Patents
Literature
717 results about "Response control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
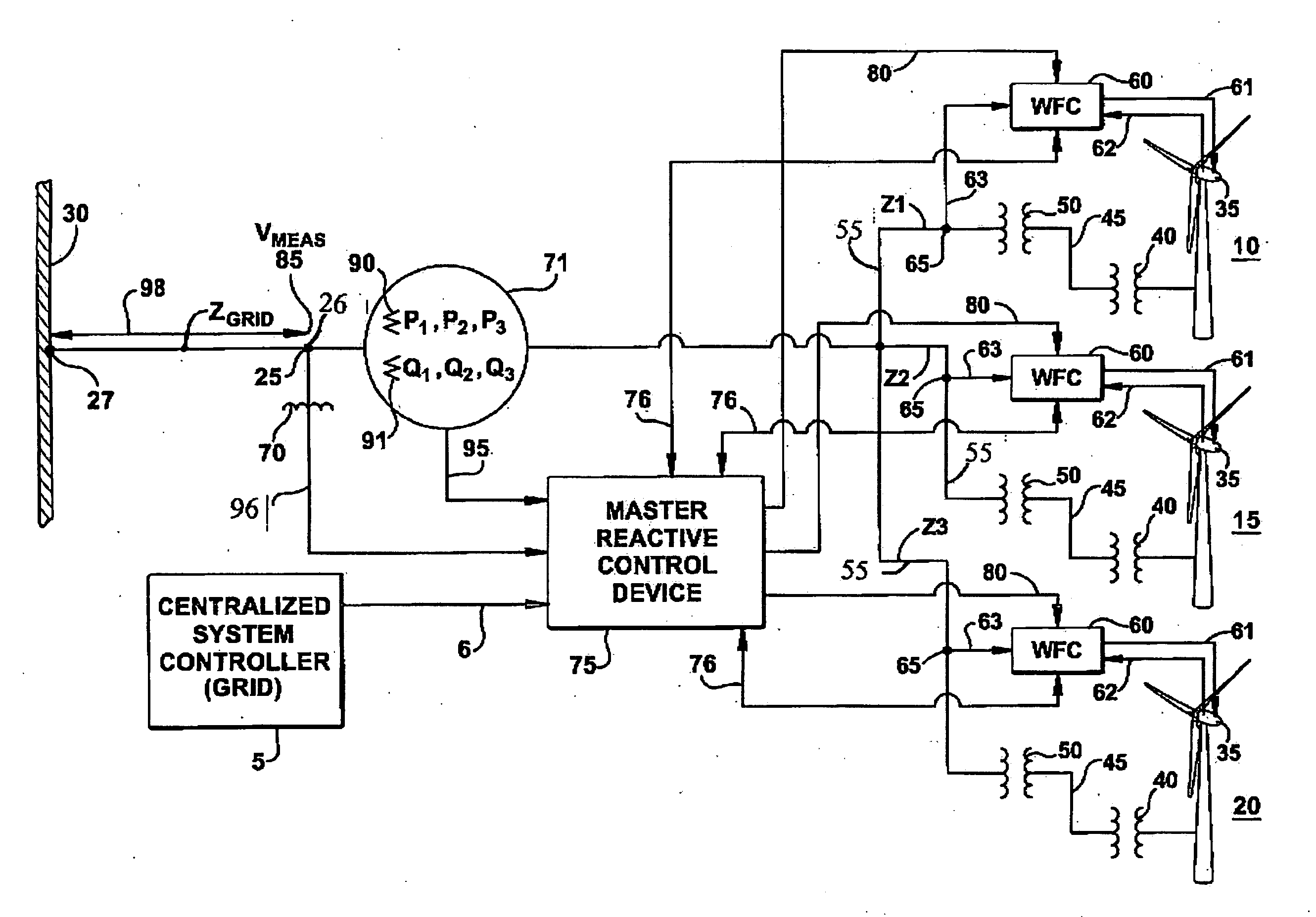
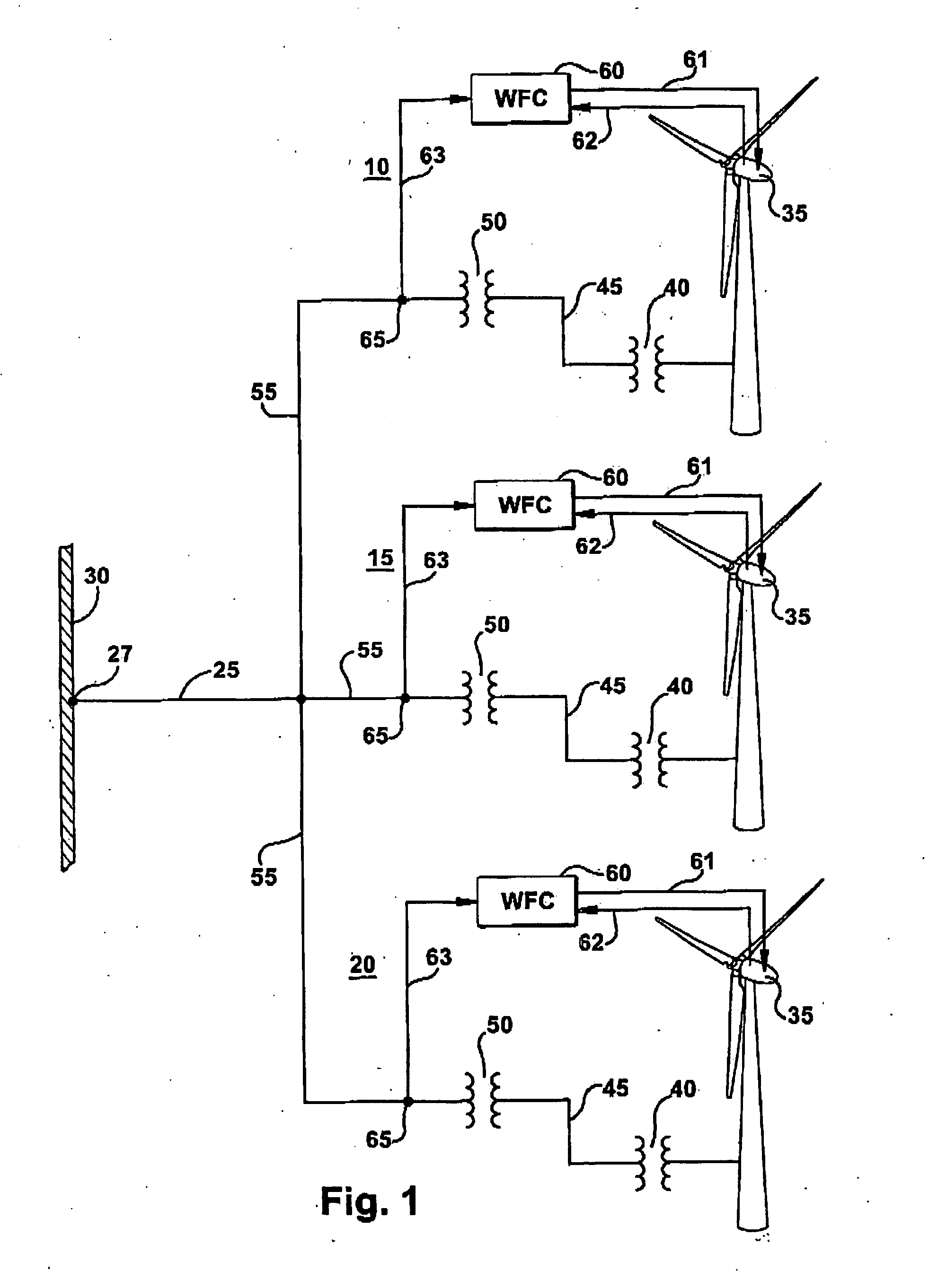
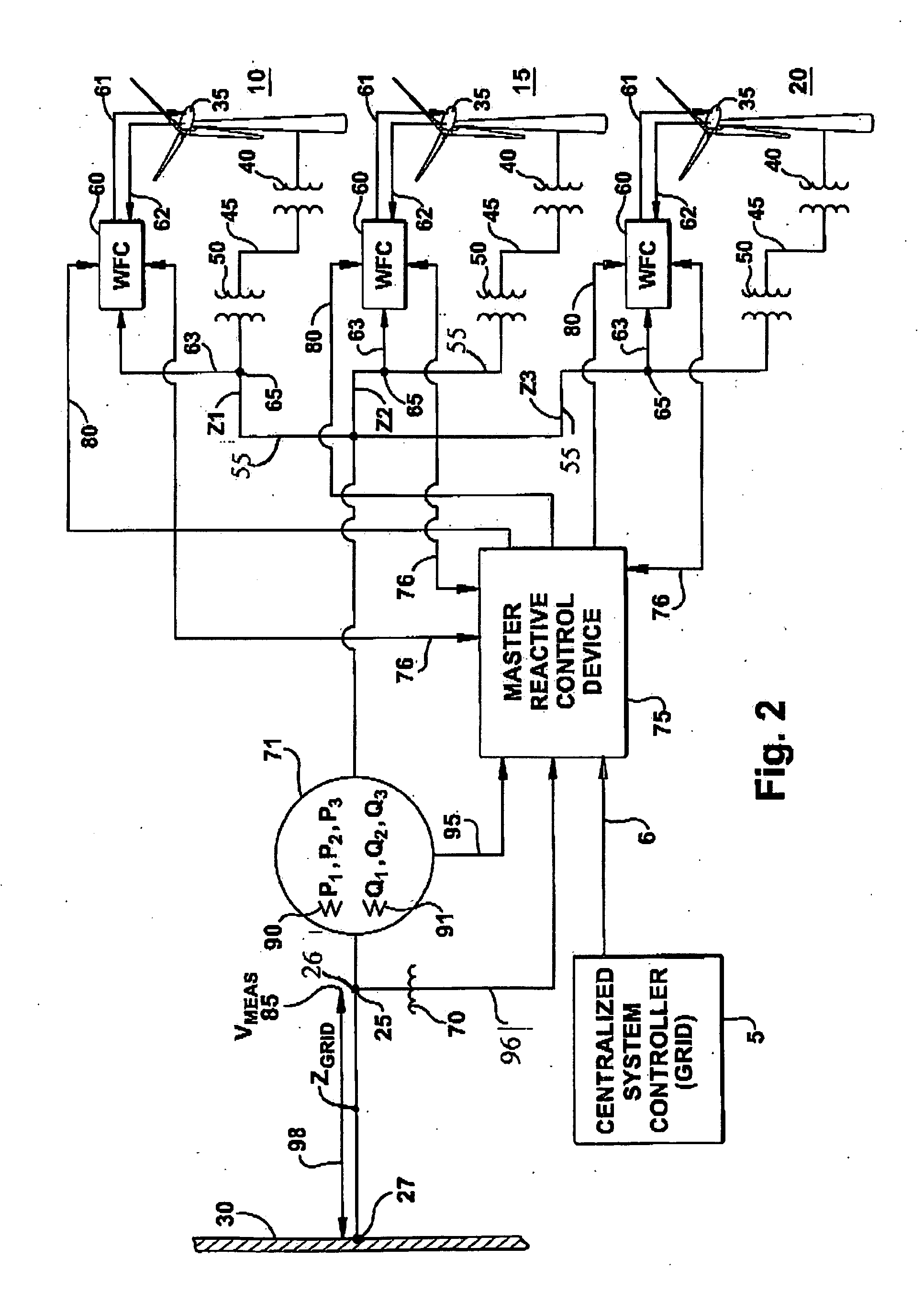
Intra-area master reactive controller for tightly coupled windfarms
ActiveUS20100025994A1Wind motor controlLoad balancing in dc networkElectric power systemPower factor
A wind turbine generator control system is provided for controlling output of a plurality of tightly-coupled windfarms connected at a point of common coupling with a power system grid. A master reactive control device employs algorithms whose technical effect is to coordinate the real power, reactive power and voltage output of the multiple windfarms. The controller incorporates a reactive power regulator that can be used to regulate reactive power, power factor or voltage at the point of common coupling and an active power regulator that can be used to regulate real power at the point of common coupling; such that each windfarm is not asked to contribute or violate its own operating capability.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
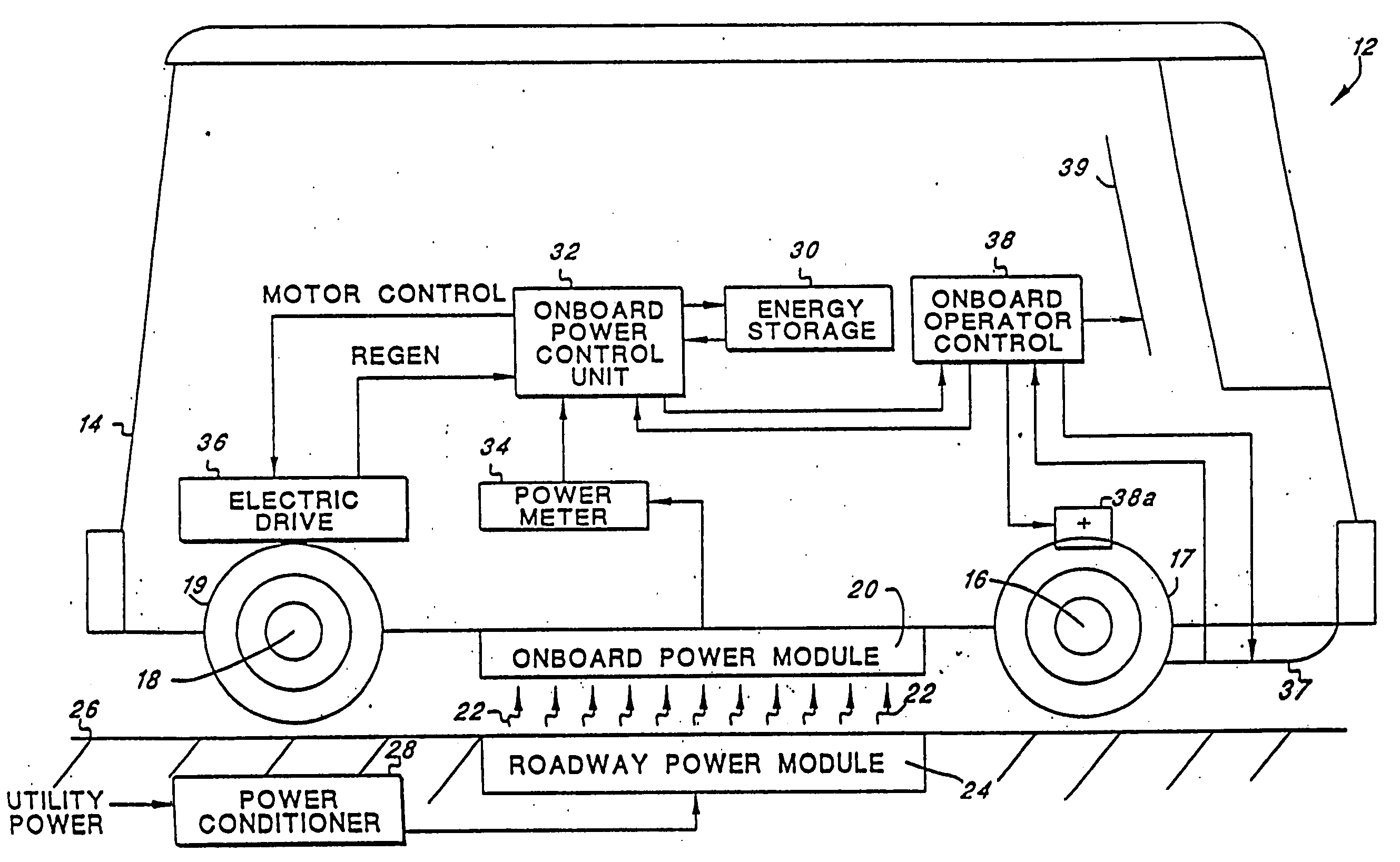
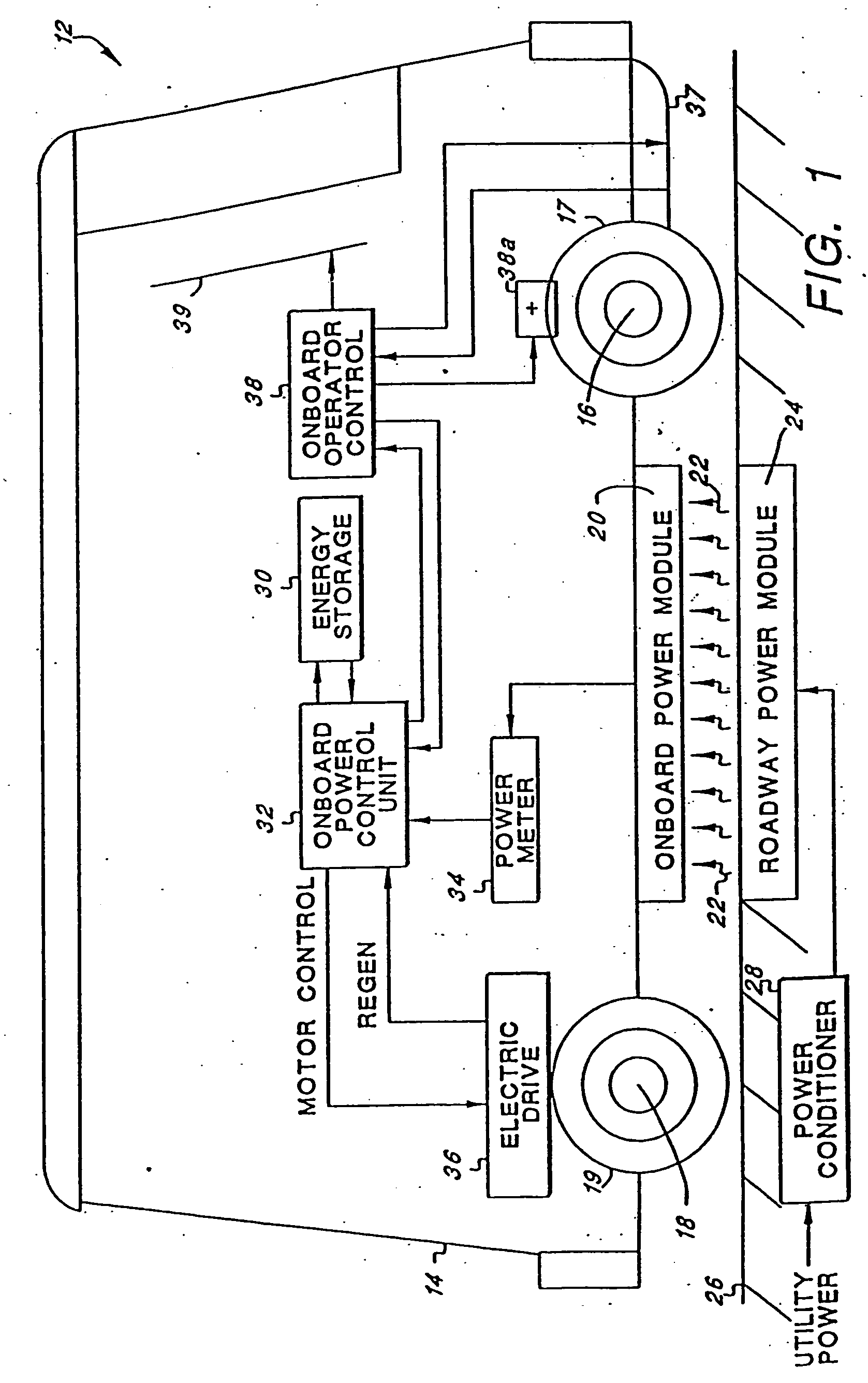
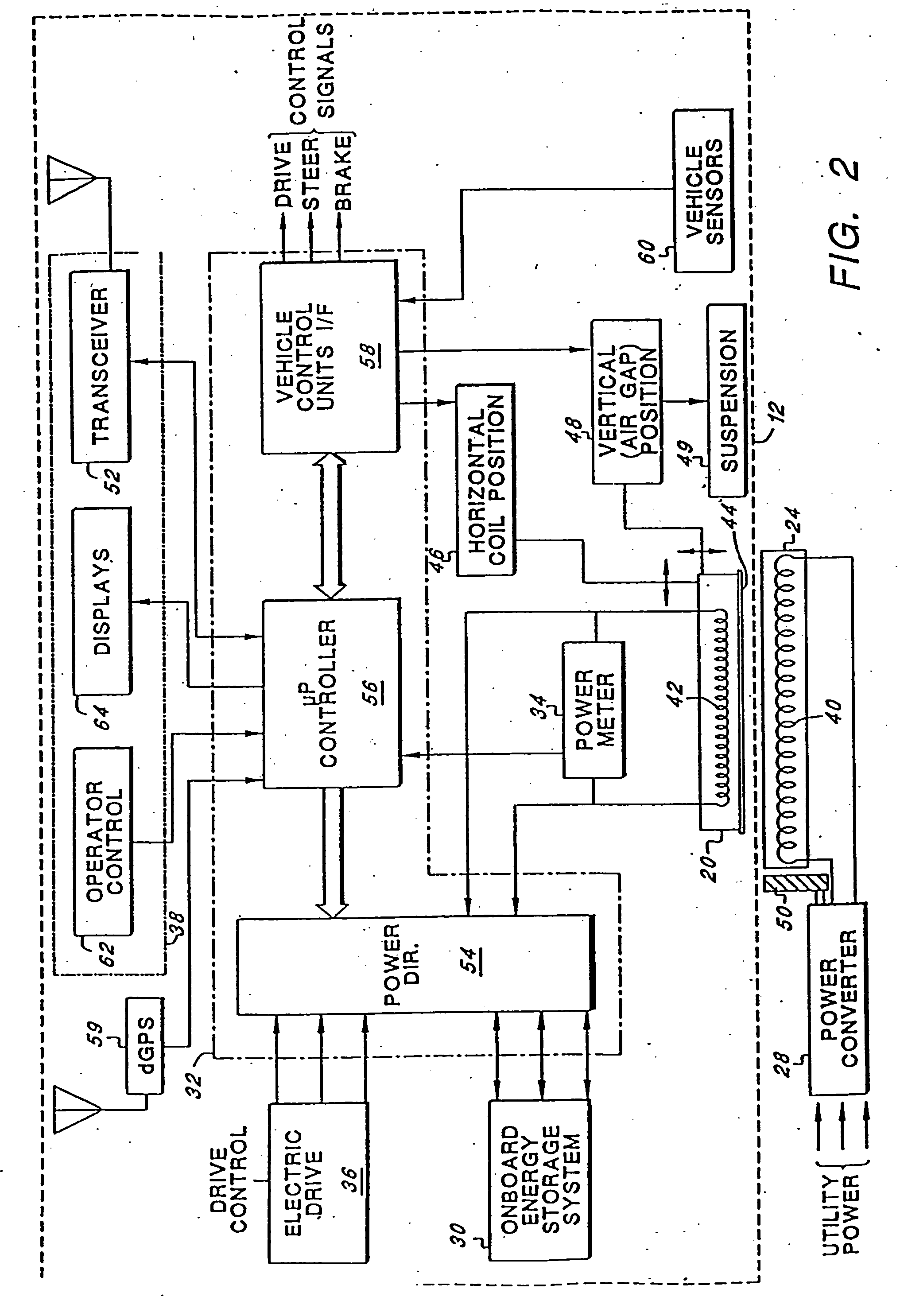
Roadway-powered electric vehicle system having automatic guidance and demand-based dispatch features
A roadway-powered electric vehicle (RPEV) system includes: (1) an all-electric vehicle; and (2) a roadway network over which the vehicle travels. The all-electric vehicle has one or more onboard energy storage elements or devices that can be rapidly charged or energized with energy obtained from an electrical current, such as a network of electromechanical batteries. The electric vehicle further includes an on-board controller that extracts energy from the energy storage elements, as needed, and converts such extracted energy to electrical power used to propel the electric vehicle. The energy storage elements may be charged while the vehicle is in operation. The charging occurs through a network of power coupling elements, e.g., coils, embedded in the roadway. The RPEV system also includes: (1) an onboard power meter; (2) a wide bandwidth communications channel to allow information signals to be sent to, and received from, the RPEV while it is in use; (3) automated garaging that couples power to the RPEV for both replenishing the onboard energy source and to bring the interior climate of the vehicle to a comfortable level before the driver and / or passengers get in; (4) electronic coupling between “master” and “salve” RPEV's in order to increase passenger capacity and electronic actuators for quick-response control of the “slave” RPEV; (5) inductive heating coils at passenger loading / unloading zones in order to increase passenger safety; (6) an ergonomically designed passenger compartment; (7) a locating system for determining the precise location of the RPEV; and (8) a scheduling and dispatch computer for controlling the scheduling of RPEV's around a route and dispatch of RPEV's based on demand.
Owner:ROSS HOWARD R
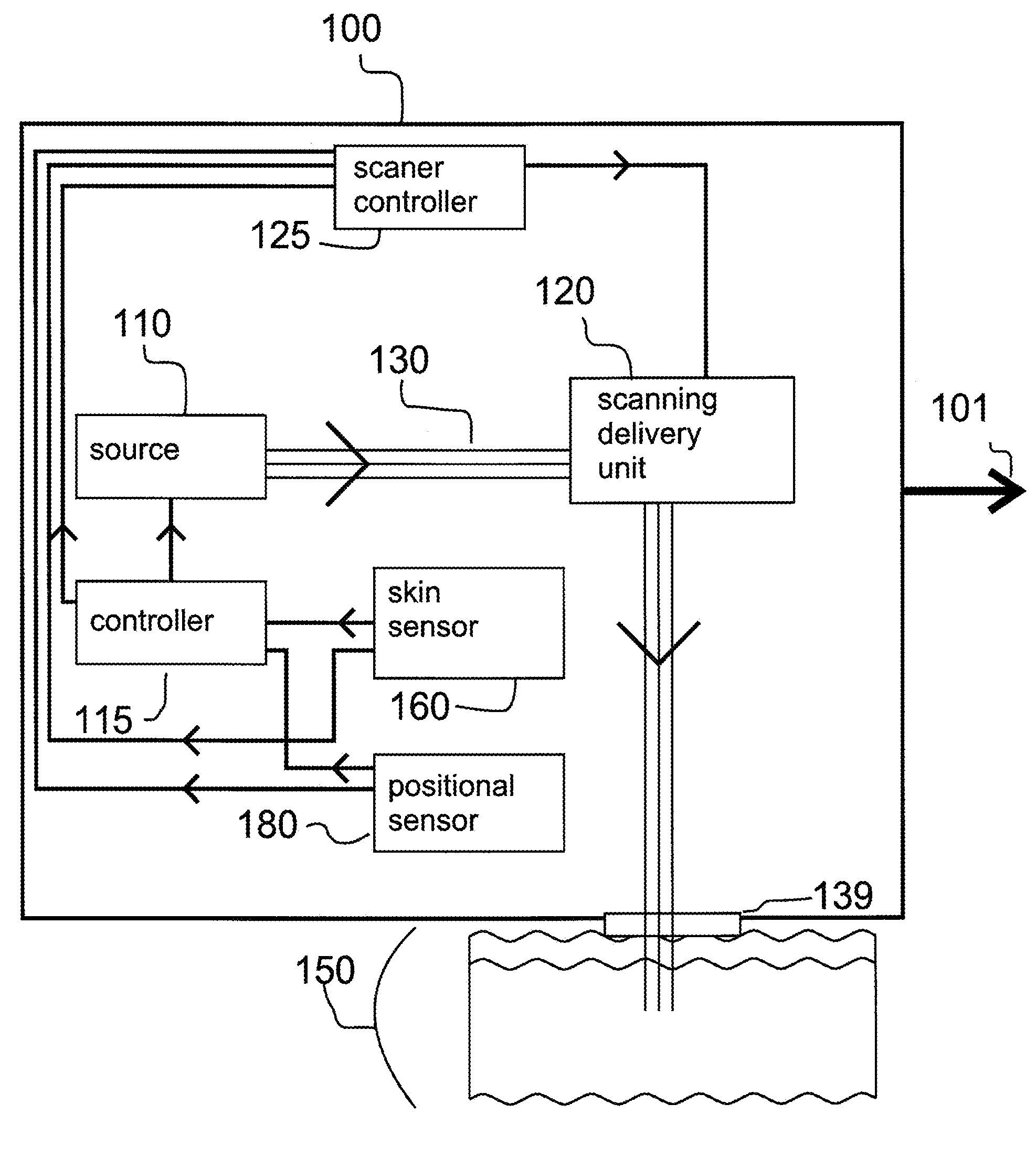
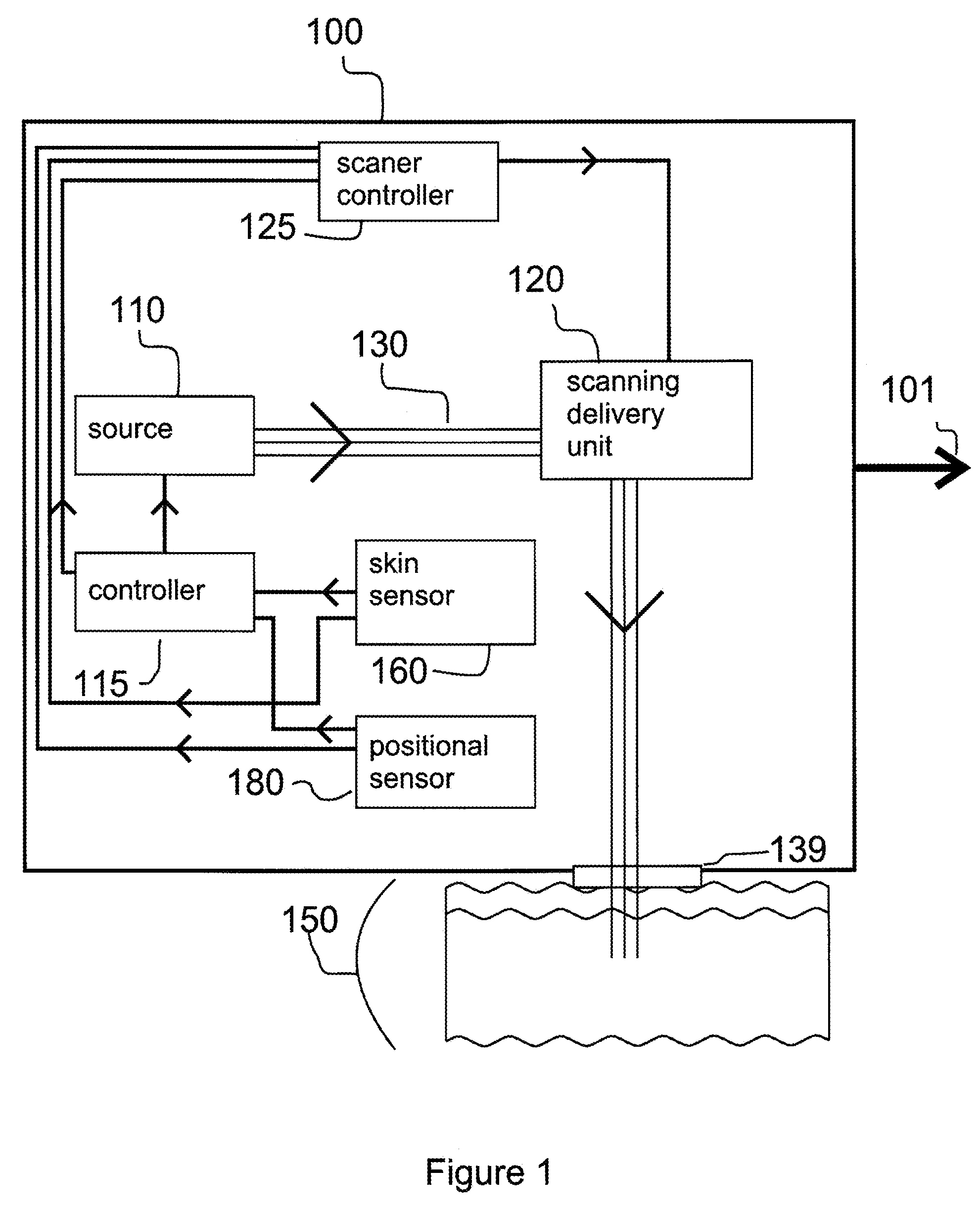
Method and apparatus for monitoring and controlling density of fractional tissue treatments
InactiveUS20080058782A1Reduce treatment intensityIncrease in sizeDiagnosticsControlling energy of instrumentMedicineVolumetric Mass Density
A method and apparatus for fractional treatment of skin by irradiating the skin with electromagnetic energy is disclosed. Sources of the electromagnetic energy can include radio frequency (RF) generators, lasers, and flashlamps. The apparatus includes at least one sensor configured to detect a positional parameter, a skin characteristic, a skin response, or combinations thereof. The sensor provides feedback to a controller. The controller controls the treatment parameters, including the treatment density. By sensing the positional parameter, skin characteristic and / or skin response to a treatment, the controller automatically adjusts treatment density in real-time in response to the sensed positional parameter, skin characteristic and / or skin response.
