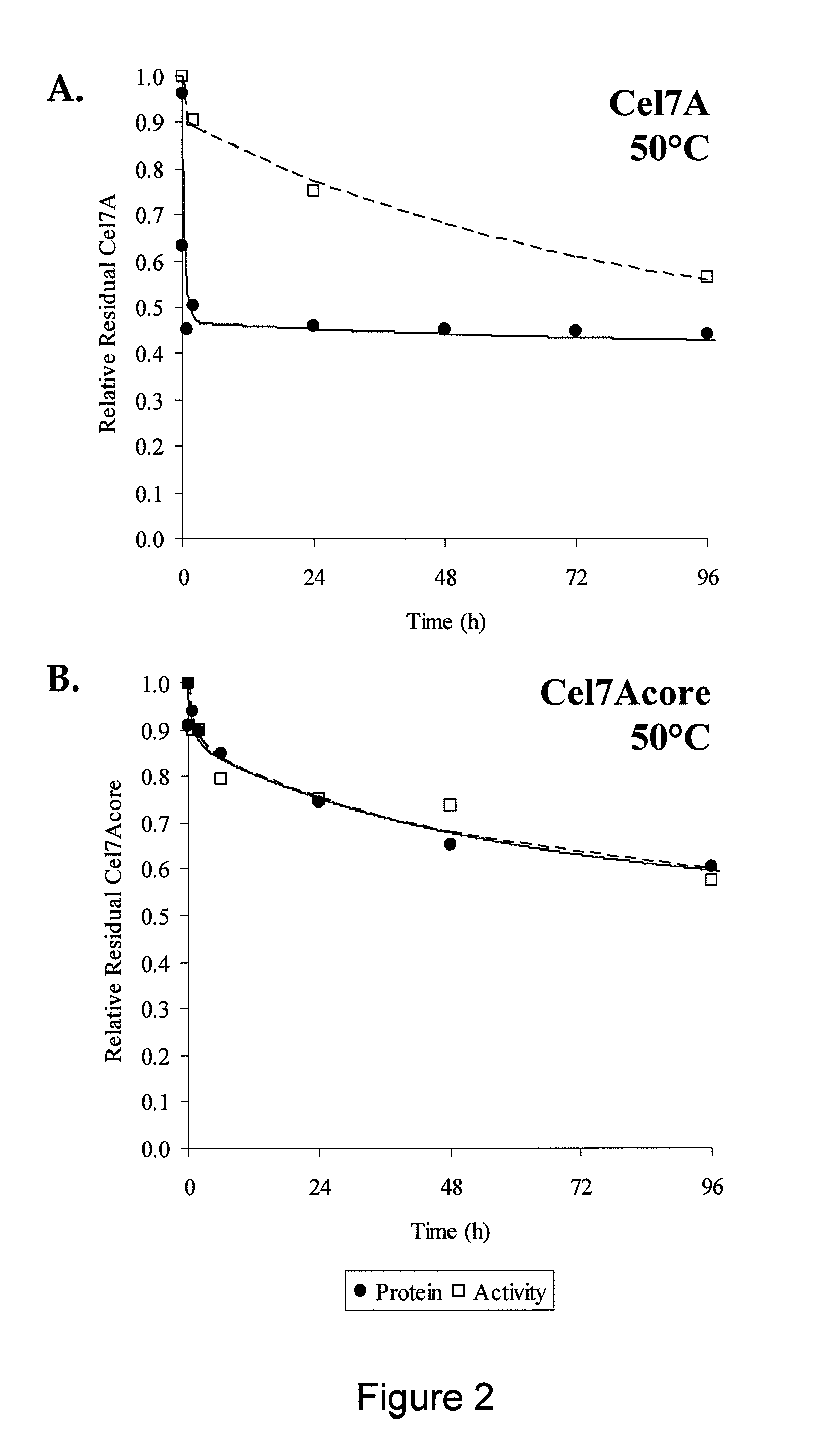
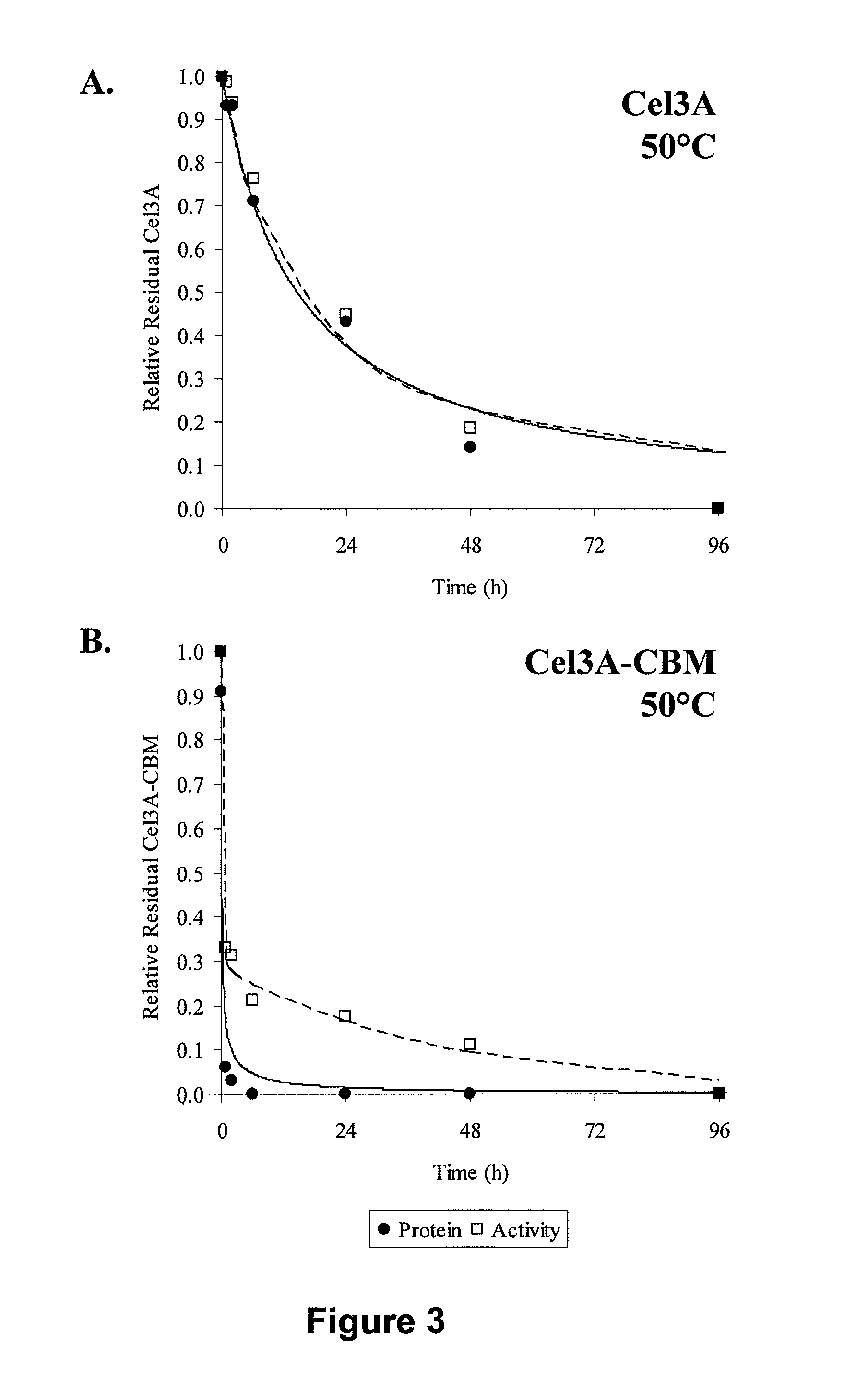
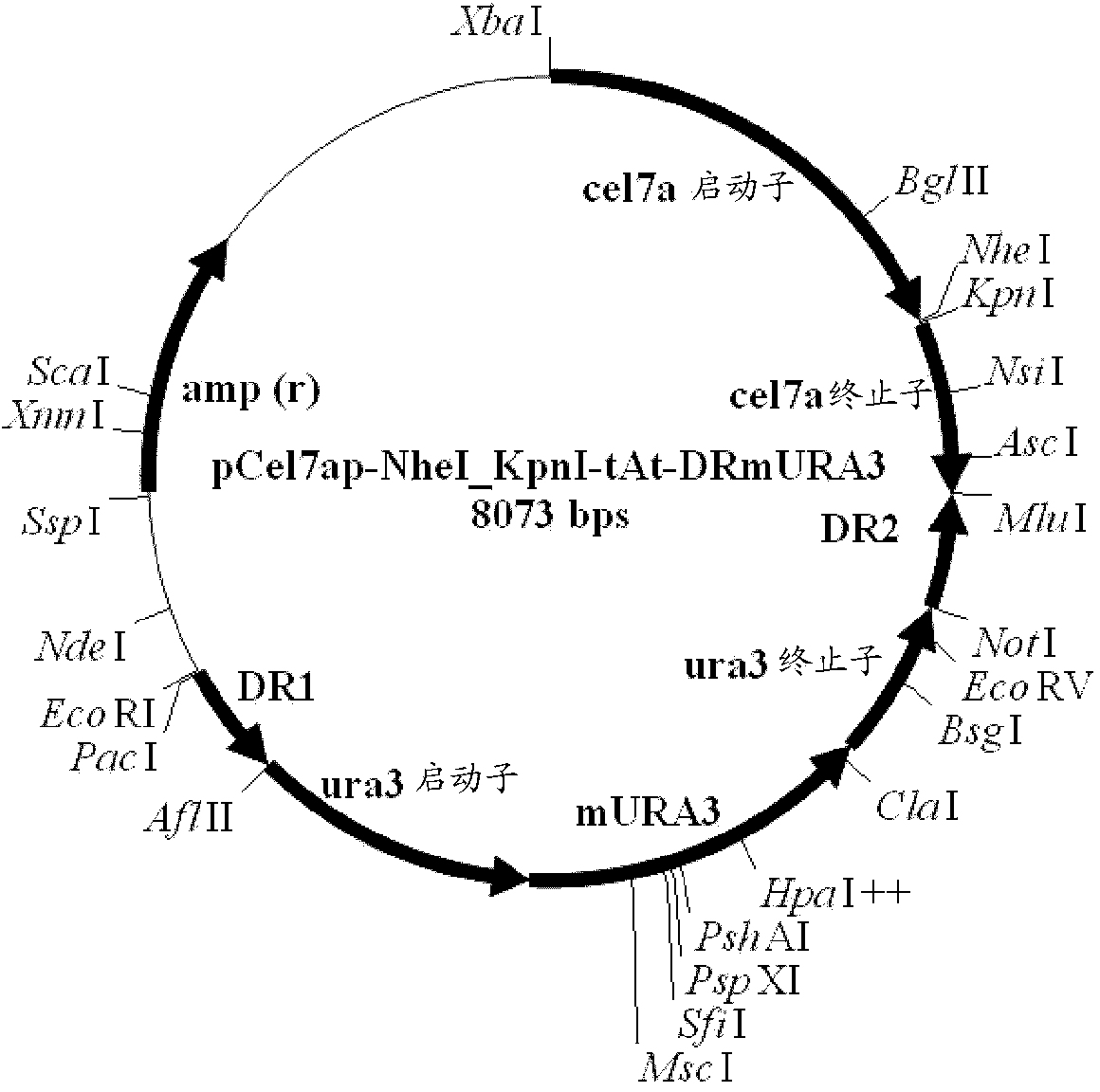
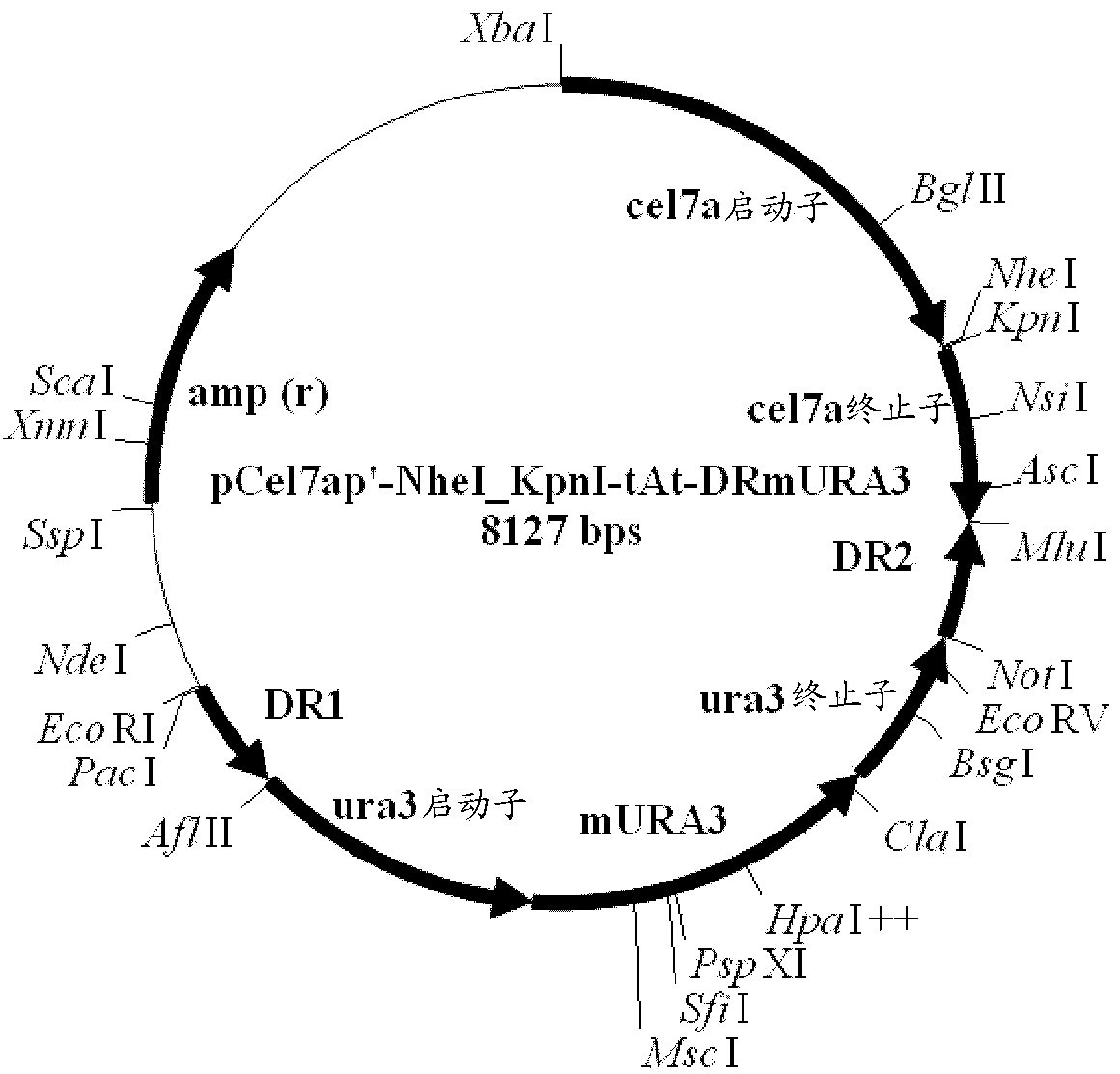
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Carbohydrate-binding protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
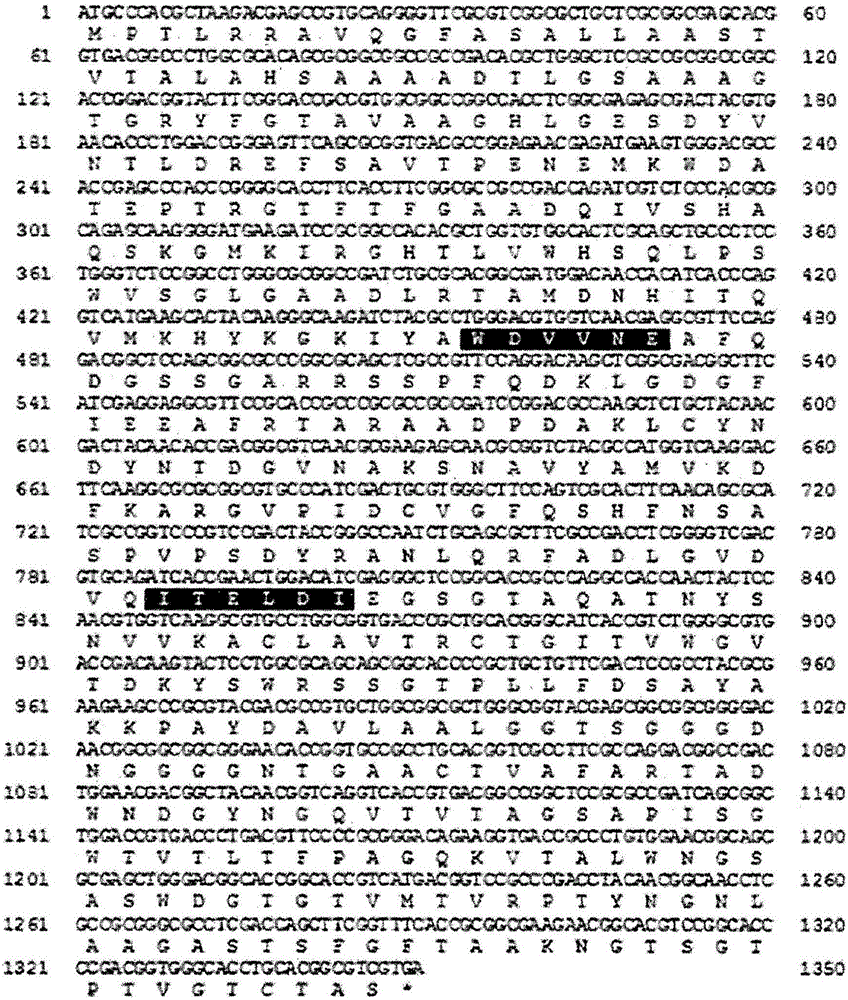
Carbohydrate-binding module family 10 (CBM10) is found in two distinct sets of proteins with different functions. Those found in aerobic bacteria bind cellulose (or other carbohydrates); but in anaerobic fungi they are protein binding domains, referred to as dockerin domains.
