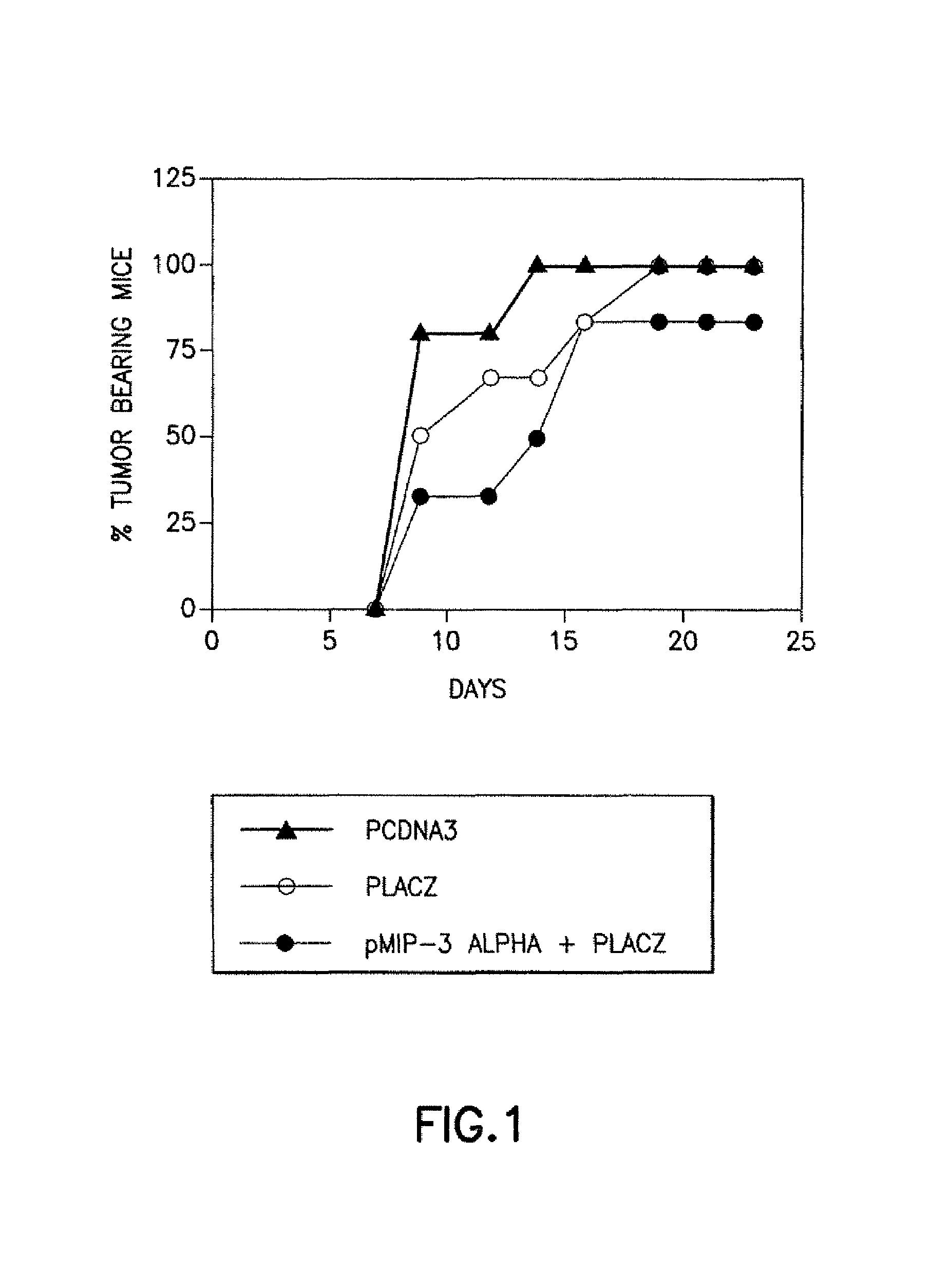
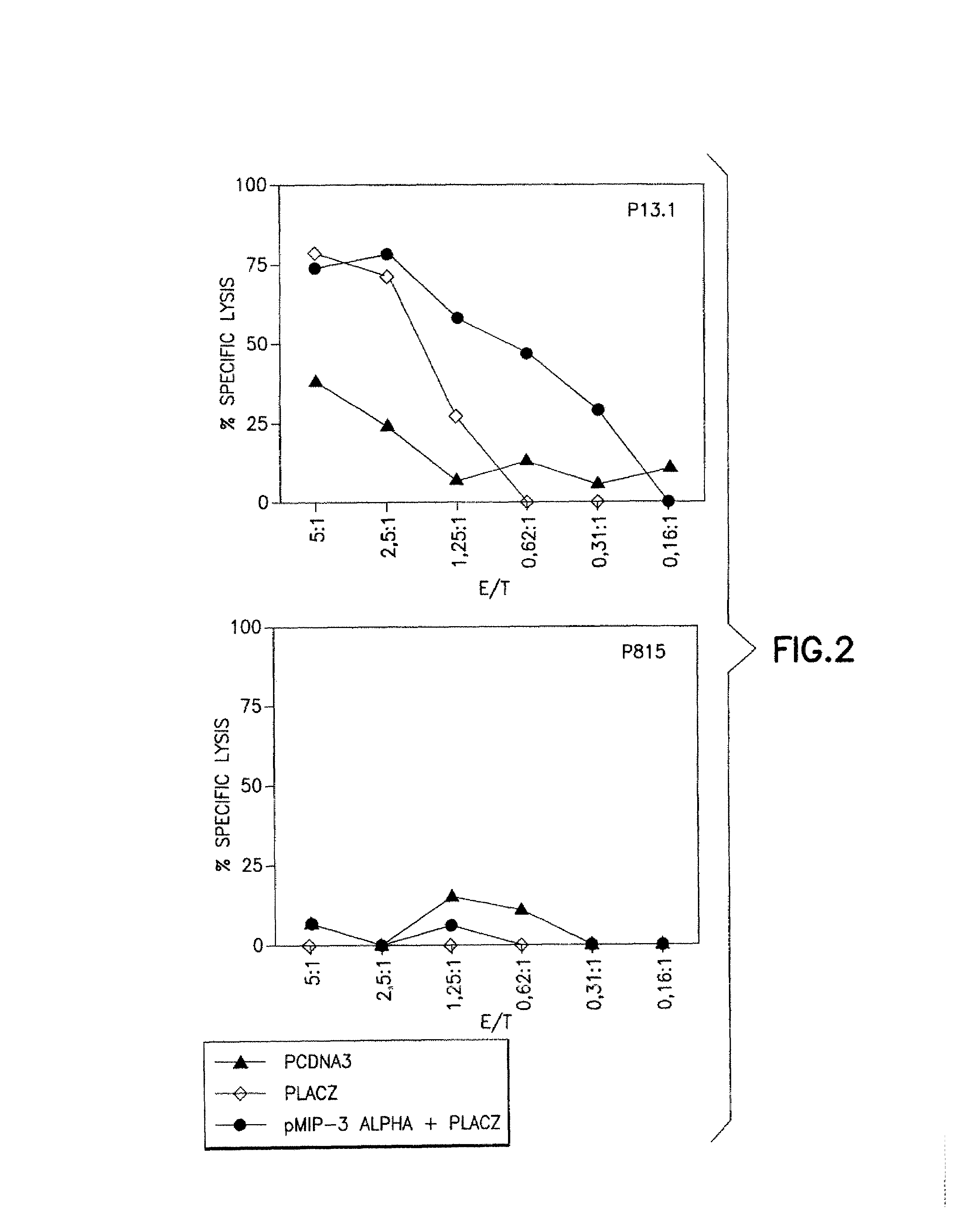
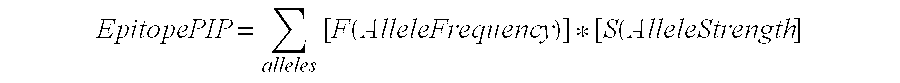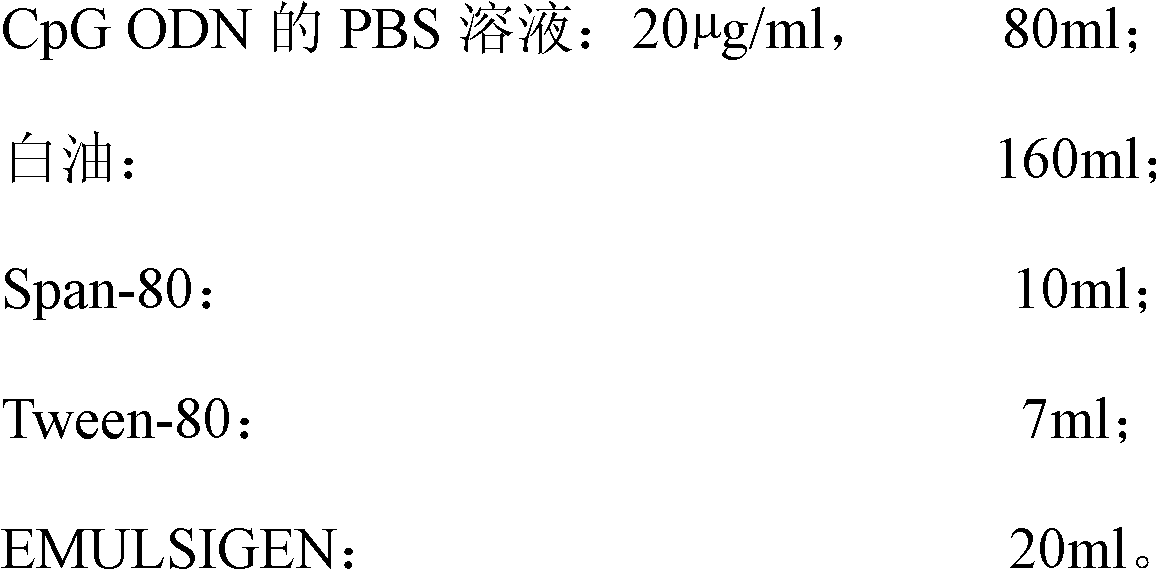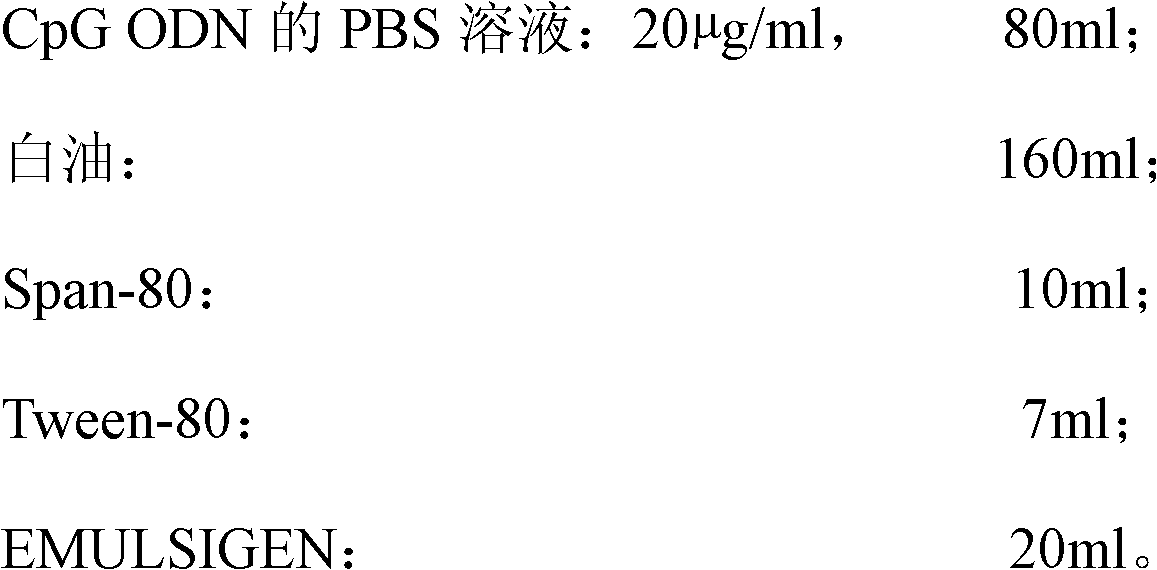Patents
Literature
32 results about "Antigen uptake" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
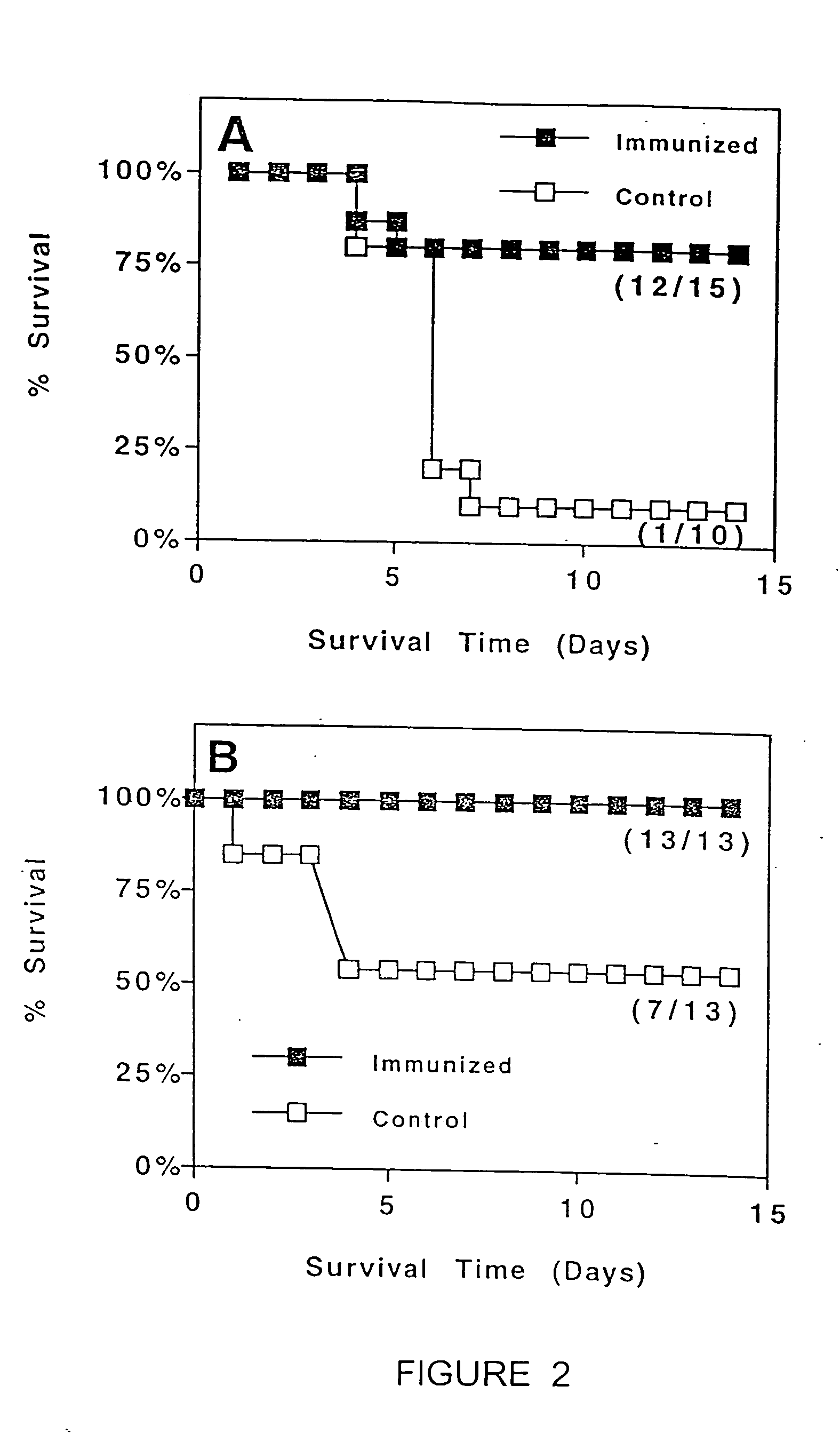
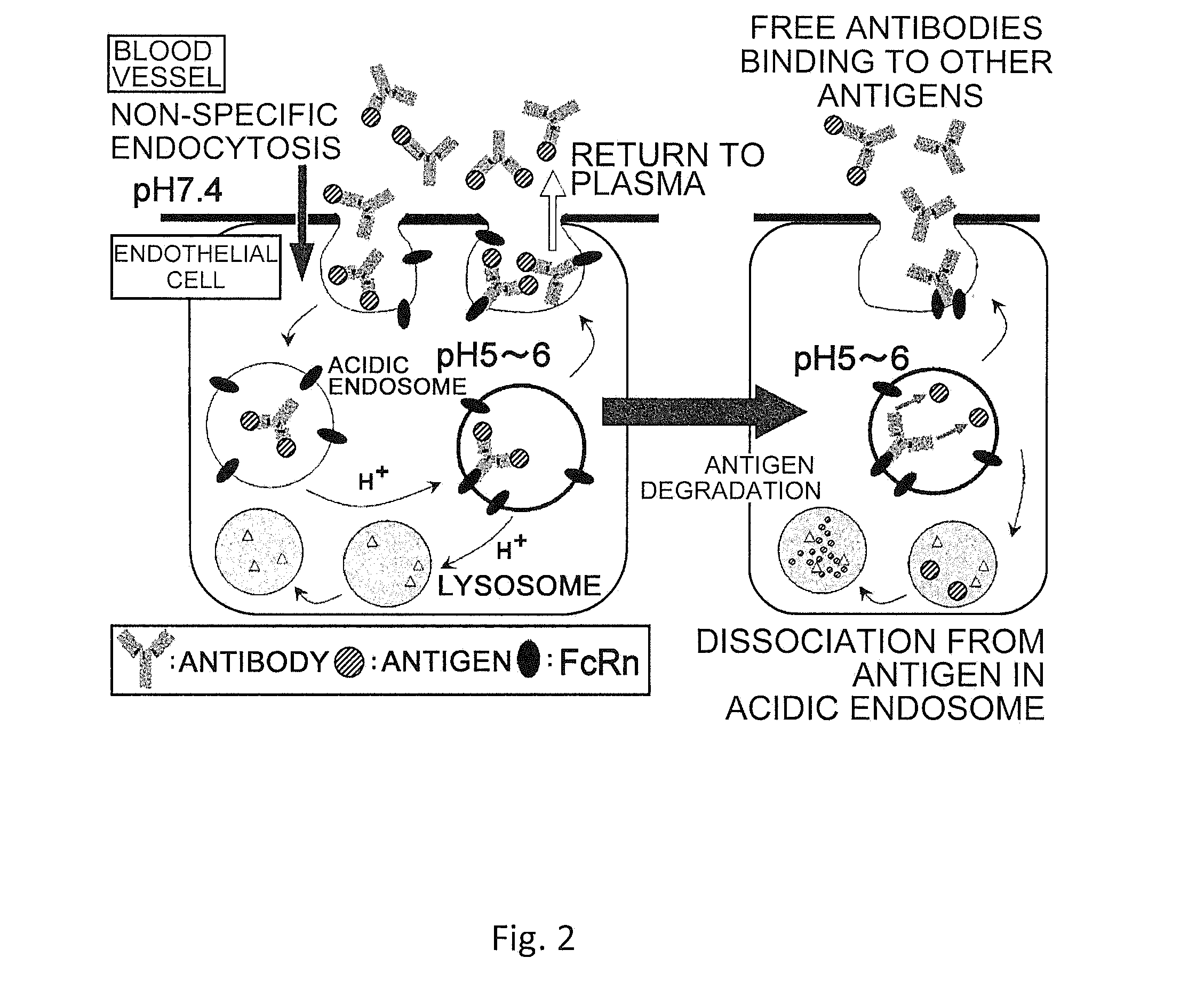
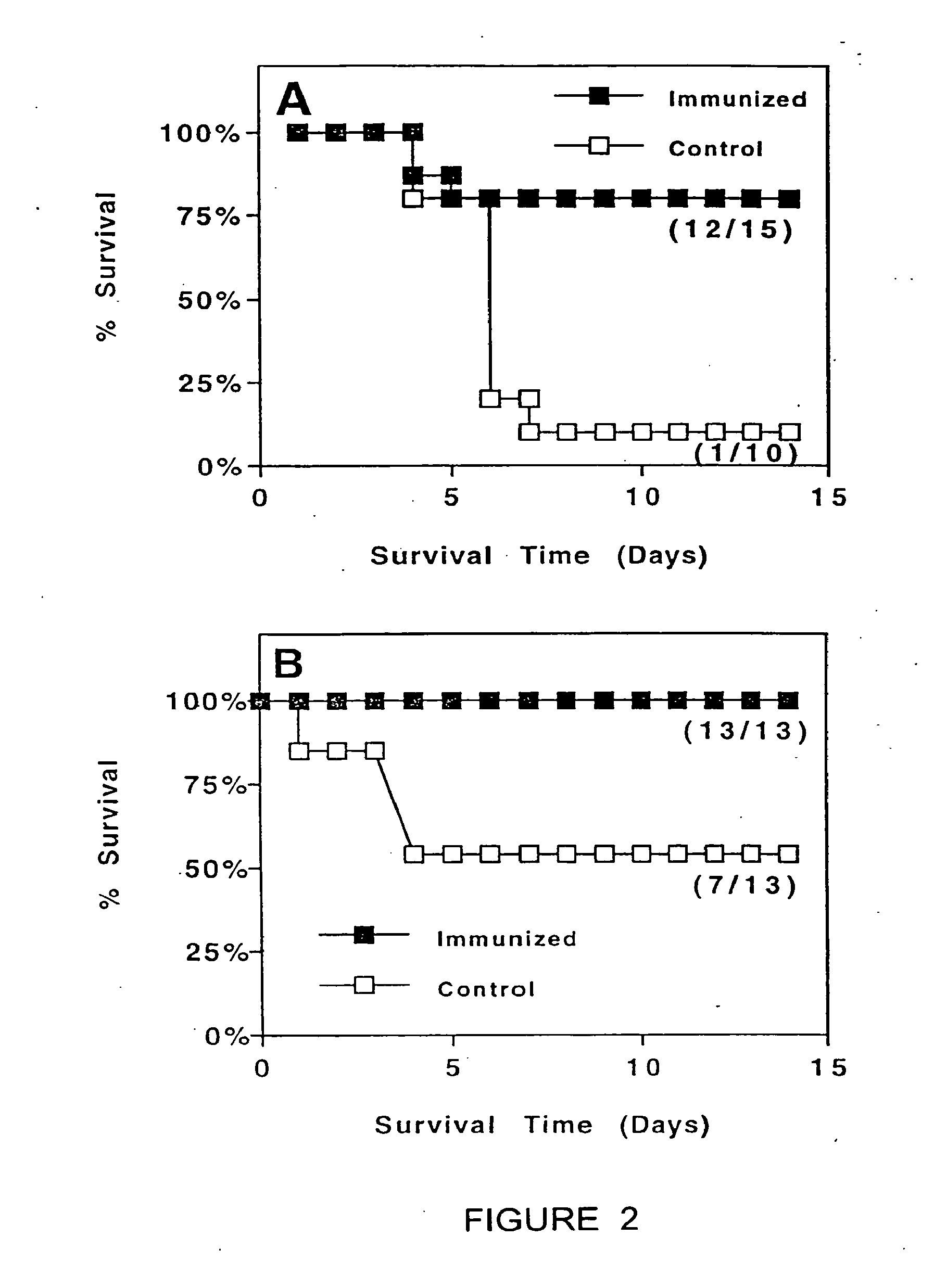
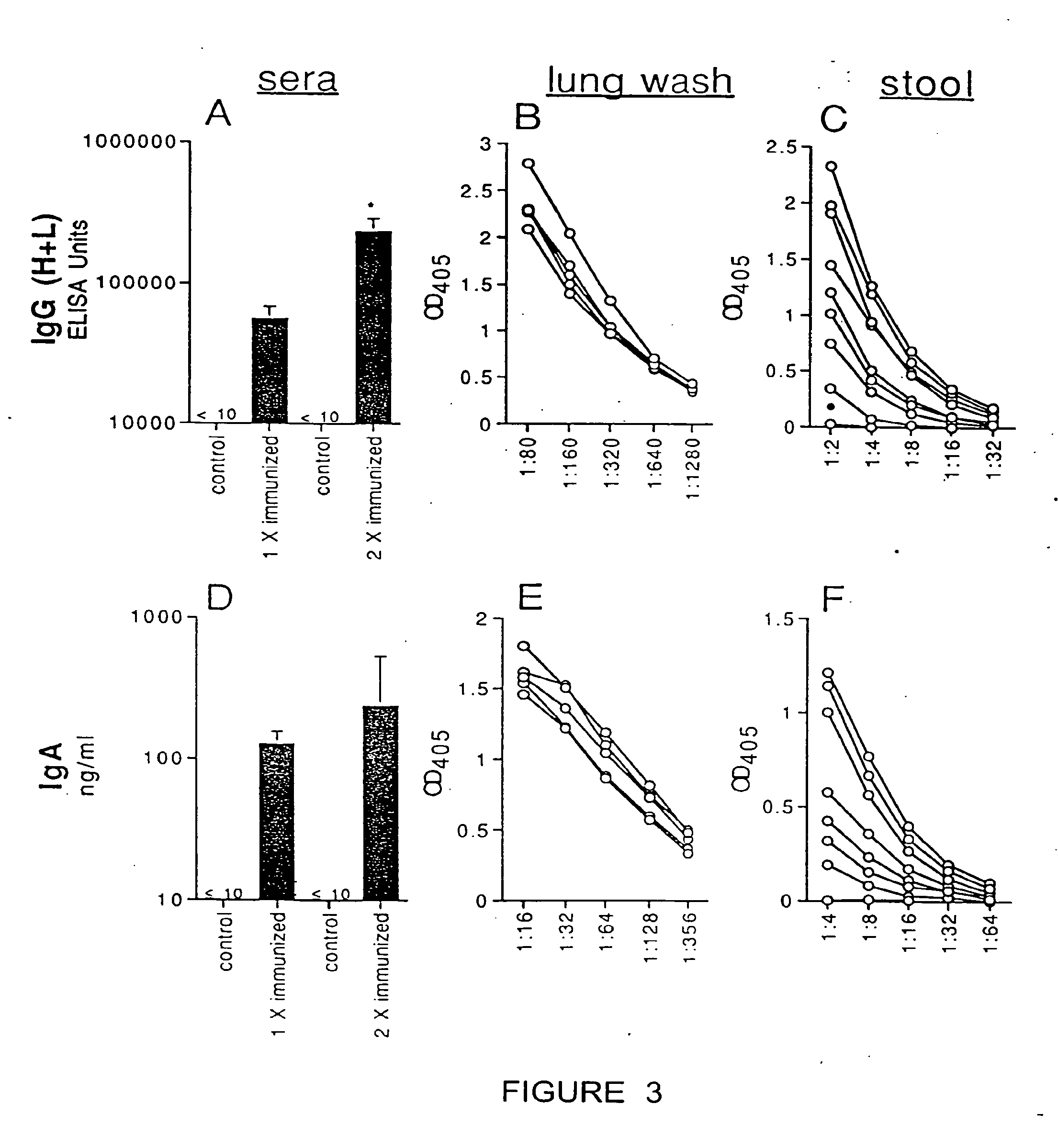
(a) Antigen uptake and delivery to the processing compartment. The antigen concentration and the mechanism of uptake (fluid phase macropinocytosis or receptor mediated) determine the amount of antigen internalized and the processing compartment to which it is delivered.
