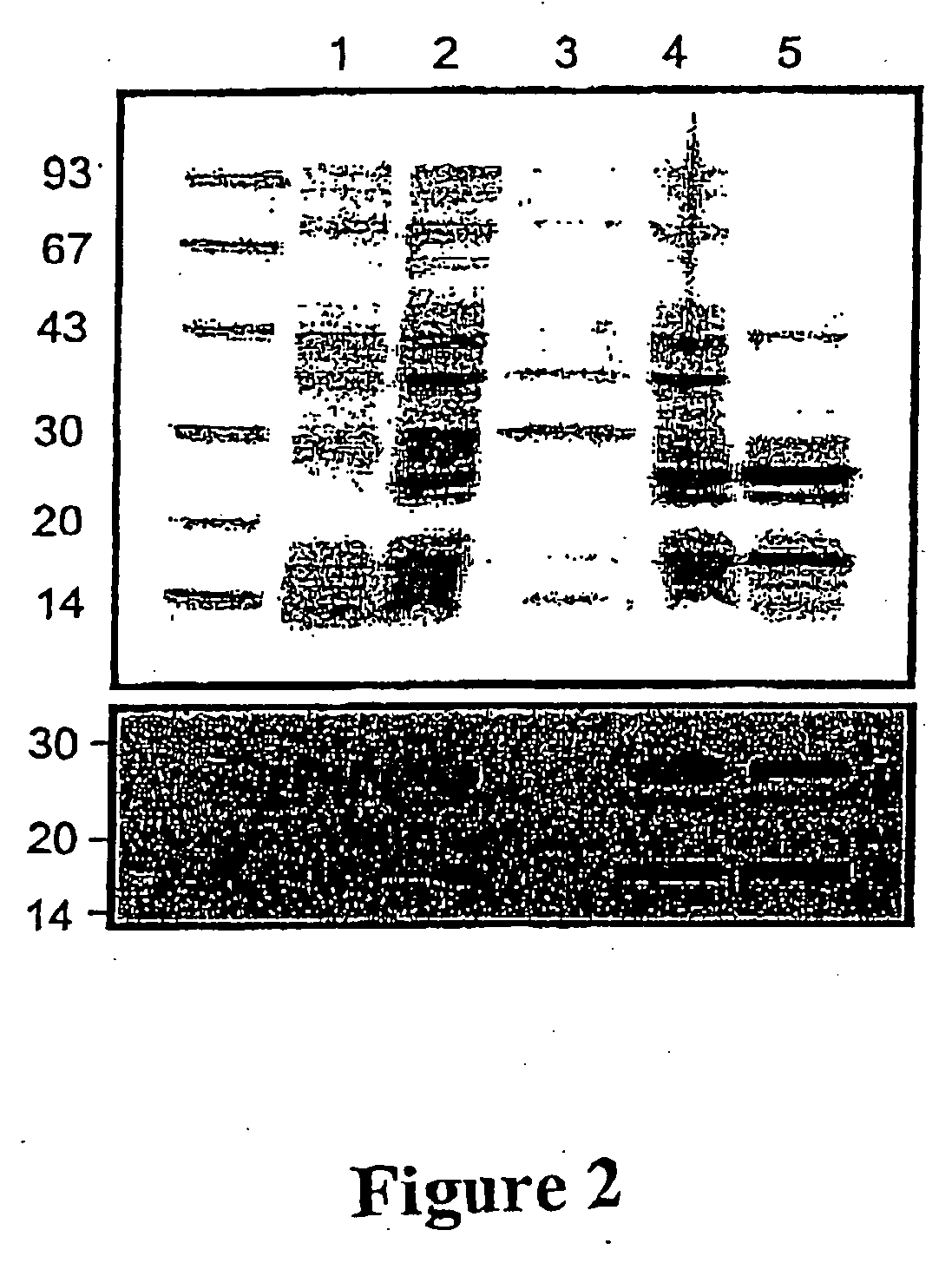
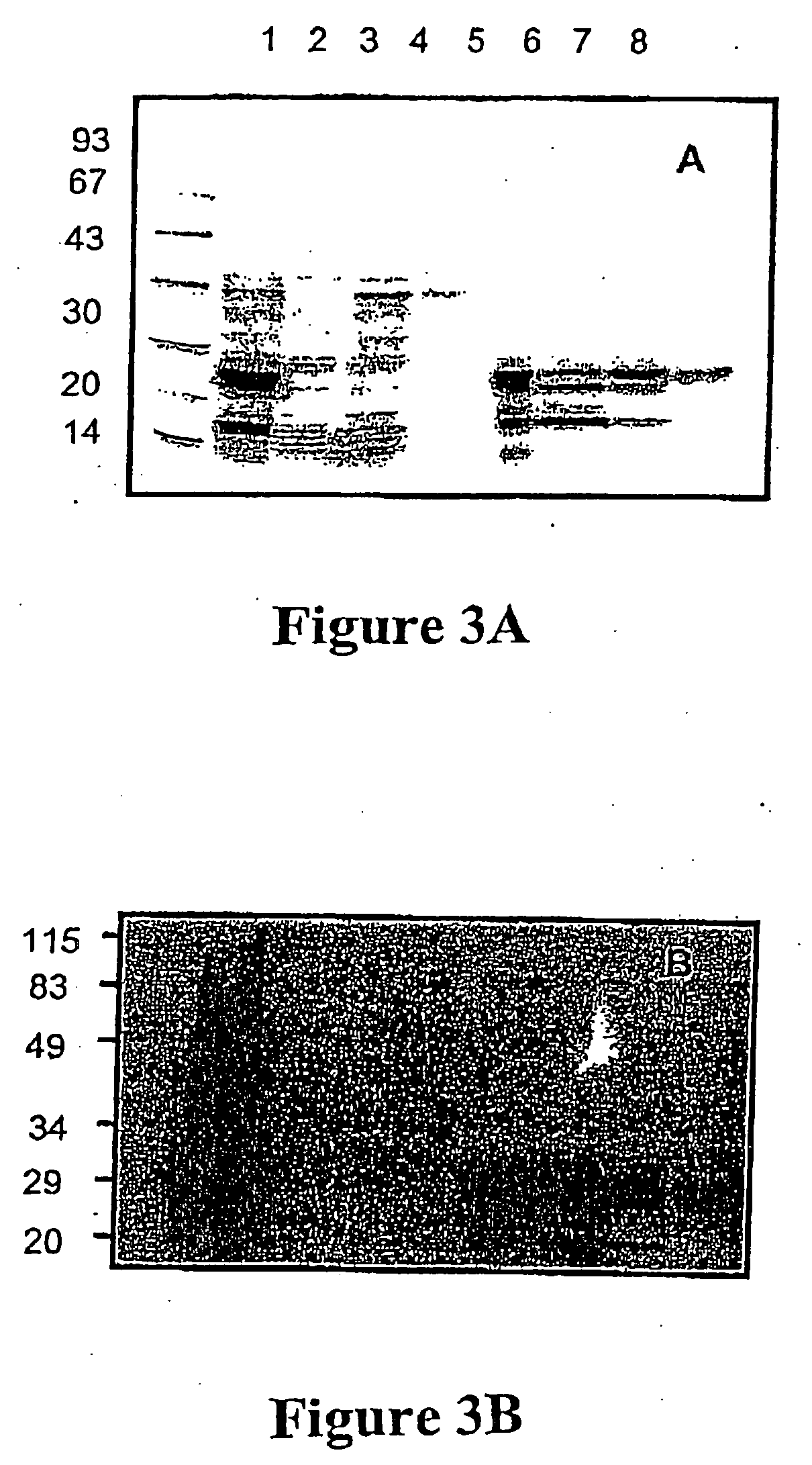
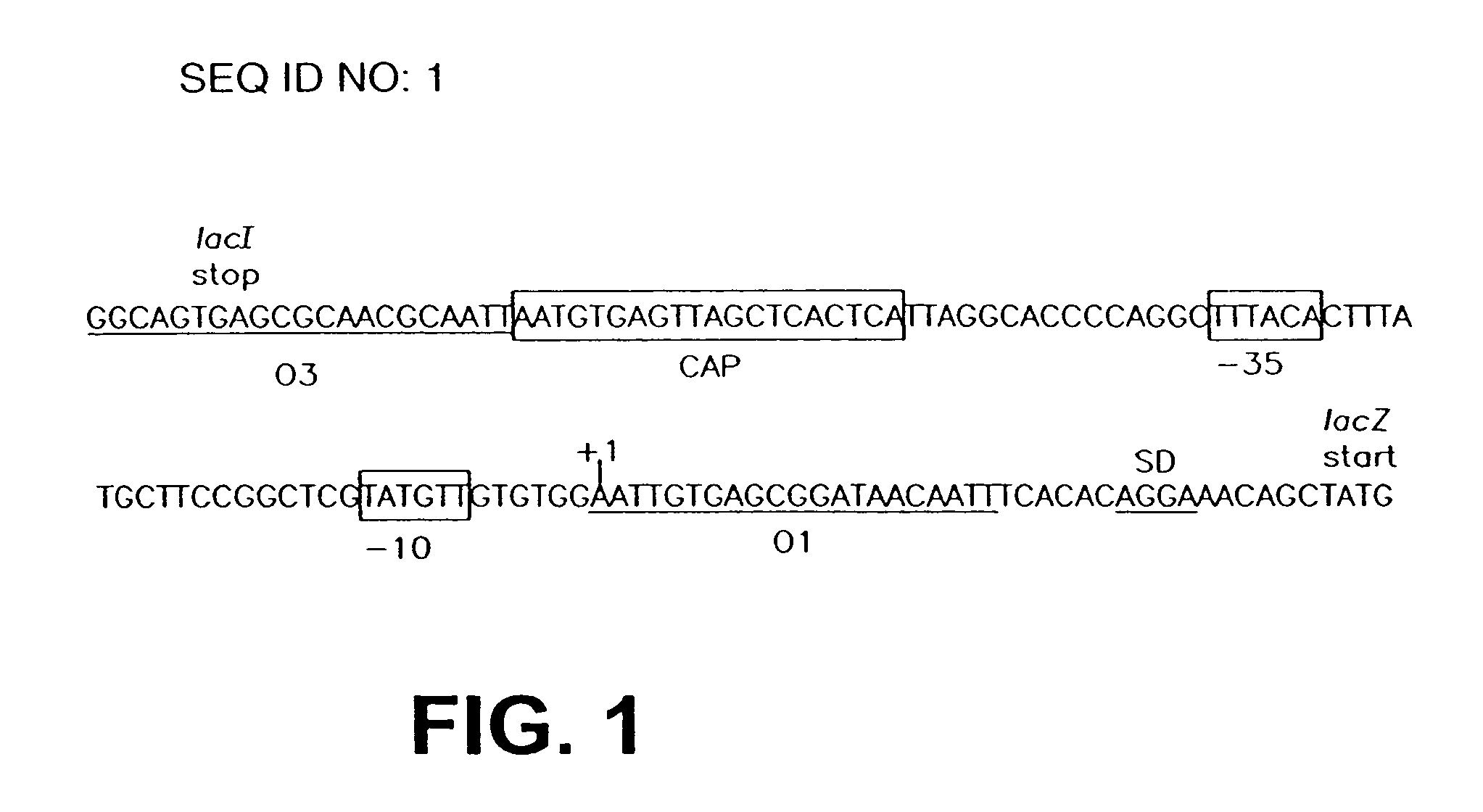
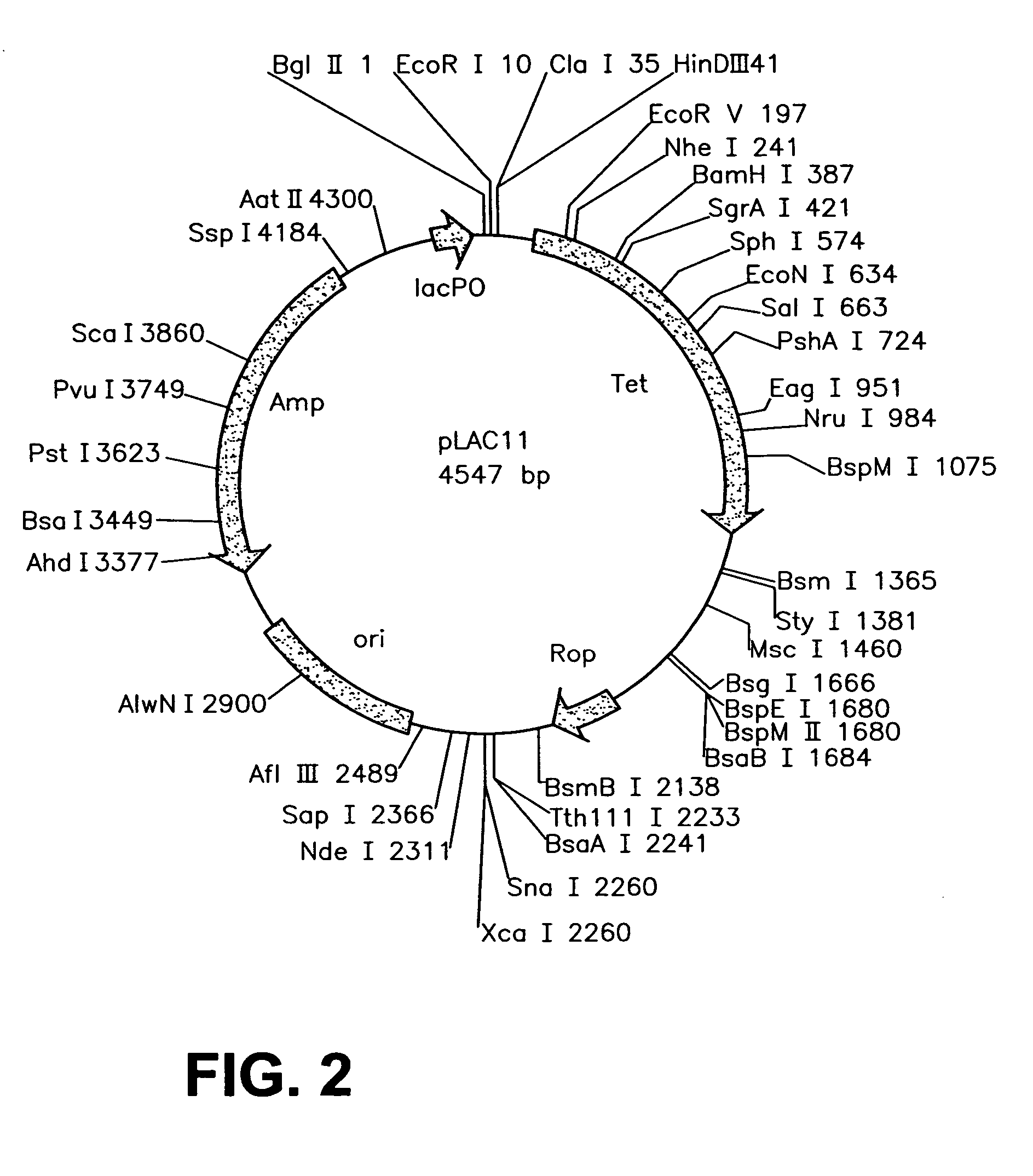
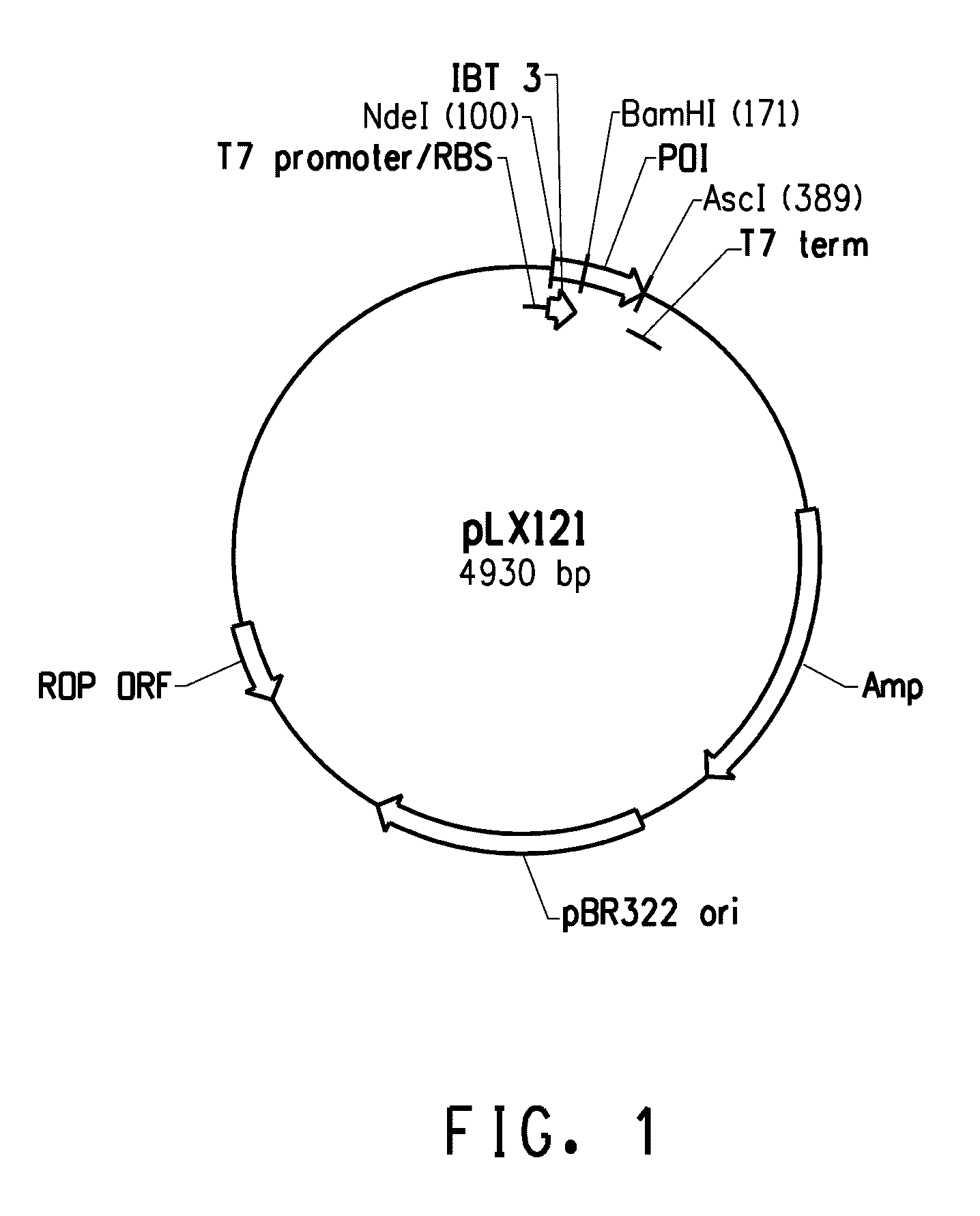
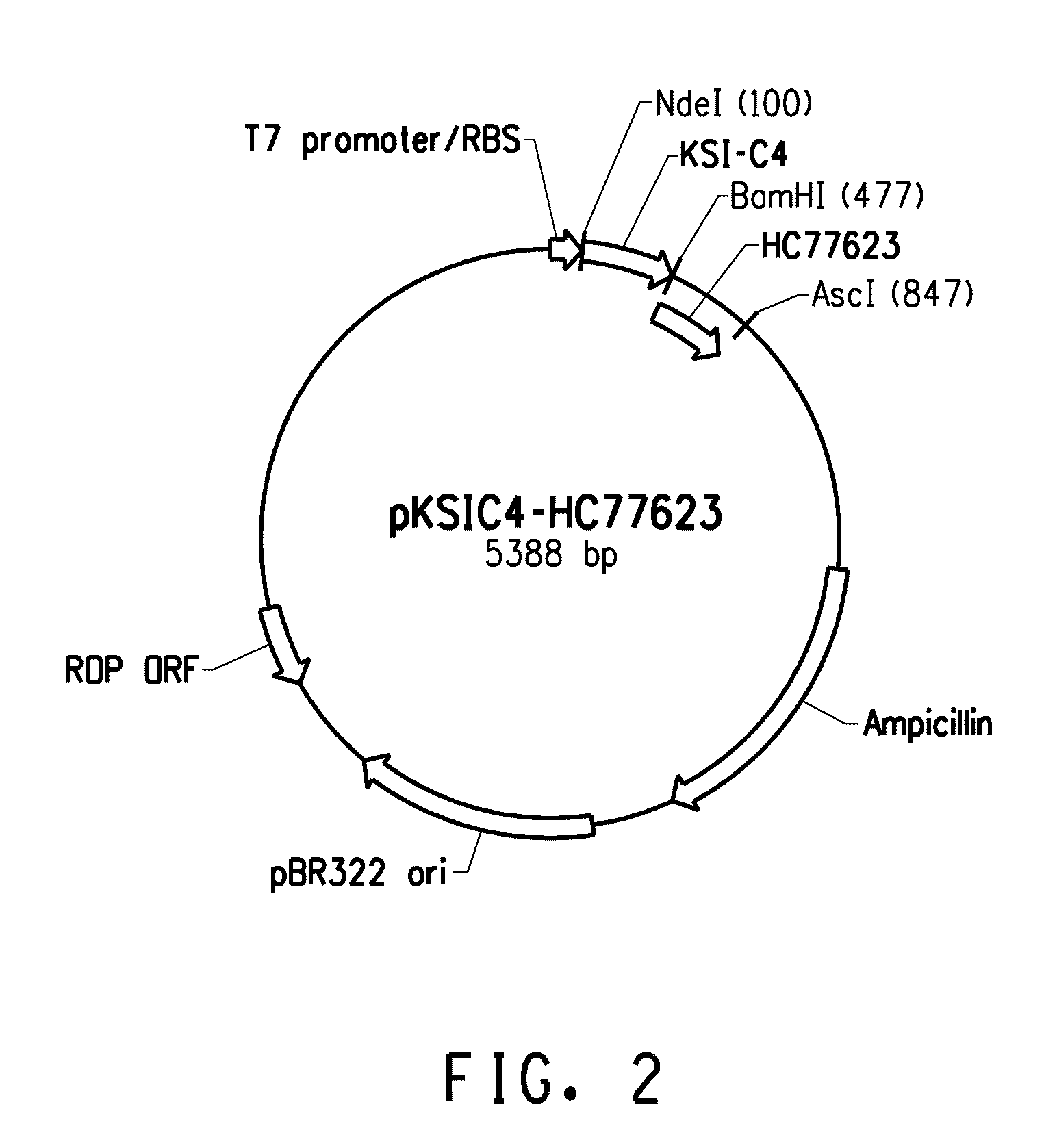
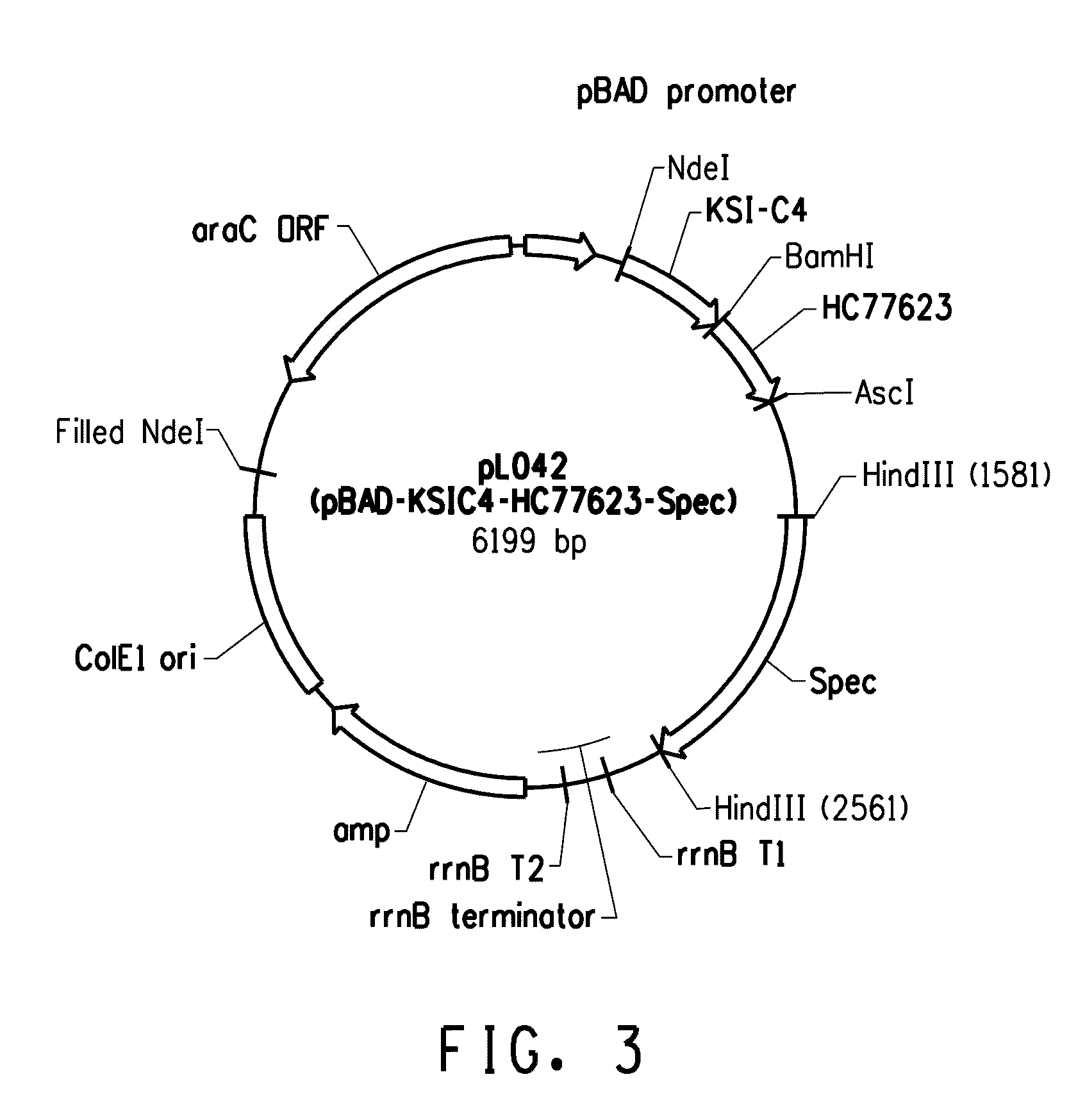
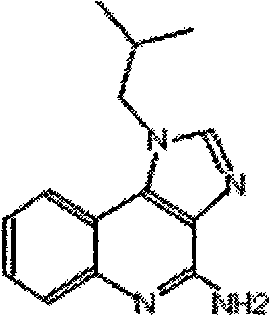
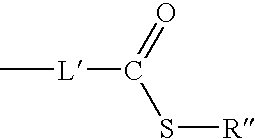
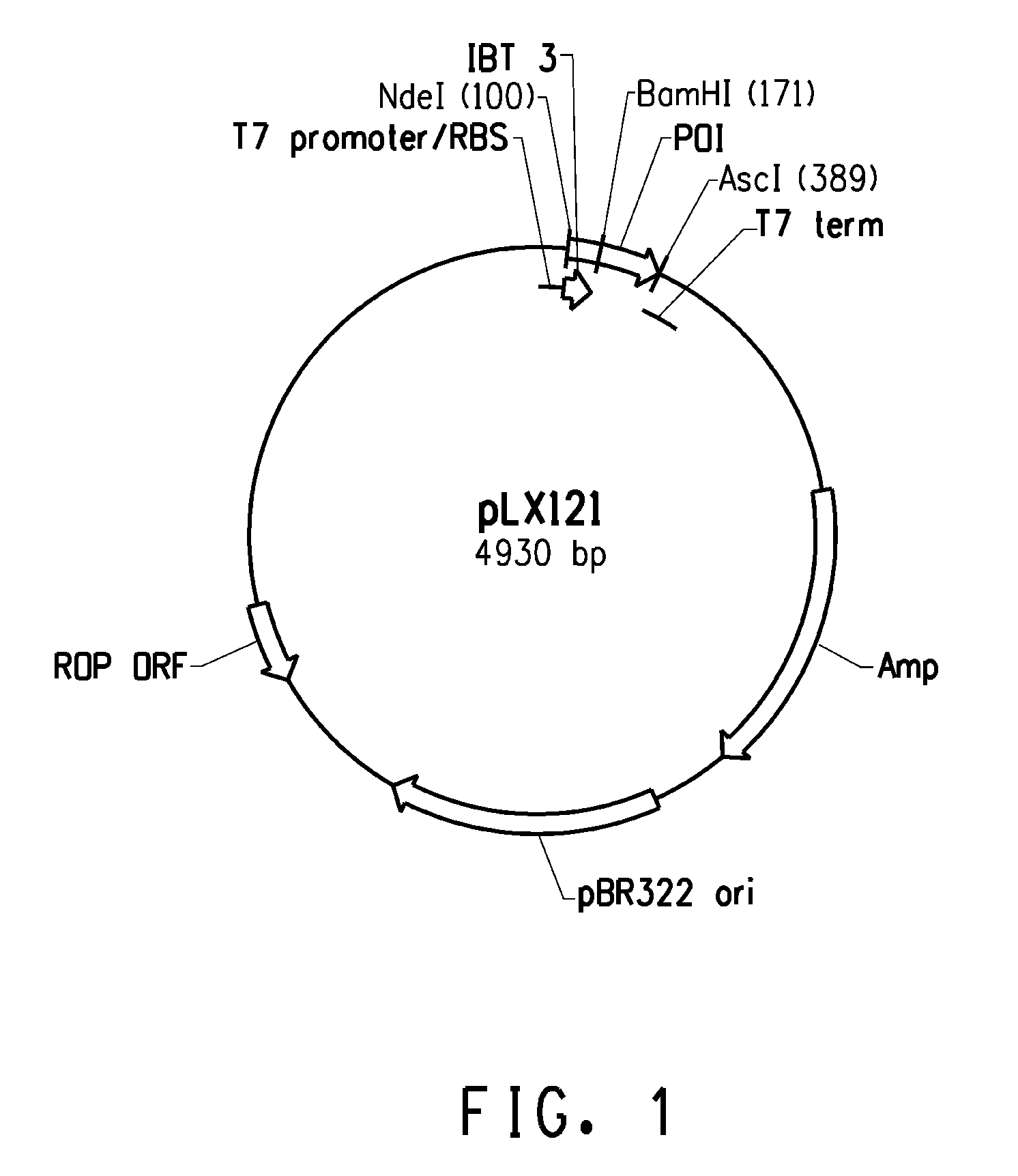
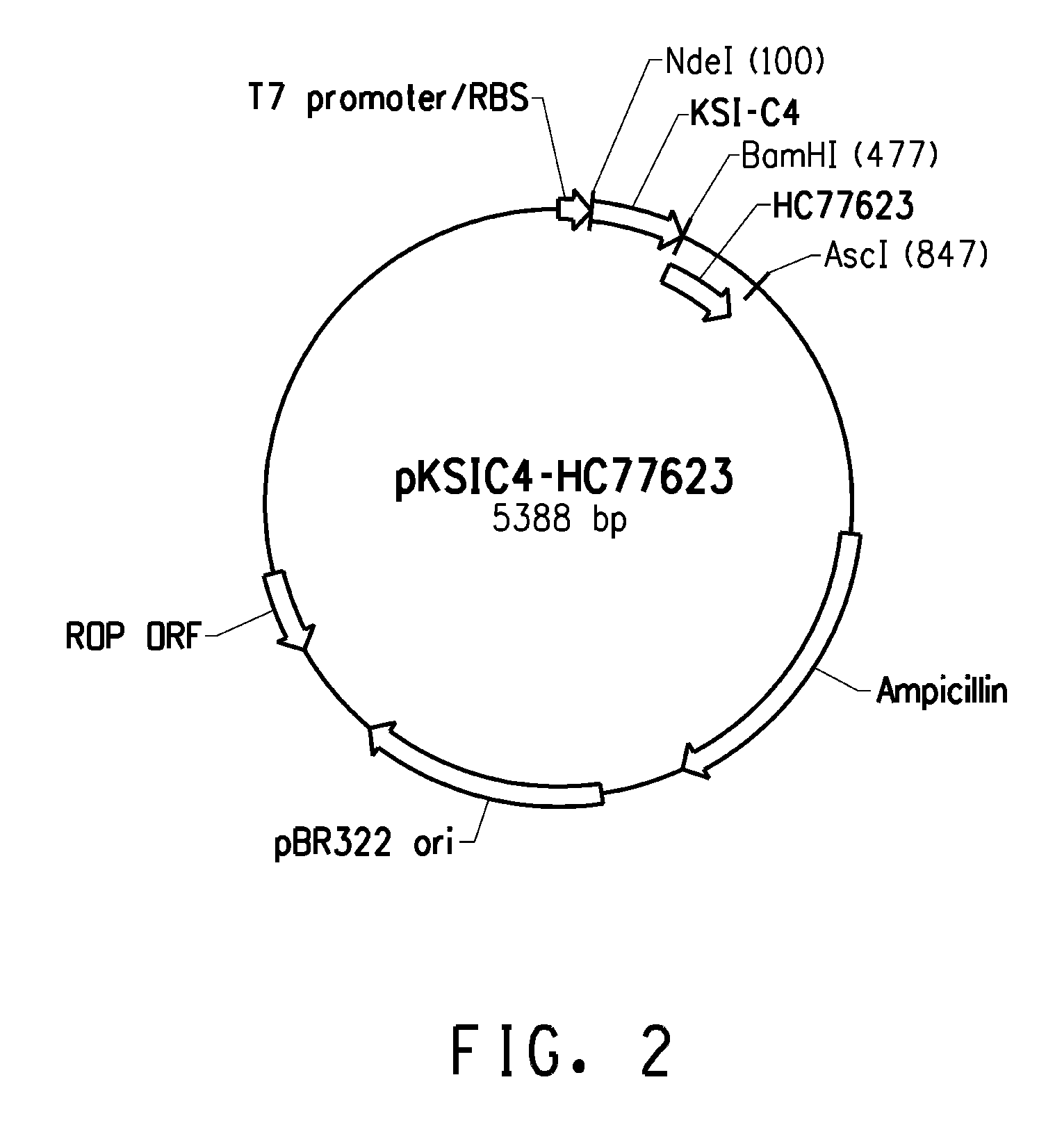
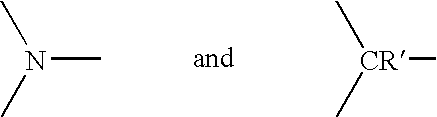Patents
Literature
103 results about "Recombinant peptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Novel peptide with osteogenic activity
The present invention provides a composition including an isolated or recombinant peptide component that has osteogenic cell proliferative activity. The peptide, which promotes proliferation of osteoblasts, is useful for treatment of fractures, as a filler in deficient sites of bone, for inhibition of decrease in bone substance related to osteoporosis and periodontic diseases, and for prevention of fractures associated with osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis. The peptide, or cells that have been genetically engineered to produce the peptide, can be combined with a bone-compatible matrix to facilitate slow release of the peptide to a treatment site and / or provide a structure for developing bone.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Recombinant peptide
InactiveUS7297516B2Simple and efficientHigh specific recrystallisation inhibiting activitiesFungiBacteriaRecombinant peptideAntifreeze activity
Use of a polypeptide or protein with amino acid sequence corresponding substantially to AFP-type III HPLC 12 as additive in a product for improvement of said product, said improvement residing in improved properties of modification of ice crystal growth processes influencing size and shape characteristics of ice in particular in regrowth thereby e.g. minimising potential freezing damage e.g. by preventing or inhibiting ice recrystallisation of the product upon freezing, said use occurring in a manner known per se for anti freeze peptides to obtain higher specific modification activity in particular antifreeze activity than obtainable with the same amount of Winter Flounder AFP.
Owner:GOOD HUMOR BREYERS ICE CREAM DIV OF CONOPCO
Peptide with osteogenic activity
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Purification of vascular endothelial growth factor-B
InactiveUS20070111944A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsHEXARecombinant peptide
The present invention provides a method for purifying recombinant peptides, polypeptides or proteins away from truncated or other full-length forms of these molecules. In particular the invention contemplates a method of purifying a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) molecule by subjecting a biological sample containing the molecule to be purified to affinity chromatography under conditions sufficient for the full length molecules to bind and not the truncated or clipped forms. In the preferred embodiment there are two columns, the first is based on affinity for a poly his tag, the second column based on heparin binding affinity. Particularly preferred VEGF molecules are untagged VEGF-B167, hexa-His-tagged VEGF-B167, hexa-His-tagged VEGF-B186 and hexa-His-tagged VEGF-B10-108.
