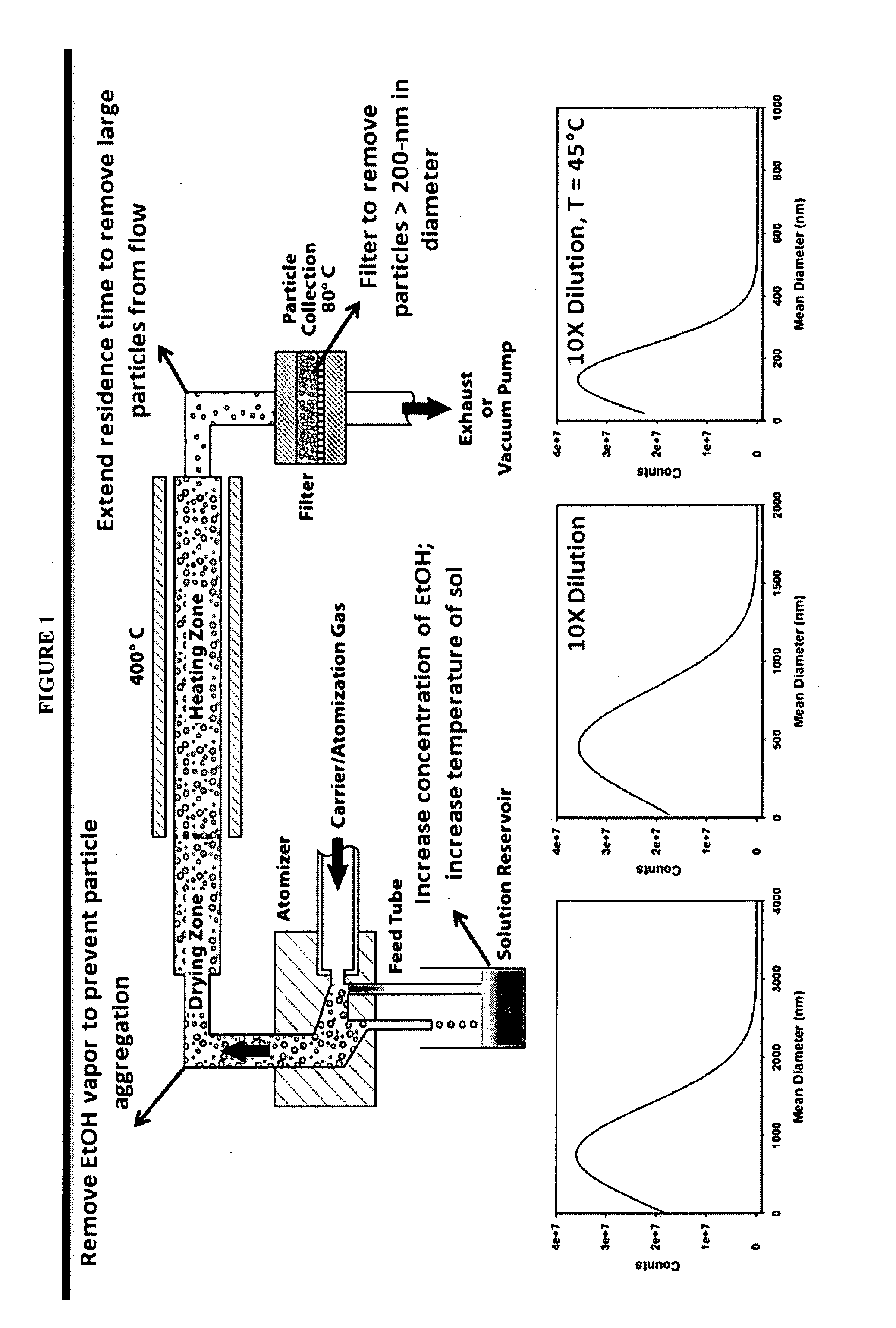
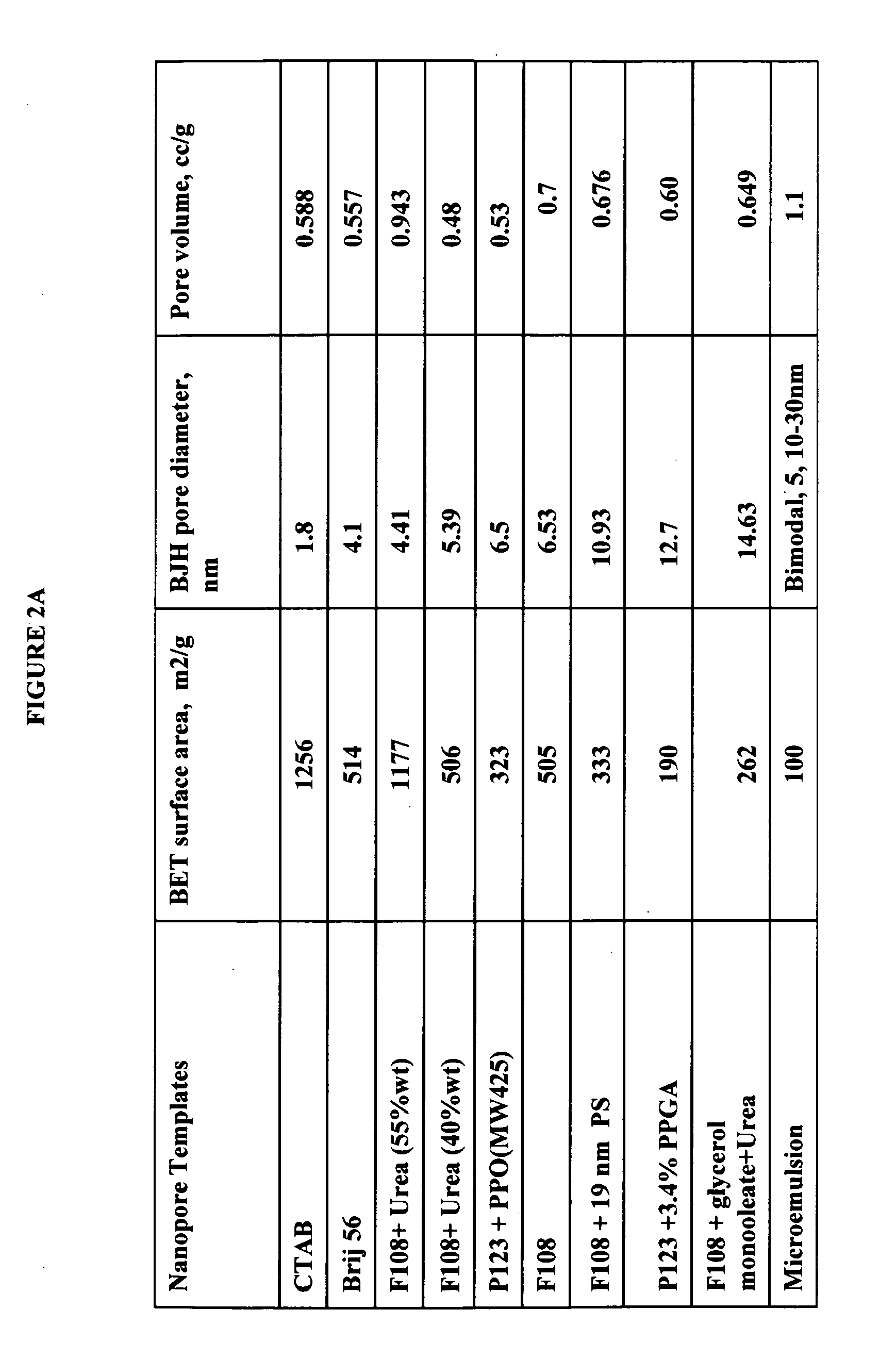
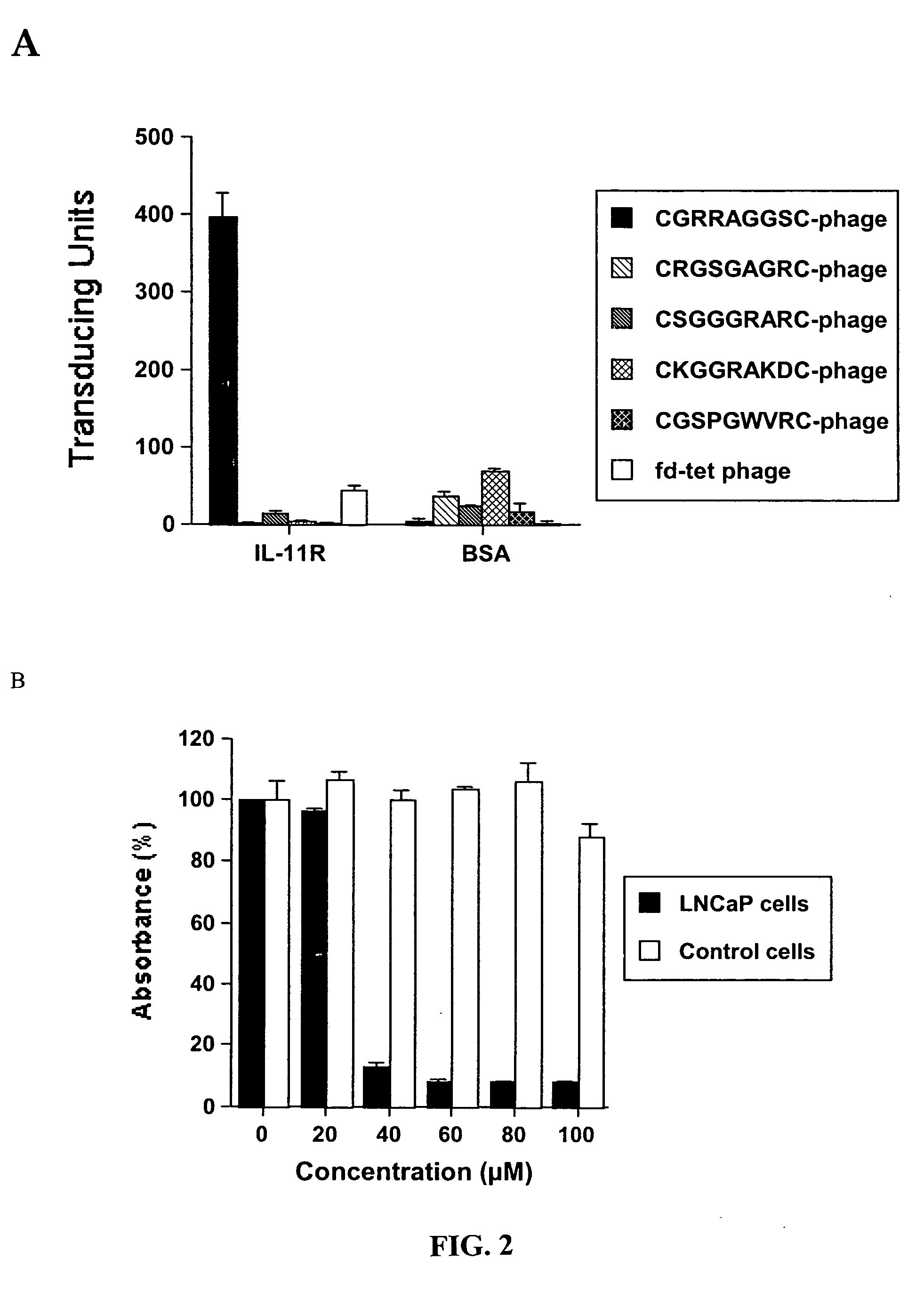
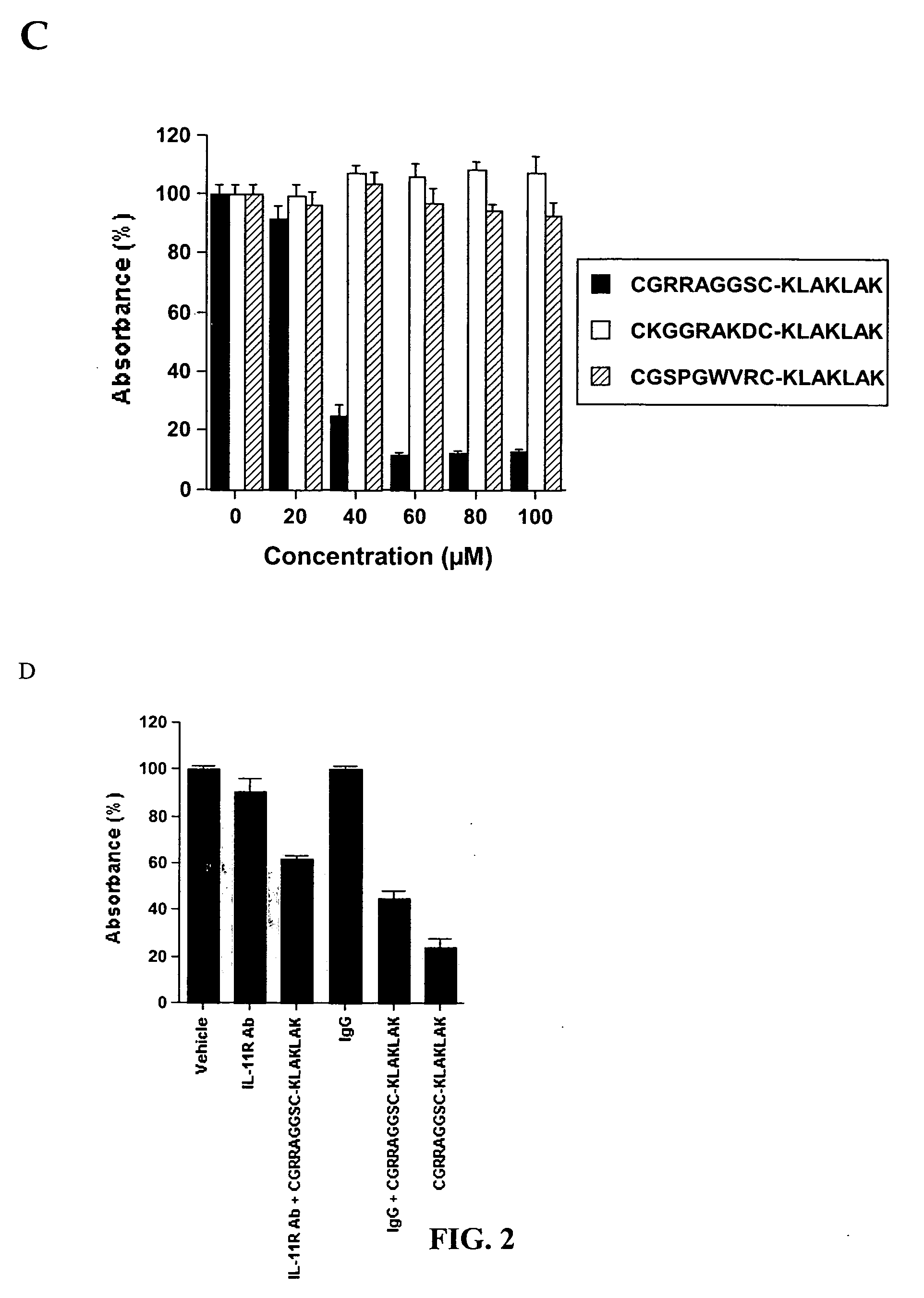
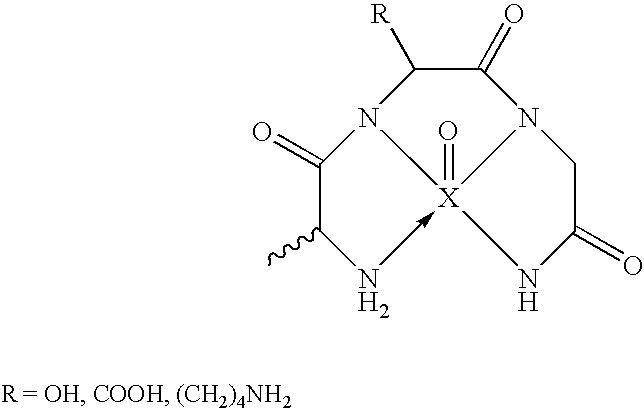
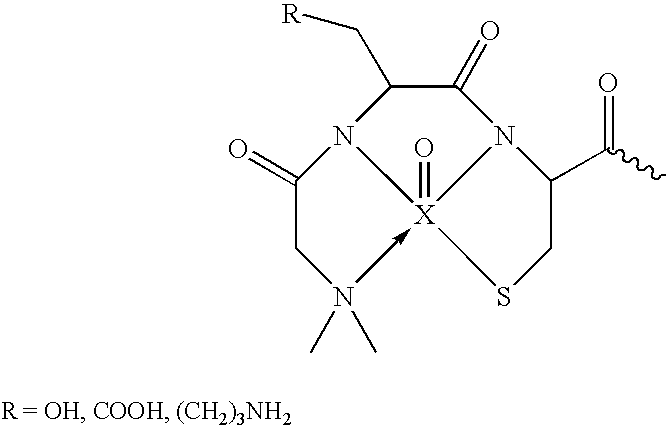
Patents
Literature
473 results about "Target peptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A target peptide is a short (3-70 amino acids long) peptide chain that directs the transport of a protein to a specific region in the cell, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), chloroplast, apoplast, peroxisome and plasma membrane. Some target peptides are cleaved from the protein by signal peptidases after the proteins are transported.