Novel proteins with altered immunogenicity
The present invention provides methods for combining computational methods for modulating protein immunogenicity with computational methods for identifying sequences with desired structural and functional properties. More specifically, the methods of the present invention may be used to identify modifications that increase or decrease the immunogenicity of a protein by affecting antigen uptake, MHC binding, T-cell binding, or antibody binding, while retaining or enhancing functional properties.
Owner:XENCOR
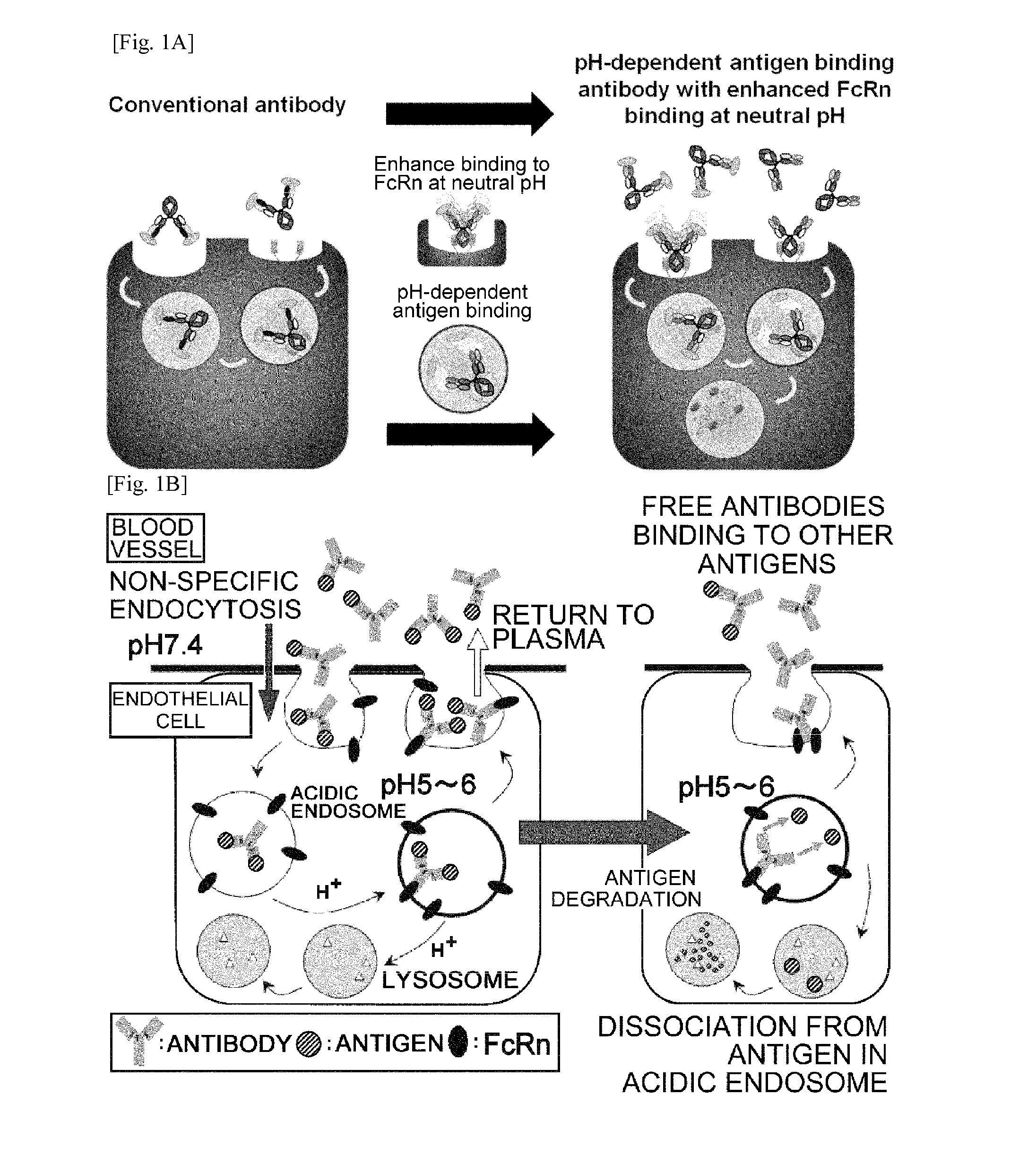
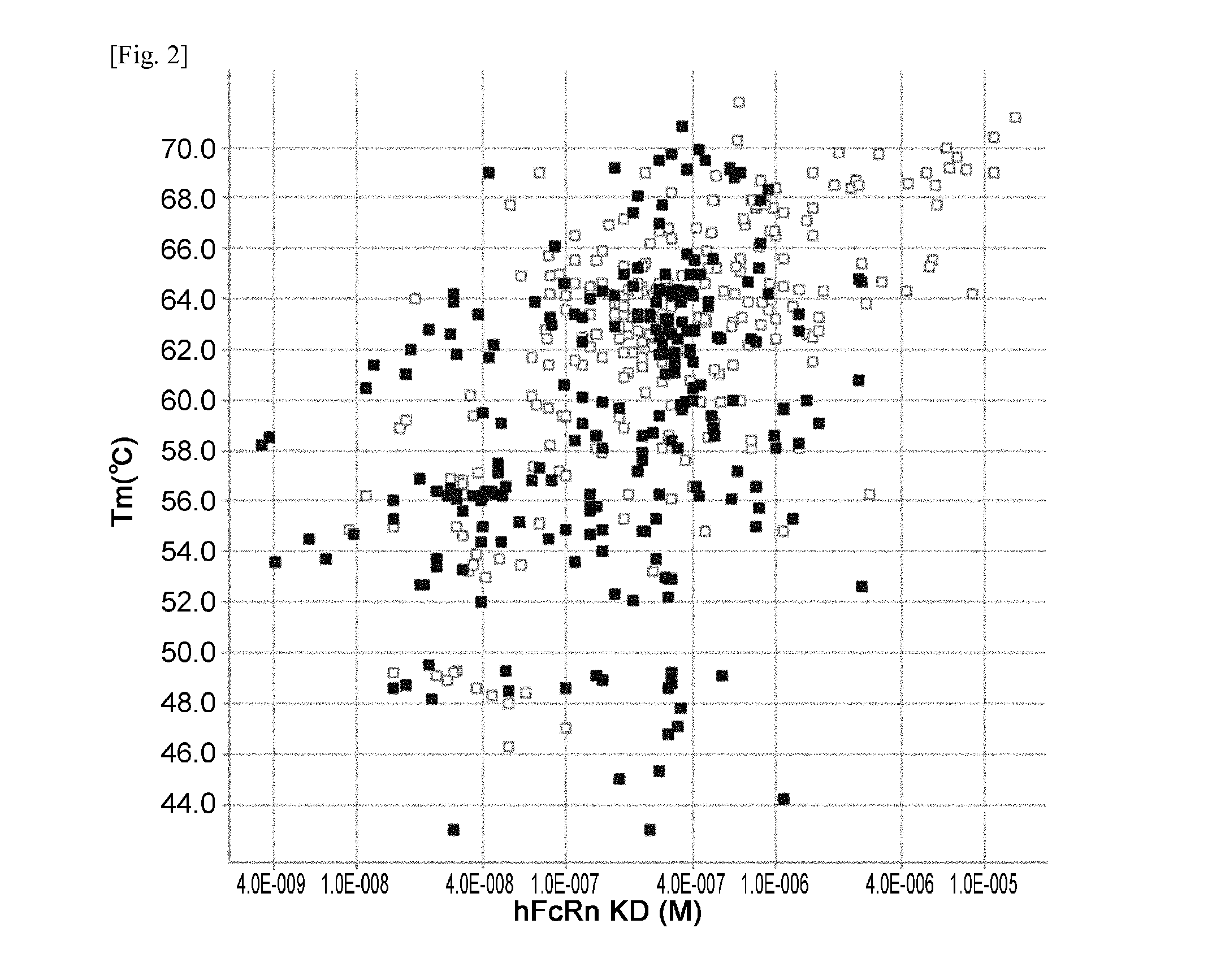
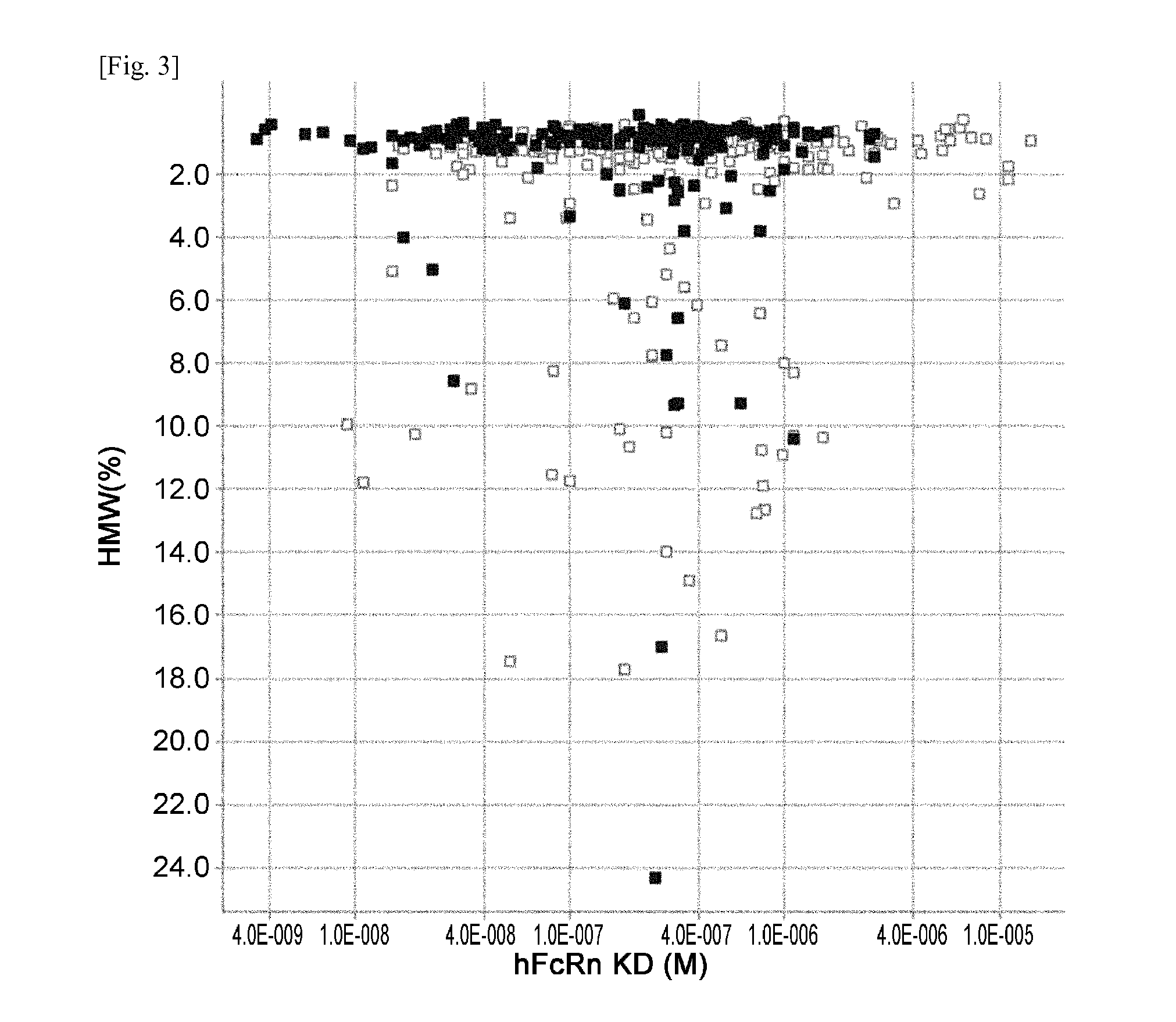
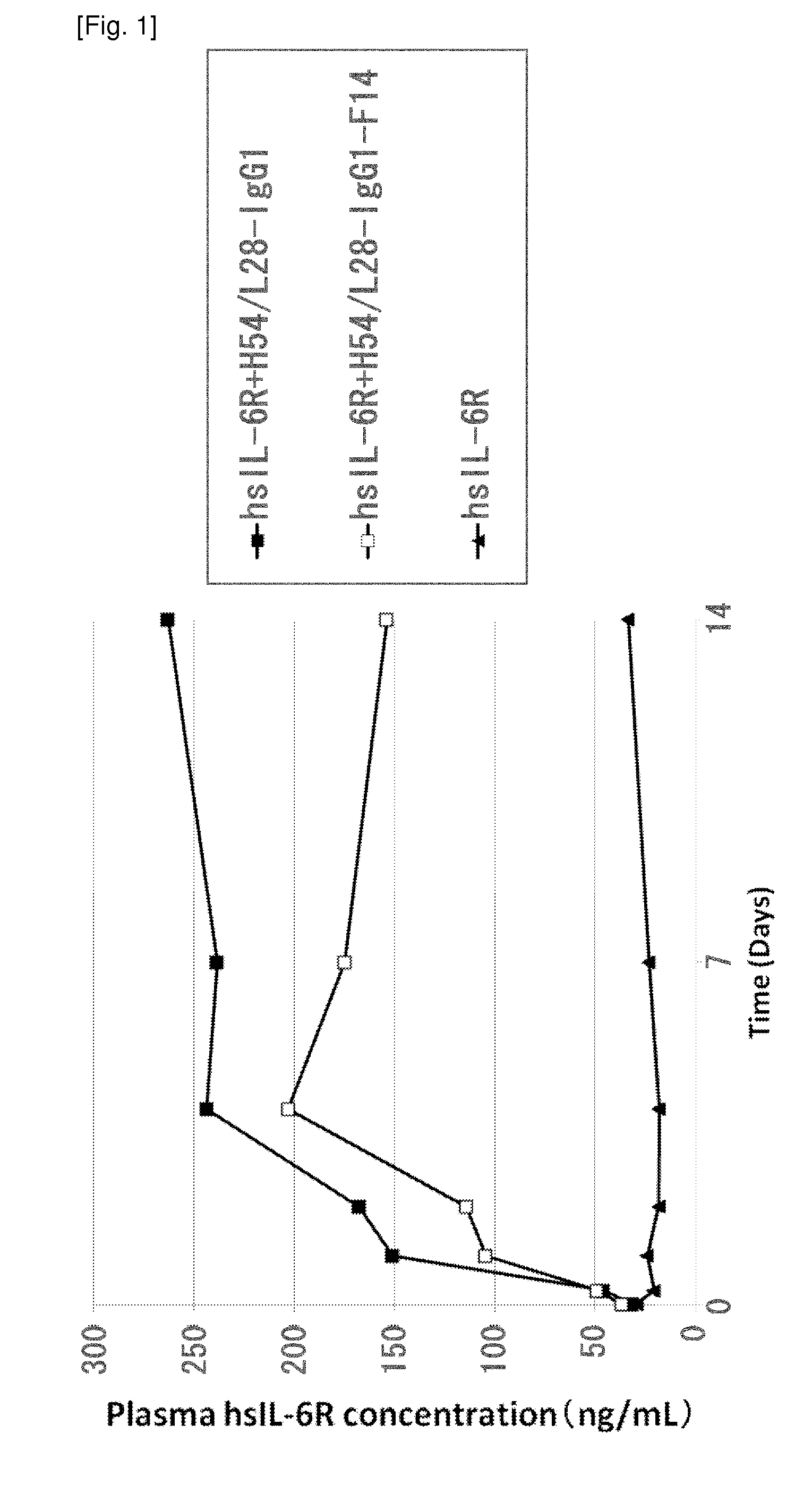
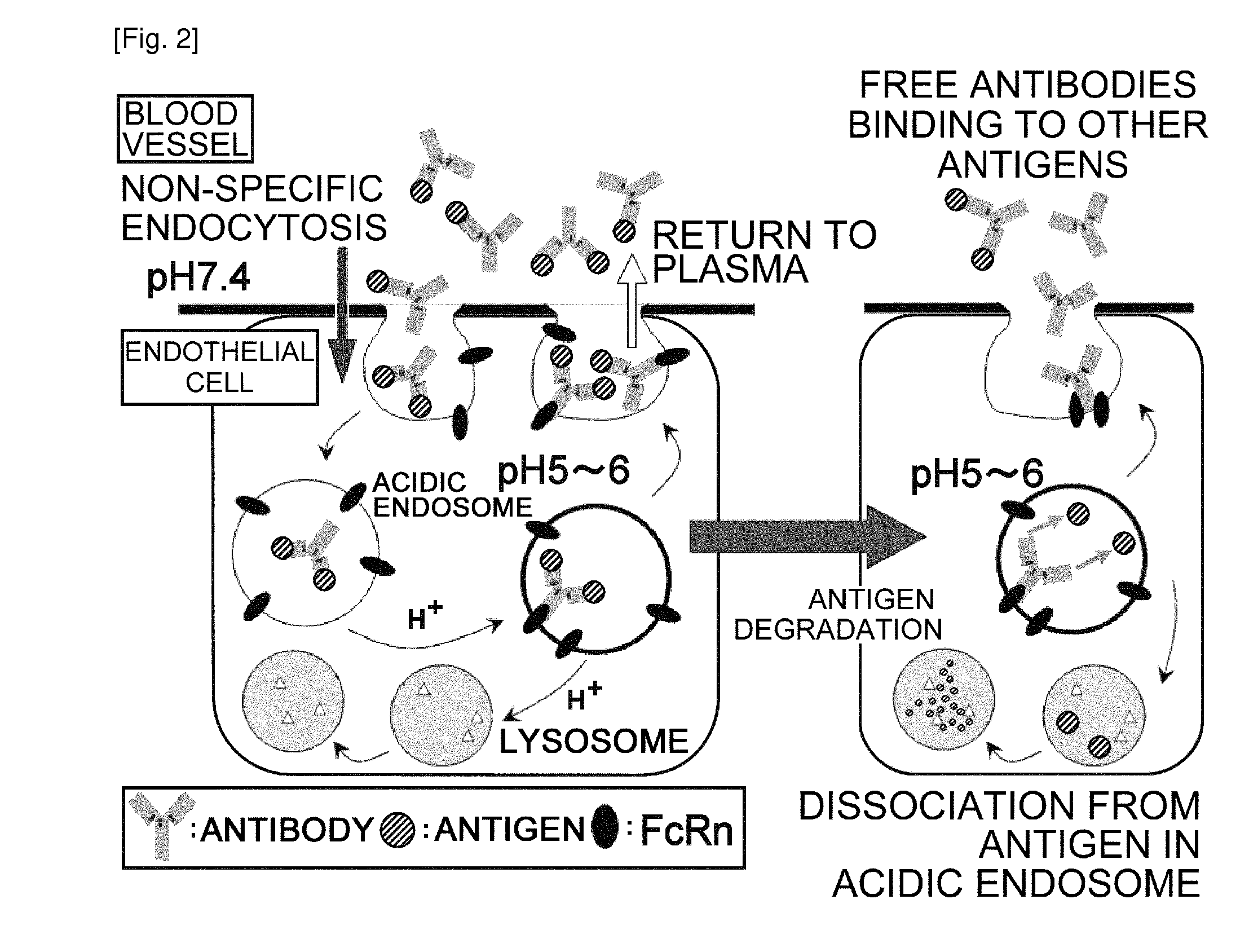
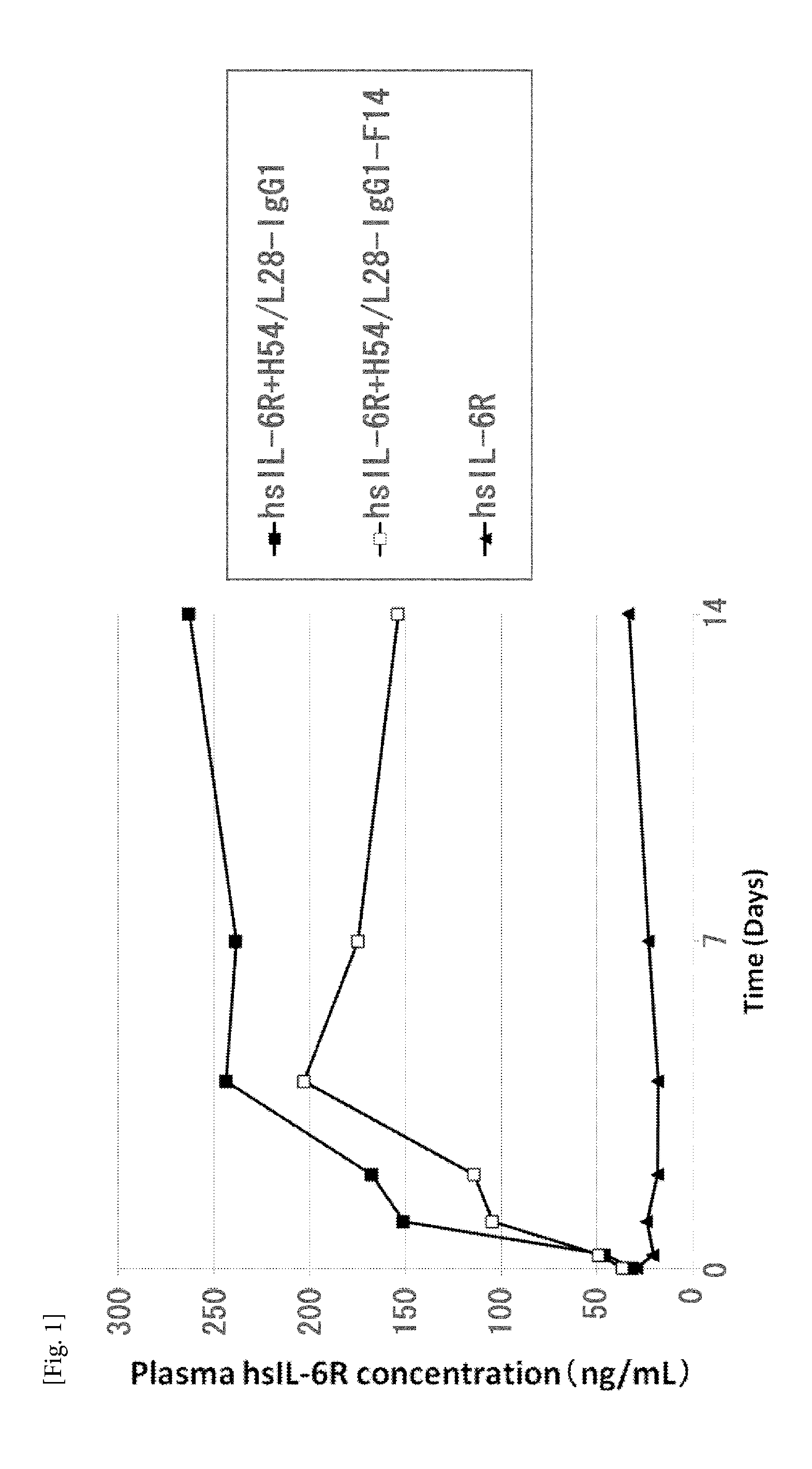
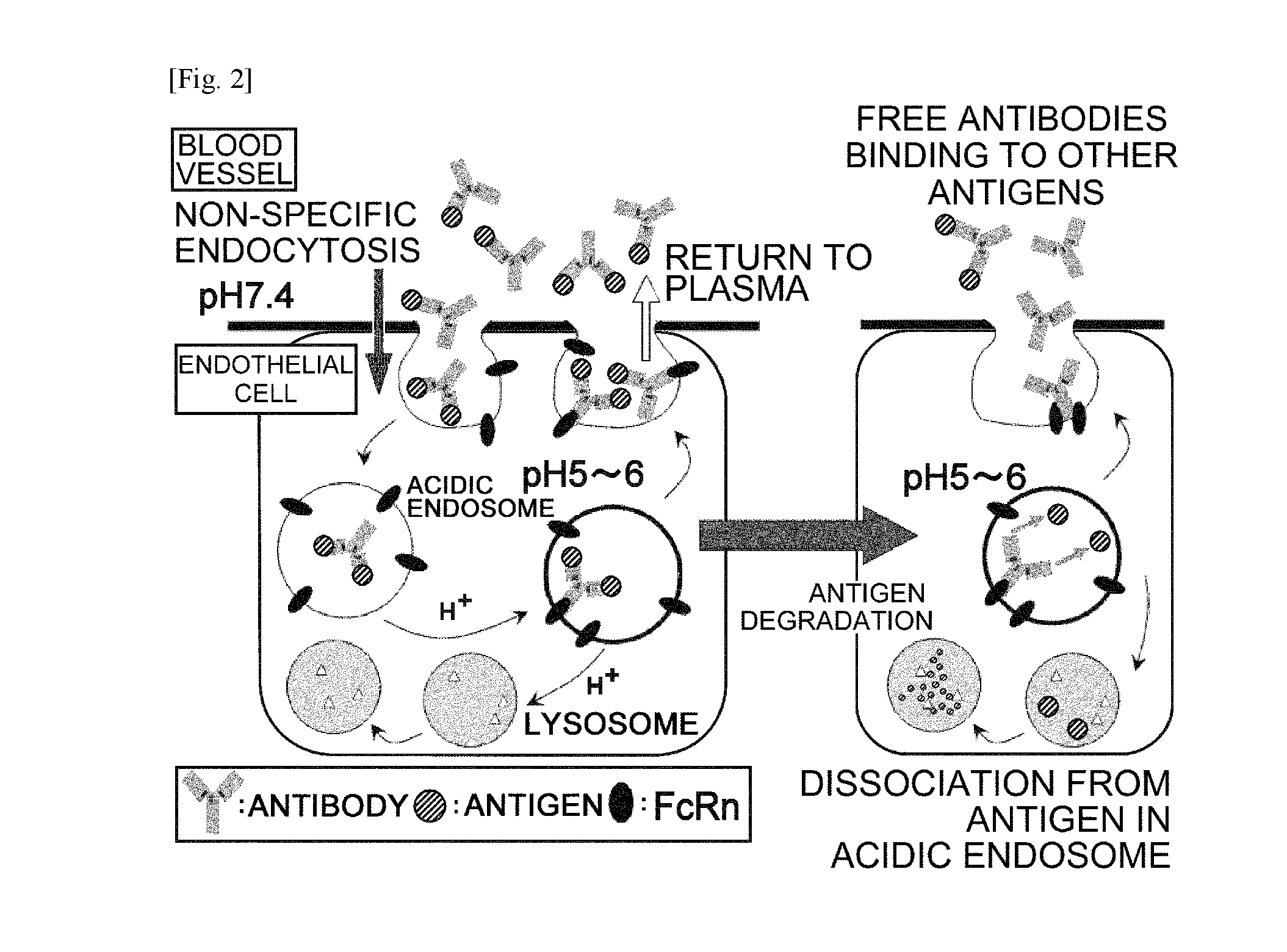
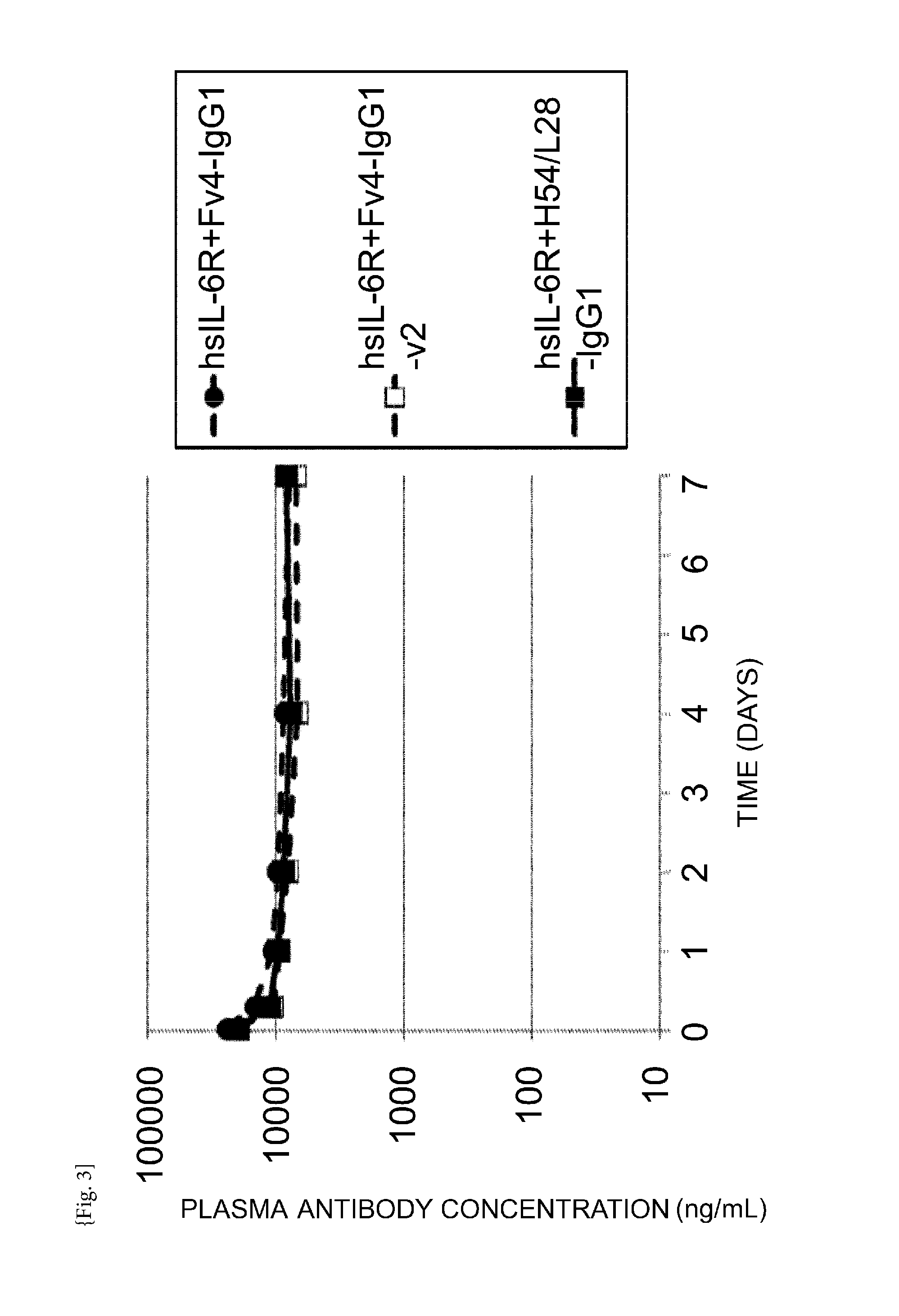
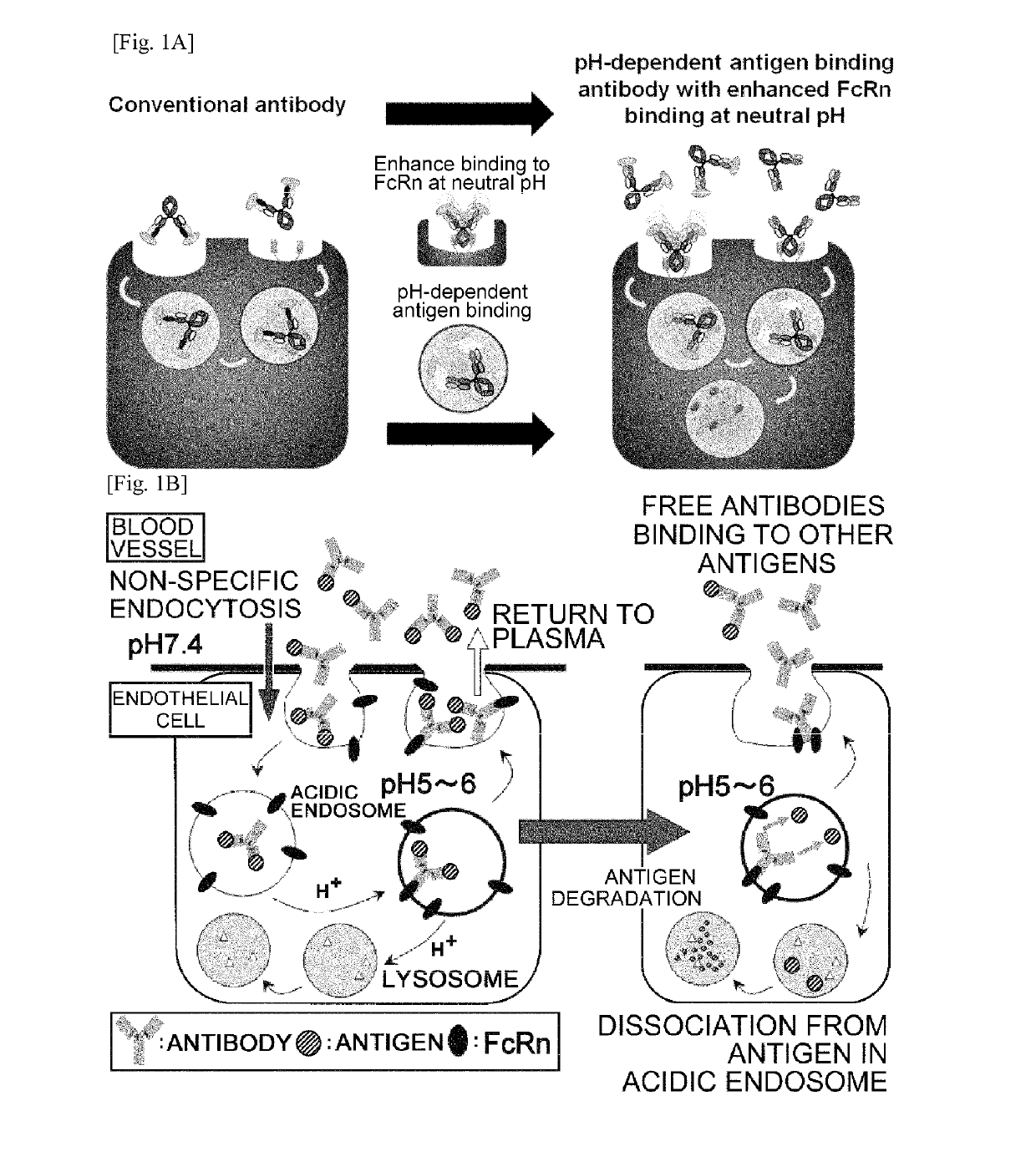
THERAPEUTIC ANTIGEN-BINDING MOLECULE WITH A FcRn-BINDING DOMAIN THAT PROMOTES ANTIGEN CLEARANCE
ActiveUS20140363428A1Low immunogenicityImprove stabilityAntipyreticAnalgesicsFc(alpha) receptorNeutral ph
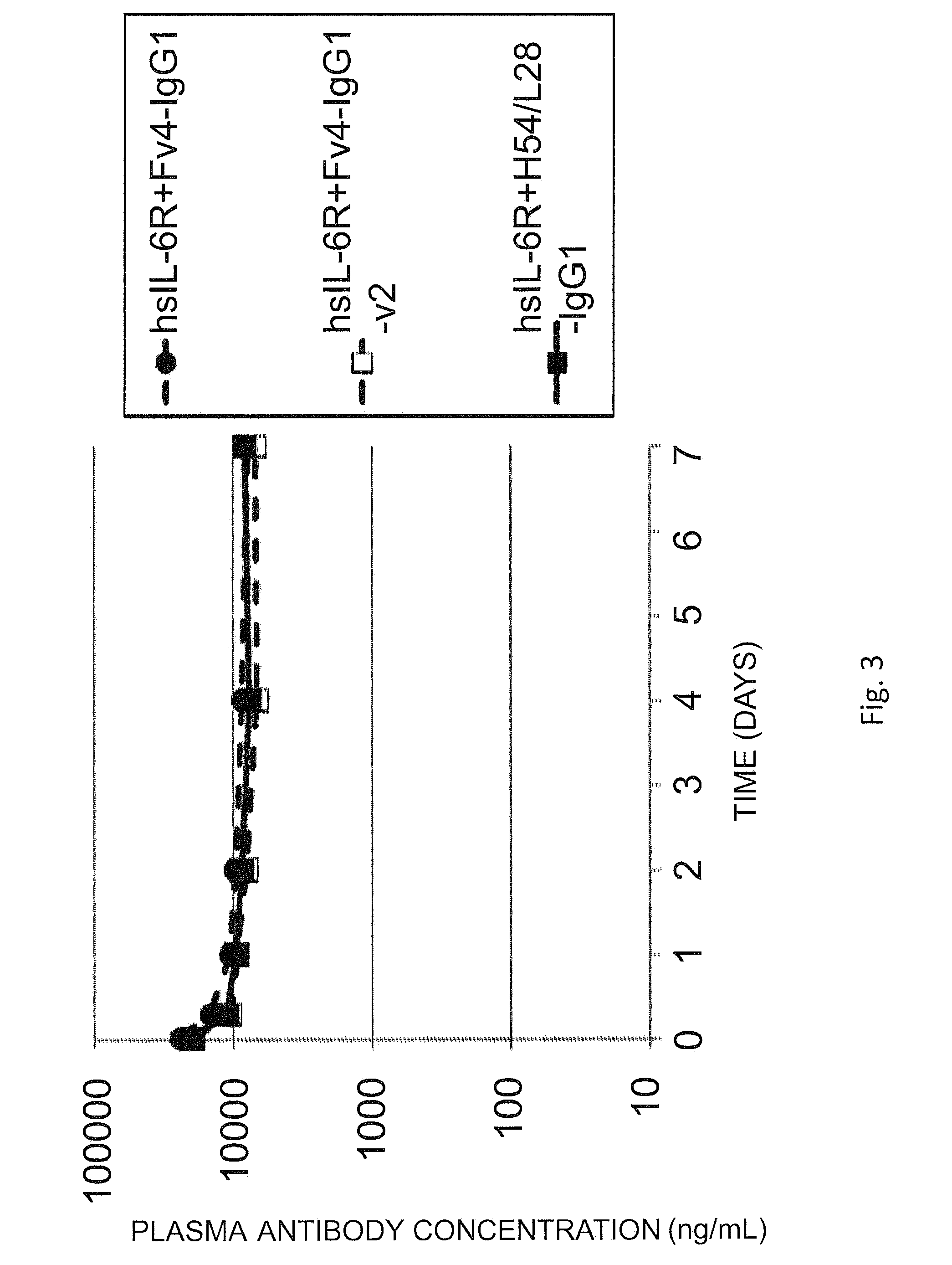
The present invention provides: a modified FcRn-binding domain having an enhanced affinity for the Fc Receptor neonatal (FcRn) at neutral pH; an antigen-binding molecule comprising said FcRn-binding domain, which has low immunogenicity, high stability and form only a few aggregates; a modified antigen-binding molecule having an increased FcRn-binding activity at neutral or acidic pH without an increased binding activity at neutral pH for a pre-existing anti-drug antibody; use of the antigen-binding molecules for improving antigen-binding molecule-mediated antigen uptake into cells; use of the antigen-binding molecules for reducing the plasma concentration of a specific antigen; use of the modified FcRn-binding domain for increasing the total number of antigens to which a single antigen-binding molecule can bind before its degradation; use of the modified FcRn-binding domain for improving pharmacokinetics of an antigen-binding molecule; methods for decreasing the binding activity for a pre-existing anti-drug antibody; and methods for producing said antigen-binding molecules.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Antibodies with modified affinity to fcrn that promote antigen clearance
InactiveUS20130131319A1Increase the number ofSuperior in vivo effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen bindingAntigen uptake