Owner:AMRAD OPERATIONS PTY LTD
Stabilized bioactive peptides and methods of identification, synthesis and use
Owner:PEPTIDE BIOSCI
Recombinant peptides derived from the Mc3 anti-BA46 antibody, methods of use thereof, and methods of humanizing antibody peptides
InactiveUS20050169915A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenRecombinant peptide
The present invention provides recombinant peptides that specifically and selectively bind to the human milk fat globule (HMFG) antigen, BA46. In particular, the present invention provides recombinant variants of the Mc3 antibody, including humanized versions of Mc3. The variant Mc3 peptides are particularly useful for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic applications in the field of breast cancer. The present invention also provides methods for the humanization of antibodies such as murine monoclonal antibodies. The novel humanization methods are applied to the production of humanized Mc3 antibodies and it is shown that these humanized antibodies retain the ability to engage in high affinity binding to their cognate antigen. Such humanization enables the use of these antibodies for immunodiagnostic and immunotherapeutic applications in humans.
Owner:CANCER RES FUND OF CONTRA COSTA
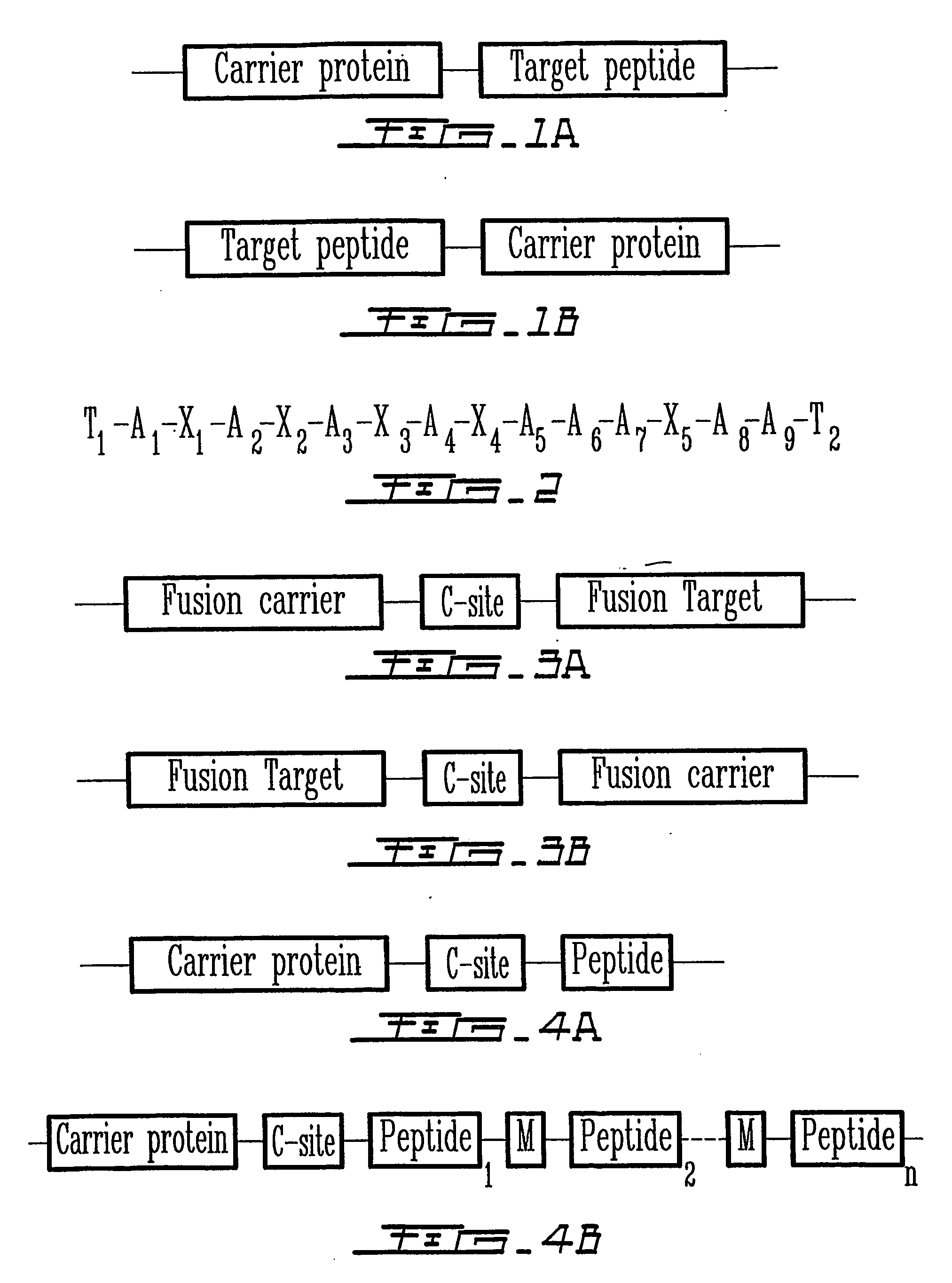
Staphylococcal nuclease fusion proteins for the production of recombinant peptides
InactiveUS7390639B2Easy to disassembleNot complicate subsequent stepSugar derivativesBacteriaInclusion bodiesHplc method
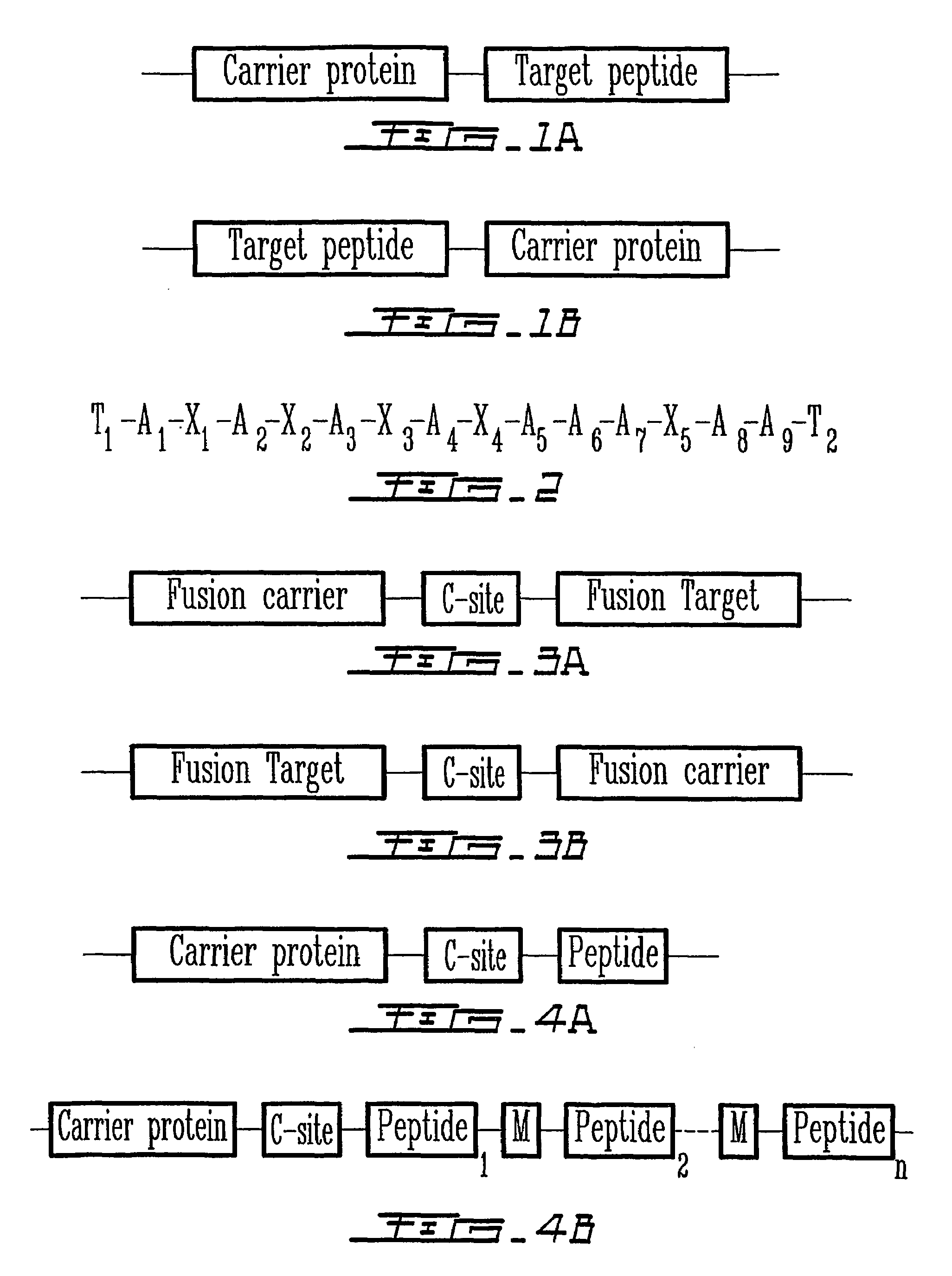
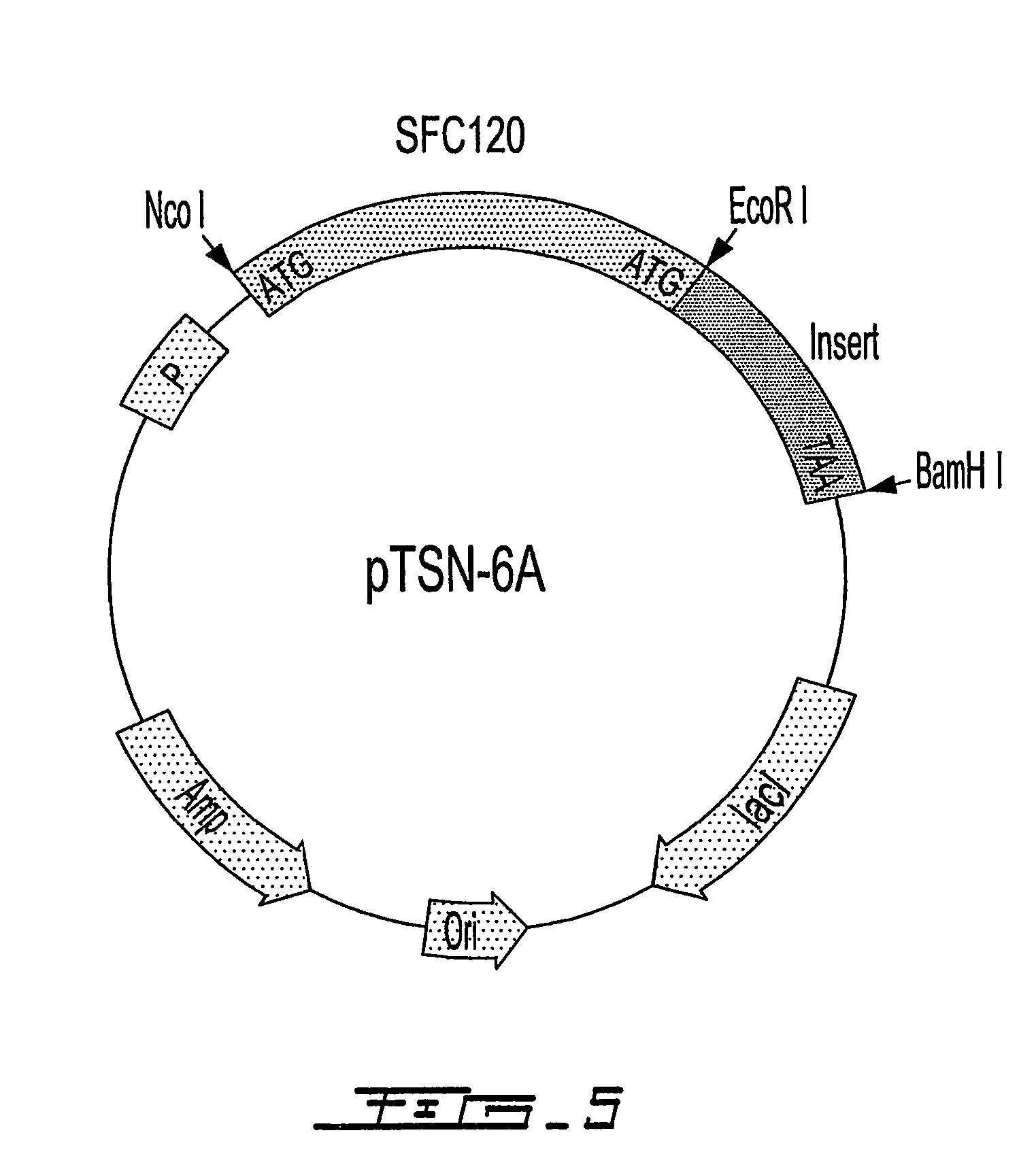
Peptides are produced as fusions with a suitable carrier protein. The carrier protein disclosed herein are adapted from the N-terminal domain of staphylococcus nuclease. This novel carrier protein acts to promote the over-expression of the peptide-protein fusion in the form of inclusion bodies, which minimizes in-cell proteolysis of desired peptides. The fusion protein is readily purified by conventional procedures or His-tag affinity chromatography when His-tag is inserted into the fusion protein. The target peptide is released from the purified fusion protein by a simple cleavage step and separated from the librated carrier protein by use of a reverse-phase HPLC process or by repeating the same affinity purification method. A particular advantage of the disclosed method, in addition to the obvious advantage of high yields, is its use for producing isotopically labeled peptides for NMR characterization of bioactive peptides and their interactions with target proteins.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Escherichia coli t7 expression vector, vectors for the co-expression and co-purification of recombinant peptides in/with carrier proteins, use of expression vectors for obtaining complexes with multiple antigens and immonomodulators
InactiveUS20180135060A1Increase productionAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliAmpicillin
