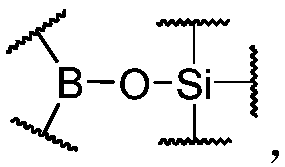Patents
Literature
896 results about "Non covalent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
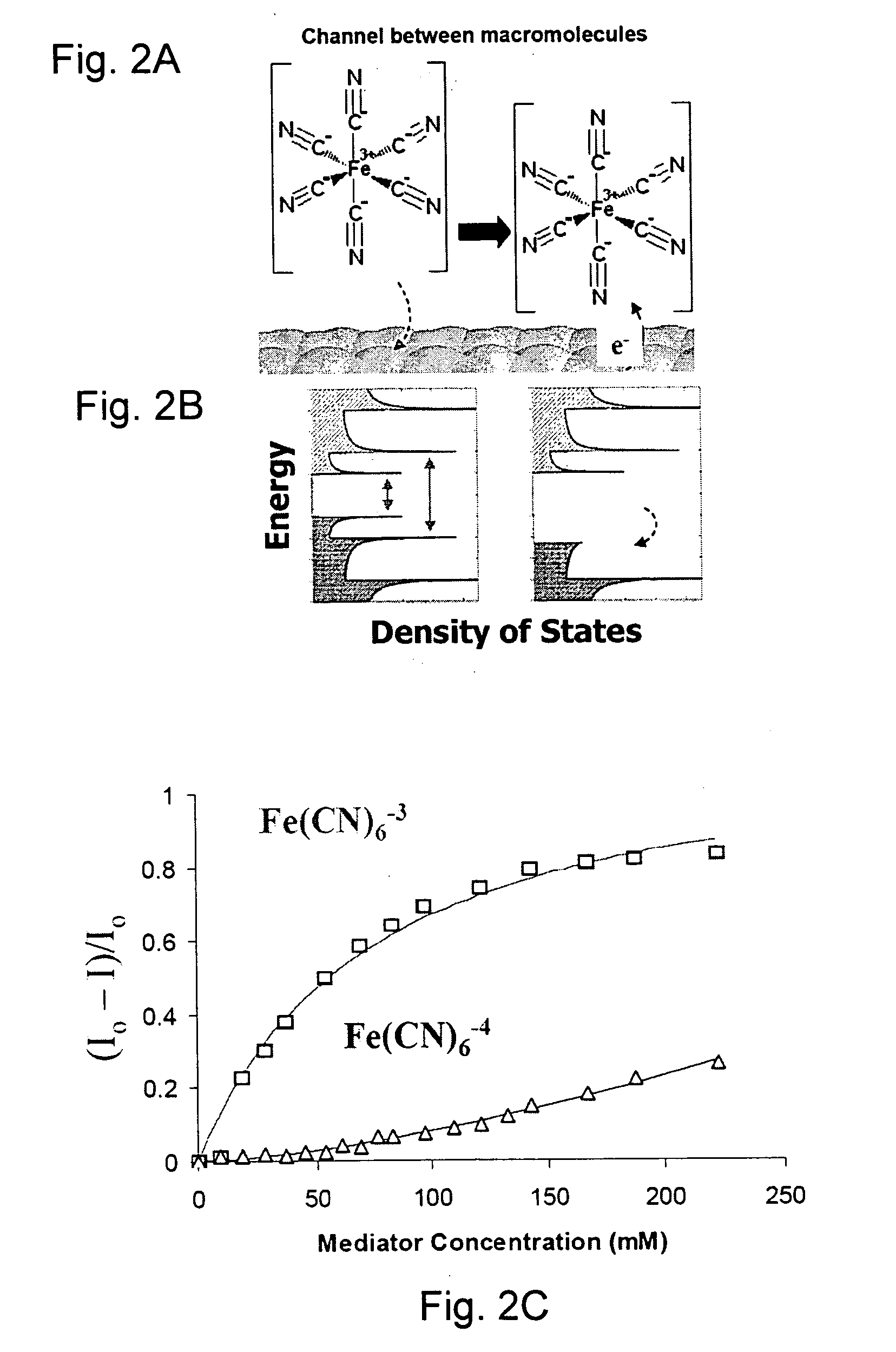
A non-covalent interaction differs from a covalent bond in that it does not involve the sharing of electrons, but rather involves more dispersed variations of electromagnetic interactions between molecules or within a molecule.
Entangled single-wall carbon nanotube solid material and methods for making same
InactiveUS6899945B2Material nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkSolvent evaporation
Buckyrock is a three-dimensional, solid block material comprising an entangled network of single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNT), wherein the block comprises greater than 75 wt % SWNT. SWNT buckyrock is mechanically strong, tough and impact resistant. The single-wall carbon nanotubes in buckyrock form are present in a random network of individual single-wall carbon nanotubes, SWNT “ropes” and combinations thereof. The random network of the SWNT or SWNT ropes can be held in place by non-covalent “cross-links” between the nanotubes at nanotube contact points. In one embodiment, SWNT buckyrock is made by forming a SWNT-water slurry, slowly removing water from the slurry which results in a SWNT-water paste, and allowing the paste to dry very slowly, such that the SWNT network of the SWNT-water paste is preserved during solvent evaporation. Buckyrock can be used in applications, such as ballistic protection systems, involving light-weight material with mechanical strength, toughness and impact resistance.
Owner:RICE UNIV
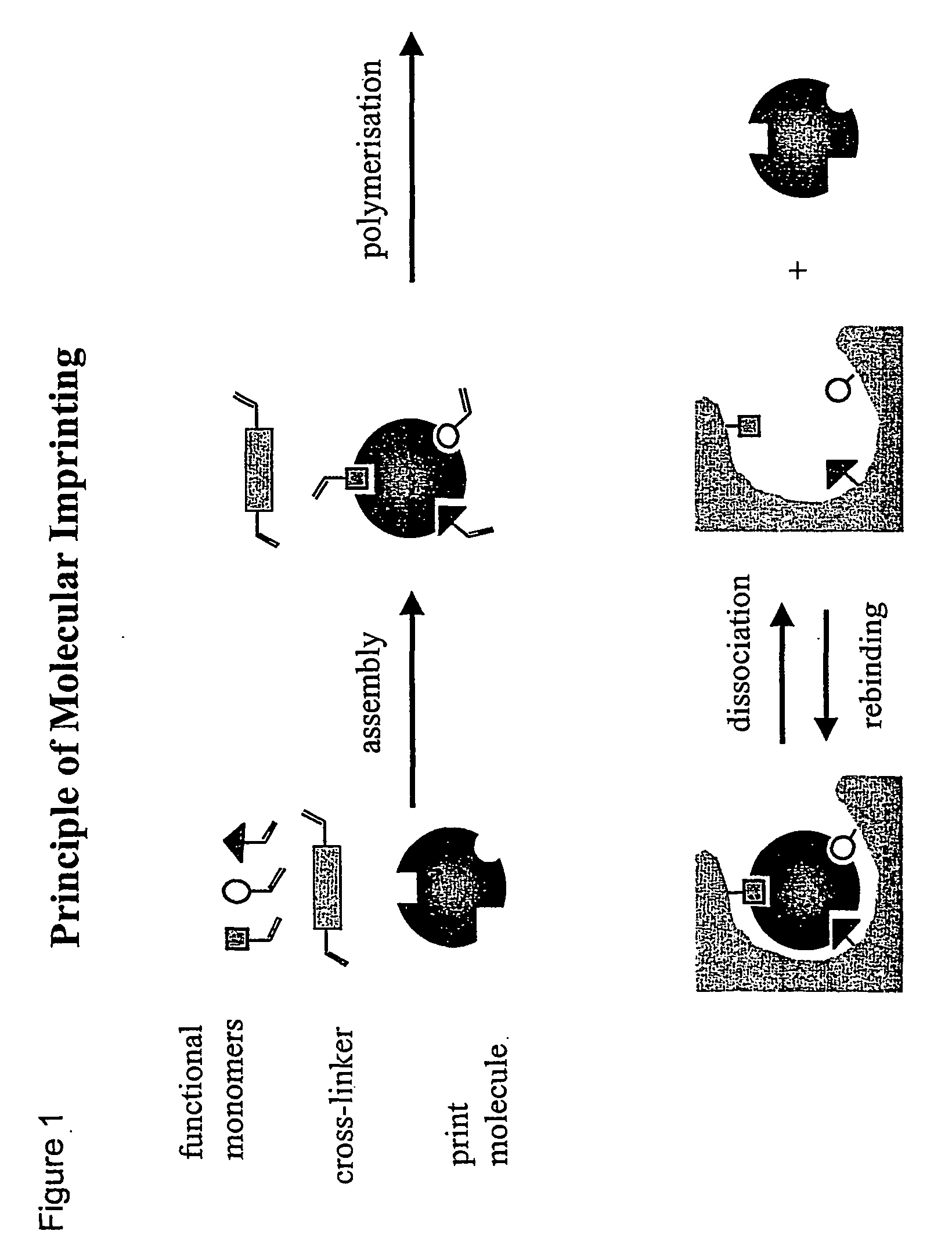
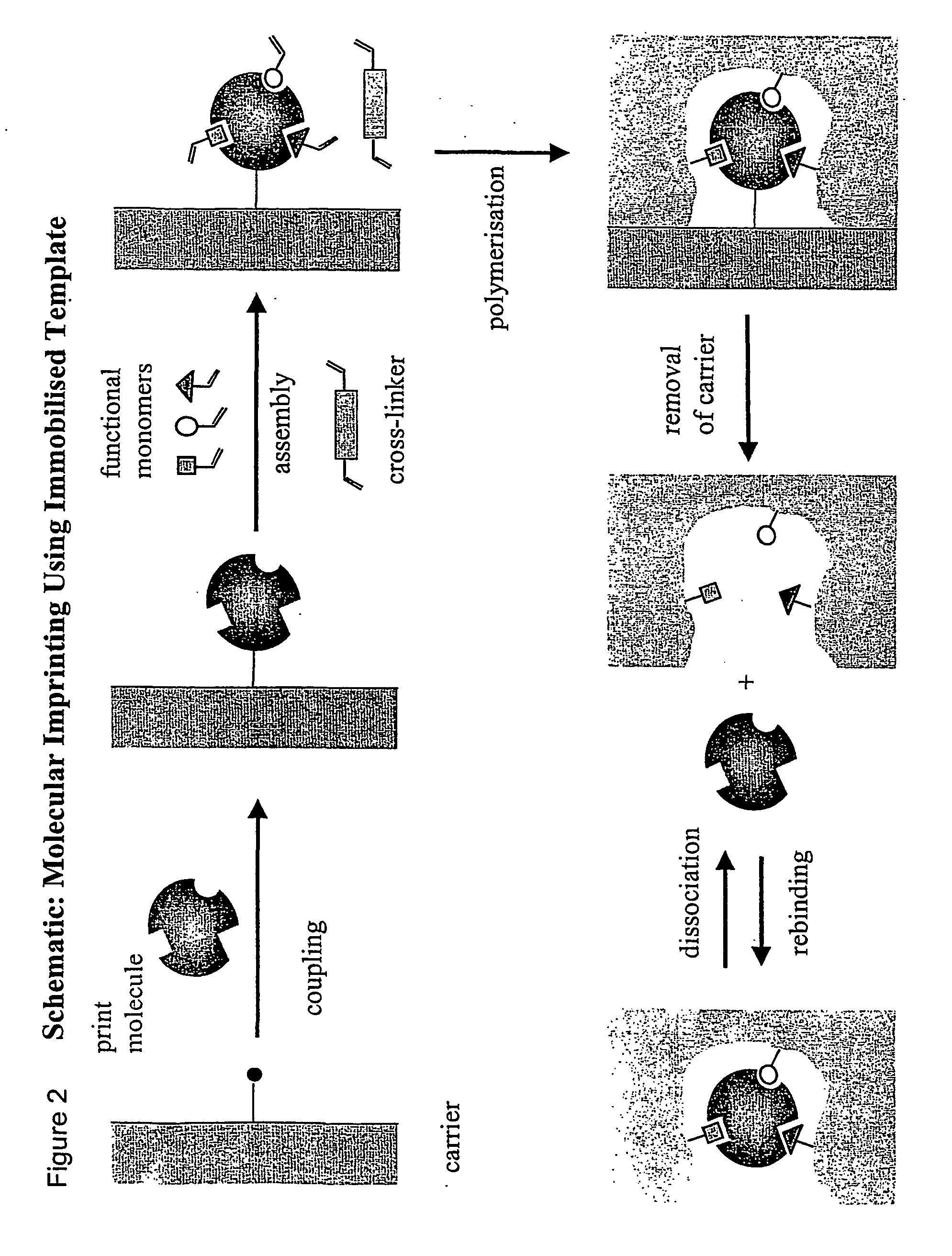
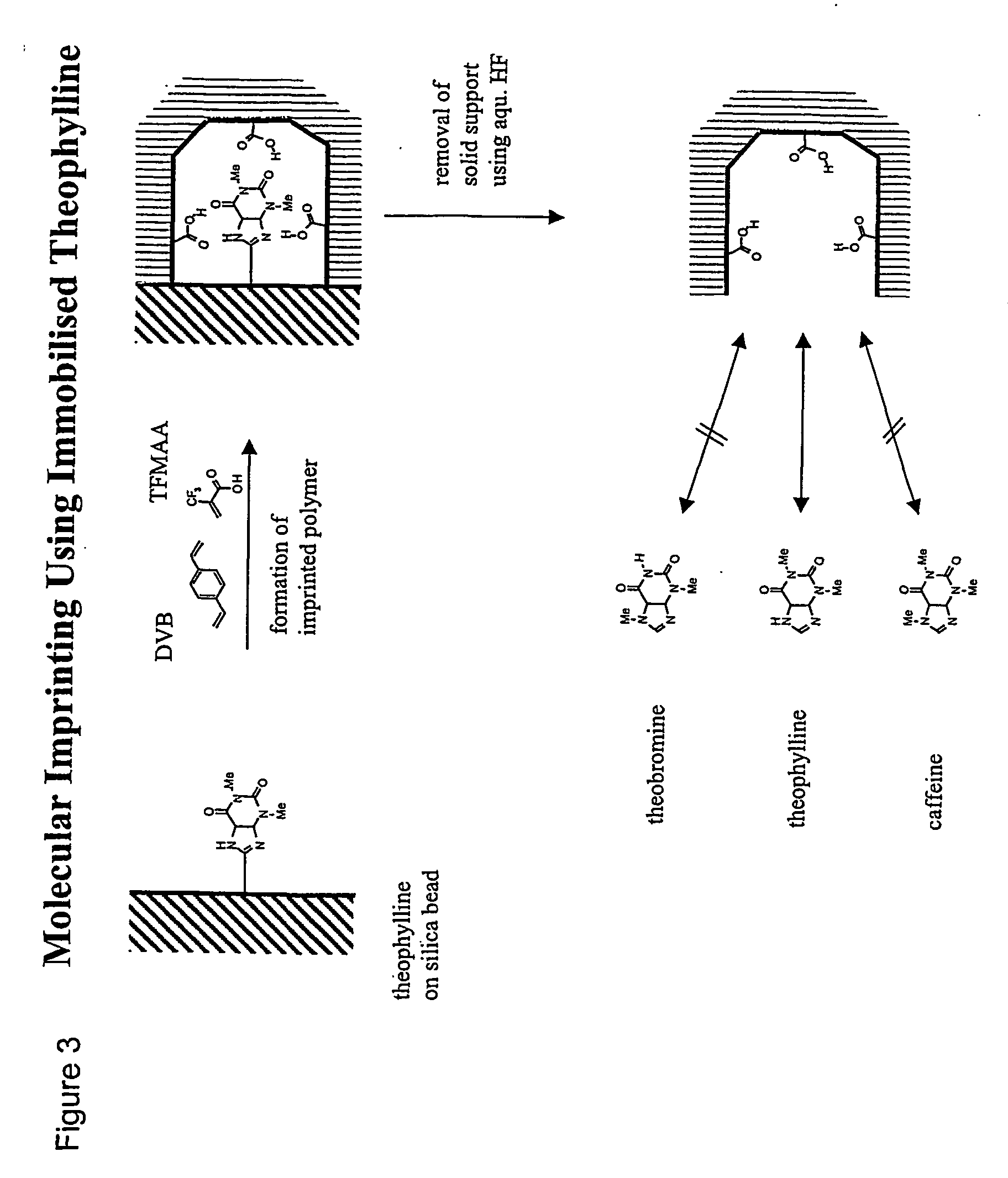
Molecular imprinting
InactiveUS20040157209A1Reduces tumbling rateImprove accessibilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyCross-linkFunctional monomer
The present invention relates to molecularly imprinted polymers comprising tailor-made recognition sites for a target in which said recognition sites are located at or close to the surface of the polymer and / or of pores in the polymer. The molecularly imprinted polymer comprising tailor-made recognition sites for a target is obtainable by polymerising functional monomers and, optionally, cross-linked, optionally in a reaction solvent, in the presence of at least one template immobilised on a support material in a polymerisation process, whereby non-covalent or covalent are formed between said functional monomers and said immobilised template(s), and removing said template(s), and said support material from the molecularly imprinted polymer.