An objective of the present invention is to provide methods for facilitating antigen-binding molecule-mediated antigen uptake into cells, methods for facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, methods for increasing the number of antigens to which a single antigen-binding molecule can bind, methods for improving pharmacokinetics of antigen-binding molecules, antigen-binding molecules improved for facilitated antigen uptake into cells, antigen-binding molecules capable of facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, antigen-binding molecules capable of repeatedly binding to antigens, antigen-binding molecules with improved pharmacokinetics, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such an antigen-binding molecule, and methods for producing those described above. The present inventors discovered that antigen uptake into cells is facilitated by an antibody having human FcRn-binding activity at the plasma pH and a lower antigen-binding activity at the early endosomal pH than at the plasma pH; such antibodies can increase the number of antigens to which a single antibody molecule can bind; the reduction of antigen in plasma can be facilitated by administering such an antibody; and antibody pharmacokinetics can be improved by using such antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Transcutaneous immunization without heterologous adjuvant
InactiveUS20060002949A1Increase skin hydrationIncrease local concentrationSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsDendritic cellSpecific immunity
Transcutaneous immunization can deliver antigen to the immune system through the stratum corneum without physical or chemical penetration to the dermis layer of the skin. This delivery system induces an antigen-specific immune response without the use of a heterologous adjuvant. Although perforation of intact skin is not required, superficial penetration or micropenetration of the skin can act as an enhancer; similarly, hydration may enhance the immune response. This system can induce antigen-specific immune effectors after epicutaneous application of a formulation containing one or more antigens. The formulation may initiate processes such as antigen uptake, processing, and presentation; Langerhans cell activation, migration from the skin to other immune organs, and differentiation to mature dendritic cells; contacting antigen with lymphocytes bearing cognate antigen receptors on the cell surface and their stimulation; and combinations thereof. Systemic and / or regional immunity may be induced. Immune responses that provide prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatments are preferred. Antigenic activities in the formulation may be found in the same molecule, two or more different molecules dissociated from each other, or multiple molecules in a complex formed by covalent or non-covalent bonds. For antigens which are proteinaceous, they may be provided in the formulation as a polynucleotide for transcutaneous genetic immunization. Besides simple application of a dry or liquid formulation to the skin, patches and other medical devices may be used to deliver antigen for immunization.