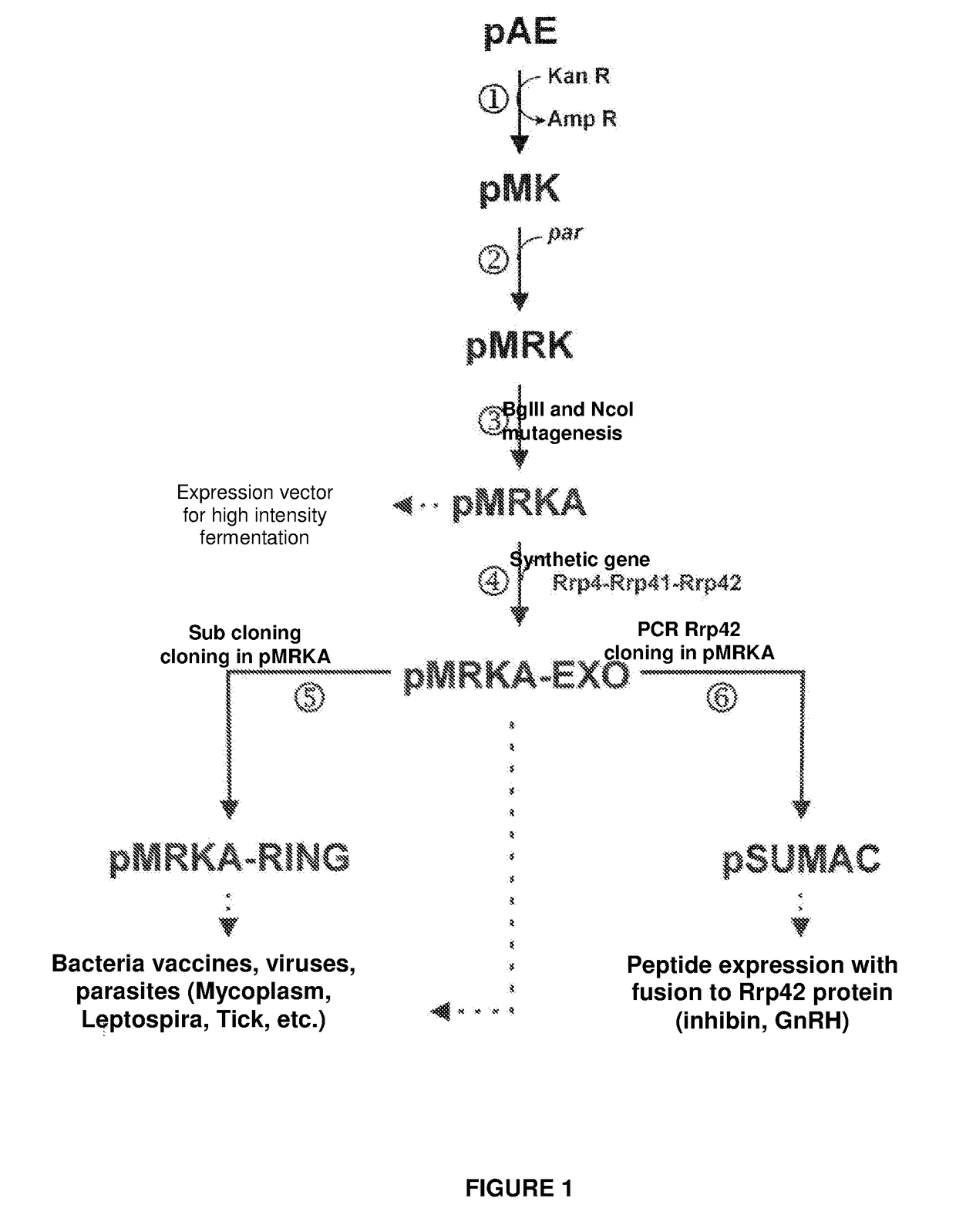
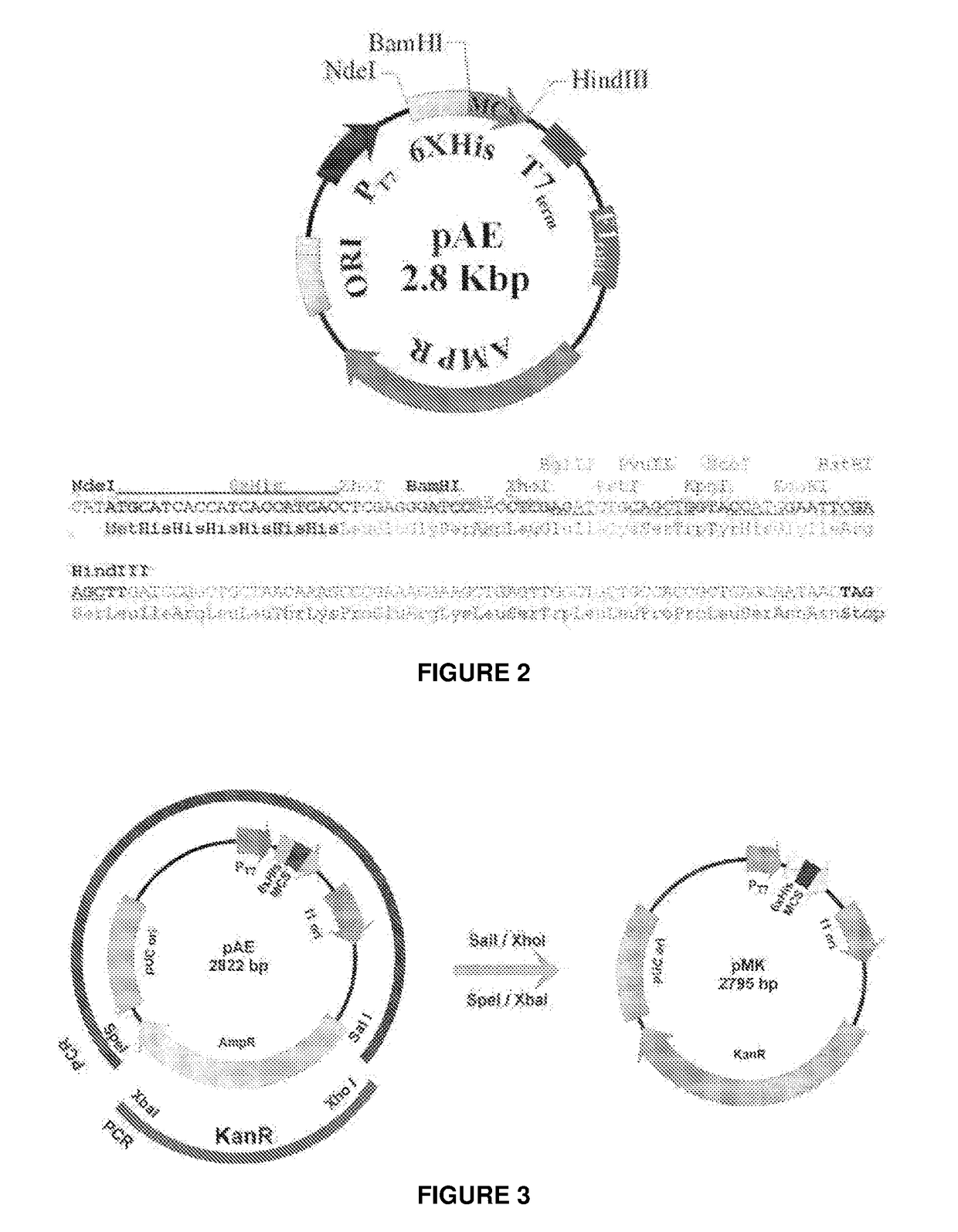
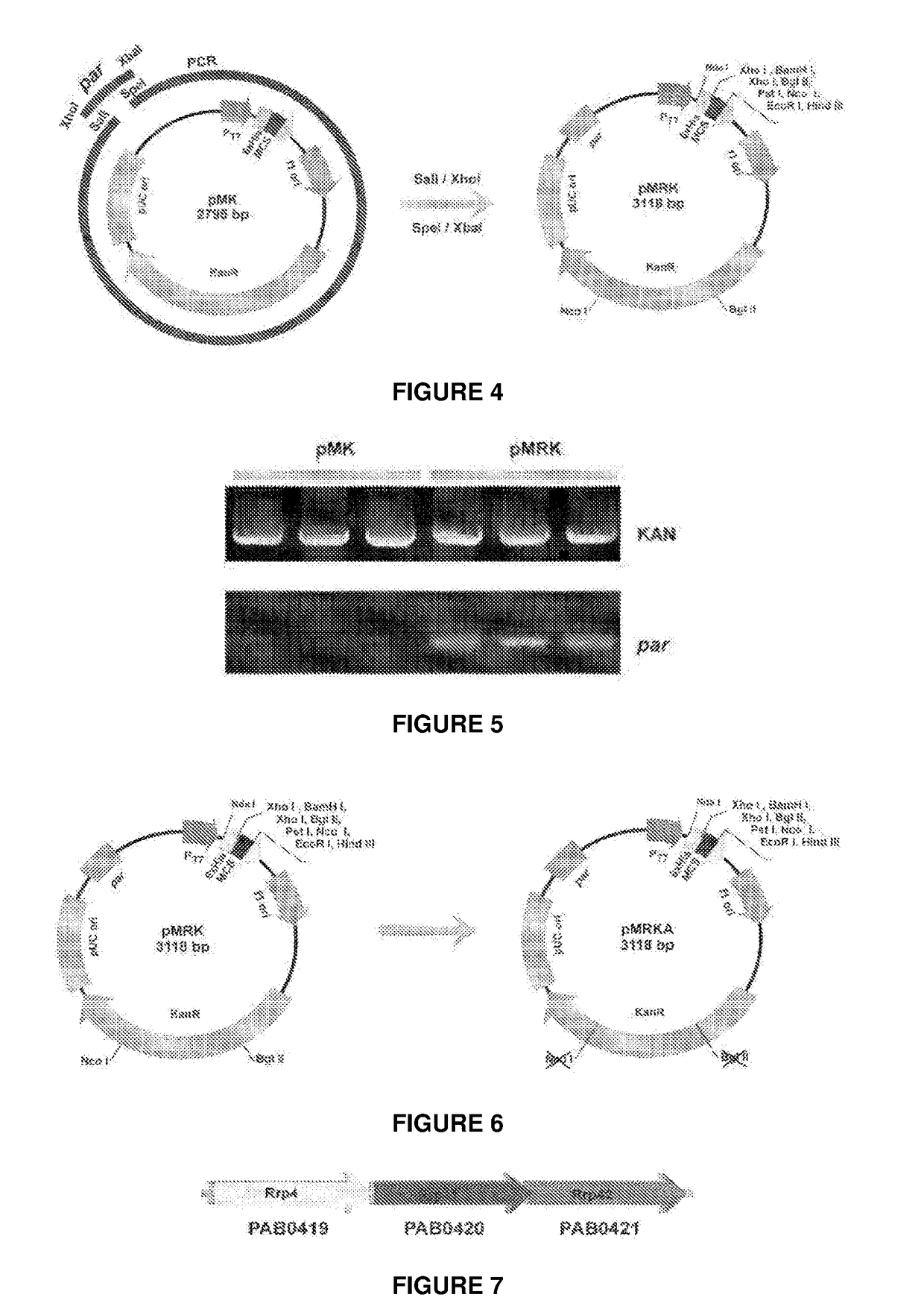
The present invention relates to a vector for the expression of recombinant proteins, antigens, pathogen-like particles and immunogenic complexes, said vector (pMRKA vector) being produced by modifying the plasmids containing the gene sequence of the T7 promoter of E. coli, this modification being mainly characterized by the substitution of the ampicillin-resistance gene by the kanamycin-resistance gene, and by the insertion of the par sequence (partition sequence which determines the efficient segregation of the plasmids in daughter cells during cell division). Also provided are expression vectors based on the pMRKA plasmid, which additionally comprise at least one of the gene sequences of the exosome of P. abyssi, which vectors are designated pMRKA-EXO, pMRKA-RING and pSUMAC. The invention also provides the vectors additionally comprising gene sequences with immunomodulatory or immunoregulatory activity, preferably the pMRKA-Z-Z-EXO and pMRKA-Z-Z-RING vectors. Other aspects of the invention include the method for producing said expression vectors and the use of the obtained vectors.
Owner:OURO FINO SAUDE ANIMAL
Methylotrophic bacterium for the production of recombinant proteins and other products
InactiveUS20060234336A1Overcome problemsLow costSugar derivativesBacteriaMethylobacterium extorquensRecombinant peptide
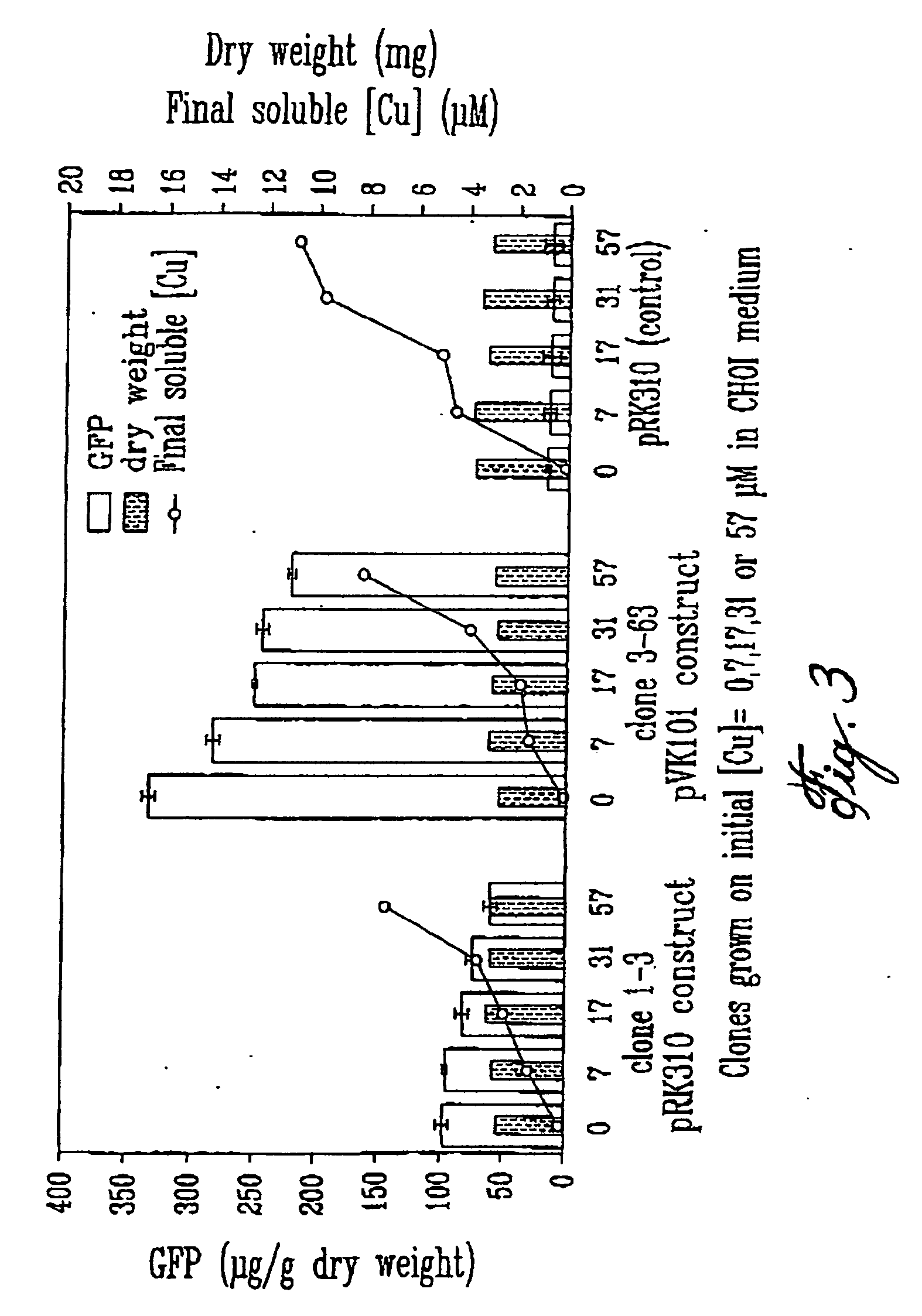
The present invention relates to a method of producing a recombinant peptide, a recombinant protein, or a product from metabolic engineering using a genetically modified methylotrophic bacterium, and more particularly to Methylobacterium extorquens ATCC 55366. The method comprises introducing am expression vector into the methylotrophic bacterium, the expression vector comprising a polynucleotide sequence, coding for a peptide or protein, or allowing for production of a product from metabolic engineering under the control of a regulated promoter. the method also comprises growing the genectically modified methylotrophic bacterium in a minimal salts medium lacking organic sugars and containing methanol. A metal ion may be used for regulating the expression of the polynucleotide sequence by the promoter.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK +1
Peptides for stimulating an immune response against melanoma
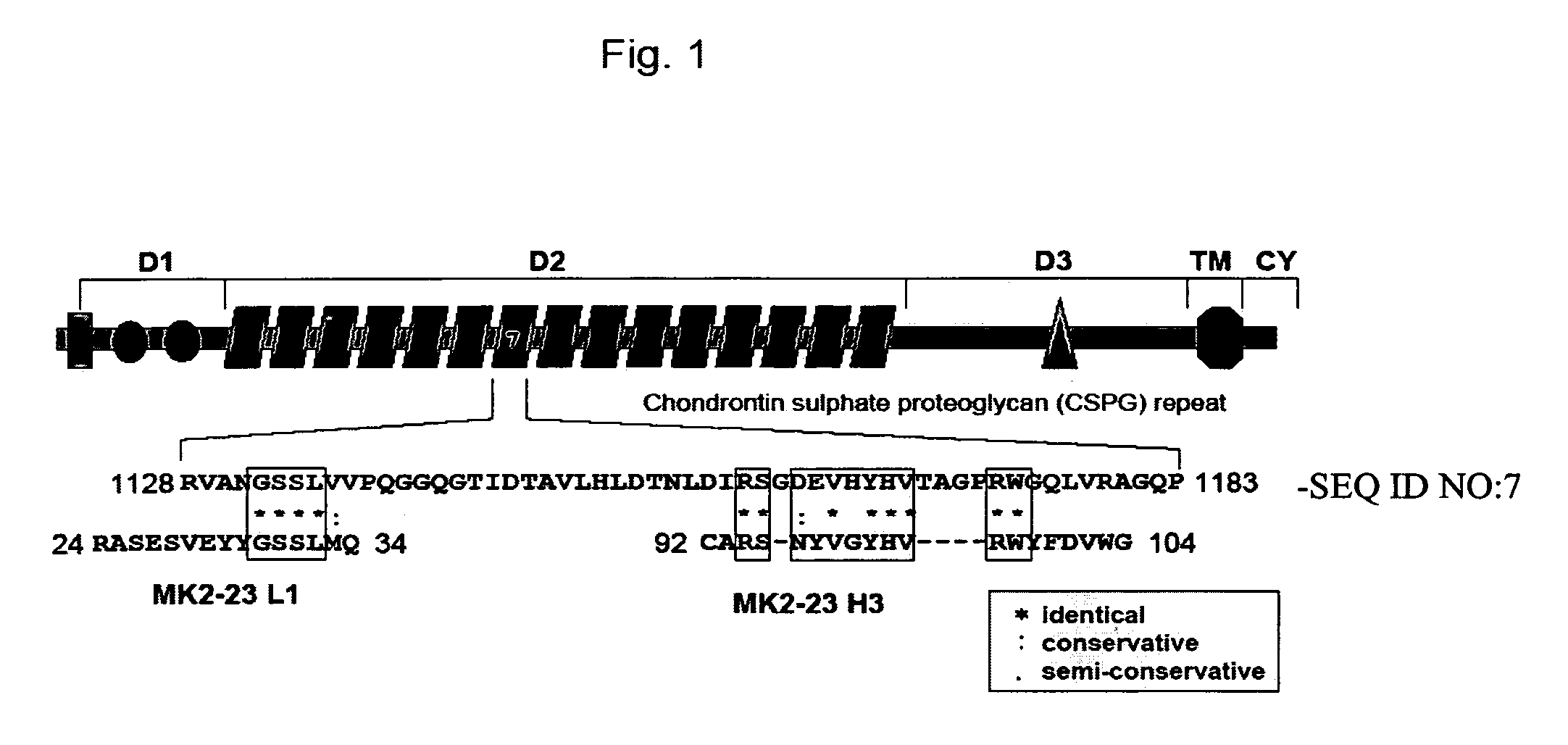
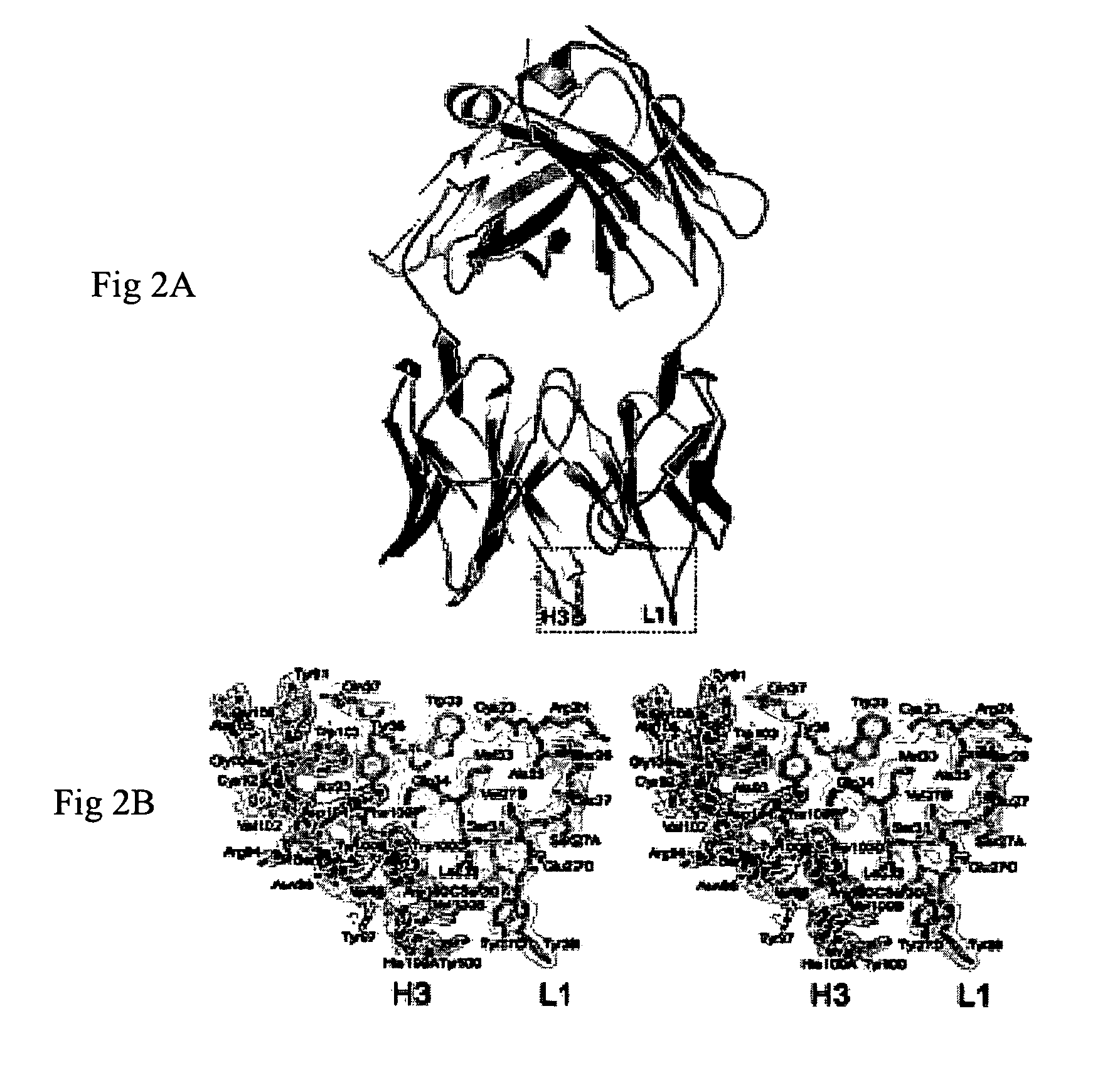
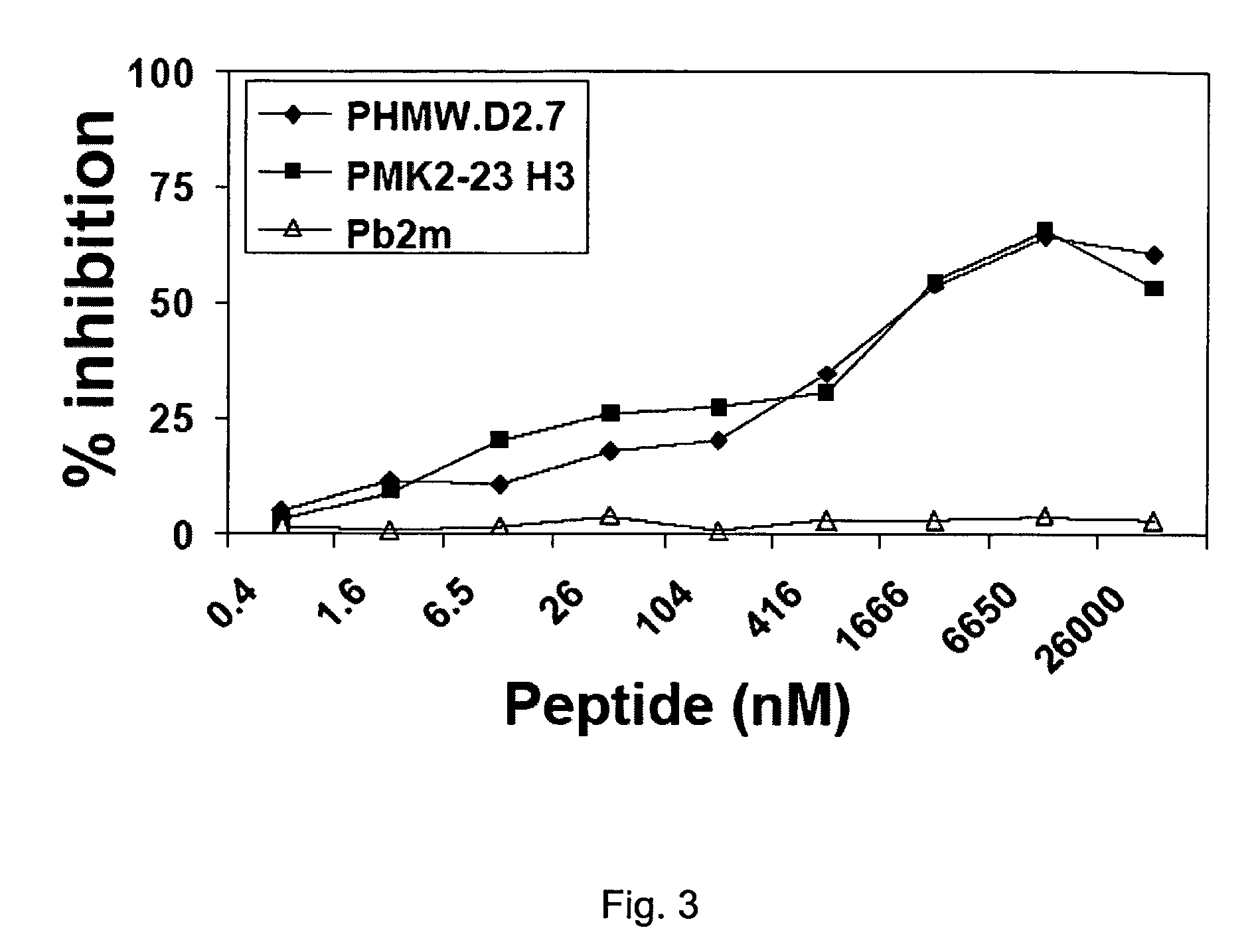
Provided in the present invention are recombinant peptides and a method for using the peptides in stimulating an immune response against human high molecular weight-melanoma associated antigen (HMW-MAA). The peptides were designed from the identification of regions of structural and amino acid sequence homology between HMW-MAA and the mouse anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody MK2-23. The method comprises the step of administering to an individual a peptide of the invention in an amount effective to elicit an immune response against HMW-MAA.