Owner:KLAUS MOSBACH
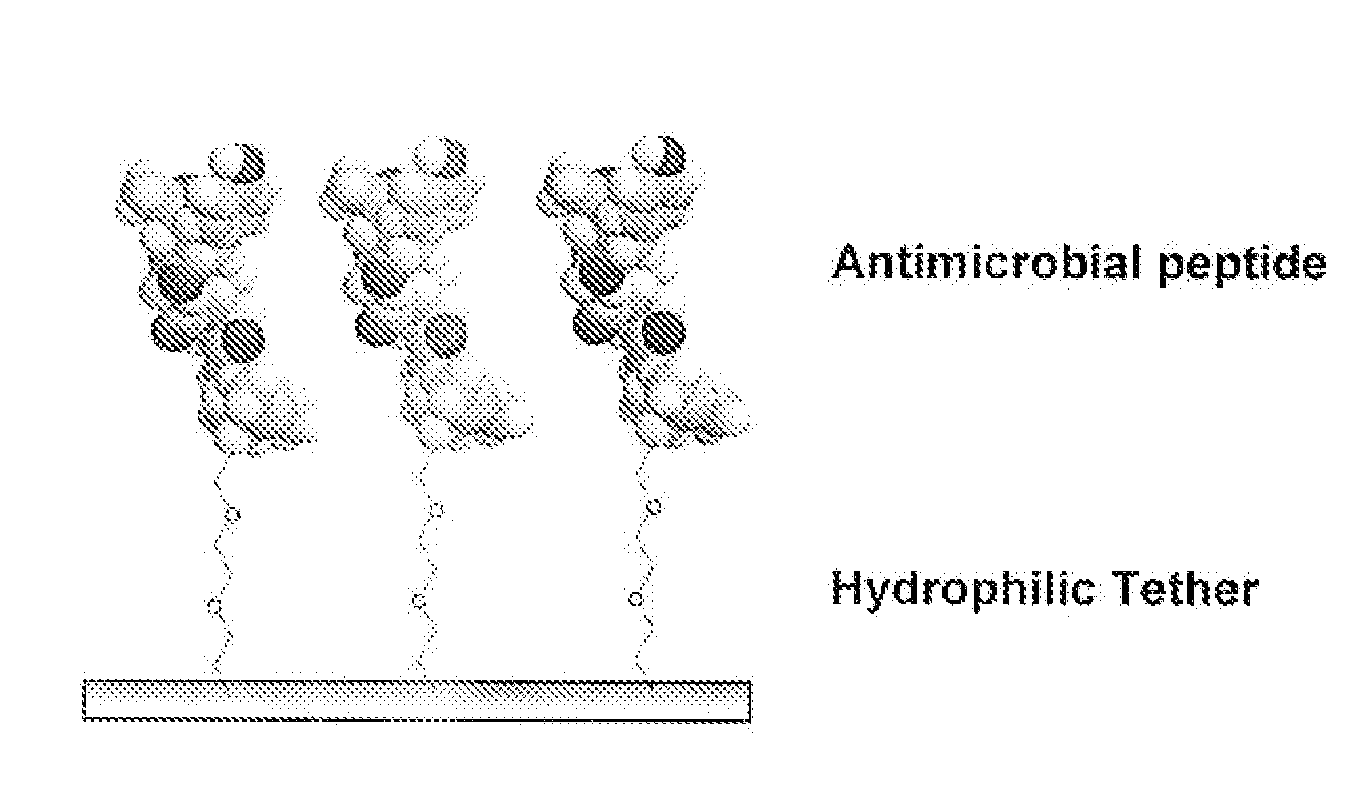
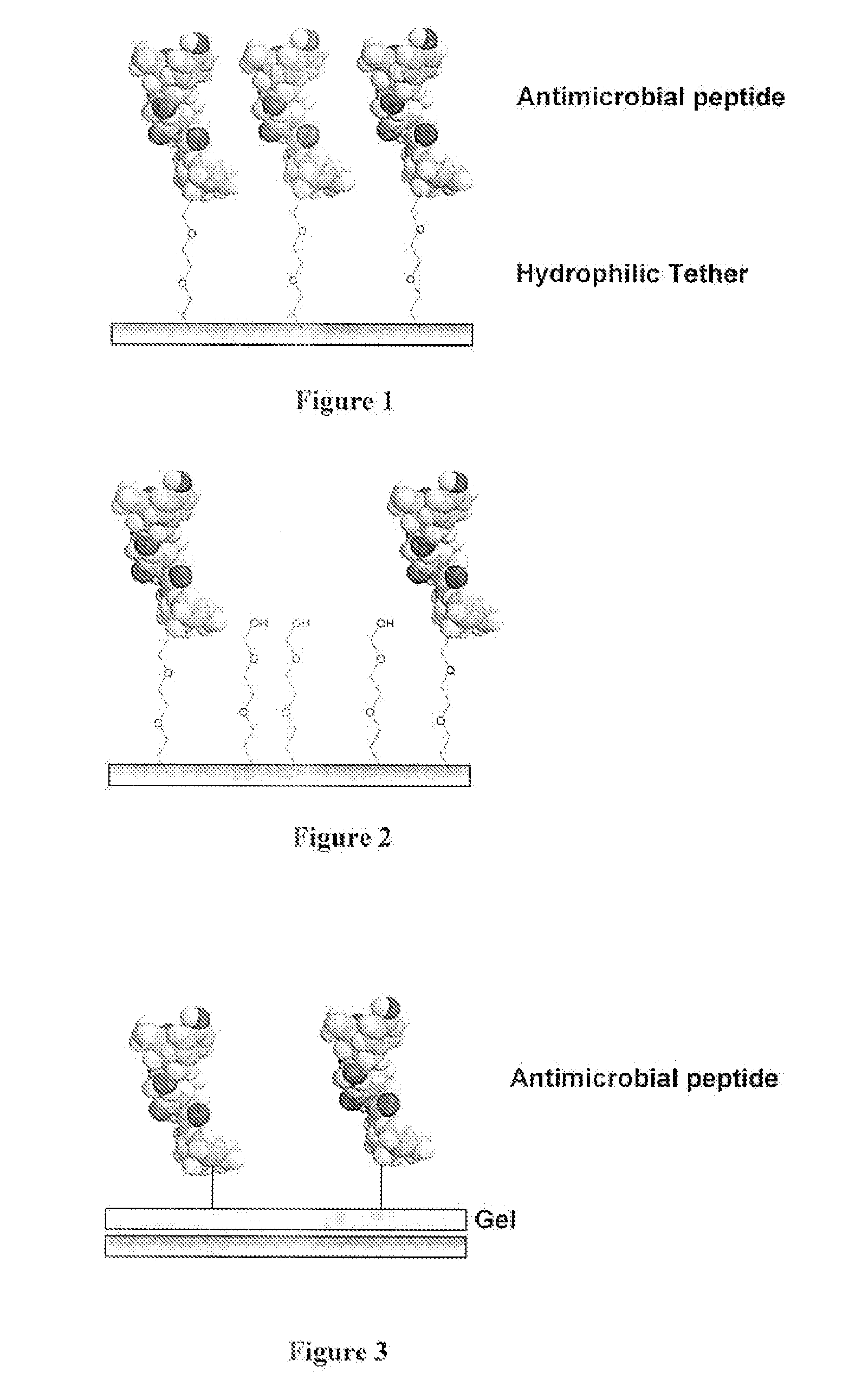
Medical Devices and Coatings with Non-Leaching Antimicrobial Peptides
InactiveUS20070254006A1Solve the lack of flexibilityPromote adequate mobilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntibiotic resistanceFungal microorganisms
Antimicrobial peptides enable an alternate approach to developing antimicrobial coatings due to their targeting of the membranes of the bacteria. High specific activity is achieved by orienting the peptides so that the antimicrobial ends of the peptides maximally contact the bacteria. In one embodiment, one end of the peptide is covalently attached directly to the substrate. In another embodiment, the peptides are immobilized on the substrate using a coupling agent or tether. Non-covalent methods include coating the peptide onto the substrate or physiochemically immobilizing the peptides on the substrate using highly specific interactions, such as the biotin / avidin or streptavidin system. The compositions are substantially non-leaching, antifouling, and non-hemolytic. The immobilized peptides retain sufficient flexibility and mobility to interact with and de endocytosed by the bacteria, viruses, and / or fungi upon exposure. Immobilizing the peptides to the substrate reduces concerns regarding toxicity of the peptides and the development of antimicrobial resistance, while presenting substantially all of the peptide at the site of action at the surface of the substrate.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method of preparing polymeric adhesive compositions utilizing the mechanism of interaction between the polymer components
InactiveUS20050113510A1Easy to handleReduce leakageCosmetic preparationsImpression capsPolymer scienceBioadhesive