Owner:RELIANT TECH INC
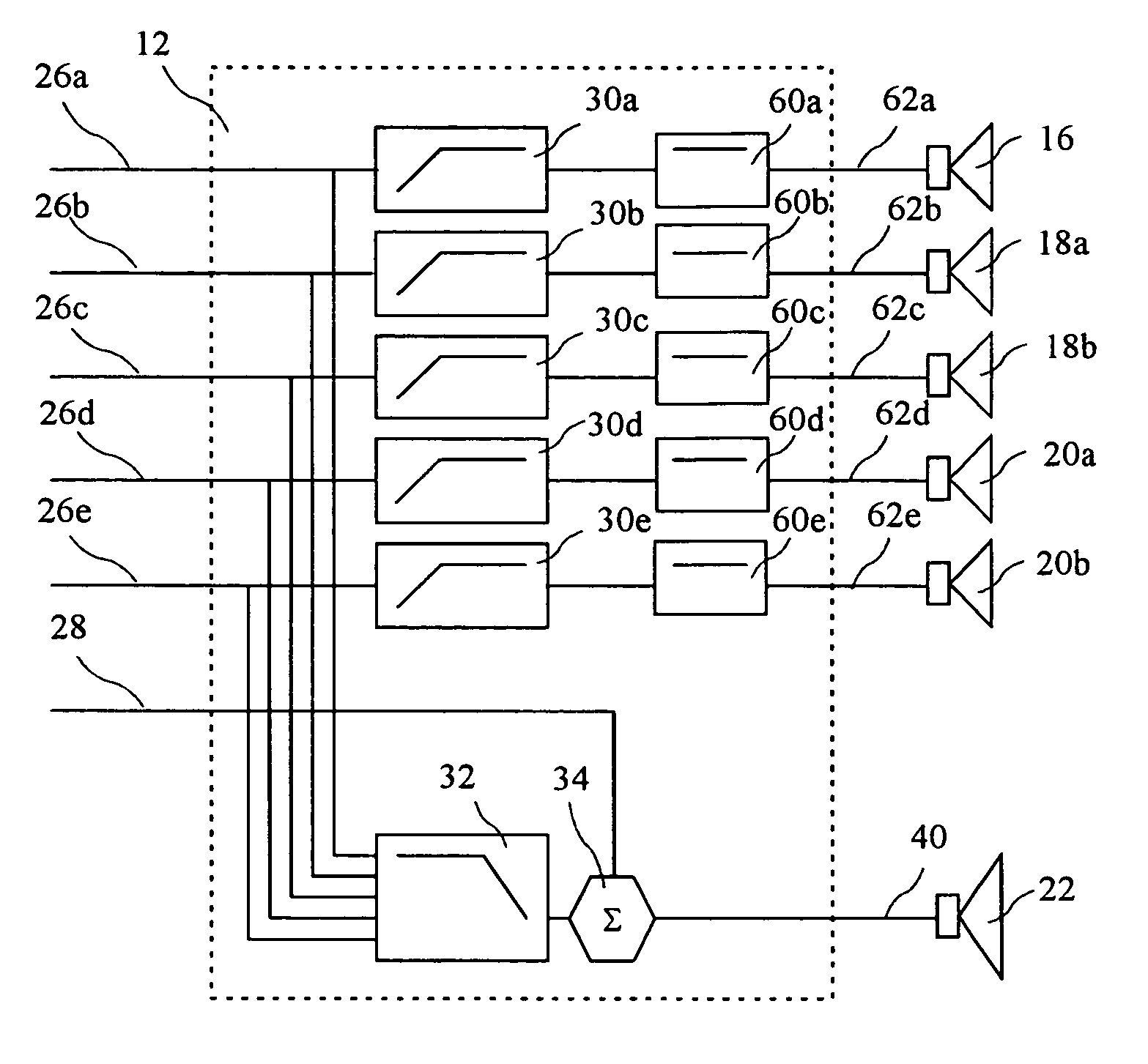
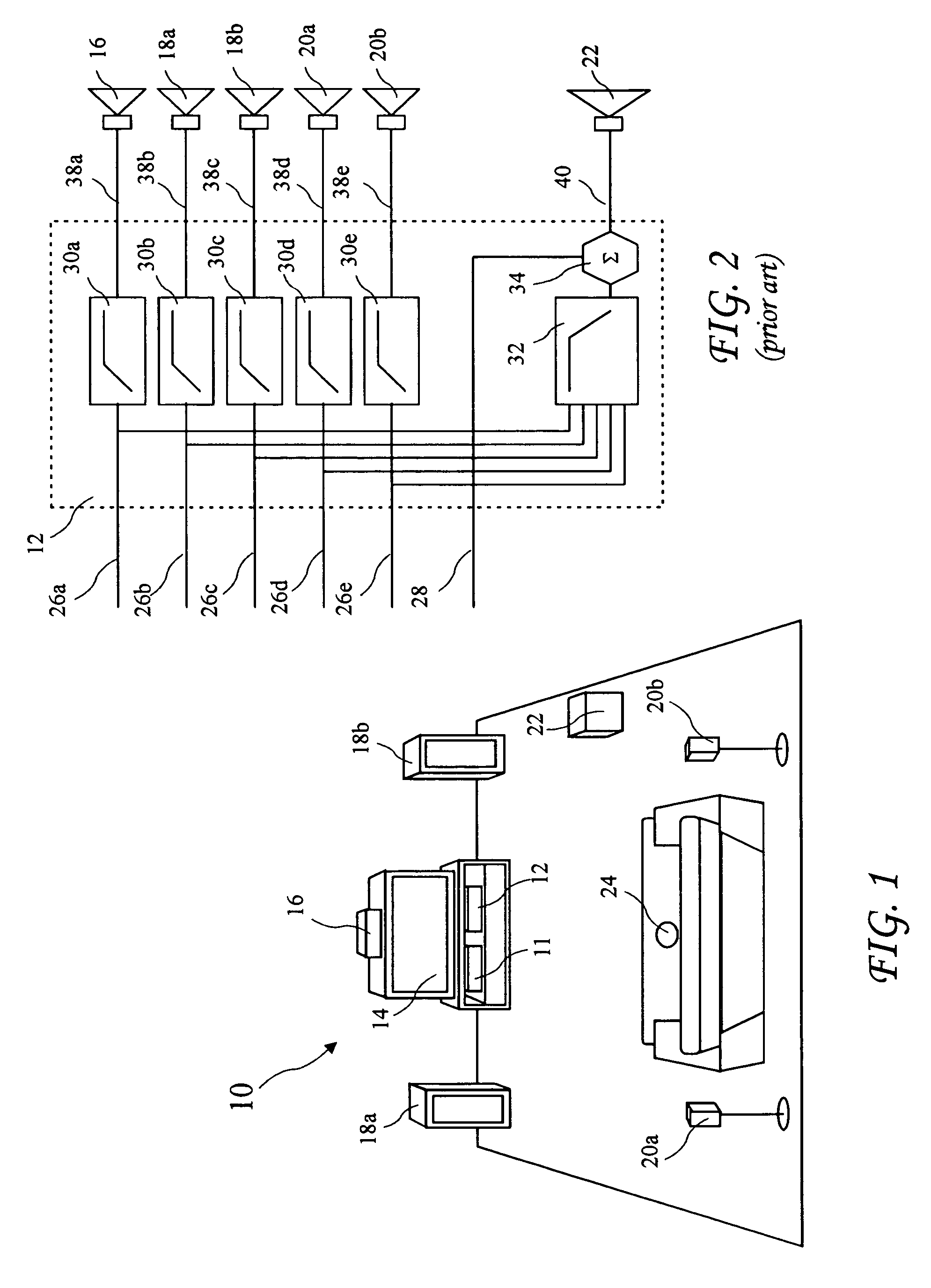
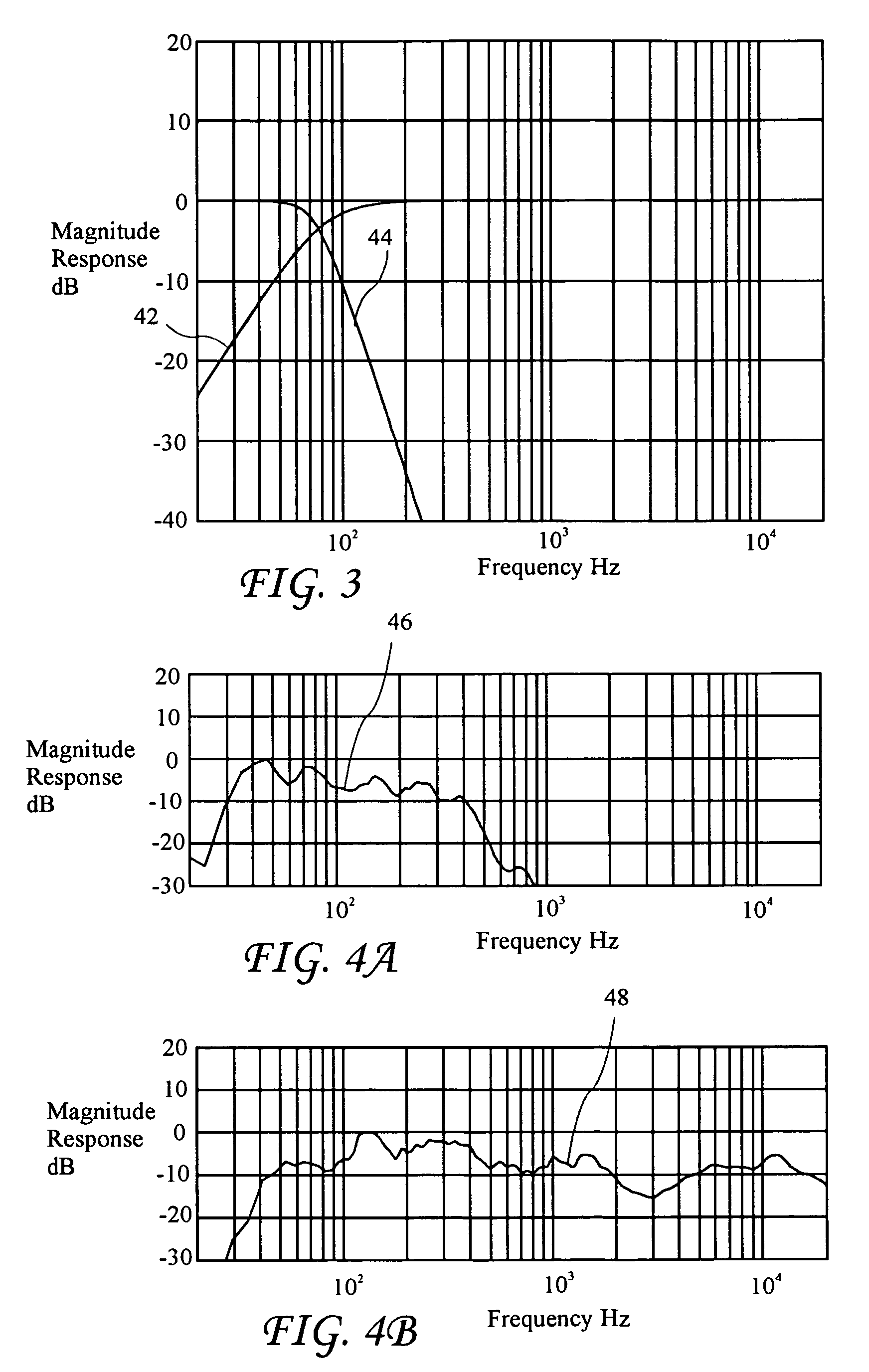
Phase equalization for multi-channel loudspeaker-room responses
ActiveUS7720237B2Improved response controlMinimize phase incoherenceFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsLine-transmissionAmplitude responseVocal tract
A system and method for minimizing the complex phase interaction between non-coincident subwoofer and satellite speakers for improved magnitude response control in a cross-over region. An all-pass filter is cascaded with bass-management filters in at least one filter channel, and preferably all-pass filters are cascaded in each satellite speaker channel. Pole angles and magnitudes for the all-pass filters are recursively calculated to minimize phase incoherence. A step of selecting an optimal cross-over frequency may be performed in conjunction with the all-pass filtering, and is preferably used to select an optimal cross-over frequency prior to determining all-pass filter coefficients.
Owner:AUDYSSEY LABORATORIES
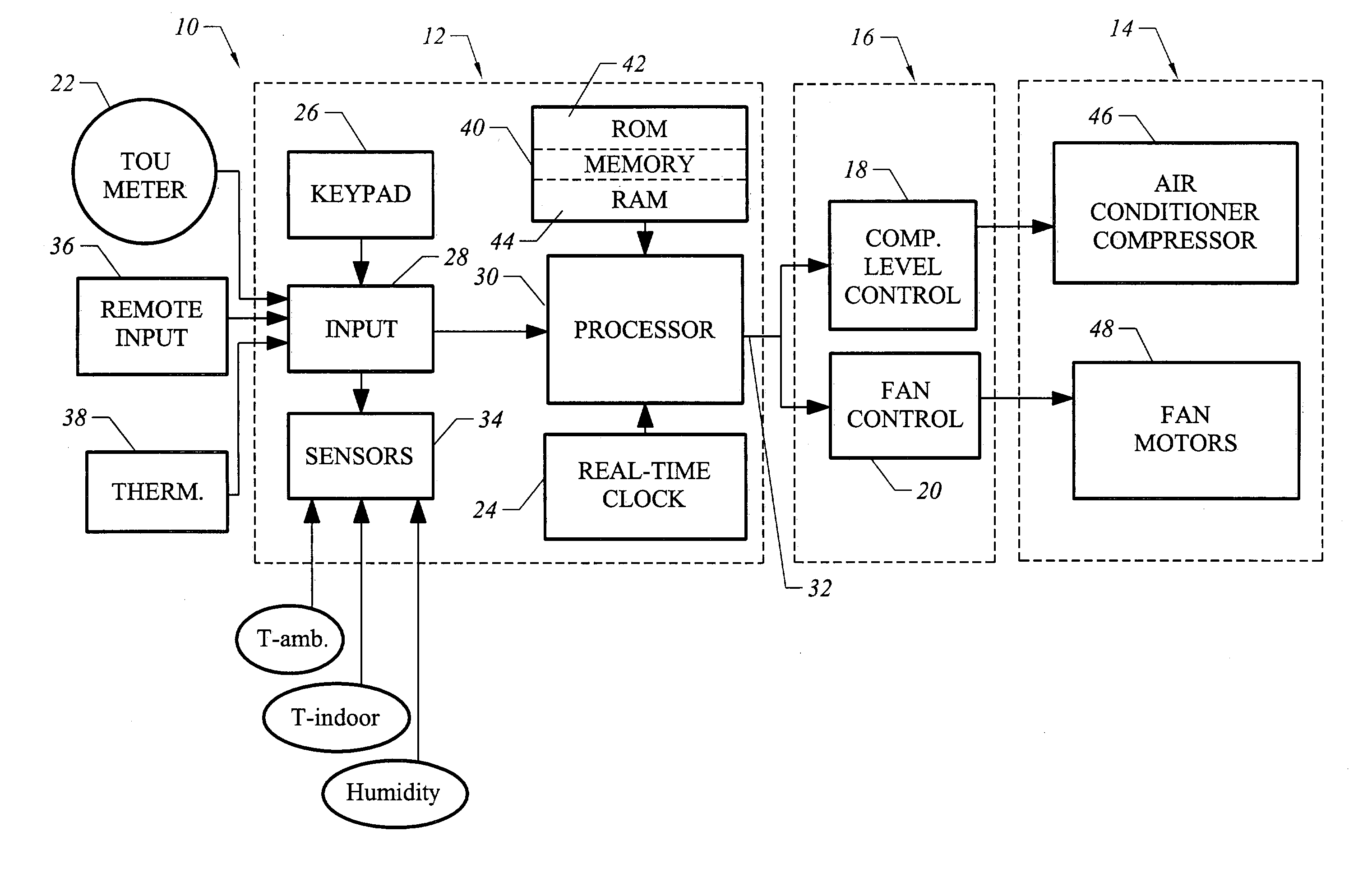
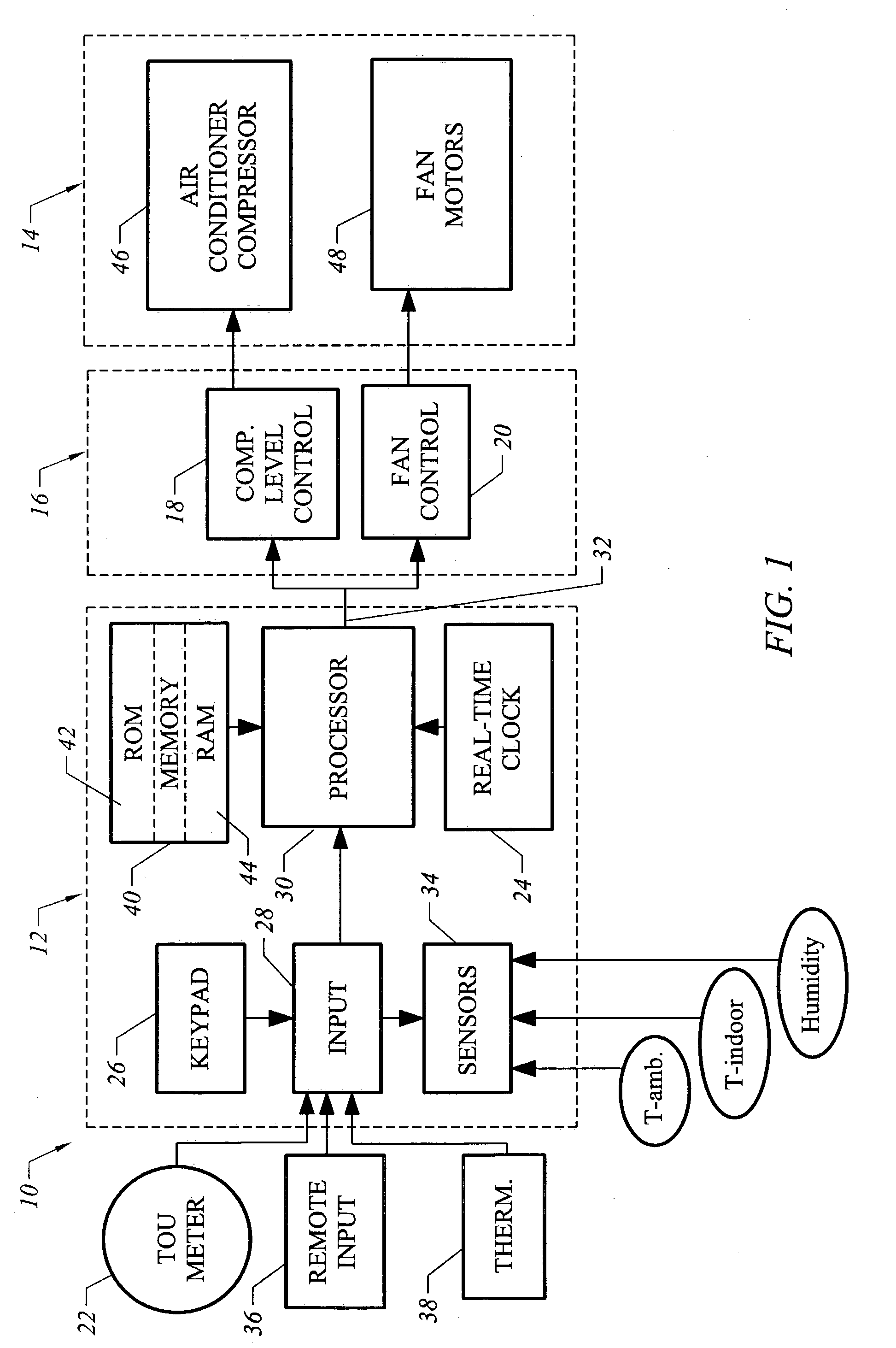
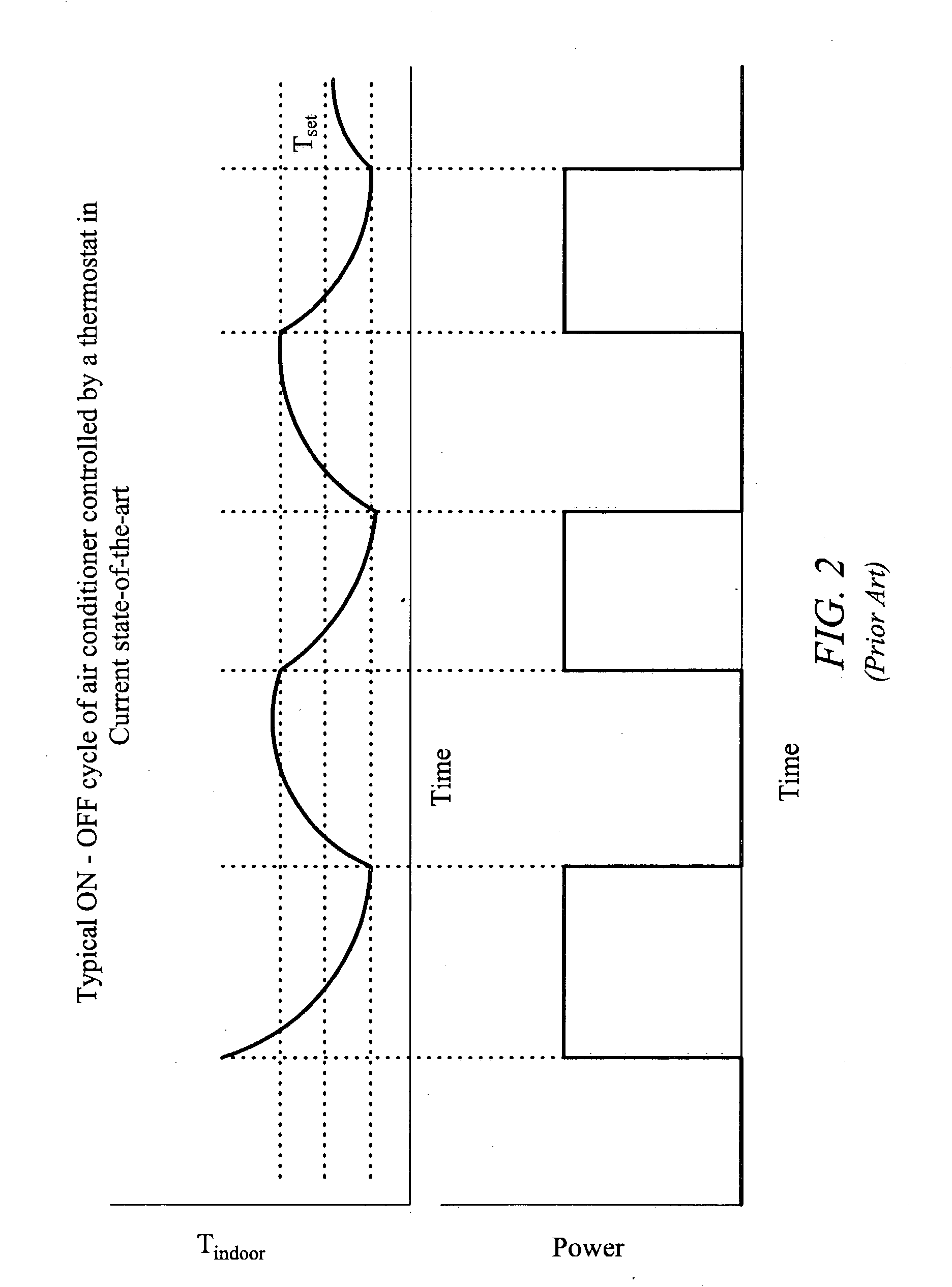
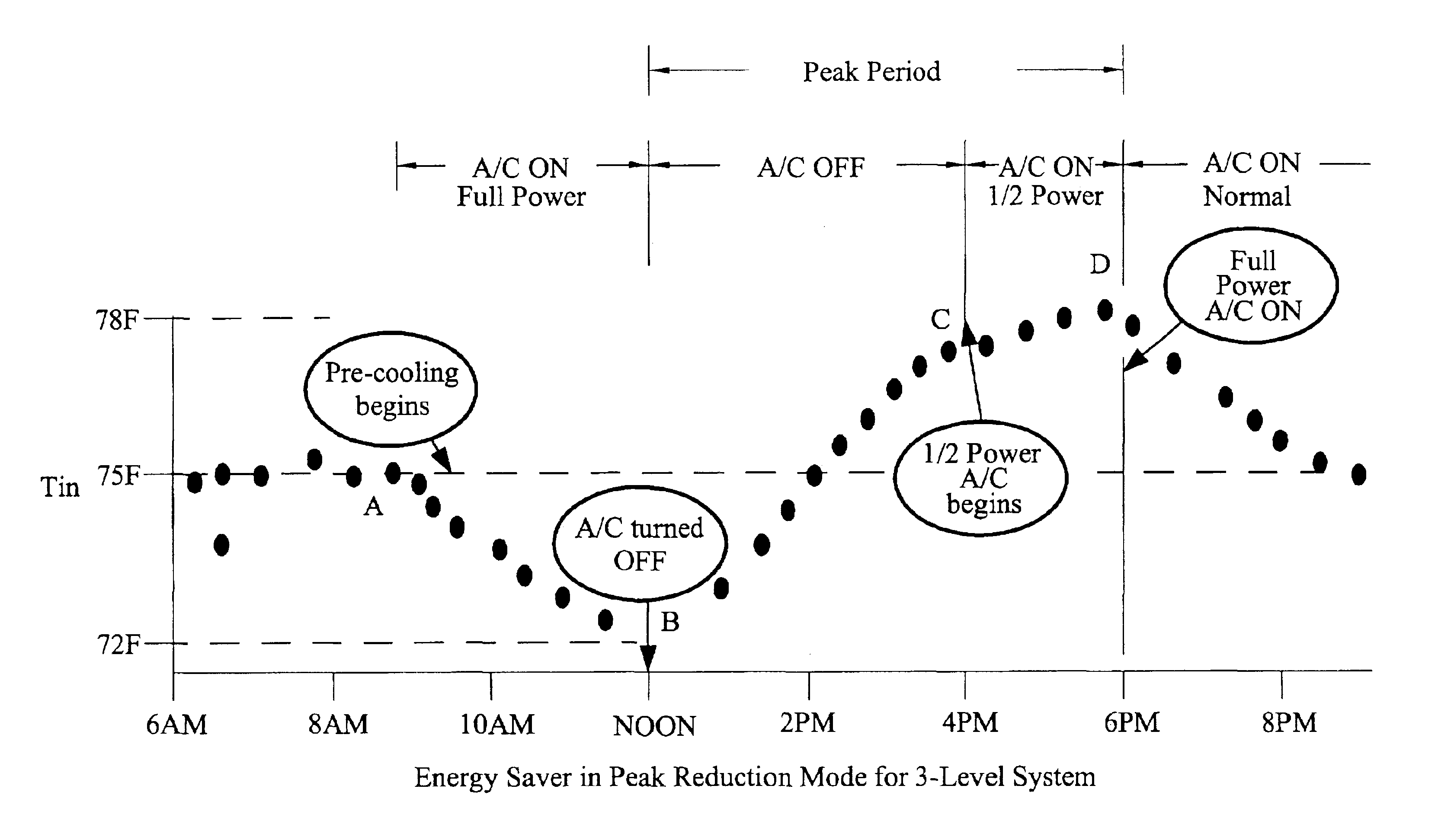
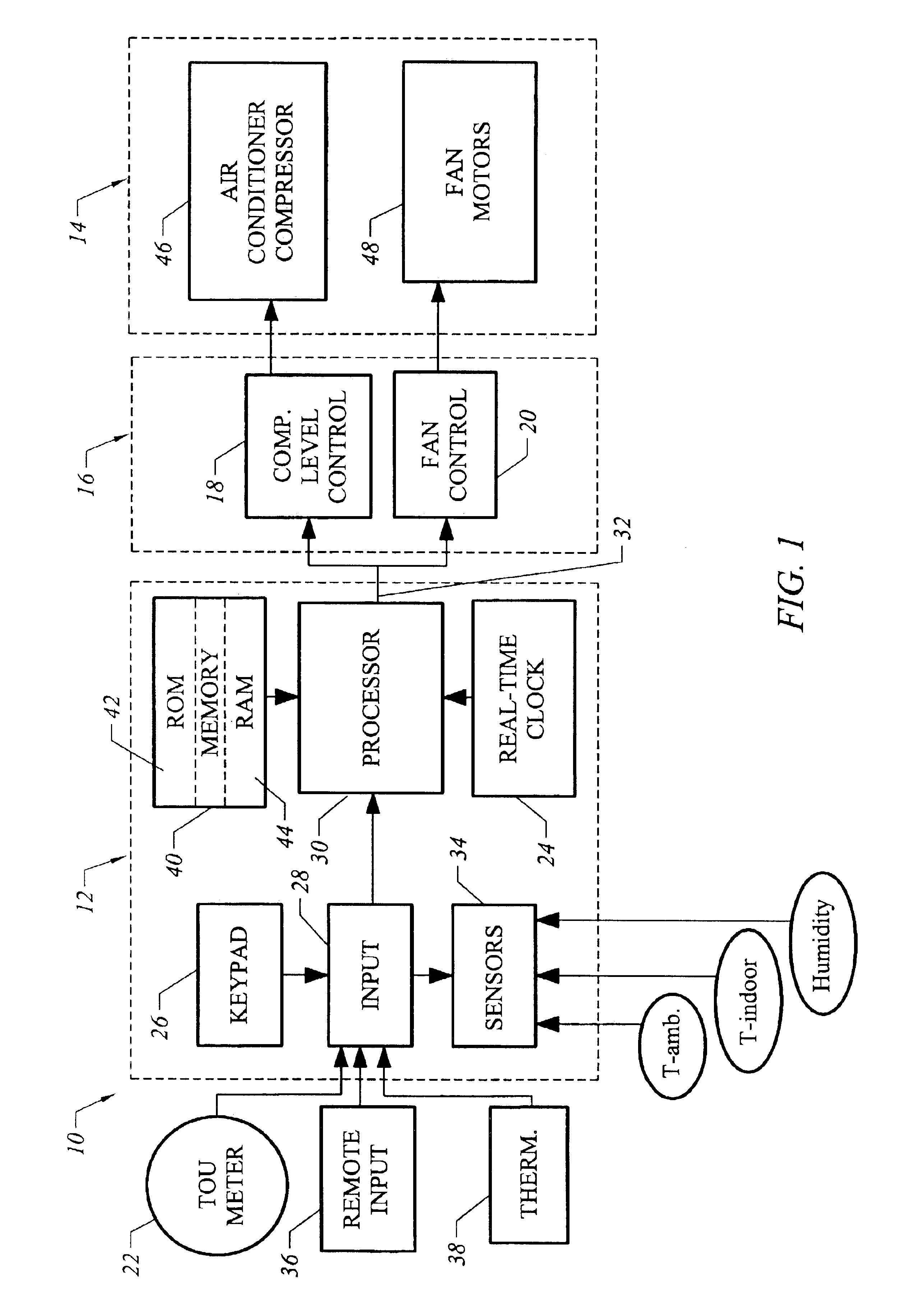
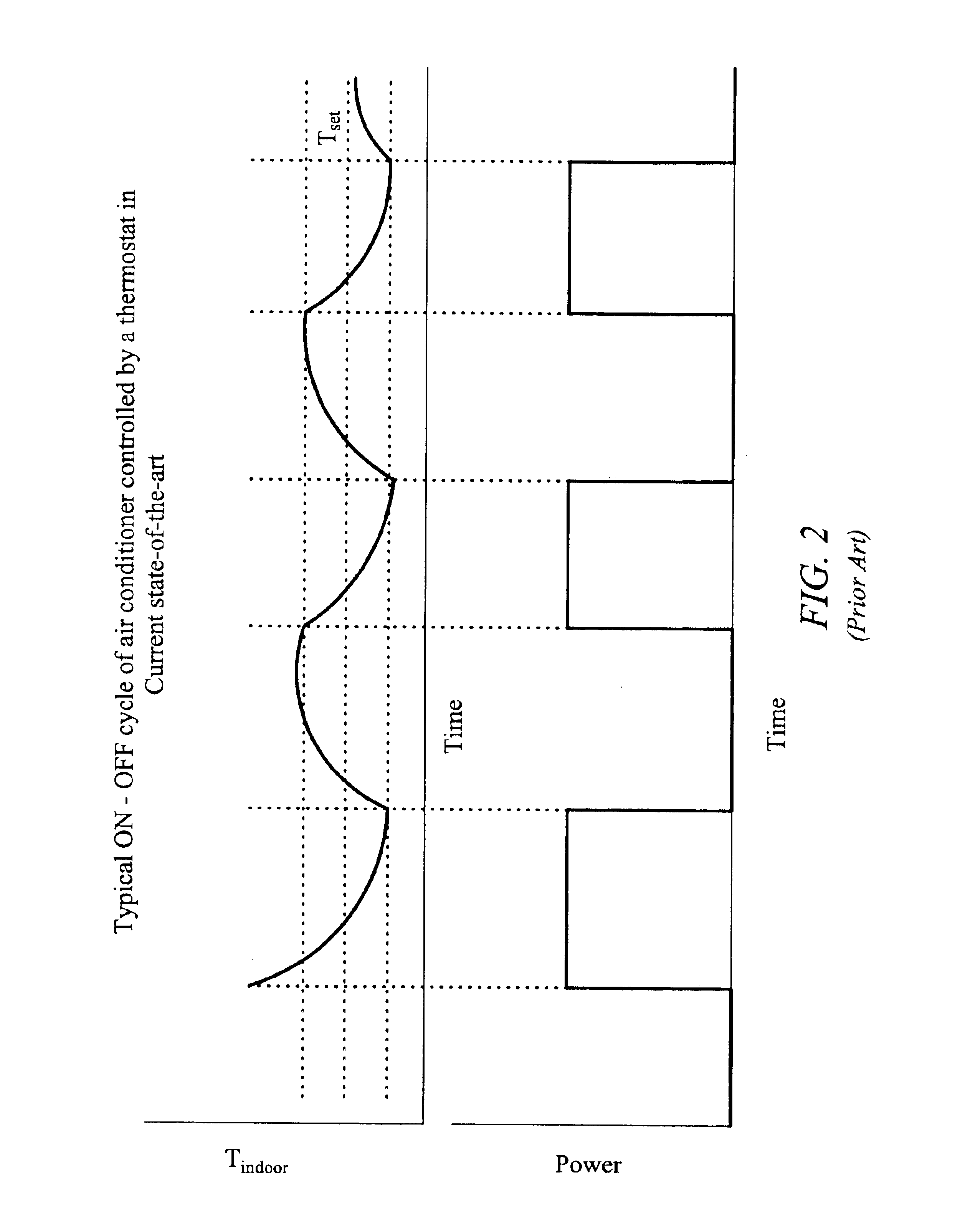
Strategic-response control system for regulating air conditioners for economic operation
InactiveUS20050005621A1Minimize adverse effectsAcceptable level of comfortDc network circuit arrangementsMechanical apparatusReal-time clockElectricity price
A strategic response control for an air conditioning system for use in an environment with increased power rates during a designated peak period. The air conditioning system includes a power board for operating the air conditioning system in one or more operating status having a controller with a processor and a real time clock, an indoor temperature sensor for generating an input signal representing the indoor temperature, an outdoor temperature sensor for generating an input signal representing the outdoor temperature, and an operating program that sets a maximum comfort level temperature, a minimum comfort level temperature and a warmup rate for the environment in which the air conditioner operates, and has a procedure for precooling the environment before the peak period, wherein on activation, the processor signals the power board to enter an operating state for precooling and an “off” or lower level operating state during the peak period.
Owner:LEVENE EDWARD R
Audience response determination
InactiveUS7555766B2Increase enjoymentAccurate responseReservationsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsAudience responseMultimedia
An audience response determination apparatus detects the state of an audience and the individual states of the members of the audience to determine the response of the audience to the content of entertainment and the like. Based on the thus determined audience response, a playback operation of the content such as a movie is controlled, so that the level of satisfaction felt by the audience to the content can be increased.
