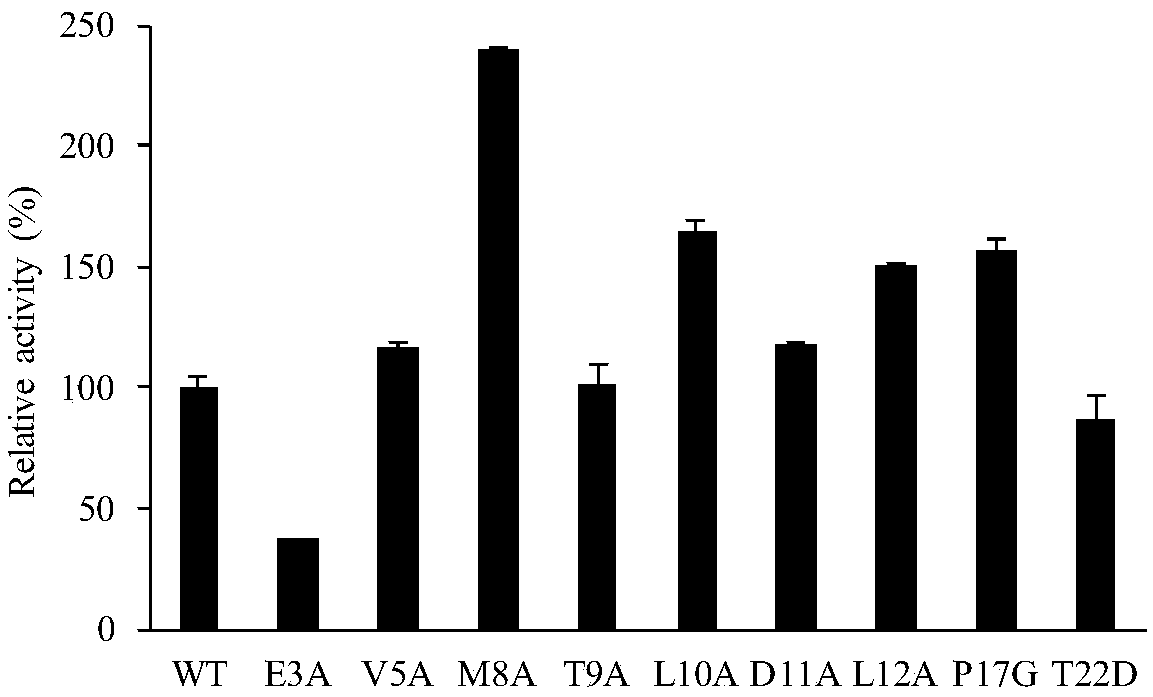
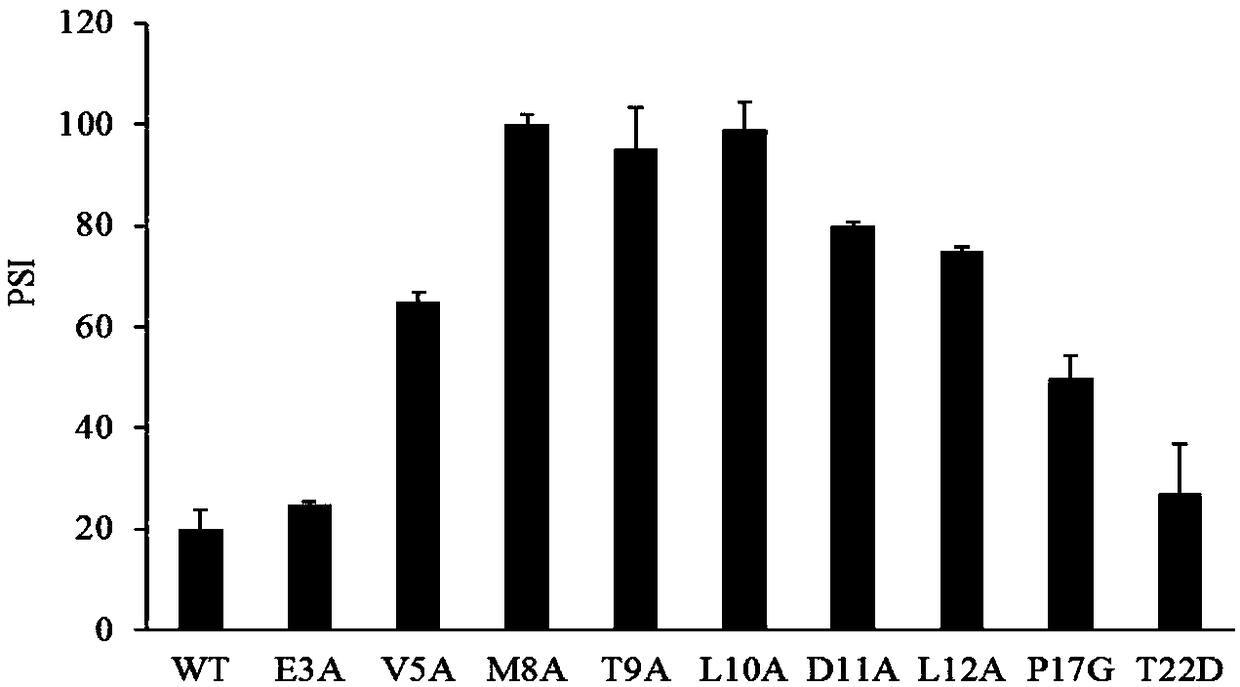
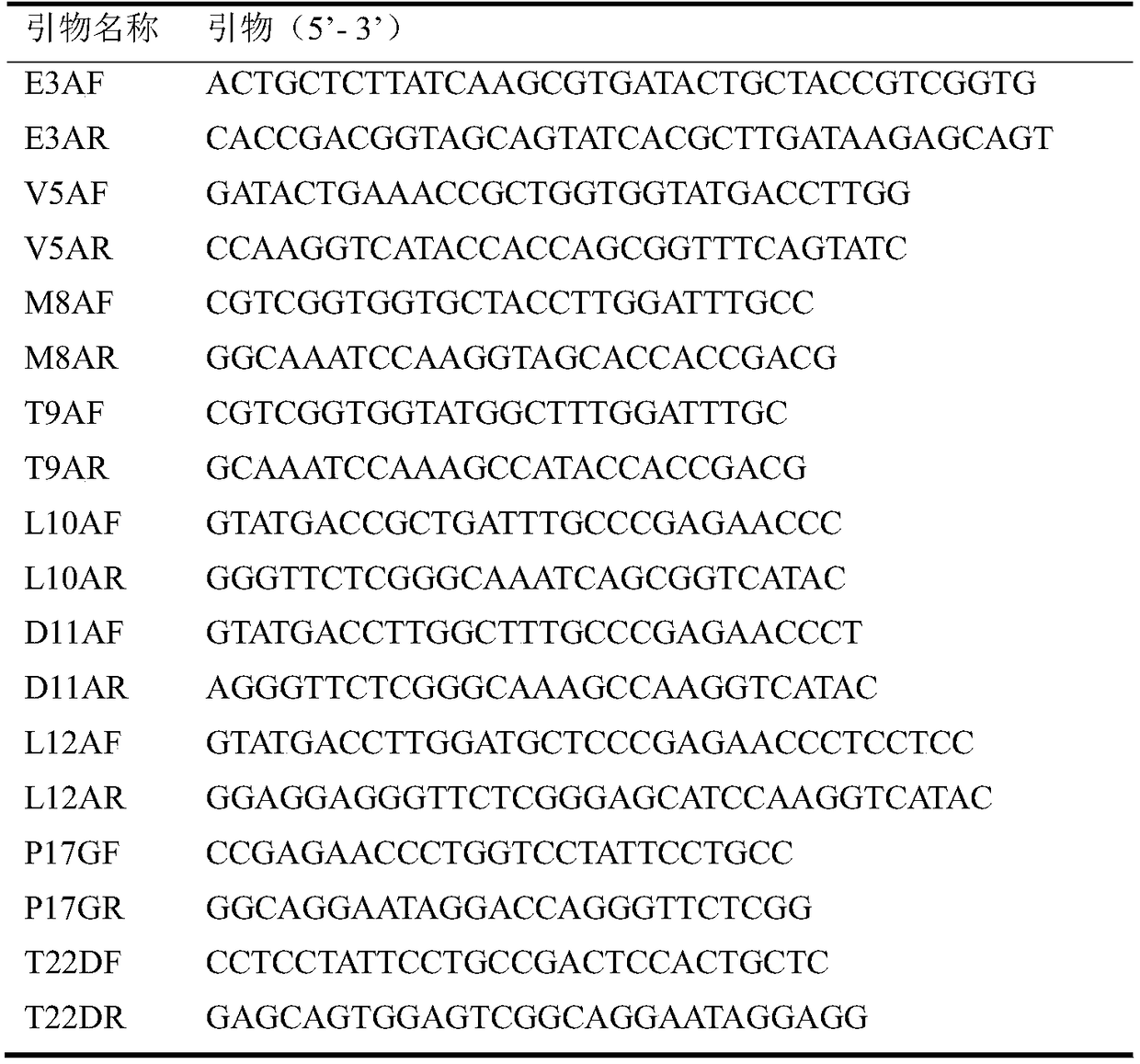
Lipase mutant with improved enzyme activity and regioselectivity and application of mutant
ActiveCN108642025AIncreased specific enzyme activityHydrolasesFermentationLipogenic enzymesRegioselectivity
The invention discloses a lipase mutant with improved enzyme activity and regioselectivity and application of the mutant and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to the lipasemutant, wild-type lipase is mutated, the enzyme activity of mutants M8A, L10A, D11A, L12A and P17G is increased by 1.1-2.4 times compared with the enzyme activity of wild-type lipase, and the 1,3-regioselectivity of the mutants M8A, L10A and T9A is increased by 4.75-5 times compared with the regioselectivity of wild-type lipase. The enzyme activity and regioselectivity are important parameters ofthe lipase mutant in structural lipid catalytic application. The lipase mutant is applied to a catalytic reaction of human milk fat substitutes and has an obvious effect.