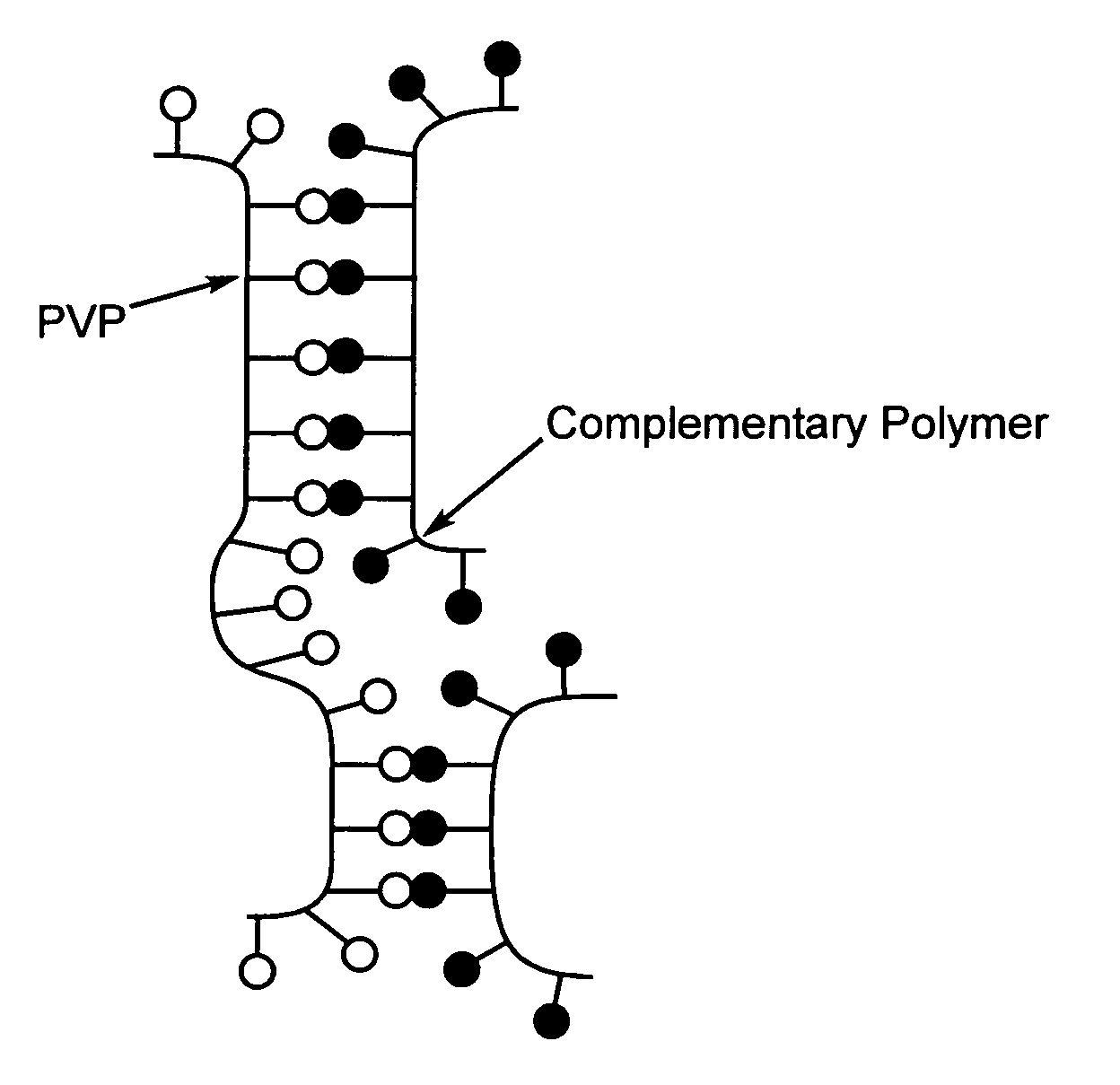
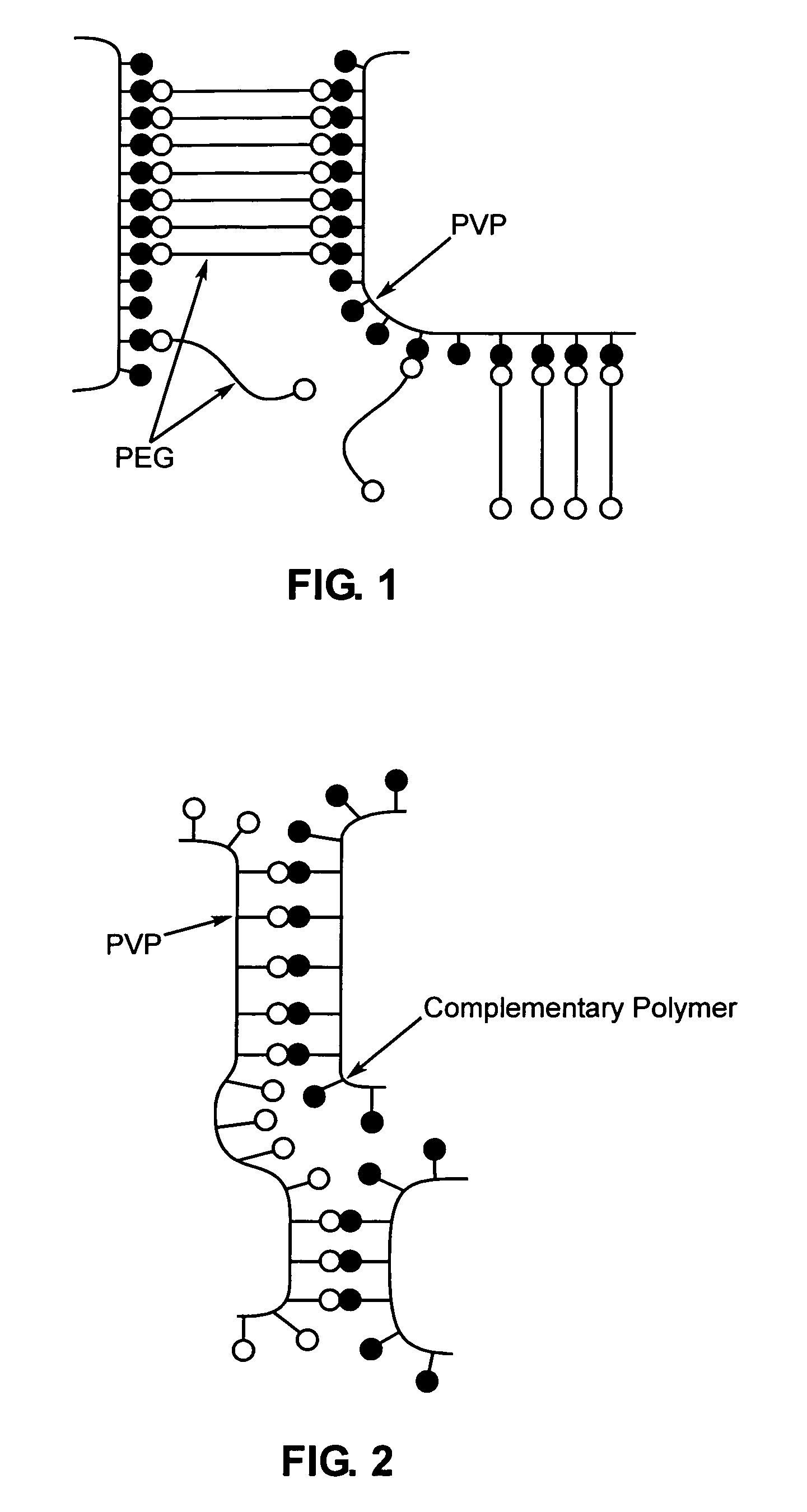
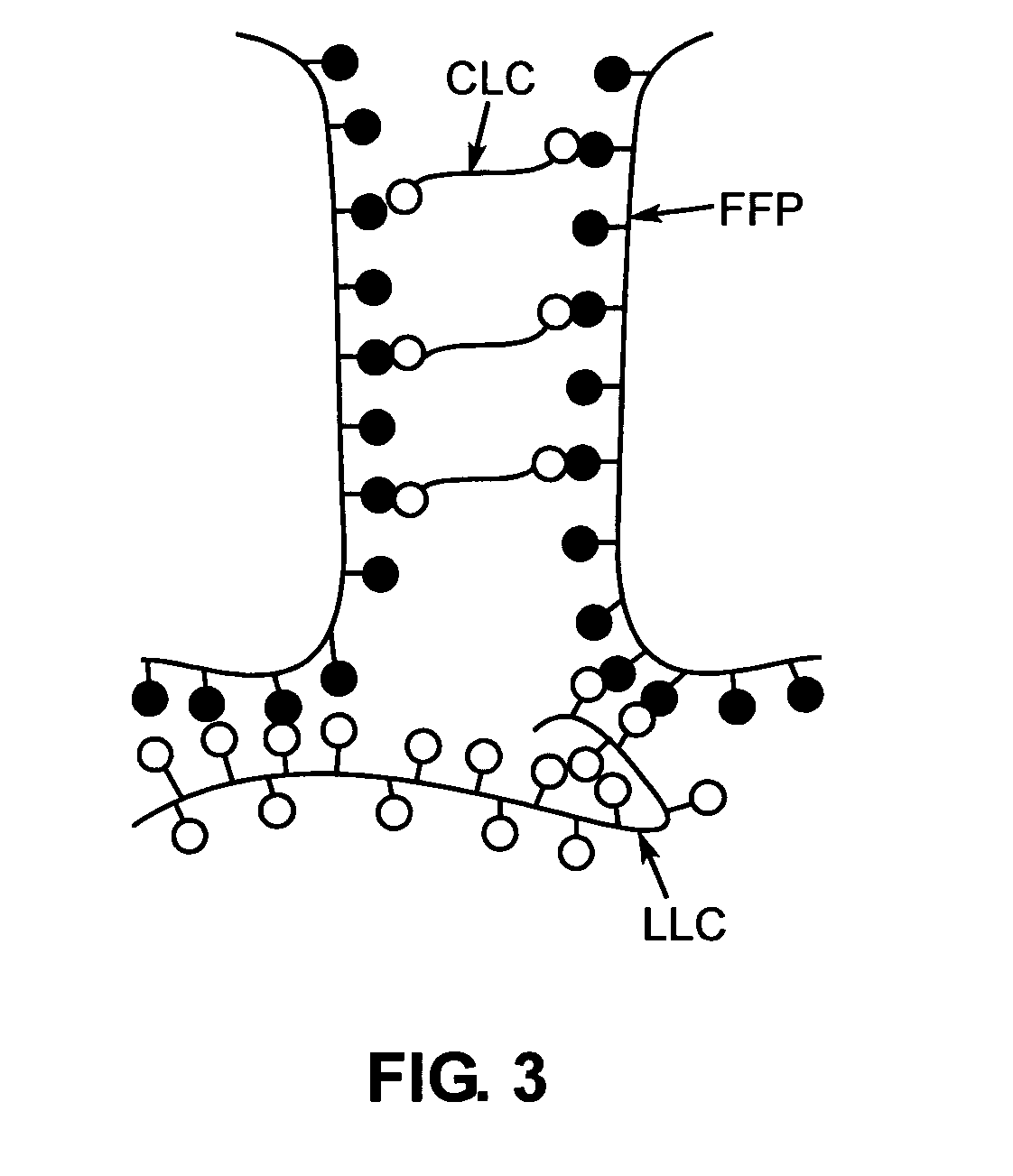
A method of selecting components for use in water-absorbing pressure-sensitive adhesive compositions is provided. The method involves selecting a film-forming polymer, a ladder-like non-covalent crosslinker that is capable of forming a ladder-like interpolymer complex with the film-forming polymer selected, and selecting a carcass-like non-covalent crosslinker that is capable of forming a carcass-like complex with at least one of the film-forming polymer selected or the ladder-like non-covalent crosslinker selected. The adhesive hydrogels provide high adhesion in a swollen state and bridge the gap between conventional pressure sensitive adhesives and bioadhesives. Methods for preparing and using the resulting compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:A V TOPCHIEV INST OF PETROCHEM +1
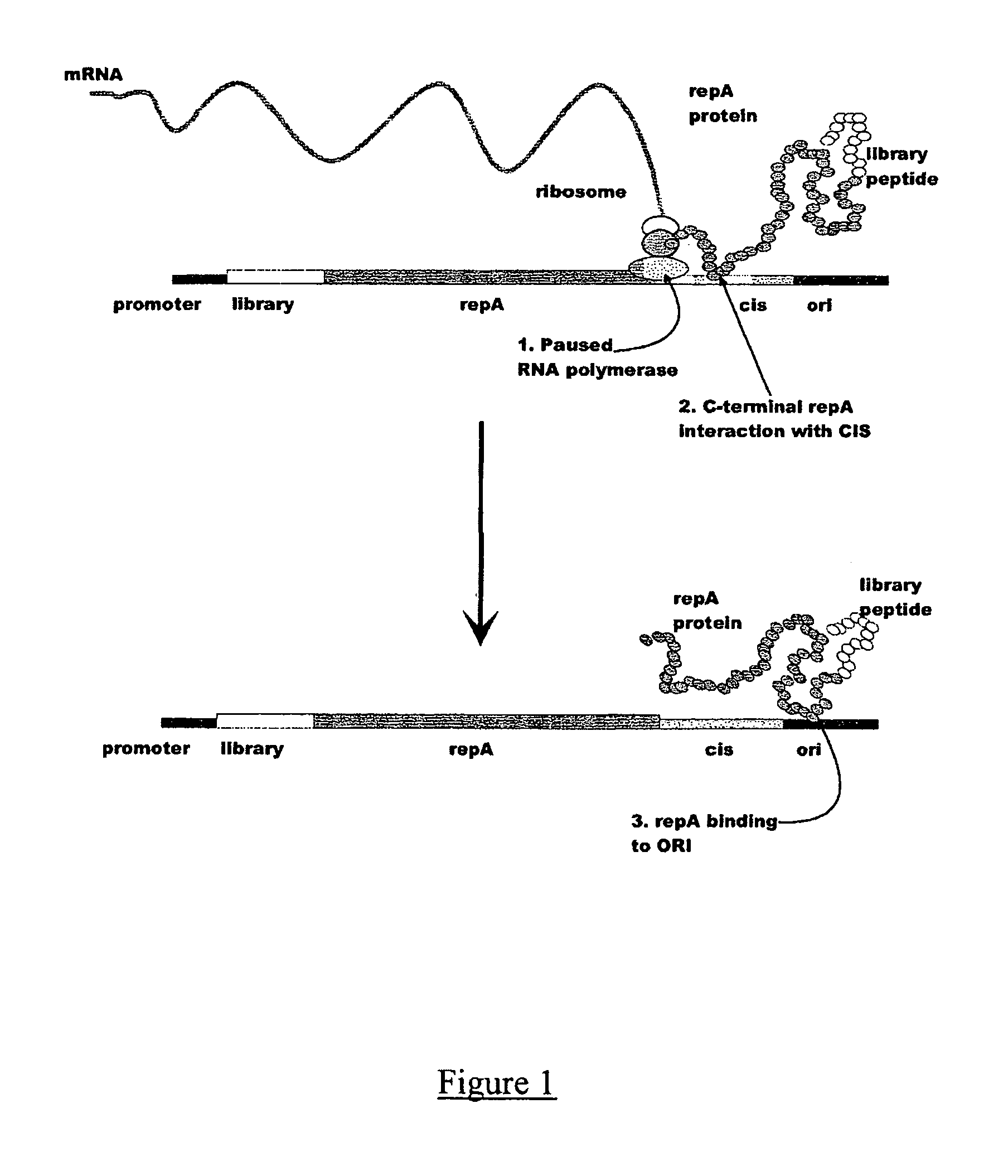
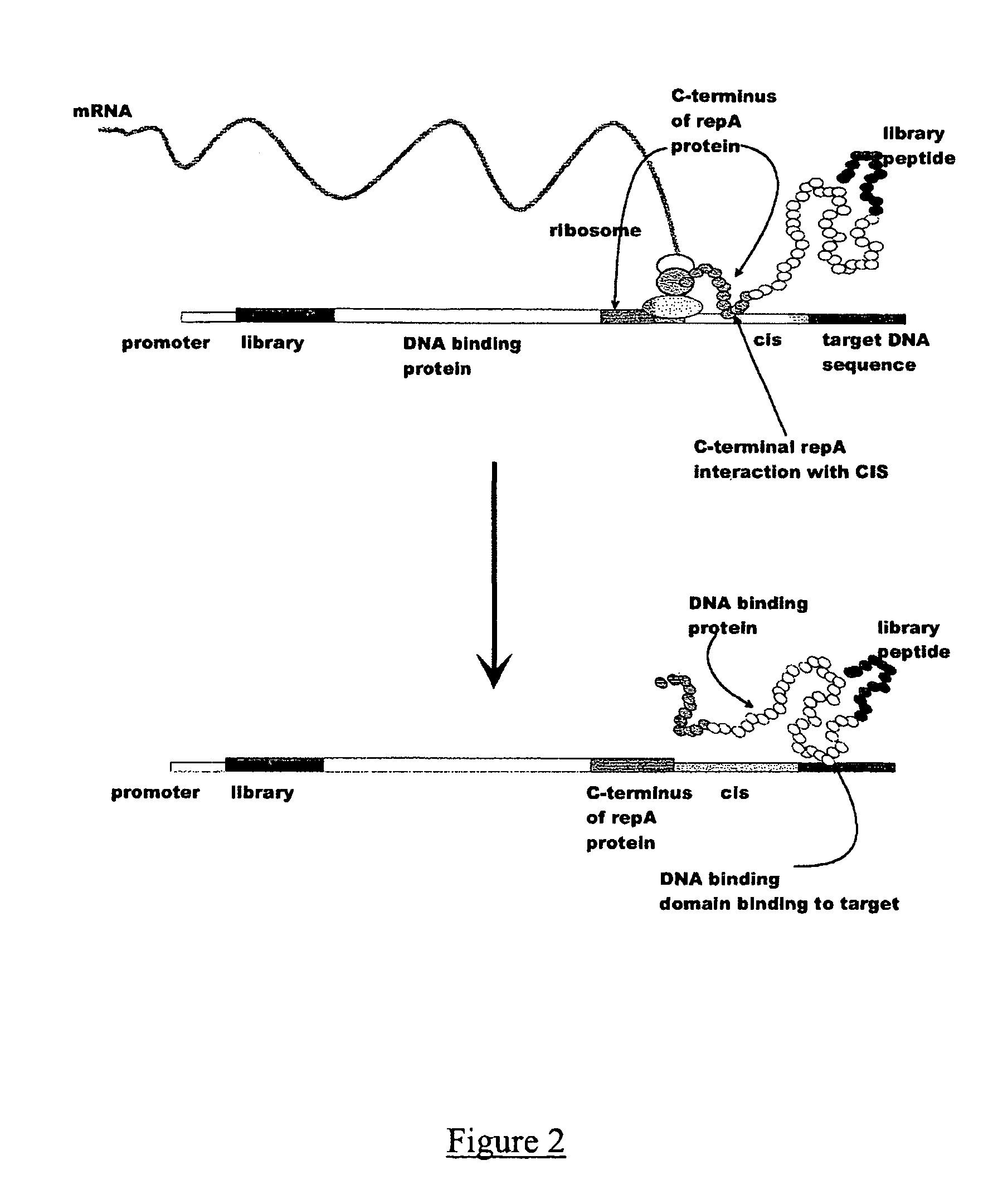
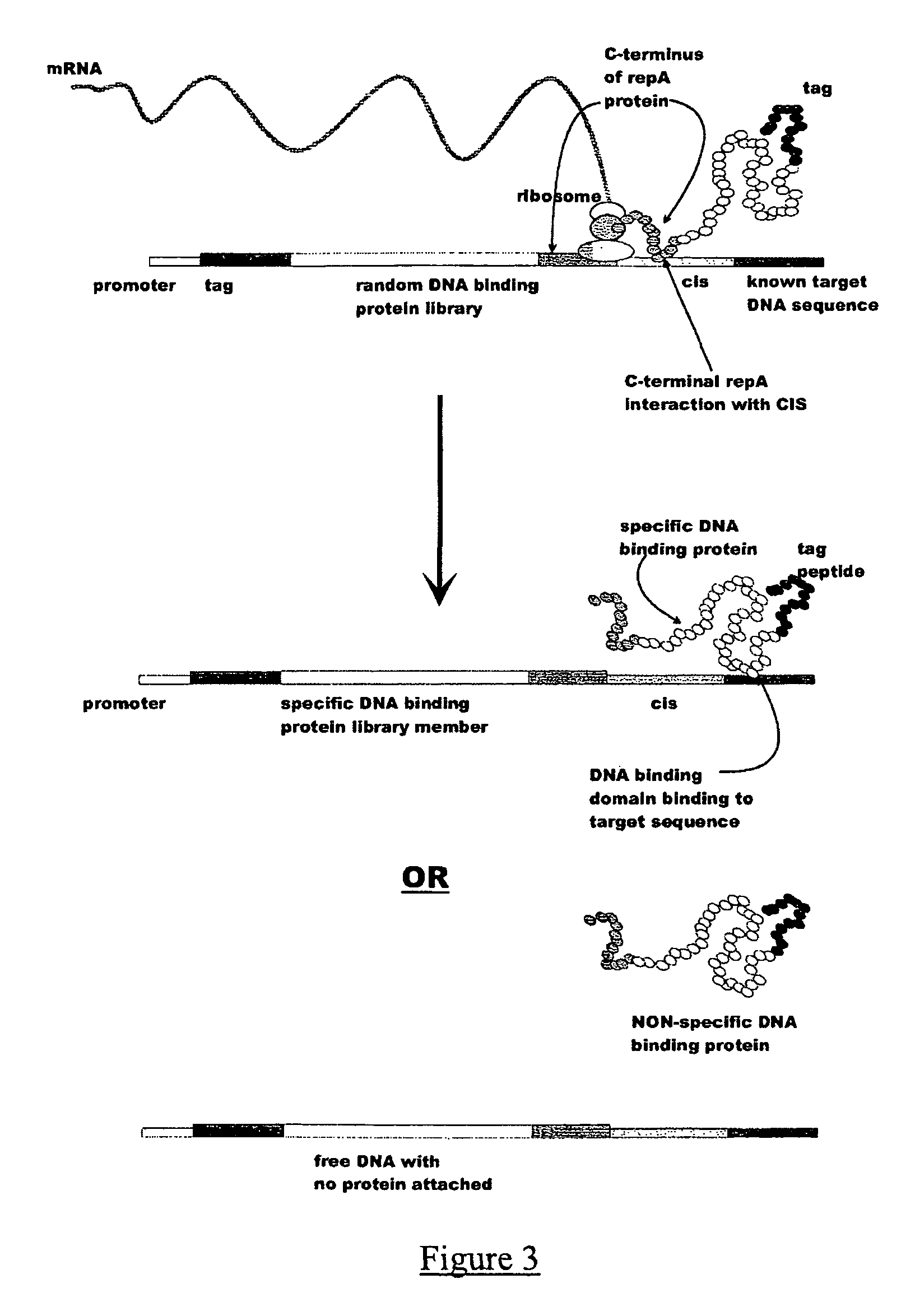
In vitro peptide expression library
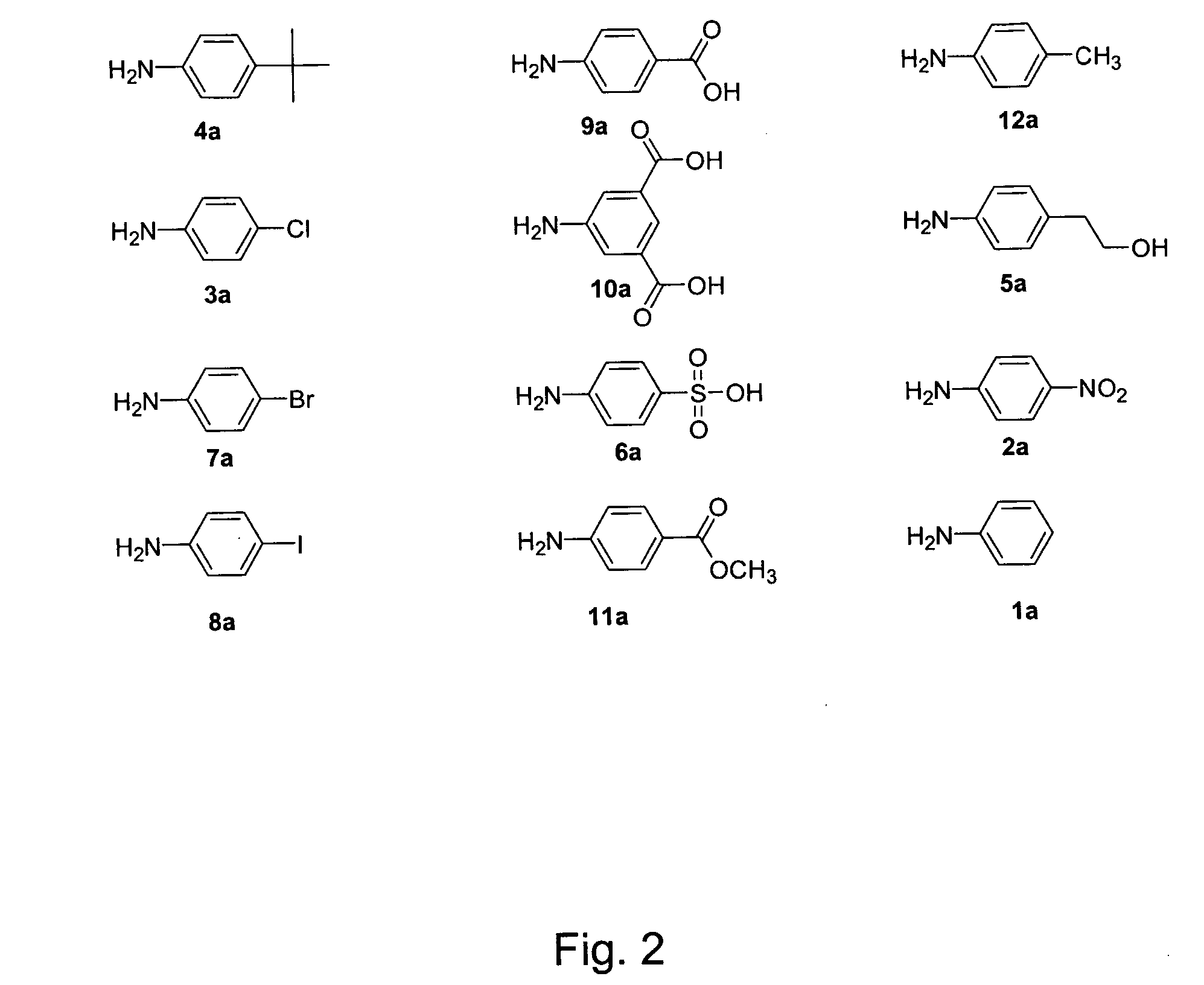
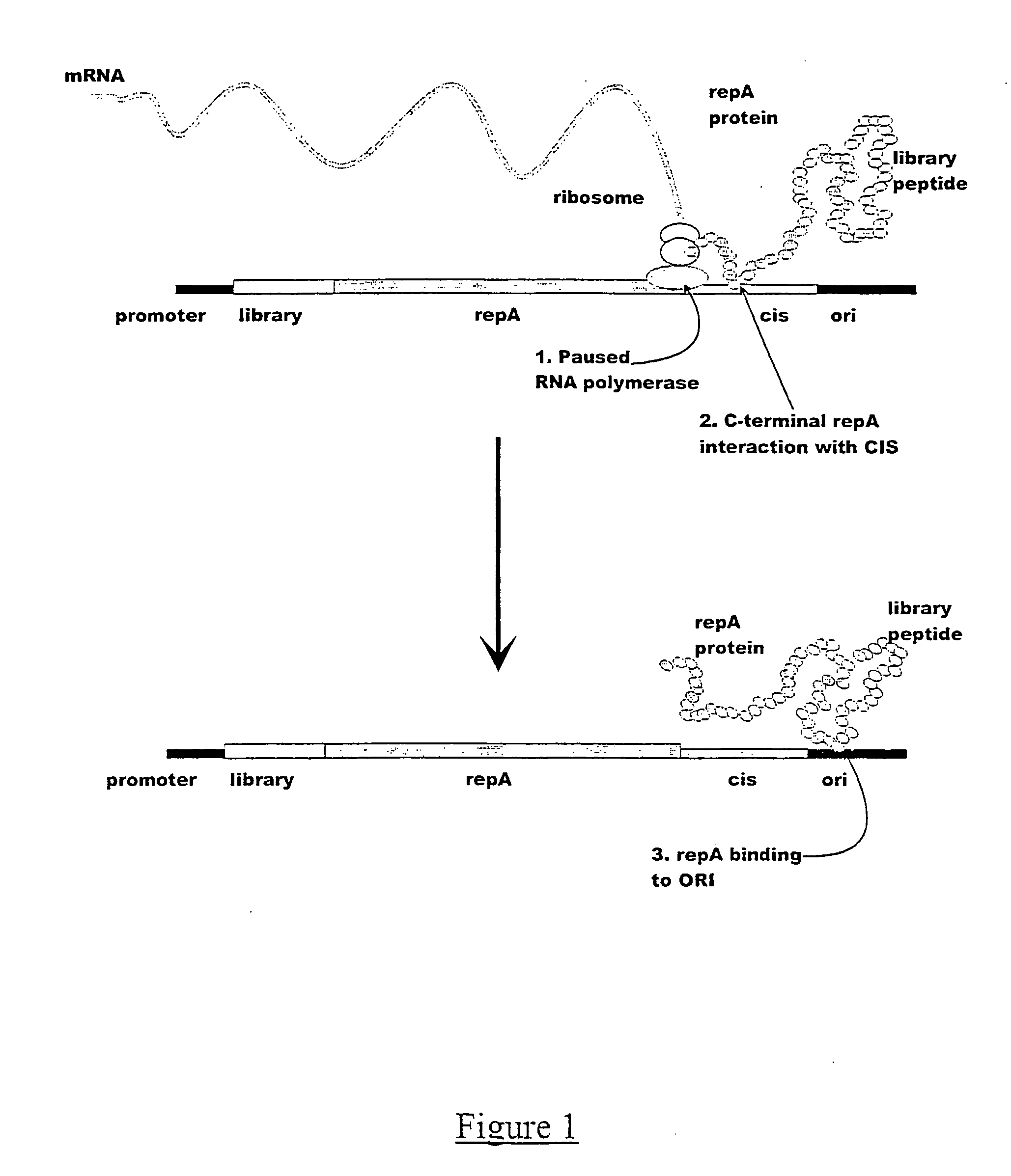
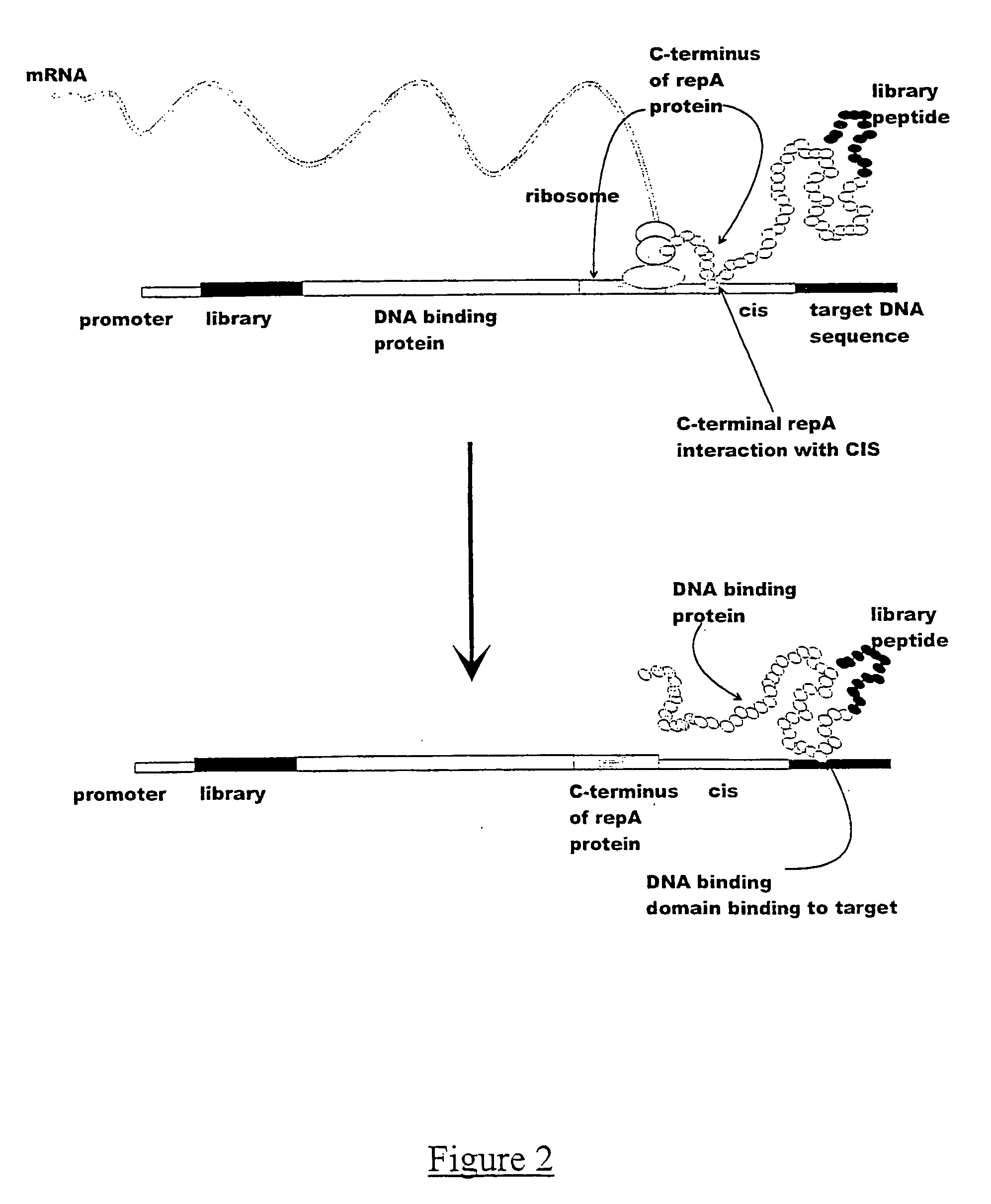
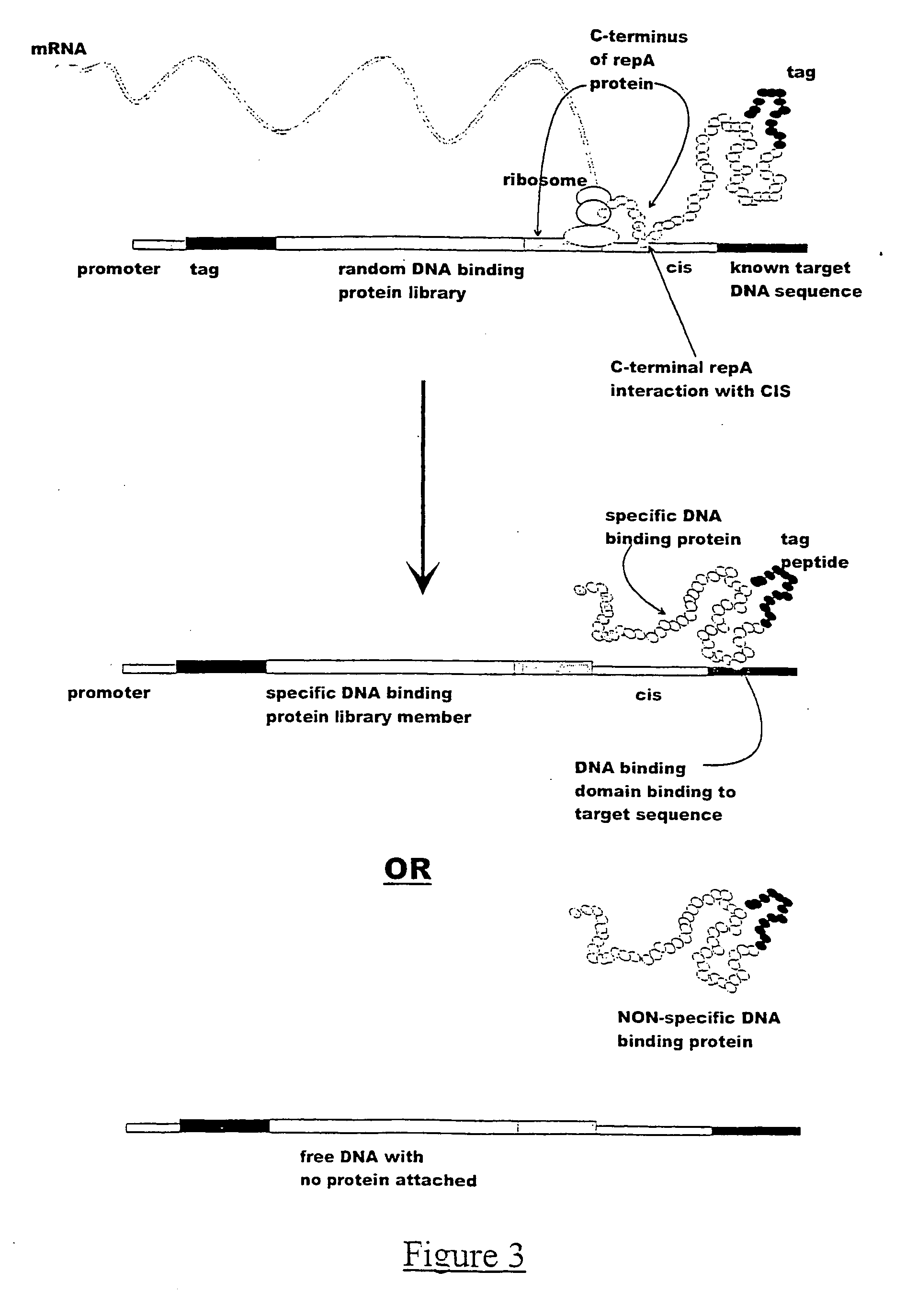
ActiveUS7842476B2Fusion with DNA-binding domainMicrobiological testing/measurementExpression LibraryNucleotide
The invention provides a method for making in vitro peptide expression libraries, and for the isolation of nucleotide sequences encoding peptides of interest, wherein the peptides or proteins are specifically associated with the DNA encoding them through non-covalent protein:DNA binding. The method describes ways of making the library itself, DNA molecules encoding the library and uses of the expression library.