Owner:ARMY GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE OFFICE OF THE COMMAND JUDGE ADVOCATE
Antibodies with modified affinity to fcrn that promote antigen clearance
InactiveUS20160244526A1Reduce additionalIncrease the number ofPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPharmaceutical drugAntigen binding
An objective of the present invention is to provide methods for facilitating antigen-binding molecule-mediated antigen uptake into cells, methods for facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, methods for increasing the number of antigens to which a single antigen-binding molecule can bind, methods for improving pharmacokinetics of antigen-binding molecules, antigen-binding molecules improved for facilitated antigen uptake into cells, antigen-binding molecules capable of facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, antigen-binding molecules capable of repeatedly binding to antigens, antigen-binding molecules with improved pharmacokinetics, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such an antigen-binding molecule, and methods for producing those described above.The present inventors discovered that antigen uptake into cells is facilitated by an antibody having human FcRn-binding activity at the plasma pH and a lower antigen-binding activity at the early endosomal pH than at the plasma pH; such antibodies can increase the number of antigens to which a single antibody molecule can bind; the reduction of antigen in plasma can be facilitated by administering such an antibody; and antibody pharmacokinetics can be improved by using such antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Skin-sctive adjuvants for transcutaneous immuization
InactiveUS20060002959A1Increase skin hydrationEnhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseDendritic cellSpecific immunity
Transcutaneous immunization can deliver antigen to the immune system through the stratum corneum without physical or chemical penetration to the dermis layer of the skin. This delivery system induces an antigen-specific immune response. Use of skin-active adjuvants is preferred. Although perforation of intact skin is not required, superficial penetration or micropenetration of the skin can act as an enhancer; similarly, hydration may enhance the immune response. This system can induce antigen-specific immune effectors after epicutaneous application of a formulation containing one or more antigen and adjuvant. The formulation may initiate processes such as antigen uptake, processing, and presentation; Langerhans cell activation, migration from the skin to other immune organs, and differentiation to mature dendritic cells; contacting antigen with lymphocytes bearing cognate antigen receptors on the cell surface and their stimulation; and combinations thereof. Systemic and / or regional immunity may be induced; immune responses that result in prophylaxis and / or therapeutic treatments are preferred. Antigen and adjuvant activities in the formulation may be found in the same molecule, two or more different molecules dissociated from each other, or multiple molecules in a complex formed by covalent or non-covalent bonds. For antigens and adjuvants which are proteinaceous, they may be provided in the formulation as a polynucleotide for transcutaneous genetic immunization. Besides simple application of a liquid formulation, patches or other medical devices may be used to deliver antigen for immunization.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Therapeutic antigen-binding molecule with a FcRn-binding domain that promotes antigen clearance
The present invention provides: a modified FcRn-binding domain having an enhanced affinity for the Fc Receptor neonatal (FcRn) at neutral pH; an antigen-binding molecule comprising said FcRn-binding domain, which has low immunogenicity, high stability and form only a few aggregates; a modified antigen-binding molecule having an increased FcRn-binding activity at neutral or acidic pH without an increased binding activity at neutral pH for a pre-existing anti-drug antibody; use of the antigen-binding molecules for improving antigen-binding molecule-mediated antigen uptake into cells; use of the antigen-binding molecules for reducing the plasma concentration of a specific antigen; use of the modified FcRn-binding domain for increasing the total number of antigens to which a single antigen-binding molecule can bind before its degradation; use of the modified FcRn-binding domain for improving pharmacokinetics of an antigen-binding molecule; methods for decreasing the binding activity for a pre-existing anti-drug antibody; and methods for producing said antigen-binding molecules.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Antibodies With Modified Affinity To FcRn That Promote Antigen Clearance
InactiveUS20170002080A1Increase the number ofReduce additionalPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen bindingAntigen uptake