Owner:无锡优普克生物科技有限公司
Phosphite dehydrogenase mutants for nicotinamide cofactor regeneration
InactiveUS7402419B2High catalytic efficiencyImprove thermal stabilitySugar derivativesBacteriaPhosphite dehydrogenaseWild type enzyme
Phosphite dehydrogenase mutant enzymes were generated that provide relaxed cofactor specificity and increased thermostability over the wild type enzyme. The mutant enzymes are useful for nicotinamide cofactor regeneration.
Owner:BIOTECH RES & DEV +1
Phosphite dehydrogenase mutants for nicotinamide cofactor regeneration
InactiveUS20050026250A1High catalytic efficiencyImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesWild type enzymeMutant enzyme
Phosphite dehydrogenase mutant enzymes were generated that provide relaxed cofactor specificity and increased thermostability over the wild type enzyme. The mutant enzymes are useful for nicotinamide cofactor regeneration.
Owner:BIOTECH RES & DEV +1
Modified carbonyl reducing enzyme and gene
An object of the present invention is to modify a wild-type enzyme that is less reactive in the presence of an organic solvent to provide altered carbonyl reductases having better reactivity in the presence of the organic solvent than the wild-type enzyme, and / or to provide transformants producing such reductases. The present inventors have found altered carbonyl reductases having better reactivity in the presence of an organic solvent than the wild-type enzyme, from among a mutant enzyme library prepared by randomly mutating the wild-type enzyme gene, thereby arriving at completion of the present invention.