Owner:HAUPTMAN WOODWARD MEDICAL RES INST +1
Recombinant peptide production using a cross-linkable solubility tag
The invention relates to the recombinant expression of a peptide of interest in the form of a fusion protein comprising a solubility tag. The fusion protein comprises at least two portions separated by a cleavable peptide sequence wherein one portion is devoid of cysteine residues and the second portion comprises an effective number of cross-linkable cysteine residues. After cell lysis and isolation of the fusion protein, the fusion protein is subsequently cleaved into a mixture of first and second portions. Oxidative cross-linking is used to selectively precipitate one of the two portions to facilitate simple and effective separation of the peptide of interest.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Compound immunological adjuvant and vaccine
ActiveCN101850117AHigh activityImprove immune responseViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsMicroorganismRecombinant peptide
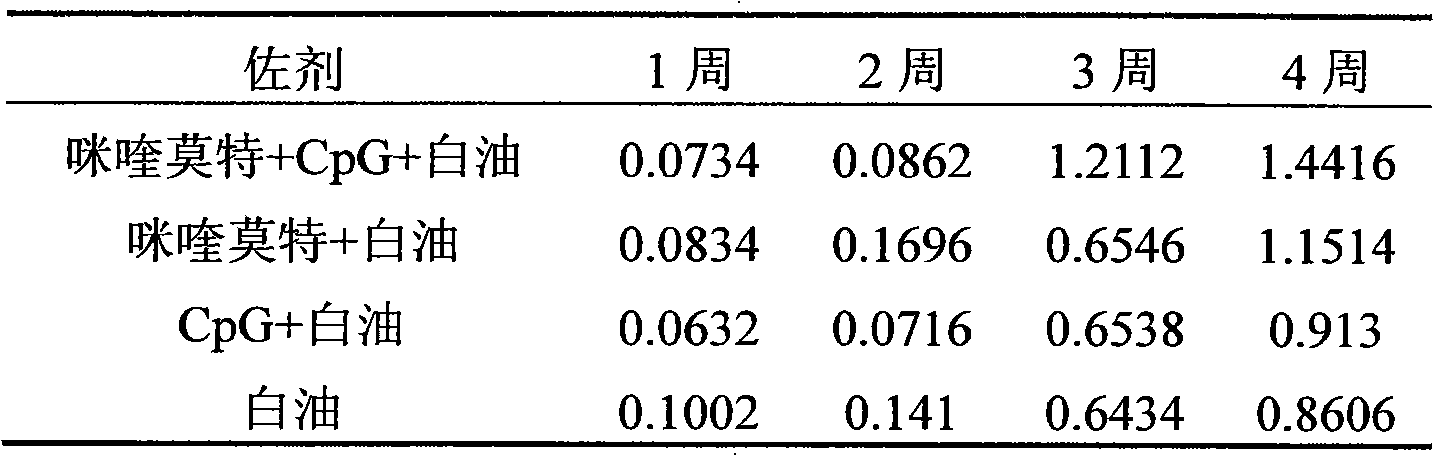
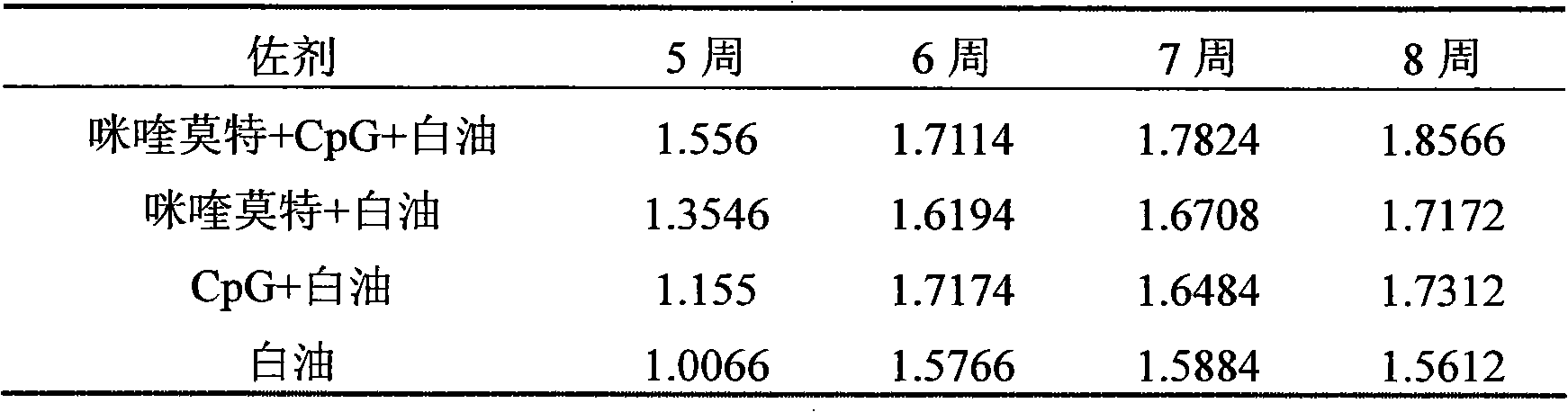
The invention relates to a compound immunological adjuvant comprising a water phase solution and an oil phase solution which are respectively prepared, wherein the water phase solution is a CpG water solution the concentration of which is 0.5 to 2.0mg / mL; the oil phase solution is an imiquimod white oil solution the concentration of which is 0.25 to 1.0mg / mL; and the volume ratio of the water phase solution to the oil phase solution is 1:6. The invention also relates to a vaccine prepared from one or more antigens selected from attenuated live full microorganisms, inactivated microorganisms, recombinant peptide and proteins, synthetic peptide and cracked microorganisms and the water phase solution and the oil phase solution in the compound immunological adjuvant according to the volume ratio of 1:1:6. By the compounding of imiquimod, CpG and a white oil component, the compound immunological adjuvant has an obvious synergistic effect and enhances the immunological activity reactions of Th1 and Th2, so that the activity of stimulated immunological cells is obviously enhanced.
Owner:国家兽用生物制品工程技术研究中心 +2
Phage display vector, phages encoded thereby, and methods of use thereof
Filamentous bacteriophages are particularly efficient for the expression and display of combinatorial random peptides. Two phage proteins are often employed for peptide display: the infectivity protein, pIII and the major coat protein, pVIII. The use of pVIII typically requires the expression of two pVIII genes: the wild type and the recombinant pVIII genes to generate mosaic phages. “Type 88” vectors contain two pVIII genes in one phage genome. A novel “type 88” expression vector has been rationally designed and constructed, which can be used to express recombinant peptides as pVIII chimeric proteins in mosaic bacteriophages. This vector is not only genetically stable but also of high copy number and produces high titers of recombinant phages.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
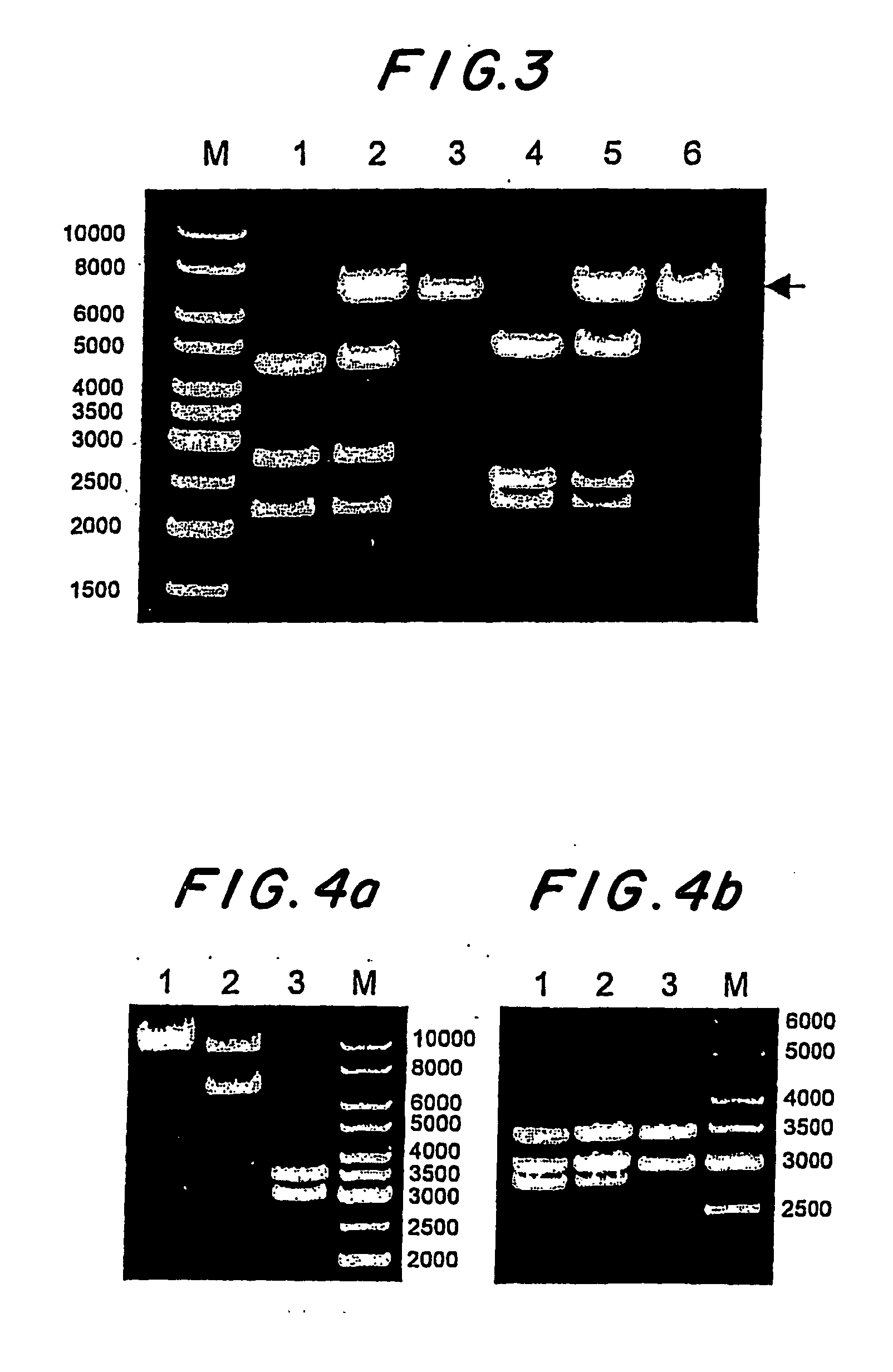
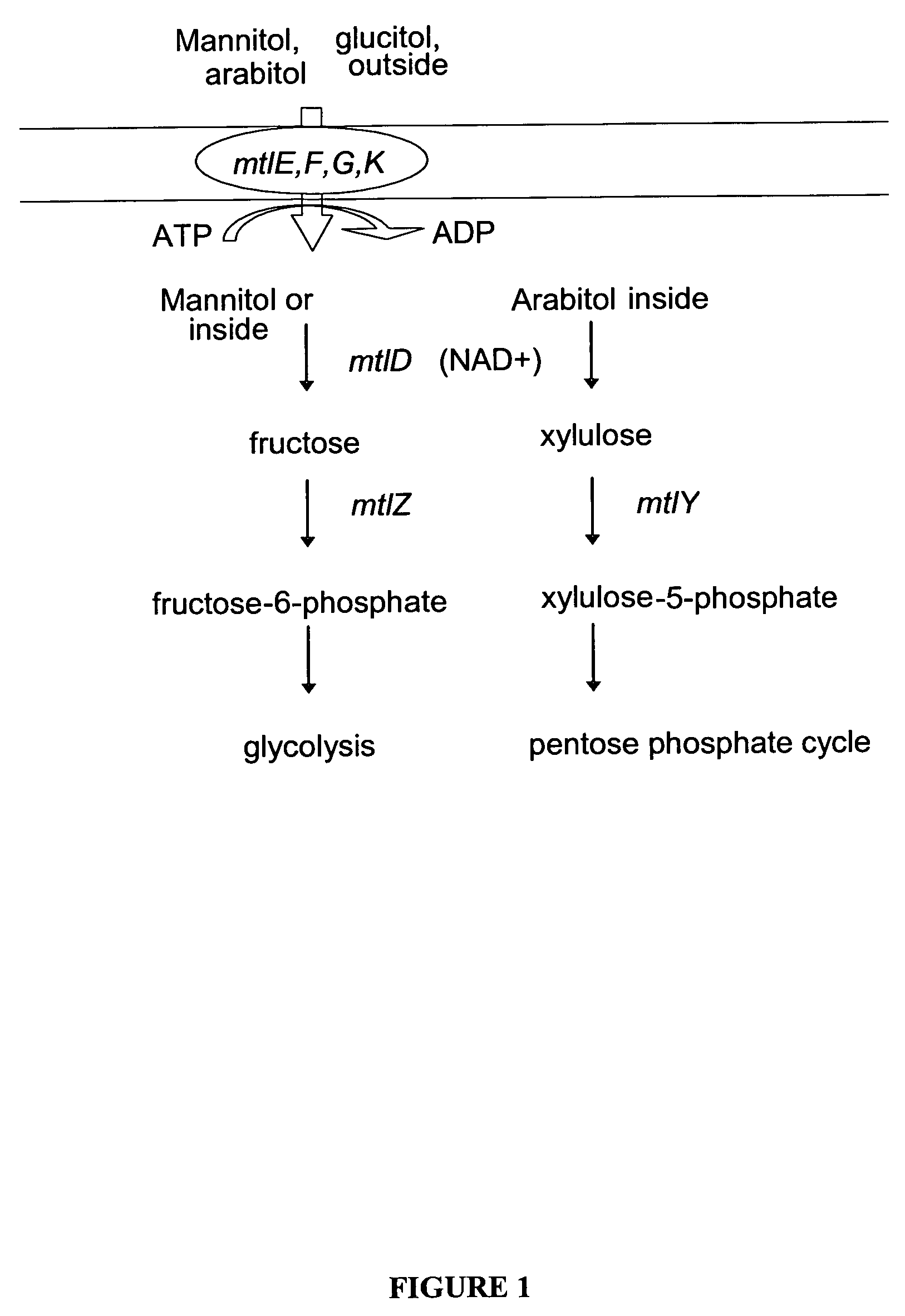
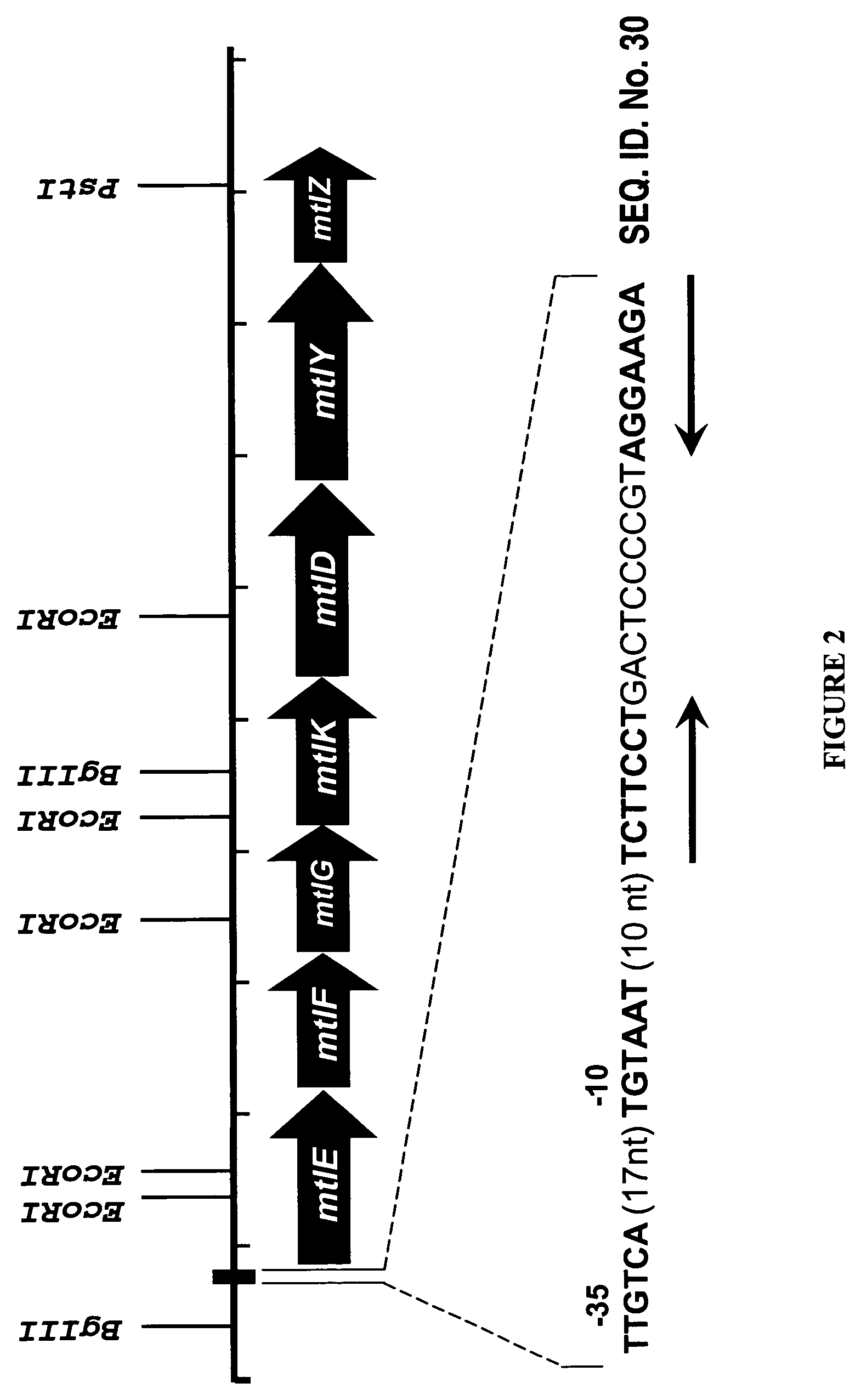
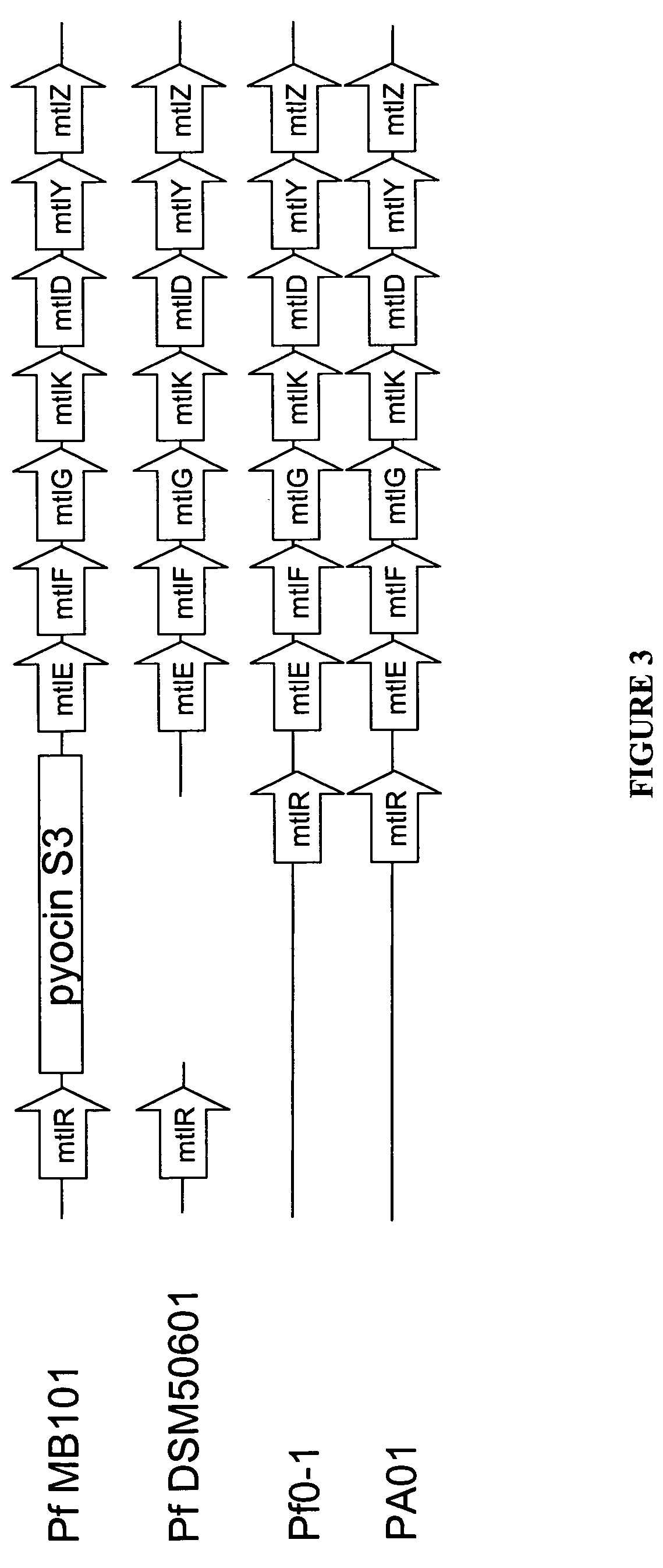
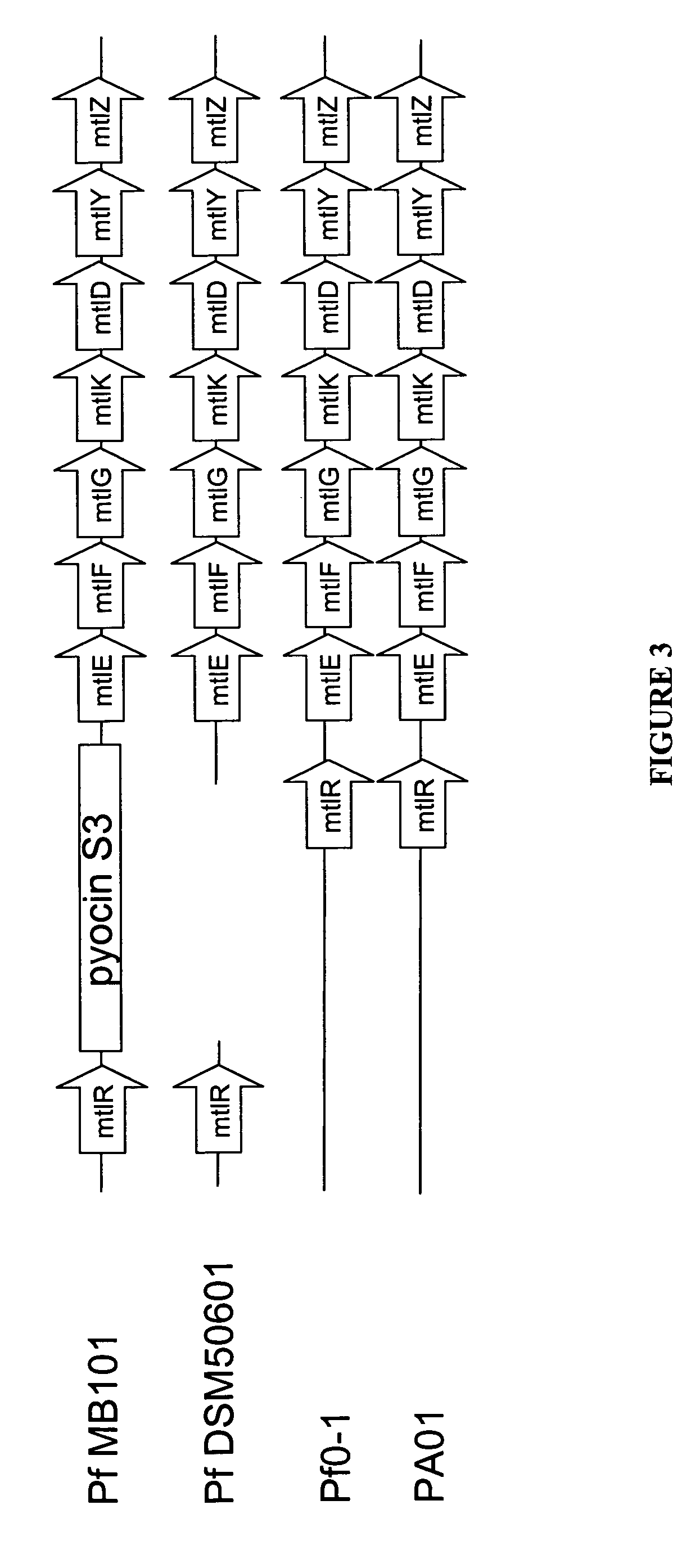
Mannitol induced promoter systems in bacterial host cells
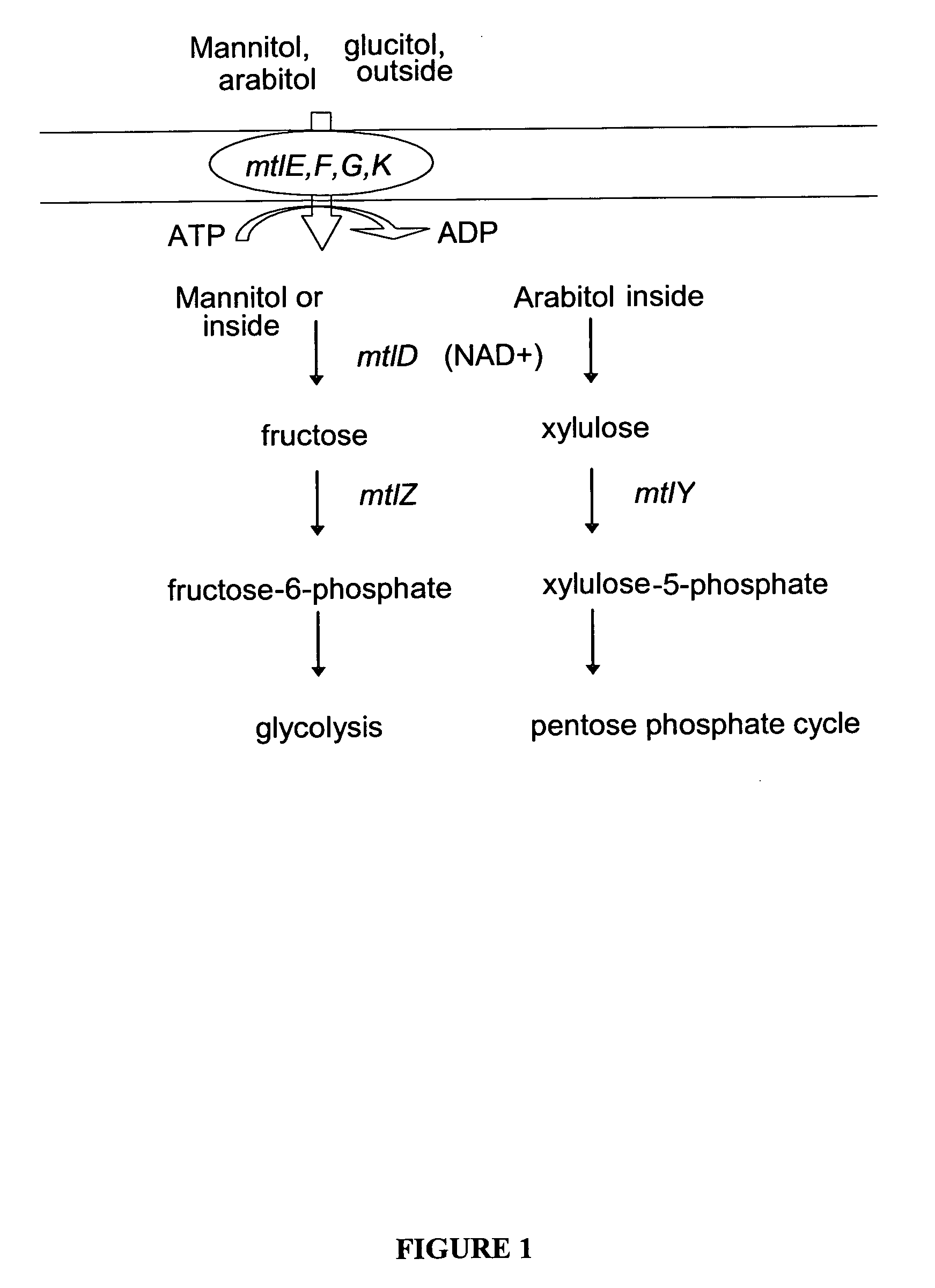
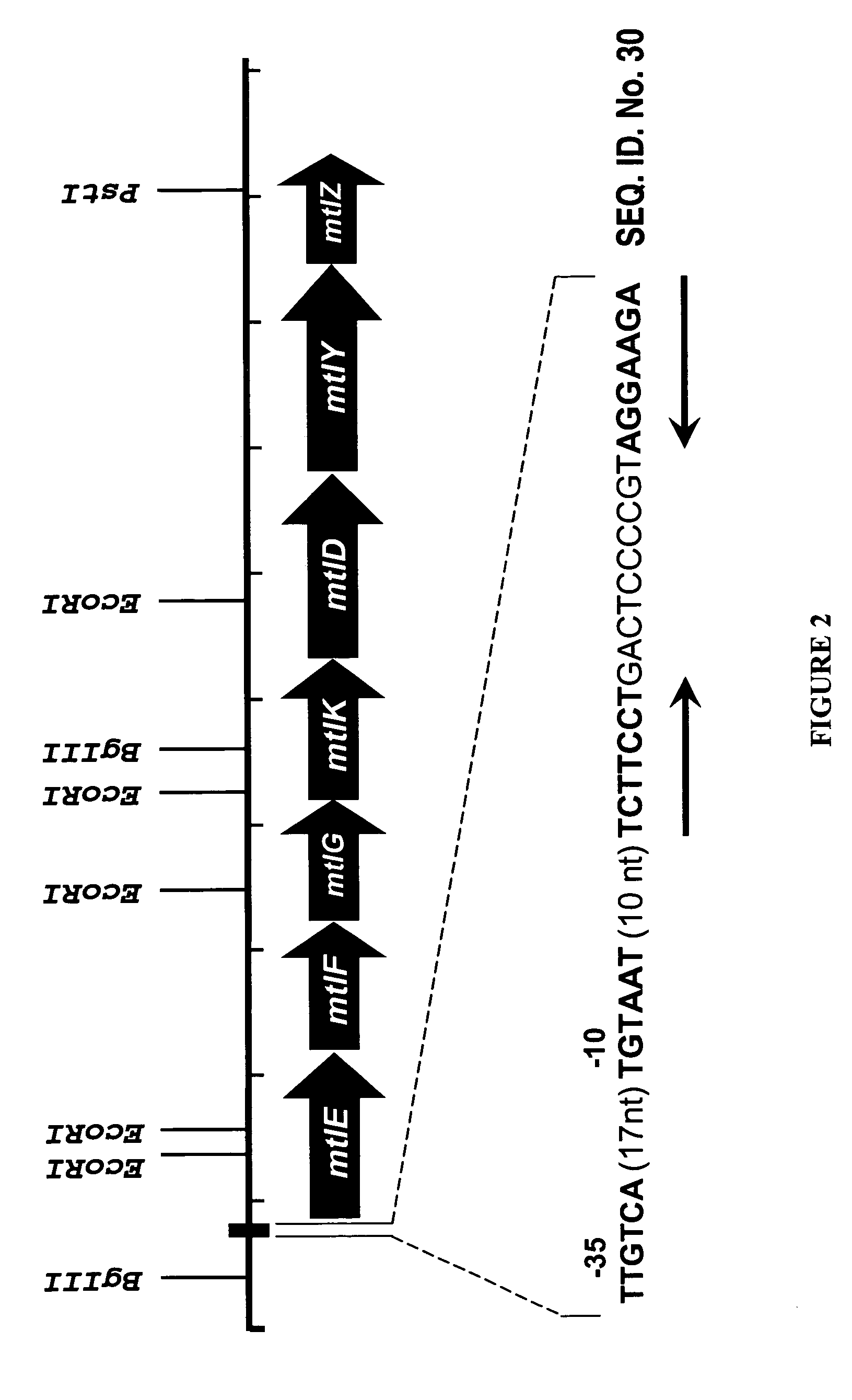
ActiveUS7476532B2Continuous and stable levelIncrease stringencyBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyBacteroides
The present invention provides methods for producing recombinant peptides in a bacterial host utilizing a mannitol, arabitol, glucitol, or glycerol-inducible promoter, wherein the host bacterial cell that produces the peptide has been rendered incapable of degrading or metabolizing mannitol, arabitol, or glucitol, or derivatives or analogues thereof. The present invention provides bacterial cells that have been genetically altered to inhibit the metabolism or degradation of mannitol, glucitol, or arabitol, or derivatives or analogues thereof. The present invention utilizes mannitol, arabitol, glucitol, or glycerol to induce expression of a target polypeptide from an inducible promoter, allowing for the use of an inexpensive and stable carbon source inducer in the fermentation processes for the production of recombinant peptides.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Separatome-based protein expression and purification platform