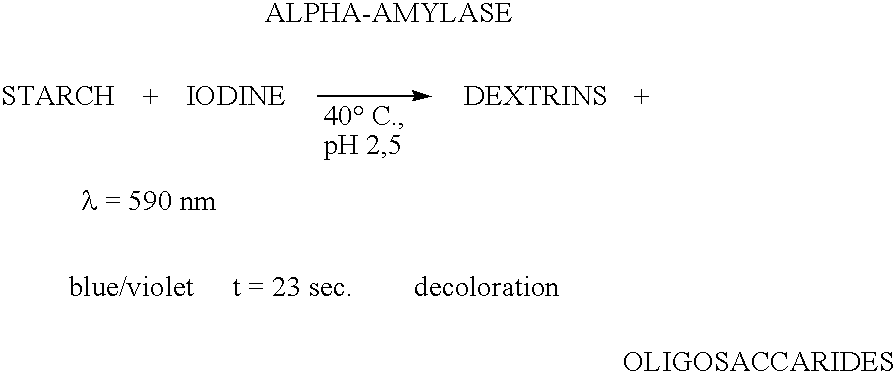
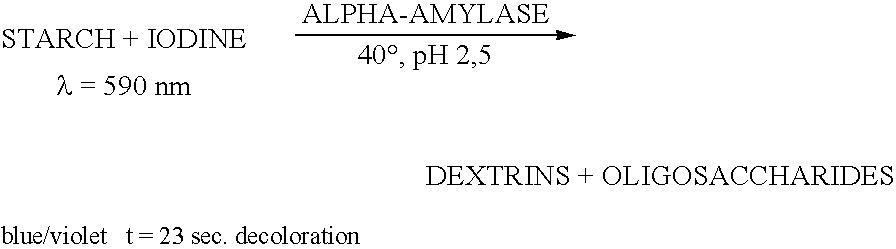
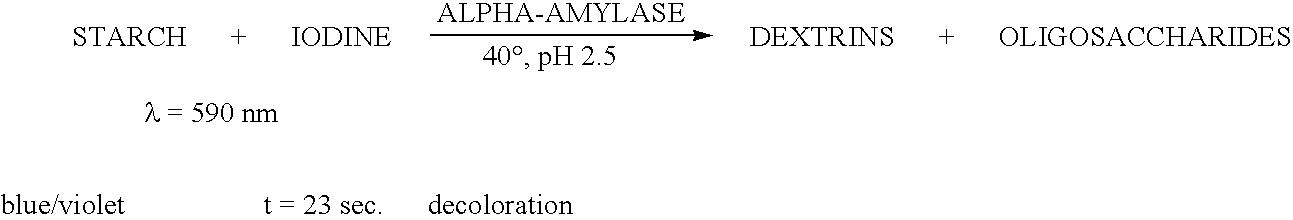
Enzymes for starch processing
InactiveUS20050054071A1Increased acid alpha-amylase activityImprove enzyme stabilitySugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyCarbohydrate-binding protein
The present invention relates to a hybrid enzyme comprising carbohydrate-binding module amino acid sequence and a fungal alpha-amylase amino acid sequence and to a variant of a fungal wild type enzyme comprising a carbohydrate-binding module and an alpha-amylase catalytic module. The invention also relates to the use of the hybrid enzyme or the variant in starch liquefaction.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Enzymes for starch processing
InactiveUS20060148054A1Good curative effectActivity be alteredFungiSugar derivativesCarbohydrate-binding proteinAlpha-amylase
The present invention relates to polypeptides comprising a carbohydrate-binding module amino acid sequence and,an alpha-amylase amino acid sequence as well as to the application of such polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Hybrid enzymes
The present invention relates to a hybrid enzyme comprising at least one carbohydrate-binding module amino acid sequence and at least the catalytic module of a glucoamylase amino acid sequence. The invention also relates to the use of the hybrid enzyme in starch processing and especially ethanol production.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Hybrid enzymes
InactiveUS20060257984A1FungiAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCarbohydrate-binding proteinCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to a hybrid enzyme comprising at least one carbohydrate-binding module amino acid sequence and at least the catalytic module of a glucoamylase amino acid sequence. The invention also relates to the use of the hybrid enzyme in starch processing and especially ethanol production.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Stabilized bioactive peptides and methods of identification, synthesis and use
Owner:PEPTIDE BIOSCI
Enzymes for starch processing
ActiveUS20140127753A1Good curative effectActivity be alteredAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPolypeptide with affinity tagCarbohydrate-binding proteinAlpha-amylase
The present invention relates to polypeptides comprising a carbohydrate-binding module amino acid sequence and an alpha-amylase amino acid sequence as well as to the application of such polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
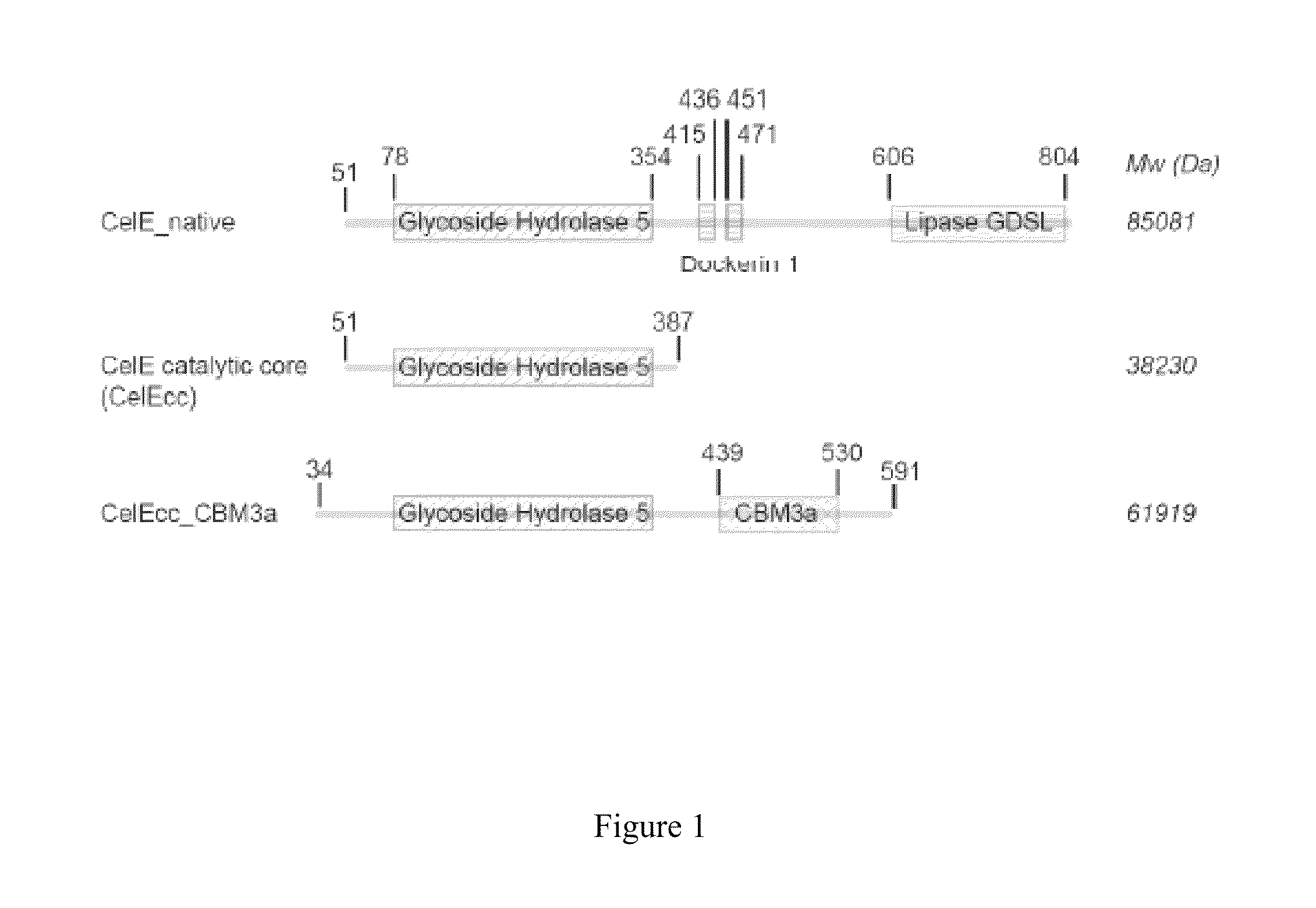
Method and DNA constructs for increasing the production level of carbohydrate degrading enzymes in filamentous fungi
ActiveUS20060014247A1Increase production levelsEasy constructionFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyFungal microorganisms
The invention is related to a method and DNA constructs for obtaining in a filamentous fungus host a higher production level of a carbohydrate degrading (CD) enzyme, having in its original state a catalytic module (CAT) and a carbohydrate binding module (CBM) separated by a linker region. The DNA construct comprising a truncated actinomycetes, preferably Nonomuraea flexuosa (NJ) derived DNA sequence encoding a truncated form of the CD enzyme, for example Nf Xyn11A, Nf Xyn10A, and is introduced into a filamentous fungal host. Said CD enzyme contains the catalytically active region of CAT but lacks part or all of the CBM, or all of the CBM and part or all of the linker region and is expressed and secreted under the control of regulatory sequences comprising at least a signal sequence, but also promoters, terminators and DNA sequences encoding a secretable carrier protein or domains thereof, preferably originating from filamentous fungi are included. The production level obtained with DNA sequence having the shortened DNA sequence encoding the truncated form of the CD enzyme is higher than the production level obtained with DNA construct encoding the corresponding full length CD enzyme.
