Patents
Literature
110 results about "Fusogenic peptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery and methods of using same
ActiveUS20140079774A1Promoting death of cancer cellEfficient packagingBiocideSpecial deliveryLipid formationBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Novel reagents for transfection of eukaryotic cells
ActiveUS20090023215A1Improve efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesDendrimerTransfection
Compositions and methods for improved delivery of macromolecules into eukaryotic cells are provided. Fusogenic peptides from fusion proteins of non-enveloped viruses enhance the efficiency of transfection of eukaryotic cells mediated by transfection agents such as cationic lipids, polycationic polymers such as PEI and dendrimers. These fusogenic peptides are used as part of a transfection complex that efficiently delivers a macromolecule, for example, a nucleic acid, into a eukaryotic cell. Novel cationic lipids and compositions of cationic lipids also are provided that may be used for the introduction of macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins and peptides into a variety of cells and tissues. The lipids can be used alone, in combination with other lipids and / or in combination with fusogenic peptides to prepare transfection complexes.
Owner:MOLECULAR TRANSFER
Fusion peptides isolatable by phase transition
InactiveUS20010034050A1Small sizePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesPurification methodsThroughput
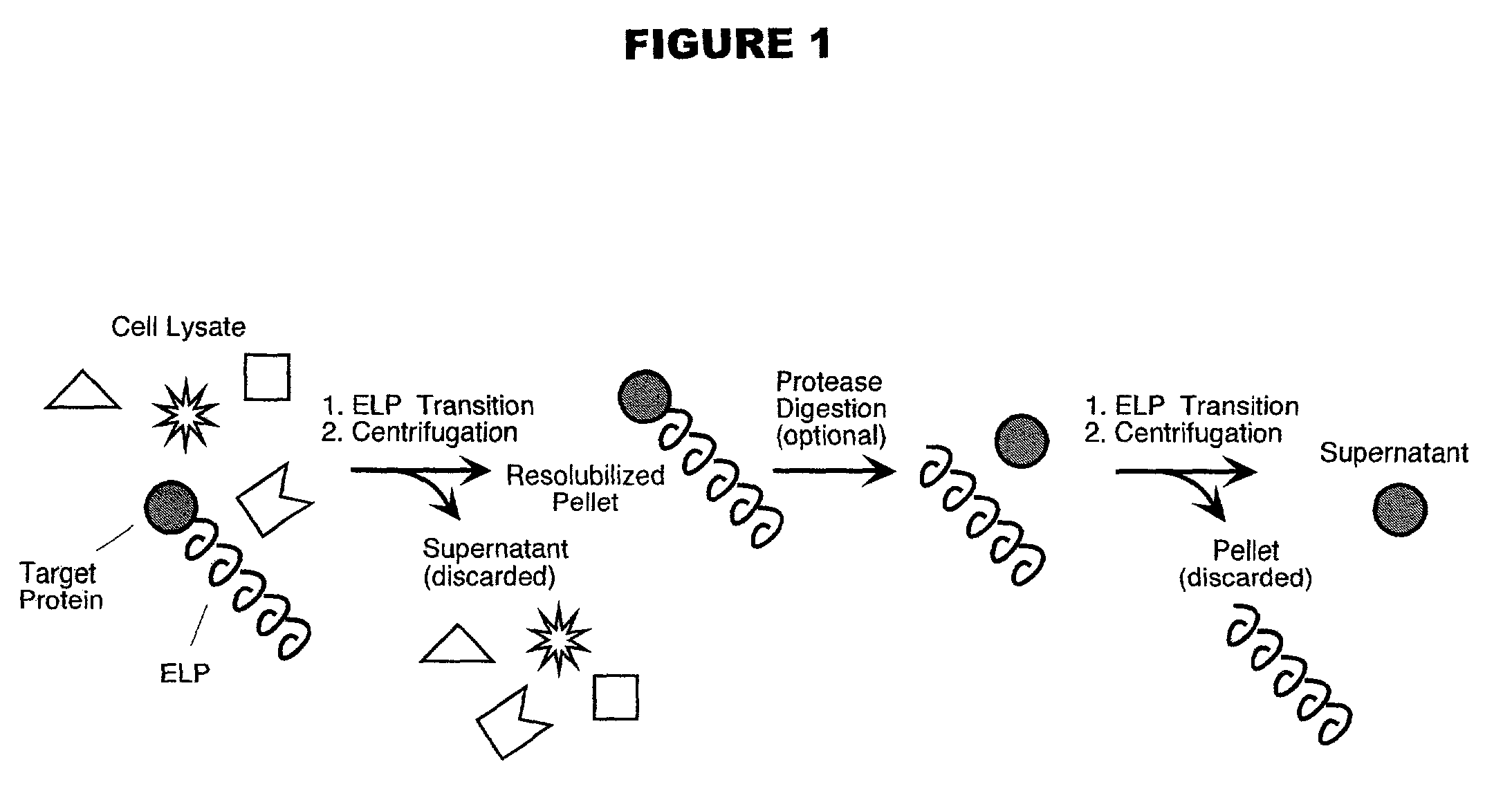
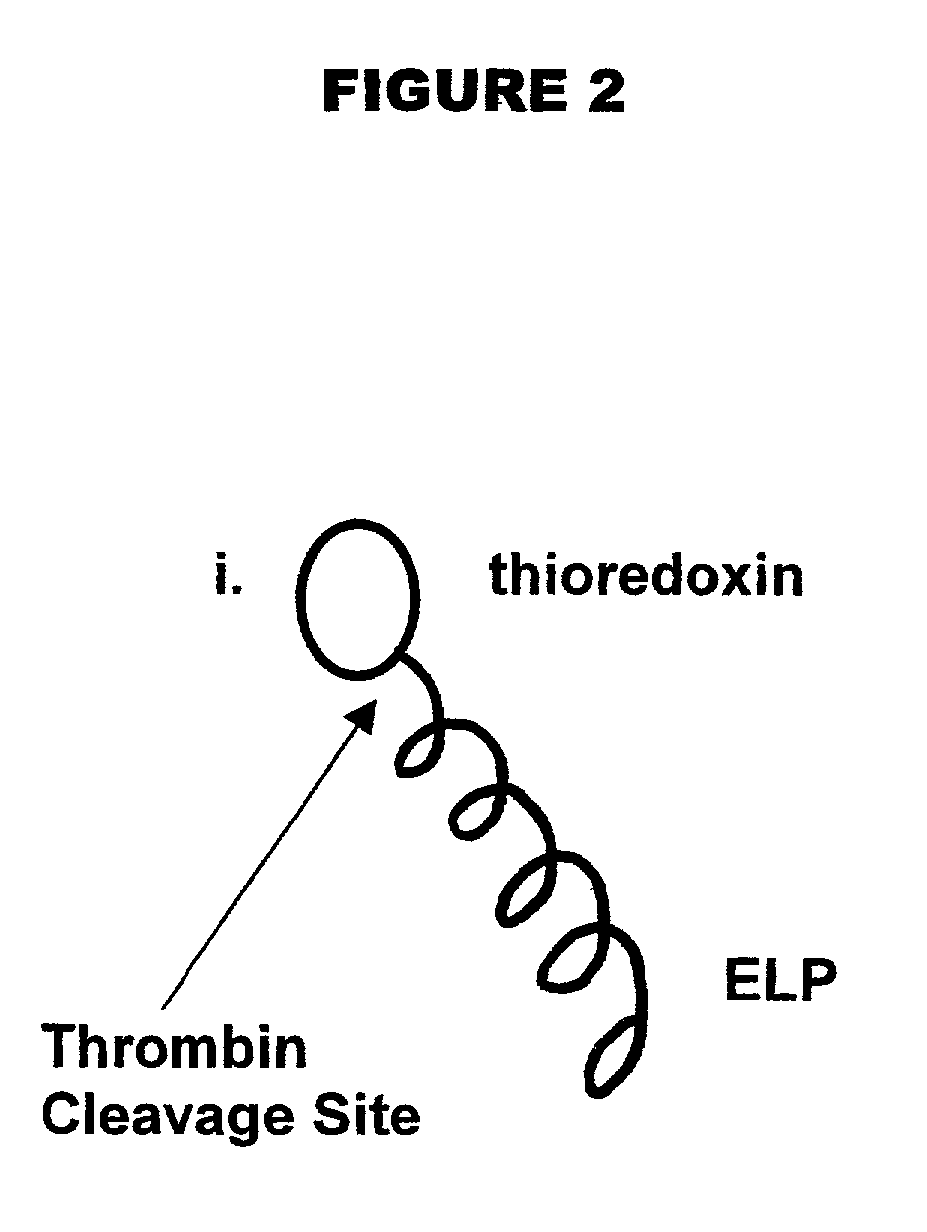
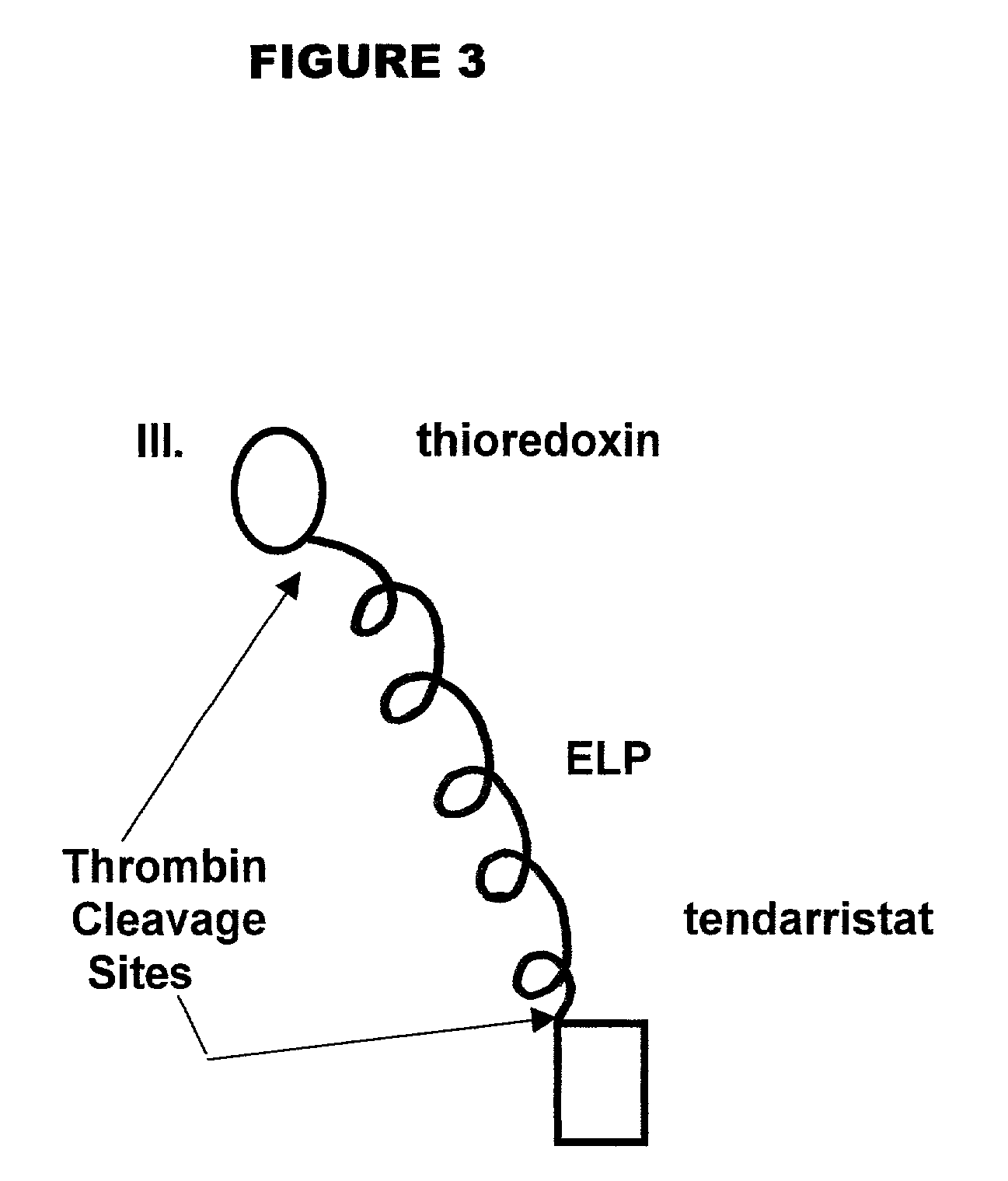
Genetically-encodable, environmentally-responsive fusion proteins comprising ELP peptides. Such fusion proteins exhibit unique physico-chemical and functional properties that can be modulated as a function of solution environment. The invention also provides methods for purifying the FPs, which take advantage of these unique properties, including high-throughput purification methods that produce high yields (e.g., milligram levels) of purified proteins, thereby yielding sufficient purified product for multiple assays and analyses. The high throughput purification technique is simpler and less expensive than current commercial high throughput purification methods, since it requires only one transfer of purification intermediates to a new multiwell plate.
Owner:PHASE BIOSCIENCE INC
Endosomolytic agents and cell delivery systems
The present invention provides improved cell delivery compositions. In particular, the invention provides biocompatible endosomolytic agents. In a preferred embodiment, the endosomolytic agents are also biodegradable and can be broken down within cells into components that the cells can either reuse of dispose of. In one aspect, the present invention provides endosomolytic agents capable of effecting the lysis of an endosome in response to a change in pH, and methods for effecting the lysis of an endosome. These inventive endosomolytic agents obviate the need for known agents (i.e., chloroquine, fusogenic peptides, inactivated adenoviruses and polyethyleneimine) that can burst endosomes and have negative effects on cells. In another aspect, the present invention provides cell delivery compositions comprising an endosomolytic component that is capable of effecting the lysis of the endosome in response to a change in pH, and an encapsulating, or packaging, component capable of packaging a therapeutic agent to be delivered to cellular or subcellular components.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Ligand/lytic peptide compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20040018967A1Inhibition of maturationLysis of tumor cells is rapidAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLytic peptideAutoimmune condition