InactiveUS8927231B2Easy to separatePromote recoveryBacteriaUnicellular algaeEscherichia coliChromatographic separation
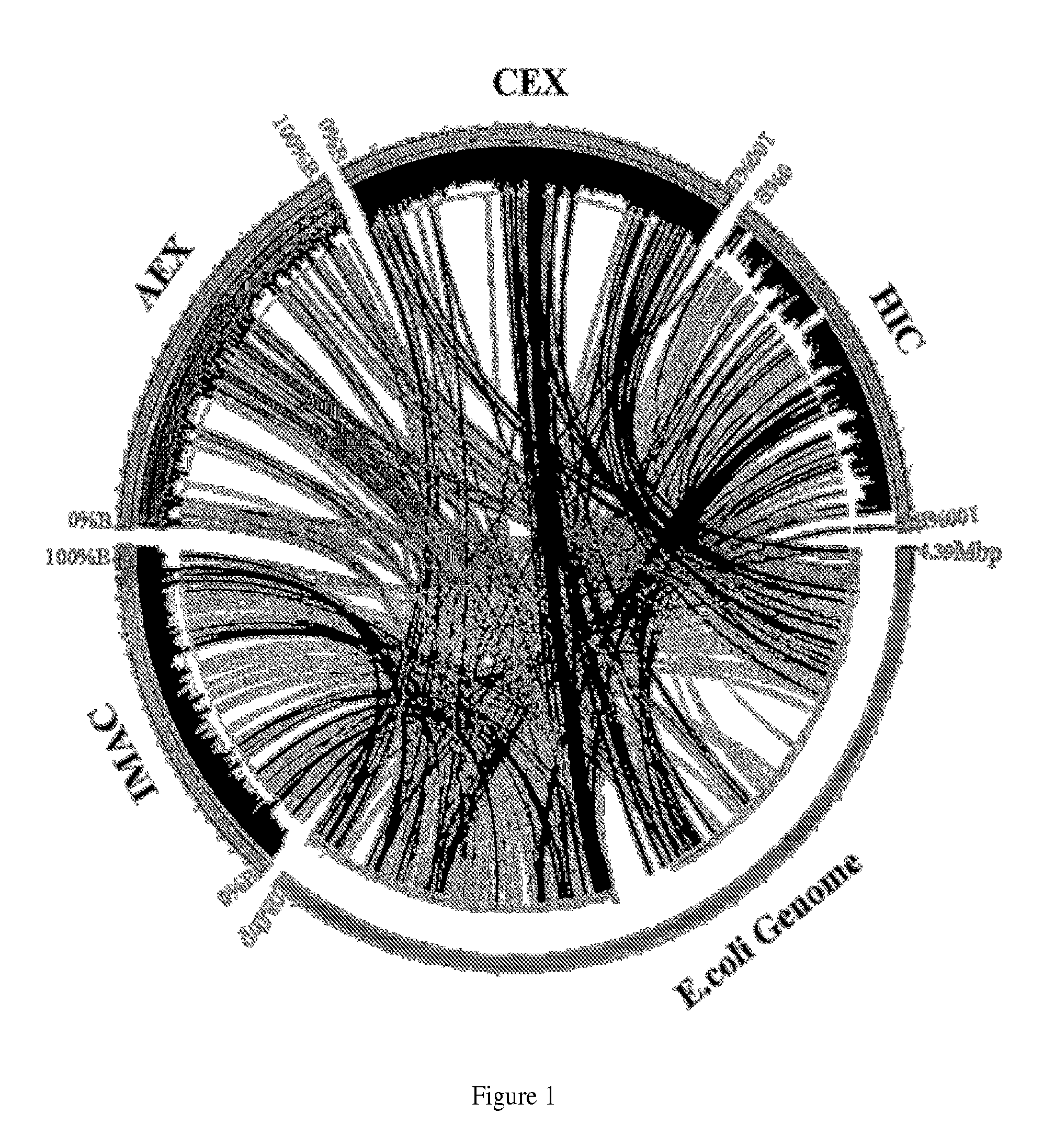
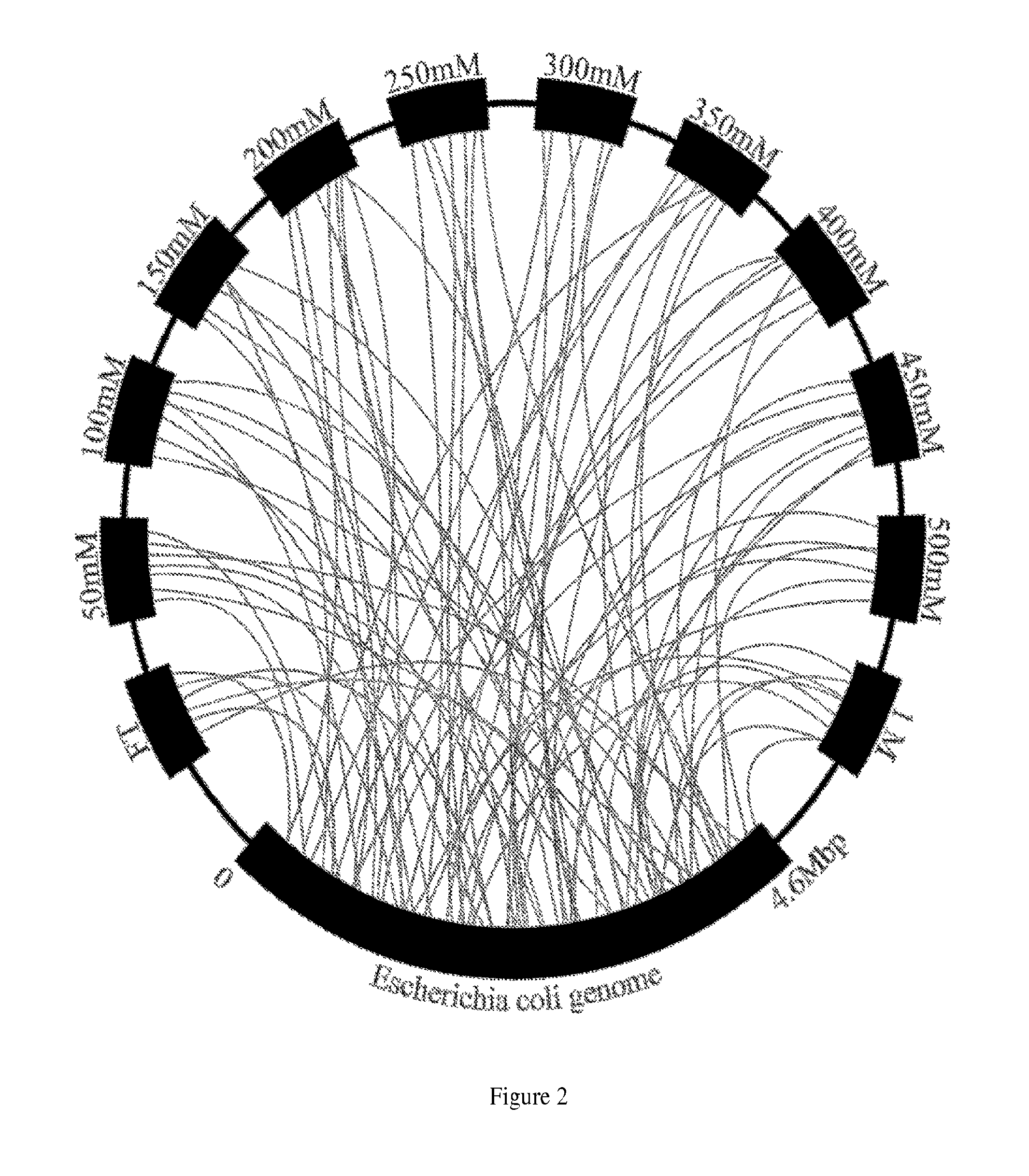
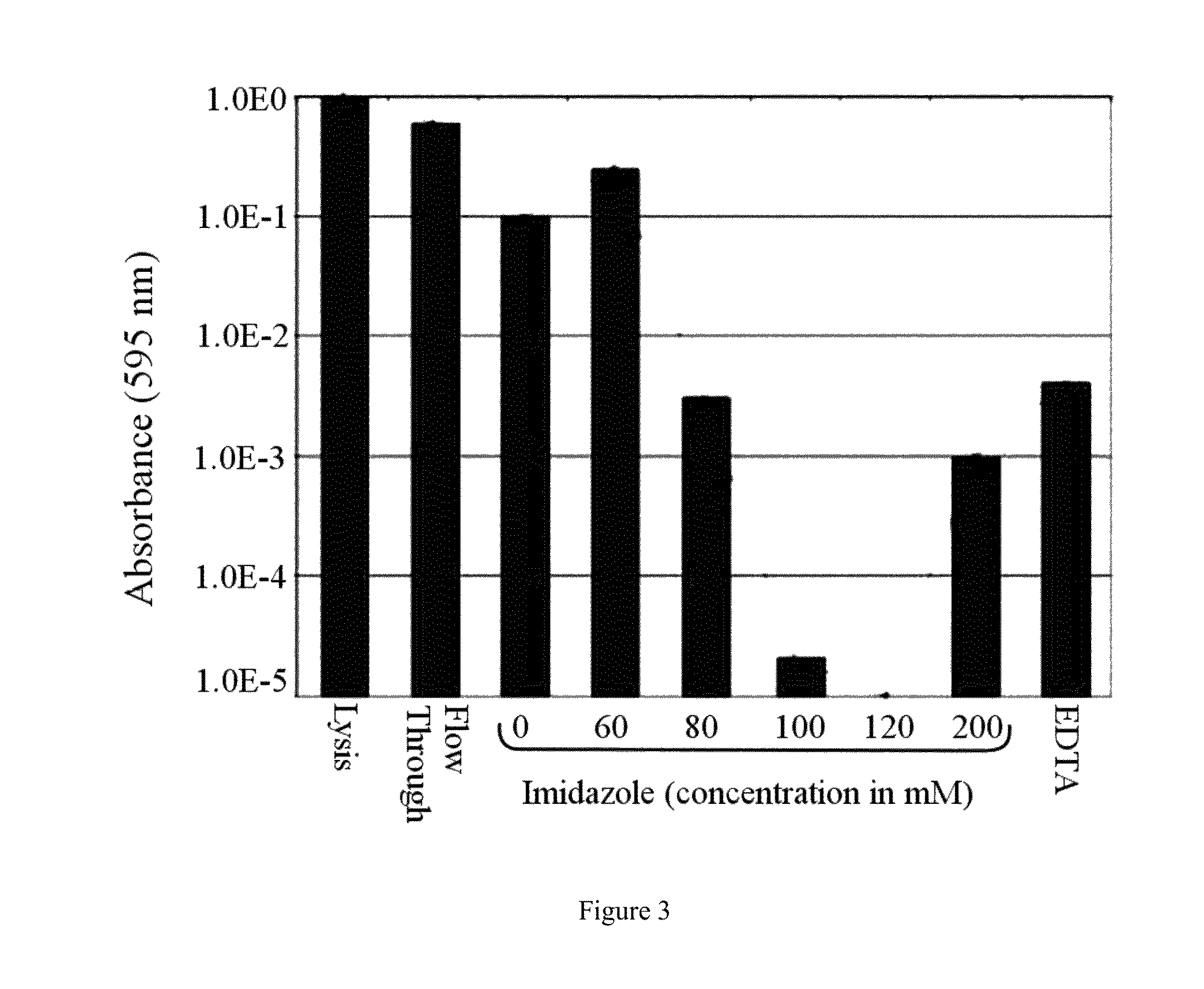
Provided is a separatome-based recombinant peptide, polypeptide, and protein expression and purification platform based on the juxtaposition of the binding properties of host cell genomic peptides, polypeptides, and proteins with the characteristics and location of the corresponding genes on the host cell chromosome, such as that of E. coli, yeast, Bacillus subtilis or other prokaryotes, insect cells, mammalian cells, etc. This platform quantitatively describes and identifies priority deletions, modifications, or inhibitions of certain gene products to increase chromatographic separation efficiency, defined as an increase in column capacity, column selectivity, or both, with emphasis on the former. Moreover, the platform provides a computerized knowledge tool that, given separatome data and a target recombinant peptide, polypeptide, or protein, intuitively suggests strategies leading to efficient product purification. The separatome-based protein expression and purification platform is an efficient bioseparation system that intertwines host cell expression systems and chromatography.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +1
Genes that increase peptide production
InactiveUS20100159513A1Increase volumeHigh expressionBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliBiotechnology
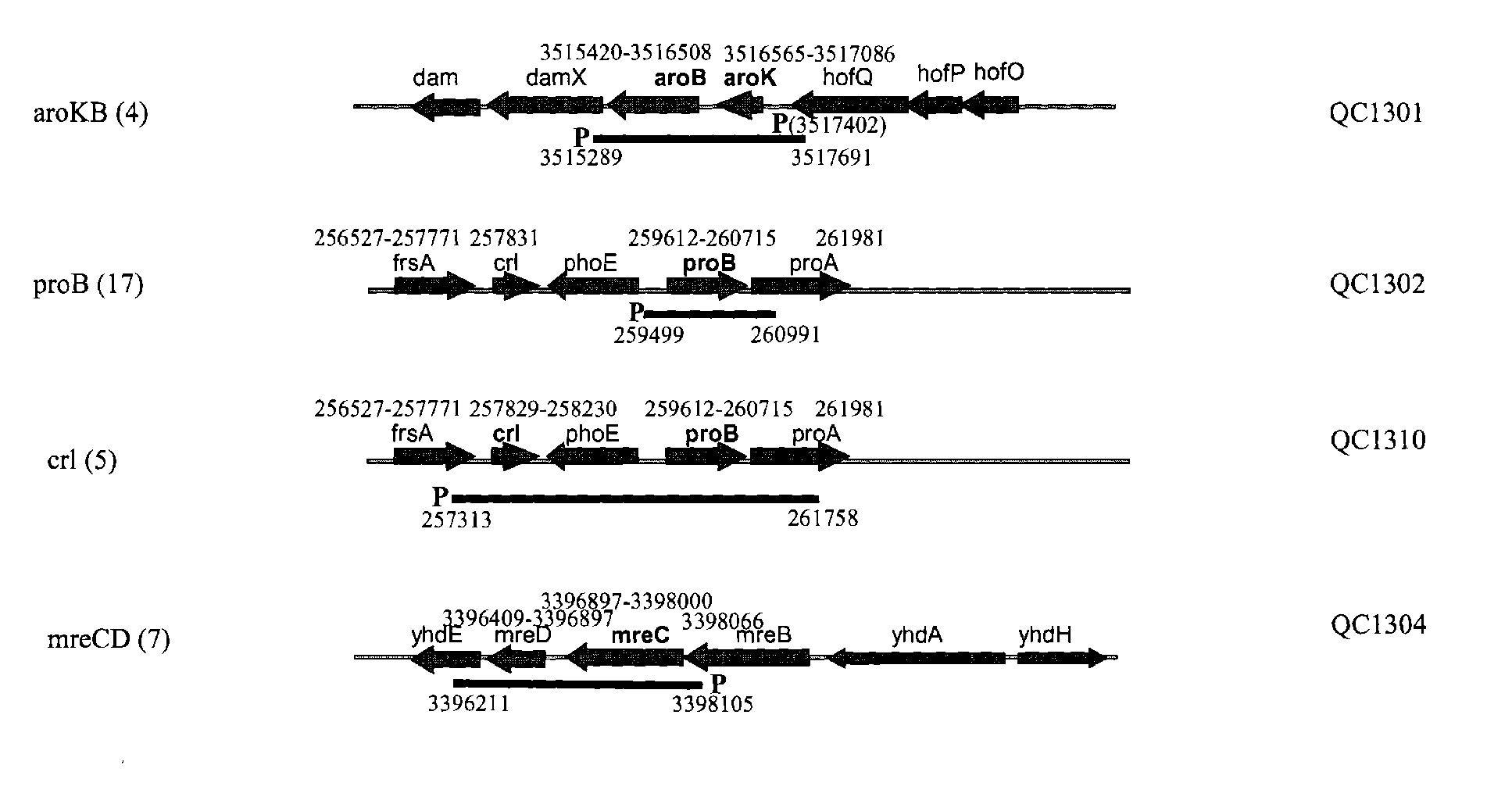
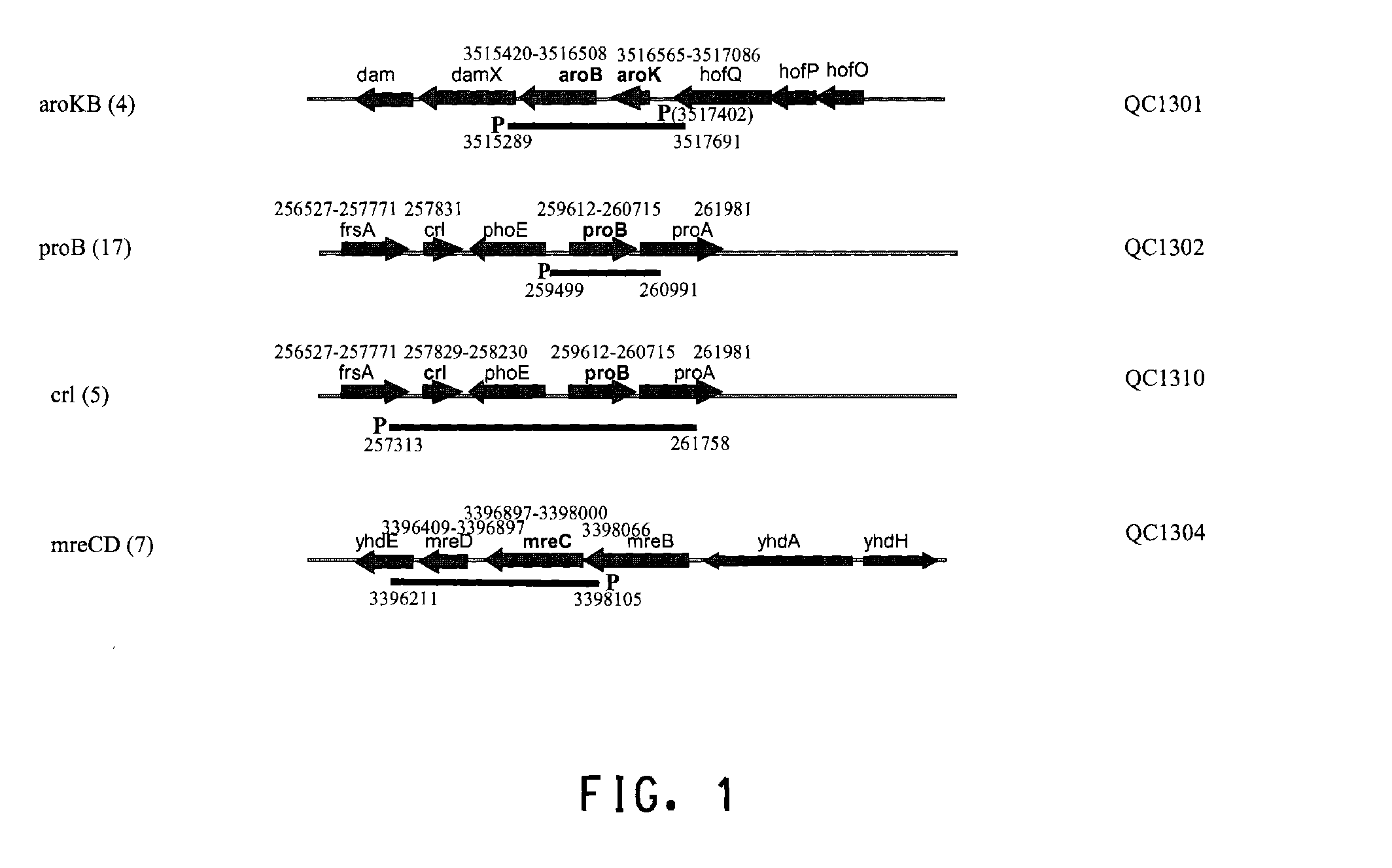
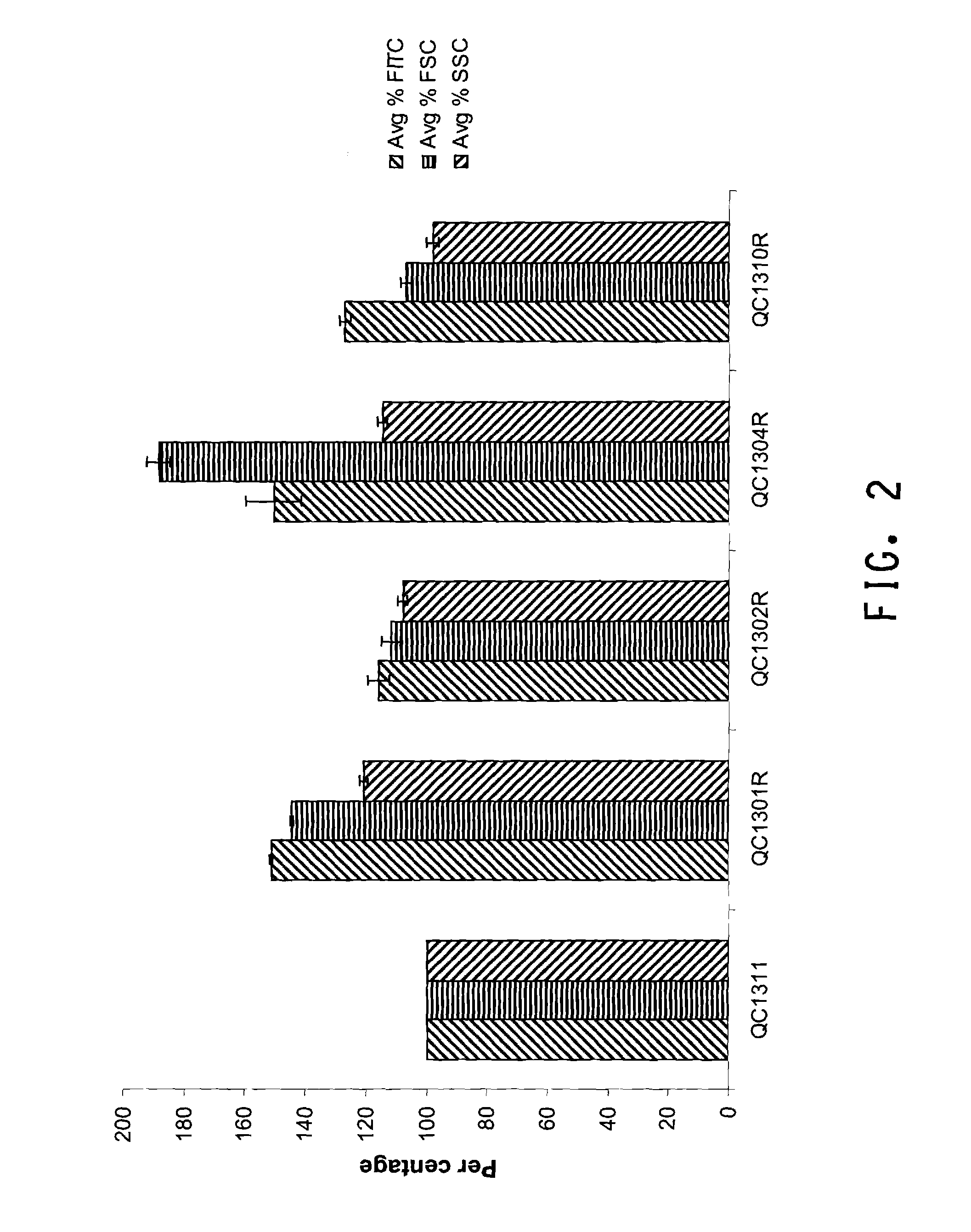
Several endogenous genes have been identified in Escherichia coli, the overexpression of which increases recombinant peptide production. Increasing the copy number of aroB, aroK, proB, or crl increases the amount of a recombinant peptide produced by a host cell. Recombinant host cells comprising at least one chimeric genetic construct encoding a peptide of interest and at least one genetic modification that increases recombinant peptide production are provided as well as methods of using such recombinant host cells
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Recombinant icosahedral virus like particle production in pseudomonads
The present invention provides an improved process for the production of recombinant peptides by fusion of recombinant peptides with icosahedral viral capsids and expression of the fusion in bacterial cells of Pseudomonad origin. The Pseudomonad cells support formation of virus like particles from icosahedral viral capsids in vivo, and allow the inclusion of larger recombinant peptides as monomers or concatamers in the virus like particle. The invention specifically provides cells expressing viral capsid fusions, nucleic acids encoding fusions of toxic proteins with icosahedral viral capsids and processes for manufacture of recombinant proteins.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for designing peptides
InactiveUS20060240510A1Potent inhibitorImprove solubilityBacteriaSugar derivativesInteinRecombinant peptide
The present invention relates to genetic engineering and; in specific, to design, generation, and modification of recombinant peptides using a combination of phage display and intein-mediated protein cleavage reaction.
Owner:KARYON CTT
Site-specific labelling of proteins using cyanine dye reporters
InactiveUS20040023408A1Methine/polymethine dyesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCyanineRecombinant peptide