Owner:AB ENZYMES OY
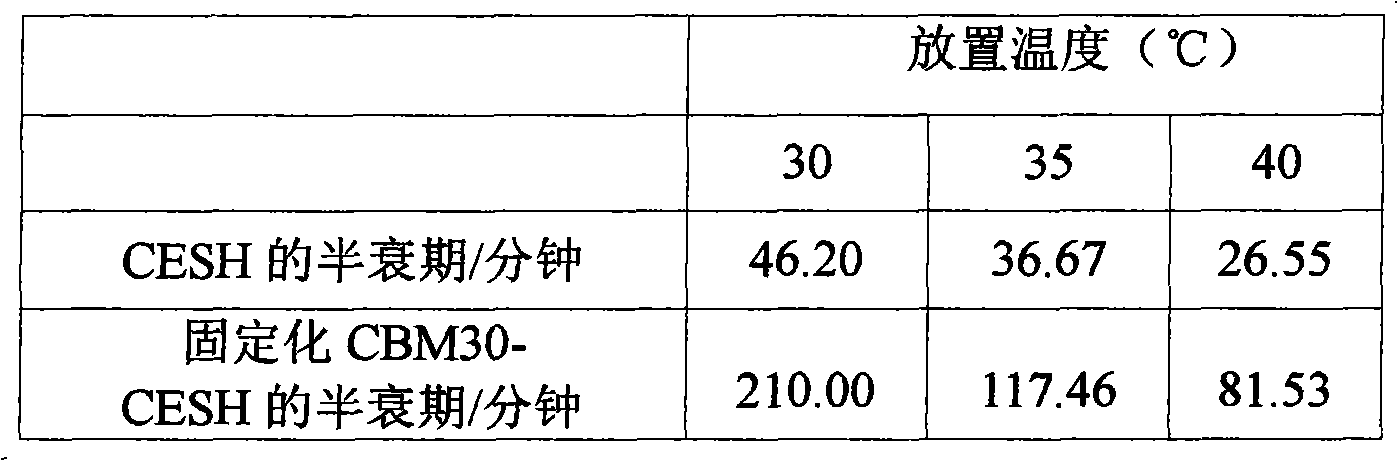
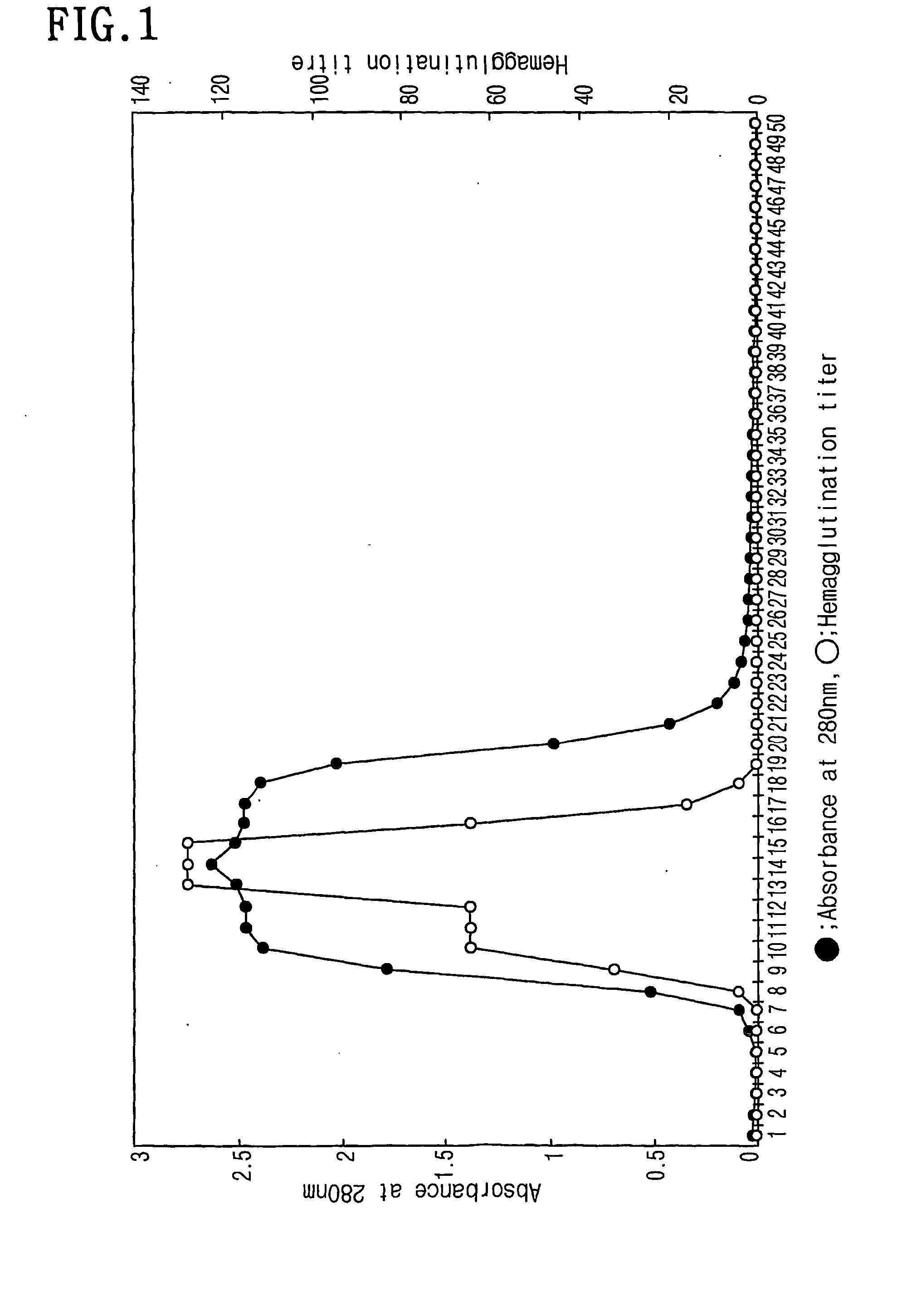
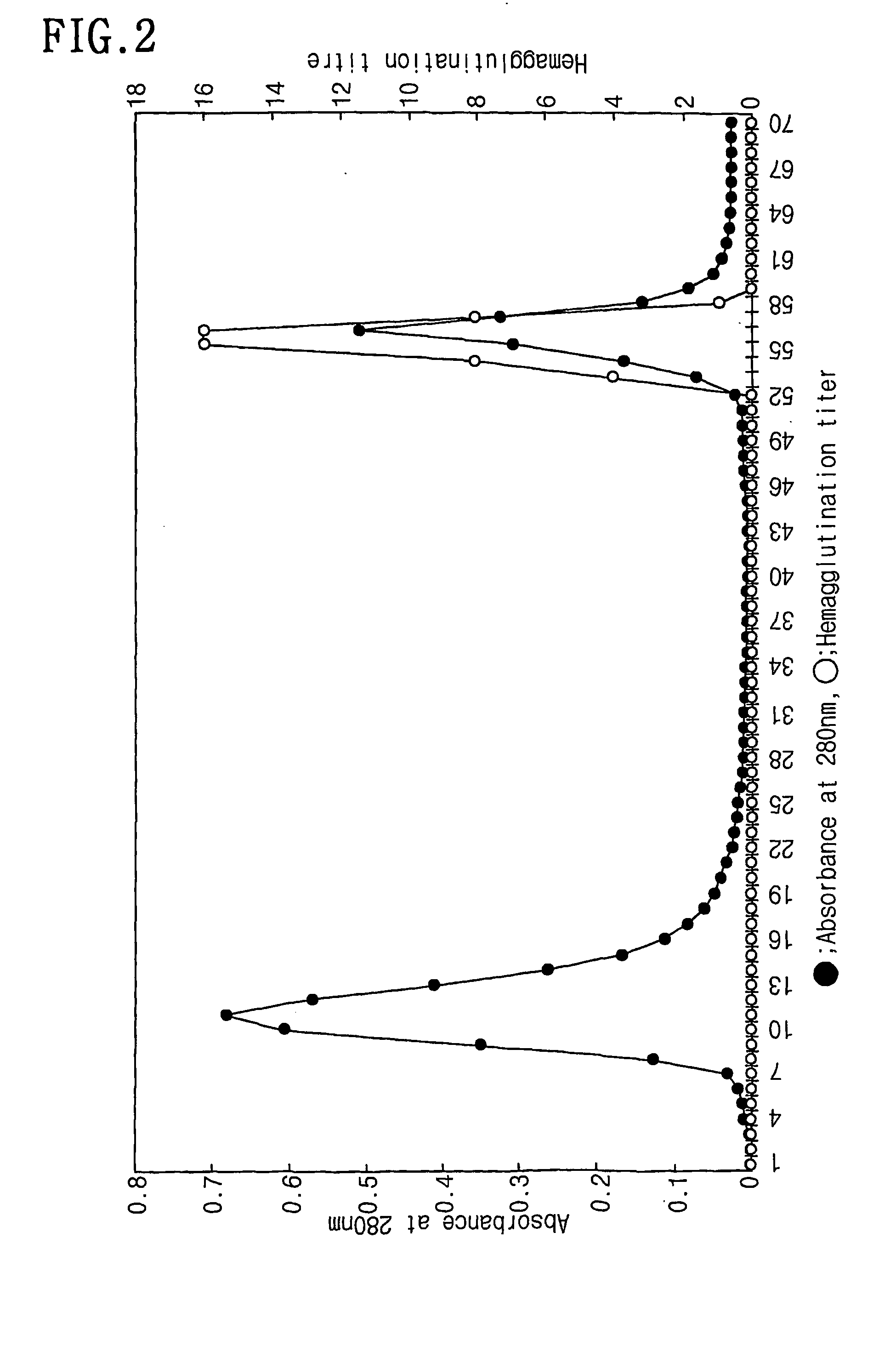
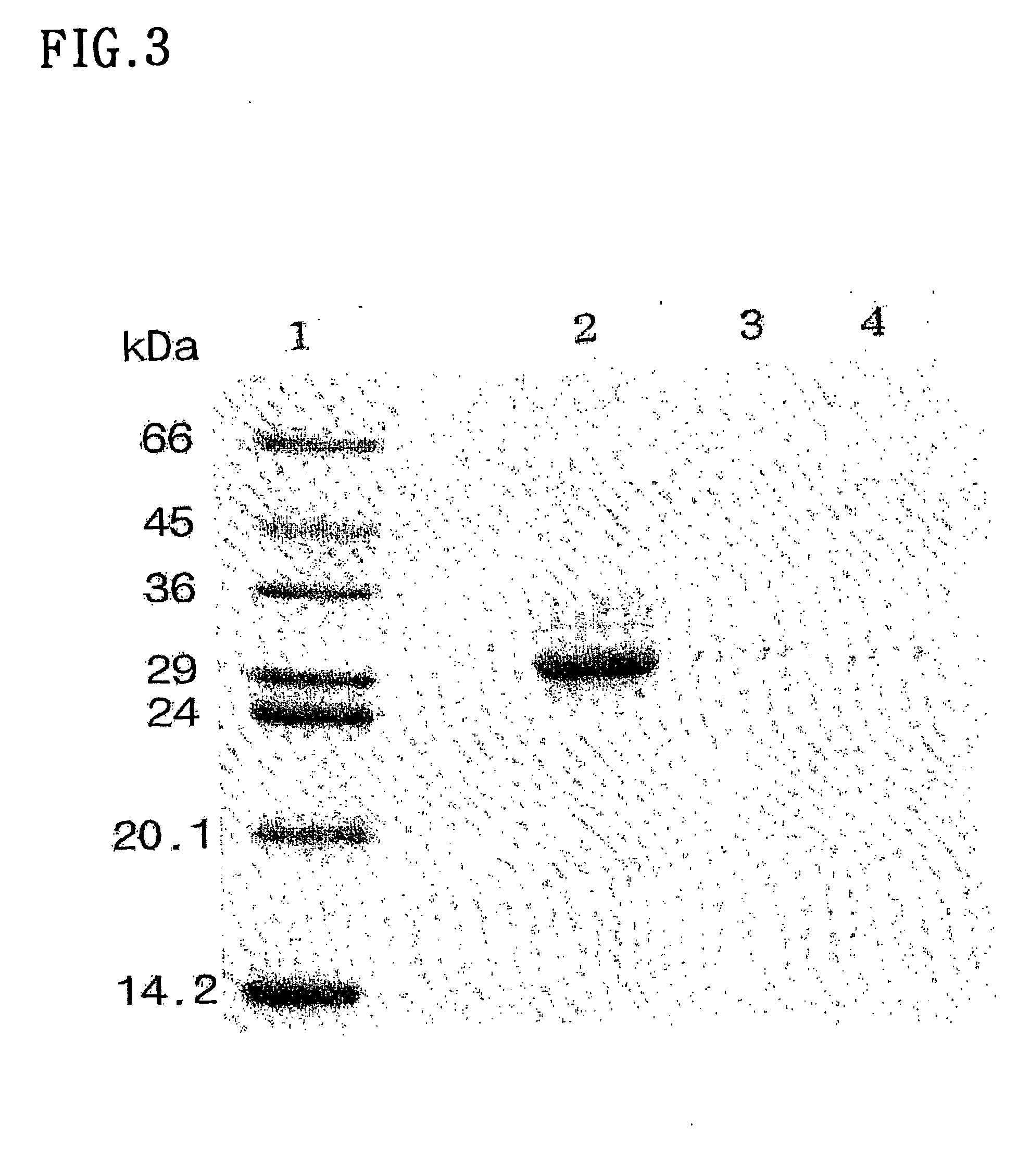
Cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase and method for preparing tartaric acid
InactiveCN102703419ALow priceWide variety of sourcesOn/in organic carrierFermentationCelluloseEscherichia coli
The invention provides a method of cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase. The method comprises the following steps: fusing gene coding cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase and carbohydrate binding module CMB30, efficiently expressing the fused gene in Escherichia coli, and then carrying out purification and immobilization on fused enzyme in crude enzyme liquid by adopting the cellulose. The invention also provides a method for catalyzing and hydrolyzing epoxy succinic acid to convert into L-tartaric acid or D-tartaric acid by adopting the cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase as biocatalyst. The method has the beneficial effects that: not only is the stability of enzyme obviously improved, but also the cellulose used as purified and fixed substrate is low in price and easy to get by adopting the cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase, and has excellent economic prospect. The method for preparing tartaric acid by adopting the cellulose immobilized cis epoxy succinic acid hydrolase has the advantages of reaction specificity, high product purity, high reaction efficiency and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Lectin protein prepared from maackia fauriei, process for preparing the same and the use thereof
InactiveUS20050084903A1Return to normal activitiesSaccharide peptide ingredientsDepsipeptidesMelanomaCancer cell
The present invention relates to a lectin protein, designated MFA isolated and purified from the bark of the Korean legume Maackia fauriei, process for preparing the same and the use thereof. This protein can be used as reagents in the study of carbohydrate binding proteins as well as to examine the distribution of N-acetylneuraminic acid in cancer cells owing to its capability that specifically recognizes N-acetylneuraminic acid which plays important structural and functional roles in the expressions of various cells or oligosaccharide terminal residue of glycoconjugates, and, in addition, used as an anti-cancer drug in view of its anti-proliferation effect against various cancers such as breast cancer, melanoma, hepatoma, etc.
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Lectin protein prepared from Maackia fauriei, process for preparing the same and the use thereof
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Biosynthesis method for obtaining high-purity and high-efficiency microcystins (MCs) degrading enzyme (MlrA)
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method for obtaining a high-purity and high-efficiency microcystins (MCs) degrading enzyme (MlrA), belonging to the field of biotechnology application or environmental protection. The method comprises the following steps: constructing the sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1 on pMAL-C2X to obtain pMAL-MlrA; transferring pMAL-MlrA to escherichia coli TB1 to obtain an expression bacterium of MlrA; carrying out induced expression on the expression bacterium of MlrA with isopropyl beta-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), collecting thalli after induced expression, crushing and purifying by using a maltose-binding protein (MBP) tag, thus obtaining the high-purity and high-efficiency MlrA. By optimizing an expression vector and expression conditions, the purity of the obtained MBP-MlrA is above 90% and the purity of MlrA after cutting off the MBP tag can be above 98%. The obtained MlrA has wide range of degradation and high degradation efficiency.
