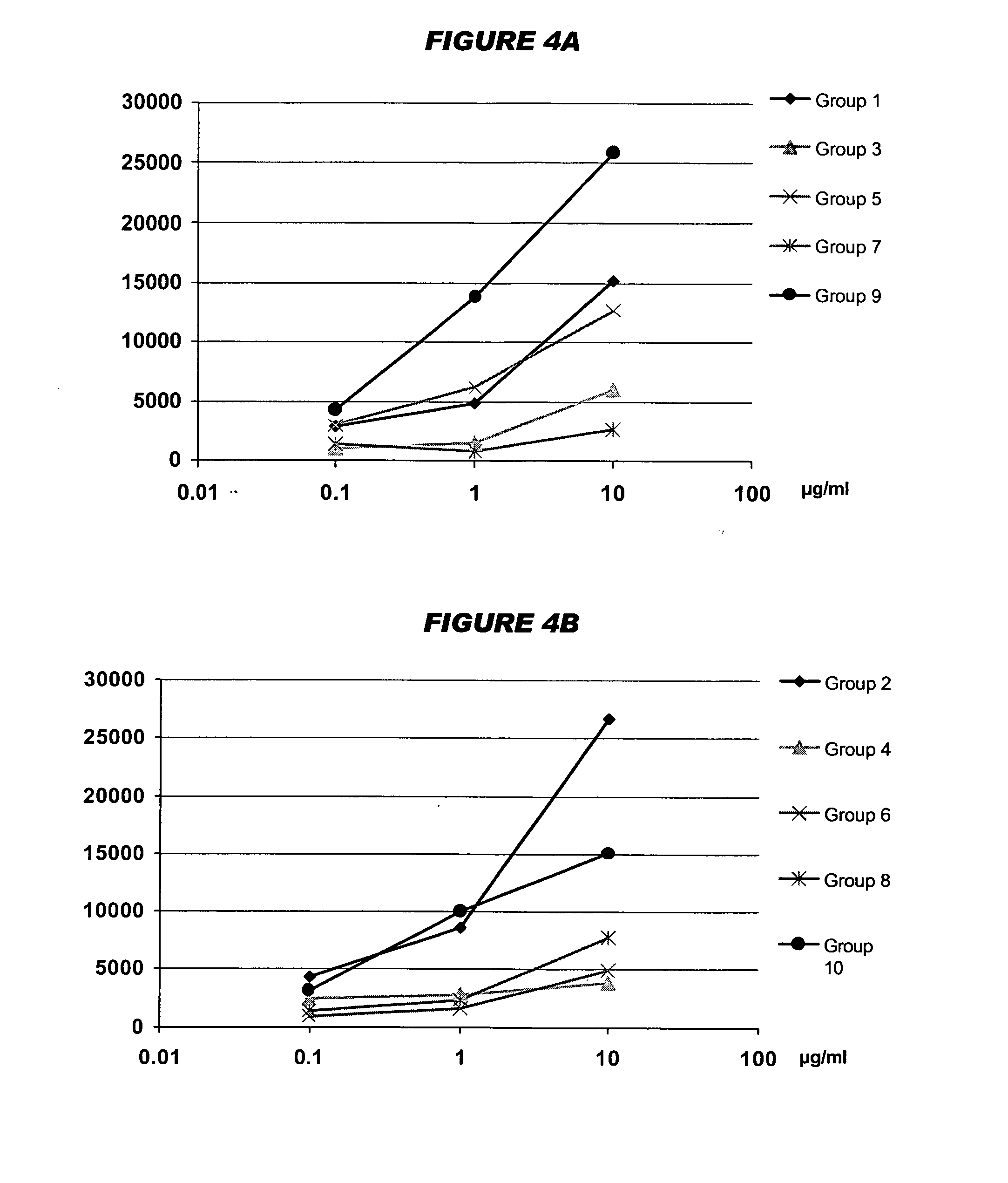
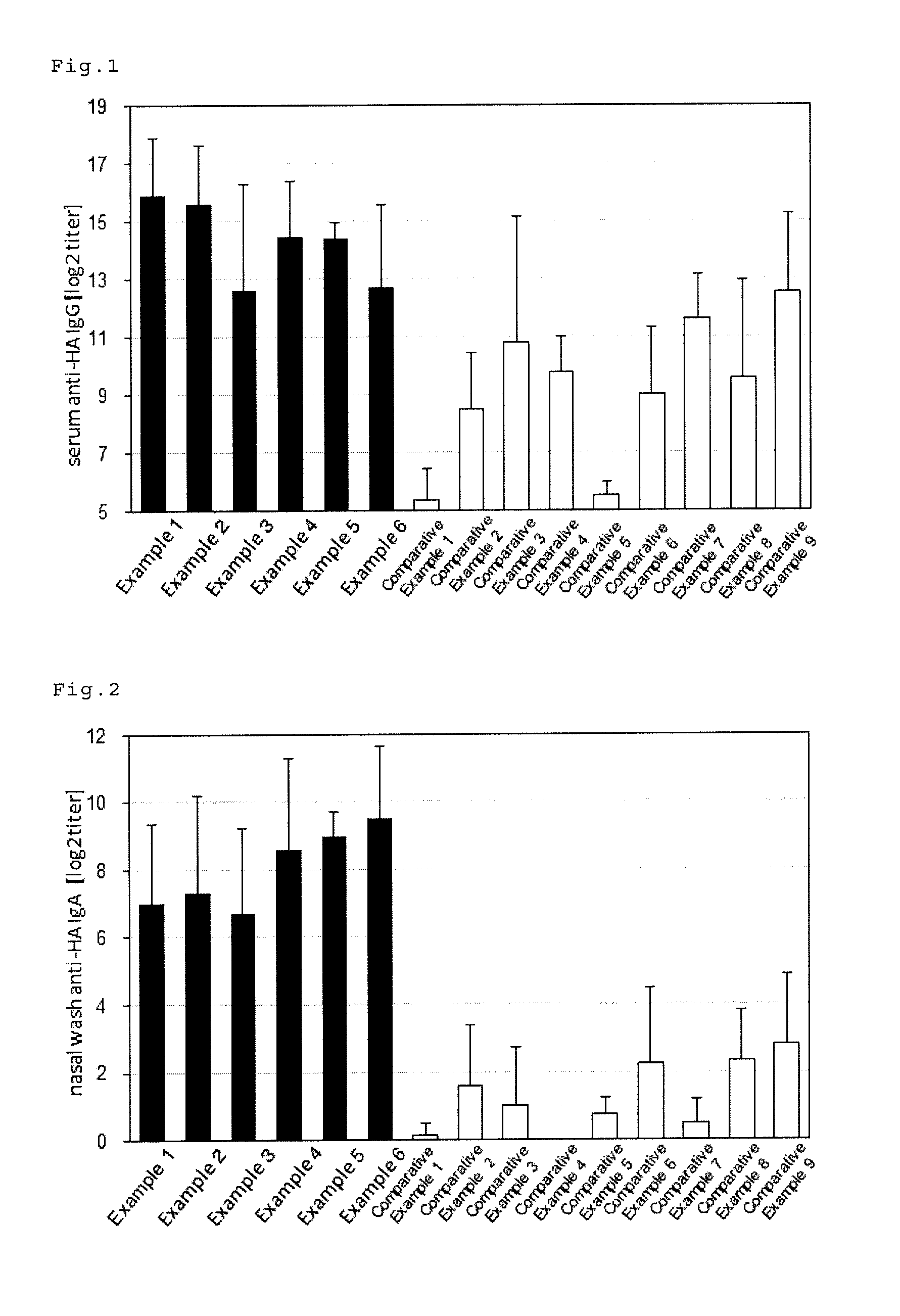
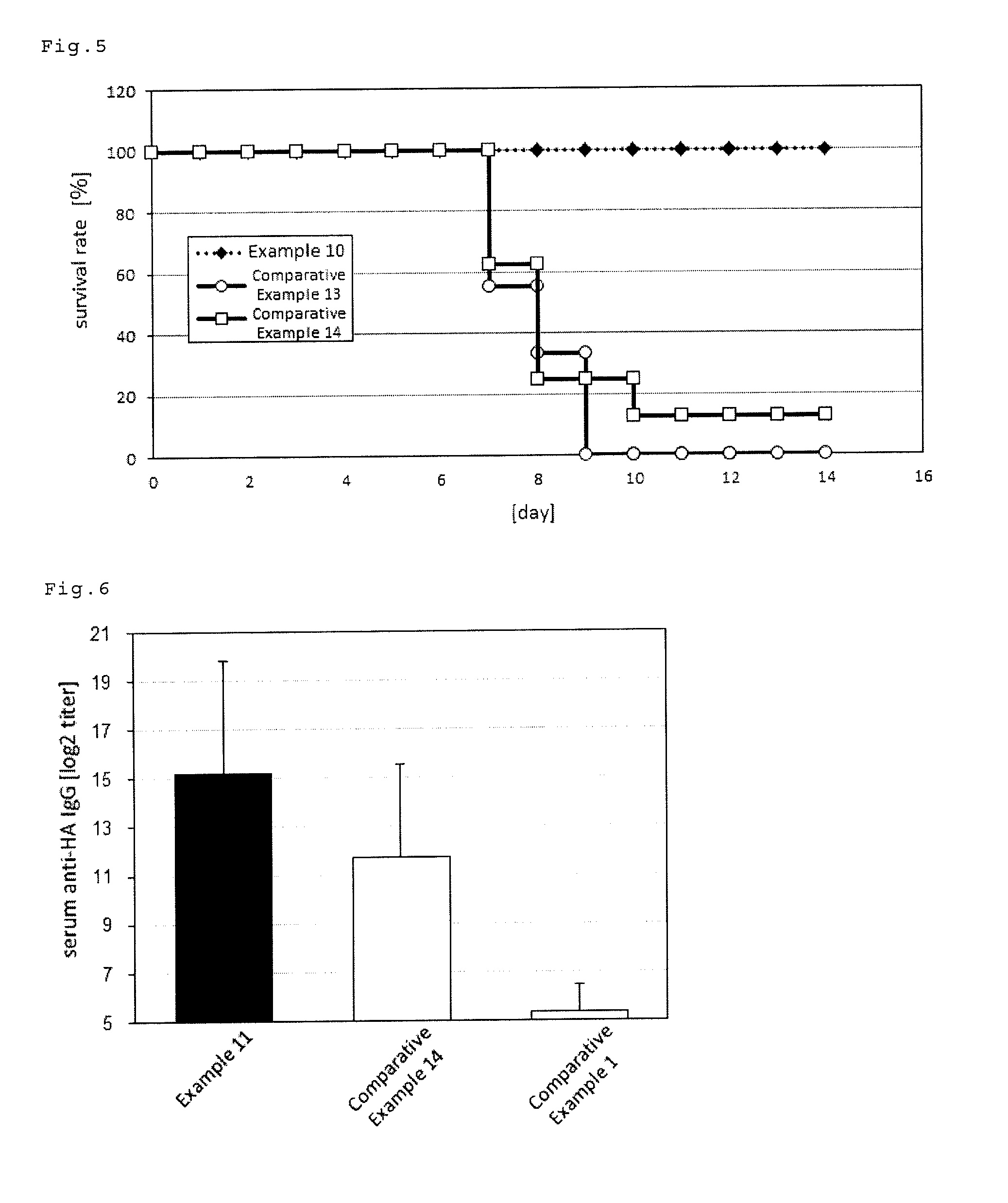
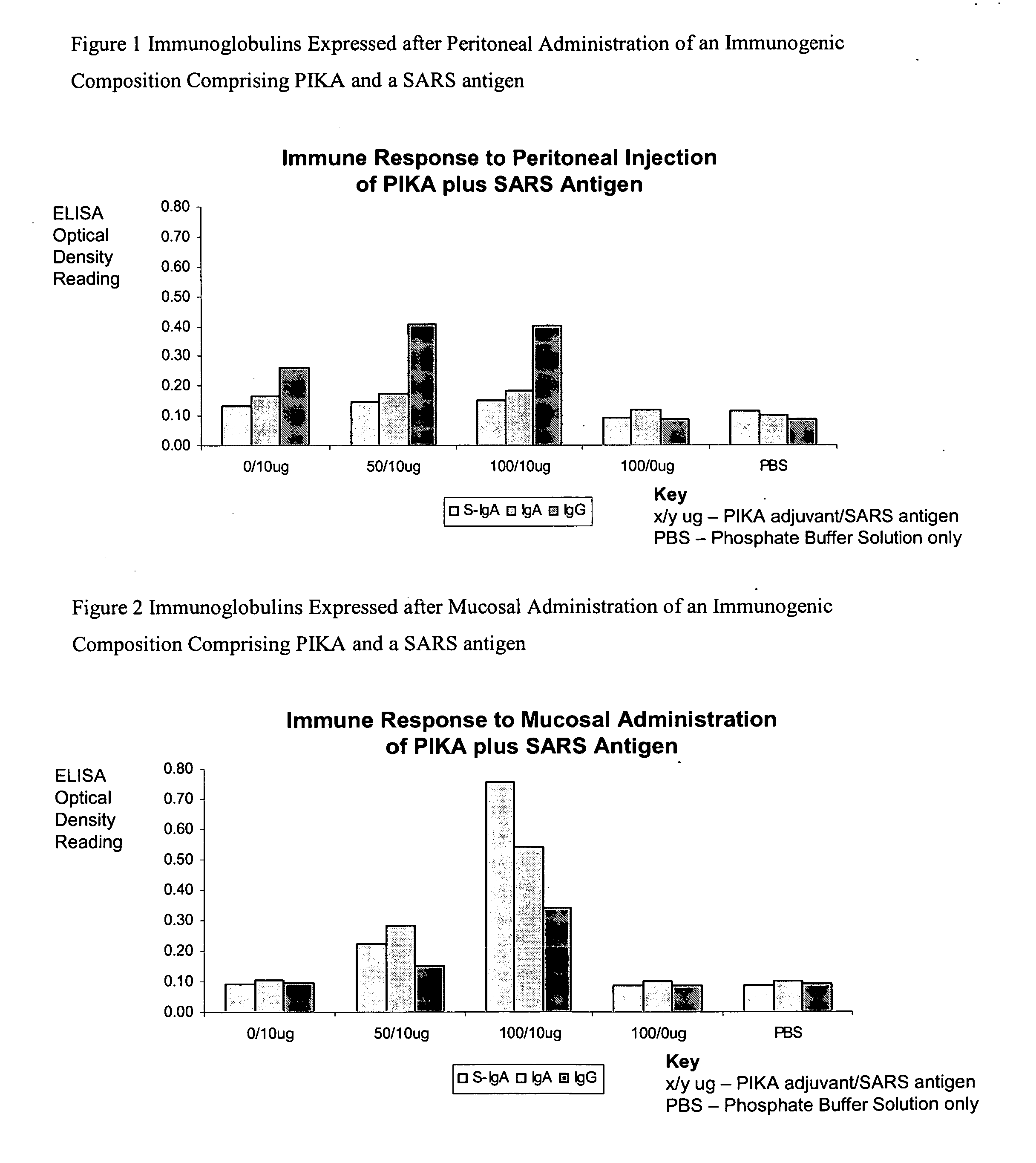
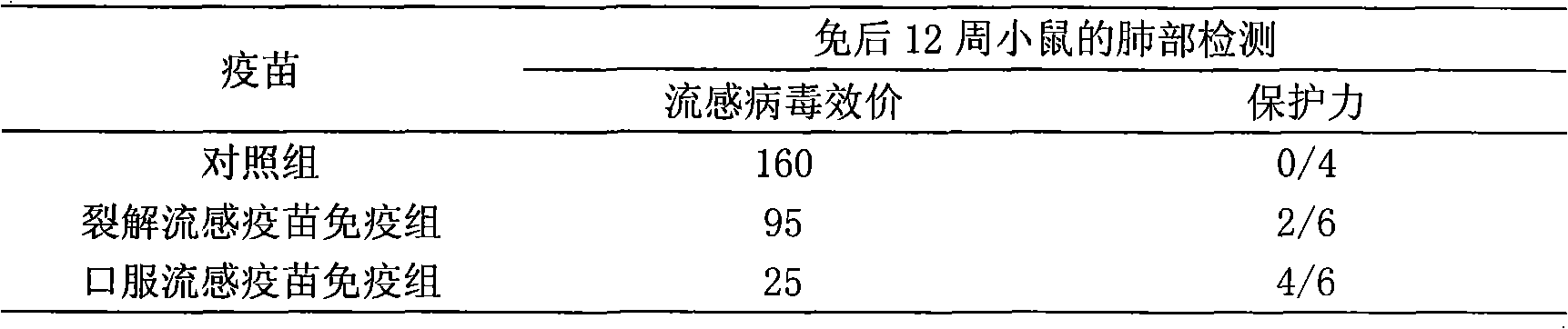
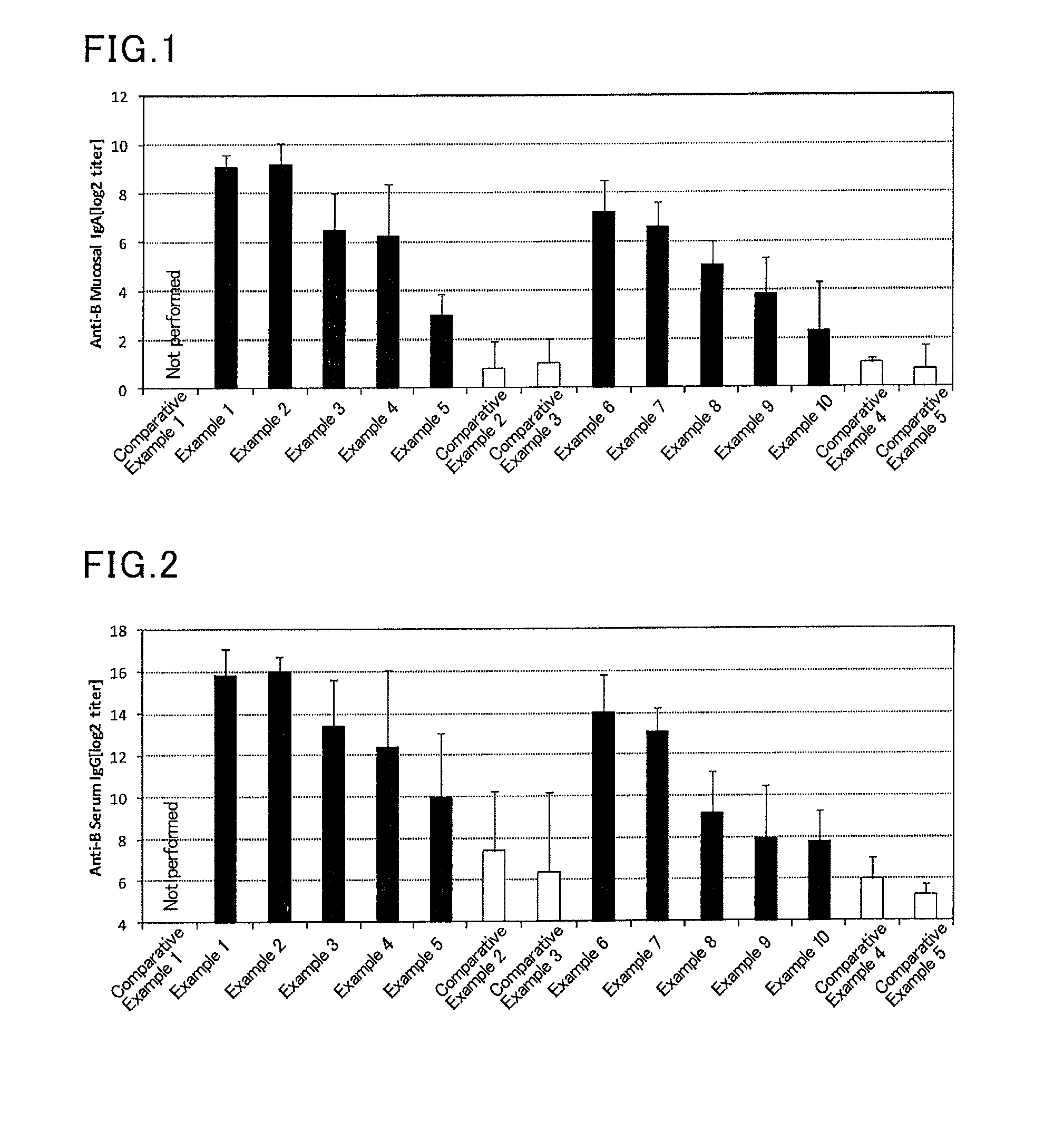
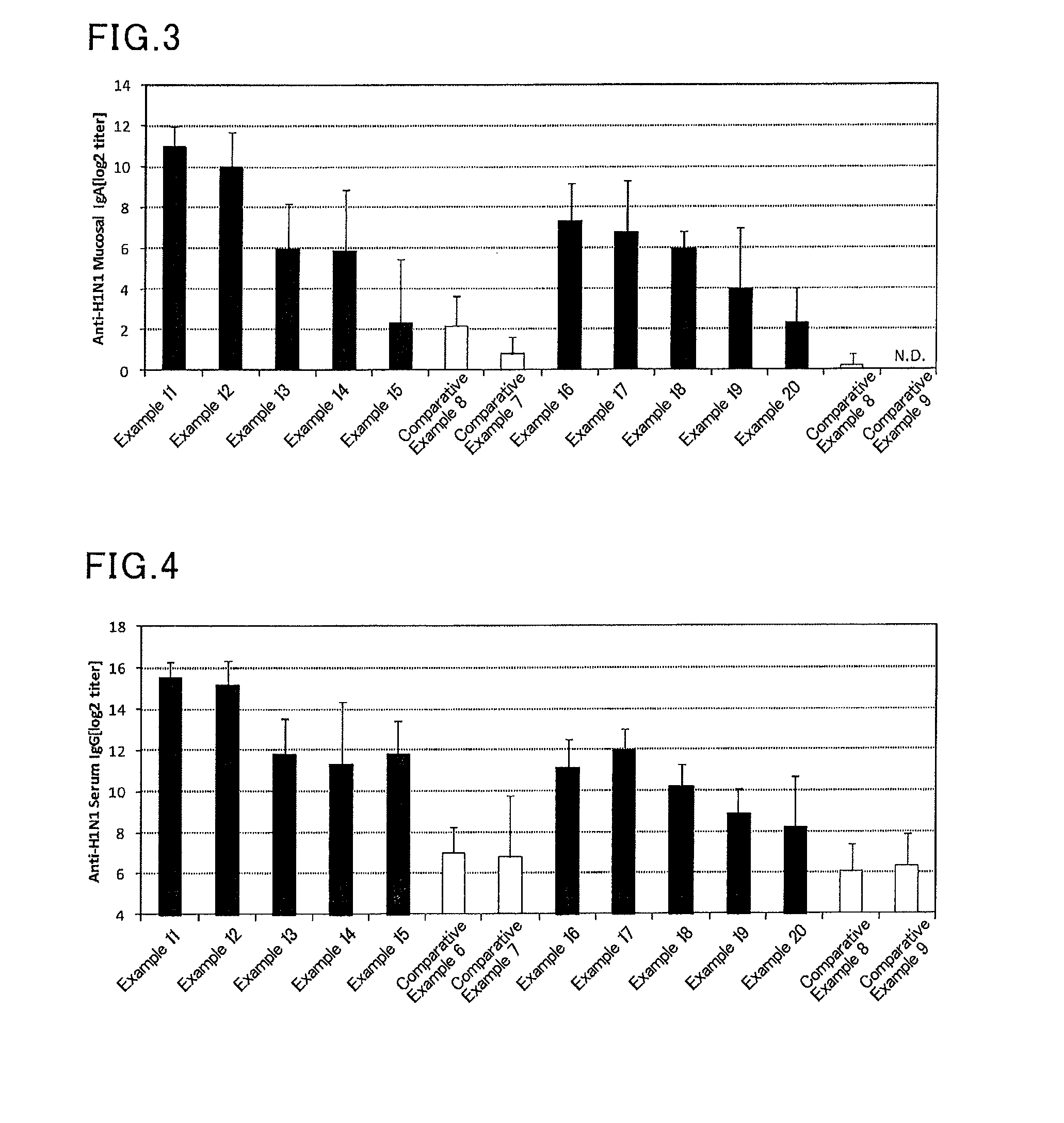
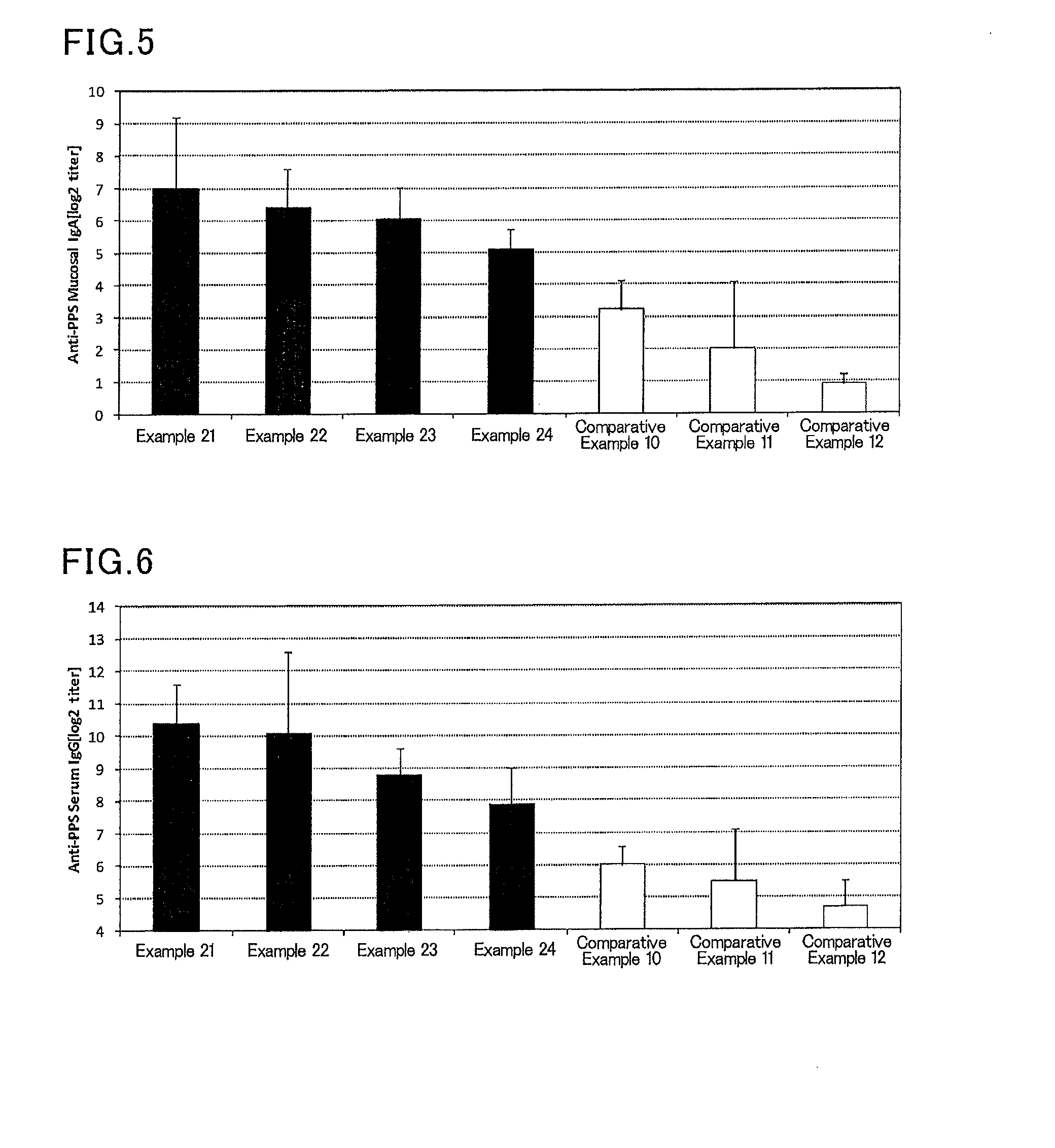
Patents
Literature
113 results about "Mucosal Immune Responses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mucosal immunology is the study of immune system responses that occur at mucosal membranes of the intestines, the urogenital tract and the respiratory system, i.e., surfaces that are in contact with the external environment.
Vaccines and Methods for Using the Same
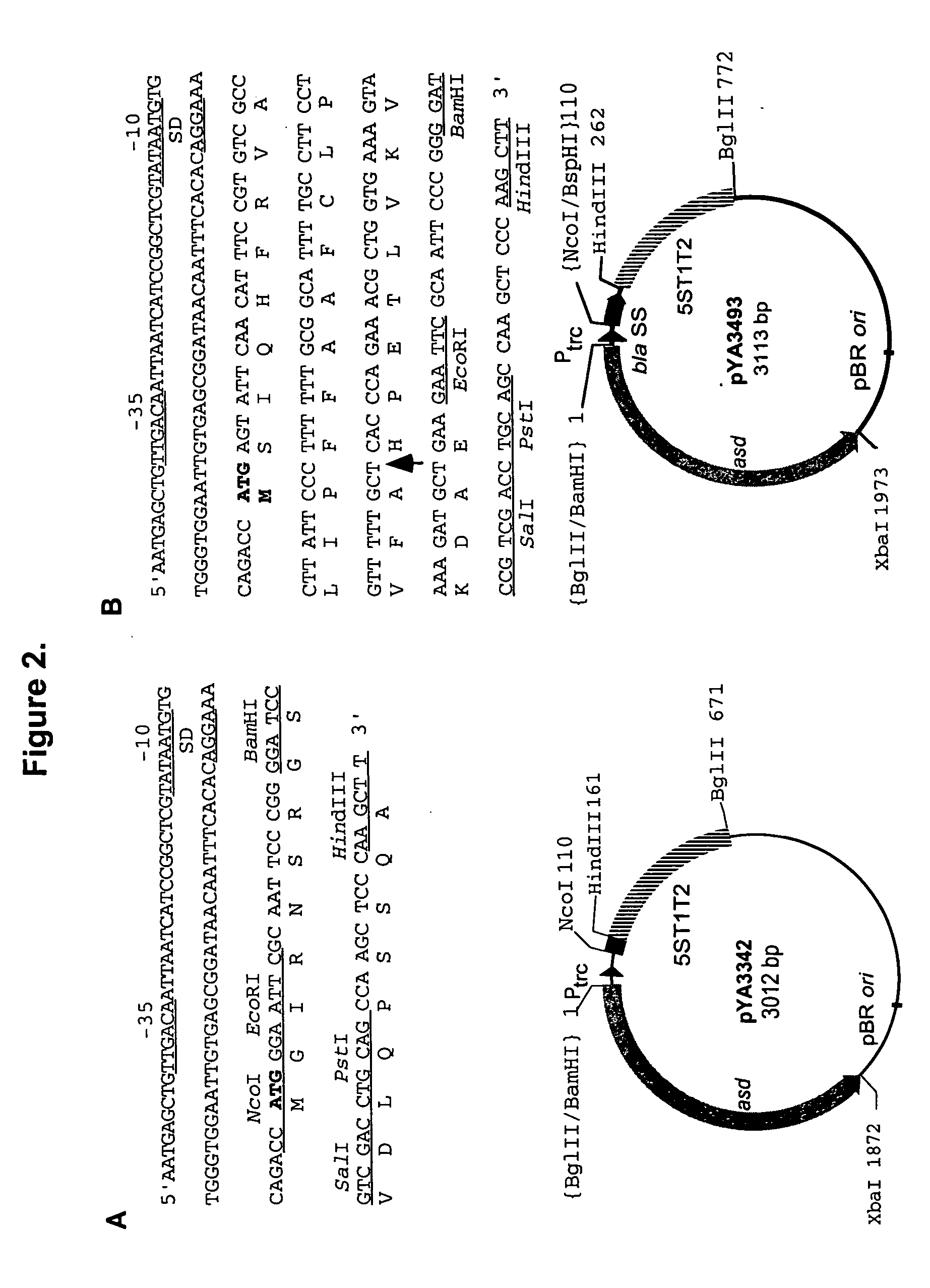
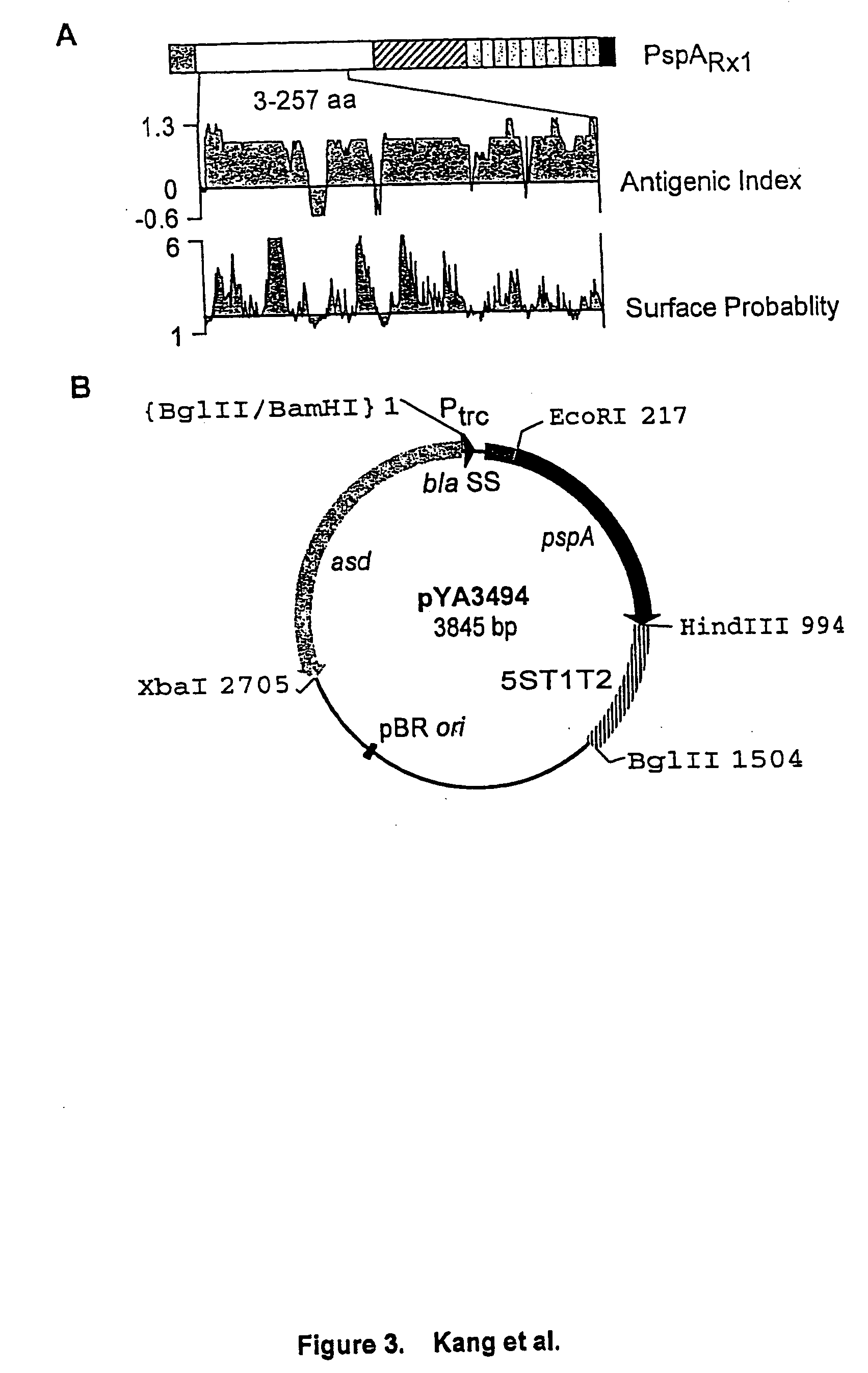
InactiveUS20080274140A1Sugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesADAMTS Proteins
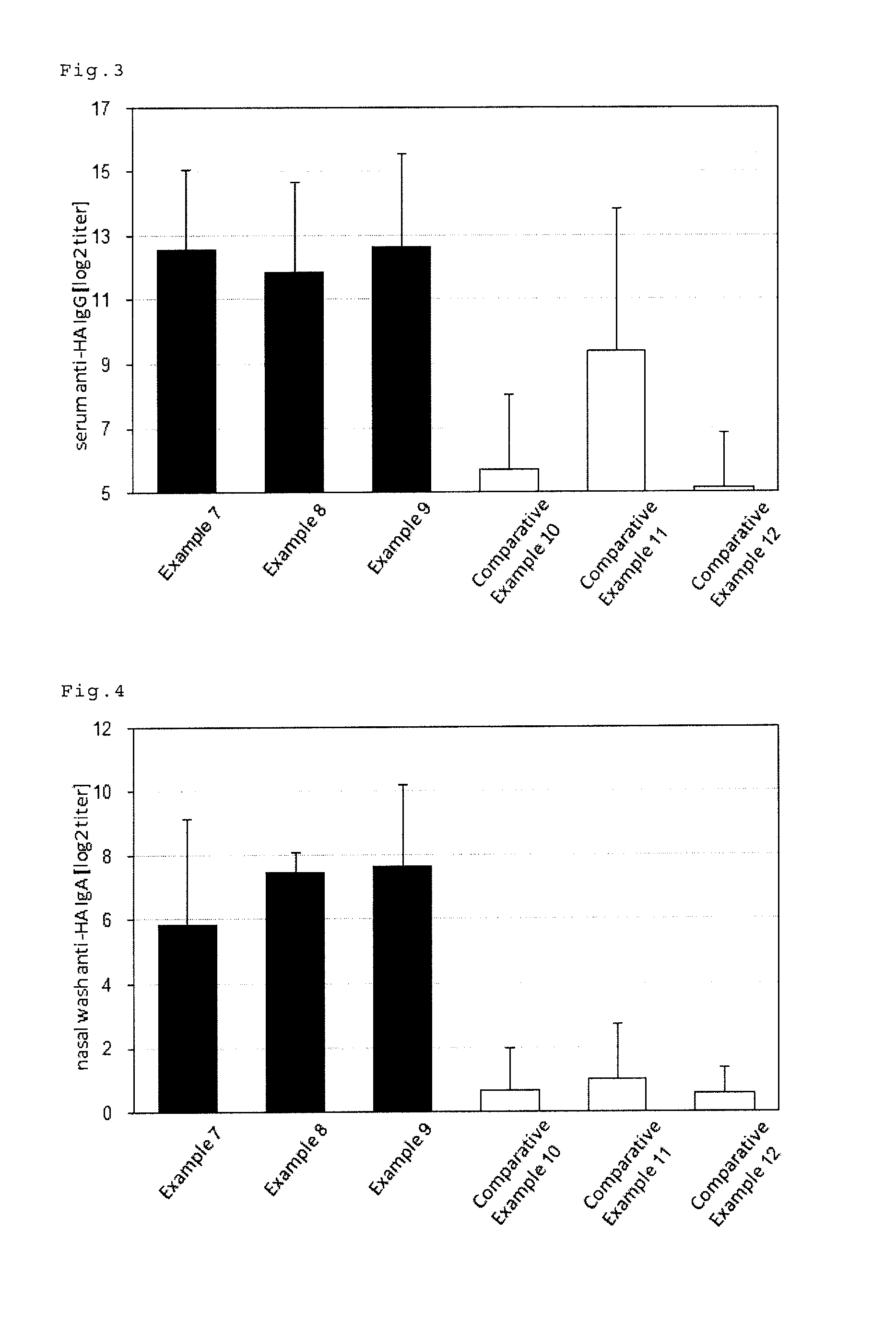
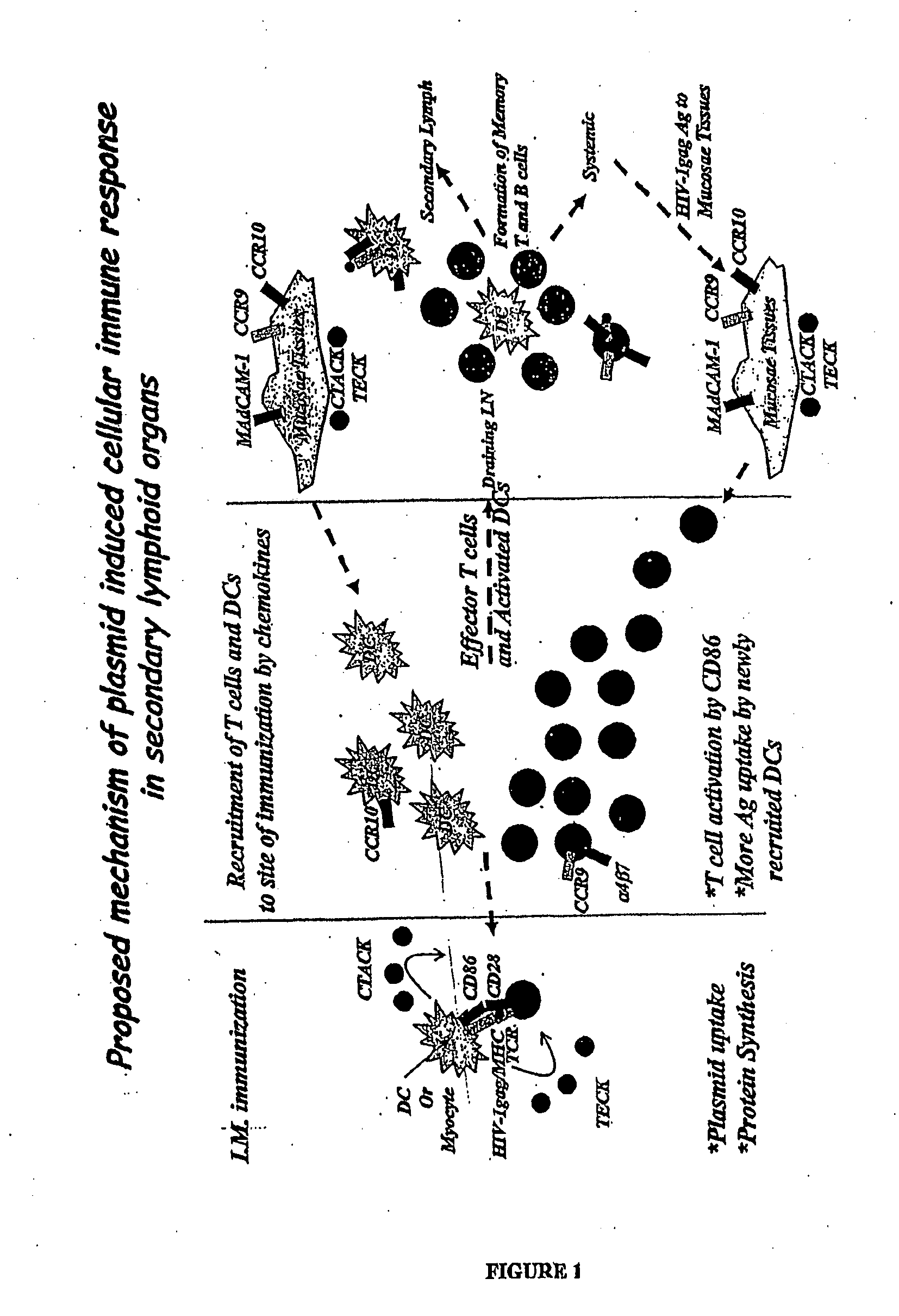
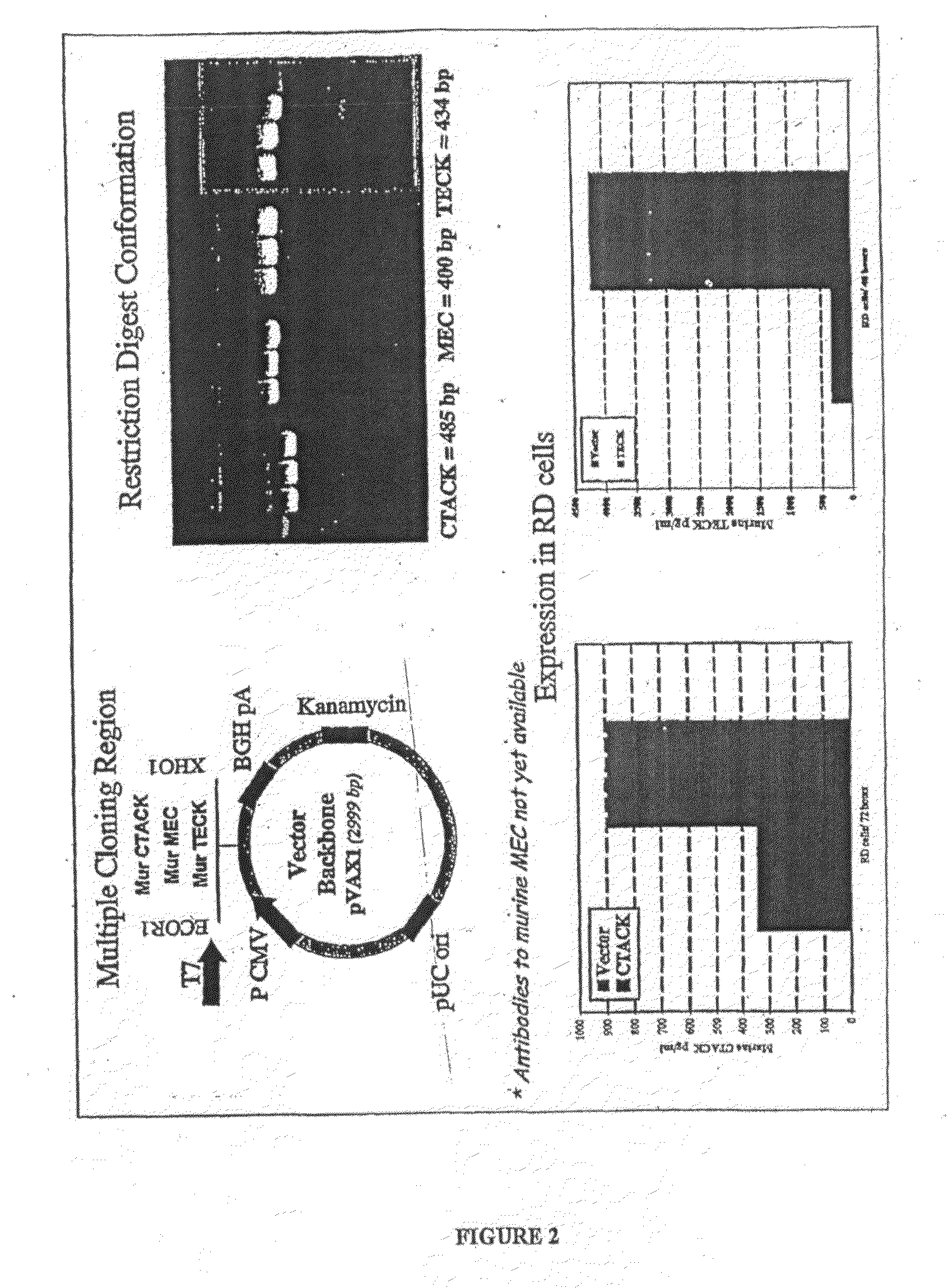
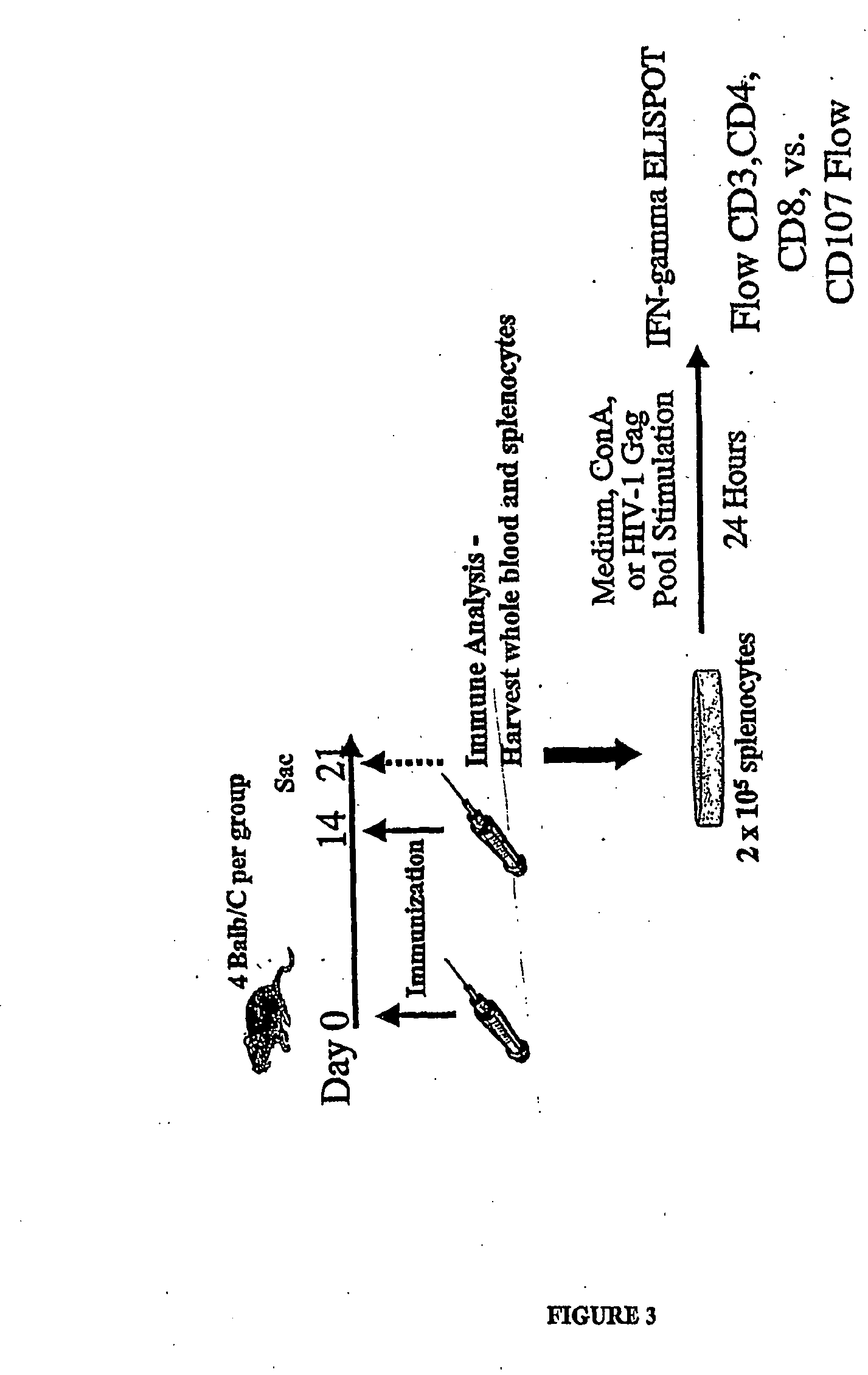
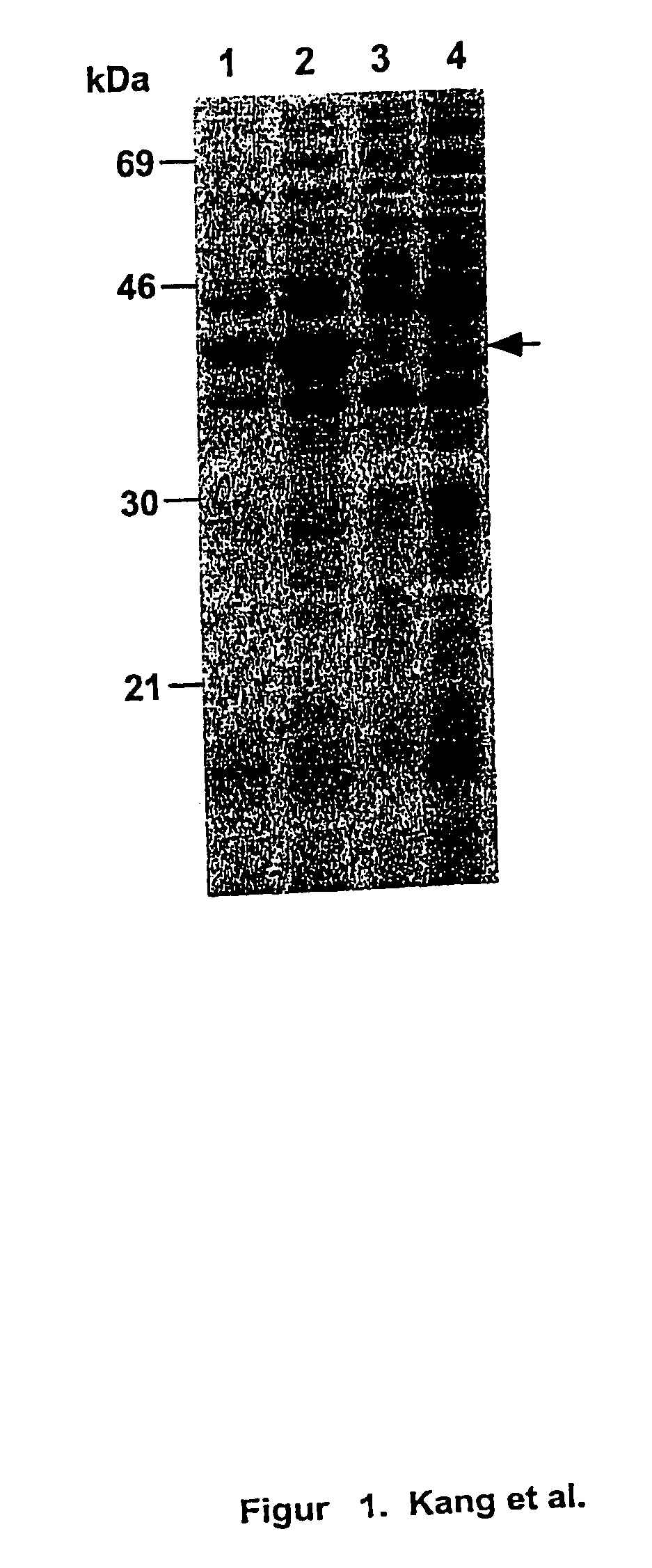
Compositions comprising one or more isolated nucleic acid molecules that encode an immunogen in combination with one or more of CTACK protein, TECK protein, MEC protein and functional fragments thereof and / or an isolated nucleic acid molecule that encodes an protein selected from the group consisting of: CTACK, TECK, MEC and functional fragments thereof are disclosed. Methods of inducing an immune response, including methods of inducing mucosal immune responses, in an individual against an immunogen, using such compositions are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Immunogenic compositions and vaccines comprising carrier bacteria that secrete antigens
InactiveUS20040101531A1Snake antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesMucosal Immune ResponsesAntigen delivery
Disclosed are vaccines and immunogenic compositions which use live attenuated pathogenic bacteria, such as Salmonella, to deliver ectopic antigens to the mucosal immune system of vertebrates. The attenuated pathogenic bacteria are engineered to secrete the antigen into the periplasmic space of the bacteria or into the environment surrounding the bacteria. The vertebrate mounts a Th2-mediated immune response toward the secreted antigen.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Mucosal meningococcal vaccines
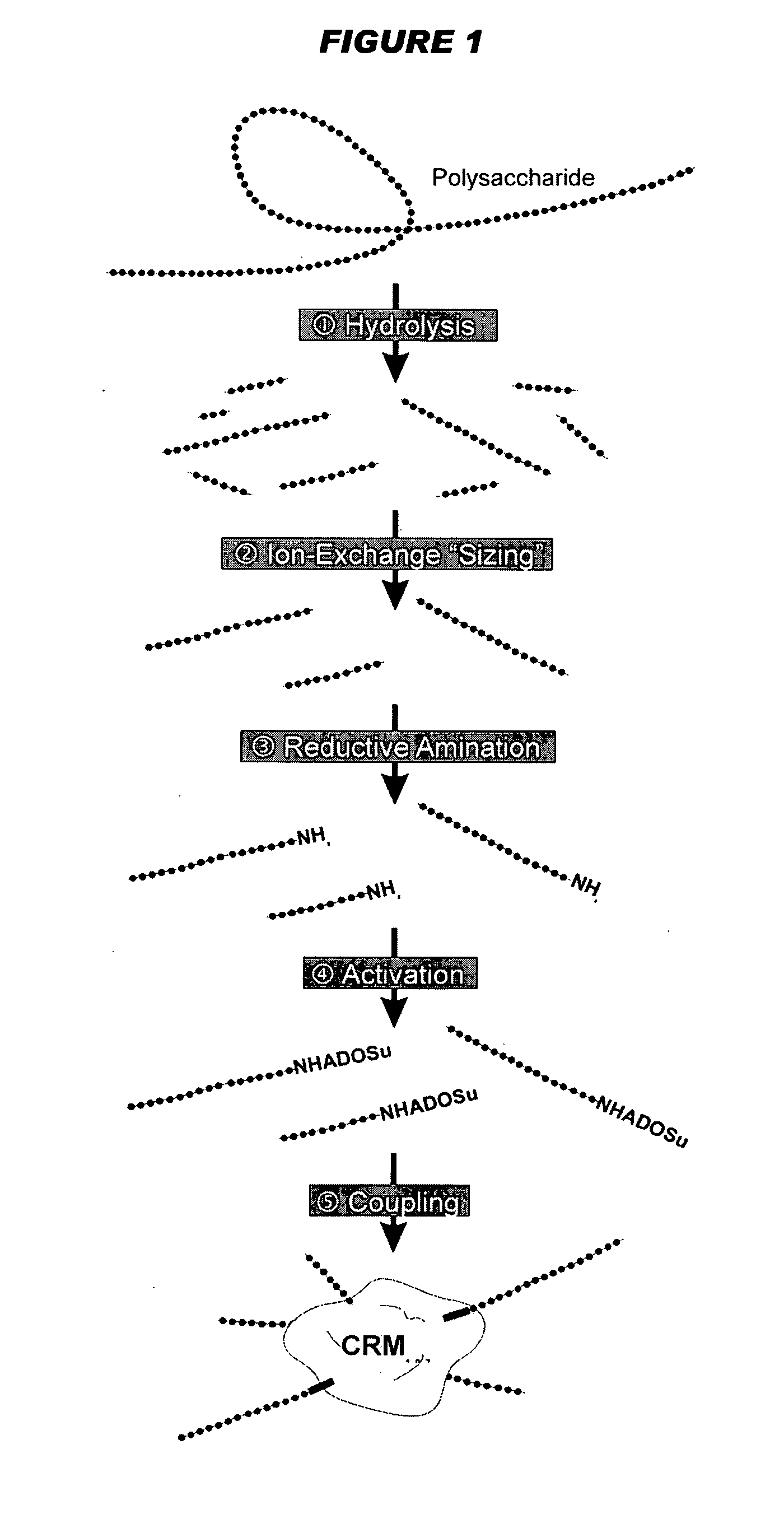
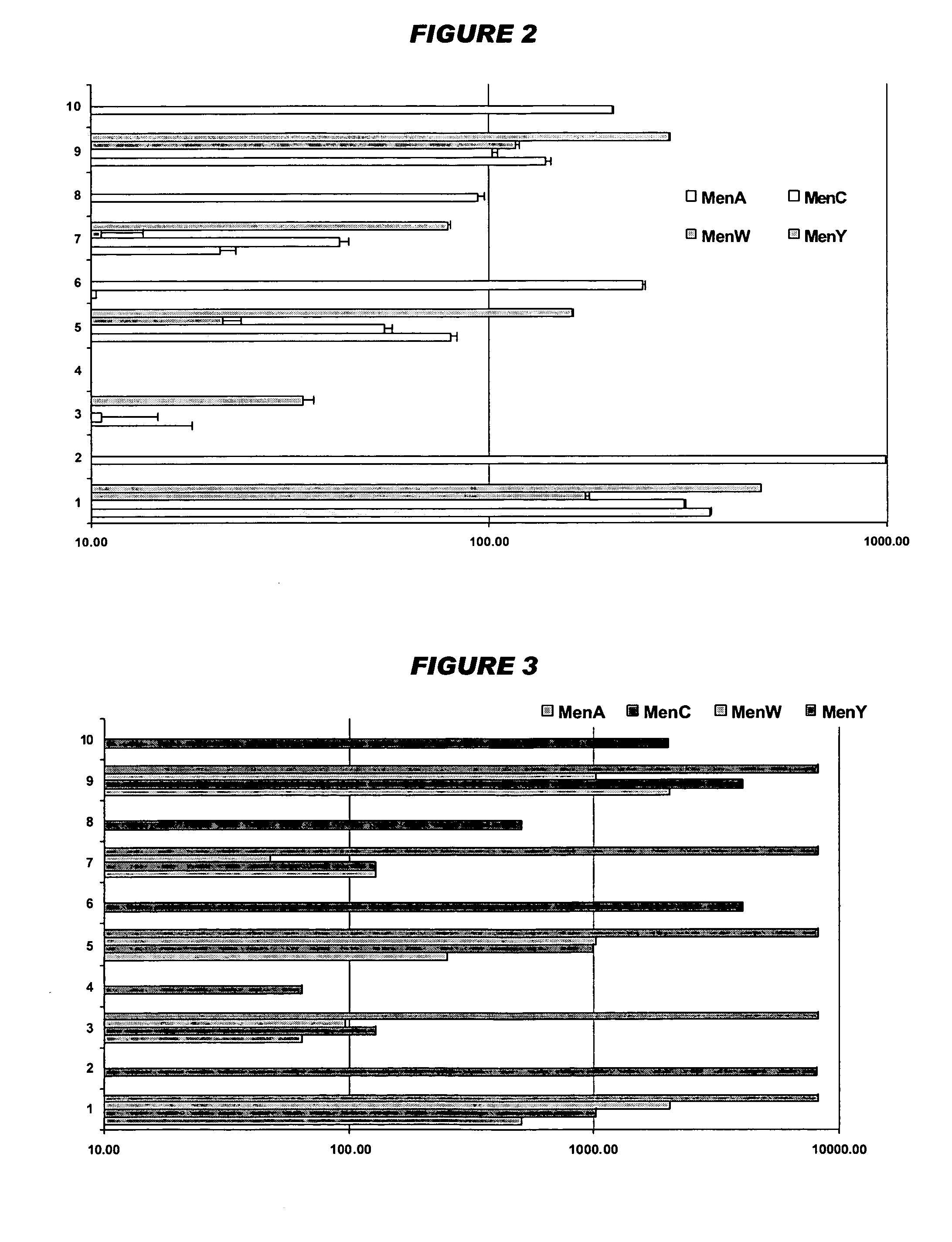
InactiveUS20070207090A1Improve securityReduced dosAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesAdjuvant
The invention provides immunogenic compositions for mucosal delivery comprising capsular saccharides from at least two of serogroups A, C, W135 and Y of N. meningitidis. It is preferred that the capsular saccharides in the compositions of the invention are conjugated to carrier protein(s) and / or are oligosaccharides. Conjugated oligosaccharide antigens are particularly preferred. The invention also provides immunogenic compositions comprising (a) a capsular saccharide antigen from serogroup C of N. meningitidis, and (b) a chitosan adjuvant. The composition preferably comprises (c) one or more further antigens and / or (d) one or more further adjuvants. The compositions are particularly suitable for mucosal delivery, including intranasal delivery. The use of chitosan and / or detoxified ADP-ribosylating toxin adjuvants enhances anti-meningococcal mucosal immune responses and can shift the Th1 / Th2 bias of the responses.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Vaccine composition
ActiveUS20130266612A1Efficient inductionSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesWhole body
An intraorally administrable vaccine composition useful to be a preventive or therapeutic agent for infectious diseases, and effectively induces a systemic immune response or a mucosal immune response is provided. A vaccine composition for administration to the oral cavity of a human or an animal, the vaccine composition containing at least one antigen derived from an infectious disease, and at least one selected from the group consisting of a toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) agonist, a toll-like receptor 2 / 6 (TLR2 / 6) agonist, and cyclic dinucleotide, or a derivative or salt thereof.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
