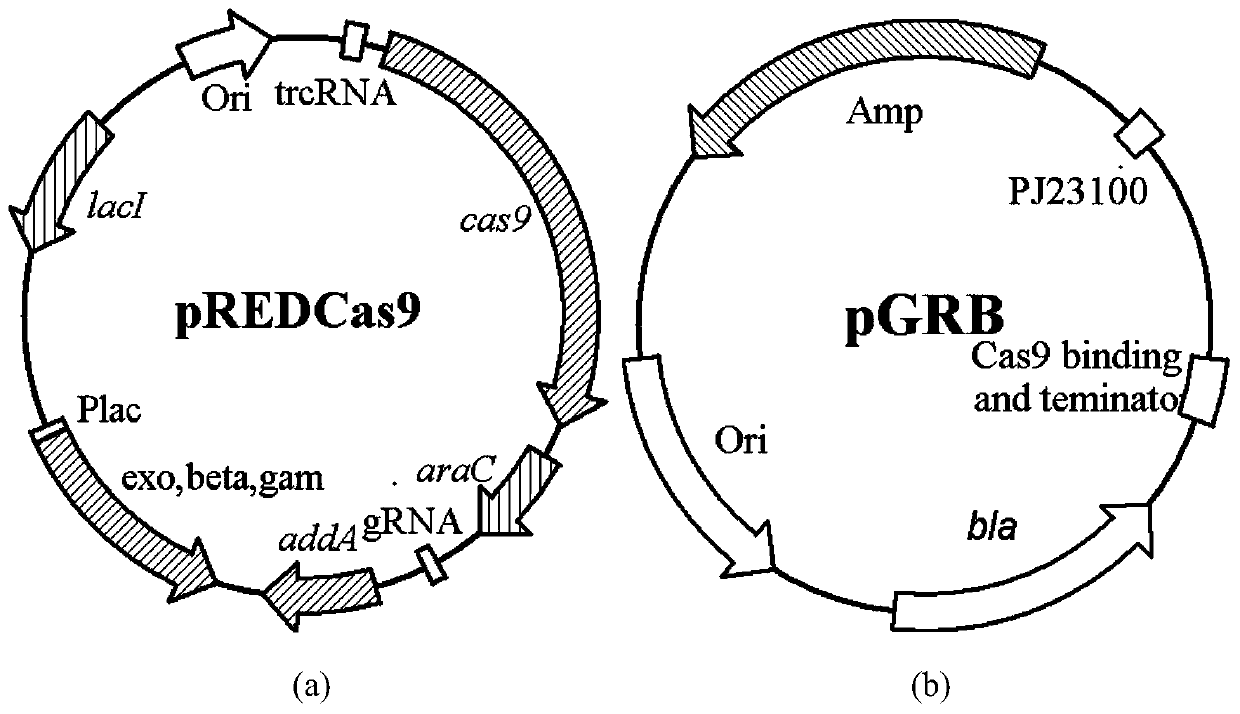
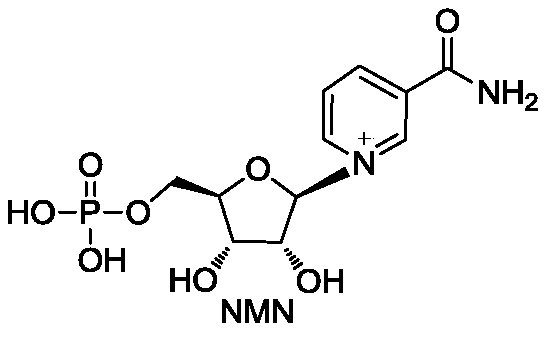
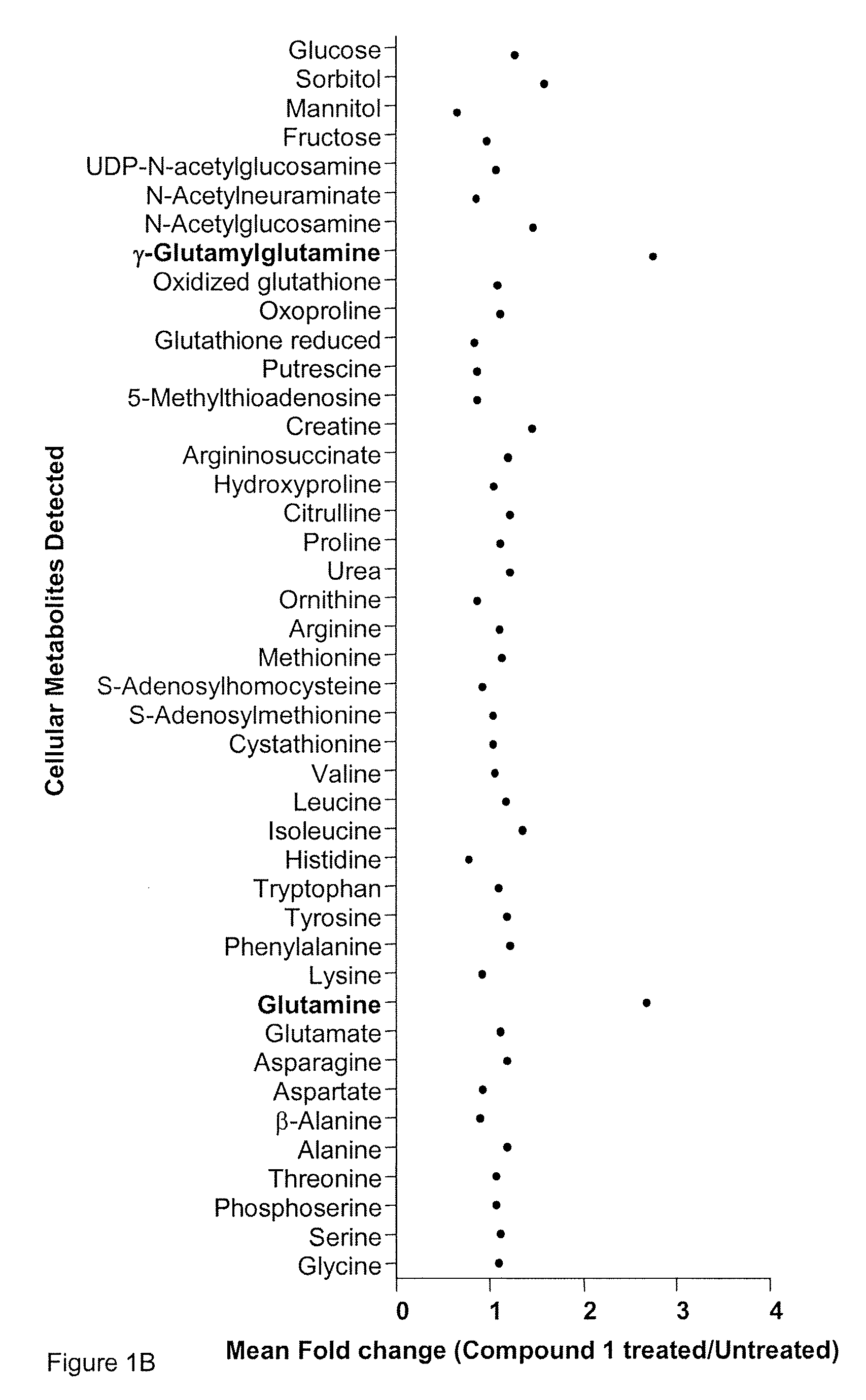
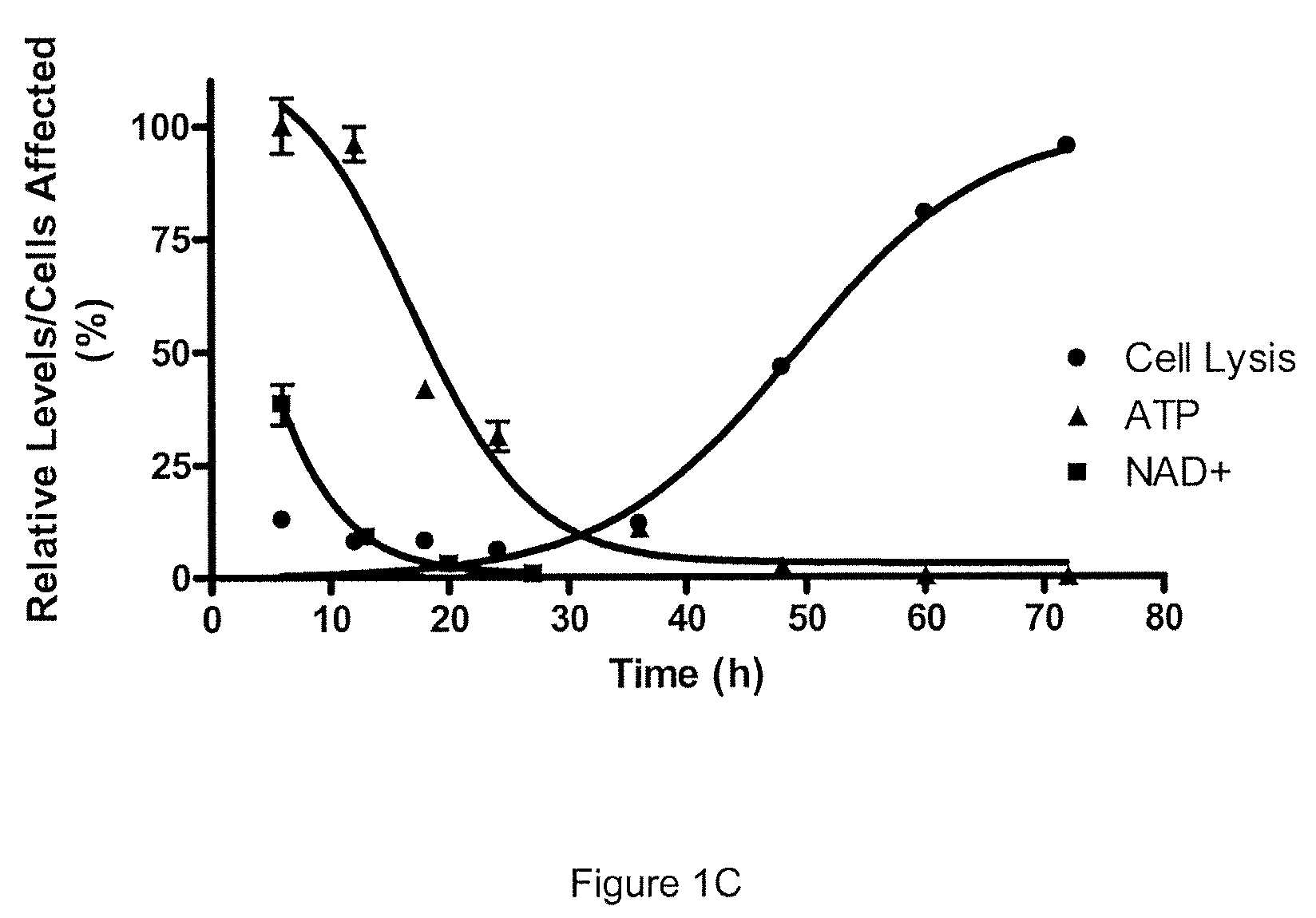
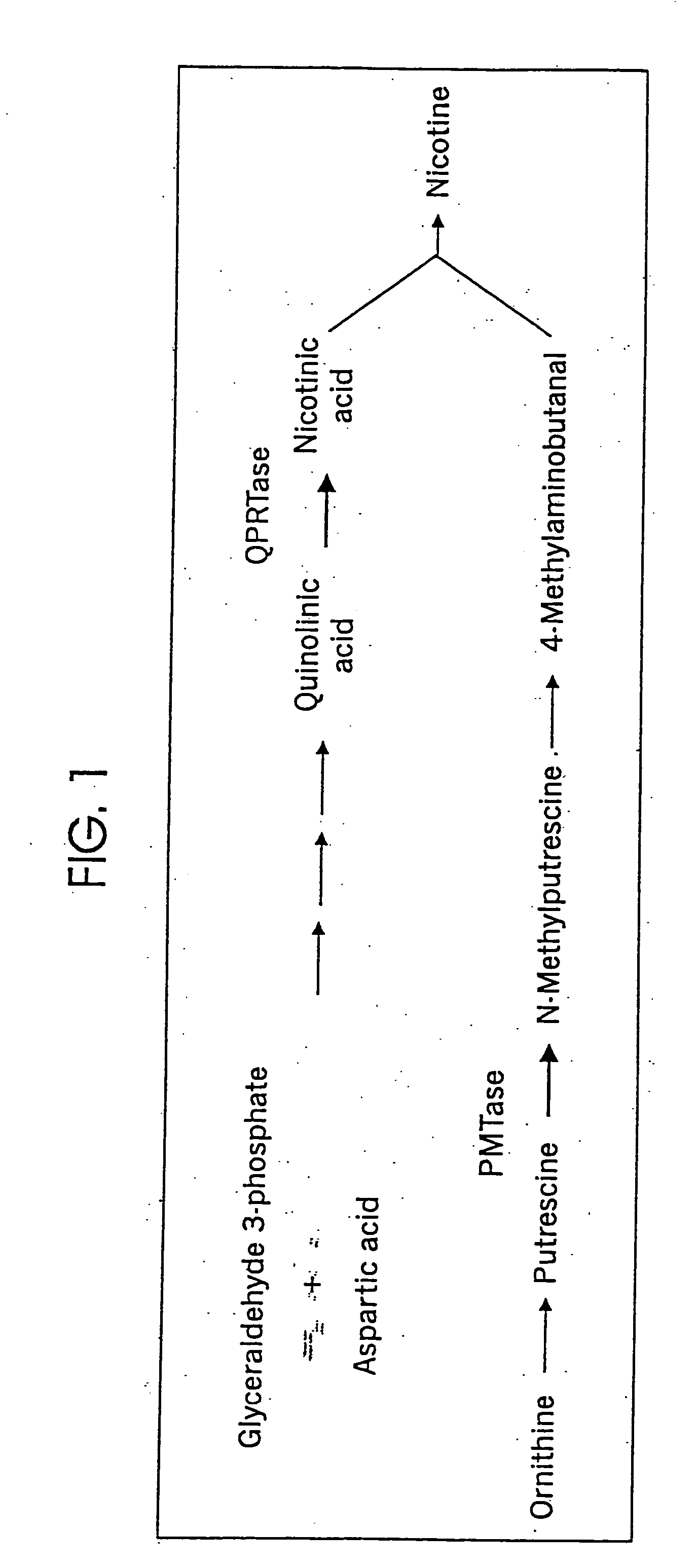
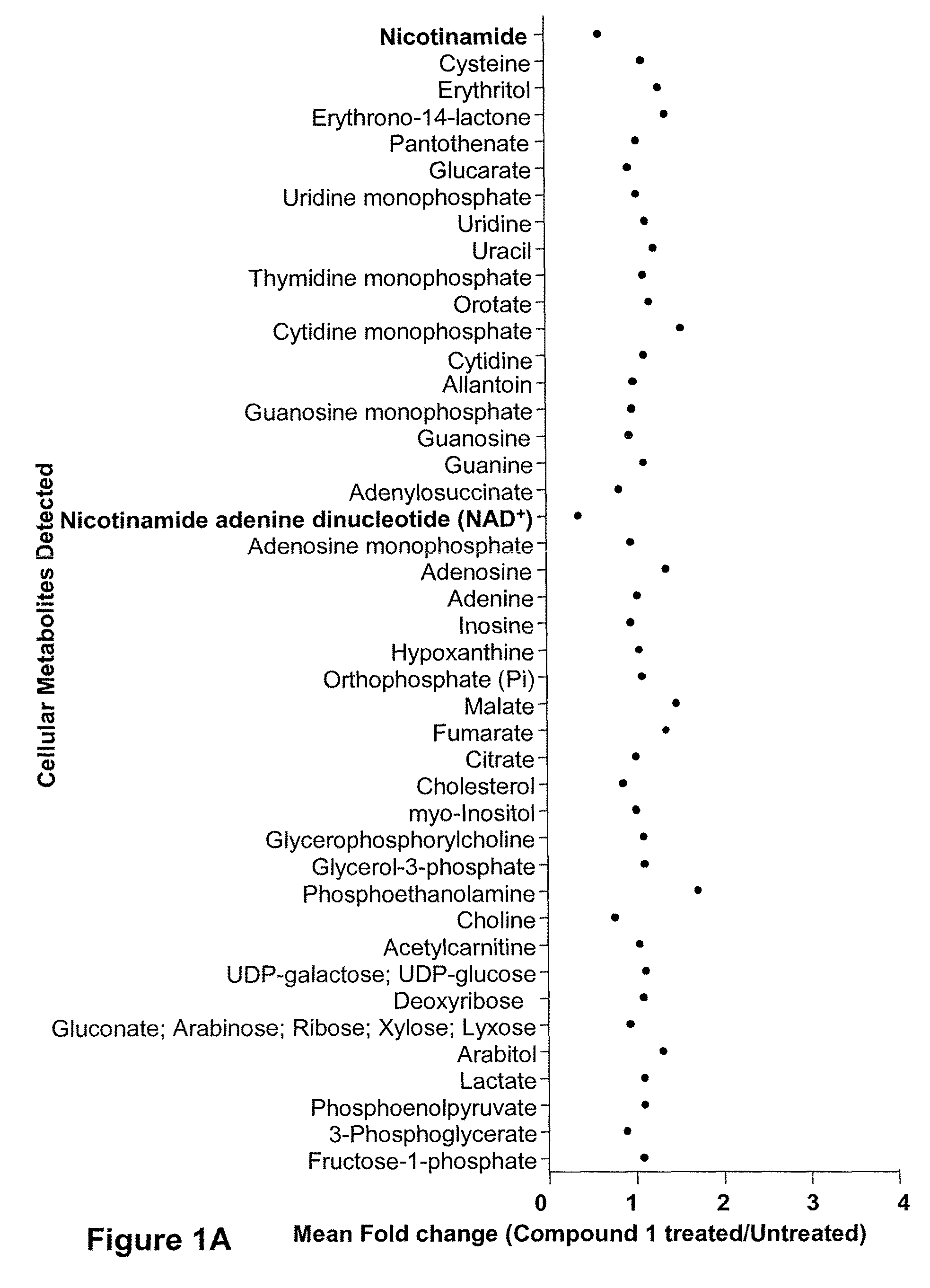
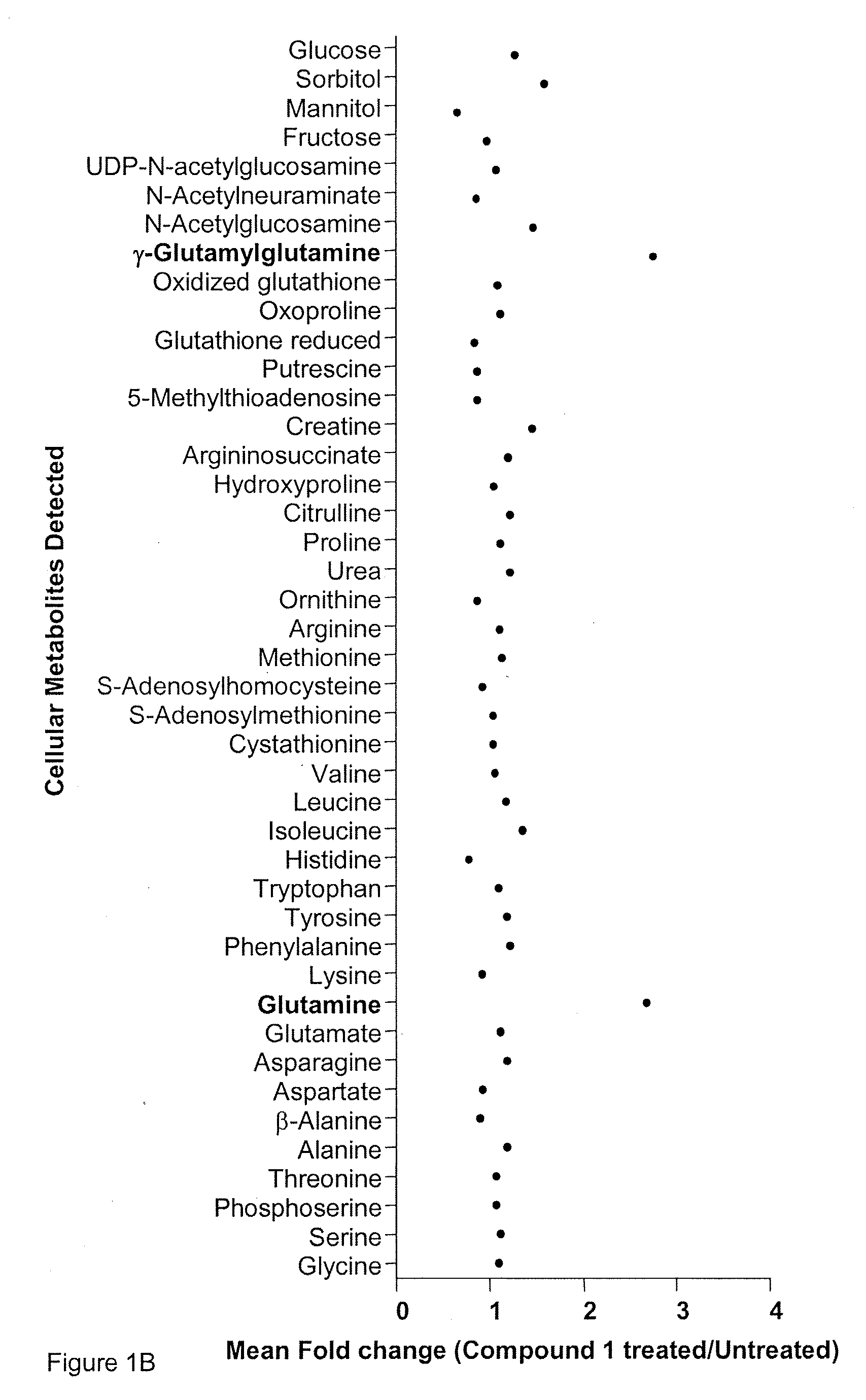
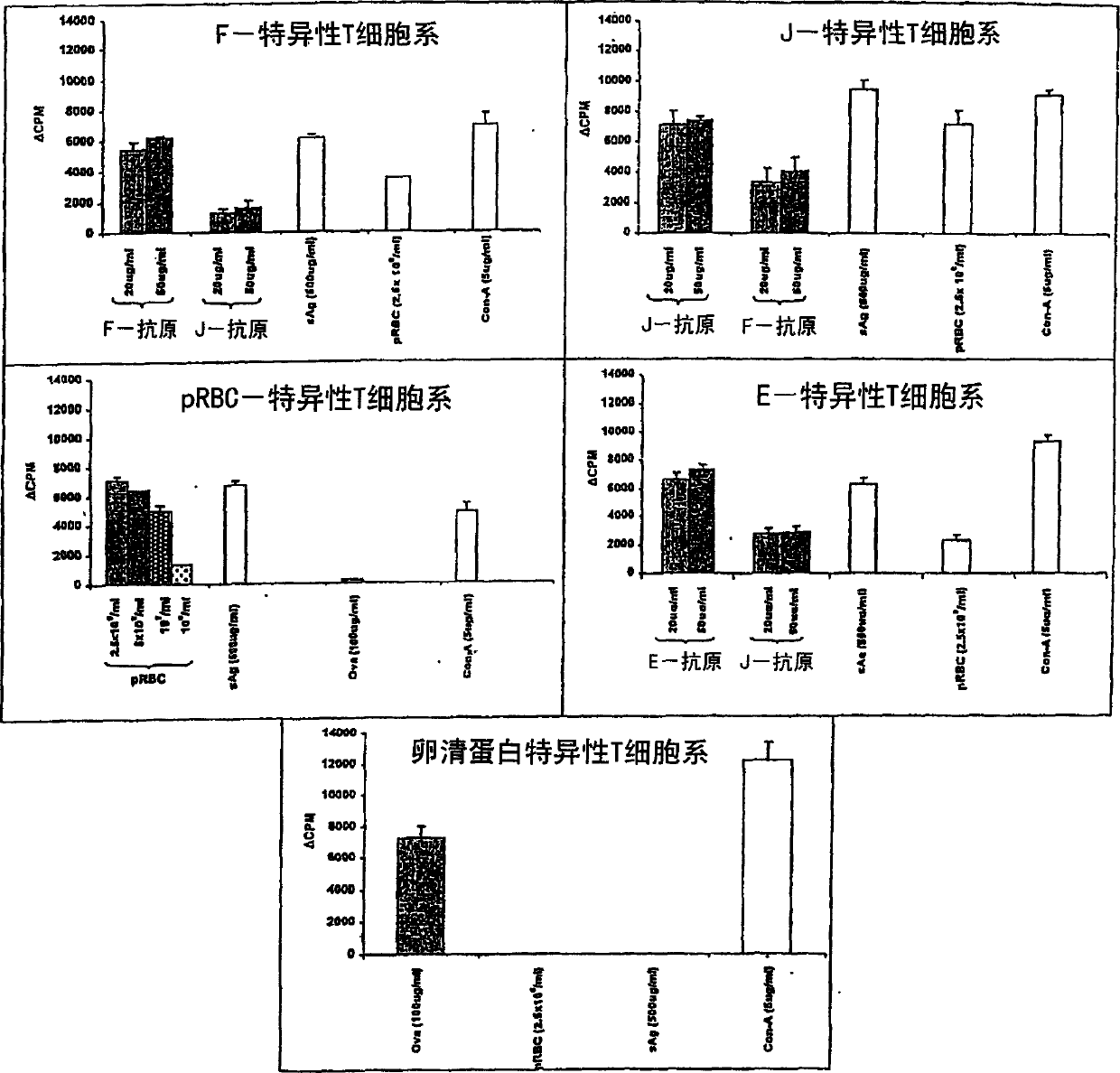
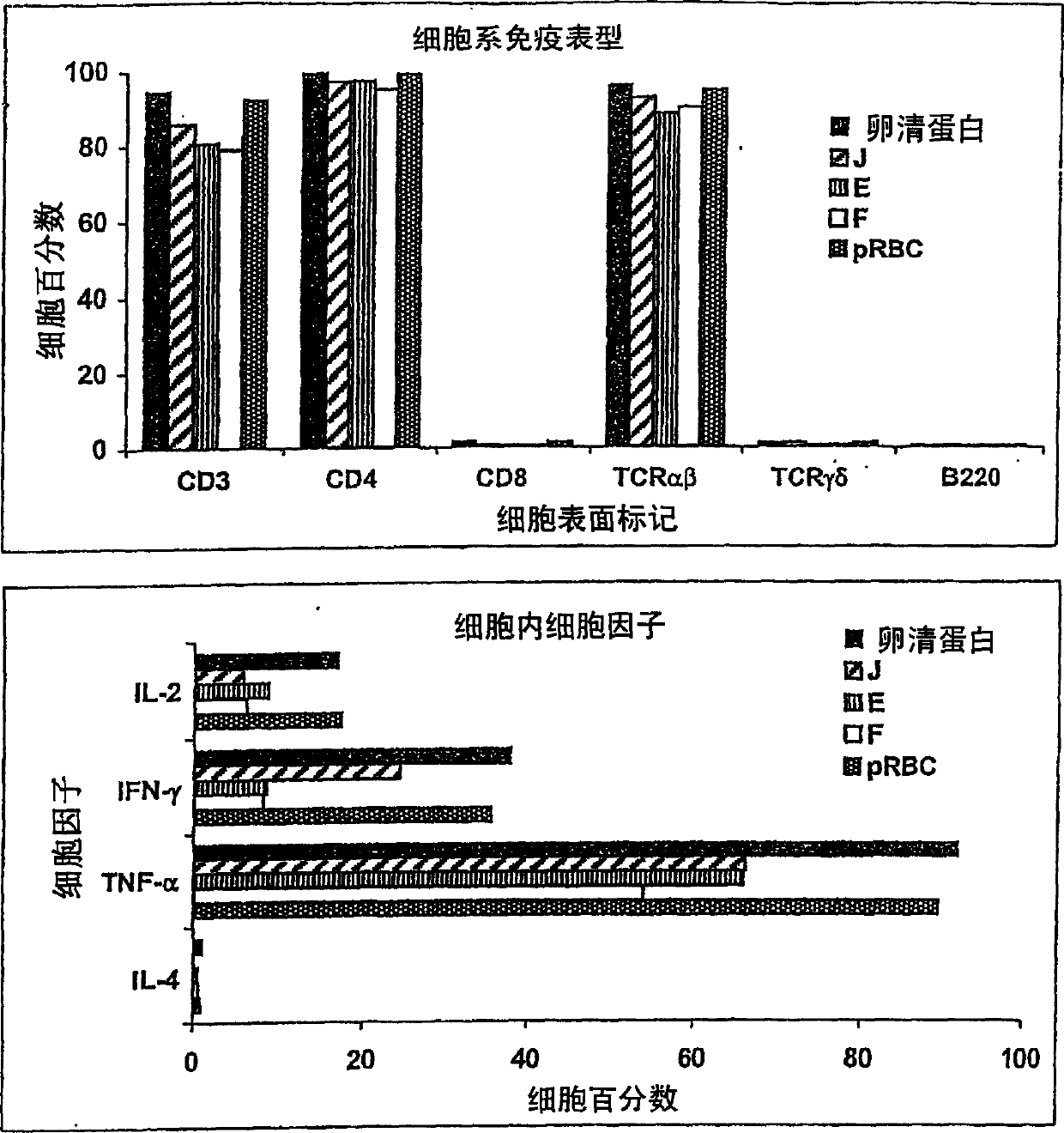
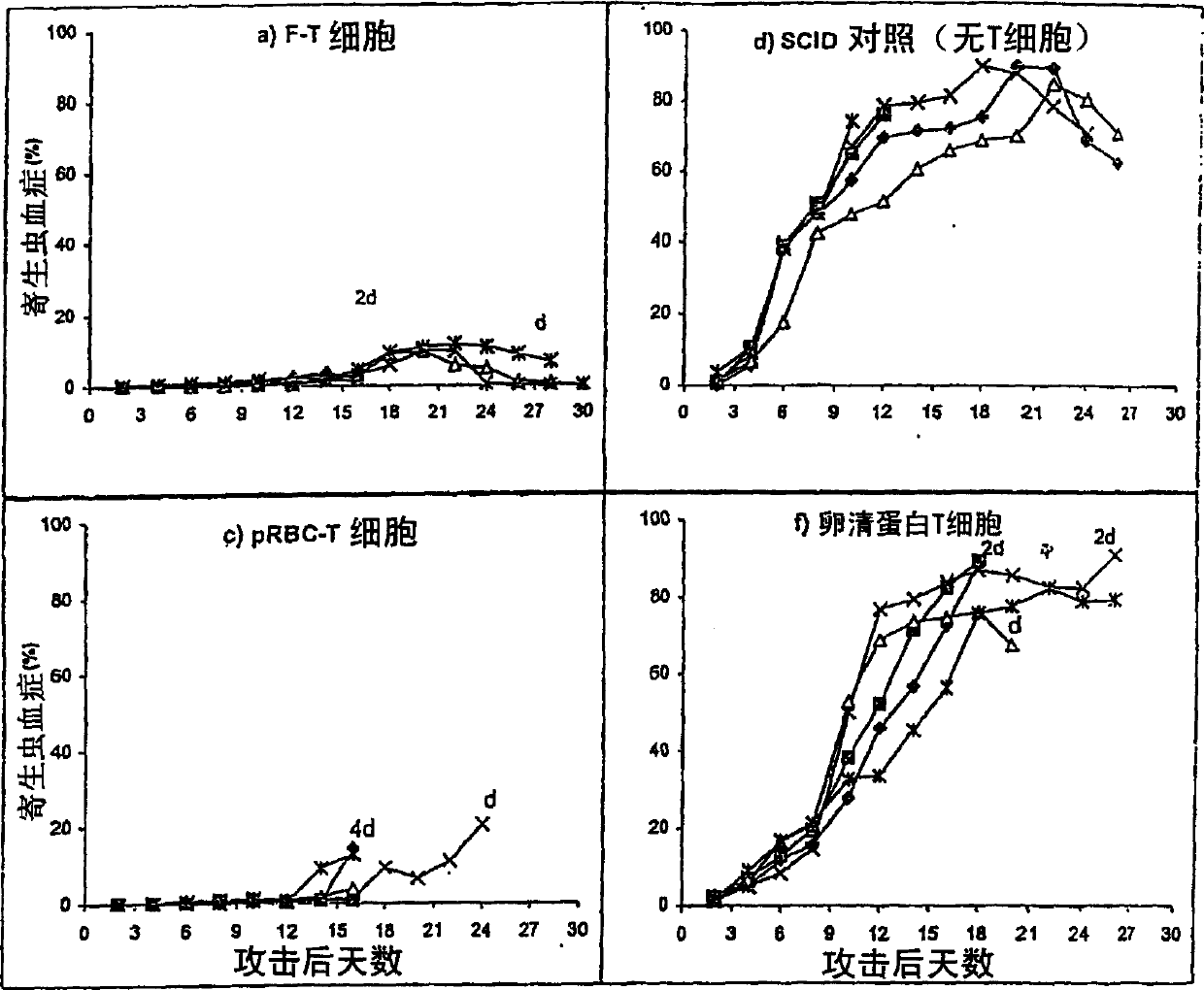
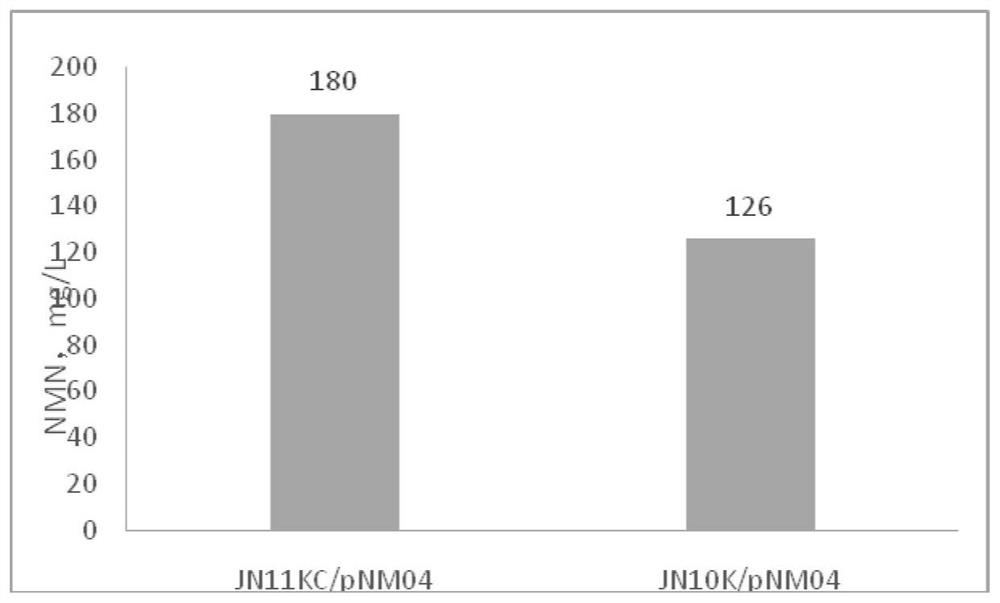
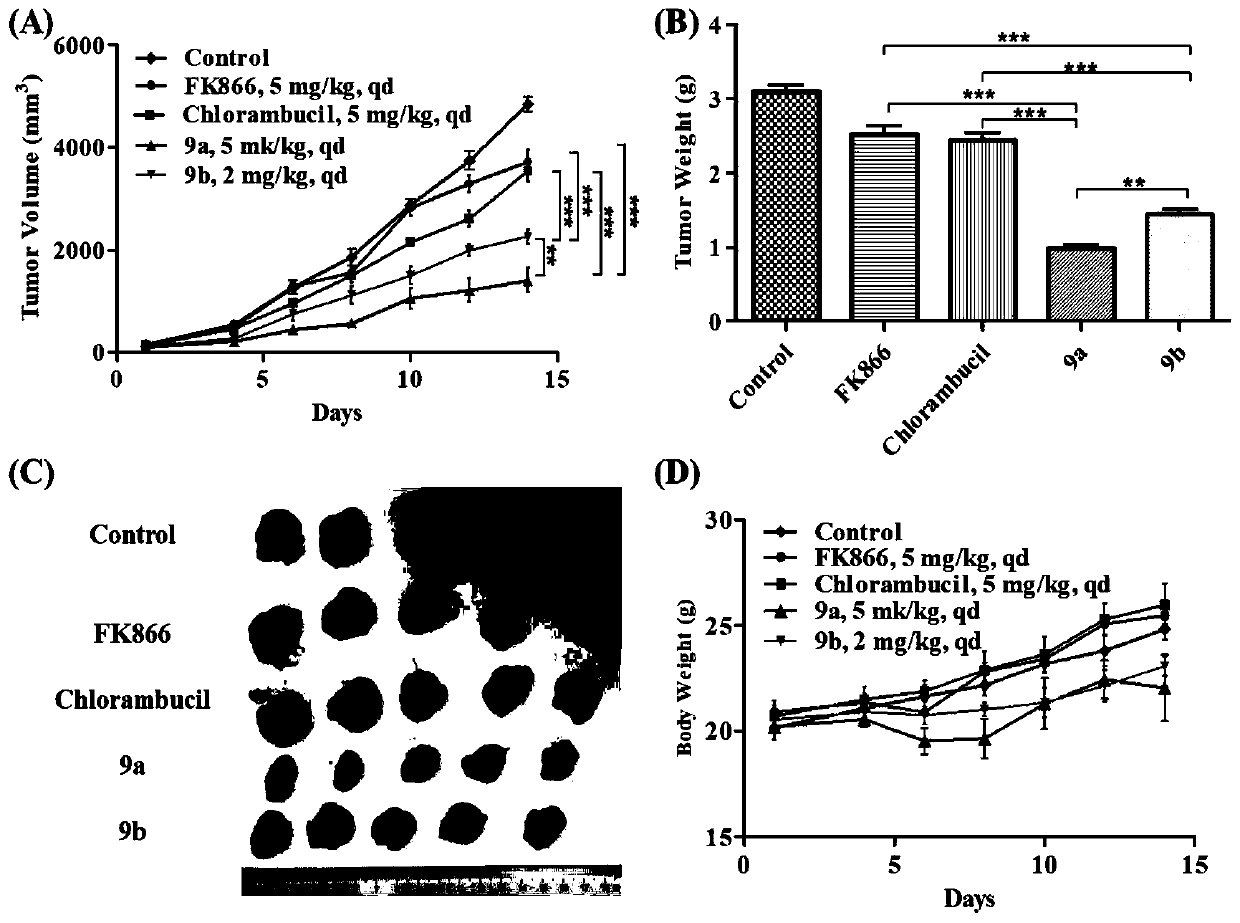
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Phosphoribosyl transferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
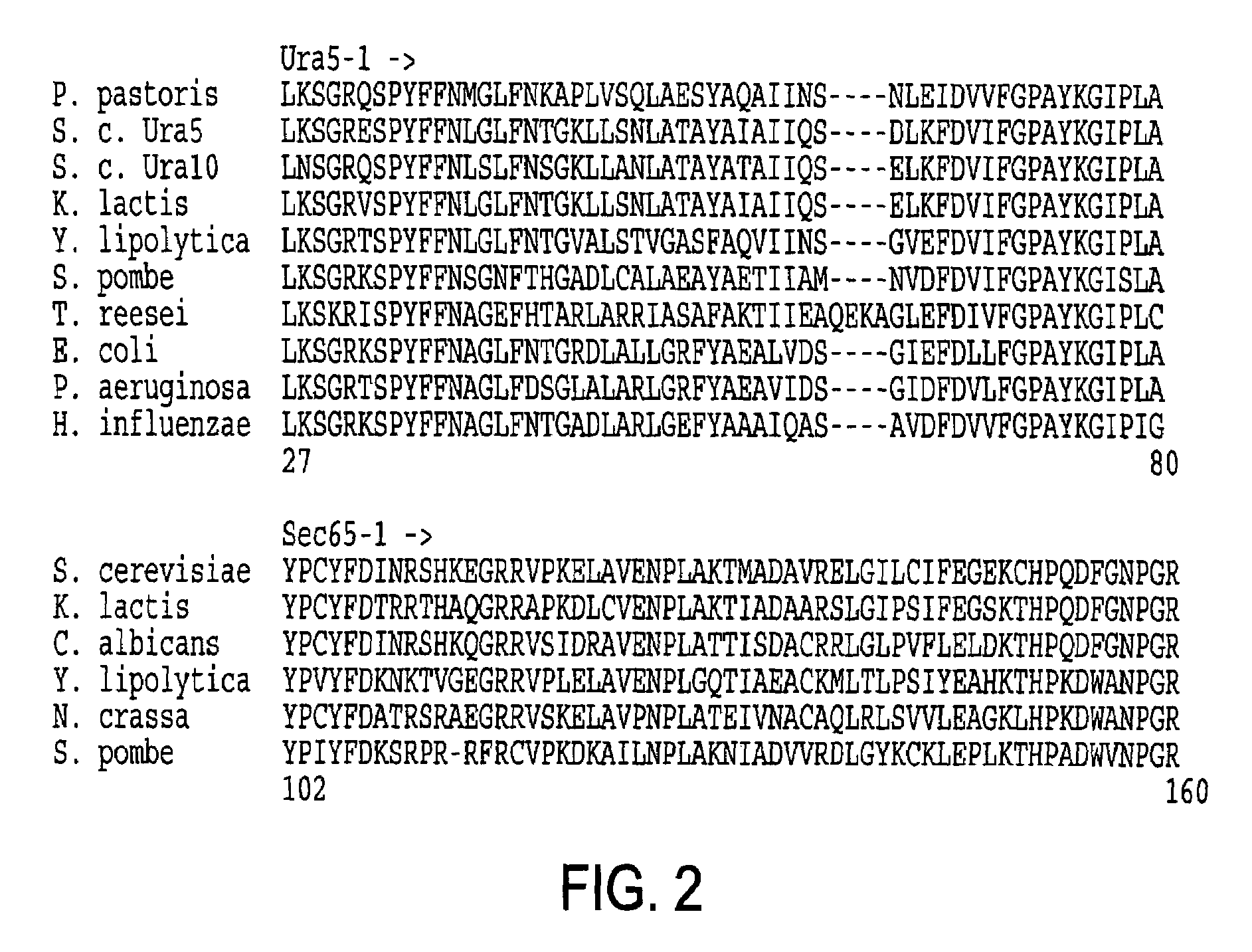