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery and methods of using same
ActiveUS20140079774A1Promoting death of cancer cellEfficient packagingBiocideSpecial deliveryLipid formationBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Compositions and methods of use of targeting peptides for diagnosis and therapy
InactiveUS20050191294A1Improve concentrationImprove bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTarget peptideBone cancer
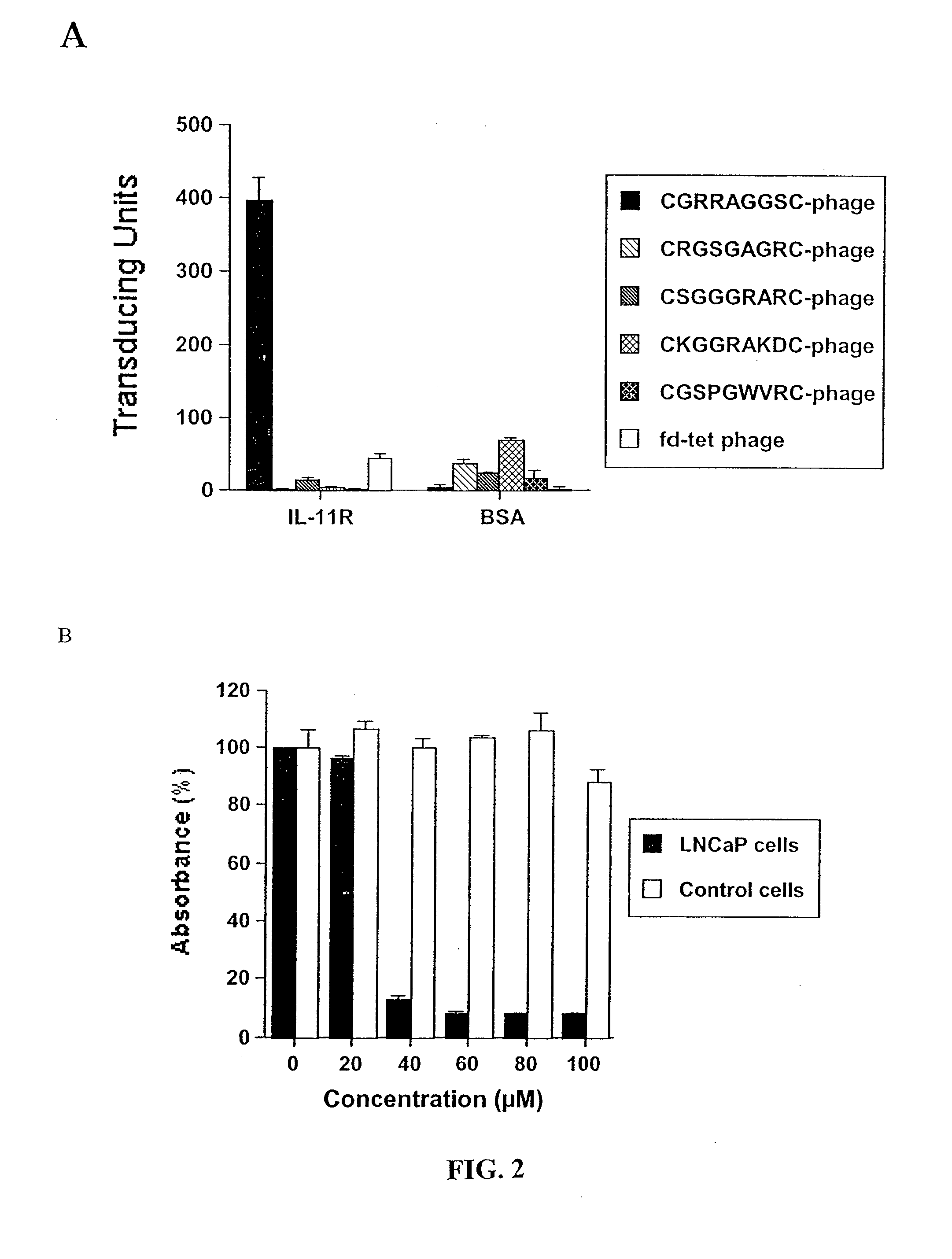
The compositions and methods include targeting peptides selective for tissue selective binding, particularly prostate and / or bone cancer, or adipose tissue. The methods may comprise targeting peptides that bind, for example, cell surface GRP78, IL-11Rα in blood vessels of bone, or prohibitin of adipose vascular tissue. These peptides may be used to induce targeted apoptosis in the presence or absence of at least one pro-apoptotic peptide. Antibodies against such targeting peptides, the targeting peptides, or their mimeotopes may be used for detection, diagnosis and / or staging of a condition, such as prostate cancer or metastatic prostate cancer.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
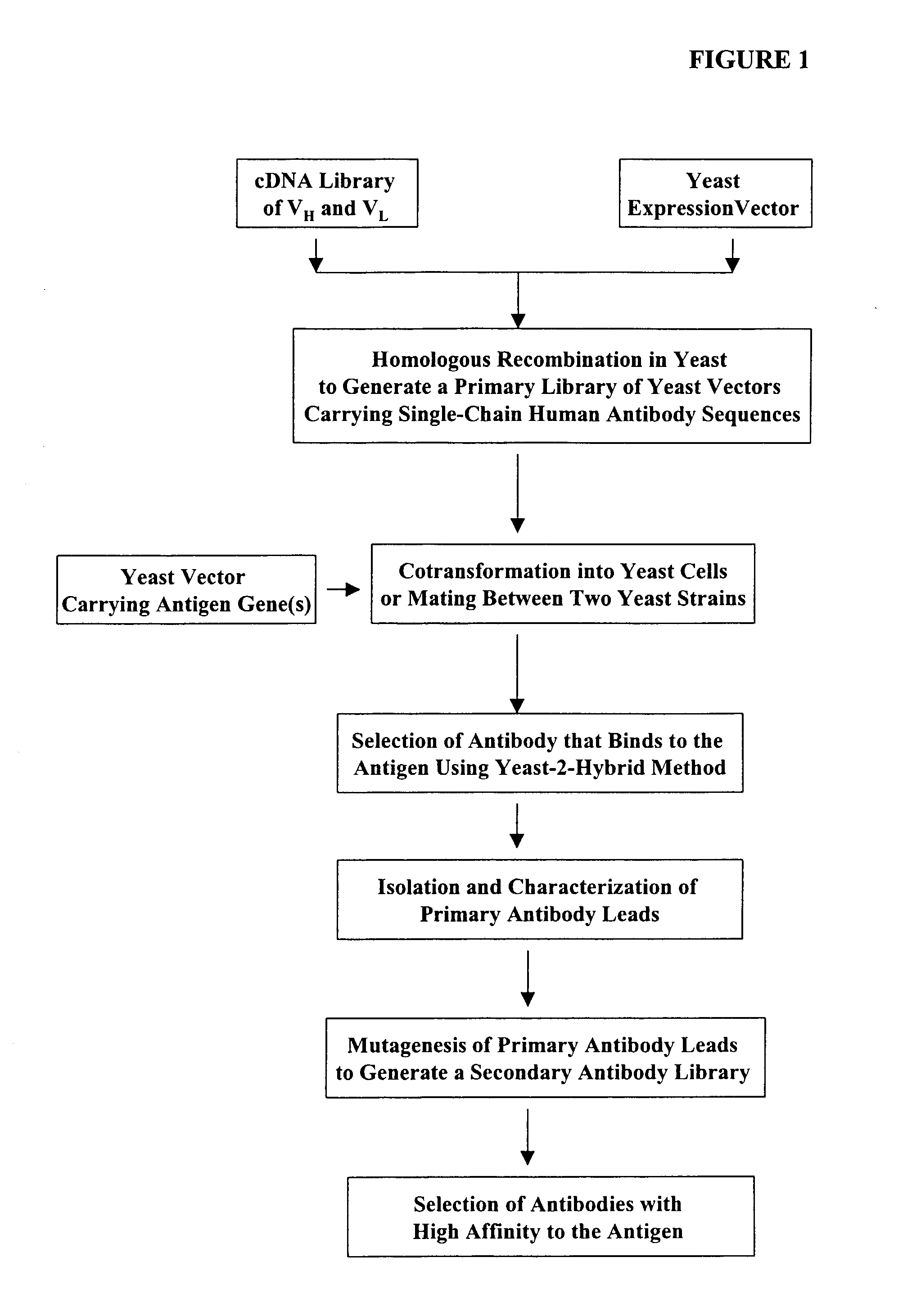
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6406863B1High affinityEasy to assembleMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsTarget peptideIn vivo
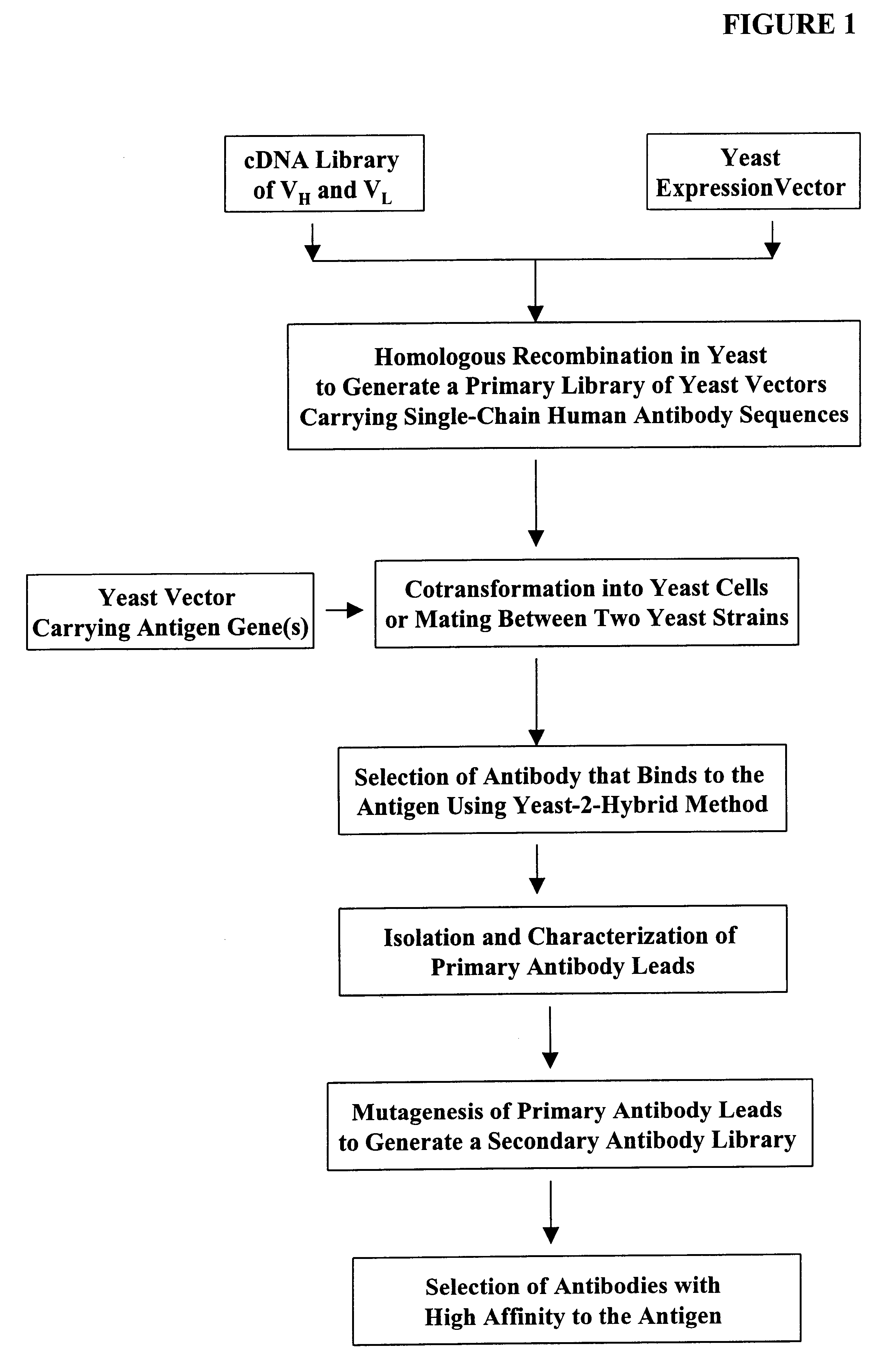
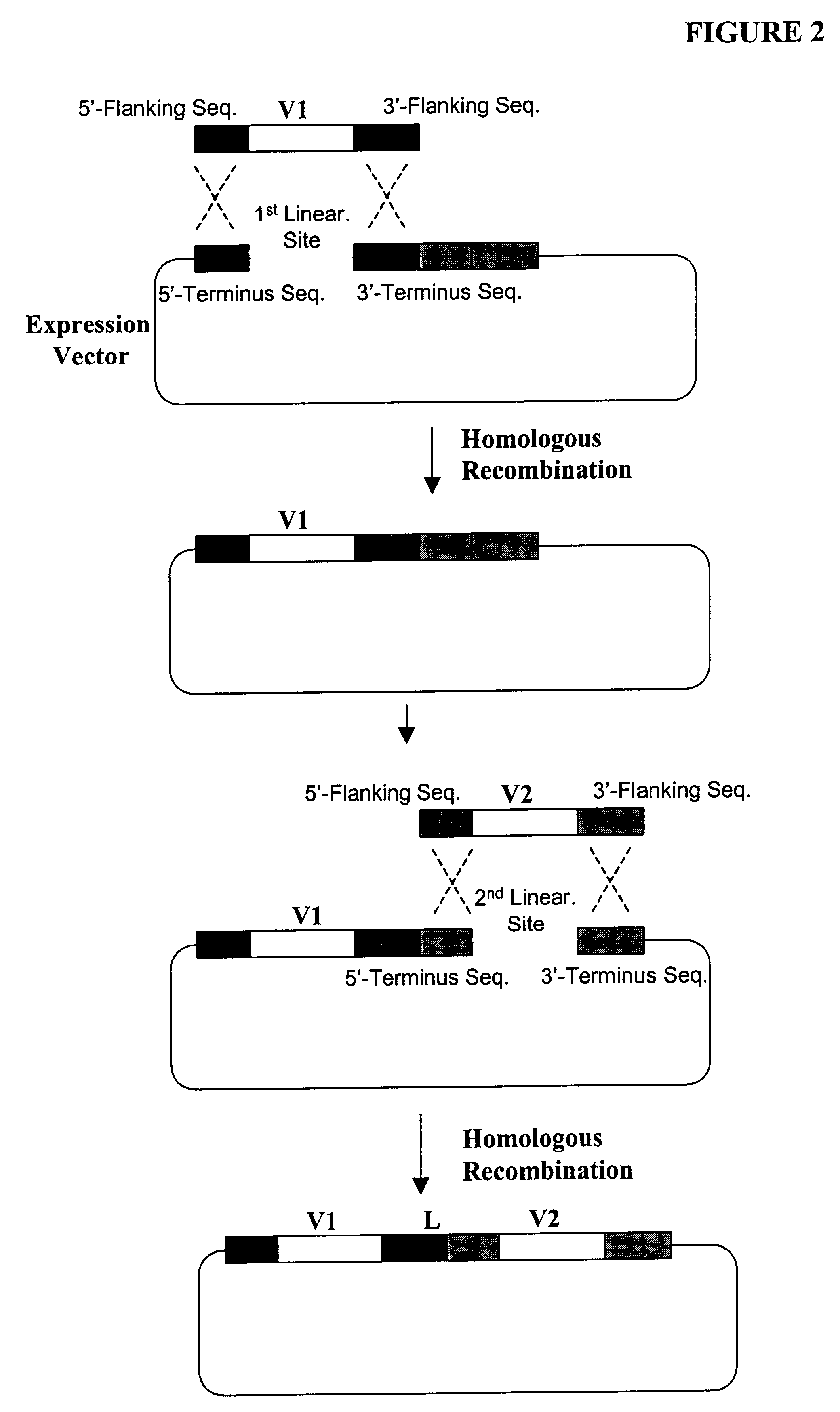
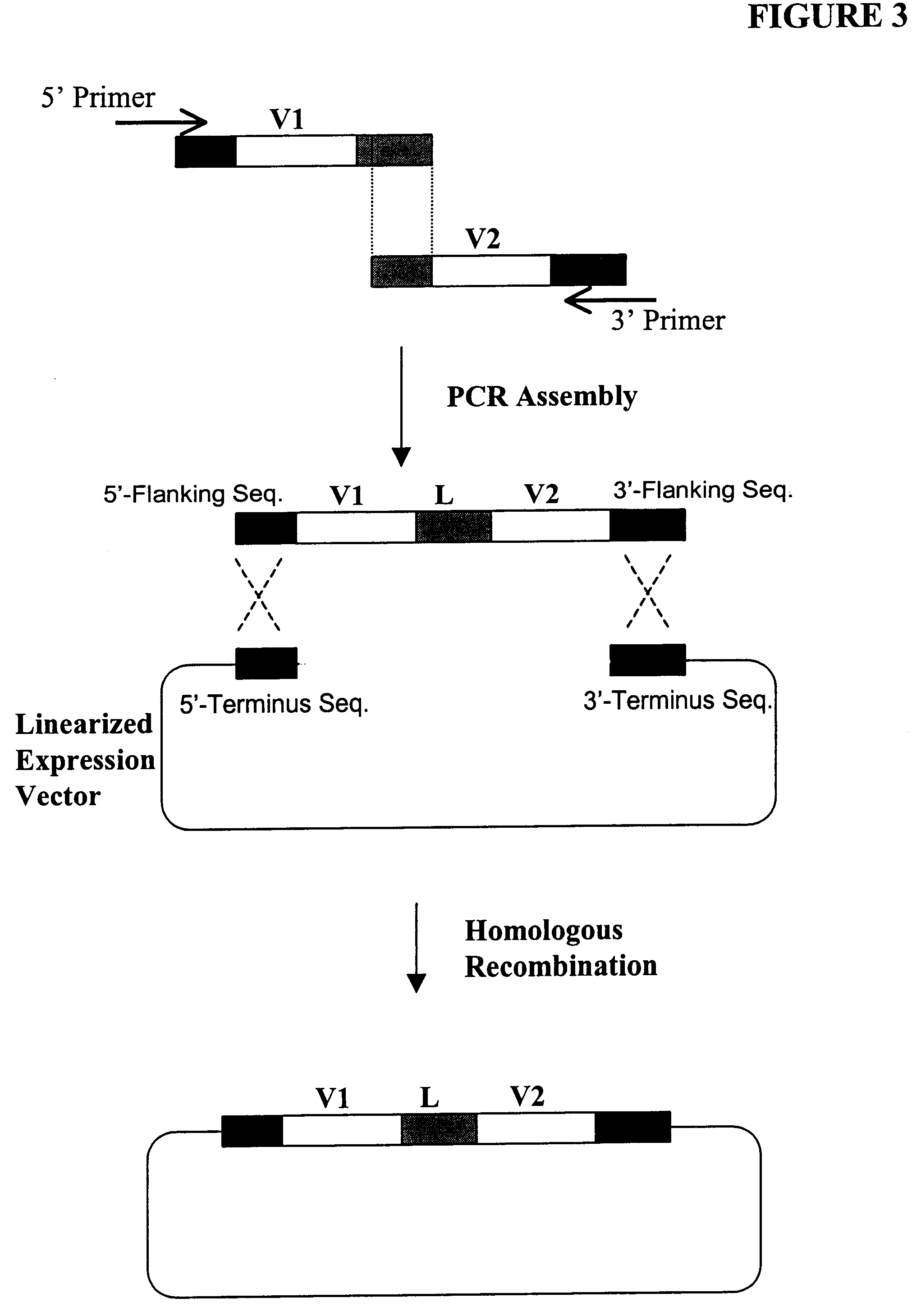
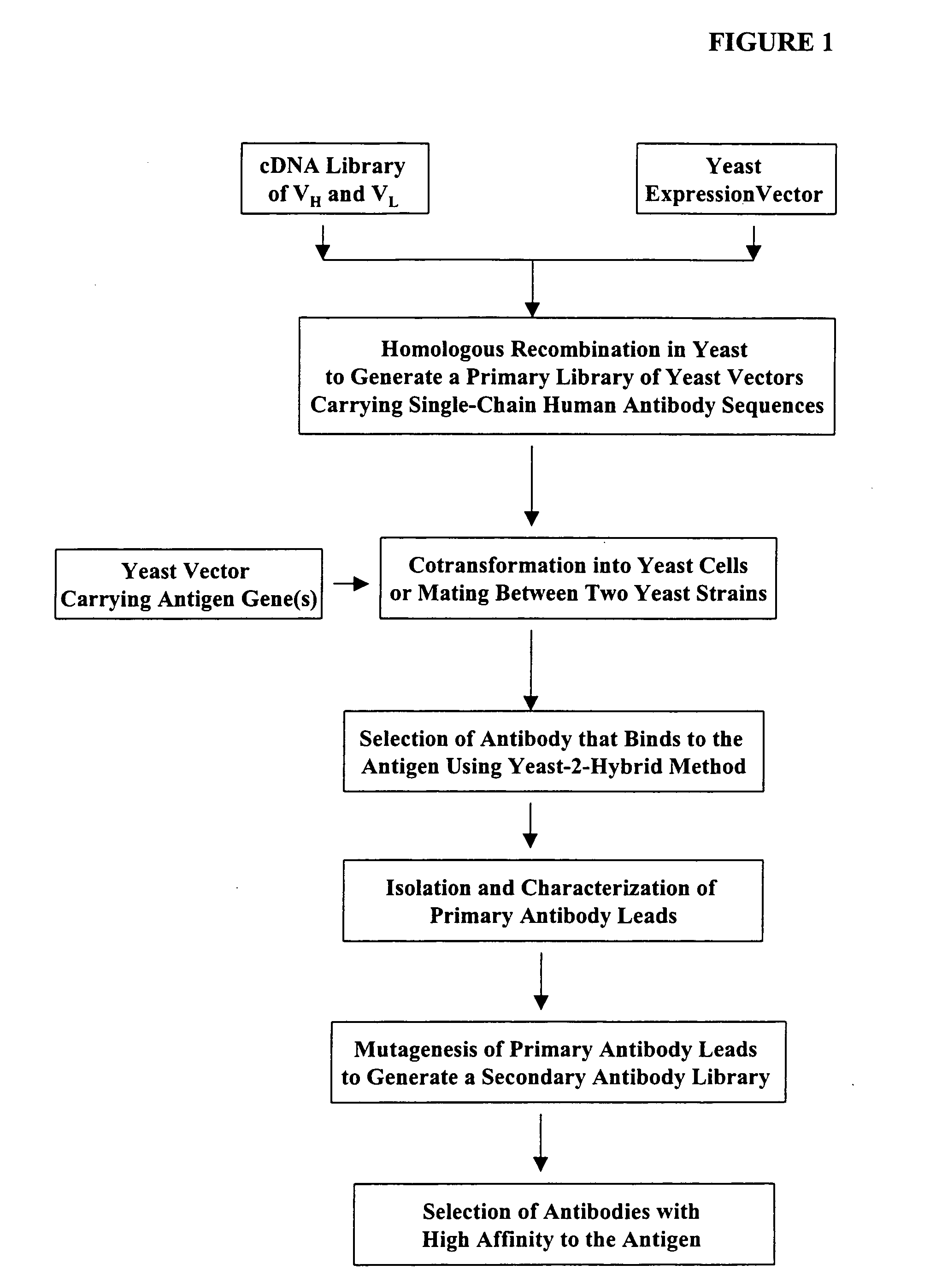
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
GRP78 targeting peptides and methods employing same
The compositions and methods include targeting peptides selective for tissue selective binding, particularly prostate and / or bone cancer, or adipose tissue. The methods may comprise targeting peptides that bind, for example, cell surface GRP78, IL-11Rα in blood vessels of bone, or prohibitin of adipose vascular tissue. These peptides may be used to induce targeted apoptosis in the presence or absence of at least one pro-apoptotic peptide. Antibodies against such targeting peptides, the targeting peptides, or their mimeotopes may be used for detection, diagnosis and / or staging of a condition, such as prostate cancer or metastatic prostate cancer.