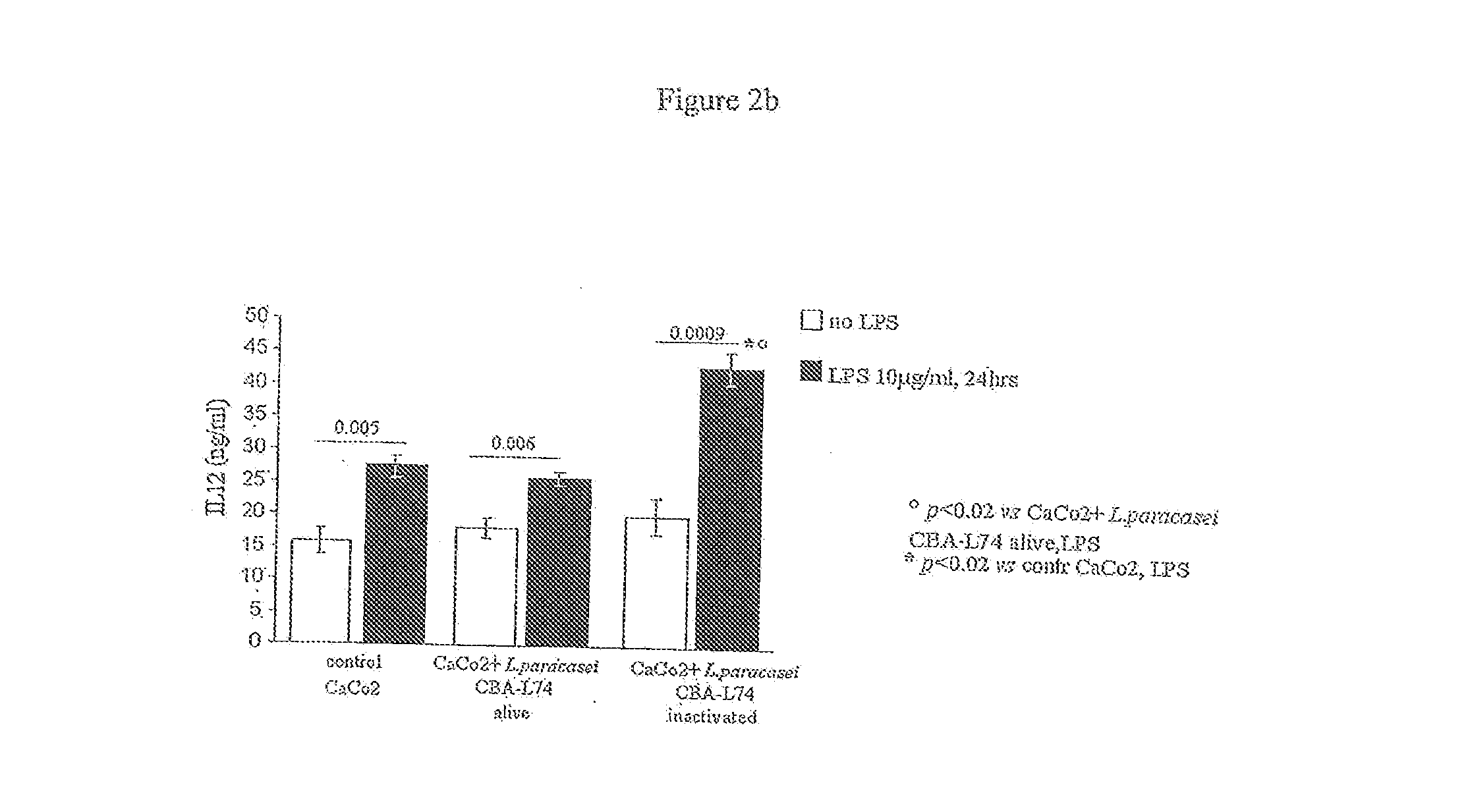
Probiotic compositions and methods
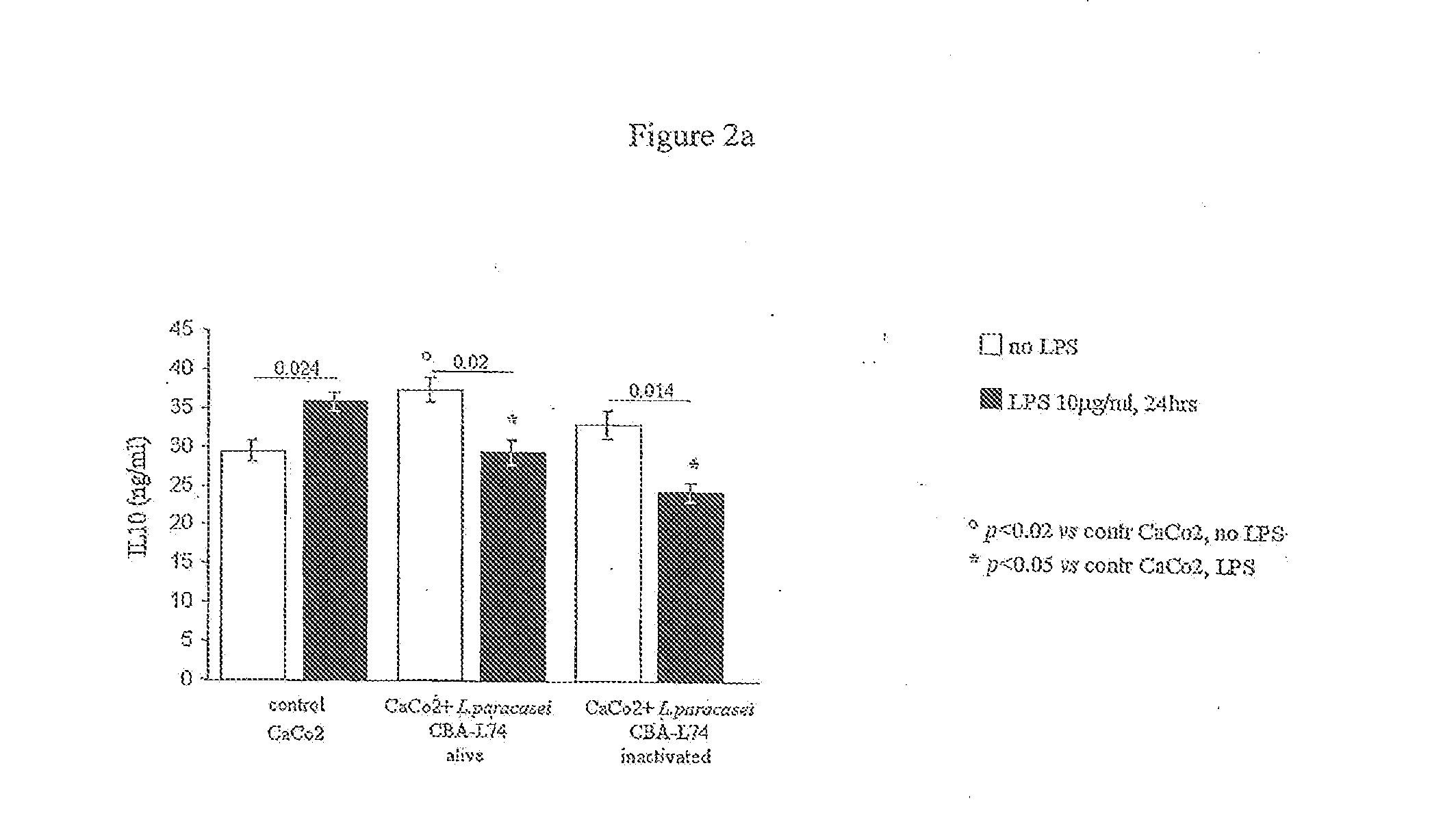
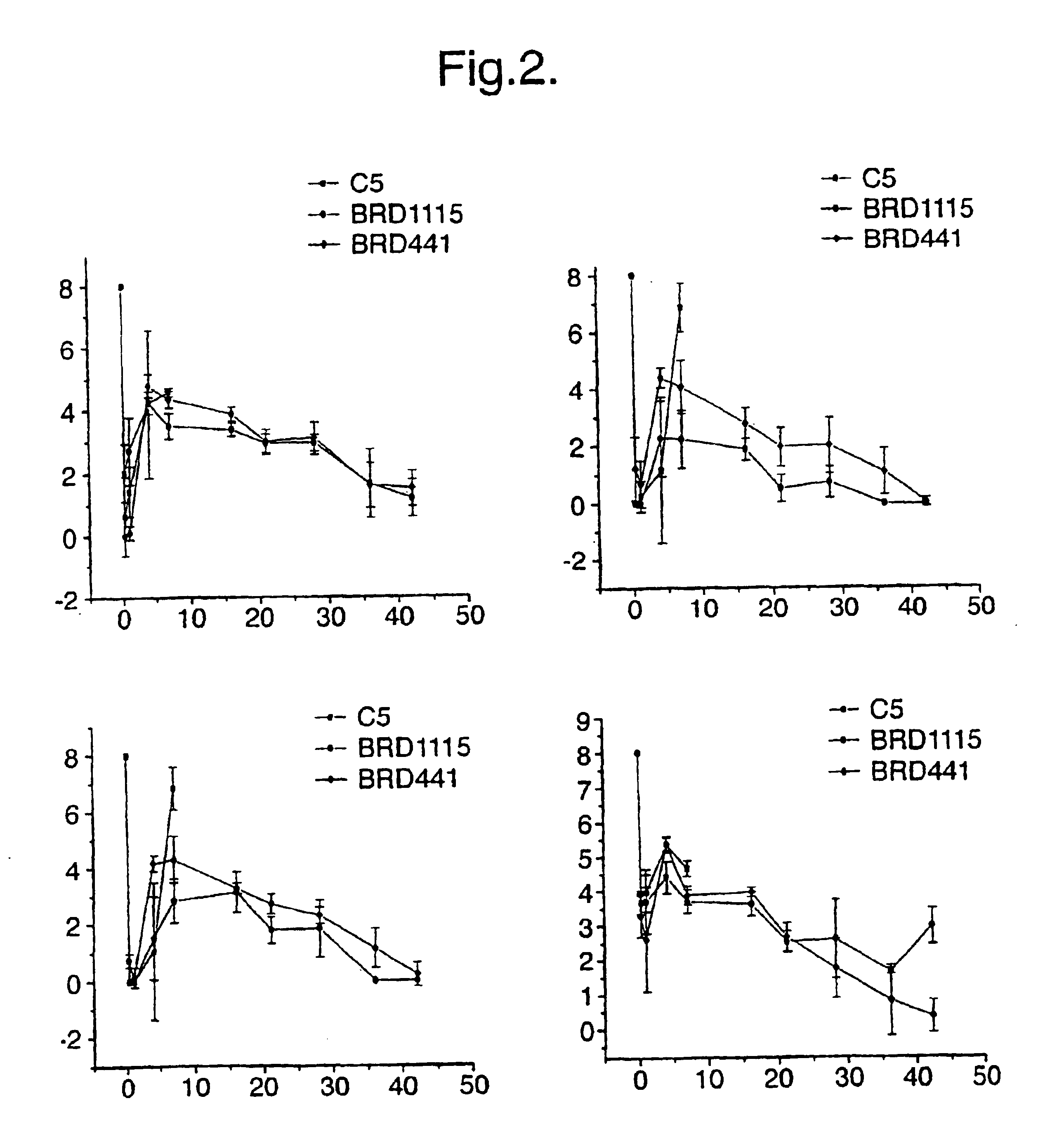
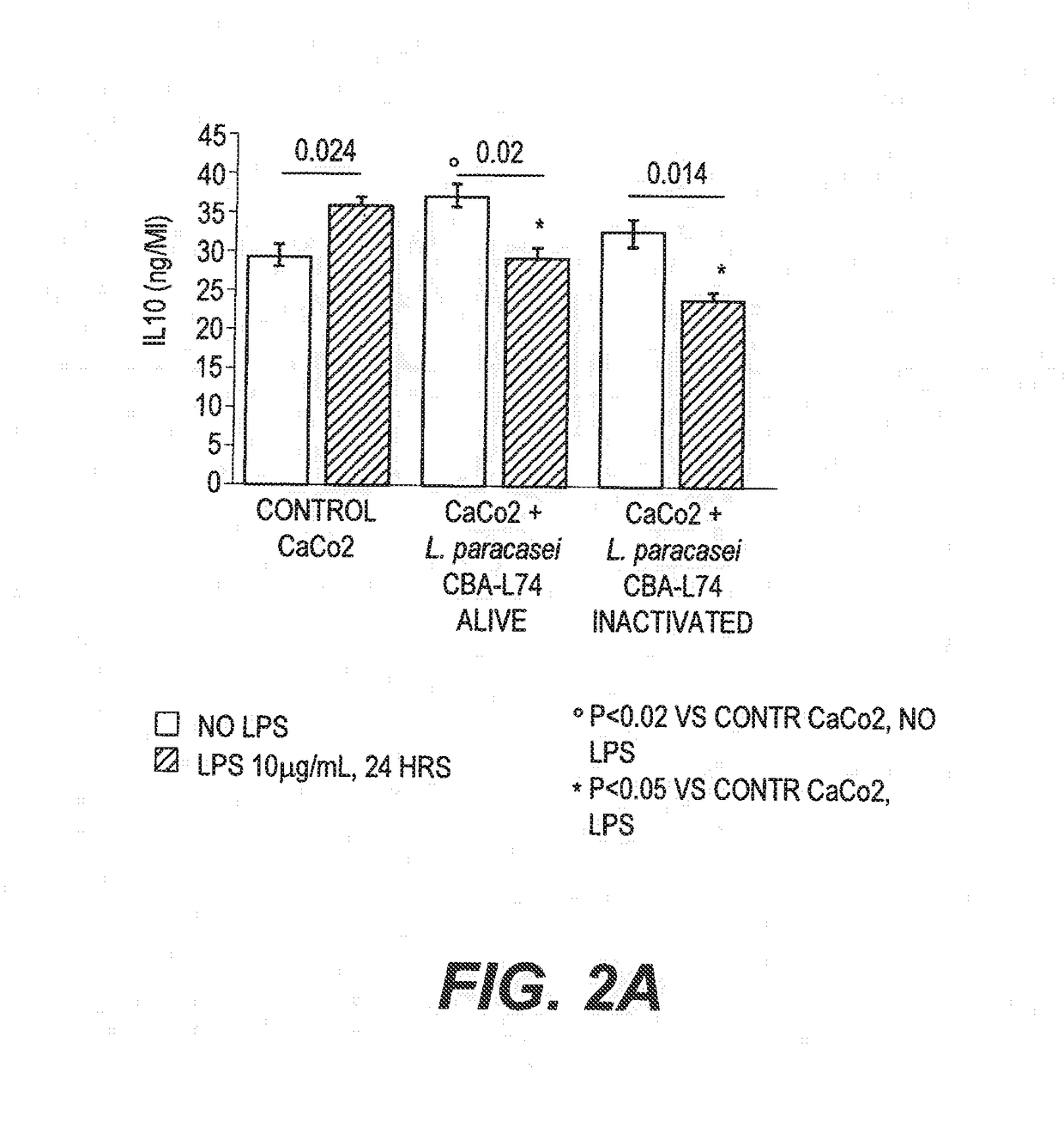
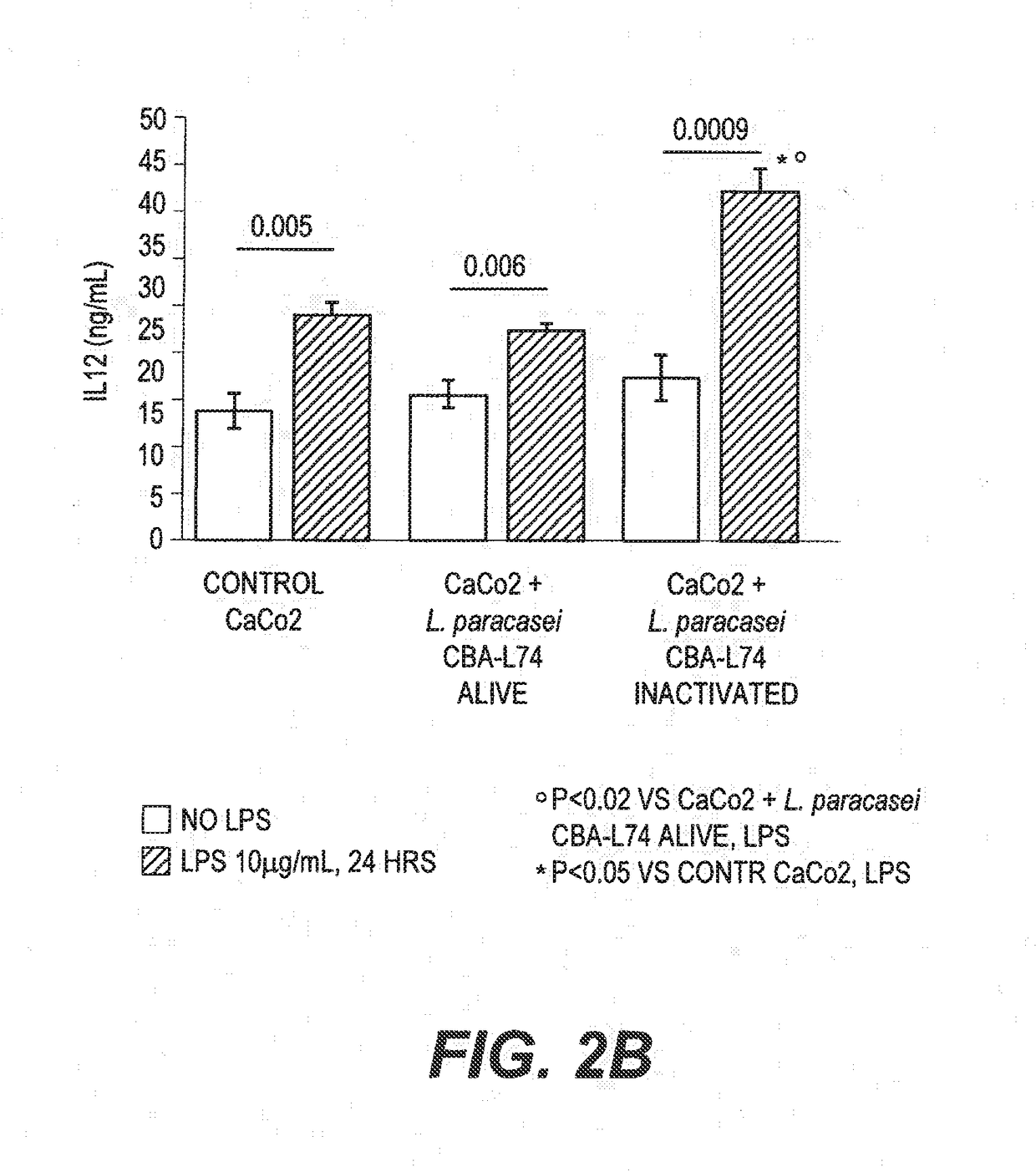
The present invention features compositions and methods for modulation of the mucosal immune system. The compositions include foods fermented by the probiotic organism, Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 (International Depository Accession Number LMG P-24778). Alternatively the compositions can include L. paracasei CBA L74 and a physiologically acceptable carrier. In some embodiments, the L. paracasei CBA L74 can be non-replicating. The compositions can be administered to a subject having or at risk for gastrointestinal disorders related to immaturity of the immune system, infection or disease.
Owner:H J HEINZ COMPANY BRANDS
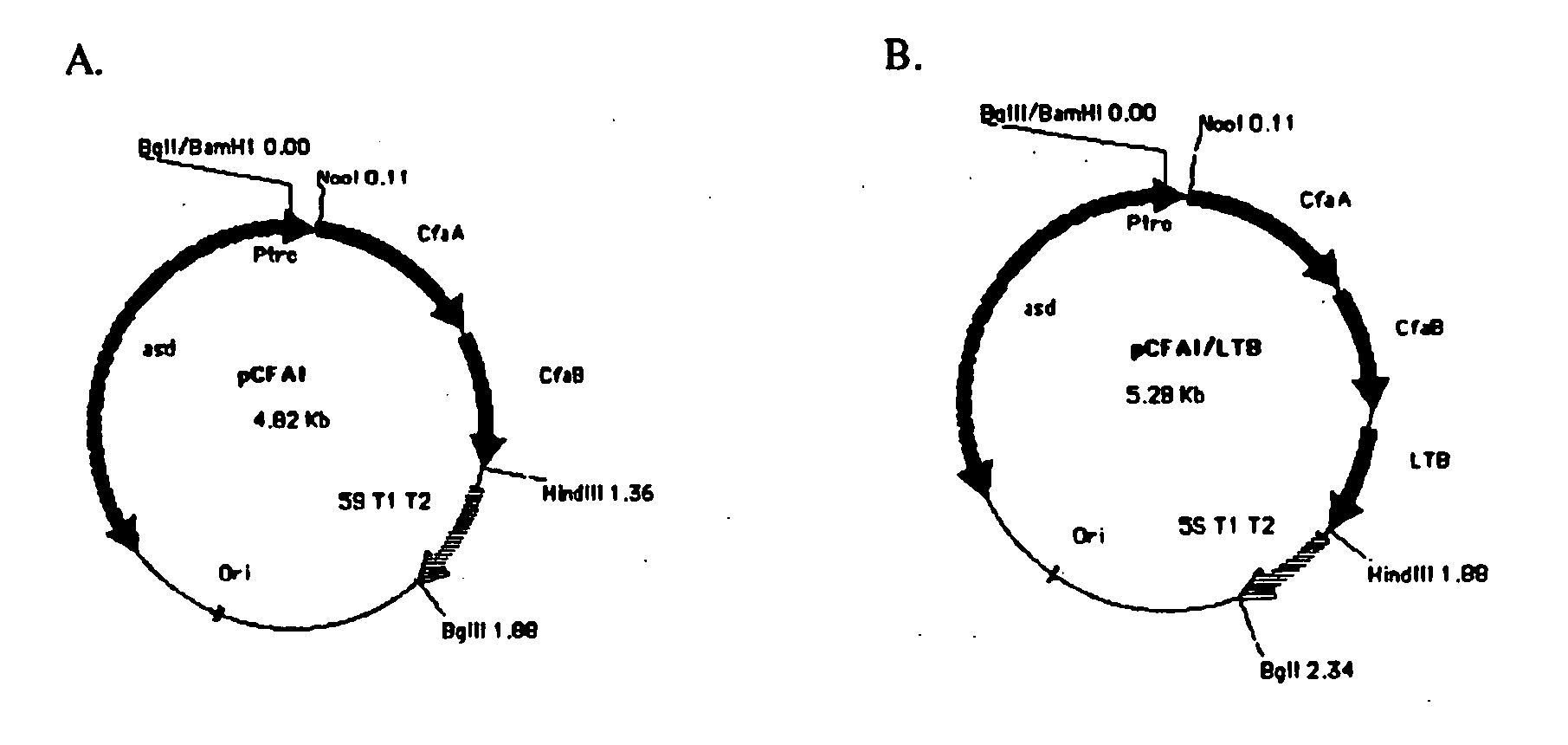
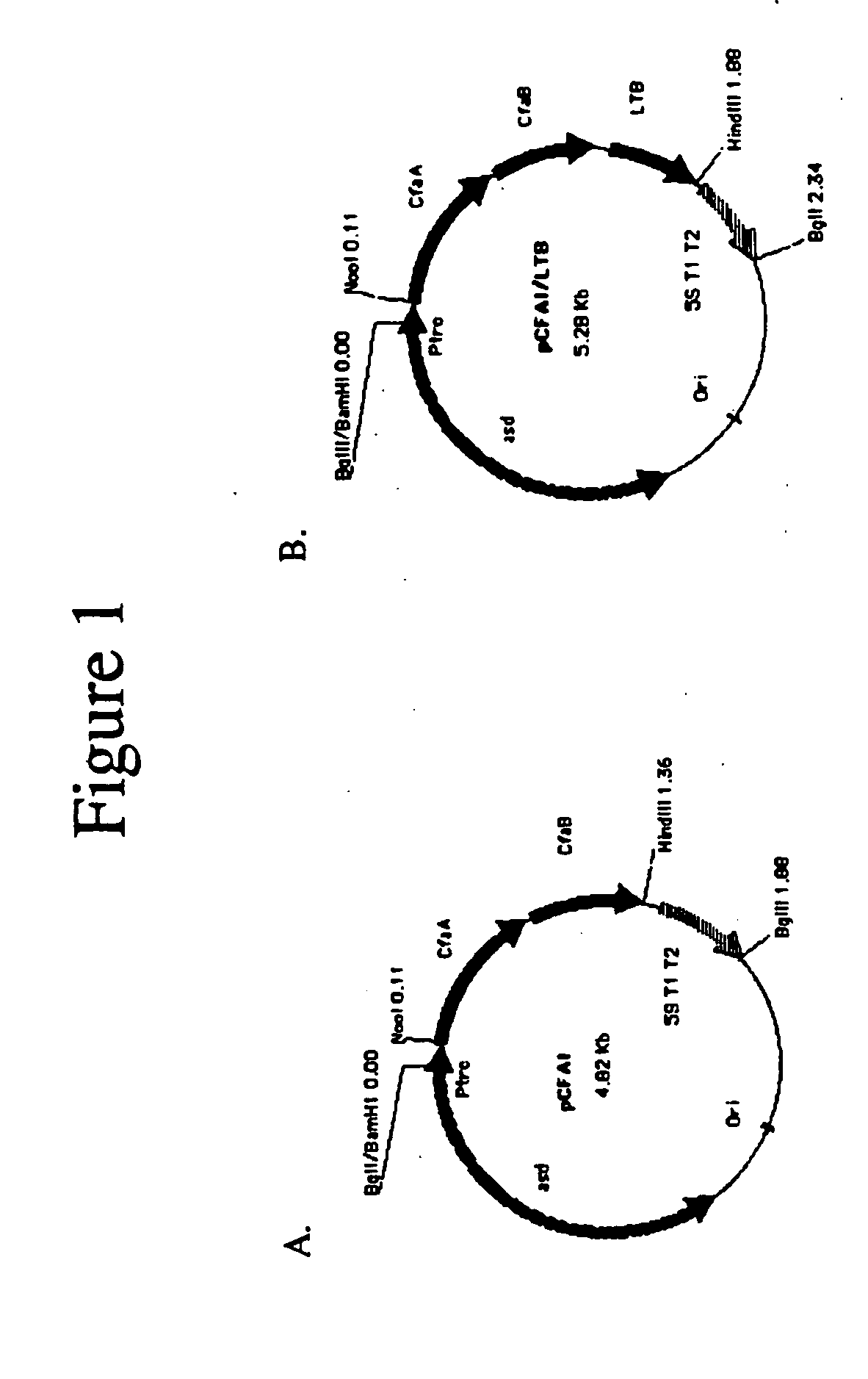
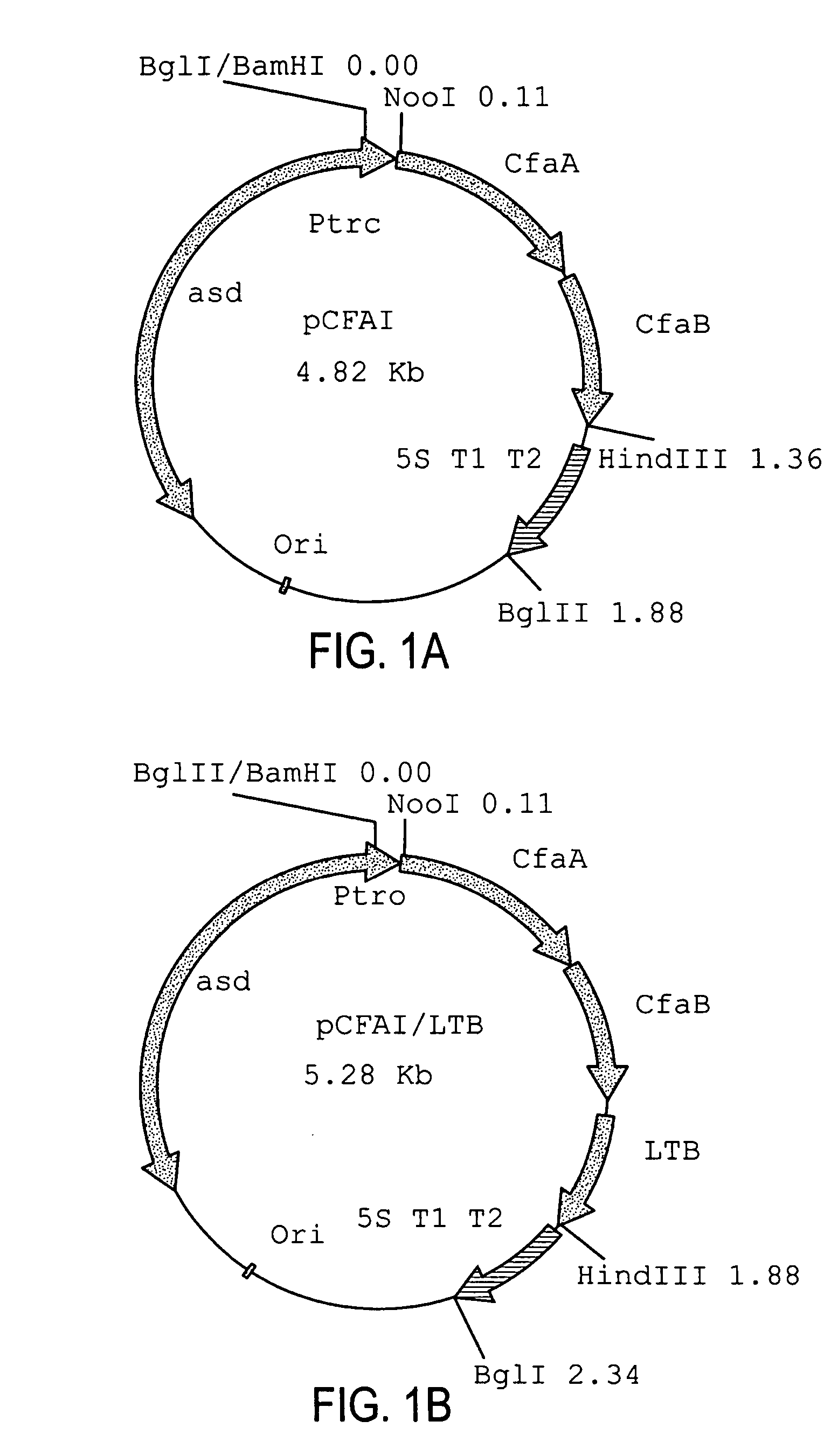
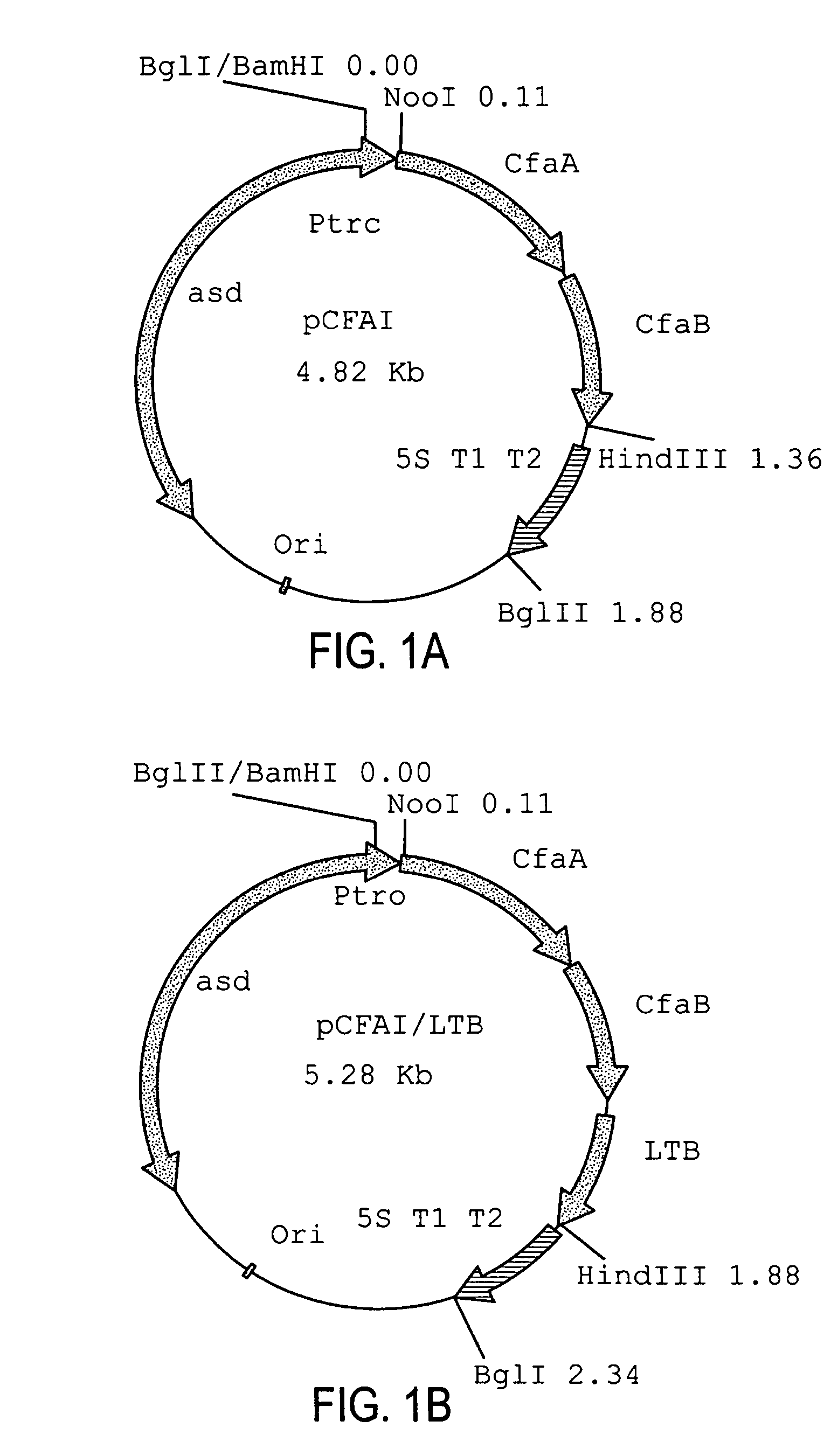
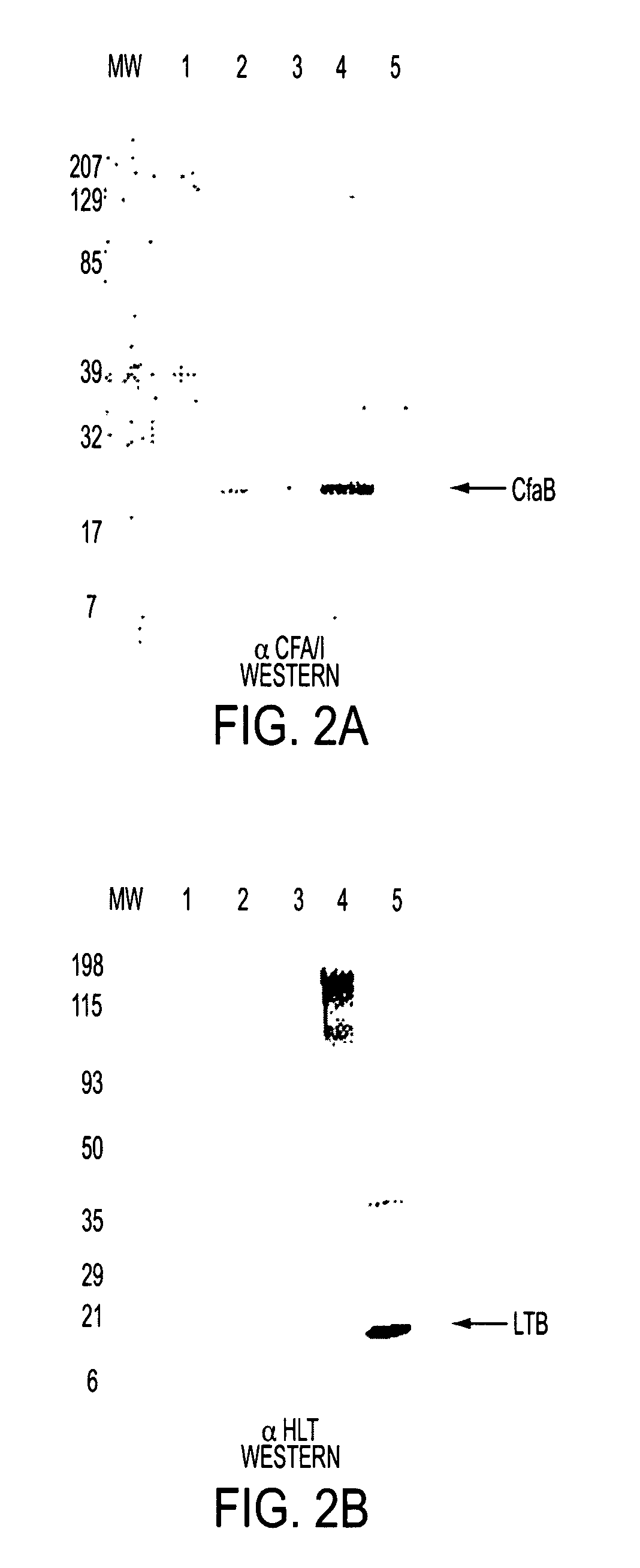
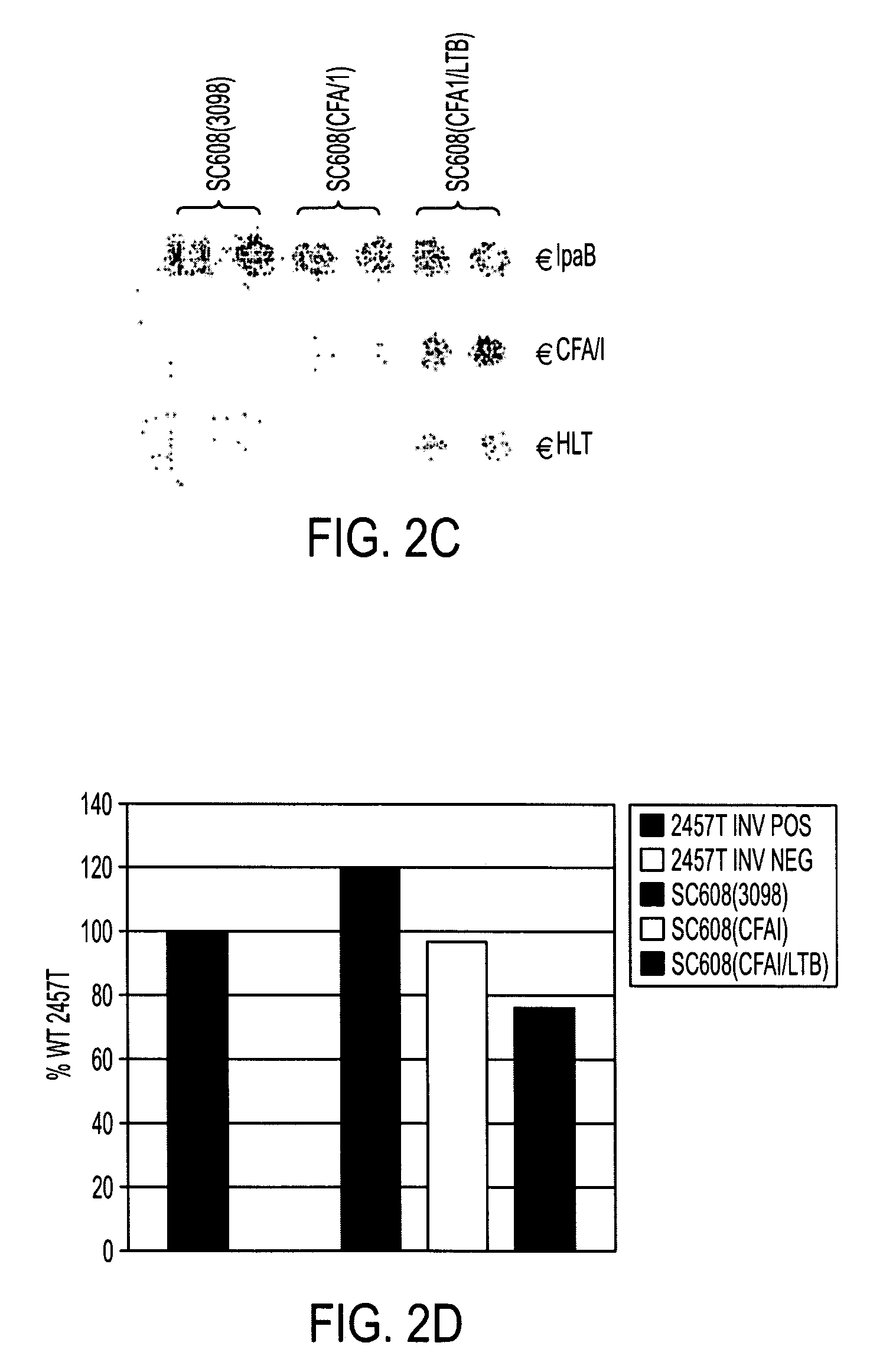