Owner:SONY CORP
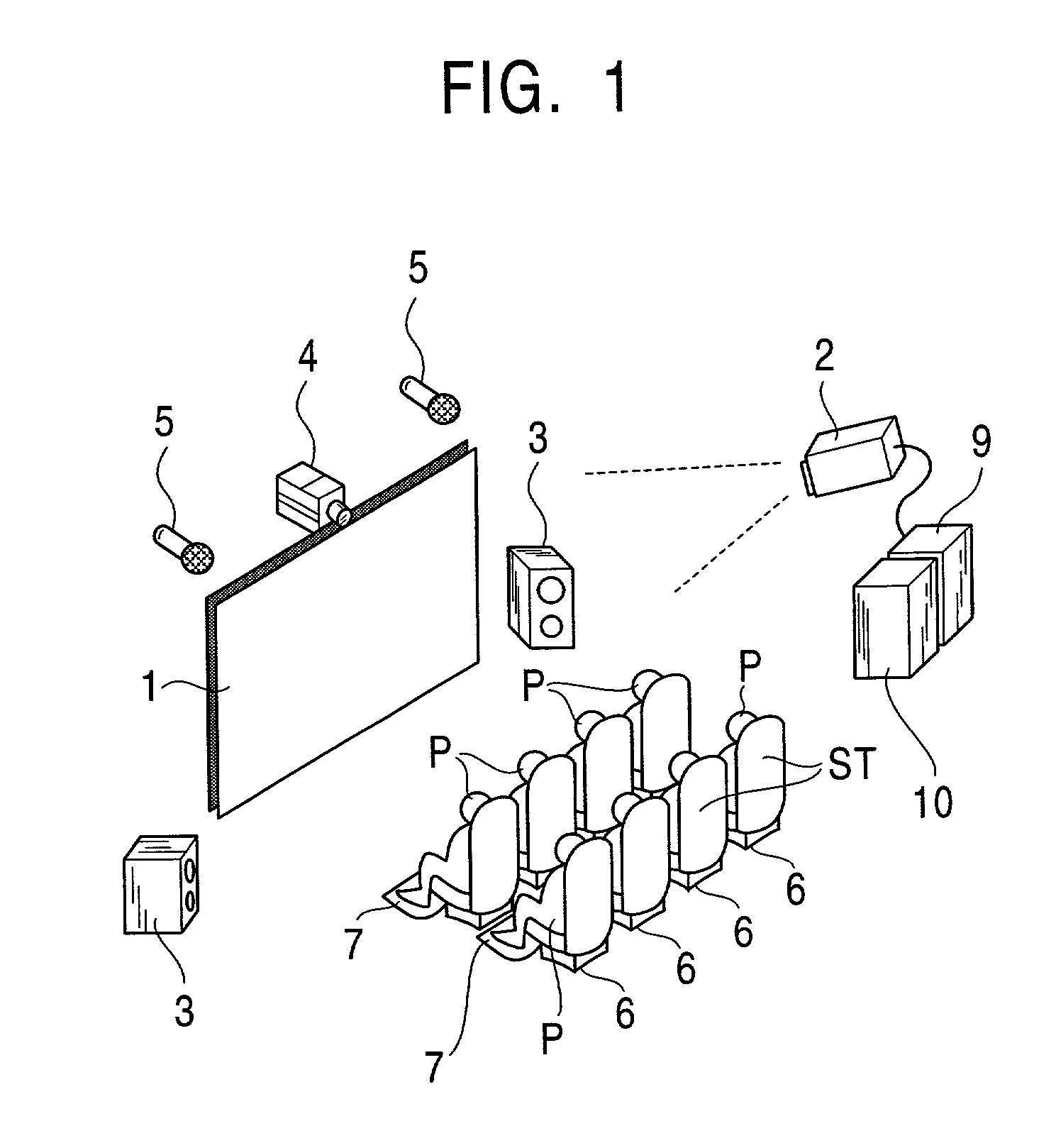
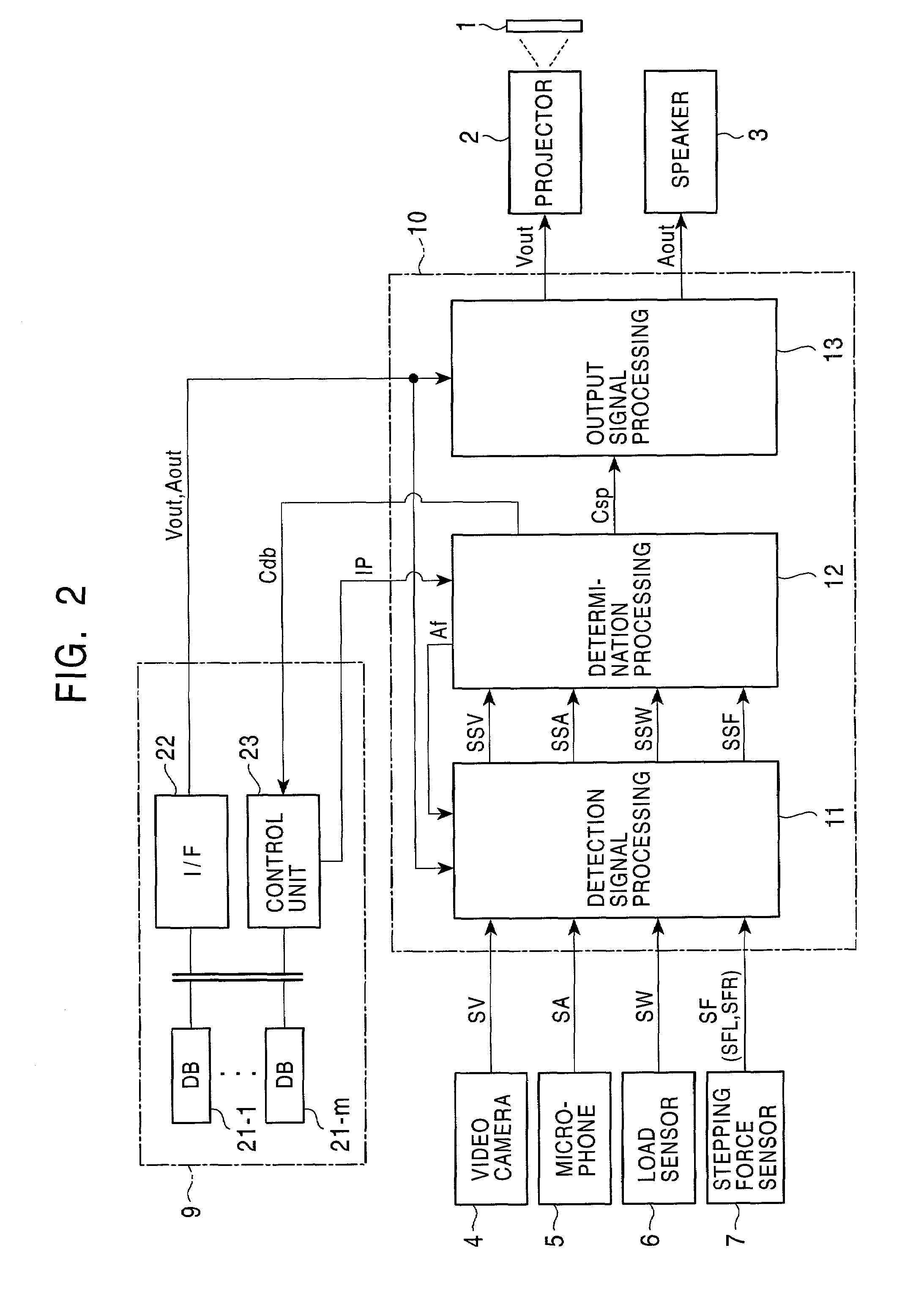
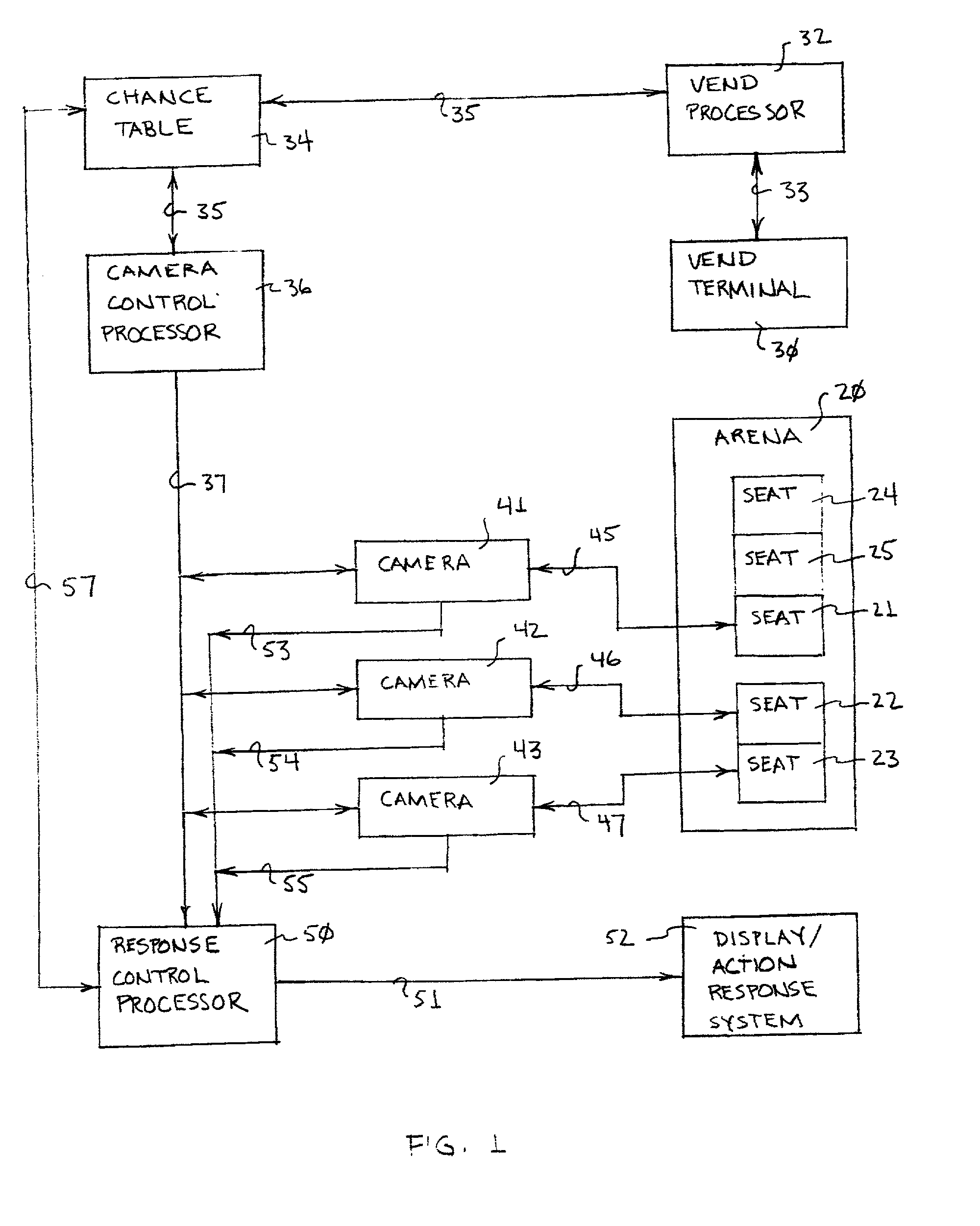
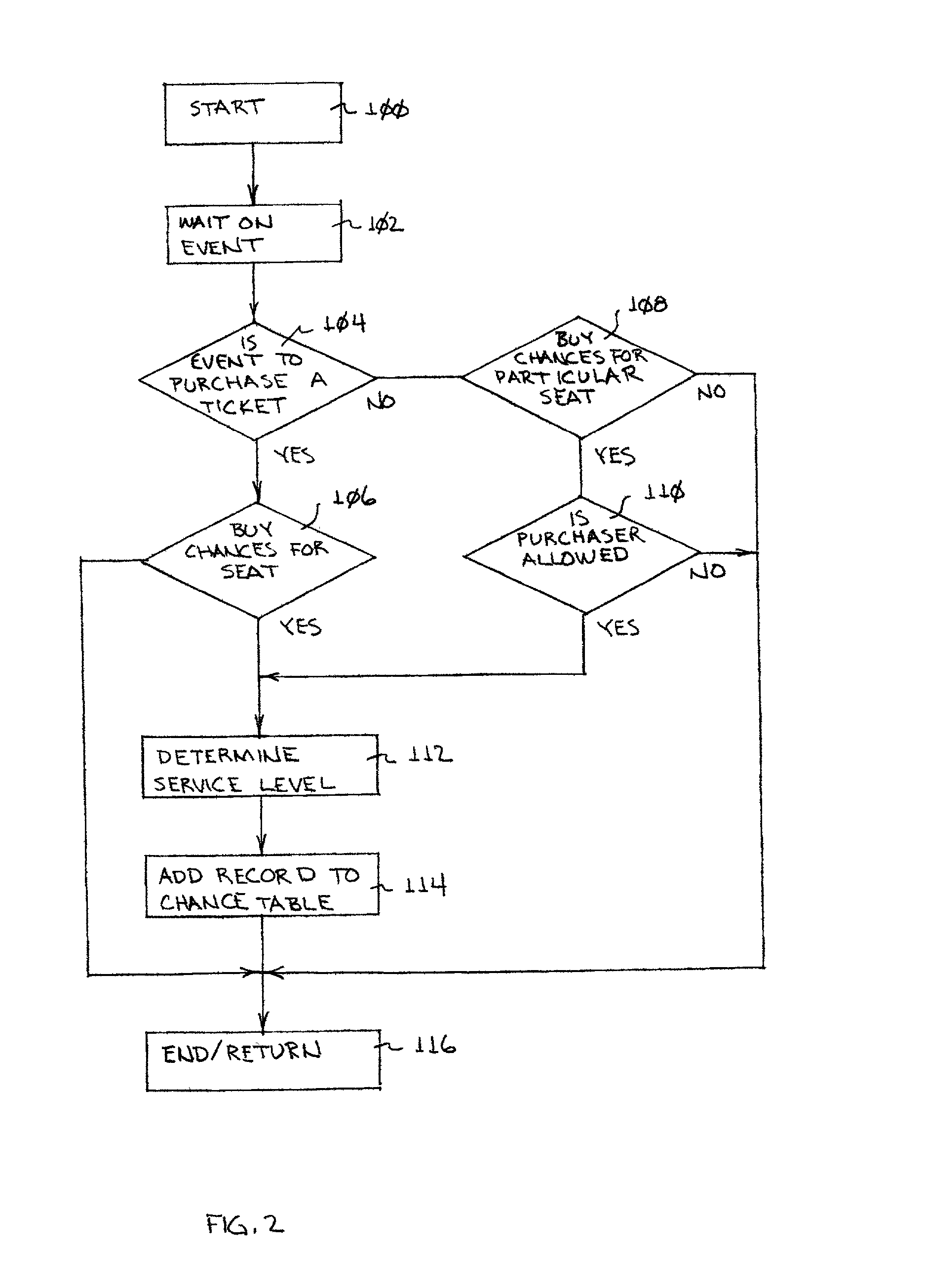
System and method for selecting arena seat locations for display
InactiveUS20030040943A1Increase opportunitiesReservationsMarketingCamera controlComputer graphics (images)
Arena locations are selected by chances sold to customers for recording and distributing video images of the location. A vend terminal / processor system is used to sell these chances and load them to a chance table. The chance table is accessed by a camera control processor and a response control processor to cause a video camera to record and transmit images of selected arena locations selectively to a TV live or delayed broadcast, a view screen at the arena, or to a remote customer for viewing at a display.
Owner:IBM CORP
Resource allocation method
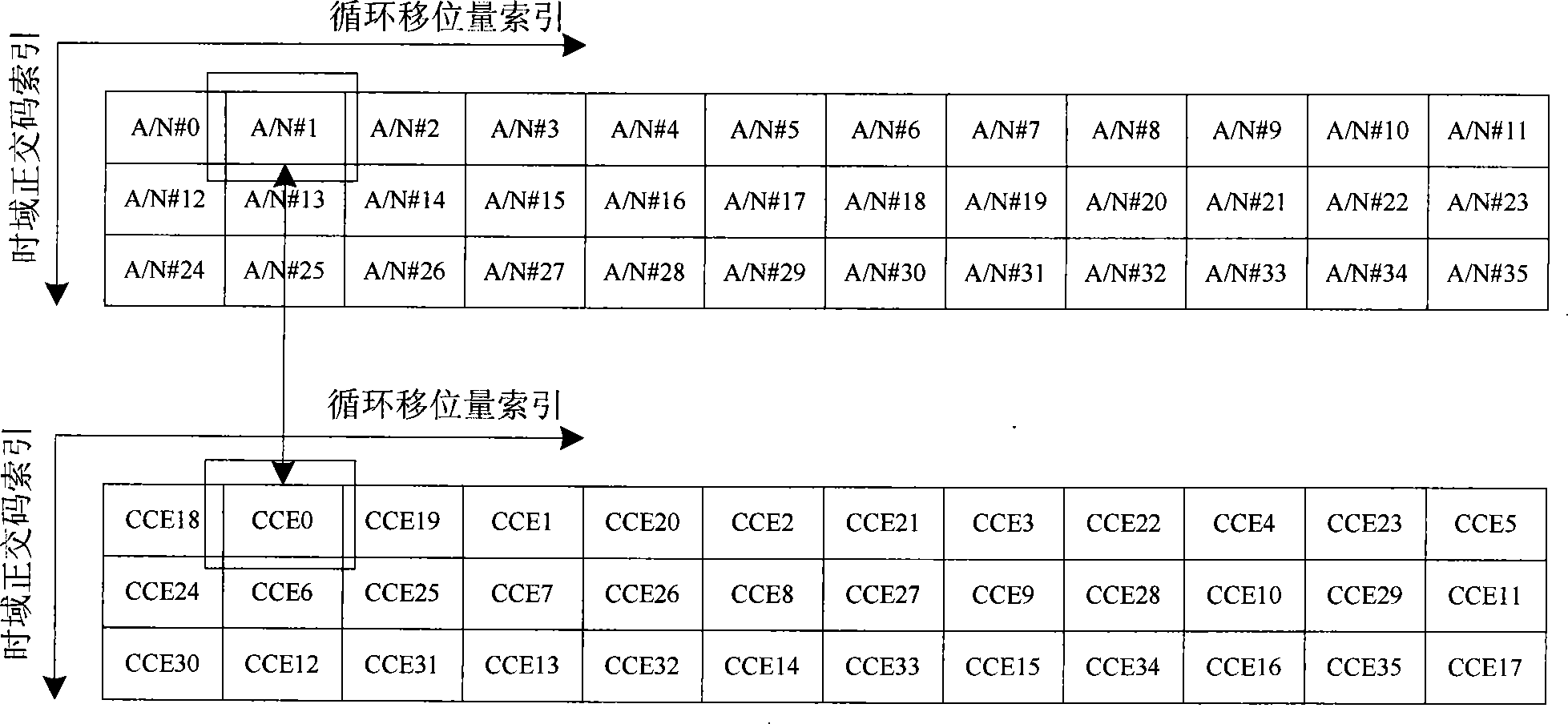
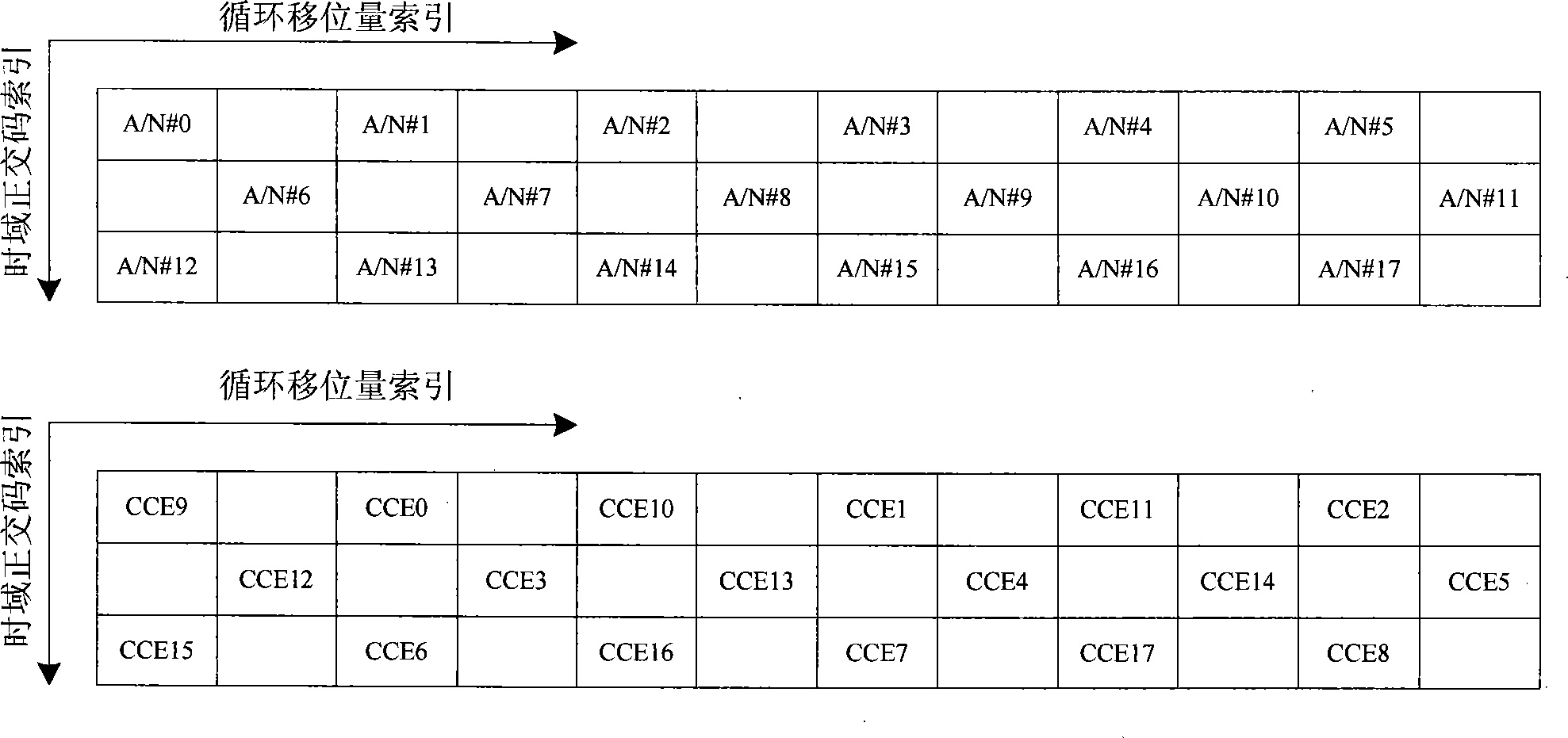
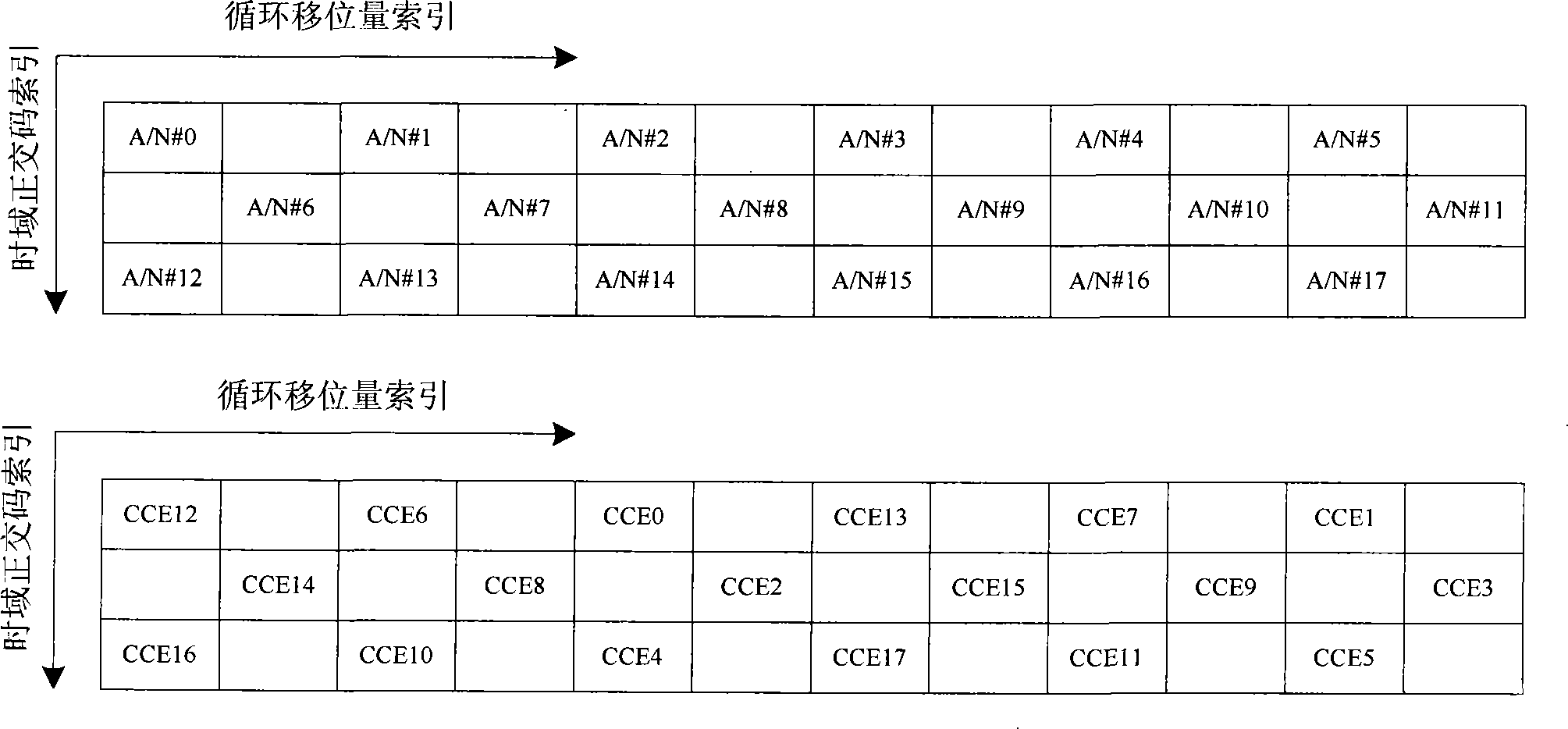
InactiveCN101252783AReduce distractionsEasy to implementError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime domainTelecommunications
The invention relates to a resource allocation method. A base station utilizes a control channel unit of a physical downlink control channel to transmit control signaling related to the downstream data to a mobile terminal; after the mobile terminal receives the control signaling, the mobile terminal obtains virtual resource block index mapped by the corresponding physical uplink response control channel, and physical uplink reply control channel index which is determined by mapped circulating motion amount index and time domain orthogonal code index in the virtual resource block according to the index of the control channel unit, and the set mapping method; the mobile terminal returns positive / negative acknowledgement control signaling on the physical uplink response control channel to the base station; when the set mapping method ensures the physical uplink response control channel corresponding to adjacent control channel unit indexes to be mapped to an identical virtual resource block, the mapped time domain orthogonal code indexes are different or identical, but the circulating motion amount indexes are not adjacent, therefore the interference between the physical uplink response control channels corresponding to the adjacent control channel units is minimized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
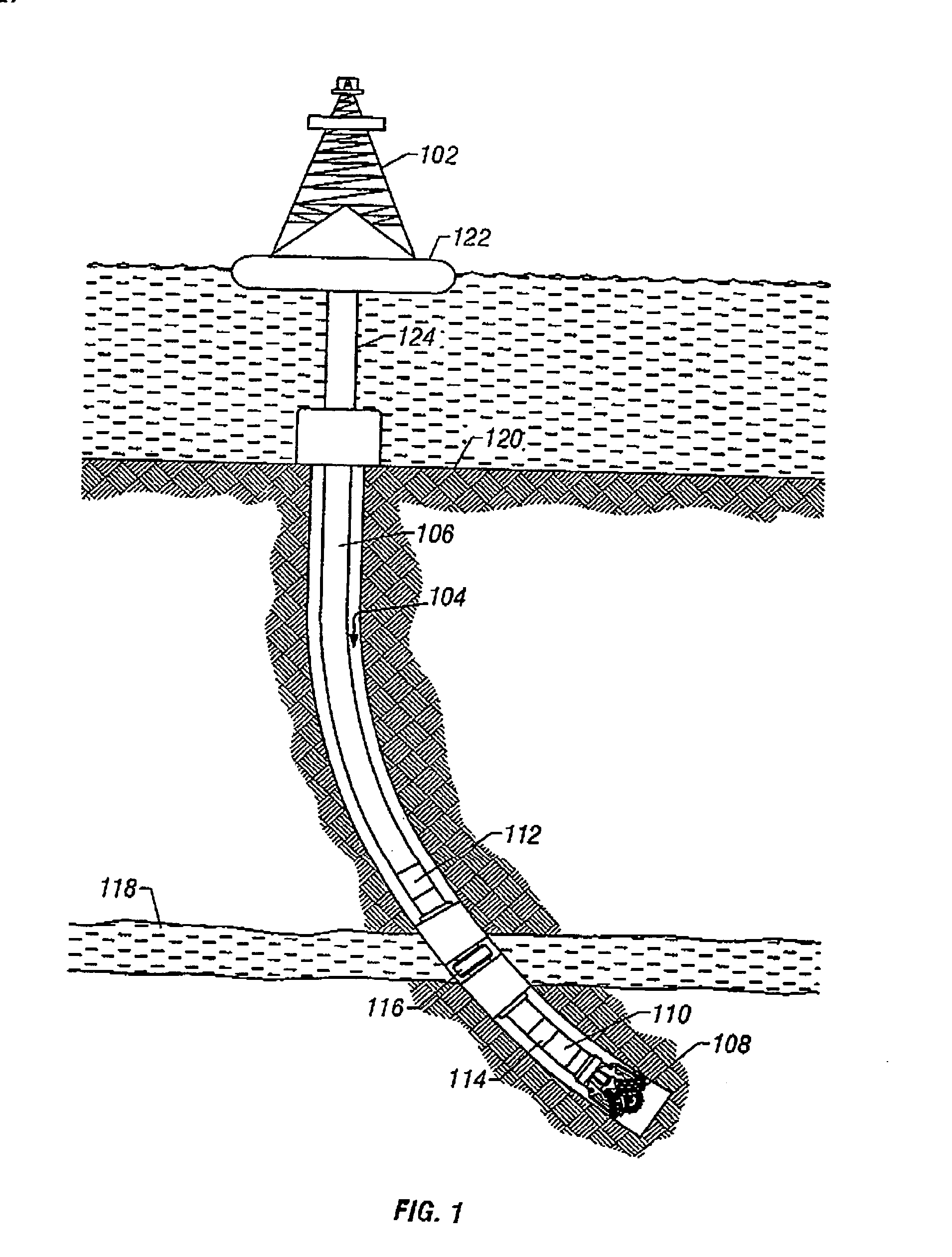
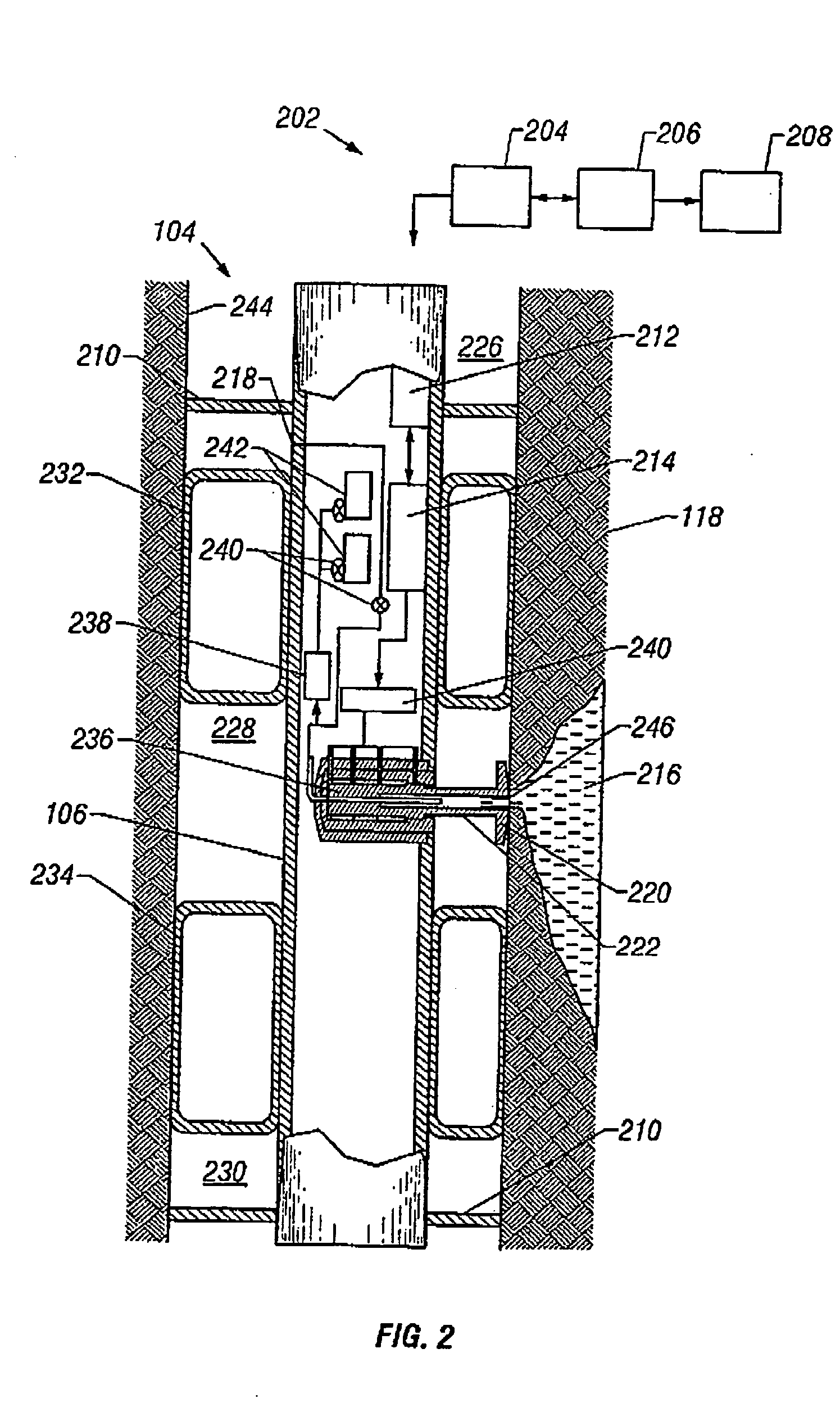
Apparatus and methods for sampling and testing a formation fluid
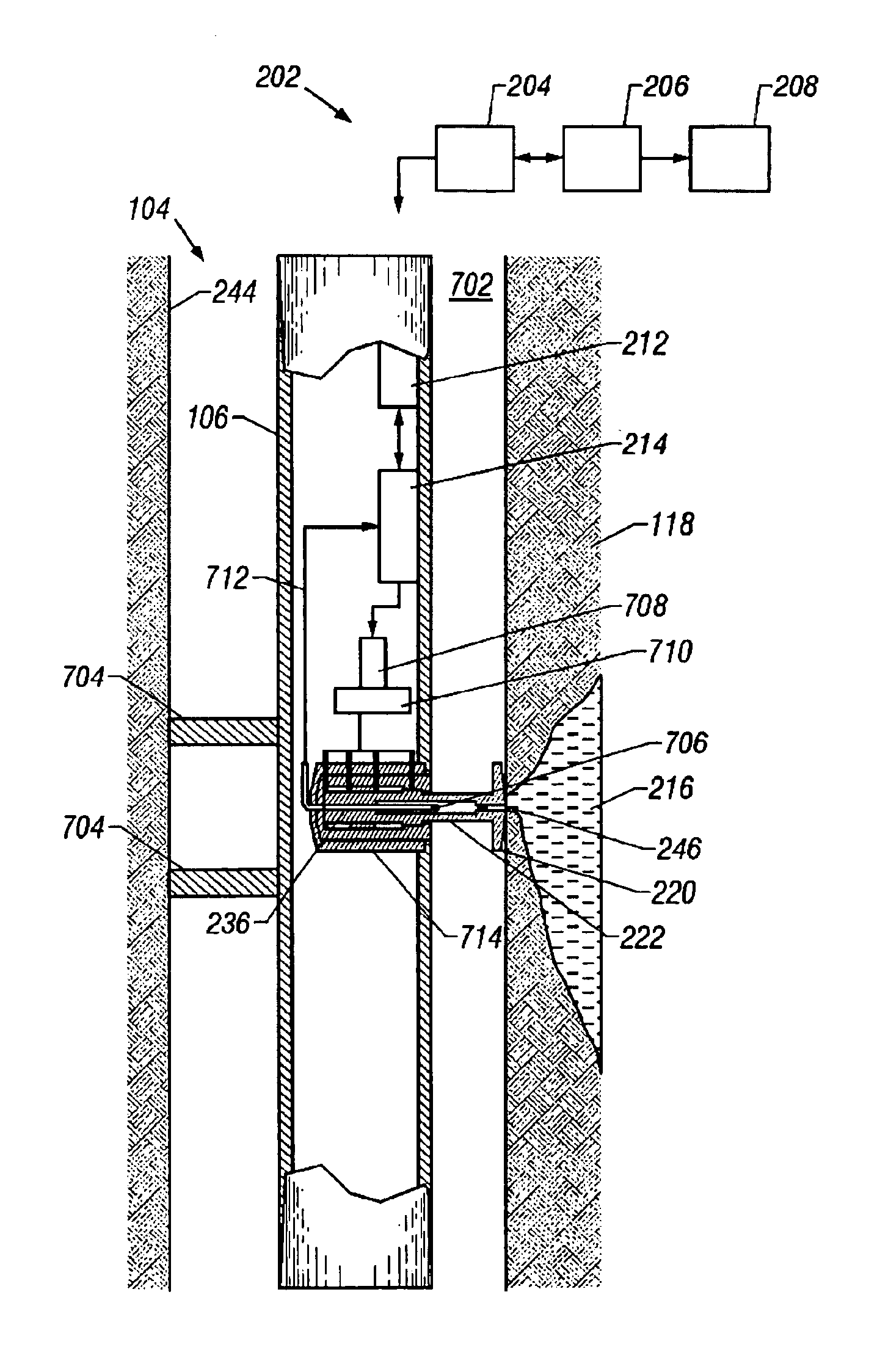
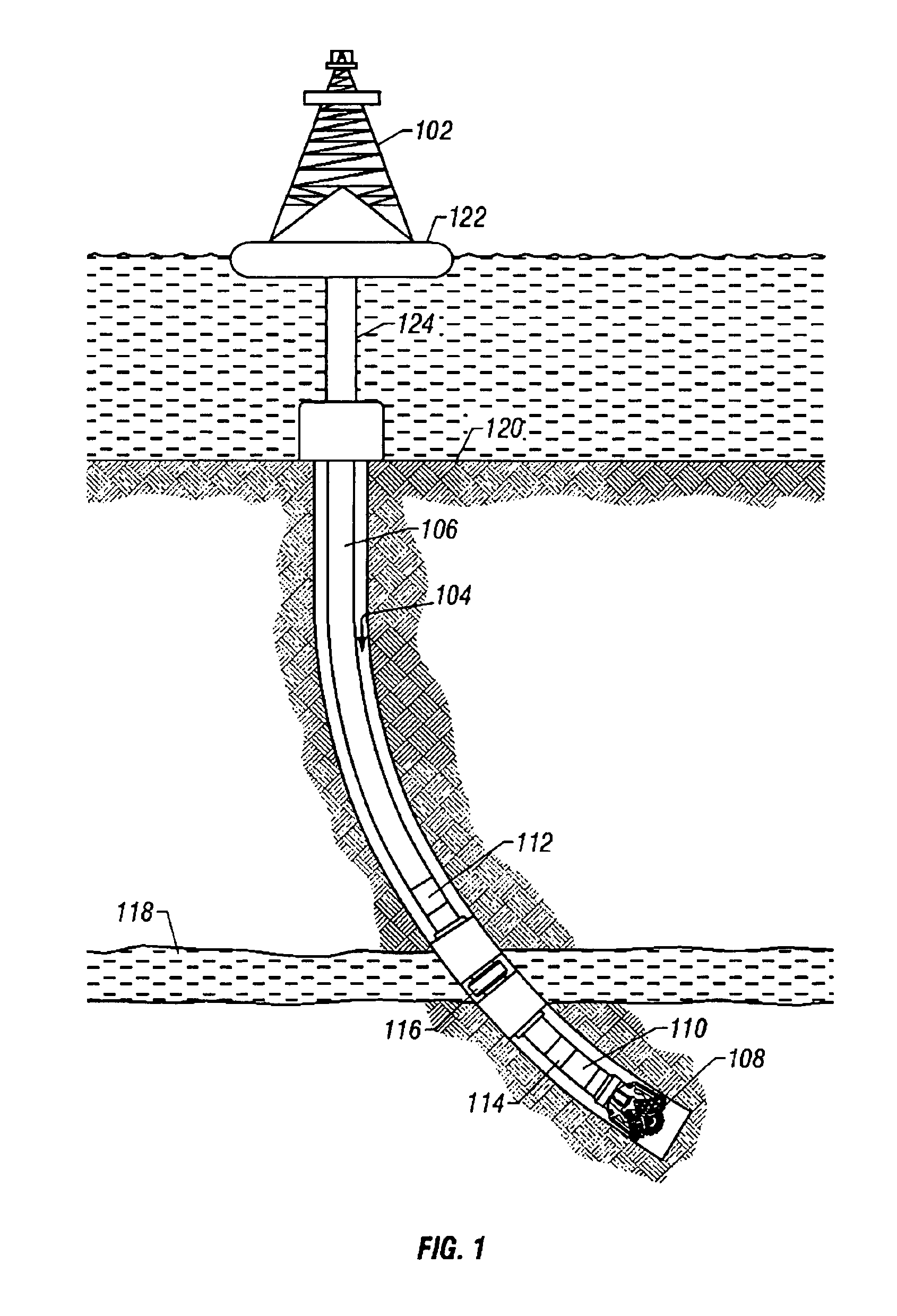
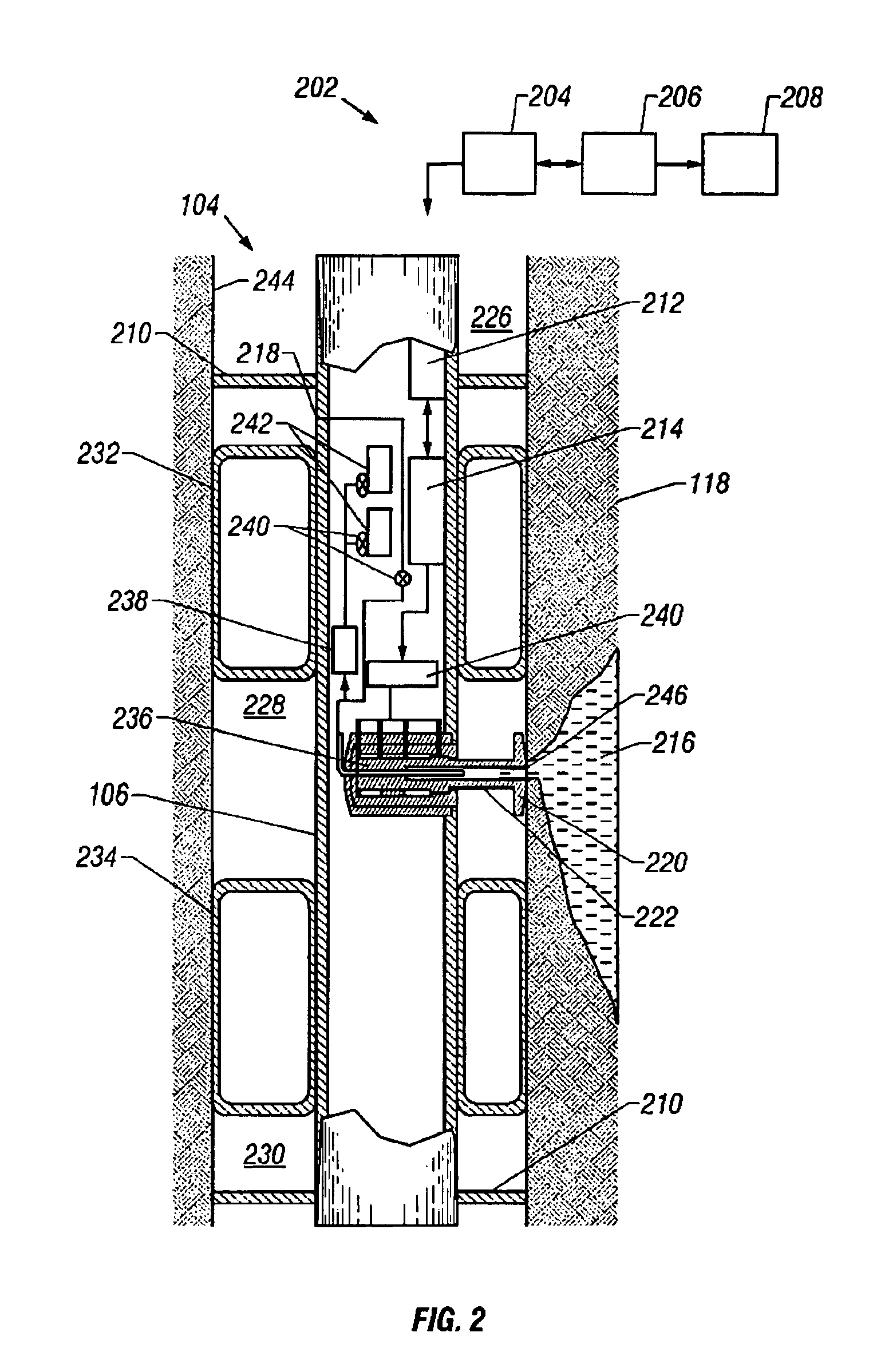
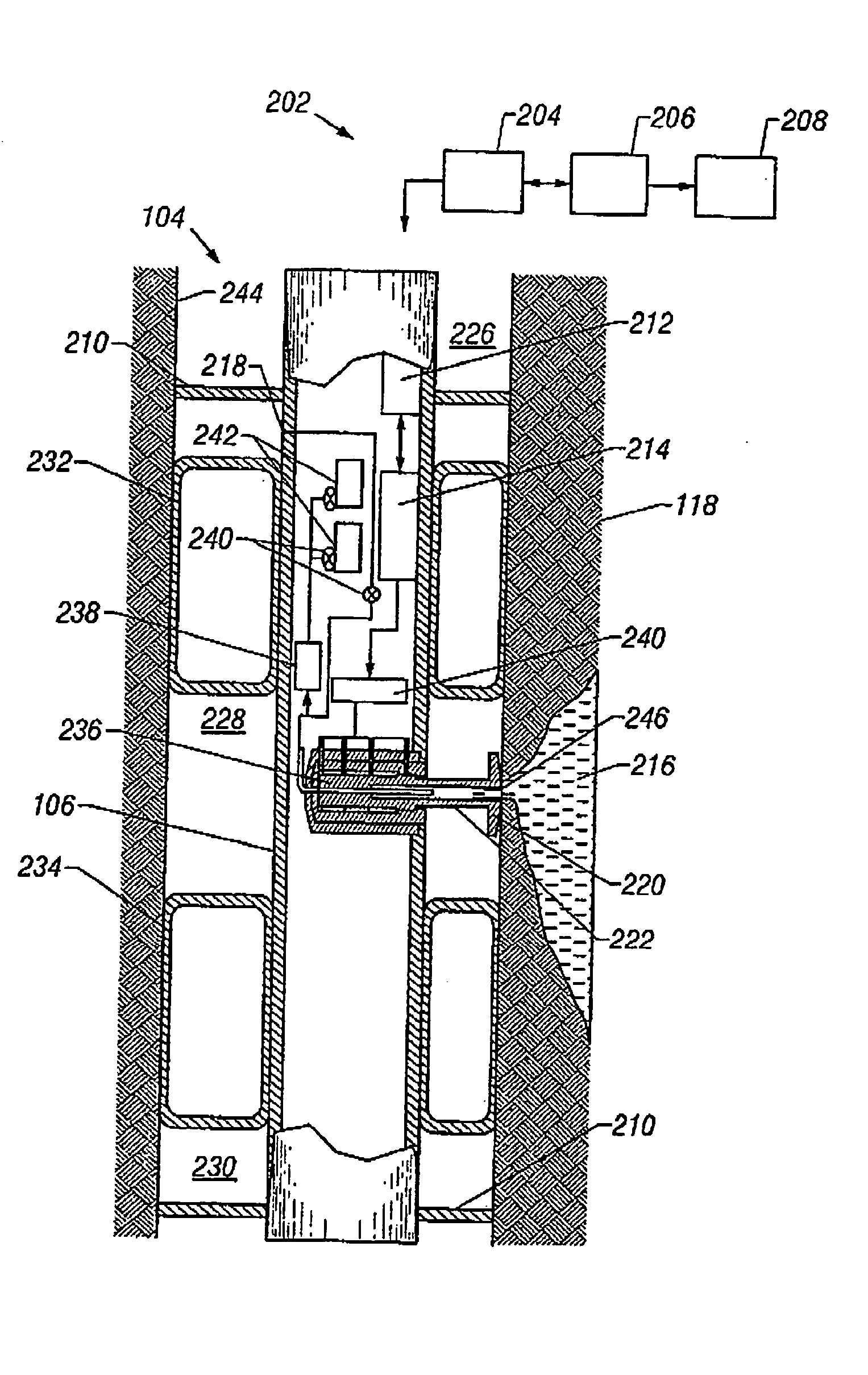
InactiveUS6871713B2Shorten the timeReduce riskSurveyAutomatic control for drillingControl systemFormation fluid
A formation test tool and methods are described that enable sampling and measurements of parameters of fluids contained in a borehole while reducing the time required for taking such samples and measurements and reducing the risk of formation damage due to sampling induced pressure spikes. The tool has a quick response control system for controlling a fluid transfer device in response to fluid pressure near a sampling port.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Apparatus and methods for sampling and testing a formation fluid
A formation test tool and methods are described that enable sampling and measurements of parameters of fluids contained in a borehole while reducing the time required for taking such samples and measurements and reducing the risk of formation damage due to sampling induced pressure spikes. The tool has a quick response control system for controlling a fluid transfer device in response to fluid pressure near a sampling port.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
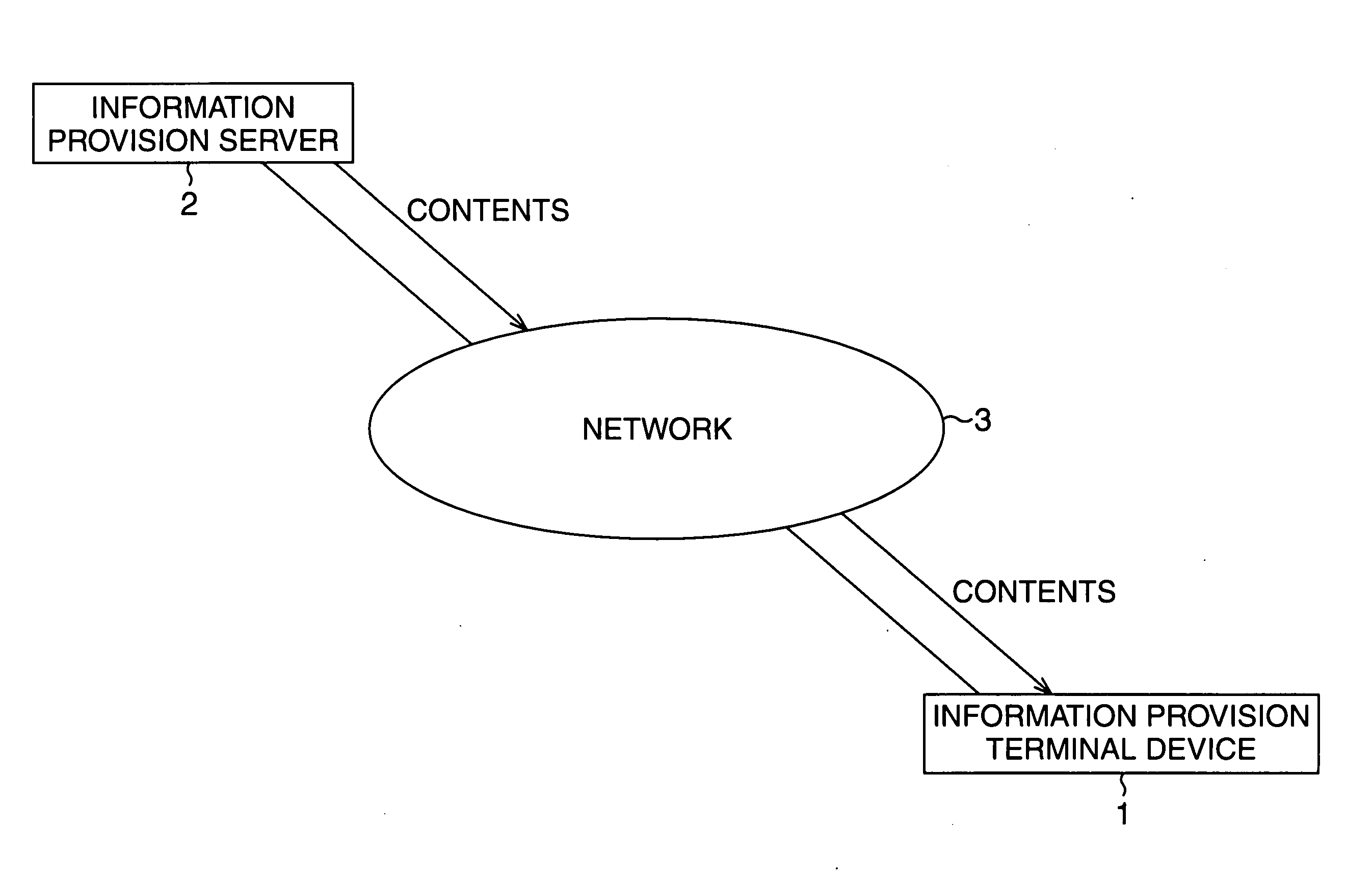
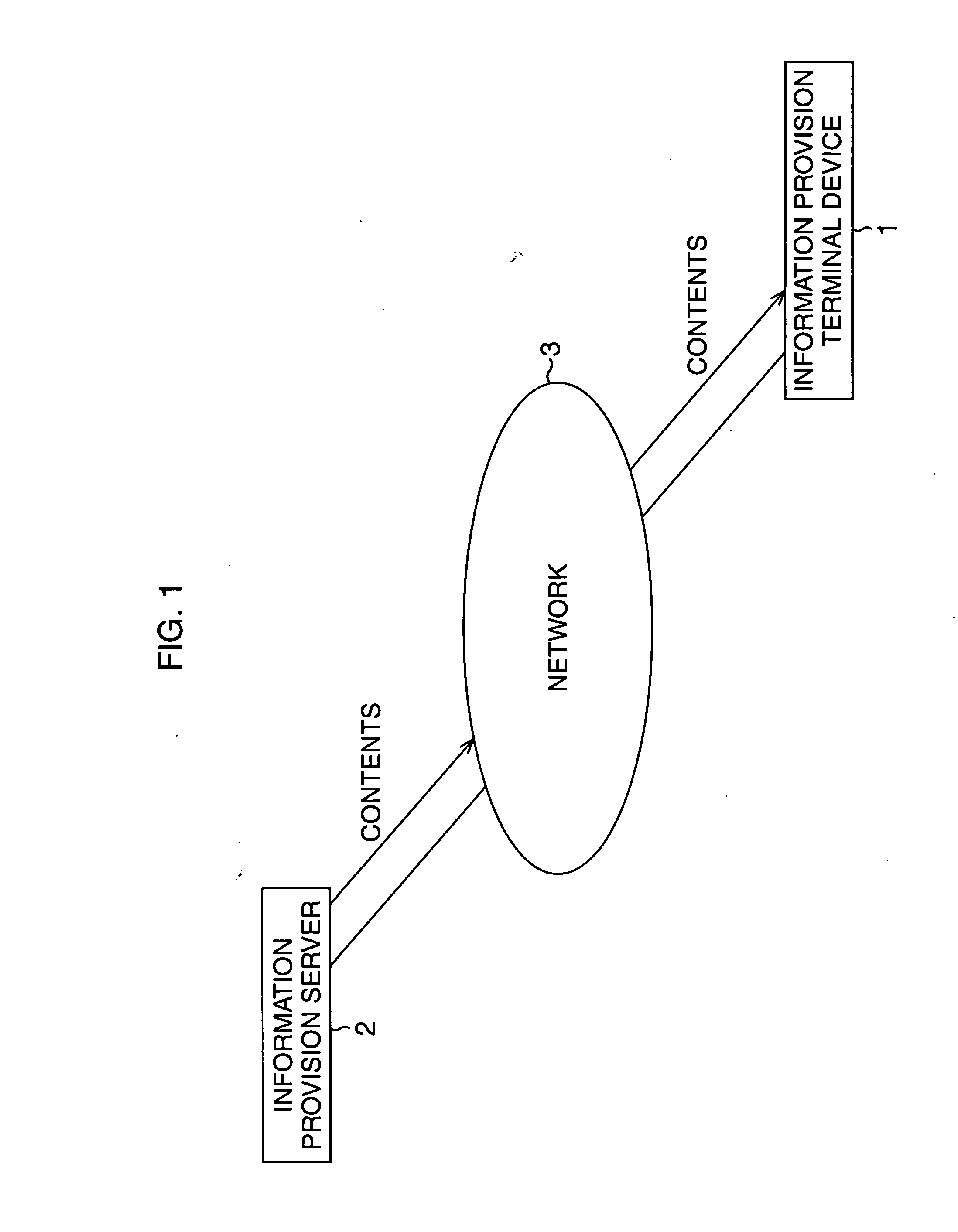
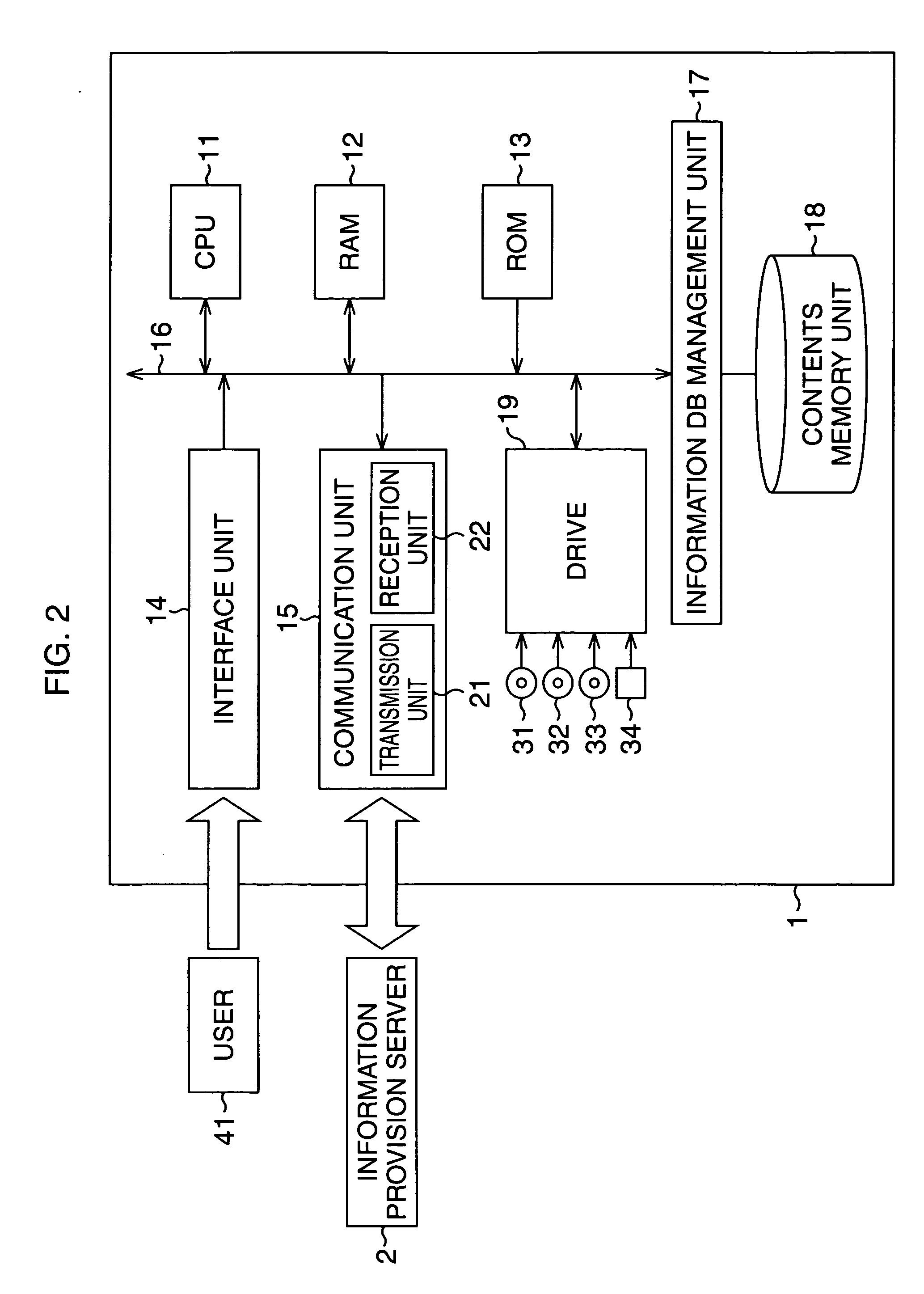
Terminal device, business designation method, contents provision device, contents provision method, recording medium, program, business management system and business management method
InactiveUS20060265228A1Minimum operationDigital computer detailsResourcesData controlCommunication unit