Owner:ARAP WADIH +3
Compositions and methods of use of targeting peptides for diagnosis and therapy of human cancer
The present invention concerns compositions comprising and methods of identification and use of targeting peptides selective for cancer tissue, particularly prostate or ovarian cancer tissue. The method may comprise identifying endogenous mimeotopes of such peptides, such as GRP78, IL-11Rα and hsp90. Antibodies against such targeting peptides or their mimeotopes may be used for detection, diagnosis and / or staging of prostate or ovarian cancer. In other embodiments, the compositions and methods concern novel type of gene therapy vector, known as adeno-associated phage (AAP). AAP are of use for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents to particular tissues, organs or cell types, such as prostate or ovarian cancer. In still other embodiments, targeting peptides selective for low-grade lipomas may be used for detection, diagnosis and targeted delivery of therapeutic agents.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
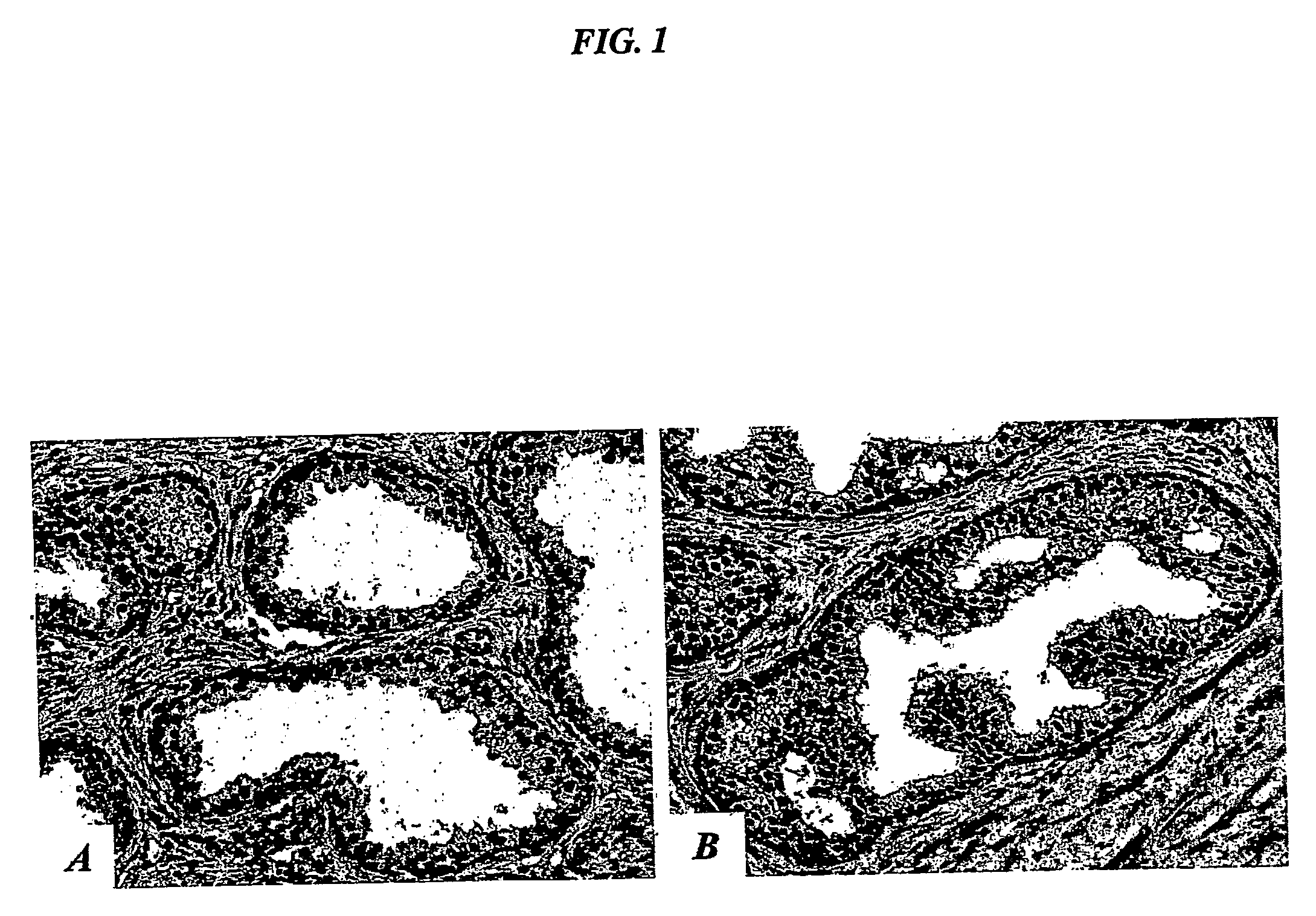
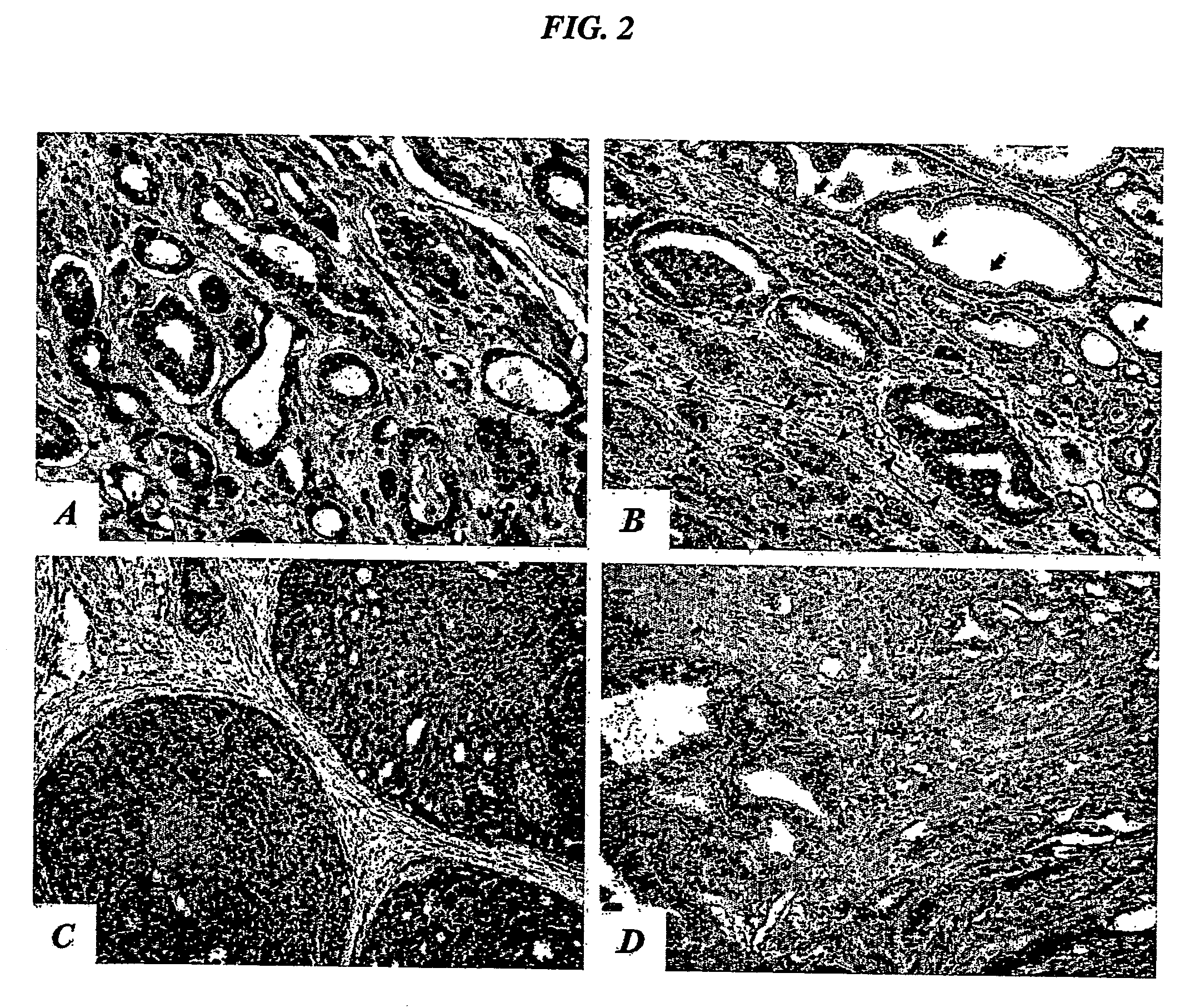
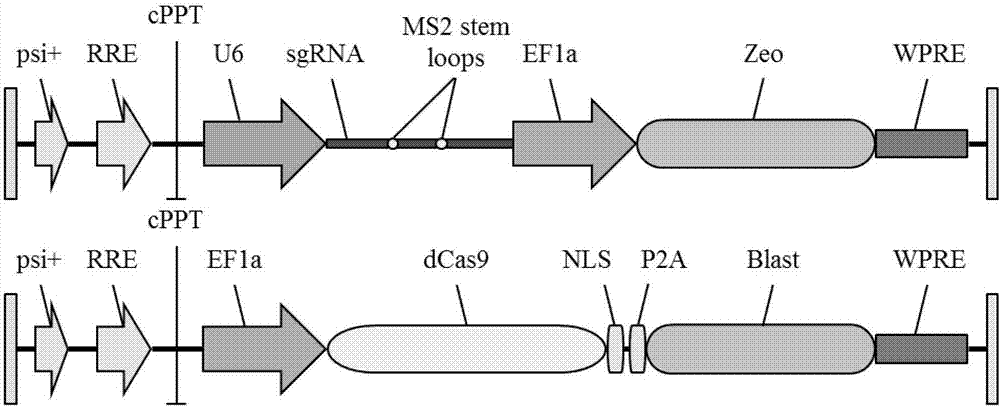
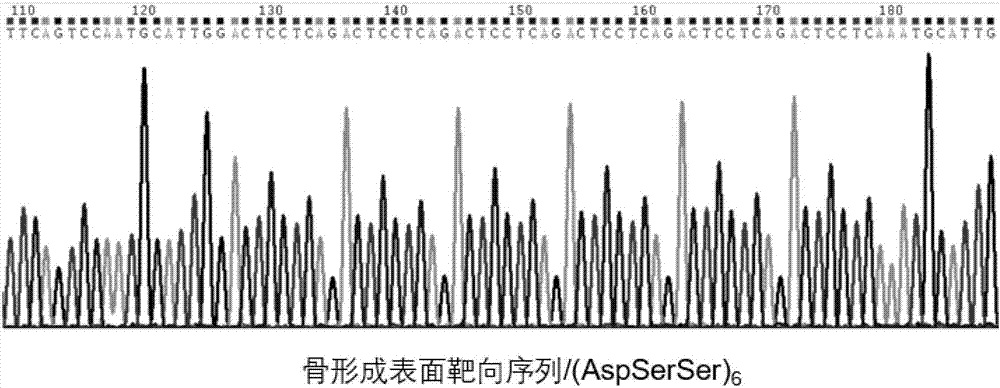
Exosome carrier of targeted bone, CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system and application
ActiveCN107034188APlay gene editingFunctionHydrolasesStable introduction of DNATarget peptideExosome
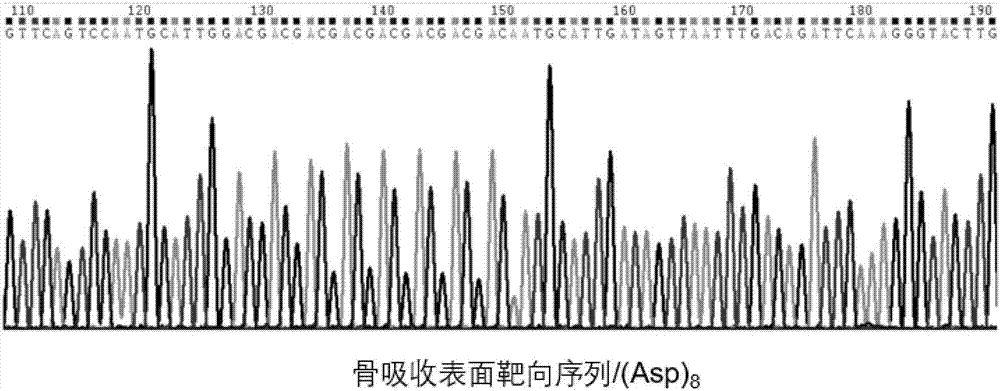
The invention relates to an exosome carrier of a targeted bone, a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system and application. The exosome carrier comprises a targeted peptide of any one of a targeted bone forming surface, a bone absorbing surface and an endothelial cell. The exosome carrier can be fused with (AspSerSer)6, (Asp)8 and a CREDVW oligopeptide respectively by transforming an exosome surface membrane protein lamp2b, so that an exosome can be fused with the targeted bone forming surface, the bone absorbing surface and the endothelial cell. Therefore, the bone targeting exosome is developed as the carrier, a CRISPR / Cas9 system serves as a gene editing and controlling tool, and the two parts are combined to play the important significance on the treatment of various bone diseases.
Owner:HOSPITAL OF STOMATOLOGY SUN YAT SEN UNIV
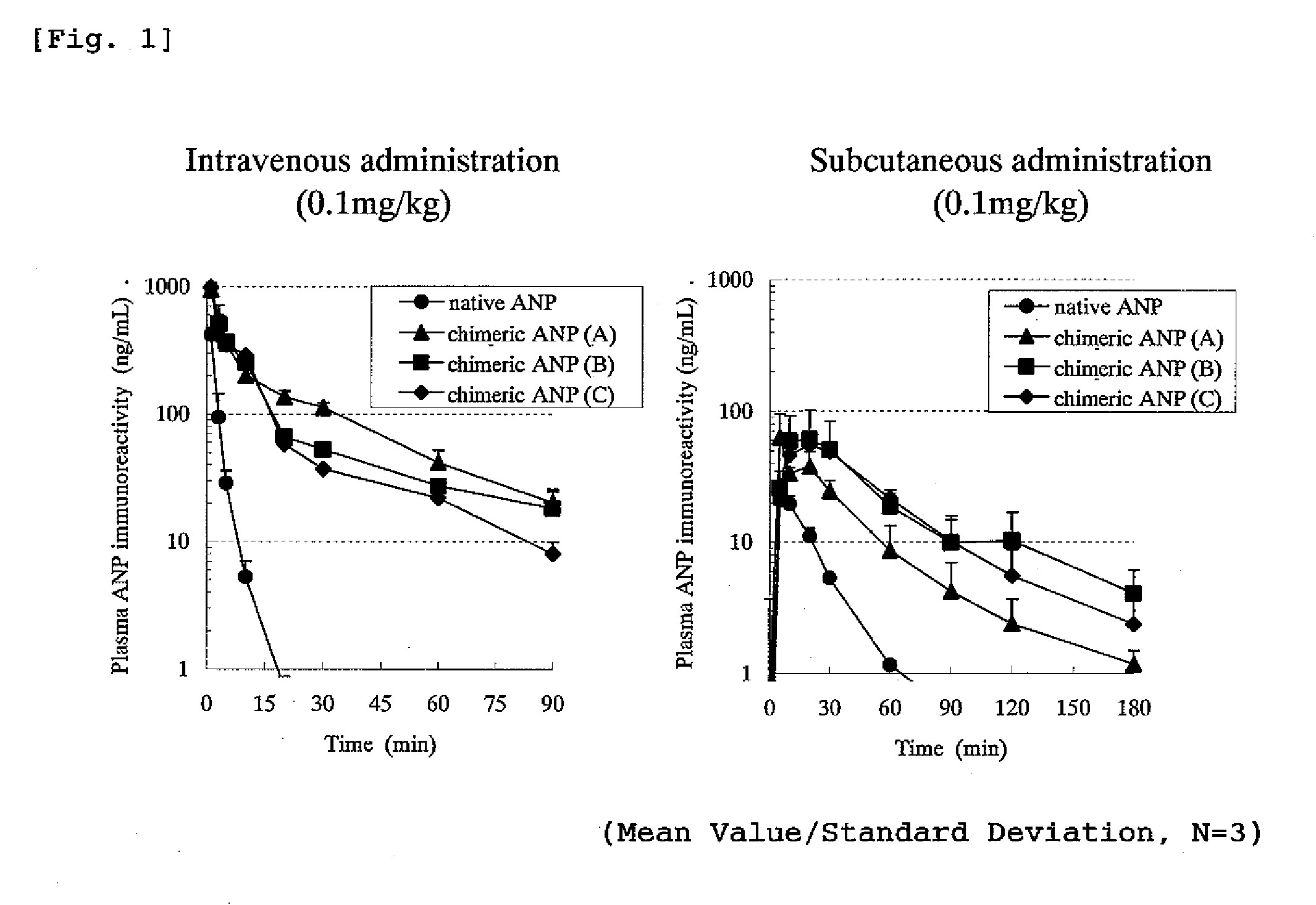
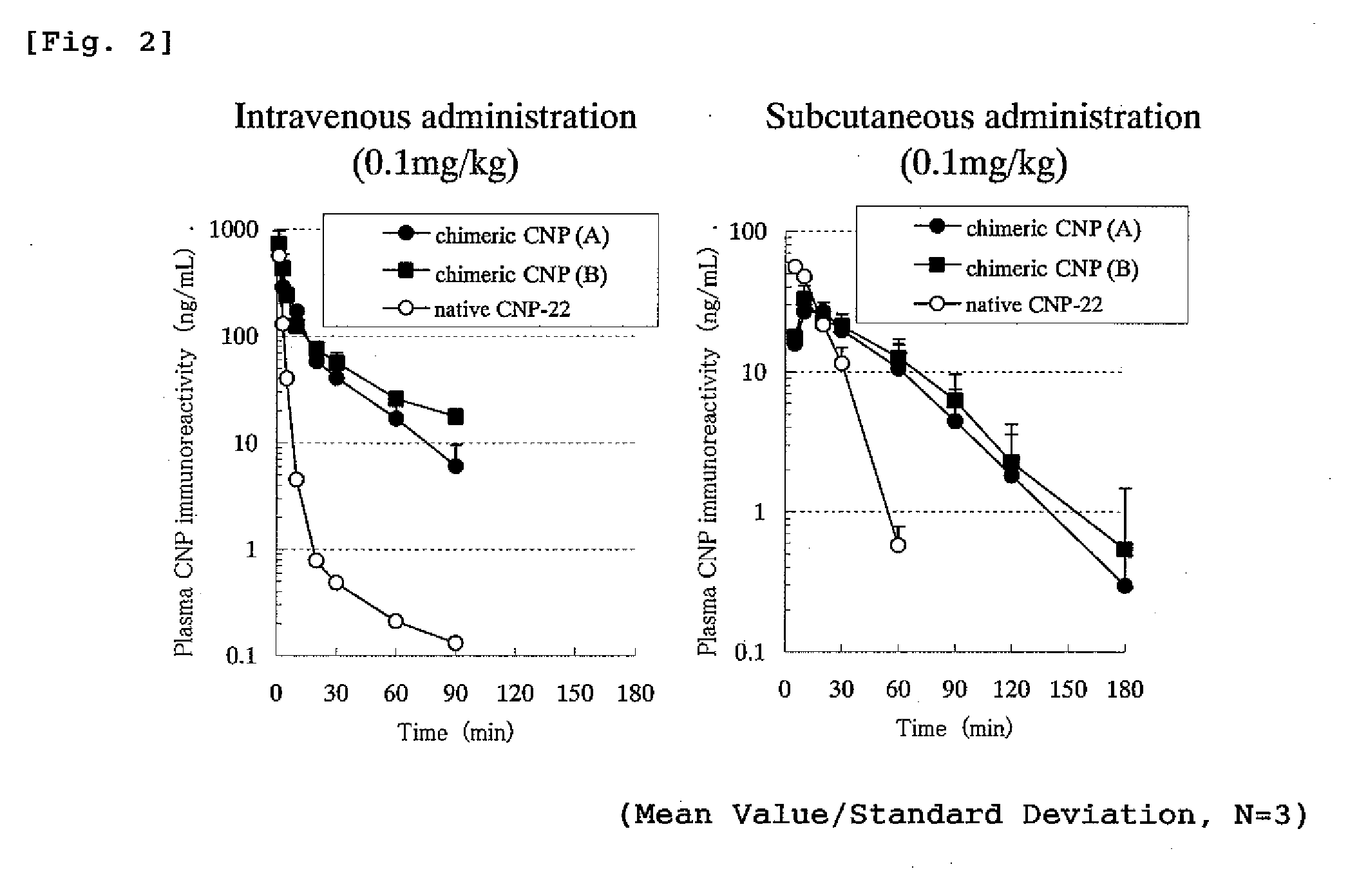
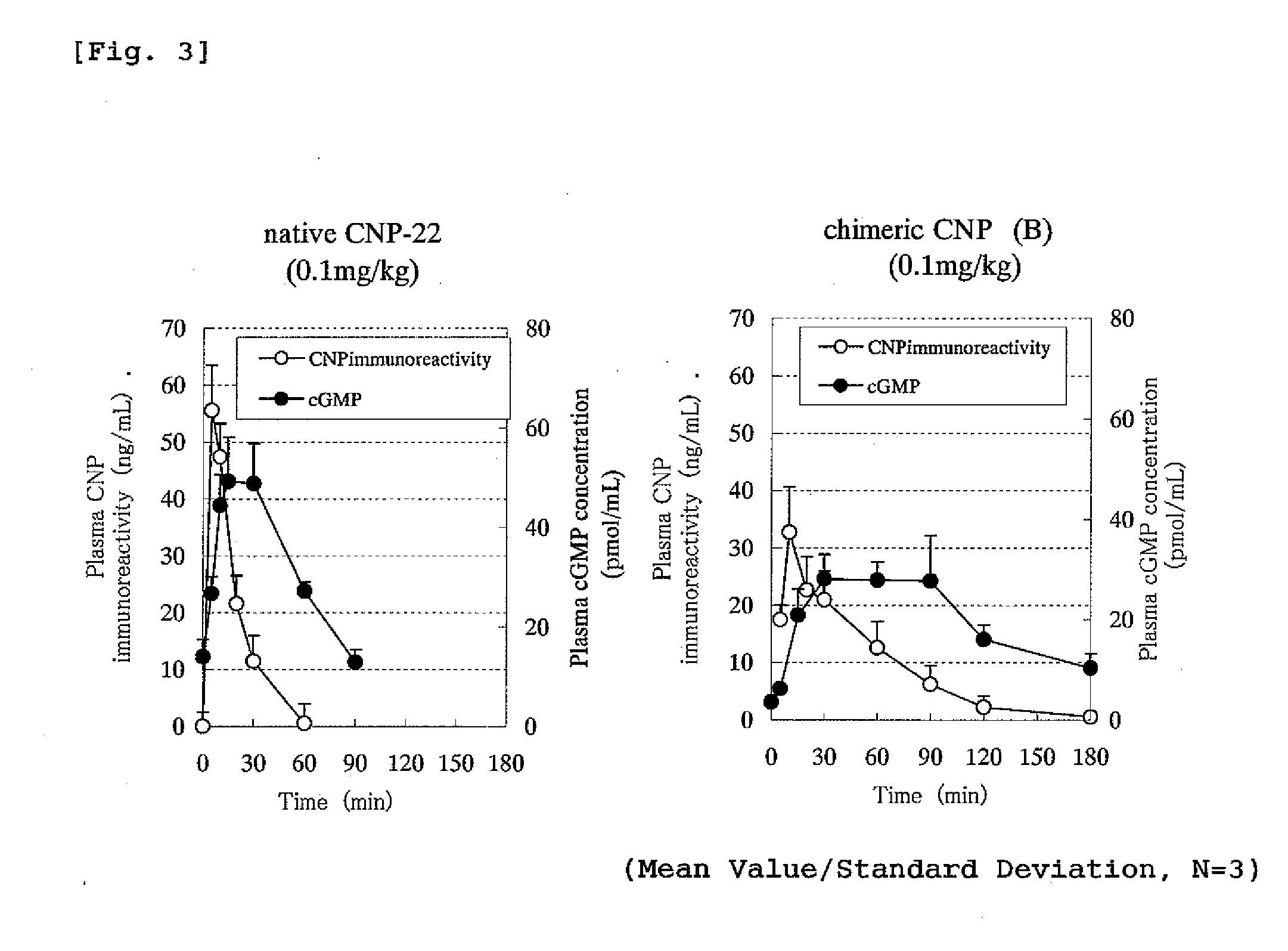
Peptide having an extending action for half-life of object peptide in plasma
ActiveUS20100305031A1Improve securityLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticHalf-lifeBlood plasma
A peptide of the following (I) or (II).(I) a peptide represented by the formula B, A-B, B-C or A-B-C in which A, B and C each is represented by the following (1), (2) and (3) and, when it is bonded to other object peptide, it is able to extent the half-life in plasma as compared with the object peptide where the physiological activity of the object peptide is still retained.(II) a peptide comprising a reversed sequence of the peptide of (I); a sequence which is represented by A-B in (I) and A or B is reversed; a sequence which is represented by B-C in (I) and B or C is reversed; or a sequence which is represented by A-B-C in (I) and A, B, C, A and B, B and C or A and C is reserved.(1) A is a peptide comprising 1 to 14 of any amino acid(s)(2) B is a peptide represented by the formula 1:(Wk-Xl-Y-Zm-Wn)-(Wo-Xp-Y-Zq-Wr)s(In the formula 1, W is a basic amino acid; X and Z are any amino acids; Y is an acidic amino acid; k is 1 or 2; l is an integer of 4≧l≧0; m is an integer of 2≧m≧0; 4≧l+m≧0; n is 1 or 2; o is 1 or 2; p is an integer of 4≧p≧0; q is an integer of 2≧q≧0; 4≧p+q≧0; r is 1 or 2; and s is 0 or 1.)(3) C is a peptide comprising 2 to 14 of any amino acids.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Direct expression of peptides into culture media
InactiveUS6210925B1Reduced viabilityImprove breathabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth phaseBiotechnology