Construction of live attenuated Shigella vaccine strains that express CFA/I antigens (cfaB and CfaE) and the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) from enterotoxigenic E.coli
ActiveUS20070237791A1Reduce intrusionBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousMucosal Immune Responses
With the goal of creating a combination vaccine against Shigella and other diarrheal pathogens we have constructed a prototype vaccine strain of Shigella flexneri 2a (SC608) that can serve as a vector for the expression and delivery of heterologous antigens to the mucosal immune system. SC608 is an asd derivative of SC602, a well-characterized vaccine strain, which has recently undergone several phase 1 and 2 trials for safety and immunogenicity. Using non-antibiotic asd-based plasmids, we have created novel constructs for the expression of antigens from enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC), including CFA / I (CfaB and CfaE) and the B-subunit from heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) in Shigella vaccine strain SC608. Heterologous protein expression levels and cellular localization are critical to immune recognition and have been verified by immunoblot analysis. Following intranasal immunization (SC608(CFAI) and SC608(CFAI / LTB) of guinea pigs, serum IgG and IgA immune responses to both the Shigella LPS and ETEC antigens can be detected by ELISA. In addition, ELISPOT analysis for ASCs from cervical lymph nodes and spleen showed similar responses. All vaccine strains conferred high levels of protection against challenge with wild-type S. flexneri 2a using the Sereny test. Furthermore, serum from guinea pigs immunized with SC608 expressing CfaB and LTB contained antibodies capable of neutralizing the cytological affects of heat-labile toxin (HLT) on Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells. These initial experiments demonstrate the validity of a multivalent invasive Shigella strain that can serve as a vector for the delivery of pathogen-derived antigens.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Mucosal immunogenic substances comprising a polyinosinic acid - polycytidilic acid based adjuvant
InactiveUS20070166239A1Enhance immune responseImprove responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesAdjuvant
The present invention provides a polynucleotide adjuvant composition and methods of use in eliciting an immune response, in particular a mucosal immune response. The present invention also provides an immunogenic composition comprising the polynucleotide adjuvant composition together with other immunogenic compositions such as an antigen (e.g., as in a vaccine). The present invention further contemplates methods of use of such adjuvant compositions, particularly in eliciting an immune response, in particular a mucosal immune response to an antigenic compound.