The present invention enables the continuous designation of appropriate business at an appropriate timing and in appropriate order with minimal operation, and enables the management side to comprehend the business condition. A master control unit 101 controls the output of an aggregate based on an event response control program associated with the aggregate containing information being output, and in correspondence with an event. A play list reader 102 controls the output of information contained in an aggregate based on ordinal data associated with the aggregate for which the output thereof has been designated by the master control unit 101. A communication unit 106 controls the transmission of business condition information indicating the condition of business to a business support server 502 for providing the contents based on the event response control program, and in correspondence with an event. The present invention may be employed in a business support system for supporting the implementation of business.
Owner:ORMON CORP
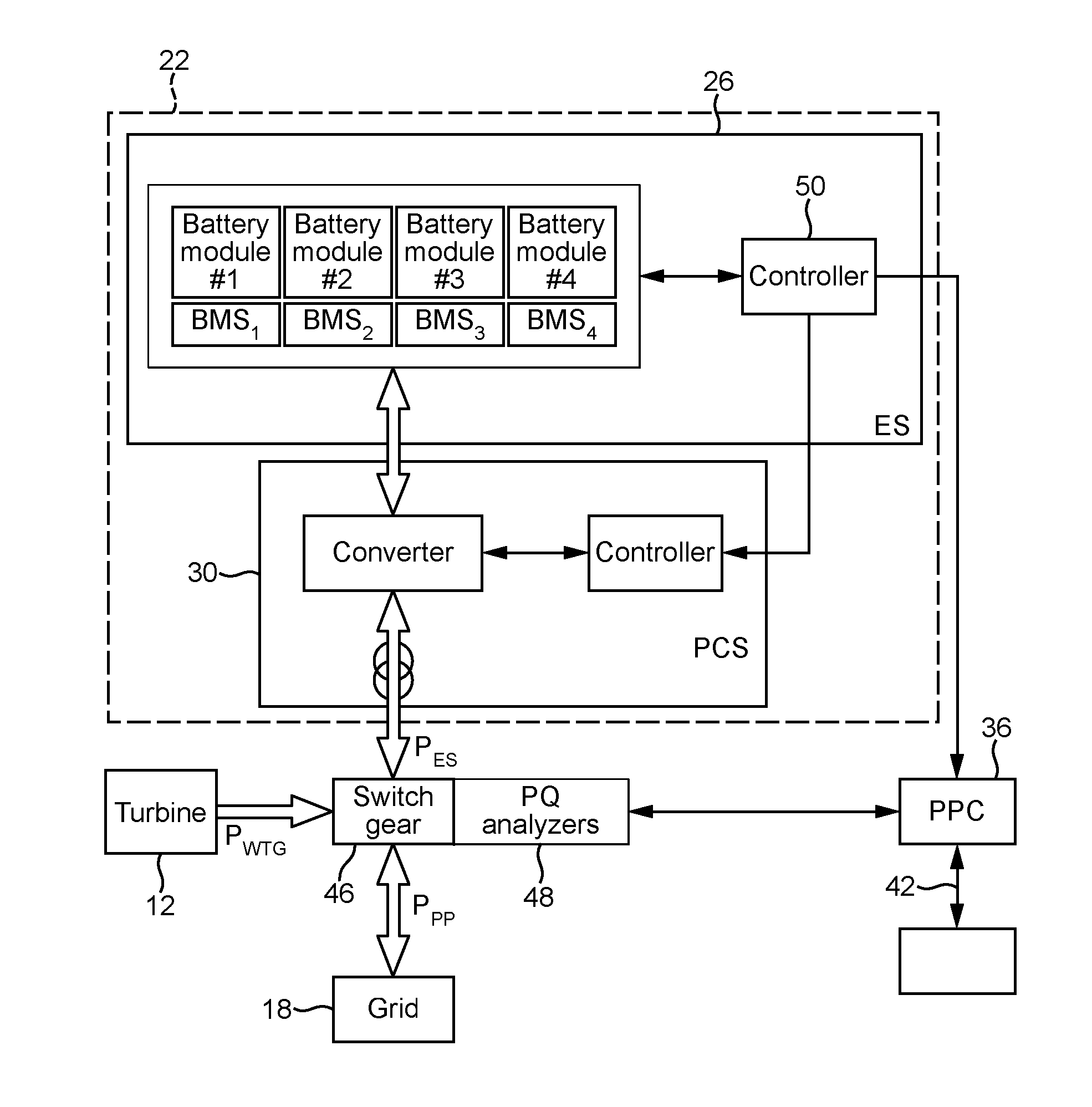
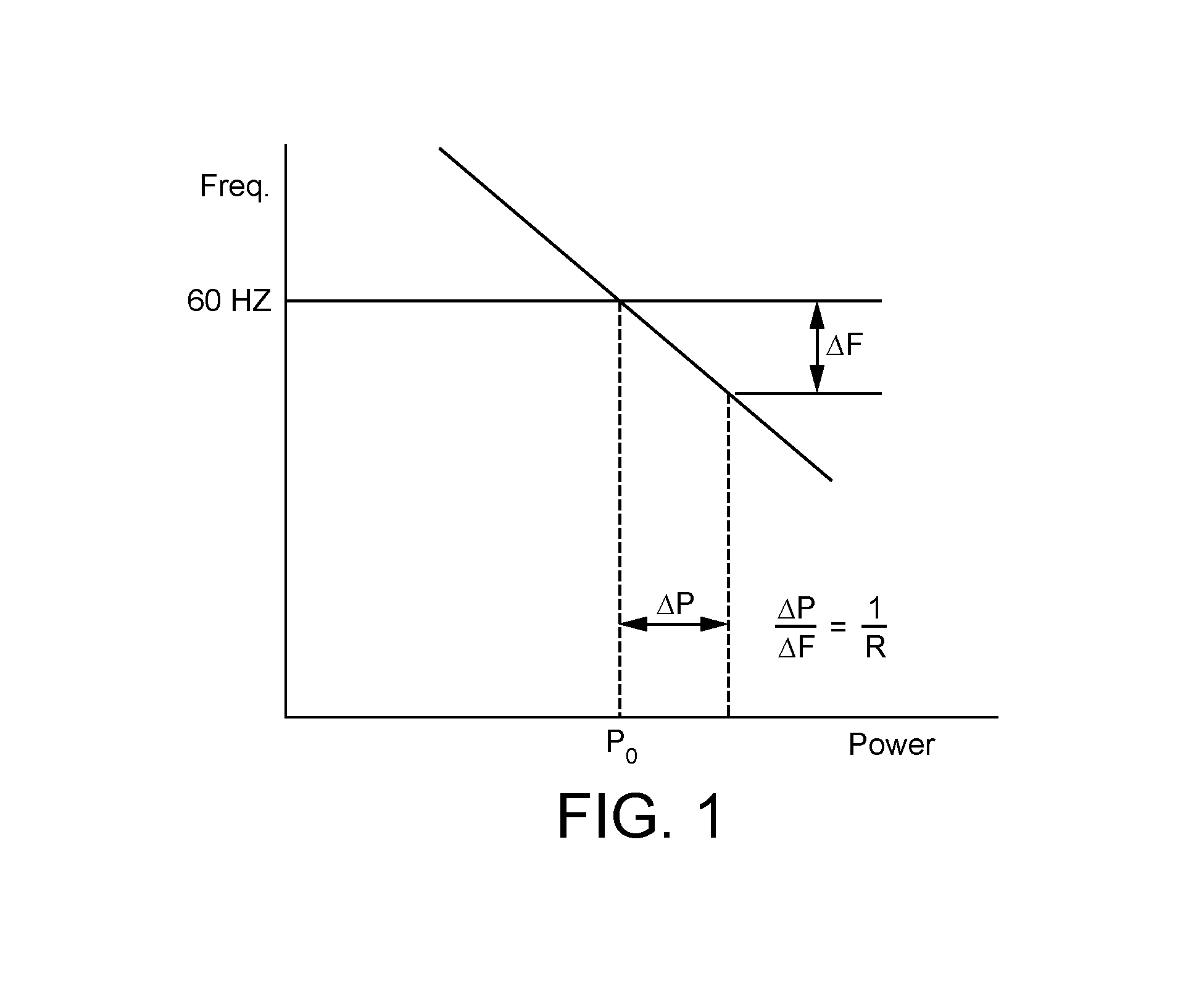
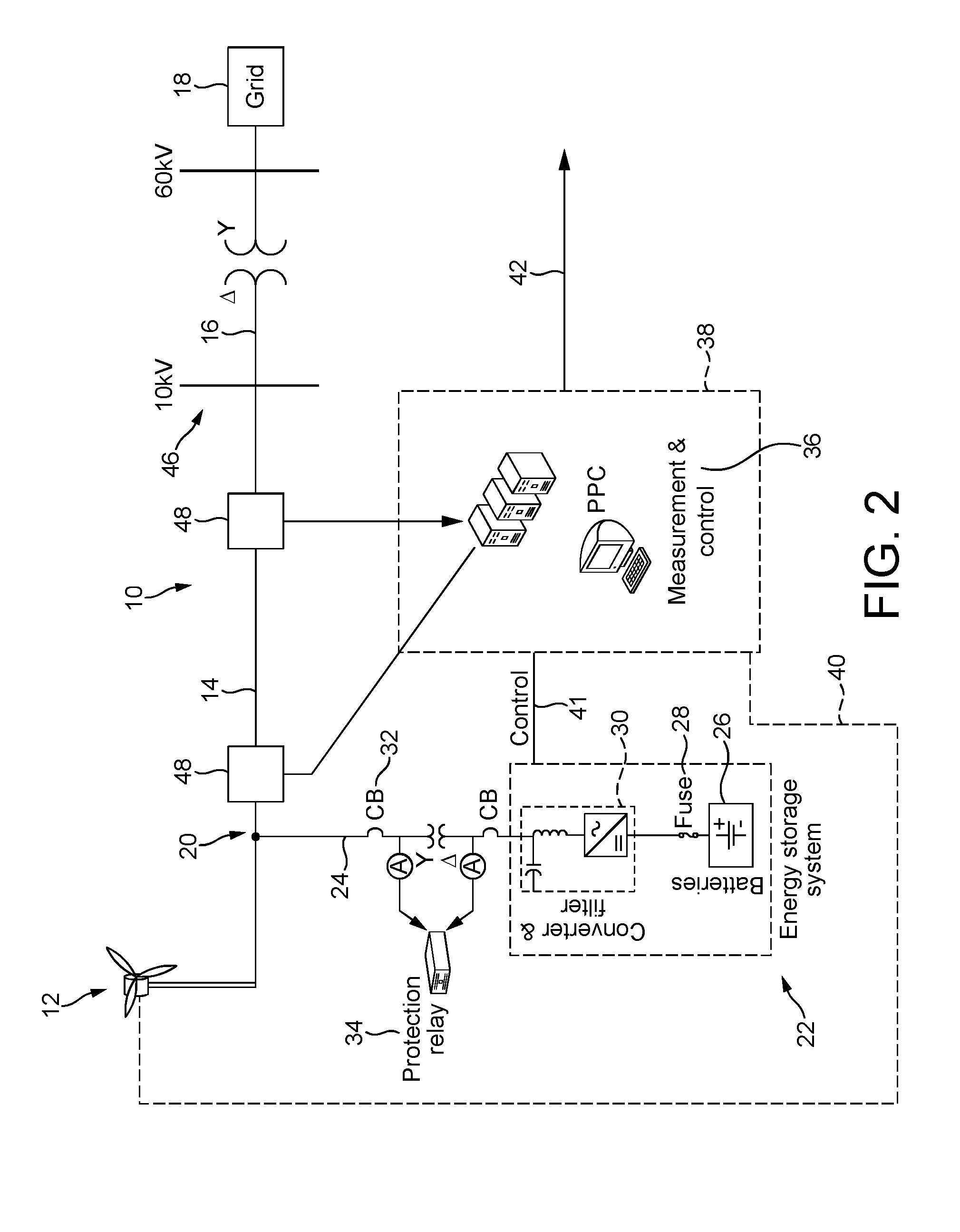
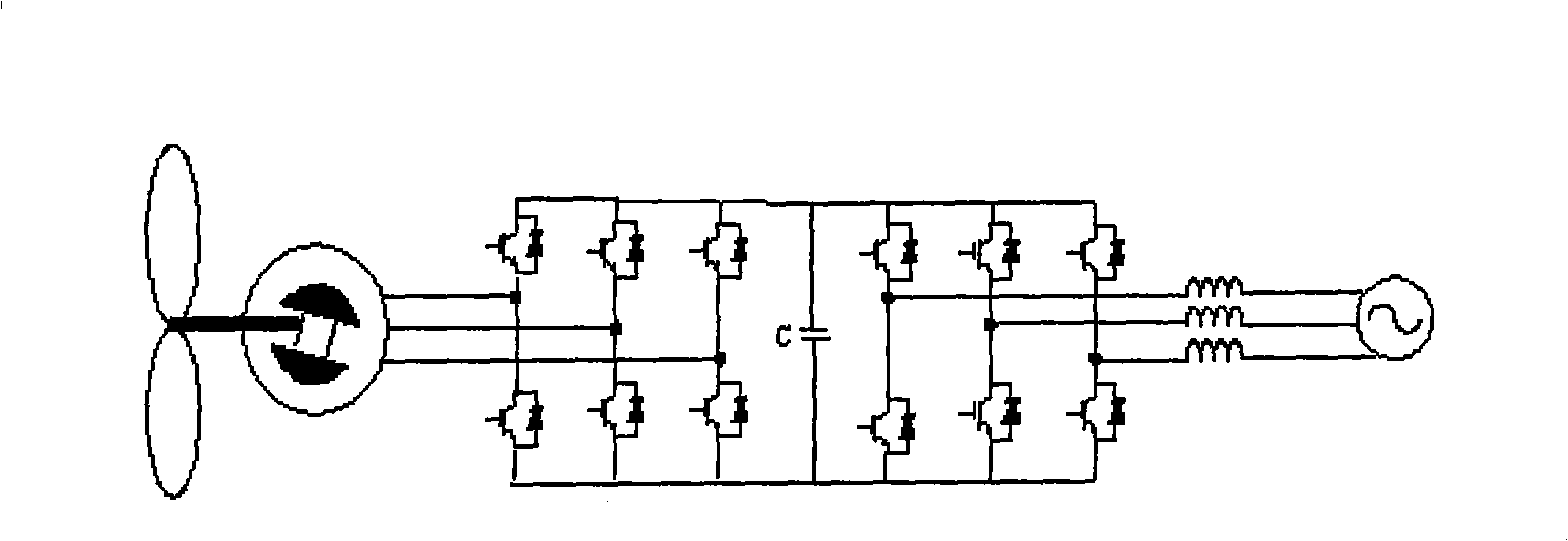
Selective droop response control for a wind turbine power plant
ActiveUS20140316592A1Reduce the amount requiredMore powerLevel controlWind motor controlPower stationPower grid
A power plant controller (36) is described. The power plant controller (36) controls a power generation system (10) having one or more power generators (12) and an energy storage system (22), and provides a utility grid or transmission system operator with the capability to select the droop response provided by the power generation system. Accordingly, an operator can request a specific generator droop response in order to provide appropriate frequency and grid control services. The power plant controller (36) operates in real time determining one or more power characteristics of the power generation system (10). Based on these characteristics and an indication of a future predicted power output for the power generation system, the power plant controller can take the necessary steps to ensure that the power generation system is capable of responding with the selected droop response, or can advise the operator that a different droop is preferred.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
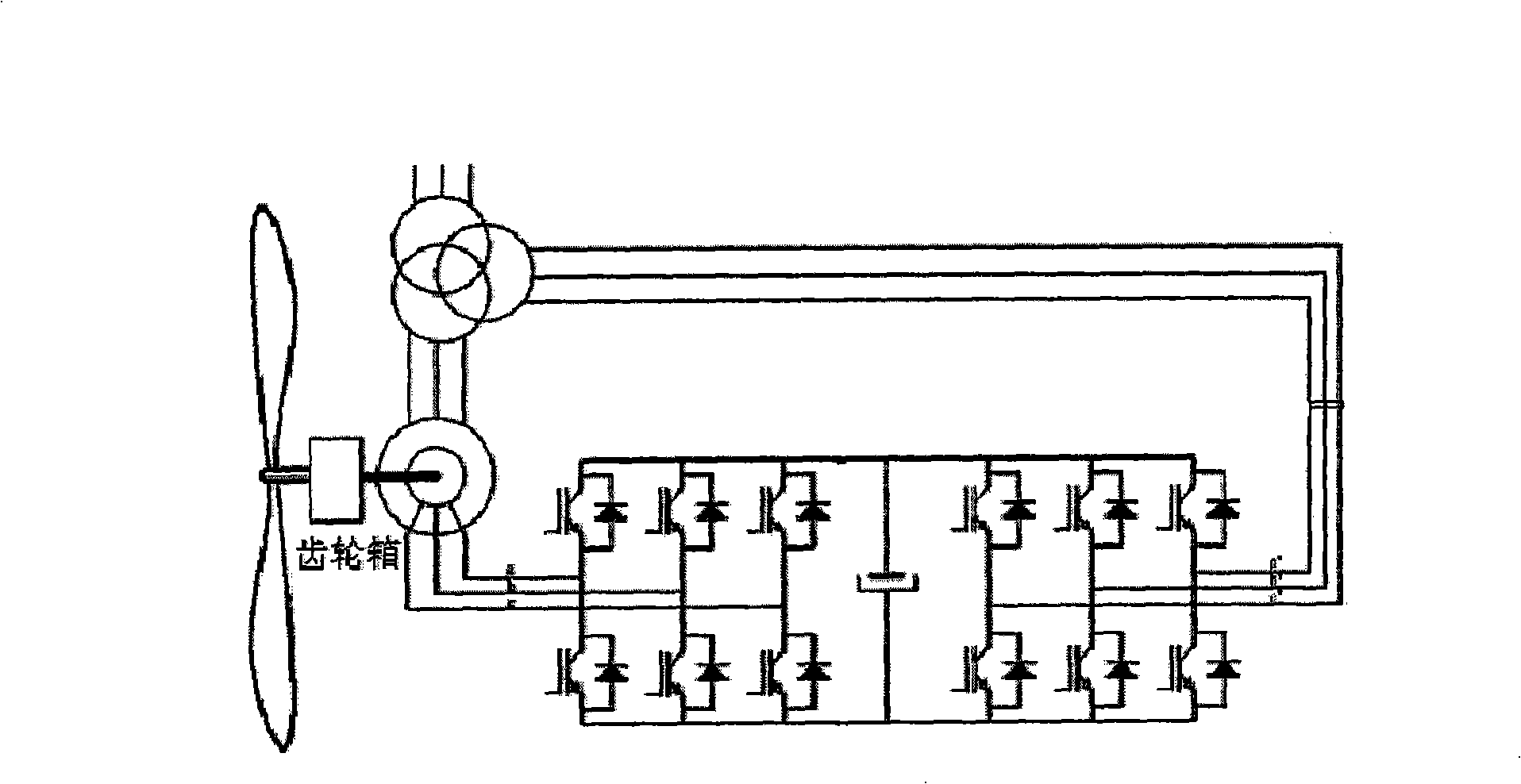
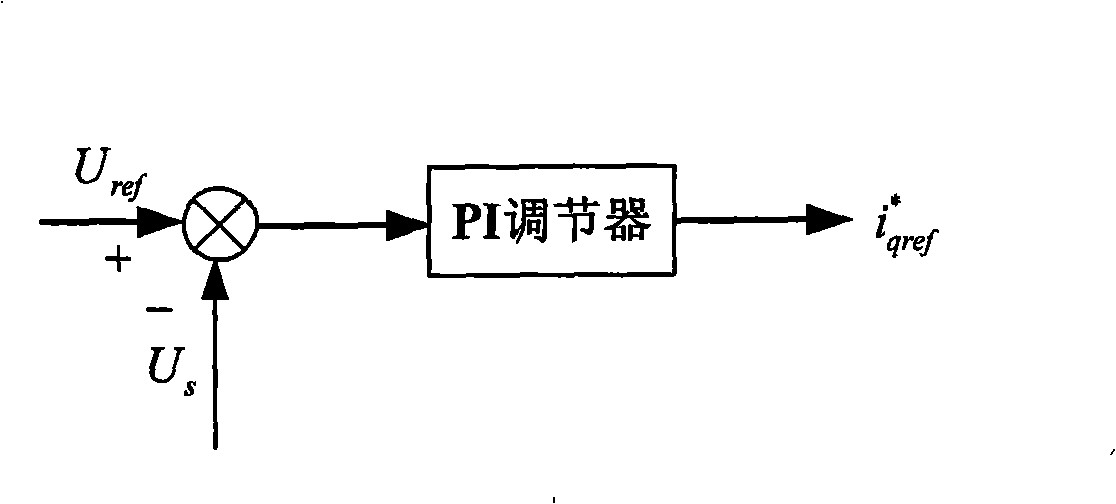
Low voltage traversing control method of wind generator set
InactiveCN101272055AWith low voltage ride through characteristicsSelf-regulatingSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network voltage adjustmentLow voltageInner loop
A response control method for the lower voltage traversing of a wind generating set is characterized in that changing situation of the voltage us of a power network is detected at any time; the power the voltage us of the power network is compared with a reference value of the voltage us of the power network, and a wattless current iqref<*> as well as an effort current idref <*> are obtained by an obtained difference value Delta u through a PI adjustor; the wattless current iqref<*> is taken as the reference value for the inner loop control of the circuit to cooperate with the control strategies of the outer loop of the voltage and the inner loop of the circuit to control a network side inverter and restrain the depreciation of the voltage of the power network as well as the effect loss of the compensating chain of the effect circuit idref<*>. Under the situation that the voltage of the power network declines instantly, the invention can flexibly feed corresponding reactive powers according to requirements, adjust the effect power correspondingly as well, lead the wind generating set to reach a transmission reliability standard similar to a fire generating set, and has the capacity of self adjustment.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Strategic-response control system for regulating air conditioners for economic operation
InactiveUS6860431B2Minimize adverse effectsAcceptable level of comfortFuel supply regulationDc network circuit arrangementsReal-time clockElectricity price
A strategic response control for an air conditioning system for use in an environment with increased power rates during a designated peak period. The air conditioning system includes a power board for operating the air conditioning system in one or more operating status having a controller with a processor and a real time clock, an indoor temperature sensor for generating an input signal representing the indoor temperature, an outdoor temperature sensor for generating an input signal representing the outdoor temperature, and an operating program that sets a maximum comfort level temperature, a minimum comfort level temperature and a warmup rate for the environment in which the air conditioner operates, and has a procedure for precooling the environment before the peak period, wherein on activation, the processor signals the power board to enter an operating state for precooling and an “off” or lower level operating state during the peak period.