Owner:湖北华大瑞尔科技有限公司
Method for continuously detecting glucose concentration in sample, kit thereof and method for using biosensor
ActiveUS20100304399A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHigh concentrationCarbohydrate-binding protein
The invention provides a method for continuously detecting glucose concentration in a sample, including: (a) providing a biosensor comprising a transducer and a polysaccharide covered on the surface of the transducer; (b) providing a carbohydrate binding protein solution, wherein the carbohydrate binding protein has at least one receptor, and the receptor is capable of binding to the polysaccharide and glucose; (c) mixing a sample and the carbohydrate binding protein solution to form a mixture; (d) contacting the mixture with the biosensor; (e) detecting the amount of carbohydrate binding proteins bound to the polysaccharide by the biosensor, wherein glucose concentration of the sample is inversely proportional to the amount of carbohydrate binding proteins bound to the polysaccharide; and (f) refreshing the surface of the biosensor with a high concentration glucose solution.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Enzymes for starch processing
ActiveUS8841091B2Good curative effectActivity be alteredSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCarbohydrate-binding proteinAlpha-amylase
The present invention relates to polypeptides comprising a carbohydrate-binding module amino acid sequence and an alpha-amylase amino acid sequence as well as to the application of such polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
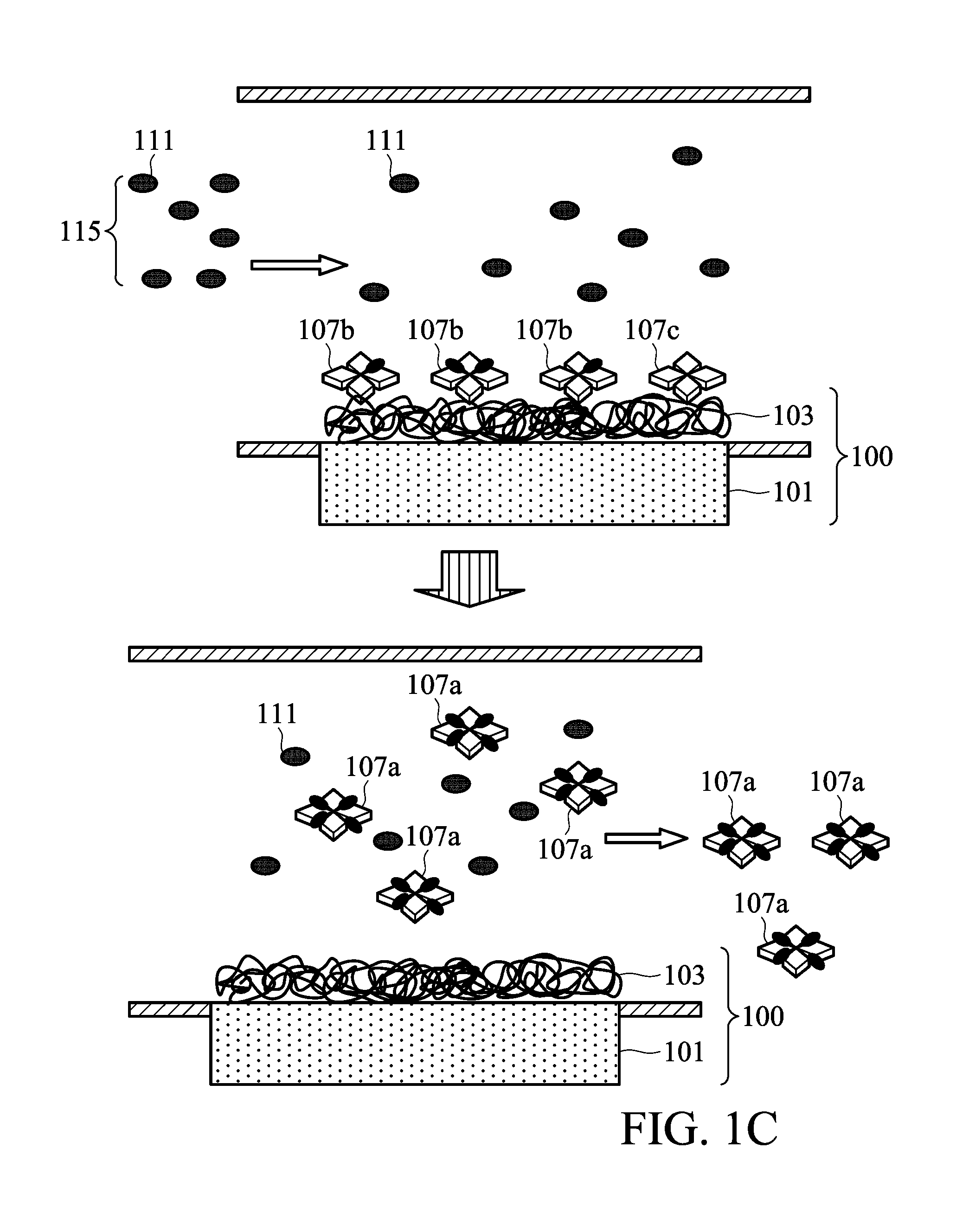
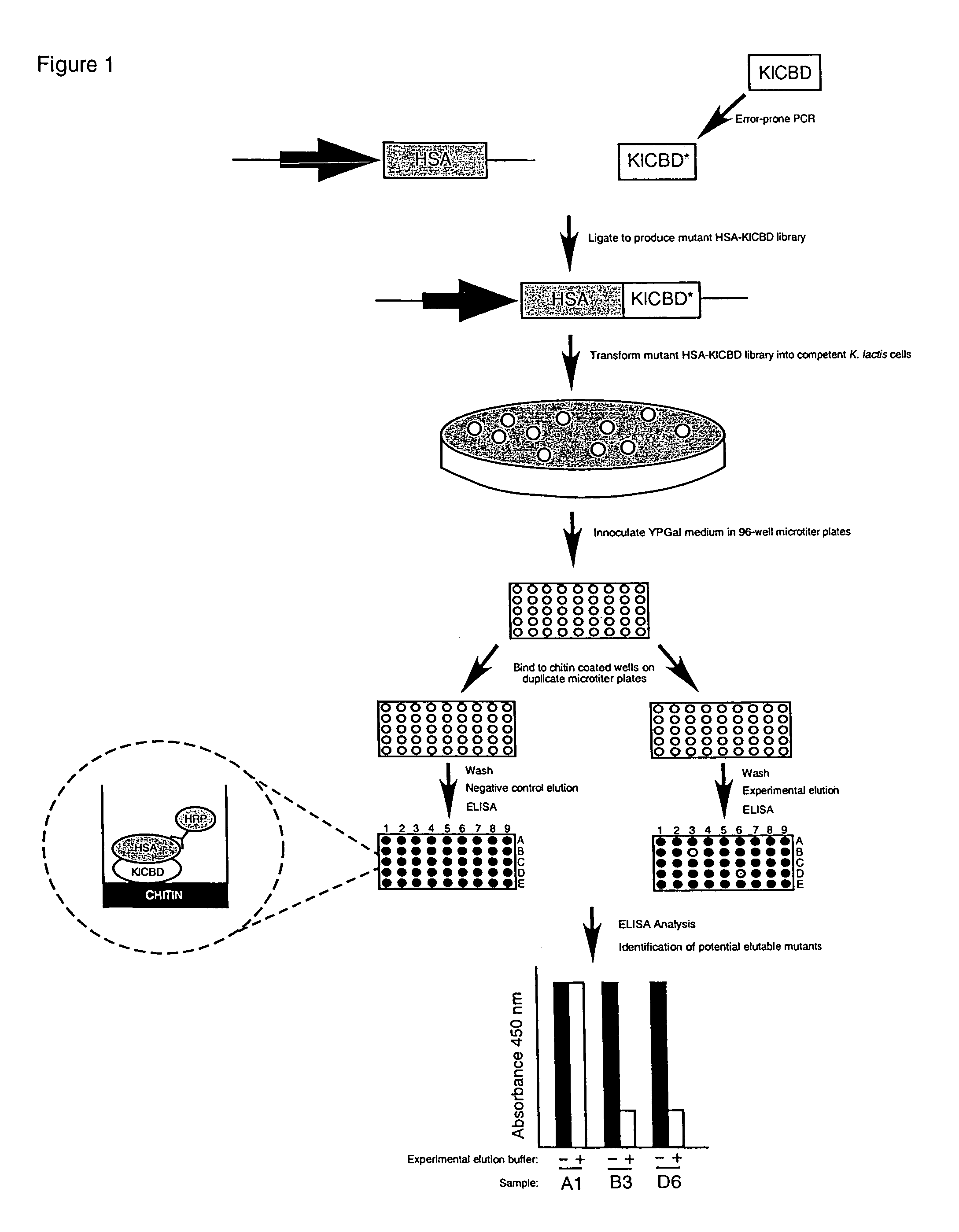
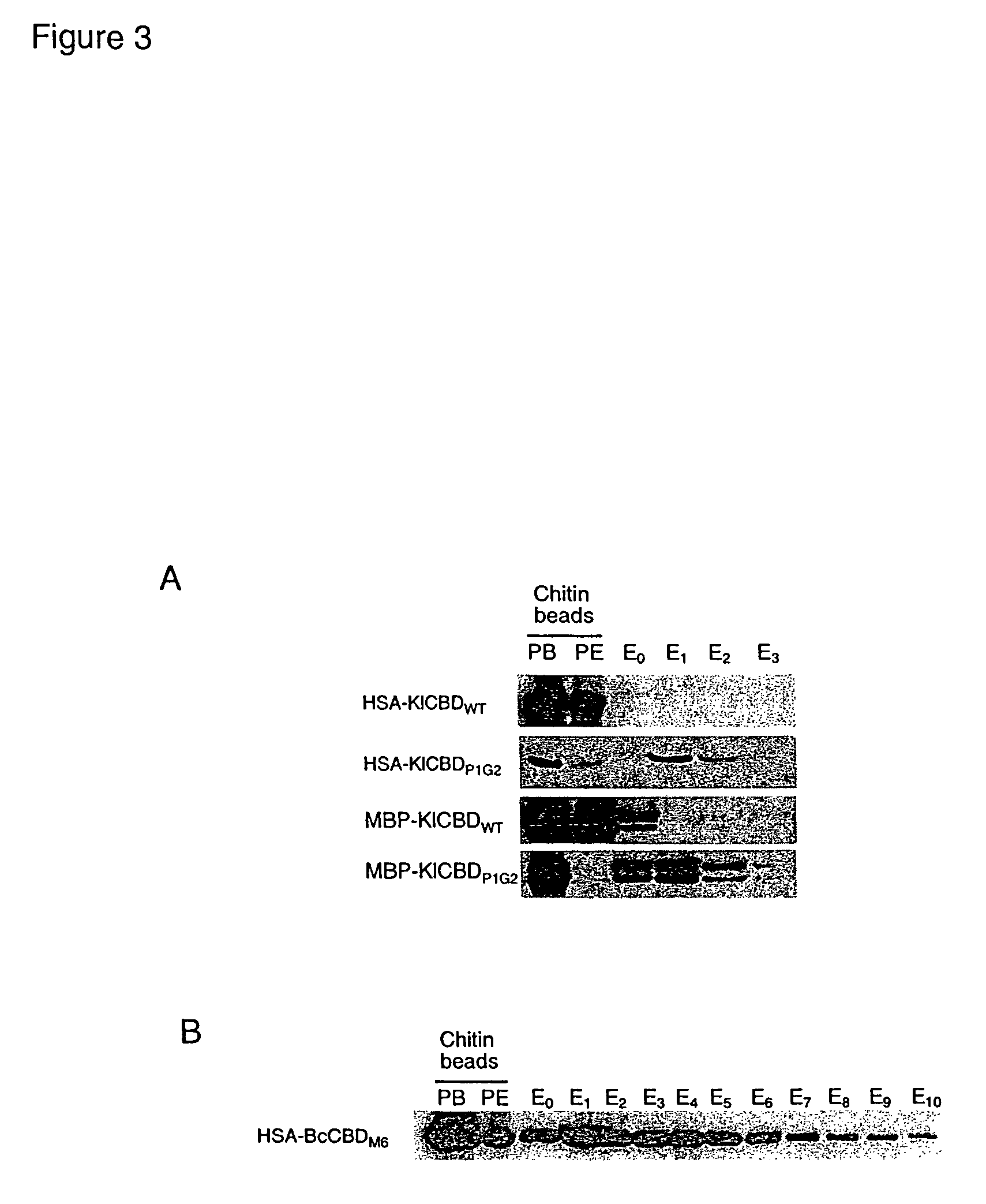
Compositions and methods relating to elutable carbohydrate-binding proteins
InactiveUS7732565B2Peptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningCarbohydrate-binding proteinChitin formation
Compositions and methods are provided for creating and identifying mutant carbohydrate-binding proteins that reversibly bind to carbohydrate substrates under conditions where the native protein remains bound. Examples of modified chitin-binding domains are provided which can be eluted from chitin in the presence of a reducing agent or at a pH within the range of 5-10.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Enzymes for starch processing
ActiveUS20110104759A1Good curative effectActivity be alteredSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCarbohydrate-binding proteinAlpha-amylase
The present invention relates to polypeptides comprising a carbohydrate-binding module amino acid sequence and an alpha-amylase amino acid sequence as well as to the application of such polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
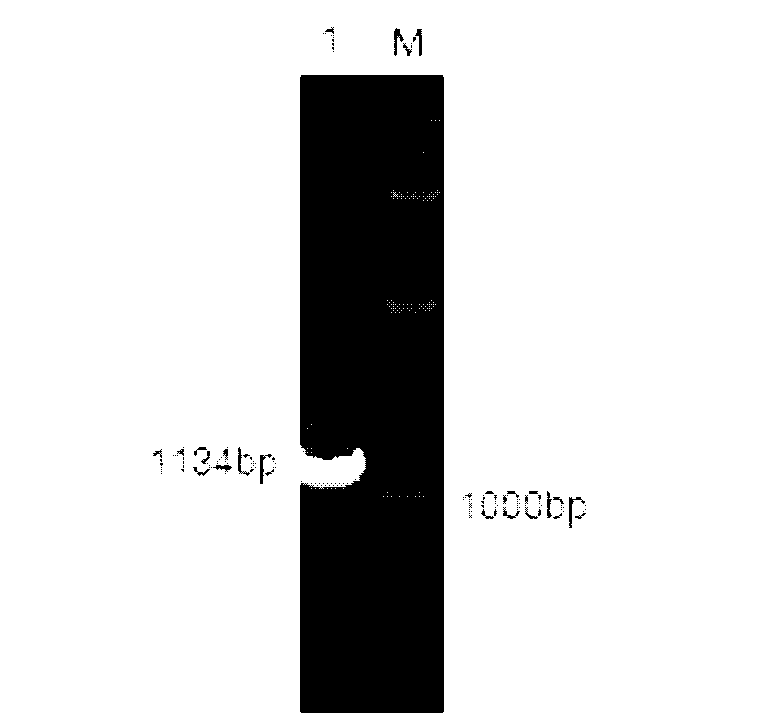
A high-temperature resisting neutral xylanase gene and engineering bacteria containing the gene
InactiveCN102191260AImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAnimal ForagingConserved sequence
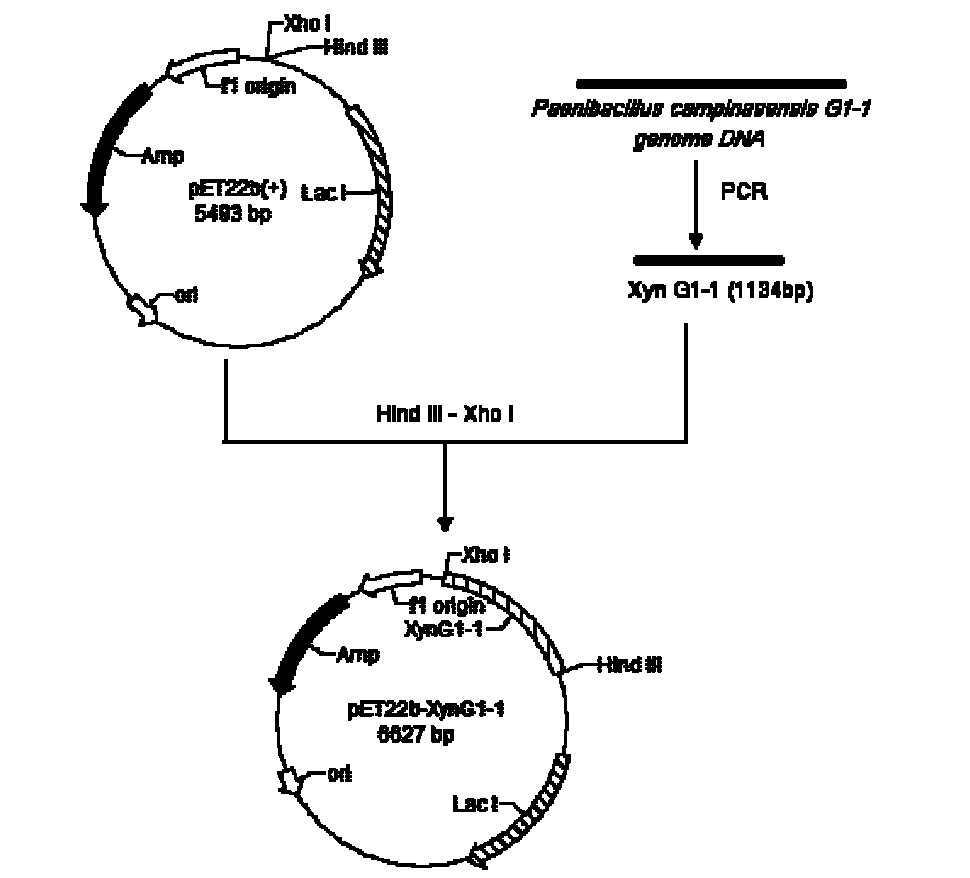
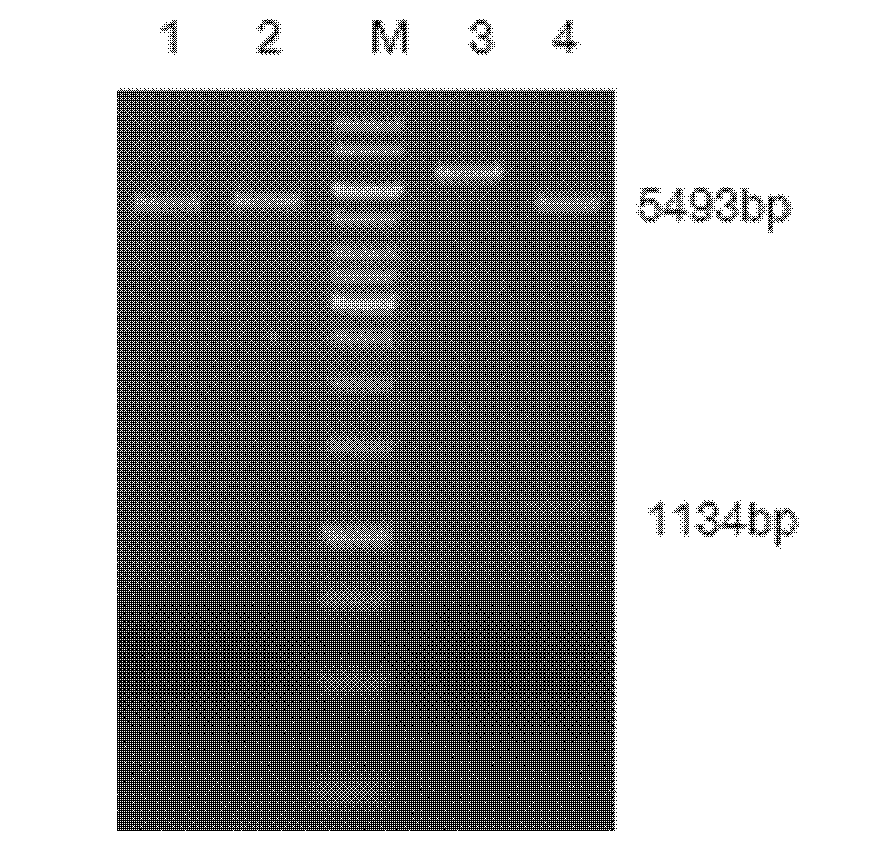
The invention relates to a high-temperature resisting neutral xylanase gene and engineering bacteria containing the gene. A gene sequence refers to a sequence 1, the whole length of the gene is 1134 bp and the gene is named as XynG1-1, the gene codes 377 amino acids, molecular weight of the gene is 41267 Da, wherein former 39 amino acids are signal peptide of the gene, the 49th to 235th amino acids are a conserved sequence of a glucosides hydrolase GH11 family, the 263rd to 377th amino acids are a conserved sequence of a carbohydrate-binding module CBM6 family. According to the invention, the recombinase obtained by fermenting the engineering bacteria has optimum temperature of 60 DEG C and optimum pH value of 7.0, heat is preserved at a pH value of 7.0 and temperature of 70 DEG C for 1 hour, the relative enzyme activity is more than 65%, and heat is preserved at a pH value of 9 and temperature of 60 DEG C for 1 hour, the relative enzyme activity is more than 60%. The xylanase of the present invention has the characteristic of good stability under high temperature, and can be applied to a plurality of industrial fields such as papermaking, foodstuff and forage, etc. The present invention has wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for continuously detecting glucose concentration in sample, kit thereof and method for using biosensor