Owner:YISHENG BIOPHARMA SINGAPORE
Influenza oral tablet vaccine, influenza oral slow-release vaccine and preparation methods thereof
ActiveCN101524537AImprove immunityEasy to useInorganic non-active ingredientsAntiviralsMucosal Immune ResponsesAdditive ingredient
The invention provides high-efficiency low-cost influenza oral tablet vaccine and influenza oral slow-release vaccine which can be produced in large amount and preparation methods thereof, relating to a novel influenza oral tablet or oral slow-release vaccine preparation suitable for oral administration and preparation processes thereof and comprising preparation of virus seed banks, production and preparation of vaccine stock solution, addition and freeze-drying of protective agents and excipients, ingredients of the oral tablet or oral slow-release preparation, forming processes and the like. The preparation method refers to that of whole-virus inactivated vaccines, split vaccines and subunit vaccines. The influenza oral vaccine can avoid pains and discomfort caused by injection, imitate route of natural infection, ensure that most surface areas of the mucosa contact the vaccine and arouse mucosal immune response and systemic immune response. As the vaccines are unnecessary to be produced under extremely strict conditions, the cost is lowered, thus relatively reducing the expenses needed due to increase of the amount of required antigens. The oral vaccine is convenient in use and does not need special personnel for inoculation and is convenient for storage and transportation.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHUA BIOLOGICAL PROD
Methods and compositions for modulating heterotypic E-cadherin interactions with T lymphocytes
InactiveUS7029676B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMucosal Immune ResponsesMonoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for modulating the heterotypic adhesion between E-cadherin expressing cells and T lymphocytes. Monoclonal antibodies which specifically bind to E-cadherin and isolated peptides which mimic the binding function of E-cadherin also are provided. The antibodies and peptides are useful in screening assays to identify pharmaceutical lead compounds which are capable of modulating adhesion between T lymphocytes and E-cadherin expressing cells. Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for modifying the mucosal immune response of a subject also are provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Streptococcus suis type 2 10-gene-deleted strain and application
ActiveCN106085936AWith cross protectionAvoid side effectsAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesOral medication
The invention discloses a streptococcus suis type 2 10 gene-deleted strain and application. The strain is obtained by knocking out 10 genes on the basis of a streptococcus suis type 2 virulent strain, and the preservation serial number is CCTCC NO: M 2015800. The virulence of the strain is significantly reduced compared with that of the parent strain, safety is high, immunogenicity is high, and immunized mice can be protected against the attack of the streptococcus suis type 2 virulent strain after being immunized in an injection or nasal drip or oral administration mode, which shows that the vaccine can effectively activate the mucosal immune system and systemic immunology of a host; meanwhile, a cross protection function on streptococcus suis type 2 virulent strains of different ST types can also be achieved. The vaccine is simple in preparation method and suitable for industrial production; meanwhile, the immunogenicity of the mutant strain is similar to that of a wild virulent strain, and thus the mutant strain can be applied to the development of rapid reagent kits as a standard substance or a whole-cell antigen.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Campylobacter jejuni chitose nano DNA vaccine and preparation method and use thereof
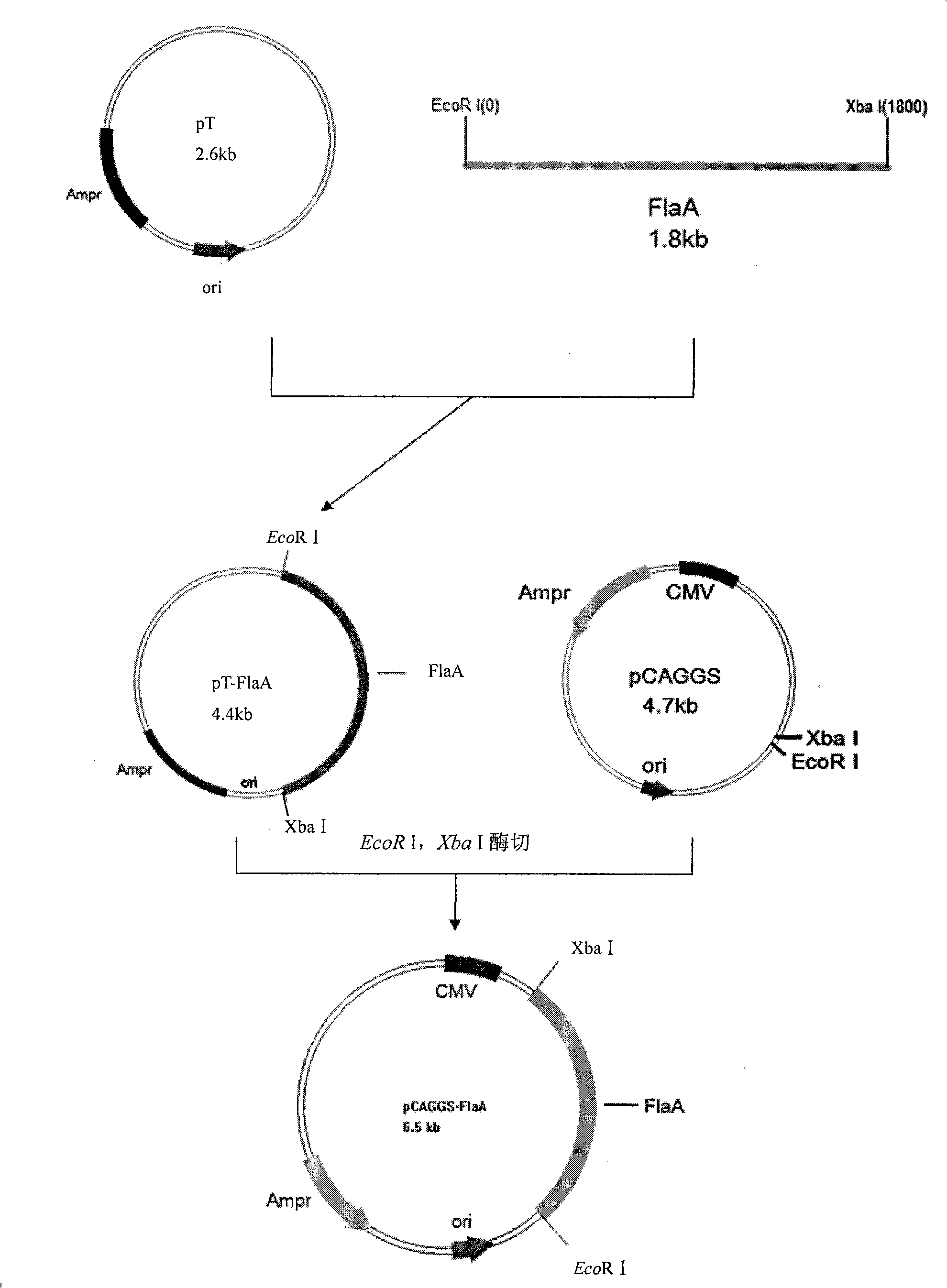
InactiveCN101332304AWeakened immunityImmune challengeAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesCloaca
The invention relates to a campylobacter jejuni chitosan nanometer DNA vaccine, a preparation method and application thereof. The campylobacter jejuni chitosan nanometer DNA vaccine is a nano-microcapsule composed of a chitosan and a recombinant plasmid; the recombinant plasmid is a pCAGGS-flaA which consists of a campylobacter jejuni flagellin gene flaA and a eukaryotic expression vector; the flagellin gene flaA has a nucleotide sequence showed by an SEQ NO.1. The campylobacter jejuni chitosan nanometer DNA vaccine is made by dissolving the constructed recombinant plasmid in chitosan solution; the vaccine can also be used for preparing the drugs for preventing chicken campylobacter jejuni. Tests prove that the vaccine can stimulate to produce specific humoral and local mucosal immune response; after oral challenge, the cloaca bacteria exhausting rate shows a significant declining trend, and the number of the campylobacter jejuni in blood, small intestine, large intestine and caecum can be decreased.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Health food suiting child dinners and having immunity enhancing function
ActiveCN101999578ASimple structureImprove developmentFood preparationMucosal Immune ResponsesFood science
The invention discloses a health food suiting child dinners and having the immunity enhancing function. The health food is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 15-100 parts of yam, 15-100 parts of tuckahoe, 12-90 parts of hawthorn, 12-90 parts of malt, 12-90 parts of mushroom, 10-80 parts of white fungus and 2-40 parts of oligo fructose. The invention is characterized in that traditional Chinese medical herbs in homology of medicine and food are carefully chosen to prepare the prescription capable of replenishing qi to invigorate the spleen and regulate the stomach to enhance the immunity, and the prebiotics (the oligo fructose) is added to the prescription to proliferate beneficial bacteria, optimize the child gastrointestinal microbial community structure and promote the development of the child intestinal mucosal immune system so as to synchronously enhance the child immunity in dual paths.
Owner:INFINITUS (CHINA) CO LTD
Use of coccidian
ActiveUS8142771B2Useful complement to the eukaryotic expression systemIncrease conversionsSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideMucosal Immune ResponsesImmune tolerance
The present invention provides a novel use of coccidian, specifically relates to the use of coccidian as a vaccine live vector. The present invention further provides a live vaccine with coccidian as a vector, which is transgenic coccidian capable of expressing exogenous protein or stably transfected coccidian that contain expression vector and can express exogenous coccidian. The present coccidian vector live vaccine can induce organisms to simultaneously generate protective humoral and cellular immune responses (including the mucosal immune response), as well as generate memory responses, which can be readily carried out and has stable effect and high biological safety without generating immune tolerance.
Owner:SUO XUN +7
Vaccines containing attenuated bacteria
InactiveUS6905691B1Easy to foldIncidenceBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaMucosal Immune ResponsesBacteroides
The invention relates to a vaccine comprising a bacterium attenuated by a non-reverting mutation in a gene encoding a protein which promotes folding of extracytoplasmic proteins. Such mutations were initially identified as being useful in vaccines from a bank of randomly inserted, transposon mutants in which attenuation was determined as a reduction in virulence of the organism in the mouse model of infection. Site directed mutation of the gene results in a strain which shows at least 4 logs of attenuation when delivered both orally and intravenously. Animals vaccinated with such a strain are protected against subsequent challenge with the parent wild type strain. Finally, heterologous antigens such as the non-toxic and protective, binding domain from tetanus toxin, fragment C, can be delivered via the mucosal immune system using such strains of bacteria. This results in the induction of a fully protective immune response to subsequent challenge with native tetanus toxin.
Owner:CELLTECH PHARMA EURO
Probiotic Compositions And Methods
The present application relates to compositions and methods for modulation of the mucosal immune system. The compositions include foods fermented by the probiotic organism, Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 (International Depository Accession Number LMG P-24778). Alternatively, the compositions can include L. paracasei CBA L74 and a physiologically acceptable carrier. In some embodiments, the L. paracasei CBA L74 can be non-replicating. The compositions can be administered to a subject having or at risk for gastrointestinal disorders related to immaturity of the immune system, infection or disease.
Owner:H J HEINZ COMPANY BRANDS
Vaccine for blocking transmission of echinococcosis pathogeny echinococcus granulosus from source
ActiveCN107510841AIncreased serum titerImprove immunityBacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesMycobacterium smegmatis
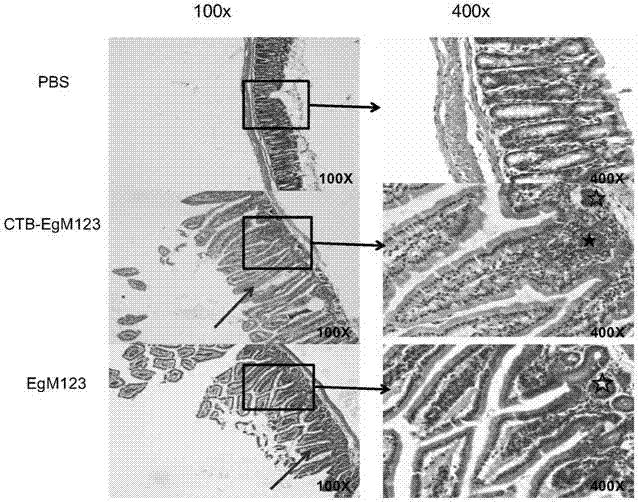
The invention discloses a vaccine for blocking transmission of echinococcosis pathogeny echinococcus granulosus from a source. The vaccine provided by the invention is a CTB-EgM123 vaccine or a complete set of vaccine consisting of the CTB-EgM123 vaccine and a subunit vaccine of an EgM123 protein recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis vaccine. An active ingredient of the CTB-EgM123 vaccine is a fusion protein formed by fusion of a cholera toxin B subunit and an echinococcus granulosus EgM123 protein; the active ingredient of the EgM123 protein recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis vaccine can express the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis of the echinococcus granulosus EgM123 protein. The vaccine provided by the invention can stimulate the immune response in a host, improves the immune level of the host, enhances the intestinal mucosal immune response, and plays an important protective role in resisting infection of echinococcosis.
Owner:THE FIRST TEACHING HOSPITAL OF XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIVERCITY +1
Vaccine composition
ActiveUS9498527B2Efficient inductionSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesWhole body
An intraorally administrable vaccine composition useful to be a preventive or therapeutic agent for infectious diseases, and effectively induces a systemic immune response or a mucosal immune response is provided. A vaccine composition for administration to the oral cavity of a human or an animal, the vaccine composition containing at least one antigen derived from an infectious disease, and at least one selected from the group consisting of a toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) agonist, a toll-like receptor 2 / 6 (TLR2 / 6) agonist, and cyclic dinucleotide, or a derivative or salt thereof.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Immunogenic Substances Comprising A Polyinosinic Acid-Polycytidilic Acid Based Adjuvant
InactiveUS20090175902A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesAdjuvant
The present invention provides a polynucleotide adjuvant (PICKCa) composition and methods of use in eliciting an immune response, in particular a mucosal immune response. The polynucleotide adjuvant comprises of a polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid (PIC), at least one antibiotic and at least one positive ion. The present invention also provides an immunogenic composition comprising the polynucleotide adjuvant composition together with other immunogenic compositions such as an antigen (e.g., as in a vaccine) selected from viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic and / or cancer antigens. The present invention further contemplates methods of use of such adjuvant compositions, particularly in eliciting an immune response, in particular a mucosal immune response to an antigenic compound.
Owner:YISHENG BIOPHARMA SINGAPORE
Mucosal vaccine composition
InactiveUS20160213773A1Safe and effectiveSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesXanthomonas
The present invention aims at providing a vaccine composition capable of being administered to an intraoral mucous membrane, ocular mucous membrane, ear mucous membrane, genital mucous membrane, pharyngeal mucous membrane, respiratory tract mucous membrane, bronchial mucous membrane, pulmonary mucous membrane, gastric mucous membrane, enteric mucous membrane, or rectal mucous membrane, that is safe, useful as a prophylactic or therapeutic agent for infectious diseases or cancers, and capable of effectively inducing the systemic immune response and mucosal immune response. The present invention provides a mucosal vaccine composition to be administered to at least one mucous membrane selected from the group consisting of a human or animal intraoral mucous membrane, ocular mucous membrane, ear mucous membrane, genital mucous membrane, pharyngeal mucous membrane, respiratory tract mucous membrane, bronchial mucous membrane, pulmonary mucous membrane, gastric mucous membrane, enteric mucous membrane, and rectal mucous membrane, the mucosal vaccine composition containing: at least one antigen; and as an adjuvant, a lipopolysaccharide derived from at least one gram-negative bacterium selected from the group consisting of Serratia, Leclercia, Rahnella, Acidicaldus, Acidiphilium, Acidisphaera, Acidocella, Acidomonas, Asaia, Belnapia, Craurococcus, Gluconacetobacter, Gluconobacter, Kozakia, Leahibacter, Muricoccus, Neoasaia, Oleomonas, Paracraurococcus, Rhodopila, Roseococcus, Rubritepida, Saccharibacter, Stella, Swaminathania, Teichococcus, Zavarzinia, Pseudomonas, Achromobacter, Bacillus, Methanoculleus, Methanosarcina, Clostridium, Micrococcus, Flavobacterium, Pantoea, Acetobacter, Zymomonas, Xanthomonas, and Enterobacter, or a salt thereof, wherein a mass ratio between the adjuvant and the antigen (total mass of the adjuvant / total mass of the antigen) is 0.002 to 500.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain capable of stably expressing porcine rotavirus VP4 protein and preparation method of lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain
InactiveCN107988130AImproving immunogenicityBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesVp4 gene
The invention discloses a lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain capable of stably expressing porcine rotavirus VP4 protein and a preparation method of the lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain. The vaccine strain is obtained through the following steps: on the basis of lactobacillus casei with uracil phosphoribosyl transferase, UPP gene deleted, the porcine rotavirus VP4 gene is inserted between a termination codon and a terminator of the neuronspecificenoluse gene of lactobacillus casei through homologous recombination, and the vaccine strain is not provided with an antibiotic selection marker. The experiment proves that after the constructed lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain capable of stably expressing the porcine rotavirus VP4 proteinis used for immunizing animals through oral administration, the local mucosal immune response can be induced, the mucous membrane antibody IgA is generated, the body is induced to generate humoral immune response, the serum antibody IgG is then generated, good immunogenicity is displayed, and the constructed lactobacillus gene engineering vaccine strain not labelled by antibiotic resistance accords with the development concept of 'no pollution and environmental protection' of veterinary vaccines.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Novel bacterial species
ActiveUS20190183941A1Sure easyQuick upgradeAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderDiseaseMucosal Immune Responses
A novel Akkermansia species has been isolated from fresh faeces obtained from the reticulated python. The species has been named Akkermansia glycaniphilus. It is capable of growing on mucus as a sole carbon and nitrogen source. The species can be used as a medicament, probiotic or cosmetic, e.g., for promoting weight loss, for promoting gut mucosal immune system function, for maintaining, restoring and / or increasing the physical integrity of the gut mucosal barrier, and for prevention or treatment of a variety of associated diseases or disorders.
Owner:WAGENINGEN UNIV
Mucosal immunogenic substances comprising a polyinosinic acid - polycytidilic acid based adjuvant
InactiveUS20090311334A1Enhance immune responseImprove responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesAdjuvant
The present invention provides a polynucleotide adjuvant (PICKCa) composition and methods of use in eliciting an immune response, in particular a mucosal immune response. The polynucleotide adjuvant comprises of a polyriboinosinic-polyri-bocytidylic acid (PIC), at least one antibiotic and at least one positive ion. The present invention also provides an immunogenic composition comprising the polynucleotide adjuvant composition together with other immunogenic compositions such as an antigen (e.g., as in a vaccine). The present invention further contemplates methods of use of such adjuvant compositions, particularly in eliciting an immune response, in particular a mucosal immune response to an antigenic compound.