Expression systems are disclosed for the direct expression of peptide products into the culture media where genetically engineered host cells are grown. High yield was achieved with novel vectors, a special selection of hosts, and / or fermentation processes which include careful control of cell growth rate, and use of an inducer during growth phase. Special vectors are provided which include control regions having multiple promoters linked operably with coding regions encoding a signal peptide upstream from a coding region encoding the peptide of interest. Multiple transcription cassettes are also used to increase yield. The production of amidated peptides using the expression systems is also disclosed.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
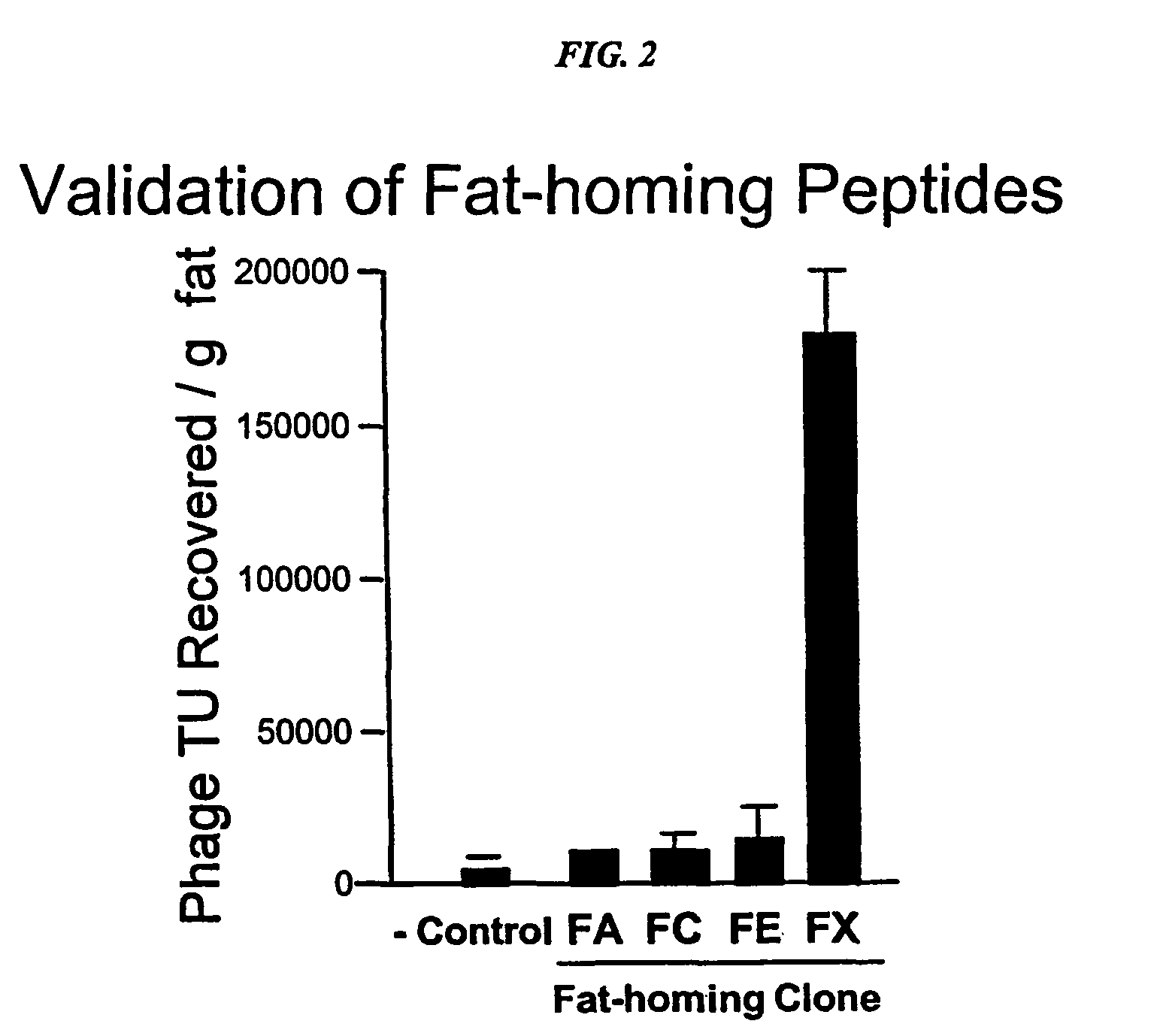
Human and mouse targeting peptides identified by phage display
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for in vivo and in vitro targeting. A large number of targeting peptides directed towards human organs, tissues or cell types are disclosed. The peptides are of use for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents, including but not limited to gene therapy vectors. A novel class of gene therapy vectors is disclosed. Certain of the disclosed peptides have therapeutic use for inhibiting angiogenesis, inhibiting tumor growth, inducing apoptosis, inhibiting pregnancy or inducing weight loss. Methods of identifying novel targeting peptides in humans, as well as identifying endogenous receptor-ligand pairs are disclosed. Methods of identifying novel infectious agents that are causal for human disease states are also disclosed. A novel mechanism for inducing apoptosis is further disclosed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
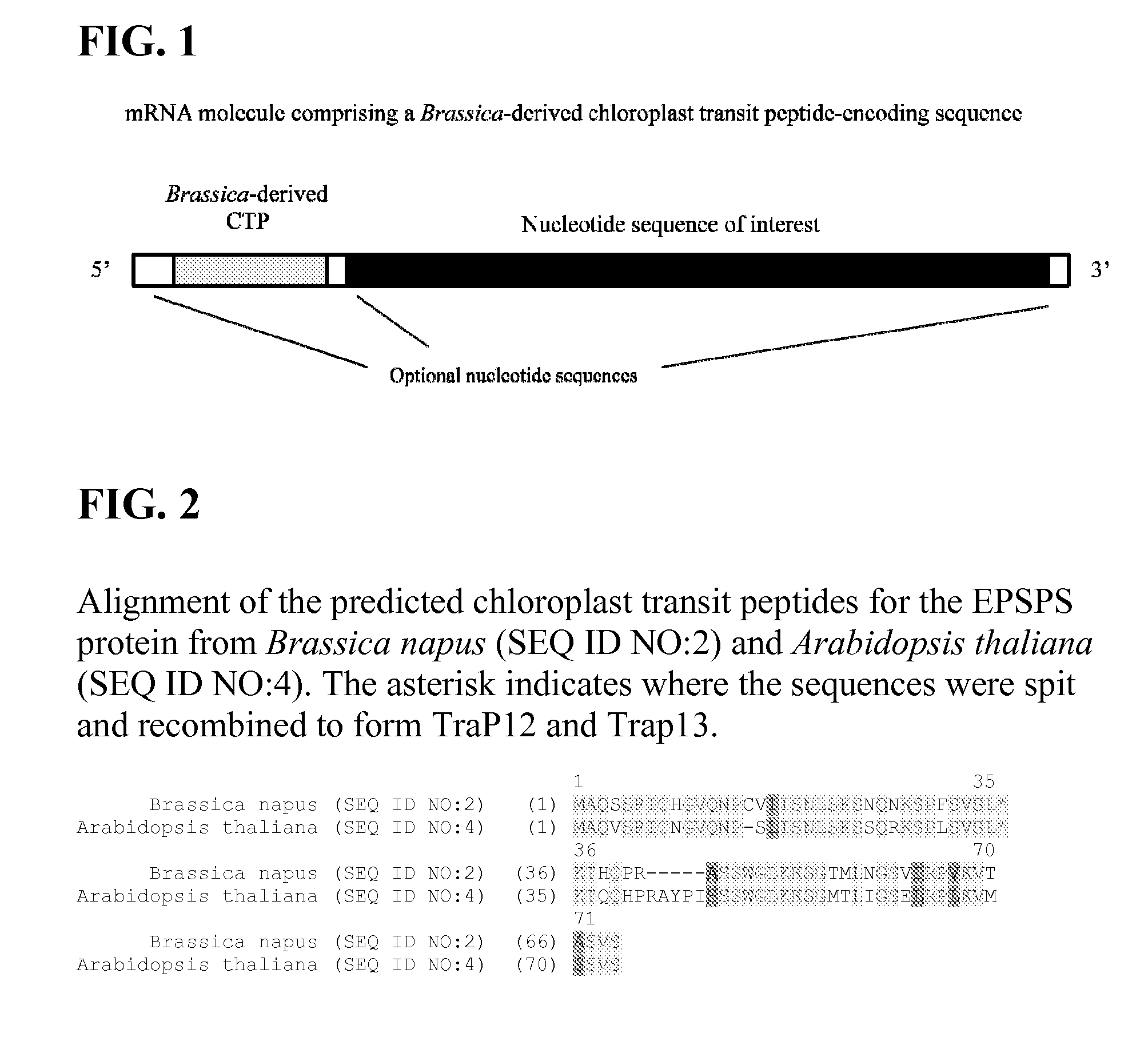
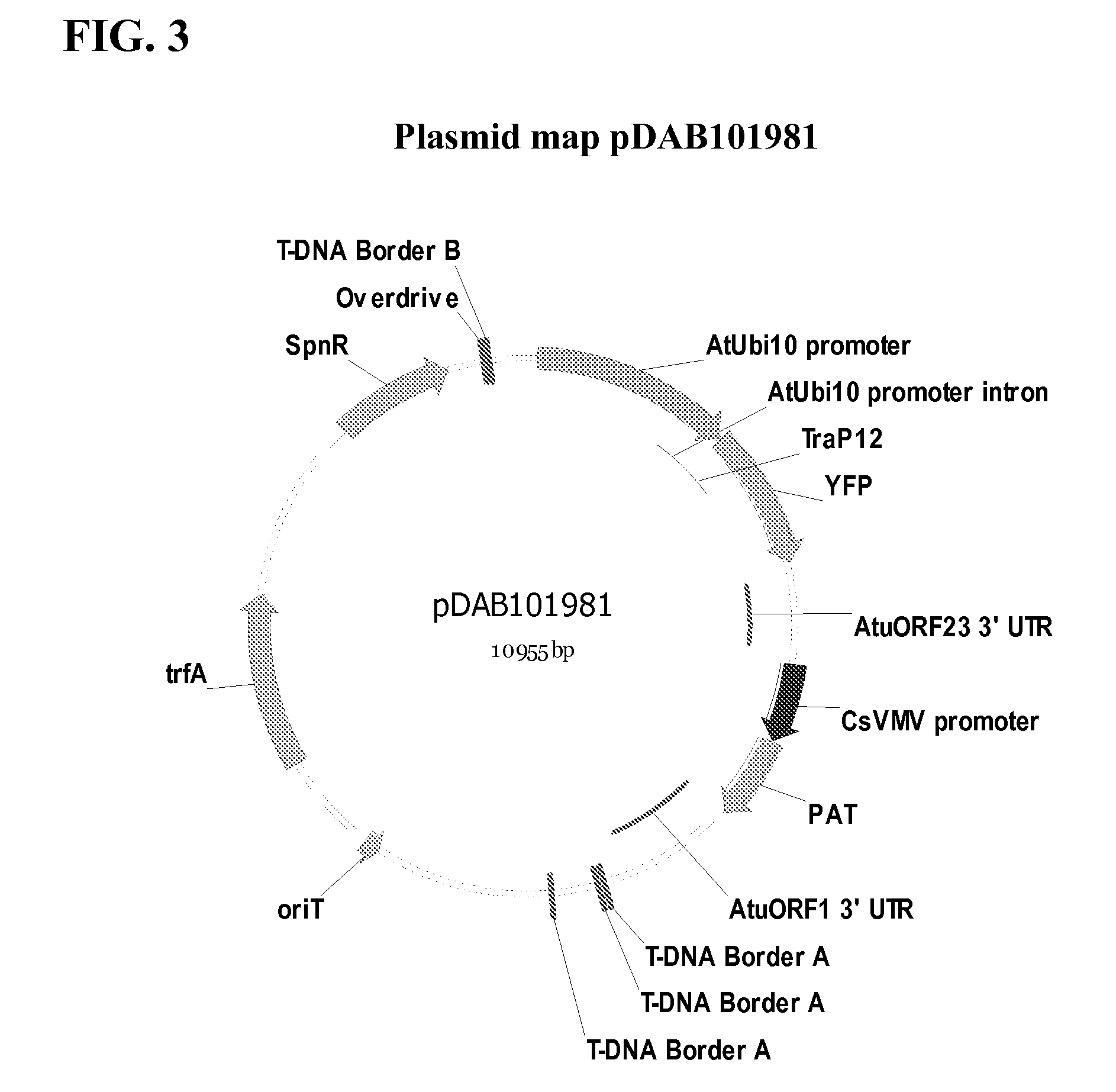
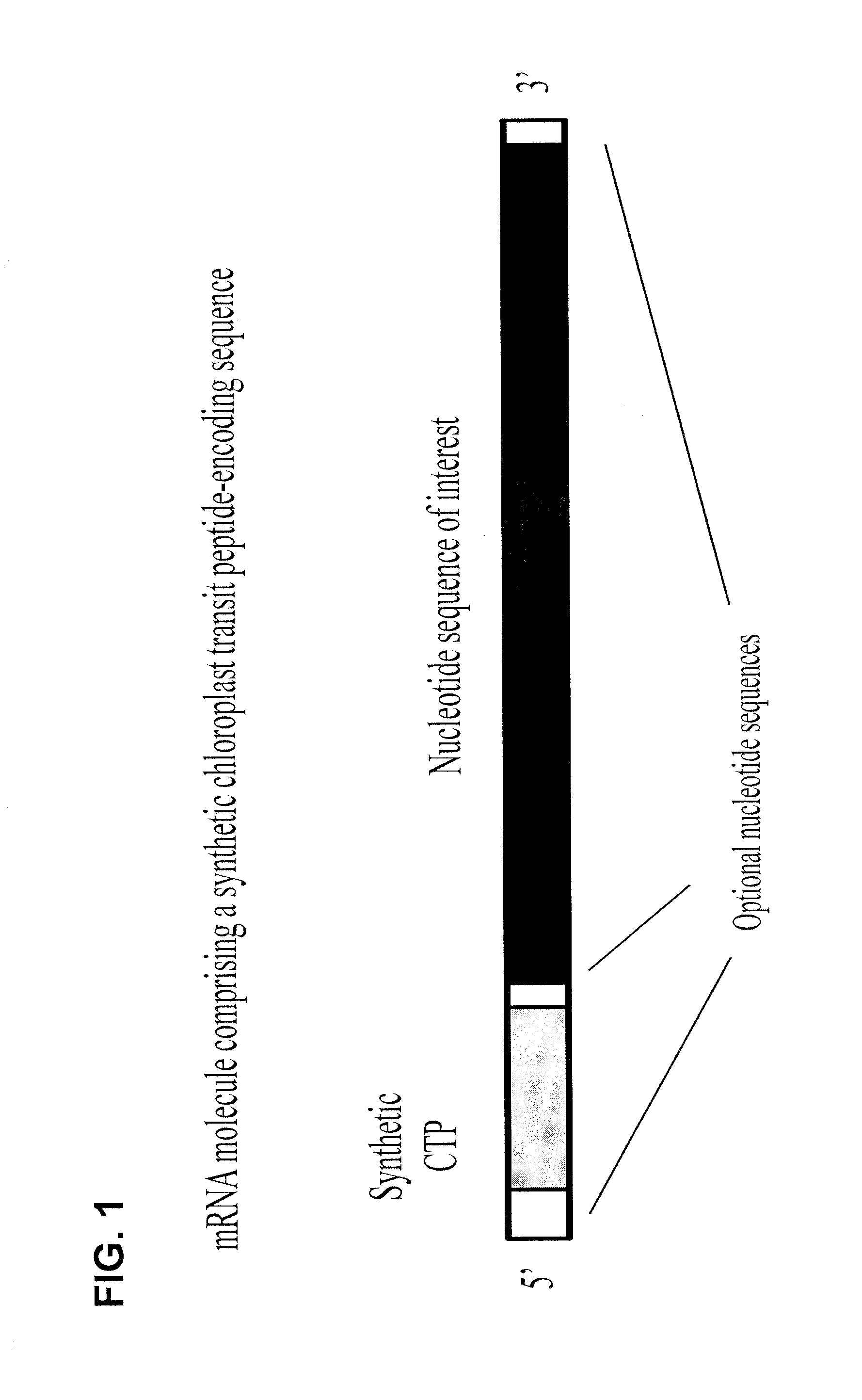
Synthetic brassica-derived chloroplast transit peptides
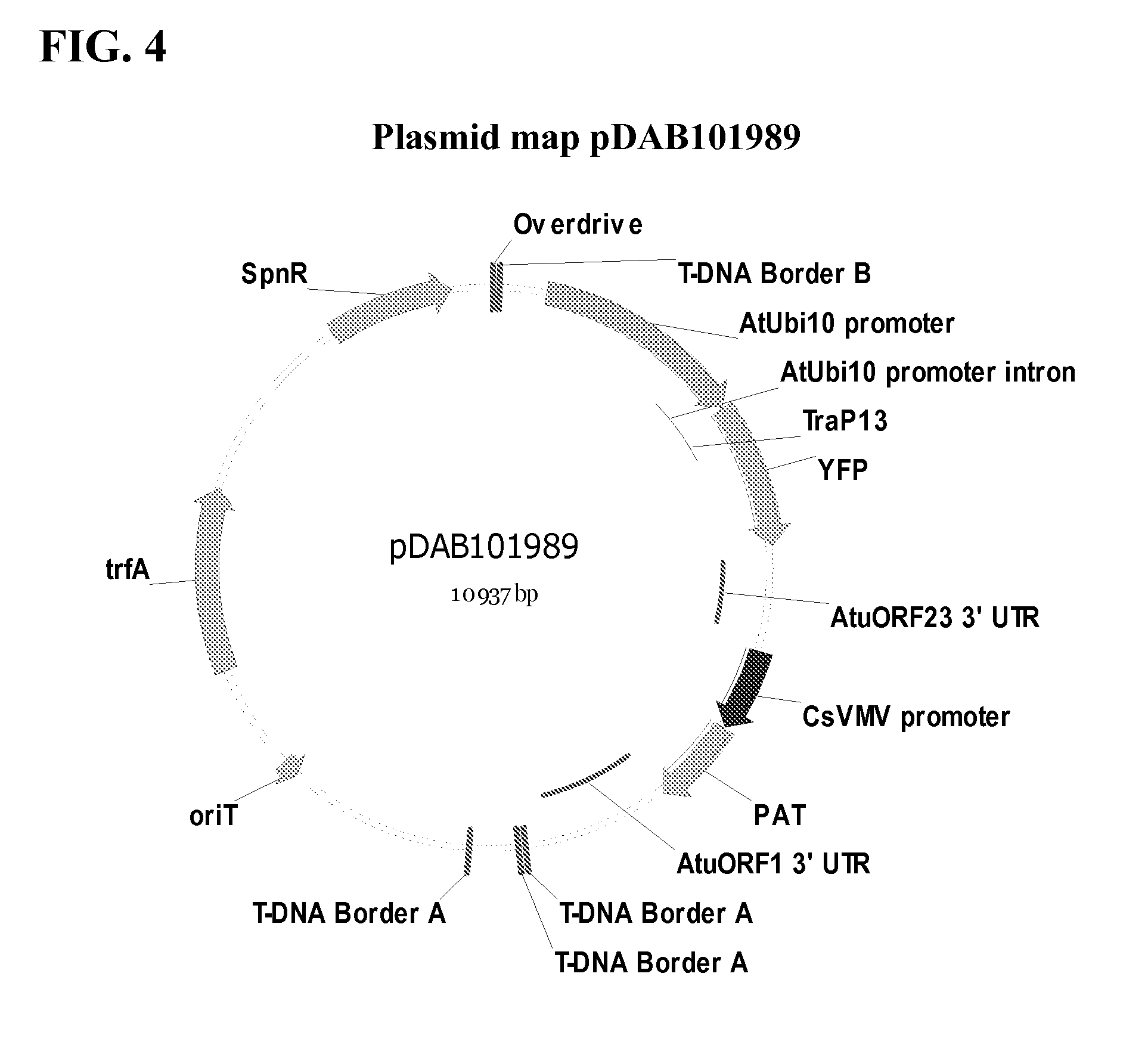
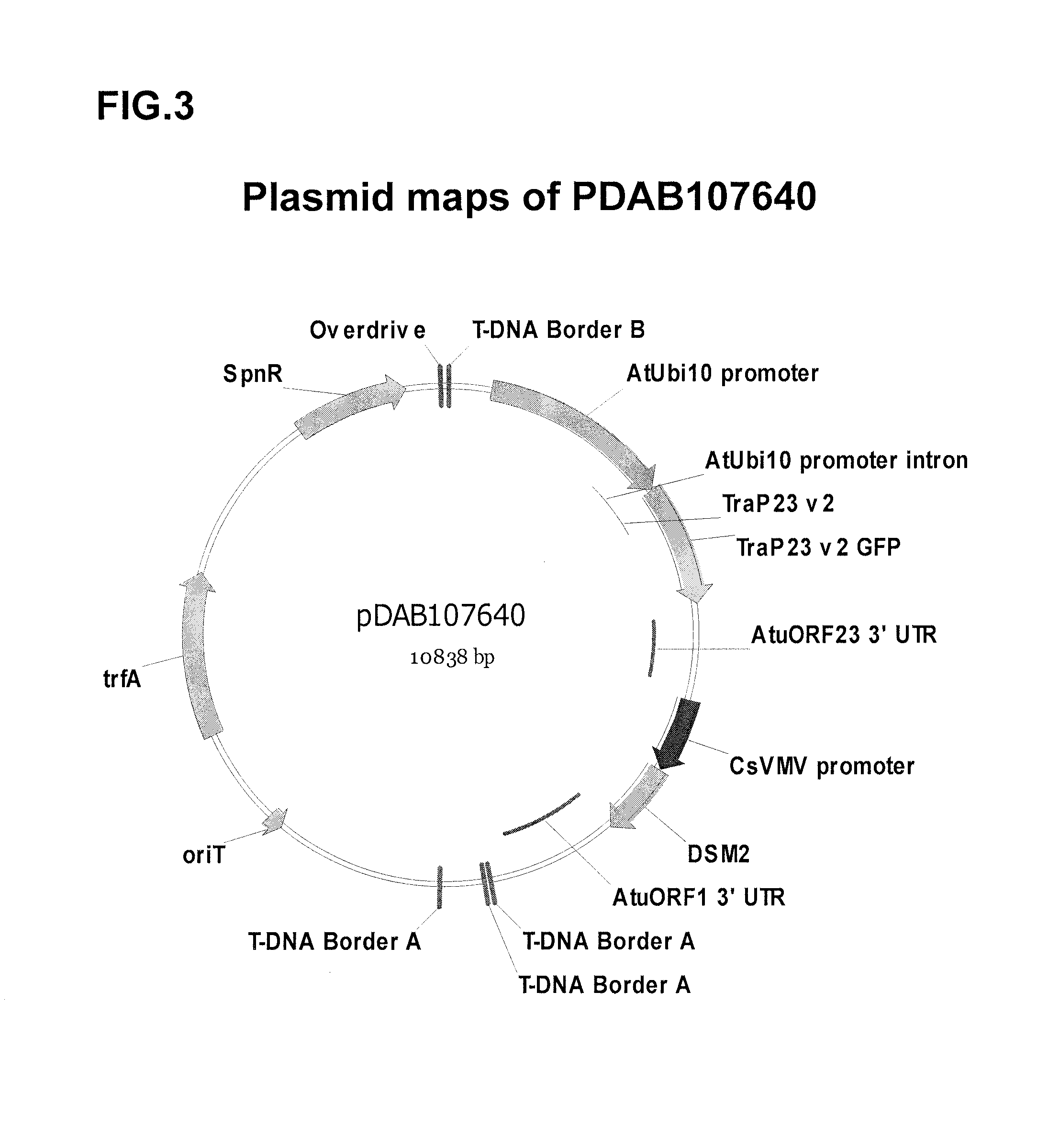
This disclosure concerns compositions and methods for targeting peptides, polypeptides, and proteins to plastids of plastid-containing cells. In some embodiments, the disclosure concerns chloroplast transit peptides that may direct a polypeptide to a plastid, and nucleic acid molecules encoding the same. In some embodiments, the disclosure concerns methods for producing a transgenic plant material (e.g., a transgenic plant) comprising a chloroplast transit peptide, as well as plant materials produced by such methods, and plant commodity products produced therefrom.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Compositions and methods of use of targeting peptides for diagnosis and therapy of human cancer
The present invention concerns compositions comprising and methods of identification and use of targeting peptides selective for cancer tissue, particularly prostate or ovarian cancer tissue. The method may comprise identifying endogenous mimeotopes of such peptides, such as GRP78, IL-11Rα and hsp90. Antibodies against such targeting peptides or their mimeotopes may be used for detection, diagnosis and / or staging of prostate or ovarian cancer. In other embodiments, the compositions and methods concern novel type of gene therapy vector, known as adeno-associated phage (AAP). AAP are of use for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents to particular tissues, organs or cell types, such as prostate or ovarian cancer. In still other embodiments, targeting peptides selective for low-grade lipomas may be used for detection, diagnosis and targeted delivery of therapeutic agents.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Blood brain barrier permeation peptides
InactiveUS20060039859A1Enough timeIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsVascular endotheliumTarget peptide
Novel blood-brain barrier permeant amyloid-targeting peptides and peptide conjugates are described. The peptide conjugates include a radioisotope or other label in a stable complex that translocates across brain capillary endothelial cell monolayers. The labeled peptide conjugate binds to amyloid plaques (Aβ) associated with Alzheimer's disease, and is useful for the targeted delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic molecules into the brain.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Specific target polypeptide self-assembled nano-carrier, drug-carrying nanoparticle and preparation method