Amphipathic lytic peptides are ideally suited to use in a ligand / cytotoxin combination to specifically inhibit cells that are driven by or are dependent upon a specific ligand interaction; for example, to induce sterility or long-term contraception, or to attack tumor cells, or to selectively lyse virally-infected cells, or to attack lymphocytes responsible for autoimmune diseases. The peptides act directly on cell membranes, and need not be internalized. Administering a combination of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) (or a GnRH agonist) and a membrane-active lytic peptide produces long-term contraception or sterilization in animals in vivo. Administering in vivo a combination of a ligand and a membrane-active lytic peptide kills cells with a receptor for the ligand. The compounds are relatively small, and are not antigenic. Lysis of gonadotropes has been observed to be very rapid (on the order of ten minutes.) Lysis of tumor cells is rapid. The two components-the ligand and the lytic peptide-may optionally be administered as a fusion peptide, or they may be administered separately, with the ligand administered slightly before the lytic peptide, to activate cells with receptors for the ligand, and thereby make those cells susceptible to lysis by the lytic peptide. The compounds may be used in gene therapy to treat malignant or non-malignant tumors, and other diseases caused by clones or populations of "normal" host cells bearing specific receptors (such as lymphocytes), because genes encoding a lytic peptide or encoding a lytic peptide / peptide hormone fusion may readily be inserted into hematopoietic stem cells or myeloid precursor cells.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Use of polymeric nanoparticles for vaccine delivery
InactiveUS20080044484A1Enhance antigen presentationImprove efficiencyBiocidePowder deliveryCancer cellT lymphocyte
The invention relates generally to the treatment and prevention of human cancer and viral diseases. More specifically, this invention relates to development of a new generation of vaccines that rely on eliciting cellular immune responses, specifically induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), against cancer cells and virus-infected cells via administration of a polymeric nanoparticle containing a vaccine comprising a fusion peptide or a modified peptide. Such a fusion peptide is composed of an insertion signal sequence and a peptide derived from a tumor antigen or a viral antigen, which improves antigen presentation and induces CTL with higher efficiency against cancer cells and virus-infected cells. An exemplary peptide utilized in the invention is Mart-1:27-35 peptide.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
InactiveUS20150272885A1Large specific surface areaAmenable to high capacity loadingOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCancers diagnosisBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
Recombinant flu vaccines
InactiveUS20090117144A1Sufficient immunogenicityReduce loadSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseInfluenza virus vaccinePlant virus
The present invention provides compositions for use as vaccines against the influenza virus, and rapid methods of producing such compositions. The composition include i) at least one peptide derived from an influenza virus, wherein the peptide is fused to a capsid protein derived from a plant virus forming a recombinant capsid fusion peptide and ii) at least one isolated antigenic protein or protein fragment derived from a human or avian influenza virus. The isolated antigenic protein or protein fragment derived from the human or avian influenza virus can be conjugated to the surface of the recombinant capsid fusion peptide.