Owner:ISOGENICA LTD
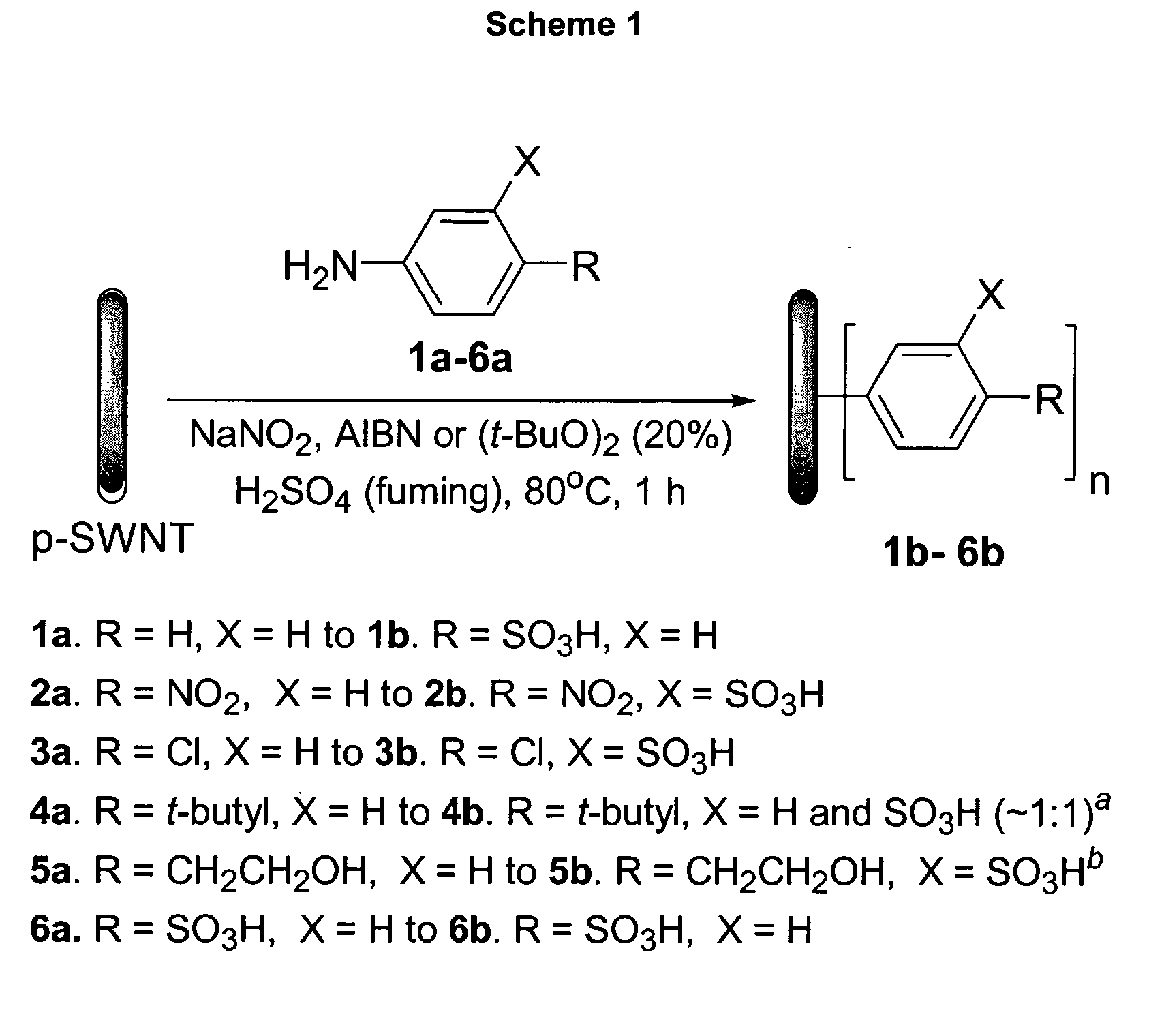
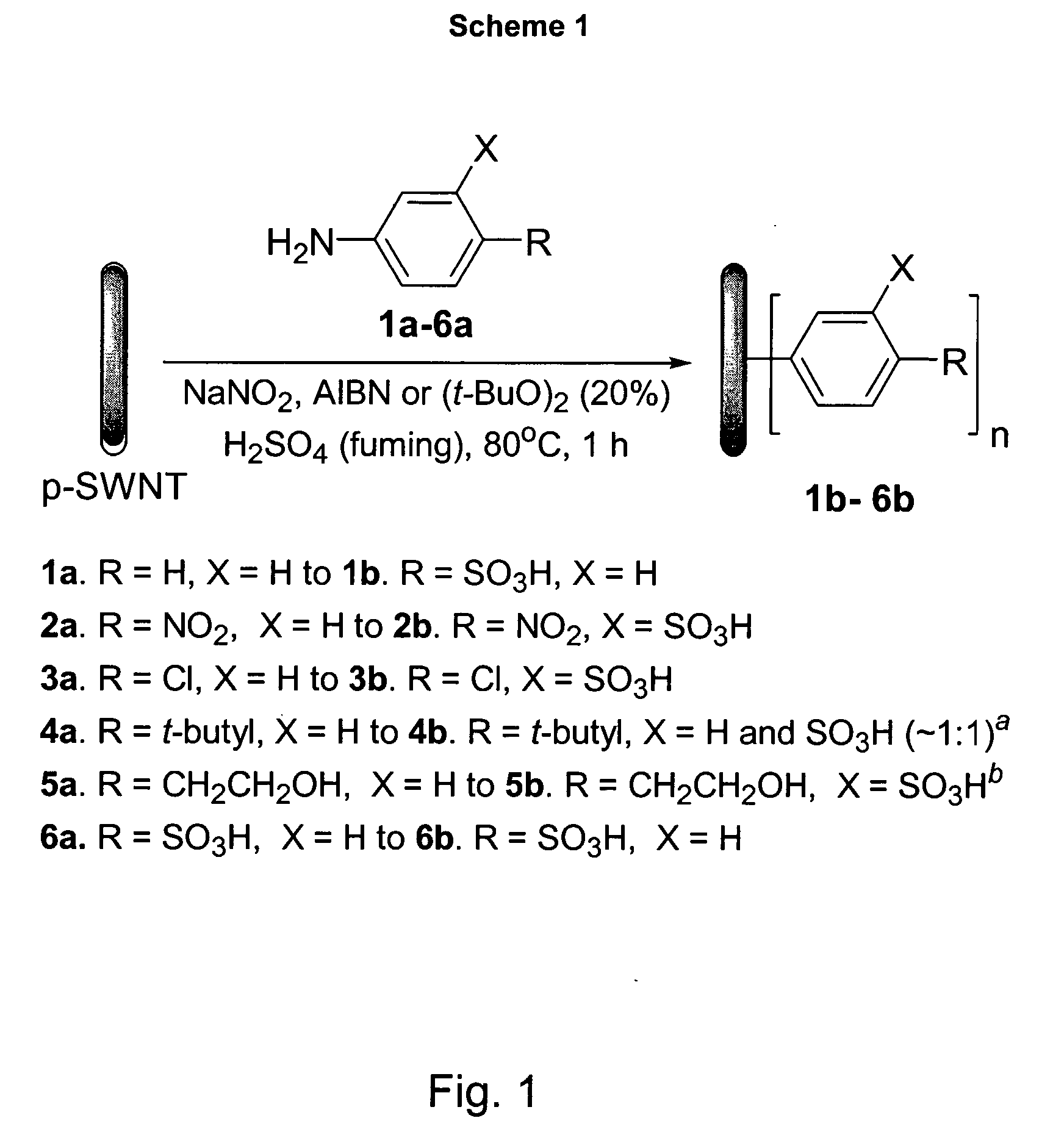
Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes in Acidic Media
InactiveUS20070280876A1Improve scalabilityEasy to functionalizePigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon nanotubeOrganic chemistry
The present invention is generally directed to methods of functionalizing carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in acidic media. By first dispersing CNTs in an acidic medium, bundled CNTs can be separated as individual CNTs, affording exposure of the CNT sidewalls, and thereby facilitating the functionalization of such CNTs, wherein functional groups are attached to the subsequently exposed sidewalls of these individualized CNTs. Once dispersed in this substantially unhundled state, the CNTs are functionalized according to one or more of a variety of functionalization processes. Typically, ultrasonication or non-covalent wrapping is not needed to afford such dispersion and subsequent functionalization. Additionally, such methods are easily scalable and can provide for sidewall-functionalized CNTs in large, industrial-scale quantities.
Owner:RICE UNIV
In vitro peptide expression library
ActiveUS20060035232A1Fusion with DNA-binding domainMicrobiological testing/measurementExpression LibraryDna encoding
The invention provides a method for making in vitro peptide expression libraries, and for the isolation of nucleotide sequences encoding peptides of interest, wherein the peptides or proteins are specifically associated with the DNA encoding them through non-covalent protein:DNA binding. The method describes ways of making the library itself, DNA molecules encoding the library and uses of the expression library.
Owner:ISOGENICA LTD
Recombinant fibrin chains, fibrin and fibrin-homologs
The invention is directed to fibrin materials for use in fibrin compositions and methods that avoid the need to use thrombin as an activating agent for fibrin monomer-based sealants. The invention provides for substantially pure fibrin chains, fibrin chain precursors, fibrin chains with other N-terminal extensions, fibrin monomer, fibrin-homolog and fibrin-analog. The invention further provides for variant fibrin .gamma.-chains. The variant gamma-chain contains one or more mutations and / or deletions in the C-terminal region following the coiled-coil forming region such that, when incorporated into fibrin-homolog, the homolog lacks the ability to self-polymerize but has the ability to form non-covalent bonds, and thereby form mixed polymers useful as sealants, with fibrinogen. The invention also provides nucleotide sequences encoding fibrin chains or fibrin chain variants and cells expressing fibrin chains, fibrin chain variants, fibrin monomer, fibrin precursor or fibrinogen-analog. The invention further provides a method of forming fibrin-related proteins in vitro from their component fibrin chains. The invention additionally provides a method for forming a fibrin sealant by a reacting a first fibrin-related protein that is incapable of self-polymerizing with a second fibrin-related protein that is incapable of self-polymerizing. Fibrin chains produced by methods of the present invention may be used as sources of substantially pure starting material for the production of important fibrin-derived factors that regulate angiogenesis, platelet aggregation, and other physiological processes.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
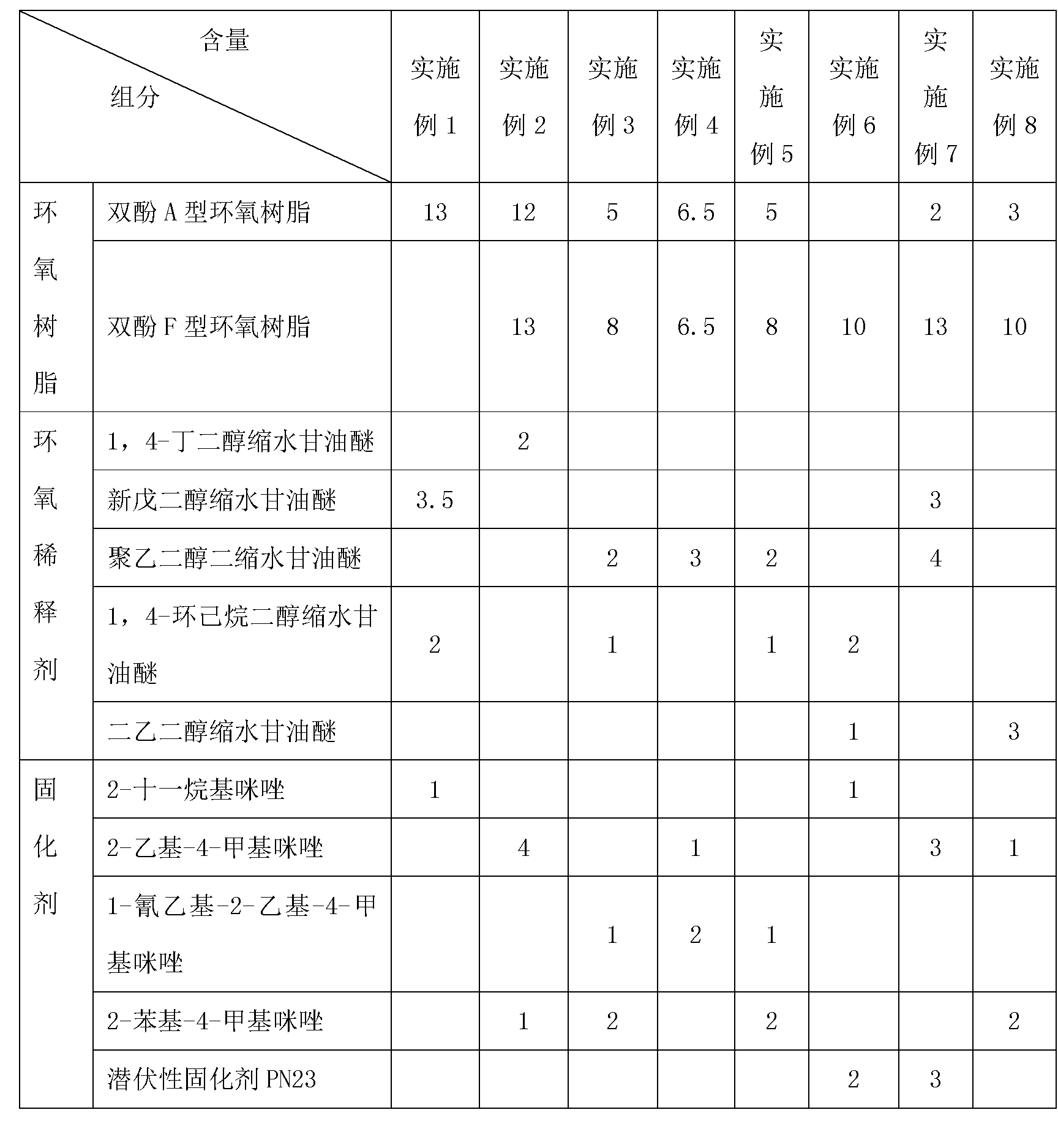
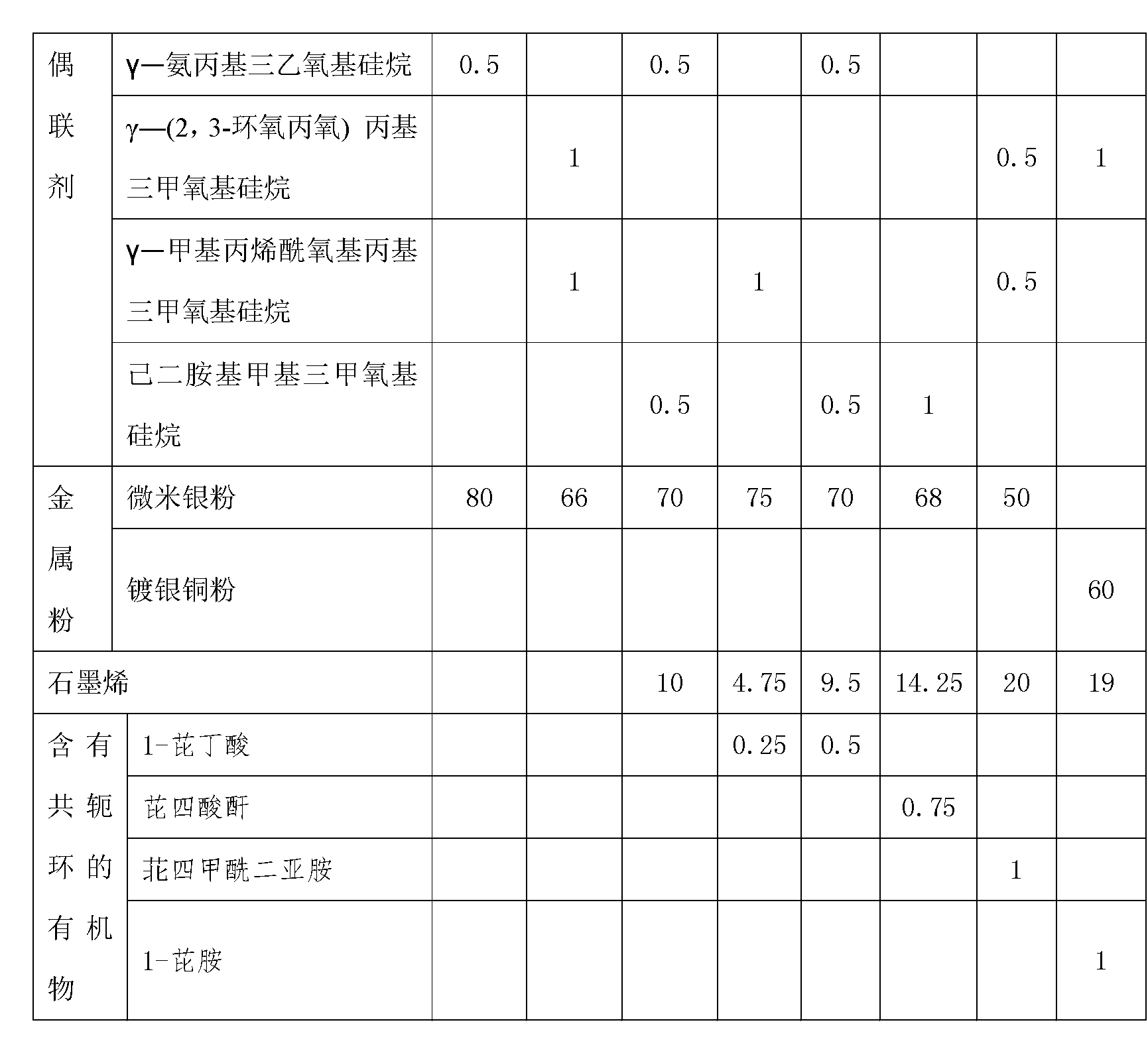
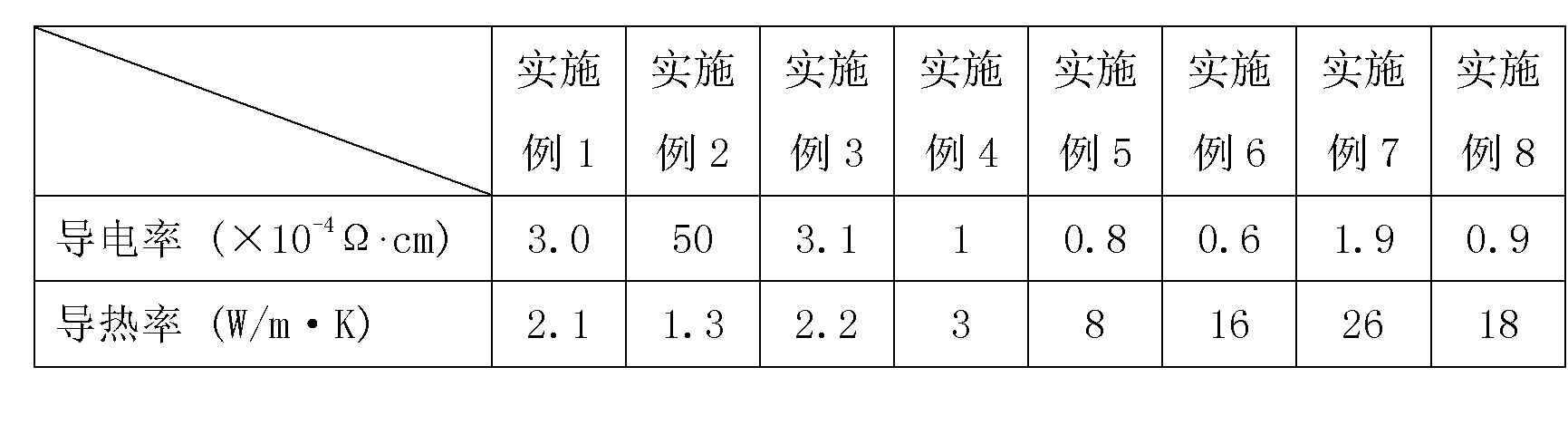
Method for preparing high-heat-conductivity conductive adhesive containing graphene
ActiveCN103194165AGood dispersionScatter to reachEpoxy resin adhesivesPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsEpoxyAdhesive
The invention provides a method for preparing high-heat-conductivity conductive adhesive containing graphene. The method comprises the steps of (1) functionalizing surface of graphene, namely adding graphene to acetone solution of an organic matter containing a conjugate ring, and strongly ultrasonically shaking for 6-48 hours at 40-100 DEG C to form non-covalent modified graphene; (2) mixing epoxy resin with an epoxy diluent for 3-30 minutes at room temperature to obtain a mixture of epoxy resin and the epoxy diluent, and sequentially adding metal powder and a coupling agent to the mixture; (3) adding the non-covalent modified graphene prepared in the step (1) to the mixture in the step (2); and (4) adding a curing agent to the mixture in the step (3) to prepare the even conductive adhesive. The method has the advantages that dispersing and enhancing interface joint in an epoxy system are facilitated by functionalizing the surface of graphene by a non-covalent bond; and then graphene is mixed with metal powder to obtain the high-heat-conductivity conductive adhesive. The high-heat-conductivity conductive adhesive has the application prospect in a high-power apparatus.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Preparing method of nanometer particle carbon nanotube compound catalyst
InactiveCN101224434AEasy to operateGood catalyticOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsModified carbonElectrostatic interaction
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nano particle carbon nanotube compound catalyst. The carbon nanotube with electric charges on surface is obtained from the materials which can generate non-covalent action with the carbon nanotube. Then nano particle with opposite electric charges on surface to that of the non-covalent modified carbon nanotube is added and completely mixed, and excess nano particle is removed to finally obtain the nano particle carbon nanotube catalyst compound. A plurality of nano particle carbon nanotube catalyst compounds can be prepared by the invention, all of which represent very good catalytic activities. The invention adopts the method of non-covalent modified carbon nanotube to obtain carbon nanotube with perfect surface. Meanwhile, the invention provides the nano particle, in particular, the morphology controllable nano particle on the load of carbon nanotube with an effective way by utilizing the electrostatic interaction of carbon nanotube and namo particle, thus extending the applications of morphology controllable nano particle in catalytic field.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Transcutaneous immunization without heterologous adjuvant
InactiveUS20060002949A1Increase skin hydrationIncrease local concentrationSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsDendritic cellSpecific immunity
Transcutaneous immunization can deliver antigen to the immune system through the stratum corneum without physical or chemical penetration to the dermis layer of the skin. This delivery system induces an antigen-specific immune response without the use of a heterologous adjuvant. Although perforation of intact skin is not required, superficial penetration or micropenetration of the skin can act as an enhancer; similarly, hydration may enhance the immune response. This system can induce antigen-specific immune effectors after epicutaneous application of a formulation containing one or more antigens. The formulation may initiate processes such as antigen uptake, processing, and presentation; Langerhans cell activation, migration from the skin to other immune organs, and differentiation to mature dendritic cells; contacting antigen with lymphocytes bearing cognate antigen receptors on the cell surface and their stimulation; and combinations thereof. Systemic and / or regional immunity may be induced. Immune responses that provide prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatments are preferred. Antigenic activities in the formulation may be found in the same molecule, two or more different molecules dissociated from each other, or multiple molecules in a complex formed by covalent or non-covalent bonds. For antigens which are proteinaceous, they may be provided in the formulation as a polynucleotide for transcutaneous genetic immunization. Besides simple application of a dry or liquid formulation to the skin, patches and other medical devices may be used to deliver antigen for immunization.