ActiveCN106822036AGrowth inhibitionInhibit synthesisOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsNanocarriersBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and in particular relates to a specific target polypeptide self-assembled nanoparticle. The nanoparticle is prepared from a hydrophobic anti-tumor drug with a therapeutic dosage and an amphipathic polypeptide which covers the periphery of the hydrophobic anti-tumor drug through a self-assembling manner, wherein the amphipathic polypeptide is a target peptide which can be used for specifically targeting a epidermal growth factor receptor of a tumor cell; a terminal N of the target peptide is coupled with a hydrophobic functional molecule. After the nanoparticle targets the tumor cell, the target peptide is exposed; the nanoparticle targets the tumor cell and enters the tumor cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis, and the drug is released to inhibit DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) synthesis and repairing; the nanoparticle has dual killing effects on the tumor cells and the growth of the tumor cell is inhibited. The amphipathic polypeptide does not generate a covalent bond in a self-assembling process and no reverse reaction is caused; the specific target polypeptide self-assembled nanoparticle is used for treating tumors and has the advantages of no toxin and good biocompatibility.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
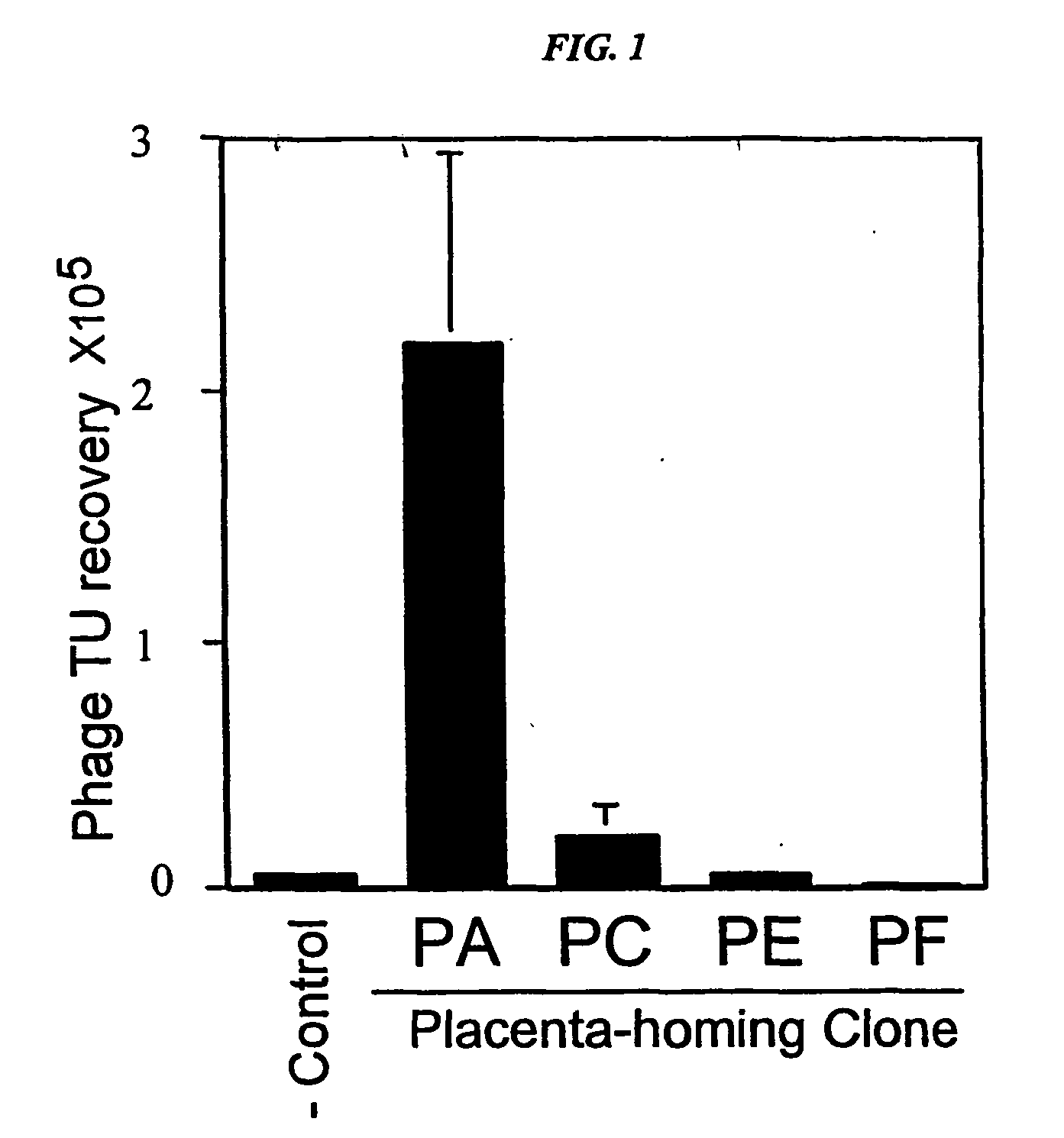
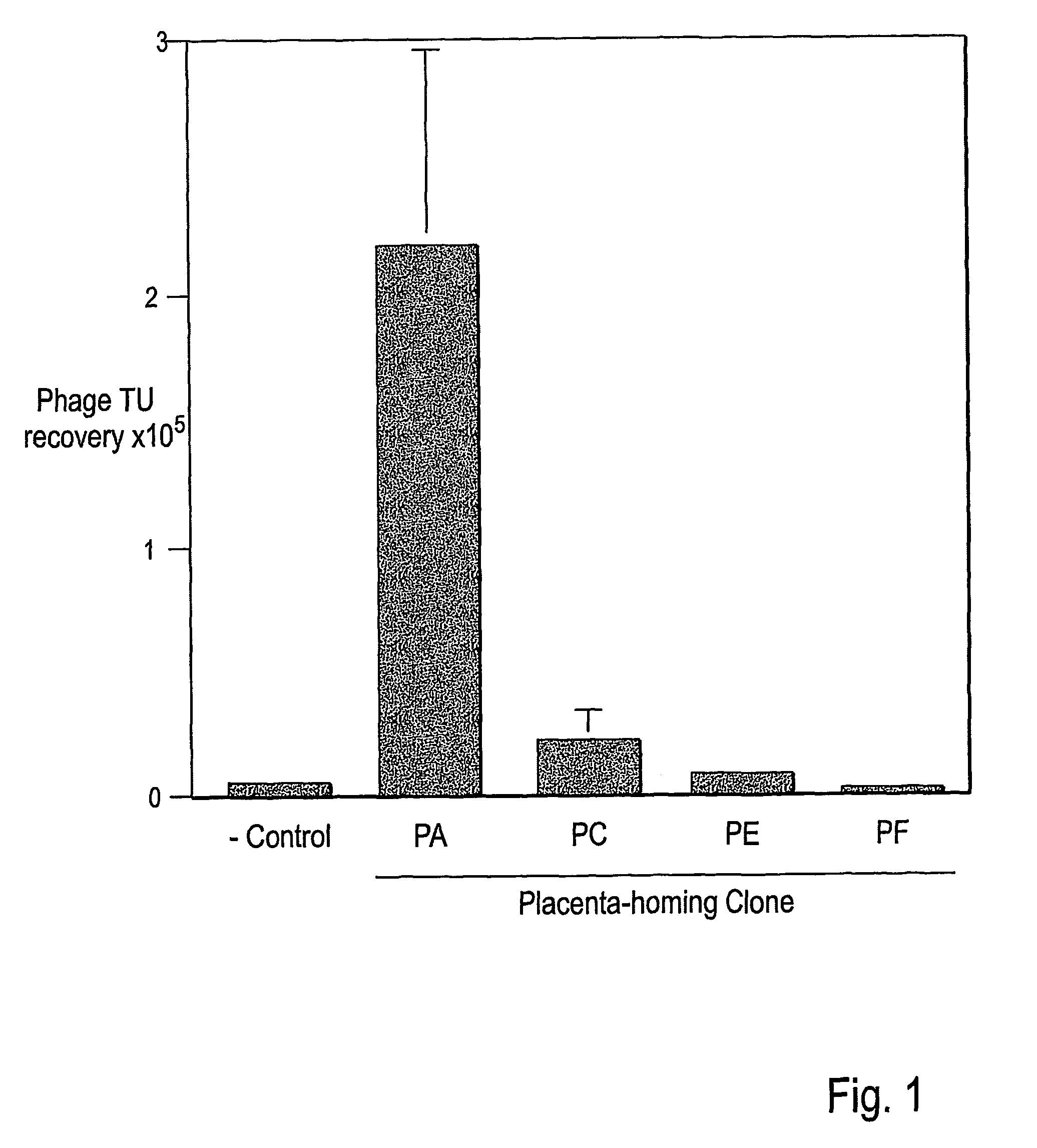
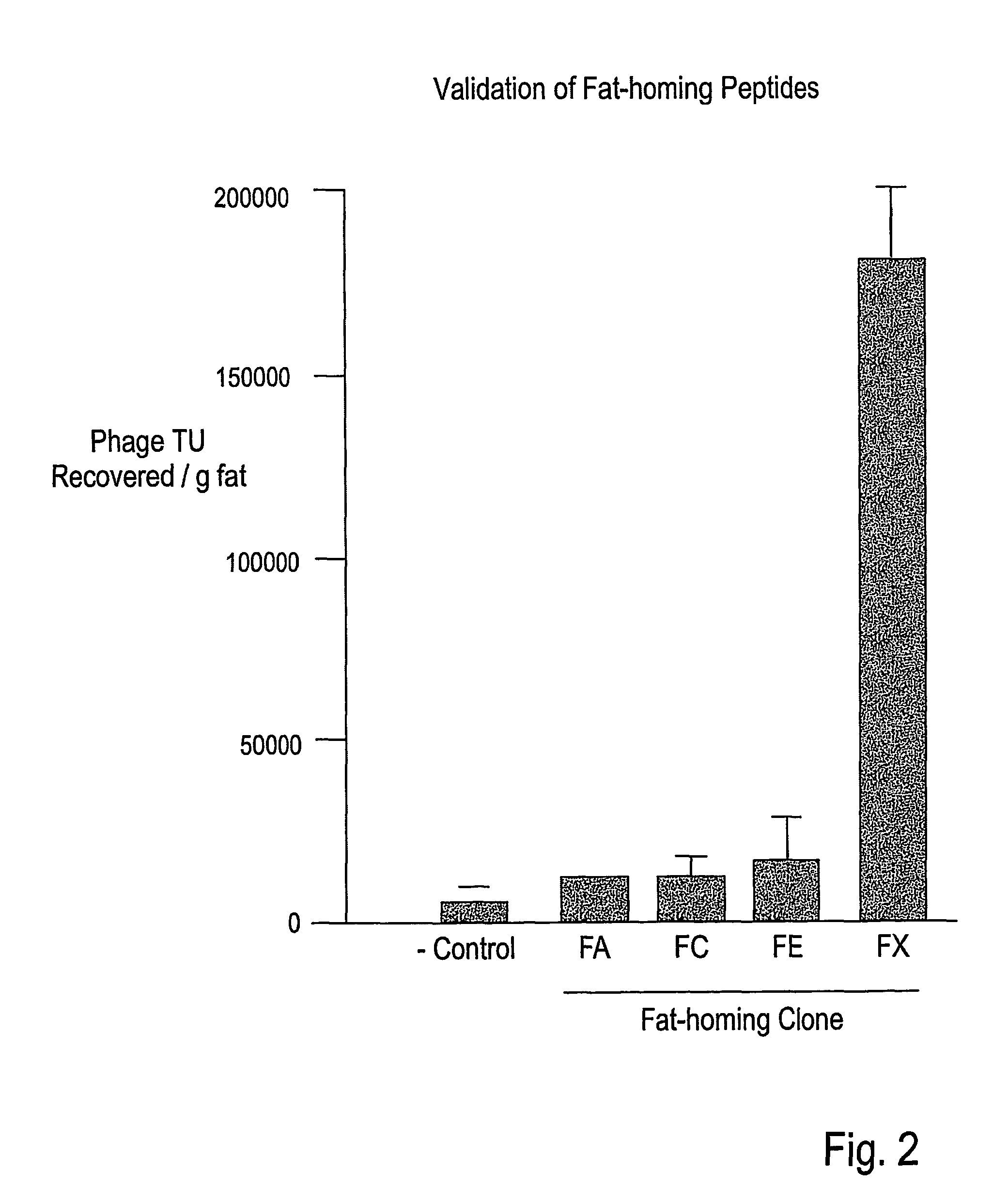
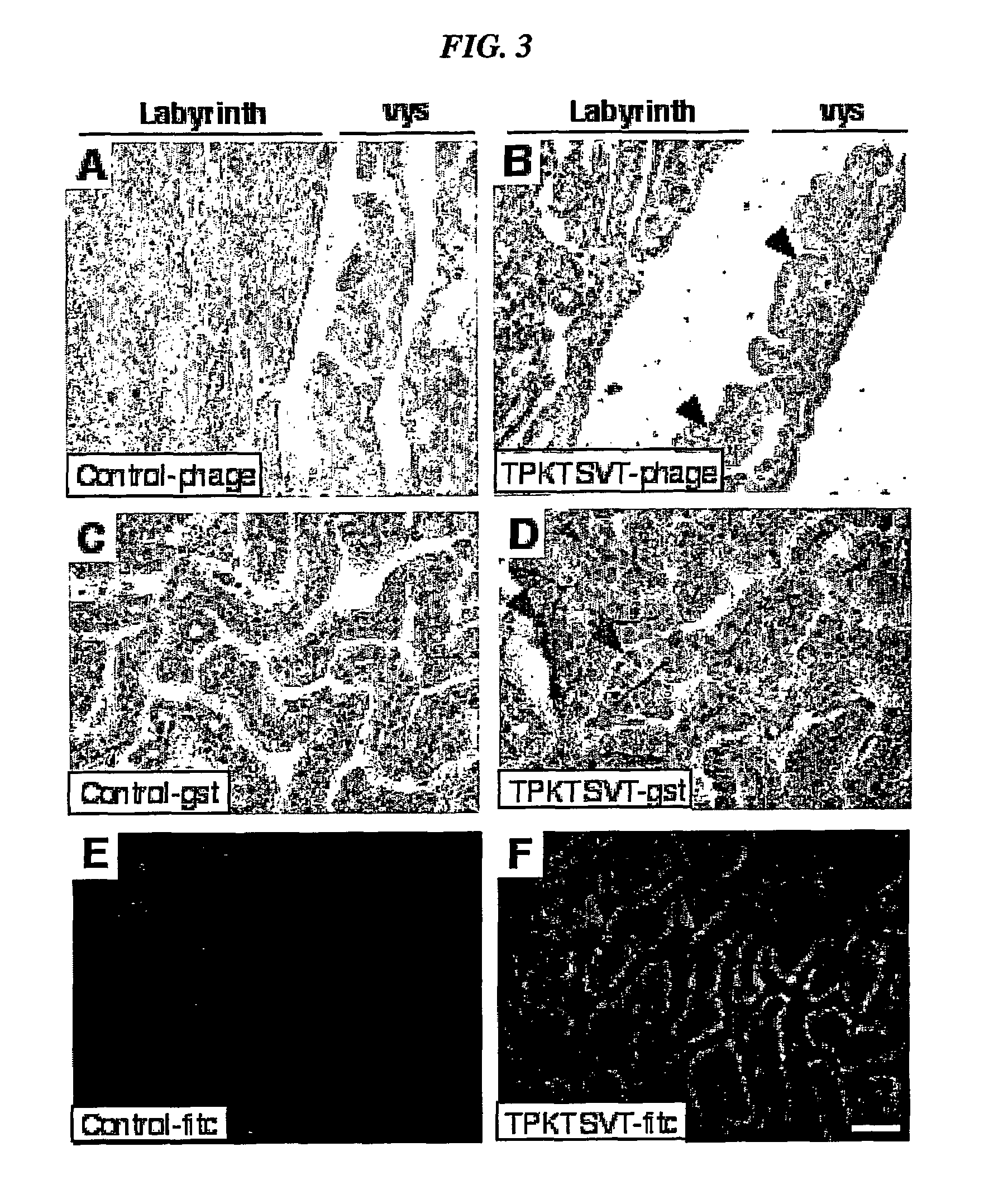
Compositions and methods of use of targeting peptides against placenta and adipose tissues
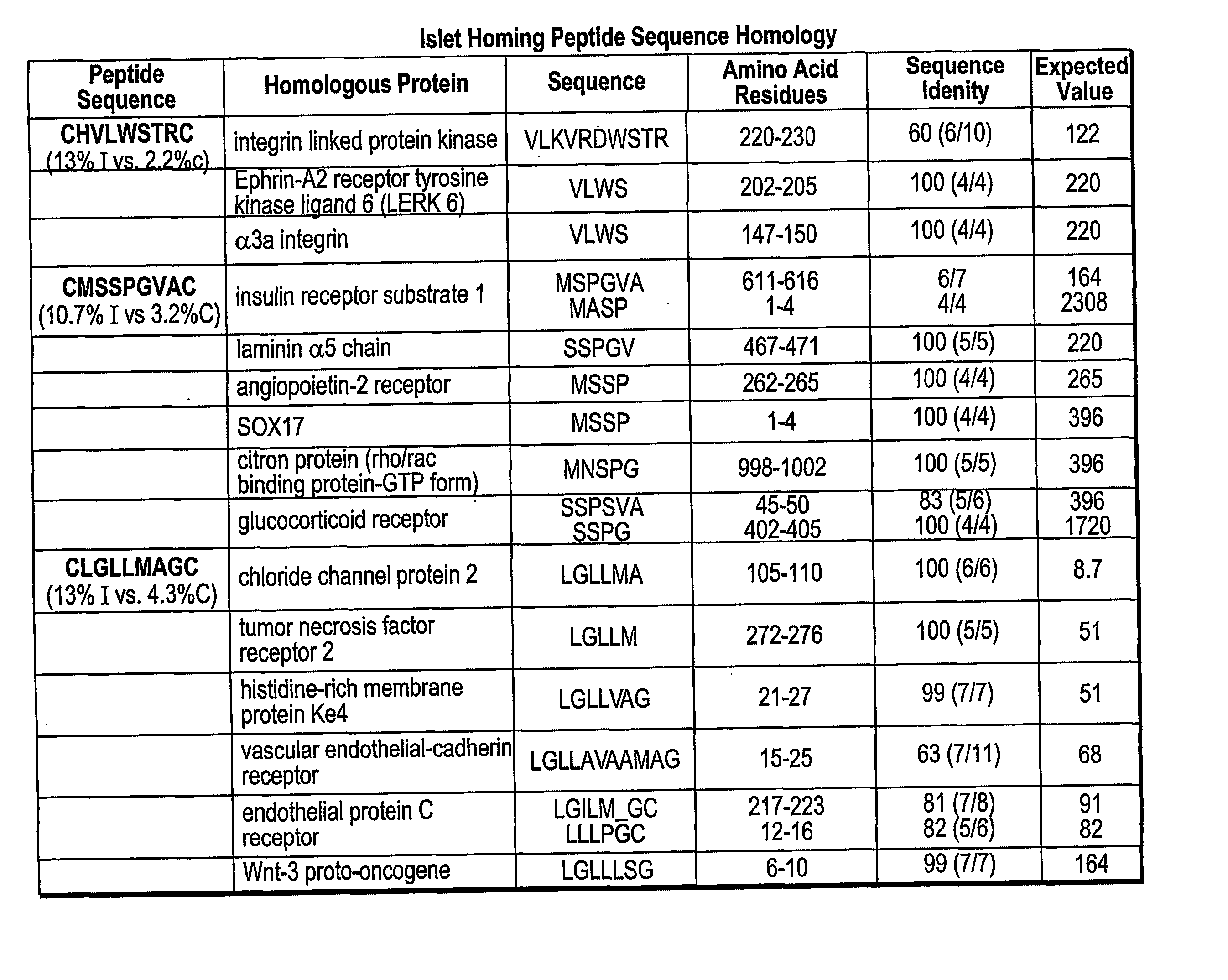
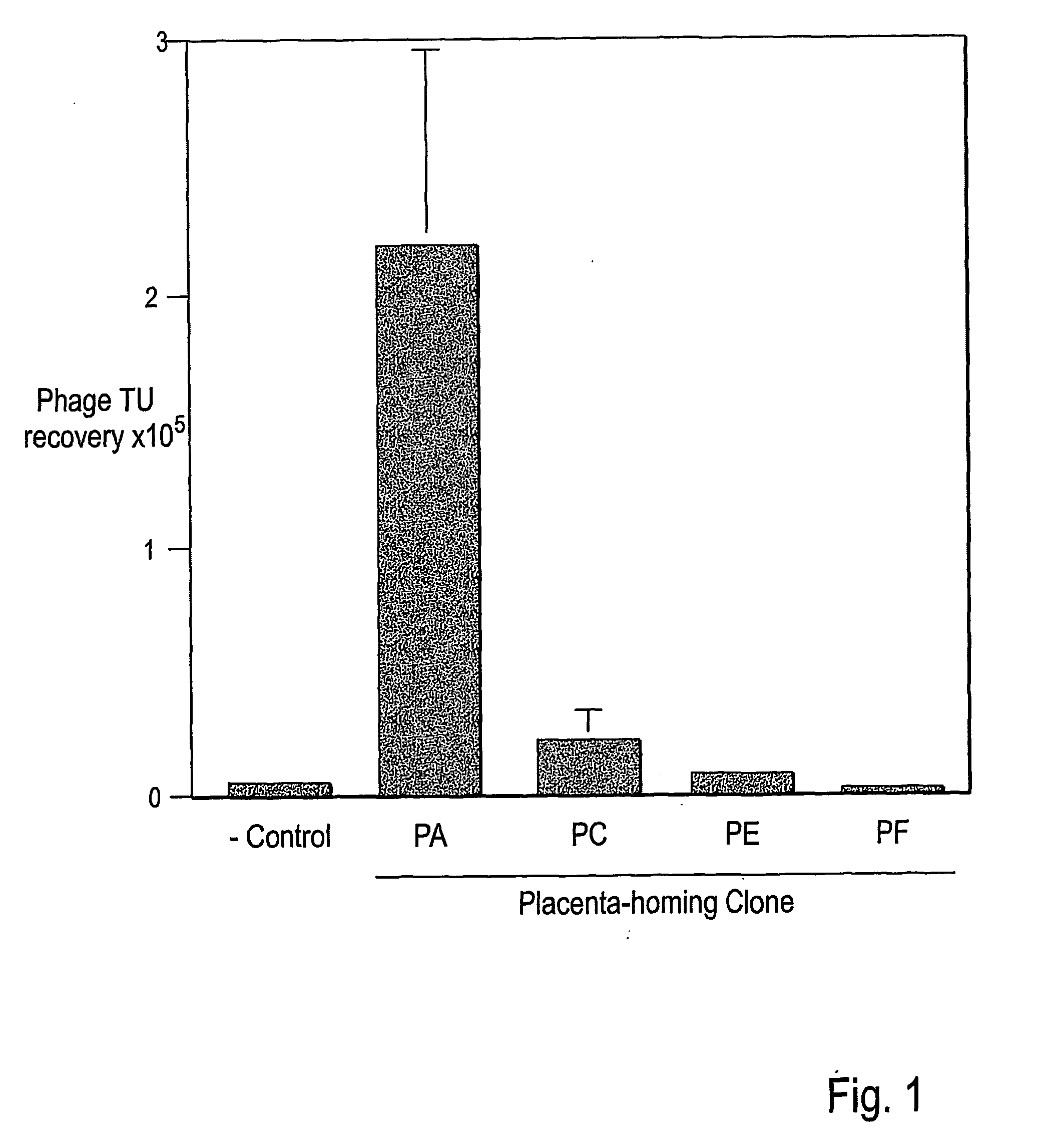
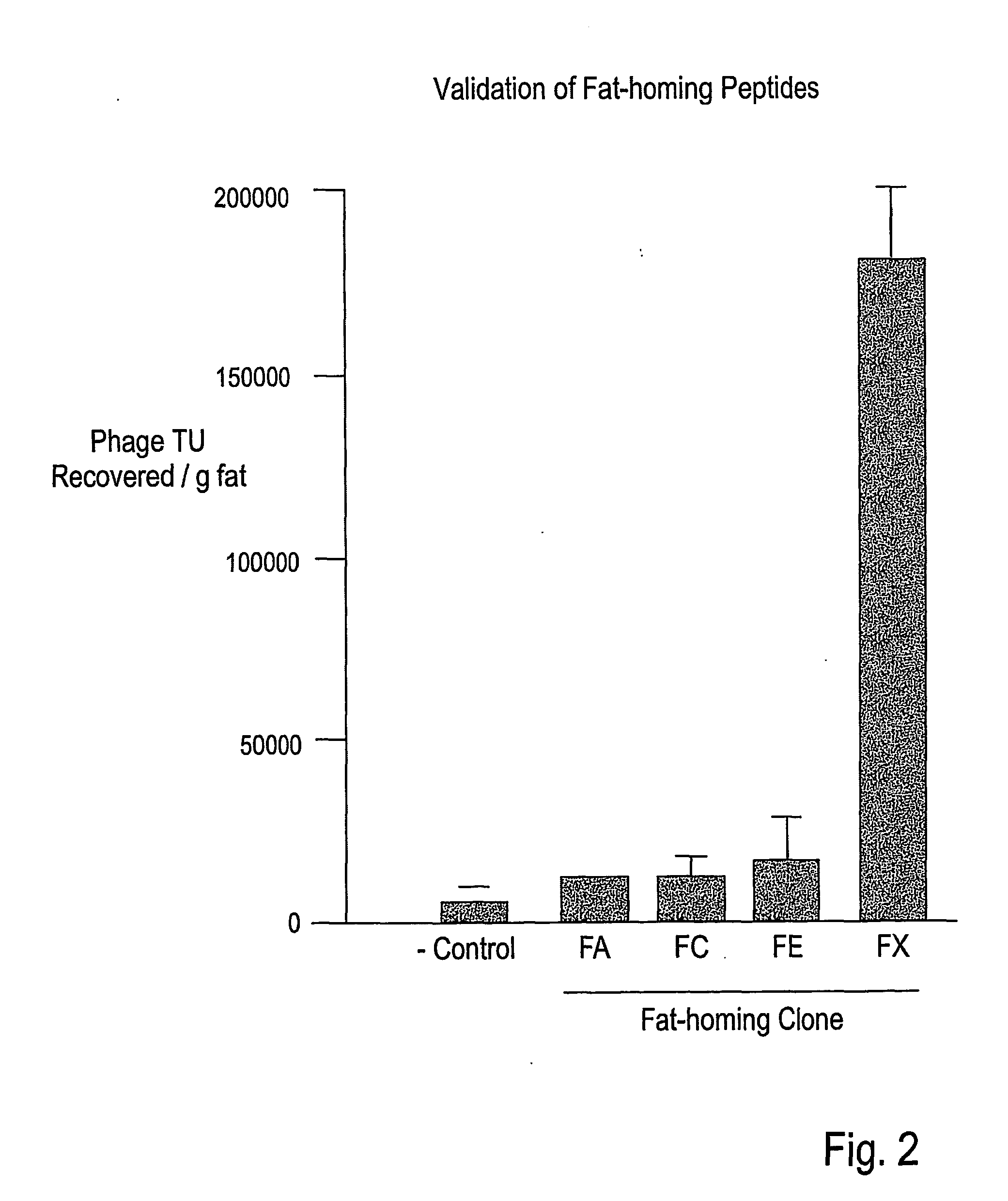
The present invention concerns compositions comprising and methods of identification and use of targeting peptides for placenta or adipose tissue. In certain embodiments, the targeting peptides comprise part or all of SEQ ID NO:5-11, SEQ ID NO:13-22 OR SEQ ID NO:144. The peptides may be attached to various therapeutic agents for targeted delivery. Adipose-targeting peptides may be used in methods for weight control, inducing weight loss and treating lipodystrophy syndrome. Adipose-targeting may also be accomplished using other binding moieties selectively targeted to adipose receptors, such as a prohibitin receptor protein complex. Placenta-targeting peptides may be used to interfere with pregnancy, induce labor and / or for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents to placenta and / or fetus. In other embodiments, receptors identified by binding to placenta-targeting peptides may be used to screen compounds for potential teratogenicity. An exemplary placental receptor is FcRn / β2M, and compounds that bind to FcRn / β2M are potential teratogens.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Fusion protein containing fluorescent protein fragment and application of fusion protein
The invention relates to fusion protein containing a fluorescent protein fragment and an application of the fusion protein. Specifically, the invention provides the fusion protein, and the fusion protein has a structure as shown in (P1-L1)s-A1-(X)n-A2-(L2-P2)t. (X)n or A1-(X)n in the fusion protein can promote the folding and expression of fusion target peptide, improve the solubility of the fusion protein and reduce the intermolecular interaction of the fusion protein, so that the fusion target peptide can be folded under the high concentration with commercial significance. (X)n or A1-(X)n inthe fusion protein can be digested into a plurality of oligopeptides of which the lengths are far less than the length of the target peptide, so that the separation of the oligopeptides from the target peptide is better facilitated, and the purification of the target peptide is more convenient.