Owner:LEVENE EDWARD R
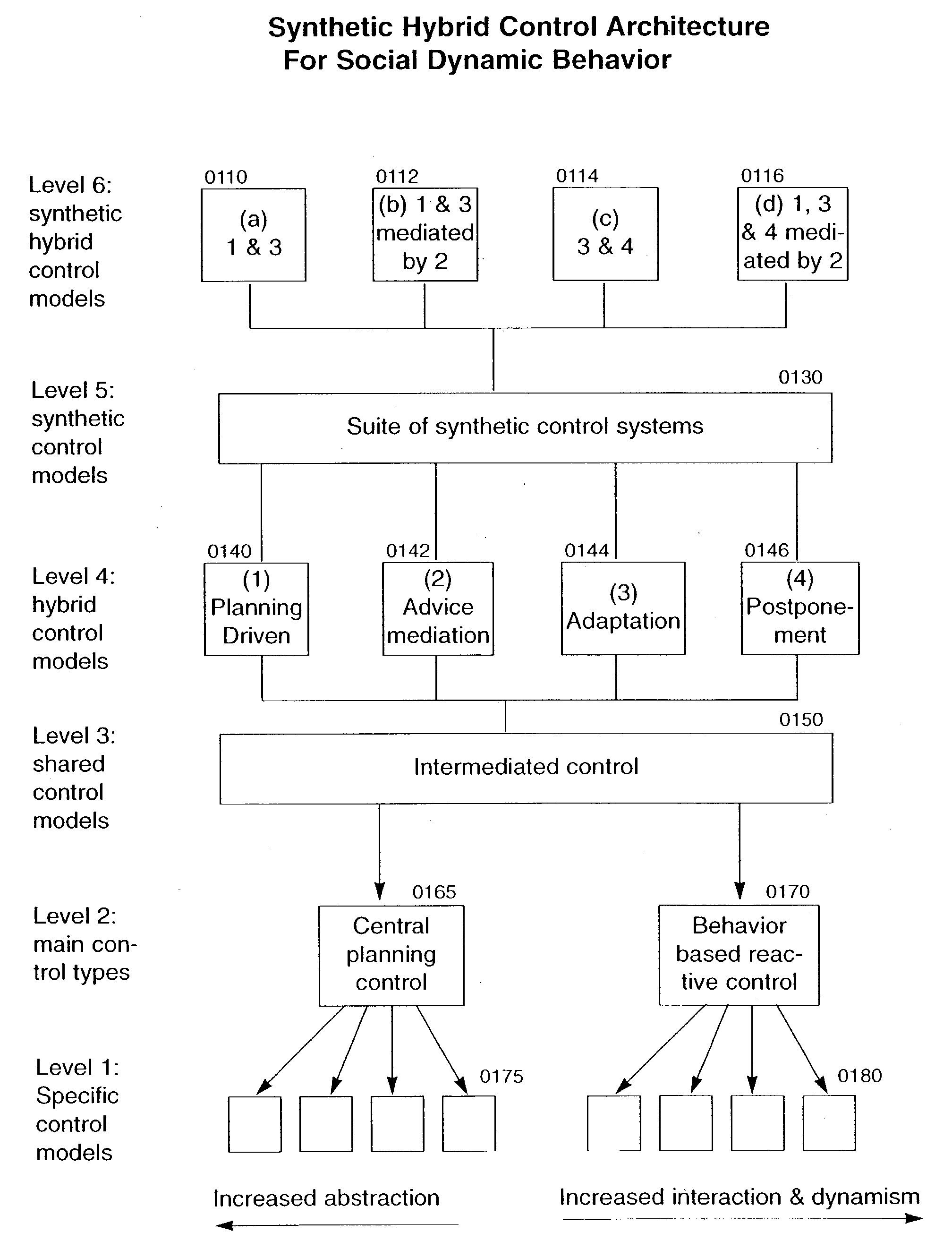
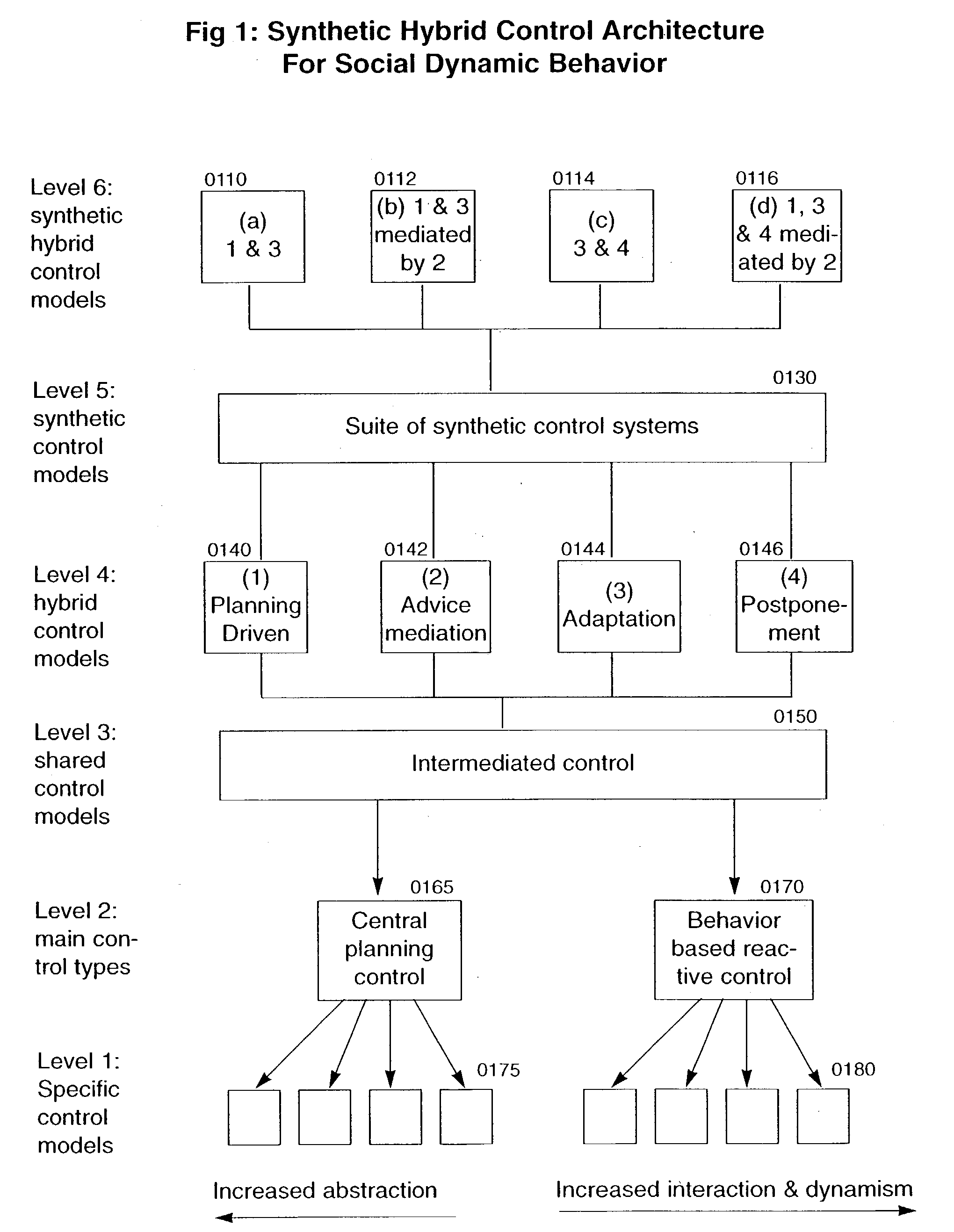
System, methods and apparatus for managing a weapon system
InactiveUS20050183569A1Sustains the moral responsibility necessaryOvercome limitationsAutonomous decision making processRemote controlled aircraftControl layerControl system
A system for managing a weapon system is provided. The system includes a number of mobile robotic vehicles (MRVs), a number of squads, each squad having a lead MRV and member MRVs, a number of central control systems, a number of reactive control systems, a central planning control configured to control the plurality of central control systems, a behavior-based reactive control configured to control the plurality of reactive control systems, an intermediated control layer configured to control the central planning control and the behavior-based reactive control, a number of hybrid control models configured to communicate with the intermediate control layer, the hybrid control models including a planning driven model and an adaptation model, a number of synthetic control models configured to communicate with the hybrid control models, and a number of synthetic hybrid control models configured based on combinations of the hybrid control models and the synthetic control models.
Owner:SOLOMON RES
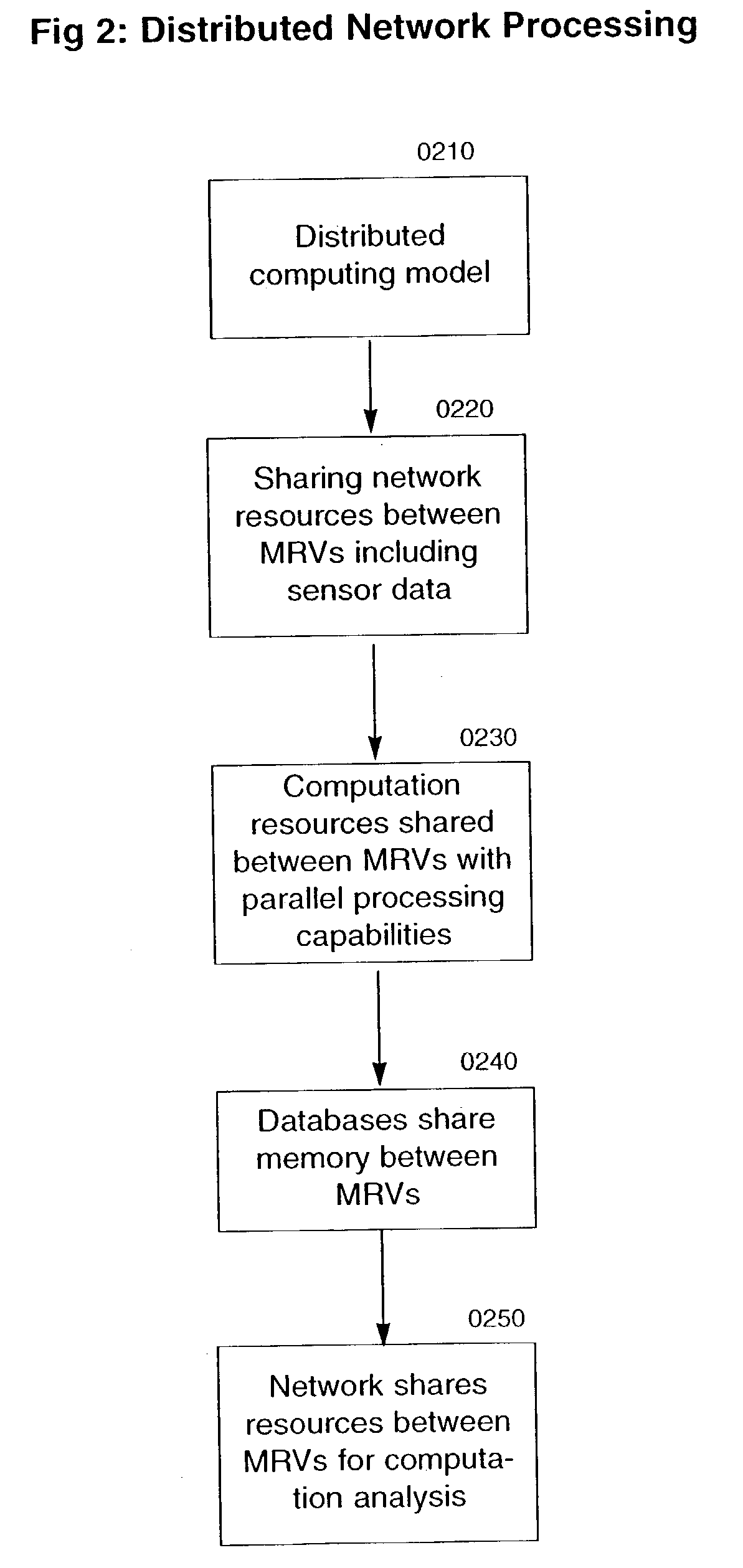
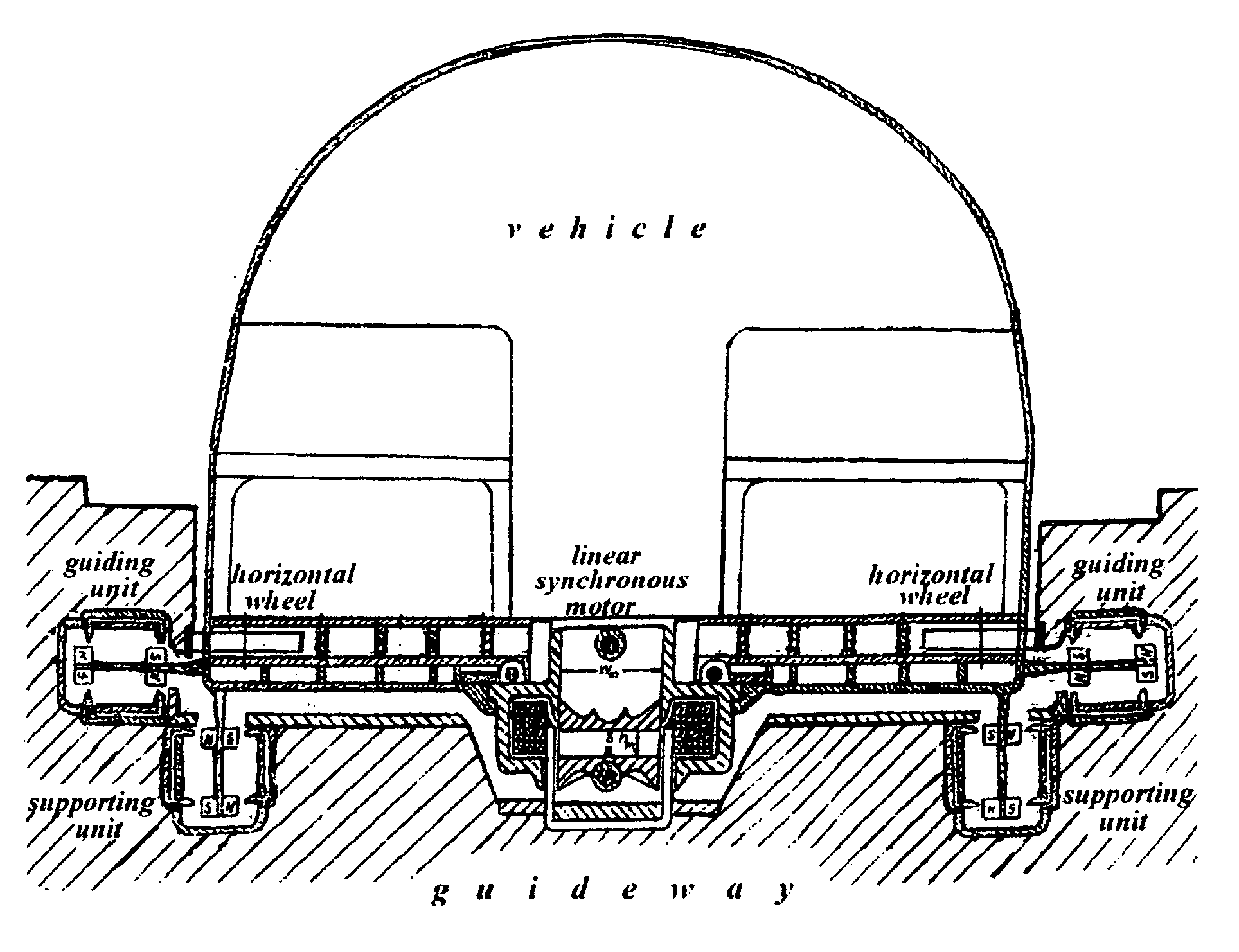
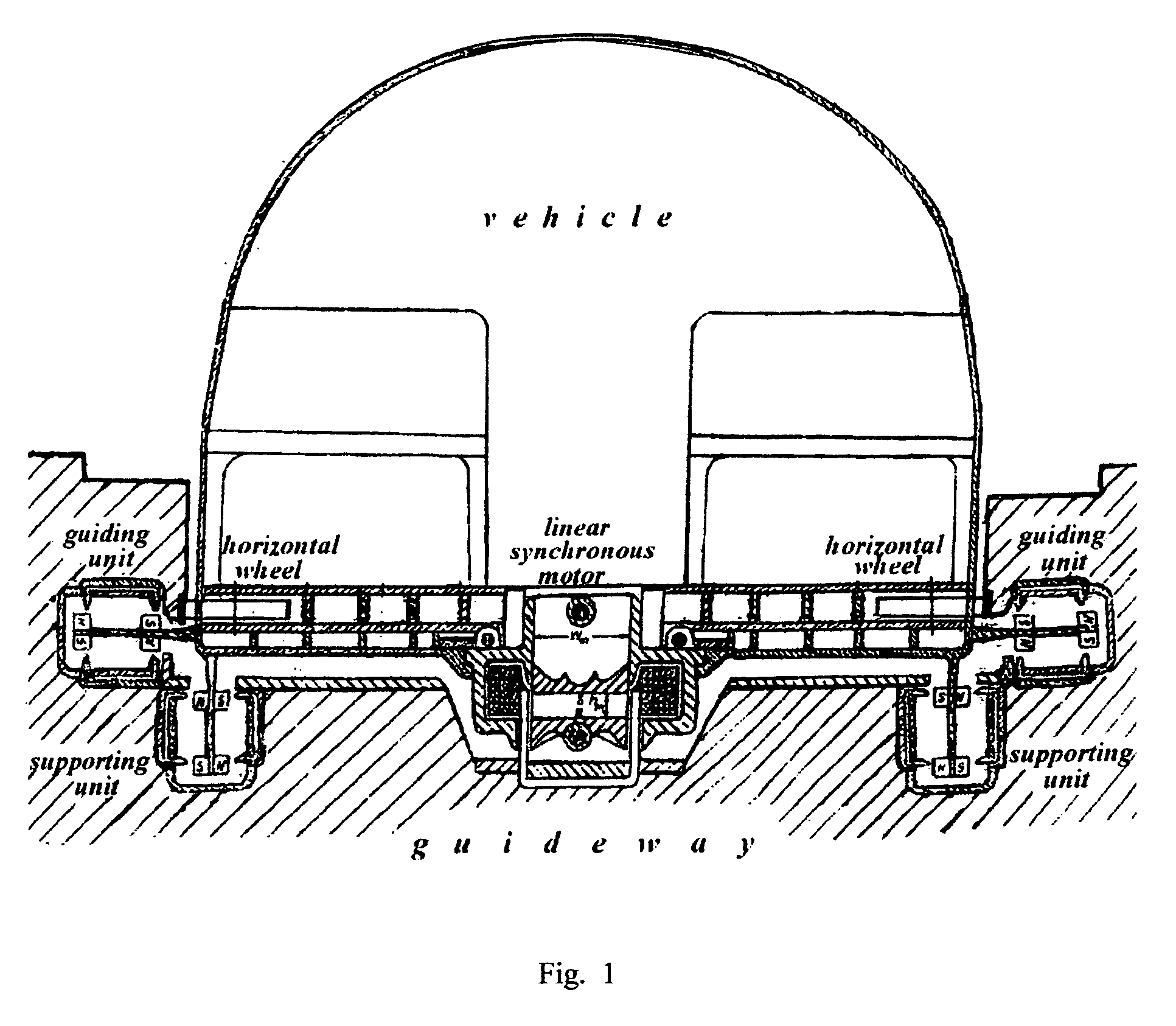
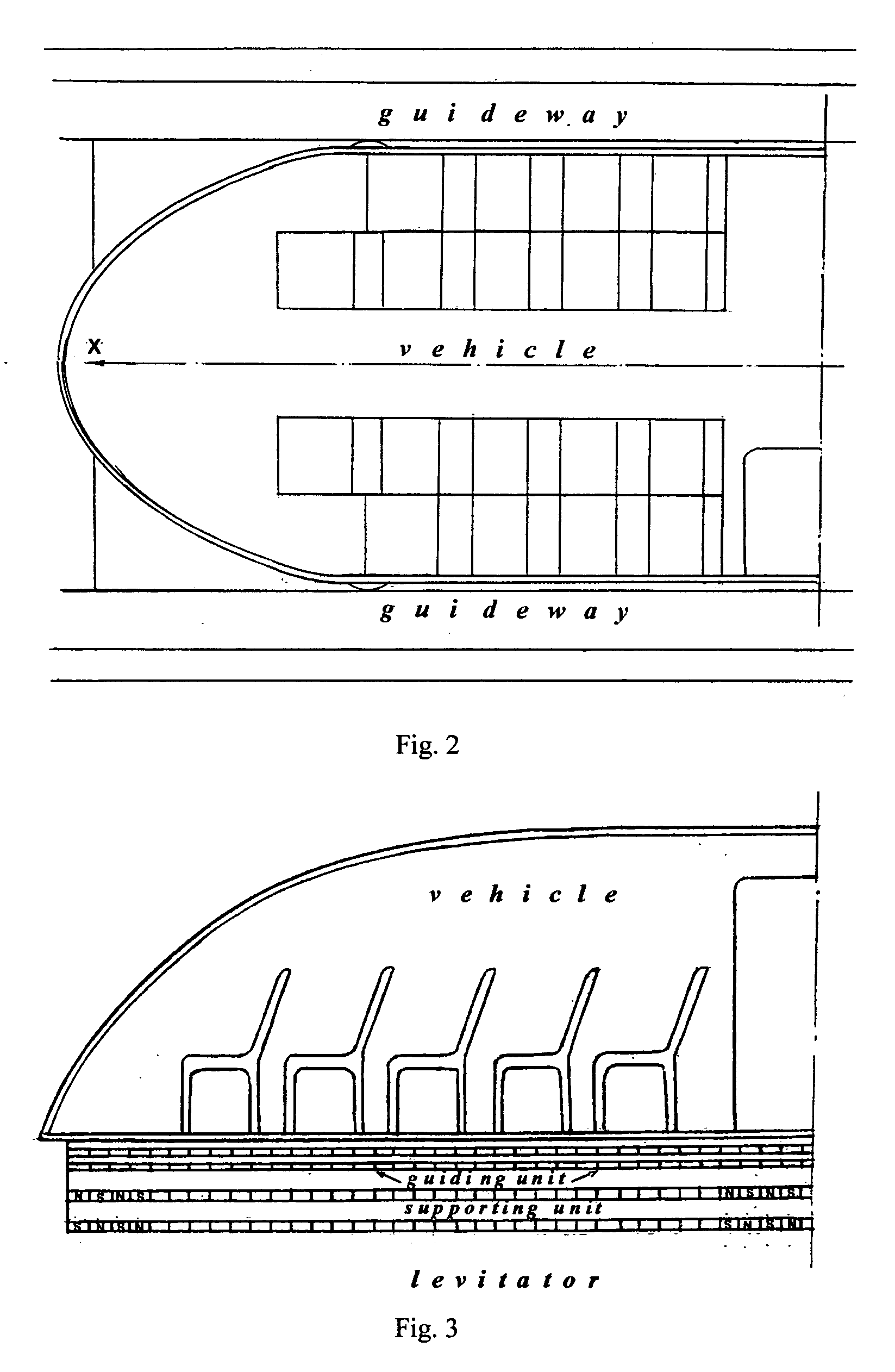
Amlev: Self-regulating type of Maglev high speed ground transportation based on permanent magnets and steel cores
The proposed Amlev Self-Regulating System of High Speed Ground Transportation Based on Permanent Magnets and Steel Cores is designated for magnetic levitation, stabilization, and propulsion of vehicles moving without friction. The proposed system comprises subsystems: a Magneto-Dynamic Levitation and Stabilizing Self-Regulating System (MDLSS), and a Permanent Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor (PMLSM). Both systems comprise permanent magnets and steel cores. MDLSS provides levitation and stabilization of vehicle while PMLSM produces propulsion force providing the assigned alternative velocity of the vehicle along the stator winding powered by the current of constant frequency 50 Hz. Each of the subsystems comprises two main parts: a fixed part—guideway / stator including extended steel cores for MDLSS and windings for PMLSM, and moving part—permanent magnets of the levitator for MDLSS and the rotor for PMLSM—both affixed to the moving vehicle. Each of the subsystems is self-regulating and operates without fast response control system. A new model is proposed for measuring destabilizing forces impacting a flying vehicle at its shifts from an assigned trajectory that allows to eliminate the stage of full-scale modeling when designing Amlev system.