Owner:PFENEX
Urease epitope fusion peptide liposome bacterin for preventing the helicobacter pylori infecting
InactiveCN101062015AEffective in inducing an immune responsePromote wound healingAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPylorusAdjuvant
The invention discloses an urea enzyme epitope fuse peptiolipid plastid vaccine to against pylorus bolt bacteria infection, which is characterized by the following: choosing fuse peptide of pylorus bolt bacteria urea enzyme B subunit and stick film adjuvant cholera morbus toxin B subunit as immunogen; coating the immunogen with liposome; producing the liposome vaccine. This liposome vaccine can evoke organism to generate special immune response and inhibit planting of pylorus bolt bacteria in stomach.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
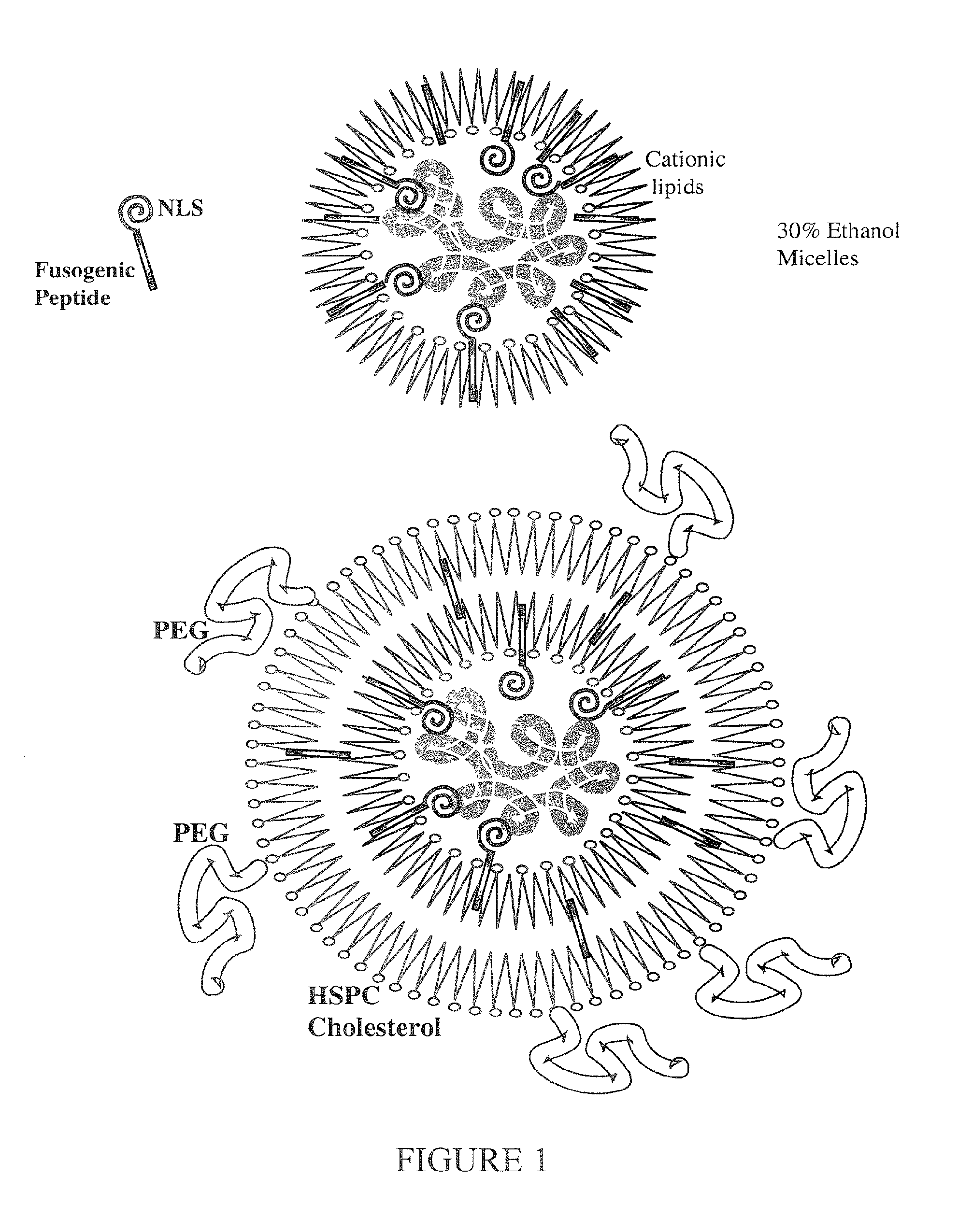
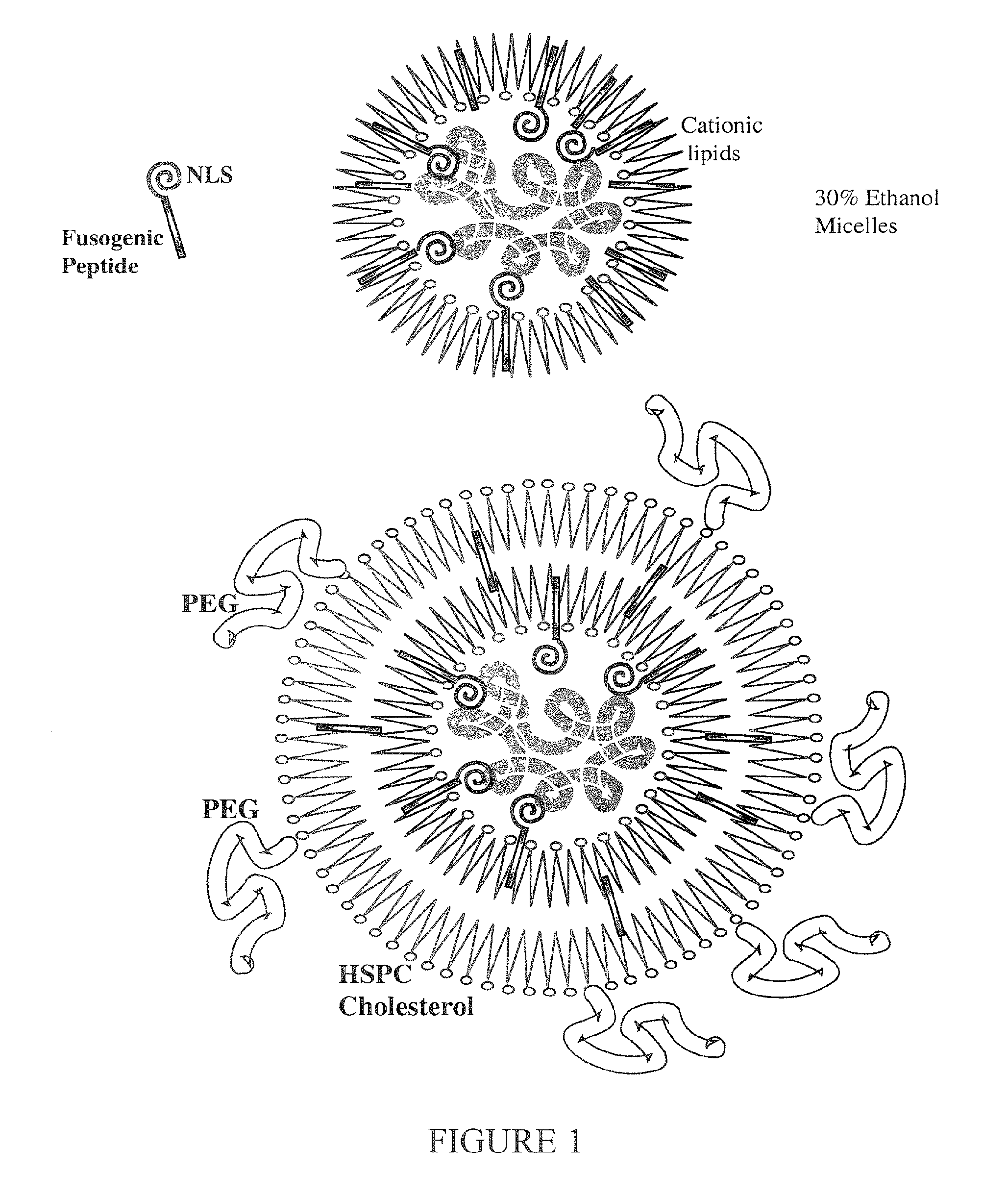
Encapsulation of Plasmid DNA (Lipogenes) and Therapeutic Agents with Nuclear Localization Signal/Fusogenic Peptide Conjugates into Targeted Liposome Complexes
InactiveUS20120183596A1Increase the entranceHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman tumorNucleotide
A method is disclosed for encapsulating plasmids, oligonucleotides or negatively-charged drugs into liposomes having a different lipid composition between their inner and outer membrane bilayers and able to reach primary tumors and their metastases after intravenous injection to animals and humans. The formulation method includes complex formation between DNA with cationic lipid molecules and fusogenic / NLS peptide conjugates composed of a hydrophobic chain of about 10-20 amino acids and also containing four or more histidine residues or NLS at their one end. The encapsulated molecules display therapeutic efficacy in eradicating a variety of solid human tumors including but not limited to breast carcinoma and prostate carcinoma. Combination of the plasmids, oligonucleotides or negatively-charged drugs with other anti-neoplastic drugs (the positively-charged cis-platin, doxorubicin) encapsulated into liposomes are of therapeutic value. Also of therapeutic value in cancer eradication are combinations of encapsulated the plasmids, oligonucleotides or negatively-charged drugs with HSV-tk plus encapsulated ganciclovir.