Owner:NINGBO KUNPENG BIOTECH CO LTD
Haploid yeast cells transformed with a library of expression vectors encoding a fully human antibody repertoire
InactiveUS20030027213A1High affinityEasy to assembleFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetTarget peptide
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
InactiveUS20150272885A1Large specific surface areaAmenable to high capacity loadingOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCancers diagnosisBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Liver cancer targeted peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN105039333AEfficient tumor targetingTumor targeting specificityRadioactive preparation carriersPeptidesTarget peptideElutriation
The invention discloses a targeted polypeptide capable of being specifically combined with tumors, particularly a targeted peptide capable of being specifically combined with liver cancer tissues and application thereof in diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer. The liver cancer targeted peptide is preferably HCC-47 of which the amino acid sequence is SQDIRTWNGTRS; and the liver cancer targeted peptide is specifically combined with the liver cancer tissues, and can not be specifically combined with cervical carcinoma cells Hela, mammary cancer cells MDA-MB231, kidney cancer cells CRL-1932 and lung cancer cells A549. The polypeptide is obtained by in-vitro biological elutriation by combining a bacteriophage display library and a living body cross sectioning technique. The polypeptide can be used in a molecular imaging preparation for early diagnosis of liver cancer. The polypeptide can also be used in targeted modification and preparation of drugs for treating liver cancer. The polypeptide can also be used for targeted modification on drug transport carriers, thereby providing a new way for diagnosing or treating patients with liver cancer.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Synthetic chloroplast transit peptides
This disclosure concerns compositions and methods for targeting peptides, polypeptides, and proteins to plastids of plastid-containing cells. In some embodiments, the disclosure concerns chloroplast transit peptides that may direct a polypeptide to a plastid, and nucleic acid molecules encoding the same. In some embodiments, the disclosure concerns methods for producing a transgenic plant material (e.g., a transgenic plant) comprising a chloroplast transit peptide, as well as plant materials produced by such methods, and plant commodity products produced therefrom.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Compositions and methods of use of targeting peptides against placenta and adipose tissues
The present invention concerns compositions comprising and methods of identification and use of targeting peptides for placenta or adipose tissue. In certain embodiments, the targeting peptides comprise part or all of SEQ ID NO:5-11, SEQ ID NO:13-22 OR SEQ ID NO:144. The peptides may be attached to various therapeutic agents for targeted delivery. Adipose-targeting peptides may be used in methods for weight control, inducing weight loss and treating lipodystrophy syndrome. Adipose-targeting may also be accomplished using other binding moieties selectively targeted to adipose receptors, such as a prohibitin receptor protein complex. Placenta-targeting peptides may be used to interfere with pregnancy, induce labor and / or for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents to placenta and / or fetus. In other embodiments, receptors identified by binding to placenta-targeting peptides may be used to screen compounds for potential teratogenicity. An exemplary placental receptor is FcRn / β2M, and compounds that bind to FcRn / β2M are potential teratogens.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Target peptides for ovarian cancer immunotherapy
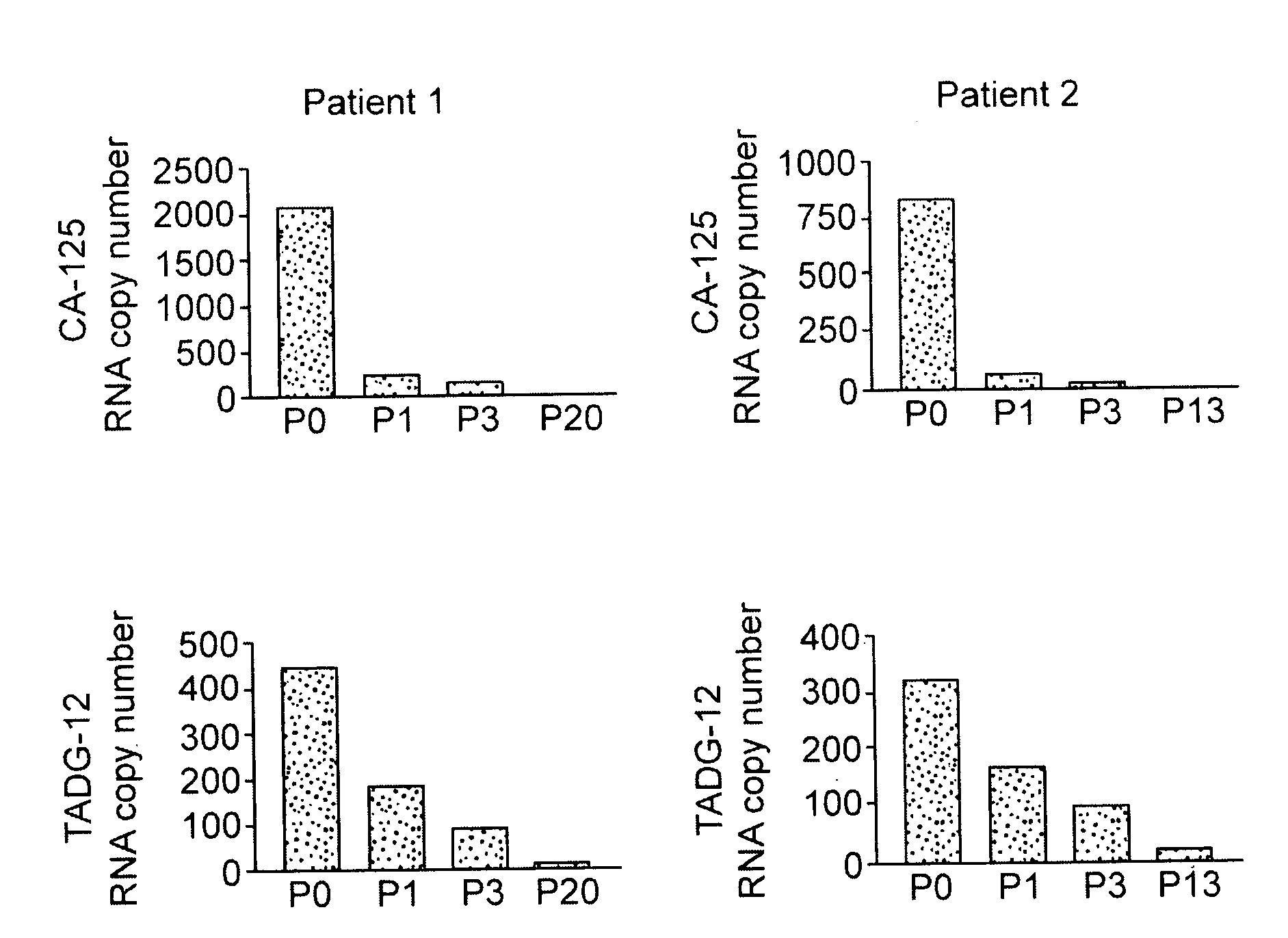
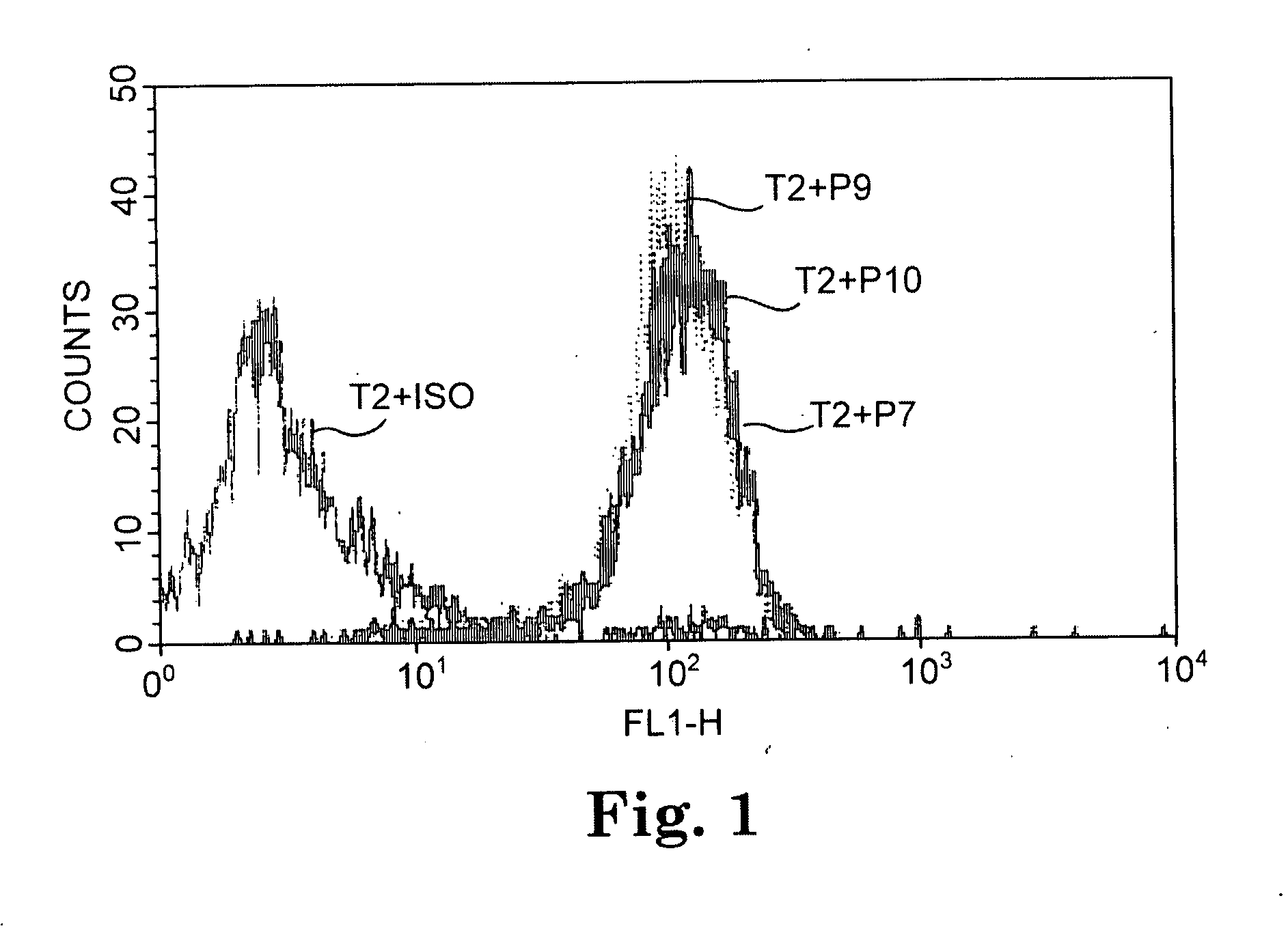
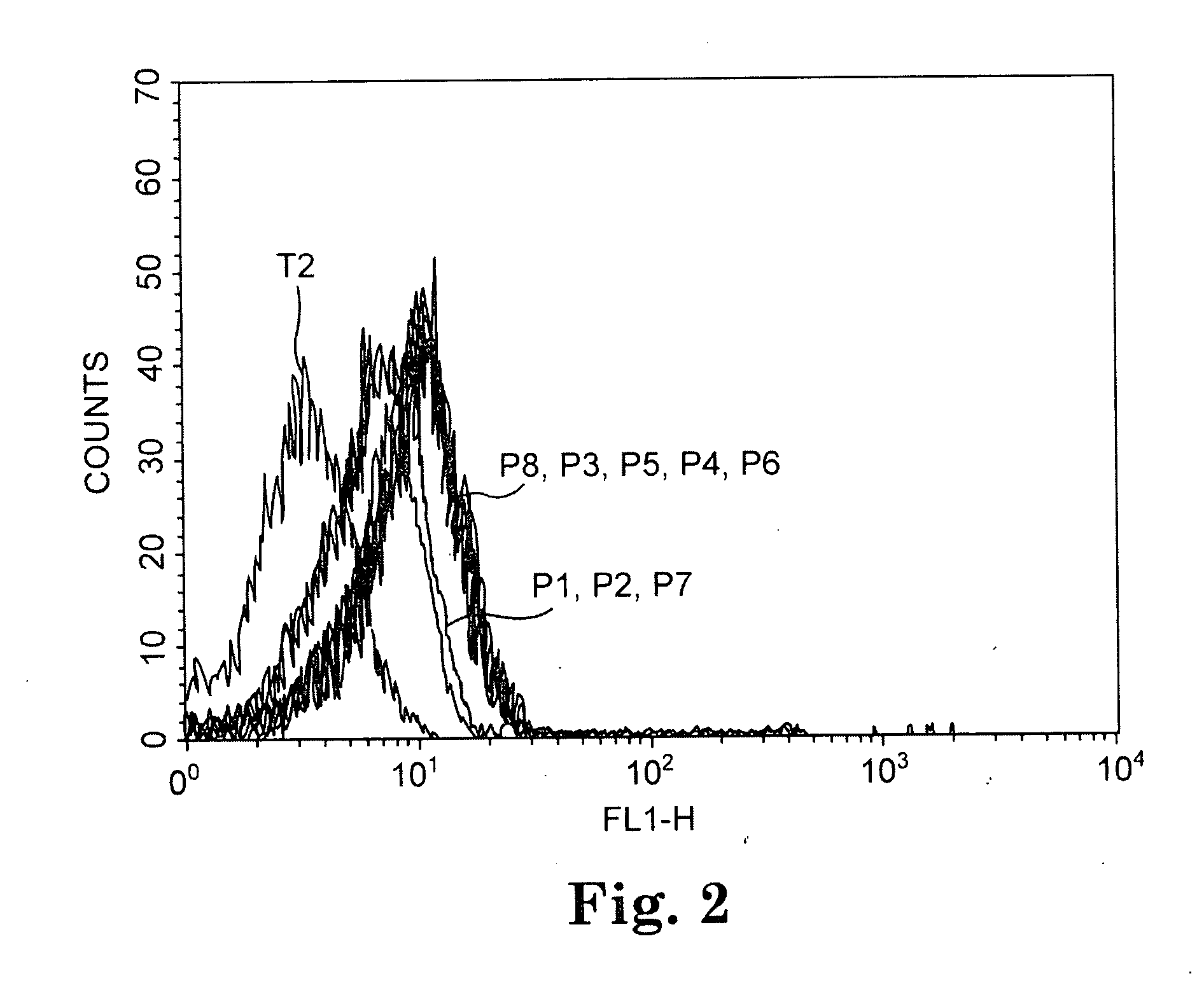
TADG-12 and CA125 are two proteins expressed with high specificity in ovarian cancer tumors. They thus would be potential antigens for immunotherapy in ovarian cancer. The invention is based on the discovery of peptides in TADG-12 and CA125 that can be used to induce an autologous T cell response that lyses ovarian cancer cells expressing TADG-12 or CA125. The peptides are contacted with dendritic cells in vitro to generate peptide-loaded dendritic cells. The peptide-loaded dendritic cells are contacted with T cells in vitro to amplify CD8+ T cells that recognize the peptide. At least one CA125 peptide and at least one TADG-12 peptide were found that amplified CD8+ T cells, even from cancer patients, that lysed autologous CA125-expressing or TADG-12-expressing tumor cells. The peptide-loaded dendritic cells can be administered to a cancer patient to amplify CD8+ T cells in vivo that attack the cancer cells. Alternatively, autologous CD8+ T cells can be amplified ex vivo and then infused into the cancer patient.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