An objective of the present invention is to provide methods for facilitating antigen-binding molecule-mediated antigen uptake into cells, methods for facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, methods for increasing the number of antigens to which a single antigen-binding molecule can bind, methods for improving pharmacokinetics of antigen-binding molecules, antigen-binding molecules improved for facilitated antigen uptake into cells, antigen-binding molecules capable of facilitating the reduction of antigen concentration in plasma, antigen-binding molecules capable of repeatedly binding to antigens, antigen-binding molecules with improved pharmacokinetics, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such an antigen-binding molecule, and methods for producing those described above.The present inventors discovered that antigen uptake into cells is facilitated by an antibody having human FcRn-binding activity at the plasma pH and a lower antigen-binding activity at the early endosomal pH than at the plasma pH; such antibodies can increase the number of antigens to which a single antibody molecule can bind; the reduction of antigen in plasma can be facilitated by administering such an antibody; and antibody pharmacokinetics can be improved by using such antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Antigen and TLR agonist targeting co-loaded cationic phospholipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticle vaccine adjuvant, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108992666AStrong activationRealize the loadCancer antigen ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDendritic cellPhospholipid
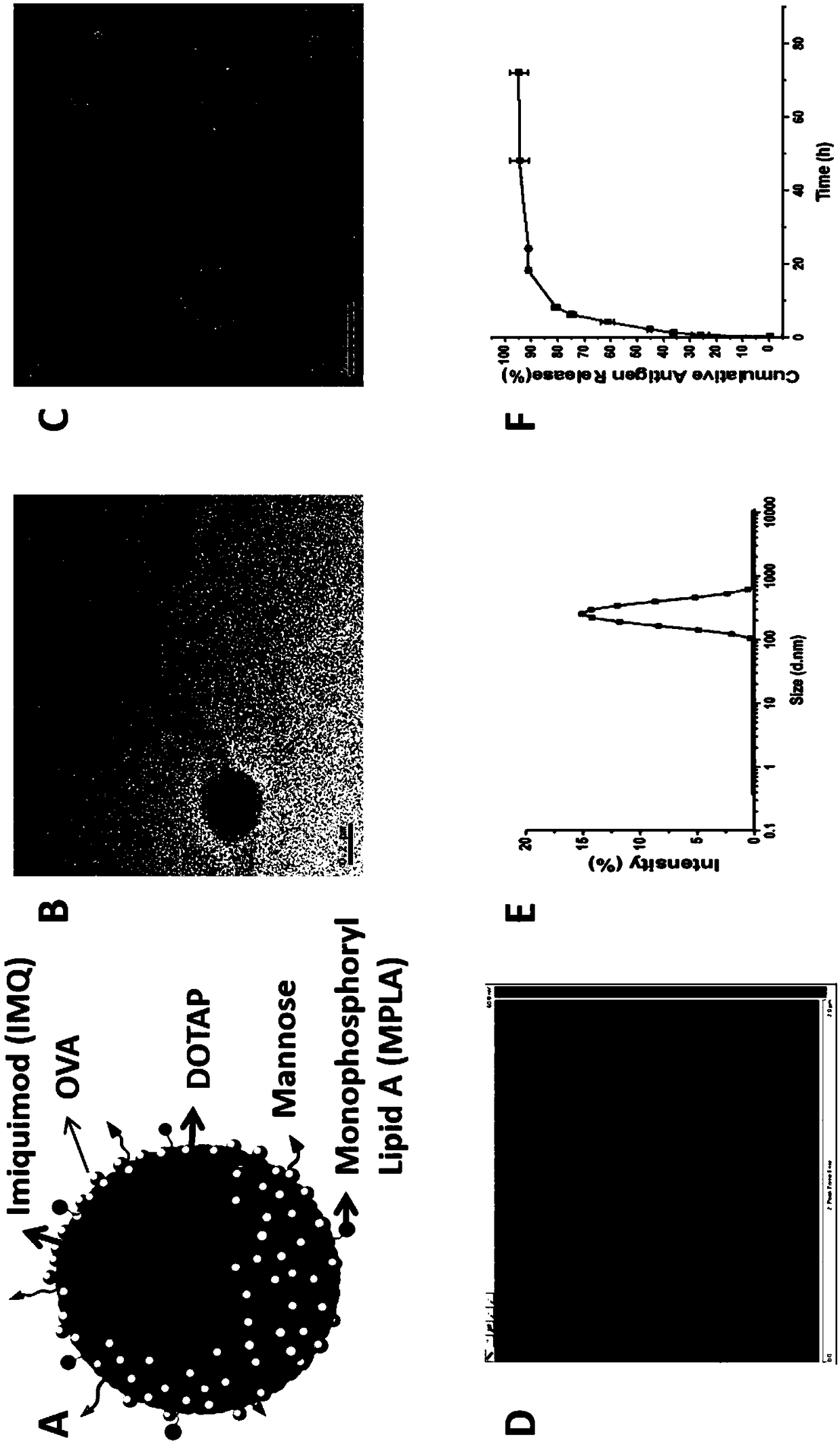
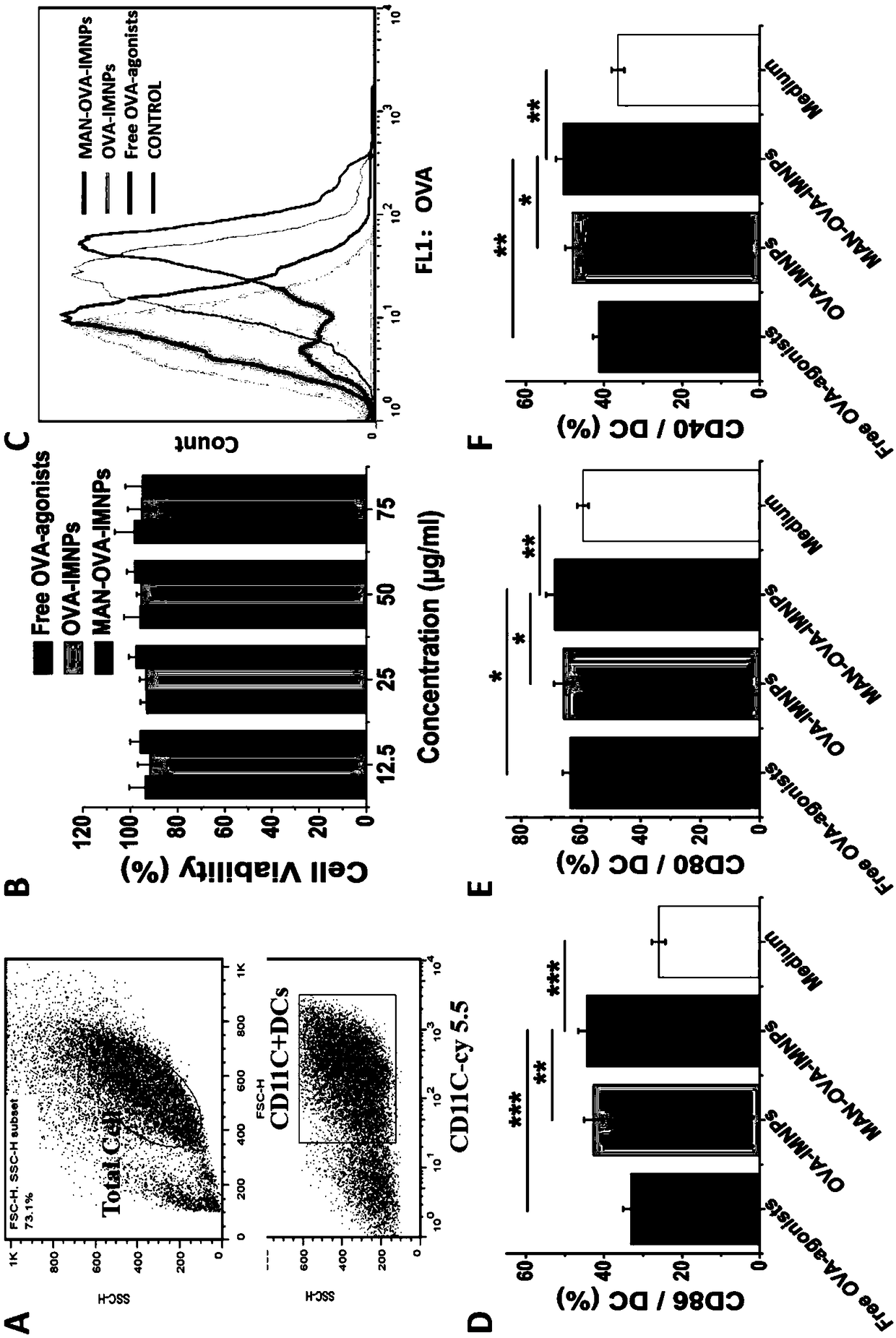
The invention relates to an antigen and TLR agonist targeting co-loaded cationic phospholipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticle vaccine adjuvant, and a preparation method and an application thereof. A hydrophobic inner core is encapsulated with a TLR7 agonist, a phospholipid layer is encapsulated with a TLR4 agonist, an antigen is adsorbed by cationic phospholipids in the phospholipid layer, and ligation of a mannose ligand makes the vaccine adjuvant like a specific targeting antigen to have the dendritic cell presenting ability, so the DC cell intake and the maturation promoting effect are enhanced; and the antigen is protected by hybridized nanoparticles, the antigen uptake by DC cells is improved, immune response after antigen stimulation is significantly enhanced by the TLR agonist, and thecross-presentation of the antigen is significantly improved, so vaccine adjuvant has a strong potent T cell killing effect, can induce cytokine secretion, has a long-acting memory T cell response, andhas an excellent prevention effect on tumors.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
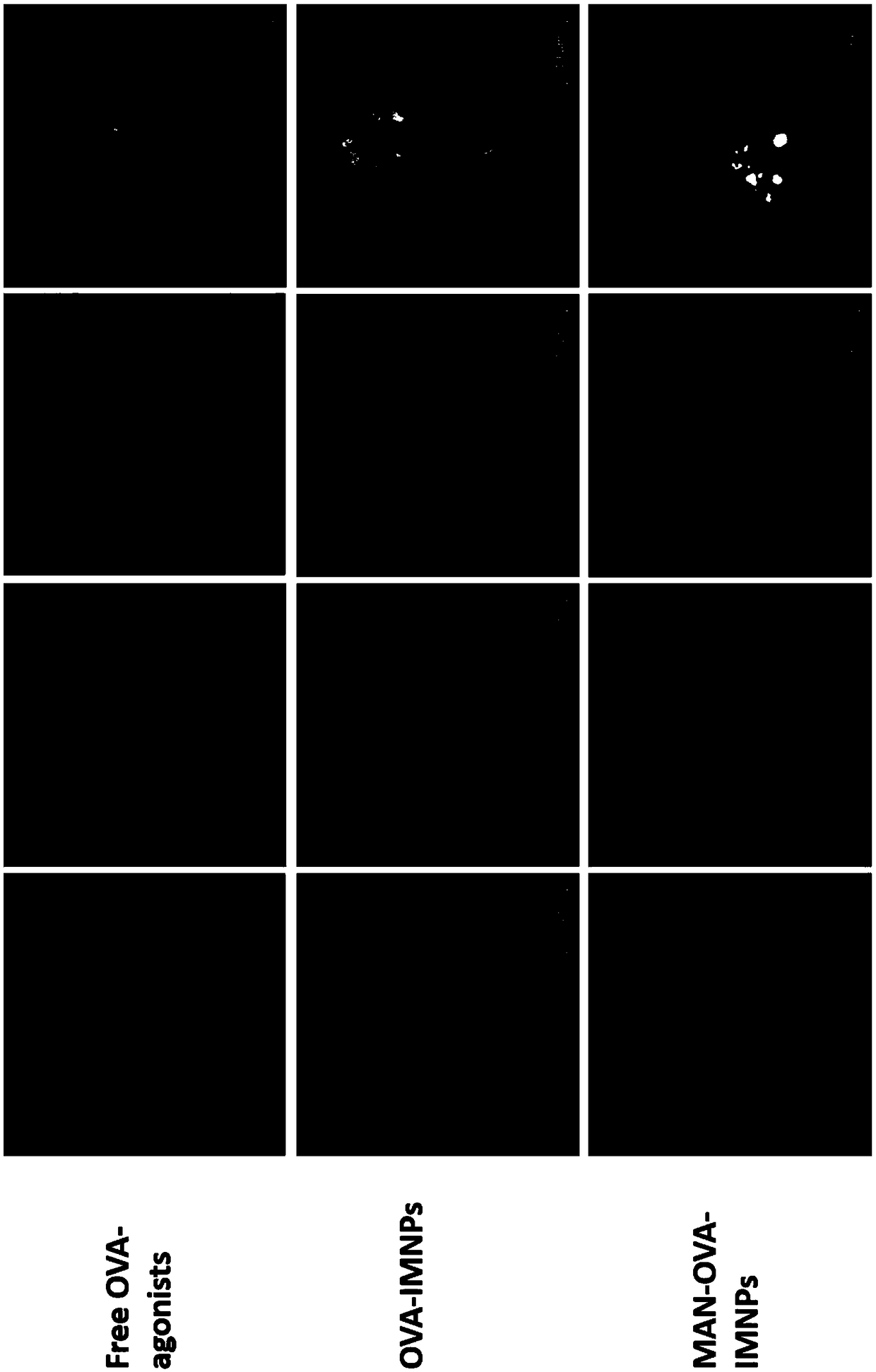
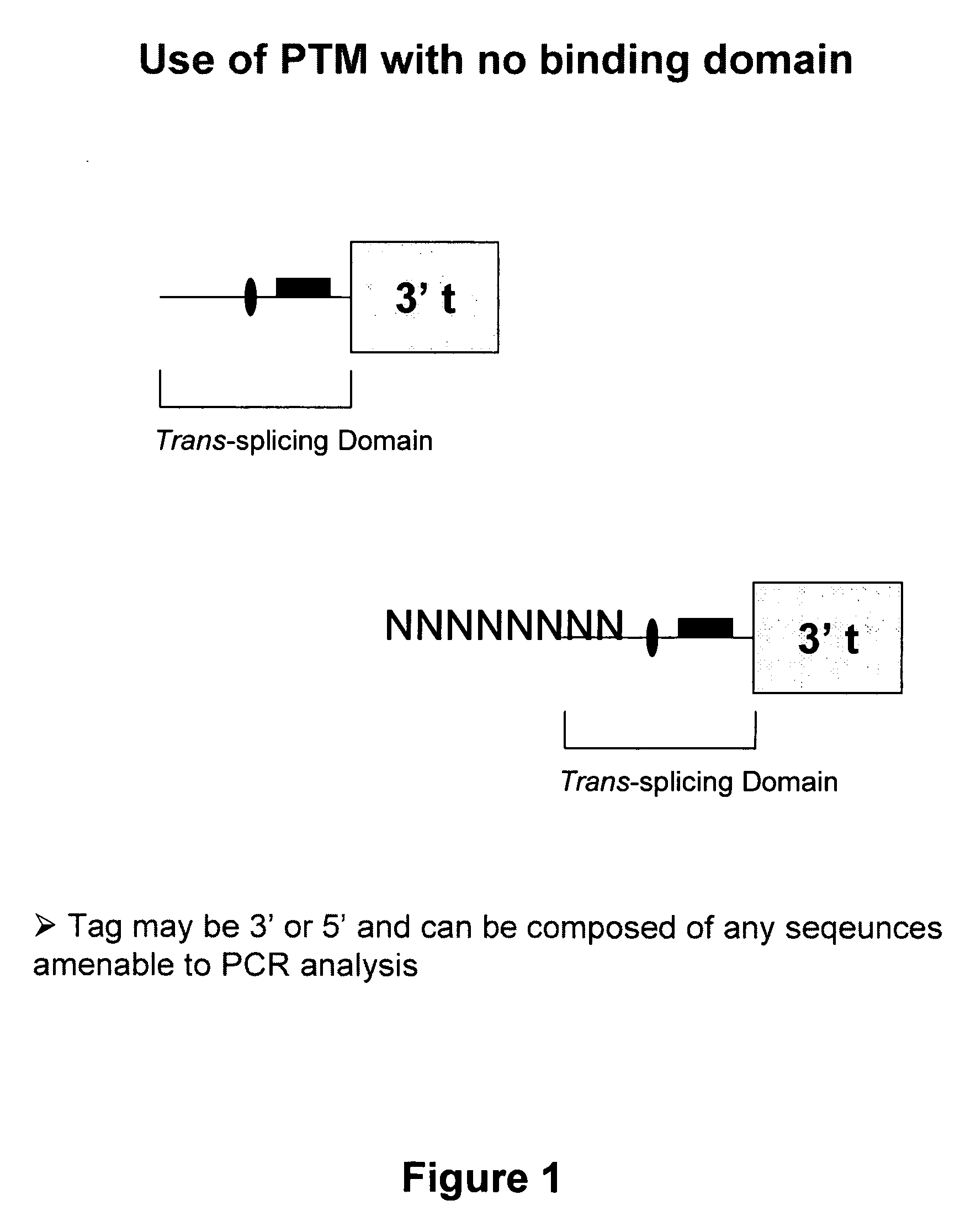
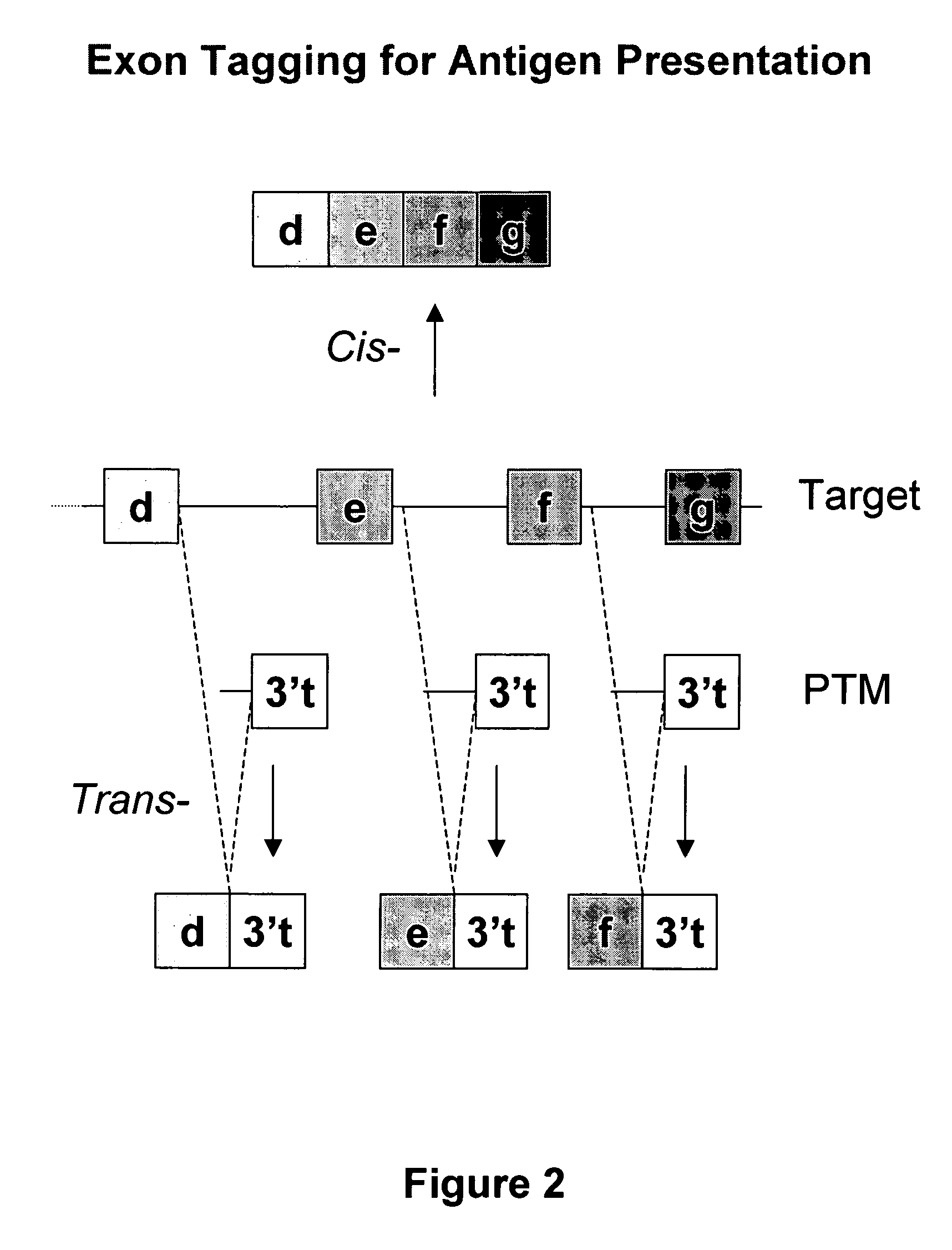
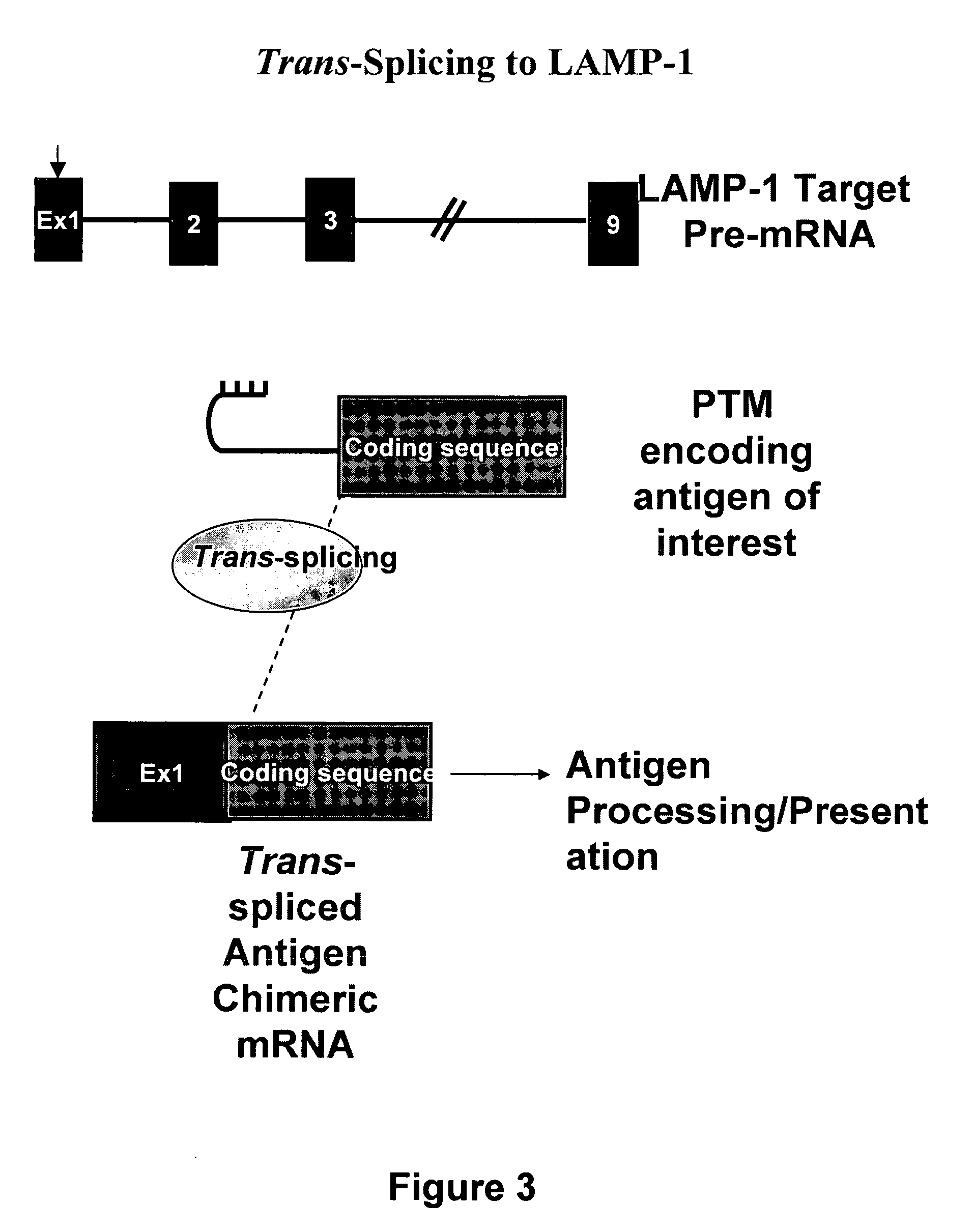
Use of spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing for immunotherapy
InactiveUS20060094110A1Stimulate immune responseGood health benefitsSugar derivativesTissue cultureRNA Trans-SplicingMessenger RNA
Methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosomal mediated trans-splicing that result in expression of an immunogenic polypeptide. The invention includes pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA) capable of encoding the immunogenic polypeptide, recombinant vector systems capable of expressing the PTMs of the invention, and cells expressing said PTMs. The target pre-mRNA are those encoding proteins that function in antigen uptake, antigen presentation and chaperoning. The methods of the invention encompass contacting the PTMs of the invention with a target pre-mRNA, under conditions in which a portion of the PTM is trans-spliced to a portion of the target pre-mRNA to form a chimeric mRNA molecule capable of encoding an immunogenic polypeptide.
Owner:VIRXSYS
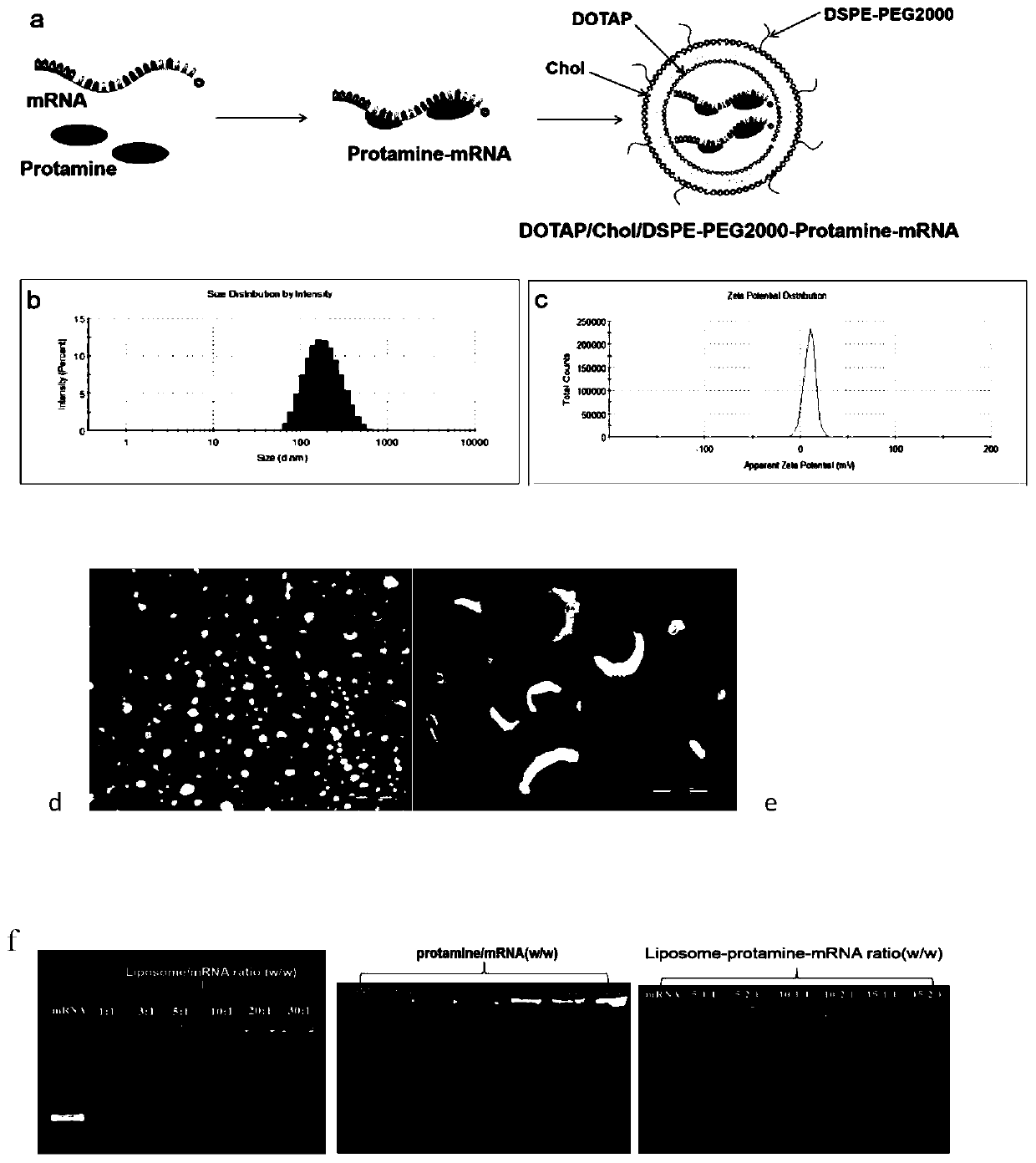
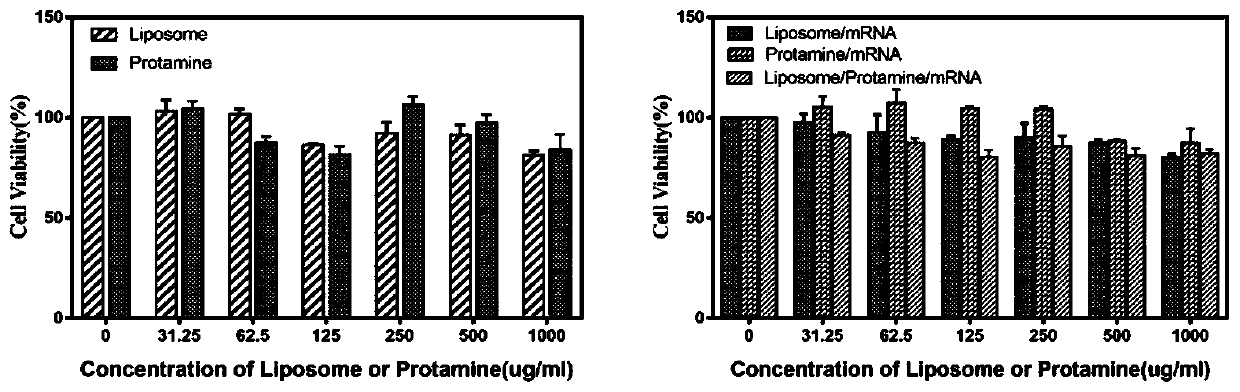
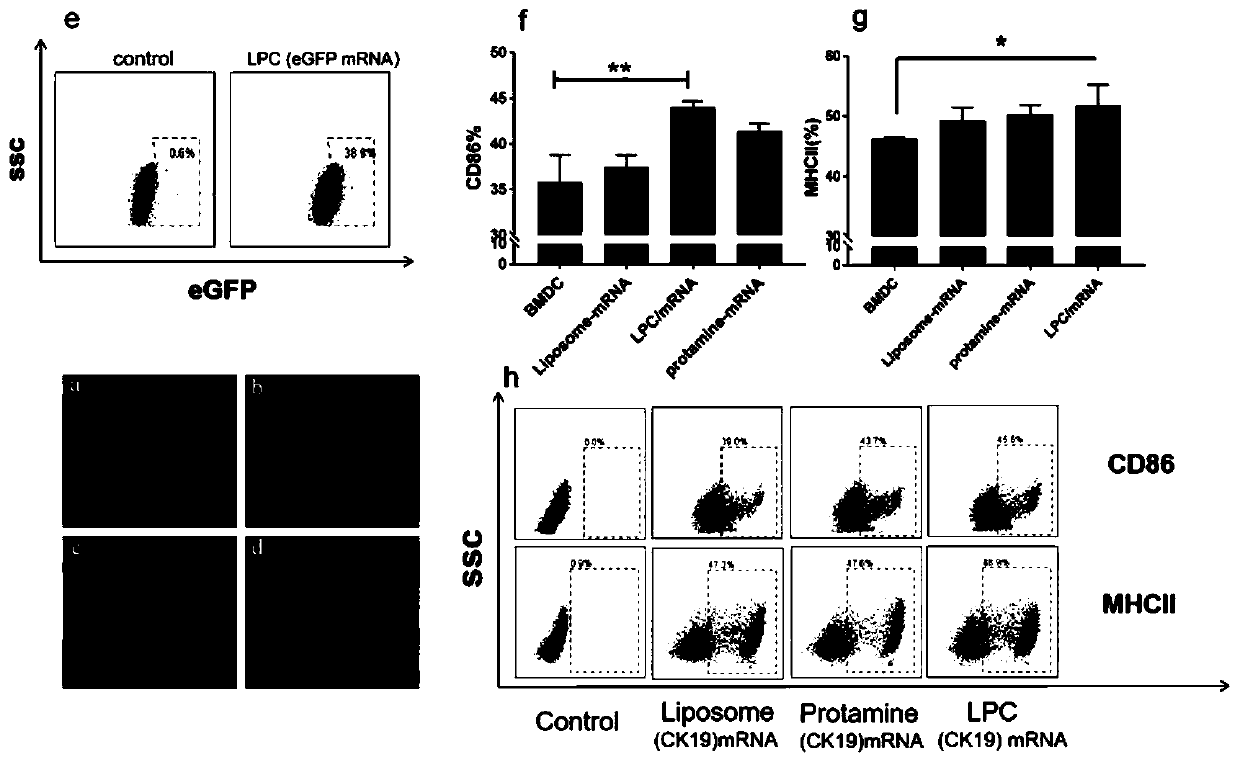
Cationic liposome-protamine-mRNA tumor vaccine and preparation method and application method thereof
PendingCN110882383ASynthesis fastRapid purificationSkin cancer vaccineCancer antigen ingredientsAdjuvantTumor therapy
The invention relates to a cationic liposome-protamine-mRNA tumor vaccine and a preparation method and an application method thereof. According to the tumor vaccine, a cationic liposome-protamine compound is used as a delivery carrier and adjuvant of mRNA, wherein the mass ratio of the cationic liposome to protamine to mRNA is 5:1: 1 to 15: 2:1, and the optimal mass ratio is preferably 10:1:1; theparticle size of the constructed cationic liposome-protamine-mRNA tumor vaccine is 50 to 800nm; the Zeta potential is 10 to 60mv; and the encapsulation efficiency is 70% to 95%. The cationic liposome-protamine-mRNA tumor vaccine prepared by the invention can effectively promote antigen uptake of APCs, induce DC stimulation and maturation, promotes secretion of cytokines and cause anti-tumor immune response. The tumor vaccine is used for immunotherapy through intramuscular and subcutaneous injection or nasal mucosa administration, wherein nasal mucosa administration can show a more excellent tumor treatment effect. The tumor vaccine has a wide application prospect in the aspect of tumor treatment.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Lipids as synthetic vectors to enhance antigen processing and presentation ex-vivo in dendritic cell therapy
ActiveUS20180353599A1Improve the level ofLow level of TregViral antigen ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsTumor targetRegulatory T cell
The invention covers the use of certain classes of lipids including cationic lipids in ex-vivo dendritic cell therapies. The cationic lipids enhance antigen uptake, processing and presentation of the processed antigens by dendritic cells to CD8+ and CD4+ T-cells via the MHC classes I and II presentation pathways respectively. Antigen uptake via cationic lipid by dendritic cells result in significant lowering of the population of the immune suppressive regulatory T cells in the tumors and a significant increase of the tumor targeting cytotoxic T-cells. Loss of regulatory T cells and increase of tumor specific cytotoxic cells are conducive to effective elimination of the tumors.