Owner:REGULON
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
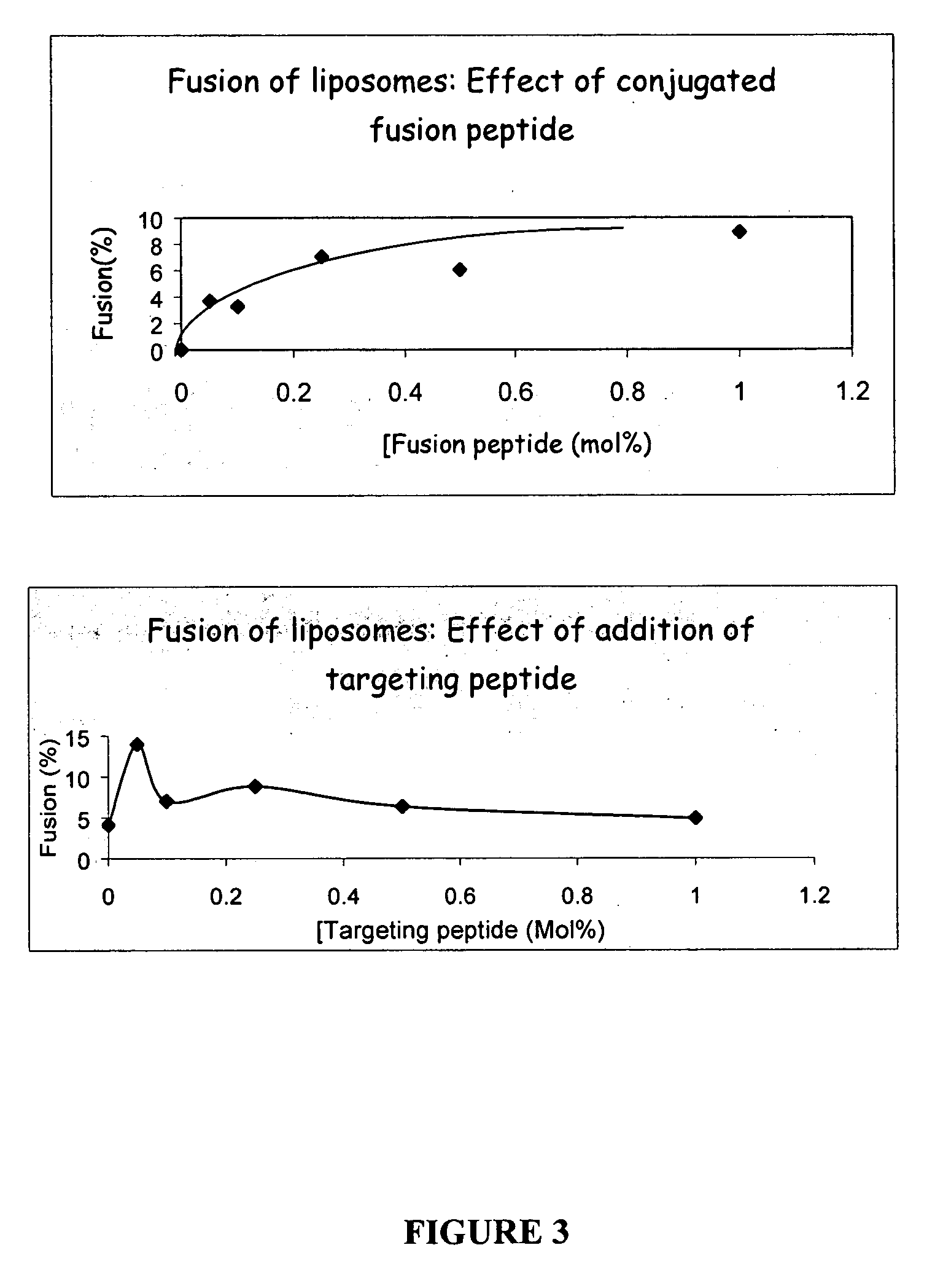
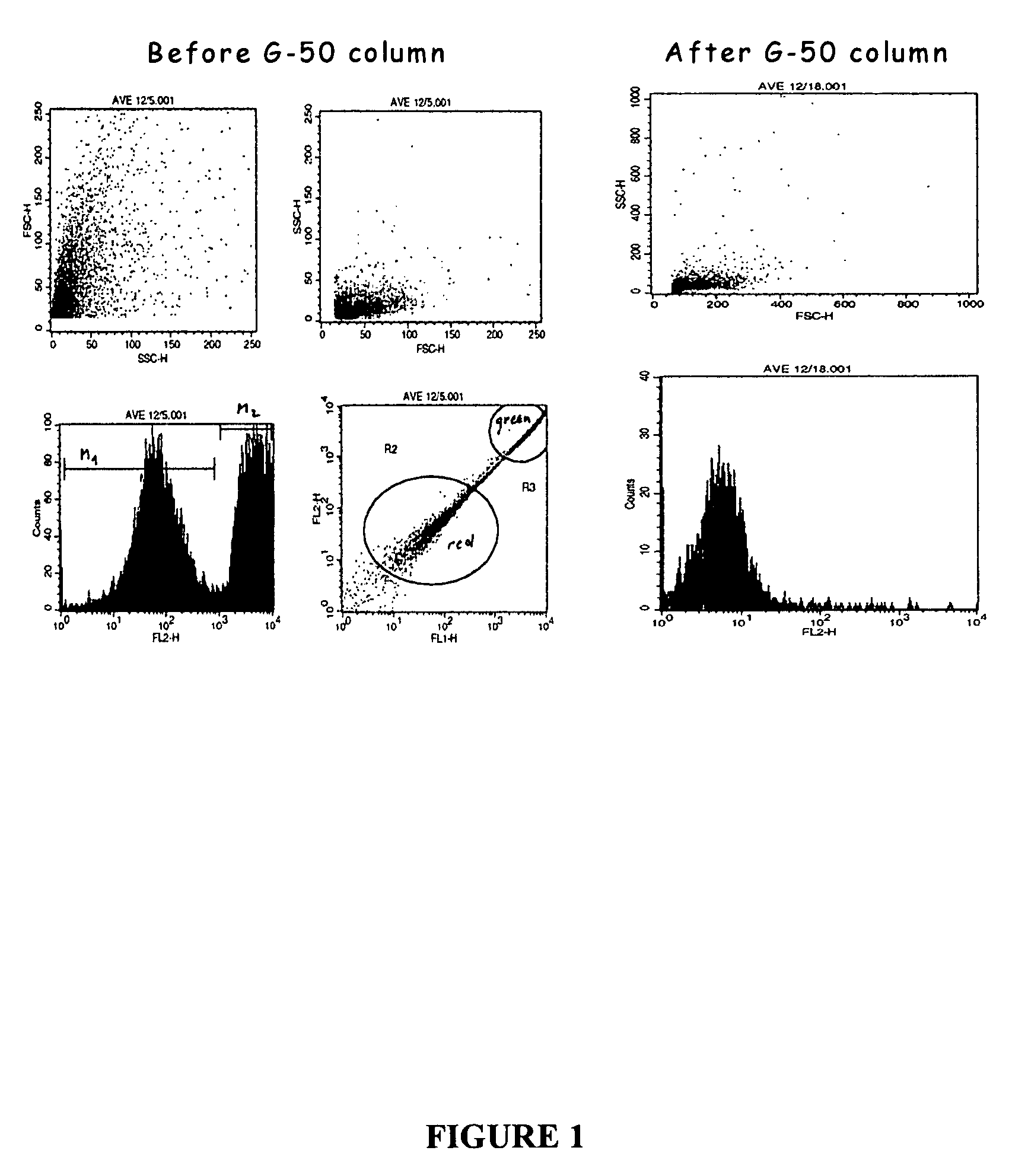
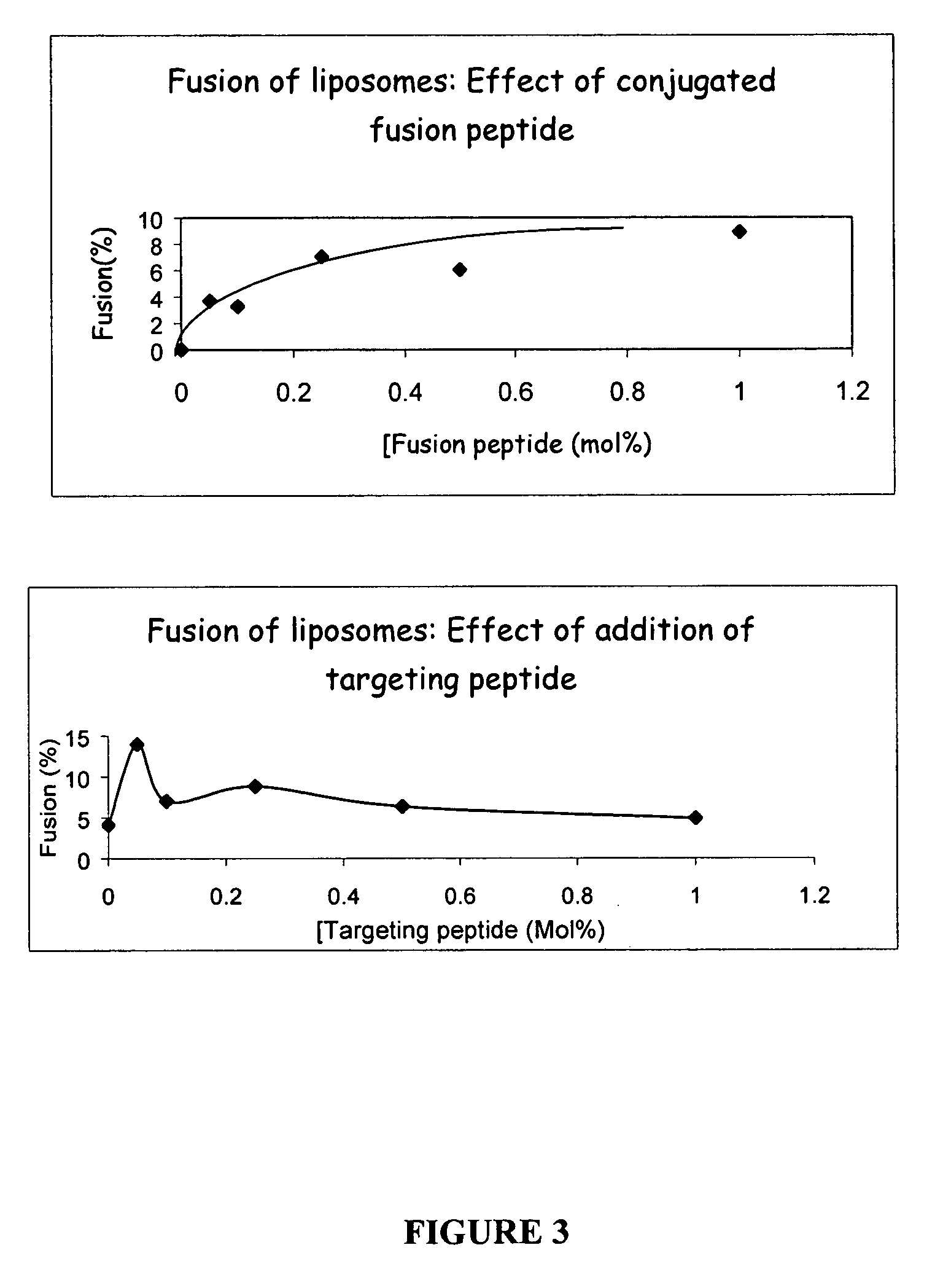
Liposomes containing novel targeting and/or fusogenic peptides, preparations containing them and therapeutic use thereof
InactiveUS20060240091A1SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHemagglutininTarget peptide
A novel targeting peptide from the C-terminal of endothelin and / or a novel fusogenic peptide from hemagglutinin are optionally conjugated to the carboxy group of 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-succinate and incorporated into liposomes for therapeutic treatment. The novel targeting peptide directs liposomes to lung cells, and, therefore, is useful for delivering liposomes encapsulating cholinesterase genes, particularly, the human serum butyryl cholinesterase (Hu BChE) gene, as a treatment against nerve agents. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader quickly to ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the appended issued claims. 37 CFR §1.72(b).