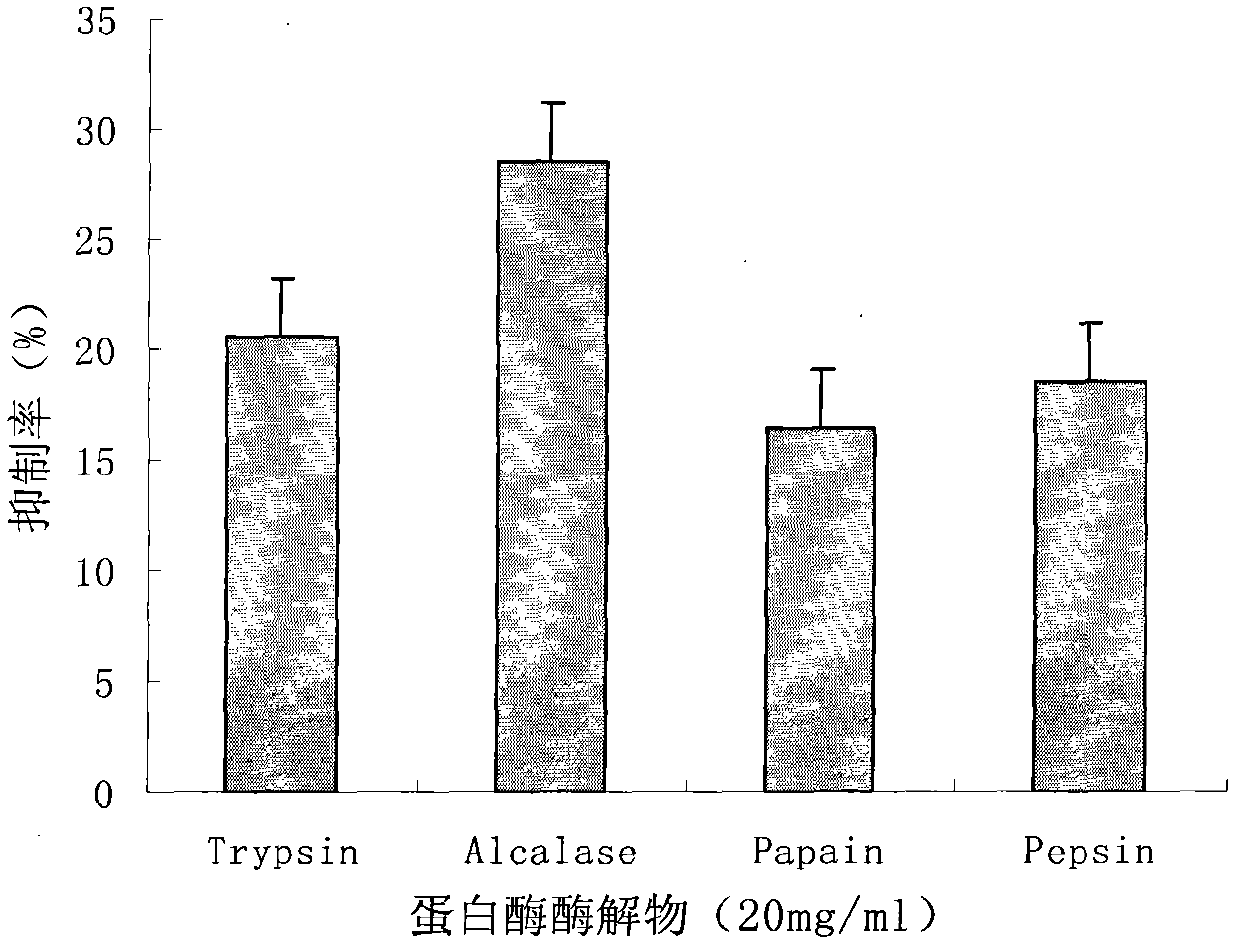
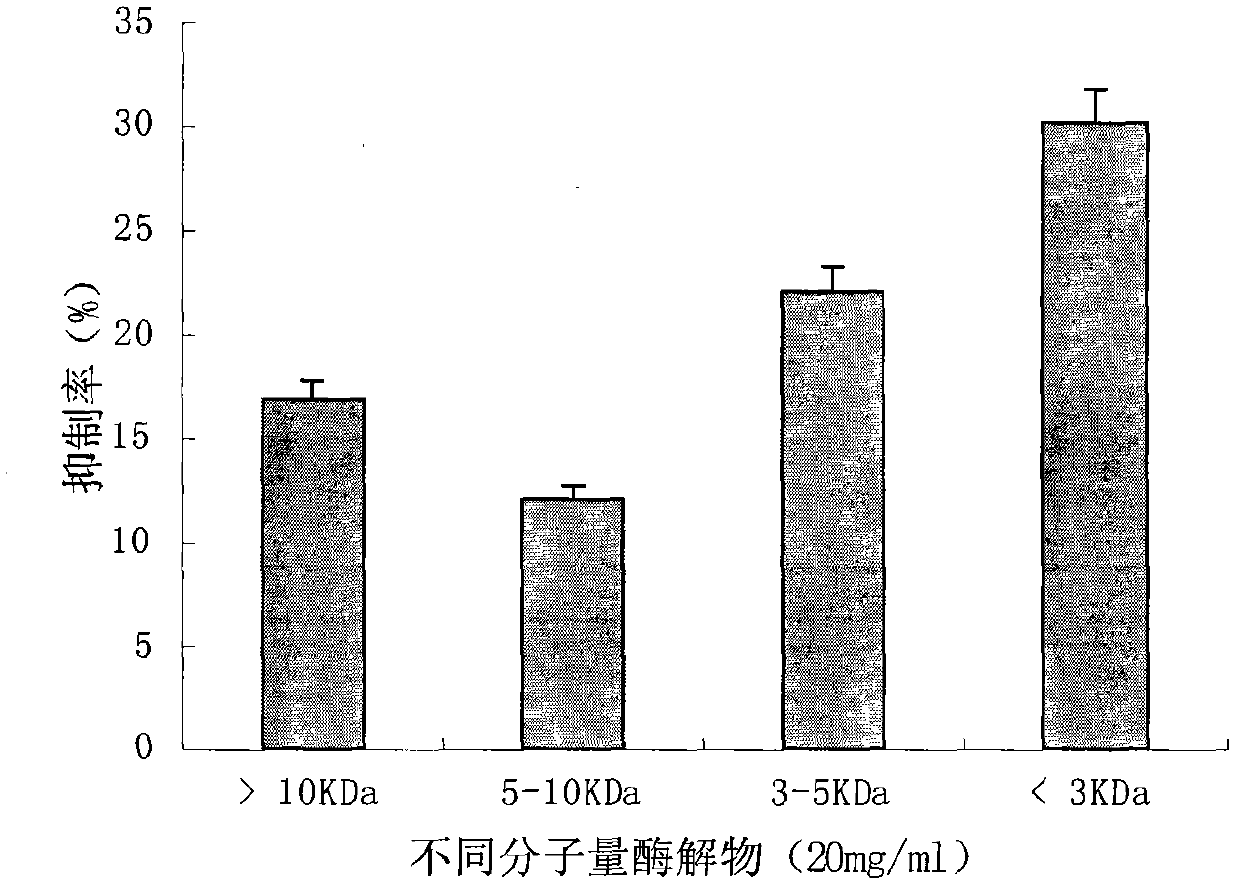
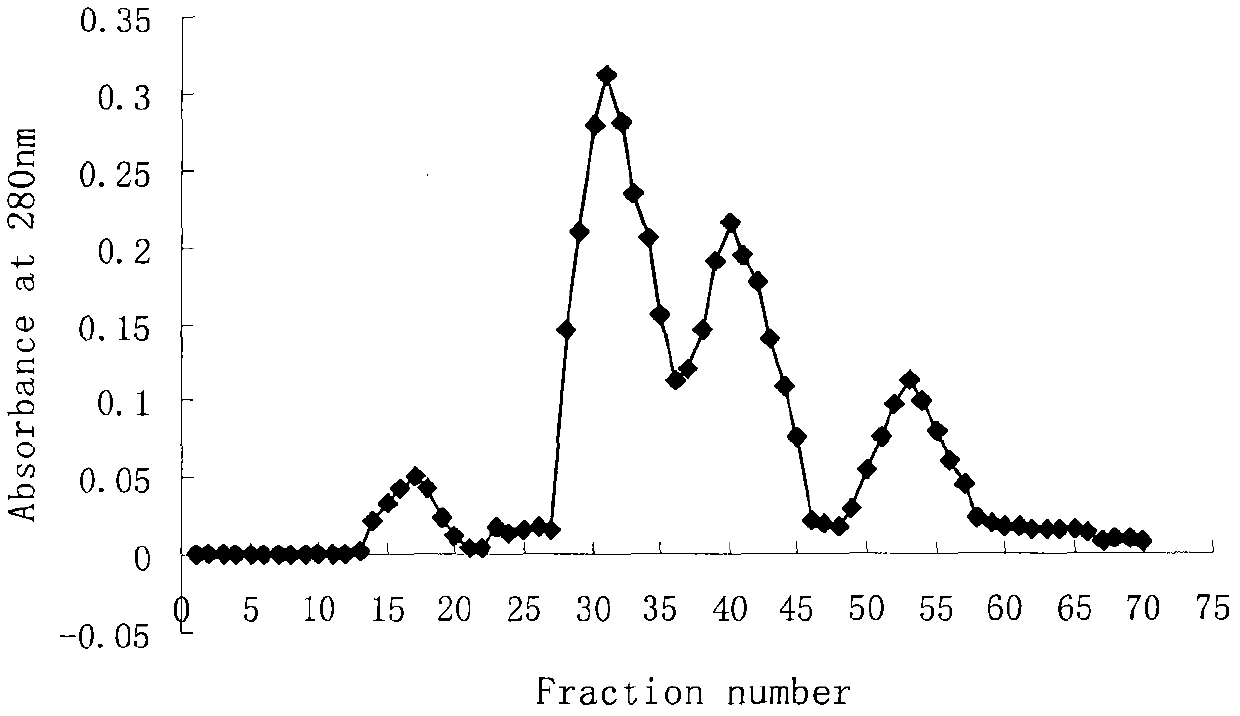
Mytilus edulis enzymolysis polypeptide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102558296AStrong inhibitory effect on proliferationSimple processHydrolysed protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsProstate cancer cellChromatographic separation
The invention discloses a mytilus edulis enzymolysis polypeptide. The mytilus edulis enzymolysis polypeptide is characterized by containing the following amino acid sequence: Asp Leu Tyr. The mytilus edulis enzymolysis polypeptide is prepared by adopting the following steps of: (1) preparing homogenate from mytilus edulis meat, adding alkaline protease, deactivating the protease, centrifuging, and taking clear solution of the upper layer; (2) performing ultra-filtration on the clear solution, collecting hydrolysate with the molecular weight of below 3K, concentrating, and performing freeze drying; (3) performing chromatographic separation by adopting a DEAE-SepharoseFF ion exchange column; (4) performing chromatographic separation by adopting a Sephadex G-25 gel column; and (5) performing high performance liquid chromatography purification. The invention also discloses application of the mytilus edulis enzymolysis polypeptide prepared by the steps in prostatic cancer resistance. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that: the mytilus edulis is subjected to enzymolysis and purification by adopting an optimal protease and an optimal technology, a strong cell proliferation inhibiting effect is achieved when the obtained target peptide is applied to prostatic cancer resistant cells, and a feasible research path is provided for resisting prostatic cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
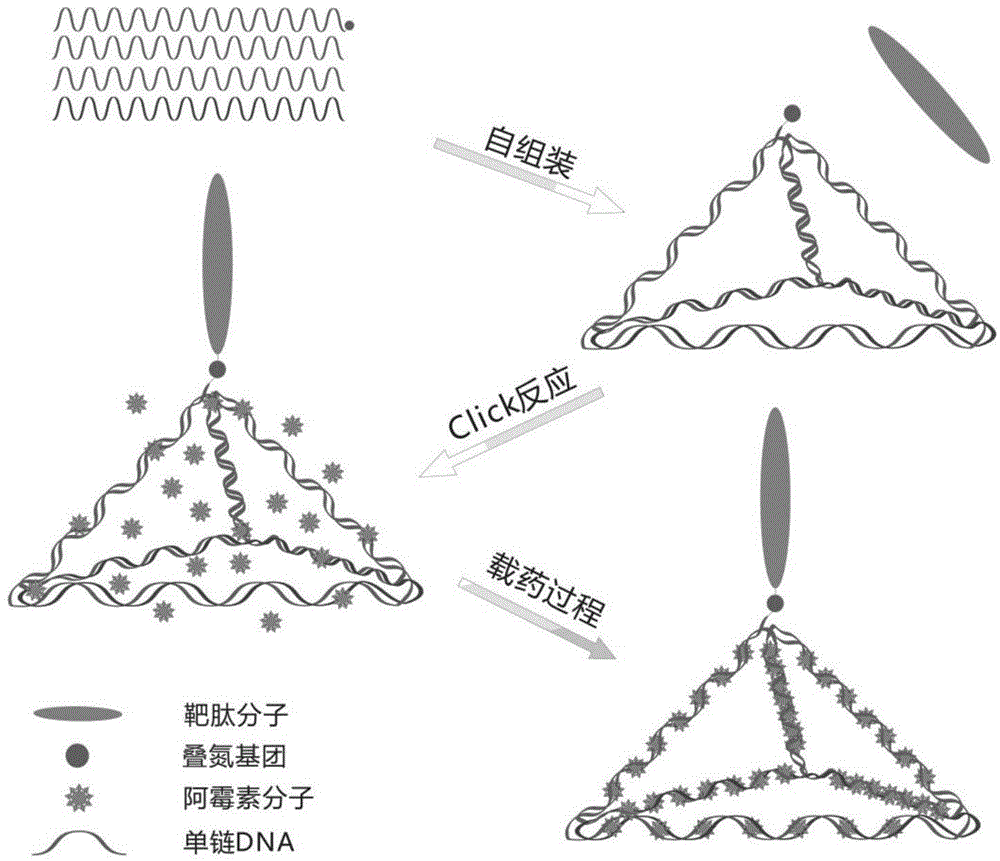
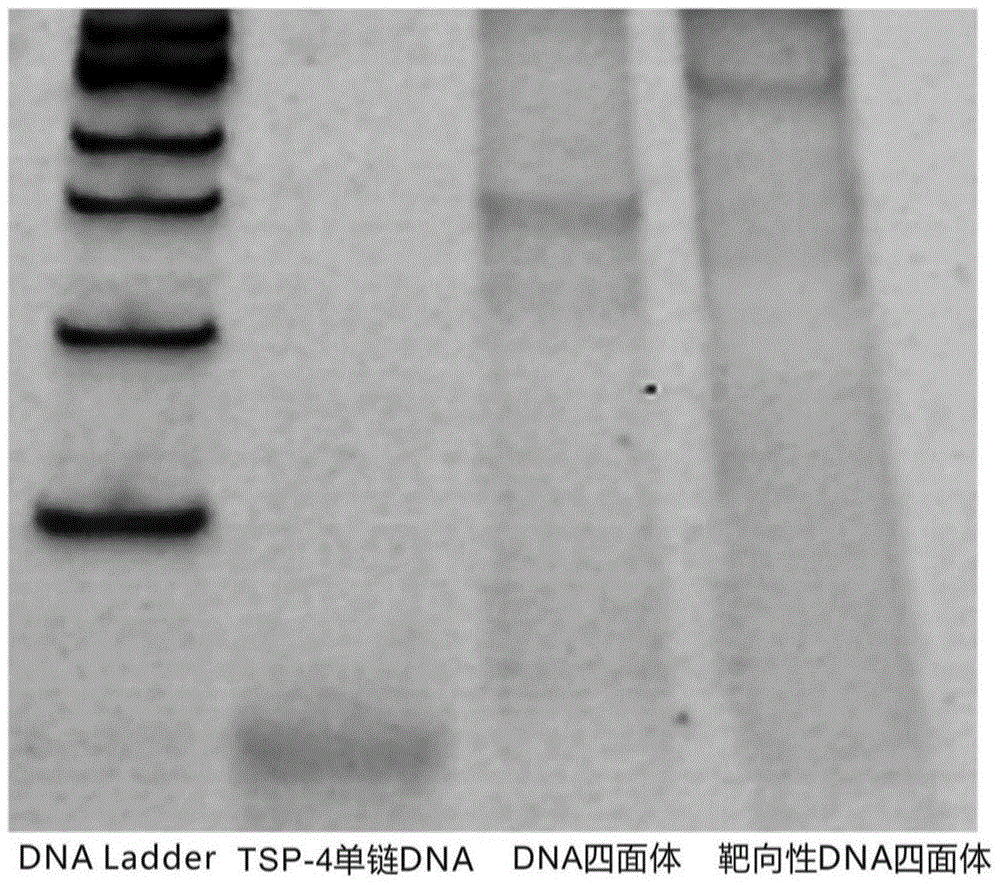
Preparation method of DNA targeting nano medicine-carrying molecule for brain tumor
InactiveCN104645338ARealize the drug loading processGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsPhosphoric acidCytotoxicity
The invention discloses a preparation method of a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) targeting nano medicine-carrying molecule for a brain tumor. The preparation method comprises the steps that a DNA single strand is added to a Tris-MgCl solution and mixed, and reacts to form a DNA tetrahedron solution; the DNA tetrahedron solution and a targeting peptide solution are added to a mixed solution of a PBS (Phosphoric acid solution), a CuSO4 solution, a TCEP (Tris-(2-carboxyethyl)-phosphine) solution and a TBTA (Tert-Butyl 2,2,2-trichloroacetimidate) solution, and subjected to thermostatic reaction; a targeting DNA tetrahedron solution is obtained; a tumor medicine is added to the targeting DNA tetrahedron solution; constant temperature oscillation, centrifugation, and supernatant removal are conducted; and an obtained sediment is the DNA targeting nano medicine-carrying molecule. According to the preparation method, peptide molecules having specificity in the tumor are modified on DNA tetrahedrons via a point-and-click reaction, so that construction of a targeting DNA nano-carrier is realized; and the targeting DNA medicine-carrying molecule has extremely high specific recognition function, low cytotoxicity and good structural stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
MUC18 targeting peptides
ActiveUS8450278B2Preventing and decreasing interactionEasy transferTumor rejection antigen precursorsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMelanomaTarget peptide
Provided are MUC 18 targeting peptides which may be used, e.g., to therapeutically target B-I lymphocytes to reduce the influence of these cells on the metastatic potential of melanoma cells and / or to target cancerous cells, including certain melanoma and leukemia cells. MUC 18 targeting peptides may be comprised in fusion constructs, imaging constructs, and / or therapeutic constructs such as fusion constructs which may be used for diagnosing or treating a cancer.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Chloroplast transit peptide
This disclosure concerns compositions and methods for targeting peptides, polypeptides, and proteins to plastids of plastid-containing cells. In some embodiments, the disclosure concerns chloroplast transit peptides that may direct a polypeptide to a plastid, and nucleic acid molecules encoding the same. In some embodiments, the disclosure concerns methods for producing a transgenic plant material (e.g., a transgenic plant) comprising a chloroplast transit peptide, as well as plant materials produced by such methods, and plant commodity products produced therefrom.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS20050142562A1High affinityHighly efficient homologous recombinationFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementTarget peptideIn vivo