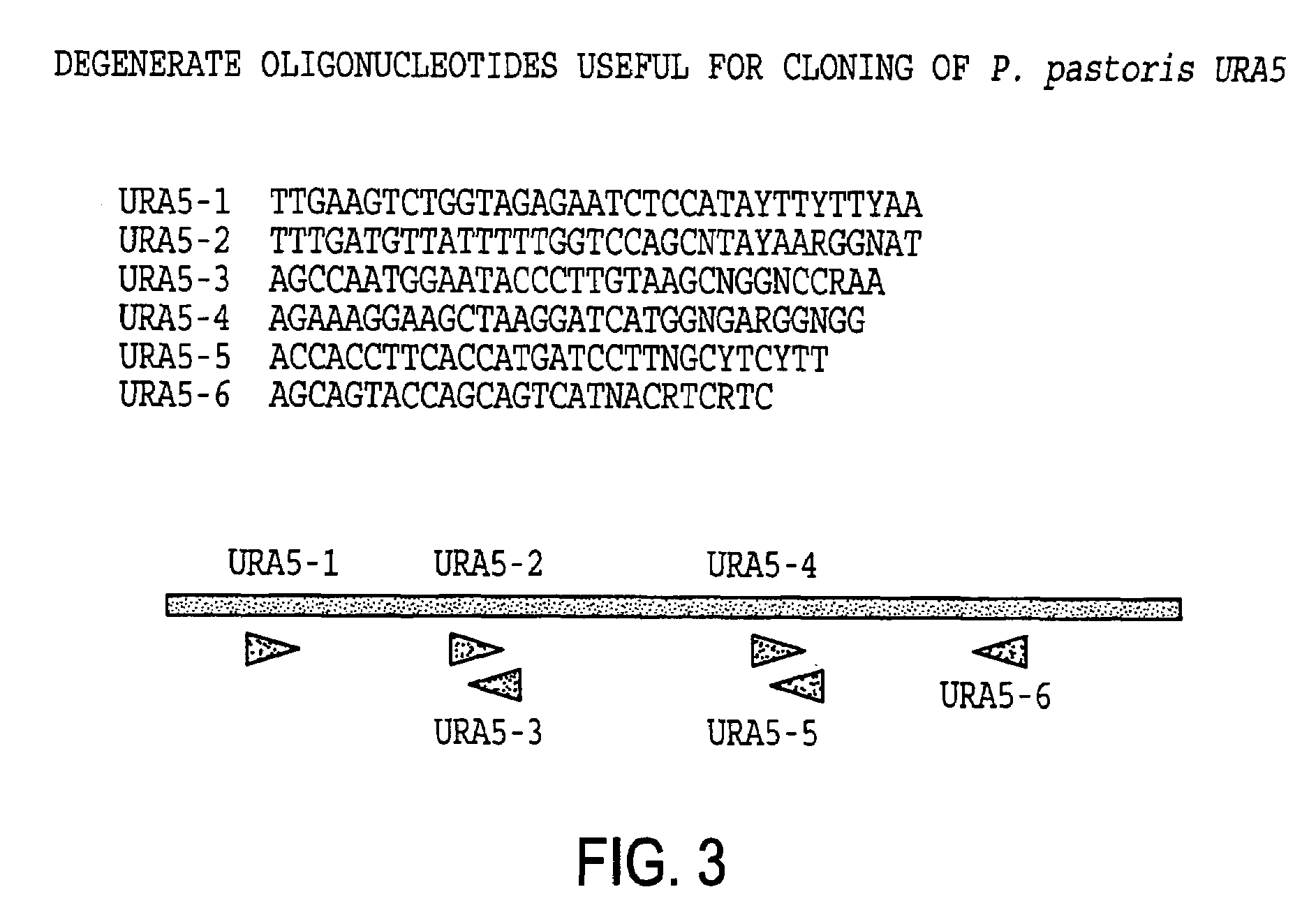
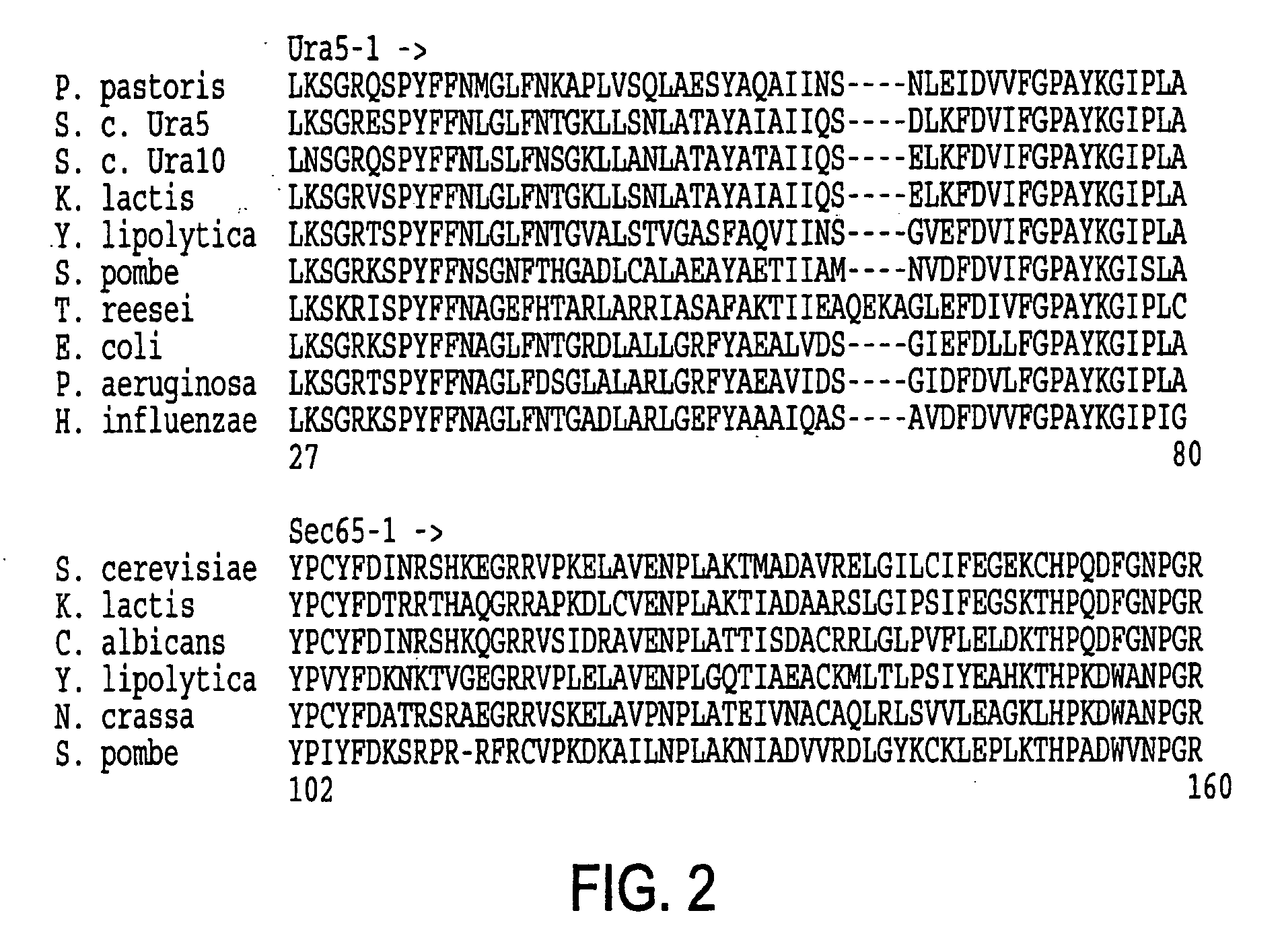
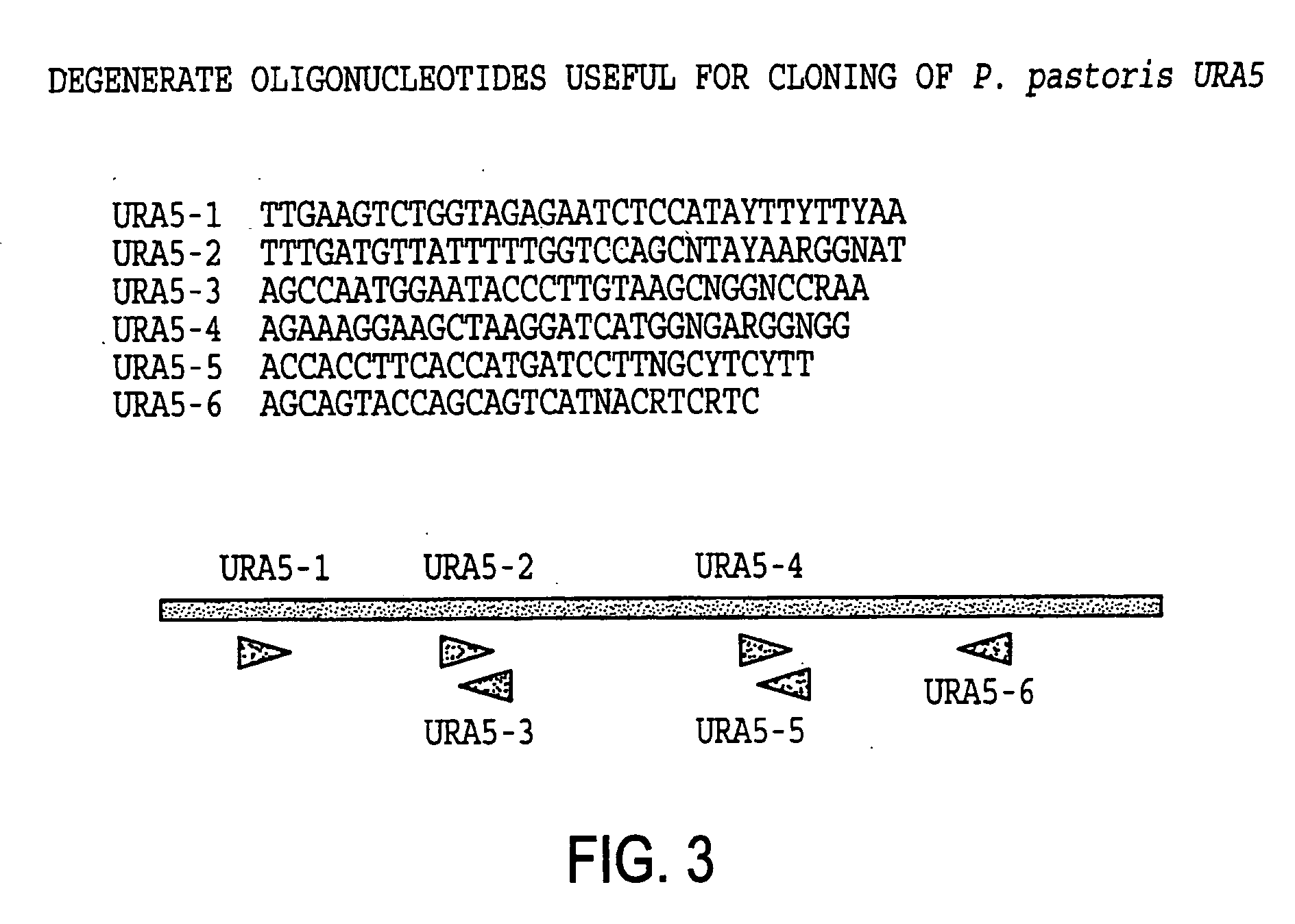
URA5 gene and methods for stable genetic integration in yeast
A novel gene encoding P. pastoris orotate-phosphoribosyl transferase (URA5) is disclosed. Methods for producing and selecting yeast strains capable of stable genetic integration of heterologous sequences into the host genome are also provided.
Owner:GLYCOFI
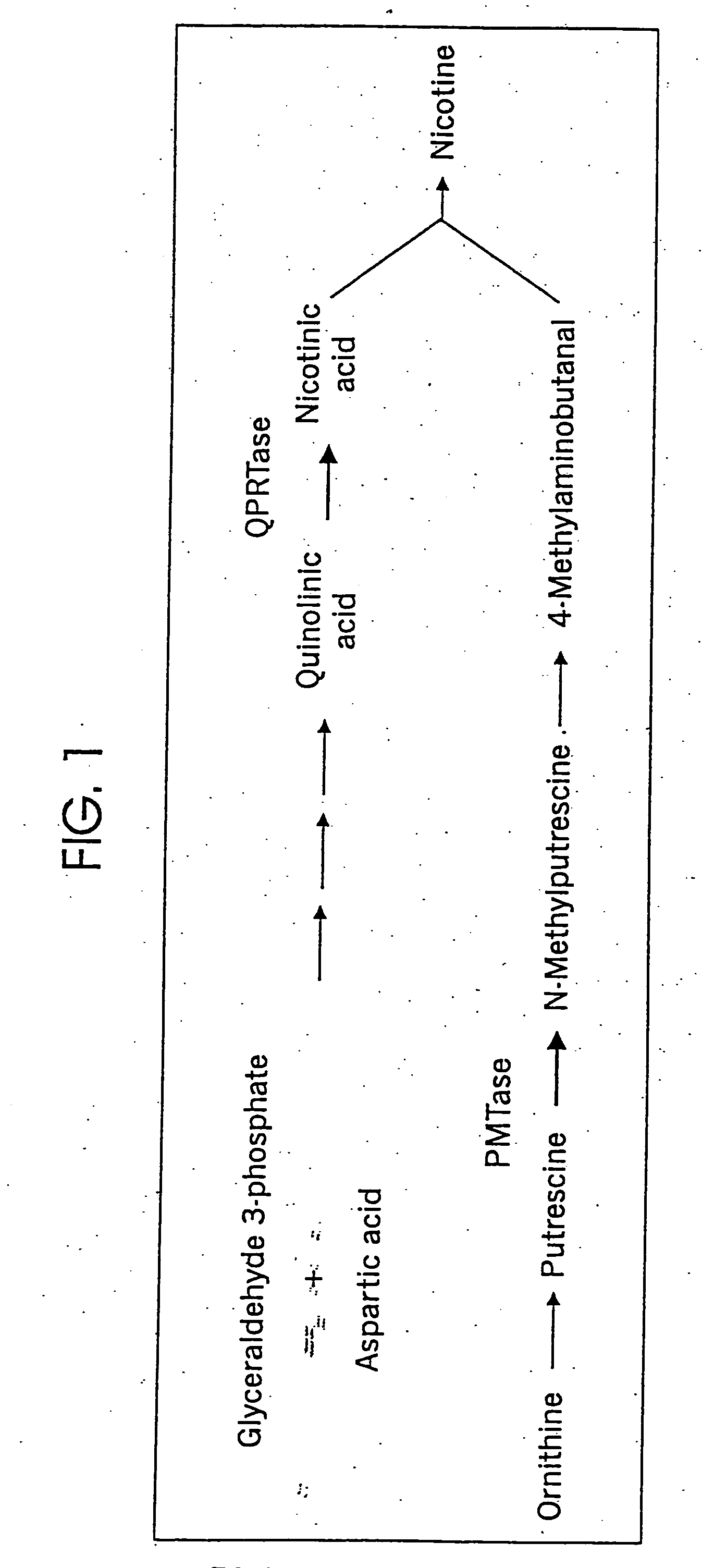
Tobacco products with increased nicotine
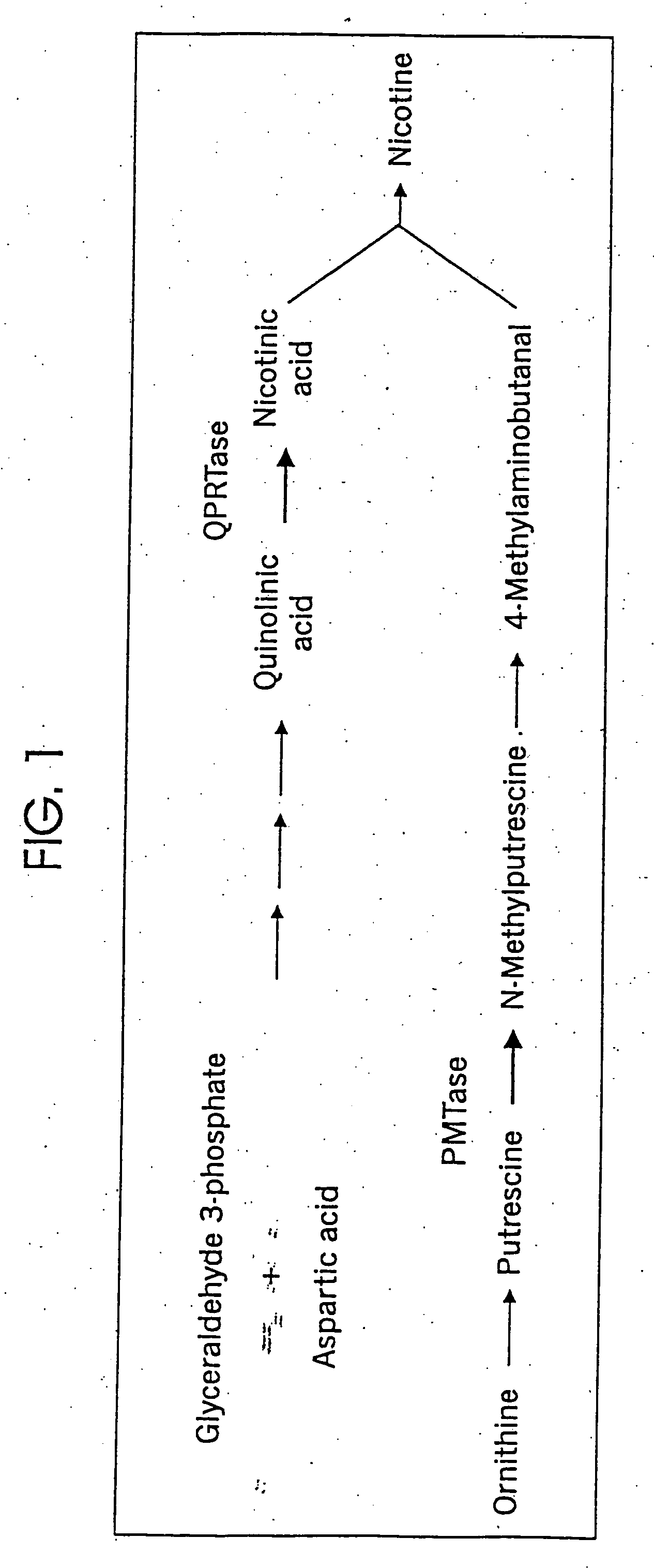
InactiveUS20060191036A1Reduce expressionDecreasing expression of endogenousTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentNicotiana tabacumDna encoding