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
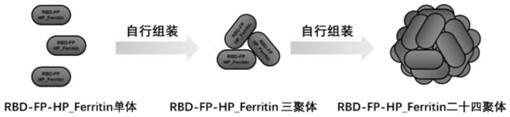
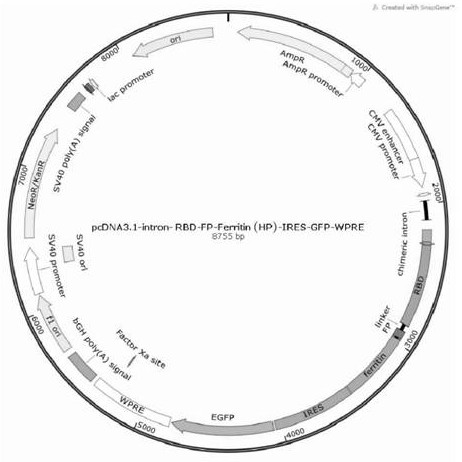
Helicobacter pylori ferritin-based novel coronavirus S protein double-region subunit nanovaccine
ActiveCN111607002AImprove the level ofOvercoming the disadvantage of insufficient immunogenicitySsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsReceptorImmunogenicity
The invention discloses a helicobacter pylori ferritin-based novel coronavirus S protein double-region subunit nanovaccine. According to the invention, a receptor binding domain (RBD) of a virus and afusion peptide (FP) are jointly used as double antigens, and the double antigens are connected with a helicobacter pylori polymer protein (HP _ Ferritin) to form a fusion protein RBD-FP-HP _ Ferritin, so that antigen multimerization is realized; and then an eukaryotic cell expression system is utilized for expression, so as to form a 24-polymer nano antigen through the self-assembly action of HP_ Ferritin. According to the scheme, the defect that RBD monomers are insufficient in immunogenicity can be overcome, the obtained vaccine can remarkably improve the level of neutralizing antibodies of a host to viruses, and the generated antibodies have the capacity of strongly preventing the viruses from invading target cells. Moreover, the vaccine is simple in preparation method, easy to purifyand high in safety, and can be quickly applied to clinical tests.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Acid-cleavable linkers exhibiting altered rates of acid hydrolysis
InactiveUS8609621B2Improve efficiencyIncrease hydrolysis ratePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaCrystallographyAcid hydrolysis
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery and methods of using same
InactiveUS20160106671A1Inhibit growthBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsLipid formationBinding peptide
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Reagents for transfection of eukaryotic cells
ActiveUS7915230B2Improve efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDendrimerLipid formation
Owner:MOLECULAR TRANSFER
Porous nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for targeted delivery including transdermal delivery of cargo and methods thereof
InactiveUS20170232115A1Amenable to high capacity loadingPorosity adjustableOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCancer cellApoptosis
The present invention is directed to protocells for specific targeting of hepatocellular and other cancer cells which comprise a nanoporous silica core with a supported lipid bilayer; at least one agent which facilitates cancer cell death (such as a traditional small molecule, a macromolecular cargo (e.g. siRNA or a protein toxin such as ricin toxin A-chain or diphtheria toxin A-chain) and / or a histone-packaged plasmid DNA disposed within the nanoporous silica core (preferably supercoiled in order to more efficiently package the DNA into protocells) which is optionally modified with a nuclear localization sequence to assist in localizing protocells within the nucleus of the cancer cell and the ability to express peptides involved in therapy (apoptosis / cell death) of the cancer cell or as a reporter, a targeting peptide which targets cancer cells in tissue to be treated such that binding of the protocell to the targeted cells is specific and enhanced and a fusogenic peptide that promotes endosomal escape of protocells and encapsulated DNA. Protocells according to the present invention may be used to treat cancer, especially including hepatocellular (liver) cancer using novel binding peptides (c-MET peptides) which selectively bind to hepatocellular tissue or to function in diagnosis of cancer, including cancer treatment and drug discovery.