The present invention therefore provides new cyanine dye reagents and methods that afford direct attachment of the cyanine dye reporter to either the N-terminus or C-terminus of a synthetic or recombinant peptide or protein and their derivatives, in a site-specific manner, coupled with purification of the resultant labelled molecule.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Construction and expression of vector of tumstatin T7 of tumstatin T7 peptide and derivative T7-NGR thereof
InactiveCN101519658ASmall molecular weightStrong penetrating powerConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsWestern blotTumstatin
The invention constructs recombinant plasmid vector containing tumstatin T7 peptide and gene sequence of derivative T7-NGR thereof and obtains recombinant T7 peptide and T7-NGR fusion protein. The amino acid sequence of the derivative T7-NGR is TMPFLFCNVNDVCNFASRNDYSYWLGSCNGRCVSGCAGRC. The invention combines the generation activity of tumstatin T7 peptide for restricting the tumor neovascularization effectively and high specificity of NGR guide peptide, so as to lead the generation activity of T7 peptide for restricting the tumor neovascularization to be greatly strengthened. The recombinant cloned vectors are respectively identified by sequencing: the direction, position and sequence of integration are correct. The expression vector is transformed into competent E.coli BL21 (DE3) and then is expressed by the induction of IPTG; electrophoresis is carried out on the thalli after cracking; and by Western-Blot identification, the expression product is in accordance with the expected. The pET7N expression vector fusion protein T7-NGR has potential application prospect in the diagnosis and treatment of tumor.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Scorpion peptide for treating arrhythmia and its preparing process and application
InactiveCN1379042AObvious antiarrhythmic effectIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationSolubilityEscherichia coli
An anti-arrhythmia scorpion peptide whose amino acid sequence is disclosed is prepared through designing PCR upstream primer containing enteric kinase cut site, using the PCR to amplify anti-arrhythmia peptide gene fragment through limited enzymatic cut of endoenzyme, clonining to pGX-5x-1 expression carrier, transferring to colibacillus BL21 to obtain recombinant colibacillus BL21 (pGEX / BmK1M); after inducing by IPTG, through purifying by glutathion transferase affinity chromatographic column, expressing the resultant fusion protein by enteric kinase and desalting to obtain the said peptide.Its advantages are high anti-arrhythmia activity, high solubility and high output.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Methods for recombinant peptide production
InactiveUS7247454B2Efficiently and economically producedSimple methodBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyRecombinant peptide
Owner:XOMA TECH LTD
Higher plant cytosolic er-based glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase genes
InactiveUS20060206960A1Modifying lipid metabolismChange outputSugar derivativesTransferasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase is the initial enzyme of the glycerolipid biosynthetic pathway. Biochemical analyses indicated that the reaction mediated by glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase represents a potential rate-limiting step for the synthesis of phospholipids and storage neutralipid, triacylglycerol. The present invention relates to the cloning of genes encoding extraplastidic membrane-bound glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases. Heterologous expression of the genes, GPAT1, GPAT2, and GPAT3 in a yeast glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase mutant demonstrated that the encoded products could efficiently utilize glycerol-3-phosphate to mediate sn-1 stereo-specific fatty acid acylation. The invention encompasses the glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase peptides disclosed and fragments and homologues thereof, the corresponding gene sequences and fragments and homologues thereof, as well as the use of the peptide and gene sequences of the present invention for use in generating recombinant proteins, and transgenic plants with altered lipid metabolism. In this way, the present invention also encompasses the use of such recombinant peptides and transgenic plants for the production of lipid products for use, for example, in pharmaceutical and nutritional applications.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Recombinant peptide production using a cross-linkable solubility tag