ActiveUS8415170B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHigh concentrationCarbohydrate-binding protein
The invention provides a method for continuously detecting glucose concentration in a sample, including: (a) providing a biosensor comprising a transducer and a polysaccharide covered on the surface of the transducer; (b) providing a carbohydrate binding protein solution, wherein the carbohydrate binding protein has at least one receptor, and the receptor is capable of binding to the polysaccharide and glucose; (c) mixing a sample and the carbohydrate binding protein solution to form a mixture; (d) contacting the mixture with the biosensor; (e) detecting the amount of carbohydrate binding proteins bound to the polysaccharide by the biosensor, wherein glucose concentration of the sample is inversely proportional to the amount of carbohydrate binding proteins bound to the polysaccharide; and (f) refreshing the surface of the biosensor with a high concentration glucose solution.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Polymer Probes And Methods
ActiveUS20170115267A1Effective wayQuick checkPeptide-nucleic acidsBiological material analysisCarbohydrate-binding proteinCarbohydrate-binding module
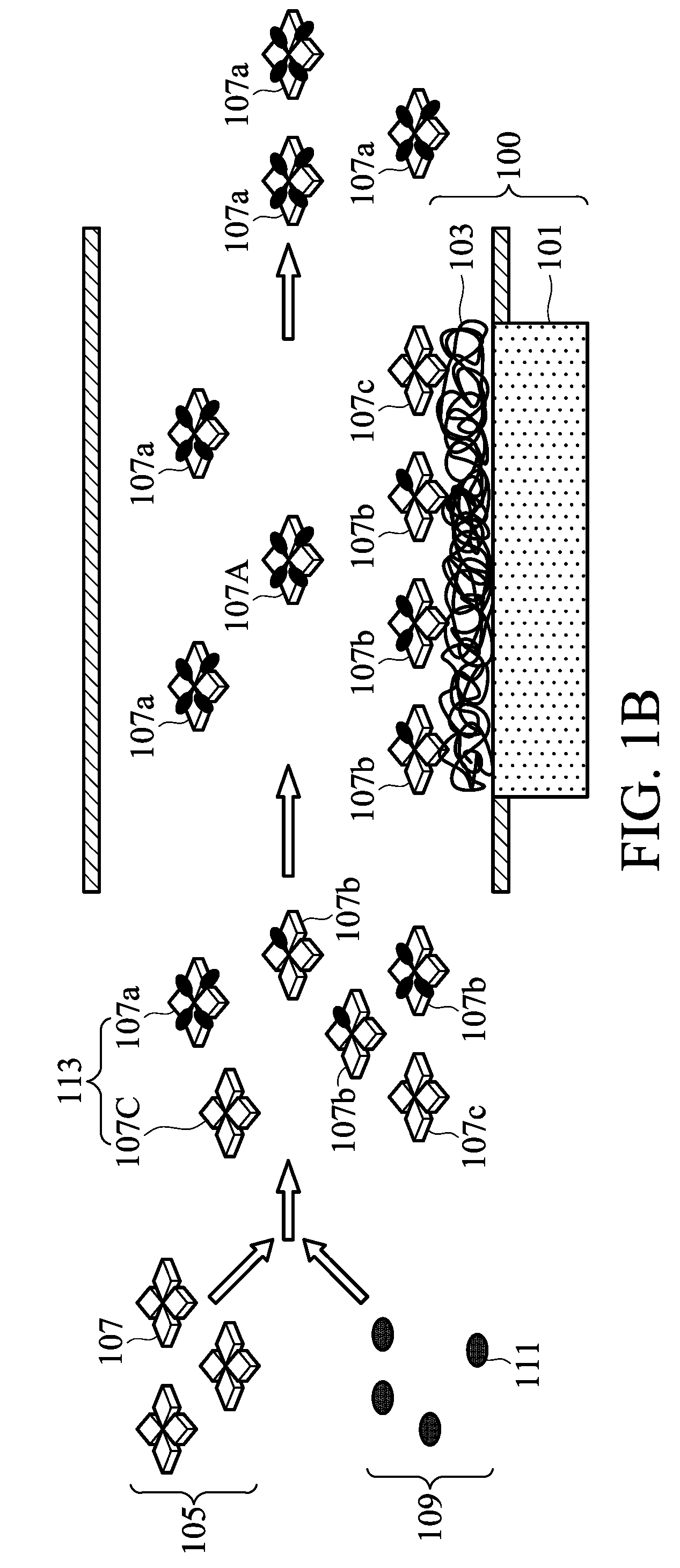
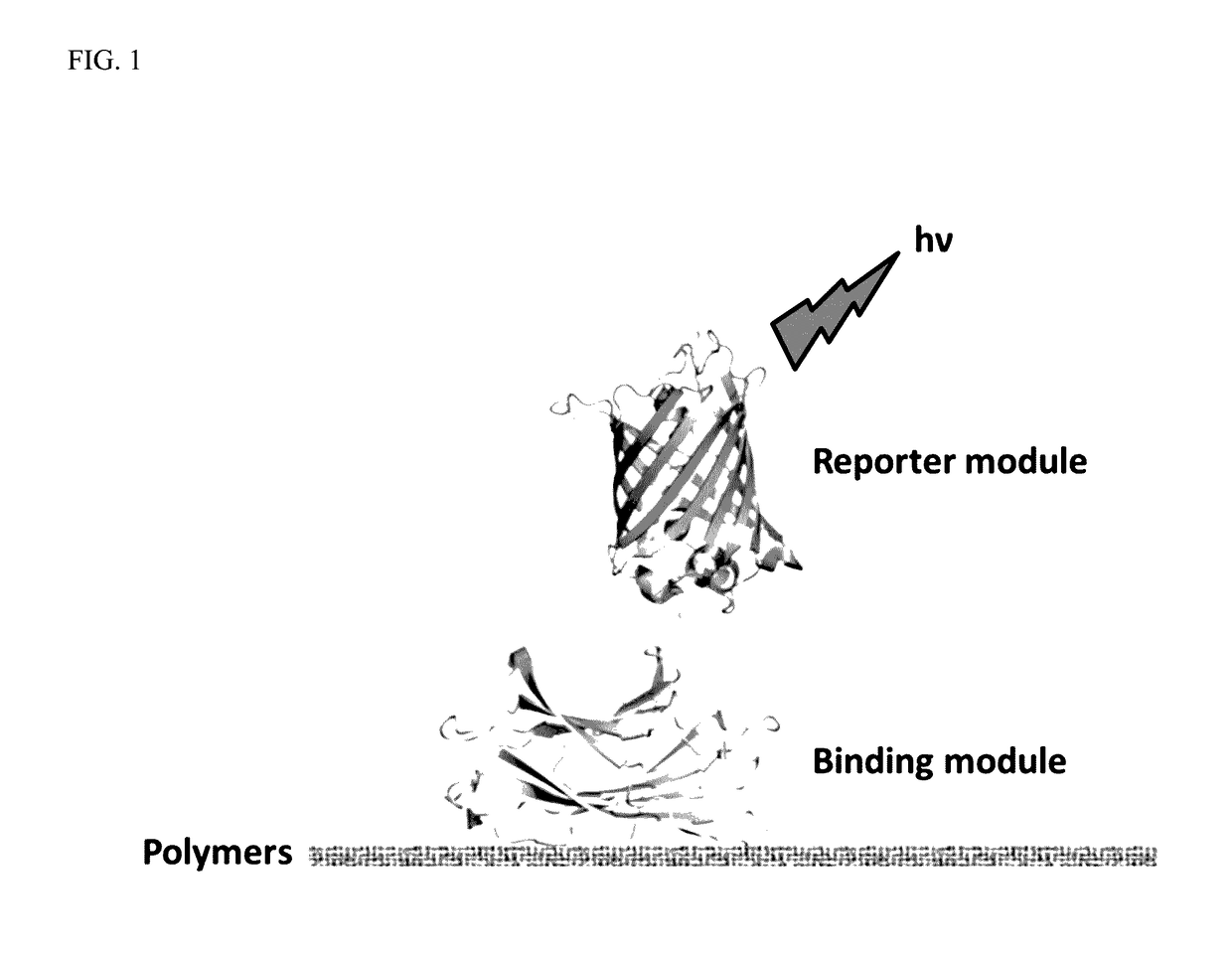
A polymer detection probe is provided that includes a binding module that specifically binds to at least one polymer and a reporter module that is spectroscopically detectable. The binding module can be a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). The reporter module can be a fluorescent protein. A complex is provided that includes a probe specifically bound to a pulp or paper product including at least one surface available lignocellulosic polymer. A pulp or paper product is provided that includes at least one surface available lignocellulosic polymer and at least one probe bound thereto. Methods are provided that employ a lignocellulosic probe. A method of detecting a lignocellulosic polymer or other type of polymer is provided. A method of determining the effectiveness of an industrial treatment on pulp or a paper product is also provided. A method of determining a physical property of pulp or a paper product is further provided.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC +1
Method and DNA constructs for increasing the production level of carbohydrate degrading enzymes in filamentous fungi
The invention is related to a method and DNA constructs for obtaining in a filamentous fungus host a higher production level of a carbohydrate degrading (CD) enzyme, having in its original state a catalytic module (CAT) and a carbohydrate binding module (CBM) separated by a linker region. The DNA construct comprising a truncated actinomycetes, preferably Nonomuraea flexuosa (NJ) derived DNA sequence encoding a truncated form of the CD enzyme, for example Nf Xyn11A, Nf Xyn10A, and is introduced into a filamentous fungal host. Said CD enzyme contains the catalytically active region of CAT but lacks part or all of the CBM, or all of the CBM and part or all of the linker region and is expressed and secreted under the control of regulatory sequences comprising at least a signal sequence, but also promoters, terminators and DNA sequences encoding a secretable carrier protein or domains thereof, preferably originating from filamentous fungi are included. The production level obtained with DNA sequence having the shortened DNA sequence encoding the truncated form of the CD enzyme is higher than the production level obtained with DNA construct encoding the corresponding full length CD enzyme.