Owner:STC UNM +1
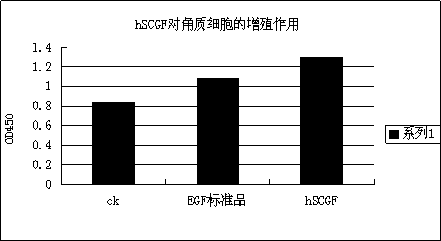
Application of fusion protein in cosmetics
InactiveCN105504066AEasy to pass throughImprove biological activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCosmetic preparationsMedicineDrug biological activity
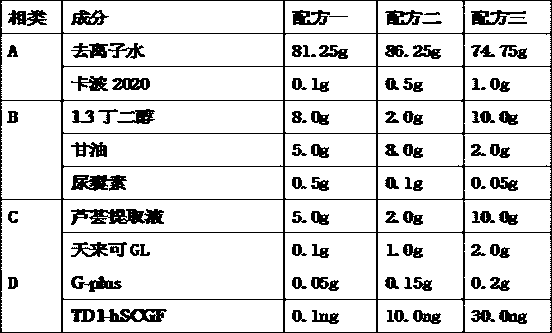
The invention provides the application of fusion protein in cosmetics. The fusion protein contains a transdermal peptide and a human stem cell growth factor (hSCGF), and the transdermal peptide is connected to the N end or C end of the hSCGF through a linker peptide or in a covalent mode. The fusion protein can penetrate through intact skin more easily, and high biological activity and skin absorptivity can be maintained.
Owner:GUANGDONG COOWAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Process for preparing and purifying Exendin-4 from colon bacillus
InactiveCN101586138AIncrease productionHigh purityPeptide preparation methodsFermentationEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention relates to a process for preparing and purifying Exendin-4 from colon bacillus, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. The purified Exendin-4 is obtained by cultivating Exendin-4 high-yielding engineering bacterial strain through bacteria, carrying out non-denatured affinity chromatography, and eliminating N-end fusogenic peptide with enterokinase. Compared with the prior art, the invention improves the formulations of lysate and eluent and adopts a gradient elution technique, thereby enhancing the yield and the purity of a target protein; and besides, the invention simplifies the operating procedures, is simple and easy to operate in operating steps and is suitable for large-batch industrial production.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
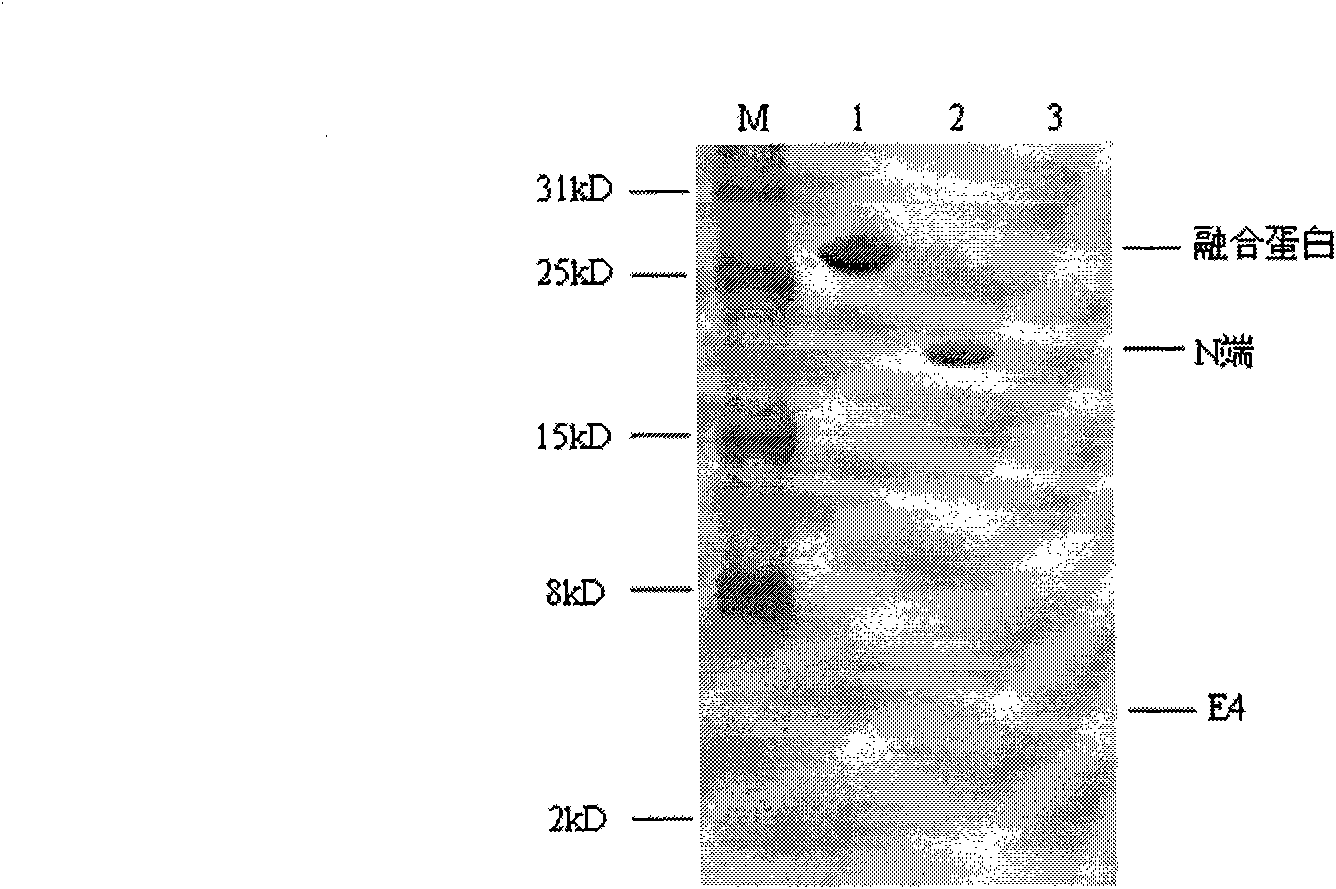
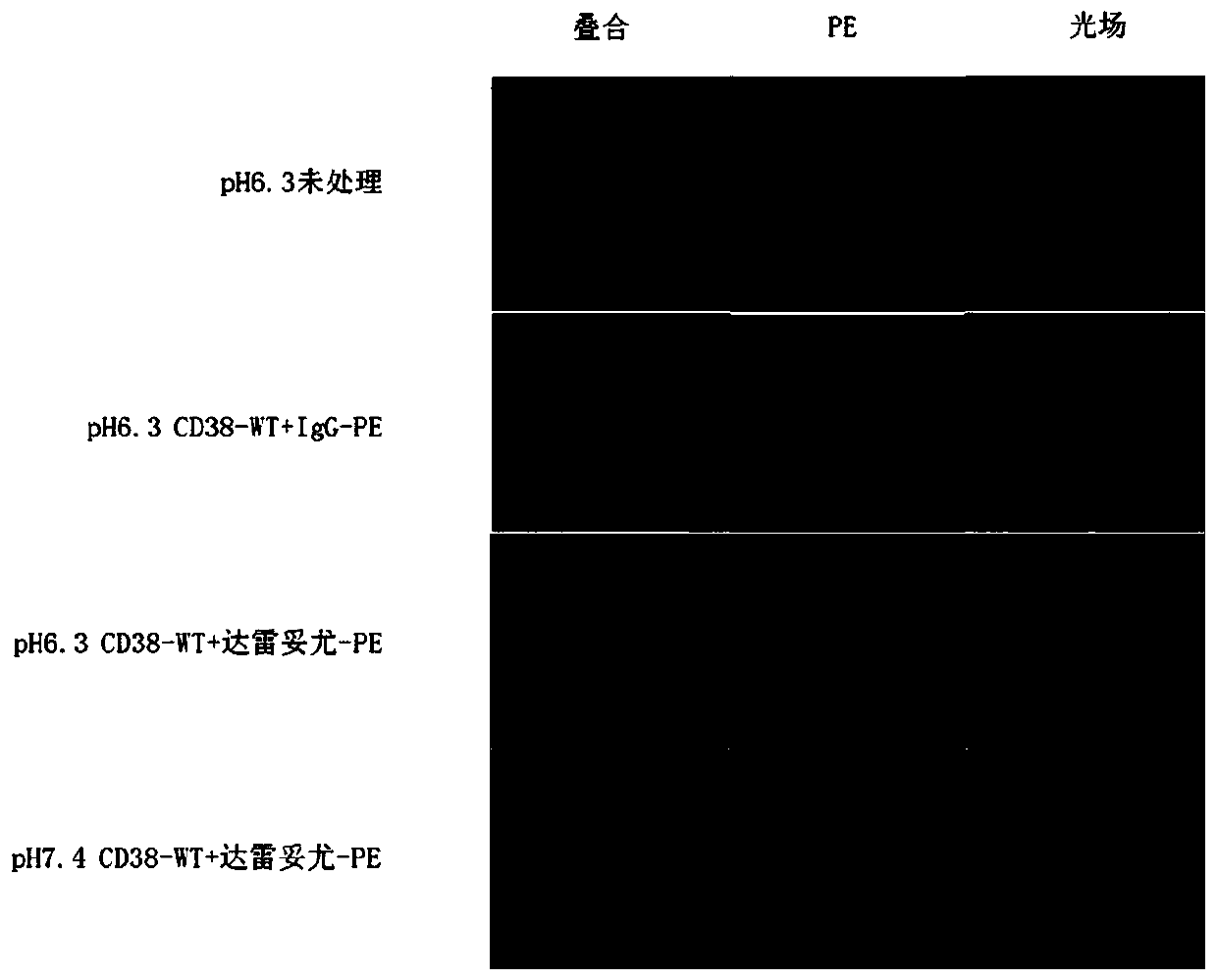
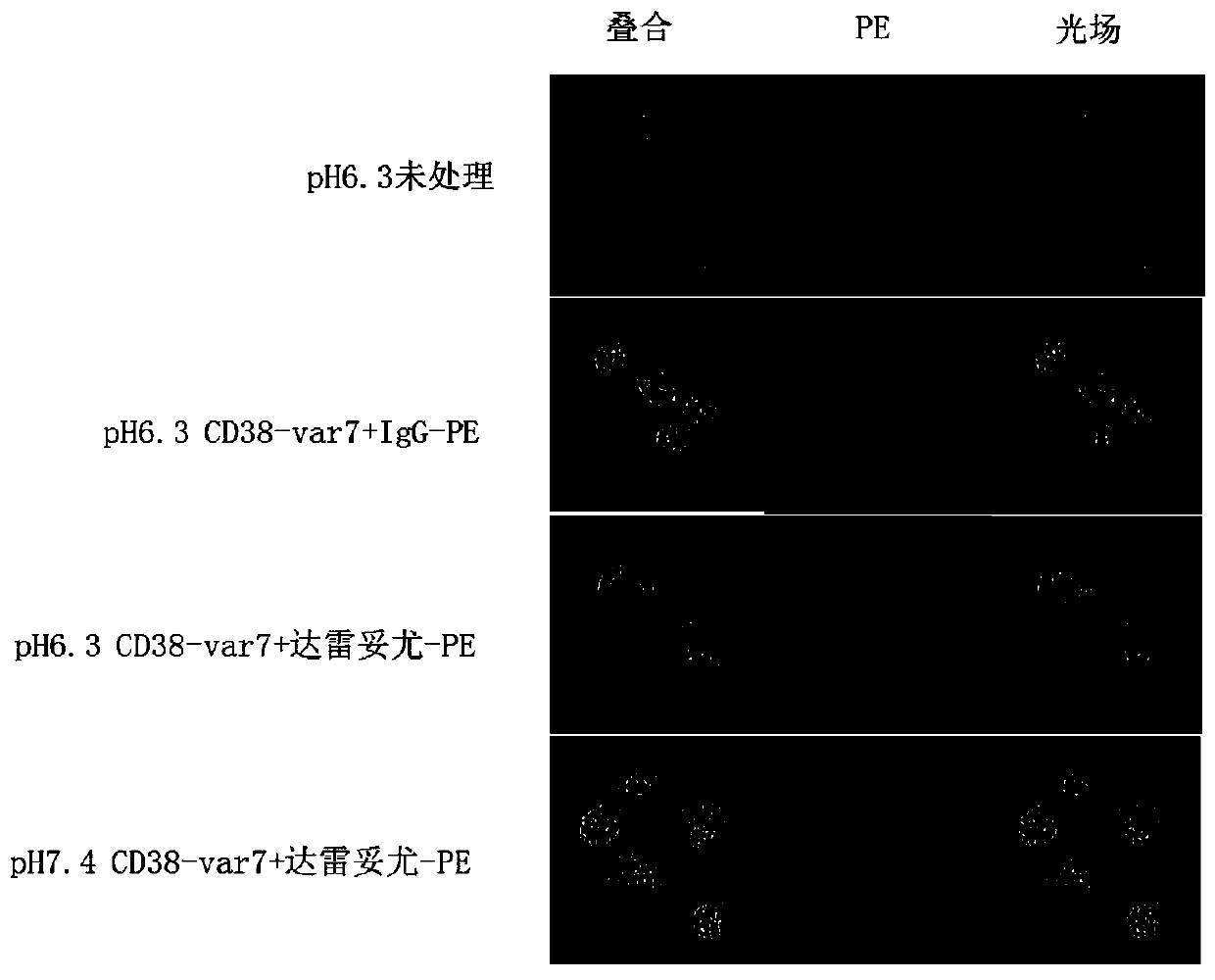
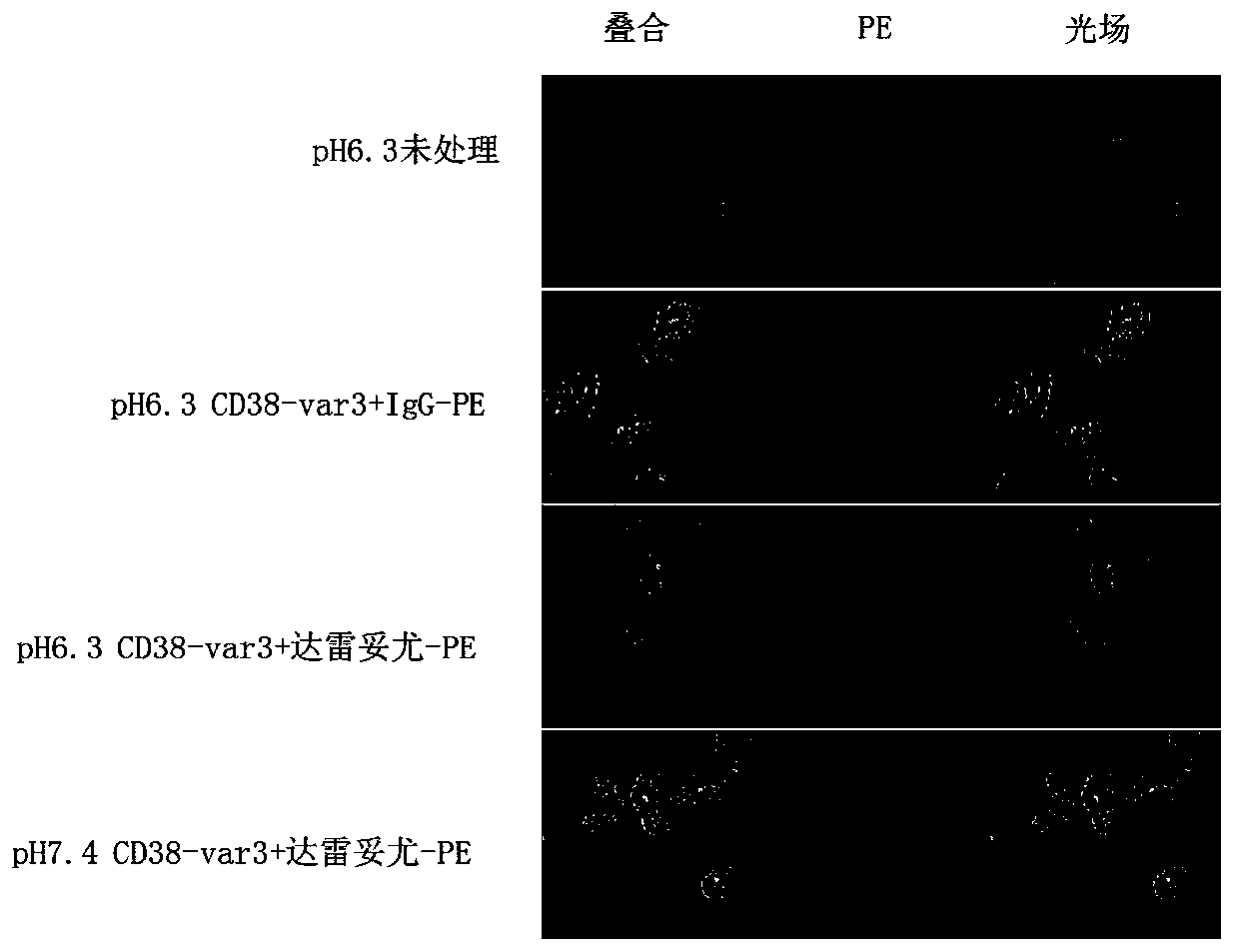
Tumor-targeted CD38-pH low insertion peptide (pHLIP) fusion peptide
PendingCN110698565APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifTumor rejection antigen precursorsAntiendomysial antibodiesCell membrane
Owner:BEIJING ZEQIN BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Solubility tags for the expression and purification of bioactive peptides
InactiveUS20090029412A1High expressionImprove purification effectBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityInclusion bodies
Peptide tags, referred to here as inclusion body tags, are disclosed useful for the generation of insoluble fusion peptides. The fusion peptides comprise at least one inclusion body tag operably linked to a peptide of interest. Expression of the fusion peptide in a host cell results in a product that is insoluble and contained within inclusion bodies in the cell and / or cell lysate. The inclusion bodies may then be purified and the protein of interest may be isolated after cleavage from the inclusion body tag.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Modified fc fusion proteins
InactiveUS20160024179A1Expand the populationLong half-lifeImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseOligosaccharide
Preparations of modified Fc fusion peptides that exhibit metabolically complete or near-complete oligosaccharide structures are provided. Also provided are methods for preparation of the modified Fc fusion peptides. These preparations exhibit enhanced serum half-life and are useful for treatment of a variety of diseases.