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Penicillin G acylase mutant
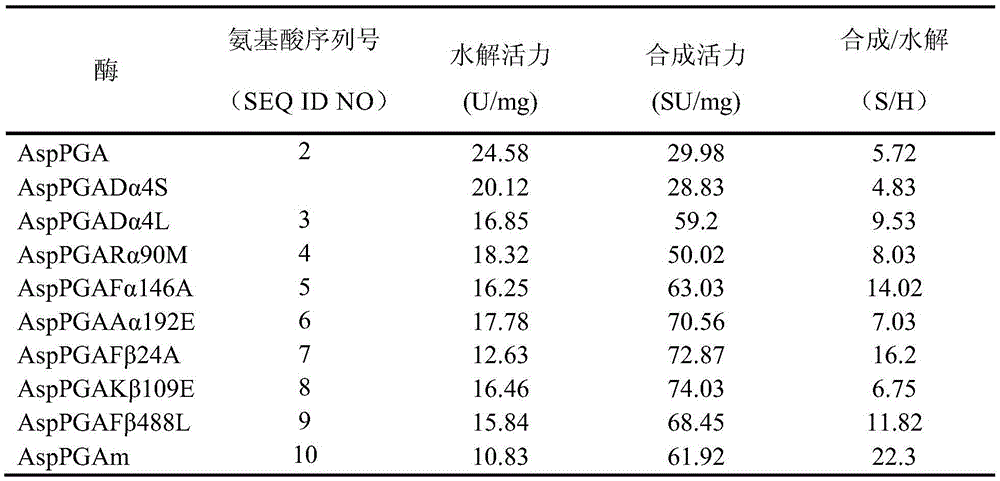
ActiveCN105483105AHigh catalytic efficiencyHydrolasesMicroorganismsBeta lactam antibioticHydrolysate
The invention relates to a penicillin G acylase mutant constructed by genetic engineering. In comparison with wild type penicillin G acylase from achromobacter (Achromobacter sp.CCM 4824), the synthesis performance of the penicillin G acylase mutant is improved substantially, the maximum synthetic product / hydrolysate value S / H reaches 22.3 and is 3.9 times that of wild type enzyme, and various beta-lactam antibiotics can be efficiently synthesized catalytically. When the ratio of side chains to mother nucleus is 1.05:1, the conversion rate of the mother nucleus 6-APA, 7-ADCA, 7-ACCA and 7-APRA reaches 99.0% or above, and the penicillin G acylase mutant has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:山西双雁生物科技有限公司
Polydatin bioconversion method using heat-resisting beta-glucosidase and mutants thereof
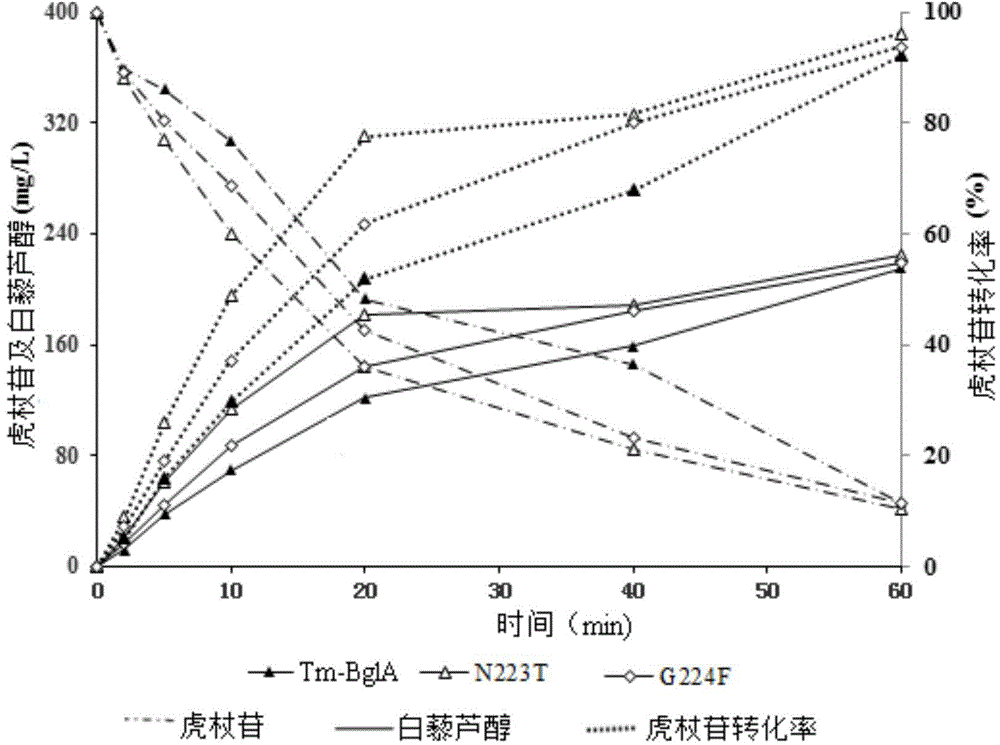
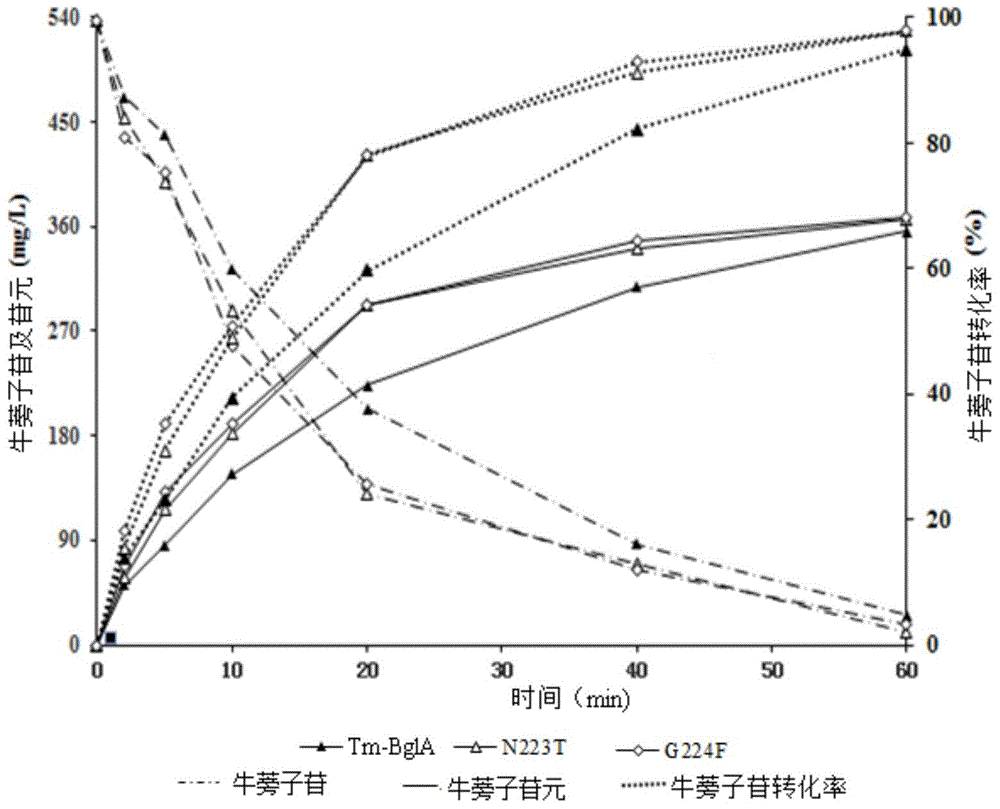
InactiveCN104818262AImprove conversion efficiencyHigh activityFermentationGlycosylasesAlgluceraseDrug biotransformation