DNA encoding a plant quinolate phosphoribosyl transferase (QPRTase) enzyme, and constructs comprising such DNA are provided. Methods of altering quinolate phosphoribosyl transferase expression are provided.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
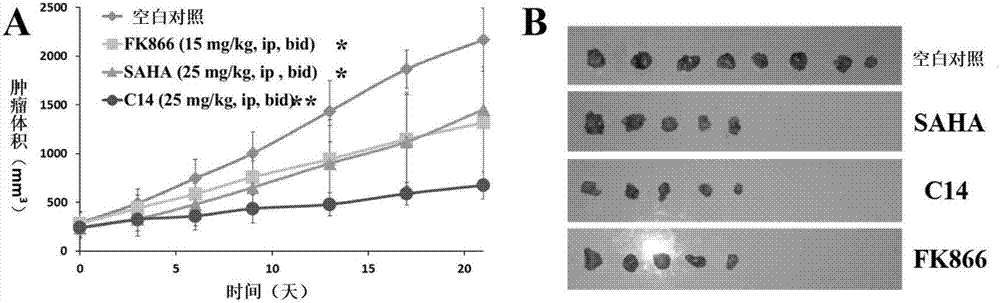
NAMPT/HDAC dual-target inhibitor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106916101AImproved potency in vivoOrganic chemistryAmide active ingredientsIn vivoHDAC inhibitor
The invention discloses an NAMPT / HDAC dual-target inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. The dual-target inhibitor is an amide derivative and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein a structure general formula is represented as the formula (I). A pharmacological experiment proves that the derivative or the salt thereof have very strong inhibition activity on the nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase and the histone deacetylase, and have high in-vitro anti-tumor activity and excellent in-vivo tumor inhibiting effect. The invention also provides a preparation method of the derivative and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and an application in preparation of an NAMPT inhibitor, a HDAC inhibitor, and anti-tumor medicines.