Owner:TOZONI MICHAEL
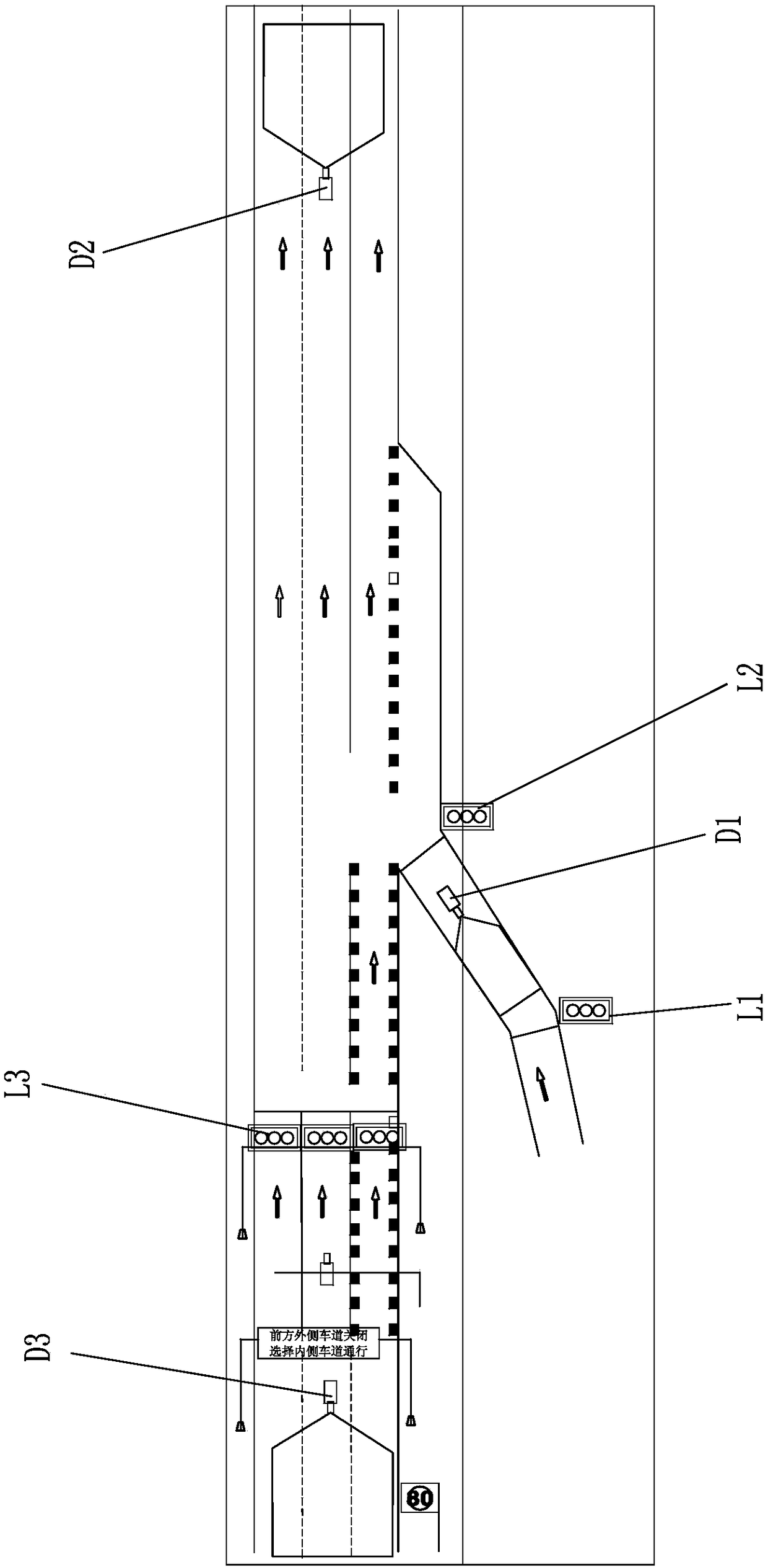
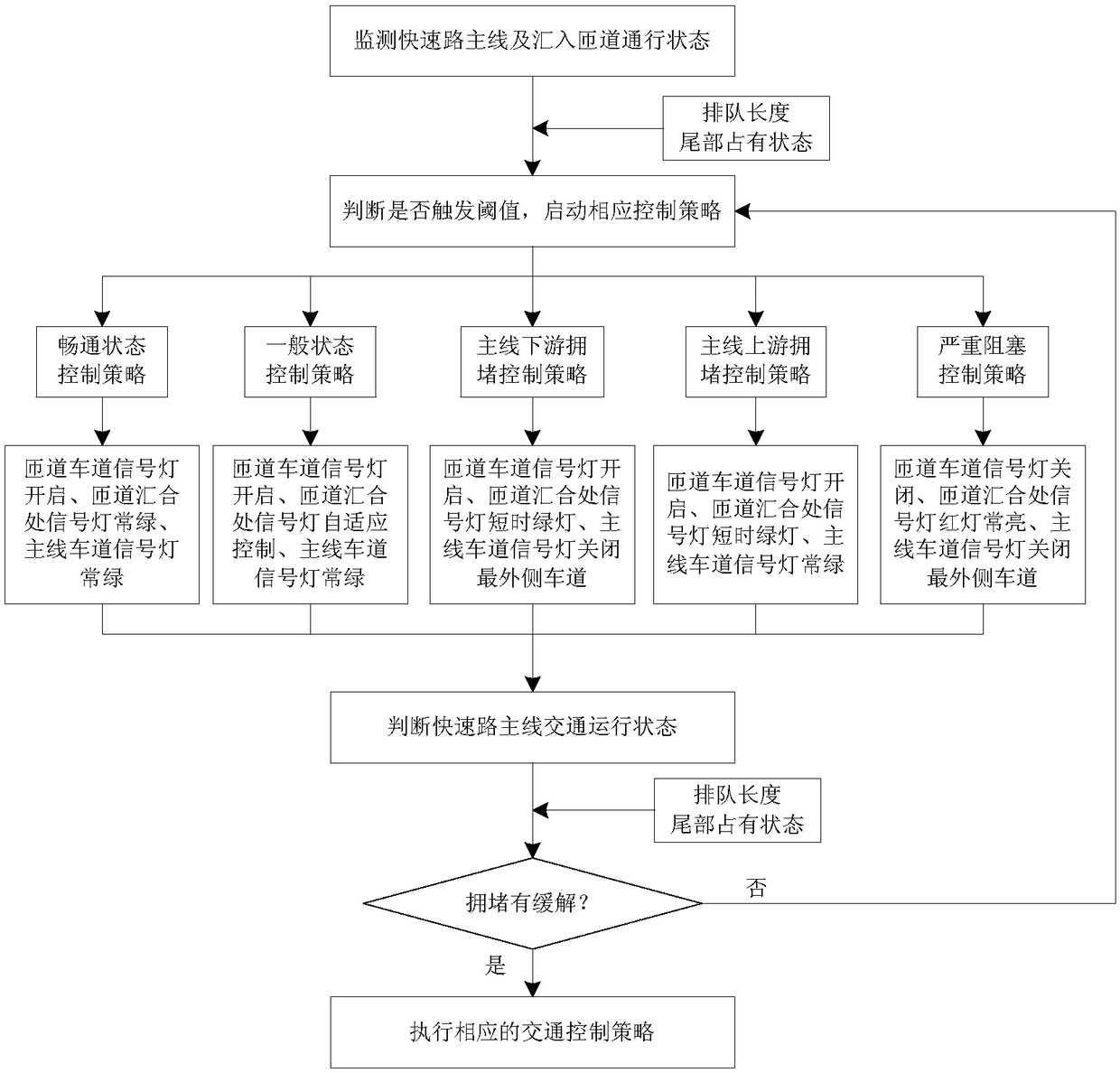
Cooperative control method and system for trunk line and ramp of city expressway
InactiveCN108122418ABreakthrough accuracyBreakthrough effectivenessControlling traffic signalsArrangements for variable traffic instructionsControl systemControl signal
The invention relates to a cooperative control method and system for the trunk line and ramp of a city expressway, and belongs to the technical field of road traffic signal control. The system is characterized in that the system comprises a detector which is used for detecting the traffic flow states of the ramp and the trunk line; a signal lamp which is used for controlling the opening, closing and discharging of the ramp and the trunk line; a signal annunciator which is connected with the detector, the signal lamp and a control system, and is used for collecting the traffic flow operation state data of the ramp and the trunk line and uploading the data to the control system, and controlling the signal lamp according to a control command of the control system; and the control system whichselects a corresponding preset scheme according to a triggering threshold value, and transmitting the preset scheme to the signal annunciator. The system solves problems that a conventional section collection index is not accurate and the effectiveness is not high. The system employs a trunk line and ramp signal lamp linkage control strategy and scheme according to different scenes, and achievesthe cooperation of traffic organization and a signal control scheme and the dynamic response control of the ramp.
Owner:TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT RES INST OF THE MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Thermal sensing
ActiveUS20050265898A1Thermometer detailsVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
Thermal detectors and thermal sensing cells can include a region of a support layer or support structure. Within the region can be reaction surfaces or other reaction regions, as well as contact pads and circuitry connecting the contact pads to other components. Also, a cell region can include a structure with reaction regions, contact pads, and control / detection circuitry connected to the contact pads; the control / detection circuitry controls occurrence of reactions in response to control signals, such as by drop merging, and also allows electrical detection of thermal signals from the reaction regions. The control / detection circuitry can include reaction control components such as drop merger electrodes and also thermal sensors such as thermistors, or it can include control / sensor elements such as semiconductor slabs that perform both functions. Each cell in an array can have control / detection circuitry that does not extend or connect outside the cell except through contact pads.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Common carrier material for targeting anticancer drug and gene and preparation and application
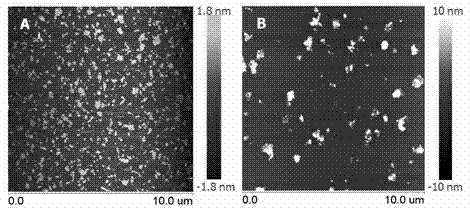
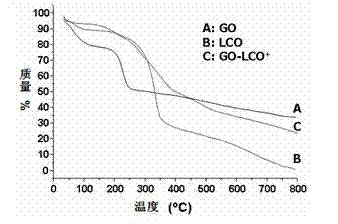
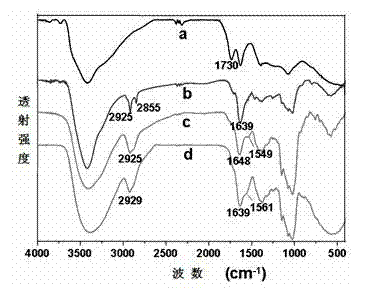
InactiveCN102949727AGood biocompatibilityEnhanced Osmotic Retention EffectGenetic material ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsTumor targetingResponse control
The invention relates to a common carrier material based on graphene oxide for a targeting anticancer drug and a gene and application and application. Folic acid, lactobionic acid and other tumor cell targeting or liver targeting molecules and part of amino groups of soluble chitosan are connected by amide bonds to prepare a conjugate, the conjugate is then connected with graphene oxide, quaternization is performed by using an epoxy compound with a quaternary ammonium group, and gene molecules are loaded by the quaternizationquaternized part of the chitosan through electrostatic attraction; and then the anticancer drug is loaded by pi-pi conjugates, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic effects in a non-covalent bond method. By adopting the targeting performance of targeting molecules and effects of graphene oxide of a particular size to enhance penetration and retention in tumor tissues and combining the performance of the graphene oxide for pH response control release of the loaded drug, the drug can be realized released in a tumor cell, an intelligent delivery system for the common carrier of the tumor targeting or liver targeting anticancer drug and the gene is synthesized from the perspective of synergetic medication, and a theoretical basis and a method basis are provided for combined therapy of tumor.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
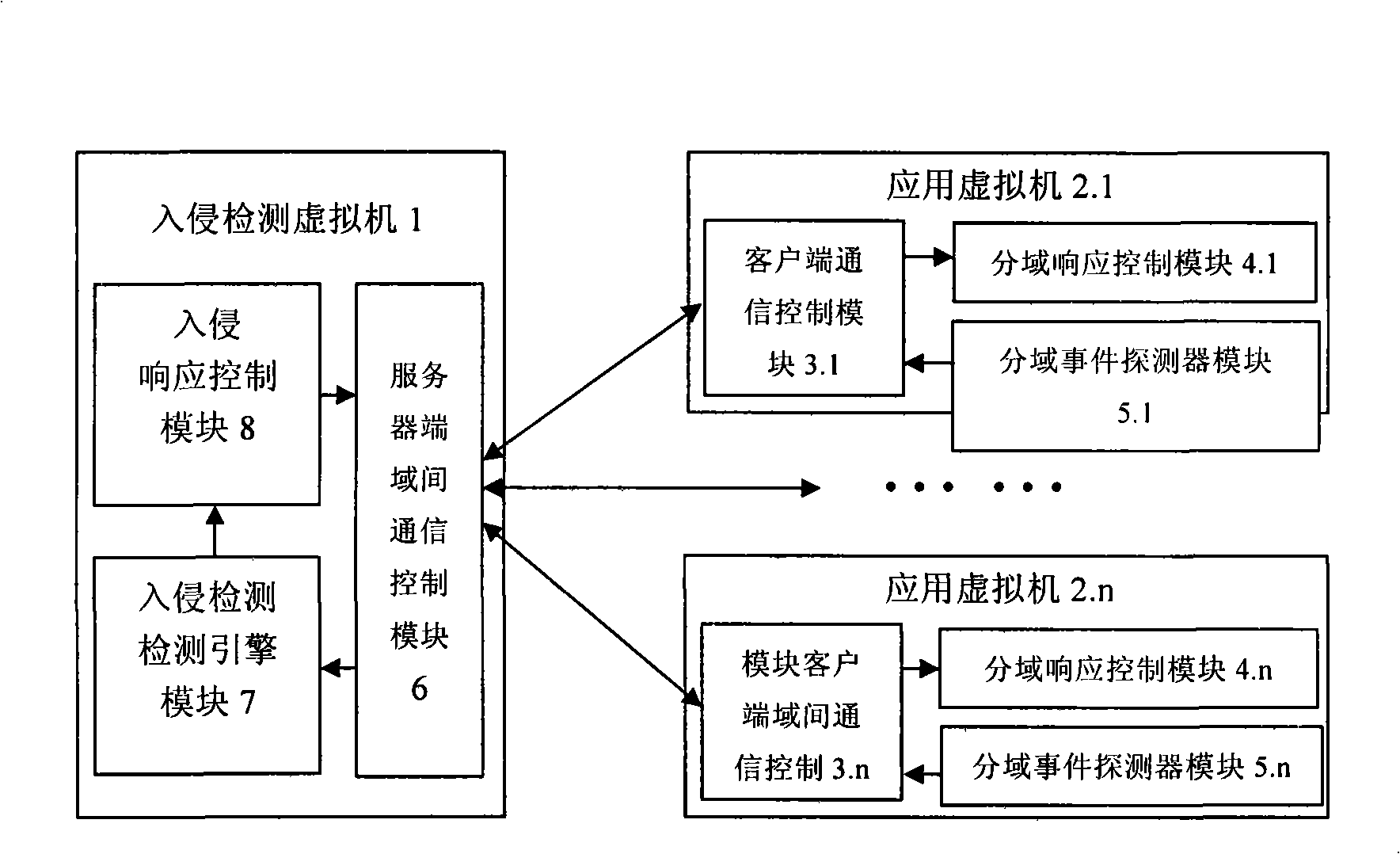
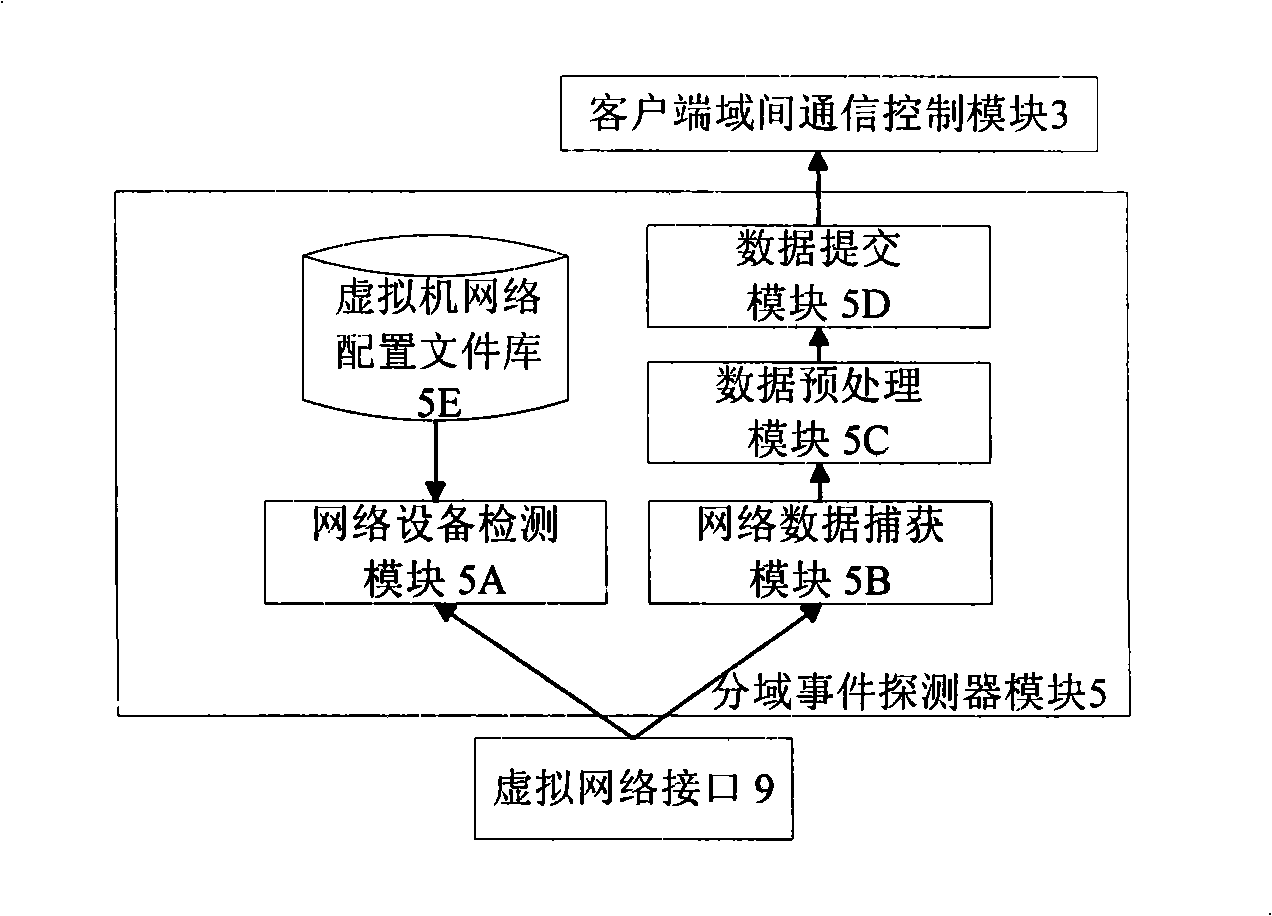
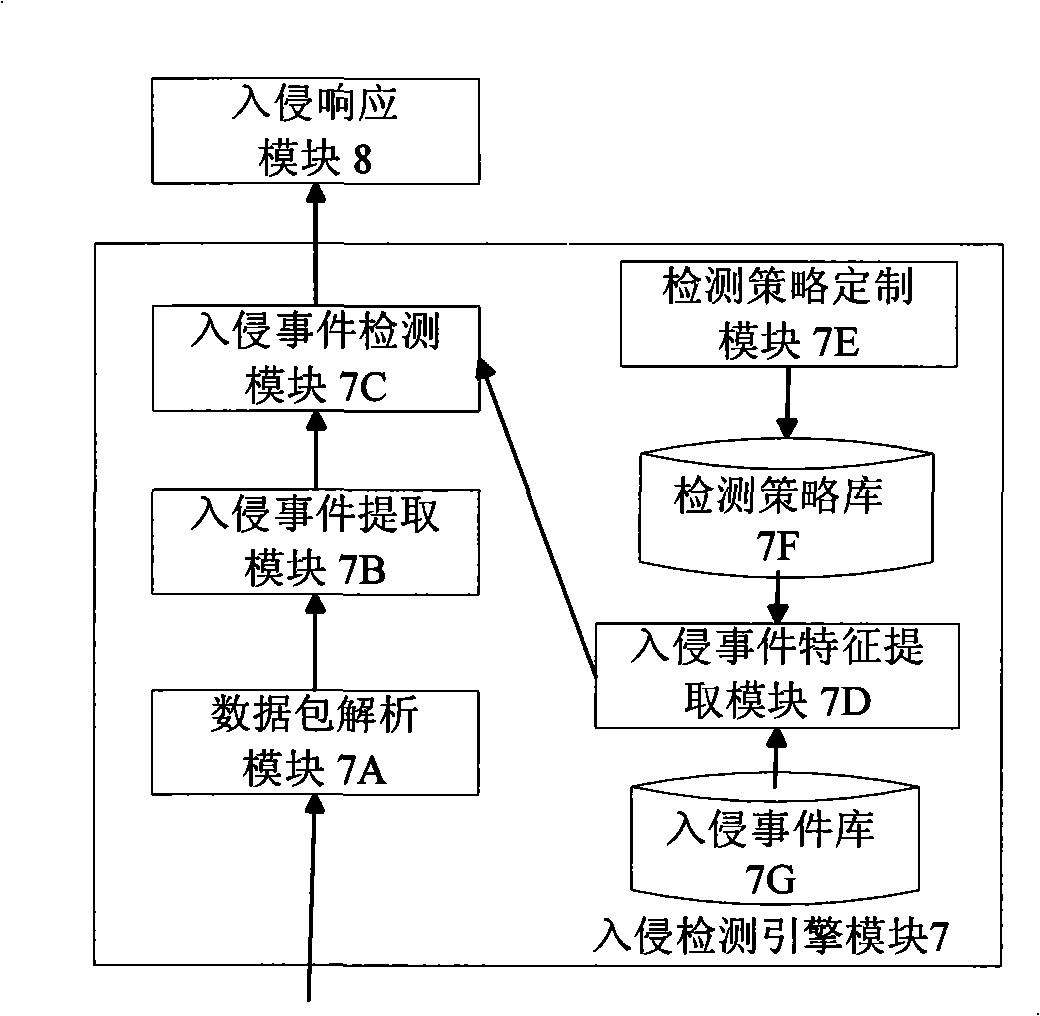
Security network invasion detection system suitable for virtual machine environment
InactiveCN101309180AGuaranteed security featuresCentralized control of intrusion detection rulesData switching networksCommunication controlA domain
The invention discloses a safe network intrusion detection system which is applicable to the virtual machine environment and includes a server inter-domain communication control module, an intrusion detection engine module, an intrusion response control module in the intrusion detection virtual machine, a client inter-domain communication control module, a domain spilt event detector module and a domain split response control module in the detected application virtual machines. According to the problem that the safety of the virtual machine system of the virtual machine needs to be improved; the current intrusion detection system cannot realize the purpose, the safe network intrusion detection system considers the layering structure of the virtual machine network sufficiently and realizes the intrusion detection protection of the virtual machine system in the internal network based on the virtual machine; the safety of the virtual machine applied in the production practice activities is improved; meanwhile, the separation of the intrusion detection system and the protected system is realized based on the separation safety property of the virtual machine; compared with the traditional network intrusion detection system, the safe network intrusion detection system has better safety and reliability.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
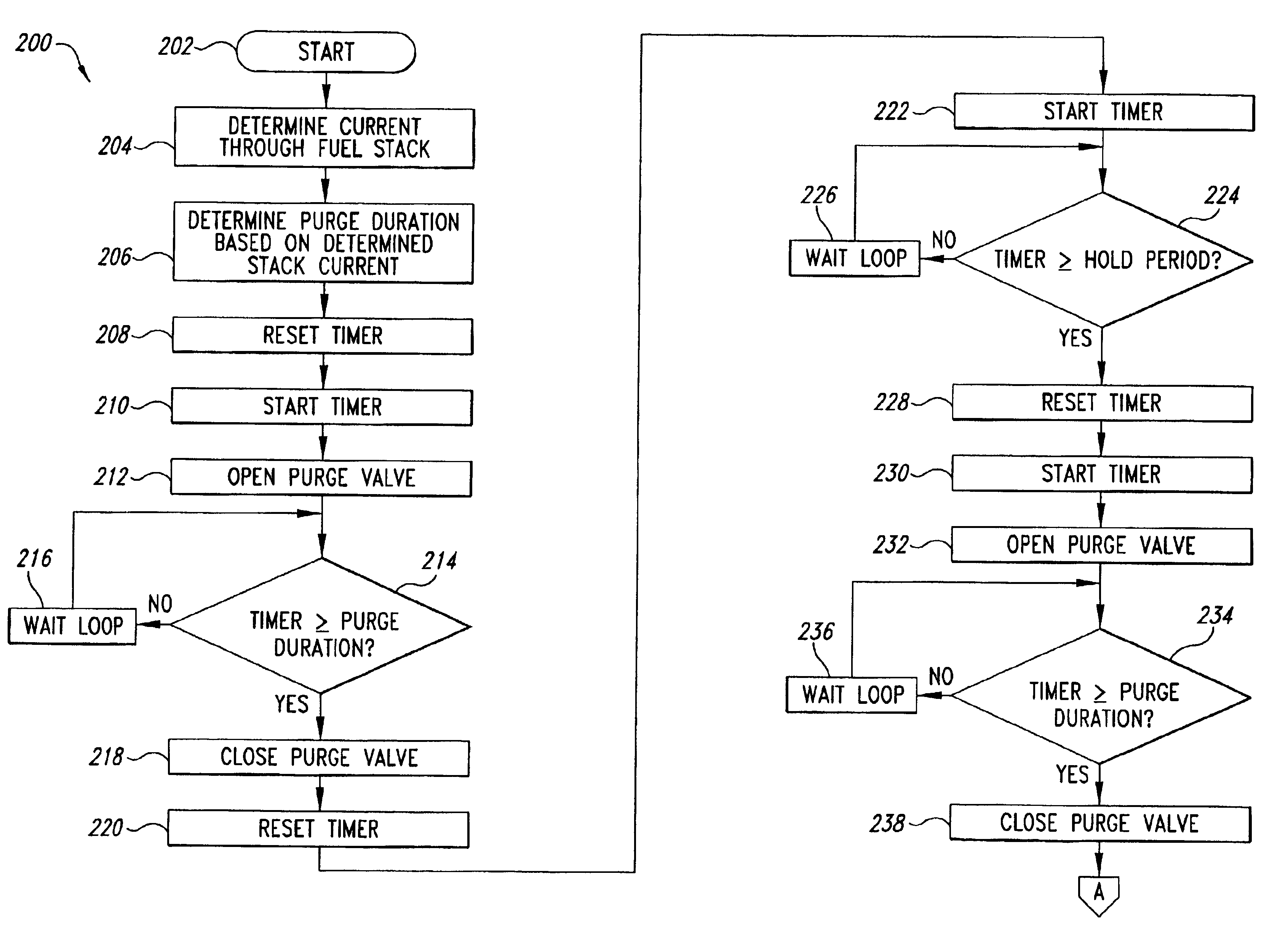
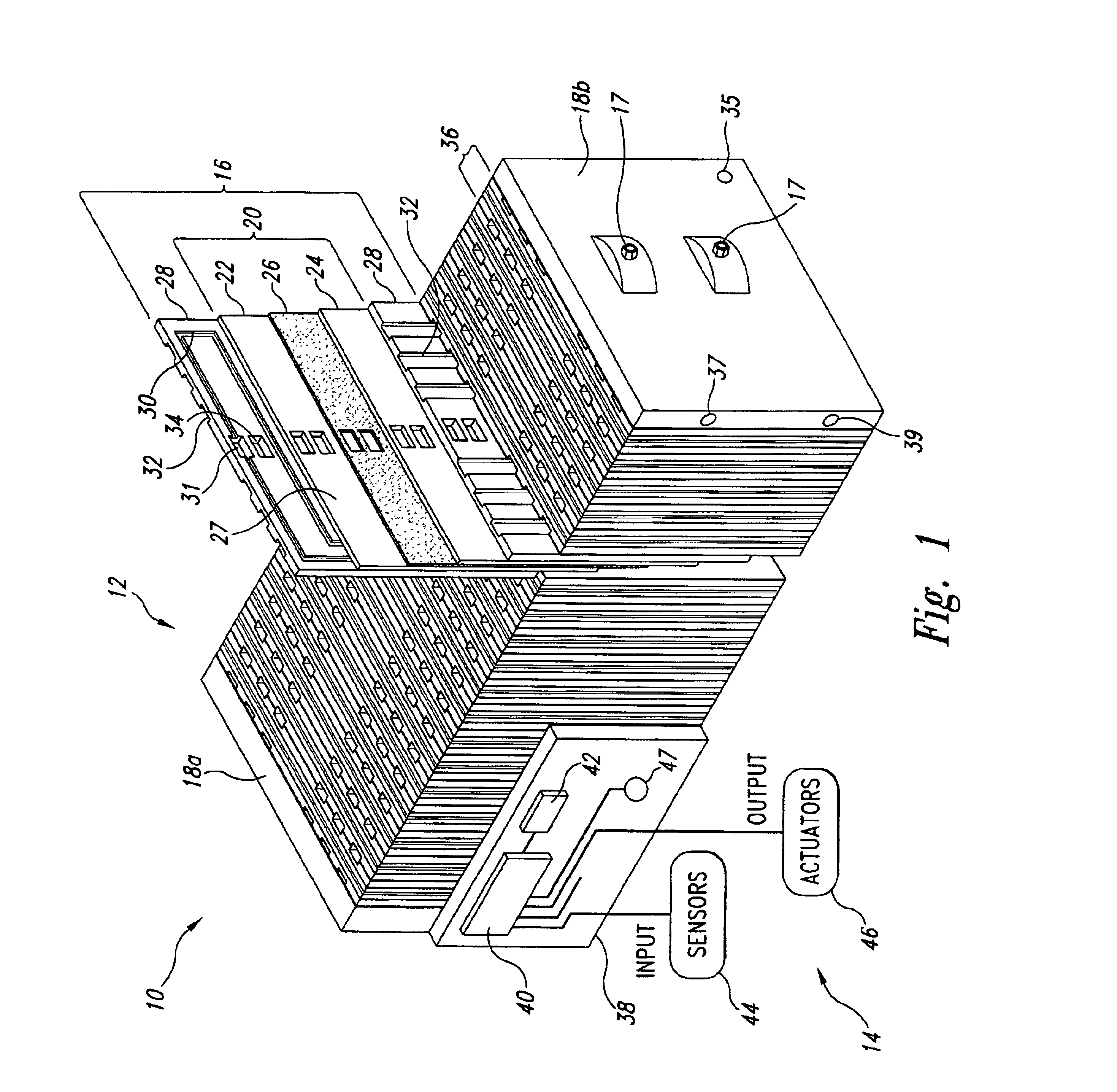
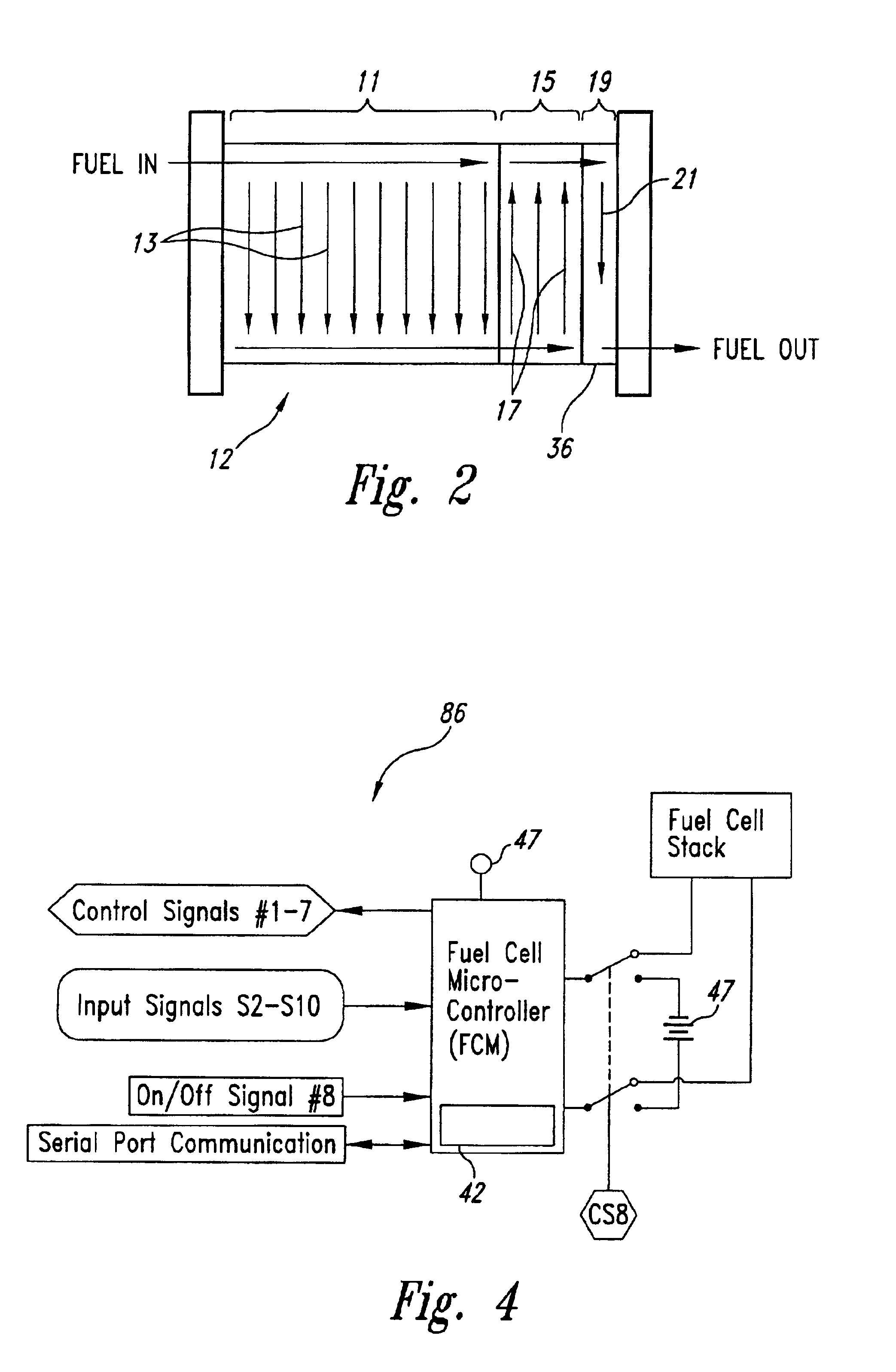
Fuel cell purging method and apparatus
A purge system for fuel cell stack includes a purge valve to regulate exhaust from the fuel cell stack in response control signals from a controller in response to a voltage across a purge cell portion of a fuel cell stack. The purge valve is opened when the voltage across the purge cell portion falls below a defined percentage of a threshold voltage. The threshold voltage can be equal to an average cell voltage of some or all of the fuel cells of the fuel cell stack. The purge may include one or more successive openings of the purge valve of controlled purge durations.