The invention discloses application of heat-resisting beta-glucosidase mutants N223T, G224F and N223T / G224F in a conversion of polydatin to resveratrol. According to the heat-resisting beta- glucosidase mutants N223T, G224F and N223T / G224F, the amino acid sequences thereof are represented as SEQ: ID NO. 1, ID NO. 2 and ID NO. 3. By the use of the heat-resisting beta- glucosidase and the mutants thereof to hydrolyze the polydatin for preparing the resveratrol, comparing to the use of wild-type enzymes, the conversion efficiency is high, the reaction byproducts are fewer, the yield and purity are high, the separation and purification are easy, and chemical pollution is less.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant, gene, vector, engineering bacterium and application of recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant
ActiveCN107058251AHigh activityIncreased substrate toleranceBacteriaOxidoreductasesWild type enzymeEnzyme
The invention discloses a recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant, a gene, a vector, an engineering bacterium and application of the recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant. The mutant is obtained by performing single-point mutation on the 95th locus, the 144th locus or the 156th locus of an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant has reduced (S)-6-chloro-5-hydroxy-3-oxohexanoate, and compared with a wild type enzyme, has the advantages that the catalytic activity and the substrate tolerance are greatly improved when such reaction is converted, and the time consumption of a reaction process is obviously reduced. Compared with a chemical method for preparing (3R,5S)-6-chloro-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoate, such a technology has the advantages that an obtained product is high in stereoselectivity, a tedious chemical catalysis step is simplified, the reaction condition is milder, the requirement on equipment is low, the reaction cost is reduced, and the technology is environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
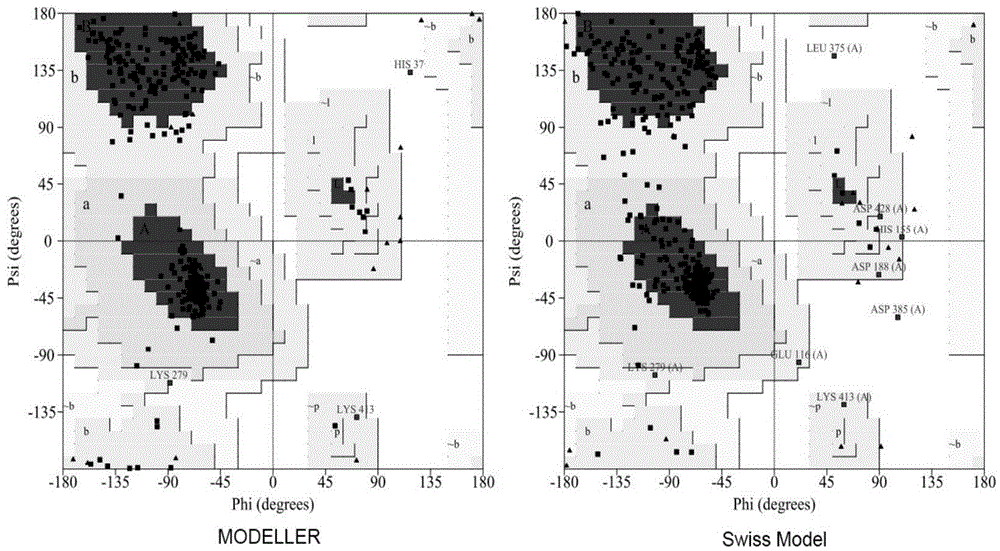
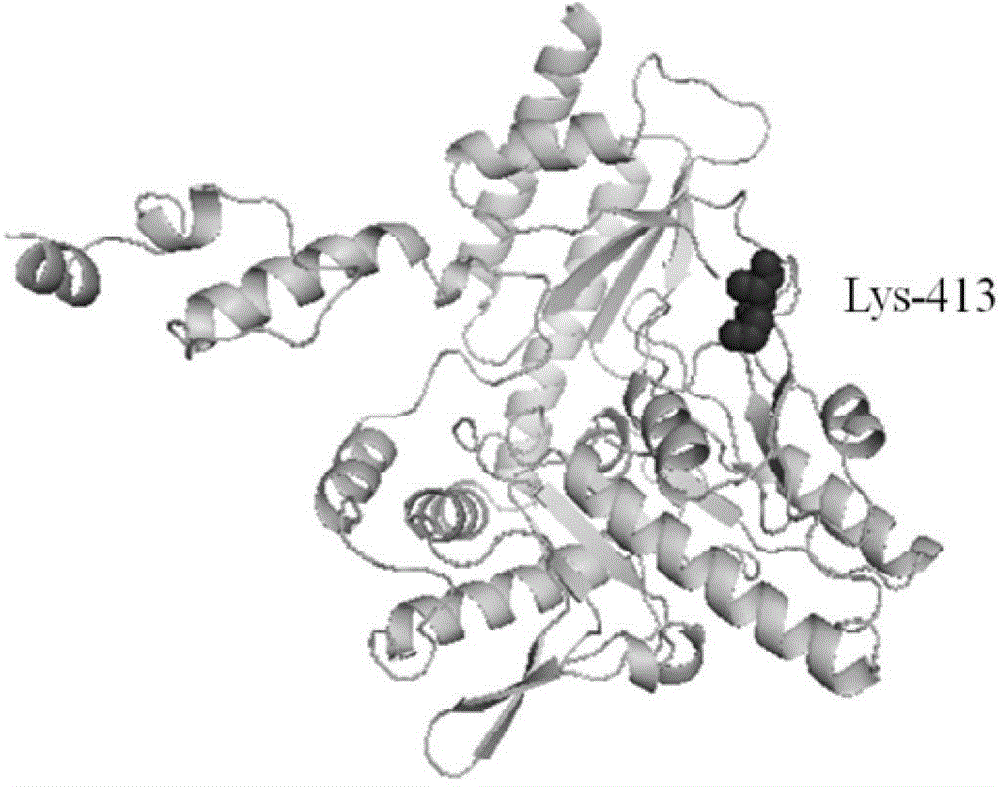
Method for preparing glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant by utilizing ramachandran map information and mutant thereof
InactiveCN104694524AIncrease reaction rateEase of industrial productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention discloses a method for preparing a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant by utilizing ramachandran map information and a mutant thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a three-dimensional structural model of glutamic acid decarboxylase, carrying out dihedral angle reasonable evaluation to generate a ramachandran map, and determining an amino acid residue site in an unreasonable conformation area from the ramachandran map; designing a site-specific mutation primer aiming at the