InactiveUS20090043075A1High molecular weightEasy to separatePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityLysis
The invention relates to the recombinant expression of a peptide of interest in the form of a fusion protein comprising a solubility tag. The fusion protein comprises at least two portions separated by a cleavable peptide sequence wherein one portion is devoid of cysteine residues and the second portion comprises an effective number of cross-linkable cysteine residues. After cell lysis and isolation of the fusion protein, the fusion protein is subsequently cleaved into a mixture of first and second portions. Oxidative cross-linking is used to selectively precipitate one of the two portions to facilitate simple and effective separation of the peptide of interest.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
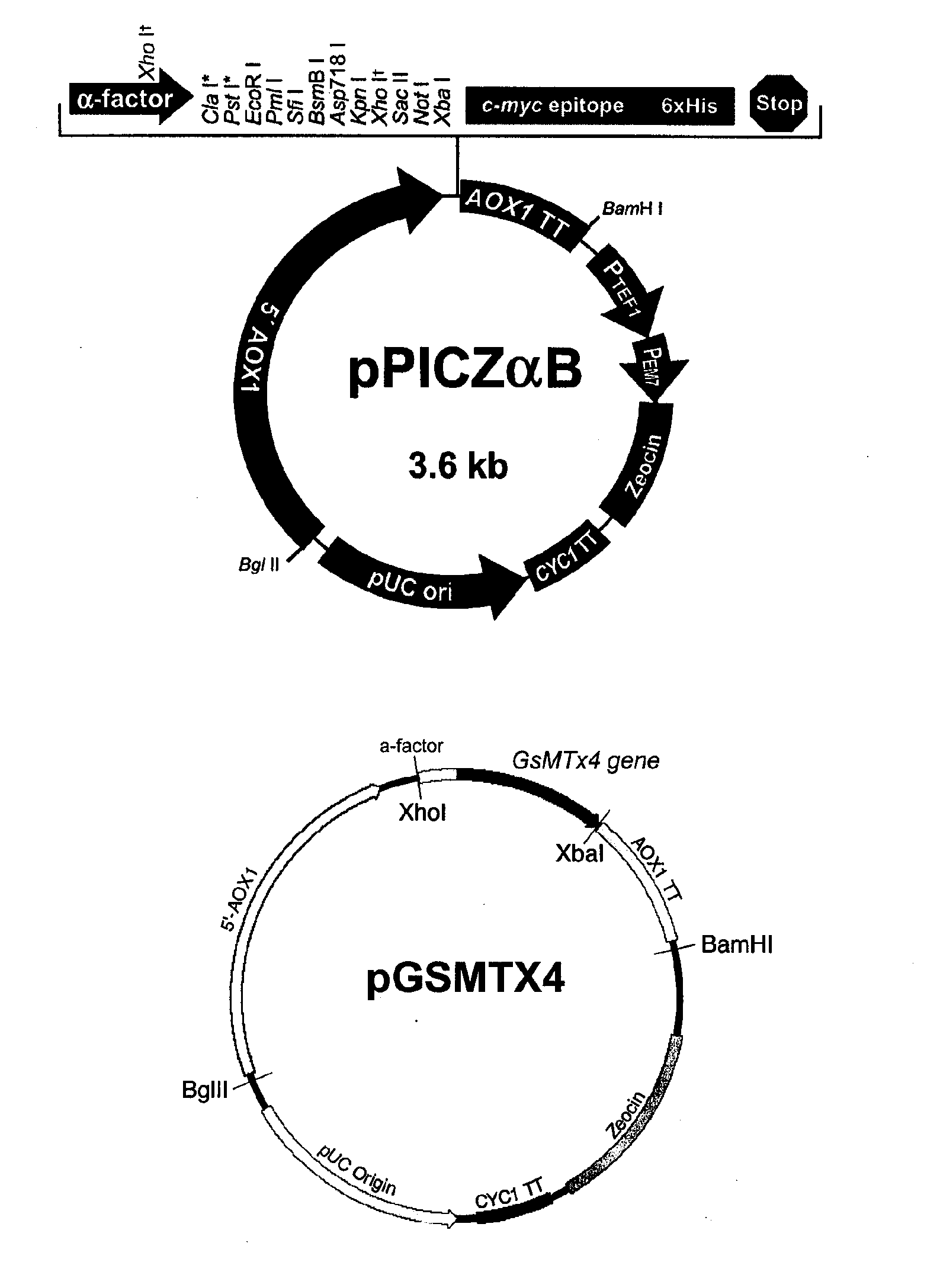
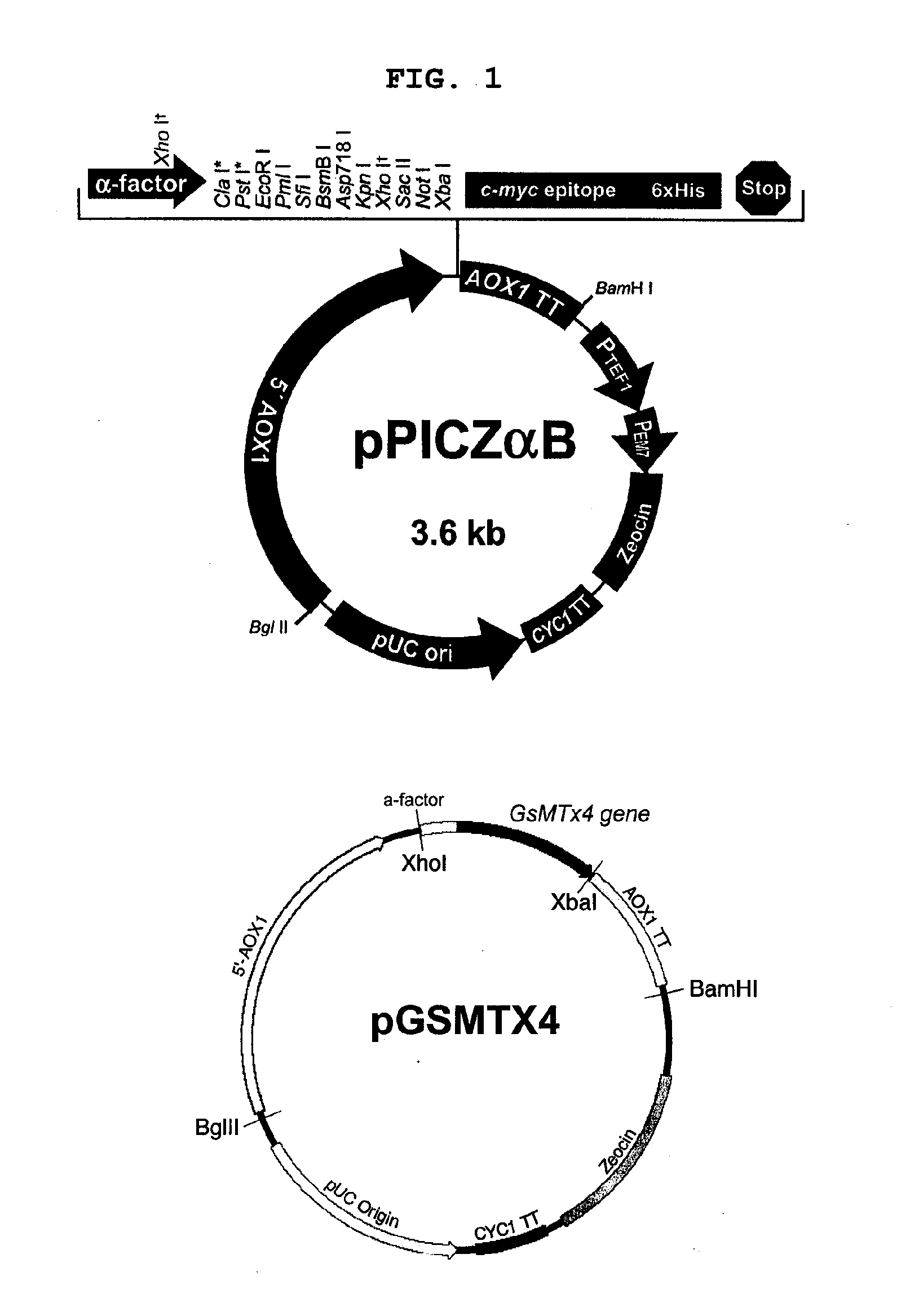
Method For Preparing Recombinant Peptide From Spider Venom and Analgesic Composition Containing The Peptide
InactiveUS20090023183A1Effective activityEffective functionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMechanosensitive ion channel
The present invention relates to a method for producing a recombinant, spider toxin peptide and analgesic compositions containing said peptide. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method in which the gene for GsMTx4 is subcloned into a vector, so that it is linked to a secretion signal sequence of the alpha factor and under the control of methanol-inducible alcohol oxidase (AOX) promoter to construct a recombinant yeast expression plasmid. Yeast cells are transformed with this plasmid to produce the GsMTx4 peptide and analgesic compositions containing said peptide. The recombinant yeast expression system of the present invention affords a more stable method for producing GsMTx4 than its natural route. Thus the GsMTx4 peptide and its derivatives produced by the method of this invention can be used in the cure of related diseases such as heart failure as the peptide specifically inhibits mechanosensitive ion channels.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Posterior silk gland gene expression unit and transgenic silkworm containing same
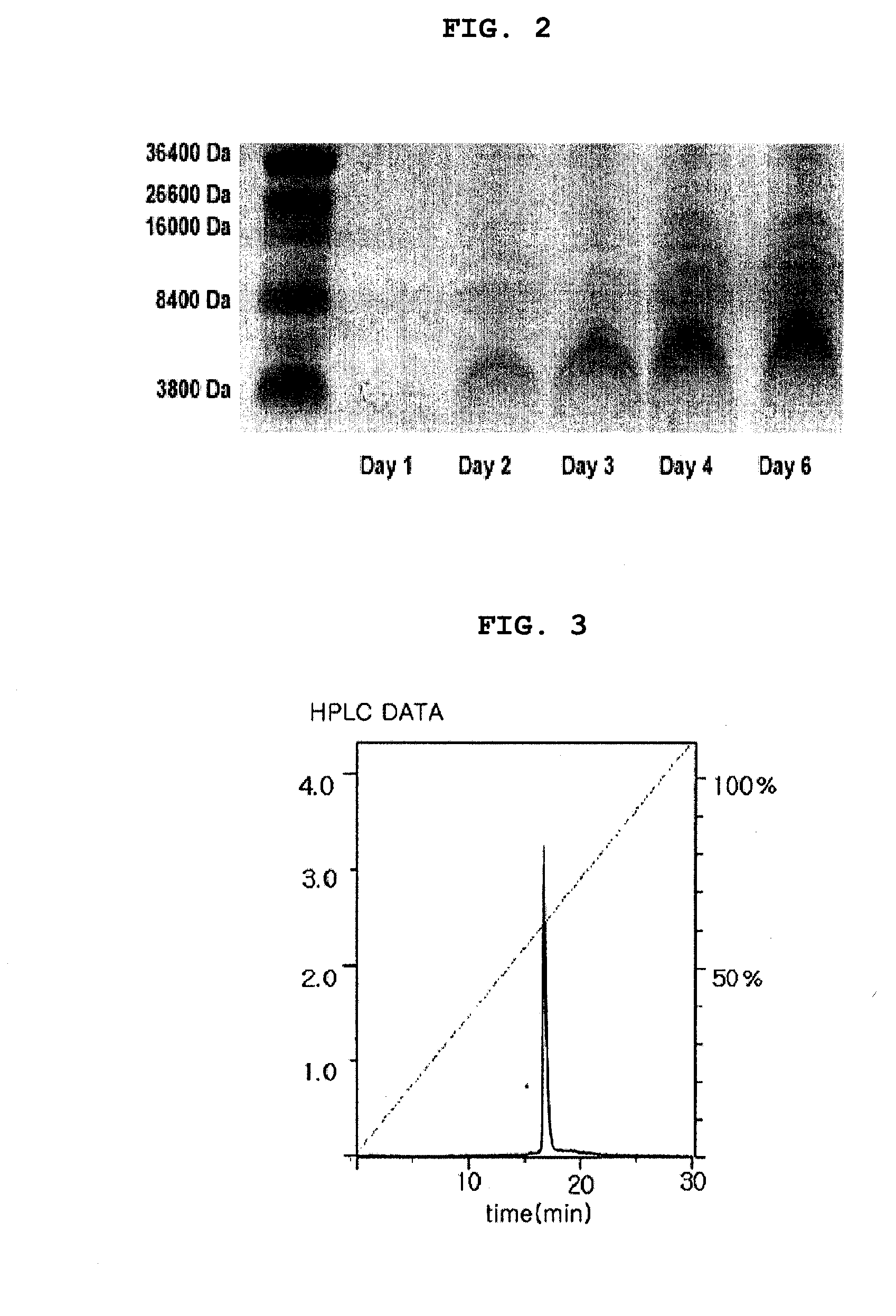
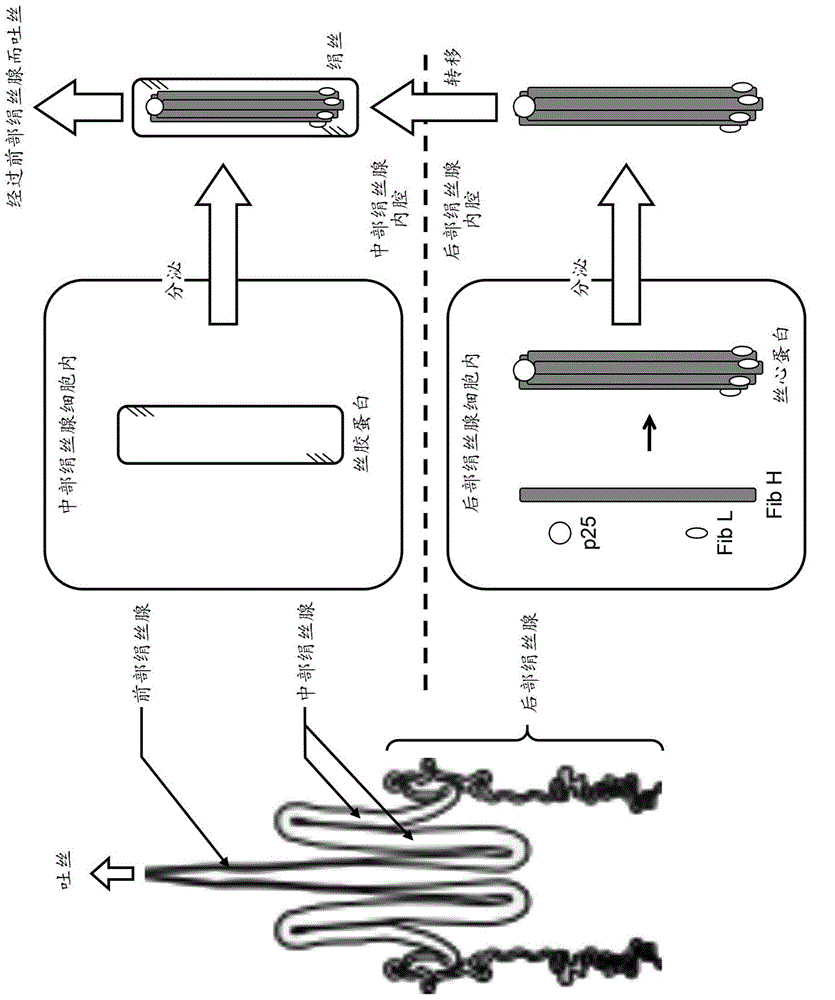
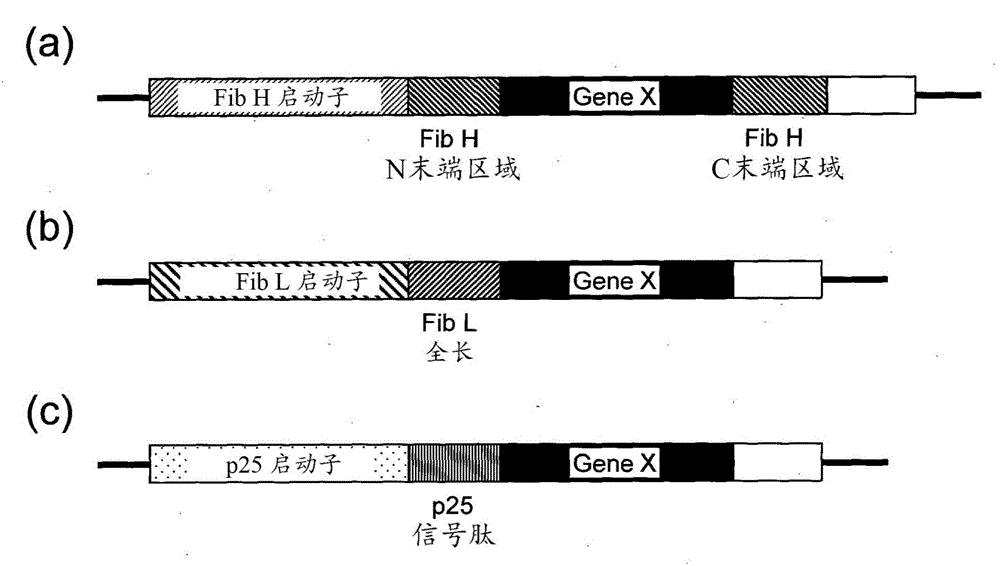
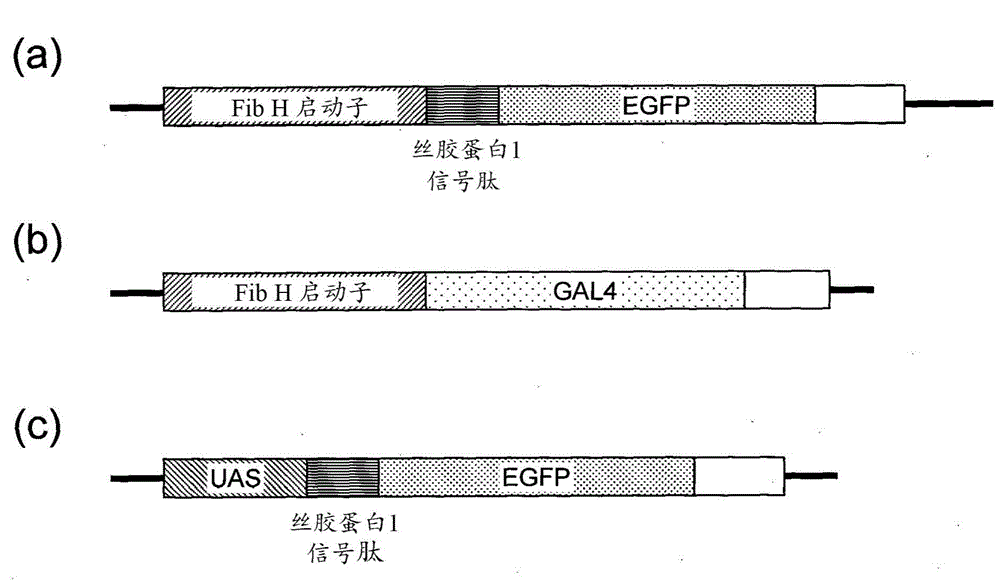
InactiveCN104903445AIncrease productivityReduce manufacturing costAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionProtein insertionRecombinant peptide
The present invention addresses the problem of providing: a posterior silk gland gene expression unit, whereby a recombinant peptide, in particular a water-soluble peptide, can be expressed in a large amount in the posterior silk gland of a silkworm such as Bombyx mori; and a transgenic silkworm into which the aforesaid gene expression unit has been transferred. Provided is a posterior silk gland gene expression unit which comprises: a promoter of a gene encoding a protein, said protein being expressed specifically in the posterior silk gland; a DNA encoding a signal peptide originating in a protein, said protein being expressed specifically in the middle silk gland, functionally bound to the downstream of the promoter; and a DNA encoding a target peptide, said peptide being free from proteins secreted as constituents of fibroin, ligated to the downstream thereof.
Owner:国立研究开发法人农业生物资源研究所
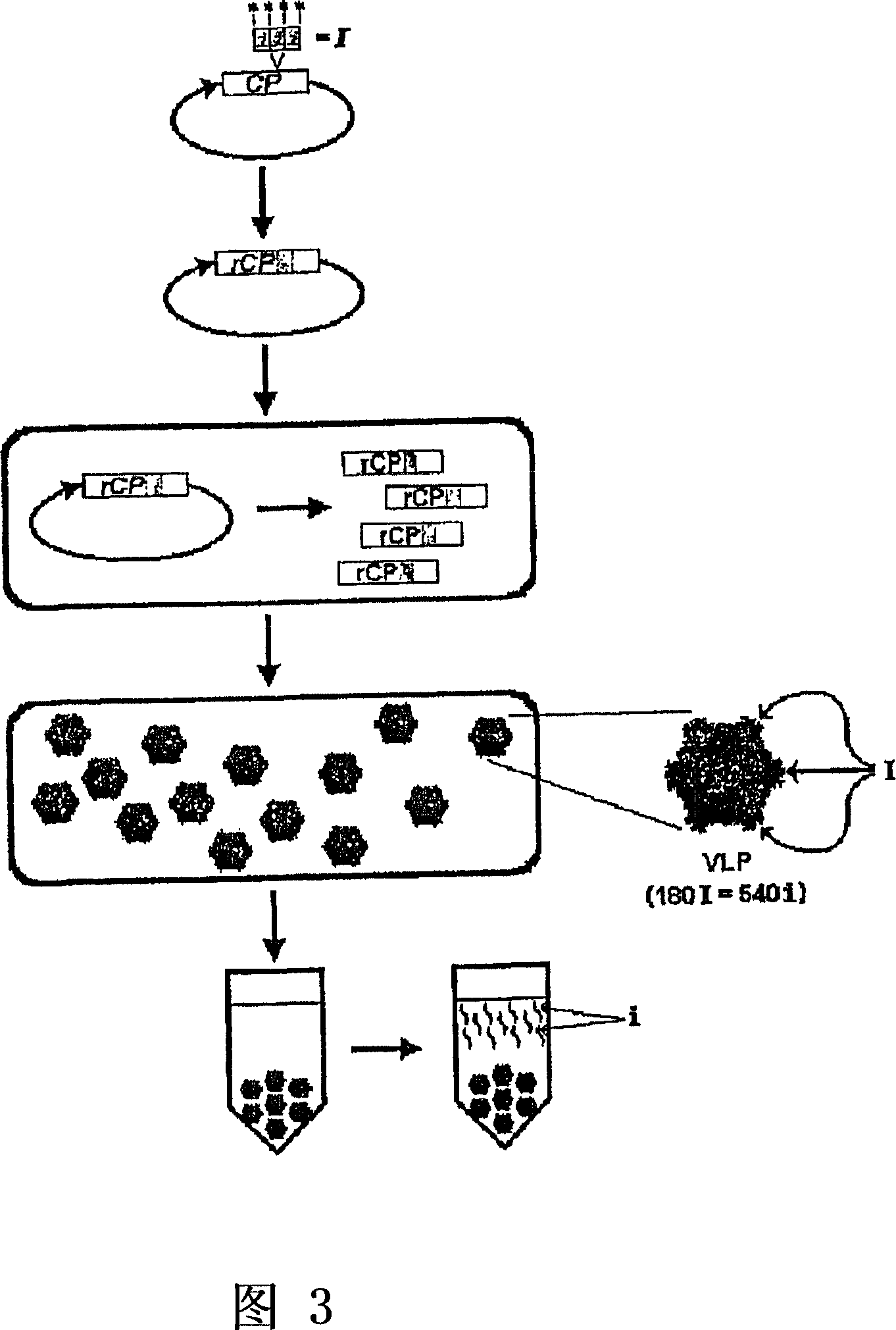
Improved production and in vivo assembly of soluble recombinant icosahedral virus-like particles
InactiveCN101784655ASsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseIcosahedral viral capsidVirus-like particle
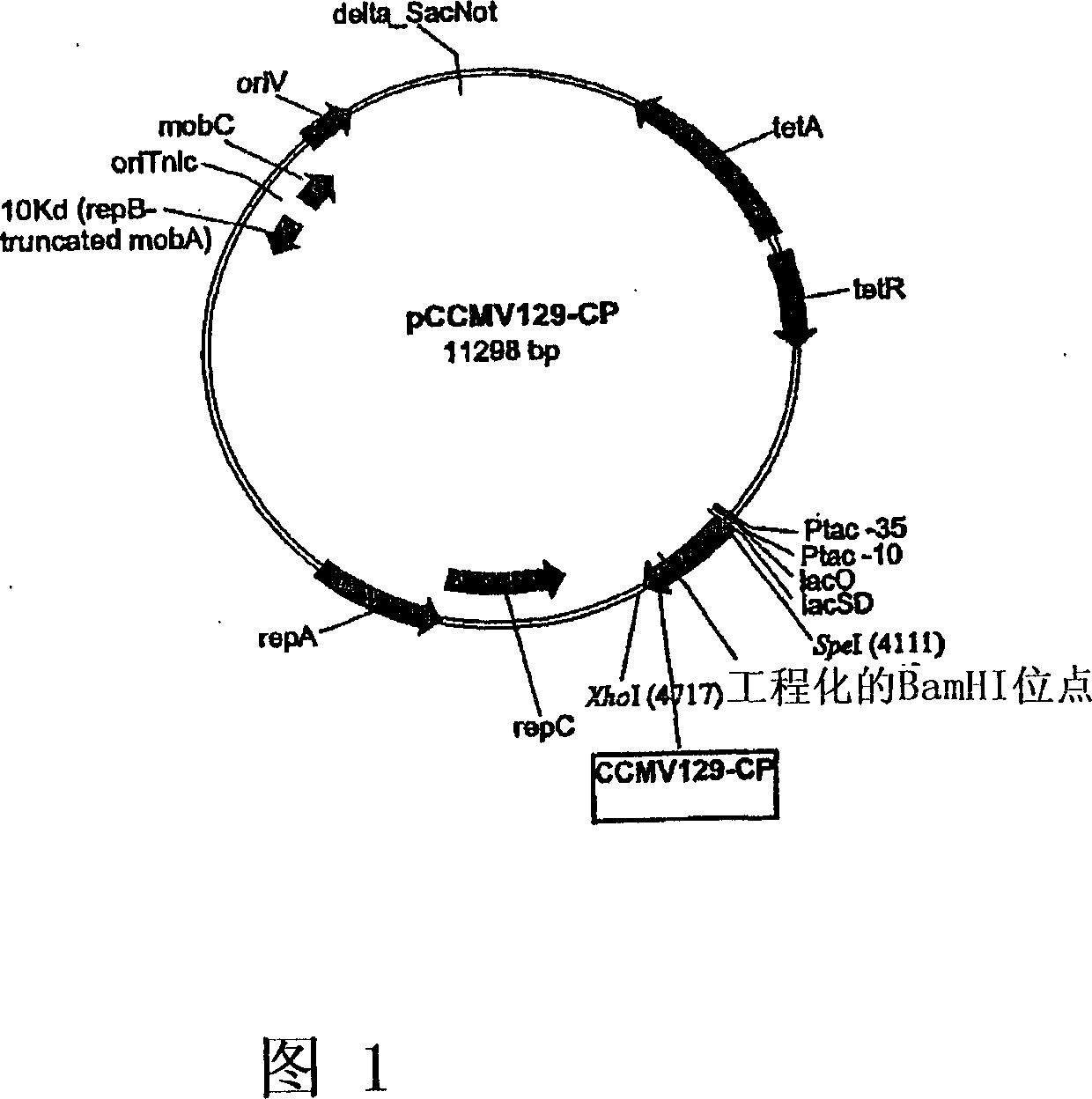
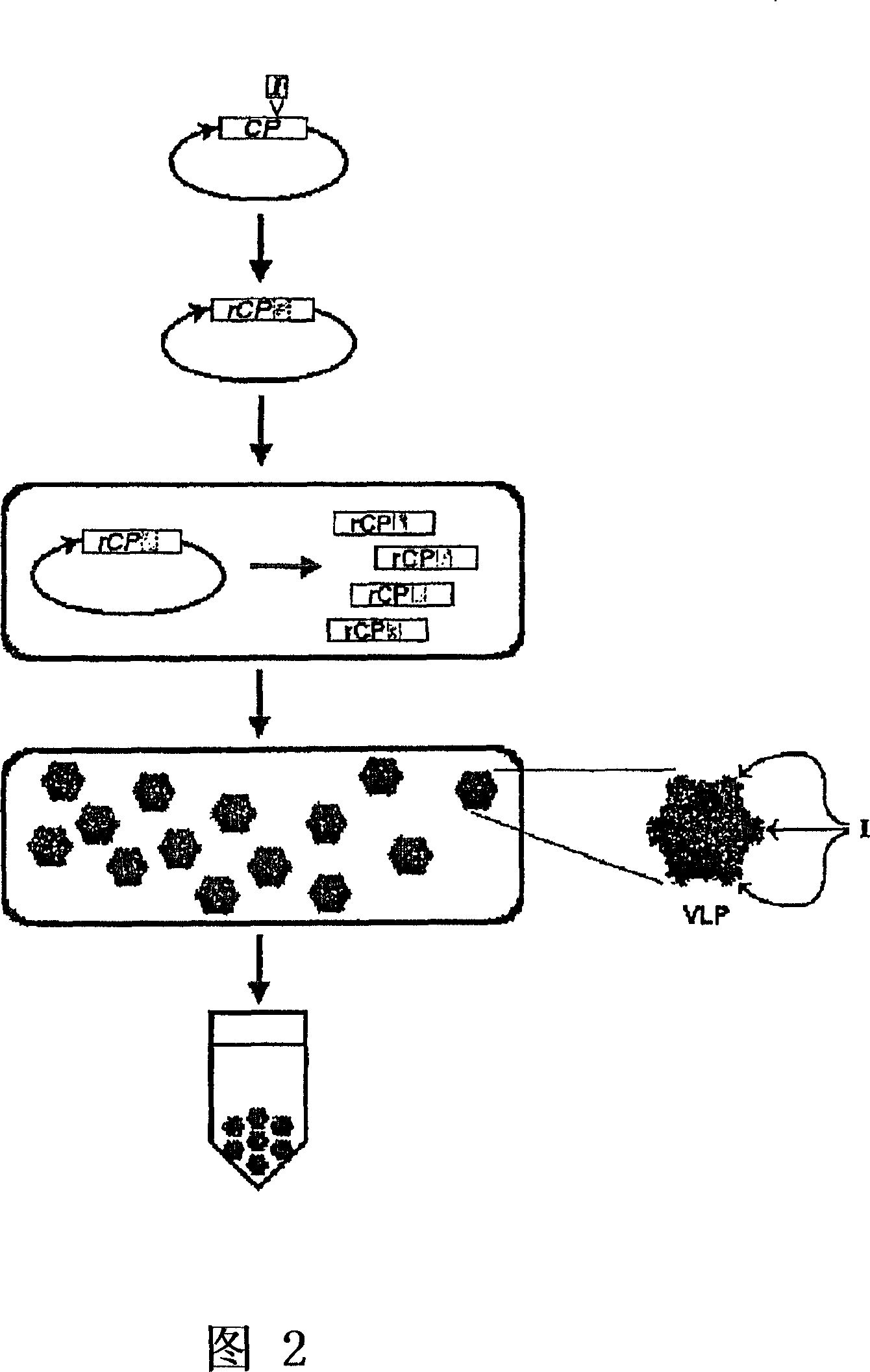
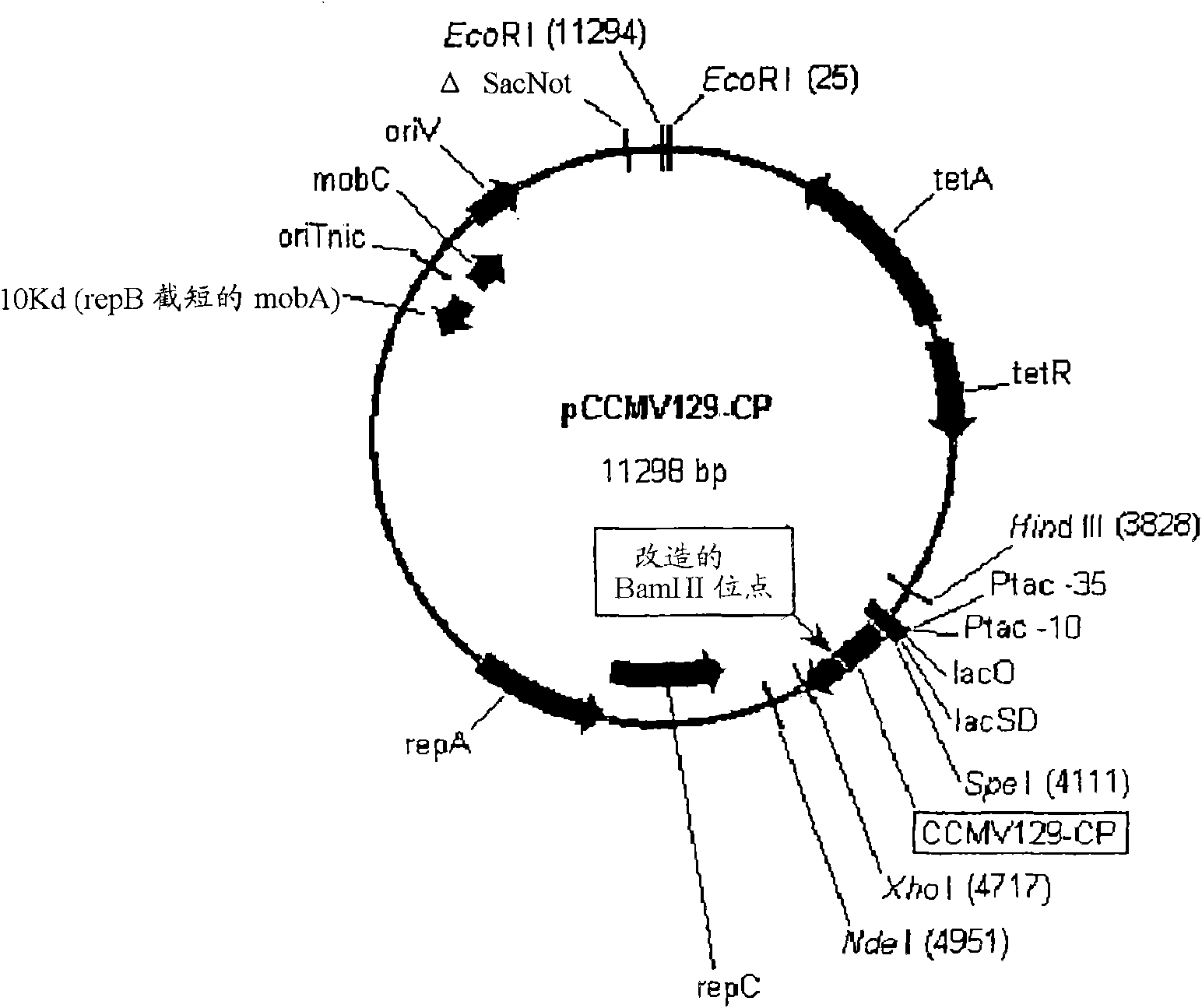
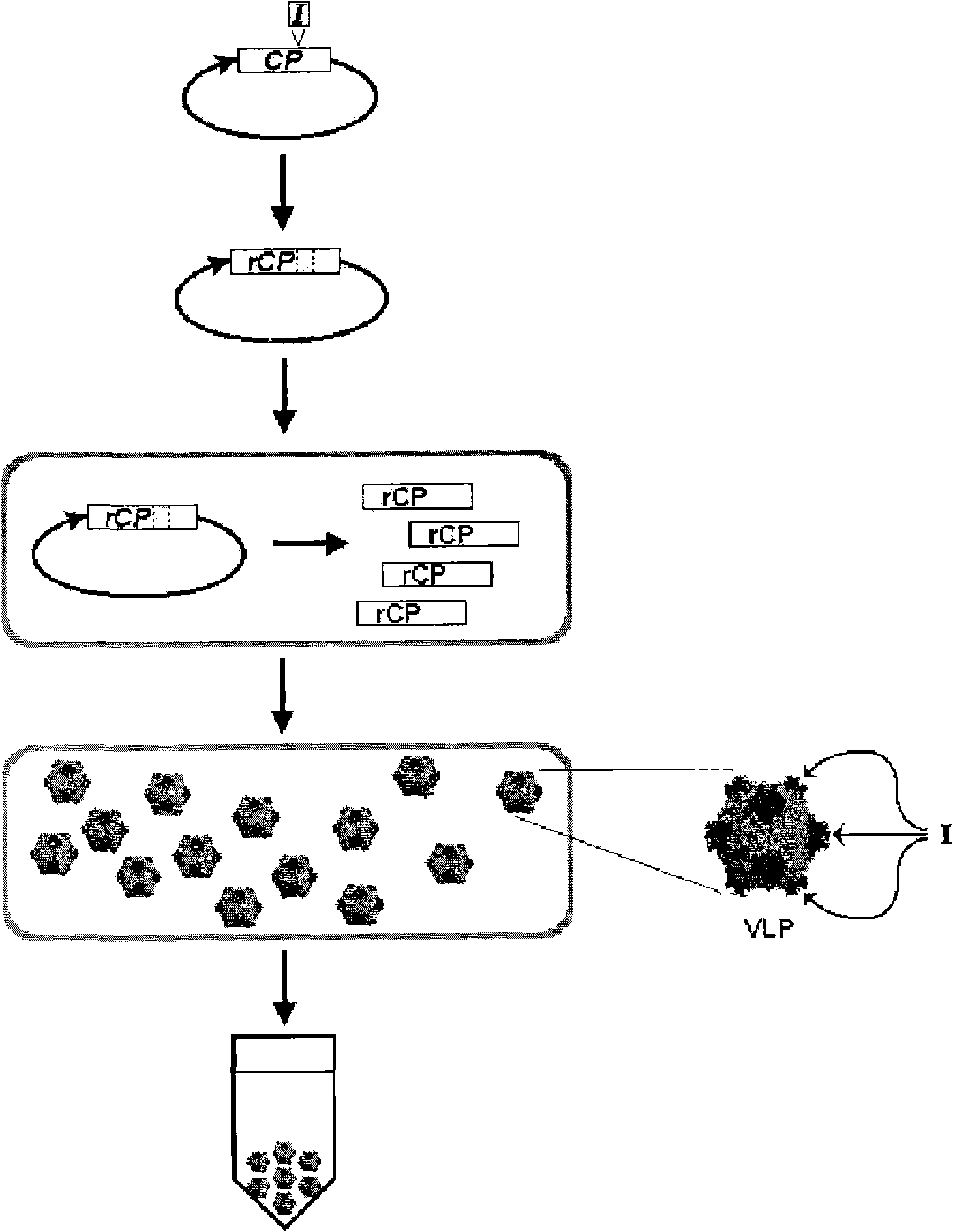
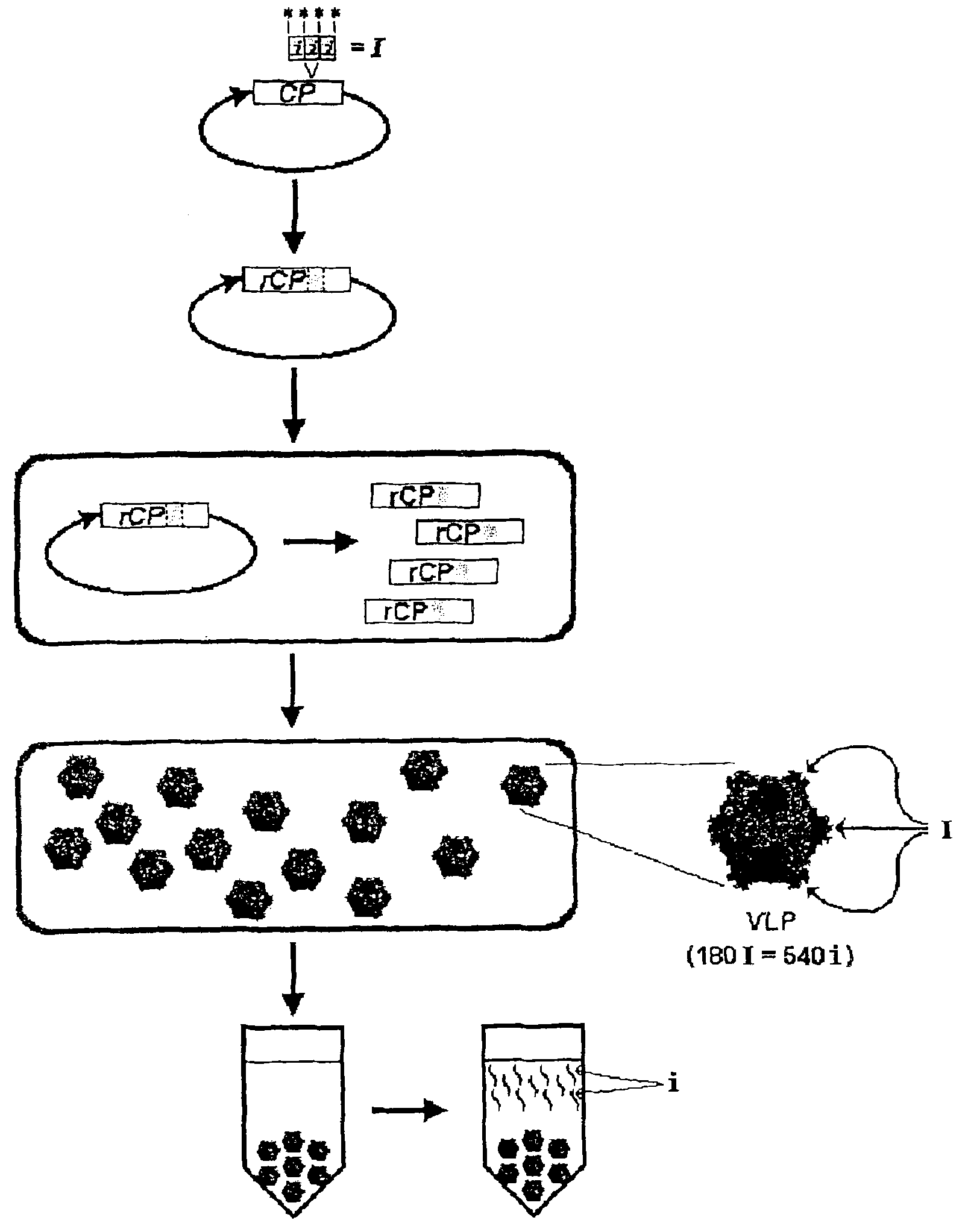