Owner:YISHENG BIOPHARMA SINGAPORE
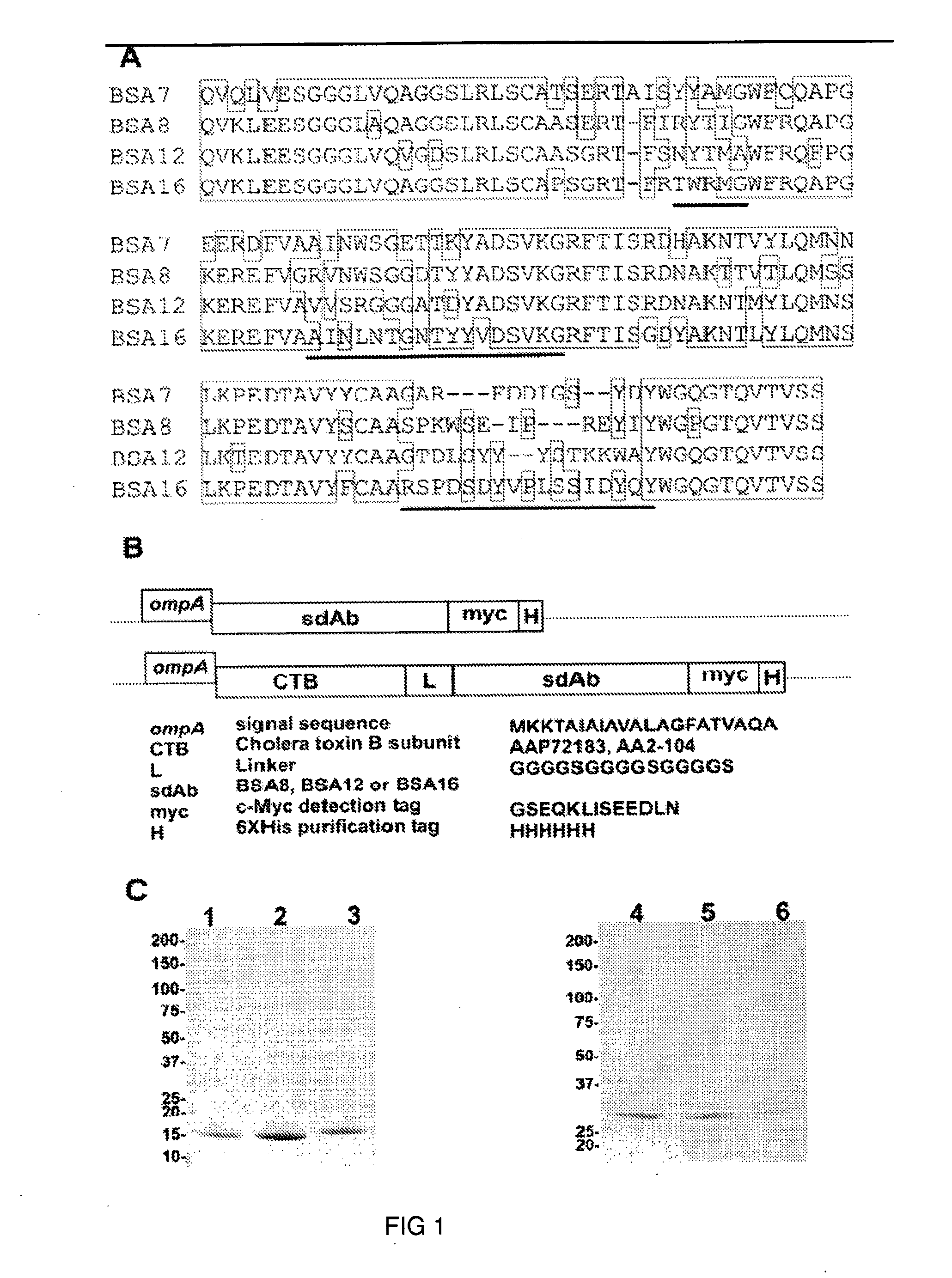
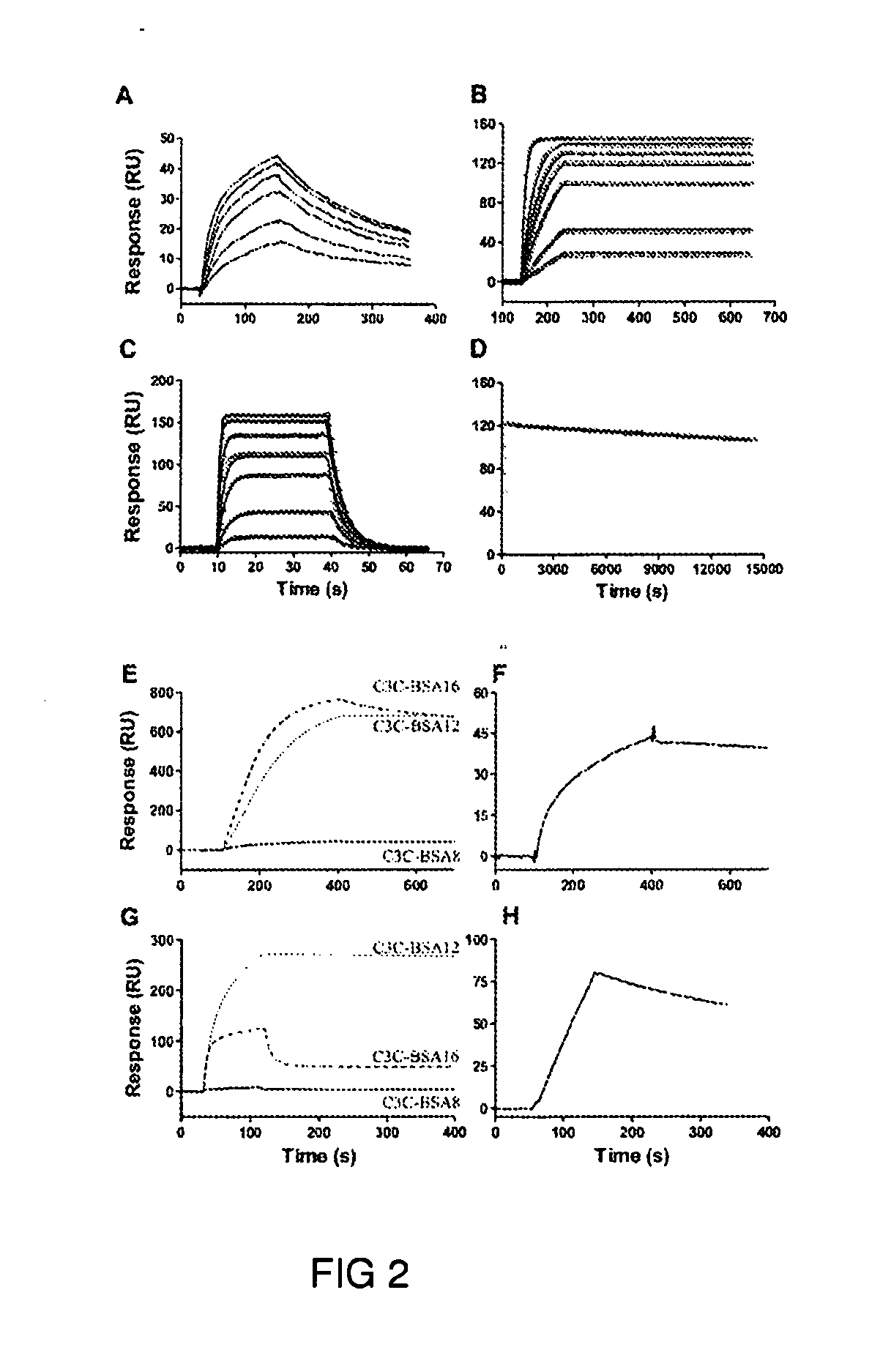
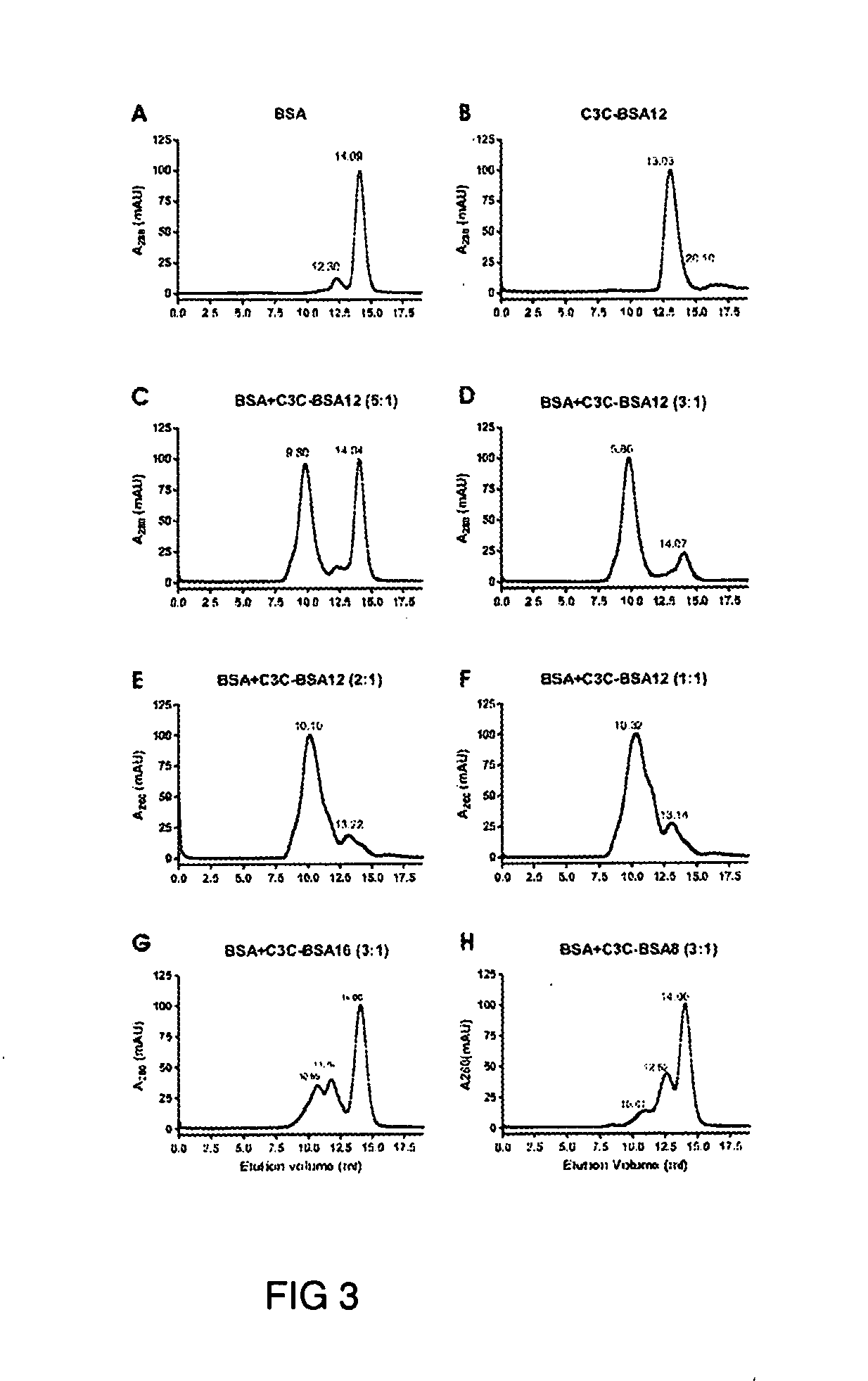
Induction of mucosal immune responses by mucosal delivery pentabody complex (MDPC)
InactiveUS20110318348A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesPentamer
The subject invention provides, for example, a novel approach to specifically induce intranasal and / or oral mucosal as well as humoral antibody response by administrating a mucosal delivery pentabody complex (MDPC). The MDPC is a complex formed by mixing a target antigen and a mucosal delivery pentabody (MDP) that has a strong affinity to the target antigen. The MDP is a fusion protein of a single domain antibody (sdAb; which binds to the target antigen specifically) to a pentamerization domain (which can include the B-subunit of an AB5 toxin family, including the B subunit of cholera toxin (CT) or heat-labile toxin (LT)). The pentamerization domain can self-assemble into a pentamer, through which a pentameric single domain antibody, or a pentabody, is formed.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Mucosal immunoadjuvant inducing Th1 immune response, and application thereof
InactiveCN103214554AStimulate Th1 type immune responseImprove immunityAntibody medical ingredientsHybrid peptidesBALB/cMucosal Immune Responses
The invention relates to a mucosal immunoadjuvant inducing Th1 immune response. A bioinformatics technology is applied in the invention, the spatial conformation of a ricin B-chain monoclonal anti-3E1 and Ricin-B compound which has obtained a Chinese invention patent is determined through the action of an antibody-antigen compound, and a molecular stimulation technology is utilized to reasonably determine four Ricin B identifying active regions of 3E1 and derive four nucleotide sequences. Four GFP-nRTB fusion proteins are obtained through a molecular cloning technology. Results of experiments that the four proteins are used to immunize BALB / C mice through a sublingual way three times show that a P1-GFP protein in the four proteins excites Th1 immune response, and a high-level IgG2a antibody is generated. The capability and the possible molecular mechanism of the targeting GFP mucosal immune response of the P1-GFP protein are discussed. The mucosal immunoadjuvant inducing Th1 immune response, which is screened through the above scheme, can be used for preparing vaccines, immunomodifiers or treatment medicines.
Owner:PLA NAVY GENERAL HOSIPTAL
Preparation method of classical swine fever spleen-lymph-sourced compound living vaccine
InactiveCN104888213AEnhance humoral immunityBreak through interferenceOrganic active ingredientsAnthropod material medical ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesMaternal antibody
The invention relates to a preparation method of a classical swine fever spleen-lymph-sourced compound living vaccine and belongs to the technical field of veterinary biological products. The preparation method of the classical swine fever spleen-lymph-sourced compound living vaccine comprises the following process steps: selecting a domestic rabbit to be inoculated; inoculating; measuring the temperature and observing; harvesting; preparing virus suspension and inspecting; carrying out mixed adsorption on the harvested full-suspension virus bulk and chicken anti-hog cholera virus egg yolk antibody; and adding freezing and drying protecting agent containing an immunopotentiator into antigen antibody compound obtained through adsorption, carrying out split charging, freezing, and carrying out vacuum drying, so that the classical swine fever spleen-lymph-sourced compound living vaccine is obtained. By adopting the preparation method of the classical swine fever spleen-lymph-sourced compound living vaccine, an antibody acquiring route is simple, animal welfare can be improved, manpower and material resources are saved, production cost is greatly reduced, humoral immunity of the living vaccine can be greatly improved, and high neutralizing antibodies can be produced; and the classical swine fever spleen-lymph-sourced compound living vaccine can be applied to piglet immunization, maternal antibody interference can be avoided, no interference is produced to other vaccines, especially a mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccine and the like, after the classical swine fever spleen-lymph-sourced compound living vaccine is applied to piglets, and strong mucosal immune response can be induced, so that protection rate is improved.
Owner:浙江美保龙生物技术有限公司
Construction of live attenuated Shigella vaccine strains that express CFA/I antigens (CfaB and CfaE) and the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) from enterotoxigenic E. coli
ActiveUS7759106B2Reduce intrusionBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousMucosal Immune Responses
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Methods for inducing an immune response via oral administration of an adenovirus
The present invention provides a method for inducing an immune response to an adenovirus in a subject which has been pre-exposed to an adenovirus or adenoviral vector. The invention further provides a method for inducing a mucosal immune response to an antigen. The methods of the invention are carried out by oral administration of adenoviral vectors.
Owner:WISTAR INST THE A CORP OF PA
Replication-defective recombinant influenza virus for simultaneously expressing HA and HEF
ActiveCN109097341AGood gene stabilityNot pathogenicSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesHemagglutinin
The invention provides a preparation method of a replication-defective A and D divalent influenza virus attenuated live vaccine. The invention constructs a recombinant virus strain; on the premise ofnot changing gene stability, the constructed recombinant virus can stably and simultaneously express surface protein hemagglutinin HA of A type influenza virus H1N1 subtype and unique surface proteinhemagglutinin esterase fusion protein HEF of D type influenza virus. The constructed attenuated strain has good gene stability and cannot be replicated in an experimental animal body, so the constructed attenuated strain has no pathogenicity; meanwhile, the constructed attenuated strain also can induce a body to produce strong mucosal immune response and cellular immune response level and keeps intense and durable immunogenicity. The key is that a vaccine candidate strain can produce an immunoprotection action on the A type influenza virus H1N1 subtype and the D type influenza virus. Therefore, the replication-defective A and D divalent influenza virus attenuated live vaccine has huge social significance in preventing and controlling A type and D type influenza.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Porcine rotavirus (PRV) VP fusion protein reconstruction body as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108359015AGut-piercing activityAvoid enteringPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaMucosal Immune ResponsesIntraperitoneal route
The invention discloses a porcine rotavirus (PRV) VP fusion protein reconstruction body as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The fusion protein VP8-VP7-TAT provided by the invention comprises truncation fragments VP8 and VP7 of a PRV coat shell structure protein VP4 and eleven core amino acids bonded to a TAT protein transduction peptide basic amino acid enrichment region at anend C. A mouse is immunized with the fusion protein VP8-VP7-TAT by means of intraperitoneal injection or oral intragastric administration, so that the organism can be effectively inducted to generatea humoral immune response and a mucosal immune response, and high immunogenicity is achieved. Through fusion expression of PRV proteins VP8, VP7 and TAT, a novel method is provided for the preventionof PRV infection, and a basis is laid for the development of a novel PRV oral vaccine.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Mucosal vaccine composition
ActiveUS20160193327A1Safe and effectiveSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsMucosal Immune ResponsesXanthomonas
The present invention aims at providing a mucosal vaccine composition that can be administered to an intraoral mucous membrane, ocular mucous membrane, ear mucous membrane, genital mucous membrane, pharyngeal mucous membrane, respiratory tract mucous membrane, bronchial mucous membrane, pulmonary mucous membrane, gastric mucous membrane, enteric mucous membrane, or rectal mucous membrane, that is useful as a prophylactic or therapeutic agent for infectious diseases or cancers, and is capable of safely and effectively inducing the systemic immune response and mucosal immune response. The present invention provides a mucosal vaccine composition to be administered to at least one mucous membrane selected from the group consisting of a human or animal intraoral mucous membrane, ocular mucous membrane, ear mucous membrane, genital mucous membrane, pharyngeal mucous membrane, respiratory tract mucous membrane, bronchial mucous membrane, pulmonary mucous membrane, gastric mucous membrane, enteric mucous membrane, and rectal mucous membrane, containing: at least one antigen; and as an adjuvant, a lipopolysaccharide derived from at least one gram-negative bacterium selected from the group consisting of Serratia, Leclercia, Rahnella, Acidicaldus, Acidiphilium, Acidisphaera, Acidocella, Acidomonas, Asaia, Belnapia, Craurococcus, Gluconacetobacter, Gluconobacter, Kozakia, Leahibacter, Muricoccus, Neoasaia, Oleomonas, Paracraurococcus, Rhodopila, Roseococcus, Rubritepida, Saccharibacter, Stella, Swaminathania, Teichococcus, Zavarzinia, Pseudomonas, Achromobacter, Bacillus, Methanoculleus, Methanosarcina, Clostridium, Micrococcus, Flavobacterium, Pantoea, Acetobacter, Zymomonas, Xanthomonas, and Enterobacter, or a salt thereof.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com