site, and carrying out site-specific PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by taking a glutamic acid decarboxylase gene as a template so as to obtain a site-specific mutation library; and screening the glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant from the site-specific mutation library. Enzyme is rationally designed through structural information provided by the ramachandran map; in combination with a site-specific mutation technology, the mutation probability is effectively increased; the time is saved; the experimental efficiency is increased; mutant enzyme the catalytic activity of which is superior to wild type enzyme can be obtained by screening; the mutant enzyme is capable of increasing the reaction rate for generating gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by catalyzing L-glutamic acid or sodium salts thereof; and thus, industrial production of GABA is easily carried out.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Heat-resisting beta-glucosidase and application of heat-resisting beta-glucosidase mutants to arctigenin preparation
InactiveCN104818261AHigh activityImprove conversion efficiencyFermentationGlycosylasesAlgluceraseTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses an application of heat-resisting beta-glucosidase mutants N223T, G224F and N223T / G224F to transforming arctiin into arctigenin. Amino acid sequences of the heat-resisting beta-glucosidase mutants N223T, G224F and N223T / G224F are indicated in SEQ: ID NO.1, ID NO.2 and ID NO.3. The arctiin is hydrolyzed to prepare the arctigenin by the aid of heat-resisting beta-glucosidase and the mutants thereof, and as compared with wild-type enzyme, the heat-resisting beta-glucosidase has the advantages of high transformation efficiency, fewer reaction by-products, high yield and purity, easiness in separation and purification, less chemical pollution and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase
InactiveUS7037698B2Reduced responseIncreased substrate specificityFungiSugar derivativesAmino acid compositionAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
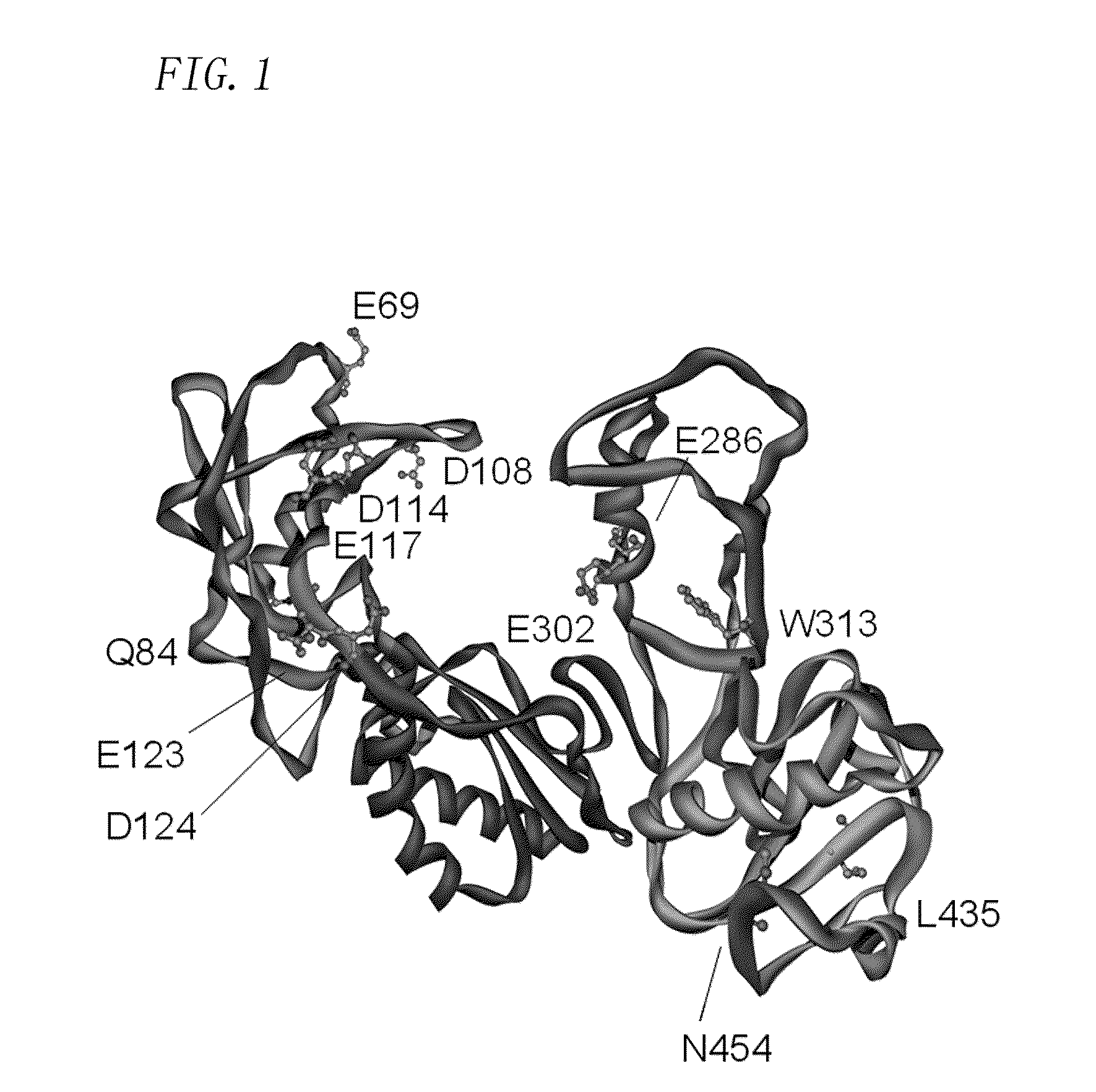
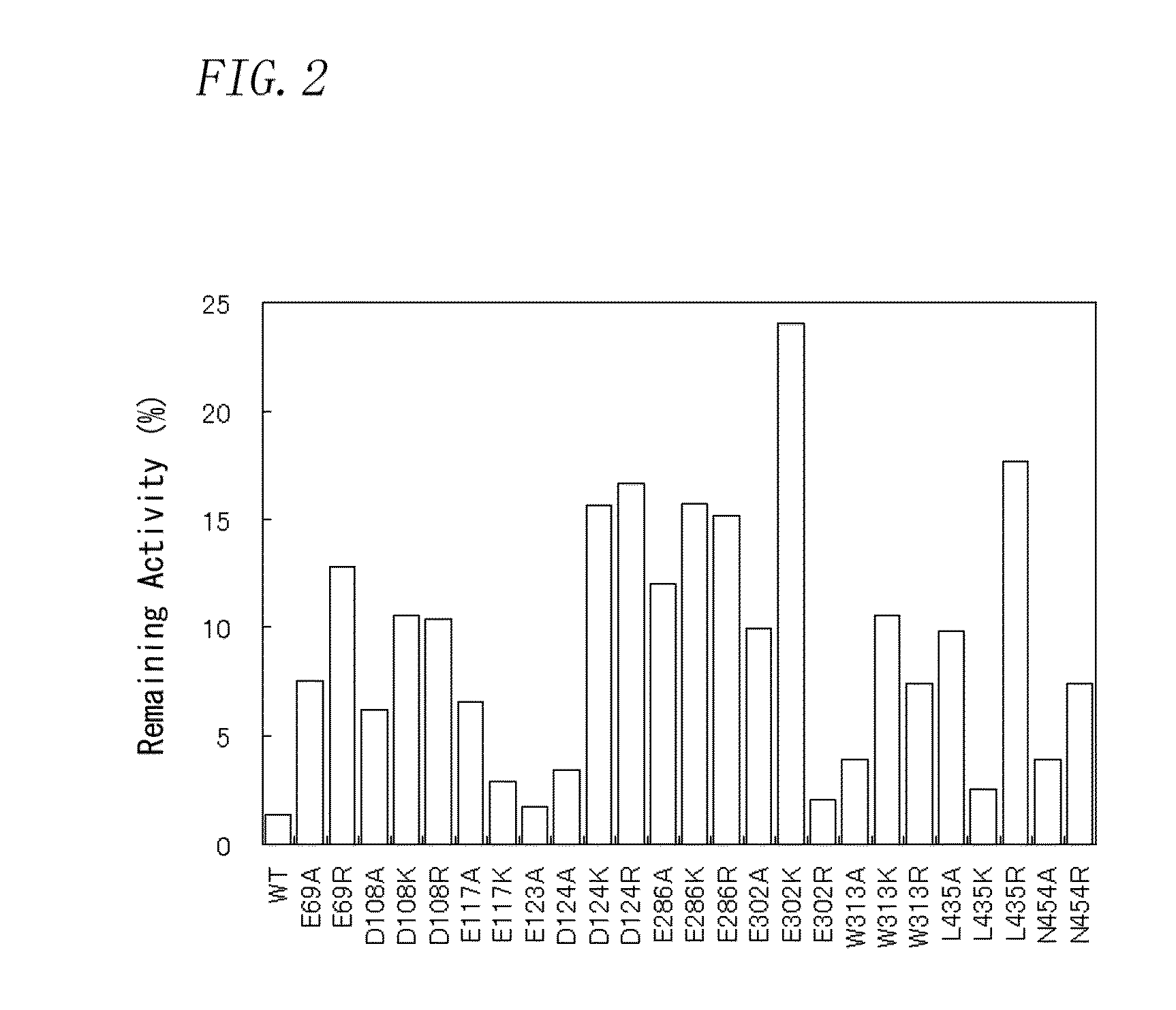
A modified pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase having a low reactivity with respect to maltose, galactose, etc. is provided. A modified pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase including an amino acid sequence in which one or more amino acids in a region corresponding to a first region consisting of amino acids at positions 326 to 354 in pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase derived from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus are substituted as compared with an amino acid sequence of the corresponding wild-type enzyme.
Owner:AMANO ENZYME INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com