Owner:BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS
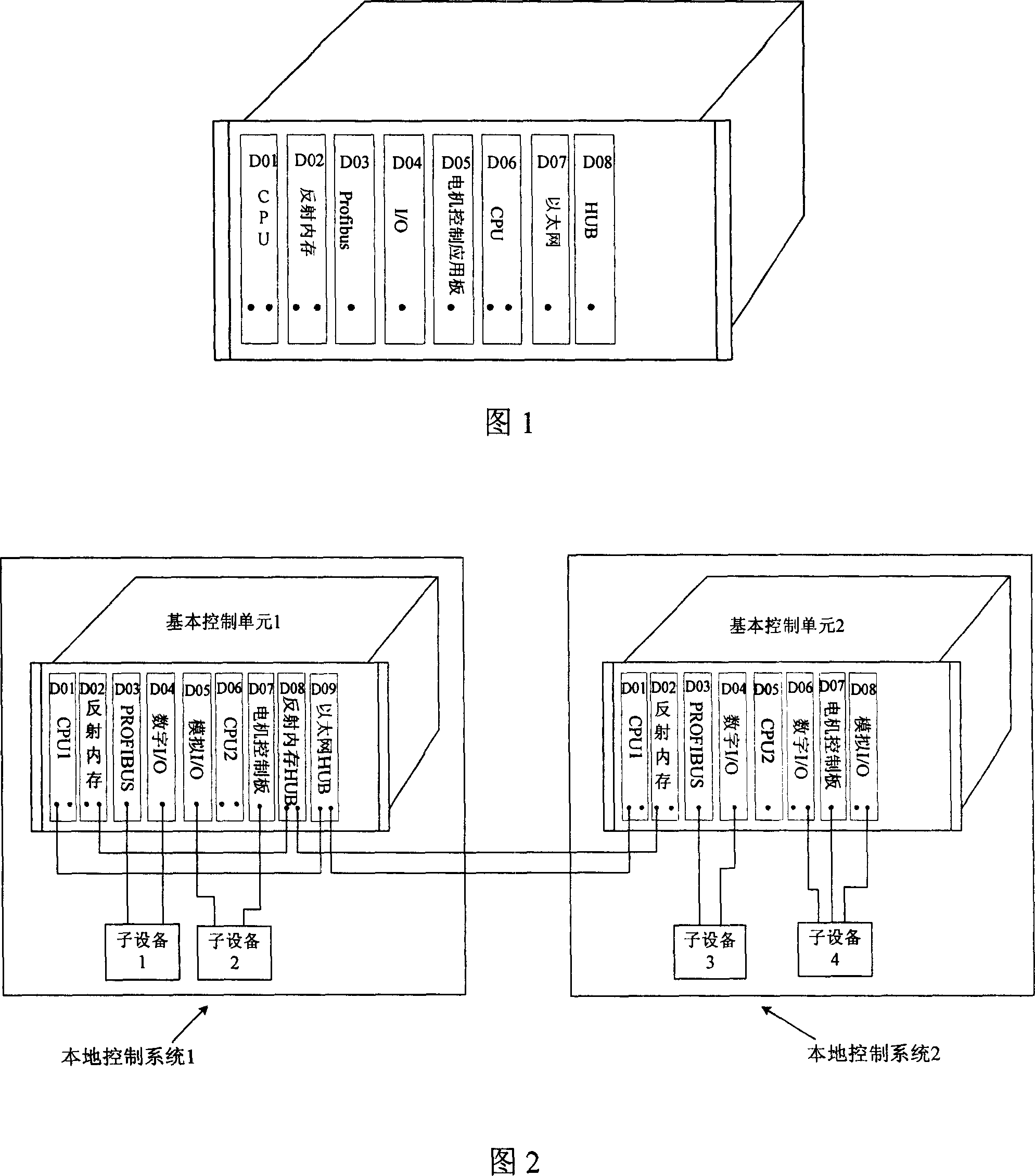
Real time multiple task distributive control system based on VME bus
ActiveCN1987705AMeet multi-functional and complex control requirementsClear functional relationshipTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlResponse controlEmbedded system
The control system includes VME bus chassis, CPU main board, Ethernet comm interface board (CIB), reflection memory CIB, PROFIBUS CIB, digital signal interface board, analog signal interface board, and electrical motor control board (MCB). Boards and cards are inserted to backboard inside the VME bus chassis. Through VME bus, boards and cards in backboards inside same chassis can communicate each other through VME bus. Each board contains VME bus controller. VME bus controller implements functions of gating board, bus arbitration, interrupt response control, and reading and writing data. Each board possesses own address. Through VME bus, gated board exchanges data to CPU board. Using shared memory exchanges data between CPU boards in same backboard bus. The reflection memory CIB executes remote comm and real time control among multiple control systems. MCB can exchange data to CPU main board, and control motor through optical fiber interface driven by power switch in bottom layer.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
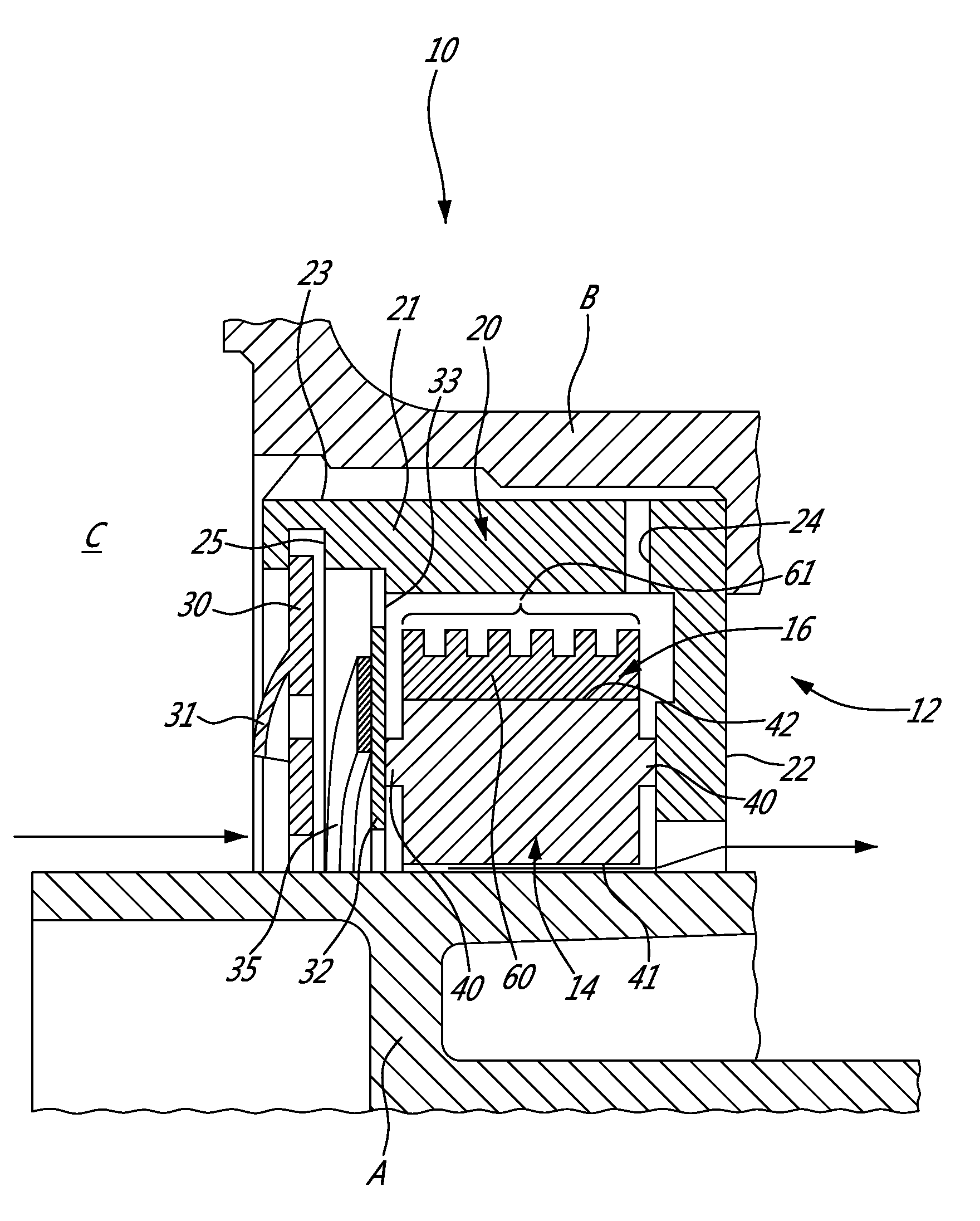
Thermally response controlled gap seal device
ActiveUS20130285331A1Controllably coolControllably shrinkEngine sealsLeakage preventionEngineeringResponse control
A controlled gap seal device is adapted to surround a shaft with an annular seal element. A ring is positioned on an outer surface of the seal element, the ring adapted to modify a diametrical dimension of the seal element by thermally expanding / contracting as a function of temperature variations. A housing assembly has an interior enclosing the seal element and the ring, with the seal configured to be generally stationary in the interior. The housing assembly has an air inlet and air outlet in fluid communication with a surrounding environment for directing a flow of gas from the surrounding environment onto the ring to controllably cool and shrink the ring. A method for modifying a diameter of a controlled gap seal relative to the shaft is also provided.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Information providing system, method of providing information and program for providing information
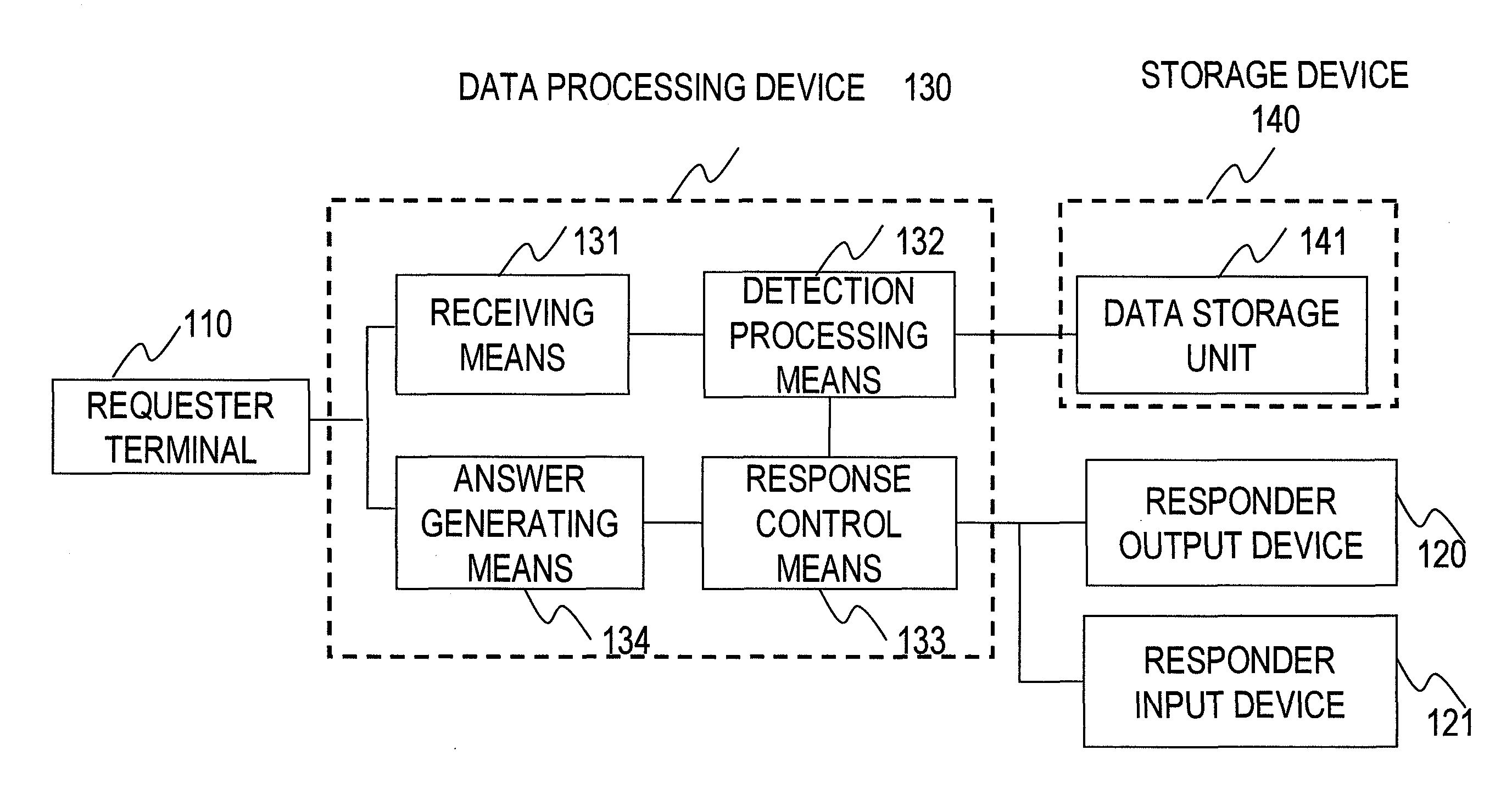
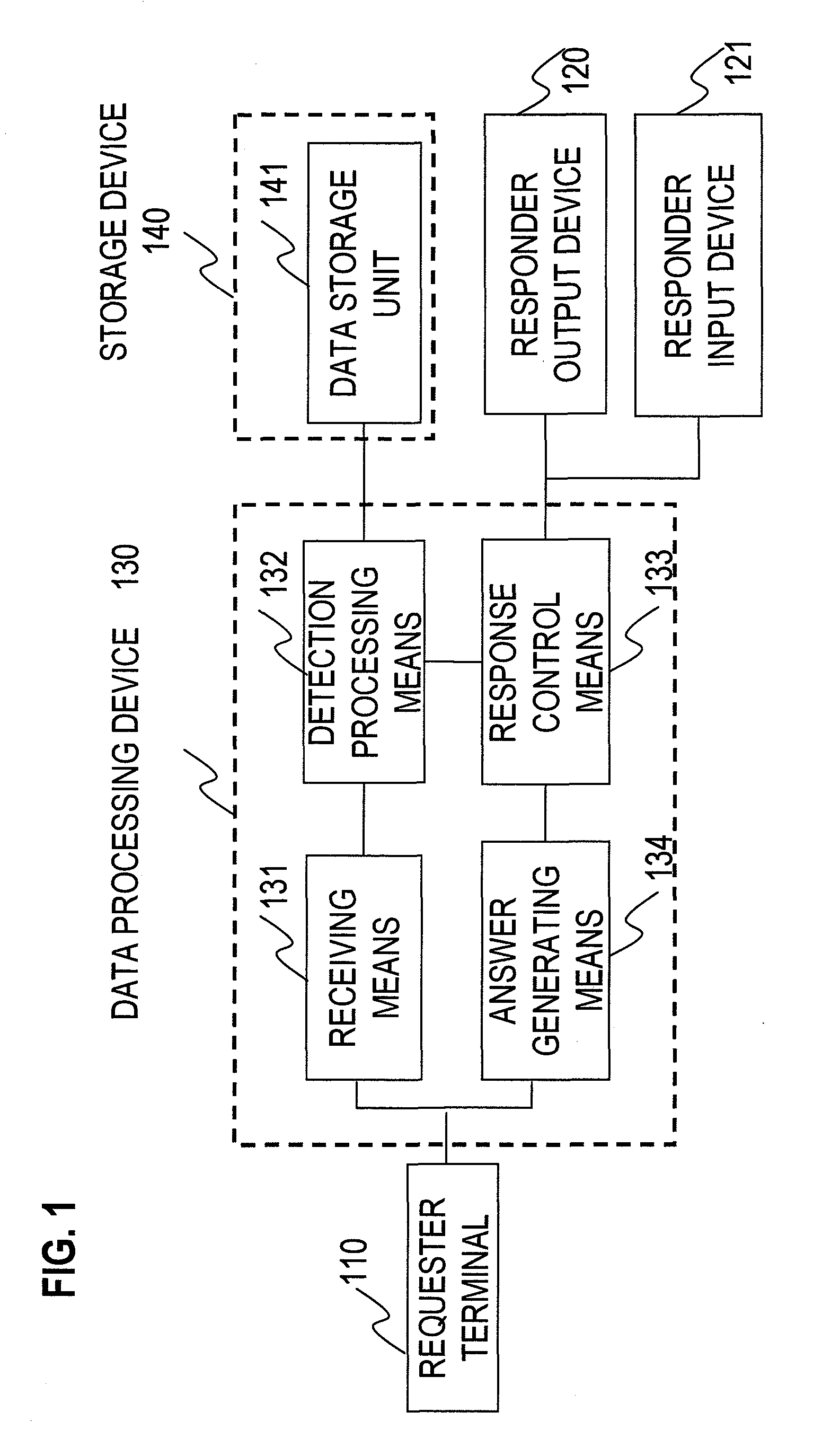
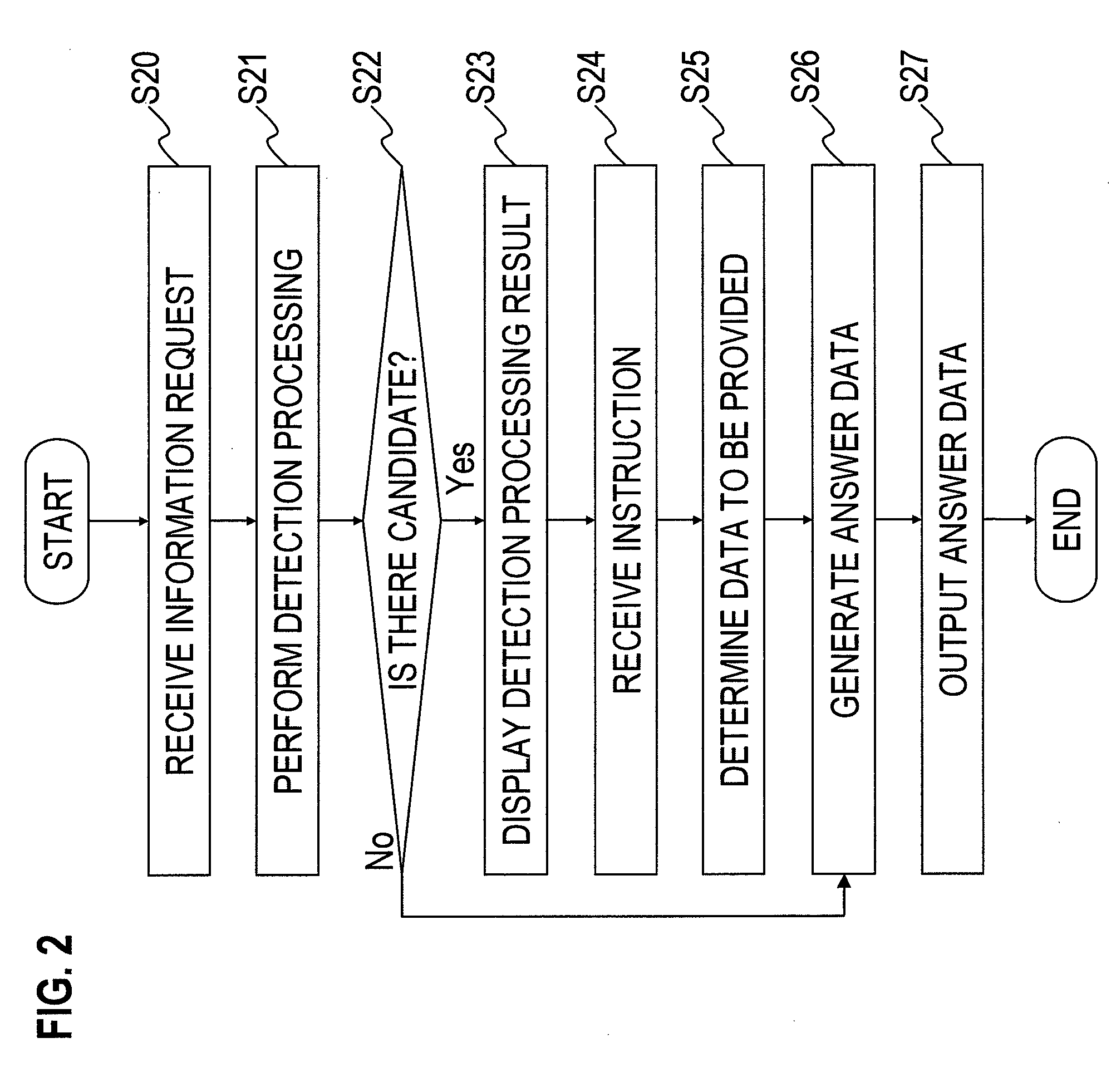
ActiveUS8306933B2Efficiently providedMaintain securityDigital data information retrievalDigital data protectionOutput deviceResponse control
Disclosed is an information providing system comprising a receiving unit that receives an information request from a requester, a data storage unit that stores data, a detection processing unit that analyzes the content of the information request and extracts provision candidate data corresponding to the information request from the data storage unit, a responder output device to which the content of the information request and the provision candidate data are output, a responder input device that receives instruction information on whether or not the provision candidate data is to be provided, a response control unit that determines whether or not there is providable data based on the received instruction information and the provision candidate data, and an answer generating unit that generates answer data using the decision result by the response control unit.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and system for intelligent driving horizontal and vertical decoupling control of great inertia electric motor coach
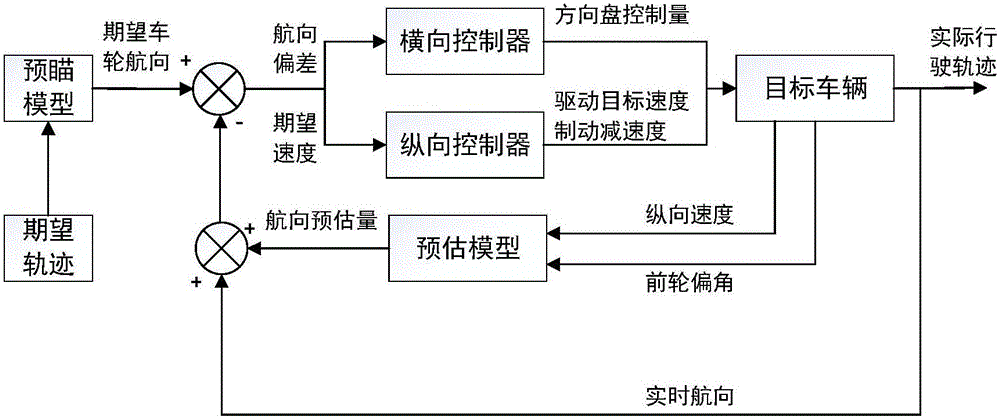
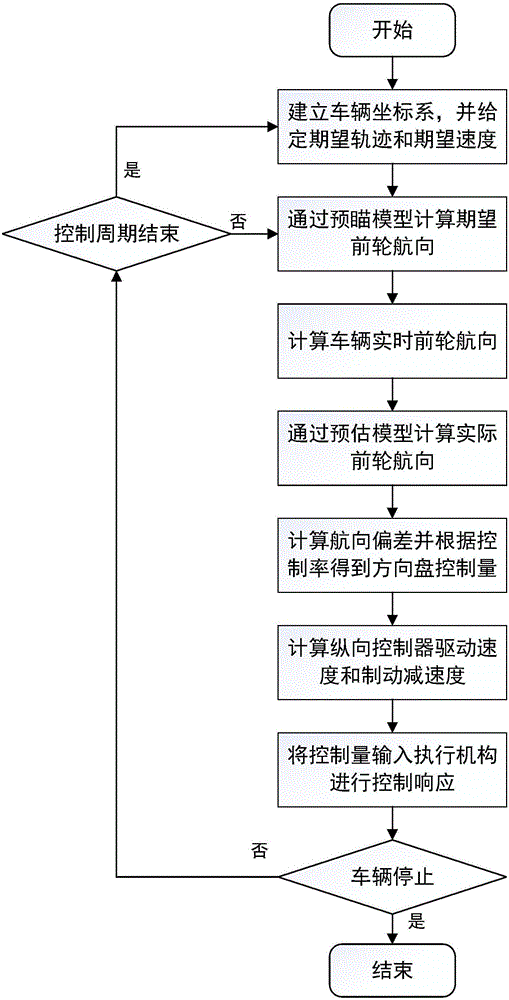
ActiveCN106681327AImplement Control ResponseOvercoming large inertia characteristicsPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesHysteresisSteering wheel
The present invention discloses a method and system for intelligent driving horizontal and vertical decoupling control of a great inertia electric motor coach. The method comprises the following steps: the step 1: establishing a coordinate system and setting an expected track and an expected speed according to a vehicle; the step 2: calculating an expected front-wheel course angle through a preview model; the step 3: calculating the real0-time front-wheel course angle of the vehicle; the step 4: calculating the estimated course angle of the vehicle; the step 5: calculating the course deviation and calculating the controlled quantity of a steering wheel according to the control rate; the step 6: calculating a vertical controller driving speed and a braking deceleration; and the step 7: inputting the controlled quantity into an execution mechanism to realize response control. The method for the intelligent driving horizontal and vertical decoupling control of the great inertia electric motor coach improves the control precision of tracking the expected track of the great inertia electric motor coach in the driverless environment, optimizes the control structure, effectively overcome the great inertia and the hysteresis quality and improve the response speed and the tracking effect of the control of the great inertia unmanned coach.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
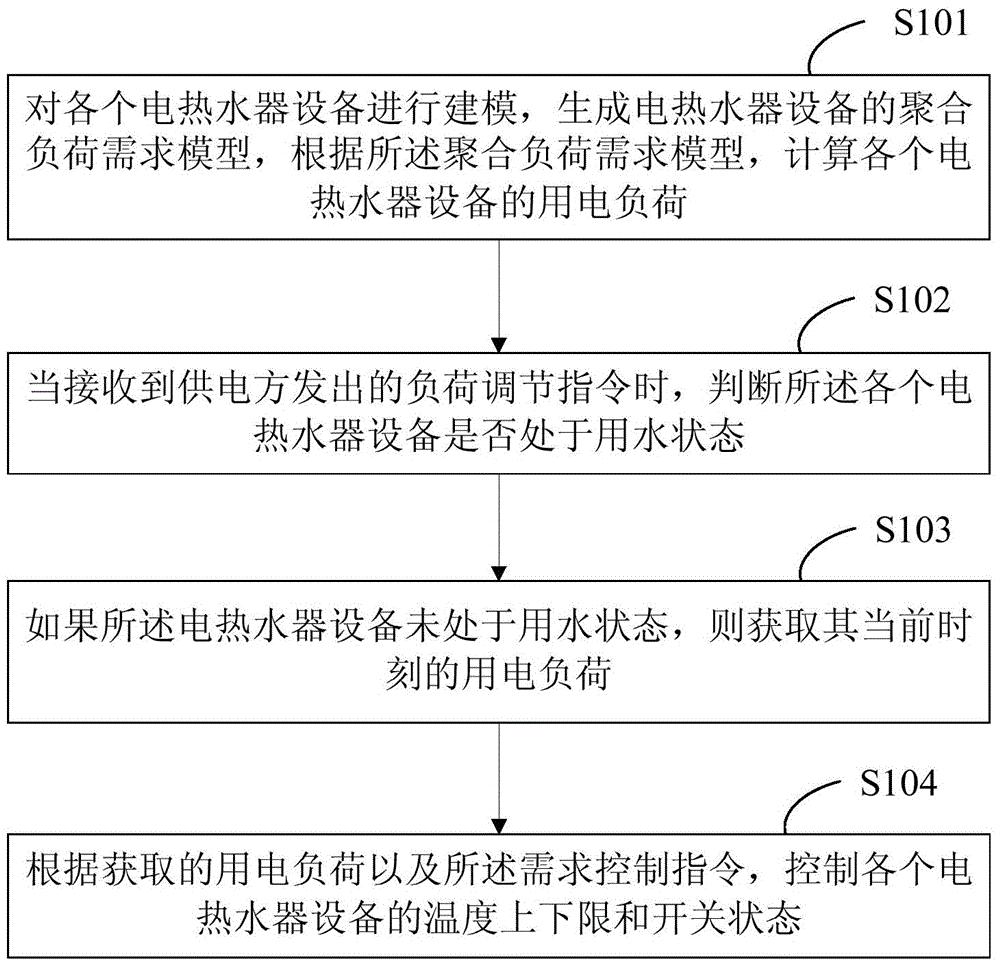
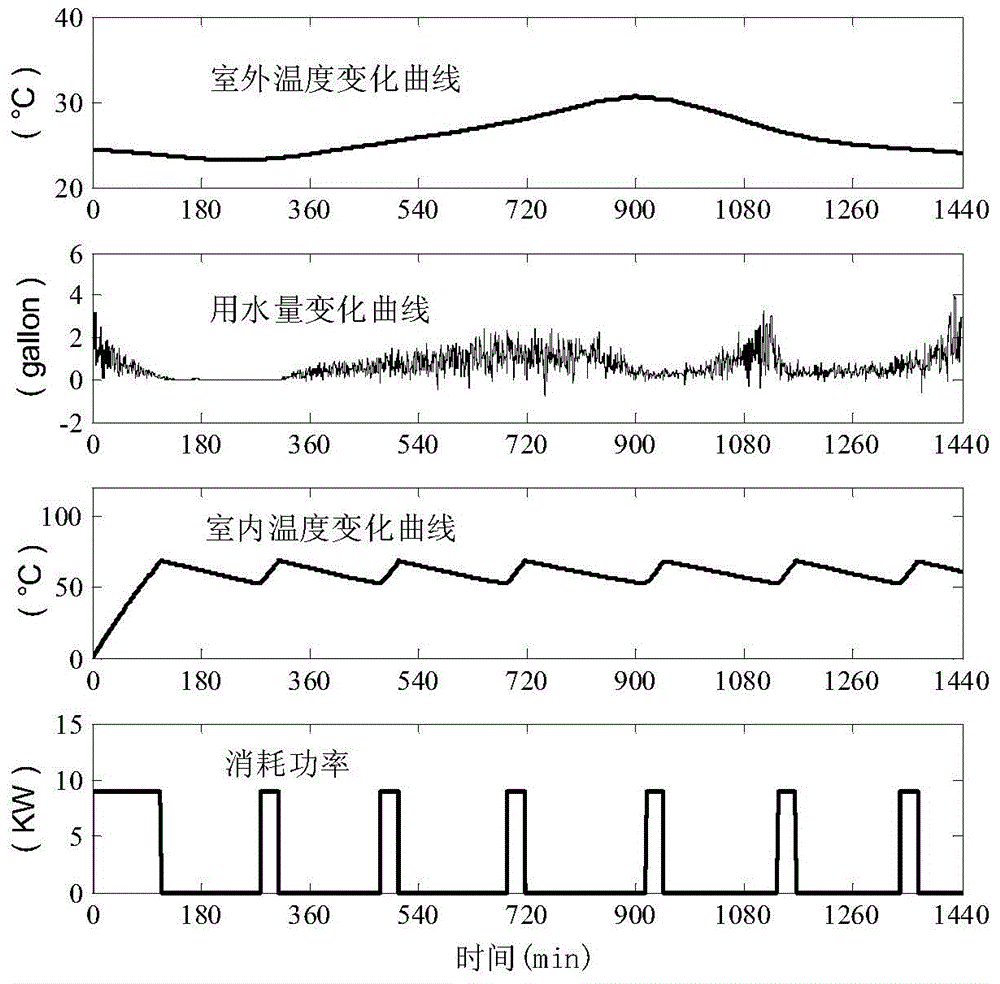
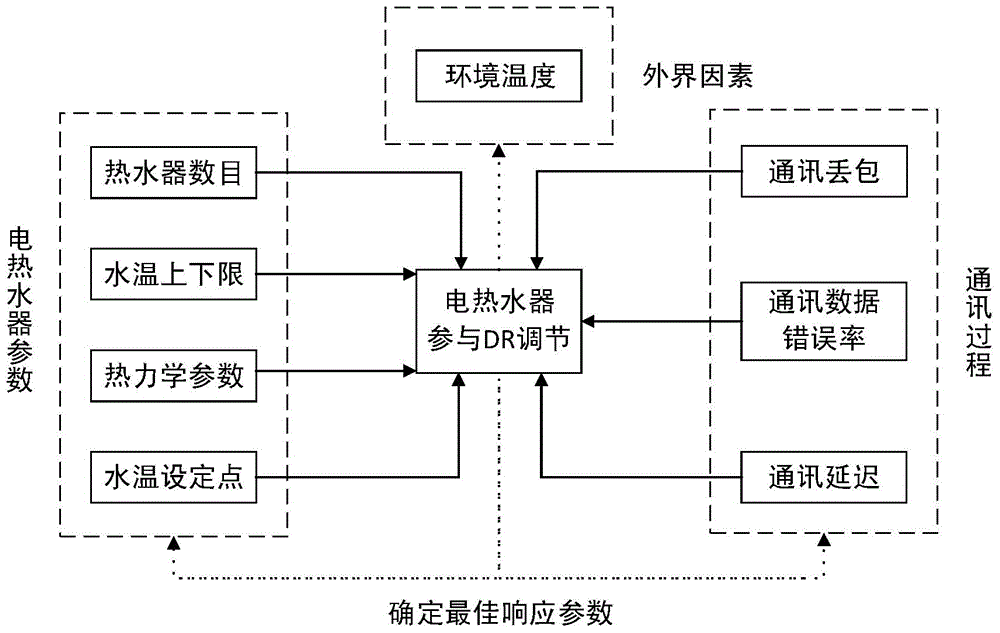
Demand side response control method based on temperature control load electric water heater and system thereof
The invention provides a demand side response control method based on a temperature control load electric water heater and a system thereof. Electric water heater equipment is molded to form an electric water heater polymerization load demand model; a water use amount of the electric water heater is considered, and an upper temperature limit, a lower temperature limit and a switch state of the electric water heater are reasonably controlled, so that a dynamic process and electric energy consumption of the electric water heater can be changed; various relevant factors such as an electric water heater parameter, an external factor and a communication process which affect response of the electric water heater are calculated so as to form a control framework for controlling the electric water heater, so that the electric water heater can effectively participate in a DR (data recorder); therefore, service is provided for a power grid, the application reliability of the electric water heater participating in the DR is improved, the relevant factors can be adjusted, and the application effect of the electric water heater to the field of the DR can be enhanced; resources are saved, and the electric energy quality can be improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
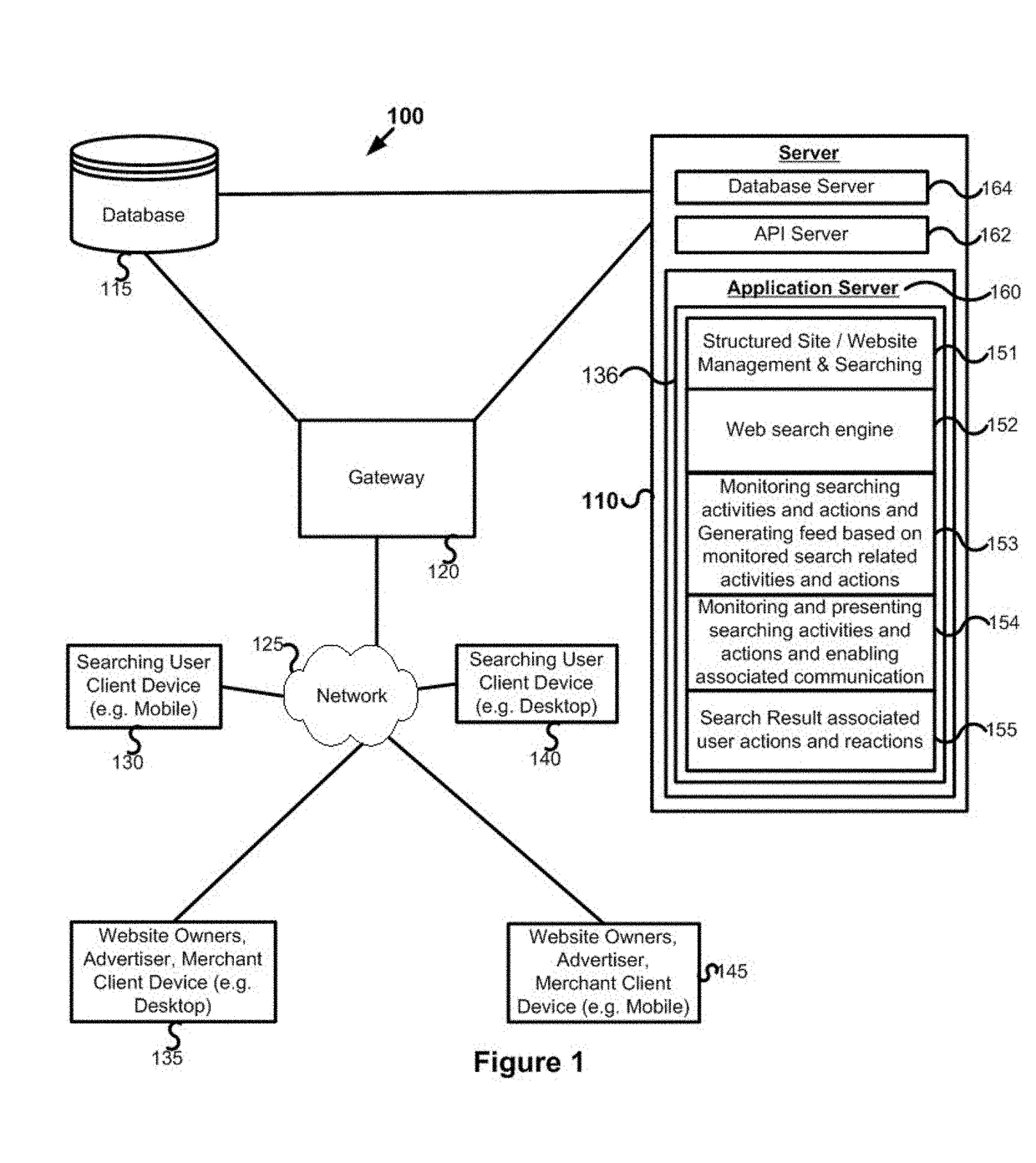
Displaying search result associated identified or extracted unique identity associated structured contents or structured website
Various embodiments of a system, methods, platform, database, search engine & device for identifying search result associate unique identity or extracting unique identity based on parsing search result associated Uniform Resource Locator (URL) or web address or metadata, automatically determining or preparing or generating query based on said identified unique identity and automatically executing said query to automatically search, identify, invoke or retrieve or generate said identified unique identity associated one or more types of structured contents, structured data or structured website. In an embodiment enable to create and manage standardized, compact, searchable and search result compatible structured site or website including pages or webpages or GUIs or categories or categories of posts, and associated one or more types of contents including posts, structured contents, user actions and reaction controls or GUIs and presenting said structured contents with corresponding search result item based on search result item associated domain name of website associated user or account or source.