Owner:聚缘(上海)生物科技有限公司 +1
Malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria and its construction and use
InactiveCN104046577AThe fermentation method is simpleGood effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFumaraseFermentation
The invention provides malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria Escherichiacoli BA043. The malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria is named as BA043 (Escherichiacoli BA043) and has a preservation registration number CCTCC NO: M2014034. The invention also provides a construction method of the malic acid-production gene engineering bacteria and a method for fermentation production of malic acid. Through knockout or inactivation of fumarase and fumarate reductase and through over coexpression of exogenous pyruvate carboxylase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase, recombinant escherichia coli can reduce by-product pyruvic acid generation by glucose metabolism growth so that a malic acid yield and production intensity are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
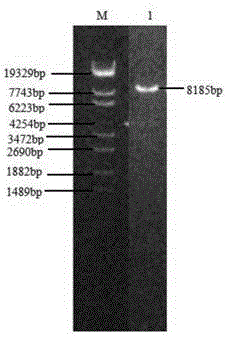
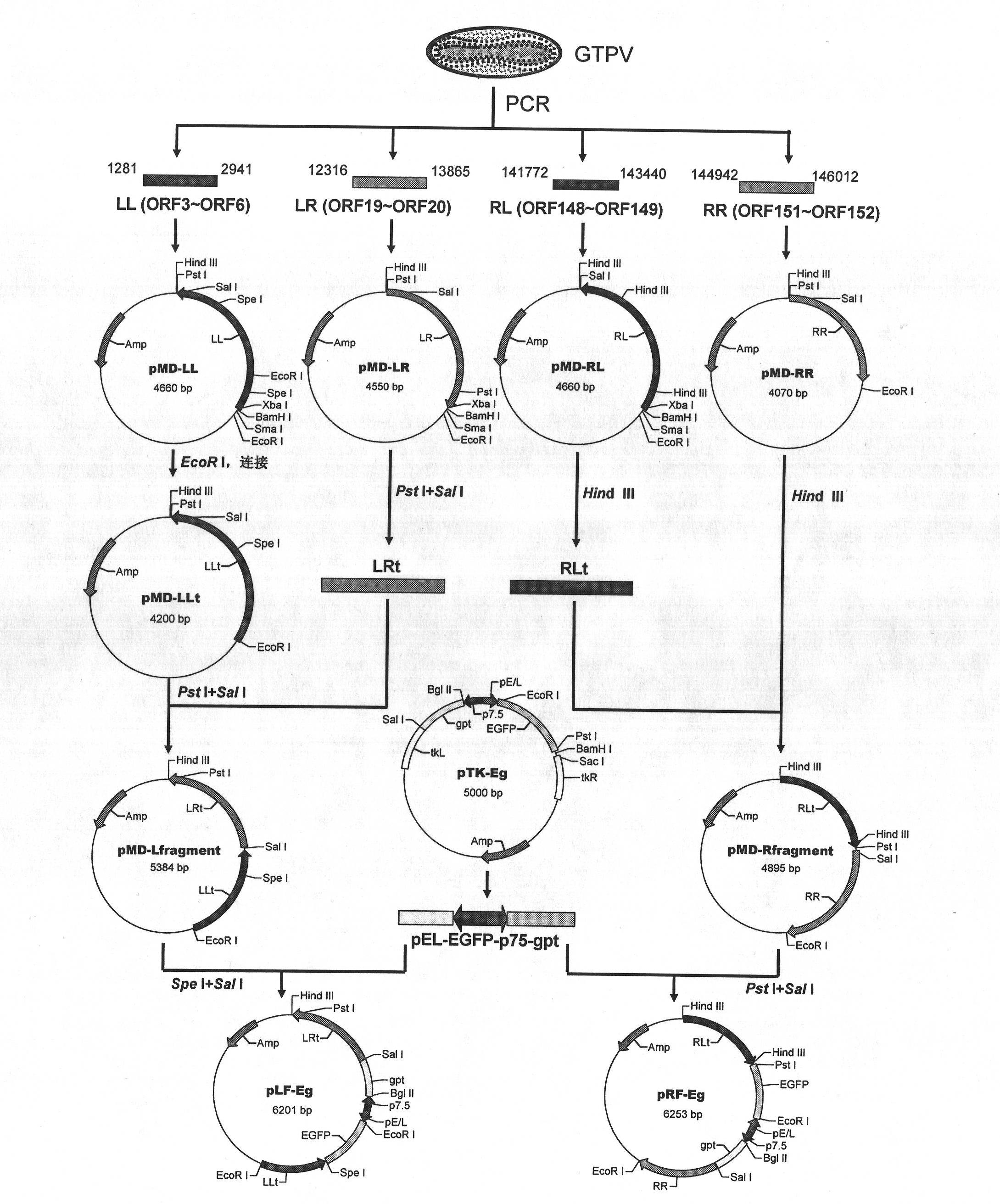
Method for screening non-essential regions for replication of goat pox virus and universal transfer vectors for same
InactiveCN102174508AImprove securitySmall virulent effectsViruses/bacteriophagesVector-based foreign material introductionScreening methodTransfer vector
The invention relates to a method for screening non-essential regions for replication of a goat pox virus and universal transfer vectors for same. The method comprises the steps of amplifying two-end gene segments of any two regions of a goat pox virus gene by using a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method; then, inserting an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene and a xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (gpt) gene expression cassette into the segments; establishing two universal transfer vectors of the goat pox virus; and acquiring a recombinant virus expressing an exogenous gene stably from the transfer vectors, thereby determining the selected regions to be non-essential regions for replication of the goat pox virus, wherein each universal transfer vector contains one unique restriction enzyme cutting site Sal I and allows gene expression cassettes of other items to insert in. The recombinant virus obtained by means of the two universal transfer vectors provided by the invention not only has a growth performance similar to a parent virus, but also has better safety because a plurality of toxicity related genes in a genome are knocked out in an orientation way, and has the potential to be developed into an attenuated vaccine strain for gene engineering.
Owner:广西壮族自治区动物疫病预防控制中心
Tobacco products with reduced nicotine
DNA encoding a plant quinolate phosphoribosyl transferase (QPRTase) enzyme, and constructs comprising such DNA are provided. Methods of altering quinolate phosphoribosyl transferase expression are provided.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
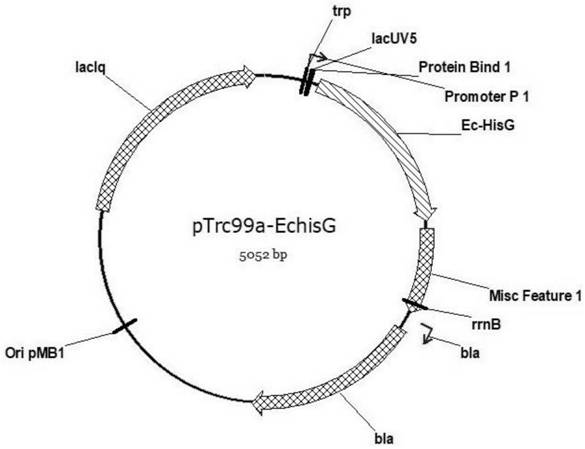
High-yield L-histidine genetically engineered bacterium strain, constructing method and application thereof
InactiveCN110184230AIncreased growth burdenClear genetic backgroundBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliArginine
The present invention provides a high-yield L-histidine genetically engineered bacterium strain and a constructing method thereof. The bacterium integrates a nucleotide sequence of a corynebacterium glutamicum ATP phosphoribosyl transferase HisG mutant encoding gene hisG* represented by SEQ ID NO:1 based on genome of escherichia coli to enhance activity of histidine-synthesizing key enzyme HisG, also increases copy number of histidine operon genes in the genome to enhance a terminal synthesis pathway of histidine, and also integrates an encoding gene lysE of arginine / lysine transportprotein derived from the corynebacterium glutamicum to promote extracellular secretion of the intracellular histidine. The genetically engineered bacterium is used for producing the L-histidine by a fermentation method, can stably produce 40-55 g / L of the histidine by fermentation in a 5L fermentation tank for 40-50 h, has a production intensity reaching 1.0-1.5 g / (Lxh), and has a conversion rate of 0.18-0.22 g histidine / g glucose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
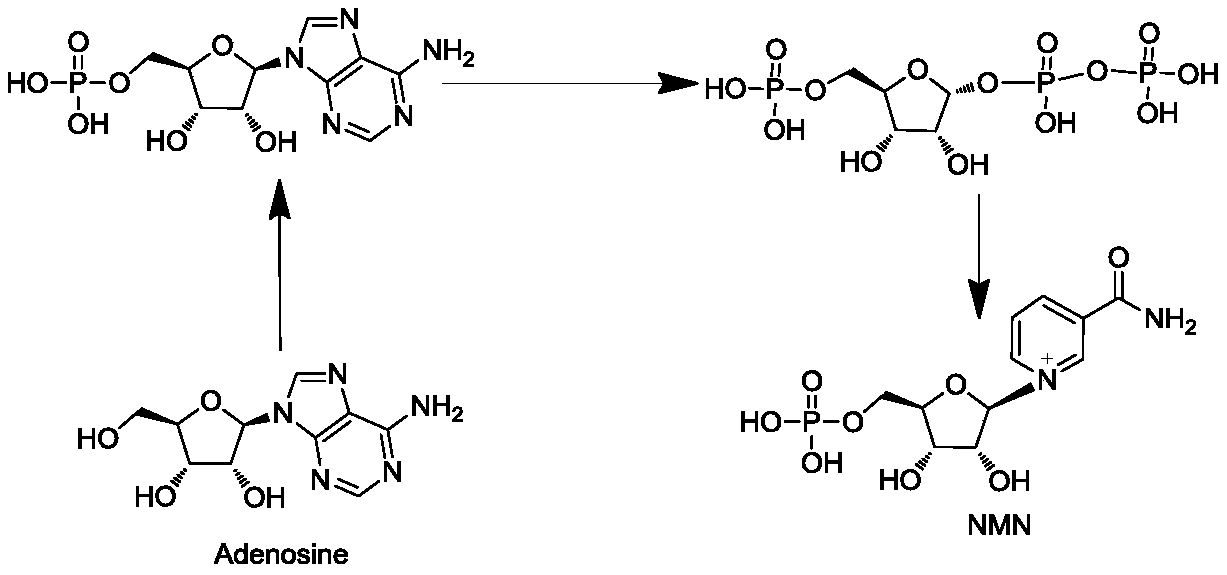
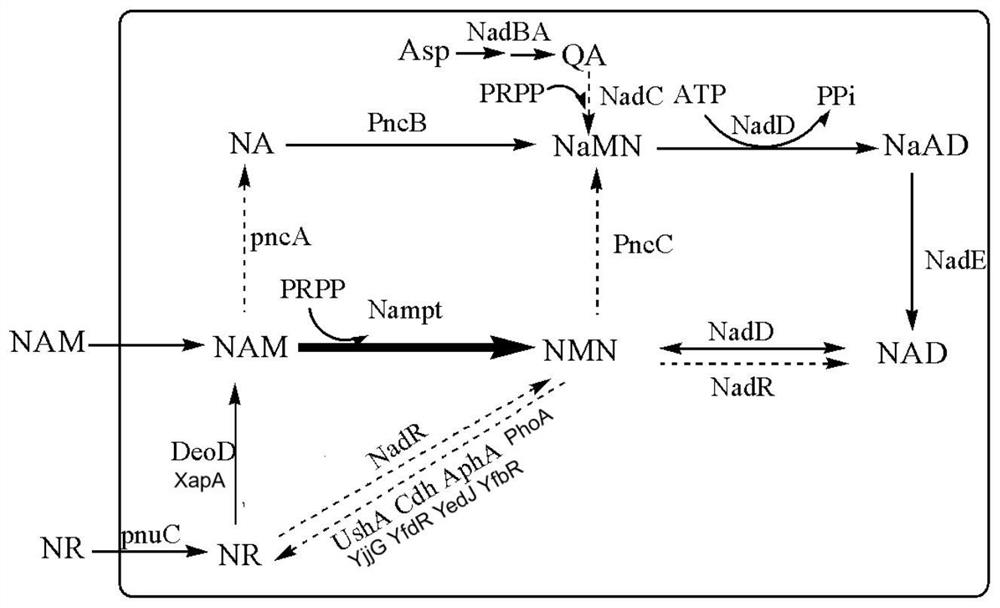
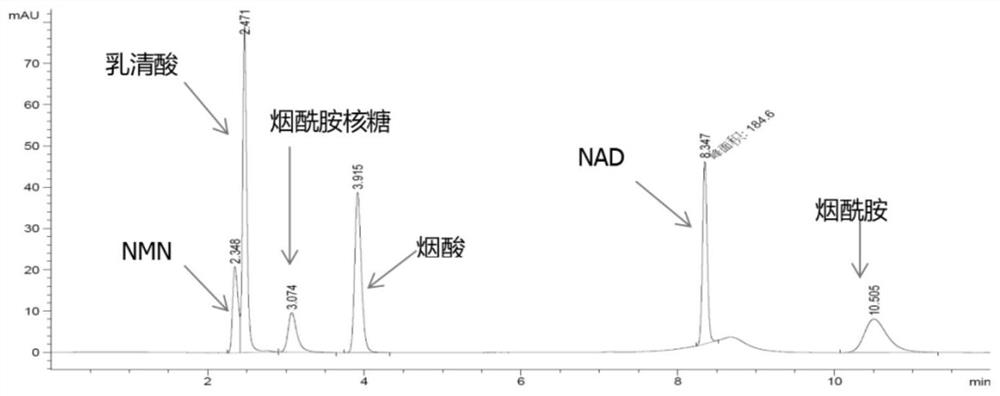
Enzyme composition for preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide and method for preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide by enzymatic process
The invention relates to the technical fields of biopharmacy and biochemical industry, and in particular relates to an enzyme composition for preparing nicotinamide mononucleotide and a method for preparing the nicotinamide mononucleotide by an enzymatic process. The enzyme composition is composed of adenosine kinase, adenine phosphoribosyl transferase and nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase.The three enzymes provided by the invention can be reasonably combined for efficient catalytic preparation of the nicotinamide mononucleotide. The enzyme composition provided by the invention can be recycled, has low costs, saves energy and protects the environment; the method for preparing the nicotinamide mononucleotide by the enzymatic process provided by the invention uses adenosine as a substrate, the enzyme composition is added, so that the nicotinamide mononucleotide can be prepared at low cost, safely and reliably, the cost of a current route can be reduced, and the method can be suitable for large-scale production and provides guarantee for the use of the nicotinamide mononucleotide in the fields of biocatalysis and drugs.
Owner:杭州唯泰生物药业有限公司 +1
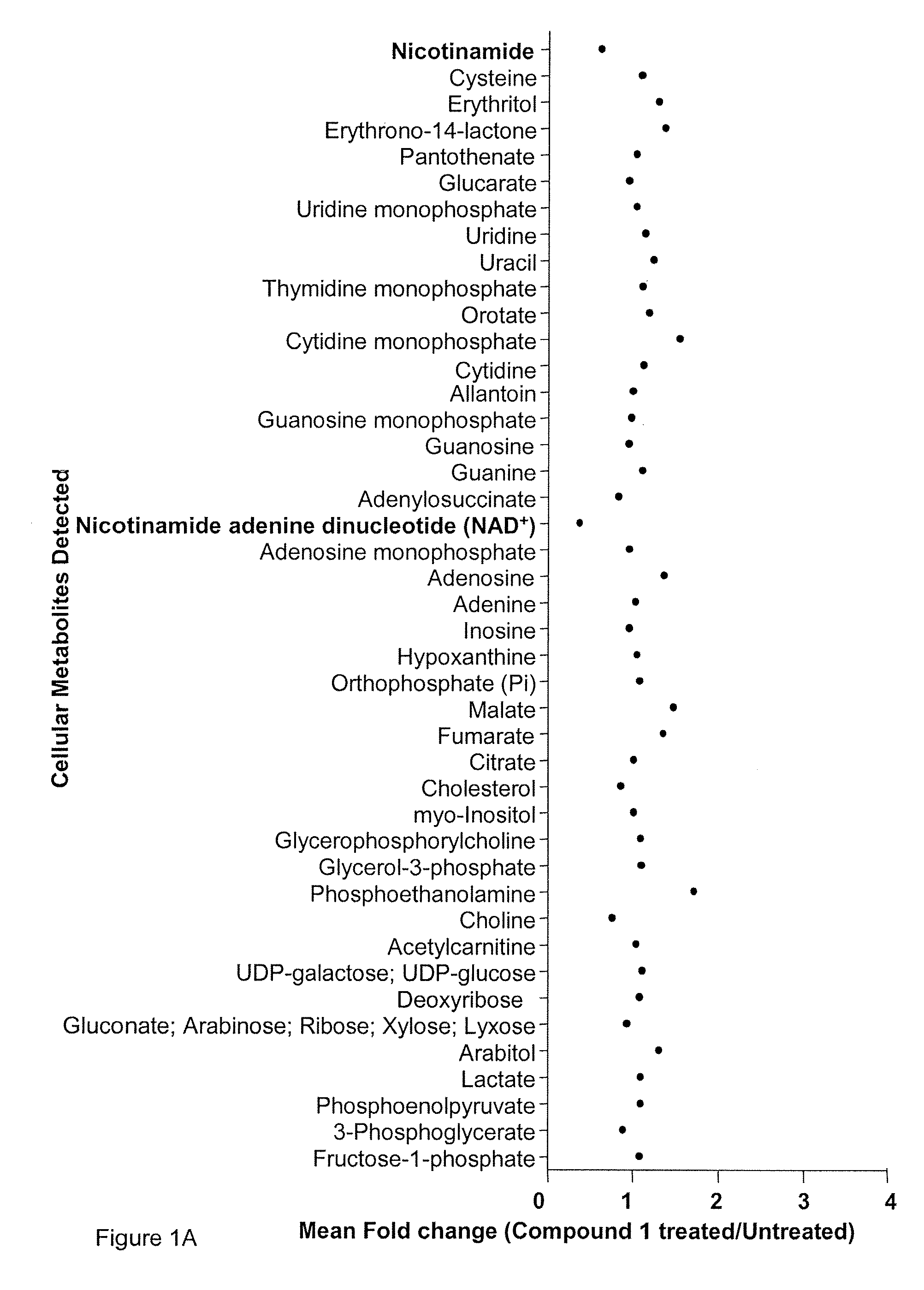
Compositions and methods for effecting nad+ levels using a nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase inhibitor
The present invention relates to methods for decreasing cellular DNA repair in a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); decreasing cellular NAD+ biosynthesis in a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL; or sensitizing a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL to a DNA damaging therapy. The invention relates to methods for treating a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL.