Owner:AB ENZYMES OY
Chitinase fused with carbohydrate binding module, preparation method for chitinase and application of chitinase
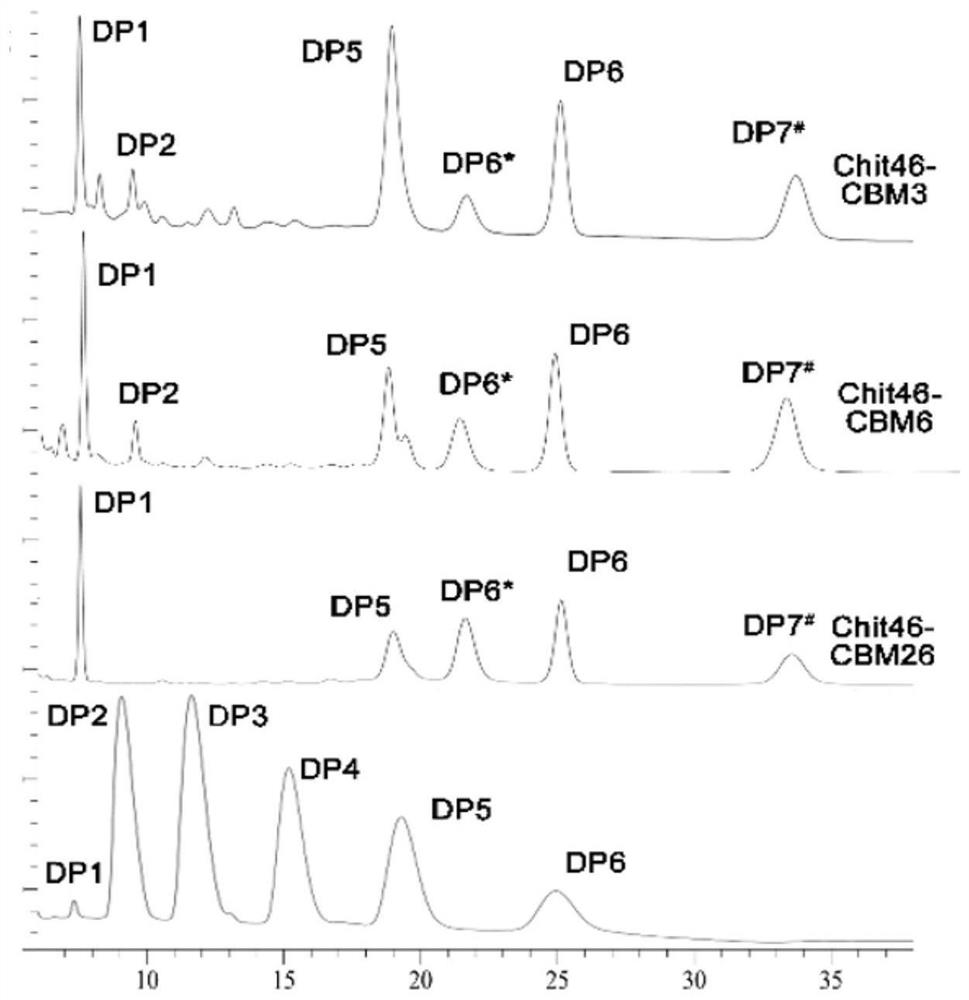
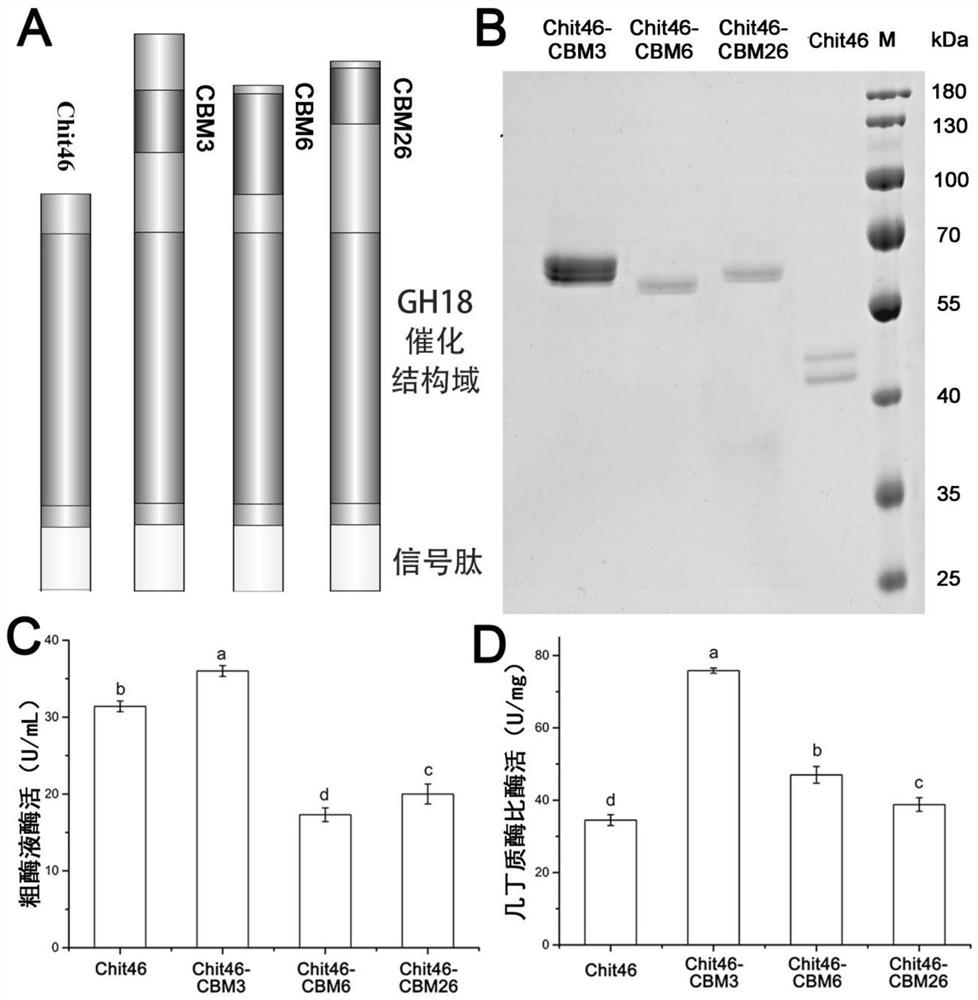
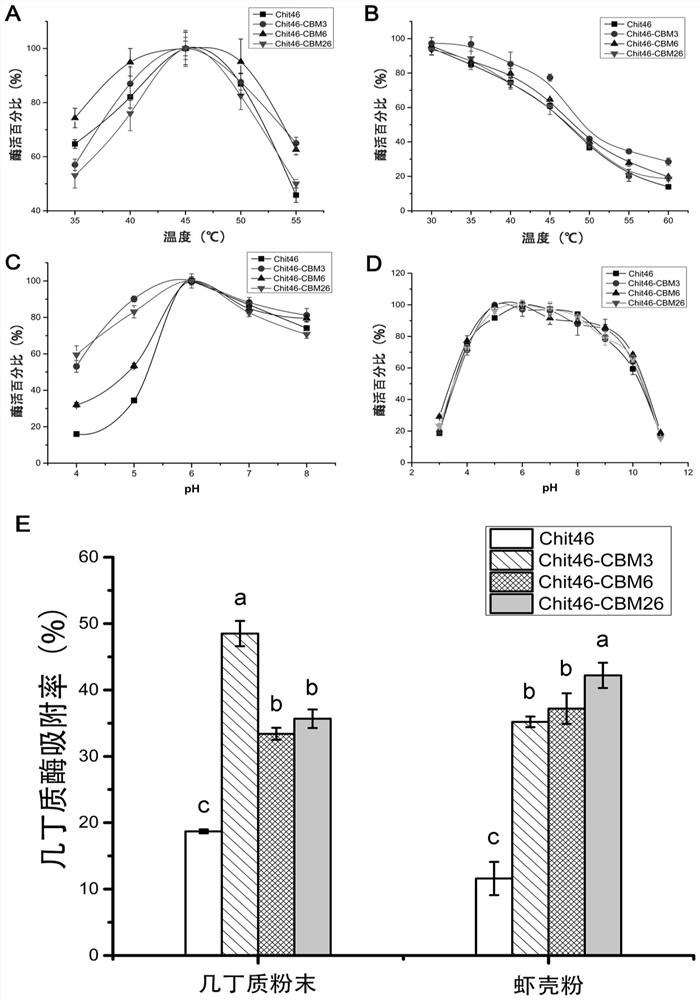
ActiveCN111944787AImprove recycling effectAvoid using effectsFungiAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCarbohydrate-binding proteinChitinase
The invention provides chitinase fused with a carbohydrate binding module, a preparation method for the chitinase and application of the chitinase, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The chitinase fused with the carbohydrate binding module comprises fusion chitinase formed by series connection of the carbohydrate binding module with a connecting peptide and a C end of chitinase Chit46. It is the first time for the invention to successfully apply the chitinase Chit46-CBM3, Chit46-CBM6 and Chit46-CBM26 fused with the carbohydrate binding module (CBM) to shrimp shell waste recovery. After the CBM is fused, the chitin in shrimp shells can be directly hydrolyzed by the fusion chitinase, and thus, the use of a strong alkali reagent and a complex pretreatment step in atraditional process are avoided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Carbohydrate binding module and use thereof
InactiveCN103097411AMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against virusesEpitopeCarbohydrate-binding protein
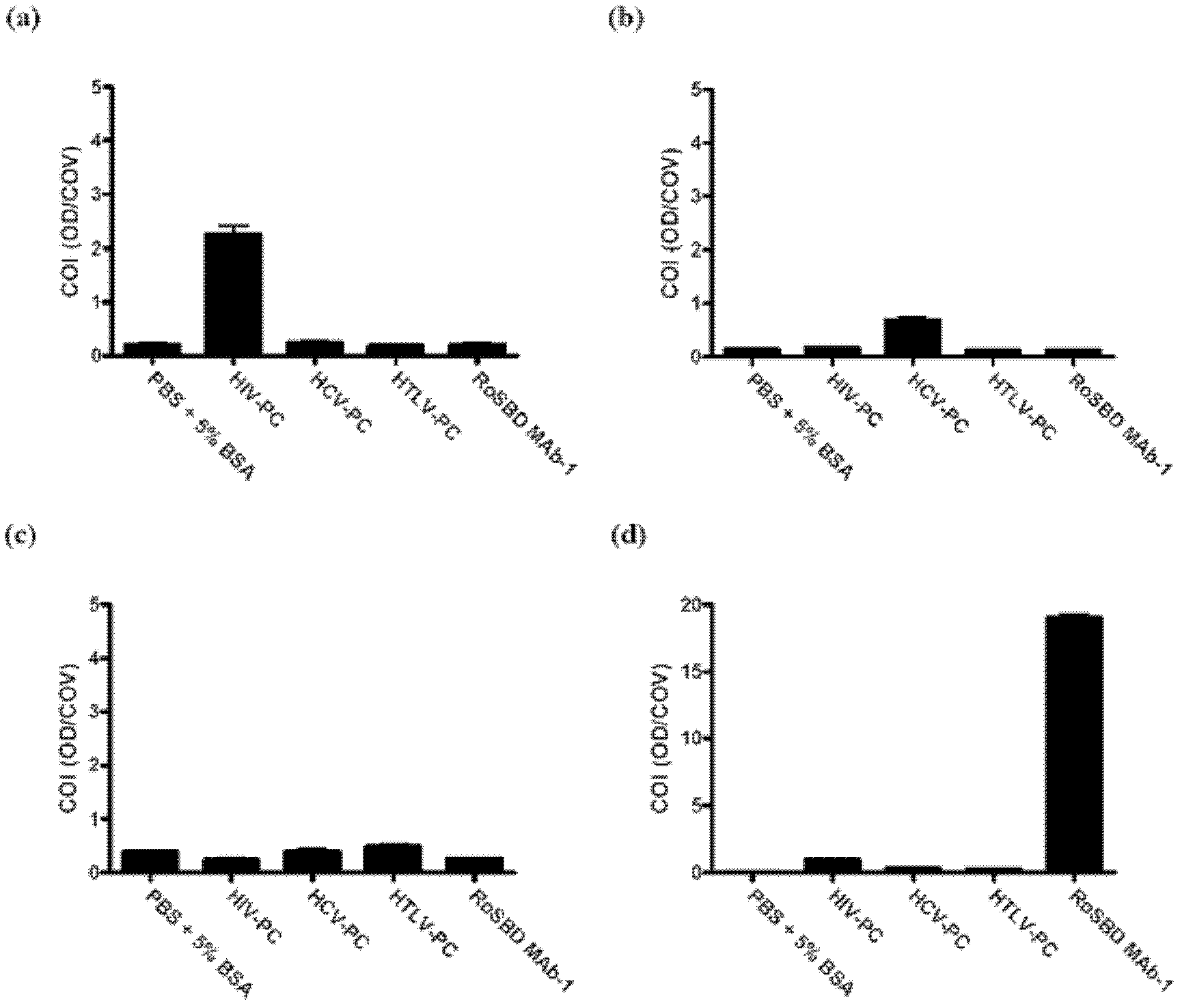
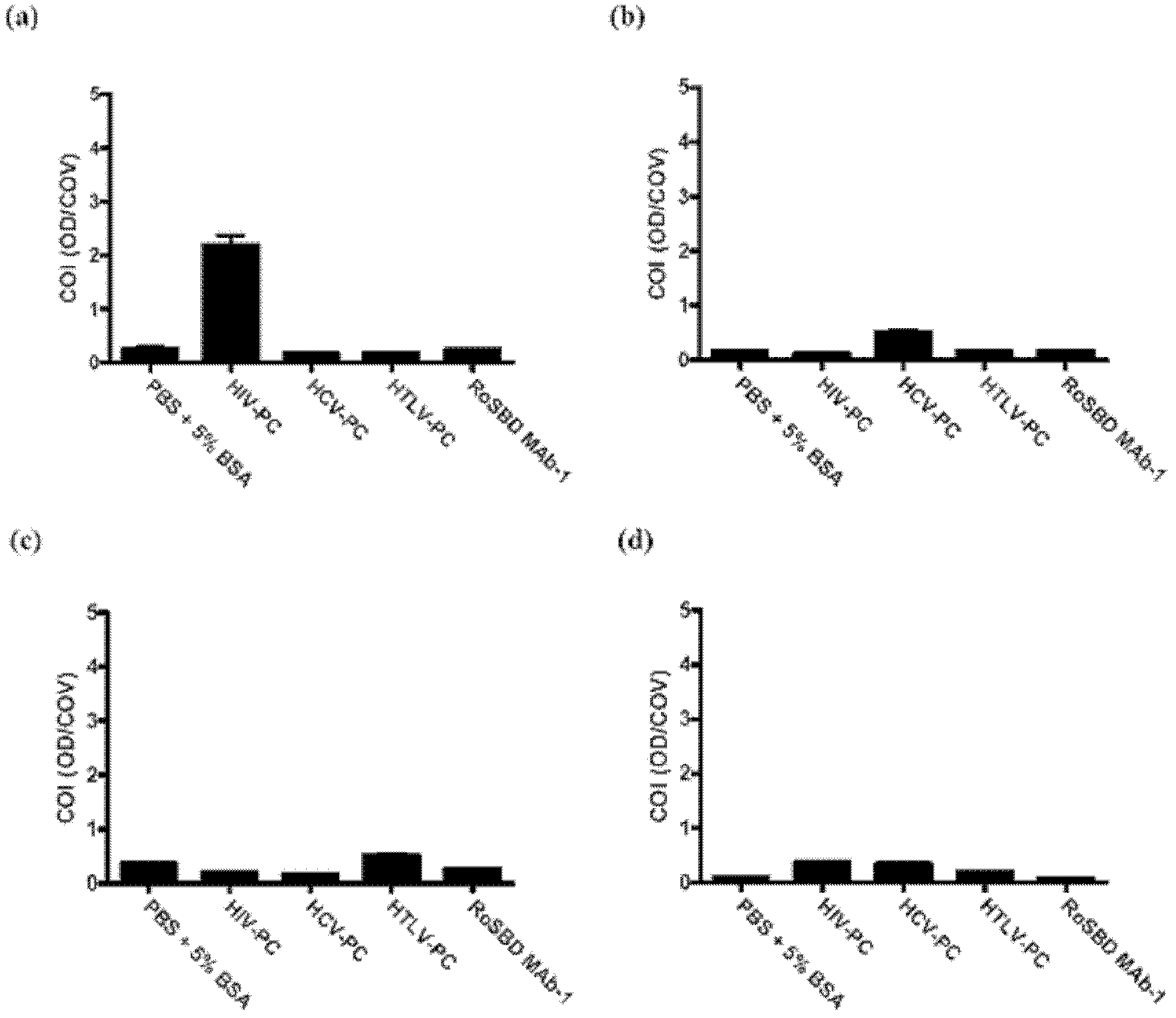
The present invention provides a method of inhibiting HIV infection of a subject, comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of an antibody mimetic of carbohydrate binding module (CBM) which specifically binds to an epitope on HIV glycoprotein. The present invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of an antibody mimetic of carbohydrate binding module and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also provides a method of inhibiting HIV infection of the subject preventionally or therapically comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of an antibody mimetic of carbohydrate binding module (CBM) which specifically binds to an epitope on HIV glycoprotein
Owner:张大慈
Feruloyl esterase as well as mutants and application thereof
ActiveCN112980812AIncrease enzyme activityHigh activityHydrolasesFood processingDisulfide bondingSide chain
The invention discloses feruloyl esterase as well as mutants and application thereof. The feruloyl esterase has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, SEQ ID No. 2 or SEQ ID No. 3, the feruloyl esterase is stable in property, the reaction pH is 6-8, and the reaction temperature is 37-54 DEG C. On the basis of the amino acid sequence of the feruloyl esterase, three feruloyl esterase mutants N.1-300, N.7-16 and N.9-98 are obtained by increasing the number of disulfide bonds in the feruloyl esterase, changing side chain groups of a carbohydrate binding module of the feruloyl esterase and changing the charges of a catalytic structural domain, and compared with original feruloyl esterase, the specific enzyme activities of the three mutants are obviously improved. The feruloyl esterase and the mutant obtained by the invention have stable properties, and are beneficial to industrial application of the feruloyl esterase.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Feruloyl esterase as well as mutant N.7-16 and application thereof