Owner:ARMY GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE OFFICE OF THE COMMAND JUDGE ADVOCATE
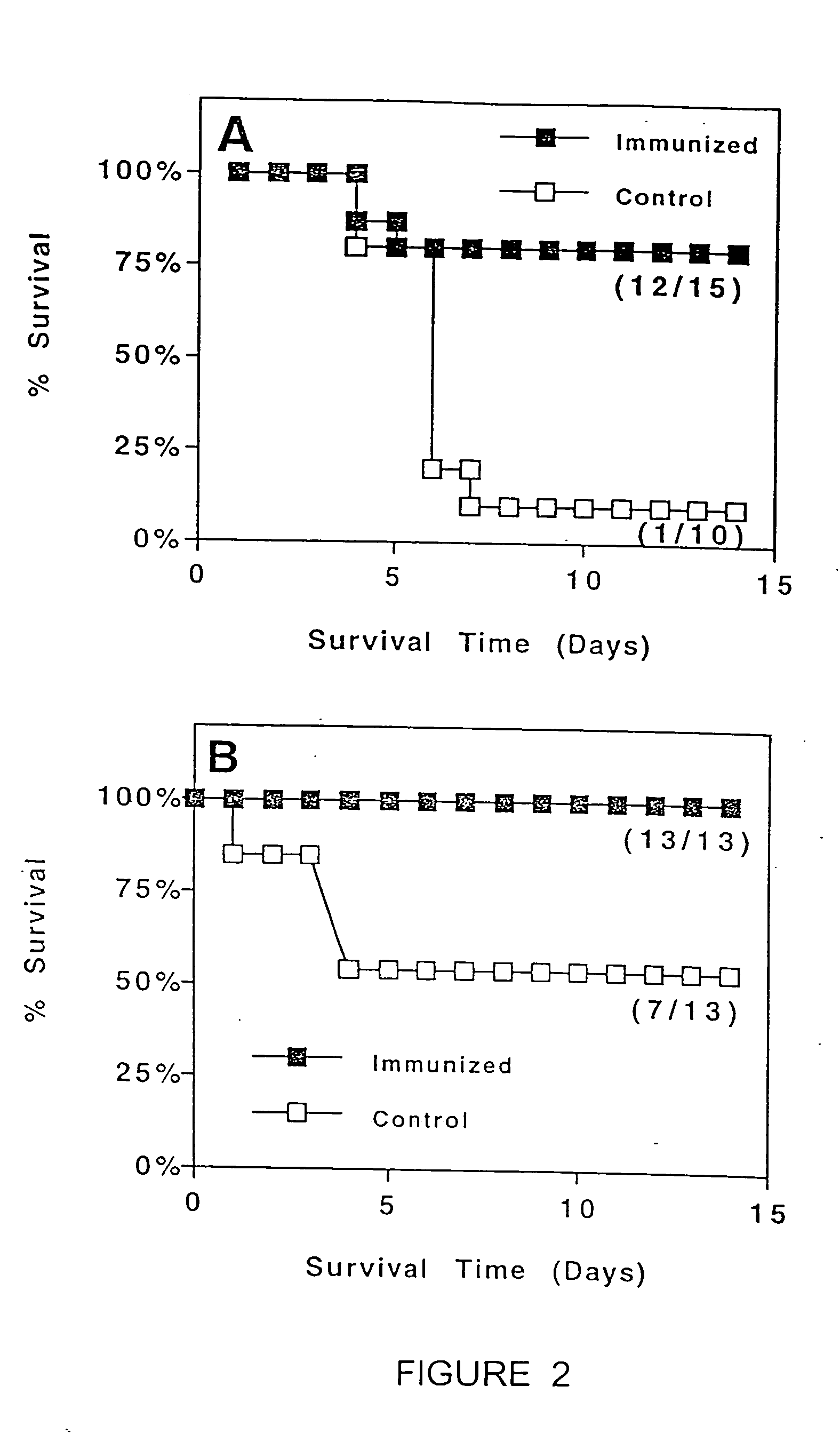
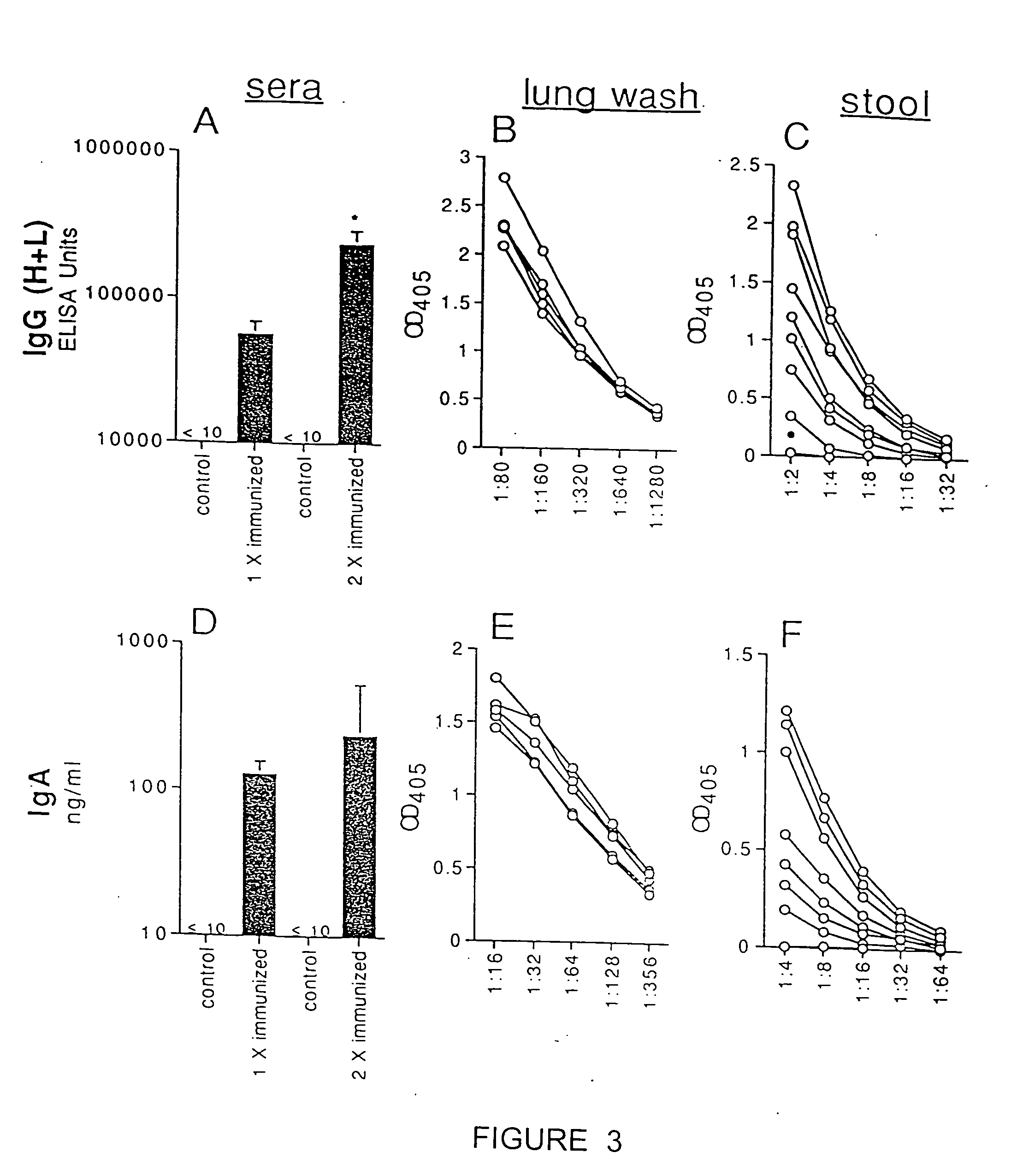
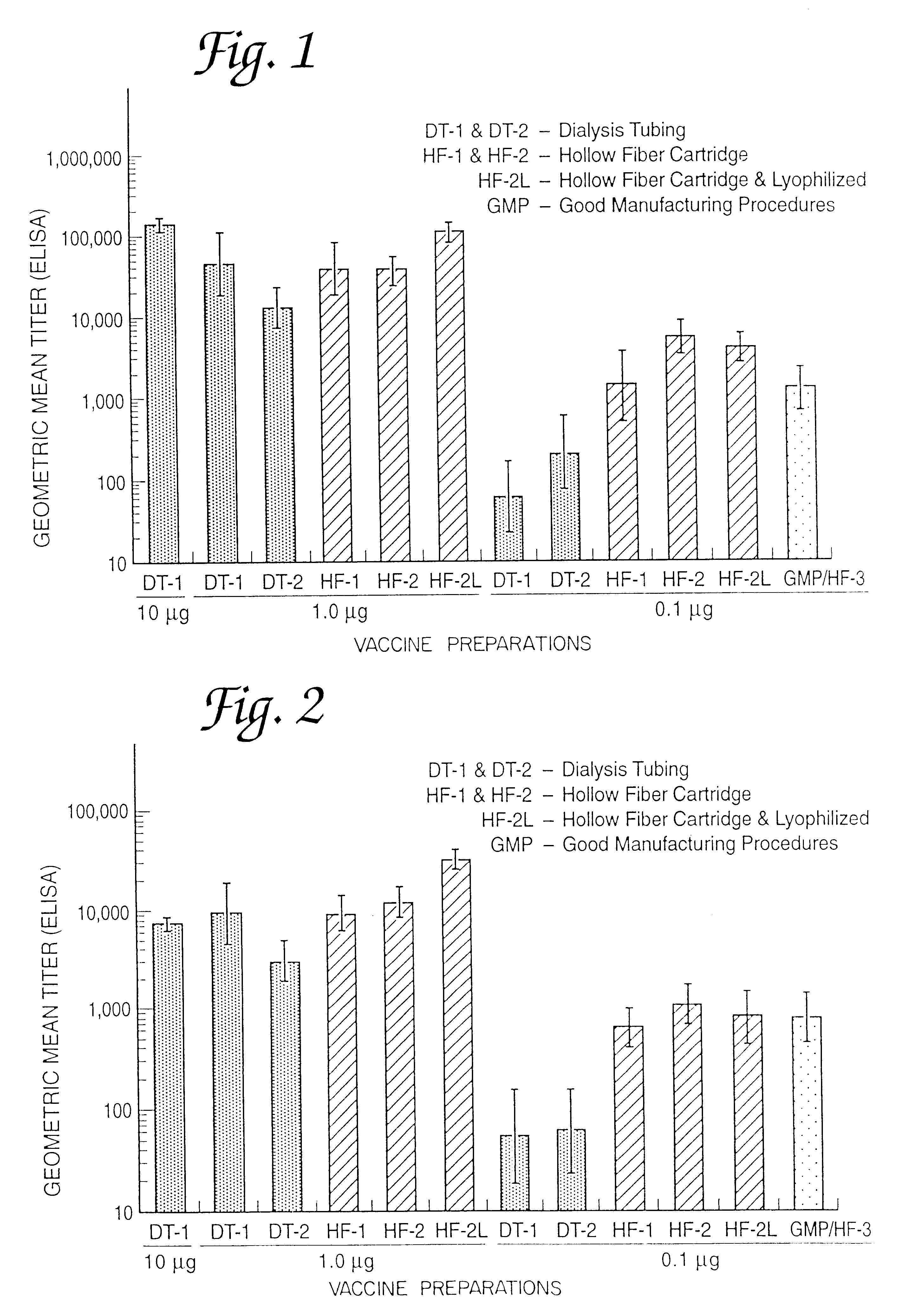
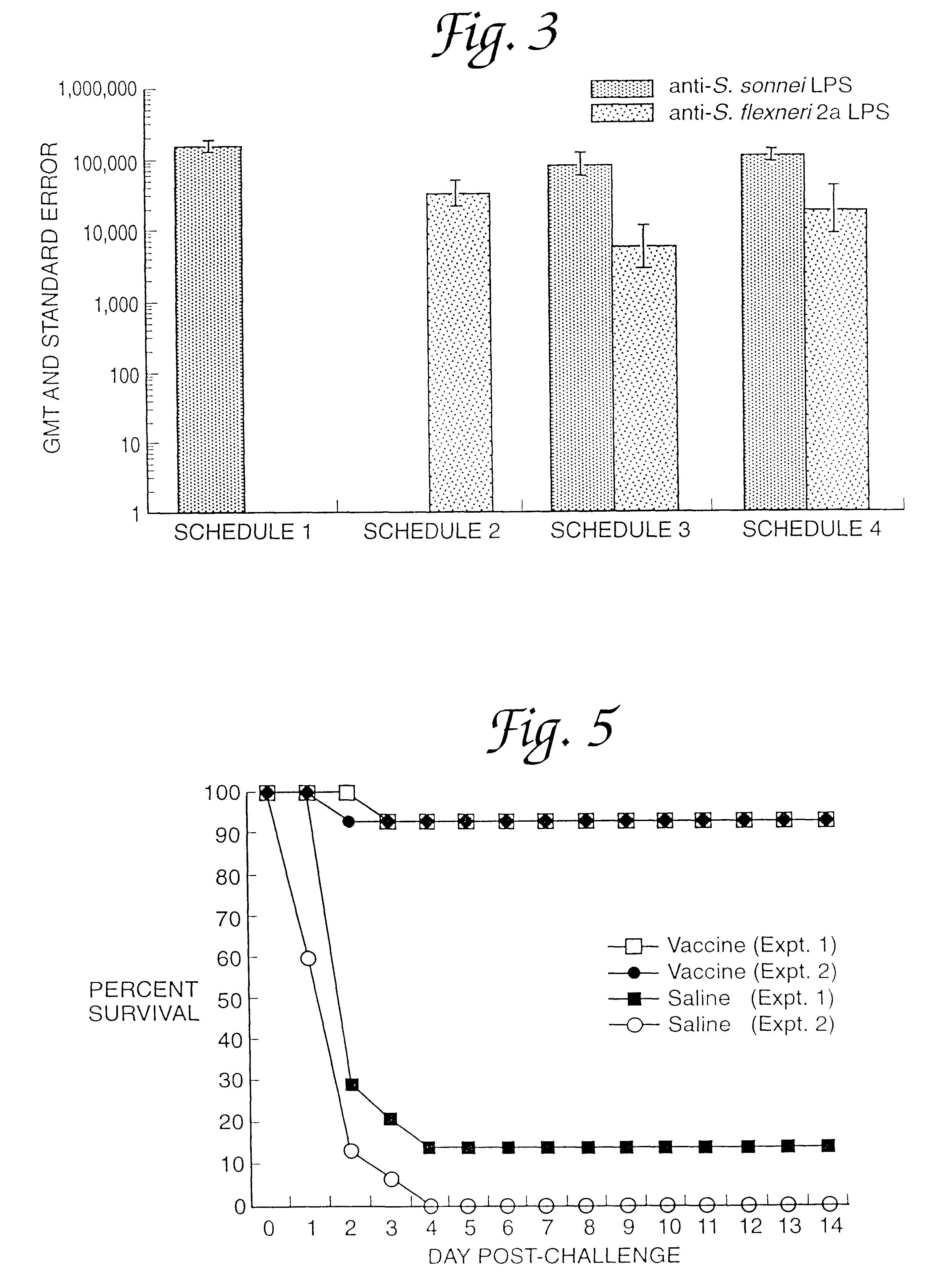
Methods for the production of non-covalently complexed and multivalent proteosome sub-unit vaccines
InactiveUS6476201B1Shorten the timeIncrease temperatureAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsContinuous monitoringContamination
A continuous method for preparing proteosome-amphiphilic determinant vaccines for parenteral or mucosal administration using diafiltration or ultrafiltration technology. The amphiphilic determinants include lipopolysaccharides from gram negative bacteria, e.g. S. flexneri, P. shigelloides and S. sonnei. Proteosomes are obtained from group B type 2b meningococci. The active proteosome-amphiphilic determinant complexes (non-covalent complexes) of the vaccine are formed using diafiltration or ultrafiltration to remove the detergent under non-static conditions. The use of diafiltration or ultrafiltration decreases processing time and the opportunity for contamination and further permits the use of ambient temperature and efficient scale-up. In addition, the process permits the reliable and continuous monitoring of the dializate which enhances the efficiency of the entire process. The time of dialysis for the production of a lot of vaccine is reduced from 7-10 days to less than 72 hours and usually less than 48 or 24 hours. The use of the process optimizes the presence of each antigenic component in the preparation of multivalent vaccines.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY +1
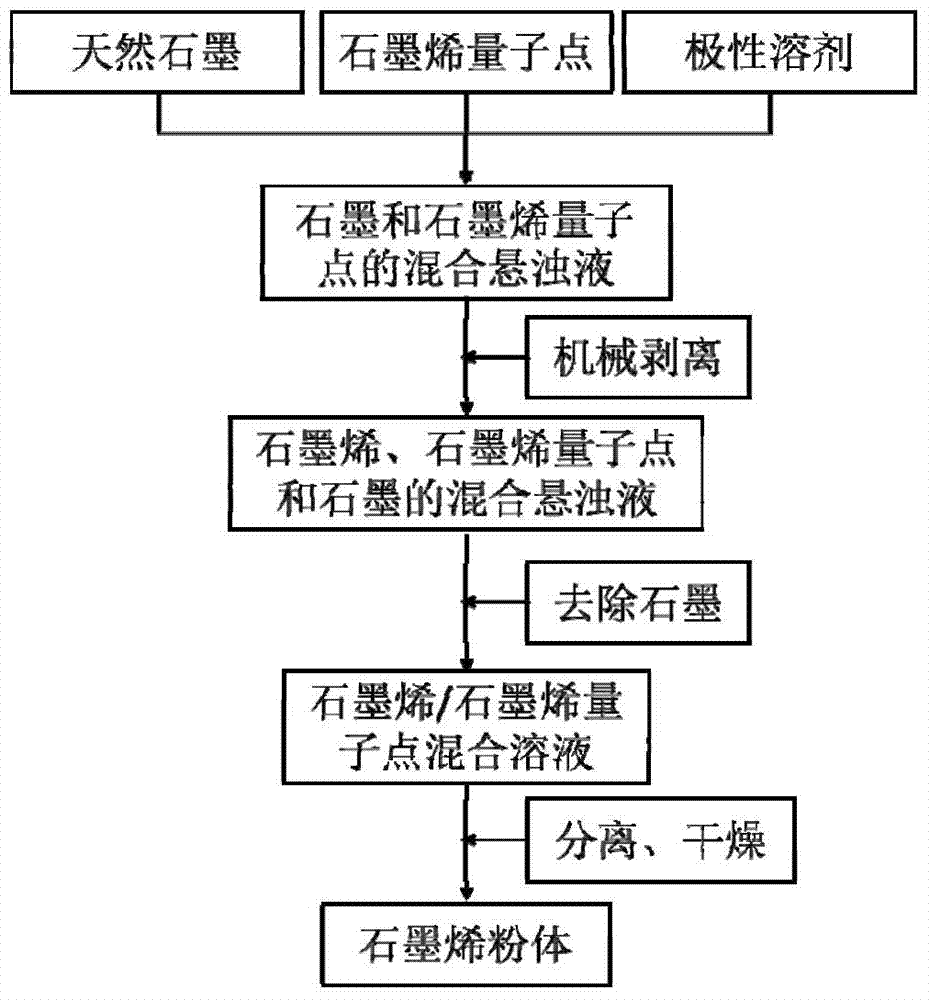
Preparation method of graphene
The invention discloses a preparation method of graphene, which is characterized in that natural graphite used as a raw material is subjected to mechanical stripping under the auxiliary action of graphene quantum dots by using a polar solvent as a dispersion medium to prepare the high-quality graphene. The stripping of the natural graphite and dispersion of the graphene nanosheets in the polar solvent are promoted by utilizing the favorable dispersivity of the graphene quantum dots in the polar solvent and the strong non-covalent bond combination between the graphene quantum dots and graphene / graphene laminae, thereby obtaining the high-quality graphene. According to the invention, the graphene powder is directly obtained from the natural graphite under the condition of not introducing any surfactant, inorganic salt, organic salt or any other impurity. Compared with the existing methods, the method is simple in technique, and can be perform in multiple polar solvents; the maximum yield of the obtained graphene can reach 50%, and the quality is good; the graphene quantum dots used for auxiliary stripping can be recycled; and thus, the method is very suitable for mass preparation of graphene.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
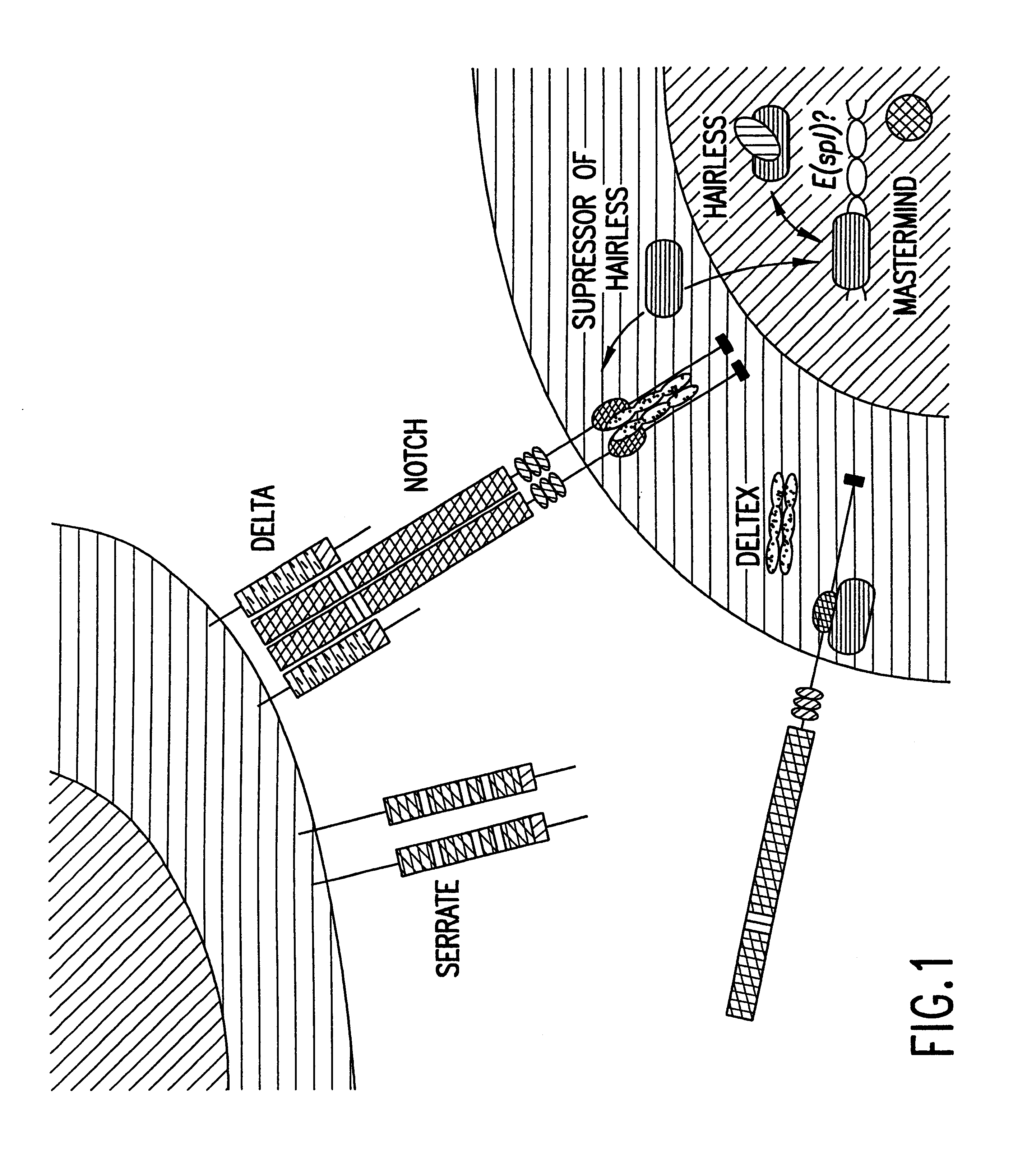
Activated forms of notch and methods based thereon
InactiveUS6692919B1Compound screeningCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological activationNotch ligand
The present invention is directed to methods for detecting or measuring Notch activation by observing or measuring the appearance of Notch on the cell surface or by observing or measuring Notch cleavage products that are indicative of Notch activation. The present invention is also directed to methods for detecting a molecule that modulates Notch activation by observing or measuring a change in the amount of Notch expressed on the cell surface or a change in the amount or pattern of Notch cleavage products. The present invention is also directed to a substantially purified activated heterodimeric form of Notch and components thereof and pharmaceutical compositions and kits thereof. The present invention is based, at least in part, on the discovery that Notch in its active form, i.e., the form that mediates signal transduction and that binds Notch ligands such as Delta, is a heterodimer of an about 180 kDa subunit (N<EC>) and an about 110 kDa subunit (N<TM>), which are tethered together through a reducing agent-sensitive linkage, in particular, a non-covalent, metal ion-dependent linkage.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Liposome compositions
The present invention provides a non-covalent coupling method for the preparation of sterically stabilized lipsomes which may be used for targeted drug delivery, e.g., pegylated liposomes. The method simplifies the attachment of targeting vectors to sterically stabilized liposomes. The present invention also provides a liposome composition comprising a compound of the formulaand a compound of the formula Z-Y, wherein Z is any compound capable of binding to a cellular receptor, and X and Y are compounds which can interact with each other non-convalently, and wherein the substituents n, F1 and F2 are as provided in the specification.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Cross-linked high amylose starch resistant to amylase as a matrix for the slow release of biologically active compounds
The present invention is concerned with a solid slow release oral pharmaceutical dosage unit resistant to amylase which comprises a solid dosage unit made up of an admixture of a therapeutic dosage of an orally effective pharmaceutical product, an optional polysaccharide or polyol, and cross-linked high amylose starch, wherein the cross-linking of the high amylose starch has been carried out with a covalent or non-covalent cross-linking agent with from about 0.1 g to about 30 g of cross-linking agent per 100 g of high amylose starch.