Owner:PDS BIOTECH
Mannose modified co-loaded antigen and double immuno-agonist phospholipid hybrid polymer vesicle as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108969771AMaximize Targeting EffectMaximize the effect of targeted immunotherapyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAdjuvantBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a mannose modified co-loaded antigen and a double immuno-agonist phospholipid hybrid polymer vesicle as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A vaccine carriertakes an amphiphilic triblock copolymer as material, OVA is loaded in the hydrophilic inner cavity, IMQ is loaded in the hydrophobic membrane layer, DOTAP cationic layer is fitted with MPLA, and cationic lipid outer layer adsorbs outer layer OVA; phospholipid with reactive group is introduced to pass the targeted mannose ligand through covalently linked to the PEG-active distal end of the polymer-loaded vesicle surface, integrating the functions of active targeting of tumors, co-delivery of antigens and adjuvants and the like; the vesicle has the characteristics of small particle size, good dispersion, high antigen loading and good biocompatibility, etc., which can promote antigen uptake, DC activation and maturation, antigen cross-presentation, antigenic lymph node migration, lymphocyteactivation, effector T cell immune response, CD8<+> T and CD4<+> T cell responses, and memory T cells immune response.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Chemokines as adjuvants of immune response
InactiveUS20070128159A1Promote migrationIncrease the number ofPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune condition
Dendritc cells play a critical role in antigen-specific immune responses. Materials and methods are provided for treating disease states, including cancer and autoimmune disease, by facilitating or inhibiting the migration or activation of antigen-presenting dendritic cells. In particular, chemokines are used to initiate, amplify or modulate an immune response. In one embodiment, chemokines are used to attract dentritic cells to the site of antigen delivery. An increase number of dendritic at the site of antigen delivery means more antigen uptake and a modified immune response.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Method of Transcutaneous Immunization Using Antigen
InactiveUS20110243979A1Easy to identifyEfficient deliverySsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsDendritic cellAdjuvant
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Application of chrysin in preparation of medicaments for treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases
InactiveCN102793712AInhibition of differentiationInhibition MaturityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDendritic cellAutoimmune condition
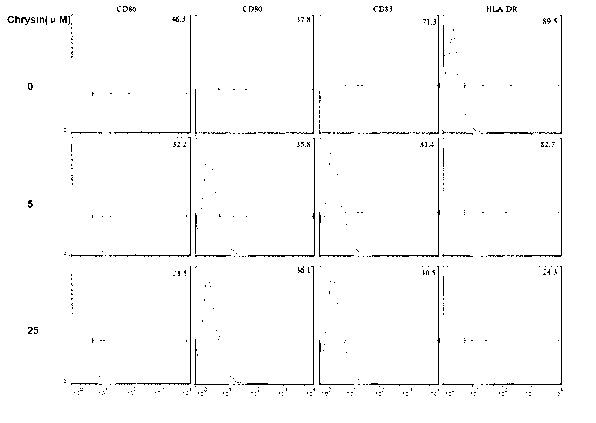
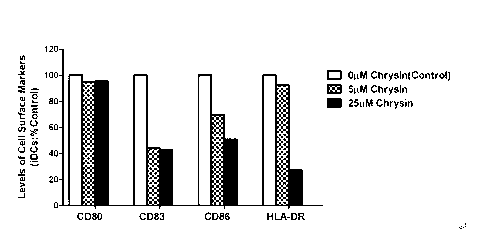
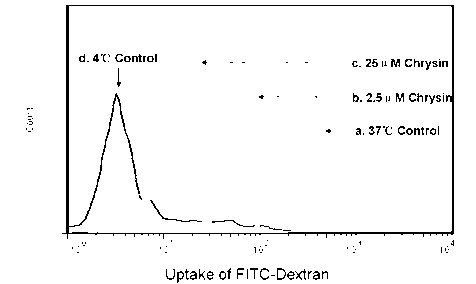
The invention discloses application of chrysin in preparation of medicaments for treating autoimmune diseases. Experimental results show that the chrysin can inhibit differentiation of human immune dendritic cells (DC) and maturity of LPS (lipopolysaccharide)-activated human immune DC, can inhibit the antigen uptake capabilities of the immature DC and the antigen presenting capabilities of the mature DC and can inhibit T cell proliferation reactions stimulated by the DC. In particular, the chrysin can reduce the average score, the highest score and the total score of clinical scores of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis of mice and can relieve myelitis cell infiltration and demyelination in spinal cords. Thus, the medicament inhibiting immune systems is expected to become the medicament for treating such autoimmune inflammatory diseases as multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis clinically.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Lipids as synthetic vectors to enhance antigen processing and presentation ex-vivo in dendritic cell therapy
ActiveUS20190358319A1Increased proliferationImprove viabilityViral antigen ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsTumor targetRegulatory T cell
Owner:PDS BIOTECH
Chemokines as adjuvants of immune response
InactiveUS7217700B2Promote migrationIncrease the number ofAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseDendritic cell
Dendritic cells play a critical role in antigen-specific immune responses. Materials and methods are provided for treating disease states, including cancer and autoimmune disease, by facilitating or inhibiting the migration or activation of antigen-presenting dendritic cells. In particular, chemokines are used to initiate, amplify or modulate an immune response. In one embodiment, chemokines are used to attract dentritic cells to the site of antigen delivery. An increase number of dendritic at the site of antigen delivery means more antigen uptake and a modified immune response.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
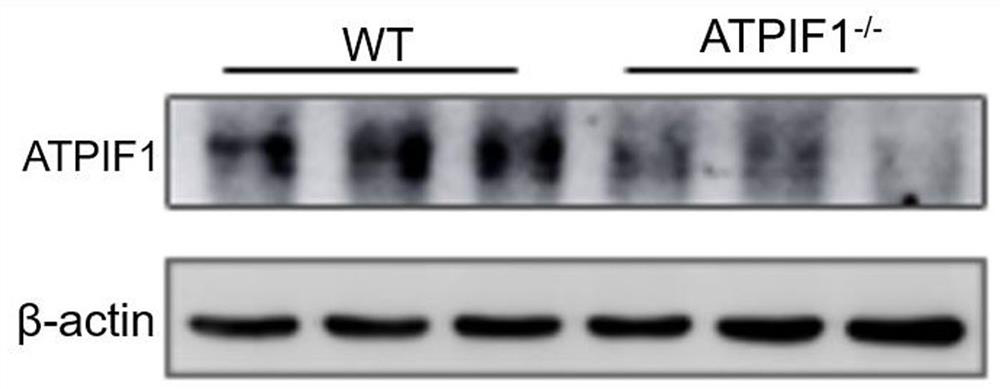
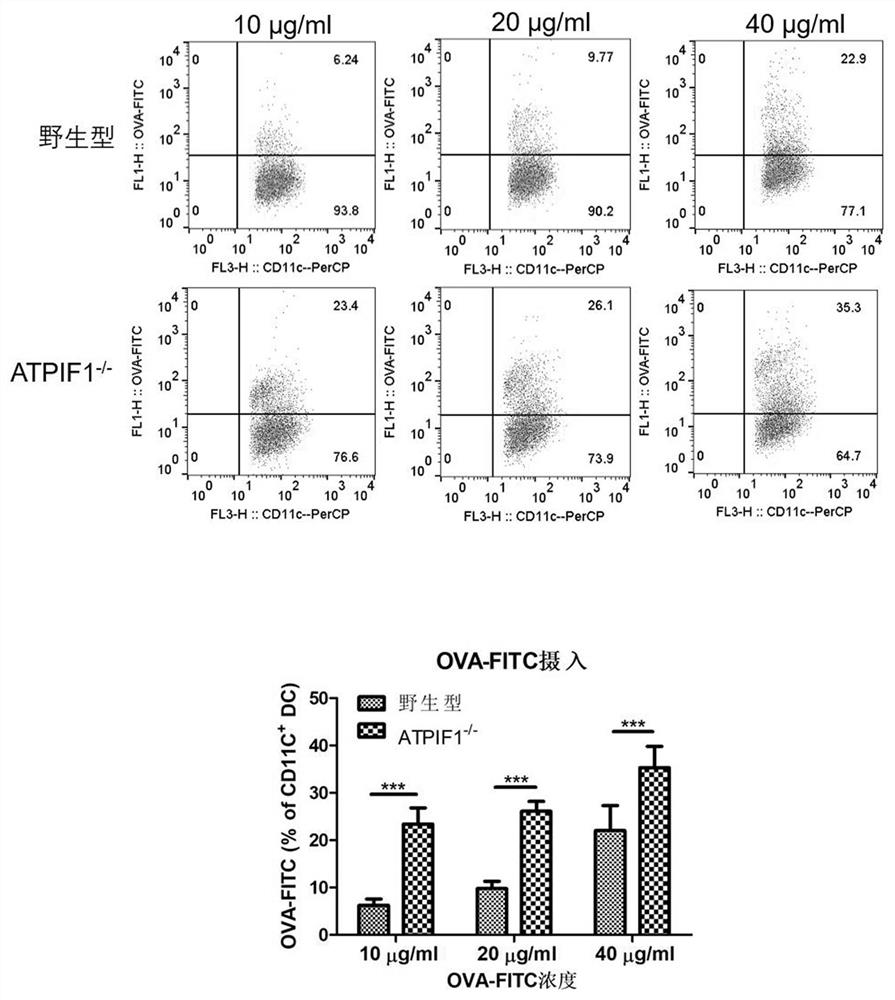
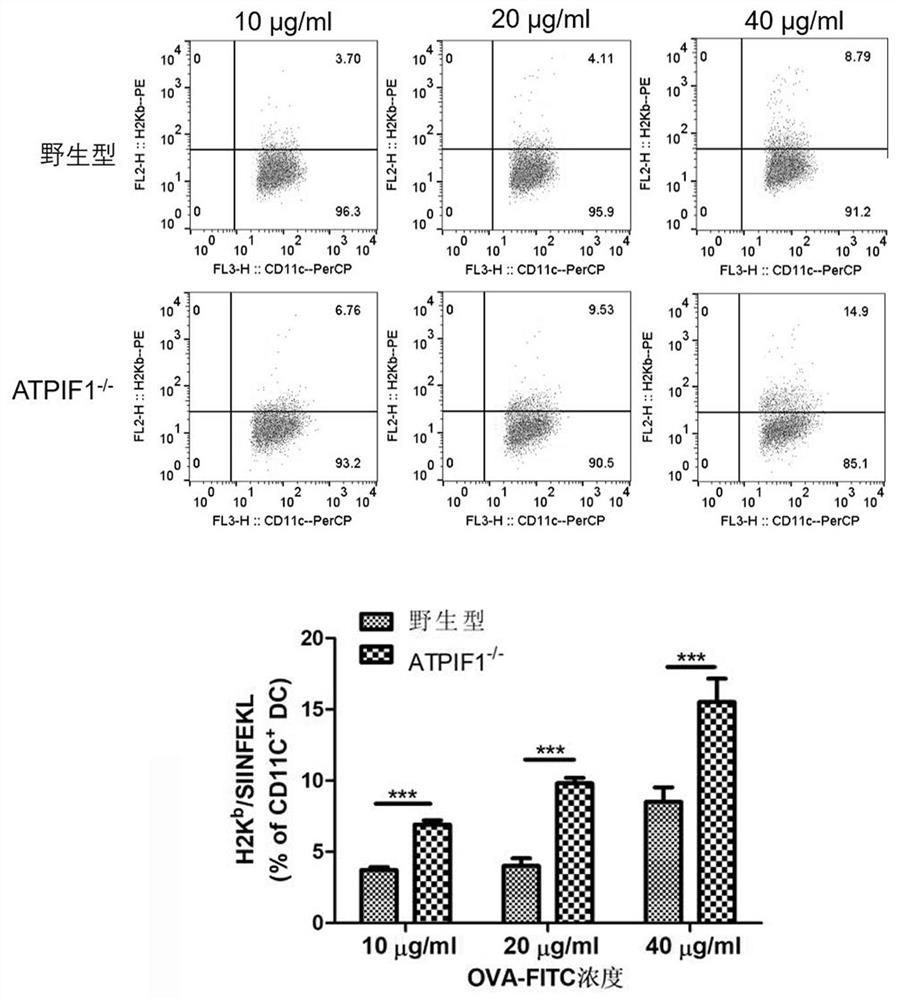
Application of dendritic cell with ATPIF1 gene knock-down expression
PendingCN112274534AImprove anti-tumor effectEnhance killing activityGenetically modified cellsPeptidesDendritic cellPharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to the fields of biotechnology and medicine, and provides a dendritic cell (DC) with ATPIF1 gene knock-down expression. The ATPIF1 gene is knocked down in the dendritic cell, sothat the antigen uptake, processing and presentation capabilities of the dendritic cell in the immune process are enhanced, the initial T cell is effectively activated, the effect function of the T cell is improved, and the killing effect of the T cell on tumor cells is enhanced. The dendritic cell with ATPIF1 knock-down expression has a potential application value in the aspect of preparing immunotherapy drugs for tumors.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
High-efficiency CpG preparation, preparation method thereof and application
ActiveCN102631675AImprove intake capacityPromote formationAntibody medical ingredientsOil/fats/waxes non-active ingredientsMedicinePhosphate