Owner:PYRANOSE BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Dual-target tumor vaccine based on tumor endothelium marker-8 gene and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101623498AEasy accessSpeed up entryGenetic material ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsTumor therapyImmunogenicity
The invention discloses a dual-target tumor vaccine based on a tumor endothelium marker-8 gene and a preparation method thereof. The tumor vaccine is formed by combining an eukaryon expression vector recombined by the tumor endothelium marker-8 gene with fusogenic peptide obtained by fusing a membrane penetrating peptide HIV-Tat49-57 and a RGD peptide in the manner of non covalent bonds. The preparation method thereof comprises the following steps: respectively preparing the eukaryon expression vector recombined by the tumor endothelium marker-8 genethe and the fusogenic peptide obtained by fusing the membrane penetrating peptide HIV-Tat49-57 and the RGD peptide; and then, polymerizing the eukaryon expression vector and the fusogenic peptide through electrostatic interaction to form a compound. The tumor vaccine not only reserves the advantages of polypeptide vaccine, such as safety, easy preparation and purification and the like, but also overcomes the shortages, such as small polypeptide molecule, weak immunogenicity and difficult absorption by antigen presenting cells and the like. The vaccine can inhibit the tumor angiogenesis as well as induce the apoptosis of tumor cells, thereby greatly improving the effectiveness and the safety of tumor therapy. The vaccine has wide application prospects in the field of tumor therapy.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
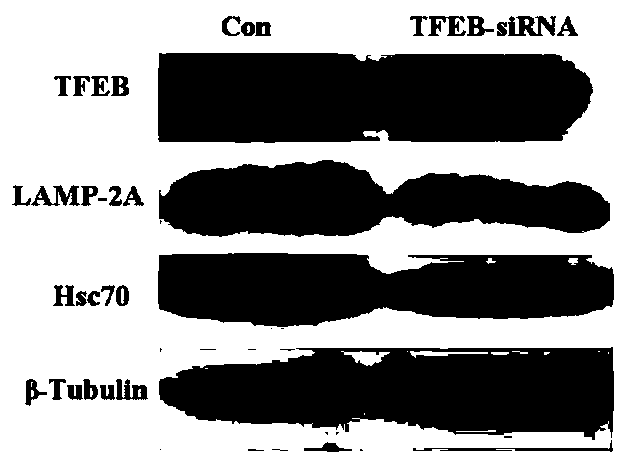
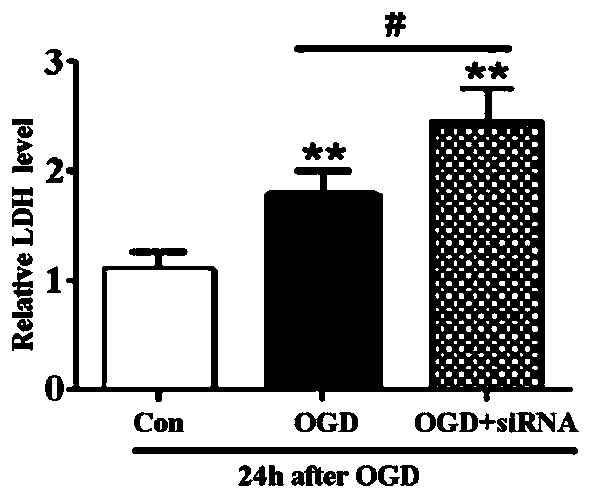
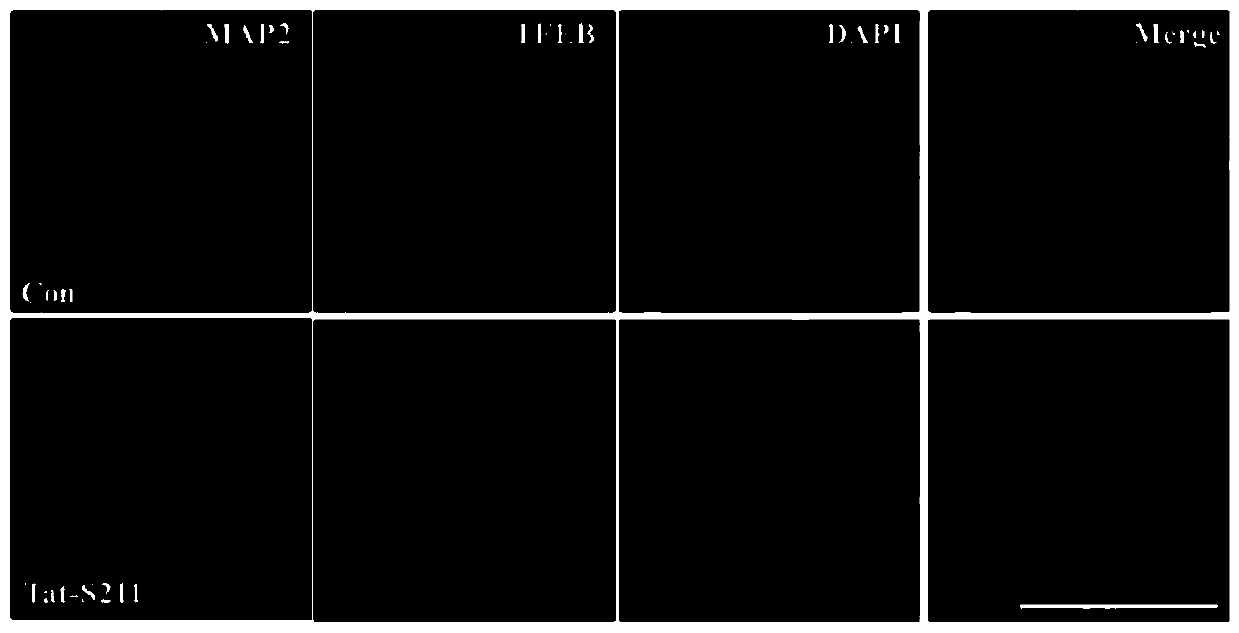
Short chain polypeptide capable of promoting TFEB nuclear translocation, linear short chain polypeptide based on short chain polypeptide, and application of short chain polypeptide to alleviating cerebral ischemia damage
ActiveCN110724203AHigh membrane penetration efficiencySmall molecular weightPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderNeurophysinsTFEB
The invention discloses short chain polypeptide capable of promoting TFEB nuclear translocation, linear short chain polypeptide based on the short chain polypeptide, and an application of the short chain polypeptide to alleviating cerebral ischemia damage, and belongs to the technical field of biological pharmaceuticals. The short chain polypeptide disclosed by the invention is short chain polypeptide obtained through fusing function areas combined from TFEB protein and 14-3-3 protein, and the nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ.ID.NO.1. The invention further discloses the linear short chain polypeptide protecting the short chain polypeptide. The linear short chain polypeptide is obtained through fusing cell-penetrating peptide with the short chain polypeptide. Experiment verifies thatthe synthesized peptide can adjust and control TFEB nuclear translocation, and promote CMA to alleviate cell injury. Therefore, the invention discloses an application of the short chain polypeptide totreatment new target points for alleviating nerve cell death and improving cerebral ischemia damage.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Subunit vaccine immunologic adjuvant and application thereof
InactiveCN102178950AImproving immunogenicityGood immune effectAntibacterial agentsAntibody medical ingredientsPasteurella caballiP. multocida
The invention provides a subunit vaccine immunologic adjuvant and application thereof. The adjuvant is a fusogenic peptide of antibacterial peptide and allanoin tripeptide and has an amino acid sequence of SEQ.ID.NO.1 and a nucleotide sequence of SEQIDNO.2. In the invention, PG-1-GGGGS-3BS fusogenic peptide is used as a molecular adjuvant, and the immunogenicity of the outer membrane protein of chicken pasteurella multocida can be enhanced effectively; when the PG-1-GGGGS-3BS fusogenic peptide is used as a molecular adjuvant, a eukaryotic yeast expression vector is selected, the fusogenic peptide can be expressed and purified easily, can be modified by glycosylation and the like, and is easy for mass production; the fusogenic peptide expressed by yeast has modifier genes of eukaryotic cells, is similar to the structure of PG-1 expression in a mammal body and has good biological activity.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Liposomes containing novel targeting and/or fusogenic peptides, preparations containing them and therapeutic use thereof
InactiveUS7741431B2SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHemagglutininTarget peptide
A novel targeting peptide from the C-terminal of endothelin and / or a novel fusogenic peptide from hemagglutinin are optionally conjugated to the carboxy group of 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-succinate and incorporated into liposomes for therapeutic treatment. The novel targeting peptide directs liposomes to lung cells, and, therefore, is useful for delivering liposomes encapsulating cholinesterase genes, particularly, the human serum butyryl cholinesterase (Hu BChE) gene, as a treatment against nerve agents. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader quickly to ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the appended issued claims. 37 CFR §1.72(b).