Owner:RATHOD YOH
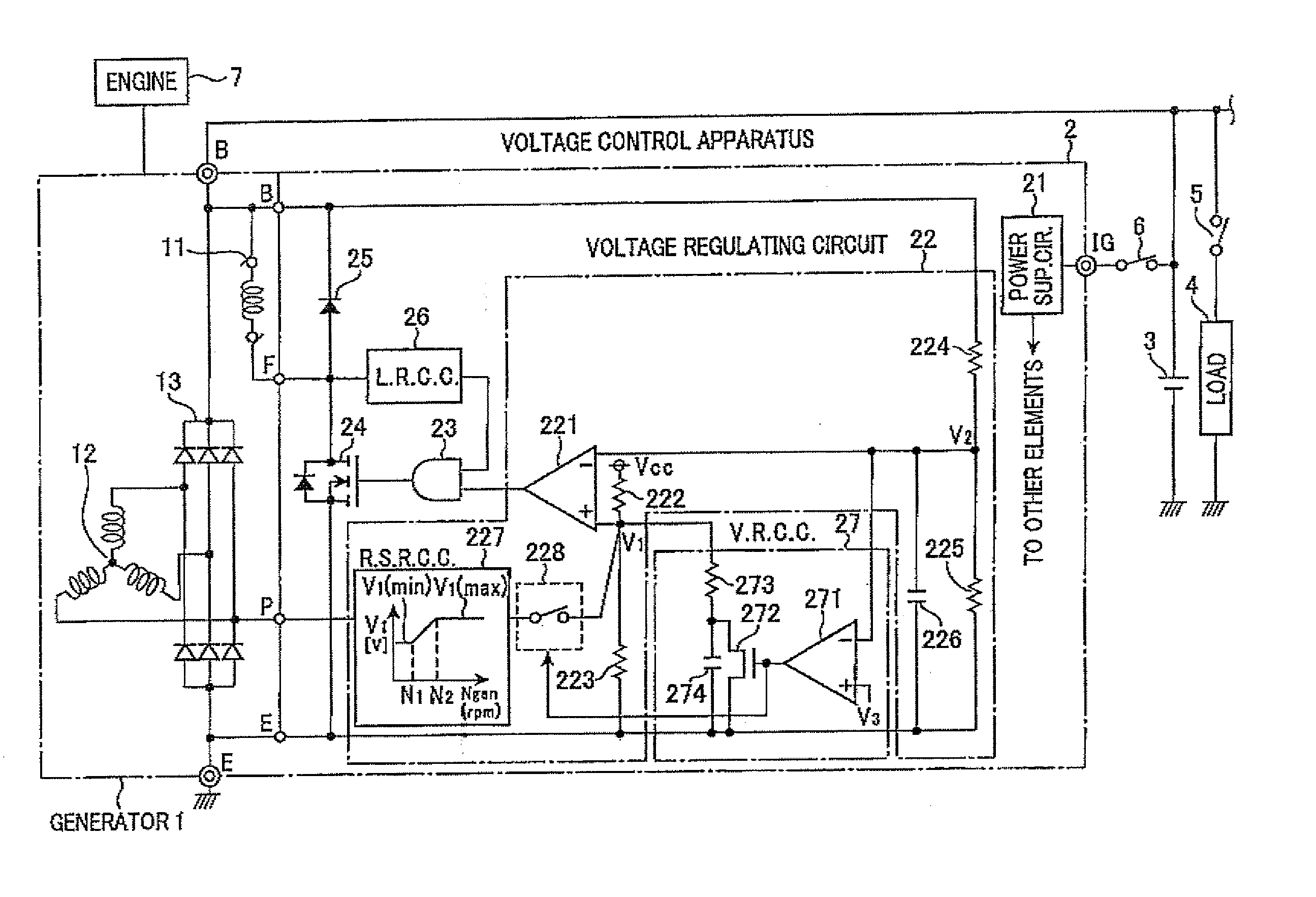
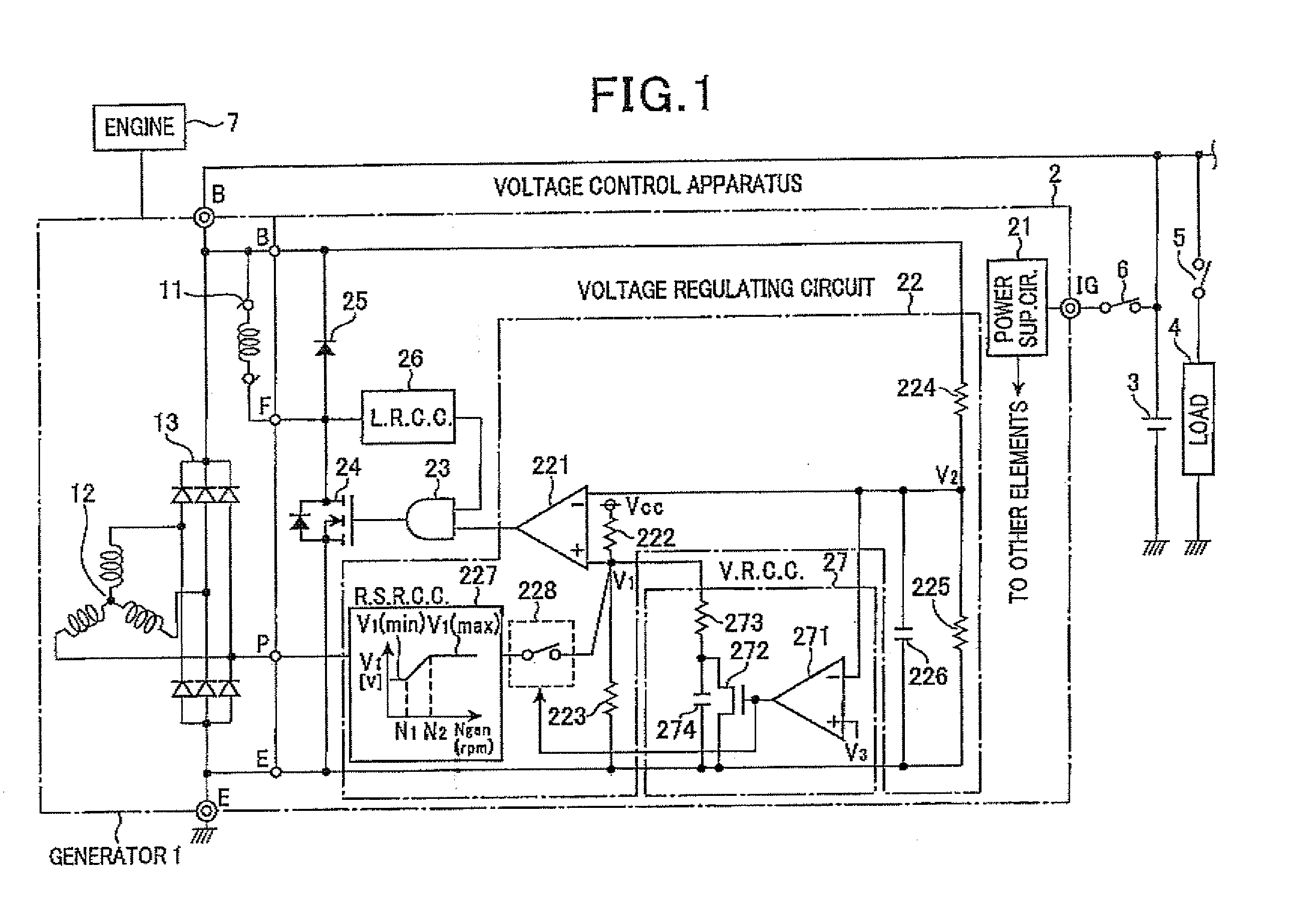
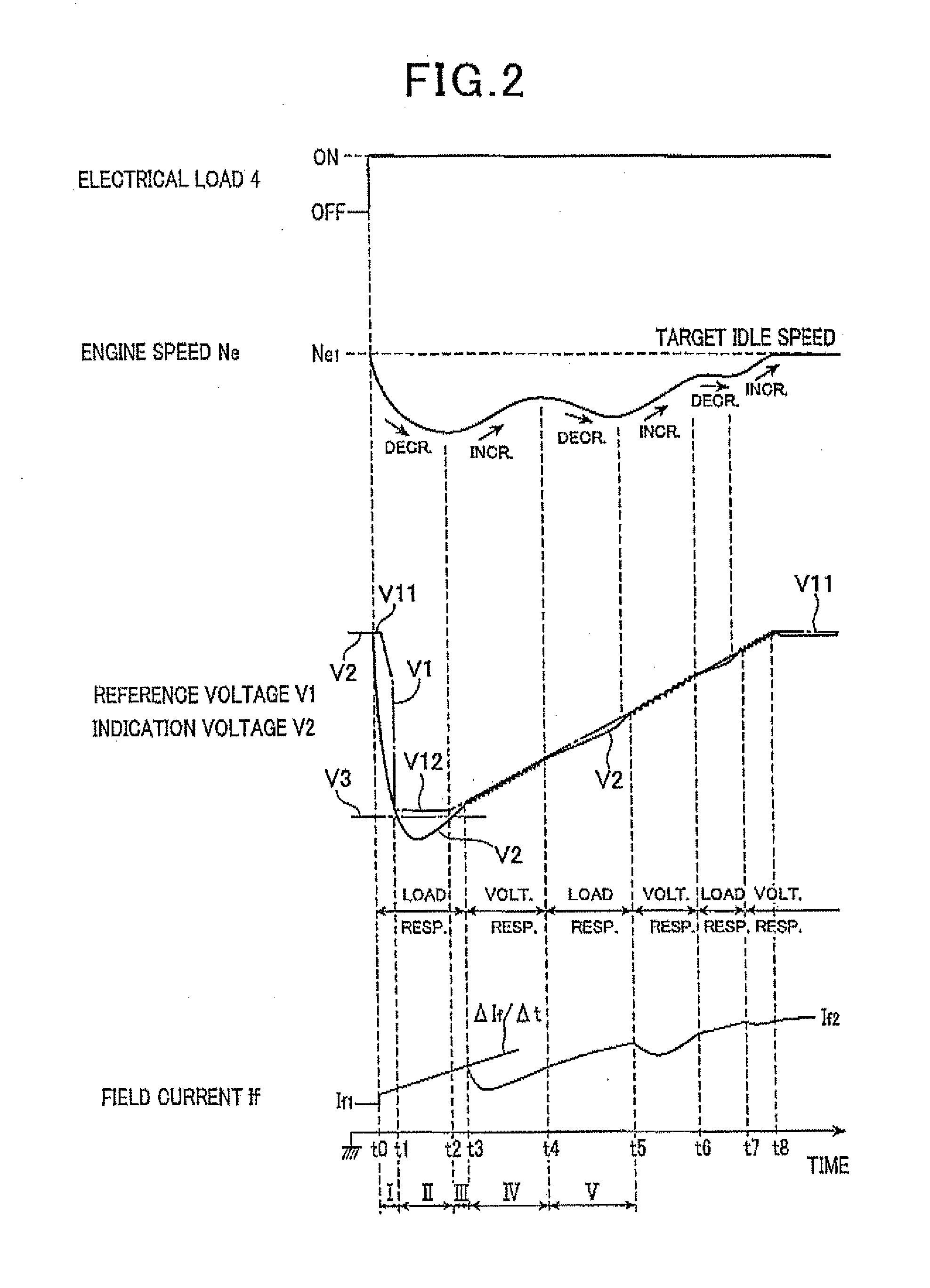
Voltage control apparatus for automotive electric generator
InactiveUS20100225284A1Increase currentSuppress increase in field currentEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlVoltage responseResponse control
A voltage control apparatus for an electric generator includes a load response controller and a voltage response controller. The electric generator includes a field winding and is driven by an engine of a motor vehicle. When the output voltage of the generator decreases below a threshold voltage upon the application of an electrical load, the rotational speed of the engine fluctuates to repeatedly increase and decrease until it is stabilized. During the time periods in which the rotational speed of the engine decreases, field current supplied to the field winding of the generator is gradually increased under a load response control performed by the load response controller. During the time periods in which the rotational speed of the engine increases, the field current is gradually increased under a voltage response control by the voltage response controller.
Owner:DENSO CORP
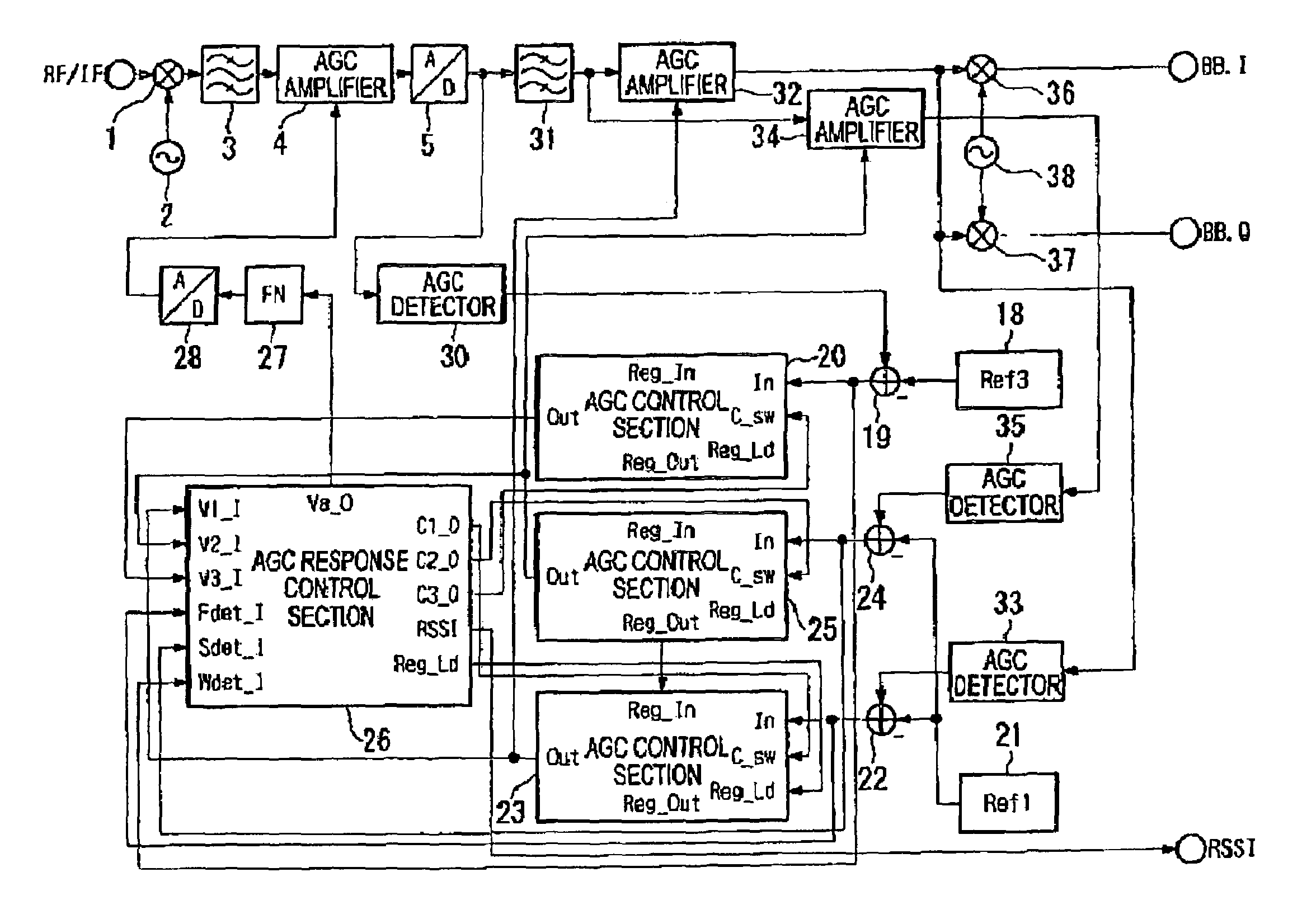
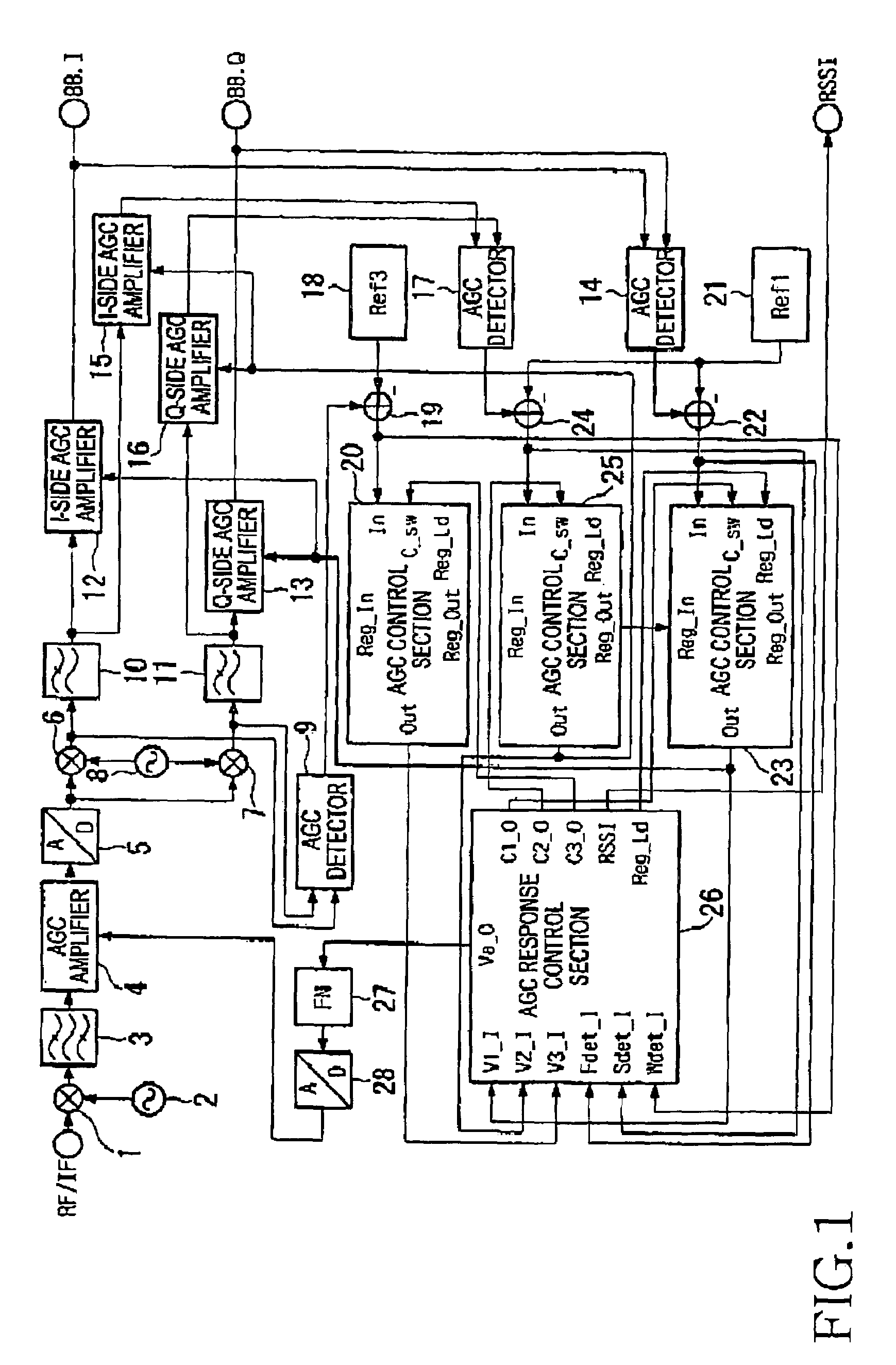
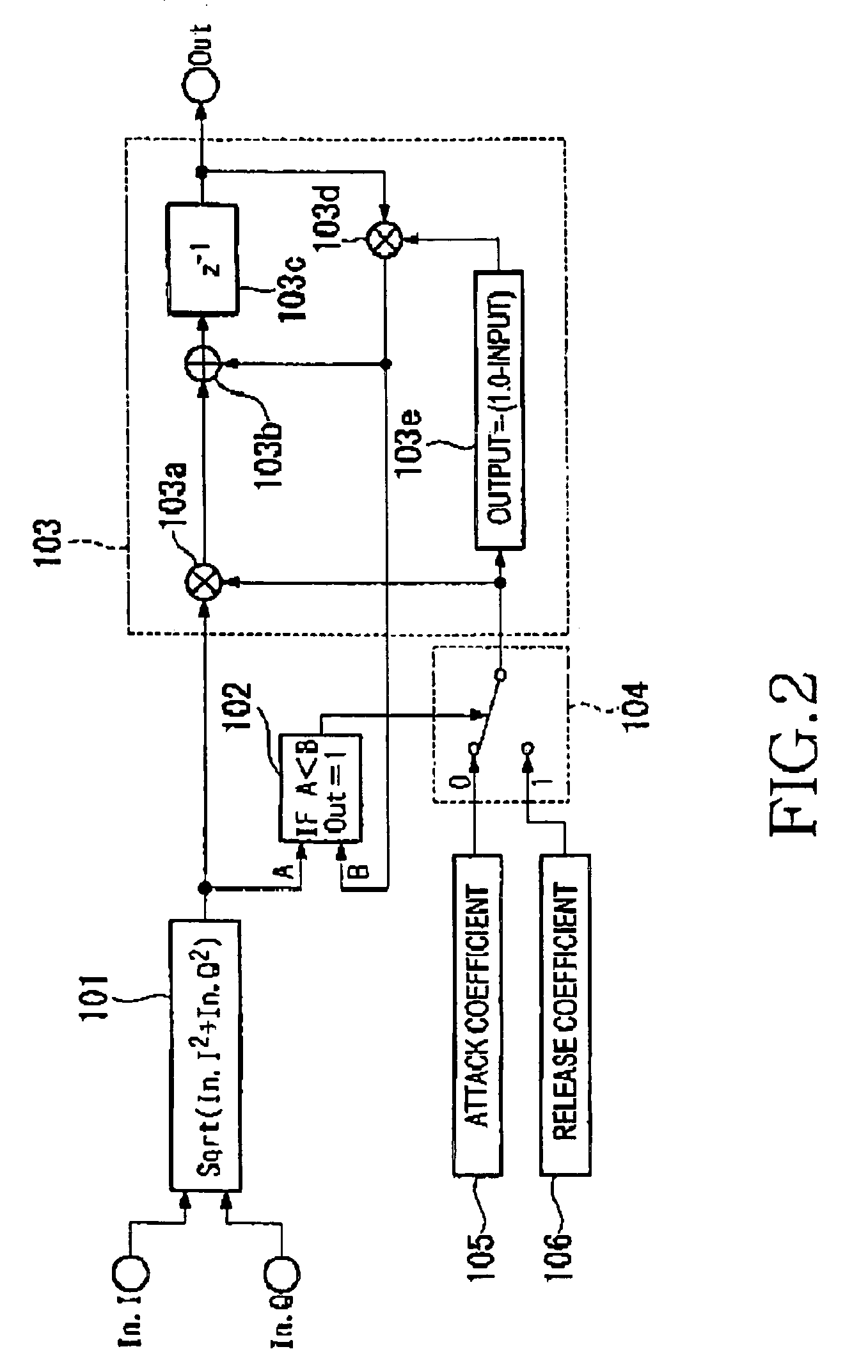
Automatic gain controller
ActiveUS7113758B2Easy to measureReduce saturationControlling traffic signalsResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierControl signal
Disclosed is an automatic gain controller capable of reducing signal saturation or signal distortion caused by out-of-band signals of a filter extracting an object signal or delay of a control signal and capable of precisely measuring a signal level in a filter band. An AGC response control section compares a level of control voltage (“V2_I terminal” signal) outputted from a first AGC control section and inputted into a “V2_I terminal” with a level of control voltage (“V3_I terminal” signal) outputted from a second AGC control section and inputted into a “V3_I terminal”. If the control voltage, which is the “V3_I terminal” signal, outputted from the second AGC control section is less than the control voltage, which is a “V2_I terminal” signal, outputted from the first AGC control section, the AGC response control section controls an AGC amplifier by using the control voltage outputted from the second AGC control section. If the control voltage, which is the “V3_I terminal” signal, outputted from the second AGC control section is greater than the control voltage, which is the “V2_I terminal” signal, outputted from the first AGC control section, the AGC response control section controls the AGC amplifier by using the control voltage outputted from the first AGC control section.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electronically-controlled suspension apparatus and damping force control method
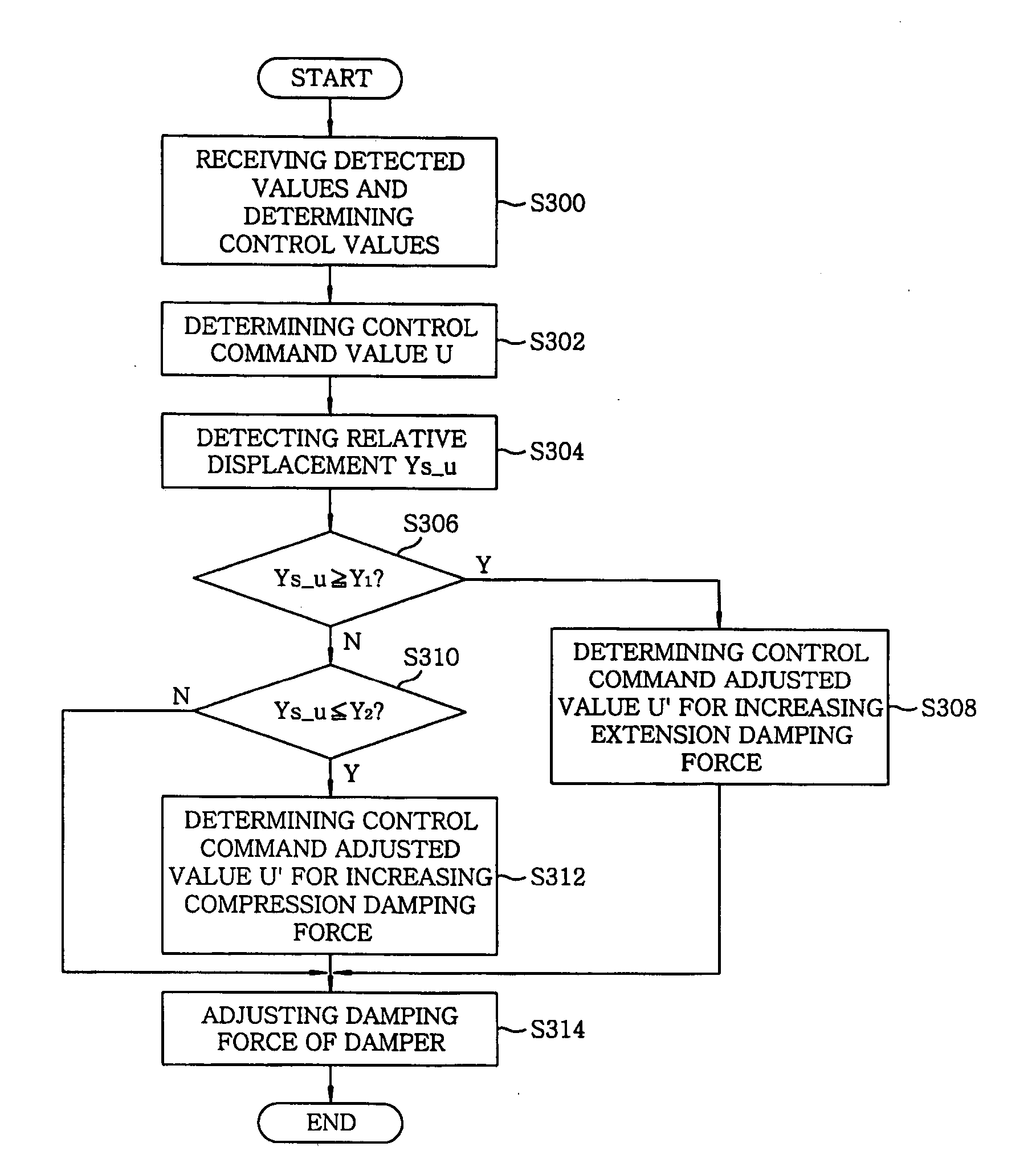
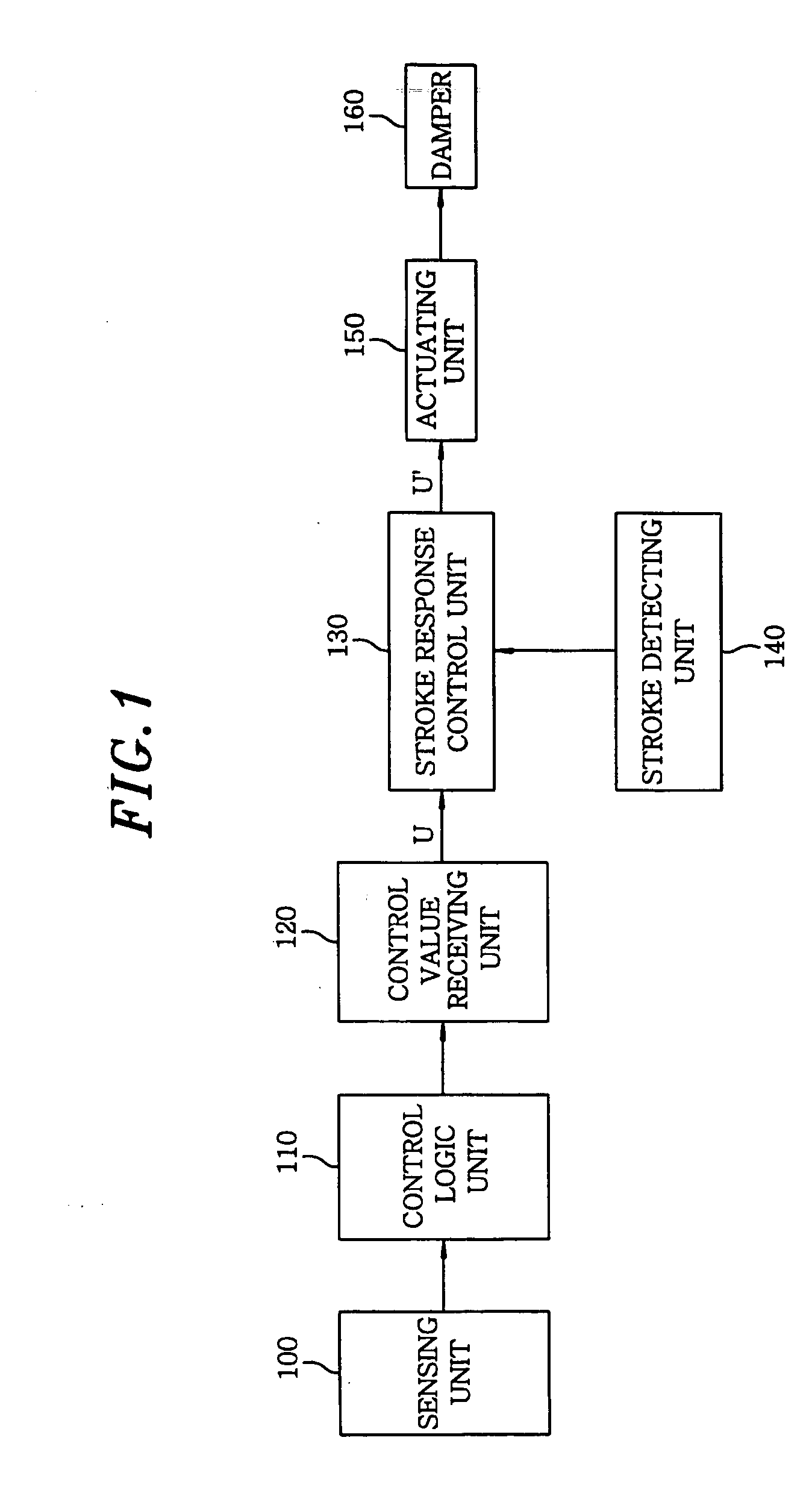
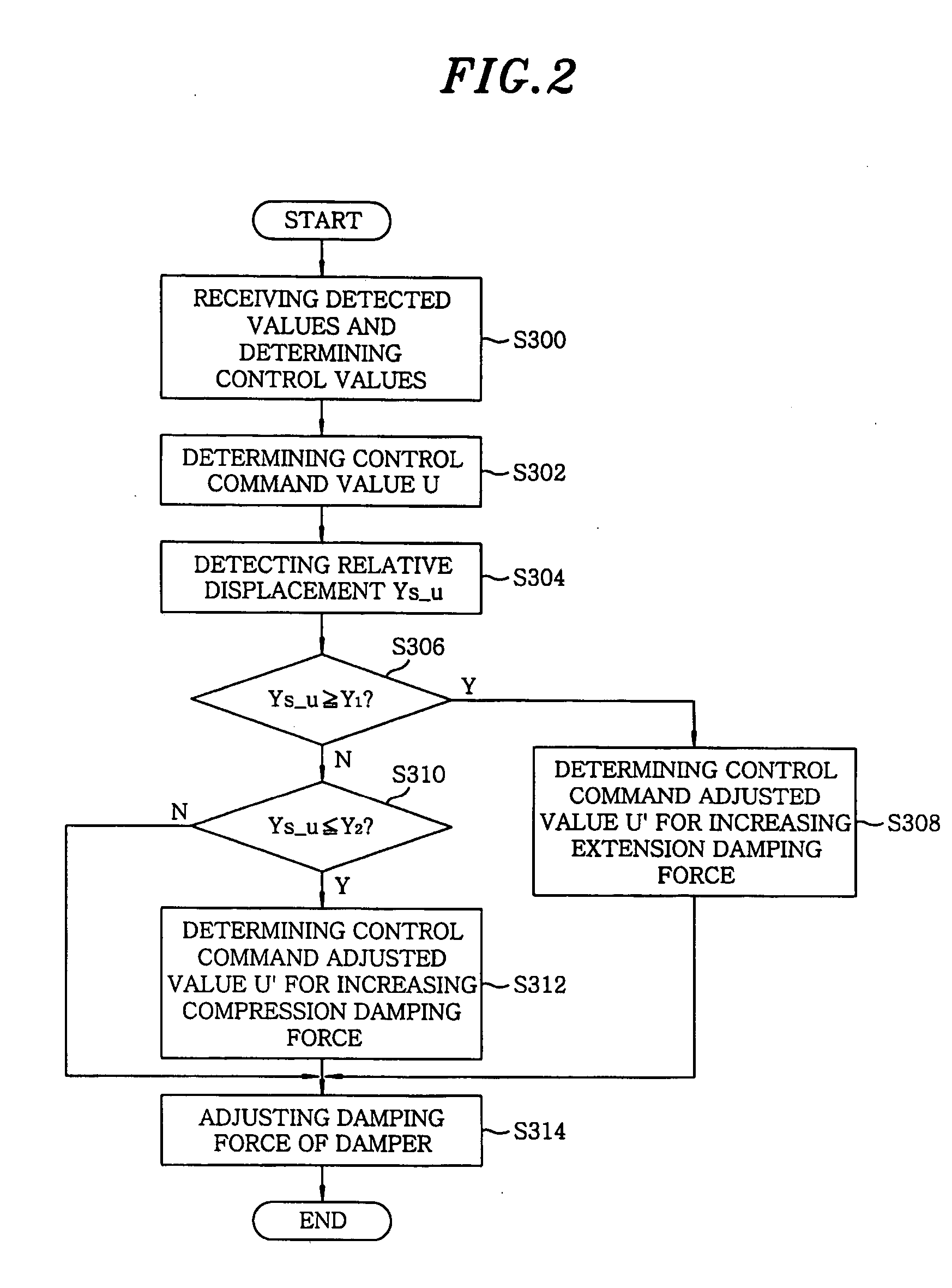
InactiveUS20050113998A1Avoid componentsHardens damping force characteristics of a damperDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesRelative displacementControl theory
An electronically-controlled suspension apparatus includes a stroke detecting unit for detecting a relative displacement of the vehicle body with respect to the wheel axle; a stroke response control unit for determining a control command adjusted valve; and an actuating unit which is operated according to the control command adjusted value, thus adjusting the extension or compression damping force of the damper. The stroke response control unit determines the control command adjusted value for increasing an extension or compression damping force of the damper when the relative displacement is equal to or greater than a first predetermined value, or is less than or equal to a second predetermined value.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com