The invention discloses a high-efficiency CpG preparation, a preparation method thereof and application. The CpG preparation consists of components including 80-120ml of PBS (phosphate buffer solution) of CpG ODN (oligodeoxynucleotide) with the concentration of 10-45mug / ml, 160-180ml of white oil, 10-14ml of span-80, 6-10ml of tween-80 and 20-40ml of EMULSIGEN. The preparation is quite favorable for strengthening antigen uptake ability of antigen presenting cells, promotes formation of Th1 type immune response, can reduce the application amount of vaccine, improves the service effect of the vaccine, and is higher in stability and more convenient to be stored.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
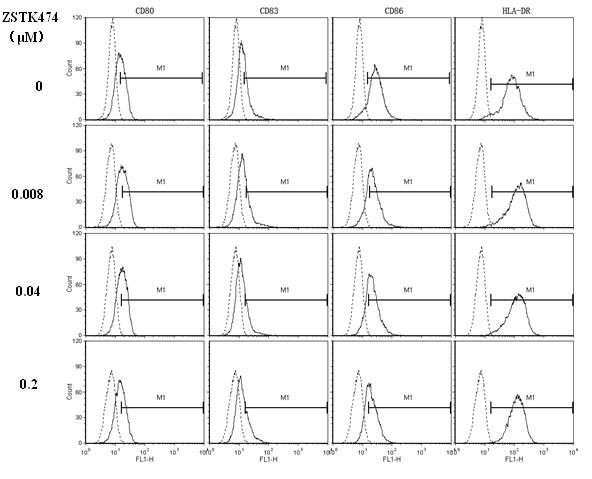
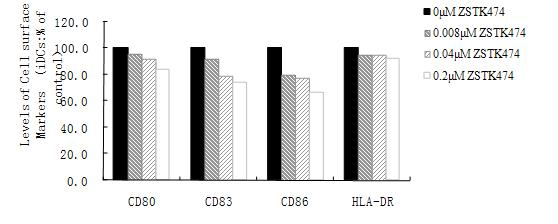
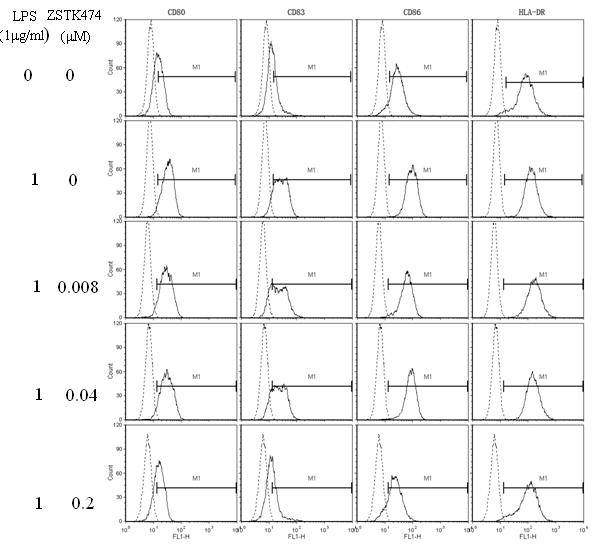
Application of ZSTK474 to preparation of medicine for treating autoimmune diseases
The invention discloses application of 2-(2-difluoromethyl benzimidazole-1-yl)-4,6-dimorpholinyl-1,3,5-triazine (ZSTK474 for short) to preparation of a medicine for treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Experimental results prove that the ZSTK474 can inhibit the differentiation of human immune dendritic cells, the maturity of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activated human immune dendritic cells, the antigen uptake capacity of immature dendritic cells, the antigen presenting capacity of mature dendritic cells and T cell proliferation reaction stimulated by the dendritic cells, and particularly can reduce the morbidity degree of mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, so the ZSTK474 is expected to become a medicine for treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis and the like clinically.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Cationic complex liposome influenza vaccine as well as preparation method and application method thereof
InactiveCN113144184AImprove immune efficiencyStrong immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesDendritic cell
The invention relates to a cationic complex liposome influenza vaccine as well as a preparation method and an application method thereof. With cationic liposome as an immune carrier and an adjuvant, the influenza vaccine comprises an immunomodulator and encapsulates an influenza vaccine antigen. The constructed cationic complex liposome influenza vaccine is 200-700nm in particle size, 5-40mV in Zeta potential, 30-90% in encapsulation efficiency, and 1-10% in drug loading capacity. The prepared cationic complex liposome influenza vaccine can significantly promote antigen uptake of dendritic cells, stimulate activation and maturation of DCs, and further cause immune response. The influenza vaccine is used for immunotherapy through intramuscular injection, subcutaneous injection or nasal mucosal administration, wherein the mucosal immune response level and the cellular immune response level of the organism are effectively enhanced through nasal mucosal administration. The influenza vaccine has a wide application prospect in influenza prevention.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
High-efficiency CpG preparation, preparation method thereof and application
ActiveCN102631675BImprove intake capacityPromote formationAntibody medical ingredientsOil/fats/waxes non-active ingredientsPhosphateMedicine
The invention discloses a high-efficiency CpG preparation, a preparation method thereof and application. The CpG preparation consists of components including 80-120ml of PBS (phosphate buffer solution) of CpG ODN (oligodeoxynucleotide) with the concentration of 10-45mug / ml, 160-180ml of white oil, 10-14ml of span-80, 6-10ml of tween-80 and 20-40ml of EMULSIGEN. The preparation is quite favorable for strengthening antigen uptake ability of antigen presenting cells, promotes formation of Th1 type immune response, can reduce the application amount of vaccine, improves the service effect of the vaccine, and is higher in stability and more convenient to be stored.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
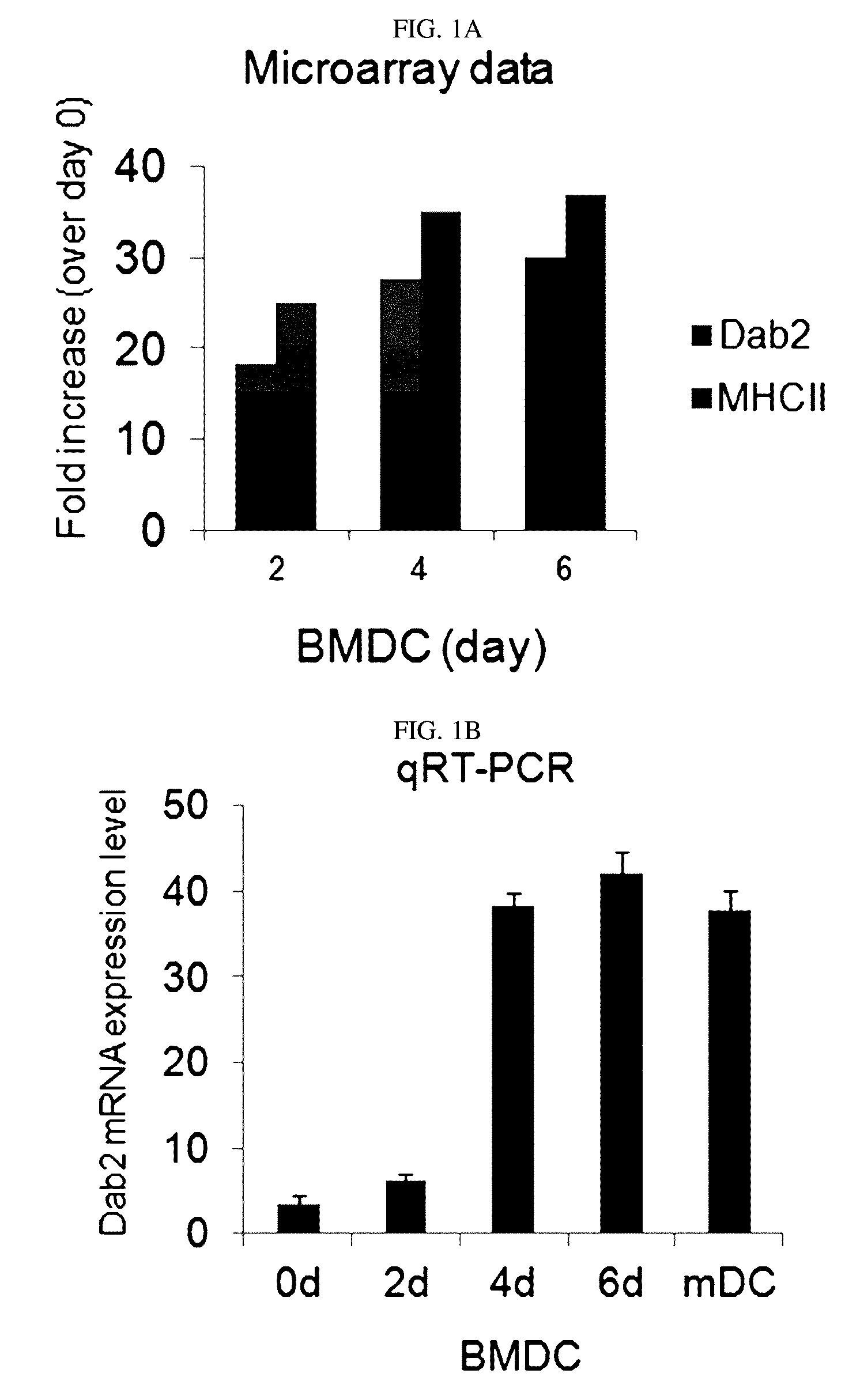
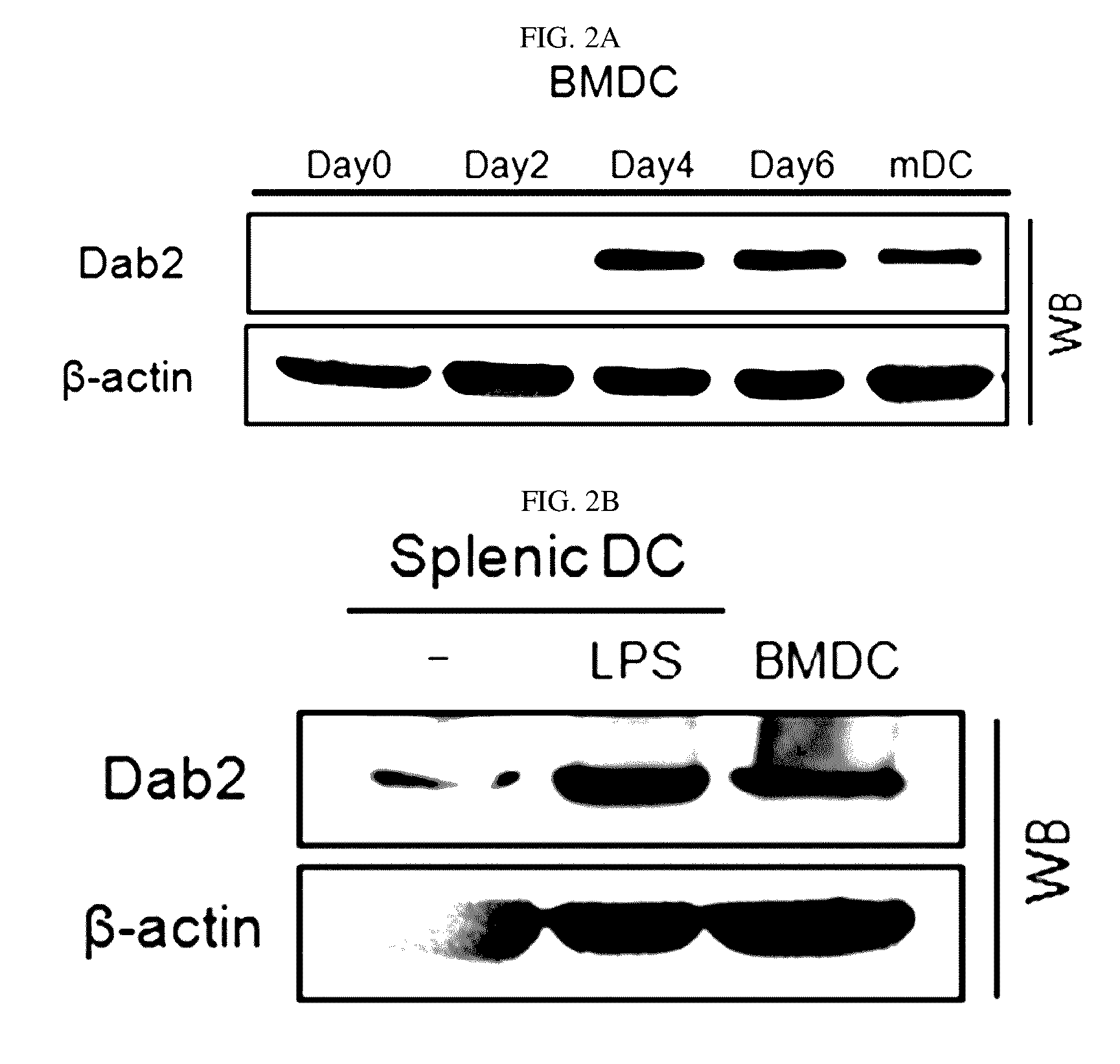
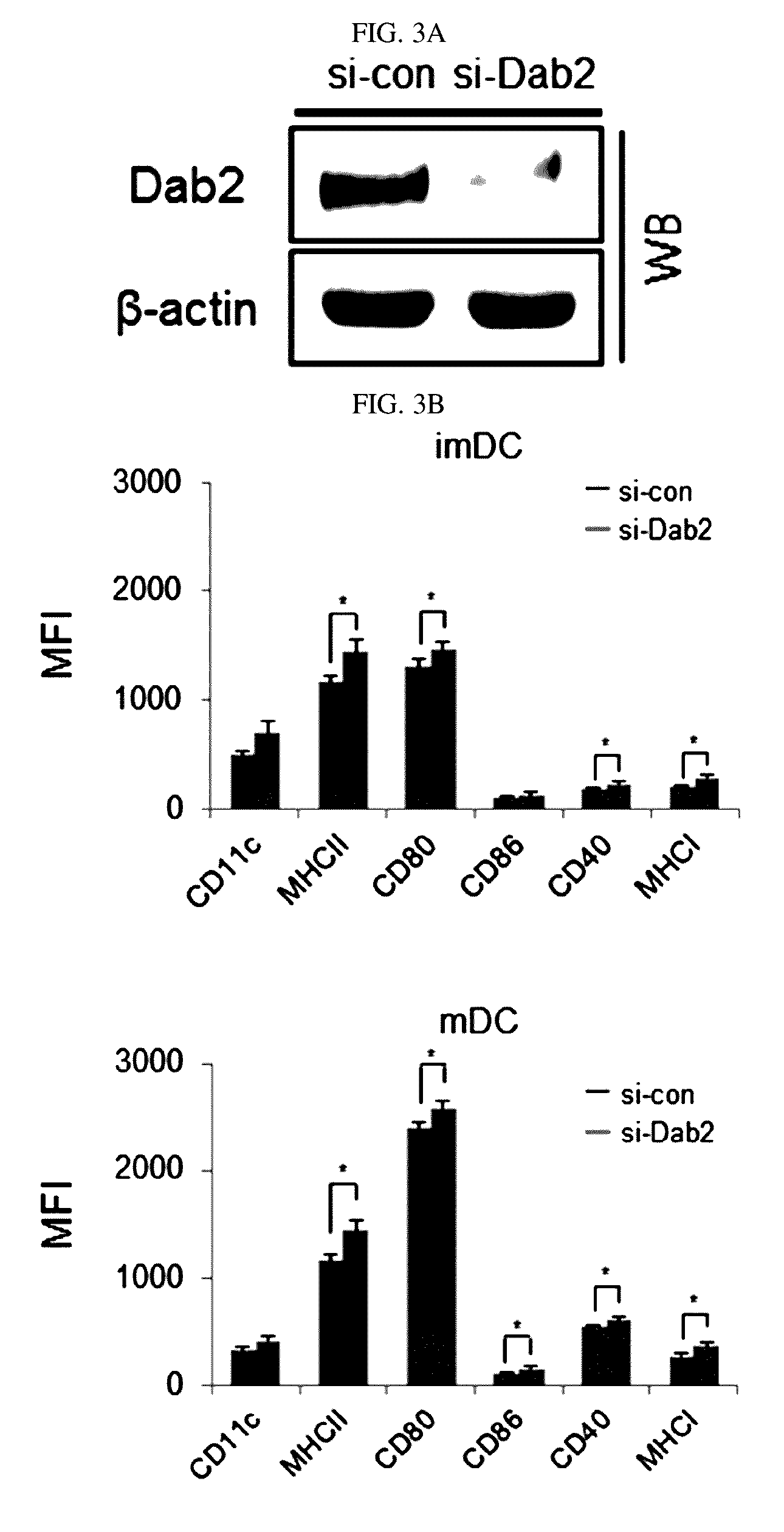
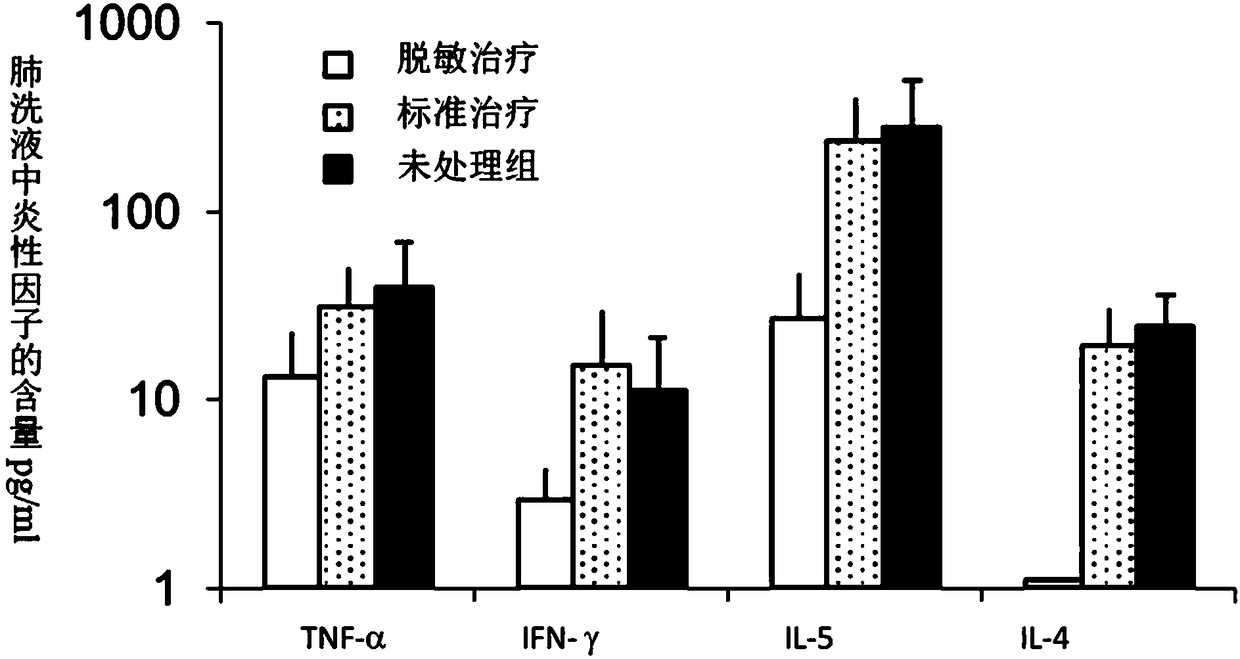
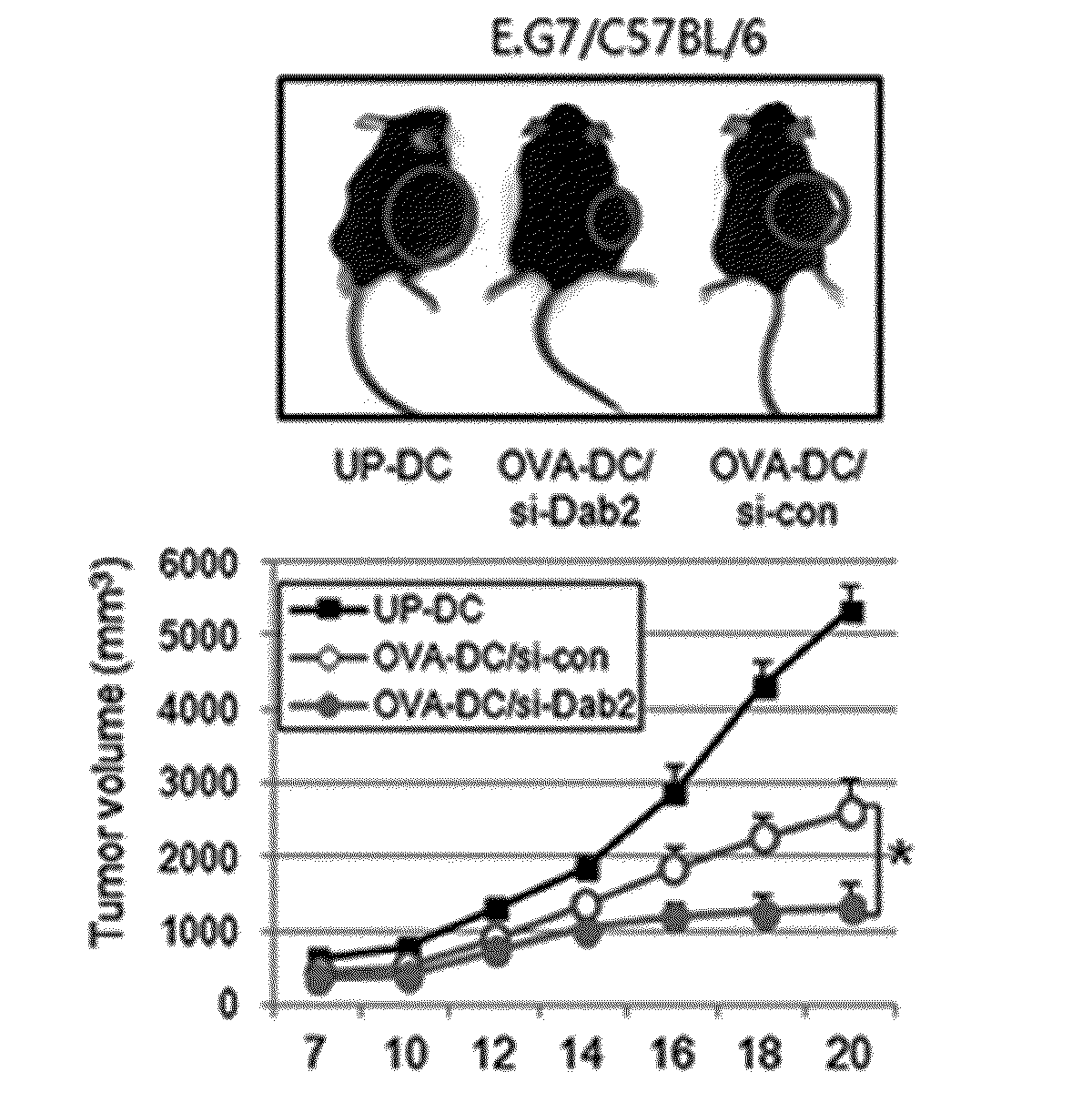
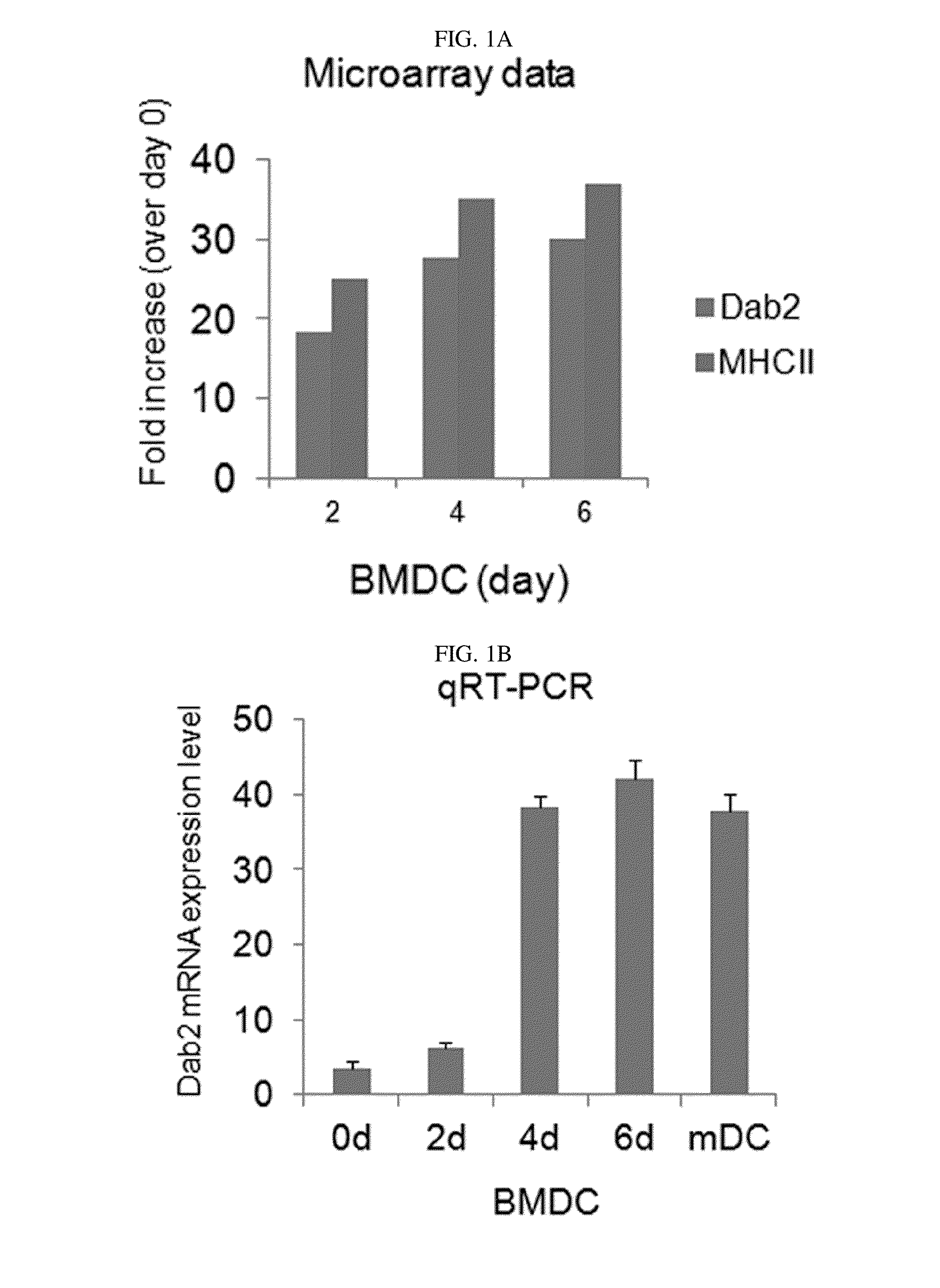
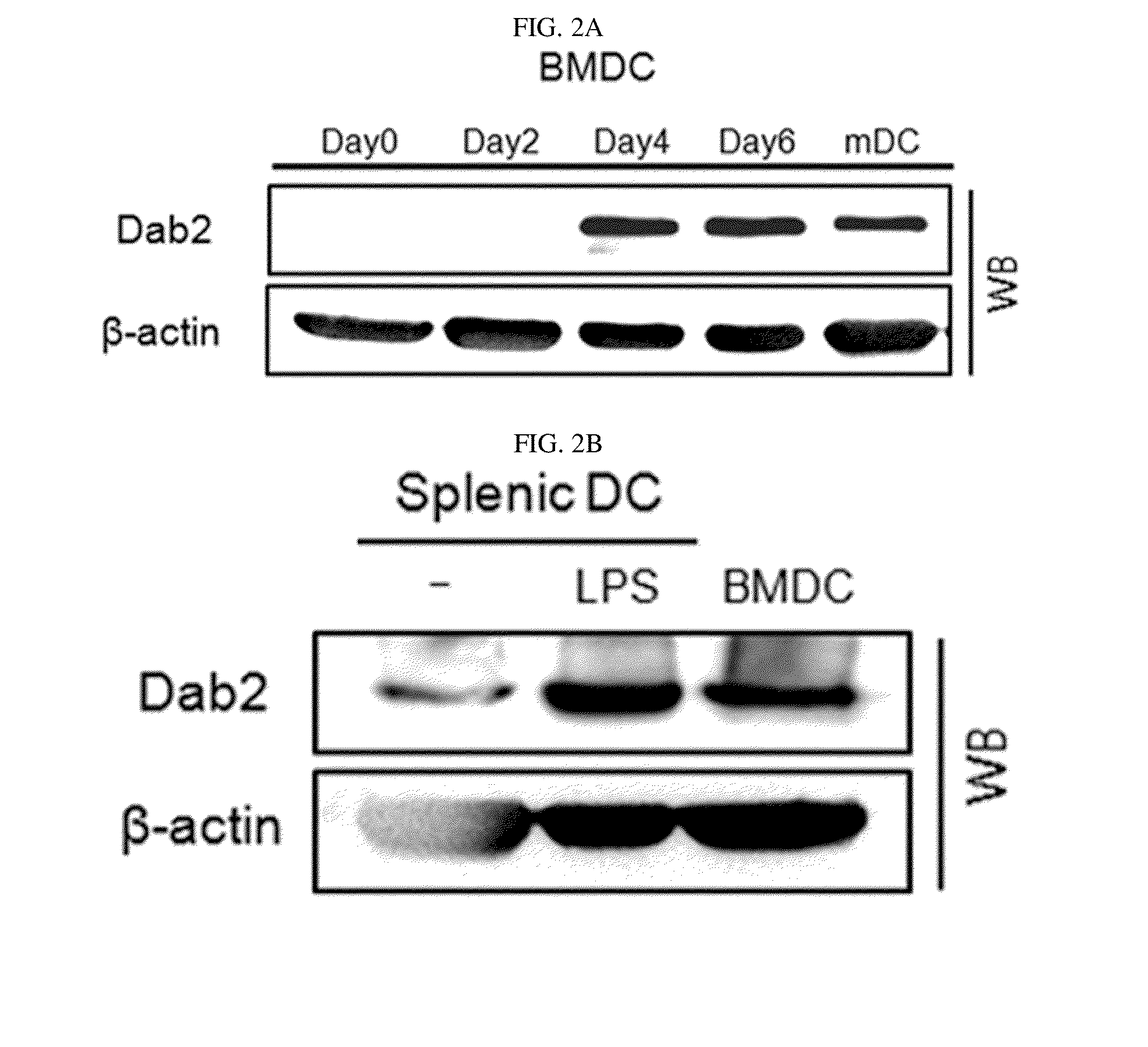
Pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancers comprising dendritic cells with Dab2 gene silenced
Provided is a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer, and more particularly, a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer, including dendritic cells with a knock-down Dab2 gene. The composition includes a dendritic cell in which a Dab2 gene is knocked down or knocked out or activity of a Dab2 protein is suppressed as an active ingredient, and thus is expected to be useful as a pharmaceutical composition to prevent, improve or treat cancer as a result of having improved antigen uptake, a migration ability of a cell to a lymph node, and expression of inflammatory cytokines, and activating antigen-specific cytotoxic T cell lymphocyte (CTL) and related T cells that can attack cancer cells, and therefore is expected to be used as the pharmaceutical composition for preventing, improving or treating cancer.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Bacterial outer membrane vesicle carrier and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112773901BFacilitate cross-presentationInduce specific immune responseBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDendritic cellSpecific immunity
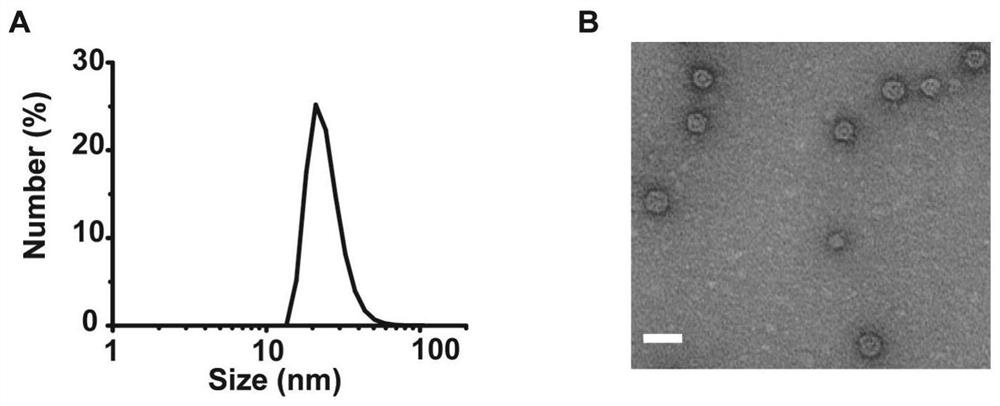
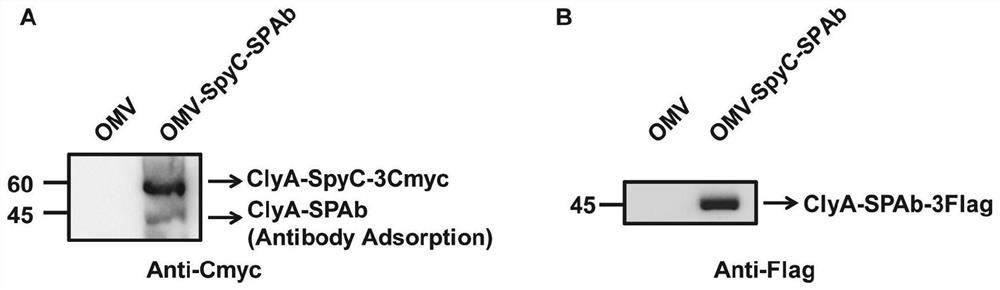
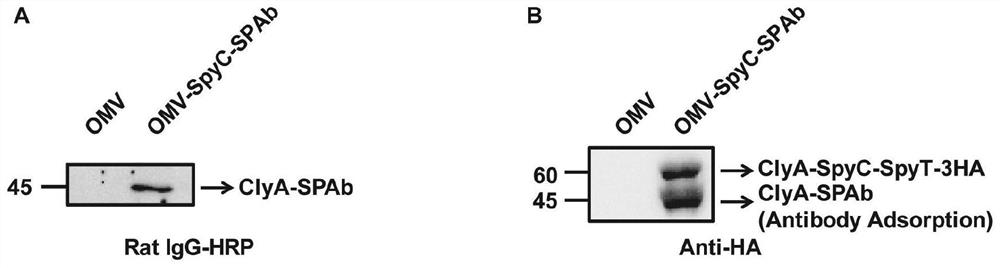
The invention provides a bacterial outer membrane vesicle carrier and its preparation method and application. The present invention provides a vaccine universal carrier OMV-SpyC-SPAb, which is based on bacterial outer membrane vesicles and can target dendritic cells, constructed on the basis of the B domain SPAb of Staphylococcus aureus protein A, Staphylococcus aureus protein The B domain of A, SPAb, is displayed on the bacterial outer membrane vesicle, which can quickly bind to dendritic cell-targeting antibodies (such as Anti-DEC205 antibody), and display the antigen in the bacterial outer membrane vesicle through SpyCatcher / SpyTag molecular glue vesicle surface, prepared a new type of OMV-OVA-DEC vaccine that can target dendritic cells and significantly enhance antigen uptake, which can promote the cross-presentation of dendritic cells to antigens, induce specific immune responses, and achieve anti-tumor purpose and has broad application prospects.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Application of embelin to preparation of medicament for treating autoimmune disease