ActiveCN114774388AIncrease enzyme activityHigh activityHydrolasesFood processingDisulfide bondingSide chain
The invention discloses feruloyl esterase, a mutant N.7-16 of the feruloyl esterase and application of the feruloyl esterase. The feruloyl esterase has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2 and is stable in property, the reaction pH is 6-8, and the reaction temperature is 37-54 DEG C. On the basis of the amino acid sequence of the feruloyl esterase, the feruloyl esterase mutant N.7-16 is obtained by increasing the number of disulfide bonds in the feruloyl esterase, changing side chain groups of a carbohydrate binding module and changing the charges of a catalytic structural domain, and compared with original feruloyl esterase, the feruloyl esterase mutant N.7-16 has the advantages that the feruloyl esterase mutant N.7-16 is obtained; the specific enzyme activity of the mutant is obviously improved. The feruloyl esterase and the mutant obtained by the invention have stable properties, and are beneficial to industrial application of the feruloyl esterase.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Novel xylanase produced from streptomyces sp. strain hy-14
The present invention relates to a novel xylanase homologous with an enzyme corresponding to a glycoside hydrolase family 10 (GH10) domain and comprising a carbohydrate-binding module family 2 (cellulose-binding module family 2, CBM2) domain, a substrate-binding module, which were isolated from Streptomyces sp. strain HY-14. Particularly, the maximum enzyme activity continues at at least 80% at a pH between 5.0 and 7.5 and the sugar substrates including xylans are significantly degraded in the xylanase, and thus the xylanase can be used as an enzyme in various industrial sectors such as food, feed, and other industries.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
A special multifunctional growth-promoting bacterium agent for soybean and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109652340BPlay a role in promoting growthPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus megaterium
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, and in particular relates to a special multifunctional growth-promoting bacterium agent for soybeans, which is fermented from the FK19 strain, and the classification of the FK19 strain is named Bacillus megaterium (Bacillus megaterium), preserved on December 27, 2018 In China Center for Type Culture Collection, the deposit number is CCTCC M 2018925. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: the multifunctional growth-promoting bacterium agent of the present invention has obvious promoting effect on soybean growth, has obvious increasing effect on phosphorus content and potassium content of soybean leaves, and can increase soybean yield. Soybean roots will produce soybean lectin, which is a sugar-binding protein or glycoprotein of non-immune origin, which can be combined with polysaccharides of bacteria. The multifunctional growth-promoting bacteria agent of the present invention has soybean lectin affinity, and can Combined, adsorbed on the soybean roots, and then promote the synthesis of more isoflavones in soybeans, mediate the colonization of the bacterial strains in the soybean roots, so as to exert the growth-promoting function of the bacterial agent.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Carbohydate binding modules with reduced binding to lignin
ActiveUS9206406B2Reduced binding to ligninPromote recoveryBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsCarbohydrate-binding proteinAmino acid substitution