Owner:GEMIN X PHARMA CANADA INC (CA)
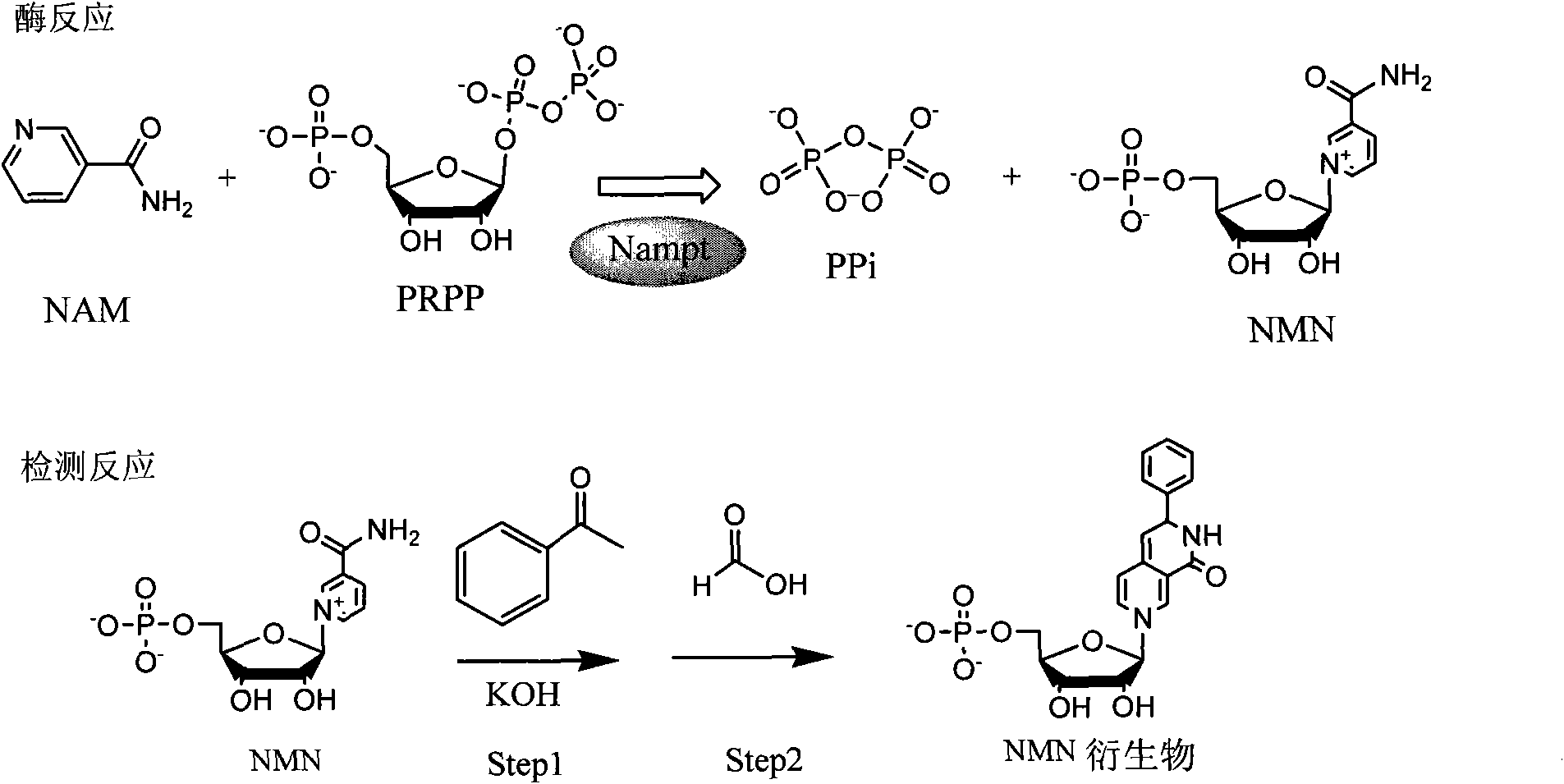
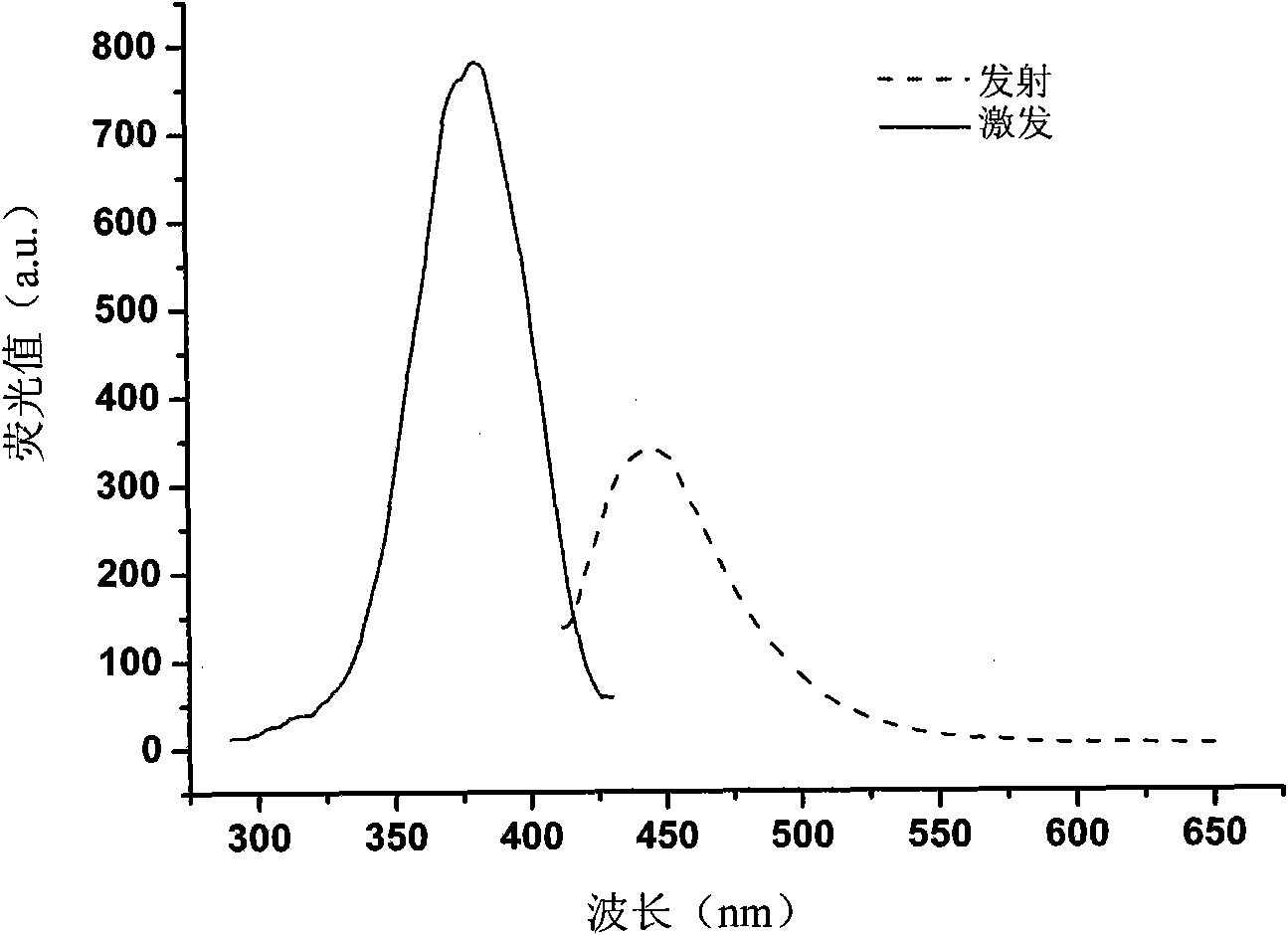
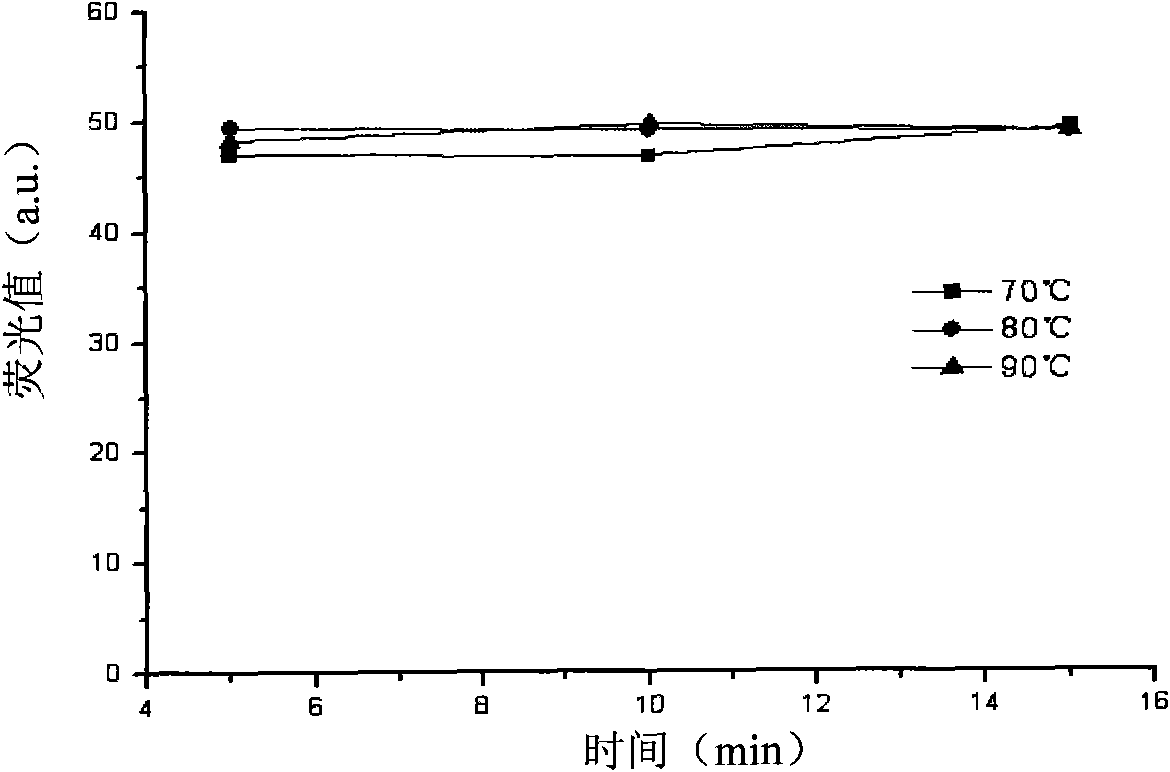
Method and kit for determining nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (Nampt) activity
InactiveCN101914614AEasy to operateMild reaction conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh fluxScreening method
The invention discloses a method and a kit for determining nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (Nampt) activity. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing the reaction for converting the Nampt catalytic substrate of nicotinamide (NAM) into the product of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN); (2) terminating the reaction by a heating method; (3) adding hypnone and strong base for thorough reaction; (4) adding formic acid for thorough reaction; (5) detecting the fluorescence intensity at the location with the excitation wavelength of 326-426nm and the transmission wavelength of 410-520nm. The invention also provides a method and a system for high-flux sieving of a Nampt inhibitor or activator. The method comprises the following steps of: incubating the compound candidate and the reacting system for the Nampt (except the substrate of NAM) in a micropore plate; determining the Nampt activity in accordance with the steps. The method has the advantages of simple operation, moderate reaction condition and high-flux operation.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Compositions and methods for effecting NAD+ levels using a nicotinamide phosphoribosyl tranferase inhibitor
ActiveUS8211912B2Reduce repairImprove efficiencyBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsToxic doseA-DNA
The present invention relates to methods for decreasing cellular DNA repair in a target patient; decreasing cellular NAD+ biosynthesis in a target patient; increasing efficiency of radiation therapy in a target patient; modulating nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase activity in a patient; or sensitizing a patient to a DNA damaging therapy. The invention relates to methods for treating a patient who received a toxic dose of an nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase inhibitor. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising a physiologically acceptable carrier; an effective amount of a NMPRT inhibitor; and nicotinic acid. The invention also relates to methods for treating a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have a cancer deficient in nicotinic acid pathway.
Owner:GEMIN X PHARMA CANADA INC (CA)
Methods and compositions for protein production in tobacco plants with reduced nicotine
InactiveUS20060191035A1Reduce expressionDecreasing expression of endogenousTobacco treatmentTransferasesNicotiana tabacumDna encoding
DNA encoding a plant quinolate phosphoribosyl transferase (QPRTase) enzyme, and constructs comprising such DNA are provided. Methods of altering quinolate phosphoribosyl transferase expression are provided.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Compositions and methods for effecting NAD+ levels using a nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase inhibitor
The present invention relates to methods for decreasing cellular DNA repair in a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); decreasing cellular NAD+ biosynthesis in a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL; or sensitizing a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL to a DNA damaging therapy. The invention relates to methods for treating a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL.
Owner:GEMIN X PHARMA CANADA INC (CA)
Genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and acidogenic fermentation method thereof
InactiveCN102533626AOvercomes the inability to utilize glucoseBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the field of biology engineering technology, and relates to a genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose and an acidogenic fermentation method of the genetic engineering strain. The genetic engineering strain for producing succinic acid by utilizing glucose is named as Escherichia coli BA205 and the preservation number is registered as CCTCC No.M2011447. In the construction process, Escherichia coli which is short of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) gene and Pyruvate formate-lyase (PFL) gene activity is mainly used as an original strain; phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PPC) gene is removed by utilizing a homologous recombination technology; and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyl transferase are excessively co-expressed; therefore the synthesis efficiency of succinic acid is greatly increased. In the fermentation method, a two-stage fermentation manner is adopted, the biomass is improved in an aerobic stage and the acidogenic fermentation is carried out in an anaerobic stage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate by enzyme method
ActiveCN110643587ALow costSafe preparationFermentationGlycosyltransferasesAdenine phosphoribosyltransferaseAdenosine
The invention belongs to the technical fields of biological pharmacy and biochemical engineering, and discloses an enzyme composition for production of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate anda method for preparing the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate by an enzyme method. The enzyme composition disclosed by the invention consists of adenine phosphoribosyl transferase, nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase, nicotinamide phosphate ribose transferase and polyphosphate dependent form NAD kinase. The four kinds of enzymes are in reasonable combination, so that the nicotinamideadenine dinucleotide phosphate can be efficiently catalyzed and prepared. The enzyme composition disclosed by the invention can be in cyclic utilization, and is low in cost, energy-saving and environmentally-friendly. According to the method for preparing the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate by an enzyme method disclosed by the invention, adenylic acid is used as a substrate, and the enzyme composition is added, so that the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate can be prepared safely and reliably at a low cost, the cost by a conventional route is reduced, the method is adaptedto large-scale production, and guarantee is provided for usage of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate in the fields of biocatalysis and medicines.