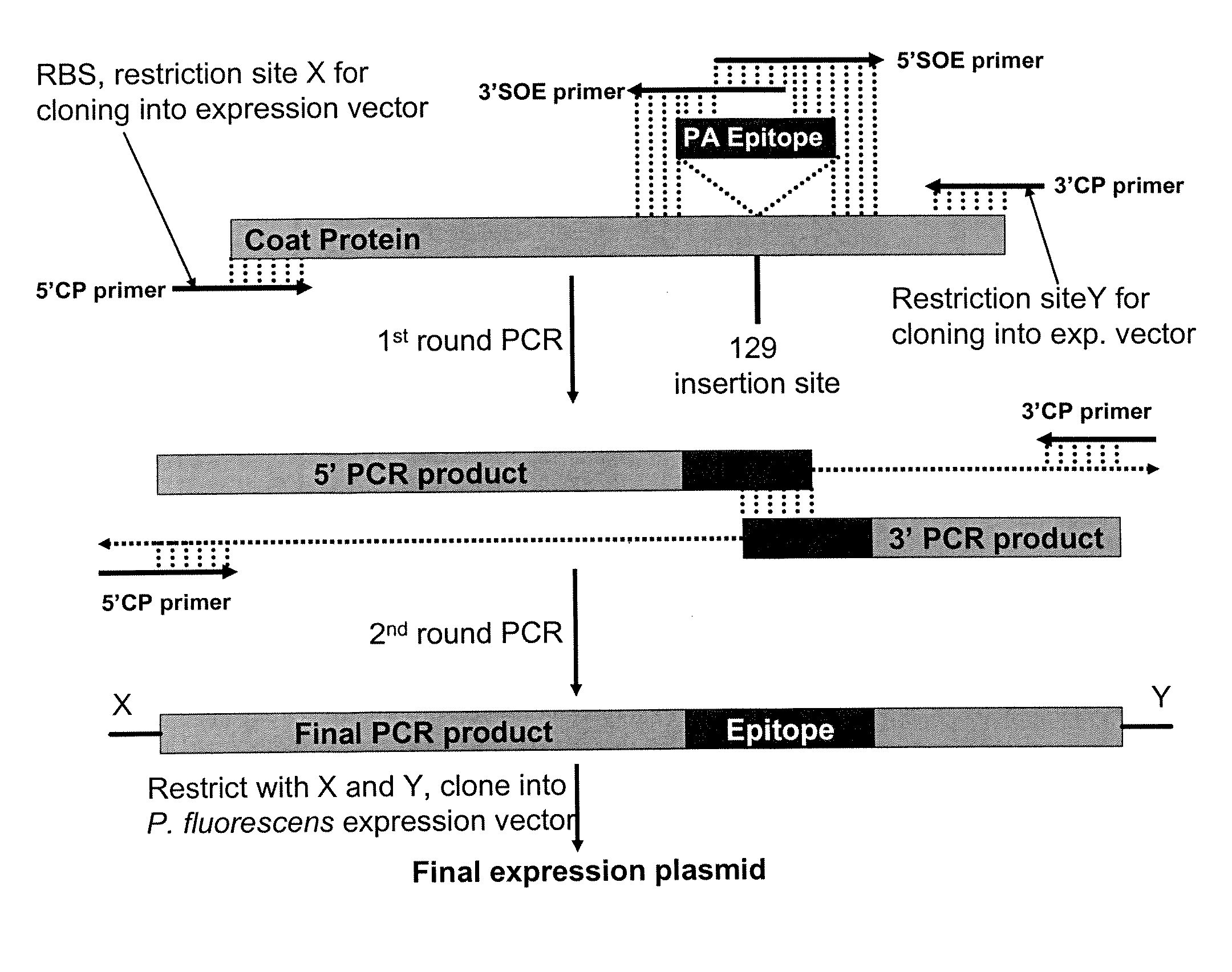
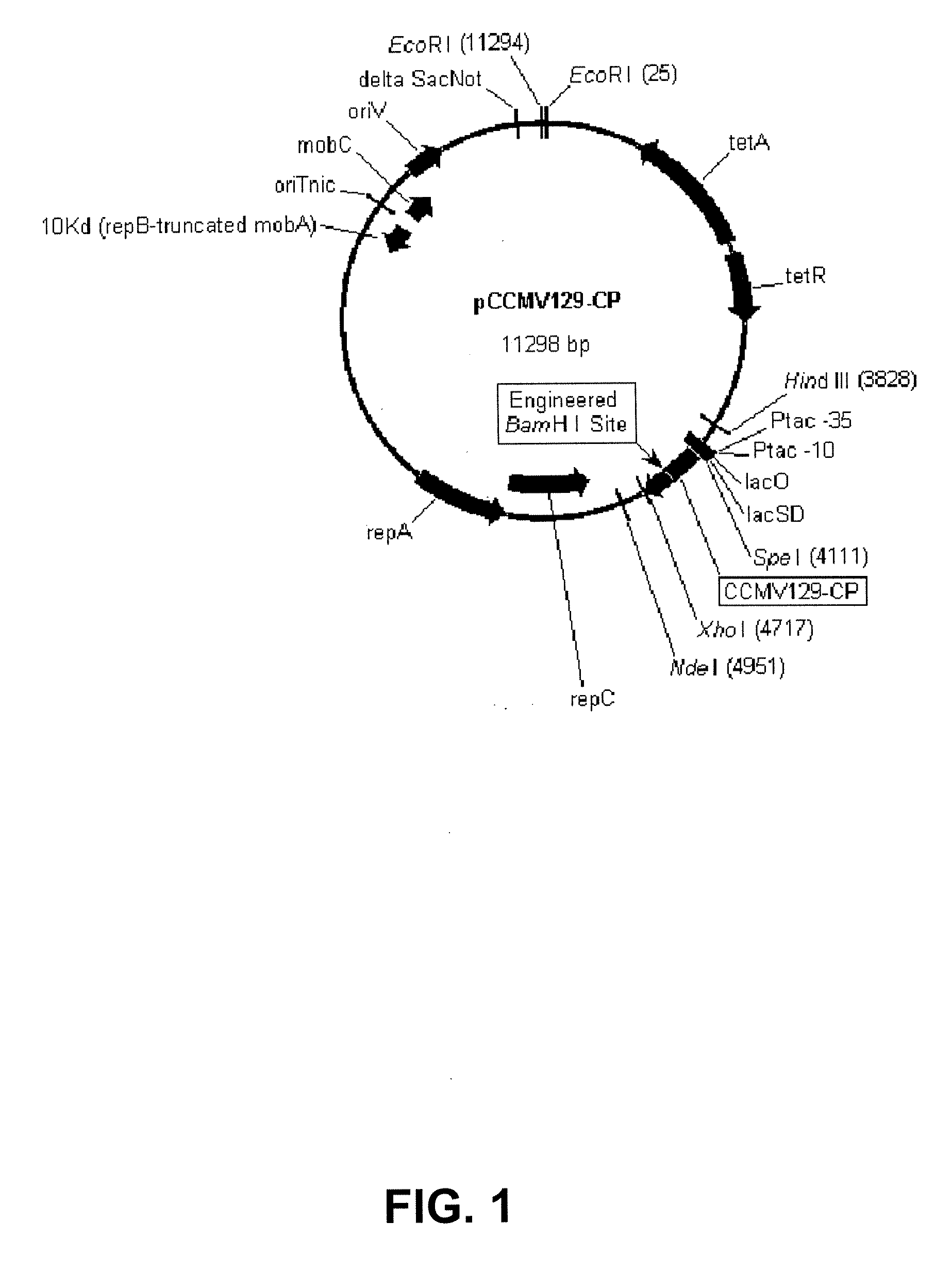
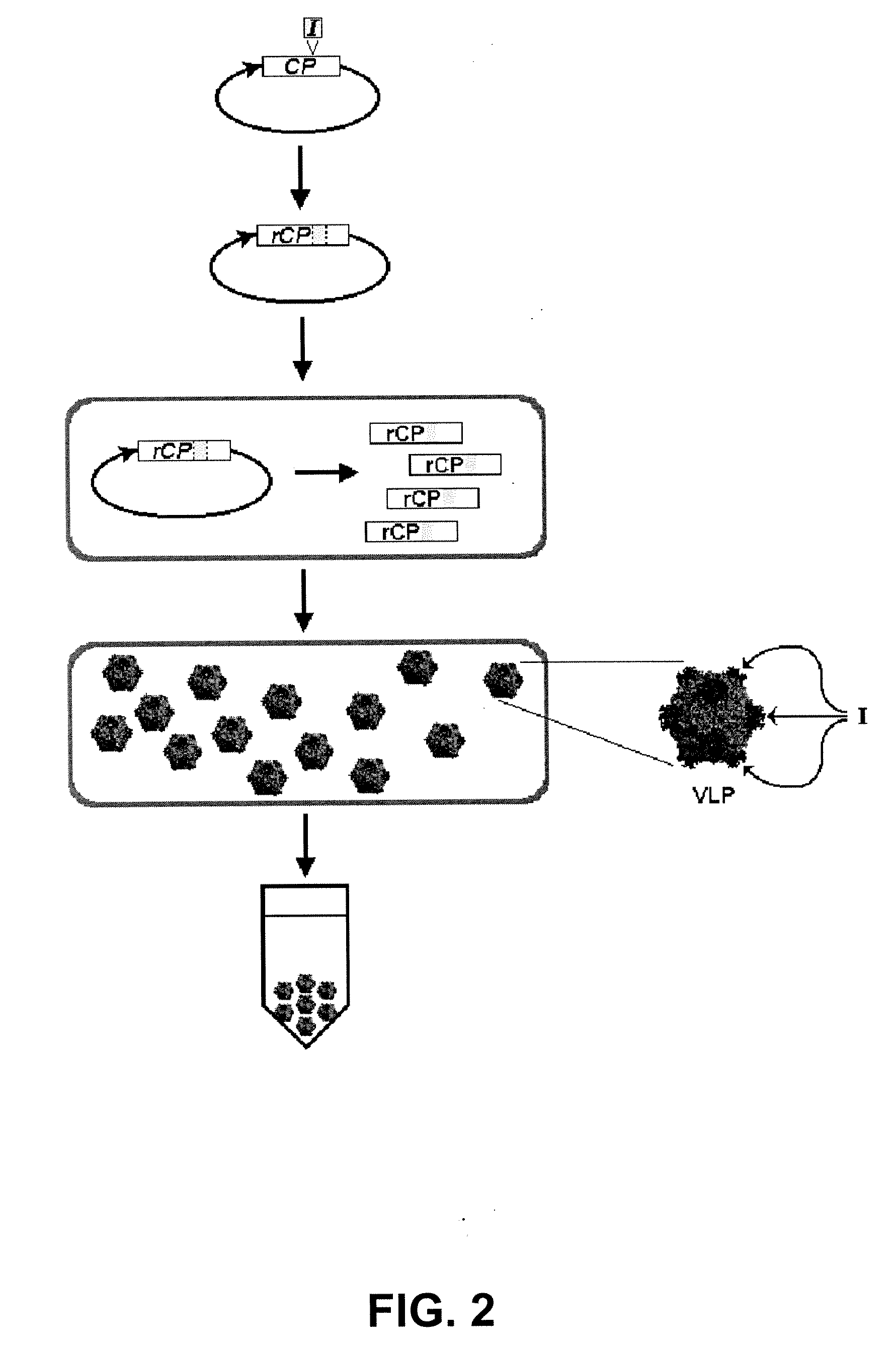
The present invention provides an improved method for the in vivo production of soluble assembled virus-like particles (''VLPs'') in bacterial cells of Pseudomonad origin. The Pseudomonad cells support assembly of VLPs from icosahedral viral capsid proteins (''CPs'') in vivo, and allow the inclusion of larger recombinant peptides as monomers or concatamers in the VLP. The invention specifically provides an improved method for the in vivo production of soluble assembled Cowpea Chlorotic Mottle Virus (''CCMV'') VLPs by introducing modifications into the CCMV CP that result in high yield production of soluble CP fusions in a Pseudomonas fluorescens bacterial system. These soluble VLPs can subsequently be purified and used as vaccines.
Owner:菲尼克斯股份有限公司
Production and in vivo assembly of soluble recombinant icosahedral virus-like particles
InactiveUS20090093019A1Increase productionImprove hydrophilicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseRecombinant peptideIn vivo
The present invention provides an improved method for the in vivo production of soluble assembled virus-like particles (“VLPs”) in bacterial cells of Pseudomonad origin. The Pseudomonad cells support assembly of VLPs from icosahedral viral capsid proteins (“CPs”) in vivo, and allow the inclusion of larger recombinant peptides as monomers or concatamers in the VLP. The invention specifically provides an improved method for the in vivo production of soluble assembled Cowpea Chlorotic Mottle Virus (“CCMV”) VLPs by introducing modifications into the CCMV CP that result in high yield production of soluble CP fusions in a Pseudomonas fluorescens bacterial system. These soluble VLPs can subsequently be purified and used as vaccines.
Owner:PFENEX
Mannitol induced promoter systems in bacterial host cells
ActiveUS20060292671A1Continuous and stable induction levelContinuous and stable levelBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyArabitol
The present invention provides methods for producing recombinant peptides in a bacterial host utilizing a mannitol, arabitol, glucitol, or glycerol-inducible promoter, wherein the host bacterial cell that produces the peptide has been rendered incapable of degrading or metabolizing mannitol, arabitol, or glucitol, or derivatives or analogues thereof. The present invention provides bacterial cells that have been genetically altered to inhibit the metabolism or degradation of mannitol, glucitol, or arabitol, or derivatives or analogues thereof. The present invention utilizes mannitol, arabitol, glucitol, or glycerol to induce expression of a target polypeptide from an inducible promoter, allowing for the use of an inexpensive and stable carbon source inducer in the fermentation processes for the production of recombinant peptides.
Owner:PFENEX
Staphylococcal nuclease fusion proteins for the produciton of recombinant peptides
InactiveUS20060173164A1Easy to disassembleNot complicate subsequent stepSugar derivativesBacteriaInclusion bodiesProtein target
Peptides are produced as fusions with a suitable carrier protein. The carrier protein disclosed herein are adapted from the N-terminal domain of staphylococcus nuclease. This novel carrier protein acts to promote the over-expression of the peptide-protein fusion in the form of inclusion bodies, which minimizes in-cell proteolysis of desired peptides. The fusion protein is readily purified by conventional procedures or His-tag affinity chromatography when His-tag is inserted into the fusion protein. The target peptide is released from the purified fusion protein by a simple cleavage step and separated from the librated carrier protein by use of a reverse-phase HPLC process or by repeating the same affinity purification method. A particular advantage of the disclosed method, in addition to the obvious advantage of high yields, is its use for producing isotopically labeled peptides for NMR characterization of bioactive peptides and their interactions with target proteins.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com