ActiveCN102488678BInhibition of differentiationInhibition MaturityOrganic active ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune responses
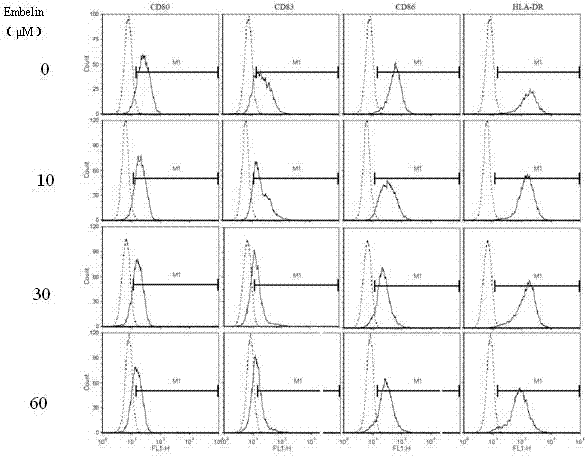
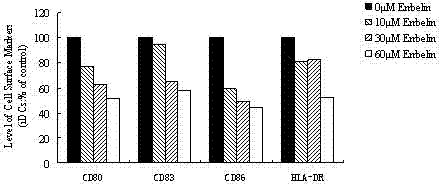
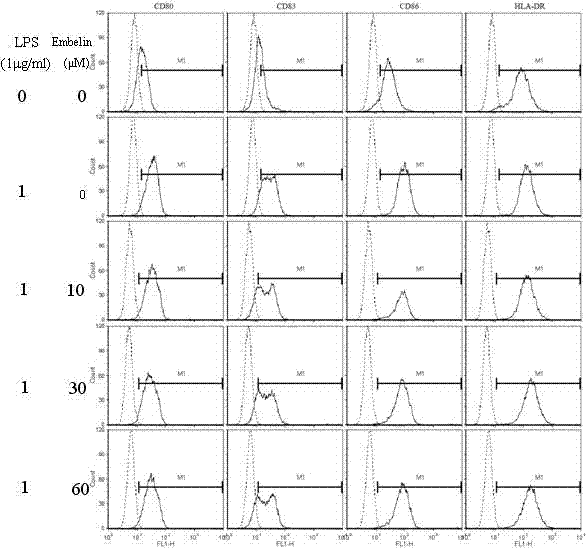
The invention discloses an application of embelin to the preparation of a medicament for treating an autoimmune disease. As proved by an experimental result, the embelin can be used for suppressing the differentiation of human immune dendritic cells, the maturity of human immune dendritic cells activated by LPS (Lipopolysaccharide), the antigen uptaking capabilities of immature dendritic cells, the antigen presenting capabilities of mature dendritic cells, cell-T breeder reactions excited by dendritic cells, and the expression of cell factors which are secreted by dendritic cells and are usedfor promoting type 1 and type 17 cell differentiation of auxiliary cells T. Particularly, the embelin can be used for lowering the pathogenic degree of mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. The invention relates to preparation of a medicament for suppressing an immune system, which can become a medicament for clinically treating autoimmune inflammatory lesions such as multiple sclerosis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
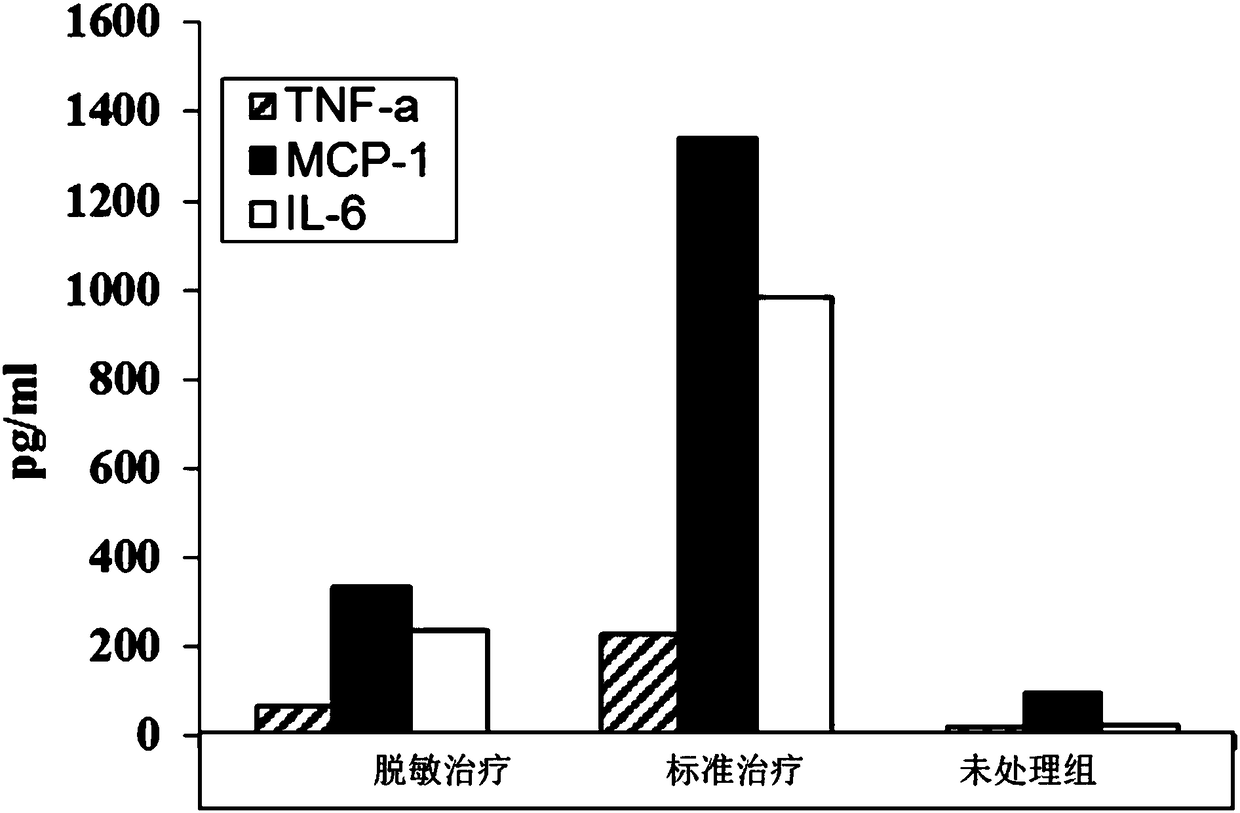
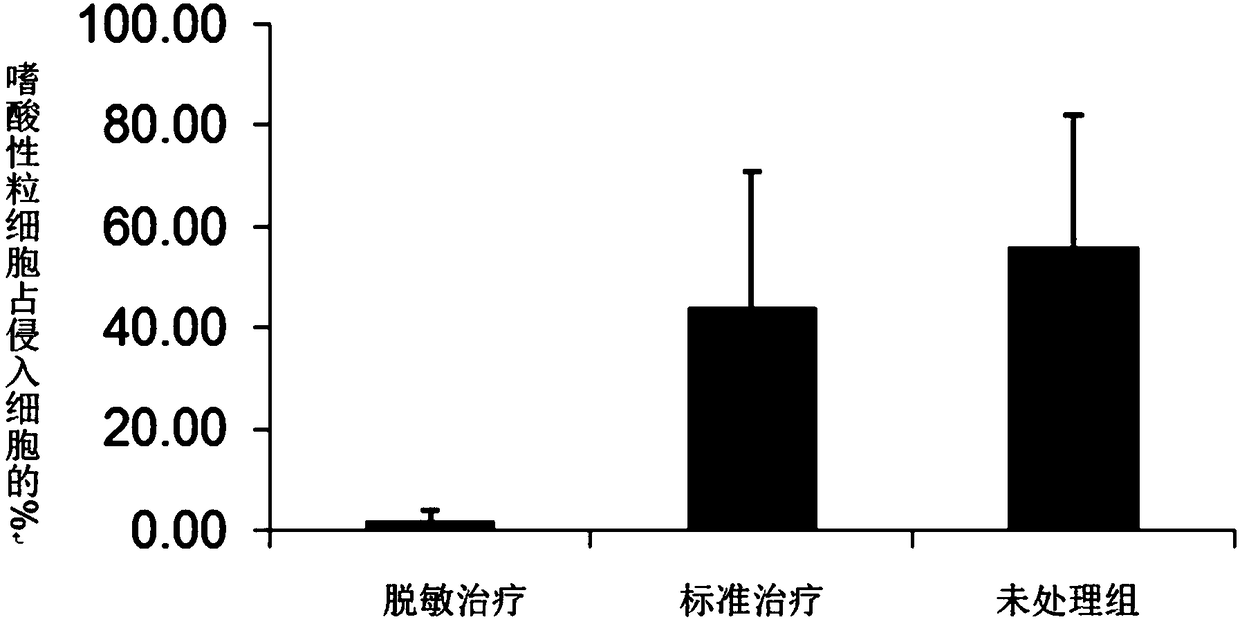
Adjuvant for desensitization vaccine and novel desensitization vaccine
ActiveCN108096575AAdjuvant effectAchieve enhanced effectOrganic active ingredientsAllergen ingredientsAdjuvantImmune tolerance
The invention provides an adjuvant for a desensitization vaccine; the adjuvant is prepared from components with immune tolerance; the components with immune tolerance are anti-inflammatory compounds.The invention also provides the novel desensitization vaccine using the anti-inflammatory compounds as the adjuvant. The anti-inflammatory compounds are used as the adjuvant and are co-injected with an allergen, so that inflammation of allergy vaccines is prevented at the injection site; the anti-inflammatory compounds have an effect of inhibiting the maturation of antigen-presenting cells; the anti-inflammatory compounds directly act on the antigen-presenting cells so as to inhibit the antigen-presenting cells from becoming mature cells during antigen uptake and presentation; the anti-inflammatory compounds realizes long-acting treatment of allergies by rapidly inducing the production of Treg cells. The desensitization vaccine provided by the invention can realize rapid, long-acting and effective treatment on the allergies from the view of sensitization mechanism.
Owner:CHENGDU MAXVAX BIOTECHNOLOGY LLC
Pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancers comprising dendritic cells with dab2 gene silenced
Provided is a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer, and more particularly, a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer, including dendritic cells with a knock-down Dab2 gene. The composition includes a dendritic cell in which a Dab2 gene is knocked down or knocked out or activity of a Dab2 protein is suppressed as an active ingredient, and thus is expected to be useful as a pharmaceutical composition to prevent, improve or treat cancer as a result of having improved antigen uptake, a migration ability of a cell to a lymph node, and expression of inflammatory cytokines, and activating antigen-specific cytotoxic T cell lymphocyte (CTL) and related T cells that can attack cancer cells, and therefore is expected to be used as the pharmaceutical composition for preventing, improving or treating cancer.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
An adjuvant for desensitization vaccine and a new type of desensitization vaccine
ActiveCN108096575BRelieve symptomsDiffusion fastOrganic active ingredientsAllergen ingredientsAdjuvantMature cell
The invention provides an adjuvant for a desensitization vaccine, which includes an immune tolerance-inducing component, and the immune tolerance-inducing component is an anti-inflammatory compound. The present invention also provides a novel desensitizing vaccine using an anti-inflammatory compound as an adjuvant. In the present invention, the anti-inflammatory compound is used as an adjuvant and co-injected with the allergen to prevent the inflammation of the allergic vaccine at the site; the anti-inflammatory compound has the effect of inhibiting the maturation of antigen-presenting cells, and the anti-inflammatory compound directly acts on the antigen-presenting cells, inhibiting They become mature cells during antigen uptake and presentation; anti-inflammatory compounds achieve long-lasting treatment of allergies by rapidly inducing the generation of Treg cells. The desensitization vaccine provided by the invention can realize rapid, long-acting and effective treatment of allergic symptoms from the mechanism of sensitization.
Owner:CHENGDU MAXVAX BIOTECHNOLOGY LLC
An affinity peptide ty peptide targeting dendritic cells and its application
ActiveCN109021078BPromote maturityImprove intake efficiencyPowder deliveryPeptidesDendritic cellNanocarriers
This application belongs to the technical field related to protein for tumor therapy, and specifically relates to an affinity peptide TY peptide targeting dendritic cells and its application patent application matters. The TY peptide is a 12-peptide, and the specific amino acid sequence is: TITHFQFGPTVY. On the basis of TY peptide, this application further designed a new type of nano-transport system that can target DC based on MSN, and loaded the model antigen OVA and immune adjuvant CpG, and successfully prepared the nano-carrier MSN‑TY / OVA / CpG. Experiments show that MSN‑TY / OVA / CpG can be effectively taken up by immature DCs, improve the efficiency of antigen uptake by DCs, promote the maturation of DCs and effectively activate DCs, and effectively promote the processing and presentation of antigens , stimulate its secretion of cytokines, and further trigger antigen-specific CTL immune response and anti-tumor immune response.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com