Owner:杭州唯泰生物药业有限公司 +1
Method for producing nicotinamide mononucleotide by utilizing recombinant bacillus subtilis
PendingCN111996208AStable passageStable expressionBacteriaStable introduction of DNANucleotideNicotinamide mononucleotide
The invention discloses a method for producing nicotinamide mononucleotide by utilizing recombinant bacillus subtilis. Particularly, a nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase expression element is integrated into optimized modified bacillus subtilis chromosomes; and nicotinamide mononucleotide is produced through fermentation by taking the bacteria as a strain, using an optimized culture medium and adding nicotinamide as a substrate. The method in the invention has the advantages that: the nicotinamide mononucleotide is produced by utilization an expression system of food safety; the foreign gene contained in the integrated expression recombinant strain could be stably passaged and expressed; and, by utilization of the optimized recombinant strain and culture medium, the yield of the nicotinamide mononucleotide is higher than that reported in other literatures.
Owner:南宁邦尔克生物技术有限责任公司 +1
Lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain capable of stably expressing porcine rotavirus VP4 protein and preparation method of lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain
InactiveCN107988130AImproving immunogenicityBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesVp4 gene
The invention discloses a lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain capable of stably expressing porcine rotavirus VP4 protein and a preparation method of the lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain. The vaccine strain is obtained through the following steps: on the basis of lactobacillus casei with uracil phosphoribosyl transferase, UPP gene deleted, the porcine rotavirus VP4 gene is inserted between a termination codon and a terminator of the neuronspecificenoluse gene of lactobacillus casei through homologous recombination, and the vaccine strain is not provided with an antibiotic selection marker. The experiment proves that after the constructed lactobacillus gene engineering subunit vaccine strain capable of stably expressing the porcine rotavirus VP4 proteinis used for immunizing animals through oral administration, the local mucosal immune response can be induced, the mucous membrane antibody IgA is generated, the body is induced to generate humoral immune response, the serum antibody IgG is then generated, good immunogenicity is displayed, and the constructed lactobacillus gene engineering vaccine strain not labelled by antibiotic resistance accords with the development concept of 'no pollution and environmental protection' of veterinary vaccines.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and Methods for Effecting NAD+ Levels Using A Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyl Tranferase Inhibitor
ActiveUS20090162454A1Reduce repairImprove efficiencyHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideToxic doseA-DNA
The present invention relates to methods for decreasing cellular DNA repair in a target patient; decreasing cellular NAD+ biosynthesis in a target patient; increasing efficiency of radiation therapy in a target patient; modulating nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase activity in a patient; or sensitizing a patient to a DNA damaging therapy. The invention relates to methods for treating a patient who received a toxic dose of an nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase inhibitor. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising a physiologically acceptable carrier; an effective amount of a NMPRT inhibitor; and nicotinic acid. The invention also relates to methods for treating a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have a cancer deficient in nicotinic acid pathway.
Owner:GEMIN X PHARMA CANADA INC (CA)
Anti-protozoal vaccine
Immunotherapy of protozoal diseases is provided by use of hypoxanthine guanine xanthine phosphoribosyl transferase protein, or peptide fragments thereof, as an immunogen in vaccines effective against protozoal diseases such as malaria and babesiosis. In particular, immunization with hypoxanthine guanine xanthine phosphoribosyl transferase or peptide fragments thereof, induces T cell immunity to blood stage malaria. In particular embodiments, the invention provides protein and DNA malaria vaccines and methods of prophylactic and therapeutic immunization that elicit T cell-mediated immune responses broadly applicable to protozoal diseases including malaria.
Owner:COUNCIL OF THE QUEENSLAND INST OF MEDICAL RES
Electrochemical detection method for gene mutation of ribosyltransferase
InactiveCN103540661ASimple meansLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesPurineBiology
The invention discloses an electrochemical detection method for gene mutation of ribosyltransferase, which relates to an electrochemical detection method for gene mutation and aims to solve the problems of complicated measures, high cost and large errors which are caused by a fact that a result can only be determined by detecting a genetic endpoint by an existing method in detection of gene mutation of cell strains and the problem that the health of a tester can be injured. The electrochemical detection method for the gene mutation of ribosyltransferase comprises the steps of 1, preparing a nano composite working electrode; 2, respectively detecting electrochemical signals of a cell lysis solution, purine base monomers and a purine base mixed solution through the prepared nano composite working electrode, and analyzing and determining a peak on which the purine base electrochemical signal is located; and 3, performing electrochemical detection every 12 hours after cells are mutated through a mutagenesis agent, and constructing an HGPRT (hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase) gene mutation electrochemical test method by taking electrochemical signal changes at different moments as indexes. The technical scheme provided by the invention is used in the field of electrochemical detection methods.
Owner:JIAMUSI UNIVERSITY
Method for improving production capacity of L-histidine producing bacteria
ActiveCN111996155AIncrease production capacityHas industrial development valueBacteriaStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for improving the production capacity of L-histidine producing bacteria. The method includes the following steps that mutating is carried out on ATP phosphoribosyl transferase derived from escherichia coli to obtain a mutant with improved enzyme activity; the gene of the mutant is designed and encoded; and the coded gene is integrated into a genome of escherichia coli to obtain genetically-engineered bacteria. The method can increase the L-histidine production capacity of L-histidine producing bacteria by more than 3.5 times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUARUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Genetically engineered strain for producing ergothioneine and application
ActiveCN112251392AShort fermentation cycleClear genetic backgroundBacteriaStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention provides a genetically engineered strain for high yield of ergothioneine and application. The stain takes escherichia coli as a host, and a coding gene hisG* of a corynebacterium glutamicum ATP phosphoribosyl transferase HisG mutant is integrated on a genome of the host; the copy number of a histidine operon gene hisDBCHAFI is further increased on the genome of the host; a mycobacterium smegmatis ergothioneine operon gene egtBCDE is further integrated on the genome of the host; an Escherichia coli glutamylcysteine ligase encoding gene gshA is integrated on the genome of the host,so that the synthesis of the ergothioneine is promoted; a neurospora crassa C-S lyase coding gene egtE<ncr> is further integrated on the genome of the host, so that the synthesis of ergothioneine isfurther promoted; and a gene egtB*<msm> of a sulfoxide synthase mutant is integrated on a genome of the host, so that synthesis of ergothioneine is further promoted.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
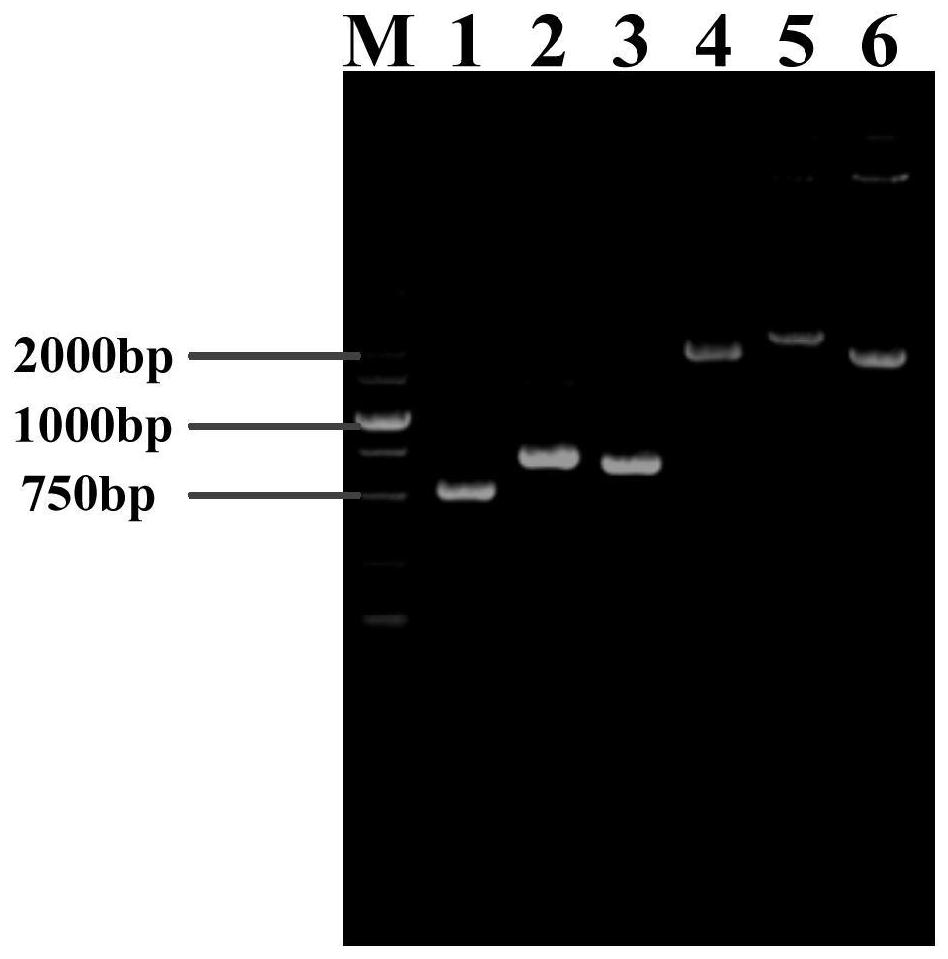