Owner:LABOPHARM INC
Sensors employing single-walled carbon nanotubes
ActiveUS20070292896A1Facilitate selective reactionFacilitate ligand-receptor binding or antigen-antibody (Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteBiopolymer
Sensing compositions, sensing element, sensing systems and sensing devices for the detection and / or quantitation of one or more analytes, Compositions comprising carbon nanotubes in which the carbon nanotubes retain their ability to luminesce and in which that luminescence is rendered selectively sensitive to the presence of an analyte. Compositions comprising individually dispersed carbon nanotubes, which are electronically isolated from other carbon nanotubes, yet which are associated with chemical selective species, such as polymers, particularly biological polymers, for example proteins, which can interact selectively with, or more specifically selectivity bind to, an analyte of interest. Chemically selective species bind, preferably non-covalently, to the carbon nanotube and function to provide for analyte selectivity. Chemically selective species include polymers to which one or more chemically selective groups are covalently attached. Chemically selective polymers include, for example, proteins and polysaccharides.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Preparation method of rare earth coordination crosslinking rubber
InactiveCN101781413AImprove mechanical propertiesSolve technical problems with poor comprehensive mechanical propertiesSizingNon covalent
The invention relates to a rare earth coordination crosslinking rubber and a preparation method thereof. The invention is characterized by (1) uniformly mixing 1-100 parts by weight of thermoplastic resin with polar functional groups, 100 parts by weight of rubber resin and 1-30 parts by weight of compatilizer for 5-25 min at the temperature of 30-260 DEG C in a mixing device of an open mill, an internal mixer or an extruder into a blending modified sizing material; and (2) adding a rare earth coordination crosslinking agent and a vulcanizing agent into the blending modified sizing material, uniformly mixing, heating to 150-190 DEG C, quickly mixing for 210min, stopping mixing and standing still for 0.5-3min; and then rapidly heating up to 200-240 DEG C, continuing to mix for 9min-12min, stopping mixing and then obtaining the rare earth coordination crosslinking rubber after standing still for 5-7min. With the method, the thermoplastic coordination crosslinking rubber with the comprehensive mechanical property equivalent to or superior to that of corresponding thermoset rubber can be prepared via optimized formula design, and the technical problem that the comprehensive mechanical properties of the non-covalent cross-linking rubbers are poorer is solved.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Hydrogel wound dressing and biomaterials formed in situ and their uses
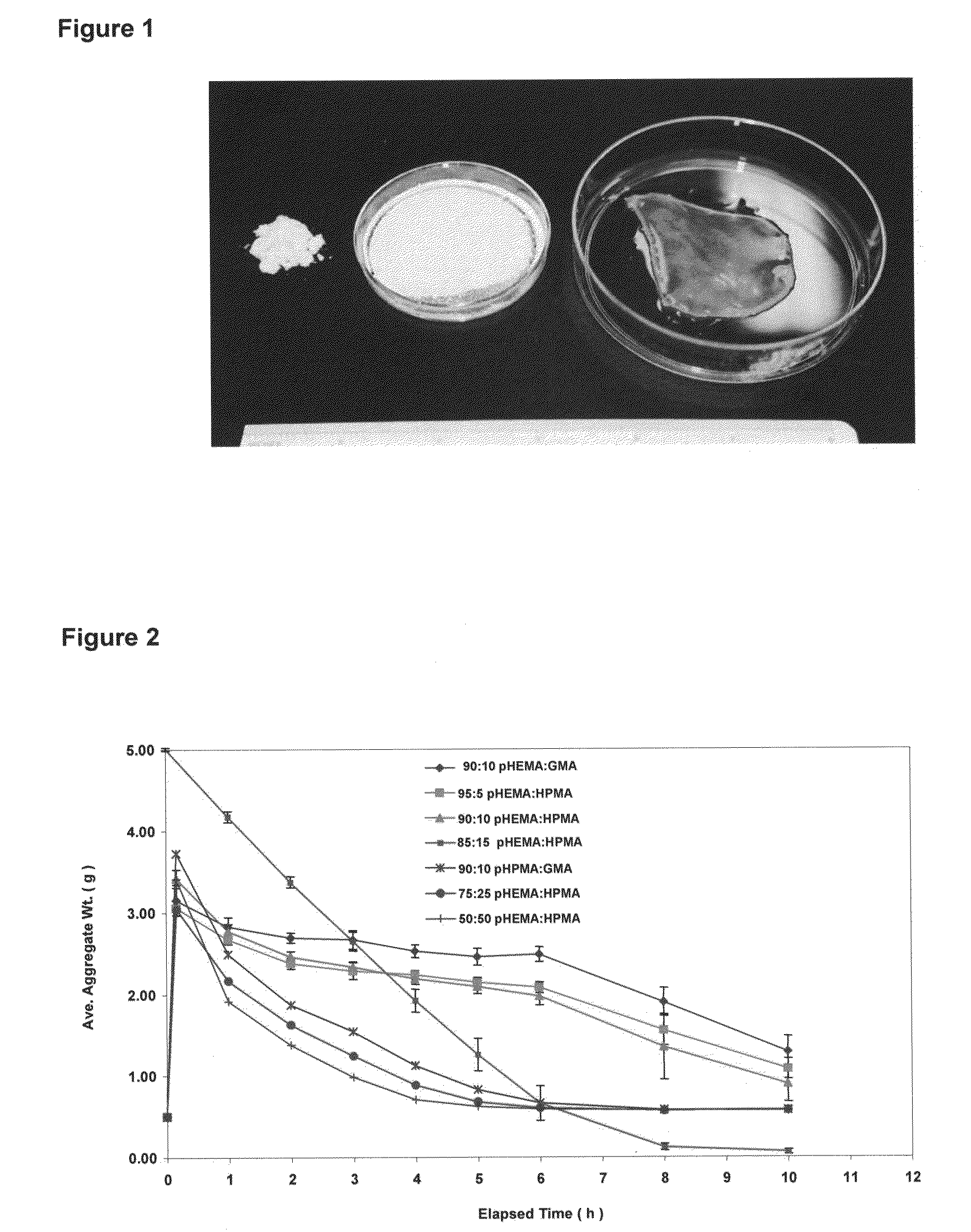
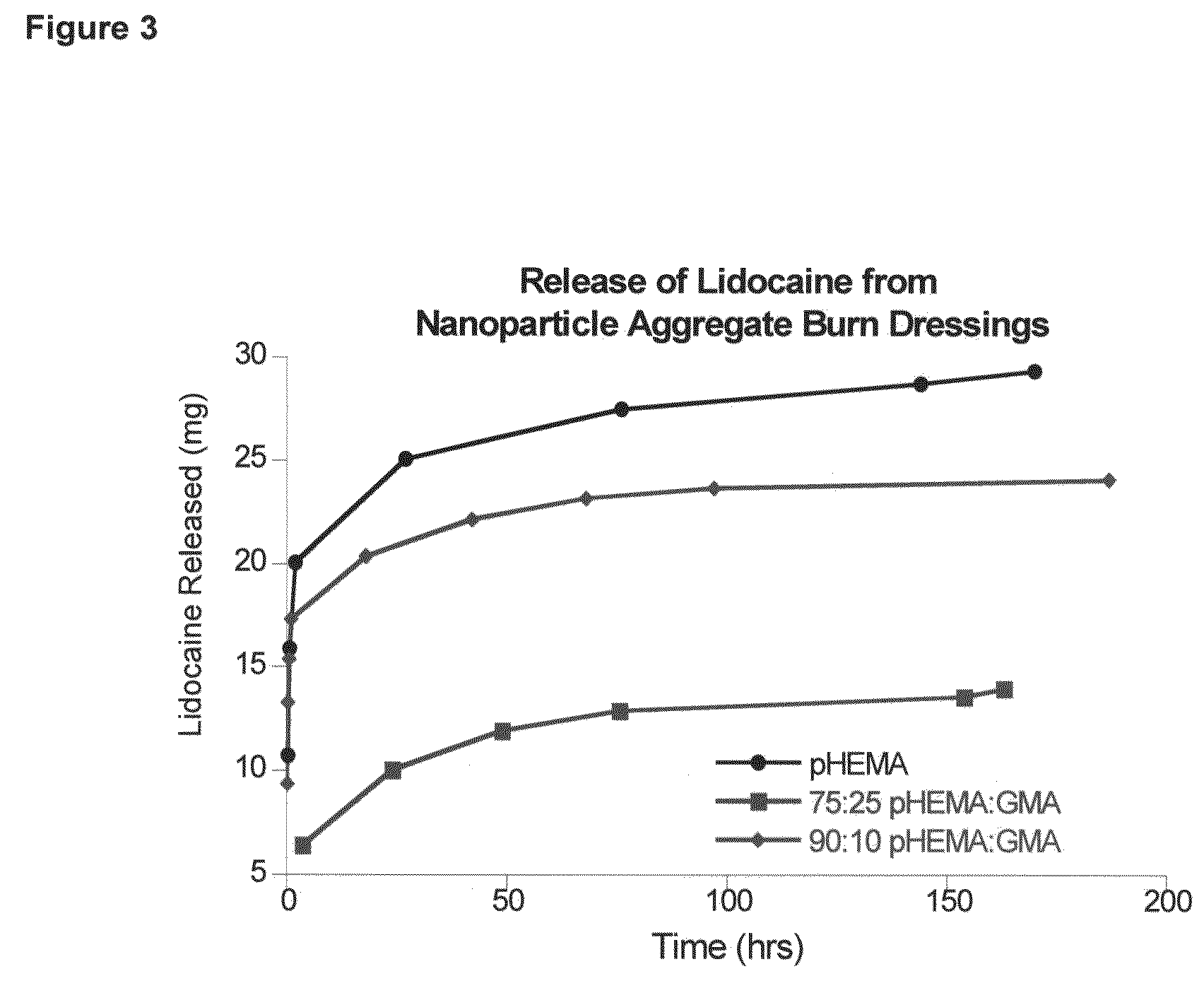
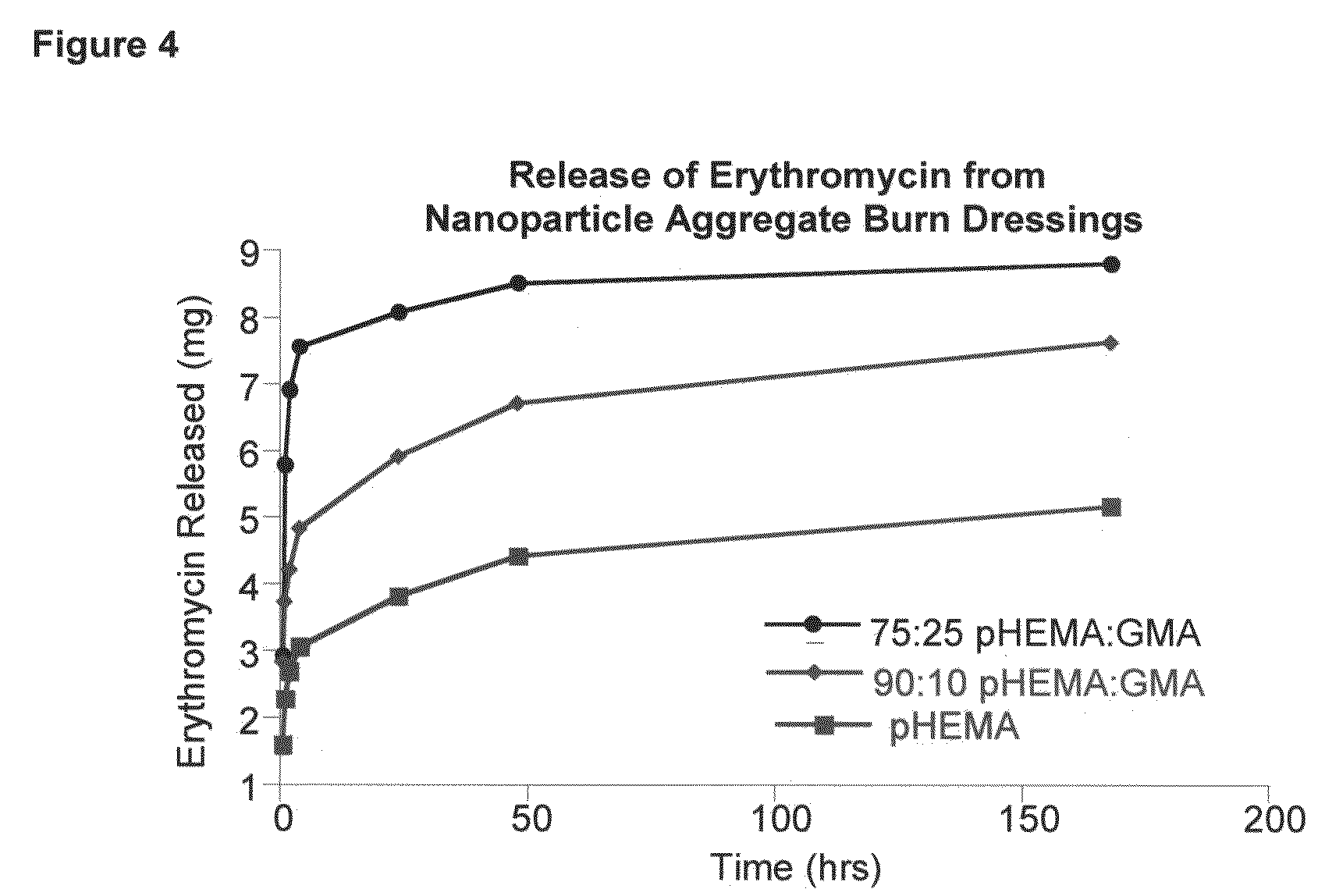
The present invention relates to a method of forming shape-retentive and shape-conforming aggregate wound dressings and biomaterials composed of gel nanoparticles and wound or bodily fluid in which the aggregates are held together by non-covalent bond physical forces such as, without limitation, hydrophobic-hydrophilic interactions and hydrogen bonds. The method comprises introducing a dry powder of gel nanoparticles to a wound site in which the nanoparticles absorb some of the blood or wound exudate and coalesce in situ into the claimed shape-retentive aggregate dressing. The method also comprises introducing the dry nanoparticle powder in or on a wet bodily tissue in vivo to form the claimed shape-retentive biomaterial. In addition, the method also comprises incorporating biomedical agents to produce medicated aggregate dressings or biomaterials for a variety of medical applications. This invention also relates to uses of the method of formation of the shape-retentive aggregates of gel nanoparticles.
Owner:ULURU INC
Common carrier material for targeting anticancer drug and gene and preparation and application
InactiveCN102949727AGood biocompatibilityEnhanced Osmotic Retention EffectGenetic material ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsTumor targetingResponse control
The invention relates to a common carrier material based on graphene oxide for a targeting anticancer drug and a gene and application and application. Folic acid, lactobionic acid and other tumor cell targeting or liver targeting molecules and part of amino groups of soluble chitosan are connected by amide bonds to prepare a conjugate, the conjugate is then connected with graphene oxide, quaternization is performed by using an epoxy compound with a quaternary ammonium group, and gene molecules are loaded by the quaternizationquaternized part of the chitosan through electrostatic attraction; and then the anticancer drug is loaded by pi-pi conjugates, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic effects in a non-covalent bond method. By adopting the targeting performance of targeting molecules and effects of graphene oxide of a particular size to enhance penetration and retention in tumor tissues and combining the performance of the graphene oxide for pH response control release of the loaded drug, the drug can be realized released in a tumor cell, an intelligent delivery system for the common carrier of the tumor targeting or liver targeting anticancer drug and the gene is synthesized from the perspective of synergetic medication, and a theoretical basis and a method basis are provided for combined therapy of tumor.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Compositions and methods for purifying and crystallizing molecules of interest
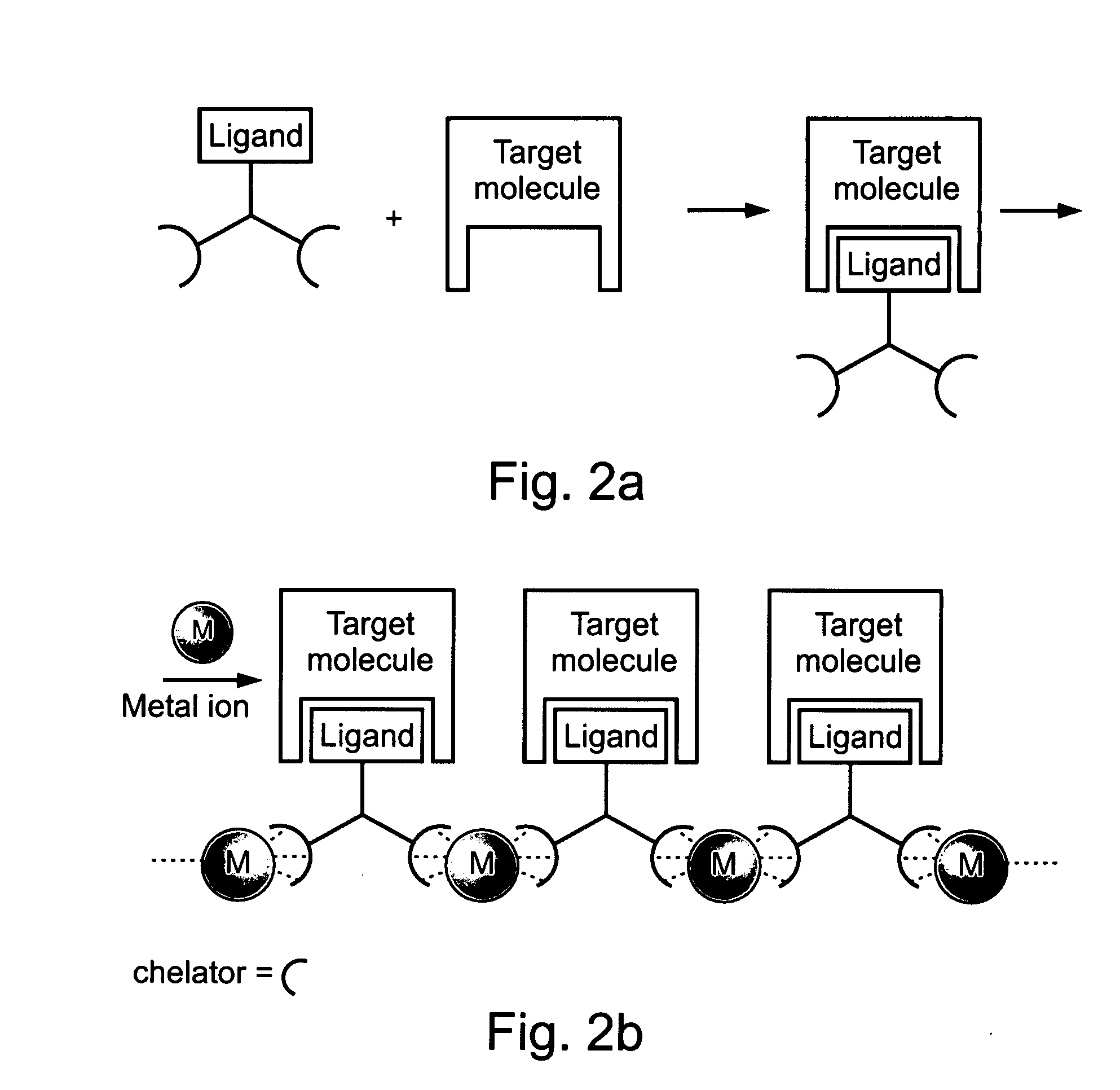
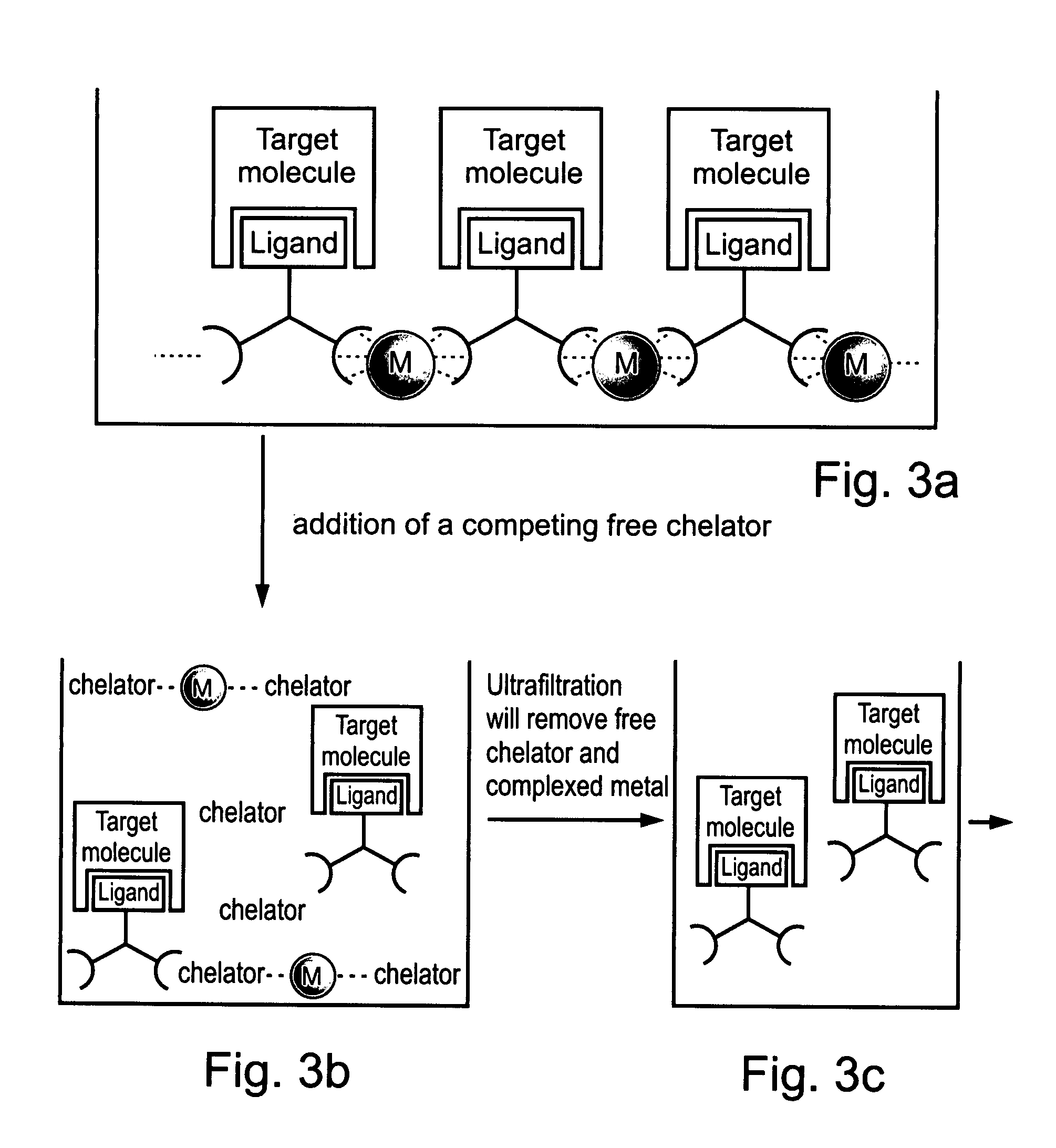
A composition-of-matter is provided. The composition comprising at least one antibody binding moiety capable of binding an antibody-labeled target molecule, cell or virus of interest, said at least one antibody binding moiety being attached to at least one coordinating moiety selected capable of directing the composition-of-matter to form a non-covalent complex when co-incubated with a coordinator ion or molecule.