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
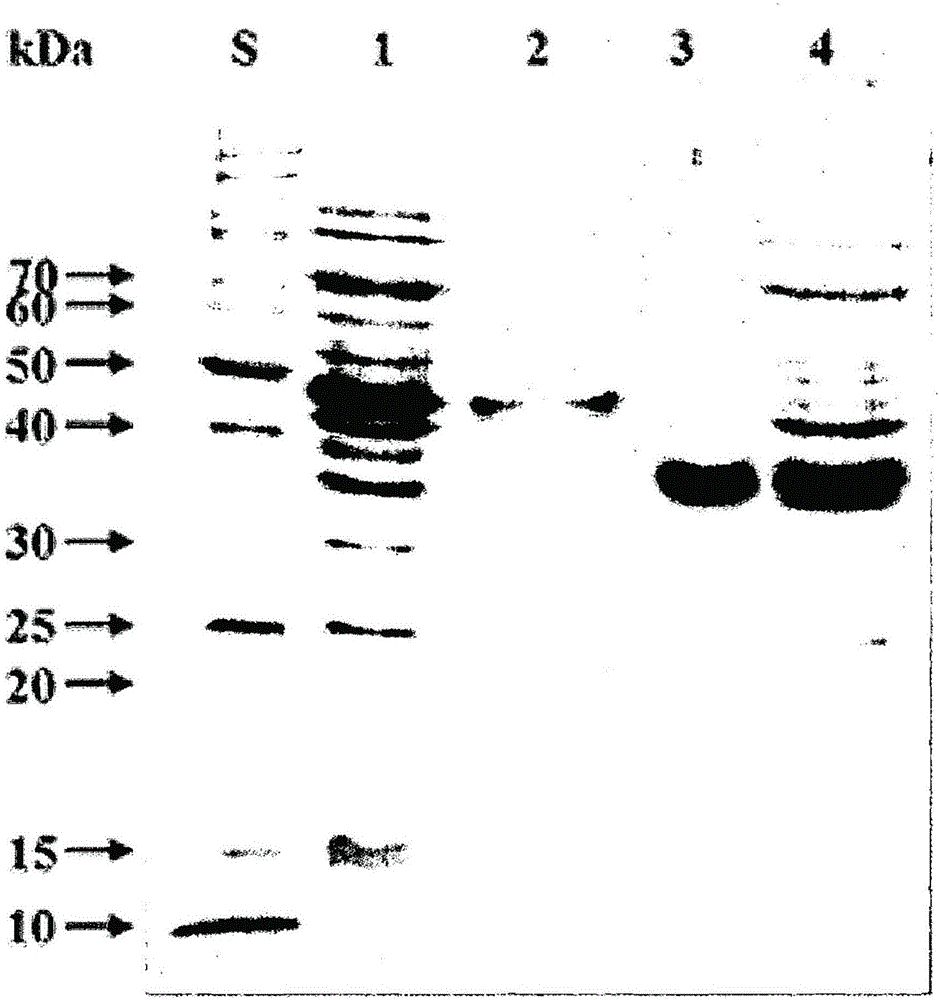
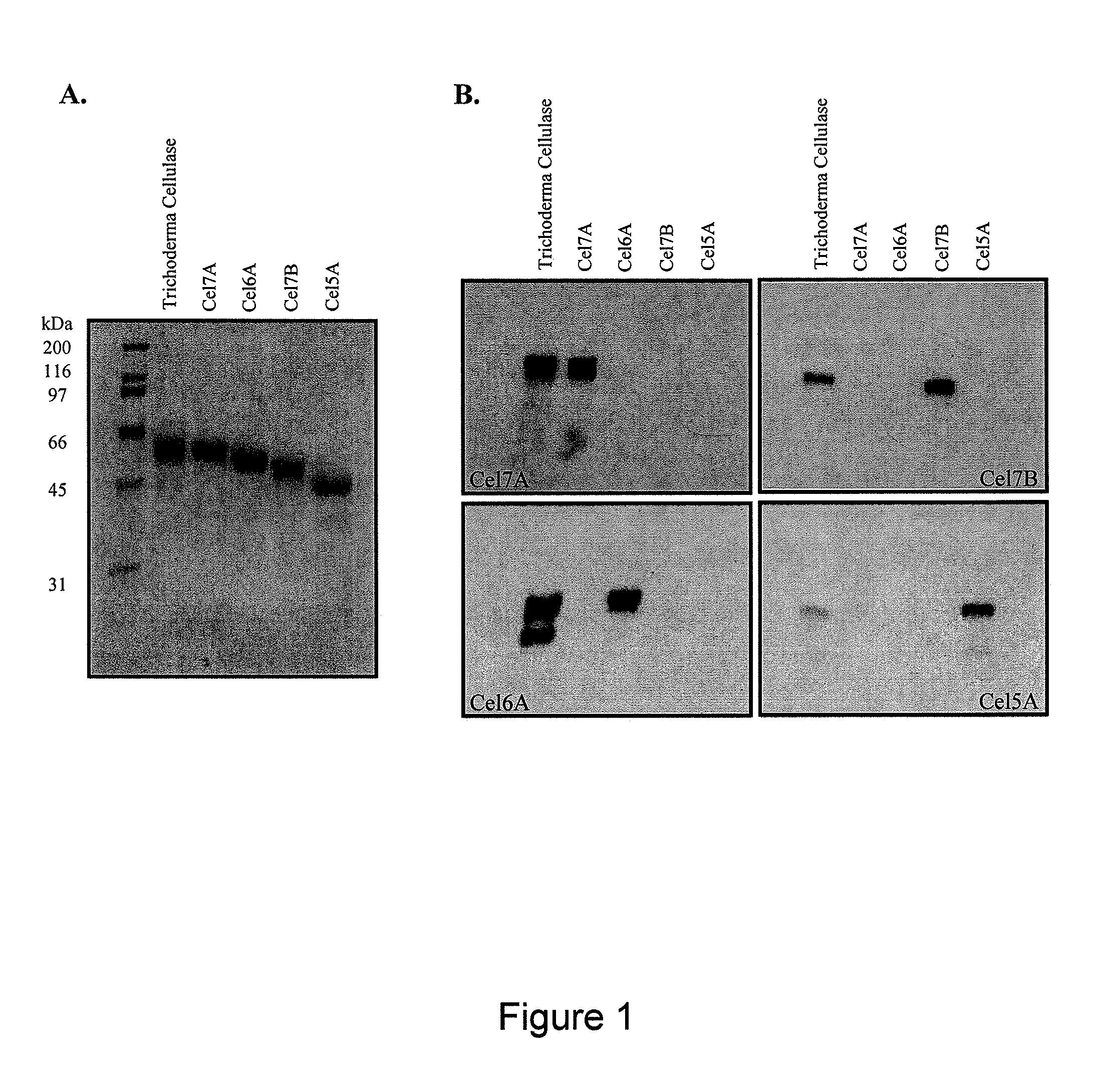
Novel cellobiohydrolase enzymes
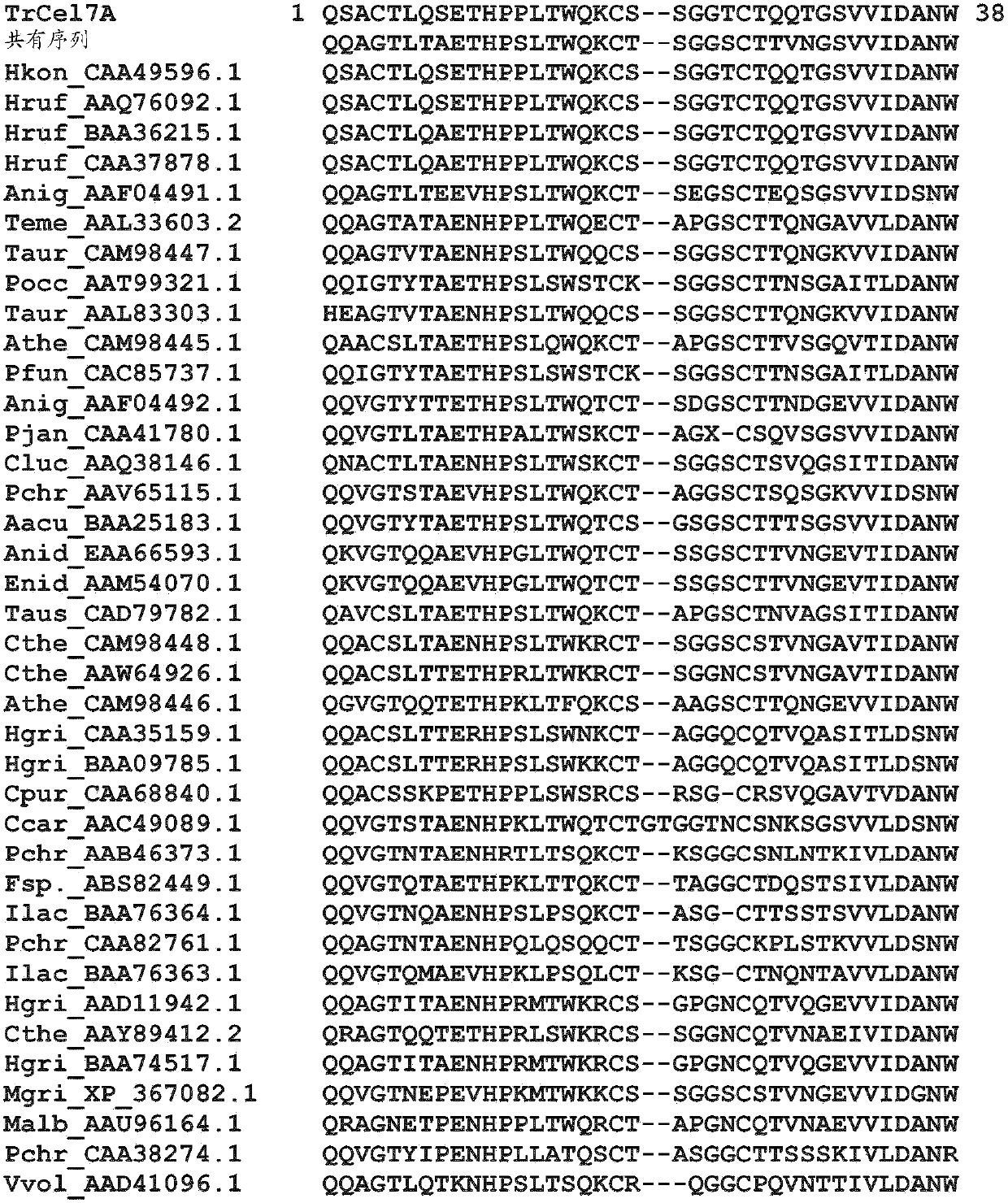
Provided are isolated cellobiohydrolases comprising a modified Glycoside Hydrolase (GH) Family 7 catalytic domain, a GH Family 7 catalytic domain and a modified Family carbohydrate binding module (CBM), or both a modified Family 7 catalytic domain and a modified Family 1 CBM. Such isolated cellobiohydrolases exhibit from 45% to about 99.9% amino acid sequence identity to amino acids 1- 436 of SEQ ID NO: 1 or to amino acids 1-438 of SEQ ID NO: 2 and improved activity on process substrates. Also provided are genetic constructs and genetically modified microbes for expressing the isolated cellobiohydrolases, a process for producing the isolated cellobiohydrolases, cellulase enzyme mixtures comprising the isolated cellobiohydrolase and a process for hydrolysing a cellulosic substrate with such cellulase enzyme mixtures.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Multifunctional cellulase and hemicellulase
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Carbohydrate binding module with affinity for insoluble xylan
InactiveUS20110237448A1Improve abilitiesPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesOpen reading frameCarbohydrate-binding protein
The present disclosure relates to isolated polynucleotides with two polynucleotide sequences linked within one open reading frame, in which the first polynucleotide sequence encodes a peptide that binds to a carbohydrate. The present disclosure also relates to vectors and genetically modified host cells containing such isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by such isolated polynucleotides. The present disclosure further relates to methods of increasing the ability of a recombinant protein to bind to a carbohydrate and methods of identifying a protein having an ability to bind to a carbohydrate.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
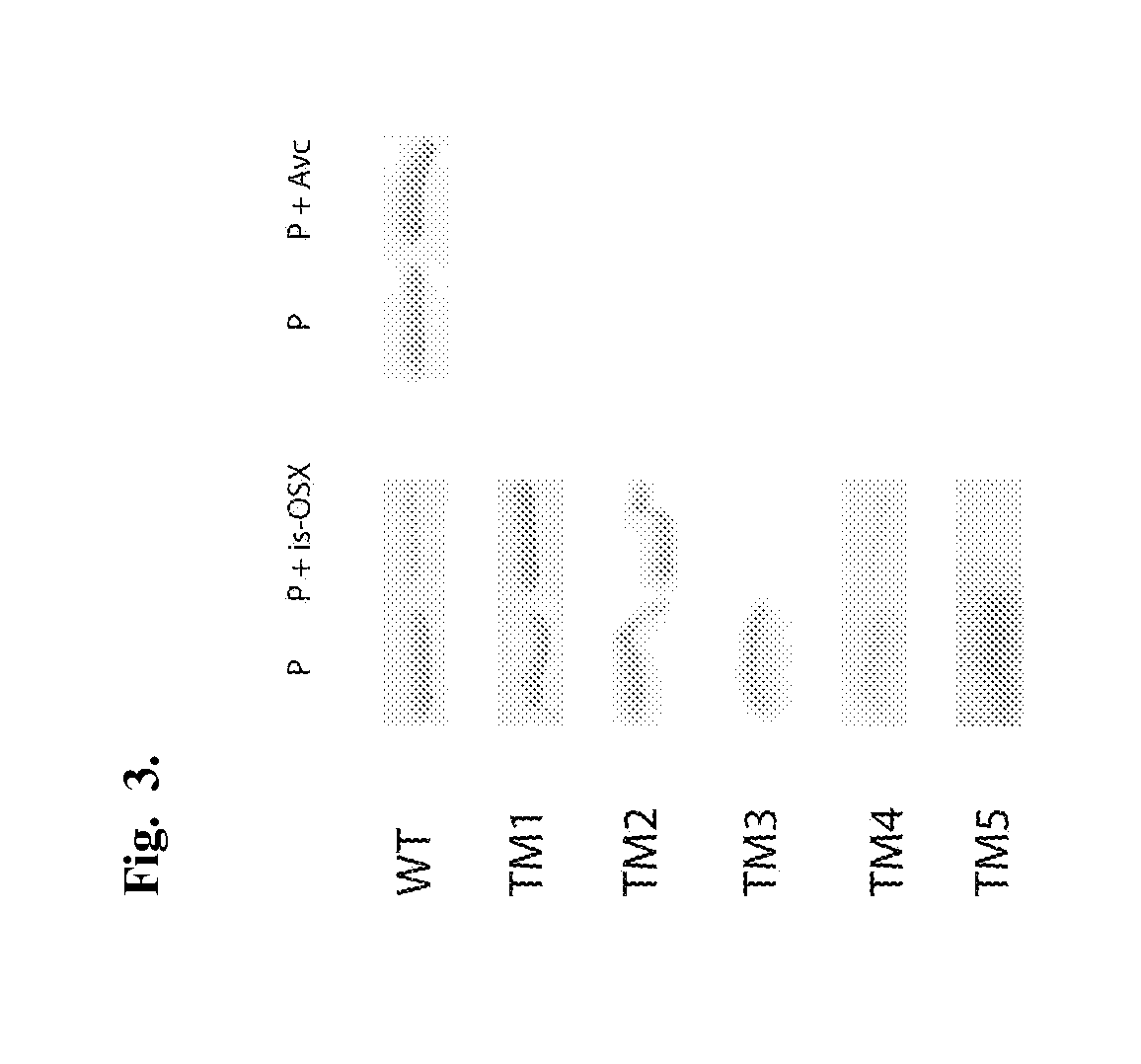
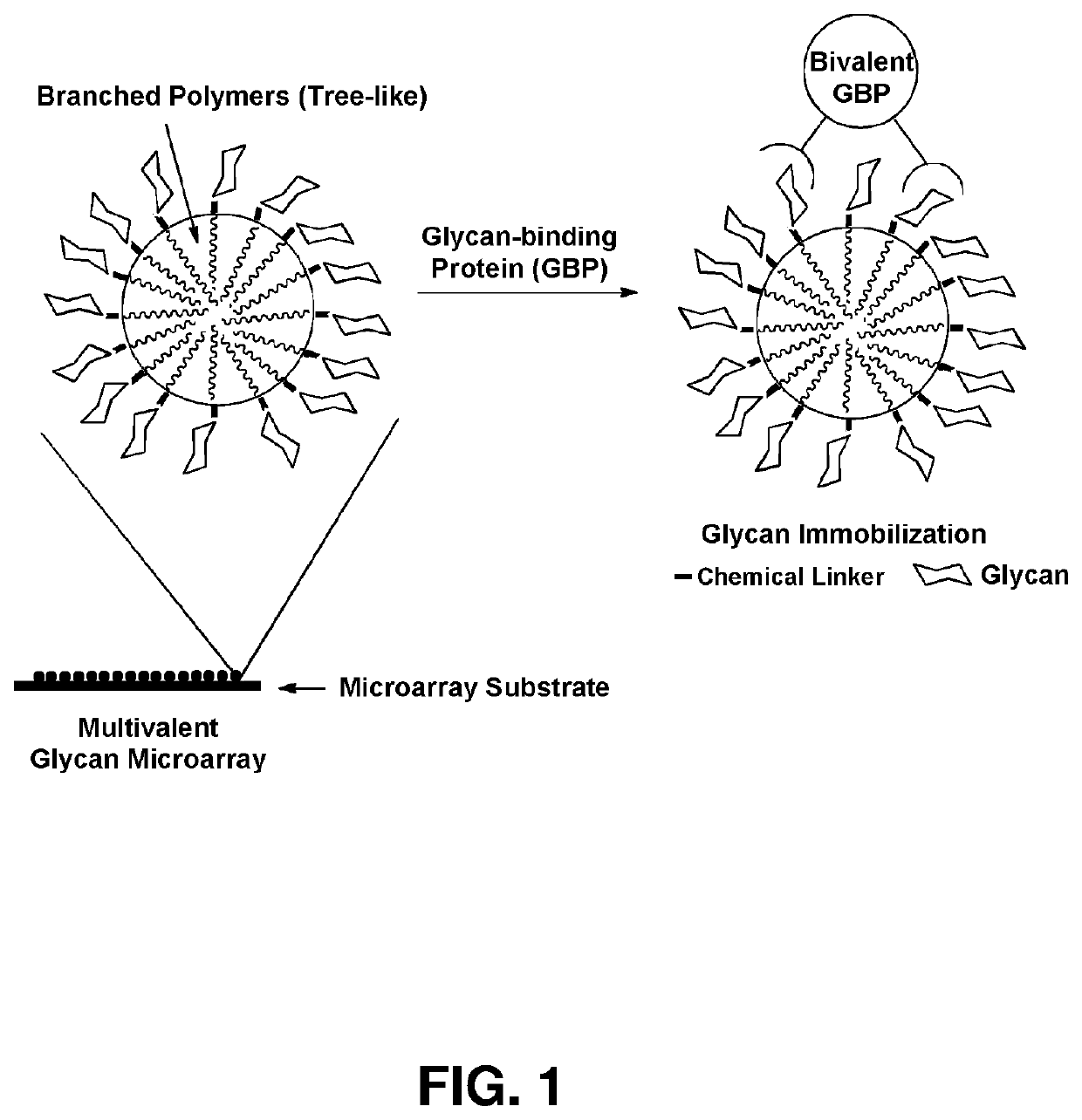
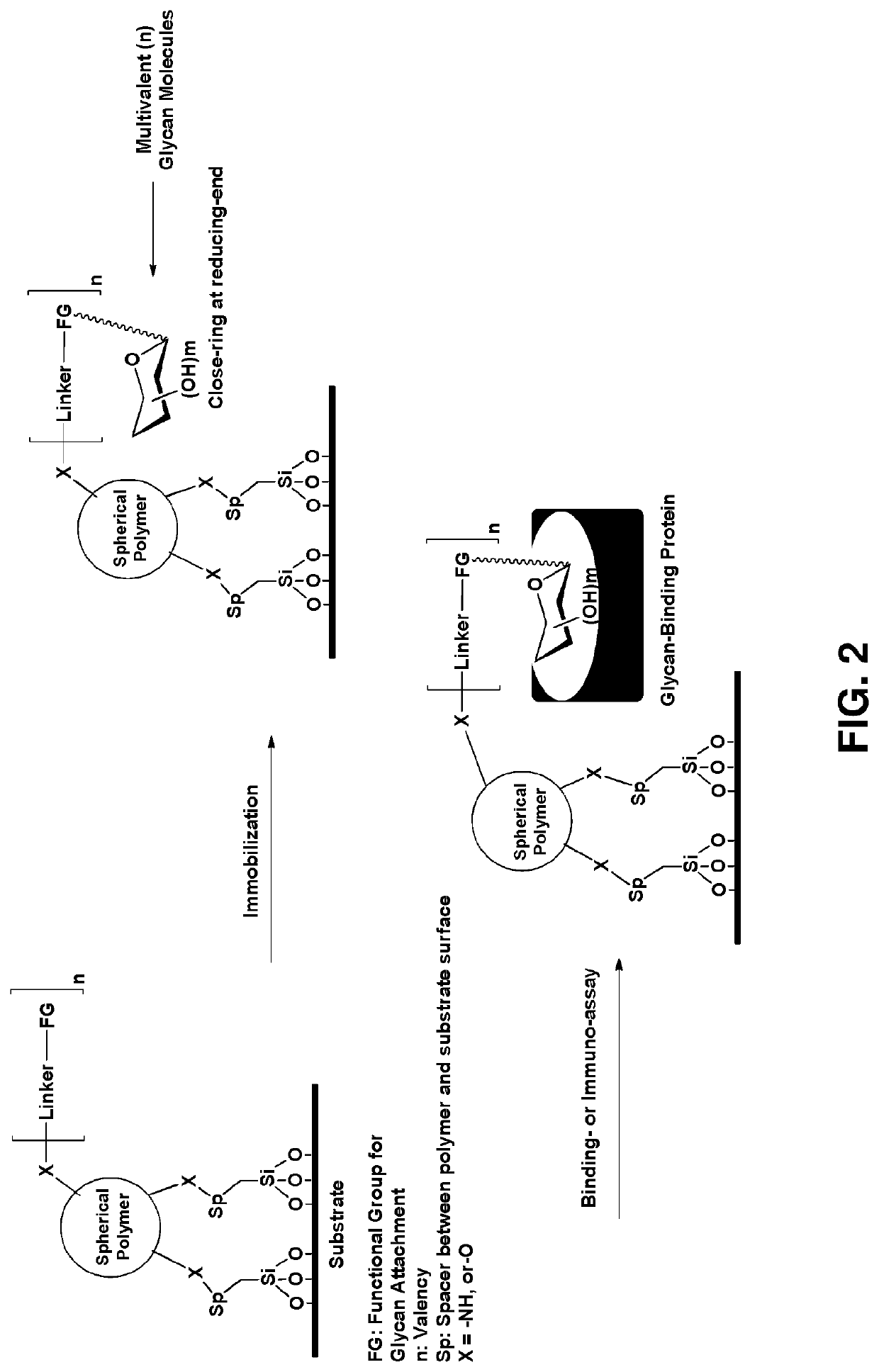
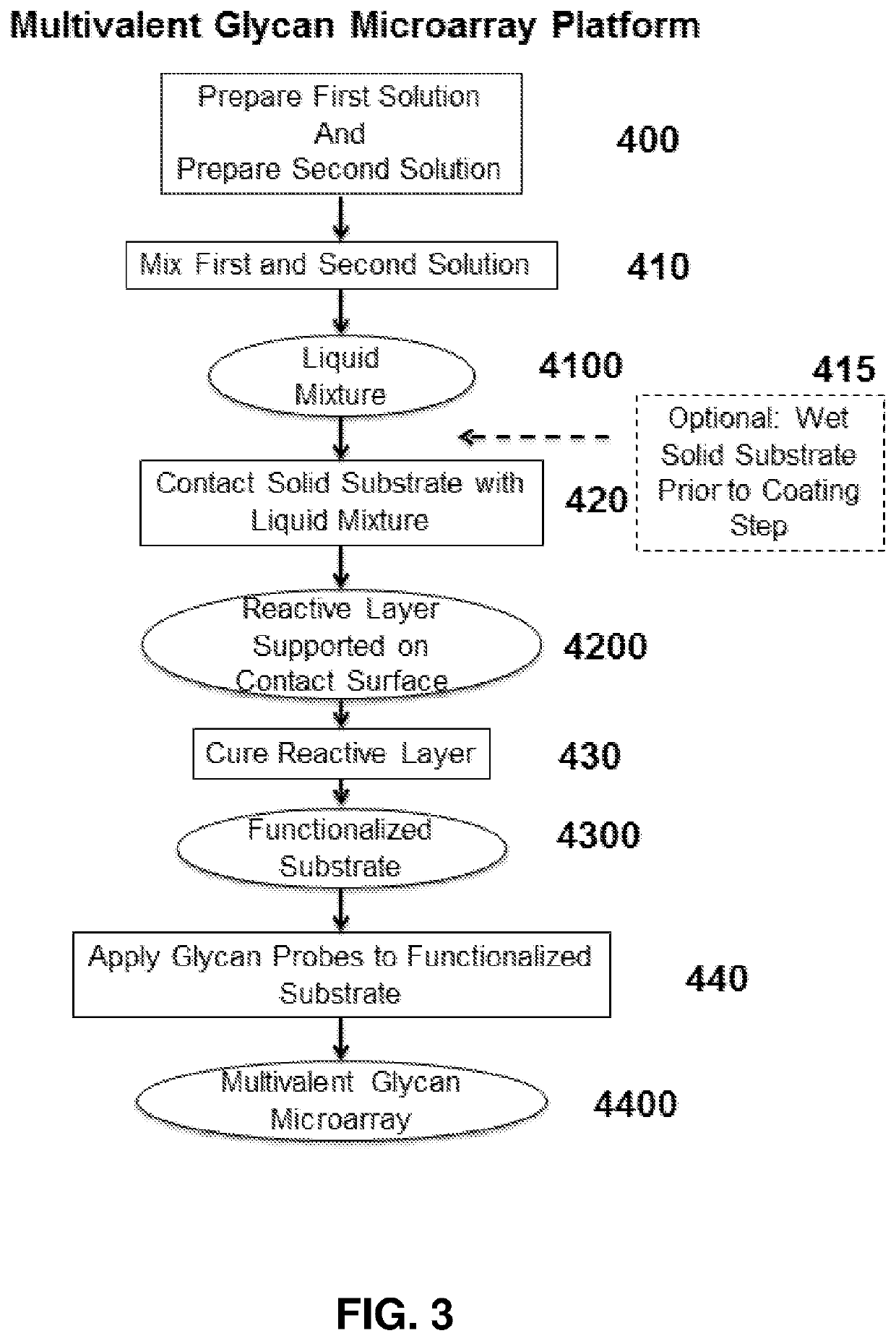
Multivalent glycan microarray platform
ActiveUS11231415B2High affinityHigh densityPeptide librariesMacromolecular librariesCarbohydrate-binding proteinActive agent
The present invention includes a multivalent glycan microarray for detection of glycan-binding proteins. The multivalent glycan microarray allows a multivalent presentation of glycan on a microarray substrate, which can enhance binding of the glycan binding protein to the glycan microarray. The multivalent microarray includes a solid substrate having one or more branched polymers bonded to it via one or more silane-based linker reagents. The branched polymer in turn is bonded to a glycan, via one or more bifunctional linkers to form the multivalent glycan microarray. Nonspecific binding of glycan binding proteins to the multivalent glycan microarray can be reduced by using a blocking reagent coated on to the microarray substrate, which includes a polyethylene glycol surfactant attached to the solid substrate via a self-crosslinking azido-functionalized silane. Methods for making multivalent glycan microarrays and methods for using same to detect glycan-binding proteins are also disclosed.
Owner:Z BIOTECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com