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
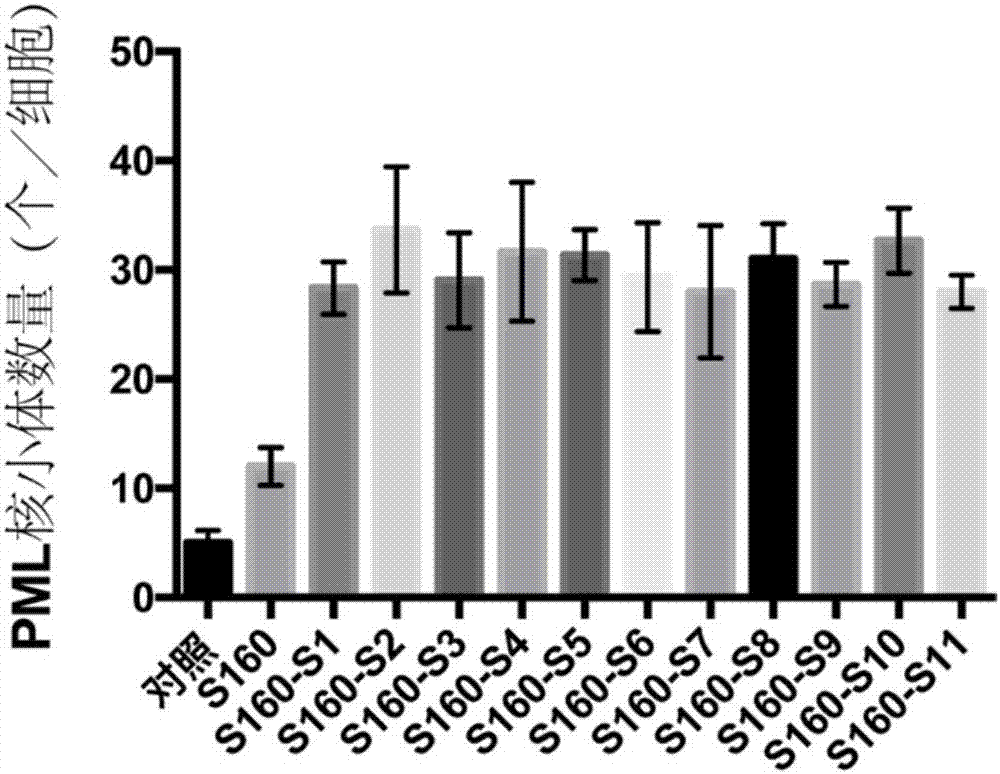
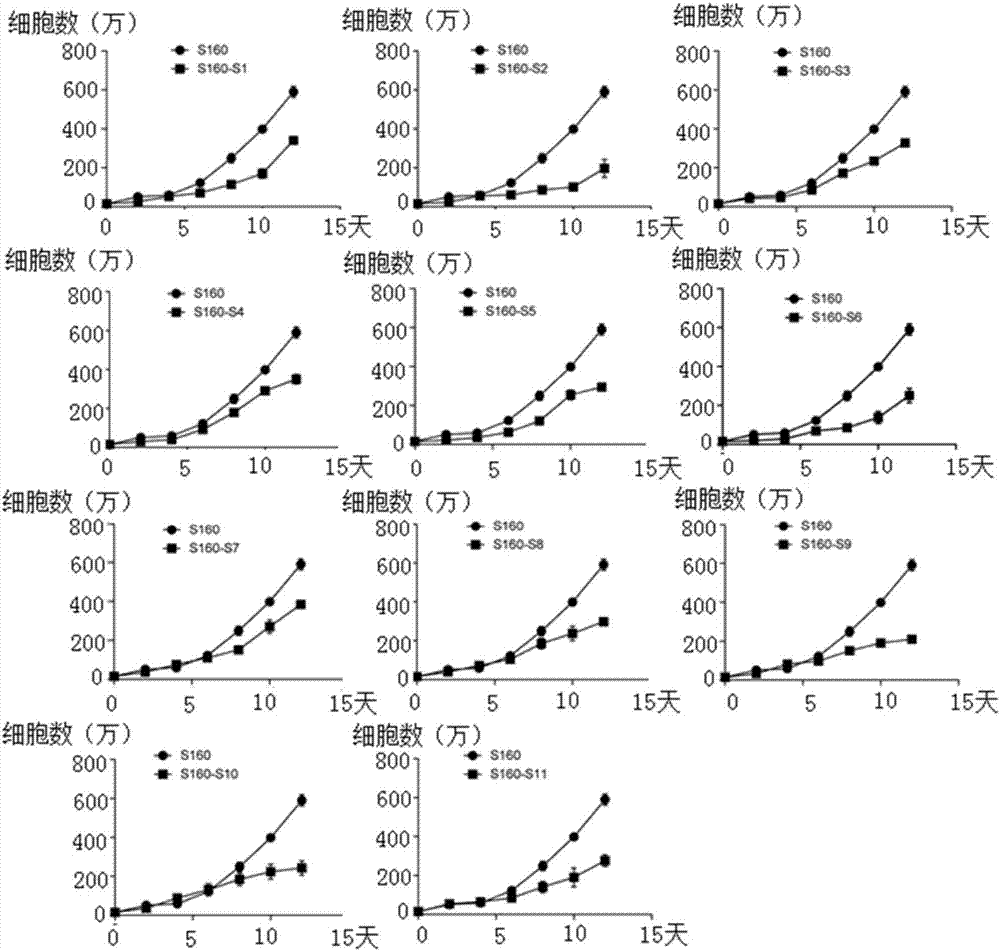
Polypeptide and application thereof to preparation of medicament for treatment and/or prevention of tumor
ActiveCN107474115ASignificant effectSmall toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesSide chainMedicine
The invention provides a polypeptide and an application thereof to preparation of medicament for treatment and / or prevention of tumor. An amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is shown in a sequence table SEQ ID No.1, or shown in the sequence table SEQ ID No.1 amino acid sequence with two or more amino acids substituted by unnatural amino acids with connectable side chains, and a derivative comprises a chimeric peptide formed by connection of the polypeptide and a cell-penetrating peptide, a fusogenic peptide formed by the polypeptide and a virus, a methylated polypeptide, a glycosylated polypeptide, and a pegylated polypeptide. The polypeptide or the polypeptide derivative can targetedly increase number of PML nucleosomes, and can be applied to preparation of medicament for treatment and / or prevention of tumor.
Owner:胡卓伟
Acid-clevable linkers exhibiting altered rates of acid hydrolysis
InactiveUS20120122153A1Improve efficiencyIncrease hydrolysis rateFungiBacteriaLytic peptideAcid hydrolysis
An acid-cleavable peptide linker comprising aspartic acid and proline residues is disclosed. The acid-cleavable peptide linker provides an altered sensitivity to acid-hydrolytic release of peptides of interest from fusion peptides of the formula PEP1-L-PEP2. The inventive linker, L, is described in various embodiments, each of which provides substantially more rapid acid-release of peptides of interest than does a single aspartic acid-proline pair. In an additional aspect, a method of increasing the stability of an acid cleavable linkage to acid hydrolysis is also provided.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
TLR4 (Toll-like receptor) compound of targeting microglia as well as preparation method and application of compound
InactiveCN103933580AIncrease uptakeHigh transfection efficiencyNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsCX3CR1Antiinflammatory drug
The invention discloses a TLR4 (Toll-like receptor) compound of targeting microglia as well as a preparation method and application of the compound in the pharmaceutical field, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. The compound is formed by binding fusion peptide of Q9 peptide (QQQKKKKKK) and T9 peptide (LTQQVVMKF) and TLR4RNAi through an electrostatic interaction; through a guiding function of the Q9 peptide, the compound can specifically target a specific CX3CR1 receptor on the surface of the microglia; when the T9 peptide acts with the CX3CR1 receptor, the TLR4RNAi is efficiently transfected into the microglia to inhibit activation of the microglia, so as to inhibit an inflammatory reaction after microglia mediated cerebral hemorrhage; the compound can be used for preparing microglia mediated anti-inflammatory drugs, and has good development and application prospects in the field of cerebral hemorrhage treatment.
Owner:中国人民解放军南京军区福州总医院四七六医院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com