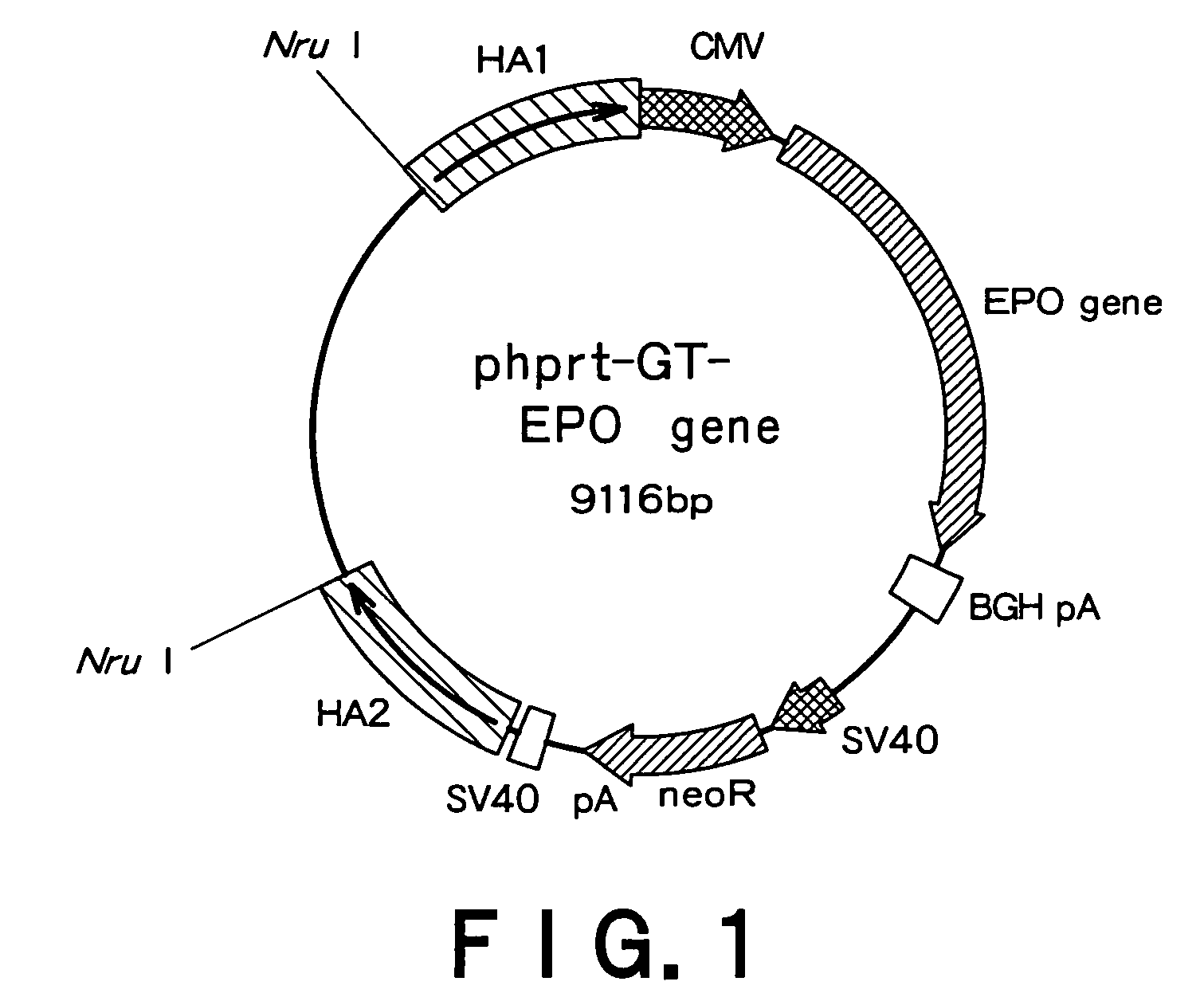
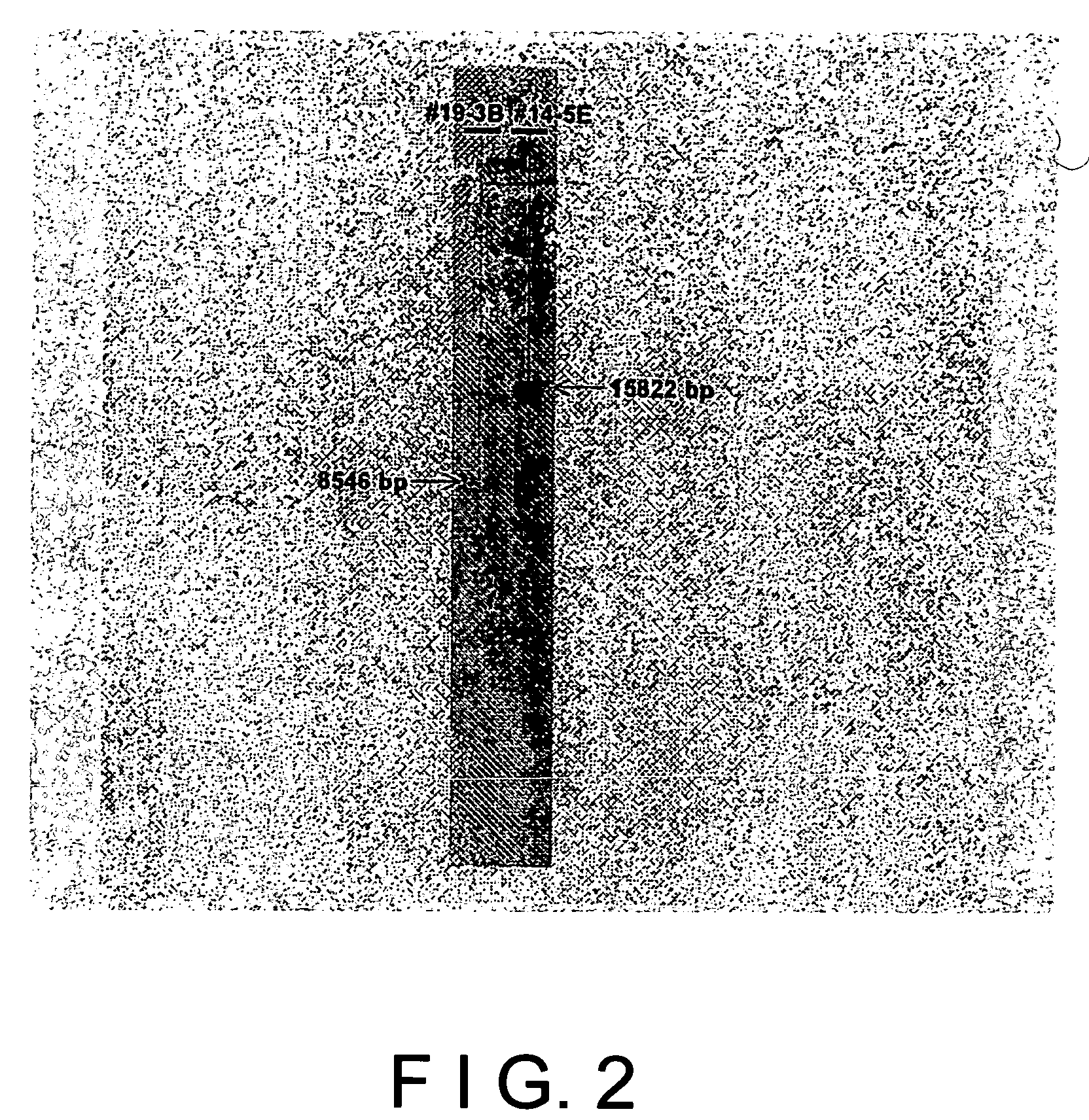
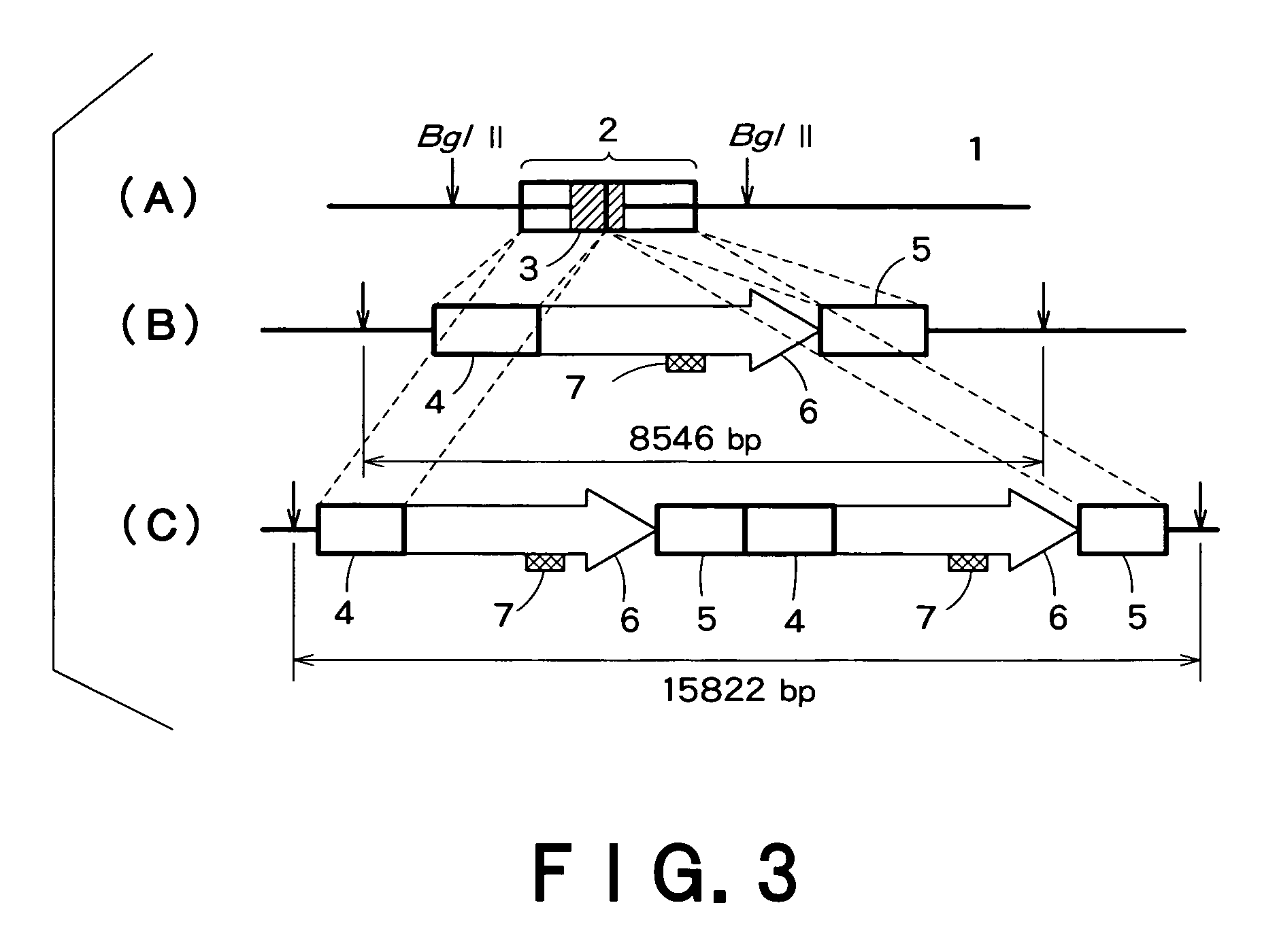
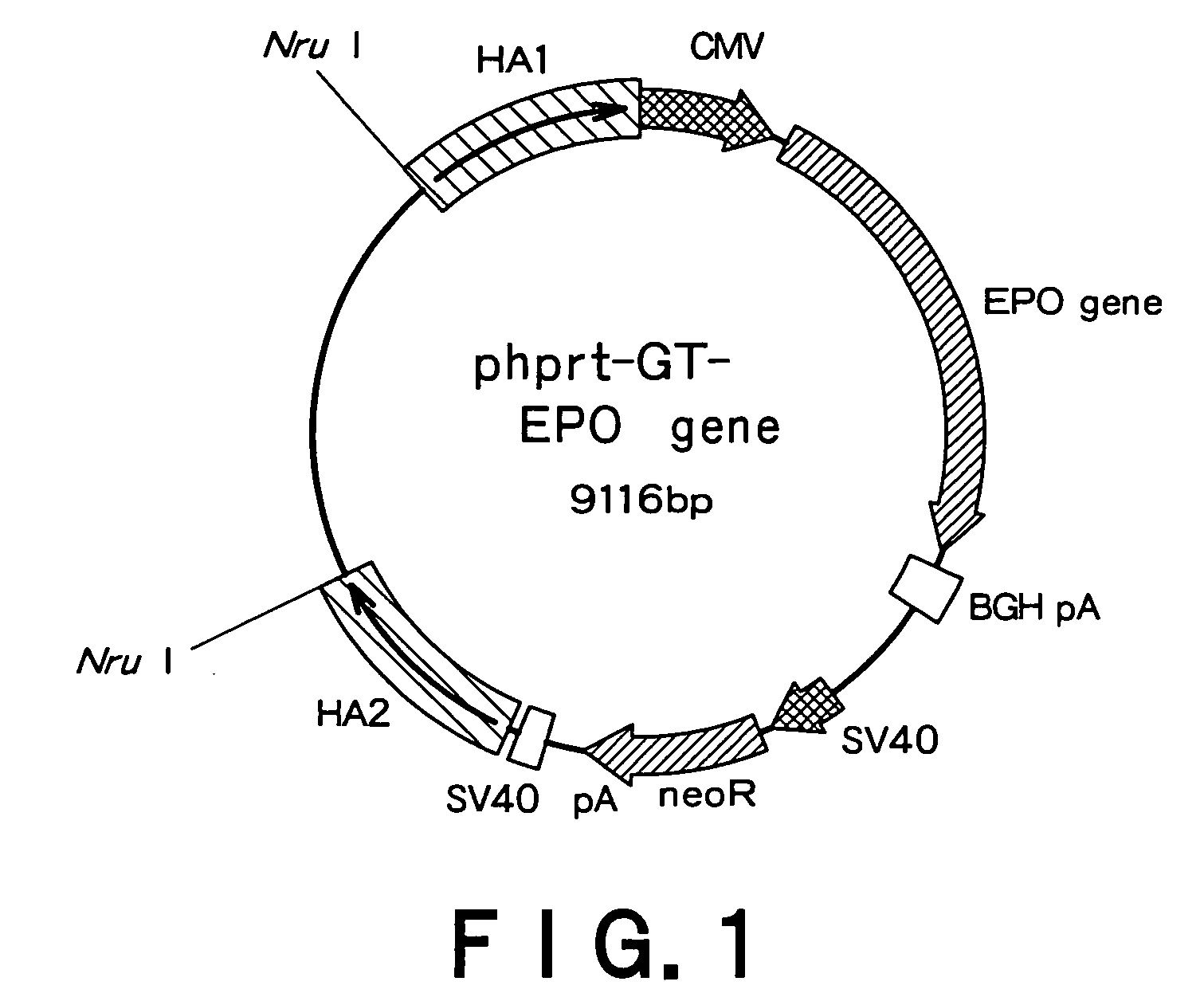
Recombinant mammal cells, method of producing thereof, and method of producing proteins of interest
ActiveUS8071332B2Maintain stabilitySpecific productivity levelArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsEnzymeGene expression
The present invention relates to a method of expressing an objective protein at a high level and stably as well as for a long period even in the absence of a selection drug with a recombinant mammal cell. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of producing an objective protein by providing a recombinant mammal cell having multiple copies of the exogenous objective protein gene expression unit integrated into a hypoxanthine-phosphoribosyl transferase enzyme (hprt) gene locus and culturing said cell.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Method for increasing yield of L-histidine
ActiveCN112779198AHigh mutation rateIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenes mutation
The invention relates to a method for increasing the yield of L-histidine. By using an ARTP mutagenesis method which is safe and mild in operation condition and high in controllability, a mutation library with the higher mutation rate is obtained; in combination with L-histidine structural analogue screening, a stable L-histidine high-yield mutant strain is obtained through ten times of passage; the mutation condition of L-histidine synthesis related genes of the mutagenic high-yield strain is further analyzed; 5-phosphoribose-1-pyrophosphate synthesis related gene Prs and ATP phosphoribosyl transferase encoding gene hisG mutants which can promote the increase of the yield of the L-histidine are obtained through comparison and screening; and one or two of the genes Prs and hisG are expressed in host bacteria for producing the L-histidine, so that the yield of the L-histidine can be effectively increased. A foundation is laid for producing the L-histidine by further transforming serratia marcescens or other strains in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant mammal cells, method of producing thereof, and method of producing proteins of interest
ActiveUS20090117615A1Maintain stabilitySpecific productivity levelArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsEnzymeGene expression
The present invention relates to a method of expressing an objective protein at a high level and stably as well as for a long period even in the absence of a selection drug with a recombinant mammal cell. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of producing an objective protein by providing a recombinant mammal cell having multiple copies of the exogenous objective protein gene expression unit integrated into a hypoxanthine-phosphoribosyl transferase enzyme (hprt) gene locus and culturing said cell.
Owner:TOTO LTD
Recombinant microorganism for producing beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide at high yield and method for producing beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide
The invention provides a recombinant microorganism for producing beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) at high yield and a method for producing beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide by using the recombinant microorganism, and the recombinant microorganism strain contains one or more of the following characteristics or all of the following characteristics, the characteristics are as follows: (1) nicotinamide is added into a fermentation culture medium, and NMN is generated through recombinant microorganism transformation; (2) the nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase is overexpressed; and (3) deletion or inactivation or enzyme activity reduction of a gene for encoding 5'-deoxynucleotidase on a recombinant microbial genome.
Owner:BIOSYNTHETICA INC
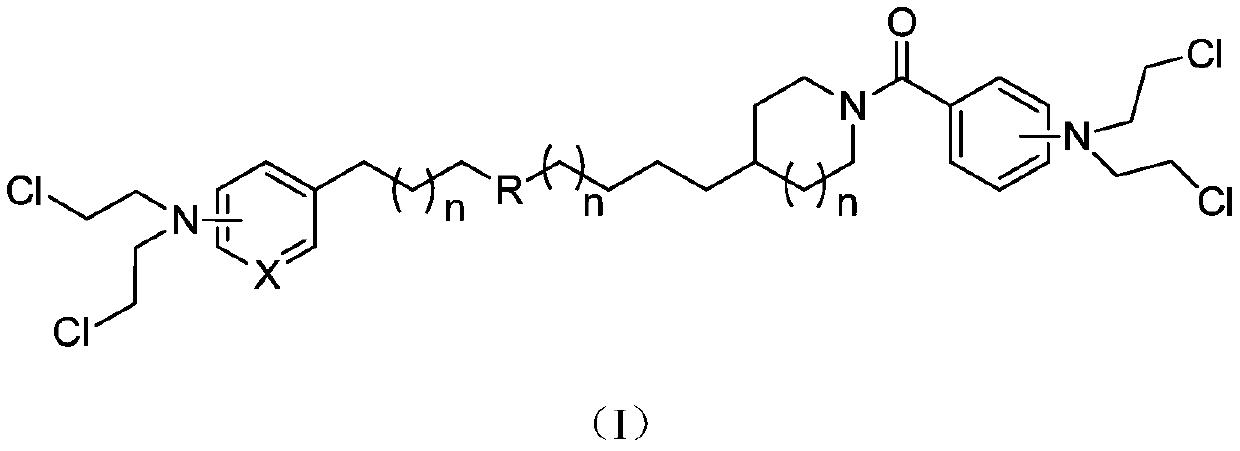
Multi-target nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase nitrogen mustard inhibitor with antitumor activity and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN109776494AStrong inhibitory activityEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsPhosphoribosyl transferaseAnti-Tumor Drugs
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, in particular to a multi-target nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase nitrogen mustard inhibitor with the antitumor activity and preparation and application thereof. The invention provides a compound based on inhibition of two targets NAMPT / DNA, and the structural general formula thereof is shown as a formula (I). The compound has excellent NAMPT enzyme inhibiting activity, has relatively strong in-vitro antitumor activity and an excellent in-vivo tumor-inhibiting effect, has low toxicity, has the characteristics of high efficiency and low toxicity, and is a superior antitumor medicine. The invention further provides a preparation method of a derivative thereof, and application thereof to preparation of an NAMPT inhibitor, a DNAinhibitor, an NAMPT / DNA two-target inhibitor and the antitumor medicine.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
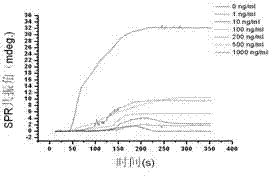
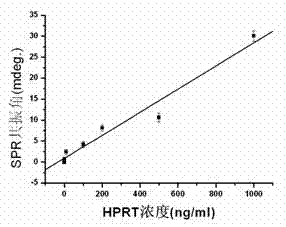
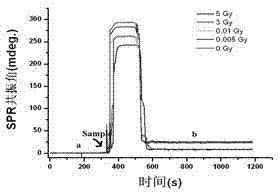
HPRT (hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase) body gene mutation detection method based on surface plasmon resonance
InactiveCN102162792AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationGenes mutationHistiocyte
The invention belongs to a quantitative detection method of an enzyme, and in particular relates to an HPRT (hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase) body gene mutation detection method based on surface plasmon resonance. The HPRT body gene mutation detection method based on surface plasmon resonance is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparation of a wild HPRT enzyme-sensitive SPR (surface plasmon resonance) gold film; (2) SPR detection of a wild HPRT standard substance; and (3) sample preparation and the SPR detection: after collected mammal cells are repeatedly washed by a hanks liquid, directly adding a histiocyte lysis solution; vibrating at the temperature of 4DEG C to cause the sample to fully crack; carrying out low-temperature centrifugation on the cracked product; collecting a supernate containing proteins; replacing the lysis solution component in the supernate by PBS (phosphate buffered saline), and storing in a refrigerator at the temperature of 4 DEG C; and carrying out SPR detection. The method has high detection sensitivity, and the content of wild HPRT of ngmL-1 order of magnitude can be detected.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
URA5 gene and methods for stable genetic integration in yeast
A novel gene encoding P. pastoris orotate-phosphoribosyl transferase (URA5) is disclosed. Methods for producing and selecting yeast strains capable of stable genetic integration of heterologous sequences into the host genome are also provided.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Full-natural cell conditioning method of high uric acid/gout
PendingCN109620948AResolve Healing EffectsNo side effectsOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsSide effectMedicine
The invention provides a full-natural cell conditioning method of high uric acid / gout, which comprises the following steps of: firstly supplementing selenium and zinc element antioxidant repair cells,and then supplementing goose carnosine to enhance the activityof hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT), combining the administration of acomposition for reducing uric acid to achieve the aim of reducing uric acid and relieving gout. The full-natural cell conditioning method solves the problem that patients with high uric acid / gout need to take medicines for prevention and treatment all the time in the prior art; and the conditioning method has no toxic or side effects and can achieve the basic aim of preventing and curing high uric acid / gout by conditioning and comprehensively repairing cells.
Owner:HUNAN KAQI E COMMERCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com