Owner:AFFISINK BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
Method of formation of shape-retentive aggregates of gel particles and their uses
The present invention relates to a method of forming shape-retentive aggregates of gel particles in which the aggregates are held together by non-covalent bond physical forces such as, without limitation, hydrophobic-hydrophilic interactions and hydrogen bonds. The method comprises introducing a suspension of gel particles in a polar liquid at a selected concentration, wherein the gel particles have an absolute zeta potential, into a medium in which the absolute zeta potential of the gel particles is decreased, resulting in the gel particles coalescing into the claimed shape-retentive aggregate. This invention also relates to uses of the method of formation of the shape-retentive aggregates of gel particles.
Owner:ULURU INC
Dynamic polymer having non-covalent crosslinking structure and application thereof
ActiveCN107805309AFast self-healingAchieve synthesisPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesFibre treatmentBoric acidBiomimetic materials
The invention discloses a dynamic polymer having a non-covalent crosslinking structure. The dynamic polymer contains organic boric acid silicon ester bonds on polymer chain backbone; wherein the organic boric acid silicon ester bonds are existed as polymeric chain contacts of the dynamic polymer, and are the necessary condition for forming or maintaining a dynamic polymer structure. The dynamic polymer has energy dissipation performance by means of the organic boric acid silicon ester bonds having strong dynamic reversibility, embodies functional characteristics of stimulation responsiveness and self-repairability, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of sport protection, a functional coating, and a bionic material.
Owner:厦门天策材料科技有限公司
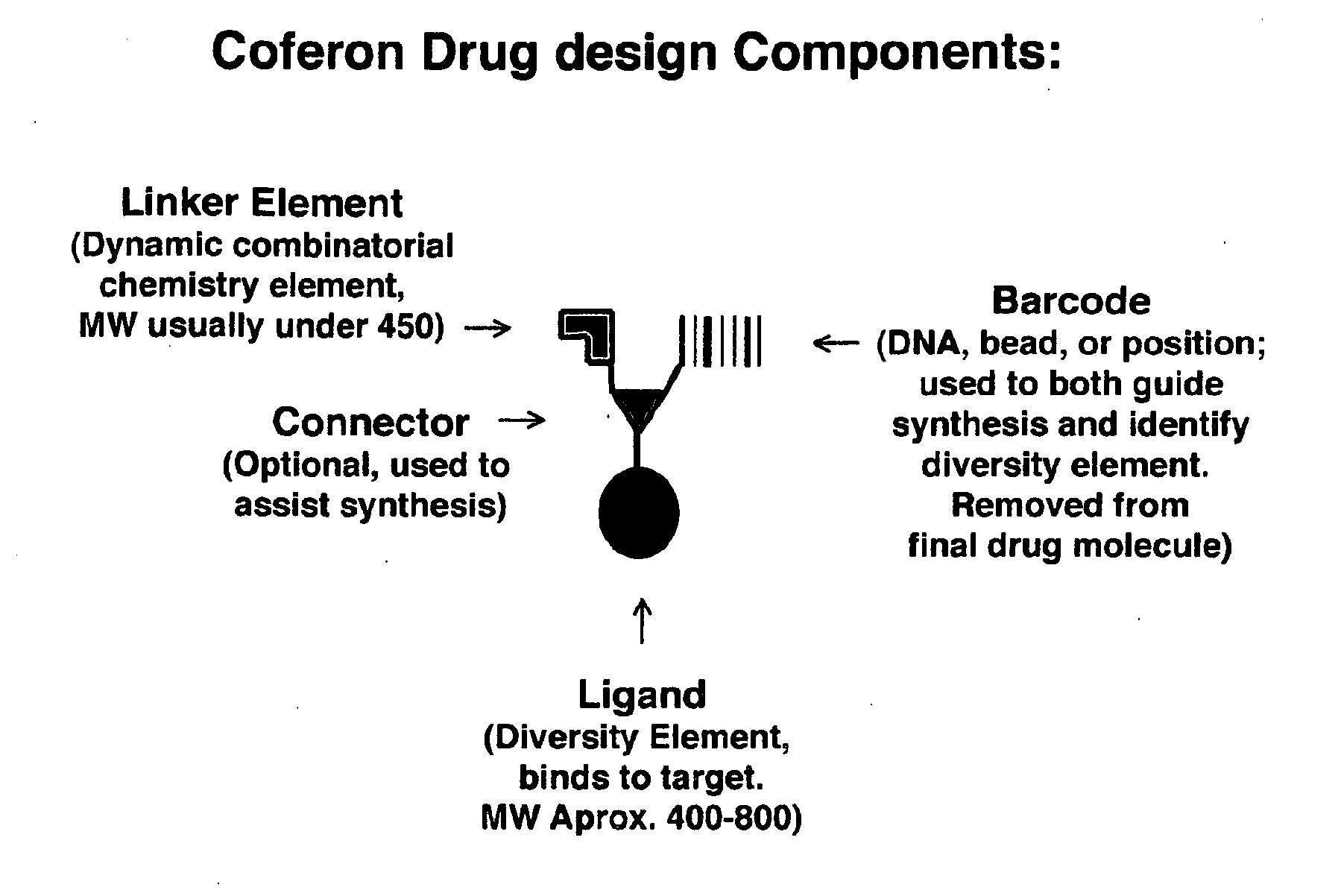
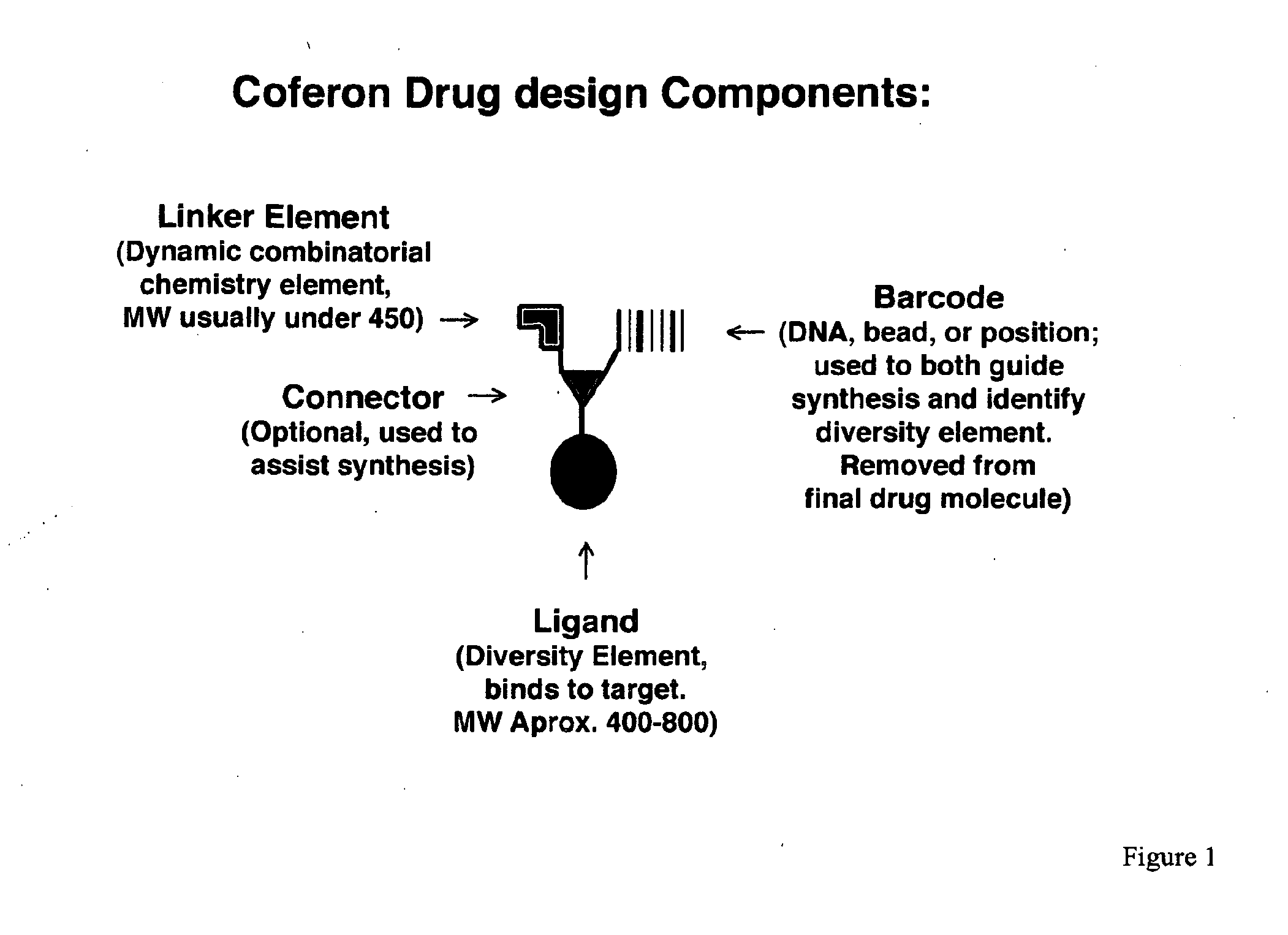
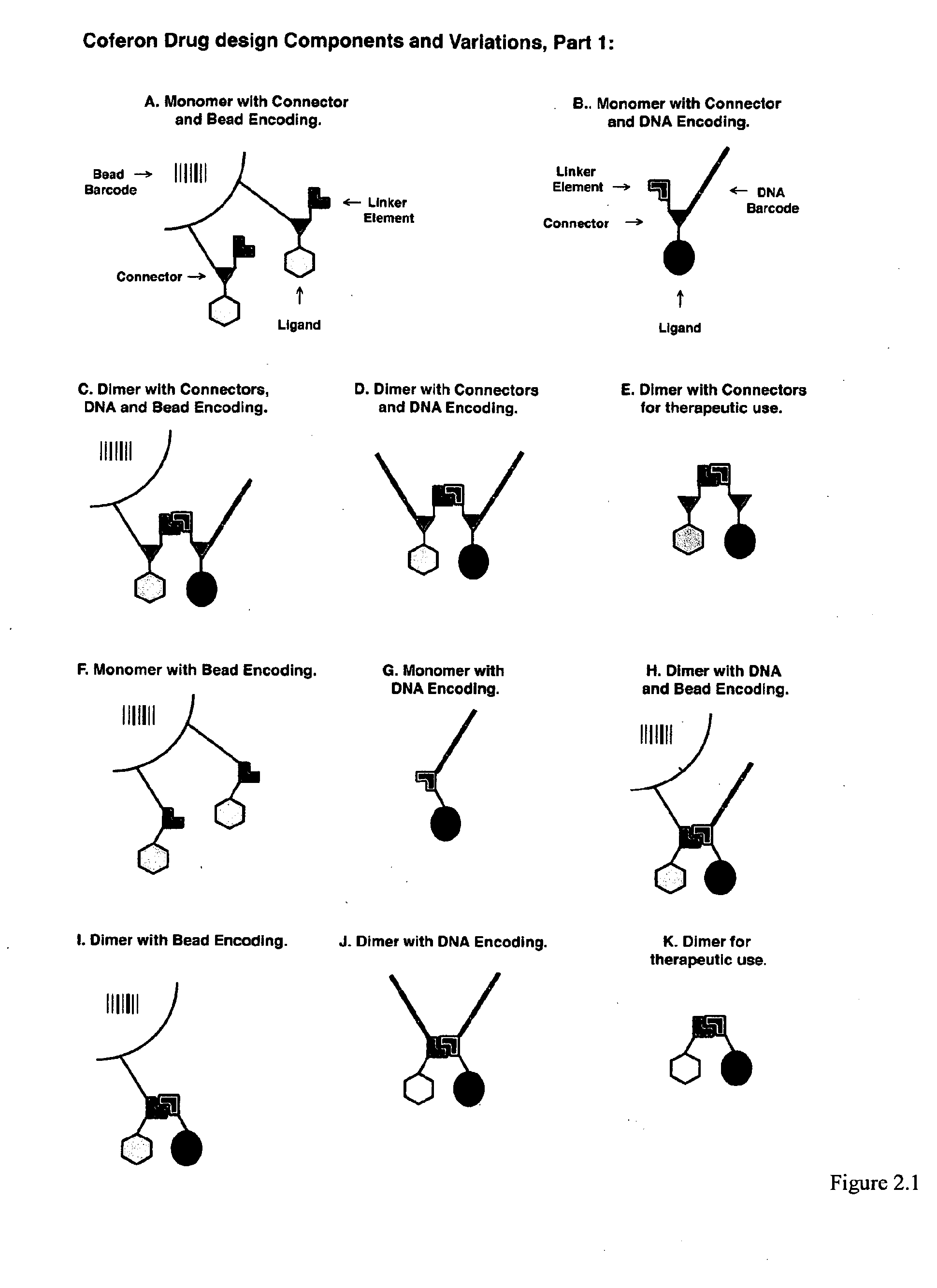
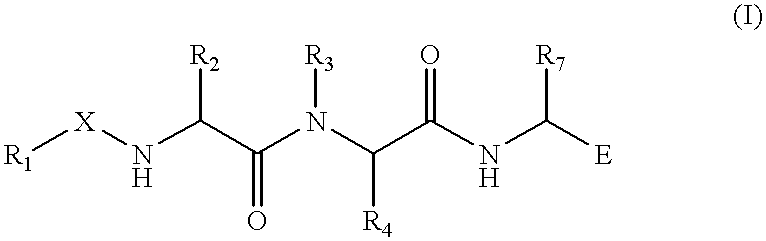
Coferons and methods of making and using them
ActiveUS20110263688A1Easy to modifyDisrupt interactionSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesChemical compoundCombinatorial chemistry
A monomer useful in prepaπng therapeutic compounds includes a diversity element which potentially binds to a target molecule with a dissociation constant of less than 300 11 M and a linker element connected to the diversity element The linker element has a molecular weight less than 500 daltons, is connected, directly or indirectly through a connector, to said diversity element, and is capable of forming a reversible covalent bond or noncovalent interaction with a binding partner of the linker element The monomers can be covalently or non-covalently linked together to form a therapeutic multimer or a precursor thereof
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
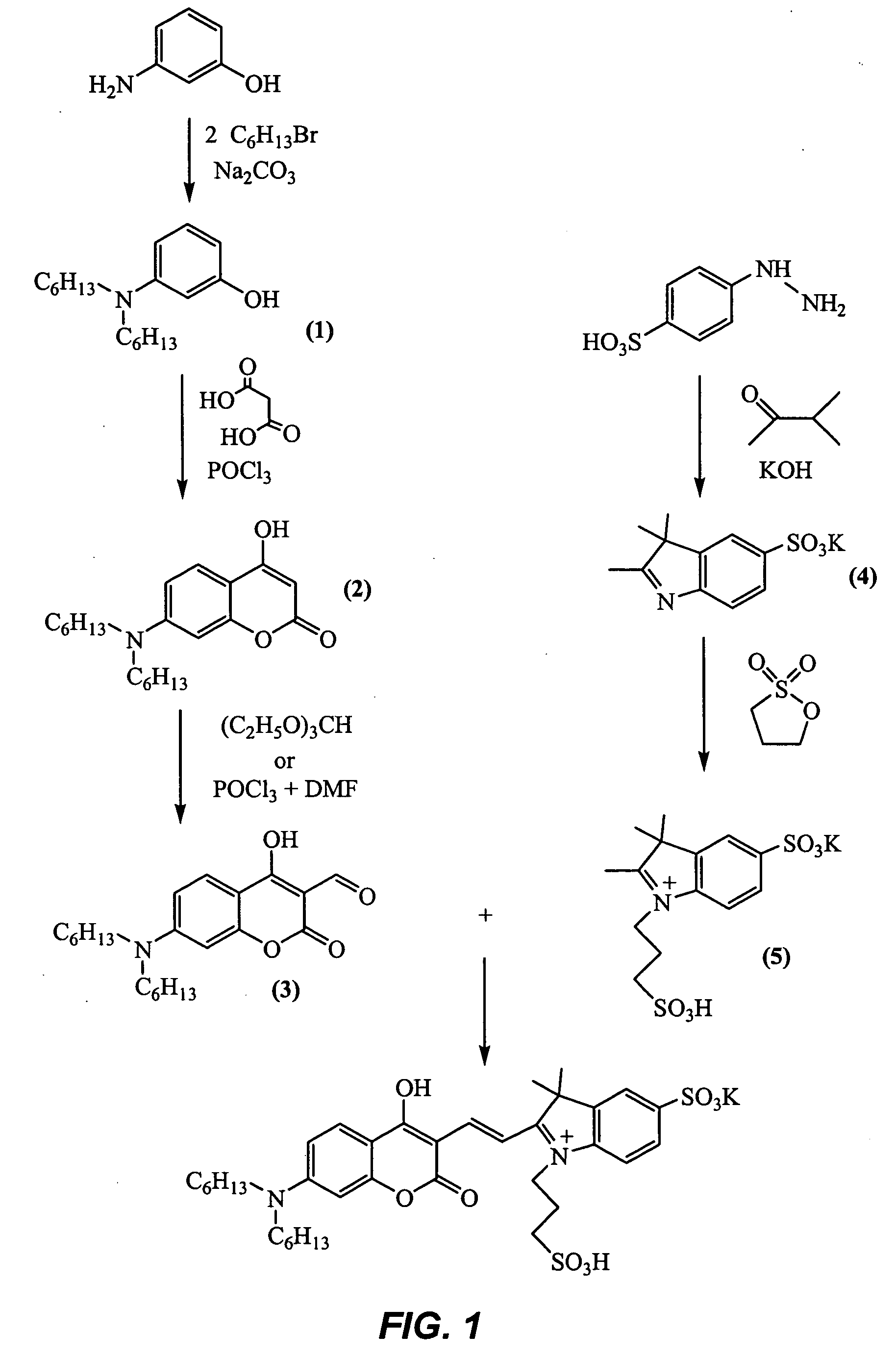
Coumarin-based cyanine dyes for non-specific protein binding
ActiveUS20060166368A1Efficient detectionFluorescence enhancementMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryFluorescenceAnalytical chemistry
Protein dyes whose molecular structure is that of a coumarin moiety coupled to a quaternary ammonium heterocycle through a vinyl or polyvinyl linkage demonstrate the ability to associate with proteins in a non-covalent, non-specific manner at low pH, where the associated form displays a significantly higher fluorescence emission than the unassociated form. This makes the dyes useful as selective labels for proteins at the low pH and eliminates the need for the removal of extraneous components from the medium in which the proteins reside prior to detection.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
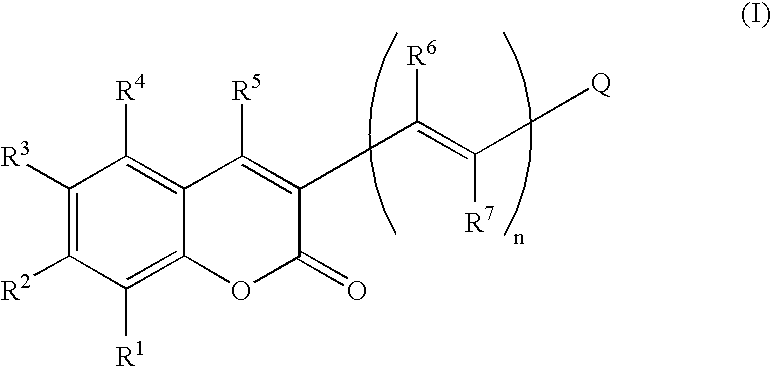
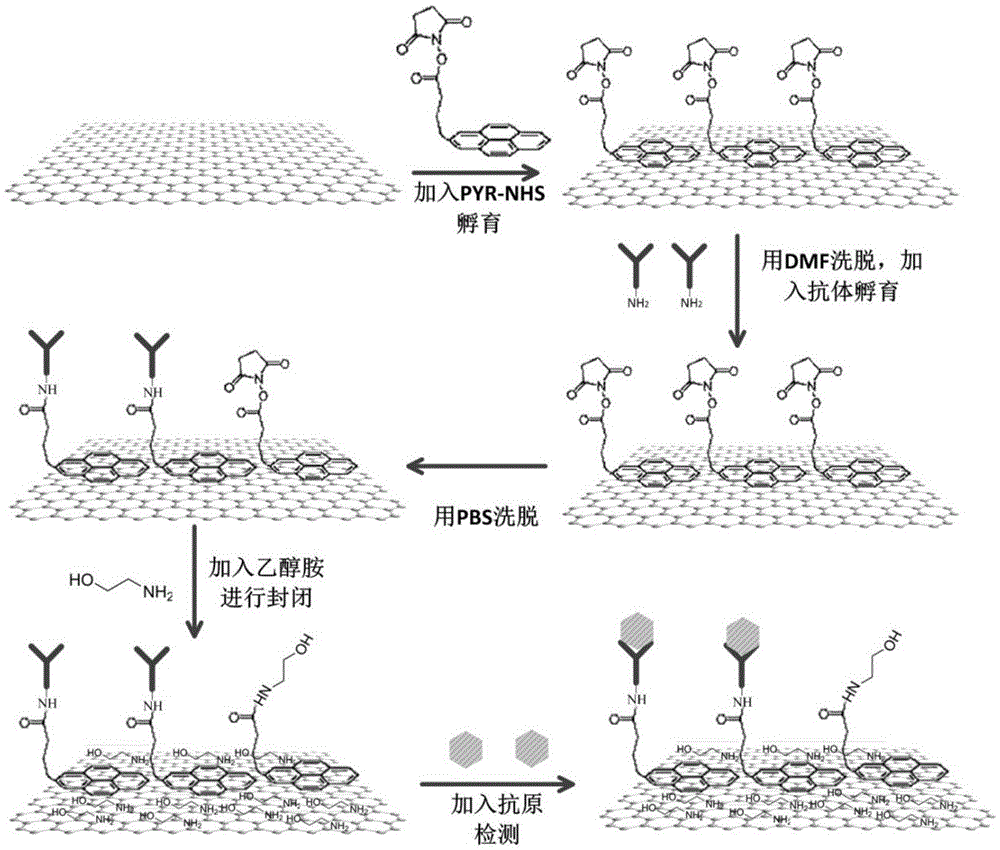
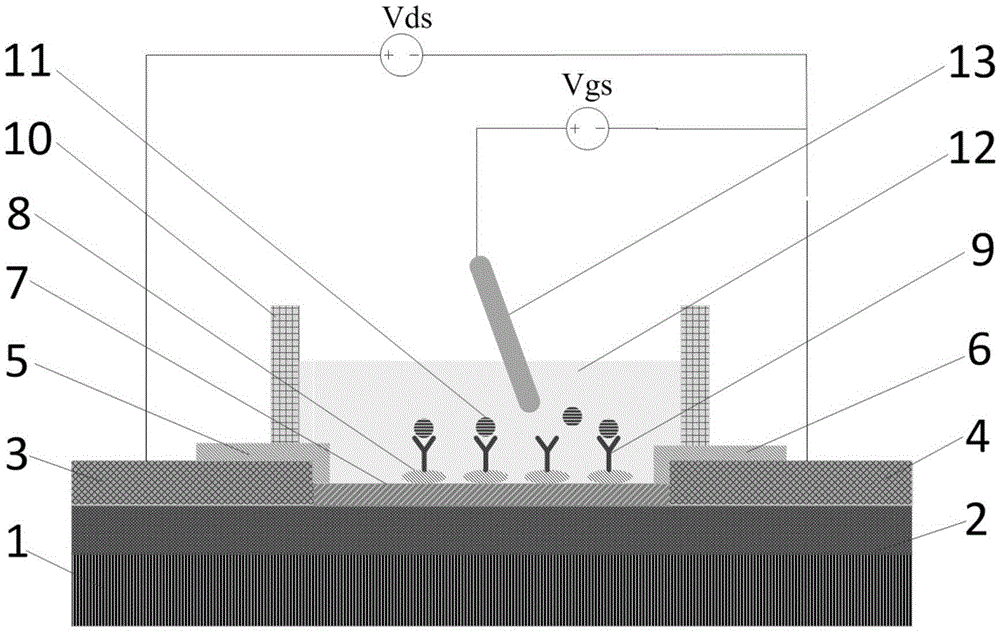
Non-covalently modified graphene field effect transistor-based tumor marker detection sensor and production method thereof
InactiveCN105651845ALittle influence on electrical characteristicsGood electrical propertiesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansInsulation layerMetal electrodes
The invention relates to a non-covalently modified graphene field effect transistor-based tumor marker detection sensor and a production method thereof. The sensor comprises a silica substrate, a graphene channel and a reaction chamber. The production method comprises the following steps: making a metal electrode, carrying out wet transfer on graphene, making the graphene channel and a protection insulation layer of the graphene channel, and modifying the surface of graphene in a non-covalent mode. The sensor has the advantages of convenient making process, simple modification process, easy operation, and high sensitivity and good specificity in application; and the making method can also be used to make most of biosensors of capture probes with amino groups, and the sensor is used to detect target molecules.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Shielded micelles for polynucleotide delivery
InactiveUS20070141134A1Highly efficient transfection agentLess cytotoxicBiocideSpecial deliverySolubilityCancer cell
The present invention relates to compositions that enhance the intracellular delivery of polynucleotides. The present invention is applicable to the fields of gene therapy and oligonucleotide or DNA therapy. Synthetic methods are disclosed, wherein a polynucleotide can be incorporated into the PEG shielded micelle particle to facilitate the delivery of the polynucleotide across a cellular membrane. Incorporation of the polynucleotide into the shielded micelle particle is provided by covalent and non-covalent means. Other cell targeting agents are provided that may also be covalently coupled to the shielded micelle particle to enhance localization in the body. The compositions herein are suitable for pharmaceutical use but are also suitable as transfection agents for in-vitro or in-vivo research. The PEG shielded polynucleotide micelles can provide favorable pharmacokinetic properties such as enhanced uptake into cancer cells, stability against nucleases, high solubility, and non-binding to serum proteins. The invention comprises a novel gene carrier which is shown to be substantially non-toxic and is suitable for parenteral, oral, pulmonary, and transmucosal delivery of polynucleotides.