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
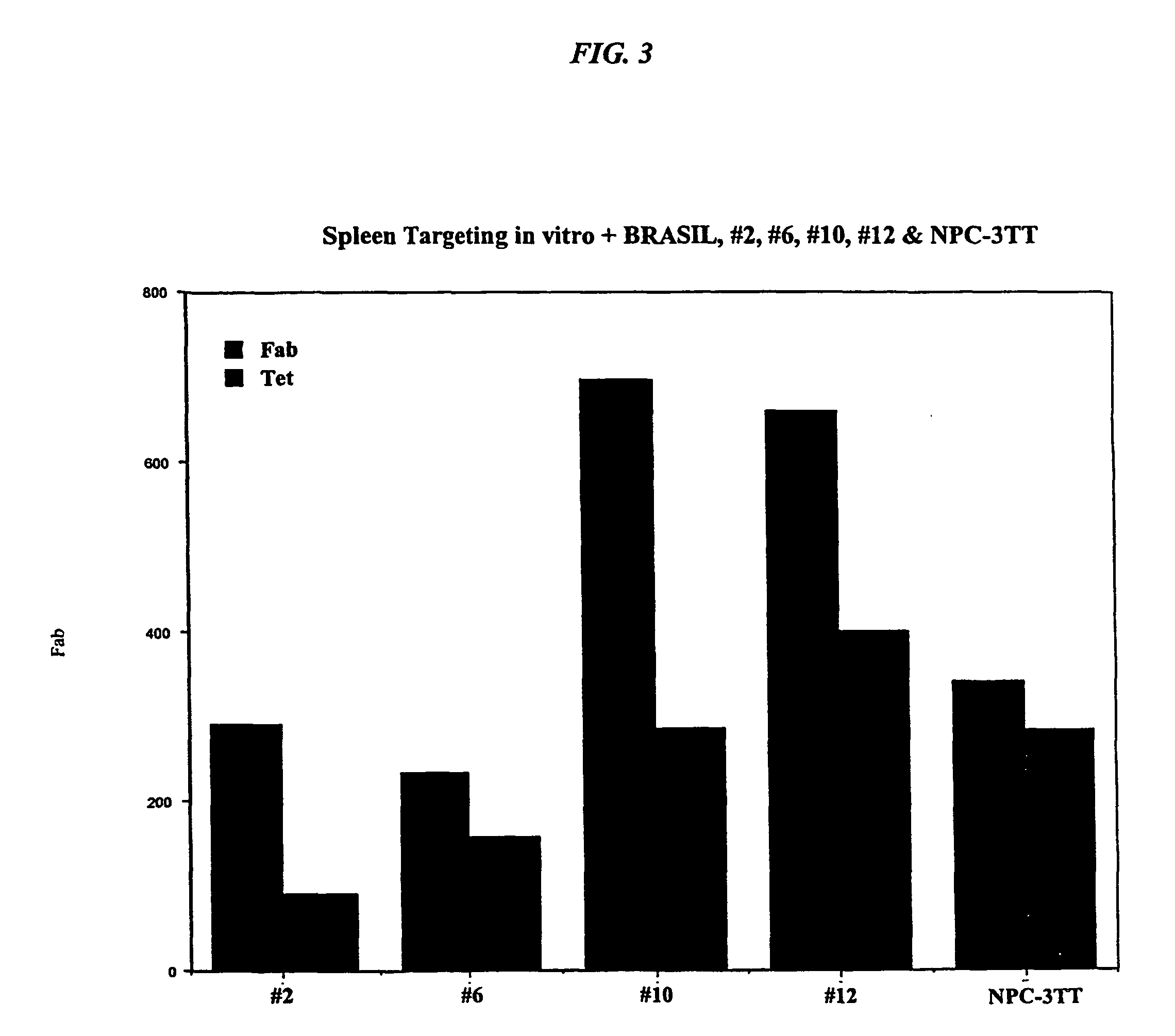
Cardiac-Specific Protein Targeting Domain
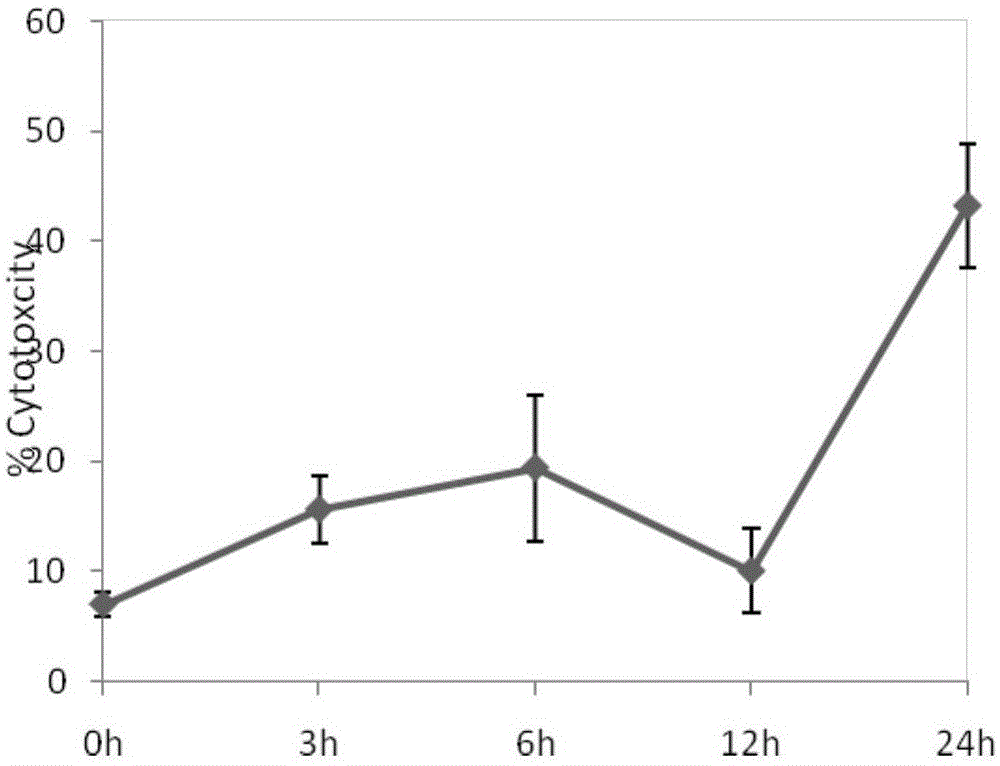
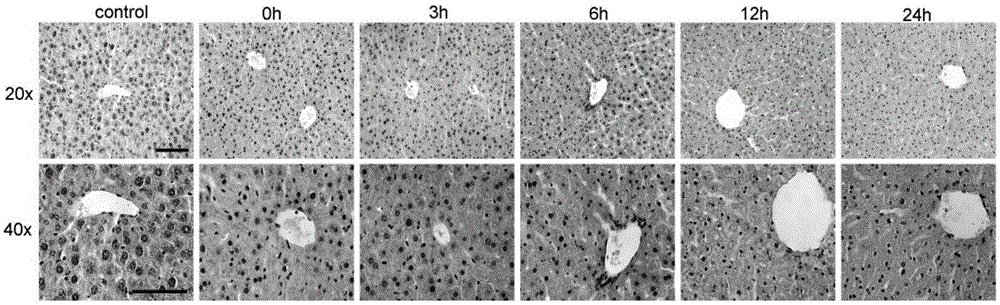
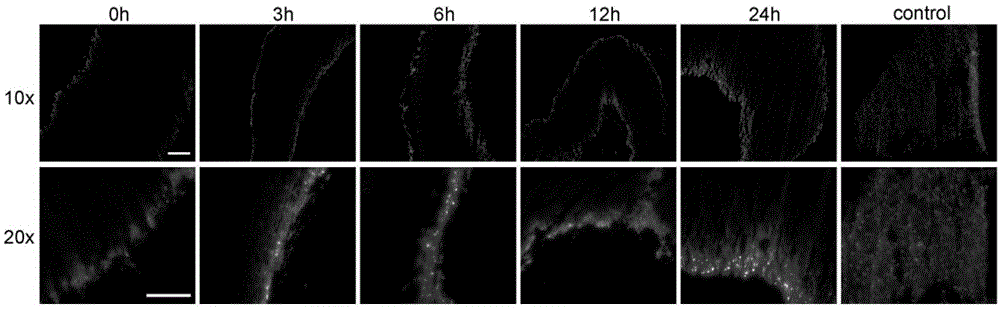
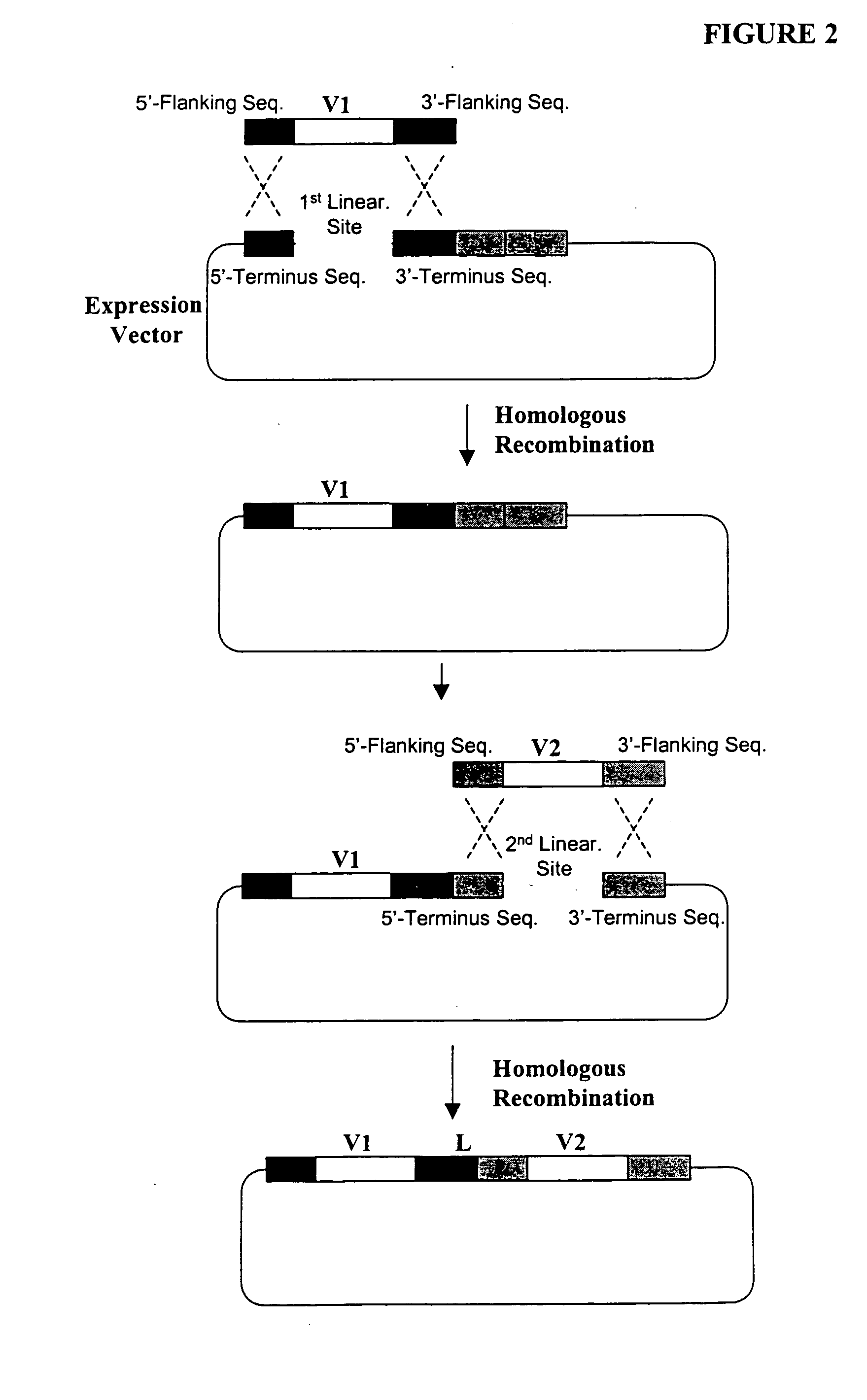
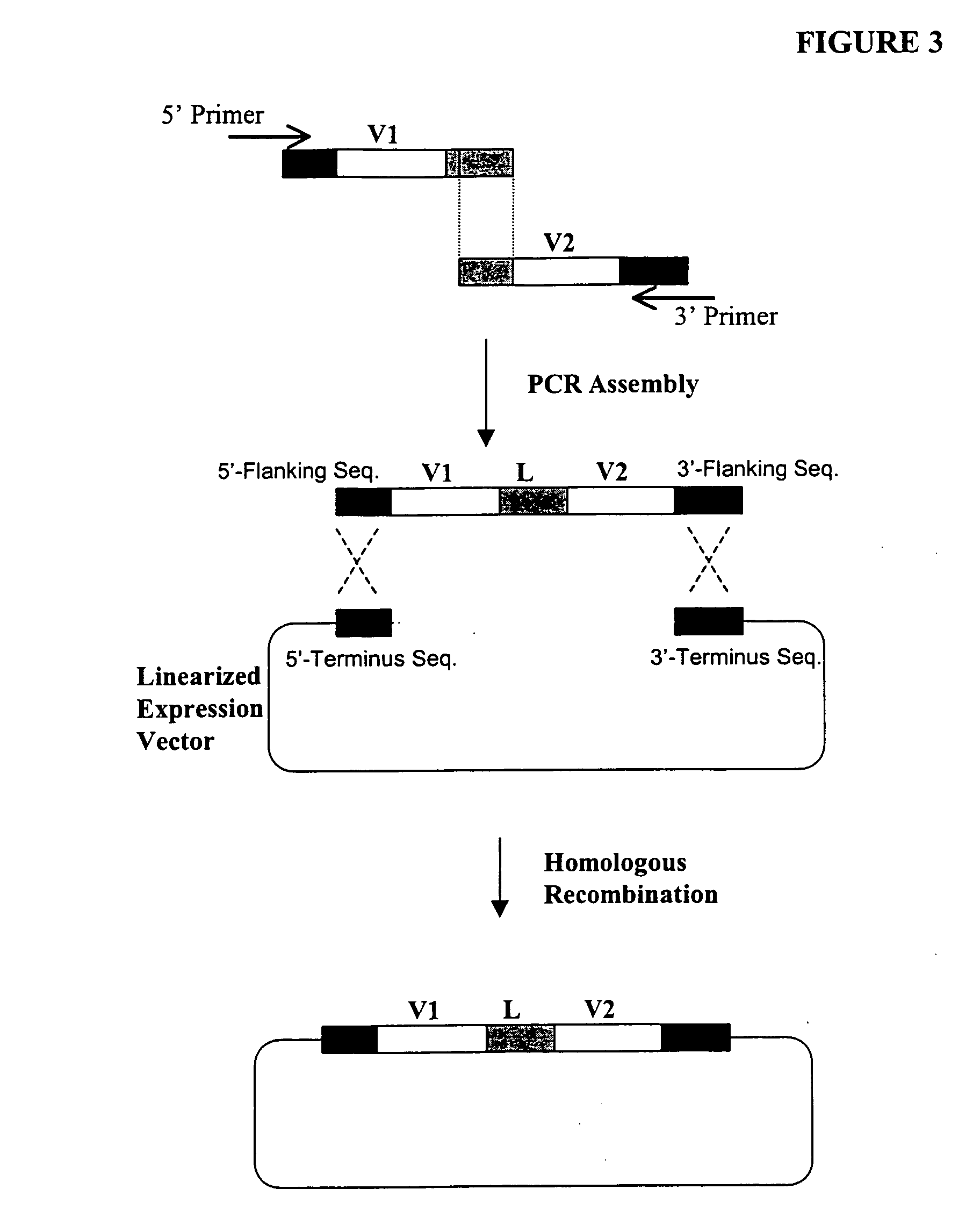
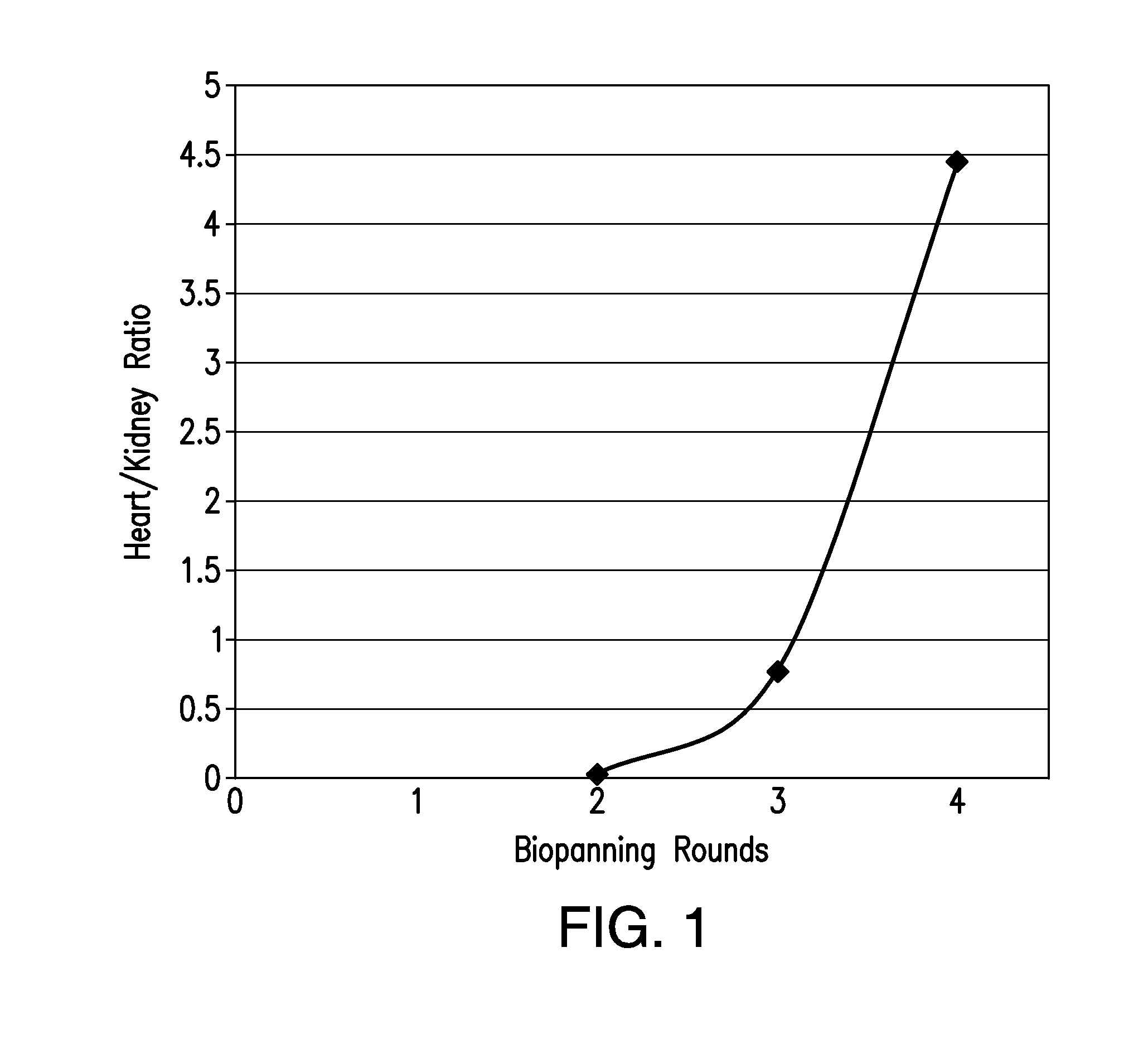
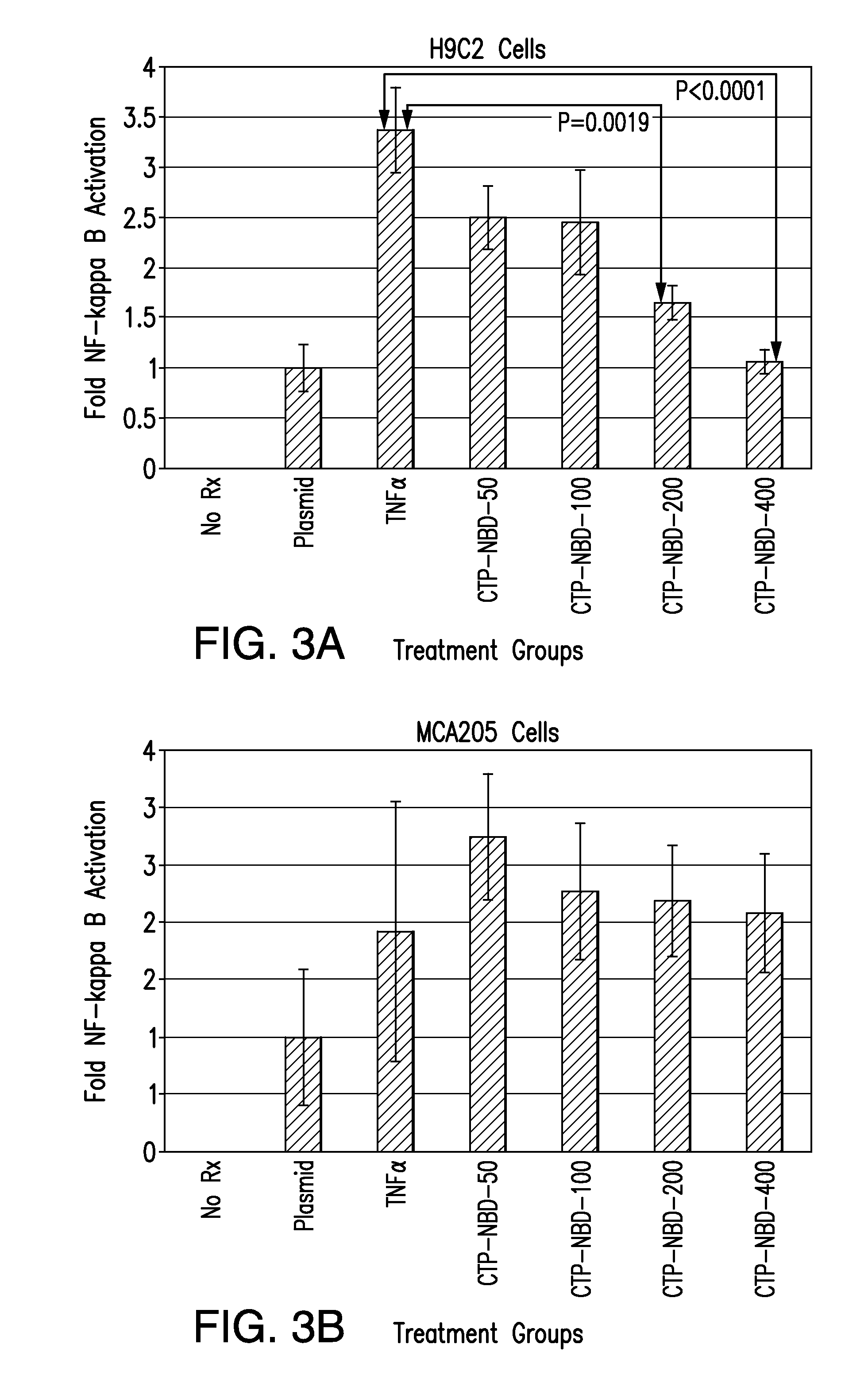
The present invention relates to Cardiac Targeting Peptides or CTPs that are able to transduce cardiomyocytes specifically in culture and in vivo, and to methods for using such peptides and their derivatives to deliver peptides, proteins or nucleic acids specifically to the heart. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that the peptide APWHLSSQYSRT (SEQ ID NO:1) functioned as a cardiac-specific protein targeting peptide and was successful in delivering a number of different cargoes to cardiac muscle cells in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Fusion proteins incorporating lysozyme
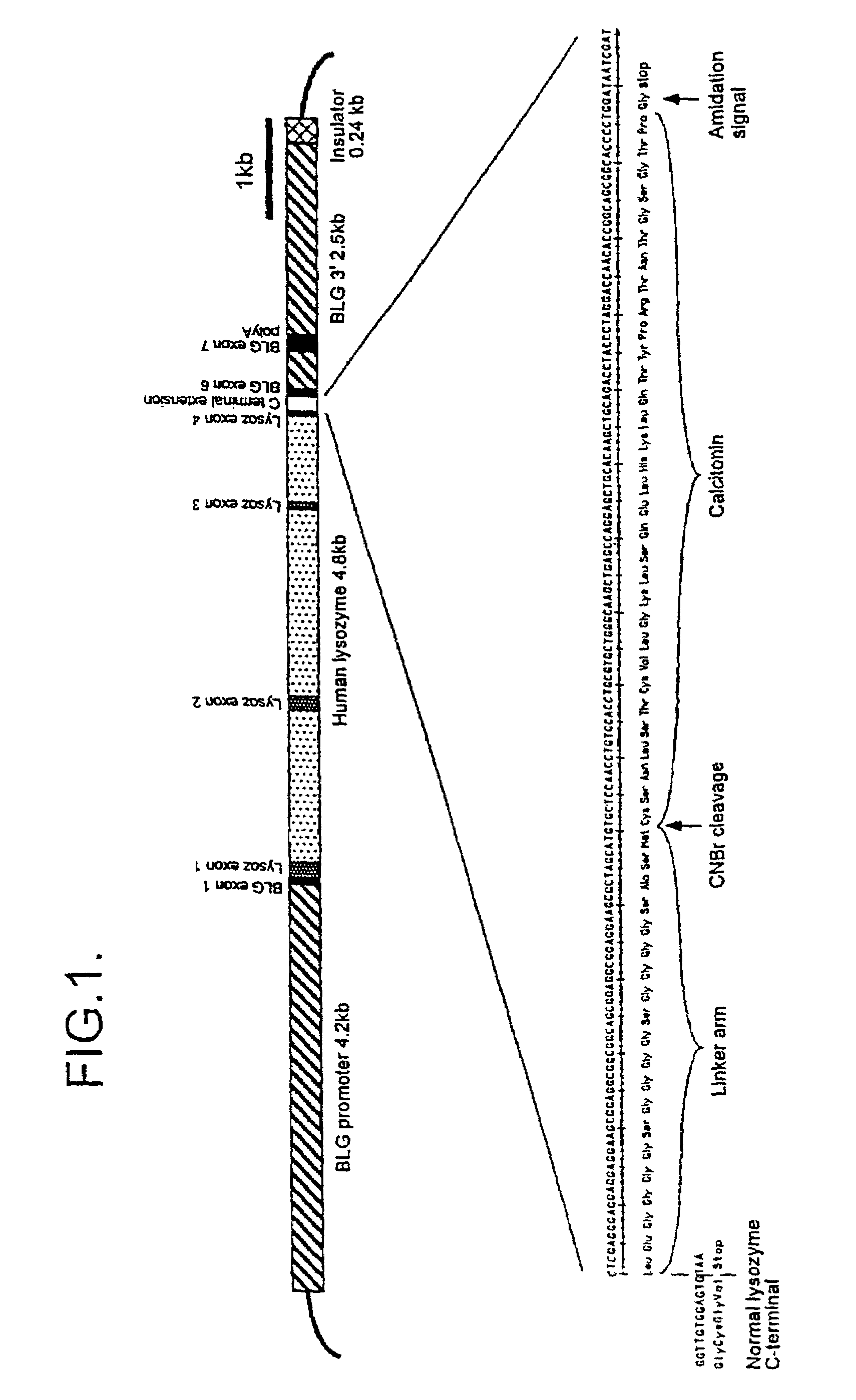
InactiveUS7045677B2High yieldSimple and inexpensive to purifyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCalcitoninsTarget peptideA-DNA
A process for the production of a peptide is disclosed, the process comprising expressing in the milk of a transgenic, non-human, placental mammal a fusion protein which comprises the peptide to be expressed linked to a fusion partner protein which is lysozyme. The fusion protein may be separate from the milk and cleaved to yield the target peptide. A transgenic, non-human, placental mammal whose genome incorporates a DNA molecule comprising a coding sequence encoding lysozyme coupled to a peptide is also described.
Owner:PHARMING INTPROP BV
Method for preparing teriparatide by fragment method and solid-liquid combination
InactiveCN105384809AHigh purityAvoid formingPeptide preparation methodsParathyroid hormonesDipeptideTarget peptide
The invention belongs to the field of polypeptide synthesis, relating to a method for preparing teriparatide by solid-liquid combination. The method adopts a liquid phase mode to synthesize a part of dipeptide and tripeptide fragments, feeding is performed by the synthesized dipeptide and tripetide fragments, 13 steps of solid phase coupled reaction are reduced, the coupling efficiency is greatly improved, not only is the generation of racemization impurities difficult to be purified and removed at the 34th site tail end avoided, but also the generation of missing peptides at multiple sites is avoided, and the purity of the final target peptide reaches 75 percent or more. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention is simple in synthetic route, less in solid phase coupling steps, mainly solves the problems that a peptide sequence is too long and coupling is difficult, and that the missing peptides are easily generated, the fragment synthesis technology is well developed, the materiel cost is lowered, and the industrialized mass production can be carried out.
Owner:JINAN KANGHE MEDICAL TECH
Method for screening feature peptide fragment for quantitatively detecting protein in food
ActiveCN107102149AMeet comprehensive screeningMeet the quantitative testing requirementsBiological testingMulti methodScreening method
The invention discloses a method for screening a feature peptide fragment for quantitatively detecting protein in food, and belongs to the technical field of protein quantitative detection. The screening method comprises the following steps: (1) comparing and analyzing matching score and interference number corresponding to a to-be-detected protein theoretical enzymolysis fragment by utilizing BLAST; (2) analyzing a mass spectrum response value and fragment abundance of a target peptide fragment through high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; (3) calculating the enzymolysis rate of the target peptide fragment when the enzymolysis is conducted for 1 to 3 hours by utilizing a fitted curve; (4) calculating the recovery rate and the precision degree of the target peptide fragment. The feature peptide fragment suitable for protein accurate quantification is comprehensively screened from the aspects of specificity, mass spectrum characteristic, enzymolysis characteristic, accuracy, stability and the like and by utilizing various methods in a combined way; the screened feature peptide fragment can meet the quantitative detection requirement of high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry on protein in food matrix, and realizes protein quantitative detection requirement with high sensitivity, high precision degree and excellent reproducibility.
Owner:杭州璞湃科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com