Owner:KOSAK MATTHEW K
Silica particle including a molecule of interest, method for preparing same and uses thereof
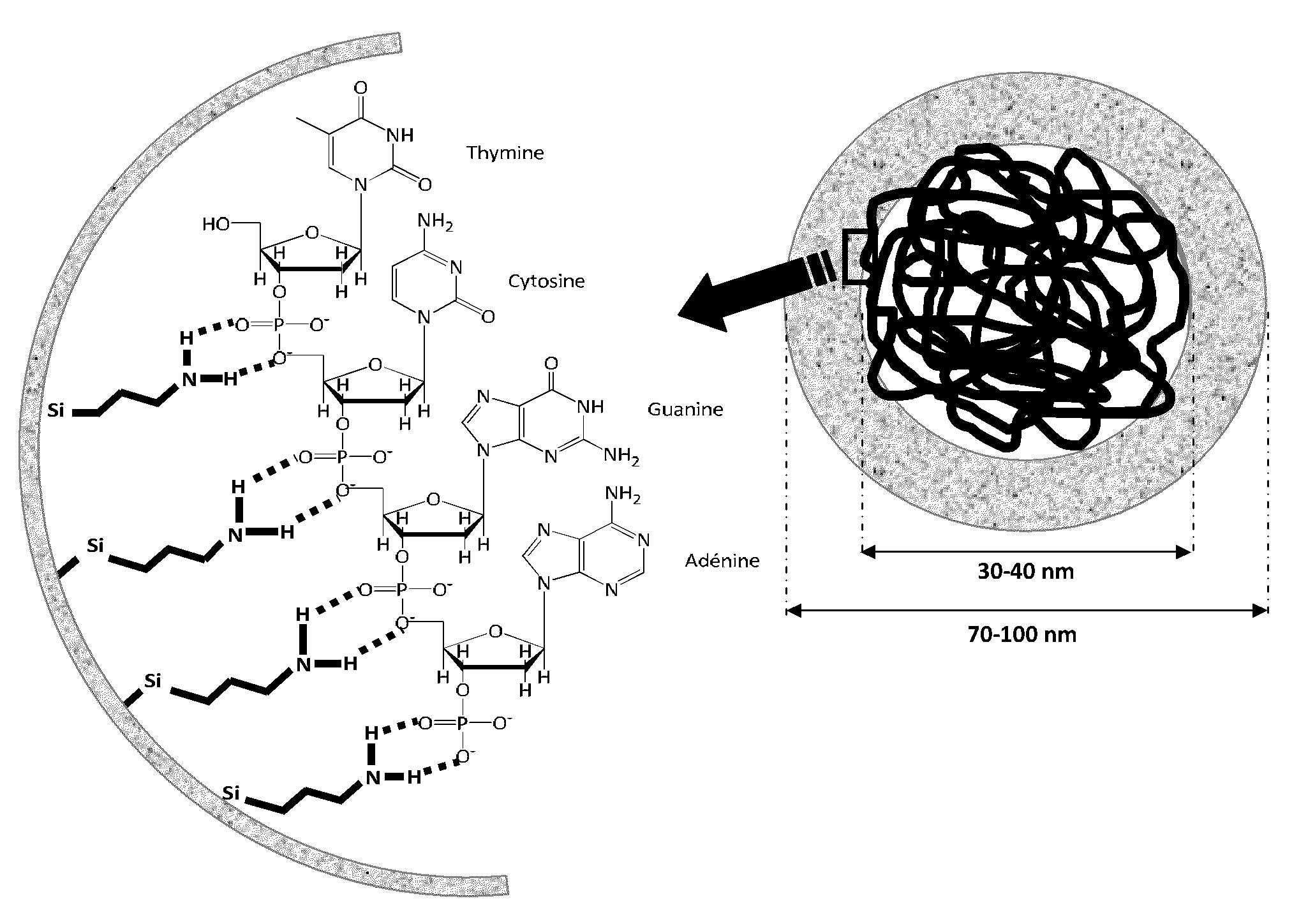
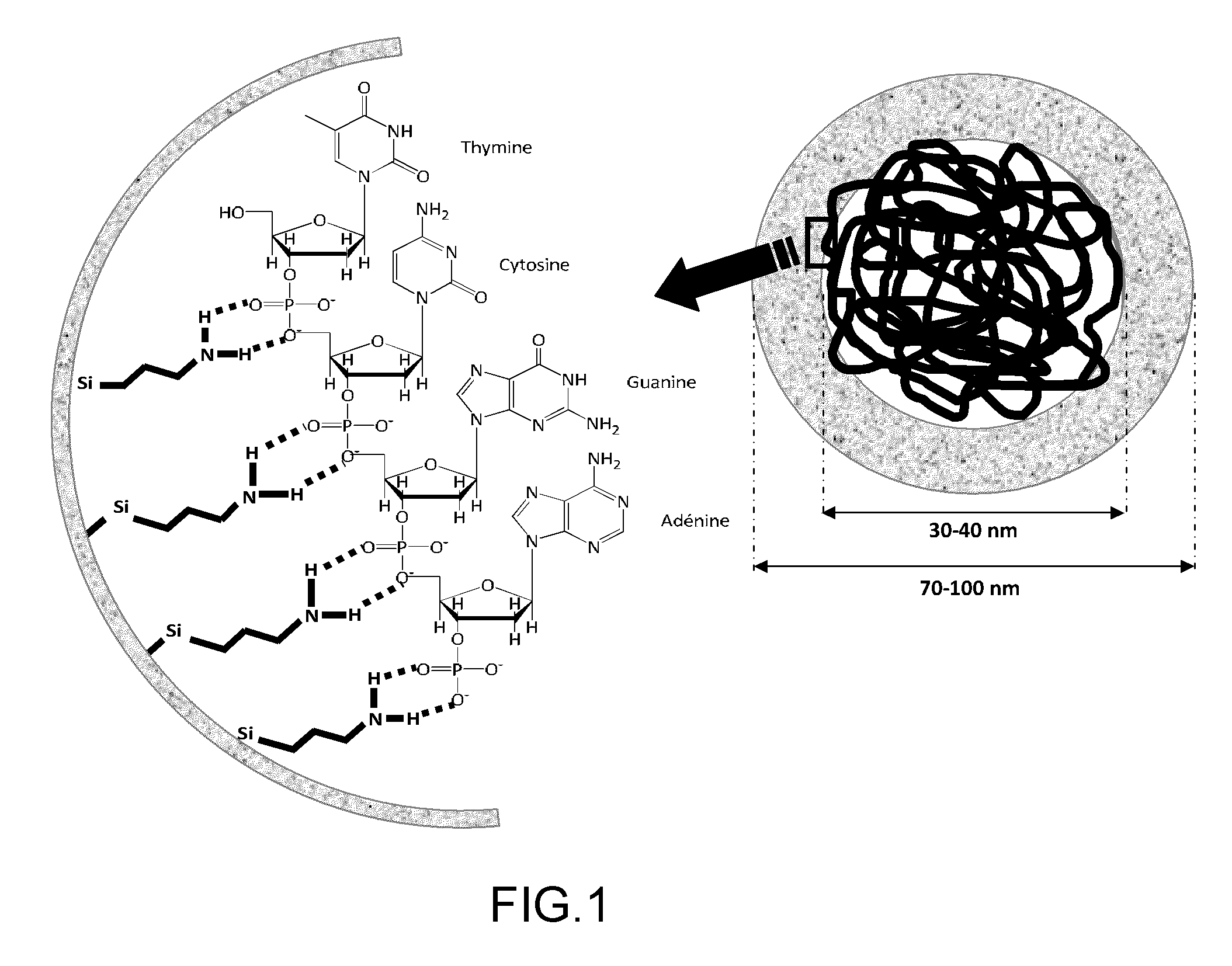
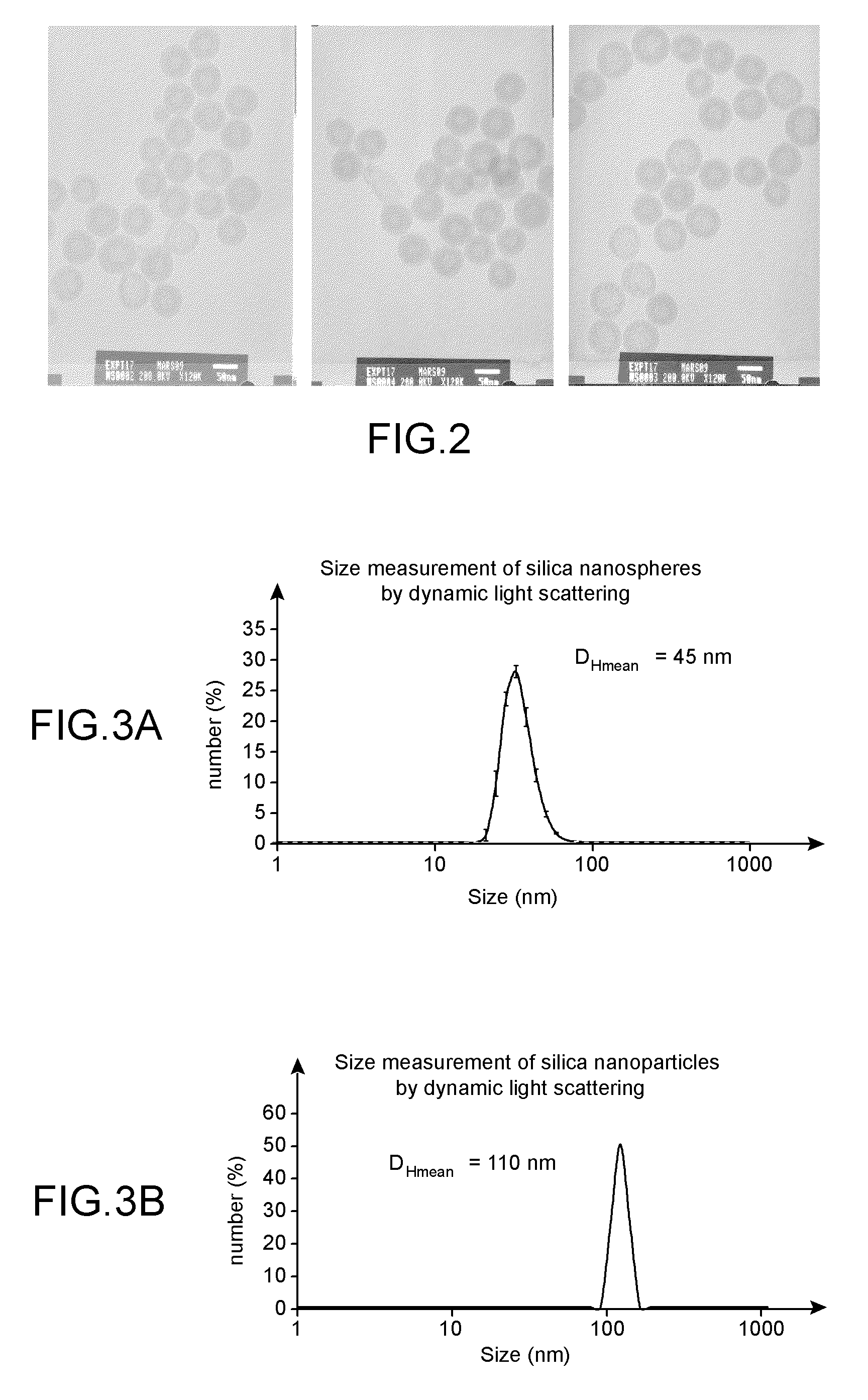
What is provided includes a nanoparticle of porous silica, incorporating at least one molecule of interest, the silica network inside said nanoparticle being functionalized by at least one group capable of setting up an ionic and / or hydrogen non-covalent bond with the molecule of interest, whereby the molecule(s) of interest is(are) linked to the silica network solely by non-covalent bonds. In addition, a method for preparing said silica particle and uses thereof is provided.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Non-covalent inhibitors of urokinase and blood vessel formation
InactiveUS20020037857A1Promote cell adhesionImprove cell adhesionDipeptide ingredientsDepsipeptidesUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorIn vivo
Novel compounds having activity as non-covalent inhibitors of urokinase and having activity in reducing or inhibiting blood vessel formation are provided. These compounds have Pi a group having an amidino or guanidino moiety or derivative thereof. These compounds are useful in vitro for monitoring plasminogen activator levels and in vivo in treatment of conditions which are ameliorated by inhibition of or decreased activity of urokinase and in treating pathologic conditions wherein blood vessel formation is related to a pathologic condition.
Owner:KEVIN S HELMBACHER GENERAL COUNSEL +1
Multifunctional Supramolecular Hydrogels as Biomaterials
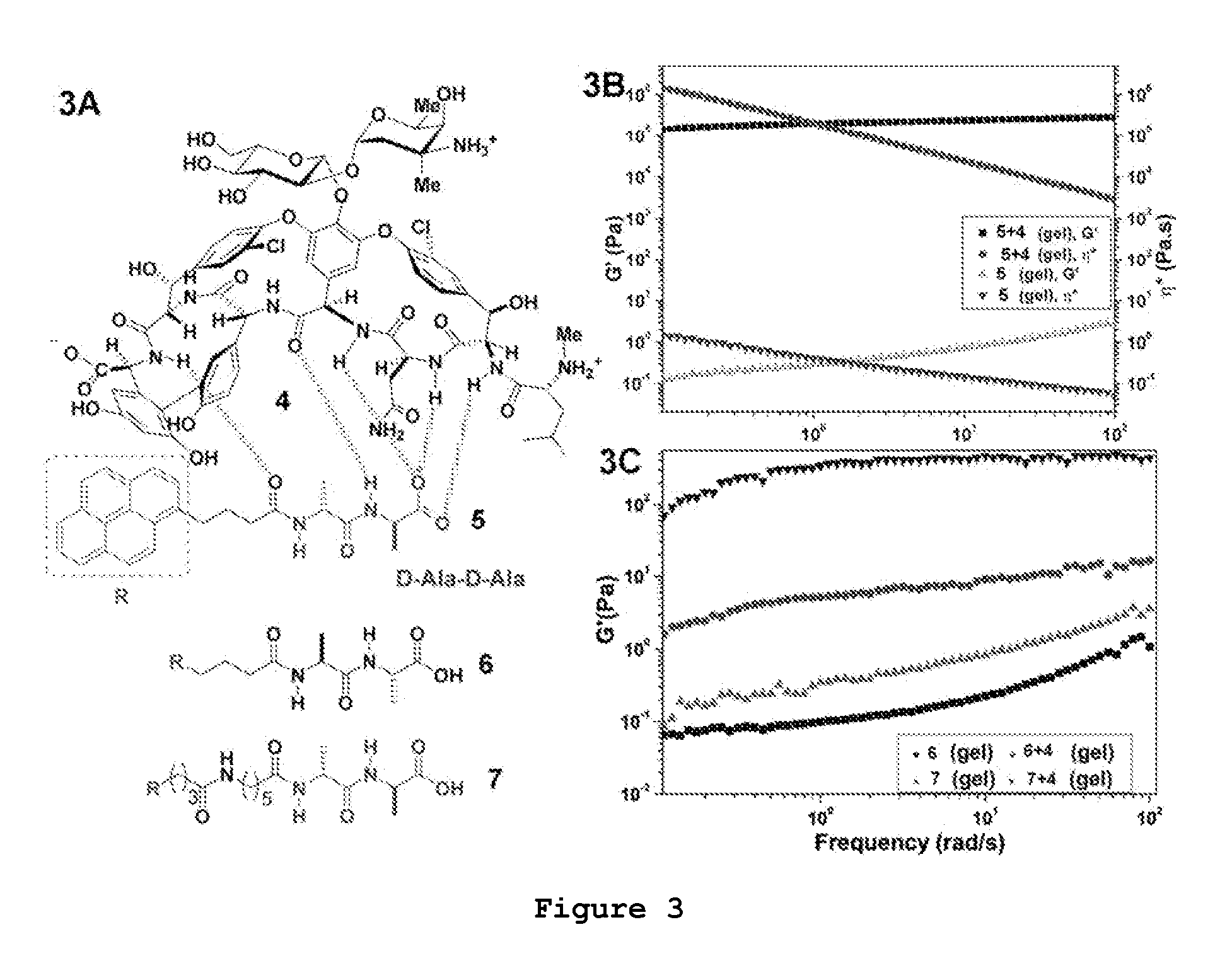
The present invention provides supramolecular hydrogels having a three-dimensional, self-assembling, elastic, network structure comprising non-polymeric, functional molecules and a liquid medium, whereby the functional molecules are noncovalently crosslinked. The functional molecules may be, for instance, anti-inflammatory molecules, antibiotics, metal chelators, anticancer agents, small peptides, surface-modified nanoparticles, or a combination thereof. Applications of the present invention include use of the supramolecular hydrogel, for instance, as a biomaterial for wound healing, tissue engineering, drug delivery, and drug / inhibitor screening.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com